Patents
Literature
39results about "Demodulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
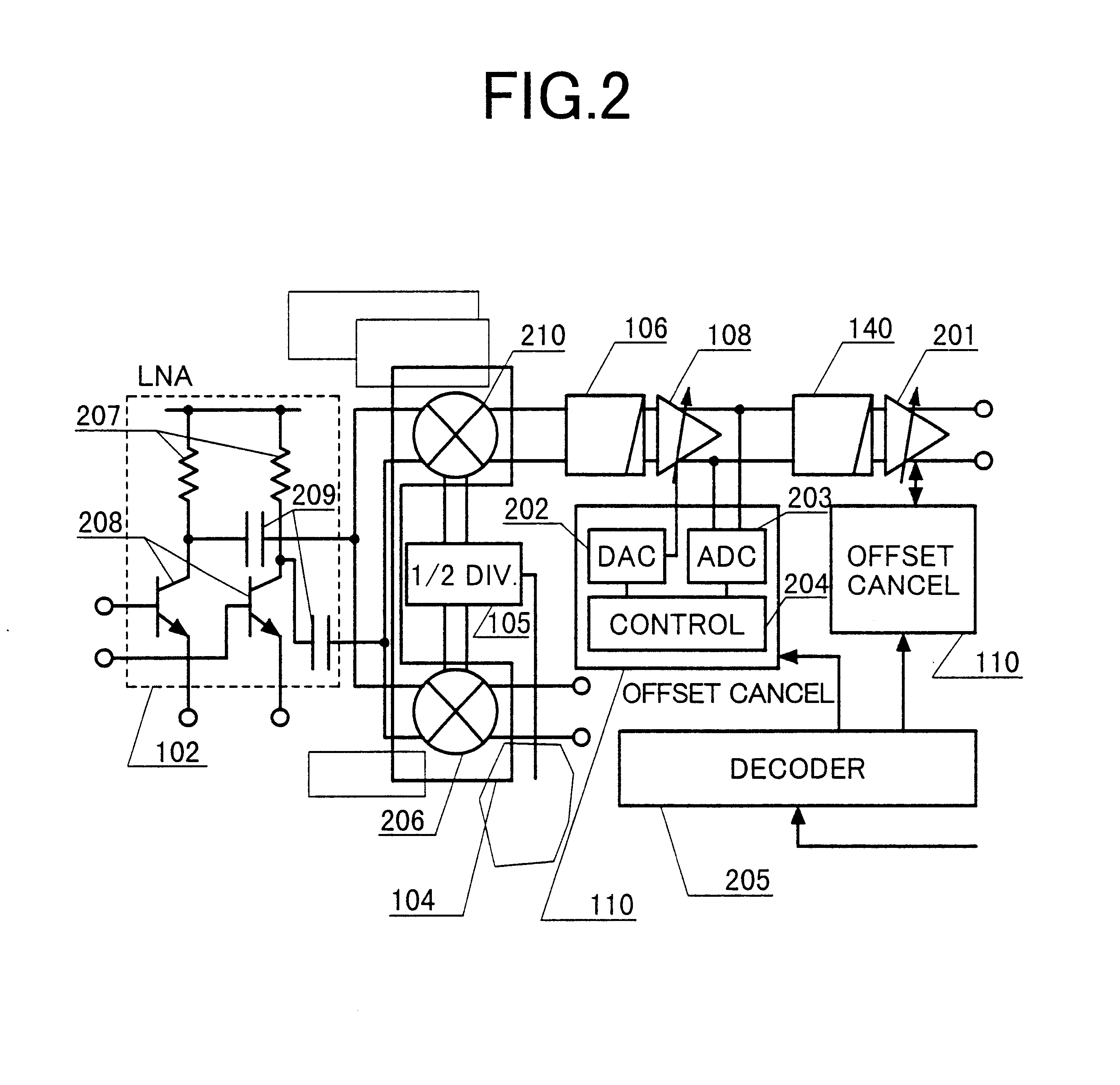
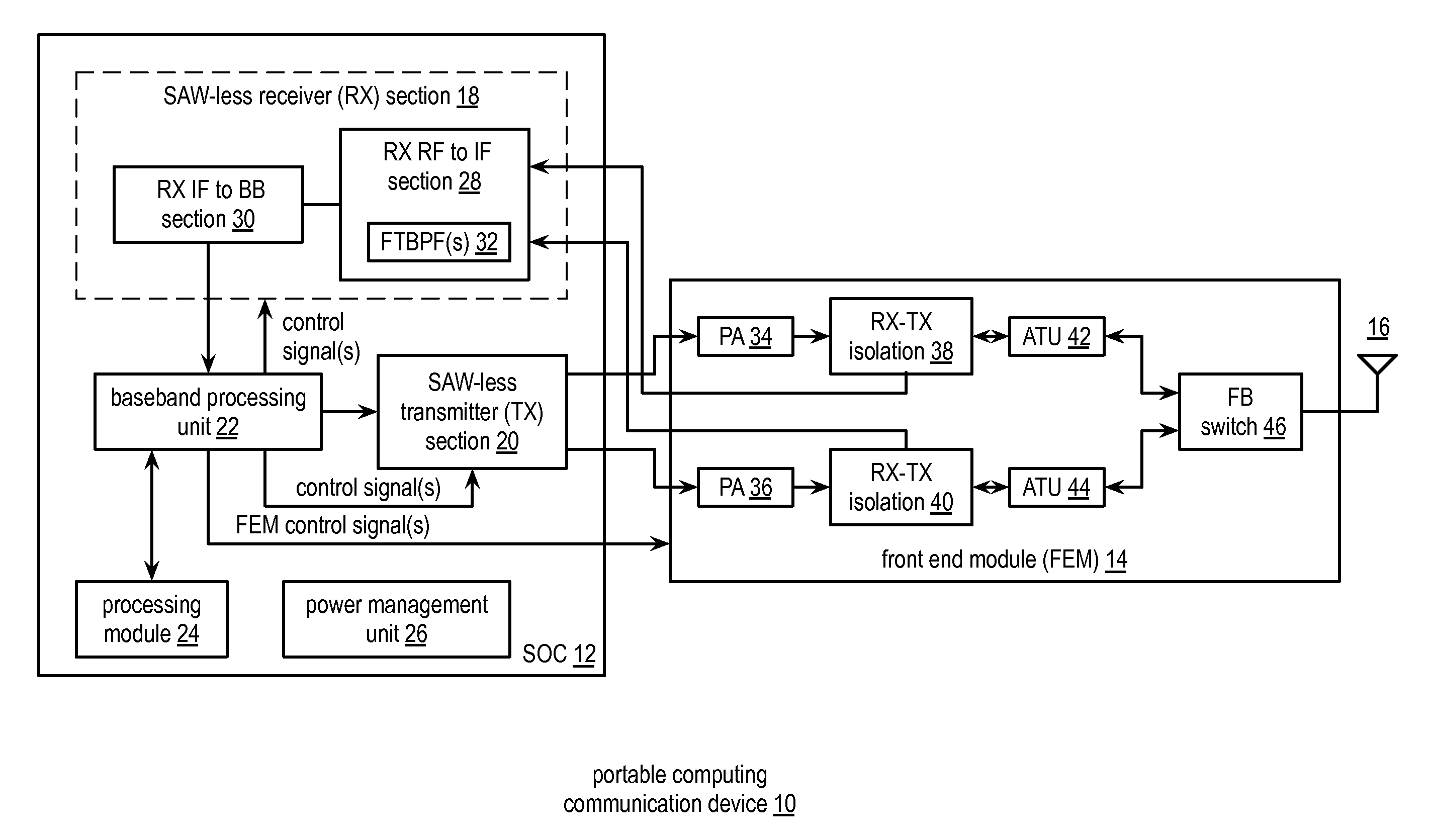
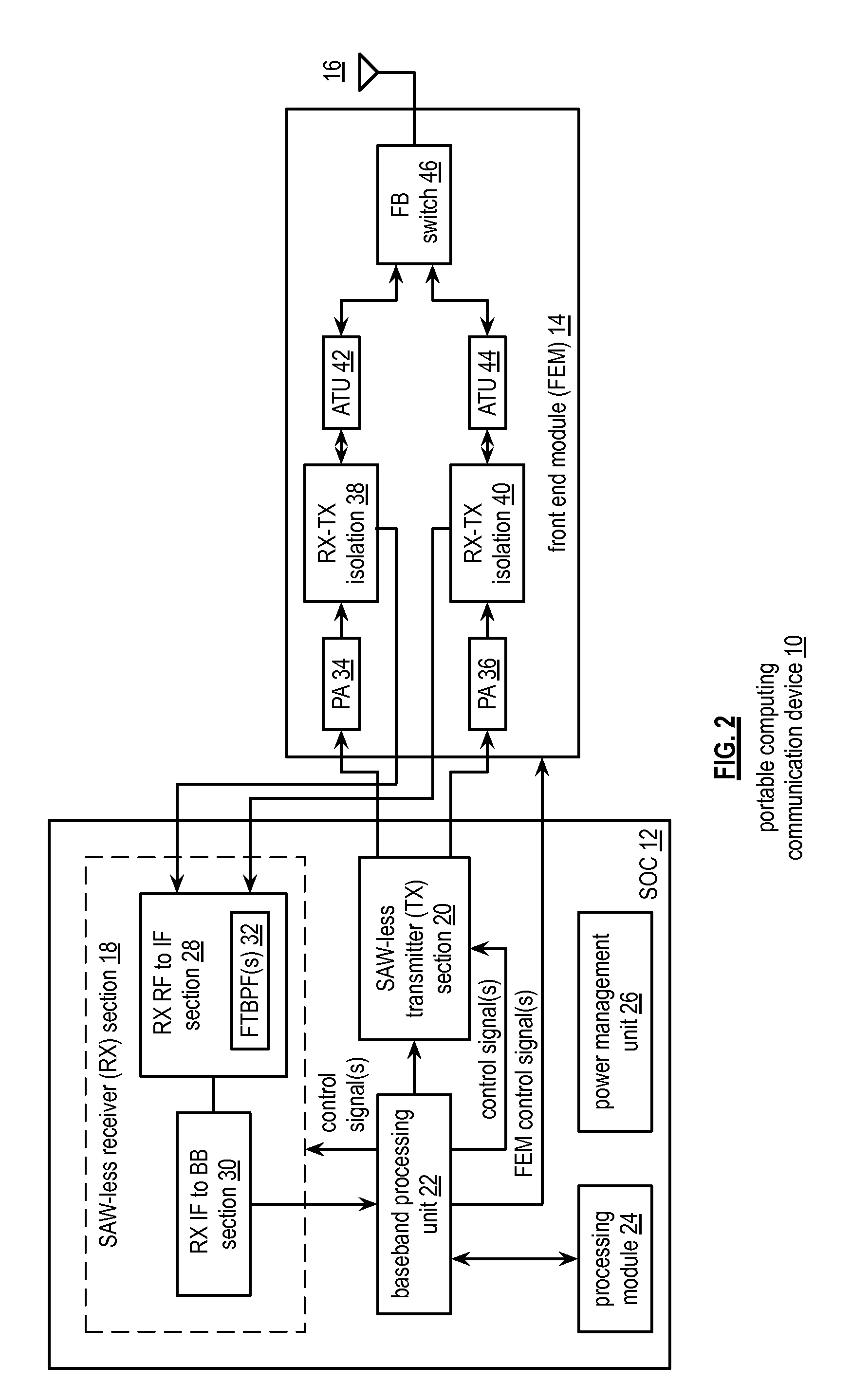
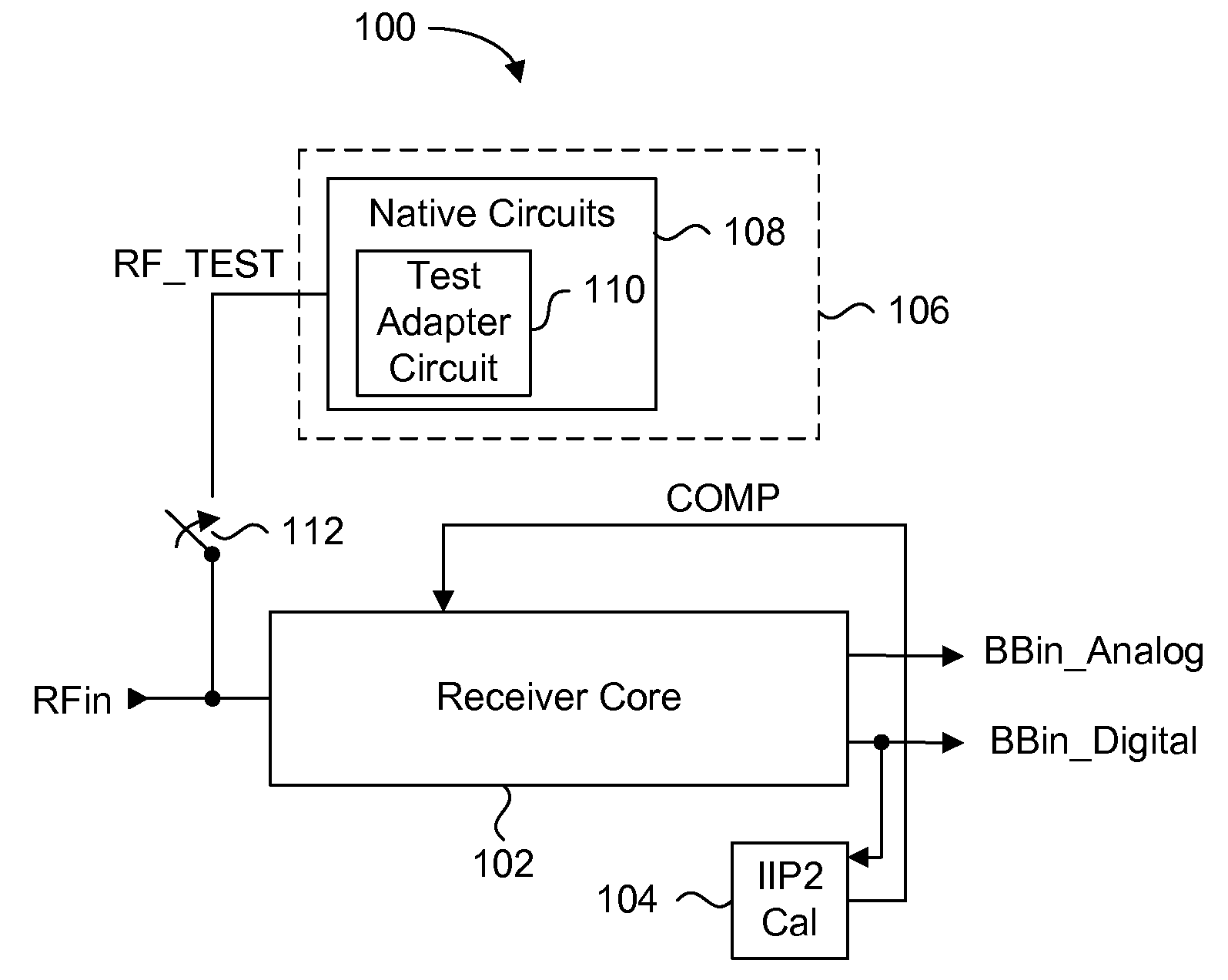
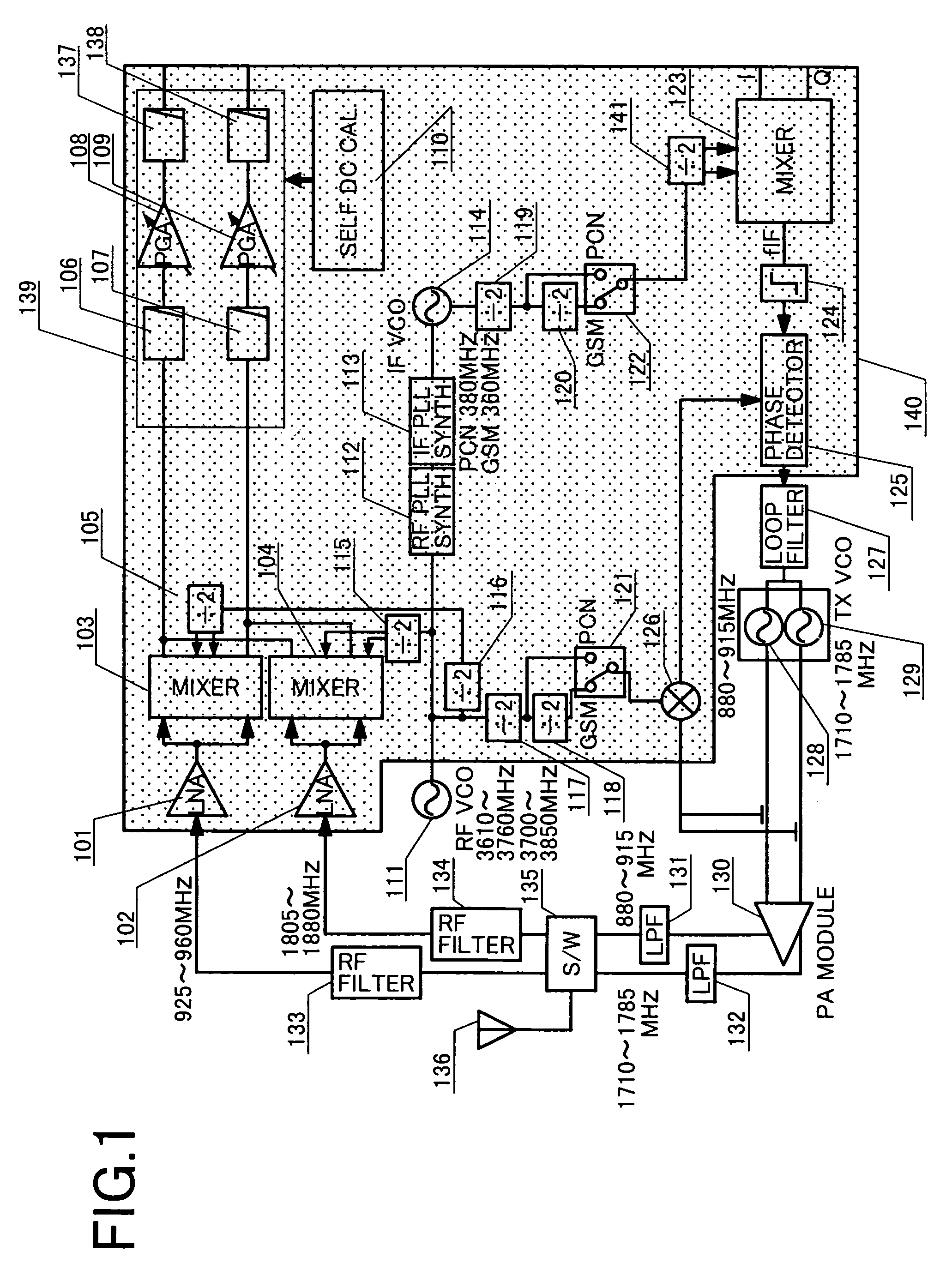
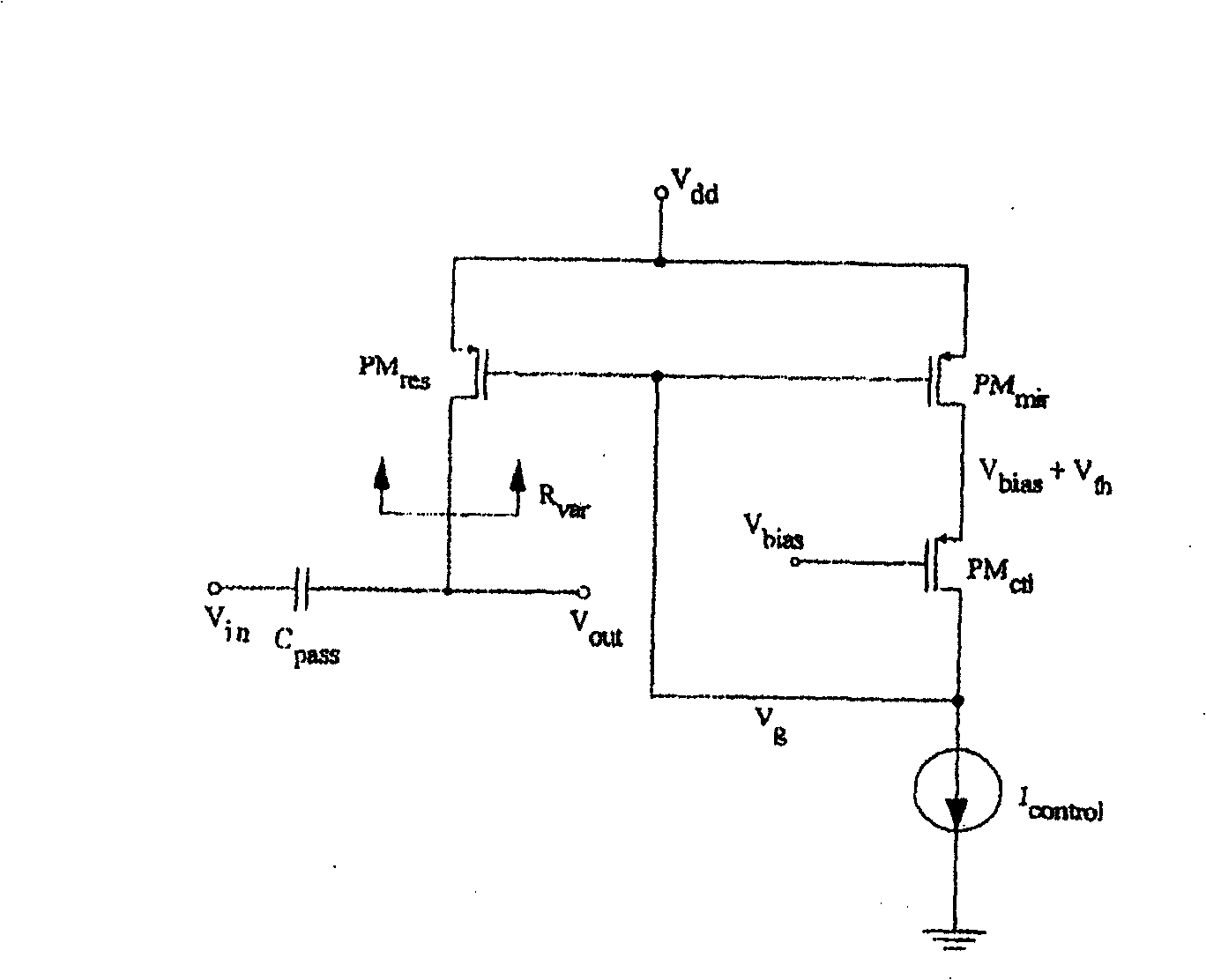
Automatic iip2 calibration architecture
ActiveUS20080182537A1Minimize circuit overheadEasing testing requirementReceivers monitoringDemodulationWireless transceiverEngineering
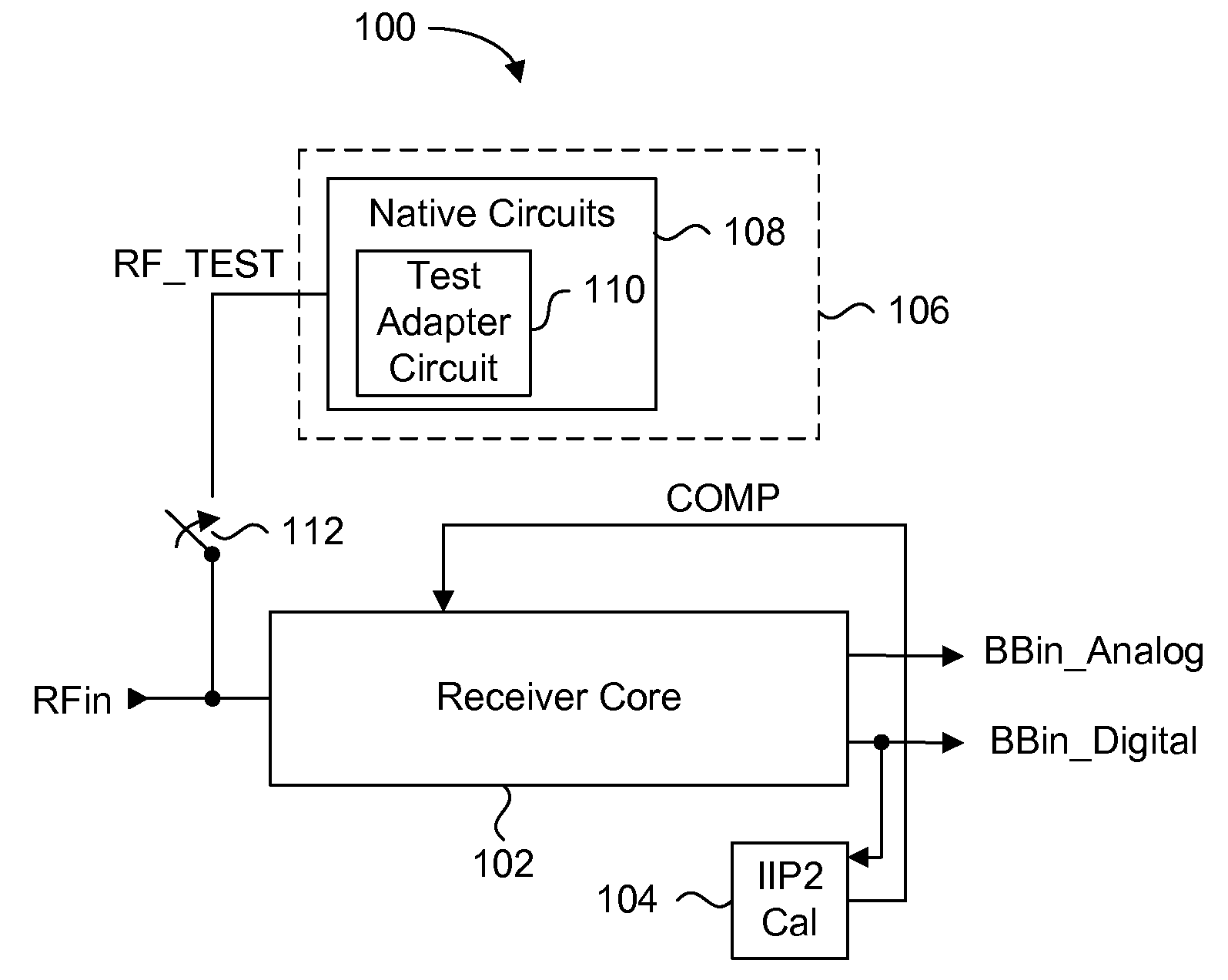
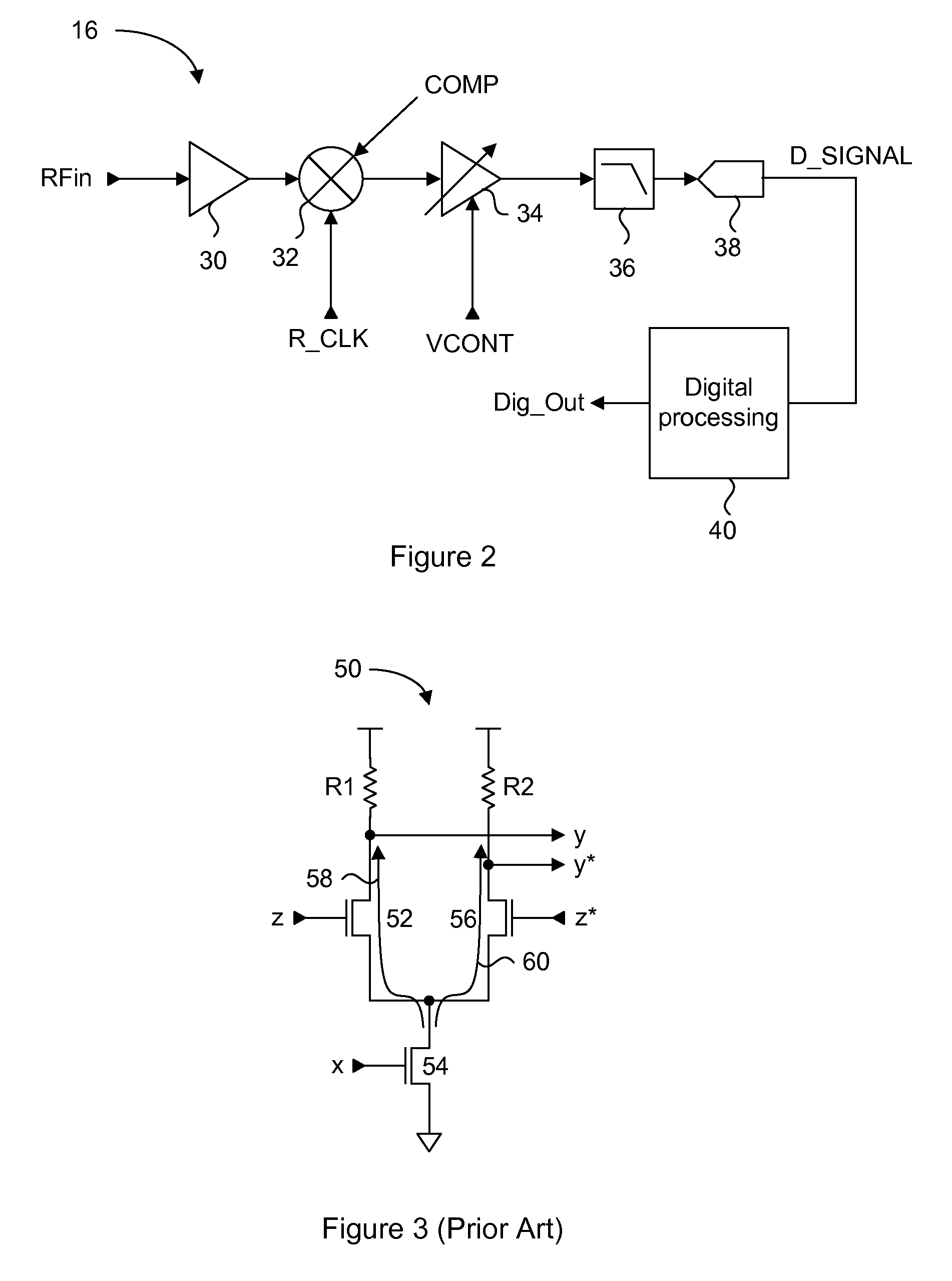
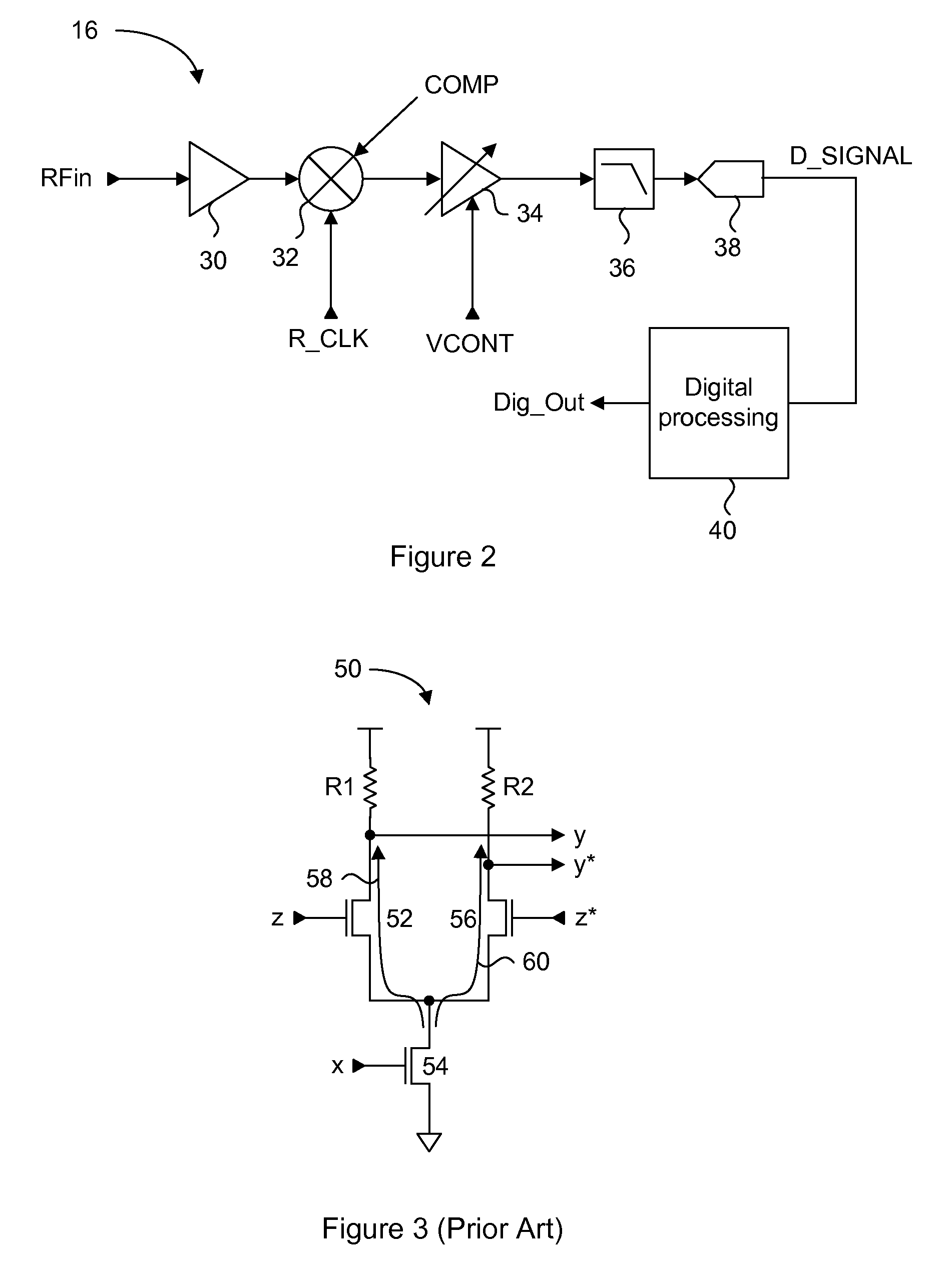
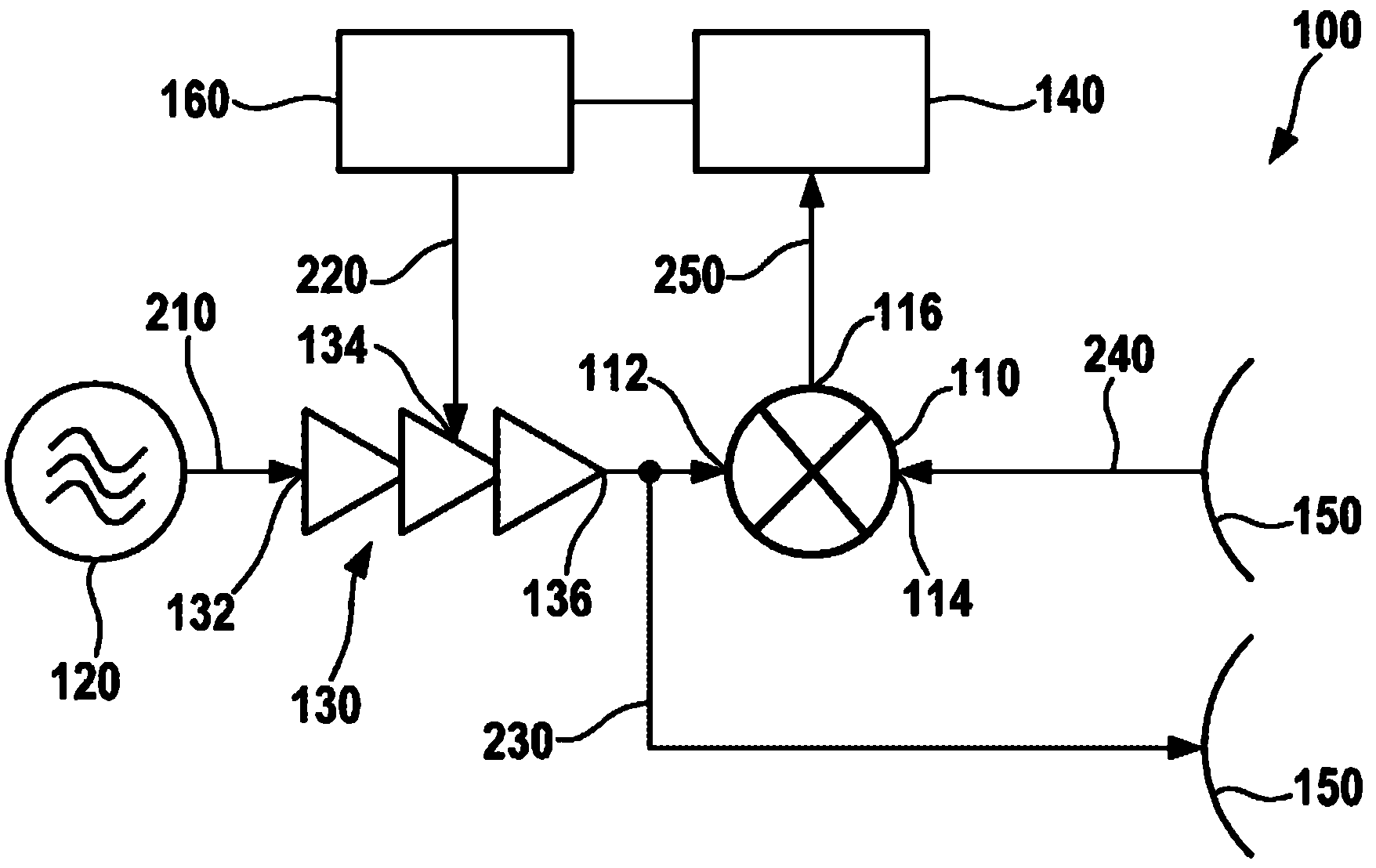
An integrated automatic IIP2 calibration architecture for wireless transceivers is disclosed. The architecture enables a wireless transceiver to generate a test radio frequency (RF) signal having a second order tone with minimal additional circuitry. In particular, the test RF signal is generated using a combination of native transceiver circuits and test adaptor circuits. Native transceiver circuits are those circuits implemented on the transceiver chip for executing native transceiver functions during normal operation, which can be used for generating the test (RF) signal. Test adaptor circuits are added to the transceiver chip, more specifically to the native circuits, for enabling the native circuits to generate the test RF signal in a self-test mode of operation. Circuits for implementing a particular IIP2 minimizing scheme can be included on the transceiver chip for automatic IIP2 calibration during the self-test mode of operation.
