Patents
Literature
38results about "Associative processors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
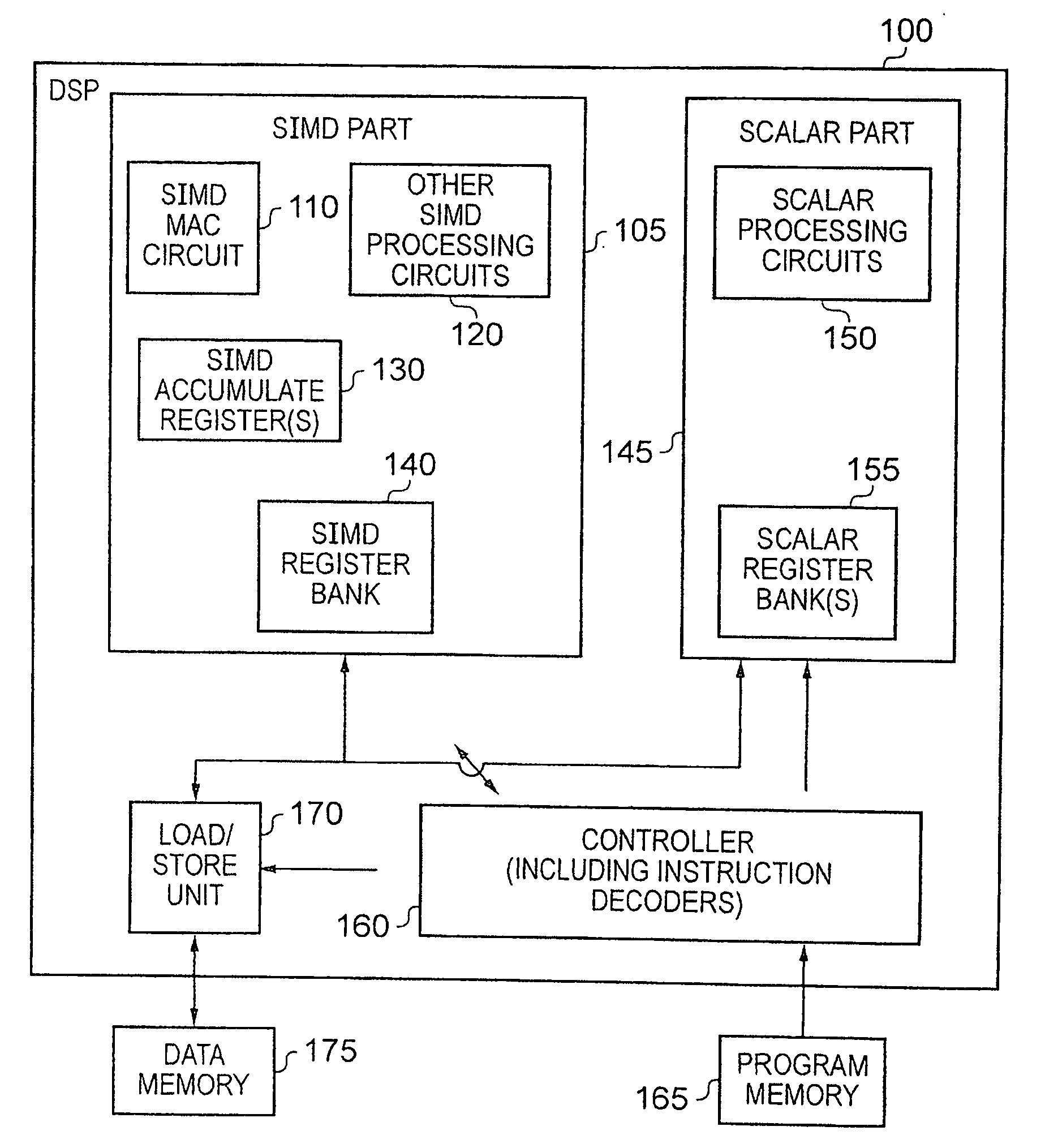
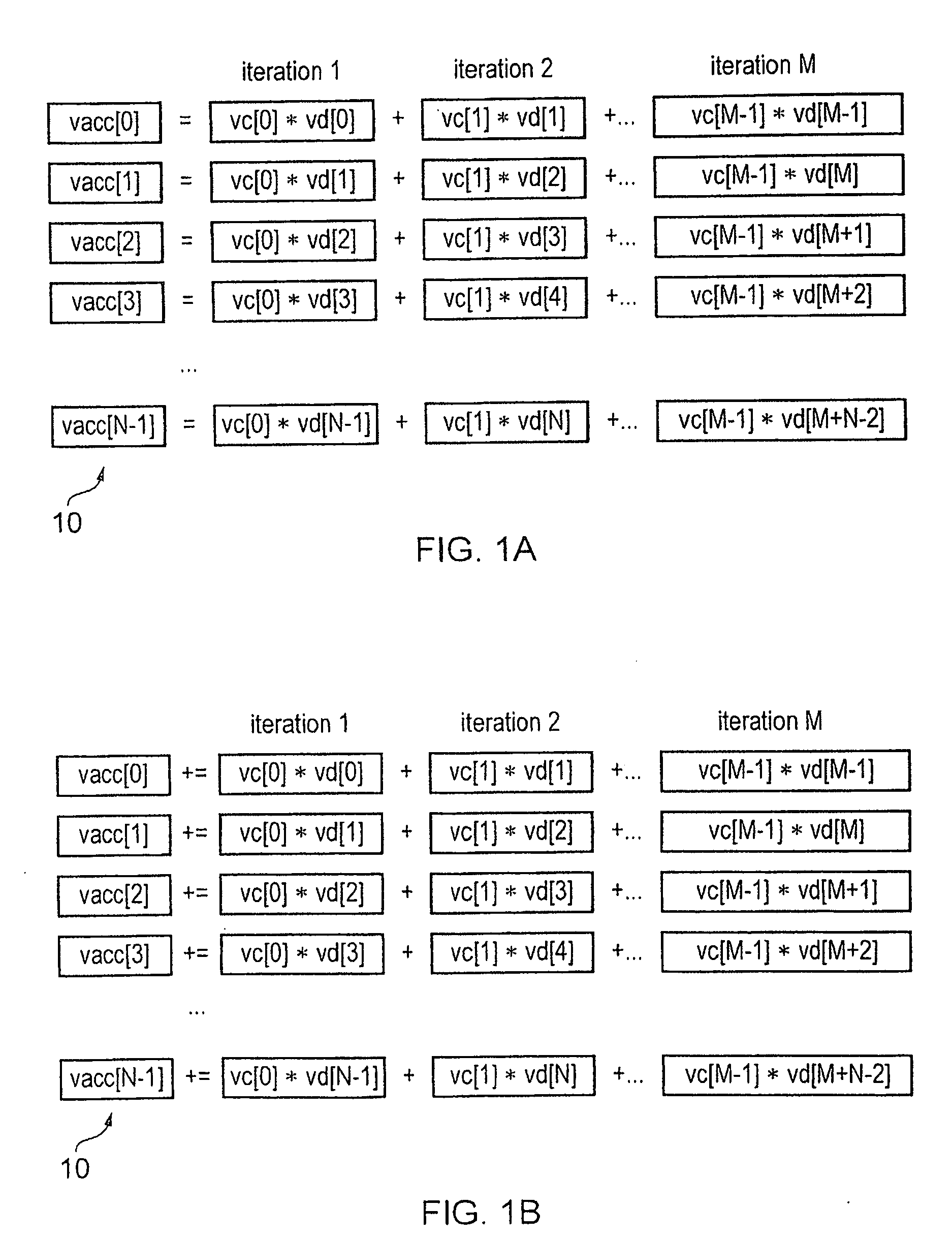
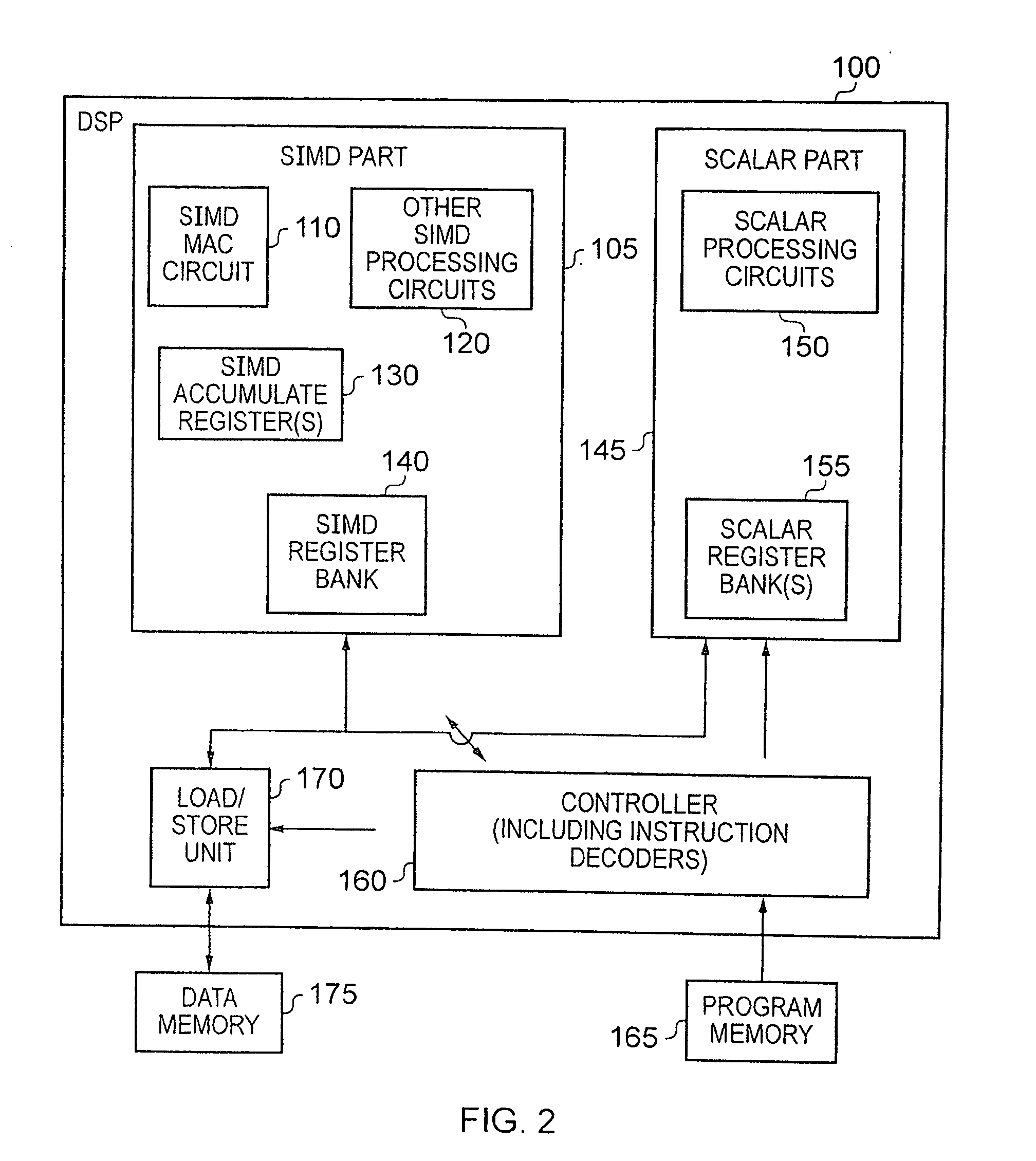
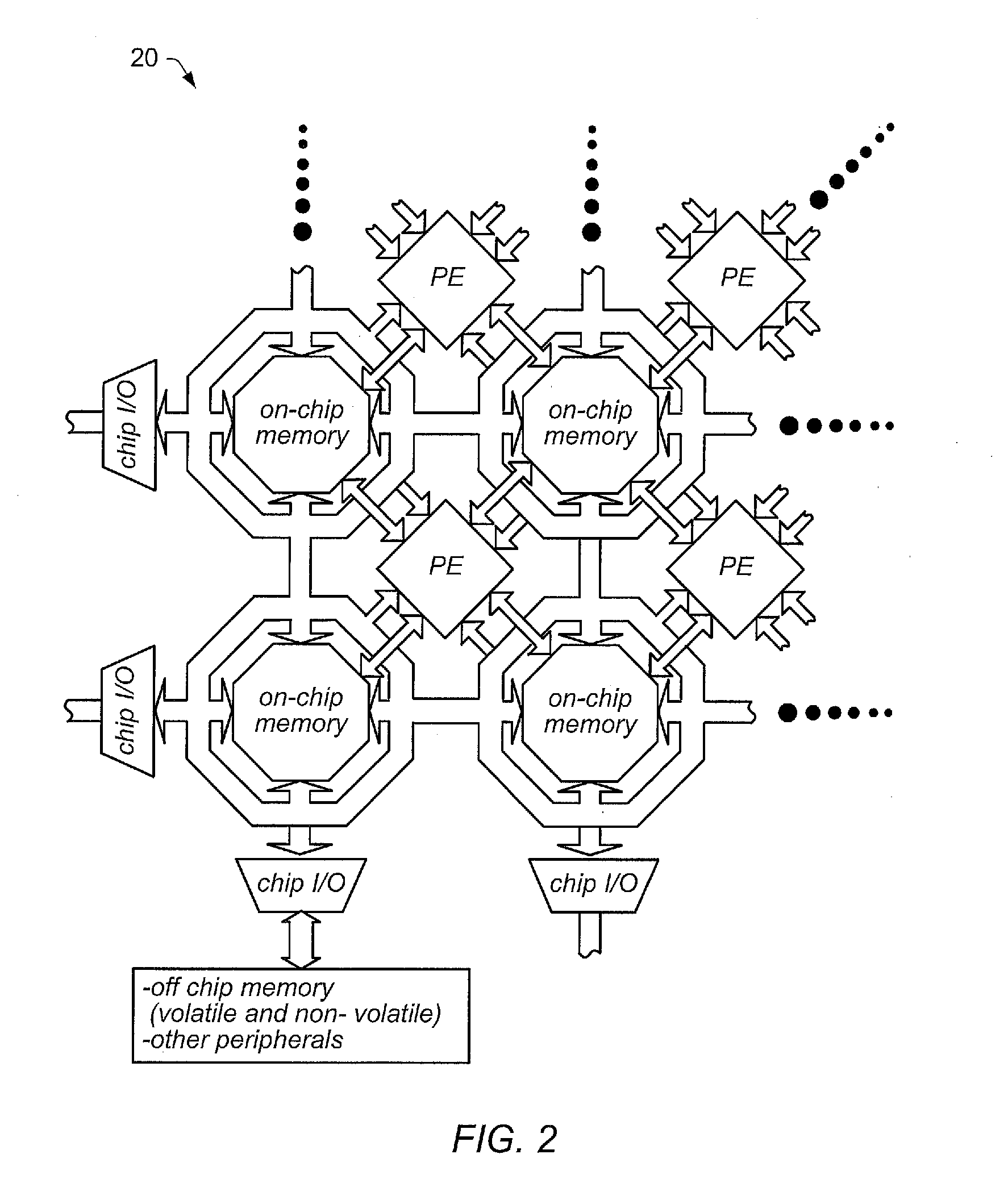
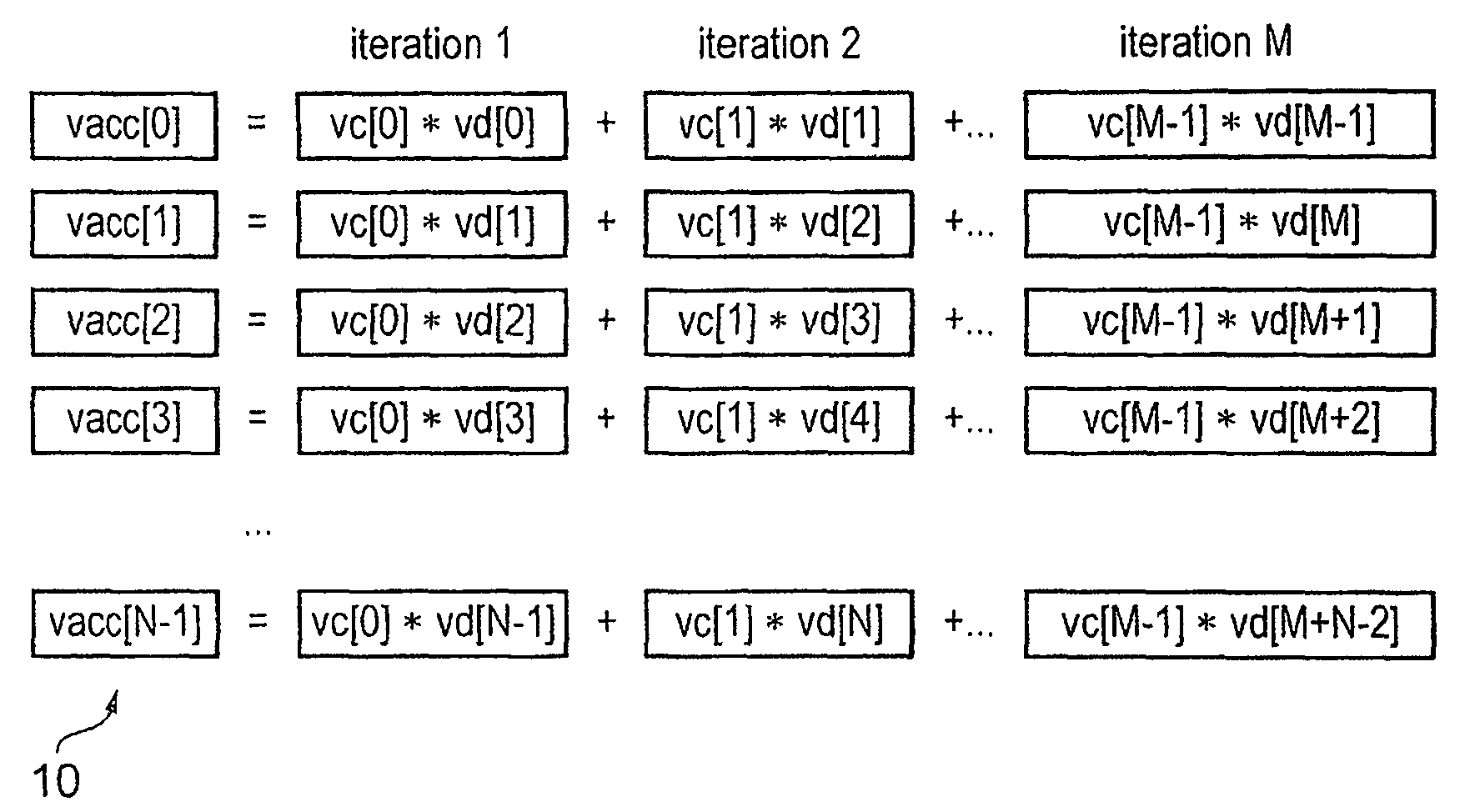
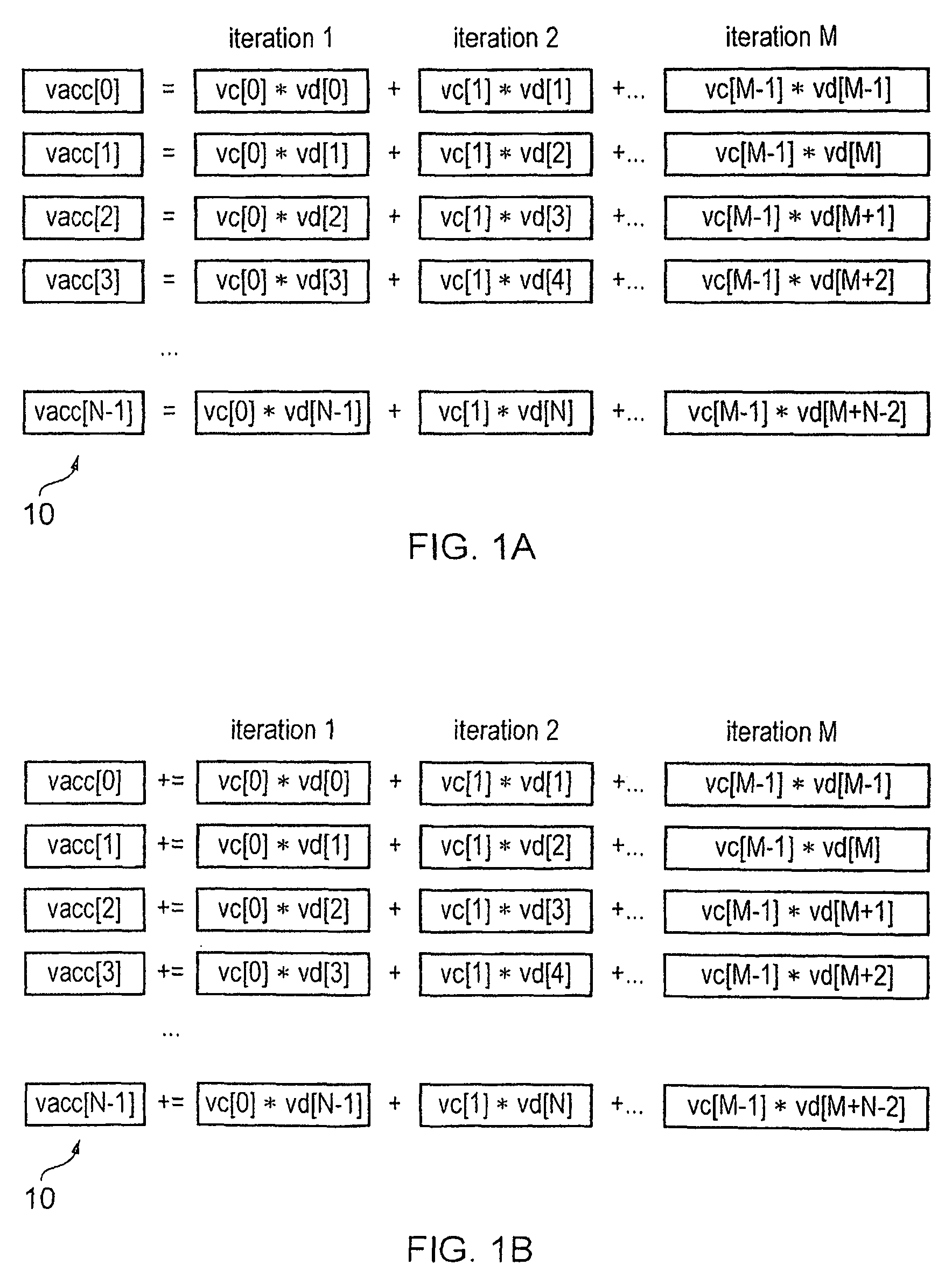
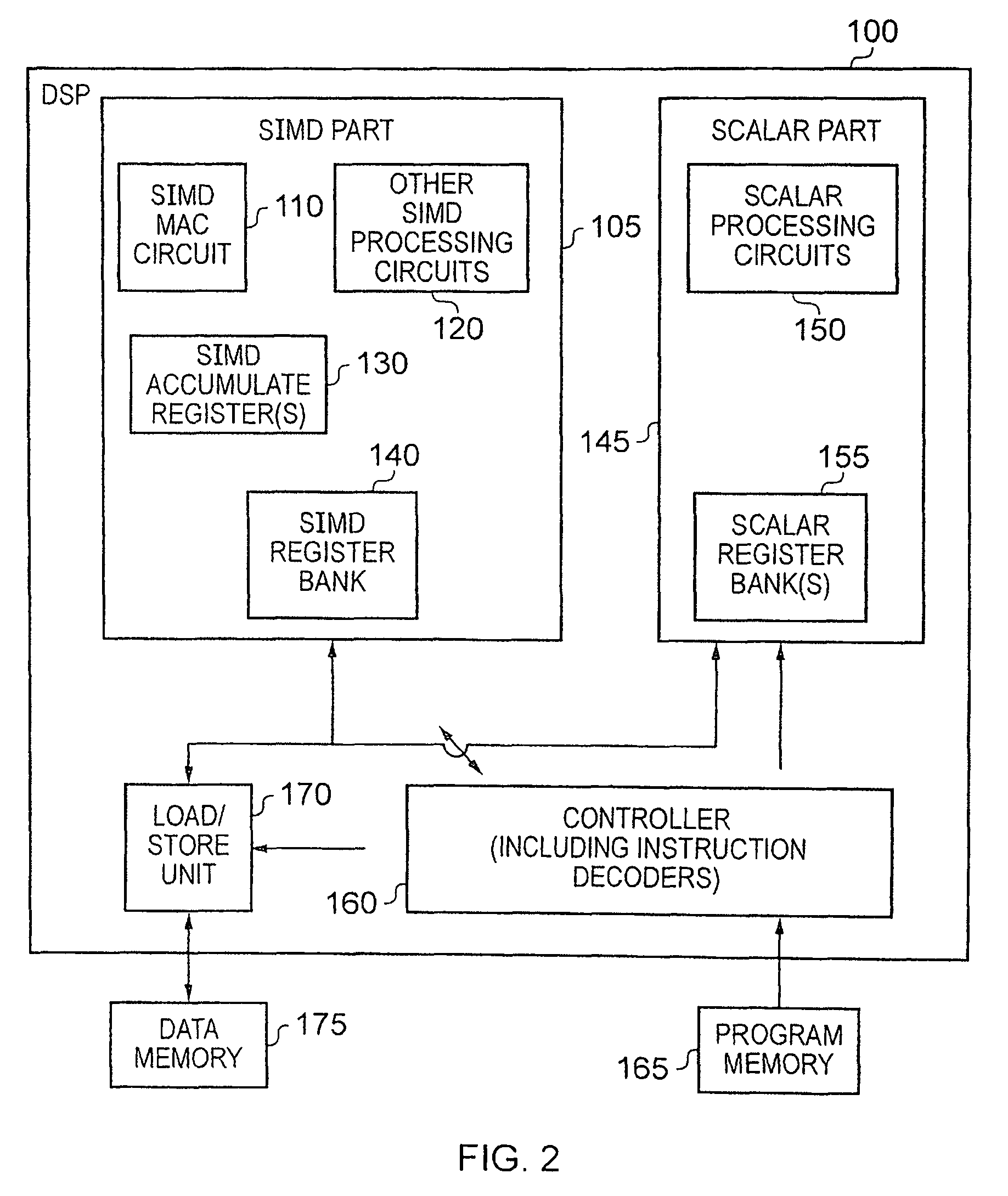
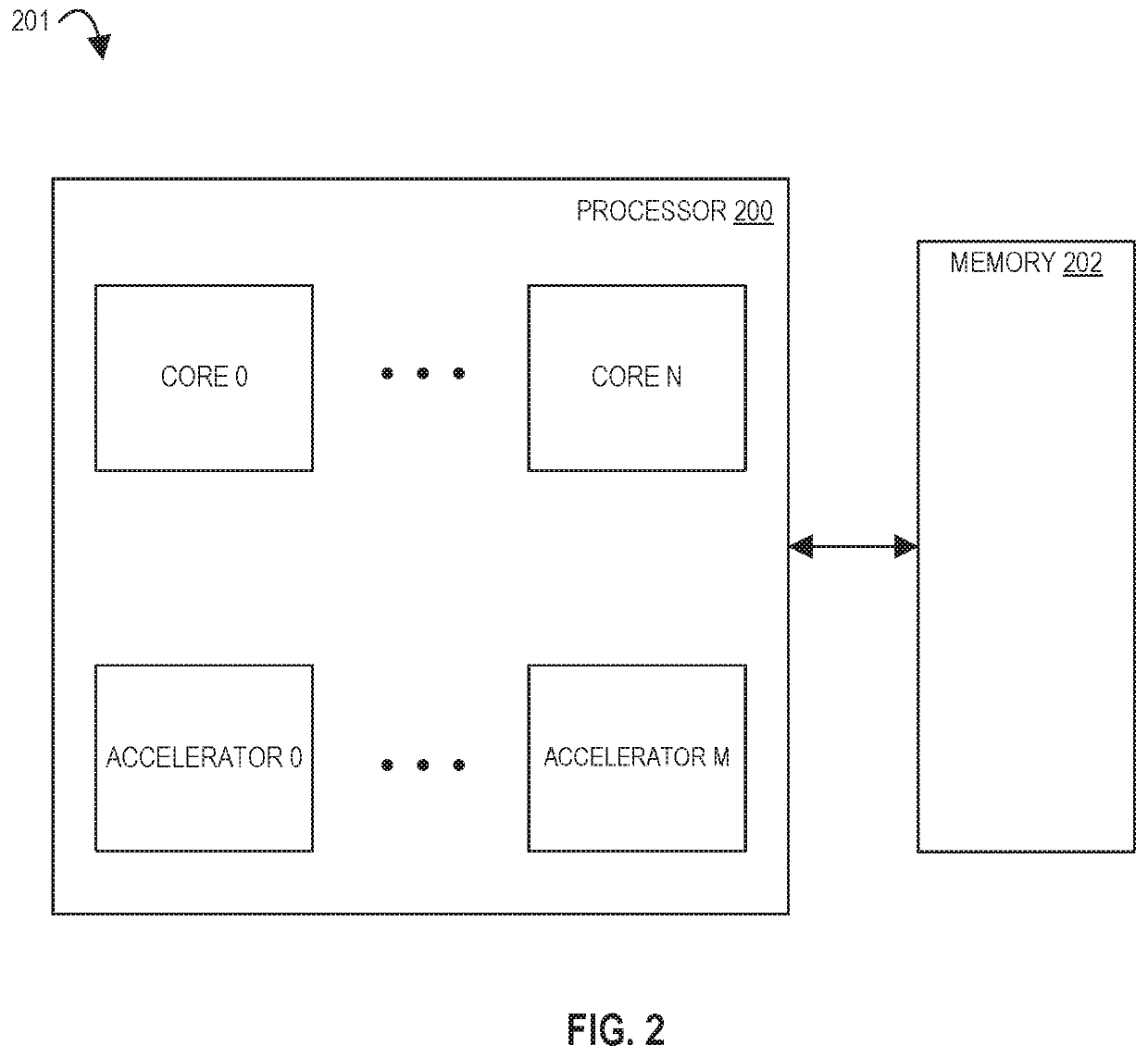
Apparatus and Method for Performing SIMD Multiply-Accumulate Operations
ActiveUS20100274990A1Reduce unnecessary power consumptionSignificant power savingAssociative processorsProgram control using wired connectionsProgram instructionScalar Value
An apparatus and method for performing SIMD multiply-accumulate operations includes SIMD data processing circuitry responsive to control signals to perform data processing operations in parallel on multiple data elements. Instruction decoder circuitry is coupled to the SIMD data processing circuitry and is responsive to program instructions to generate the required control signals. The instruction decoder circuitry is responsive to a single instruction (referred to herein as a repeating multiply-accumulate instruction) having as input operands a first vector of input data elements, a second vector of coefficient data elements, and a scalar value indicative of a plurality of iterations required, to generate control signals to control the SIMD processing circuitry. In response to those control signals, the SIMD data processing circuitry performs the plurality of iterations of a multiply-accumulate process, each iteration involving performance of N multiply-accumulate operations in parallel in order to produce N multiply-accumulate data elements. For each iteration, the SIMD data processing circuitry determines N input data elements from said first vector and a single coefficient data element from the second vector to be multiplied with each of the N input data elements. The N multiply-accumulate data elements produced in a final iteration of the multiply-accumulate process are then used to produce N multiply-accumulate results. This mechanism provides a particularly energy efficient mechanism for performing SIMD multiply-accumulate operations, as for example are required for FIR filter processes.
