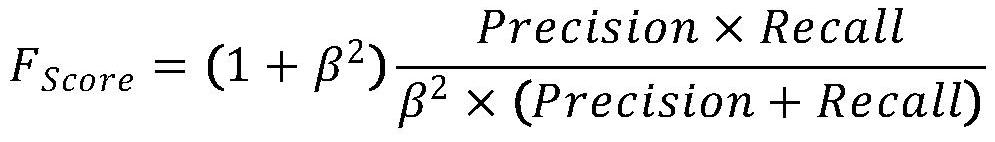Patents
Literature
33 results about "Sunspot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
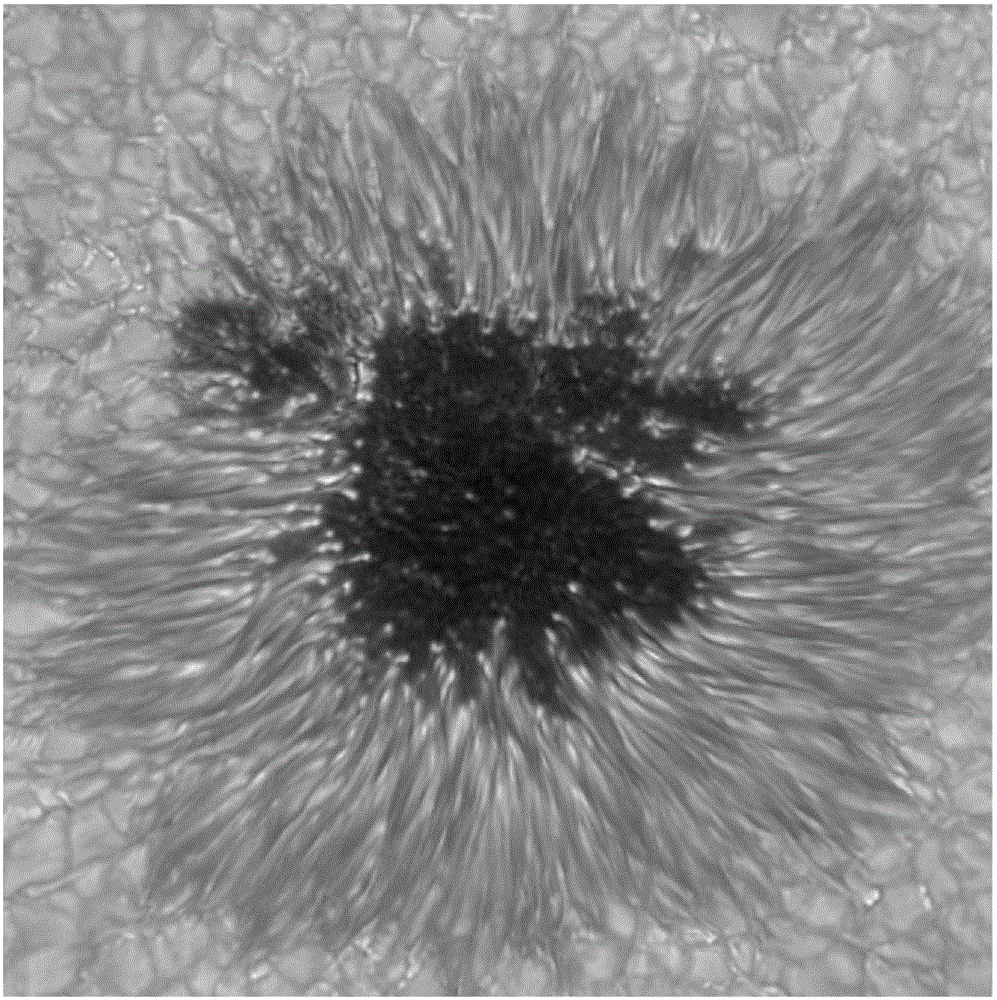
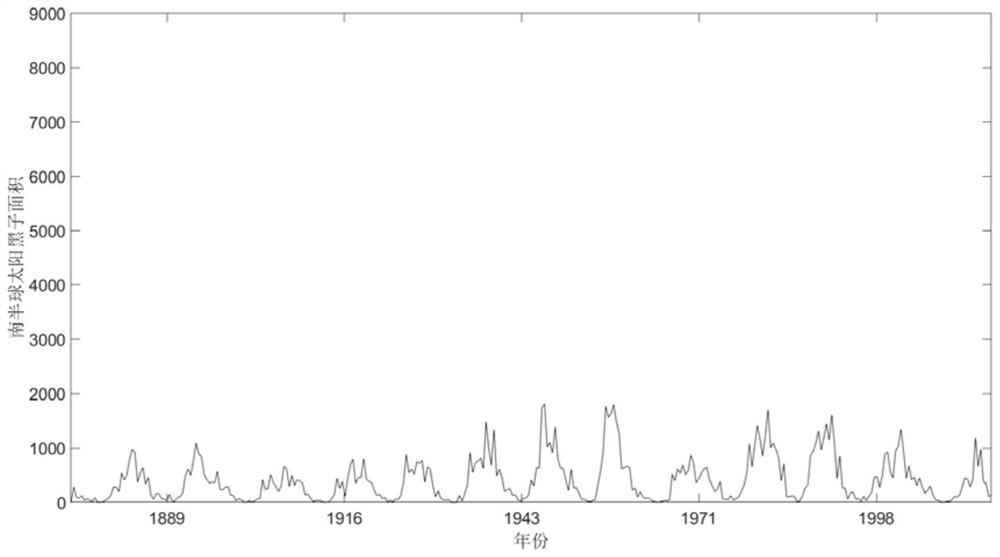
Sunspots are temporary phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as spots darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic field flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots usually appear in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle.
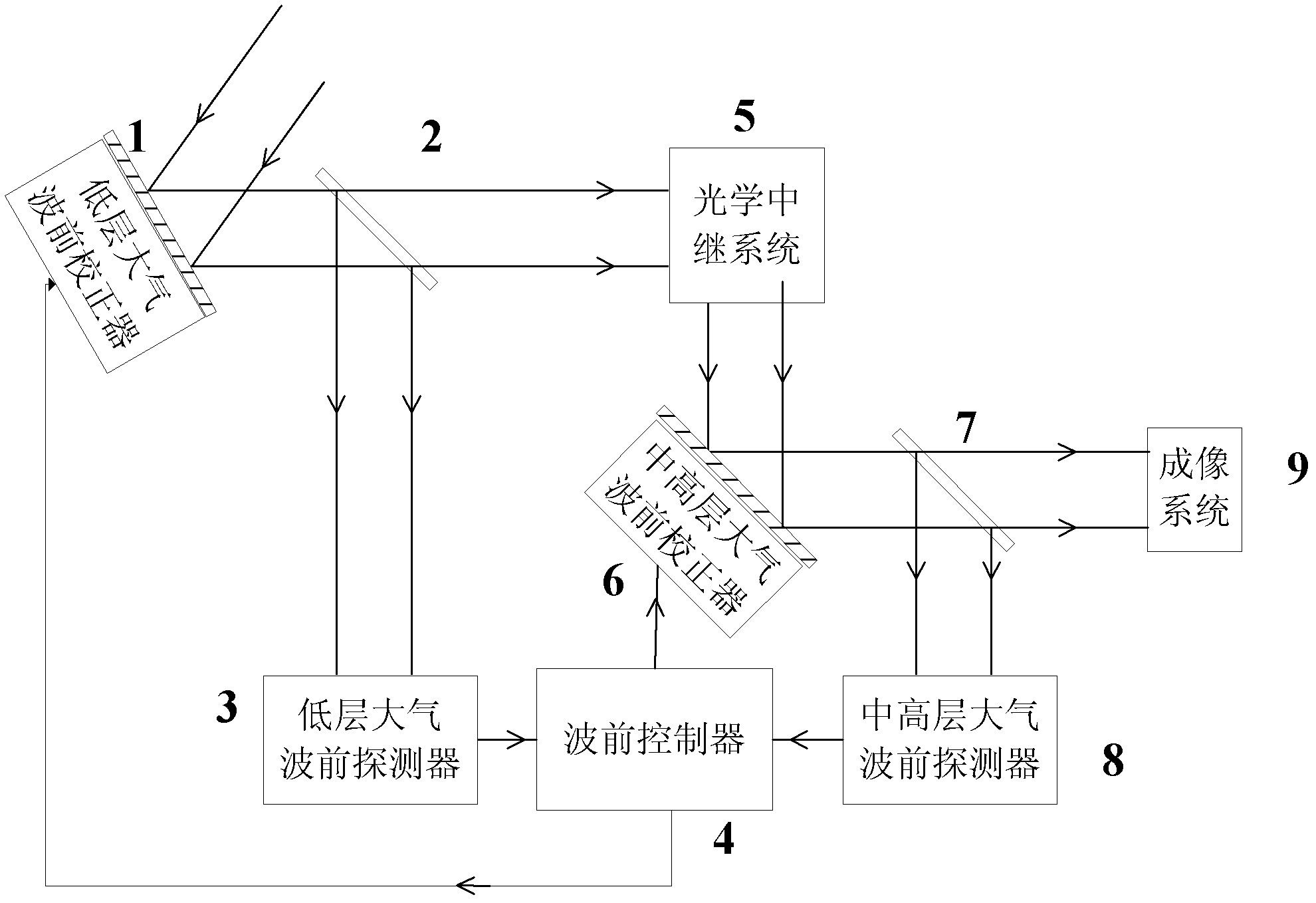
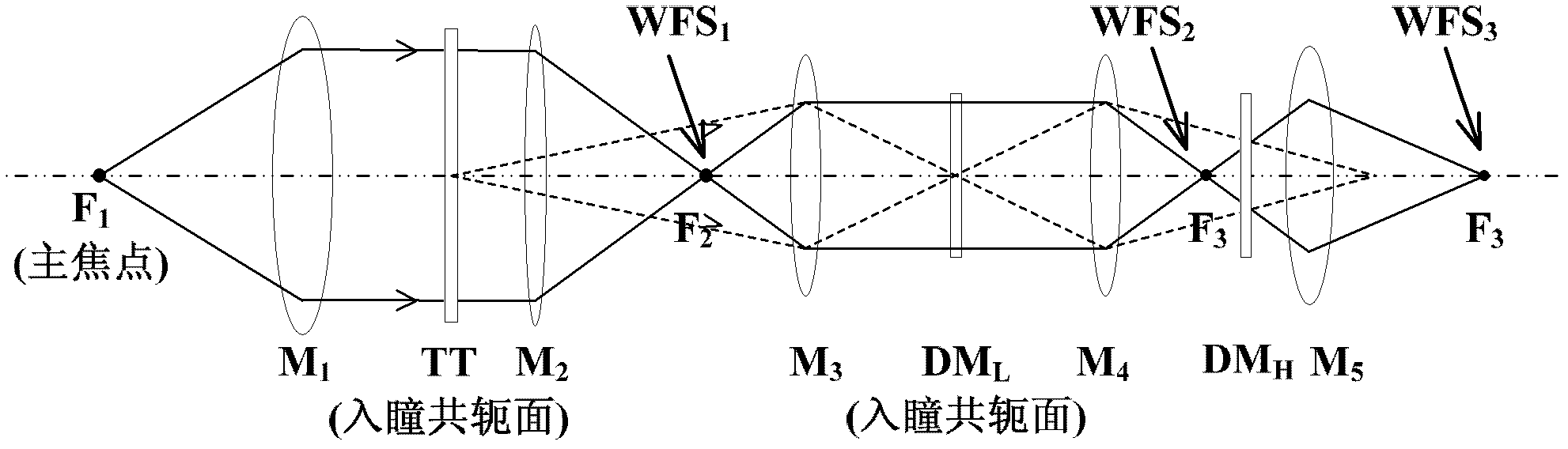
Solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system
ActiveCN102621687ARealize high-resolution imagingSimplify the difficulty of decouplingOptical measurementsOptical elementsHigh resolution imagingCoupling
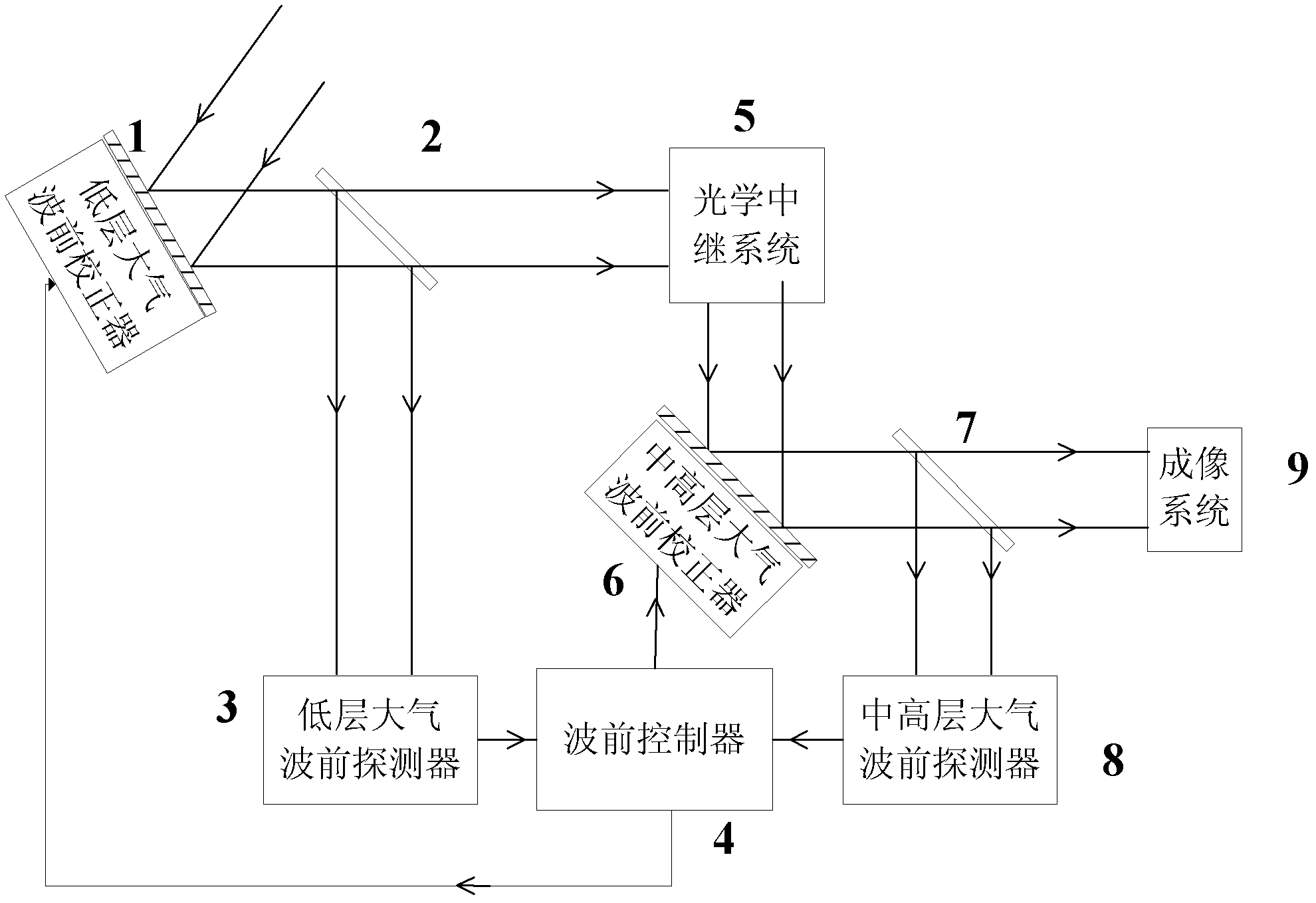
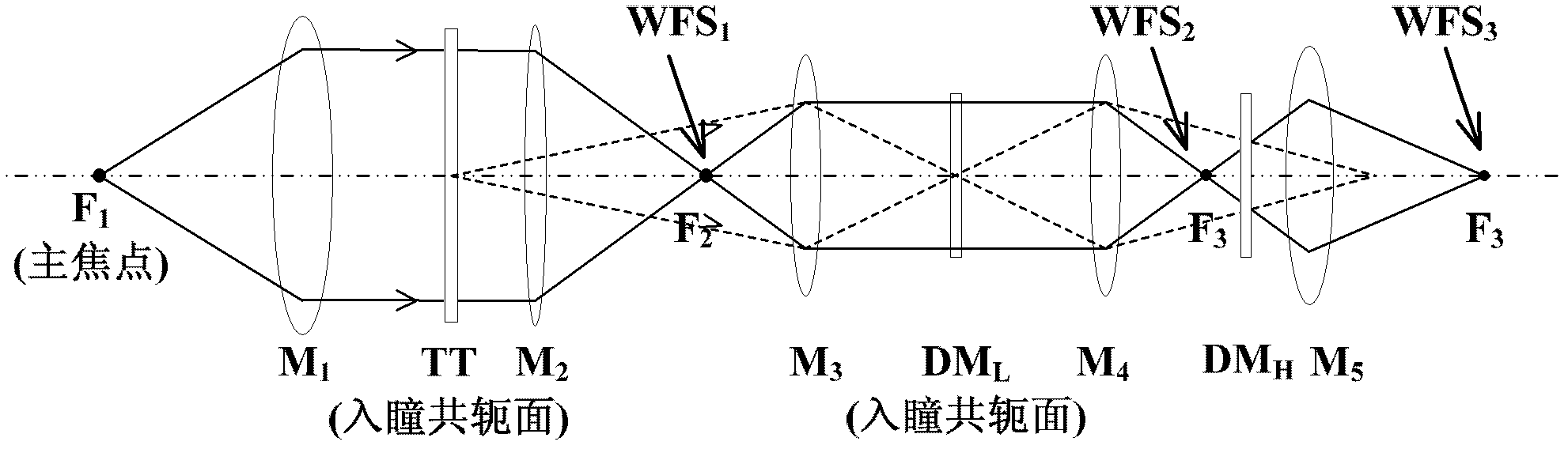
The invention provides a solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system. The solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system comprises a lower atmospheric wave front sensor, a middle and upper atmospheric wave front sensor, a lower atmospheric wave front corrector, a middle and upper atmospheric wave front corrector, a wave front controller, an optical relay system, an imaging subsystem and other necessary optical components. The system has the advantages that sunspots or grain structures on the surface of the sun are taken as beacons and wave front detection is conducted on multiple areas at the same time, so as to obtain wave front distortion caused by turbulence in a large field range; wave front aberration caused by different turbulent layers is calculated by utilizing a tomography algorithm; and at last, the wave front correctors positioned in conjugate positions of the corresponding turbulent layers are controlled to correct the atmospheric turbulence in a layered manner, so as to finally realize high-resolution imaging in the large field range. The solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system has the advantages that the sequence of the conjugate positions of the high and the lower turbulent layers is adjusted through the optical relay system, so that the lower turbulent layer is firstly compensated and corrected and the accuracy of the detection and the correction is increased; and due to the use of the tomography algorithm, errors caused by the coupling of the wave front aberrations of the different turbulent layers are reduced.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
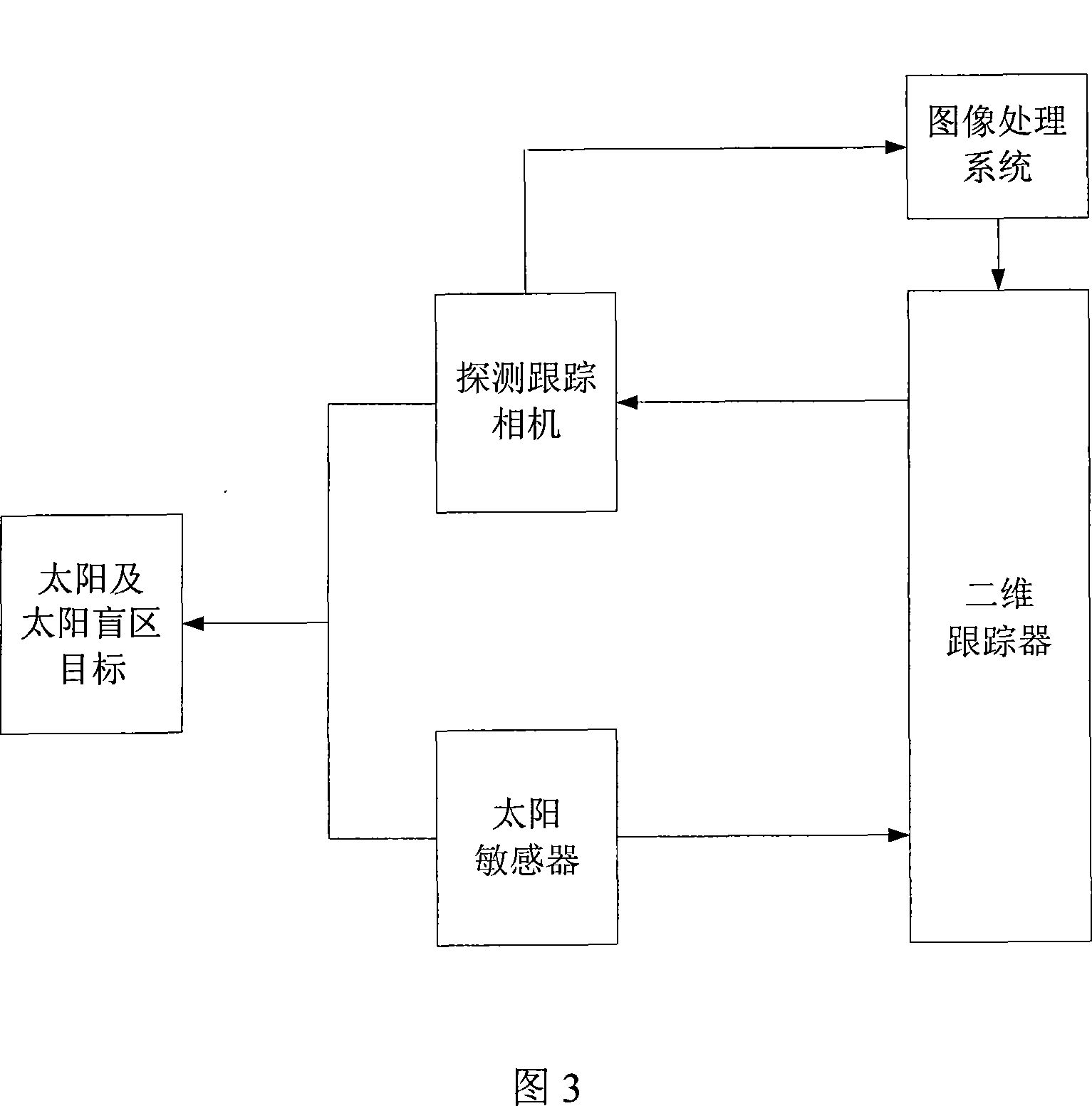
Spaceborne target detection tracing camera in sun viewing blind zone
InactiveCN101173984AFill in the observation blind spotWith detectionElectromagnetic wave reradiationBlind zoneData treatment
The invention discloses a probing and tracking camera for targets on solar observation blind areas, which can be arranged on a satellite to observe and track targets on the solar observation blind areas. The camera comprises an attenuation filter, an optical system, a probe and a data processing circuit; wherein, a ray of light from an object space passes through the attenuation filter and the optical system and forms an image on the probe. The attenuation filter is used to adjust the intensity of light coming into the camera, and the optical system adopts a double-Gauss near infrared teleobjective system; the probe adopts a CMOS probe, and the dynamic range is designed as follows: the brightness of the sun, sunspot images is designed out of the dynamic range of the camera, and the brightness of the observed targets is designed within the saturation value of the camera. The data processing circuit conducts reverse-phase processing over the images output by the probe, so as to enable the system to acquire higher positioning precision of the targets. The probing and tracking camera in the invention, together with a sun sensor, a two-dimensional tracker and an image processing system, forms a whole probing and tracking system for targets.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for automatically recognizing macula based on Huairou full-disk single-color image
InactiveCN104615990AExtraction sensitiveInstrument Noise CancellationScene recognitionColor imageSolar physics
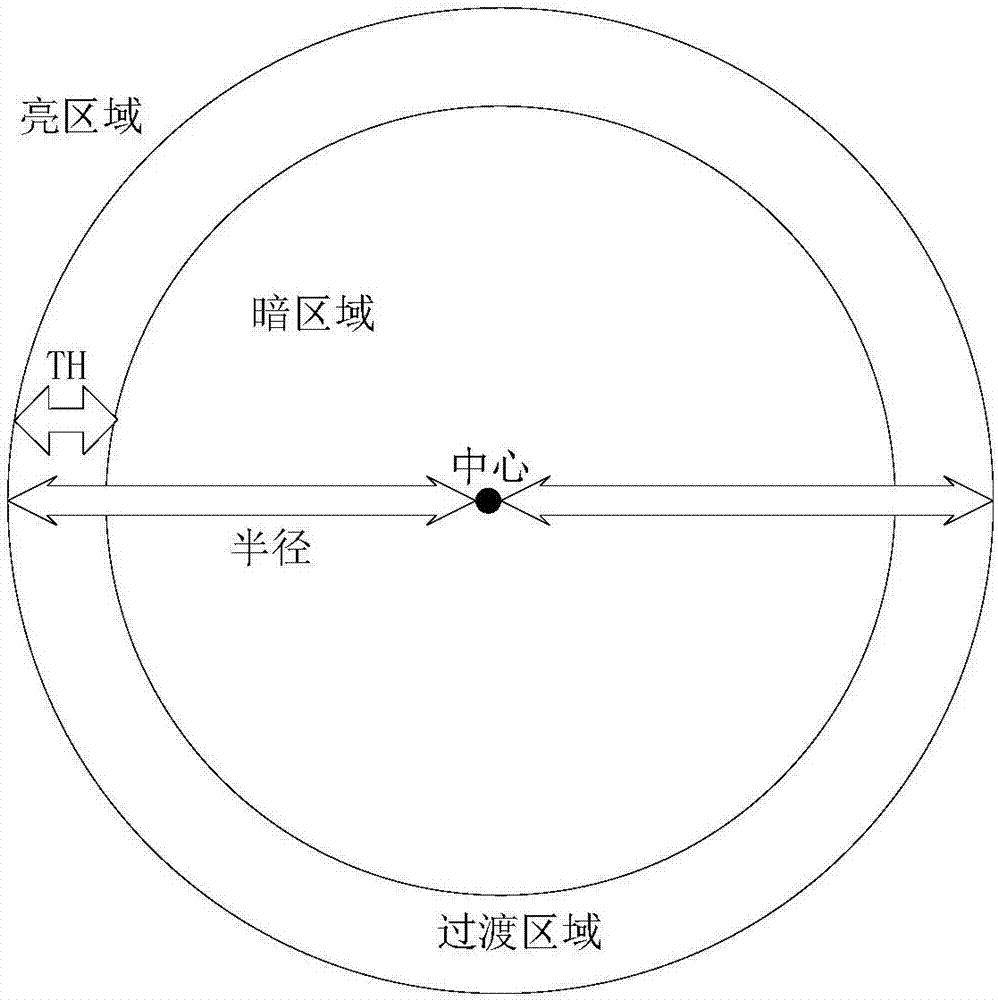
The invention relates to a method for automatically recognizing macula based on a Huairou full-disk single-color image, and aims at solving the problems of extremely low efficiency caused by manually recognizing the profile of macula on disk and that mass data cannot be met in the solar physics in the domestic astronomy field. The method comprises the steps of extracting gradient information of the disk by the morphology bot-hat transformation according to the full-disk single-color image of the Huairou solar observing station of National Astronomical Observatories of China; removing the influence of inherent limb darkening rule of the disk by the fragmentation threshold method, so as to automatically recognize macula. Compared with other algorithms for recognizing the macula based on high-quality solar space data, the method has the characteristic that the macula of the ground images with relatively low quality and suffering from the interference of instrument noise can be precisely recognized. The method is applicable to automatic recognition of macula in the single-color images or white light images at other wave bands and can provide directly service to the fields of generator theory, solar action predication and space environment monitoring.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mobile communication sea area coverage system
