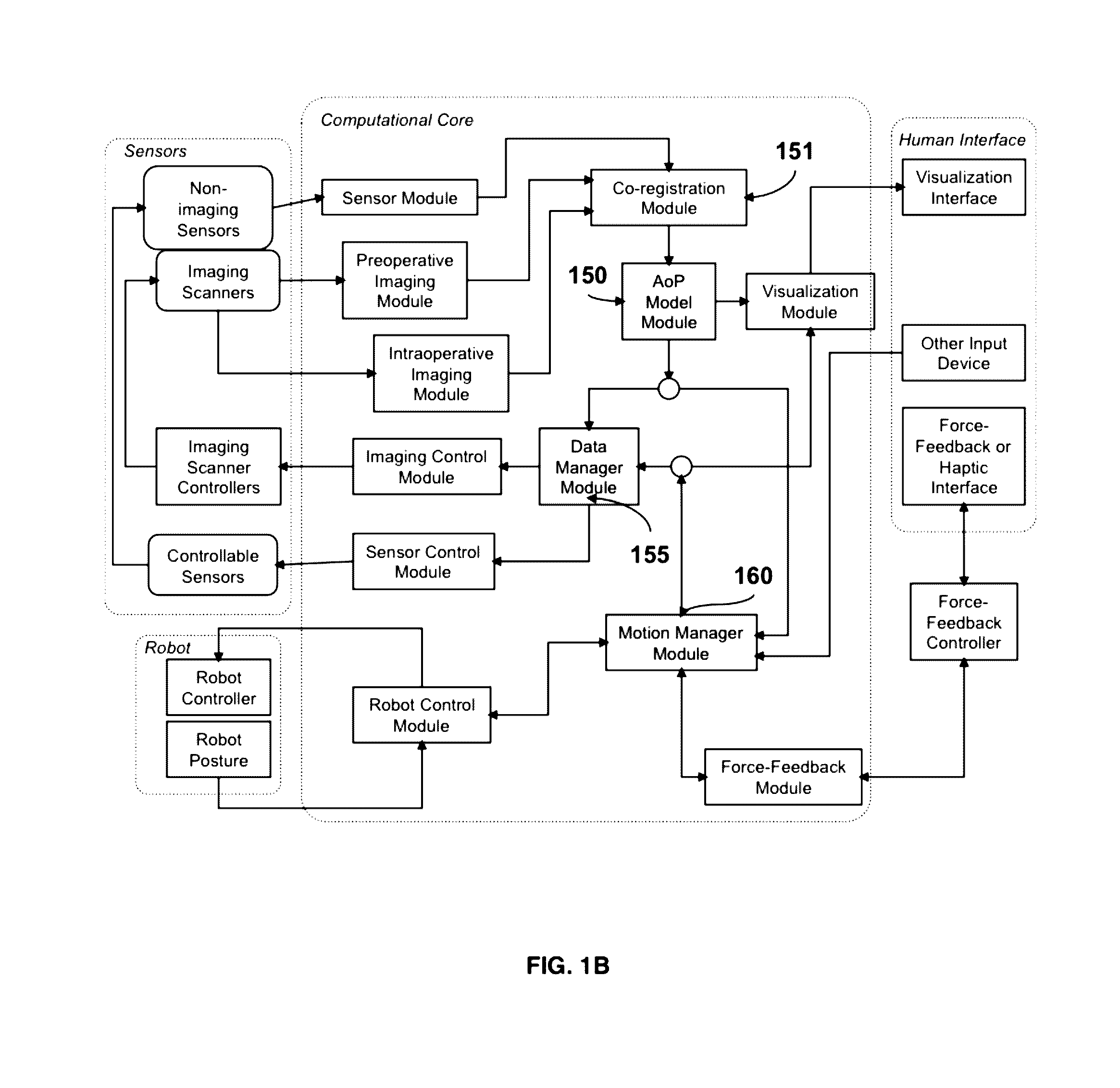
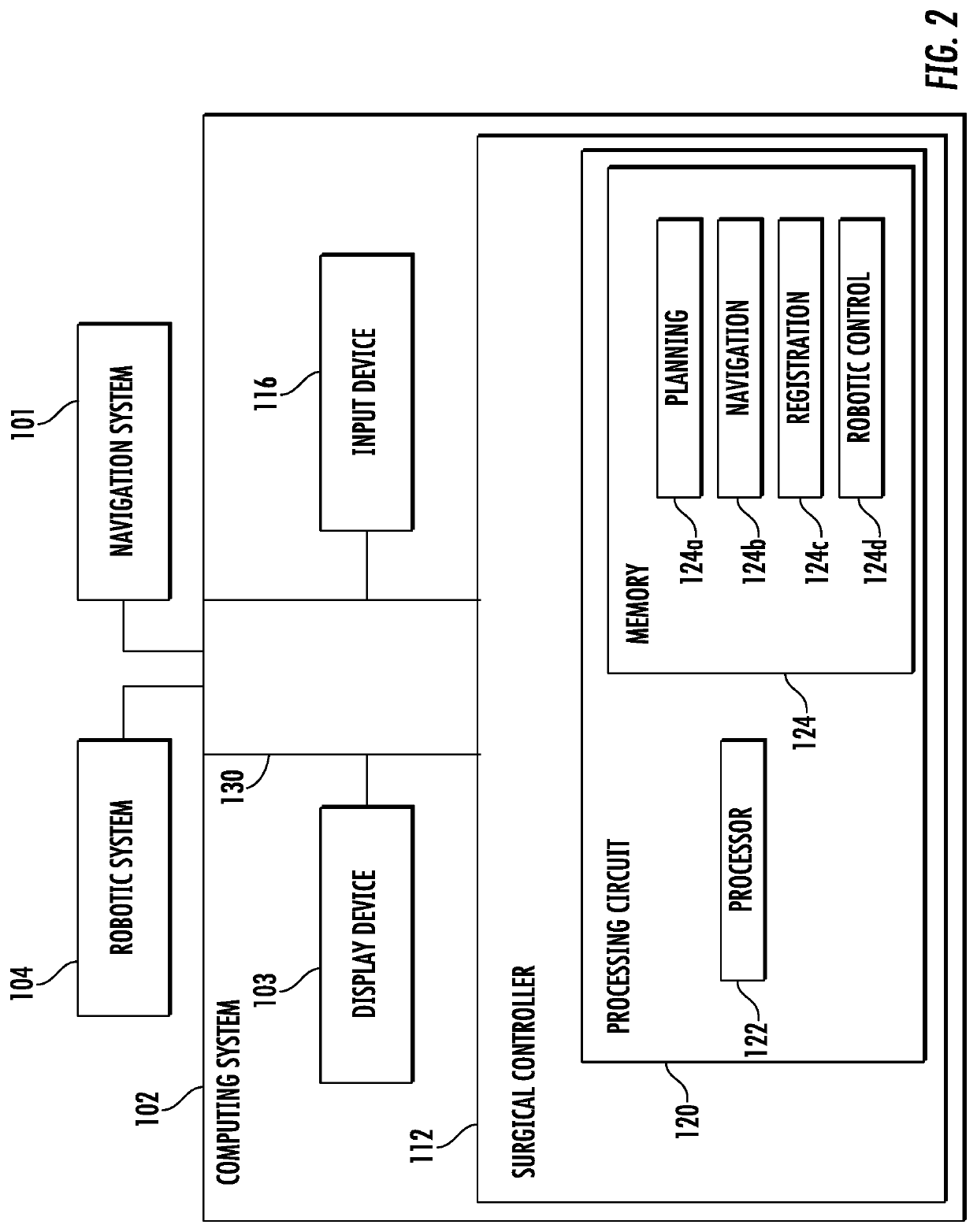
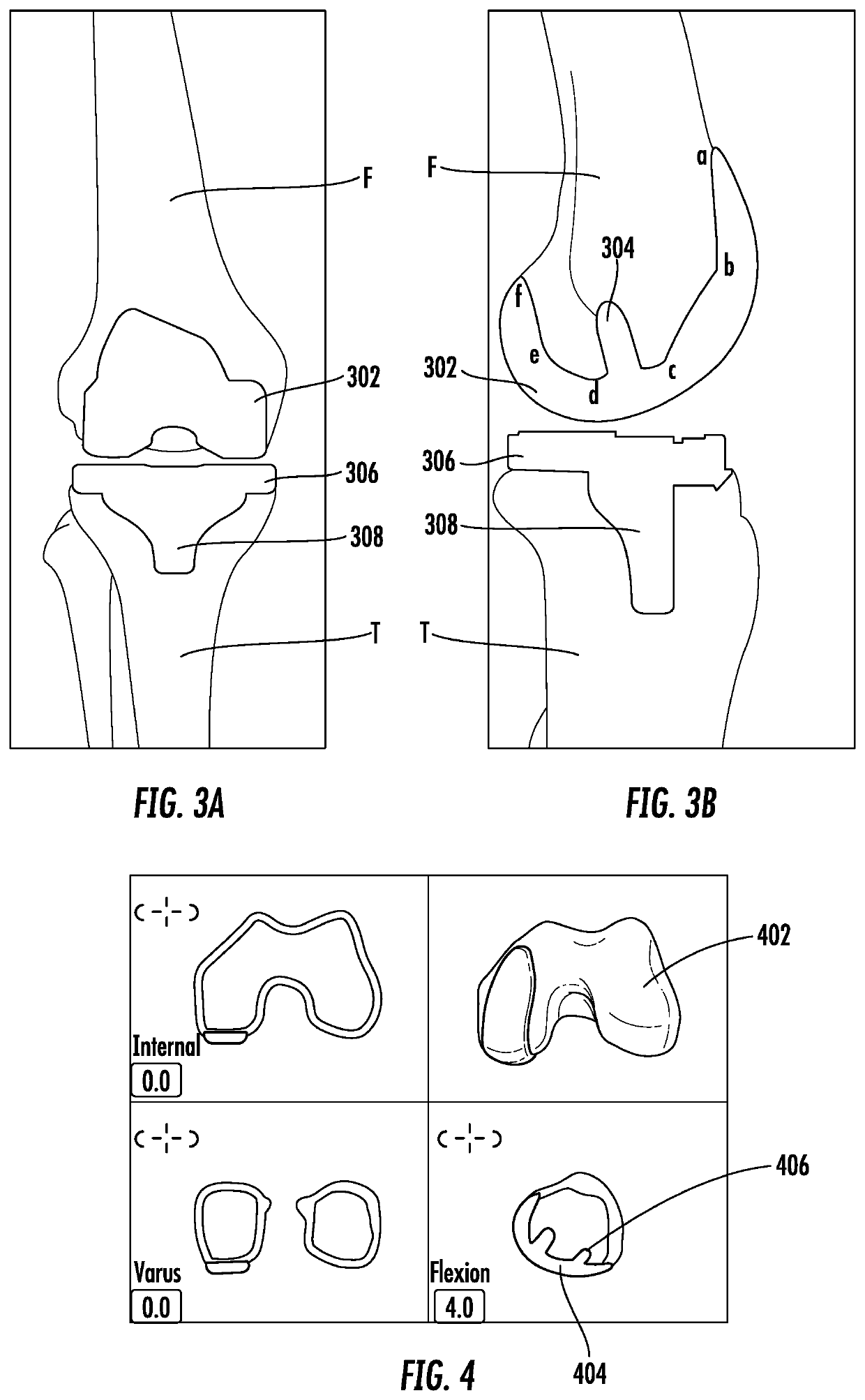
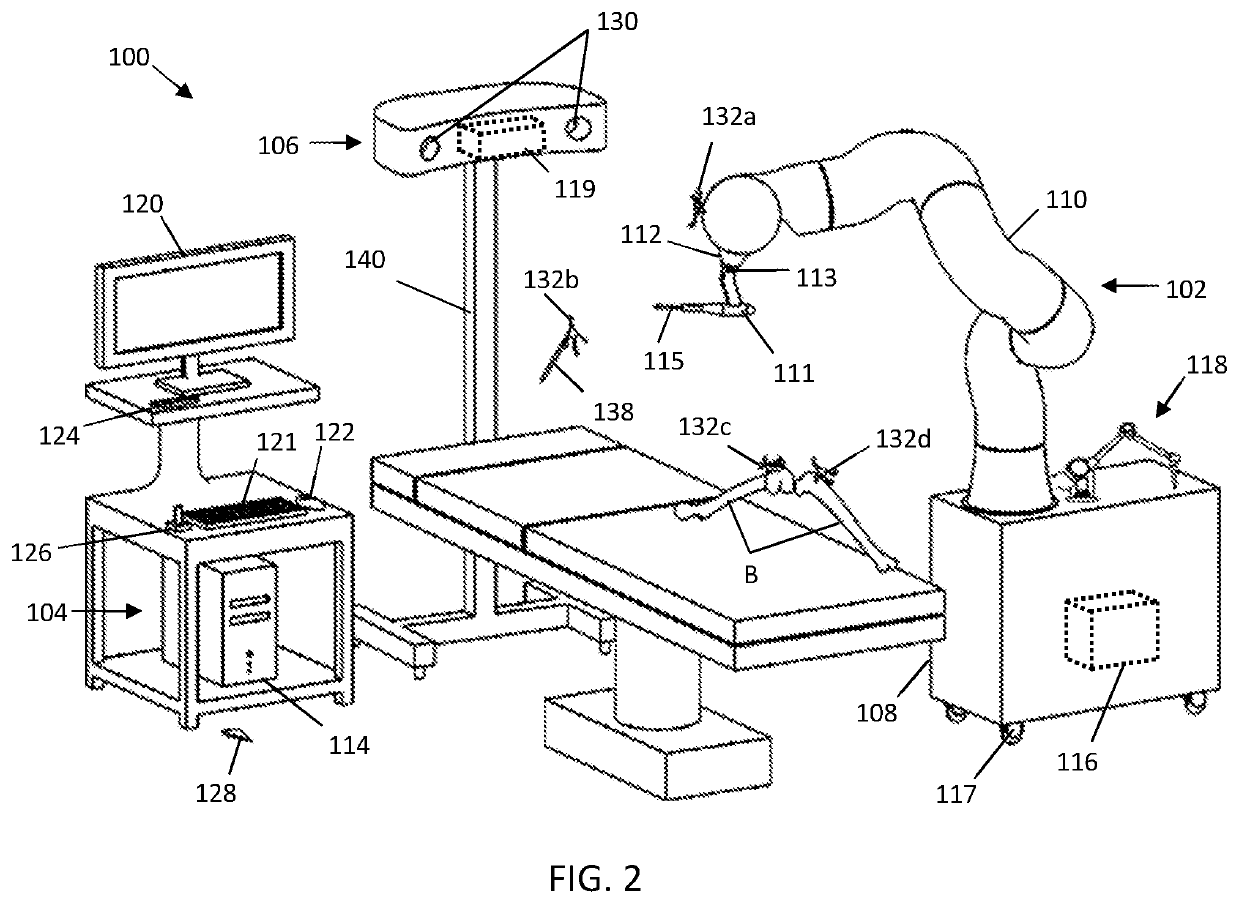
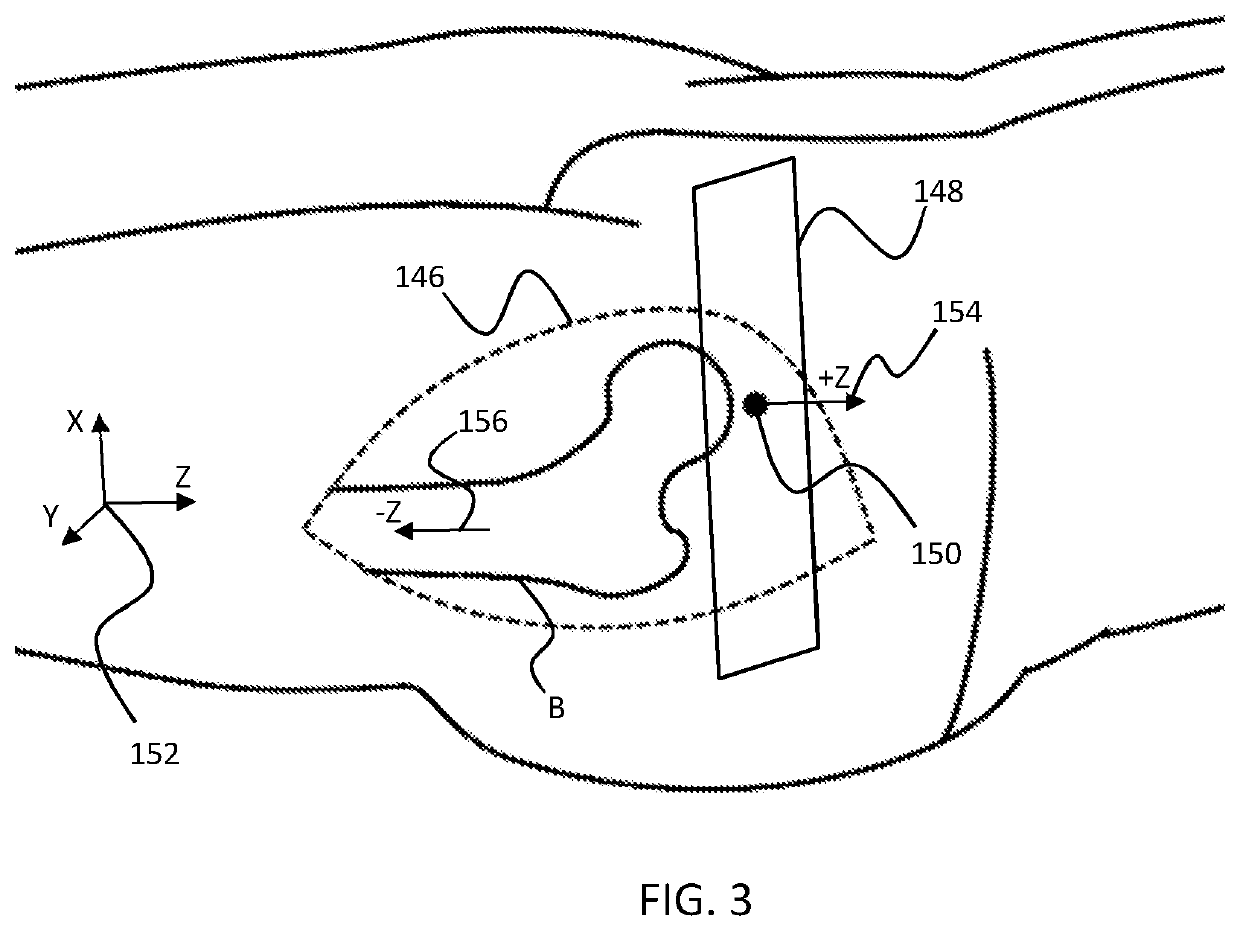
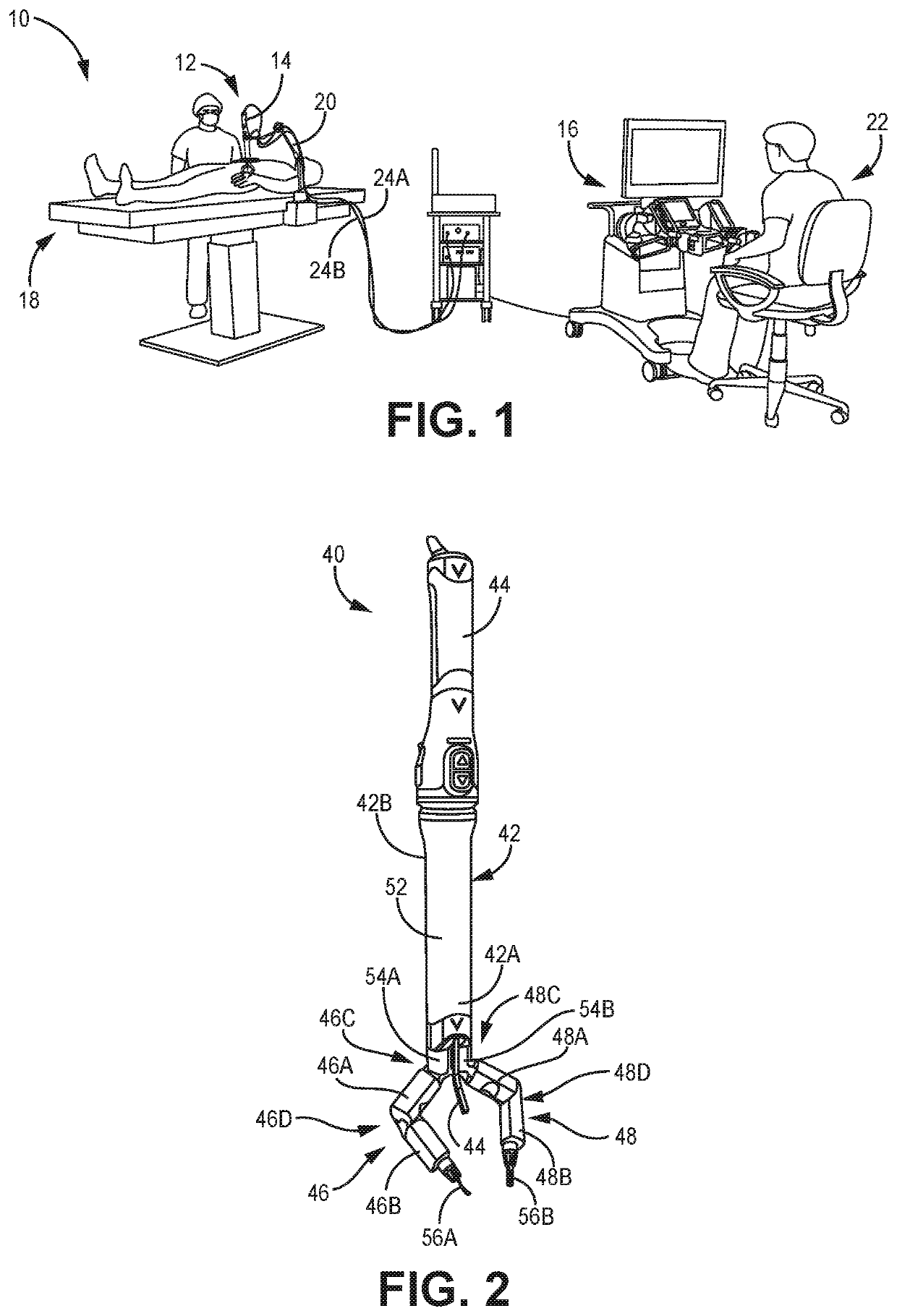
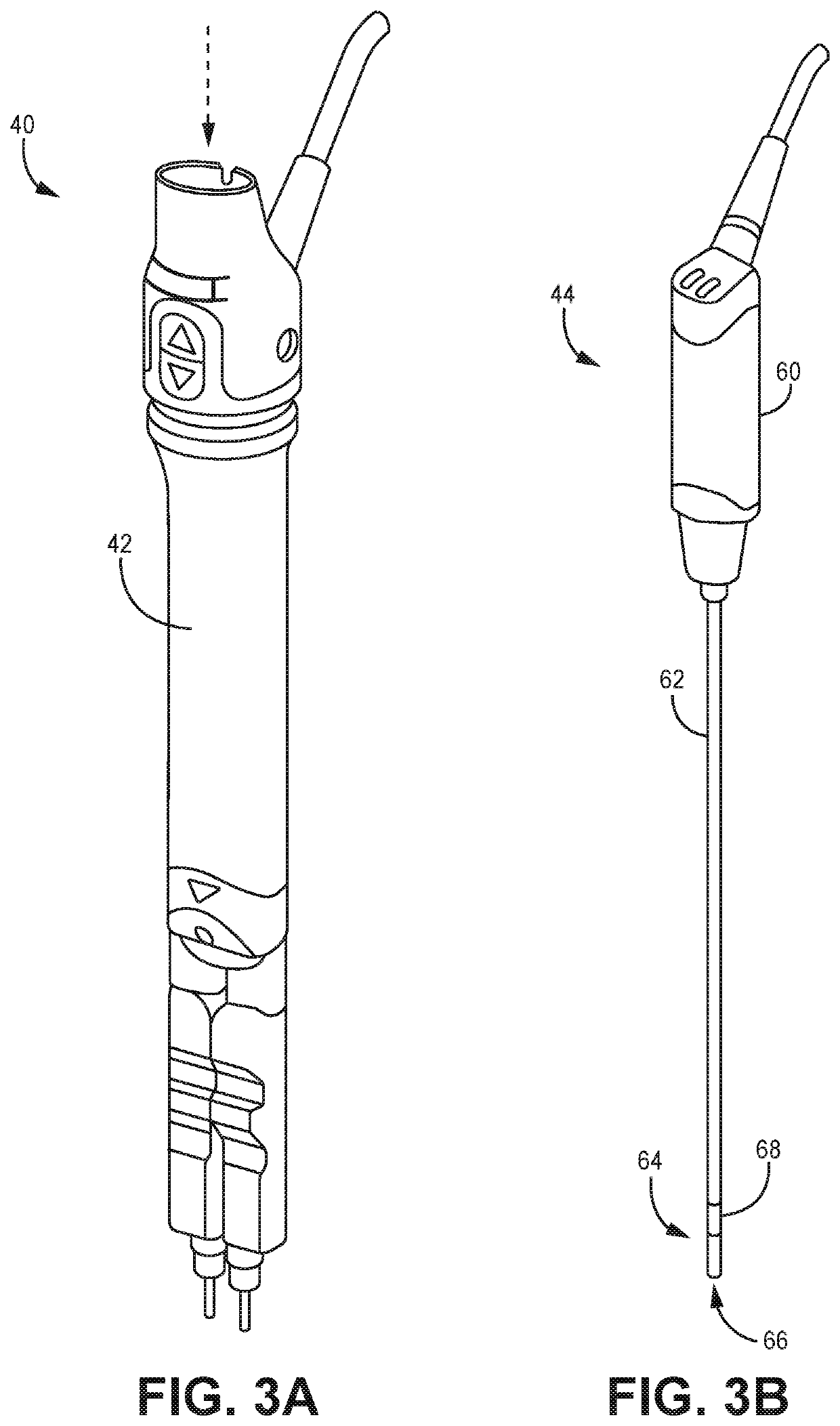
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Robotic assisted surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Robot surgery is developed on the technique of endoscopic surgery where surgical tools are inserted into the patient through ports that are connected to robotic arms which are controlled by the surgeon.
