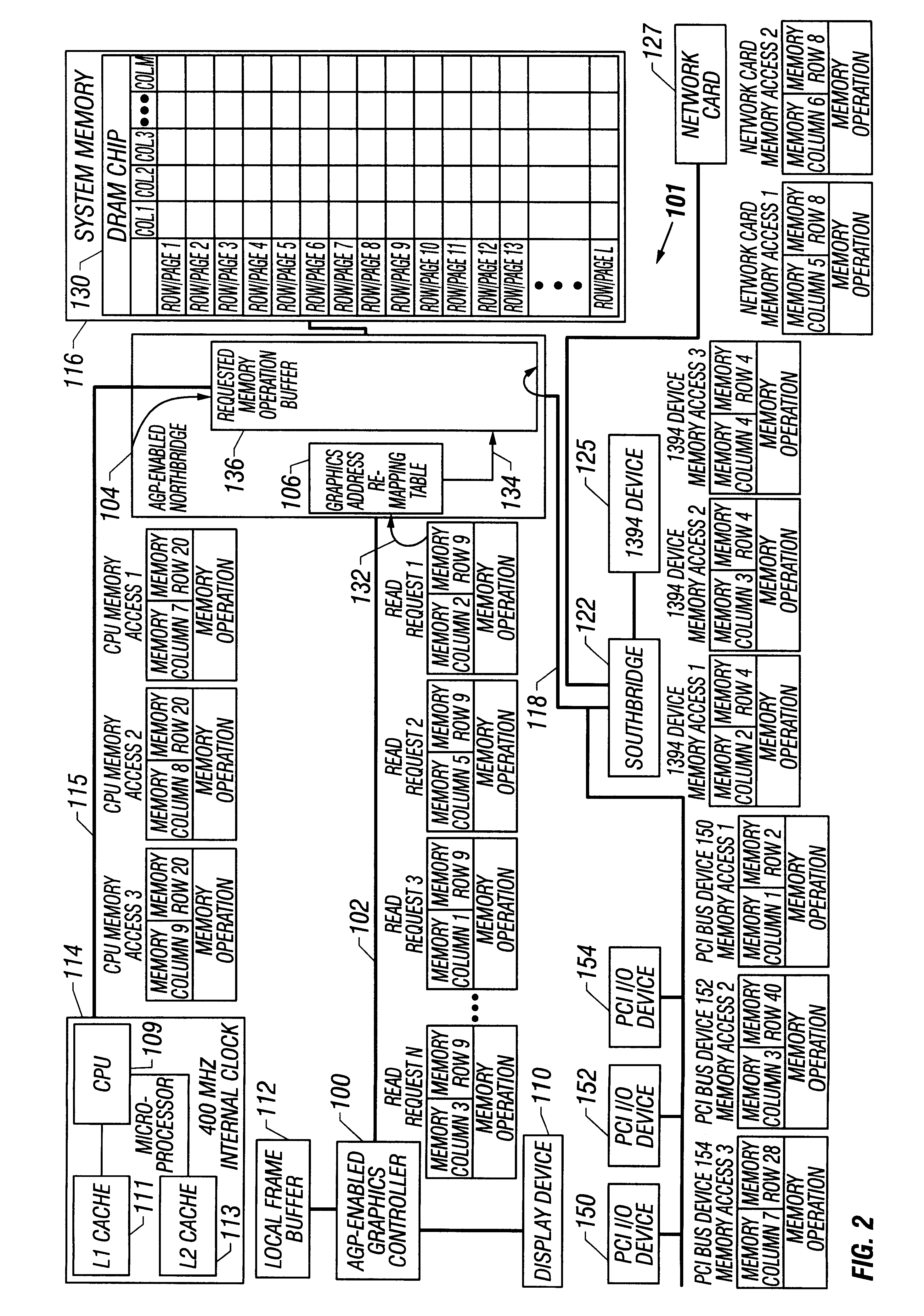
Patents
Literature
91 results about "Synchronous Data Flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synchronous Dataflow is a restriction of Kahn process networks where nodes produce and consume a fixed number of data items per firing. This allows static scheduling.
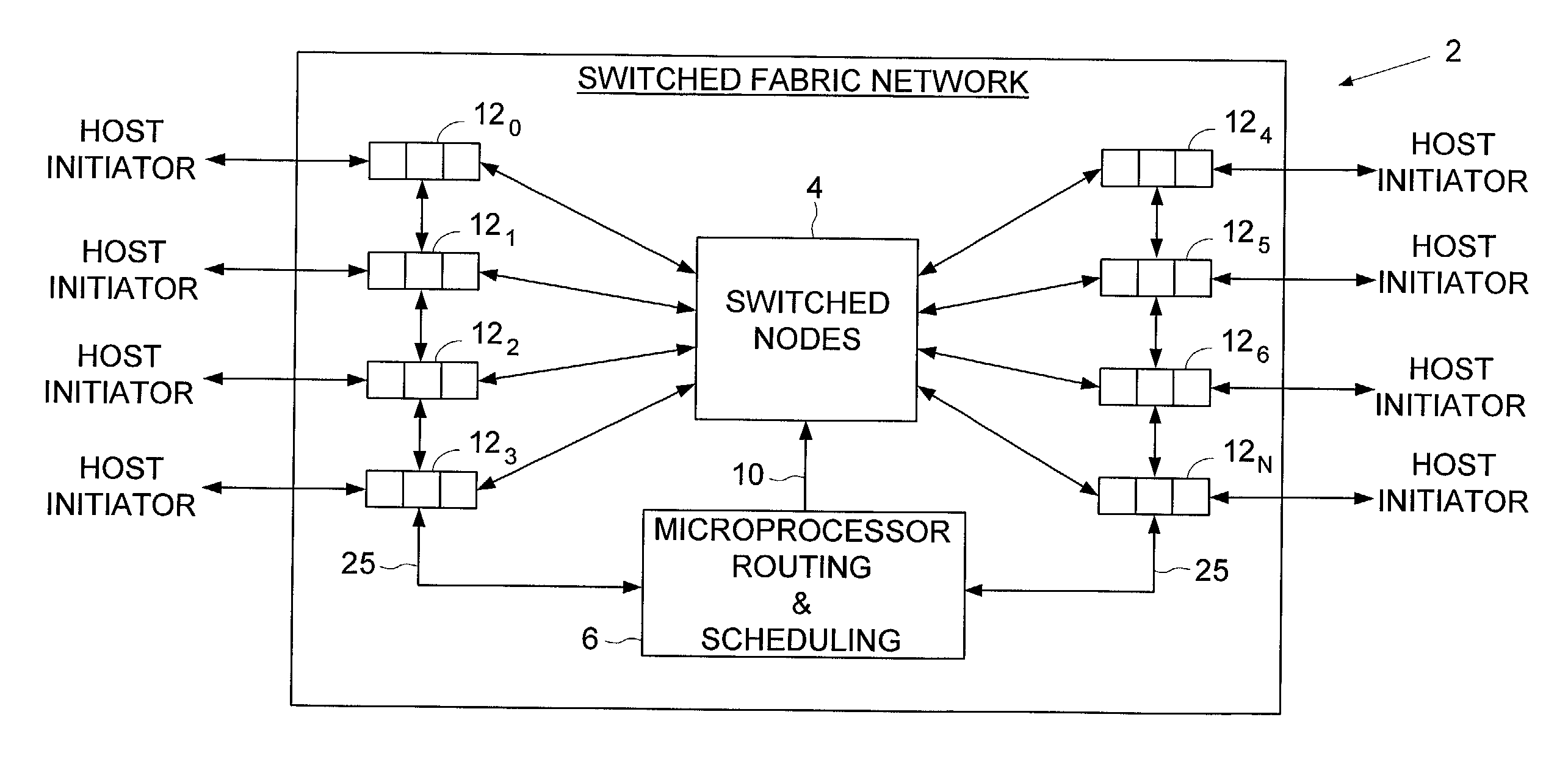
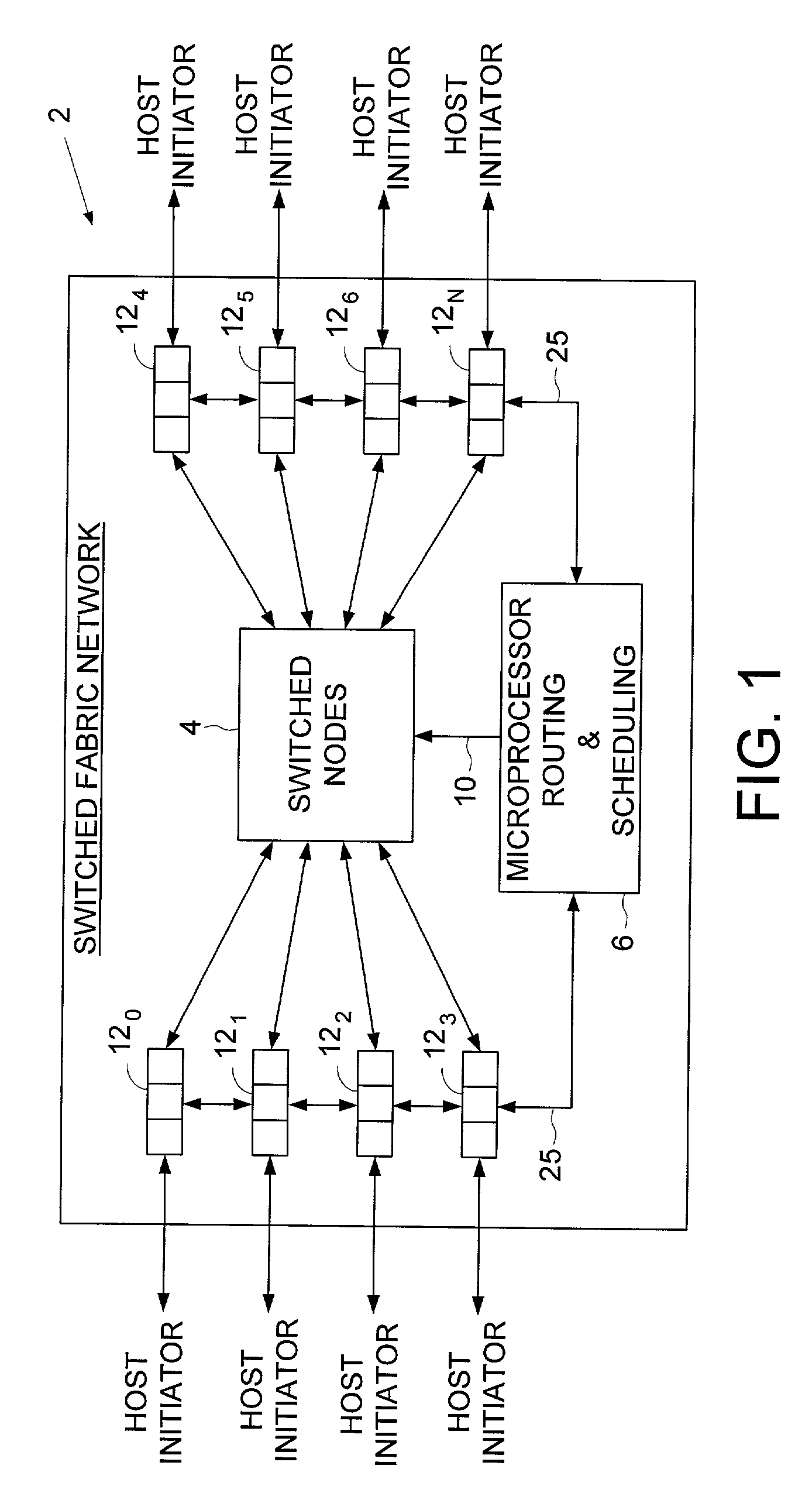
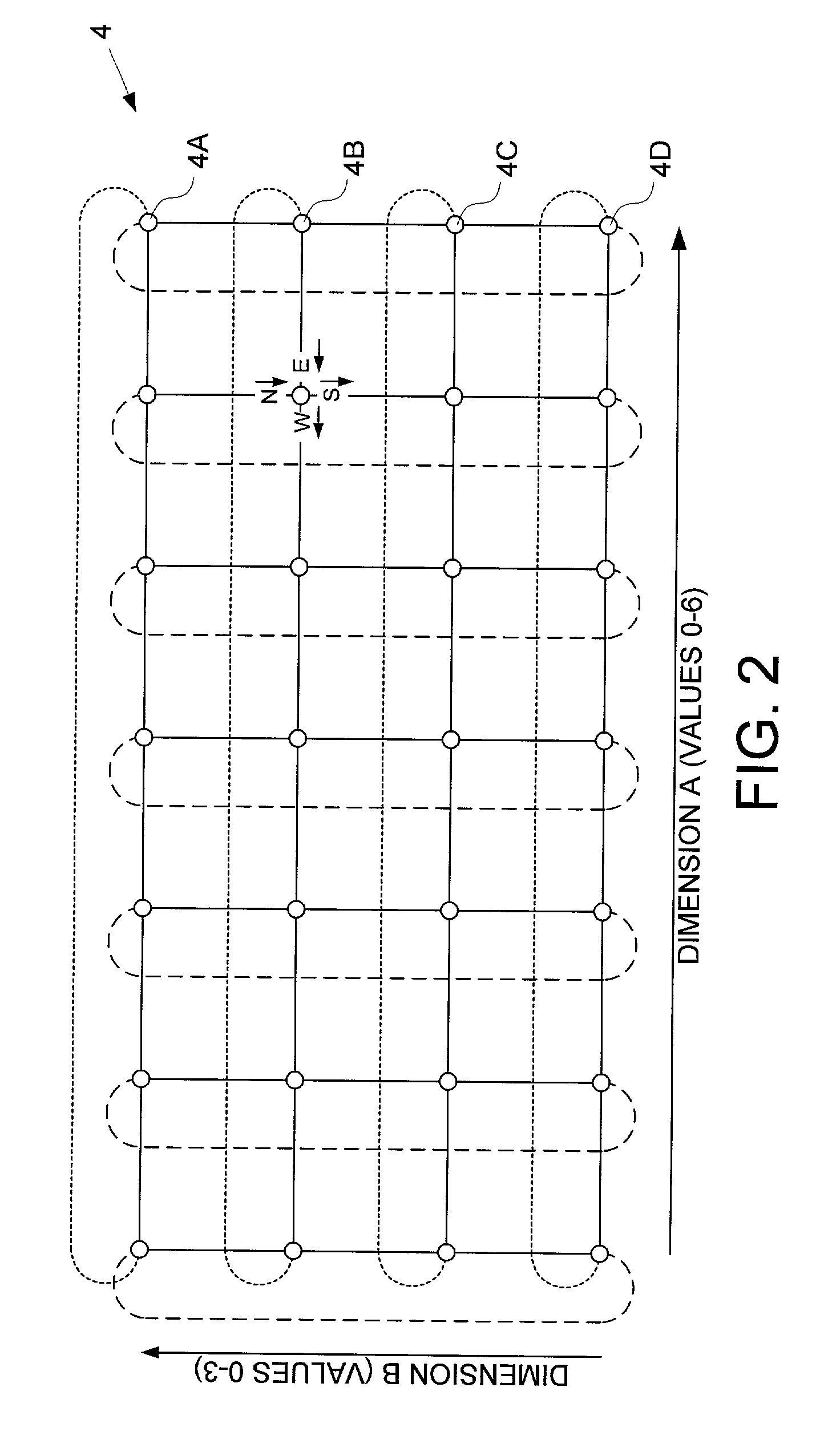
Isochronous switched fabric network
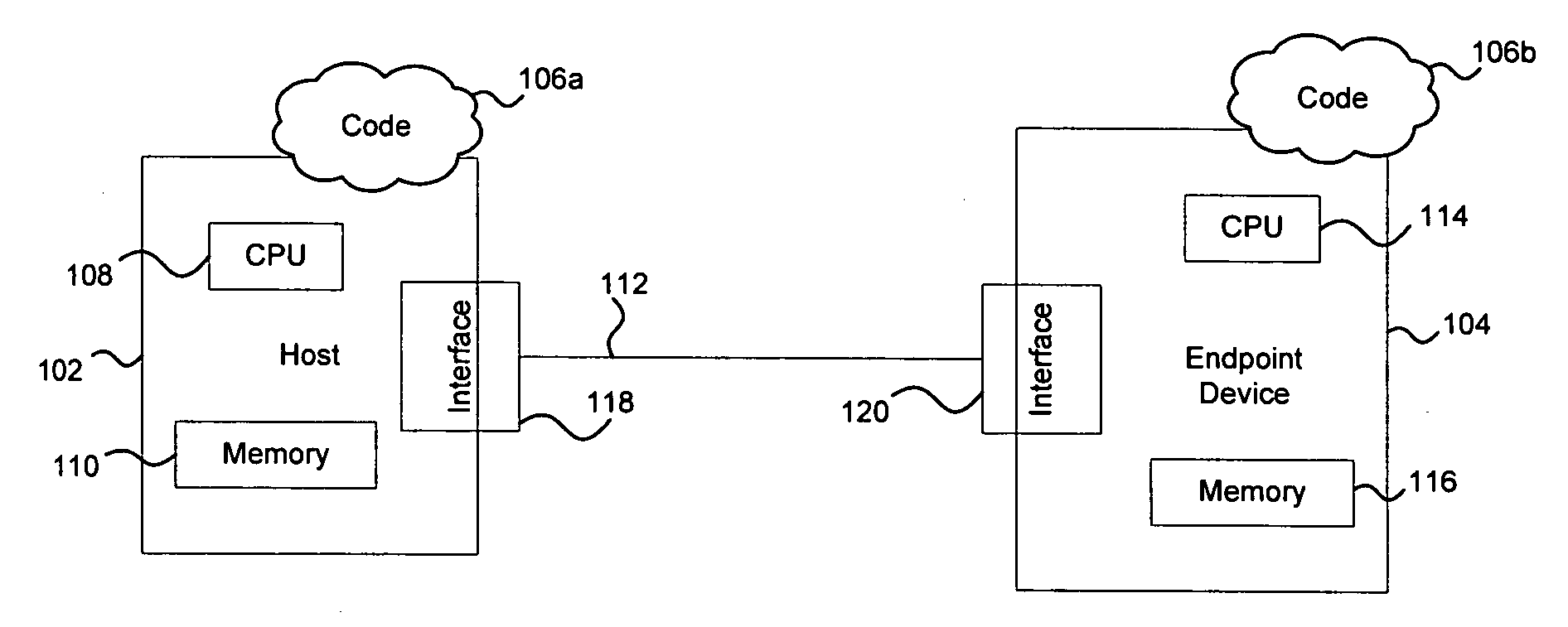
An isochronous switched fabric network is disclosed comprising a plurality of interconnected switched nodes forming multiple dimensions, each switched node comprising an upstream port and a downstream port for each dimension, each upstream and downstream port comprising an input port and an output port. A discovery facility discovers a depth of each dimension, and discovers resources within each switched node. An addressing facility assigns a matrix address to each switched node, a resource reservation facility reserves resources within each switched node to establish a path through the switched fabric network for transmitting an isochronous data stream, and a scheduling facility schedules isochronous data transmitted through the switched fabric network.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
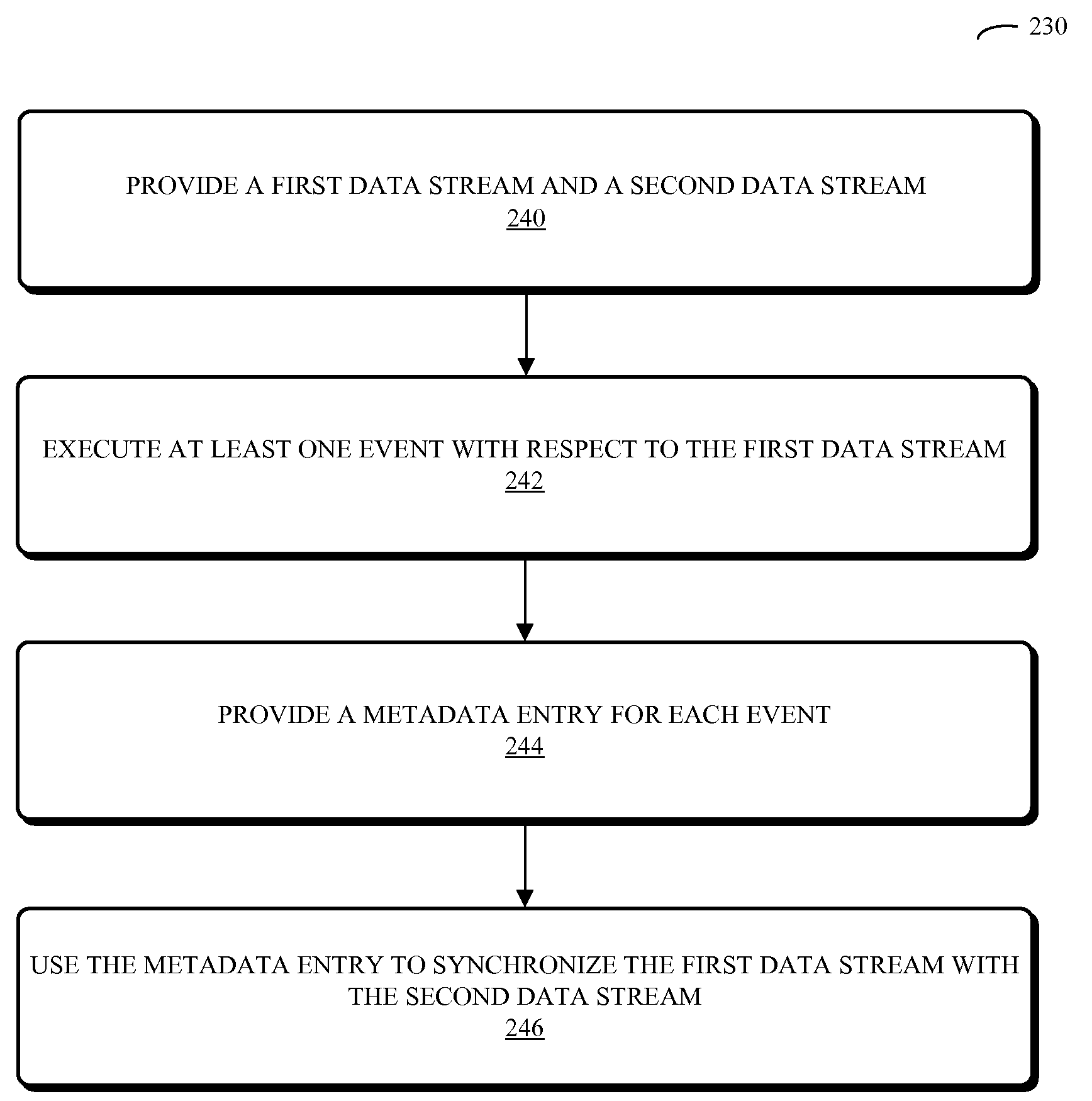
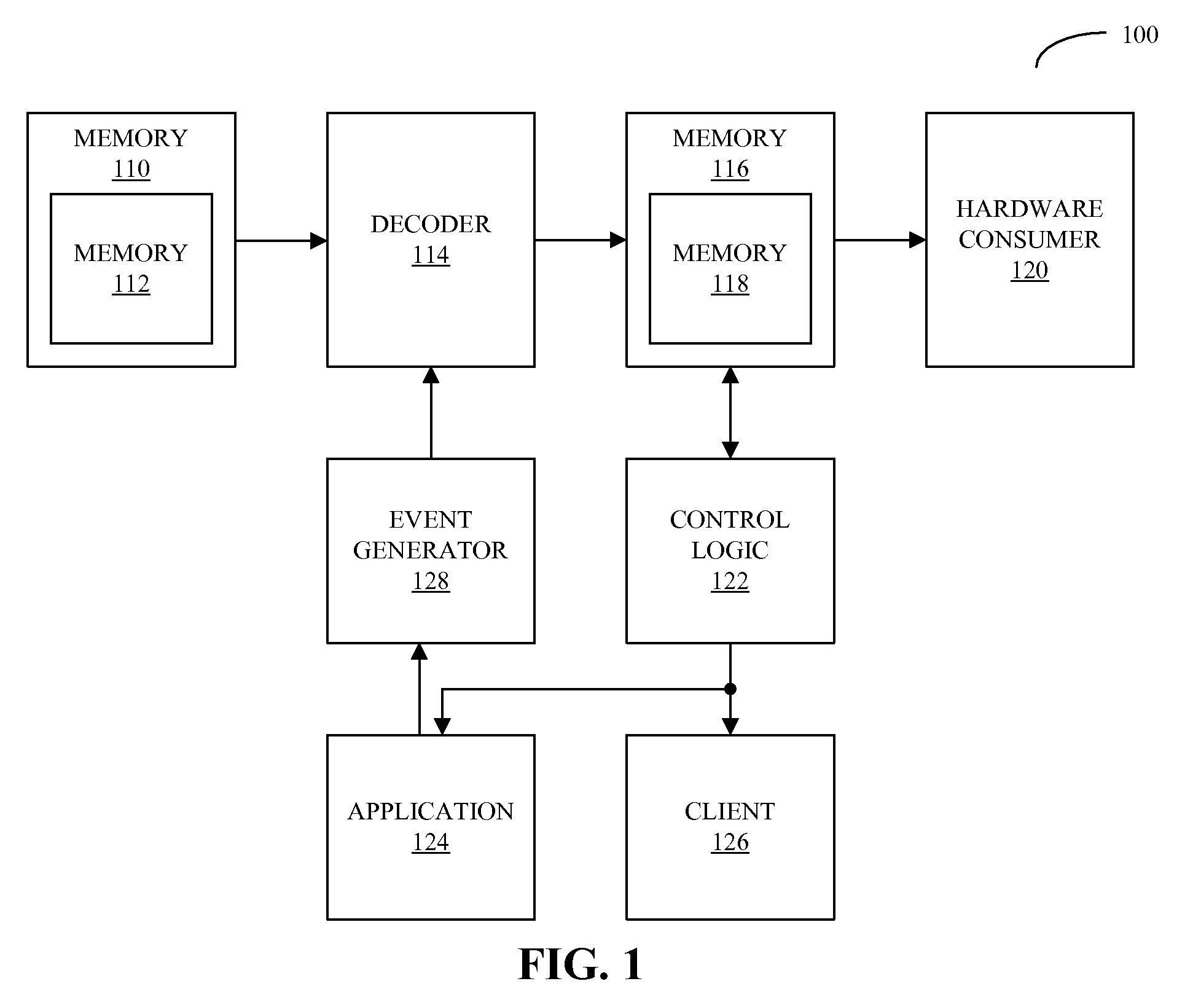
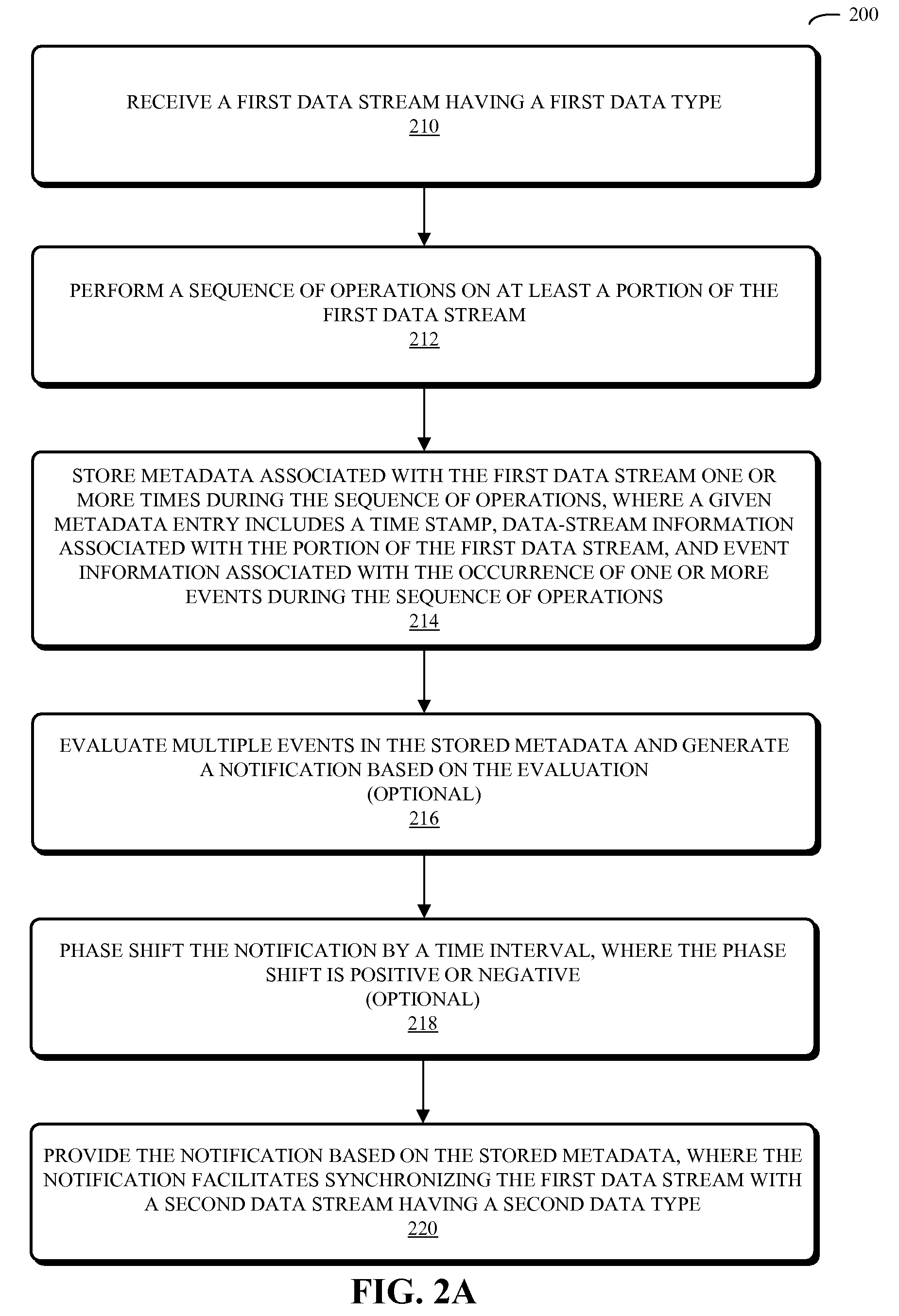
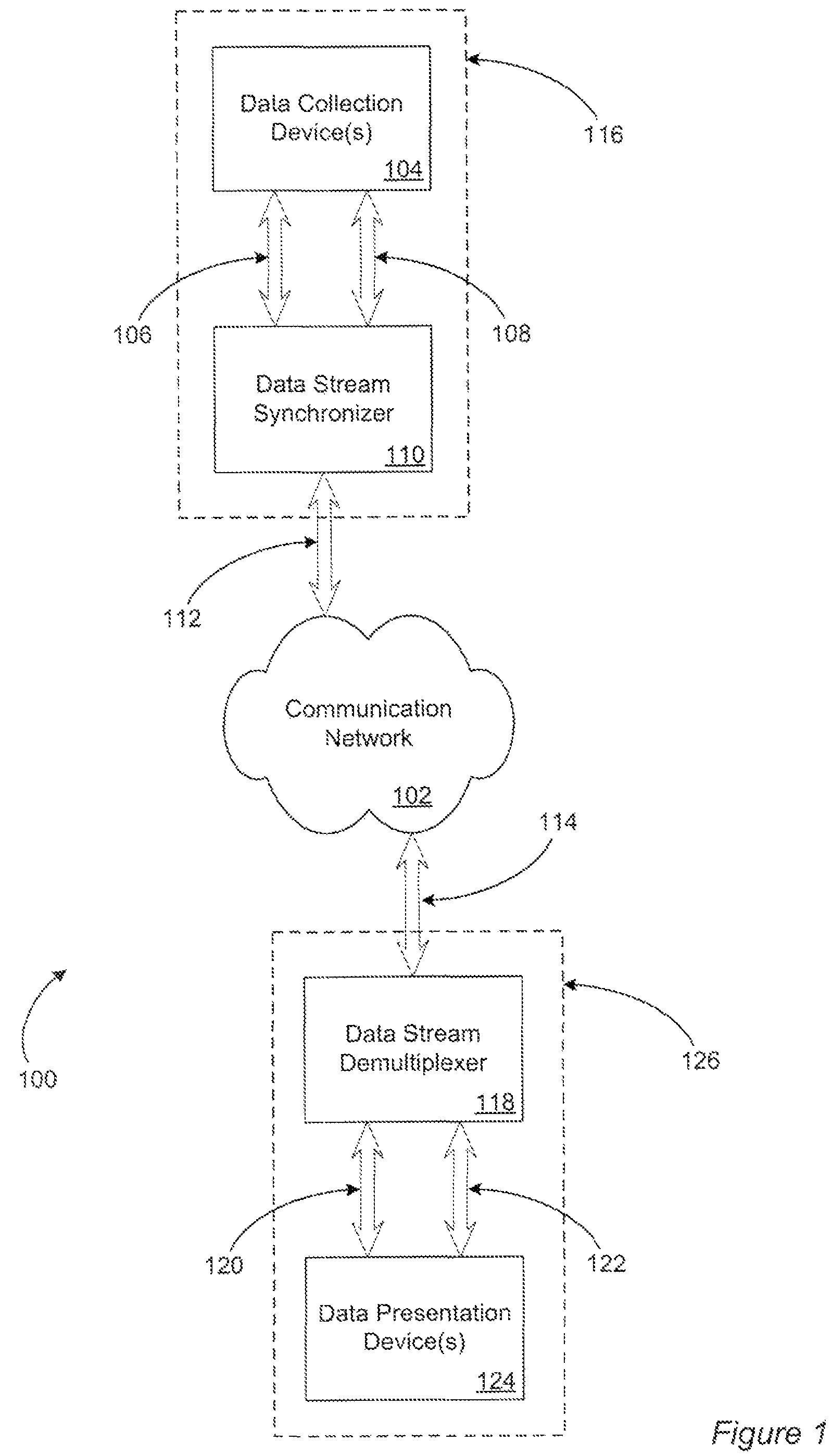
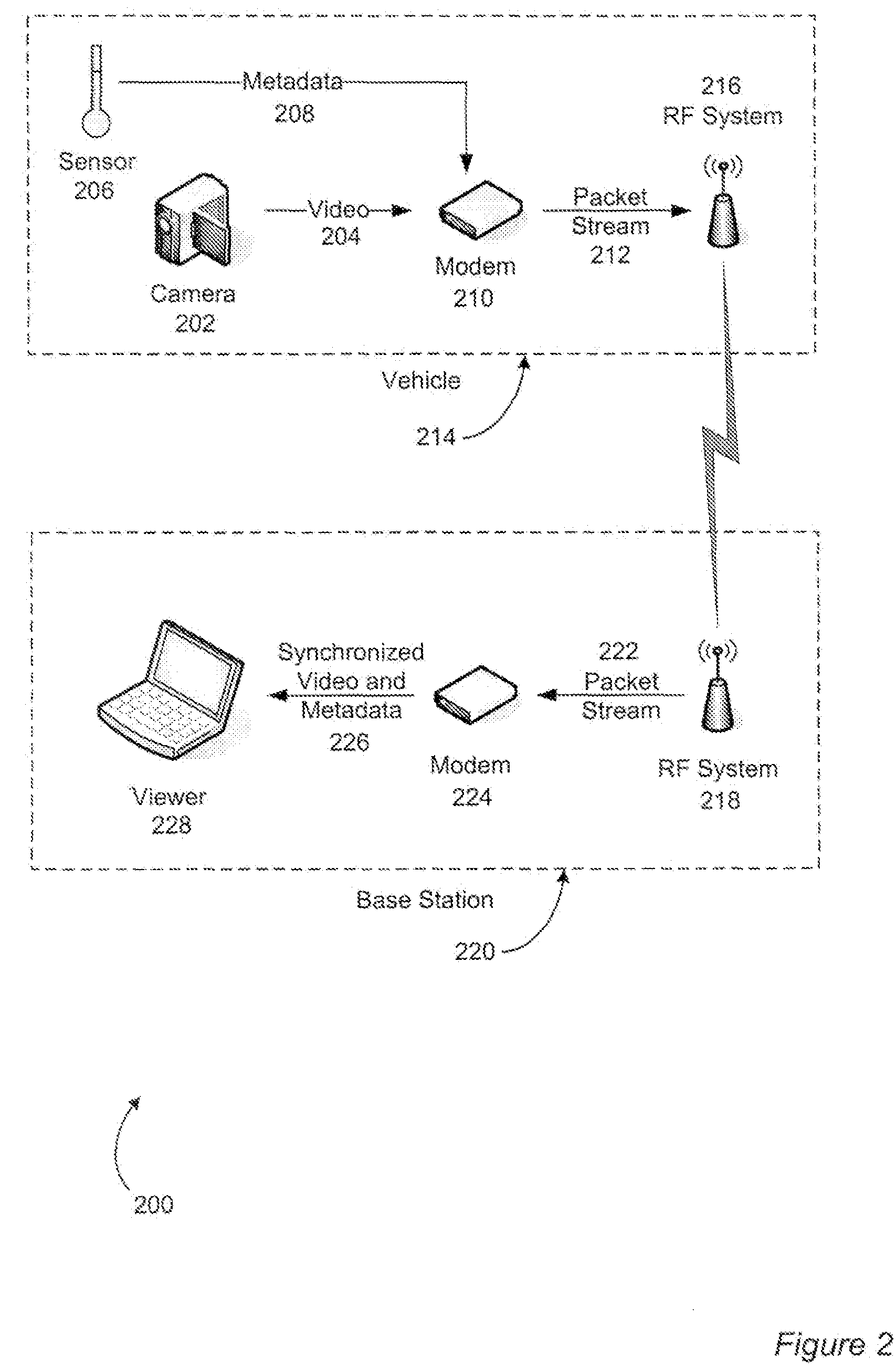
Using time-stamped event entries to facilitate synchronizing data streams
ActiveUS20090006488A1Good synchronizationReducing and eliminating delaySelective content distributionSpecial data processing applicationsData streamData type
An embodiment of a system to synchronize data streams is described. During operation, the system receives a first data stream having a first data type and performs a sequence of operations on at least a portion of the first data stream. Next, the system stores metadata associated with the first data stream one or more times during the sequence of operations. Metadata can include a time stamp, data-stream information associated with the portion of the first data stream, and event information associated with the occurrence of one or more events during the sequence of operations. Moreover, the system provides a notification based on the stored metadata, the notification to facilitate synchronizing the first data stream with a second data stream having a second data type.
