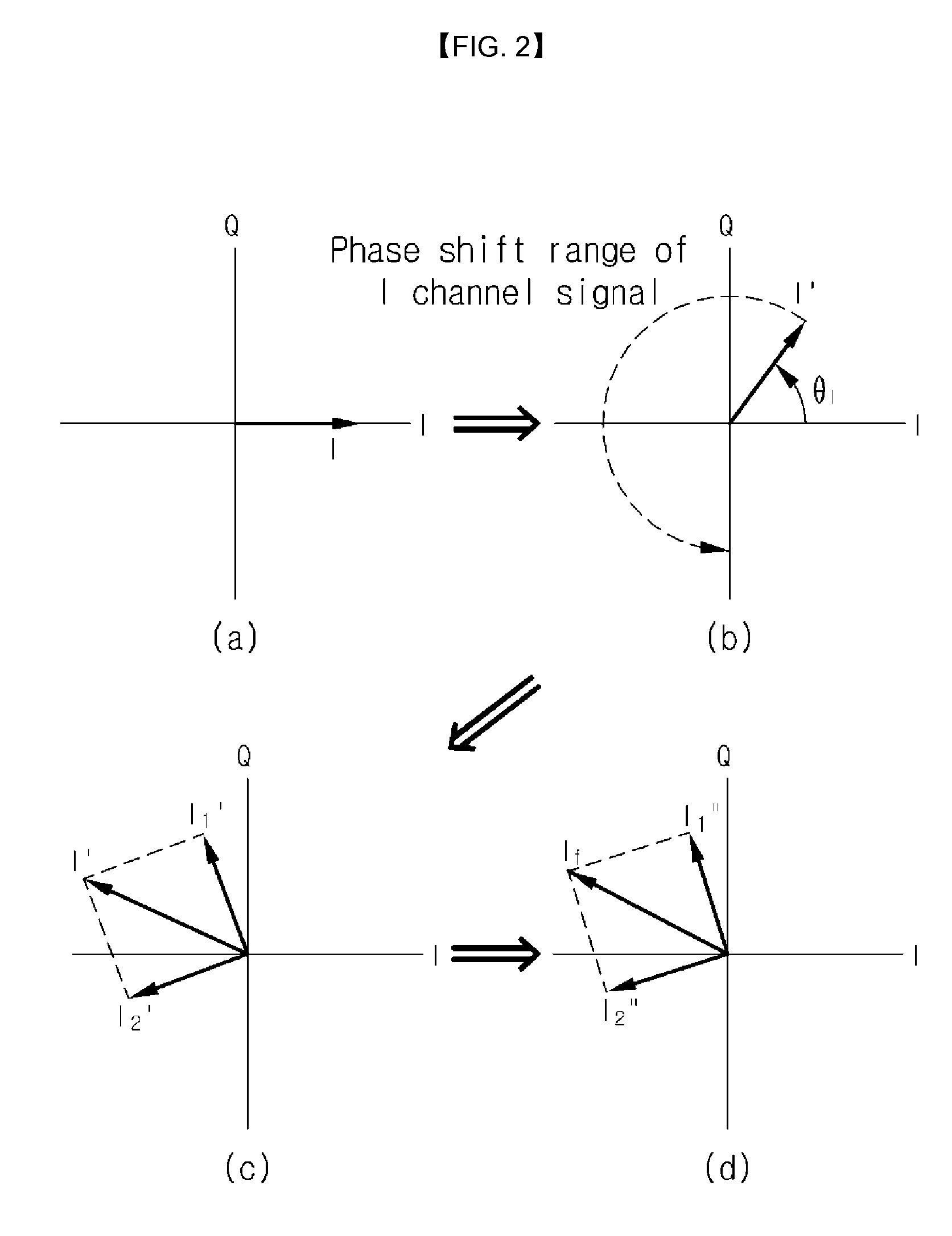Patents
Literature
70results about "Angle to amplitude modulation conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
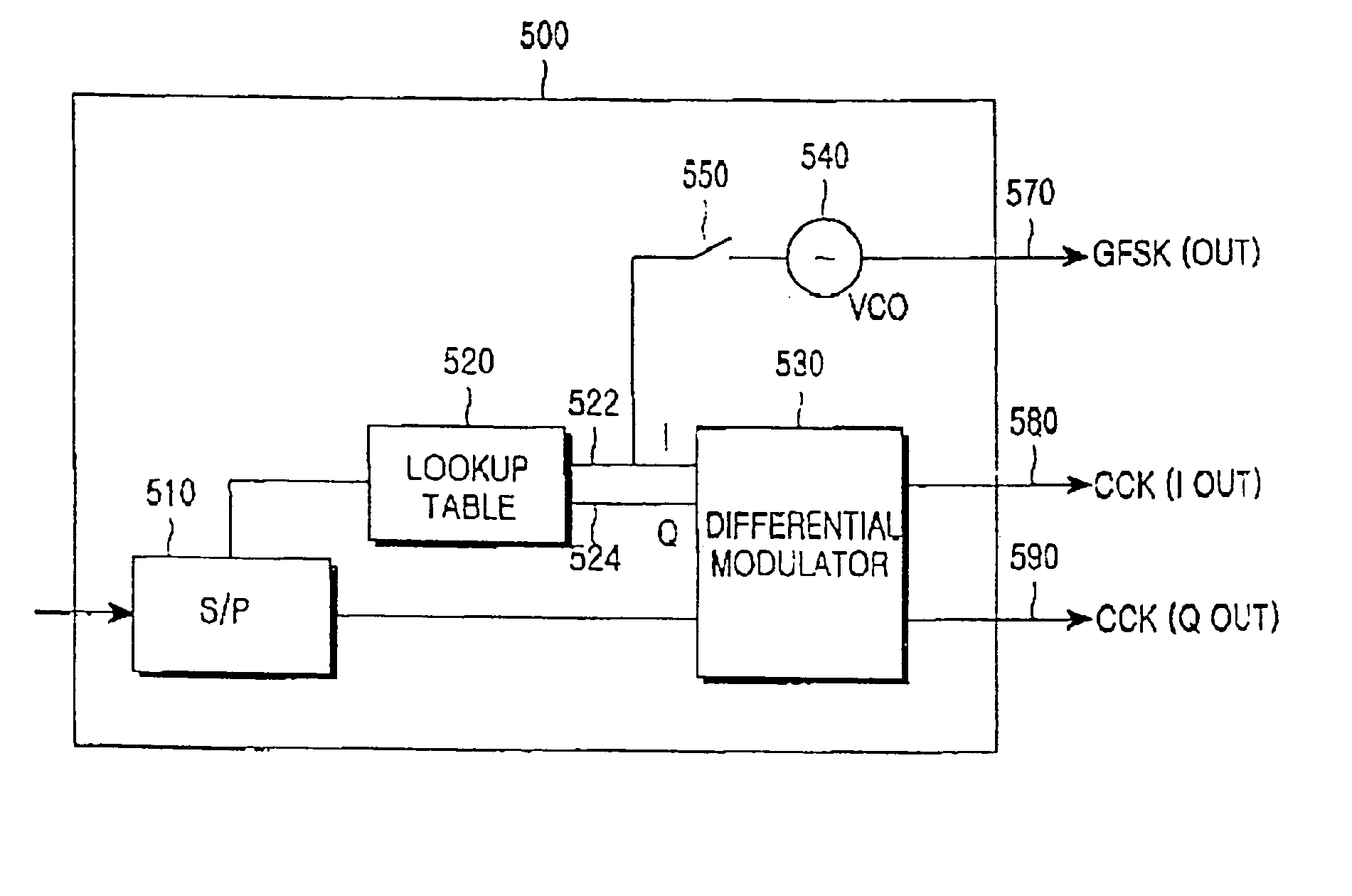
Ultra wide band transmitter
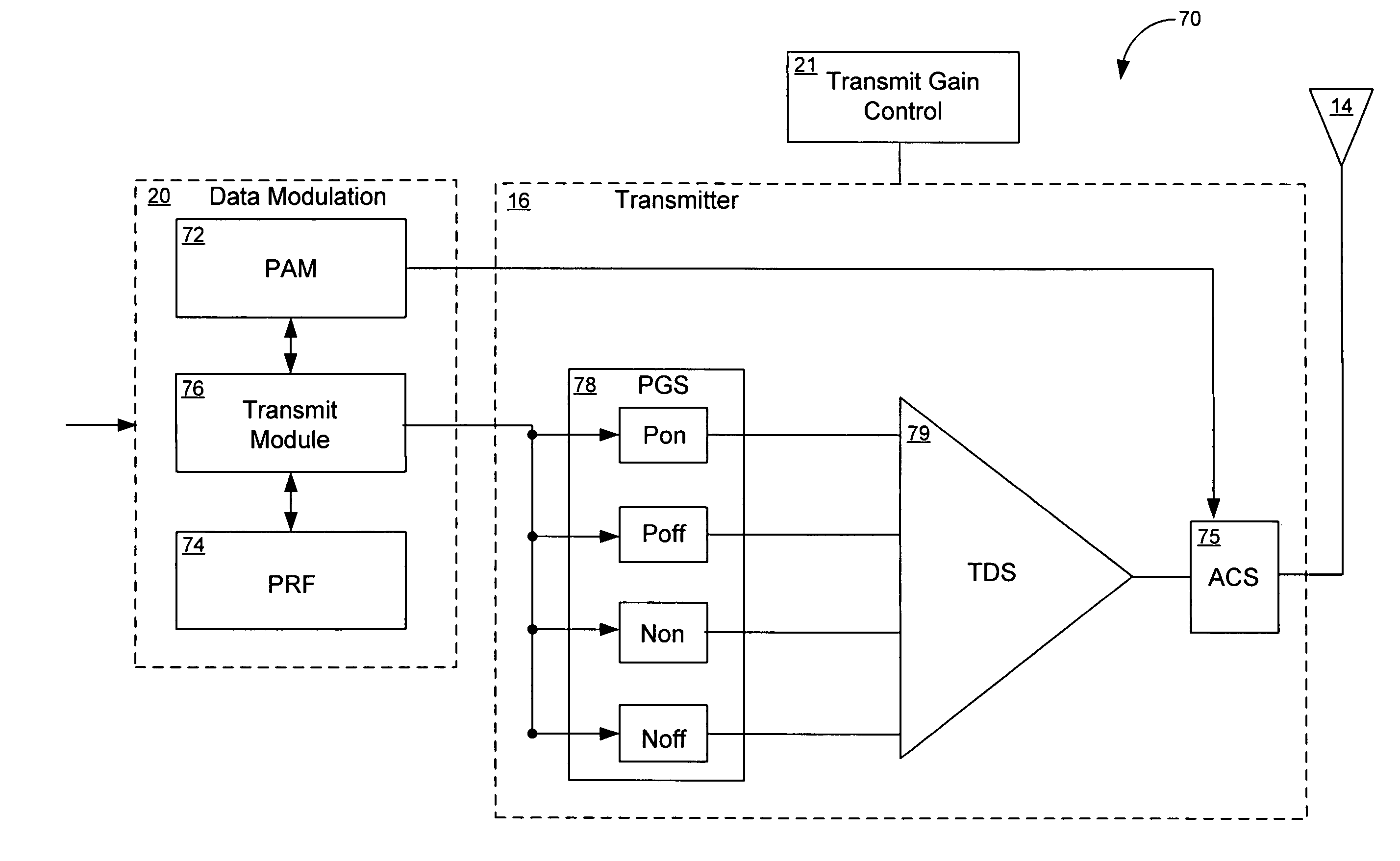
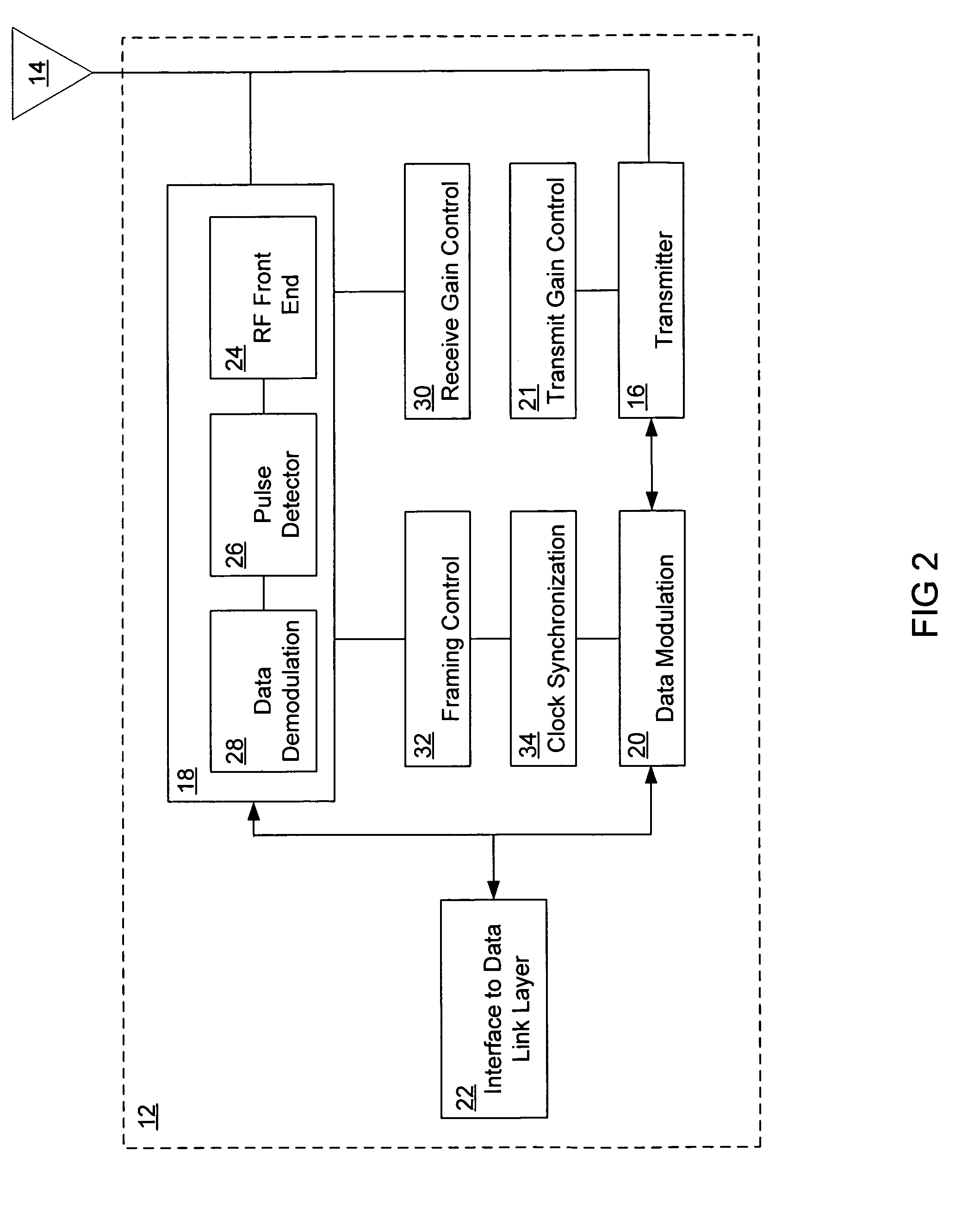
InactiveUS6952456B1Reduced clock speedMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsAngle to amplitude modulation conversionMultiplexerSubject matter
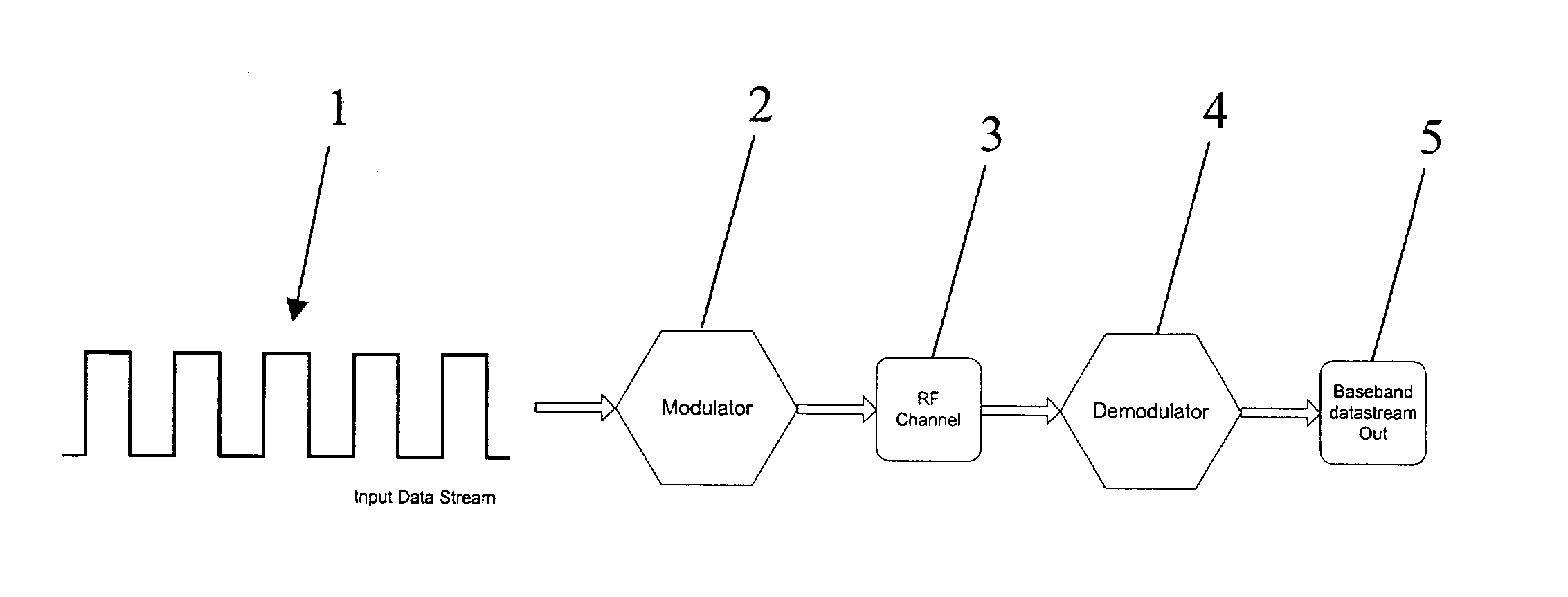
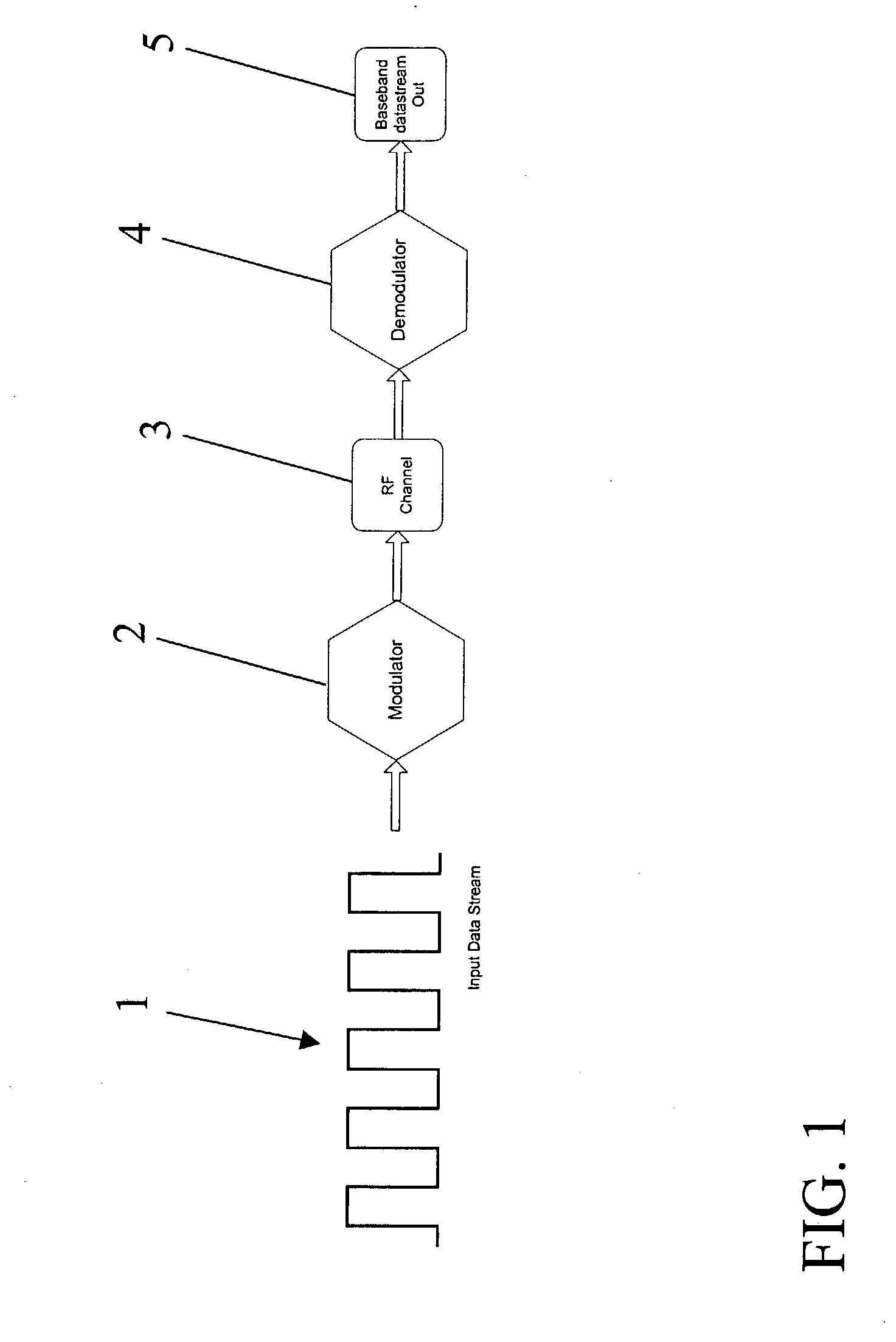
A transmitter system is provided. In one embodiment, the transmitter system includes a data modulation unit, which generates a stream of data that is synchronized with a master clock. The transmitter system additionally includes a transmitter that transmits the stream of synchronized data by way of an attached antenna. In another embodiment the transmitter system includes a Medium Access Control (MAC) layer that includes a clock synchronization device, a frequency divider, a slot allocation unit, and a multiplexer / demultiplexer. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
Adaptive modulation and coding
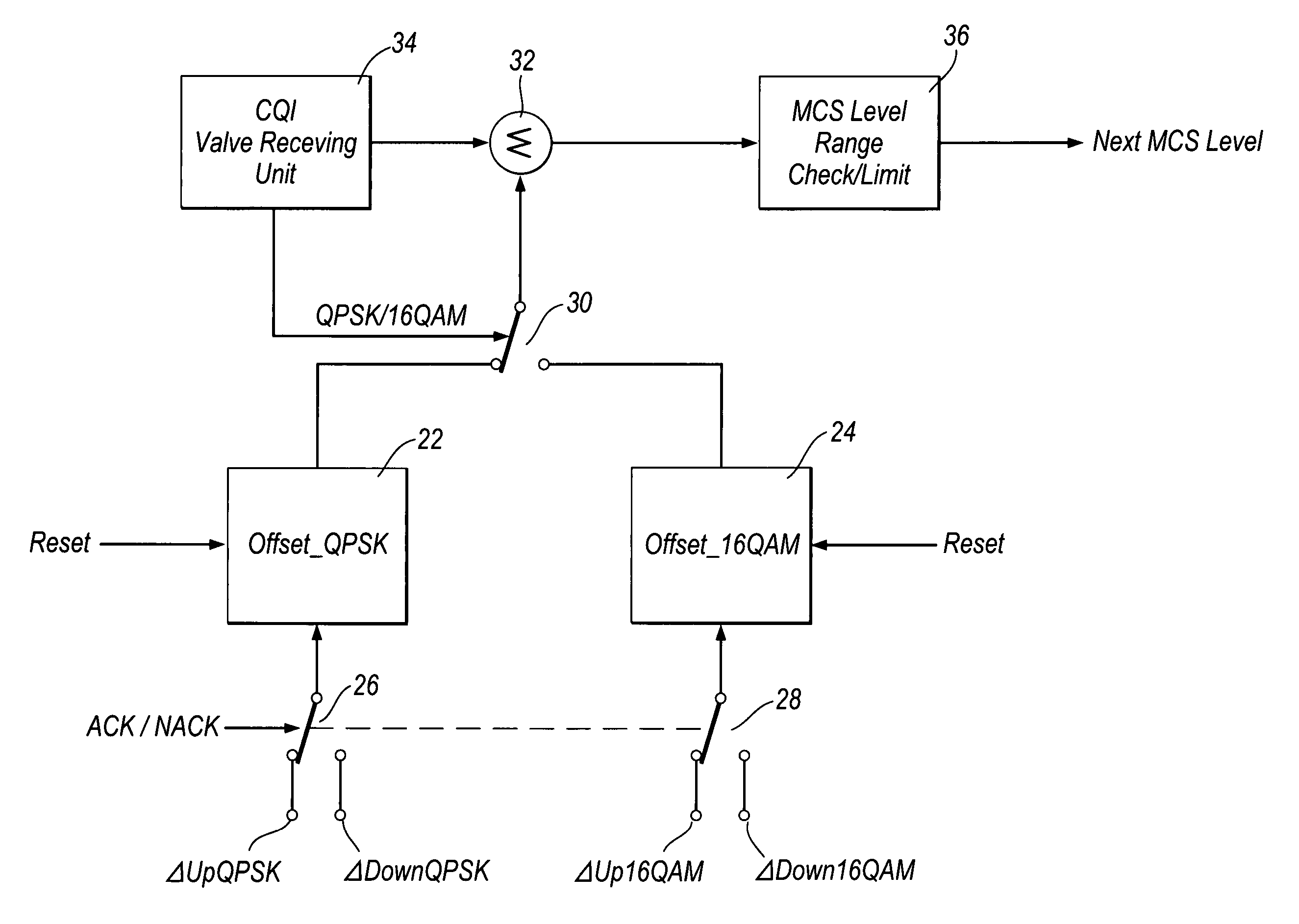
InactiveUS7590181B2Choose simpleRetrieval and updating of the values can be quick and efficientModulated-carrier systemsAngle to amplitude modulation conversionEngineeringTransmitter
In an adaptive modulation and coding method one or more adjustable values are created (S1), each corresponding to at least one of a plurality of available modulation and coding levels applicable to a signal transmitted from a transmitter to a receiver, and each representing a change to the level(s) to which it corresponds. One or more of said adjustable values is / are adjusted in dependence upon whether or not the signal is received successfully by the receiver (S2-S5). One of said available modulation and coding levels is selected (S6-S8) to apply to the signal based on such an adjustable value. Such a method can enable the appropriate modulation and coding level to be selected even when the path and channel conditions vary. The method is applicable to selecting modulation and coding levels in a high-speed downlink packet access system of a wireless communication network.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method of and apparatus for performing modulation
InactiveUS6937668B2Ensure integrityPower amplifiersAngle to amplitude modulation conversionPhysicsPhase modulation
A modulator and a method of modulating utilizes phase or frequency modulation and amplitude modulation. A delay circuit or synchronization circuit is utilized to coordinate the performance of amplitude modulation and phase modulation. The amplitude modulation can be provided after phase modulation is provided to the signal. The modulation circuit can be utilized in any frequency range including high frequency and low frequency circuits.
Owner:INSILICA
Amplitude modulator
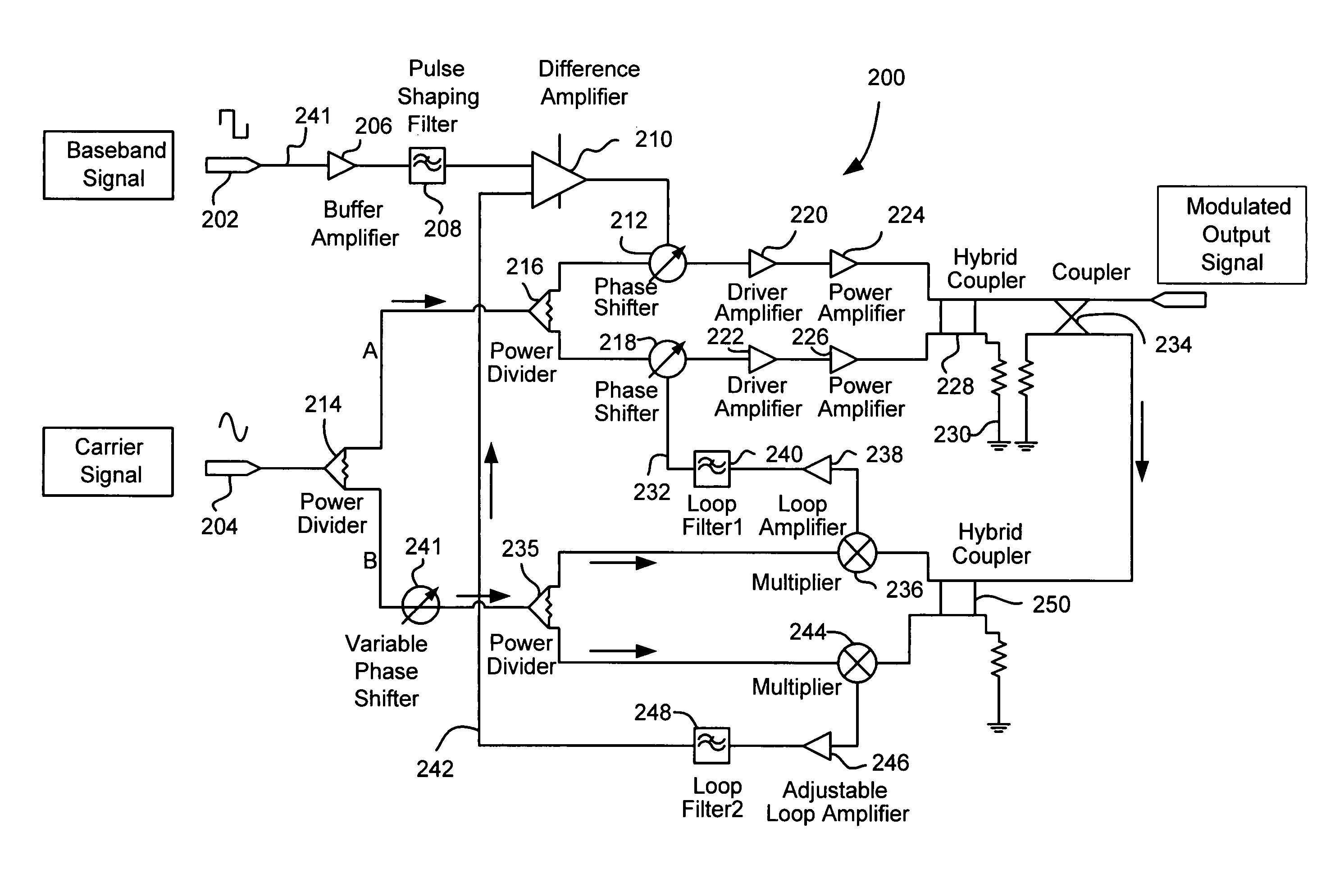
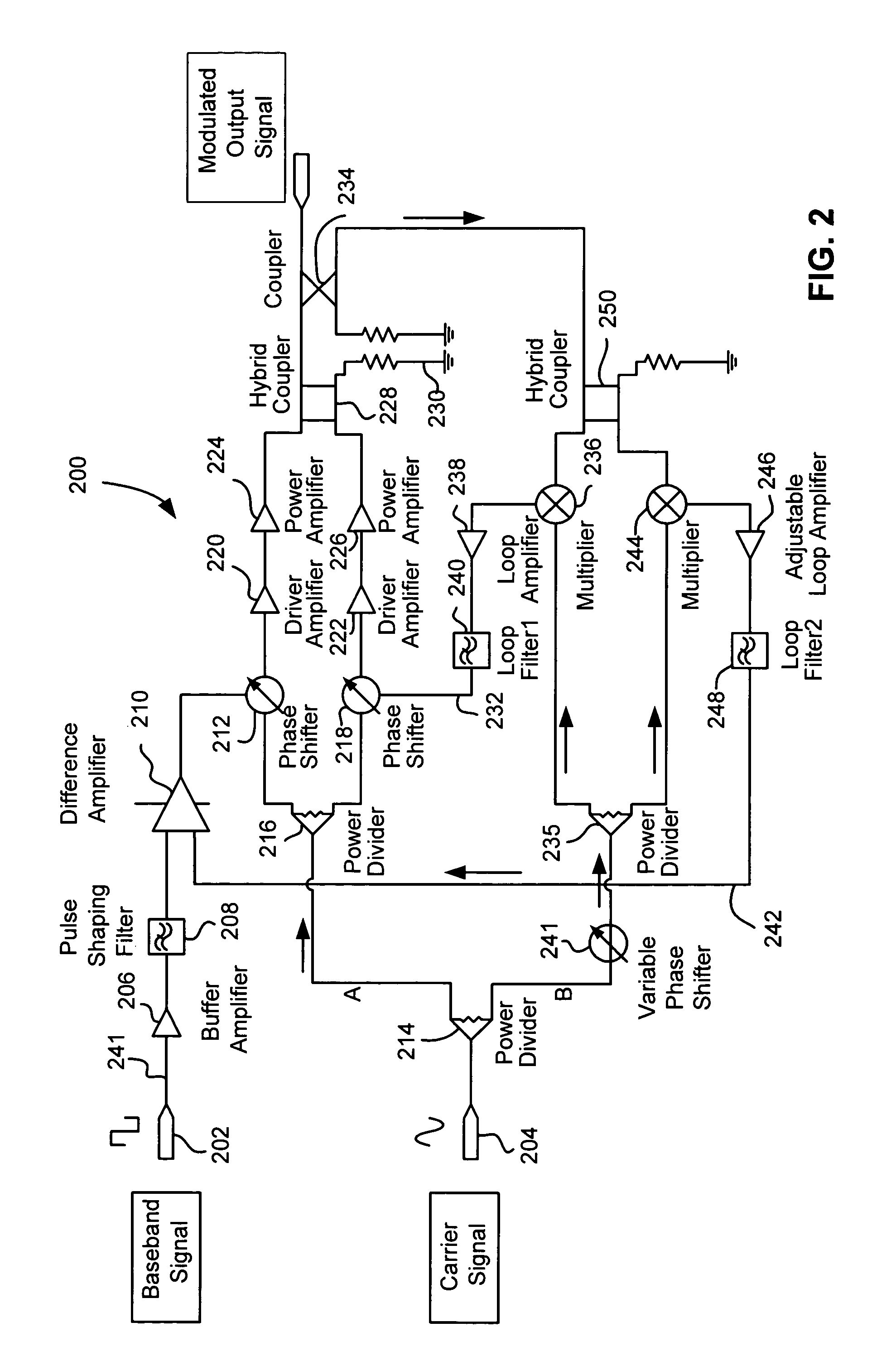
ActiveUS7773695B2Reduce residual phase variationAmplitude modulation detailsAngle to amplitude modulation conversionPhase shiftedCarrier signal
A circuit for amplitude modulating a carrier signal includes a carrier signal input, circuitry for splitting the carrier signal into first and second paths, circuitry for phase modulating the carrier signal on the first path, circuitry for phase modulating the carrier signal on the second path, and circuitry for combining the phase modulated carrier signal on the first path with the phase modulated carrier signal on the second path for generating an amplitude modulated output signal. Feedback loops virtually eliminate residual phase shift and make the amplitude modulated output signal linearly proportional to the baseband signal.