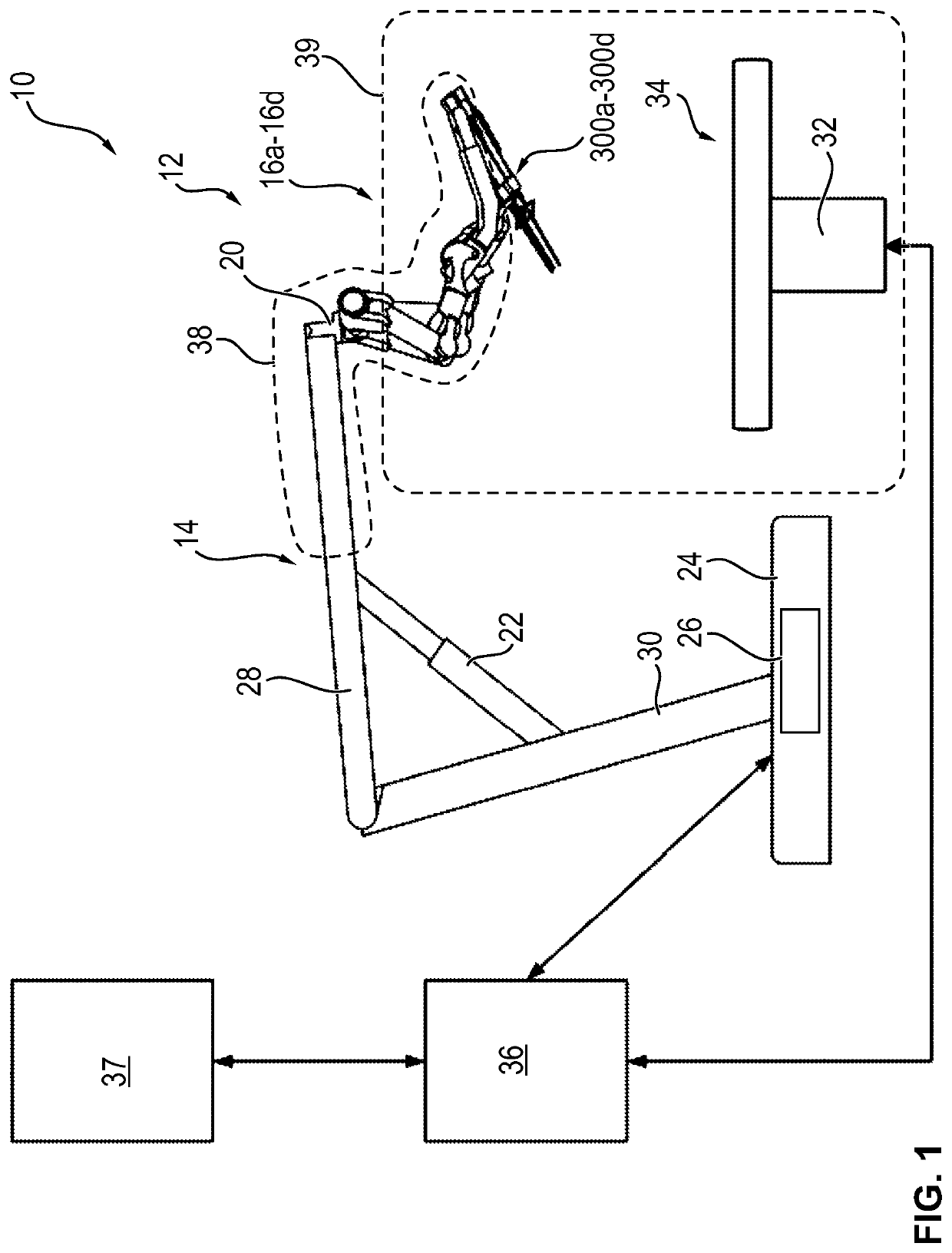
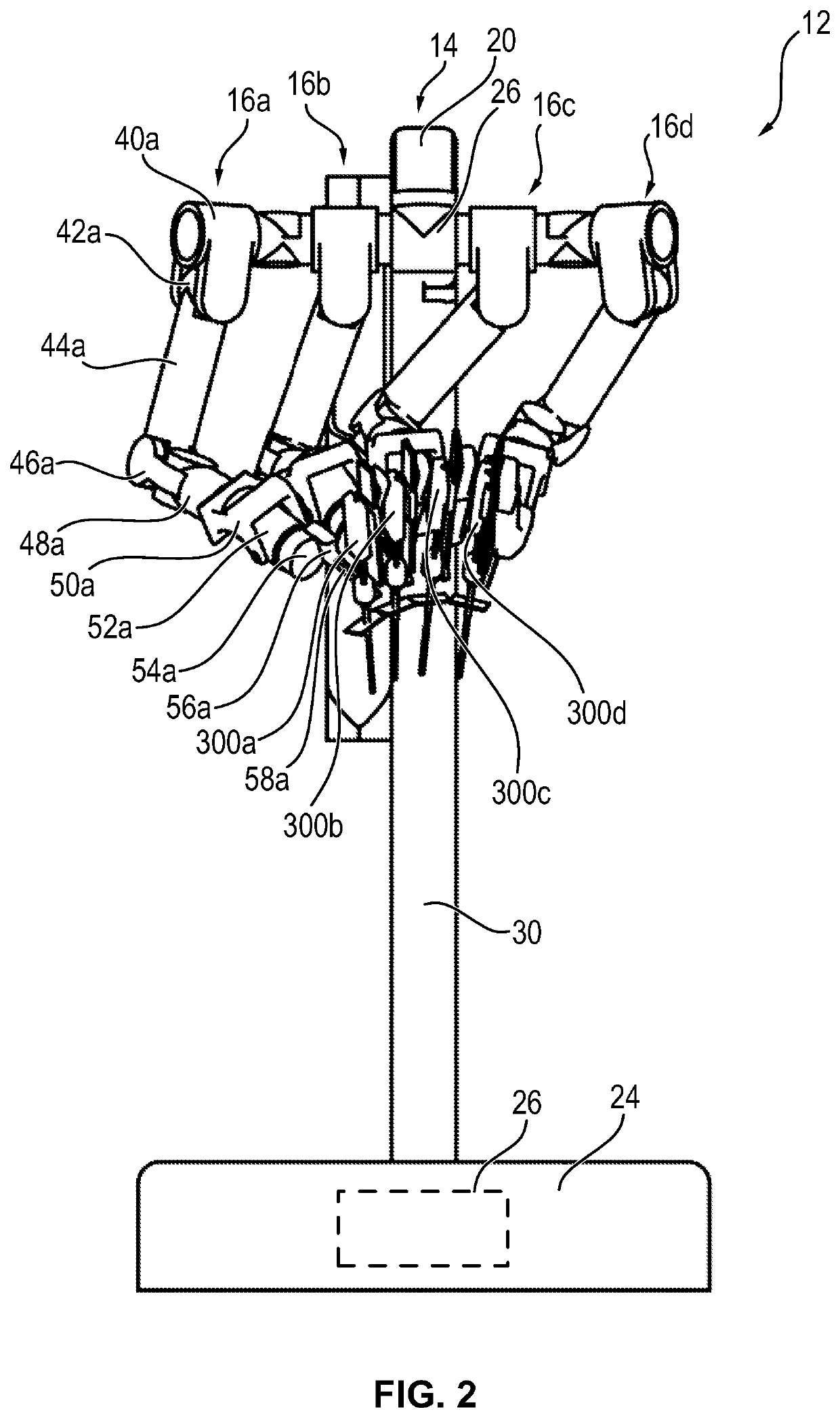
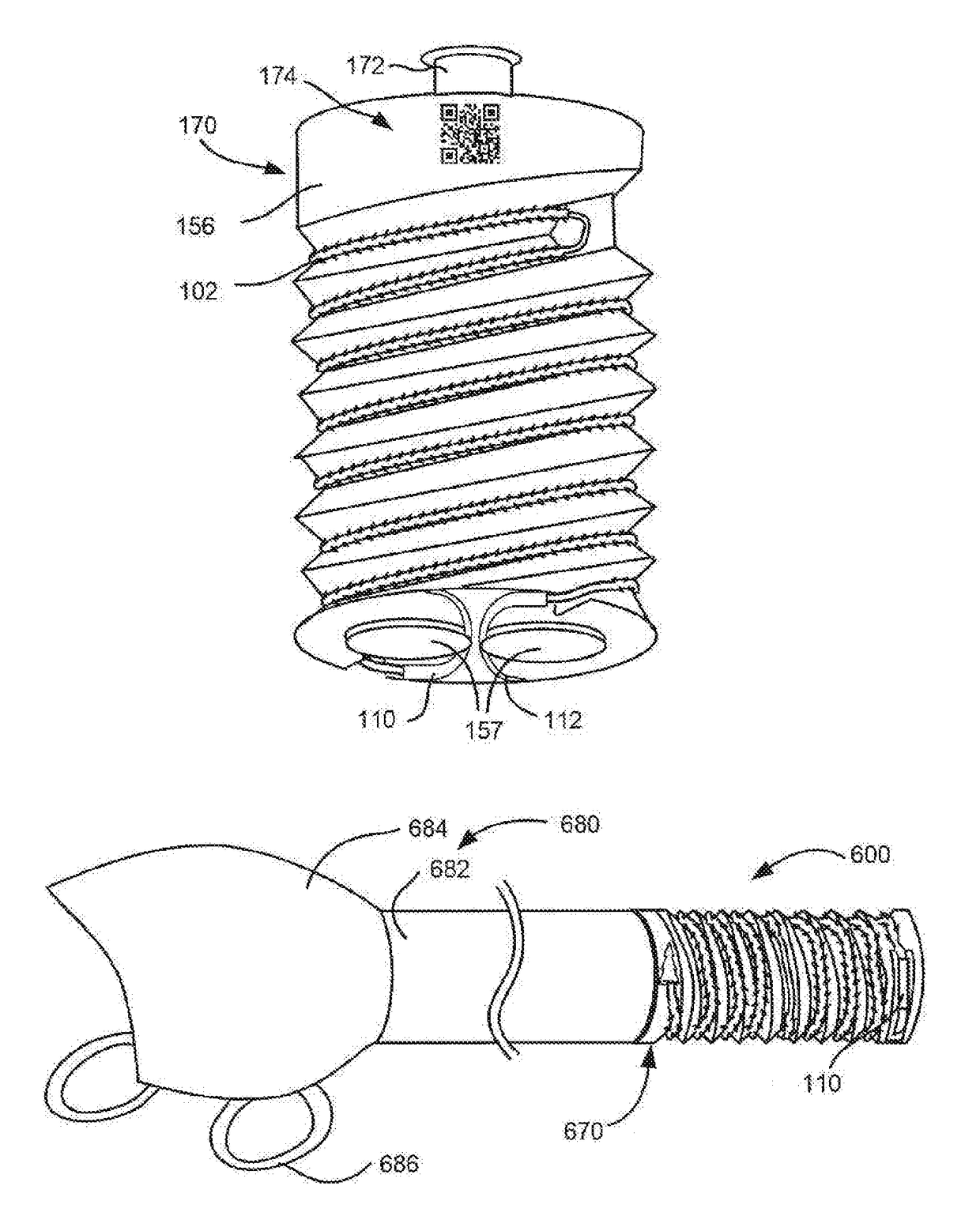
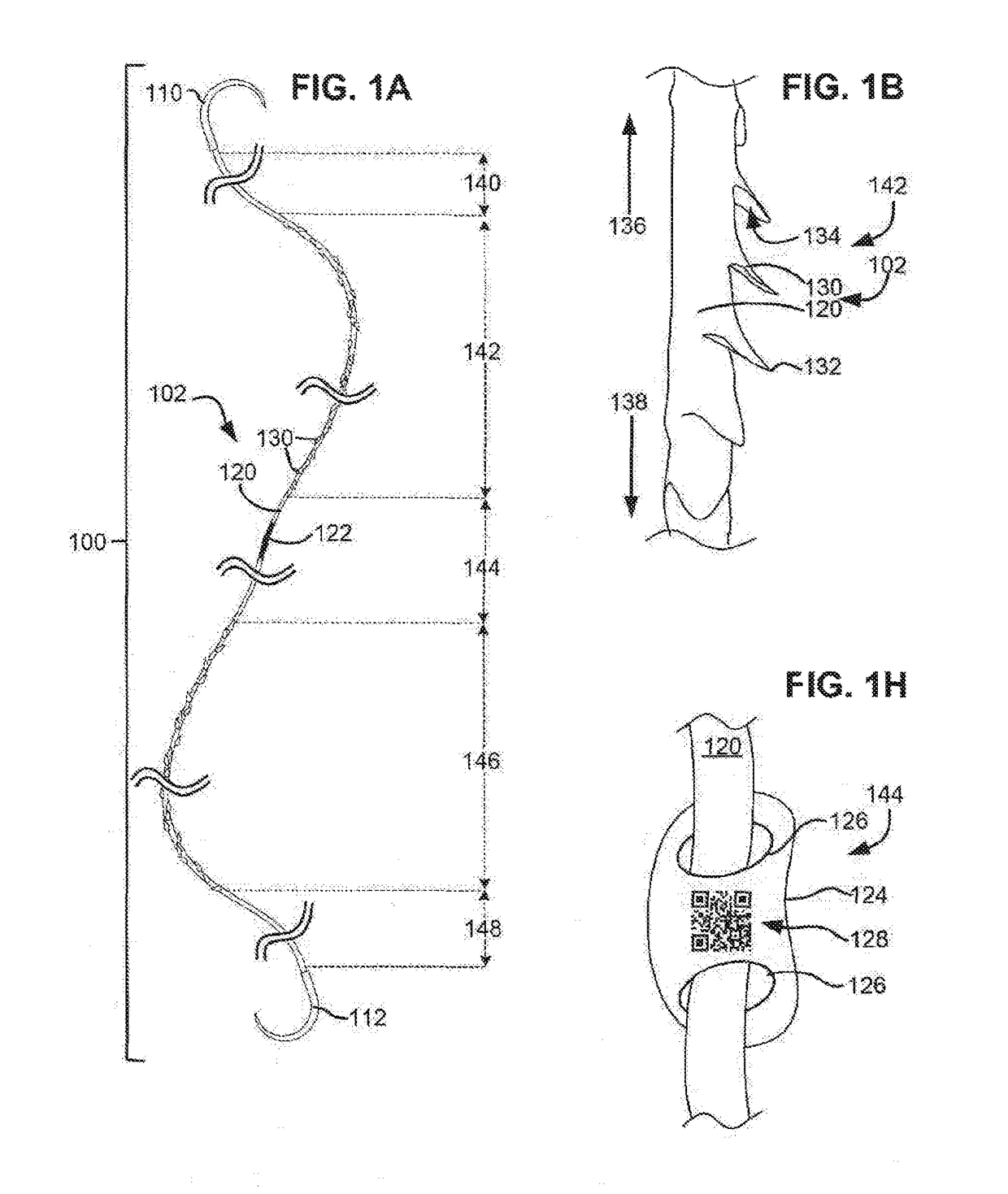
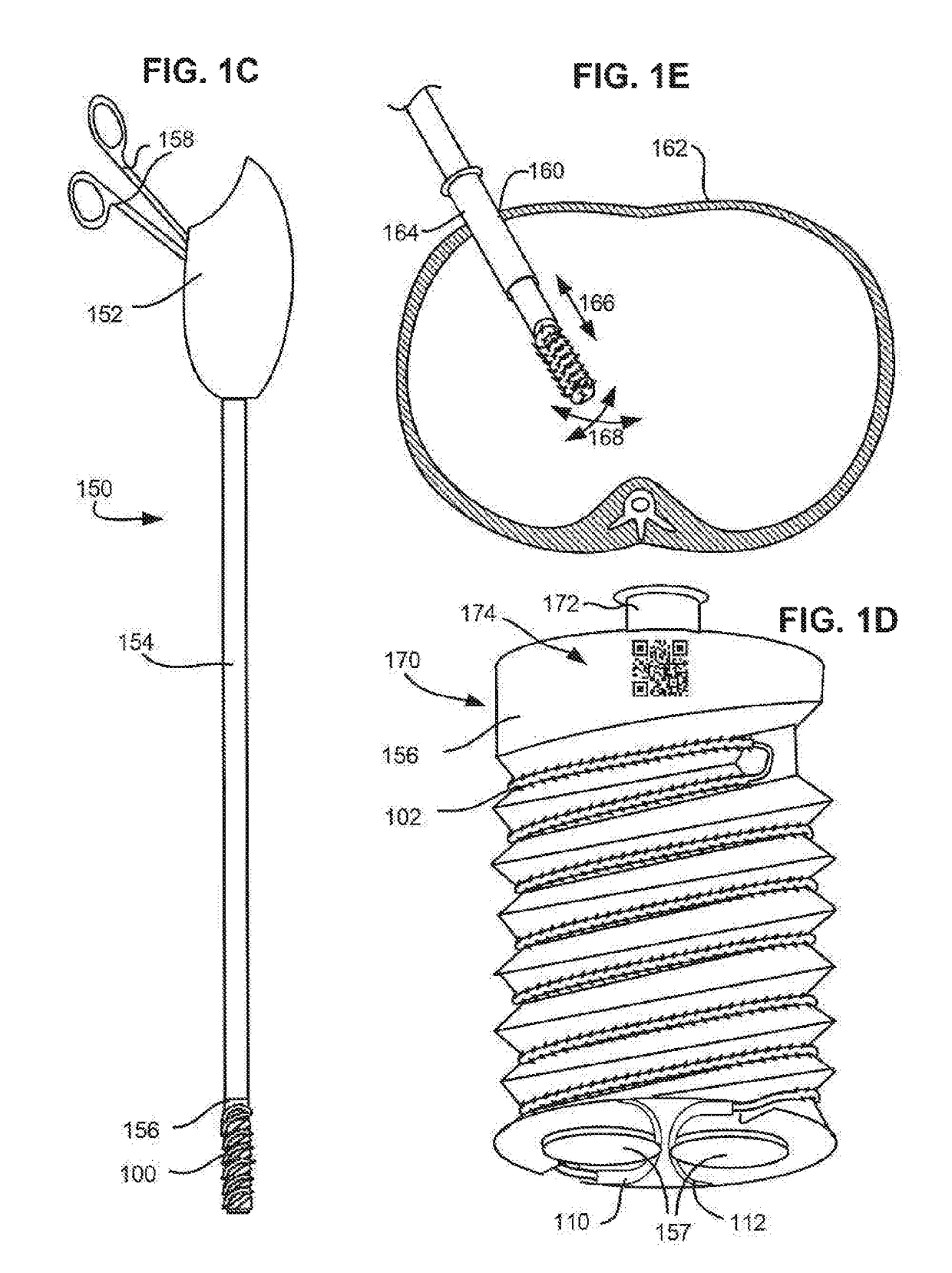
Method, apparatus and a system for robotic assisted surgery
A solution to facilitate robotic assisted surgery is discussed that allows for improved vision and manipulation.
