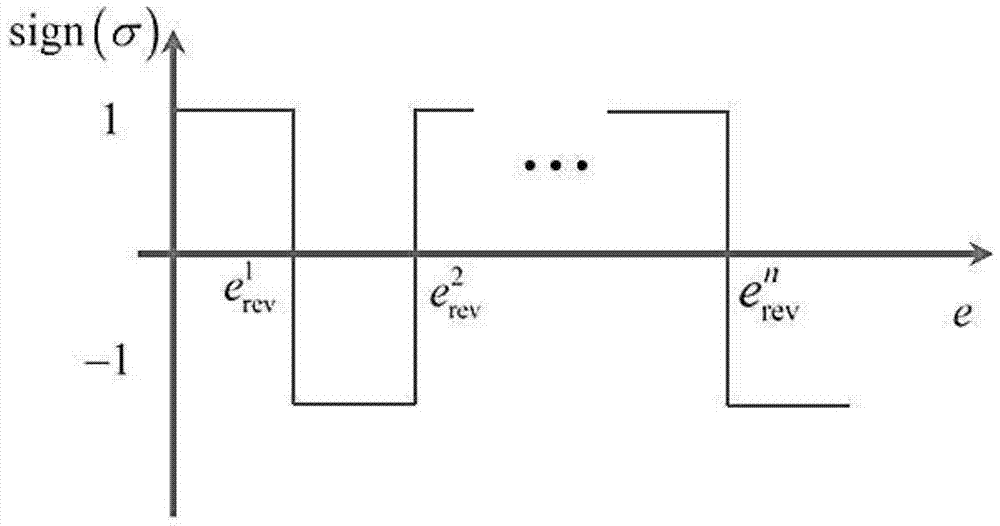
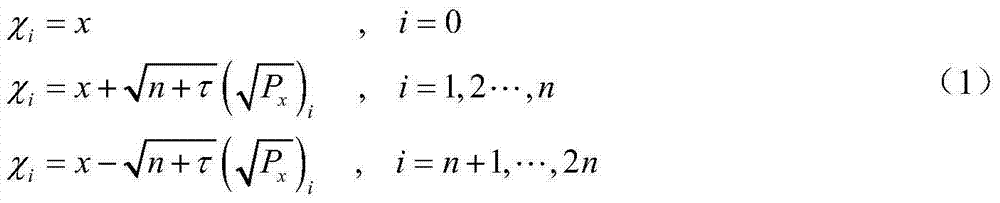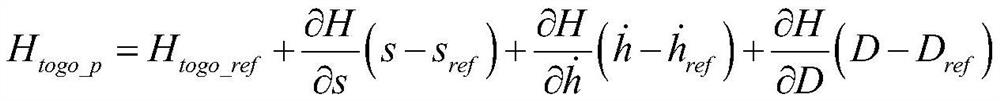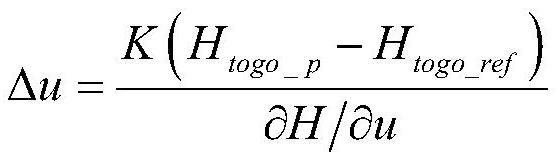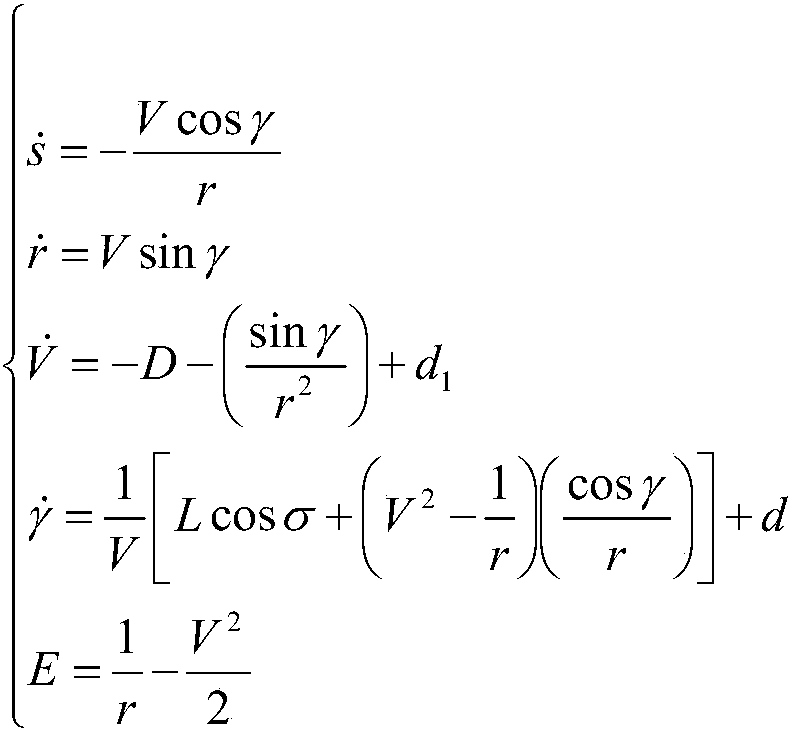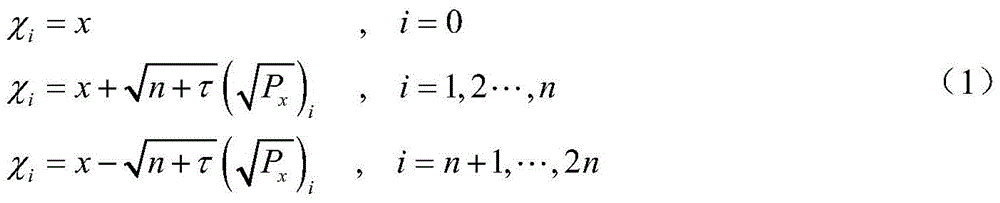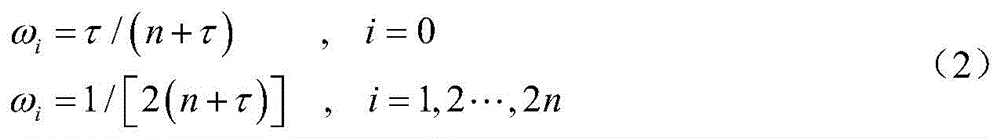Patents
Literature
30 results about "Atmospheric entry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
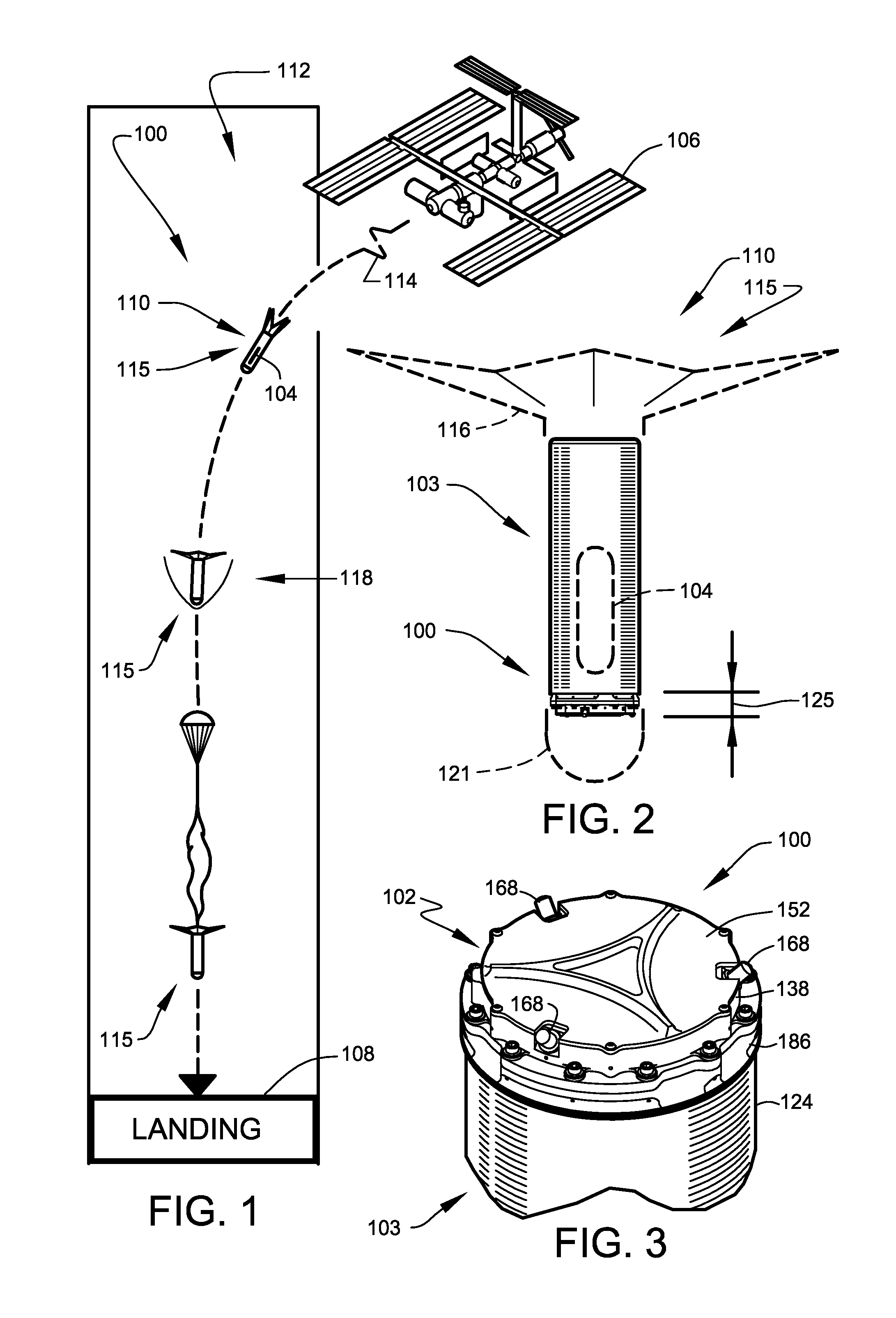
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: uncontrolled entry, such as the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides; and controlled entry (or reentry) of a spacecraft capable of being navigated or following a predetermined course. Technologies and procedures allowing the controlled atmospheric entry, descent, and landing of spacecraft are collectively termed as EDL.