Owner:KOTAB DOMINIC
Multi-protocol modulator
InactiveUS6865235B2Reducing physical size and power requirementMultiplex communicationModulation type identificationData streamMulti protocol
A multi-protocol modulator capable of supporting two or more different modes of operation, each mode of operation corresponding to a different type of modulation, comprises an m-level phase shift keying (m-PSK) modulator which receives a serial input data stream and maps data contained therein into a constellation including m equidistant phases in accordance with a predetermined mapping scheme. The m-PSK modulator is shared by at least two different modulation protocols by allowing the mapping scheme to be selectively changed depending upon the modulation protocol used. The multi-protocol modulator further includes a phase rotator operatively coupled to the output of the m-PSK modulator. The phase rotator selectively rotates the phase of the m-PSK signal by a predetermined phase rotation value. The phase rotator is shared by the two or more modulation protocols by allowing the phase rotation value to be selectively modified depending upon the modulation protocol used. A phase rotated signal is then passed through a pulse shaping filter having a linearized Gaussian response.
Owner:AGERE SYST GUARDIAN
System and method for dynamic output back-off
ActiveUS20110075772A1Improve throughputMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsAngle to amplitude modulation conversionEngineeringGain factor
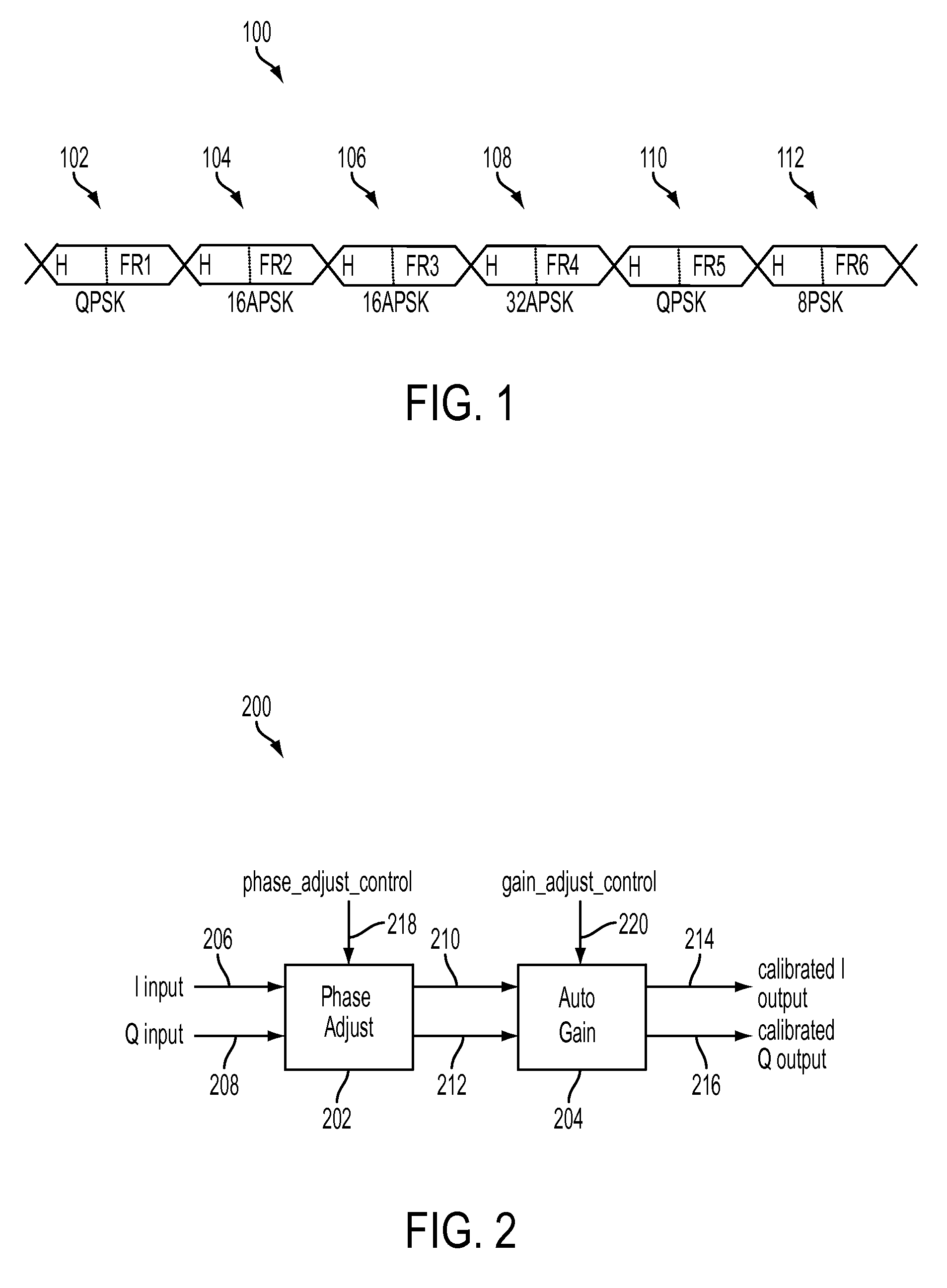
A device is provided for use with an input signal including a first packet of a first modulation type in series with a second packet of a second modulation type. The device includes a gain adjustment portion and a gain portion. The gain adjustment portion can output a first gain adjustment signal based on the first packet or can output a second gain adjustment signal based on the second packet. The gain portion can output a first signal corresponding to the first packet and can output a second signal corresponding to the second packet. The first signal is based on the input signal and a first gain factor. The second signal is based on the input signal and a second gain factor. The first gain factor is based on the first gain adjustment signal. The second gain factor is based on the second gain adjustment signal.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Modulator arrangement and method for signal modulation
InactiveUS7830220B2Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
A modulator arrangement includes a power amplifier which receives a carrier signal and has a current control input and a voltage supply input. The modulator arrangement further includes a supply voltage modulator having an output coupled to the voltage supply input and an input coupled to the data input and a bias current modulator with an output coupled to the current control input and an input coupled to the data input. A control unit is provided which has a power control output coupled to the supply voltage modulator and to the bias current modulator to control the supply voltage modulator and the bias current modulator depending on a power control signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Polar modulation using amplitude modulated quadrature signals