Owner:U-BLOX
Input/output methods for associative processor
InactiveUS6405281B1Increase speedImprove efficiencyAssociative processorsMemory systemsProcessor registerParallel computing
A data processing device includes an associative processor that in turn includes one or more arrays of content addressable memory (CAM) cells and two or more tags registers. The device also includes a memory for storing the data and a bus for exchanging the data with the associative processor. During input and output operations, data are exchanged in parallel, via one of the tags registers. Another tags register is used to select rows of CAM cells for input or output. By appropriately shifting the bits in the buffer tags register between write or compare operation cycles, entire words are exchanged between the selected CAM cell rows and the buffer tags register. During arithmetical operations, in an embodiment with multiple CAM cell arrays, different tags registers are associated with different CAM cell arrays at will. If, in the course of performing arithmetical operations using one of the CAM cell arrays, so many columns of intermediate data are produced that insufficient columns remain for subsequent arithmetical operations, the columns of intermediate data are written to the memory, via the buffer tags registers. These columns of intermediate data are retrieved subsequently from the memory as needed, also via the buffer tags register.
Owner:GSI TECH ISRAEL LTD
Processing System With Interspersed Processors DMA-FIFO
ActiveUS20140143470A1Associative processorsError detection/correctionDirect memory accessMulti processor
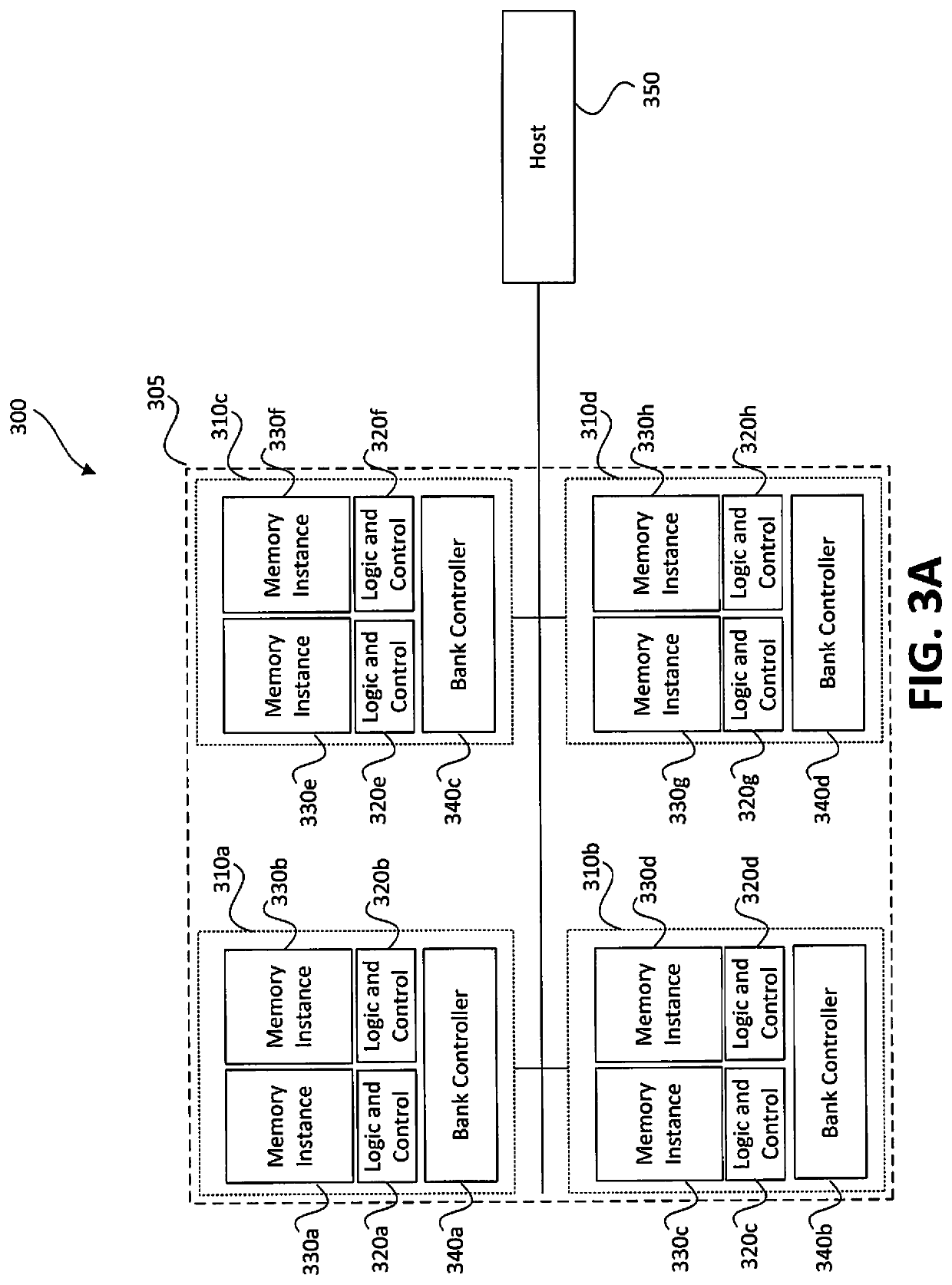
Embodiments of a multi-processor array are disclosed that may include a plurality of processors, local memories, configurable communication elements, and direct memory access (DMA) engines, and a DMA controller. Each processor may be coupled to one of the local memories, and the plurality of processors, local memories, and configurable communication elements may be coupled together in an interspersed arrangement. The DMA controller may be configured to control the operation of the plurality of DMA engines.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
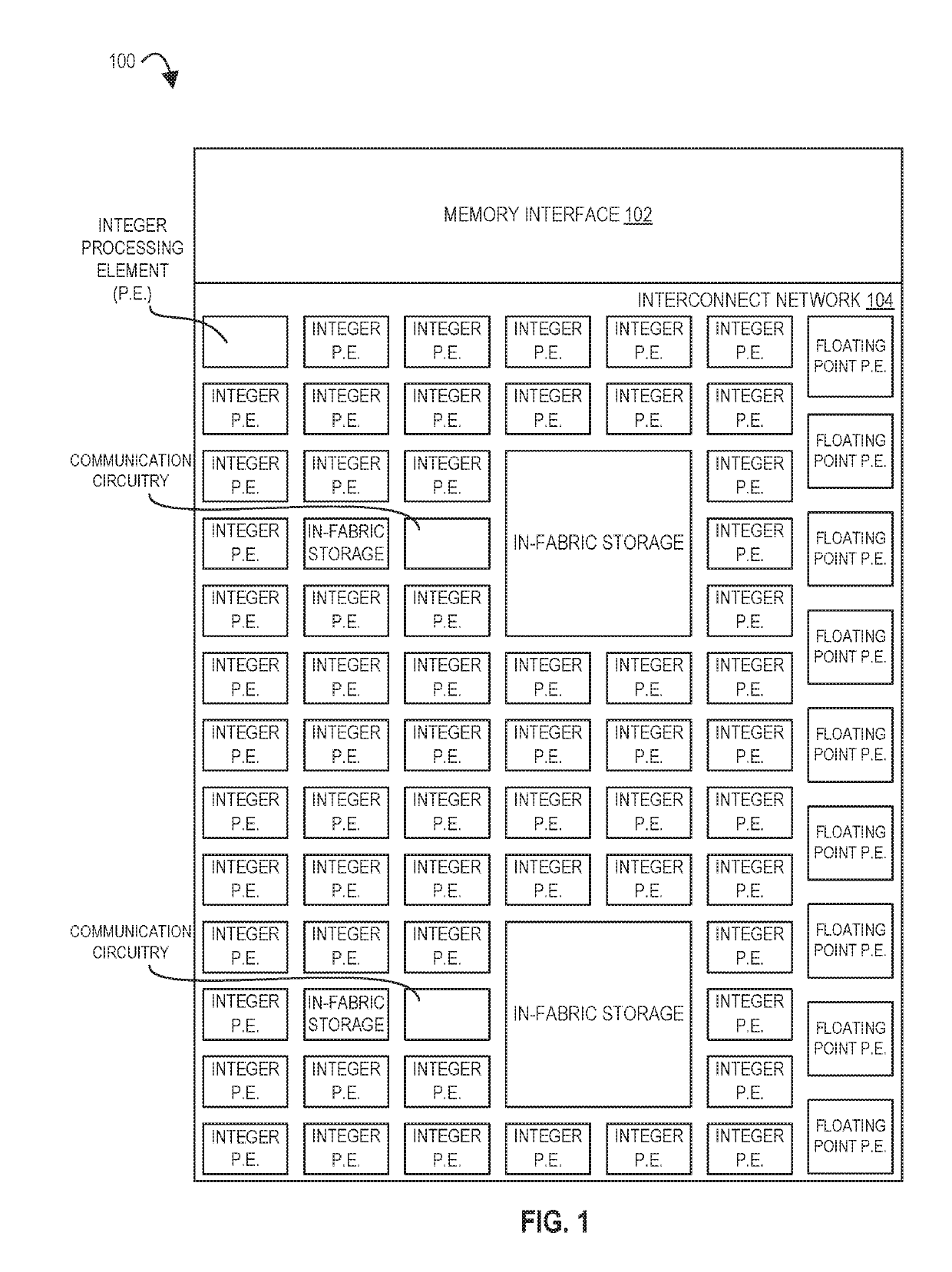
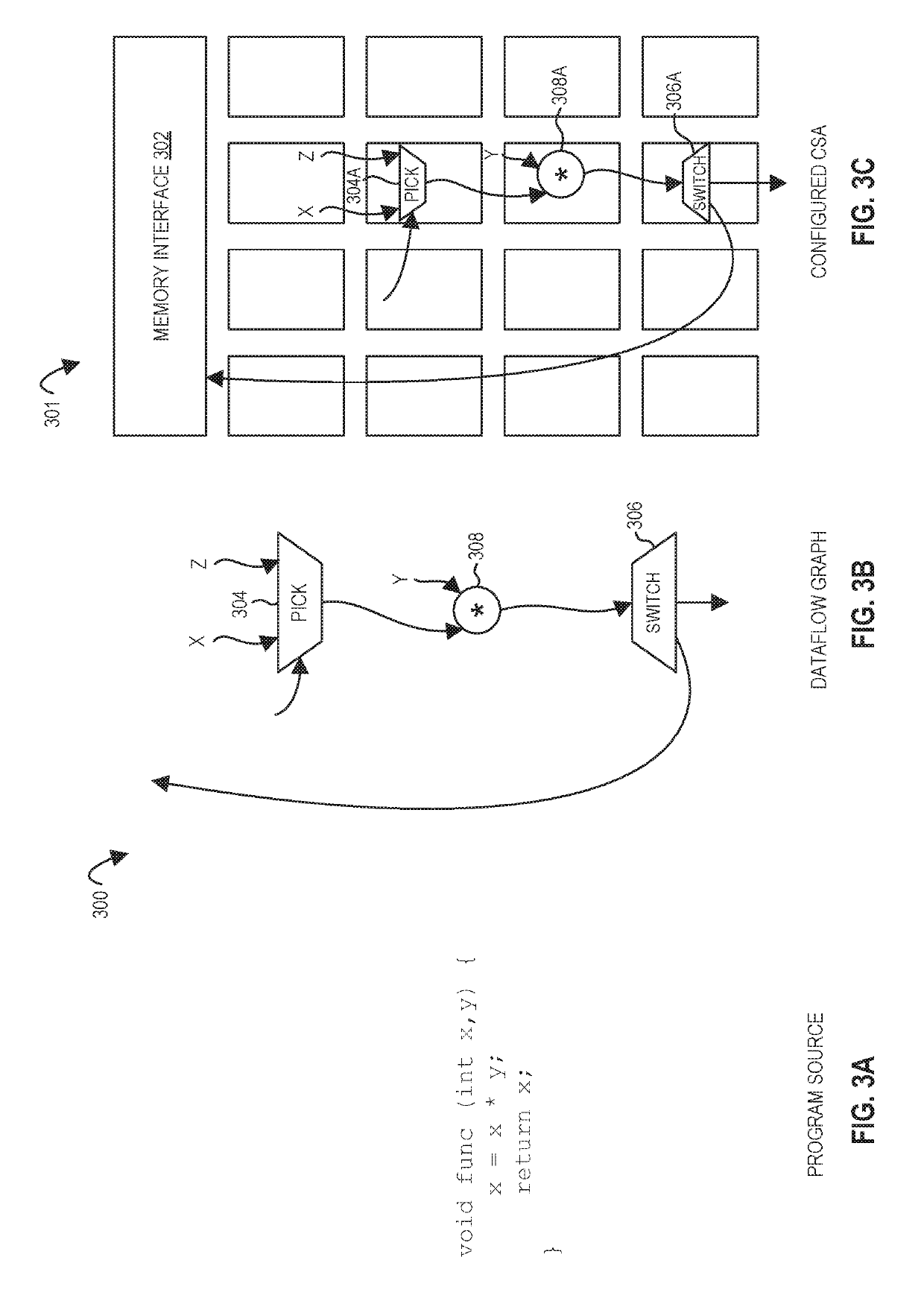
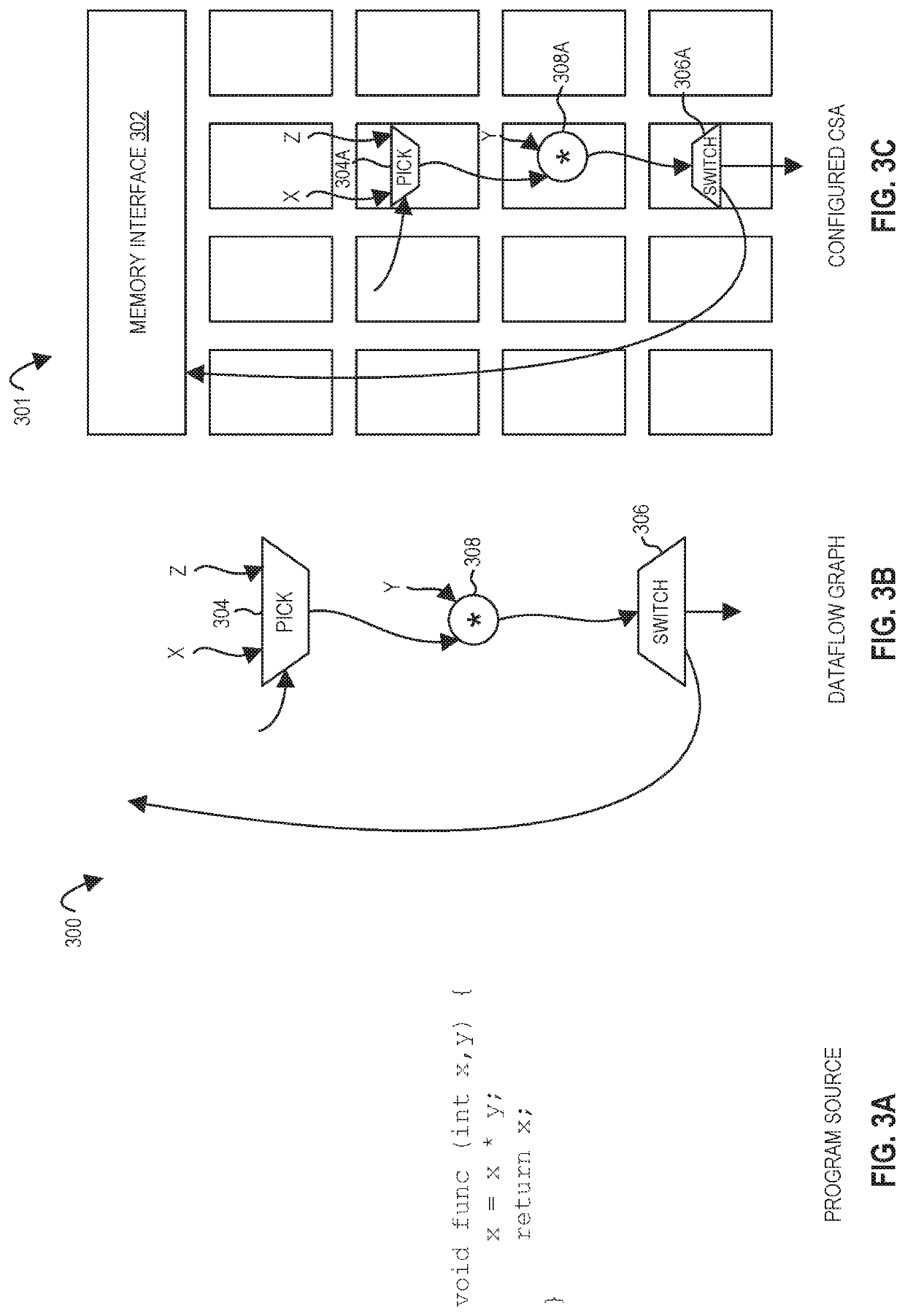
Processors, methods, and systems for debugging a configurable spatial accelerator
ActiveUS20190095383A1Easy to adaptImprove performanceAssociative processorsDataflow computersProcessing elementOperand
Systems, methods, and apparatuses relating to debugging a configurable spatial accelerator are described. In one embodiment, a processor includes a plurality of processing elements and an interconnect network between the plurality of processing elements to receive an input of a dataflow graph comprising a plurality of nodes, wherein the dataflow graph is to be overlaid into the interconnect network and the plurality of processing elements with each node represented as a dataflow operator in the plurality of processing elements, and the plurality of processing elements are to perform an operation by a respective, incoming operand set arriving at each of the dataflow operators of the plurality of processing elements. At least a first of the plurality of processing elements is to enter a halted state in response to being represented as a first of the plurality of dataflow operators.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and method for performing SIMD multiply-accumulate operations
ActiveUS8443170B2Reduce energy consumptionImprove energy consumptionAssociative processorsNext instruction address formationProgram instructionControl signal
An apparatus and method for performing SIMD multiply-accumulate operations includes SIMD data processing circuitry responsive to control signals to perform data processing operations in parallel on multiple data elements. Instruction decoder circuitry is coupled to the SIMD data processing circuitry and is responsive to program instructions to generate the required control signals. The instruction decoder circuitry is responsive to a single instruction (referred to herein as a repeating multiply-accumulate instruction) having as input operands a first vector of input data elements, a second vector of coefficient data elements, and a scalar value indicative of a plurality of iterations required, to generate control signals to control the SIMD processing circuitry. In response to those control signals, the SIMD data processing circuitry performs the plurality of iterations of a multiply-accumulate process, each iteration involving performance of N multiply-accumulate operations in parallel in order to produce N multiply-accumulate data elements. For each iteration, the SIMD data processing circuitry determines N input data elements from said first vector and a single coefficient data element from the second vector to be multiplied with each of the N input data elements. The N multiply-accumulate data elements produced in a final iteration of the multiply-accumulate process are then used to produce N multiply-accumulate results. This mechanism provides a particularly energy efficient mechanism for performing SIMD multiply-accumulate operations, as for example are required for FIR filter processes.
Owner:U-BLOX
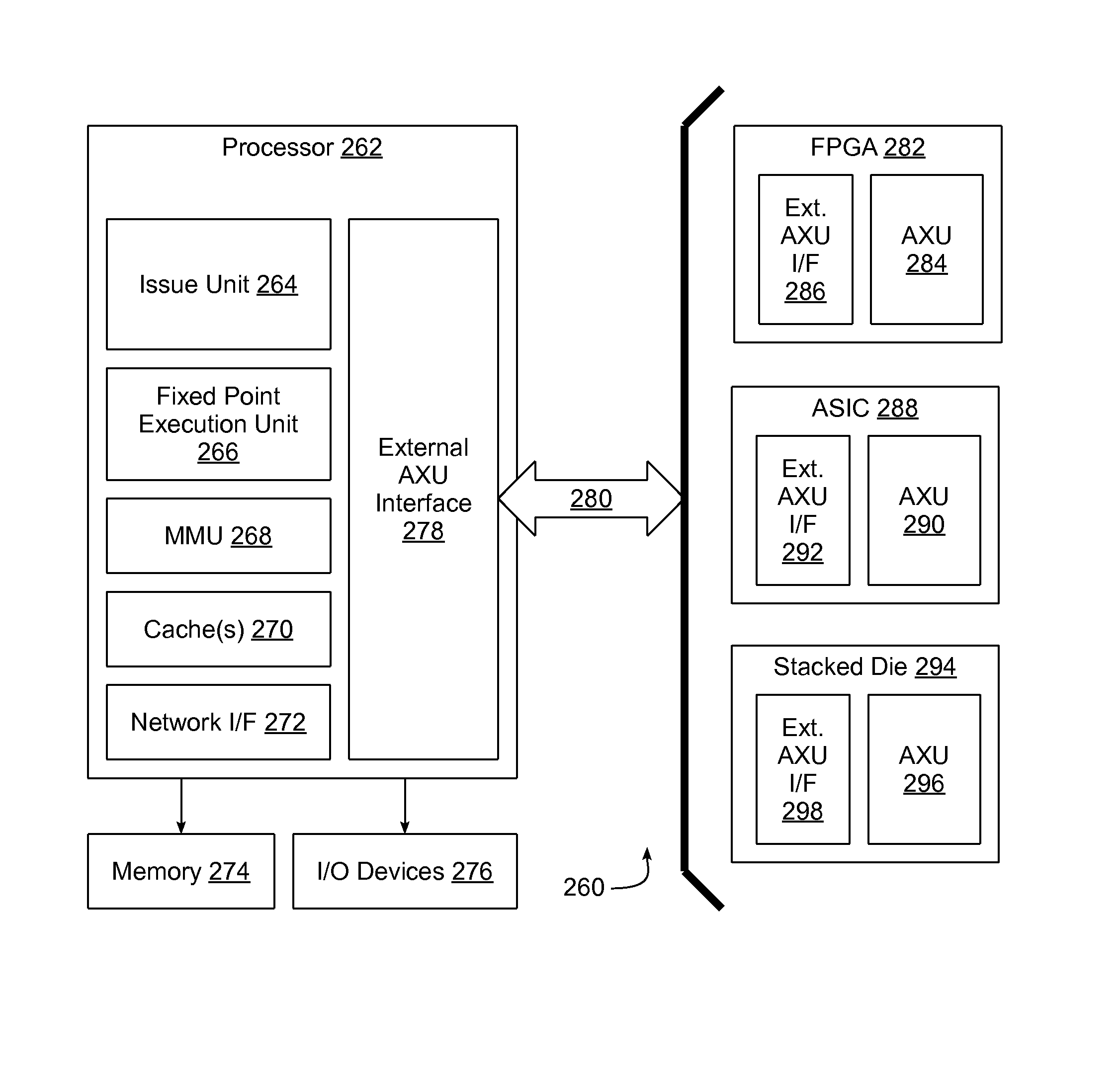
External auxiliary execution unit interface to off-chip auxiliary execution unit
An external Auxiliary Execution Unit (AXU) interface is provided between a processing core disposed in a first programmable chip and an off-chip AXU disposed in a second programmable chip to integrate the AXU with an issue unit, a fixed point execution unit, and optionally other functional units in the processing core. The external AXU interface enables the issue unit to issue instructions to the AXU in much the same manner as the issue unit would be able to issue instructions to an AXU that was disposed on the same chip. By doing so, the AXU on the second programmable chip can be designed, tested and verified independent of the processing core on the first programmable chip, thereby enabling a common processing core, which has been designed, tested, and verified, to be used in connection with multiple different AXU designs.