Owner:APPLE INC
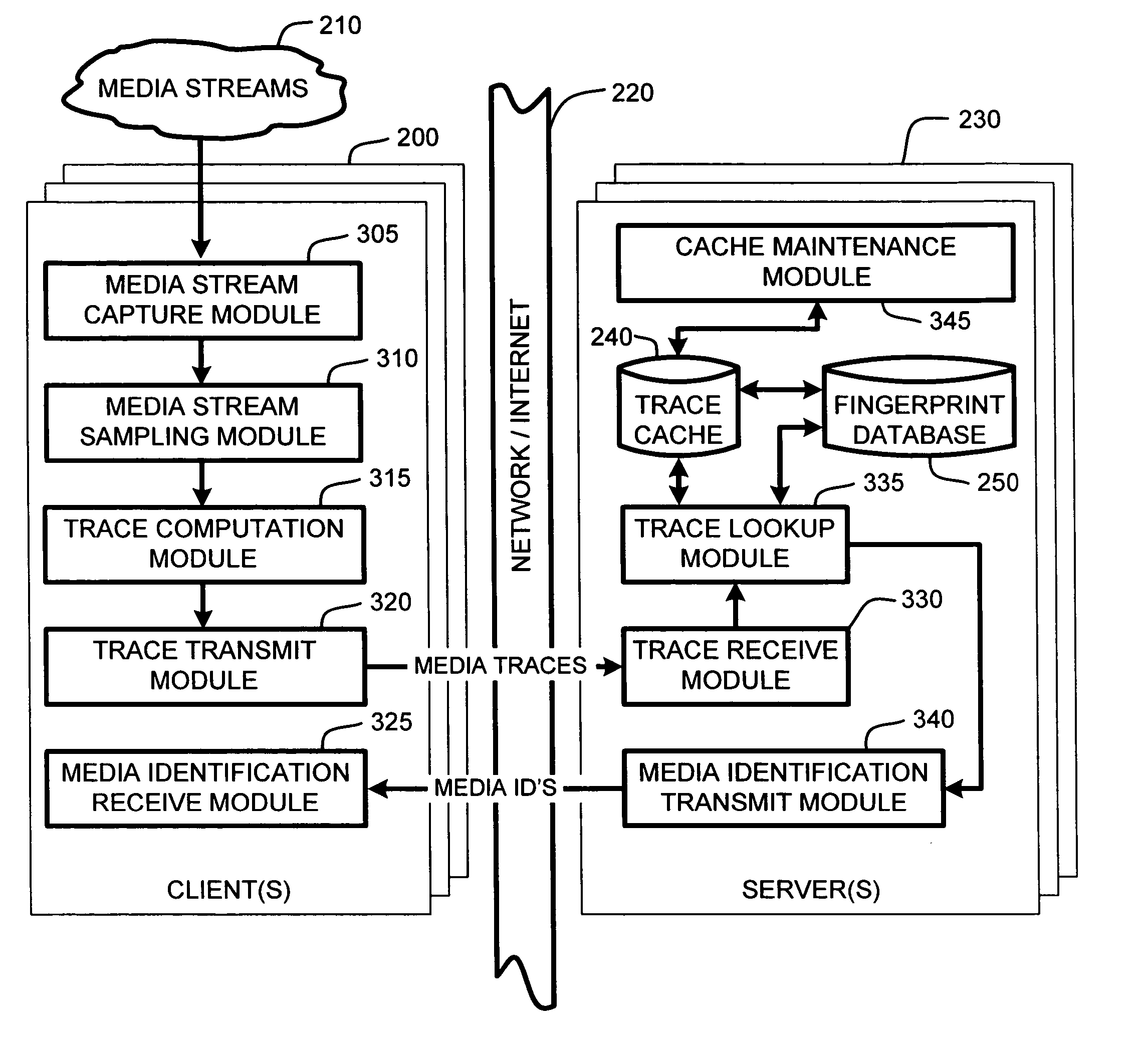
System and method for speeding up database lookups for multiple synchronized data streams
InactiveUS20060106867A1Increase loadImprove accuracyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData streamReal time services
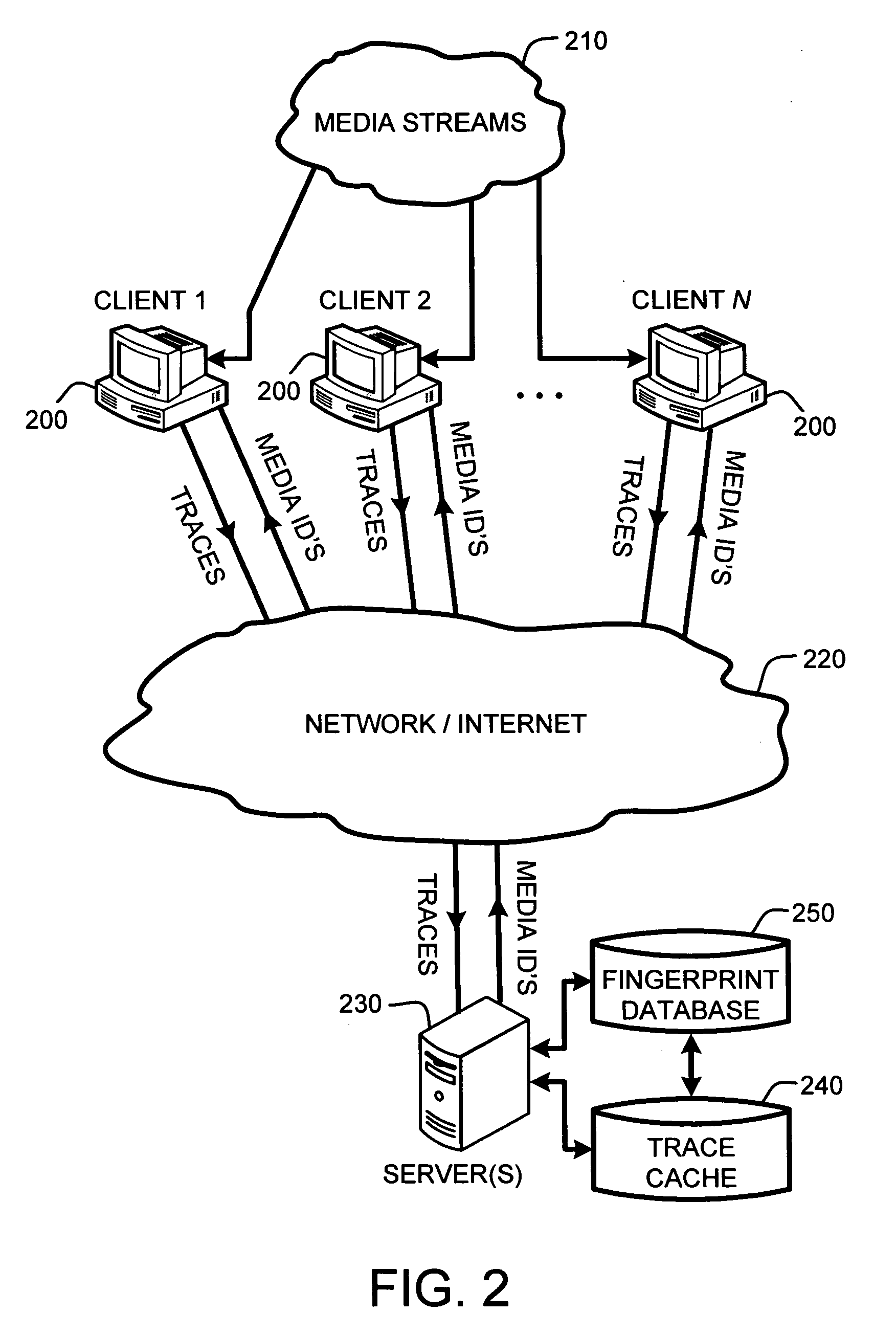
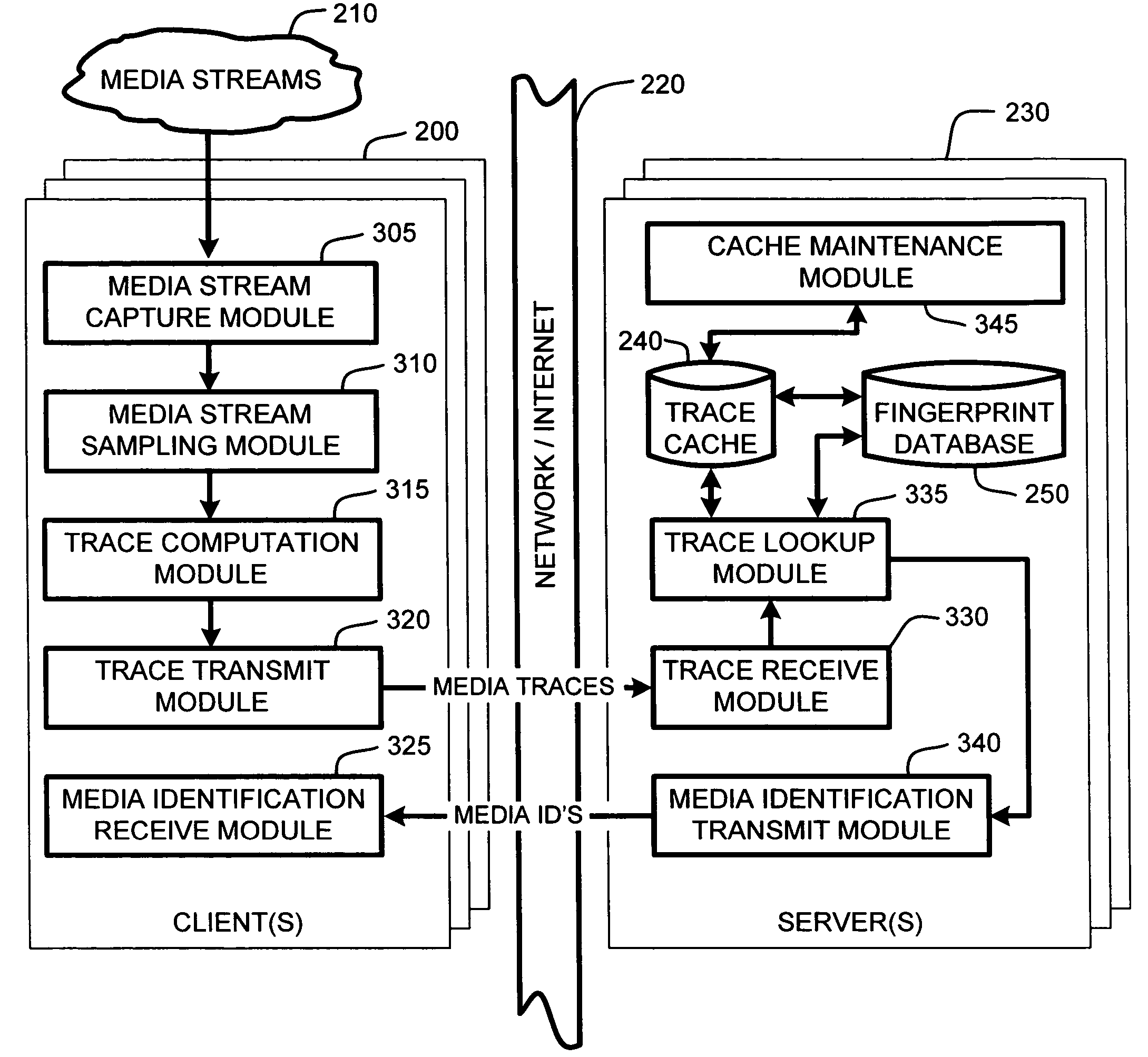
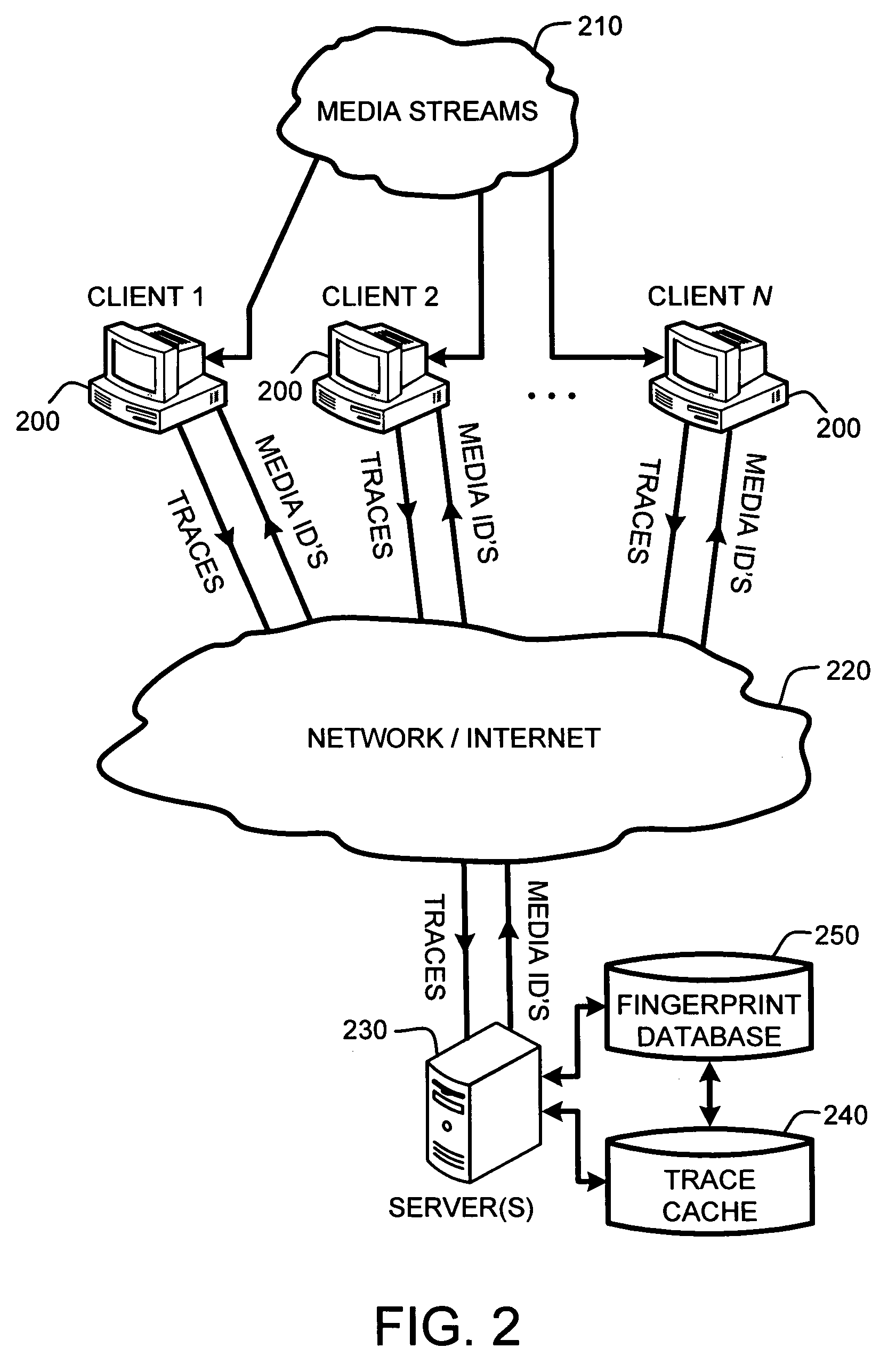
A “Media Identifier” operates on concurrent media streams to provide large numbers of clients with real-time server-side identification of media objects embedded in streaming media, such as radio, television, or Internet broadcasts. Such media objects may include songs, commercials, jingles, station identifiers, etc. Identification of the media objects is provided to clients by comparing client-generated traces computed from media stream samples to a large database of stored, pre-computed traces (i.e., “fingerprints”) of known identification. Further, given a finite number of media streams and a much larger number of clients, many of the traces sent to the server are likely to be almost identical. Therefore, a searchable dynamic trace cache is used to limit the database queries necessary to identify particular traces. This trace cache caches only one copy of recent traces along with the database search results, either positive or negative. Cache entries are then removed as they age.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Ultra wide band transmitter
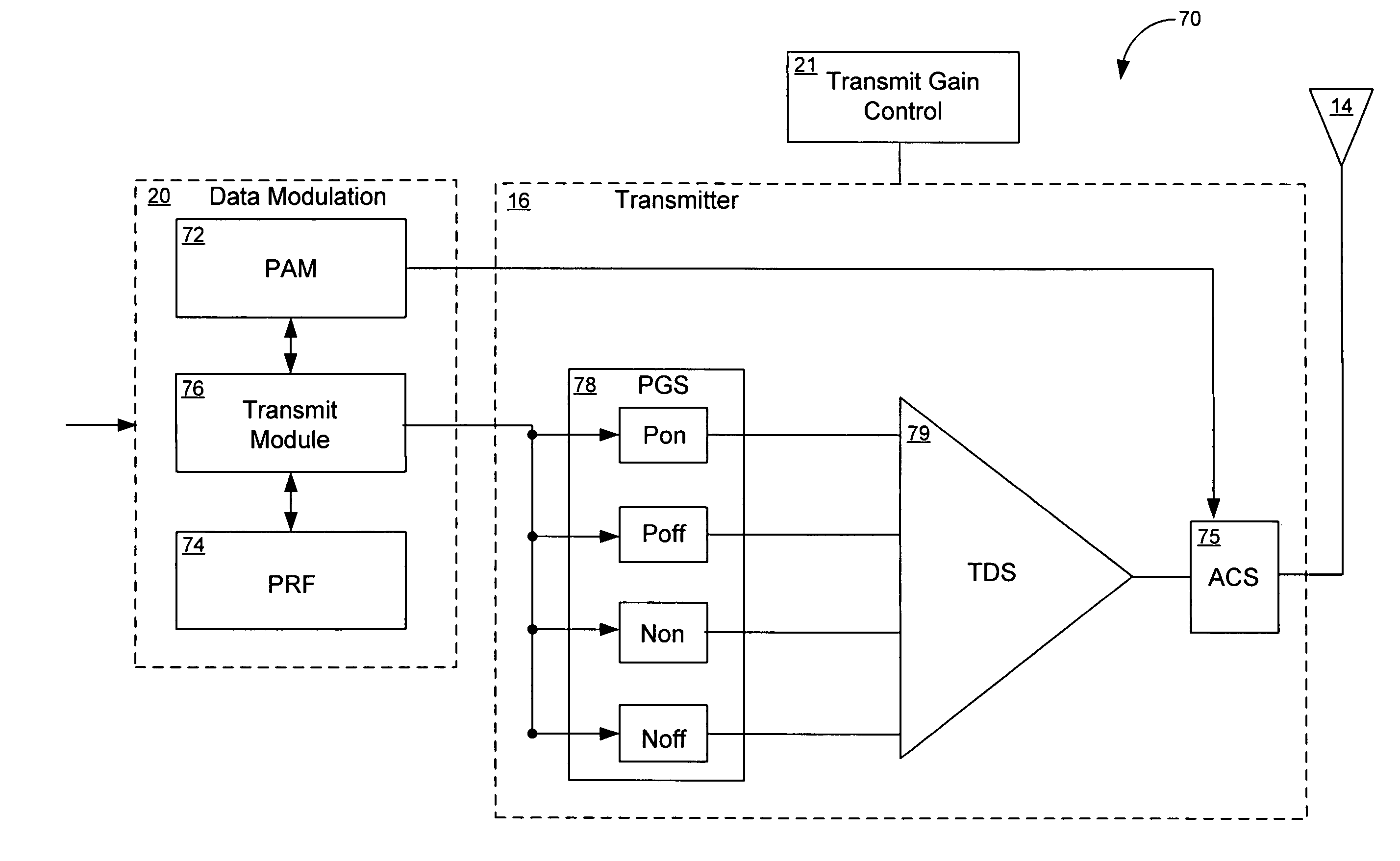
InactiveUS6952456B1Reduced clock speedMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsAngle to amplitude modulation conversionMultiplexerSubject matter
A transmitter system is provided. In one embodiment, the transmitter system includes a data modulation unit, which generates a stream of data that is synchronized with a master clock. The transmitter system additionally includes a transmitter that transmits the stream of synchronized data by way of an attached antenna. In another embodiment the transmitter system includes a Medium Access Control (MAC) layer that includes a clock synchronization device, a frequency divider, a slot allocation unit, and a multiplexer / demultiplexer. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
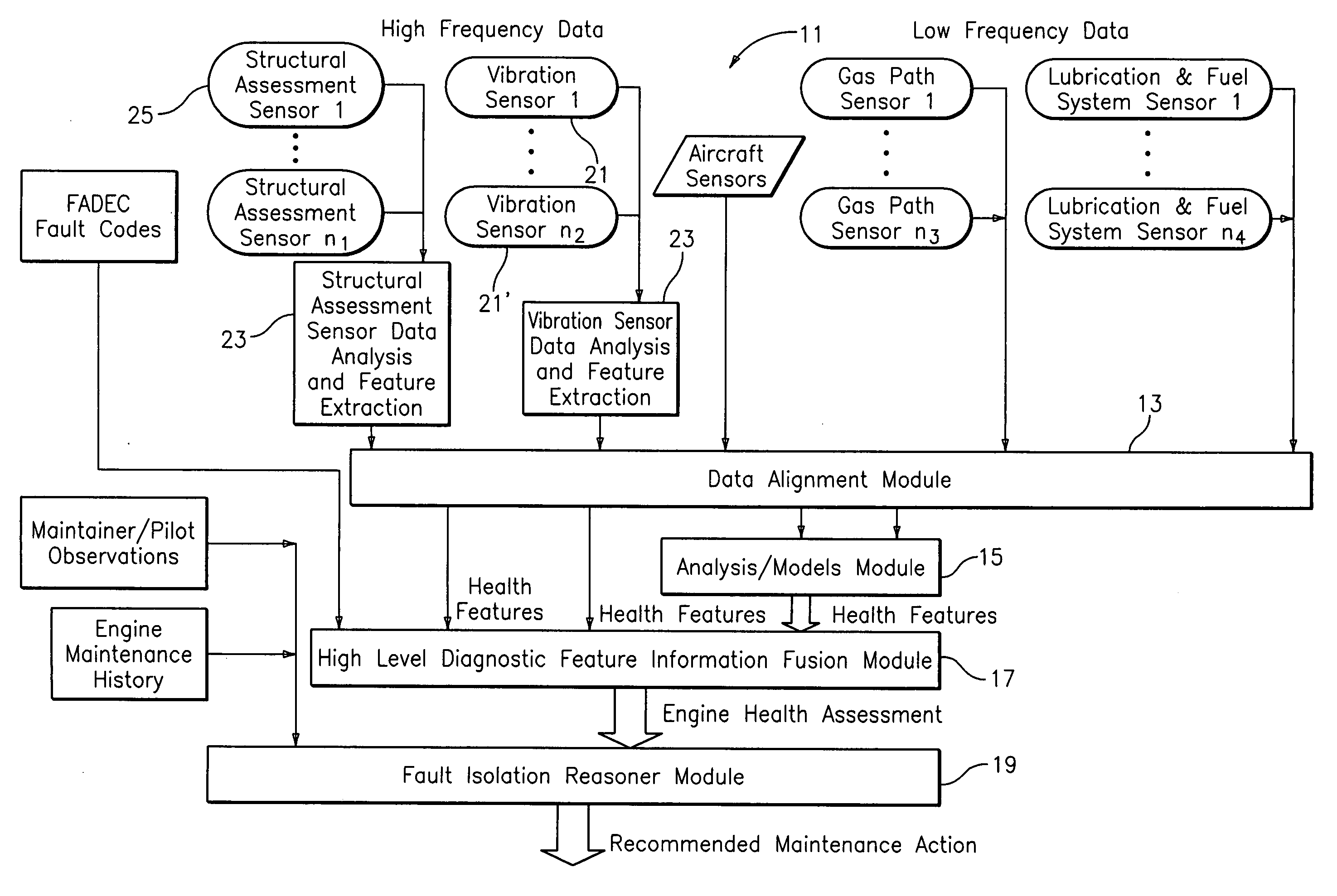
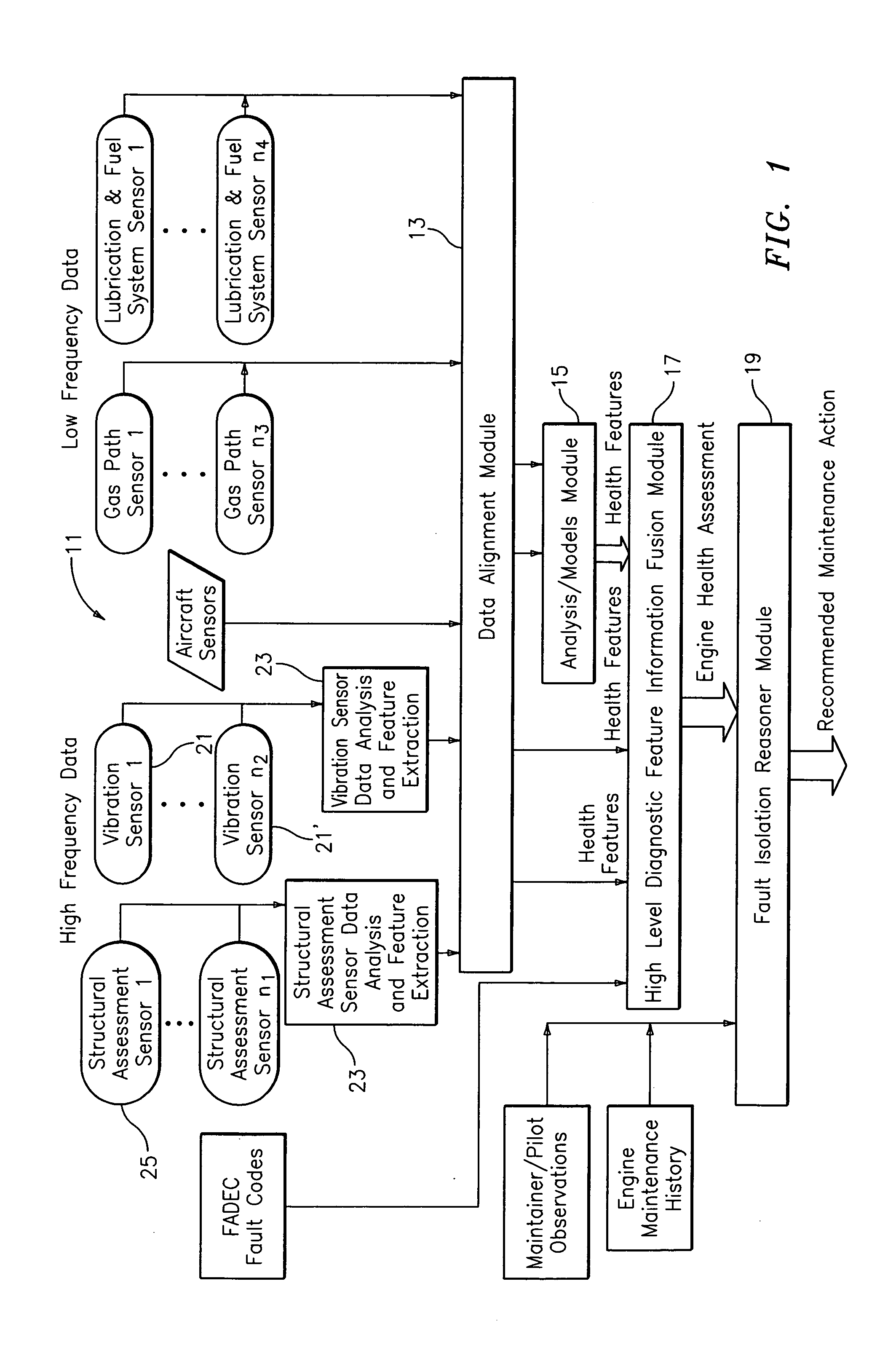
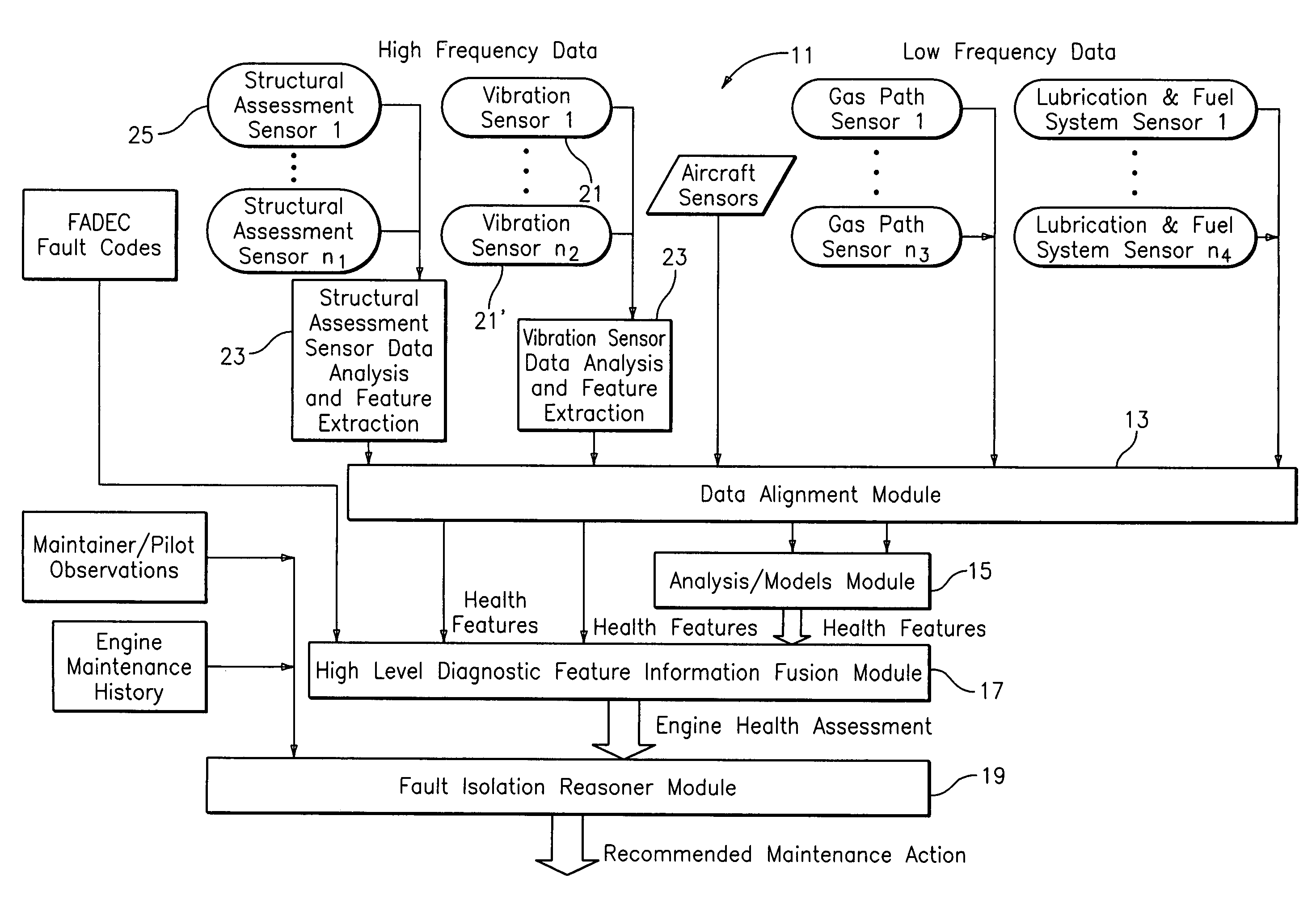
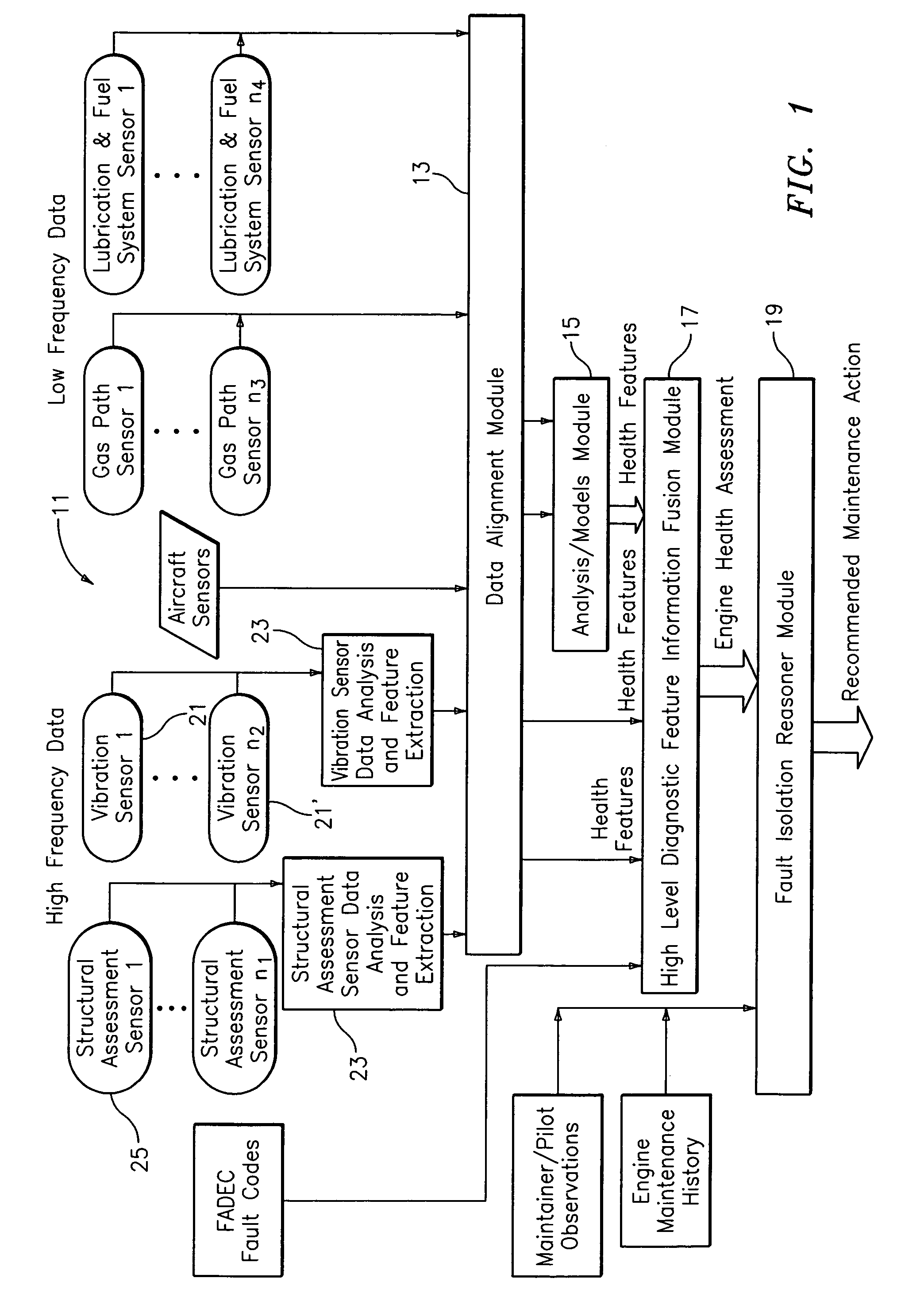
System for gas turbine health monitoring data fusion
An apparatus for assessing health of a device comprising a data alignment module for receiving a plurality of sensory outputs and outputting a synchronized data stream, an analysis module for receiving the synchronized data stream and outputting at least one device health feature, and a high level diagnostic feature information fusion module for receiving the at least one device health feature and outputting a device health assessment.