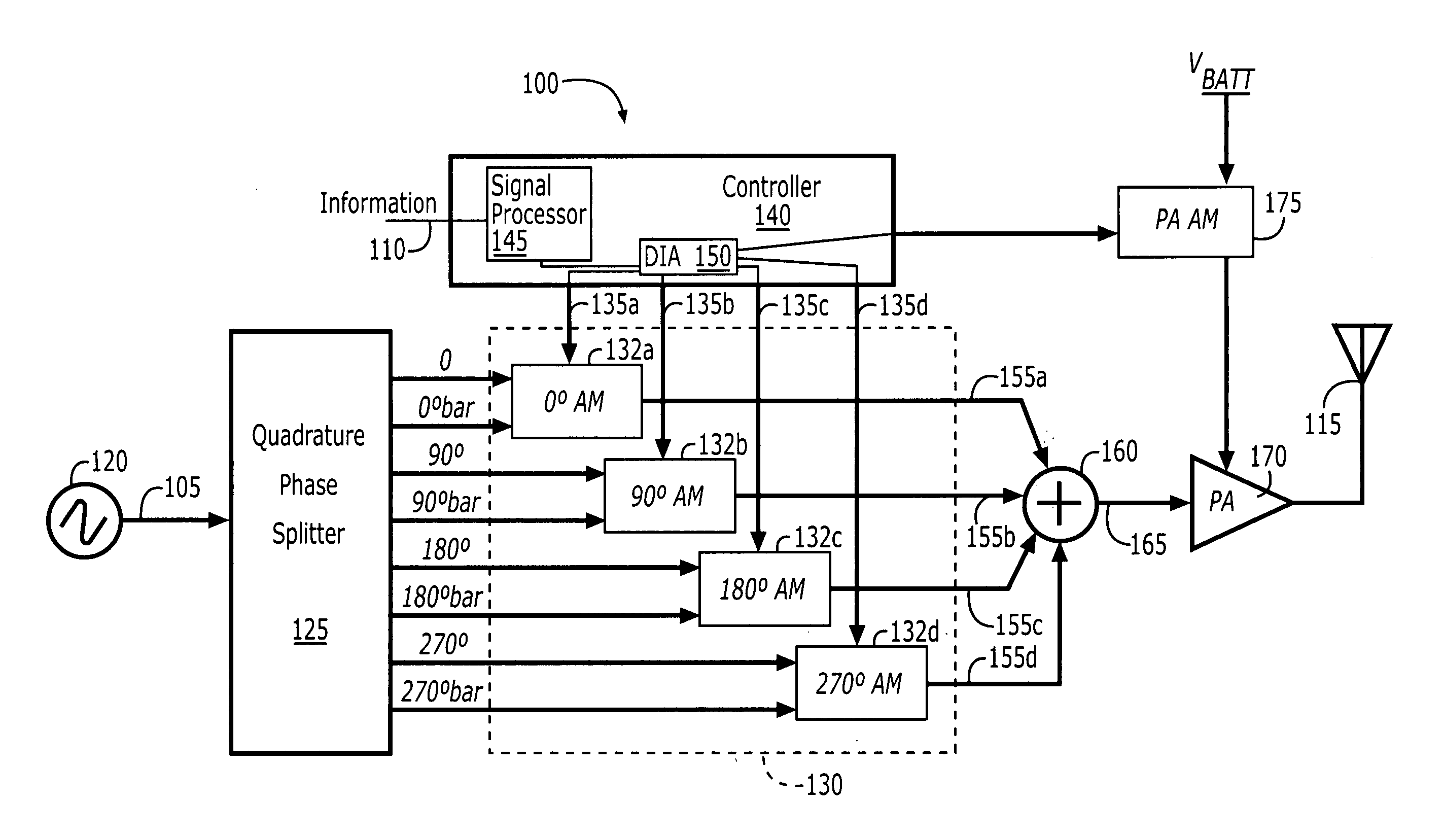
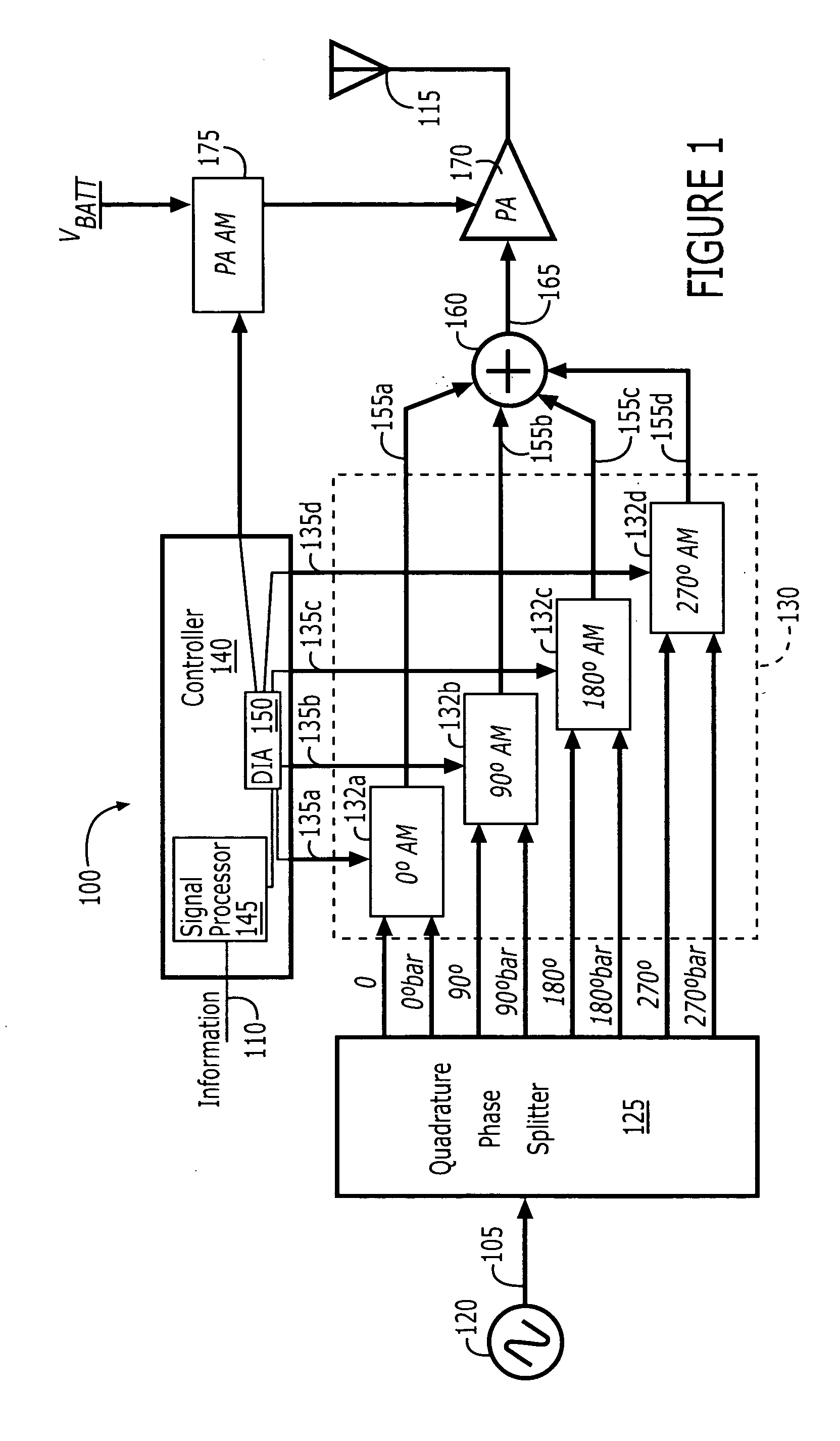
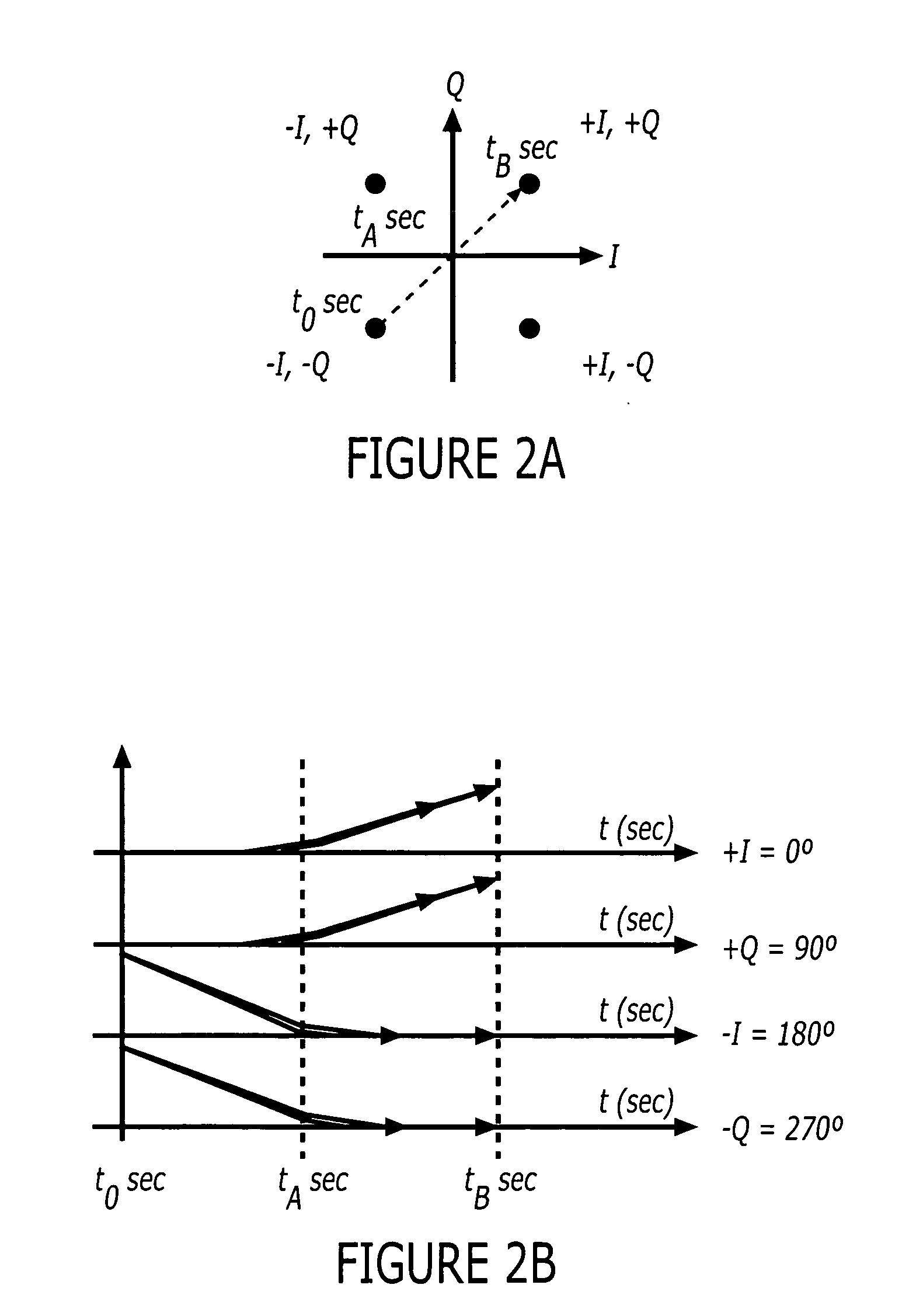
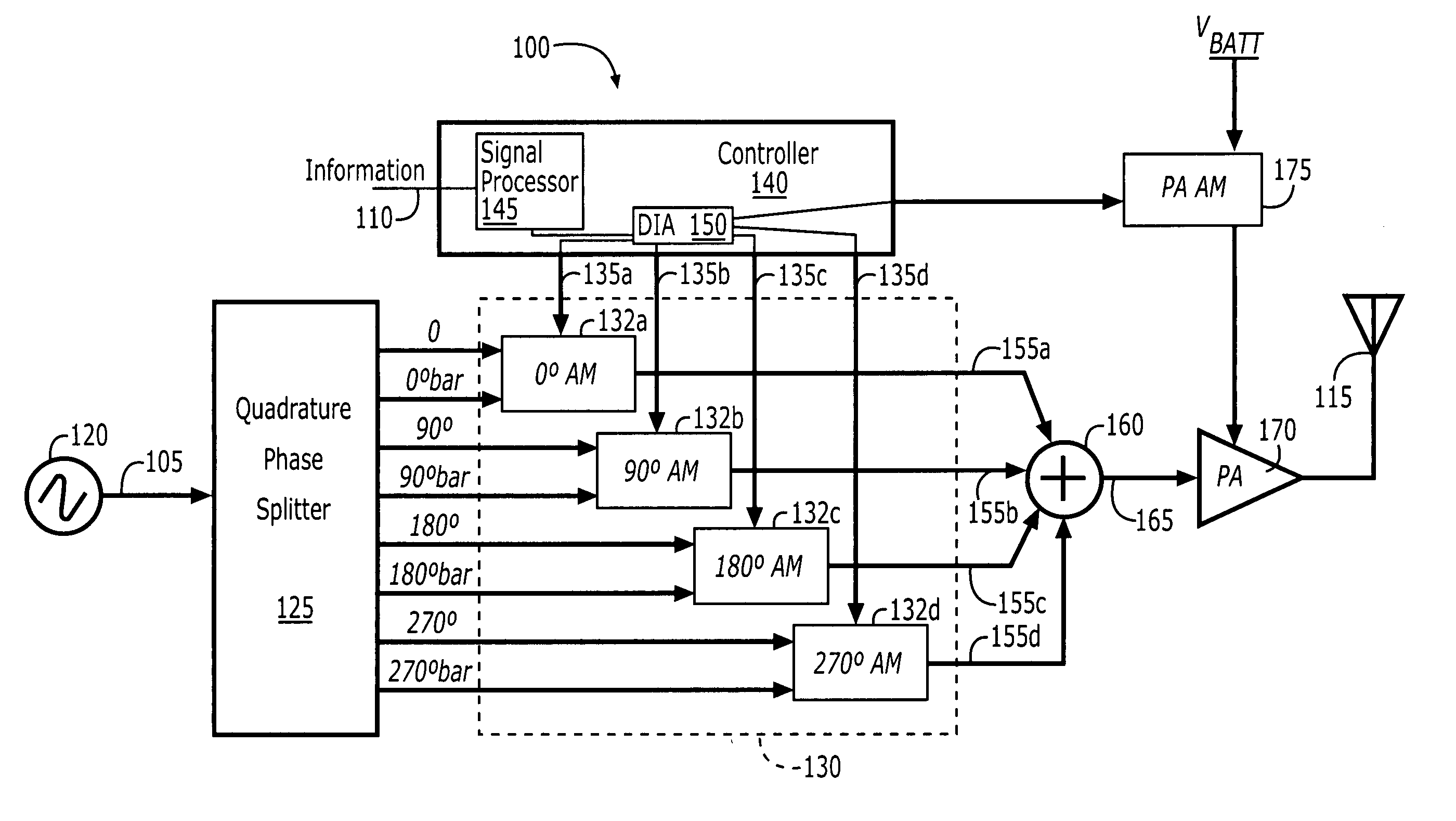
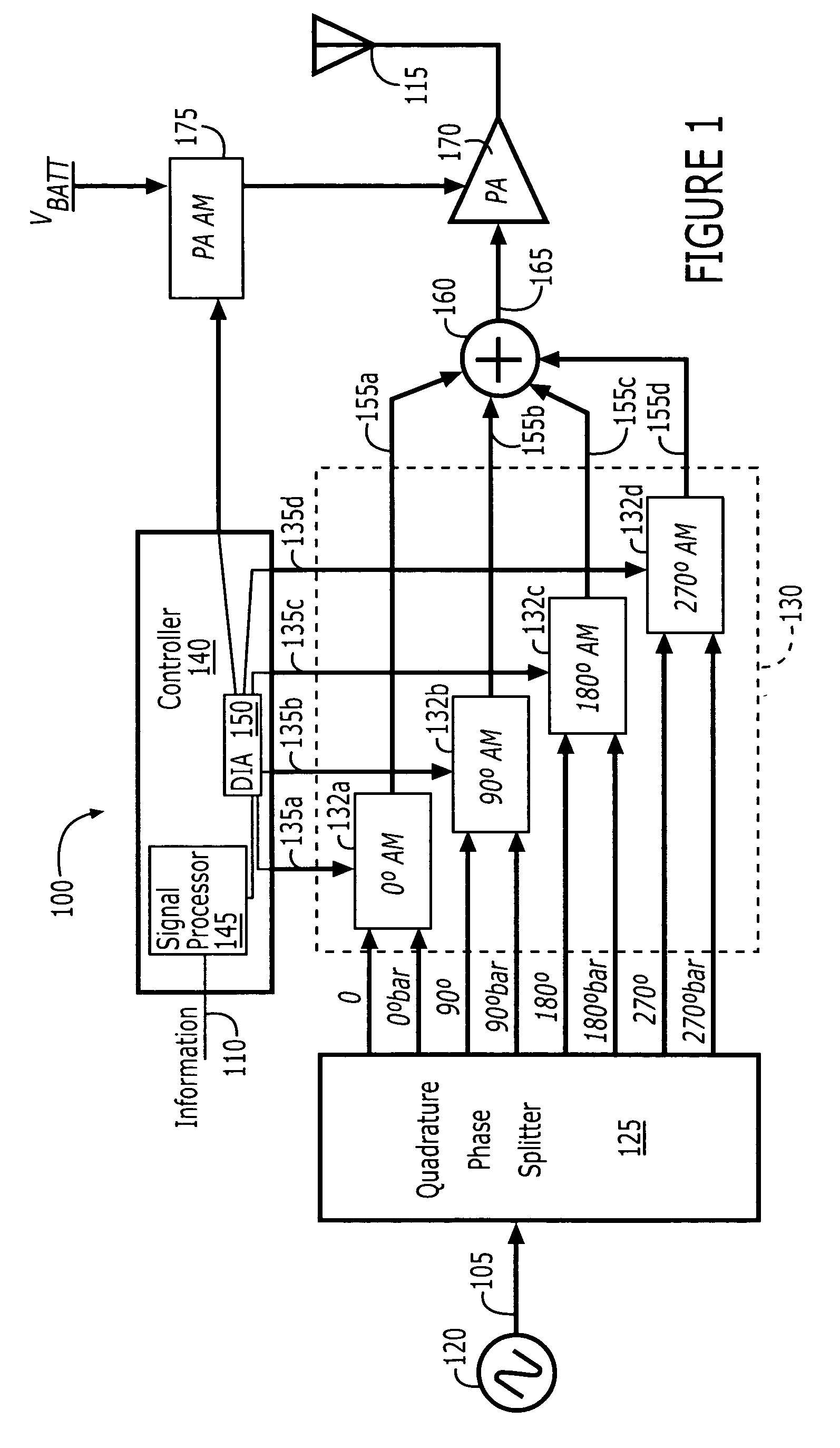
ActiveUS20050134396A1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAngle to amplitude modulation conversionPhase splitterControl signal
Polar modulators include a phase splitter, a controller, variable current sources, transistor circuits, and a combiner. The phase splitter splits a RF carrier signal into quadrature component signals that are 90 degrees out of phase with each other. The controller generates modulation control signals based on information that is to be transmitted. The variable current sources each generate a variable amplitude current signal based on a different one of the modulation control signals. Each of the transistor circuits amplify a different one of the quadrature component signals with a variable amplification based on the variable amplitude current signal from a different one of the variable current sources to generate an amplitude adjusted quadrature component signal. The combiner combines the amplitude adjusted quadrature component signals from each of the transistor circuits to generate a phase-modulated RF carrier output signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
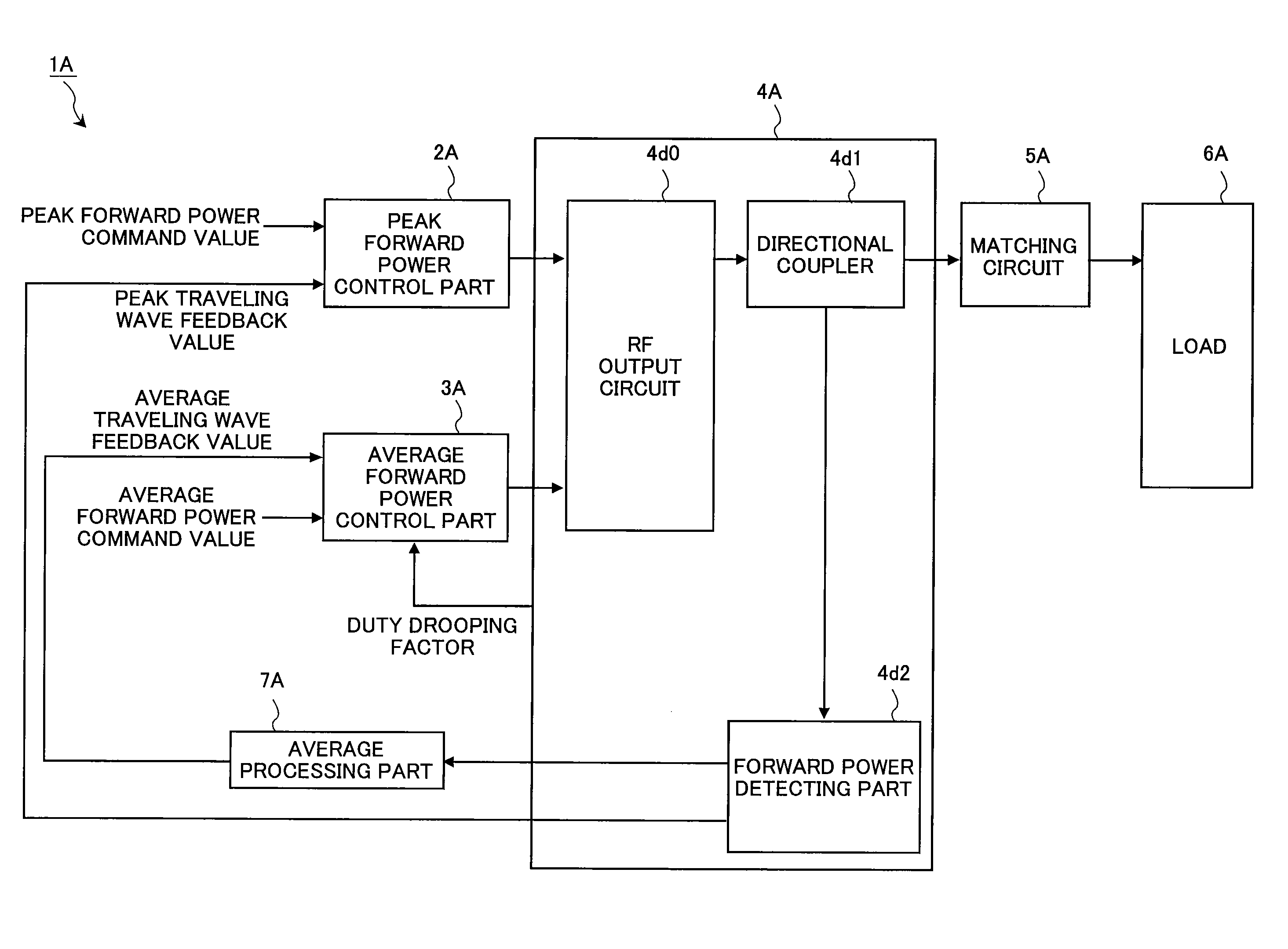
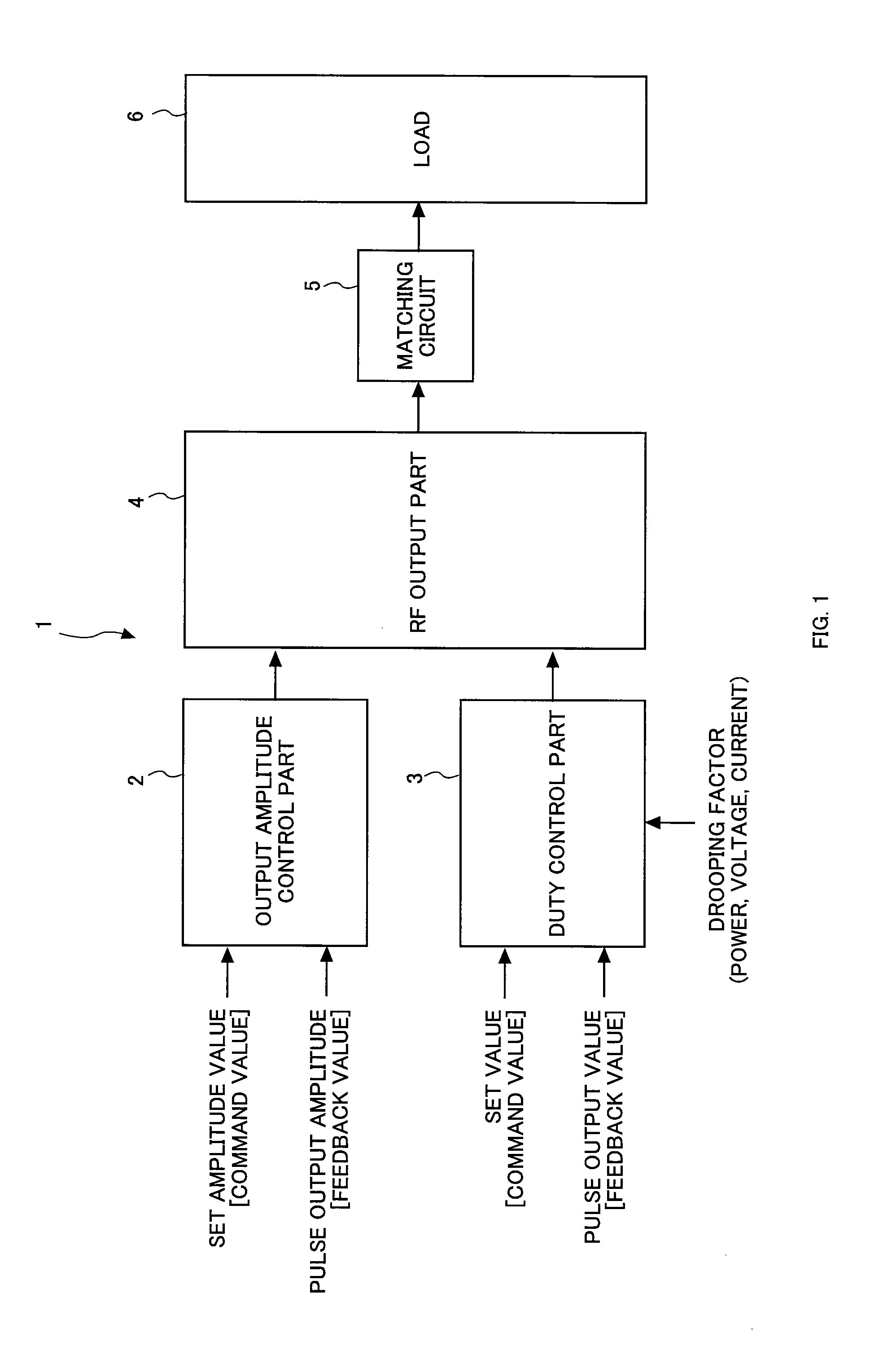
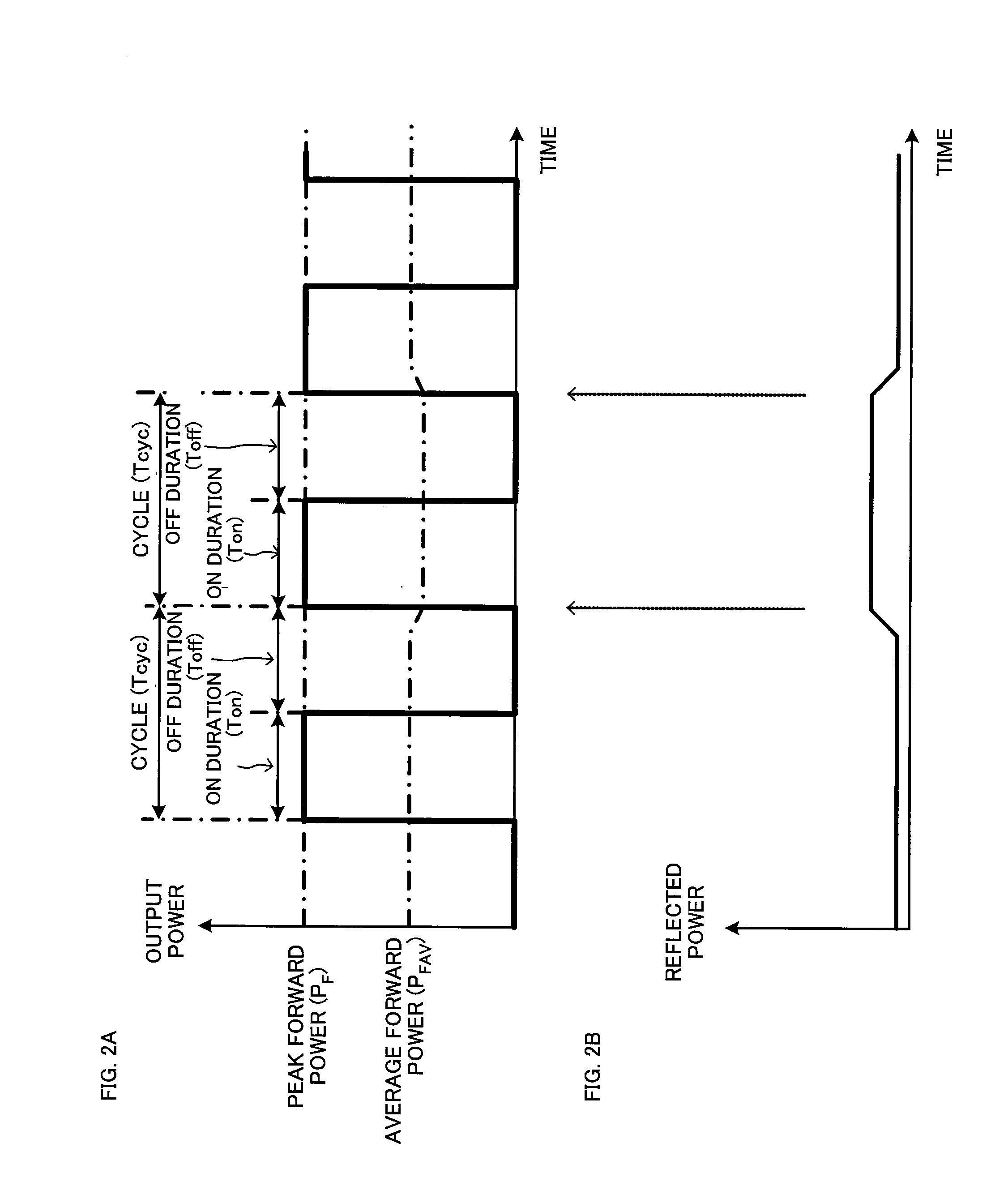
Pulse modulated RF power control method and pulse modulated RF power supply device
ActiveUS8704607B2Limit amplitudeIncrease powerElectric discharge tubesGain controlAmplitude controlPower control
Owner:KYOSAN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
Modulator arrangement and method for signal modulation
InactiveUS20080074209A1Well formedSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierEngineering
A modulator arrangement includes a power amplifier which receives a carrier signal and has a current control input and a voltage supply input. The modulator arrangement further includes a supply voltage modulator having an output coupled to the voltage supply input and an input coupled to the data input and a bias current modulator with an output coupled to the current control input and an input coupled to the data input. A control unit is provided which has a power control output coupled to the supply voltage modulator and to the bias current modulator to control the supply voltage modulator and the bias current modulator depending on a power control signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Transmission apparatus, communication apparatus and mobile radio apparatus
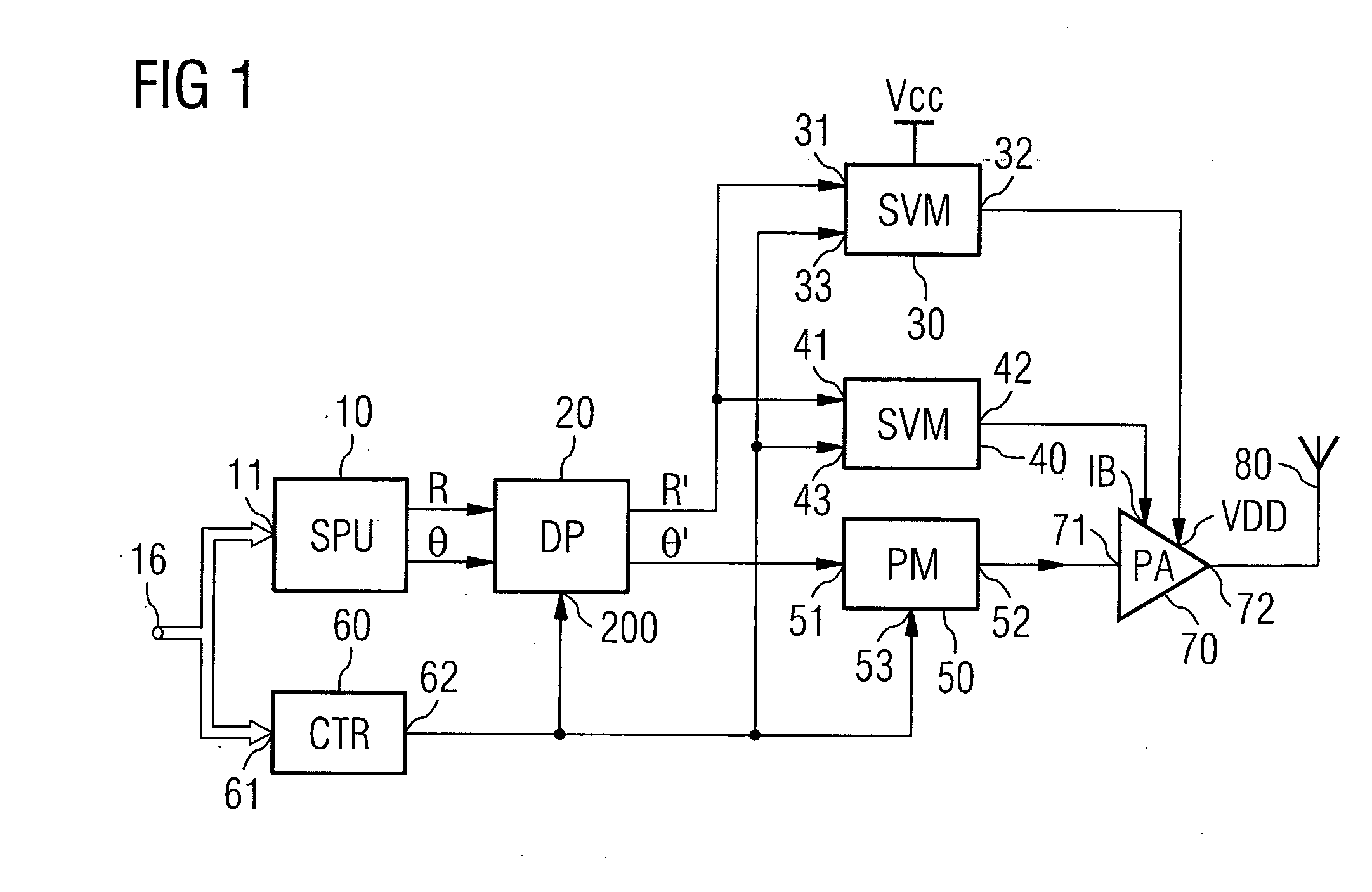
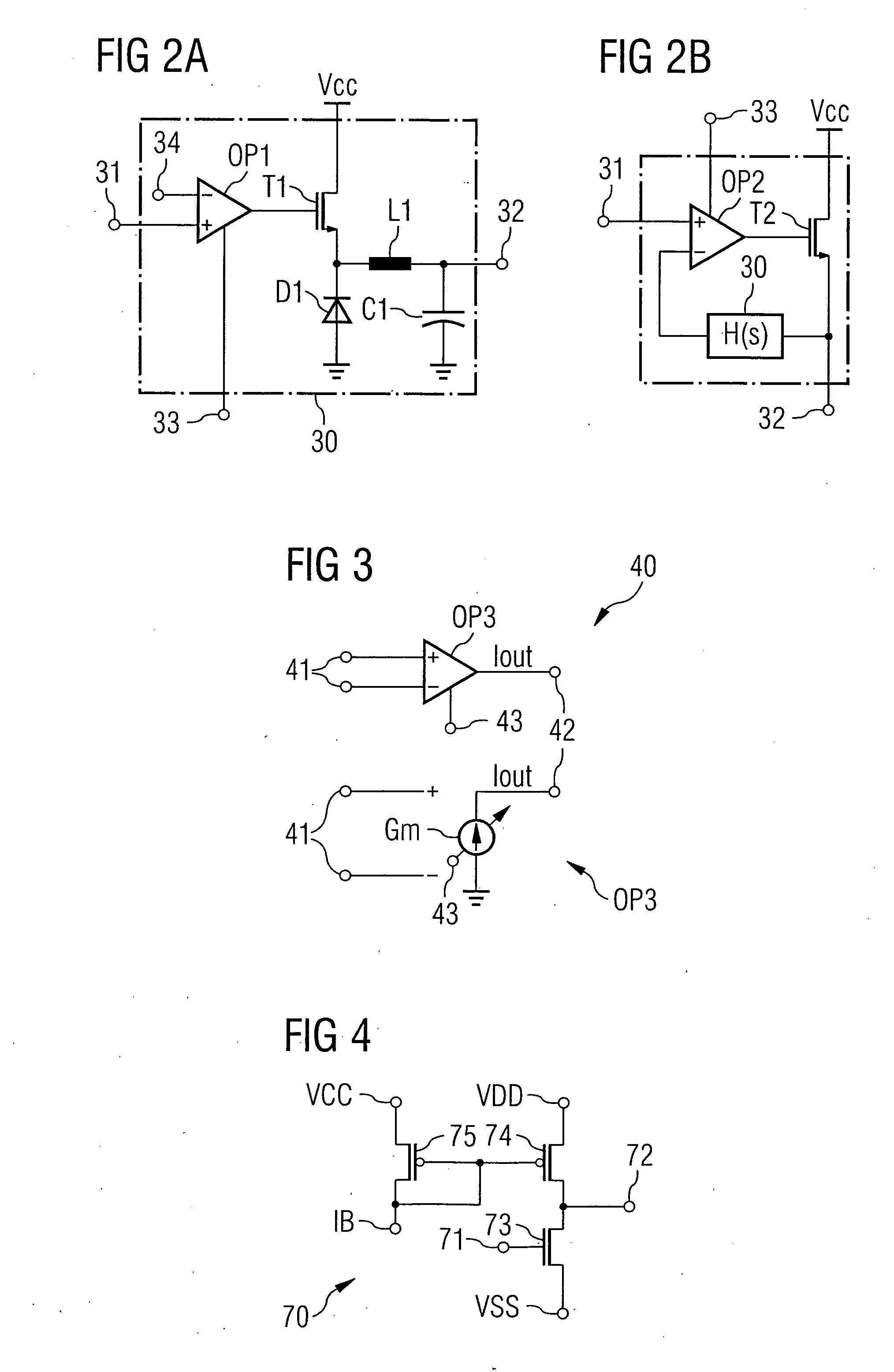
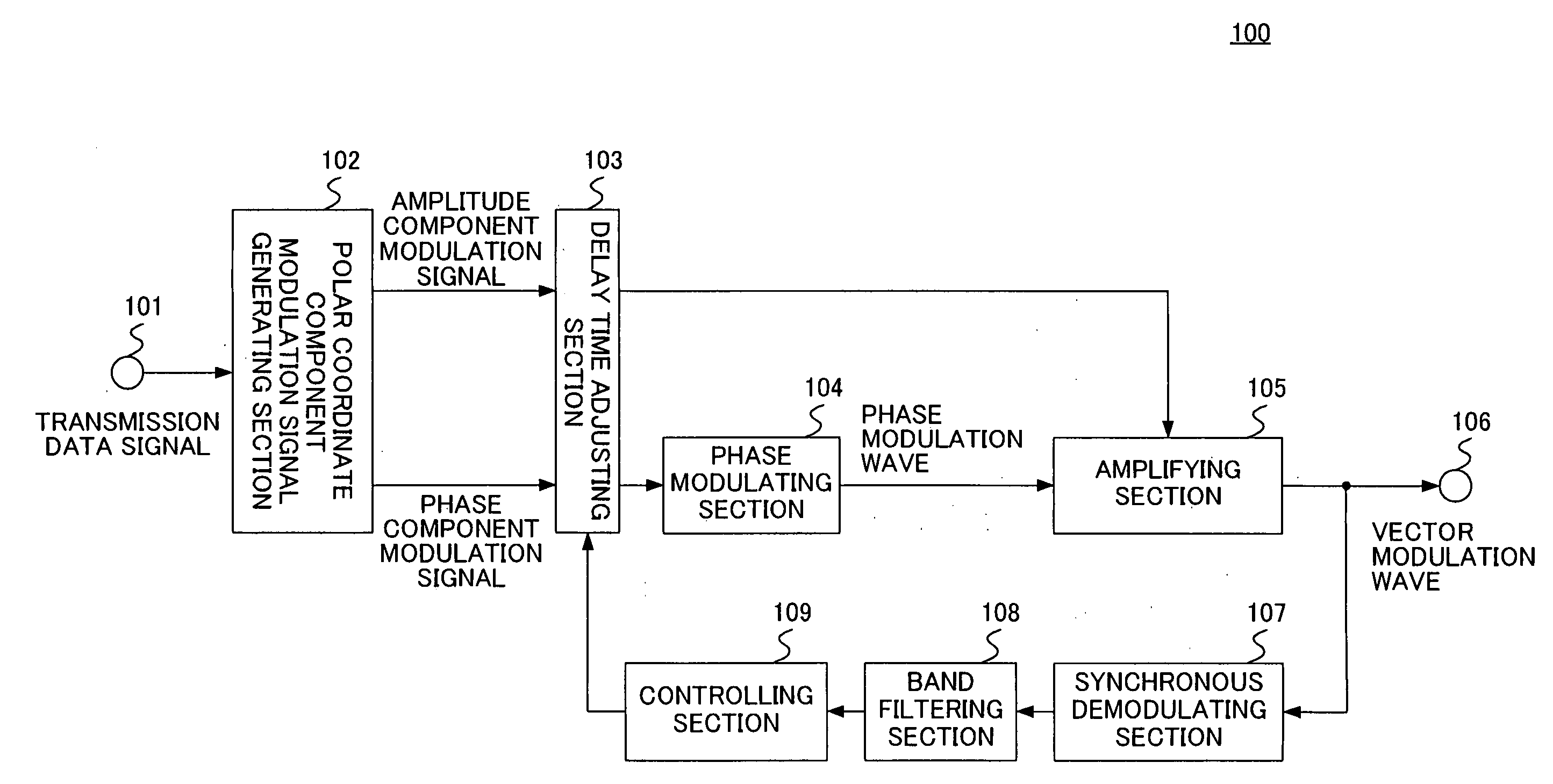
InactiveUS20060234652A1Reliable CorrectionReliable controlAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasDelayed timeMobile radio
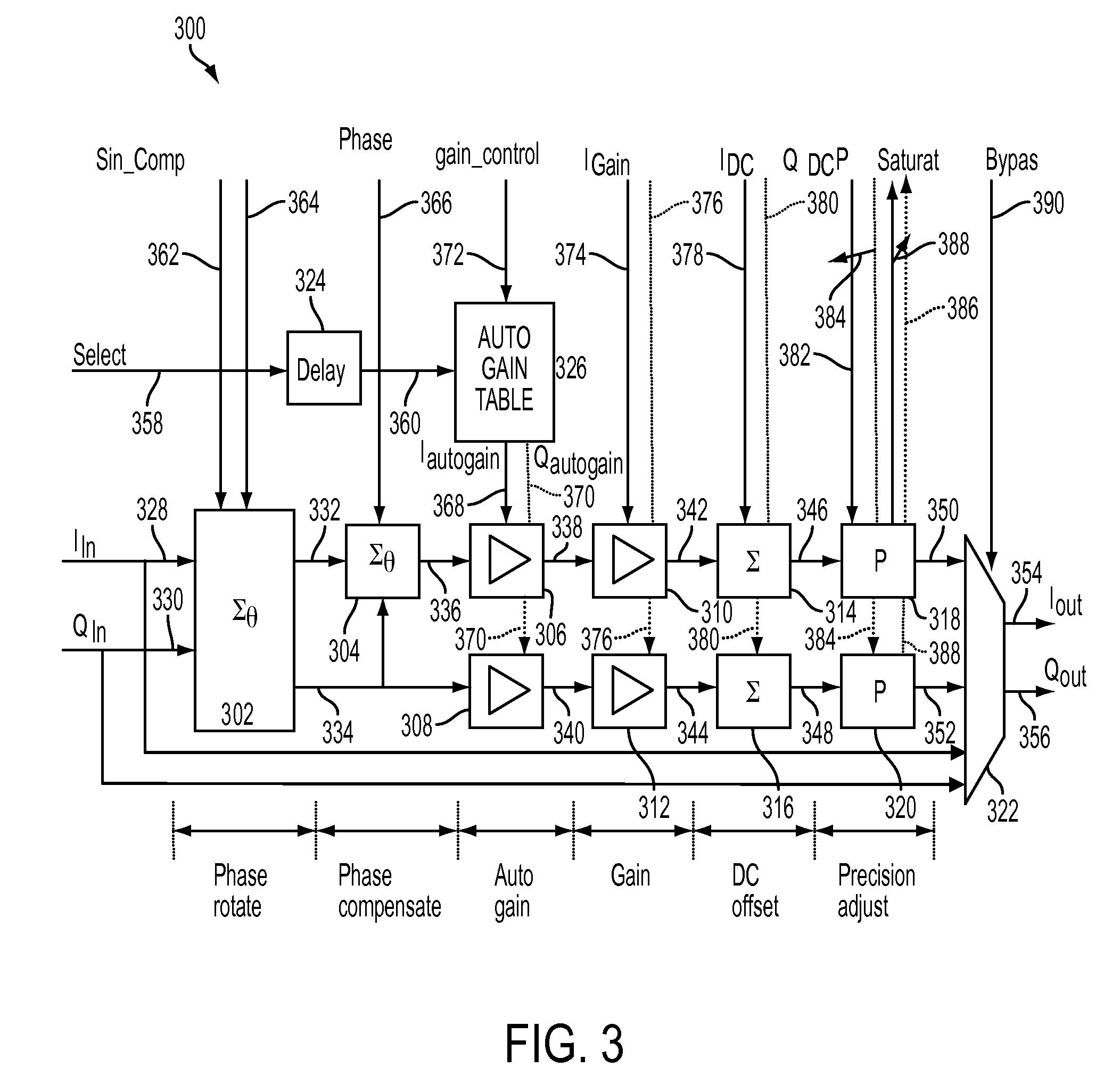
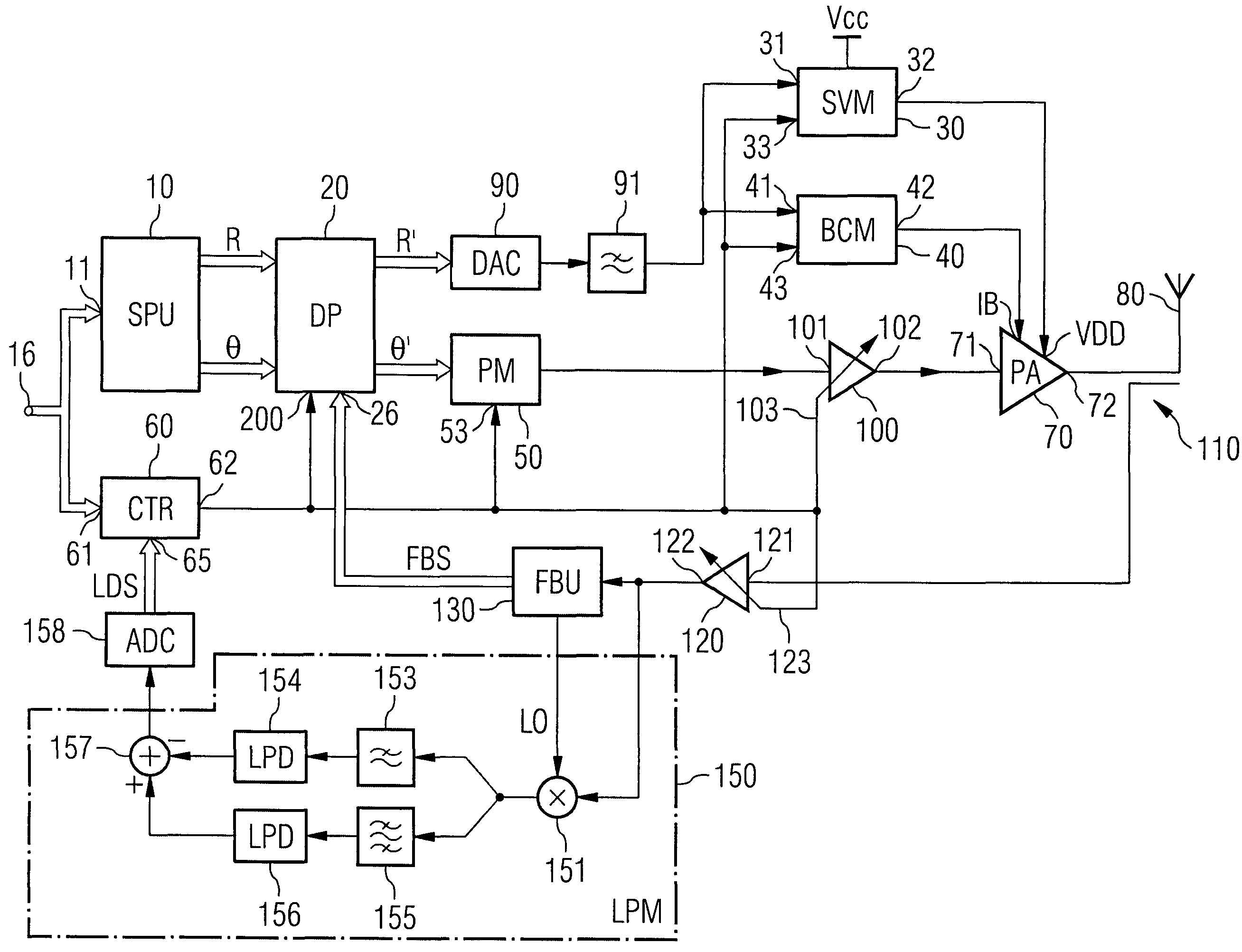
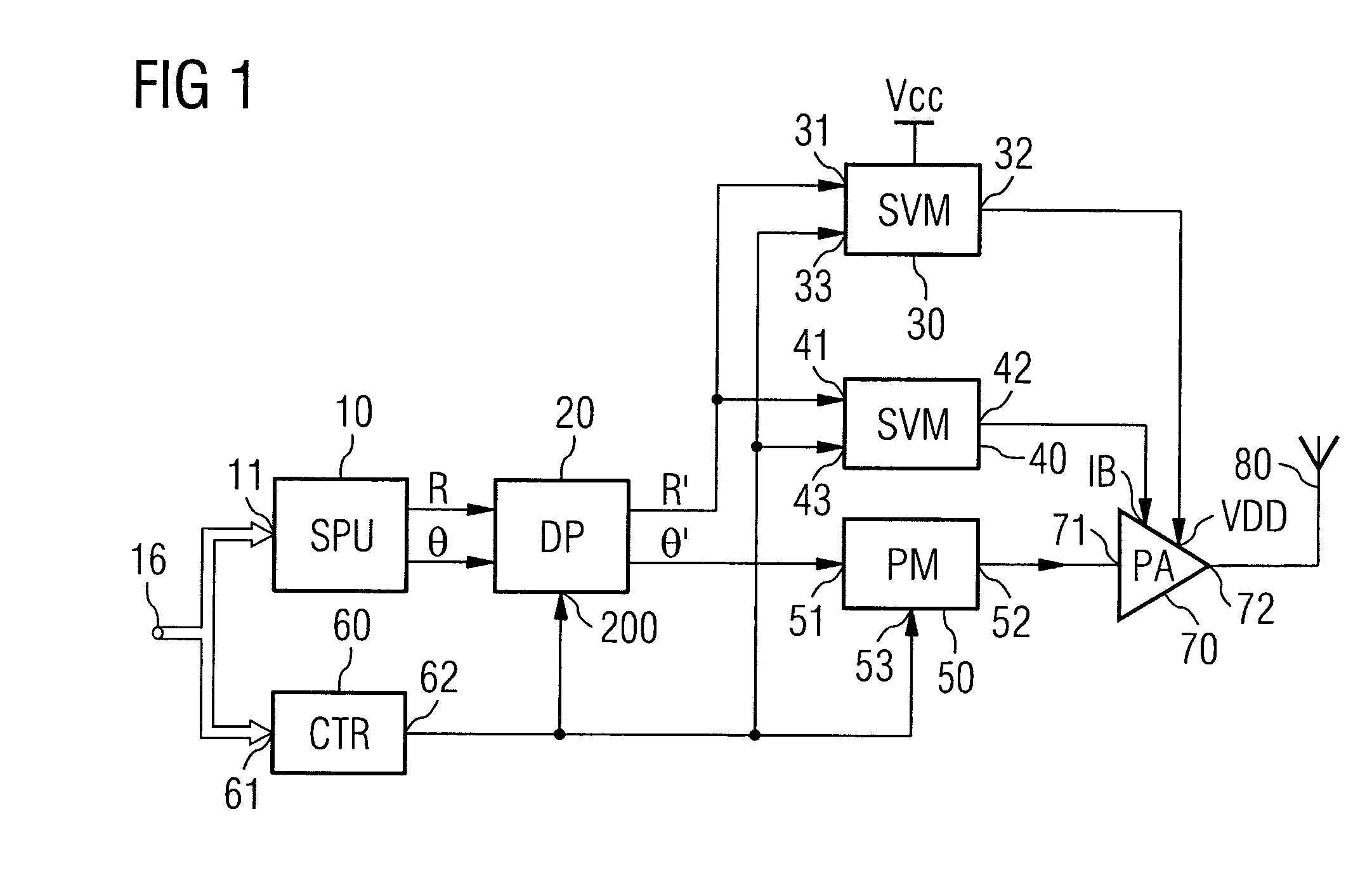
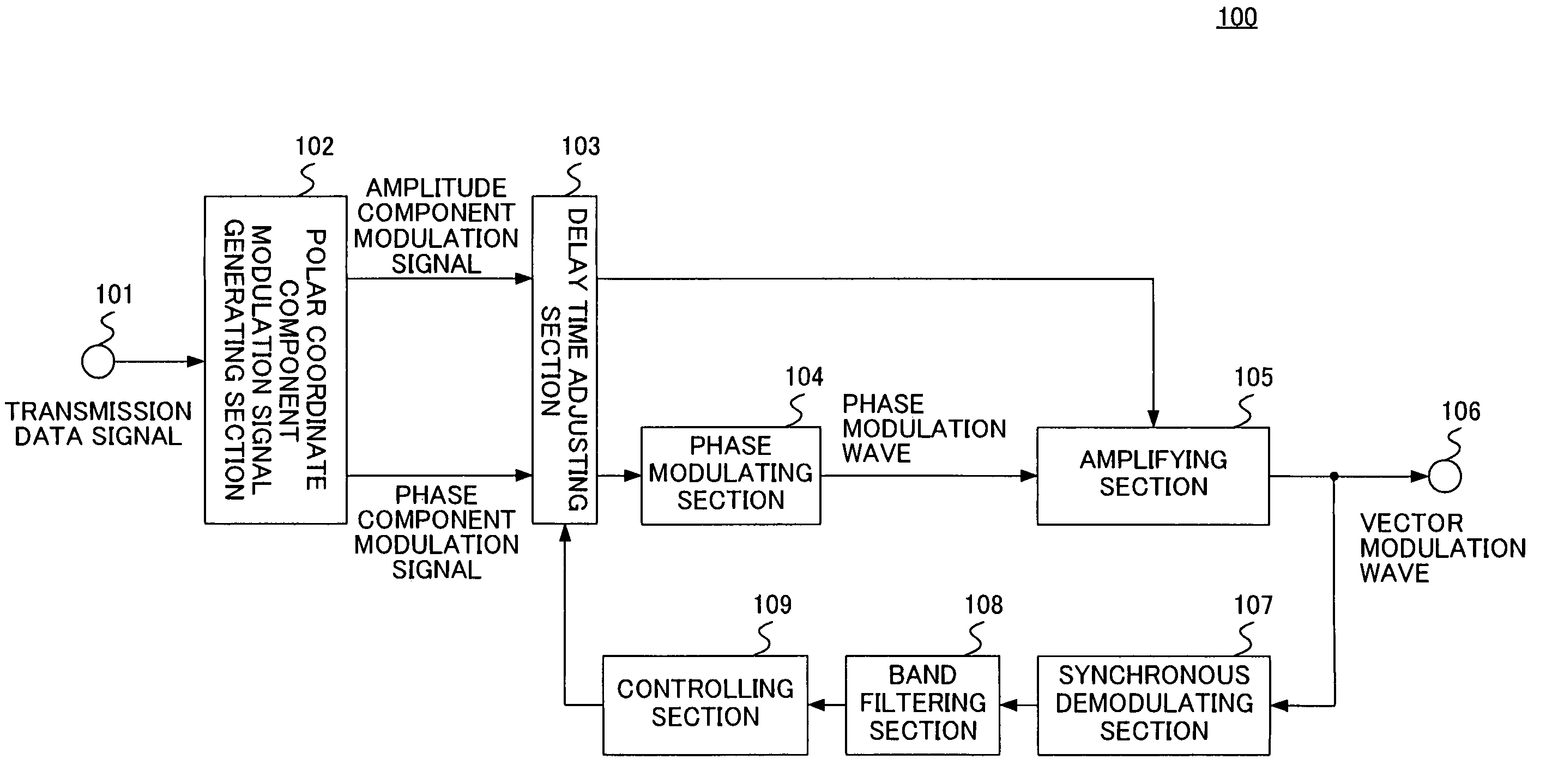
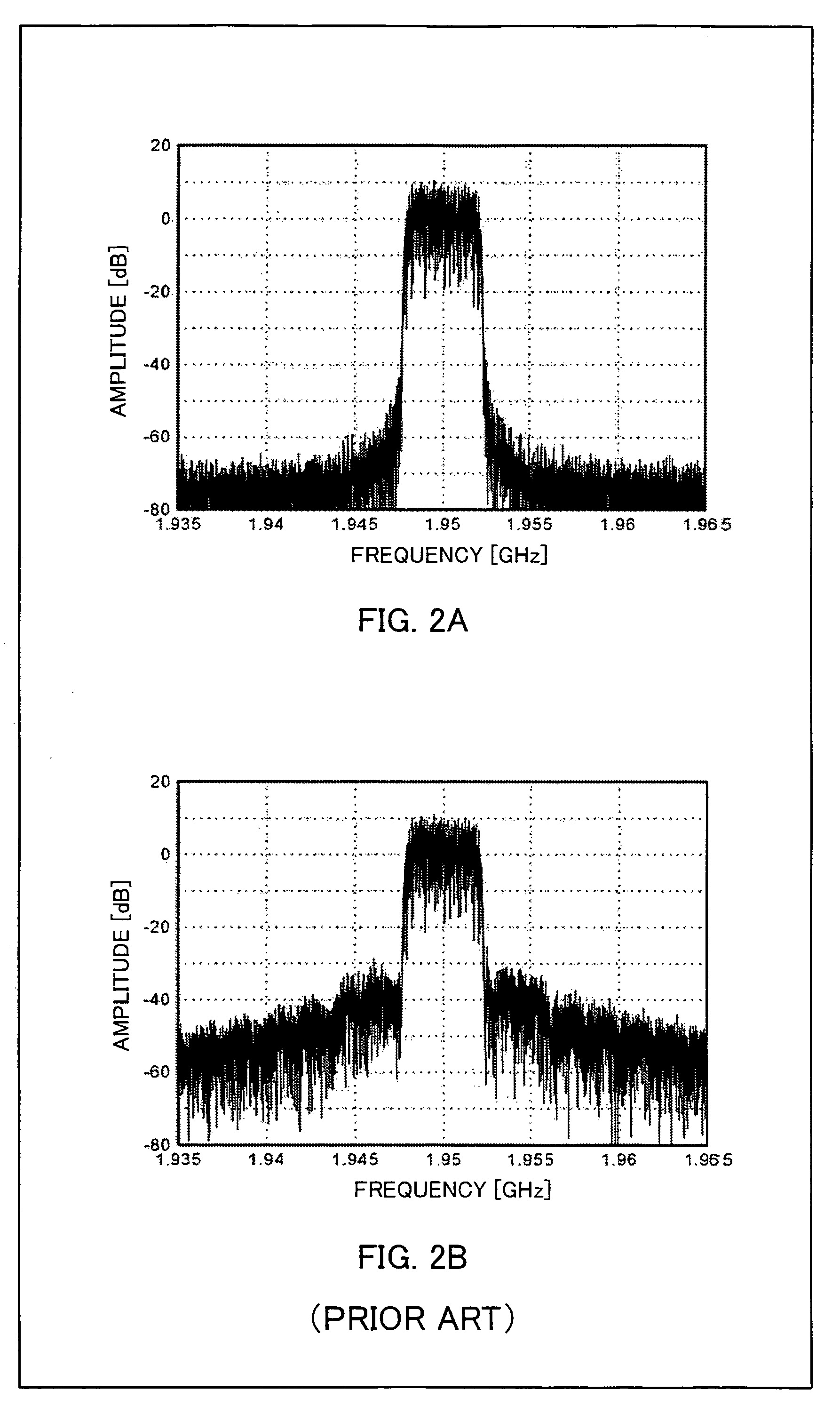