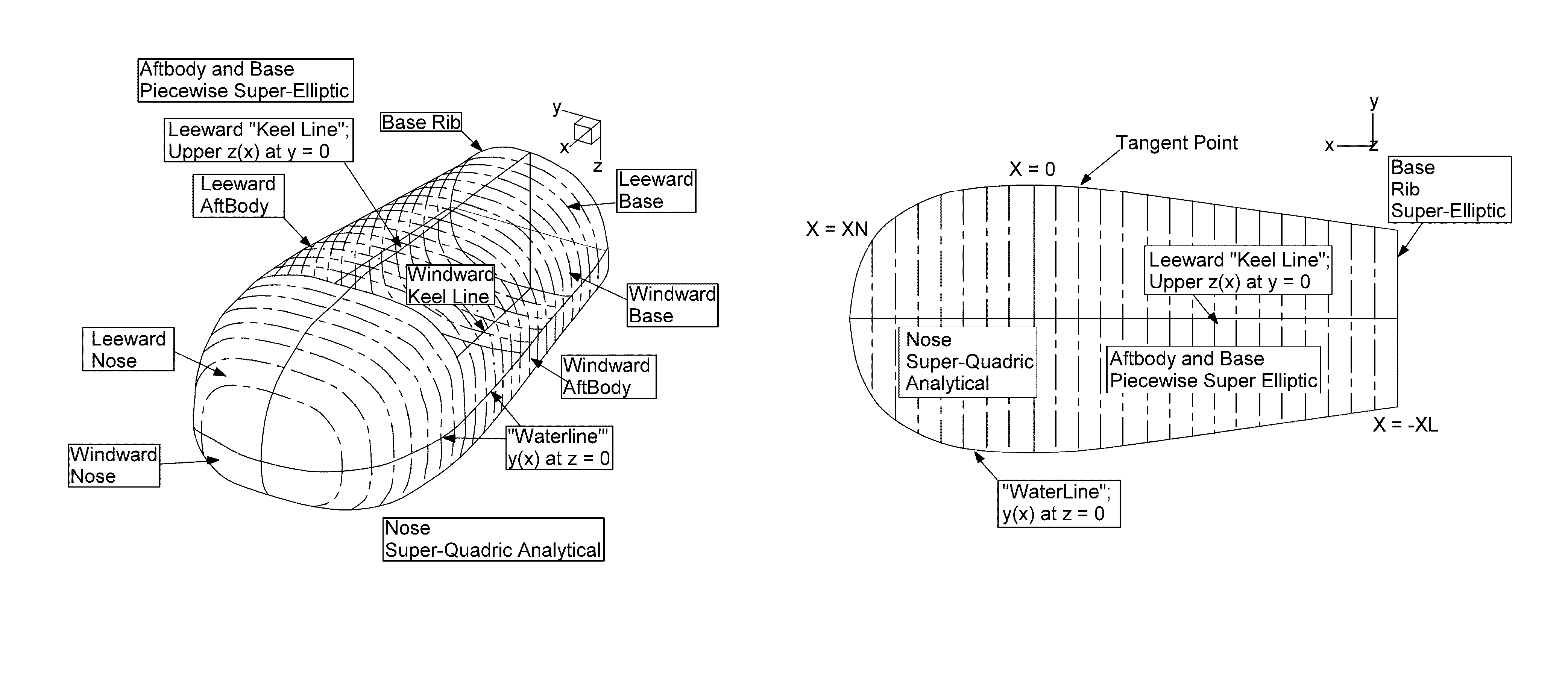
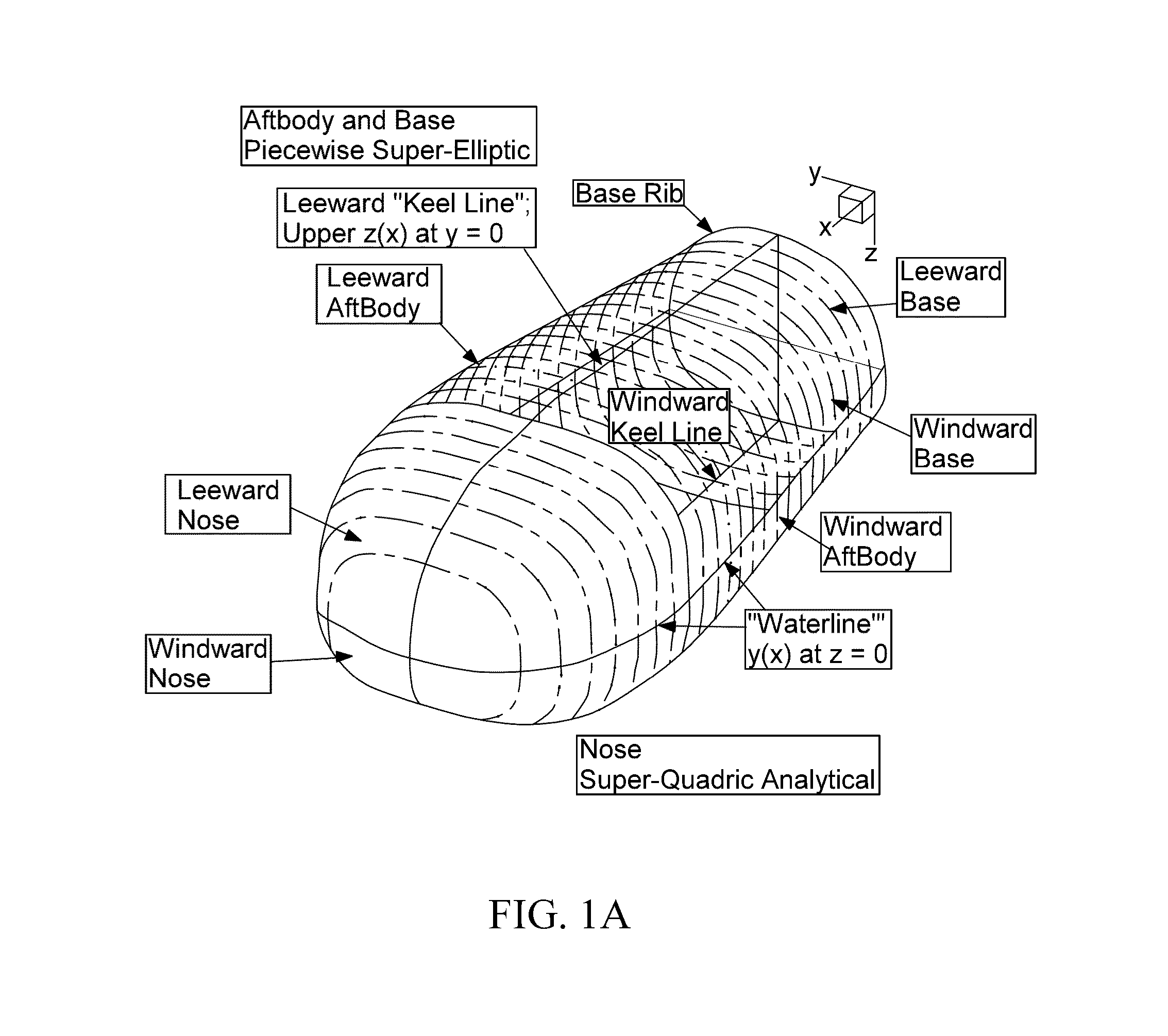
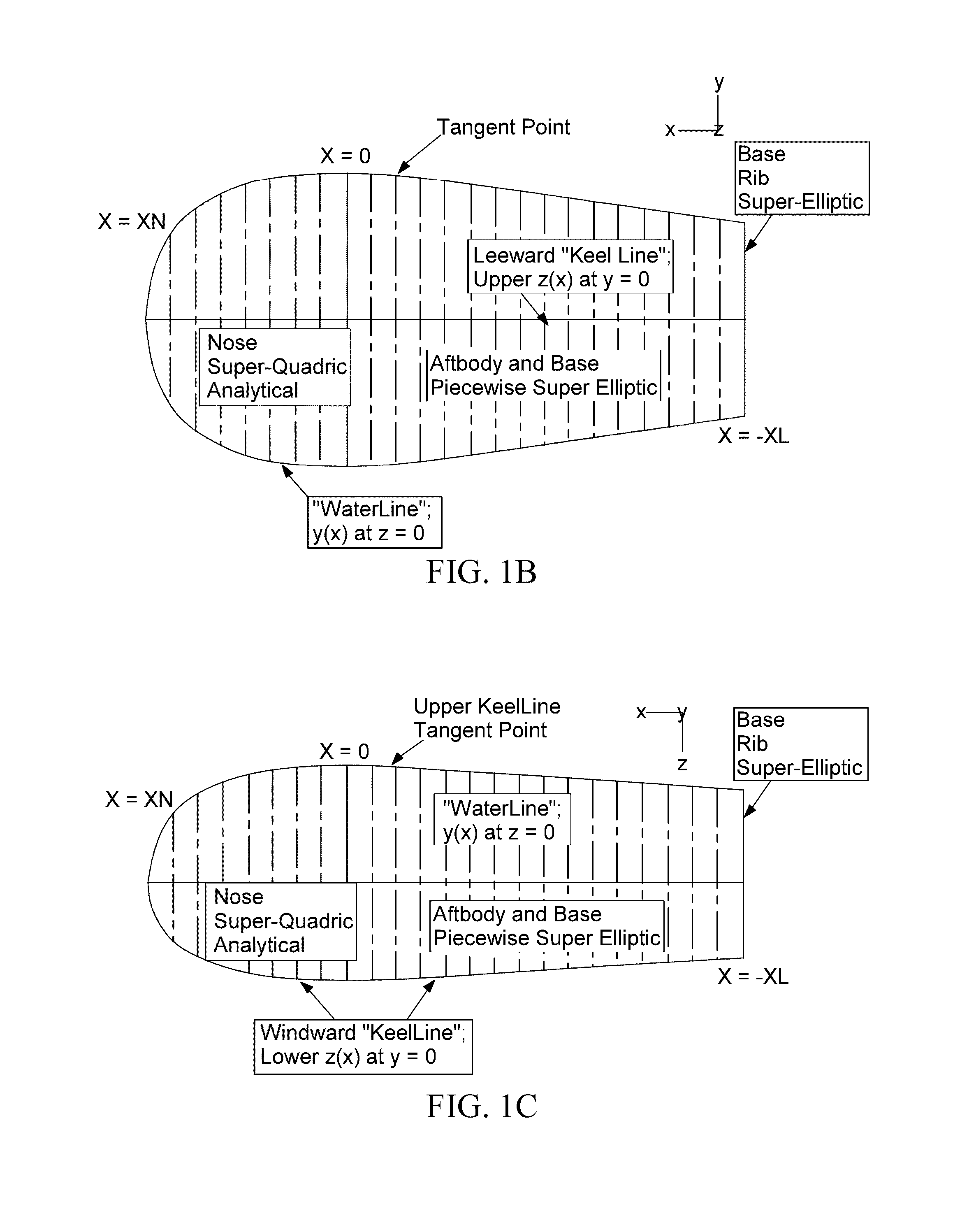
Co-optimization of blunt body shapes for moving vehicles
A method and associated system for multi-disciplinary optimization of various parameters associated with a space vehicle that experiences aerocapture and atmospheric entry in a specified atmosphere. In one embodiment, simultaneous maximization of a ratio of landed payload to vehicle atmospheric entry mass, maximization of fluid flow distance before flow separation from vehicle, and minimization of heat transfer to the vehicle are performed with respect to vehicle surface geometric parameters, and aerostructure and aerothermal vehicle response for the vehicle moving along a specified trajectory. A Pareto Optimal set of superior performance parameters is identified.