InactiveCN101778397AAvoid specular reflectionsGuaranteed recognition effectNetwork planningHigh level techniquesUltrasound attenuationCommunication quality
The invention provides a mobile communication sea area coverage system with low construction cost and good communication quality, which comprises a near-end machine, a relay antenna, a far-end machine, a far-end relay antenna and a repeat antenna, wherein the input end and the output end of the near-end machine are respectively connected with a base station and the relay antenna, and the input end and the output end of the far-end machine are respectively connected with the far-end relay antenna and the repeat antenna. The near-end machine and the far-end machine respectively compress and decompand a channel through a data companding module, and simultaneously adopt IF transmission to prevent the power attenuation caused by specular reflection of the sea level and sunspots, and the invention is suitable for the signal coverage of coastal water within 120km.
Owner:泉州泽仕通科技有限公司
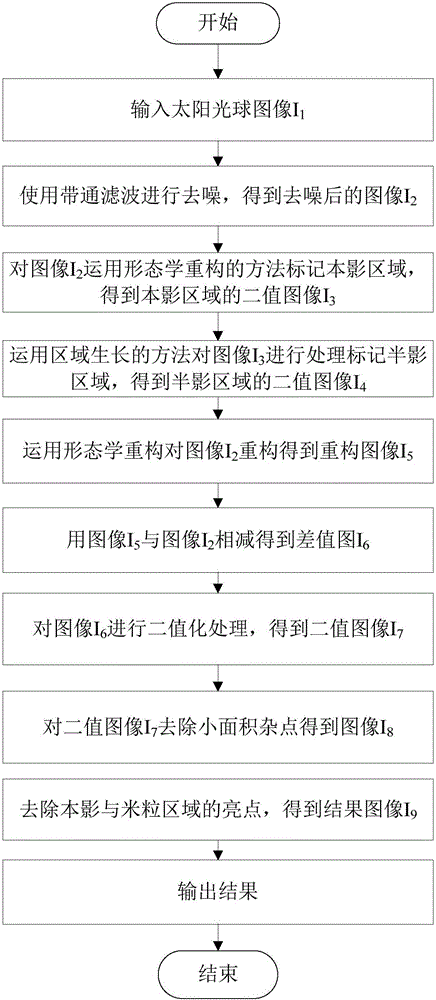
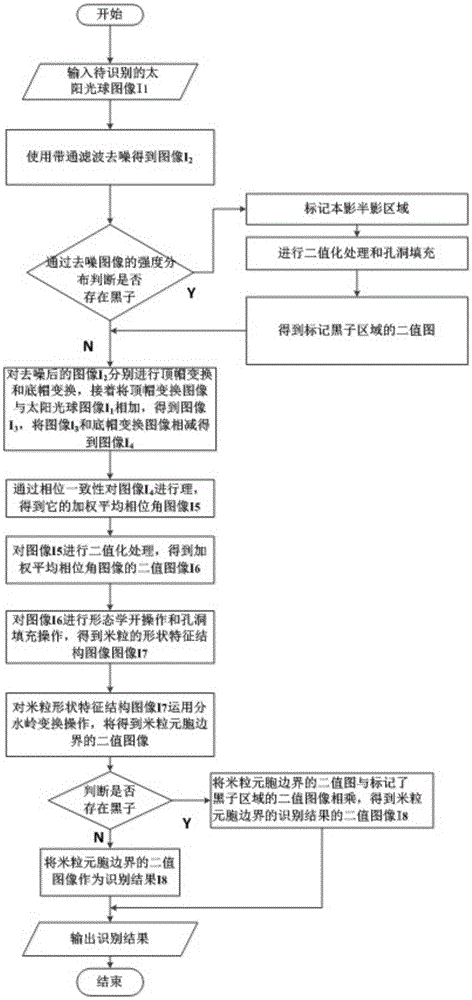
Method of identifying penumbra fiber bright spots in astronomical image sunspot
InactiveCN105844613AStable extractionSteadily extract the corresponding shape in the image to achieve image analysisImage enhancementImage analysisFiberImaging processing
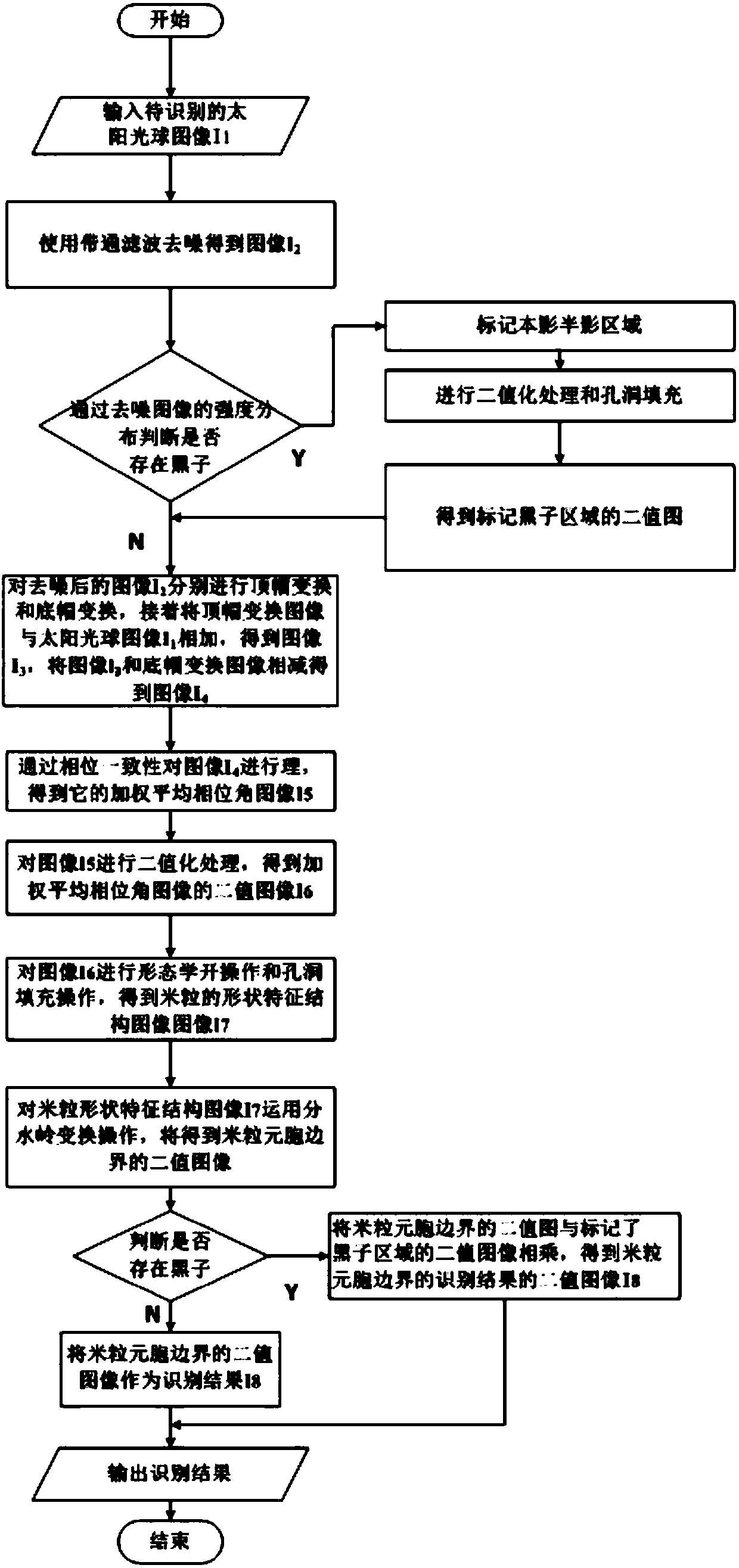
The invention relates to a method of identifying penumbra fiber bright spots in the astronomical image sunspot, and belongs to the field of astronomical technology and image processing. The method comprises the steps of denoising a solar photosphere image I1 using band-pass filtering, to obtain an image I2; marking an umbra region for the image I2 using a morphological reconstruction method, to obtain a binary image I3 of the umbra region; processing the identified image I3 by using a region growth method to mark a penumbra region, to obtain a binary image I4 of the penumbra region; reconstructing the image I2 using the morphological reconstruction method, to obtain a reconstructed image I5; subtracting the image I2 from the image I5 to obtain a differential image I6; binarizing the image I6 to obtain a binary image I7; removing small area miscellaneous points to obtain a binary image I8; and multiplying the image I8 by the image I3 and the image I4 to remove points in the umbra region and a granule region, and obtaining an image I9. The invention is advantageous over the identification method based on high-pass filtering, and the identification result is reliable and accurate.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
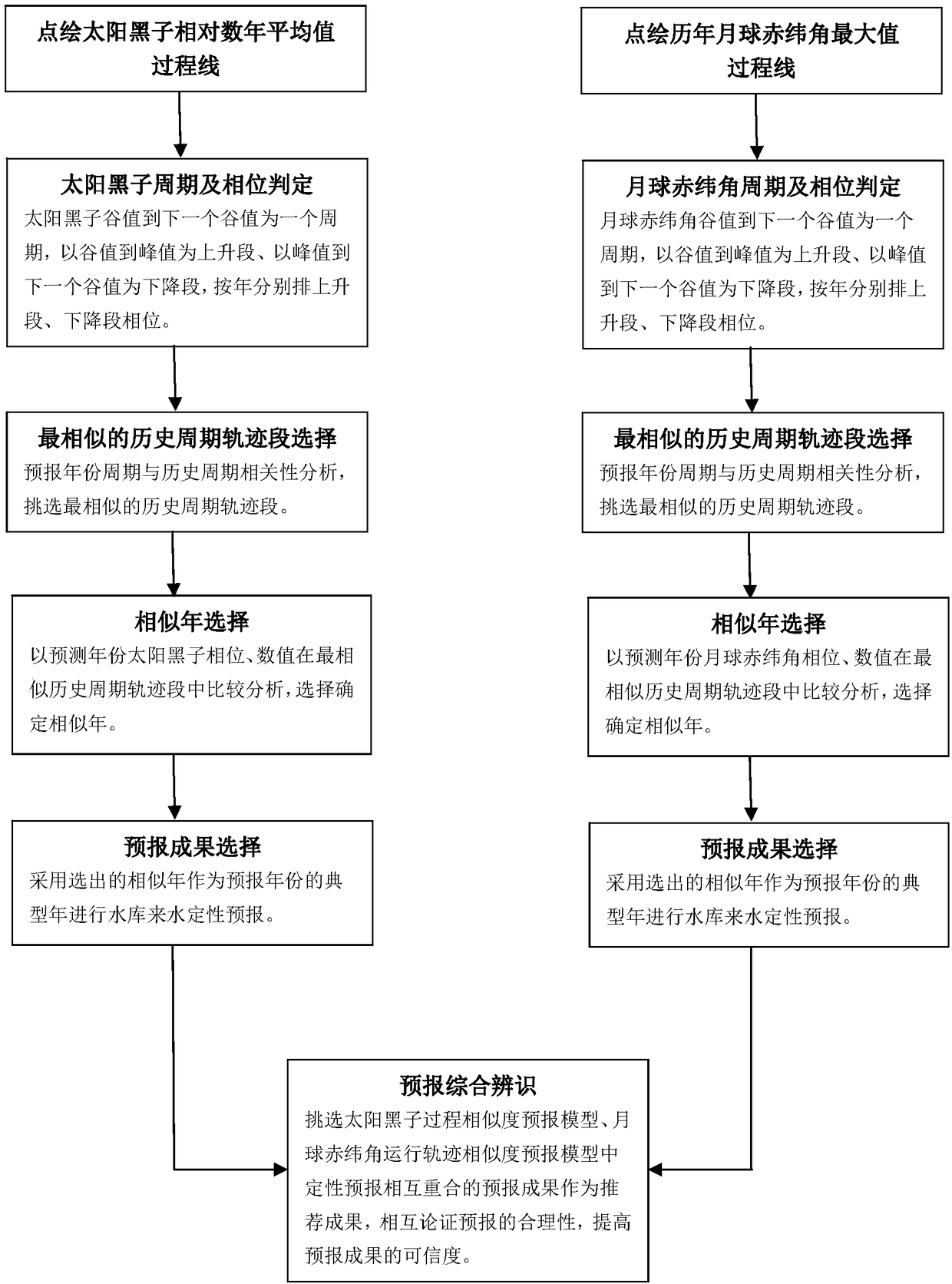
Sunspot and moon declination angle information-based reservoir inflow forecast method
InactiveCN108446487AHuge power generation benefitsHuge benefits of flood control and disaster reductionData processing applicationsClimate change adaptationEngineeringFlood control
The invention discloses a sunspot and moon declination angle information-based reservoir inflow forecast method. The method comprises the steps of (1) building a sunspot process similarity forecast model; (2) building a moon declination angle running track similarity forecast model; and (3) performing forecast and comprehensive identification. The method greatly improves the forecast precision, can be effectively applied to power generation scheduling and flood control scheduling of reservoirs, and creates huge power generation benefits and huge flood control and disaster reduction benefits for enterprises and society respectively.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Method for identifying solar granule in astronomic image
ActiveCN105551025AEasy to identifyStable extractionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingBand-pass filter
The invention relates to a method for identifying a solar granule in an astronomic image, and belongs to the fields of astronomy technology and image processing. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, receiving a solar photospheric image I1, using band-pass filtering to carry out de-noising, and obtaining a de-noised image I2; then according to intensity distribution of the image I2, judging whether sunspots exist in the image; carrying out top-hat transformation and bottom-hat transformation respectively on the image I2, and obtaining a top-hat transformation image and a bottom-hat transformation image; then adding the top-hat transformation image to the solar photospheric image, obtaining an image I3, and carrying out subtraction between the image I3 and the bottom-hat transformation image to obtain an image I4; respectively subjecting the image I4 respectively to open operation of a phase congruency method, binaryzation and morphology and hole filling operation, and obtaining an image I7; and carrying out watershed transformation operation on the image I7, and obtaining a binary image of a granule cellular boundary. By adopting the method for identifying the solar granule in the astronomic image, the granule organization high in contrast and clear in edge can be well identified, and the granule characteristics low in contrast and fuzzy in edge can also be well identified.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