Transmission apparatus capable of reducing distortion of the vector modulation wave that is the transmission output to a sufficiently small level is provided. An amplifying section (105) generates a vector modulation wave based on an amplitude component modulation signal and a phase modulation wave. A synchronous demodulating section (107) detects the vector modulation wave, generates a synchronous demodulation signal, and sends this to a band filtering section (108). The band filtering section (108) extracts a signal of the frequency component of the distortion from a synchronous demodulation signal outputted by the synchronous demodulating section (107). A controlling section (109) then refers to the distortion component signal extracted by the band filtering section (108), controls a delay time adjusting section (103) in such a manner that the signal level of the distortion component becomes small, adjusts a delay time difference between the amplitude component modulation signal and the phase component modulation signal, and reduces distortion of the modulation wave.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
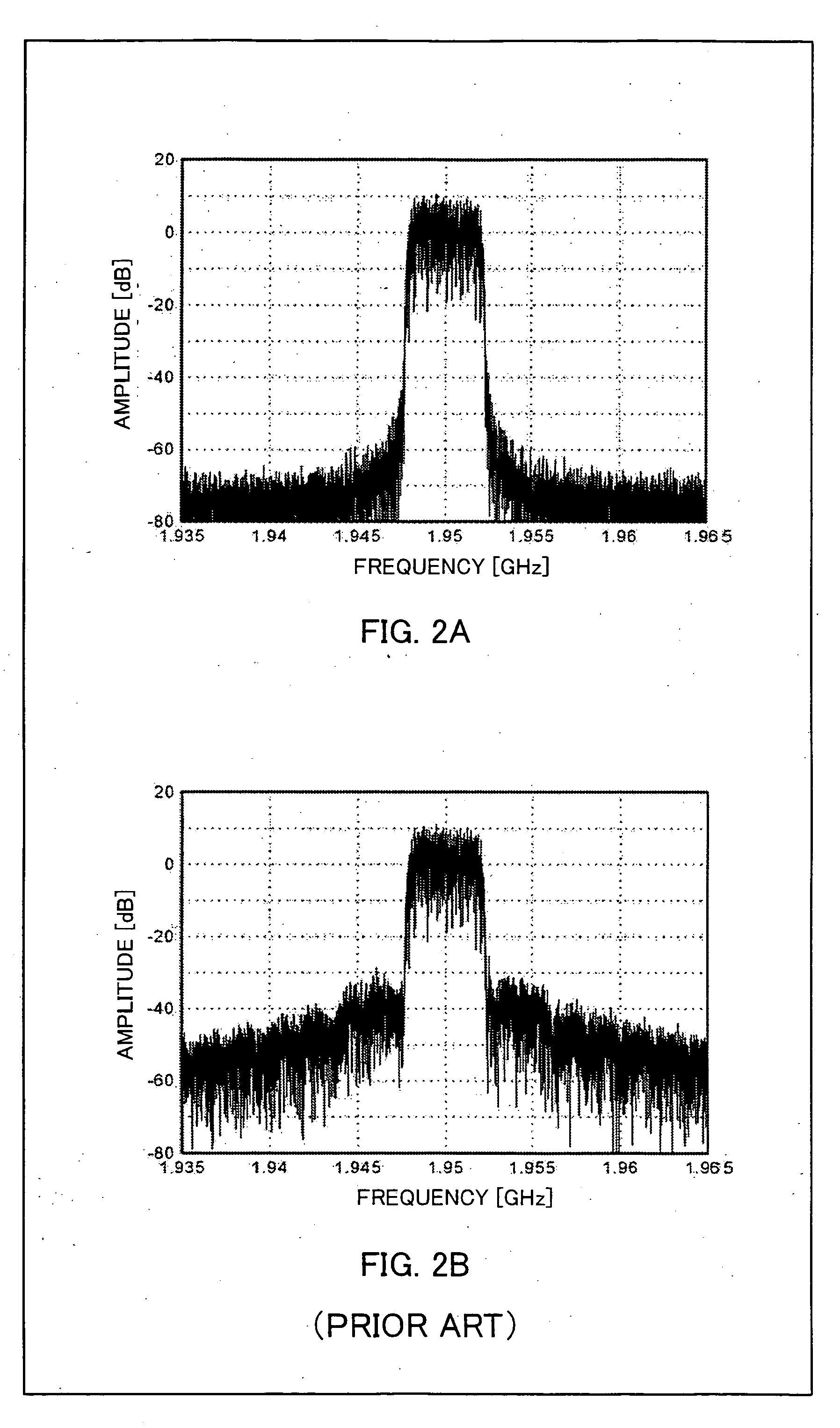
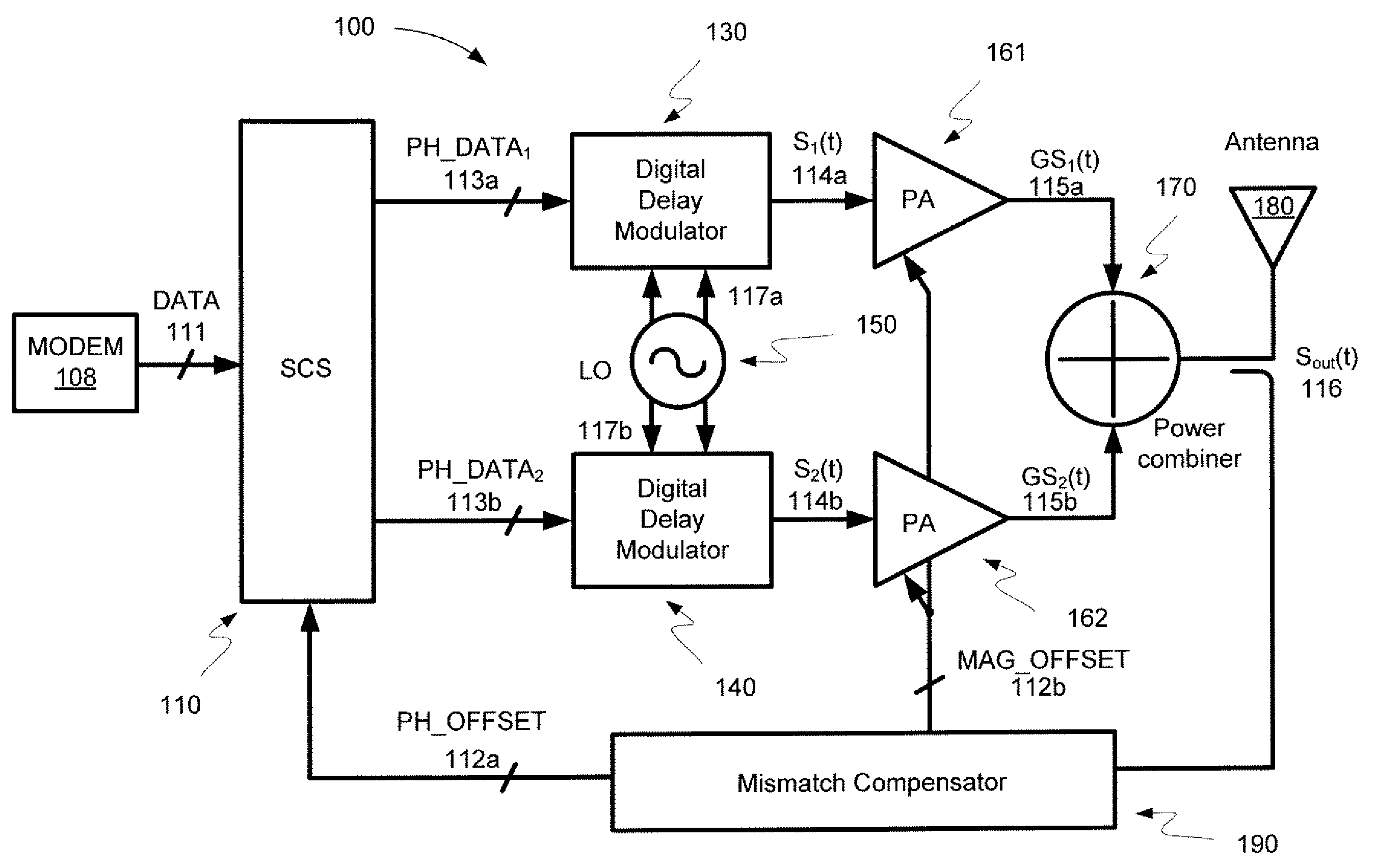
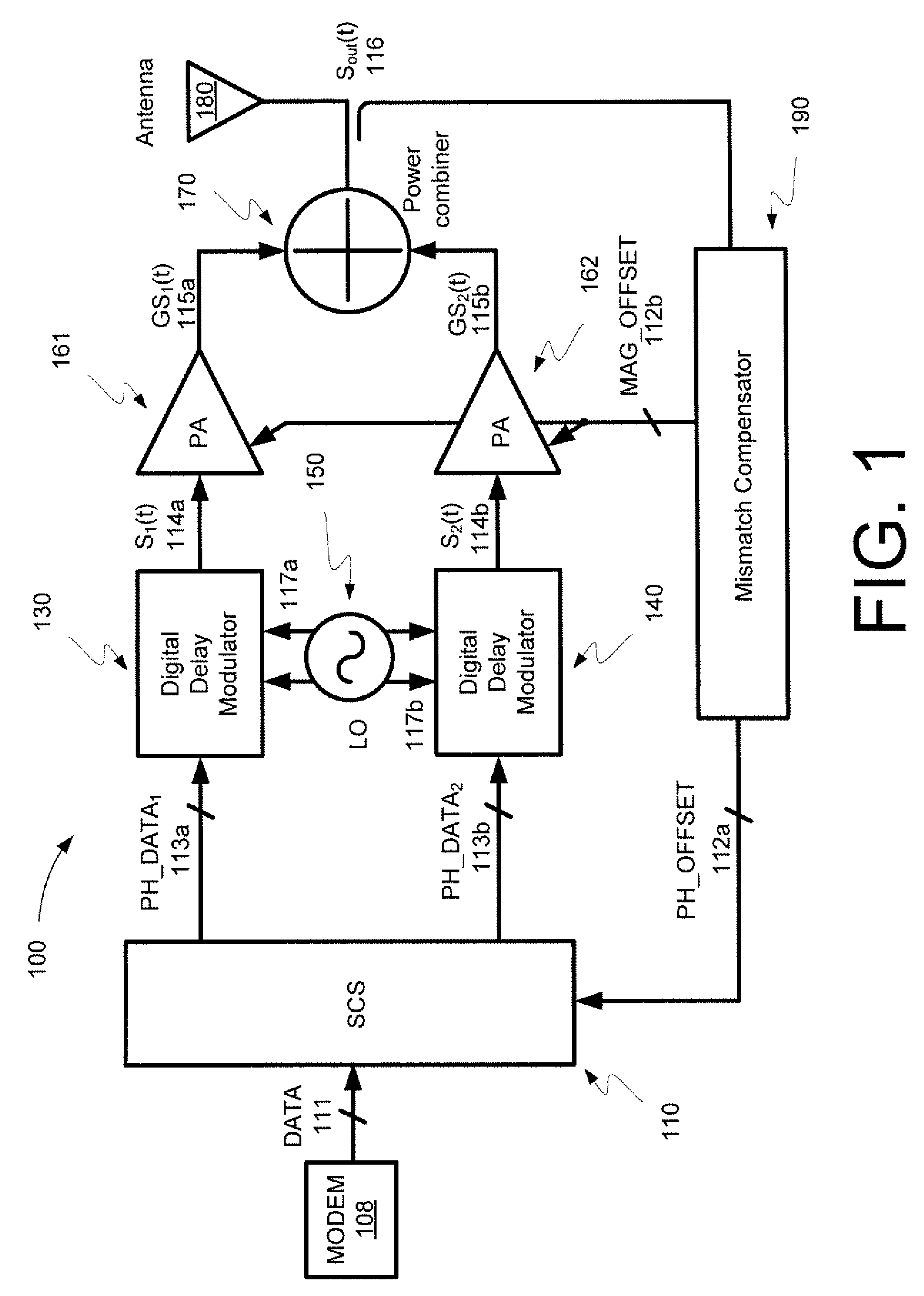
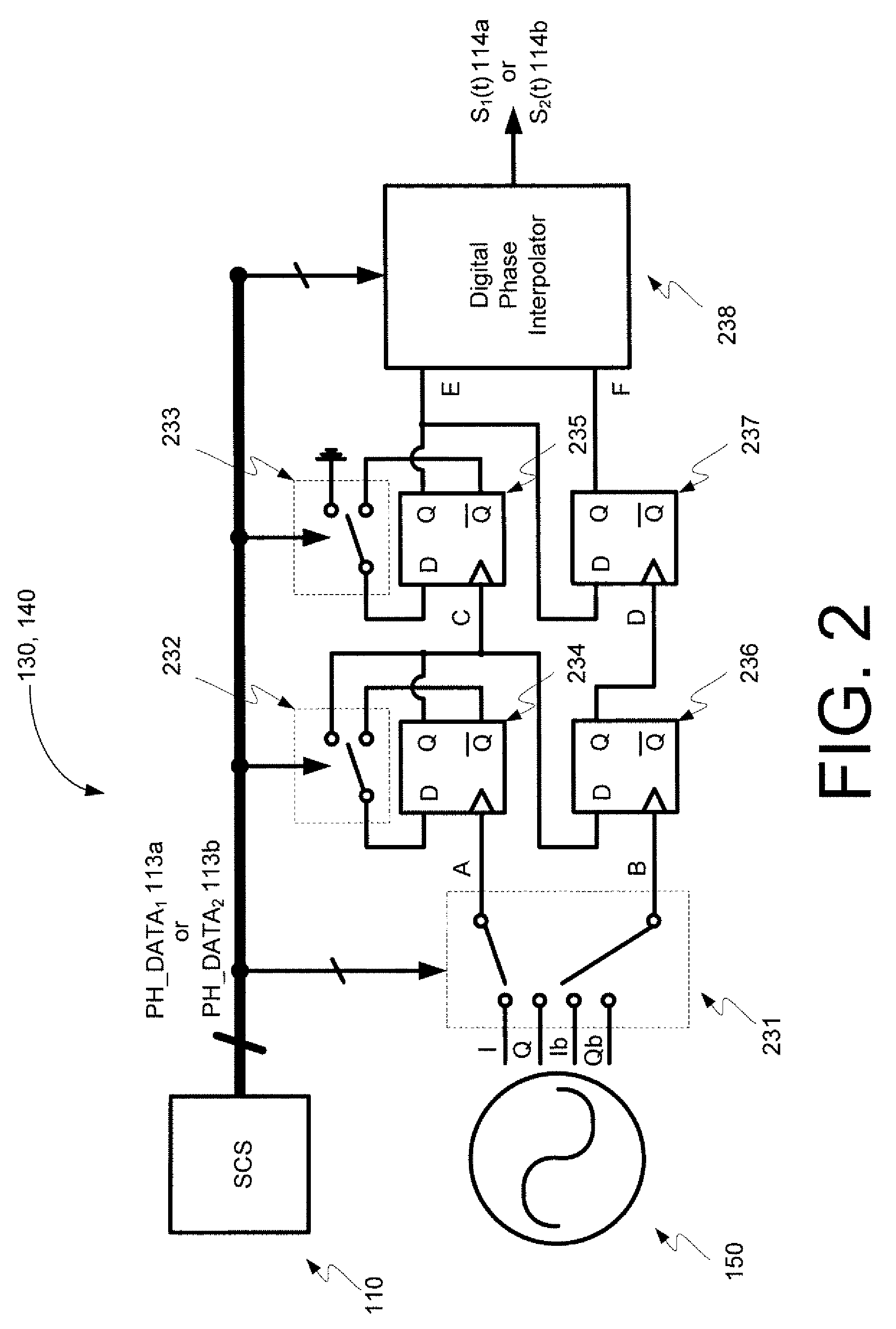
Digital linear amplification with nonlinear components (LINC) transmitter
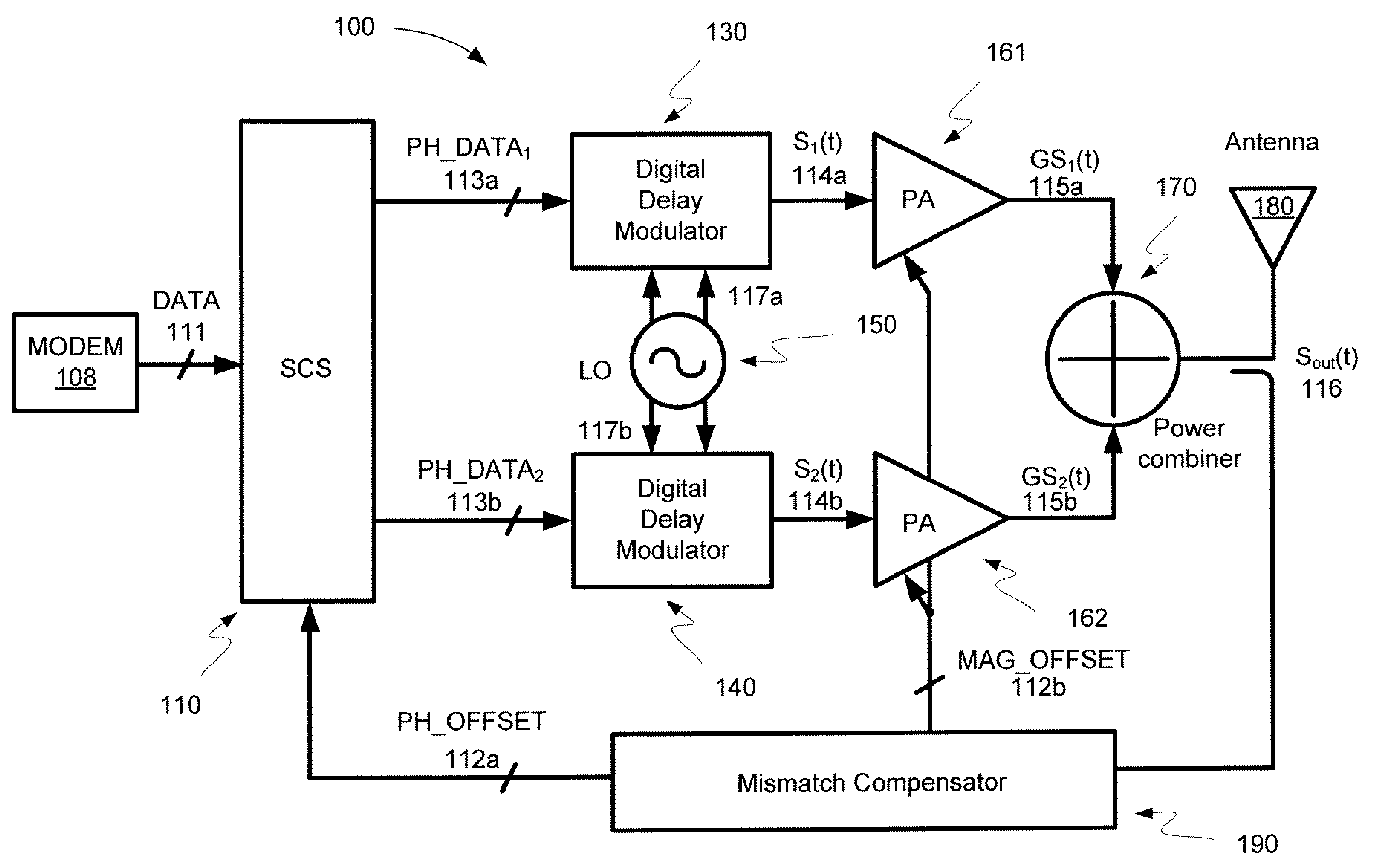
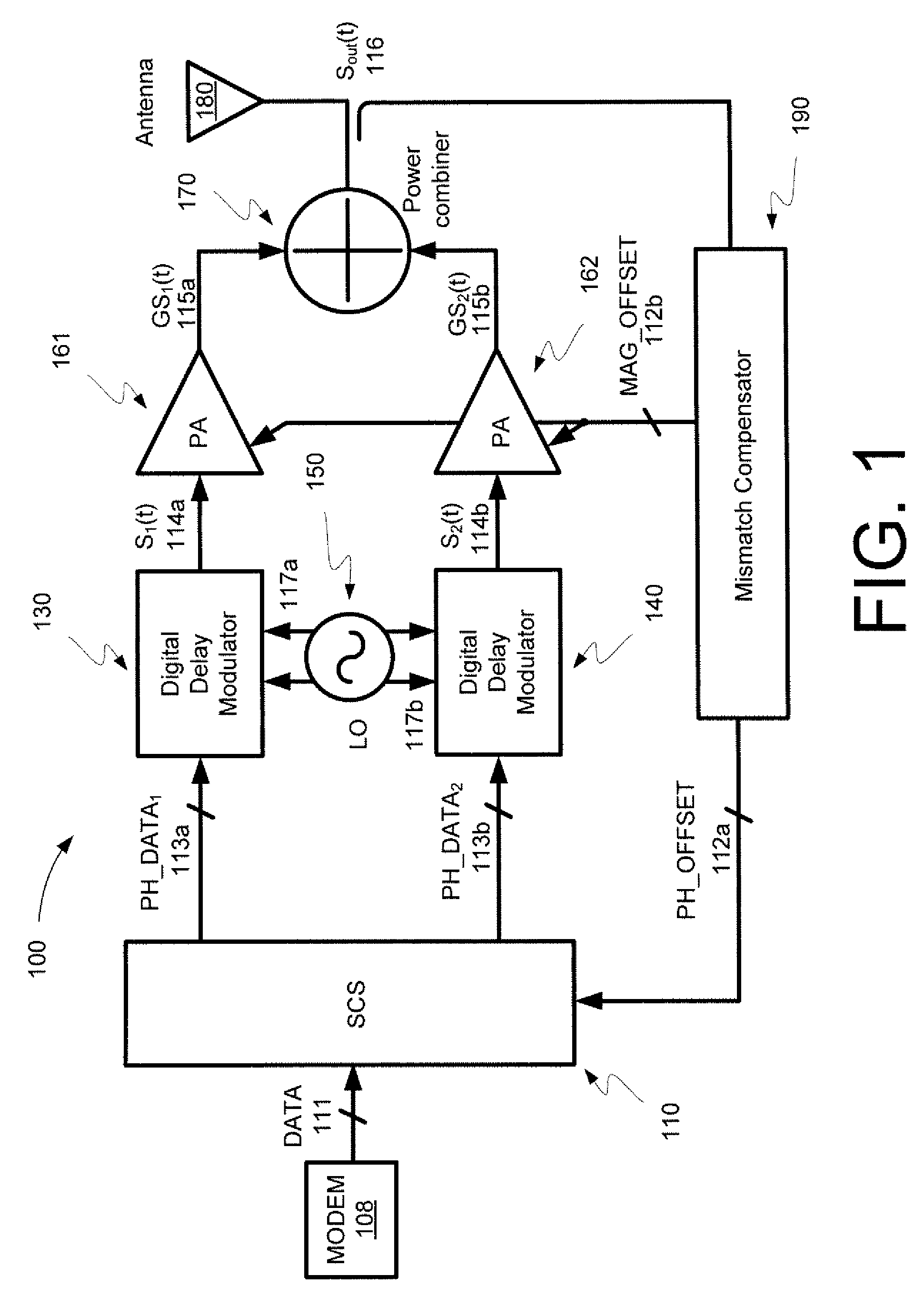
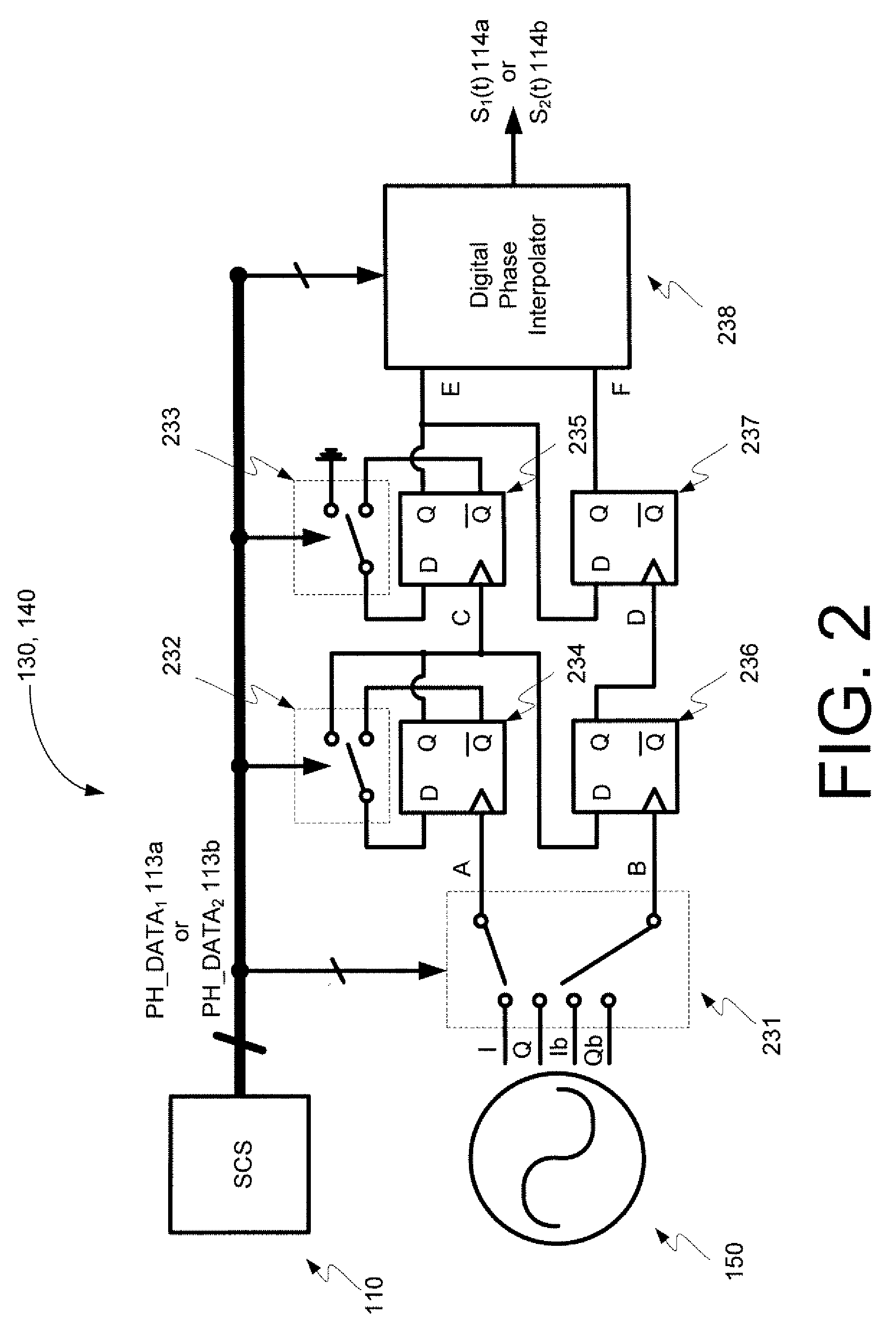
InactiveUS7889811B2Power amplifiersAngle to amplitude modulation conversionAudio power amplifierPower combiner
Embodiments of the invention may provide for a digital LINC (linear amplification with nonlinear components) transmitter. The digital LINC transmitter may include a signal component separator, at least one digital delay modulator, a frequency synthesizer, at least one power amplifier, a power combiner, an antenna, and a mismatch compensator. Additionally, systems and methods may be provided for compensating for phase and amplitude mismatches between two signal paths.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
Digital linear amplification with nonlinear components (LINC) transmitter
InactiveUS20090067541A1Power amplifiersAngle to amplitude modulation conversionPower combinerAudio power amplifier
Embodiments of the invention may provide for a digital LINC (linear amplification with nonlinear components) transmitter. The digital LINC transmitter may include a signal component separator, at least one digital delay modulator, a frequency synthesizer, at least one power amplifier, a power combiner, an antenna, and a mismatch compensator. Additionally, systems and methods may be provided for compensating for phase and amplitude mismatches between two signal paths.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
Transmission modulation apparatus, communication apparatus and mobile wireless apparatus
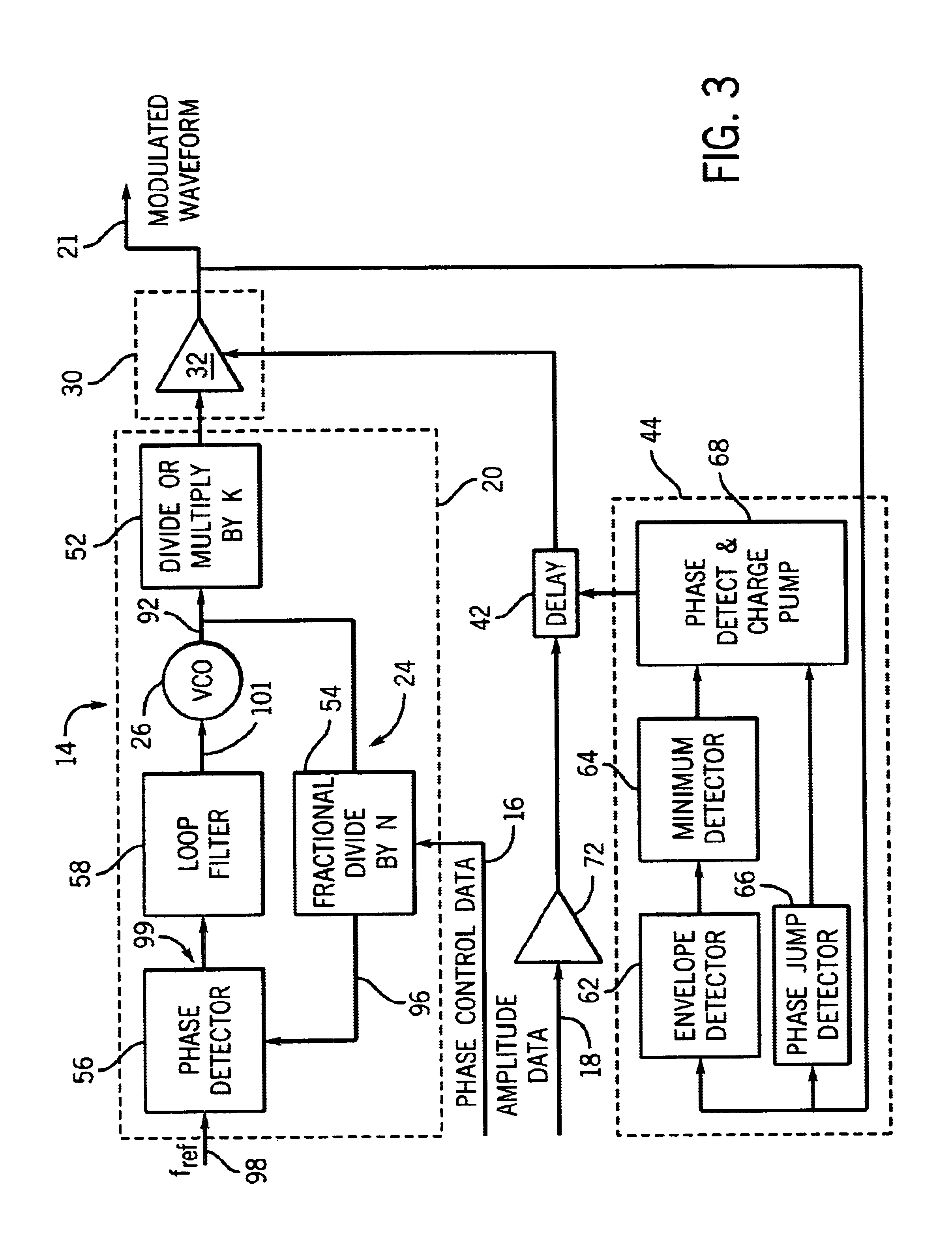
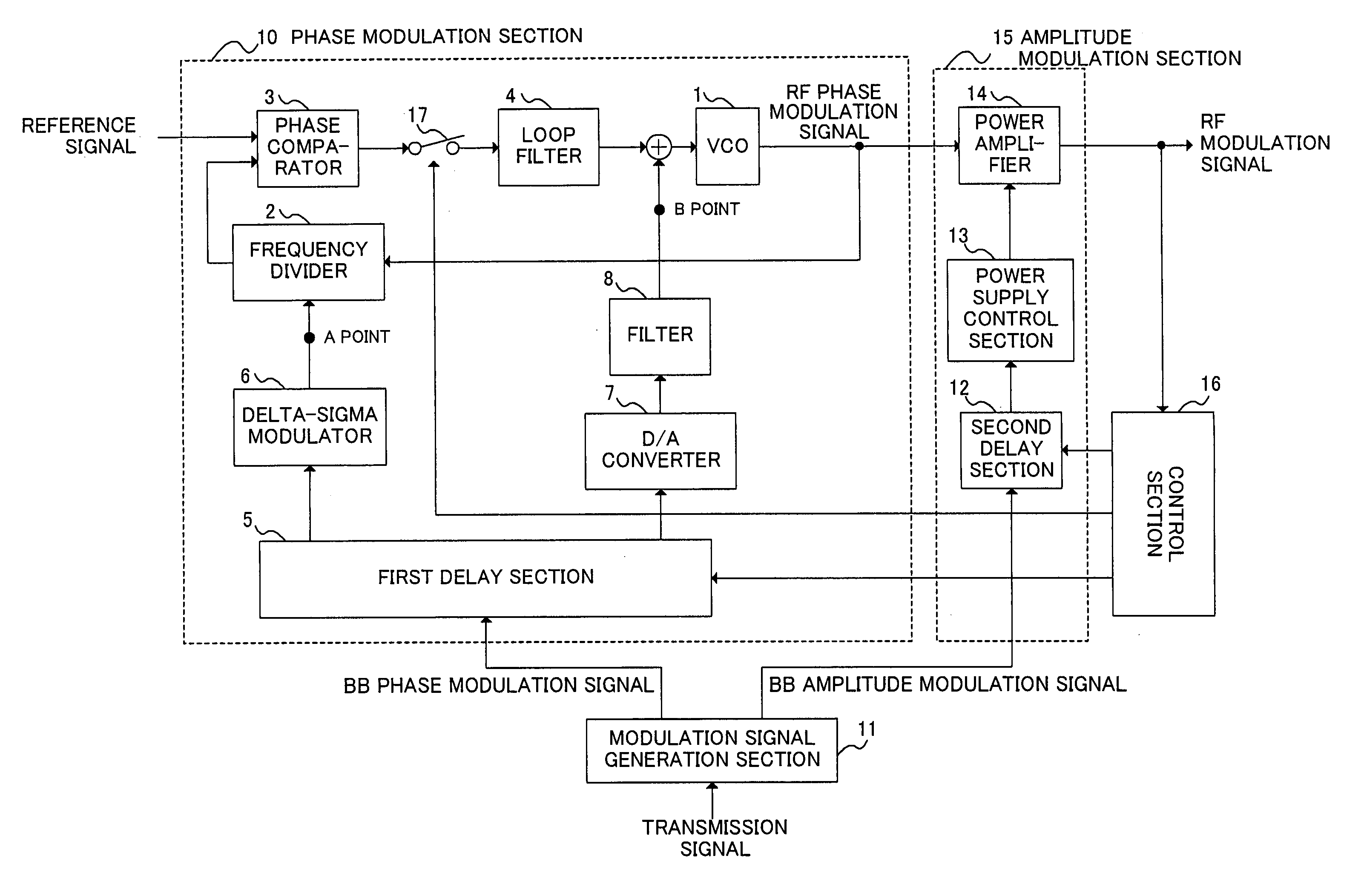
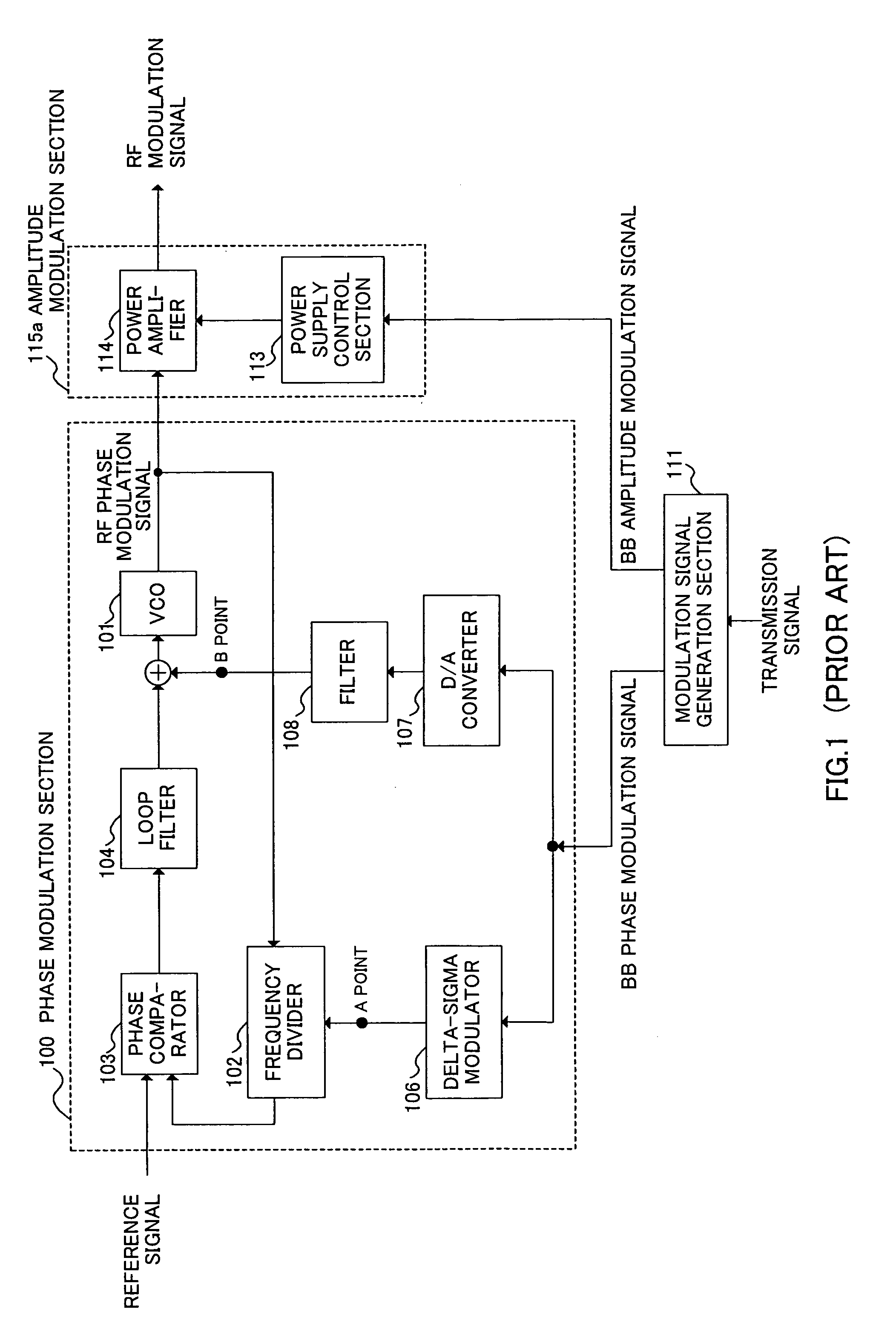
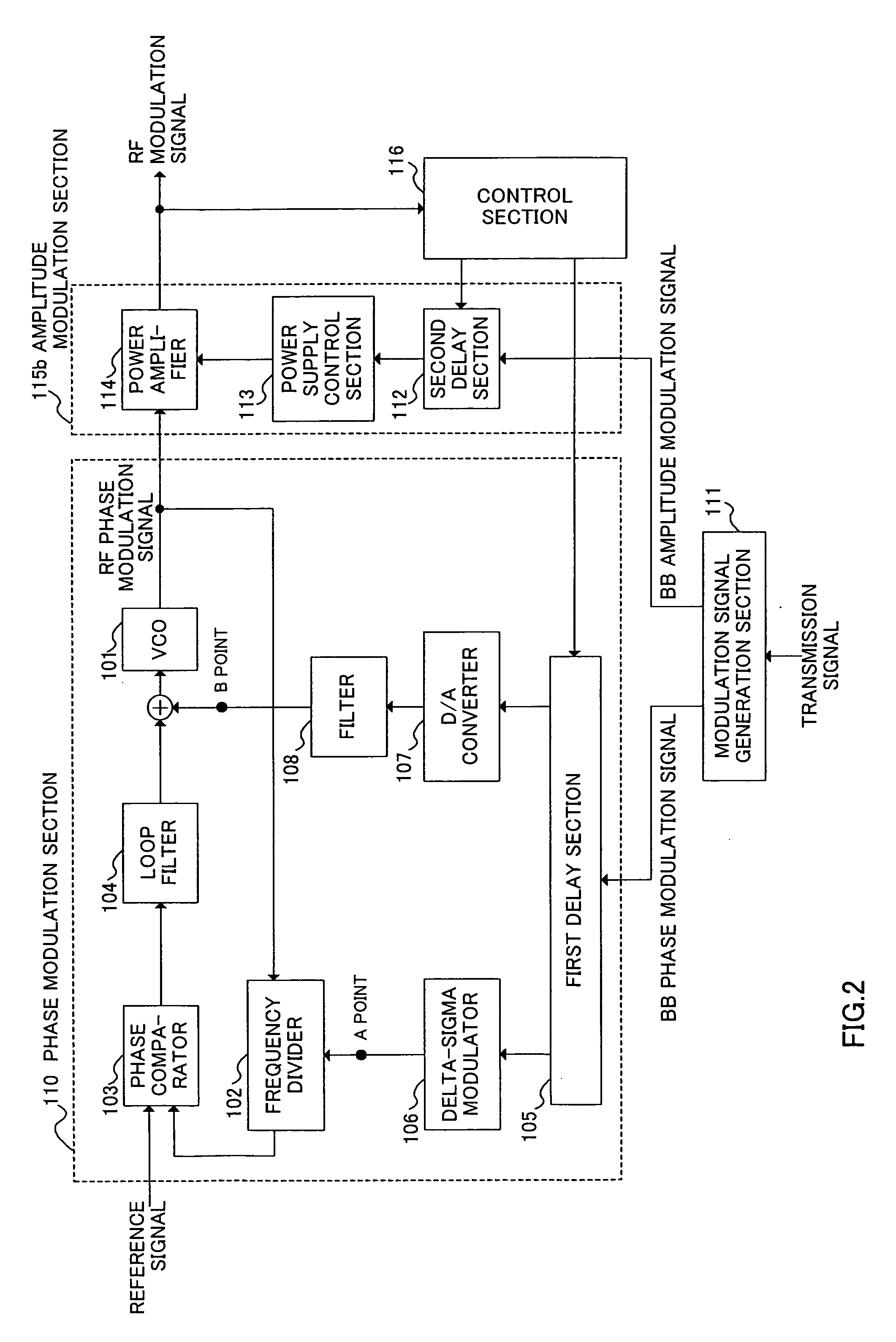
ActiveUS7276985B2Short timeAvoid delayAngle modulation detailsAngle to amplitude modulation conversionEngineeringPolar modulation