Owner:ICERA CANADA ULC
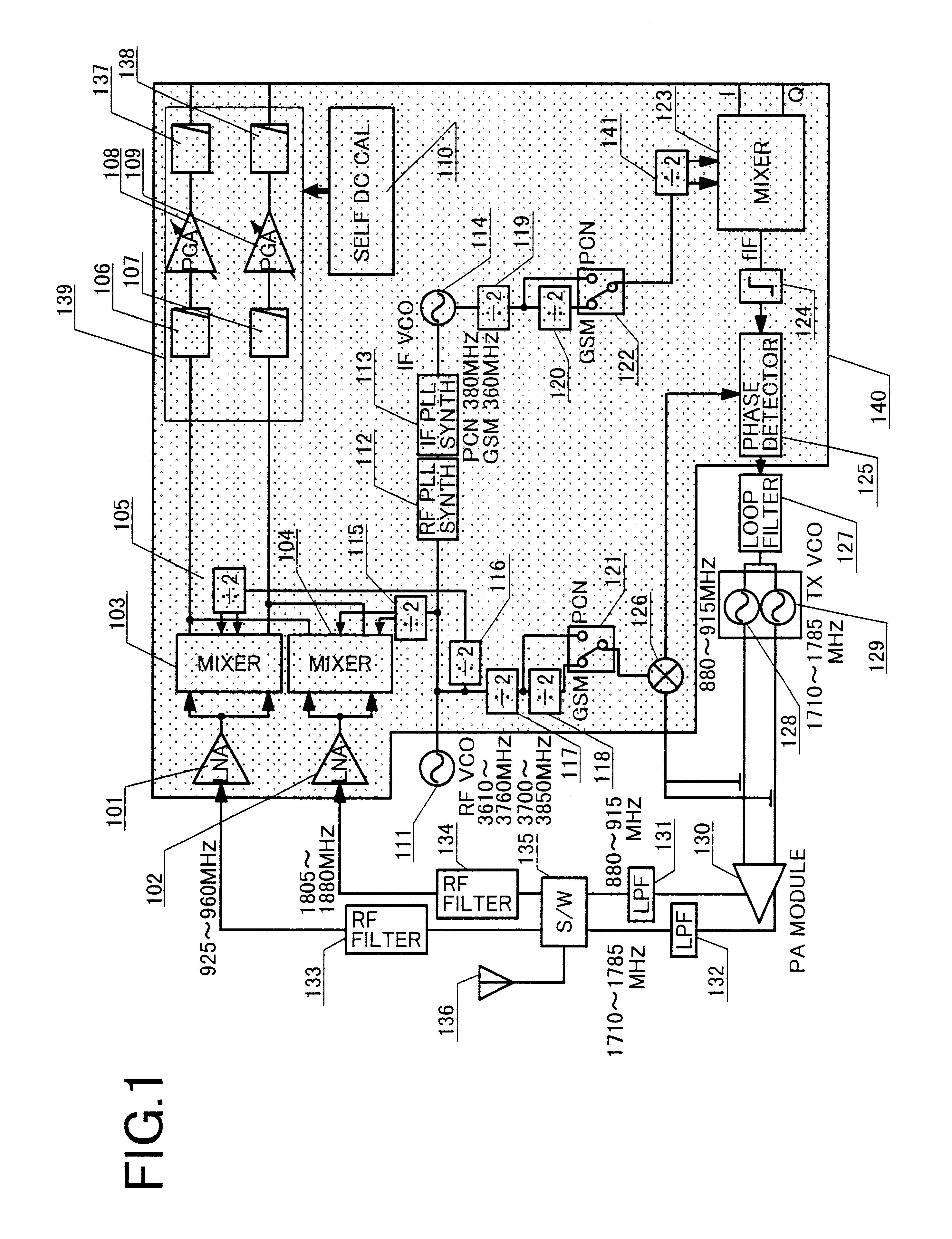
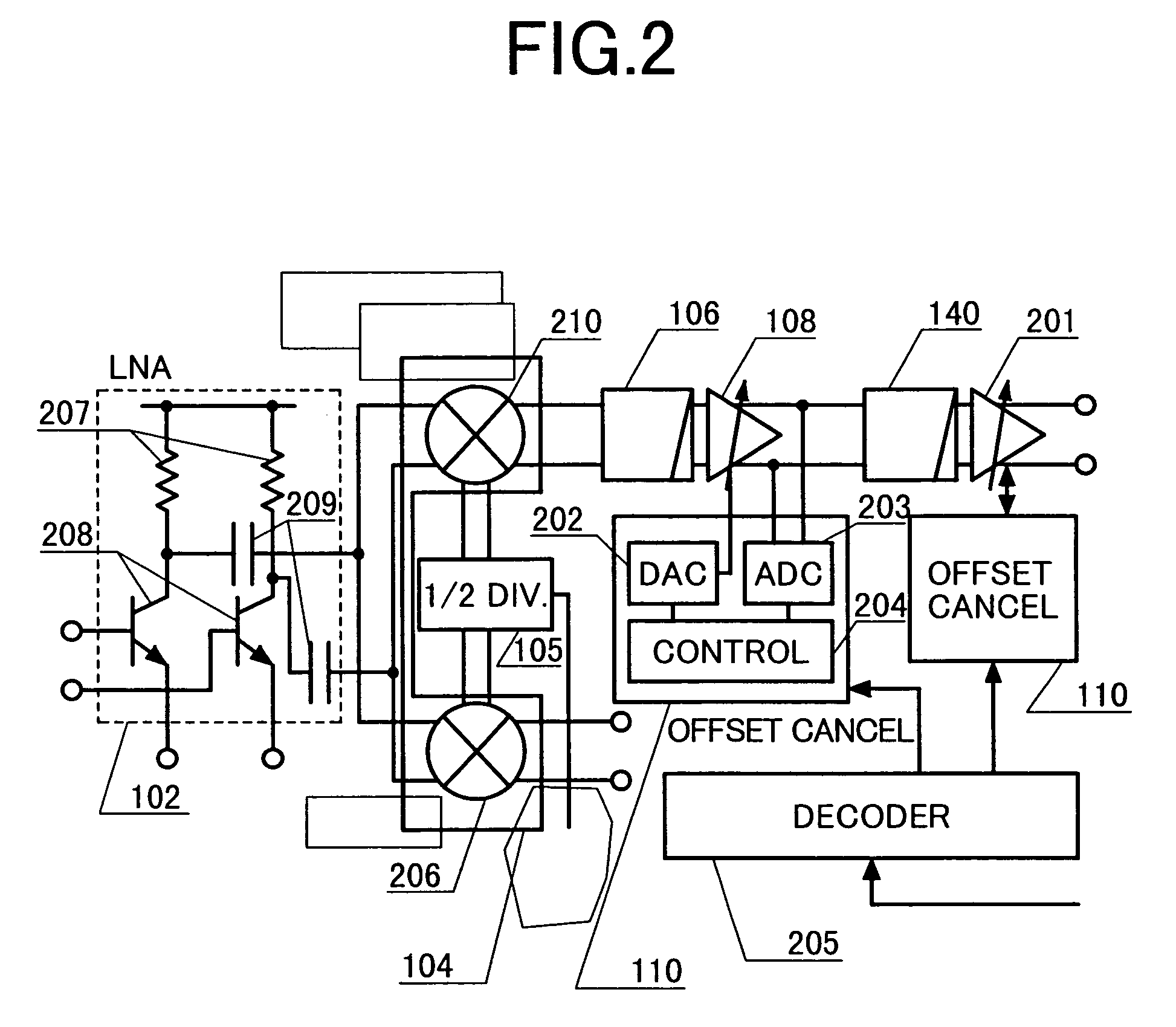
Mobile communication apparatus including dividers in transmitter and receiver
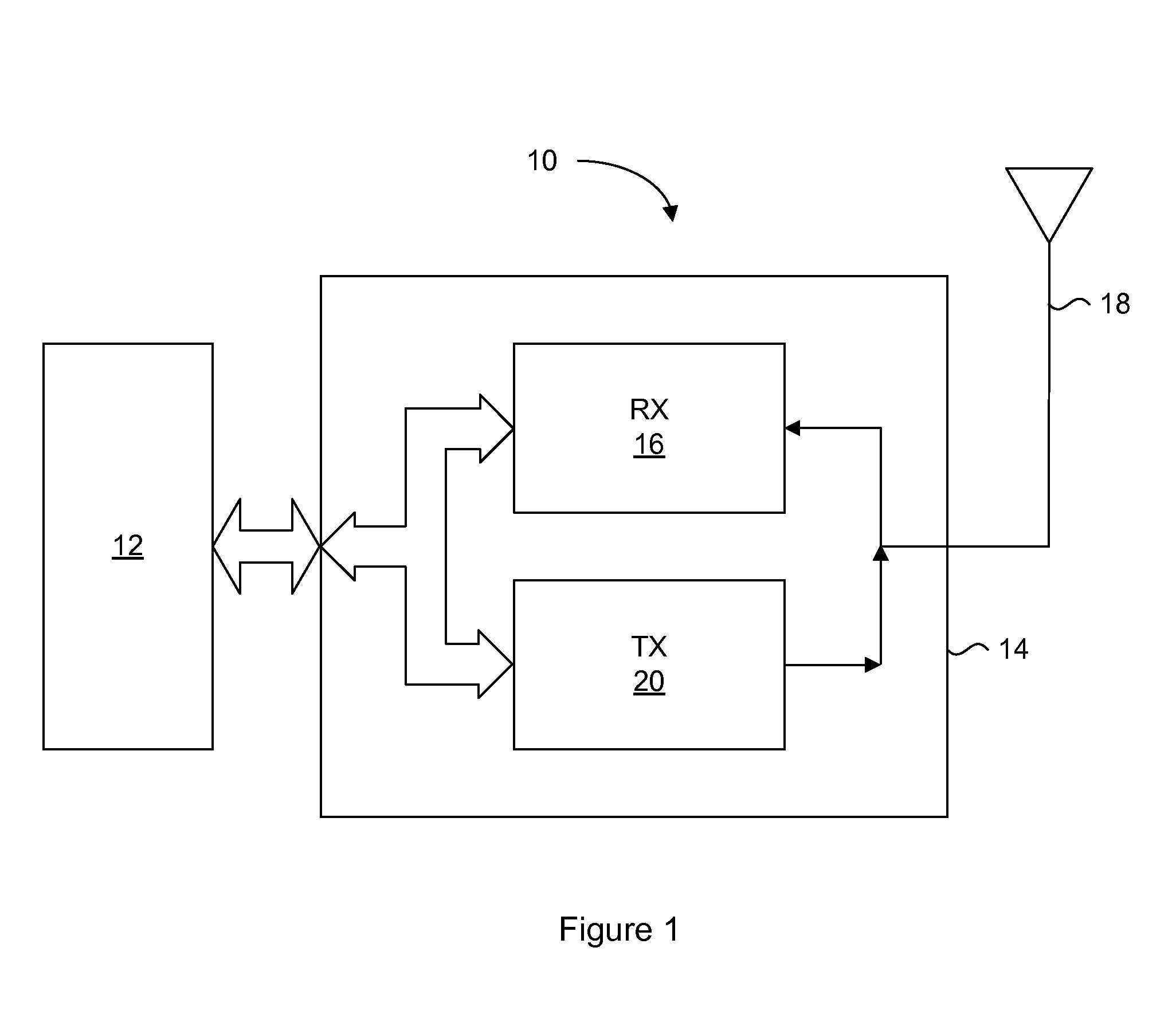
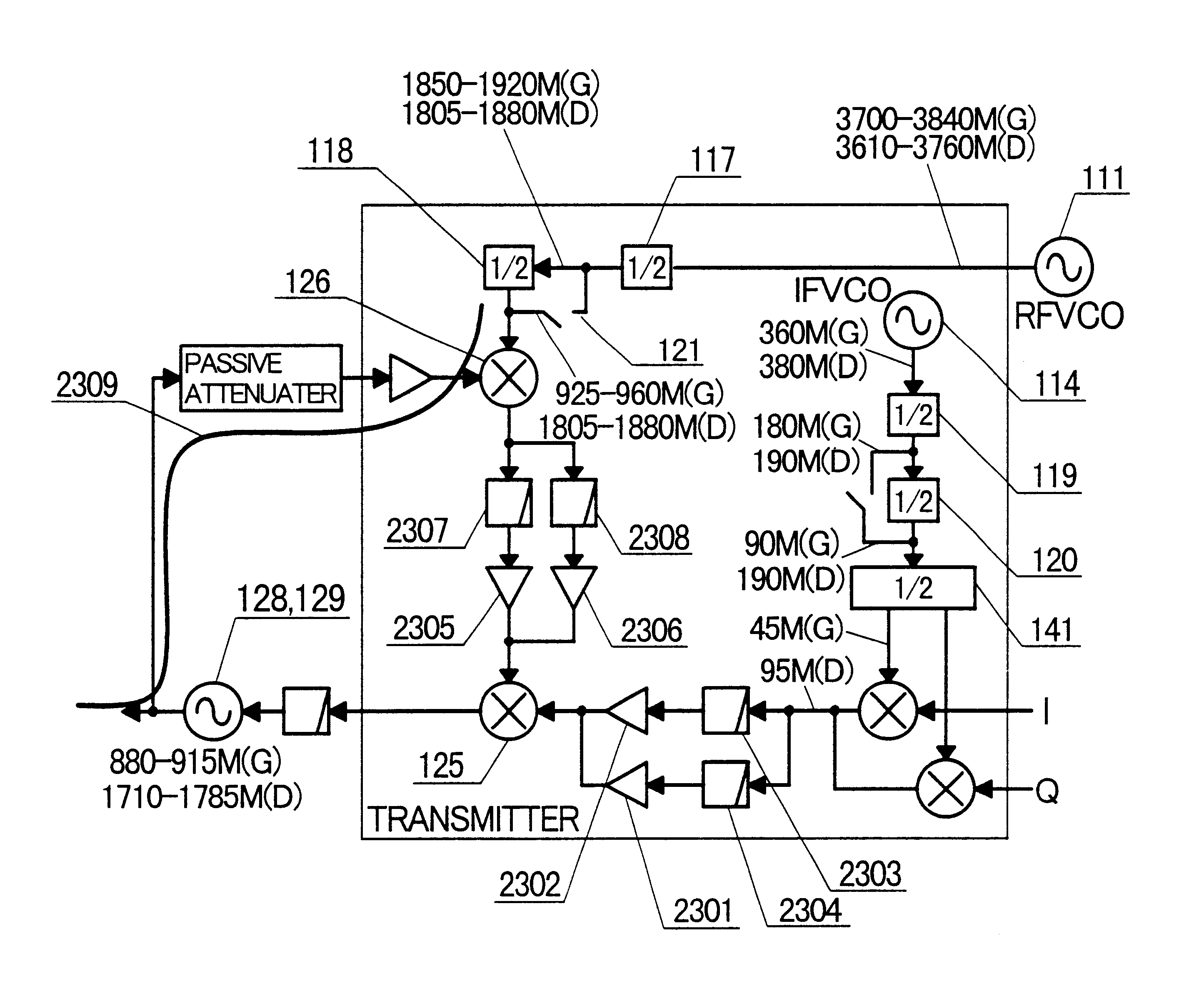
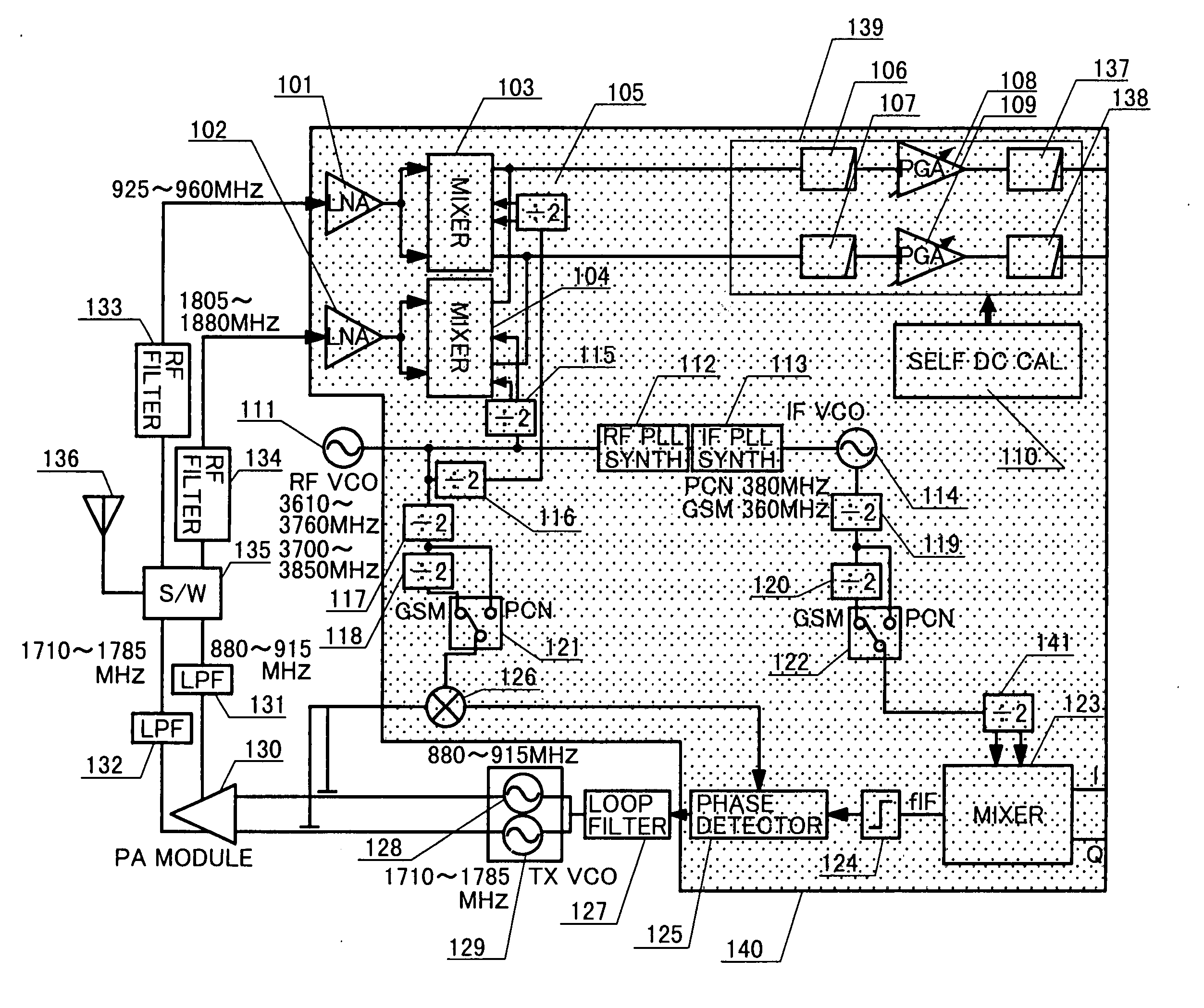
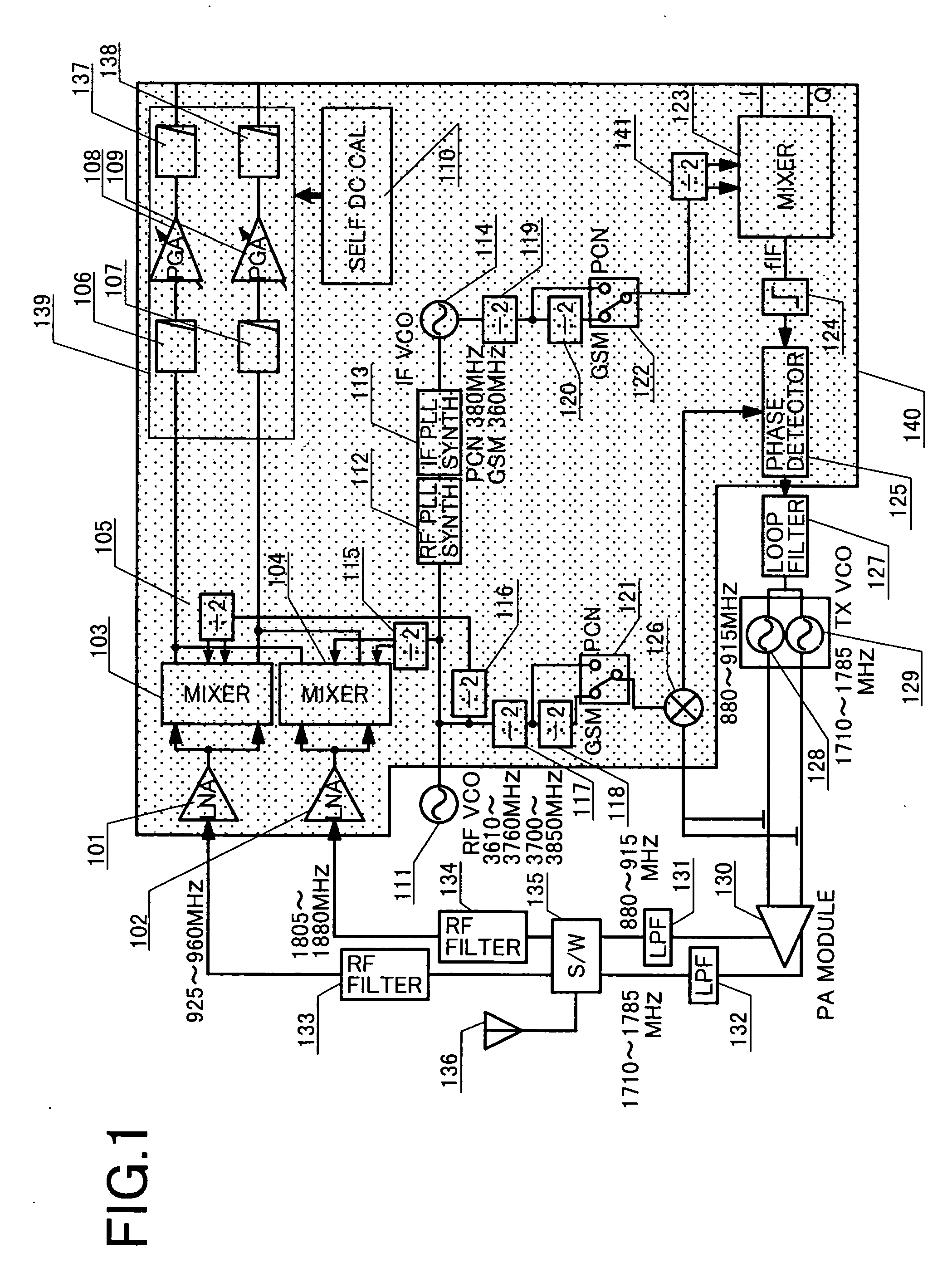
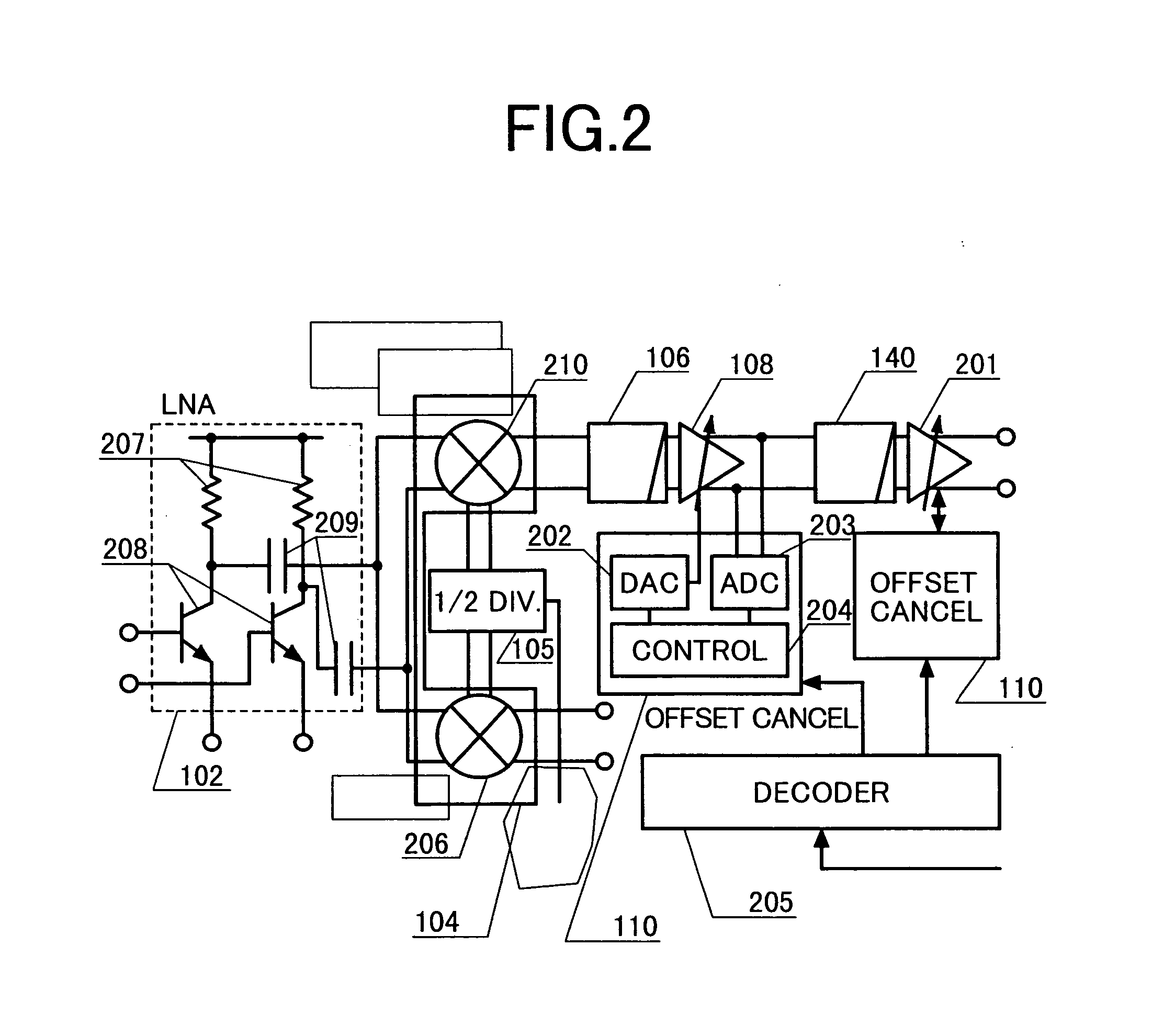
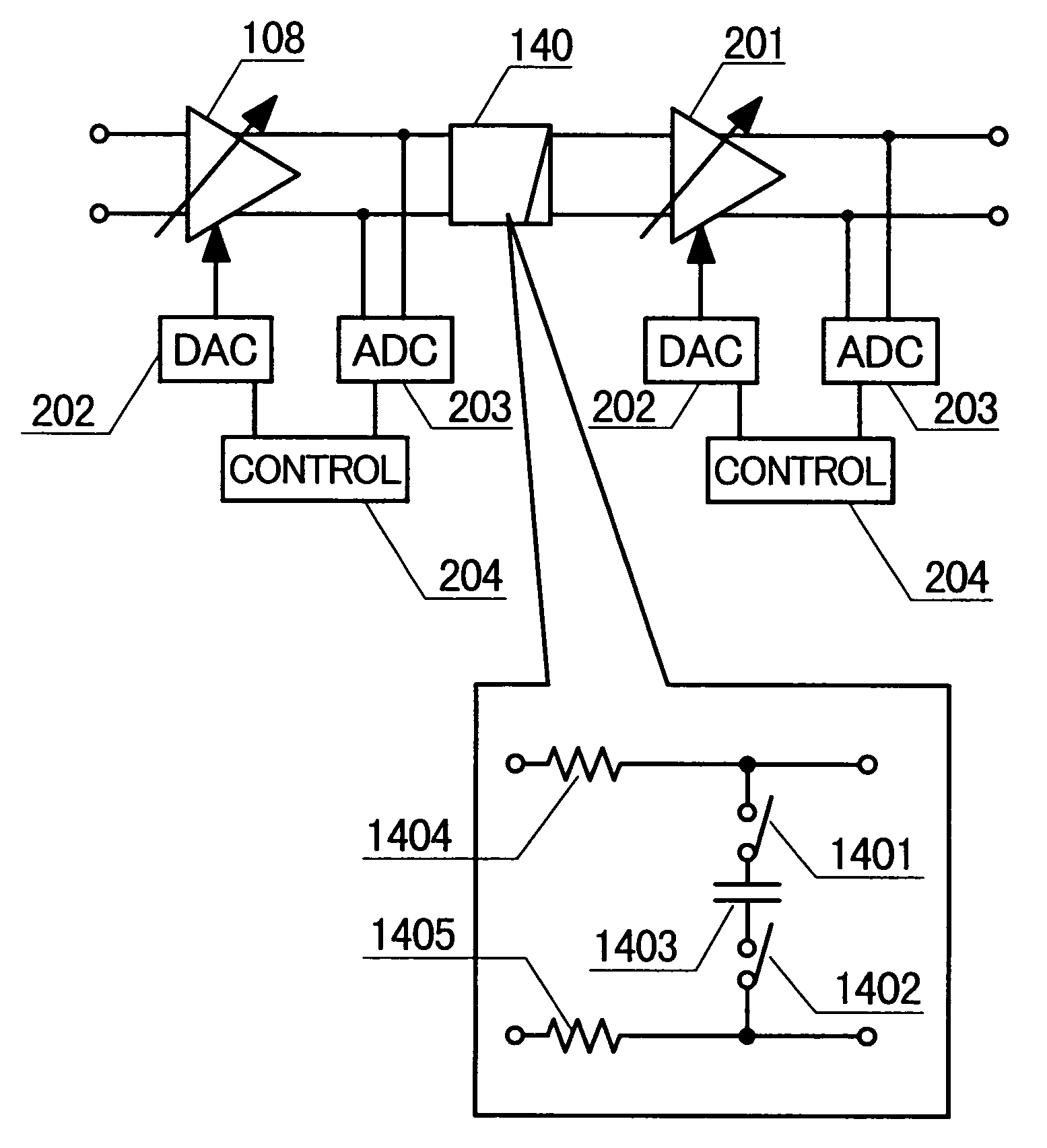
A transceiver suitable for larger scale of integration employs direct conversion reception for reducing the number of filters. Also, the number of VCOs is reduced by utilizing dividers to supply a receiver and a transmitter with locally oscillated signals at an RF band. Dividers each having a fixed division ratio are used for generating locally oscillated signals for the receiver, while a divider having a switchable division ratio are used for generating the locally oscillated signal for the transmitter. In addition, a variable gain amplifier for baseband signal is provided with a DC offset voltage detector and a DC offset canceling circuit for supporting high speed data communications to accomplish fast cancellation of a DC offset by eliminating intervention of a filter within a feedback loop for offset cancellation.