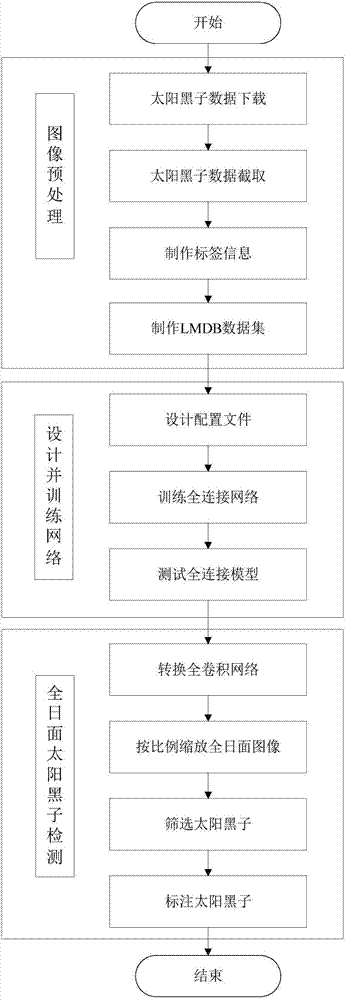
Sunspot identification method based on deep learning
The invention relates to a sunspot identification method based on deep learning, and belongs to the field of astronomical technology, image processing and artificial intelligence. The sunspot identification method comprises the steps that firstly a sunspot data sample is extracted and tag information and an LMDB data set are made; then the configuration file of a convolutional neural network is set, a convolutional neural network model including a data layer, a convolutional layer and a full connection layer is trained and tested and the full connection layer of the network is converted into the convolutional layer; then the full sun-face image is proportionally scaled and then inputted to the converted full convolutional neural network to calculate the probability; and finally the sunspots meeting the threshold are selected out through screening, and the positions of the sunspots are marked on the full sun-face image by using non-maximum suppression. Application of the method of deeplearning to the problem of sunspot identification is unprecedented and effective, and the problems of misidentification and leak identification of the conventional sunspot identification method can besolved to a great extent.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Solar system planetary planetarium display system
The invention provides a solar system planetary planetarium display system which comprises solar system star and planetary models including Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth, Moon, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune models. Projection in a model is adopted by the Sun model, the content of a projection video comprises the structure of the Sun, the Sun as a source of energy, sunspots and cycles, solar activity, the lepton miracle in the Sun, sun storm and the Sun and the Earth. Spherical touch control is used by the mercury model, and the content of a projection video comprises the internal structure of Mercury, topography, star magnetic field, the planetary extremes and star motion. Spherical touch control is used by the Venus model, and the content of a projection video comprises star characteristics, basic parameters, volcanic distribution, an atmospheric environment and physical observation. Internal projection is adopted by the Earth model, a spherical touch control is adopted by the Moon model which is associated with the Earth model, and the content of a projection video comprises the observation of the Earth from outer space, the moon, the surface of the Moon, the rotation ofthe Moon around the Earth, tides, and the origin of the Moon.
Owner:上海诚唐文旅科技集团股份有限公司
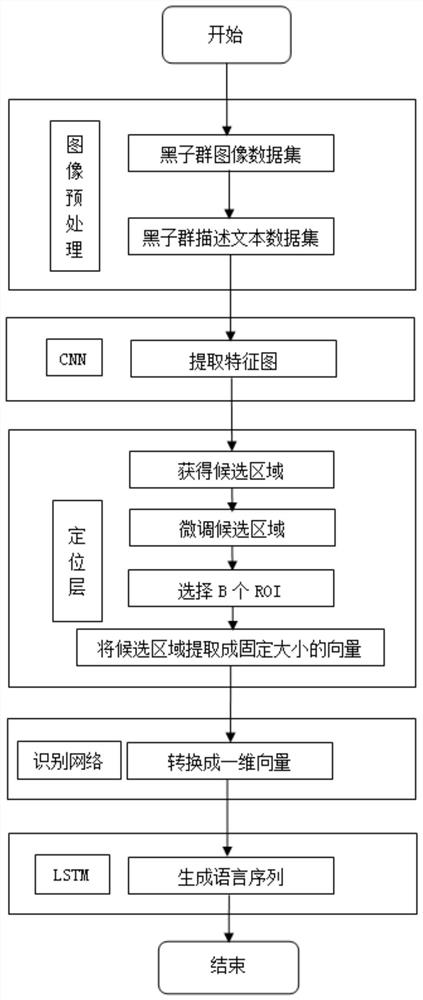
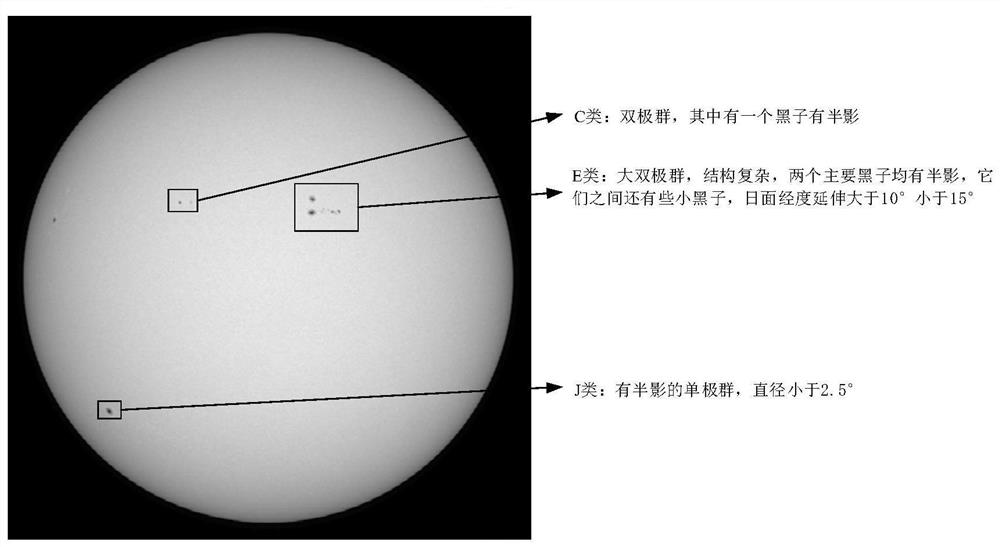
A method for describing sunspot group in full-sun image
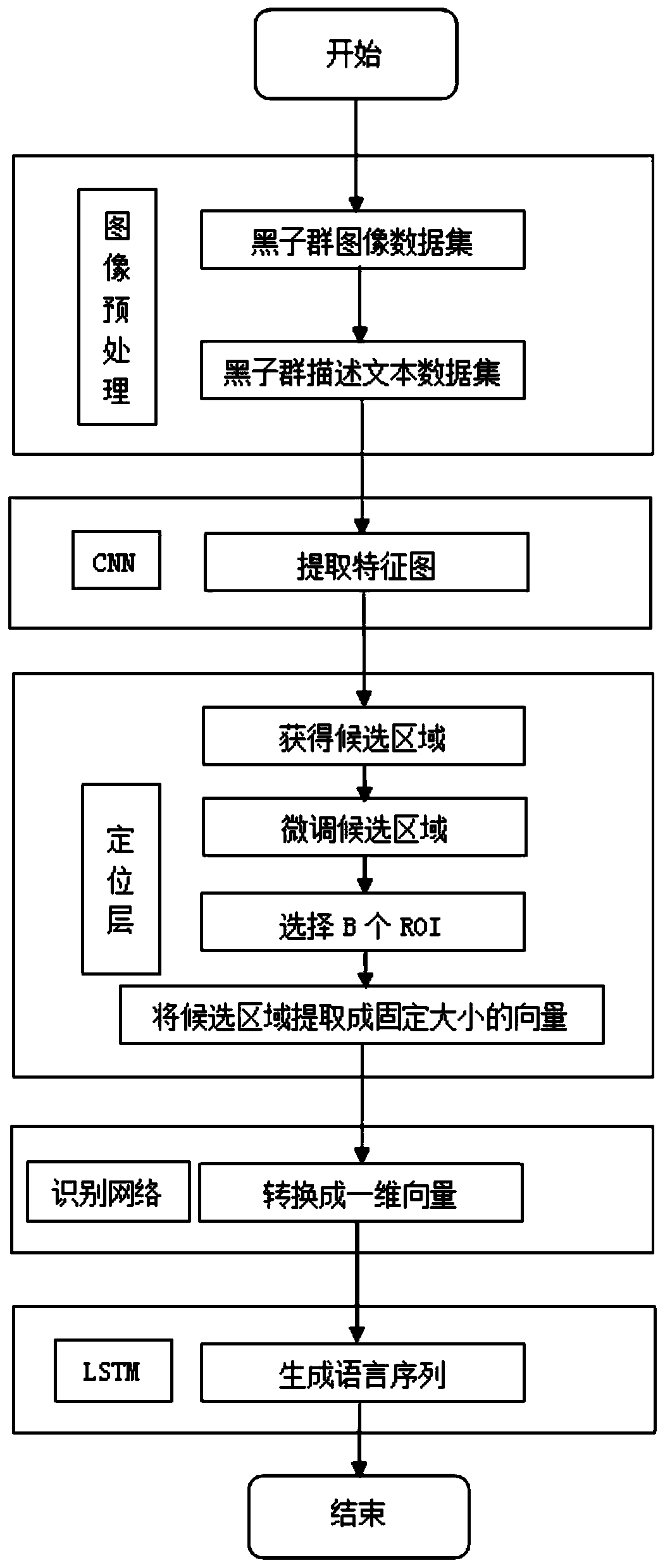
ActiveCN110851627AImprove description qualityStill image data indexingCharacter and pattern recognitionData setComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to a method for describing a sunspot group in a full-sun image, and belongs to the field of computer vision and natural language processing. The method comprises the following steps of: making a sunspot group image and a data set for describing a text, sending an original image into an improved VGG-16 network to generate a feature map; sending the output feature map to a positioning layer, generating candidate regions through improved Inception-RPN, processing the candidate regions into region features with fixed sizes, processing the region features into one-dimensionalvectors capable of being processed by LSTM after passing through an identification network, and finally generating description statements; compared with a traditional method, the method has the advantages that more accurate candidate regions can be obtained, so that the description quality of the whole network is improved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
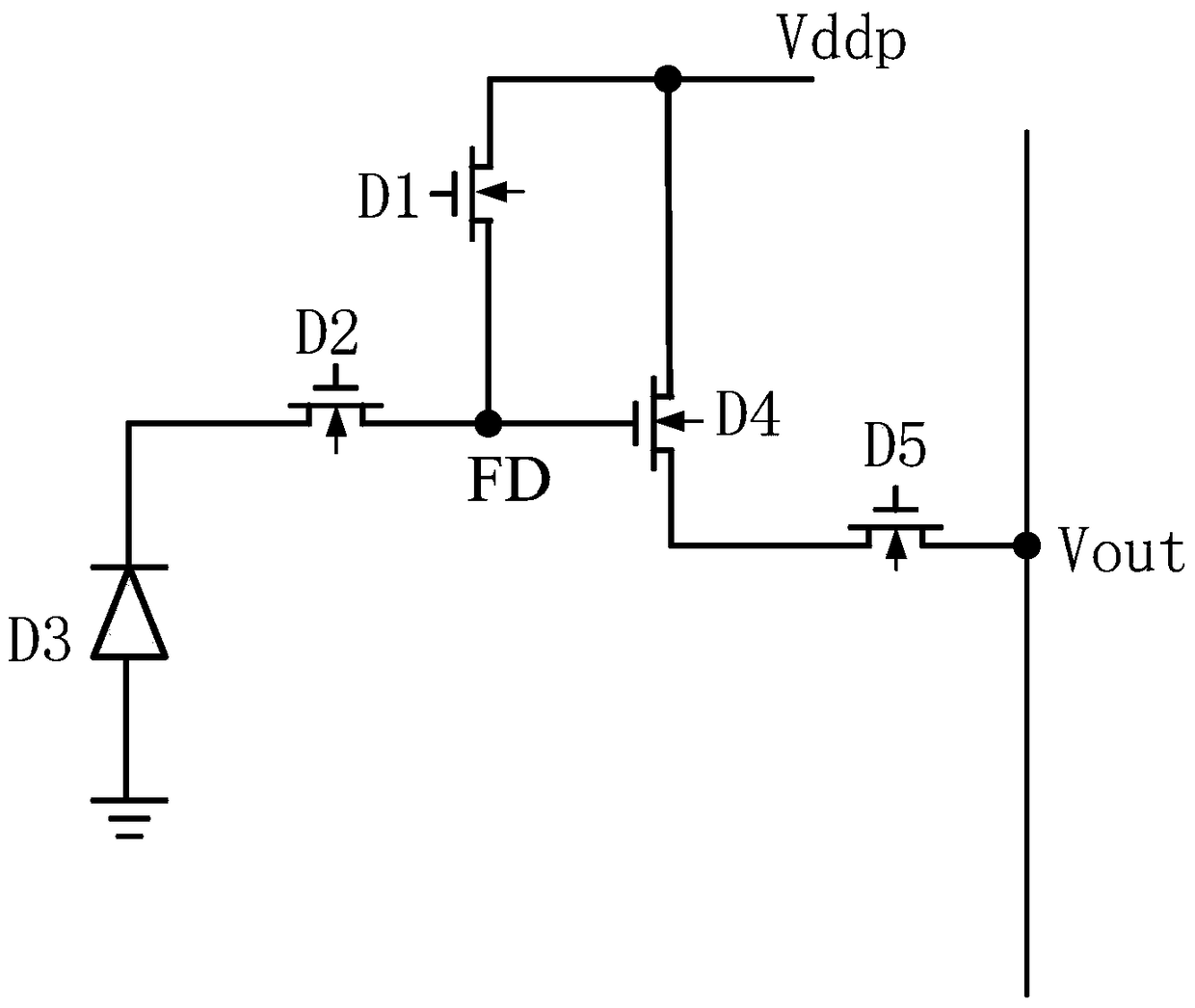
Method and circuit for eliminating sunspots of image sensor, and image sensor
ActiveCN112261325AElimination GuaranteeNo gray dotsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsIlluminanceBlack spot
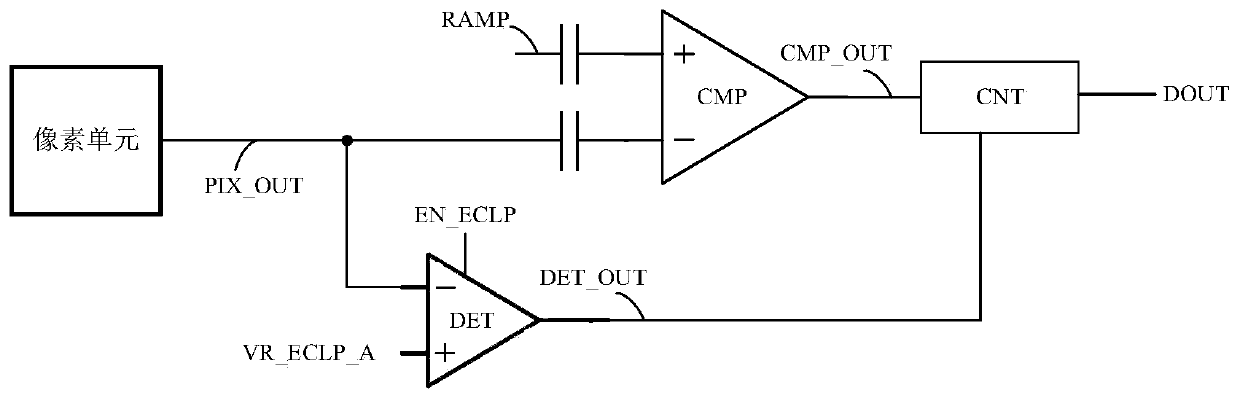
The invention discloses a sunspot elimination method and circuit of an image sensor, and the image sensor, and the method comprises the steps: firstly judging whether a sunspot phenomenon happens to acorresponding pixel or not, and locking all sunspots of a counter at a high level through a latch circuit if the sunspot phenomenon happens, so as to enable the corresponding pixel to be displayed asa bright spot. Based on this, the rated count value of the counter can be locked to be a full amplitude when the sunspot phenomenon occurs, and it is guaranteed that the occurring black spots can becompletely eliminated when the sunspot phenomenon occurs. And moreover, sunspots appearing under the irradiation of light intensity with different illuminance can be completely eliminated, so that theimage quality is ensured, and gray spots are avoided.