Owner:AURIS SURGICAL ROBOTICS
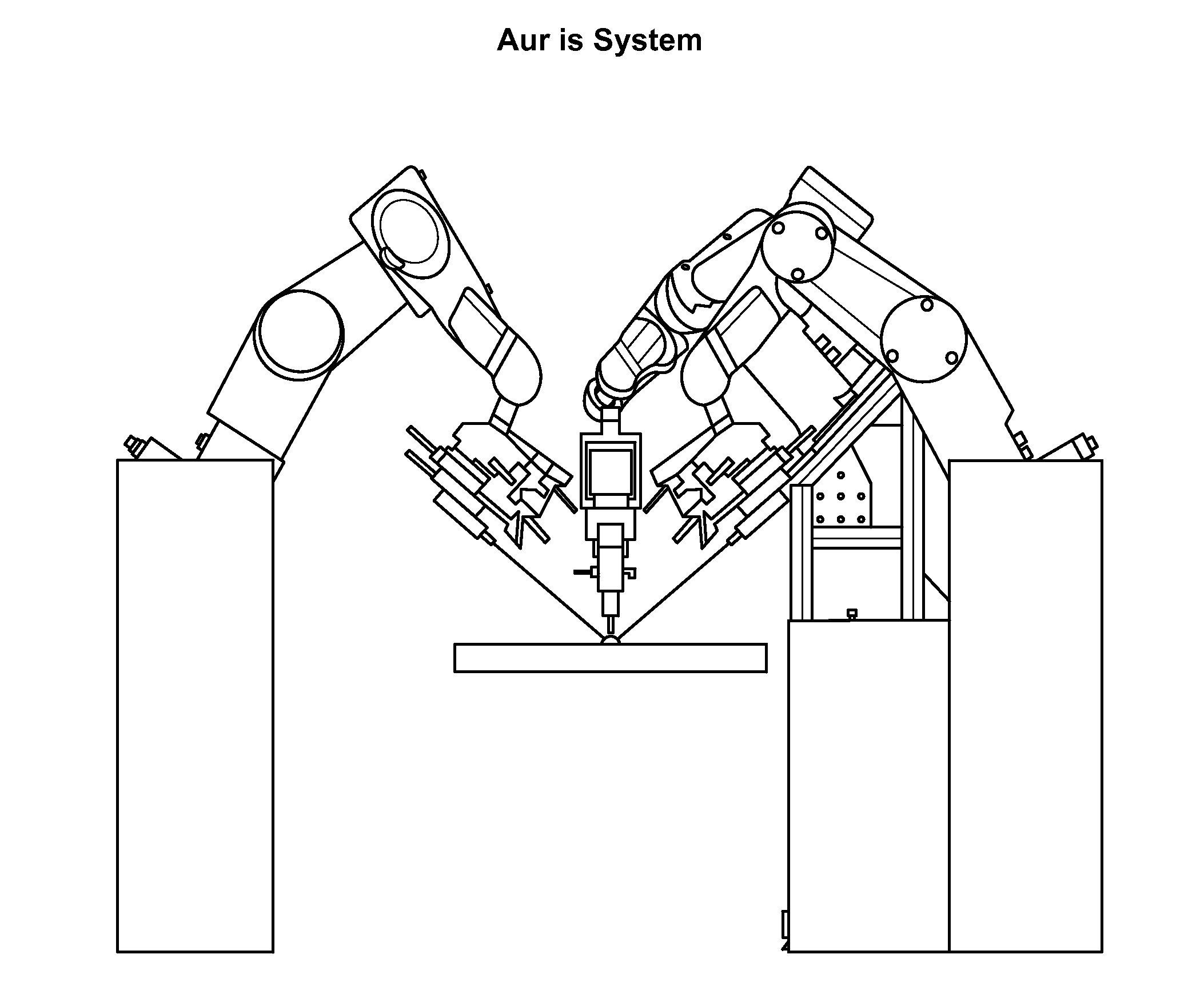
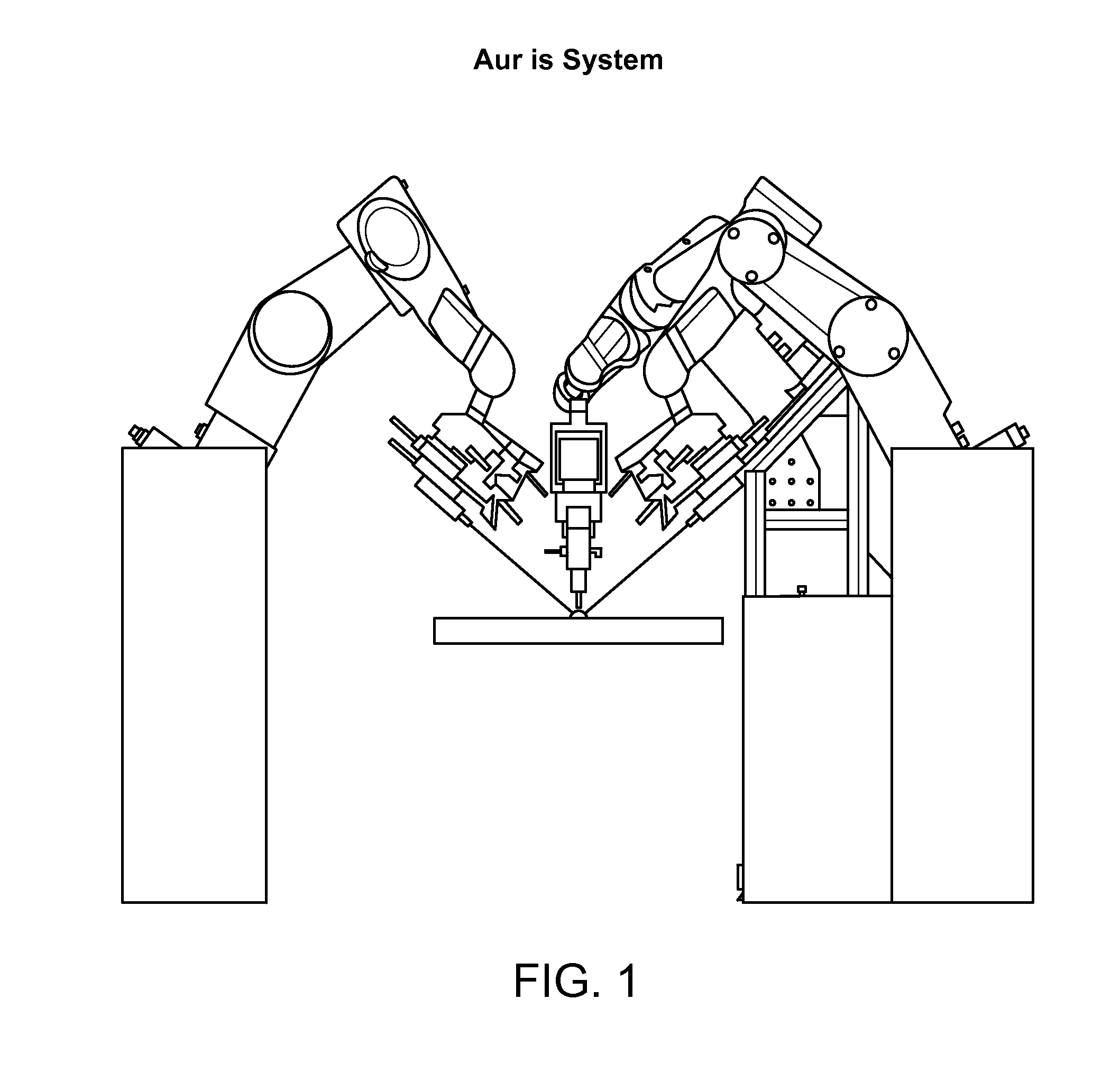
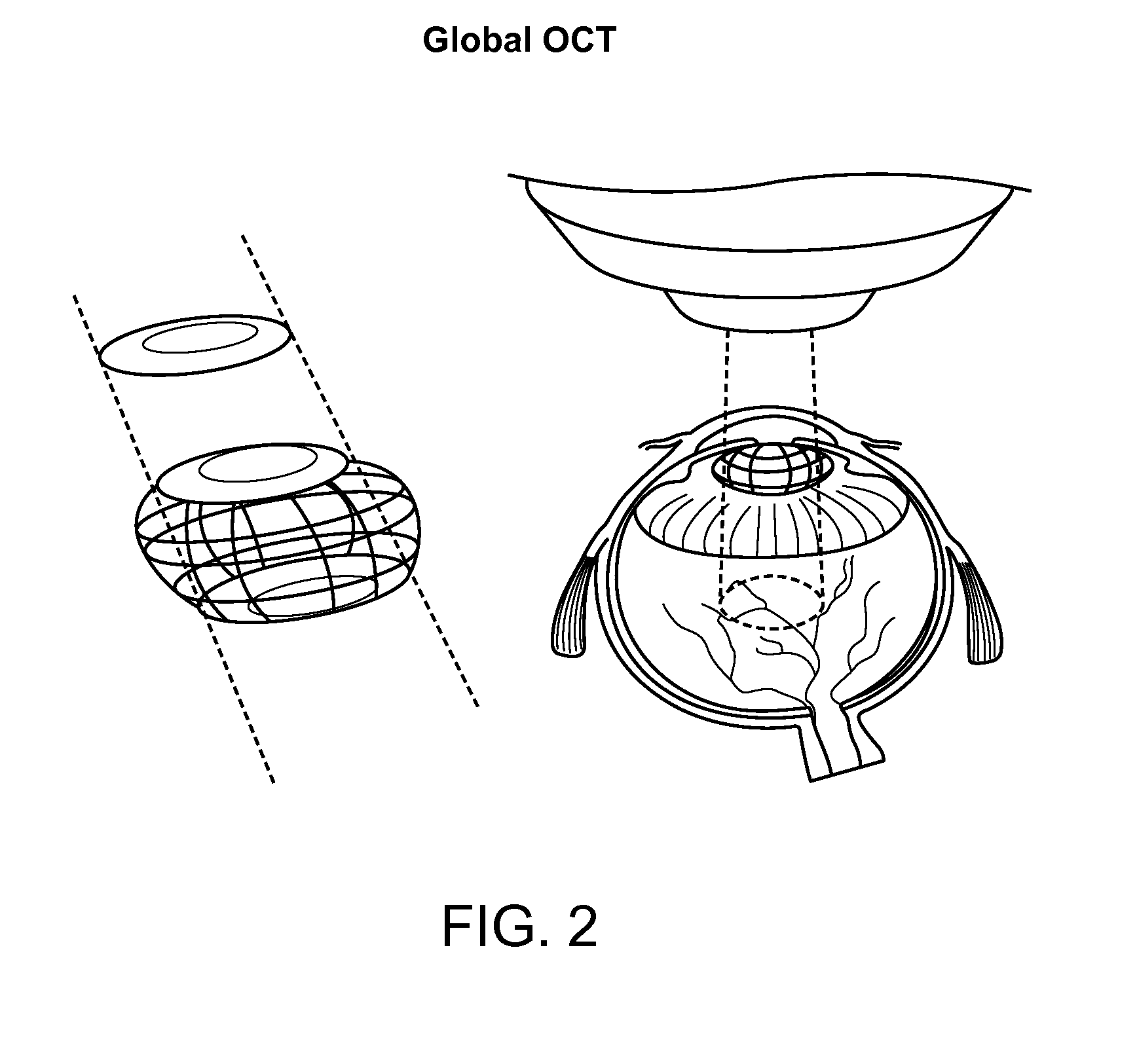
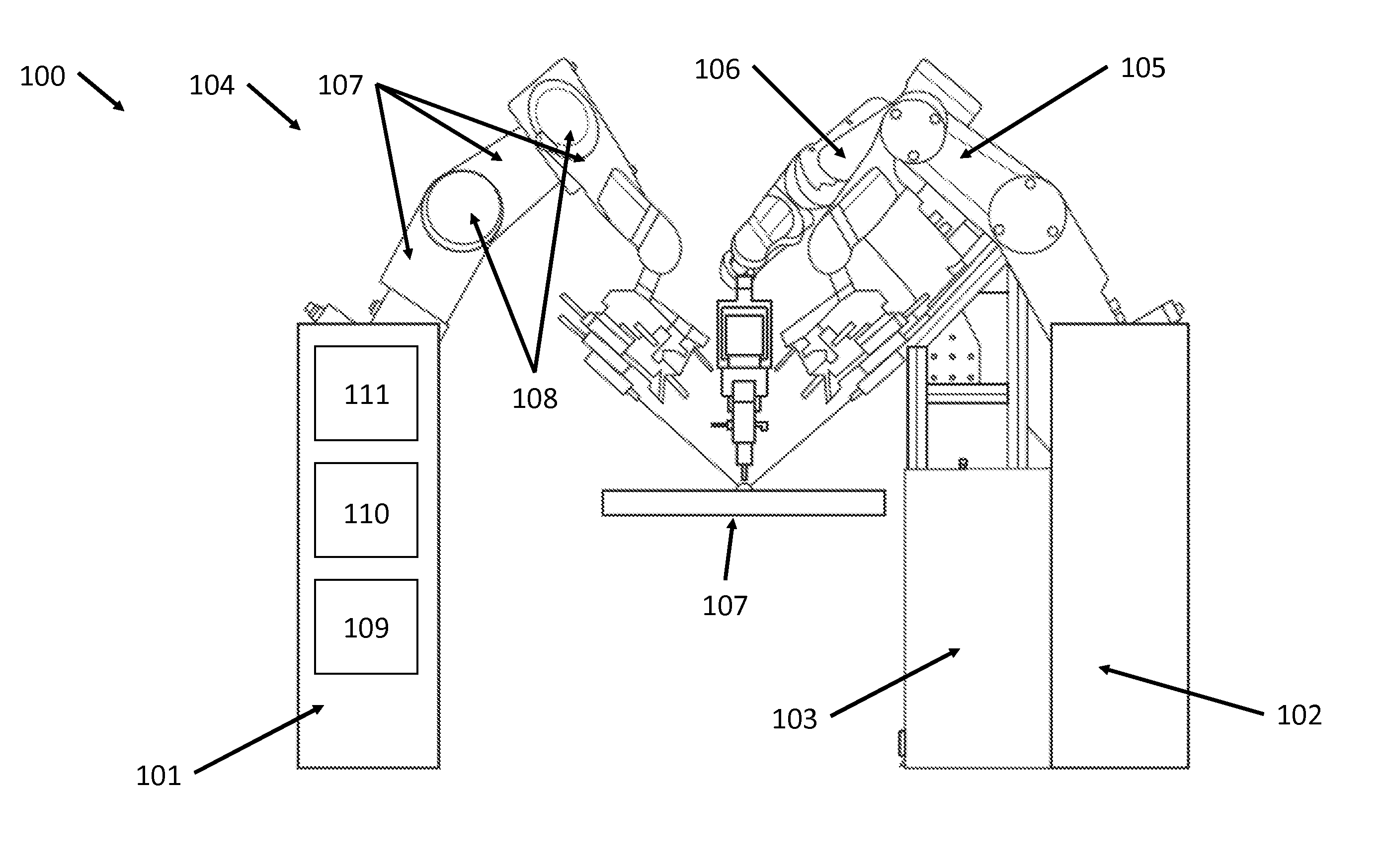
Apparatus and method for a global coordinate system for use in robotic surgery
ActiveUS20150335480A1Facilitating robotic surgeryDiagnostics using lightEye surgeryKinematicsEngineering
An apparatus and method for establishing a global coordinate system to facilitate robotic assisted surgery. The coordinate system may be established using a combination of the robotic data, i.e., kinematics, and optical coherence tomographic images generated by an overhead optical assembly and a tool-based sensor. Using these components, the system may generate a computer-registered three-dimensional model of the patient's eye. In some embodiments, the system may also generate a virtual boundary within the coordinate system to prevent inadvertent injury to the patient.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Robotic Device and Systems for Image-Guided and Robot-Assisted Surgery
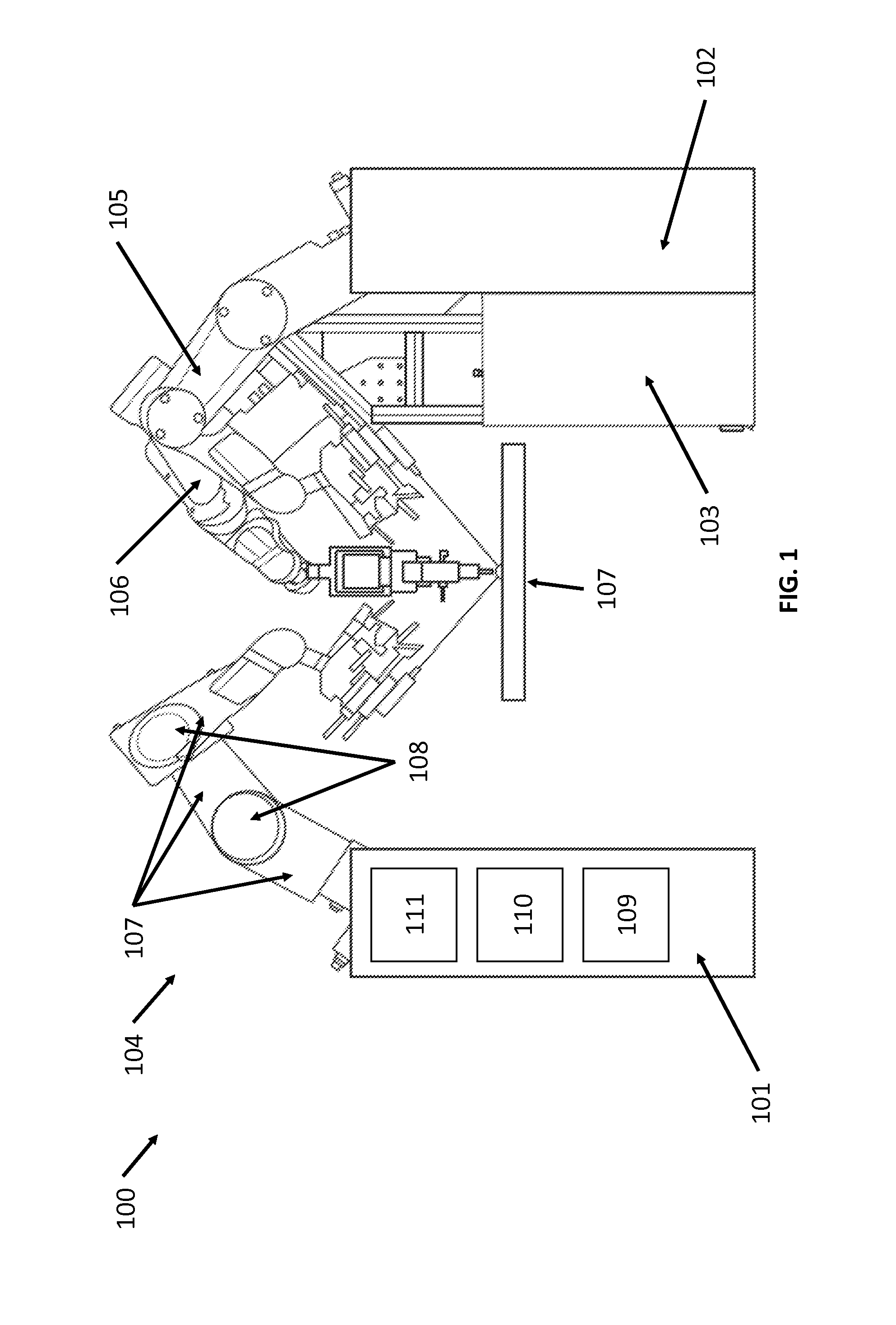
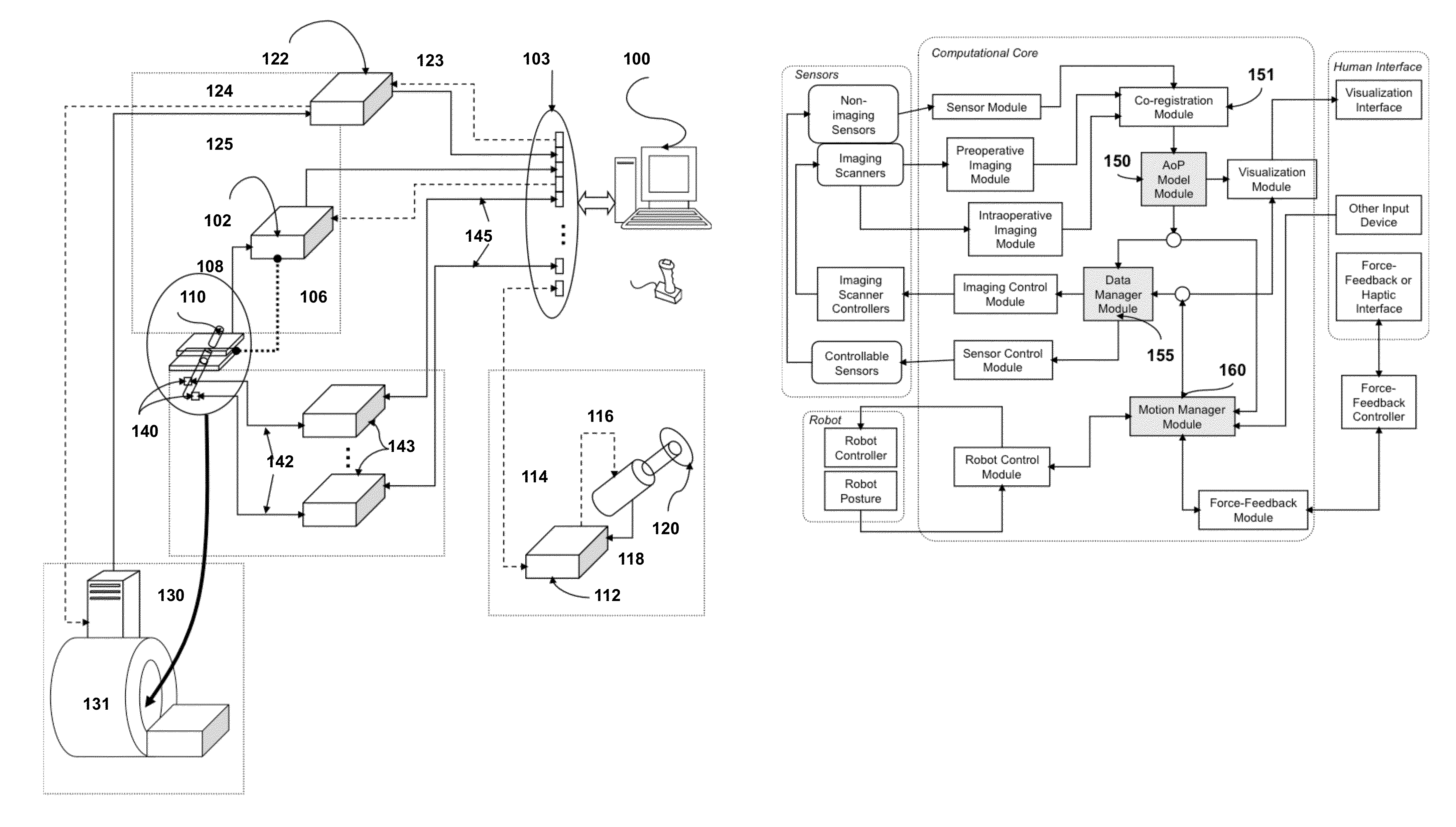
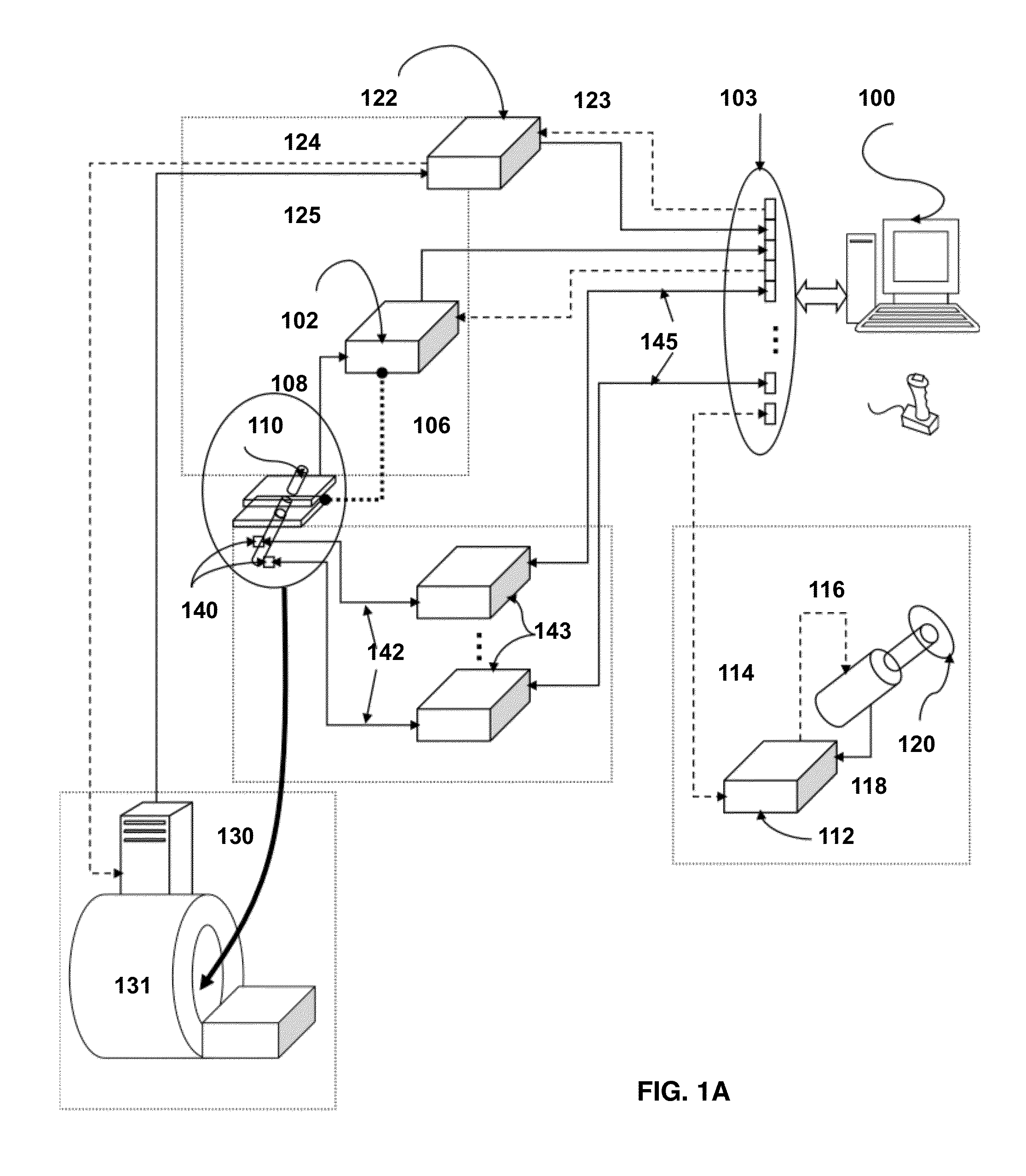
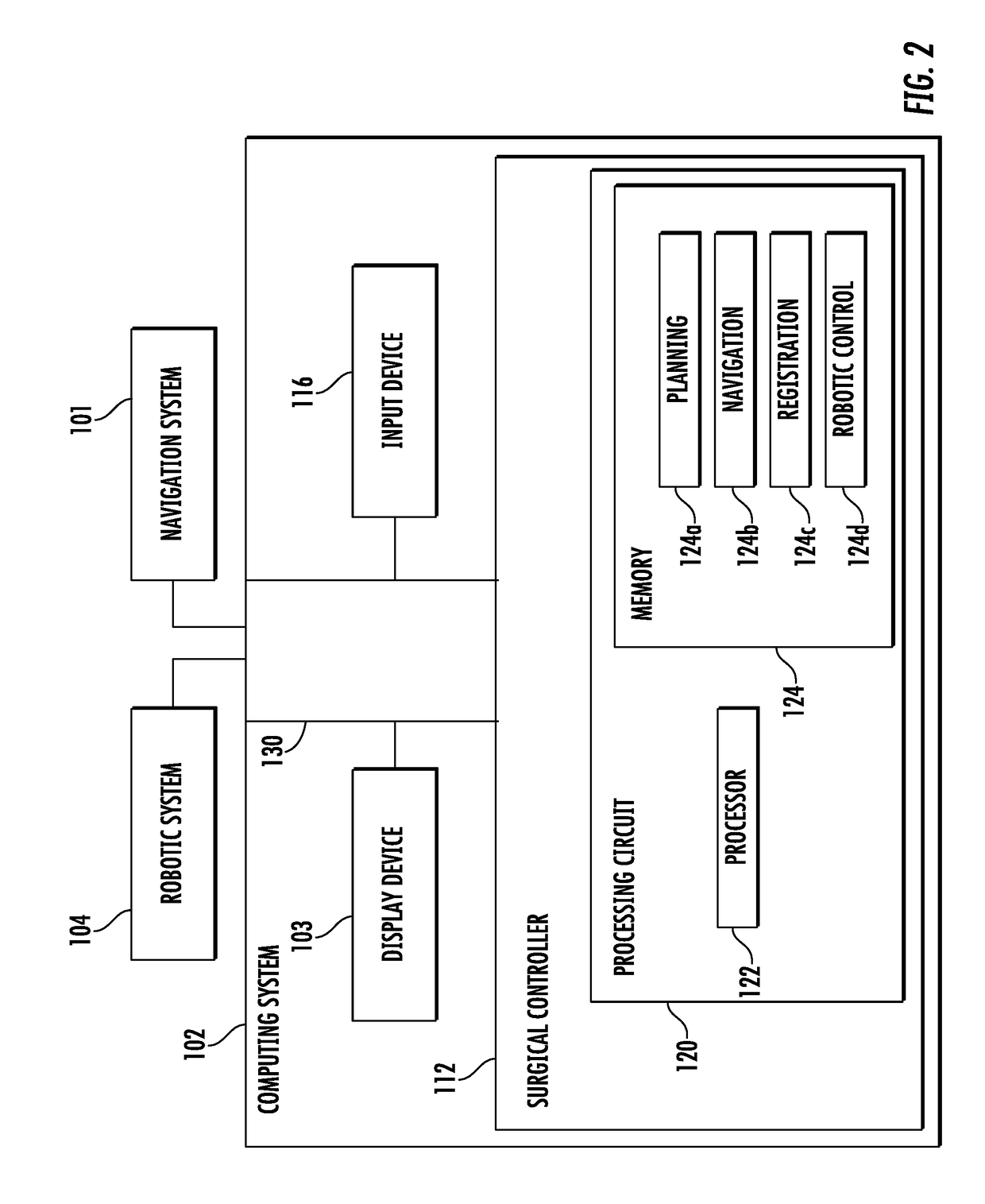
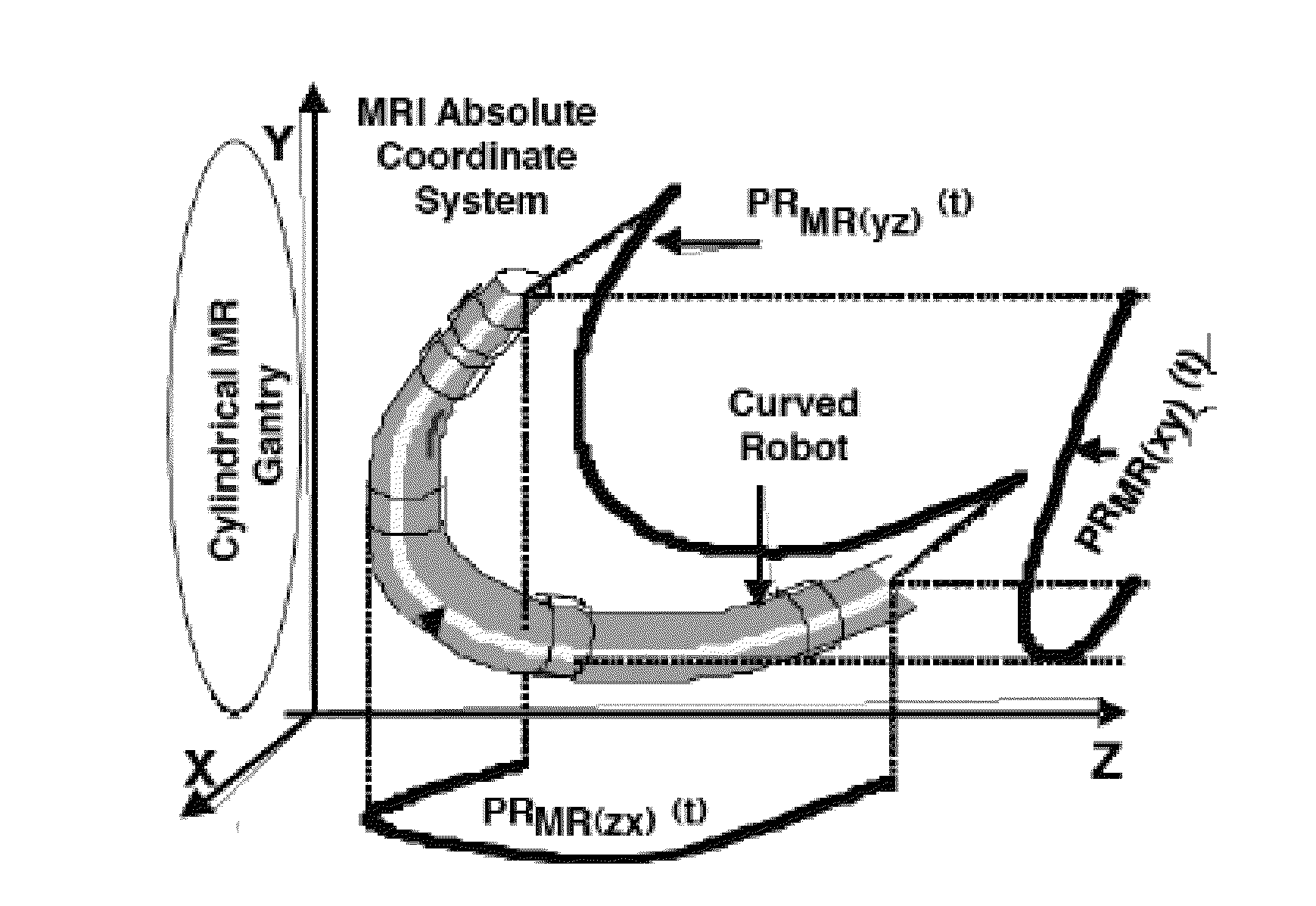
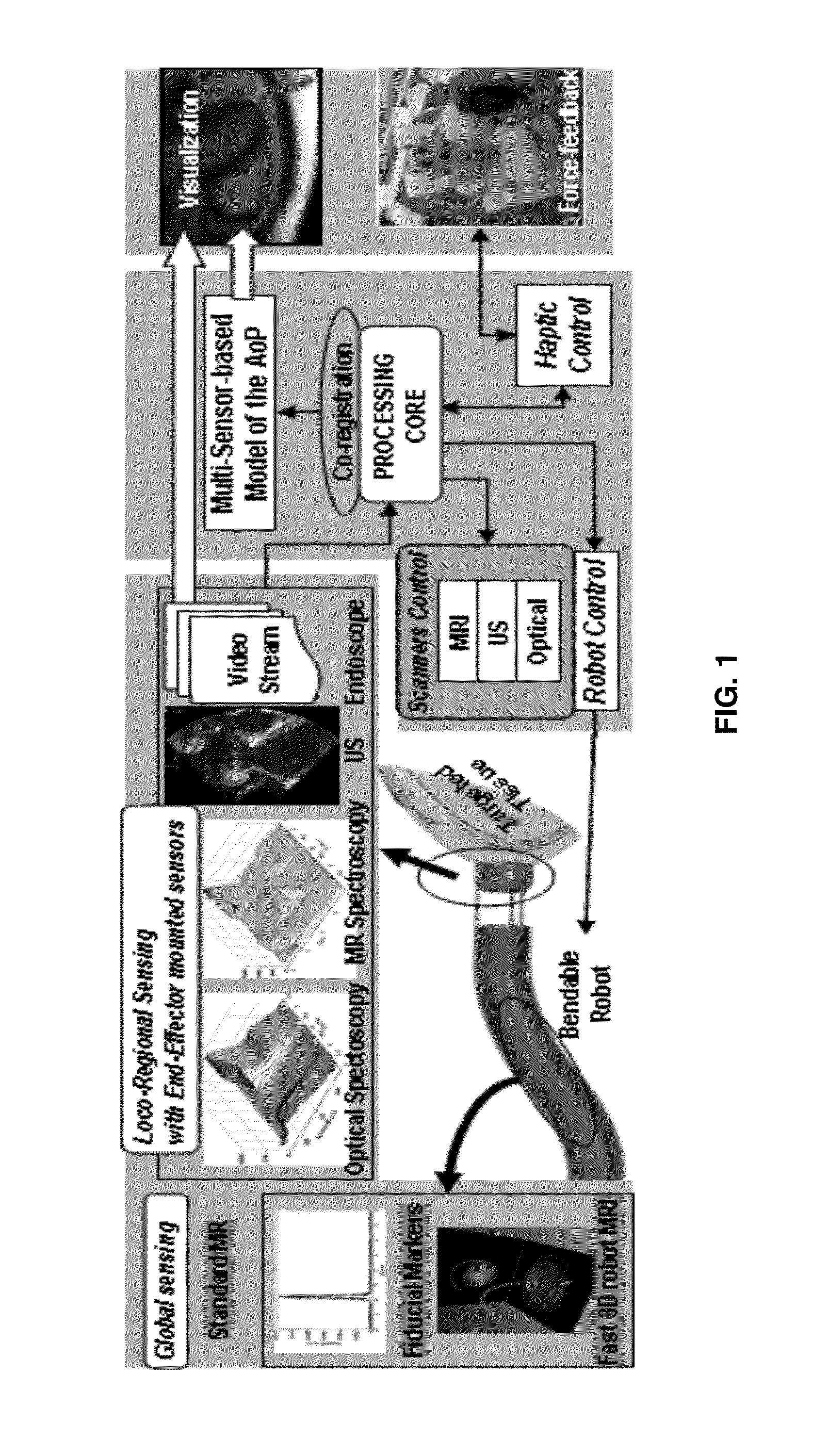
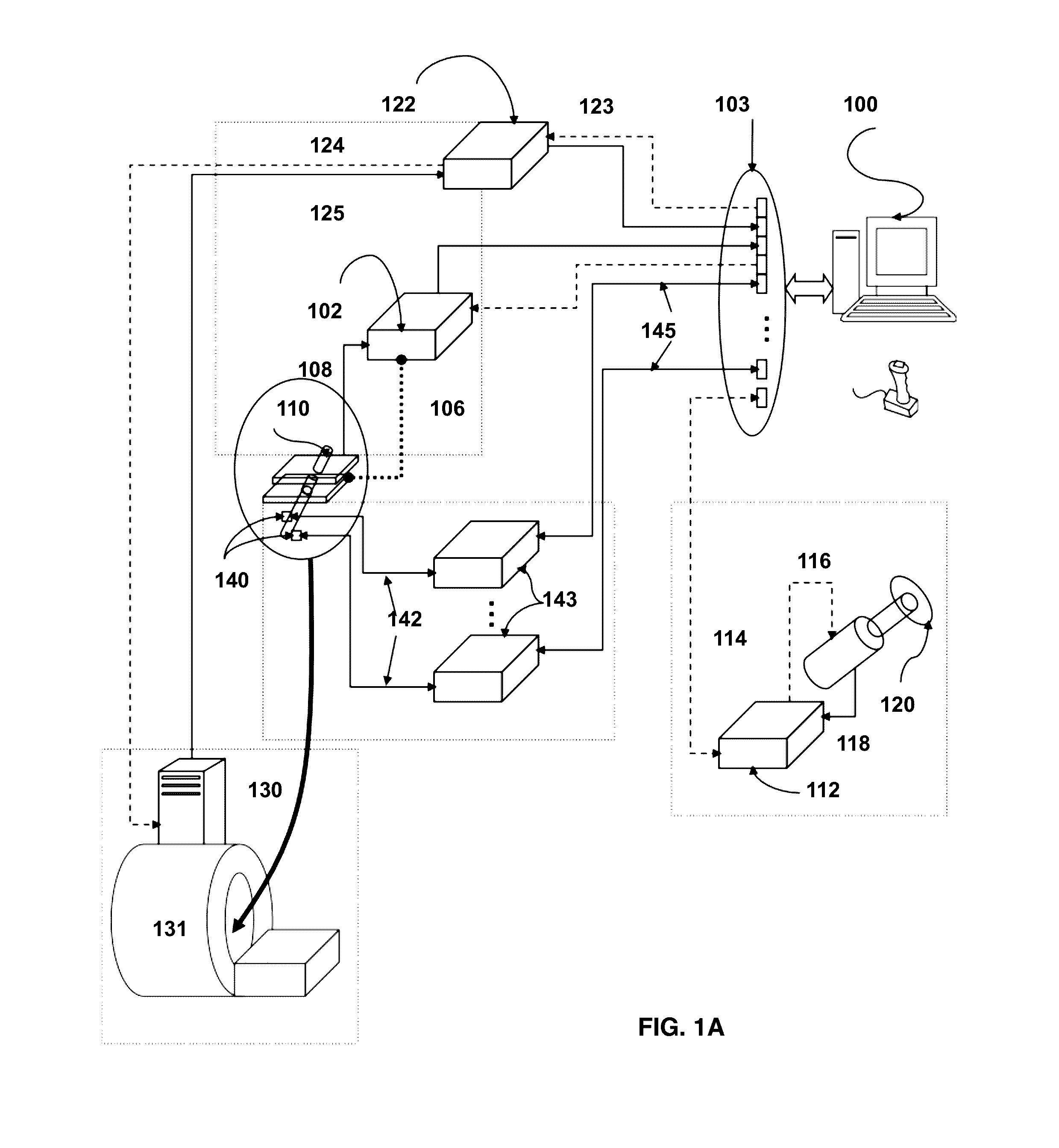
Provided herein are robotic systems, for example, MRI guided robots, for image-guided robot-assisted surgical procedures and methods for using the same to perform such surgical procedures on a patient. The robotic systems comprise a robotic manipulator device or global positioner, means for actuating the robotic manipulator or global positioner that is mechanically linked thereto and a computer having a memory, a processor and at least one network connection in electronic communication with the robotic system. The actuating means comprises at least one transmission line having a flexible component comprising a displaceable medium, a rigid component comprising rigid pistons or a combination through which actuation is transmitted to the robotic manipulator or global positioner. The computer tangibly stores in memory software modules comprising processor-executable instructions to provide interfaces between the robotic system, an imaging system and an operator and to control operation thereof.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Apparatus and method for a global coordinate system for use in robotic surgery
ActiveUS10383765B2Facilitating robotic surgeryDiagnostics using lightEye surgeryKinematicsEngineering
An apparatus and method for establishing a global coordinate system to facilitate robotic assisted surgery. The coordinate system may be established using a combination of the robotic data, i.e., kinematics, and optical coherence tomographic images generated by an overhead optical assembly and a tool-based sensor. Using these components, the system may generate a computer-registered three-dimensional model of the patient's eye. In some embodiments, the system may also generate a virtual boundary within the coordinate system to prevent inadvertent injury to the patient.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
System and method for a surveillance marker in robotic-assisted surgery
InactiveUS20170172669A1Surgical navigation systemsDiagnostic markersEngineeringRobotic assisted surgery