Owner:NASA
Reusable high temperature thermal protection system
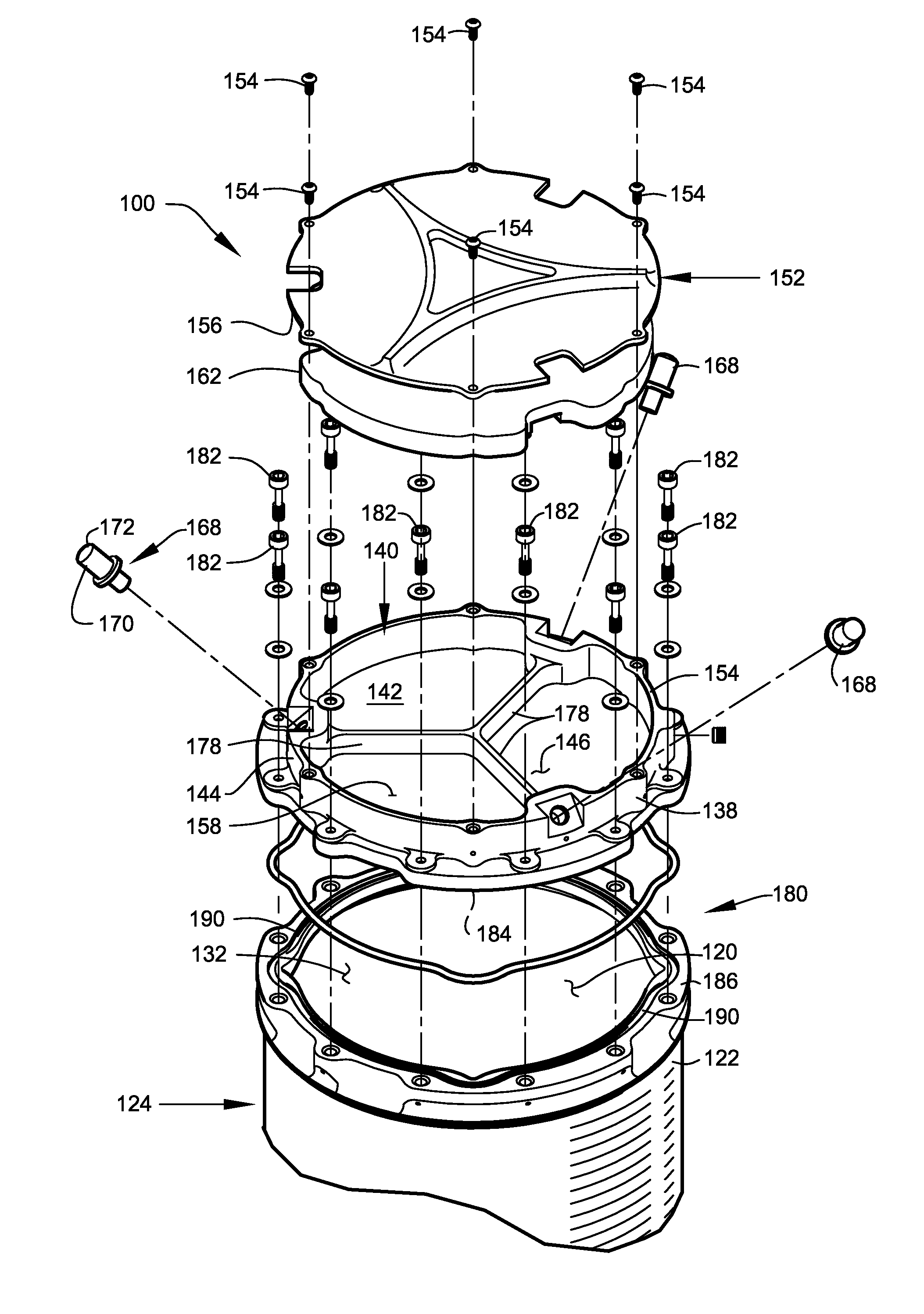
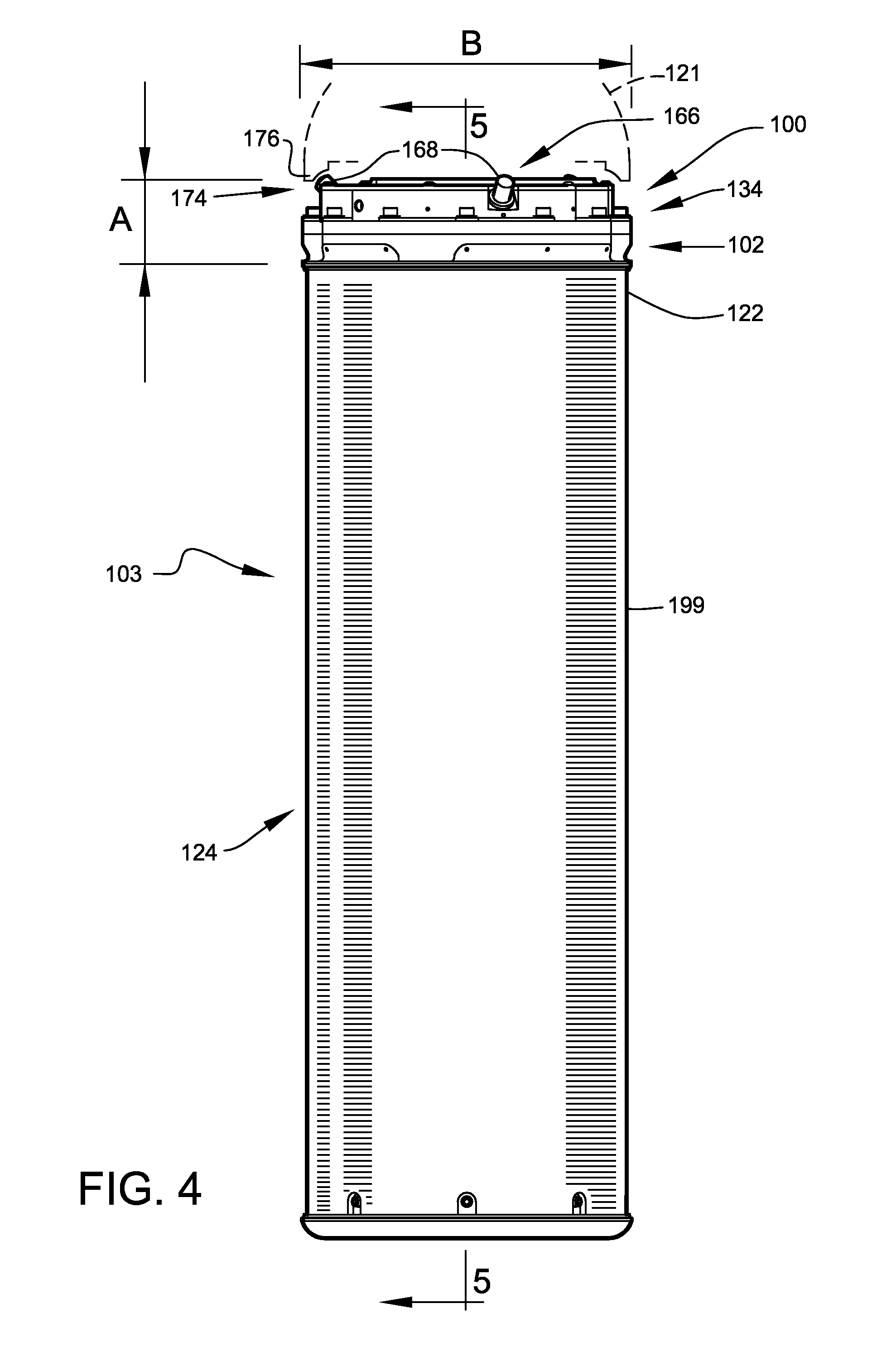
A reusable phase change material (PCM) heat shield is disclosed. The heat shield comprises: a thermally conductive casing, PCM, thermally conductive open cell foam, and heat pipes. The heat flows through the casing and open cell foam into the PCM, heating it up. The PCM changes phase twice, from solid to liquid. During the solid liquid phase change, heat pipes begin to draw heat away from the PCM to a secondary location that re-radiates the heat away. The open cell foam serves to help channel hear into the PCM. In one embodiment, the PCM heat shield can be used for thermal protection of an atmospheric entry vehicle (ARV). In another, the PCM heat shield may be applied to an aircraft engine to transfer extracted heat to preheat incoming air. In another, the PCM heat shield is integrated into the structure of a spacecraft, and used to both carry loads and protect against high temperatures.
Owner:SINHA SUMONTRO +1
Leading edge channel for enhancement of lift/drag ratio and reduction of sonic boom
The leading edges of wings, nose assemblies, tails, fins, struts, and other components of aircraft, atmospheric entry vehicles and missiles in which the leading edge is blunted and the flight Mach number is supersonic, are provided with passive airflow channel, resulting in significantly reduced wave drag and total drag, significantly increased lift-to-drag ratio, and reduced sonic boom.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Atmospheric entry thermal protection system
InactiveUS20060145020A1Economical and reliableAvoid cloggingCosmonautic thermal protectionSpace shuttlesControl systemTranspiration
A reusable system for reliably protecting a spacecraft from atmospheric entry heating is described. It includes a transpiration medium reservoir, apparatus for injecting transpiration medium through portions of the heat shield of the spacecraft, and a control system configured to inject a cleaning medium during the early portion of the launch and a transpiration cooling medium during reentry. Injecting a cleaning medium through the heat shield during ascent minimizes the likelihood of an insect or other debris clogging any of the transpiration pores.
