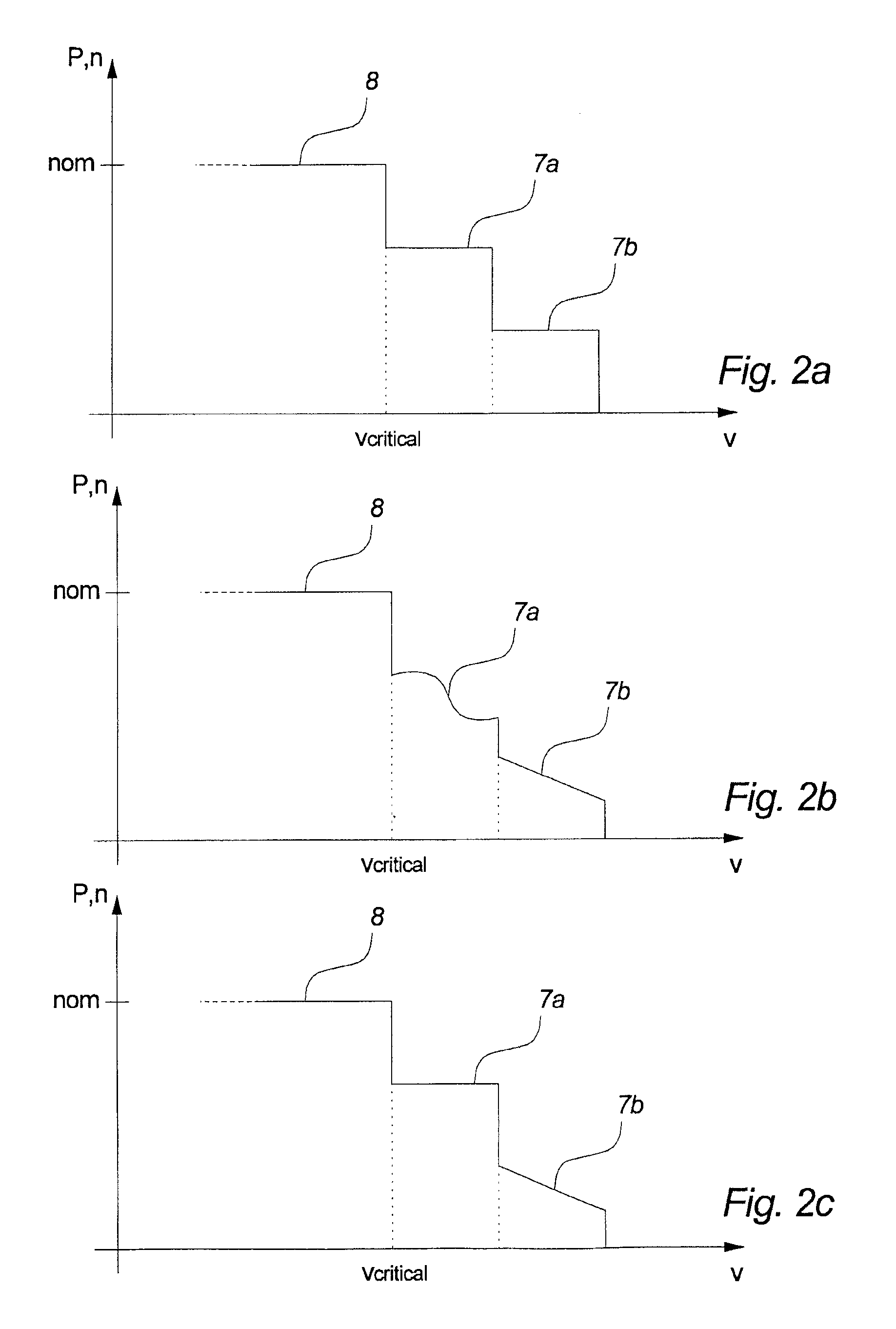
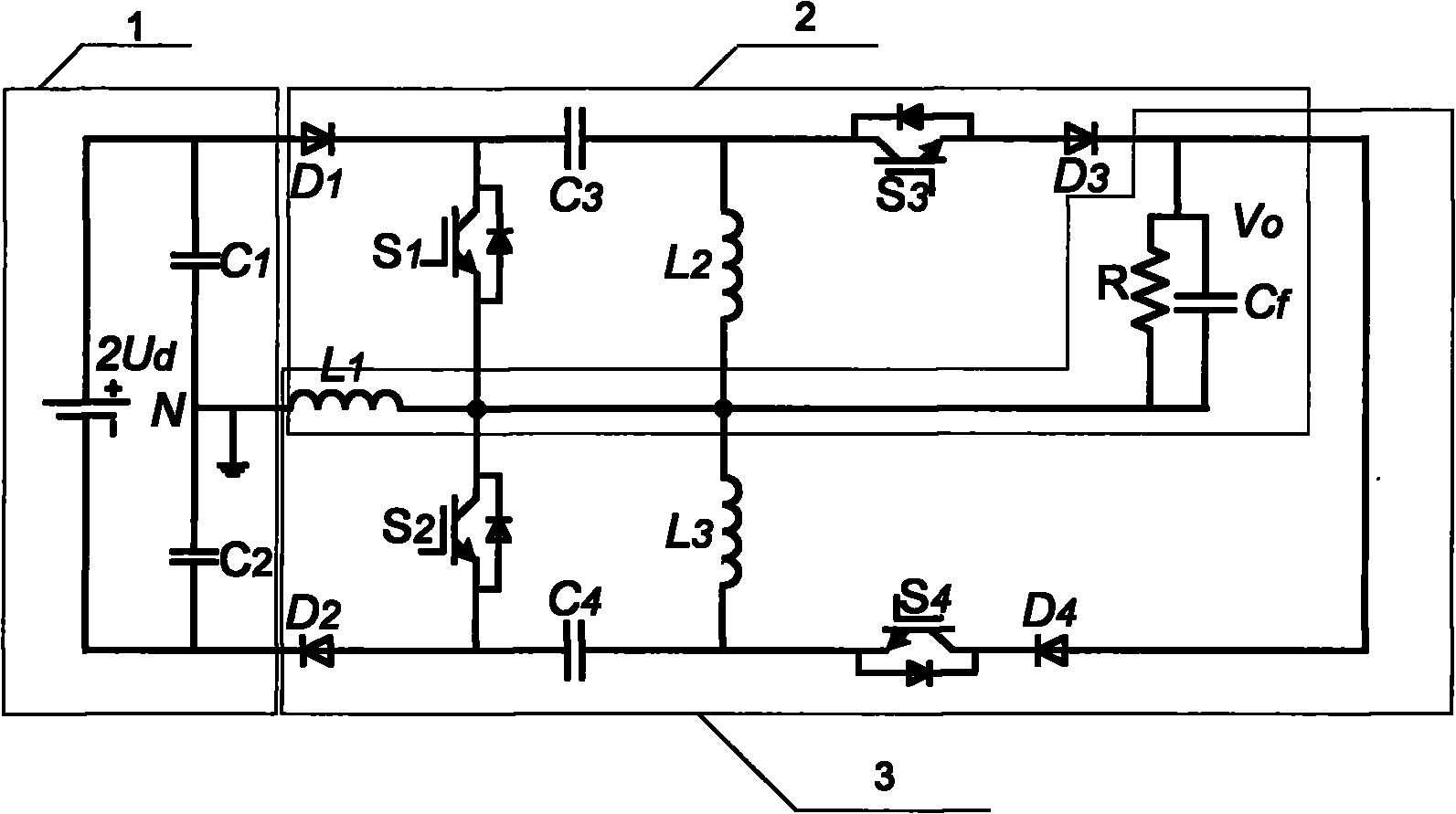
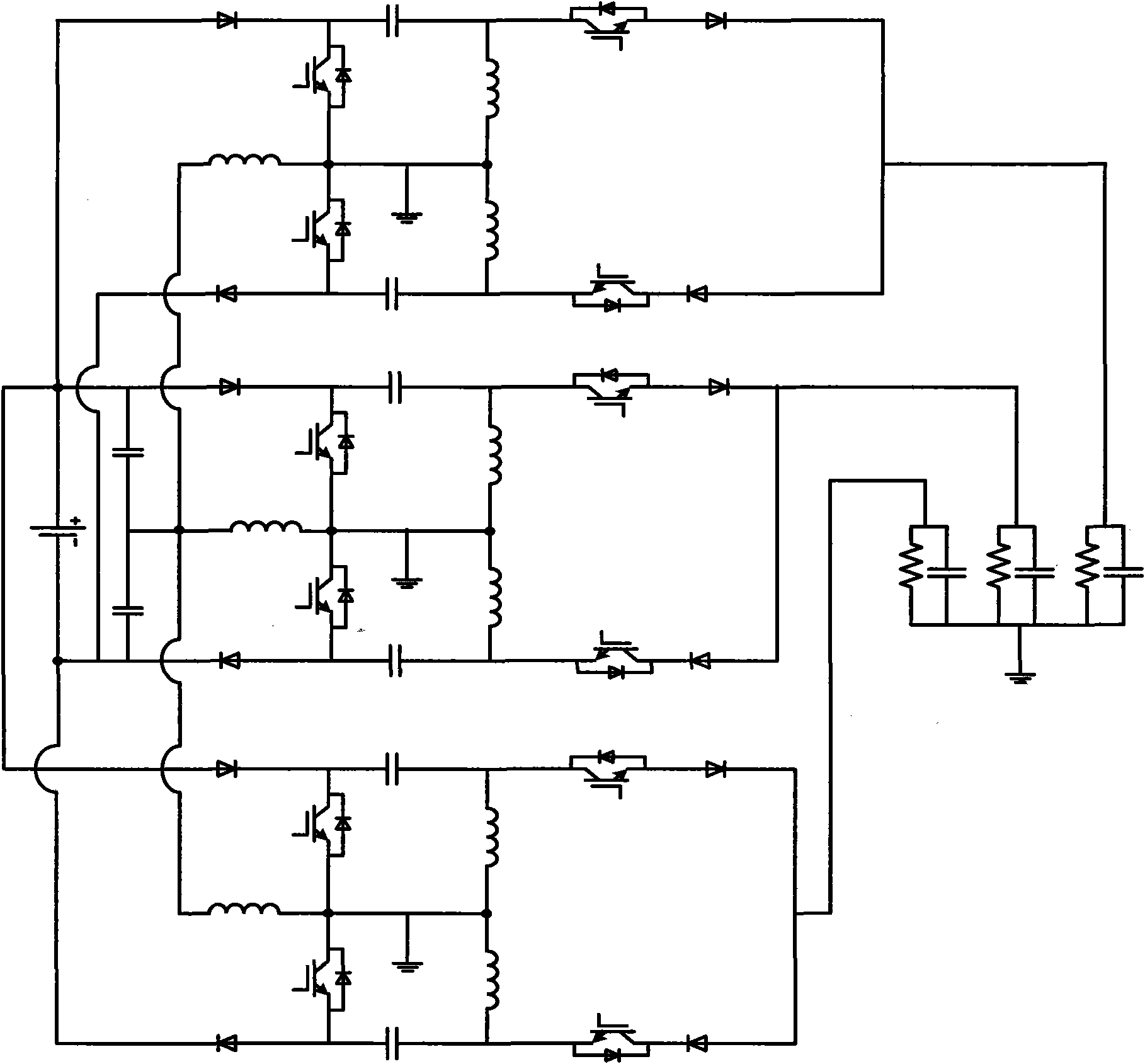
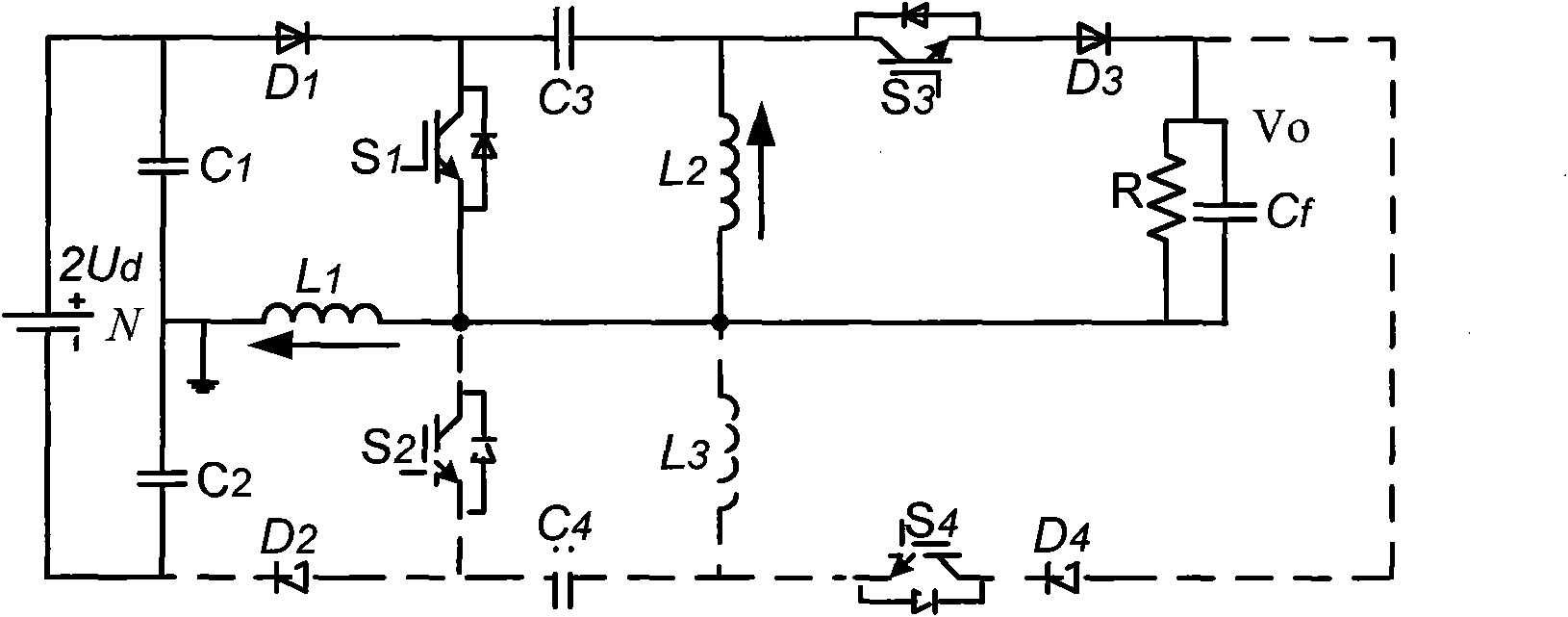
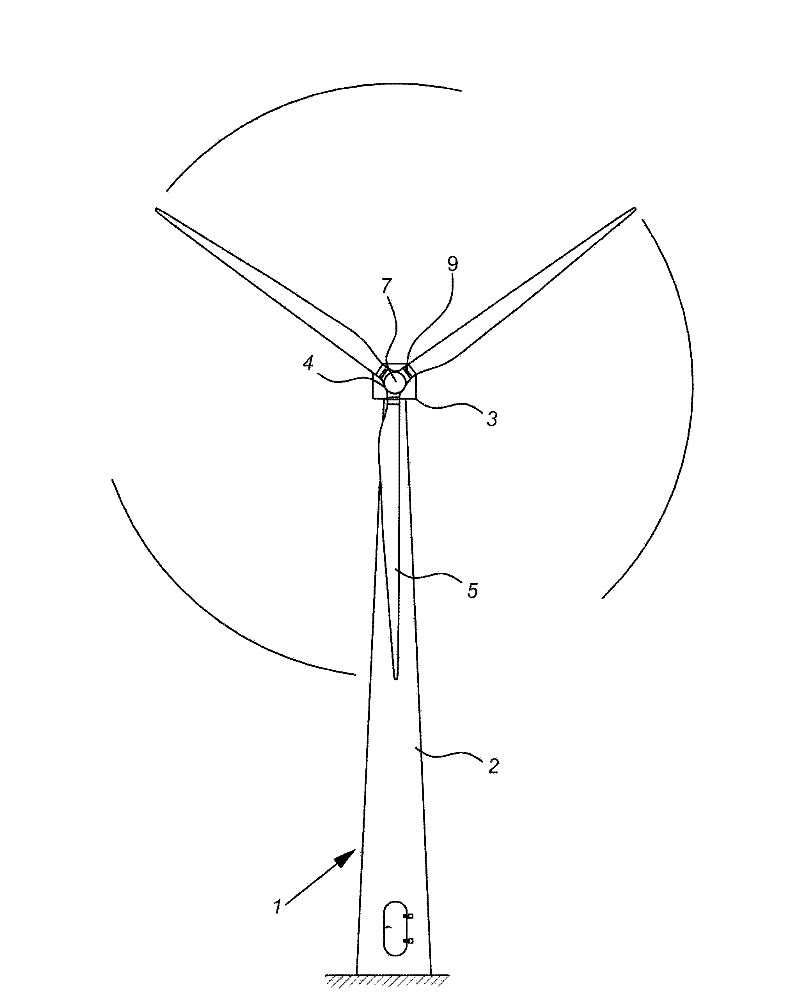
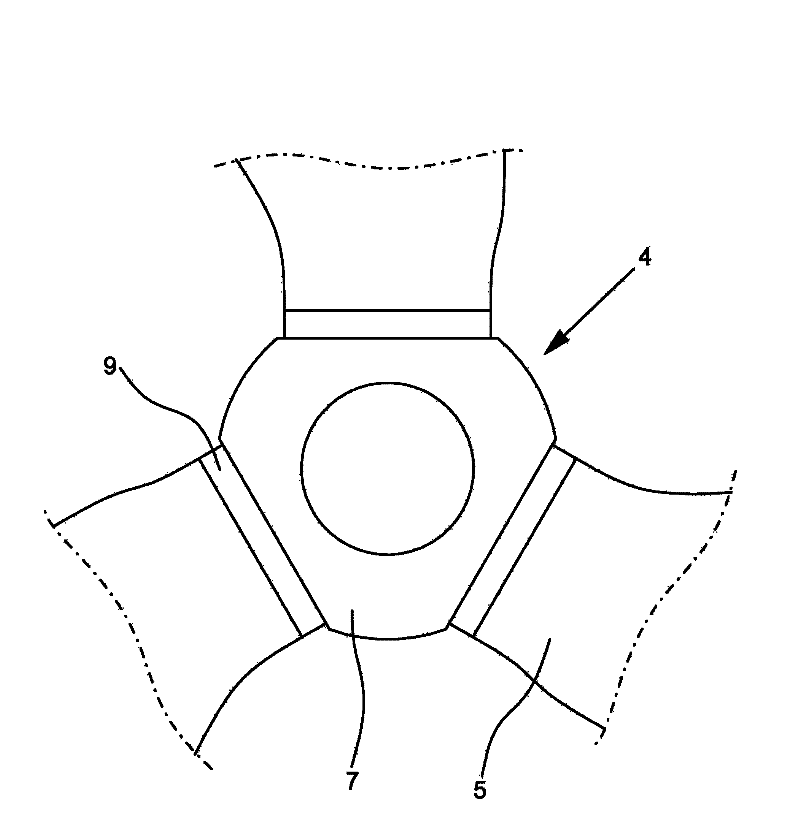
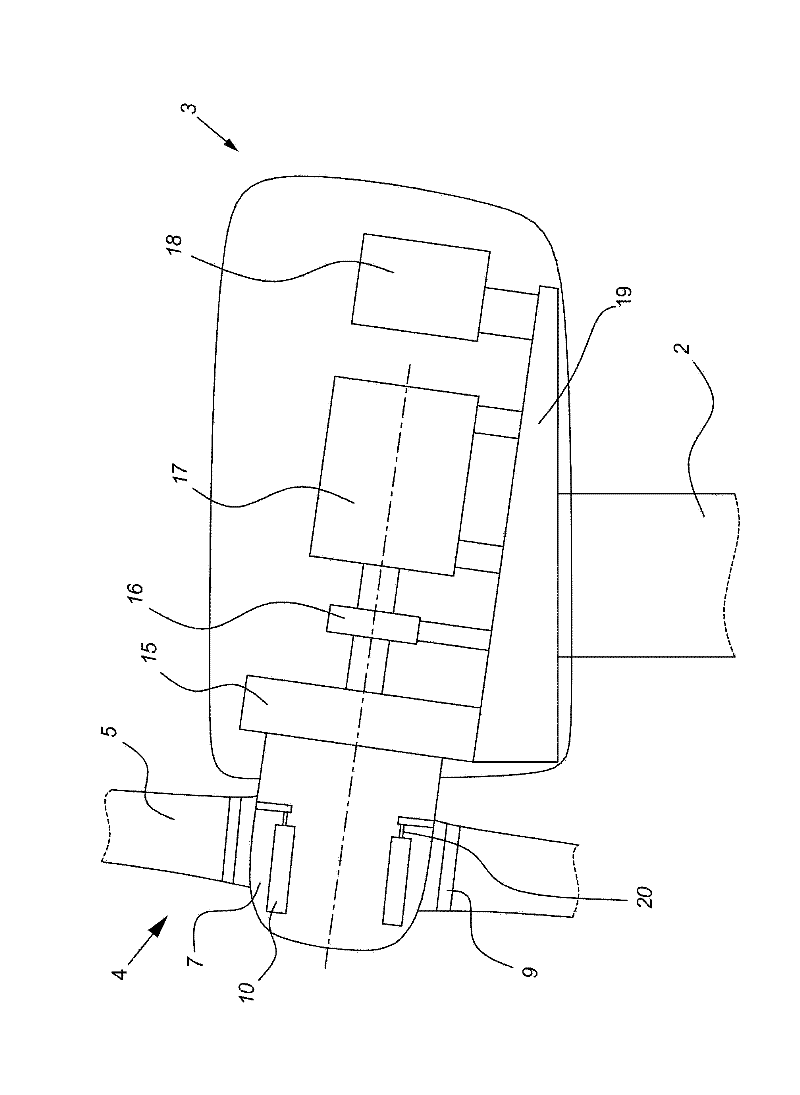
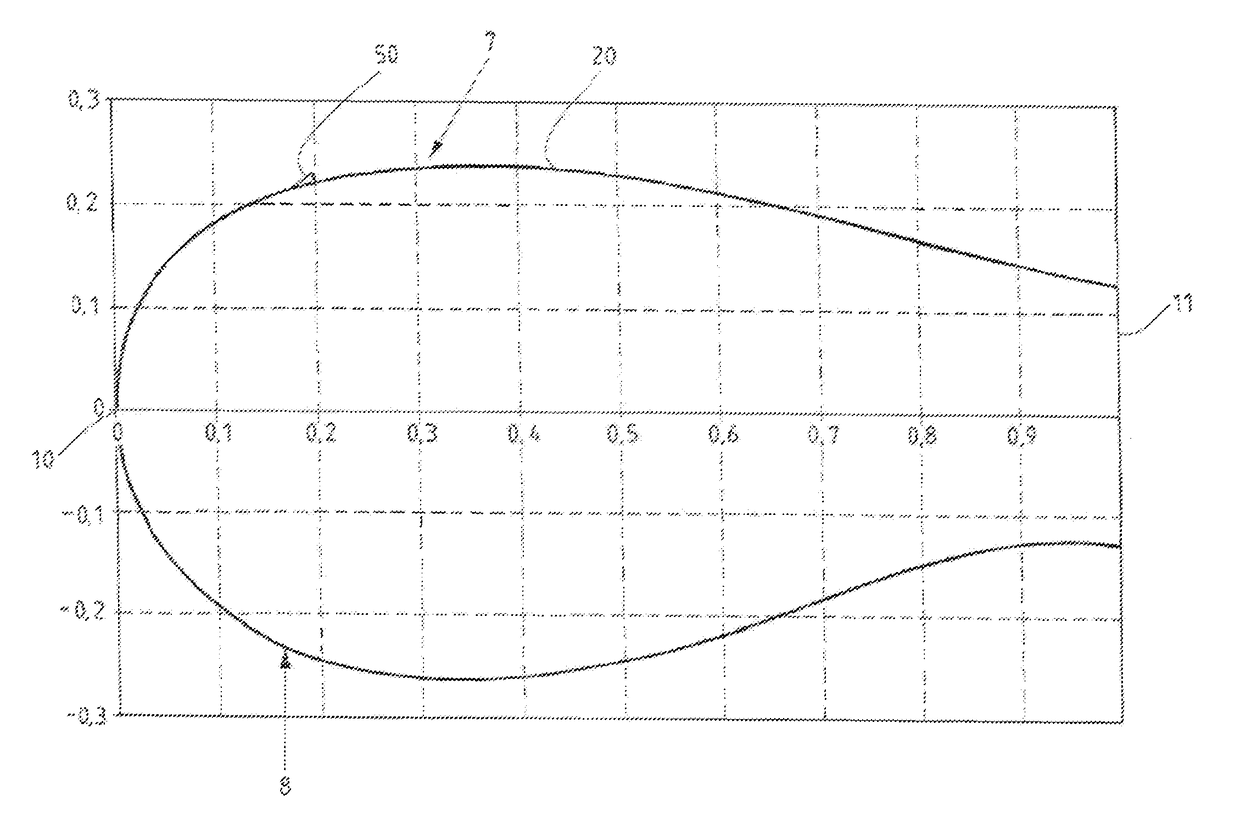
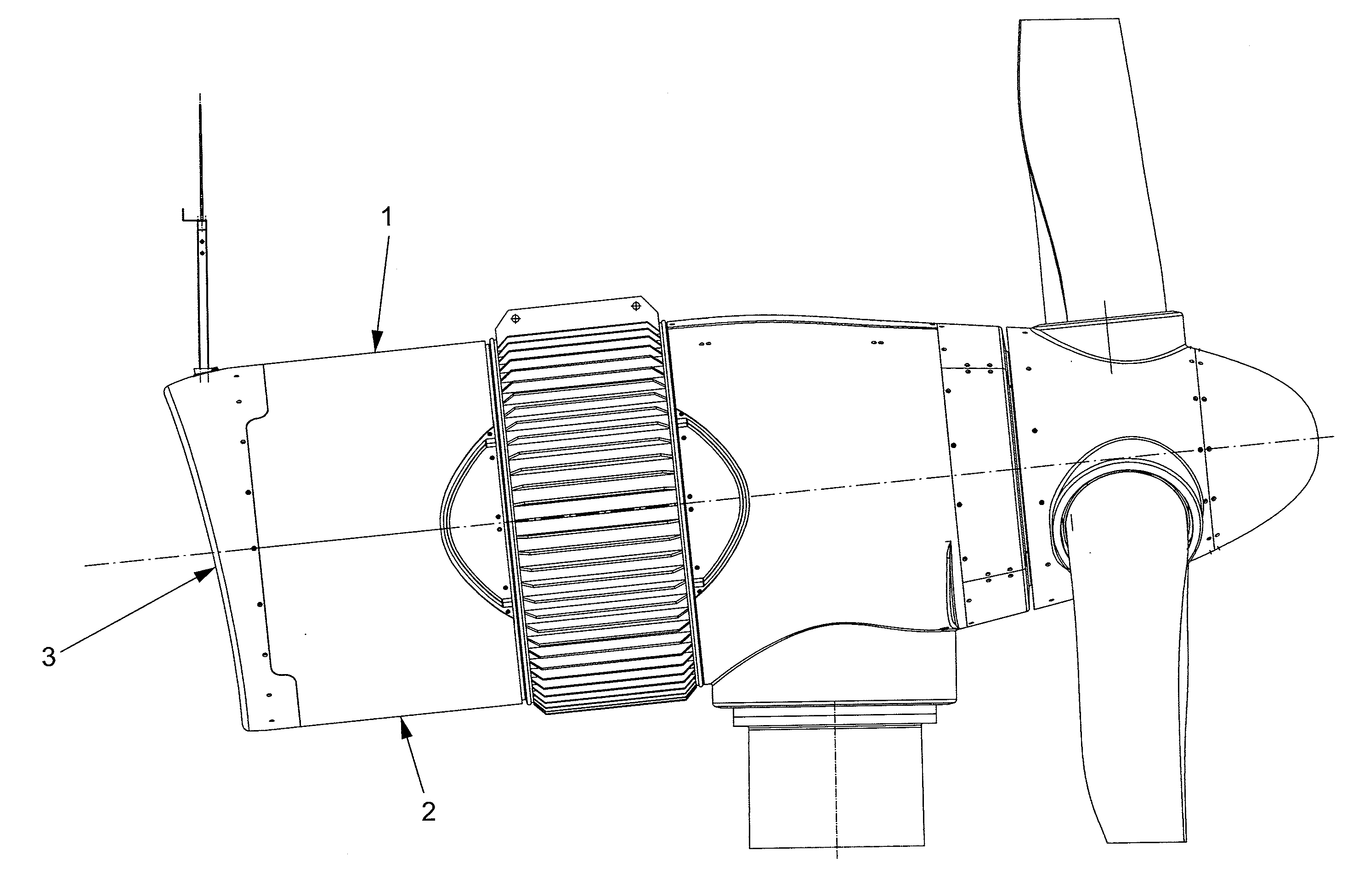
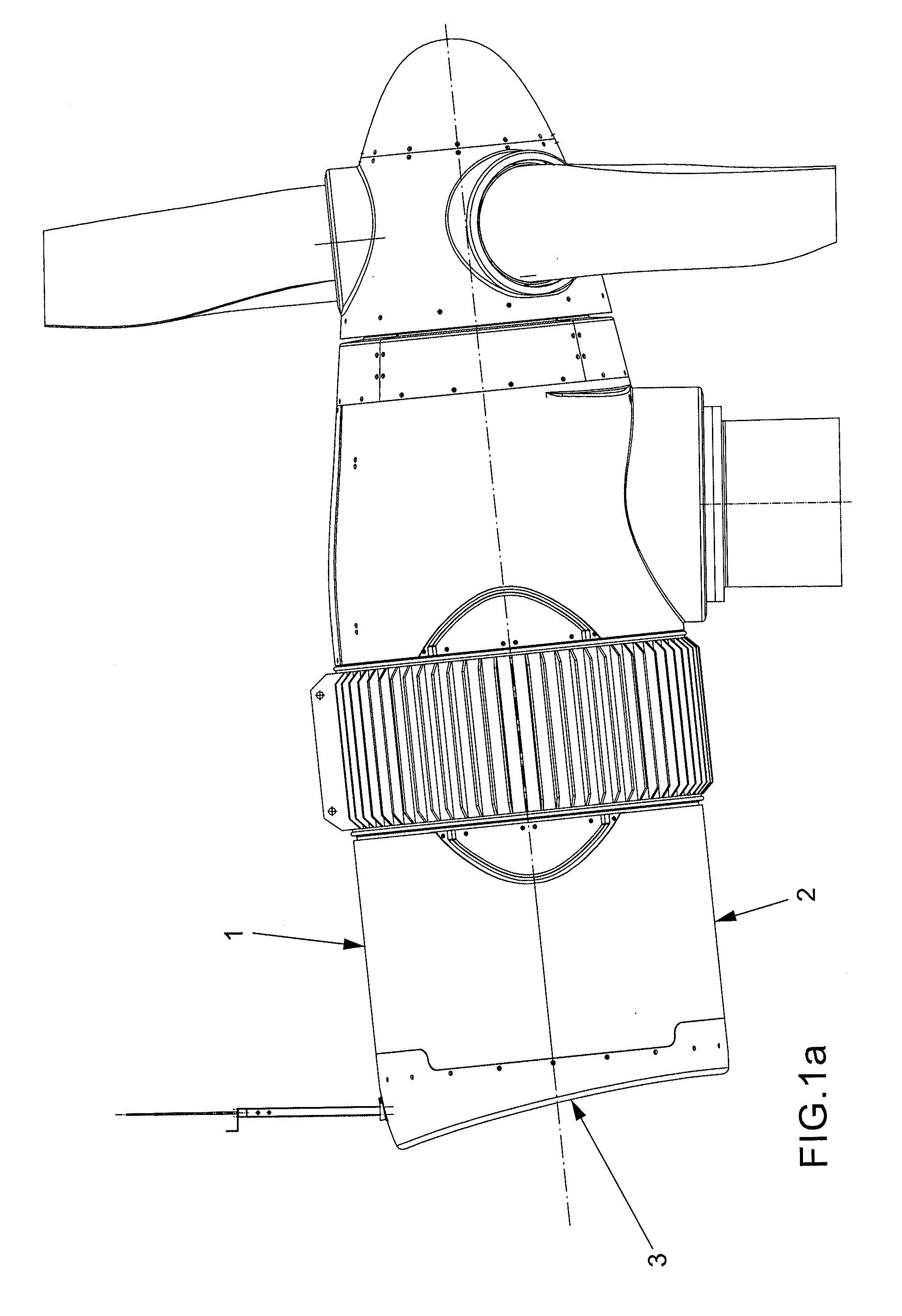
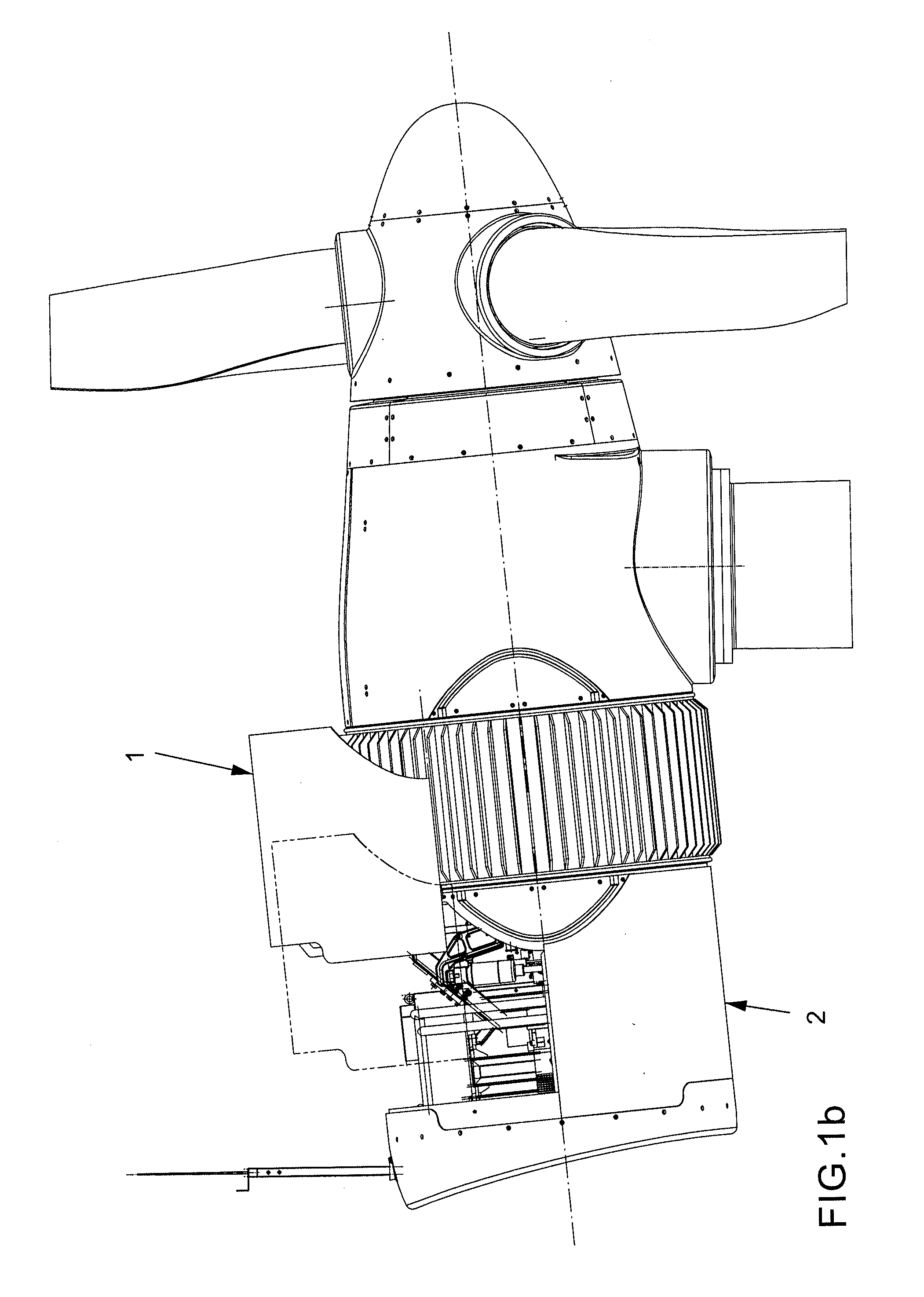
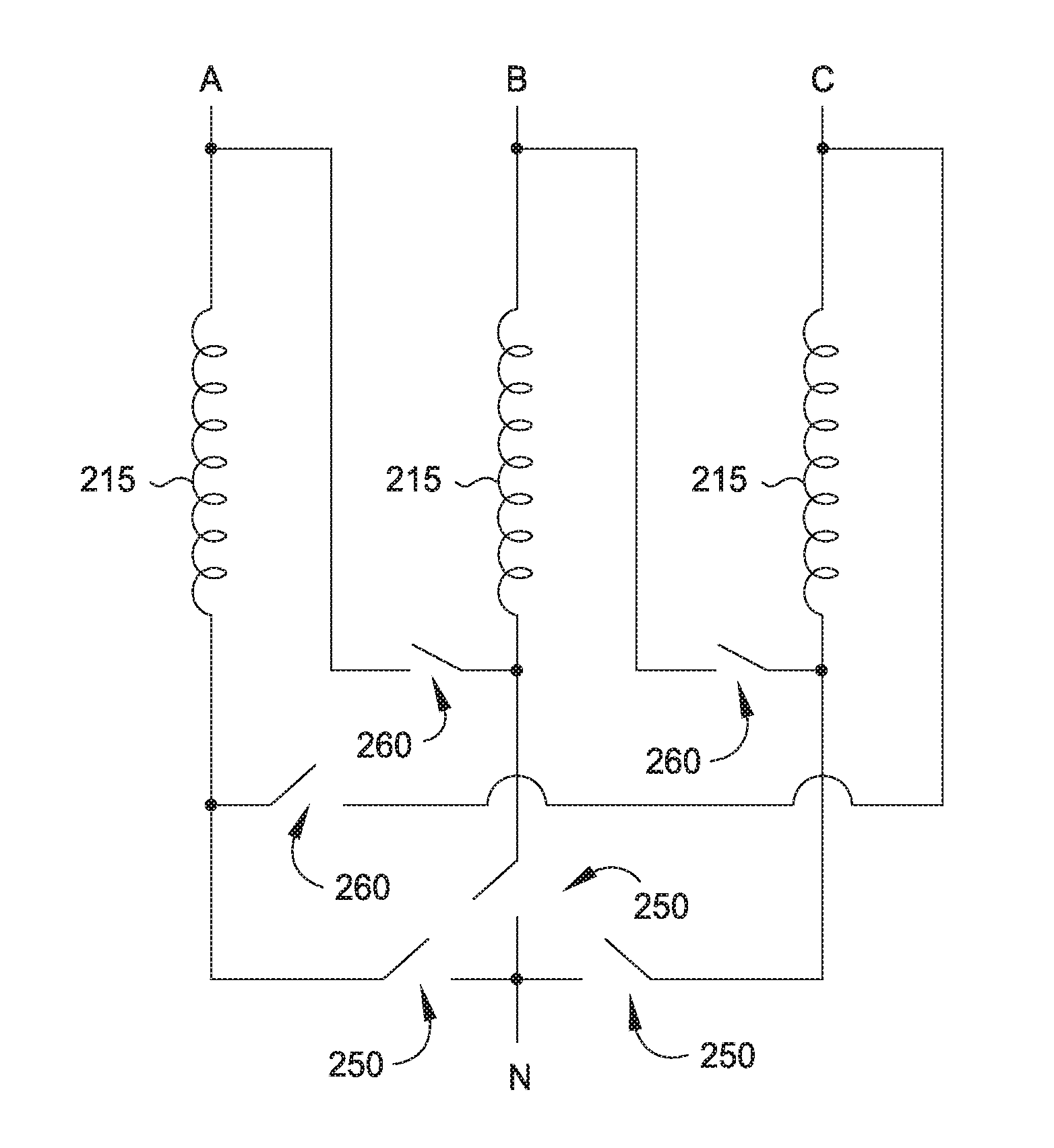
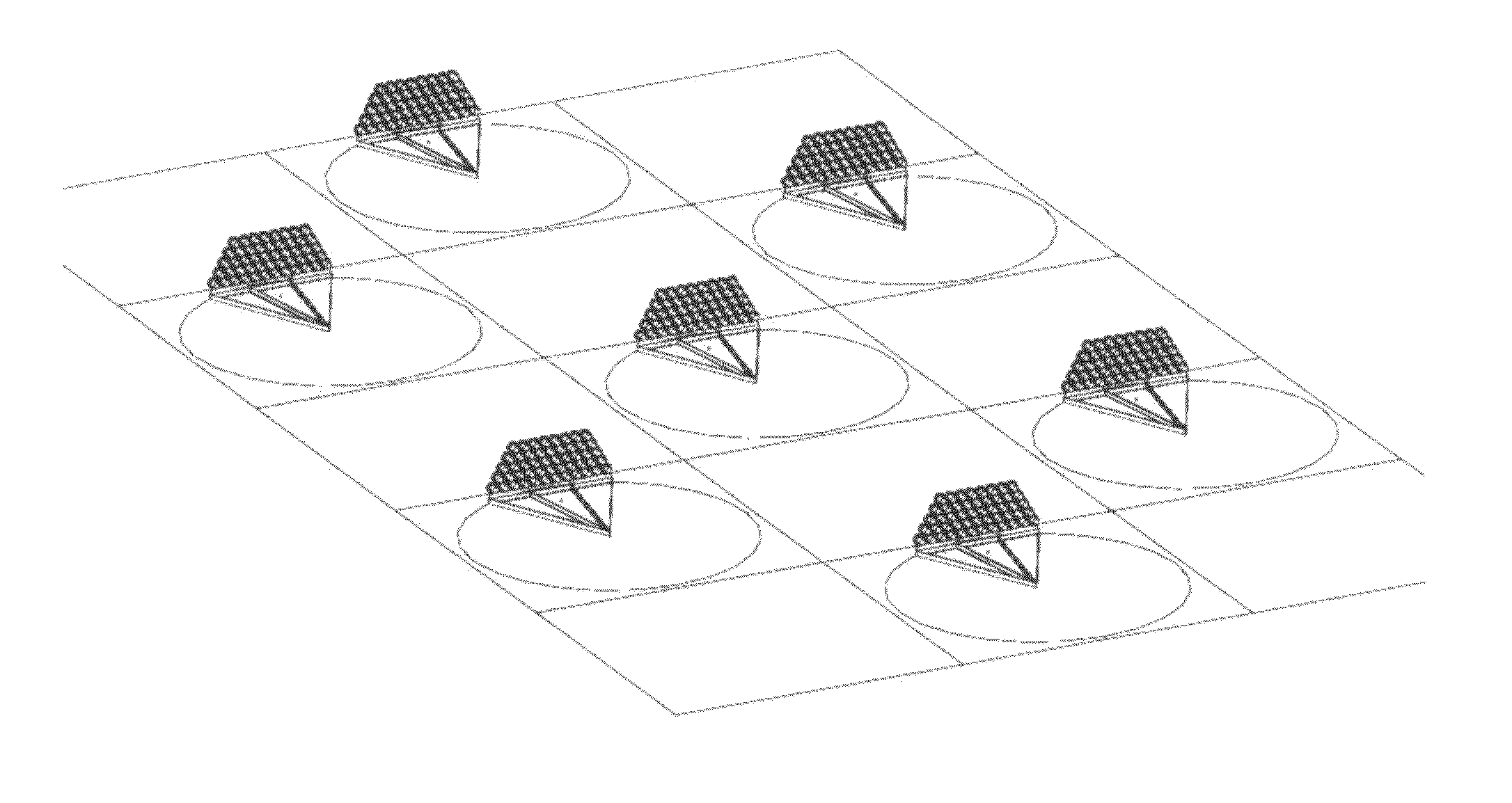
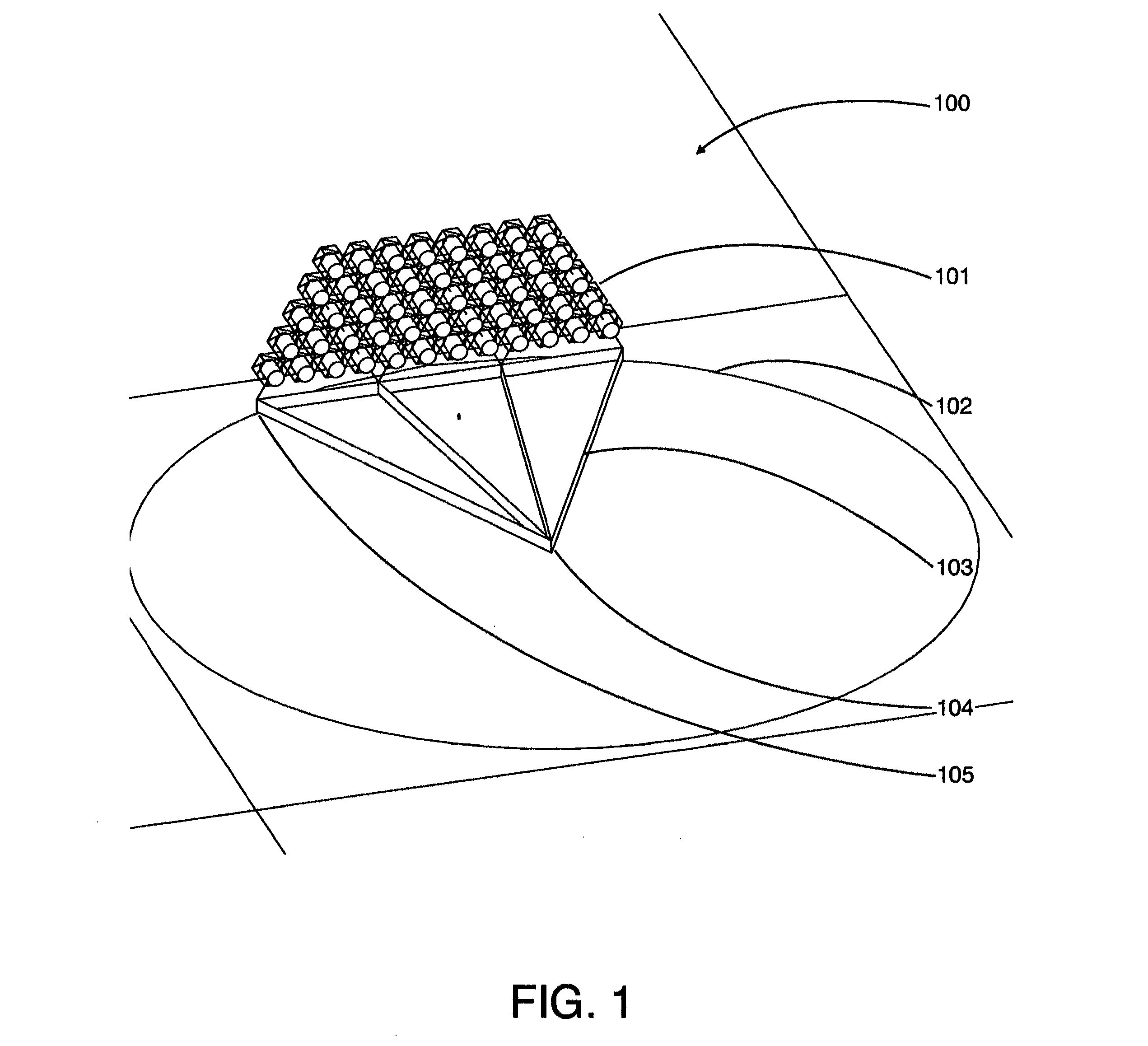
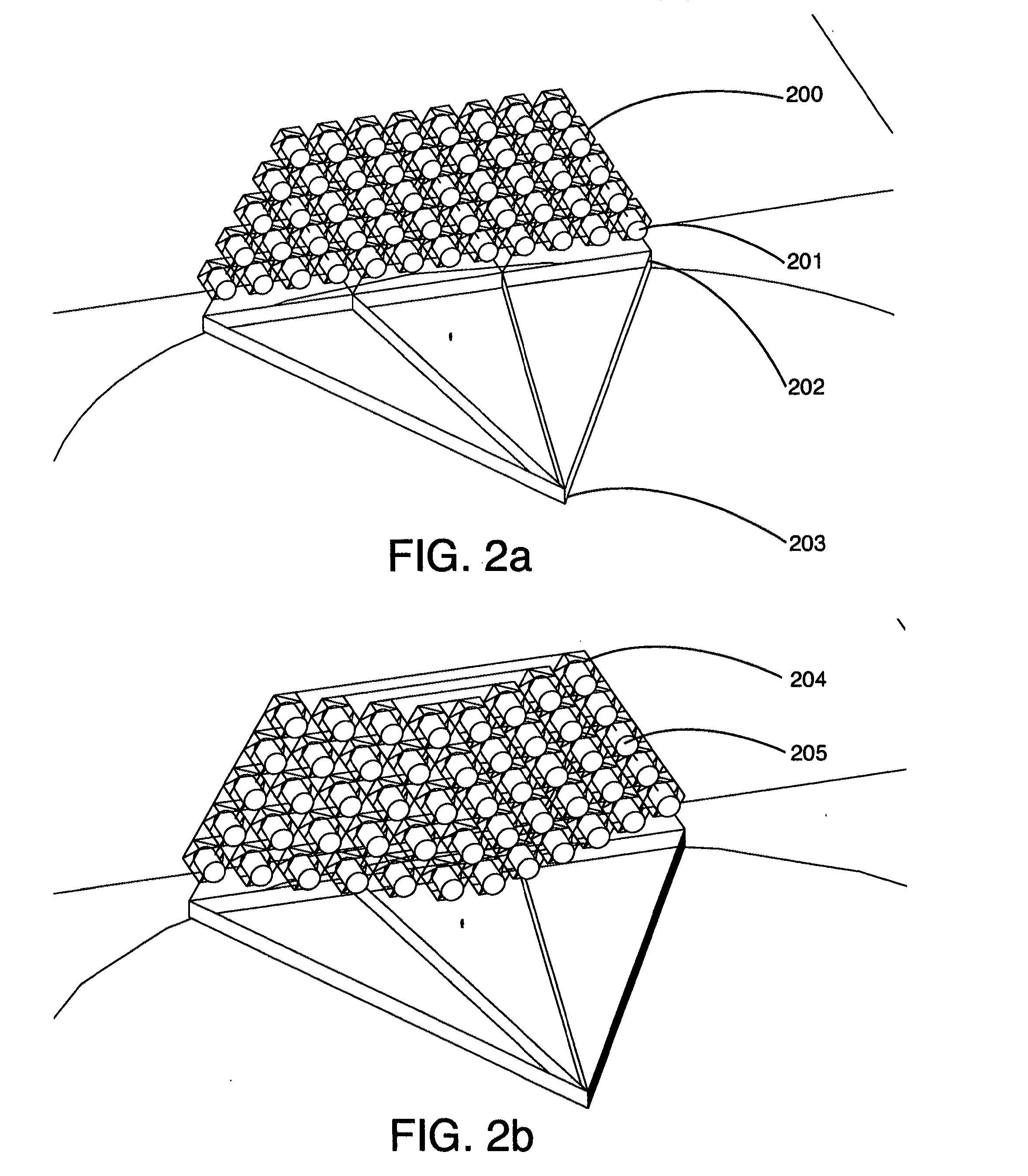
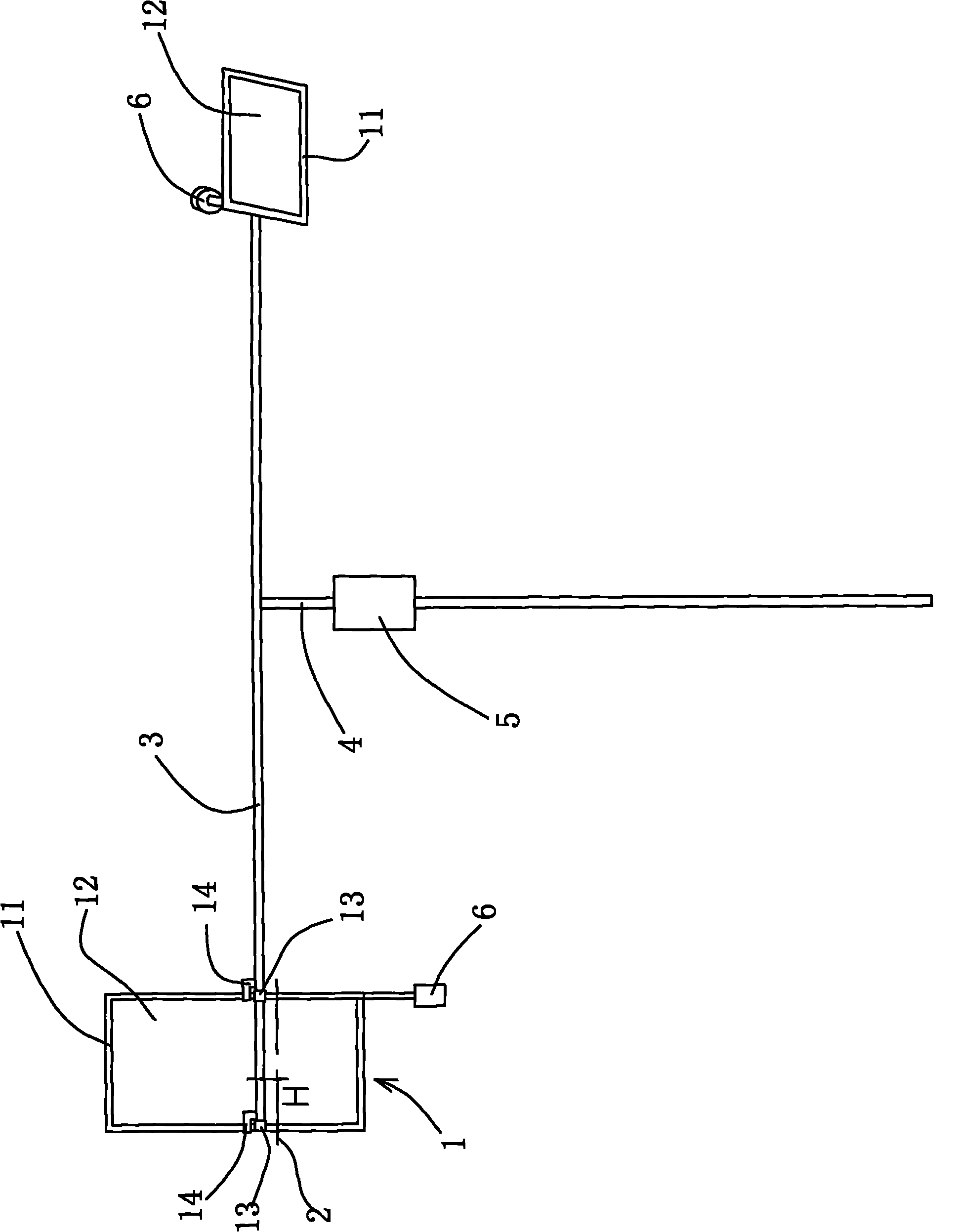
Patents
Literature
95 results about "Small wind turbine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
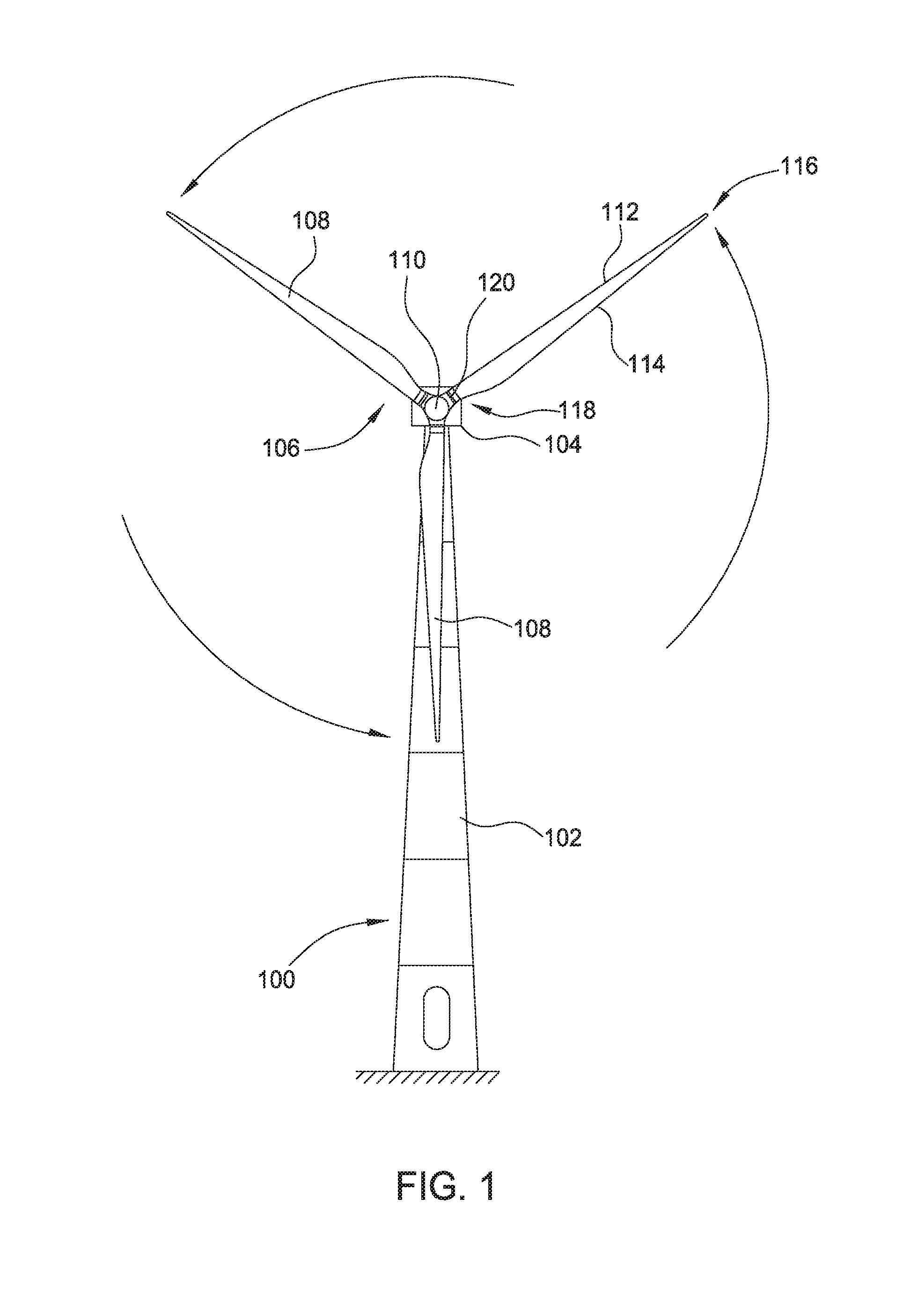
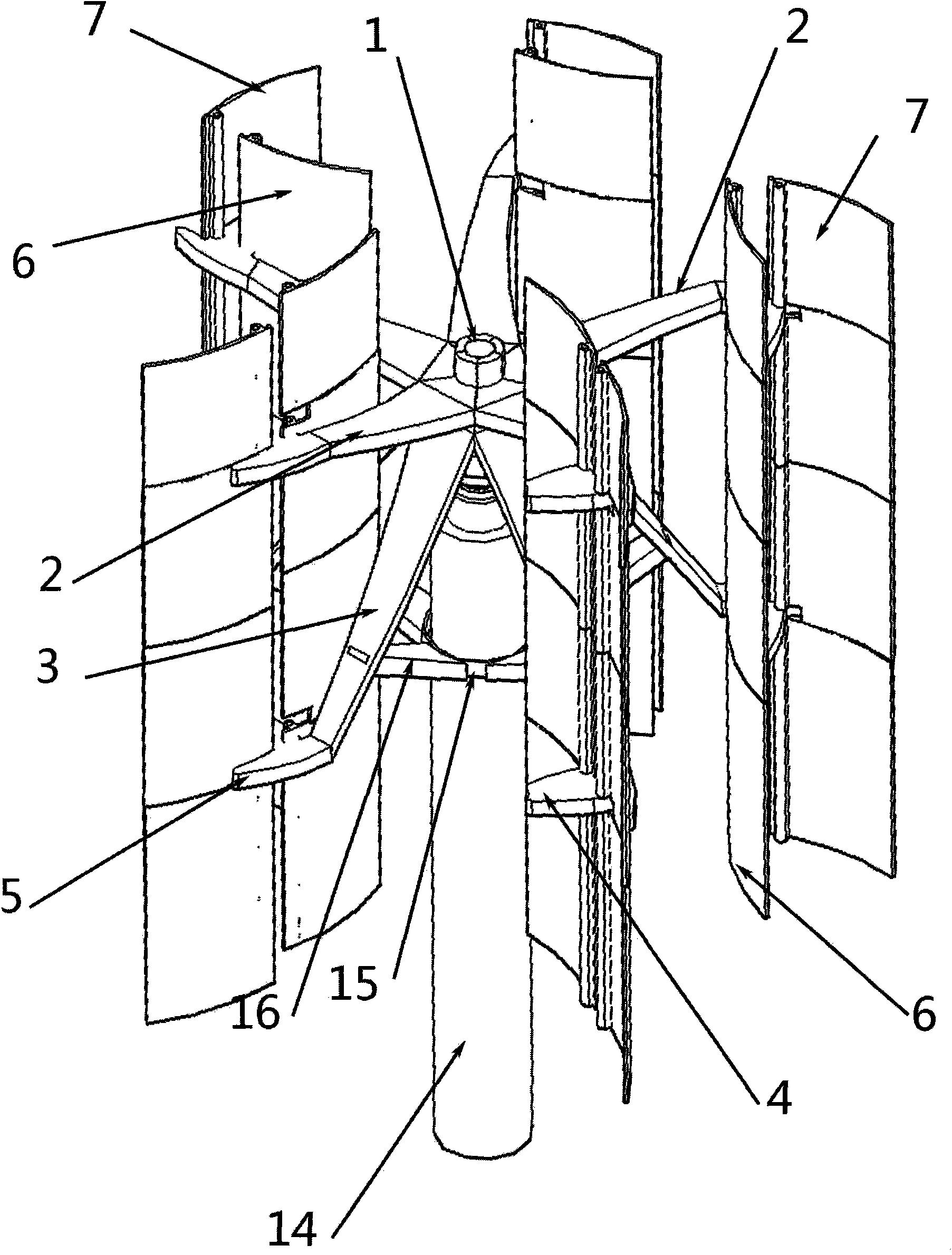
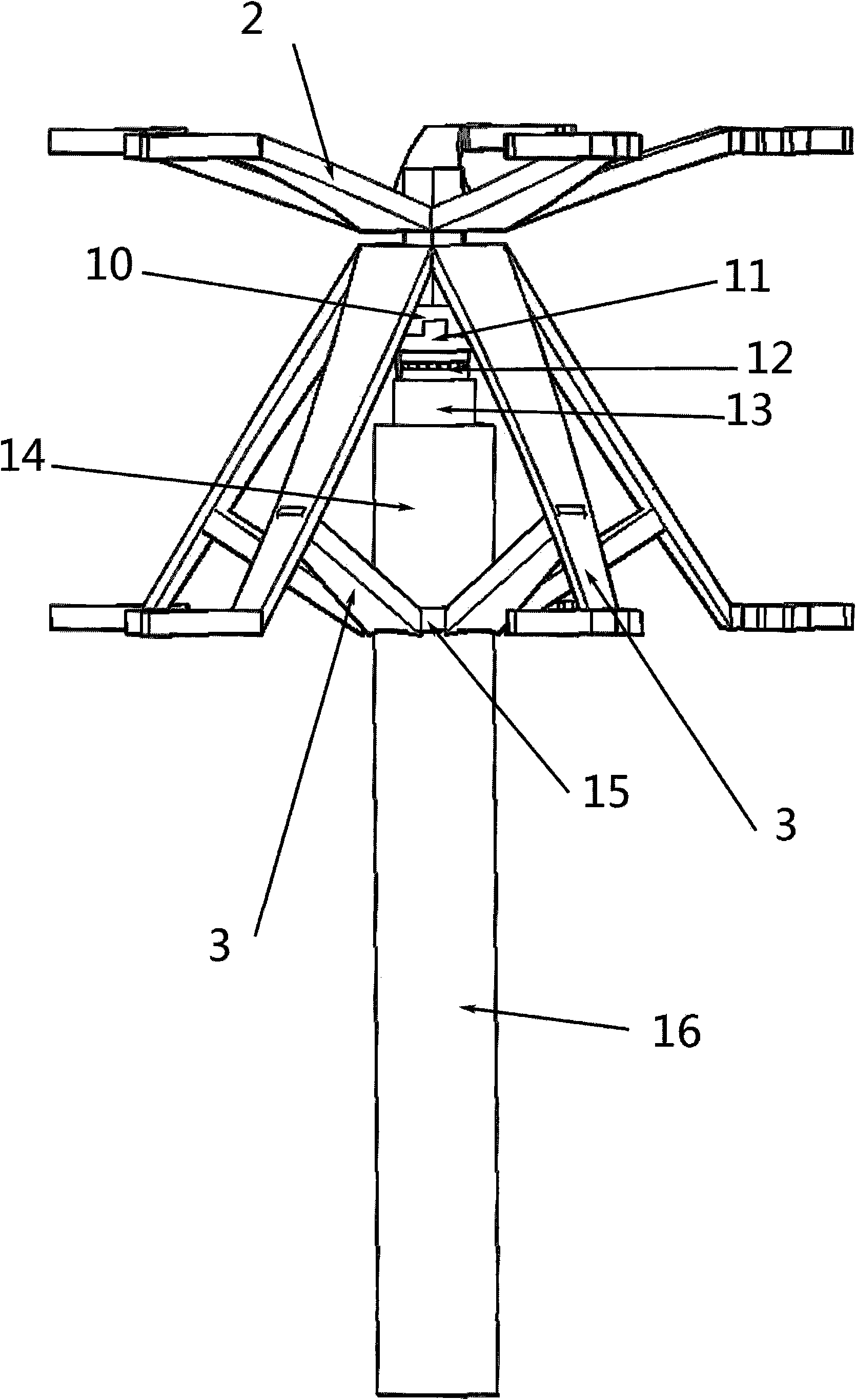
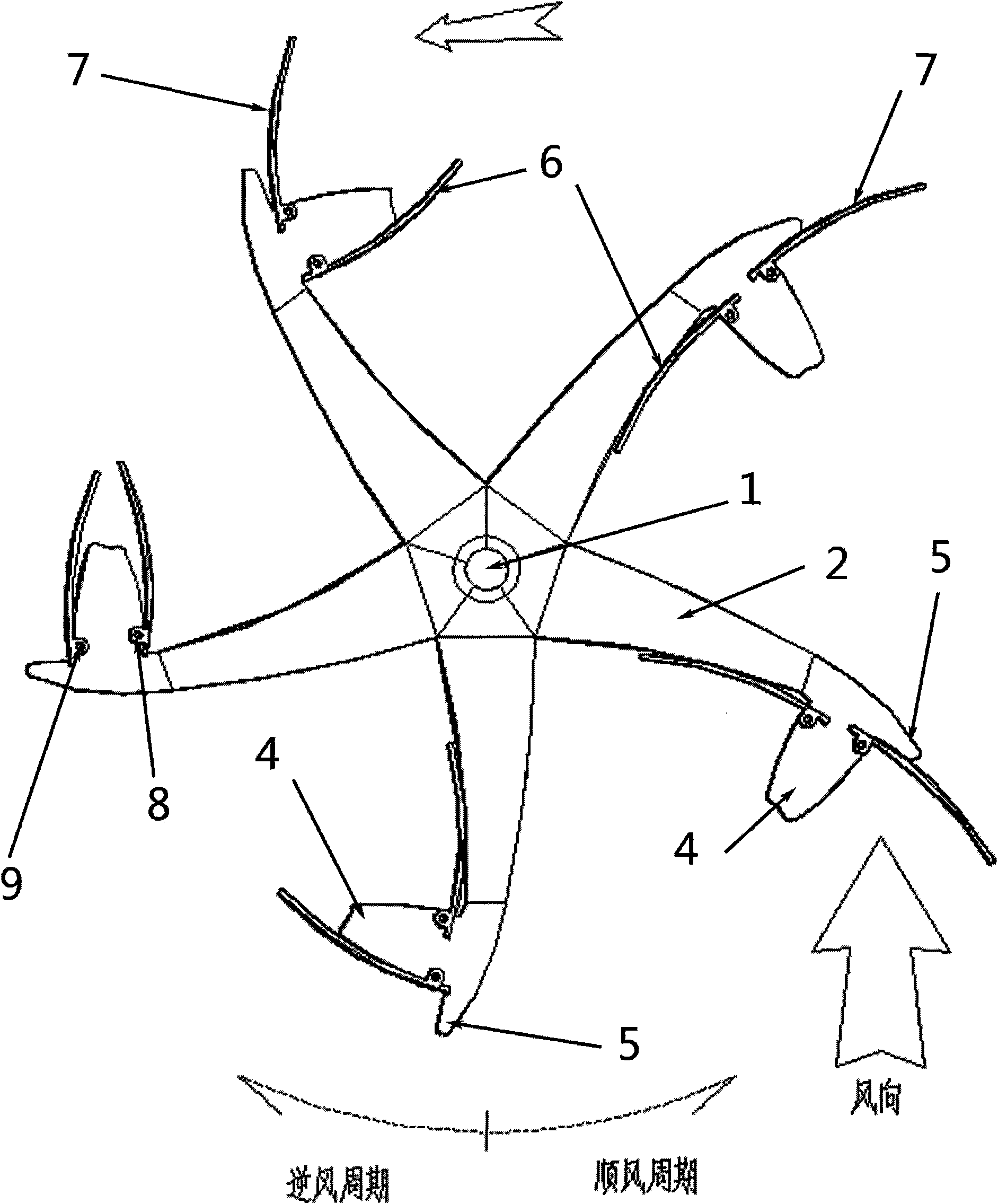
A small wind turbine is a wind turbine used for microgeneration, as opposed to large commercial wind turbines, such as those found in wind farms, with greater individual power output. The Canadian Wind Energy Association (CanWEA) defines "small wind" as ranging from less than 1000 Watt (1 kW) turbines up to 300 kW turbines. The smaller