Patents
Literature
105results about "Assembling head elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
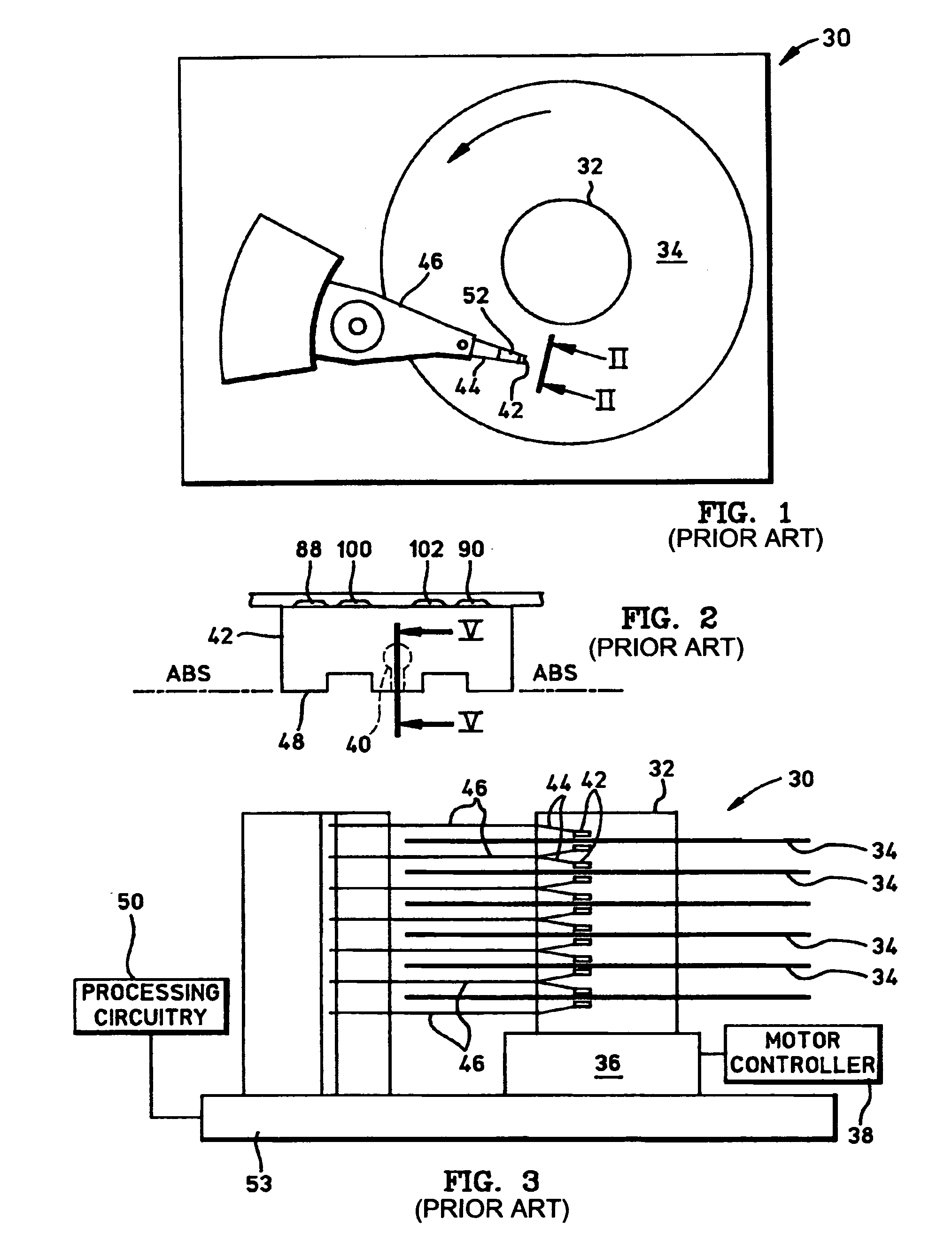
Methods of orienting an easy axis of a high-aspect ratio write head for improved writing efficiency
InactiveUS7237320B2Efficient switchingElectrical transducersRecord information storageIn planeEngineering
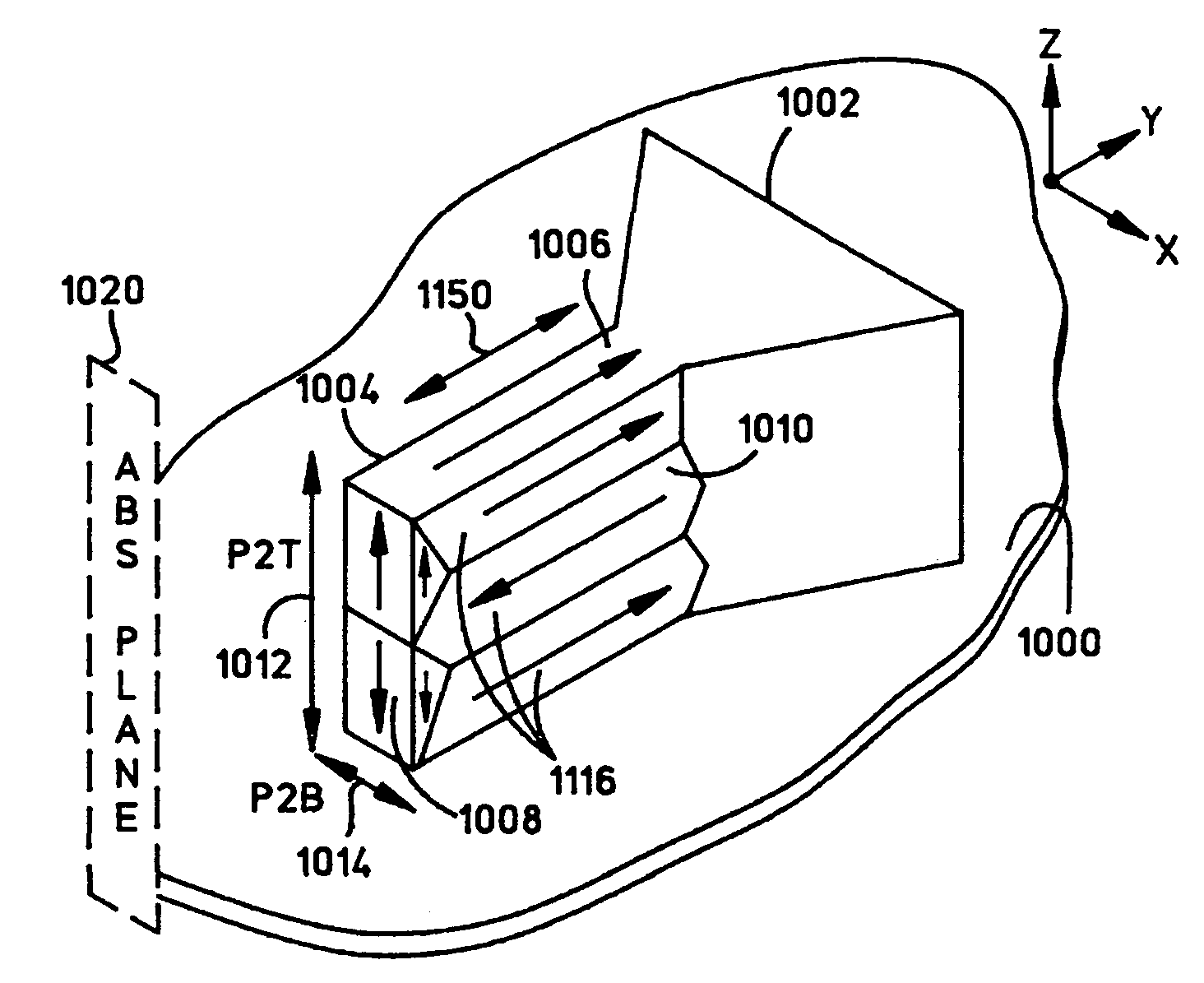
A pole piece of a magnetic write head is formed over a substrate and includes a pole tip having a width that is less than its height which is normal the substrate. Due to stress-anisotropy, the pole tip structure has an inherent easy-axis which is oriented in an unfavorable direction (i.e. perpendicular to the ABS and almost collinear with a driving field of the write head). To alleviate this problem, during electroplating or annealing of the pole piece a magnetic field is applied to the pole tip in a direction which is out-of-plane from the substrate but in-plane with a side wall of the pole tip which vertically projects from the substrate. By applying the magnetic field in this manner, the easy axis of the pole piece is oriented in the direction of the applied magnetic field to facilitate more efficient switching in the write head. Ideally, the angle θ is about 90° for Hexagonal-Closed Packed (HCP) materials or about 50° for Face-Centered Cubic or Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) materials (e.g. NiFe and CoFe).
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
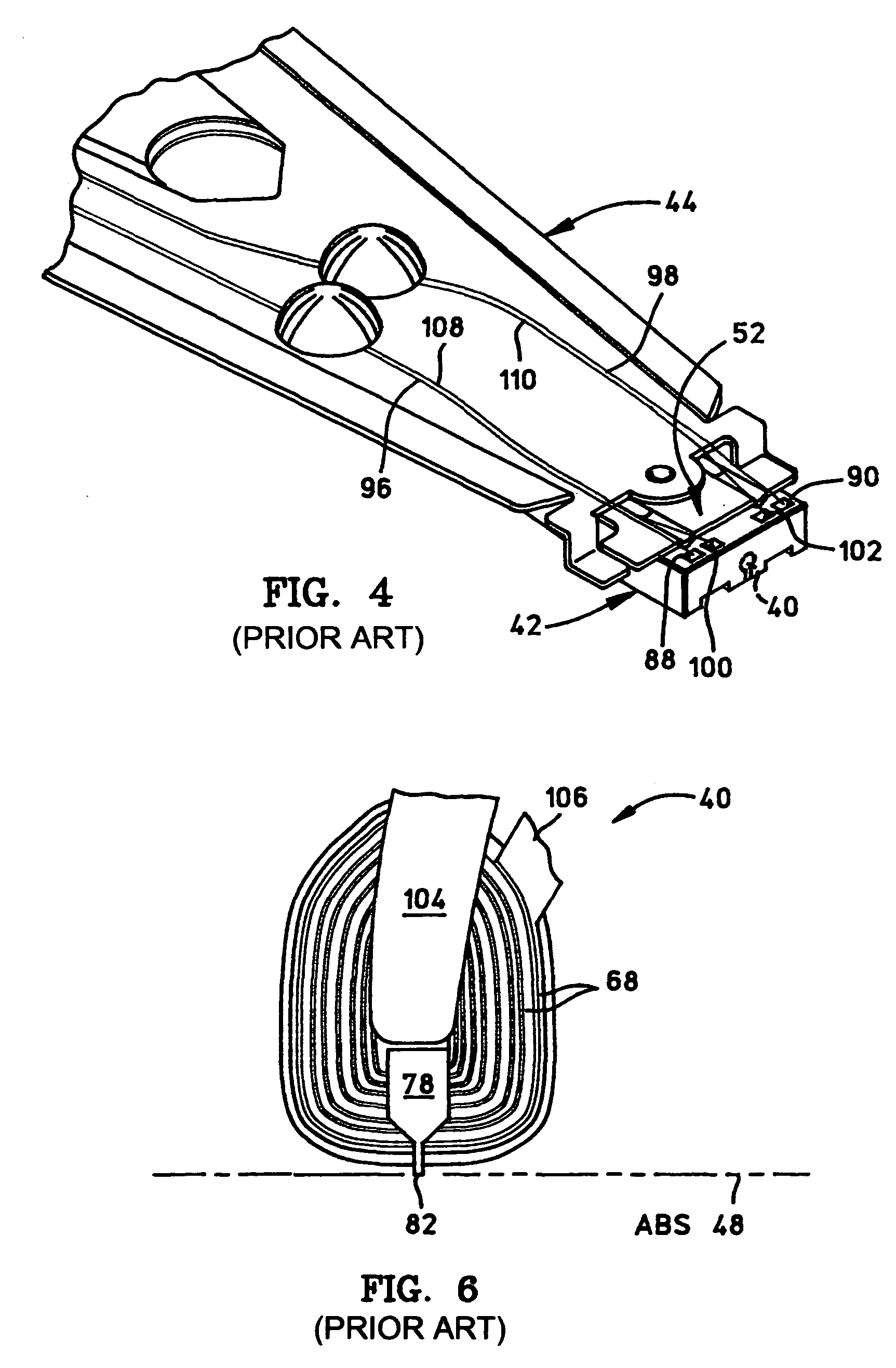
Method for use in making a write coil of magnetic head
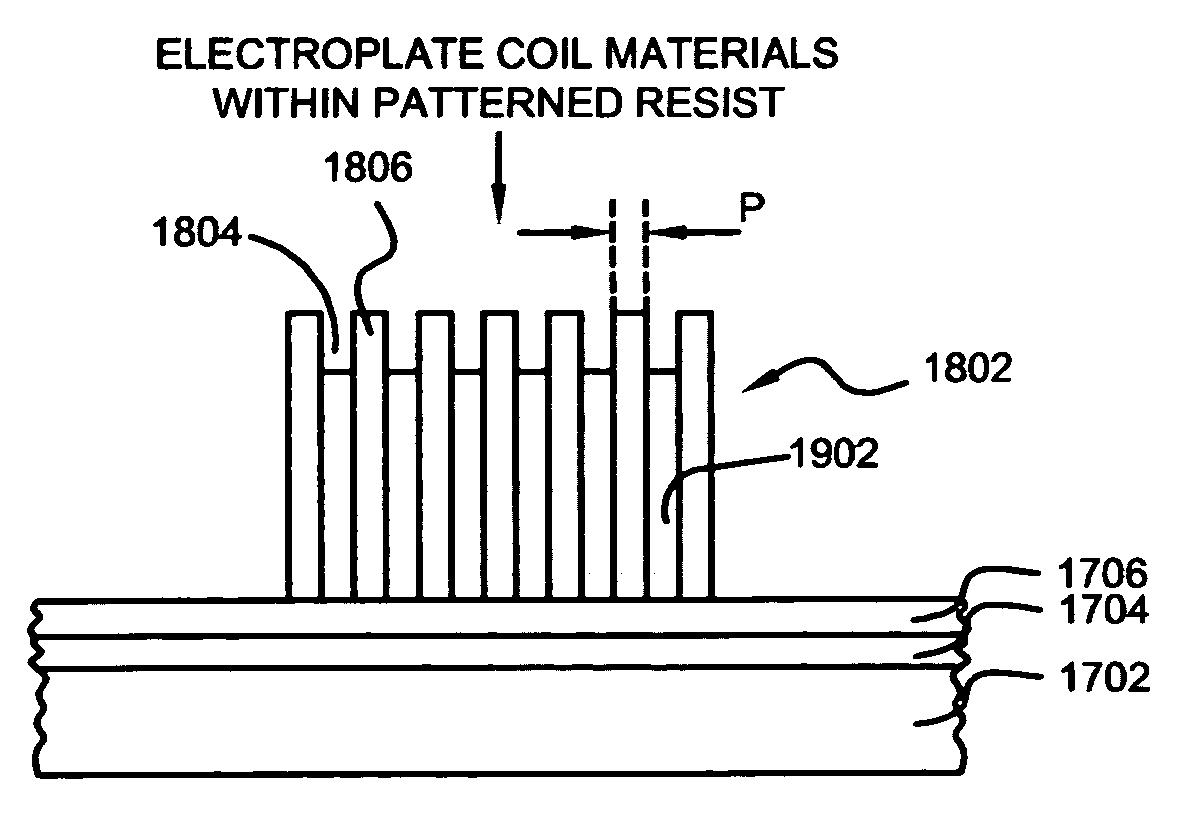
Methods suitable for use in making a write coil of a magnetic head includes the steps of forming a seed layer made of ruthenium (Ru) over a substrate; forming, over the seed layer, a patterned resist having a plurality of write coil trenches patterned therein; electroplating electrically conductive materials within the plurality of write coil trenches to thereby form a plurality of write coil layers; removing the patterned resist; and performing a reactive ion etch (RIE) in ozone gas (O3) for removing exposed seed layer materials in between the plurality of write coil layers. Advantageously, the write coil layers remain undamaged from the RIE in the ozone gas. Other structures may be fabricated in a similar manner.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Perpendicular magnetic head and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050057852A1Reduce noisePrevents side fringing and erasureElectrical transducersManufacture head surfaceMagnetic polesEngineering
A perpendicular magnetic recording head includes a primary magnetic pole having a flat top surface. The magnetic head also includes a shield layer over the primary magnetic pole and at the sides of the primary magnetic pole in a single piece. The distance in the direction perpendicular to the thickness direction between the side surfaces of the primary magnetic pole and the side shield layer is longer than the distance in the thickness direction between the top surface of the primary magnetic pole and the shield layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
ESD-protected slider and head gimbal assembly
ActiveUS6972930B1Reduce couplingElectrical connection between head and armRecord information storageHemt circuitsControl theory
A Head Gimbal Assembly (HGA) for use in a disk drive and comprising an ESD-protected slider comprising a head formed on a slider substrate. The slider may comprise an electrical-isolation circuit; an electrically-resistive path between head input connections and the slider; or both isolation circuits and resistive paths for reducing electrostatic charge on the slider while remaining connected during disk drive operations.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Head for thermal assisted magnetic recording device, and thermal assisted magnetic recording device
InactiveUS20070096854A1Reduce decreaseReduce lightCombination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic poles
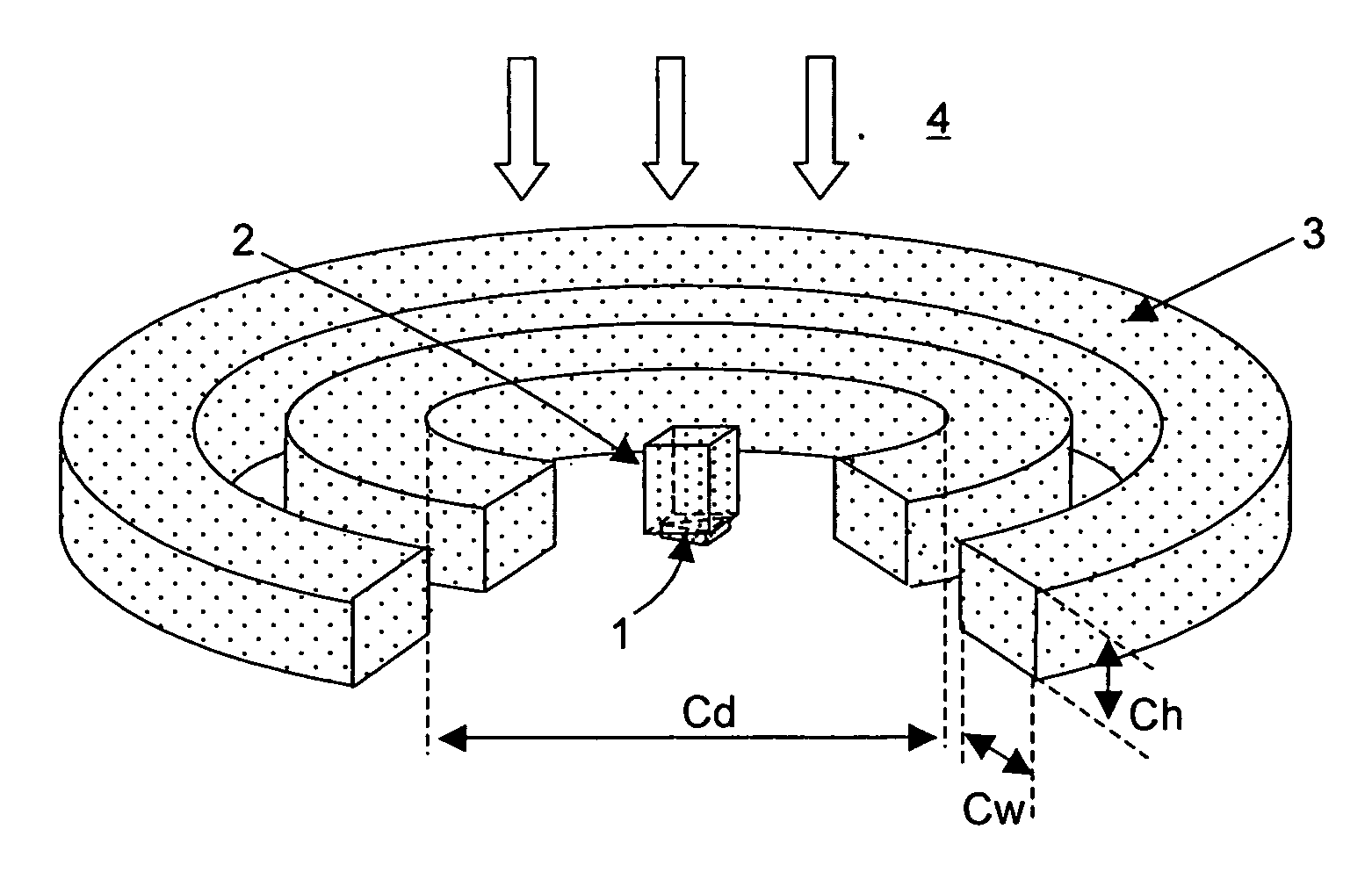
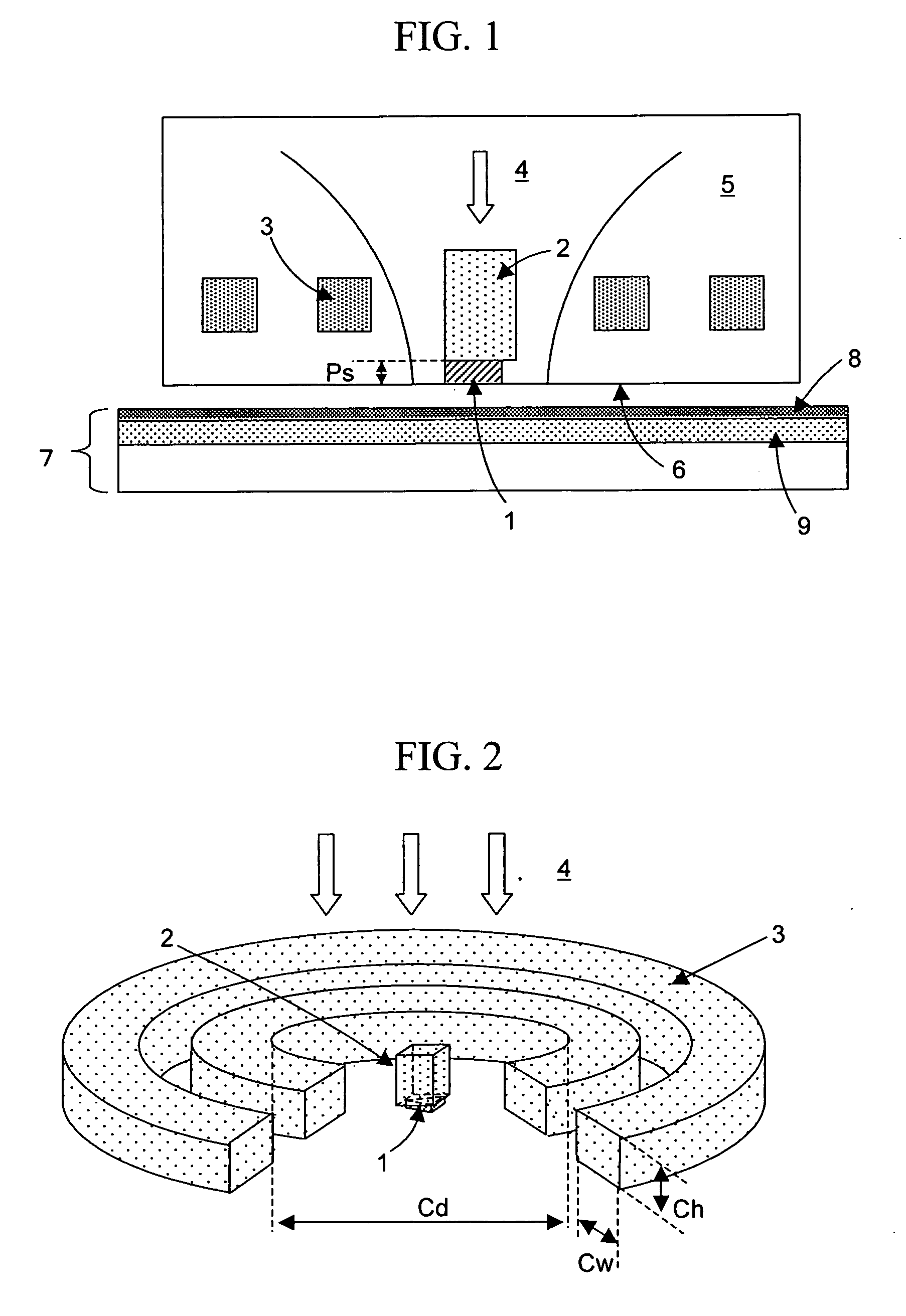
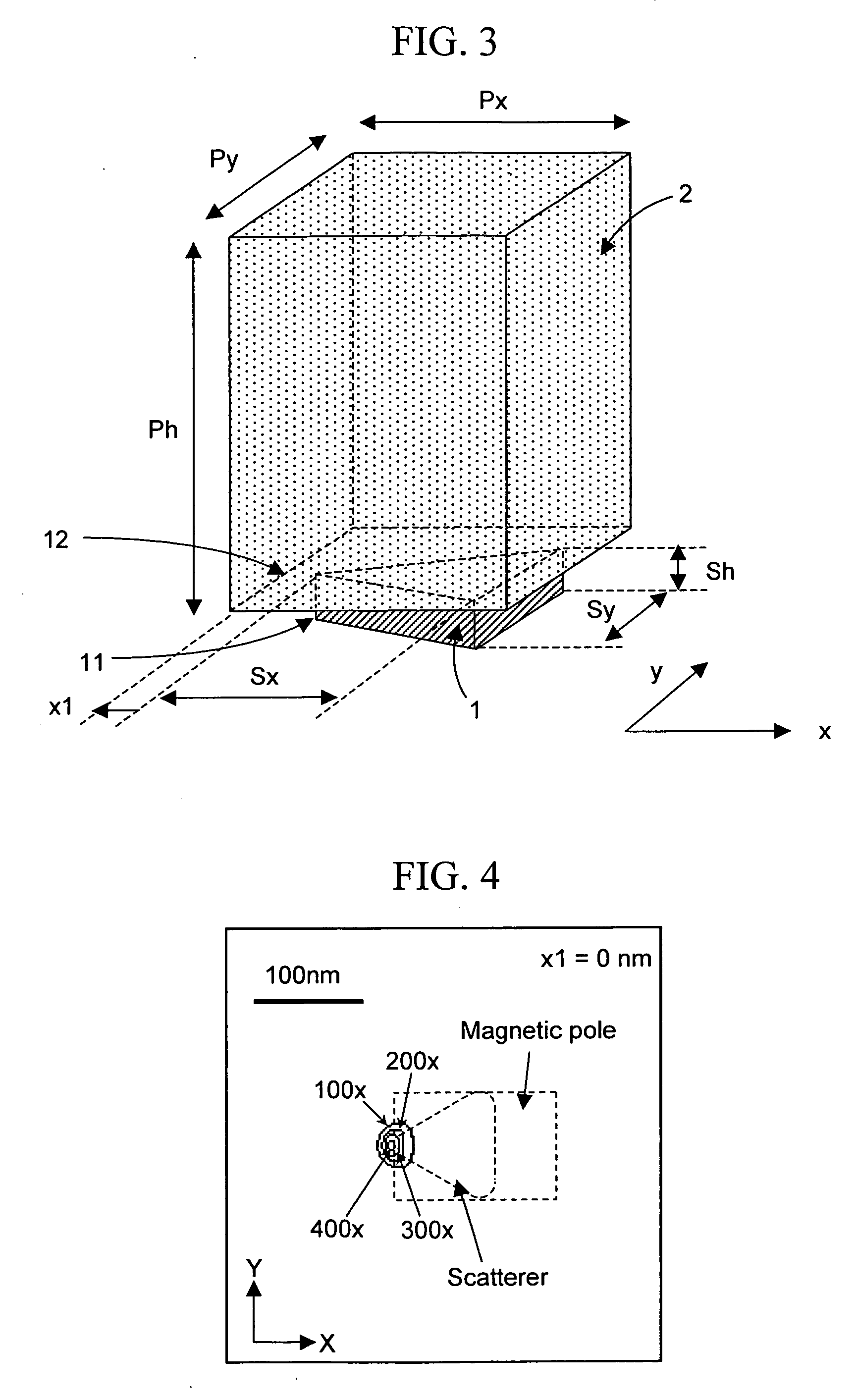
The aim of the present invention is to apply an intense magnetic field to a portion where an optical near-field is generated by a thermal assisted magnetic recording head with a scatterer having conductivity as an optical near-field generating element. To this end, a scatterer for generating an optical near-field is formed in a bottom portion of a slider, and a magnetic field is applied thereto using a coil. In order to increase the intensity of the magnetic field, a magnetic pole made of a soft magnetic material is formed over the scatterer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for manufacturing a read head having conductive filler in insulated hole through substrate
