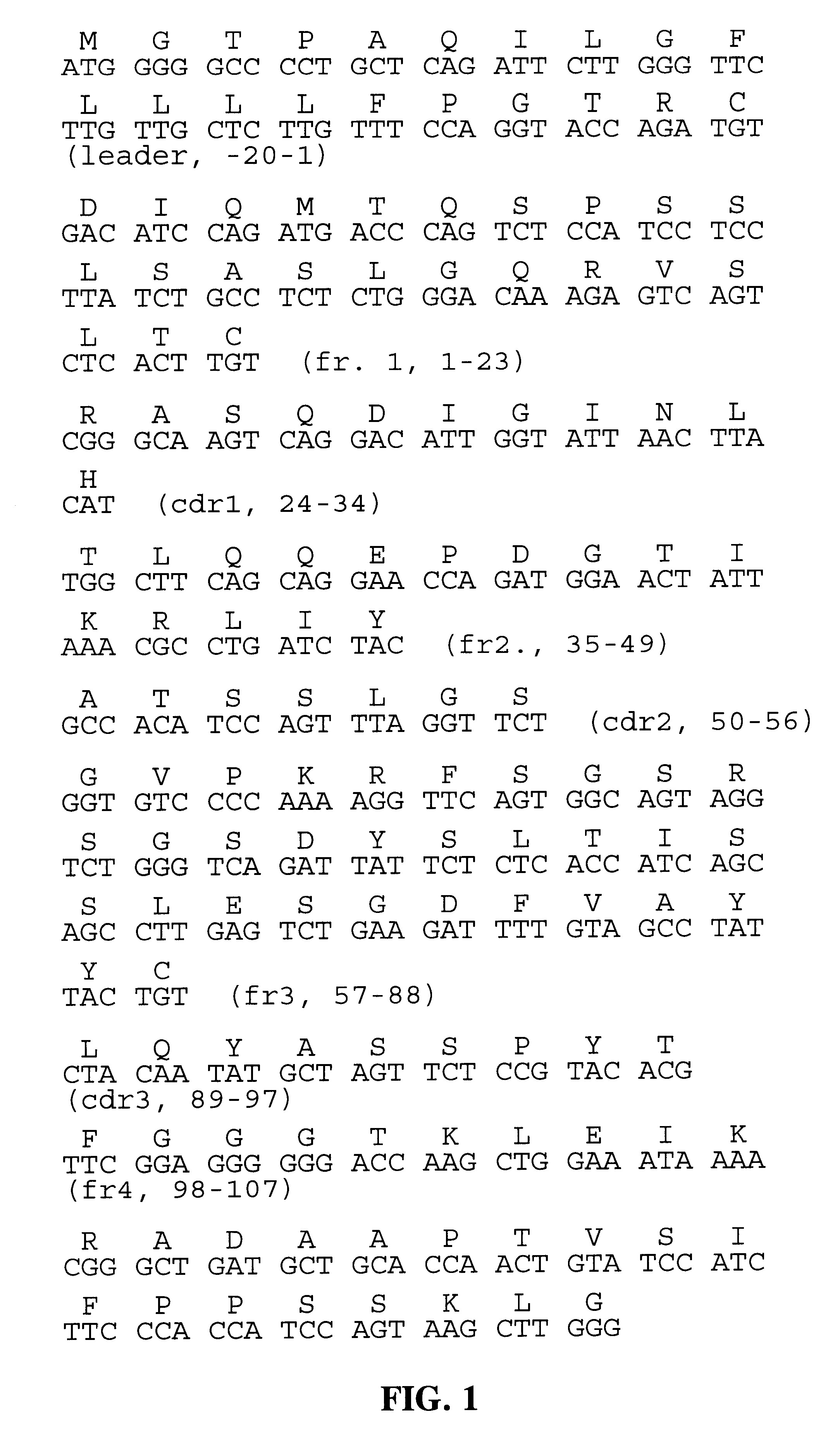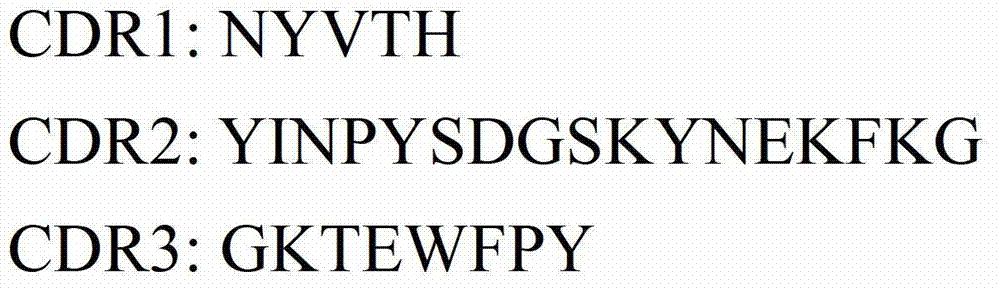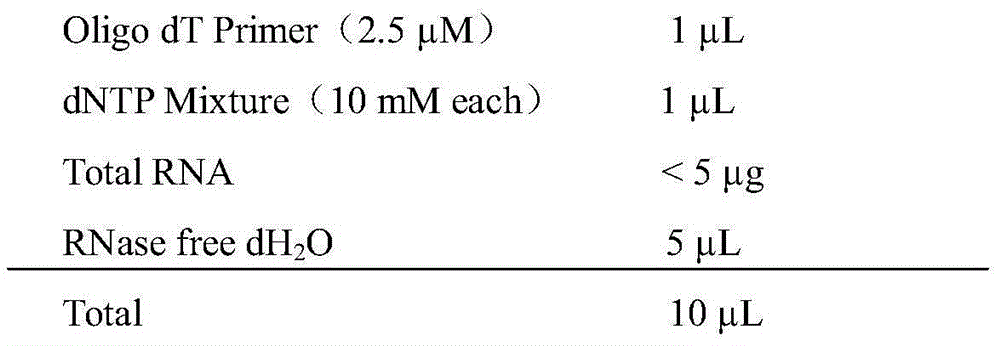Patents
Literature
52 results about "Anti-Idiotype Antibody" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical Definition of anti-idiotype. : an antibody that binds to the antigen combining site of another antibody either suppressing or enhancing the immune response. Anti-idiotypes are secondary antibodies manufactured by the immune system in reaction to the presence of antibodies, the body's basic germ fighters.
Murine monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody 11D10 and methods of use thereof
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY
Vaccines against cancer and infectious diseases
InactiveUS6440416B1Promote antibody productionPromote productionOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProtozoaPrimate
A method of stimulating an immune response in a human against malignant cells or an infectious agent comprises the step of administering to the human an immunogenic amount of a primate anti-idiotype antibody or antibody fragment that acts as an immunogenic functional mimic of an antigen produced by or associated with a malignant cell or an infectious agent. Sub-human primate anti-idiotype antisera, especially from baboons, are preferred. Such anti-idiotype antibodies are used to make vaccines for inducing preventive immunity or a therapeutic immune response against tumors, viruses, bacteria, rickettsia, mycoplasma, protozoa, fungi and multicellular parasites.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
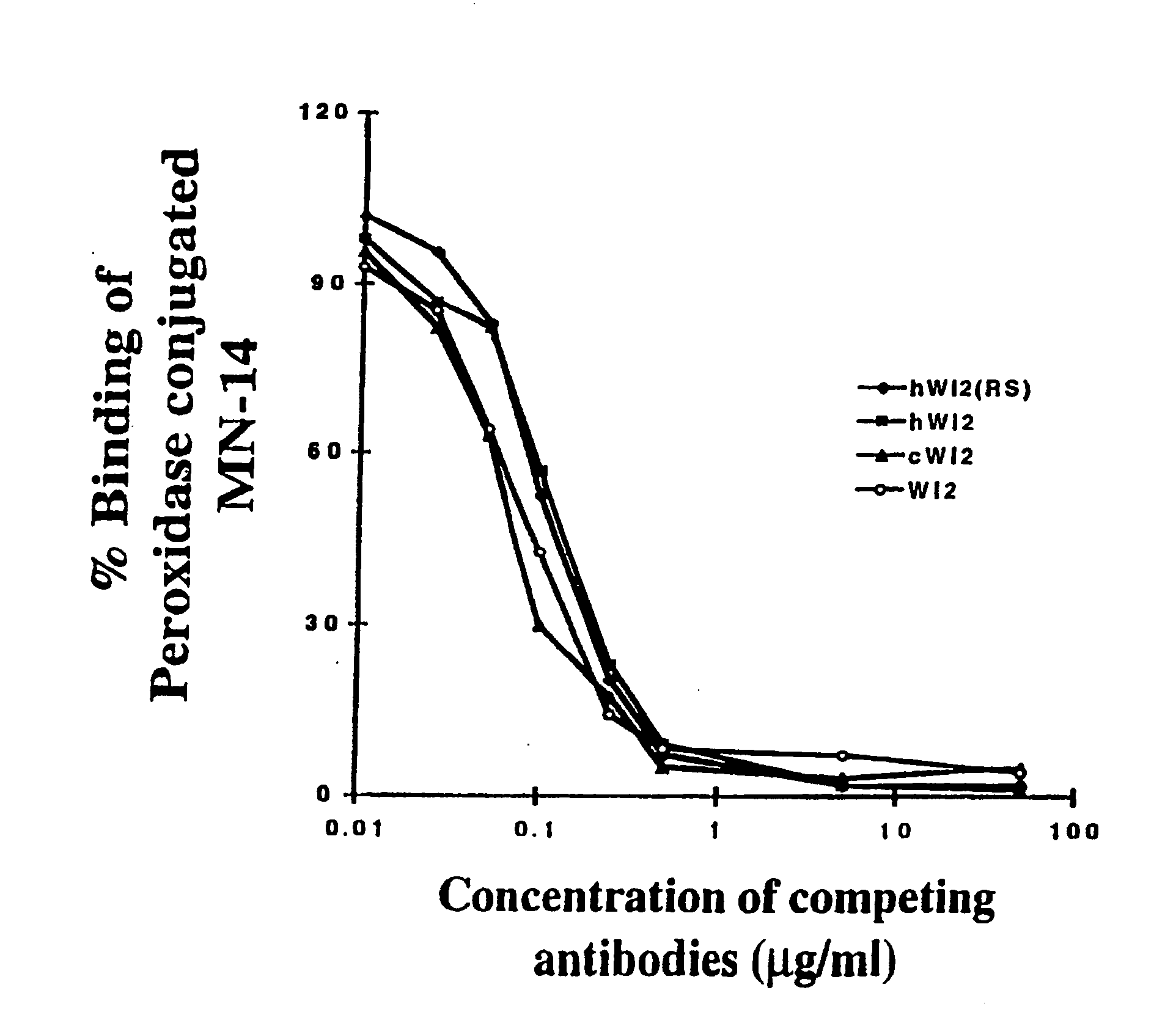
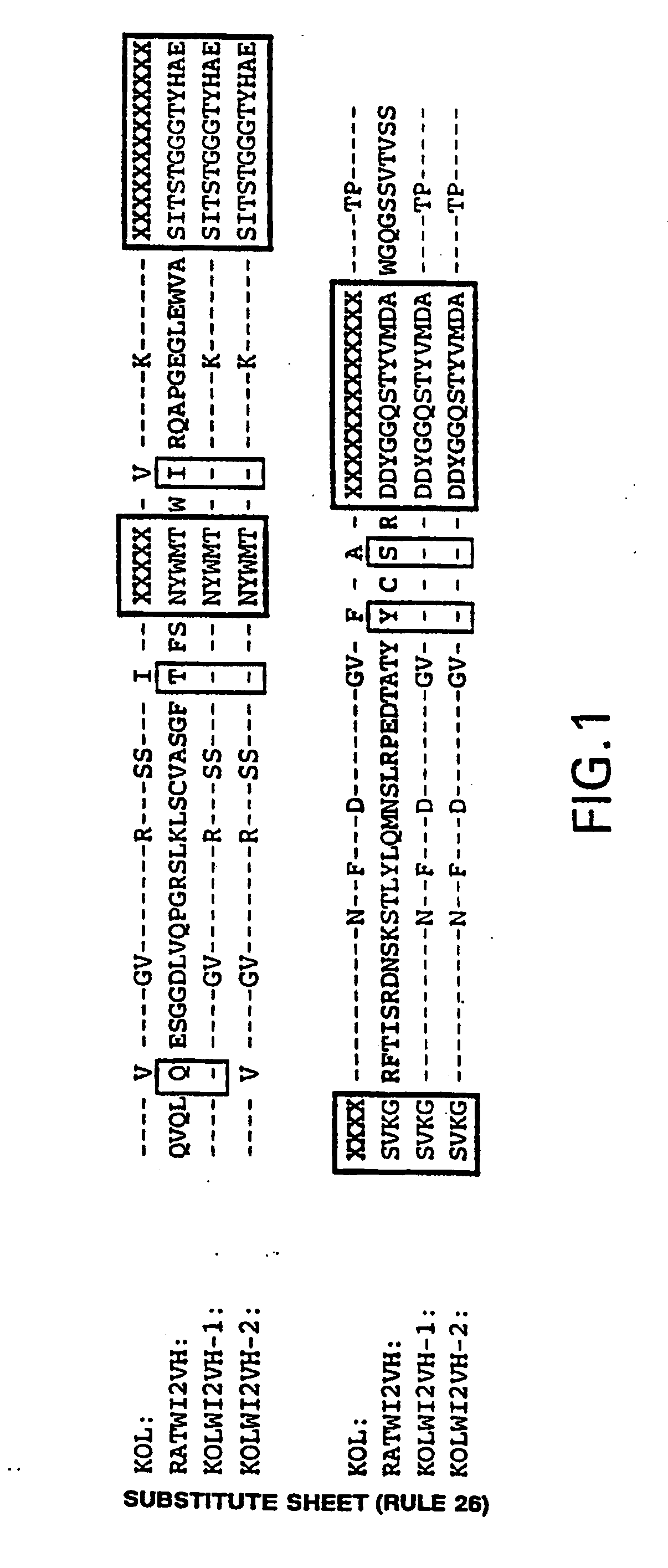
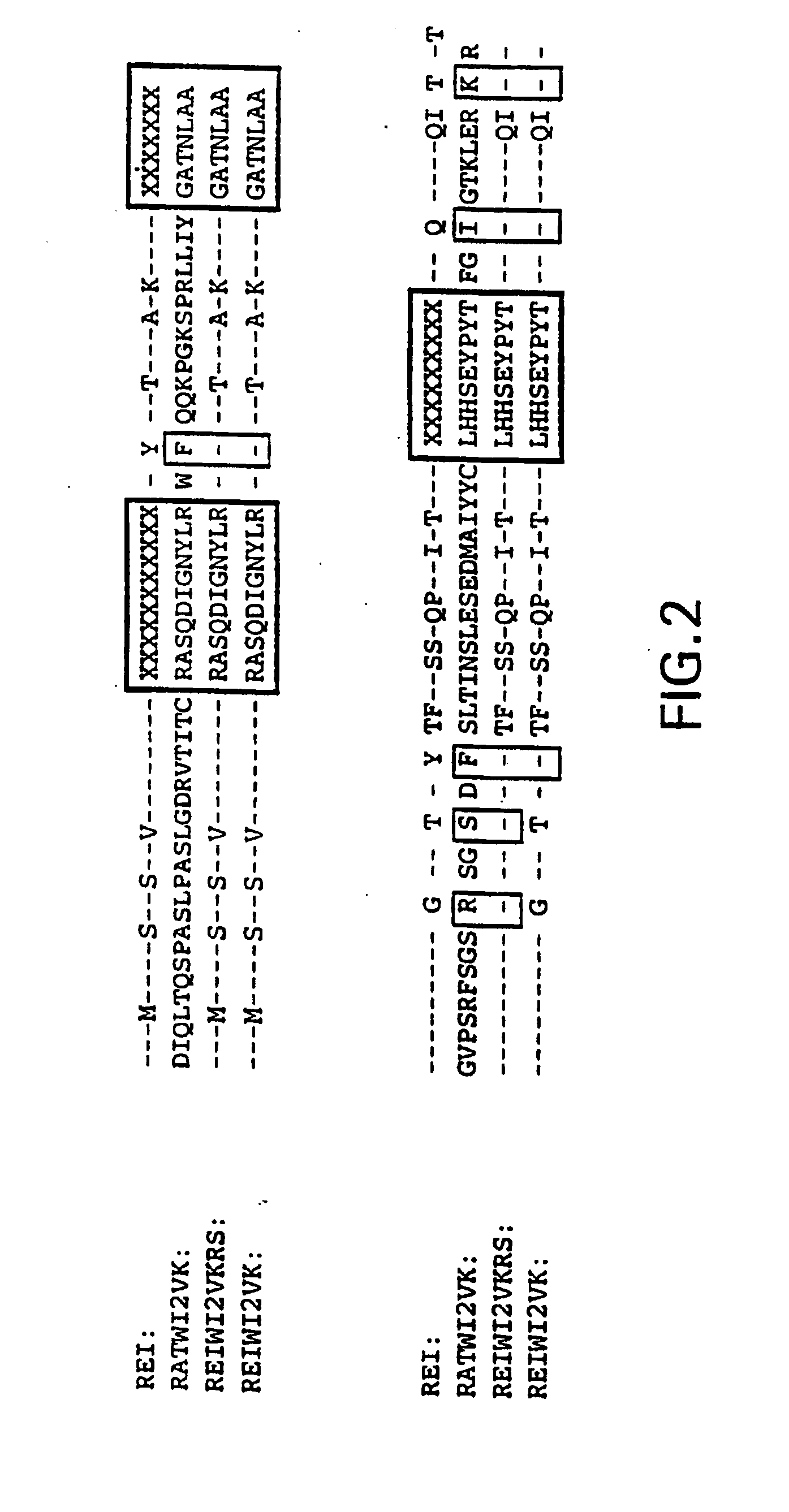
Humanization of an Anti-carcinoembryonic antigen Anti-idiotype antibody as a tumor vaccine and for targeting applications
InactiveUS20080069775A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsAntibody fragmentsAnti-CEA Antibody
A humanized form of an anti-idiotype antibody to CEA, e.g., hWI2, has conserved immunoreactivity. The clinical benefits of anti-CEA antibodies are maximized by using the humanized anti-idiotype as a clearing agent for anti-CEA antibodies or antibody fragments. The humanized anti-idiotype also can be used as an immunogenic vaccine.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Surrogate tolerogenesis for the development of tolerance to xenografts
InactiveUS6060049AIncrease differentiationIncreased proliferationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHematopoietic cellTolerability