Owner:CHENGDU LIGHT COLLECTOR TECH
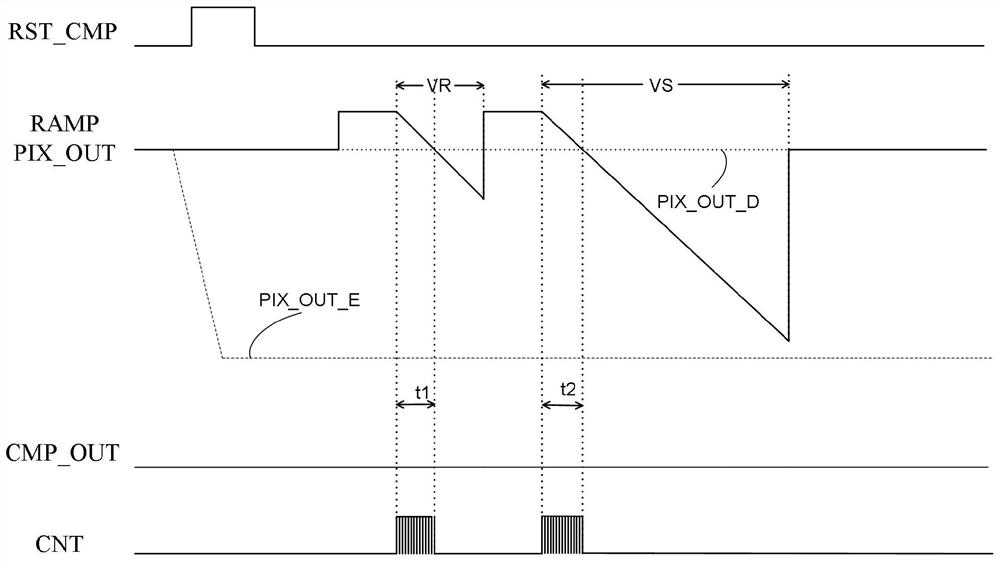
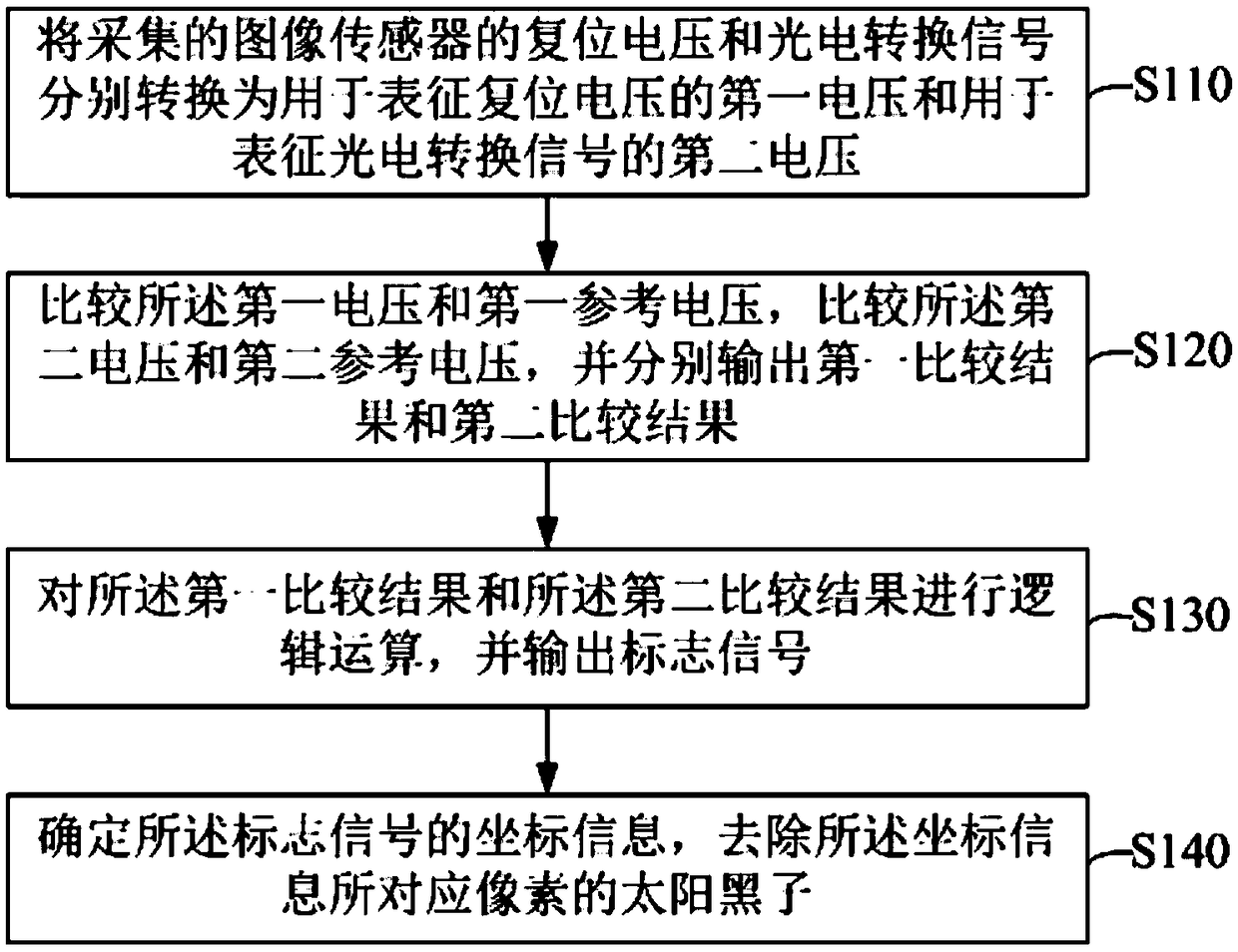
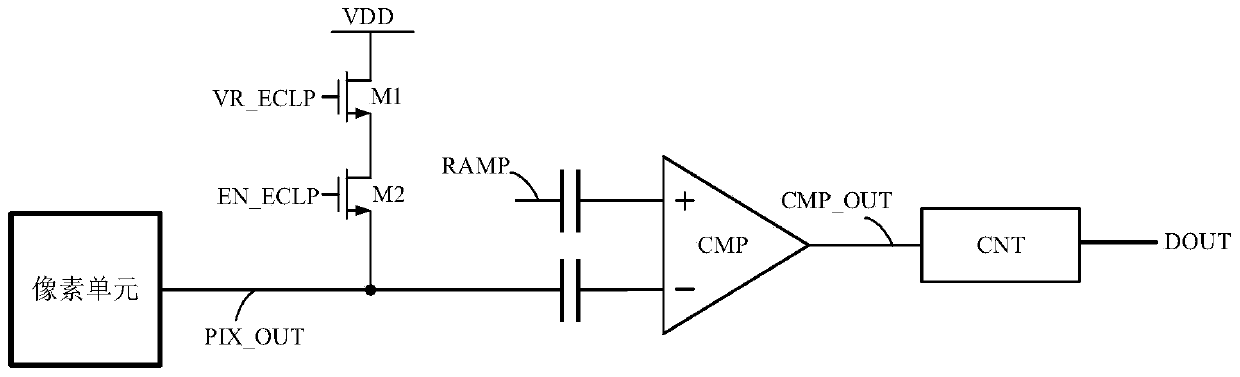
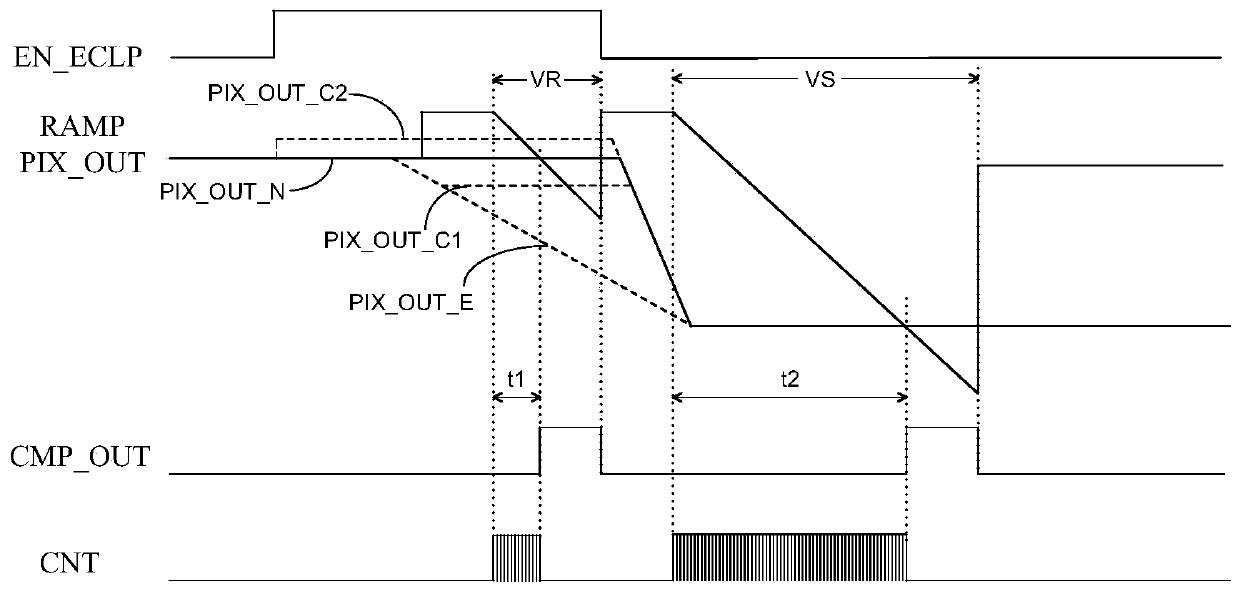
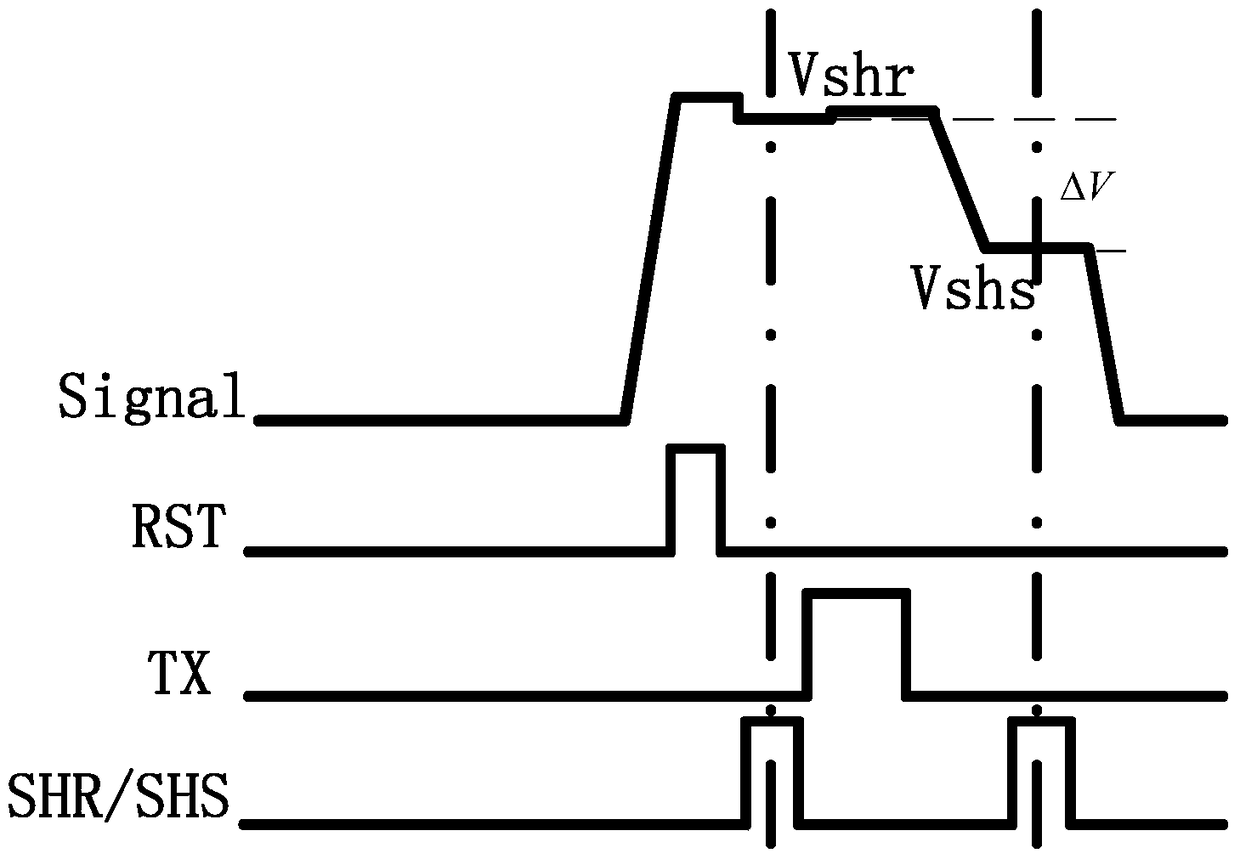
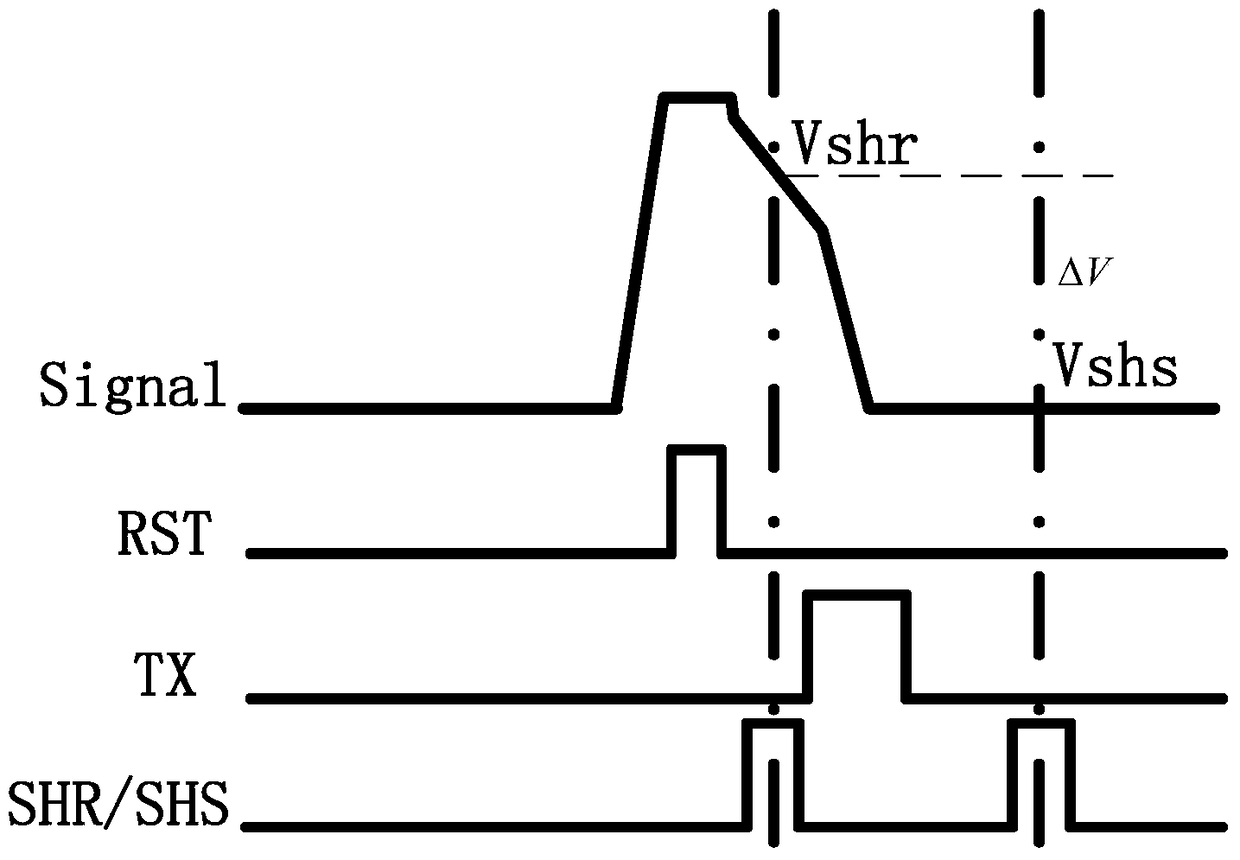
Sunspot real-time processing method and image processor
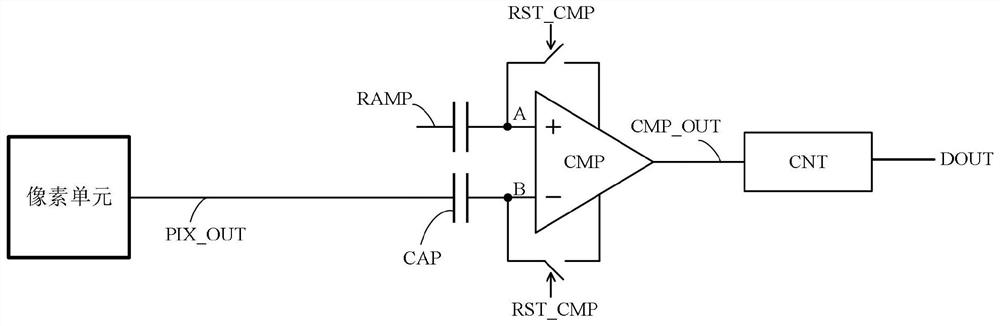
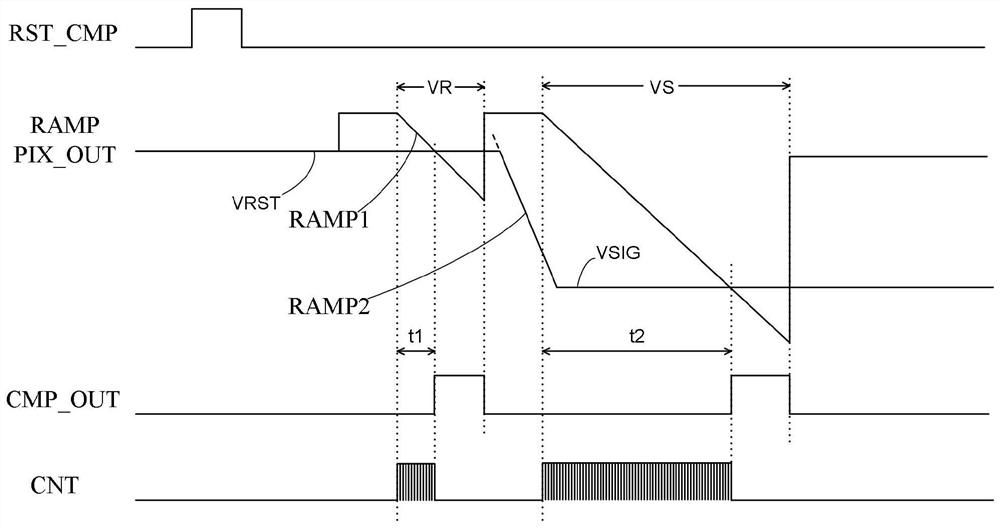
ActiveCN108924386AReduce latencyReduce demandTelevision system detailsColor television detailsReal time analysisImaging processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing and provides a sunspot real-time processing method. The method comprises the following steps of converting a collected reset voltage and photoelectric conversion signal of an image sensor into a first voltage for representing the reset voltage and a second voltage for representing the photoelectric conversion signal; comparing the first voltage with a first reference voltage, comparing the second voltage with a second reference voltage, and outputting a first comparison result and a second comparison result; carrying out logicaloperation on the first comparison result and the second comparison result, and outputting a marking signal; determining coordinate information of the marking signal, and removing a sunspot of pixel corresponding to the coordinate information. Features of the reset voltage and the voltage of the photoelectric conversion signal are analyzed in real time, the sunspot is corrected in real time, the correction delay is reduced, the frame storage space required by analyzing a whole frame image is effectively avoided, and cost and power consumption are reduced.