Owner:TTPCOM
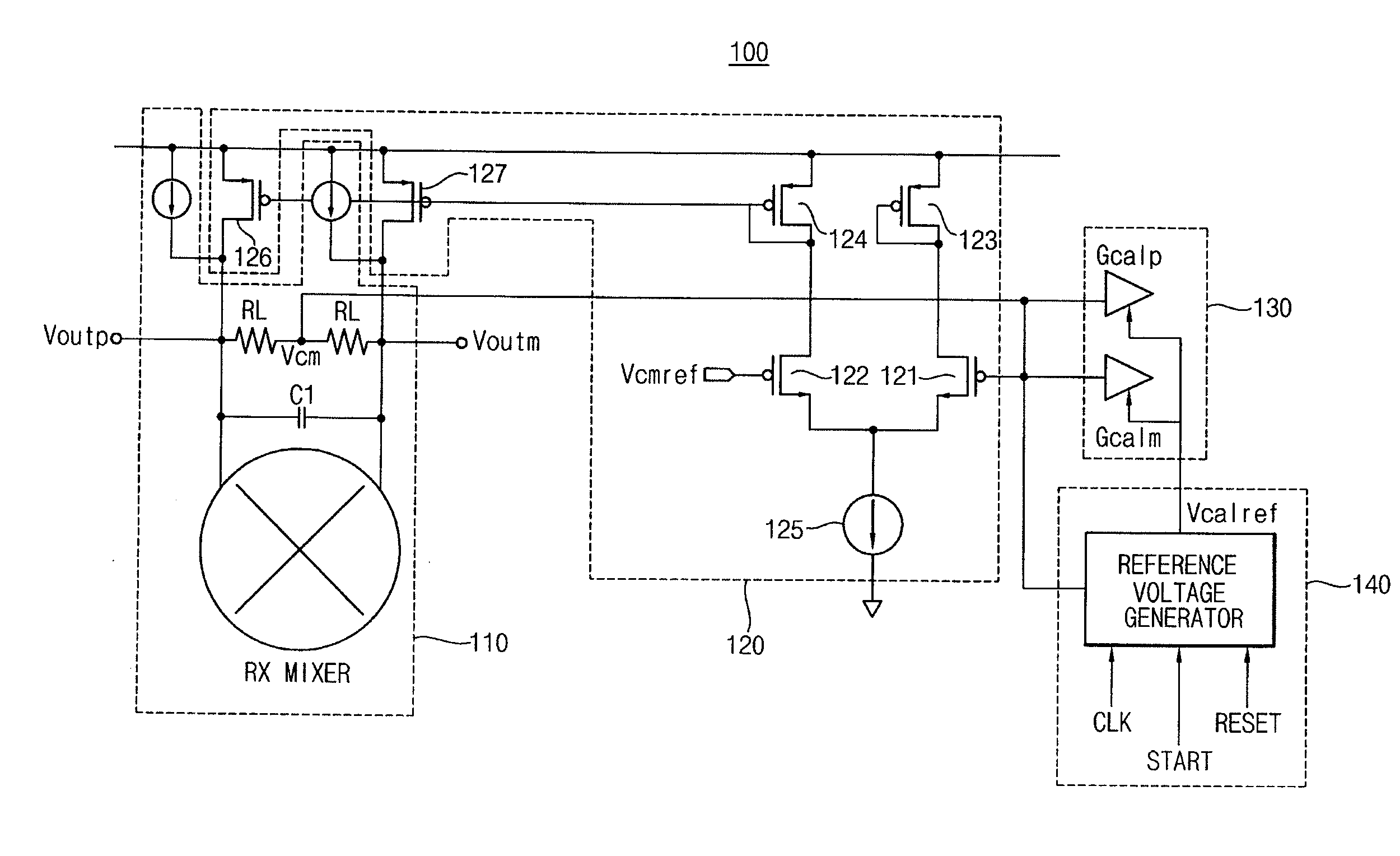
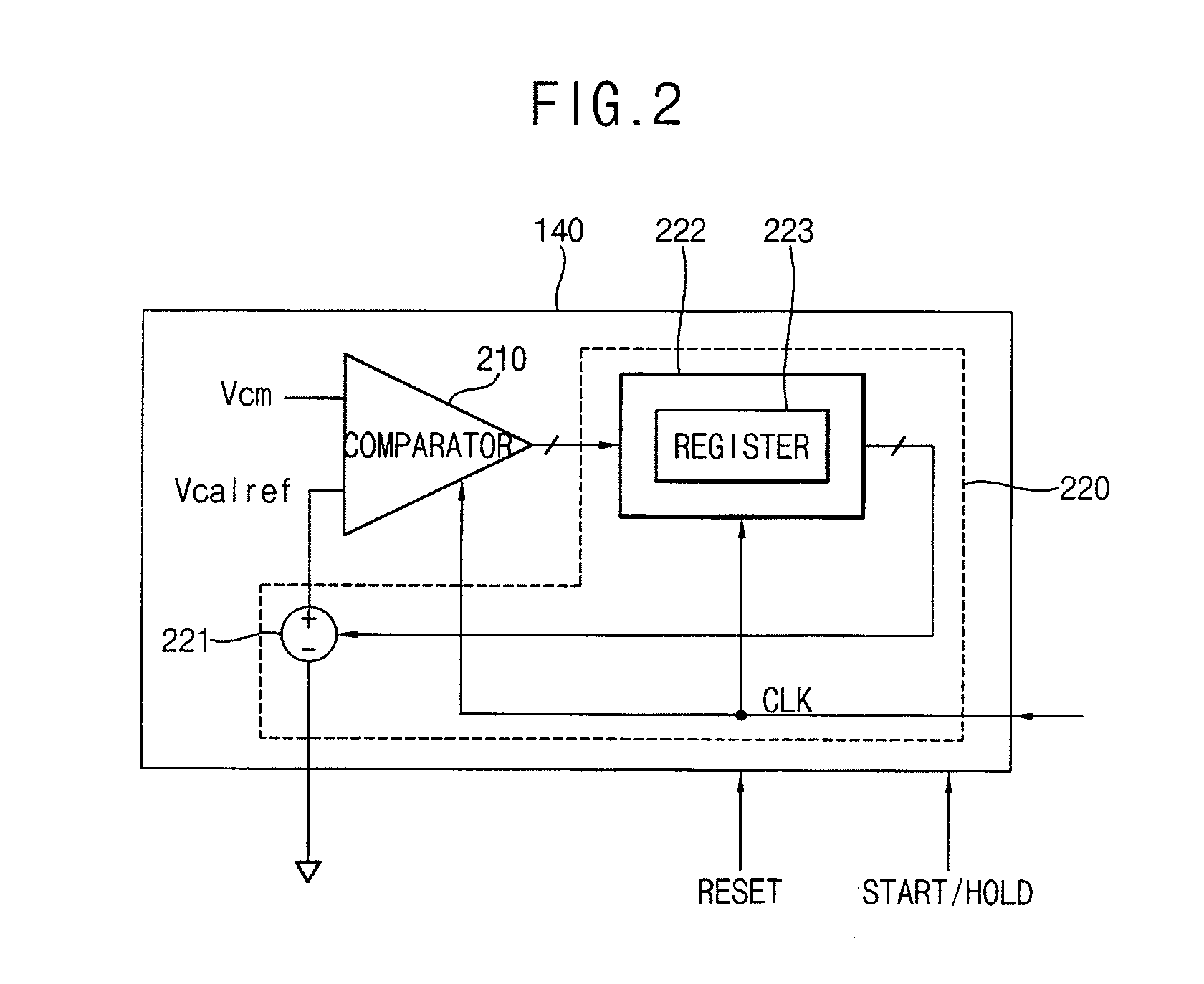
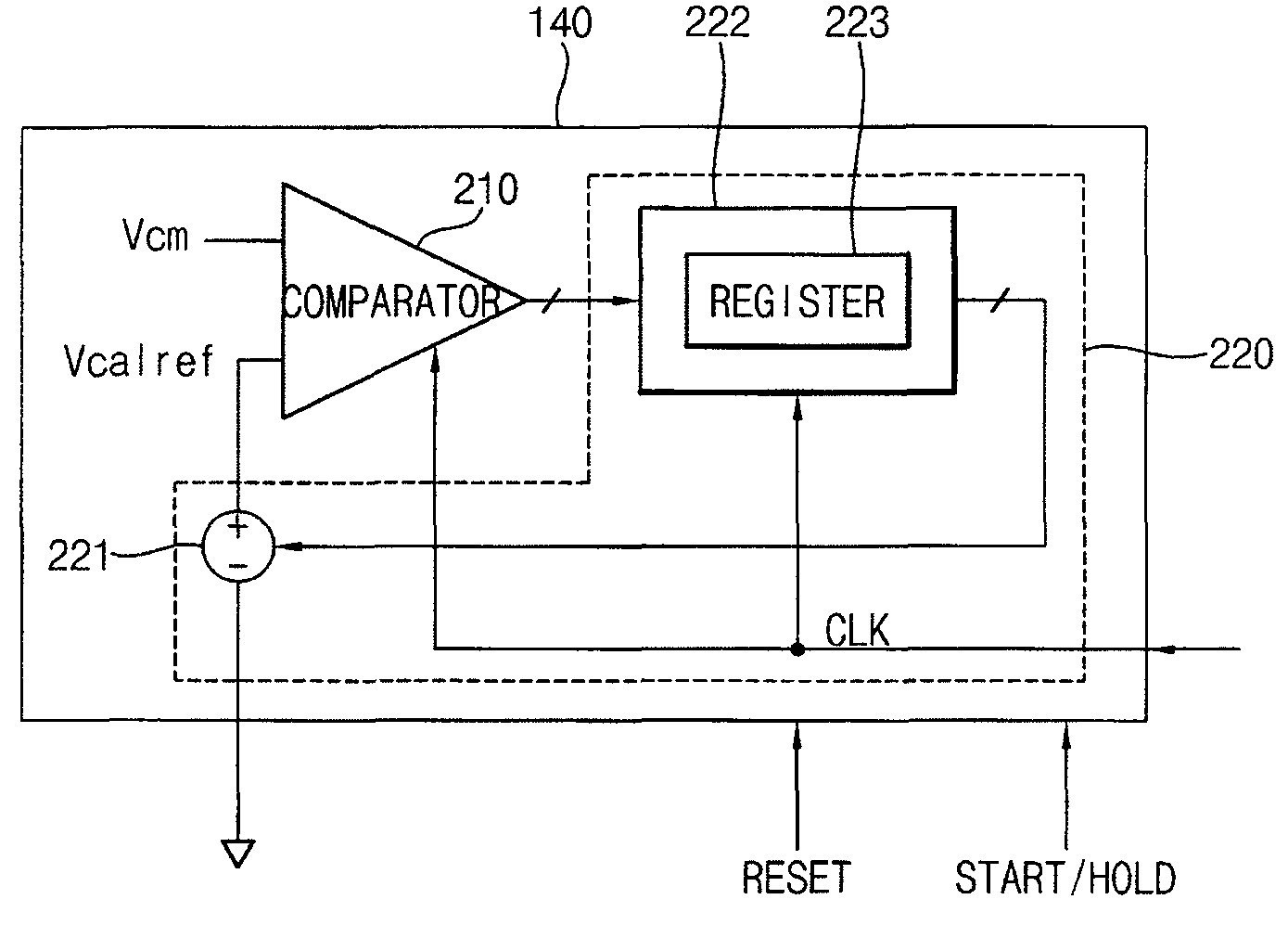
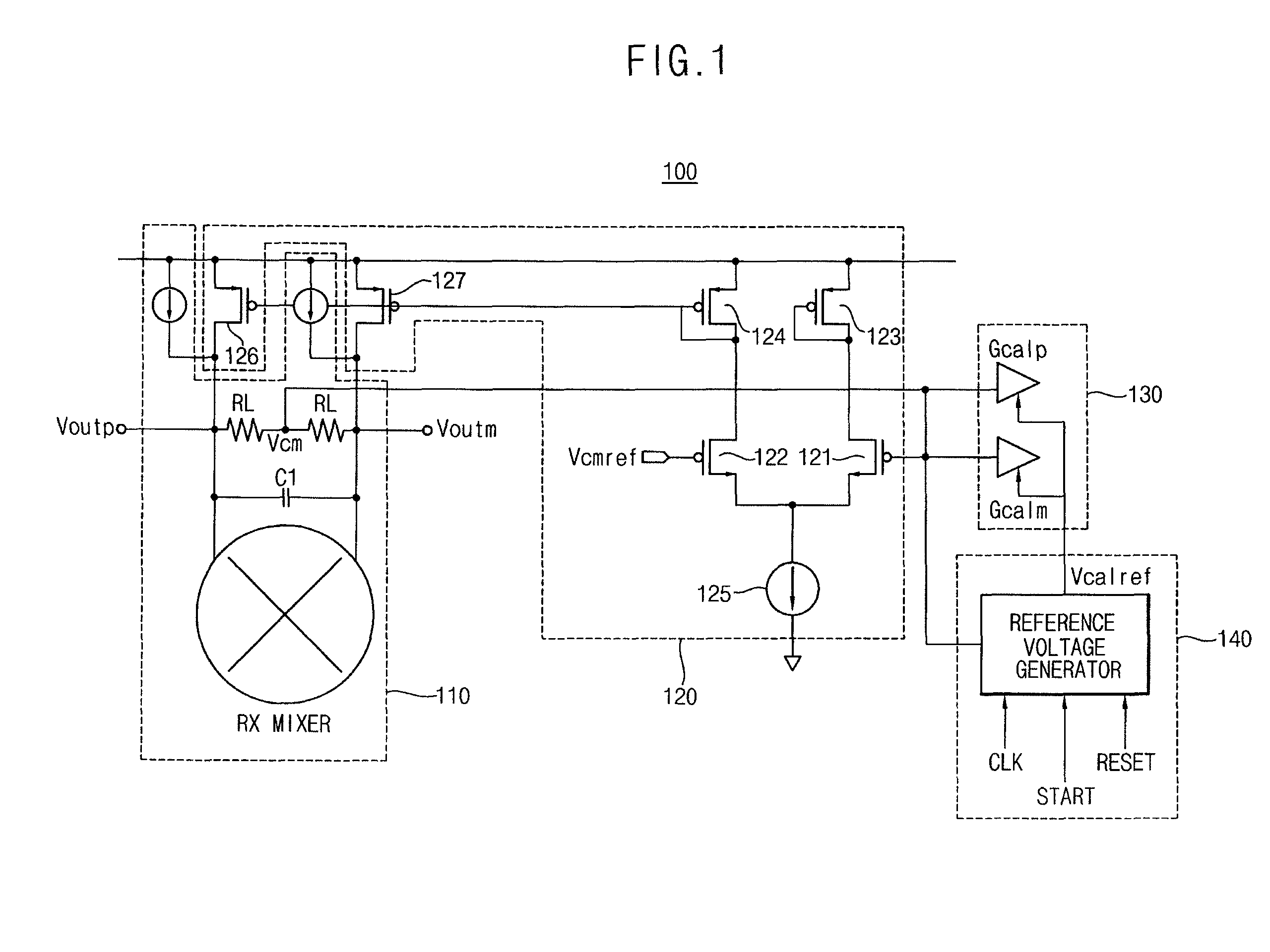
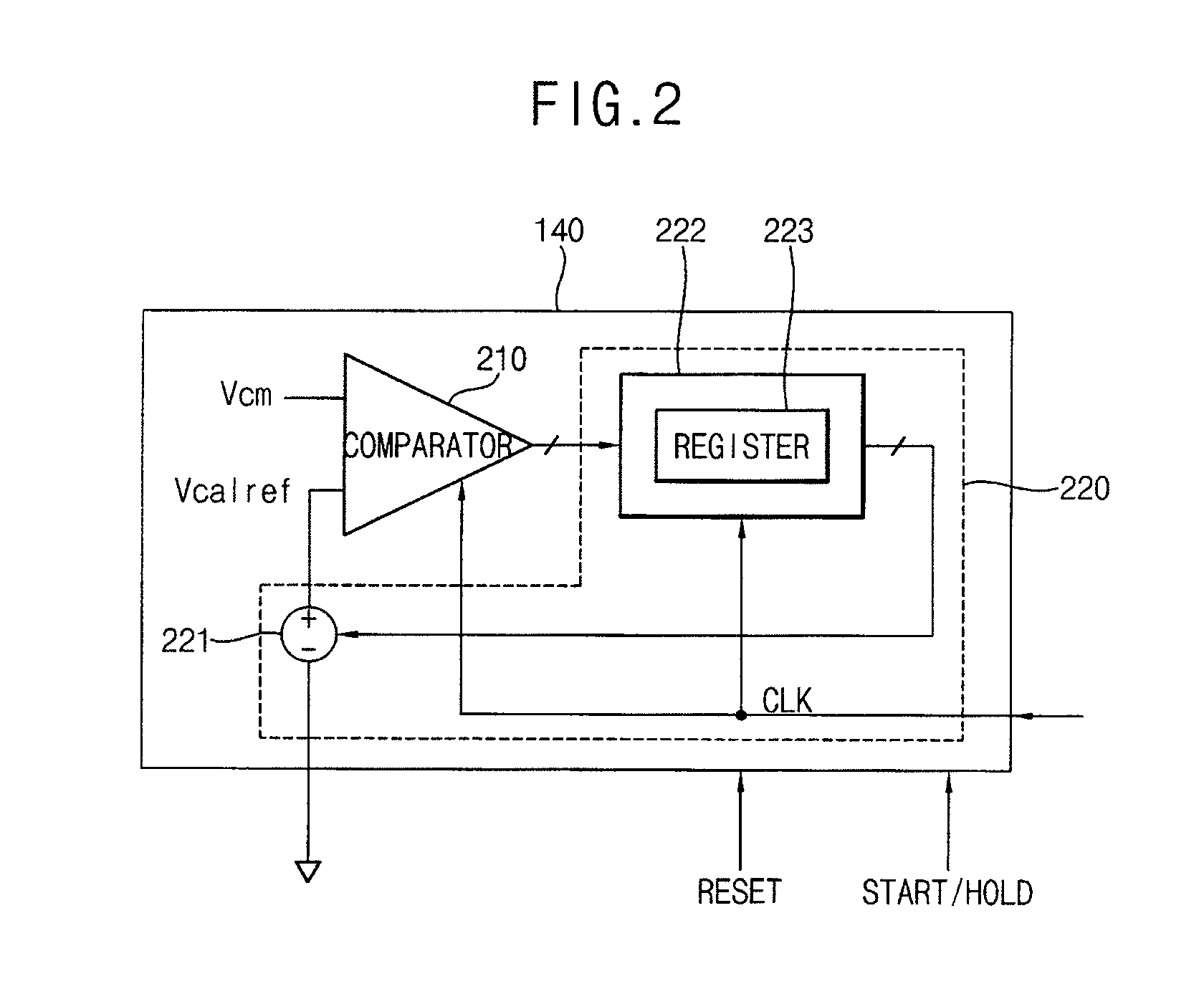
Second intercept point (IP2) calibrator and method for calibrating ip2
InactiveUS20080116902A1Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationFrequency mixerEngineering
A second intercept point (IP2) calibrator and a method for calibrating IP2 are disclosed. The IP2 calibrator and the method for calibrating IP2 remove any direct current (DC) offset by comparing a common-mode reference voltage with the common-mode voltage measured between a first output terminal and a second output terminal of a mixer, and calibrates the IP2 of the mixer by comparing the common-mode voltage with a calibration reference voltage. The calibration reference voltage is independent of the common-mode reference voltage and may be a quantized variable voltage generated according to digital control code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for processing a transmission signal in communication system
ActiveUS20150333944A1Significant valueTransmission path divisionSecret communicationCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
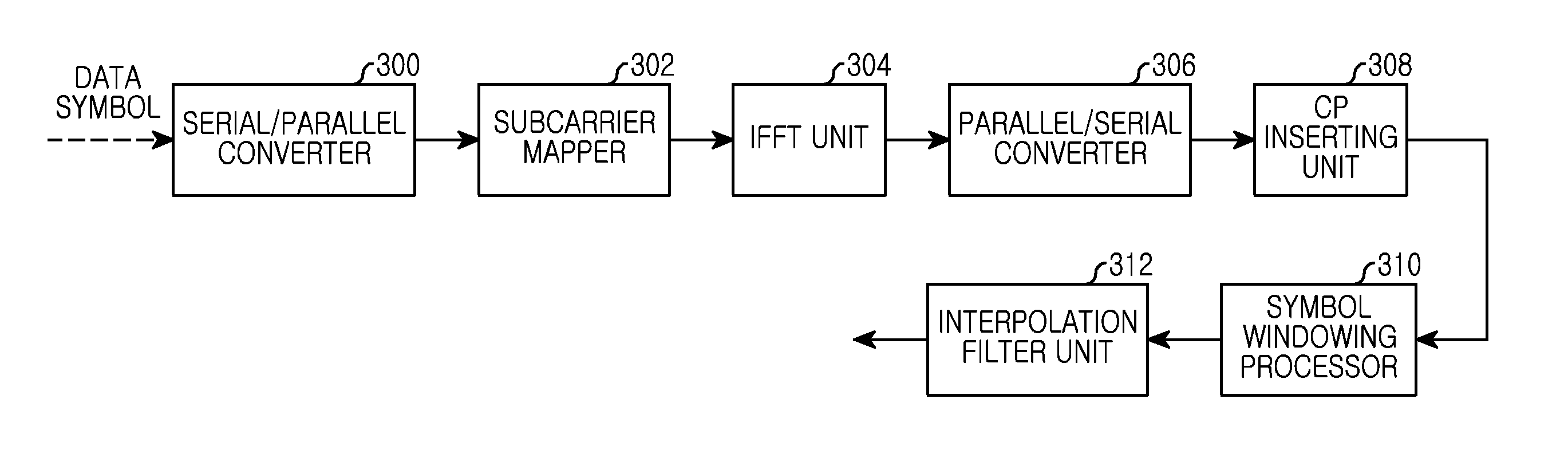
Disclosed are a method and apparatus for processing a transmission signal using a window function that changes a spectrum characteristic of a symbol. A transmission apparatus includes a symbol generator that generate a plurality of consecutive symbols, and a symbol windowing processor that is coupled with the symbol generator. The symbol windowing processor applies a first window function and a third window function that uses a difference between the first window and a second window, and changes a spectrum characteristic of each of the plurality of consecutive symbols, and processes neighboring symbols from among the plurality of consecutive symbols of which spectrum characteristics are changed, such that the symbols partially overlap one another.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
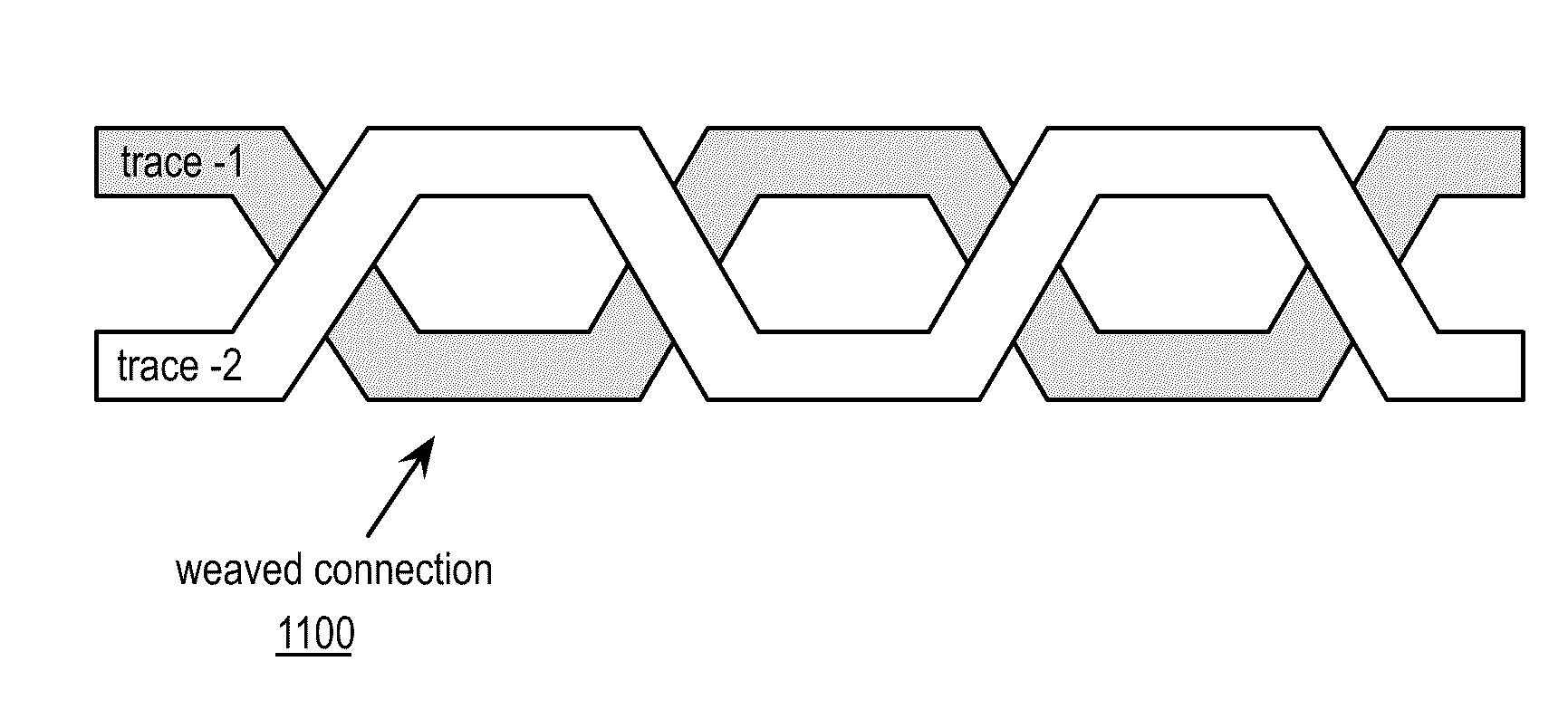
Transceiver including a weaved connection
A transceiver includes a local oscillation module, a transmitter section, and a receiver section. The local oscillation module is operable to generate a transmit local oscillation and a receive oscillation. The transmitter section includes a transmit mixing module and a transmit weaved connection that is operable to high frequency filter the transmit location oscillation. The transmit mixing module mixes the filtered transmit location oscillation with a transmit signal to produce an up-converted signal. The receiver section includes a receive mixing module and a receive weaved connection that is operable to high frequency filter the receive location oscillation. The receive mixing module mixes the filtered receive location oscillation with an RF received signal to produce a down-converted signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
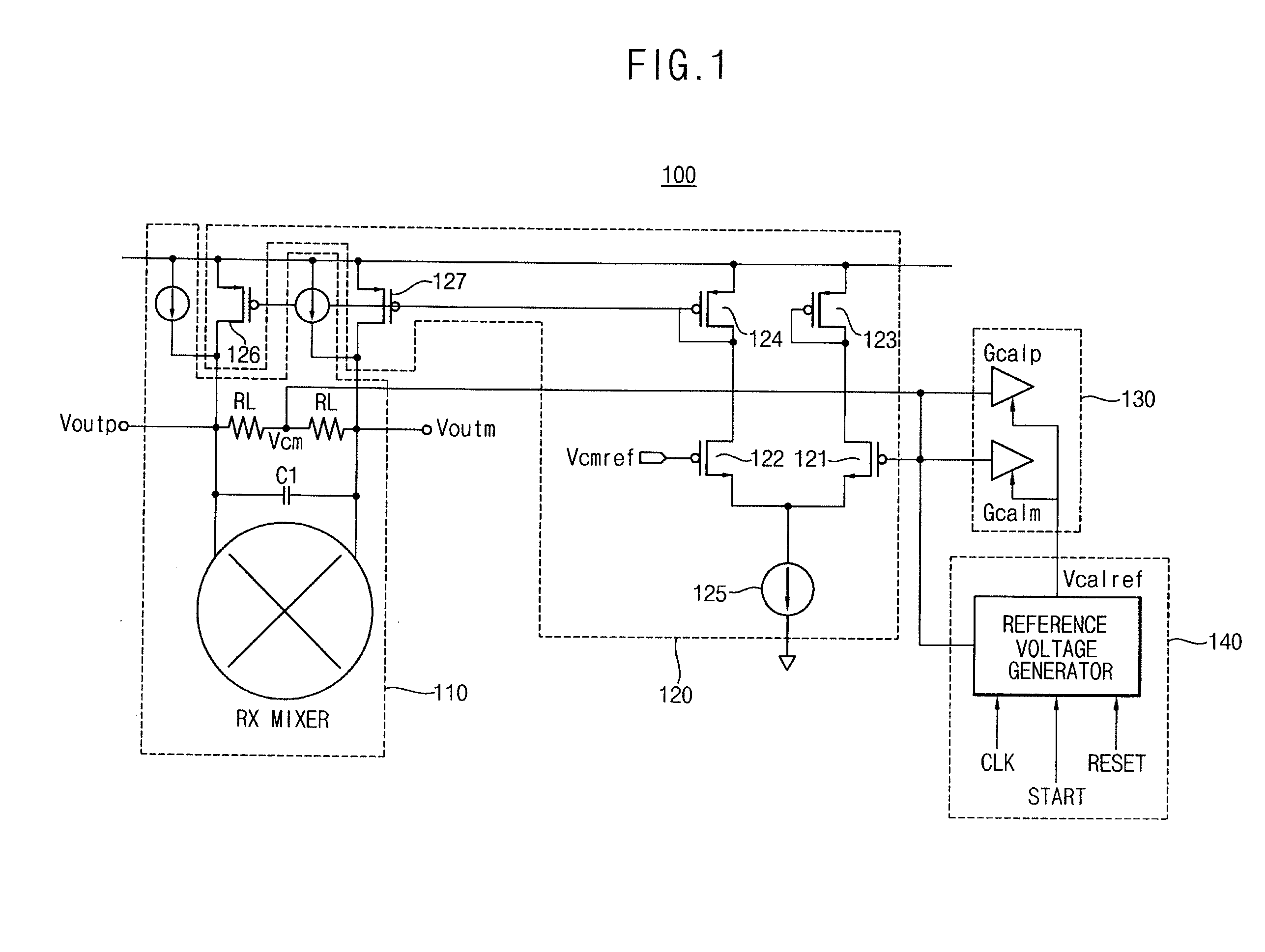
Second intercept point (IP2) calibrator and method for calibrating IP2
InactiveUS8000676B2Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationVoltage referenceDigital control
A second intercept point (IP2) calibrator and a method for calibrating IP2 are disclosed. The IP2 calibrator and the method for calibrating IP2 remove any direct current (DC) offset by comparing a common-mode reference voltage with the common-mode voltage measured between a first output terminal and a second output terminal of a mixer, and calibrates the IP2 of the mixer by comparing the common-mode voltage with a calibration reference voltage. The calibration reference voltage is independent of the common-mode reference voltage and may be a quantized variable voltage generated according to digital control code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
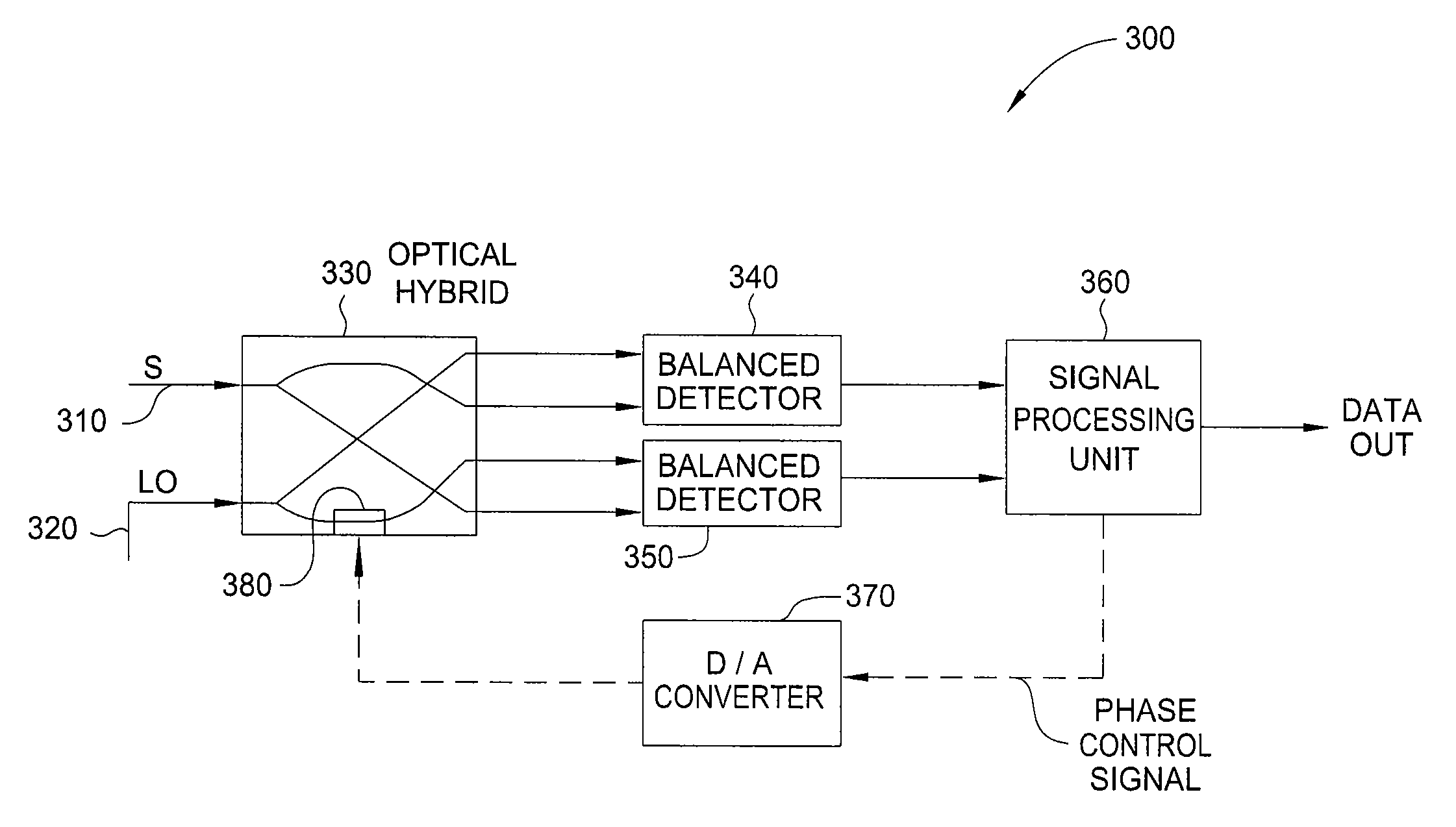
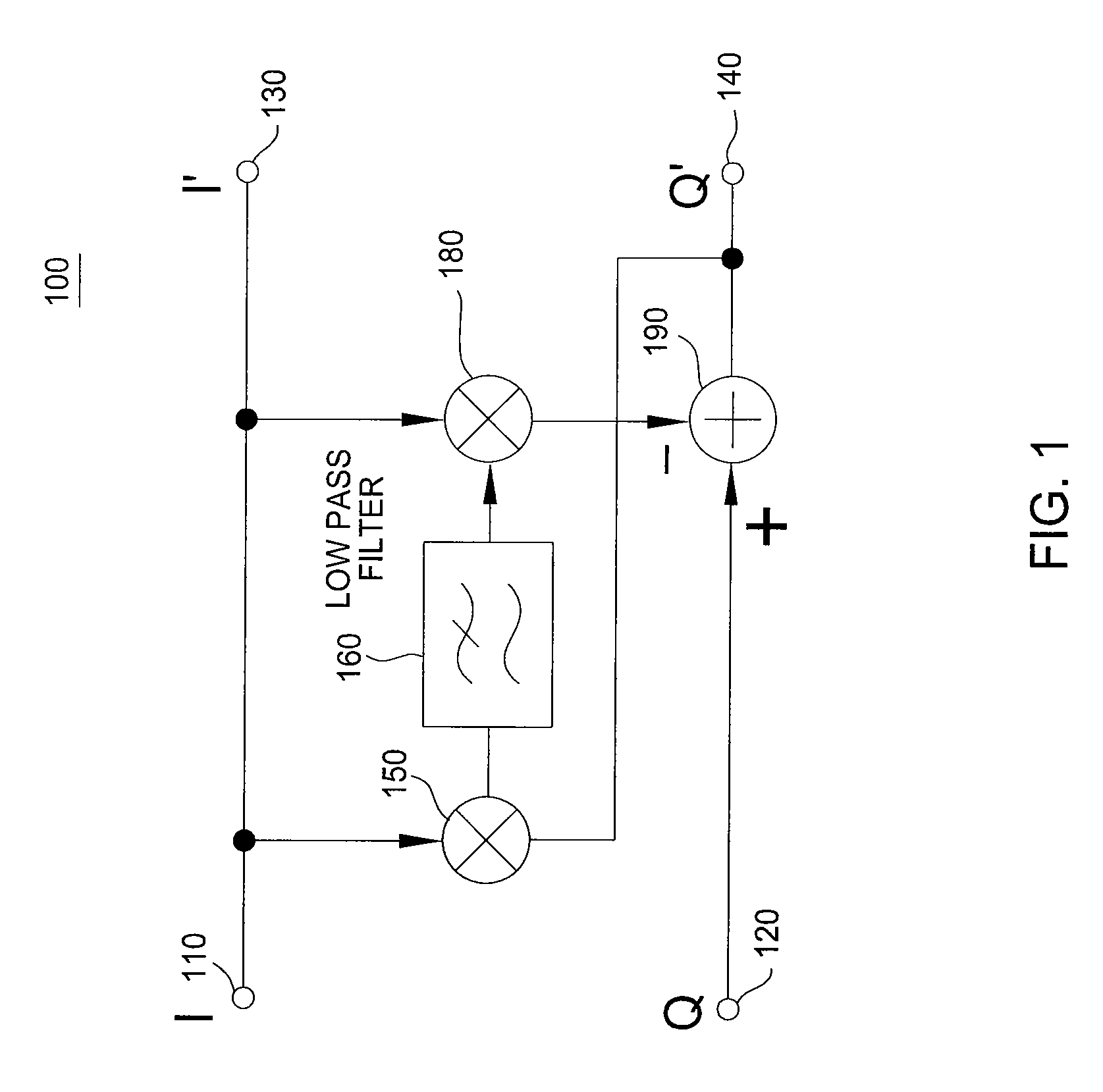
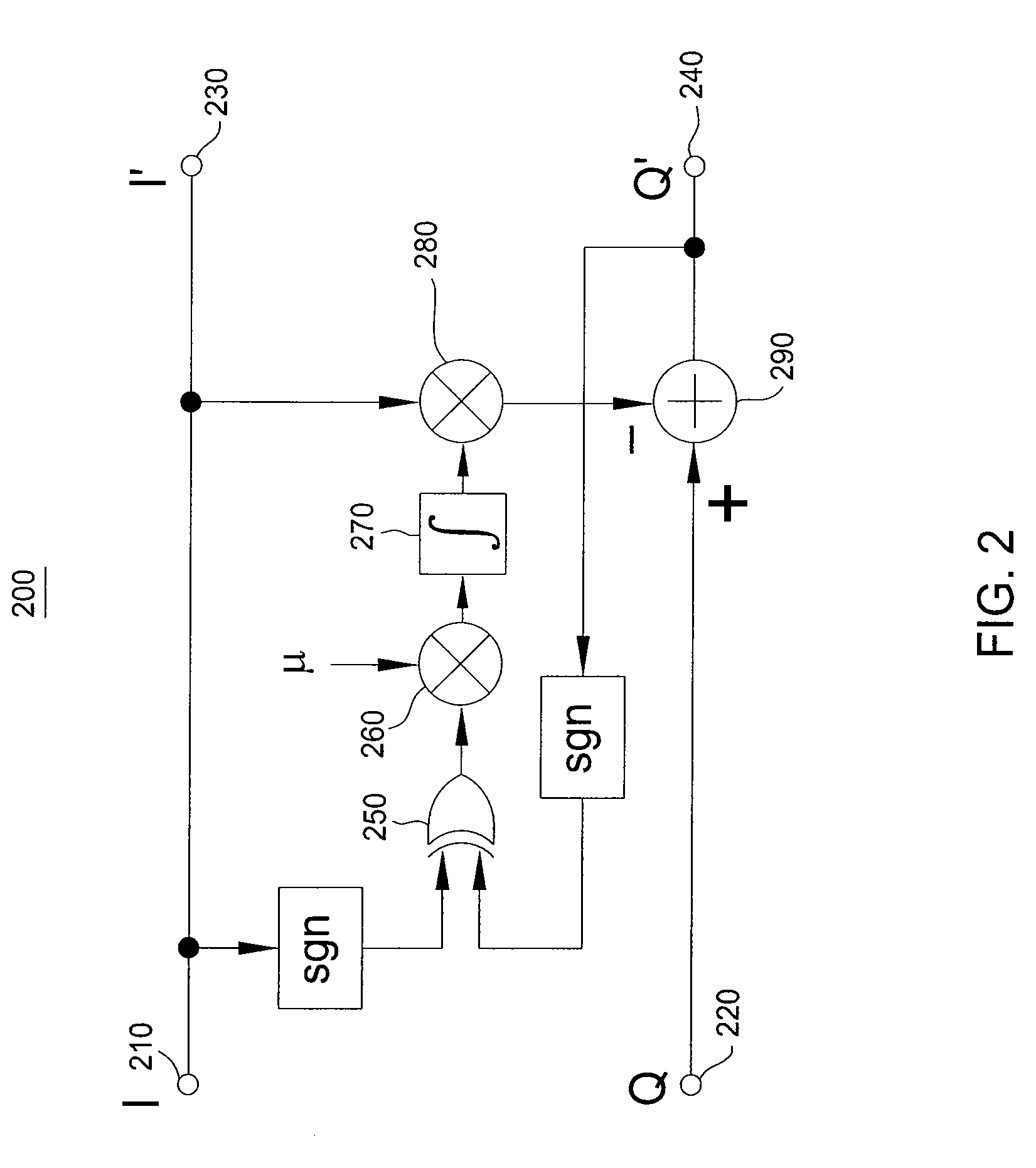
Phase error correction in a coherent receiver
A method and apparatus for correcting of phase errors in a coherent optical receiver are disclosed. Embodiments include a method for calculating a phase error between in-phase and quadrature-phase component signals, multiplying the phase error by one of the component signals and subtracting the result from the other component signal to output a corrected signal.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