PCT No. PCT / US94 / 05844 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 6, 1995 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 6, 1995 PCT Filed May 24, 1994 PCT Pub. No. WO94 / 27622 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 8, 1993This invention provides a method for developing immune tolerance in xenogeneic organ graft recipients, in which lympho-hematopoietic cells from an intended organ graft recipient are differentiated within a xenogeneic surrogate, such as a fetal animal. After birth of the surrogate, the matured lympho-hematopoietic cells containing antigen specific regulatory cells, including suppressor cells, veto cells, select B cells, anti-idiotype antibodies, and other related factors responsible for antigen specific tolerance in a surrogate animal are reintroduced into the intended organ graft recipient, in conjunction with an organ transplant or a tissue transplant from the xenograft surrogate. The invention also provides an organ graft repopulated with cells from the intended organ graft recipient produced in a surrogate animal.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
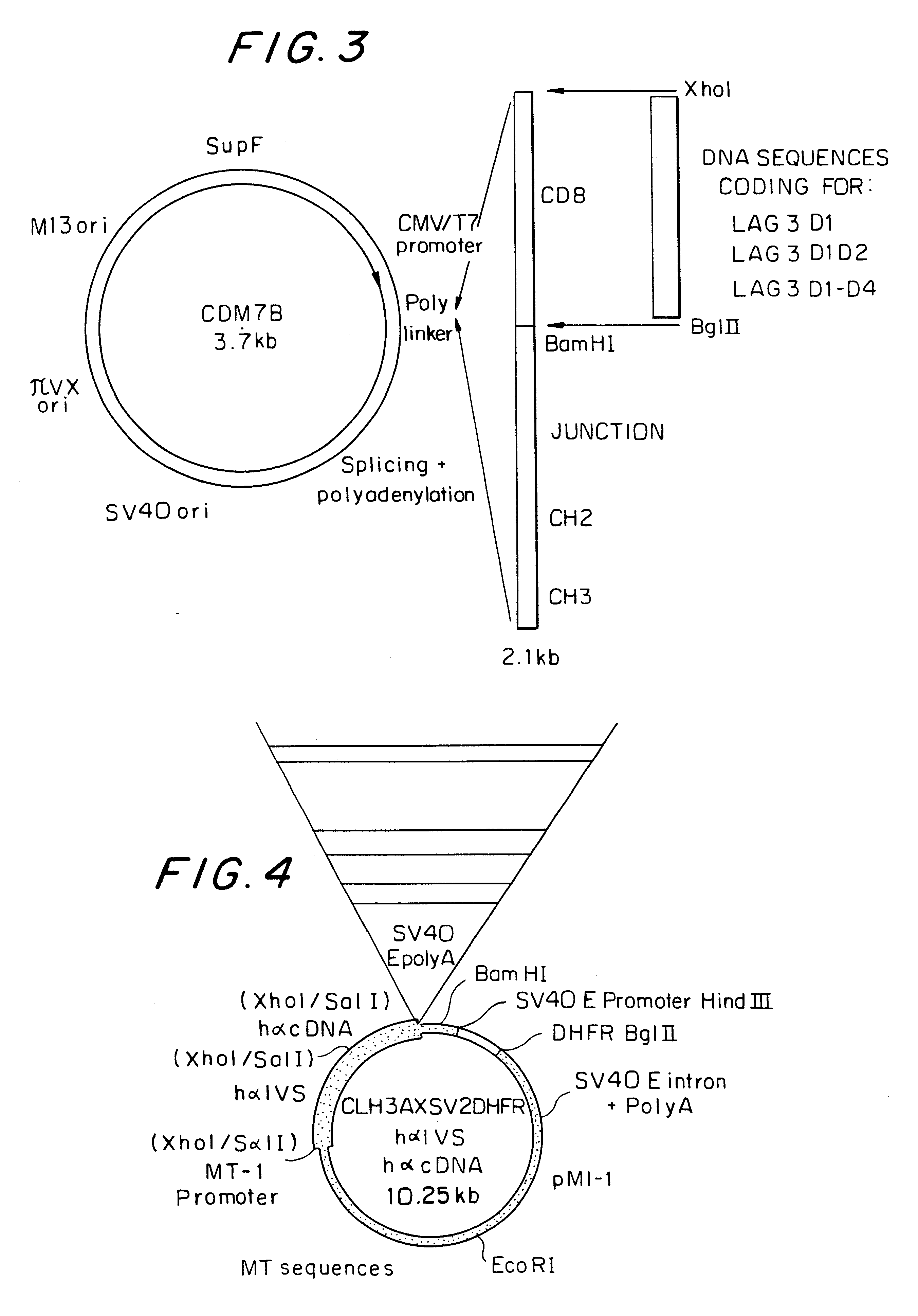
Soluble polypeptide fractions of the LAG-3 protein, production method, therapeutic composition, anti-idiotype antibodies
Soluble polypeptide fraction consisting of all or part .[.one.]. .Iadd.of .Iaddend.at least .Iadd.one .Iaddend.of the four immunoglobulin-type extracellular LAG-3 protein domains (amino acids 1-159, 160-.[.230.]. .Iadd.239.Iaddend., 240-330 and 331-412 of the SEQ ID NO:1 sequence) or consisting of one peptide sequence derived from these domains by replacement, addition or deletion of one or more amino acids. The fraction of the invention has a specificity at least equal to that of LAG-3 in relation to its ligand.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
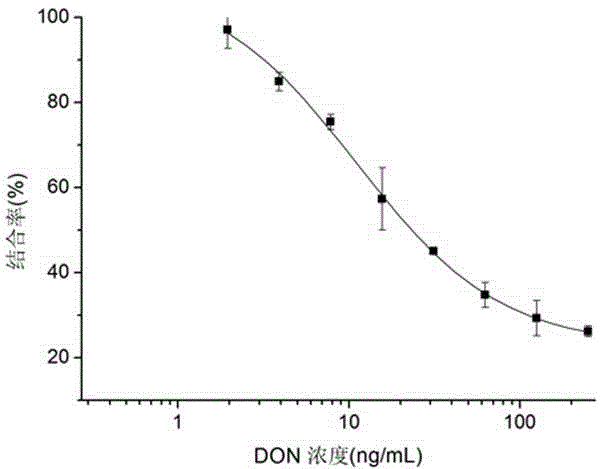
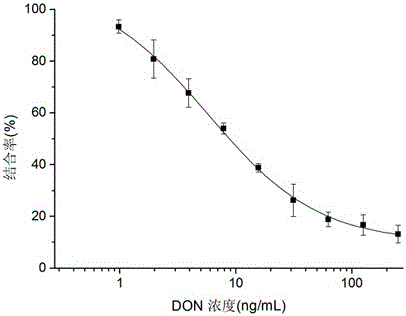
Nano antibody of anti-deoxynivalenol antibody
InactiveCN104592389AHave immune response propertiesGood effectImmunoglobulinsGenetic engineeringEpitopeEndurance capacity
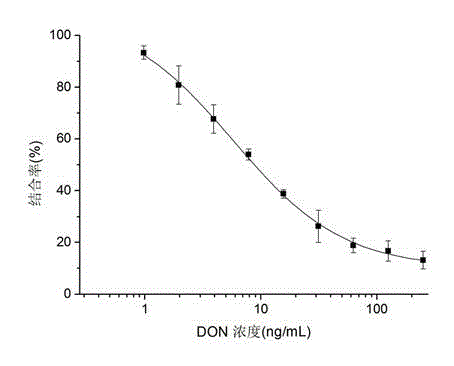
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and specifically relates to a preparation method and an application of a nano antibody capable of specially binding with an anti-deoxynivalenol antibody. The amino acid sequence of the nano antibody is SEQ ID No. 1. The invention also relates to a nucleotide for encoding amino acid. The nano antibody is capable of taking the place of the expensive high-toxicity DON standard substances, and can be applied to the immunological detection of the DON as a competitive antigen or a solid-phase envelope antigen; the nano antibody has immunoreaction characteristic similar to that of natural DON molecule, and is excellent in effect. Compared with the traditional antigen mimic epitopes based on polypeptides and the traditional anti-idiotype antibodies based on IgG, the nano antibody has the characteristics of more stable structure, acid-alkali resistance, high temperature resistance, high detection sensitivity and the like, and therefore, the immunodetection stability of the nano antibody is greatly improved, and meanwhile, the endurance capacity of the nano antibody to the environment is also improved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