Provided is a transmission modulation apparatus, using polar modulation of two-point modulation scheme, capable of completing a timing adjustment of a BB phase modulation signal and BB amplitude modulation signal in a short time. A phase modulation section (10) that performs two-point modulation with a PLL circuit is provided with a switch (17) to make the PLL circuit open loop, and when a first delay section (5) corrects the deviation in synchronization between the BB phase modulation signal and BB amplitude modulation signal, the switch (17) is turned off to make the PLL circuit open loop.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods and apparatus for offset chirp modulation
ActiveUS20050058218A1Relatively large bandwidthResolving range ambiguityFrequency-division multiplex detailsAngle to amplitude modulation conversionData streamTime delays
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
RF transmission error detection and correction module
A radio frequency (RF) transmission correction module includes an RF transmission error detection module and a correction module. The error detection module includes an RF envelope detector, a signal conversion module, and an error detection module. The RF envelope detector is operably coupled to produce an envelope signal from a transmit RF signal, wherein the envelope signal represents at least one of local oscillation leakage and in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) imbalance. The signal conversion module is operably coupled to convert the envelope signal into an error signal in accordance with baseband processing of the transmit RF signal. The error detection module is operably coupled to determine at least one of a local oscillation leakage value and an I and Q imbalance value from the error signal. The correction module is operably coupled to produce at least one of a local oscillation leakage correction signal and an I and Q imbalance correction signal based on the at least one of the local oscillation leakage value and the I and Q imbalance value, respectively.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Transmission apparatus, communication apparatus and mobile radio apparatus
InactiveUS7358829B2Reduce distortion problemsEasy to adjustAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasDelayed timeControl delay
Transmission apparatus capable of reducing distortion of the vector modulation wave that is the transmission output to a sufficiently small level is provided. An amplifying section (105) generates a vector modulation wave based on an amplitude component modulation signal and a phase modulation wave. A synchronous demodulating section (107) detects the vector modulation wave, generates a synchronous demodulation signal, and sends this to a band filtering section (108). The band filtering section (108) extracts a signal of the frequency component of the distortion from a synchronous demodulation signal outputted by the synchronous demodulating section (107). A controlling section (109) then refers to the distortion component signal extracted by the band filtering section (108), controls a delay time adjusting section (103) in such a manner that the signal level of the distortion component becomes small, adjusts a delay time difference between the amplitude component modulation signal and the phase component modulation signal, and reduces distortion of the modulation wave.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