Owner:BUEHLER DAVID BENJAMIN
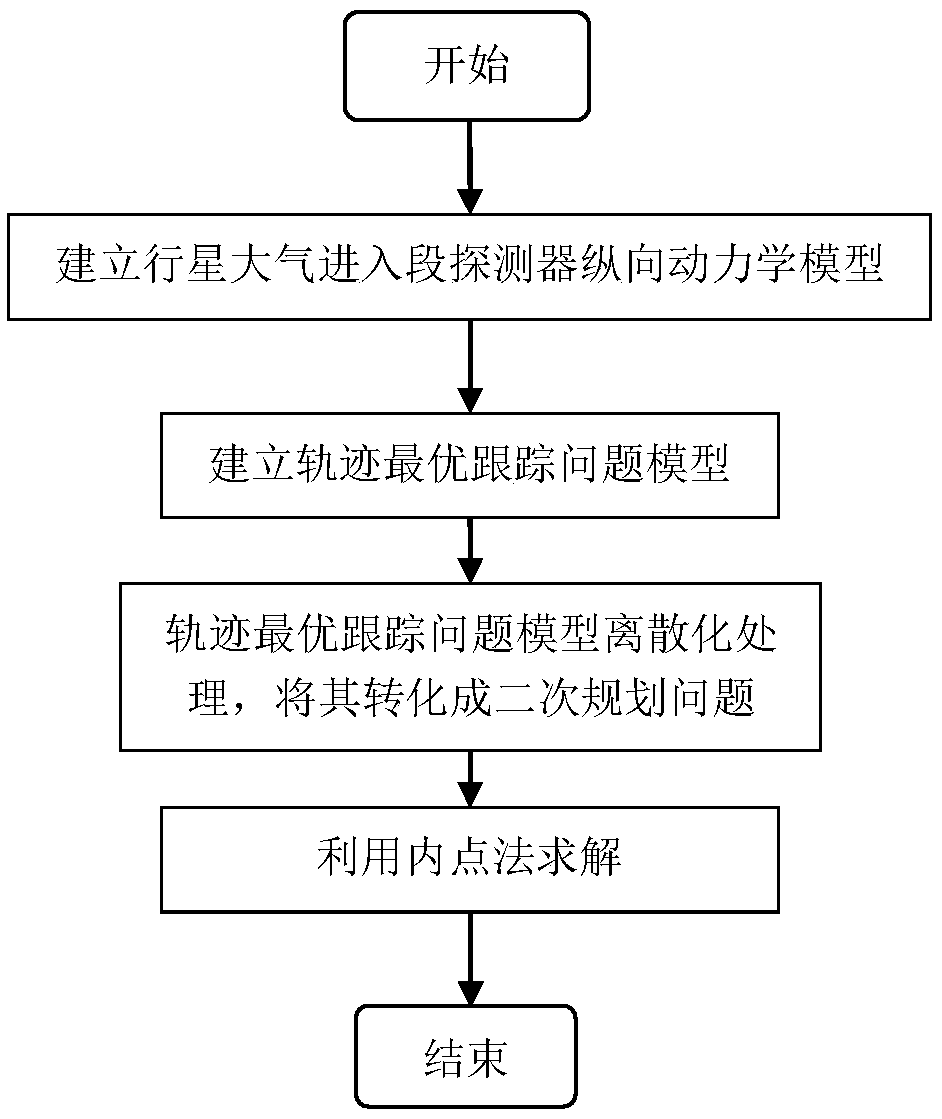
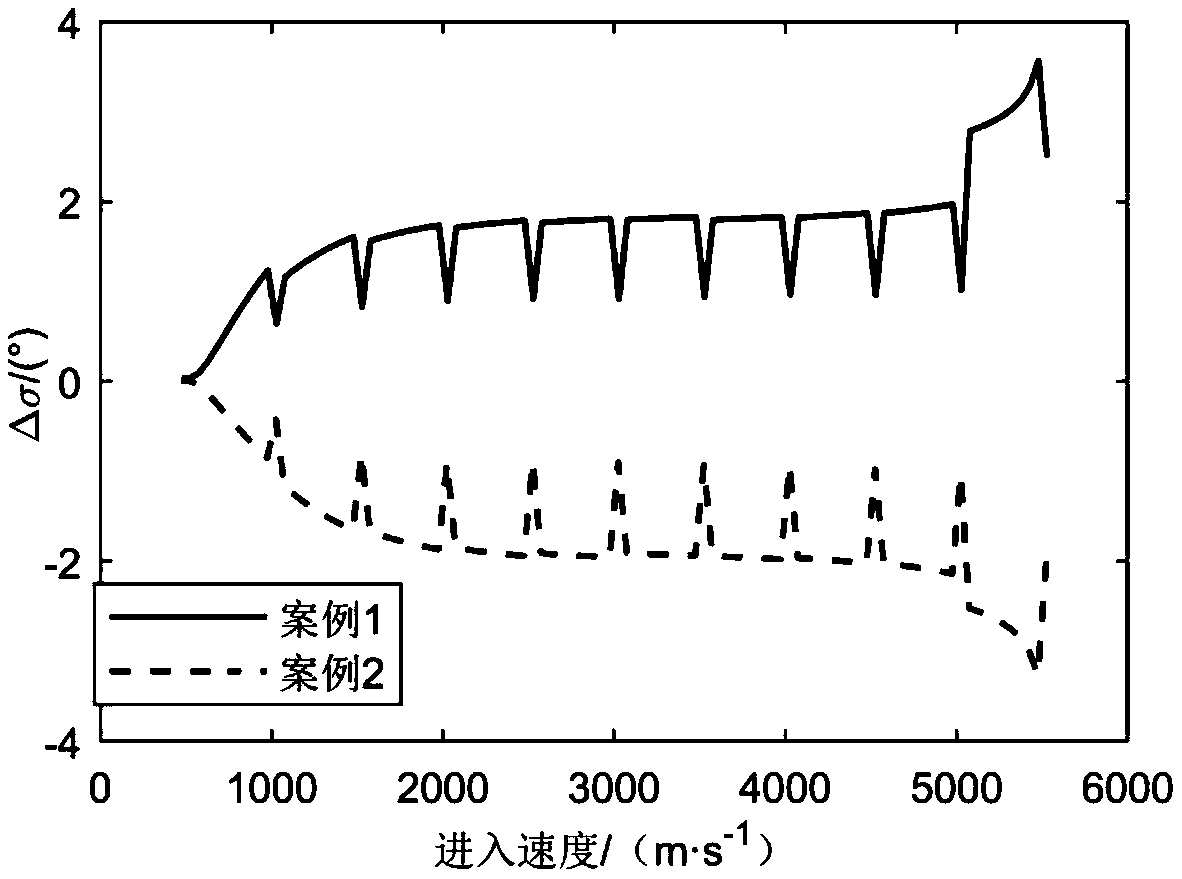
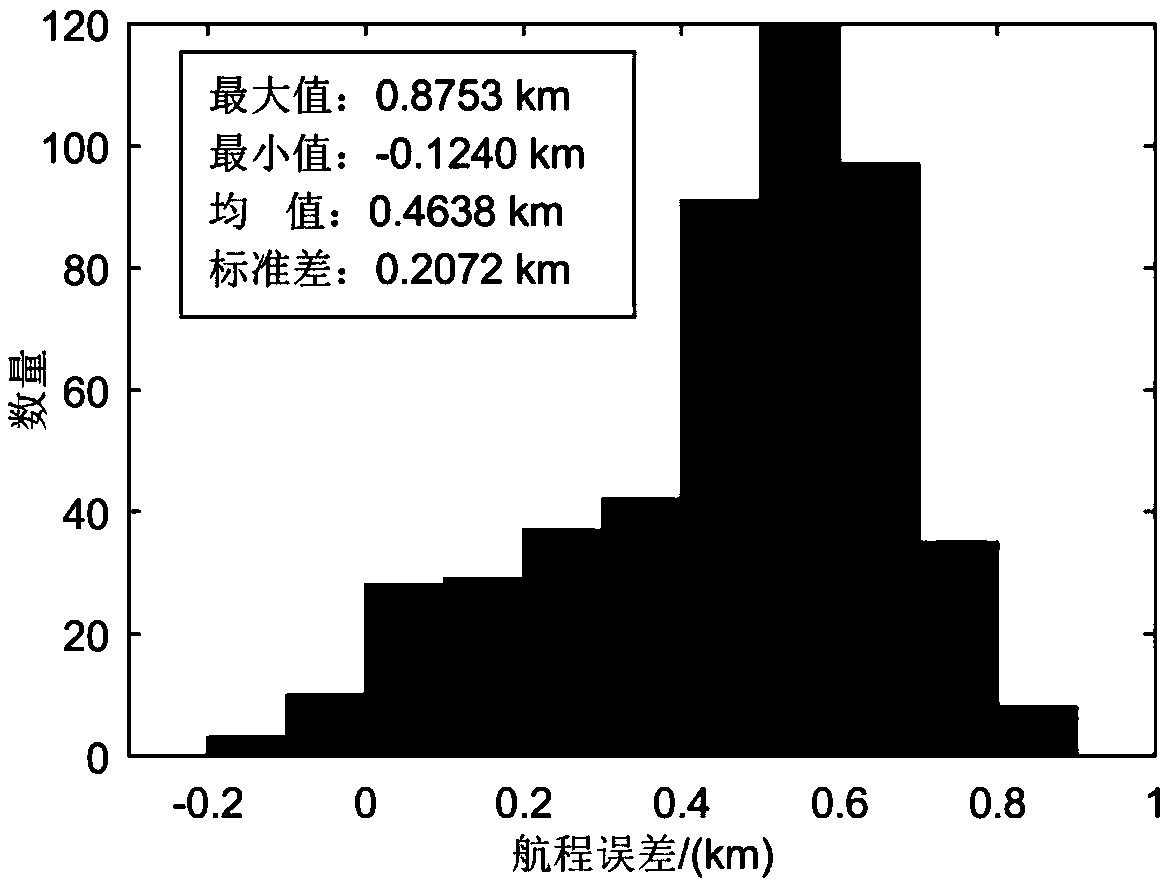
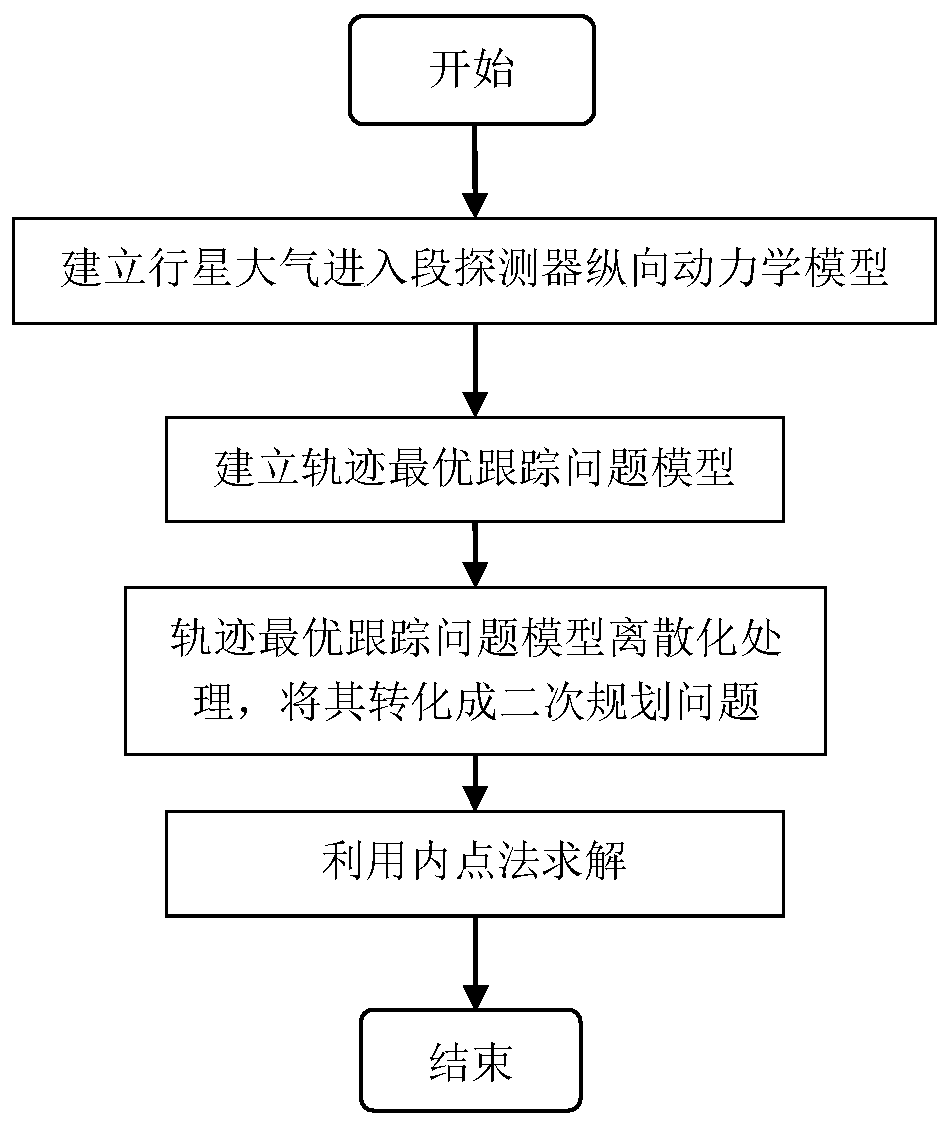
Optimal trajectory tracking guidance method for Mars atmospheric entry phase
ActiveCN109250153AReal-time online guidanceImprove solution efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusDynamic modelsInterior point method
The invention discloses an optimal trajectory tracking guidance method for Mars atmospheric entry phase, belonging to the field of deep space exploration. The realization method of the invention comprises the follow steps: (1) establishing a longitudinal dynamic model of a Mars atmospheric entry stage probe; (2), performing convexification processing on the path constraint and the control constraint, and selecting the quadratic performance index to establish a trajectory optimal trajectory tracking problem model; (3), discretizing that trajectory optimal tracking problem model in the step (2),converting the model into a quadratic programming problem, so that the problem can be solved in polynomial time by an interior point method, the discretized quadratic programming problem can be solved by a numerical method, the solution efficiency is improved, and the real-time online guidance of the Martian atmosphere entry section is realized. The invention converts the trajectory tracking guidance problem into an optimal control problem for solving, and the parachute opening accuracy can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
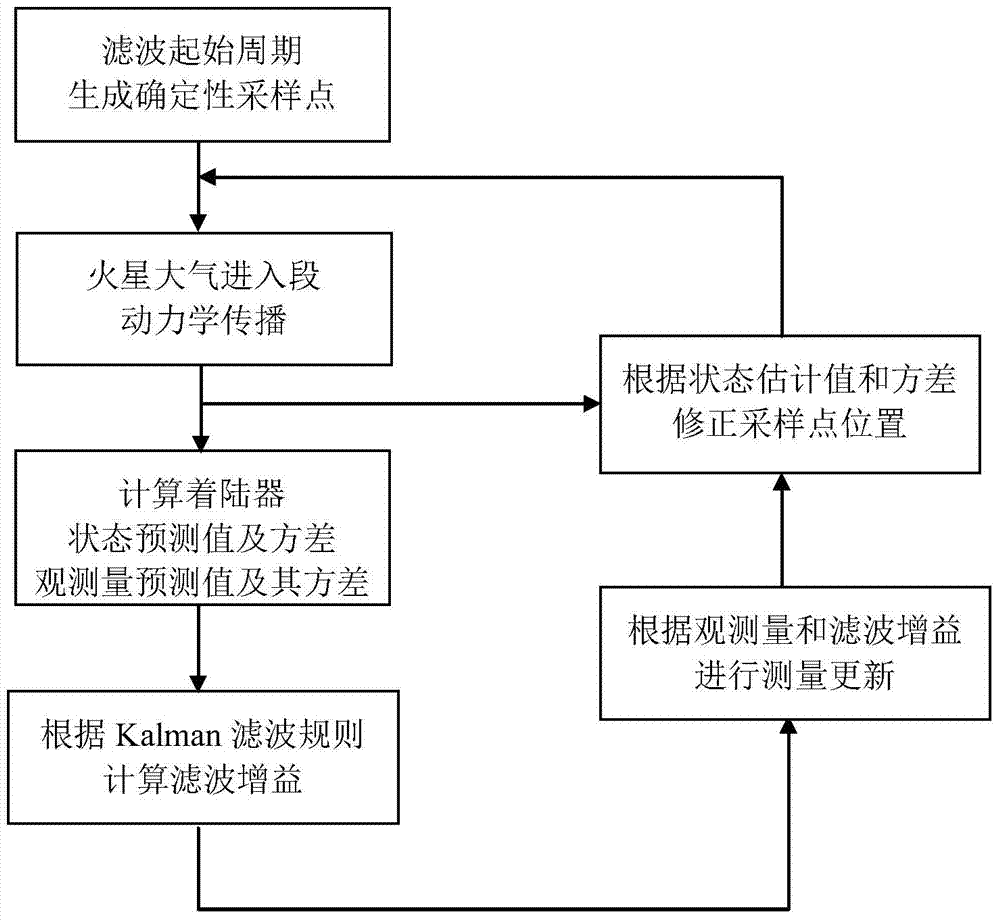
Method for atmospheric entry section navigation of mars lander based on sampling point inheritance strategy
InactiveCN104266650AHigh state prediction accuracyImprove State Estimation AccuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationCovarianceAtmospheric entry
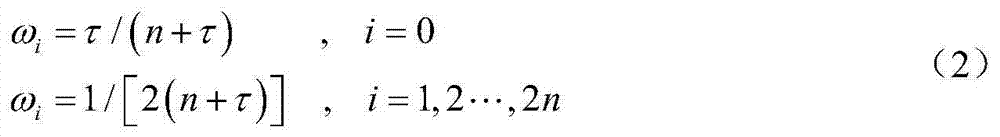
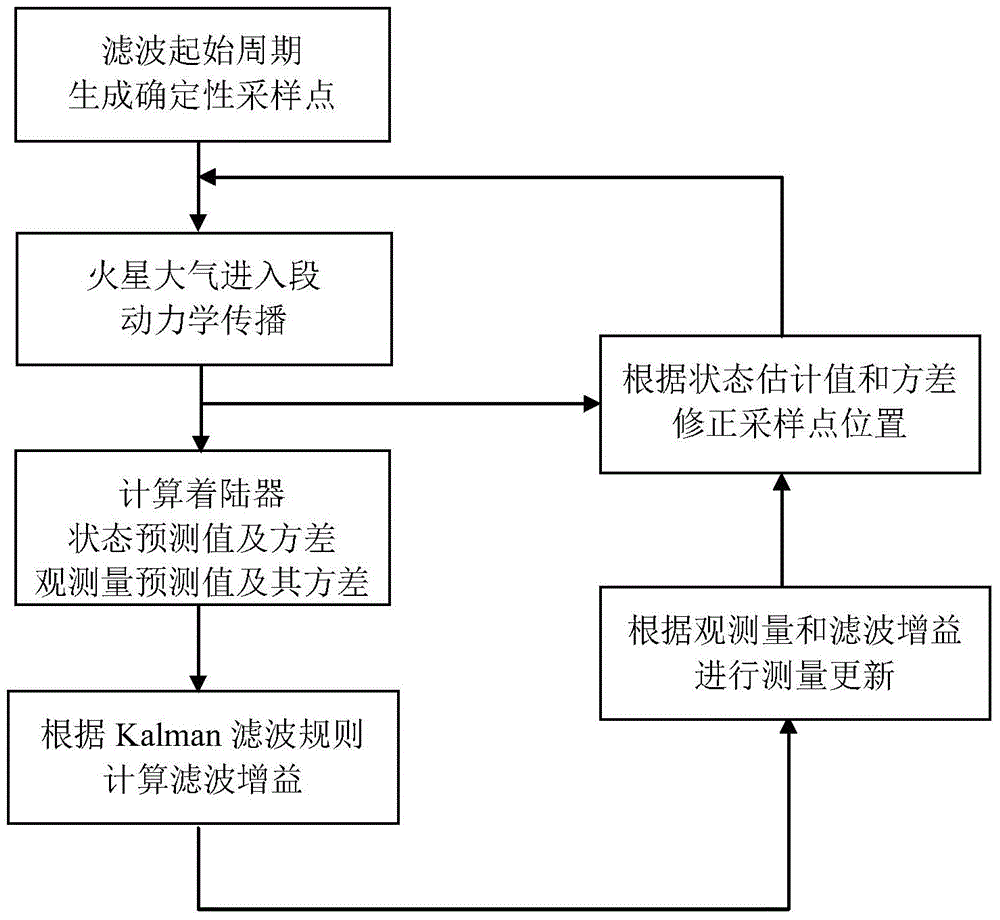
A method for the atmospheric entry section navigation of a mars lander based on a sampling point inheritance strategy relates to the technical field of navigation guidance and control, in particular to a method for the atmospheric entry section navigation of the mars lander. The invention aims at solving the problem that the precision is low when the status of the lander is estimated according to the conventional filtering method. The method comprises the following steps: in a filtering beginning cycle, providing a sampling point and a sampling point weight according to sampling point generating rules of unscented Kalman filtering; providing a lander