Owner:SMARTSENS TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD
Solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system
ActiveCN102621687BRealize high-resolution imagingSimplify the difficulty of decouplingOptical measurementsOptical elementsHigh resolution imagingCoupling
The invention provides a solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system. The solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system comprises a lower atmospheric wave front sensor, a middle and upper atmospheric wave front sensor, a lower atmospheric wave front corrector, a middle and upper atmospheric wave front corrector, a wave front controller, an optical relay system, an imaging subsystem and other necessary optical components. The system has the advantages that sunspots or grain structures on the surface of the sun are taken as beacons and wave front detection is conducted on multiple areas at the same time, so as to obtain wave front distortion caused by turbulence in a large field range; wave front aberration caused by different turbulent layers is calculated by utilizing a tomography algorithm; and at last, the wave front correctors positioned in conjugate positions of the corresponding turbulent layers are controlled to correct the atmospheric turbulence in a layered manner, so as to finally realize high-resolution imaging in the large field range. The solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system has the advantages that the sequence of the conjugate positions of the high and the lower turbulent layers is adjusted through the optical relay system, so that the lower turbulent layer is firstly compensated and corrected and the accuracy of the detection and the correction is increased; and due to the use of the tomography algorithm, errors caused by the coupling of the wave front aberrations of the different turbulent layers are reduced.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
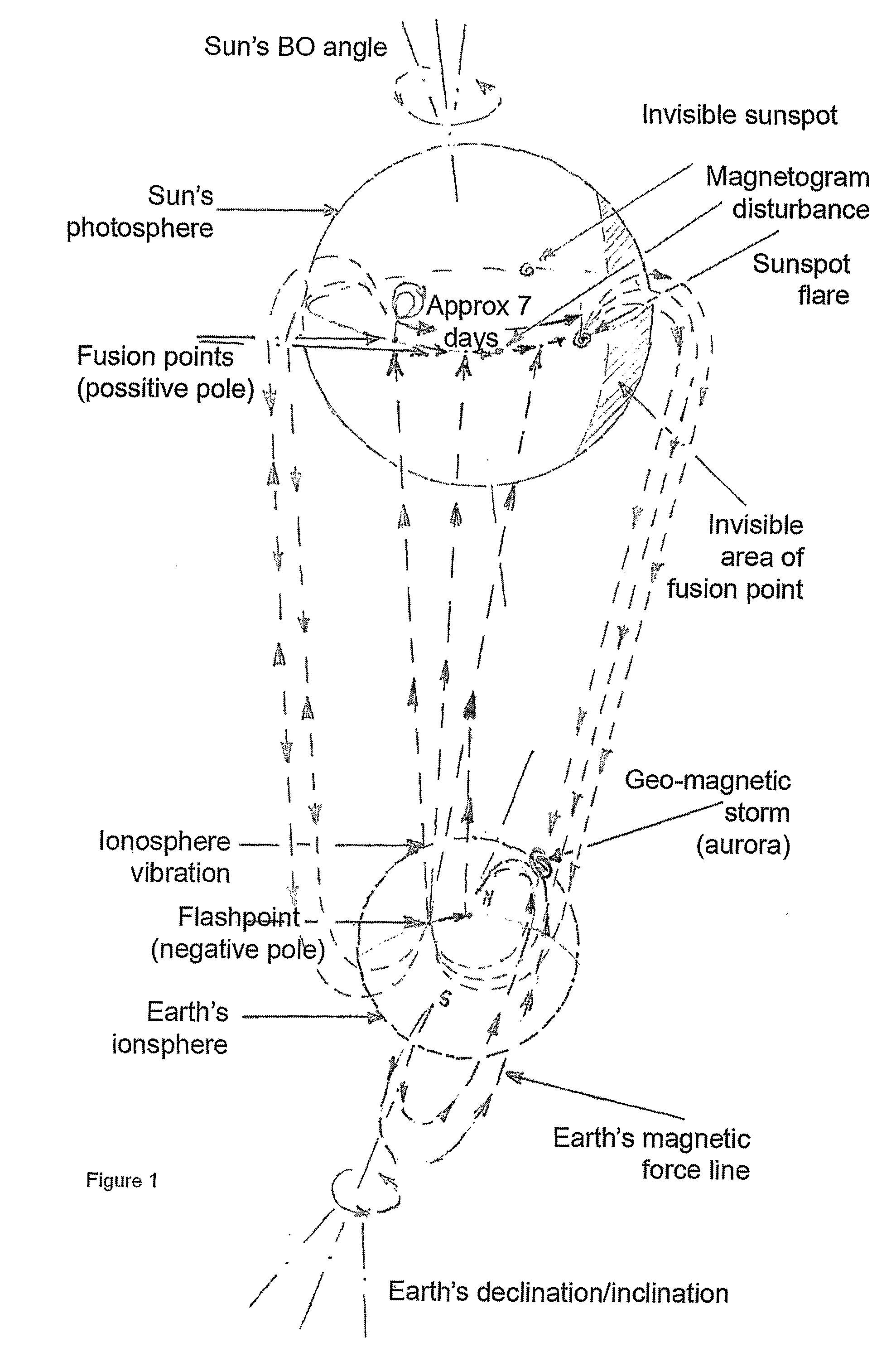
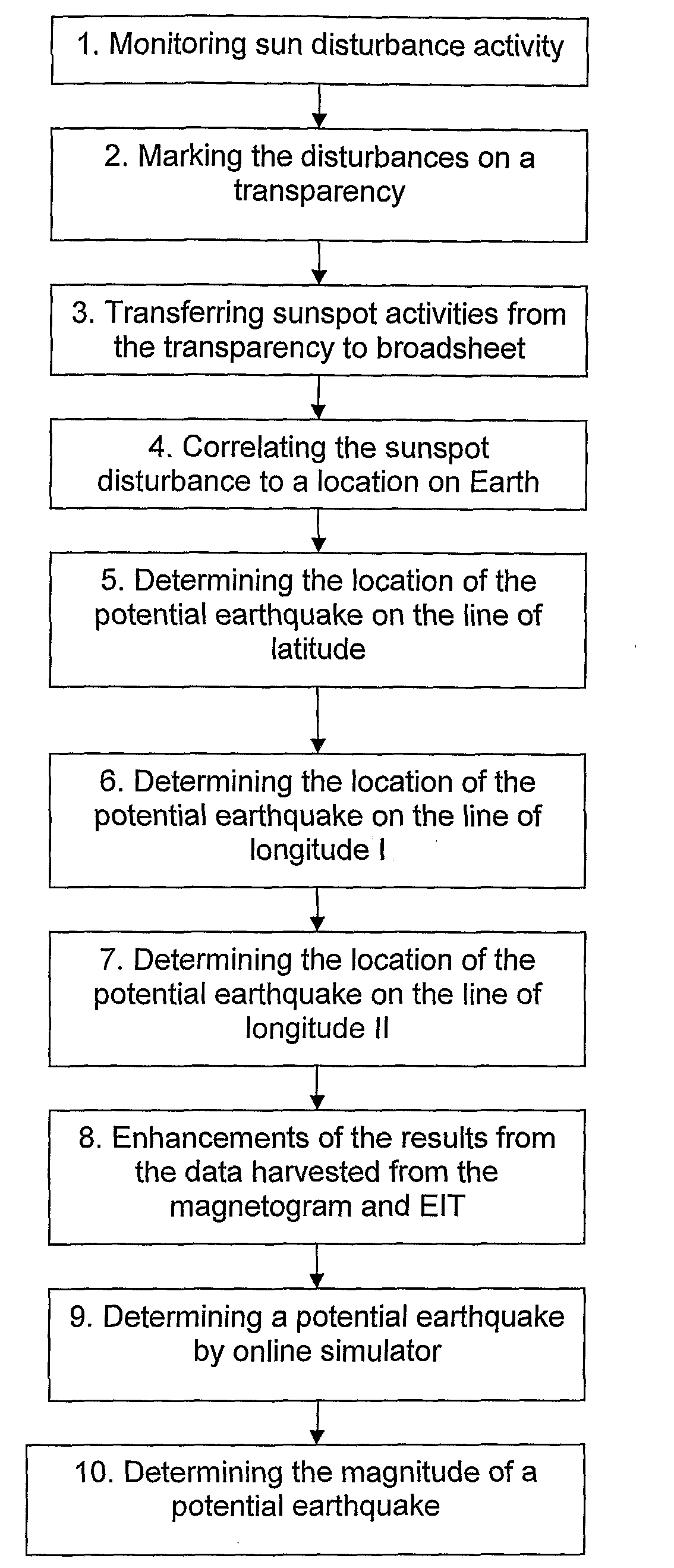
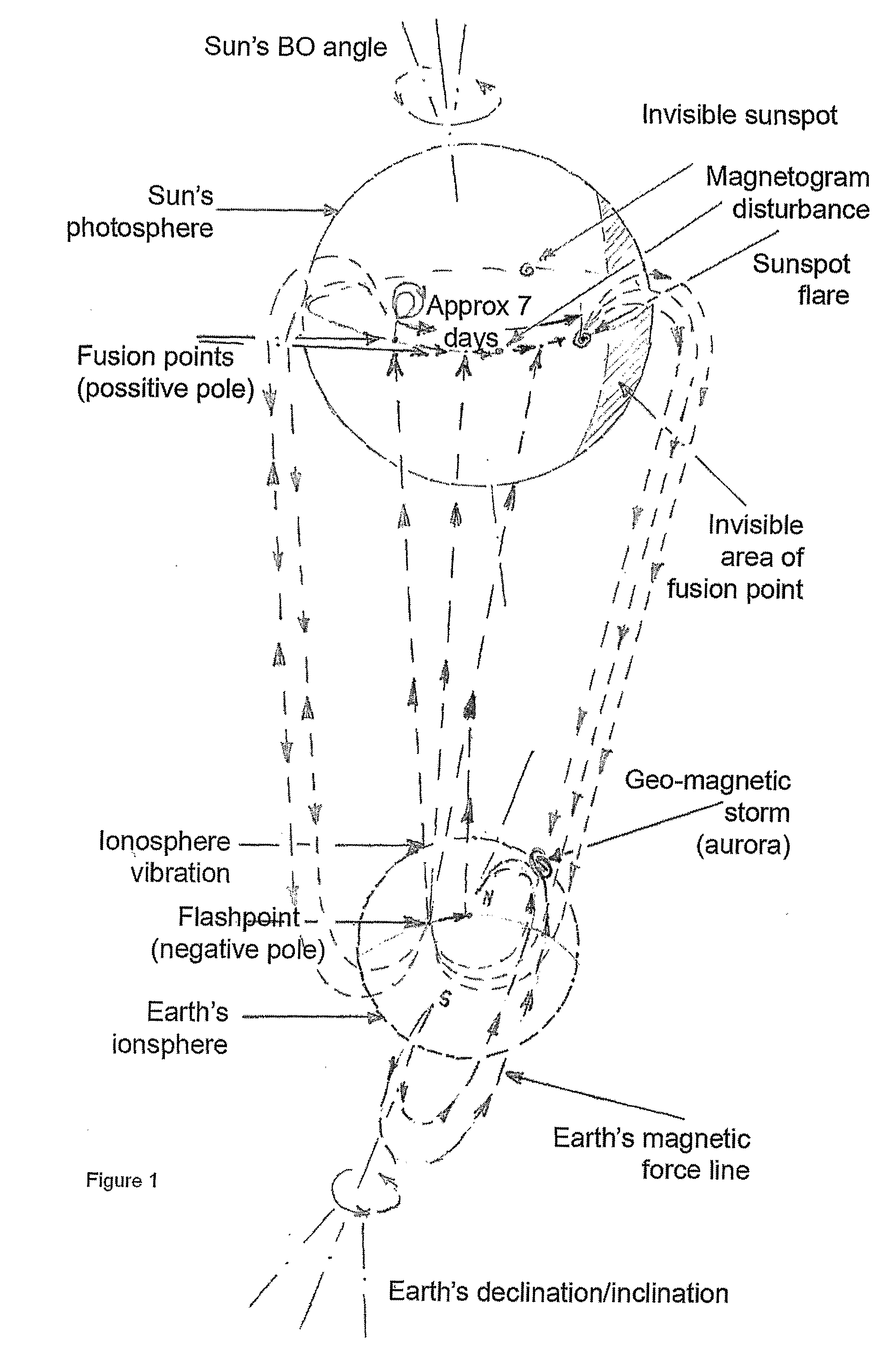
Earthquakes and sun disturbances
Owner:MIZRAHI EZRA
A medium-and long-term flood forecasting method based on cause analysis
InactiveCN109409597ASimple methodEasy to operateClimate change adaptationForecastingSocial benefitsFlood forecast
The invention discloses a medium and long-term flood forecasting method based on cause analysis. Precursor indicators for genetic analysis include sunspots, West Pacific Subtropical High Ridge, Reservoir Inflow and Precipitation. The specific method includes a sunspot, west pacific subtropical high ridge, annual runoff point scatter diagram method, a West Pacific Subtropical High Ridge, Precipitation, Annual Runoff Point scatter diagram method, and a Previous Inflow, Previous Runoff, Annual Runoff Point scatter diagram method. The invention establishes an intuitive distribution graph by utilizing the precursory index and the occurrence law of the major flood, provides a reference for the medium and long-term major flood forecast of the reservoir, improves the accuracy of the medium and long-term major flood forecast, and can bring huge economic benefit and social benefit to the reservoir.