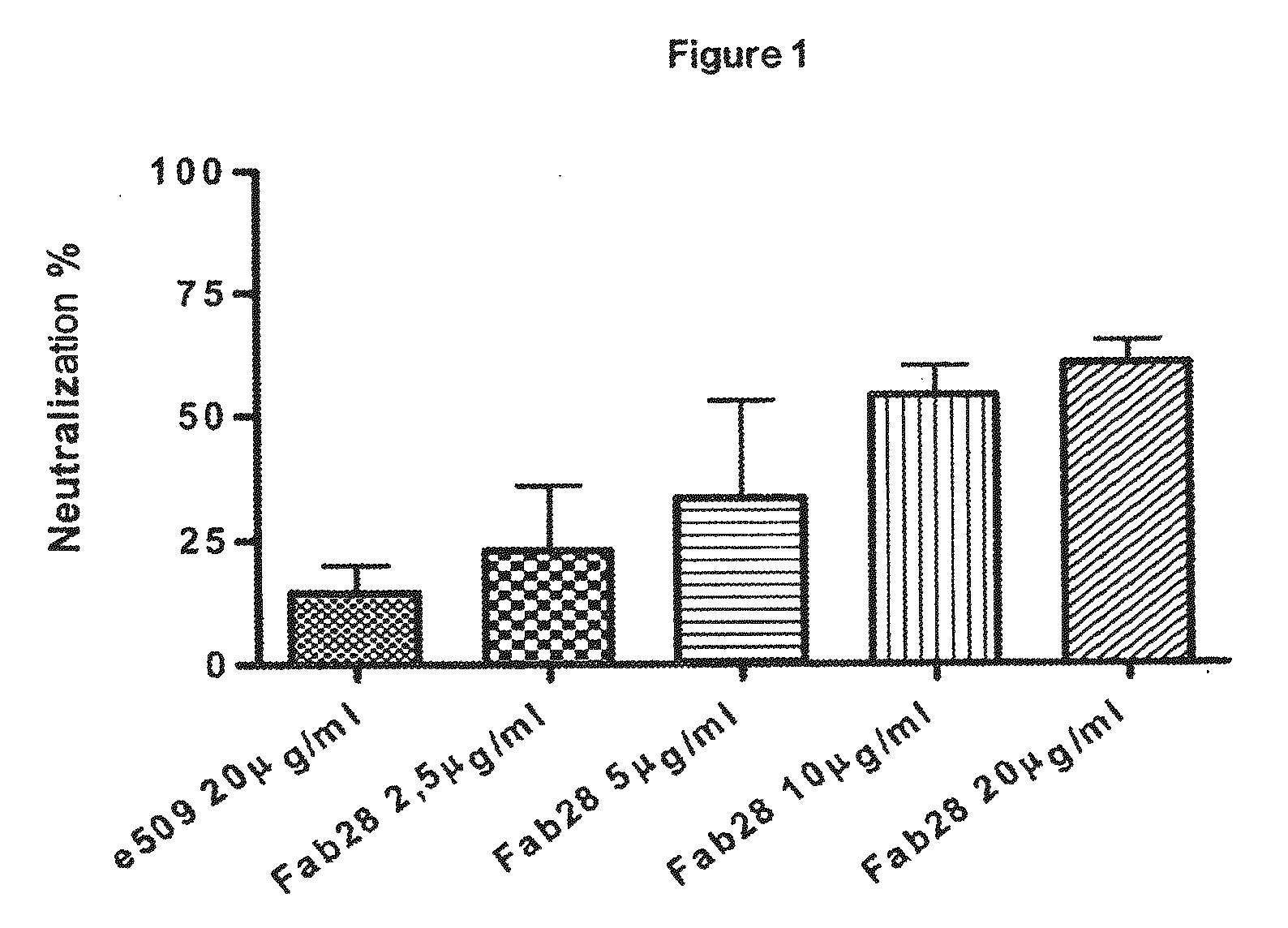
Monoclonal antibodies capable of reacting with a plurality of influenza virus a subtypes
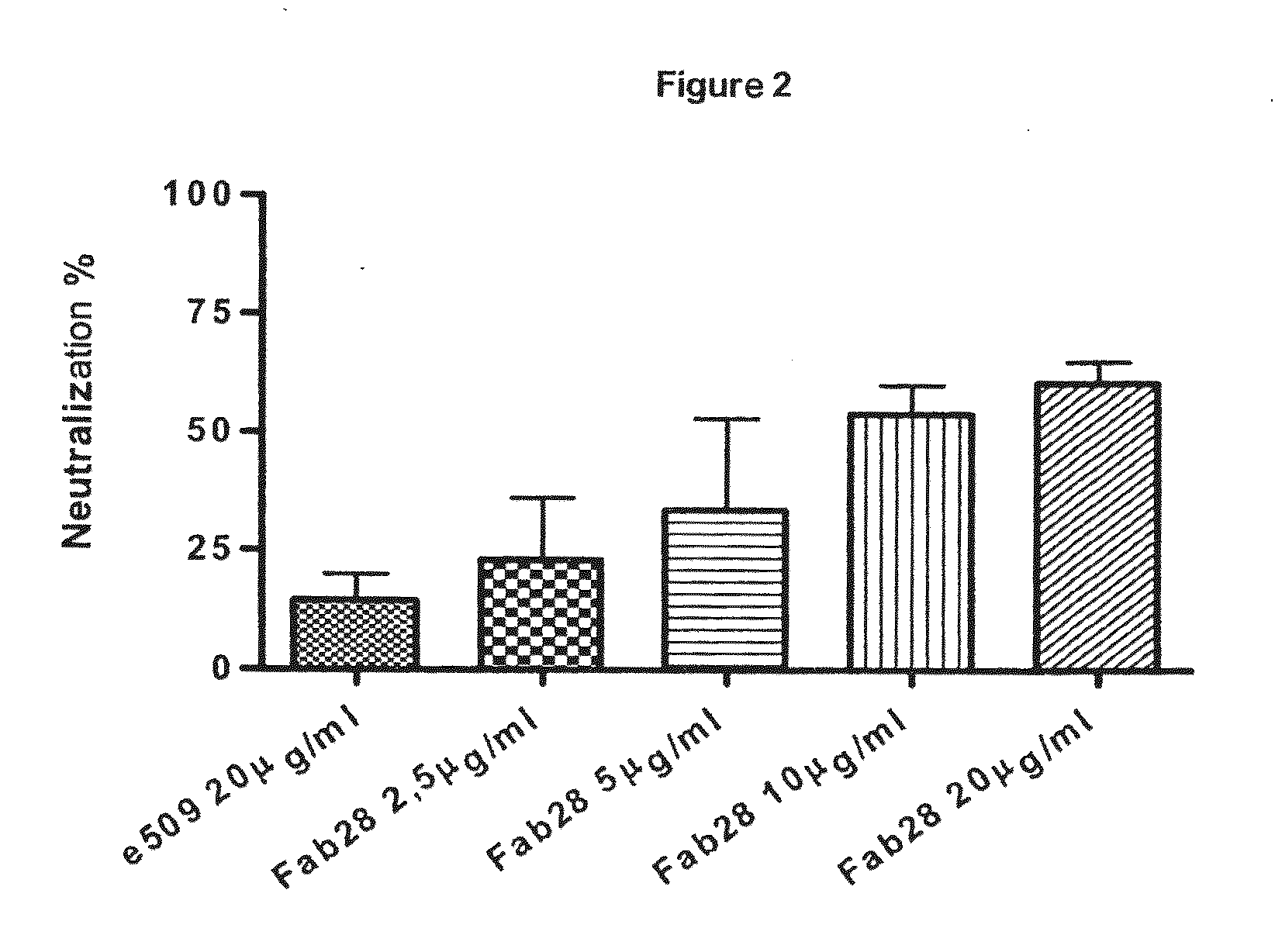
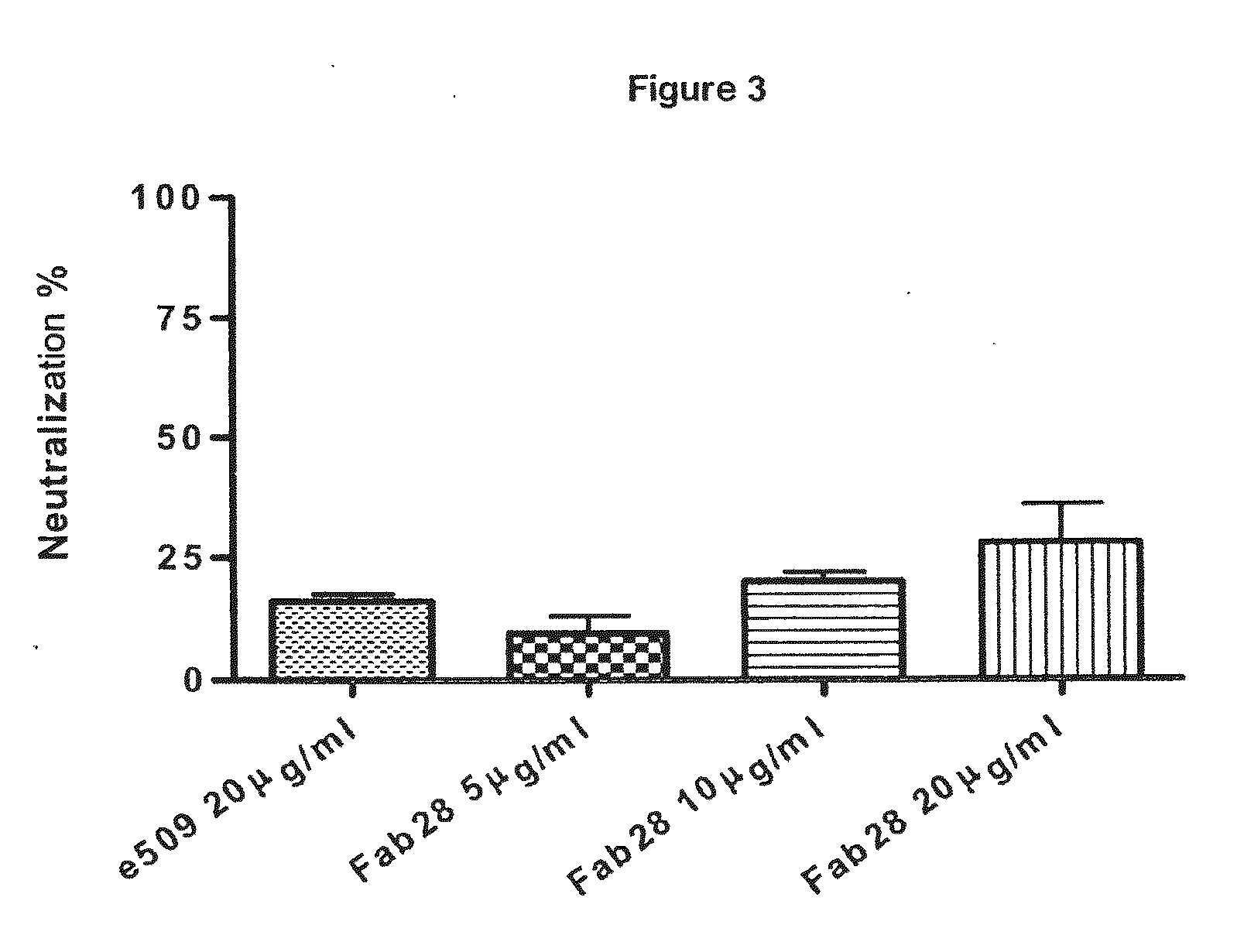
ActiveUS20110014187A1EffectiveEffective preventionImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsAnti idiotypeImmunogenicity
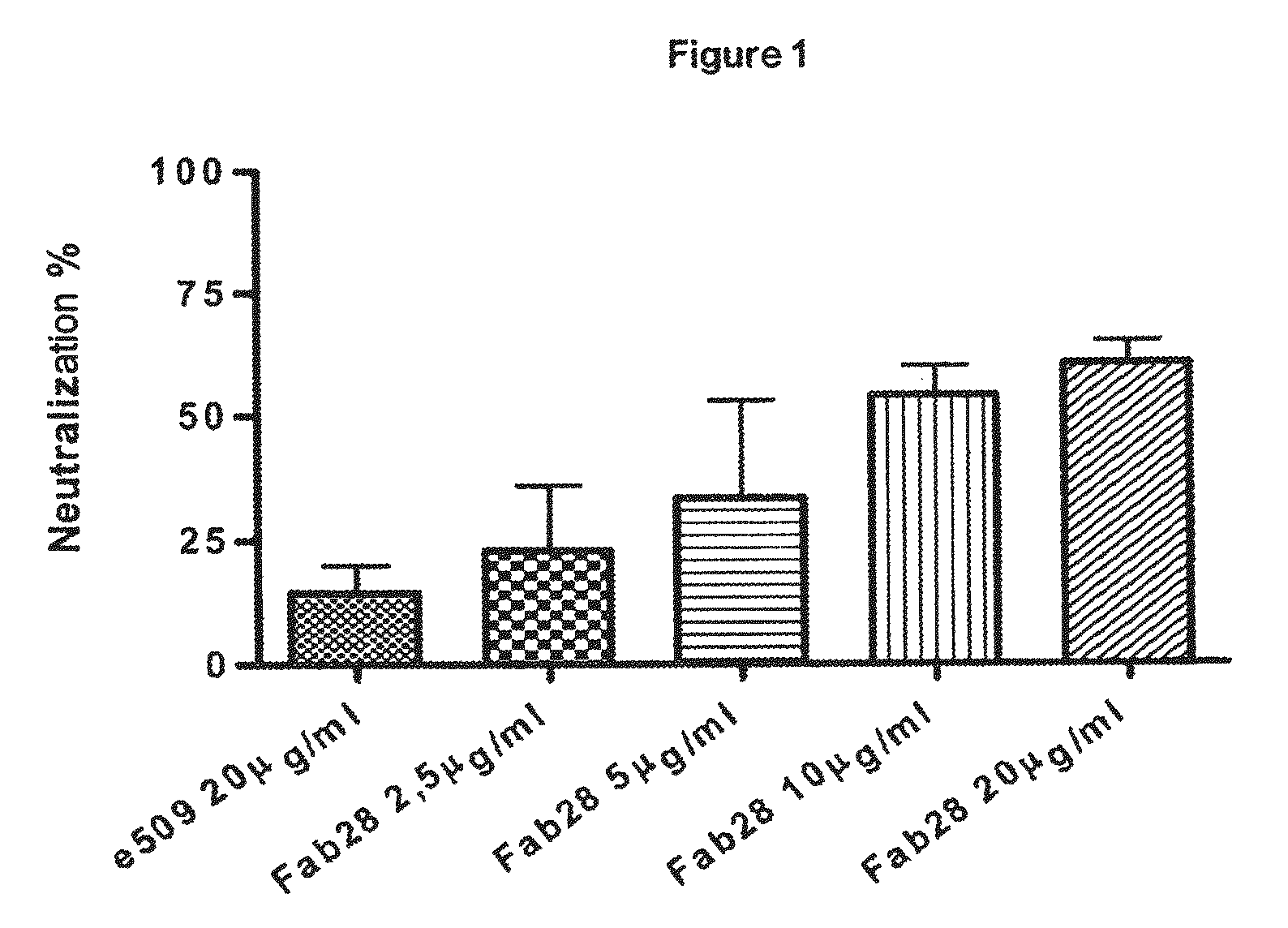
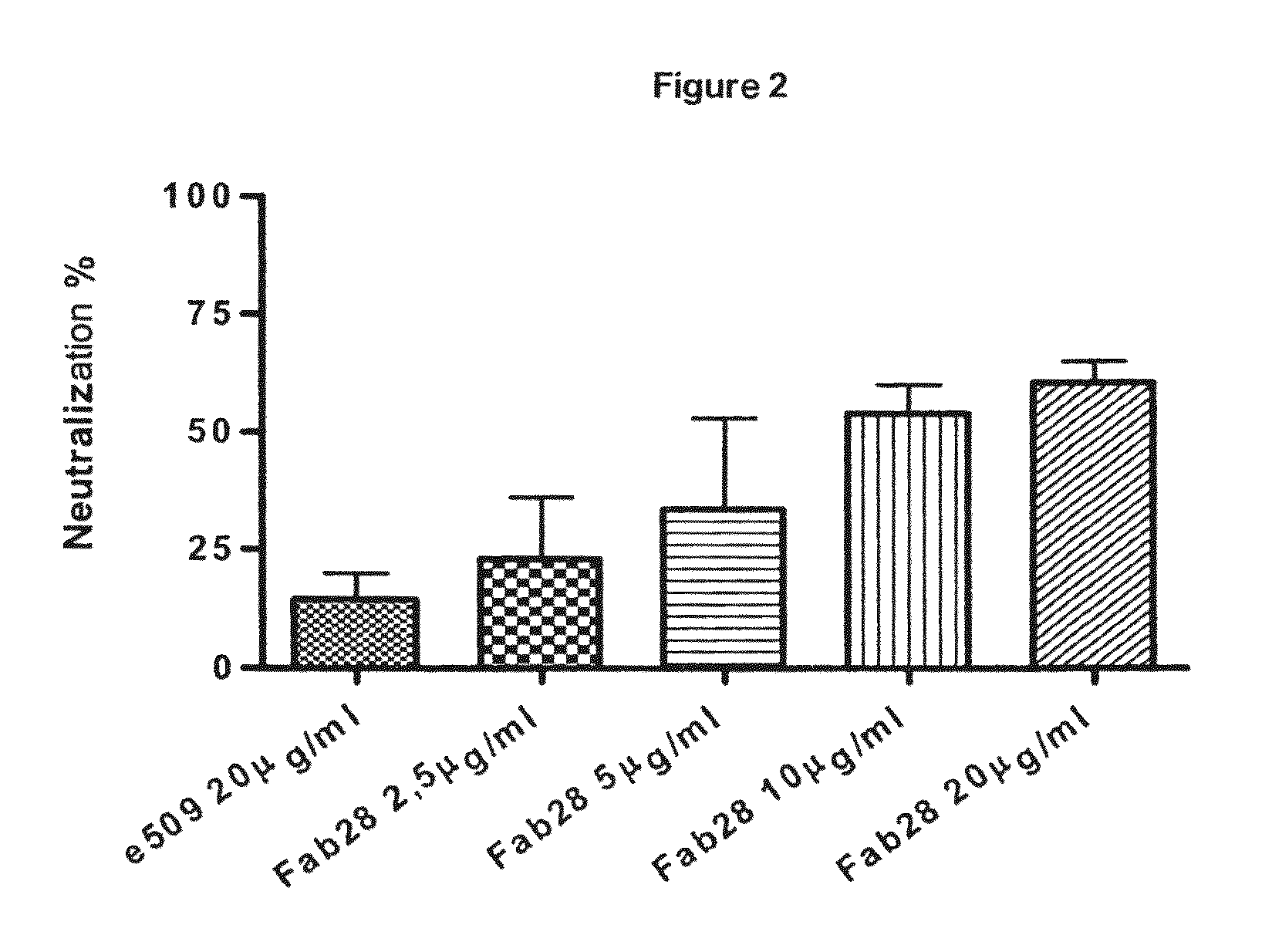
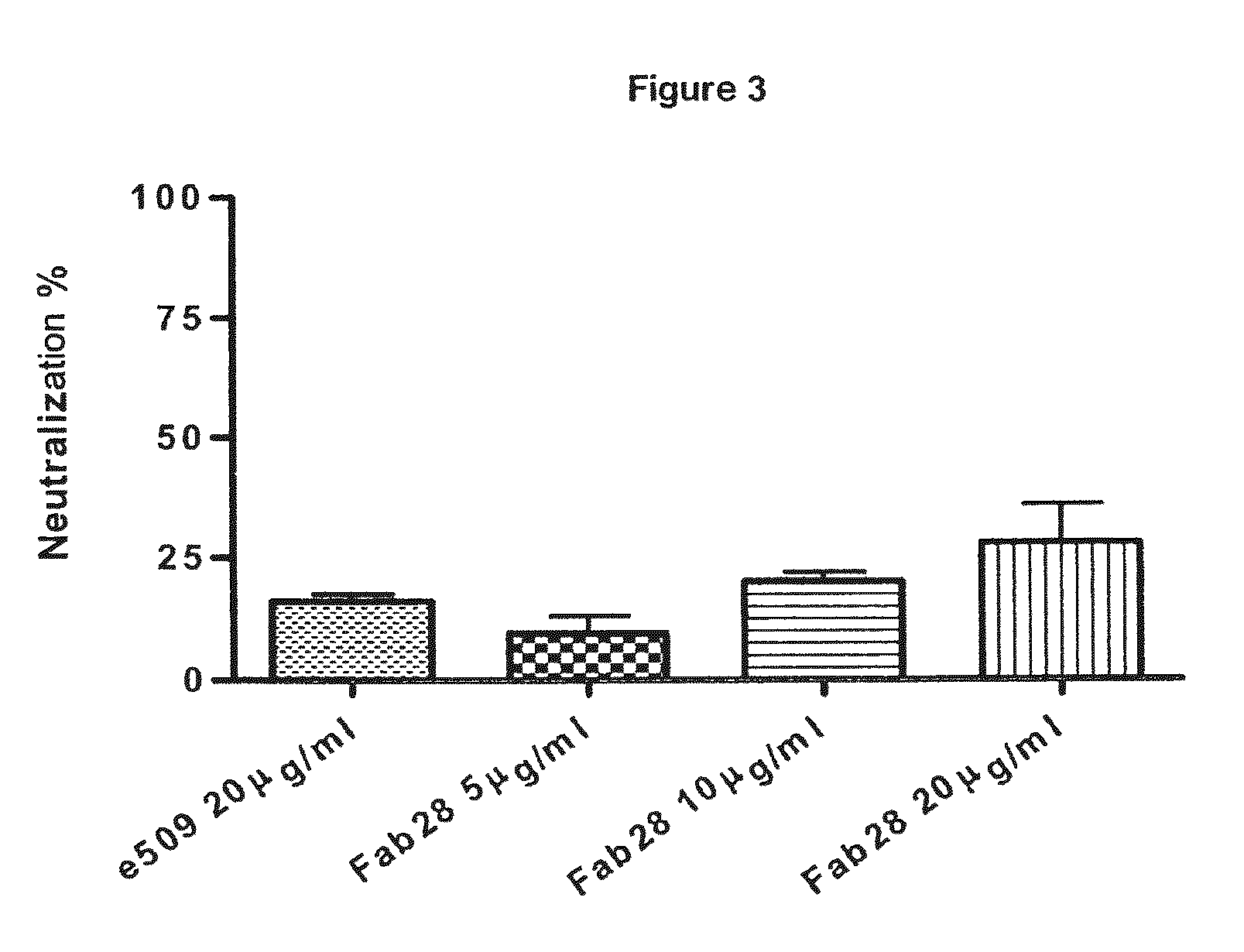
Monoclonal antibodies directed against the influenza A virus are described, which have the advantageous and unpredicted property of being able to bind a plurality of subtypes of the influenza A virus. One preferred embodiment is the antibody designated as Fab28, which displays a neutralizing activity against a plurality of subtypes of the influenza A virus. Anti-idiotype antibodies directed against the monoclonal antibodies of the invention, immunogenic or vaccine compositions comprising the monoclonal antibodies of the invention are also described, as well as therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic applications for the monoclonal antibodies of the invention. The monoclonal antibodies of the invention can also be used for testing antibody preparations to be used as vaccines.
Owner:POMONA RICERCA
Anti-cd22 Anti-idiotypic antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150175711A1Not applyBiological material analysisArtificial cell constructsComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody fragments
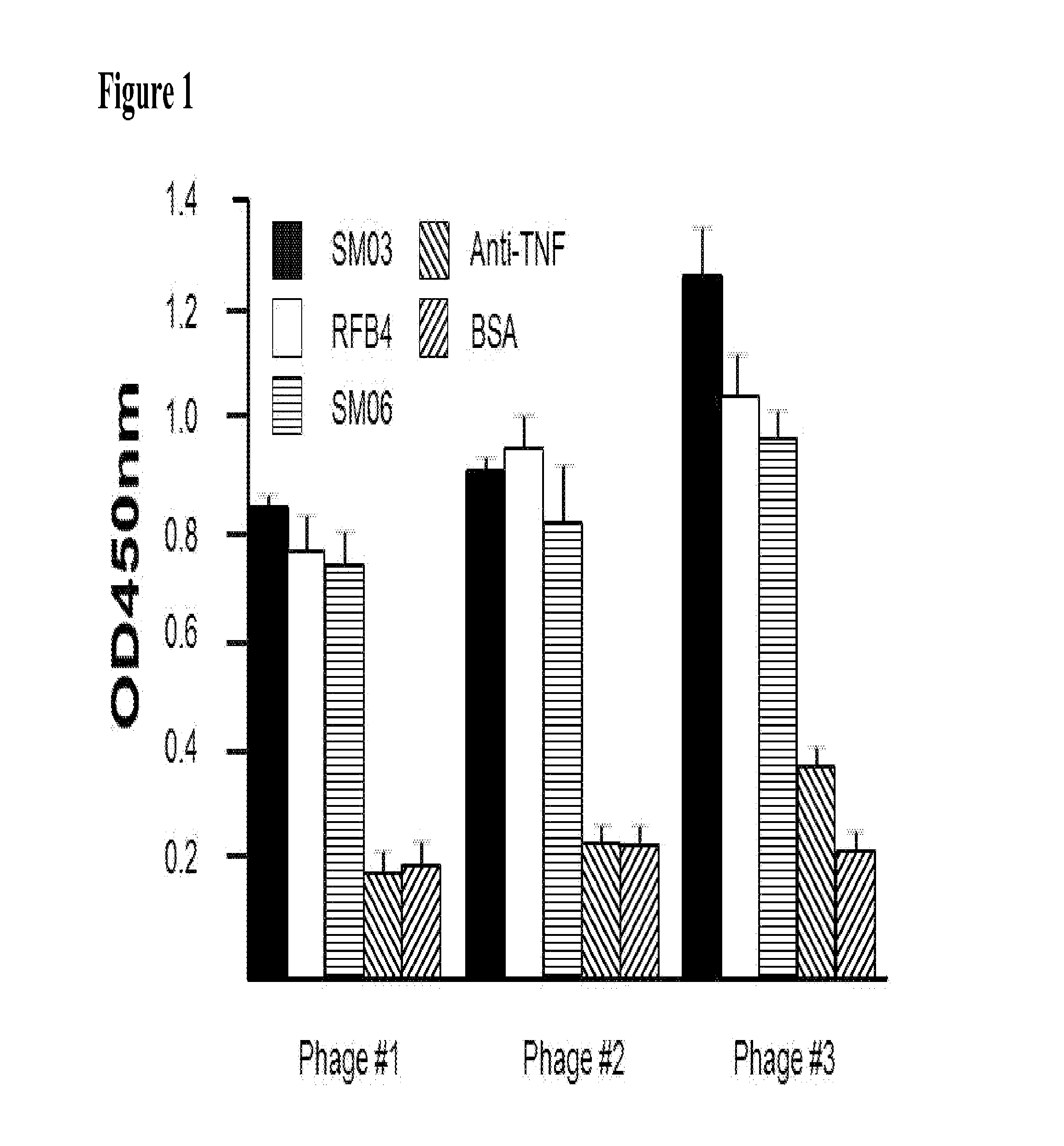
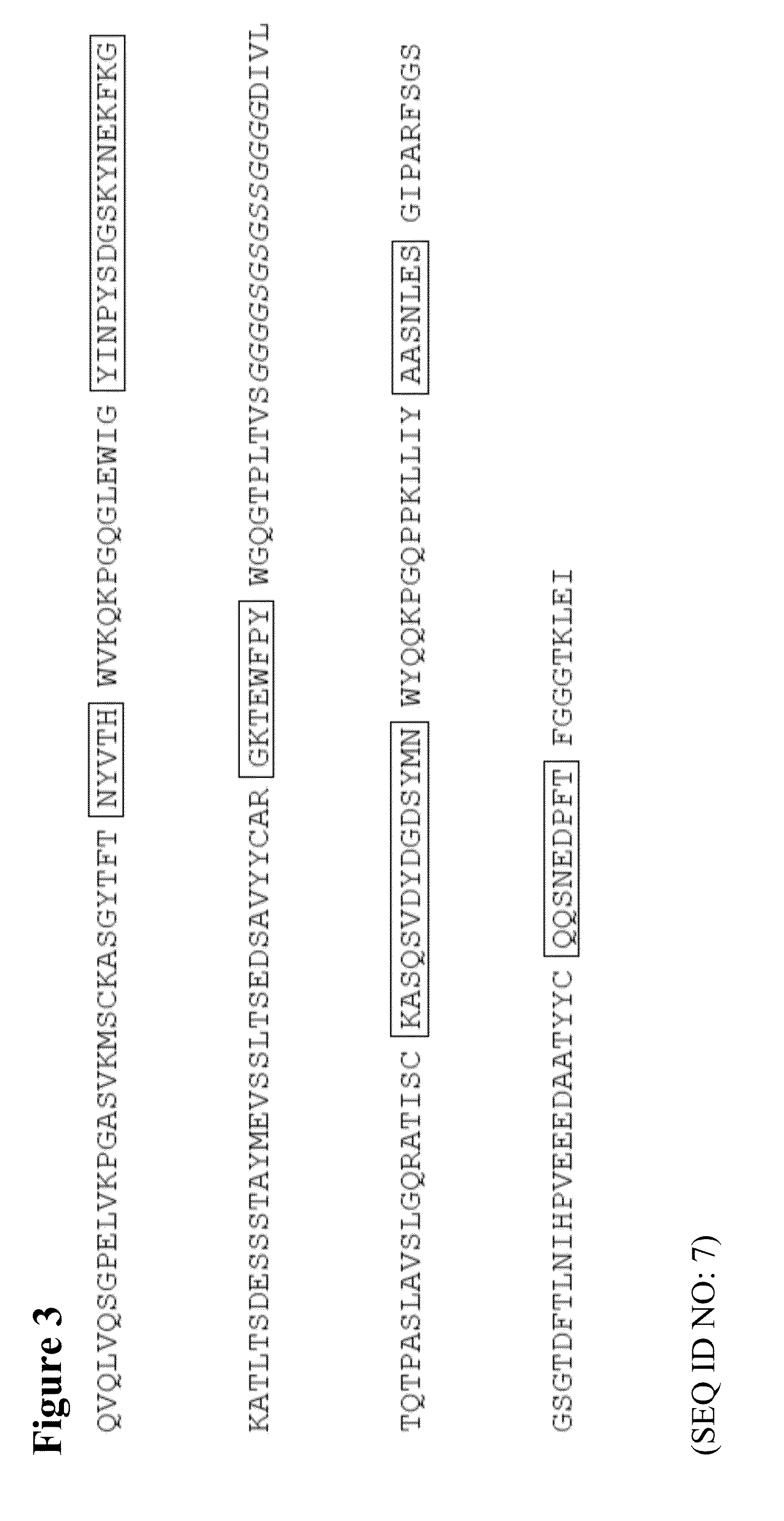
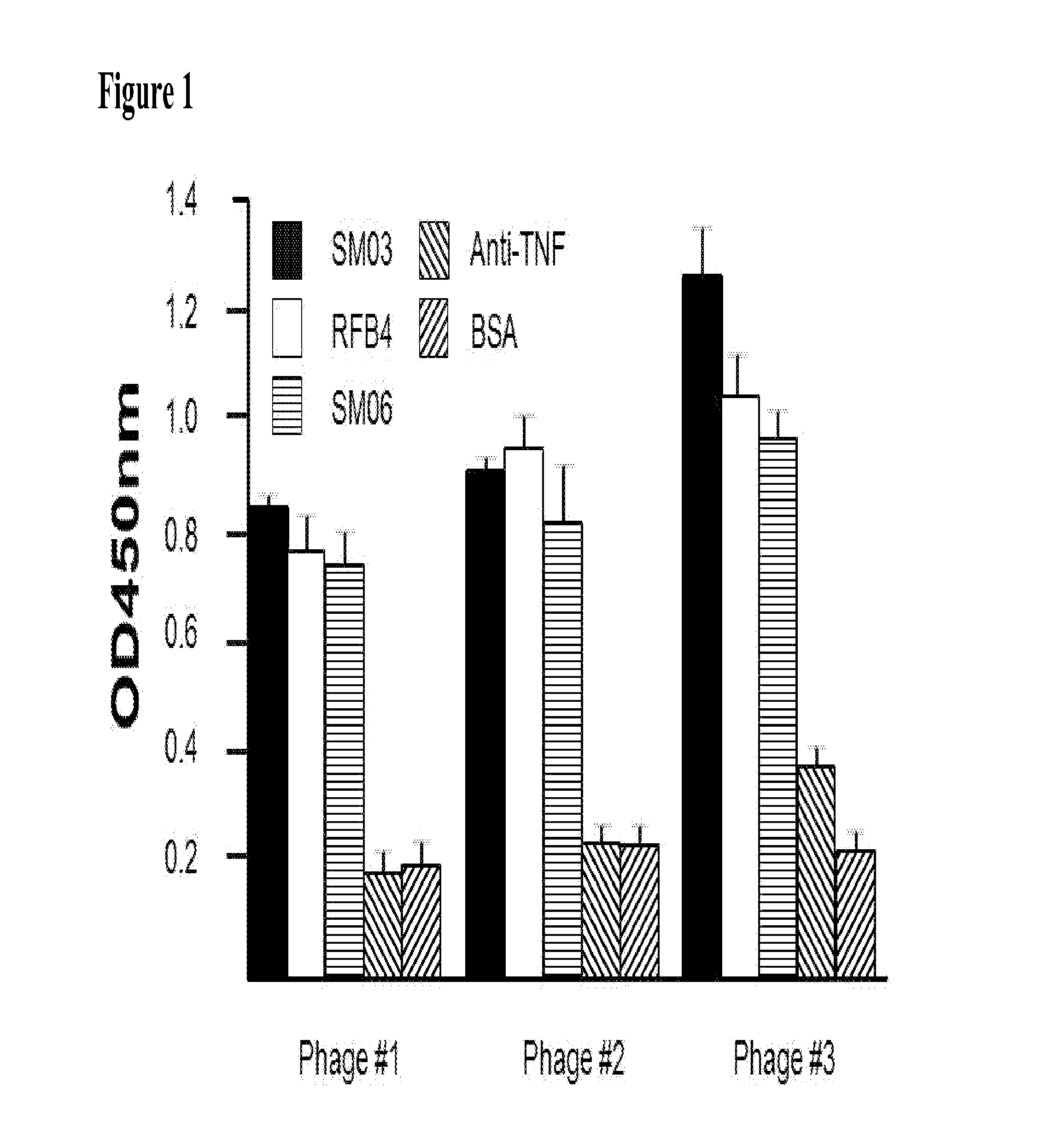
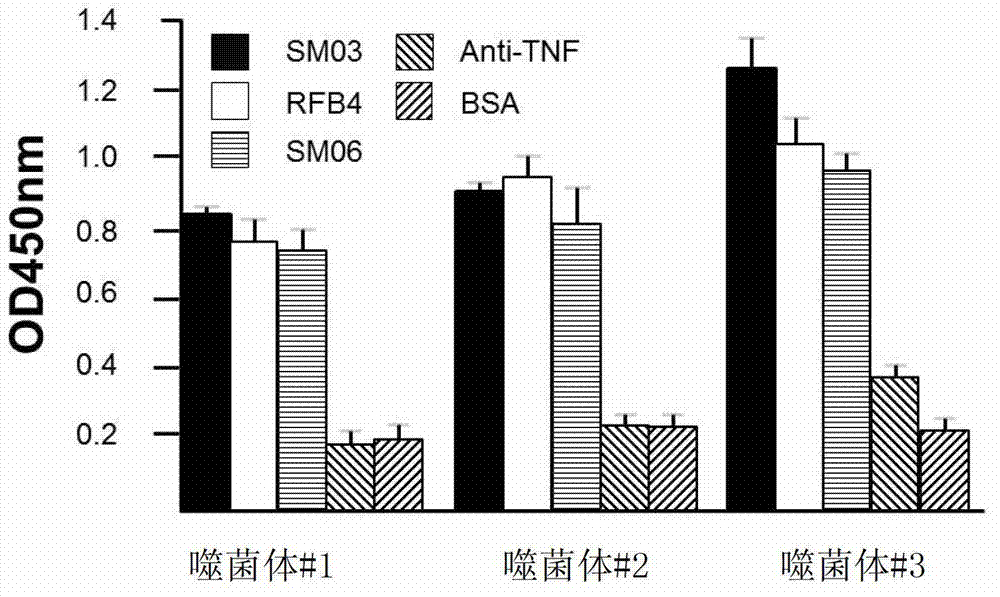
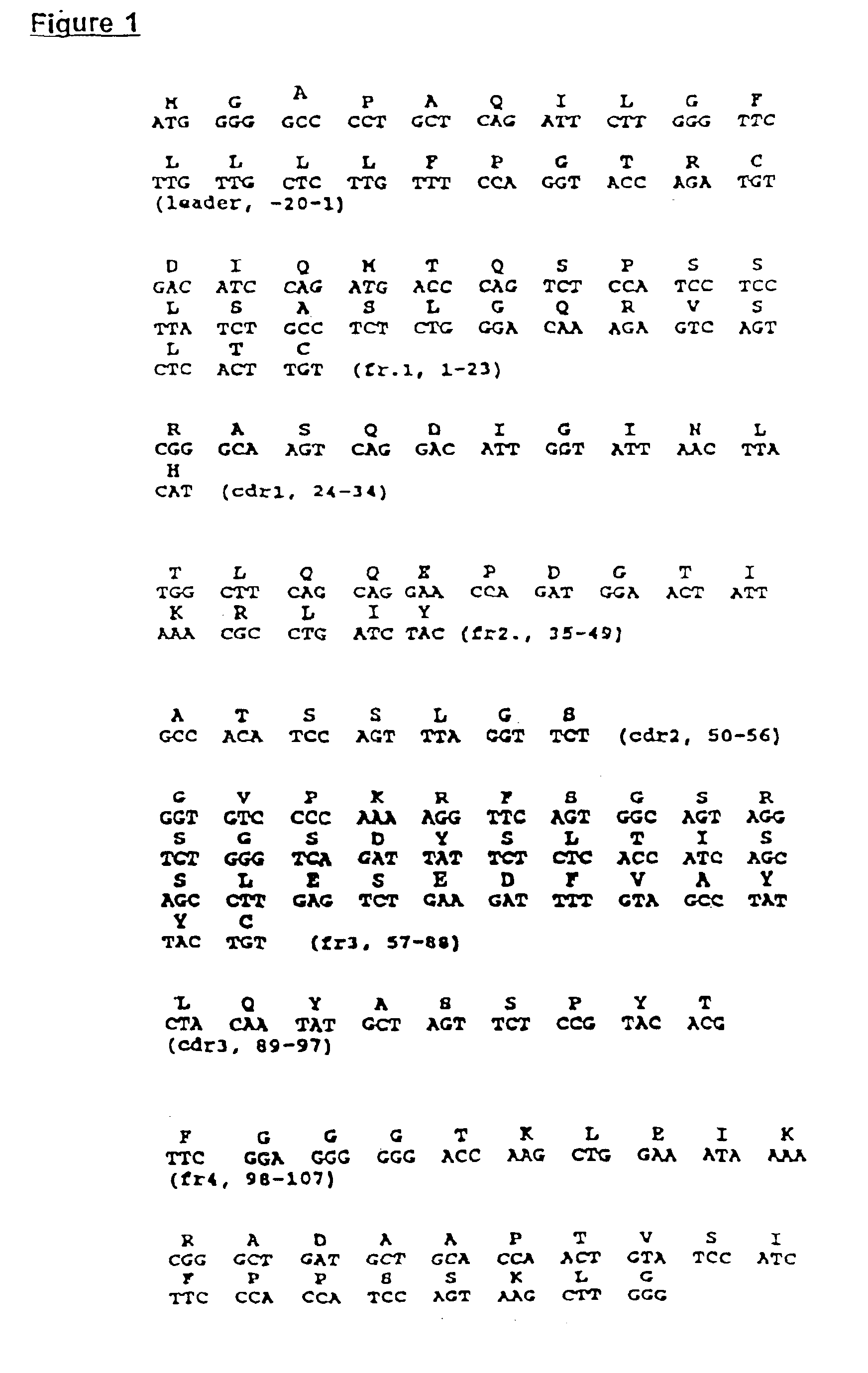
The present invention describes the generation of an anti-idiotype single-chain Fv (scFv) antibody specific for the murine (RFB4), chimeric (SM03) and humanized (SM06) versions of an anti-CD22 antibody (the anti-CD22 antibodies). The present invention further describes the construction of a murine IgG2a / kappa immunoglobulin carrying the variable region sequences of the anti-idiotype scFv sequences. Additionally, the present invention provides a cell line capable of producing an anti-idiotype murine antibody specific for the anti-CD22 antibodies. The present invention is directed against a method for identifying and evaluating the activities and concentration of the anti-CD22 antibodies. Additionally, the present invention provides a method for evaluating serum concentration of the anti-CD22 antibodies that are being used clinically. The present invention is also directed against a method to detect HAMA, HACA and HAHA responses in patients treated with the anti-CD22 antibodies. Specifically, the present invention is directed against the establishment of a cell line expressing surface concentration of the antibody of the invention; the said cell line expressing surface anti-idiotype antibodies or antibody fragments will be used as the target cell line for evaluating the functional activities of the anti-CD22 antibodies via complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and / or antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) activities.