status predicted value x' and a lander status variance Px according to a transmitted sampling point and a generated weight; calculating a measurement predicted value y', a variance Py and a covariance Pxy according to unscented Kalman filtering rules; updating measurement and correcting the estimate value of the lander status; estimating x'<+> and a lander status variance Px<+> according to the lander status, correcting the transmitted sampling point Xi and obtaining the sampling point Xi<+> with the corrected value. The method has higher status estimate precision and is suitable for navigation in the atmospheric entry section of the mars lander.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Lifting entry/atmospheric flight (LEAF) unified platform for ultra-low ballistic coefficient atmospheric entry and maneuverable atmospheric flight at solar system bodies
InactiveUS20150210407A1Cosmonautic vehiclesEnergy efficient board measuresAtmospheric airEngineering
An aerial vehicle including a collapsible and inflatable vehicle body capable of being filled with a lighter than air gas so as to make the vehicle semi-buoyant or 100% buoyant at a predetermined altitude in an atmosphere above a solar system body. The vehicle body has a shape suitable to provide aerodynamic lift. The vehicle may include a propulsion device coupled to and extending from the vehicle body, where the device provides power to aerodynamically lift the vehicle above the 100% buoyant altitude to a higher altitude where the vehicle can maintain that altitude through the aerodynamic lift and vehicle buoyancy. The vehicle is configured to be deployed / inflated from a collapsed and stowed configuration to a deployed / inflated configuration in an orbit above the atmosphere of the solar system body, and is configured to enter the atmosphere in the inflated configuration and descend without propulsion.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Cooling systems
ActiveUS9395123B1Avoid overall overheatingCosmonautic environmental control arrangementSpace suitsEngineeringThermal control system
A portable thermal-control system adapted to support space-related research and exploration. Embodiments of the present invention assist in preventing overheating of small payloads being transported from an orbiting space vehicle to a planetary surface by small atmospheric-entry vehicles. Other embodiments of the present invention provide thermal control within an extra-vehicular activity (EVA) suit. Each embodiment utilizes at least one phase-change material, cooled significantly below the freezing temperature, to absorb heat.