turbines may be as small as a 50 Watt auxiliary power generator for a boat, caravan, or miniature refrigeration unit. The IEC-61400-2:2006 Standard defines small wind turbines as wind turbines with a rotor swept area smaller than 200 m2, generating at a voltage below 1000 Va.c. or 1500 Vd.c.
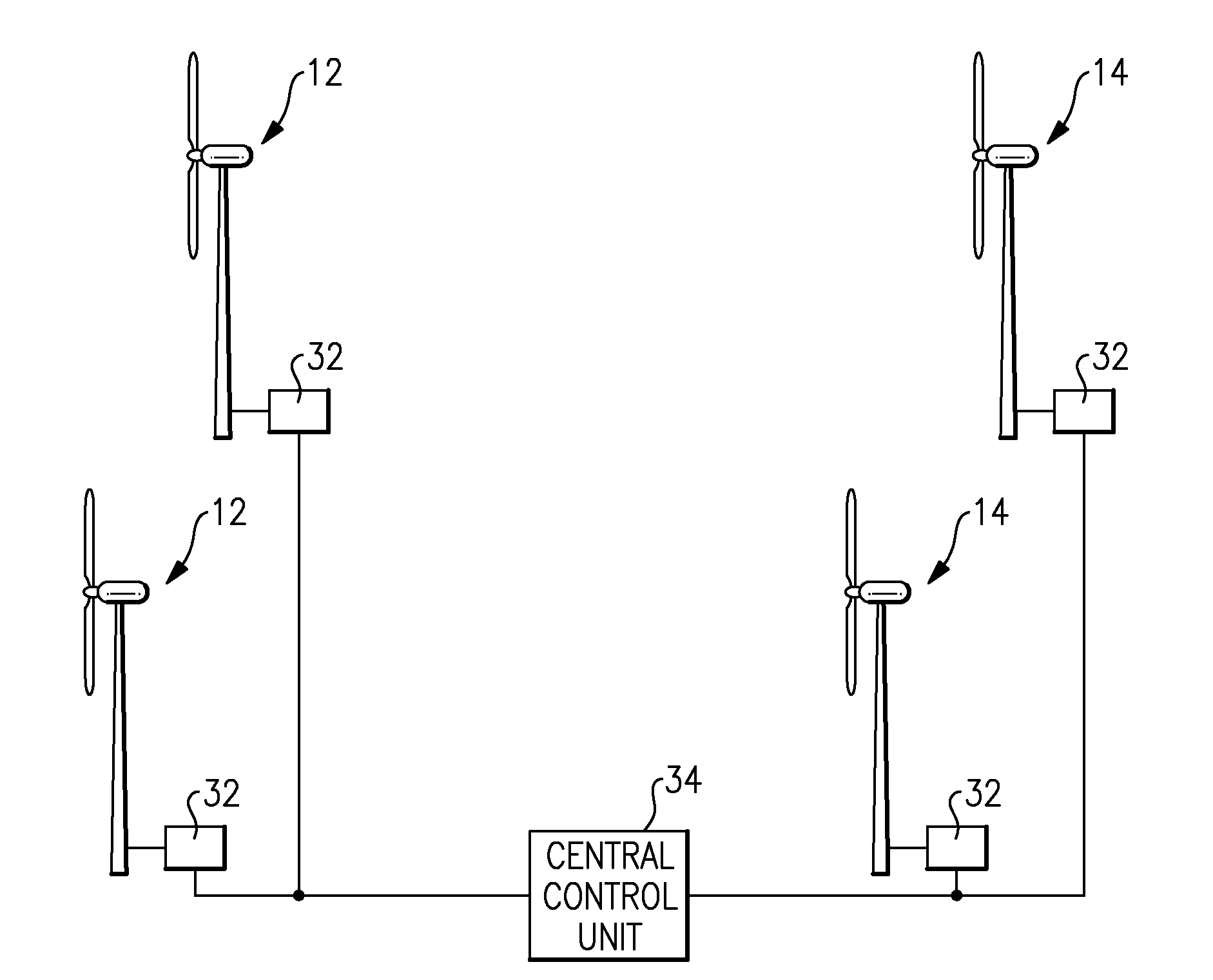
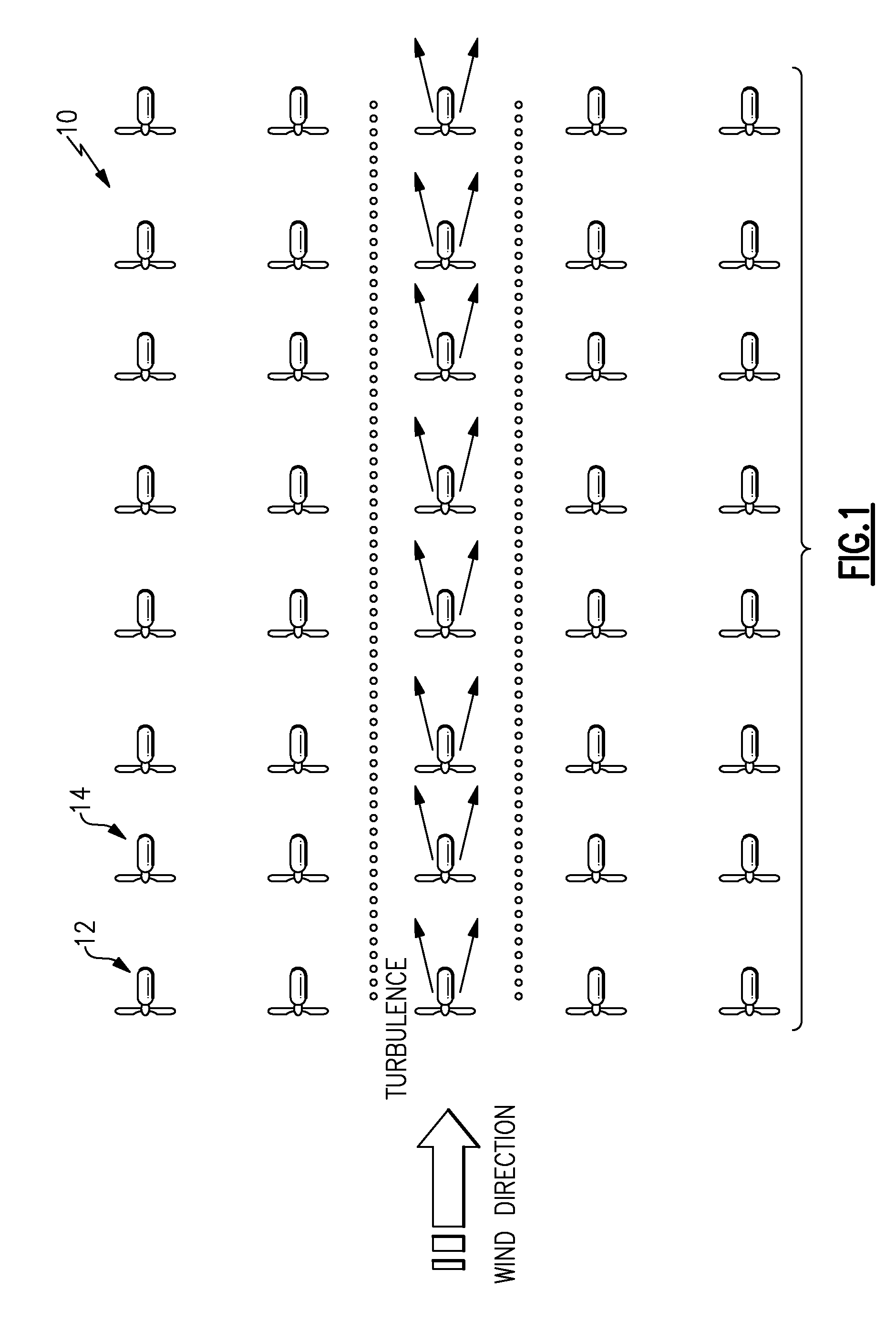
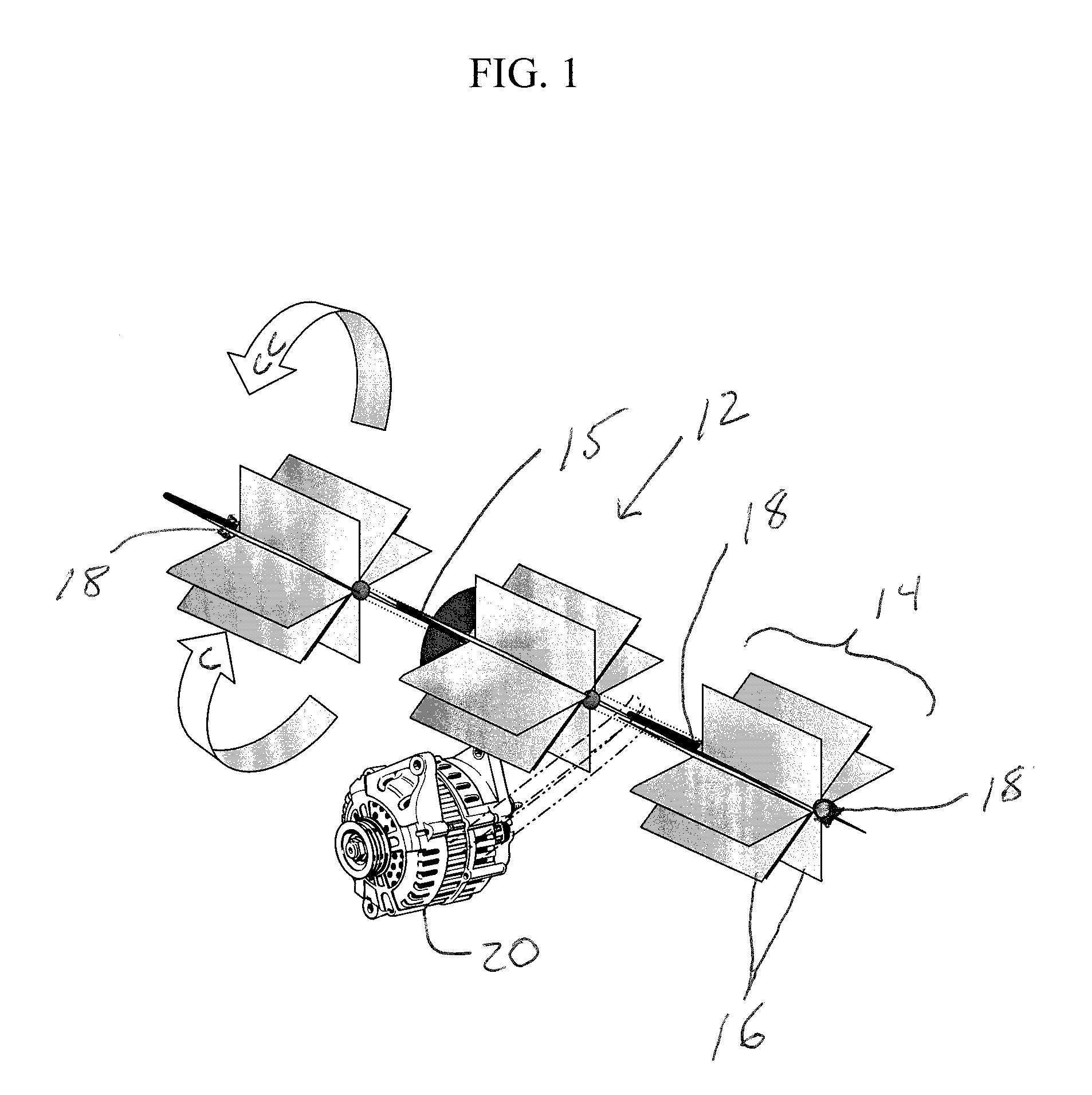
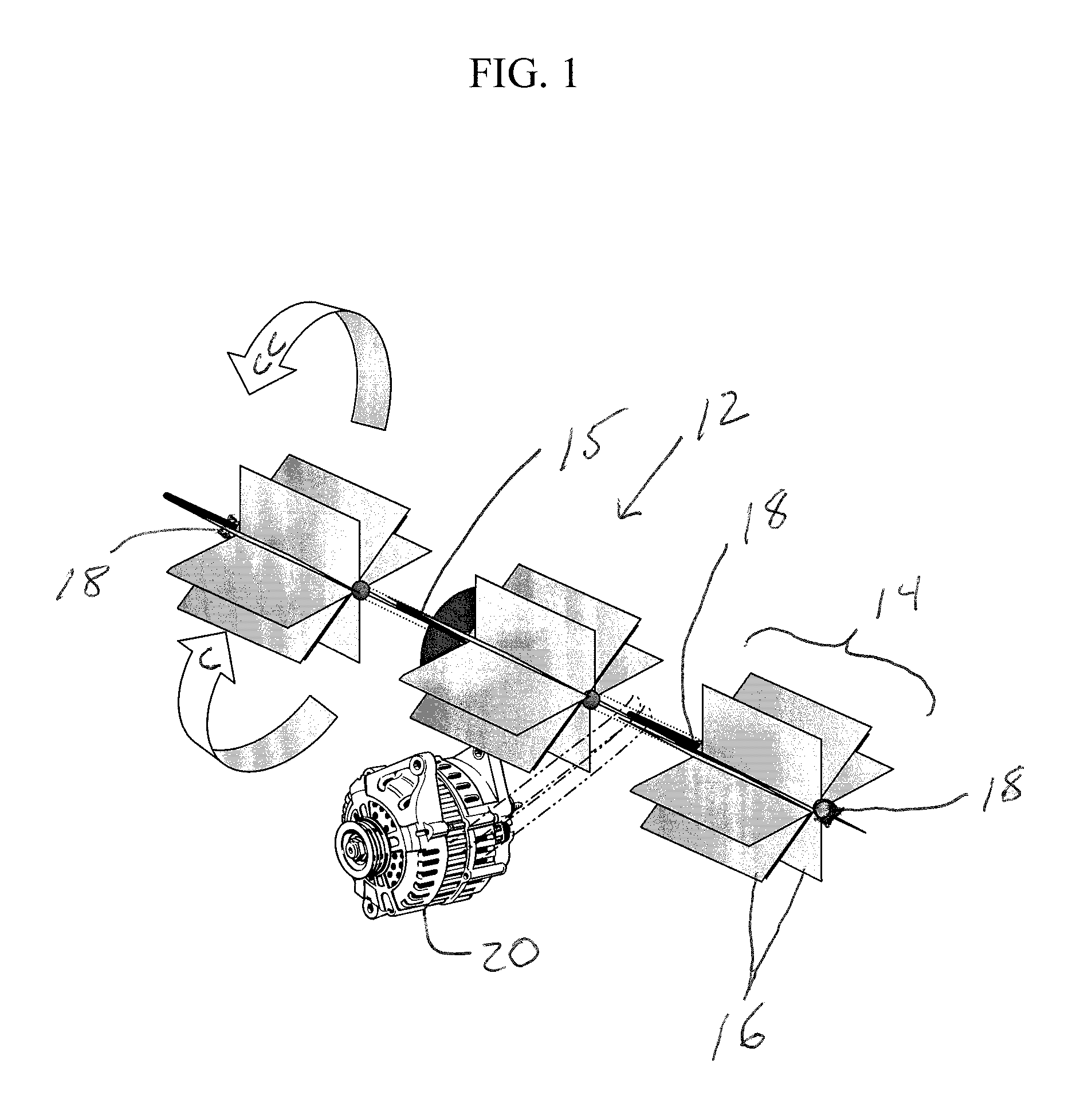
System and method for optimizing wake interaction between wind turbines
InactiveUS20090099702A1Increased energy captureEasy to captureLevel controlWind motor controlSmall wind turbineWind force
A system and method to increase the overall power output of a windpark during conditions when the wake created by an upstream turbine effects the power production of a downstream turbine. Minimizing the wake effects created by an upstream turbine on a downstream turbine increases the net power produced by both the upstream and downstream turbines. The invention is an implementation of an algorithm to determine the controller settings of one or more upstream turbines to increase total energy capture of the turbines in the windpark. The algorithm also reduces the fatigue loads on the downstream turbines by reducing the turbulence created by the wake effects of the upstream turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