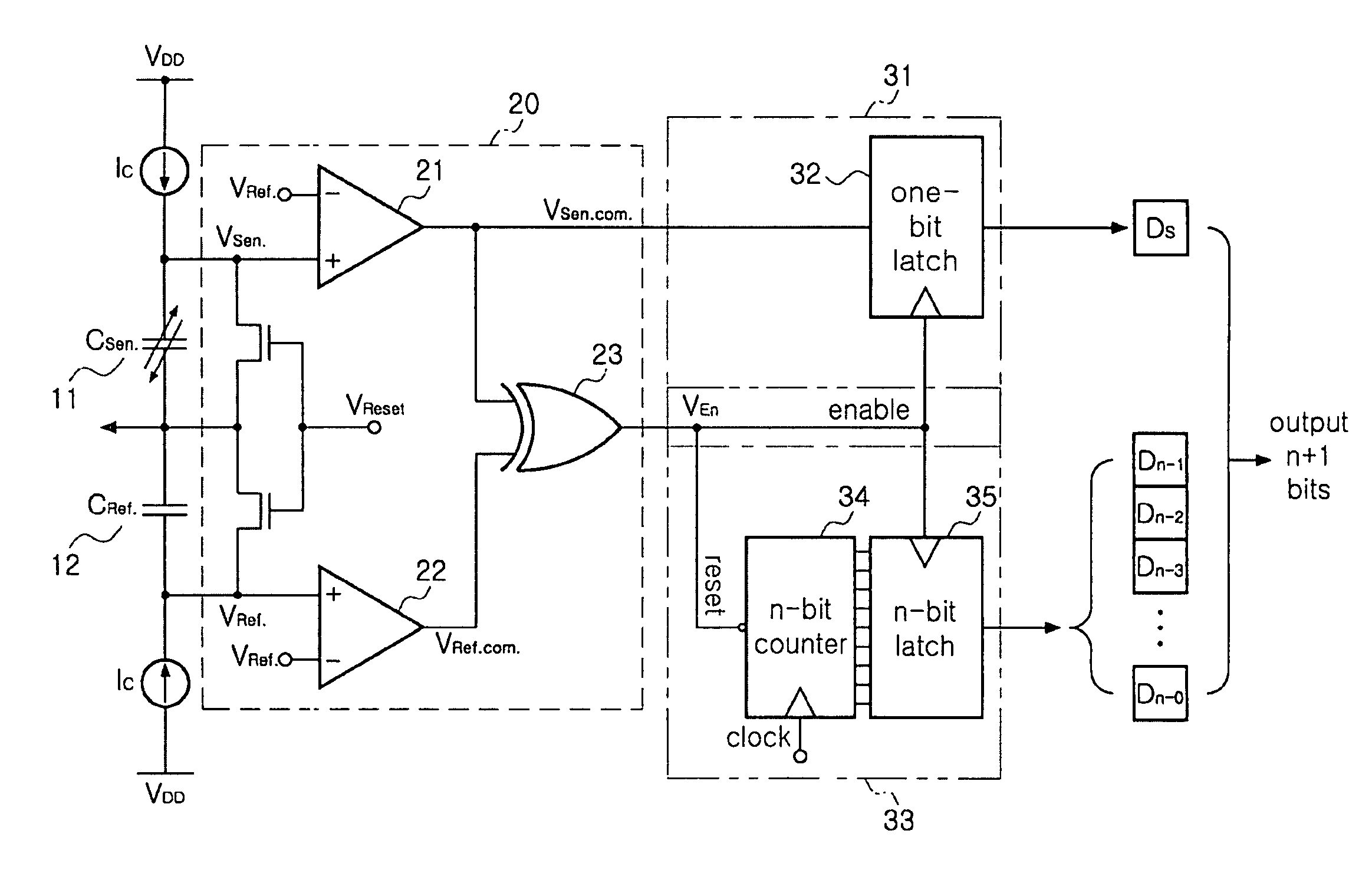
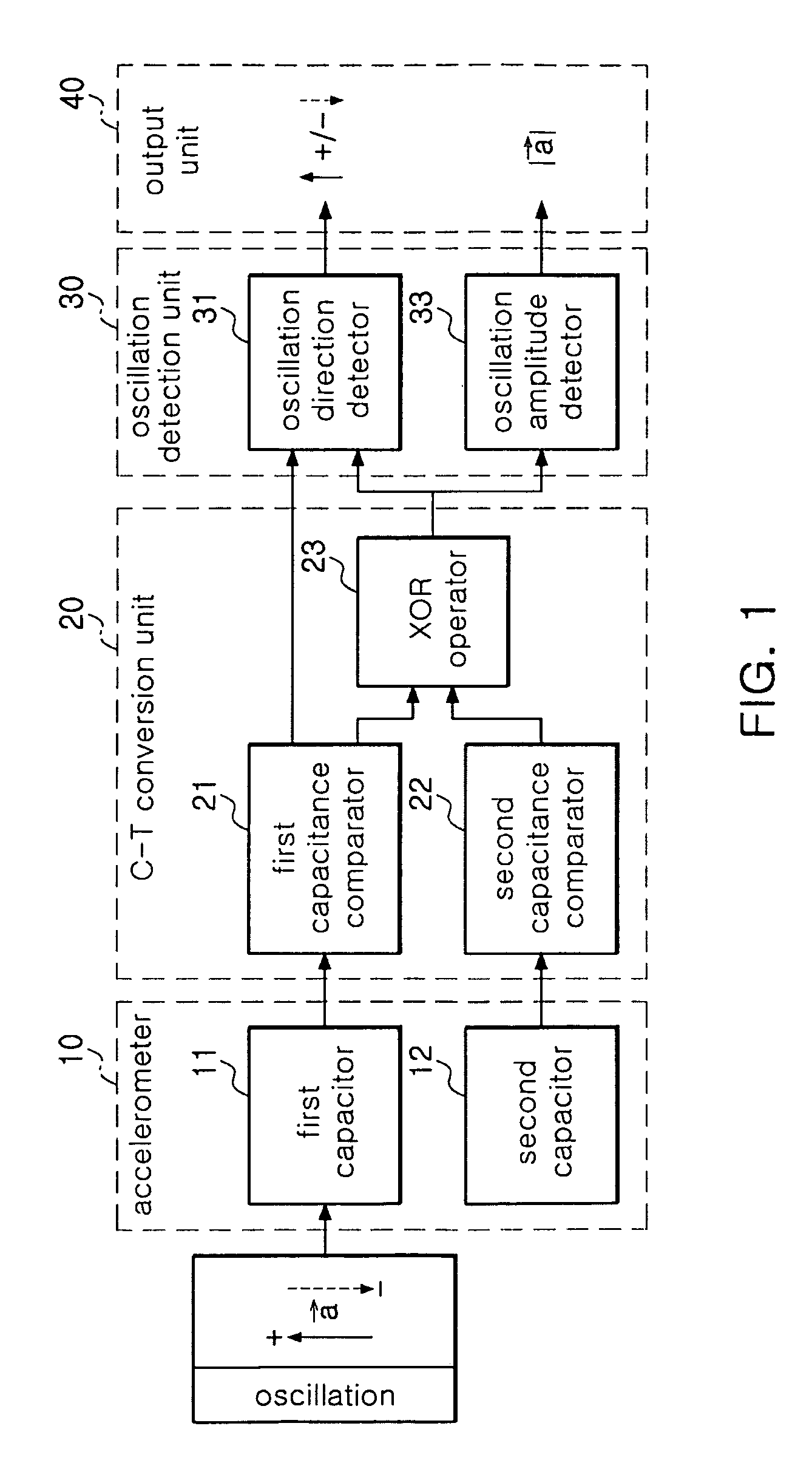
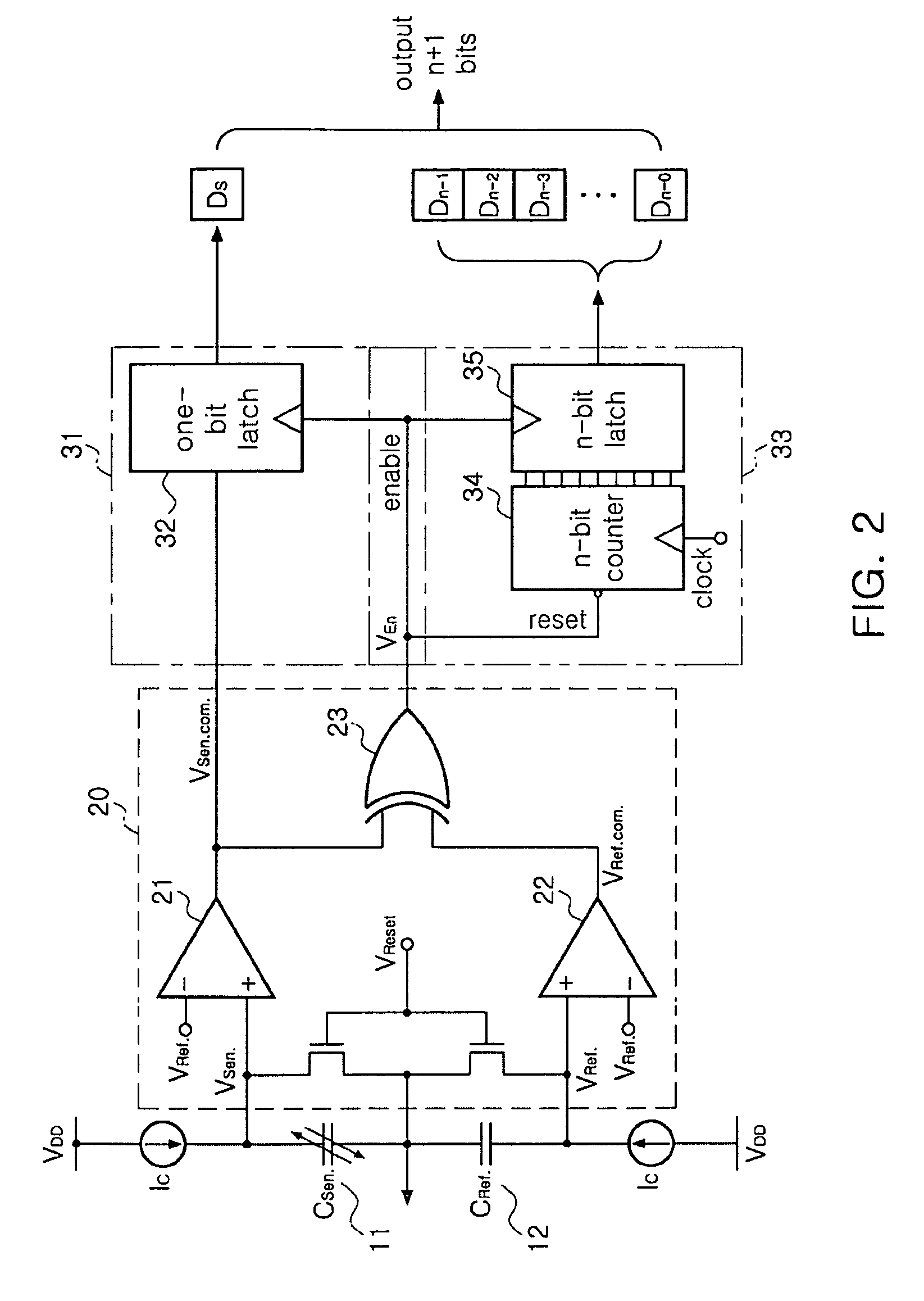
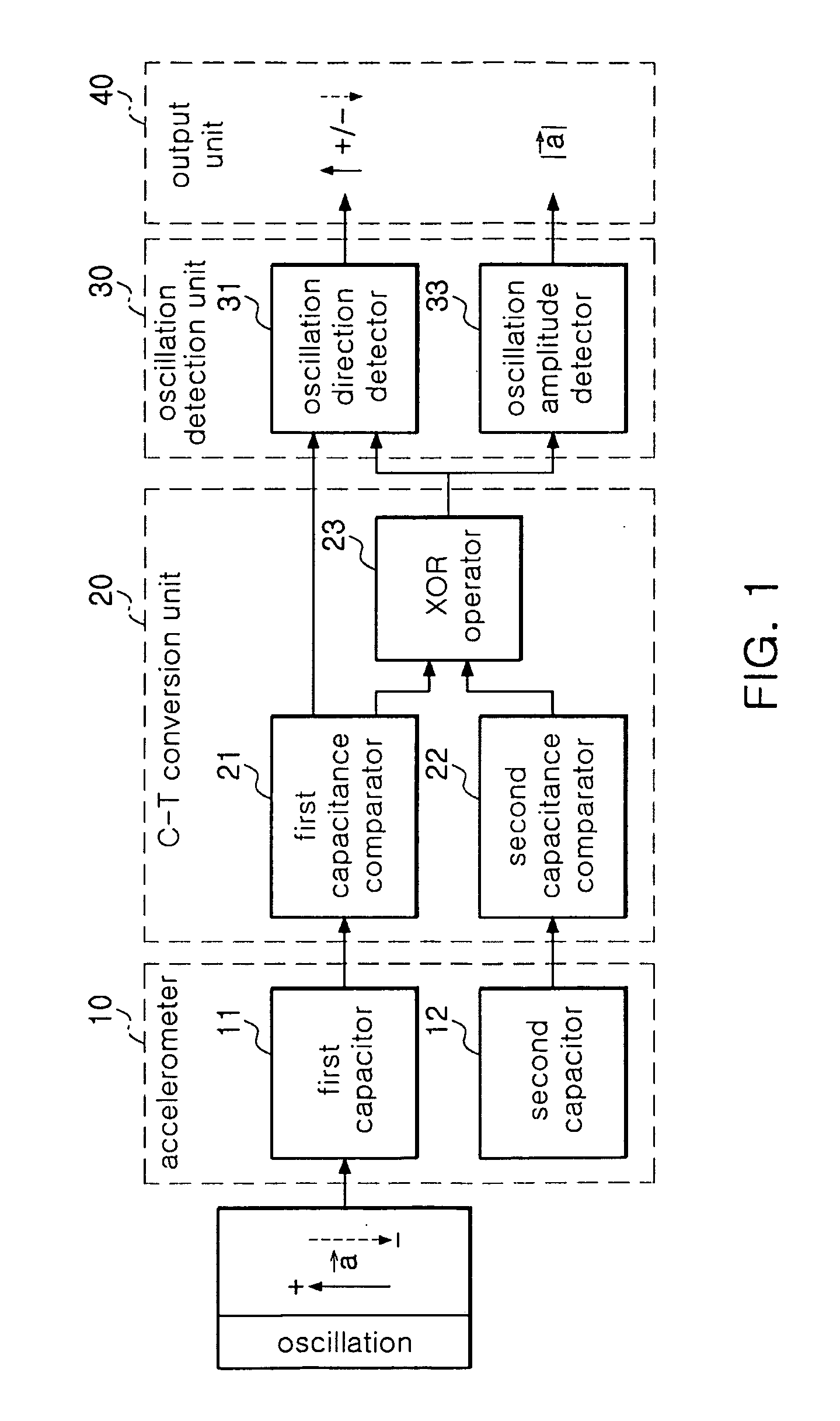
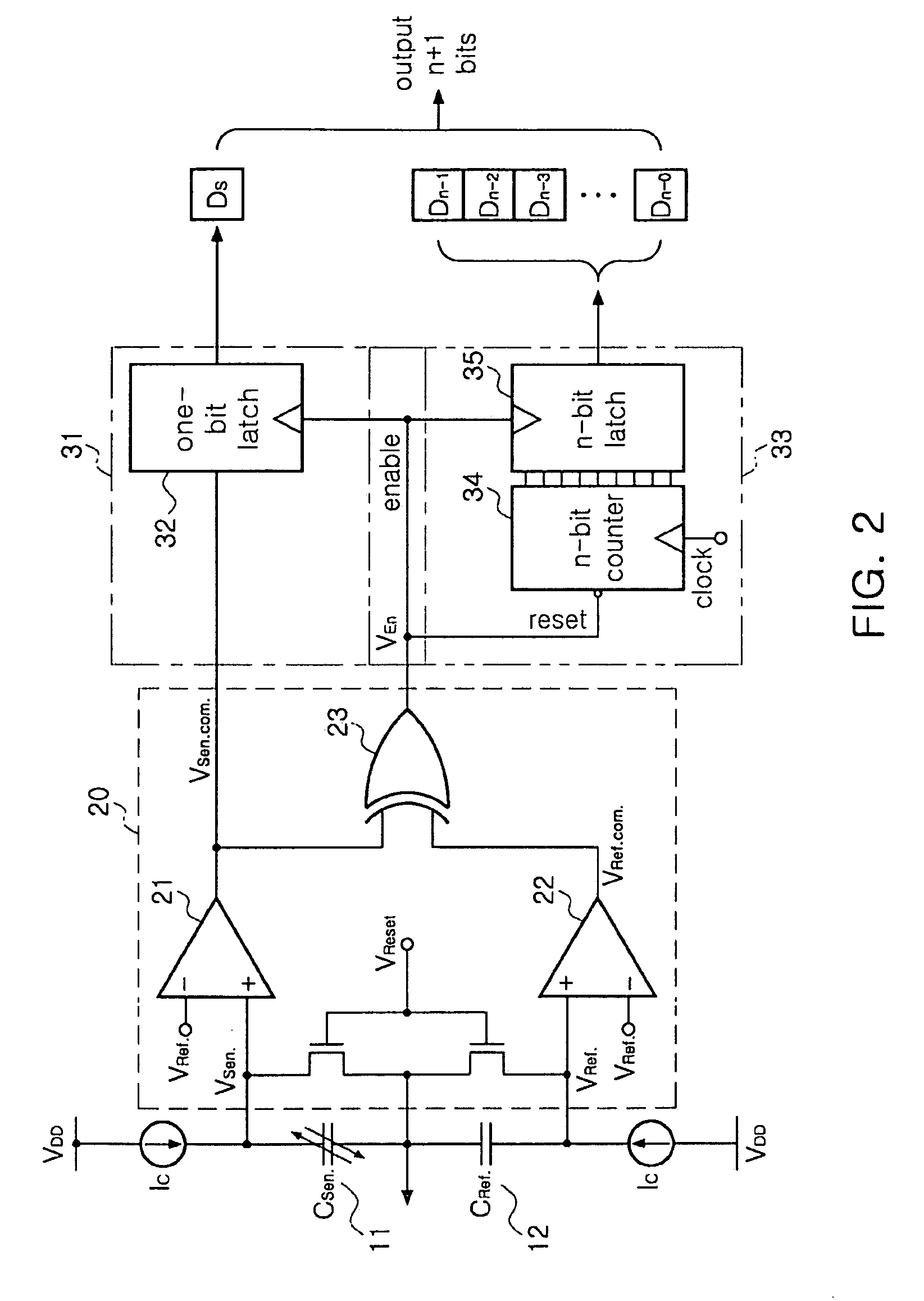
Bidirectional readout circuit for detecting direction and amplitude of capacitive MEMS accelerometers
InactiveUS7997137B2High resolutionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementTime changesMems sensors
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Mobile communication apparatus
InactiveUS20040137853A1Substation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverVariable-gain amplifier
A transceiver suitable for larger scale of integration employs direct conversion reception for reducing the number of filters. Also, the number of VCOs is reduced by utilizing dividers to supply a receiver and a transmitter with locally oscillated signals at an RF band. Dividers each having a fixed division ratio are used for generating locally oscillated signals for the receiver, while a divider having a switchable division ratio are used for generating the locally oscillated signal for the transmitter. In addition, a variable gain amplifier for baseband signal is provided with a DC offset voltage detector and a DC offset canceling circuit for supporting high speed data communications to accomplish fast cancellation of a DC offset by eliminating intervention of a filter within a feedback loop for offset cancellation.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Bidirectional readout circuit for detecting direction and amplitude of capacitive MEMS accelerometers
ActiveUS20090056448A1High Resolution FeaturesHigh resolutionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceAccelerometer
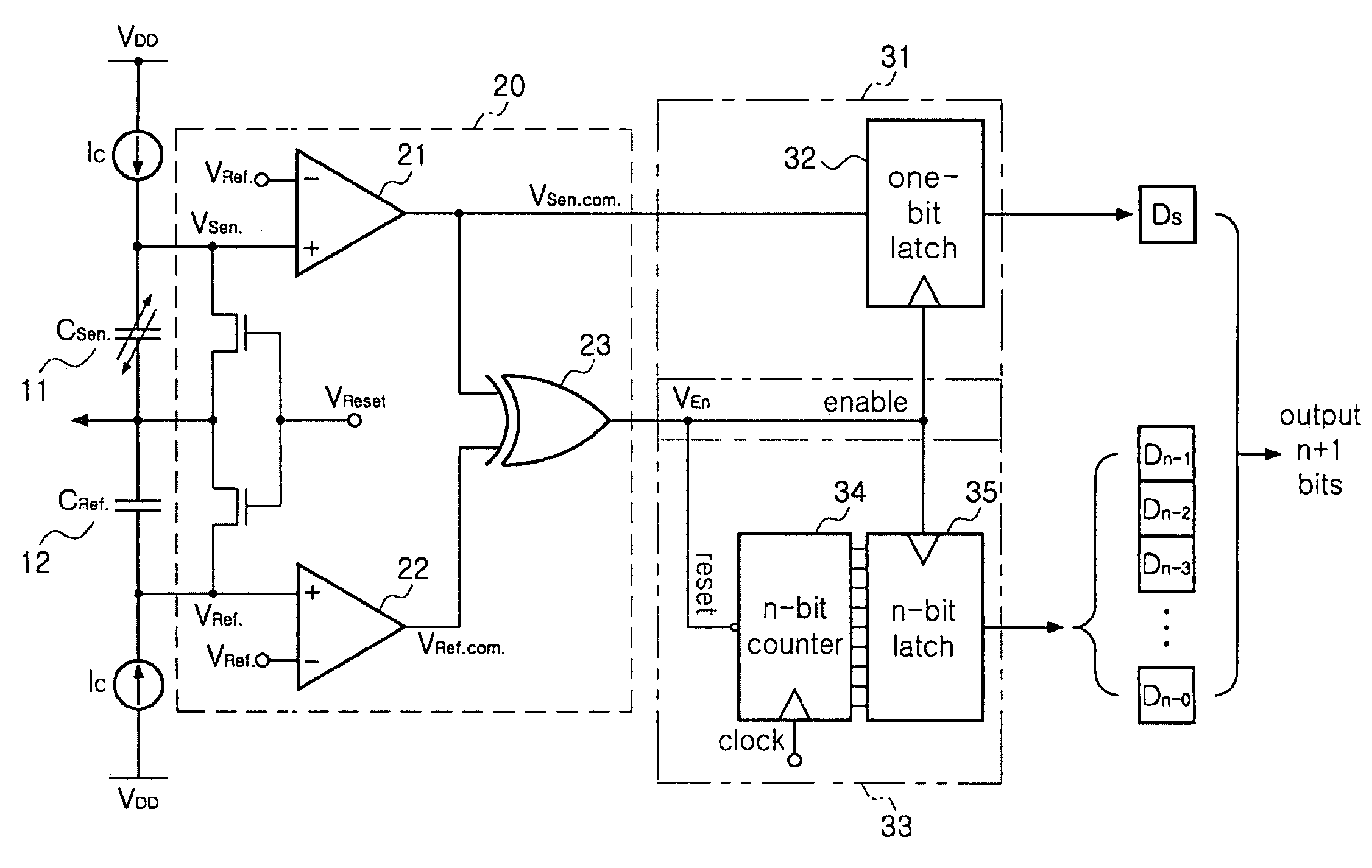
There is provided a bidirectional readout circuit for detecting direction and amplitude of an oscillation sensed at a capacitive microelectromechanical system (MEMS) accelerometer, the bidirectional readout circuit converting capacitance changes of the capacitive MEMS accelerometer into a time change amount by using high resolution capacitance-to-time conversion technology and outputting the time change amount as the direction and the amplitude of the oscillation by using time-to-digital conversion (TDC) technology, thereby detecting not only the amplitude of the oscillation but also the direction thereof, which is capable of being applied to various MEMS sensors.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
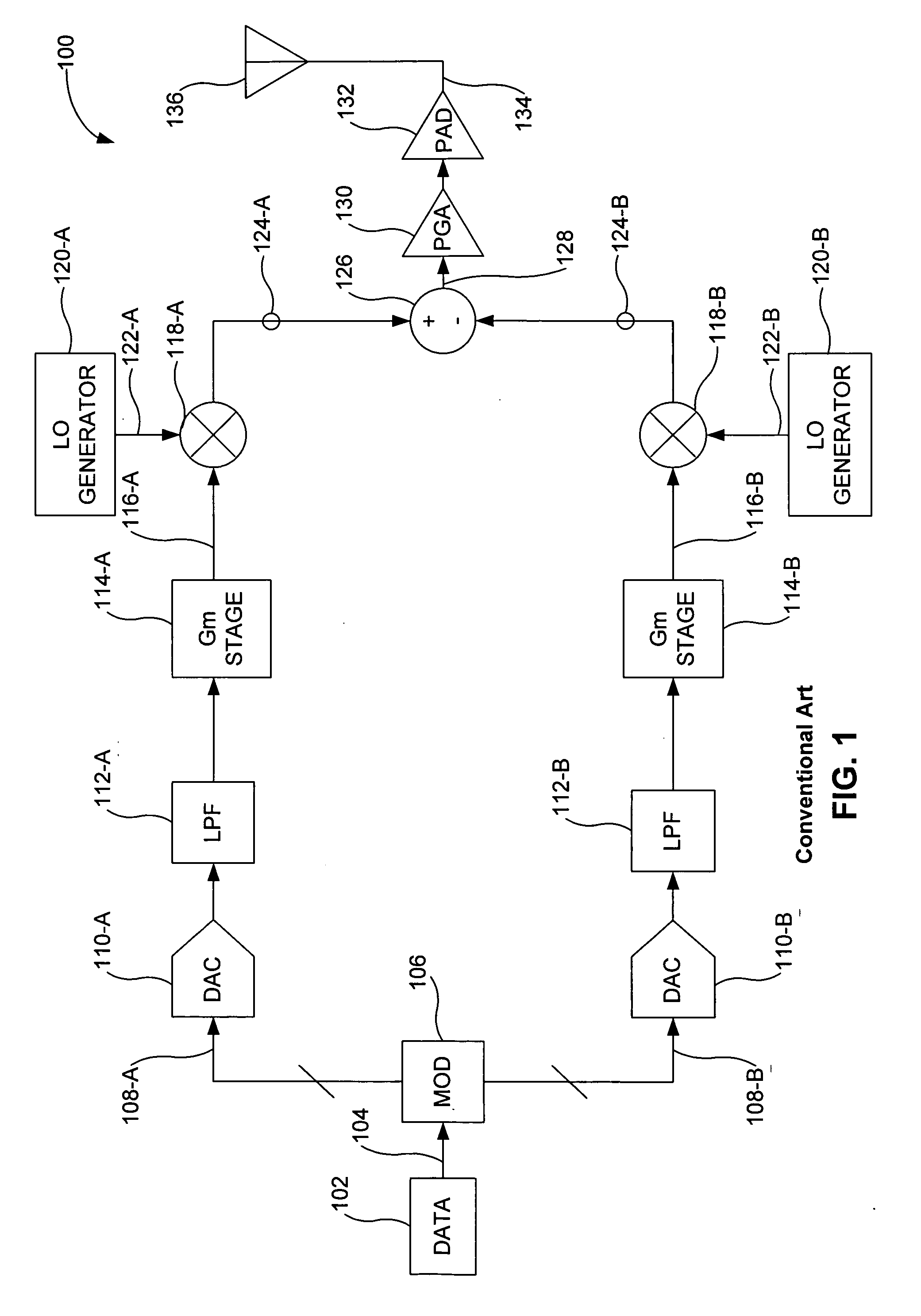
Apparatus and method of local oscillator leakage cancellation
InactiveUS7440732B2Reduce eliminateReduce the required powerResonant long antennasSecret communicationFrequency mixerLocal oscillator
A transmitter includes a first mixer to generate a first output signal by up-converting a first baseband signal having a first DC offset component. A second mixer generates a second output signal by up-converting a second baseband signal having a second DC offset component. The second output signal is subtracted from the first output signal to generate a transmitter output signal. The transmitter output signal includes a local oscillator (LO) leakage signal caused by the first and / or second DC offset components. A third mixer produces a third output signal by up-converting the first DC offset component. A fourth mixer produces a fourth output signal by up-converting the second DC offset component. The fourth output signal is subtracted from the third output signal to generate a LO leakage cancellation signal. The LO leakage cancellation signal is subtracted from the transmitter output signal, thereby reducing a power of the LO leakage signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
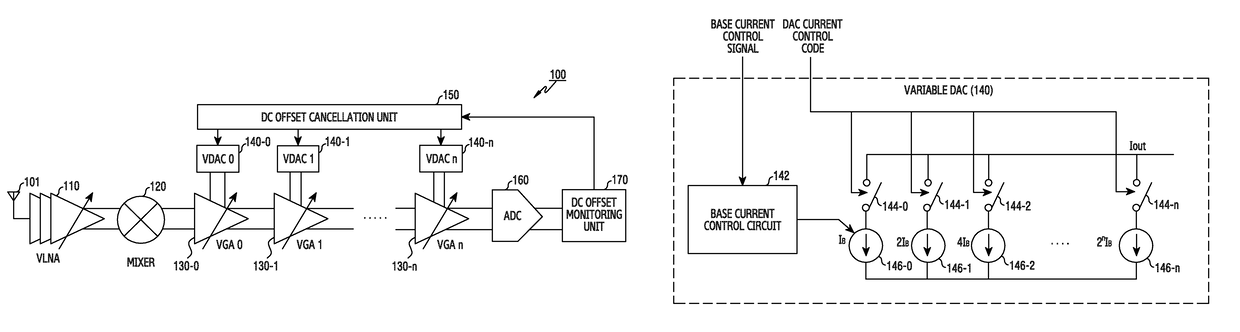
Method and apparatus for direct conversion receiver correcting direct current offset
ActiveUS20160330049A1Minimize Direct Current (DC) offsetPerformance degradation can be preventedDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionDemodulationAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
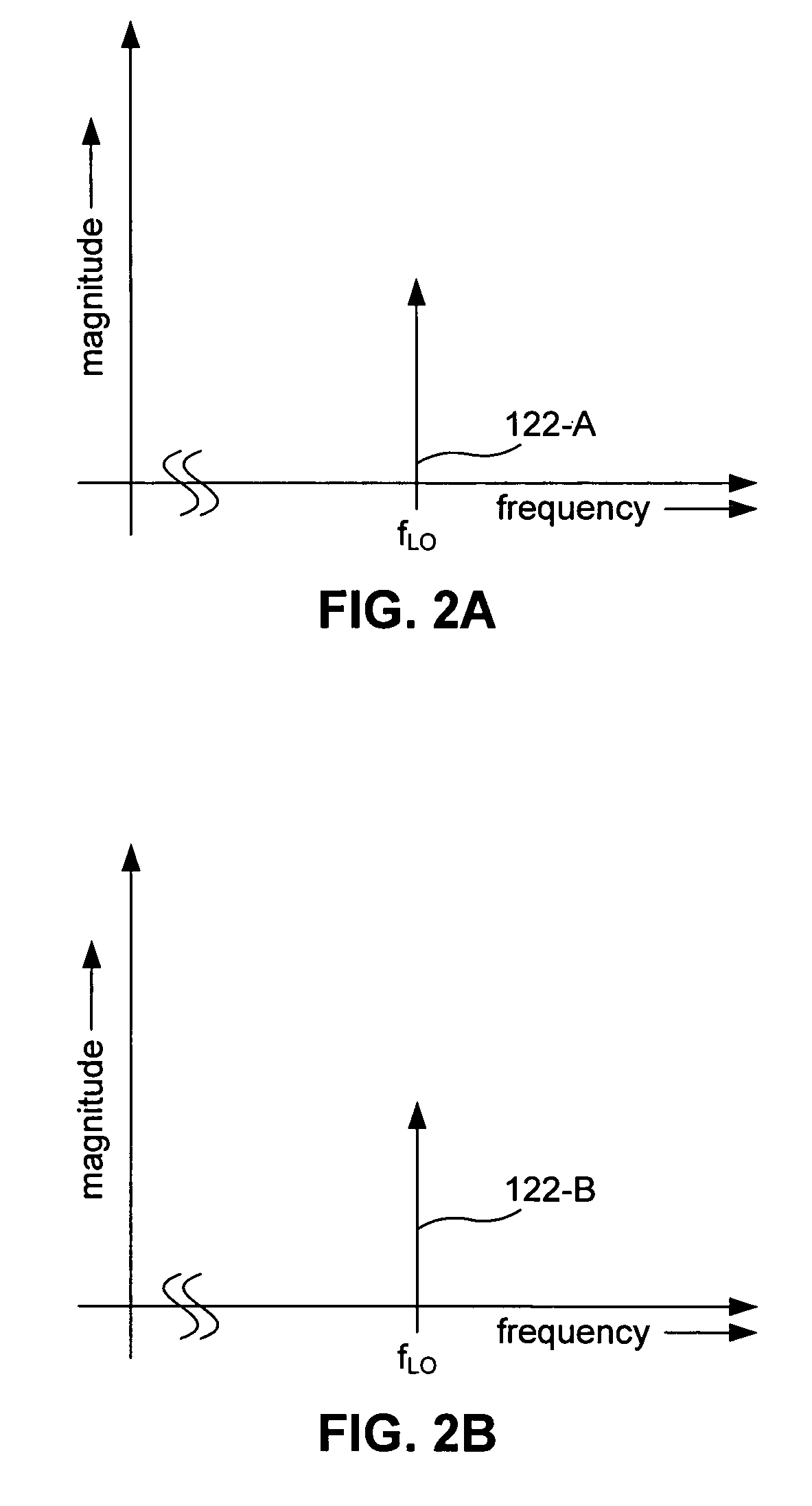
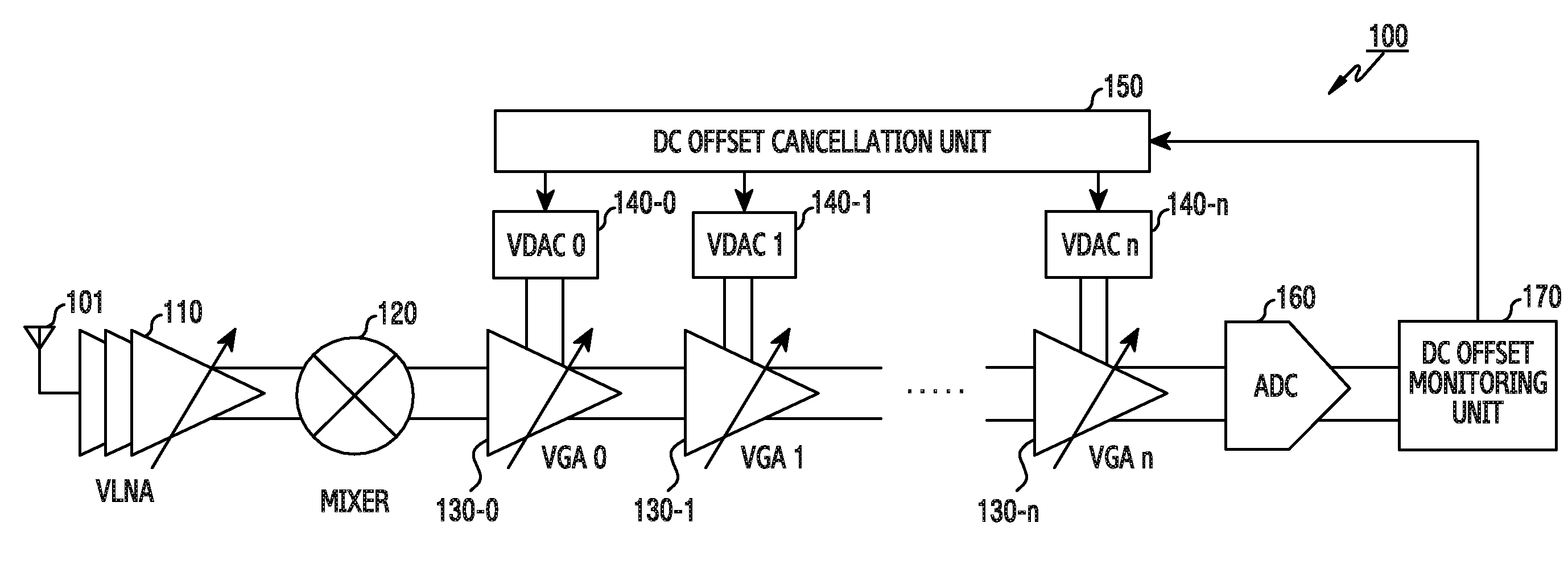
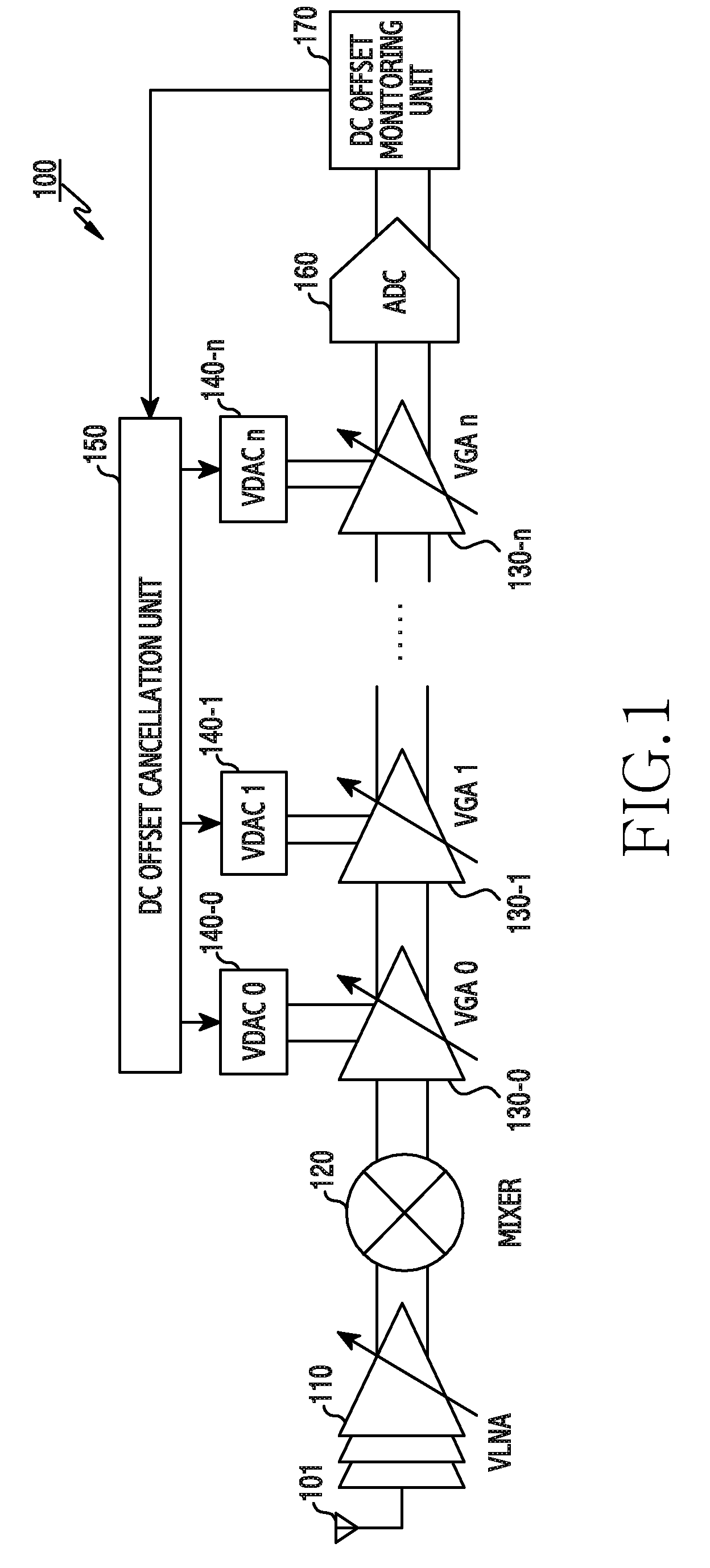
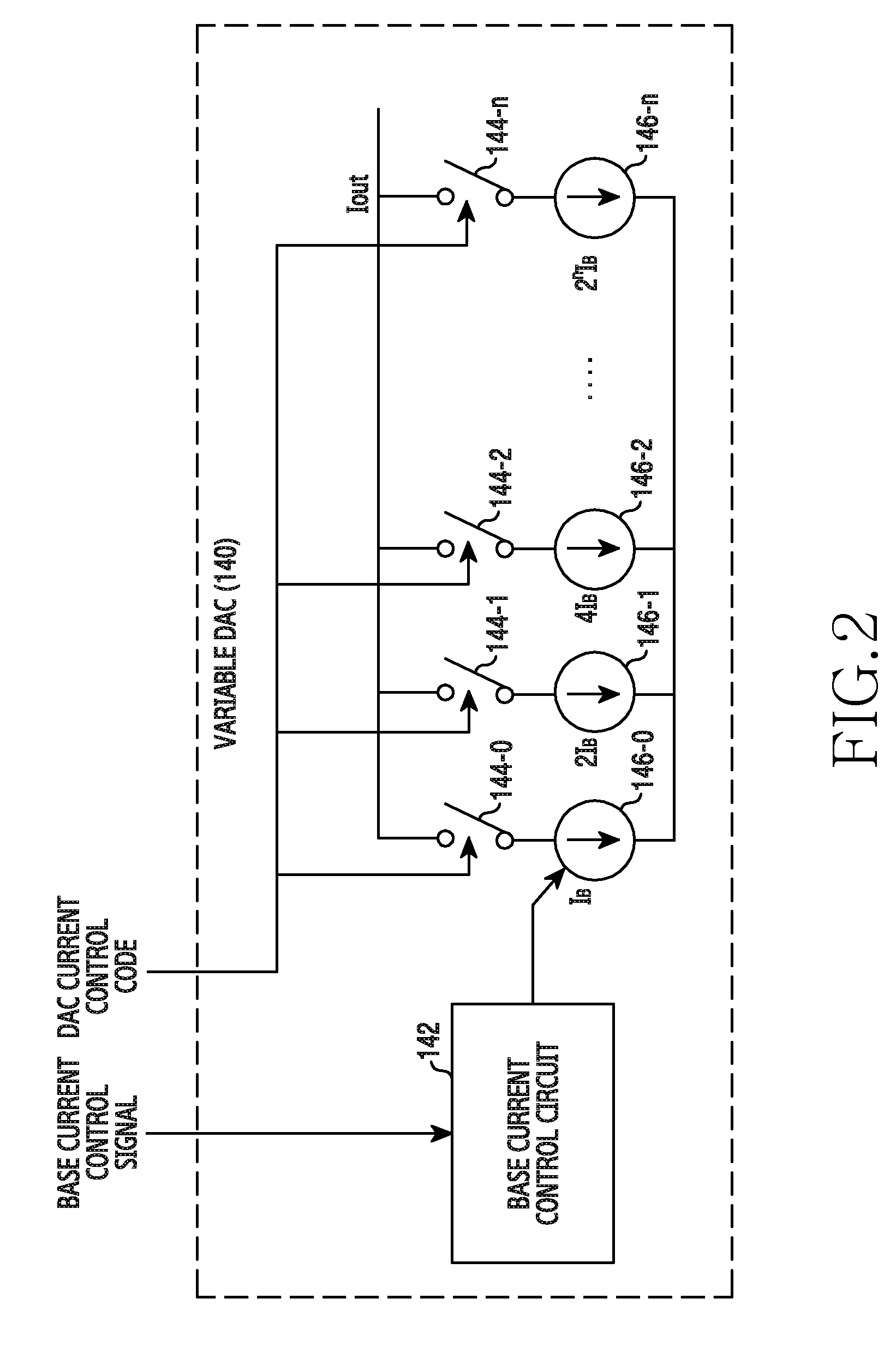
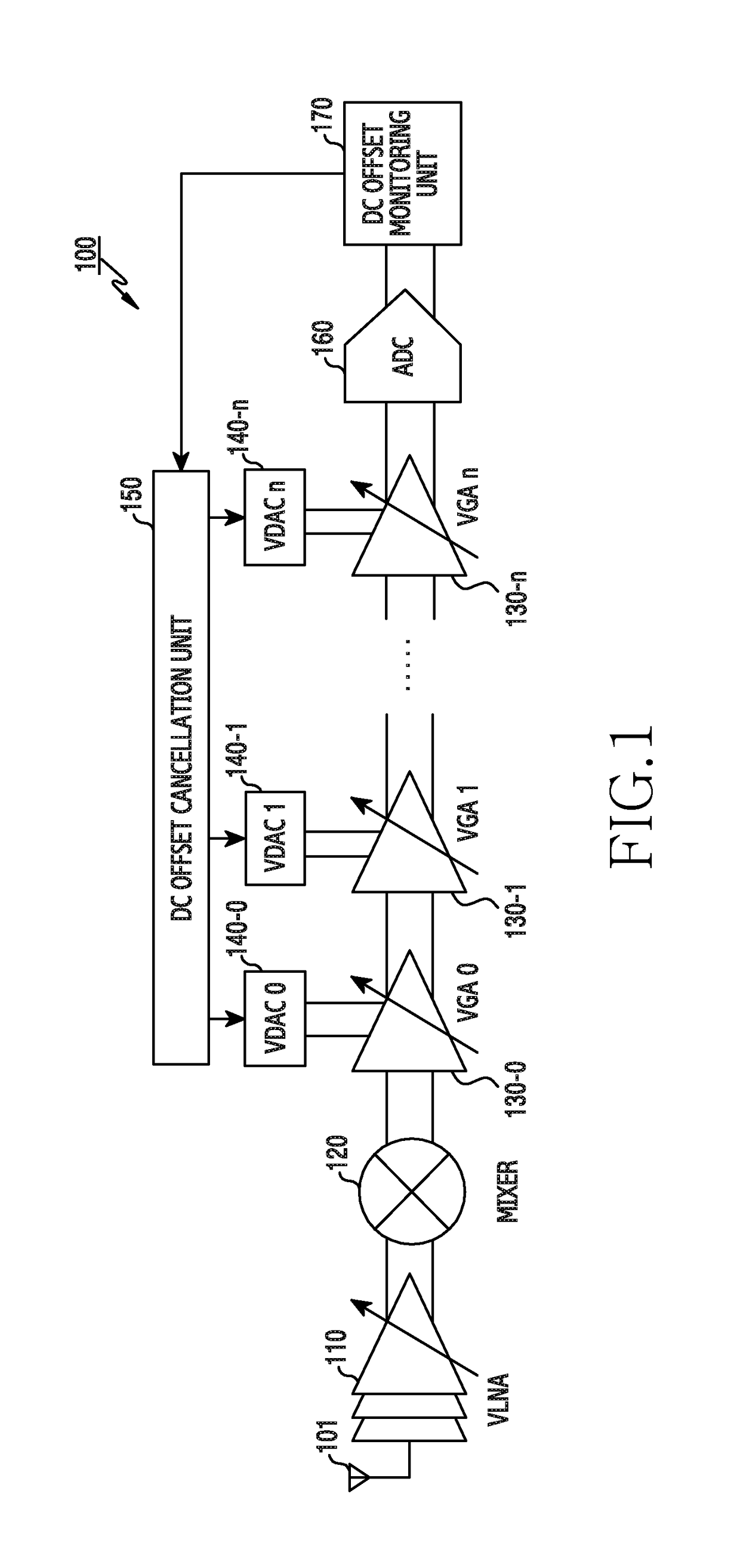
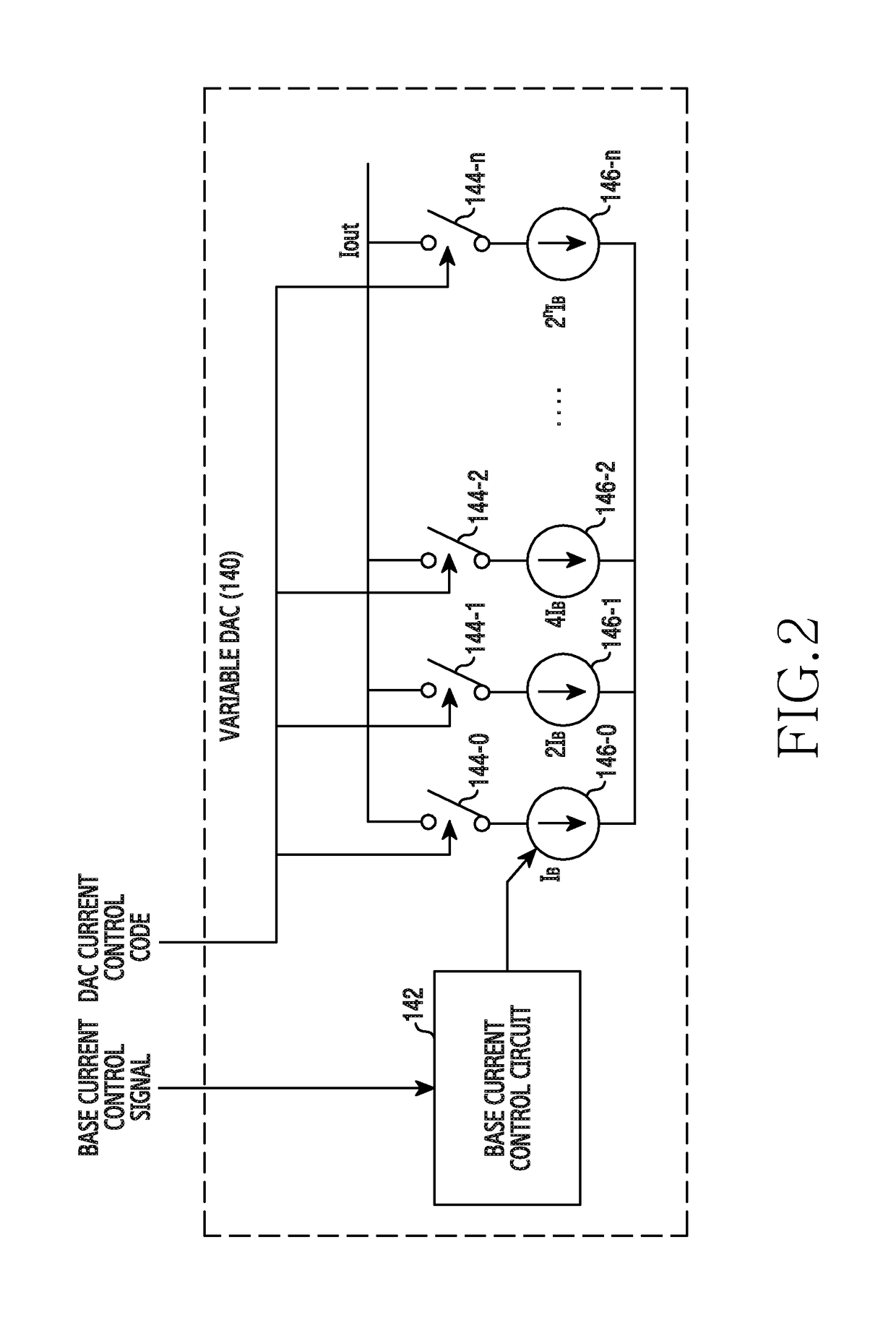