InactiveUS8756795B1Electrical connection between head and armFluid-dynamic spacing of headsTransducerElectrical contacts
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic head
InactiveUS7392577B2Reduce noisePrevents side fringing and erasureElectrical transducersManufacture head surfaceMagnetic polesCondensed matter physics
A method of manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic head is disclosed, including perpendicular magnetic recording head includes forming a primary magnetic pole having a flat top surface, where a shield layer over the primary magnetic pole and at the sides of the primary magnetic pole is formed in a single piece. The distance in the direction perpendicular to the thickness direction between the side surfaces of the primary magnetic pole and the side shield layer is longer than the distance in the thickness direction between the top surface of the primary magnetic pole and the shield layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
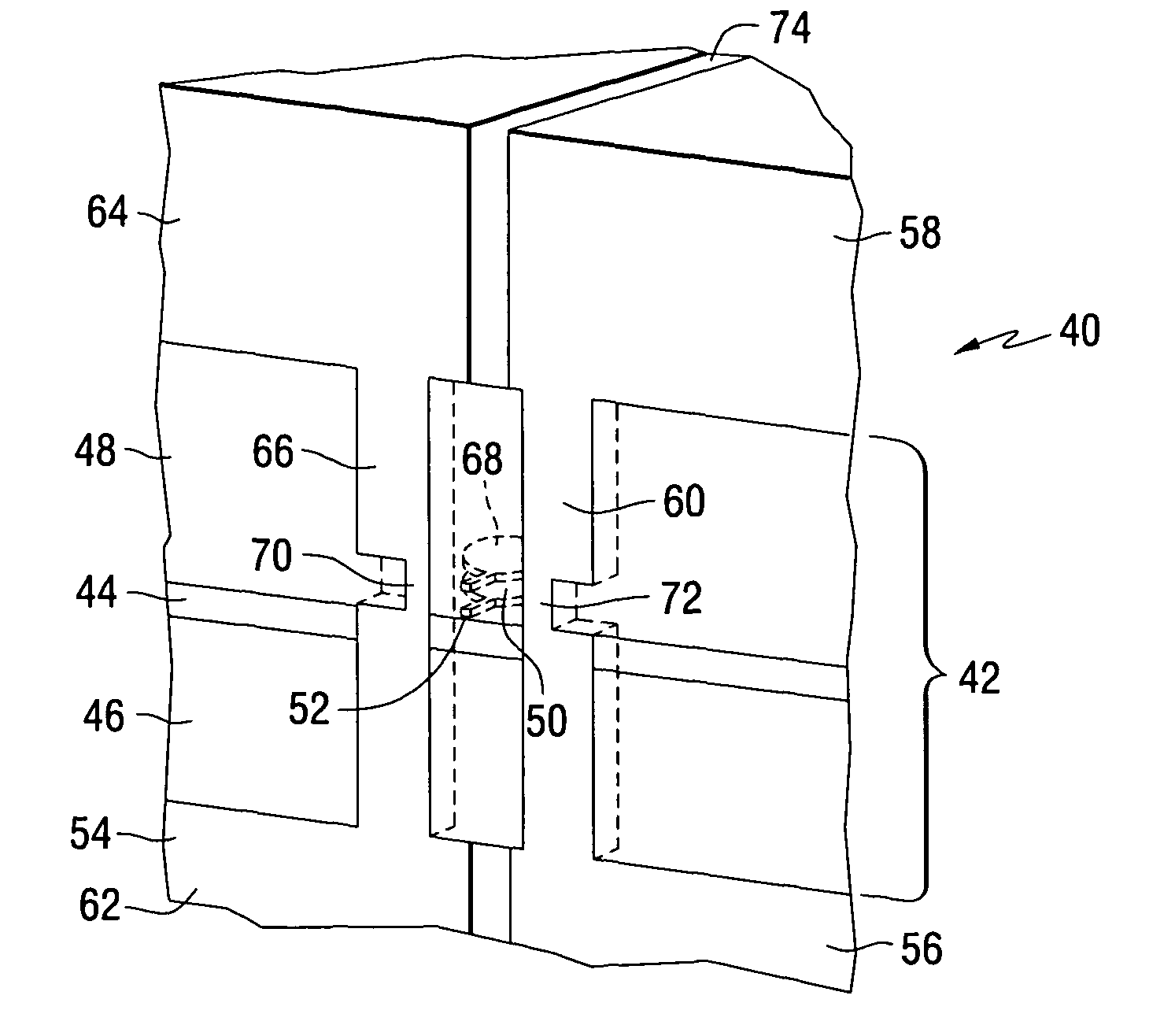
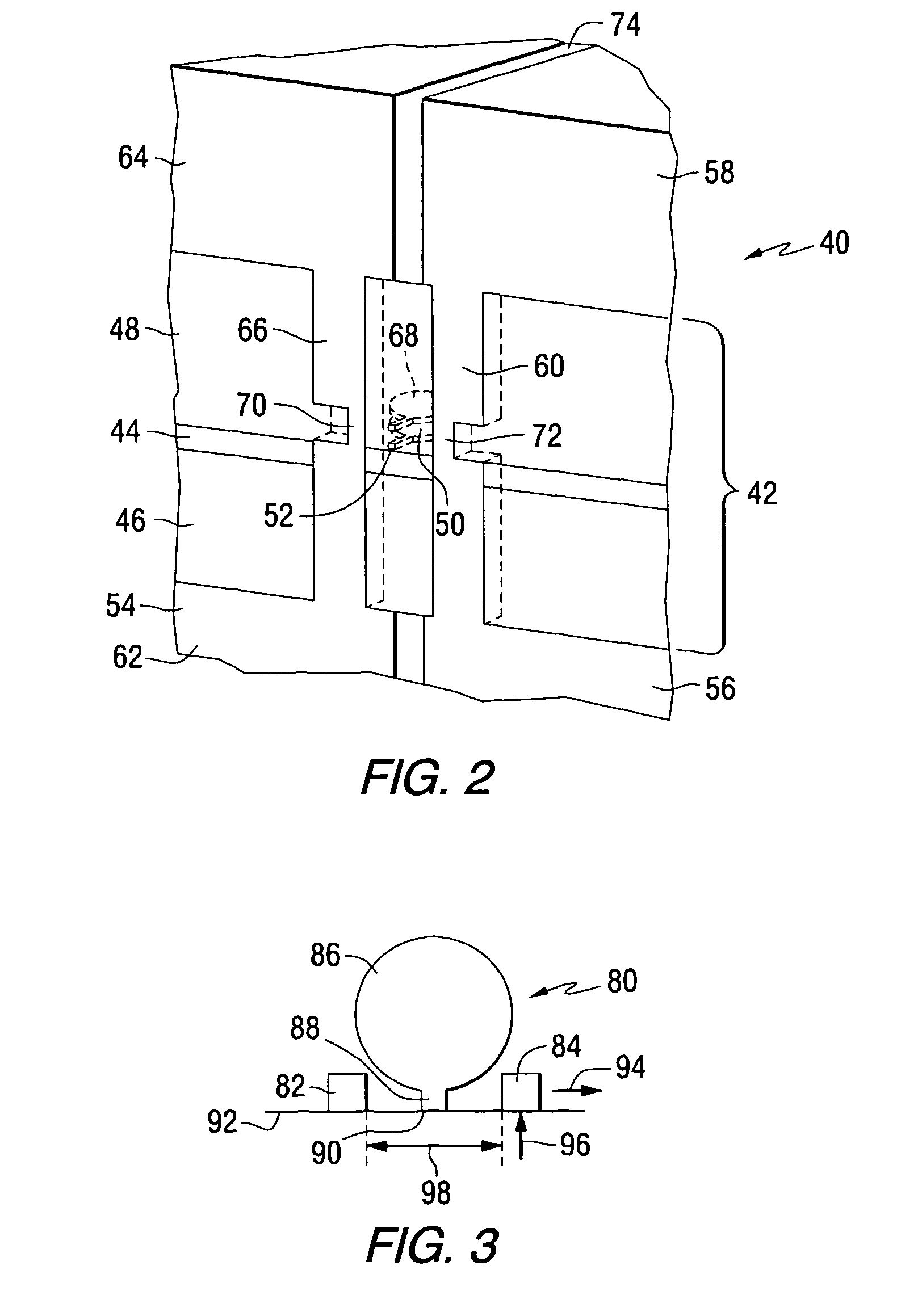
Recording head for reducing side track erasure
InactiveUS20060002020A1Construction of head windingsRecord information storageNon magneticMechanical engineering
The present invention relates to a head having an air bearing surface for confronting the surface of a storage medium. The head includes a first pole that is spaced apart from a second pole. At least one non-magnetic spacer is positioned between the first pole and the second pole such that the first pole is magnetically decoupled from the second pole. In a further aspect, one or both of the first pole and the second pole can be elliptical in shape.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
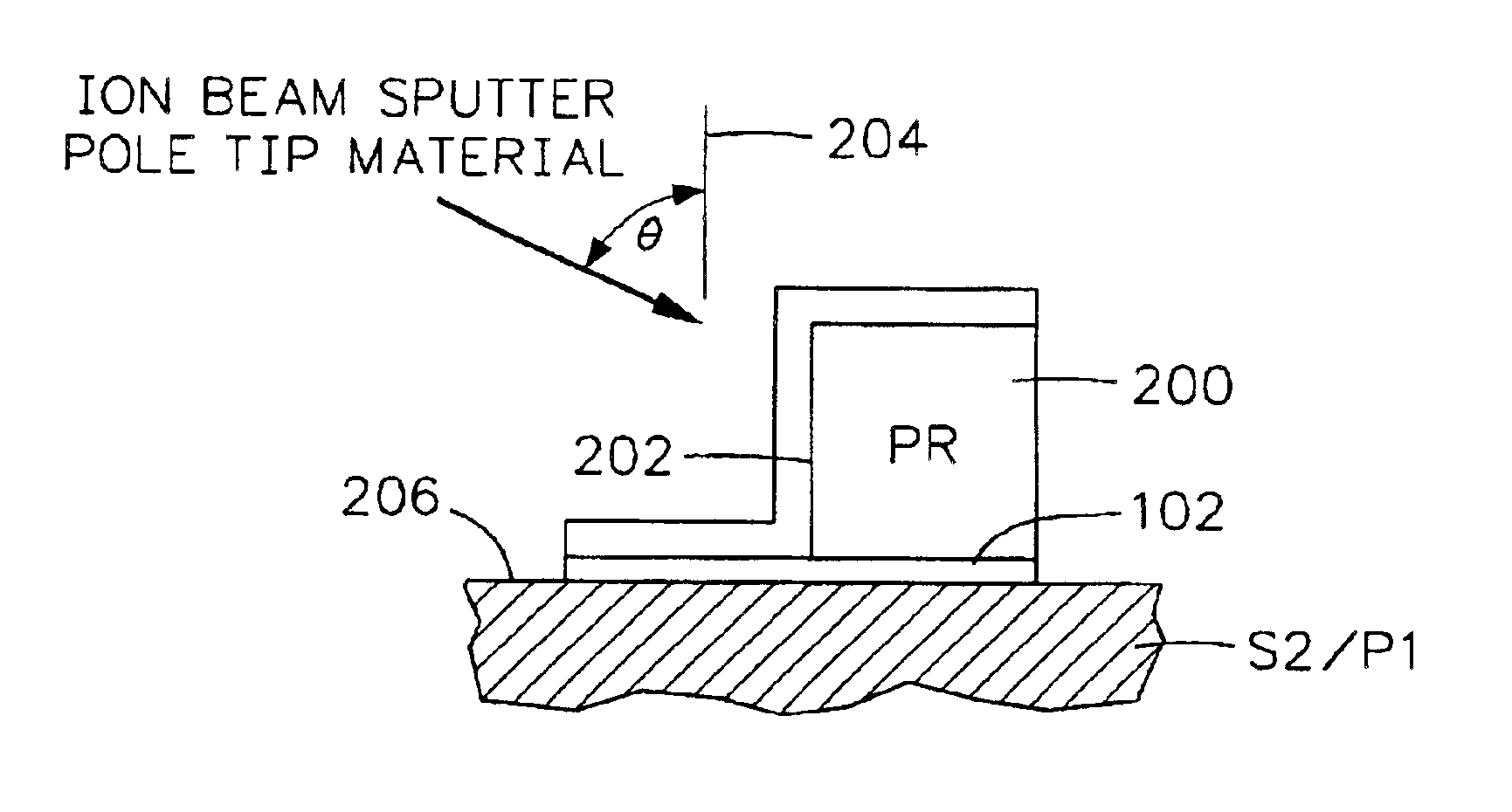
Method of making a narrow pole tip by ion beam deposition
InactiveUS6862798B2Manufacture head surfaceElectrical transducersIon beam depositionElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of making a magnetic head assembly wherein the magnetic head assembly has a write head with a pole tip includes the steps of forming a shaping layer on an underlying layer wherein the shaping layer has a side surface and a top surface, ion beam sputter depositing a ferromagnetic material layer on the underlying layer and on the side and top surfaces of the shaping layer and removing first and second portions of the ferromagnetic material layer from the underlying layer and the top surface of the shaping layer, respectively, leaving a remaining portion of the ferromagnetic material layer on the side surface of the shaping layer which is the aforementioned pole tip.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Dual wire integrated WAMR/HAMR writing head
ActiveUS20070036040A1Combination recordingRecord information storageEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
An apparatus comprises a waveguide, an optical transducer for coupling electromagnetic radiation from the waveguide to a point adjacent to an air bearing surface to heat a portion of a storage medium, and a first wire positioned adjacent to the air bearing surface, wherein current in the wire produces a magnetic field in the heated portion of the storage medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
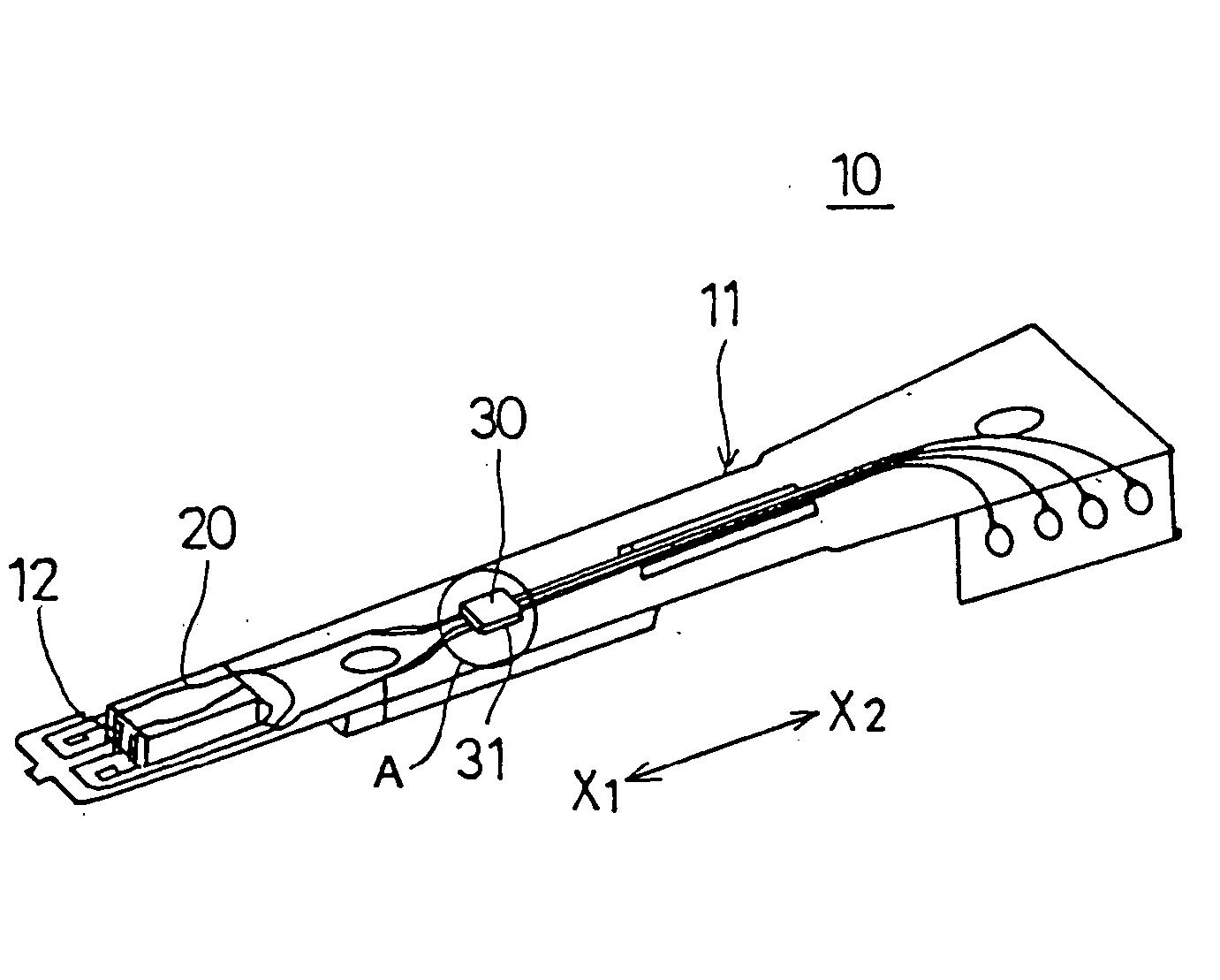
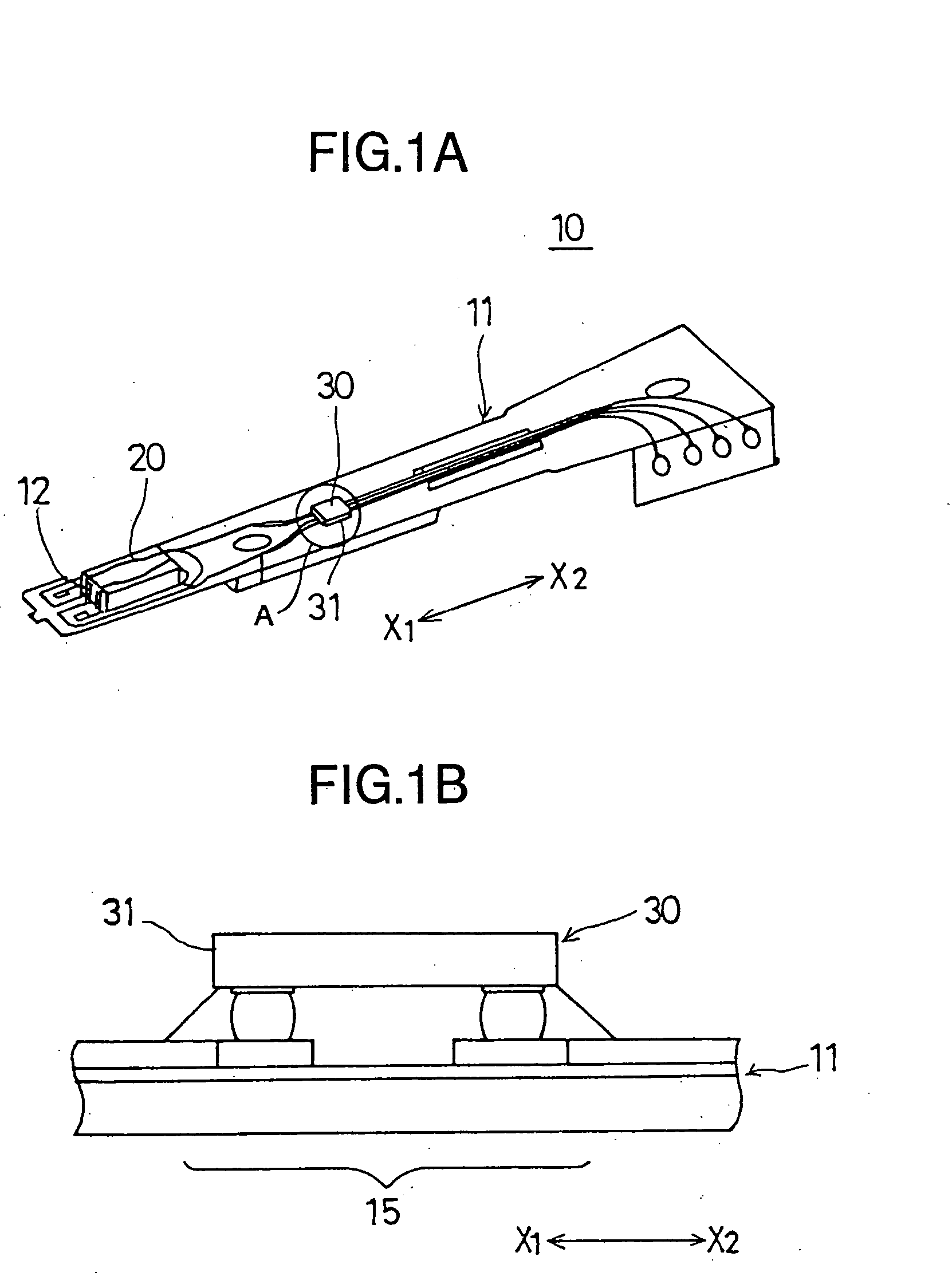
Head stack assembly and information recording apparatus
InactiveUS20080158730A1Unnecessary light emission can be preventedIncreasing and reducing amount of lightCombination recordingRecord information storageEngineering
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dual wire integrated WAMR/HAMR writing head
An apparatus comprises a waveguide, an optical transducer for coupling electromagnetic radiation from the waveguide to a point adjacent to an air bearing surface to heat a portion of a storage medium, and a first wire positioned adjacent to the air bearing surface, wherein current in the wire produces a magnetic field in the heated portion of the storage medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic recording head and method for high coercivity media, employing concentrated stray magnetic fields
InactiveUS20060187580A1High gradientImprove coercive forceMagnetic bodiesRecord information storageFlux loopMagnetization
In methods and arrangements for concentrating stray magnetic fields, a pair of permanent magnets is employed in combination with a magnetic flux circuit, the permanent magnets in the pair having respective magnetizations that are oriented oppositely to each other. The permanent magnets produce a stray magnetic field that adds to a magnetic field produced by the magnetic flux circuit.