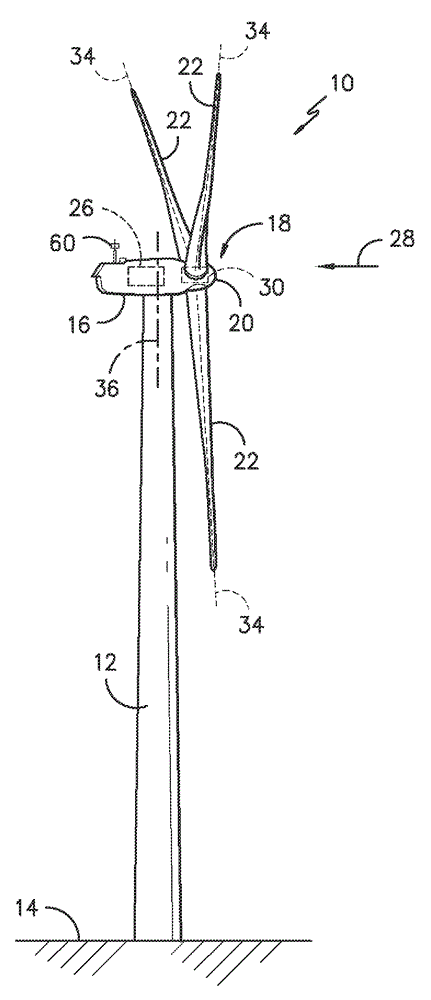
Method and apparatus to determine the wind speed and direction experienced by a wind turbine
ActiveUS20070086893A1Low costSimple and robust and low cost apparatusPropellersWind motor controlNacelleEngineering
An apparatus and a method used to determine the speed and direction of the wind experienced by a wind turbine are provided. The apparatus comprises at least one sensor fixed to the rotor of the wind turbine, an angular sensor to measure the angular position of the rotor of the wind turbine, and a circuit which converts the relationship between the output of the at least one sensor and the output of the angular sensor into the speed and direction of the wind experienced by the wind turbine. According to the invention, the sensing apparatus can measure the wind speed and direction in three dimensions. In addition, mounting the sensors directly to the rotor of the wind turbine results in a very simple and robust installation. Mounting the sensors directly to the rotor also eliminates the turbulence from the rotor and the nacelle of the wind turbine from affecting the sensors.