Owner:SINOMAB BIOSCI
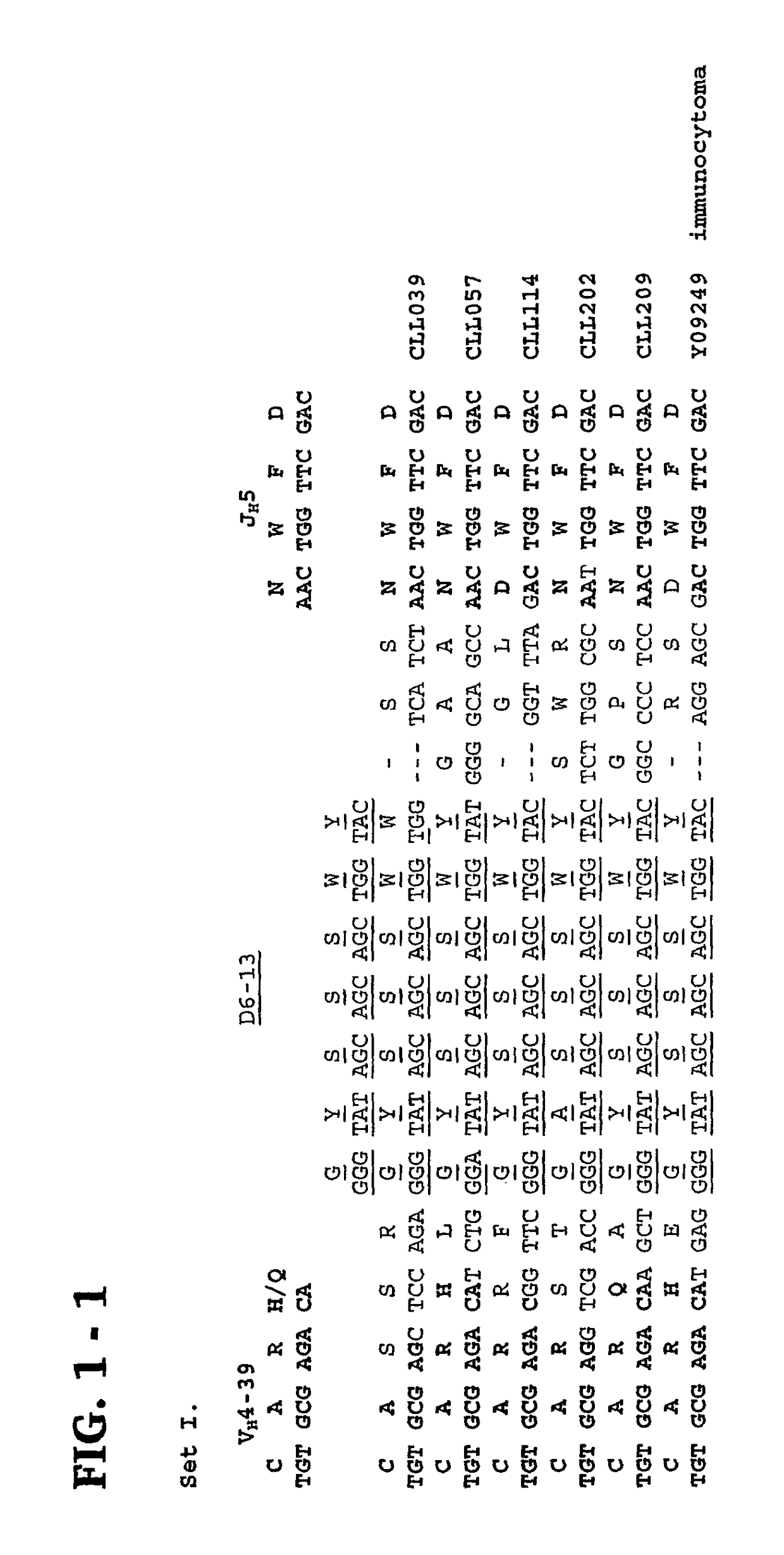
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and treatment of b cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
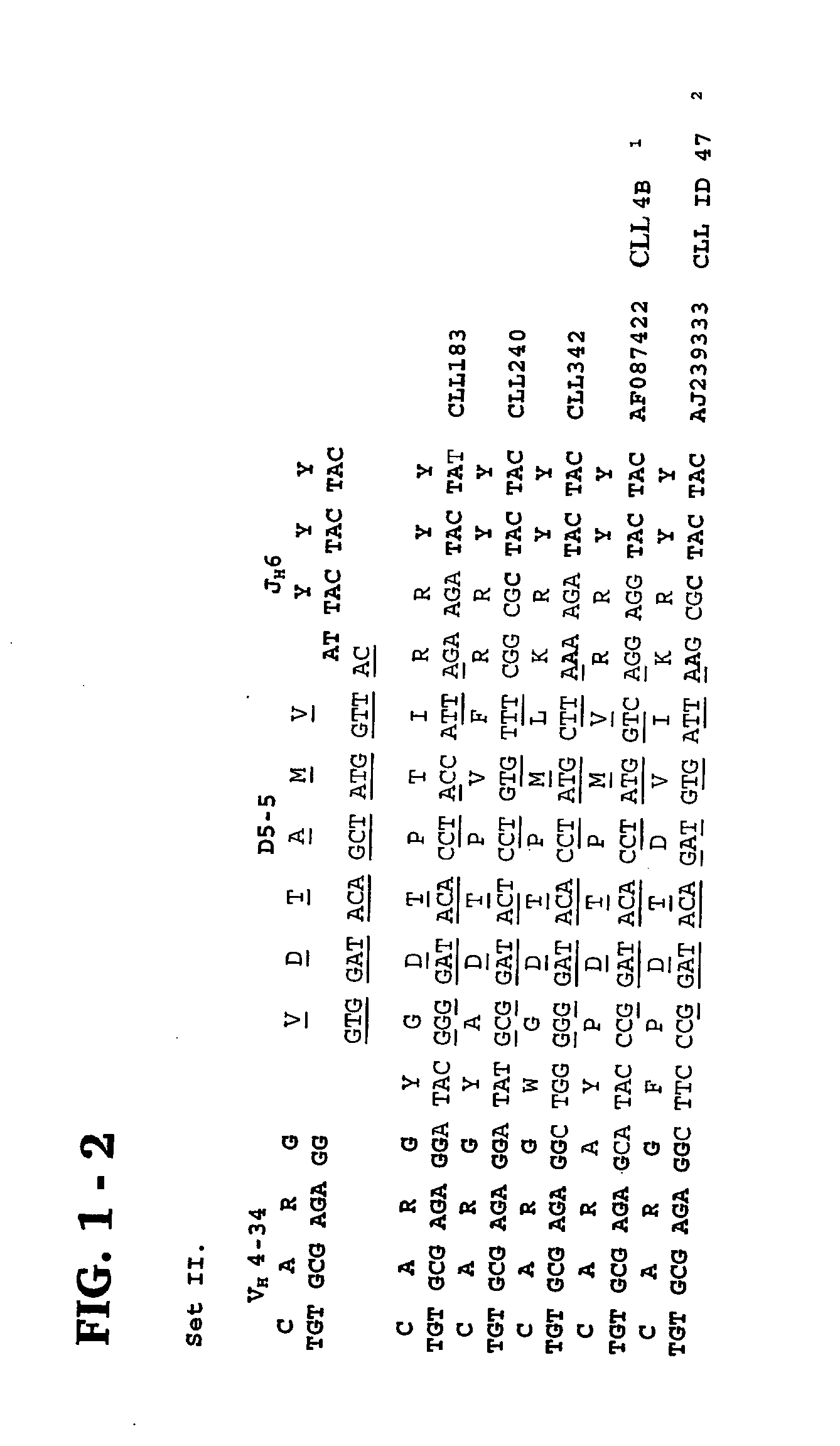
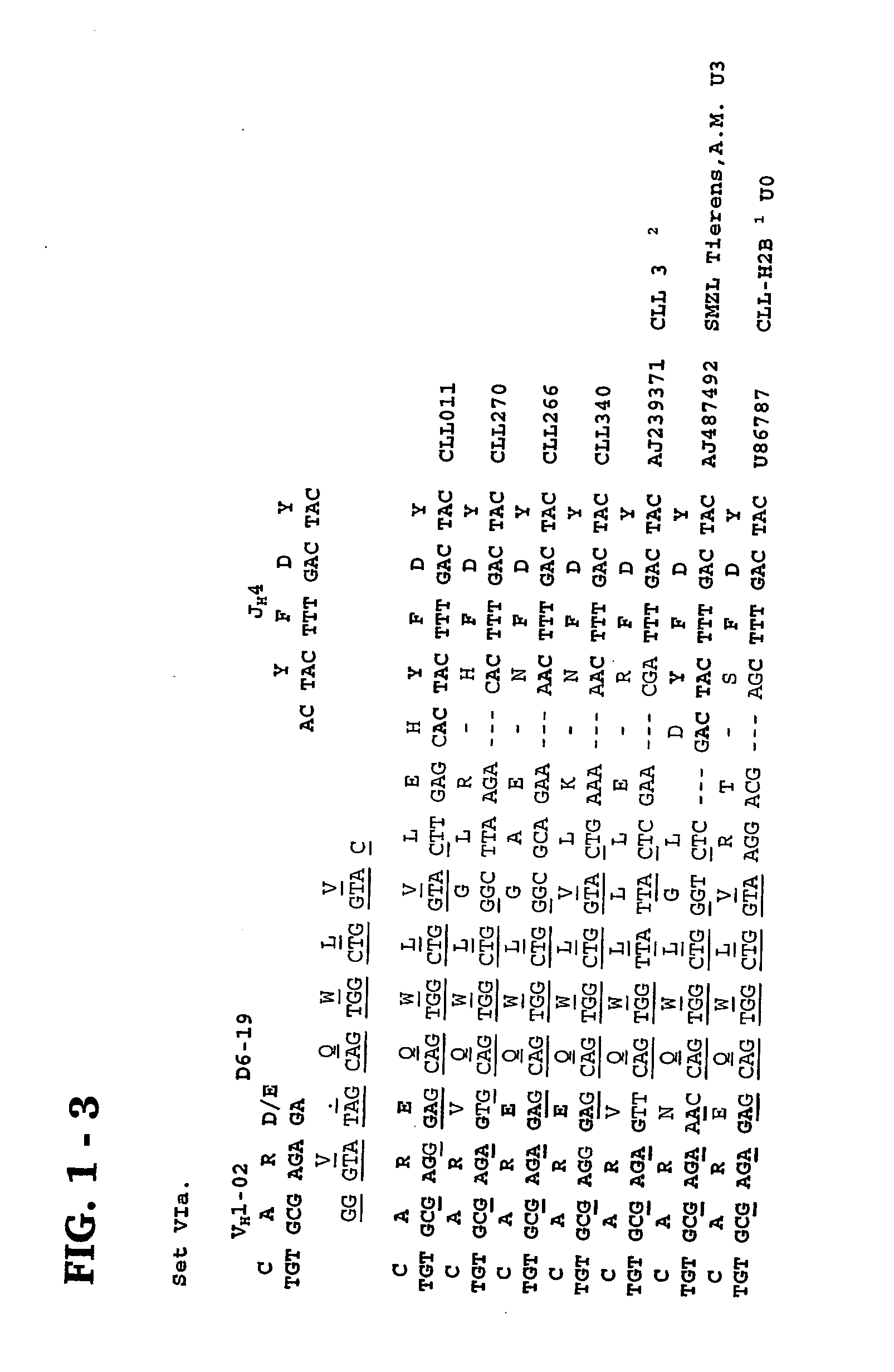
Provided are isolated and purified preparations of a combination of a light chain antibody gene and a heavy chain antibody gene, where the light chain and heavy chain antibody genes are the same among more than one patient with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Vectors comprising those genes and cells comprising those vectors are also provided, as are isolated and purified antibodies encoded by the antibody genes. Anti-idiotype antibodies, peptides, and aptamers that bind to the antigen-binding region of an antibody encoded by the antibody genes are additionally provided, as are multimeric molecules comprising multiple binding sites that bind to the antigen-binding region of an antibody encoded by the antibody genes. Methods of determining whether a patient with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) has a form of B-CLL that is susceptible to treatment directed to eliminating idiotype specific B cell receptor-bearing B-CLL cells are also provided, as are methods of following the progression of treatment of B-CLL in the patient. Additionally, methods of treating a patient having B-CLL are provided, as are methods of identifying a therapeutic agent for B-CLL.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
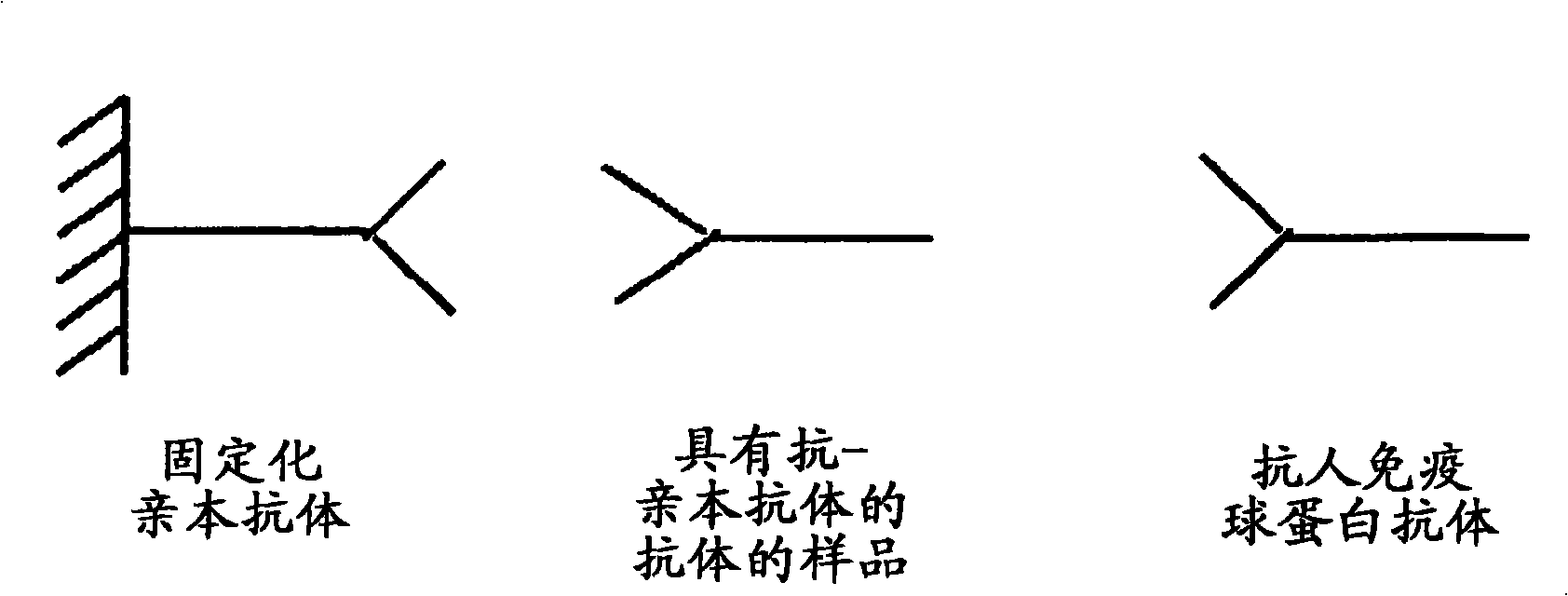
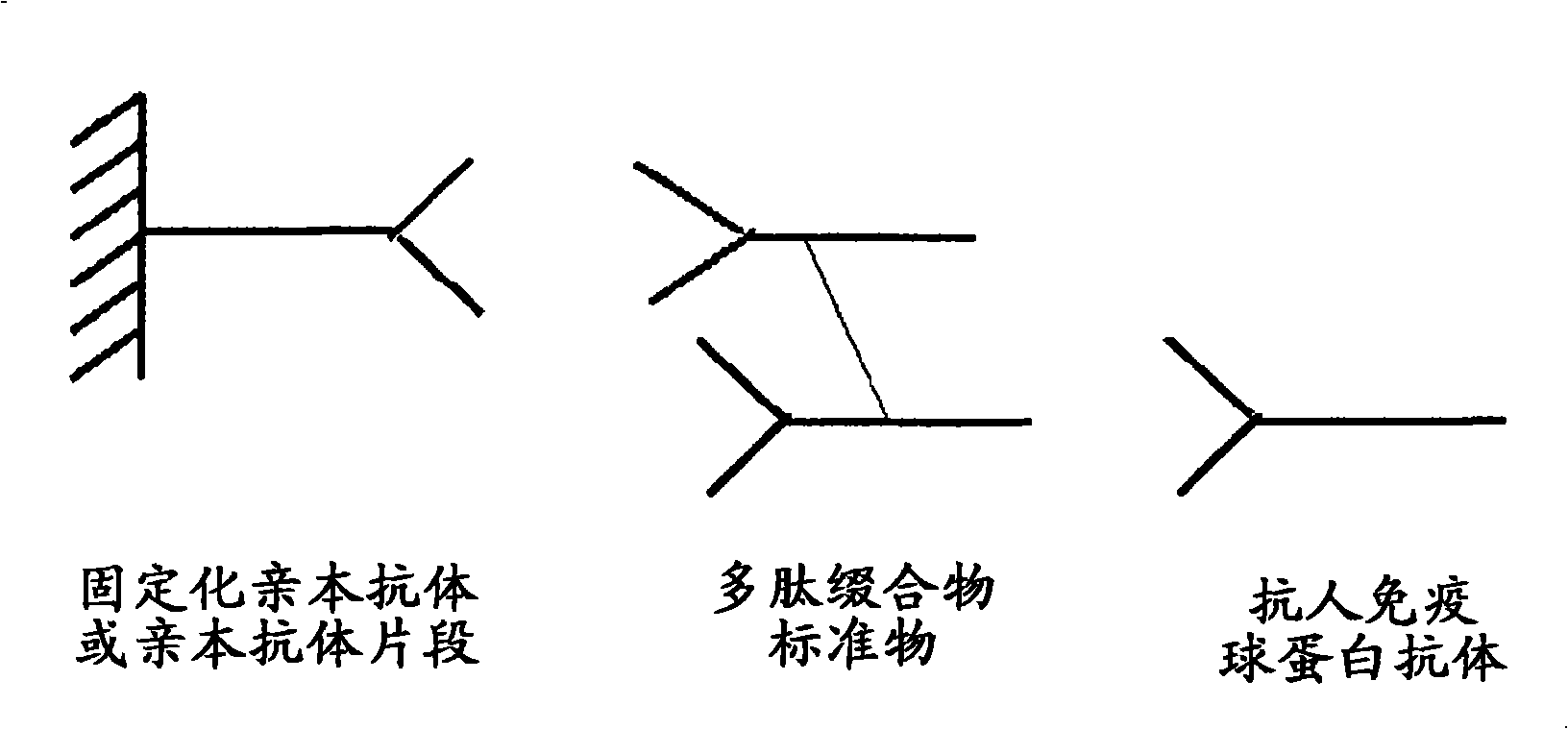
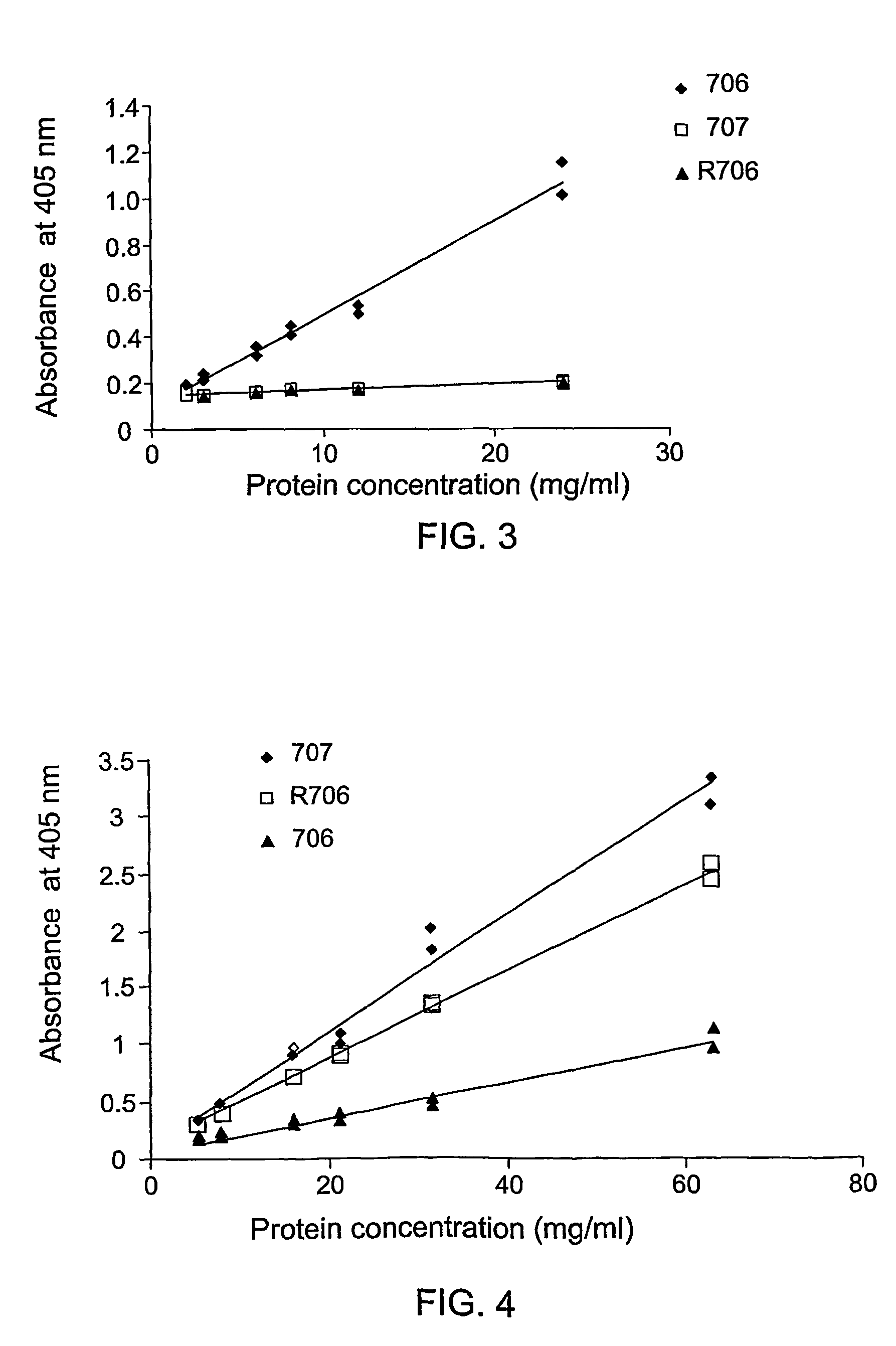
Anti-idiotype conjugate and its use as a standard in an immunassay
ActiveCN101541835AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMaterial analysis by optical meansAnti idiotypeChemistry
A composition comprising a conjugate of an anti-idiotype antibody specifically binding to a CDR region of a parent antibody and method of using polyclonal human serum immunoglobulin of class E, G, M, or A, and the use of said composition as a standard in an immunoassay is presented.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Anti-CD22 anti-idiotypic antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS9371396B2Biological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody fragments