Owner:TANDBERG DATA STORAGE
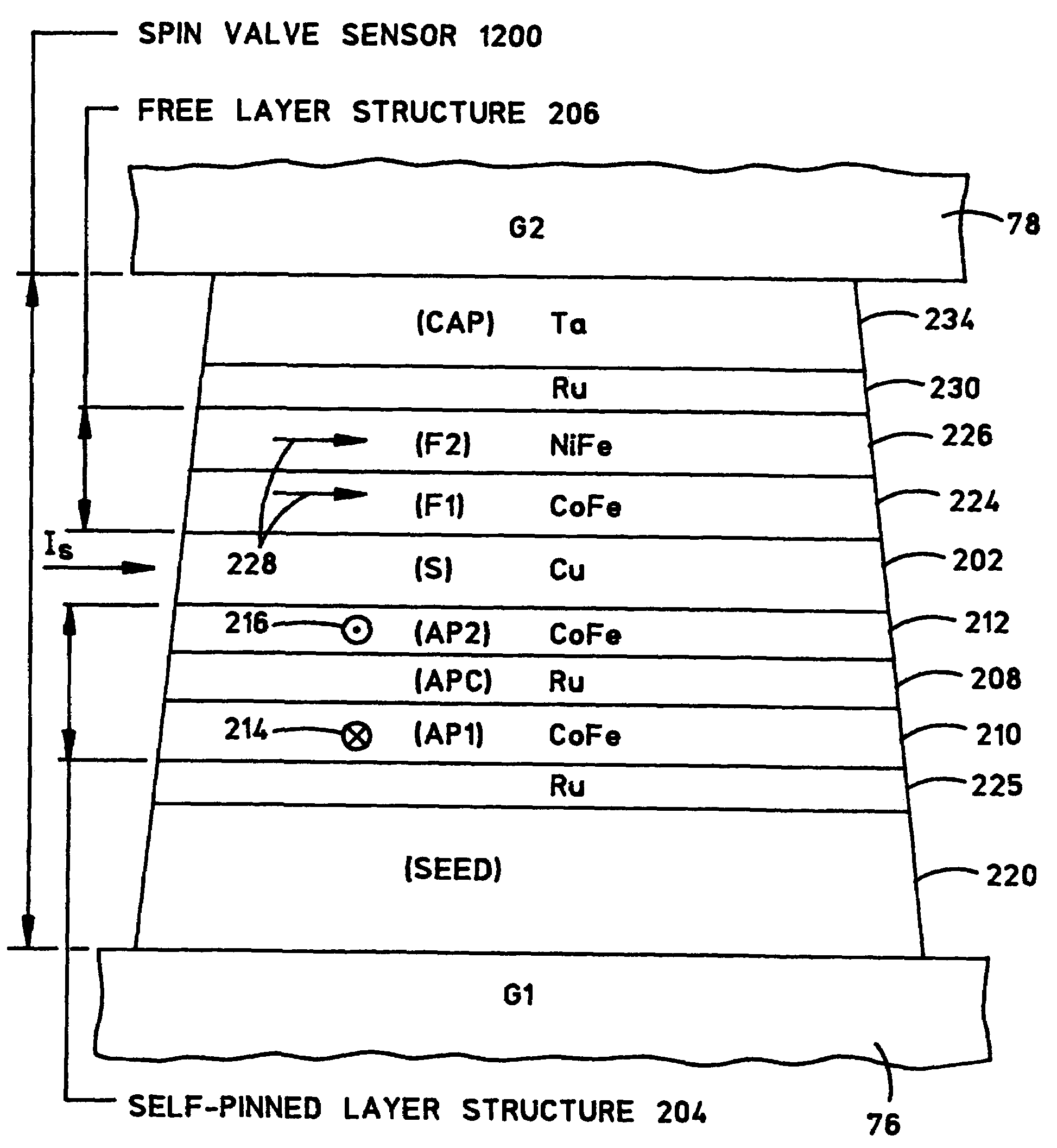
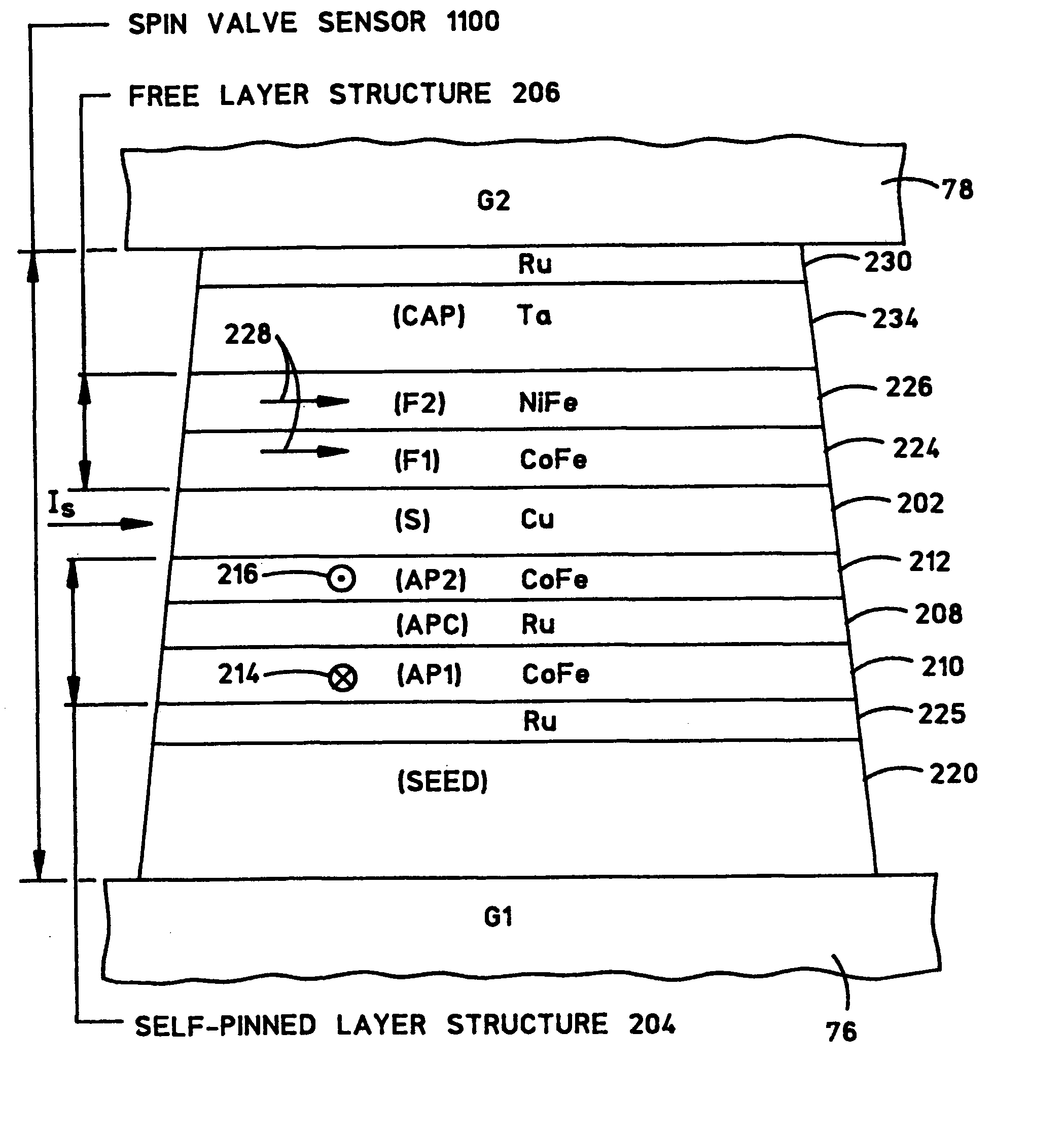
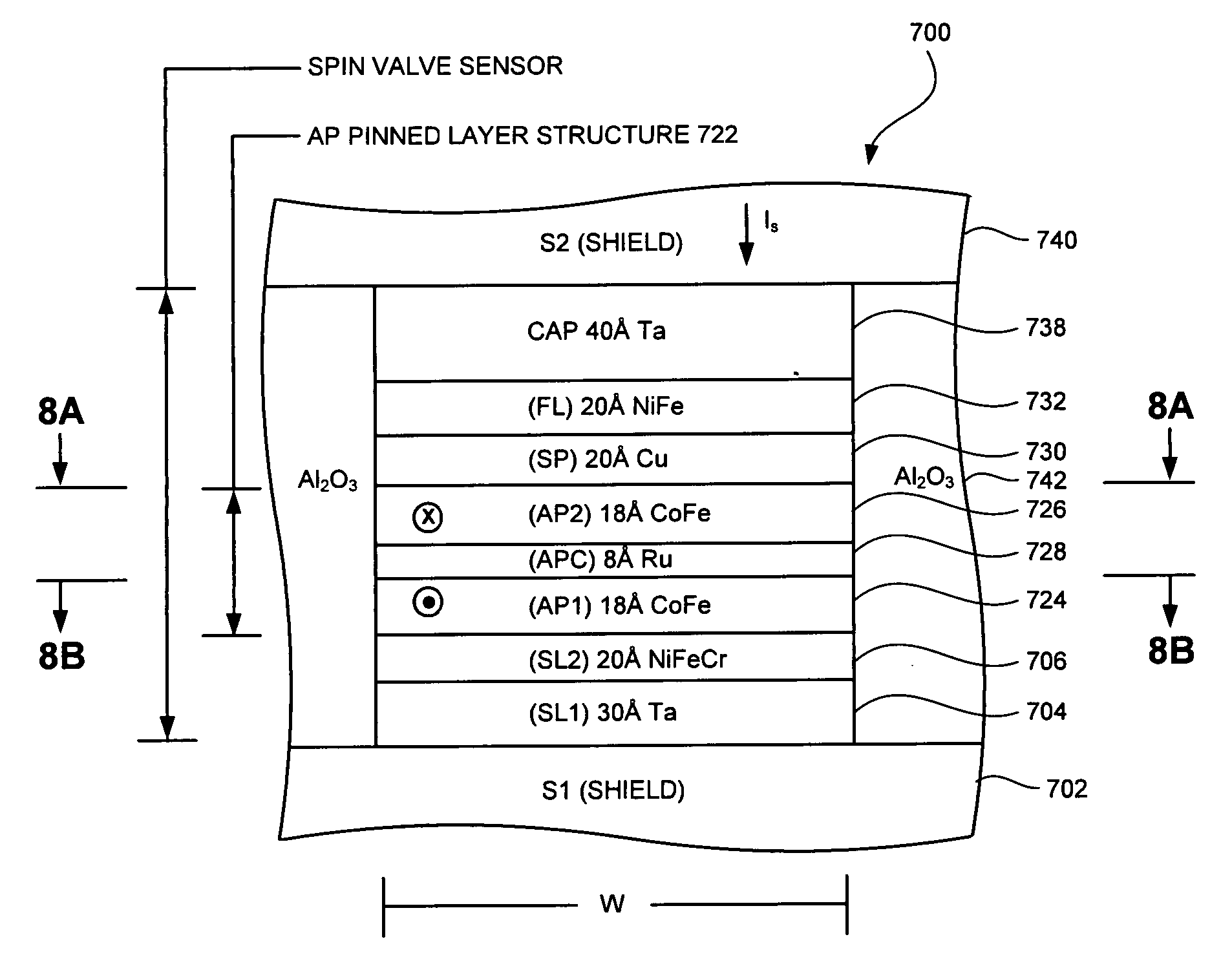
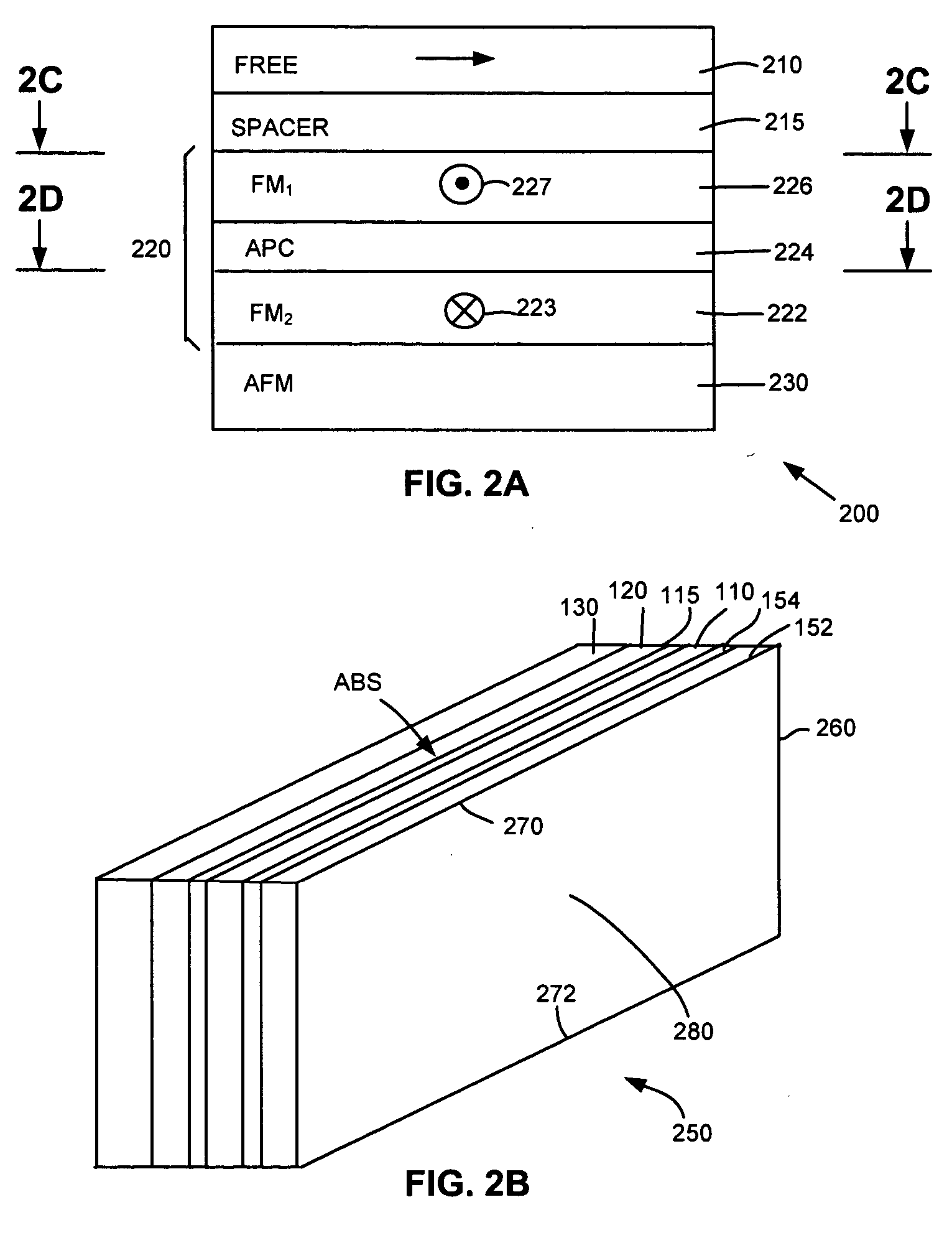
Self-pinned spin valve sensor with stress modification layers for reducing the likelihood of amplitude flip
InactiveUS7196878B2Reduce the possibilityRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsSpin valvePhysics
A spin valve (SV) sensor of the self-pinned type includes one or more compressive stress modification layers for reducing the likelihood that the pinning field will flip its direction. The spin valve sensor includes a capping layer formed over a spin valve structure which includes a free layer, an antiparallel (AP) self-pinned layer structure, and a spacer layer in between the free layer and the AP self-pinned layer structure. A compressive stress modification layer is formed above or below the capping layer, adjacent the AP self-pinned layer structure, or both. Preferably, the compressive stress modification layer is made of ruthenium (Ru) or other suitable material.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Head assembly having integrated circuit chip covered by layer which prevents foreign particle generation
InactiveUS6885522B1Avoid it happening againDisposition/mounting of recording headsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringParticle generation
A head assembly is provided with a mounting surface, and an integrated circuit chip which is mounted on the mounting surface and processes signals. The integrated circuit chip is covered by a layer which prevents generation of foreign particles from the integrated circuit chip by the provision of the layer.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
Perpendicular magnetic writer with magnetic potential control shield
InactiveUS7106554B2Easy to controlIncreased reluctanceManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageMagnetic reluctanceEngineering
Conventional perpendicular writers that utilize an extended return pole are subject to large undershoot fields. This problem has been reduced by replacing the prior art extended return pole by one whose magnetic potential has been increased relative to both the main and return poles. In a first embodiment, a second non-magnetic gap is inserted between the extended return pole and the return pole. In a second embodiment, the extended return pole is made very thin, thereby increasing its reluctance, while a third embodiment combines both reluctance-increasing features in a single design.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
TMR/CPP reader for narrow reader gap application