Owner:ROMO WIND AG
Wind turbine tower, a wind turbine, a wind turbine tower elevator and a method for assembling a wind turbine tower
ActiveUS20090016897A1Avoid transportMade preciselyEngine manufactureFinal product manufactureTowerSmall wind turbine
The invention relates to a wind turbine tower comprising at least two annular tower rings placed vertically on top of each other. The wind turbine tower is characterized in that, a first tower ring overlaps at least a further tower ring of the at least two tower rings. The invention further relates to a wind turbine, a wind turbine tower elevator for use in a wind turbine tower and a method for assembling a wind turbine tower.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
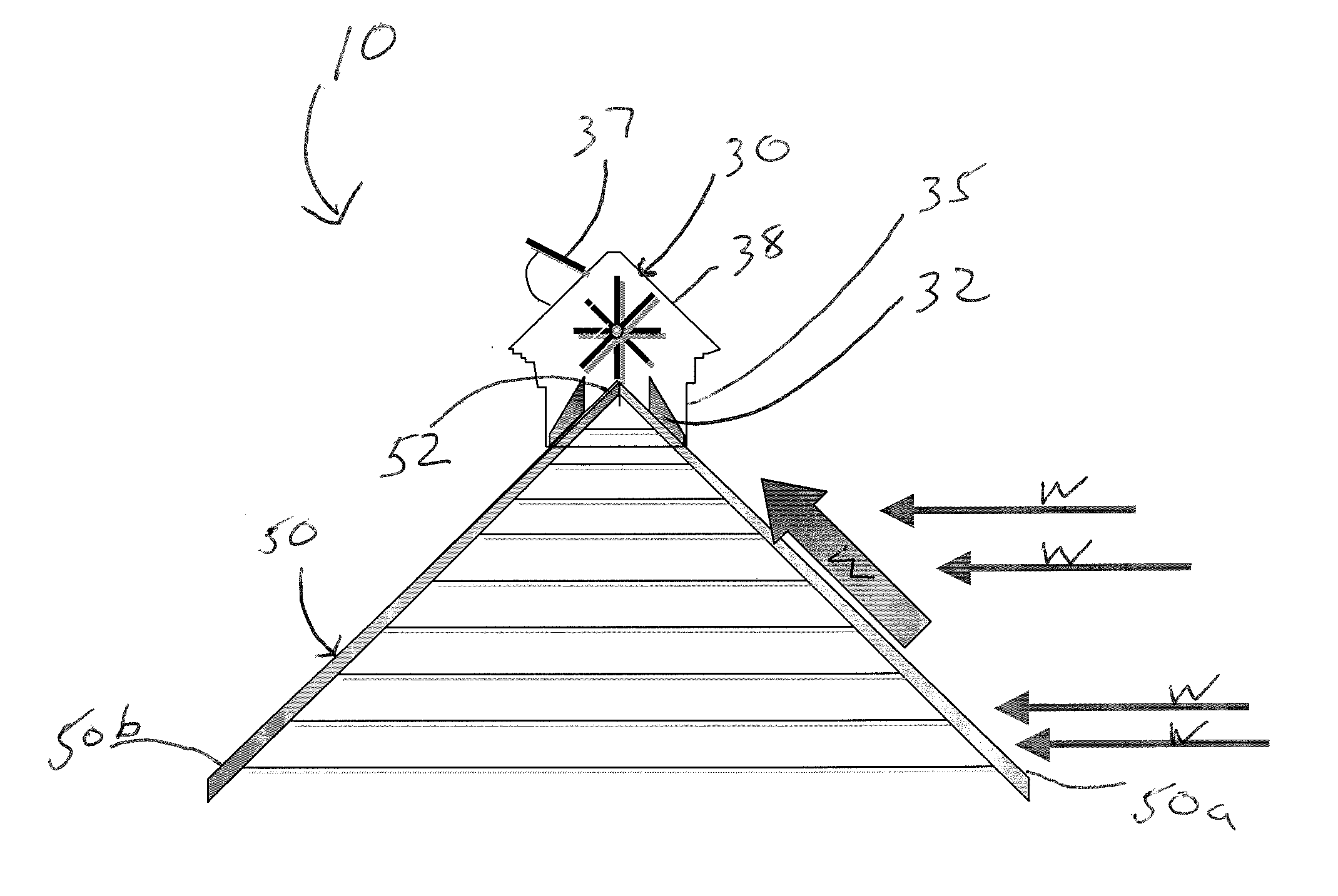
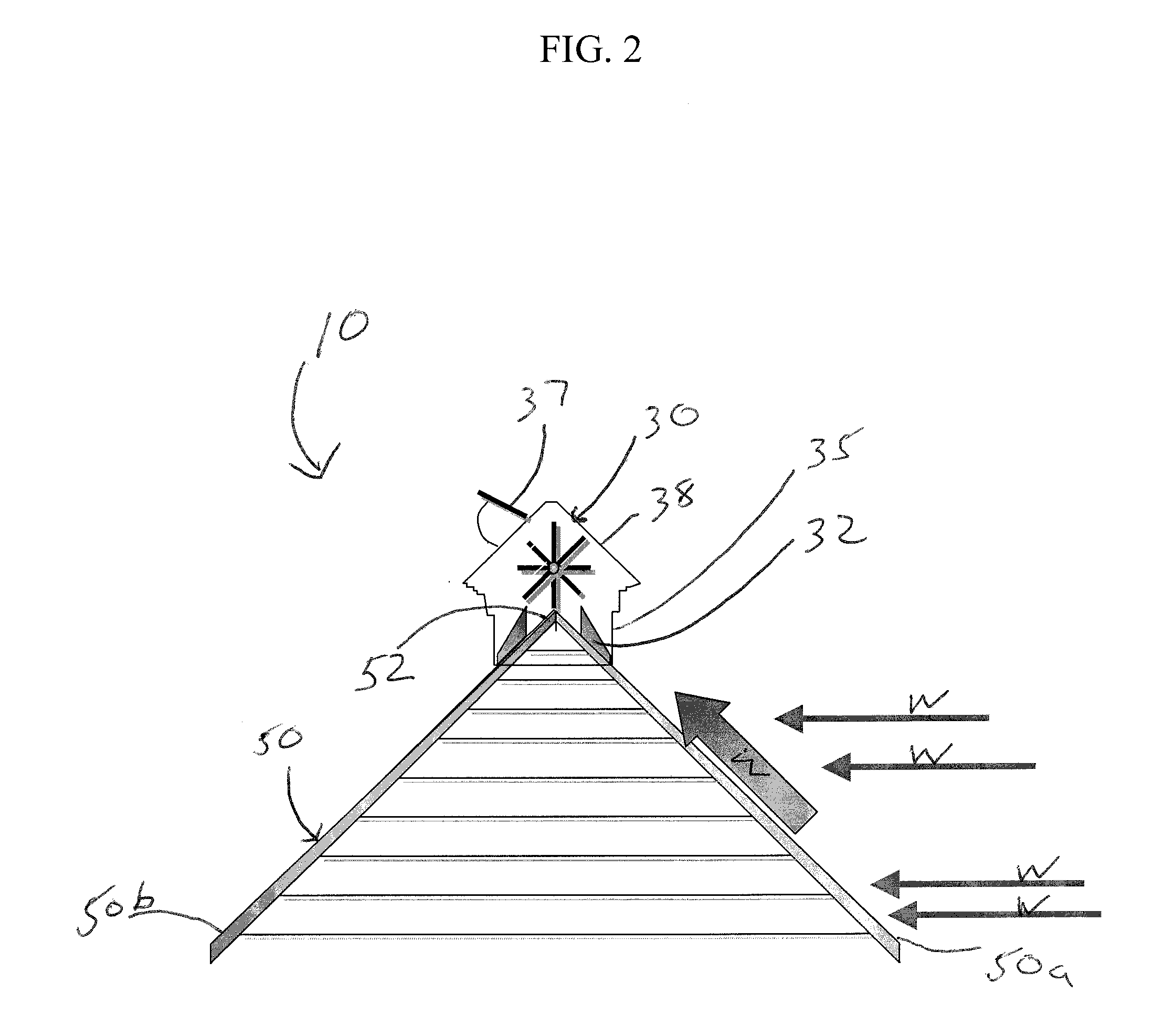
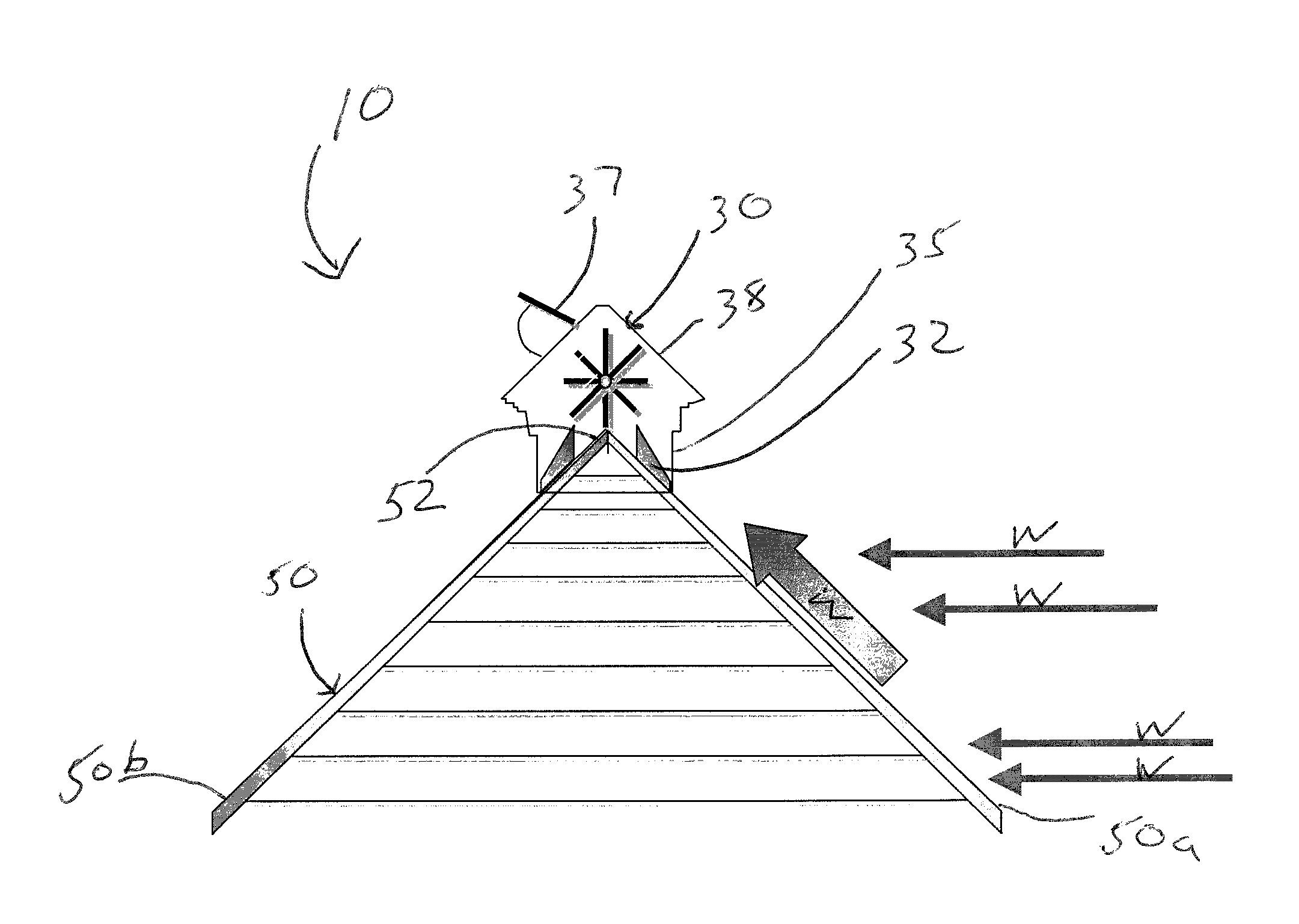
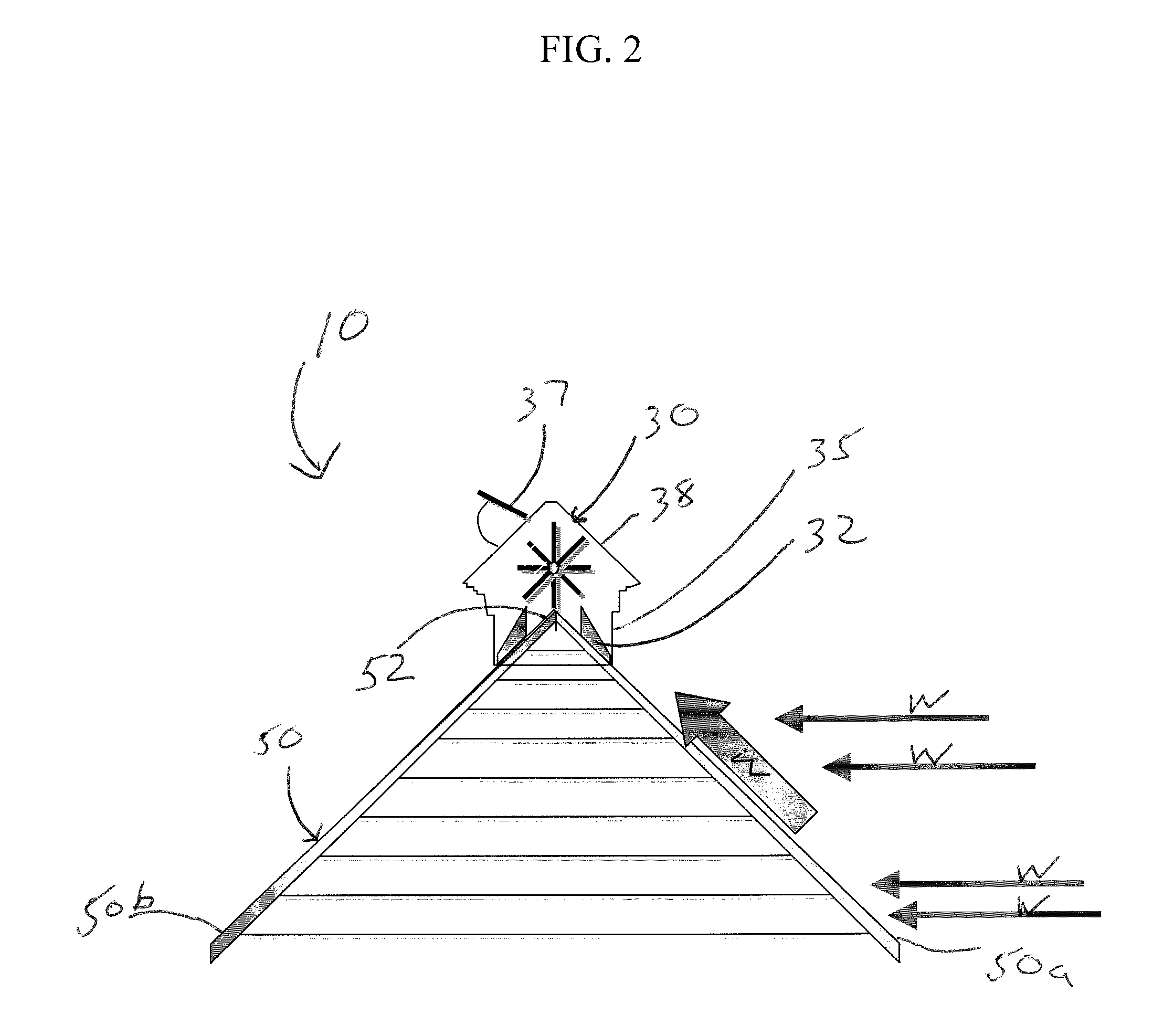
Roof ridge wind turbine
InactiveUS20100126086A1Increase wind speedReduce air pressureSpace heating and ventilationRotary non-positive displacement pumpsSmall wind turbineLouver
Disclosed are systems and method that generally relate to the capture of wind energy by small wind turbines mounted on buildings with gabled roofs. Wind energy harnessing system for gabled roof buildings having a roof ridge including a low silhouette visually appealing enclosure mounted along the roof ridge of a building and extending down both sides of the roof forming the ridge. The enclosure includes airflow guides defined by columns extending down a length of both sides of the building roof forming sidewalls and a roof formed of pivoting louvers above the columns. A paddle-wheel type wind turbine consists of a multiple-bladed cylindrical shaft that contacts the wind and provides rotational work mounted within the enclosure and a generator connected to the wind turbine for converting the rotational work from the wind turbine to electrical energy. The enclosure for the wind turbine functions to capture wind and directs the airflow via the airflow guides before it reaches the ridge.