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for direct current offset calibration of a direct conversion receiver, a Direct Current (DC) offset calibration apparatus of a direct conversion receiver includes a plurality of variable gain amplifiers for amplifying an input signal based on a gain control value, a DC offset monitoring unit for monitoring a DC offset for an output signal of the plurality of variable gain amplifiers, a plurality of variable Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) for controlling a current applied to each of the plurality of variable gain amplifiers according to a current control code, and a DC offset cancellation unit for determining a current control code set which minimizes the DC offset value per preset gain control value, and thus the DC offset can be precisely cancelled without being affected by external factors such as a signal modulation method and heat and performance degradation of the receiver can be prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Automatic IIP2 calibration architecture
ActiveUS7742747B2Minimize overheadEasing testing requirementReceivers monitoringCommunication jammingWireless transceiverOperation mode
Owner:ICERA CANADA ULC
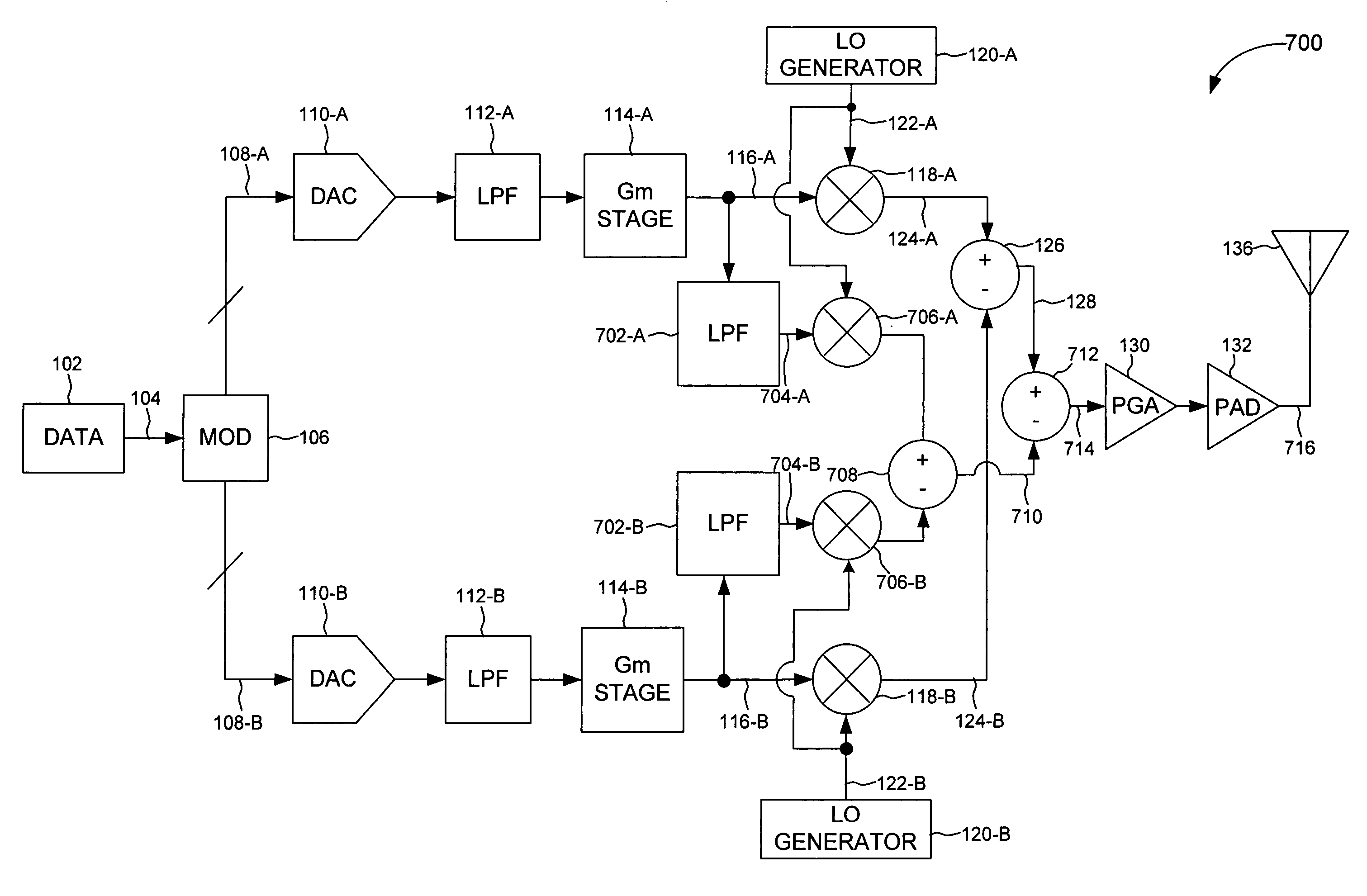
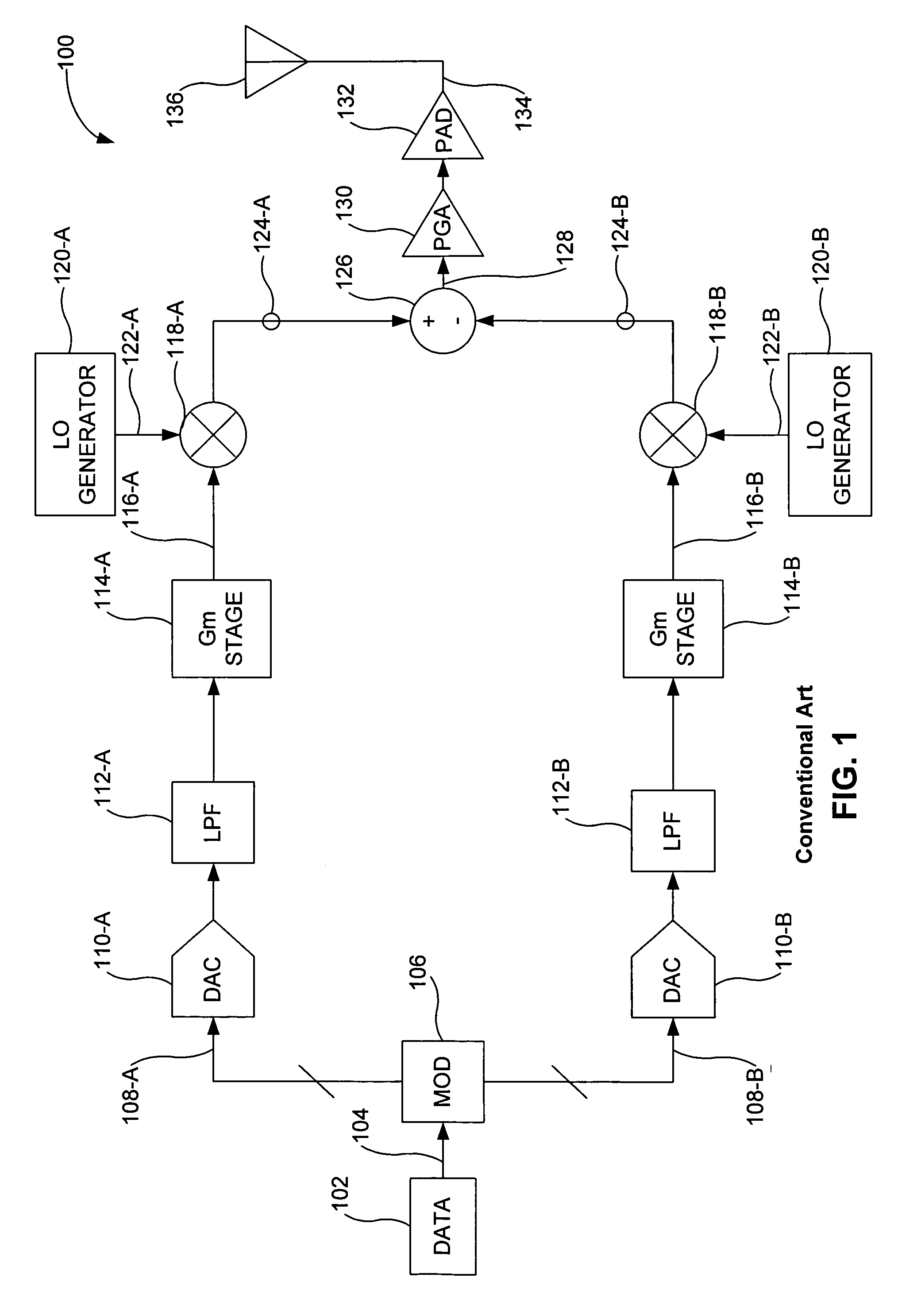
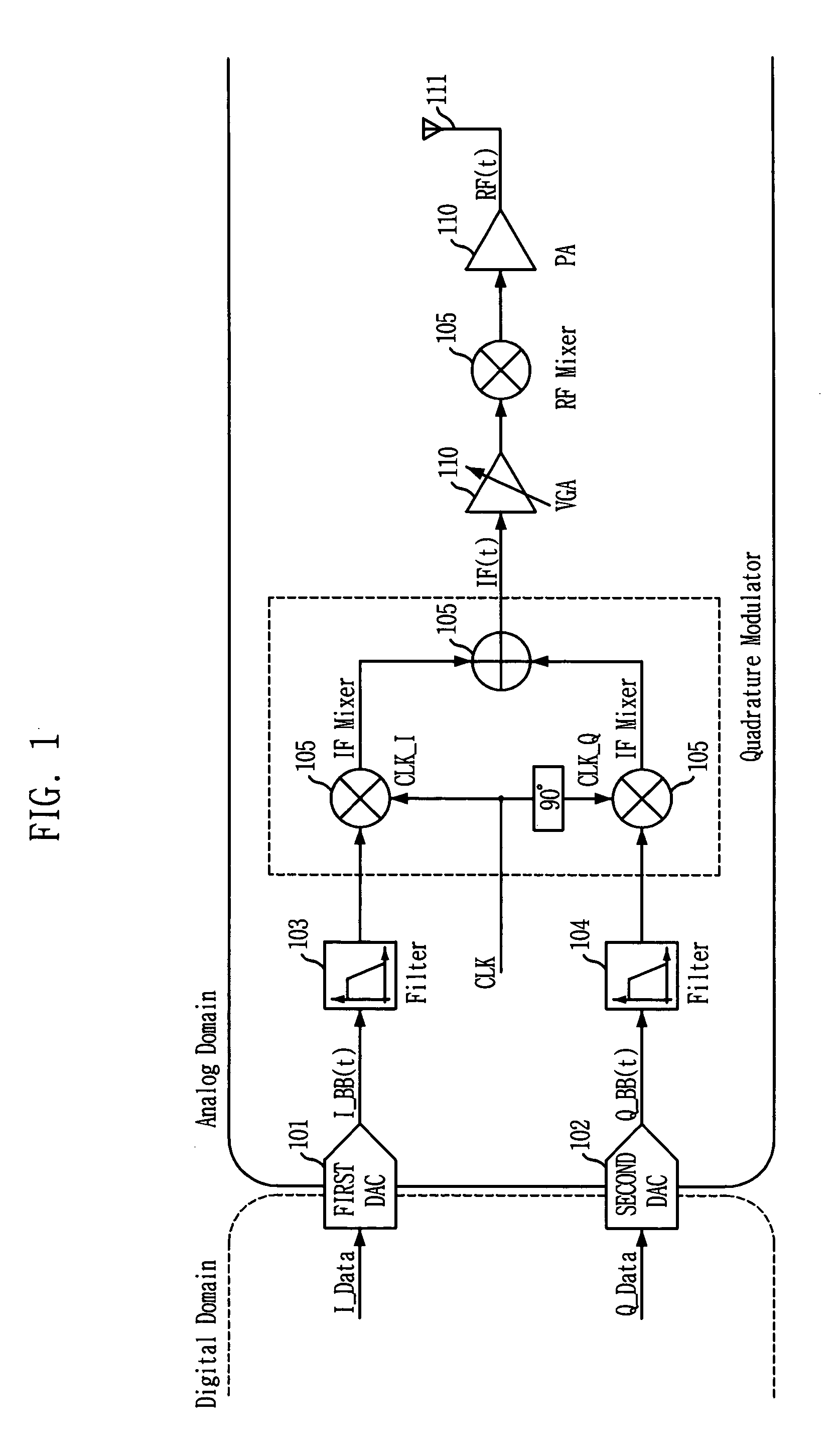
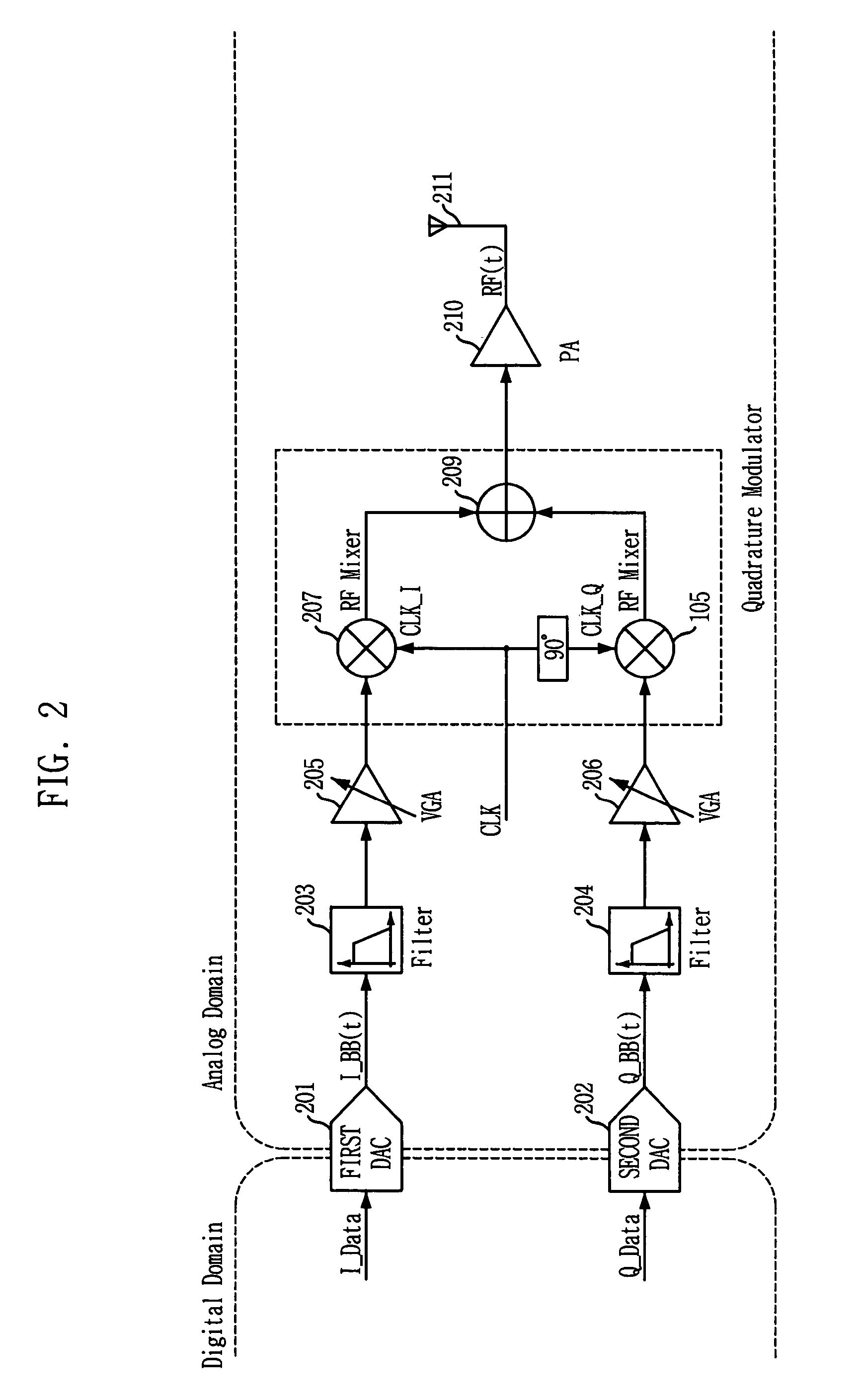
Quadrature modulation transmitter
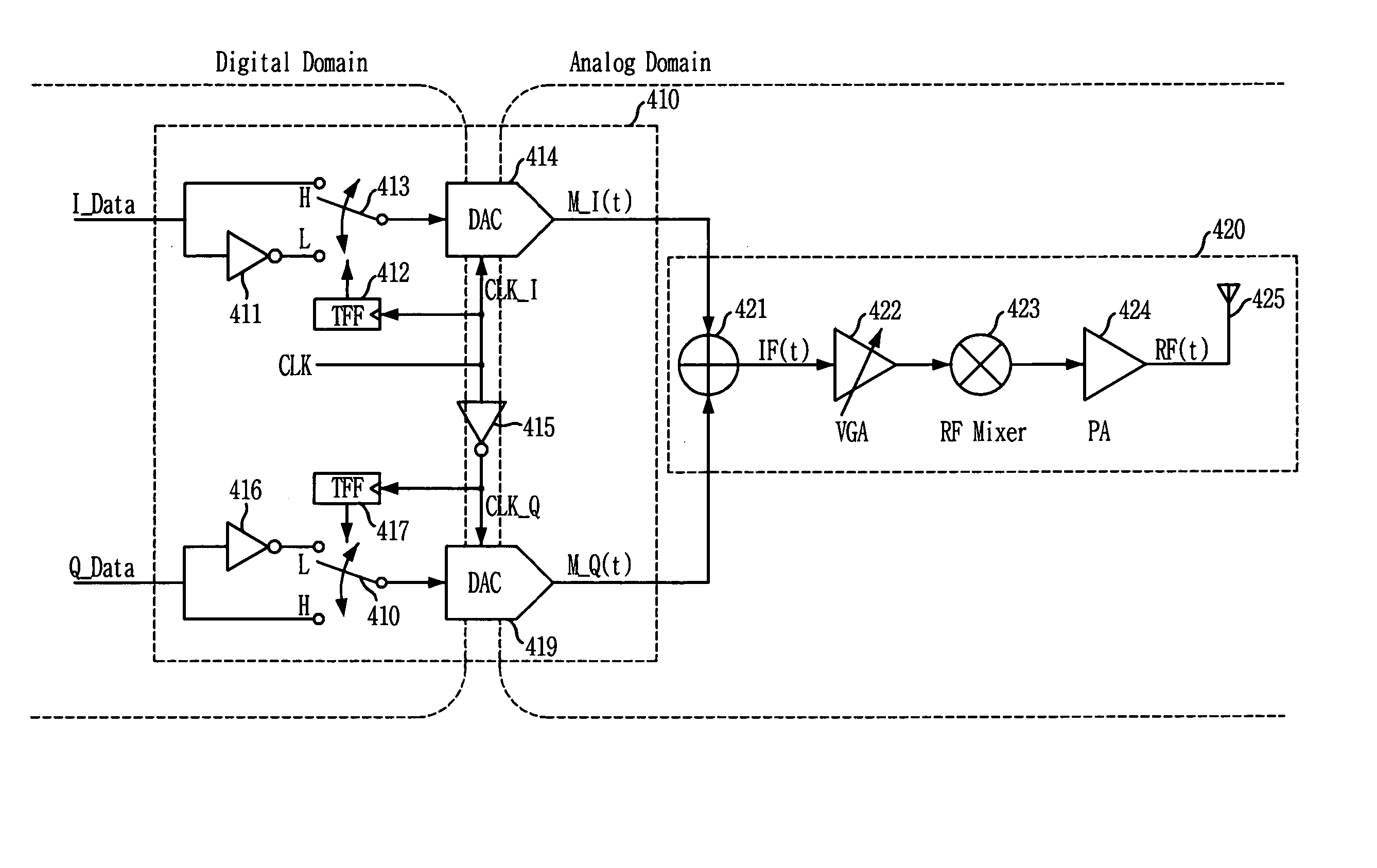
ActiveUS7212585B2Simple circuit structureReduce power consumptionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsChannel dataQuadrature modulation
There is provided a quadrature modulation transmitter which is capable of solving several problems of the conventional transmitter while performing the same function as the heterodyne transmitter or the digital IF transmitter, in which a circuit structure is simplified and a power consumption is reduced compared with the conventional transmitter. The quadrature modulation transmitter includes: a digital processing block for receiving an I-channel data, a Q-channel data and a clock signal, modulating the I-channel data or an inverted I-channel data into a first analog signal by means of an I-channel DAC according to a switching of an I-clock signal identical to the clock signal, and modulating the Q-channel data and an inverted Q-channel data into a second analog signal by means of a Q-channel DAC according to a switching of a Q-clock signal, the Q-clock signal being an inverted clock signal; and an analog processing block for receiving the first and second analog signals from the digital processing block, adding the first and second analog signals, converting the added signal into an RF domain signal through a mixing operation, and amplifying and transmitting the RF domain signal.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Mobile communication apparatus
InactiveUS7366489B2Low costReduce in quantityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentVariable-gain amplifierTransceiver
A transceiver suitable for larger scale of integration employs direct conversion reception for reducing the number of filters. Also, the number of VCOs is reduced by utilizing dividers to supply a receiver and a transmitter with locally oscillated signals at an RF band. Dividers each having a fixed division ratio are used for generating locally oscillated signals for the receiver, while a divider having a switchable division ratio are used for generating the locally oscillated signal for the transmitter. In addition, a variable gain amplifier for baseband signal is provided with a DC offset voltage detector and a DC offset canceling circuit for supporting high speed data communications to accomplish fast cancellation of a DC offset by eliminating intervention of a filter within a feedback loop for offset cancellation.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Apparatus and method of local oscillator leakage cancellation
InactiveUS20070049220A1Reduce eliminateReduce the required powerResonant long antennasSecret communicationFrequency mixerLocal oscillator
A transmitter includes a first mixer to generate a first output signal by up-converting a first baseband signal having a first DC offset component. A second mixer generates a second output signal by up-converting a second baseband signal having a second DC offset component. The second output signal is subtracted from the first output signal to generate a transmitter output signal. The transmitter output signal includes a local oscillator (LO) leakage signal caused by the first and / or second DC offset components. A third mixer produces a third output signal by up-converting the first DC offset component. A fourth mixer produces a fourth output signal by up-converting the second DC offset component. The fourth output signal is subtracted from the third output signal to generate a LO leakage cancellation signal. The LO leakage cancellation signal is subtracted from the transmitter output signal, thereby reducing a power of the LO leakage signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