Owner:PARAGON SPACE DEVMENT
Cooling systems
ActiveUS8342454B1Avoid overall overheatingCosmonautic environmental control arrangementCosmonautic vehiclesEngineeringThermal control system
A portable thermal-control system adapted to support space-related research and exploration. Embodiments of the present invention assist in preventing overheating of small payloads being transported from an orbiting space vehicle to a planetary surface by small atmospheric-entry vehicles. Other embodiments of the present invention provide thermal control within an extra-vehicular activity (EVA) suit. Each embodiment utilizes at least one phase-change material, cooled significantly below the freezing temperature, to absorb heat.
Owner:PARAGON SPACE DEVMENT
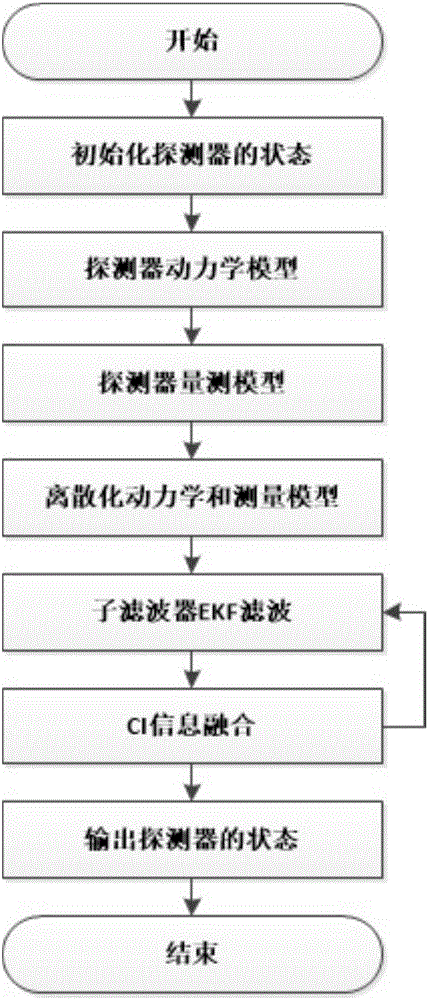
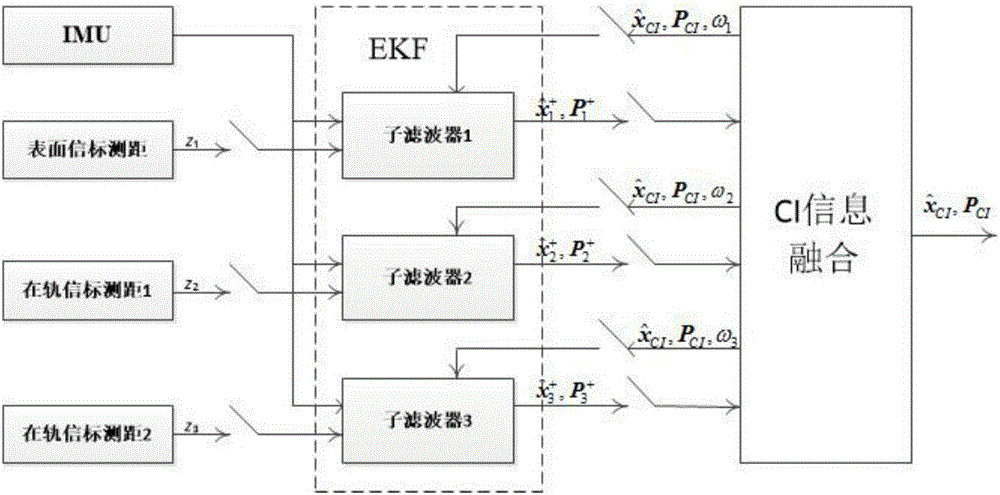
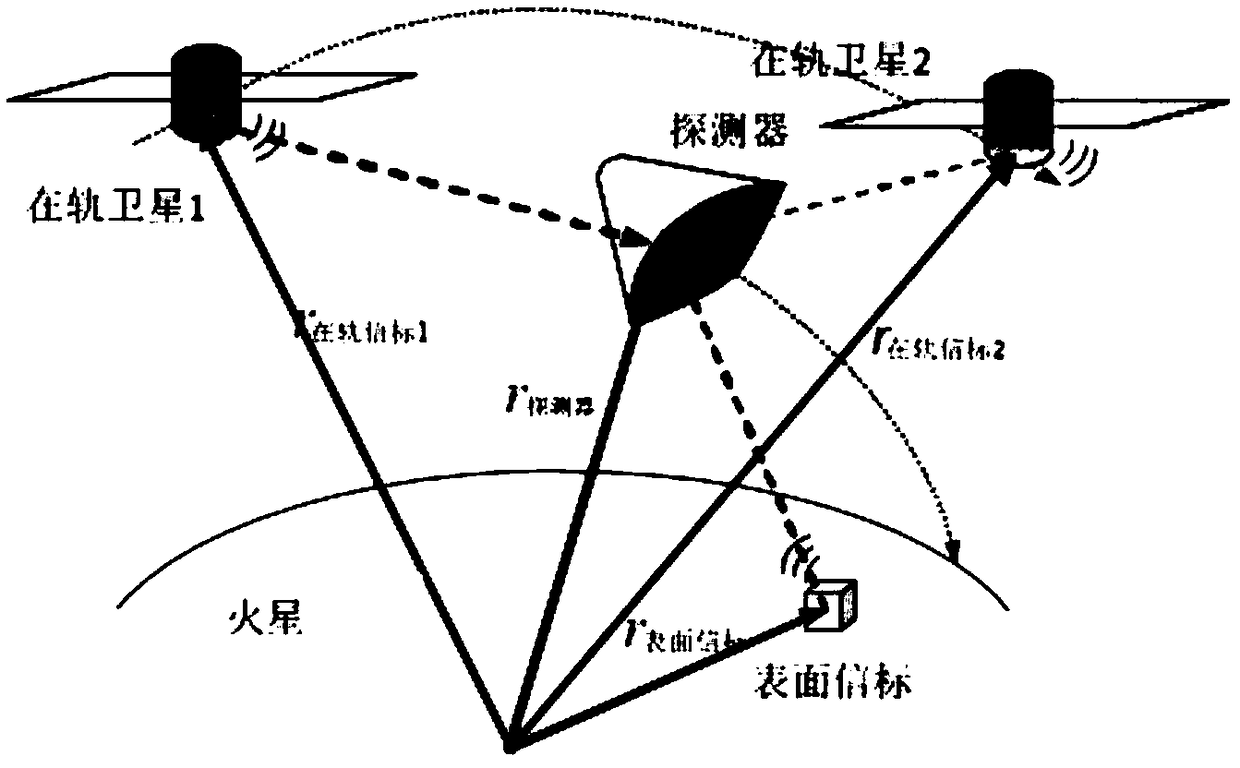
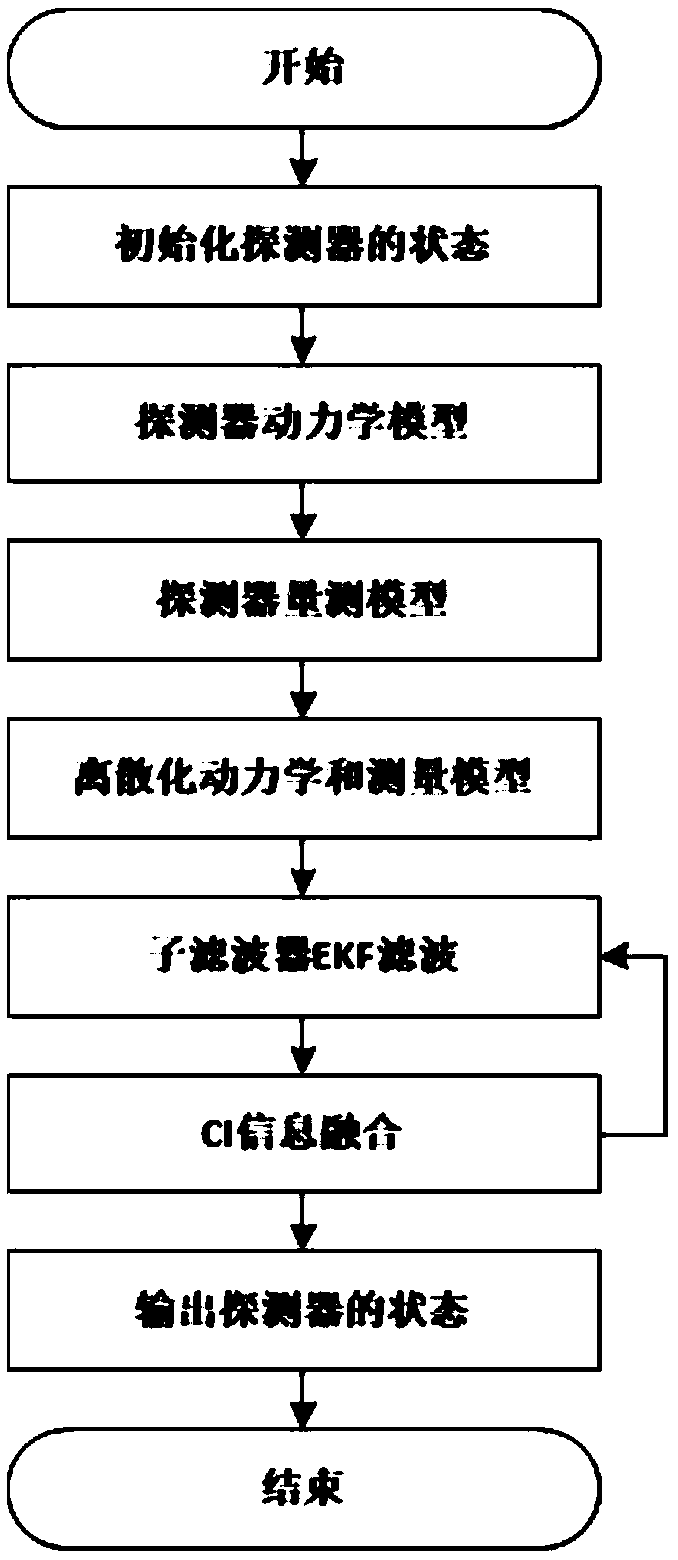
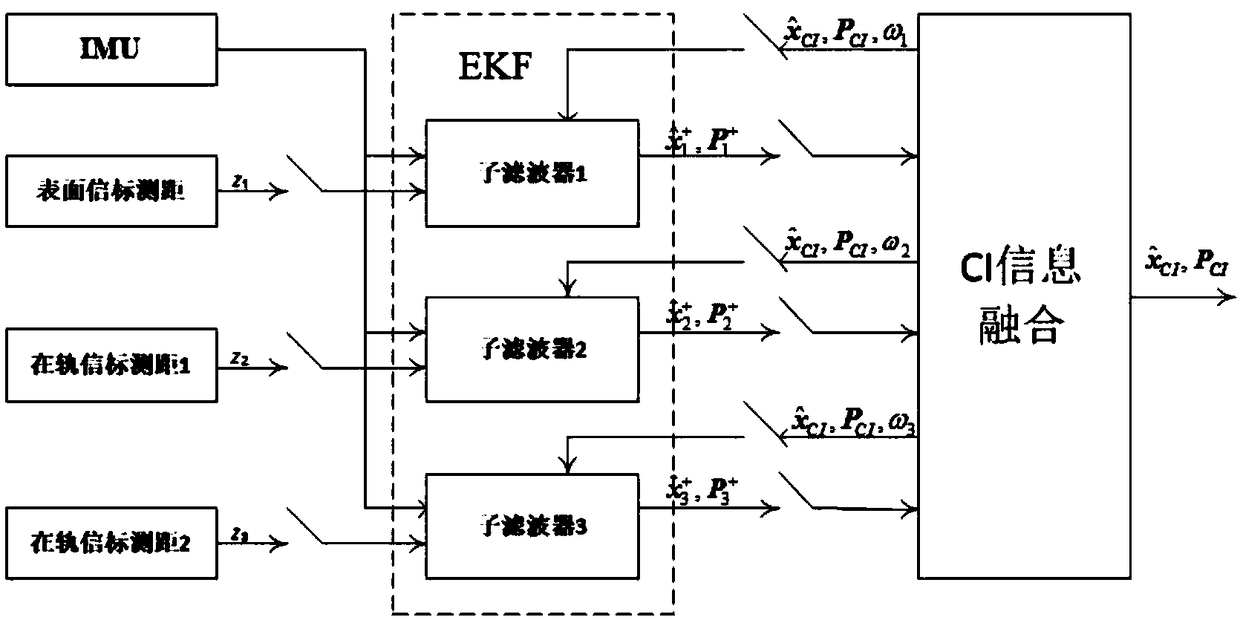
Covariance intersection and fusion based Mars entry section distribution type autonomous navigation method
ActiveCN106441309AImprove fault toleranceImprove stabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationFault toleranceAutonomous Navigation System
The invention provides a covariance intersection and fusion based Mars entry section distribution type autonomous navigation method which comprises the following steps of establishing a three-degree-of-freedom kinetic model of a Mars atmospheric entry section navigation system; establishing a measurement model of a Mars atmospheric entry section; establishing a distribution type fault-tolerant autonomous navigation system; dispersing and linearizing a three-degree-of-freedom kinetic model and a measurement model of the distribution type fault-tolerant autonomous navigation system; establishing a subfilter based on an EKF (Extended Kalman Filter) navigation filtering algorithm; and establishing an information fusion