Owner:TURBOROOF
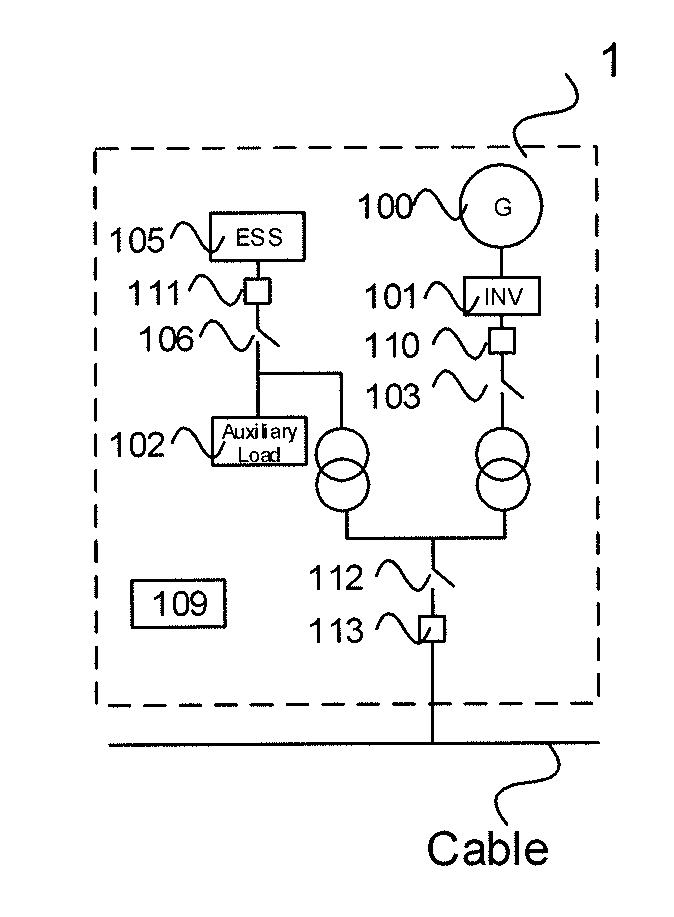
Method for black starting wind turbine, wind farm, and restoring wind farm and wind turbine, wind farm using the same
ActiveUS20170074244A1Reduce communicationVoltage and frequency stabilityWind motor controlWind energy with electric storageElectricityIslanding
A method for black starting a wind turbine and a wind farm following islanding operation, a method for restoring the wind farm following the islanding operation, and the wind turbine and wind farm. The wind turbine comprises auxiliary equipment, a generator, a converter electrically connectable to the generator, and an energy storage system, the generator is electrically connectable to the auxiliary equipment via the converter, the energy storage system is electrically connectable to the auxiliary equipment. The method for black staring the wind turbine including: measuring wind blowing smoothness degree; selecting a first power source to supply first power to the auxiliary equipment in V / f control mode and selecting a second power source to adjust an amount of active power and reactive power fed to the auxiliary equipment by the first power source in consideration of the amount of active power and reactive power demand suitable for powering the auxiliary equipment; and connecting the power sources to the auxiliary equipment.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
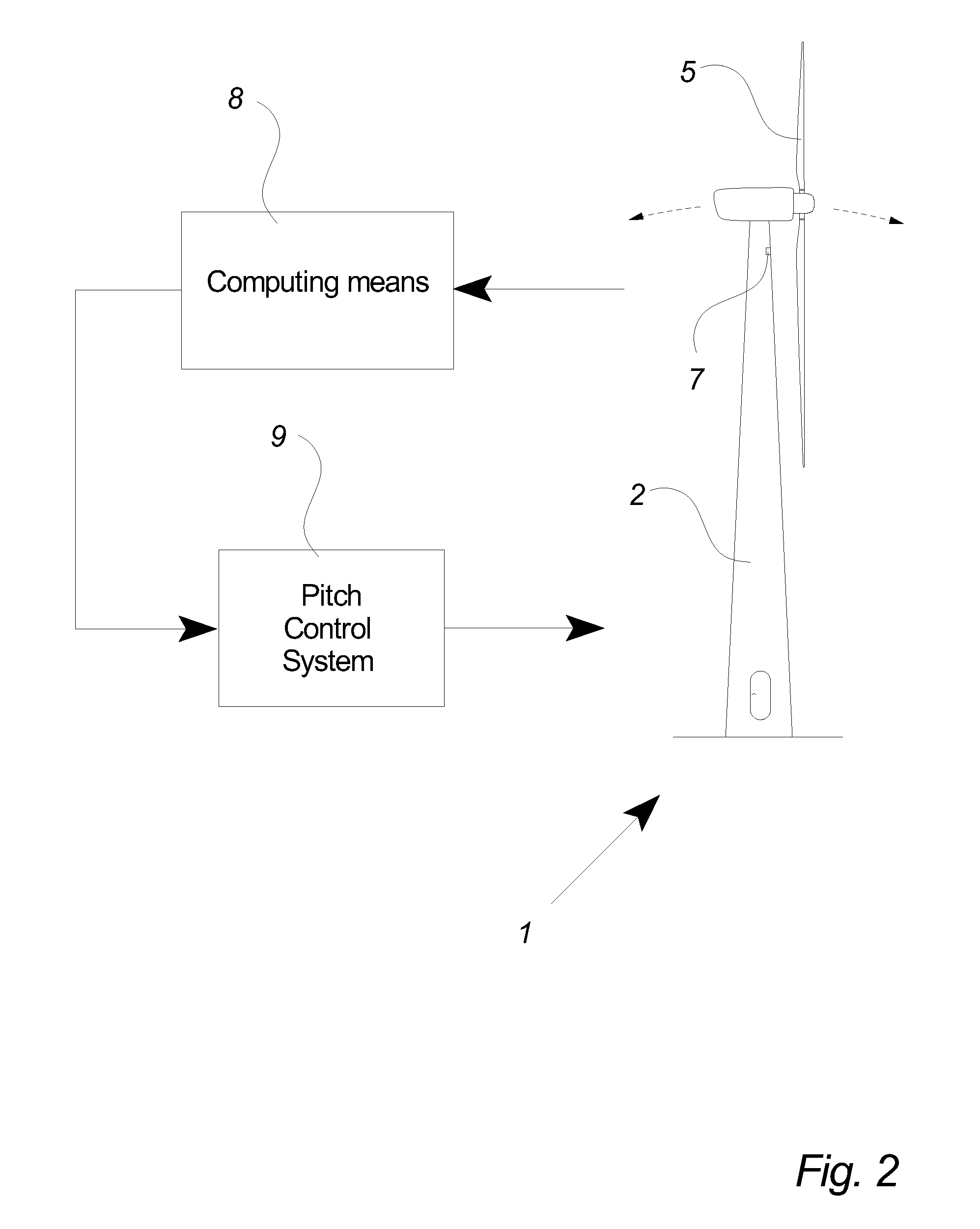
Method of operating a wind turbine with pitch control, a wind turbine and a cluster of wind turbines
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Dual-Sepic buck-boost output parallel combined inverter
InactiveCN101958660AAvoid thruSuppress fluctuationsAc-dc conversionPhotovoltaic energy generationNew energyEngineering
The invention discloses a dual-Sepic buck-boost output parallel combined inverter, which comprises two buck-boost Speic DC / DC circuits that are connected in parallel at the output side, and which can realize the buck-boost single-phase inversion and expand the buck-boost single-phase inversion in a three-phase system to realize the three-phase inversion output. The inverter has the basic function of realizing buck-boost inversion; when the direct-current voltage at the input side is lower or the change range is larger, the dual-Sepic buck-boost output parallel combined inverter still can realize the inversion function; two high-frequency switching tubes adopt a non-complementary work manner and do not work simultaneously, therefore, the bridge through problem is prevented; the circuit parameter designing principle can be designed according to the mature direct-current Sepic converter designing principle; the inductive current works under the continuous state and reduces the influence of the EMI (Electro-Magnetic interference). The invention is mainly applied to the field of renewable energy source or new energy source generation with lower direct-current voltage, faster change or larger fluctuation range, such as photovoltaic power generation, a small Wind turbine generator system, fuel cell generation, and the like.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Stratum deployment of wind turbines
InactiveUS7909567B2Introducing energyFirmly connectedPropellersWind motor controlEngineeringSmall wind turbine
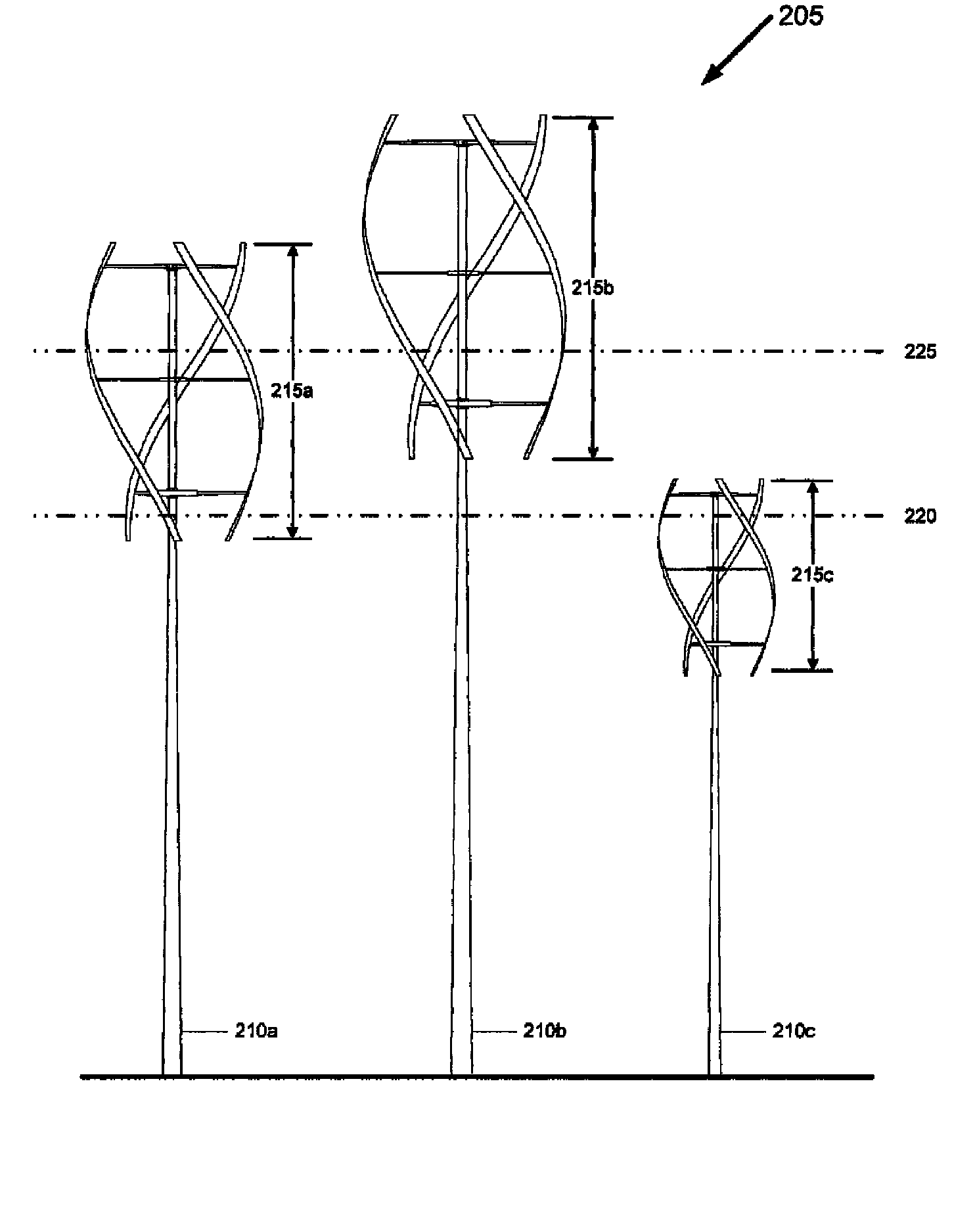
Installing large-sized wind turbines creates numerous challenges and limitations, hindering acceptance of wind generated energy. With small-sized wind turbines, such hindrances are omitted or minimized. Sized ever smaller, more small-sized wind turbines may be installed per installation. Accordingly, a method and corresponding apparatus for maximizing wind energy gathering potential of a plurality of wind turbines, each wind turbine having a sweep height, for a given location is provided. The present invention includes sizing sweep heights of substantially all wind turbines of the plurality of wind turbines to intersect at least one horizontal plane unique from horizontal planes intersected by a sweep height of at least one immediately adjacent wind turbine. Because the sweep height of each wind turbine of the plurality is individually sized in a prescribed manner, the present invention maximizes the wind energy gathering potential of the plurality of wind turbines especially for deployment of small-sized wind turbines.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
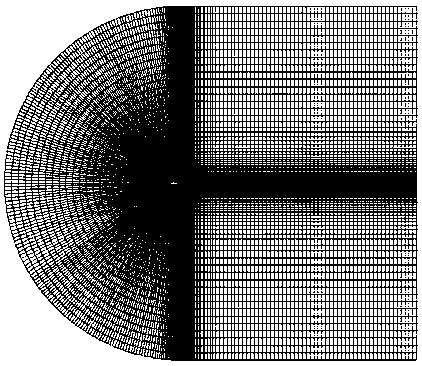
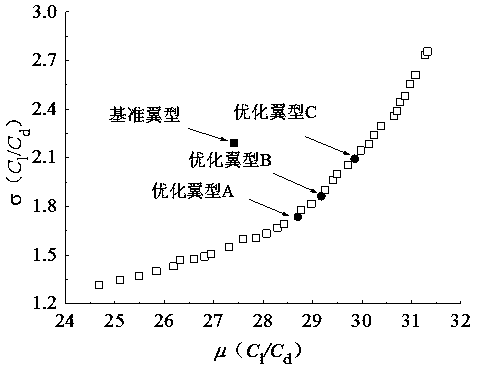
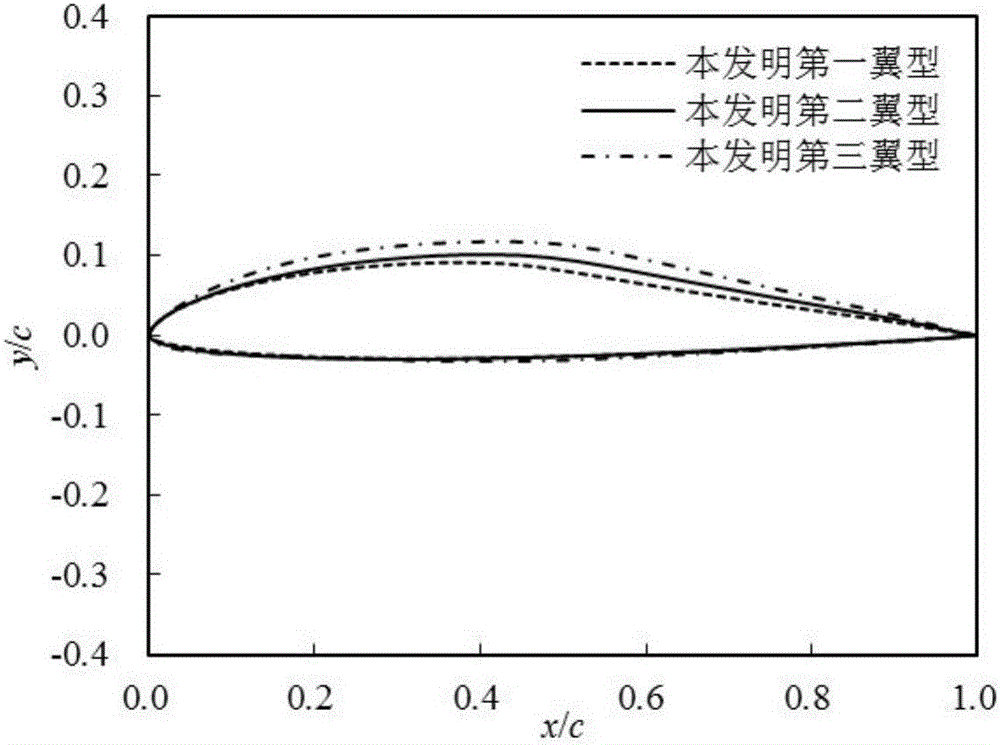
Small wind turbine wing type aerodynamic robust optimization design method suitable for turbulent working conditions
ActiveCN109376418AImprove the lift-to-drag ratioImprove capture efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelEngineering
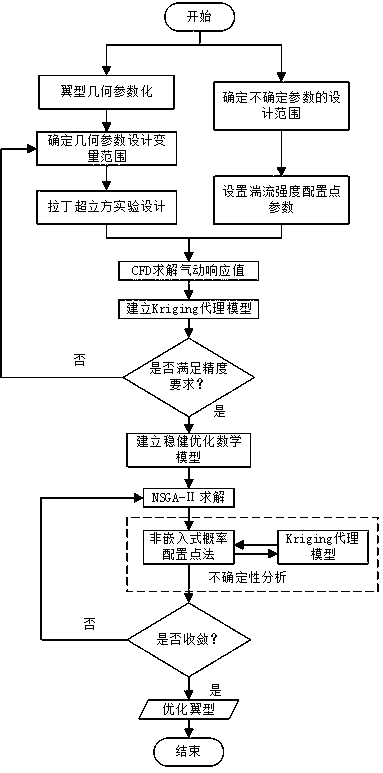
The invention discloses a small wind turbine wing type aerodynamic robust optimization design method suitable for turbulent working conditions, belonging to the technical field of wind turbines. The invention adopts the non-embedded probability collocation point method in the design to realize the quantitative characterization of the turbulence intensity of the uncertain parameter. Through the improved Hick-Henne type function parameterization method, Latin hypercube test method and CFD numerical calculation method, the kriging agent model between design variables, uncertain parameters and themaximum lift-to-drag ratio of the airfoil is established. On this basis, a robust optimization mathematical model is established to maximize the mean value of the maximum lift-to-drag ratio and minimize the standard deviation of the wind turbine wing under uncertain turbulent conditions. The non-embedded probabilistic configuration point method, the kriging proxy model, and the NSGA-II optimization algorithm are used to optimize the wind turbine airfoil. The invention improves the maximum lift-drag ratio of the airfoil, reduces the fluctuation range, improves the wind energy capture efficiency, and enhances the aerodynamic robustness under the turbulent condition. At the same time, the computational workload of robust optimization design is reduced, and the optimization efficiency is improved, which provides an important reference for the optimization design of wind turbine wing under turbulent conditions.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Methods for controlling a wind turbine connected to the utility grid, wind turbine and wind park
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
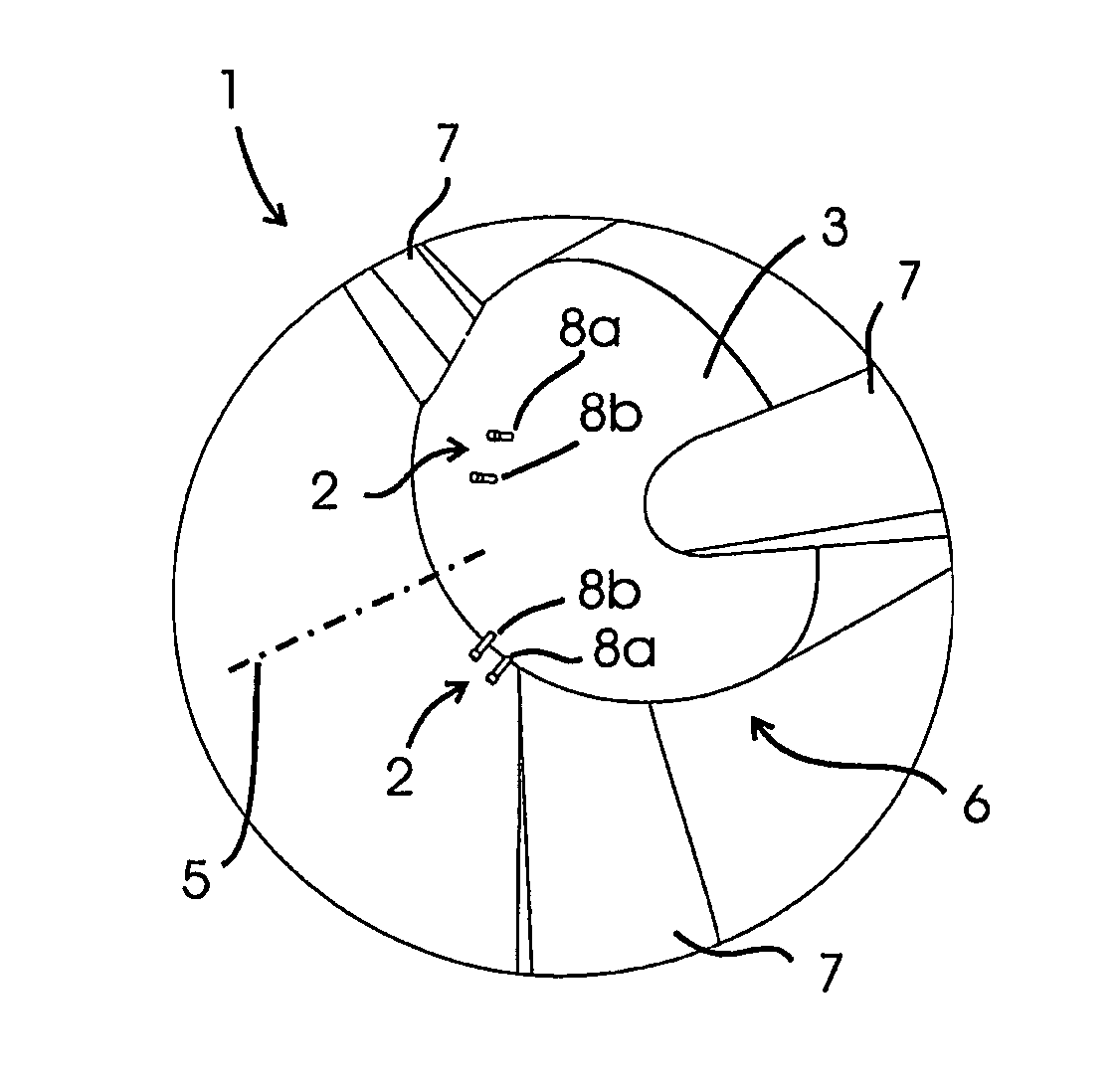
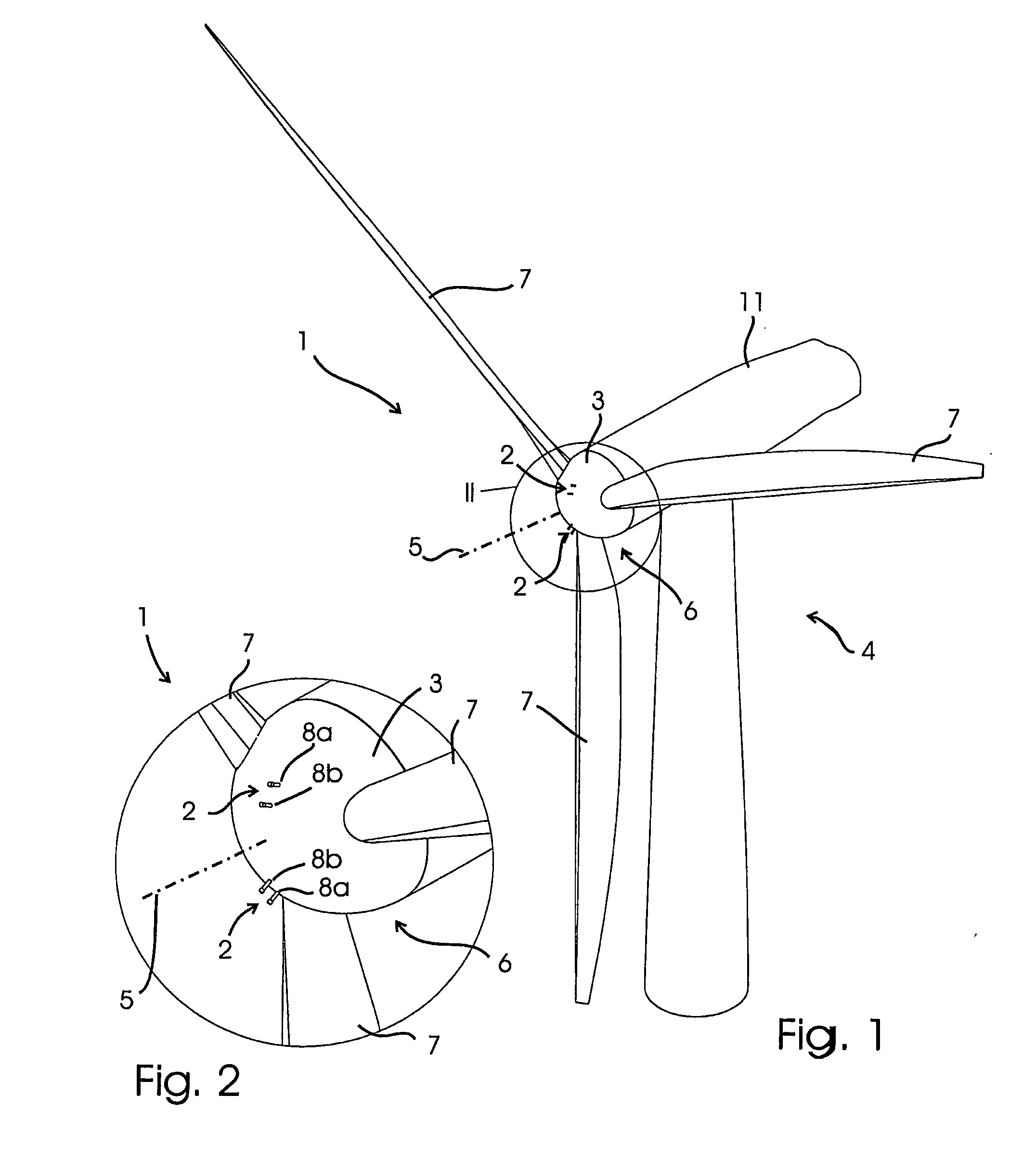
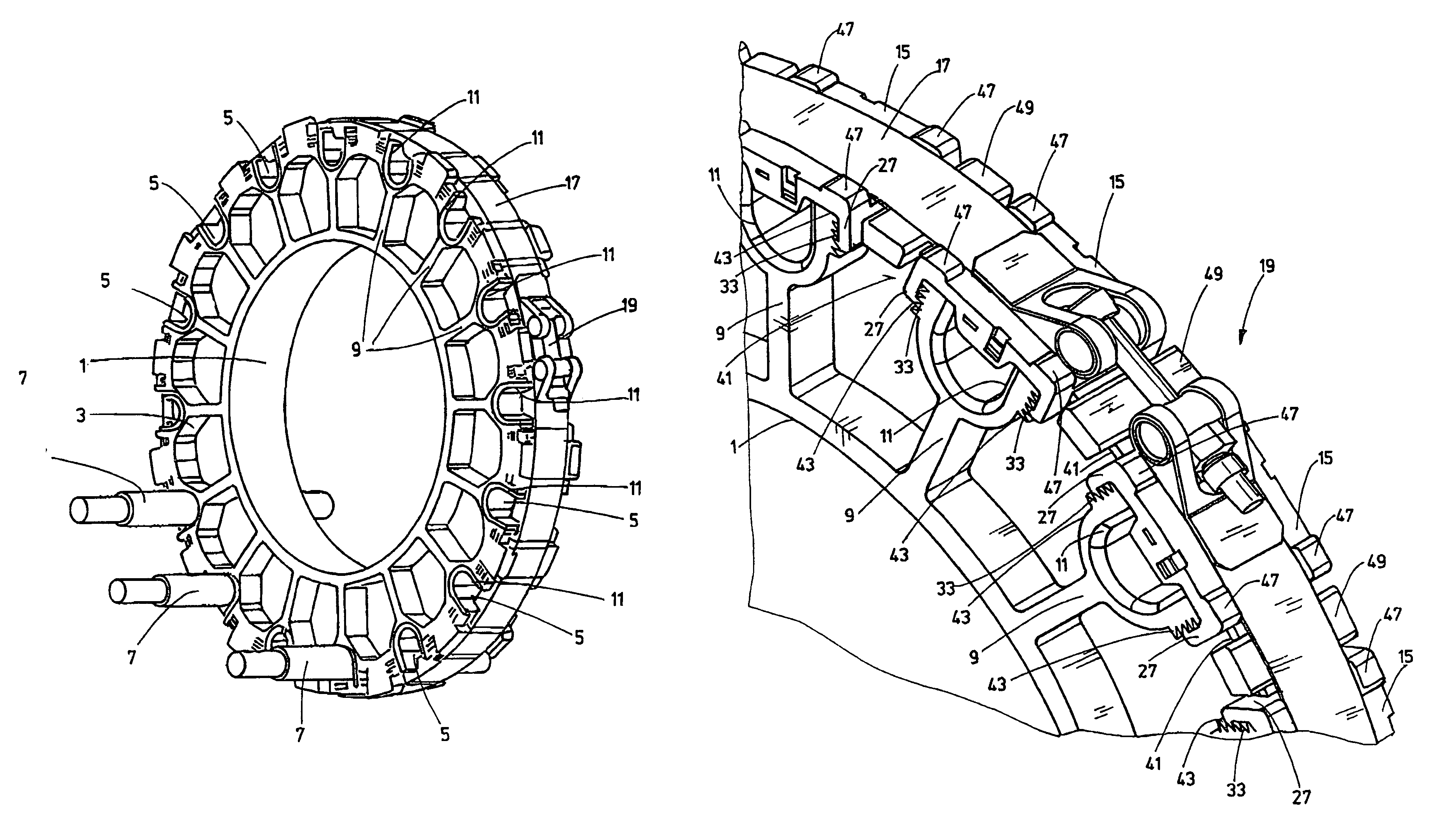
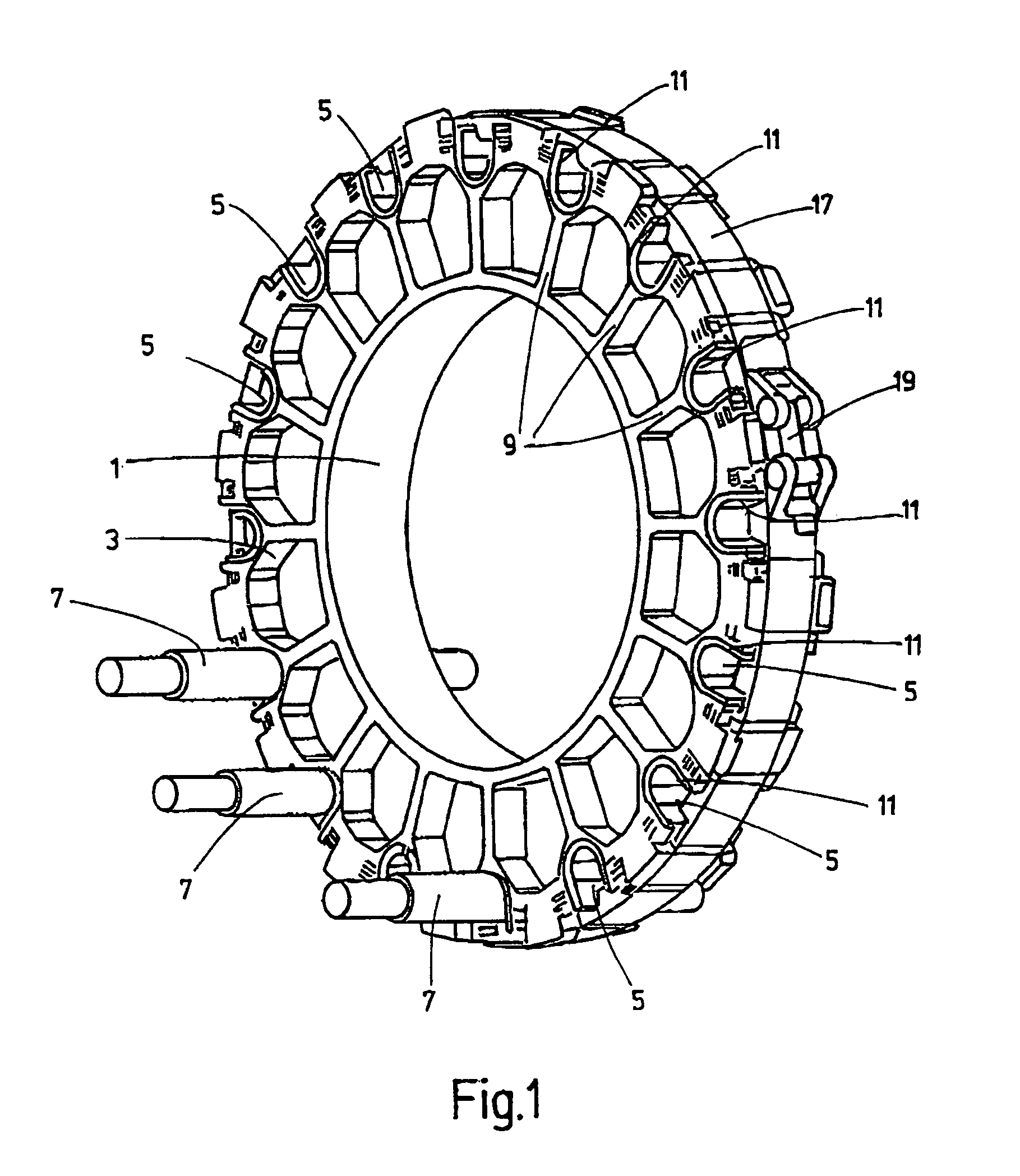
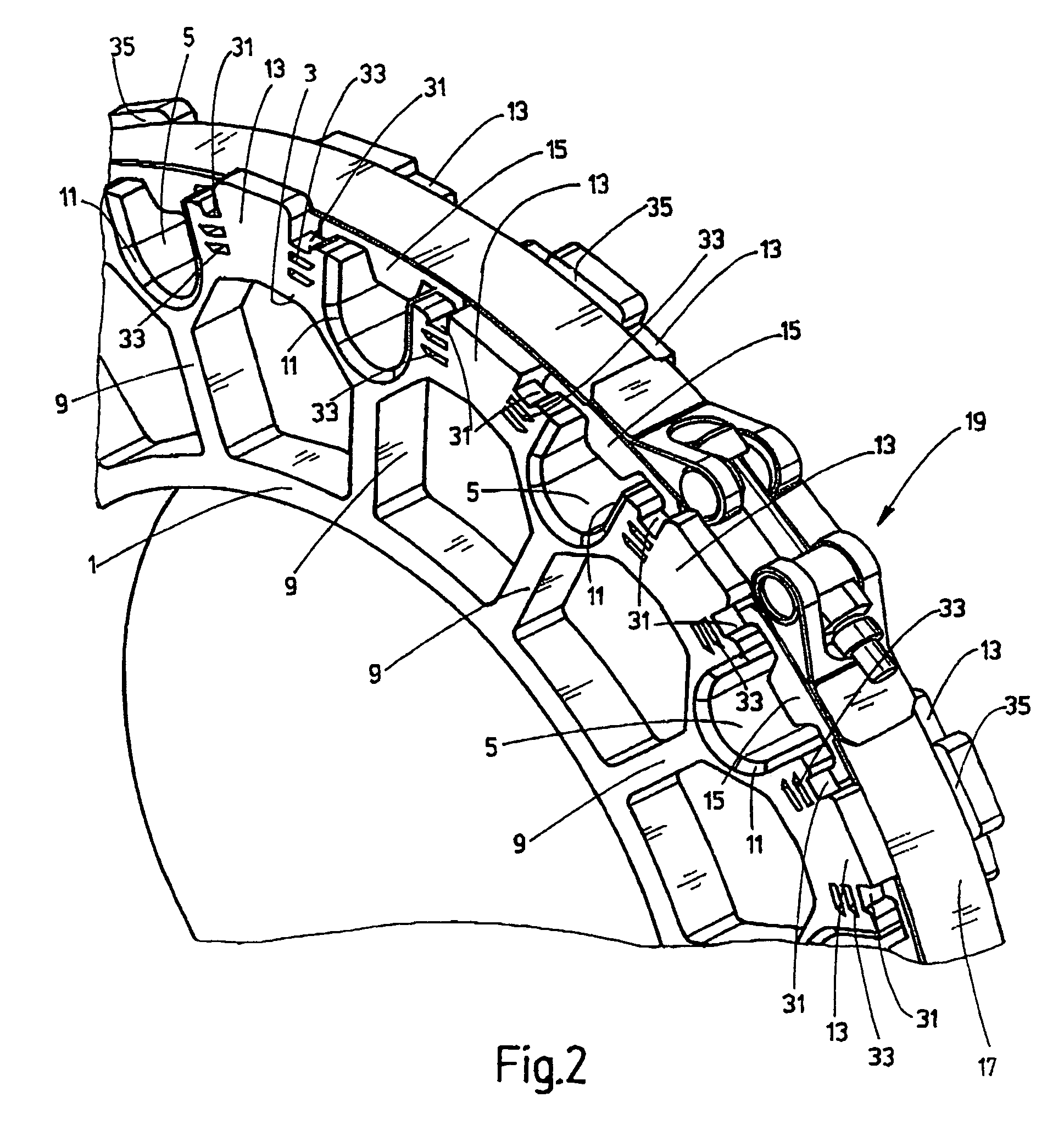
Attachment system for cables, in particular for wind turbines
InactiveUS8664544B2Easy to insertAdvantageouslySubstation/switching arrangement detailsInsulated cablesSmall wind turbine
An attachment system for cables (7), in particular for wind turbines, has a base body (1, 3) securable to a support structure and forming cable bushings (5) with openings for cables (7). The openings can be closed by a cover (17) applying retaining forces to the cables (7). The cable bushings (5) on the base body (1, 3) are arranged at least over part of a ring, with an outside opening. The cover (17) has retaining bodies lockable to the base body (1, 3) for preliminary fixing of the cables (7) inserted into the cable bushings (5) and a tightening strap (17) encompassing the base body (1, 3) and applying retaining forces to the cables (7) via the retaining bodies.