Owner:IBM CORP
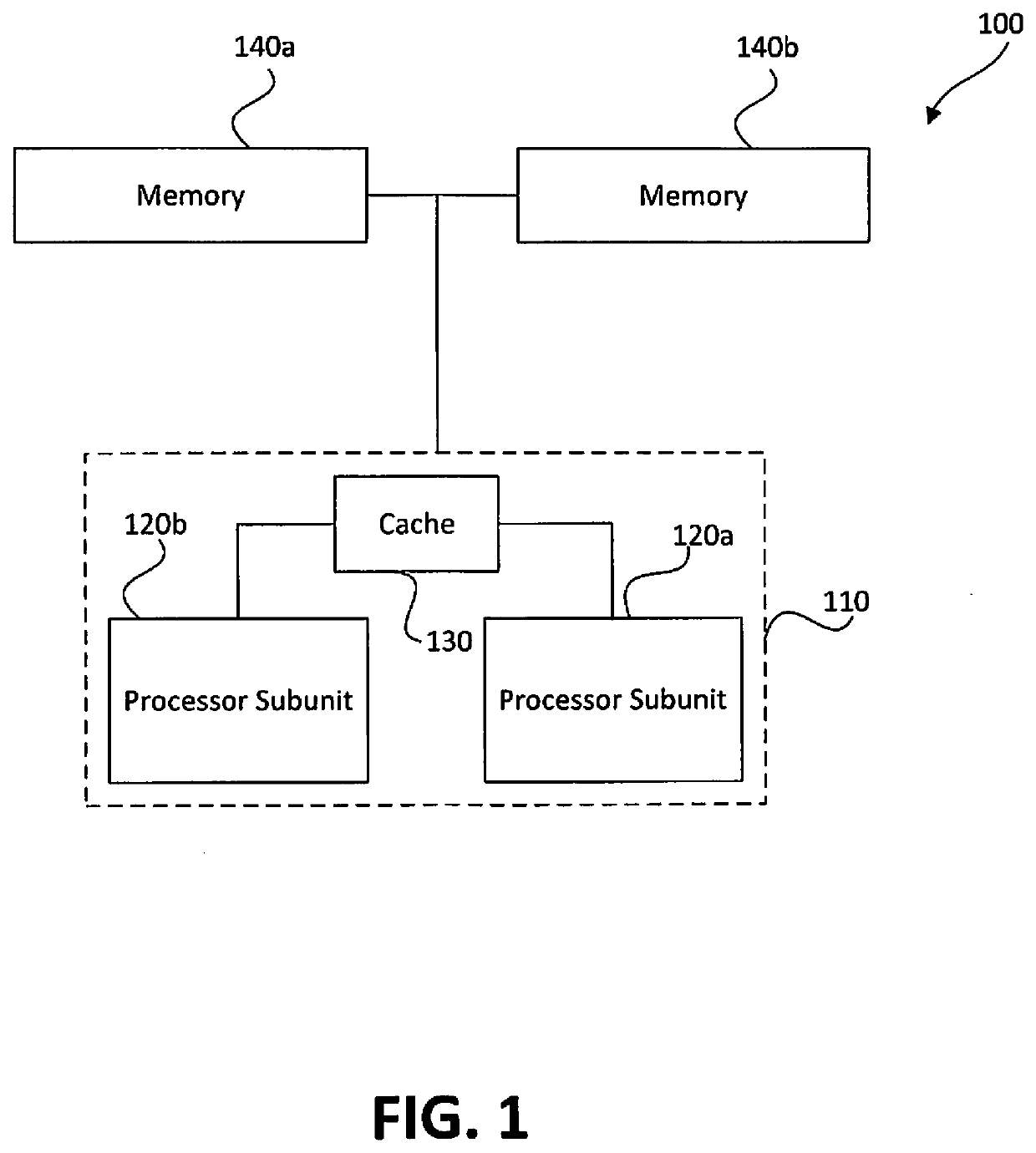
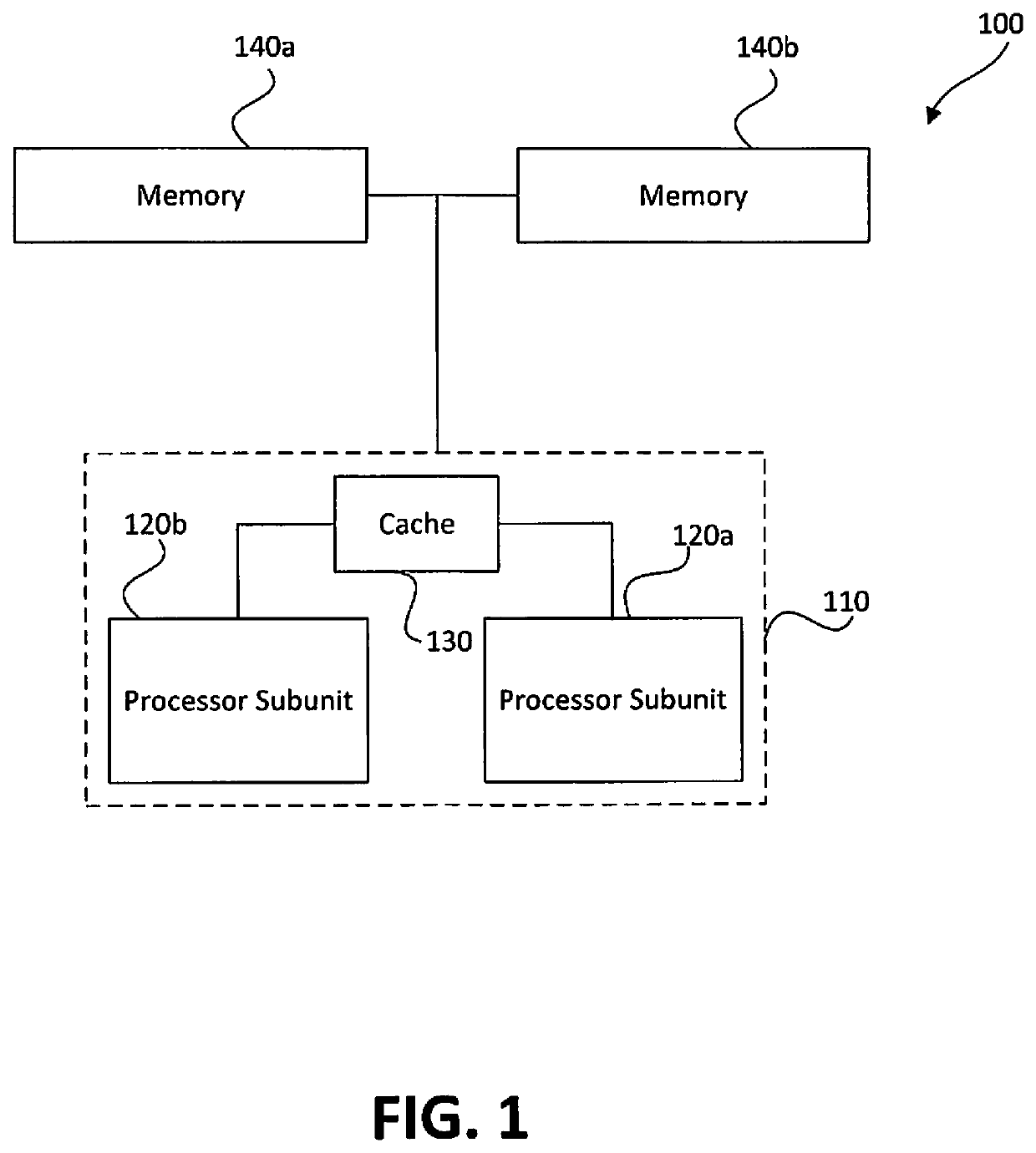
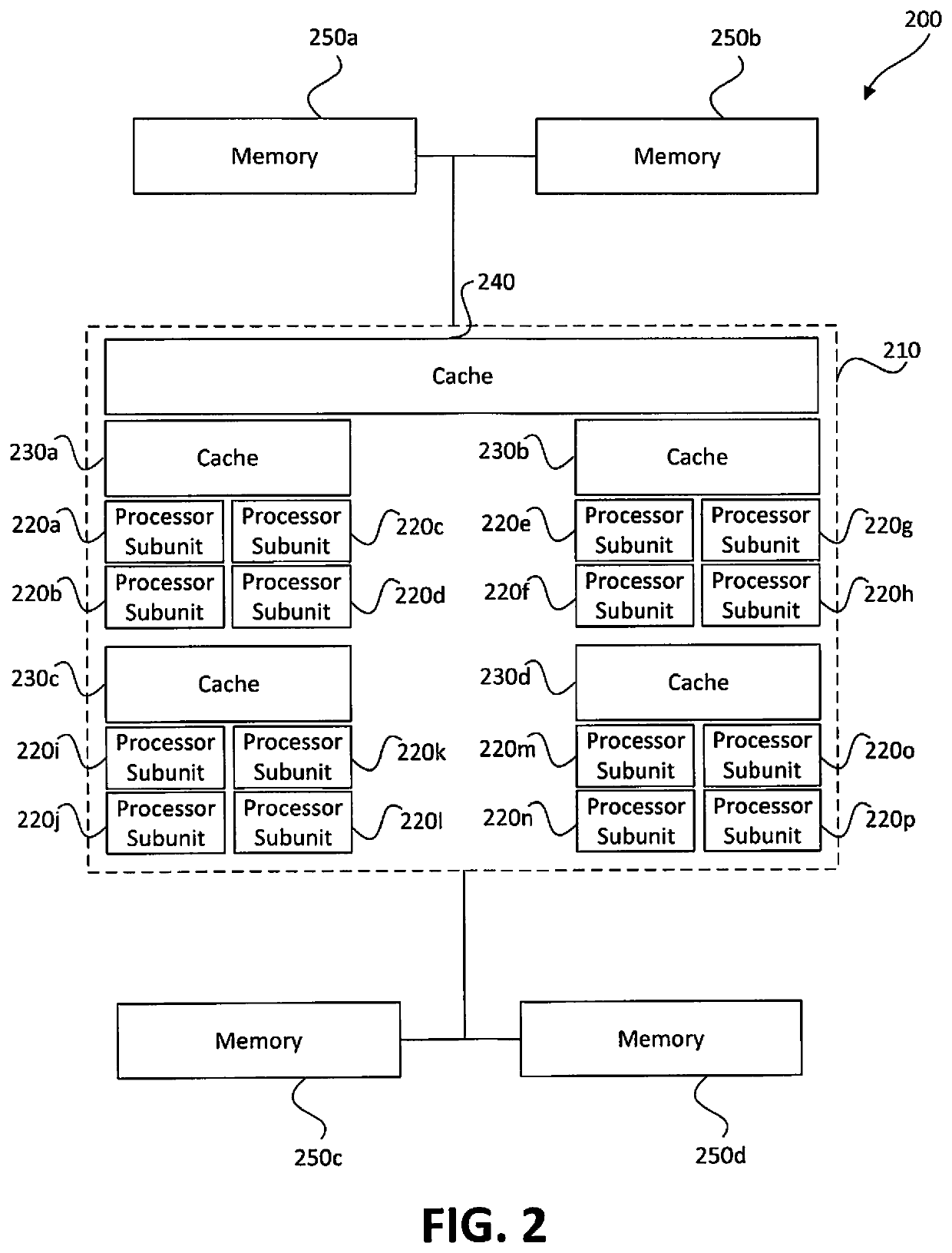
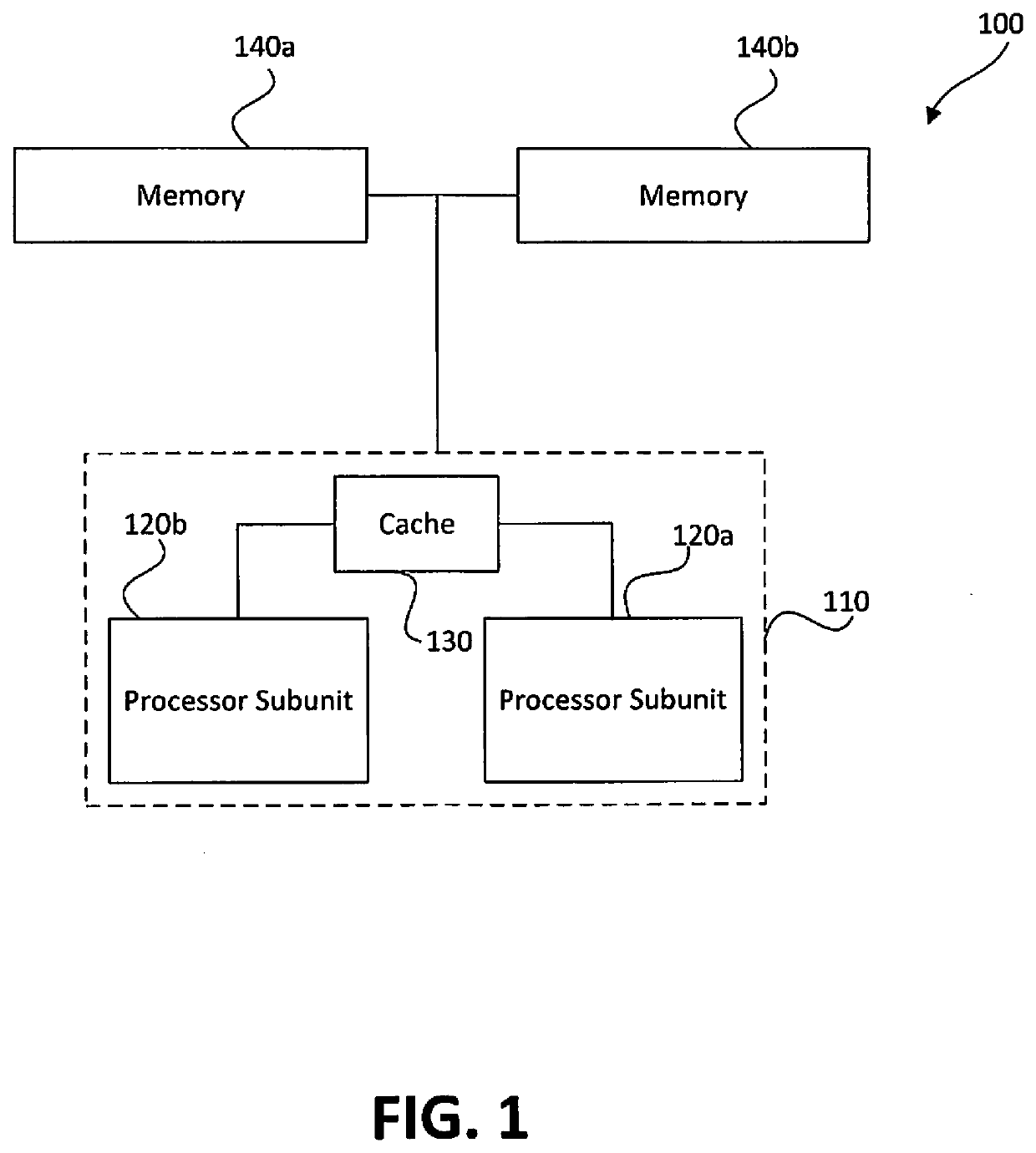
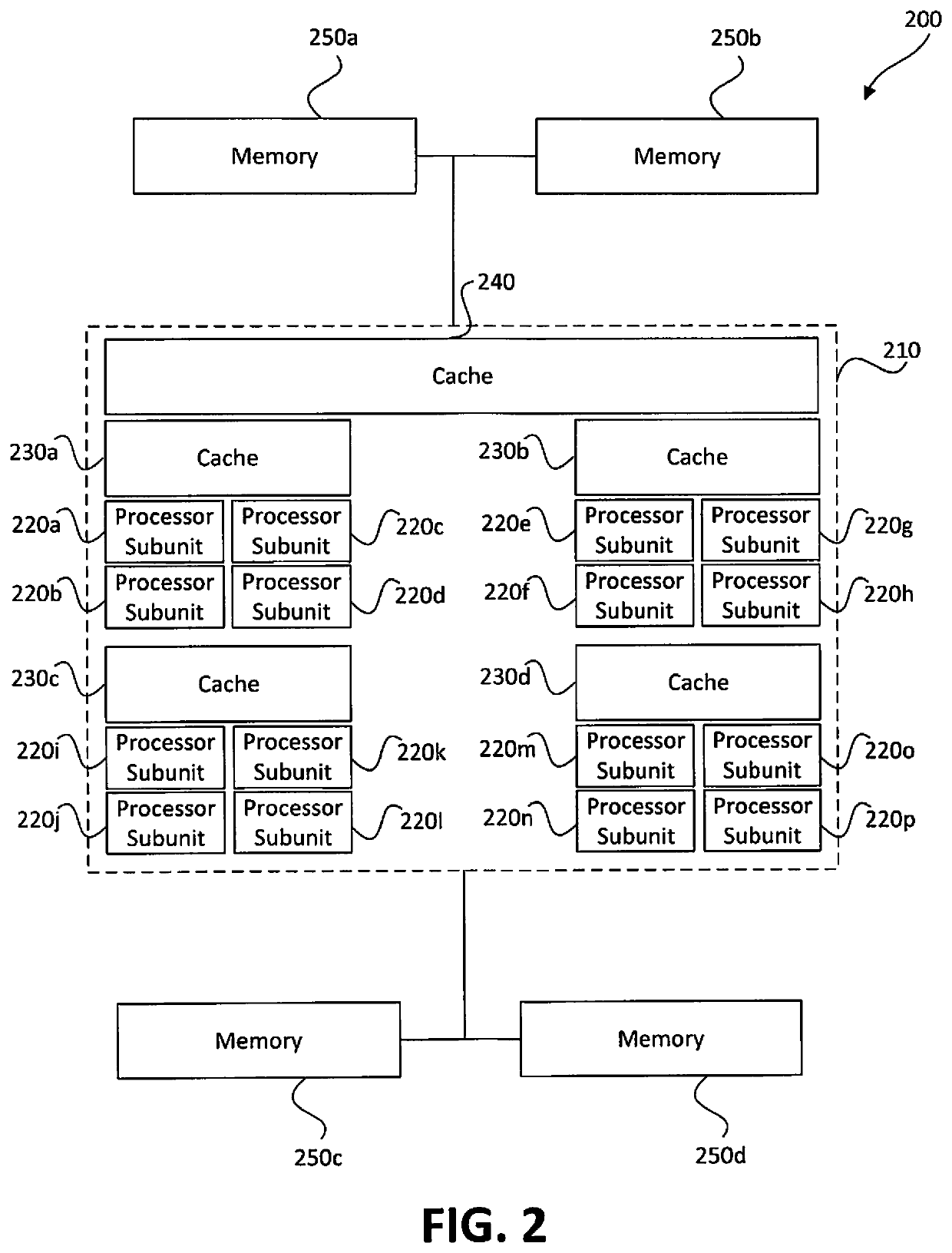
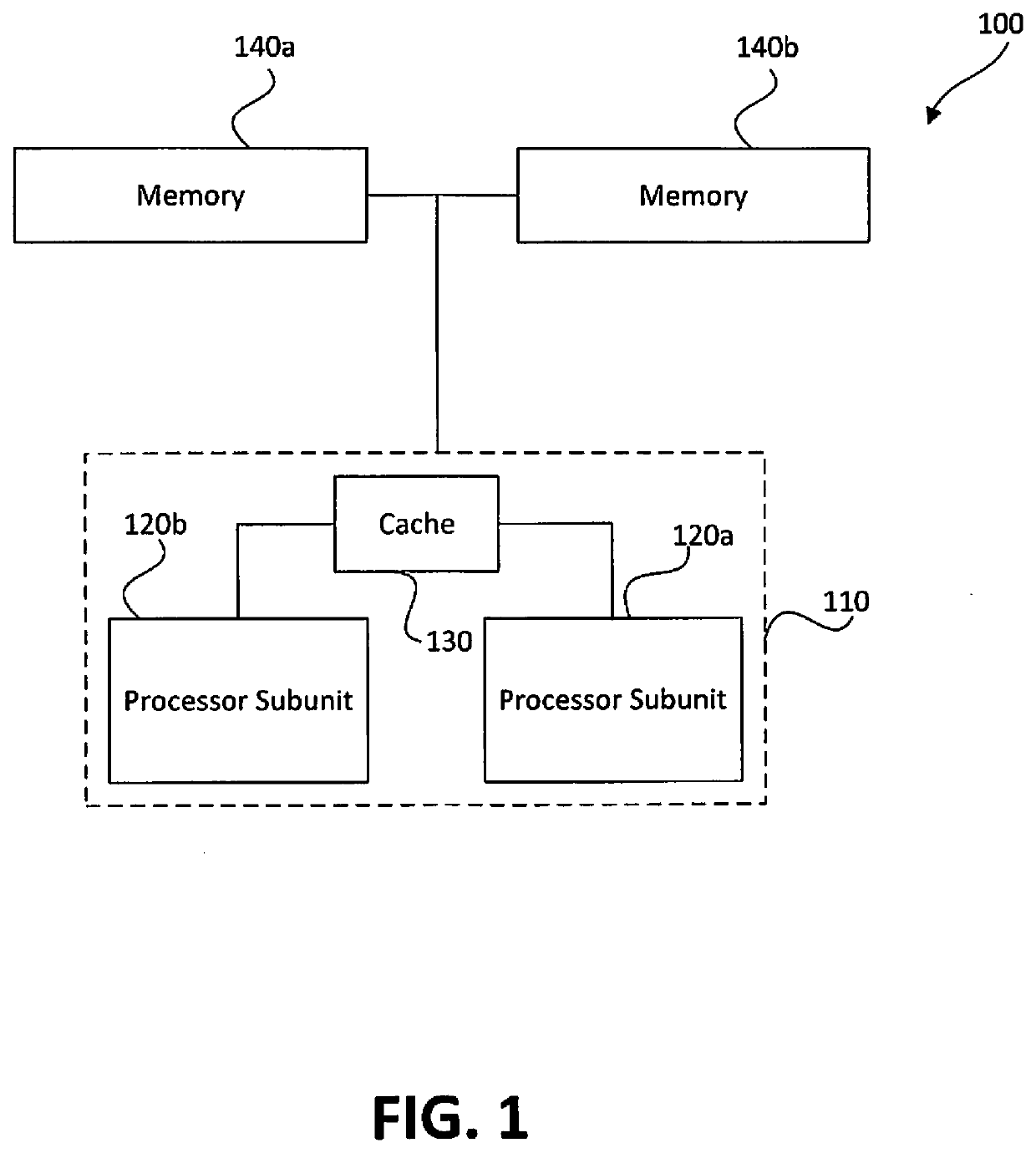
Memory-based distributed processor architecture
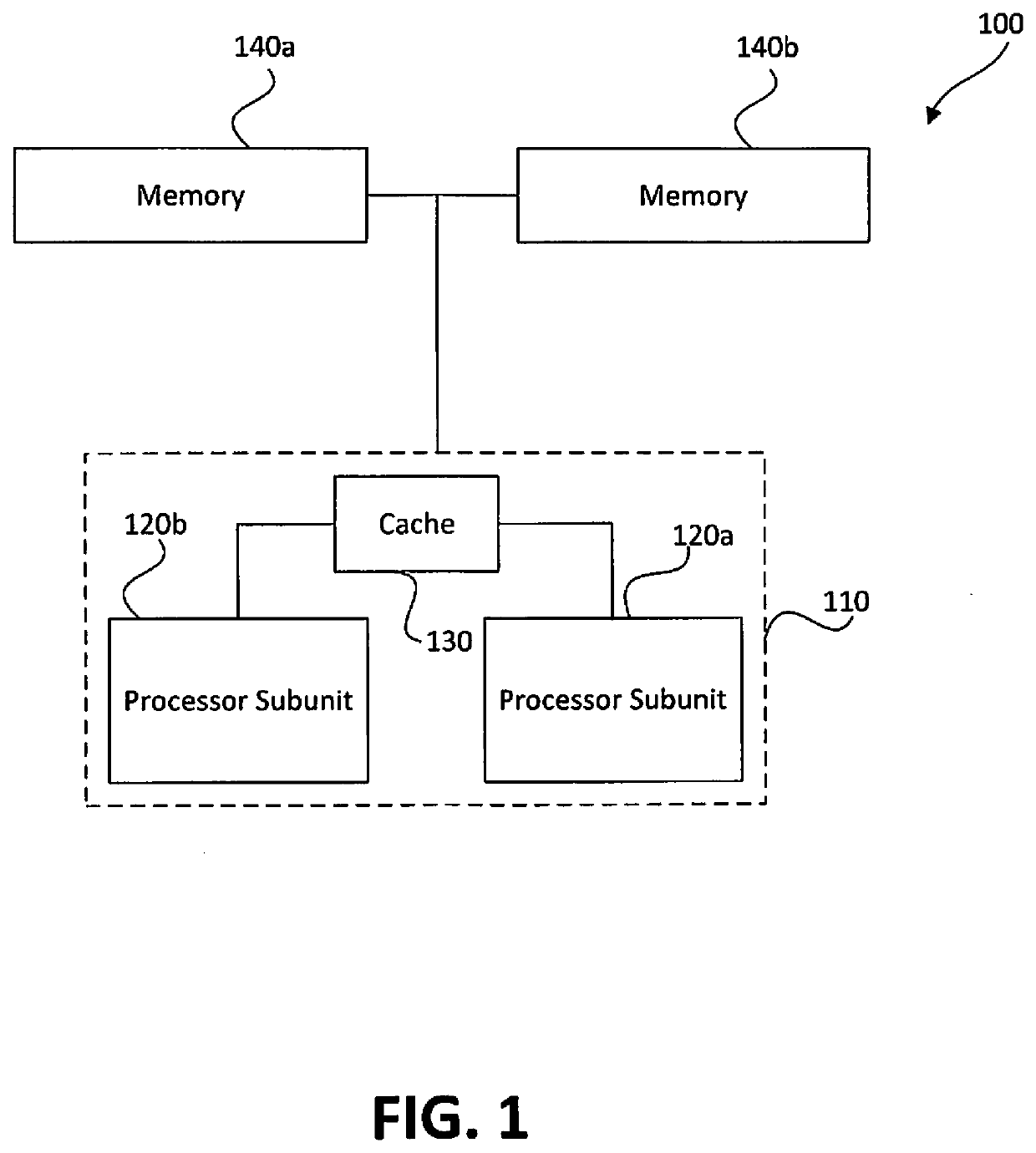
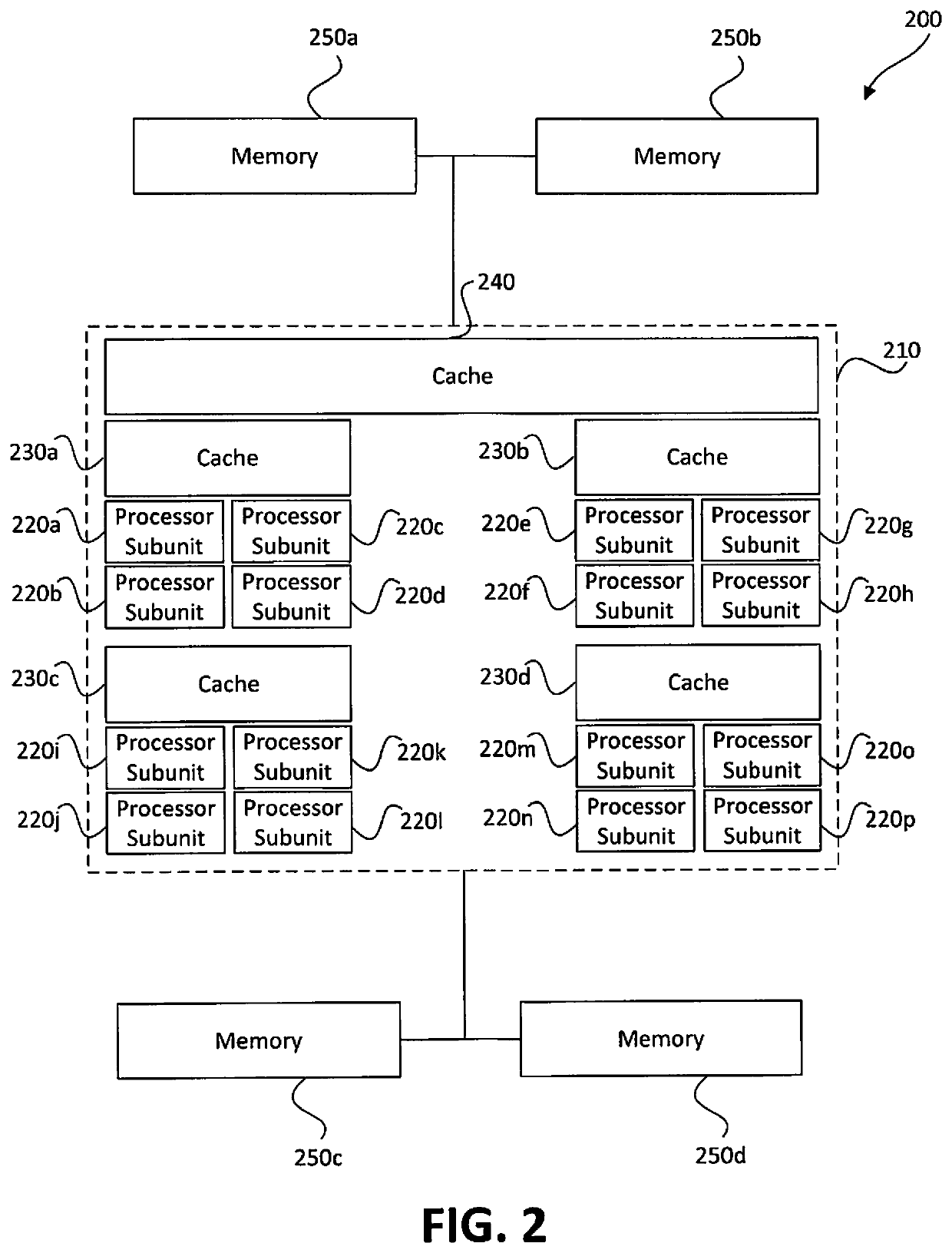
ActiveUS20190341091A1Associative processorsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory bankParallel computing
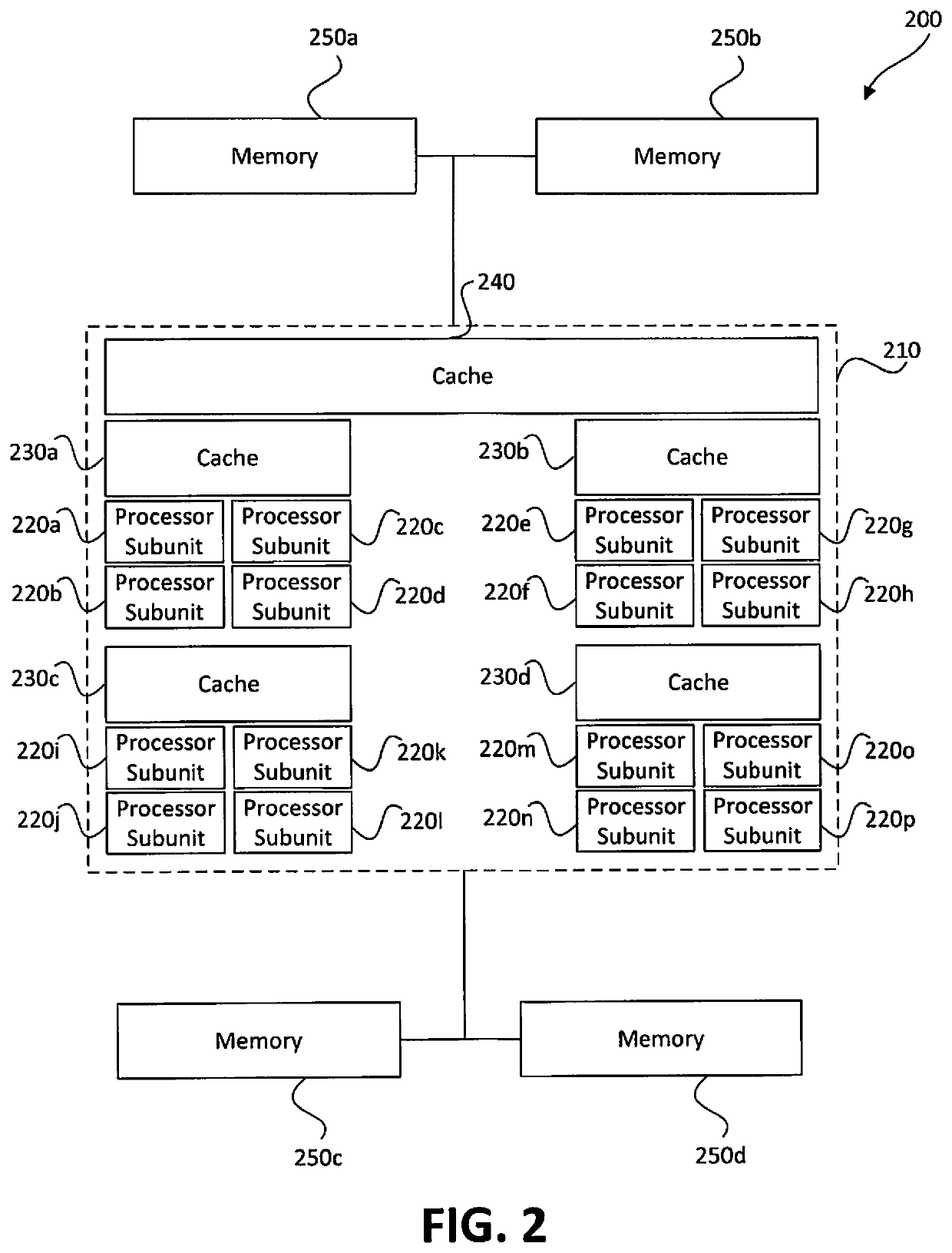
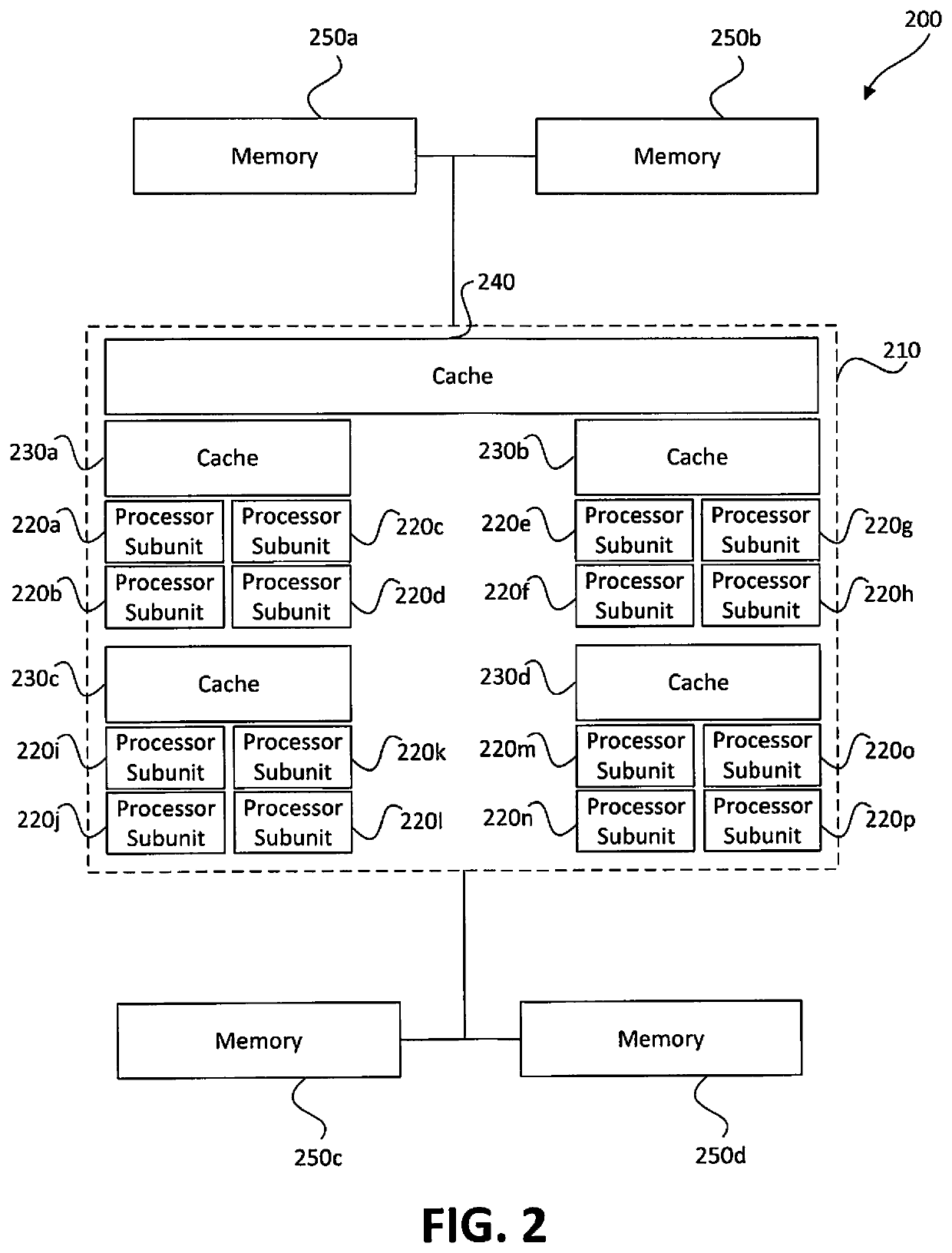
Distributed processors and methods for compiling code for execution by distributed processors are disclosed. In one implementation, a distributed processor may include a substrate; a memory array disposed on the substrate; and a processing array disposed on the substrate. The memory array may include a plurality of discrete memory banks, and the processing array may include a plurality of processor subunits, each one of the processor subunits being associated with a corresponding, dedicated one of the plurality of discrete memory banks. The distributed processor may further include a first plurality of buses, each connecting one of the plurality of processor subunits to its corresponding, dedicated memory bank, and a second plurality of buses, each connecting one of the plurality of processor subunits to another of the plurality of processor subunits.