Devices, systems, and methods for providing a surveillance marker configured to detecting movement of a dynamic reference base attached to a patient a robot-assisted surgical procedure are provided. The surveillance marker and the dynamic reference base are connected to a bony structure independent of each other.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
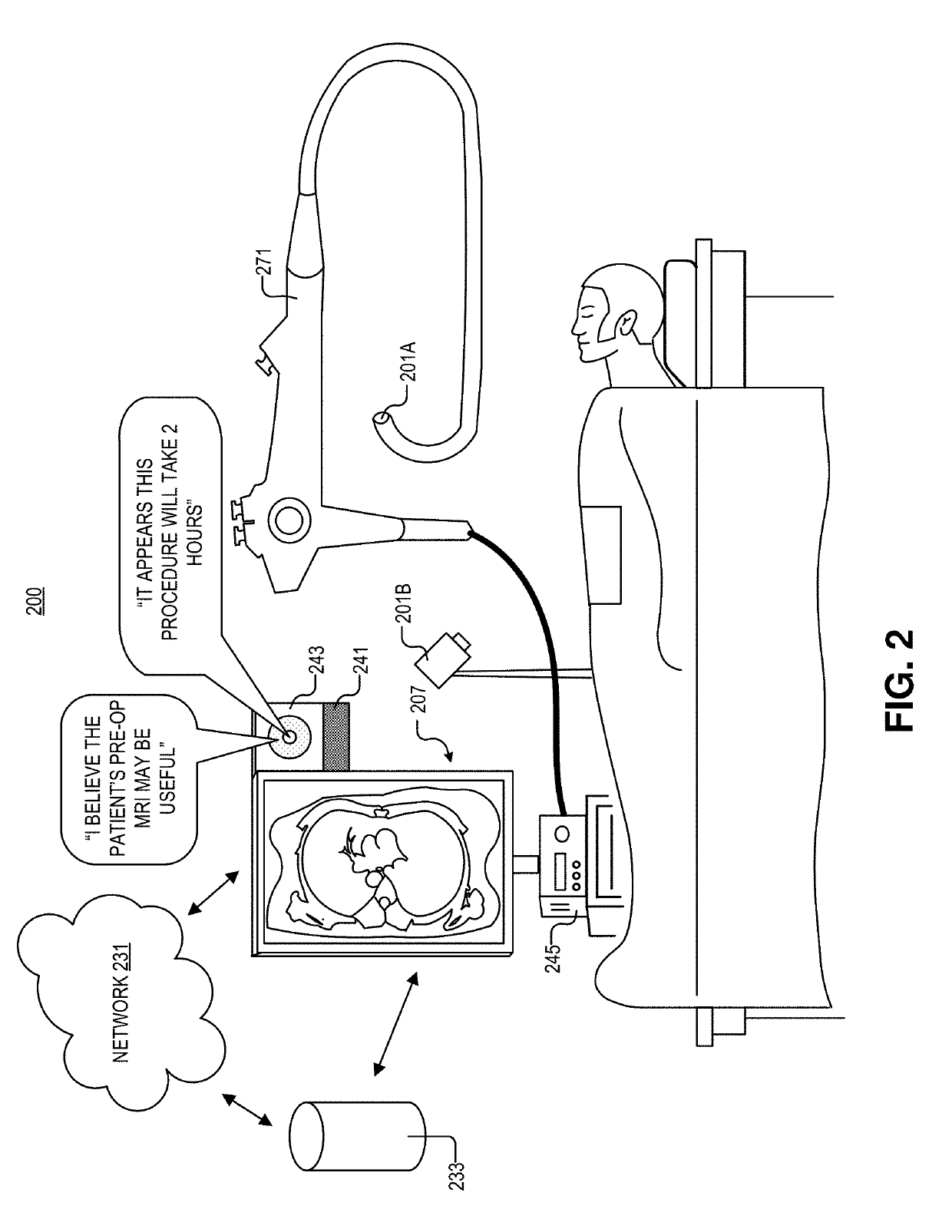
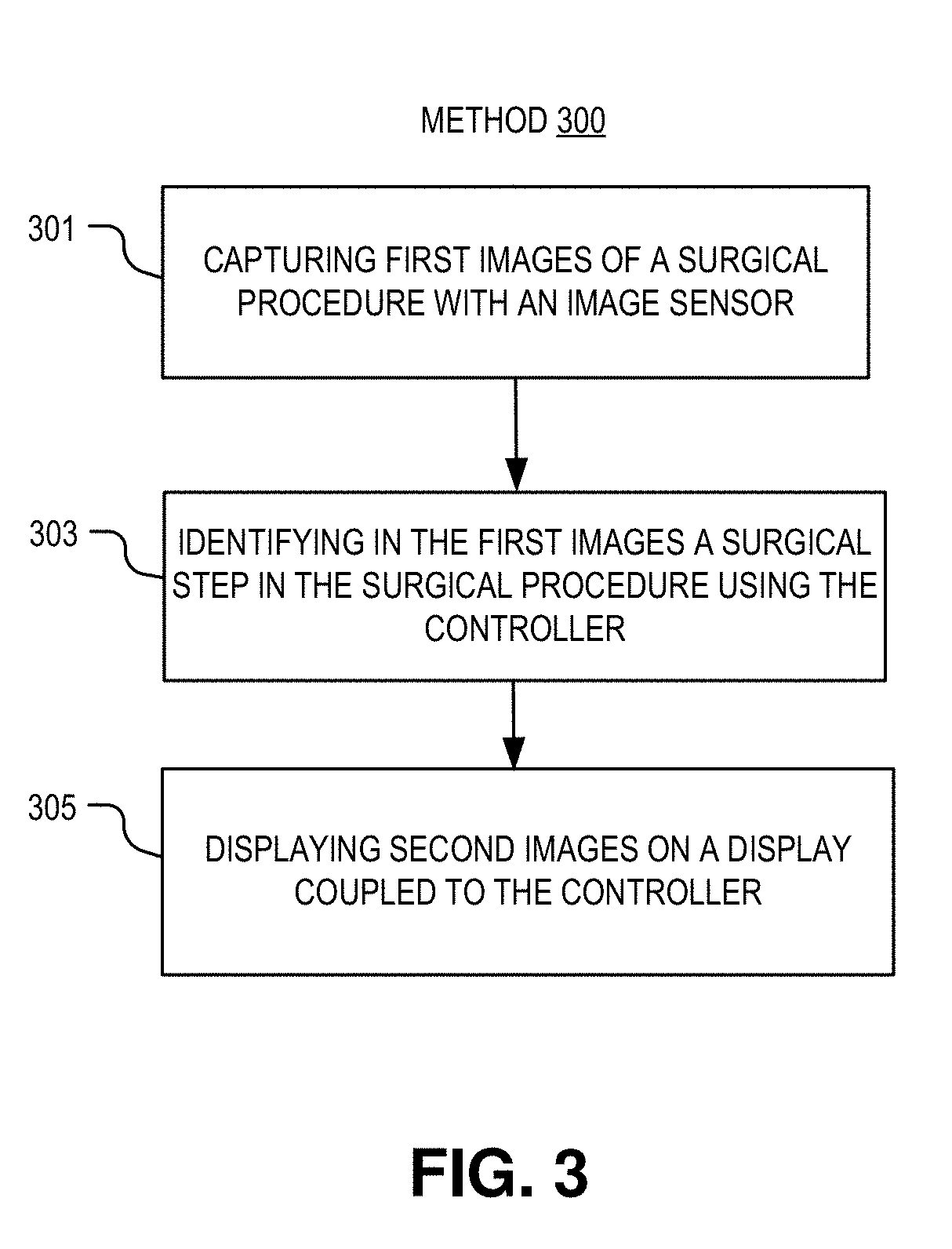
Step-based system for providing surgical intraoperative cues
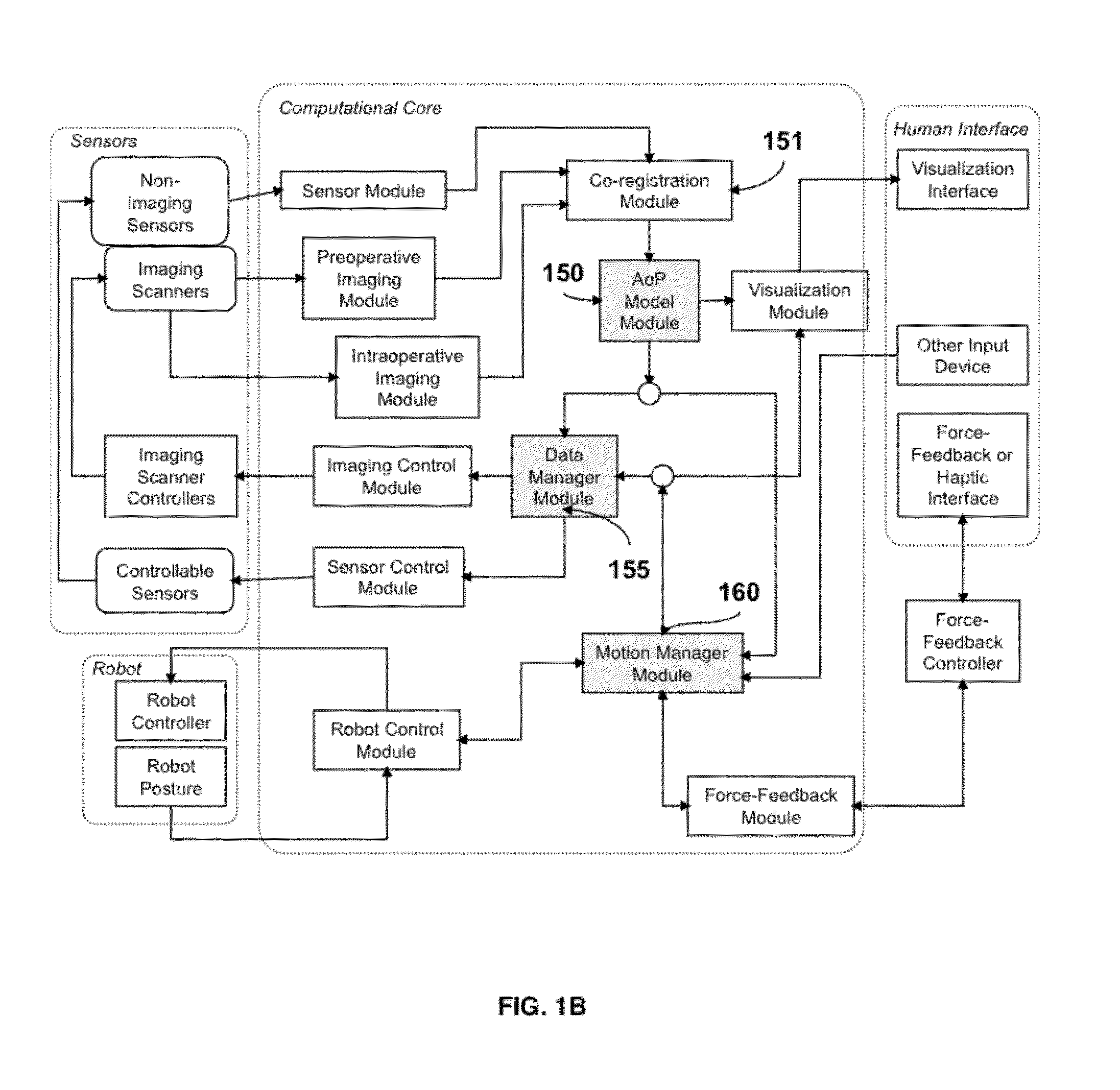
A system for robot-assisted surgery includes an image sensor and a display. The system further includes a controller coupled to the image sensor and the display, where the controller includes logic that when executed by the controller causes the system to perform operations. The operations may include acquiring first images of a surgical procedure with the image sensor, and analyzing the first images with the controller to identify a surgical step in the surgical procedure. The operations may further include displaying second images on the display in response to identifying the surgical step; the second images may include at least one of a diagram of human anatomy, a preoperative image, an intraoperative image, or an annotated image of one of the first images.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
Systems and methods for a robotic-assisted revision procedure
ActiveUS20180014891A1Accurate guideMinimize overcuttingComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhysical spaceRobotic assisted surgery
A method for performing a revision surgery using a robotic-assisted surgery system includes determining information related to an interface area between an implant component and a bone, and generating a planned virtual boundary associated with a portion of the interface area to be removed in a representation of the implant and the bone, based at least in part on the information related to the interface area. The method further includes tracking movement in the physical space of a cutting tool such that movement of the cutting tool is correlated with movement of a virtual tool, and providing a constraint on the cutting tool while the cutting tool removes the portion of the interface area. The constraint is based on a relationship between the virtual tool and the planned virtual boundary. The portion of the interface area is removed to remove the implant component from the bone.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Robotic Device and System Software, Hardware and Methods of Use for Image-Guided and Robot-Assisted Surgery
InactiveUS20140058407A1Fast data collectionDiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
Provided herein are systems, modules and methods of using the same for in-situ real time imaging guidance of a robot during a surgical procedure. The systems comprise a plurality of modules that intraoperatively link an imaging modality, particularly a magnetic resonance imaging modality, a medical robot and an operator thereof via a plurality of interfaces. The modules are configured to operate in at least one computer having a memory, a processor and a network connection to enable instructions to generally control the imaging modality, track the robot, track a tissue of interest in an area of procedure, process data acquire from imaging modality and the robot and visualize the area and robot. Also provided are non-transitory computer-readable data storage medium storing computer-executable instructions comprising the modules and a computer program produce tangibly embodied in the storage medium.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