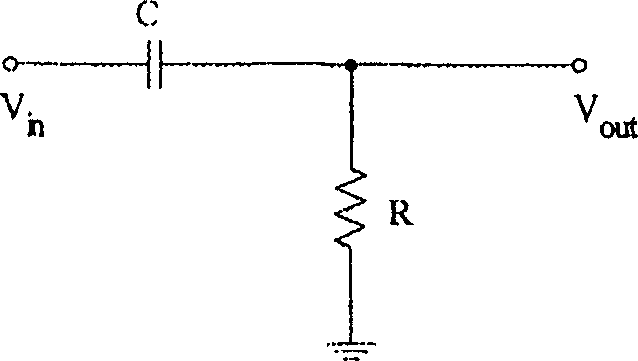
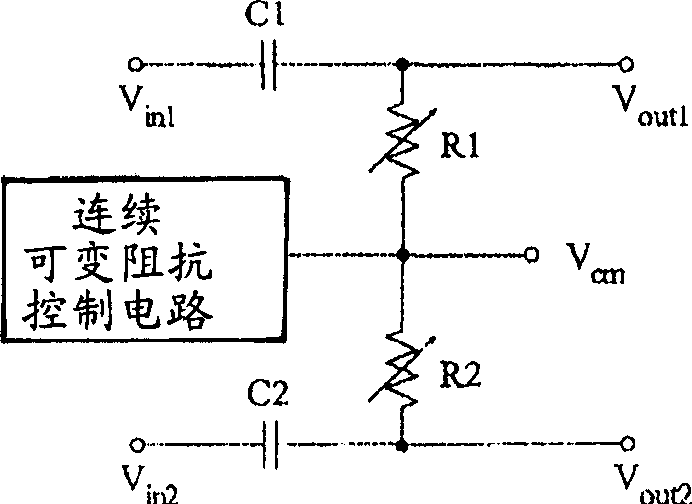
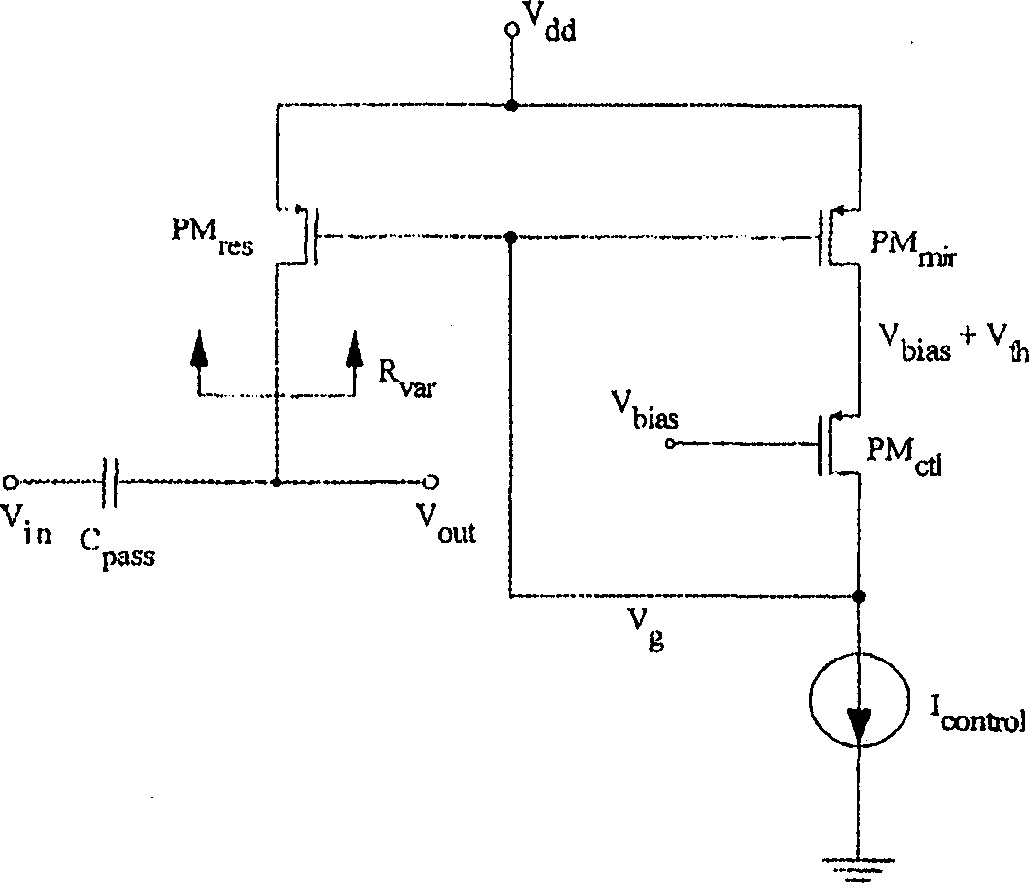
Fast-settling DC offset removal circuits with continuous cutoff frequency switching
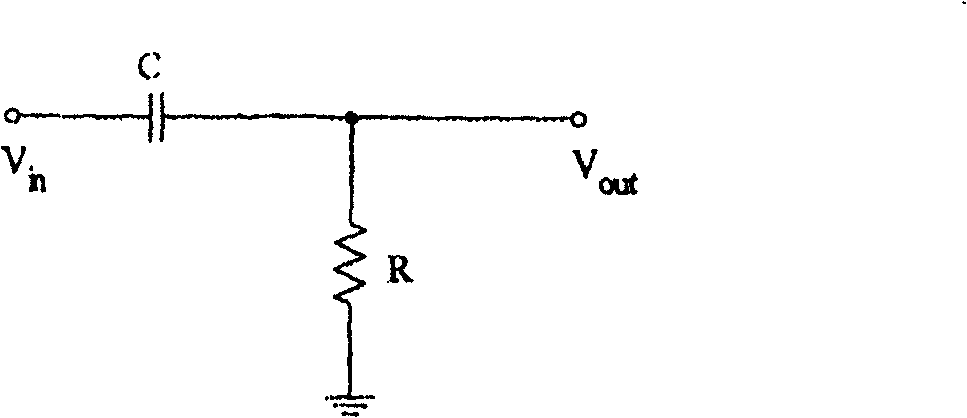
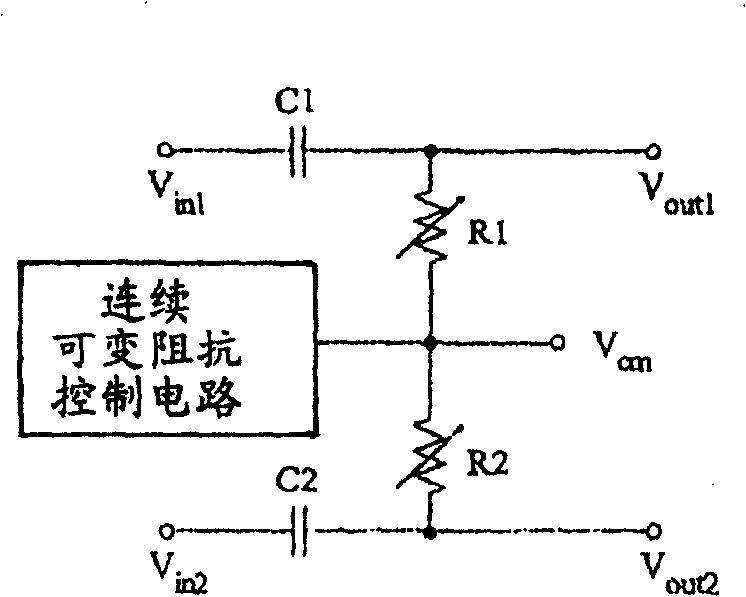
A fast-setting DC offset removal circuit with continuous cutoff frequency switching is disclosed. In the preferred embodiment, the circuit is implemented using a pair of RC filters for receiving a differential signal pair and a continuous, variable resistance control circuit. The control circuit can be current-controlled or voltage controlled to provide fast settling of the received signal and the removal of the DC offset components. Additionally, by using a current-controlled control circuit, the cutoff frequency of the RC filter can be ramped from high to low in a continuous manner, thereby minimizing the generation of DC offsets.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method and apparatus for direct conversion receiver correcting direct current offset
ActiveUS9948484B2Performance degradation can be preventedMinimise currentDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for direct current offset calibration of a direct conversion receiver, a Direct Current (DC) offset calibration apparatus of a direct conversion receiver includes a plurality of variable gain amplifiers for amplifying an input signal based on a gain control value, a DC offset monitoring unit for monitoring a DC offset for an output signal of the plurality of variable gain amplifiers, a plurality of variable Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) for controlling a current applied to each of the plurality of variable gain amplifiers according to a current control code, and a DC offset cancellation unit for determining a current control code set which minimizes the DC offset value per preset gain control value, and thus the DC offset can be precisely cancelled without being affected by external factors such as a signal modulation method and heat and performance degradation of the receiver can be prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
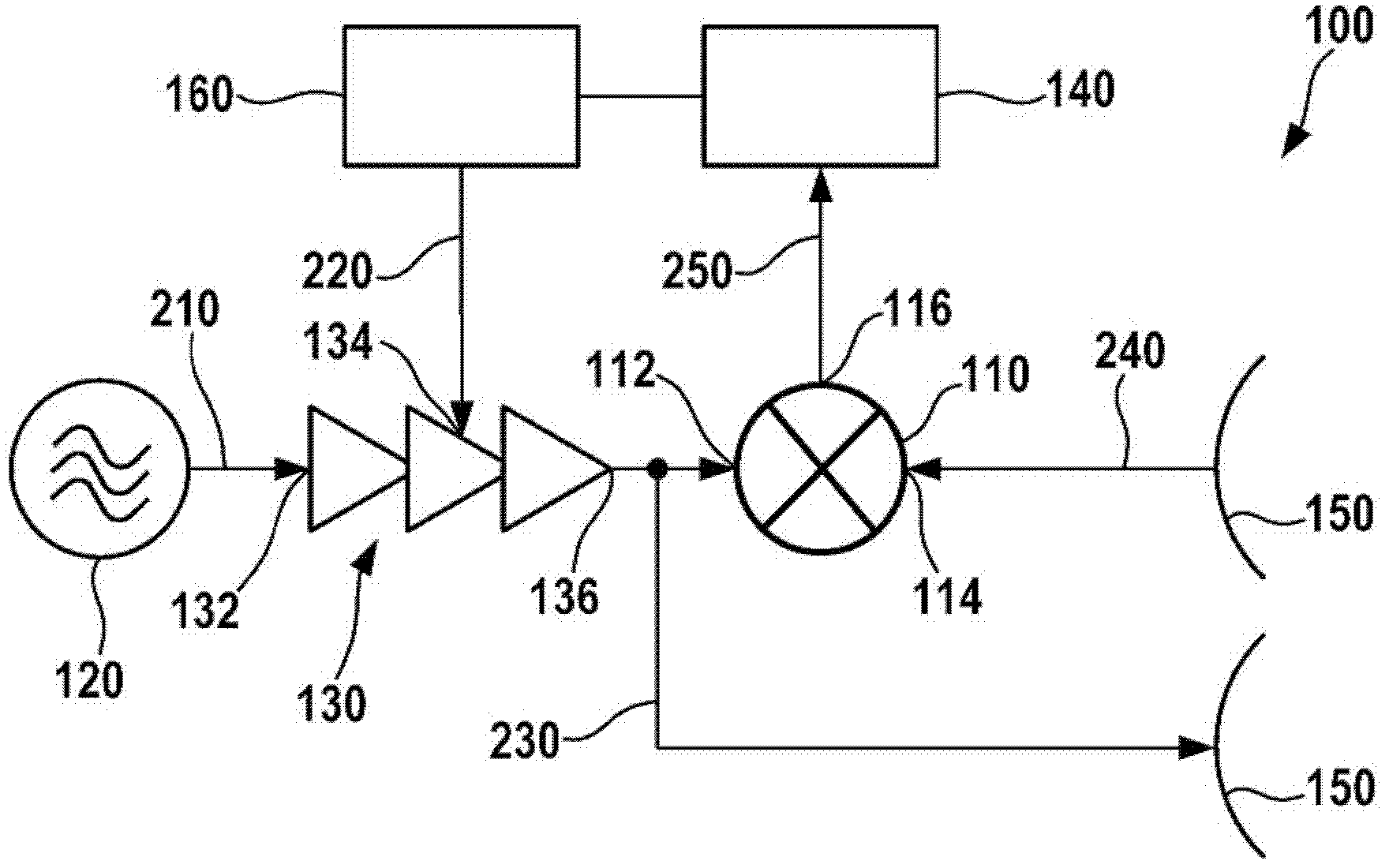
Mixer monitoring
InactiveUS20120182177A1Easy to carryEasy to controlWave based measurement systemsDemodulationEngineeringBaseband
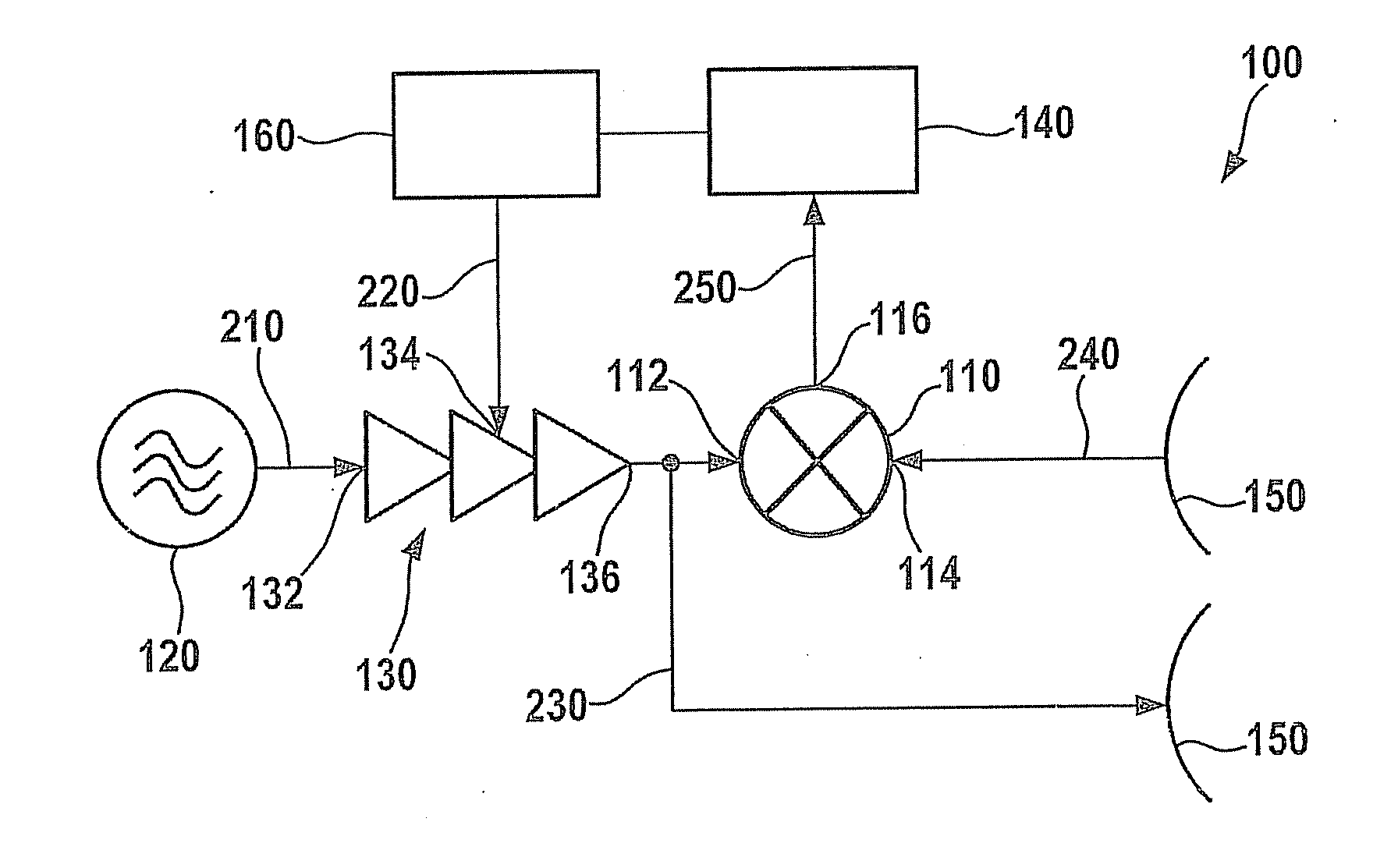
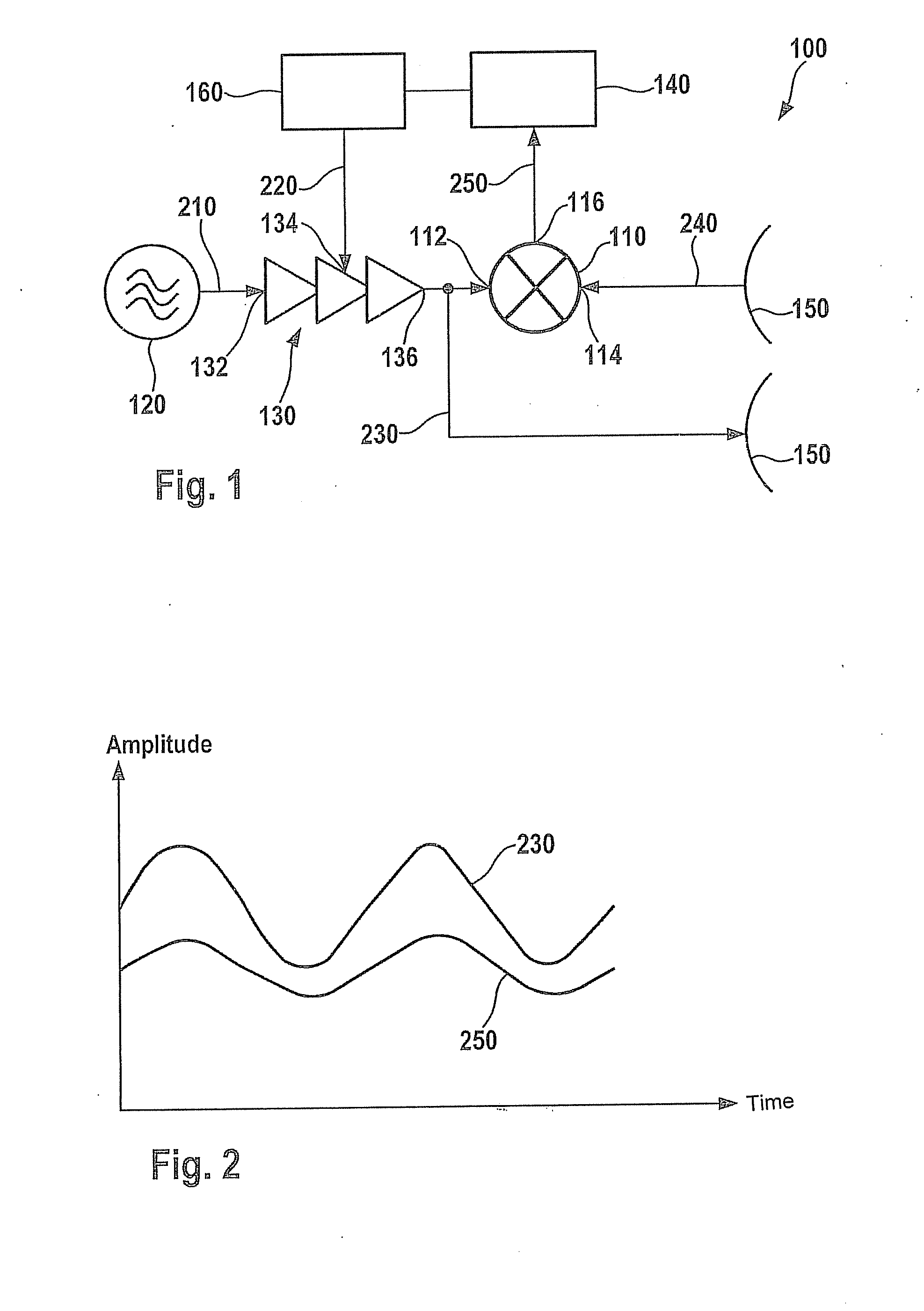
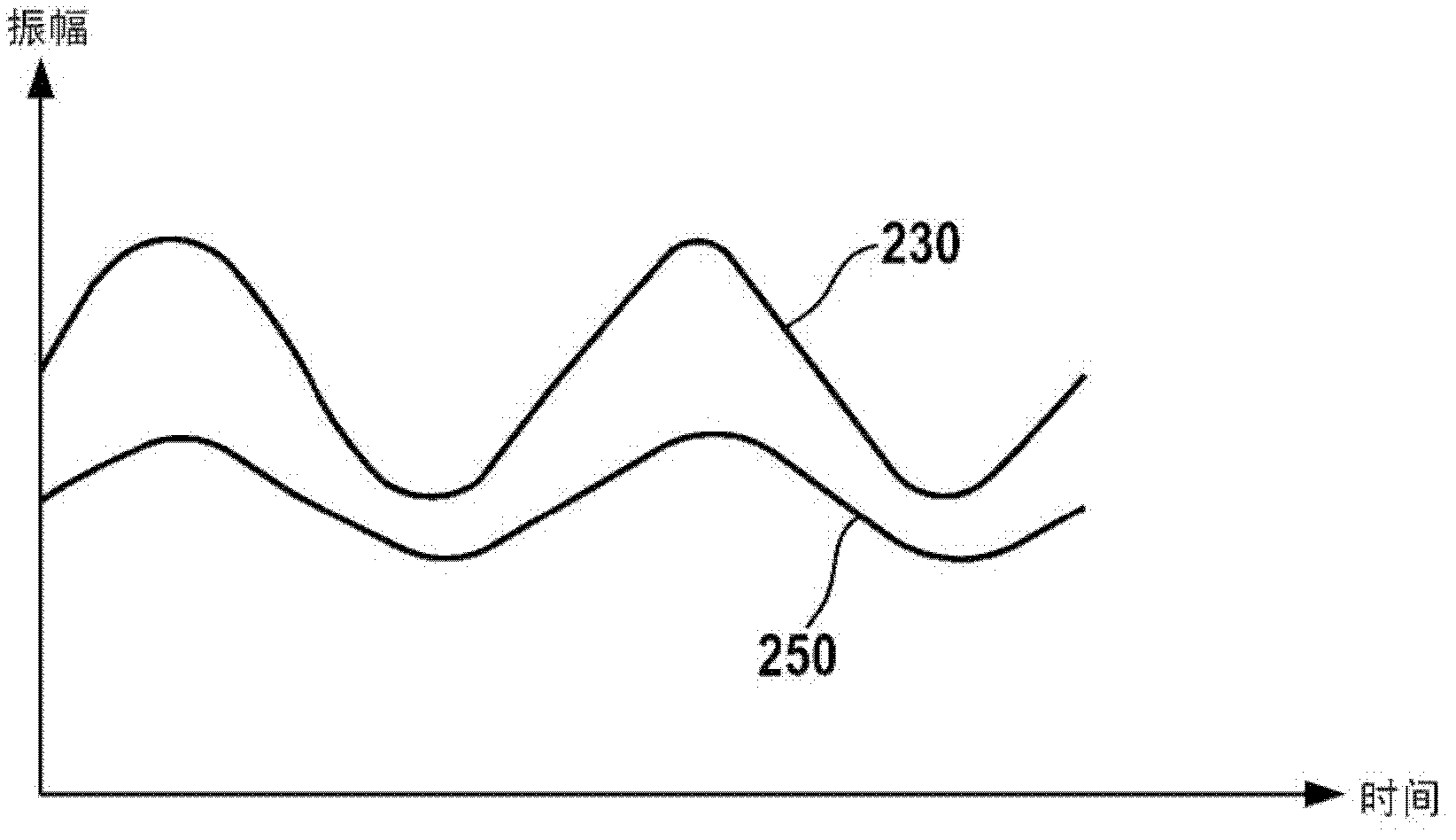
In a method for checking the functionality of a mixer, the mixer is supplied with a high-frequency signal and a high-frequency comparison signal in order to generate a baseband signal. The amplitude of the high-frequency signal is modified as a function of time. A direct-current voltage component of the baseband signal which is output by the mixer is analyzed to determine the functionality of the mixer.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
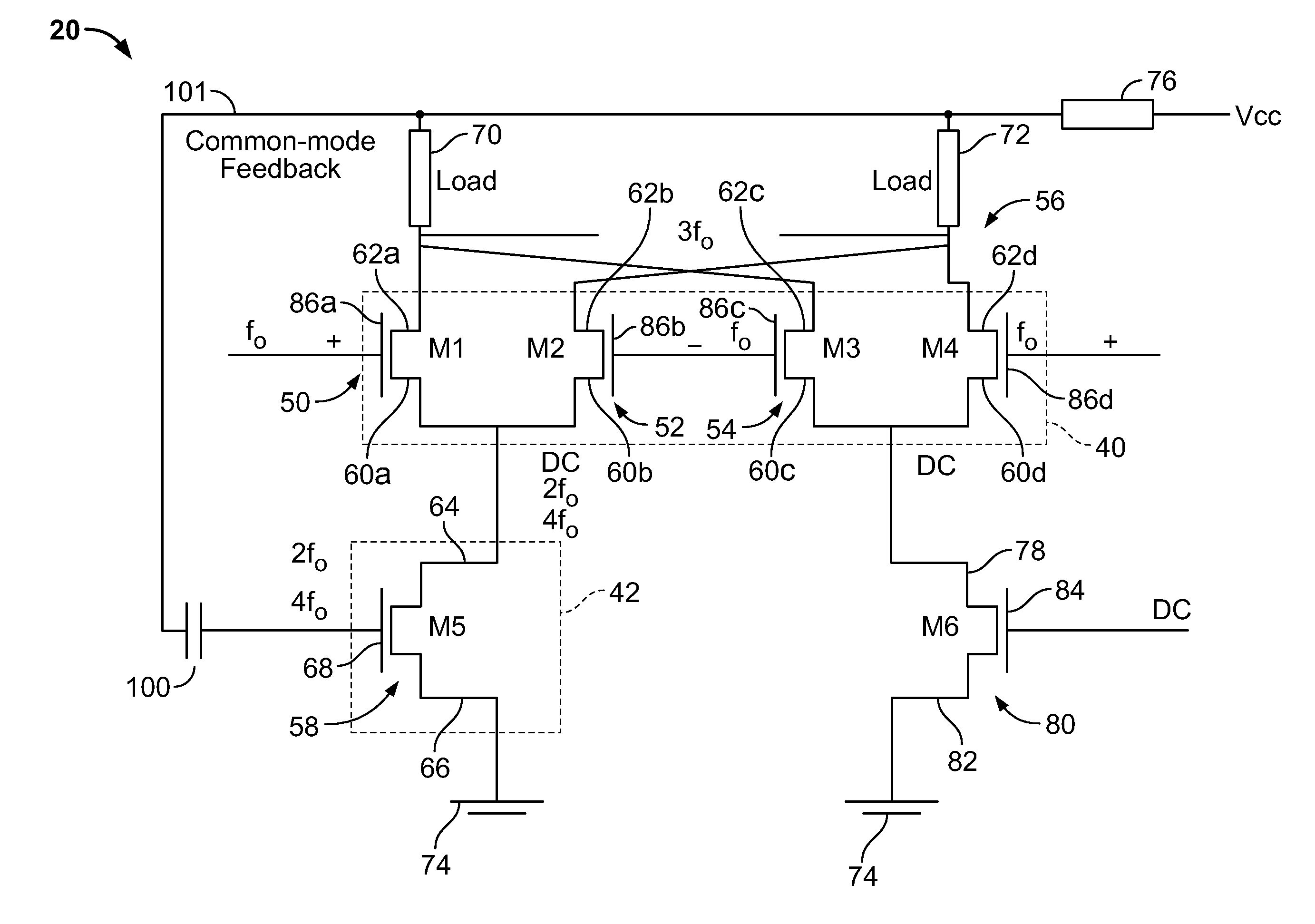
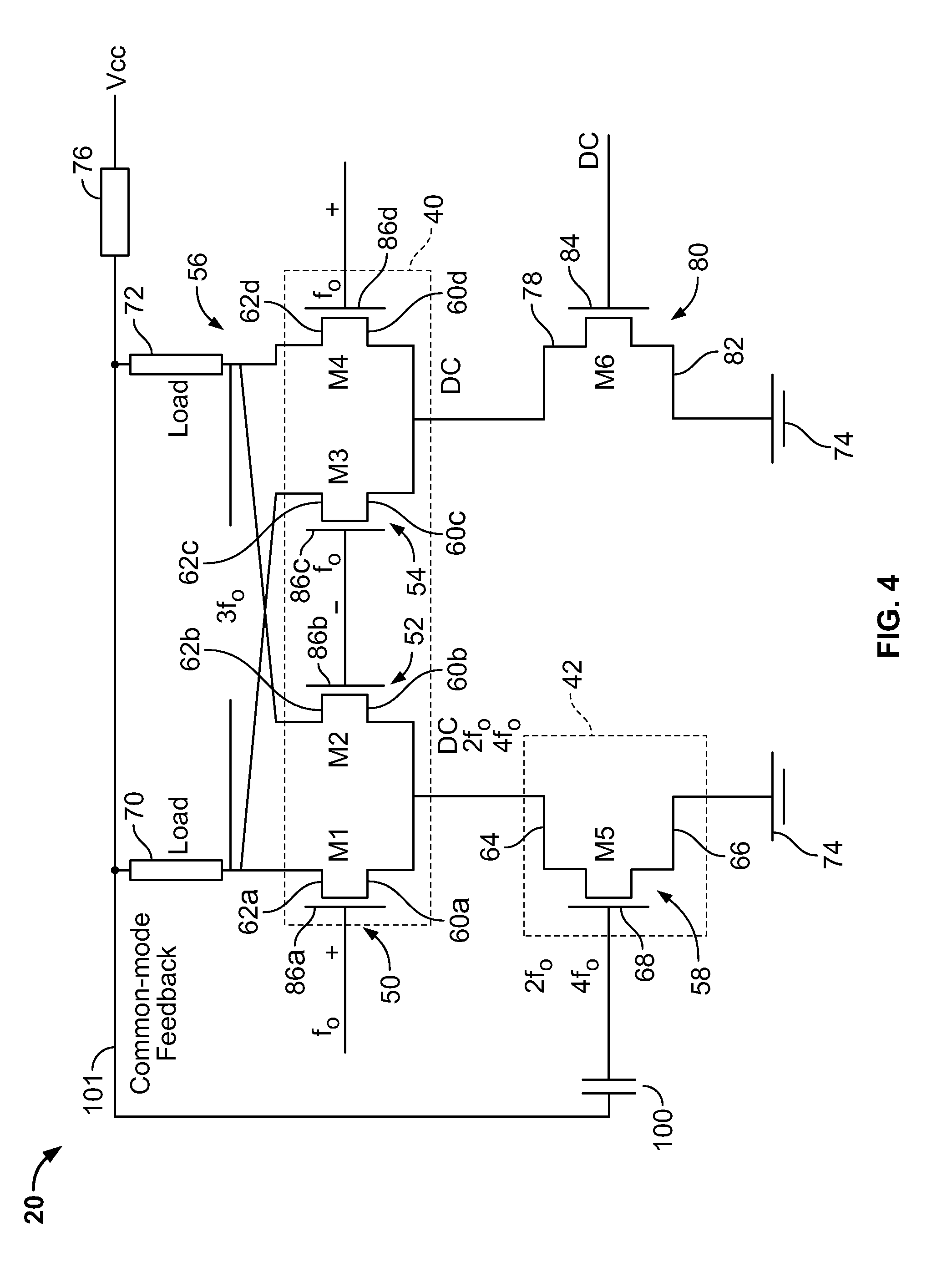
Frequency multiplier
A frequency multiplier is provided that includes a switching component having a plurality of differential pairs of transistors. The frequency multiplier further includes a gain stage. A common mode feedback generated by the switching component is also provided to the gain stage.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
Method and apparatus for processing a transmission signal in communication system
ActiveUS9479272B2Significant valueTransmission path divisionTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumCommunications system
Disclosed are a method and apparatus for processing a transmission signal using a window function that changes a spectrum characteristic of a symbol. A transmission apparatus includes a symbol generator that generate a plurality of consecutive symbols, and a symbol windowing processor that is coupled with the symbol generator. The symbol windowing processor applies a first window function and a third window function that uses a difference between the first window and a second window, and changes a spectrum characteristic of each of the plurality of consecutive symbols, and processes neighboring symbols from among the plurality of consecutive symbols of which spectrum characteristics are changed, such that the symbols partially overlap one another.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device for and a method of generating signals