Owner:NEUROBLADE LTD
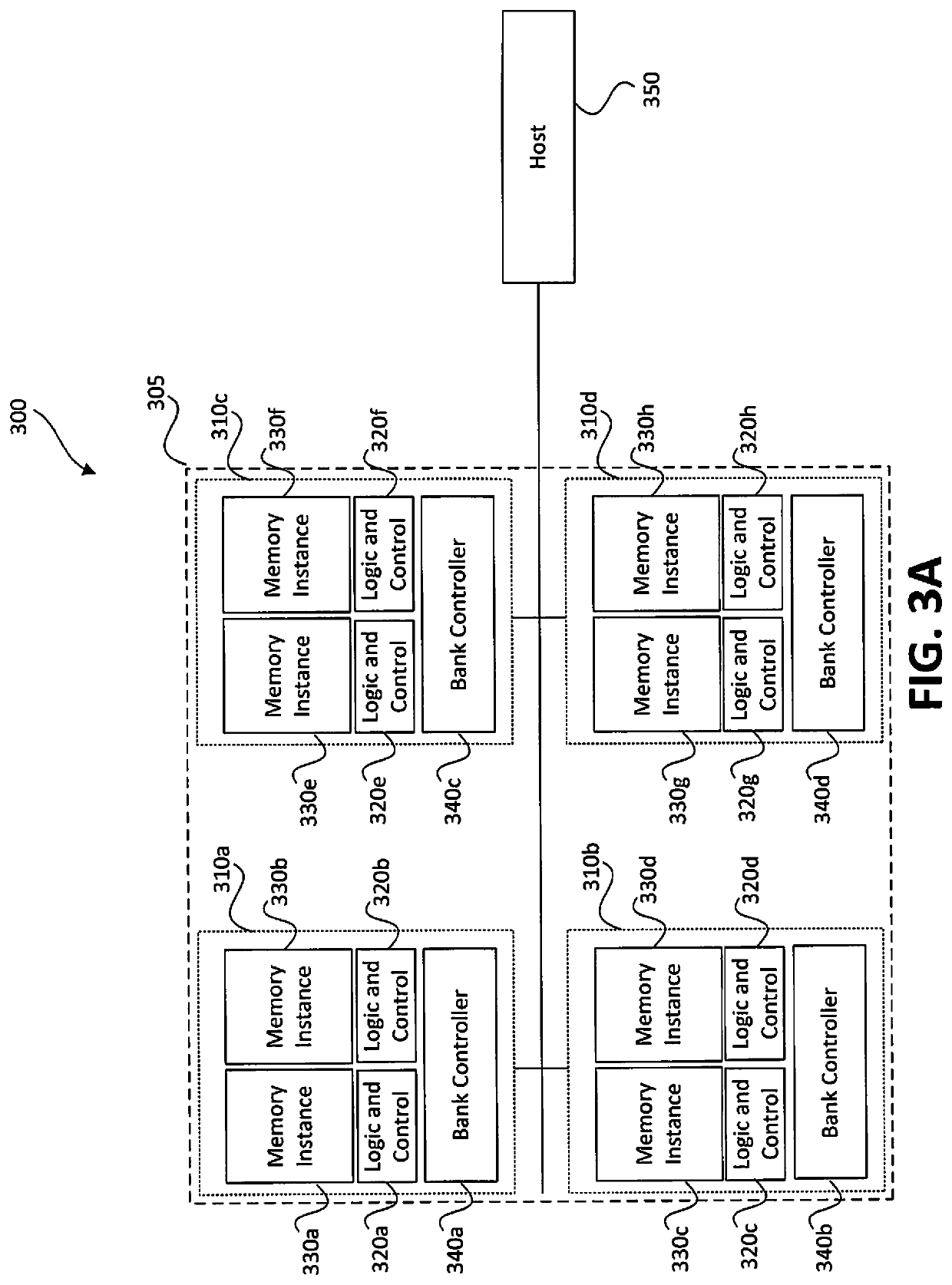
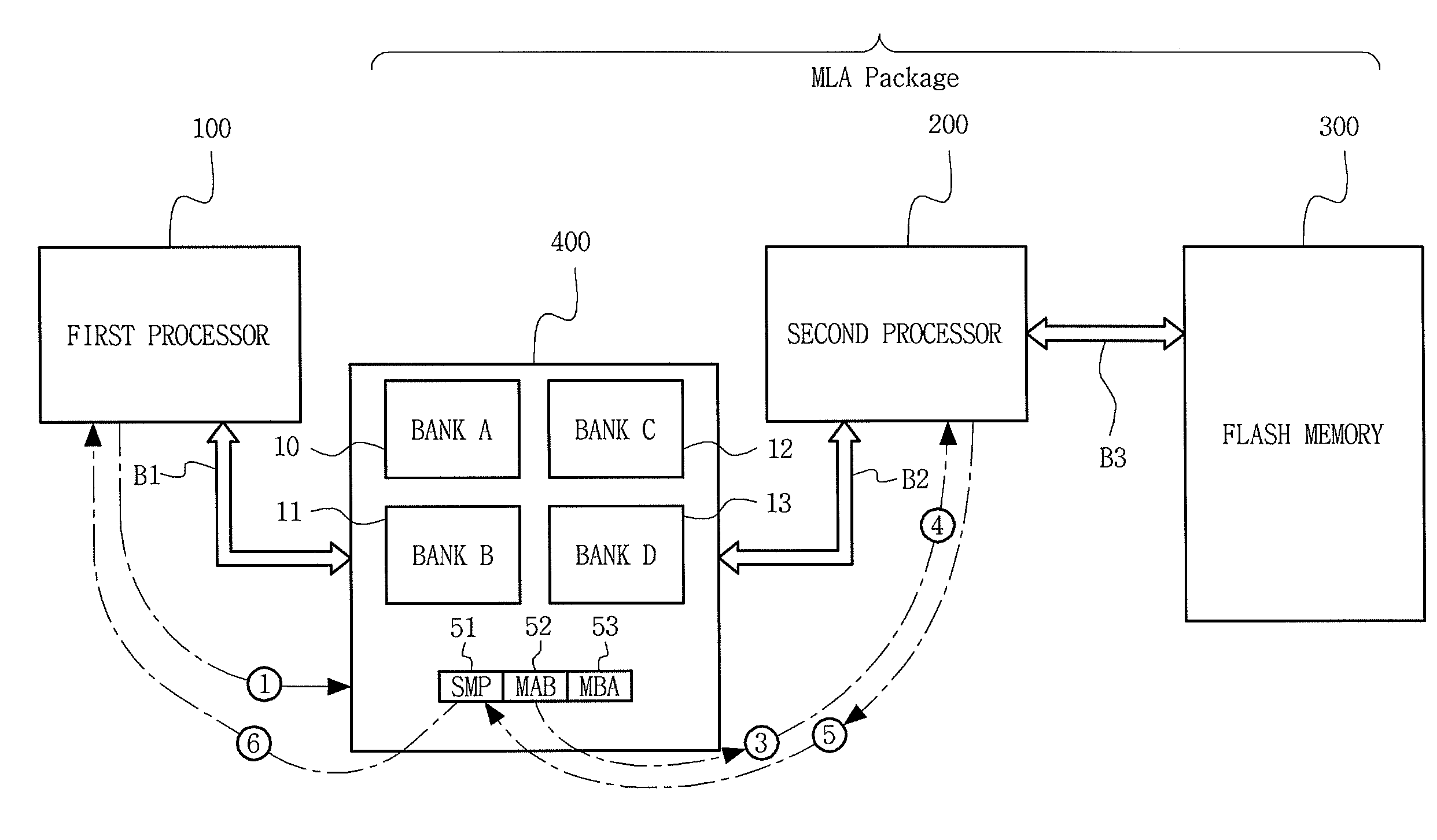
Multiprocessor System Having Direct Transfer Function for Program Status Information in Multilink Architecture
InactiveUS20090249030A1Improve data storage capacityReduce errorsAssociative processorsProgram control using wired connectionsMulti processorProgram completion
A multiprocessor system can directly transmit storage-state information in a multilink architecture. The multiprocessor system includes a first processor; a multiport semiconductor memory device coupled to the first processor; a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device; and a second processor coupled with the multiport semiconductor memory device and the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device in a multilink architecture, storing data, having been written in a shared memory area of the multiport semiconductor memory device by the first processor, in the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device, and directly transmitting storage-state information on whether the storing of the data in the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device has been completed, in response to a request of the first processor, without passing it through the multiport semiconductor memory device. Accordingly a processor indirectly coupled to a nonvolatile memory can directly check a program completion state for write data and thus enhancing a data storage performance of the system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
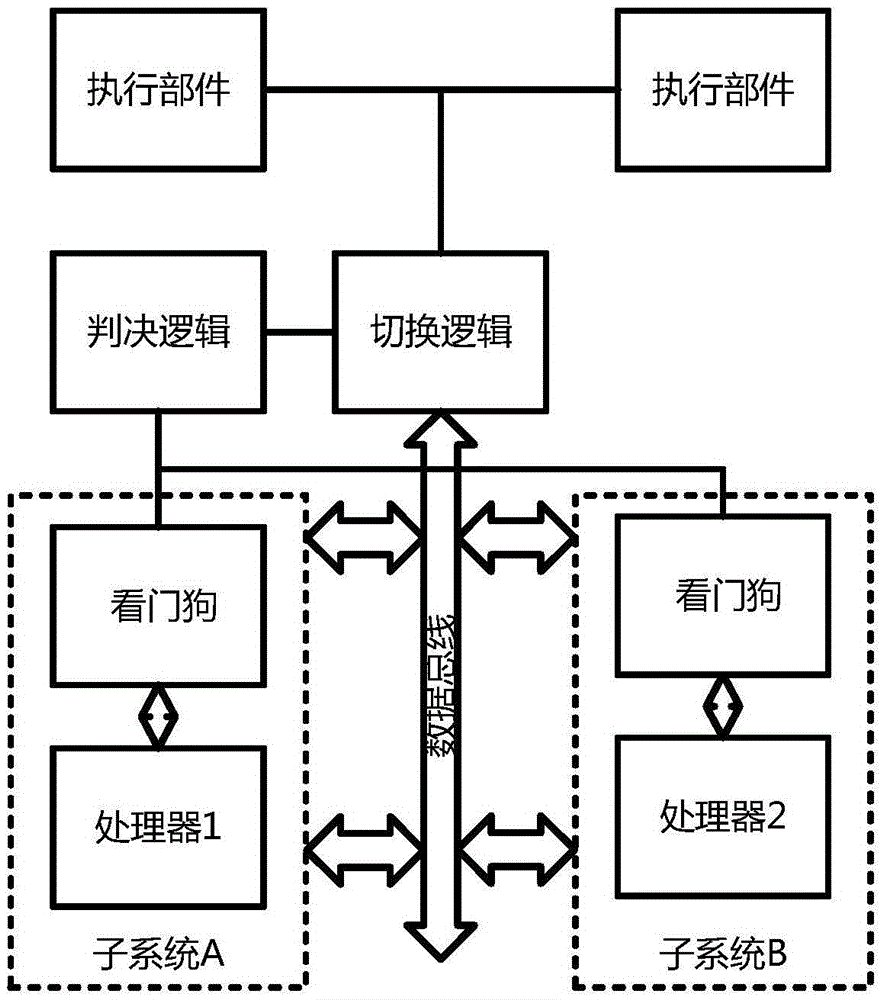
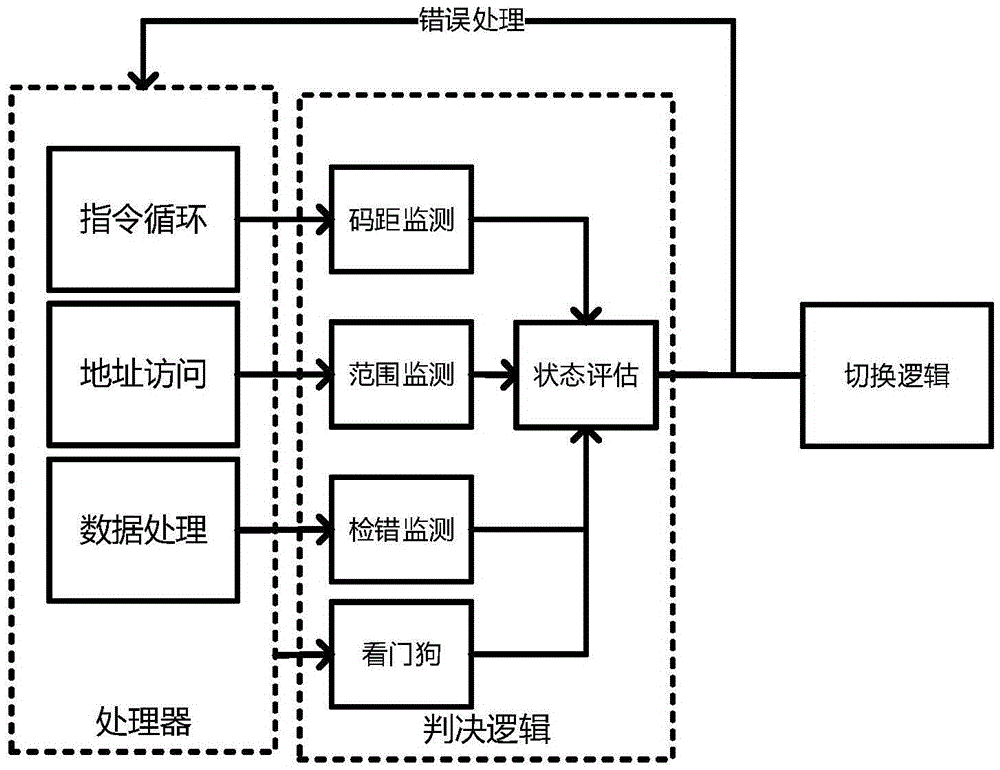
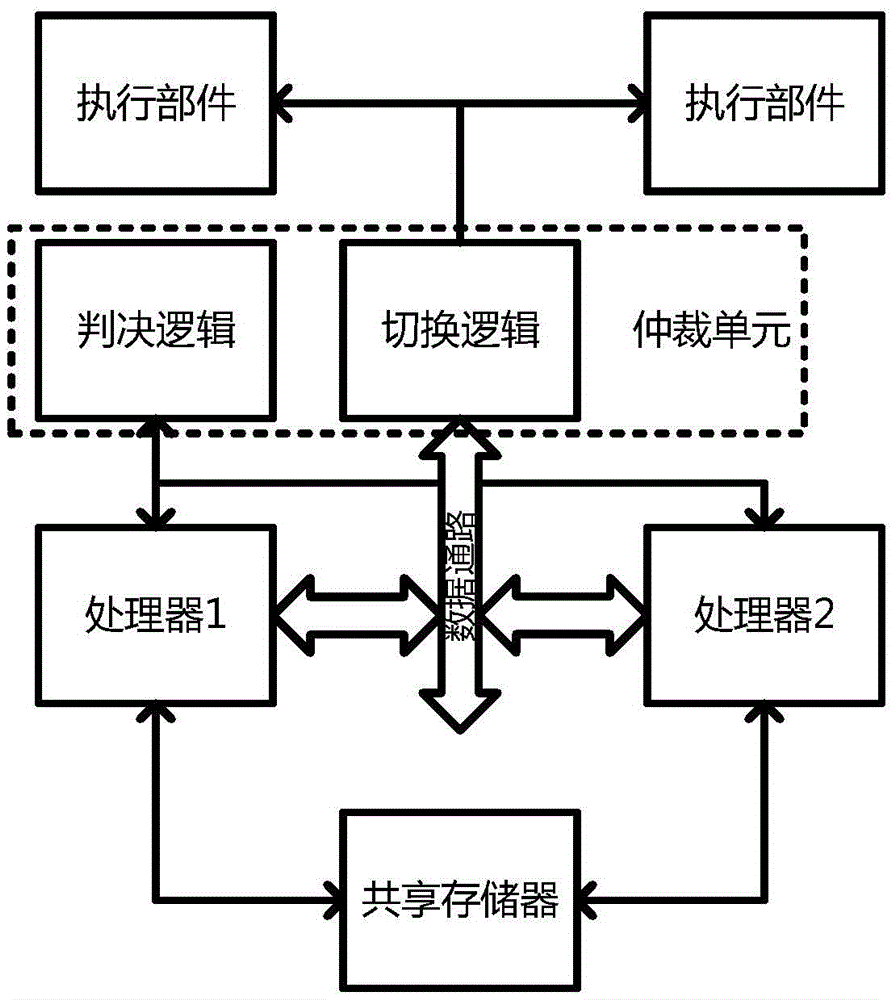
Hot switching method for dual-mode redundant microprocessor
ActiveCN105630732AGood conditionImprove fault toleranceAssociative processorsFault responseFault toleranceDual mode
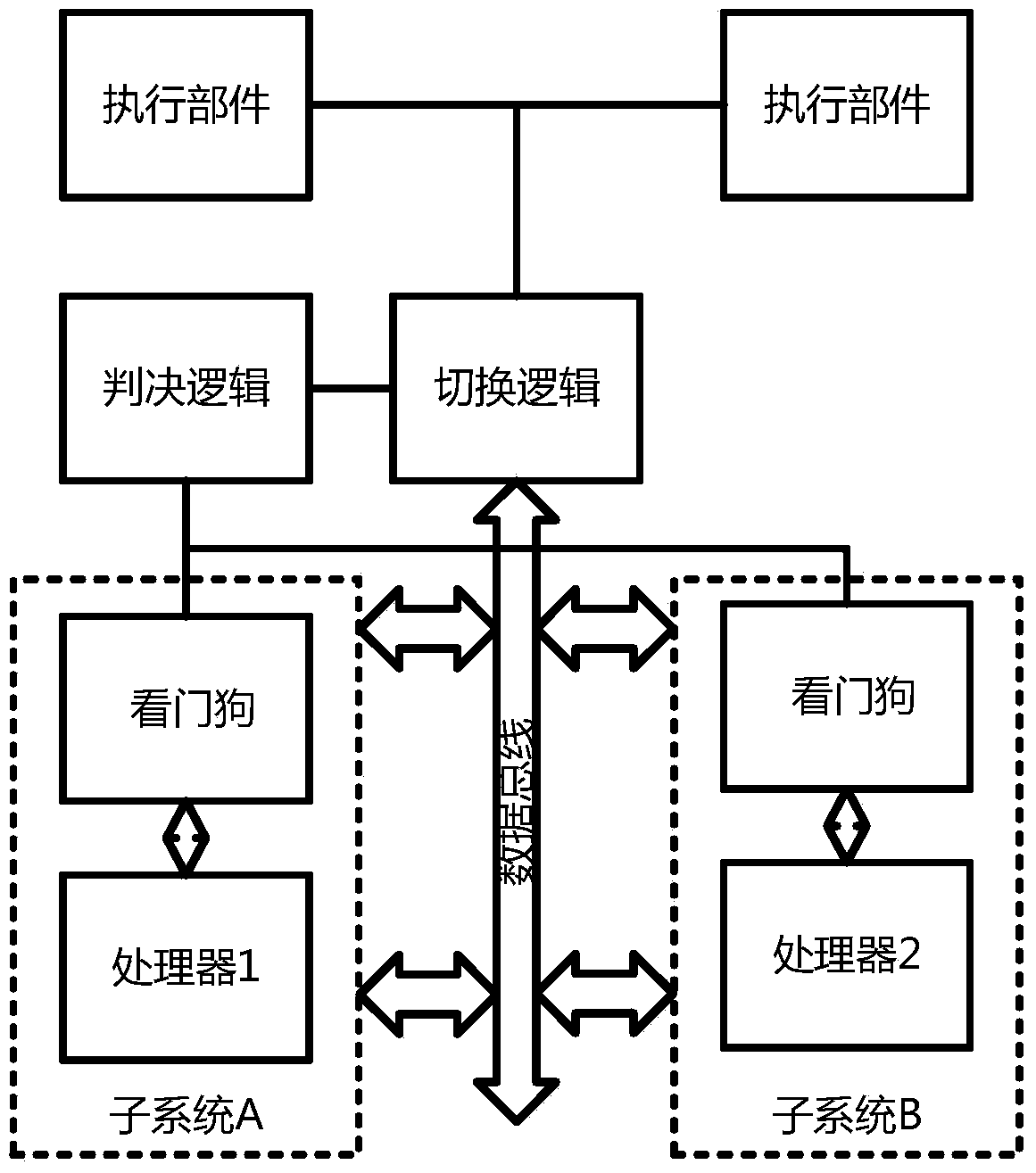
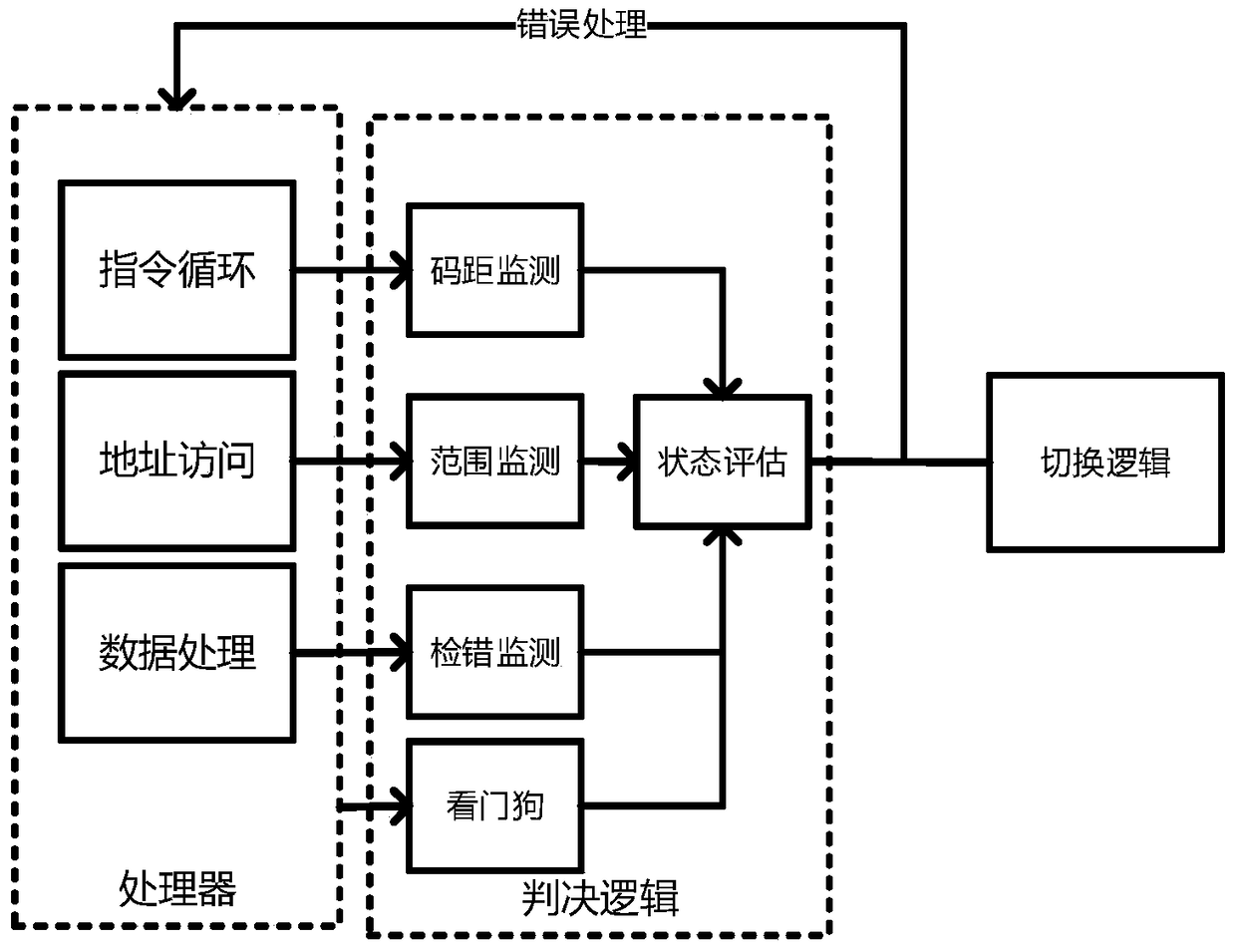
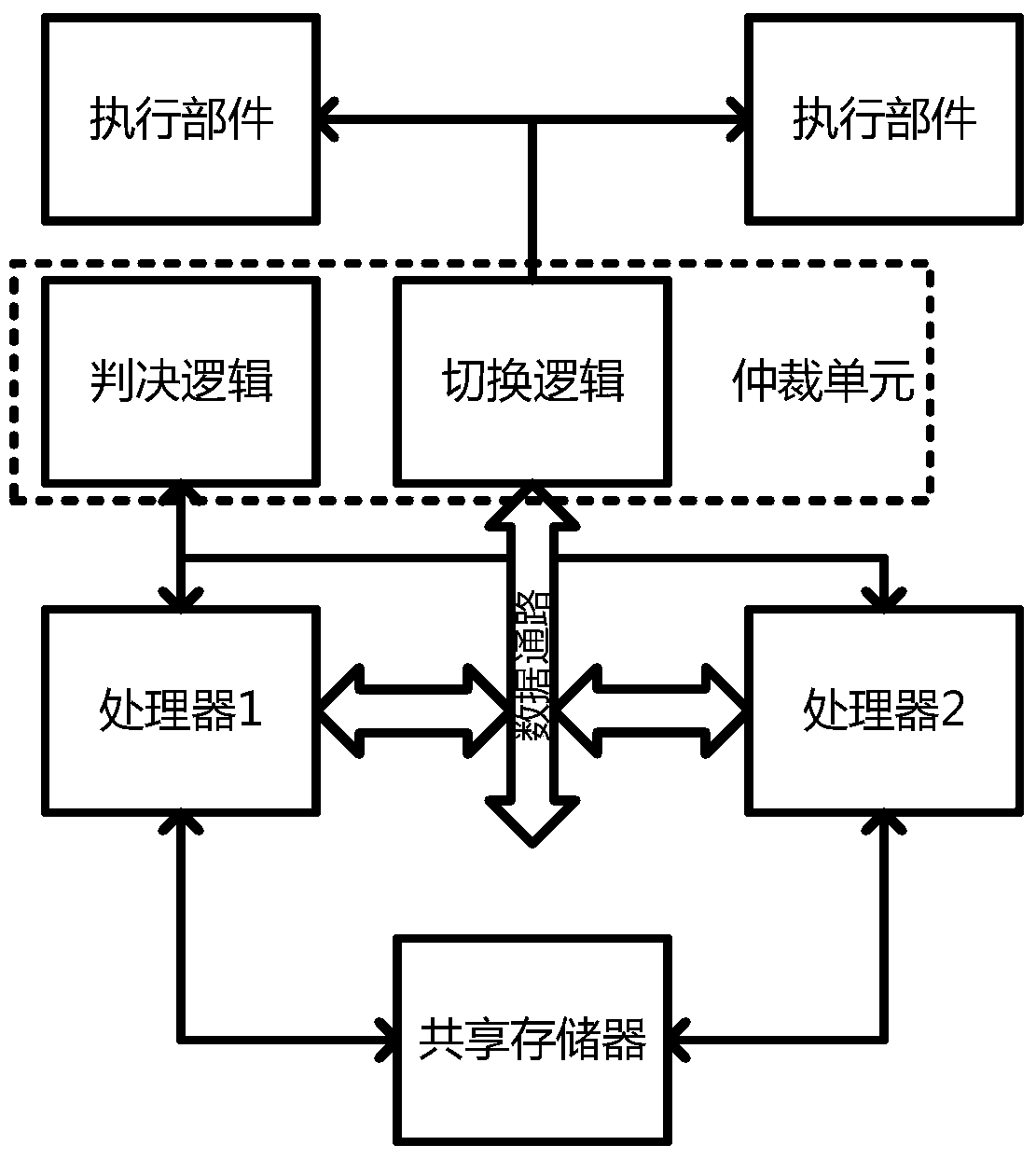
The invention discloses a hot switching method for a dual-mode redundant microprocessor, and aims to provide better processor state monitoring and fault-tolerance effects and endow a processor with a hot switching capability so as to improve the stability and adaptability of an embedded microprocessor in a radiation environment. The adopted technical scheme is that a judgment logic of a dual-mode redundant processor is established; an instruction state machine, address access, data flow processing and a processor state are monitored separately; the processor state is evaluated; during resetting, a second processor is in an idle state, a first processor executes the instruction content in a memory in sequence until the first processor has an error, at the moment, processor switching is performed, and a bus switching logic cuts off a data path of the first processor, transfers data to the second processor and sends a switching interruption request to the second processor; and the second processor uses data in a shared data memory to restore an execution state of the first processor and continues to execute an instruction, thereby realizing the hot switching.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Memory-based distributed processor architecture
ActiveUS20190339981A1Efficient effective processing speedAssociative processorsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory bankParallel computing
Distributed processors and methods for compiling code for execution by distributed processors are disclosed. In one implementation, a distributed processor may include a substrate; a memory array disposed on the substrate; and a processing array disposed on the substrate. The memory array may include a plurality of discrete memory banks, and the processing array may include a plurality of processor subunits, each one of the processor subunits being associated with a corresponding, dedicated one of the plurality of discrete memory banks. The distributed processor may further include a first plurality of buses, each connecting one of the plurality of processor subunits to its corresponding, dedicated memory bank, and a second plurality of buses, each connecting one of the plurality of processor subunits to another of the plurality of processor subunits.