The present invention describes the generation of an anti-idiotype single-chain Fv (scFv) antibody specific for the murine (RFB4), chimeric (SM03) and humanized (SM06) versions of an anti-CD22 antibody (the anti-CD22 antibodies). The present invention further describes the construction of a murine IgG2a / kappa immunoglobulin carrying the variable region sequences of the anti-idiotype scFv sequences. Additionally, the present invention provides a cell line capable of producing an anti-idiotype murine antibody specific for the anti-CD22 antibodies. The present invention is directed against a method for identifying and evaluating the activities and concentration of the anti-CD22 antibodies. Additionally, the present invention provides a method for evaluating serum concentration of the anti-CD22 antibodies that are being used clinically. The present invention is also directed against a method to detect HAMA, HACA and HAHA responses in patients treated with the anti-CD22 antibodies. Specifically, the present invention is directed against the establishment of a cell line expressing surface concentration of the antibody of the invention; the said cell line expressing surface anti-idiotype antibodies or antibody fragments will be used as the target cell line for evaluating the functional activities of the anti-CD22 antibodies via complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and / or antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) activities.
Owner:SINOMAB BIOSCI
Anti-idiotype antibody for human CD22 antibody, and application thereof
The invention discloses an anti-idiotype antibody for a human CD22 antibody, and an application thereof. The anti-idiotype antibody for the human CD22 antibody comprises three antibody heavy chain complementary determining regions and three antibody light chain complementary determining regions, wherein amino acid sequences of the three antibody heavy chain complementary determining regions are shown as 31-35 sites, 50-66 sites and 99-106 sites of a sequence 1 in a sequence table respectively; and amino acid sequences of the three antibody light chain complementary determining regions are shown as 154-168 sites, 184-190 sites and 223-231 sites of a sequence 1 in the sequence table. The anti-idiotype antibody for the human CD22 antibody can inhibit combination of the human CD22 antibody with a natural ligand of human CD22 antigen.
Owner:SINOMAB BIOSCI
Polynucleotides related to murine anti-idiotype antibody 11D10 and methods of use thereof
The present invention provides a monoclonal and-idiotype antibody 11D10 that elicits an immune response against a specific epitope of a high molecular weight mucin of human milk fat globule (HMFG) and a hybridoma that produces 11D10. The hybridoma that produces 11D10 was selected by specific procedures. 11D10 inducts an Immunological response to HMFG in mice, rabbits, monkeys and patients with advanced HMFG-associated tumors. This invention provides compositions derived from polynucleotide sequences encoding the variable light and / or variable heavy regions of monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody 11D10, as well as polypeptides encoded thereby. The invention also provides compositions which can be used in the detection or treatment of HMFG-associated tumors.