Owner:RTX CORP
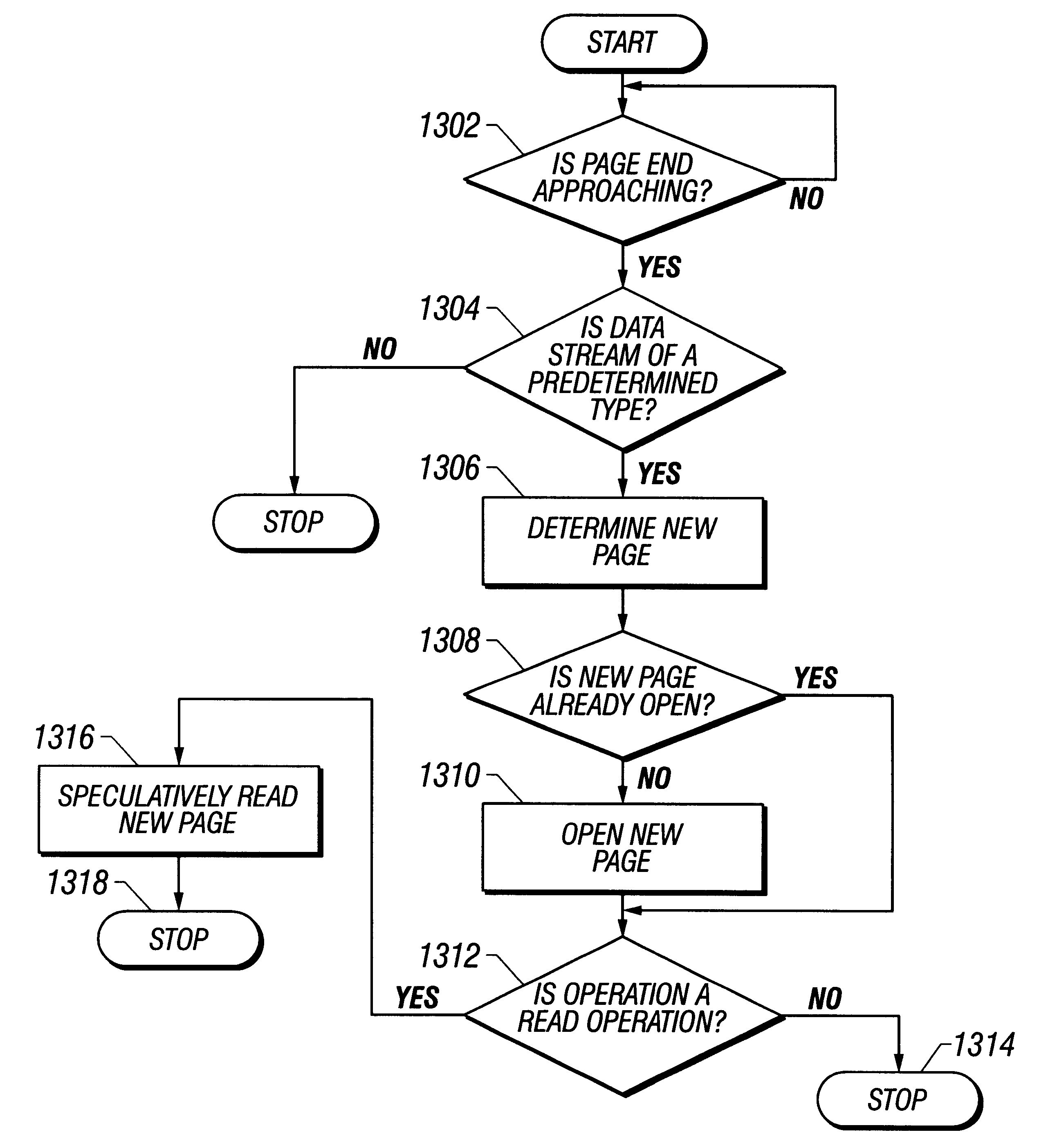
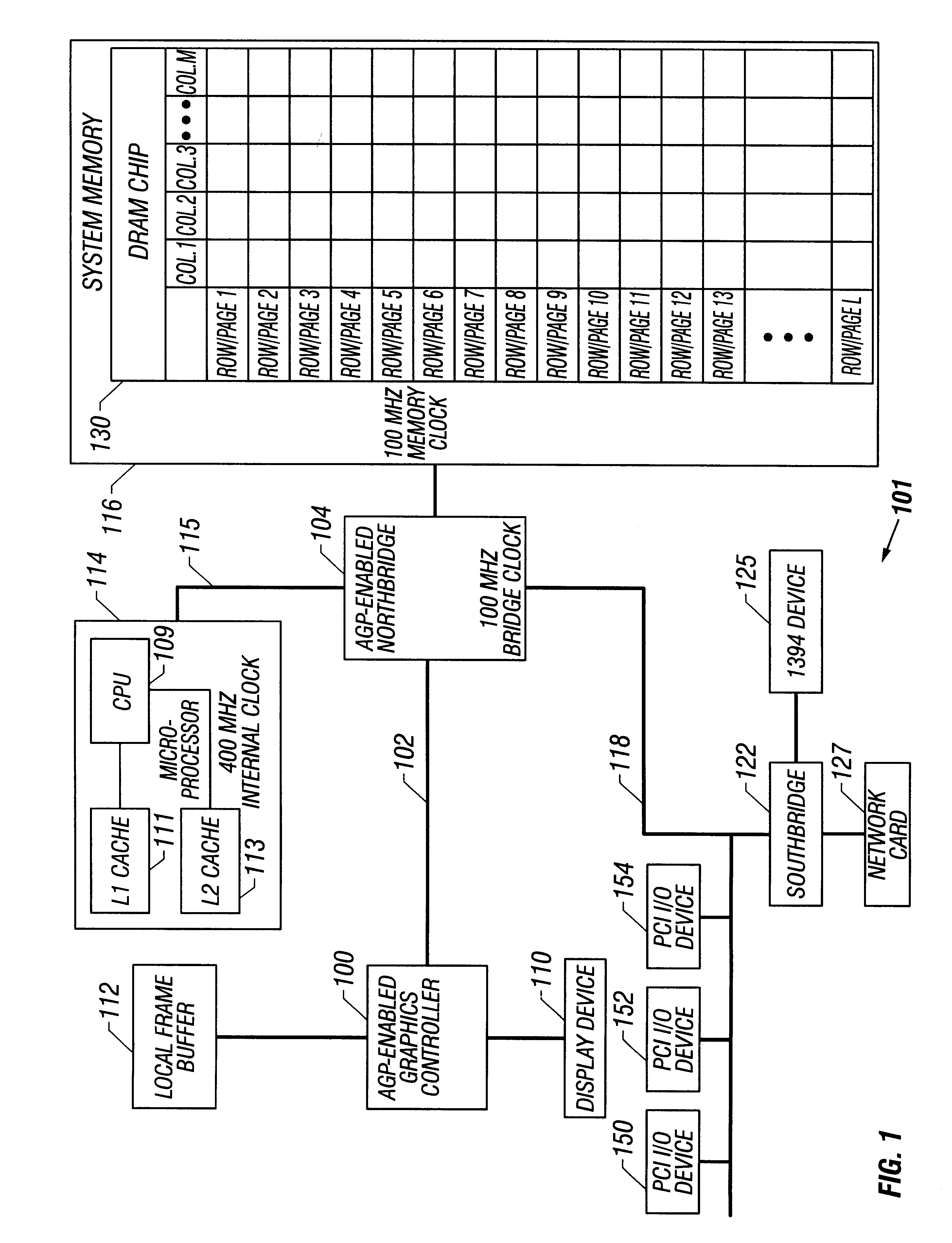
Speculative opening of a new page when approaching page boundary during read/write of isochronous streams
A memory controller detects an approaching end of a currently open page for an access operation for a particular data stream. The memory controller, in response to detecting the approaching end of the currently open page and if the particular data stream is of a predetermined type, such as an isochronous data stream, the memory controller speculatively opens a next page in the memory.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
System for gas turbine health monitoring data fusion
Owner:RTX CORP
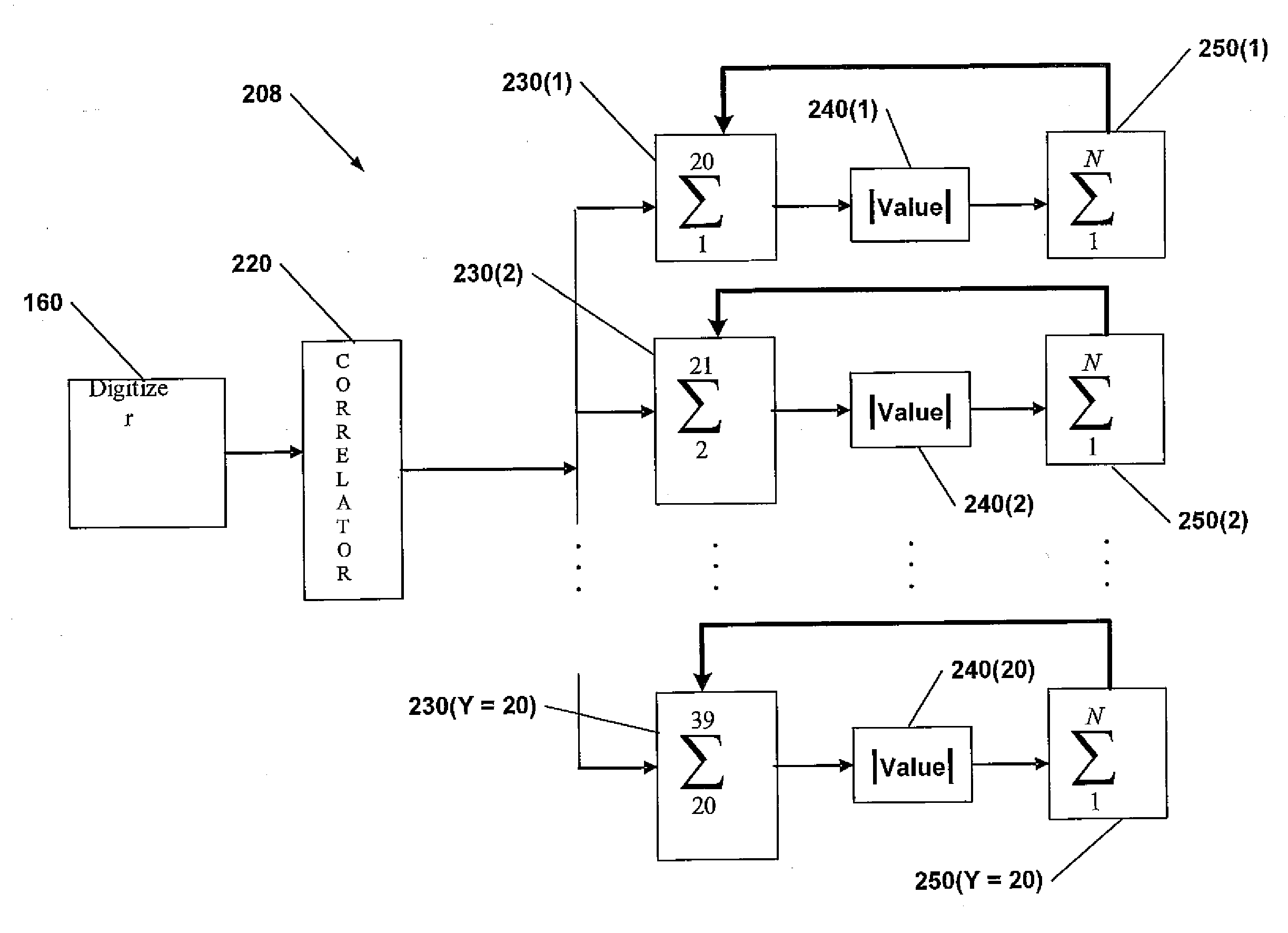
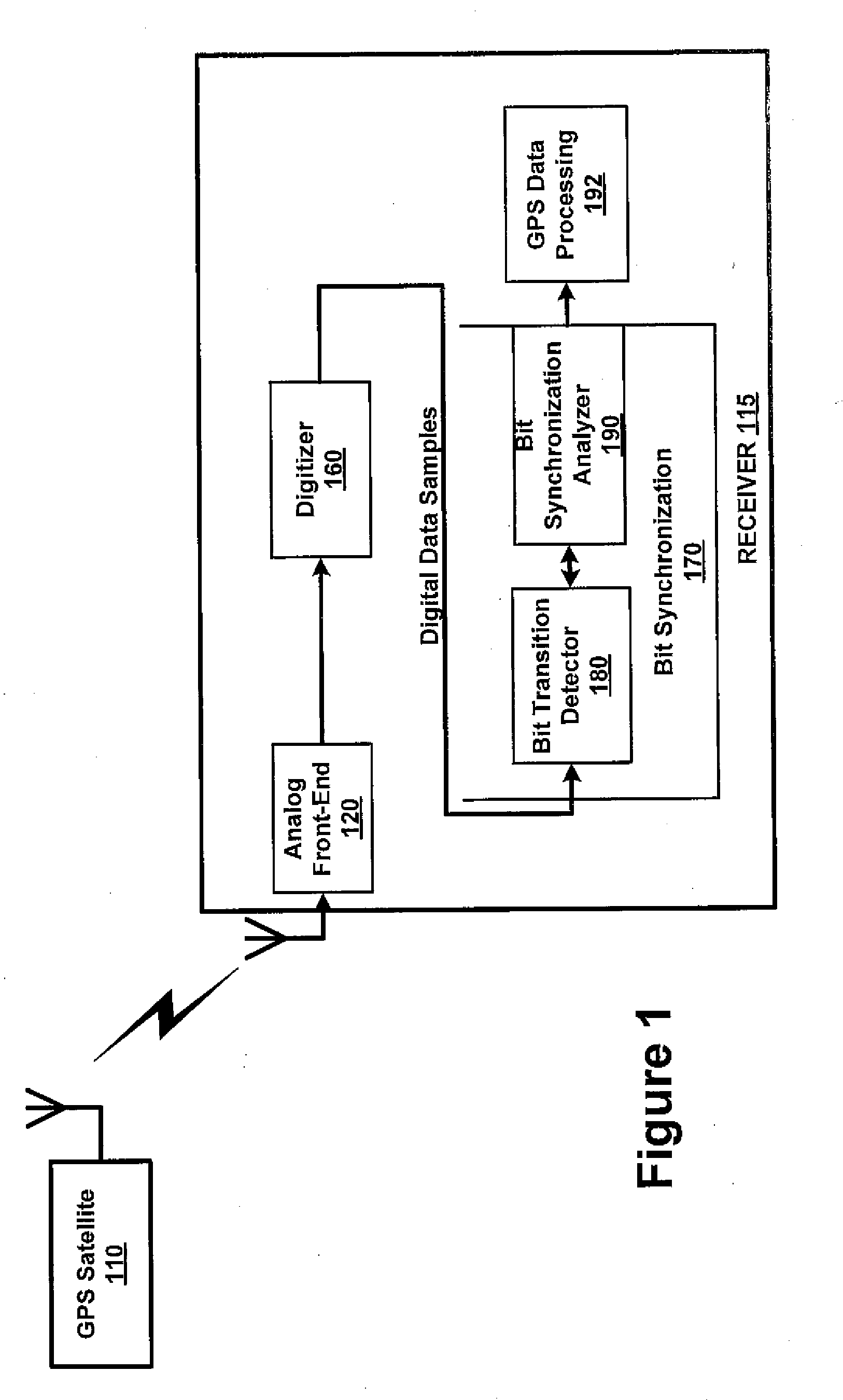
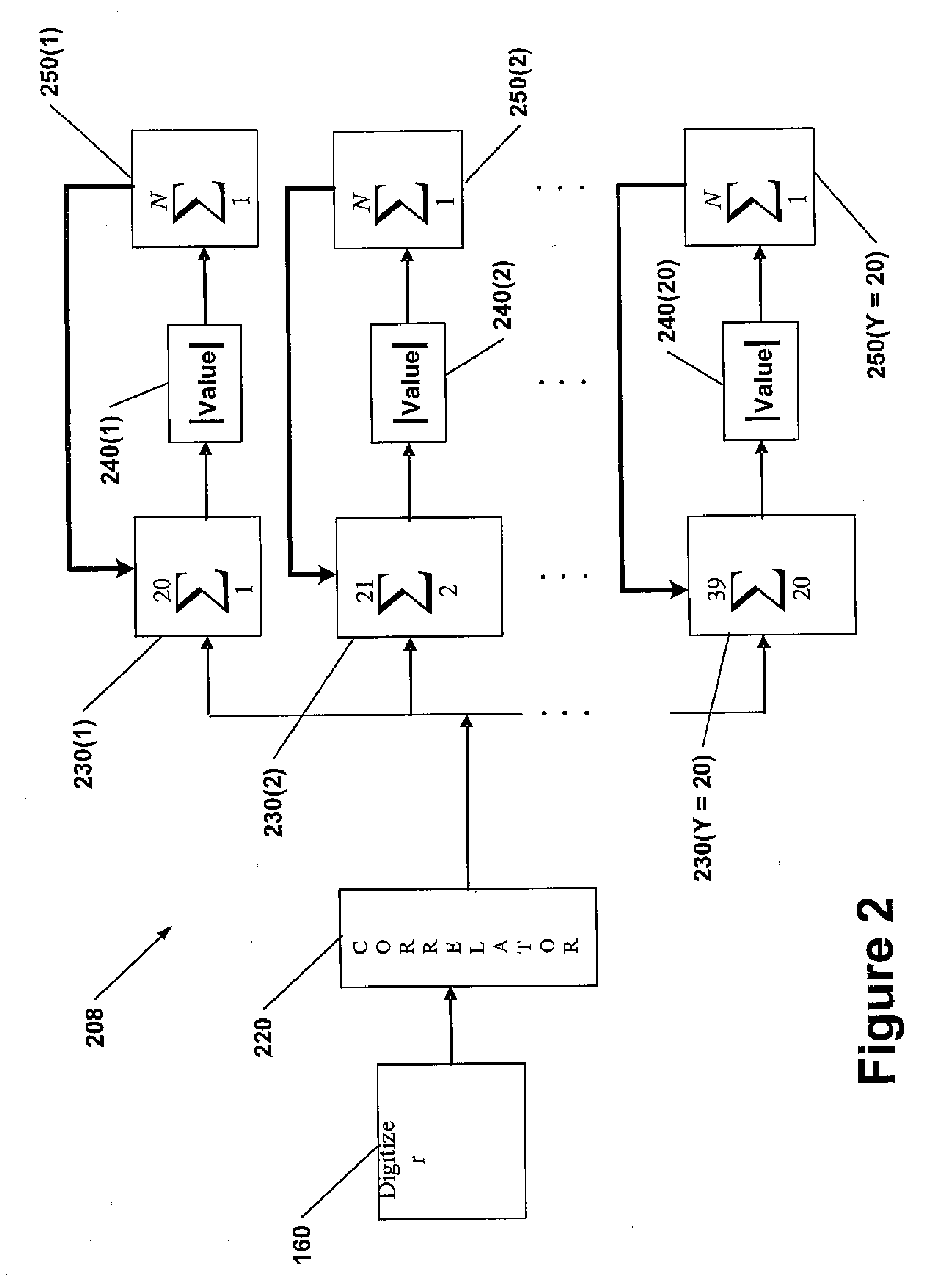
System and Method for Synchronizing Digital Bits in a Data Stream
InactiveUS20080002797A1Satellite radio beaconingSynchronising arrangementData streamComputer science
A system and method for synchronizing a receiver of a bit stream to the bit stream include a correlator to remove the PN code modulation and to generate a stream of time sequence values (samples) from the received bits. A plurality of accumulators are included, each accumulator corresponding to an offset in a series of time intervals starting with a first time period. The accumulators add a number of values equal to a number of samples in a bit period. The values added by each accumulator is a set of values starting with the value at the offset corresponding to the accumulator. A plurality of magnitude calculators receives a sum from the corresponding accumulator and calculates a magnitude. A plurality of non-coherent summers are then used to add the magnitudes for each offset in each bit period for all of the received bits. The total sum in each non-coherent summer is then analyzed to find the highest value, such that the offset corresponding to the non-coherent summer with the highest value represents the location of the bit transition in the bit period.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
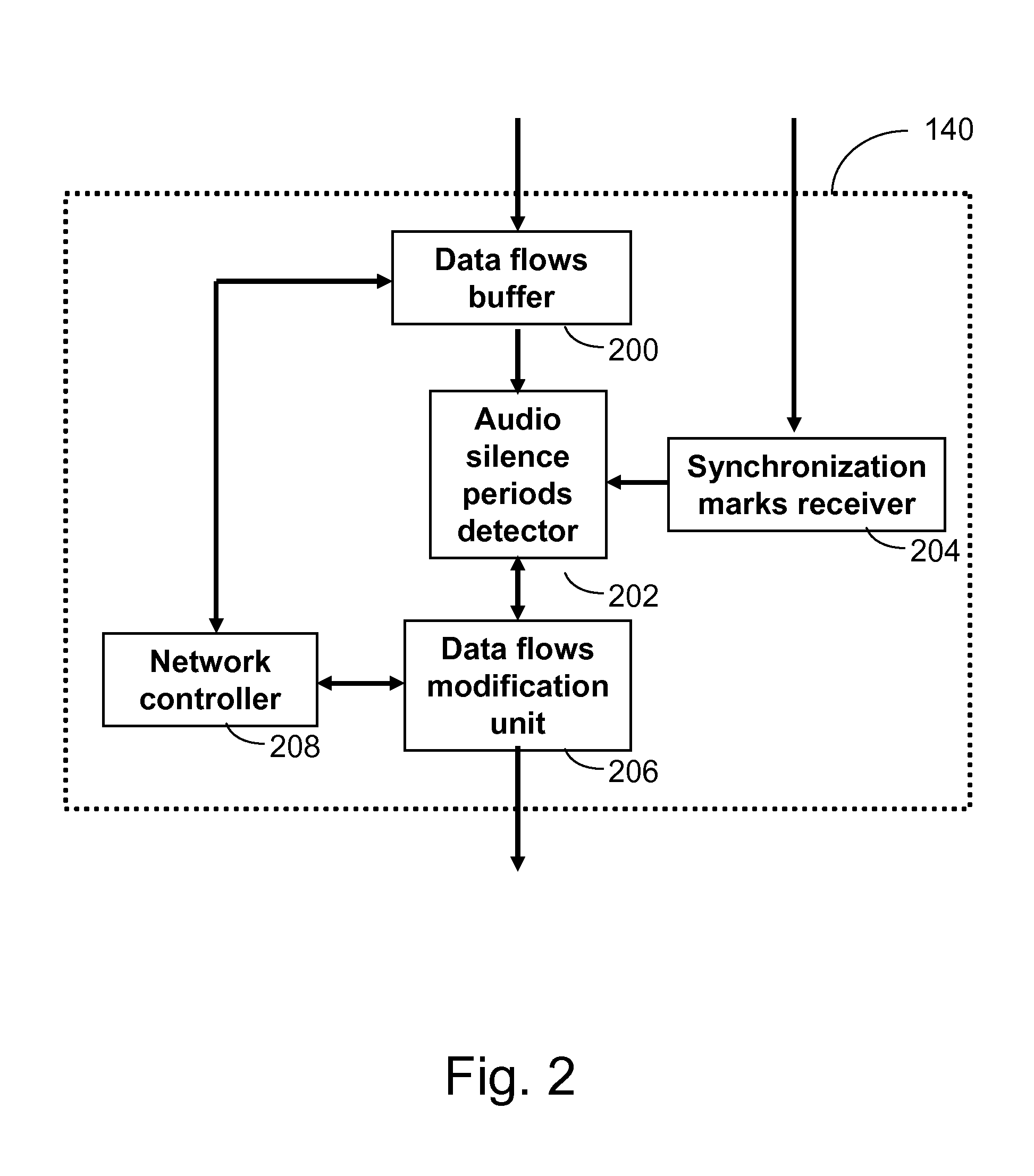
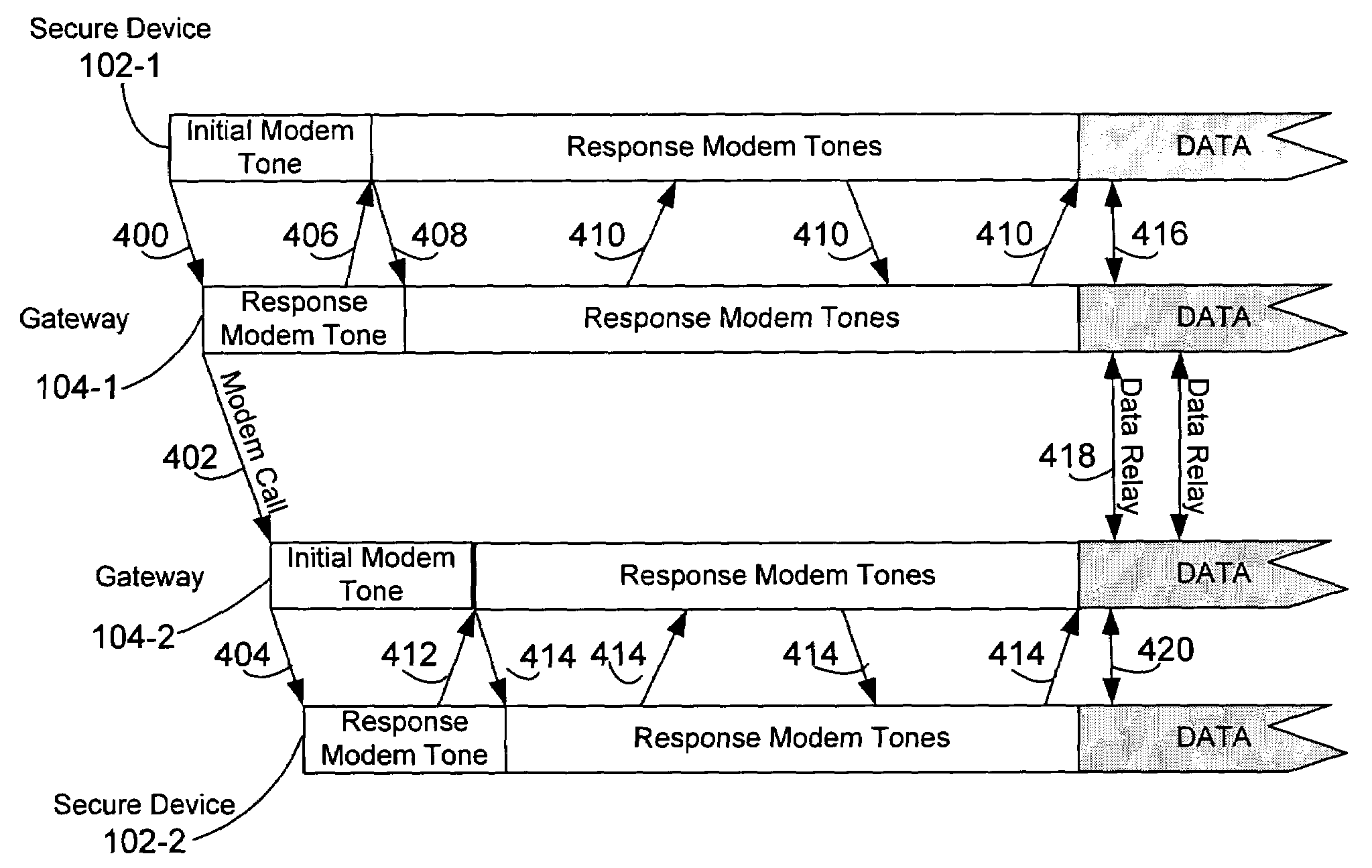
Method for synchronizing data flows
InactiveUS20090060458A1Extended durationTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionData streamParallel computing
The first data flow is buffered at a receiver, and the buffer contents are scanned for metadata. Where metadata are found indicating a second data flow which has not yet arrived, the system enters a stalling phase during which the length of any silent periods in the first data flow are stretched. As the point in the first data flow at which the second data flow is necessary gets closer, the factor by which silent periods are stretched increases exponentially. Once the expected second data flow in fact arrives, playback of two data flows is accelerated by compressing silent periods so as to clear the backlog of additional data that built up in the buffer during the stalling phase.