ActiveUS9001473B1Magnetic measurementsRecord information storageCard readerElectrical and Electronics engineering
The embodiments disclosed generally relate to a read head in a magnetic recording head. The read head utilizes a sensor structure having: a pinned magnetic structure recessed from a media facing surface; and a reader gap structure. The reader gap structure has a spacer layer recessed from the media facing surface and disposed on top of the pinned magnetic structure, a recessed first free layer partially recessed from the media facing surface and disposed on top of the barrier layer, a second free layer extending to the media facing surface an disposed on top of the barrier layer, and a cap layer extending to the media facing surface disposed atop the second free layer. The pinned magnetic structure, the spacer, and the first free layer have a common face which is on an angle relative to the media facing surface.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
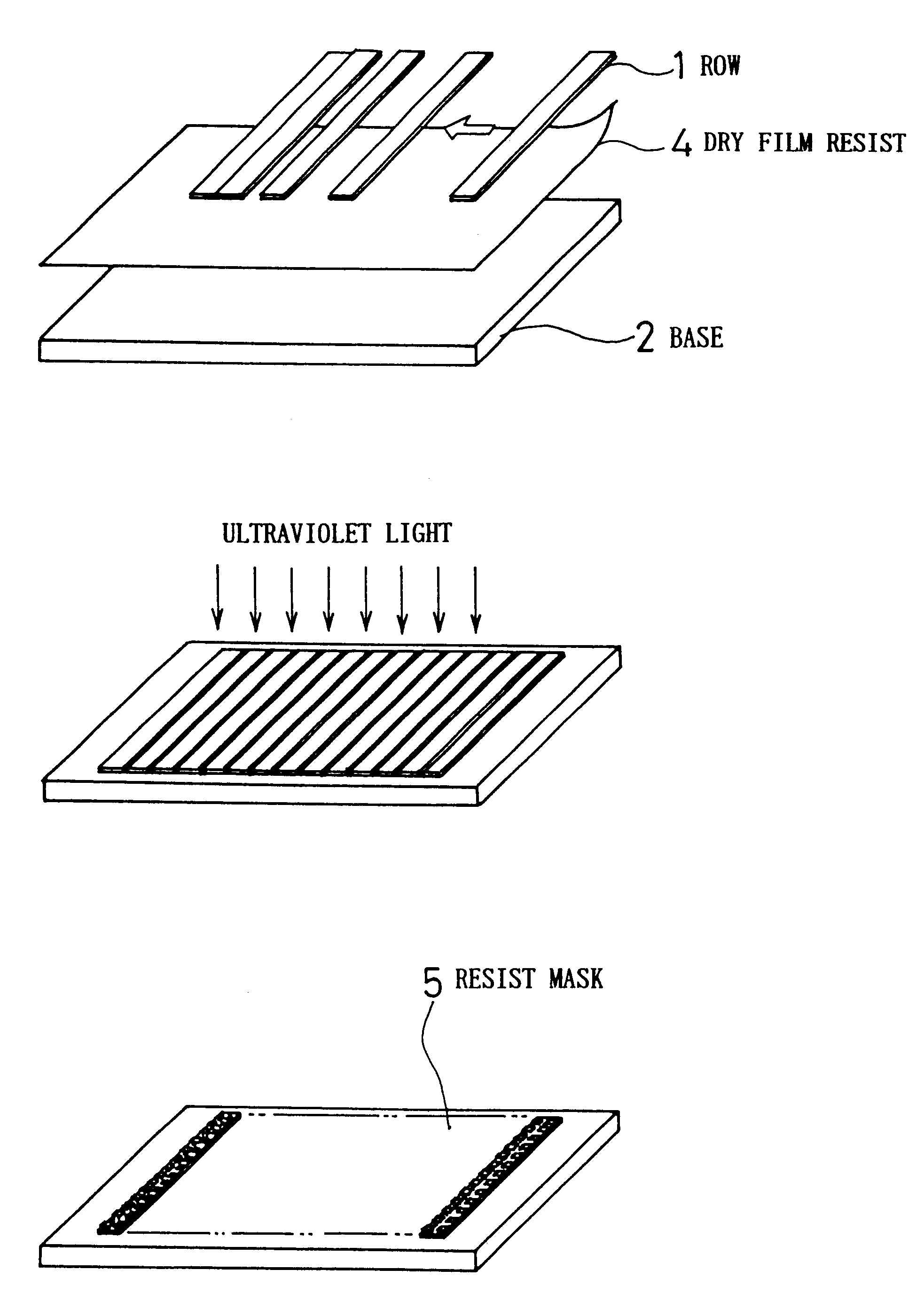
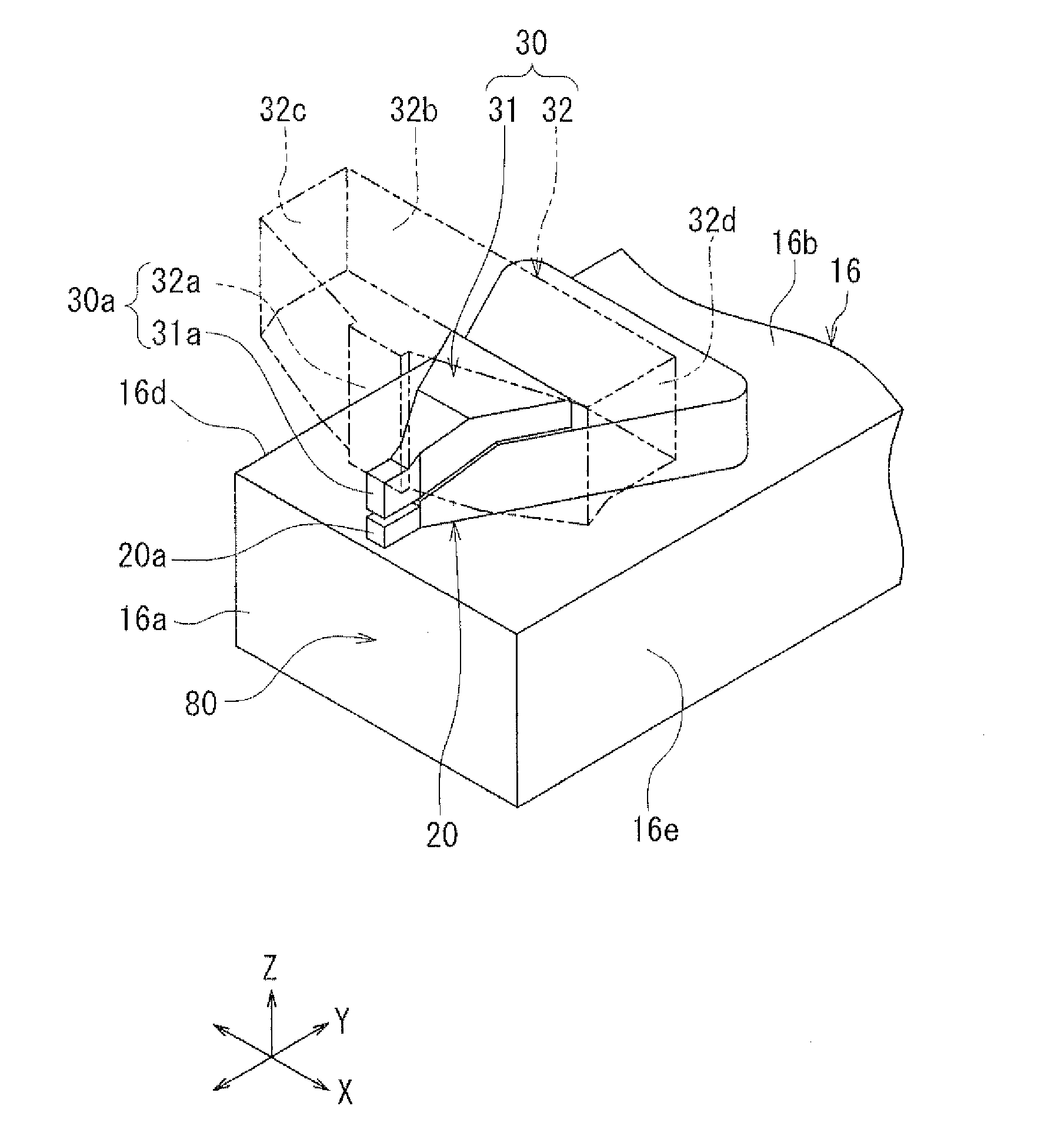
Magnetic head slider manufacturing method
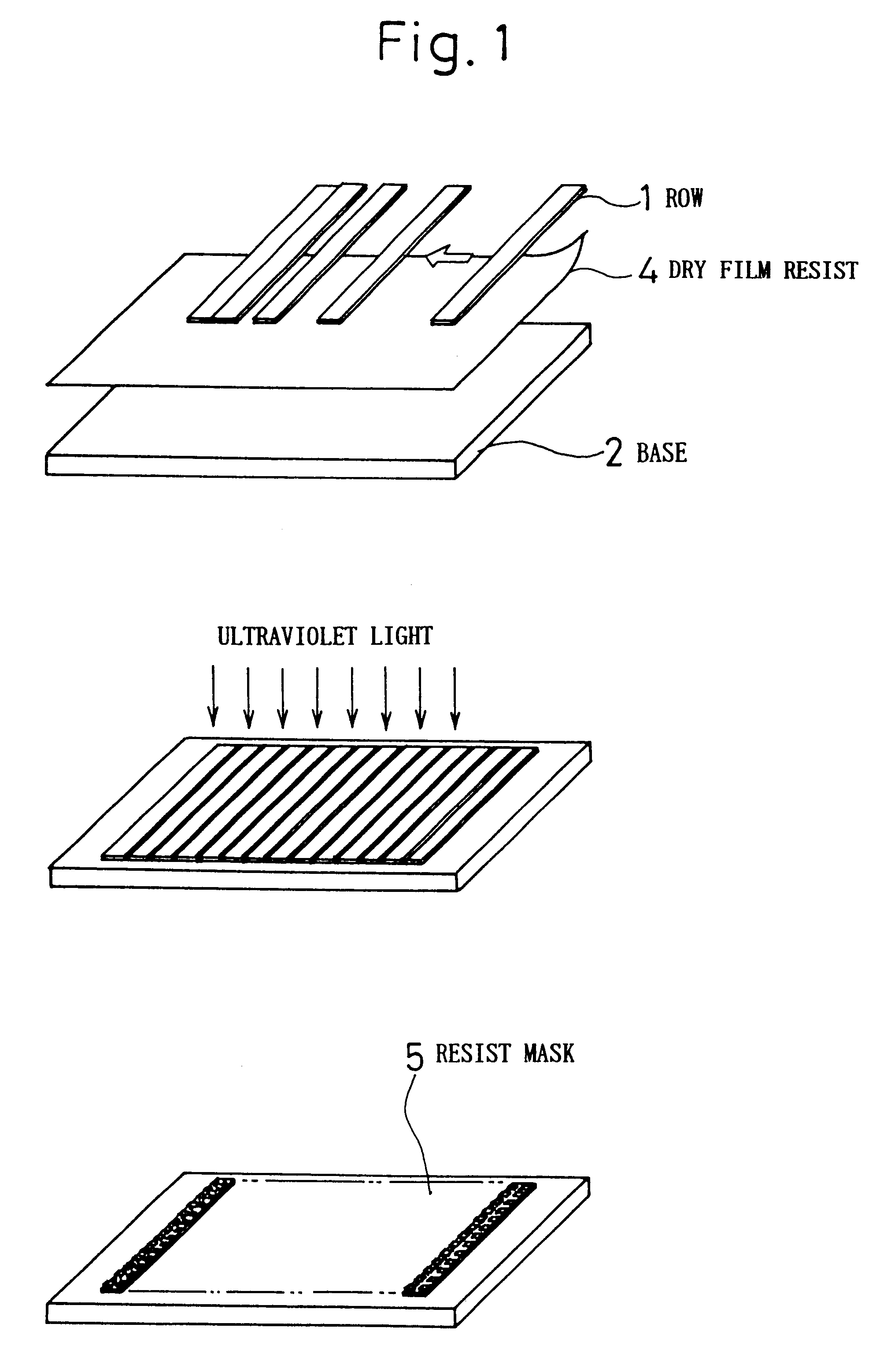
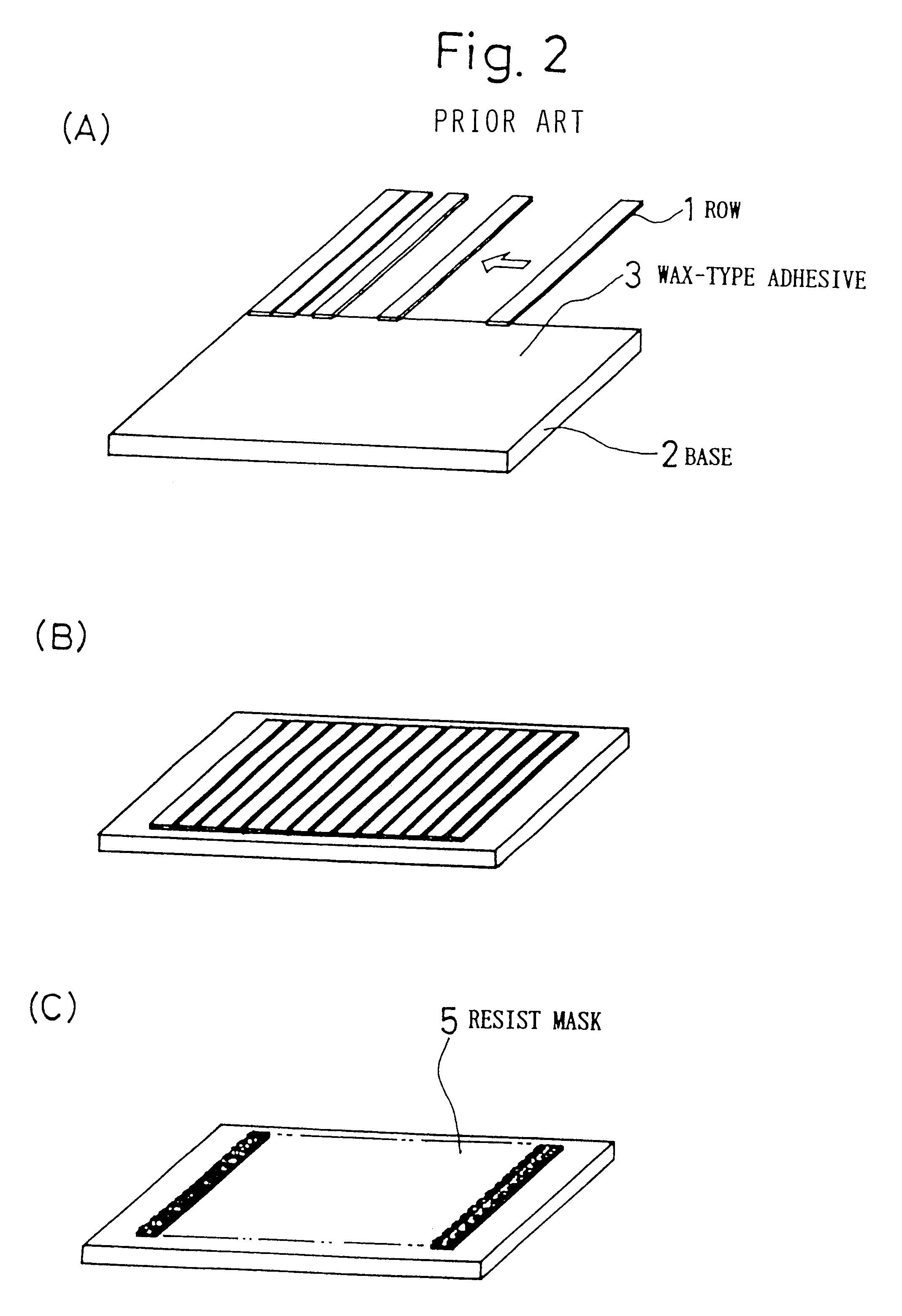
When forming a floating-type magnetic head slider for a hard disk drive or the like using dry etching, a method for manufacturing the magnetic head slider provides a method for adhering the slider being processed to an appropriate processing fixture, and when a plurality of magnetic head sliders are being processed at one time, a row (bar) array of sliders that is prepared beforehand is adhered to a metal or ceramic base, after which a dry etching method is used to form the air bearing, dry film photo-resist being used for the adhering of the row and the base. Ion milling or reactive ion etching (RIE) can be used as the dry etching method.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
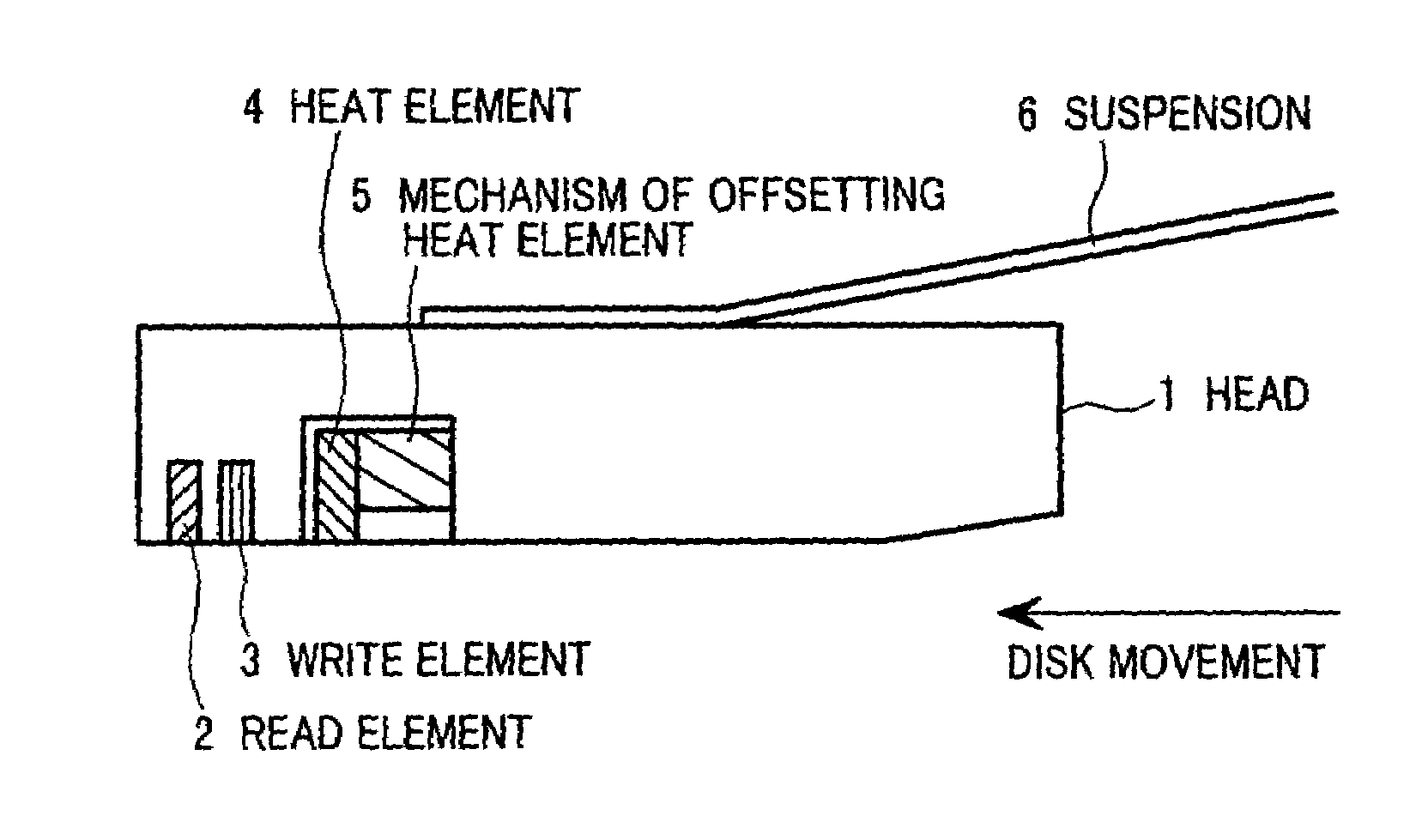
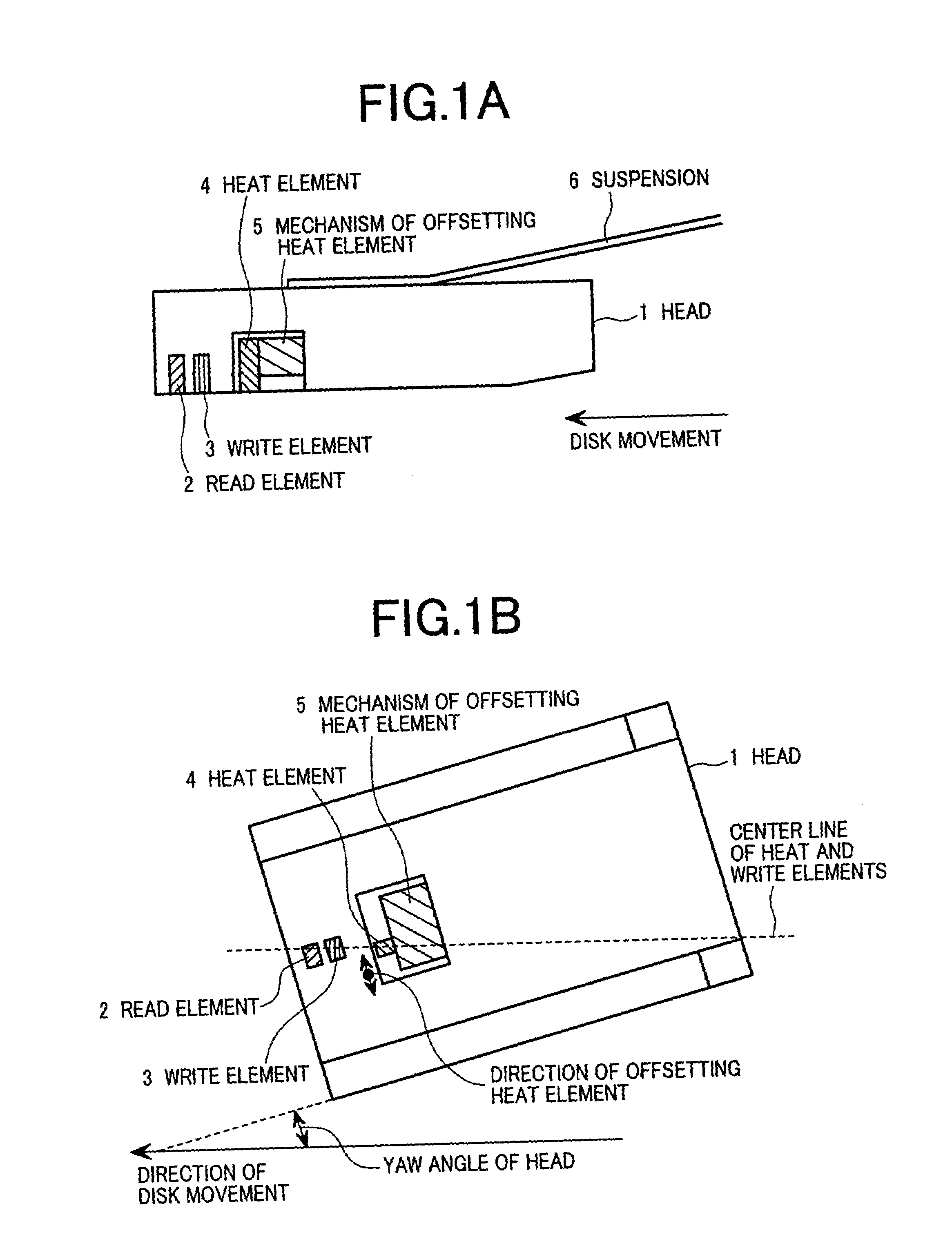
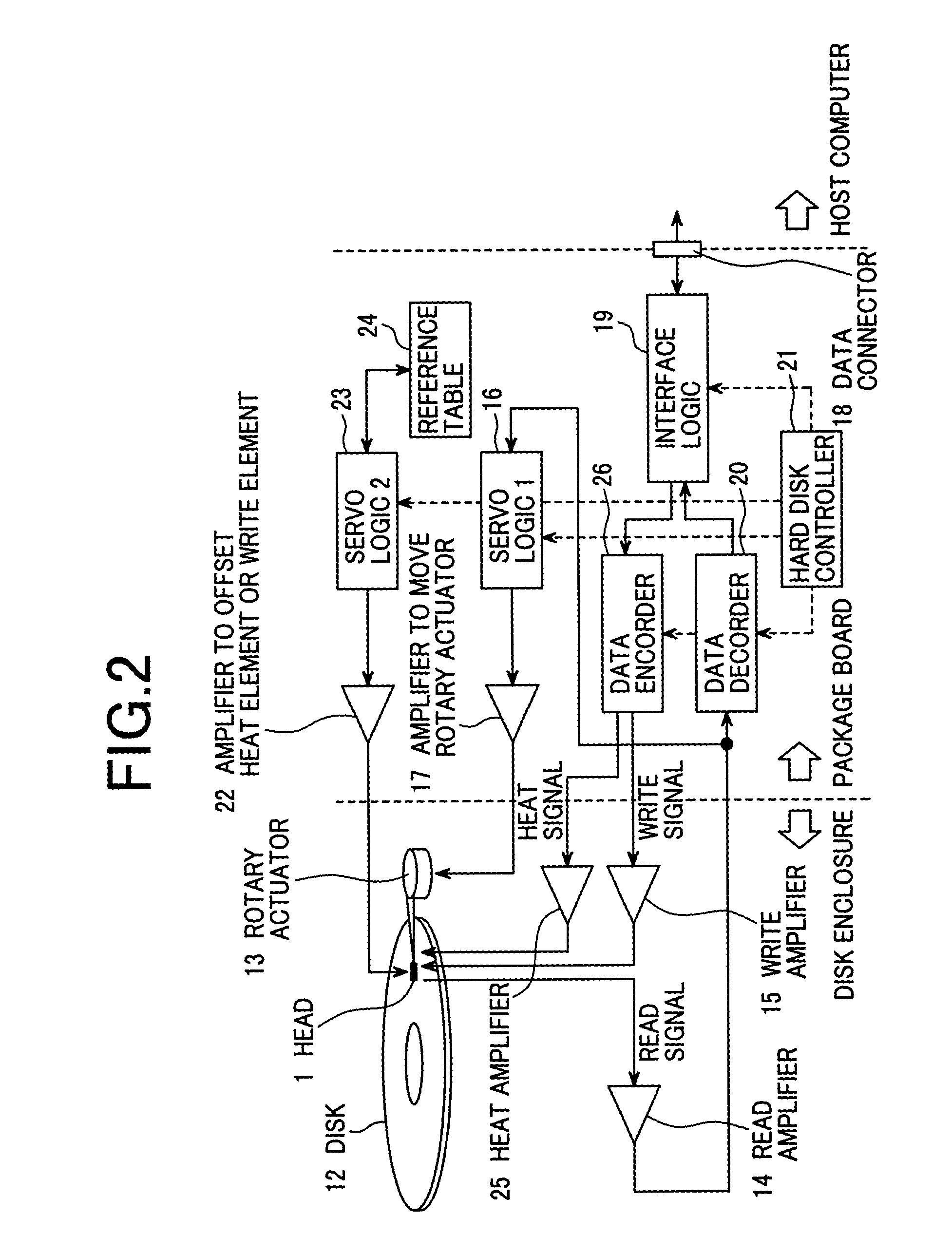
Magnetic disk apparatus having an adjustable mechanism to compensate write or heat element for off-tracking position with yaw angle
InactiveUS7027248B2Large storage capacityTrack finding/aligningManufacturing heads with multiple gapsRotary actuatorDeflection angle
In a thermal assisted type magnetic disk apparatus having a head holding a heat element and a write element, in which coercivity of a disk is locally reduced by temperature-increasing the disk and writing is performed by the write element, along with a seek operation to move the head by a rotary actuator in a radial direction, a yaw angle is changed and a heat area and the write element are track-shifted. A mechanism to offset one of the heat area and the write element in a width direction of a slider, to array the heat element and the write element in a track running direction in correspondence with the yaw angle of the head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC +1