Owner:NANJING NARI GROUP CORP
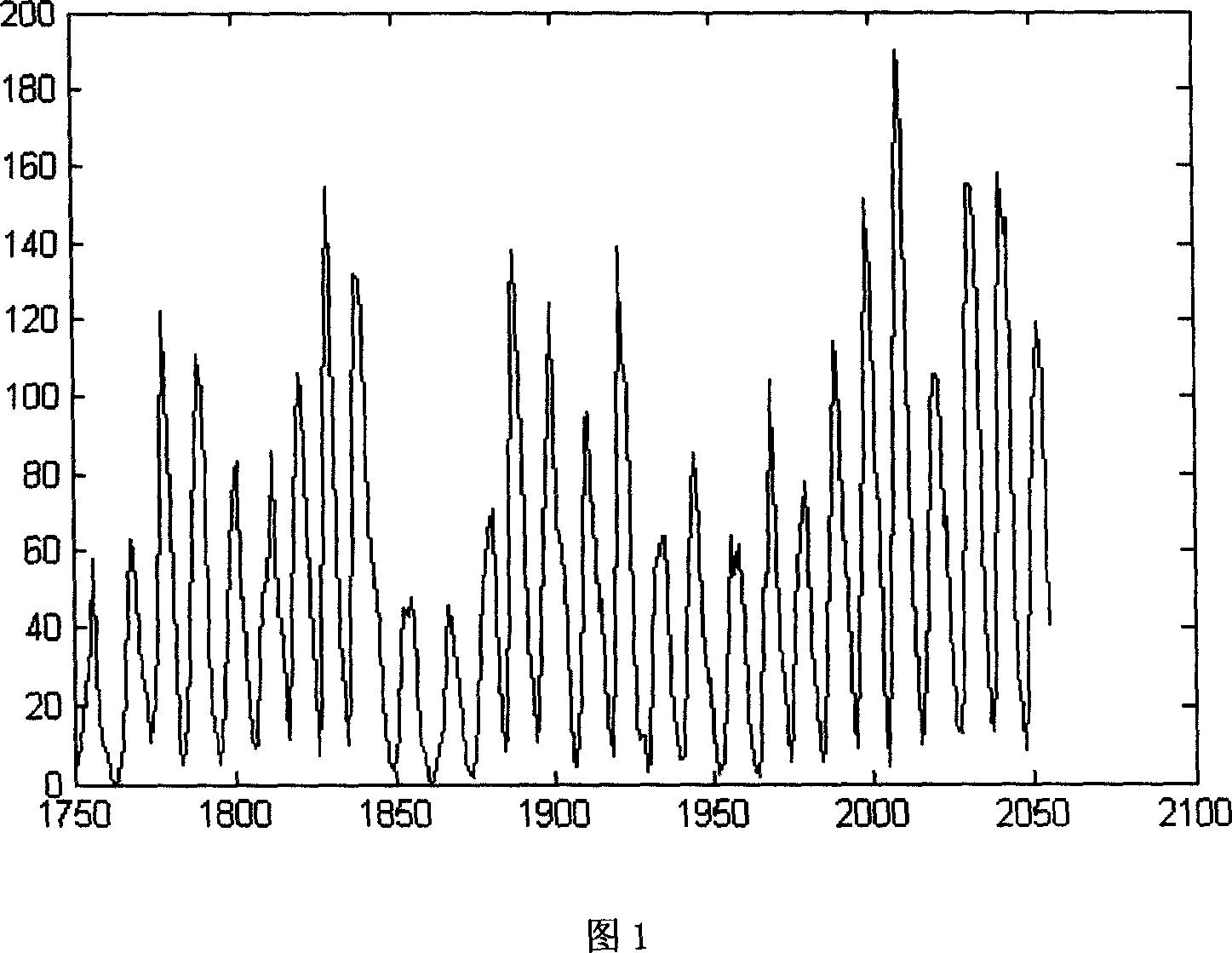
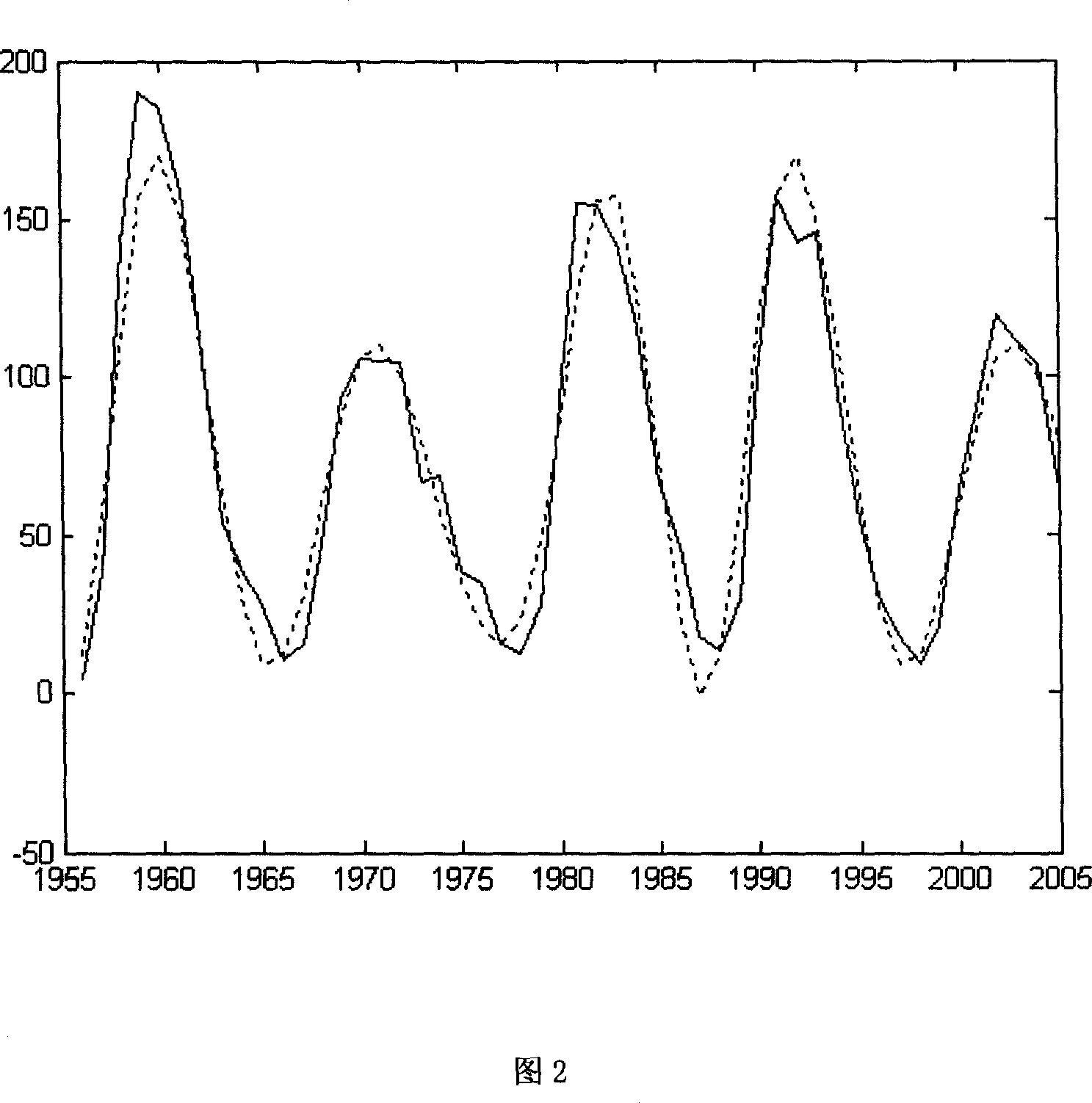
Sun-spot dynamic model and tractive predicting method based on particle filter technology
InactiveCN101075224AImplement trackingAchieve forecastSpecial data processing applicationsHigh dimensionalityAnalysis study
A sunspot dynamic model based on particle filtering technology is prepared as applying dynamic parameter mechanism, using historical data of sunspot as example, comparing the fitting property of model with set domain value and dynamically regulating model parameters when property index is less than set domain value. The said particle filtering technology is analyzing method of nonlinear time sequence.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS
Image sensor reading circuit and reading method for suppressing sunspot effect
PendingCN110798637AGuaranteed image qualityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsBlack spotLight irradiation
The invention discloses an image sensor reading circuit for suppressing a sunspot effect. The circuit comprises a detection unit, a comparator and a counter. The detection unit comprises two input ends, an enabling control end and an output end; wherein two input ends of the detection unit are respectively connected with an output end of a pixel unit and a reference voltage; the enabling control end of the detection unit is connected with an enable signal; wherein the output end of the detection unit is connected with the input end of the counter, one end of the comparator is connected with the output end of the pixel unit, the other end of the comparator is connected with an oblique wave signal, the output end of the comparator is connected with the input end of the counter, and the output end of the counter outputs the exposure digital quantity of the pixel unit. The image sensor reading circuit capable of suppressing the sunspot effect can ensure that abnormal black spots do not appear on an image when the sunspot effect occurs due to strong light irradiation, and does not influence the image quality.
Owner:CHENGDU LIGHT COLLECTOR TECH
Method for removing sunspot regions in image, image processor and photographing device
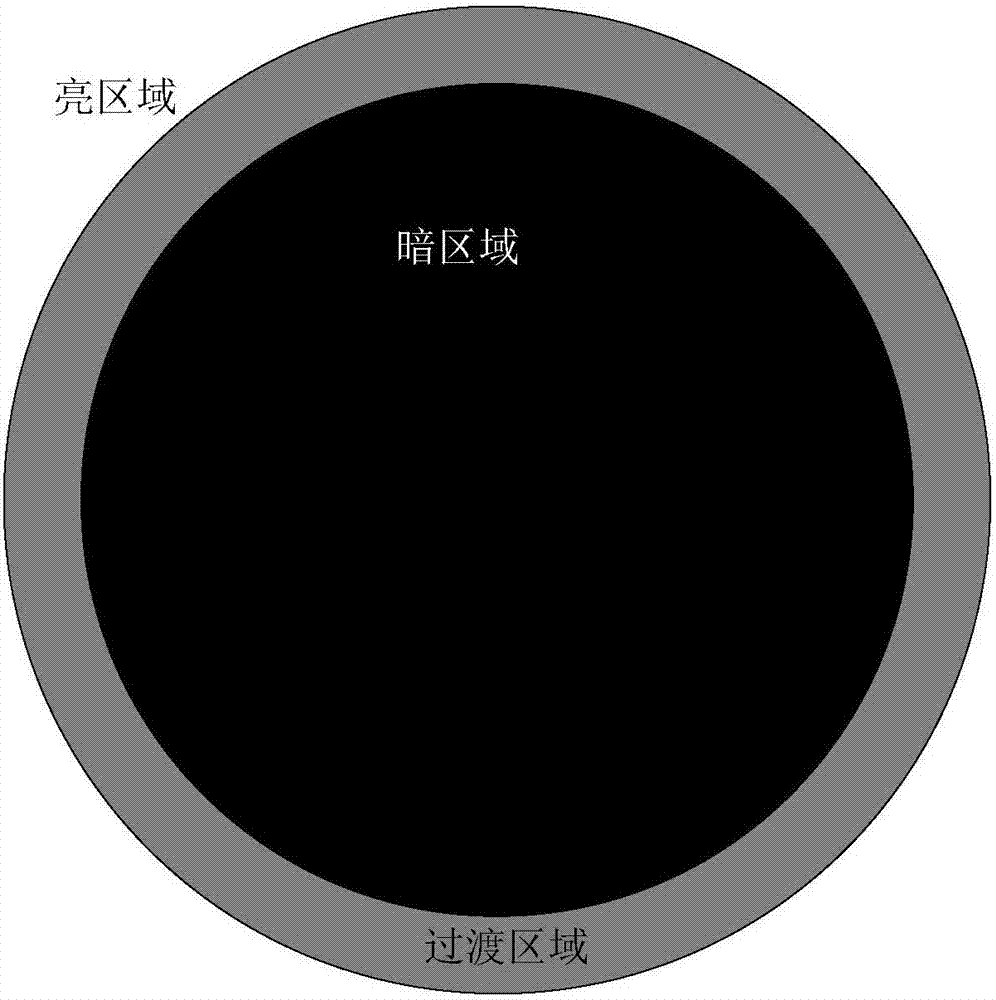
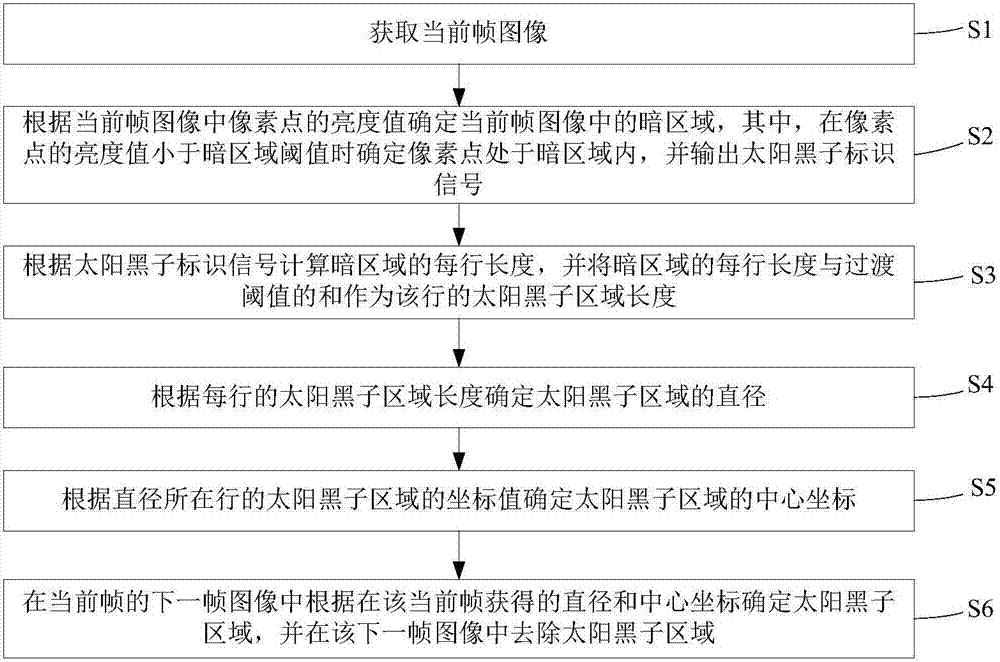
InactiveCN107580160AAvoid residueEnhance the imageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Sunspot
The invention discloses a method for removing sunspot regions in an image. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a current frame image; and determining a dark region in the current frame image according to the brightness value of the pixel points in the current frame image, wherein the pixel points are determined to be in the dark region when the brightness value of the pixel points is smaller than the threshold value of the dark region, and generating a sunspot identification signal; calculating the length of each row of the dark region according to the sunspot identification signal, and taking the sum of the length of each row of the dark region and the transition threshold value as the length of the sunspot region of the row; determining the diameter of the sunspot region according to the length of the sunspot region of each row; determining the center coordinate according to the coordinate value of the sunspot region where the diameter is located; determining the sunspot region according to the diameter and the center coordinate in the next frame of the image, and removing the sunspot region in the next frame of the image. According to the method, no transition region residue exists when the sunspot region is removed, and the image effect is better. The invention further discloses an image processor and a photographing device.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
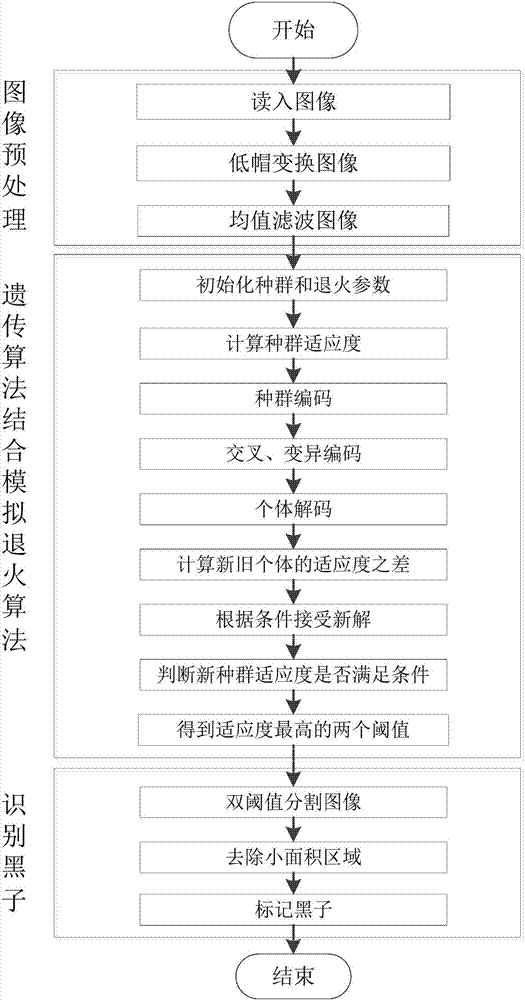
Macula identification method based on genetic algorithm and simulated annealing algorithm
InactiveCN108009471AAccurate identificationSolve the problem of selectivityCharacter and pattern recognitionGenetic algorithmsPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention, which belongs to the astronomy technology and the image processing field, relates to a macula identification method based on a genetic algorithm and a simulated annealing algorithm. Pretreatment is carried out on an image; expansion and corrosion processing is carried out on a full-disk solar image respectively; a background image after expansion and corrosion is subtracted from thefull-disk solar image to obtain a full-disk solar image with the uniform background; mean smoothing filtering is carried out on the full-disk solar image with the uniform background and noise reduction is carried out; two groups of thresholds are evolved by using a genetic algorithm; the two groups of thresholds are processed by using a simulated annealing algorithm respectively to obtain a new population; whether an exit condition is met is determined; if so, two thresholds of an optimal entropy are found out from the population to segment the image; small area block removing processing is carried out on a segmentation result; and then a segmented image is marked and displayed.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Earthquakes And Sun Disturbances
InactiveUS20080234940A1Promote resultsEarthquake measurementAlarmsElectromagnetic interferenceSunspot
Owner:MIZRAHI EZRA
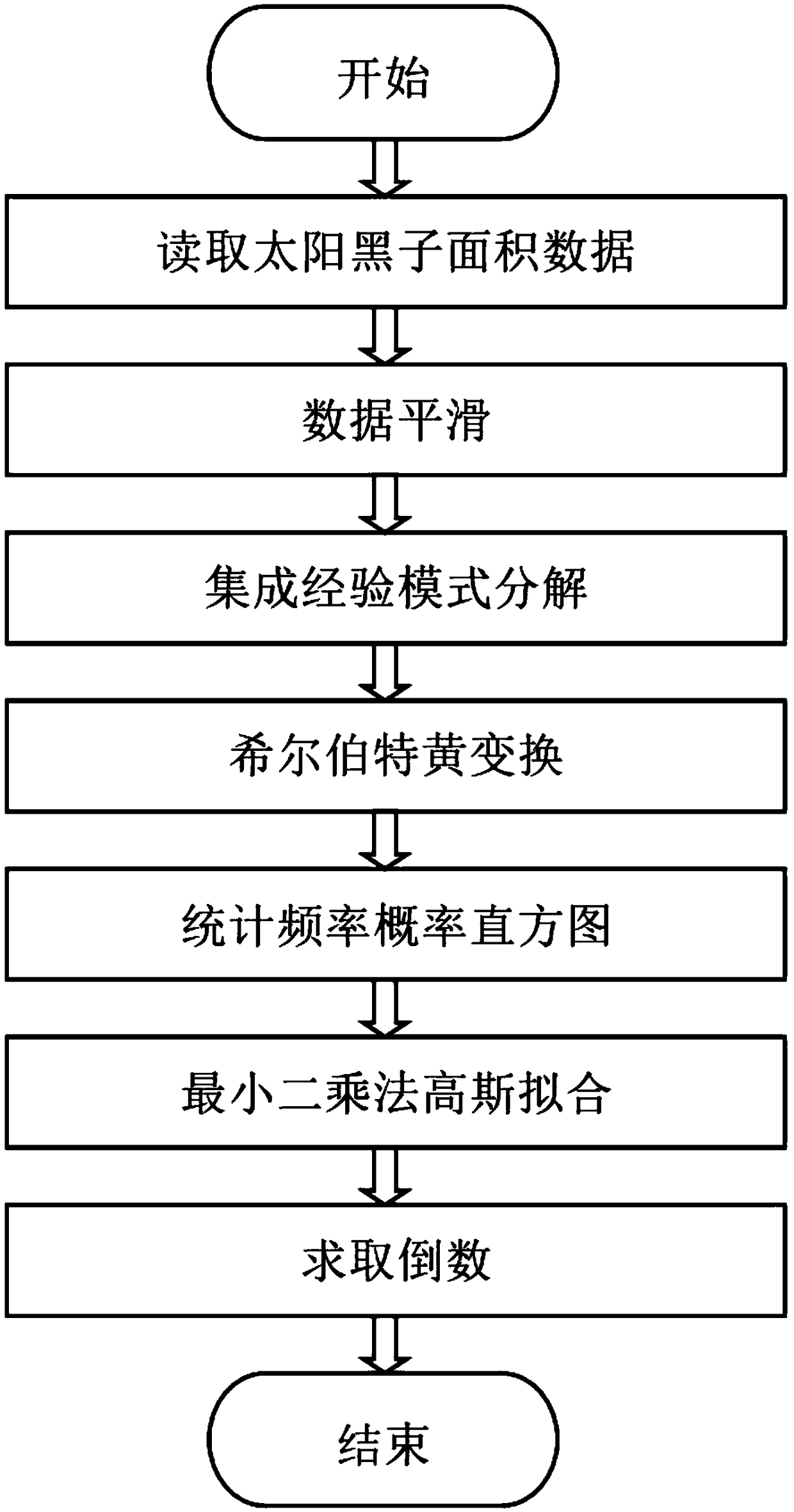
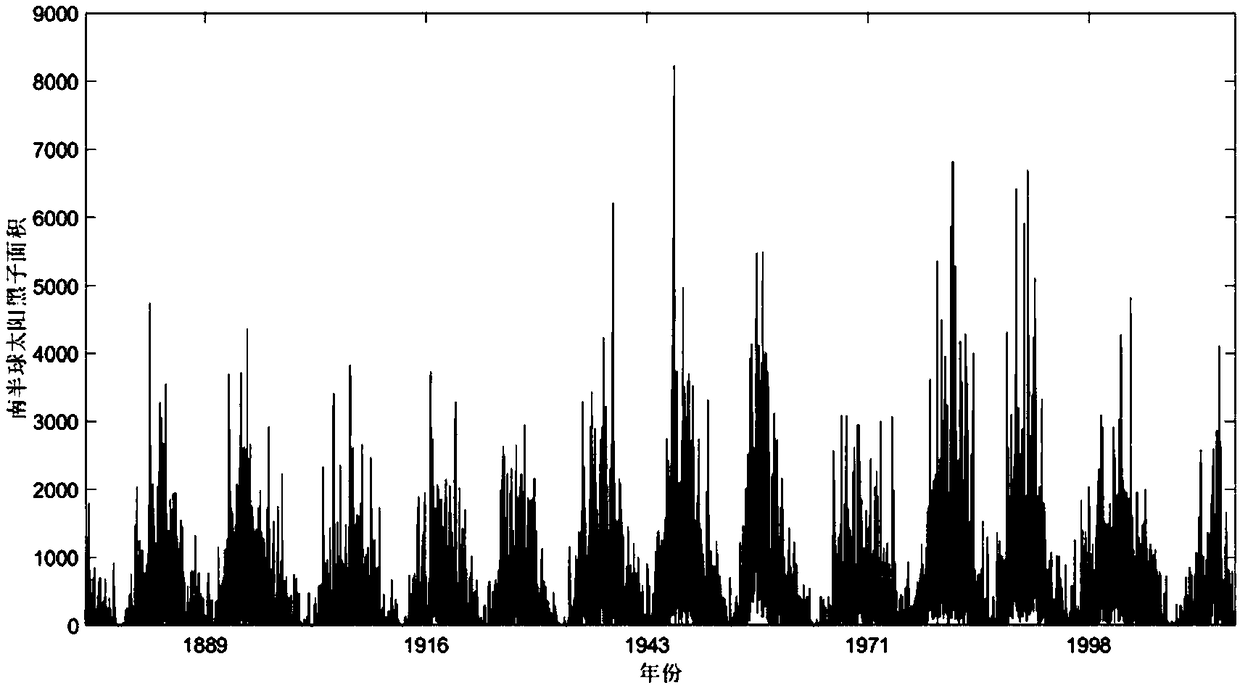
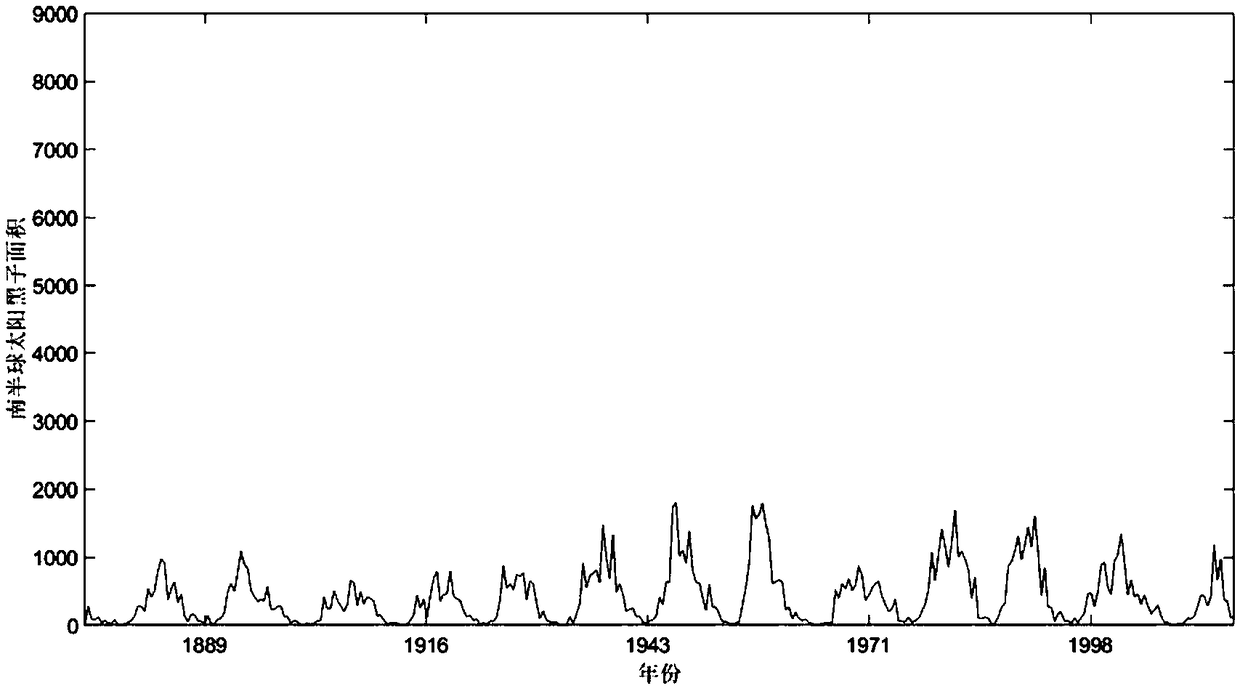
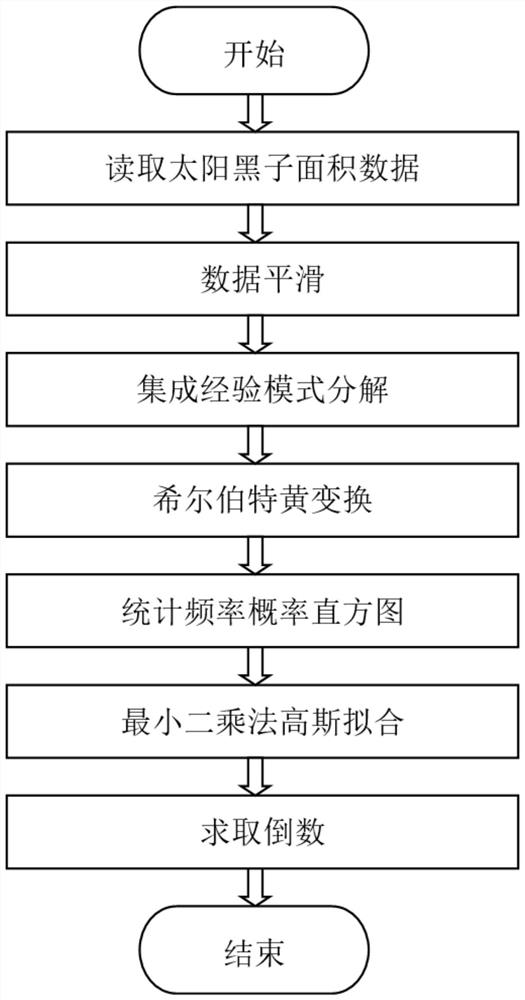
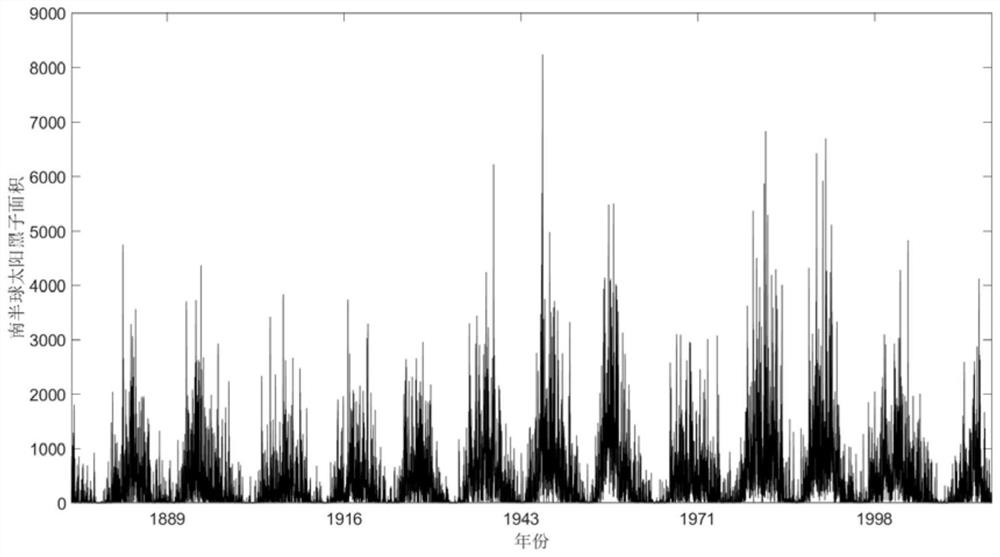
Sunspot area periodic characteristic analysis method based on HHT of EEMD
ActiveCN108804388AThe solution is constrained by basis functionsResolve accuracyComplex mathematical operationsOriginal dataDecomposition