Owner:NEUROBLADE LTD
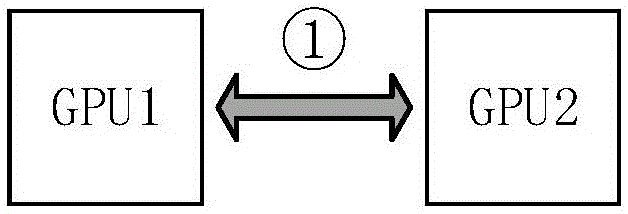
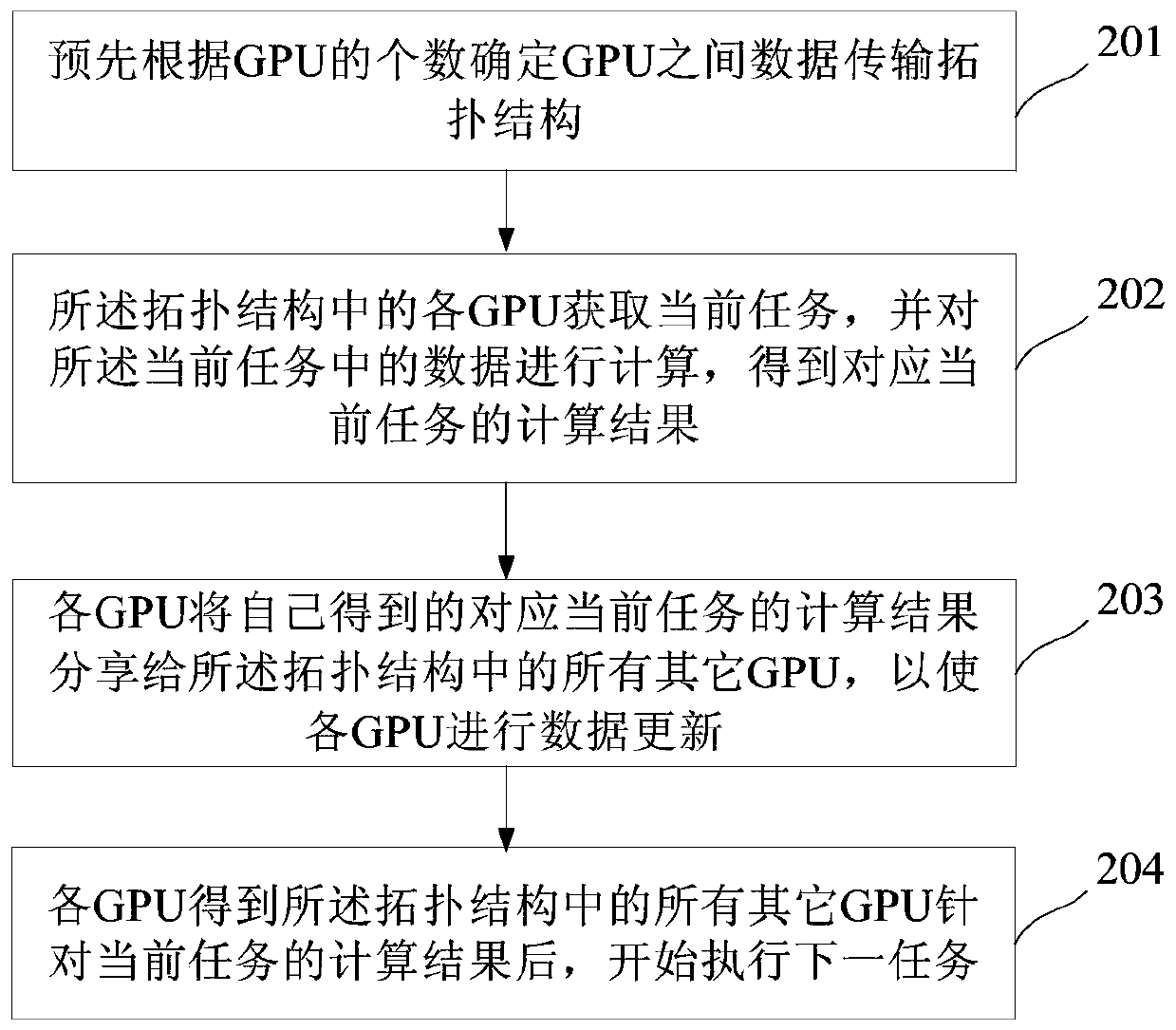
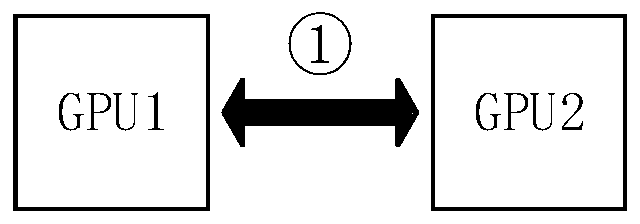
Parallel accelerating method and system in heterogeneous computation
ActiveCN106776014AProcessing speedReduce bandwidth requirementsAssociative processorsResource allocationBandwidth requirementData transmission
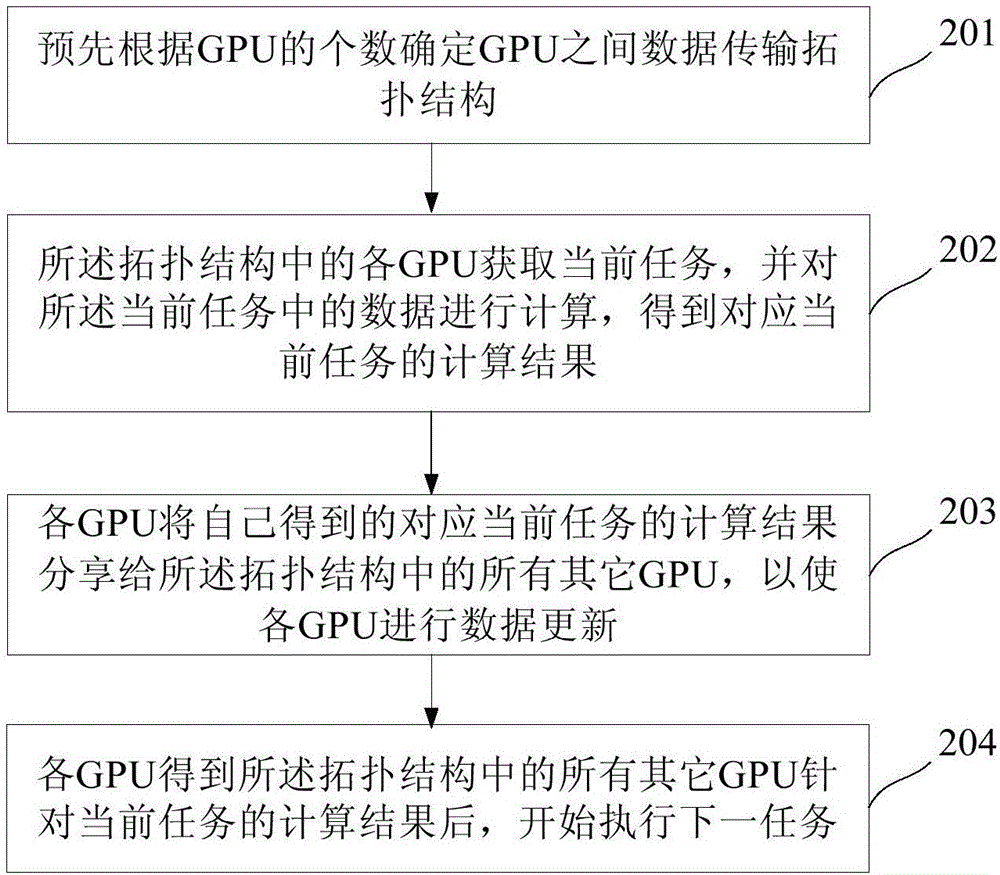
The invention discloses a parallel accelerating method and system in heterogeneous computation. The method comprises the following steps: determining a topological structure of data transmission between GPUs (Graphics Processing Unit) in advance according to the quantity of the GPUs; acquiring a current task by each GPU in the topological structure and computing data in the current task, so as to obtain a calculating result corresponding to the current task; sharing the calculating result which is obtained by each GPU and corresponds to the current task to the other GPUs in the topological structure; after obtaining the calculating results of the other GPUs in the topological structure by each GPU, starting to execute the next task. By adopting the parallel accelerating method and system in the heterogeneous computation, the parallel computation capability of the GPUs can be improved and the bandwidth requirements on nodes of each GPU are reduced.
Owner:安徽智慧皆成数字技术有限公司
Memory-based distributed processor architecture
ActiveUS10664438B2Associative processorsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer architectureMemory bank
Distributed processors and methods for compiling code for execution by distributed processors are disclosed. In one implementation, a distributed processor may include a substrate; a memory array disposed on the substrate; and a processing array disposed on the substrate. The memory array may include a plurality of discrete memory banks, and the processing array may include a plurality of processor subunits, each one of the processor subunits being associated with a corresponding, dedicated one of the plurality of discrete memory banks. The distributed processor may further include a first plurality of buses, each connecting one of the plurality of processor subunits to its corresponding, dedicated memory bank, and a second plurality of buses, each connecting one of the plurality of processor subunits to another of the plurality of processor subunits.
Owner:NEUROBLADE LTD
Memory-based distributed processor architecture
ActiveUS20190340064A1Associative processorsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory bankParallel computing
Distributed processors and methods for compiling code for execution by distributed processors are disclosed. In one implementation, a distributed processor may include a substrate; a memory array disposed on the substrate; and a processing array disposed on the substrate. The memory array may include a plurality of discrete memory banks, and the processing array may include a plurality of processor subunits, each one of the processor subunits being associated with a corresponding, dedicated one of the plurality of discrete memory banks. The distributed processor may further include a first plurality of buses, each connecting one of the plurality of processor subunits to its corresponding, dedicated memory bank, and a second plurality of buses, each connecting one of the plurality of processor subunits to another of the plurality of processor subunits.
Owner:NEUROBLADE LTD
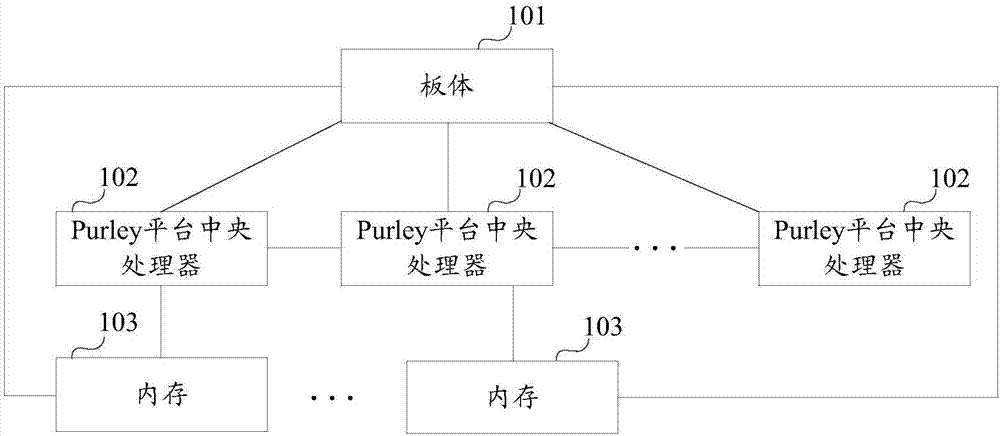
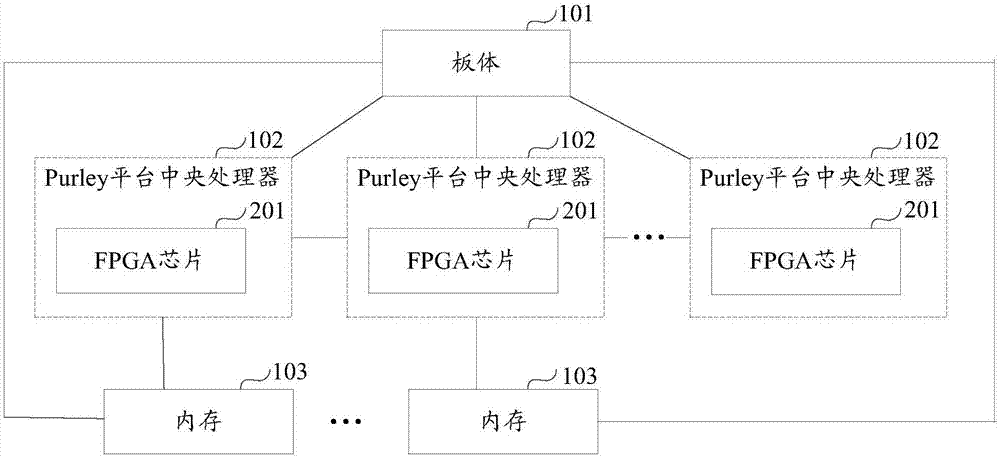
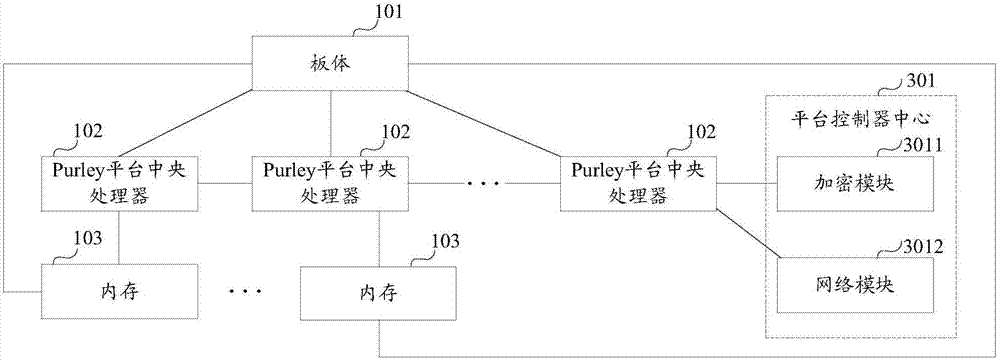
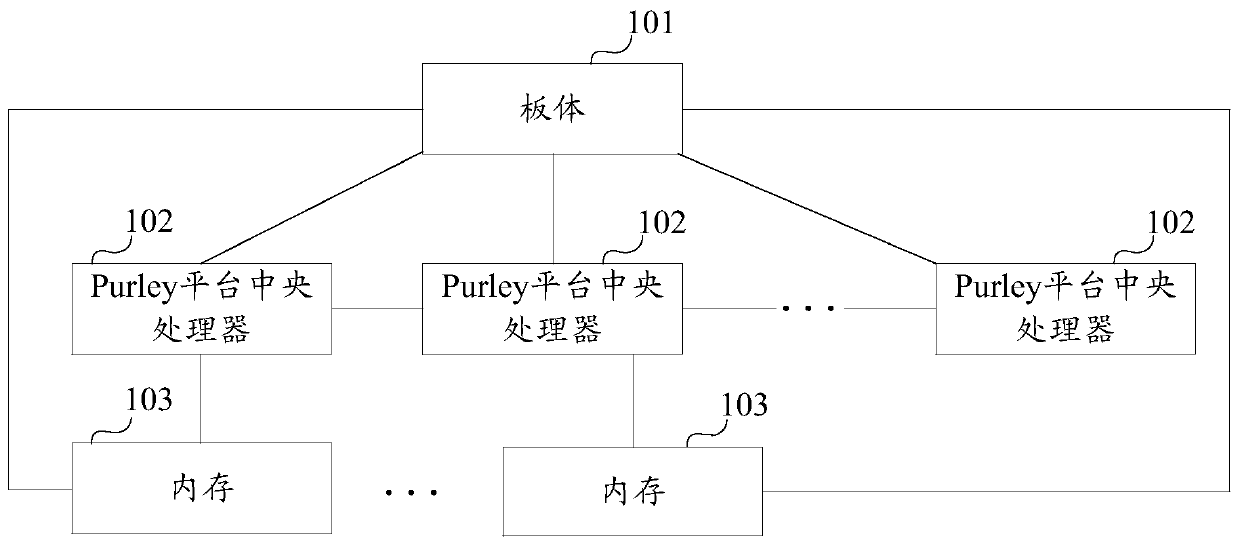
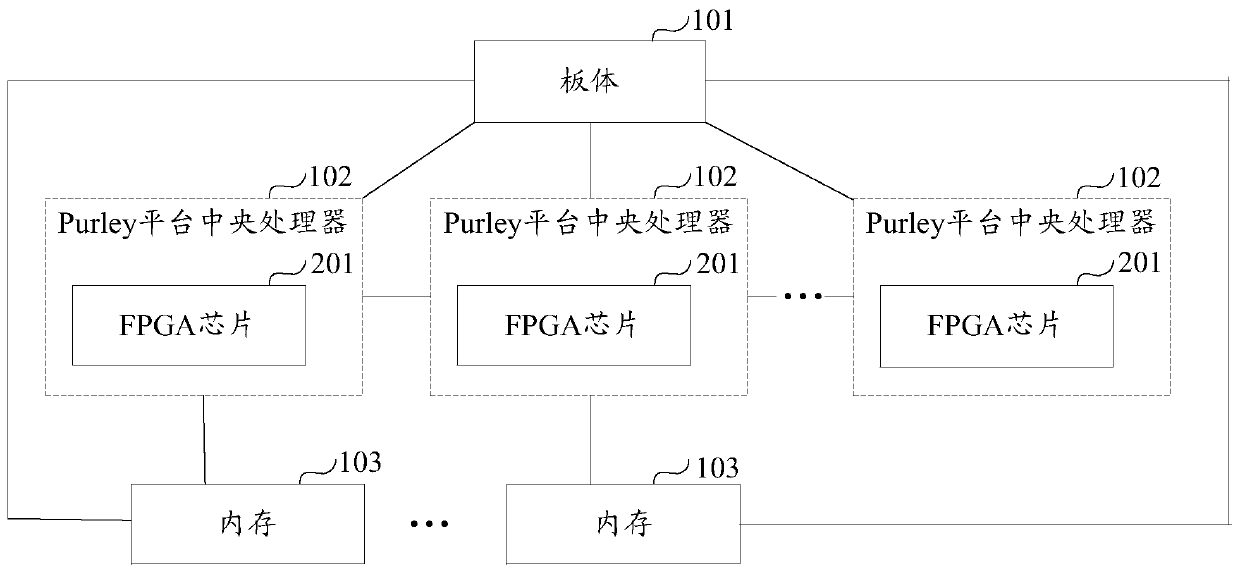
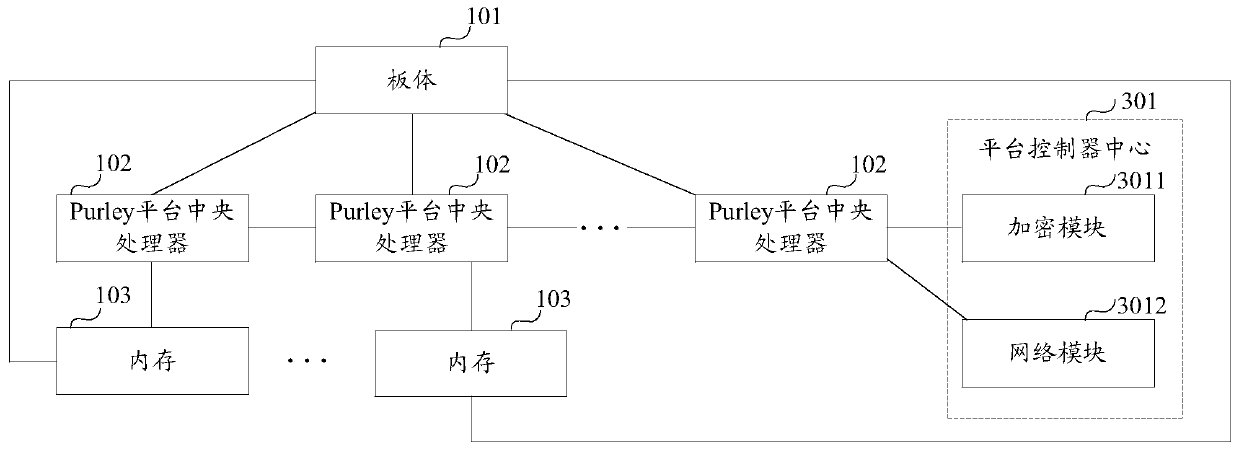
Motherboard and server
ActiveCN107301151AImprove function scalabilityAssociative processorsProgram loading/initiatingComputer scienceMotherboard
The invention provides a motherboard and a server. The motherboard comprises a motherboard body, a preset quantity of Purley platform central processing units and at least one memory. The Purley platform central processing units and the memories are mounted on the motherboard body; the Purley platform central processing units are sequentially connected with one another; each memory is connected with one of the Purley platform central processing units; each memory is used for transmitting externally inputted to-be-burned data to the Purley platform central processing unit connected with the memory when the externally inputted to-be-burned data are received; each Purley platform central processing unit is used for burning the corresponding to-be-burned data when the to-be-burned data transmitted by the corresponding memory connected with the Purley platform central processing unit are received, so that the motherboard can have functions corresponding to the to-be-burned data. According to the scheme, the motherboard and the server have the advantage that the functional expansibility of the motherboard can be improved.