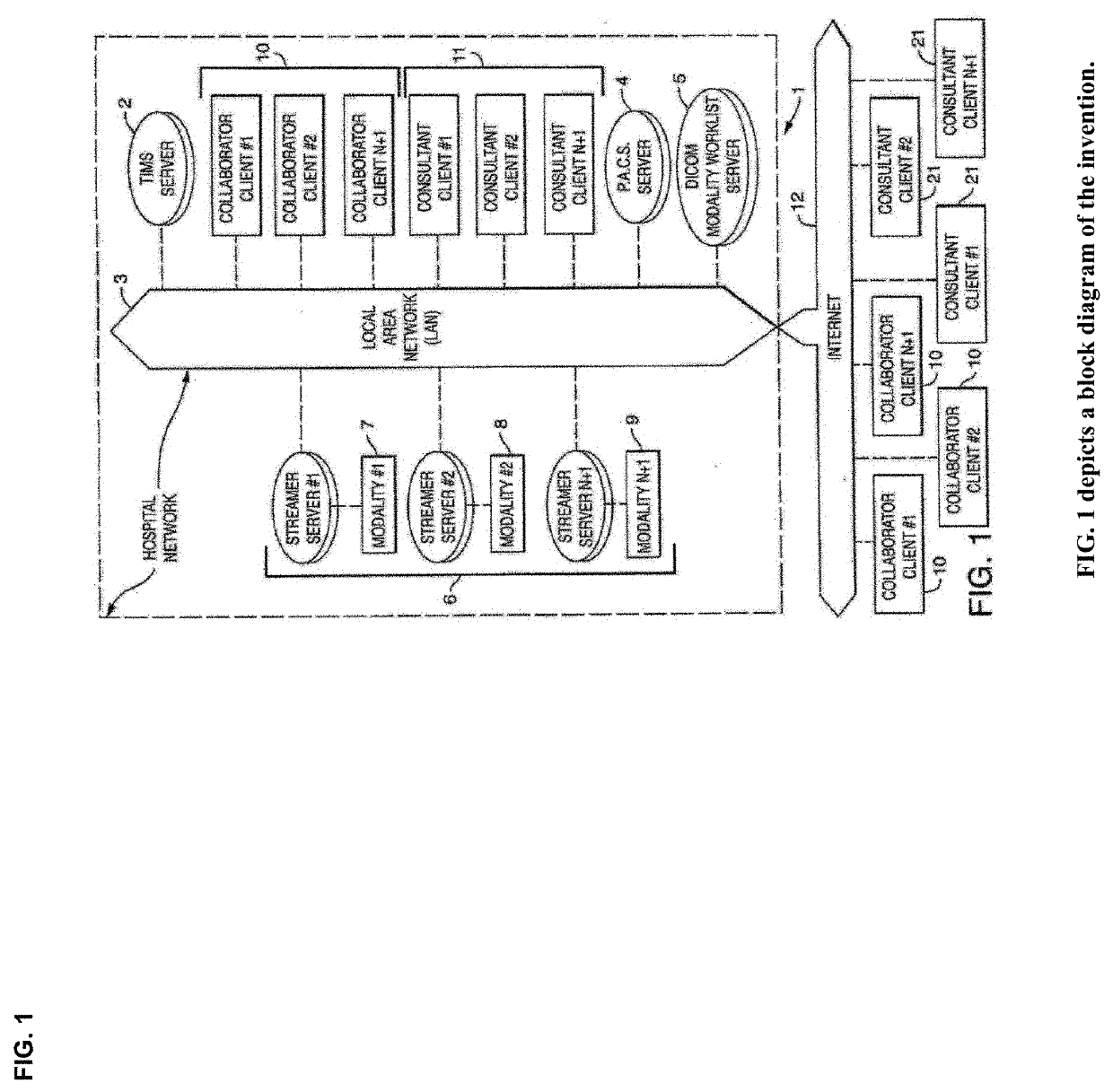
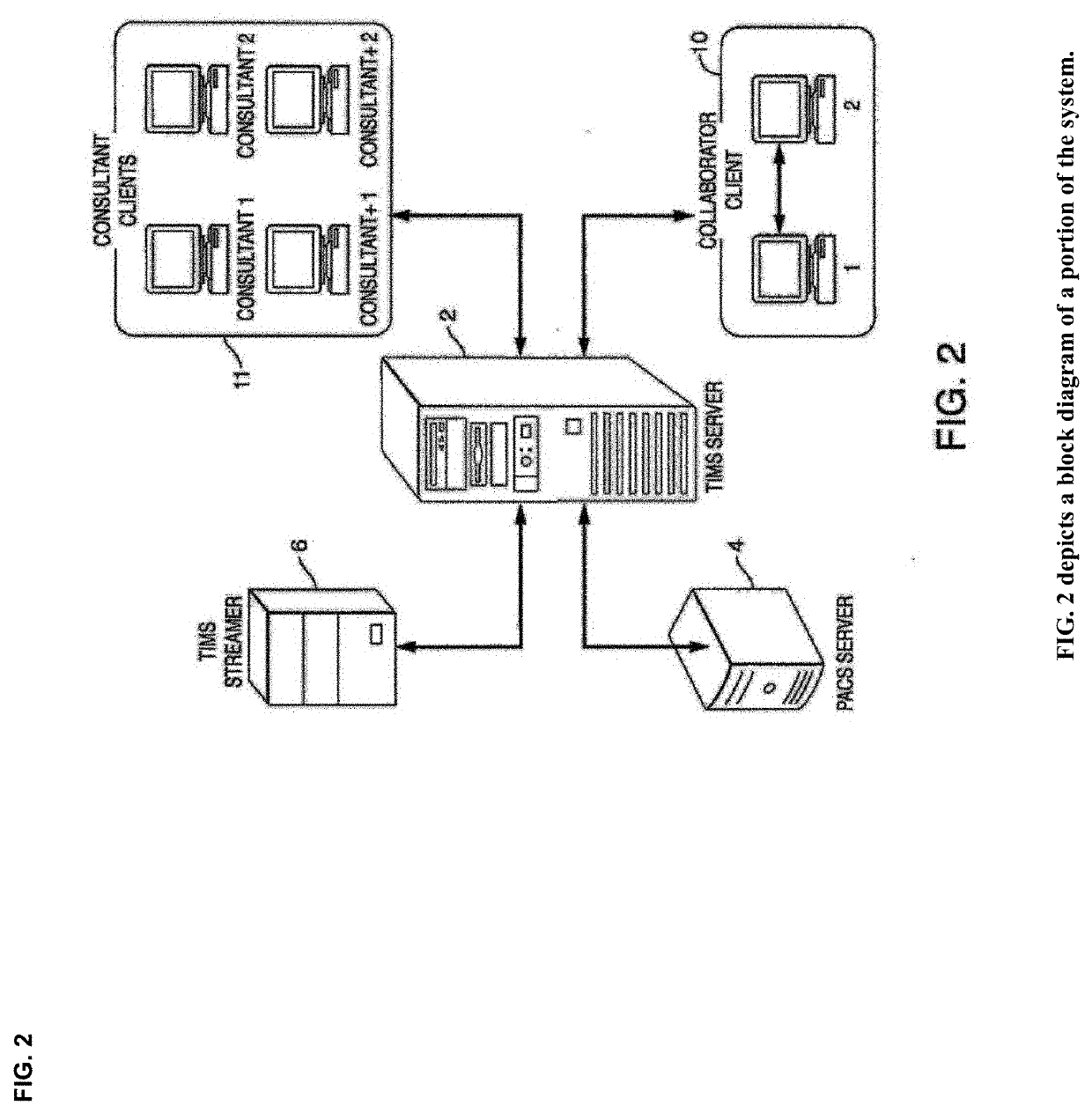
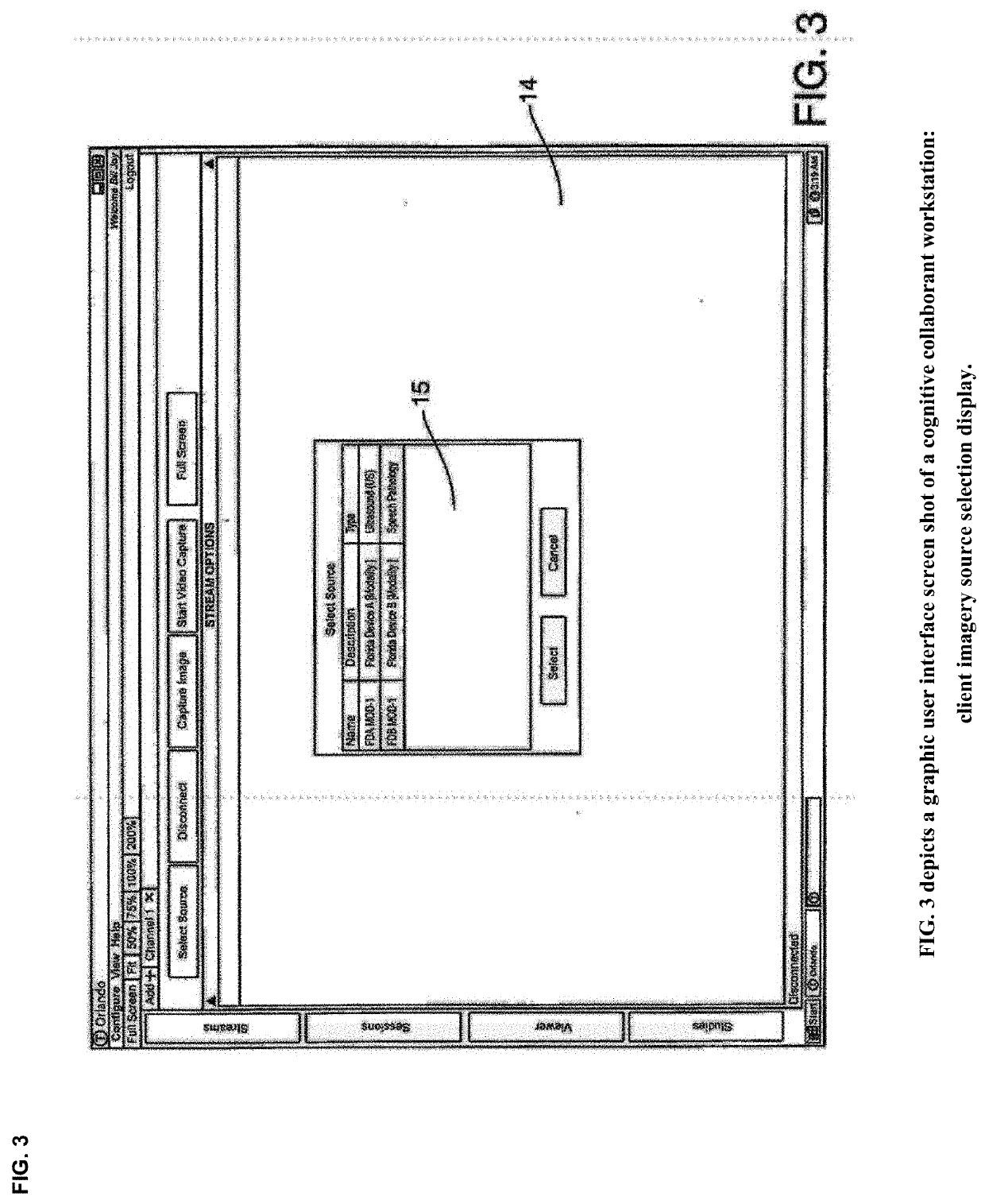
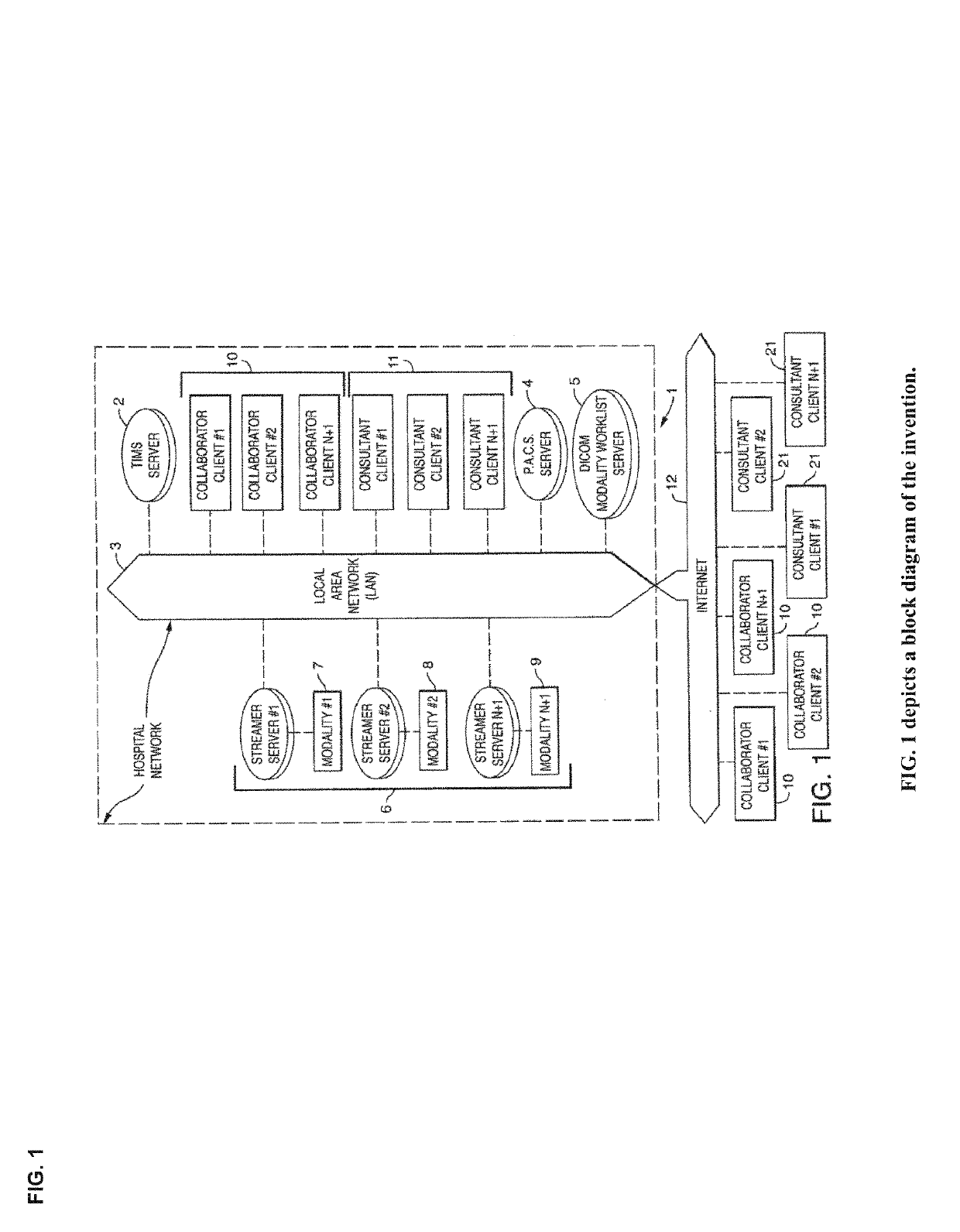
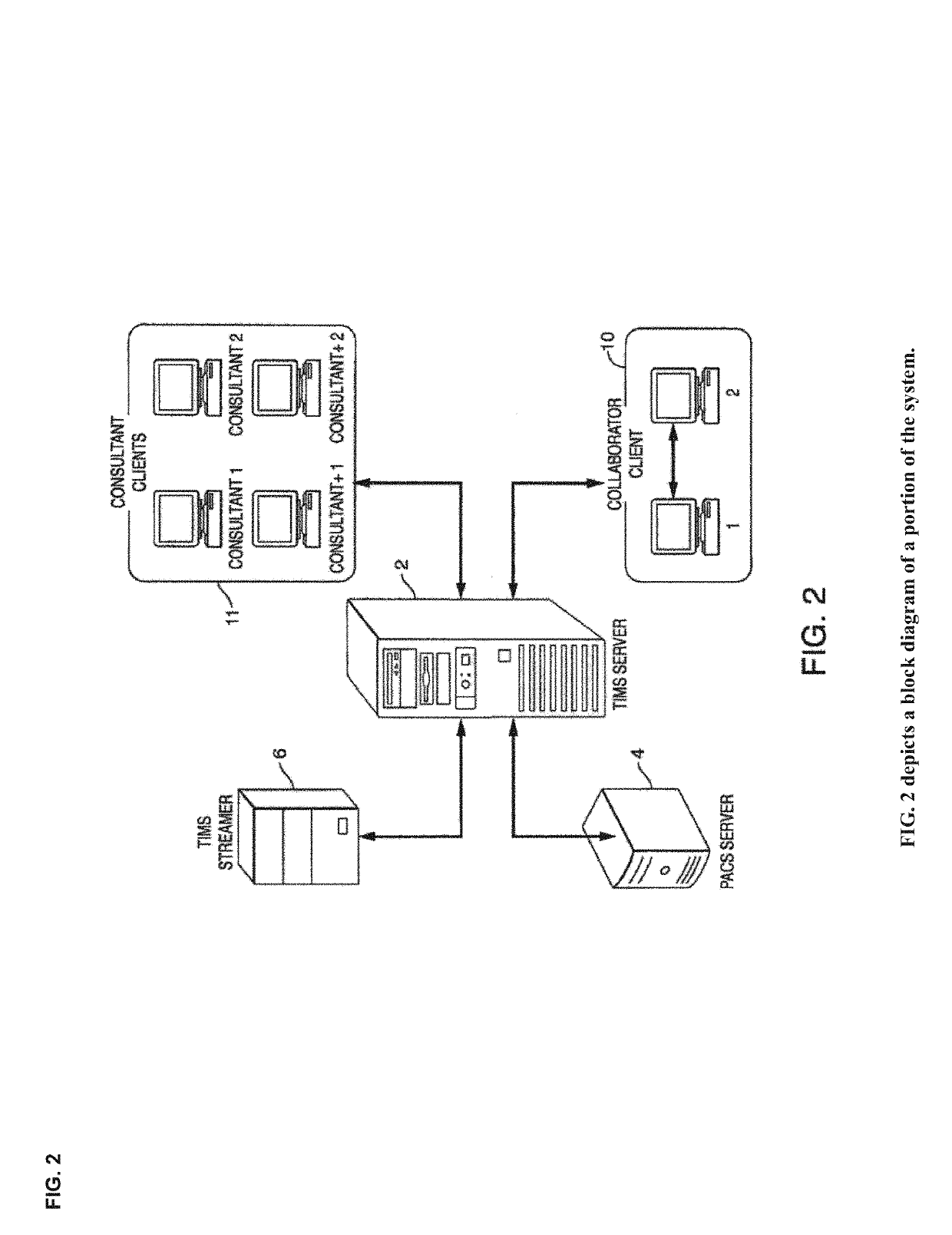
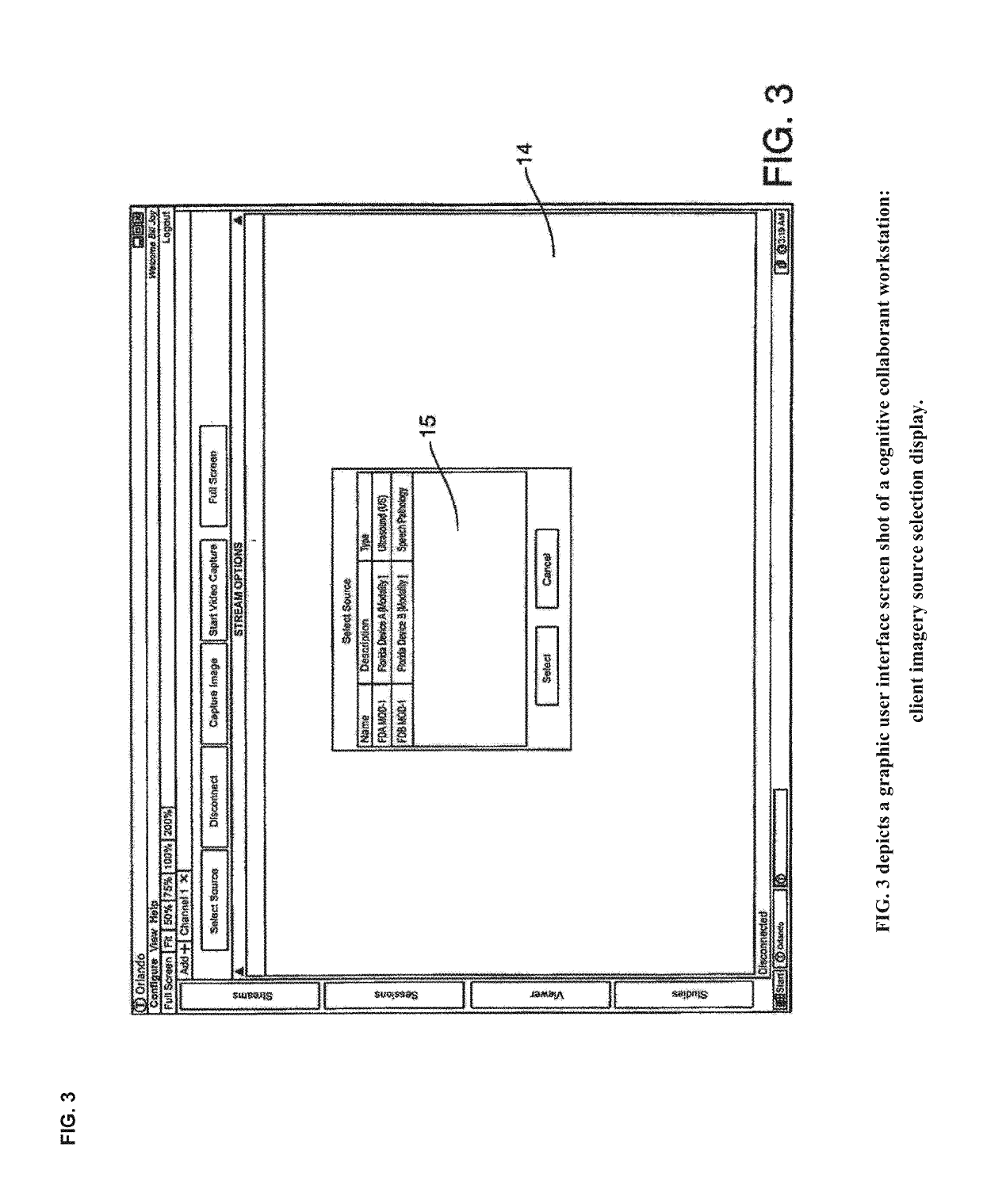
Cognitive Collaboration with Neurosynaptic Imaging Networks, Augmented Medical Intelligence and Cybernetic Workflow Streams
ActiveUS20190355483A1Improve business performanceReduces image latencyTelevision conference systemsTwo-way working systemsDiseaseIntervention measures
The invention integrates emerging applications, tools and techniques for machine learning in medicine with videoconference networking technology in novel business methods that support rapid adaptive learning for medical minds and machines. These methods can leverage domain knowledge and clinical expertise with cognitive collaboration, augmented medical intelligence and cybernetic workflow streams for learning health care systems. The invention enables multimodal cognitive communications, collaboration, consultation and instruction between and among heterogeneous networked teams of persons, machines, devices, neural networks, robots and algorithms. It provides for both synchronous and asynchronous cognitive collaboration with multichannel, multiplexed imagery data streams during various stages of medical disease and injury management—detection, diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, measurement, monitoring and reporting, as well as workflow optimization with operational analytics for outcomes, performance, results, resource utilization, resource consumption and costs. The invention enables cognitive curation, annotation and tagging, as well as encapsulation, saving and sharing of collaborated imagery data streams as packetized medical intelligence. It can augment packetized medical intelligence through recursive cognitive enrichment, including multimodal annotation and [semantic] metadata tagging with resources consumed and outcomes delivered. Augmented medical intelligence can be saved and stored in multiple formats, as well as retrieved from standards-based repositories. The invention can incorporate and combine various machine learning techniques [e.g., deep, reinforcement and transfer learning, convolutional and recurrent neural networks, LSTM and NLP] to assist in curating, annotating and tagging diagnostic, procedural and evidentiary medical imaging. It also supports real-time, intraoperative imaging analytics for robotic-assisted surgery, as well as other imagery guided interventions. The invention facilitates collaborative precision medicine, and other clinical initiatives designed to reduce the cost of care, with precision diagnosis and precision targeted treatment. Cybernetic workflow streams—cognitive communications, collaboration, consultation and instruction with augmented medical intelligence—enable care delivery teams of medical minds and machines to ‘deliver the right care, for the right patient, at the right time, in the right place’—and deliver that care faster, smarter, safer, more precisely, cheaper and better.