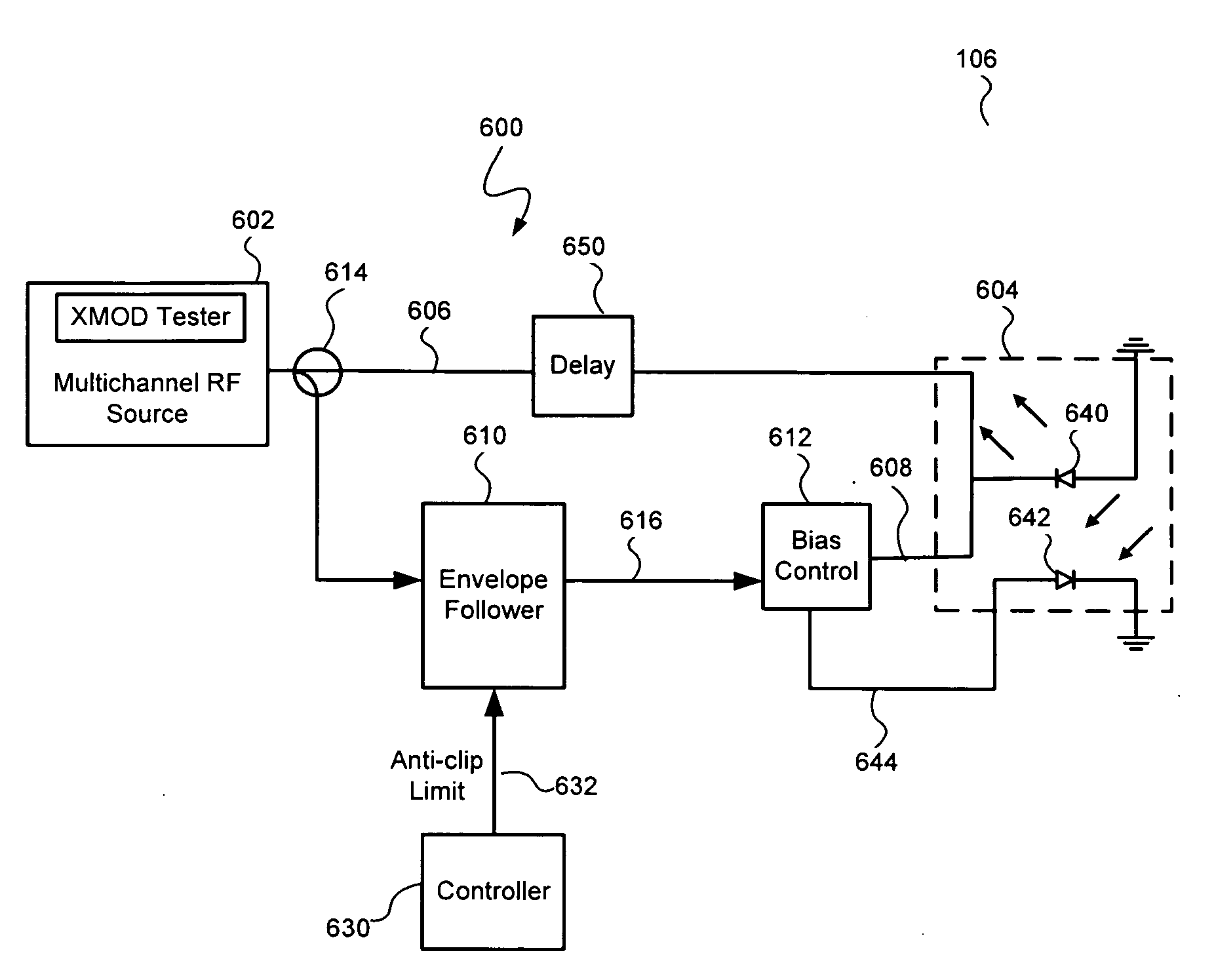
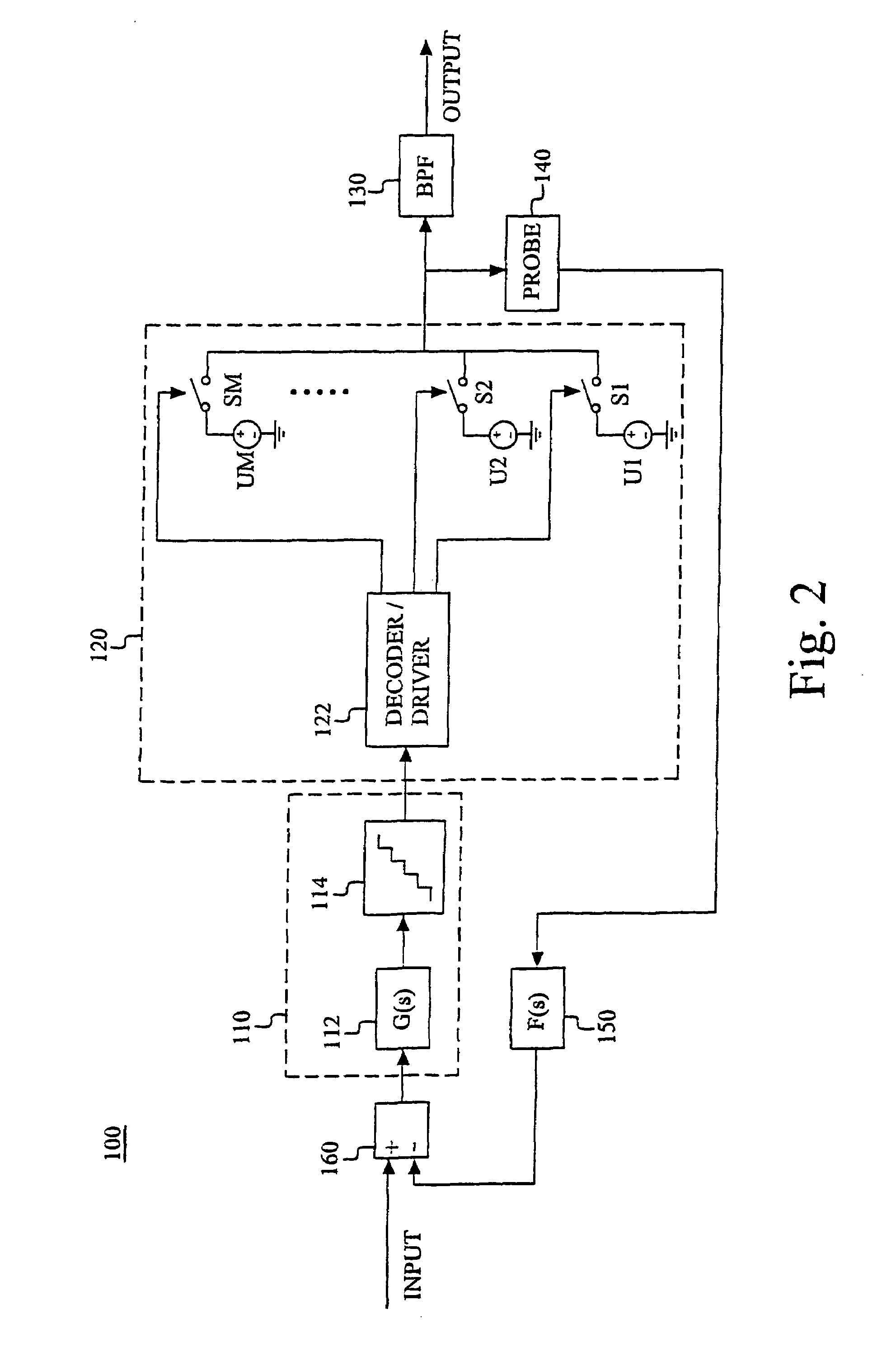
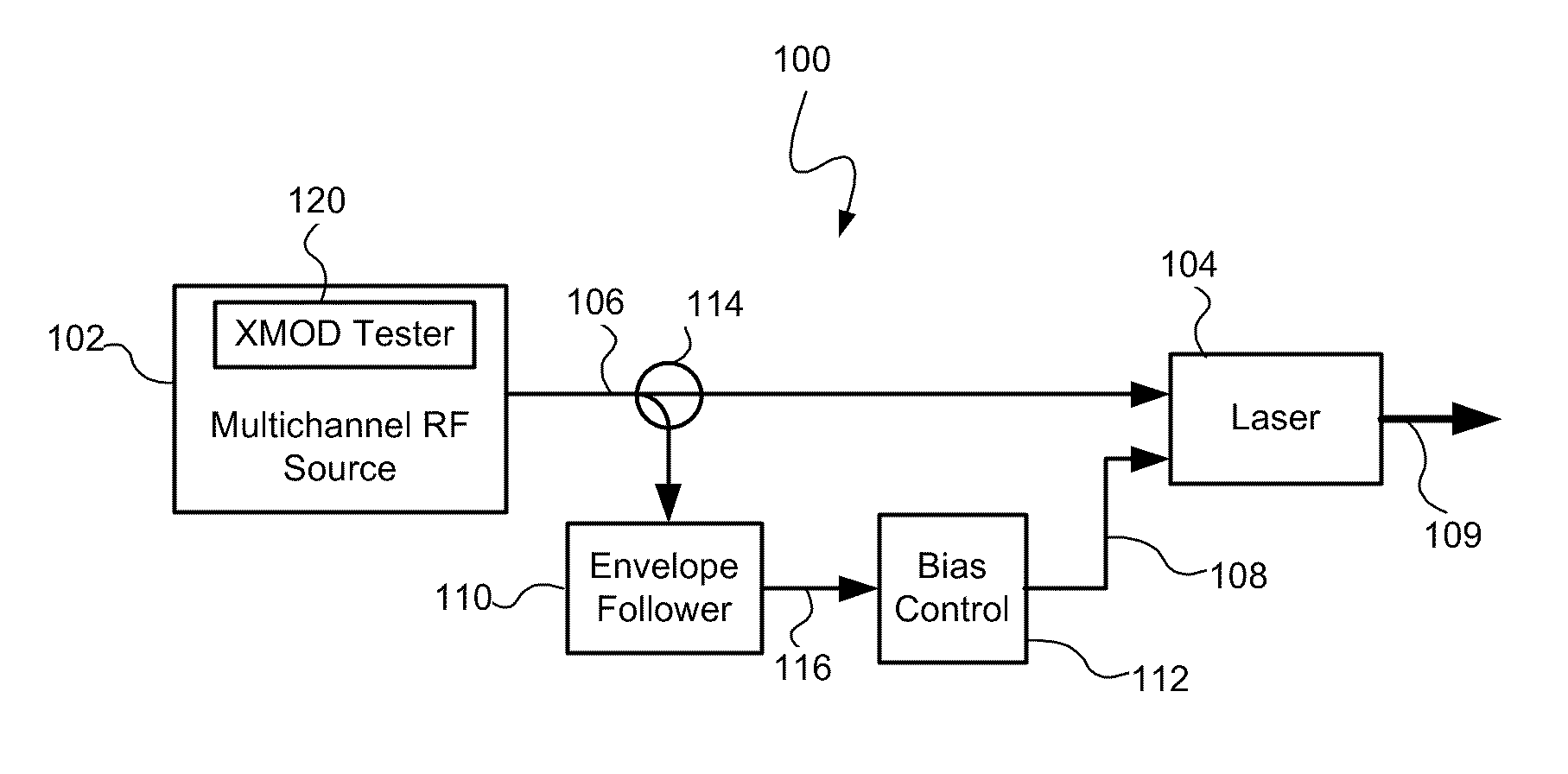
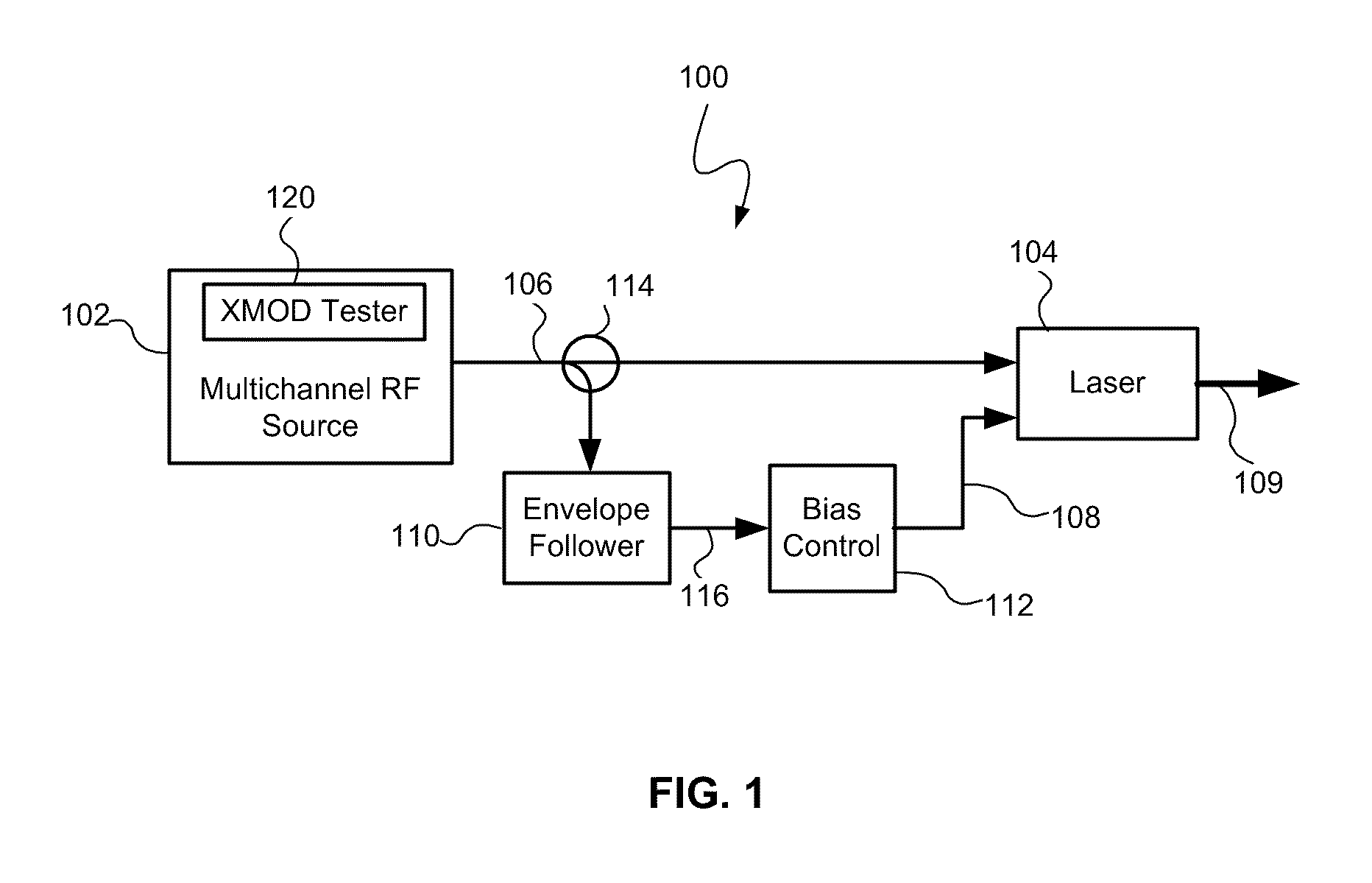
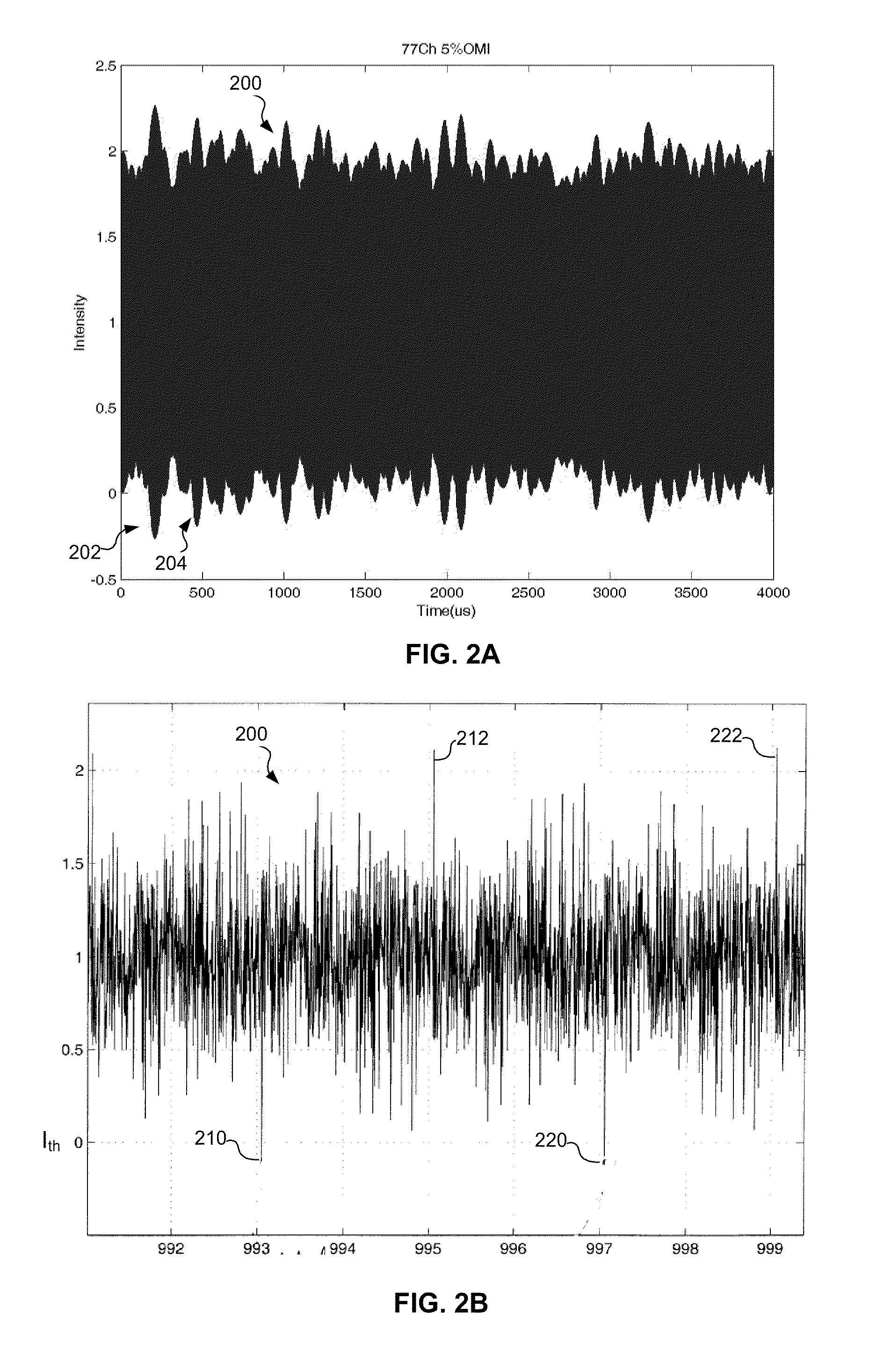
Reducing cross modulation in multichannel modulated optical systems with Anti-clipping
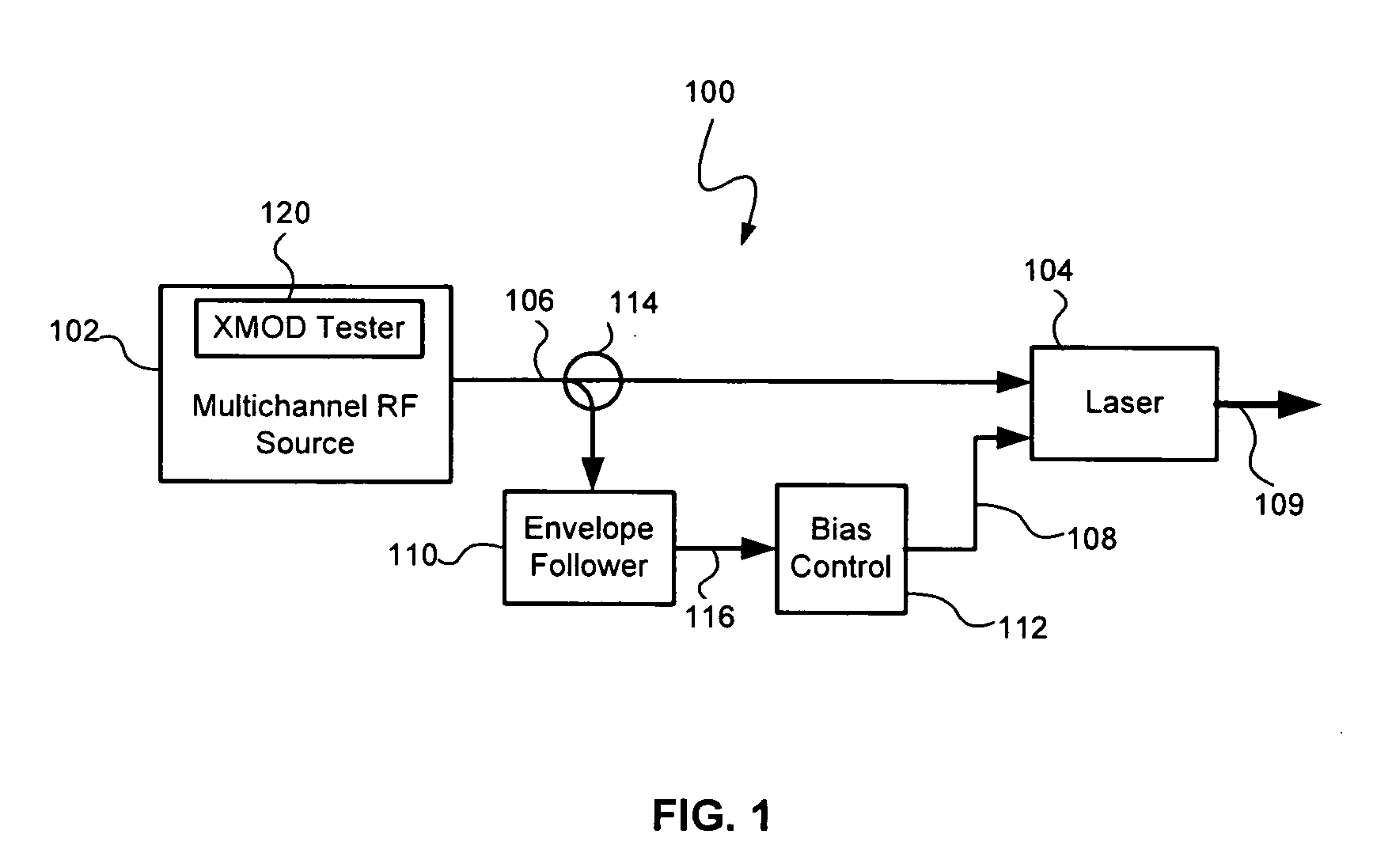
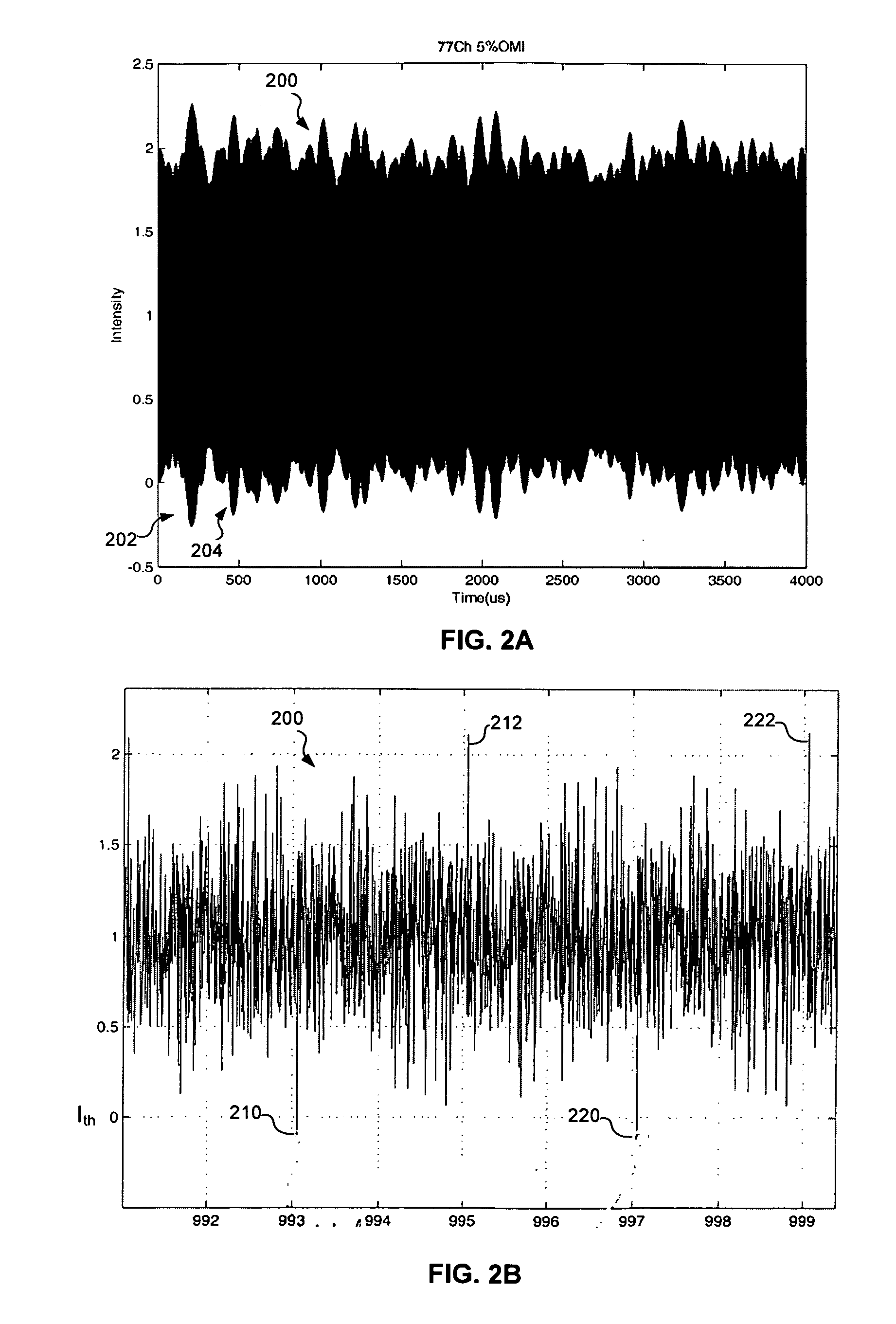
A modulated optical system with anti-clipping reduces or corrects clipping that might occur in the laser as a result of negative spikes or peaks in a multichannel RF signal. The system generally detects an envelope of the RF signal to generate an anti-clipping signal that follows at least a portion of the envelope and prevents one or more negative peaks from causing clipping by adjusting a bias current in response to the anti-clipping signal. The system may also reduce cross modulation by clamping the anti-clipping signal at an anti-clipping limit during lower power periods of the RF signal.
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
Polar modulation using amplitude modulated quadrature signals
ActiveUS7023292B2Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAngle to amplitude modulation conversionControl signalPhase splitter
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Electromagnetic wave transmitter systems, methods and articles of manufacture
InactiveUS6903619B2Amplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsPower amplifiersTransceiverWide band
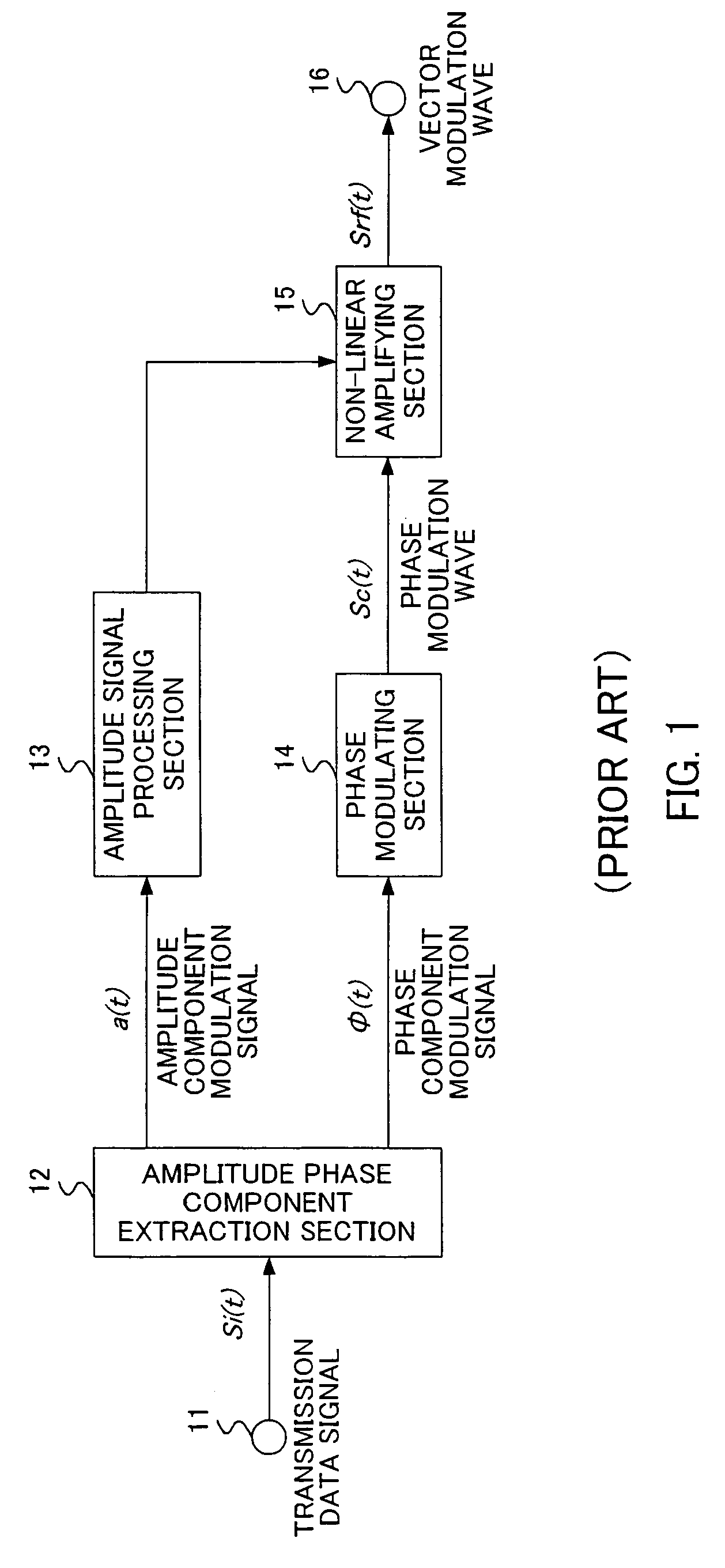
A transceiver and transmitter are shown. A baseband processor receives a signal for transmission. It converts the signal into amplitude and phase polar components. Each component is then processed—the phase component through a wideband phase modulator and the amplitude component through a wideband amplitude modulator, and the components are then recombined for further processing or transmission.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Integrated modulators and demodulators
InactiveUS20040091031A1Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsAngle to amplitude modulation conversionEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
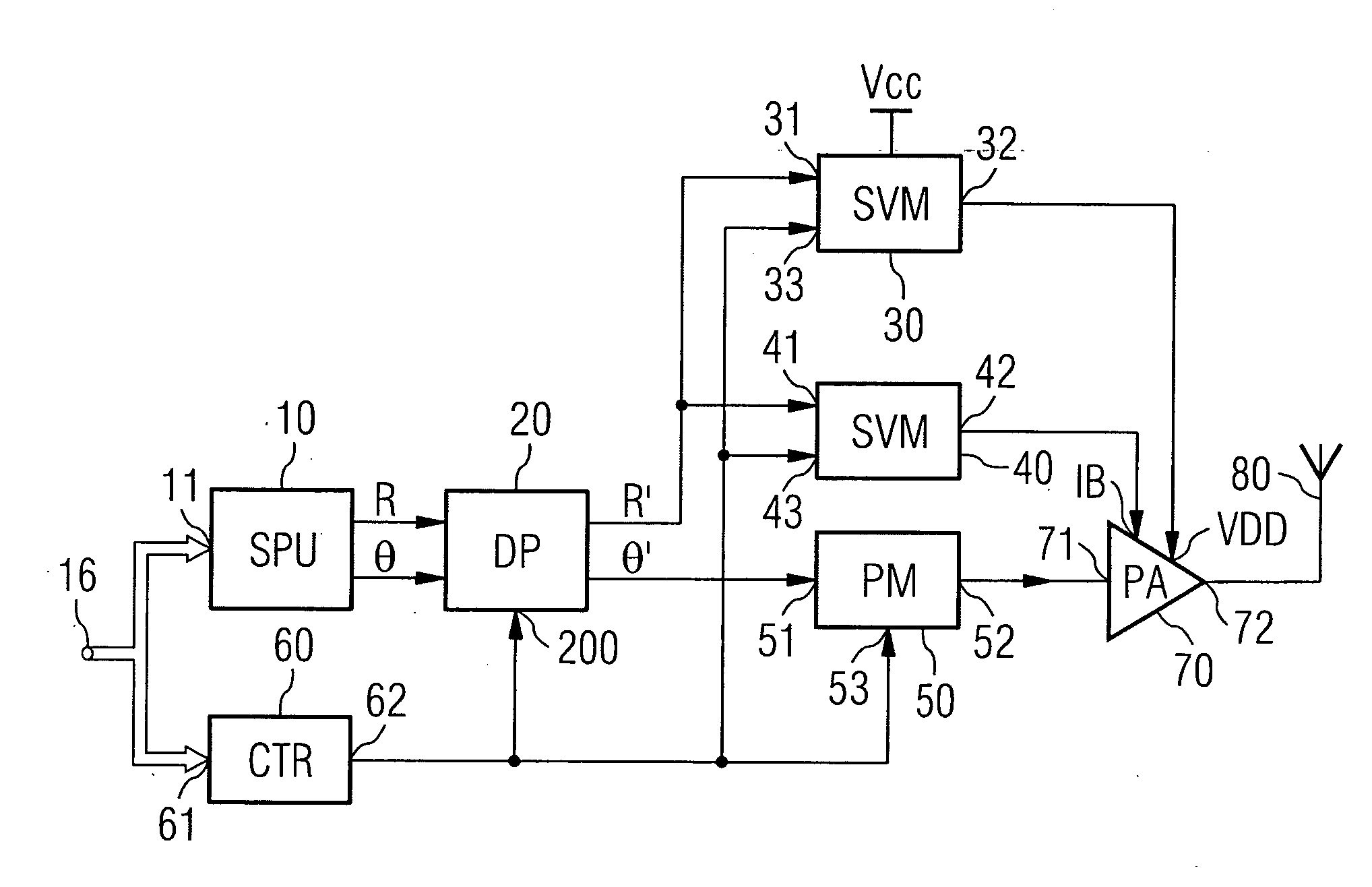
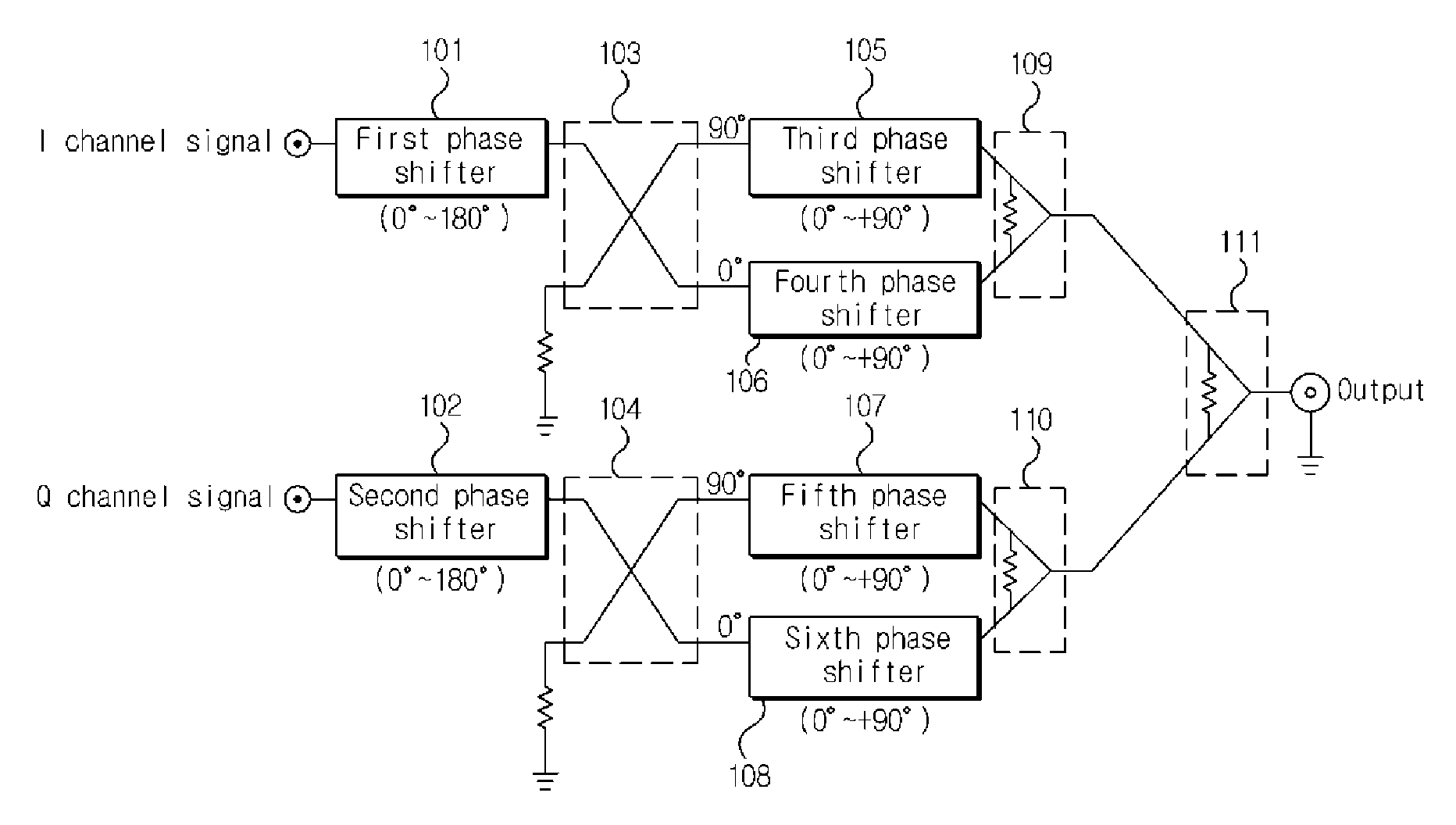
Vector modulator
InactiveUS20120294388A1Simple system configurationModulation of signal can be easilySimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAngle to amplitude modulation conversionEngineeringMechanical engineering
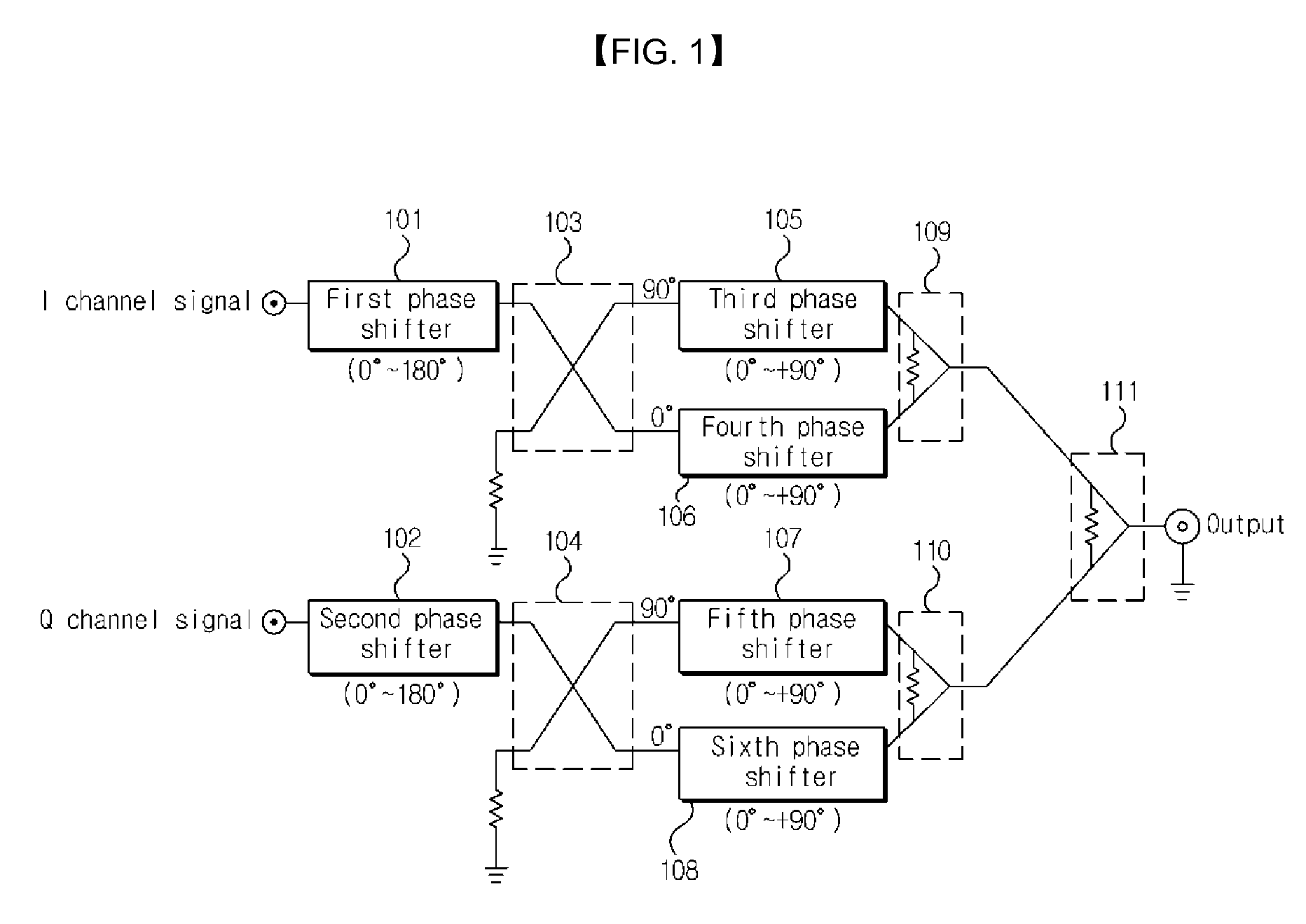
Disclosed is a vector modulator. The vector modulator can control the amplitude and phase of an input signal, by not using amplitude variable attenuators but using phase shifters. Further, the vector modulator has a simple configuration and enables an input signal to be exactly modulated. Furthermore, the vector modulator can modulate the phase of an input signal throughout all areas in the polar coordinate system.