Owner:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Automatic Real-Time Calibration of Qubit Chip
Apparatus and methods for real time calibration of qubits in a quantum processor. For example, one embodiment of an apparatus comprises: a quantum processor comprising a plurality of qubits, each of the qubits having a state; a quantum controller to generate sequences of electromagnetic (EM) pulses to manipulate the states of the plurality of qubits based on a set of control parameters; a qubit measurement unit to measure one or more sensors associated with a corresponding one or more of the qubits of the plurality of qubits to produce one or more corresponding measured values; and a machine-learning engine to evaluate the one or more measured values in accordance with a machine-learning process to generate updated control parameters, wherein the quantum controller is to use the updated control parameters to generate subsequent sequences of EM pulses to manipulate the states of the plurality of qubits.
Owner:INTEL CORP
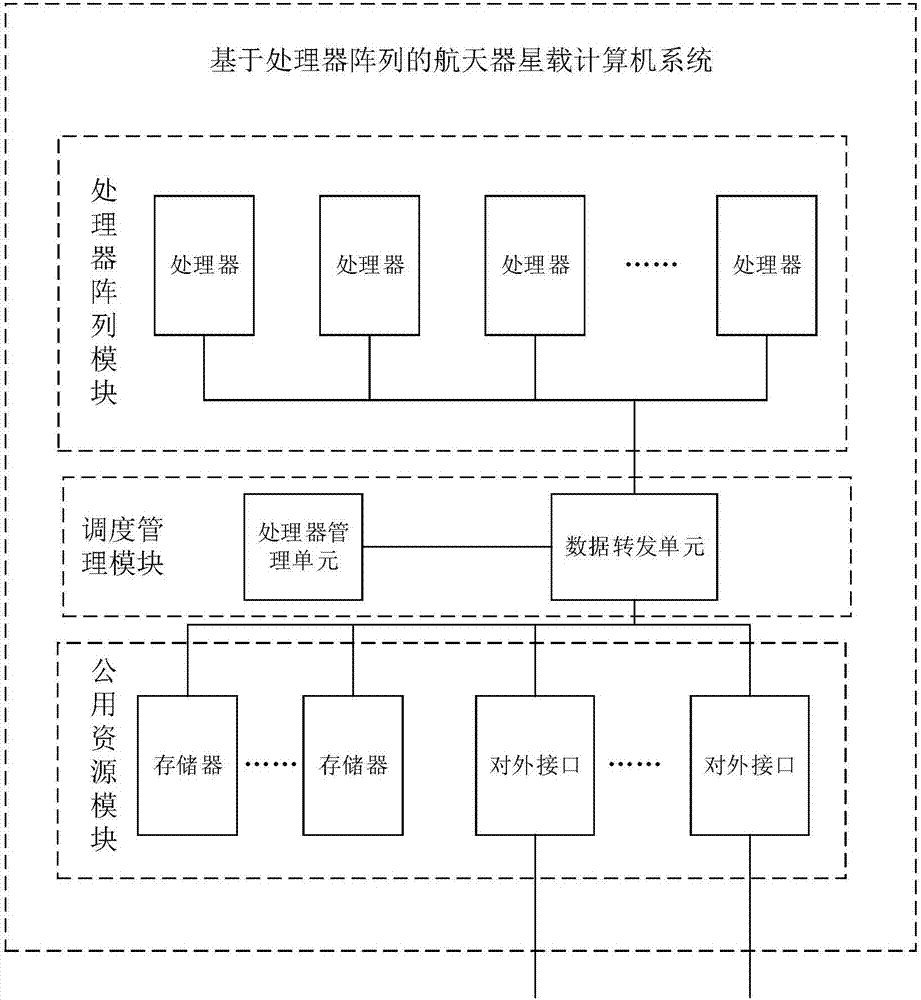
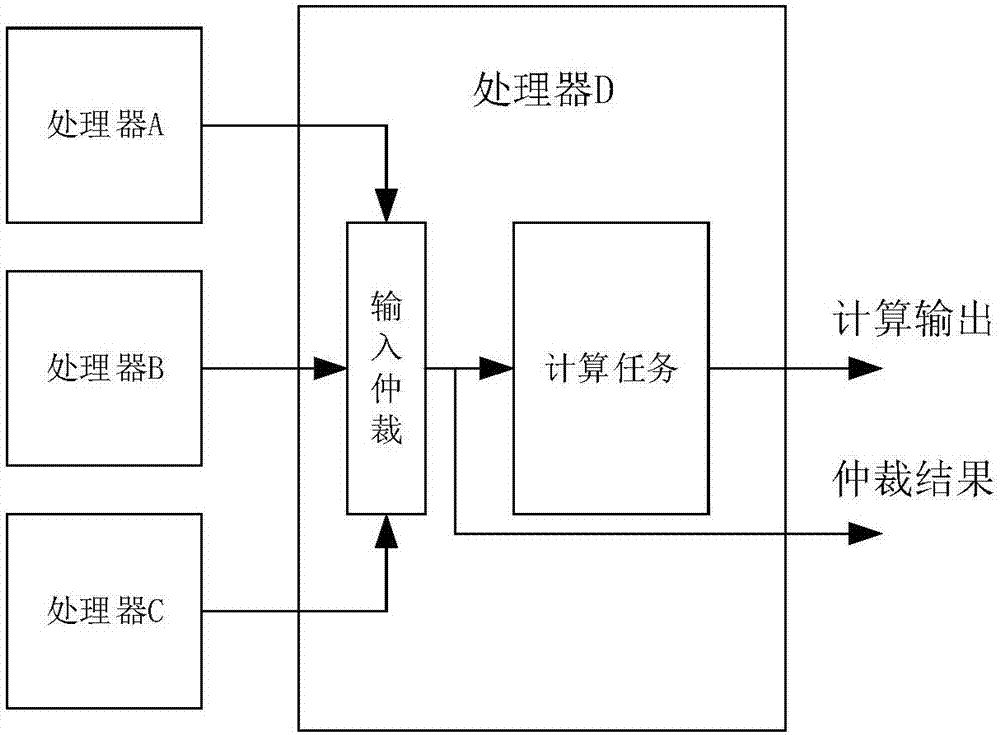
Processor array-based on-board computer system of spacecraft and fault processing method
ActiveCN106933692AImprove reliabilityGuaranteed operational reliabilityAssociative processorsFault response safety measuresComputer architectureOn board
The invention discloses a processor array-based on-board computer system of a spacecraft and a fault processing method, relates to a processor array-based on-board computer design method, and aims to solve the problems that the processing capability is poor, complex software cannot run and fault phenomena of running errors, resetting and the like often occur in the prior art. The processor array-based on-board computer system comprises a processor array module used for finishing on-board computing tasks, a public resource module used for providing data storage and external communication functions for the processor array module, and a scheduling management module used for providing a data interaction channel for the processor array module and the public resource module and identifying a fault processor in the processor array module. Through autonomous recovery of the fault processor, system operation continuity is ensured; and a plurality of processors are connected to form a processor array, thereby realizing further expansion of system computing capacity. The system and the method are used in the field of on-board computer design.
Owner:哈尔滨工大卫星技术有限公司
Processors, methods, and systems for debugging a configurable spatial accelerator
ActiveUS11086816B2Easy to adaptImprove performanceAssociative processorsDataflow computersComputer architectureData stream
Systems, methods, and apparatuses relating to debugging a configurable spatial accelerator are described. In one embodiment, a processor includes a plurality of processing elements and an interconnect network between the plurality of processing elements to receive an input of a dataflow graph comprising a plurality of nodes, wherein the dataflow graph is to be overlaid into the interconnect network and the plurality of processing elements with each node represented as a dataflow operator in the plurality of processing elements, and the plurality of processing elements are to perform an operation by a respective, incoming operand set arriving at each of the dataflow operators of the plurality of processing elements. At least a first of the plurality of processing elements is to enter a halted state in response to being represented as a first of the plurality of dataflow operators.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Processing system with interspersed processors DMA-FIFO
Embodiments of a multi-processor array are disclosed that may include a plurality of processors, local memories, configurable communication elements, and direct memory access (DMA) engines, and a DMA controller. Each processor may be coupled to one of the local memories, and the plurality of processors, local memories, and configurable communication elements may be coupled together in an interspersed arrangement. The DMA controller may be configured to control the operation of the plurality of DMA engines.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
Parallel control method and electronic device
ActiveCN109254795AEnsure safetyAssociative processorsConcurrent instruction executionOperational systemNetwork packet
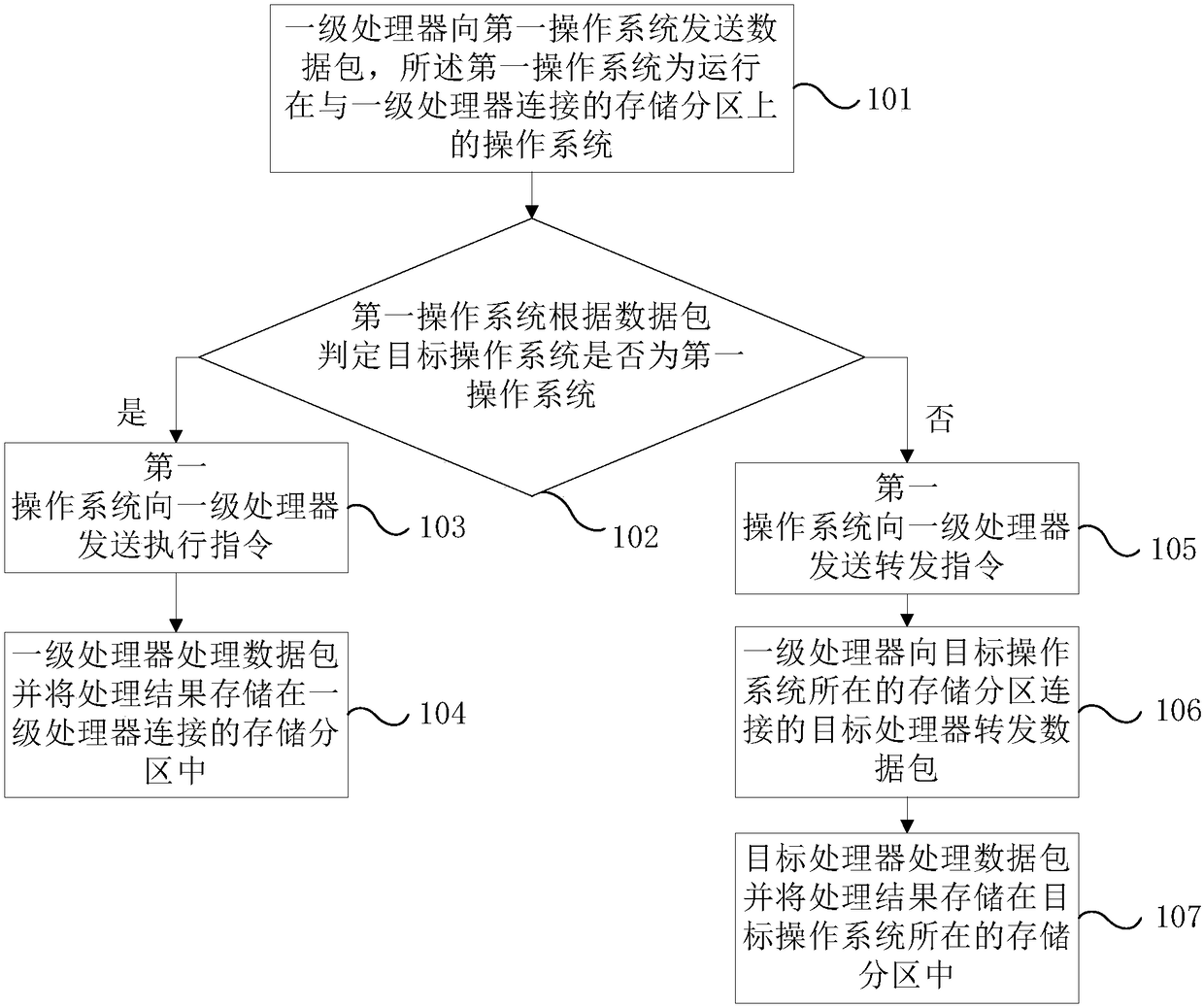
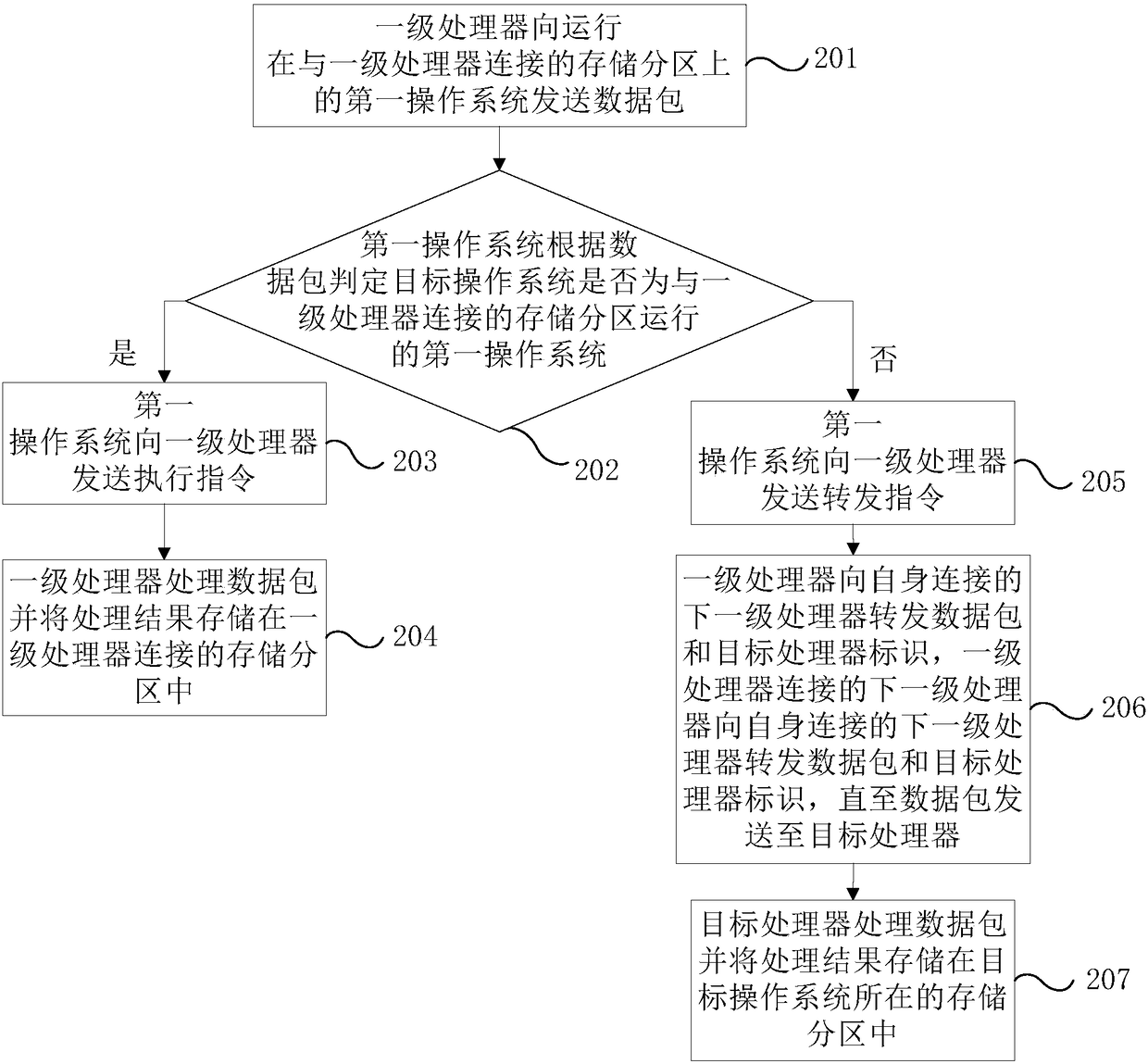
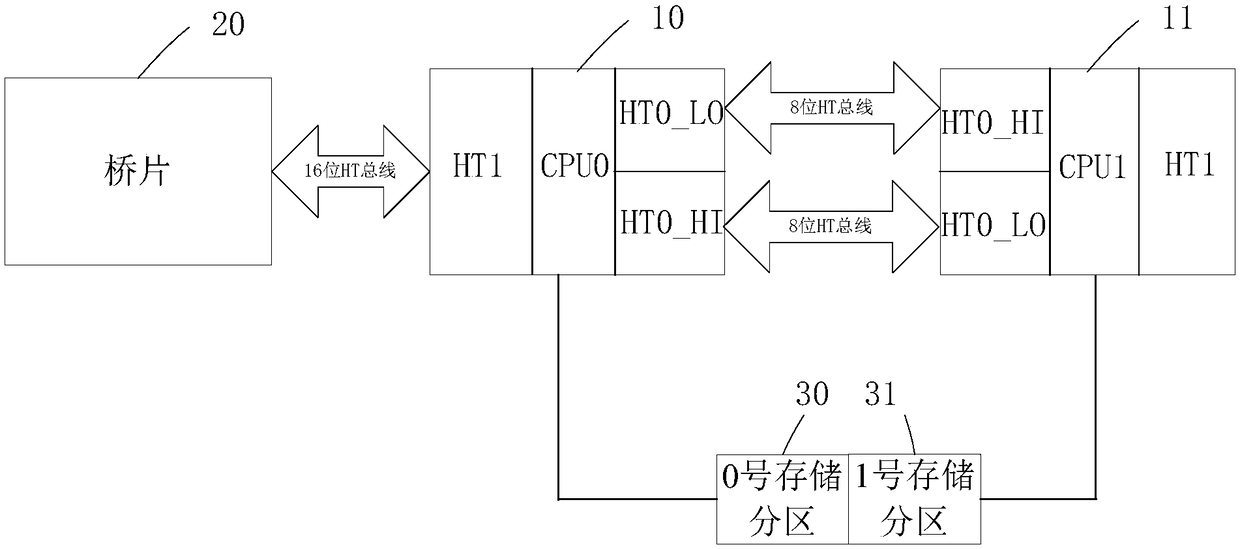
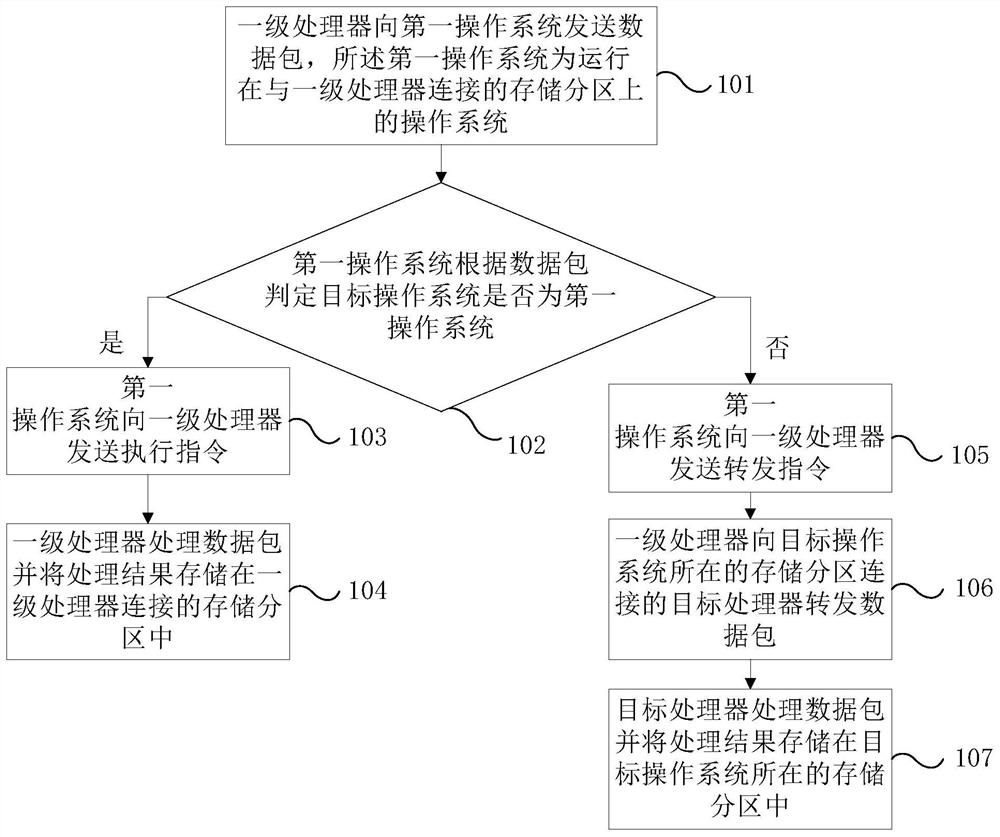
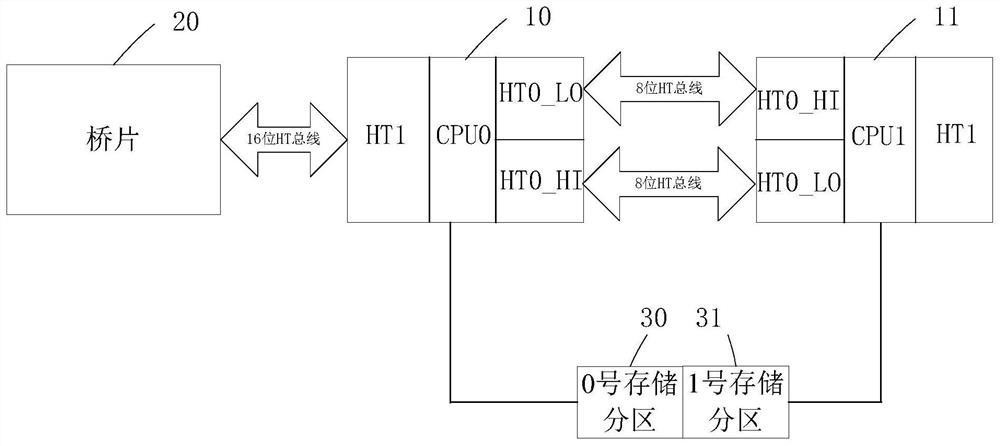
The invention provides a parallel control method and an electronic device.The electronic device compreses a memory, at least two annularly interconnect processors, and at least one bridge, the at least two processor includes at least one primary processor connected with a bridge, the memory includes several storage partitions, each storage partition is connected to a processor, each storage partition runs an operating system, a primary processor receives a send execution instruction or a forward instruction determined by its respective first operating system according to the data packet, and stores the processing result in the storage partition connected with the primary processor according to the execution instruction processing data packet, forwards the data packet to the target processor corresponding to the target operating system according to the forwarding instruction, and the target processor processes the data packet and stores the processing result in the corresponding storagepartition, so that the hardware resources of each operating system on the single board card can be physically isolated and the data security can be improved.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
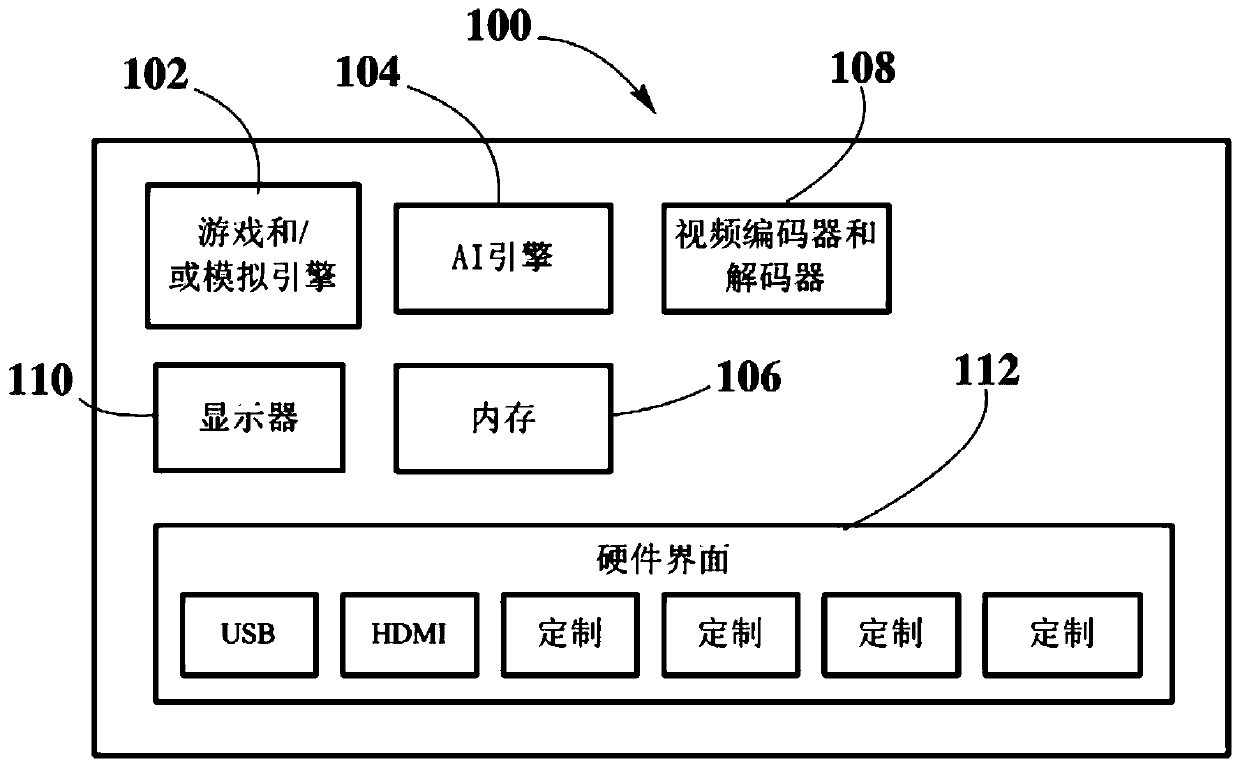
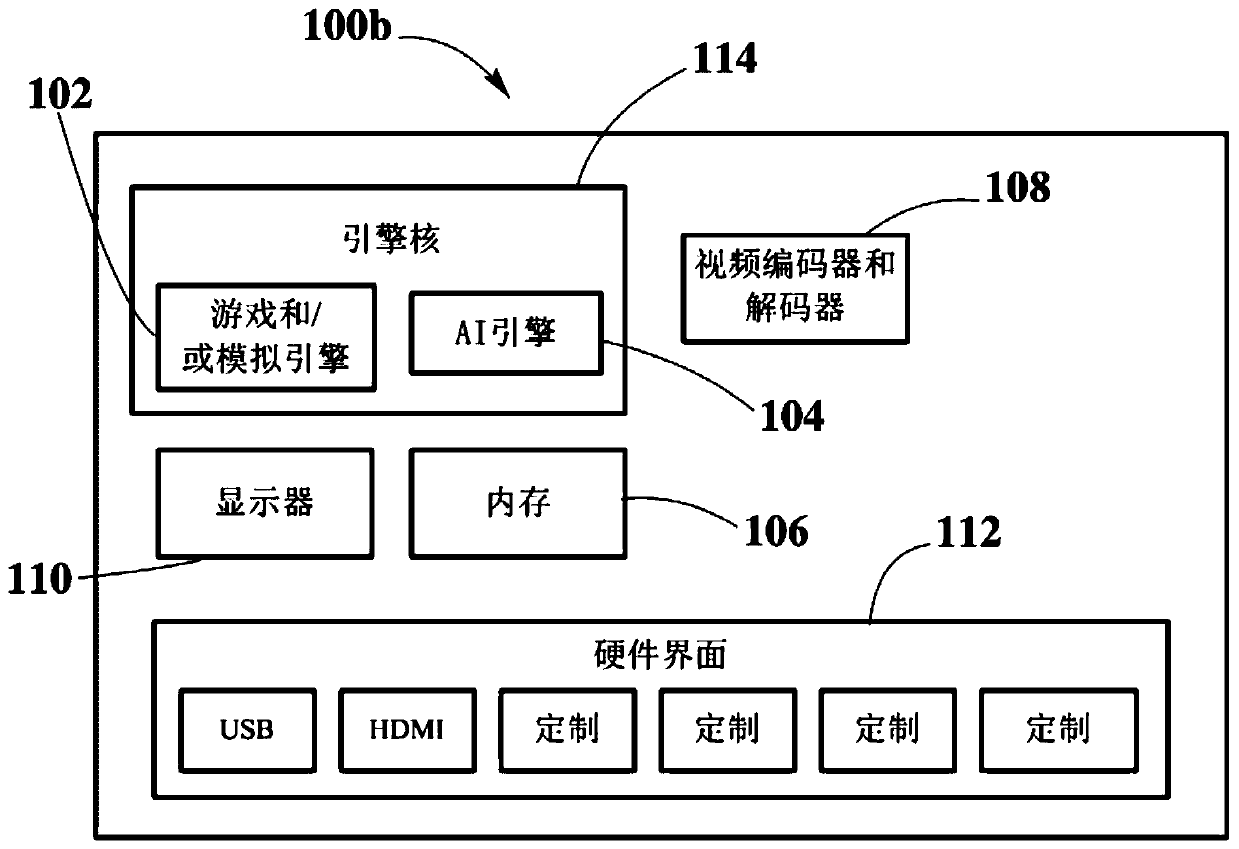
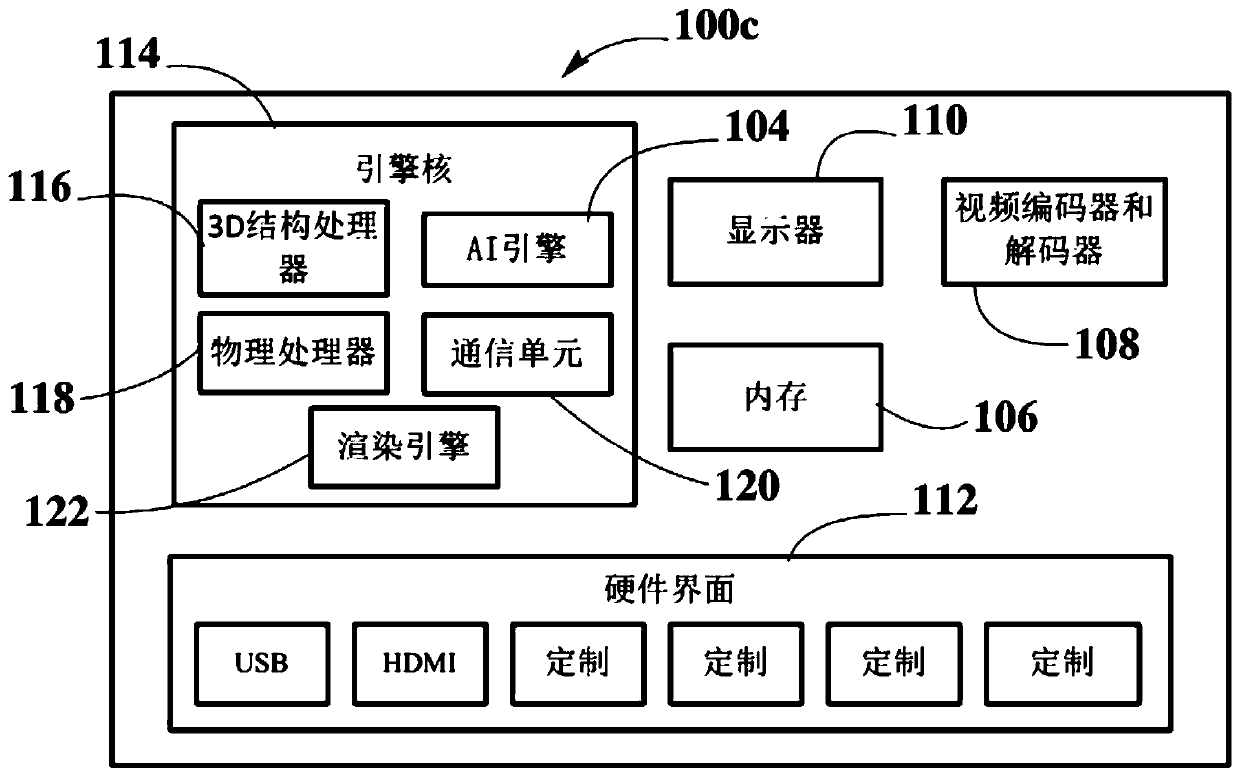
Game engine and artificial intelligence engine on a chip
PendingCN110275859AEasy to controlSimple interfaceAssociative processorsEnsemble learningData setProcessing core
An electronic chip, a chip assembly, a computing device, and a method are described. The electronic chip comprises a plurality of processing cores and at least one hardware interface coupled to at least one of the one or more processing cores. At least one processing core implements a game engine and / or a simulation engine and one or more processing cores implements an artificial intelligence engine, whereby implementations are on-chip implementations in hardware by dedicated electronic circuitry. The one or more game and / or simulation engines perform tasks on sensory data, generating data sets that are processed through machine learning algorithms by the hardwired artificial intelligence engine. The data sets processed by the hardwired artificial intelligence engine include at least contextual data and target data, wherein combining both data and processing by dedicated hardware results in enhanced machine learning processing.