Owner:IBM CORP
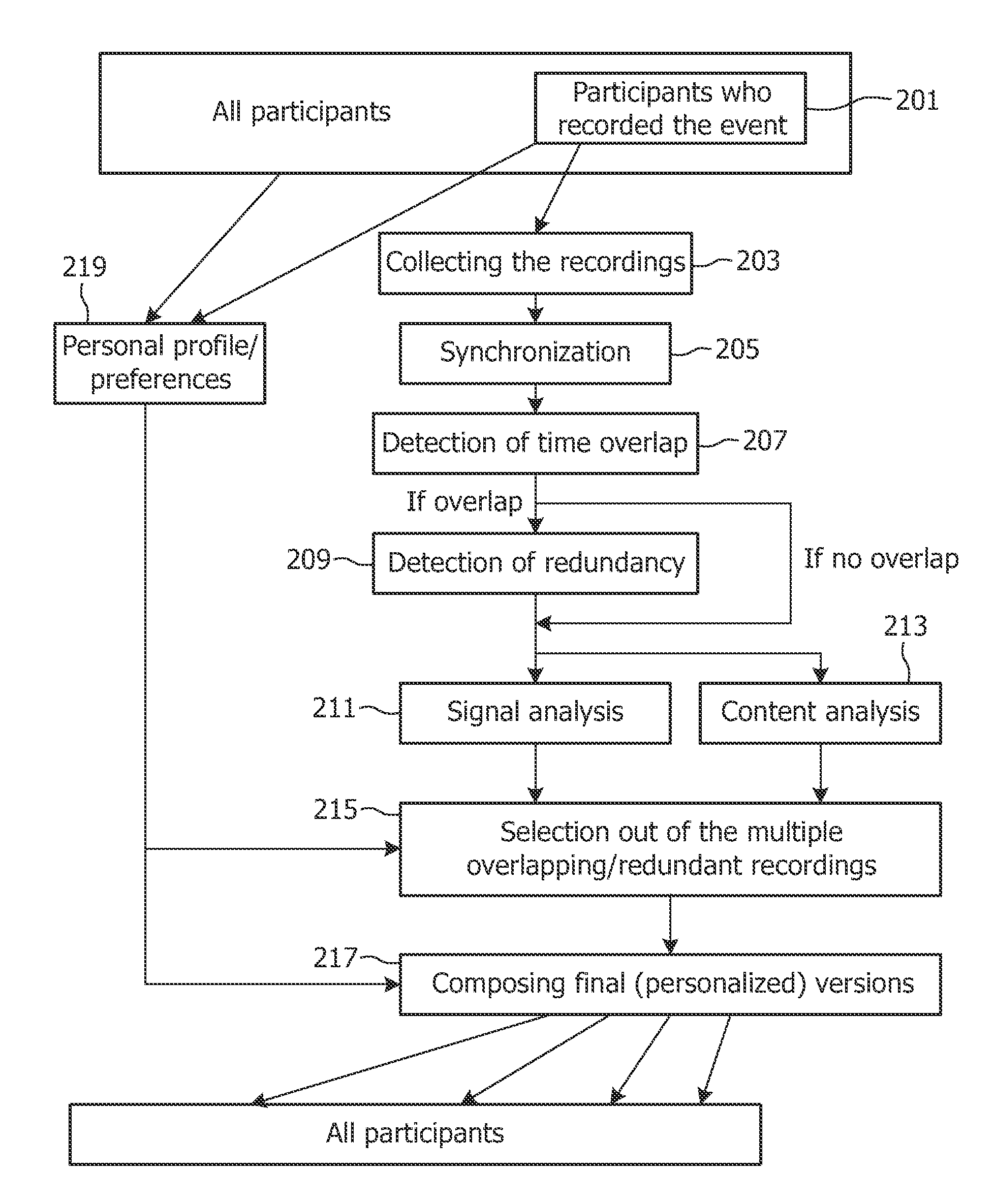
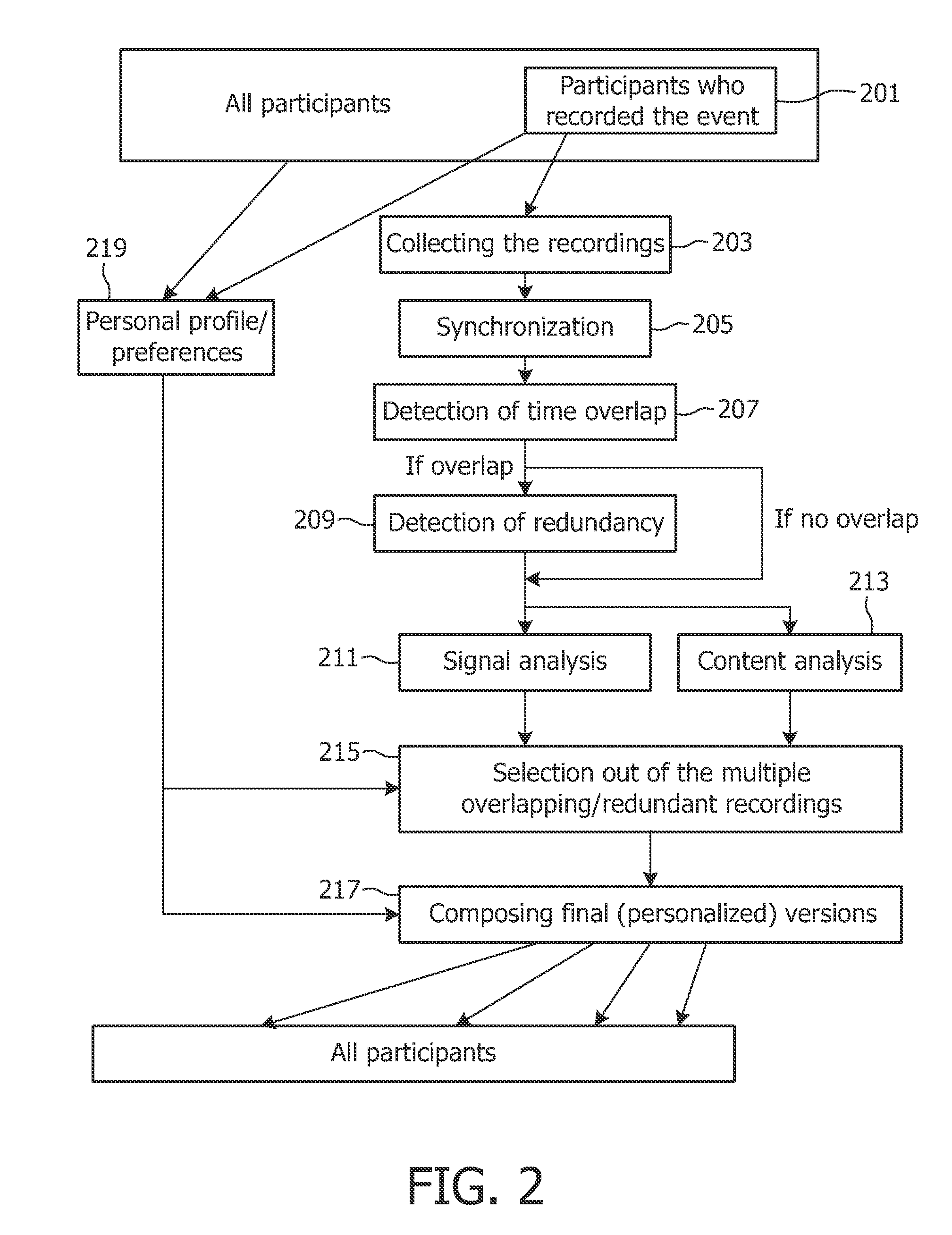
Method and apparatus for generating a summary
InactiveUS20100017716A1Easy to recordLarge audienceInput/output for user-computer interactionElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsData streamReal-time computing
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for speeding up database lookups for multiple synchronized data streams
InactiveUS7574451B2Increase loadImprove accuracyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData streamReal time services
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for synchronization of data streams
ActiveUS7772963B2Eliminate needSubscribers indirect connectionTransmissionData streamRadio frequency signal
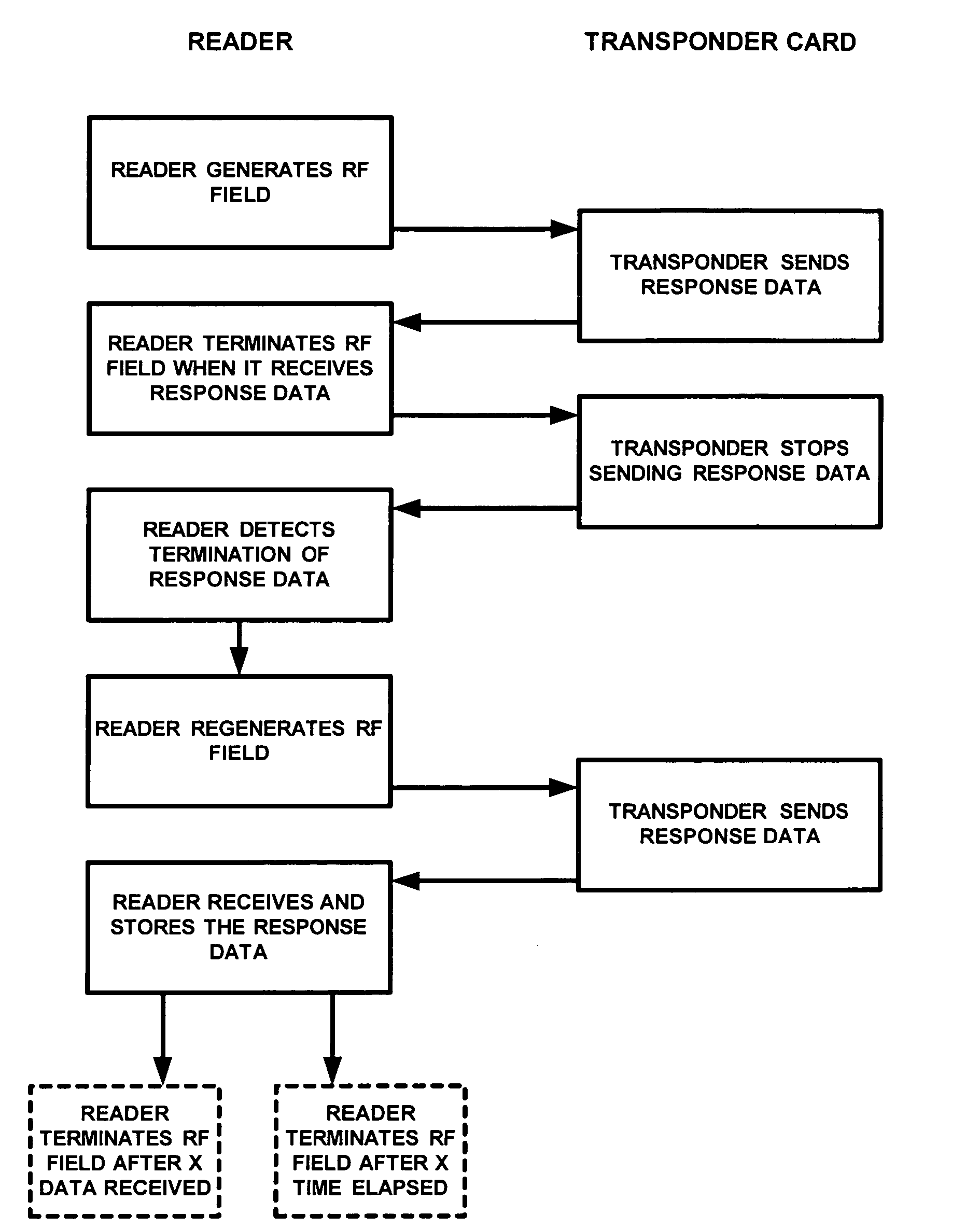
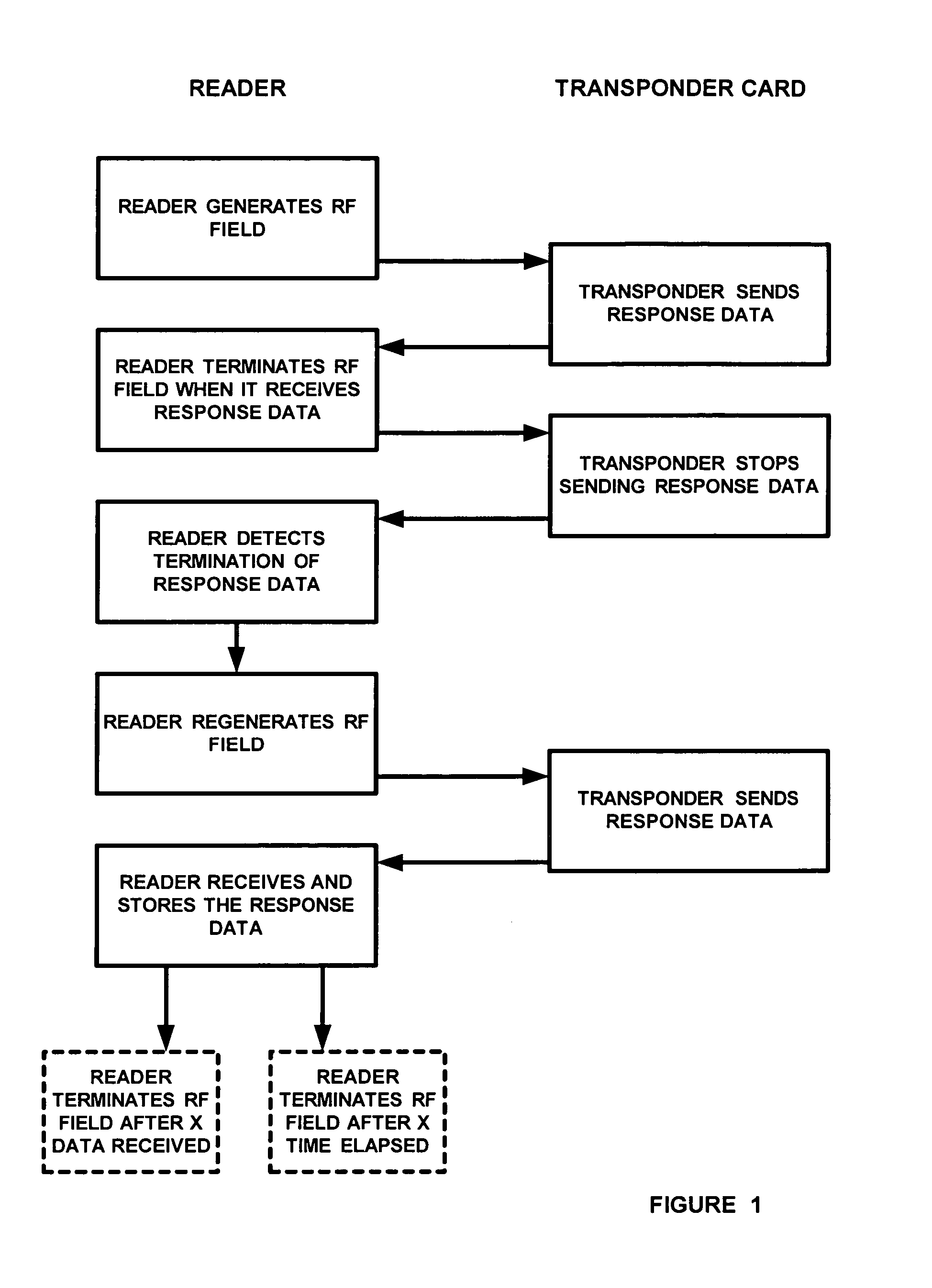
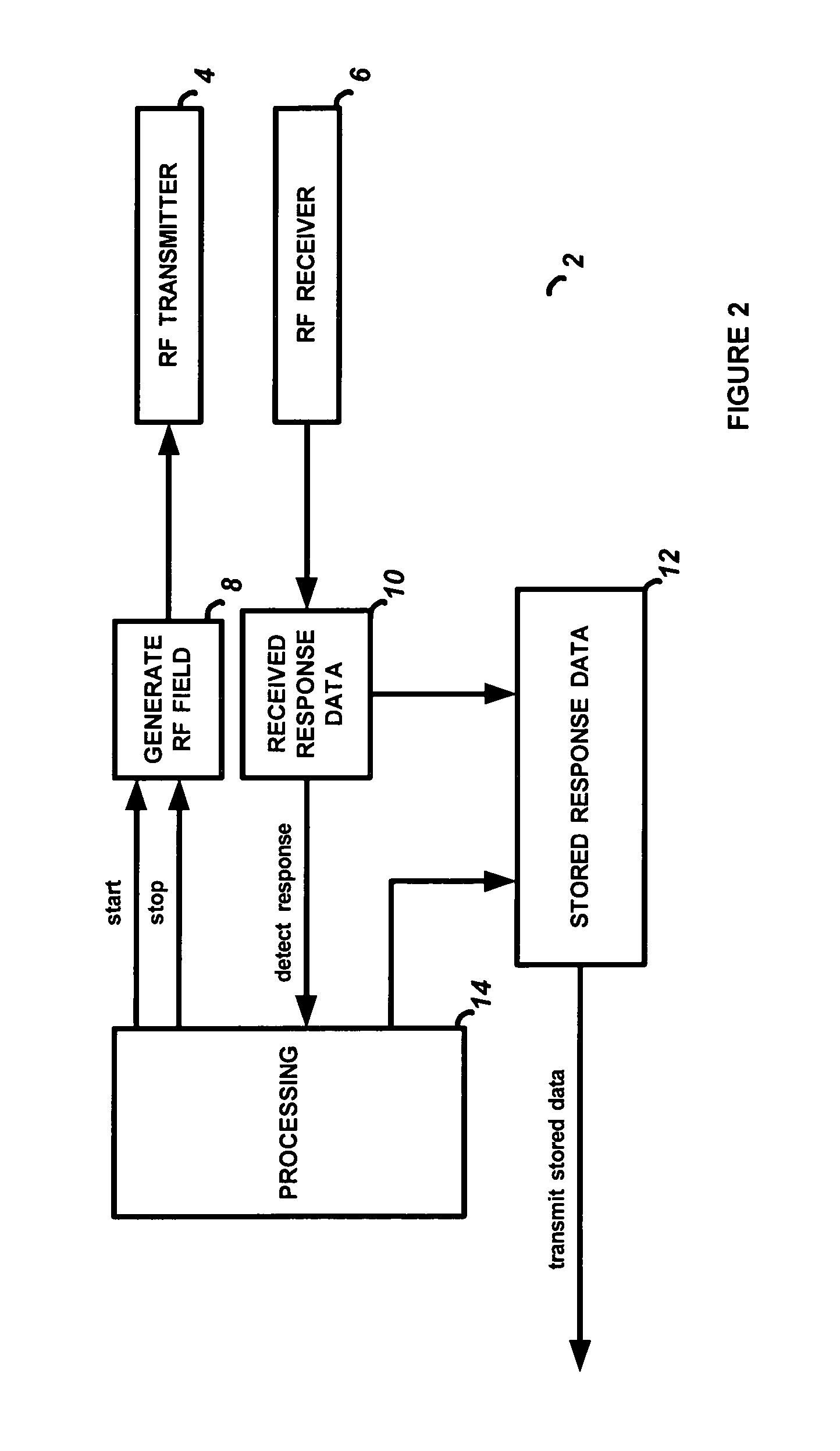
A method of and system for acquiring data by a data reader from a transponder in which the data from the transponder does not require a preamble to denote the beginning of the data sequence. A radio frequency signal is continuously transmitted by the card reader to generate a radio frequency field. Once a transponder enters the RF field, then response data is generated by the transponder and received by the card reader. The transmission of the radio frequency signal by the card reader is temporarily stopped on detection of the response data from the transponder, and then reinitiated by the card reader after it stops receiving response data from the transponder in order to regenerate the radio frequency field. The response data subsequently received from the transponder in the radio frequency field is then stored in memory.
Owner:ADEMCO INC
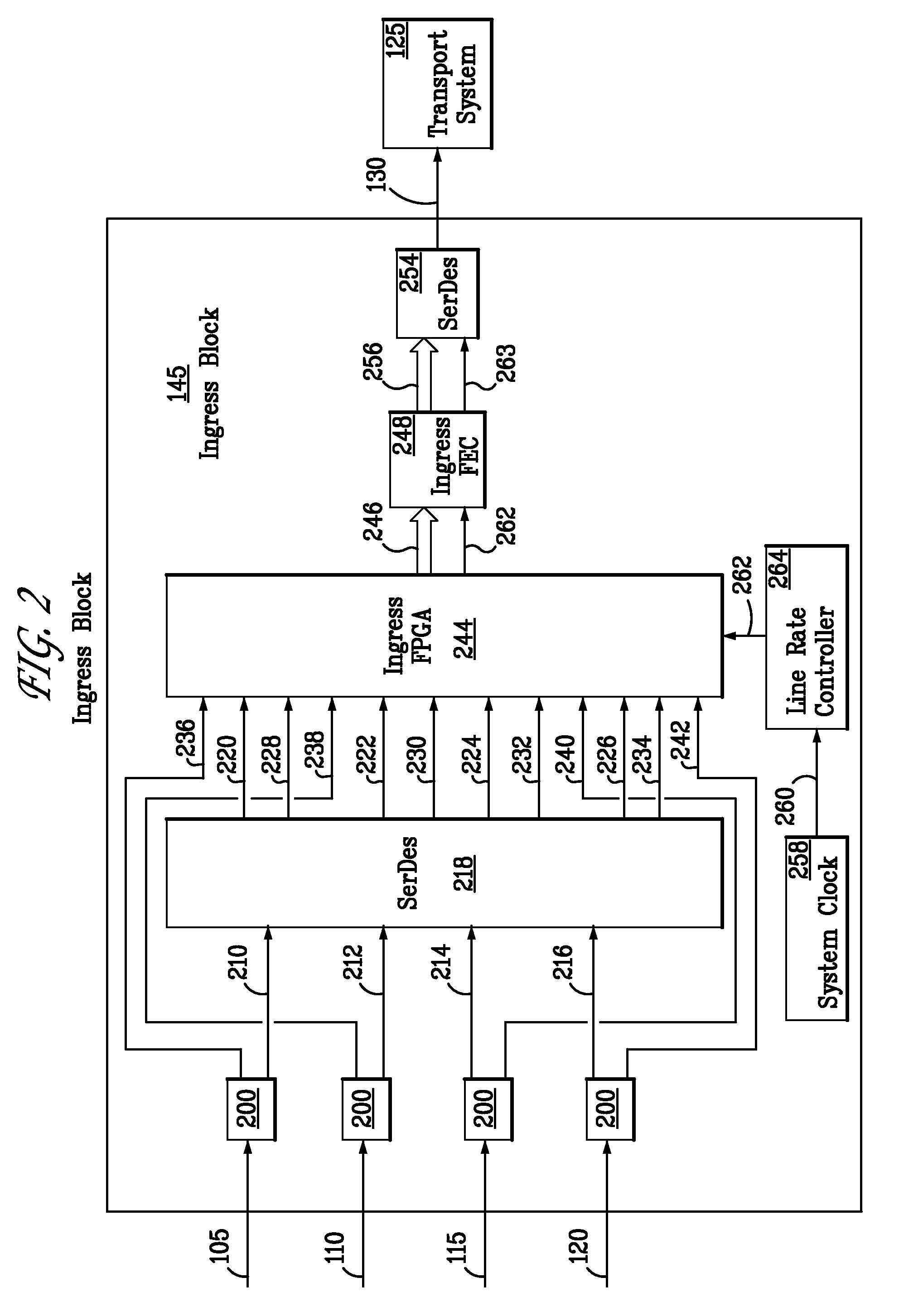
Apparatus and method for aggregation and transportation of gigabit ethernet and other packet based data formats
ActiveUS7656905B2Transparent data communicationLow costTime-division multiplexData switching networksData streamData signal
The invention provides an apparatus and method for transparently transporting four plesiochronous Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel or other packet-based data signals over a network. Multiple plesiochronous Gigabit Ethernet data streams are aggregated onto an independent clock source at an ingress circuit through the use of transparent IDLE character insertion. The independent clock is selected such that the output data rate is greater than the composite input data rate of all the plesiochronous data streams. The signals are encapsulated with forward error correction and mapped to a reciprocal FEC interface prior to transport. An egress circuit at the receiving end recovers the modulated signal and extracts the data stream. Each independent data stream is mapped to a local clock domain via IDLE character insertion or removal. Therefore, the input and output signals are transparent and identical in content.
Owner:XYLON LLC
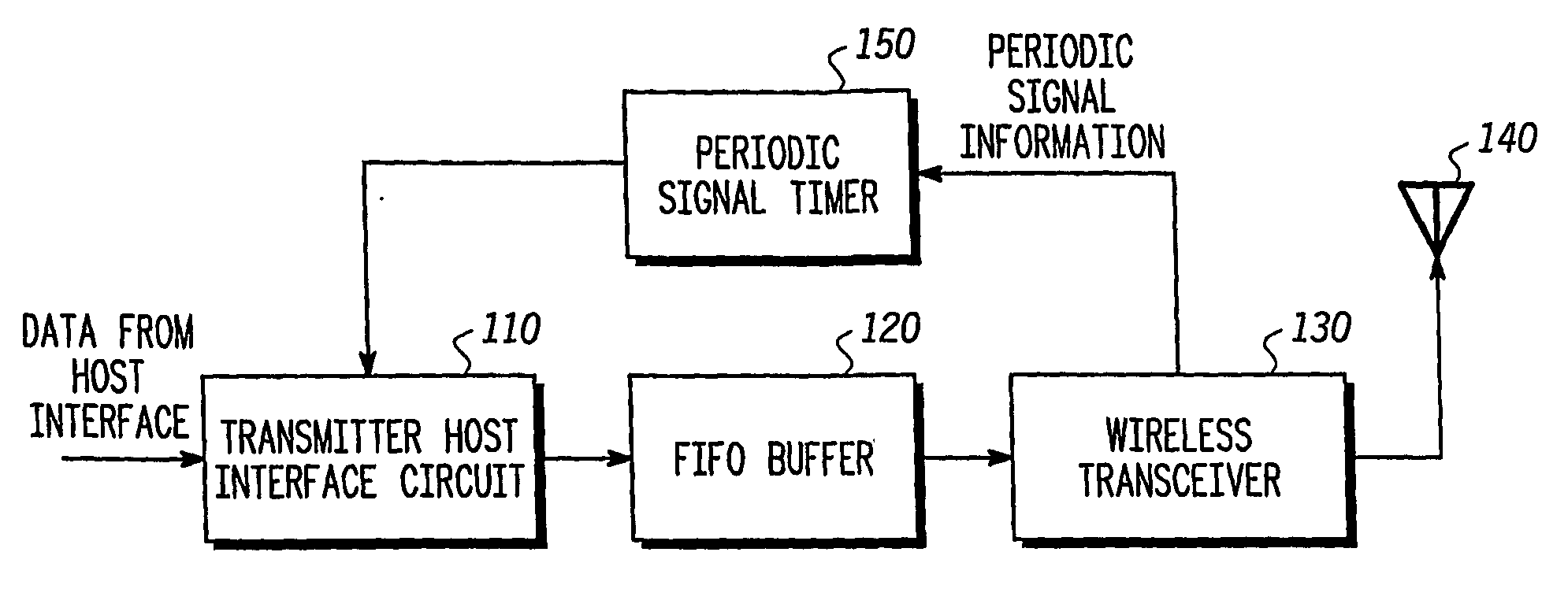
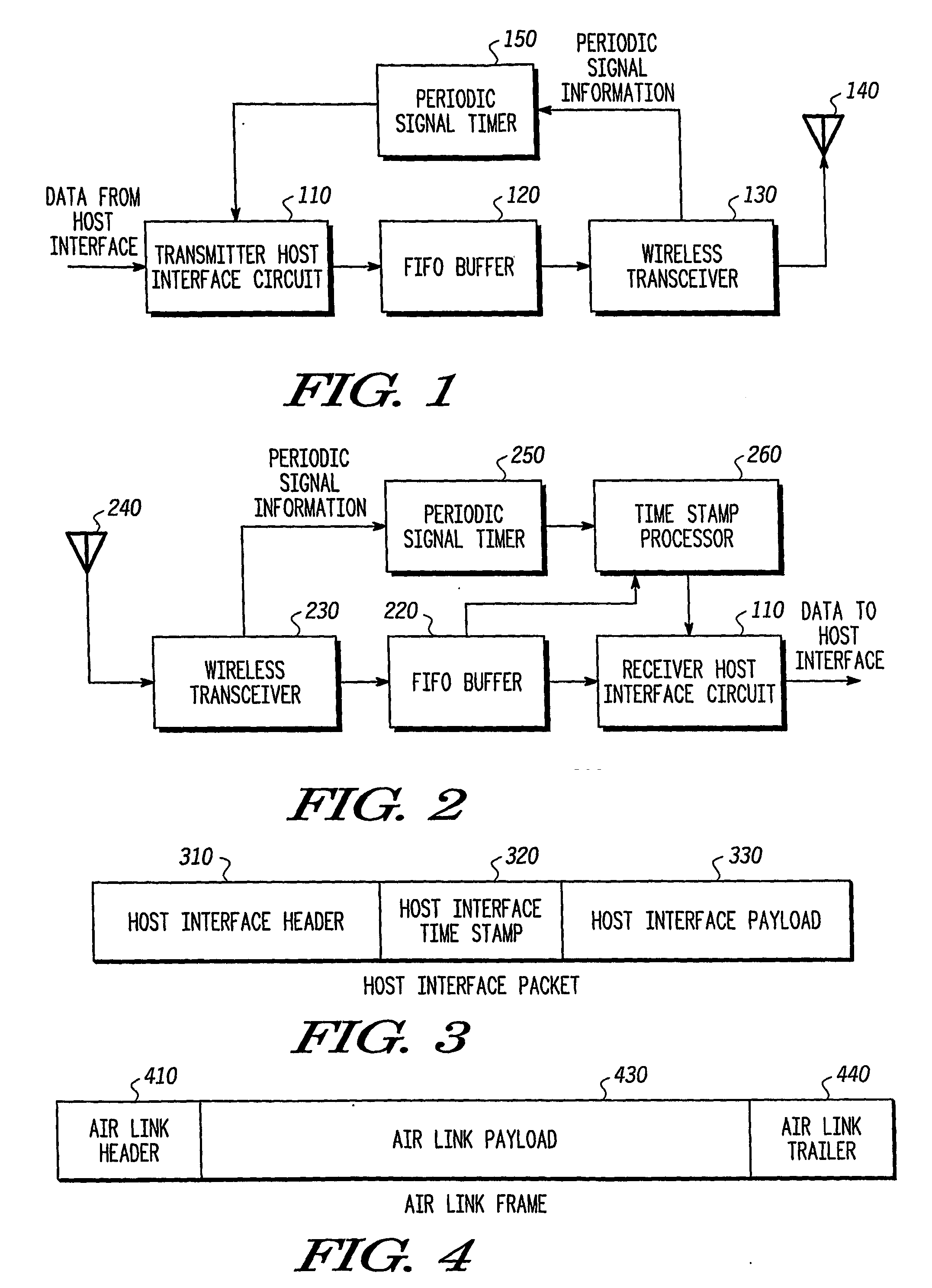
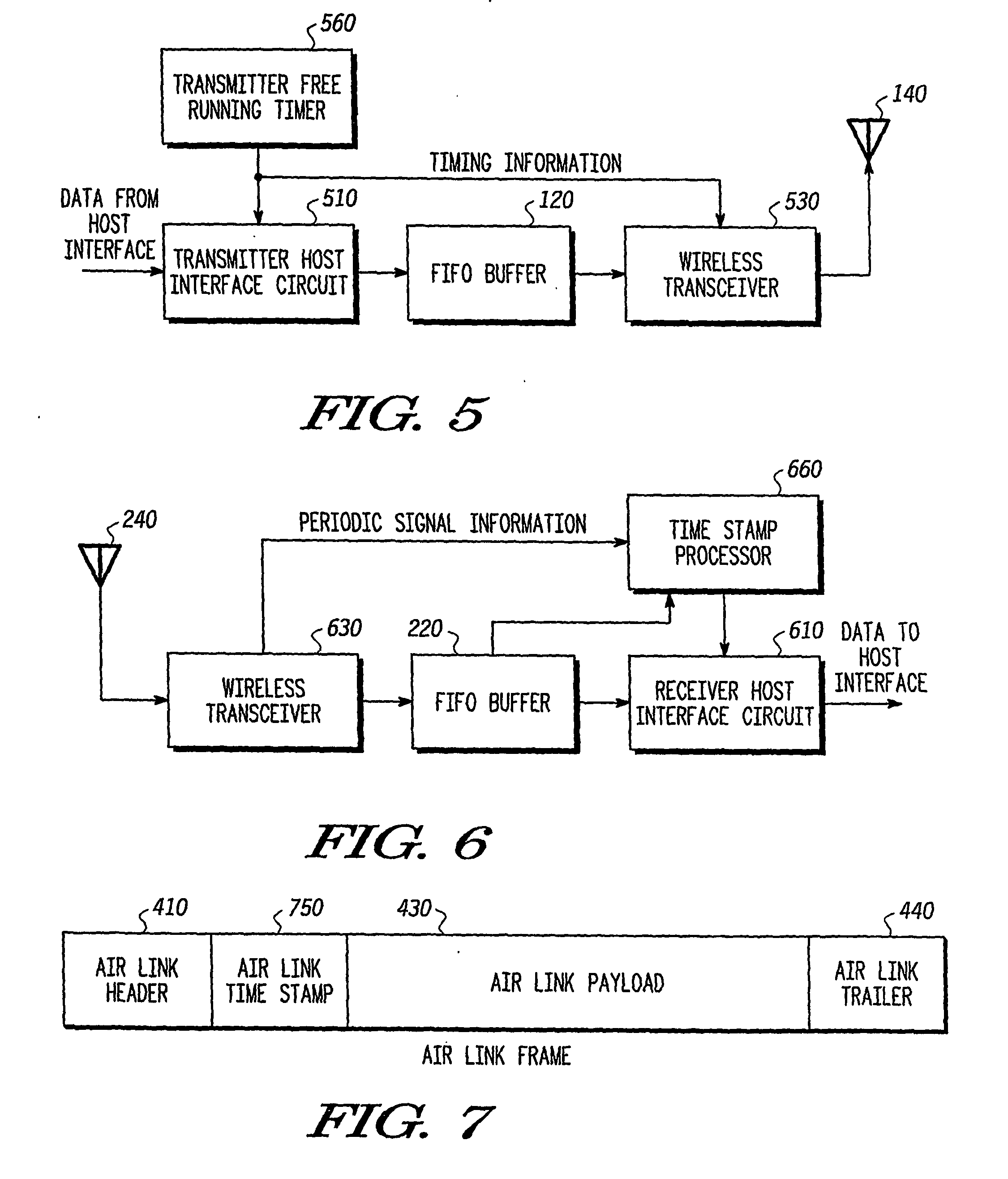
System and method for synchronization of isochronous data streams over a wireless communication link
InactiveUS20070100473A1Synchronisation arrangementPosition fixationTelecommunications linkData stream
A transmitter (500) is provided for transmitting host data over a wireless channel. The transmitter (500) includes a free-running timer (560) that provides a series of increasing free-running timing values; a host interface circuit (510) that receives host data from a local host circuit and a first free-running timing value from the series of increasing free-running timing values; a detection circuit (530) for detecting a global synchronizing event and receiving a second free-running timing value from the series of increasing free-running timing values, and for placing the host data and the first free-running timing value into a host interface packet; and a wireless transceiver (530) for adding the second free-running timing value and an identifier for the global synchronizing event to the host interface packet to form an air link frame, and transmitting the air link frame over a wireless channel to a remote wireless device.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
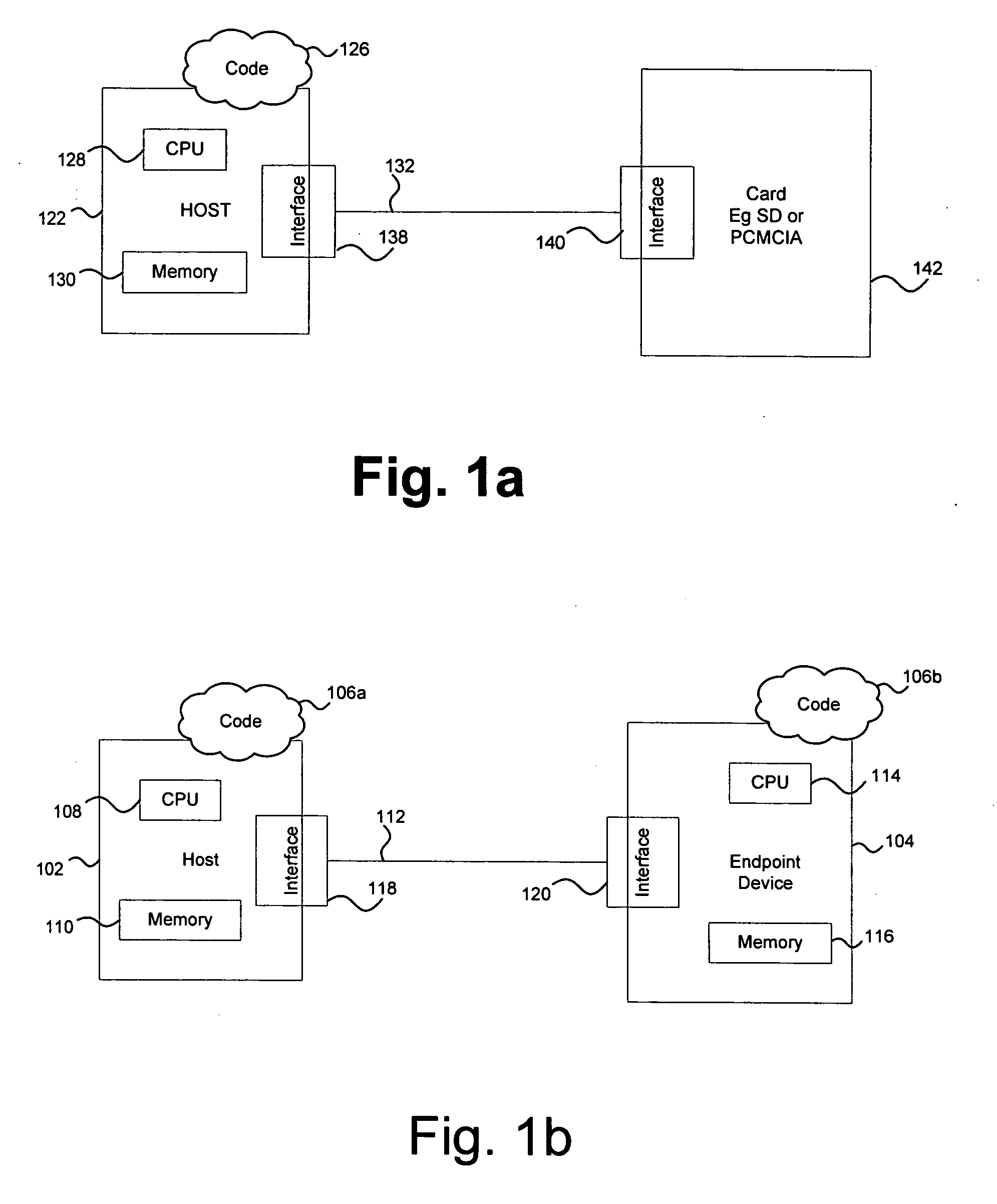
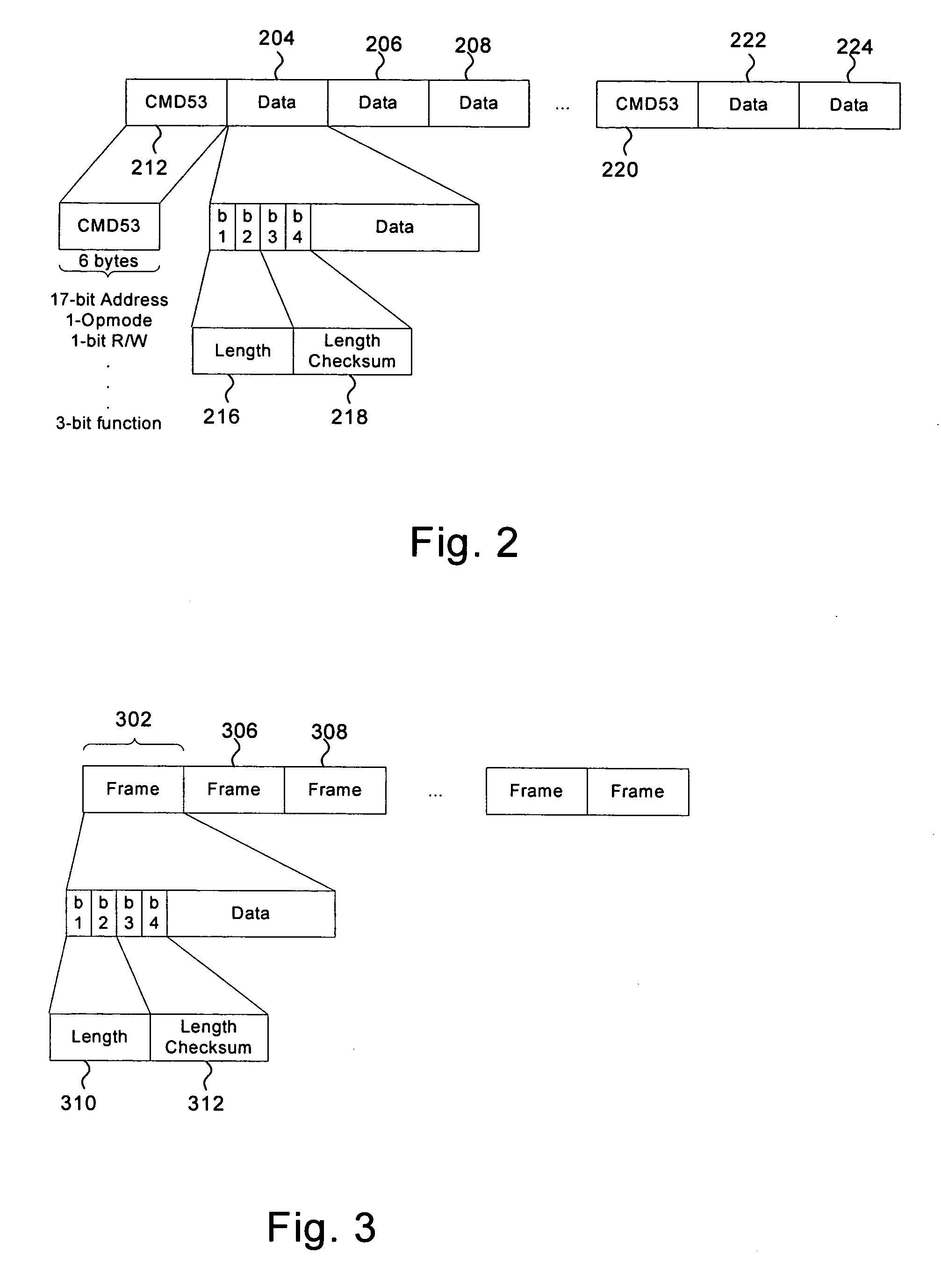
Method and system for efficient framing on addressed buses