Owner:HYDAC ACCESSORIES
Wind turbine and a method for pitching a blade of a wind turbine
ActiveCN102661238AEvenly distributedReduce load concentrationWind motor controlMachines/enginesRotational axisTurbine blade
The present invention relates to a wind turbine and a method for pitching a blade of a wind turbine. The wind turbine (1) comprises at least one wind turbine blade assembly (28). The blade assembly (28) includes a blade (5) and a pitch bearing arranged between the blade (5) and a hub of the wind turbine, the blade assembly further including two or more hydraulic pitch cylinders for pitching the blade in relation to the hub The wind turbine (1) is characterised in that the two or more hydraulic pitch cylinders (10) are arranged to expand in the same angular direction around the rotational axis of the pitch bearing (9).
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Rotor blade of a wind turbine
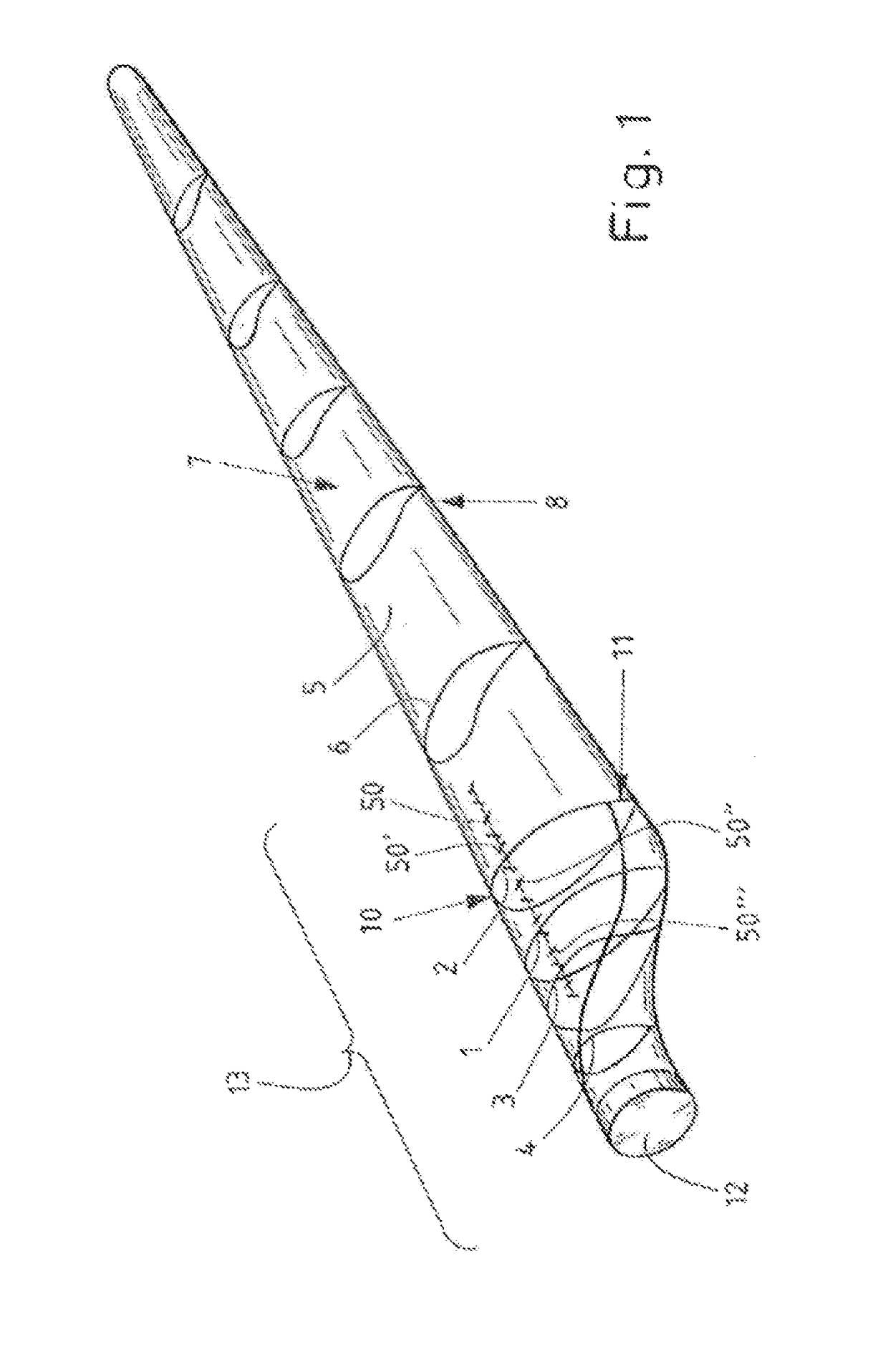
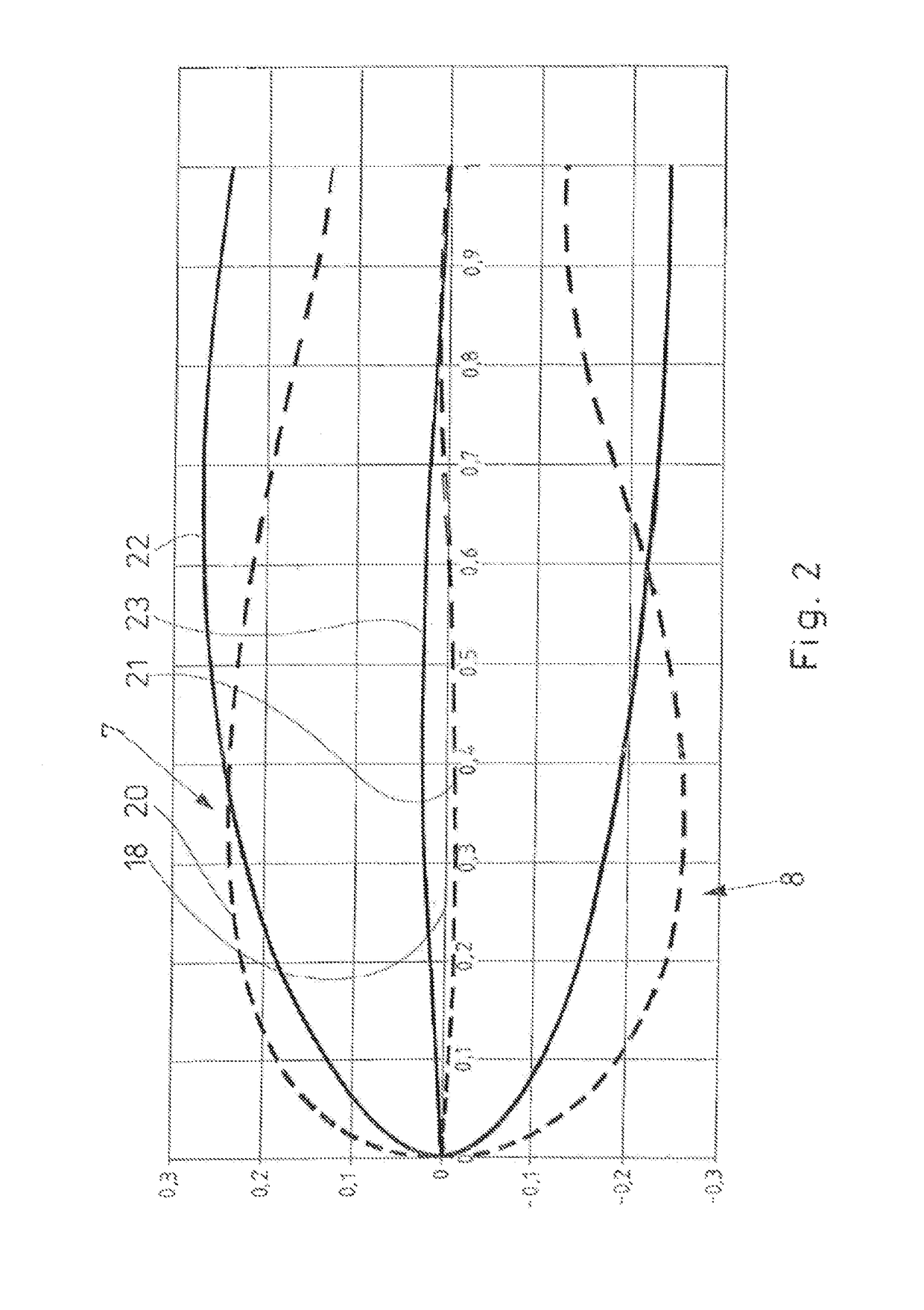
ActiveUS9932960B2Good attackImprove compatibilityMachines/enginesEngine componentsLeading edgeTrailing edge
A rotor blade (5) of a wind turbine, which has a profile (1-4) having an upper side (suction side) (7) and an underside (pressure side) (8). The profile (1-4) includes a camber line (21, 25) and a chord (18) between a leading edge (10) and a trailing edge (11) of the profile (1-4). The profile (1-4) has a relative profile thickness of more than 45%. At least one vortex generator (50, 50′, 50″, 50′″) is disposed, in the region of the profile (1-4), on the suction side (7) of the rotor blade (5). The profile (1-4) is provided with a blunt trailing edge. And, The thickness of the trailing edge is between 15% and 70% of the chord length.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
Smart power management during voltage dip in wind turbines
ActiveUS9528495B2Increase dampingReduce mechanical loadWind motor controlMachines/enginesPeak valueSmall wind turbine
The present invention is directed to a method of reducing a mechanical load on the occurrence of voltage dip in the wind turbines. The wind turbine generator controller and the converter control unit work in combination to control the oscillation generated due to voltage dip in the wind turbine 100. The method applies a ramp in power recovery to allow the enhanced DTD damp oscillations before the peak in torque happens. The method involves the step of: delivering a maximum active power value by the converter control unit to the wind turbine generator controller. Next step is setting a saturation value for the set points to enhance the drive train limits. In the next step, ramping is applied to the power set points of the wind turbine generator. And finally an enhanced drive train damping s applied to the ramped value of the power in order to reduce the mechanical load in the wind turbine and to damp the oscillation in the wind turbine generator.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
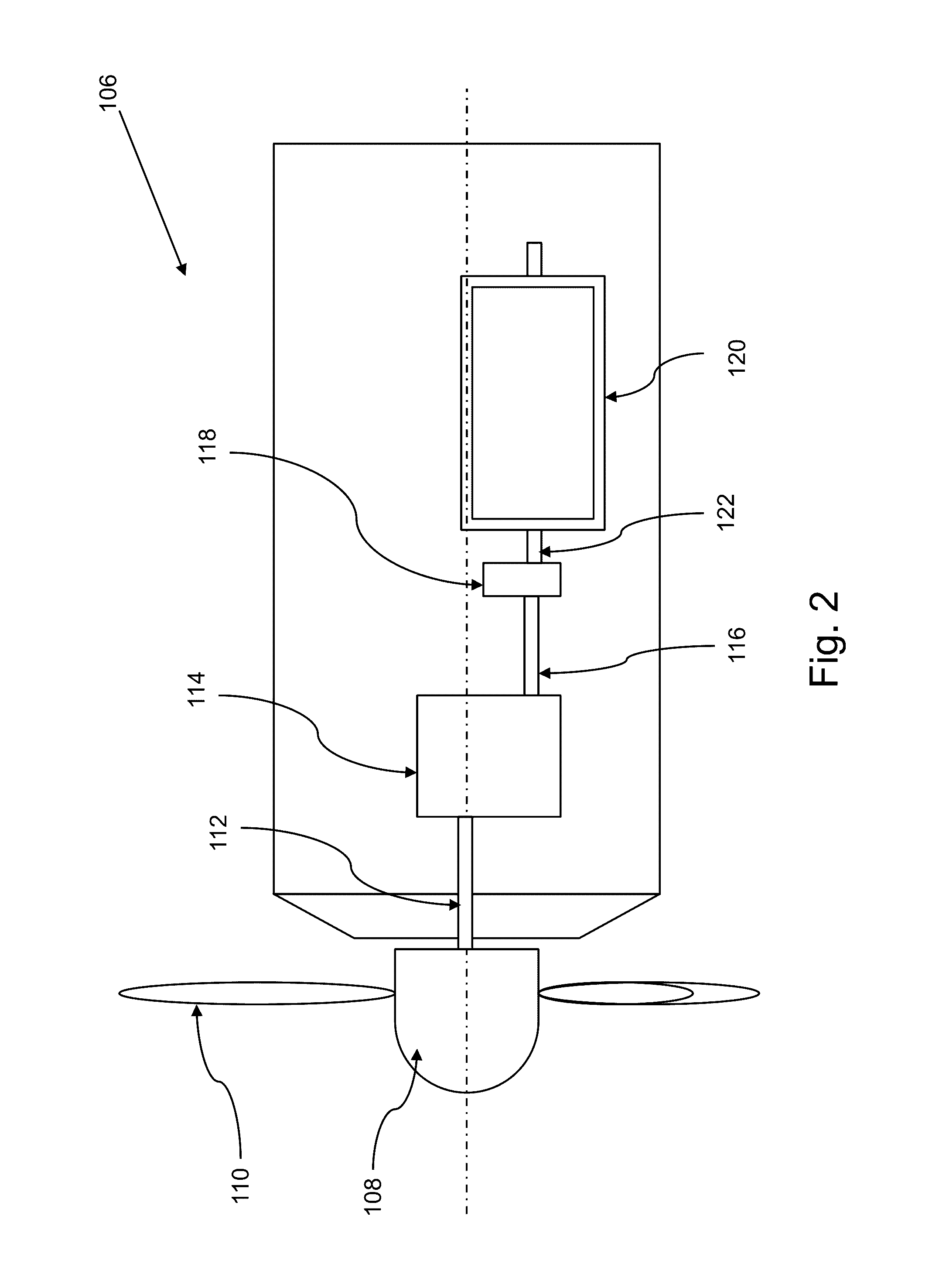
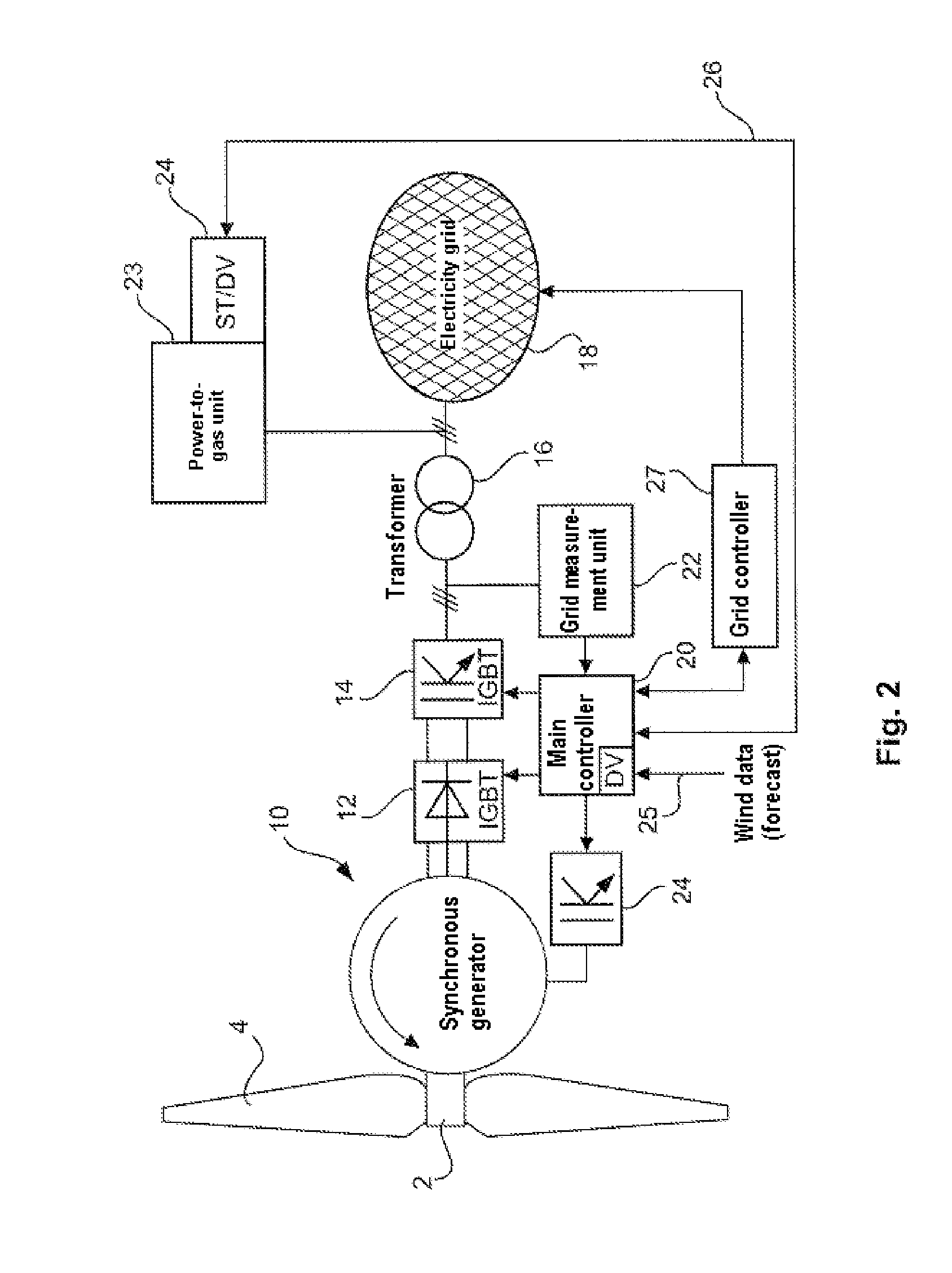
Method for operating a wind turbine or a wind farm
ActiveUS20140352311A1Guaranteed safe generationEasy to controlReciprocating combination enginesWind motor controlTime segmentCombustible gas
Thus, a method for operating a wind turbine, a wind farm or the like and a power-to-gas unit connected electrically thereto is provided. The wind turbine or the wind farm generates electric power if there is sufficient wind and feeds this power into an electrical grid connected to the wind turbine or to the wind farm. Each wind turbine is operated with a predetermined power curve. Electric power is generated by the wind turbine or the wind farm once a first wind speed (starting wind) has been reached. The wind turbine or the wind farm is in a partial-load operating mode as long as the wind speed is between the first wind speed (starting wind) and a second wind speed (nominal wind). The wind turbine or the wind farm is in a nominal power range when the wind speed is in a range which is greater than the second wind speed (nominal wind speed). Electric power generated by the wind turbine or the wind farm, preferably at least a predetermined proportion of said power, is consumed in the power-to-gas unit, with the result that a combustible gas, in particular hydrogen and / or methane gas or the like, is generated in the power-to-gas unit. The proportion of the electric power which is generated by the wind turbine or the wind farm in the partial-load operating mode and is not consumed in the power-to-gas unit is set to be virtually constant for a predetermined time segment, for example 10 minutes or more, for example 1 hour.
Owner:WOBBEN PROPERTIES GMBH
Convertible wind turbine nacelle cover
InactiveUS20130089433A1Minimizing attachmentReduce usageEngine manufactureFinal product manufactureNacelleSmall wind turbine
A convertible nacelle cover with an integrated platform for avoiding the use of auxiliary devices when performing maintenance operations on the components of a wind turbine nacelle, in cases in which the nacelle is not large enough to allow workers standing in it.The cover has at least two movable parts, which can be opened for maintenance operations, in such a manner that one of them becomes a working platform. Therefore, the nacelle cover is, per se, the place where the operator stands to perform the maintenance operations. It is especially designed to be used in small and medium size wind turbines.