device based on a covariance intersection and fusion algorithm. According to the covariance intersection and fusion based Mars entry section distribution type autonomous navigation method, autonomous navigation is carried out by adopting a mode of distribution type information fusion with stronger fault tolerance, so that improvement of utilization efficiency of wireless communication is facilitated, the calculated amount of autonomous navigation filtering is reduced, and the fault tolerance of the Mars atmospheric entry section autonomous navigation system, the navigation filtering stability and the autonomous navigation accurate of the Mars atmospheric entry section to a prober are improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Leading edge channel for enhancement of lift/drag ratio and reduction of sonic boom
The leading edges of wings, nose assemblies, tails, fins, struts, and other components of aircraft, atmospheric entry vehicles and missiles in which the leading edge is blunted and the flight Mach number is supersonic, are provided with passive airflow channel, resulting in significantly reduced wave drag and total drag, significantly increased lift-to-drag ratio, and reduced sonic boom.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
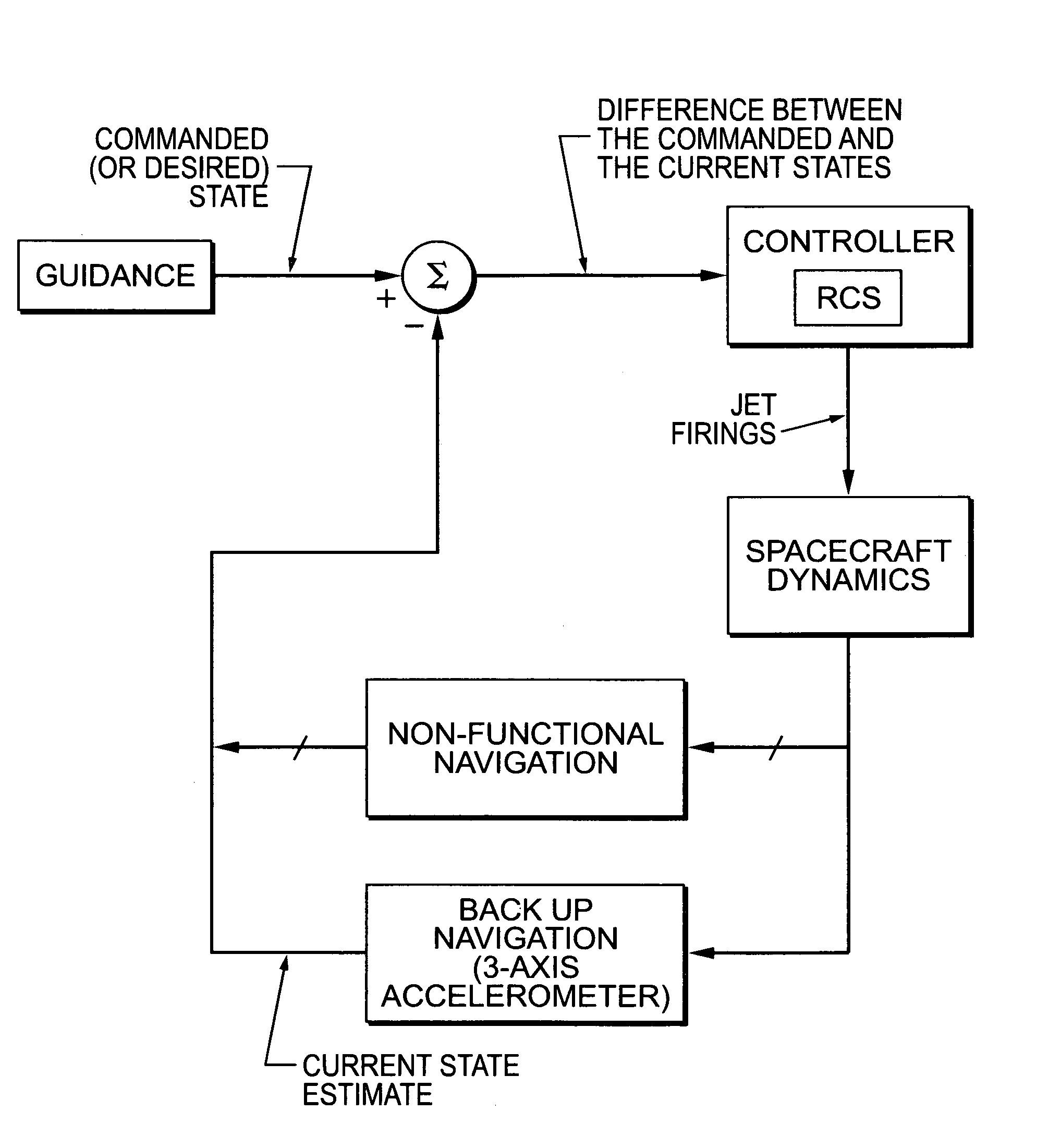
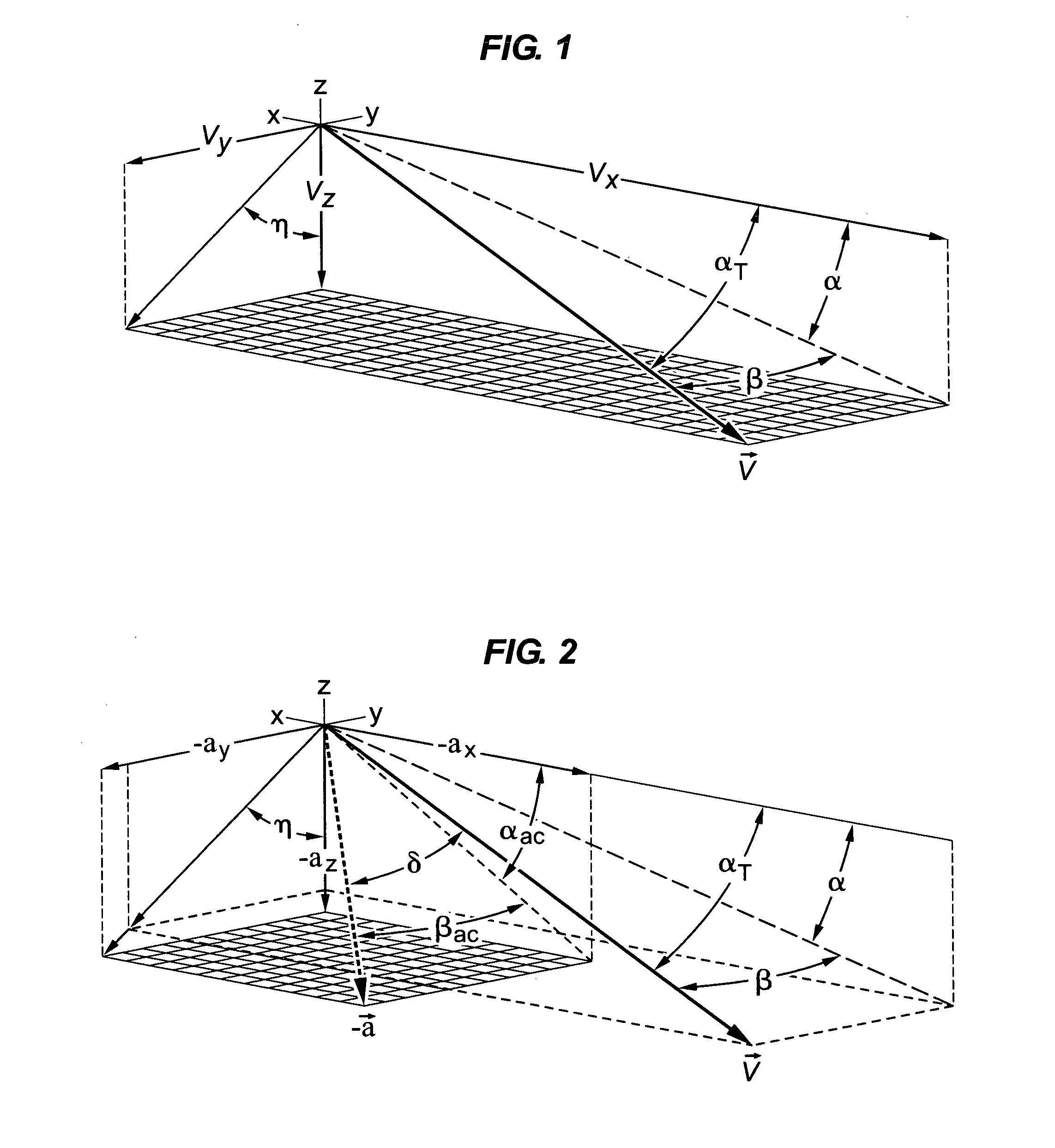
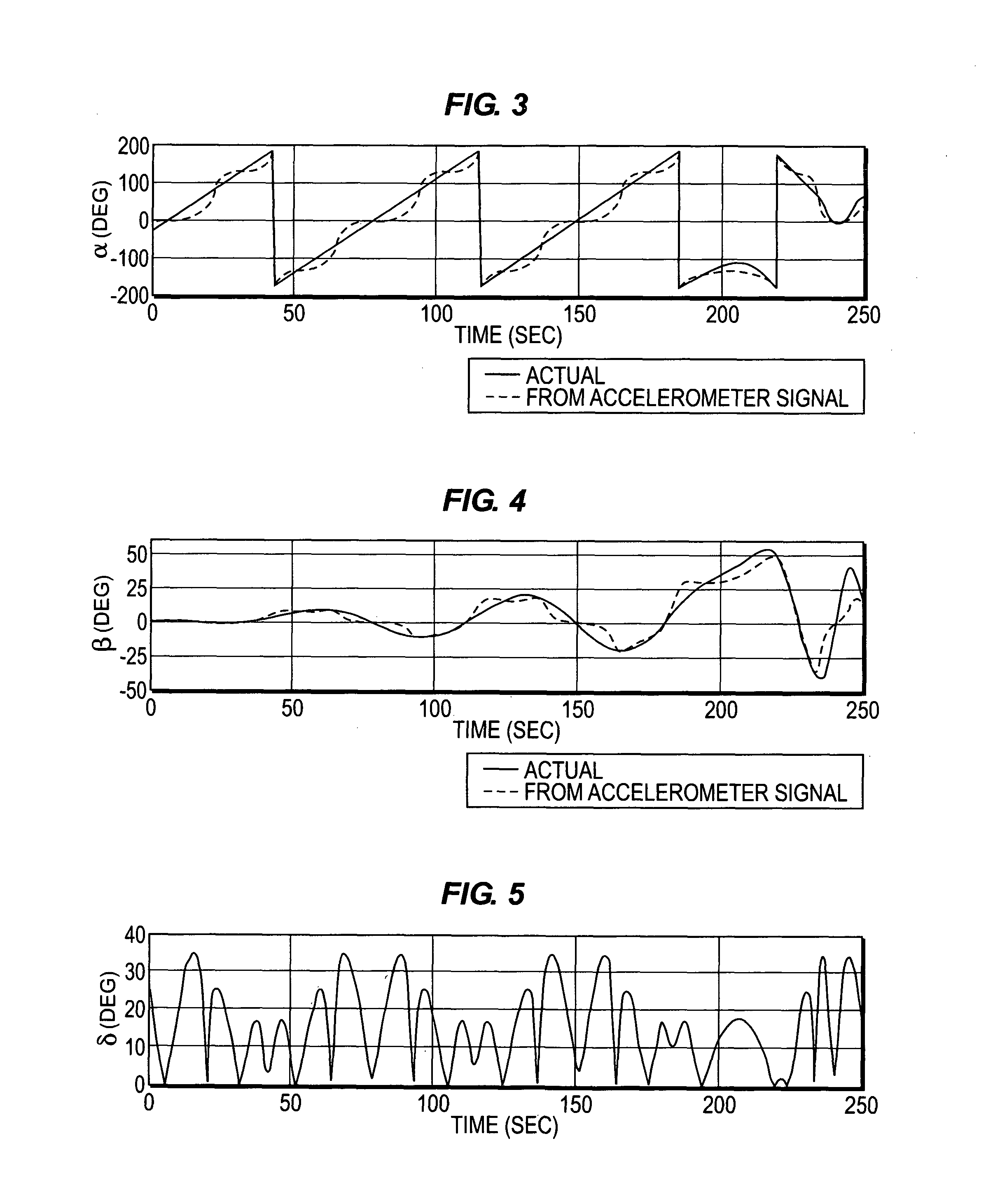
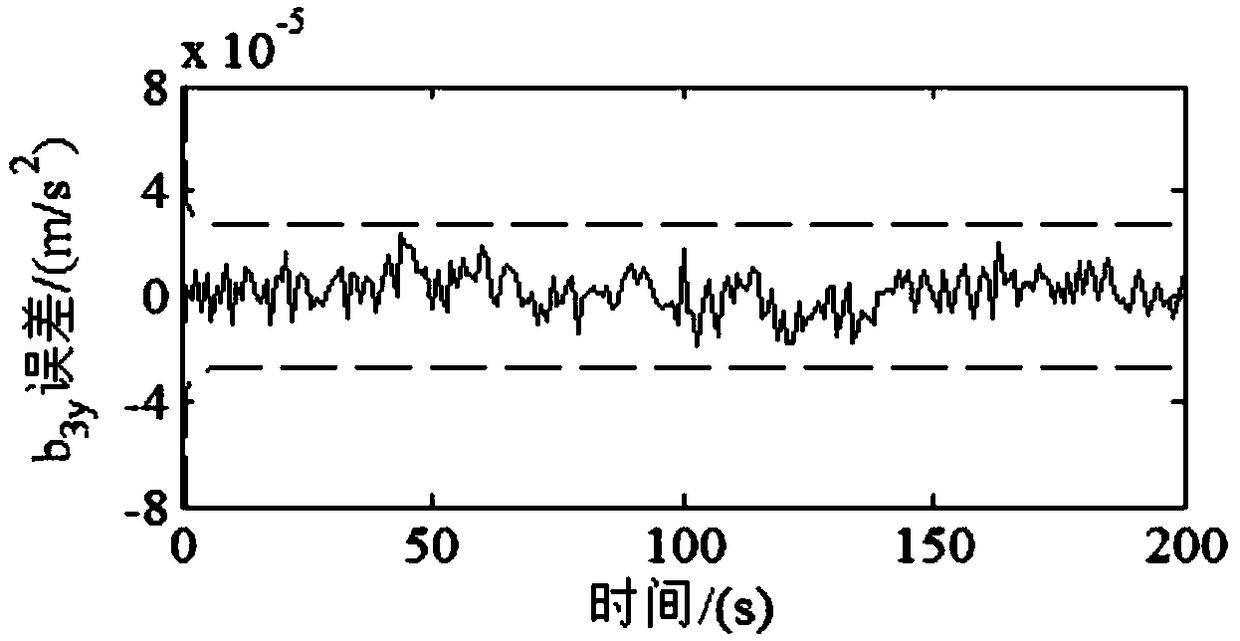
Attitude determination with three-axis accelerometer for emergency atmospheric entry
ActiveUS8321077B1Cosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
Two algorithms are disclosed that, with the use of a 3-axis accelerometer, will be able to determine the angles of attack, sideslip and roll of a capsule-type spacecraft prior to entry (at very high altitudes, where the atmospheric density is still very low) and during entry. The invention relates to emergency situations in which no