A framing mechanism may be provided that enables passing of messages over an addressed bus. This creates a form of information hiding, which passes information by converting an addressed bus interface to a message-based bus interface. Address-based information in a transaction may be replaced with additional information that specifies framing details comprising, for example, a check pattern and length information. The check pattern provides a mechanism for determining whether frame information may be valid. An end device may utilize this length information to determine an actual length of an incoming frame. The combination of the check pattern and the length information may provide a pattern for resynchronizing a data stream when errors are detected. The framing mechanism may operate over existing addressed buses without requiring host side controller hardware modifications and additional host side software driver may be utilized to add the framing information.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
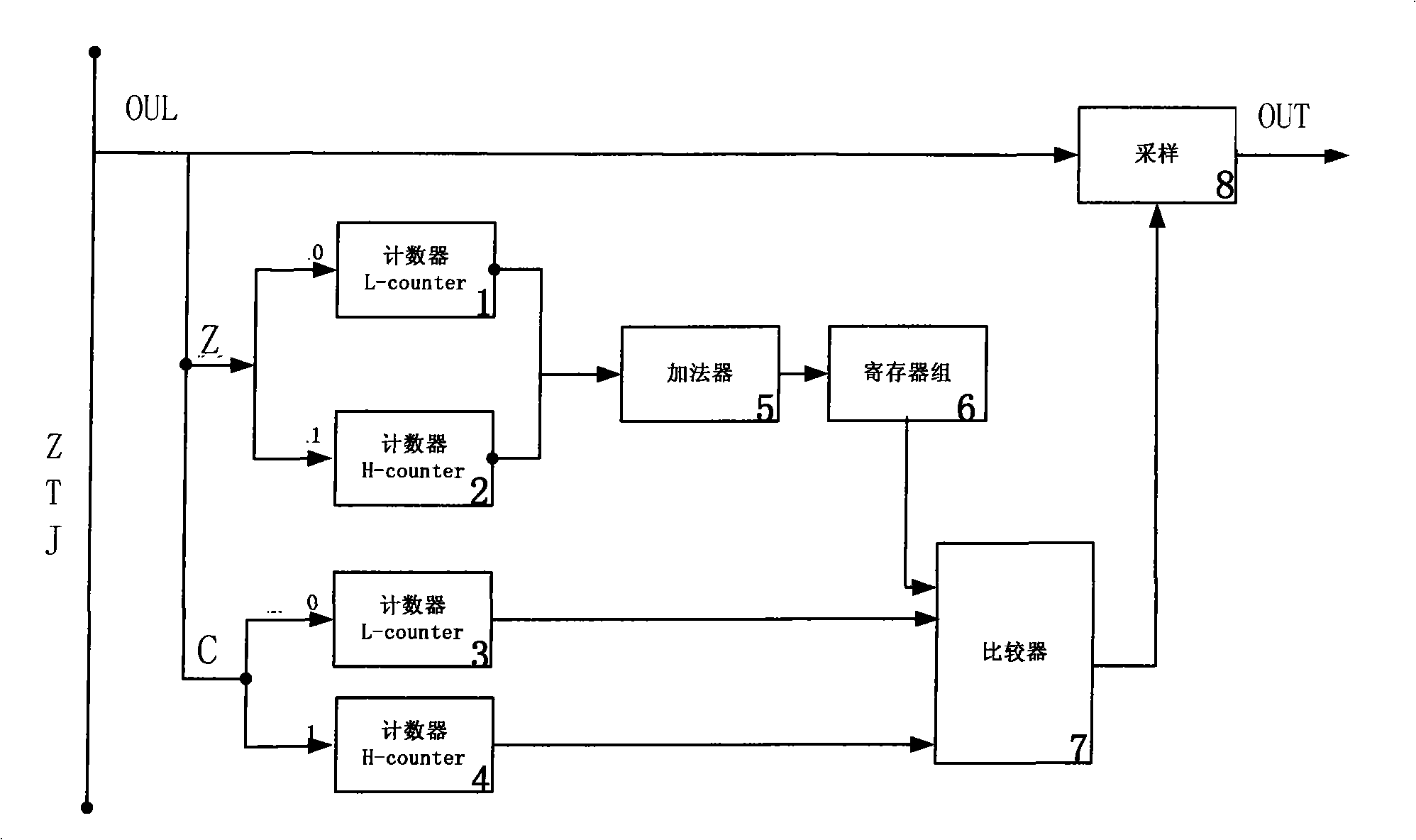
Radio frequency identification label chip data receiving synchronous method
InactiveCN101408924AAdaptableRealize simple structureSensing record carriersMachine controlProcessor register
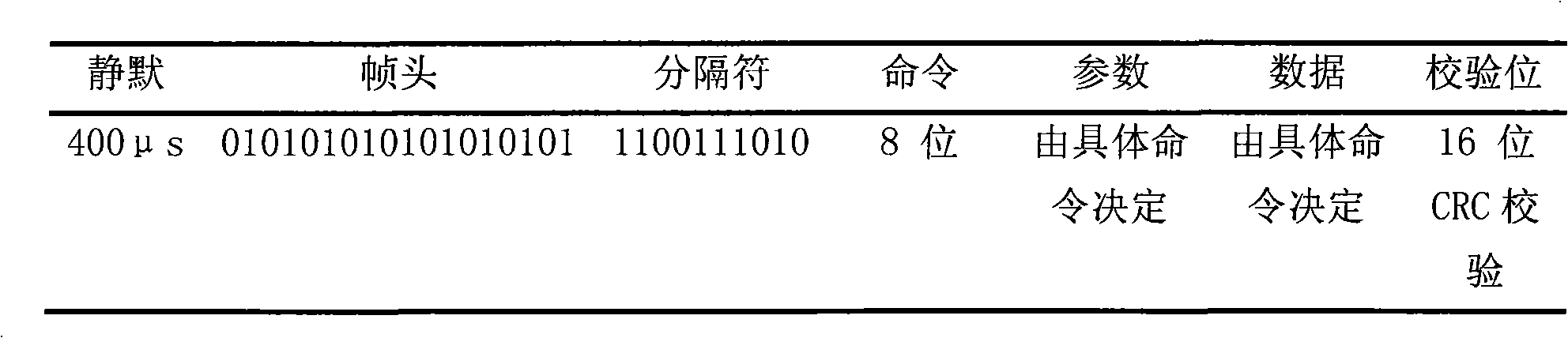
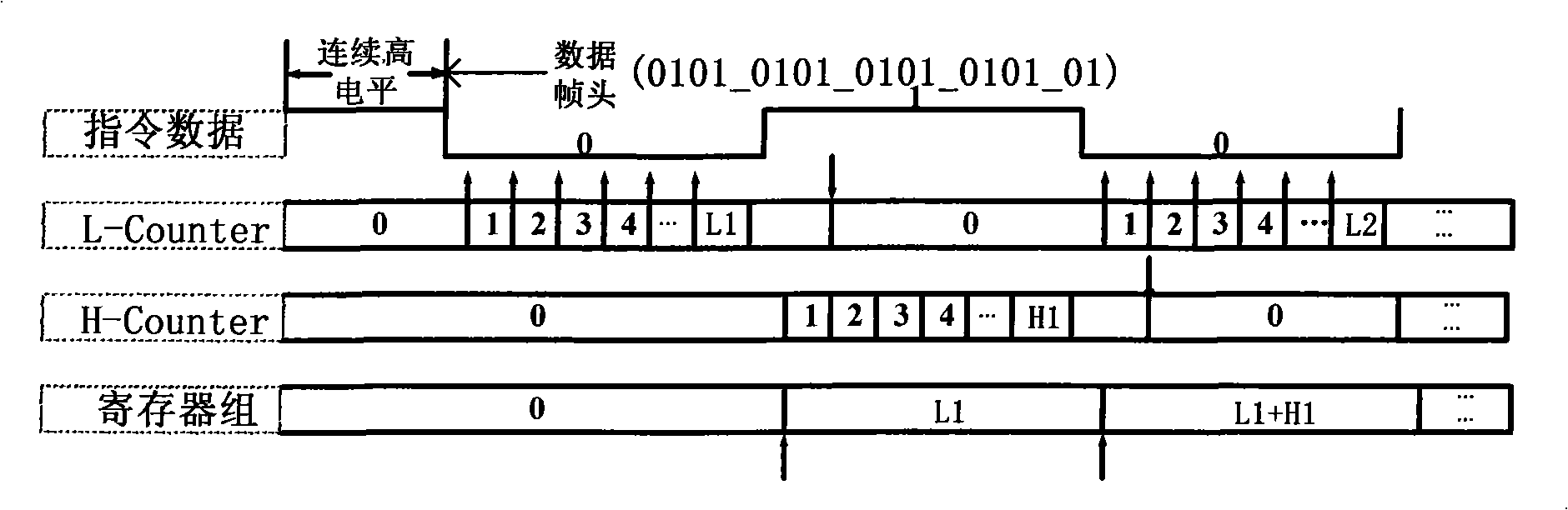
The method provides a method for synchronously receiving data of an RF identification tag chip which is applicable to an ISO / IEC 18000-6 Type B protocol. In the method, two counters are used to respectively count the lengths of a high level and a low level in an instruction format which conform to the ISO / IEC 18000-6 Type B protocol, and an adder matched with the bits of the counter is used to perform an accumulation operation, a synchronous count value is temporarily stored in a register block, and a comparator is used during sampling to compare the count value with a reference value obtained by the accumulation operation and a division operation to give a correct sampling clock edge. The specific method comprises a stage of counting the length of the high level by a high-level counter in a set time; a stage of waiting for an instruction frame header to start; a stage of receiving the instruction frame header; a stage of receiving an identification separator and a stage of receiving sampling data. The method has strong adaptability to low-stability on-chip clocks, a simple circuit realization structure, and just needs two counters, i.e. the adder and the comparator, a plurality of registers and a small state machine controlling the synchronous data flow.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
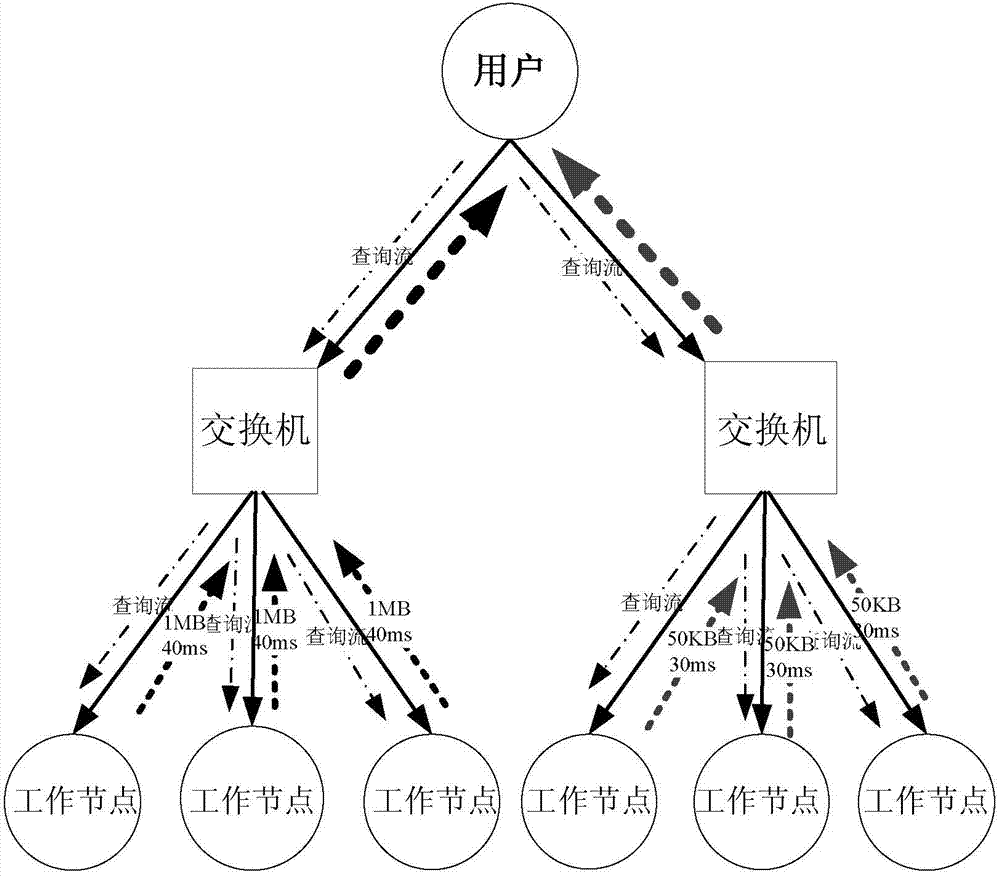
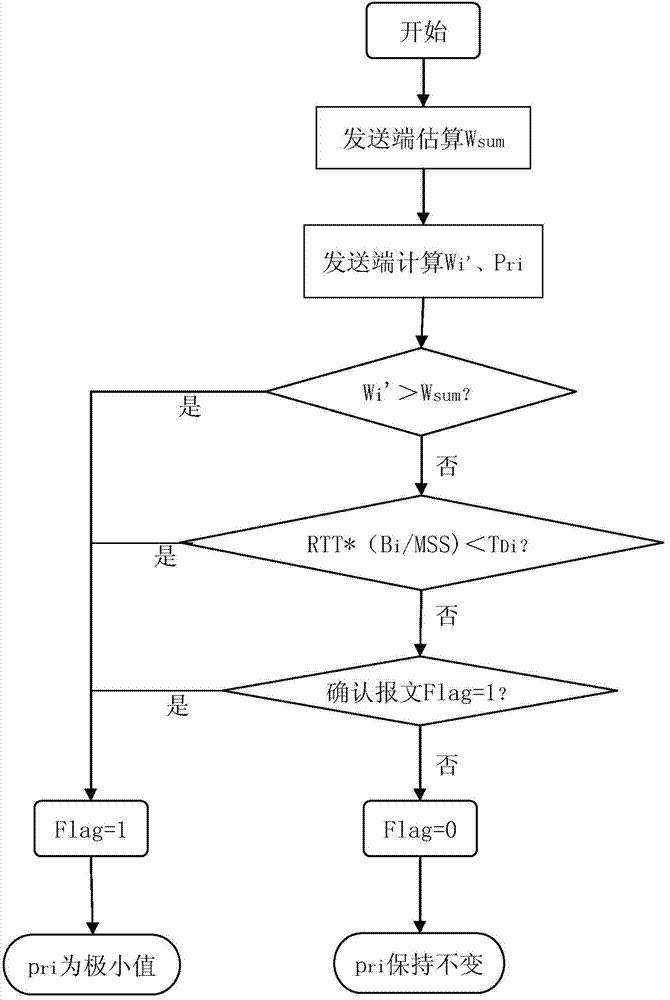
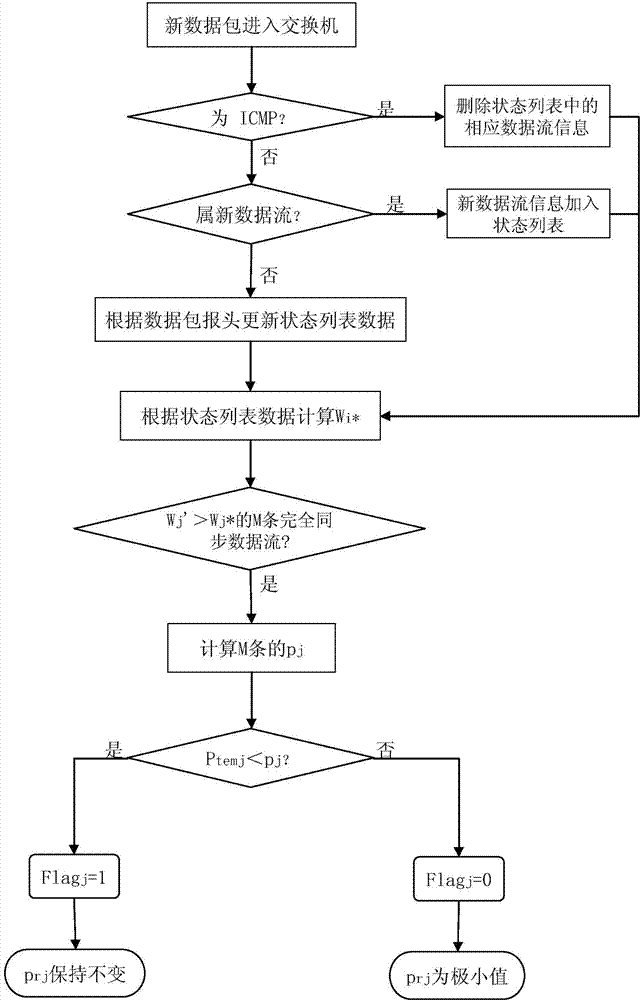
Method for processing synchronous priority bursty flow in data center network
The invention provides a method for processing synchronous priority bursty flow in a data center network. The method comprises the steps that the order of distribution priorities of the data flow is determined according to the magnitude of values of urgency factors pri, the urgency factor pri having the minimal value in a default mode has the lowest priority; an exchanger calculates the speed reduction probability pj for M strips of priority synchronous data flow with request window values larger than expectation window values in the same link; MXpj strips of data flow are randomly selected according to the M strips of data flow, urgency factors prj of the MXpj strips of data flow are regulated into minimal values, sending speed of the MXpj strips of data flow is reduced, and MX(1-pj) strips of data flow of the M strips of data flow are smoothly transmitted under the wire. The method resolves the problem of the synchronous priority bursty flow in the data center network, avoids network congestion, and meanwhile reduces the deadline missing rate.
Owner:广西优耐信息技术有限公司
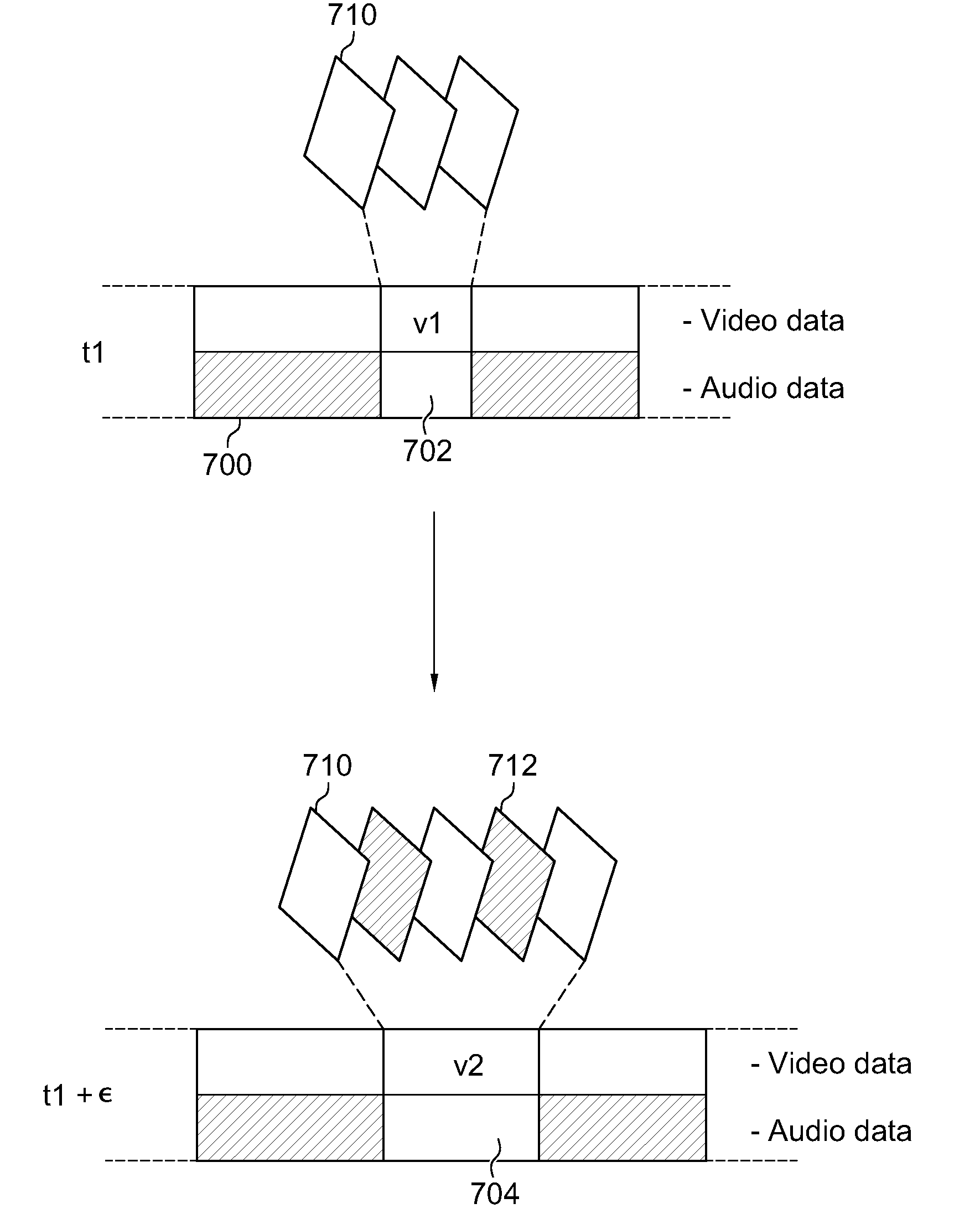
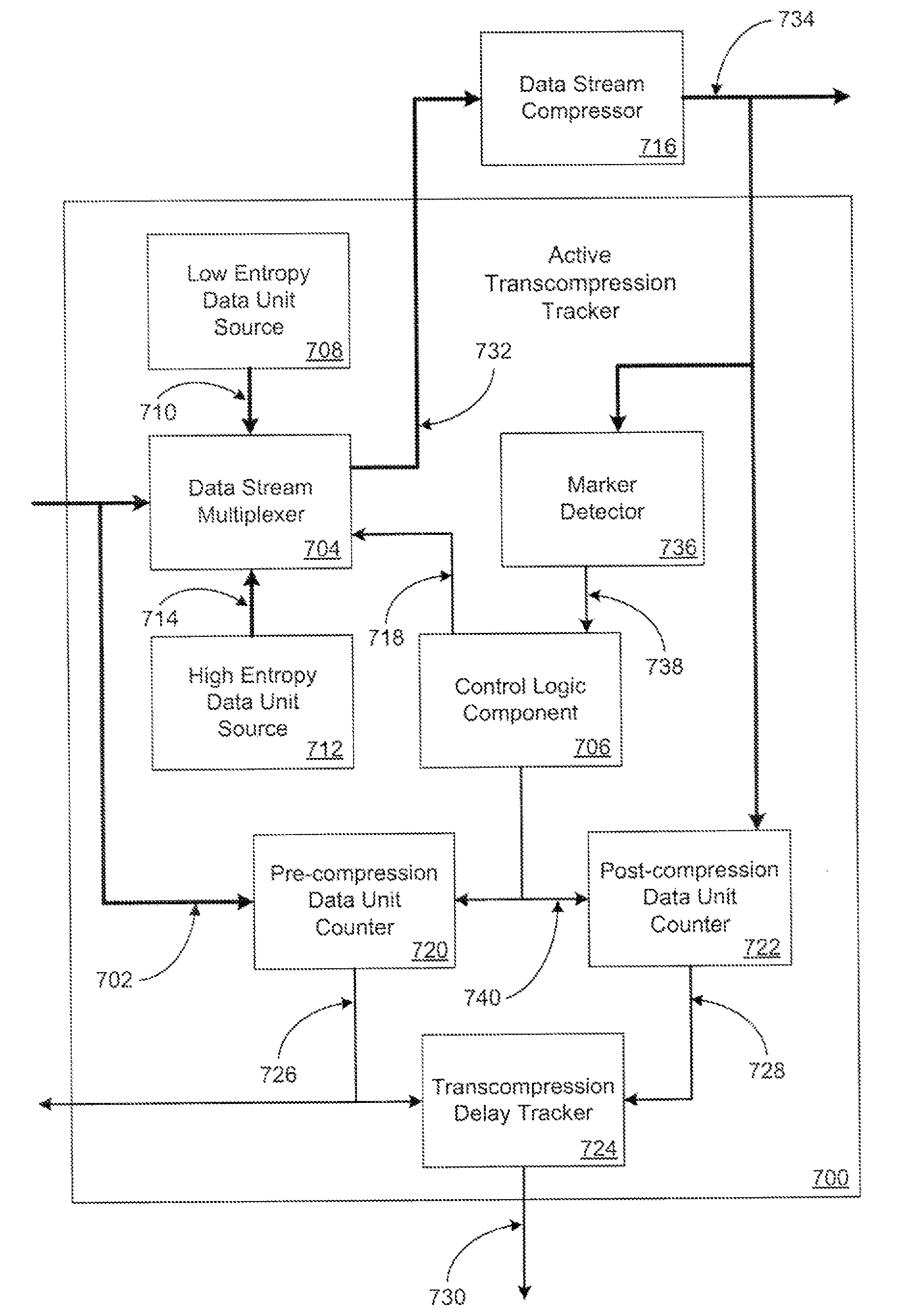
Maintaining synchronization of compressed data and associated metadata
ActiveUS8509315B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData compressionData stream
Synchronization of data streams is enabled. Synchronized data streams may include compressed data streams. Conventional data compression components may be utilized to generate the compressed data streams. As an example, compressed digitized video and associated metadata may be synchronized in this way. Synchronization may be enabled based on causing data compression components to generate detectable data units. For example, patterns of data units having well characterized entropies may be passed through data compression components to generate detectable patterns of compressed data units.