Owner:CHATTERJEE MALAYA +2
Production of specific micro-antibody for oarium cancer
InactiveCN1854295AHigh expressionImprove stabilityBacteriaImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEscherichia coliProcess optimization
The invention provides a nucleotide sequence encoding ovarian cancer anti-idiotypic microantibodies, a production method for efficiently producing ovarian cancer anti-idiotypic microantibodies, and related engineering cell construction, expression and purification processes. The optimized ovarian cancer anti-idiotypic microantibody gene is very suitable for expression in Escherichia coli. At the same time, by optimizing the combination of expression plasmids and host bacteria and optimizing the fermentation process, the expression level has been increased, and it has the advantages of high expression and high stability. The invention can obtain pure ovarian cancer anti-idiotypic micro-antibody with high efficiency, convenience and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEWSUMMIT BIOPHARMA
Vaccines against cancer and infectious diseases
InactiveUS20020192227A1Promote productionRepress the development of cancerOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProtozoaInfectious Disorder
A method of stimulating an immune response in a human against malignant cells or an infectious agent comprises the step of administering to the human an immunogenic amount of a primate anti-idiotype antibody or antibody fragment that acts as an immunogenic functional mimic of an antigen produced by or associated with a malignant cell or an infectious agent. Sub-human primate anti-idiotype antisera, especially from baboons, are preferred. Such anti-idiotype antibodies are used to make vaccines for inducing preventive immunity or a therapeutic immune response against tumors, viruses, bacteria, rickettsia, mycoplasma, protozoa, fungi and multicellular parasites.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
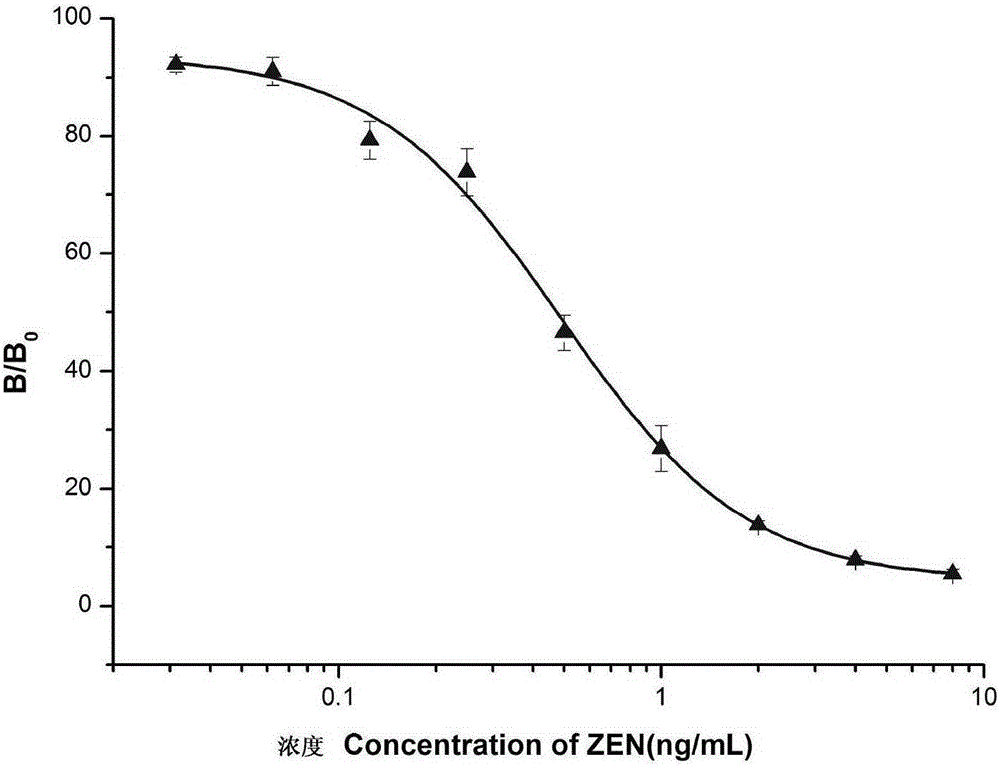
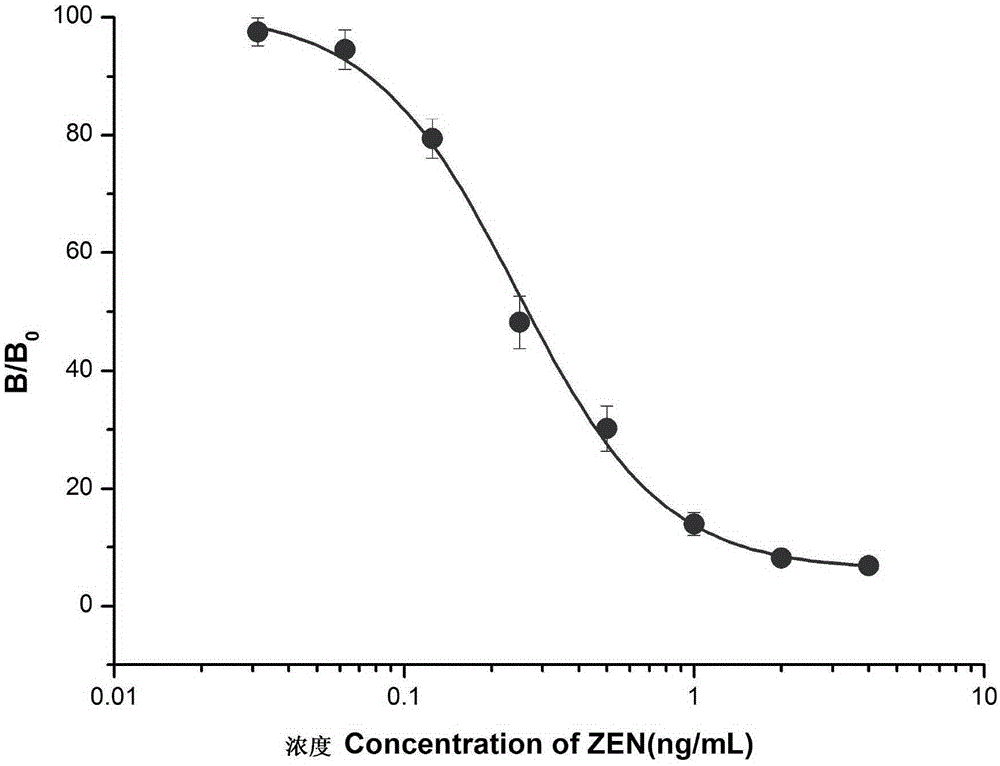
Preparation and application of zearalenone anti-idiotype nano antibody
ActiveCN105218676AHave immune response propertiesGood effectImmunoglobulinsBiological testingEpitopeNucleotide
The invention belongs to the biological technical field, and in particular relates to preparation and application of a zearalenone anti-idiotype nano antibody, which has an amino acid sequence SEQ ID No.1, also relates to the nucleotides encoding the amino acid. The nano antibody of the invention can replace the expensive toxic Zen standard, and can be used in immunological detection of Zen as a competitive antigen or solid coating antigen. the nano antibody has similar immunological properties to natural Zen molecule, and good effect. Compared to a traditional antigen mimicking epitope based on polypeptide and a traditional anti-idiotype antibody based on IgG, the nano antibody has the advantages of more stable structure, acid resistance, alkali resistance, high temperature resistance and high detection sensitivity, so that the immune detection stability has been greatly improved, and the tolerance on the environment has also been improved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Peptides and nucleic acid sequences related to the Epstein Barr Virus
InactiveUS7507804B2Effective protectionEasy to insertAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesAnti-EBV AntibodyViral nucleic acid
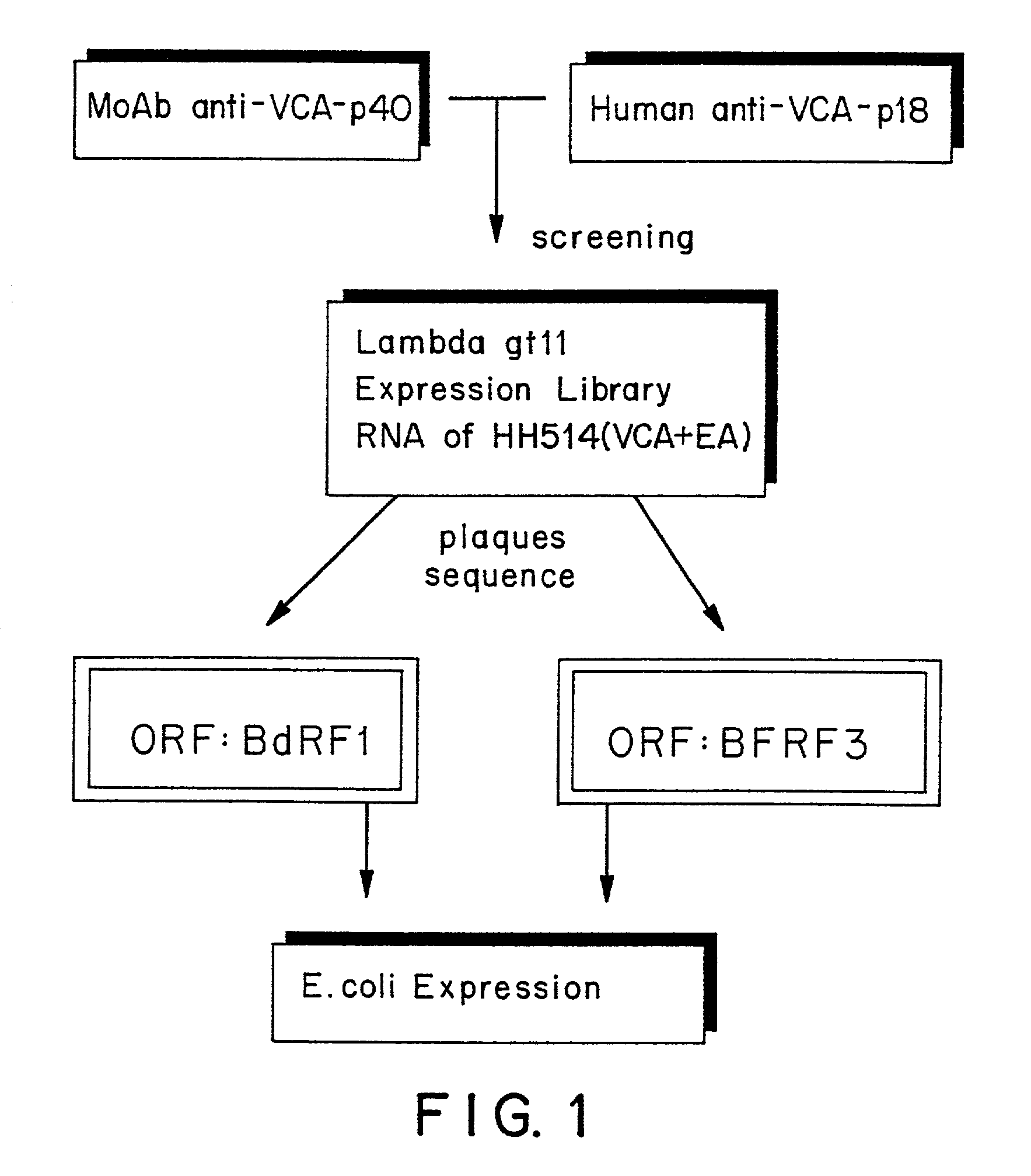
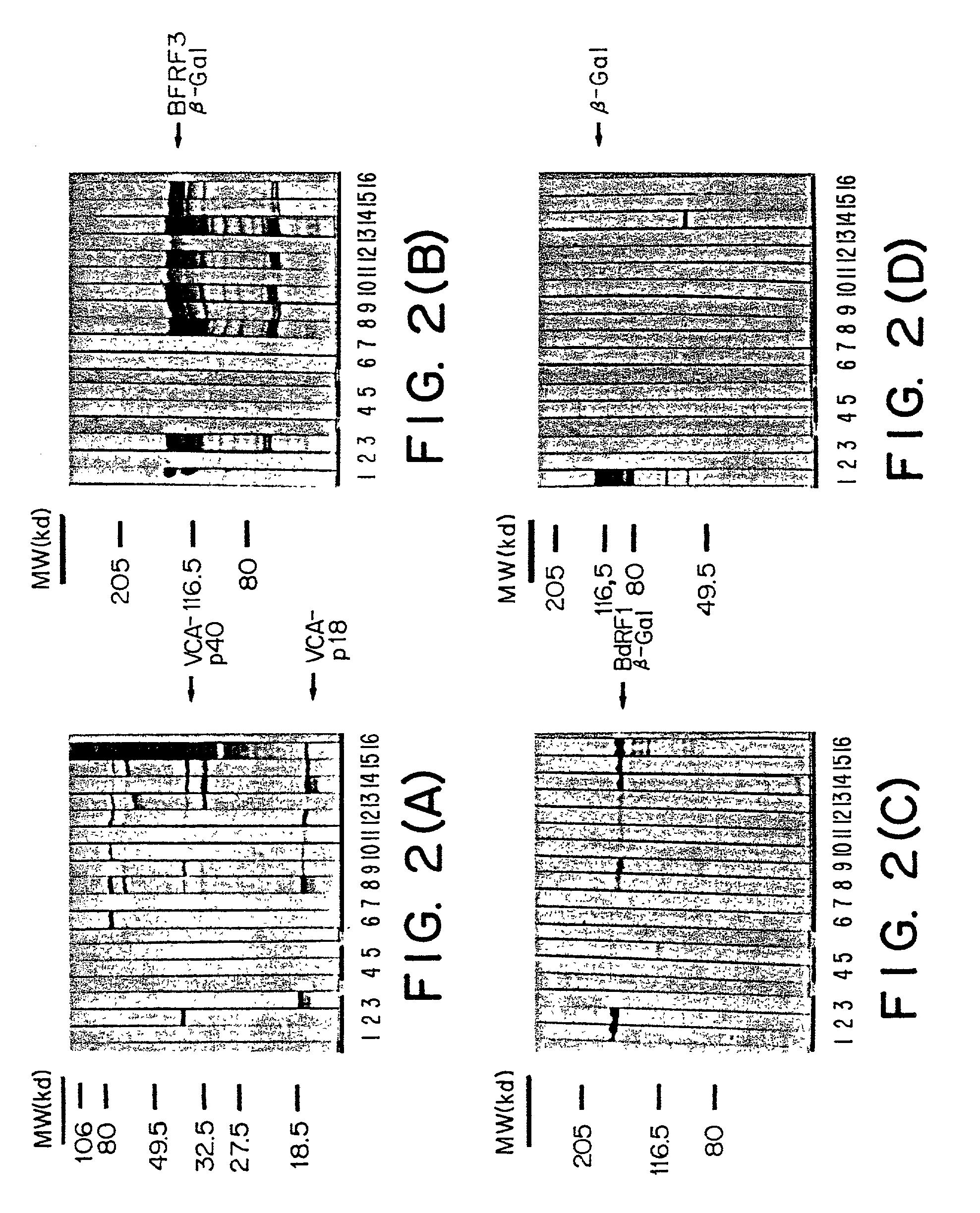
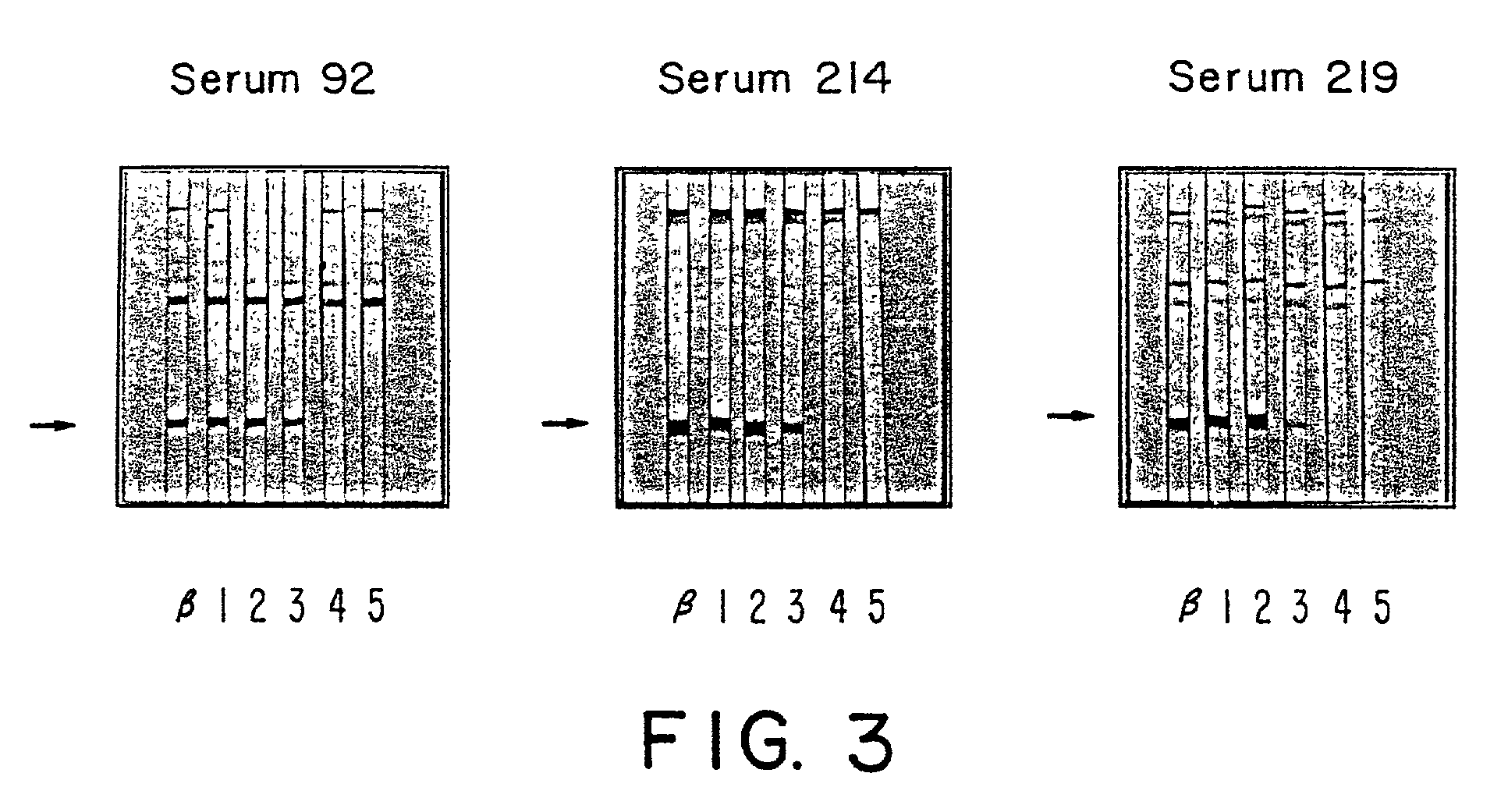
The present invention relates to peptides immunochemically reactive with antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), nucleic acid sequences encoding these peptides, monoclonal antibodies against these peptides, cell lines capable of producing monoclonal antibodies and anti-idiotype antibodies. The invention also relates to recombinant vector molecules comprising a nucleic acid sequence according to the invention and host cells transformed or transfected with these vector molecules. The invention is further concerned with immunological reagents and methods for the detection of EBV or anti-EBV antibodies and a method for the amplification and detection of Epstein Barr viral nucleic acid.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL NV
Immunoassay device and method
InactiveUS20090246795A1Rapid and highly sensitive quantitative measurementEasy to operateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteImmuno assay
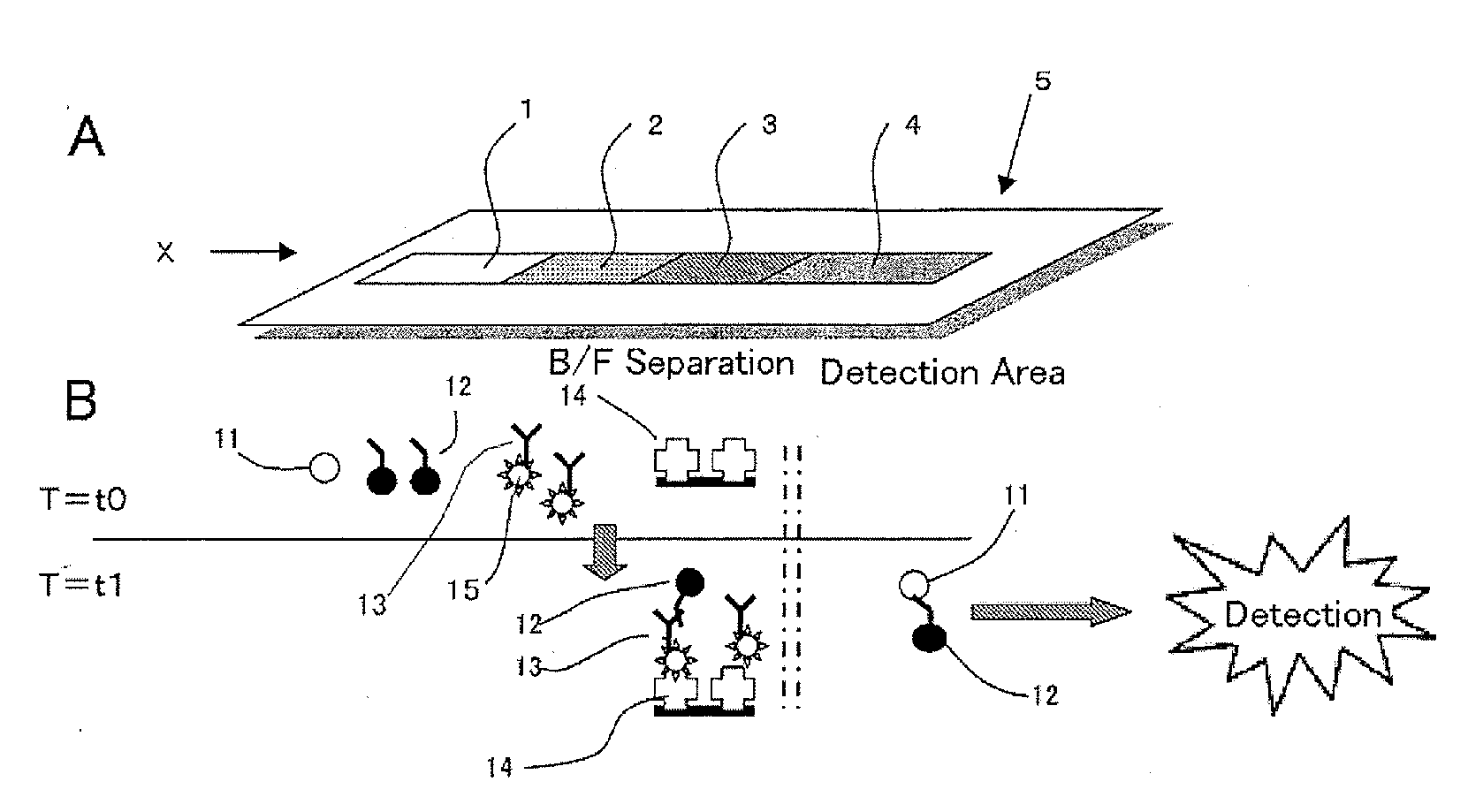
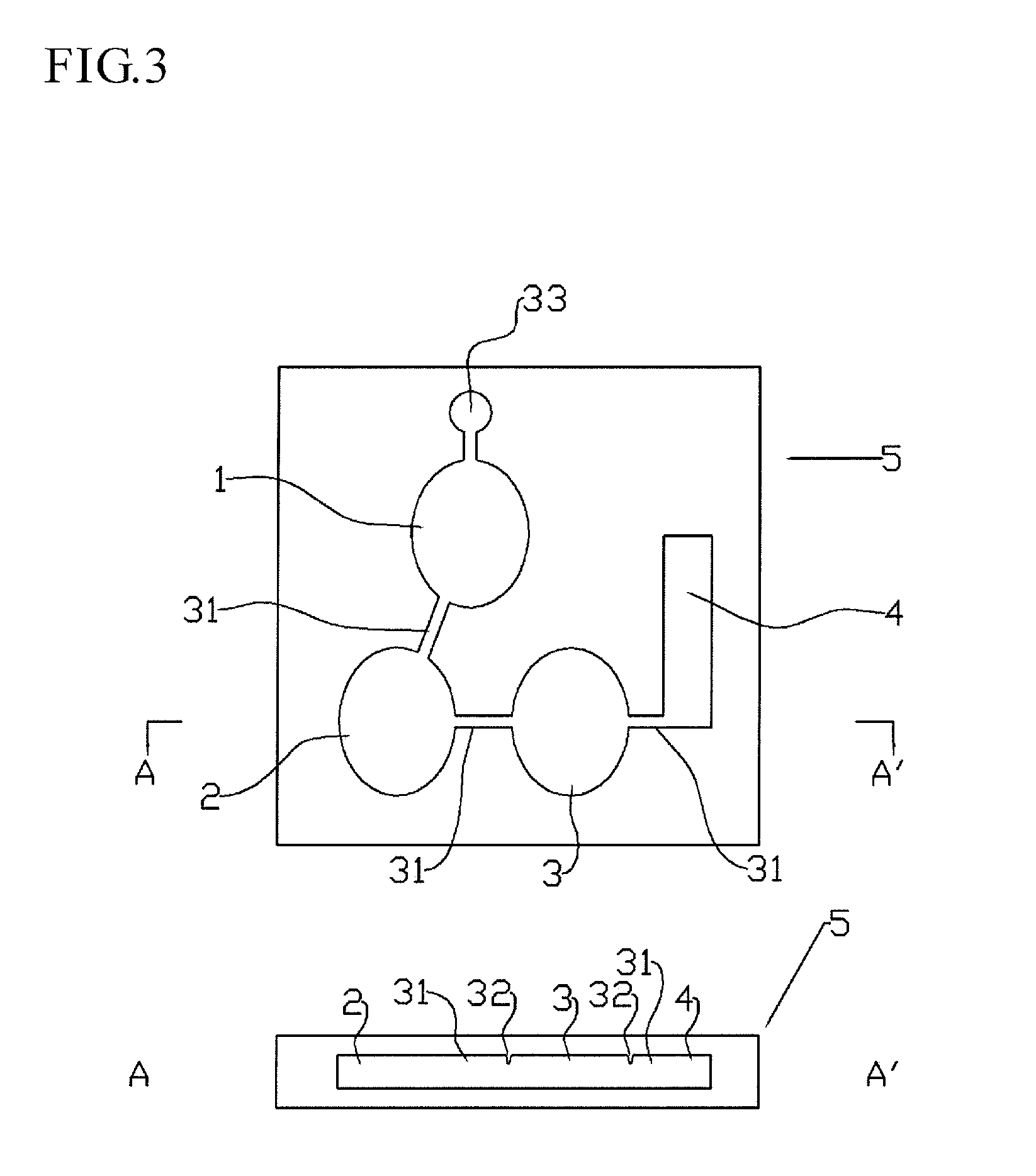
An immunoassay device capable of assaying amount of an antigen by allowing a labeled antibody to specifically bind to a antigen analyte in a sample and assaying a label of a bound product, an interior of a single device has four regions comprises: (1) a first region where the antigen in the sample reacts with a first antibody that is the labeled antibody capable of specifically binding to the antigen, (2) a second region where first antibody that has not bound to the antigen reacts with a second biotin- or avidin-bound antibody, (3) a third region where, depending on whether the second antibody is biotin-bound antibody or avidin-bound antibody, either avidin or biotin is immobilized by immobilization means so as to be unable to move to the fourth region, and the second antibody is captured by the immobilized avidin or biotin, and (4) a fourth region where the label of the first antibody that has bound to the antigen is detected, being constructed in such a way that a solution can move sequentially through each region, the first antibody, which is the labeled antibody such that an antibody component is an F(ab′) fragment or reduced IgG, the F(ab′) fragment or reduced IgG being bound with the label in a predetermined proportion, is included in the first region or an adjacent region, and the second antibody is a biotin- or avidin-bound antibody, being of anti-idiotype antibody against the first antibody and a type that cannot bind to the bound product of the antigen and first antibody, and is included in the second region or an adjacent region.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Nano antibody-based deoxynivalenol mimic antigen and application thereof
ActiveCN104311643AHave immune response propertiesGood effectDepsipeptidesBiological testingEndurance capacityNucleotide
The invention belongs to the biotechnical field and relates to nano antibody-based deoxynivalenol mimic antigen and application thereof. The amino acid sequence is shown in SEQIDNO:1. The invention further relates to nucleotide which codes the amino acid. The nano antibody-based deoxynivalenol mimic antigen provided by the invention can be used for replacing a DON (deoxynivalenol) standard substance which is high in price and strong in toxicity and is used as competitive antigen or solid phase coated antigen which is applied to immunological detection of DON. The mimic antigen has an immunoreaction characteristic which is similar to that of a natural DON molecule and is good in effect. Compared with conventional polypeptide-based antigen mimic epitopes and IgG-based conventional anti-idiotype antibody, VHH has the characteristics of being more stable in structure, resistant to acid and base and high temperature, high in detection sensitivity and the like. Therefore, the immunodetection stability is extremely enhanced, and meanwhile, the endurance capacity on the environment is further enhanced.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Murine monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody 3H1 sequences for human carcinoembryonic antigen
This invention provides compositions derived from the sequences encoding the variable light and / or variable heavy regions of monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody 3H1 and methods for using these compositions.