The invention relates to a sunspot area periodic characteristic analysis method based on HHT of EEMD and belongs to the fields of astronomical technology and signal processing. By the adoption of thesunspot area periodic characteristic analysis method based on Hilbert-Huang transformation (HHT) of an ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) algorithm, fluctuations on different time scales areseparated from original data, and changes of different frequencies over time are clearly manifested. Compared with common methods, the method is direct and self-adaptive and is based on data itself,and the problems that a traditional periodic analysis method is constrained by a base function and is inaccurate in time scale are effectively solved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A Method for Describing Sunspot Groups in Full Sun Surface Images
ActiveCN110851627BImprove description qualityStill image data indexingCharacter and pattern recognitionData setComputer graphics (images)
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A Method for Analyzing the Periodic Characteristics of Sunspot Area Based on eemd's hht
The invention relates to a method for analyzing the period characteristic of sunspot area based on HHT of EEMD, which belongs to the field of astronomical technology and signal processing. The present invention adopts the sunspot area cycle characteristic analysis method of the Hilbert-Huang Transform (HHT) based on the Integrated Empirical Mode Decomposition (EEMD) algorithm, separates the fluctuations on different time scales from the original data, and the different frequencies change with time. The change of is also clearly shown. Compared with the commonly used methods, it is a direct, adaptive, data-based method, which effectively solves the problem that the traditional cycle analysis method is constrained by the basis function and the time scale is not accurate. The problem.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method for identifying solar rice grains in astronomical images
ActiveCN105551025BEasy to identifyStable extractionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingBand-pass filter
The invention relates to a method for identifying a solar granule in an astronomic image, and belongs to the fields of astronomy technology and image processing. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, receiving a solar photospheric image I1, using band-pass filtering to carry out de-noising, and obtaining a de-noised image I2; then according to intensity distribution of the image I2, judging whether sunspots exist in the image; carrying out top-hat transformation and bottom-hat transformation respectively on the image I2, and obtaining a top-hat transformation image and a bottom-hat transformation image; then adding the top-hat transformation image to the solar photospheric image, obtaining an image I3, and carrying out subtraction between the image I3 and the bottom-hat transformation image to obtain an image I4; respectively subjecting the image I4 respectively to open operation of a phase congruency method, binaryzation and morphology and hole filling operation, and obtaining an image I7; and carrying out watershed transformation operation on the image I7, and obtaining a binary image of a granule cellular boundary. By adopting the method for identifying the solar granule in the astronomic image, the granule organization high in contrast and clear in edge can be well identified, and the granule characteristics low in contrast and fuzzy in edge can also be well identified.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
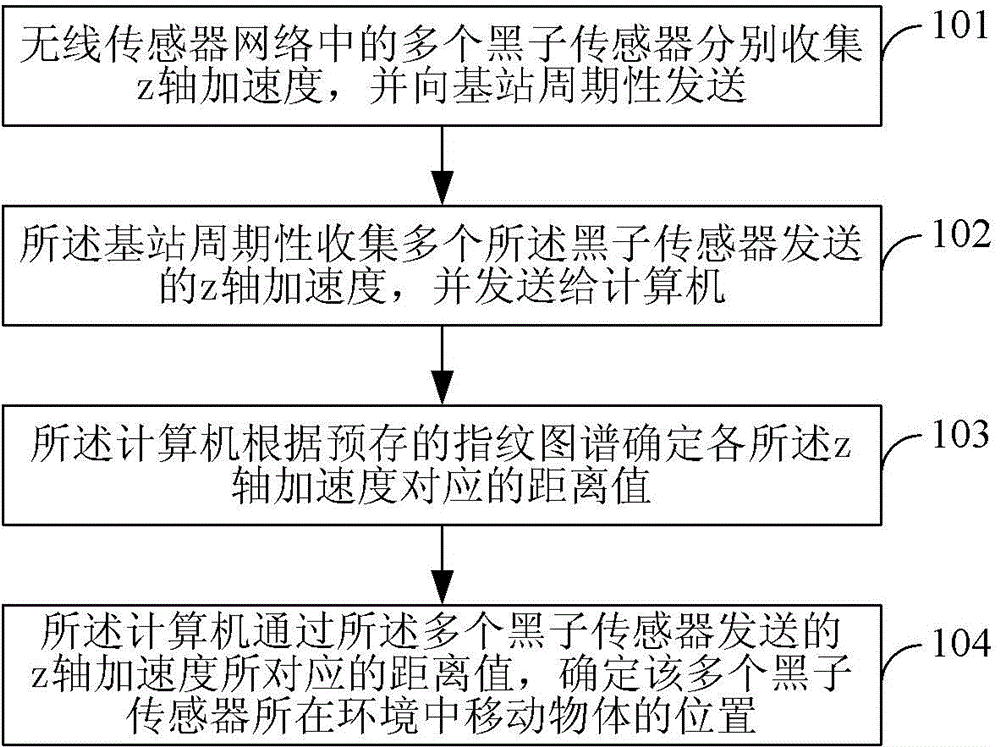
Method and system for monitoring moving objects
ActiveCN104159220BImprove securityPrevent tamperingNetwork topologiesSecurity arrangementWireless sensor networkingComputer science
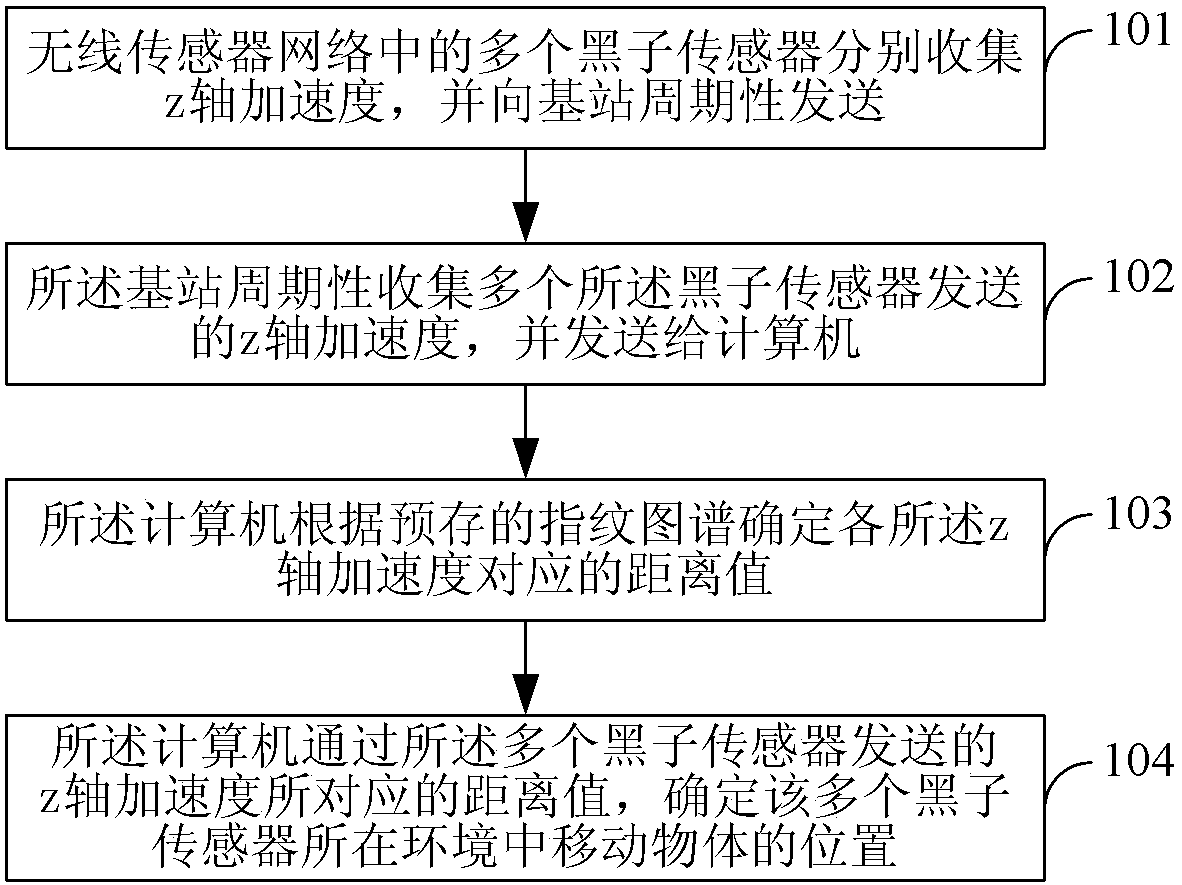
The invention provides a method and a system for monitoring a moving object. The method comprises the following steps: 101, z-axis accelerations are respectively collected by a plurality of sunspot sensors in a wireless sensor network and are periodically transmitted to a base station; 102, the z-axis accelerations respectively collected by the sunspot sensors are periodically collected by the base station and are transmitted to a computer; 103, the computer determines a distance value corresponding to each z-axis acceleration according to a pre-stored fingerprint; and 104, the computer determines a position of the moving object in the environment, in which the sunspot sensors are positioned, through the distance values corresponding to the z-axis accelerations transmitted by the sunspot sensors. The method and the system can adopt lightweight data to complete monitoring of the moving object and have the advantages of high reliability and easy implementation.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
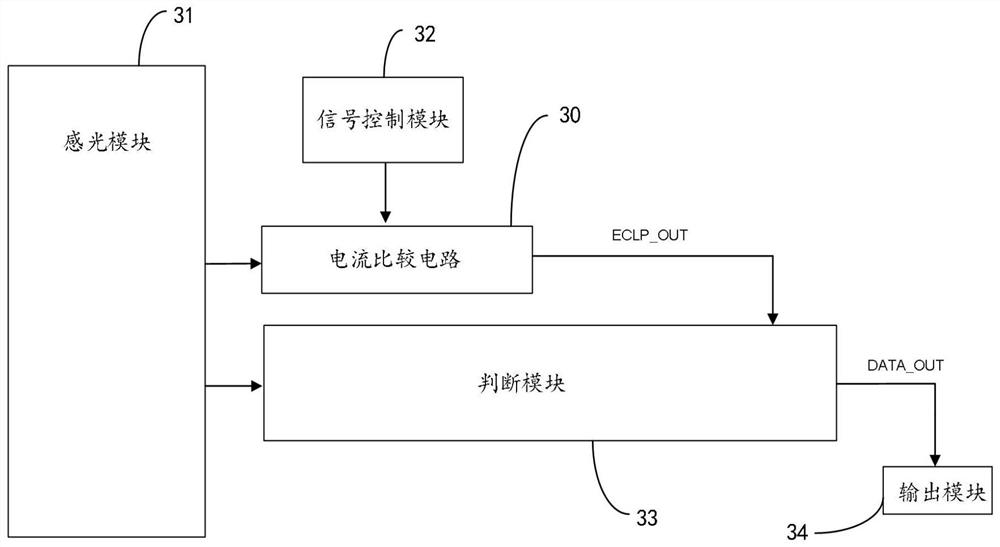
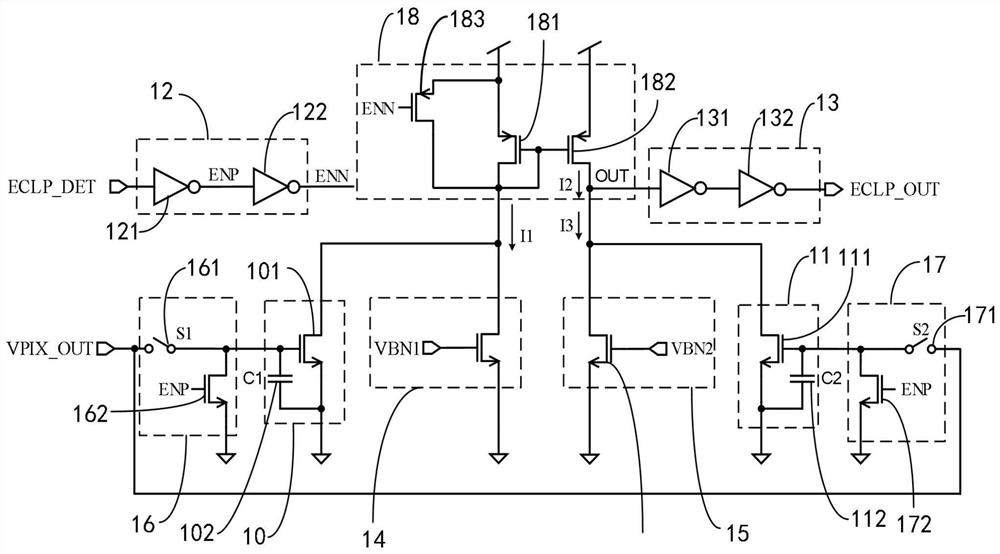
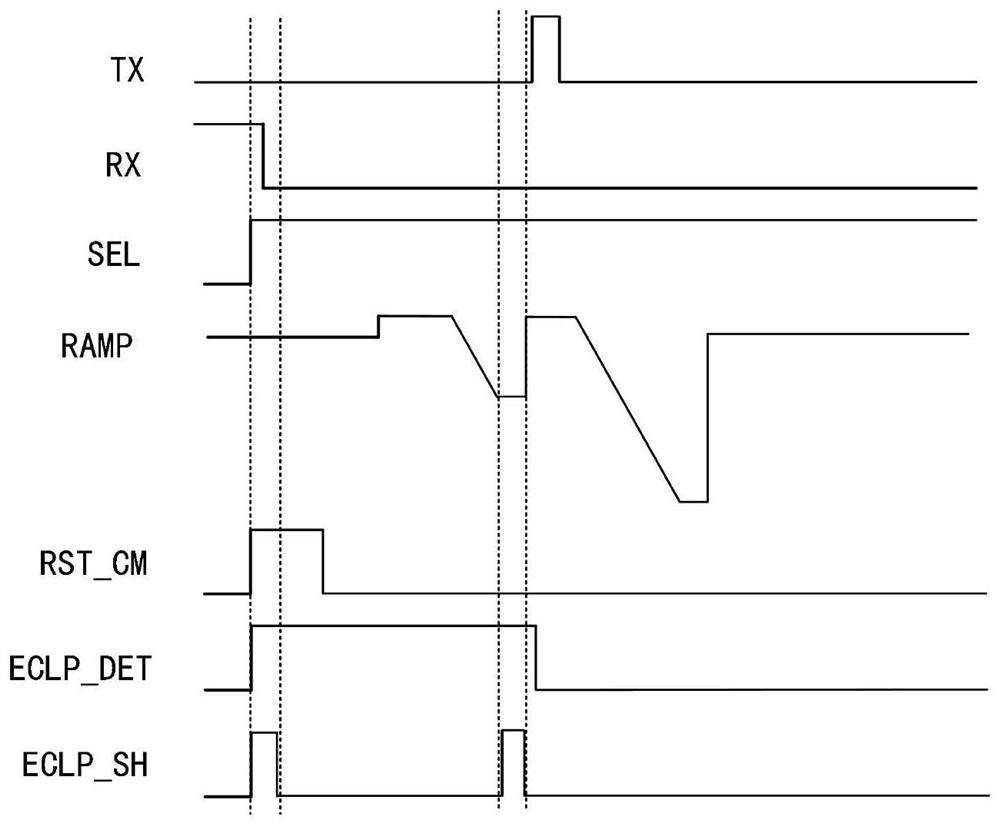
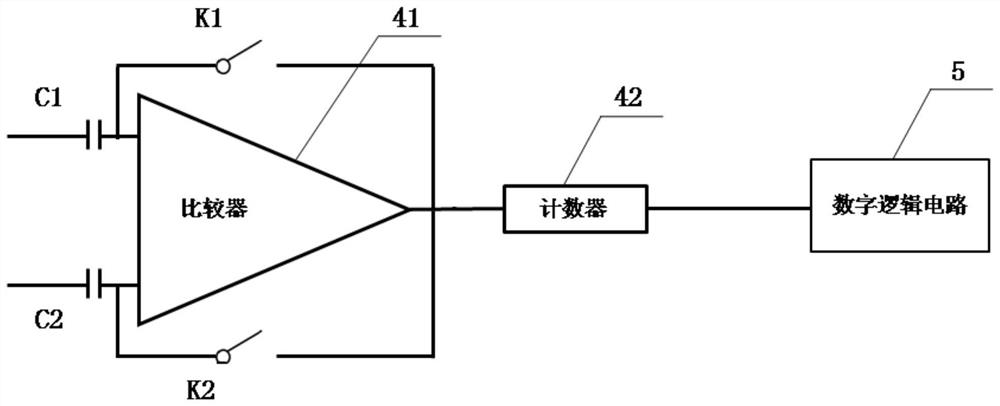
Current comparison circuit and image sunspot effect detection device and method
PendingCN113960356AReduce power consumptionGuaranteed to be normalCurrent/voltage measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionLight sensingControl signal