Owner:SMURRO JAMES PAUL
System and method for a surveillance marker in robotic-assisted surgery
PendingUS20190269467A1Surgical navigation systemsDiagnostic markersComputer scienceRobotic assisted surgery
Devices, systems, and methods for providing a surveillance marker configured to detecting movement of a dynamic reference base attached to a patient a robot-assisted surgical procedure are provided. The surveillance marker and the dynamic reference base are connected to a bony structure independent of each other.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Robotic device and systems for image-guided and robot-assisted surgery
Provided herein are robotic systems, for example, MRI guided robots, for image-guided robot-assisted surgical procedures and methods for using the same to perform such surgical procedures on a patient. The robotic systems comprise a robotic manipulator device or global positioner, means for actuating the robotic manipulator or global positioner that is mechanically linked thereto and a computer having a memory, a processor and at least one network connection in electronic communication with the robotic system. The actuating means comprises at least one transmission line having a flexible component comprising a displaceable medium, a rigid component comprising rigid pistons or a combination through which actuation is transmitted to the robotic manipulator or global positioner. The computer tangibly stores in memory software modules comprising processor-executable instructions to provide interfaces between the robotic system, an imaging system and an operator and to control operation thereof.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Systems and methods for a robotic-assisted revision procedure
ActiveUS10716630B2Dissect the bone implantAccurate guideComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhysical spaceEngineering
A method for performing a revision surgery using a robotic-assisted surgery system includes determining information related to an interface area between an implant component and a bone, and generating a planned virtual boundary associated with a portion of the interface area to be removed in a representation of the implant and the bone, based at least in part on the information related to the interface area. The method further includes tracking movement in the physical space of a cutting tool such that movement of the cutting tool is correlated with movement of a virtual tool, and providing a constraint on the cutting tool while the cutting tool removes the portion of the interface area. The constraint is based on a relationship between the virtual tool and the planned virtual boundary. The portion of the interface area is removed to remove the implant component from the bone.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
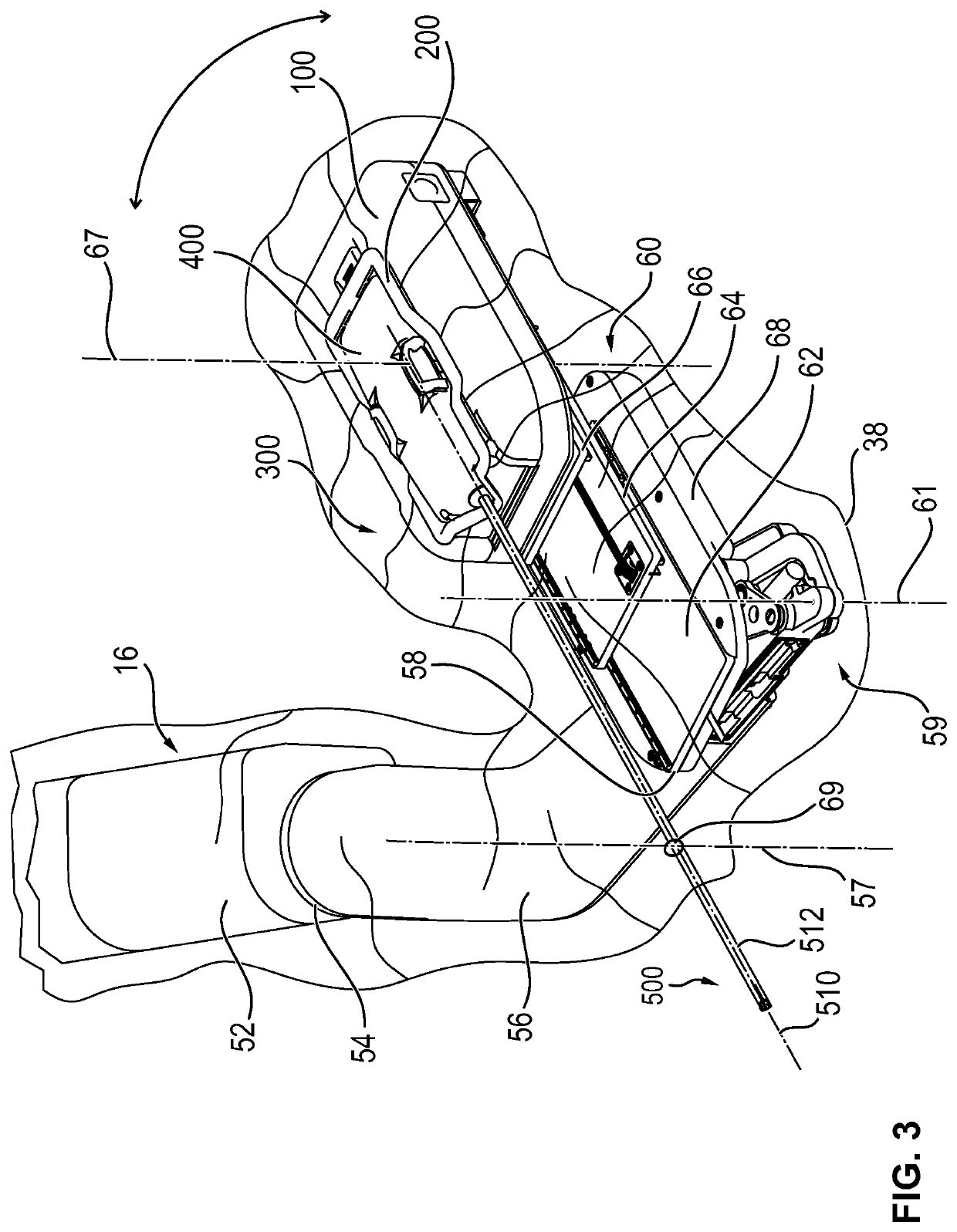
Device for robot-assisted surgery
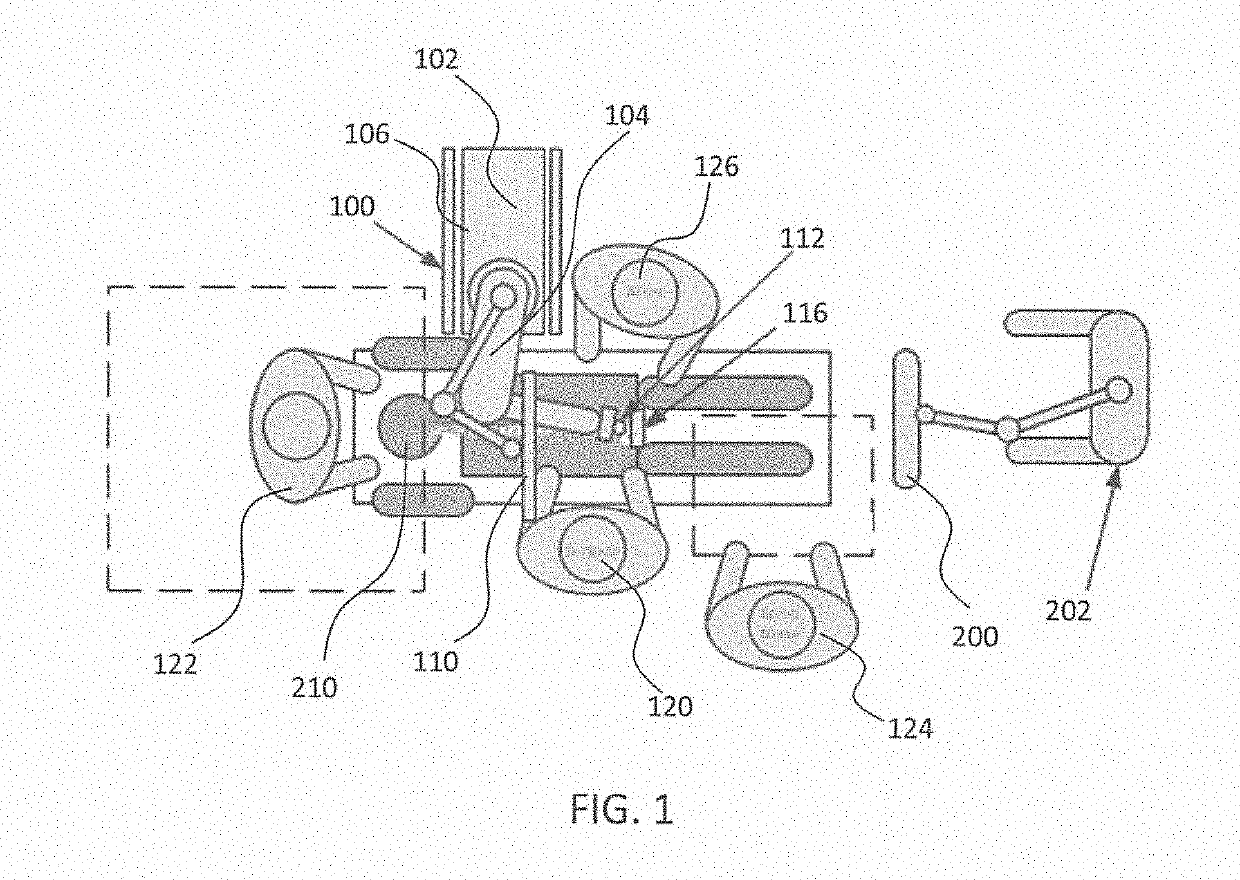
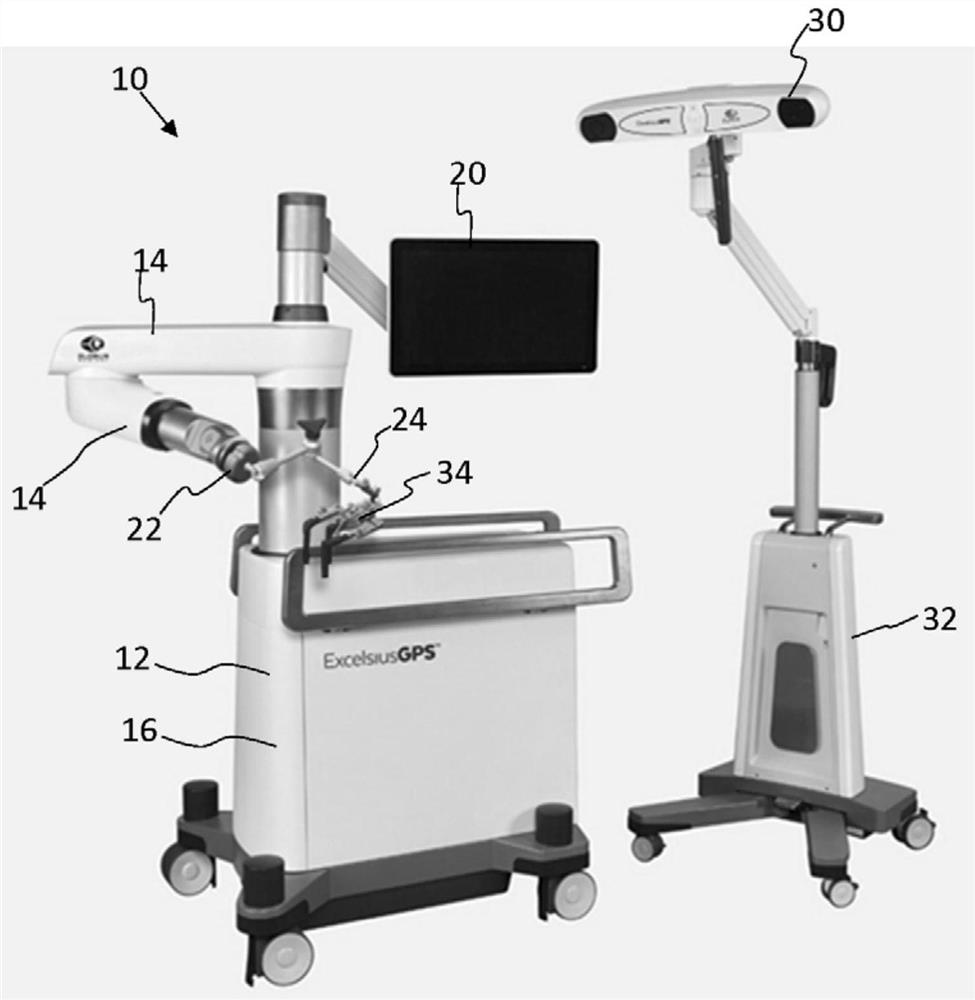
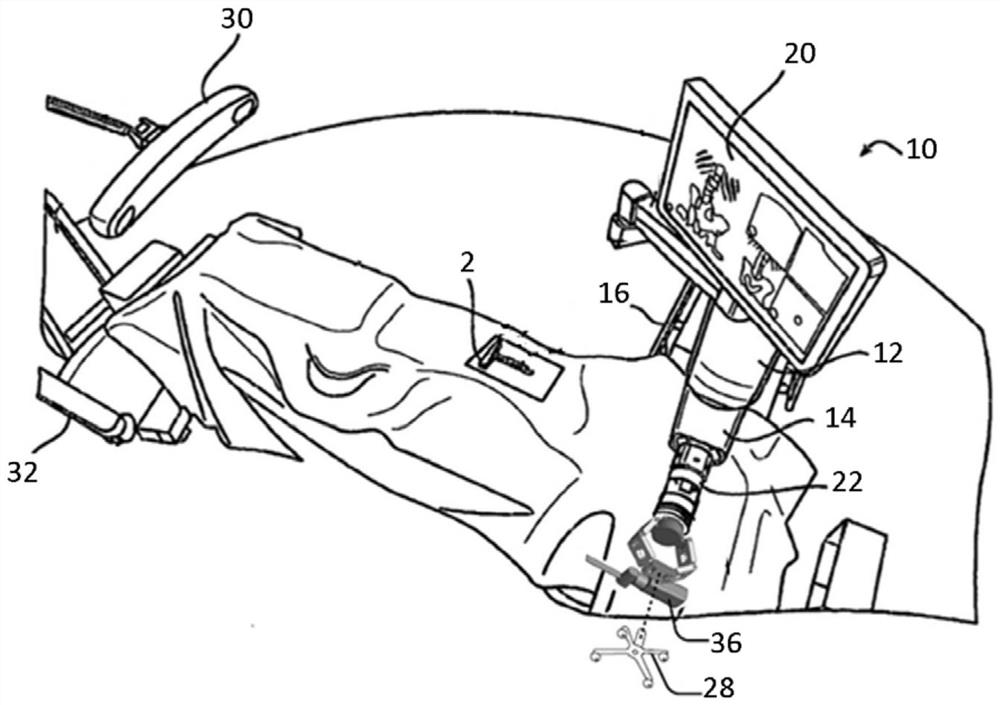
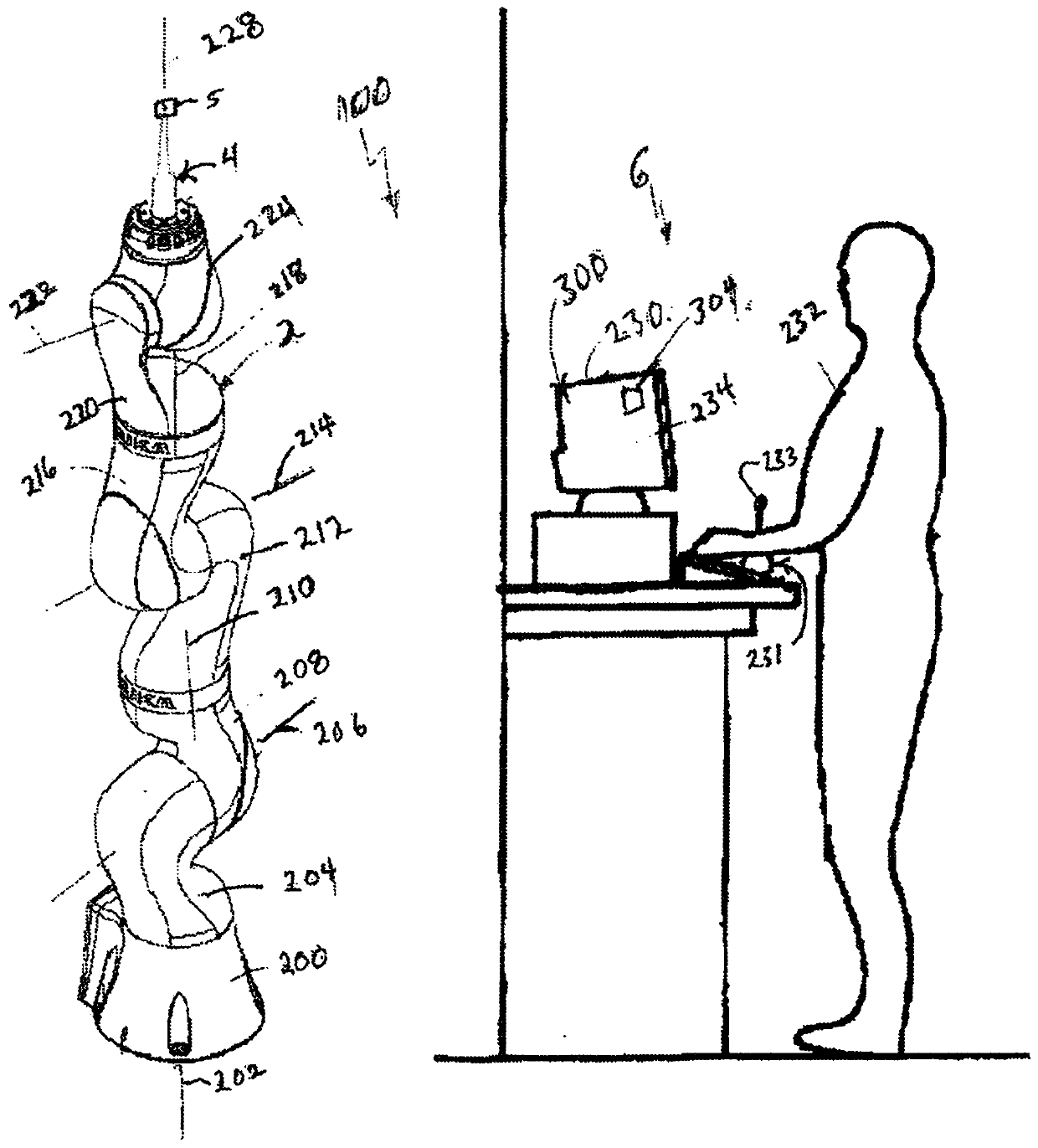
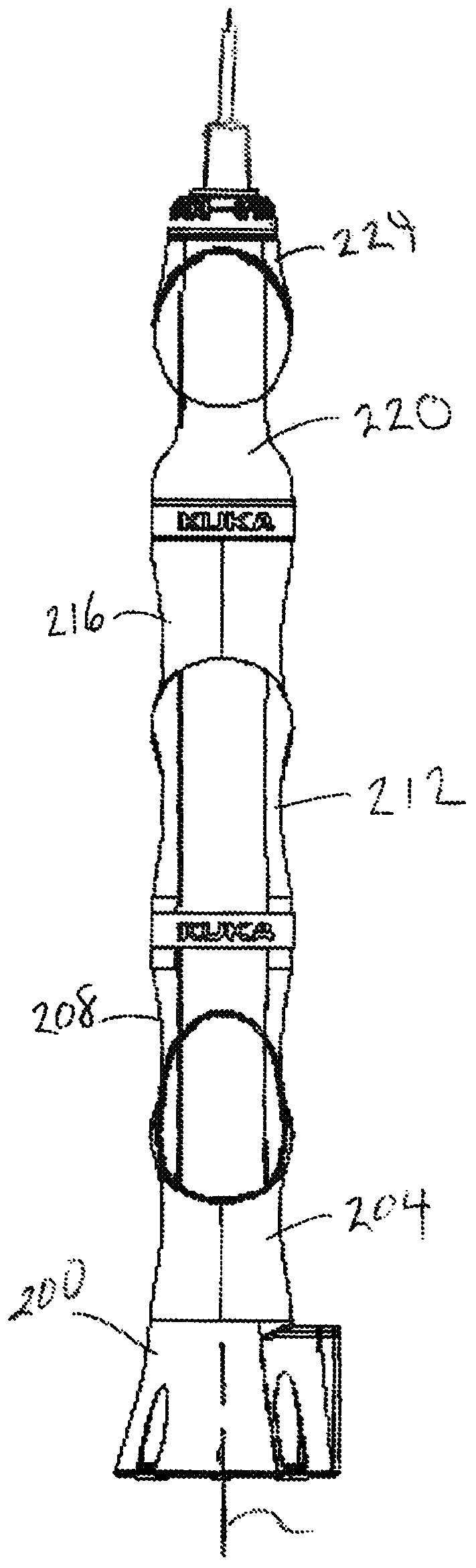
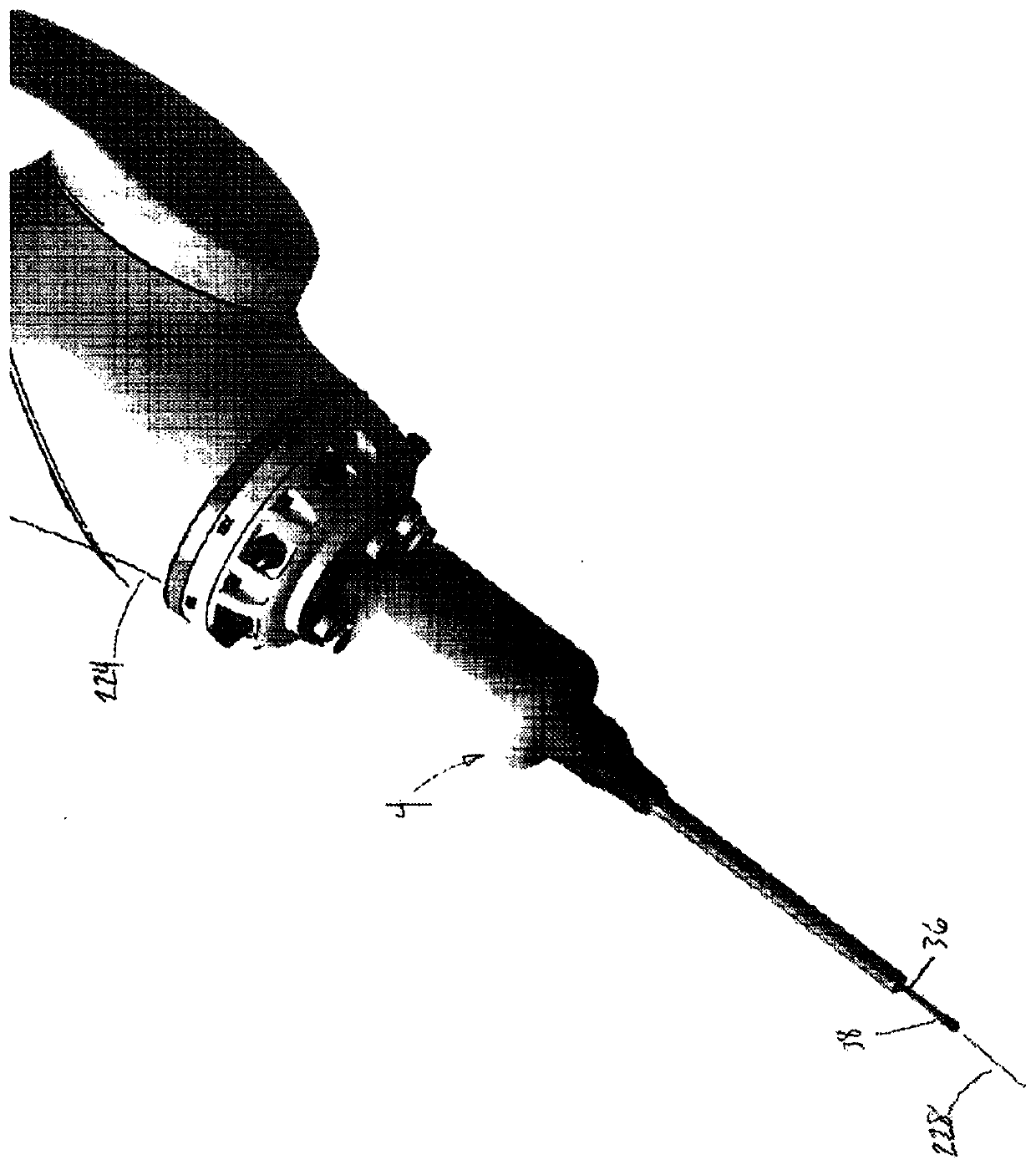
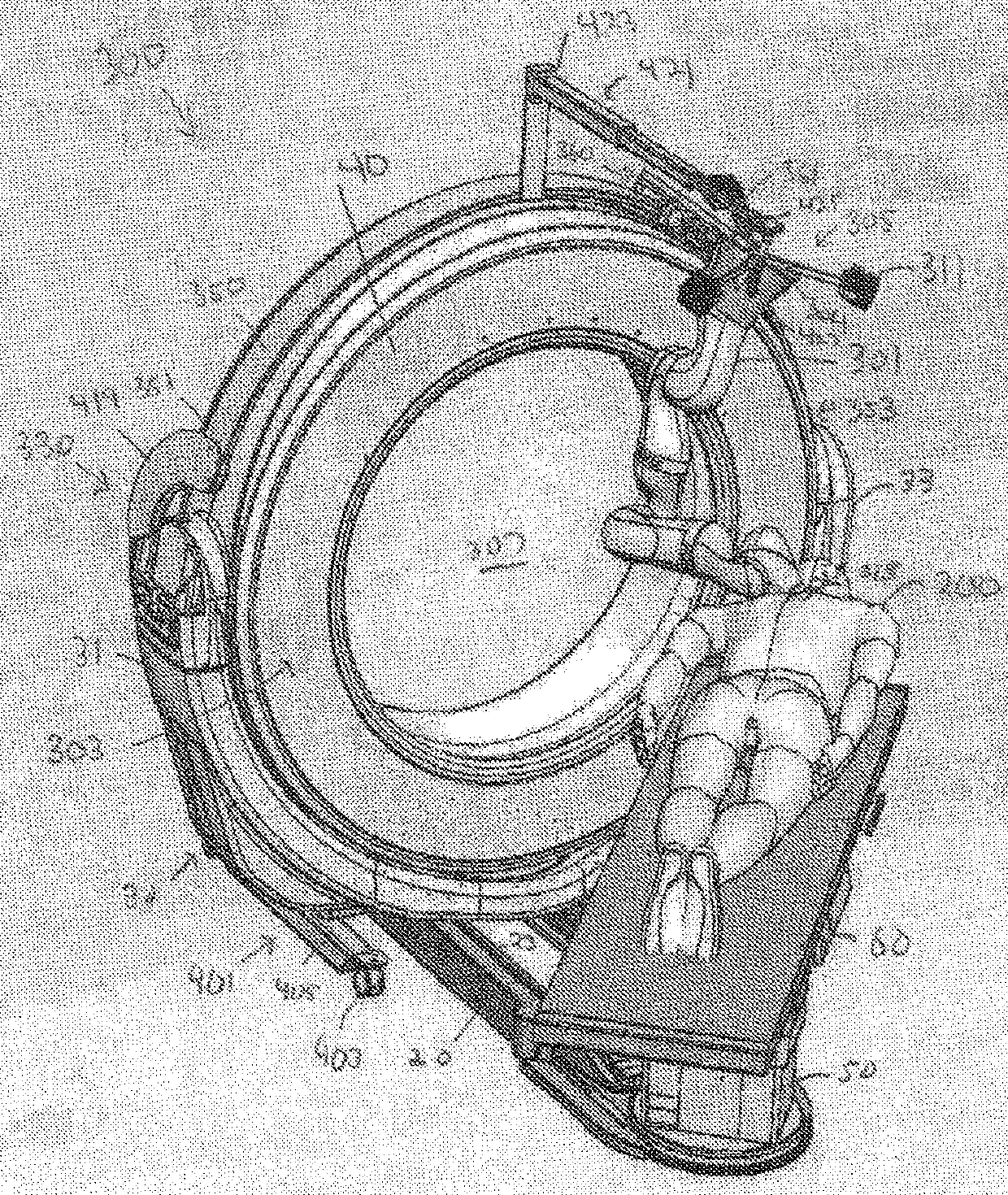
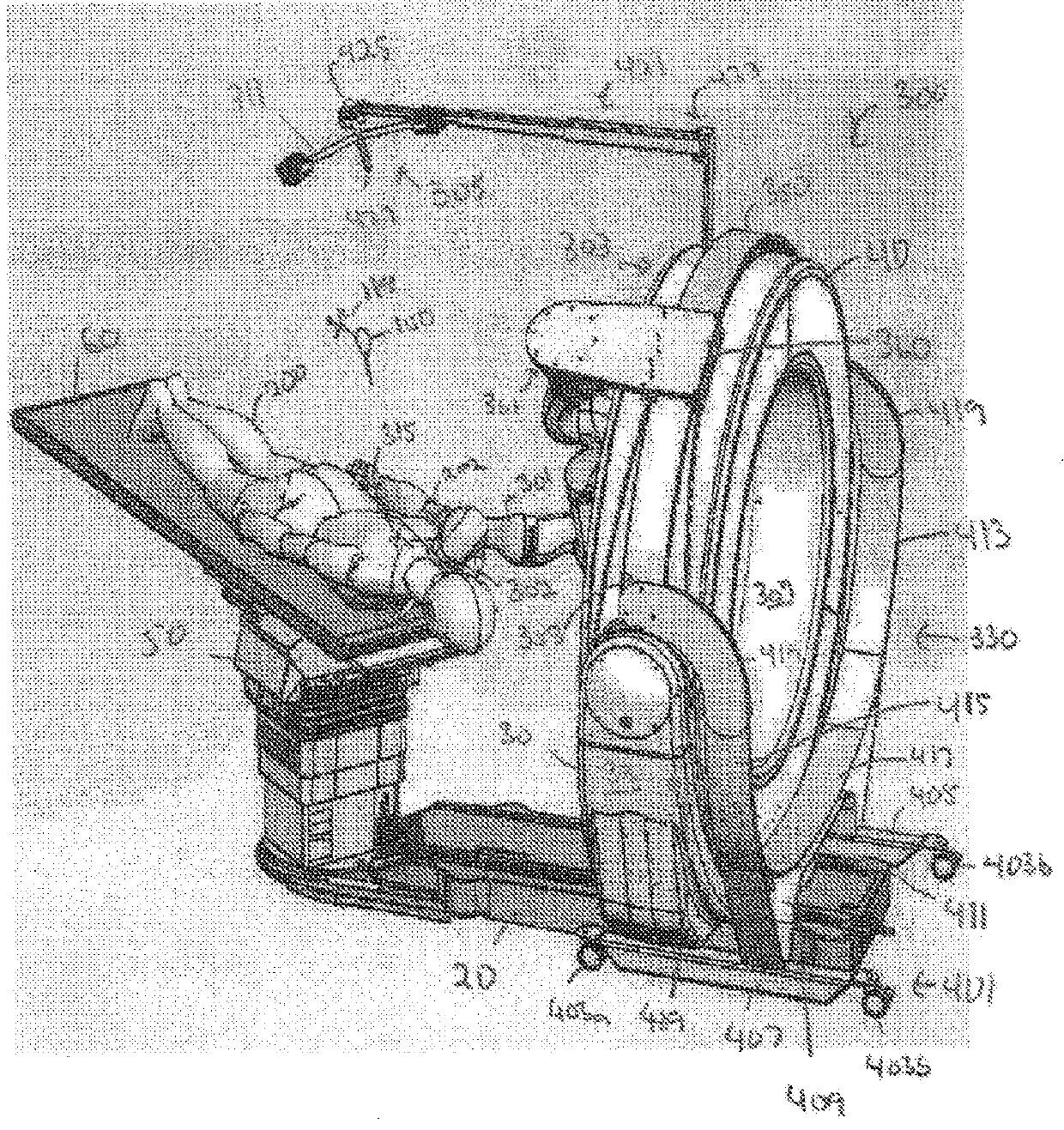
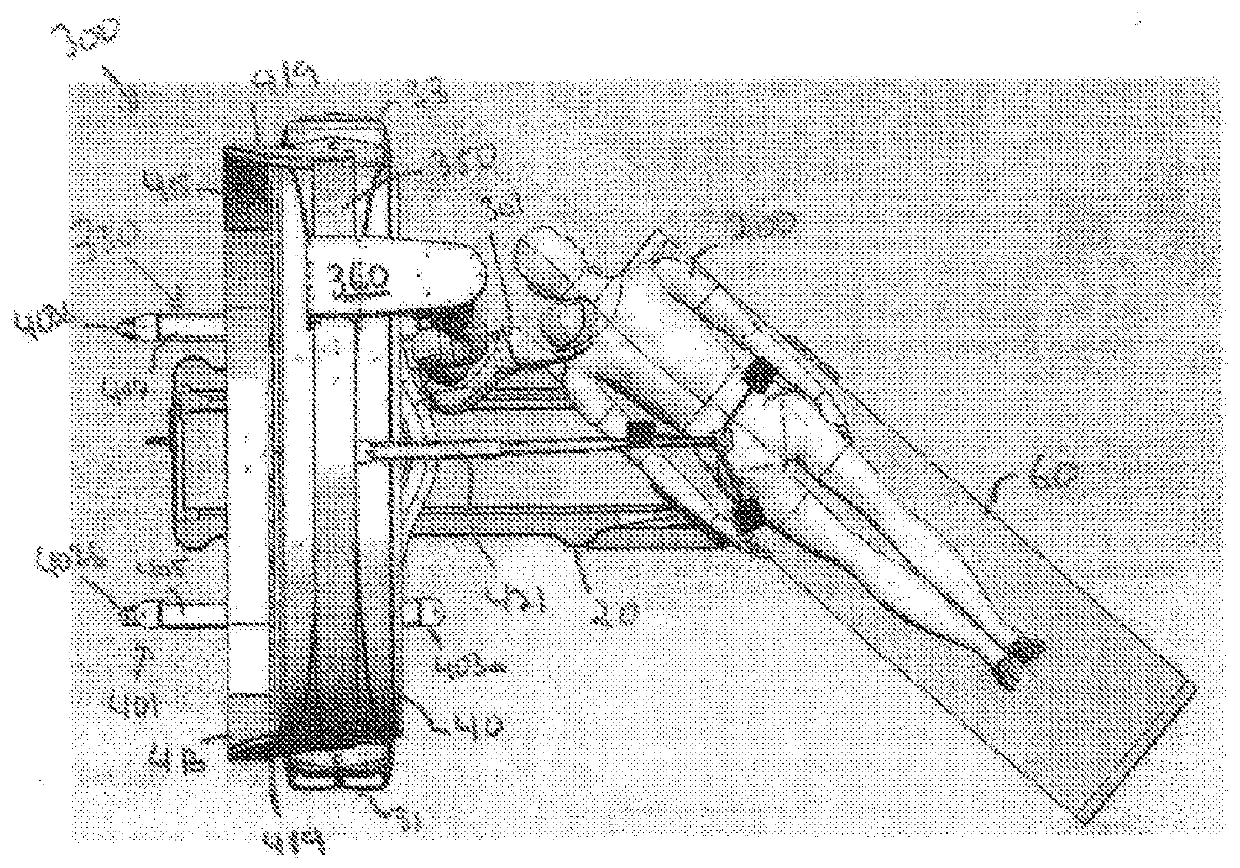
A device for robot-assisted surgery, comprising at least one non-sterile manipulator arm (12) having a coupling unit (100) with drive elements. The device further has an instrument unit (300) which comprises a surgical instrument (500) and a sterile sterile unit (400) for coupling the surgical instrument (500) to the drive elements of the coupling unit (100). The coupling unit (100) comprises a translatory drive element (110, 112) for generating a translatory drive movement and a rotatory drive element (114, 116) for generating a rotatory drive movement. The sterile unit (400) has a translationally driven element (408, 410) couplable to the translatory drive element (110, 112) and a rotationally driven element (412, 414) couplable to the rotatory drive element (114, 116). The device has a sterile lock (200) which is capable of being coupled to the coupling unit (100) and to the sterile unit (400).
Owner:AVATERAMEDICAL GMBH
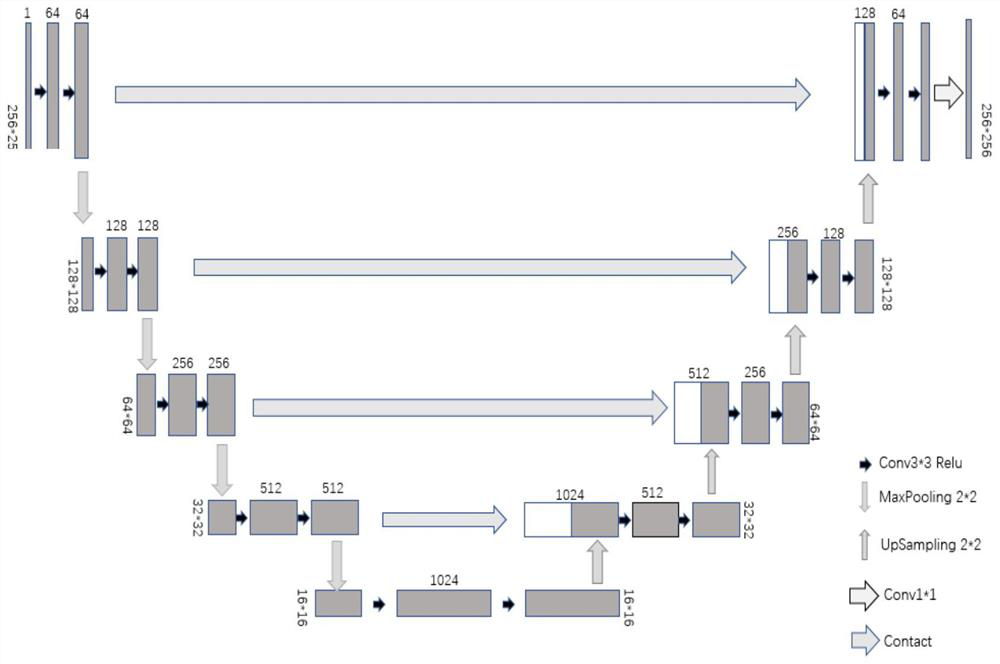
Robot surgery positioning method and device
PendingCN112773508AHigh positioning accuracyHigh control precisionImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of robot-assisted surgery, and particularly relates to a robot surgery positioning method and device based on ultrasonic guidance. Firstly, a focus is accurately positioned by adopting an image segmentation technology based on deep learning, the focus and spatial position information of the focus are accurately identified in an ultrasonic image which changes in real time, and a robot with a mechanical arm carrying ultrasound and an instrument simultaneously generates relative motion and compensates position errors in the process that ultrasonic scanning does not leave a human body, so that the position precision of instrument control is improved. According to the device, one mechanical arm is used for carrying ultrasonic and surgical tools at the same time, a multi-degree-of-freedom movement mechanism is additionally arranged, and it is guaranteed that an ultrasonic probe and the surgical tools can move relatively; and real-time position detection is performed on a part through ultrasonic image analysis, and when a focus position is displaced, a method of performing position compensation by adopting multi-degree-of-freedom provided by an additional mechanism is adopted, so that the surgical position precision is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Grinding Drill for Robotic Assisted Cervical Disc Replacement Surgery System