Owner:THE CALANY HLDG SARL
Memory-based distributed processor architecture
ActiveUS20190340153A1Efficient effective processing speedAssociative processorsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory bankParallel computing
Distributed processors and methods for compiling code for execution by distributed processors are disclosed. In one implementation, a distributed processor may include a substrate; a memory array disposed on the substrate; and a processing array disposed on the substrate. The memory array may include a plurality of discrete memory banks, and the processing array may include a plurality of processor subunits, each one of the processor subunits being associated with a corresponding, dedicated one of the plurality of discrete memory banks. The distributed processor may further include a first plurality of buses, each connecting one of the plurality of processor subunits to its corresponding, dedicated memory bank, and a second plurality of buses, each connecting one of the plurality of processor subunits to another of the plurality of processor subunits.
Owner:NEUROBLADE LTD
Parallel control method and electronic device
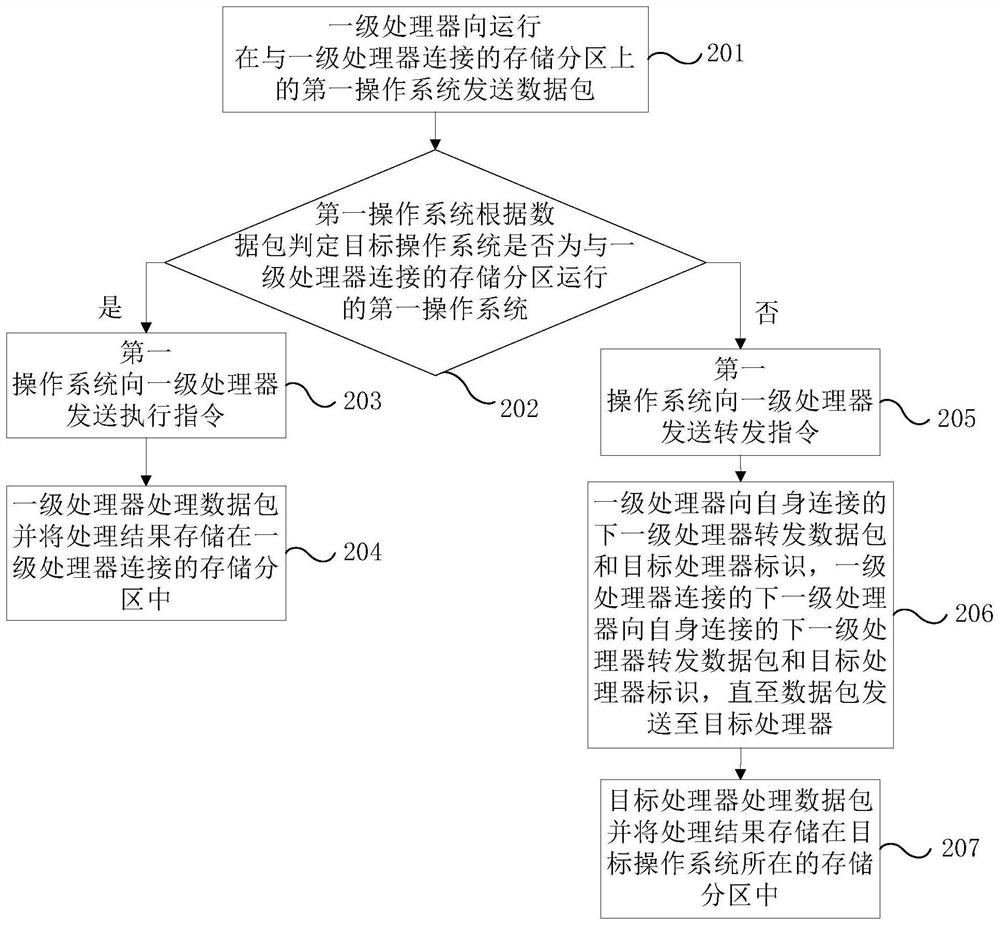
ActiveCN109254795BEnsure safetyAssociative processorsConcurrent instruction executionData packComputer architecture
In the parallel control method and electronic equipment provided by the present invention, by using memory, at least two ring interconnected processors, and at least one bridge chip, the at least two processors include at least one first-level processor connected to the bridge chip, The memory includes a number of storage partitions, each of which is connected to a processor, and each storage partition runs an operating system, and the first-level processor receives the sending and executing instructions or forwarding instructions determined by its corresponding first operating system according to the data packet , and process the data packet according to the execution instruction, and store the processing result in the storage partition connected to the first-level processor, and forward the data packet to the target processor corresponding to the target operating system according to the forwarding instruction, and the target processor processes the data packet and will process the The results are stored in the corresponding storage partitions, so that the hardware resources of each operating system on the single board can be physically isolated to improve data security.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
A Hot Switching Method of Dual-mode Redundant Microprocessor
ActiveCN105630732BGood conditionImprove fault toleranceAssociative processorsFault responseFault toleranceDual mode
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Apparatus and method for dynamic control of microprocessor configuration
ActiveUS11301298B2Associative processorsProgram initiation/switchingPower controllerComputer architecture
An apparatus and method for intelligently scheduling threads across a plurality of logical processors. For example, one embodiment of a processor comprises: a plurality of cores to be allocated to form a first plurality of logical processors (LPs) to execute threads, wherein one or more logical processors (LPs) are to be associated with each core of the plurality of cores; scheduling guide circuitry to: monitor execution characteristics of the first plurality of LPs and the threads; generate a first plurality of LP rankings, each LP ranking including all or a subset of the plurality of LPs in a particular order; and store the first plurality of LP rankings in a memory to be provided to a scheduler, the scheduler to schedule the threads on the plurality of LPs using the first plurality of LP rankings; a power controller to execute power management code to perform power management operations including independently adjusting frequencies and / or voltages of one or more of the plurality of cores; wherein in response to a core configuration command to deactivate a first core of the plurality of cores, the power controller or privileged program code executed on the processor are to update the memory with an indication of deactivation of the first core, wherein responsive to the indication of deactivation of the first core, the scheduler is to modify the scheduling of the threads.
Owner:INTEL CORP
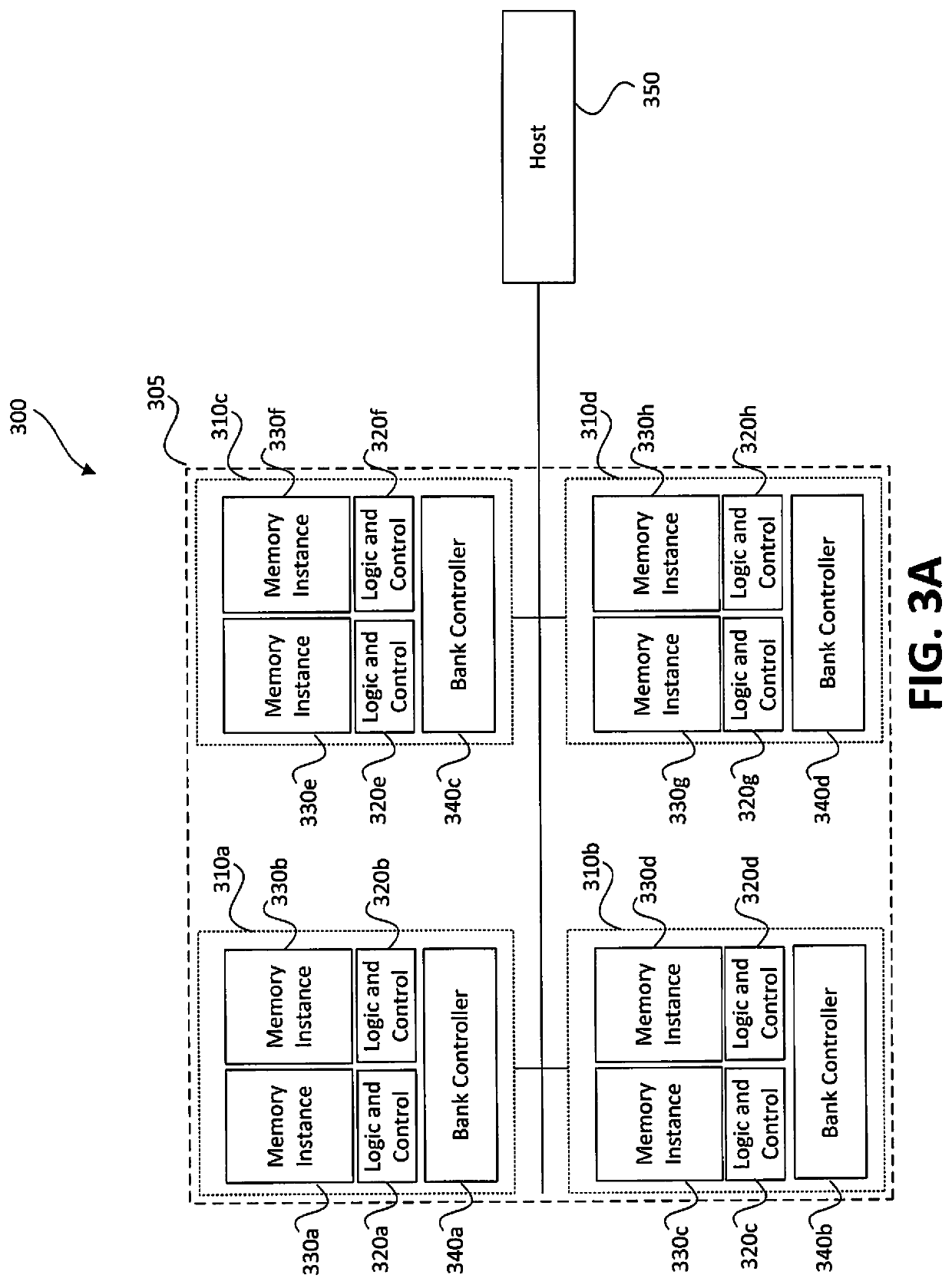
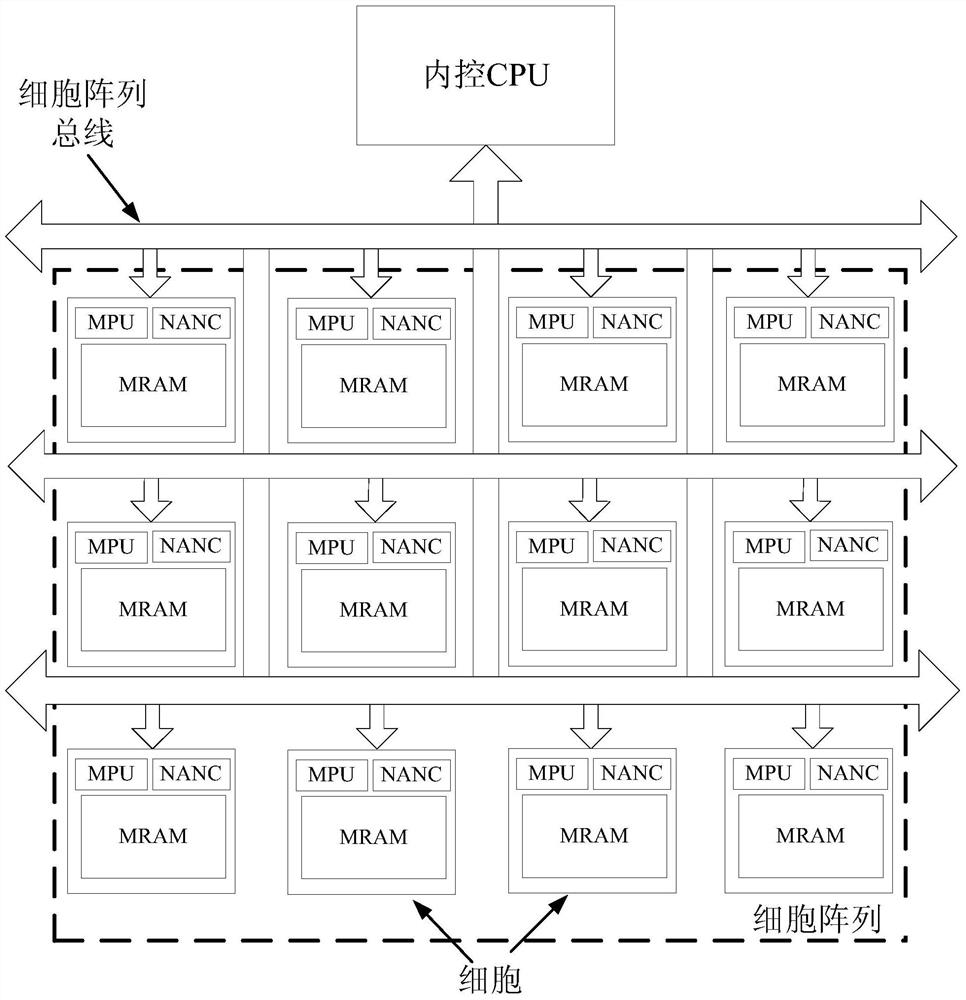
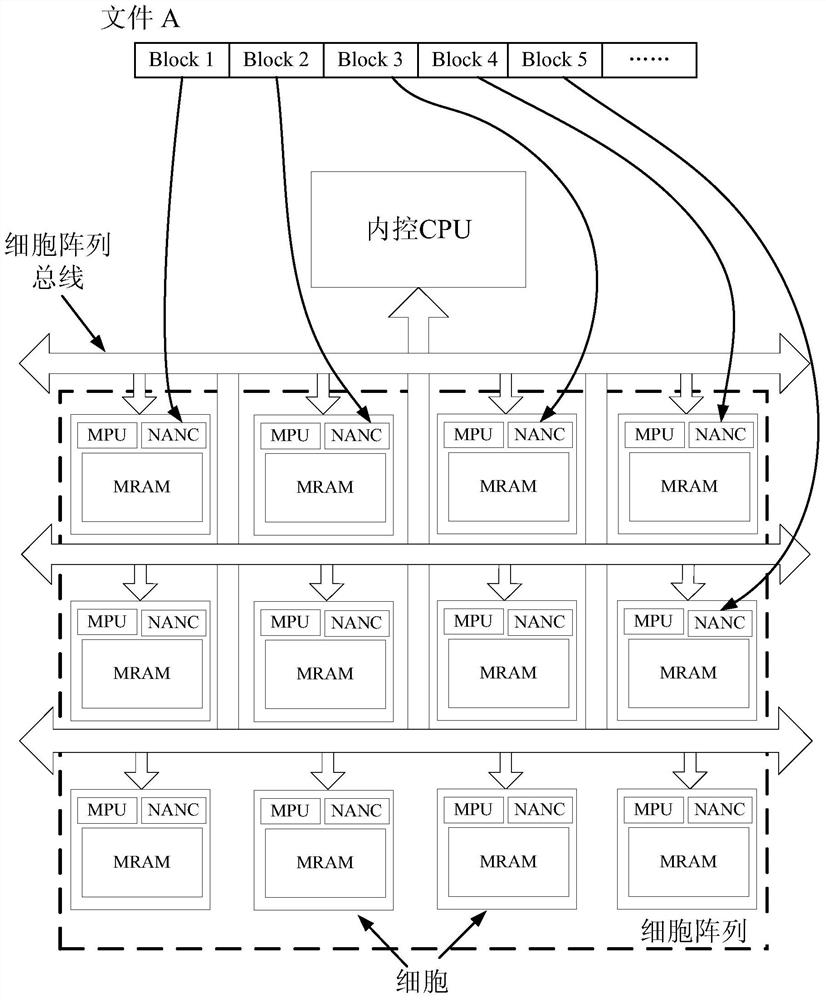
Cell Array Computing System
ActiveCN107291209BAvoid communication bottlenecksProcessing speedAssociative processorsSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsInternal memoryTerm memory
A cell array calculation system comprises an internal control CPU (Central Processing Unit), a cell array, a cell array bus, a bus controller, an external interface, a storage interface and at least one nonvolatile memory which adopts integrated reading and writing, wherein the cell array is a two-dimensional or three-dimensional array formed by more than one cells with calculation and storage functions; each cell includes a microprocessor and the nonvolatile memory; each cell stores a respective position in the cell array as an ID (Identity) so as to be read by software or hardware in the cell; the internal control CPU controls the storage interface, manages storage data and communicates with each cell in the cell array through the cell array bus, and distributes resources in the cell to complete a calculation task; the bus controller coordinates the control power of each main apparatus for the cell array bus. According to the cell array calculation system, communication bottlenecks among the CPU, an internal memory and storage can be overcome, the power consumption of a calculation system is greatly reduced, the processing speed is enhanced, the storage capability of large-scale data is expanded and the overall performance of the system is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI CIYU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
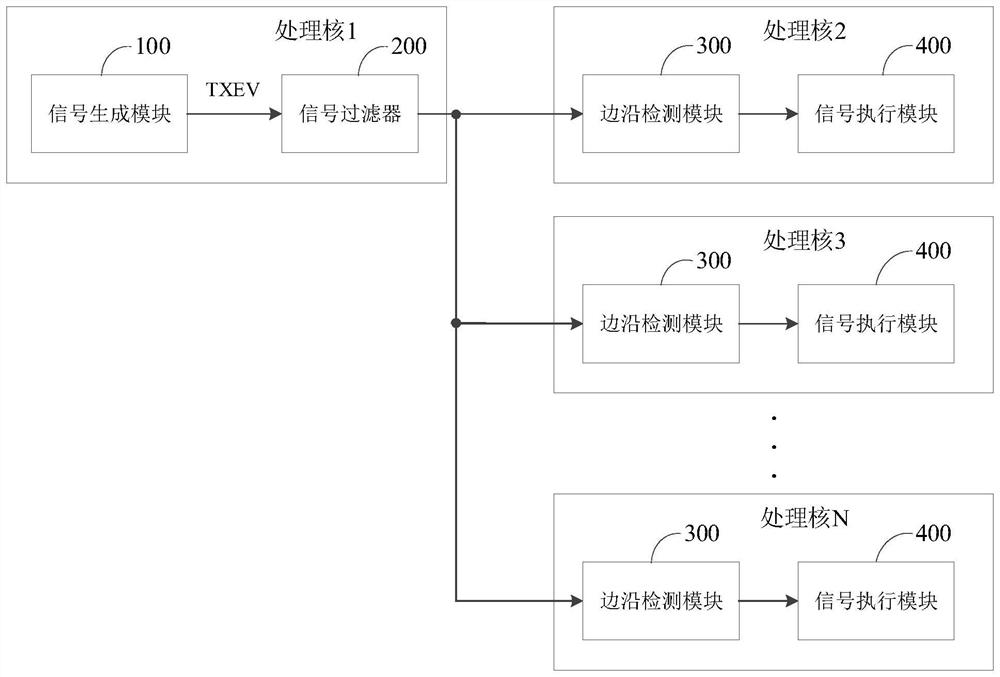
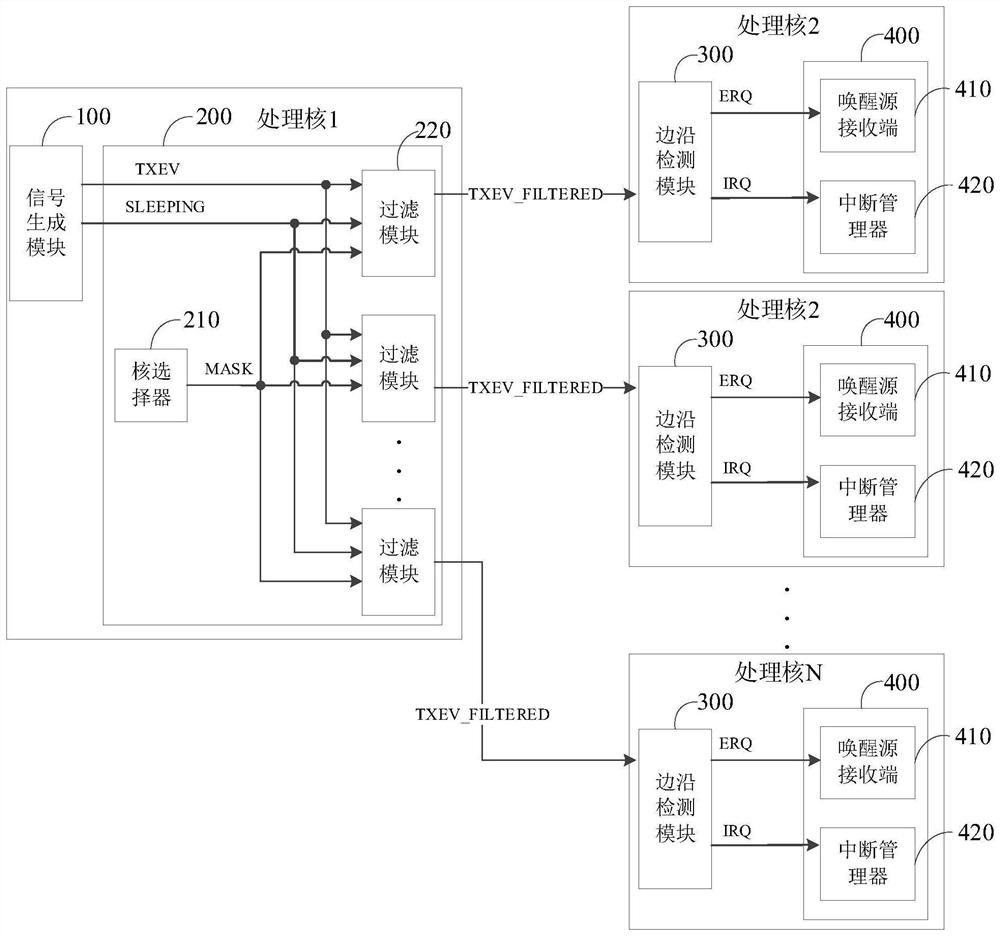
Multi-core microprocessor and control method thereof
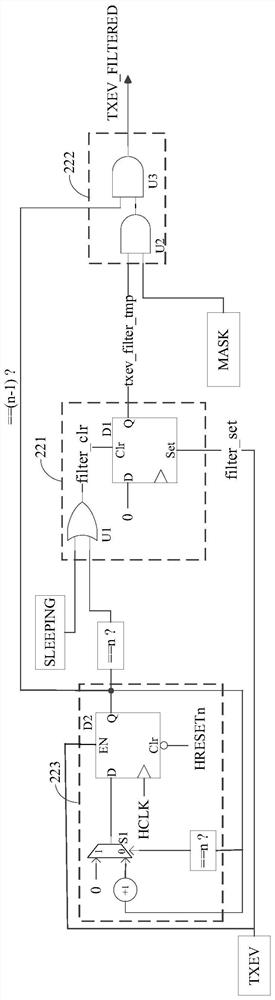
PendingCN114791897AAssociative processorsElectric digital data processingProcessing coreControl signal
The invention discloses a multi-core microprocessor and a control method thereof. The multi-core microprocessor comprises a plurality of processing cores, each processing core comprises a signal generation module, a signal filter, an edge detection module and a signal execution module, the signal filter is electrically connected with the edge detection modules of the other processing cores, the signal filter is configured to filter an initial control signal through a preset logic operation, and the signal execution module is configured to execute the filtering operation; the control signal set comprises at least one effective control signal and at least one invalid control signal. According to the method and the device, the technical problem that interruption false triggering or false awakening of other cores is easily caused due to lack of a corresponding filtering mechanism for a control signal sent by a certain processing core during control among a plurality of processing cores in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN HANGSHUN CHIP TECH DEV CO LTD
Parallel Acceleration Method and System in Heterogeneous Computing
ActiveCN106776014BProcessing speedReduce bandwidth requirementsAssociative processorsResource allocationComputational scienceConcurrent computation
The invention discloses a parallel accelerating method and system in heterogeneous computation. The method comprises the following steps: determining a topological structure of data transmission between GPUs (Graphics Processing Unit) in advance according to the quantity of the GPUs; acquiring a current task by each GPU in the topological structure and computing data in the current task, so as to obtain a calculating result corresponding to the current task; sharing the calculating result which is obtained by each GPU and corresponds to the current task to the other GPUs in the topological structure; after obtaining the calculating results of the other GPUs in the topological structure by each GPU, starting to execute the next task. By adopting the parallel accelerating method and system in the heterogeneous computation, the parallel computation capability of the GPUs can be improved and the bandwidth requirements on nodes of each GPU are reduced.