InactiveUS8183894B2Increase the output frequencyEasy to measureTransistorHigh frequency amplifiersEngineeringTransistor
Owner:NXP BV
Transceiver including a weaved connection
ActiveUS9031515B2Multiple-port networksNetworks with variable switch closing timeTransceiverTransmitter
A transceiver includes a local oscillation module, a transmitter section, and a receiver section. The local oscillation module is operable to generate a transmit local oscillation and a receive oscillation. The transmitter section includes a transmit mixing module and a transmit weaved connection that is operable to high frequency filter the transmit location oscillation. The transmit mixing module mixes the filtered transmit location oscillation with a transmit signal to produce an up-converted signal. The receiver section includes a receive mixing module and a receive weaved connection that is operable to high frequency filter the receive location oscillation. The receive mixing module mixes the filtered receive location oscillation with an RF received signal to produce a down-converted signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
High frequency signal generation apparatus
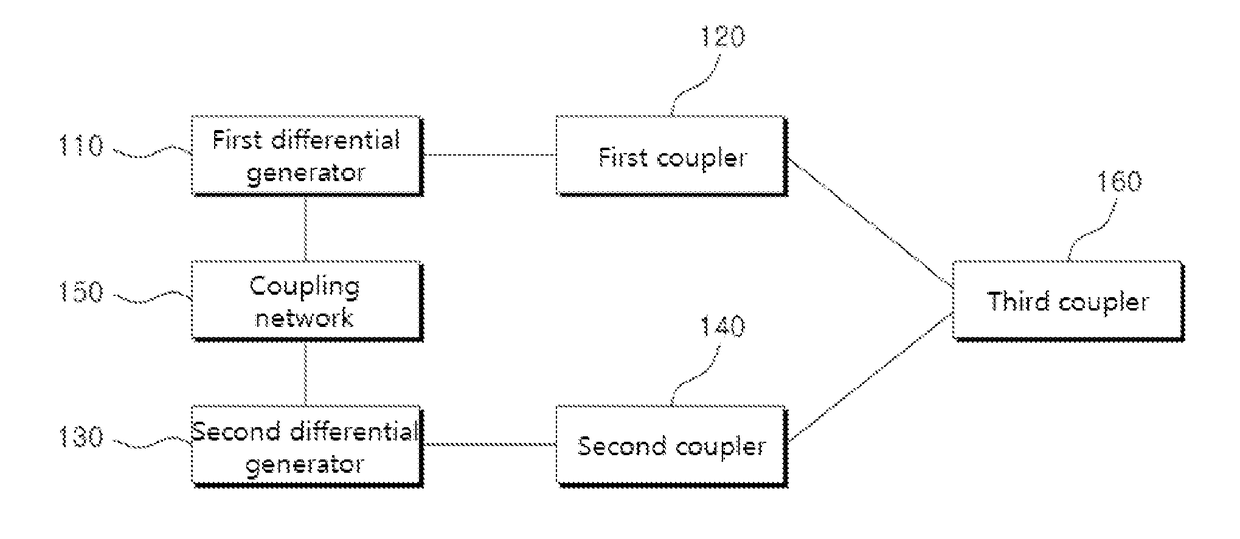
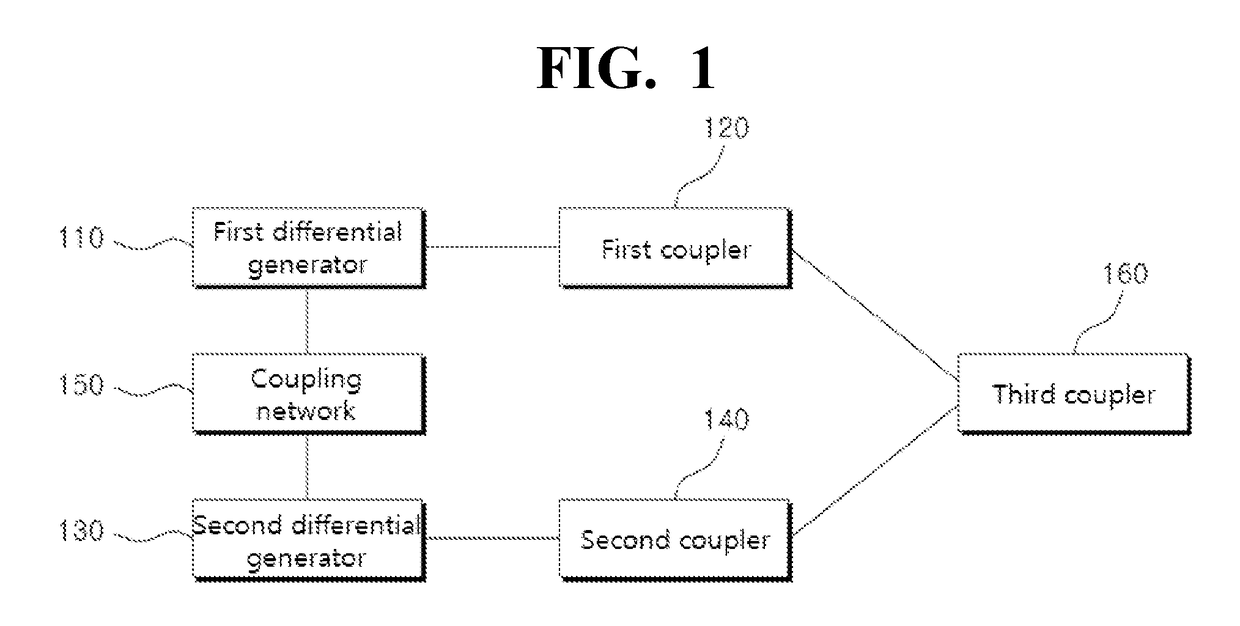
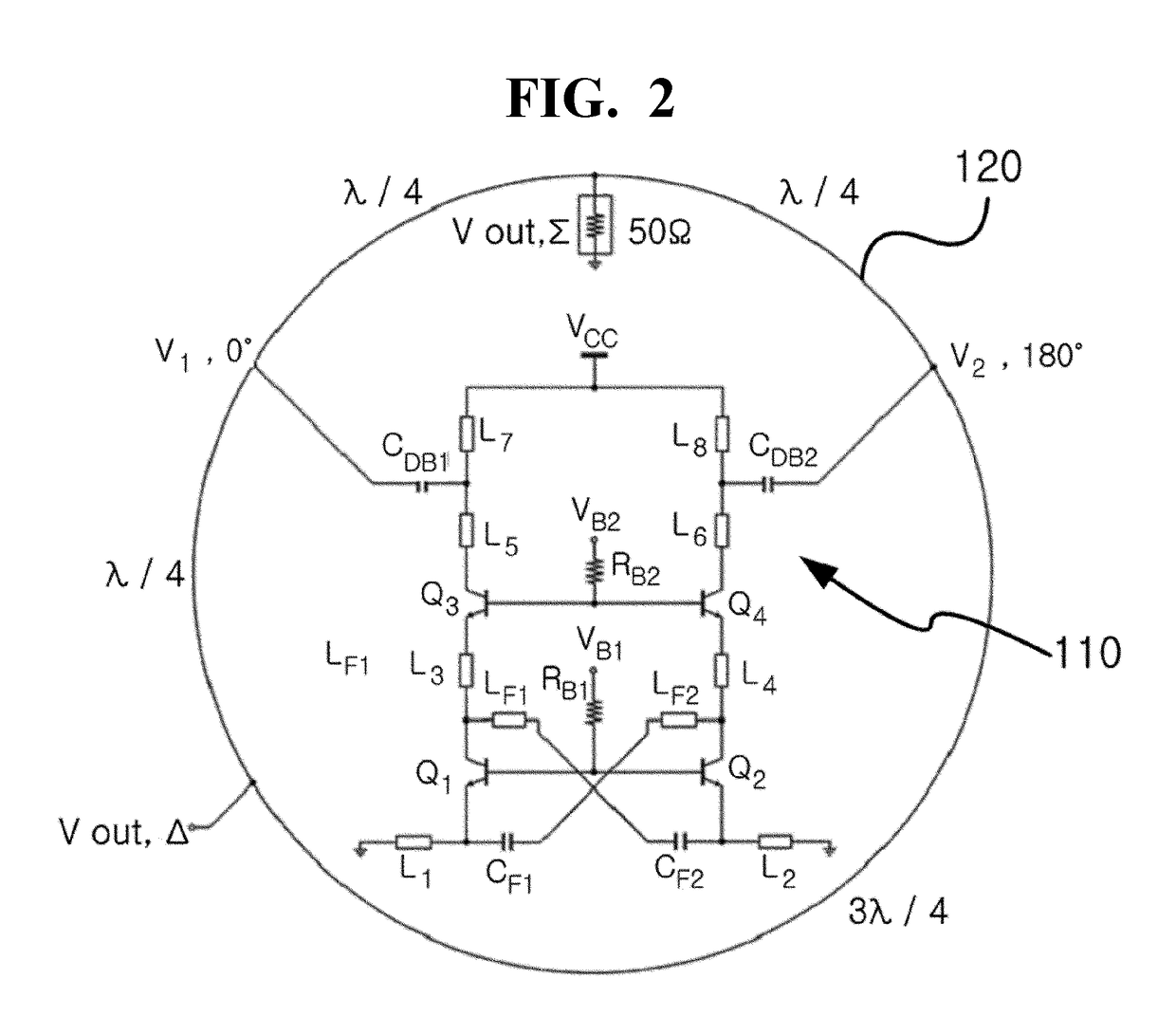
ActiveUS20170257062A1Reduce areaIncrease output powerDemodulationOscillations generatorsPhase differenceCoupling
The apparatus comprises a first coupler configured to receive two output signals, having 180° phase difference, outputted from a first differential generator as two input signals, and output a first voltage signal generated by adding the two input signals and a second voltage signal corresponding to subtraction of the two input signals, a second coupler configured to receive two output signals, having 180° phase difference, outputted from a second differential generator as two input signals, and output a third voltage signal generated by adding the two input signals and a fourth voltage signal corresponding to subtraction of the two input signals, a coupling network connected to the first differential generator and the second differential generator and a third coupler configured to output a signal generated by adding the voltage signal outputted from the first coupler and corresponding voltage signal outputted from the second coupler.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
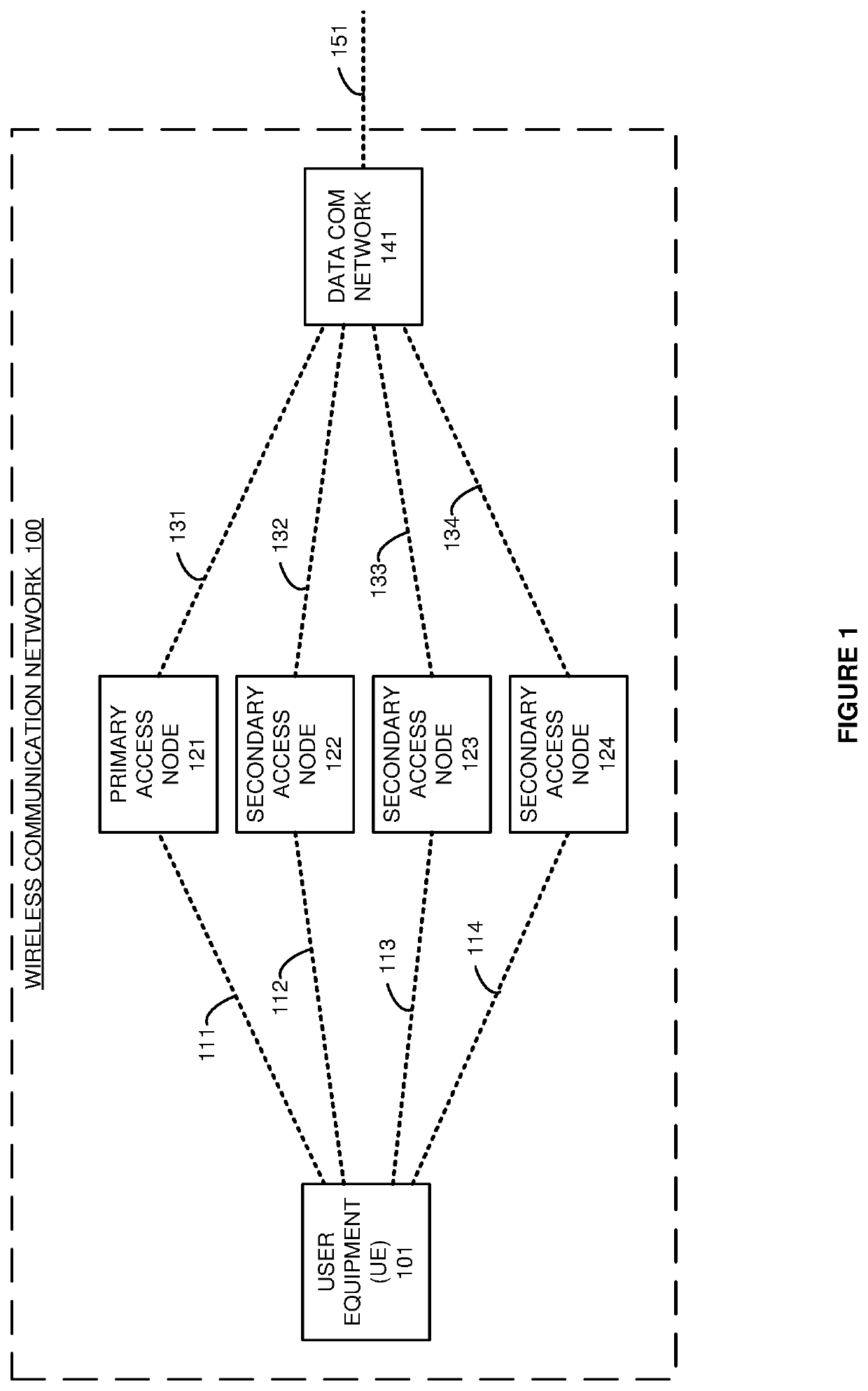
Multi-frequency data communication service over multiple wireless access nodes
ActiveUS11240748B1Assess restrictionColor television signals processingComputer networkTelecommunications
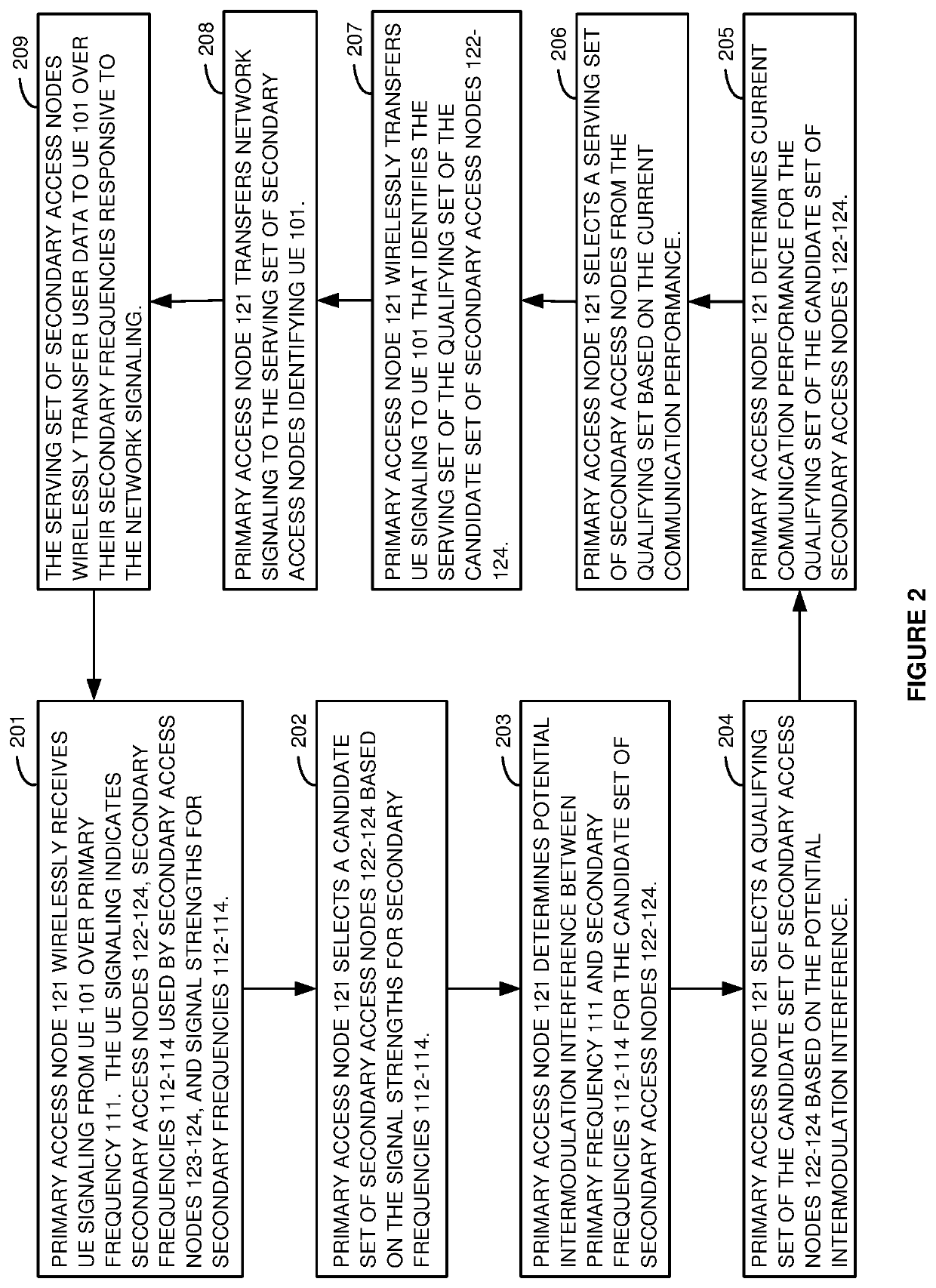
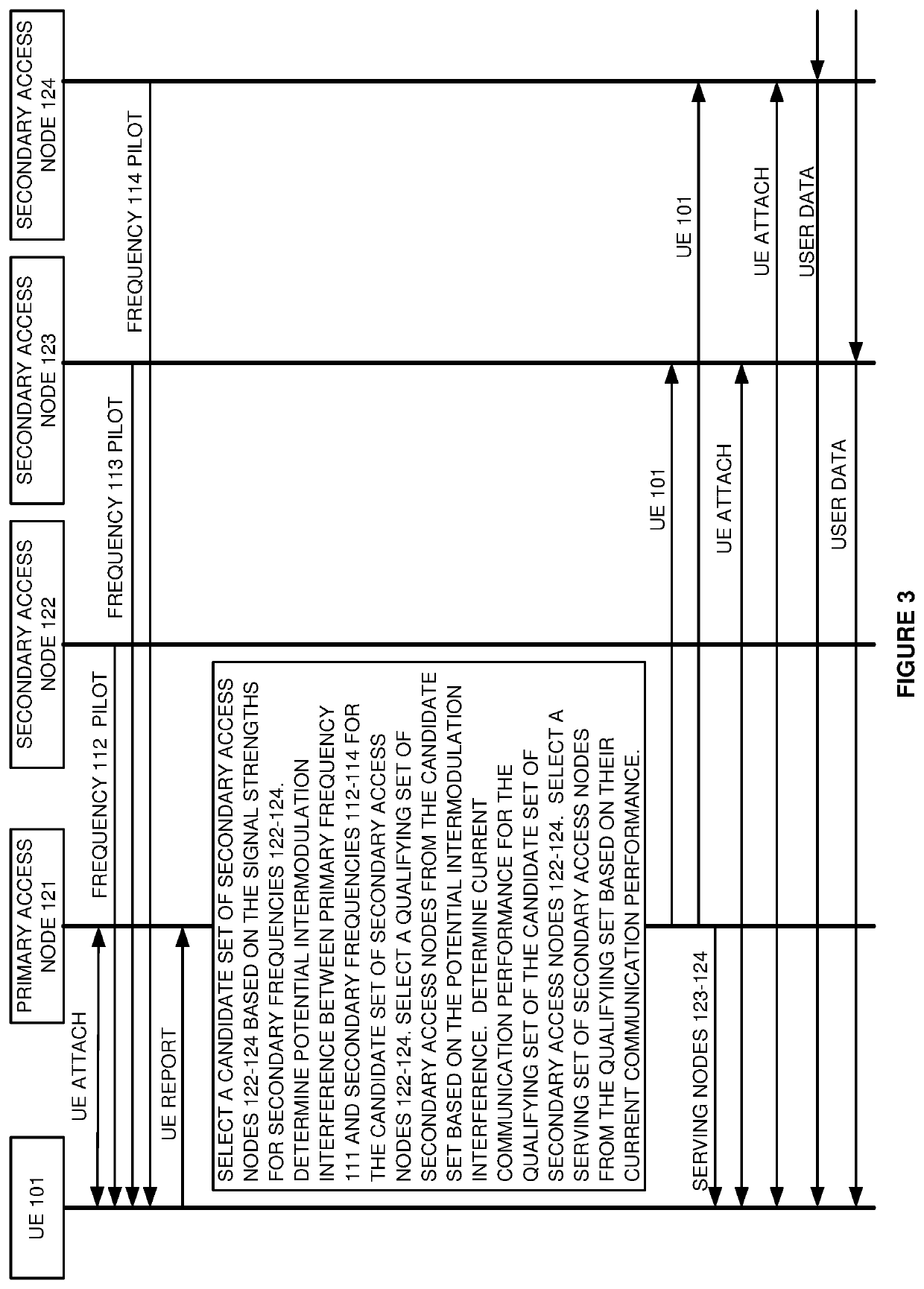
A wireless communication network delivers multi-frequency service to User Equipment (UE). A primary node receives signaling from the UE that indicates secondary nodes along with their frequencies and signal strengths. The primary node selects candidate nodes based on the signal strengths for the secondary nodes. The primary node determines potential intermodulation interference between the primary frequency and the frequencies for the candidate set. The primary node selects a qualifying set from the candidate set based on the potential intermodulation interference. The primary node determines communication performance for the qualifying set and selects a serving set from the qualifying set based on the communication performance. The primary node wirelessly transfers signaling to the UE identifying the serving set and transfers signaling to the serving set identifying the UE. The serving set of secondary access nodes wirelessly transfer user data to the UE over their frequencies responsive to the signaling.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
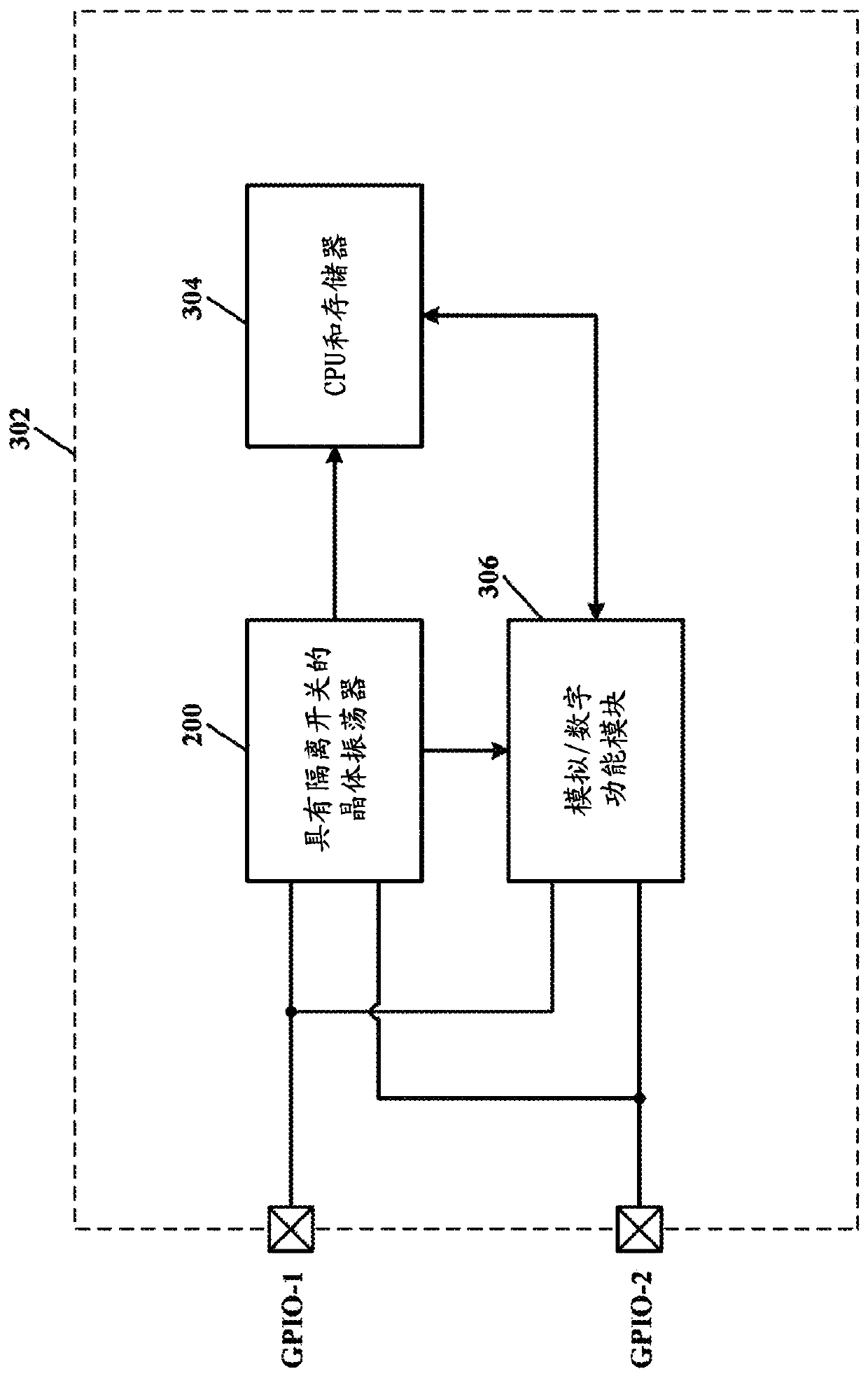
Low-voltage crystal oscillator circuit compatible with GPIO
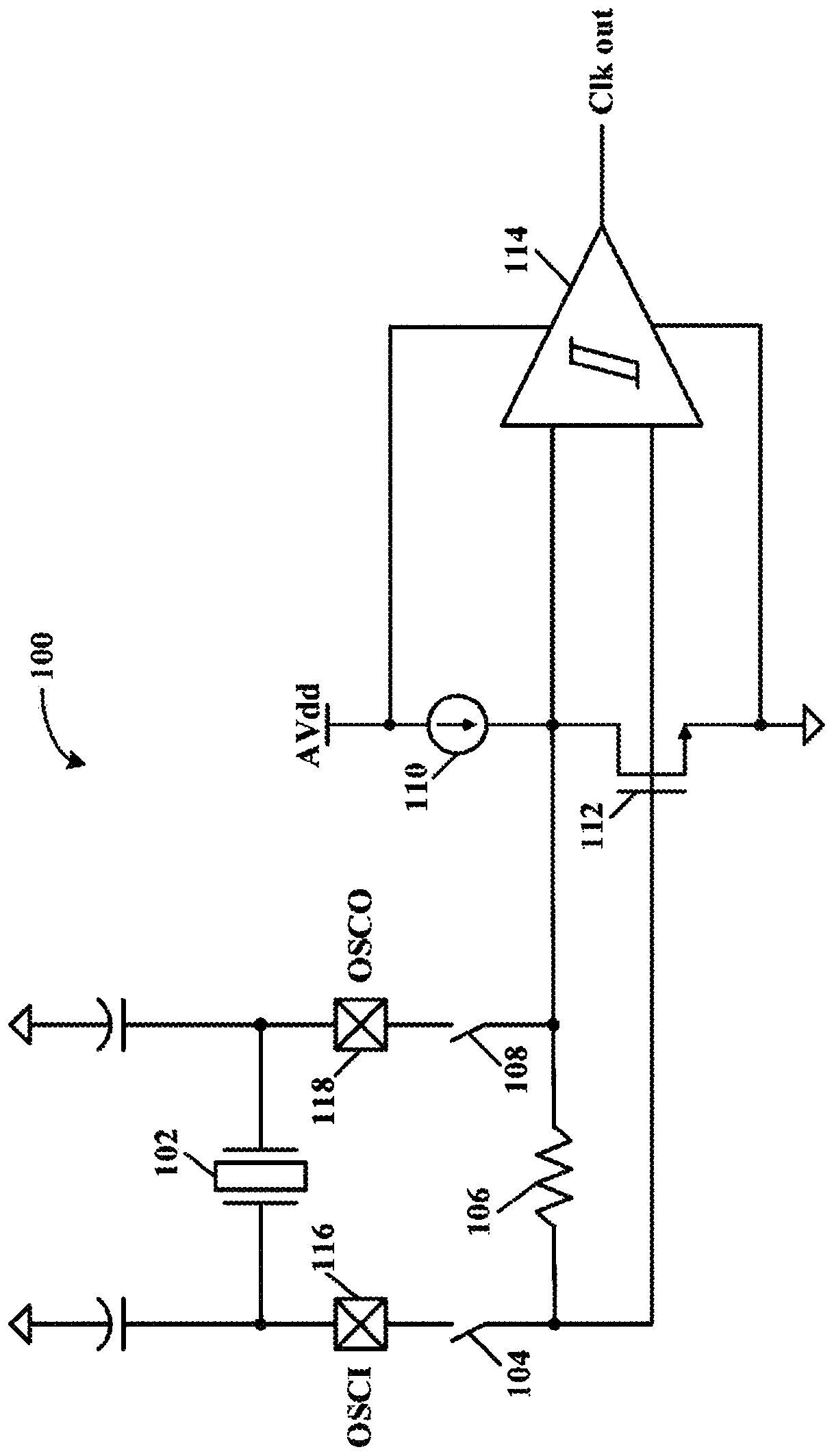
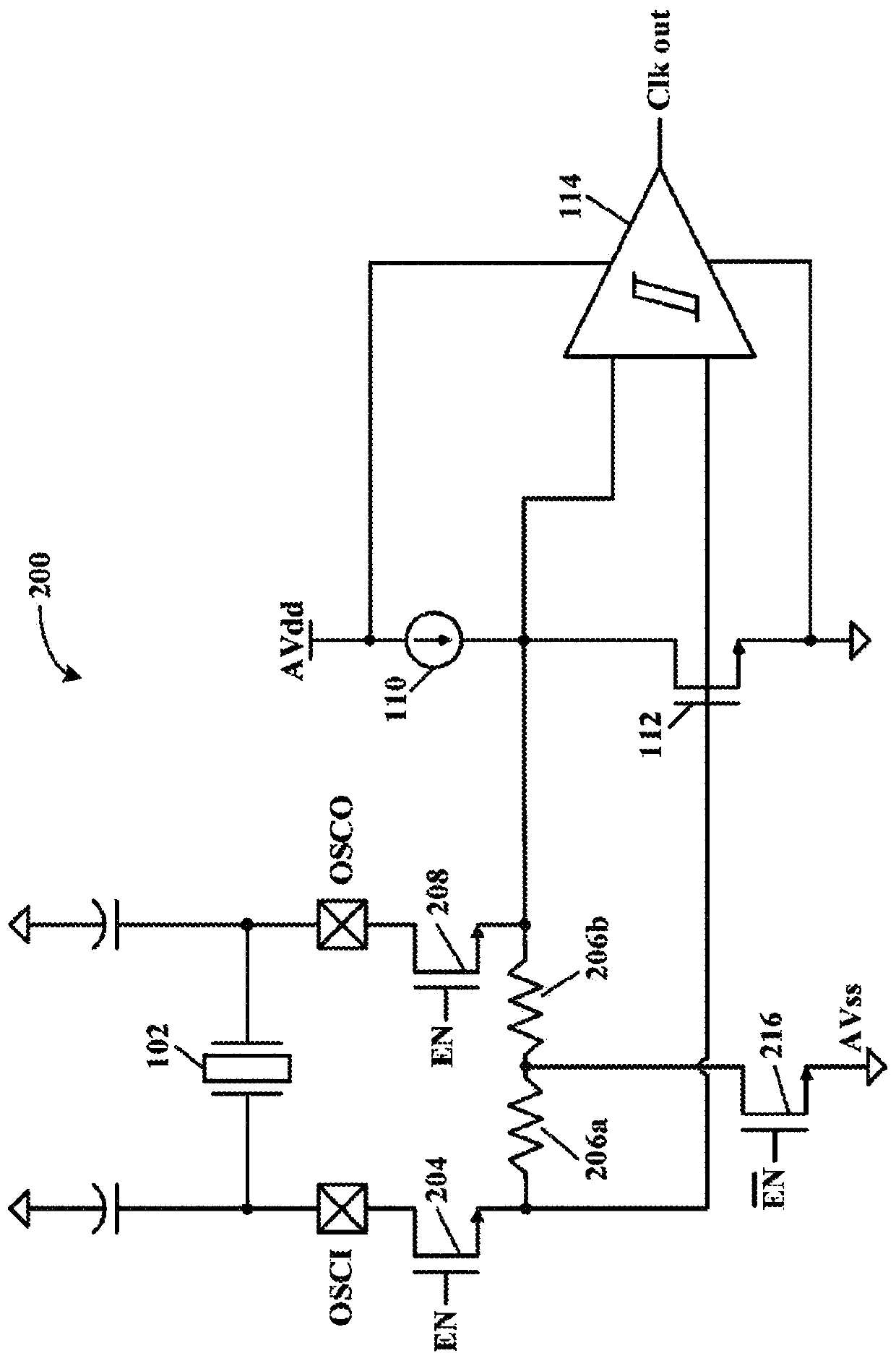