Owner:LS IND SYETEMS CO LTD
Data receiving apparatus for receiving data frame using constellation mapping scheme and data transmission apparatus for transmitting the data frame
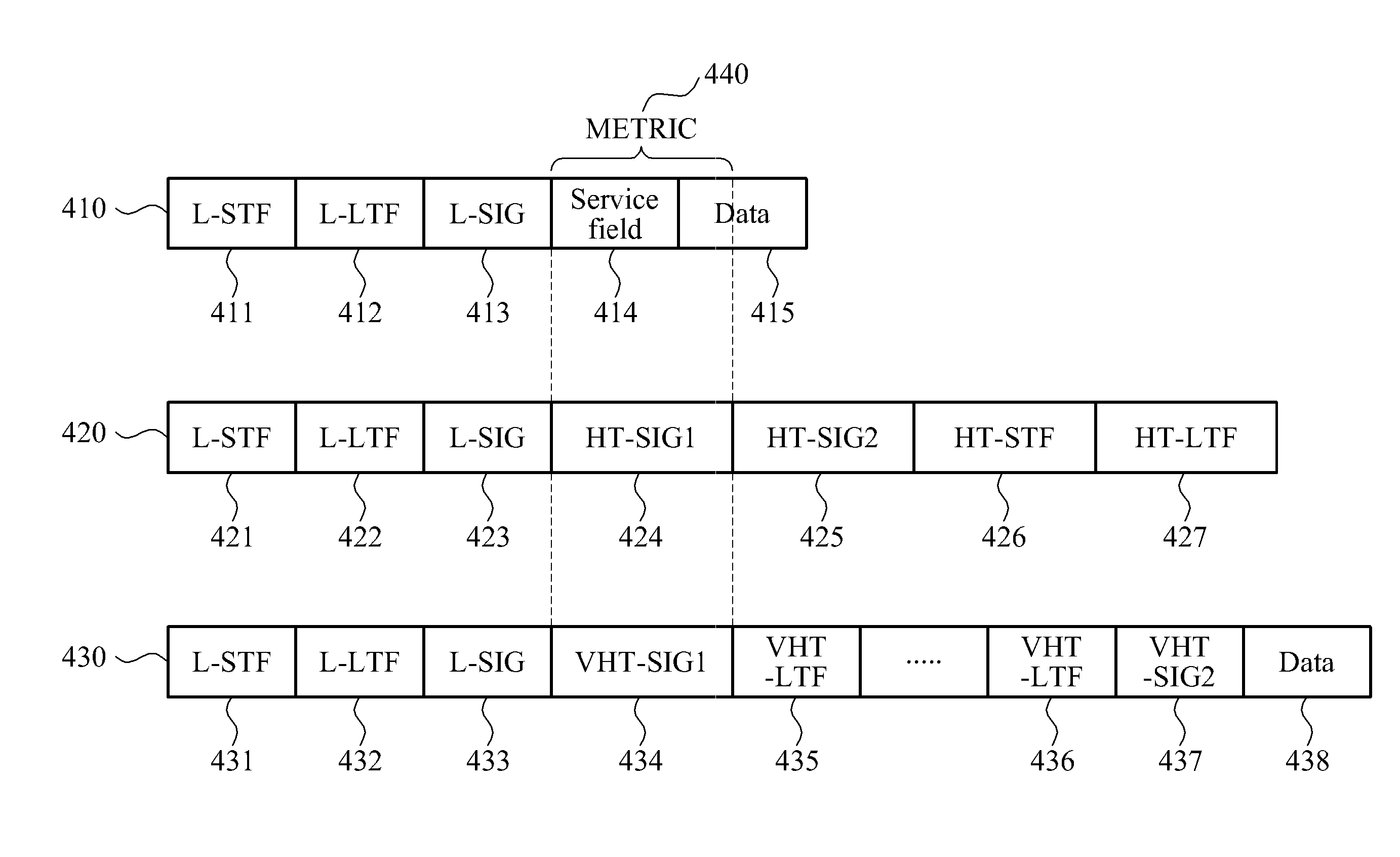
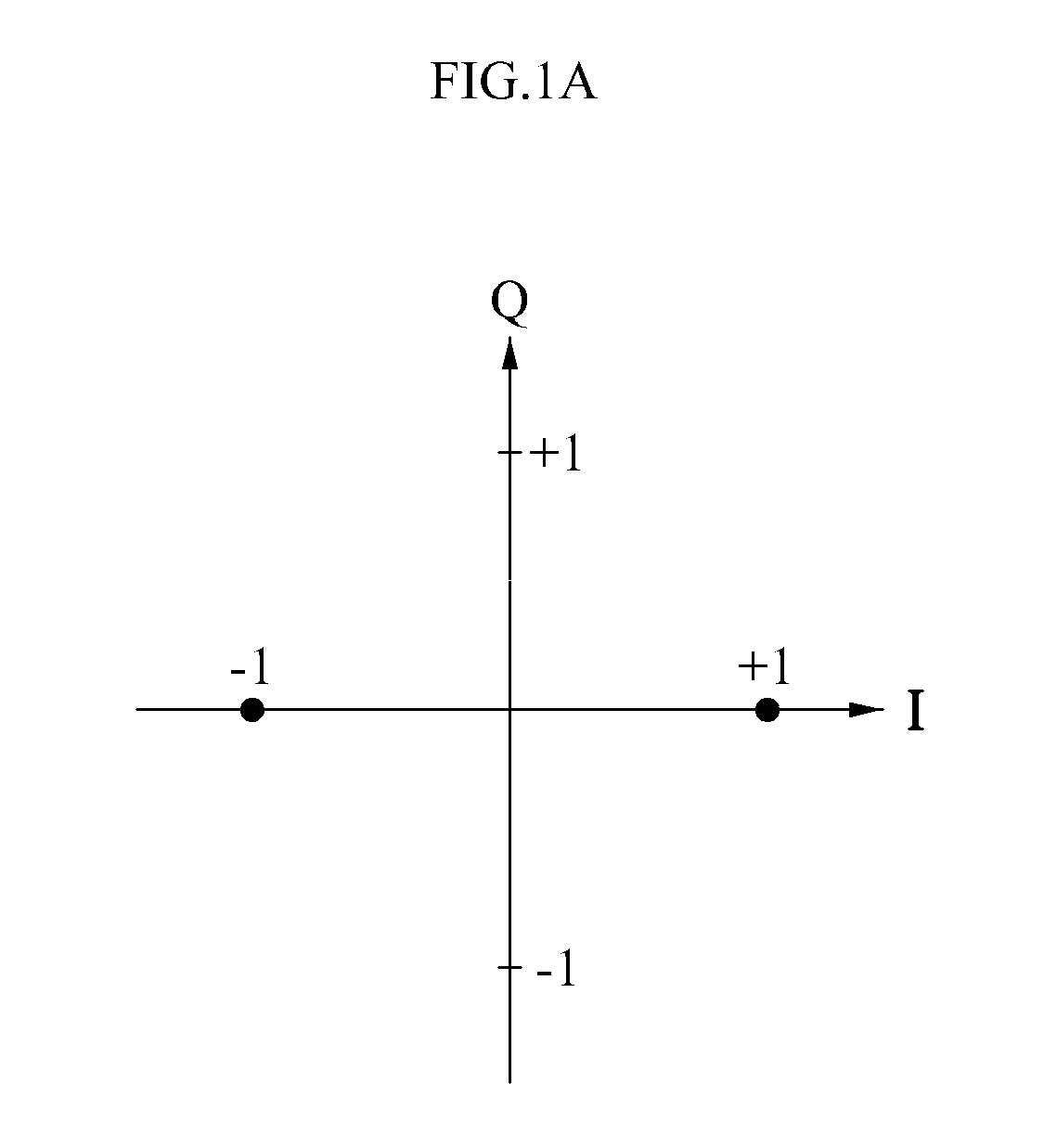
ActiveUS20110110443A1Reduce the valuePolarisation/directional diversityModulation type identificationInternet privacyData transmission
Disclosed are a data receiving apparatus that may discriminate a type of a received data frame, and a data transmission apparatus that may apply a constellation mapping scheme to a data frame so that a data receiving apparatus may discriminate the data frame in accordance with the constellation mapping scheme applied to the data frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
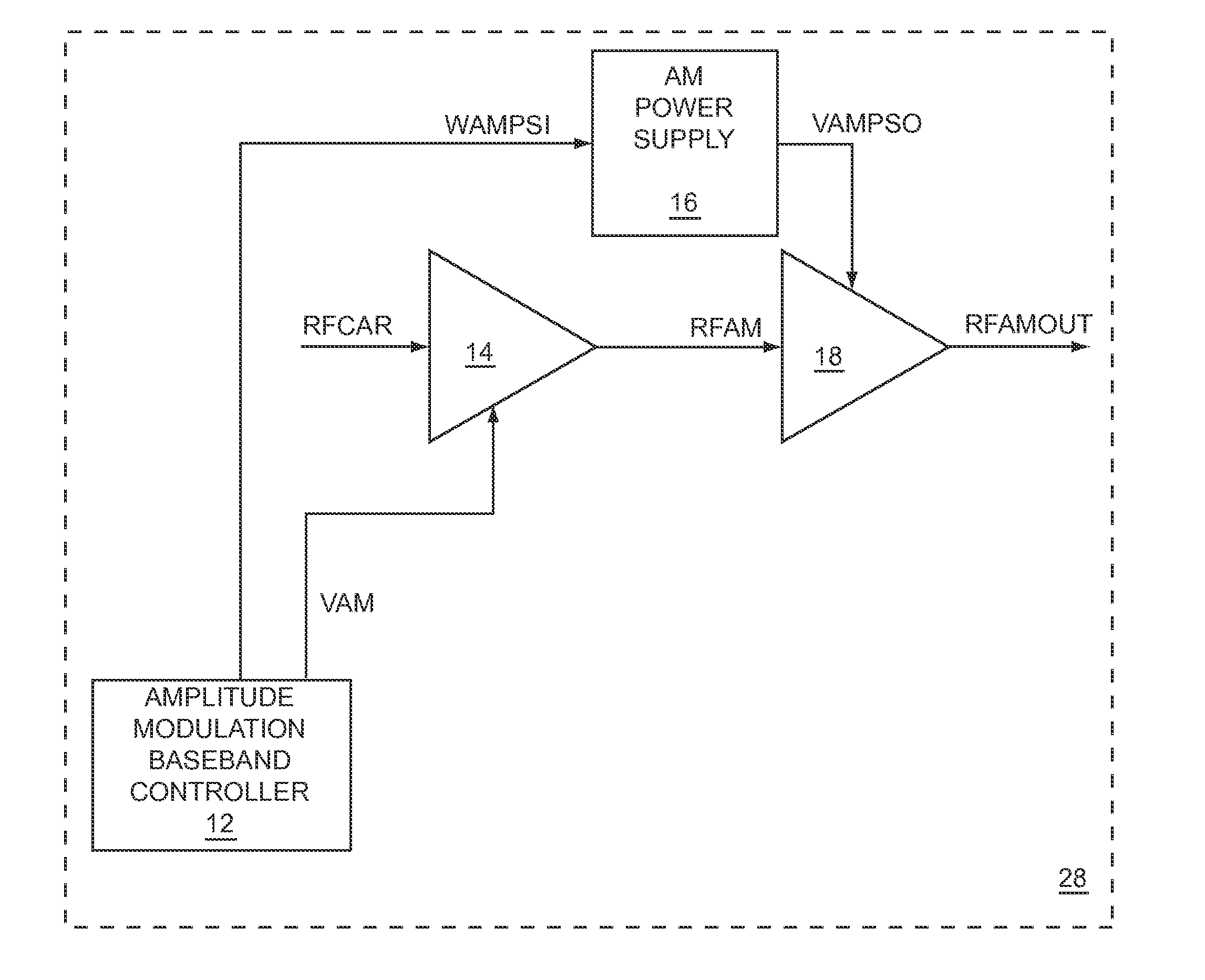
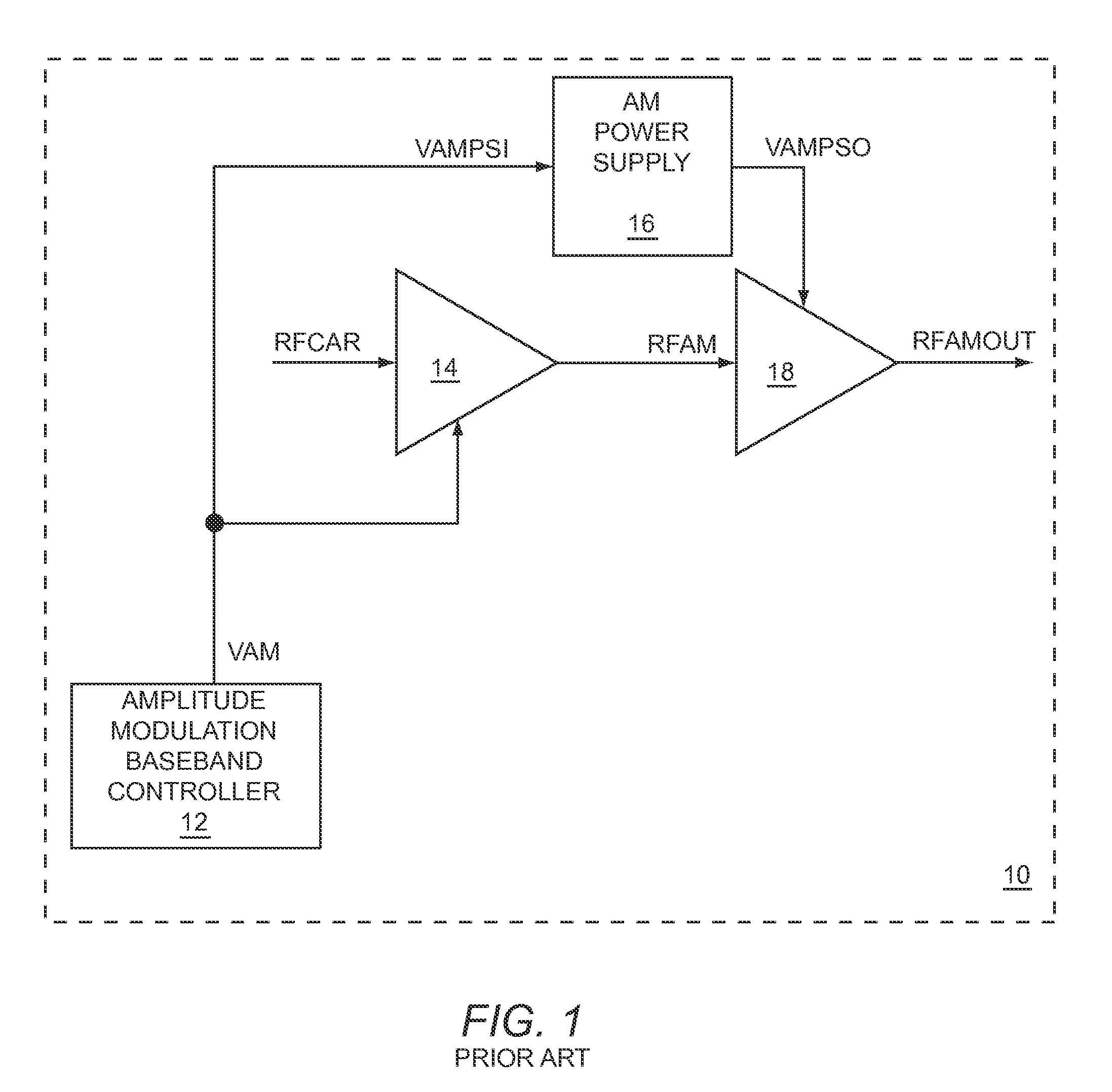
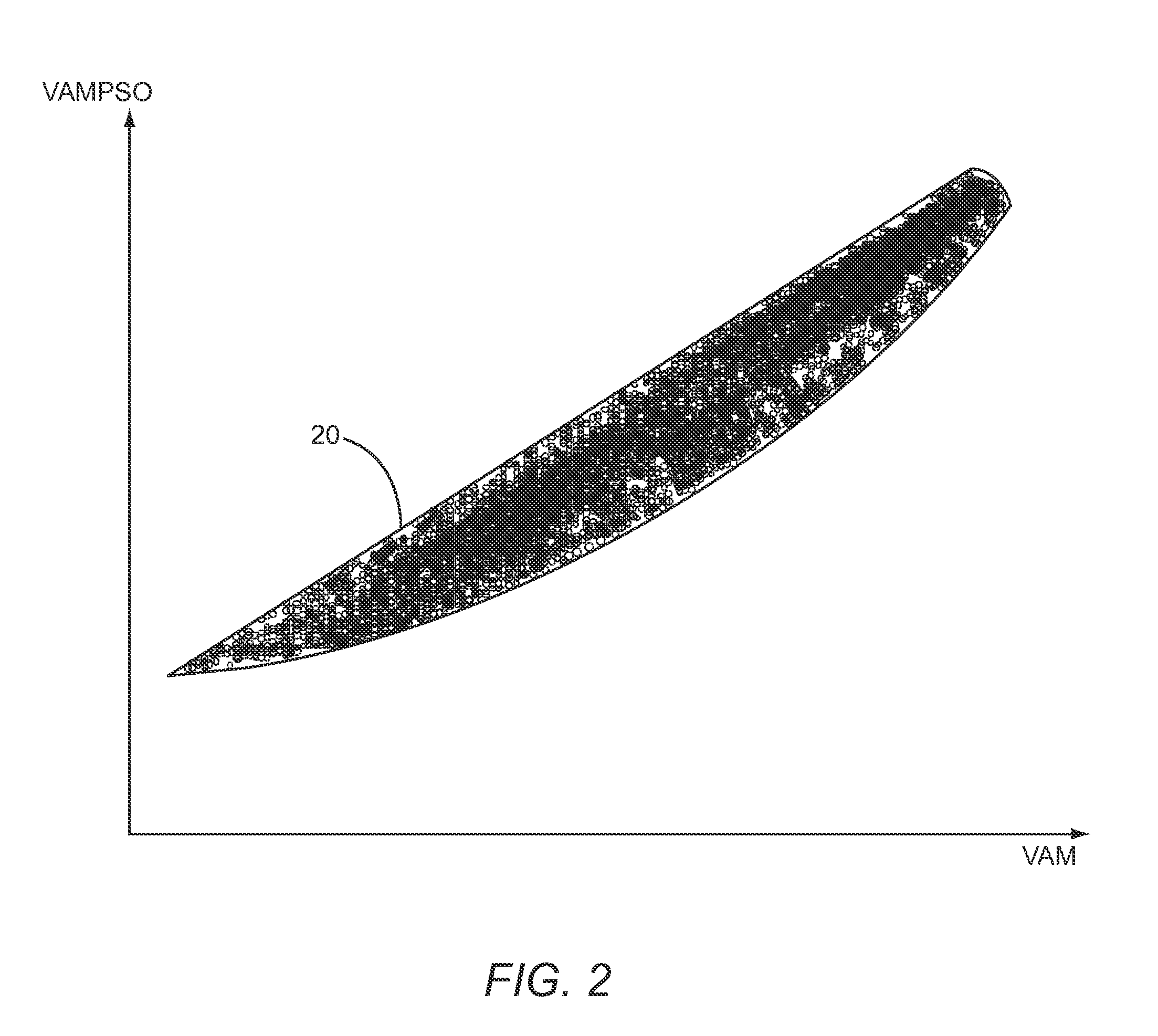
Windowing to narrow a bandwidth of an amplitude modulation power supply input signal
ActiveUS8159309B1Attenuation bandwidthReduce supplyOrganic chemistryAmplitude modulation detailsNoise levelEngineering
The present disclosure relates to using windowing to reduce the bandwidth of an amplitude modulation (AM) power supply input signal (PSIS), which is fed to an AM power supply to provide envelope power to an RF power amplifier stage via an AM power supply output signal. By reducing the bandwidth, noise levels from the AM power supply may be reduced. However, although the bandwidth of the AM PSIS is reduced, the AM power supply output signal may track the AM of the RF power amplifier stage closely enough to meet linearity requirements and to provide high efficiency. The windowing may be based on dividing a stream of AM input samples into a stream of input windows, from which a stream of output windows is created to provide a stream of windowed AM input samples that are used to provide a windowed AM PSIS to the AM power supply.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Polar Modulation Transmission Circuit and Communication Device
InactiveUS20090079511A1Increase output powerImprove efficiencySimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasUltrasound attenuationLow distortion
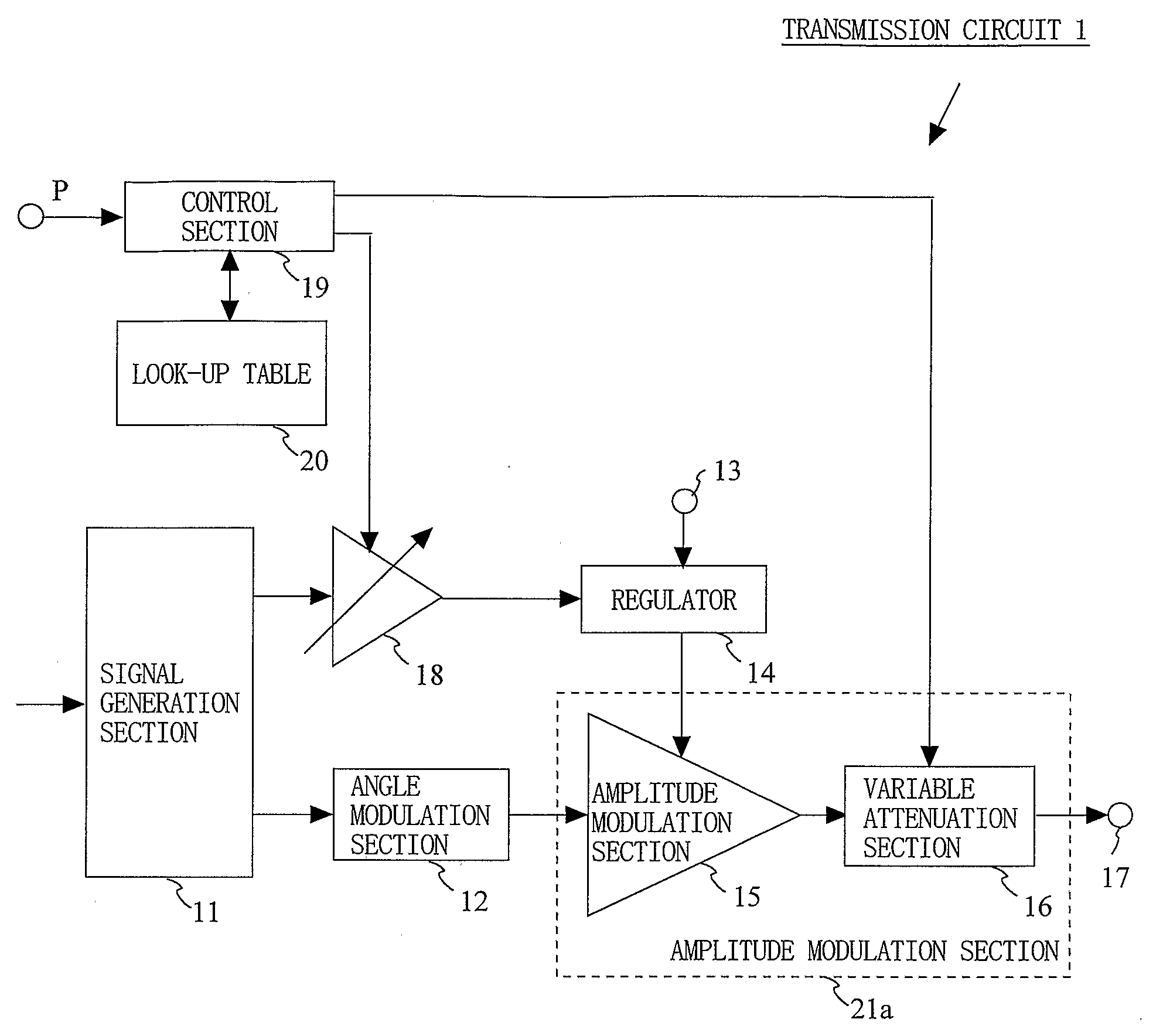
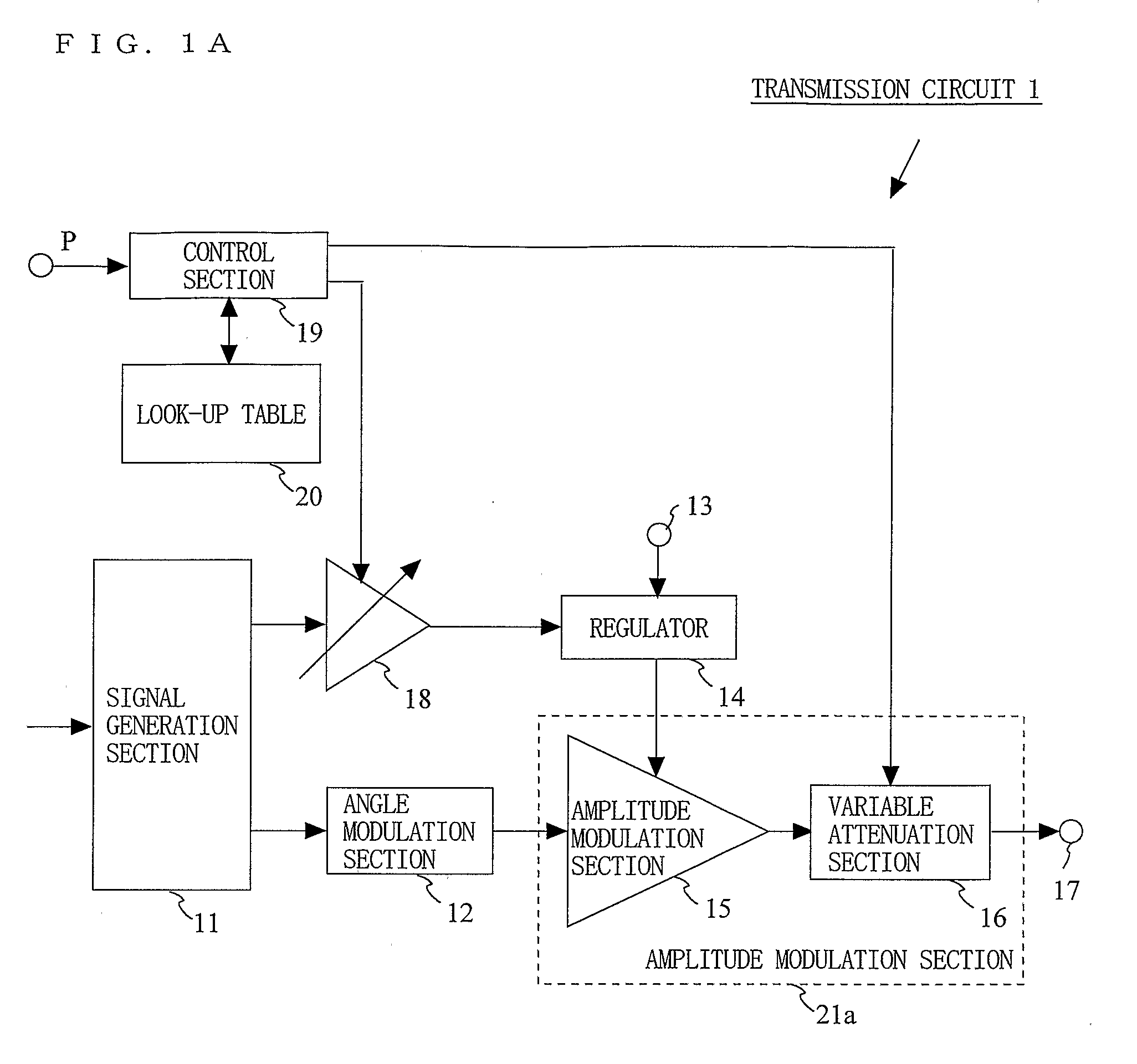
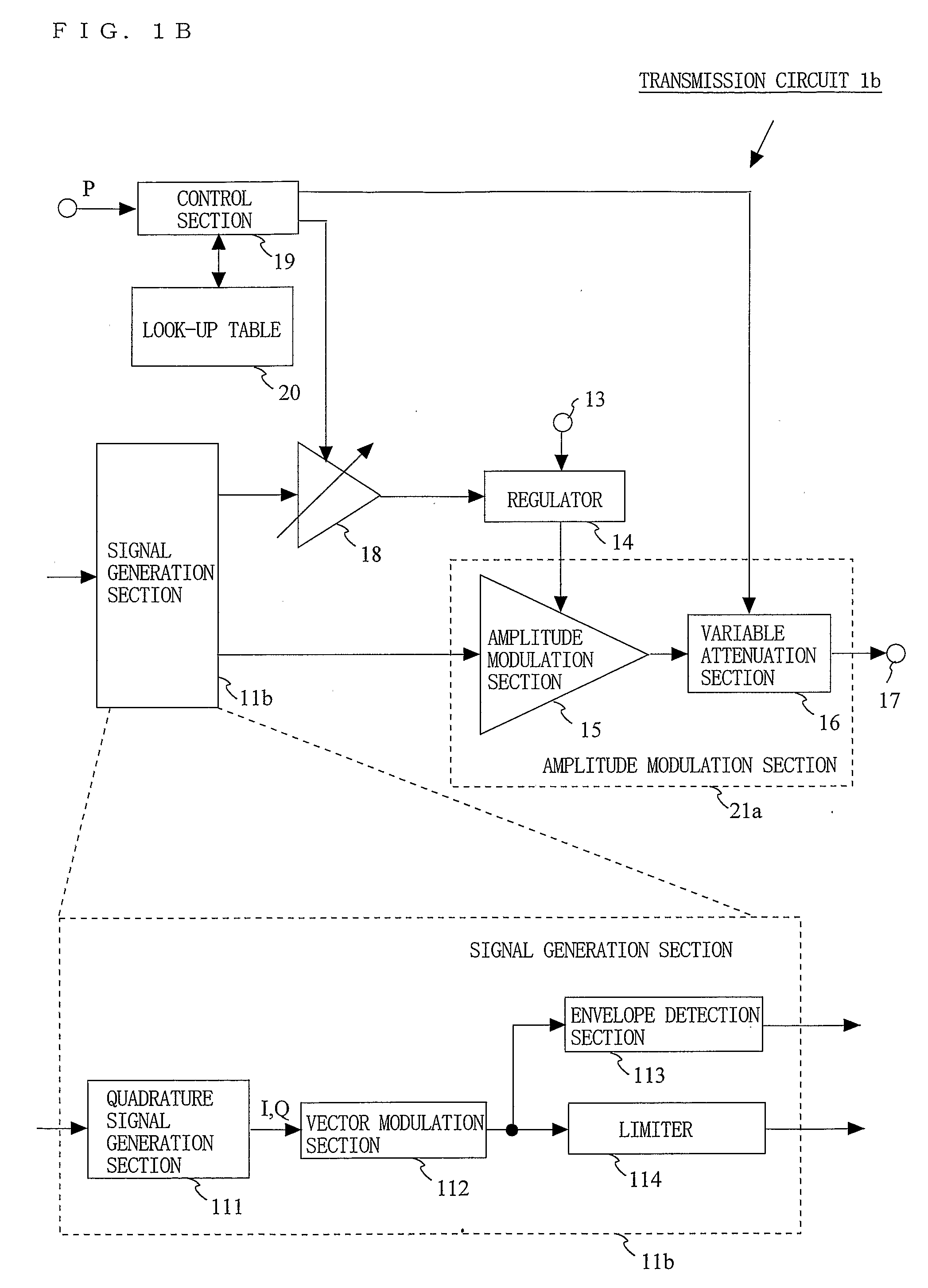
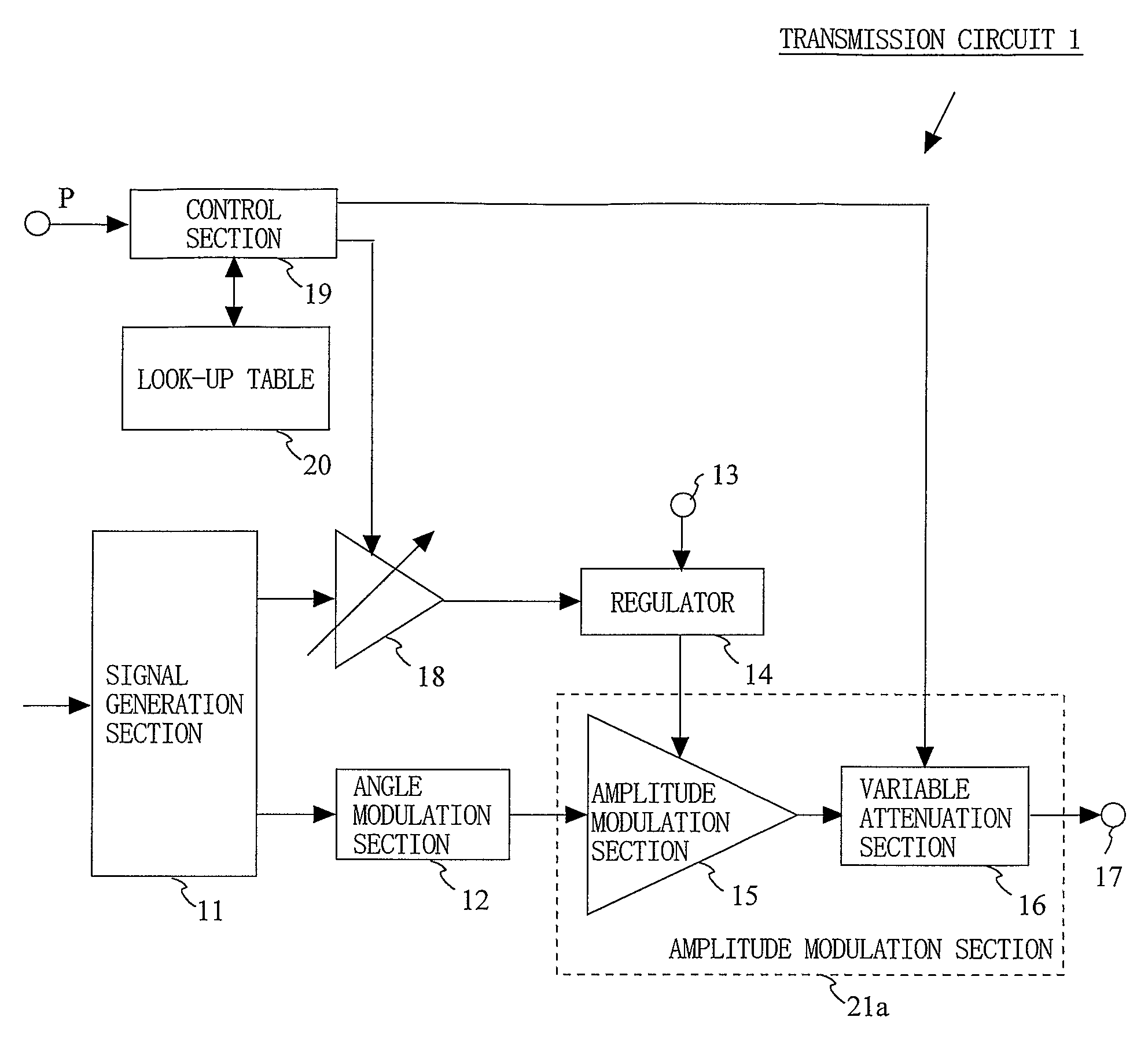
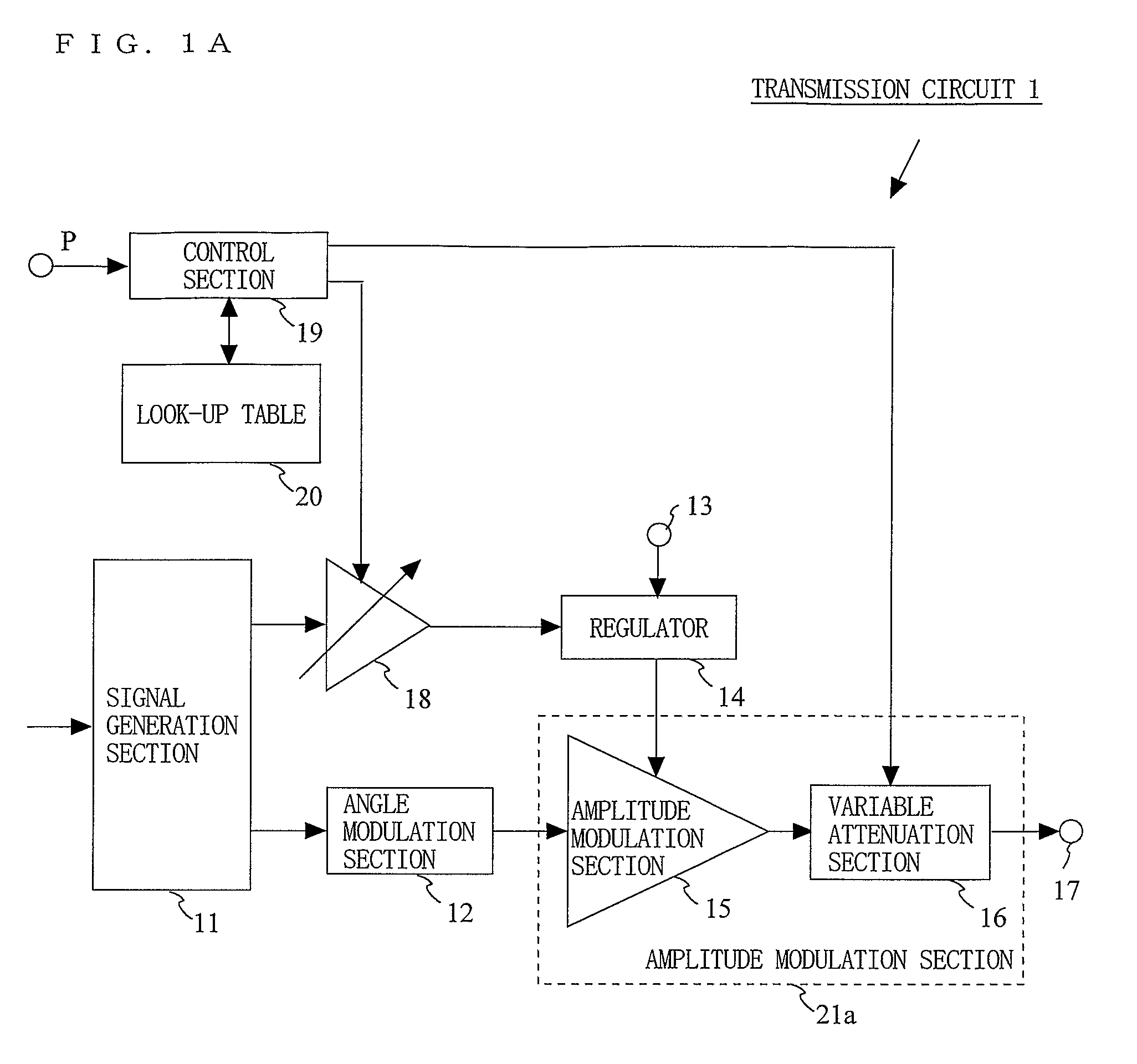
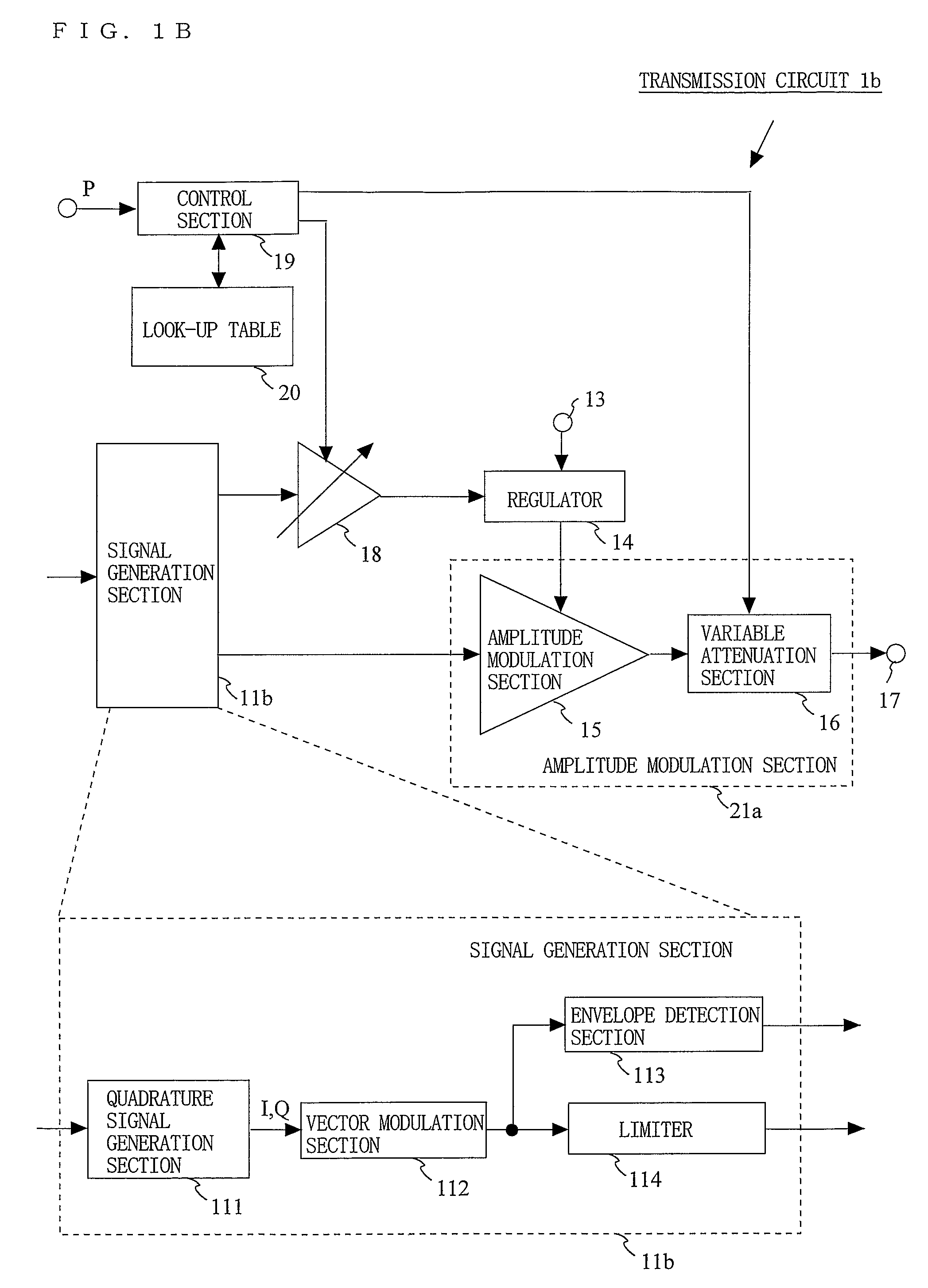
A transmission circuit for outputting transmission signals with a low distortion and a high efficiency over a wide range of output power is provided. A signal generation section (11) generates an amplitude signal and a phase signal. An angle modulation section (12) performs angle modulation on the phase signal and outputs an angle-modulated signal. A regulator (14) receives the amplitude signal via a variable gain amplification section (18) and supplies a voltage controlled based on the magnitude of the amplitude signal to the amplitude modulation section (15). The amplitude modulation section (15) performs amplitude modulation on the angle-modulated signal and outputs a modulated signal to the variable attenuation section (16). When the value of power information is smaller than a predetermined threshold value, the control section (19) increases the gain of the variable gain amplification section (18) and the attenuation of the variable attenuation section (16).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Polar modulation transmission circuit and communication device
InactiveUS7688156B2Reduce power consumptionReduce distortion problemsResonant long antennasAngle modulation detailsUltrasound attenuationLow distortion