Magnetic recording head with compact yoke
A compact magnetic recording head is provided. The recording head includes a write pole and a substantially planar yoke, which is coupled to the write pole. The yoke is configured to support a substantially single vortex configuration of magnetization.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magneto resistive (MR) head
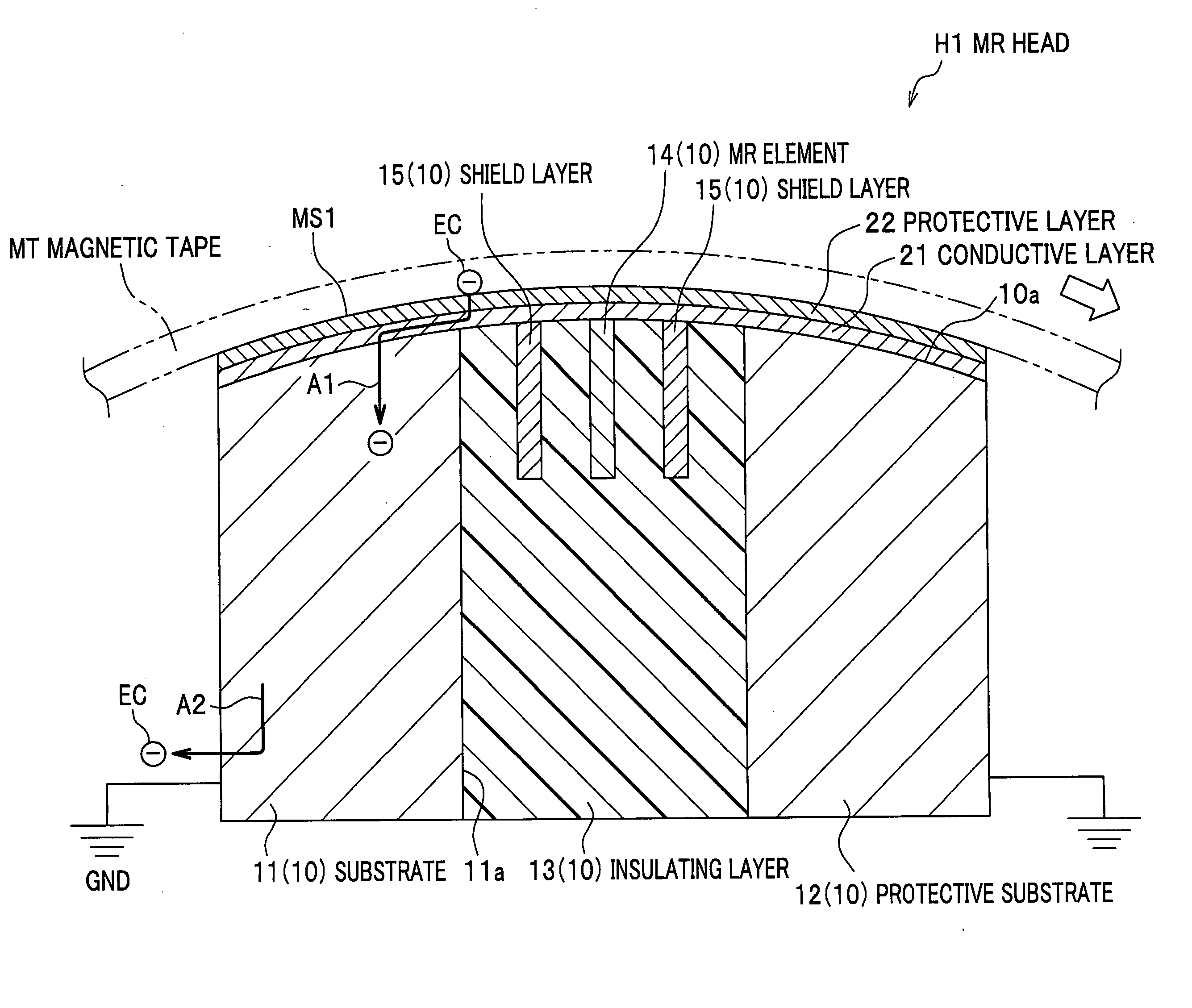
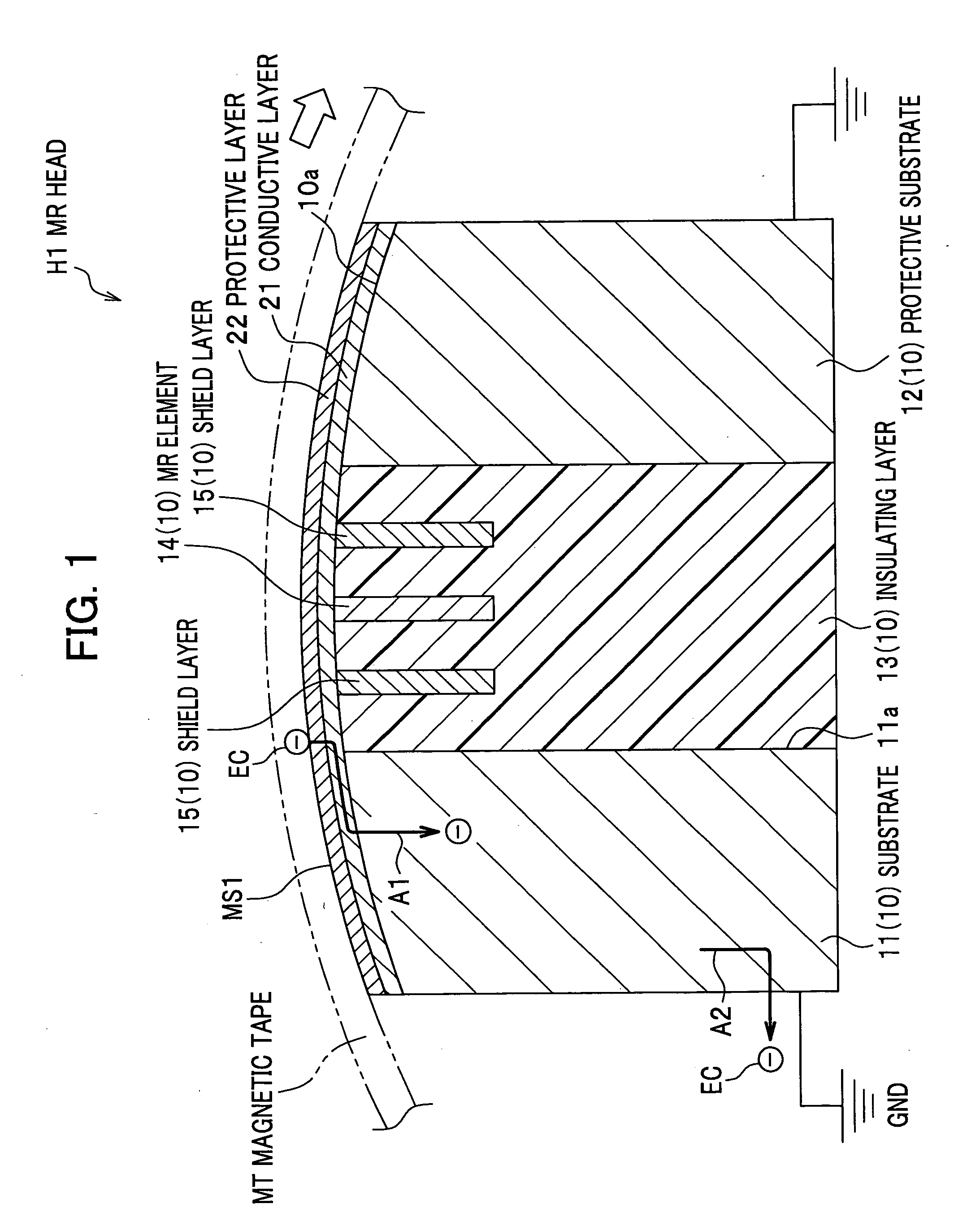
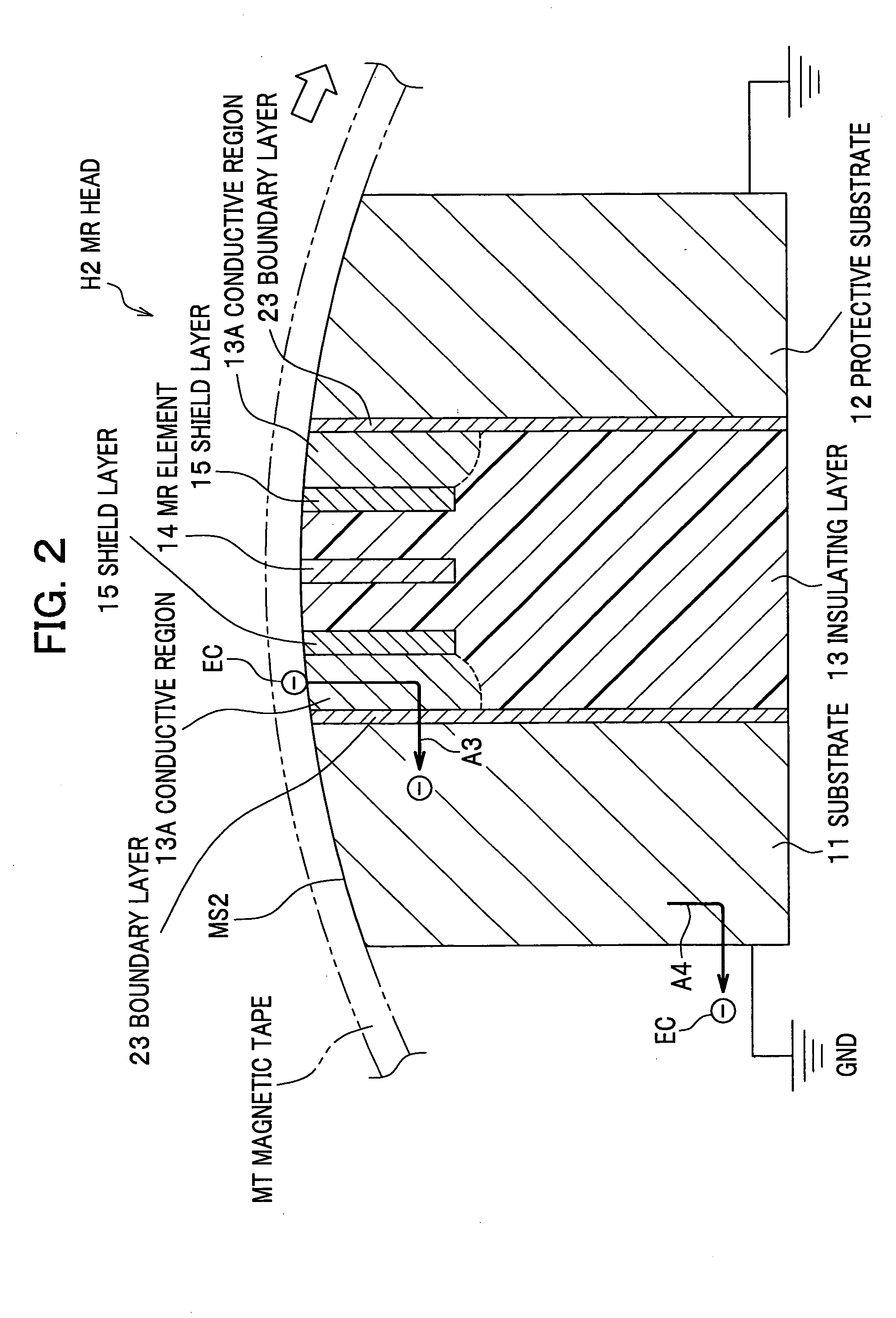
InactiveUS20050207069A1Easy dischargePrevented from being scratchedRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsMagnetic tapeMagnetic reluctance
Disclosed is an MR head in which the MR element resists damage due to ESD. A magneto resistive head to be in contact with a running magnetic tape includes a substrate, an insulating layer, a magneto resistive element located in the insulating layer, at least one shield layer for shielding the magneto resistive element from magnetic fields, and a conductive layer that has a conductive surface being in contact with the magnetic tape and that is electrically connected to the substrate. In this head, static electricity accumulated on the magnetic tap is discharged through the conductive layer and the substrate.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Glass composition, sealing glass for magnetic head and magnetic head using the same
InactiveUS6778355B2Low pour pointImprove waterproof performanceManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageSoftening pointElectronic equipment
In order to provide a practically lead-free glass composition having a low softening point and an excellent water resistance for use in various parts of electronic equipment and a magnetic head using the same, a glass composition is provided, which contains 0.5 to 14 wt % of SiO2, 3 to 15 wt % of B2O3, 4 to 22 wt % of ZnO, 55 to 90 wt % of Bi2O3, 0 to 4 wt % of Al2O3, 0 to 5 wt % of at least one selected from the group consisting of Li2O, Na2O and K2O, and 0 to 15 wt % of at least one selected from the group consisting of MgO, CaO, SrO and BaO.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Solderable pad fabrication for microelectronic components
InactiveUS20130277863A1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface oxidationDiffusion barrier