Owner:安徽智慧皆成数字技术有限公司
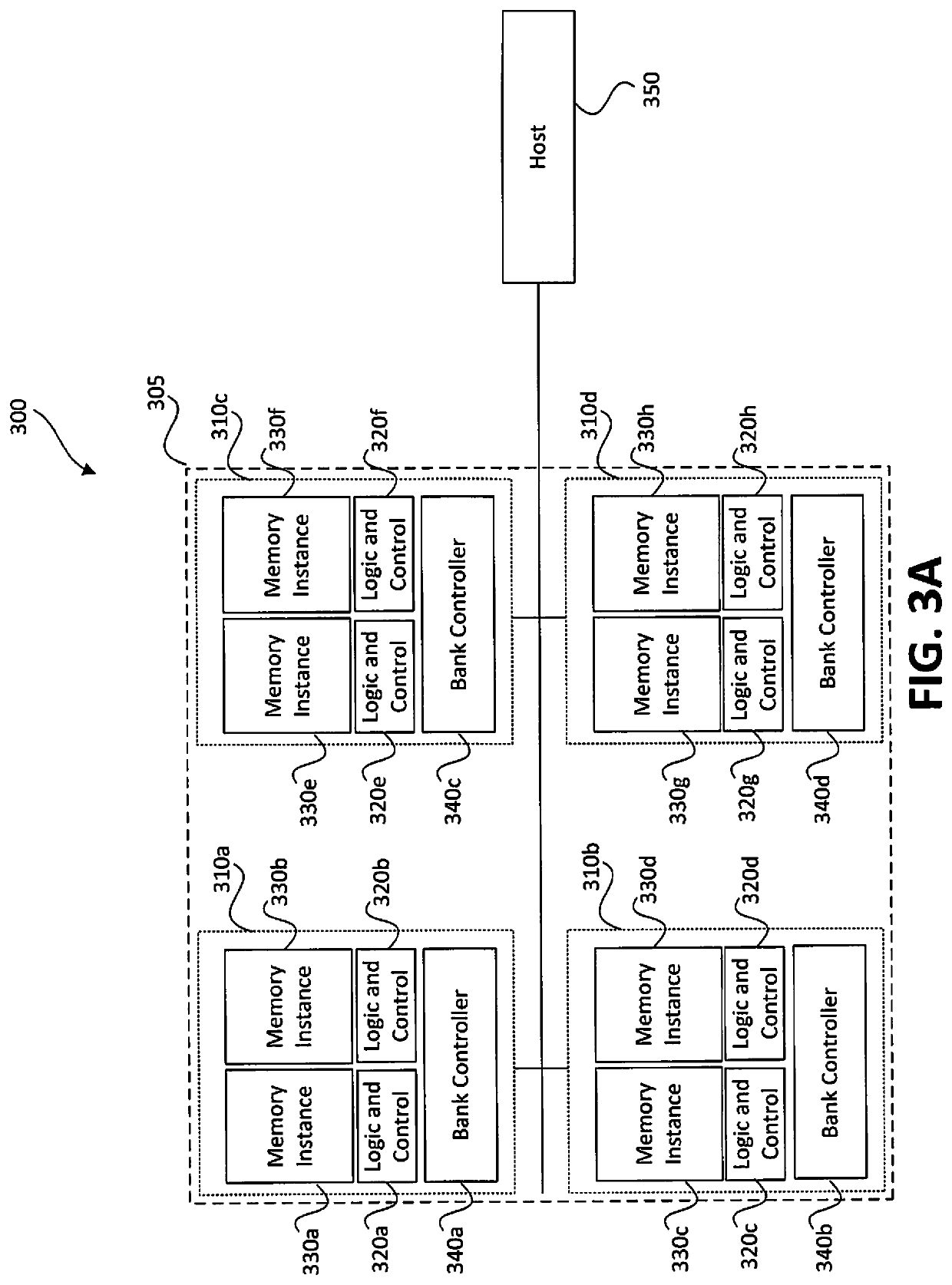
Scalable processing network for searching and adding in a content addressable memory
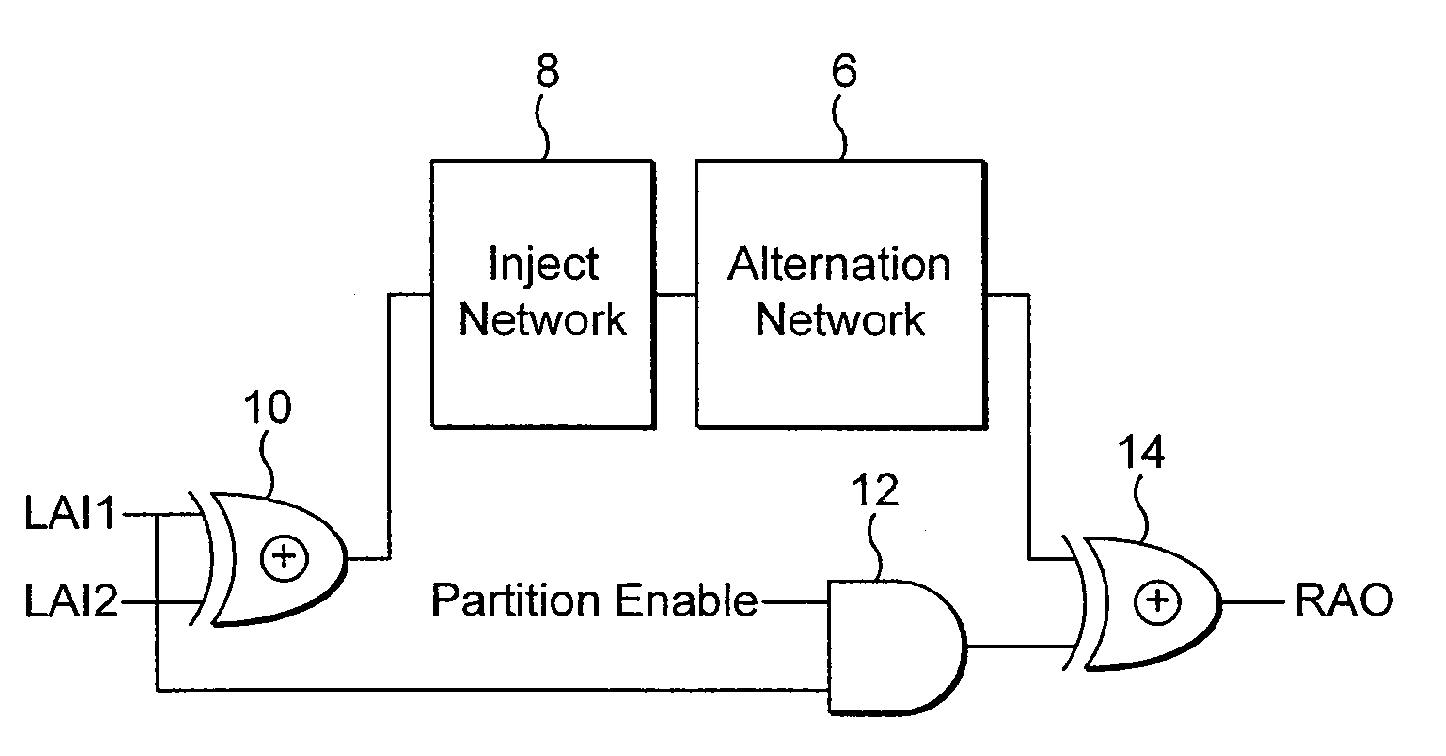
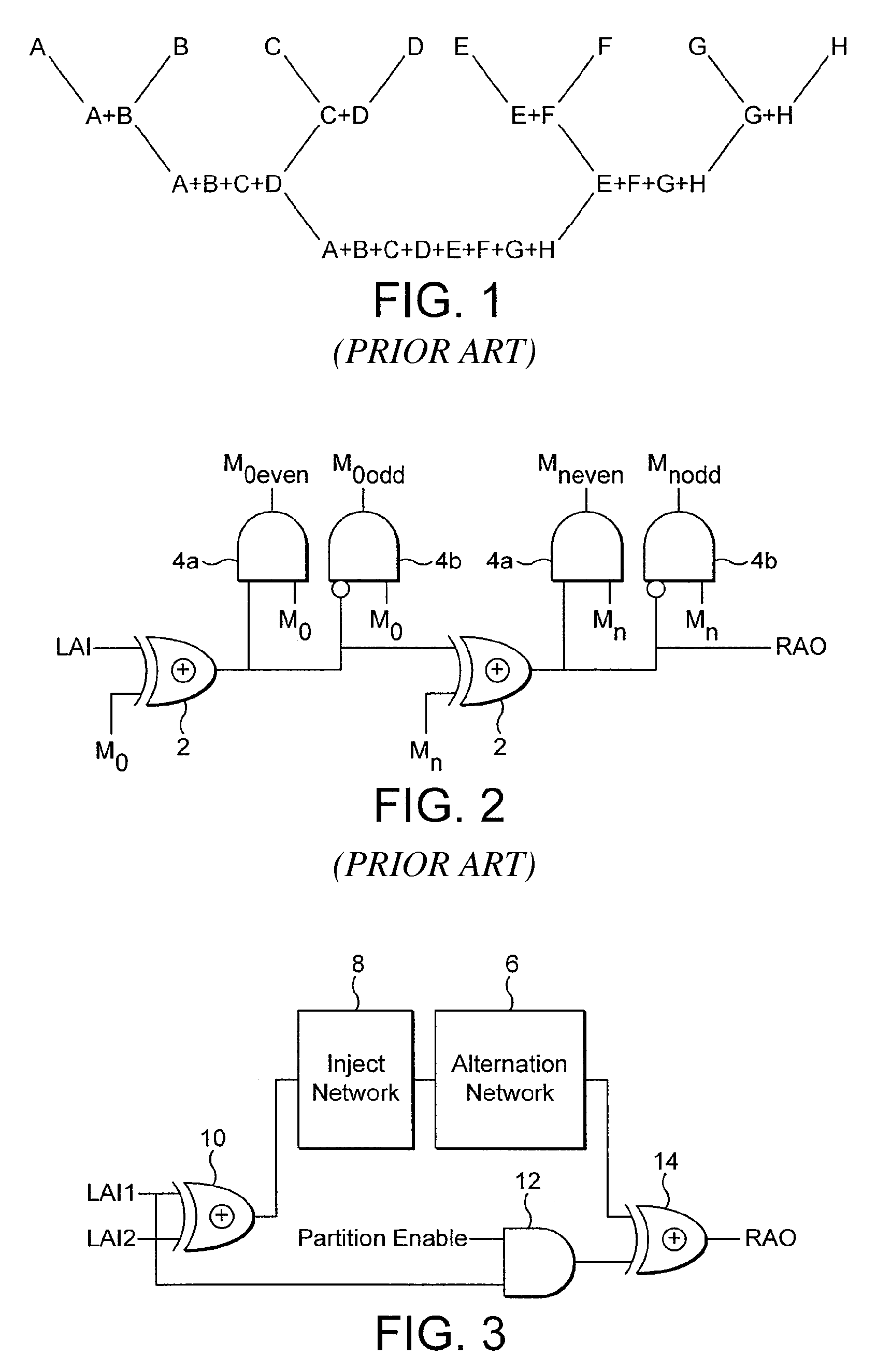
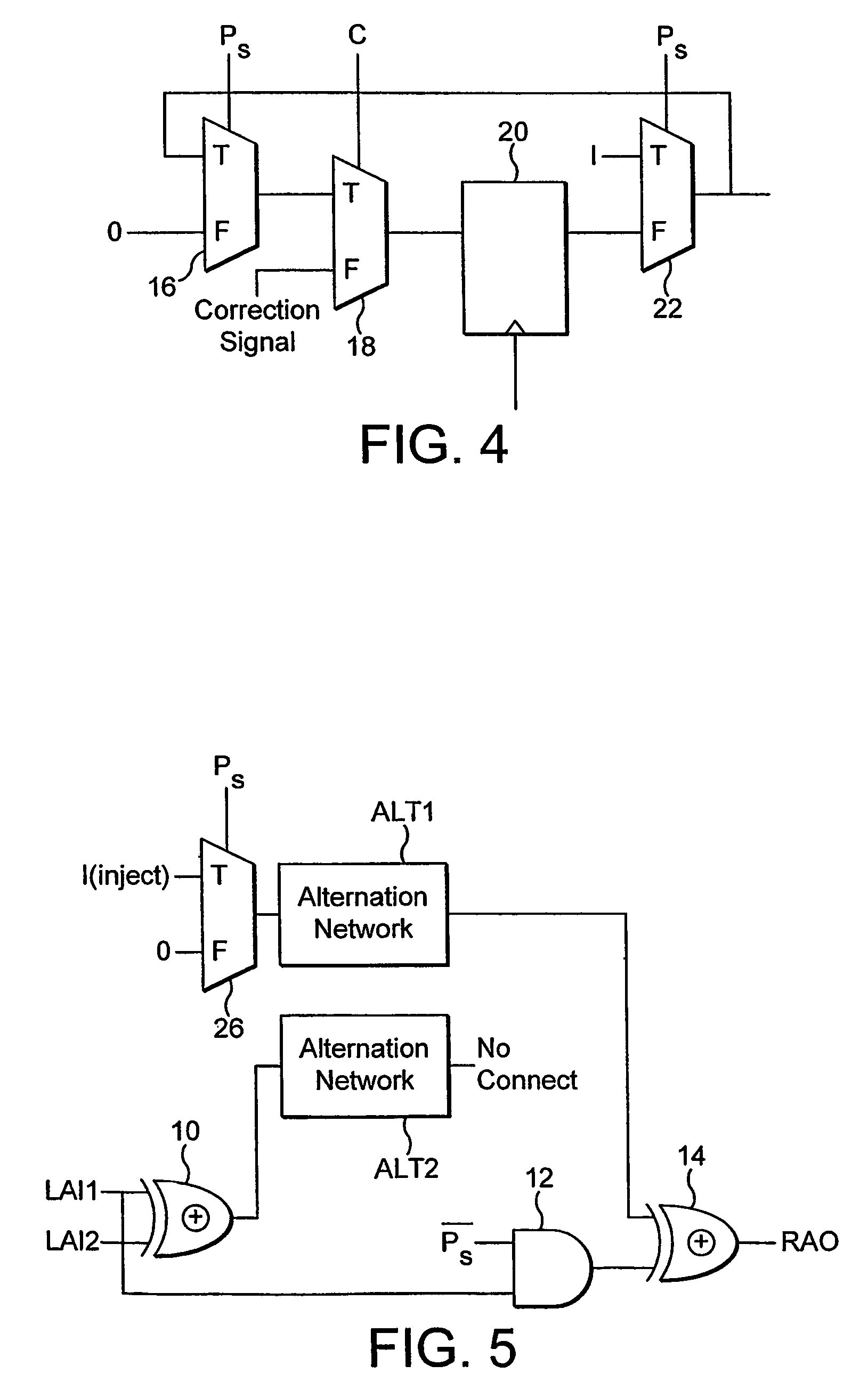
ActiveUS7865662B2Applied effectively and efficientlyEasy to useAssociative processorsMemory systemsDivide and conquer algorithmsParallel computing
An alternation network for use with a content addressable memory for implementing a divide and conquer algorithm is described. The alternation network comprises: a plurality of alternation modules connected in series together, each module comprising: a plurality of cascaded logic gates arranged to propagate a match parity signal via the gates along at least part of a matching result vector, the matching result vector being generated by execution of a matching instruction on the content addressable memory, and the logic gates being configured to change the parity of the match parity signal in accordance with the matching result vector; and a vector output arranged to output a parity level vector of the propagated match parity signal present at the each gate of the plurality of logic gates; a logic network for dividing the matching result vector into an odd match vector and an even match vector representing respectively odd and even numbered elements of the matching result vector, by use of the parity level vector, and means for writing a selected one of the odd and even match vectors to the content addressable memory.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
A kind of motherboard and server
ActiveCN107301151BImprove function scalabilityAssociative processorsDigital data protectionComputer architectureEngineering
The invention provides a motherboard and a server, the motherboard includes: a board body, a preset number of Purley platform CPUs and at least one memory; a preset number of Purley platform CPUs and at least one memory are respectively installed on the board body ; The preset number of Purley platform CPUs are connected in turn; each memory is connected to one of the preset number of Purley platform CPUs; each memory is used for receiving external input waiting When burning data, send the data to be burned to the connected Purley platform CPU; each Purley platform CPU is used to burn the data to be burned when receiving the data to be burned sent by the connected memory , to have functions corresponding to the data to be programmed. Therefore, the solution provided by the present invention can improve the function expandability of the motherboard.
Owner:SUZHOU METABRAIN INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
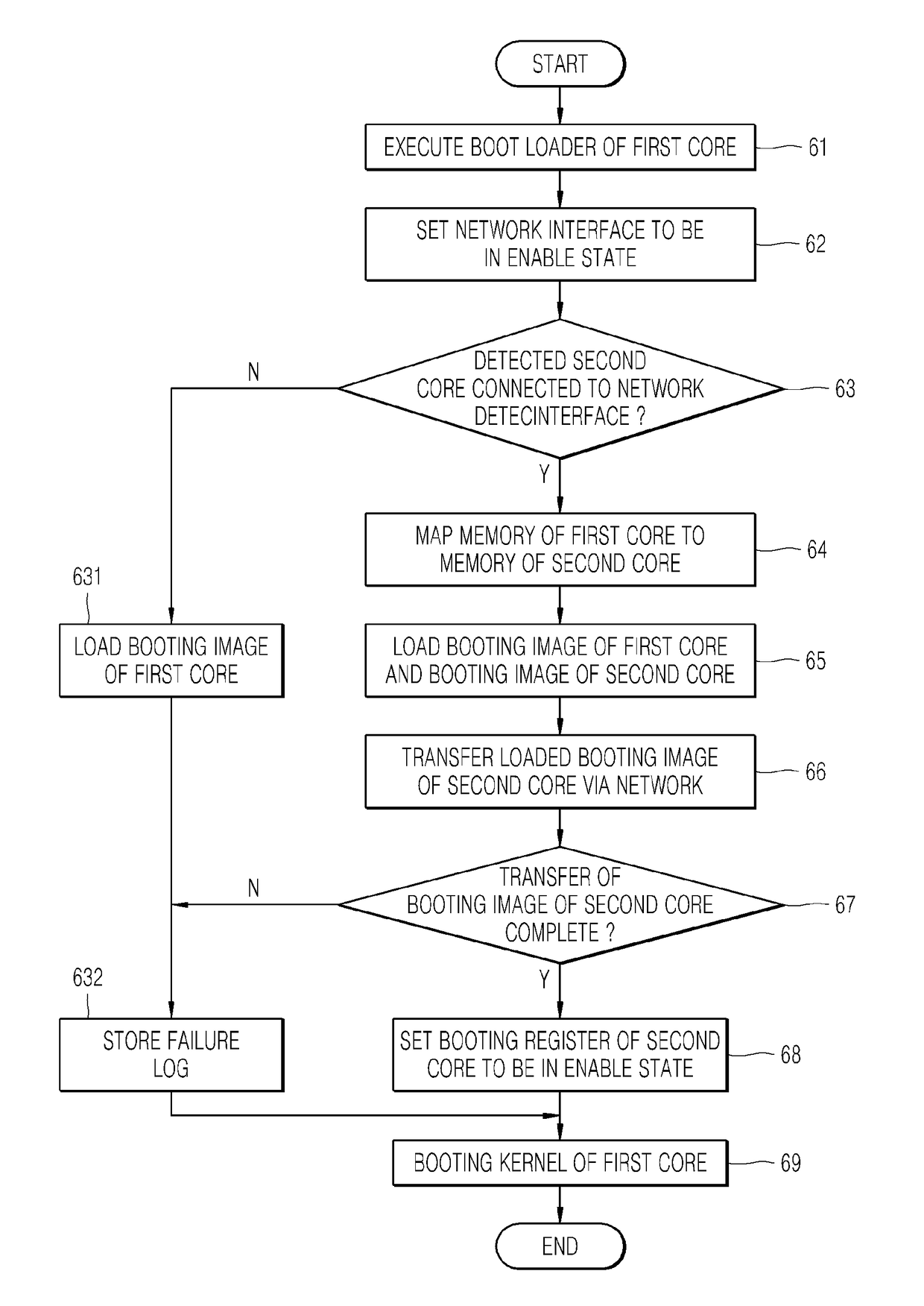
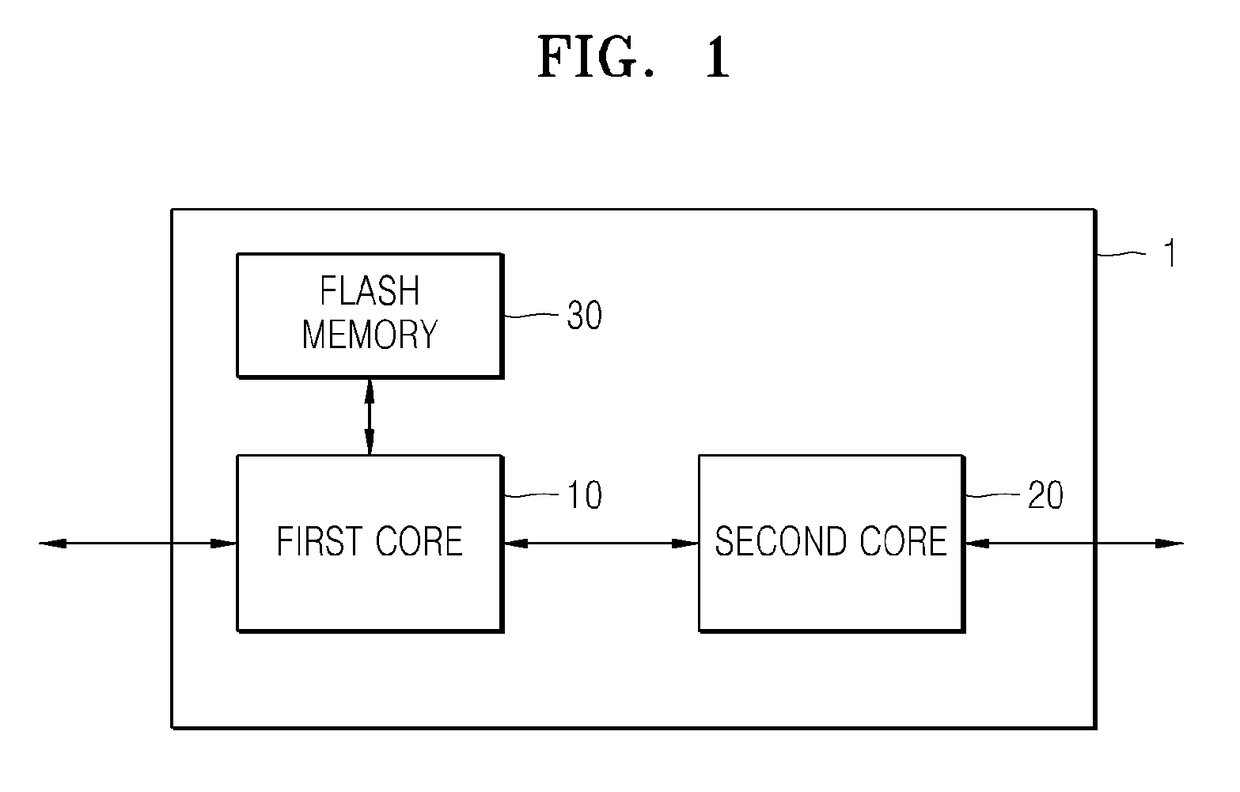
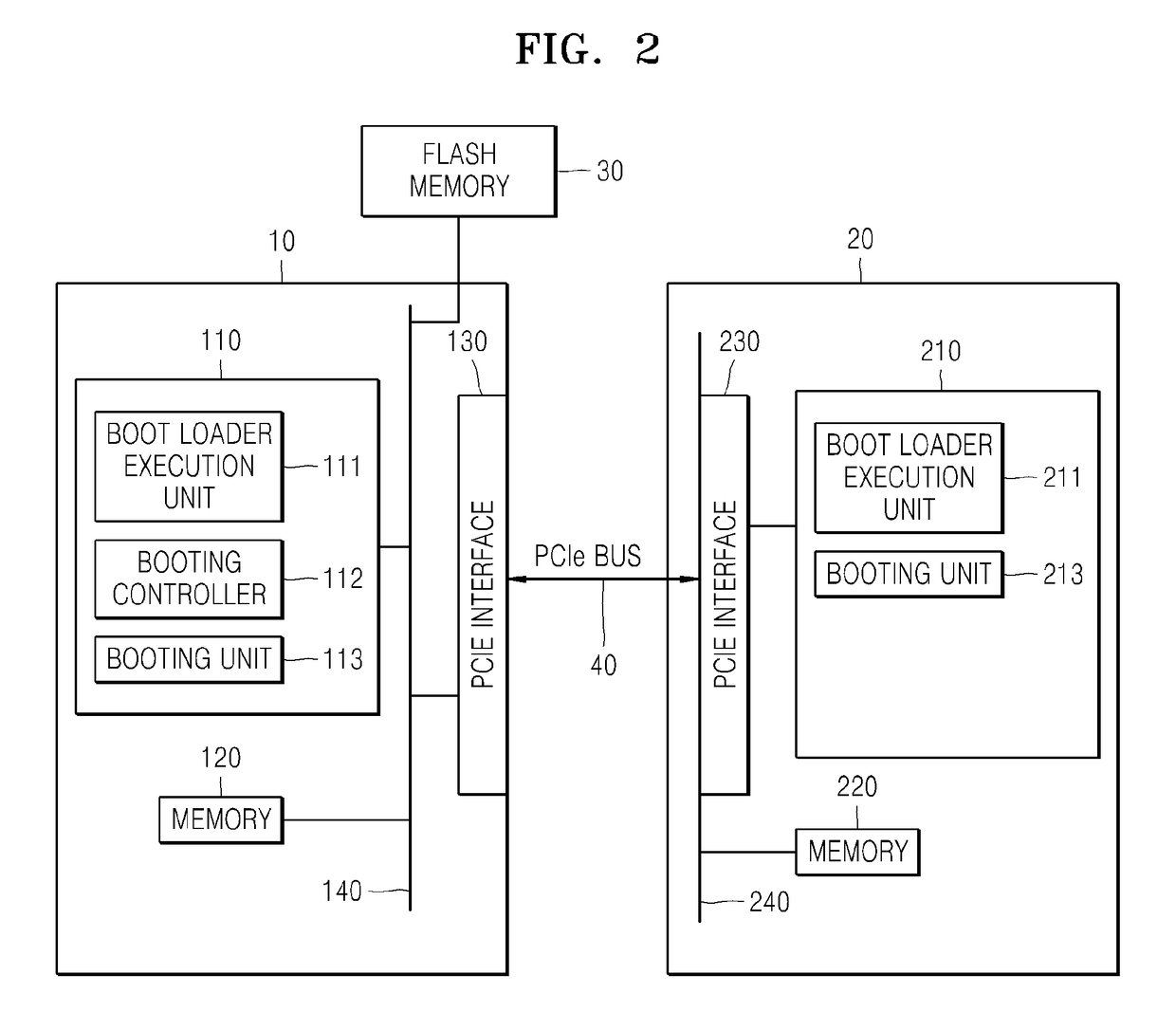
Multisystem and method of booting the same
A method of booting a multisystem including a first core and a second core, the method includes: executing a boot loader of the first core; setting a network interface of the first core to be in an enable state; detecting the second core that is connected to the network interface of the first core; mapping a first memory of the first core to a second memory of the second core; loading a booting image of the first core and a booting image of the second core on the first memory; and transferring the booting image of the second core loaded on the first memory to the second core via a network.
Owner:HANWHA VISION CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com