Owner:VIASAT INC
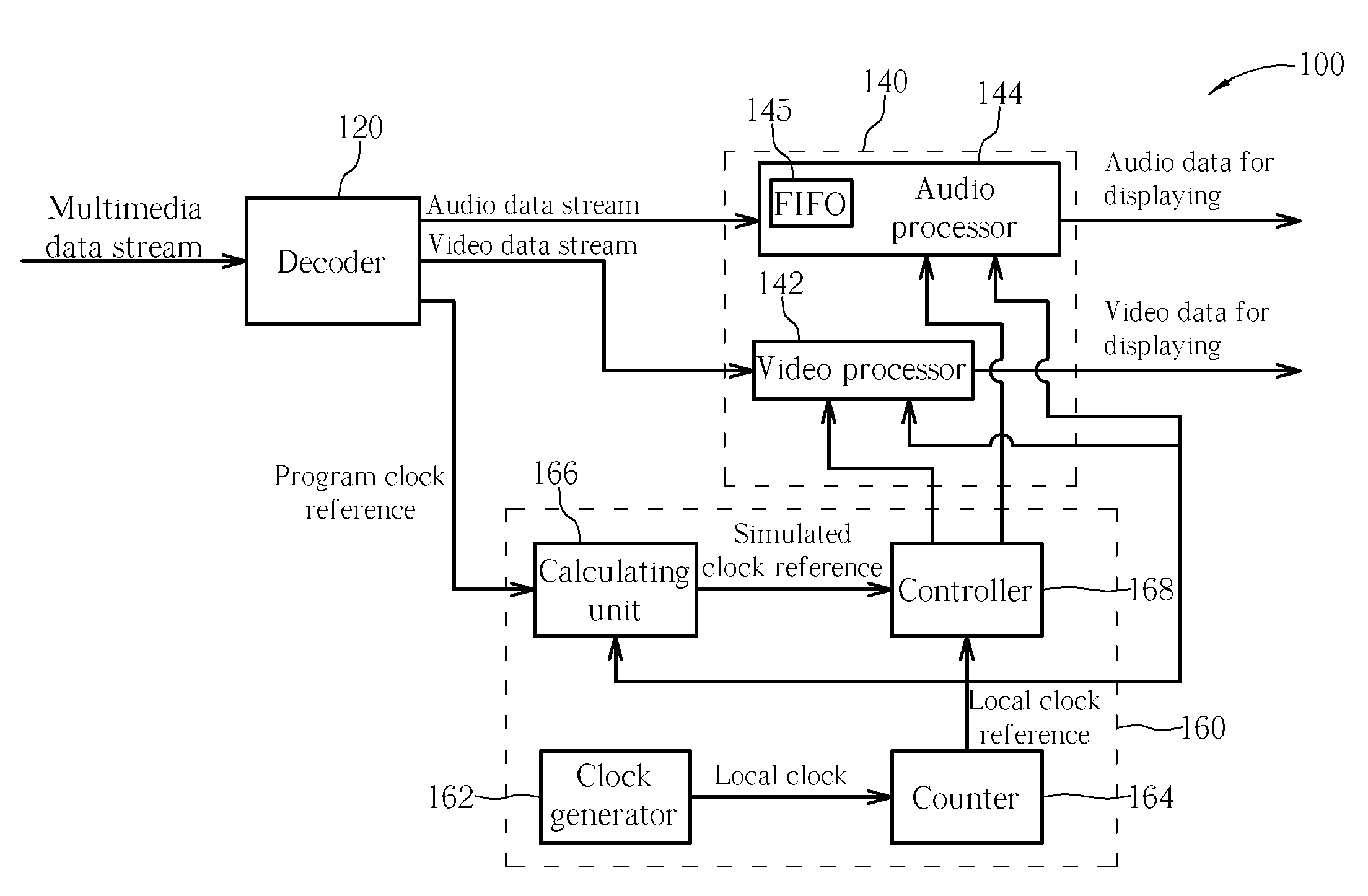
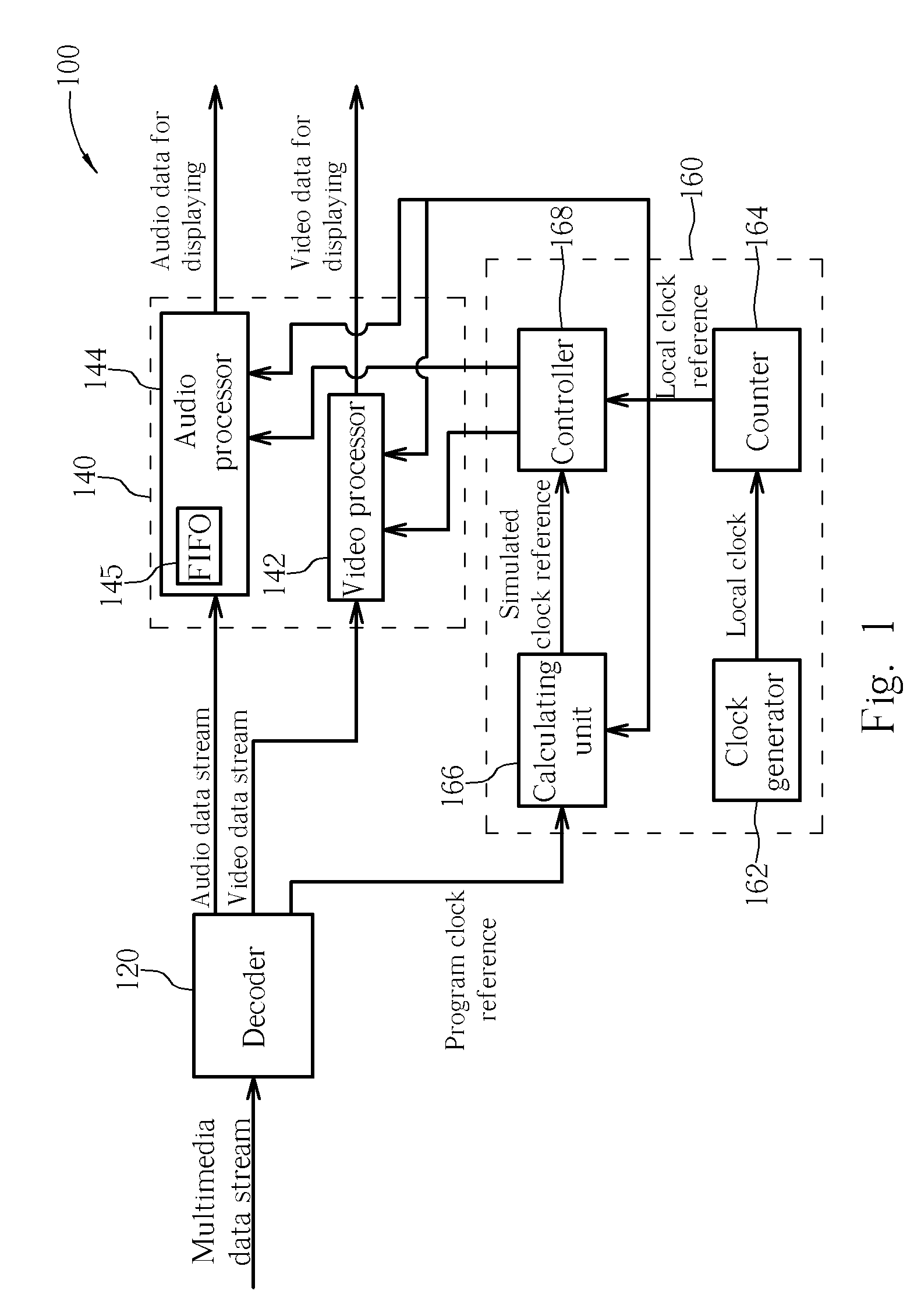
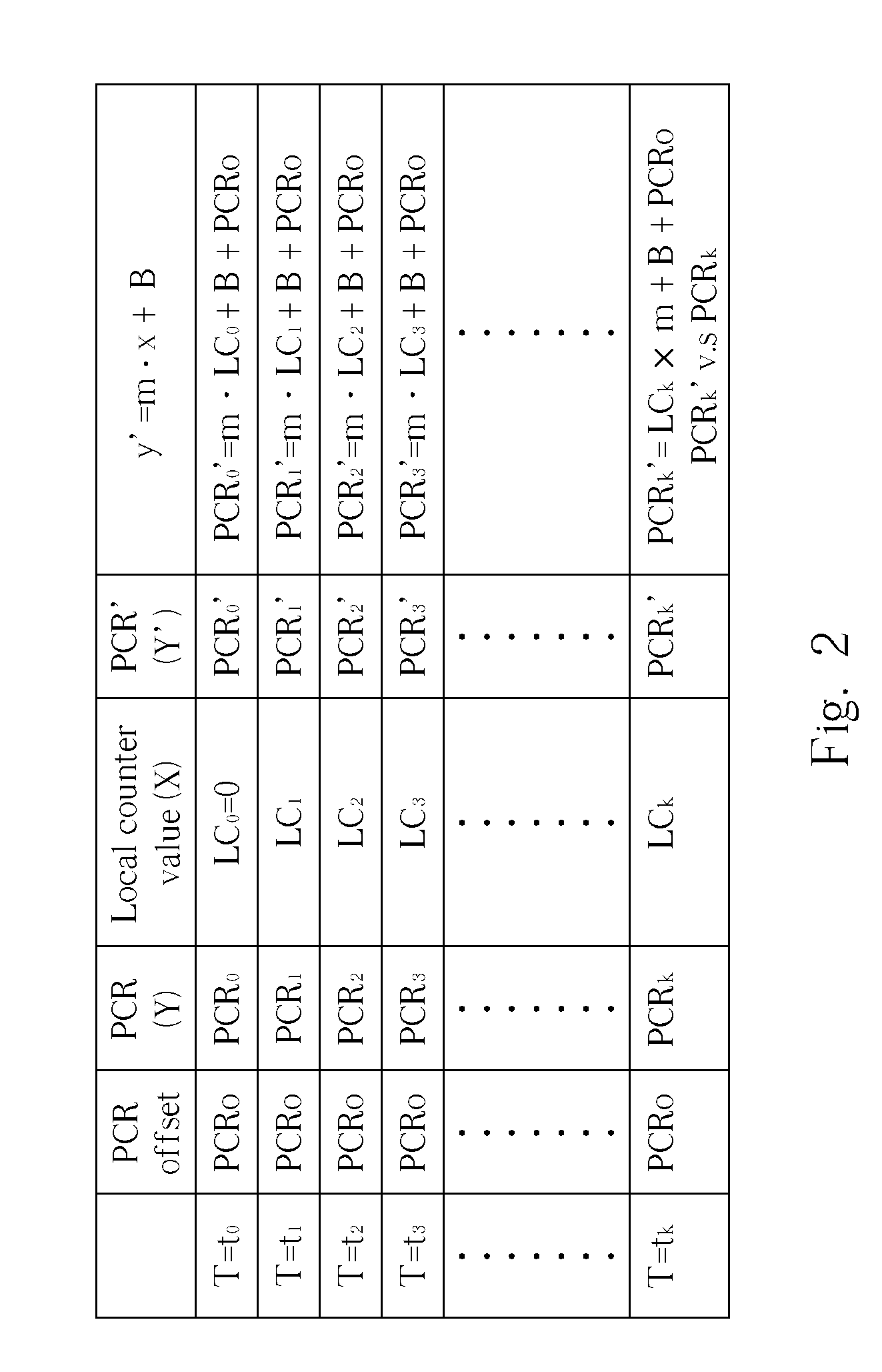
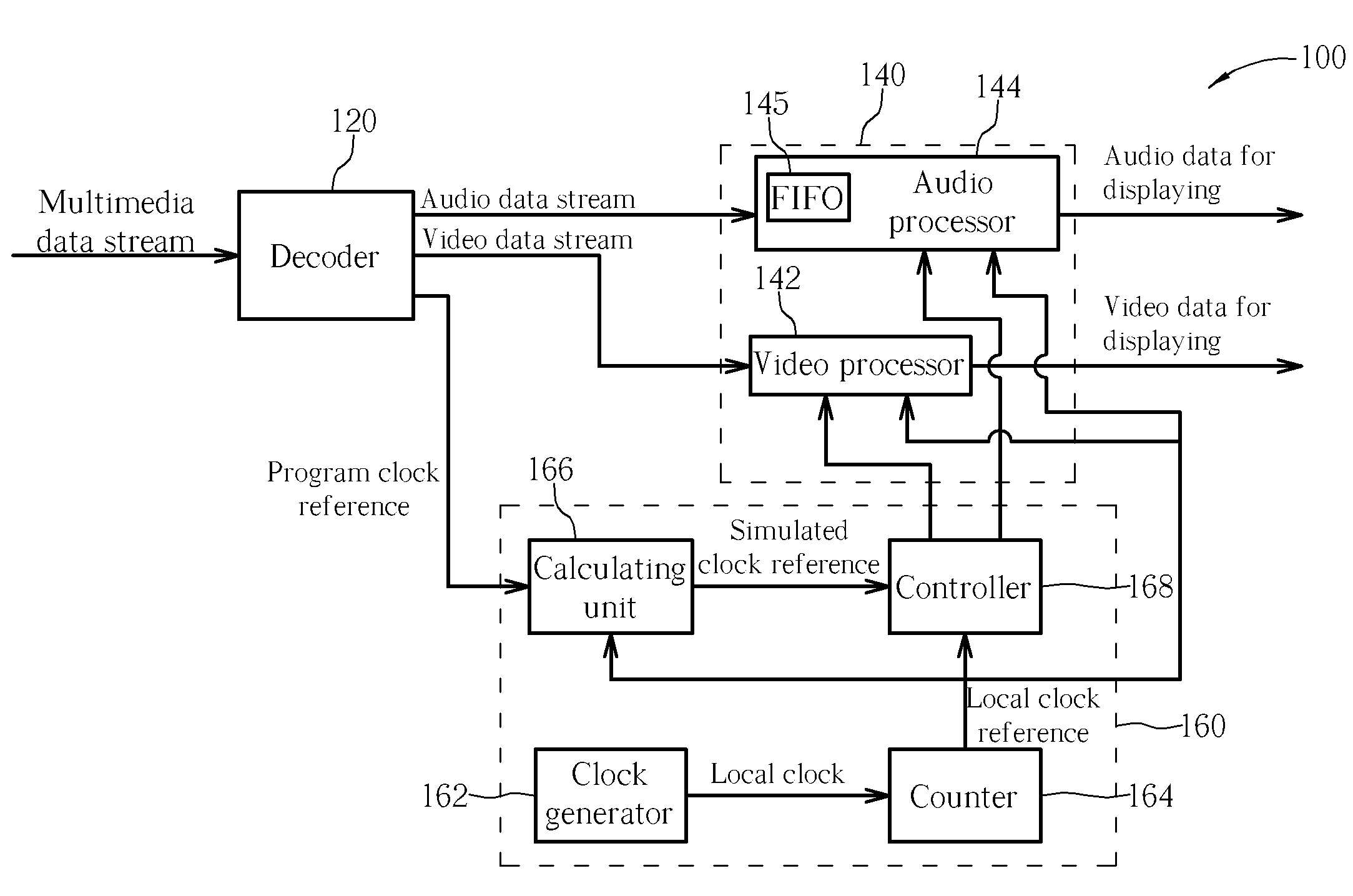
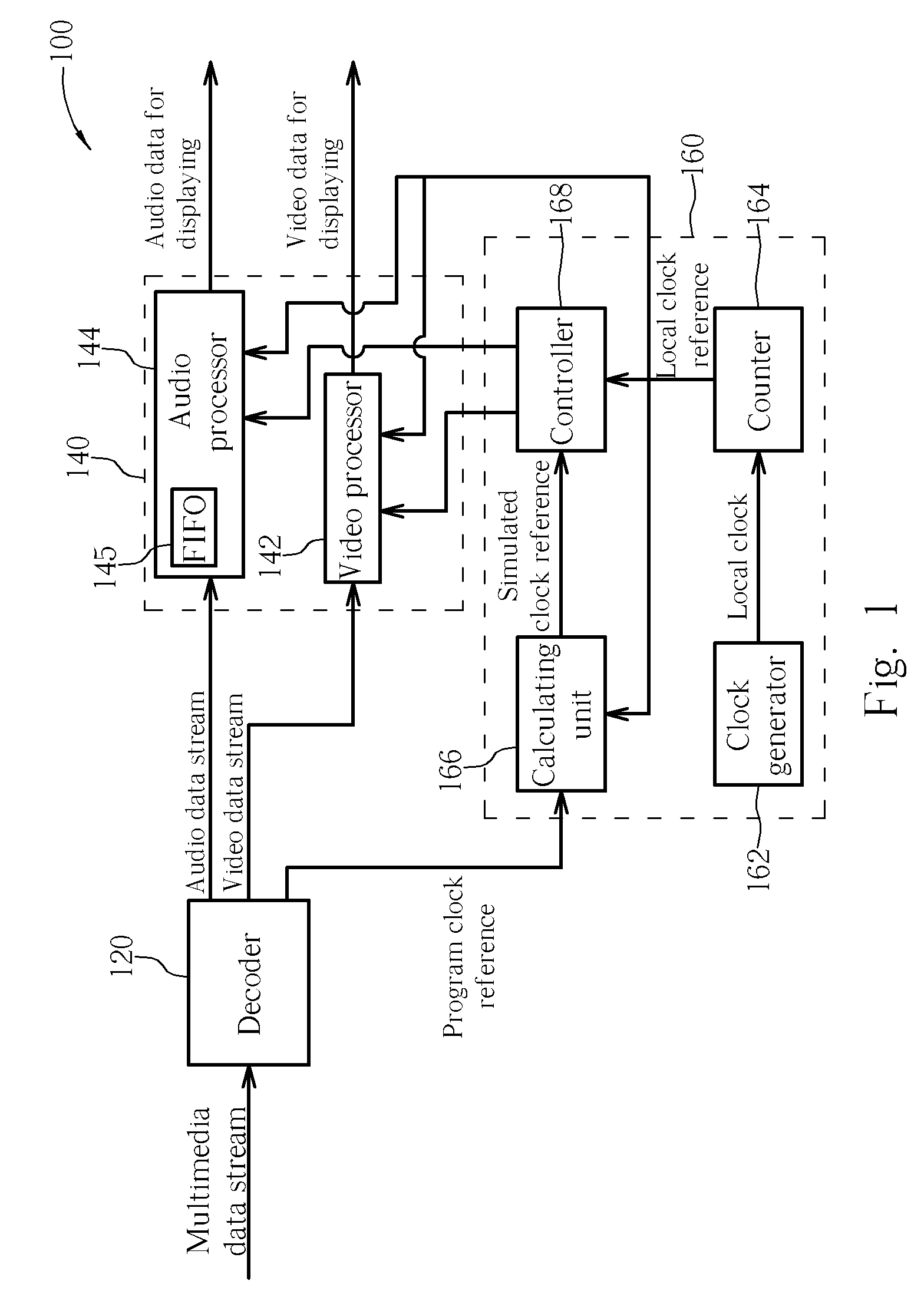
Method and apparatus for synchronizing multimedia data stream
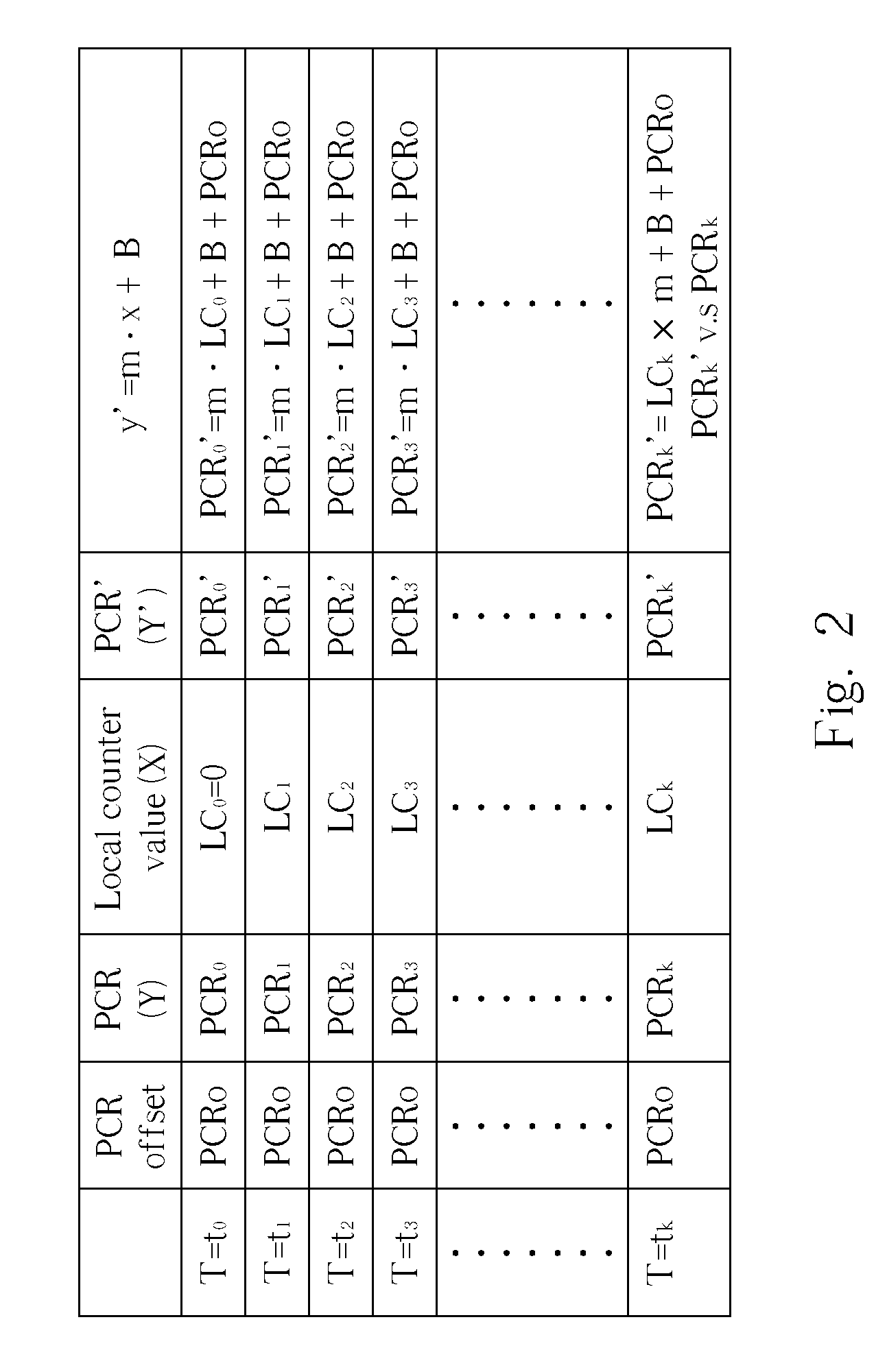
ActiveUS20070013811A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareProgram clock reference
A method and an apparatus for synchronizing a data stream are disclosed. The method includes: decoding the data stream to generate a decoded data stream and program clock references; generating a local clock reference; generating a simulated clock reference according to the program clock references and the local clock reference; comparing the local clock reference with the simulated clock reference to generate a comparison result; adjusting a processing timing of the decoded data stream according to the comparison result; and processing the decoded data stream according to the processing timing.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
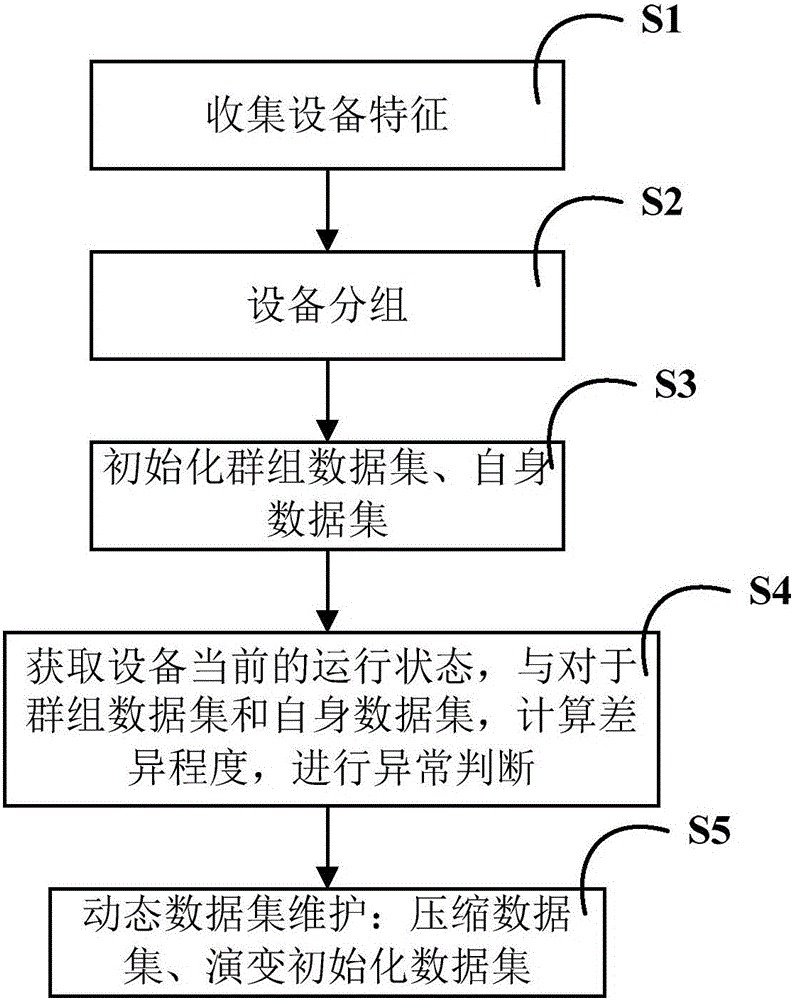
Real-time detection method of equipment exceptions on the basis of synchronous data flow compression
InactiveCN106126385AAbnormal real-time detectionImprove accuracyHardware monitoringData setAnomaly detection
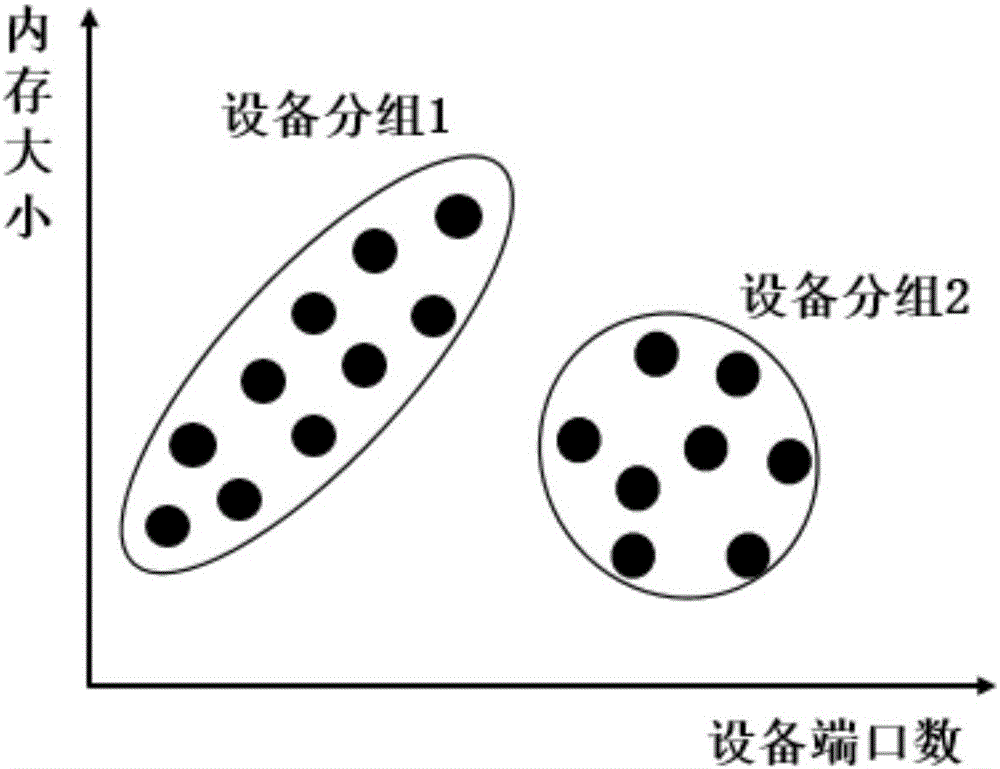
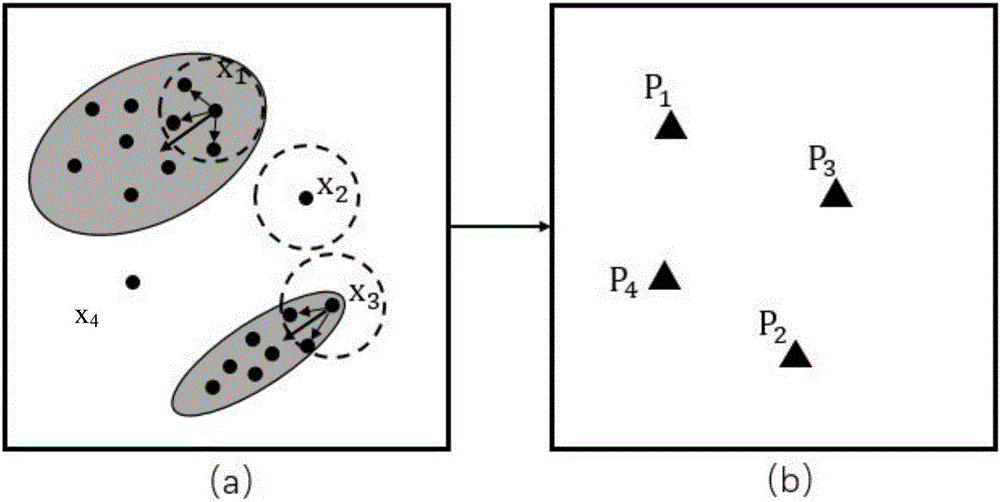
The invention discloses a real-time detection method of equipment exceptions on the basis of synchronous data flow compression. The characteristics of each piece of equipment are collected and are grouped, a group dataset which represents the normal operation state of the group of equipment and an own dataset which represents the normal operation state of the equipment are constructed, so that the records of the two datasets are compared to comprehensively obtain an exception detection result, and detection accuracy is improved. Meanwhile, since the operation states of the equipment are different under different environments, a concept drifting detection method based on principal component analysis is adopted to detect operation state data, whether the operation state data is evolved or not is judged, the two datasets are initialized again if the operation state data is evolved, and therefore, detection accuracy is further improved. In addition, the synchronous data flow compression is adopted to reduce a calculated amount of a comparison process so as to realize the real-time detection of the equipment exceptions.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fast classification method, method and device for EEG signals based on FPGA
InactiveCN109376843AEnable configurabilityIncrease flexibilityBiological neural network modelsSignal classificationClassification methods
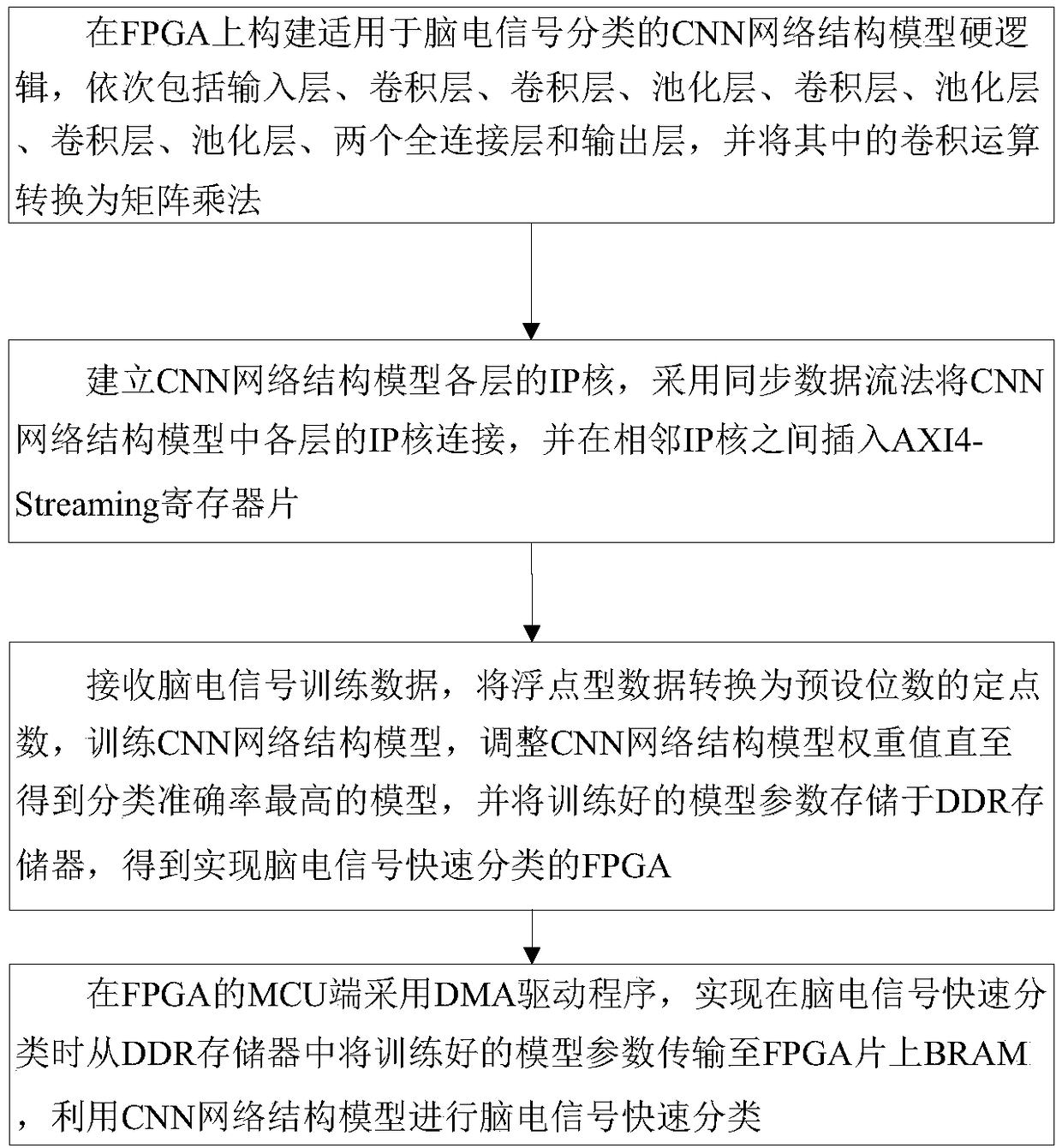
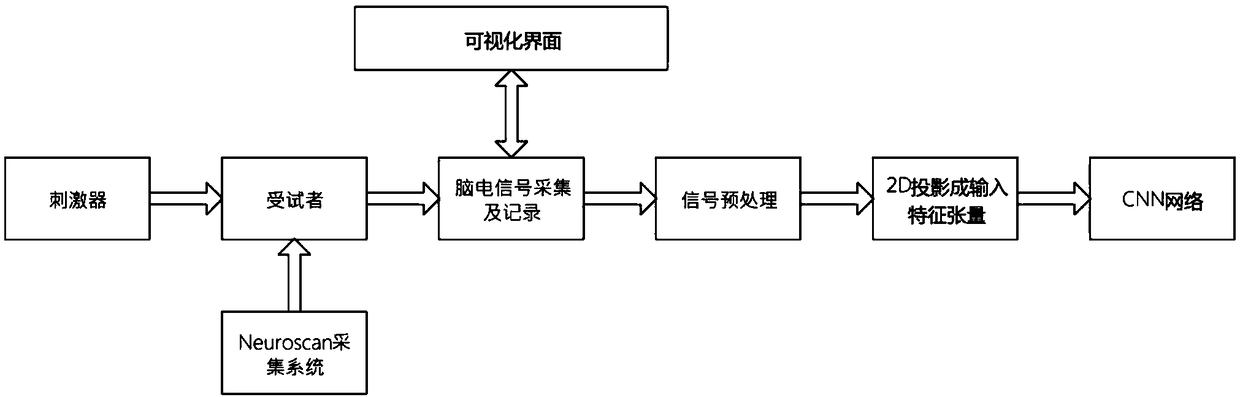
The invention discloses a fast classification method of EEG signals based on FPGA, a realization method and a device thereof. The hard logic of a CNN network structure model suitable for the classification of EEG signals is constructed on FPGA, and the convolution operation is converted into matrix multiplication. The IP cores of each layer in the CNN network structure model are established, and the IP cores of each layer in the CNN network structure model are connected by using the synchronous data flow method, and AXI4-Streaming register chip is inserted between the adjacent IP cores; the EEG training data is received, the floating-point data is converted to a fixed-point number with a preset number of bits, training the CNN network structure model, adjusting the CNN network structure model weight value until the highest classification accuracy model is obtained, and the trained model parameters are stored in DDR memory, so as to obtain FPGA which can realize the fast classificationof EEG signals, and the fast classification of EEG signals is carried out by using the CNN network structure model.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
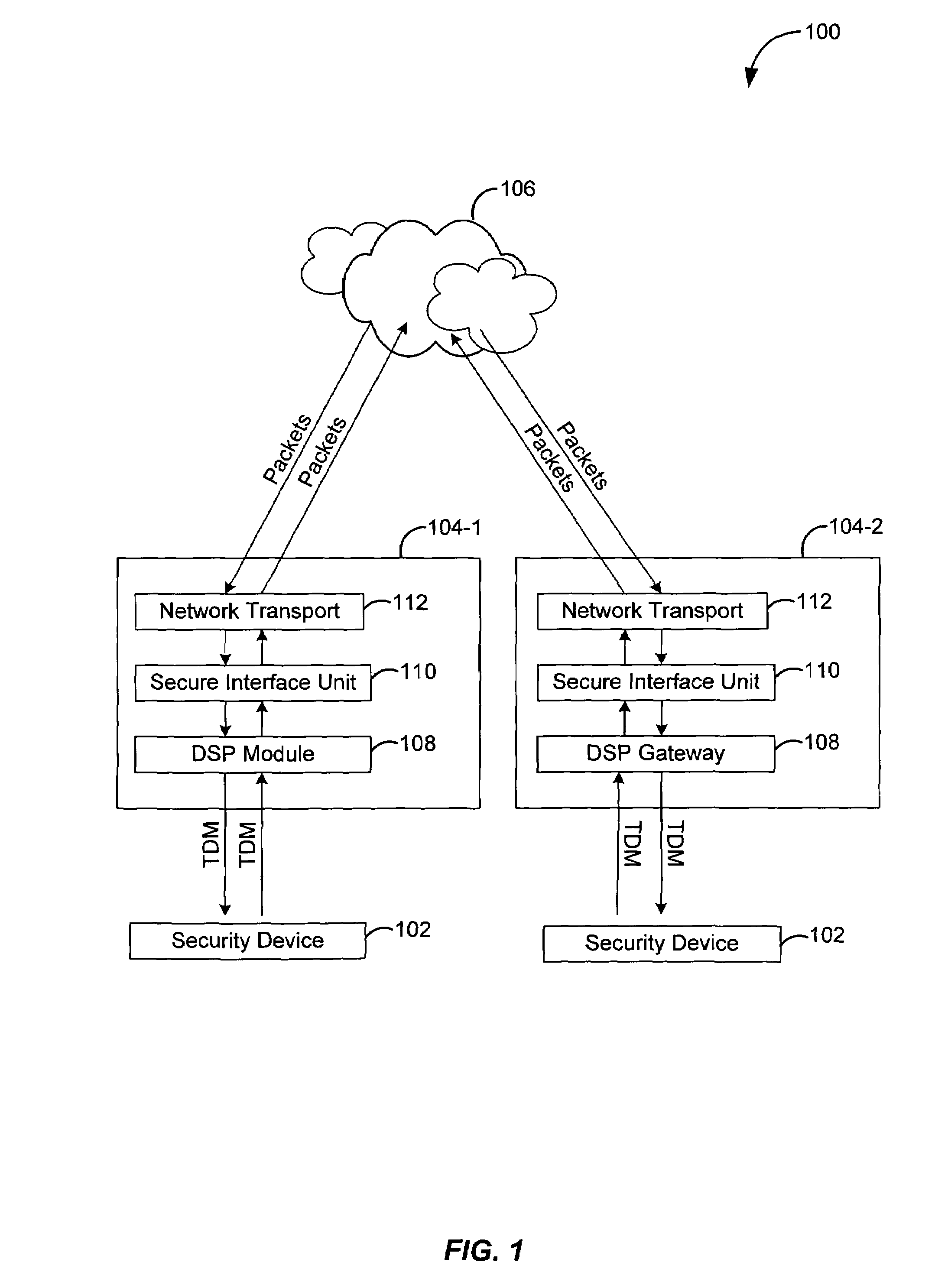
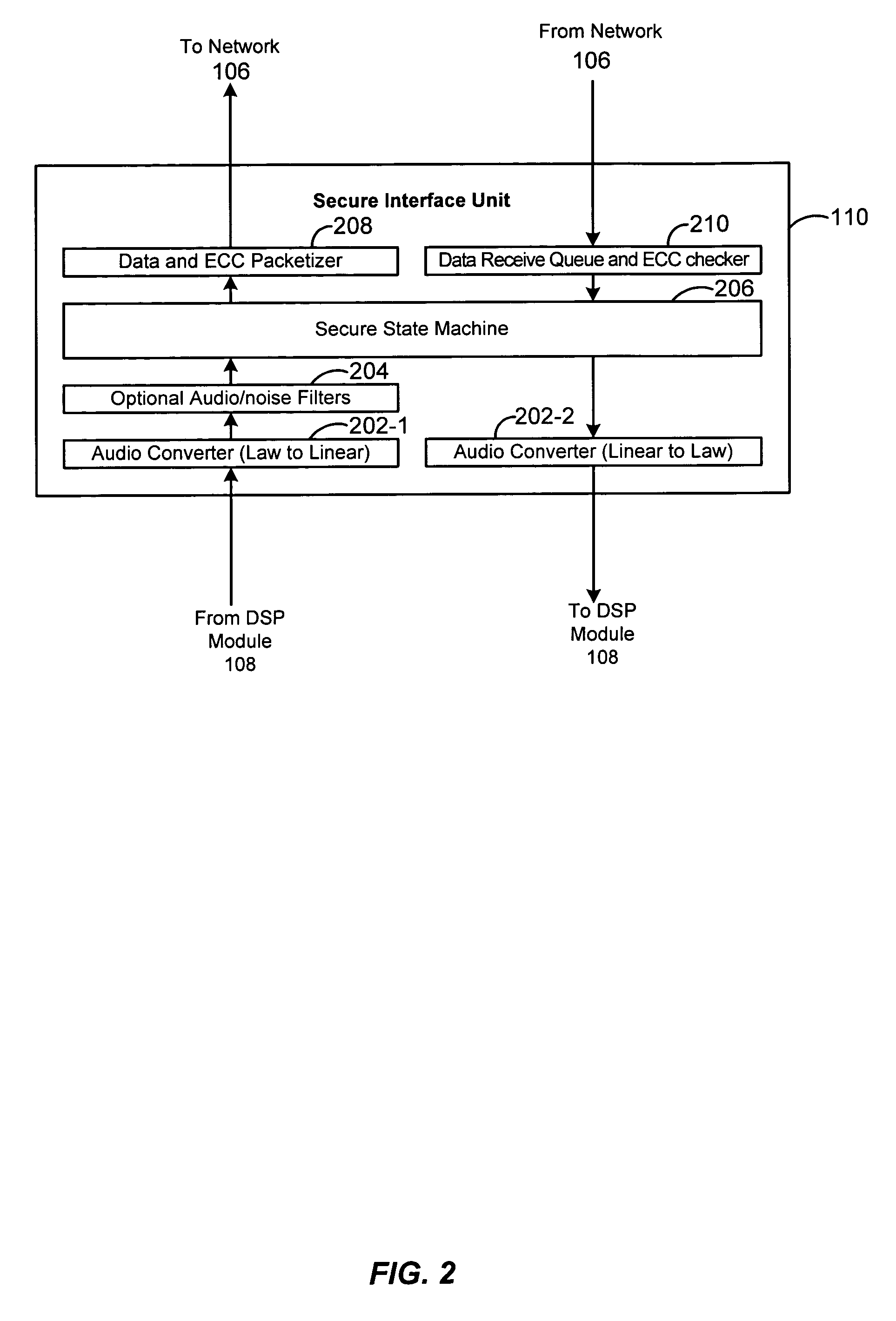
Techniques for asynchronous compensation for secure communications
Techniques for compensating for synchronous data stream transported over an asynchronous system are provided. The techniques include compensating for network jitter for an asynchronous connection over an asynchronous transport, using frame slip control for compensating for a synchronous connection over an asynchronous transport, and dropping filler frames for compensating for a synchronous connection over an asynchronous transport.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