Two microelectronic components can be attached by flowing solder between solderable pads patterned on interfacing surfaces. According to one implementation, the microelectronic components can include the solderable pads patterned onto first respective surfaces and other surface features patterned onto second respective surfaces. In another implementation, the solderable pads can include an adhesion layer, a diffusion barrier layer, and surface oxidation layer.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Lapping system with mutually stabilized lapping carriers
InactiveUS7115020B1Prevent rotationRecord information storageGrinding feed controlEngineeringCantilever
A lapping system for eliminating crowning in a surface to be lapped includes a first lapping carrier adapted to carry a first workpiece and a second lapping carrier adapted to carry a second workpiece. A stabilizer assembly interconnects the first and second lapping carriers in a mutually stabilizing arrangement that stabilizes the first and second workpieces against rotation. The stabilizer assembly includes first and second stabilizer arms extending between the first lapping carrier and the second lapping carrier. Each lapping carrier and an associated stabilizer arm collectively defines a fixture having a carrier portion and a stabilizer portion, and which may be generally T-shaped. One end of each stabilizer arm is cantilevered from its associated lapping carrier, while the free end of each stabilizer arm is pivotally mounted to the opposite lapping carrier. Downward lapping forces are applied independently to each lapping carrier. In an alternative embodiment, the stabilizer arm extending from the lapping carrier is mounted to an anchor that is not another lapping carrier.
Owner:IBM CORP
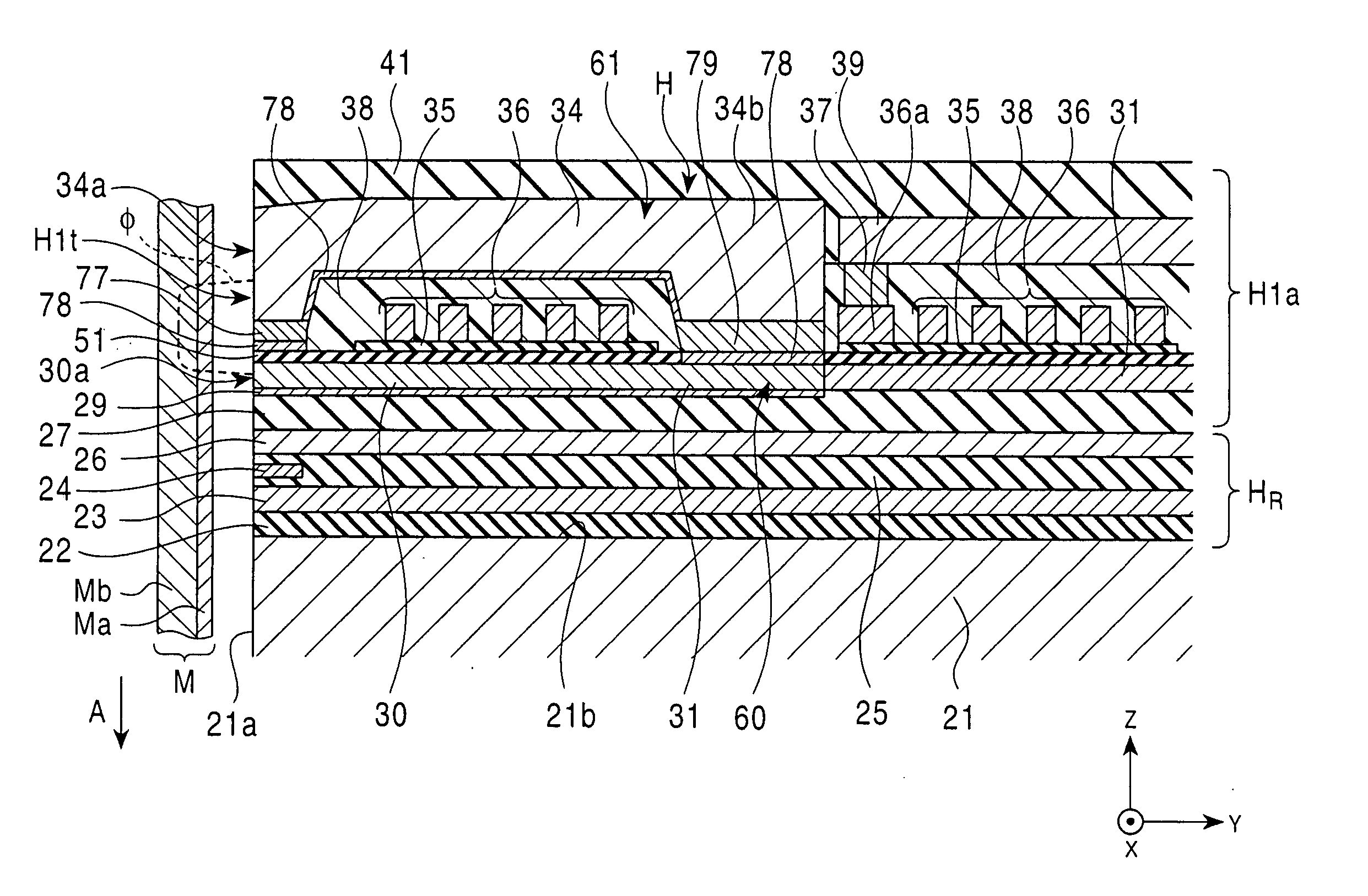
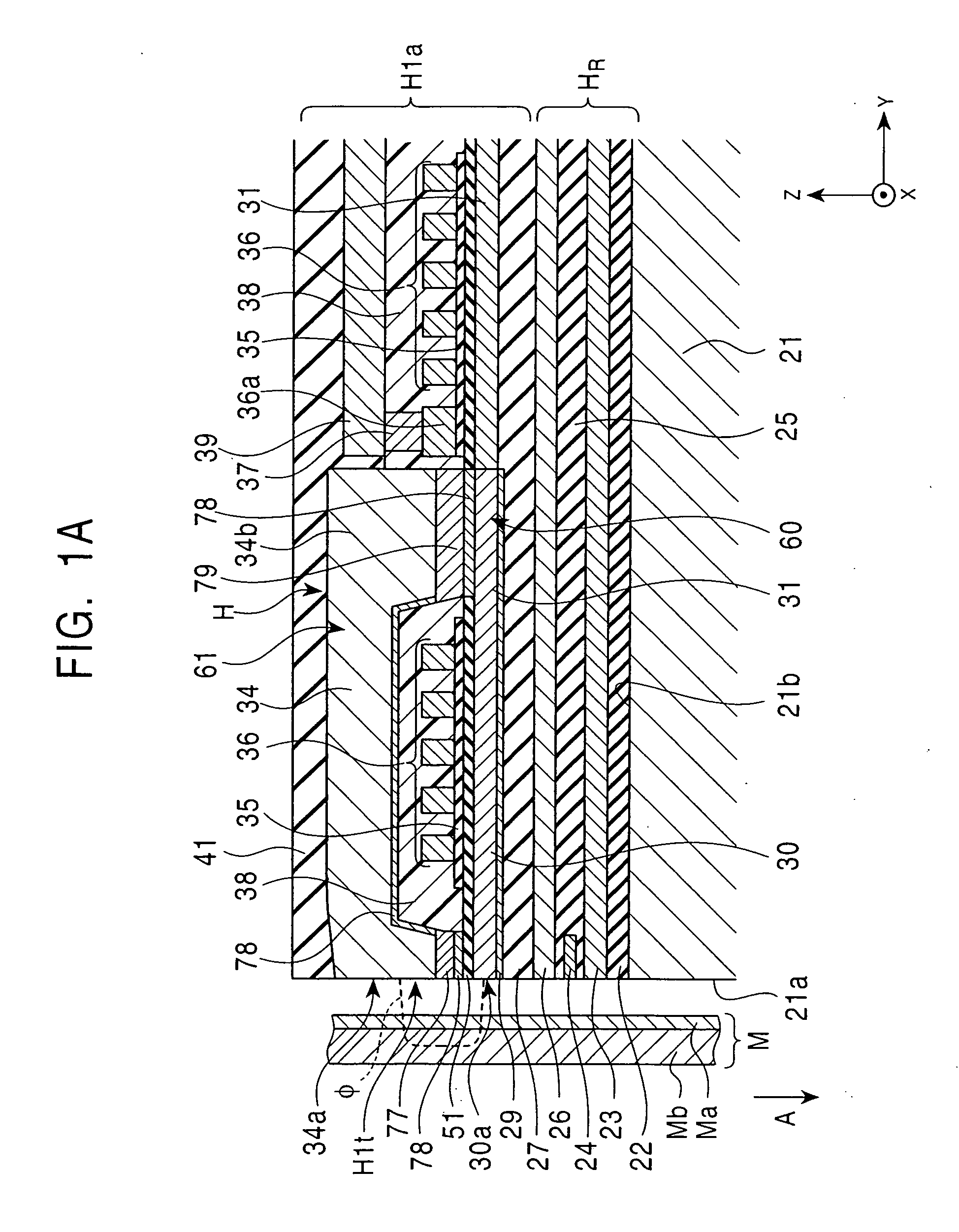
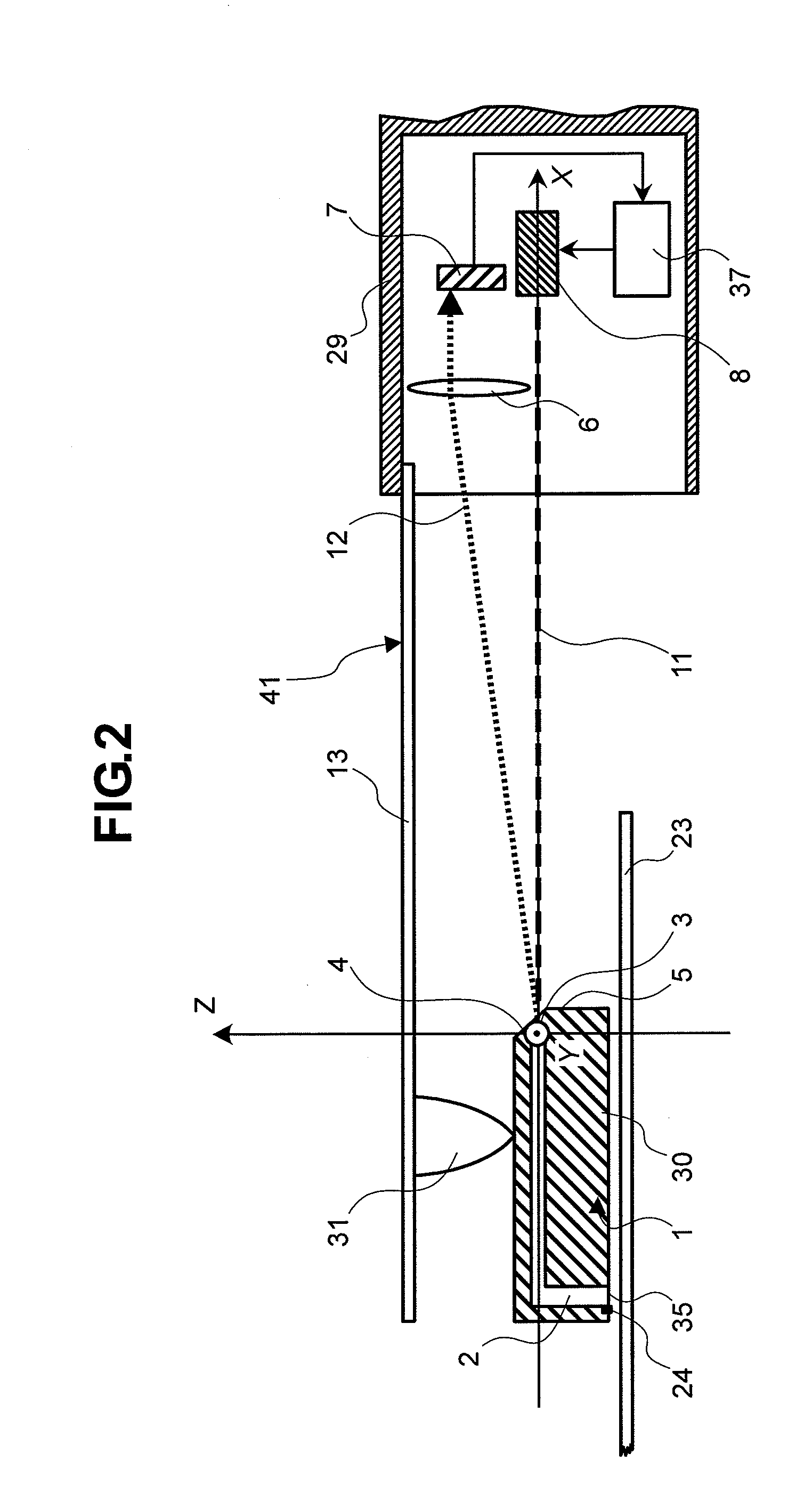
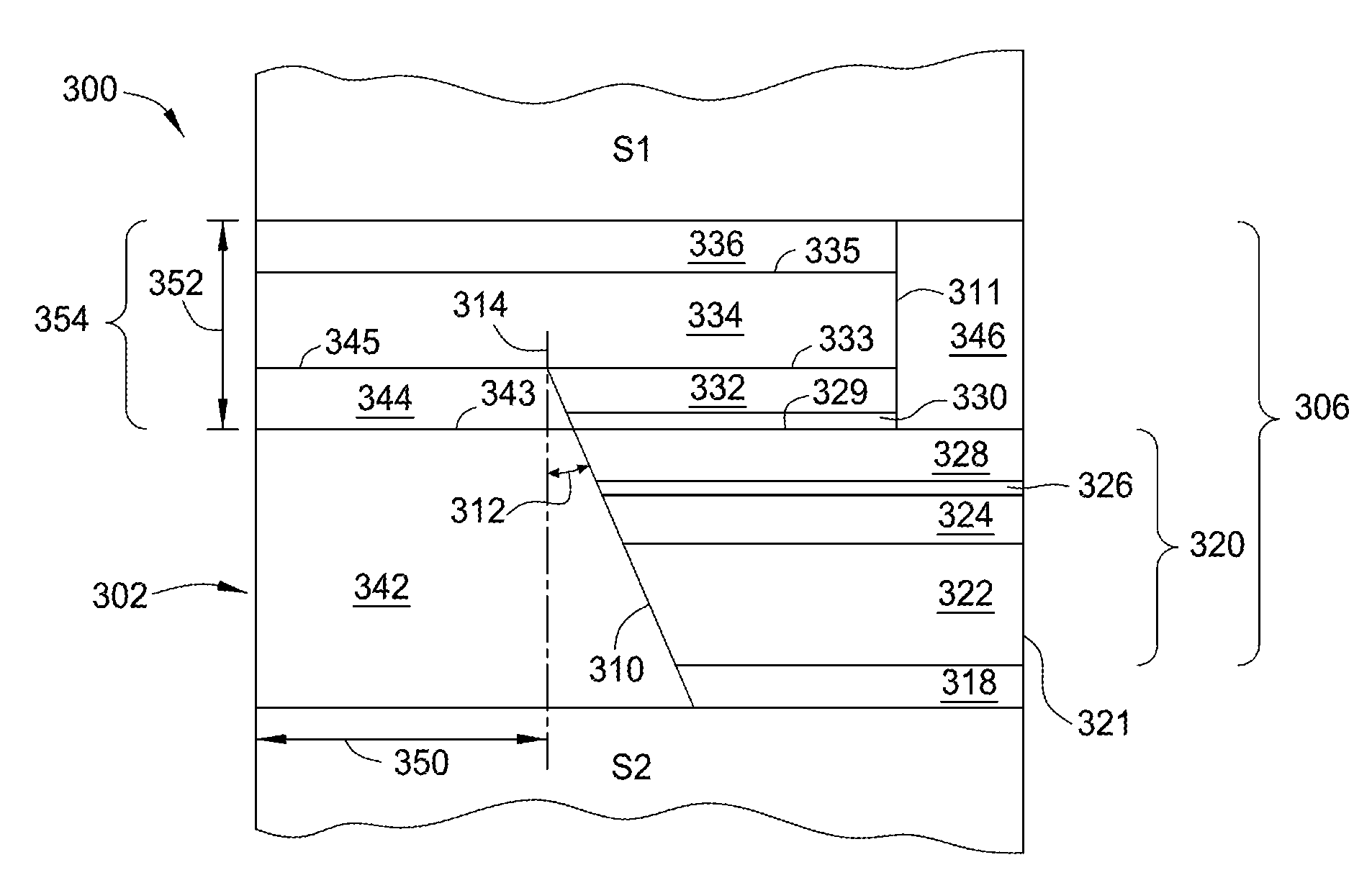
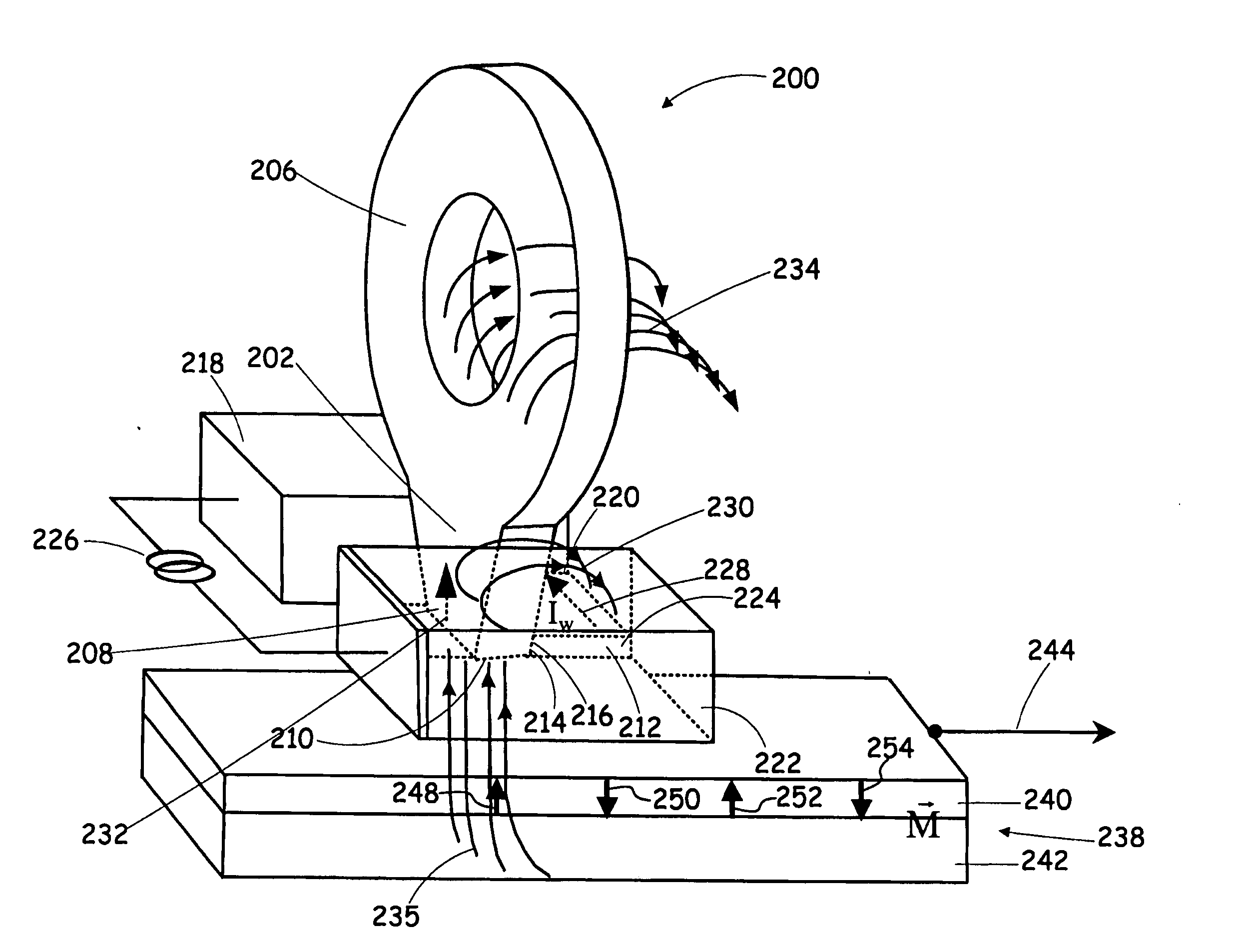
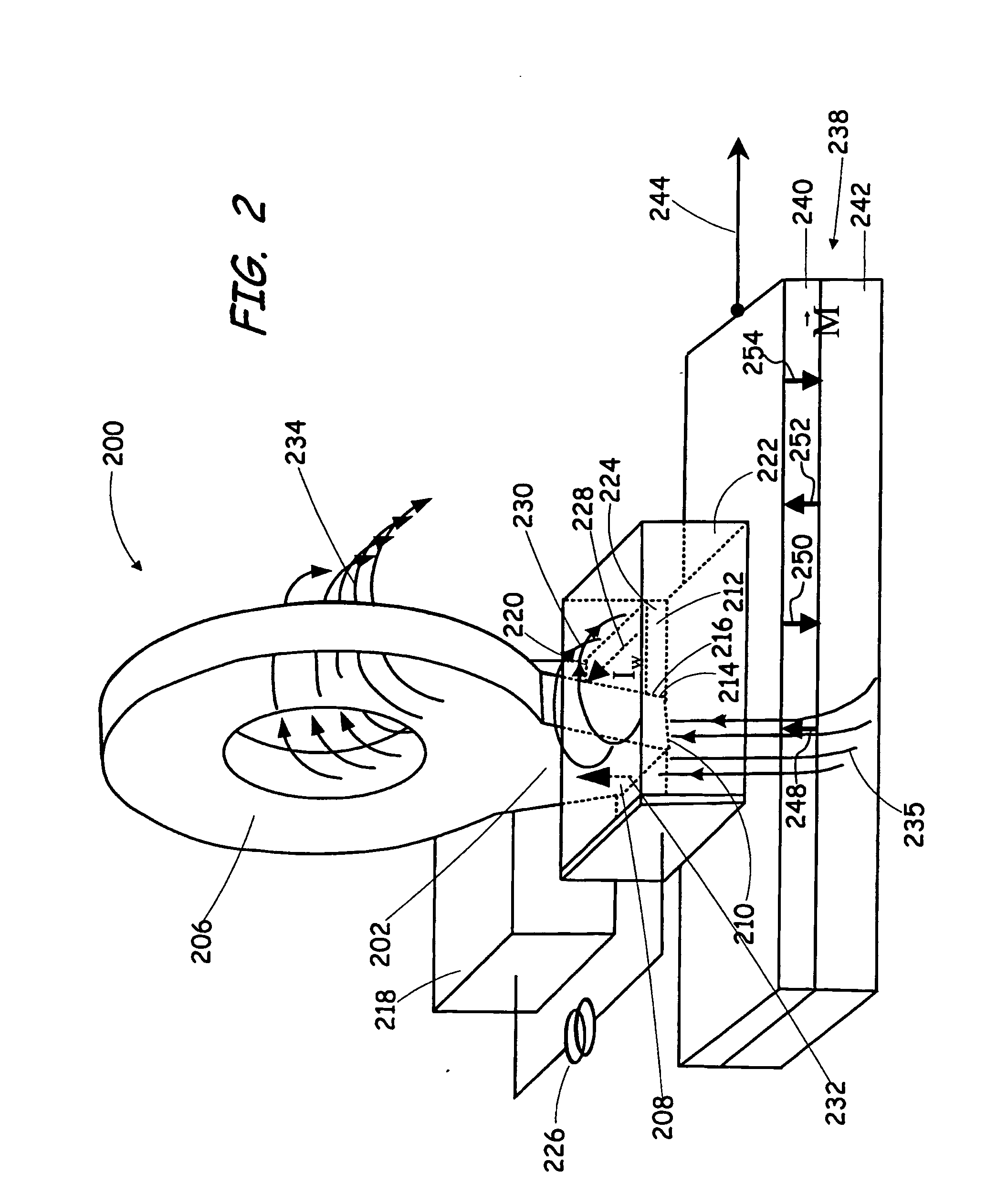
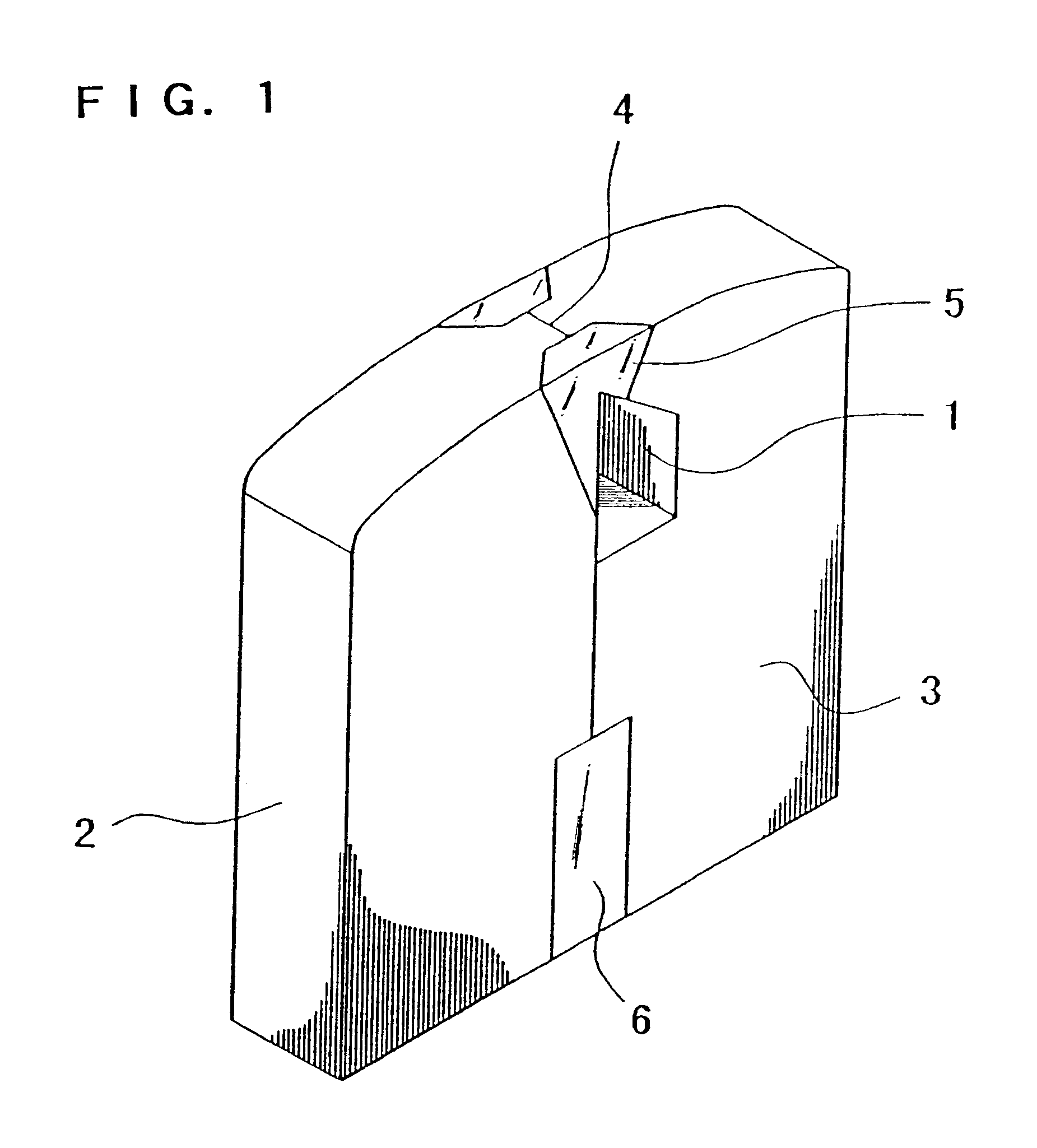
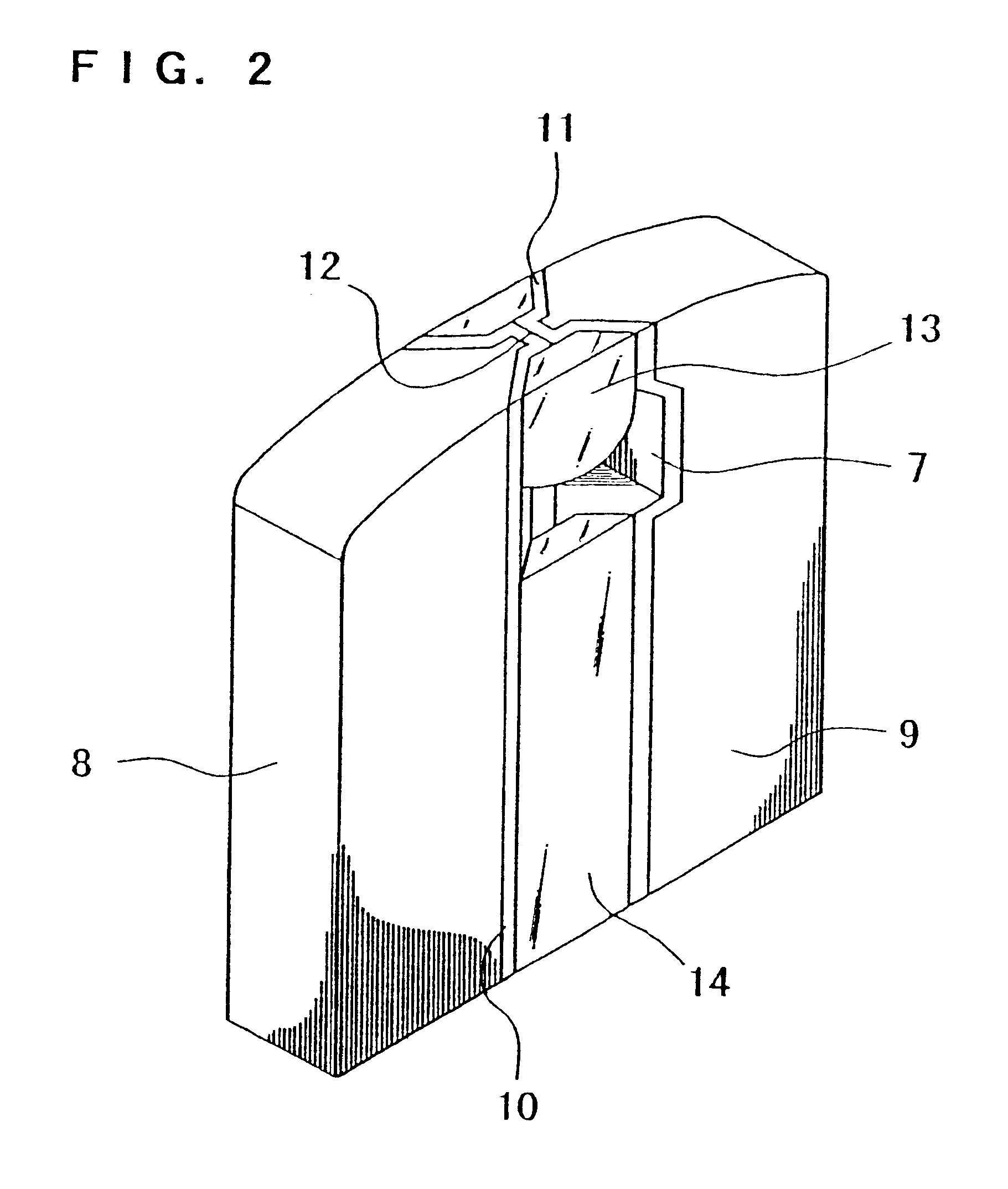
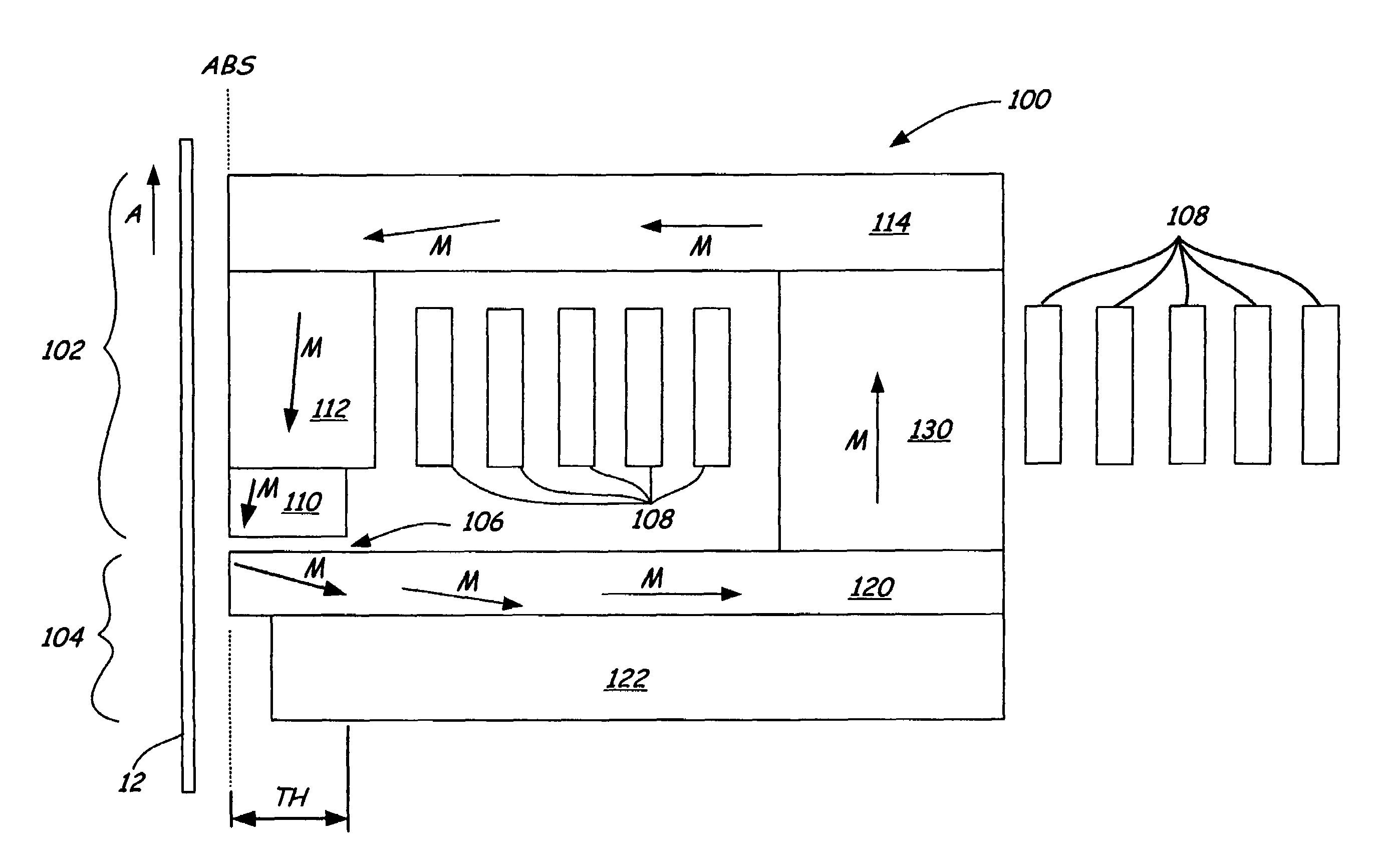
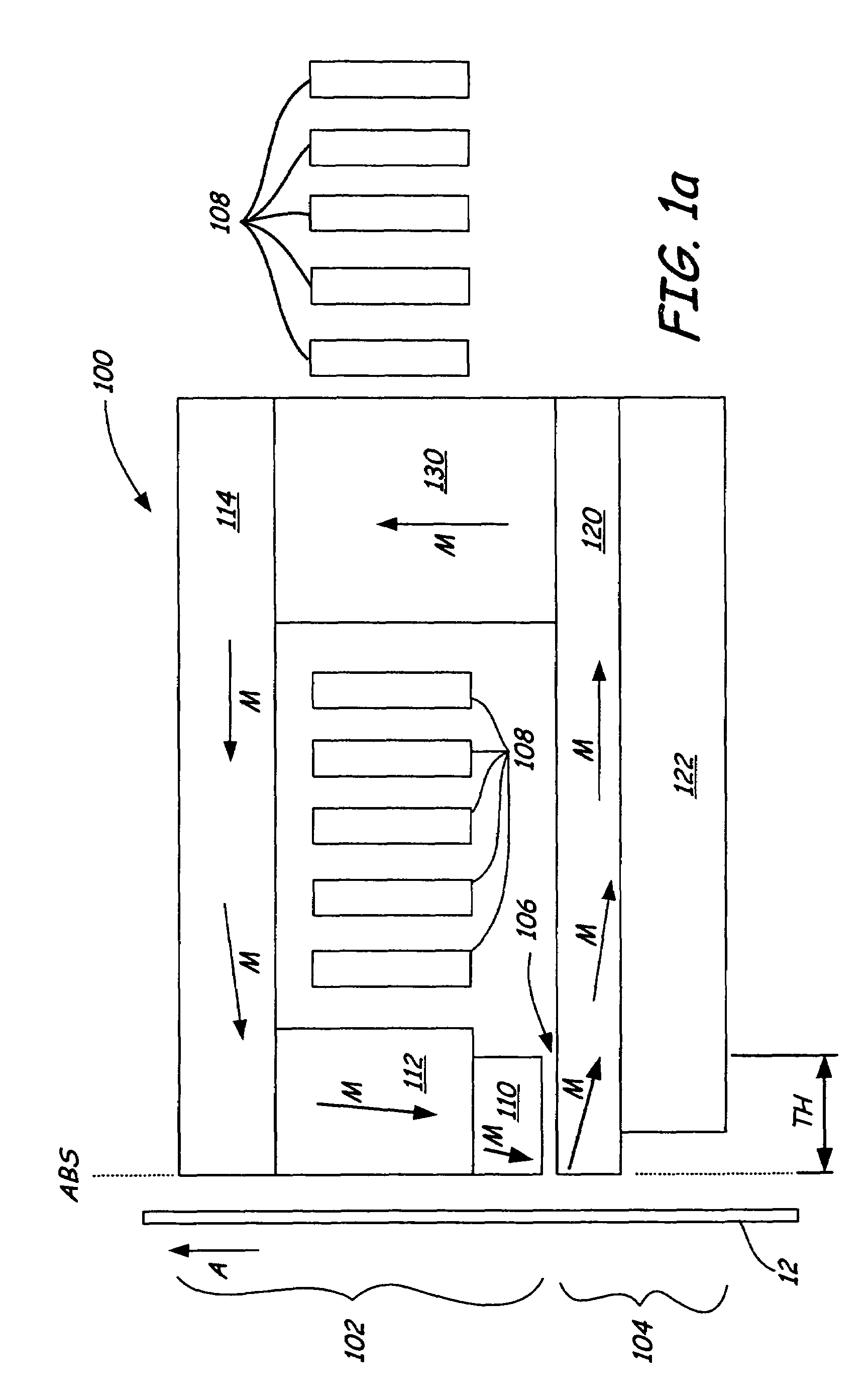
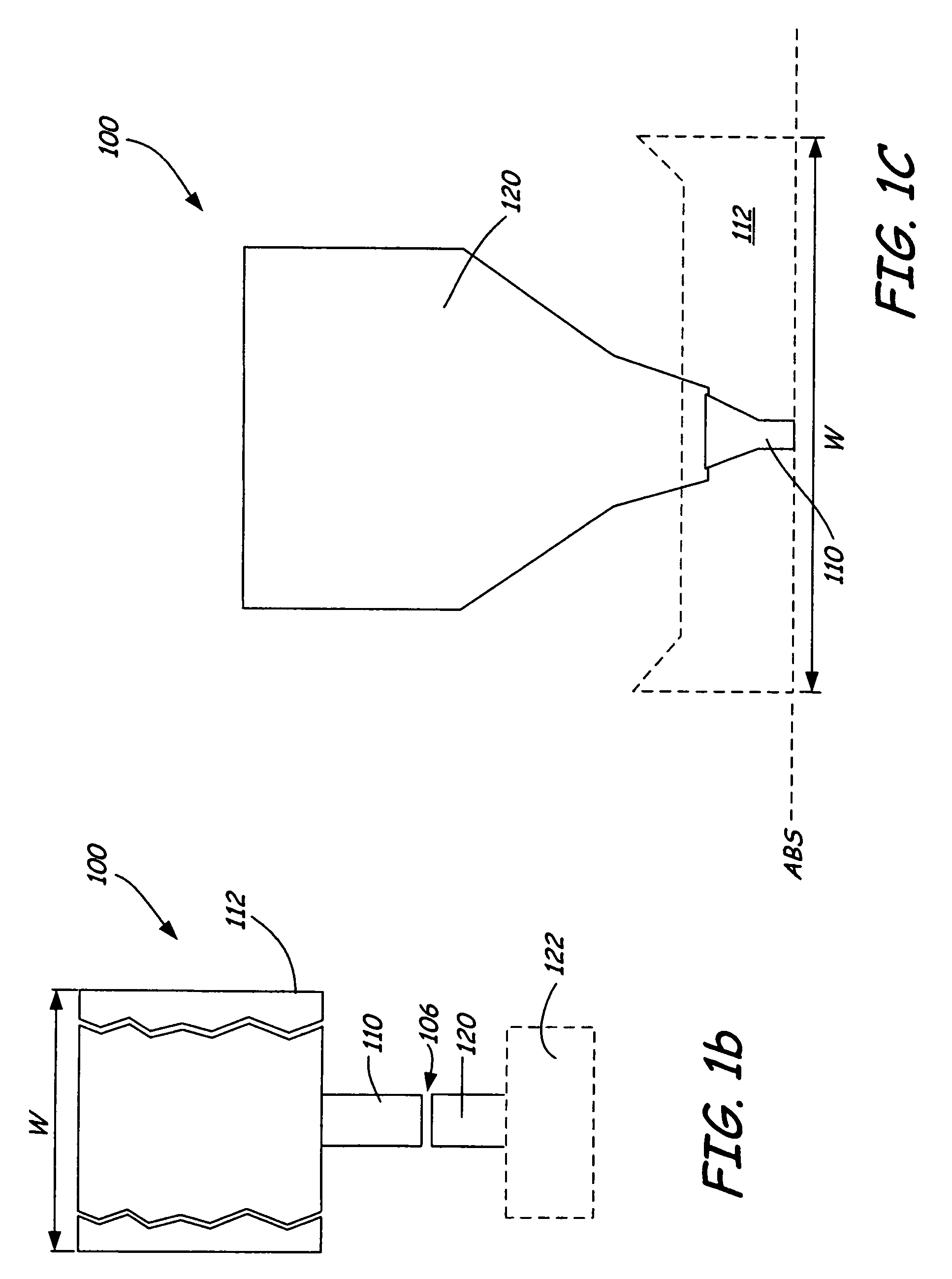
High gradient disc drive writer
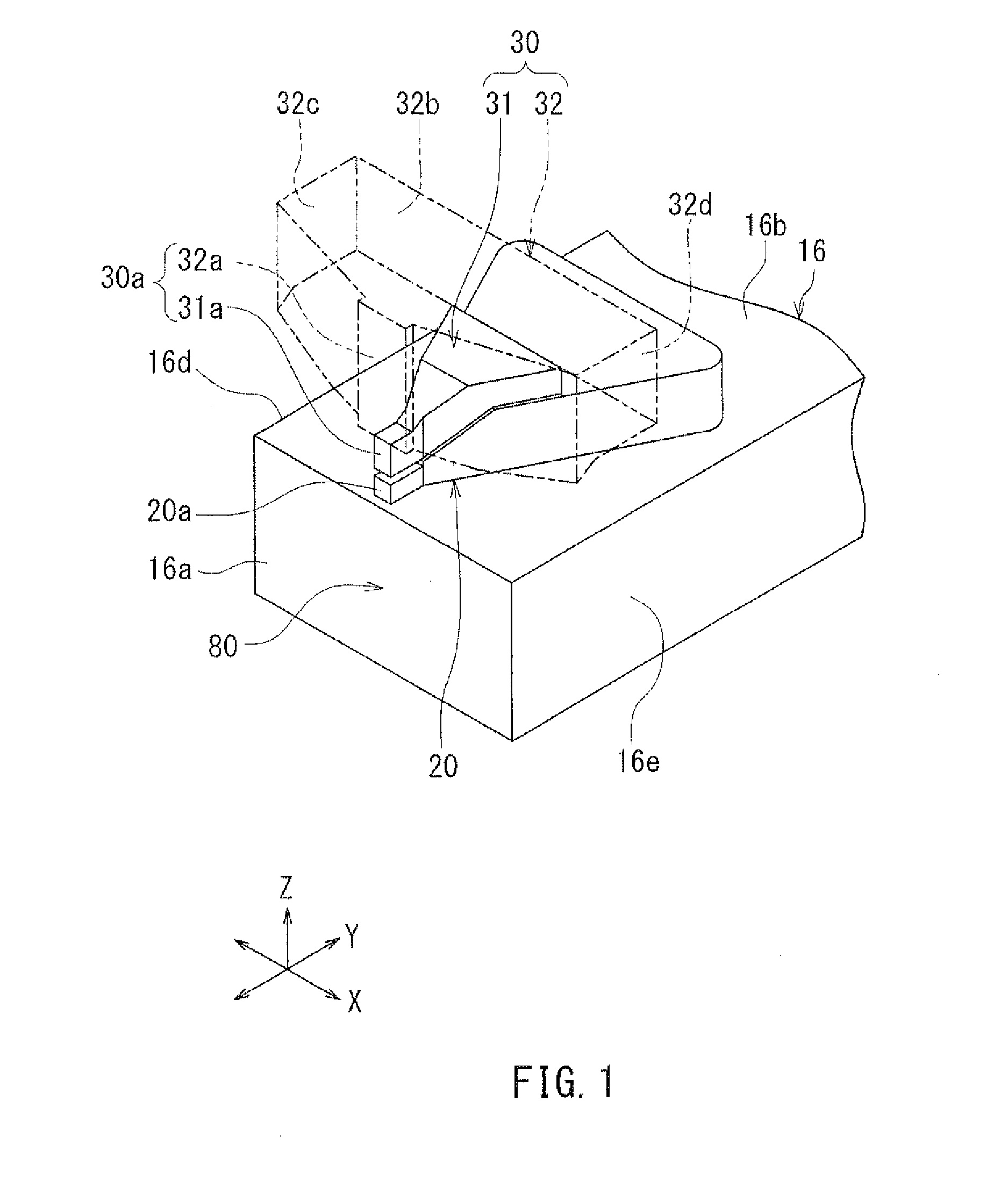
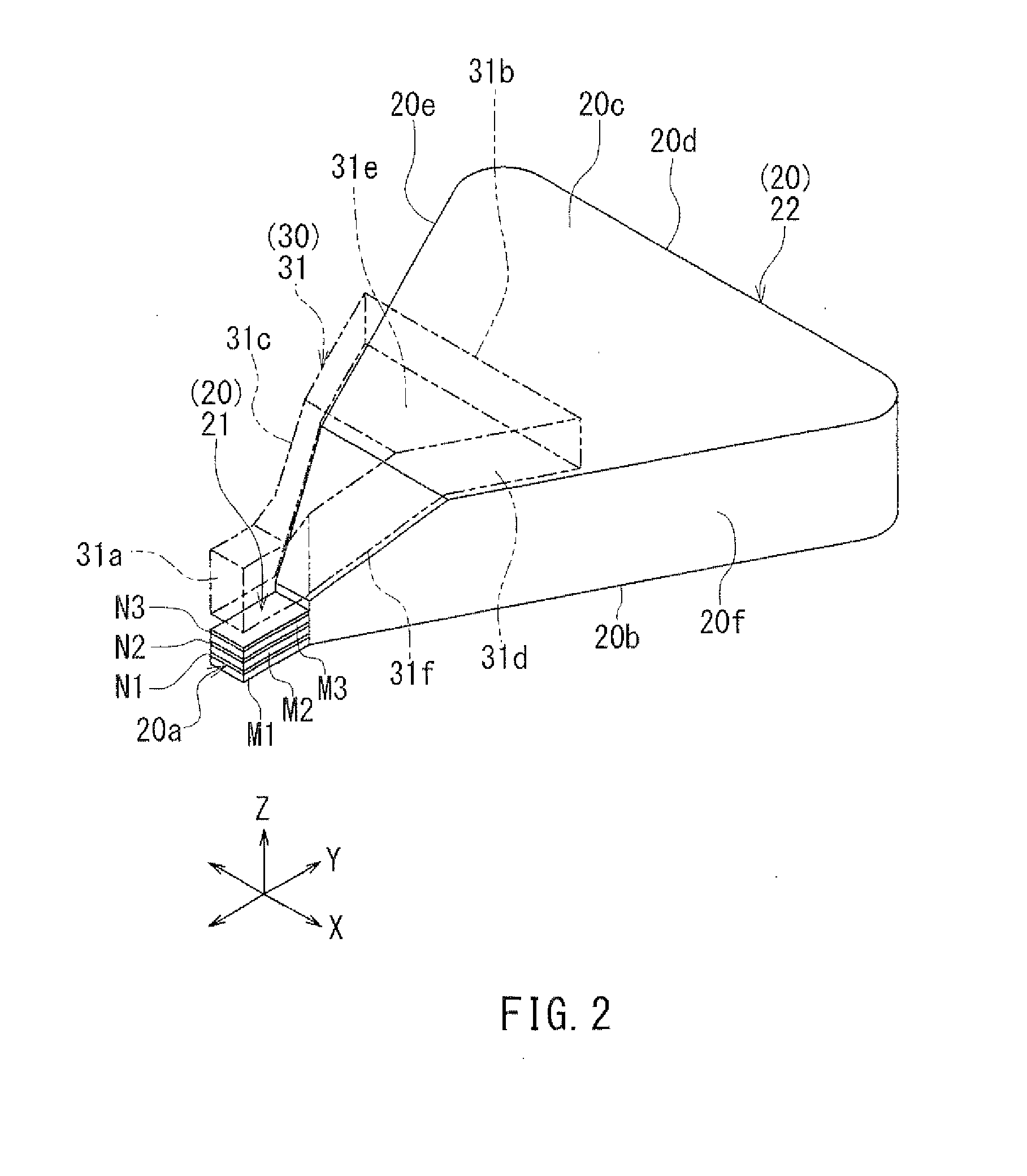
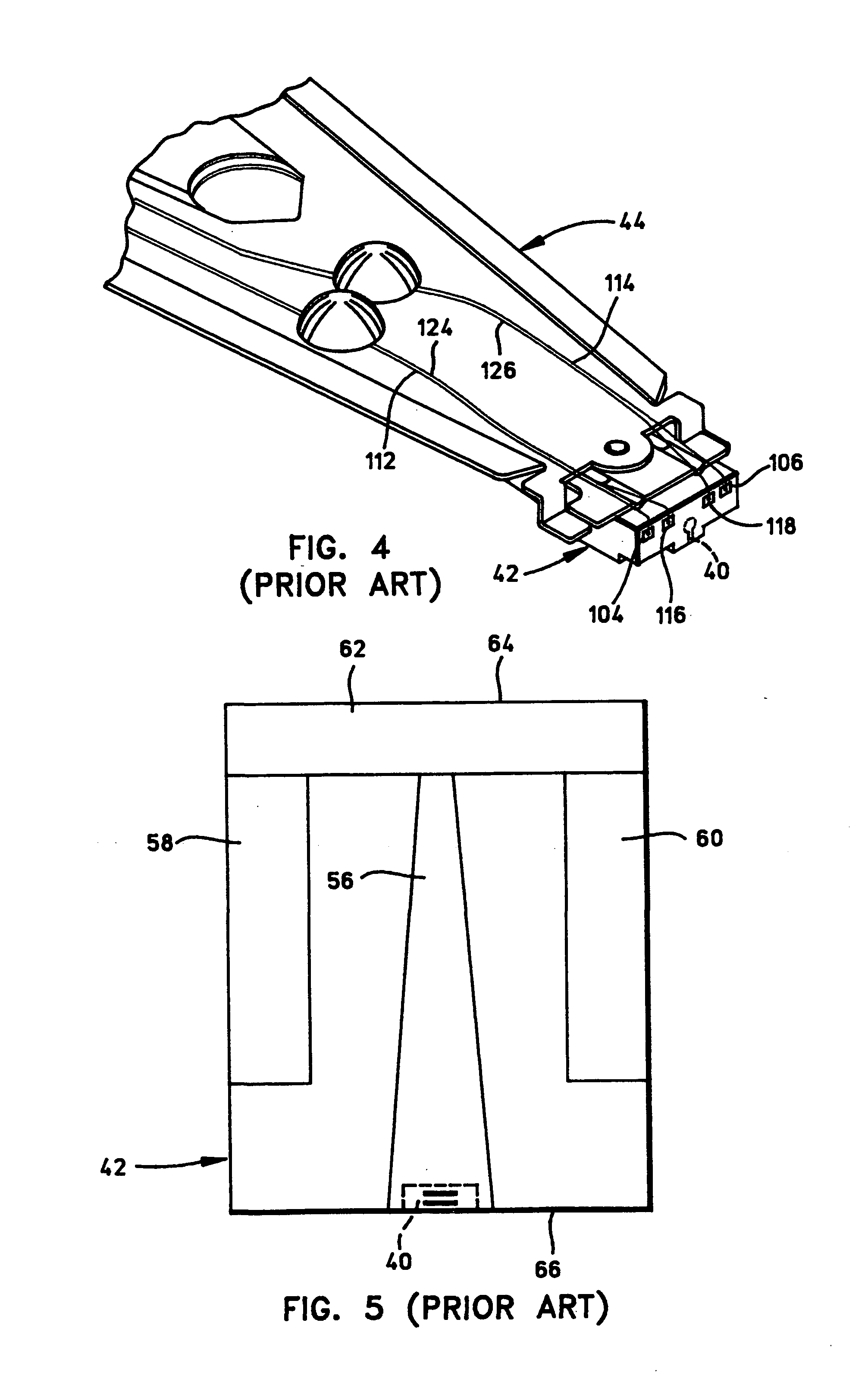
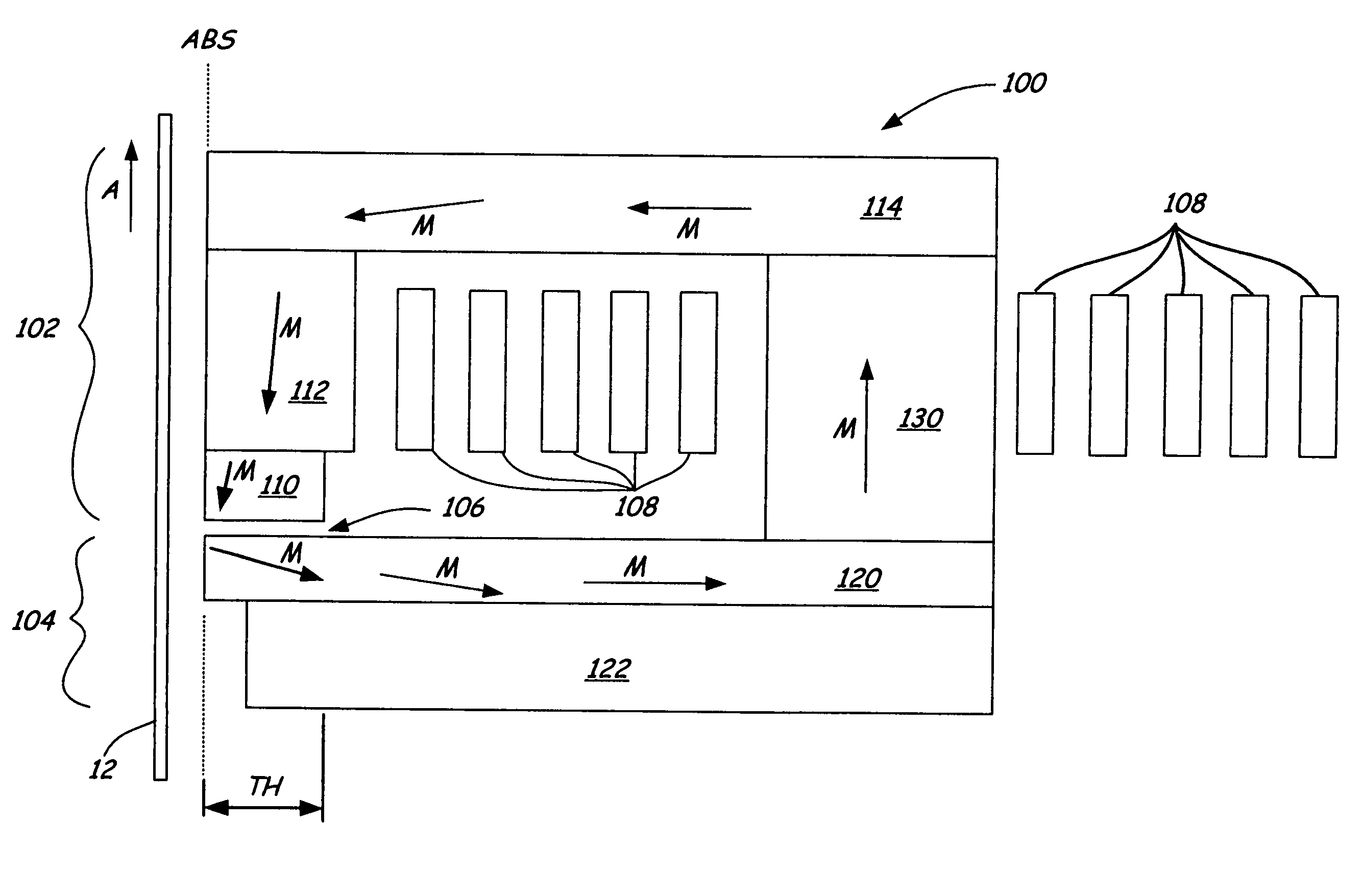
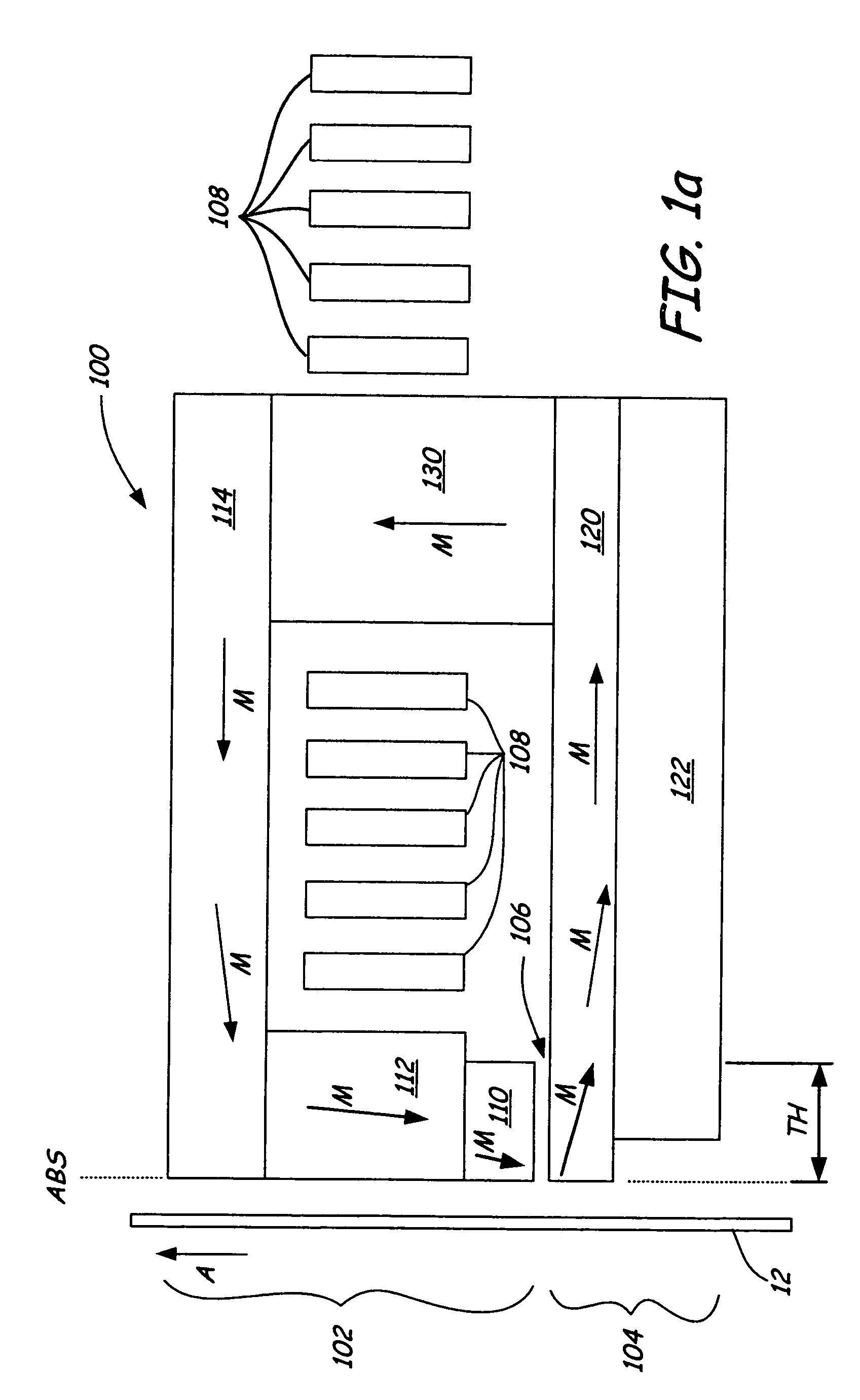
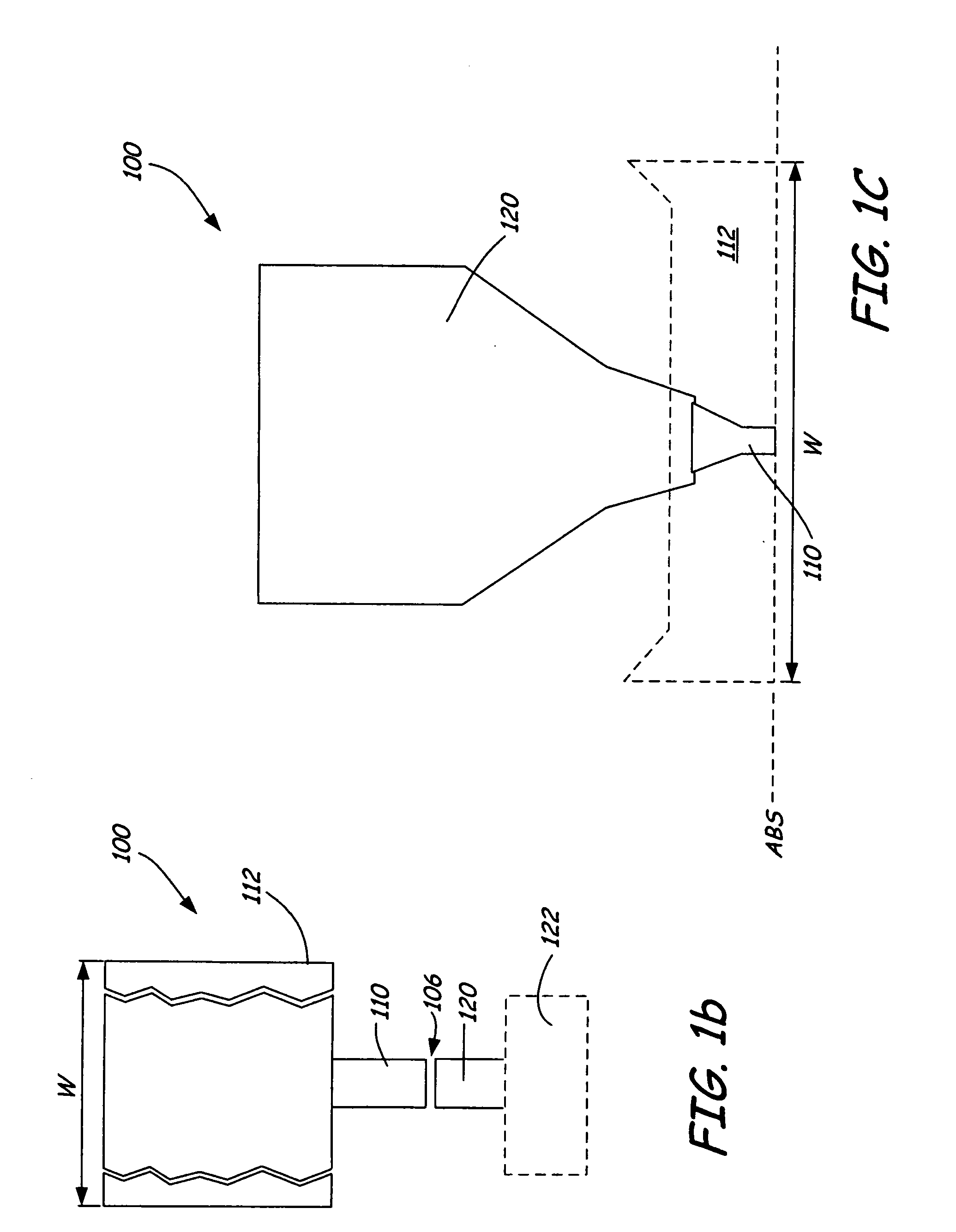
InactiveUS7187519B2Avoid distortionUniform widthRecord information storageAssembling head elementsMagnetizationMagnetic poles