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Linearized switch-based power amplifier
InactiveUS7310382B2Slow switchingLess-expensiveNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
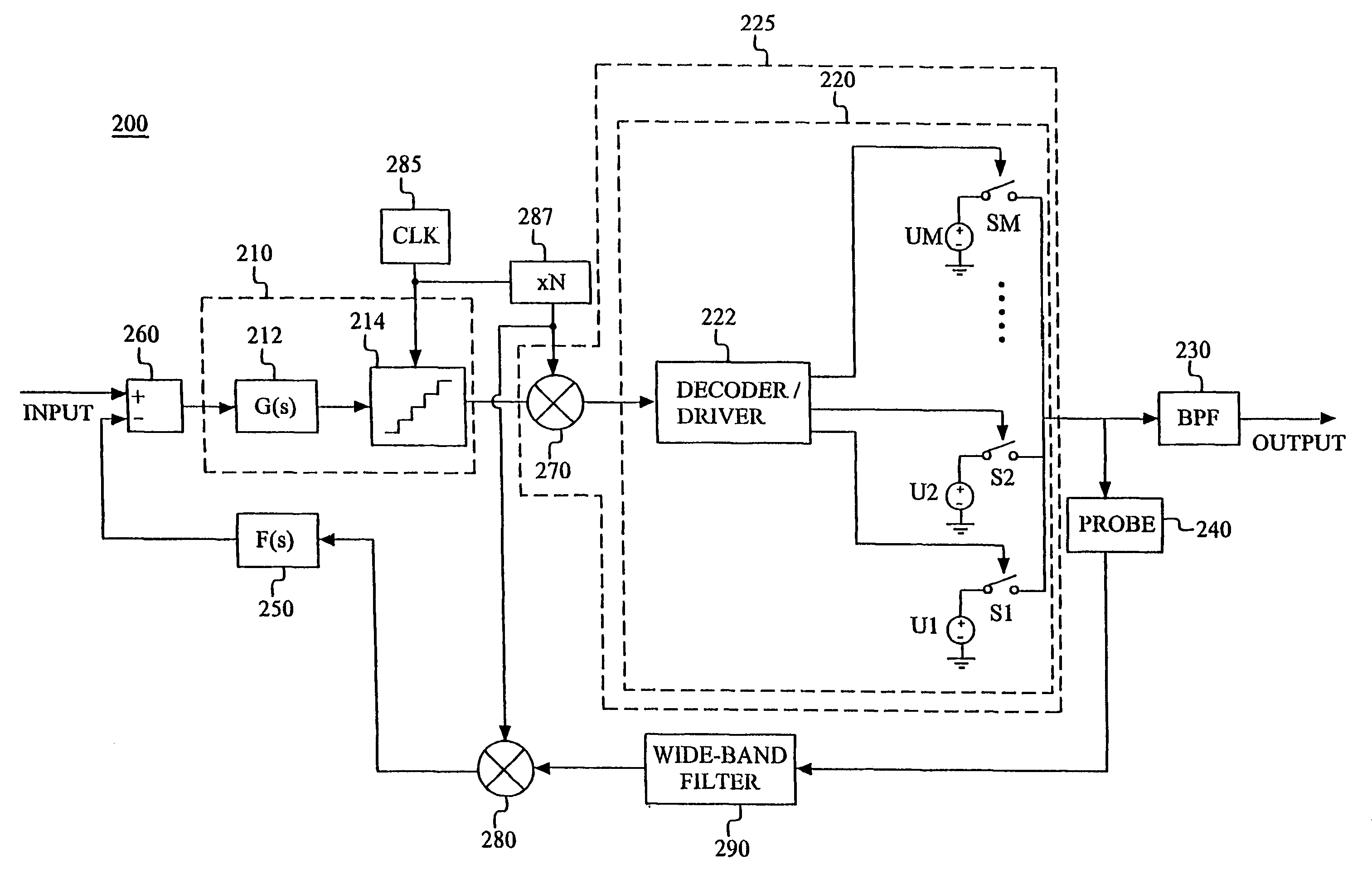
A power amplifier comprises a level-discretization modulator (210) and a mixing and amplifying stage (225), in combination with a properly designed negative feedback path. The feedback path forms an error compensation loop together with a properly selected forward path. The forward path includes at least the mixing and amplifying stage (225), which provides frequency up-conversion to the radio frequency band and switch-based amplification. The negative feedback path includes a down-conversion mixer (280) for down-conversion to the initial frequency band, and compensates for distortion caused by components of the forward path.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Reducing cross modulation in multichannel modulated optical systems with anti-clipping
A modulated optical system with anti-clipping reduces or corrects clipping that might occur in the laser as a result of negative spikes or peaks in a multichannel RF signal. The system generally detects an envelope of the RF signal to generate an anti-clipping signal that follows at least a portion of the envelope and prevents one or more negative peaks from causing clipping by adjusting a bias current in response to the anti-clipping signal. The system may also reduce cross modulation by clamping the anti-clipping signal at an anti-clipping limit during lower power periods of the RF signal.
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
Digital-to-radio frequency conversion device, chip set, transmitter, user terminal and data processing method
ActiveUS7345612B2Broadcast with distributionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital dataData signal
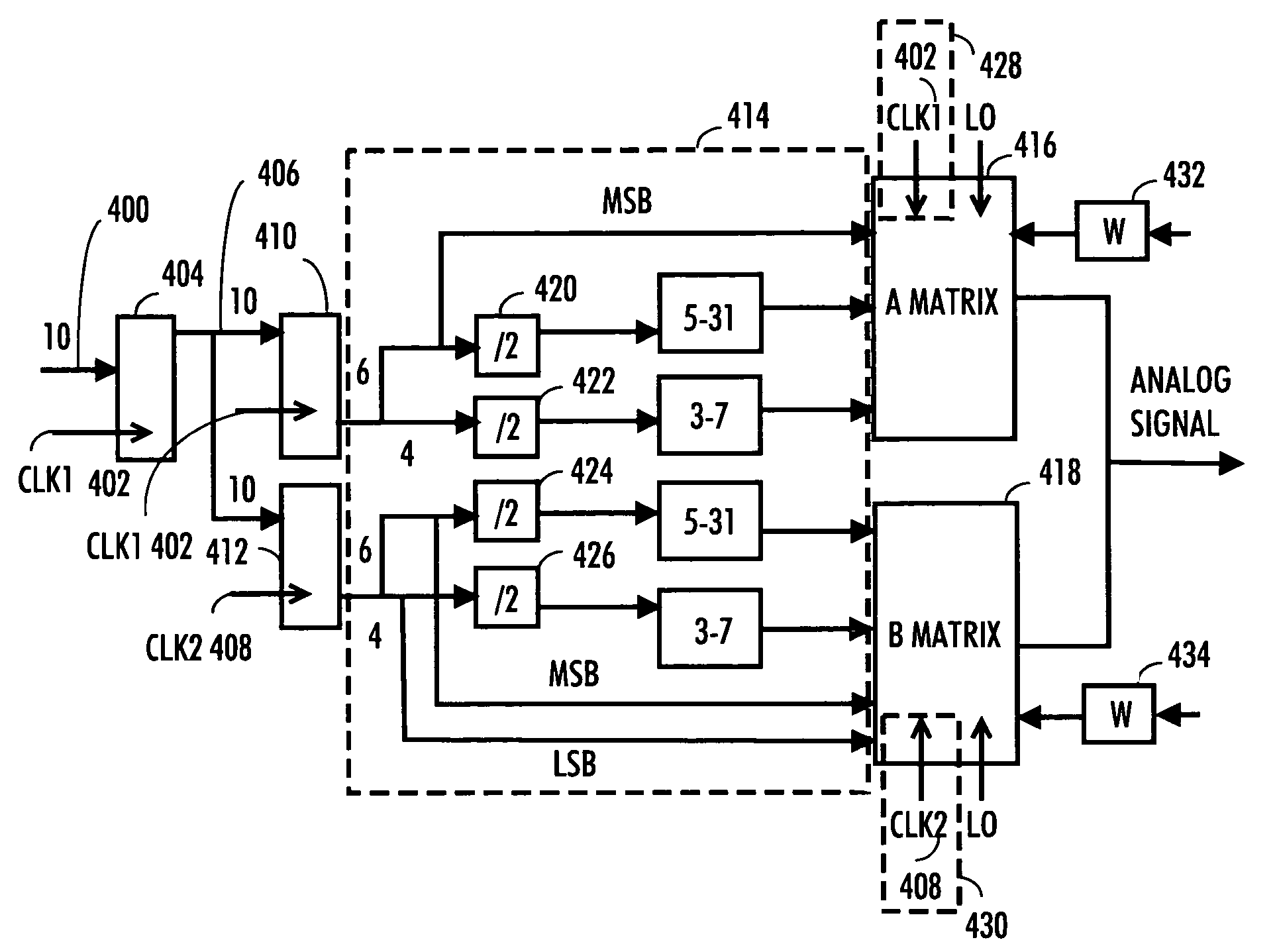
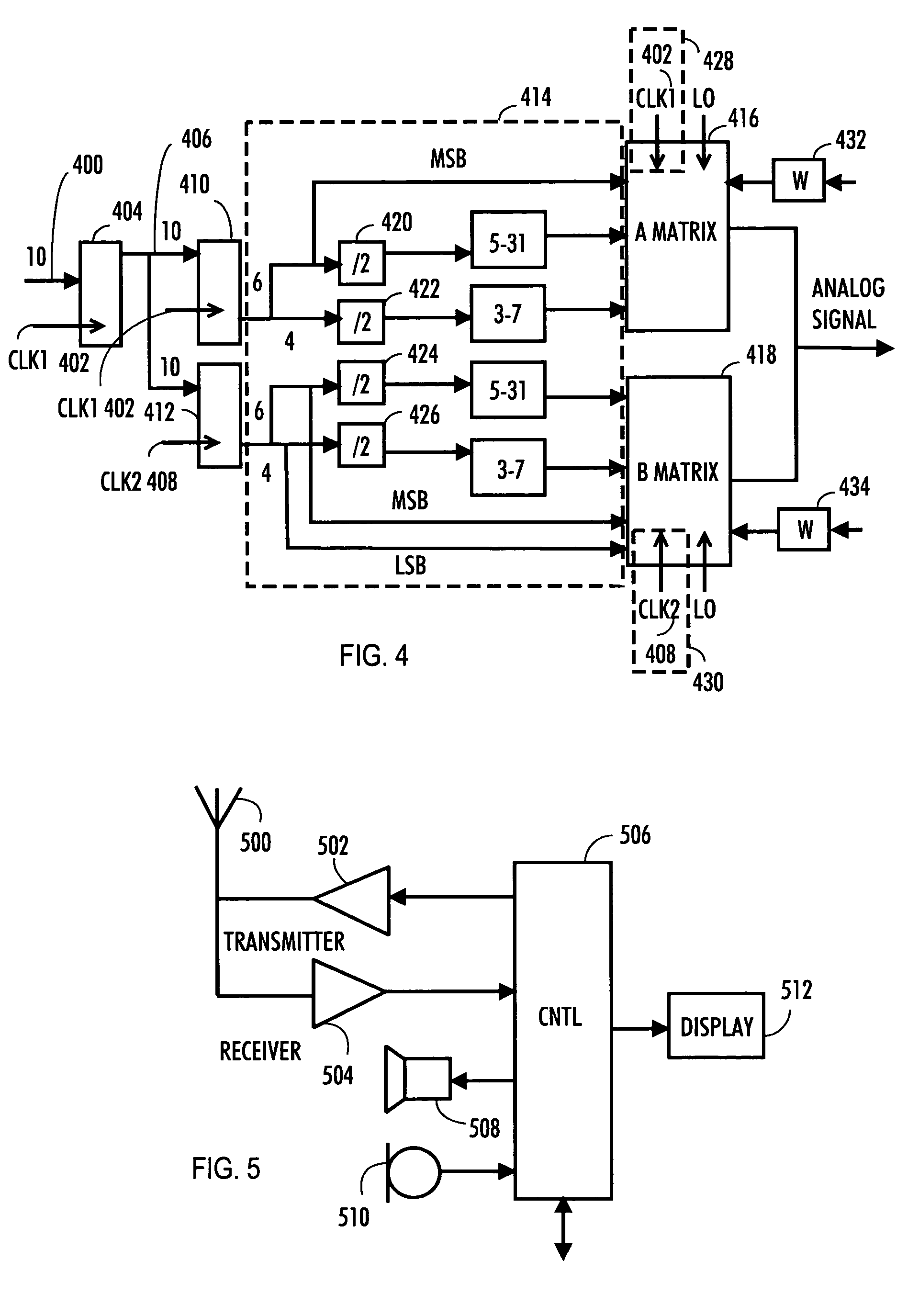
The invention relates to a device for digital-to-radio frequency conversion, the device comprising: conversion cell matrices for digital-to-radio frequency conversion; means for providing a digital data signal; means for dividing the digital data signal into data signal groups; means for generating clock signals, the clock signals having different phases, the number of clock signals being the same as the number of data signal groups; means for synchronizing the data signal groups by using the clock signals; means for conveying the synchronized data signal groups to the conversion cell matrices, the number of conversion cell matrices being the same as the number of data signal groups; and means for synchronizing each conversion cell matrix by using the clock signal with which the synchronized data signal group conveyed thereto was synchronized for generating interpolation values.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
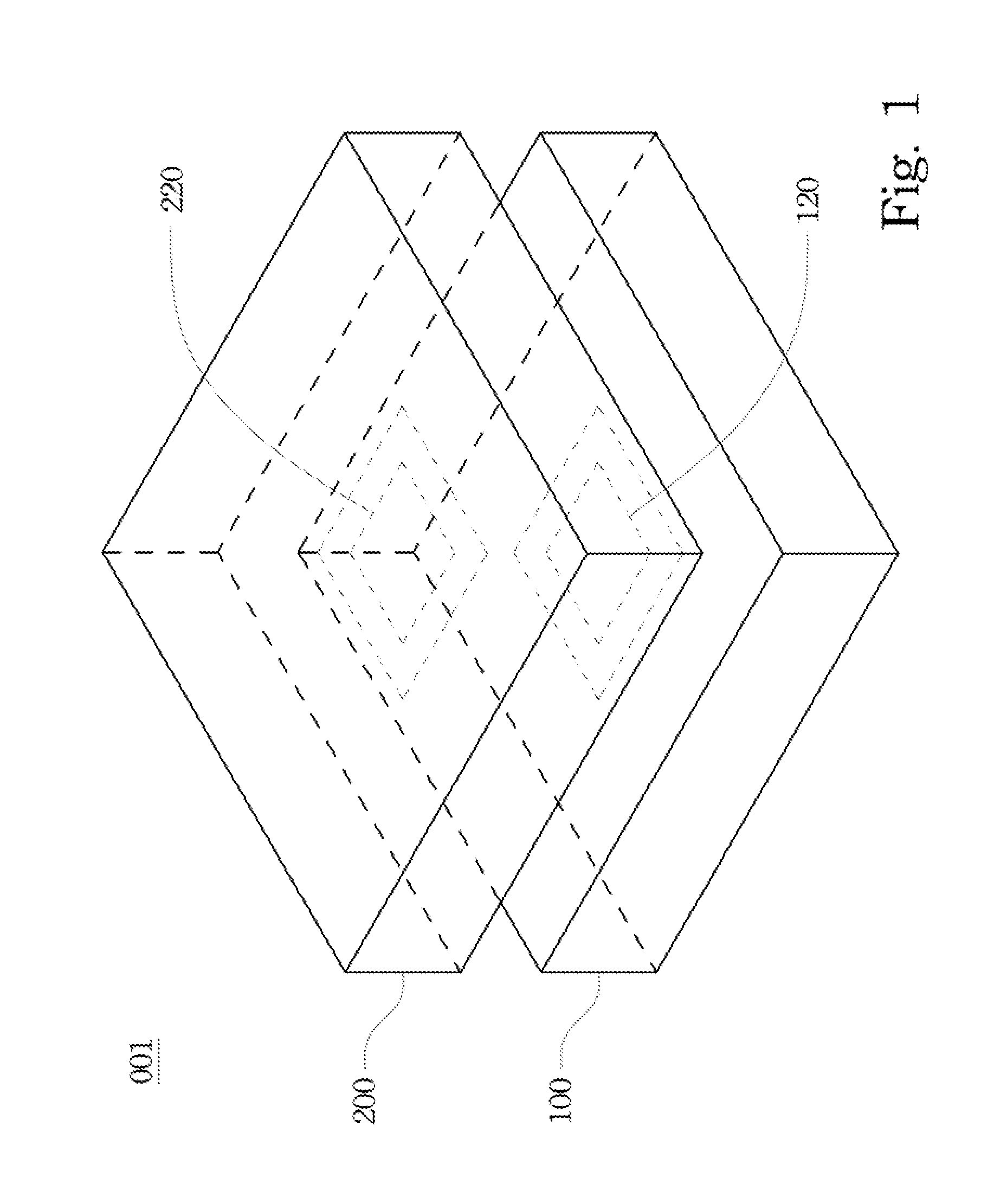
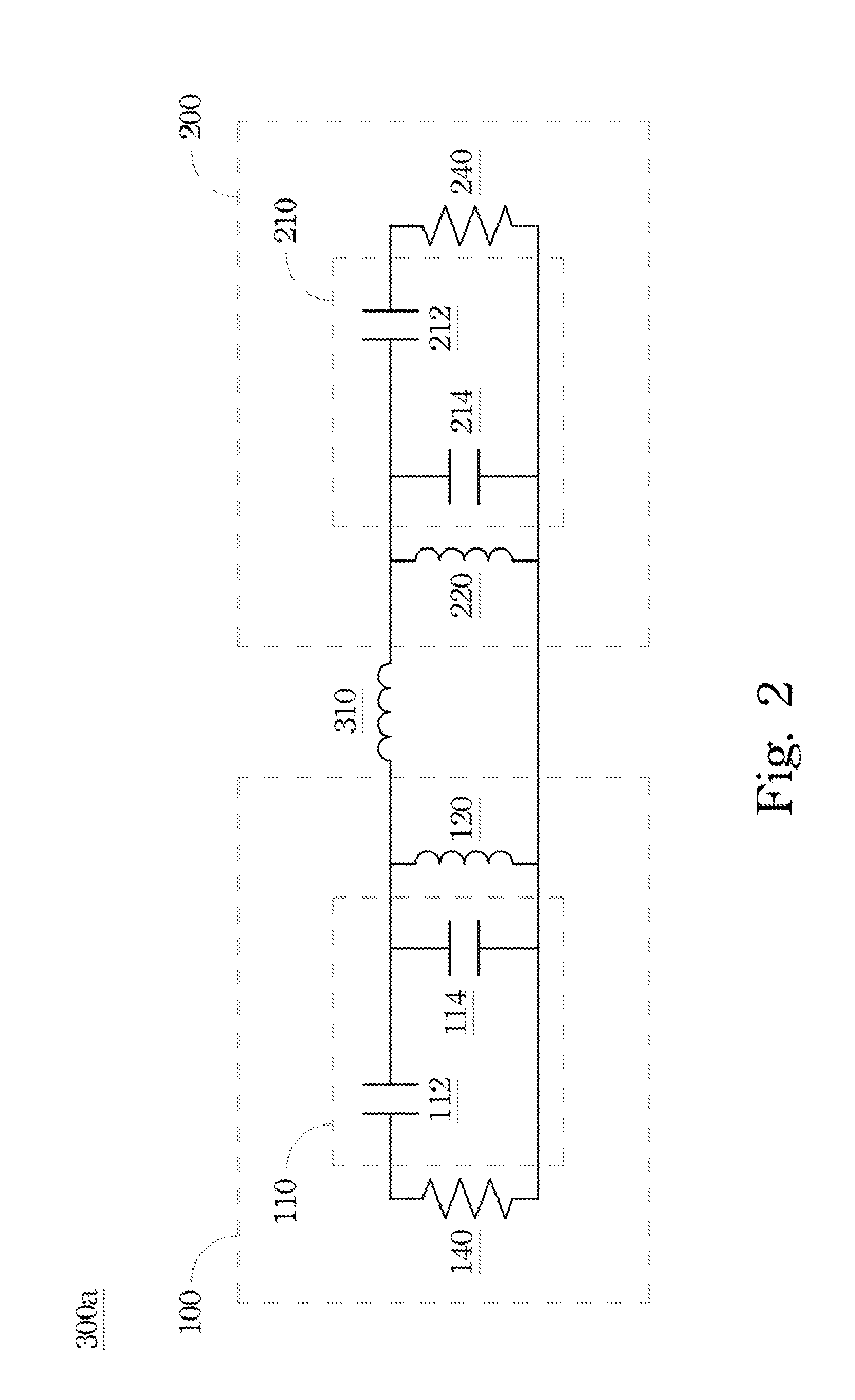
Multi-chip stack structure and signal transmission method thereof
ActiveUS20110050336A1Improve the overall coefficientImprove communication qualityMultiple-port networksAngle to amplitude modulation conversionCouplingEngineering
A multi-chip stack structure and a signal transmission method are disclosed in specification and drawing, where the multi-chip stack structure includes first and second chips. The first chip includes a first inductance coil with a first series capacitor, and the second chip includes a second inductance coil with a second series capacitor. The first and second inductance coils are magnetically coupled to each other. The magnetically coupled inductance coils and the capacitors constitute a coupling filter.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com