Low voltage crystal oscillator having native NMOS transistors used for coupling / decoupling to / from GPIO. The native NMOS transistors function properly at a low supply voltage when on (low resistance)and a high supply voltage when off (high resistance). Oscillator Gm driver bias resistors are repurposed to degenerate the native NMOS transistors when they are off, thereby reducing the leakage current thereof (oscillator circuit decoupled from GPIO nodes). This ensures compliance with the CMOS IIH leakage current specification during an external clock (EC) mode at a high supply voltage.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
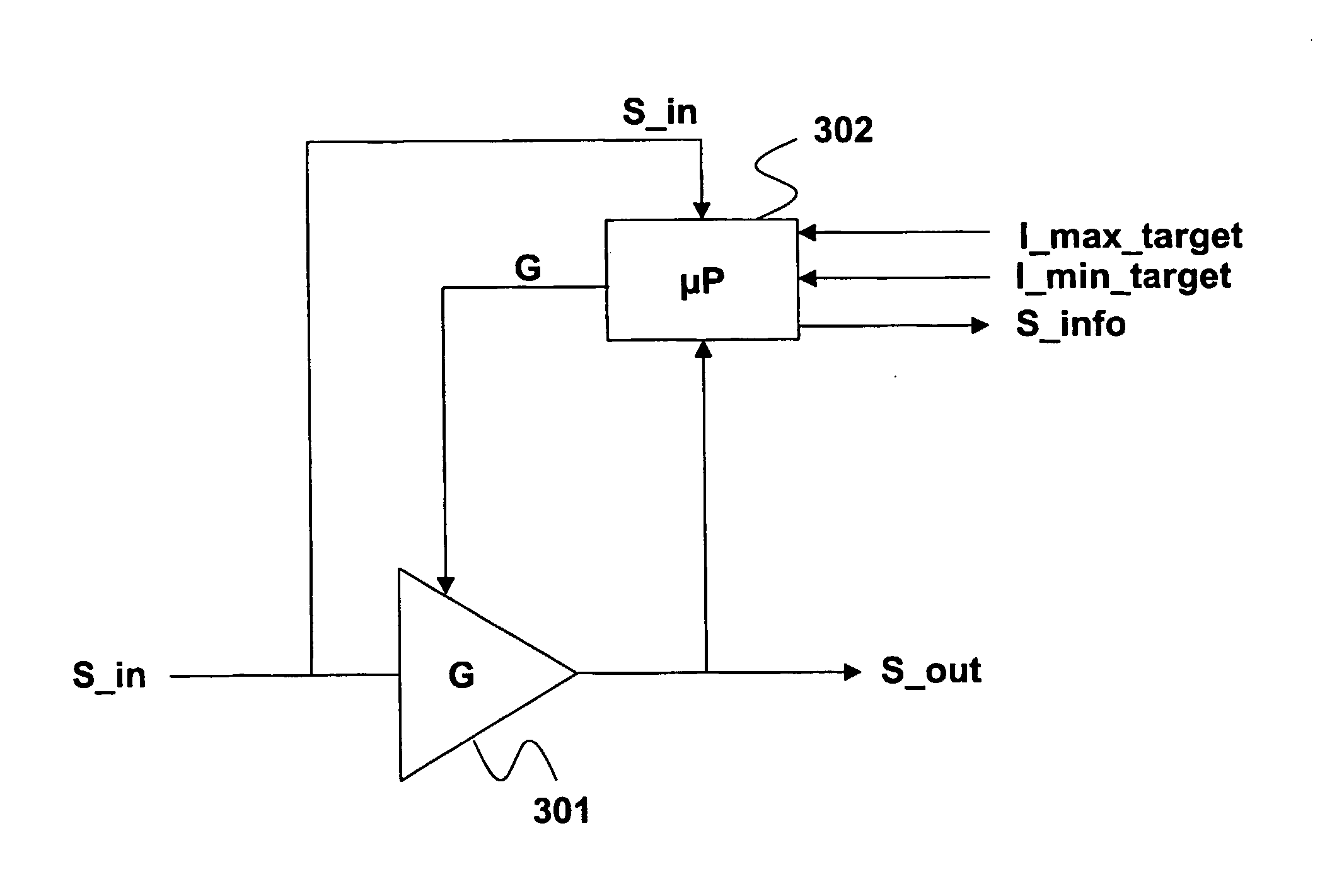
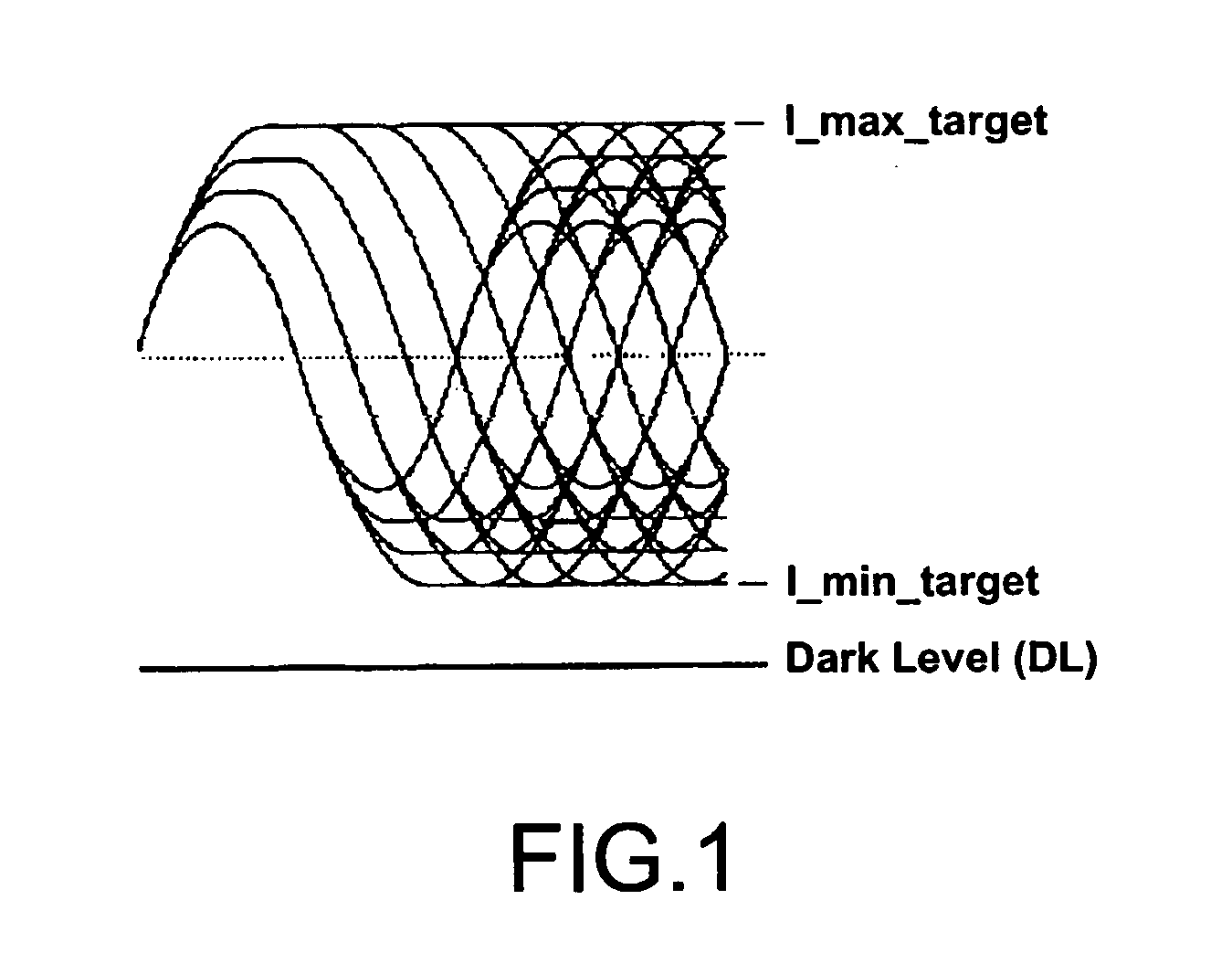
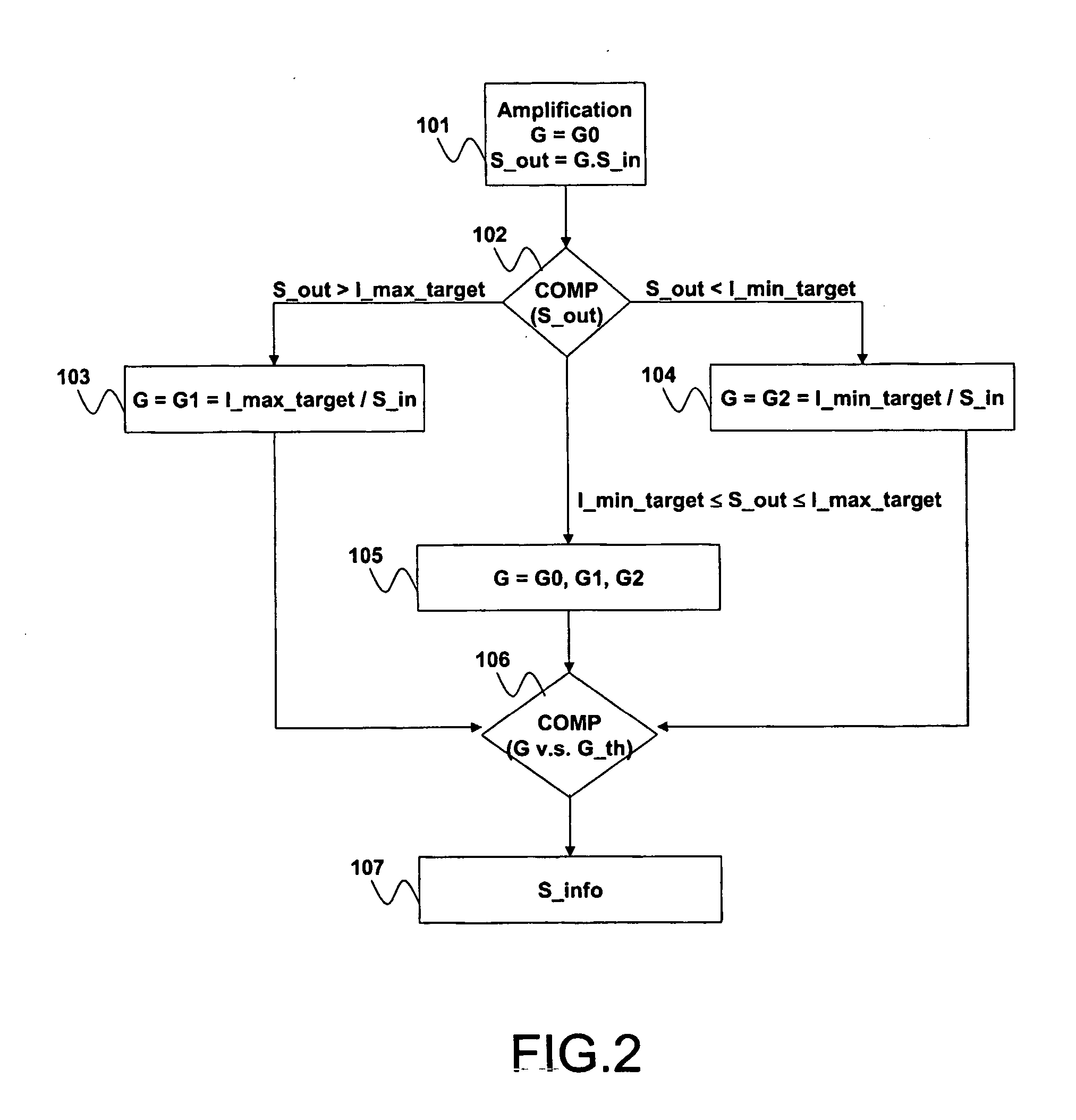
Method and system for controlling the level of a data signal read from an optical disc
InactiveUS20070121475A1Improve reading strategyReduce reflectivityModification of read/write signalsGain controlLoop controlData signal
The invention relates to a method of controlling the level of an input readout signal read from an optical disc. The method proposes to use an amplification step for amplifying the input readout signal by an adjustable gain factor for generating an amplified output readout signal having an amplitude in the range [I min target, I max target]. The value of this gain is derived from a feedback loop control in charge of comparing the level of the output readout signal with that of target levels I min target and I max target, and deriving a gain value taking into account the level of the input readout signal. This loop control renders it possible to clamp the input readout signal, counteracting as a consequence the decrease of the input readout signal in the case of a reflectivity reduction of the optical disc. Use: Optical disc reader.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
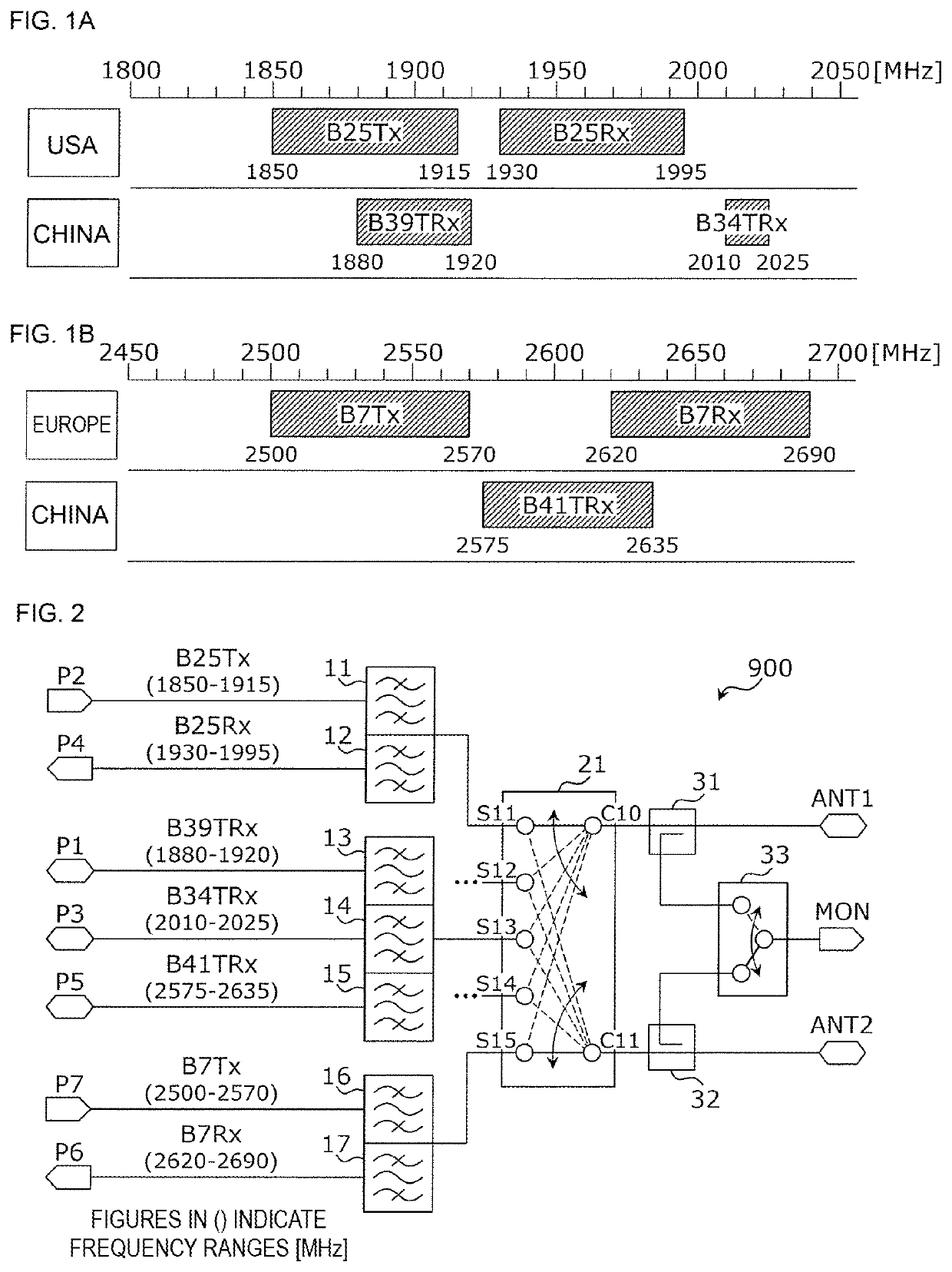
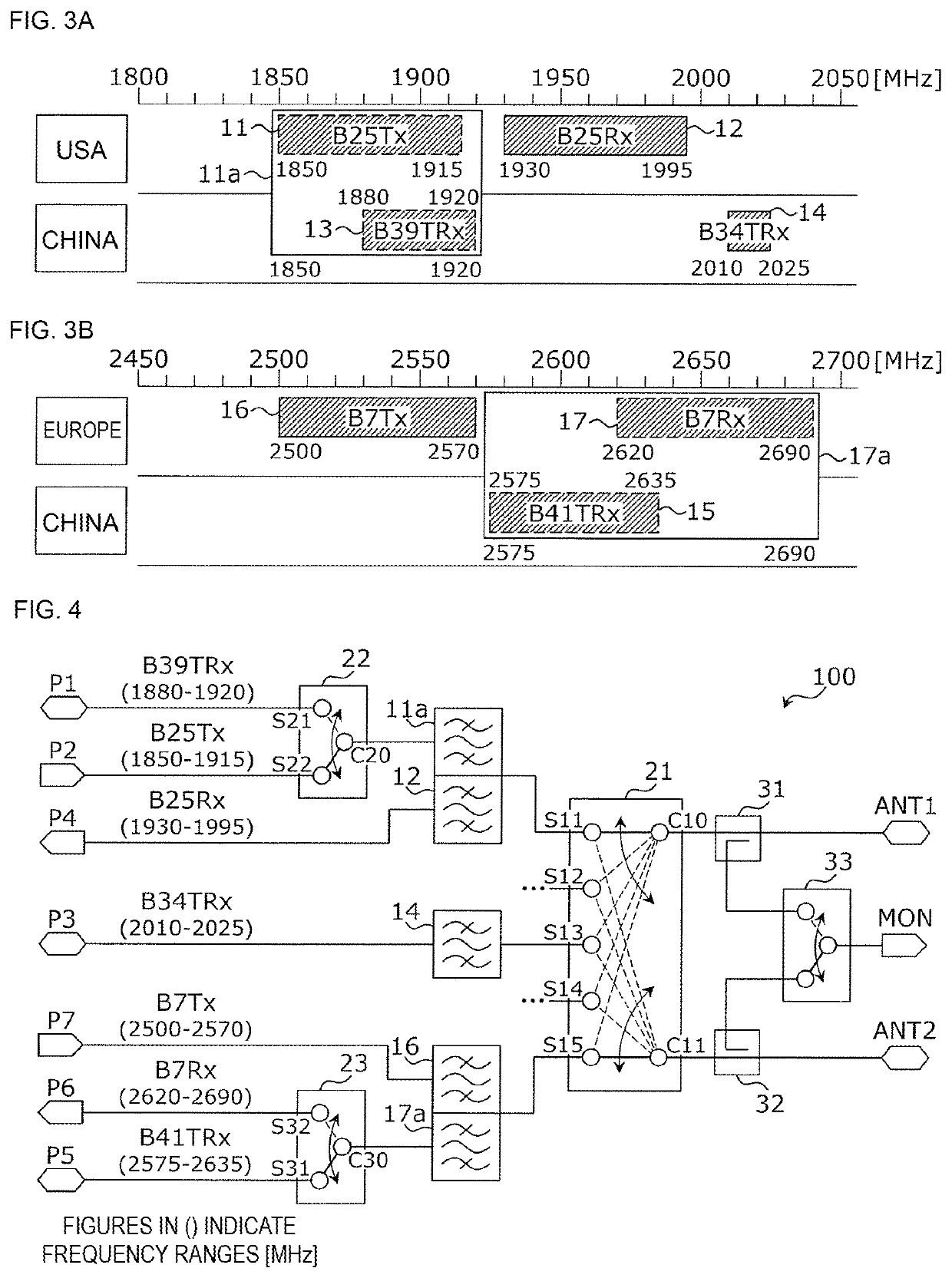
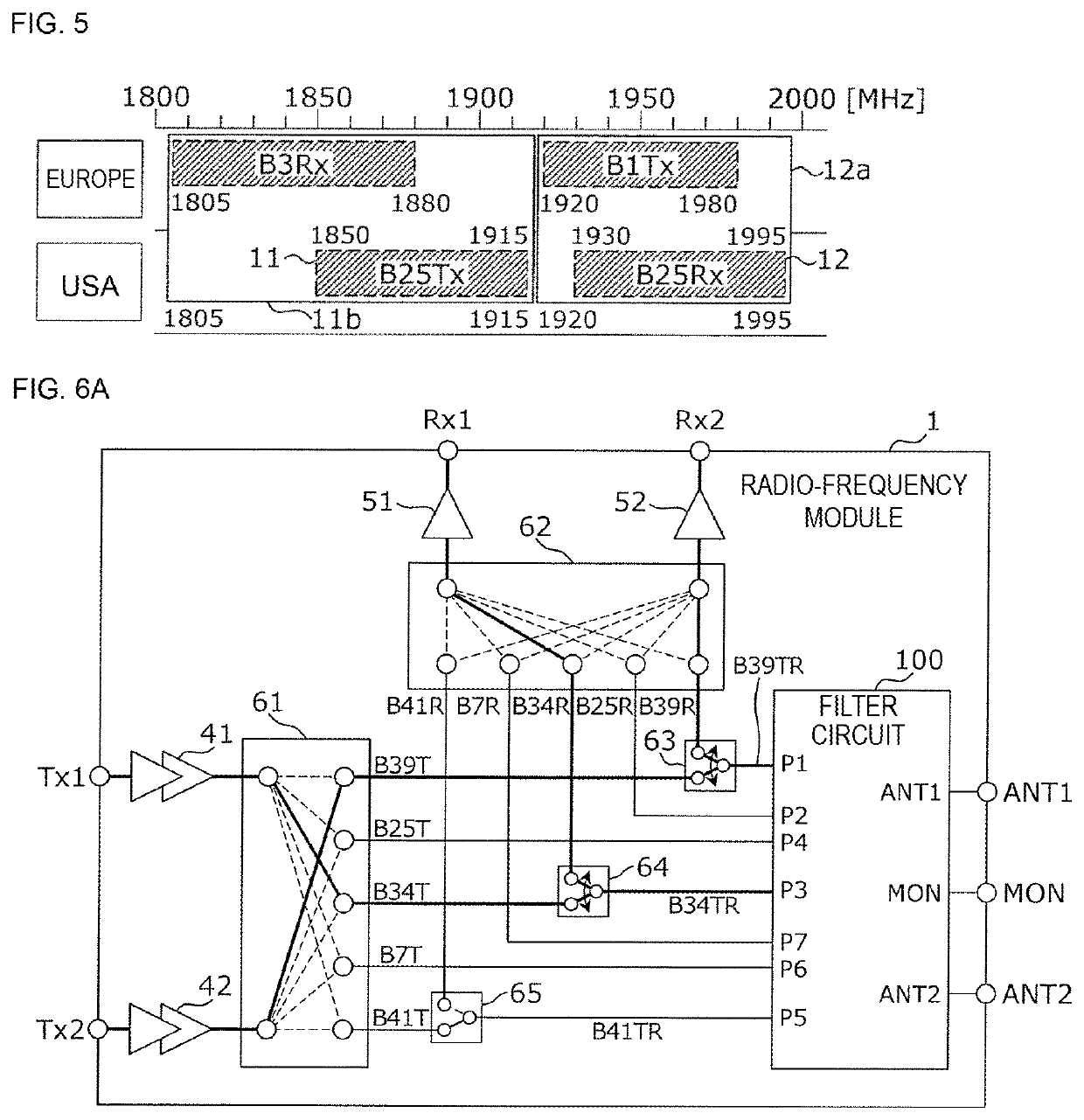
Filter circuit and radio-frequency module
ActiveUS11323193B2Increase in sizeReduce in quantityFrequency-division multiplex detailsElectronic switchingBand-pass filterRF module
A filter circuit includes a first switch circuit that exclusively connects a first common terminal to either of a first selection terminal and a second selection terminal; a first signal terminal that is connected to the first selection terminal and that is for communicating a first communication signal belonging to a first frequency range, which is a frequency range of a first communication band; a second signal terminal that is connected to the second selection terminal and that is for communicating a second communication signal belonging to a second frequency range, which is the frequency range of a second communication band and which is at least partially overlapped with the first frequency range; and a first band pass filter one end of which is connected to the first common terminal and which uses both the first frequency range and the second frequency range as pass bands.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Mixer monitoring
InactiveCN102472813AFunctional determinationLow costDemodulationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency mixerRadio frequency signal
A method for checking the operability of a mixer (110) involves the mixer (110) being supplied with a radio-frequency signal (230) and a radio-frequency comparison signal (240) in order to produce a baseband signal (250). In this case, the amplitude of the radio-frequency signal (230) is altered on the basis of time. A DC voltage component of the baseband signal (250) which is output by the mixer (110) is evaluated in order to assess the operability of the mixer (110).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fast-settling DC offset removal circuits with continuous cutoff frequency switching
A fast-setting DC offset removal circuit with continuous cutoff frequency switching is disclosed. In the preferred embodiment, the circuit is implemented using a pair of RC filters for receiving a differential signal pair and a continuous, variable resistance control circuit. The control circuit can be current-controlled or voltage controlled to provide fast settling of the received signal and the removal of the DC offset components. Additionally, by using a current-controlled control circuit, the cutoff frequency of the RC filter can be ramped from high to low in a continuous manner, thereby minimizing the generation of DC offsets.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com