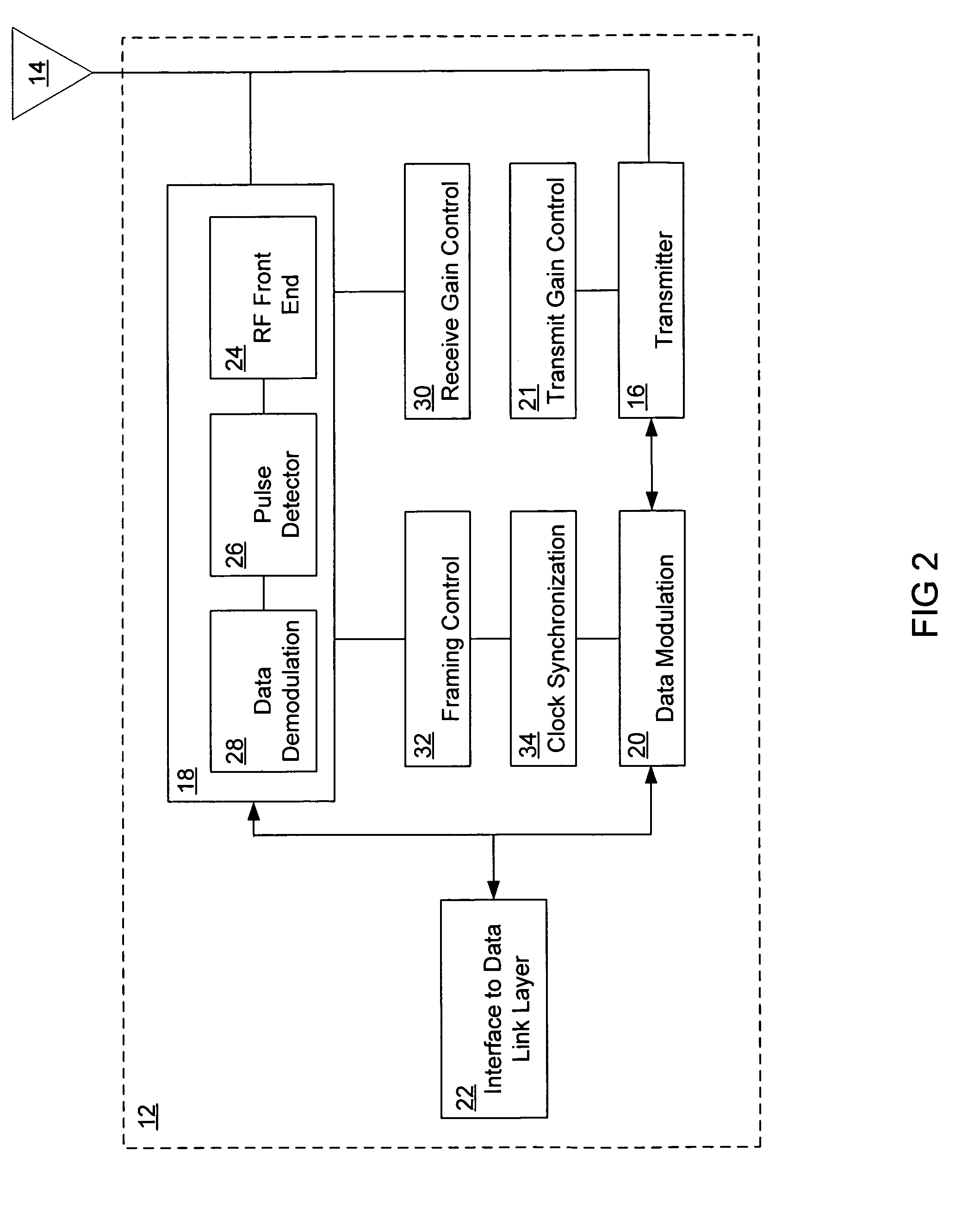
Clock synchronization of data streams
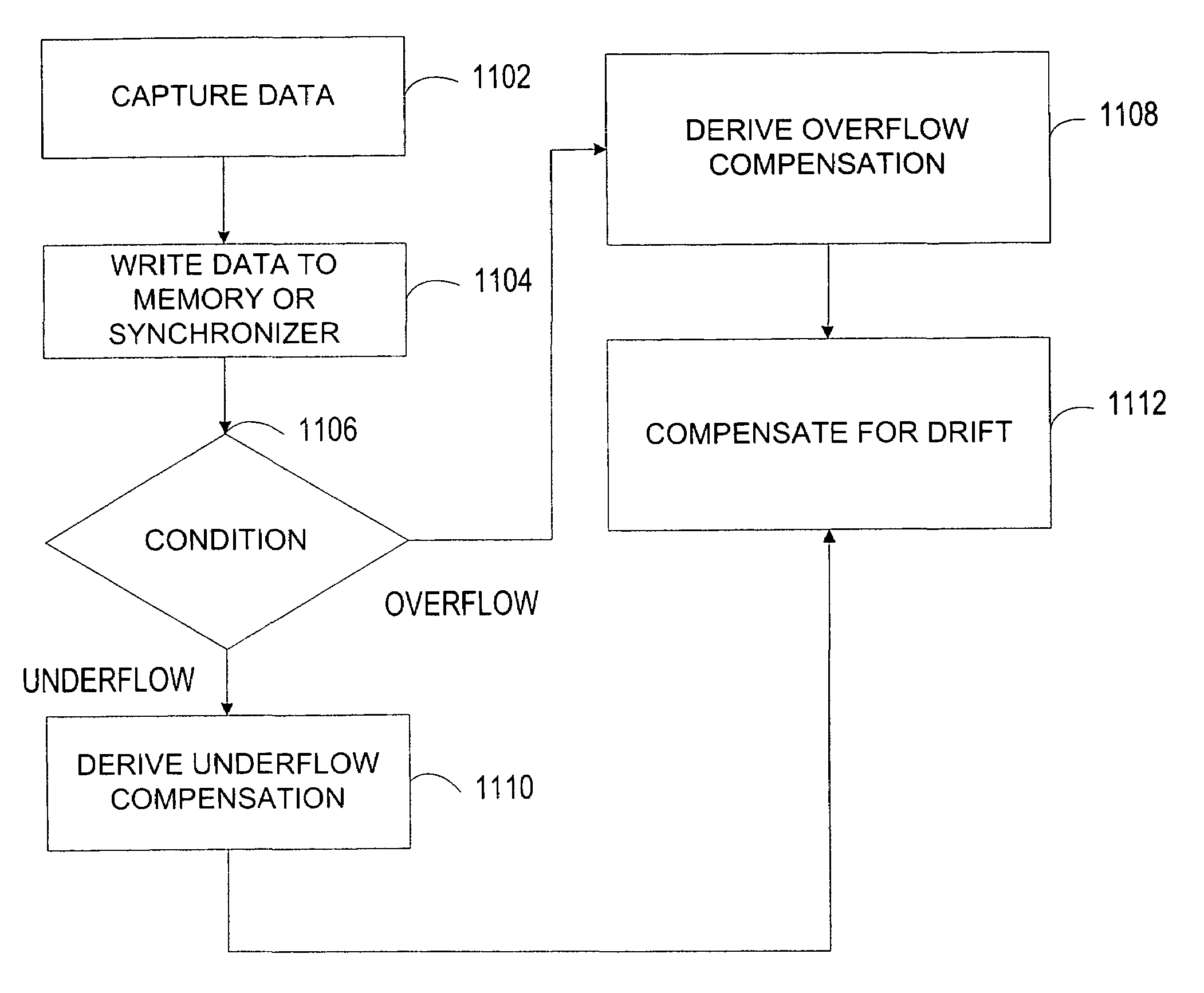
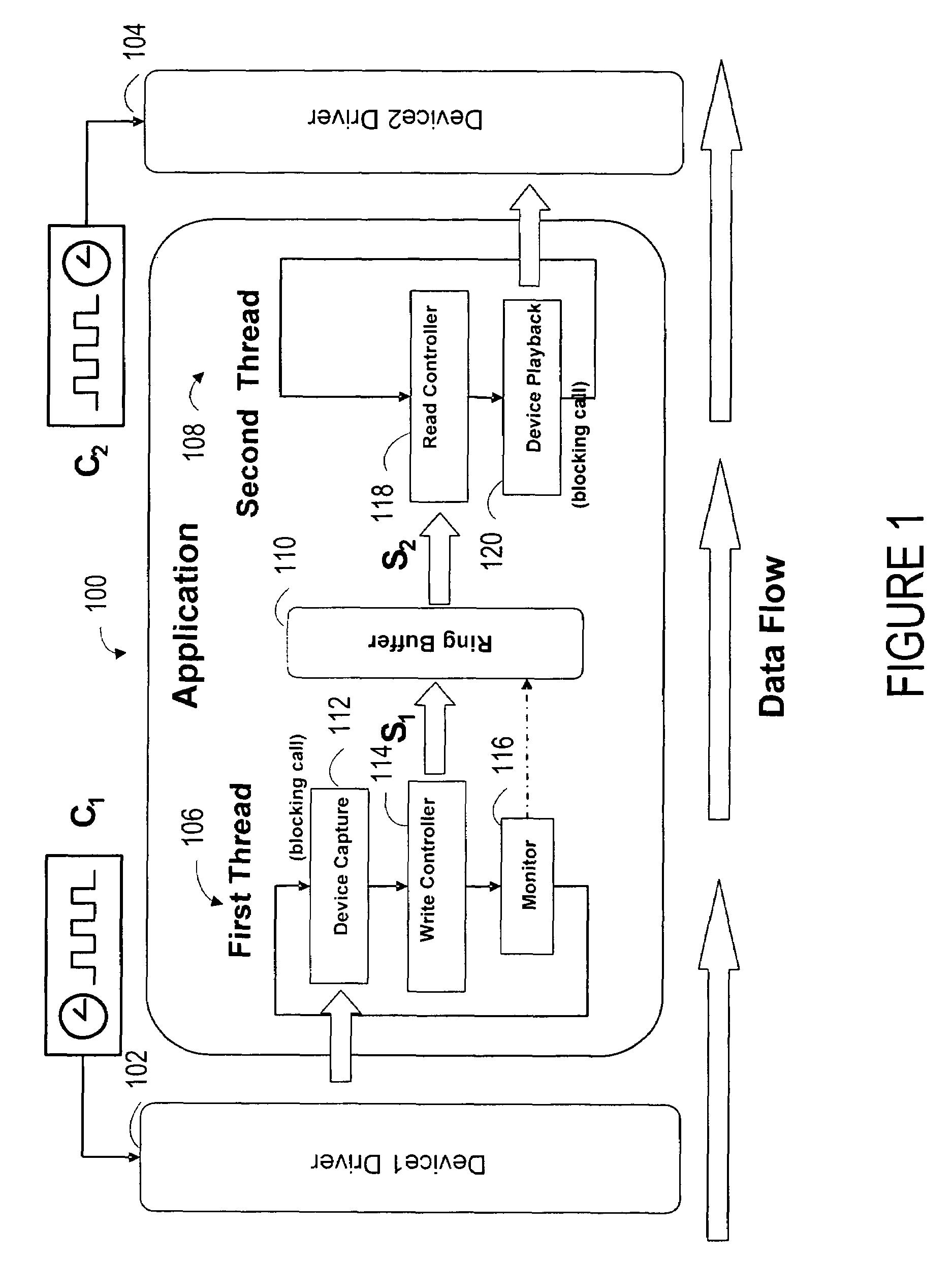
ActiveUS20080043276A1Synchronisation signal speed/phase controlDigital output to print unitsComputer hardwareData stream
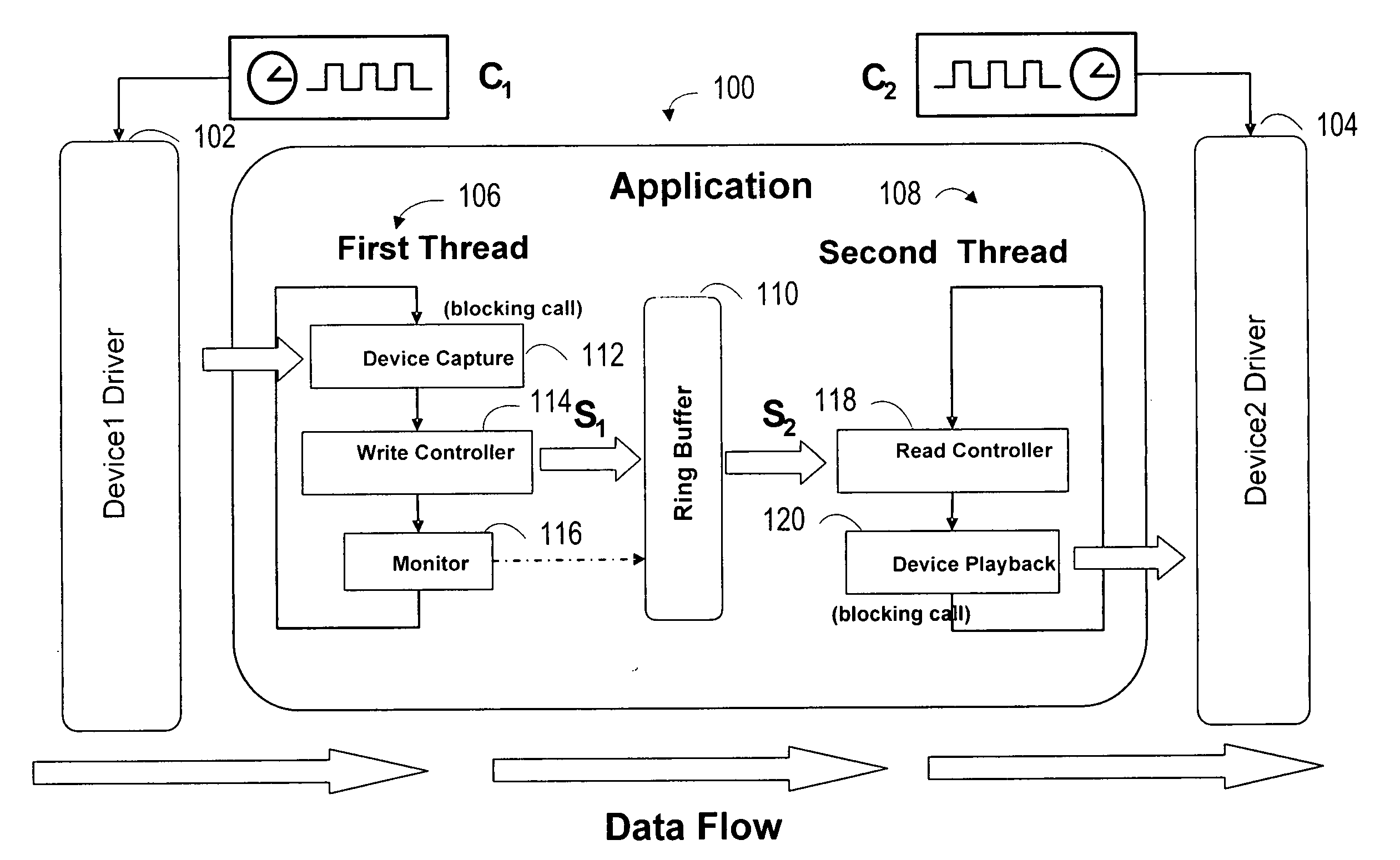
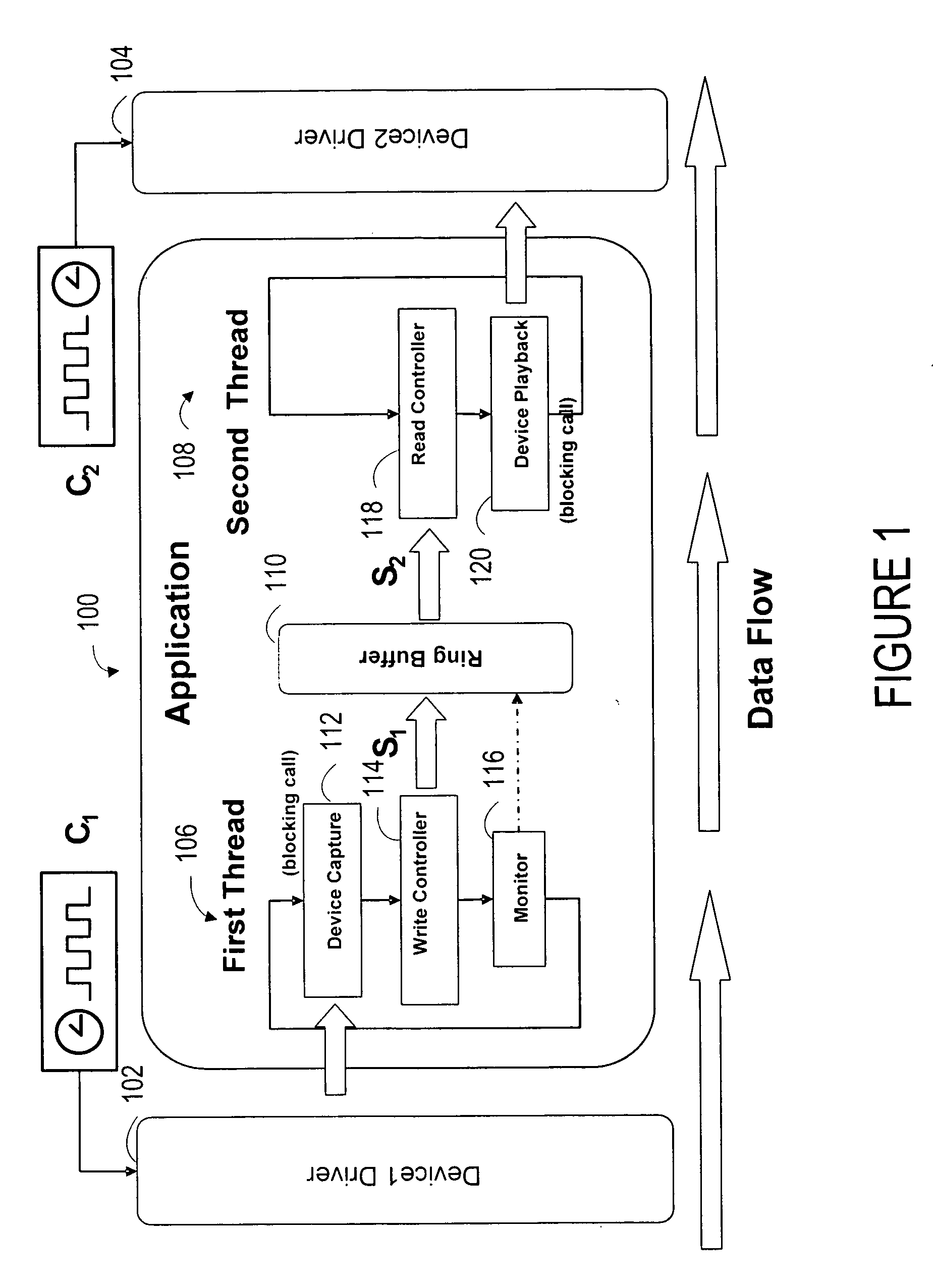
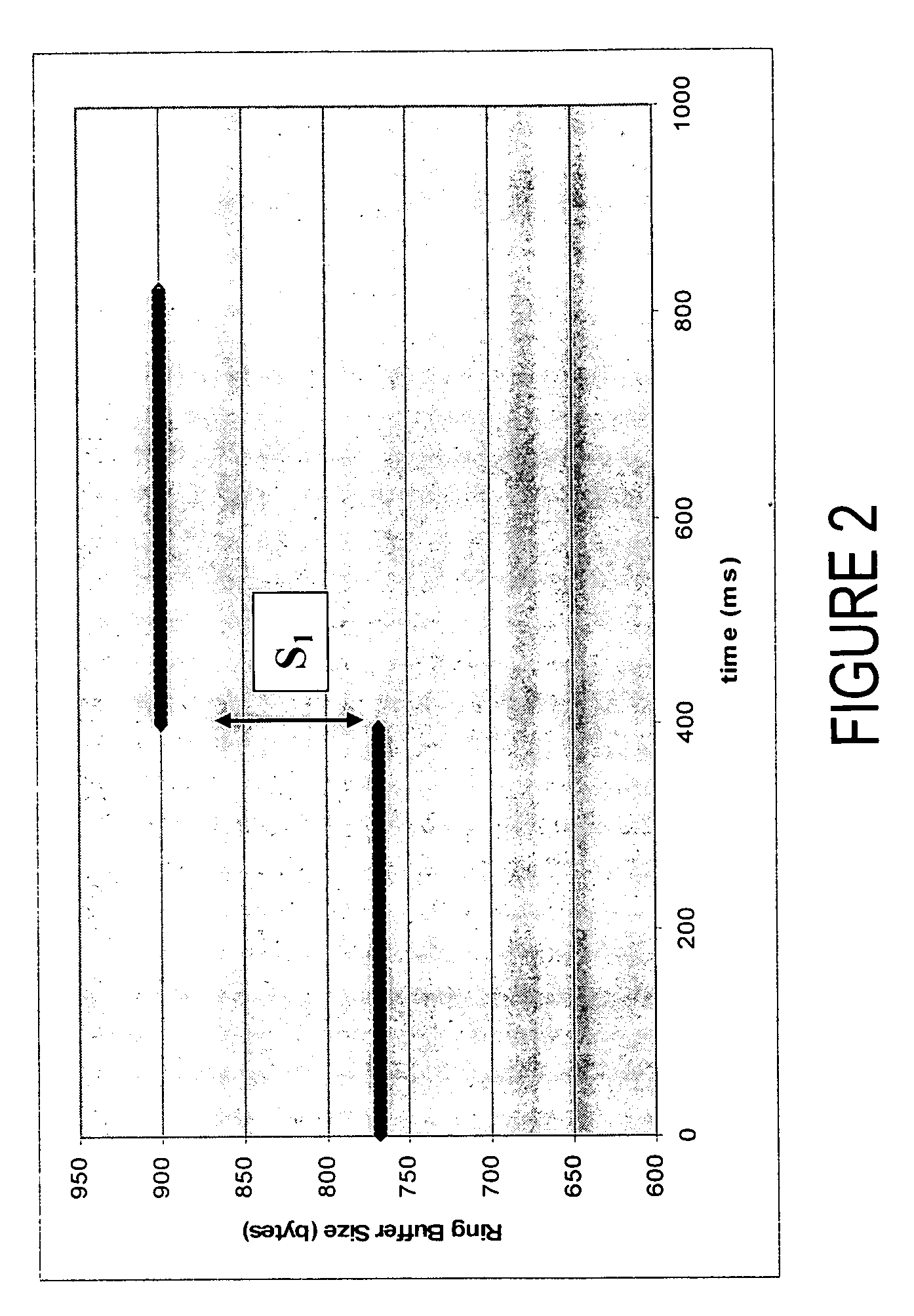
A system synchronizes data flow between a first device and a second device. The system includes a data link that connects two or more devices that are capable of sending and receiving data through a bus. A capture device senses and transfer information through the bus. A ring buffer temporarily stores data transmitted through the bus. A read controller copies or reconstructs data in a length that is different from the length of the data received. A monitor detects underflow or overflow conditions into or out of the ring buffer and compensates for clock drift.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
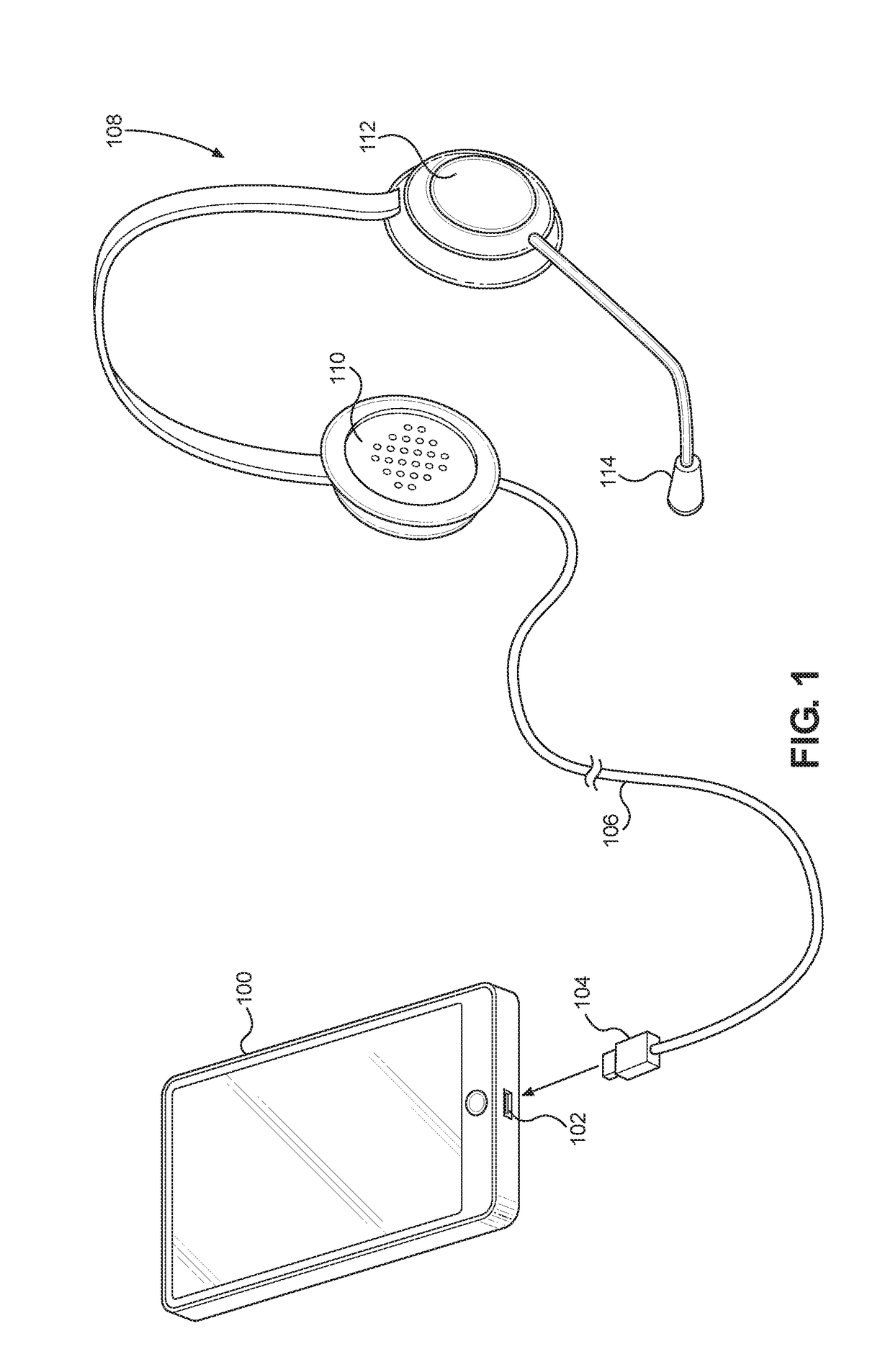
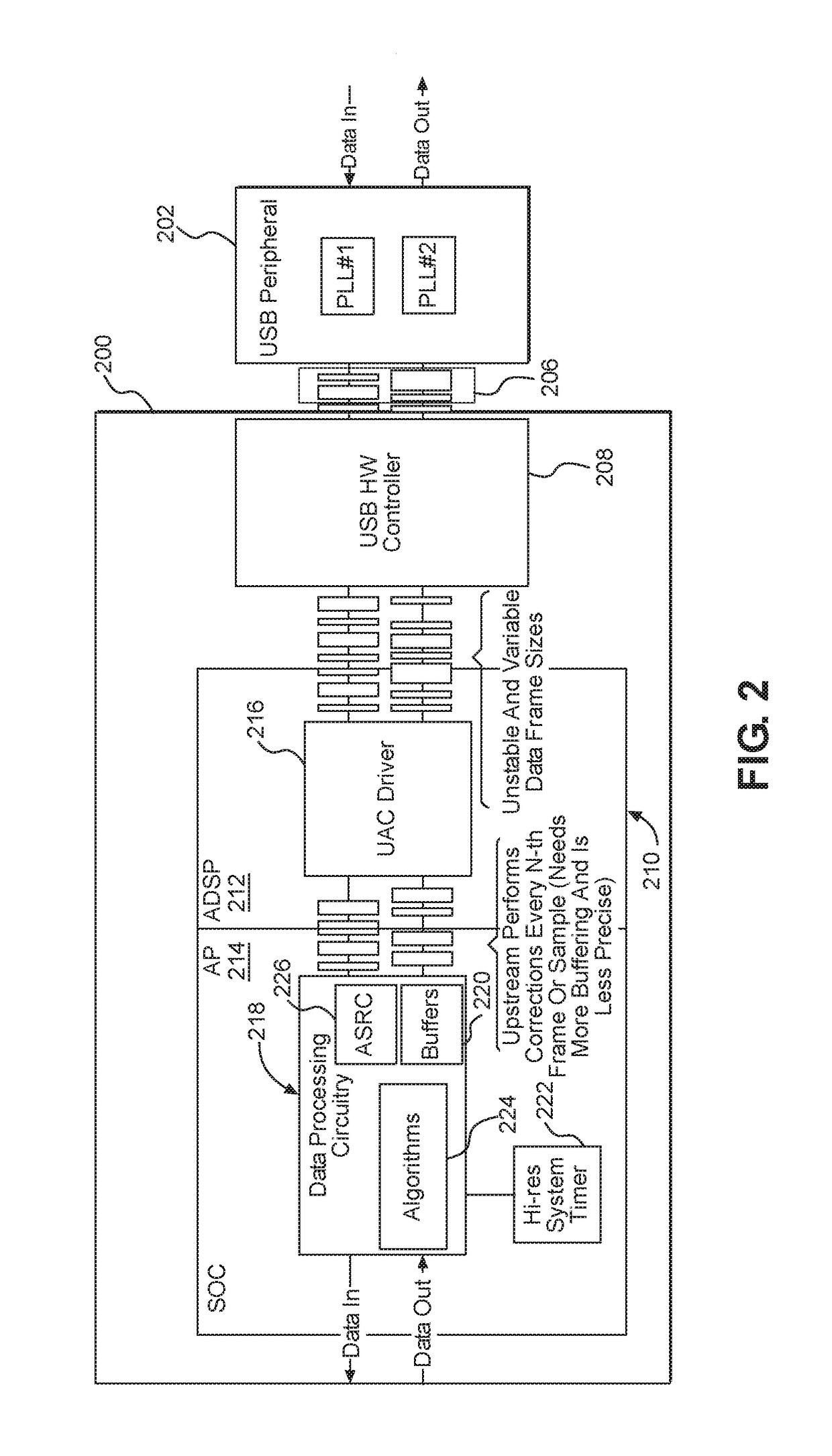
Systems and methods for controlling isochronous data streams
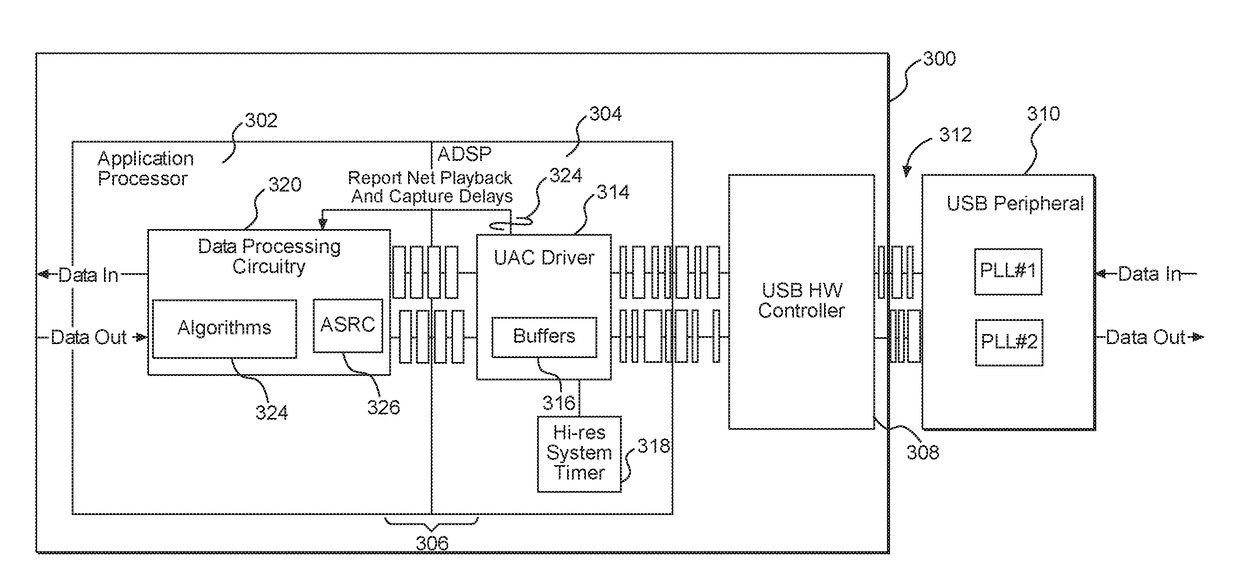
InactiveUS20170373881A1Improve user experienceEliminate needTime-division multiplexEnergy efficient computingData streamSystem time
Systems and methods for controlling isochronous data streams are disclosed. Particular aspects of the present disclosure are designed to be used with almost any isochronous data stream, but are well-suited for use with the Universal Serial Bus (USB) protocol. Further, aspects of the present disclosure are flexible to accommodate existing configuration possibilities within the USB protocol as well as accommodate proposed future changes in the USB protocol. The flexibility of the systems and methods is provided by calculating: (1) drift between a USB host system time and the application and (2) drift between the USB host system and a USB device clock. Based on these two drift calculations, a time stamp may be synthesized to program a next delivery schedule. Using this time stamp, jitter correction can take place and uniformly-sized packets may be assembled to pass to an application processor.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Bit slicer system and method for synchronizing data streams
InactiveUS20050031055A1Less latencyDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsShift registerData stream
Owner:INDESIGN
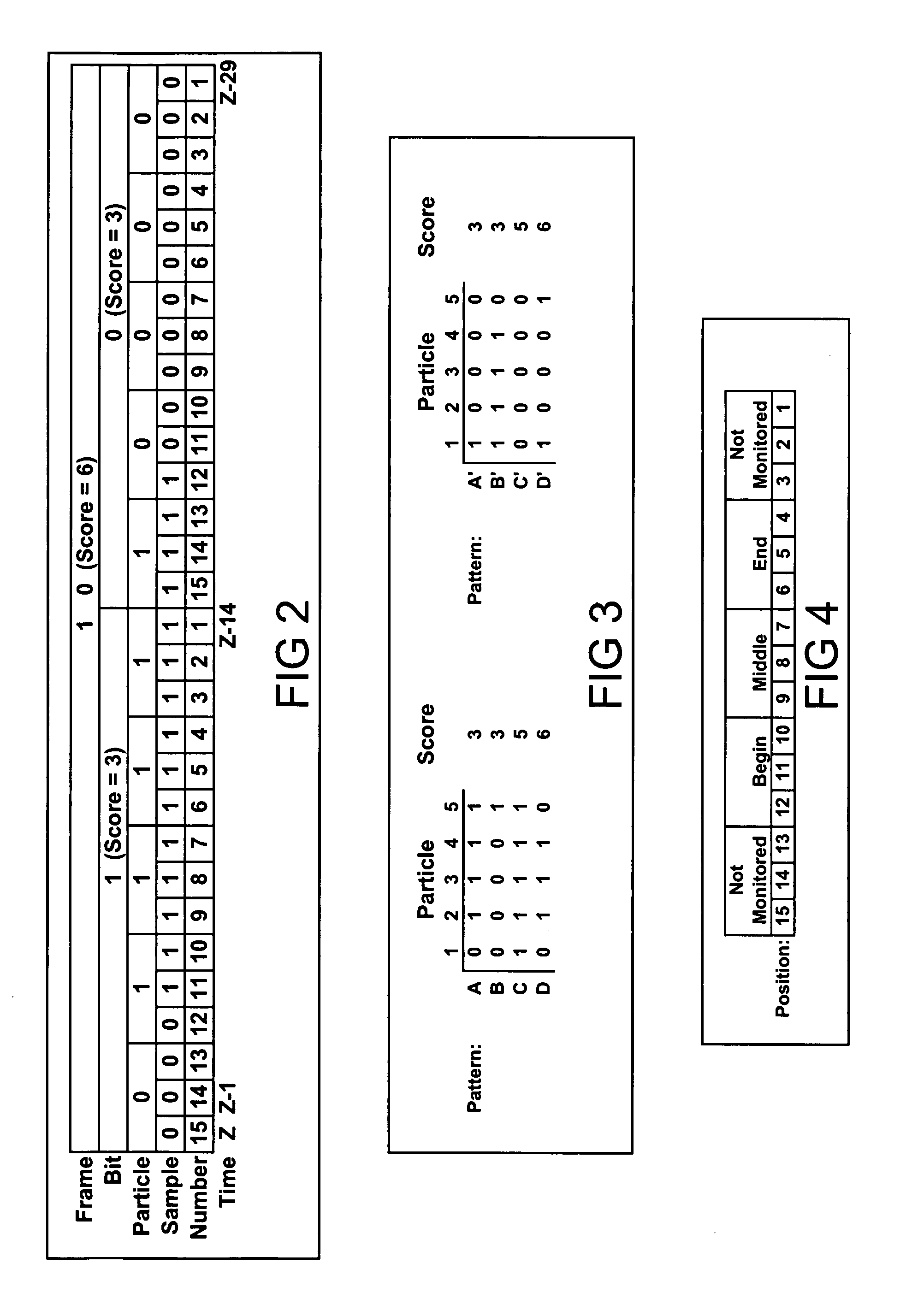
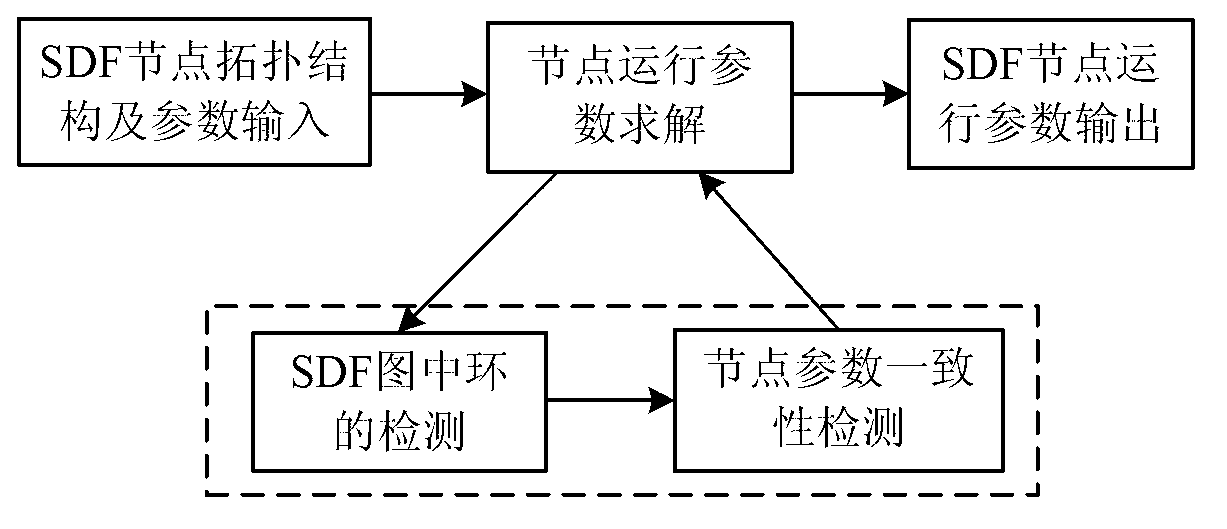
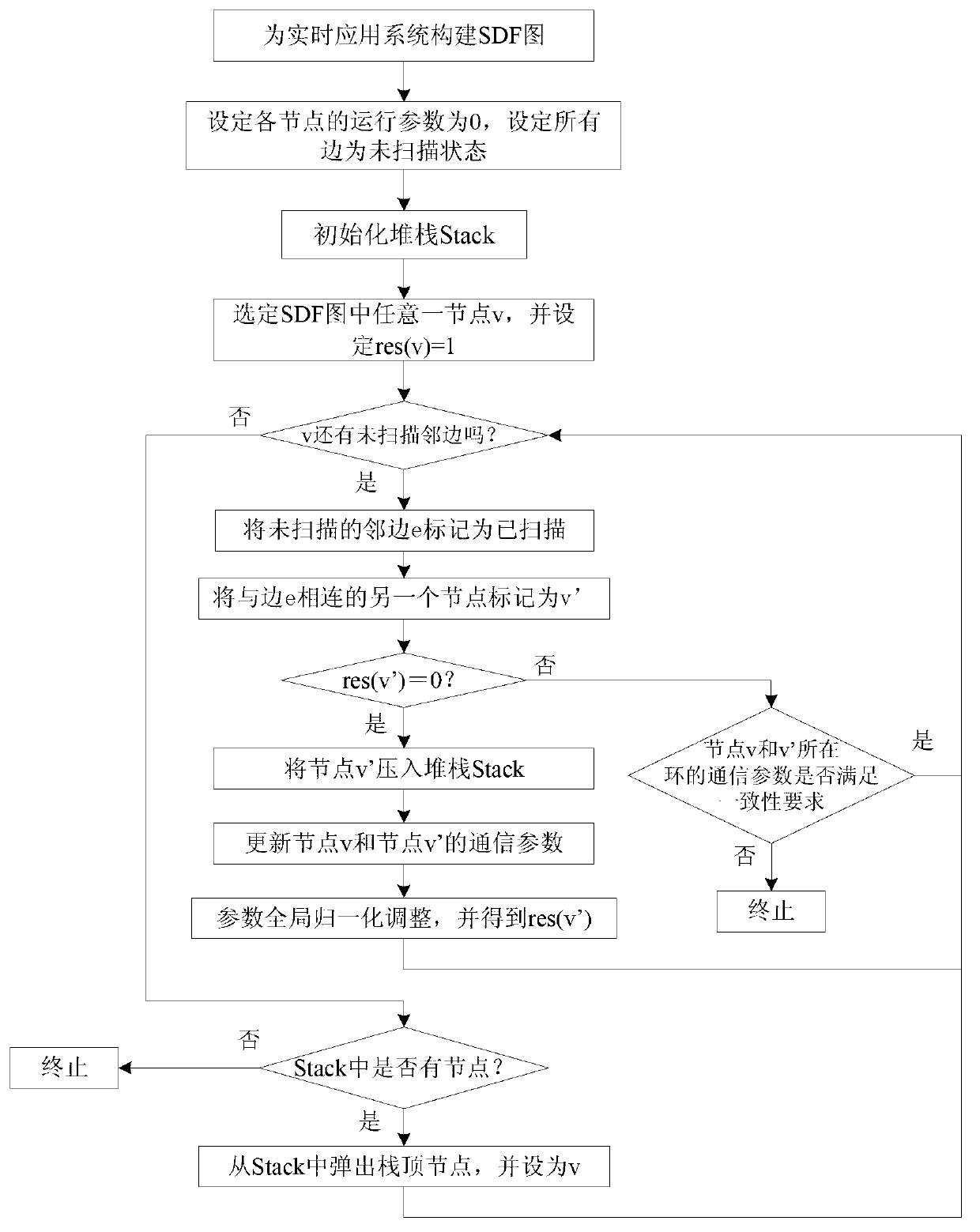
Fast ergodic synchronous data flow system node parameter processing method based on graphs
InactiveCN103136334AGeneralizedAvoid calculationSpecial data processing applicationsSynchronous Data FlowTime system
The invention discloses a fast ergodic synchronous data flow (SDF) system node parameter processing method based on graphs. The fast ergodic synchronous data flow system node parameter processing method includes that an SDF graph is built for a real-time system, communication parameters of nodes connected at two ends on the side are marked at the two ends of each side in the graph, a node needed to be temporarily stored in the SDF graph stacking and storing ergodic process is built, any one node in the SDF is selected and operation parameters of the selected node are initialized, scanning is started, whether rings exist in the graph can be judged when each node is scanned, operation parameter consistency judgment is performed on yes judgment, otherwise, the operation parameters of the node are determined on the basis of communication parameters of the node, and the operation parameters of the scanned nodes in the graph are subjected to overall normalized adjustment. The fast ergodic synchronous data flow system node parameter processing method is few in processing steps, small in calculating amount, high in efficiency and accurate in calculating result, has the universalizaion advantage of being capable of processing parameters in different attributes, and improves speed and efficiency of computers for processing real-time SDF system node operation parameters.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