The invention provides a current comparison circuit and an image sunspot effect detection device and method. The image sunspot effect detection device comprises the current comparison circuit, a light sensing module, a signal control module and a judgment module, and the light sensing module is used for outputting pixel voltage signals according to image signals; the current comparison circuit is connected with the photosensitive module and is used for carrying out current detection and comparison on the output end of the photosensitive module; the signal control module is connected with the current comparison circuit and is used for providing a control signal for the current comparison circuit; the judgment module is connected with the output end of the light sensing module and the output end of the current comparison circuit and used for conducting image sunspot judgment according to comparison signals of the current comparison circuit, whether the sunspot effect exists in an image or not can be rapidly detected through simple logic control, and meanwhile the overall circuit is low in power consumption.
Owner:CHENGDU LIGHT COLLECTOR TECH
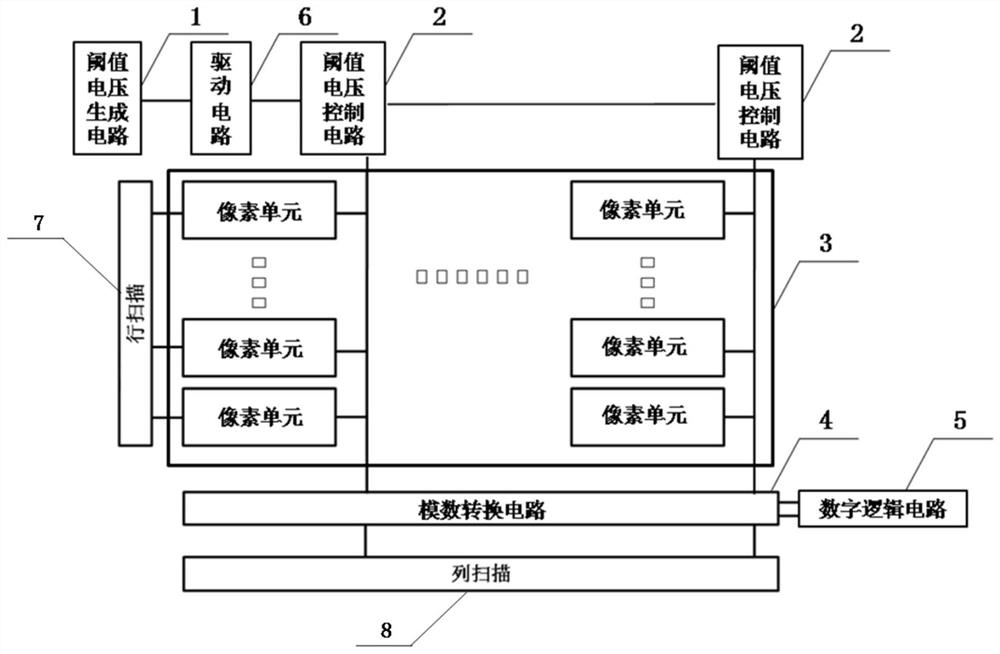
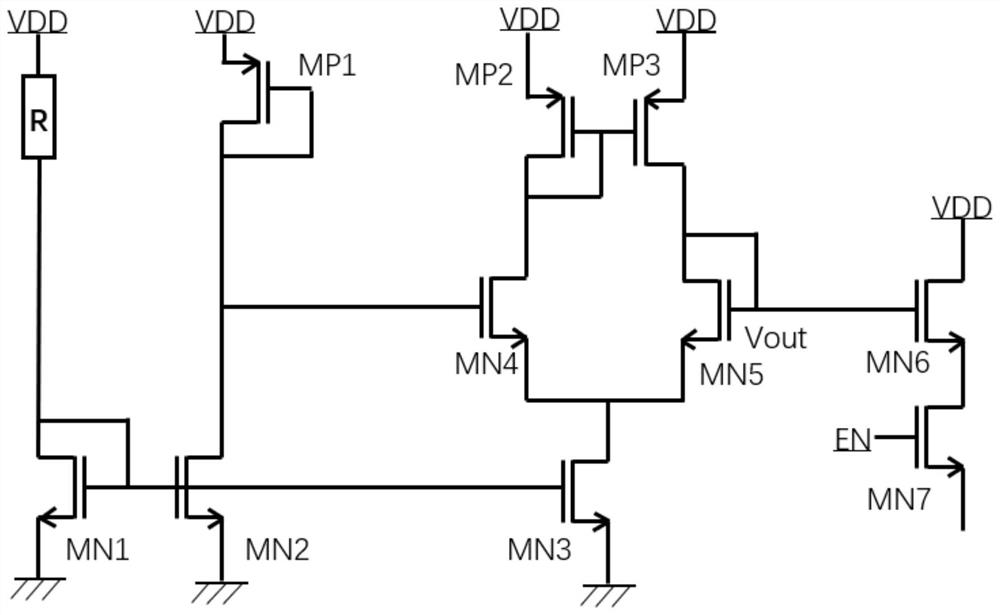
Correction structure and method for eliminating sunspot phenomenon of image sensor
ActiveCN114125337ASolve the problem of low reset voltageGuaranteed analog-to-digital conversionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsEngineering
The invention discloses a correction structure and method for eliminating a sunspot phenomenon of an image sensor. The correction structure comprises a threshold voltage generation circuit, a plurality of threshold voltage control circuits, a pixel module, an analog-to-digital conversion circuit and a digital logic circuit, the plurality of threshold voltage control circuits are connected in parallel on a bus, and the threshold voltage generation circuit is connected with the input end of the bus; the pixel module comprises a plurality of columns of pixel units, and the threshold voltage control circuits are connected with the single columns of pixel units in a one-to-one correspondence manner; and the pixel module, the analog-to-digital conversion circuit and the digital logic circuit are connected in sequence. According to the method, the sunspots can be logically judged, and the sunspot phenomenon can be effectively eliminated.
Owner:四川创安微电子有限公司
Method and system for monitoring moving object
ActiveCN104159220AImprove securityPrevent tamperingNetwork topologiesSecurity arrangementWireless sensor networkingSunspot
The invention provides a method and a system for monitoring a moving object. The method comprises the following steps: 101, z-axis accelerations are respectively collected by a plurality of sunspot sensors in a wireless sensor network and are periodically transmitted to a base station; 102, the z-axis accelerations respectively collected by the sunspot sensors are periodically collected by the base station and are transmitted to a computer; 103, the computer determines a distance value corresponding to each z-axis acceleration according to a pre-stored fingerprint; and 104, the computer determines a position of the moving object in the environment, in which the sunspot sensors are positioned, through the distance values corresponding to the z-axis accelerations transmitted by the sunspot sensors. The method and the system can adopt lightweight data to complete monitoring of the moving object and have the advantages of high reliability and easy implementation.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
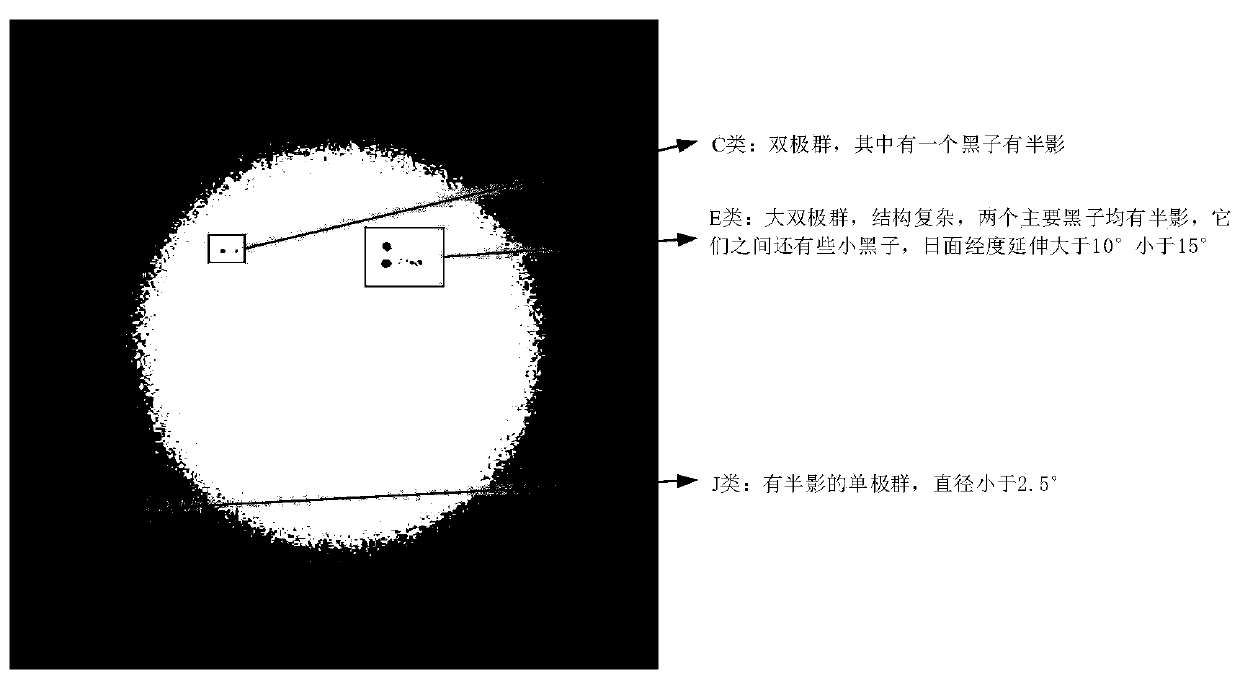
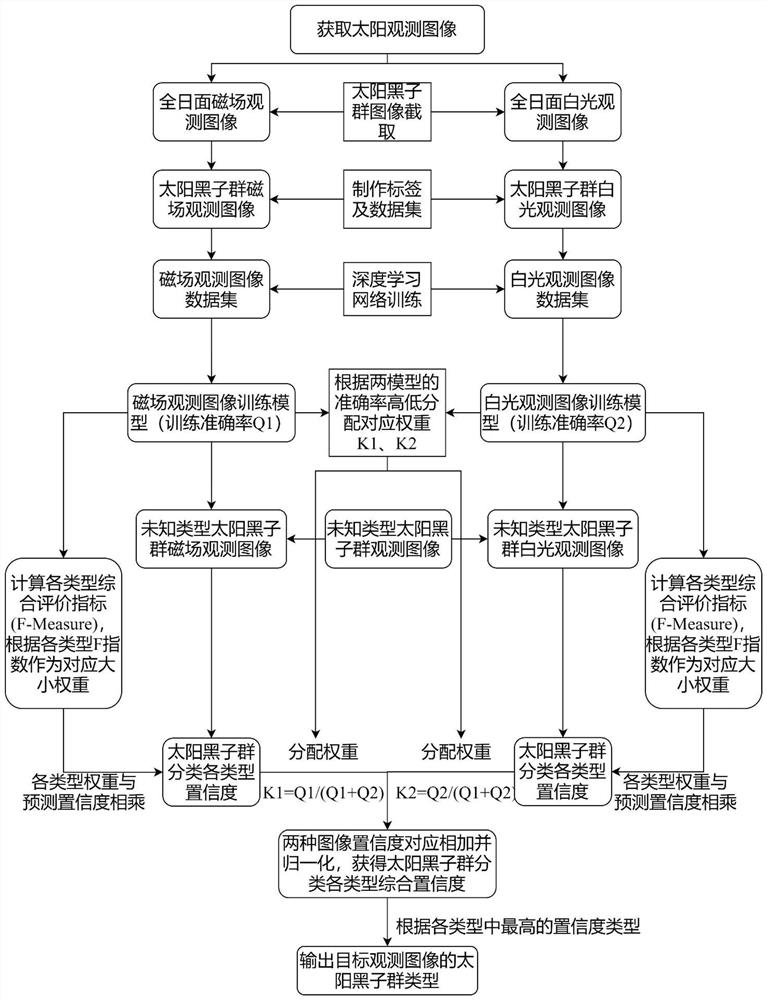
Sunspot group classification method based on deep learning
InactiveCN112949701AImprove classification accuracyReduce the probability of misclassificationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsRadiologyClassification methods
The invention provides a sunspot group classification method based on deep learning. The classification method comprises the following steps: observing two images by using a sunspot group magnetic field and white light, and respectively processing the two images by using a deep learning network; performing certain weight processing on the prediction results of the two images according to the training precision of the deep learning model to obtain a comprehensive prediction result of the two images of the same sunspot group. Compared with an existing sunspot group classification method, the method utilizes two observation images of the sunspot group, predicts the same target through the deep learning network, comprehensively evaluates the predicted target according to the training precision of the two images, weights the prediction confidence, and further improves the classification precision of the sunspot group.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Image sensor, sunspot removal method and sunspot removal device thereof
ActiveCN105338268BAccurate removalReduce noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsBlack spotComputer science
The invention discloses a method for removing sunspots of an image sensor, comprising: obtaining a reset sampling signal value of a pixel unit in an image sensor pixel array; Generate a comparison signal when the value is less than the preset sampling signal threshold; generate the position information corresponding to the pixel unit of the reset sampling signal value according to the comparison signal; replace the reset sampling signal value corresponding to the position information with the brightest value of the image to remove the pixel unit corresponding to the position information sun spots. The sunspot removal method of the image sensor of the present invention can accurately remove all sunspots without using a fixed level value as the reset sampling signal value, effectively reducing the noise of the signal chain. The invention also discloses a device for removing sunspots of an image sensor and an image sensor comprising the device for removing sunspots of the image sensor.
Owner:BYD SEMICON CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com