A burr used in a robot-assisted cervical intervertebral disc replacement surgery system relates to a burr. The present invention solves the problem that there is no dedicated grinding drill for robot-assisted cervical intervertebral disc replacement surgery system at present. One end of the fixed ring passes through the output shaft of the high-speed DC motor and is fixed on the end face of the output shaft end of the high-speed DC motor, and the other end of the fixed ring is fixed on an end face of the housing. One end of the drive shaft is installed in the housing through a bearing, one end of the drive shaft of the grinder is fixedly connected to the output shaft of the high-speed DC motor through a coupling, the grinding head is fixed on the other end of the drive shaft of the grinder, and the end The cover is machined with a first central through hole in the axial direction, the end cover is fixed on the other end surface of the housing through the drive shaft of the mill drill, and the connecting platform is machined with a second central through hole in the axial direction, so The connecting platform passes through the high-speed DC motor and is fixedly connected with the fixed ring. The invention is a burr used in a robot-assisted cervical intervertebral disc replacement operation system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Cognitive collaboration with neurosynaptic imaging networks, augmented medical intelligence and cybernetic workflow streams
ActiveUS10332639B2Avoid the needImprove responsivenessMedical communicationTelevision conference systemsDiseaseData stream
The invention integrates emerging applications, tools and techniques for machine learning in medicine with videoconference networking technology in novel business methods that support rapid adaptive learning for medical minds and machines. These methods can leverage domain knowledge and clinical expertise with cognitive collaboration, augmented medical intelligence and cybernetic workflow streams for learning health care systems. The invention enables multimodal cognitive communications, collaboration, consultation and instruction between and among cognitive collaborants, including heterogeneous networked teams of persons, machines, devices, neural networks, robots and algorithms. It provides for both synchronous and asynchronous cognitive collaboration with multichannel, multiplexed imagery data streams during various stages of medical disease and injury management—detection, diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, measurement and monitoring, as well as resource utilization and outcomes reporting. The invention acquires both live stream and archived medical imagery data from network-connected medical devices, cameras, signals, sensors and imagery data repositories, as well as multiomic data sets from structured reports and clinical documents. It enables cognitive curation, annotation and tagging, as well as encapsulation, saving and sharing of collaborated imagery data streams as packetized medical intelligence. The invention augments packetized medical intelligence through recursive cognitive enrichment, including multimodal annotation and [semantic] metadata tagging with resources consumed and outcomes delivered. Augmented medical intelligence can be saved and stored in multiple formats, as well as retrieved from standards-based repositories. The invention provides neurosynaptic network connectivity for medical images and video with multi-channel, multiplexed gateway streamer servers that can be configured to support workflow orchestration across the enterprise—on platform, federated or cloud data architectures, including ecosystem partners. It also supports novel methods for managing augmented medical intelligence with networked metadata repositories [inclduing imagery data streams annotated with semantic metadata]. The invention helps prepare streaming imagery data for cognitive enterprise imaging. It can be incorporate and combine various machine learning techniques [e.g., deep, reinforcement and transfer learning, convolutional neural networks and NLP] to assist in curating, annotating and tagging diagnostic, procedural and evidentiary medical imaging. It also supports real-time, intraoperative imaging analytics for robotic-assisted surgery, as well as other imagery guided interventions. The invention facilitates collaborative precision medicine, and other clinical initiatives designed to reduce the cost of care, with precision diagnosis [e.g., integrated in vivo, in vitro, in silico] and precision targeted treatment [e.g., precision dosing, theranostics, computer-assited surgery]. Cybernetic workflow streams—cognitive communications, collaboration, consultation and instruction with augmented medical intelligence—enable care delivery teams of medical minds and machines to ‘deliver the right care, for the right patient, at the right time, in the right place’ - and deliver that care faster, smarter, safer, more precisely, cheaper and better.
Owner:SMURRO JAMES PAUL
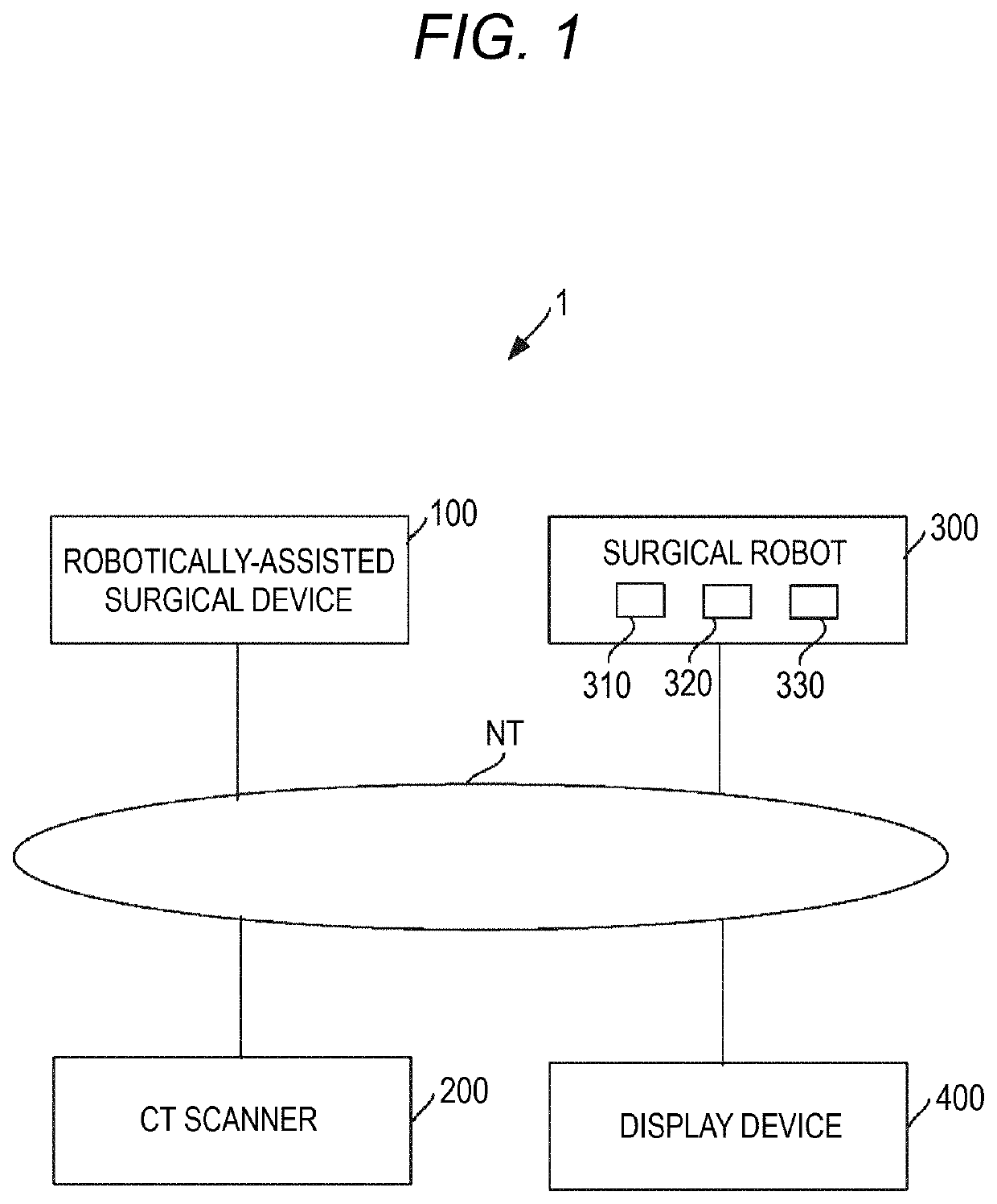
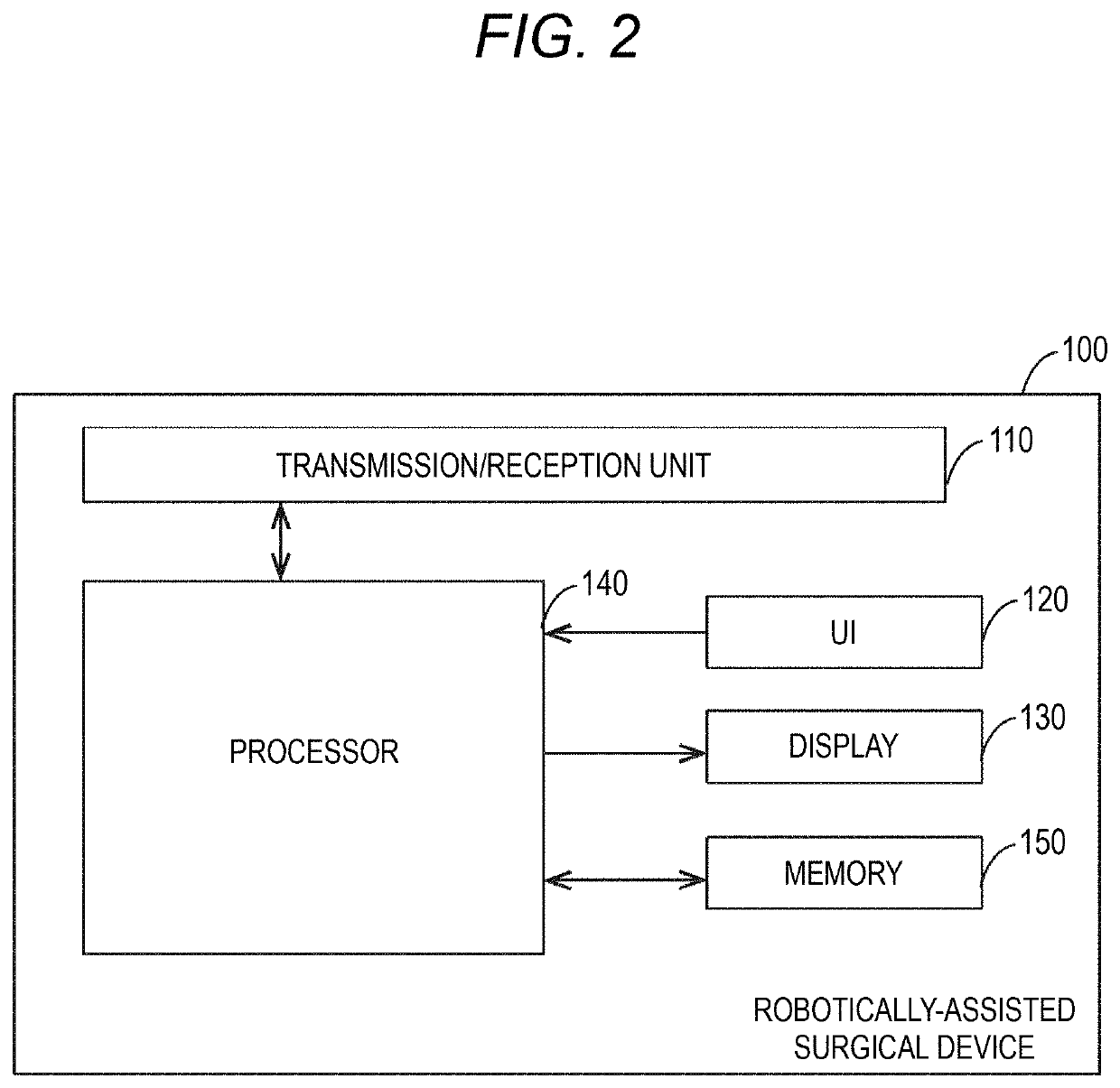
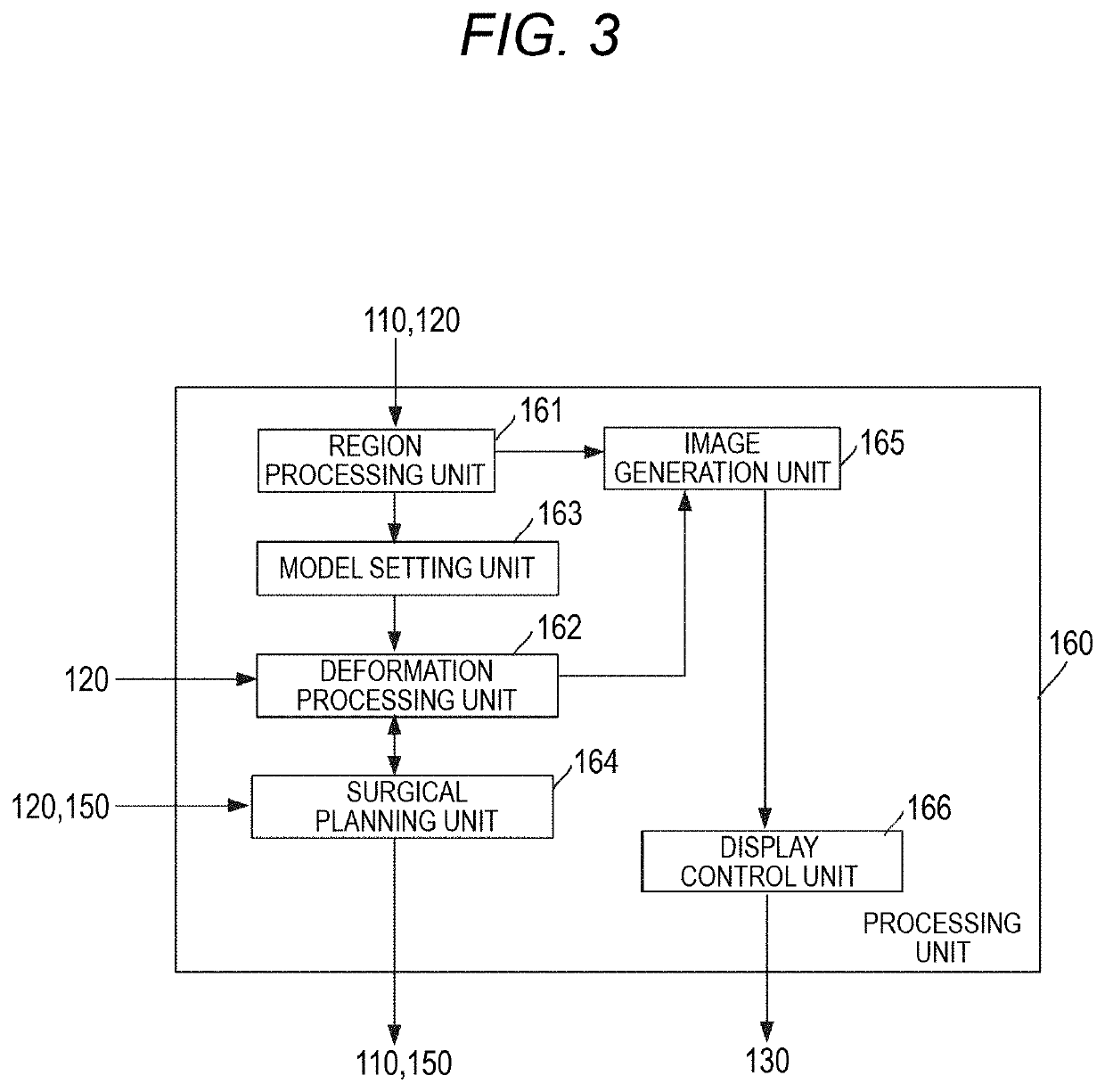
Robotically-assisted surgical system, robotically-assisted surgical method, and computer-readable medium
PendingUS20210315637A1Computer-aided planning/modellingSurgical robotsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationReoperative surgery
A robotically-assisted surgical system that assists robotic surgery by a surgical robot having a robot main body includes one or more processors. The one or more processors are configured to plan a position of a port to be perforated on a body surface of a subject which is a target of the robotic surgery, acquire a captured image obtained by capturing the subject including at least a part of the subject by an overview camera included in the robot main body, recognize a planned position of the port in the captured image based on the captured image and the planned position of the port, and show the captured image and port position information indicating the planned position of the port in the subject illustrated in the captured image, on a display unit.