Owner:KENTUCKY UNIV OF THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF
Monoclonal antibodies capable of reacting with a plurality of influenza virus A subtypes
ActiveUS9200063B2EffectiveEffective preventionImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsAnti idiotypeImmunogenicity
Monoclonal antibodies directed against the influenza A virus are described, which have the advantageous and unpredicted property of being able to bind a plurality of subtypes of the influenza A virus. One preferred embodiment is the antibody designated as Fab28, which displays a neutralizing activity against a plurality of subtypes of the influenza A virus. Anti-idiotype antibodies directed against the monoclonal antibodies of the invention, immunogenic or vaccine compositions comprising the monoclonal antibodies of the invention are also described, as well as therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic applications for the monoclonal antibodies of the invention. The monoclonal antibodies of the invention can also be used for testing antibody preparations to be used as vaccines.
Owner:POMONA RICERCA
Antigenic substance inductor, vaccine precursor, vaccine, antibody, neutralizing antibody, antitoxin, idiotype antibody and/or anti-idiotype antibody which is induced by its idiotype antibody
InactiveUS20020009467A1Induce productionEasy to disassembleBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsAntigenProtozoa
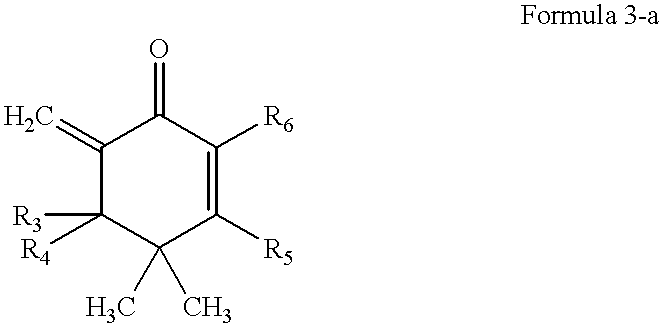
This invention provides antigen substance inductors which produce highly selective and / or specific vaccine precursor, vaccine, antibody (including idiotype antibody), neutralizing antibody, antitoxin. This invention is to produce and / or manufacture highly selective and / or specific vaccine precursor, vaccine, antibody (including idiotype antibody), neutralizing antibody, antitoxin by quantum thermodynamic and chemical control of molecular functions and morphogenesis, inducing non-functional complex macromolecules which form organism and / or non-organism and which become to be substance with fundamental structure more closed to an induction of the functions, utilizing the fundamental structure of molecule which is indicated in Formula 3-a as a representative molecule. Moreover, by those produced substances, this invention is to produce and / or manufacture antimicrobial agent, antiviral agent, neutralizing antibody, antitoxin, antitumor agent, anti-protozoa agent (malaria, spirochaeta et. al), molecular discriminating agent, antibody as labeled compounds, histocompatible accelerator on tissues or organs, immuno-response accelerator or immuno-response controller, complement chain reaction accelerator.
Owner:KOYAMA SHOZO +1
Preparation and application of nano antibody capable of specifically combining with anti-zearalenone antibody
ActiveCN105218675AHave immune response propertiesGood effectImmunoglobulinsBiological testingEpitopeNucleotide
The invention belongs to the biological technical field, and in particular to preparation and application of nano antibody capable of specifically combining with anti-zearalenone antibody and with an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID No.1; and the invention also relates to the nucleotides encoding the amino acid. The nano antibody of the invention can replace the expensive toxic Zen standard, and can be used in immunological detection of Zen as a competitive antigen or solid coating antigen. The nano antibody has similar immunological properties to natural Zen molecule, and good effect. Compared to a traditional antigen mimicking epitope based on polypeptide and a traditional anti-idiotype antibody based on IgG, the nano antibody has the advantages of more stable structure, acid resistance, alkali resistance, high temperature resistance and high detection sensitivity, so that the immune detection stability has been greatly improved, and the tolerance on the environment has also been improved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Deoxynivalenol mimetic antigen based on nanobody and its application
ActiveCN104311643BHigh detection sensitivityHas acid and alkali resistance and heat resistanceDepsipeptidesBiological testingNucleotideImmuno detection
The invention belongs to the biotechnical field and relates to nano antibody-based deoxynivalenol mimic antigen and application thereof. The amino acid sequence is shown in SEQIDNO:1. The invention further relates to nucleotide which codes the amino acid. The nano antibody-based deoxynivalenol mimic antigen provided by the invention can be used for replacing a DON (deoxynivalenol) standard substance which is high in price and strong in toxicity and is used as competitive antigen or solid phase coated antigen which is applied to immunological detection of DON. The mimic antigen has an immunoreaction characteristic which is similar to that of a natural DON molecule and is good in effect. Compared with conventional polypeptide-based antigen mimic epitopes and IgG-based conventional anti-idiotype antibody, VHH has the characteristics of being more stable in structure, resistant to acid and base and high temperature, high in detection sensitivity and the like. Therefore, the immunodetection stability is extremely enhanced, and meanwhile, the endurance capacity on the environment is further enhanced.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Anti-human ovarian carcinoma anti-anti-idiotype antibody hybridoma cell line, and monoclonal antibody and application thereof