Owner:NORVENTO ENERGIA DISTRIBUIDA
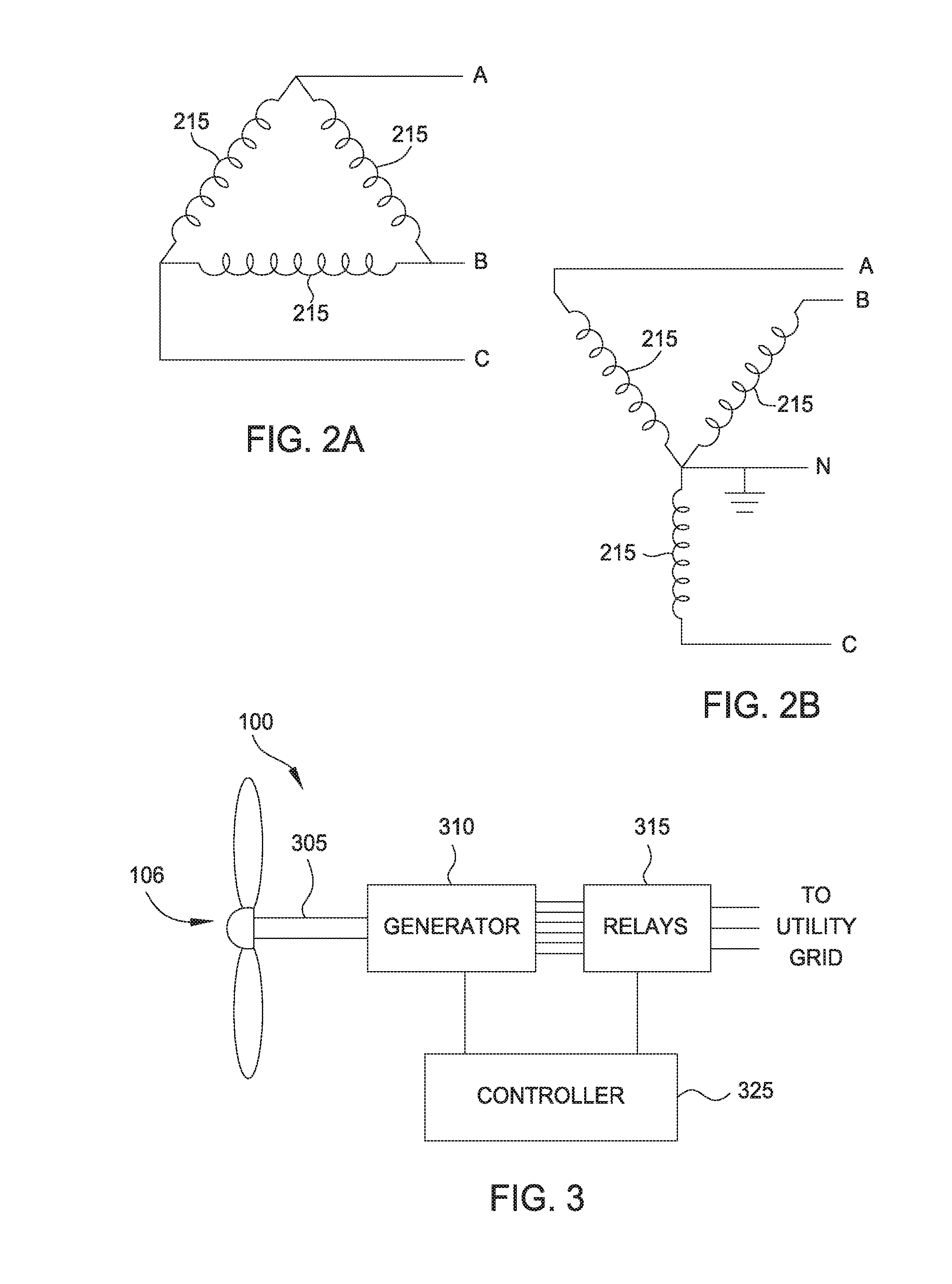
Speed management of a wind turbine when switching electrical configurations
ActiveUS20160208781A1Reduce output powerIncrease output powerLevel controlWind motor controlSmall wind turbineStructural failure
To efficiently nm a wind turbine in varying wind speeds, the wind turbine may be configured to switch between two different electrical configurations that offer different efficiencies depending on wind speed. For example, a star configuration may be preferred during low wind speeds while a delta configuration is preferred for high wind speeds. Before switching, the power output by the turbine's generator may be driven to zero. Doing so, however, removes load from the rotor blades which cause the rotor speed to increase. Instead, the rotor speed may be controlled such that the speed stays at or above the speed of the rotor immediately before the generator power is ramped down. Maintaining rotor speed at or slightly above the current speed while switching between electrical configurations may mitigate the torque change experienced by the turbine and reduce the likelihood of structural failure.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
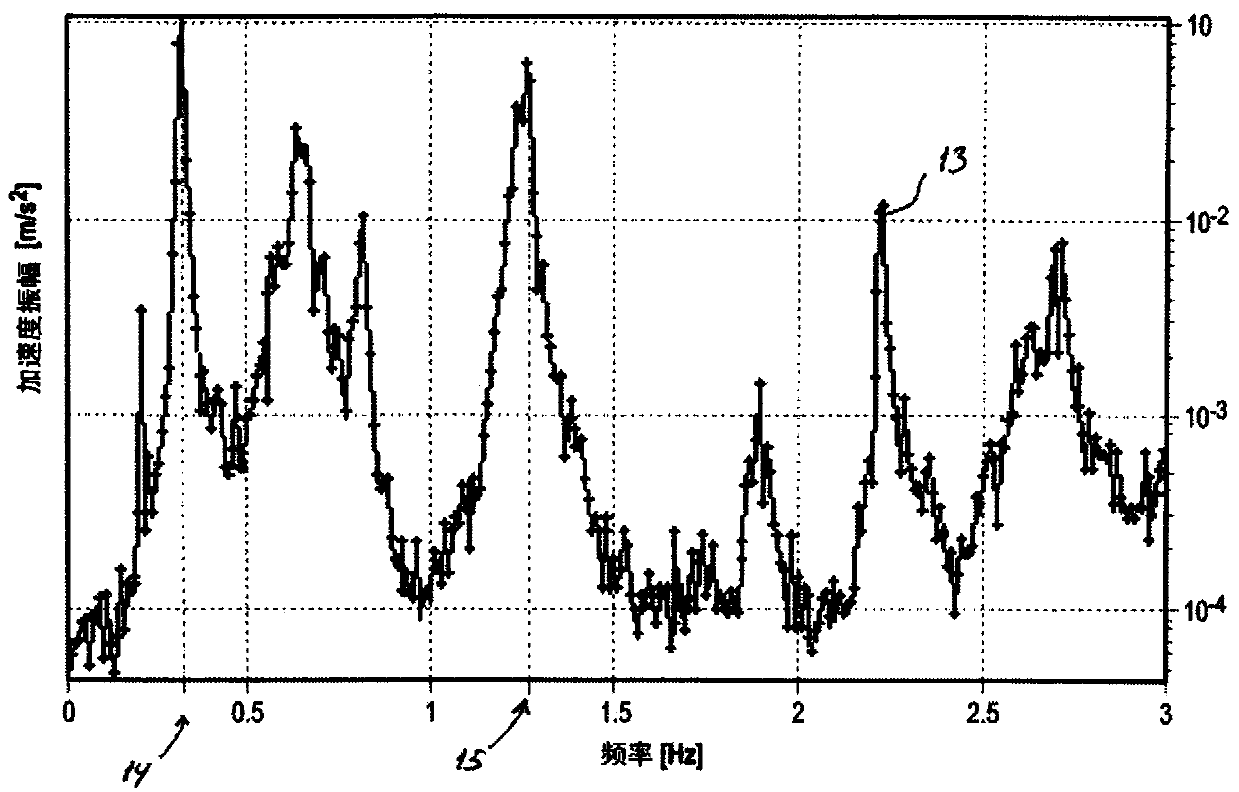
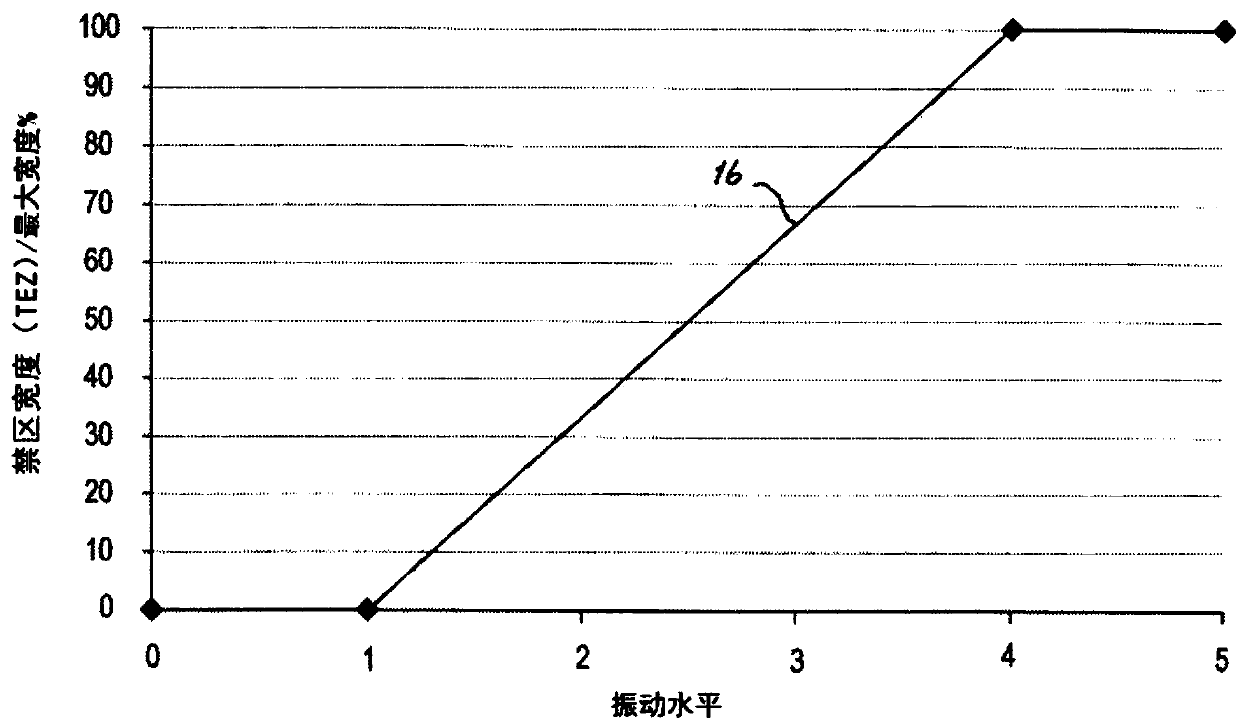
A wind turbine and a method of operating a wind turbine with a rotational speed exclusion zone
ActiveCN108026895AAvoid vibrationAvoid loadWind motor controlMachines/enginesControl systemResonance
The present invention relates to a wind turbine (1) and a method of operating a wind turbine with at least one rotational speed exclusion zone (18, 19), wherein the wind turbine (!) comprises a wind turbine control system (10) monitoring the vibrations of the wind turbine tower (2) and the rotational speed of the rotor. The wind turbine control system (10) controls the rotational speed of the rotor based on the measured vibration level (13), wherein the control system (10) uses the at least one exclusion zone (18, 19) to avoid rotational speeds that coincide with the eigenfrequency (14) of thewind turbine tower (2). The at least one exclusion zone (18, 19) has a variable width, which is determined based on the measured vibration level ( 13) so that resonance in the wind turbine tower (2)is avoided while minimizing the power loss.
Owner:YUANJIAN WIND POWER JIANGYINENVISION ENERGY CO LTD
Convertible wind turbine nacelle cover
InactiveUS9228562B2Minimizing attachmentReduce usageEngine manufactureFinal product manufactureNacelleSmall wind turbine
A convertible nacelle cover with an integrated platform for avoiding the use of auxiliary devices when performing maintenance operations on the components of a wind turbine nacelle, in cases in which the nacelle is not large enough to allow workers to stand on it. The cover has at least two movable parts, which can be opened for maintenance operations, in such a manner that one of them becomes a working platform. Therefore, the nacelle cover is, per se, the place where the operator stands to perform the maintenance operations. It is especially designed to be used in small and medium size wind turbines.
Owner:NORVENTO ENERGIA DISTRIBUIDA
Vertical-axis wind turbine with simply mounted inner and outer movable fan blades
InactiveCN101603508AEasy to startImprove efficiencyWind motor combinationsMachines/enginesLow speedGear wheel
The invention relates to a vertical-axis wind turbine with simply mounted inner and outer movable fan blades. An inner movable fan blade and an outer movable fan blade simultaneously run and play respective role at different upwind angles. The rotation of the two movable fan blades increases the upwind stress area of the fan blades in downwind period to greatly improve the efficiency of the prior vertical wind turbine and increases the starting torque force in the condition of low wind speed to enable a small wind turbine to be more popular and practical. In the invention, the gravity center of the whole device including a main shaft, an upper fan blade bracket, a lower fan blade bracket and the inner and the outer movable fan blades is lowered on purpose, the installation method of simply connecting upper and lower gears is cooperated with a vertical middle and small power ultra-low speed generator to reduce the costs of products and installation, thereby the small wind turbine is popularized easily.
Owner:李善昌
Plateau dispersion-type oxygen-enriched tent
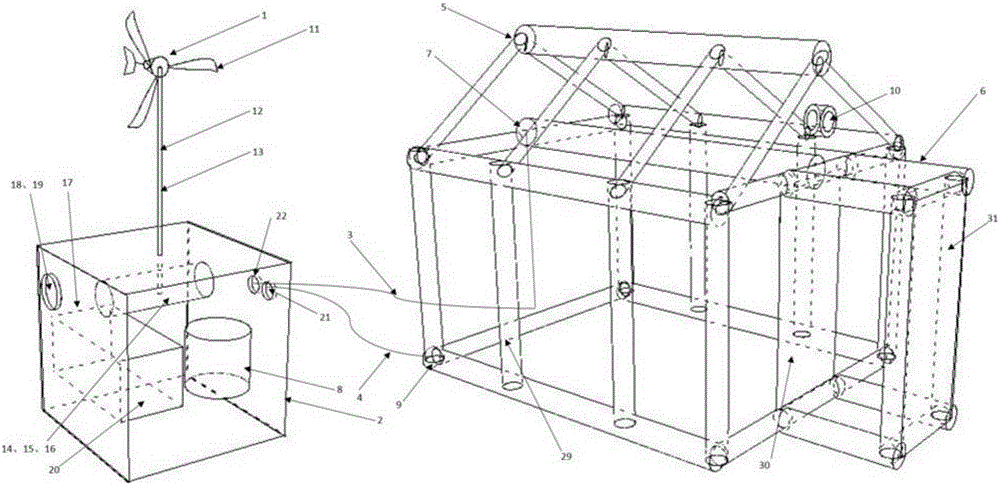
InactiveCN105257079AEasy to installExpand quicklyTents/canopiesOxygen preparationField trainingDual purpose
The invention discloses a plateau dispersion-type oxygen-enriched tent which is characterized by comprising two parts, namely, an air-rib-type inflation tent and an oxygen generator outside the inflation tent, wherein a generation unit is arranged in the housing of the oxygen generator, and is connected with a small wind turbine above the housing through a transmission mechanism; an oxygen-enriched film component is also arranged in the housing and connected with a dual-purpose vacuum pump capable of both pumping and beating; the dual-purpose vacuum pump is driven by the generation unit to inflate the inflation tent fast or provide oxygen-enriched gas to the inflated tent. The plateau dispersion-type oxygen-enriched tent is very suitable for transition of troops rushed or stationed to a plateau for execution of field training and combat mission, as well as field work of a civil engineering team.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Air conditioner
InactiveUS7051548B2Easy to transportEfficient and reliable and economical and simple and effectiveFree-cooling systemsStationary conduit assembliesEvaporative coolerEngineering
A process and the required apparatus for air conditioning the interior of a structure located within a harsh desert like exterior environment. The air conditioning system is particularly effective at times when the exterior temperature is in excess of approximately 90 to 95 degrees Fahrenheit, and the exterior relative humidity is less than approximately 35 to 40 percent. A tube and shell heat exchanger wherein the shell side is wet and the tube side is dry is employed to air condition the interior of the structure. In the operation of the air conditioner, a mass of distributed water, for example, a spray, is established on the wet shell side, and a flow of ambient air is passed through the wet shell side to form a resulting stream of moist air. A flow of ambient air is passed through the dry tube side and a resulting stream of dry cooled air is recovered. The streams of moist and cooled air are combined and the resulting stream of combined air is discharged into the exterior of the structure. The structure is not hermetically sealed so there is little or no pressure difference between the interior of the structure and the surrounding environment. The system requires so little power that it can be operated on a battery system charged from an ambient energy source harvested by, for example, a small wind turbine or an array of conventional 30 volt 4 amp hour solar power cells. The water consumption rate is generally less then approximately 10 percent that of a conventional evaporative cooler. The humidity in the interior of the structure is generally no more than approximately 2 to 2.3 times that of the exterior environment.
Owner:GPM INC
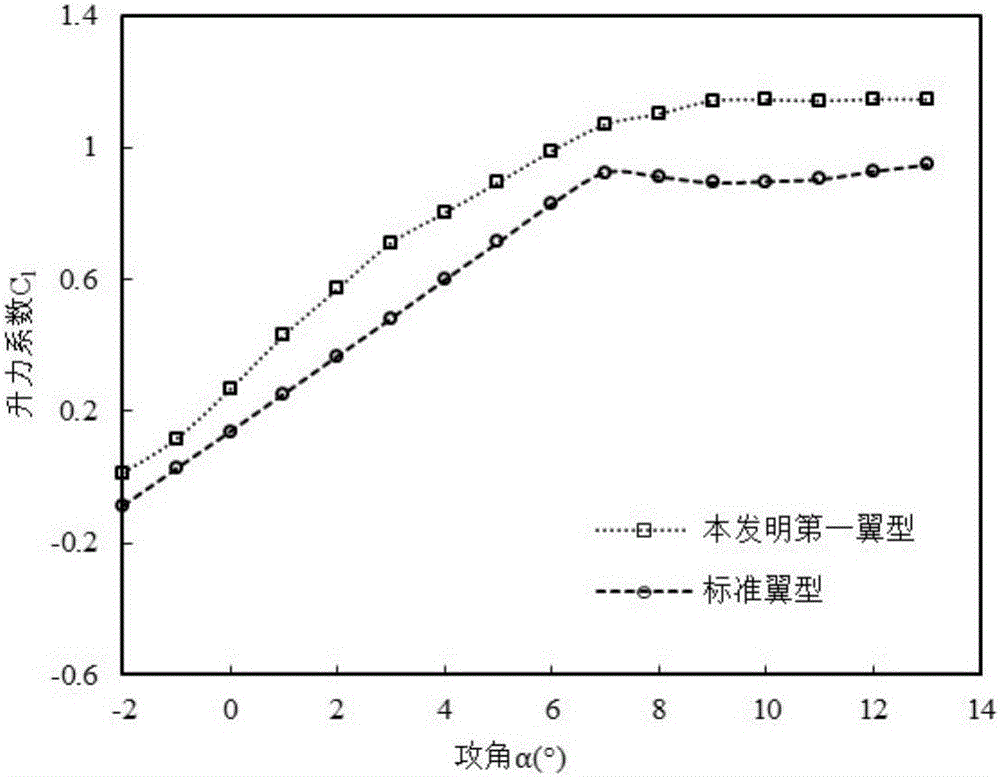
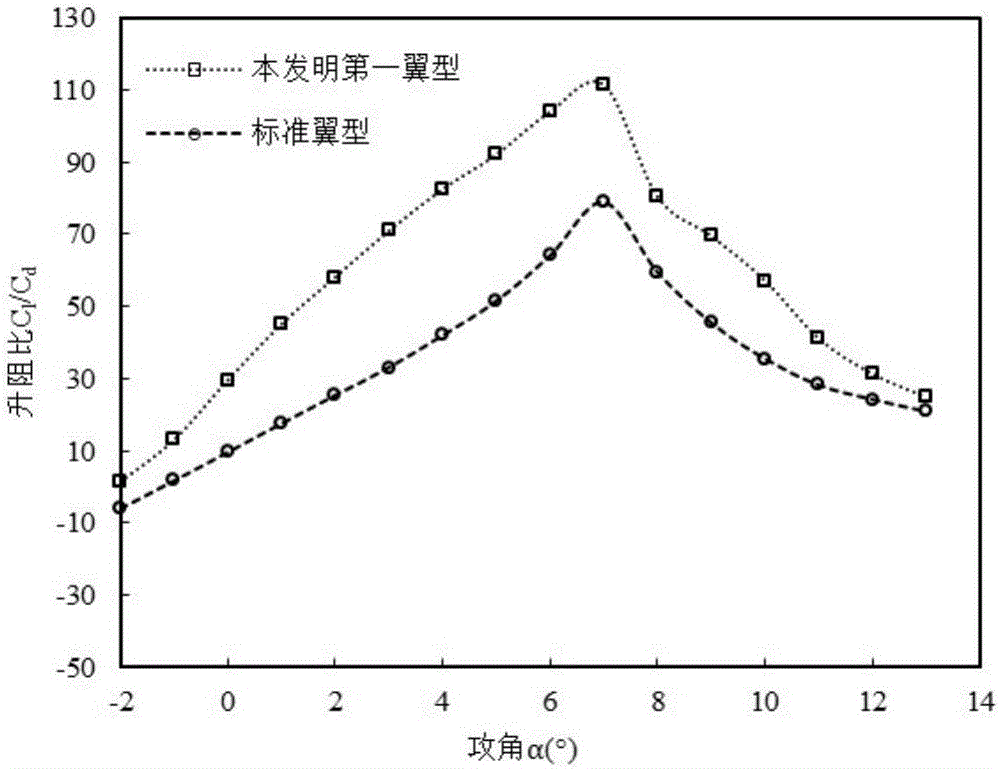
Small wind turbine blade wing section suitable for low Reynolds number flowing
InactiveCN106089569AEasy to liftImprove the lift-to-drag ratioMachines/enginesWind energy generationTurbine bladeEngineering
The invention discloses a small wind turbine blade wing section suitable for low Reynolds number flowing, and belongs to the field of wind turbine blade wing section design. The maximum thickness of the wind turbine blade wing section is 12%-15% of the chord length, the distance between the maximum-thickness position and the front edge is 35.9%-40.7% of the chord length, the maximum camber is 3.1%-4.3% of the chord length, the distance between the maximum-camber position and the front edge is 36.0%-44.3% of the chord length, and the power of a small wind turbine is smaller than or equal to 10 KW. The small wind turbine blade wing section has the higher lift coefficient and the larger lift-drag ratio under the low Reynolds number flowing, the wind energy utilization efficiency of the small wind turbine can be improved, and the small wind turbine blade wing section is more suitable for being applied to small wind turbines in low-wind-speed areas in China.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Wind turbine
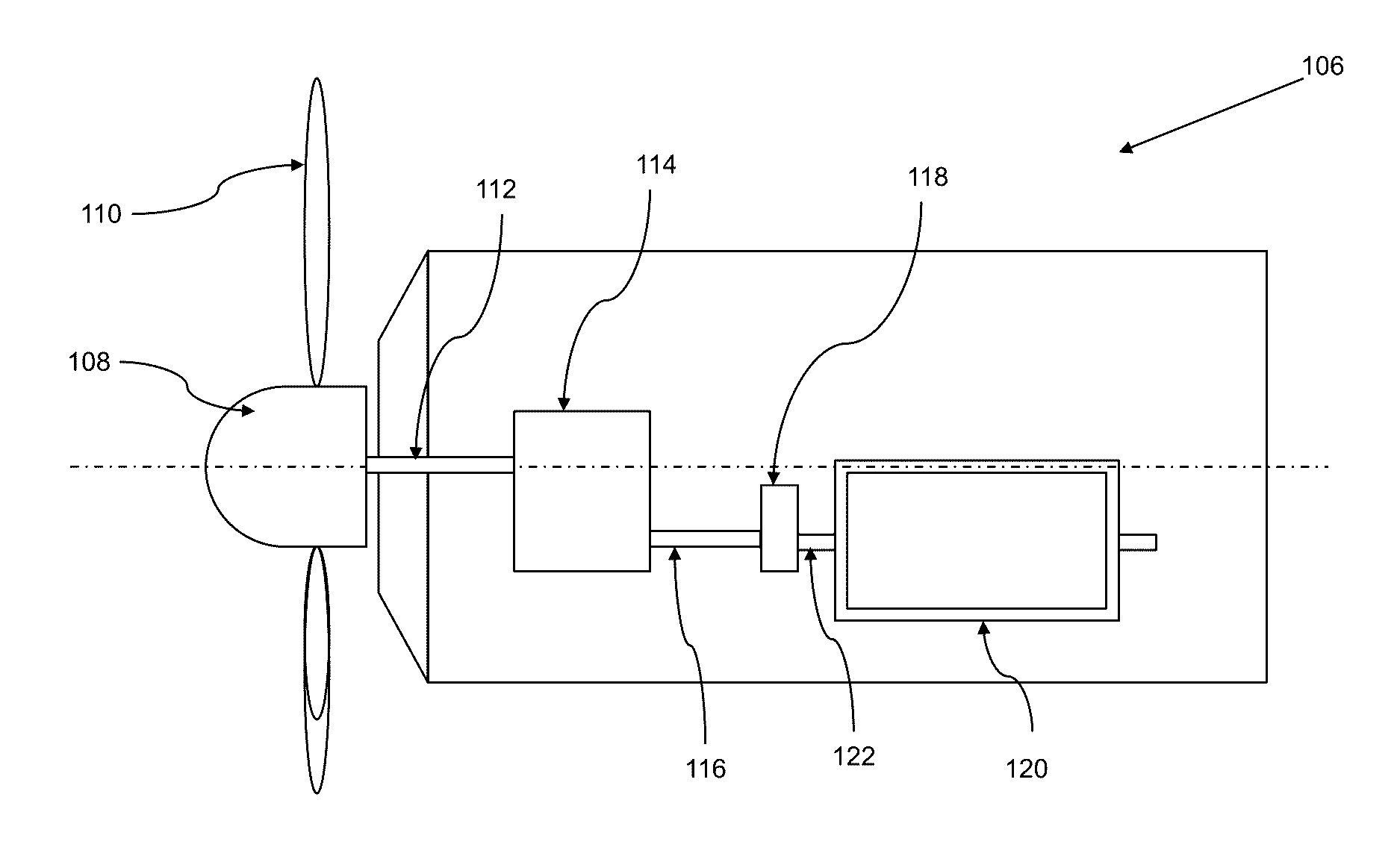
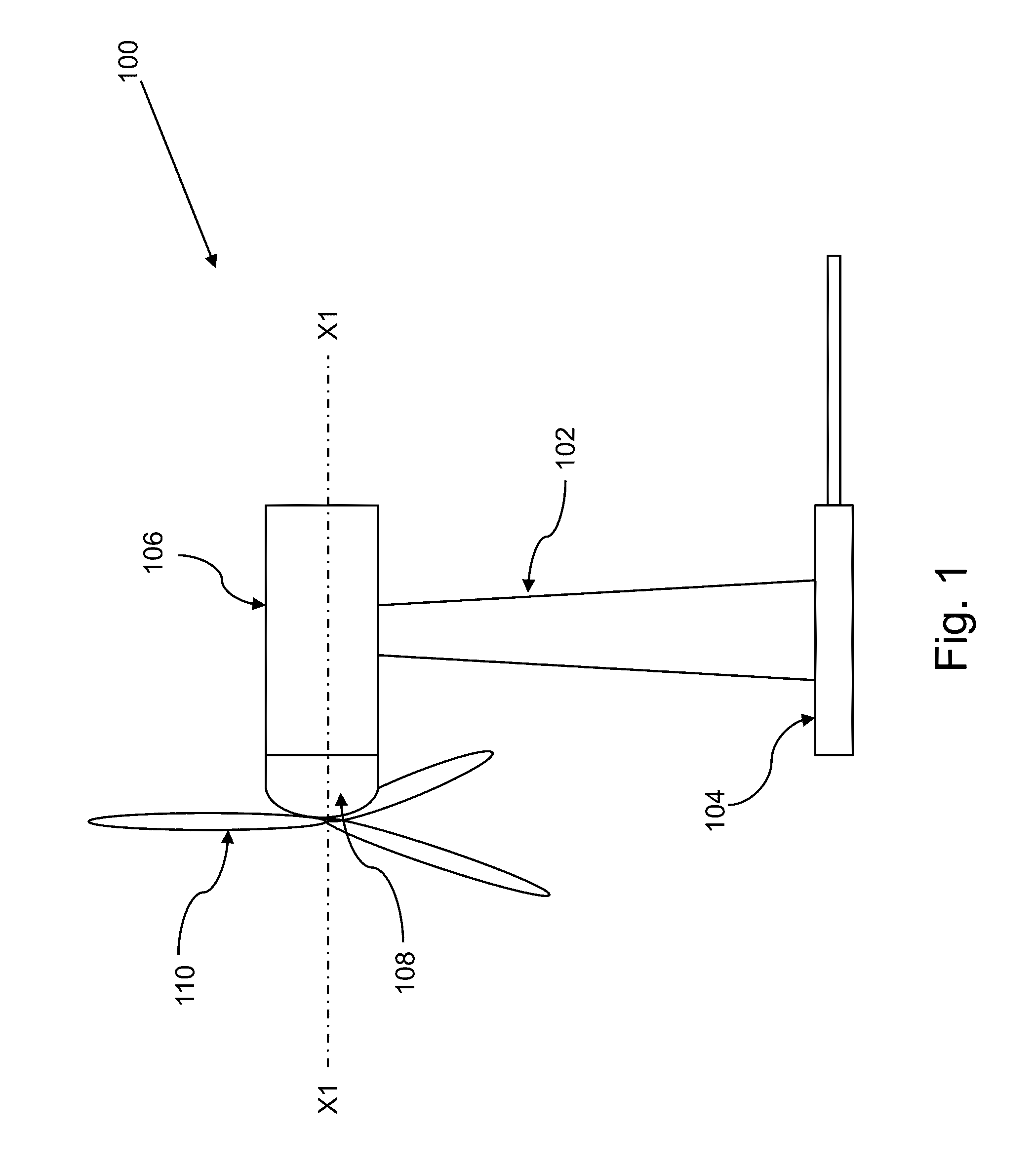
InactiveUS8338974B2Reducing and completely eliminating technical problemEfficient and effective to generateWorking fluid for enginesMachines/enginesElectricityMechanical energy
A wind turbine for generating an electric voltage from mechanical energy derived from wind is provided. The invention includes a specially designed turbine enclosure through which the wind passes. The enclosure has a Venturi area which results in movement of the wind at a rapid speed through the turbine. An electric generator with a rotable blade also is provided within the Venturi area in order to take advantage of the faster moving wind. The faster the wind moves, the more energy can be converted by the generator. The generator can be constructed with a plurality of electric coils and magnets which can be arranged in series / parallel combinations depending on the power requirements of a particular application.