Owner:MEDICAROID CORP +1
Environmental mapping for robotic assisted surgery
A system and method of use thereof are provided for dynamically generating an environmental map for use in robotic assisted surgery. The generated environmental map is used to plan a recovery tool path that an end-effector tool can safely and efficiently follow to re-position the tool back to a cutting position following the displacement of the tool from the cutting position. Additionally, the environmental map is used to update a virtual representation of a bone to provide a user with visual feedback as to the progression of the end-effector tool as the tool removes material from the bone during a surgical procedure.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
Robotically Assisted Surgical System and Related Devices and Methods
Disclosed herein are various robotic surgical systems having various robotic devices. Further, disclosed herein are removable coupleable connection ports, each of which can be coupled to a robotic device and a camera assembly that is disposed into and through the robotic device. Also disclosed herein are removable connection ports having at least one of a elongate device body coupling mechanism, a camera assembly coupling mechanism, and / or a presence detection mechanism. Further discussed herein is a camera assembly with at least one actuation mechanism for actuating movement of the steerable distal tip thereof.
Owner:VIRTUAL INCISION CORP
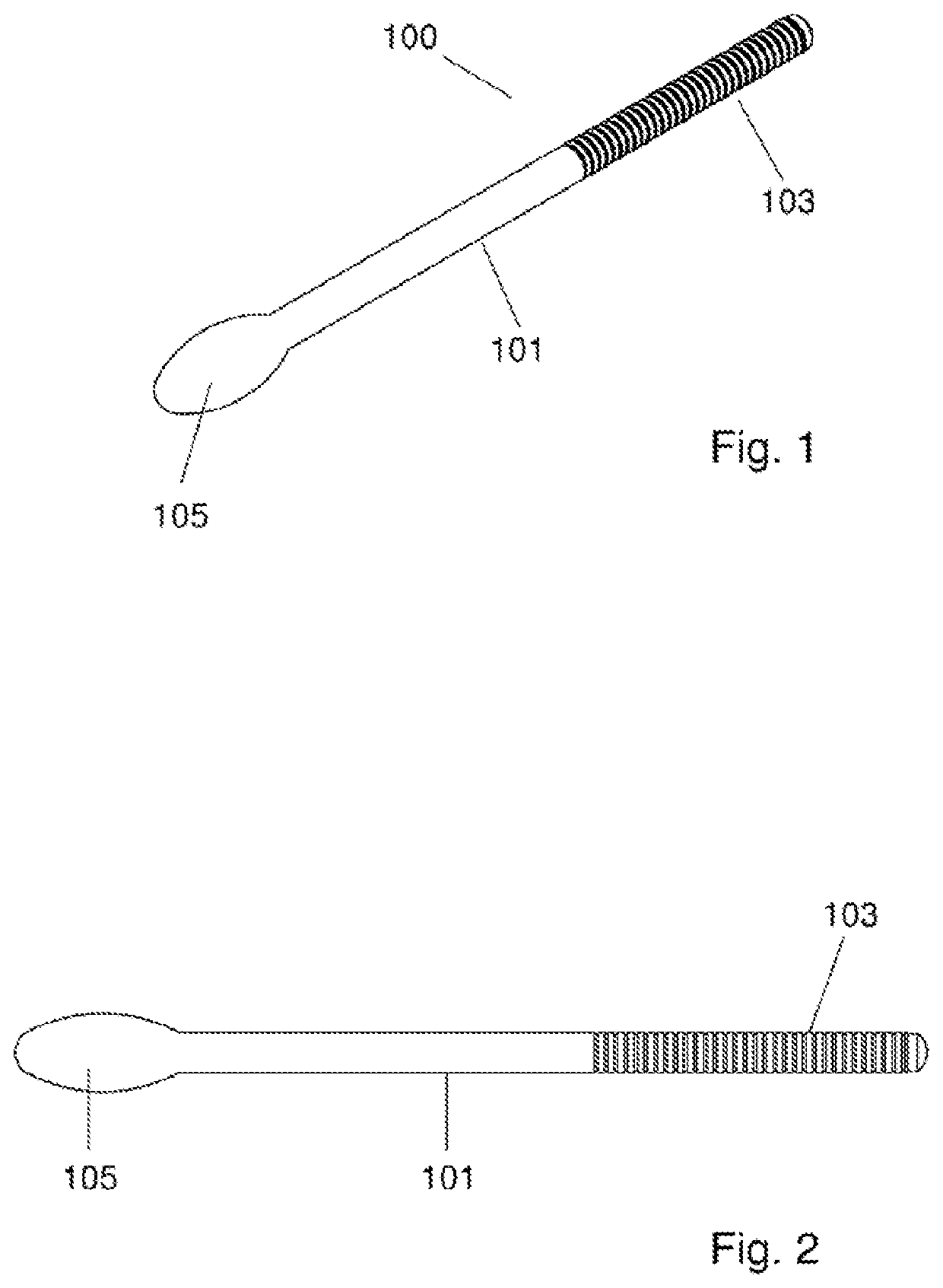
Device And Methods For Use In Robotic Assisted Surgery For Treatment Of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
ActiveUS20180280016A1Improved accuracy and reach and visualizationMinimal painSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsHyoid boneForceps
There is provided a suture passer device used in procedures of robotic assisted minimally invasive suspension of the hyoid and tongue base in treatment of sleep apnea. The suture passer device is a dual use suture passer, having both suture insertor and extractor functionality on a single unitary instrument section of the device by means of insertion and extraction hooks positioned on an elongated needlelike body which is connected to a handle grip. The insertion and extraction hooks receive a suture via an opening in the body of the instrument, with the suture capable of removal and fastening to the extraction hook by robotic forceps. Procedures for using the device are disclosed which include a single point of entry on a patient and the device moved to first and second positions above and below the hyoid bone during robotic assisted surgery.
Owner:VALENT MEDICAL INC
Suture delivery tools for endoscopic and robot-assisted surgery and methods
ActiveUS9955962B2Function increaseShorten the timeSuture equipmentsCannulasSurgical siteRobotic assisted surgery
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Method for positioning prosthesis rotation angle safety area in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
ActiveCN112402076AMeeting Kinematics-Kinetics NeedsReduce the impactJoint implantsKnee jointsUnicompartmental knee arthroplastyArticularis genus
The invention relates to a method for positioning a prosthesis rotation angle safety area in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of, 1) acquiring a personalized kinematics range of a knee joint of a patient before an operation or personalized kinematics data of the knee joint simulated in the operation of the patient; 2) performing three-dimensional dynamic preoperative planning based on the acquired personalized kinematics range of the knee joint of the patient to obtain a personalized tibial plateau prosthesis rotation safety areaof the patient; and 3) making a preoperative plan report, operative navigation, a patient-specific 3D printing operation tool and a robot-assisted operation scheme based on the personalized tibial plateau prosthesis rotation safety area of the patient obtained in the step 2). According to the method, tibial plateau prosthesis rotating direction safety range adapting to the personalized movement requirements of the patient is established on the basis of the knee joint kinematics data of different personalized postures and functions of the patient, the kinematics and dynamics requirements of the patient can be met, and therefore the method can be widely applied to the field of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty research.
Owner:BEIJING JISHUITAN HOSPITAL
Surgical visualization and medical imaging devices and methods using near infrared fluorescent polymers
A surgical visualization and medical imaging device and related computer based imaging methods and systems are disclosed. The surgical devices of the present invention use indocyanine green dye combined with a plastic, and are used in enhanced surgical imaging in applications such as robotically assisted surgeries. A near infrared light source, such as an 805 nm laser, may be used to excite the surgical device so that the device emits 835 nm light. Both the excitation and emission wavelengths penetrate tissue and blood, and provide enhanced imaging of surgical procedures. The resulting fluorescence image allows a user to readily determine relative tissue depth, to identify tissue inhomogeneity, to detect masses or tissue irregularities, to pinpoint anatomical holes, and to visualize tears.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Cervical vertebra positioning device and operating bed
PendingCN114099217APrevent movementConsistent posture of the cervical vertebraeOperating tablesPatient positioning for diagnosticsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
The invention discloses a cervical vertebra positioning device and an operating bed, and the cervical vertebra positioning device comprises a shoulder rest assembly which is arranged on the operating bed to abut against the shoulders of a patient; the traction assembly is arranged on the operating bed, and the traction assembly drives the head of the patient to move in the direction close to the traction assembly by restraining the lower jaw of the patient; the bottom plate assembly, the shoulder rest assembly and the traction assembly are arranged on the bottom plate assembly, a patient lies on the bottom plate assembly, and the height of the bottom plate assembly relative to the operating bed can be adjusted so as to adjust the height of the patient. Therefore, the cone posture of the cervical vertebra of the patient can be kept consistent before and after the operation, the cone posture of the patient can be kept consistent when CT images are shot twice before and after the operation, the accuracy of surgical image registration is ensured, and the surgical safety and the surgical success rate when the robot is used for assisting the surgery are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRICGROUP CORP
Systems and methods for robotic infection treatment of a prosthesis
A method for debriding an infected implant area using a robotic-assisted surgery system. The method includes determining, by a processing circuit associated with a computer, an area to be debrided, the debridement area including at least a surface of an implant or patient tissue, and generating, by the processing circuit, a plan for debriding the debridement area. The method further includes controlling a debridement tool, by the robotic-assisted surgery system, while the debridement tool is used to carry out the debridement plan, and monitoring the debridement by the processing circuit.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
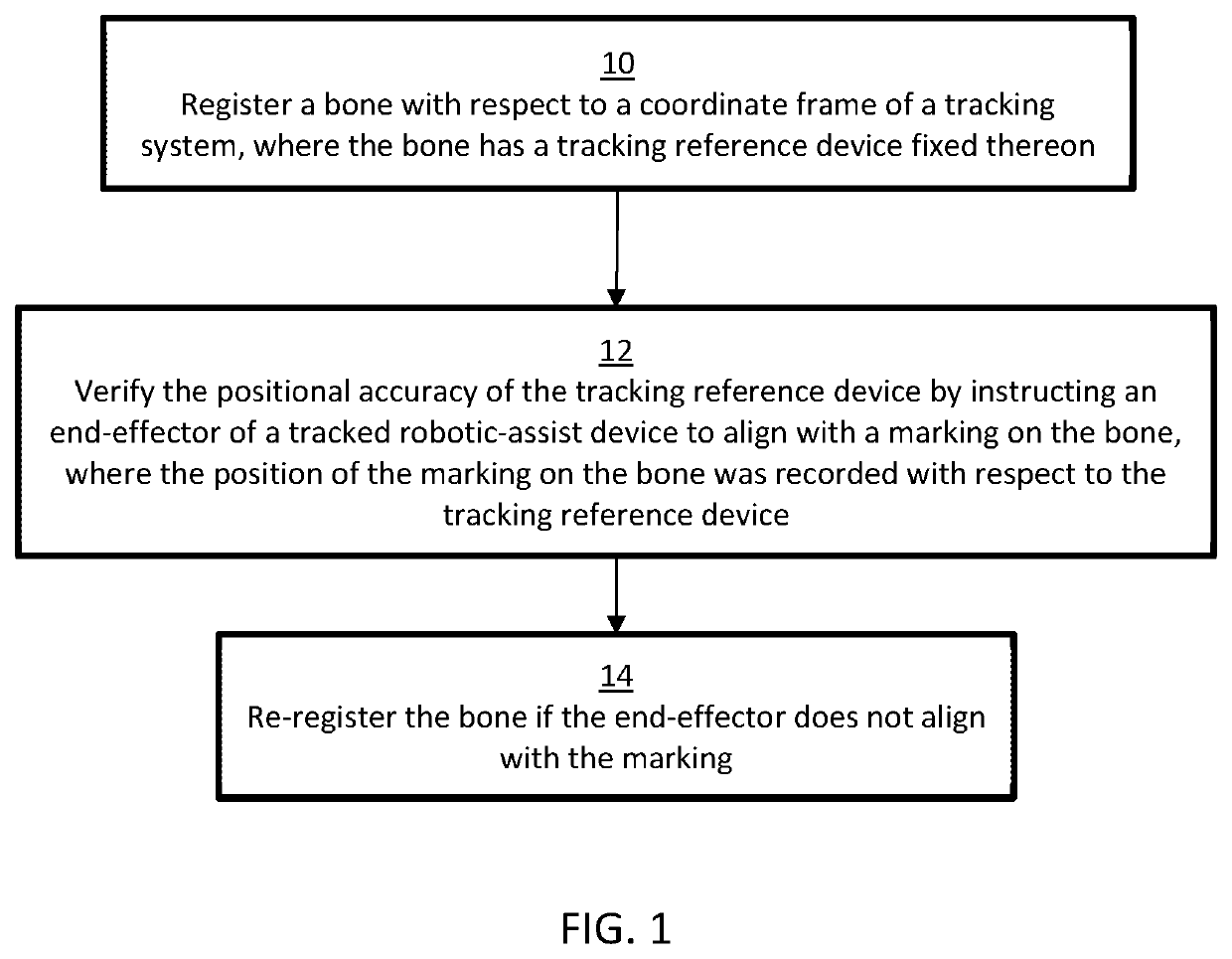
Method of verifying tracking array positional accuracy
PendingUS20220071713A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceRadiologyReference device
A method for verifying the positional accuracy of a tracking reference device is provided that includes a tracking reference device attached to a bone. The bone is then registered with respect to a coordinate frame of the tracking reference device. A verification mark on the bone is then created where the position of the verification mark is recorded, by way of a tracking system, with respect to the tracking reference device. The positional accuracy of the tracking reference device is verified by instructing an end-effector of a robotic-assisted surgical device to align with the verification mark on the bone, and wherein if the end-effector does not align with the verification mark, the positional accuracy of the tracking reference device is compromised. A surgical system for performing the computerized method is also provided.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
Instruments for navigated orthopedic surgeries
PendingCN113907878ASurgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceOrthopedics surgeryPhysical therapy
Devices, systems, and methods for computer-assisted navigation and / or robot-assisted surgery are disclosed. Navigable instrumentation, which are capable of being navigated by a surgeon using a surgical robot system, allow for the navigated movement of instruments or other surgical devices. The instruments may be suitable for procedures involving navigated and / or robotic total knee arthroplasty, for example.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Robotic surgical system
ActiveCN110114021AAllow interchangeQuick exchangeSurgical robotsReoperative surgeryBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides an apparatus, system and method for providing robotically assisted surgery that involves the removal of bone or non-fibrous type tissues during a surgical procedure. Thesystem utilizes a multi-axis robot having a reciprocating tool that is constructed and arranged to remove hard or non-fibrous tissues while leaving soft tissues unharmed. The multi-axis robot may becontrolled via computer or telemanipulator, which allows the surgeon to complete a surgery from an area adjacent to the patient to thousands of miles away.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
System and method for mounting a robotic arm in a surgical robotic system
ActiveCN109862845AProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical navigation systemsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationRobotic arm
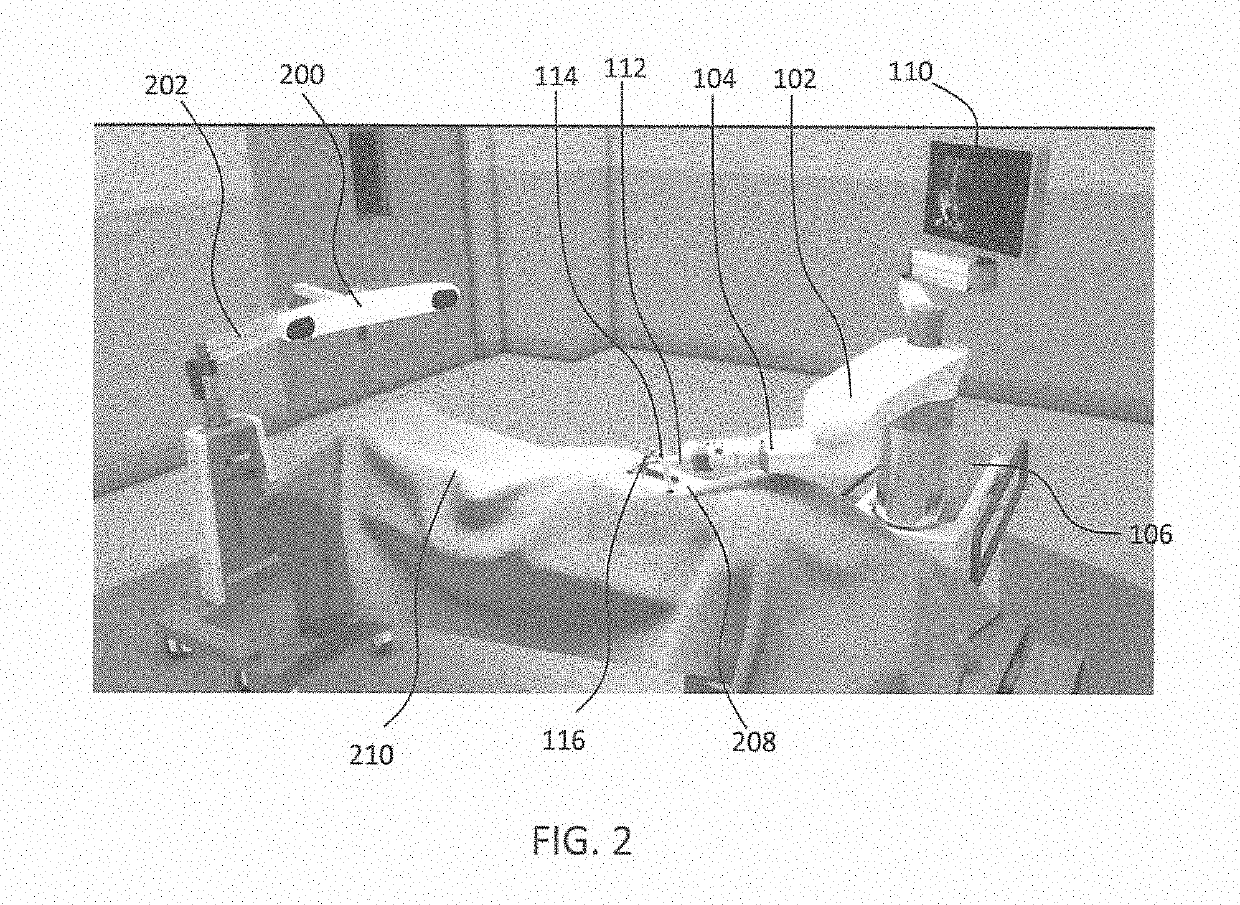
Systems and methods for mounting a robotic arm for use in robotic-assisted surgery, including a mobile shuttle that includes a support member for mounting the robotic arm that extends at least partially over a gantry of an imaging device. Further embodiments include a mounting apparatus for mounting a robotic arm to a base or support column of an imaging device, to a patient table, to a floor or ceiling of a room, or to a cart that extends over the top surface of the patient table.
Owner:MOBIUS IMAGING
Apparatus and method for a global coordinate system for use in robotic surgery
PendingUS20190374383A1Facilitating robotic surgeryDiagnostics using lightEye surgeryKinematicsEngineering
An apparatus and method for establishing a global coordinate system to facilitate robotic assisted surgery. The coordinate system may be established using a combination of the robotic data, i.e., kinematics, and optical coherence tomographic images generated by an overhead optical assembly and a tool-based sensor. Using these components, the system may generate a computer-registered three-dimensional model of the patient's eye. In some embodiments, the system may also generate a virtual boundary within the coordinate system to prevent inadvertent injury to the patient.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com