A magnetic writer having an air bearing surface for confronting a surface of a rotating disc is disclosed. The magnetic writer includes a bottom pole and a top pole. The top pole includes a first top pole portion and a second top pole portion connected by a top pole extension. The top pole extension, which preferably has a uniform width at the air bearing surface, orients a magnetization of the first top pole portion substantially parallel to an air bearing surface of the magnetic writer. The bottom pole includes a base pole and a notch pole. The base pole is recessed from the air bearing surface to prevent or reduce fringe erasure fields. The notch pole, which abuts the base pole and extends from the air bearing surface to at least a magnetic throat height of the magnetic writer, has a magnetization oriented perpendicular to the air bearing surface.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Thermally-assisted magnetic recording head including a main pole and a plasmon generator
ActiveUS20160210994A1Reduced track widthSufficient magnitudeCombination recordingConstruction of head windingsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
A thermally-assisted magnetic recording head includes a main pole and a plasmon generator. The main pole has a front end face located in the medium facing surface. The plasmon generator has a near-field light generating surface located in the medium facing surface. The front end face of the main pole includes a first end face portion and a second end face portion. The second end face portion is located farther from the near-field light generating surface than is the first end face portion, and is greater than the first end face portion in width in the track width direction. The first end face portion and the near-field light generating surface are equal in width.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Self-pinned spin valve sensor with stress modification layers for reducing the likelihood of amplitude flip
InactiveUS20050190509A1Reduce the possibilityRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsSpin valvePhysics
A spin valve (SV) sensor of the self-pinned type includes one or more compressive stress modification layers for reducing the likelihood that the pinning field will flip its direction. The spin valve sensor includes a capping layer formed over a spin valve structure which includes a free layer, an antiparallel (AP) self-pinned layer structure, and a spacer layer in between the free layer and the AP self-pinned layer structure. A compressive stress modification layer is formed above or below the capping layer, adjacent the AP self-pinned layer structure, or both. Preferably, the compressive stress modification layer is made of ruthenium (Ru) or other suitable material.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