Owner:AGLOBAL TECH
Wind turbines and methods for controlling wind turbine loading
Wind turbines and methods for controlling wind turbine loading are provided. In one embodiment, a method includes the steps of determining a current wind speed. The method further includes determining a tip speed ratio and a pitch angle that maximize a power coefficient under at least one of the following conditions: a thrust value is less than or equal to a pre-established maximum thrust, a generator speed value is less than or equal to a pre-established maximum generator speed, or a generator torque is less than or equal to a pre-established maximum generator torque. The method further includes calculating a desired generator speed value based on the current wind speed and a tip speed ratio. The method further includes calculating a desired generator power value based on the desired generator speed value.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Roof ridge wind turbine
InactiveUS8545298B2Provides liftMultiplying the wind speedSpace heating and ventilationRotary non-positive displacement pumpsSmall wind turbineGable roof
Disclosed are systems and method that generally relate to the capture of wind energy by small wind turbines mounted on buildings with gabled roofs. Wind energy harnessing system for gabled roof buildings having a roof ridge including a low silhouette visually appealing enclosure mounted along the roof ridge of a building and extending down both sides of the roof forming the ridge. The enclosure includes airflow guides defined by columns extending down a length of both sides of the building roof forming sidewalls and a roof formed of pivoting louvers above the columns. A paddle-wheel type wind turbine consists of a multiple-bladed cylindrical shaft that contacts the wind and provides rotational work mounted within the enclosure and a generator connected to the wind turbine for converting the rotational work from the wind turbine to electrical energy. The enclosure for the wind turbine functions to capture wind and directs the airflow via the airflow guides before it reaches the ridge.
Owner:TURBOROOF
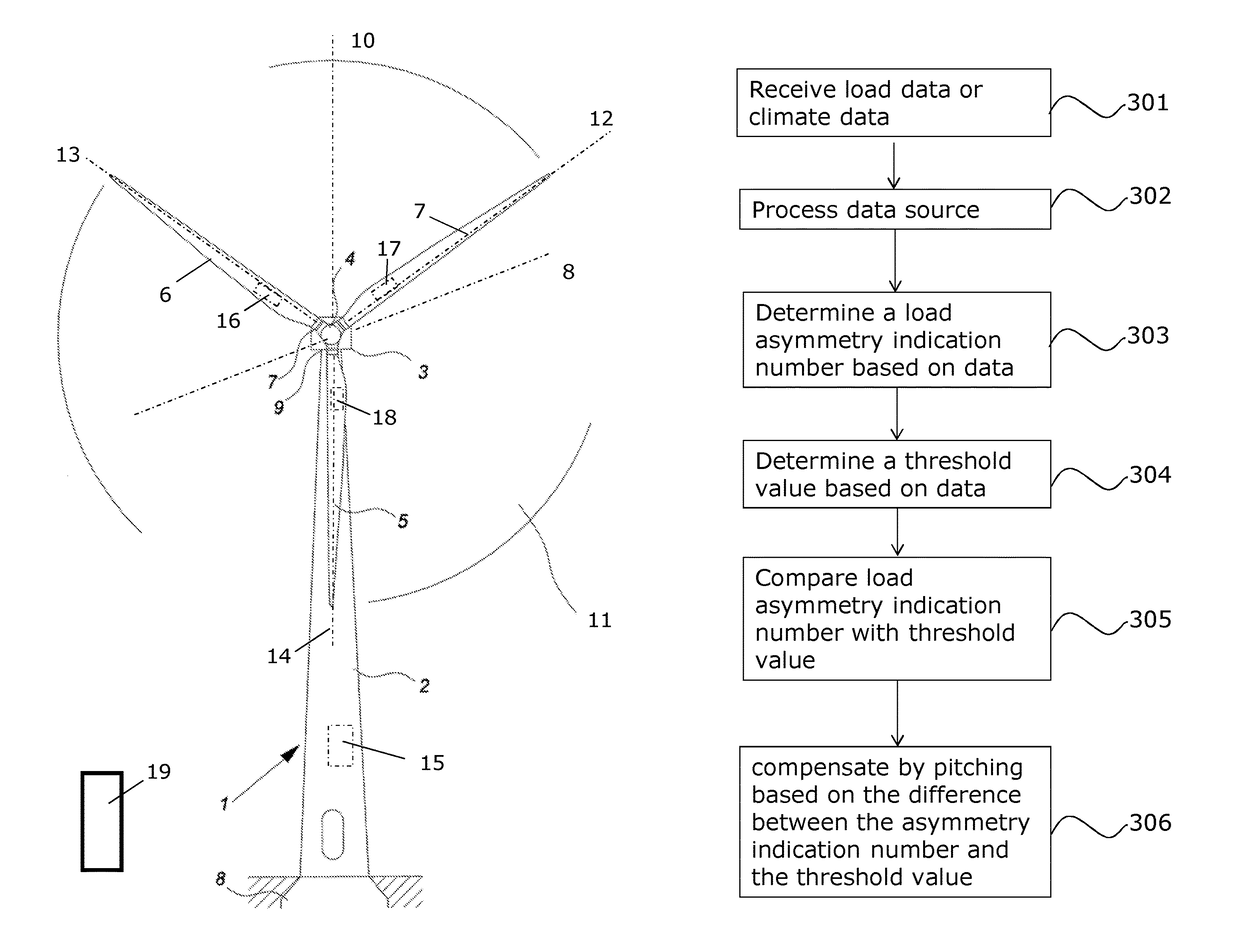
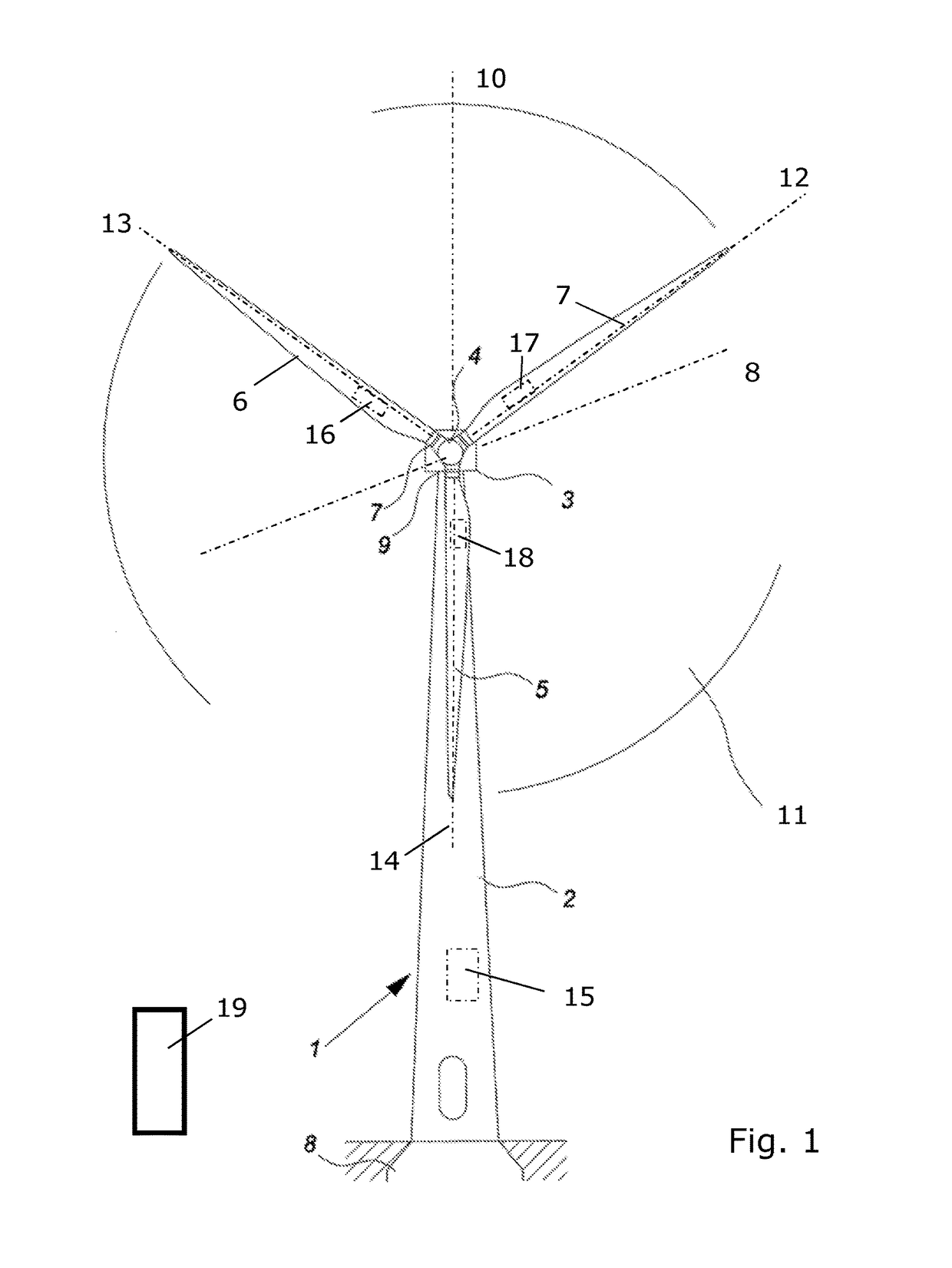
Wind turbine with a load controller
ActiveUS9970413B2Increase blade tower clearanceExtreme loadWind motor controlEngine fuctionsControl systemLoad distribution
The invention provides a wind turbine, a control system for a wind turbine and a method for controlling a wind turbine where asymmetry in load on the rotor is compensated by individual pitching by comparing a load distribution over the rotor plane with a threshold value. To avoid unnecessary compensation, the threshold value is adjusted based on a loading of the wind turbine or based on climate conditions under which the turbine operates.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Pivoting structural cellular wall for wind energy generation
InactiveUS20120114501A1Add flexiblyIncreased swayReaction enginesEngine componentsModularityEngineering
The present invention relates to a device and method associated with the device. It is a wall for collecting wind energy, holds multiple wind turbines at increased heights, the device also pivots around a central point and keeps the turbines aligned into the direction of the wind. This device can be used to increase the yield of energy collected from the wind and to place wind turbines in stronger winds. The device enables turbines to be located within the structure. The rotation is around a center pivot point with the outer vertexes of the triangle free to move. With respect to the method, the modular cells locate the wind turbines in higher wind speeds. The wind flows around and through the cell structure creating beneficial vortexes. The wind is converted into energy at the turbine, at the conclusion of these steps wind energy is converted into electrical power.
Owner:RUTHERFORD JOHN
Blade system of vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveCN101886610ASolve sheddingResolve the breakWind motor controlFinal product manufactureVertical axis wind turbineTower
The invention relates to a blade system of a vertical axis wind turbine, comprising at least two blades. A blade shaft is arranged above a balance axis in the horizontal direction of each blade; the distance between the blade shaft and the balance axis in the horizontal direction is required to meet the requirement of difference of upper and lower forces of the blade shaft so that the blades are quickly changed into a vertical condition from a horizontal condition under the action of force difference in the absence of wind; the blades rotate around the blade shaft in the presence of wind; one end of the blade shaft is fixedly connected with a wind wheel shaft; the blades are movably connected with the blade shaft; the wind shield surfaces of the blades and the axis of the blade shaft are in the same plane; and the blade shaft is provided with a limiter which is used for limiting the blades to only rotate horizontally in an unidirectional mode under the vertical condition. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, easy maintenance, low cost, light weight, low requirement for a wind tower, and the like. The invention is suitable for large, medium and small wind turbines, can be disassembled for transportation, can be used for manufacturing ultralarge blades to improve the power capacity of a single wind turbine, has no requirement for wind direction and is adaptive to wind direction.
Owner:魏彬
A small horizontal axis wind turbine axial trust measuring device
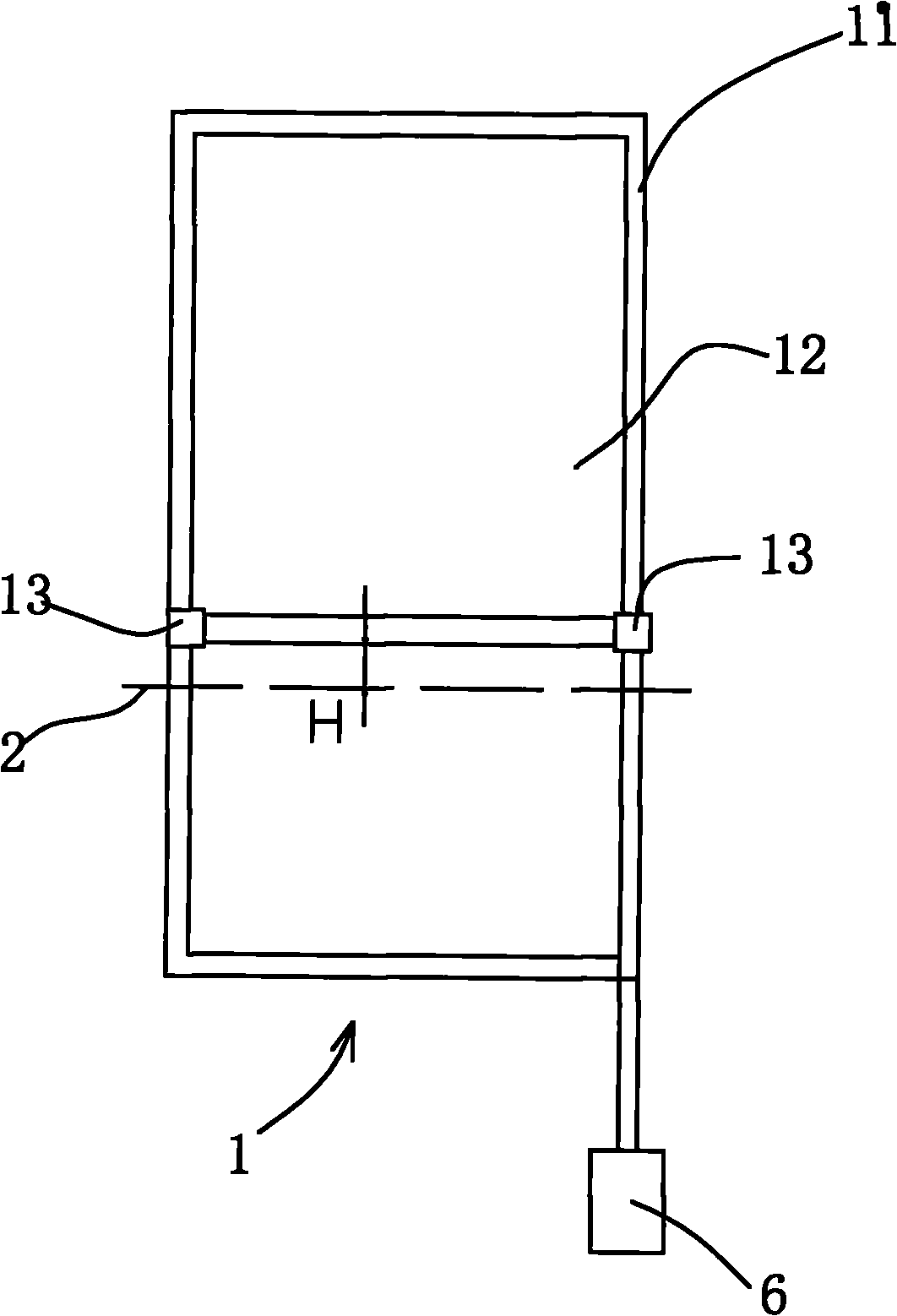
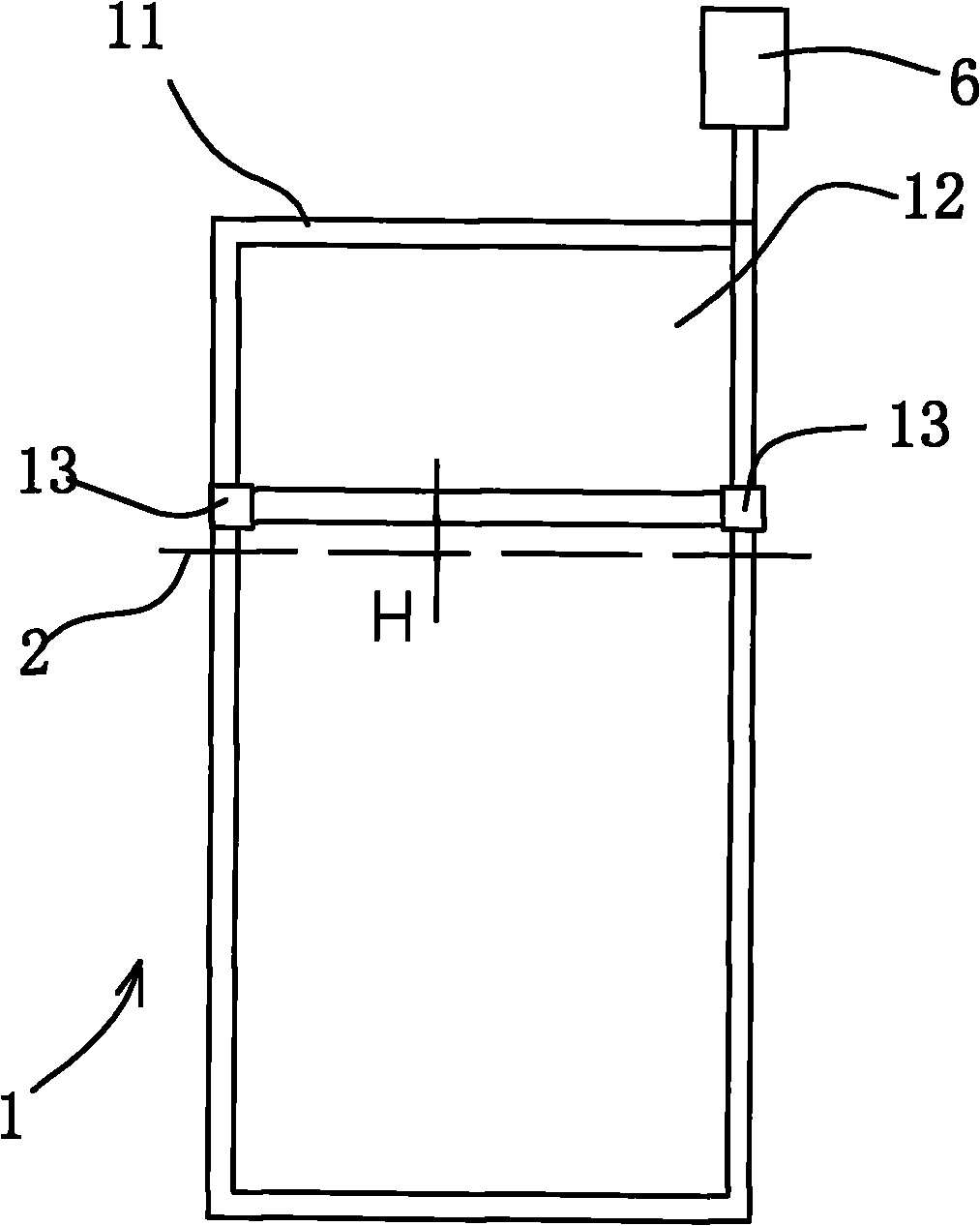
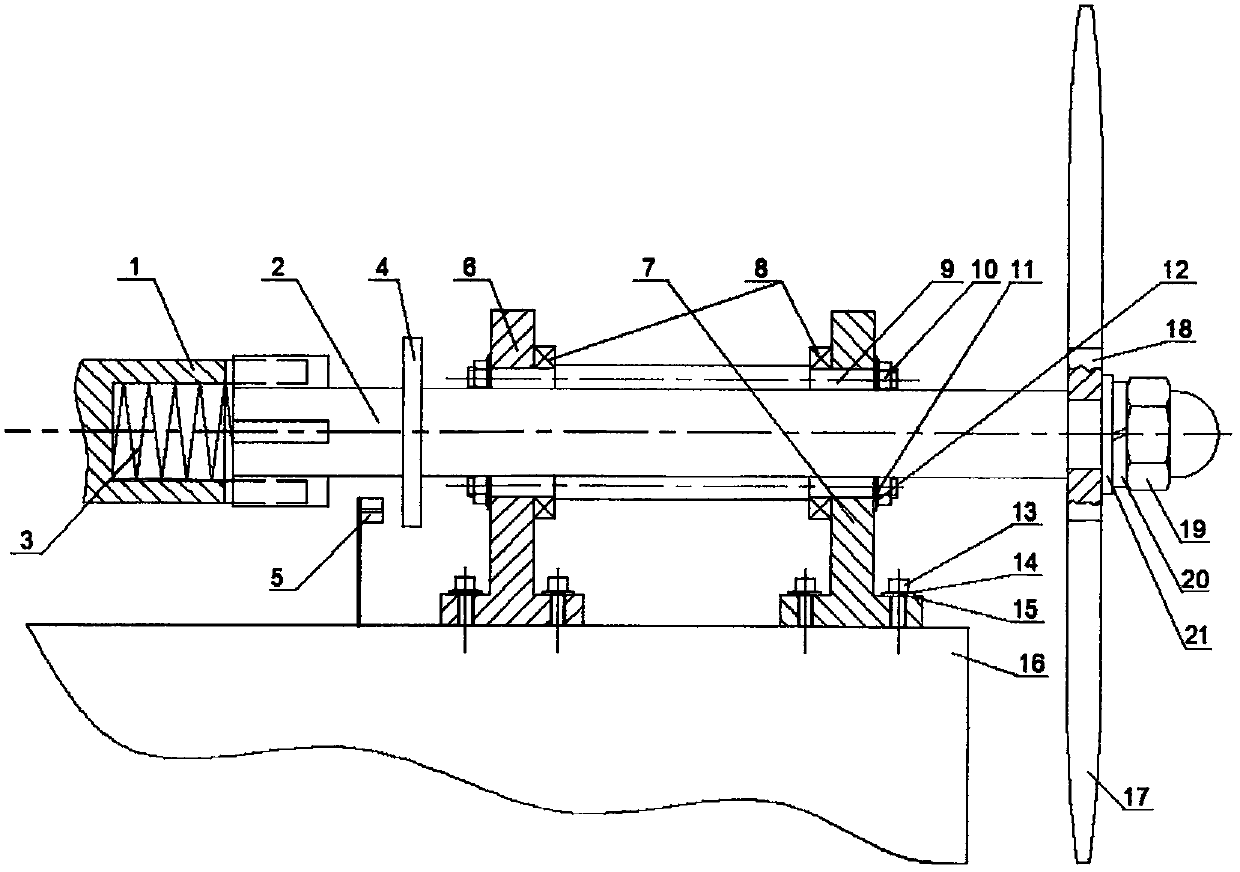
PendingCN107655605AEfficient power transmissionGuaranteed power transmissionApparatus for force/torque/work measurementAxial displacementImpeller
The invention provides a small horizontal axis wind turbine axial trust measuring device comprising a base and a small horizontal axis wind turbine arranged at the top of the base. The small horizontal axis wind turbine comprises a horizontal input shaft, a horizontal output shaft and impellers at the front end of the horizontal input shaft; the top of the base is also provided with an optical fiber sensor; when axial thrust is applied to the horizontal input shaft, the horizontal input shaft can move backward in the axial direction; an elastic body is arranged in a hollow drum body at the front end of the horizontal output shaft; the elastic body is compressed only when the horizontal input shaft encounters axial thrust; a sensing surface of the optical fiber sensor right faces a front side or rear side end face of an annular protruding shoulder; the optical fiber sensor is used for measuring the axial displacement of the annular protruding shoulder when axial thrust is applied to thehorizontal input shaft, and elastic force of the elastic body can be calculated according to the Hooke's law, which is the axial thrust of the small wind turbine. The device has the advantages of compact structure, simple operation, reliable operation, high sensitivity, high measuring precision, great anti-jamming capability and long service life.
Owner:YICHUN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com