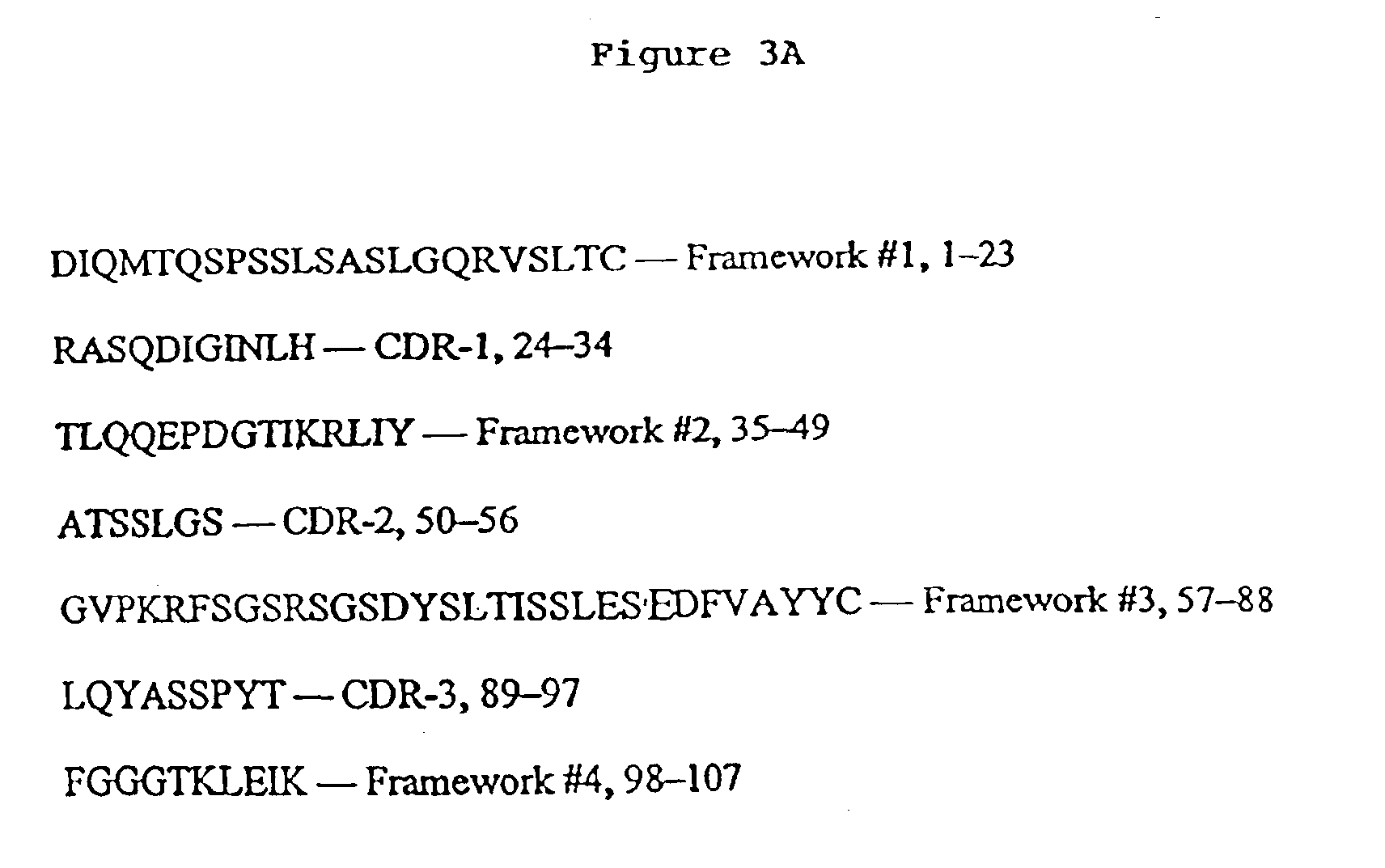
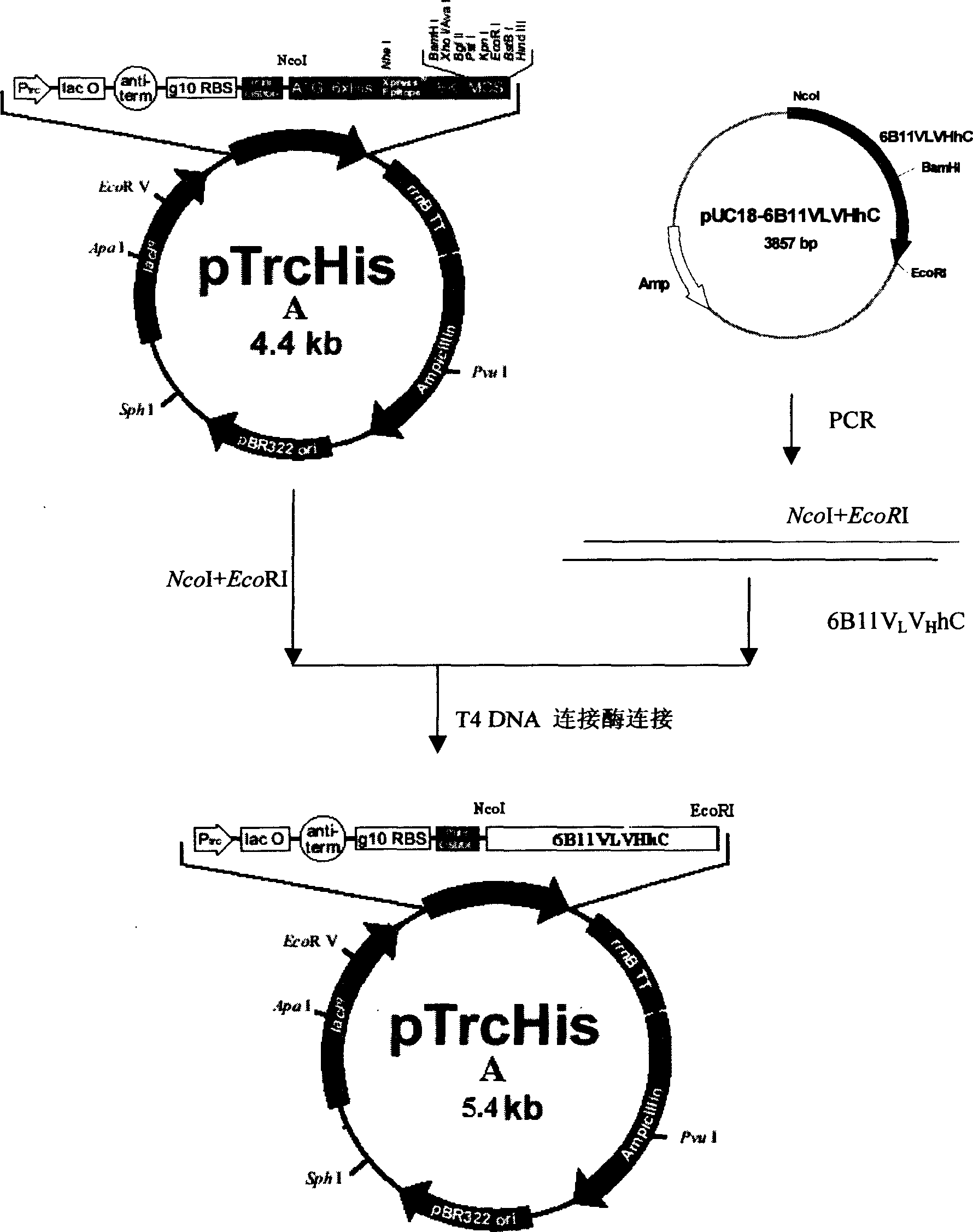
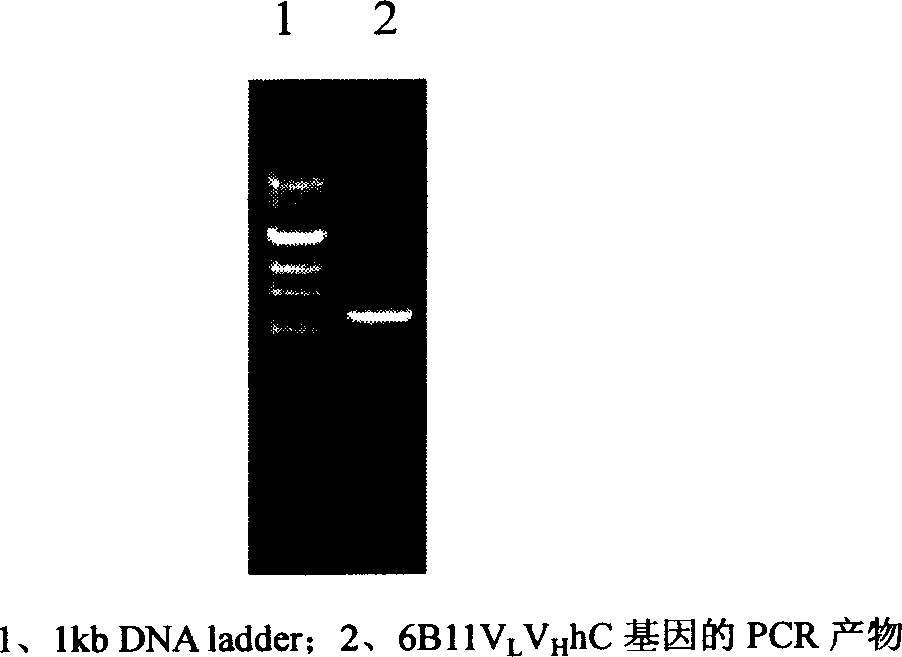
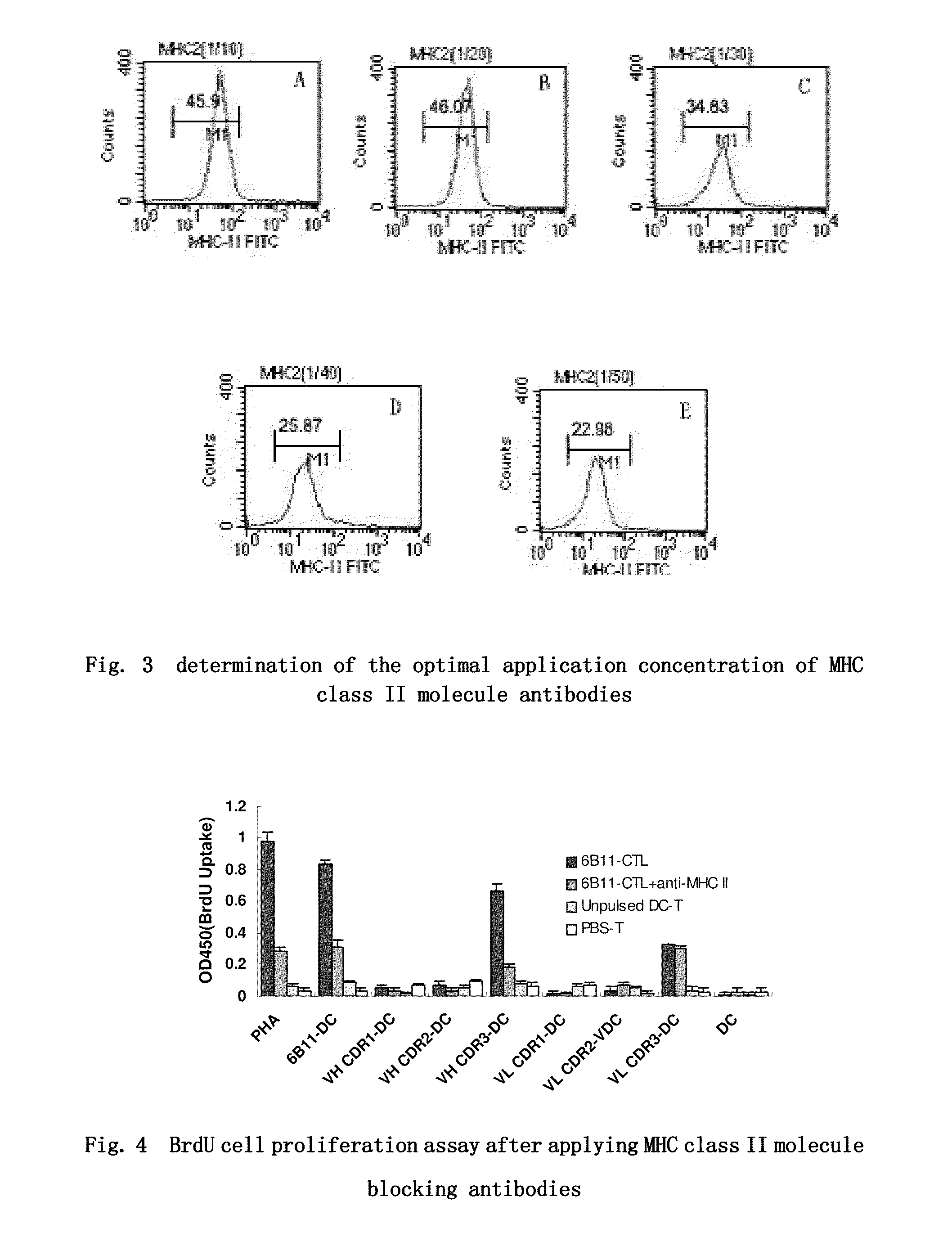
The invention belongs to the biotechnology and cell engineering field and relates to the establishment of two hybridoma cell lines secreting anti-oophoroma anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies. The invention is mainly technically characterized by taking a murine anti-oophoroma anti-idiotype monoclonal antibody as an immunogen to immunize a Balb / C mouse and using the hybridoma technology to obtain the hybridoma cell lines stably secreting anti-oophoroma anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies through fusion, screening and repeated cloning. The two hybridoma cell lines which are respectively named as OVCAMab3D12 and OVCAMab32F2 are preserved by the common microorganism center of China Committee of Culture Collection for Microorganisms with respective collection numbers of CGMCCNo.2144 and CGMCCNo.2145. The invention also discloses monoclonal antibodies 6B11Ab3(IgM) and 6B11Ab3(IgG) respectively through the two hybridoma cell lines. The antibodies can be applicable to an ELISA kit capable of detecting oophoroma associated antigen for early diagnosis of oophoroma. Simultaneously the antibodies can be used for the development of oophoroma curative medicines, particularly targeted therapeutic medicines, and for the therapy of oophoroma.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
T cell epitope peptides of 6b11 ovarian cancer Anti-idiotypic antibody
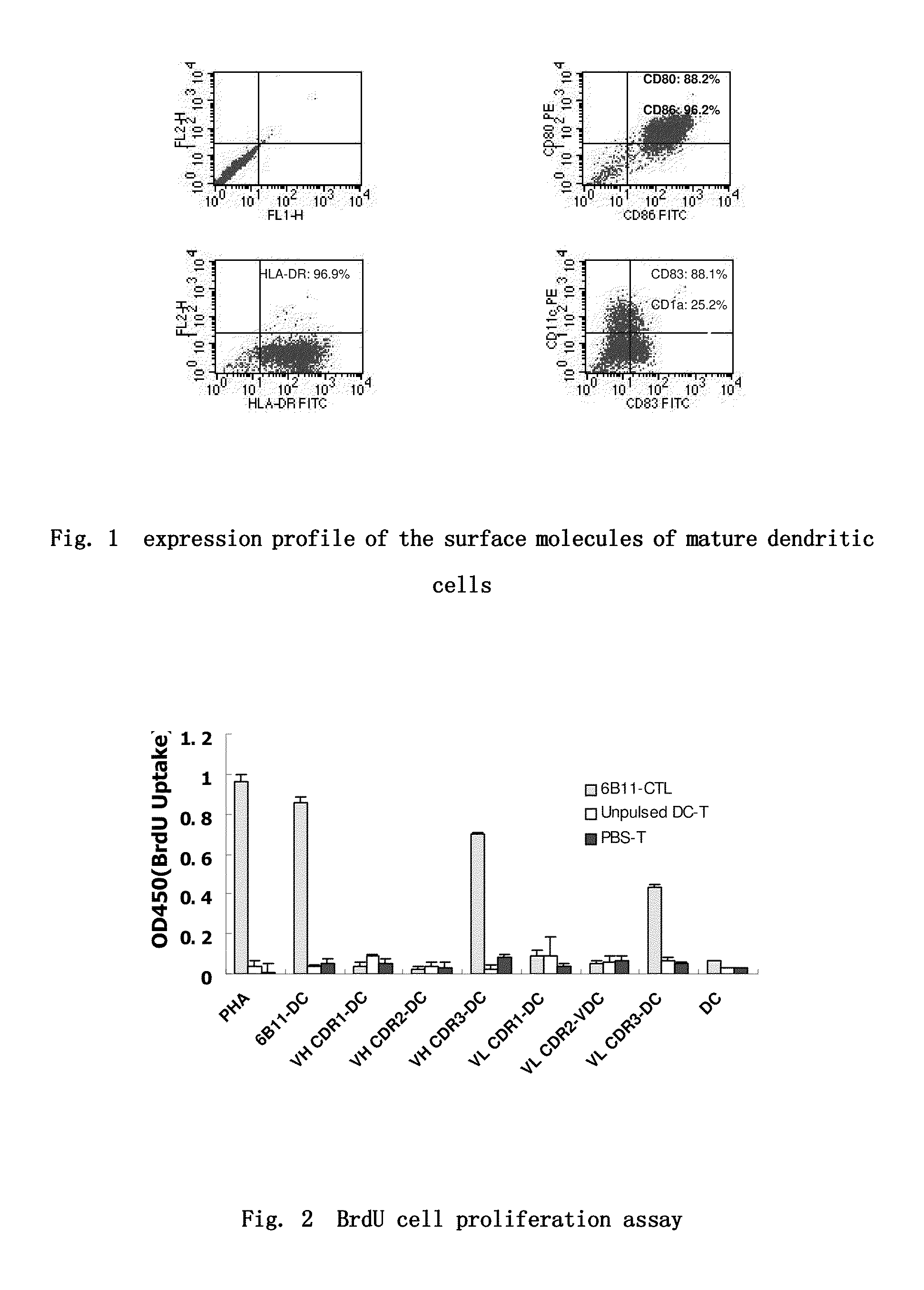
ActiveUS20090269366A1Efficient inductionAvoid negative effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsOvarian cancer cellsAntibody
The present invention provides two T-cell epitode peptides of anti-idiotype antibody 6B11 of ovarian cancer, the sequences of which are shown in SEQ ID NO:3 or 6. The present invention also provides the use of such T-cell epitope peptides in the manufacture of vaccines against ovarian cancer and in the treatment and prevention of ovarian cancer. The T-cell epitope peptides of the present invention could specifically kill ovarian cancer cells which are OC166-9 positive, and could find a wide use in the treatment and prevention of ovarian cancer.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Method for obtaining anti-idiotype antibodies
Owner:OMRIX BIOPHARM
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and treatment of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Provided are isolated and purified preparations of a combination of a light chain antibody gene and a heavy chain antibody gene, where the light chain and heavy chain antibody genes are the same among more than one patient with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Vectors comprising those genes and cells comprising those vectors are also provided, as are isolated and purified antibodies encoded by the antibody genes. Anti-idiotype antibodies, peptides, and aptamers that bind to the antigen-binding region of an antibody encoded by the antibody genes are additionally provided, as are multimeric molecules comprising multiple binding sites that bind to the antigen-binding region of an antibody encoded by the antibody genes. Methods of determining whether a patient with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) has a form of B-CLL that is susceptible to treatment directed to eliminating idiotype specific B cell receptor-bearing B-CLL cells are also provided, as are methods of following the progression of treatment of B-CLL in the patient. Additionally, methods of treating a patient having B-CLL are provided, as are methods of identifying a therapeutic agent for B-CLL.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Anti-Lewis Y Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080268459A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFused cellsAntigenScreening method
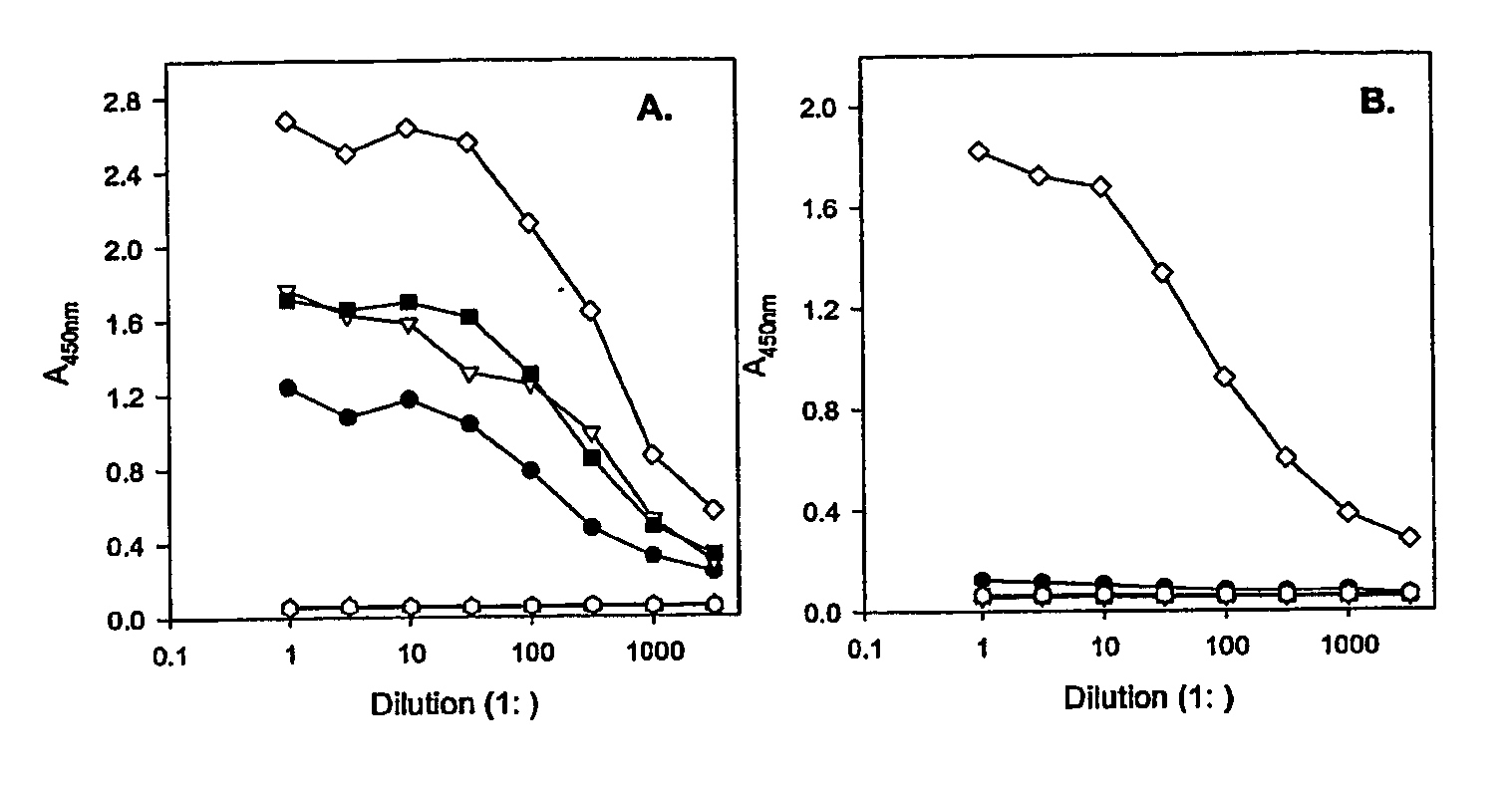
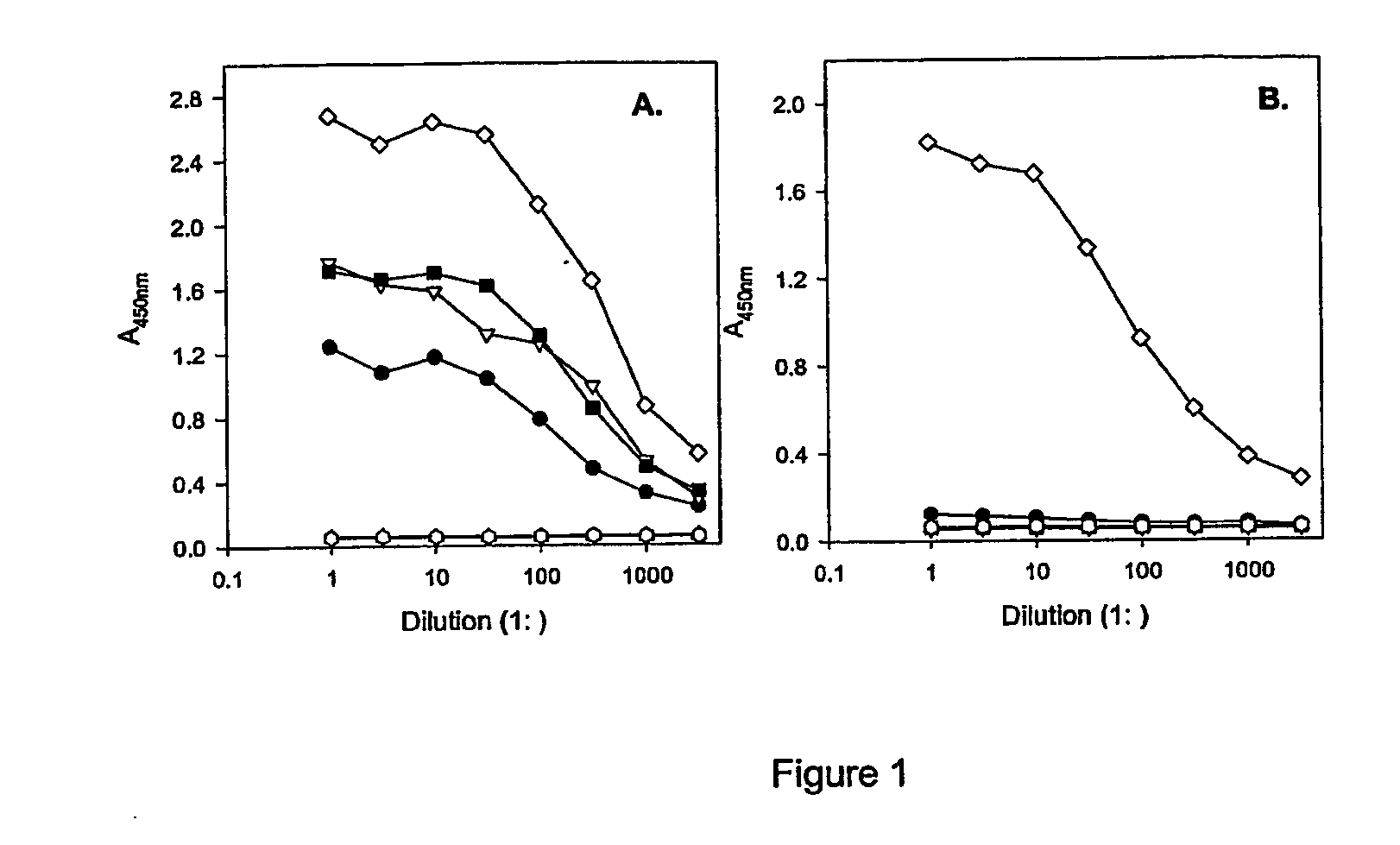
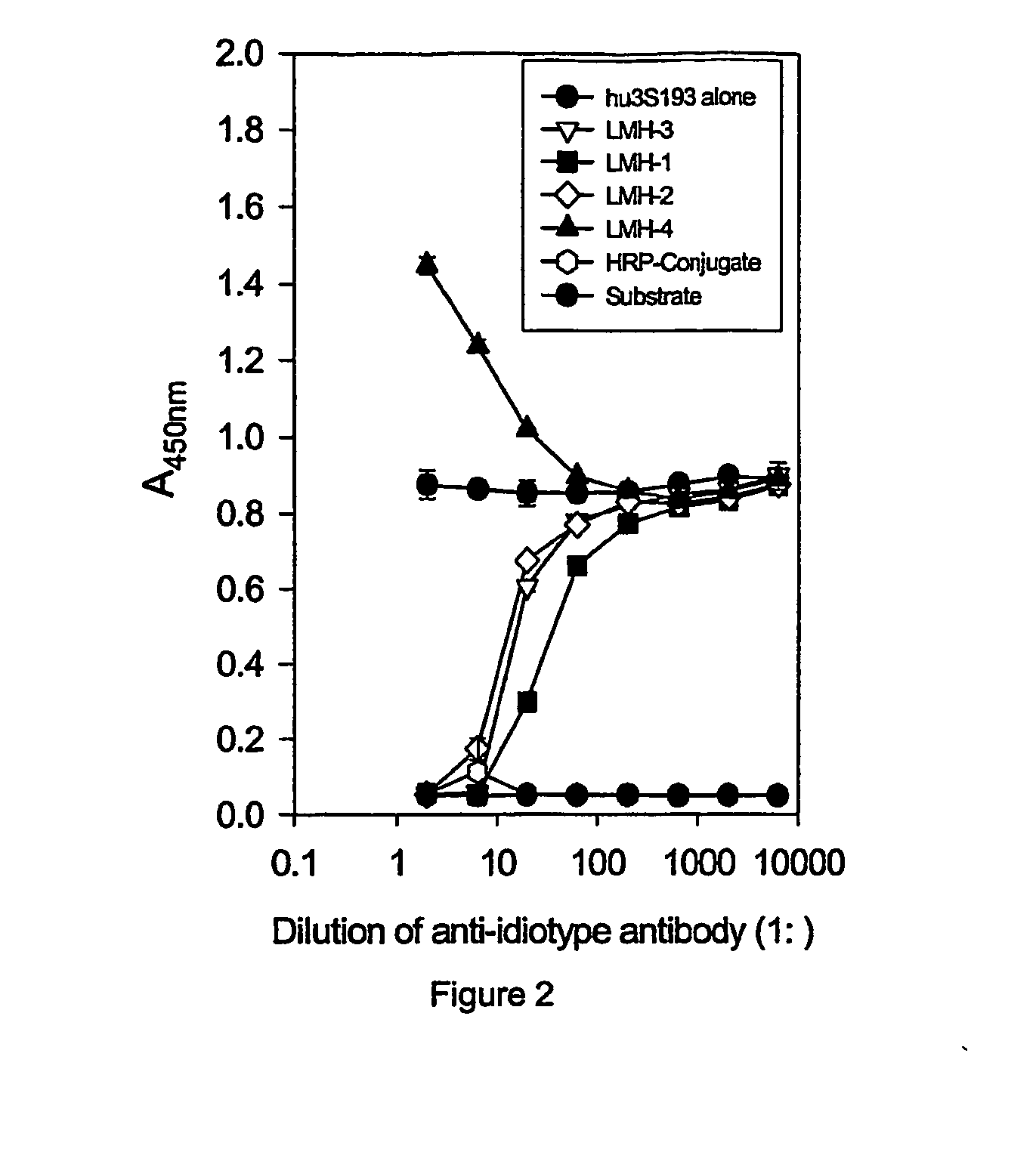
This invention provides anti-idiotype antibodies specific for Anti-Lewis Y monoclonal antibodies. The present invention also directed against an ELISA screening method of mAbs produced by hybridoma clones for specific binding to the variable regions of hu3S193 and the ability of the anti-idiotypic mAB to inhibit hu3S193 binding to Lewis Y antigen. Additionally, the present invention provides a hybridoma capable of producing an anti-idiotype antibody specific for anti-Lewis Y monoclonal antibody. A further aspect of the invention is to provide a hybridoma, which is specific for anti-Lewis Y monoclonal antibody selected from the group consisting of LMH-1, LMH-2, LMH-3, or LMH-4. The present invention is also directed against a method to detect HAMA, HACA and HAHA responses using the antibody of the invention.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com