High gradient disc drive writer
InactiveUS20050122619A1Minimize distortionPrevent and reduce fringe erasure fieldRecord information storageAssembling head elementsMagnetizationEngineering
A magnetic writer having an air bearing surface for confronting a surface of a rotating disc is disclosed. The magnetic writer includes a bottom pole and a top pole. The top pole includes a first top pole portion and a second top pole portion connected by a top pole extension. The top pole extension, which preferably has a uniform width at the air bearing surface, orients a magnetization of the first top pole portion substantially parallel to an air bearing surface of the magnetic writer. The bottom pole includes a base pole and a notch pole. The base pole is recessed from the air bearing surface to prevent or reduce fringe erasure fields. The notch pole, which abuts the base pole and extends from the air bearing surface to at least a magnetic throat height of the magnetic writer, has a magnetization oriented perpendicular to the air bearing surface.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
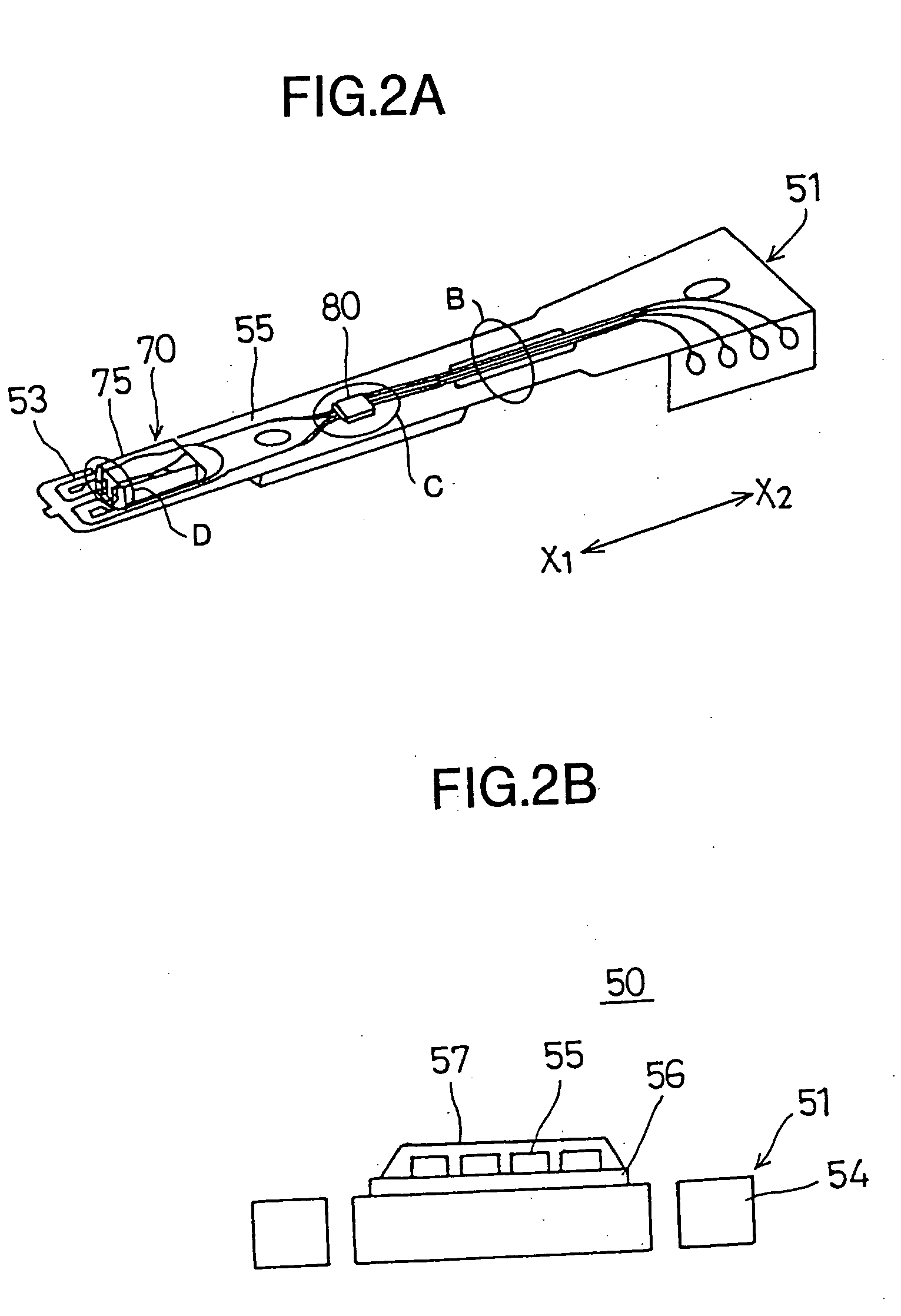
Head assembly, disk unit, and bonding method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050057856A1Efficient productionEliminate excessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsWelding/cutting auxillary devicesEngineeringIntegrated circuit
A head assembly is provided with a mounting surface, and an integrated circuit chip which is mounted on the mounting surface and processes signals. The integrated circuit chip is covered by a layer which prevents generation of foreign particles from the integrated circuit chip by the provision of the layer.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
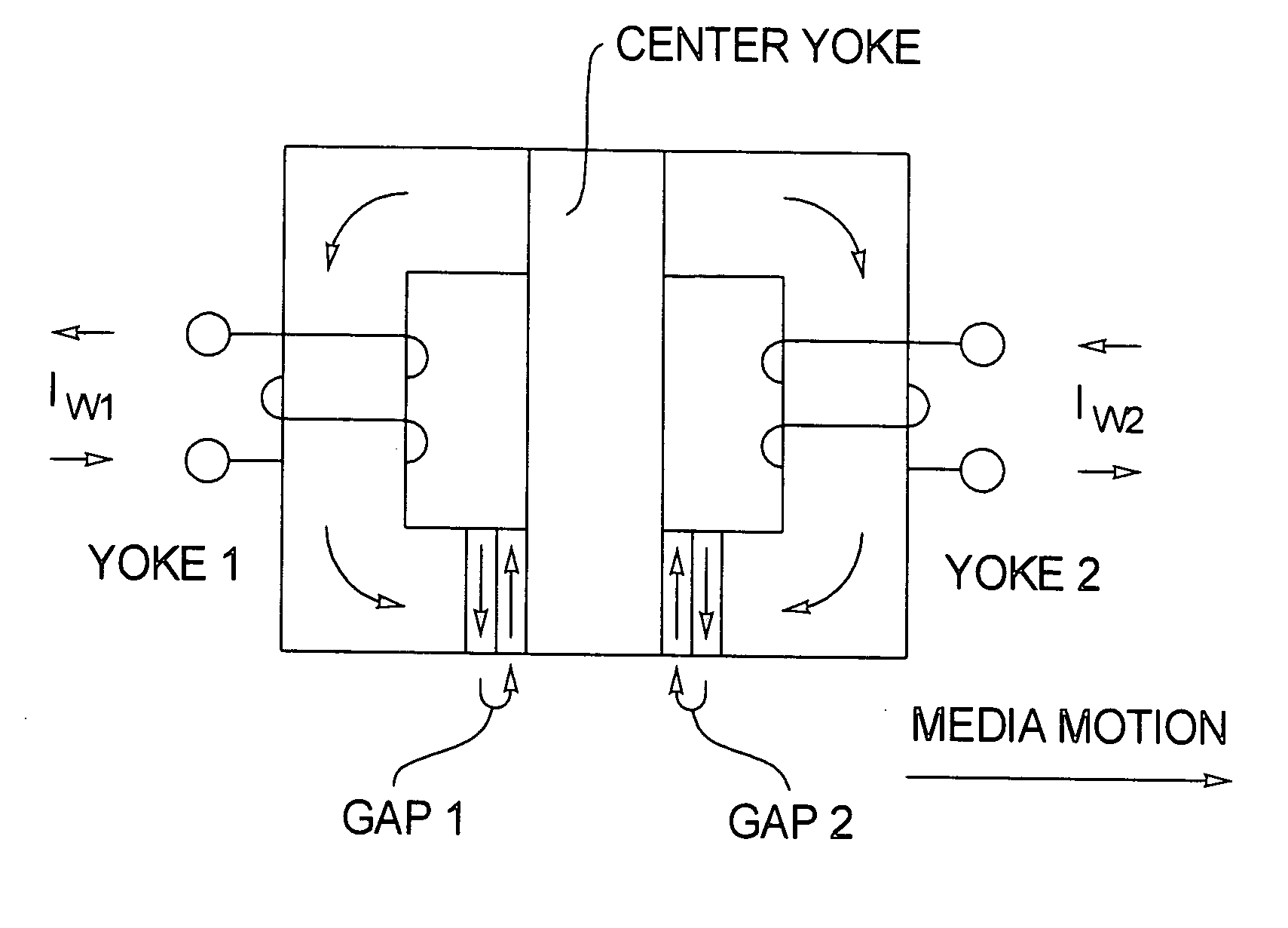
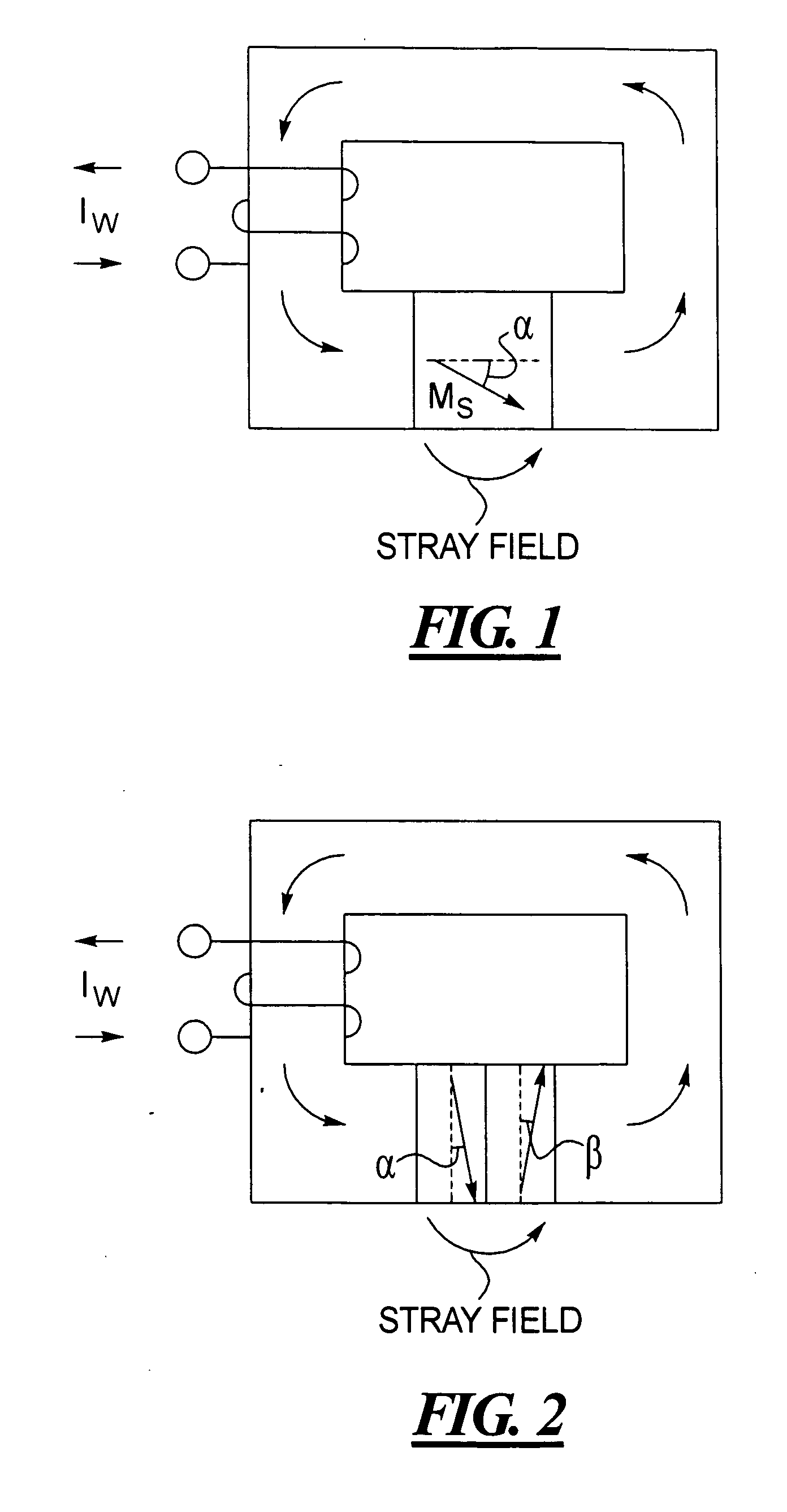
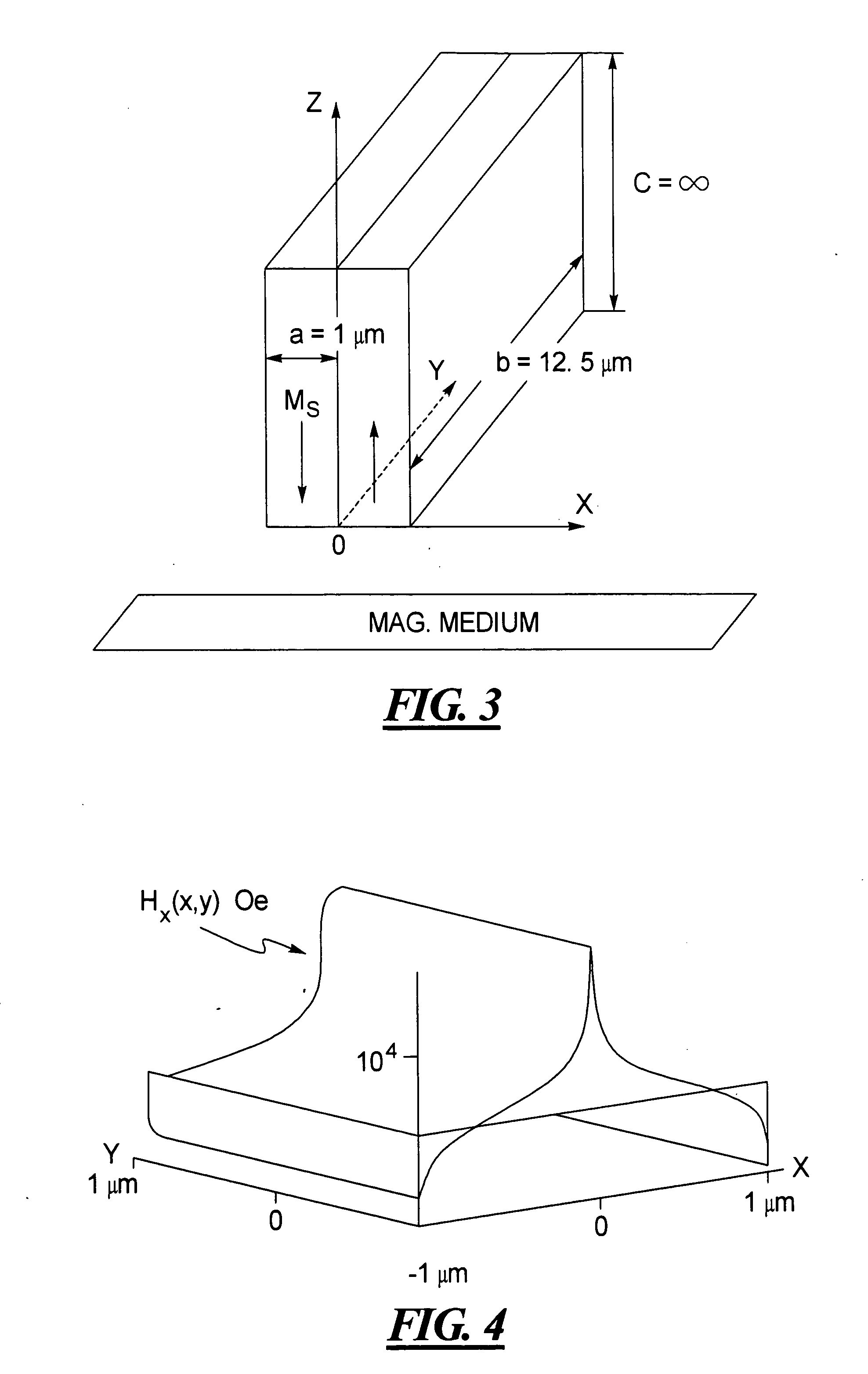
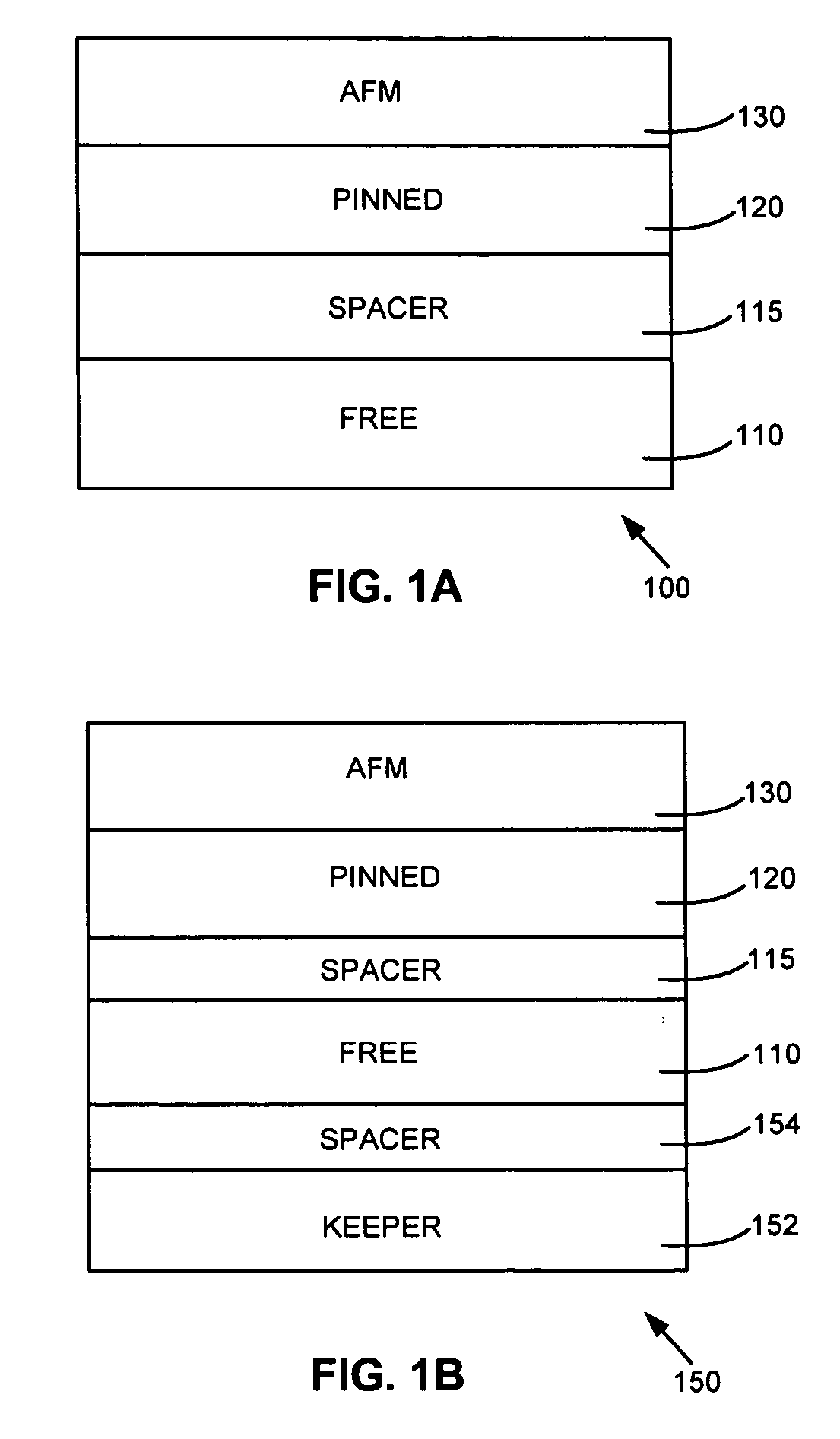
Canted easy axis in self-pinned layers
InactiveUS20050190508A1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsCouplingMolecular physics
A magnetic head having a free layer and an antiparallel (AP) pinned layer structure spaced apart from the free layer, the AP pinned layer structure including at least two AP-pinned layers having magnetic moments that are self-pinned antiparallel to each other, the AP-pinned layers being separated by an AP coupling layer. An easy axis of a first or both of the AP-pinned layers is oriented at an angle of at least 5° from the ABS along a plane of the first AP-pinned layer.
Owner:ACCULEON +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com