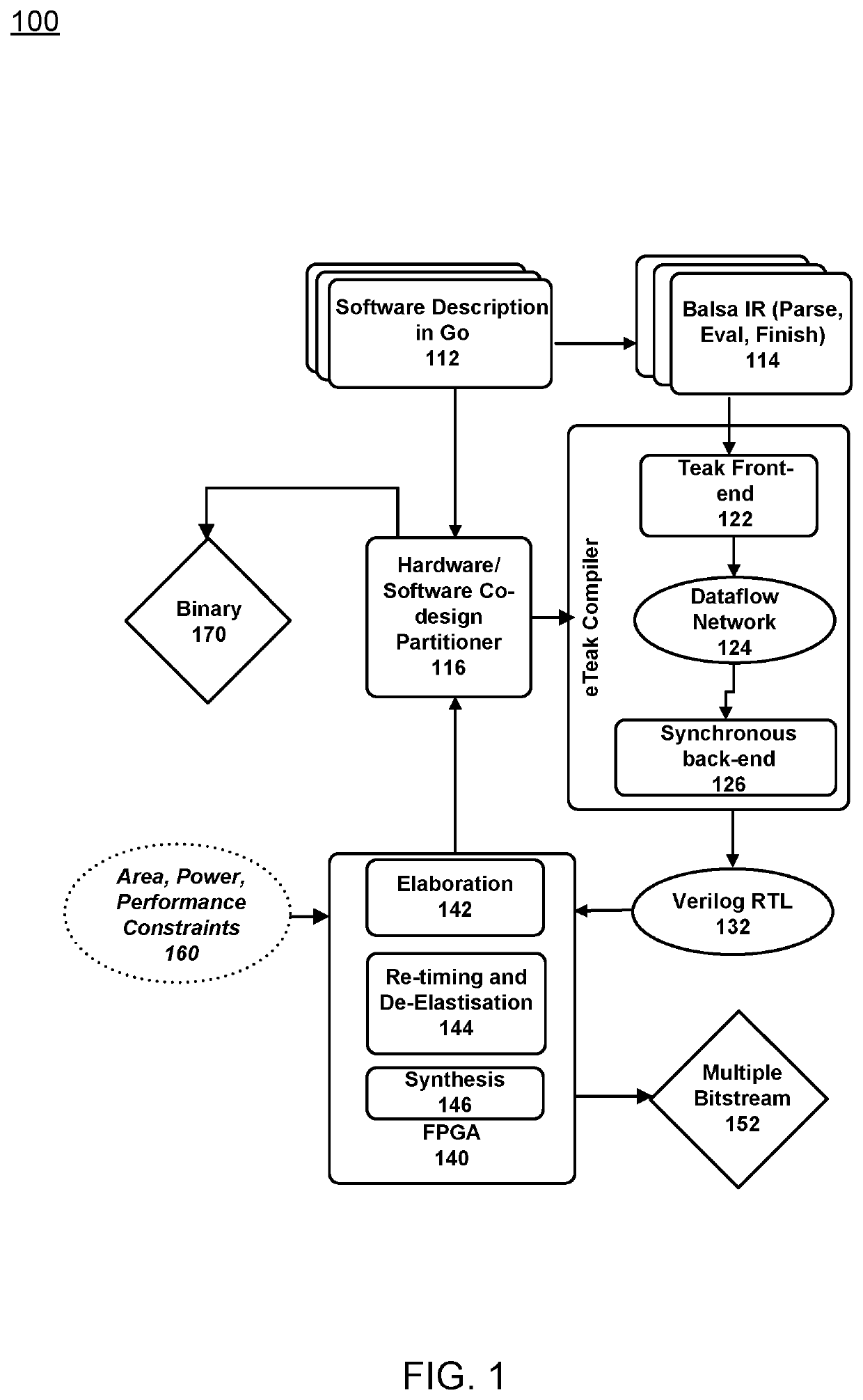
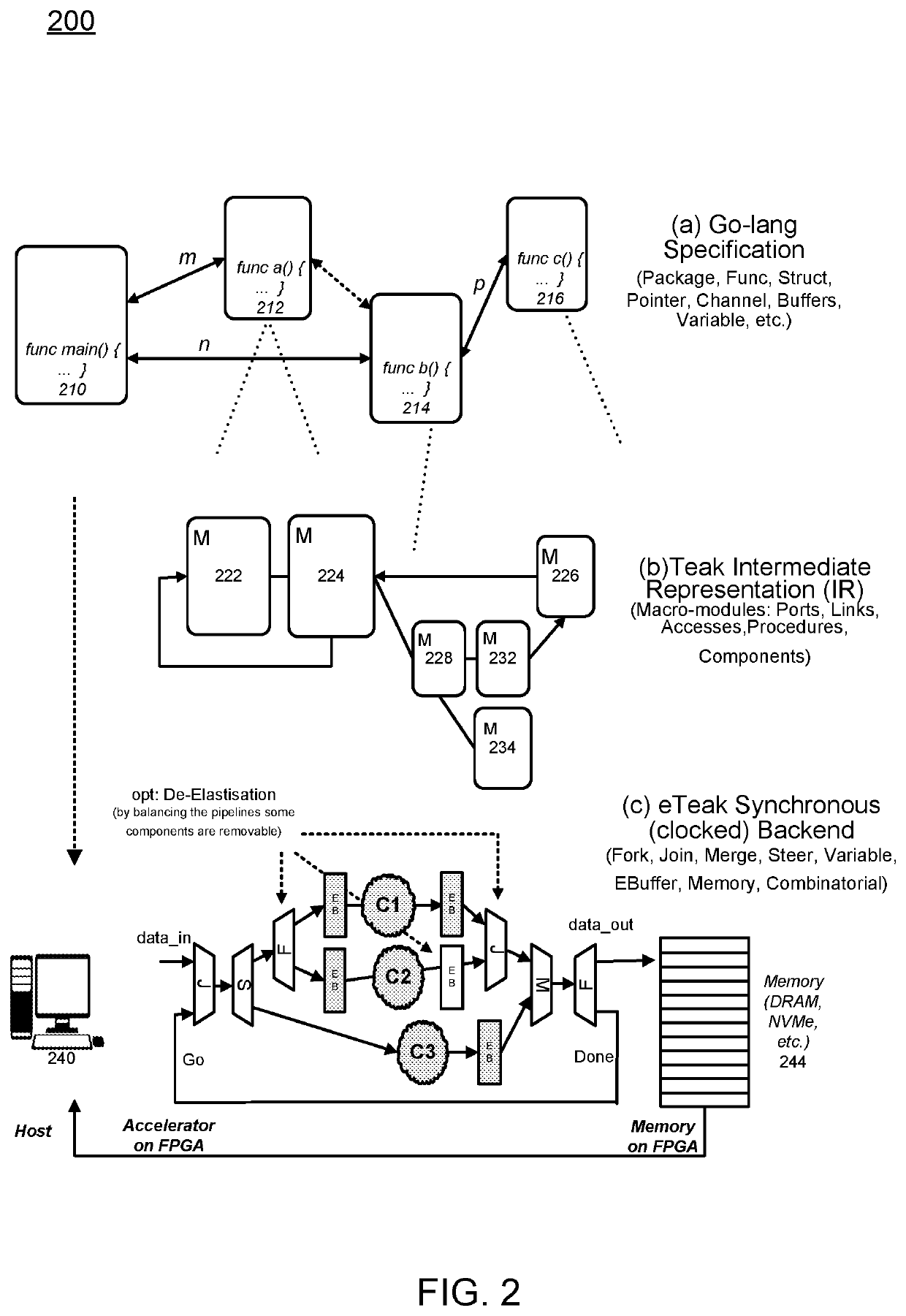
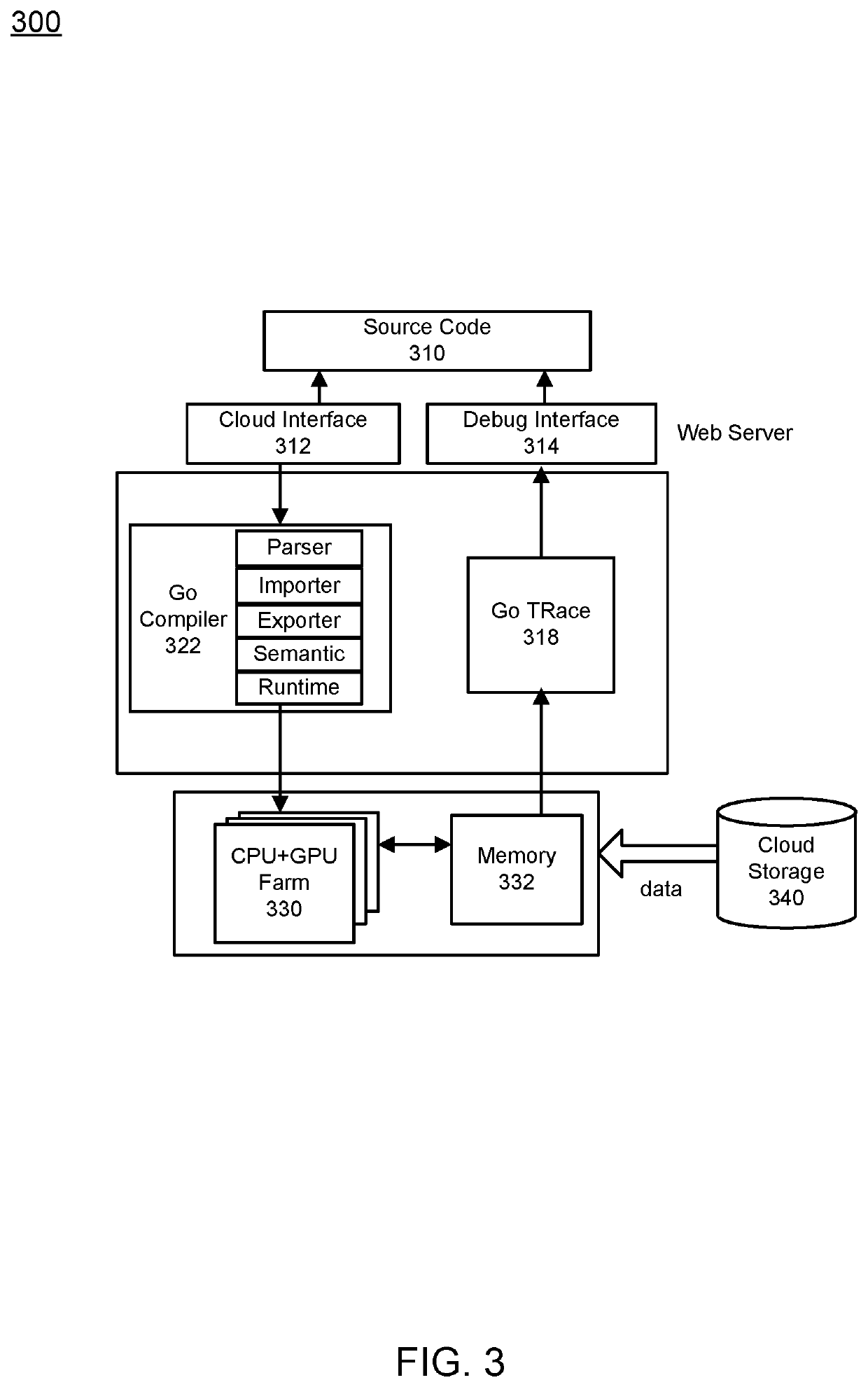
Synthesis Path For Transforming Concurrent Programs Into Hardware Deployable on FPGA-Based Cloud Infrastructures
Exploiting FPGAs for acceleration may be performed by transforming concurrent programs. One example mode of operation may provide one or more of creating synchronous hardware accelerators from concurrent asynchronous programs at software level, by obtaining input as software instructions describing concurrent behavior via a model of communicating sequential processes (CSP) of message exchange between concurrent processes performed via channels, mapping, on a computing device, each of the concurrent processes to synchronous dataflow primitives, comprising at least one of join, fork, merge, steer, variable, and arbiter, producing a clocked digital logic description for upload to one or more field programmable gate array (FPGA) devices, performing primitive remapping of the output design for throughput, clock rate and resource usage via retiming, and creating an annotated graph of the input software description for debugging of concurrent code for the field FPGA devices.
Owner:RECONFIGURE IO LTD
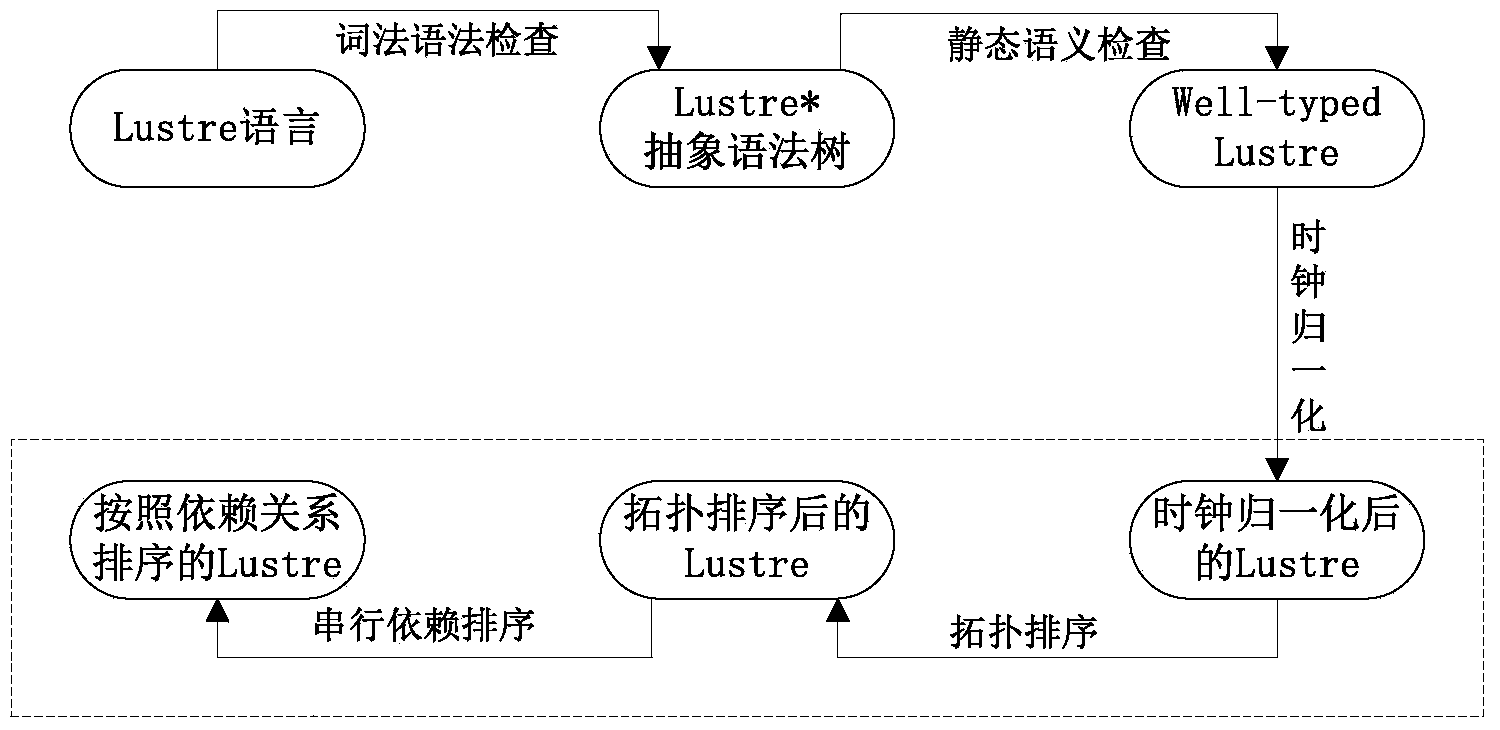
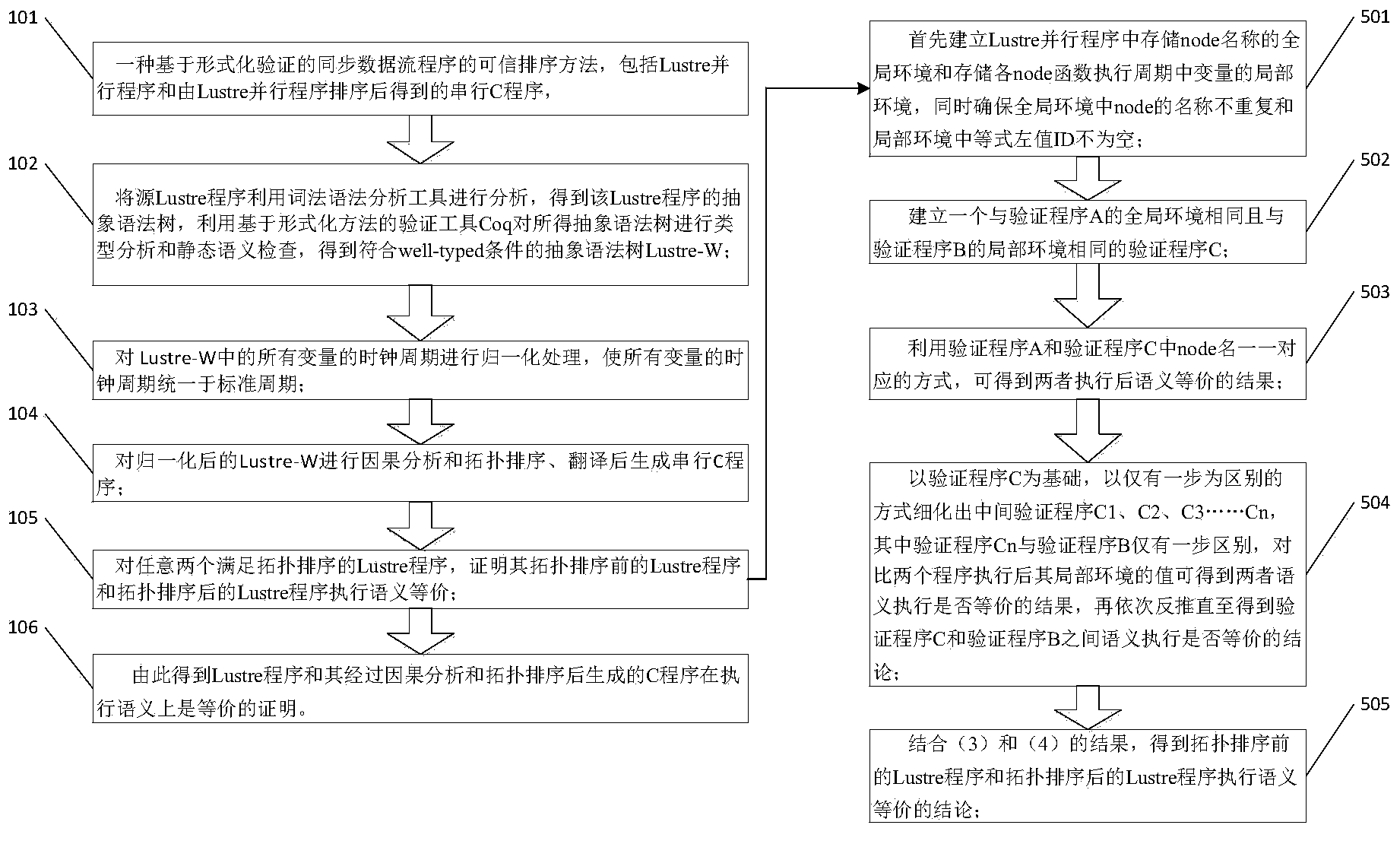
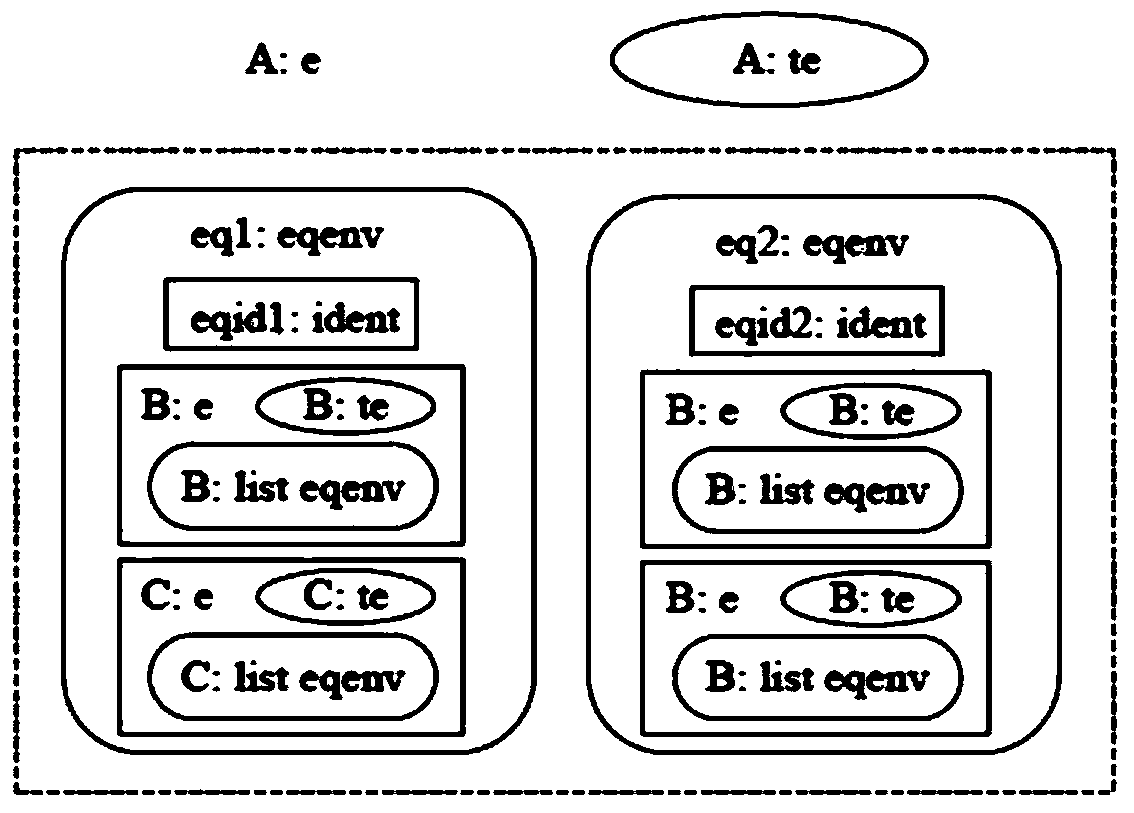
Credible sorting method of synchronous data flow procedures based on formal verification
ActiveCN103646194AImprove securityImprove reliabilityError detection/correctionProgram/content distribution protectionData streamSorting algorithm
The invention discloses a credible sorting method of synchronous data flow procedures based on formal verification. The credible sorting method comprises a Lustre parallel program and a serial C program obtained after sorting of the Lustre parallel program. For any two Lustre programs meeting the requirement for topological sorting, execution semantic equivalence of a Lustre program before topological sorting and a Lustre program after topological sorting is proved, and a C program after sorting and the Lustre program before sorting are equivalent in semantic execution. The credible sorting method of synchronous data flow procedures based on formal verification is developed and achieved based on a formalized language and with a 'vertex topological sorting algorithm with the in-degree as zero' as the theoretical basis. By means of the provement that any two programs meeting the topological sorting property are equivalent in serial semantic execution, during formal verification, all the situations in the process that a parallel language is converted into a serial language, each situation is proved, the program after sorting meets the topological sorting property, so that correctness of a scheme is ensured, and safety and reliability of a whole software system are improved.
Owner:CHINA TECHENERGY +1
Method and apparatus for synchronizing multimedia data stream
ActiveUS7787578B2Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareProgram clock reference
A method and an apparatus for synchronizing a data stream are disclosed. The method includes: decoding the data stream to generate a decoded data stream and program clock references; generating a local clock reference; generating a simulated clock reference according to the program clock references and the local clock reference; comparing the local clock reference with the simulated clock reference to generate a comparison result; adjusting a processing timing of the decoded data stream according to the comparison result; and processing the decoded data stream according to the processing timing.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Clock synchronization of data streams
ActiveUS7657668B2Synchronisation signal speed/phase controlDigital output to print unitsClock driftData stream
A system synchronizes data flow between a first device and a second device. The system includes a data link that connects two or more devices that are capable of sending and receiving data through a bus. A capture device senses and transfer information through the bus. A ring buffer temporarily stores data transmitted through the bus. A read controller copies or reconstructs data in a length that is different from the length of the data received. A monitor detects underflow or overflow conditions into or out of the ring buffer and compensates for clock drift.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com