reliable attitude and attitude rate are available. Provided that the spacecraft would not attempt a guided entry without reliable attitude information, the objective of the entry system in such case would be to attempt a safe ballistic entry. A ballistic entry requires three controlled phases to be executed in sequence: First, cancel initial rates in case the spacecraft is tumbling; second, maneuver the capsule to a heat-shield-forward attitude, preferably to the trim attitude, to counteract the heat rate and heat load build up; and third, impart a ballistic bank or roll rate to null the average lift vector in order to prevent prolonged lift down situations. Being able to know the attitude, hence the attitude rate, will allow the control system (nominal or backup, automatic or manual) to cancel any initial angular rates. Also, since a heat-shield forward attitude and the trim attitude can be specified in terms of the angles of attack and sideslip, being able to determine the current attitude in terms of these angles will allow the control system to maneuver the vehicle to the desired attitude. Finally, being able to determine the roll angle will allow for the control of the roll ballistic rate during entry.
Owner:GB TECH
Enveloping aerodynamic decelerator
ActiveUS9884693B2Cosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic thermal protectionAtmospheric entryAerodynamic force
An inflatable aerodynamic deceleration method and system is provided for use with an atmospheric entry payload. The inflatable aerodynamic decelerator includes an inflatable envelope and an inflatant, wherein the inflatant is configured to fill the inflatable envelope to an inflated state such that the inflatable envelope surrounds the atmospheric entry payload, causing aerodynamic forces to decelerate the atmospheric entry payload.
Owner:GLOBAL AEROSPACE
Occultation atmosphere detection system based on tail sub-level cluster
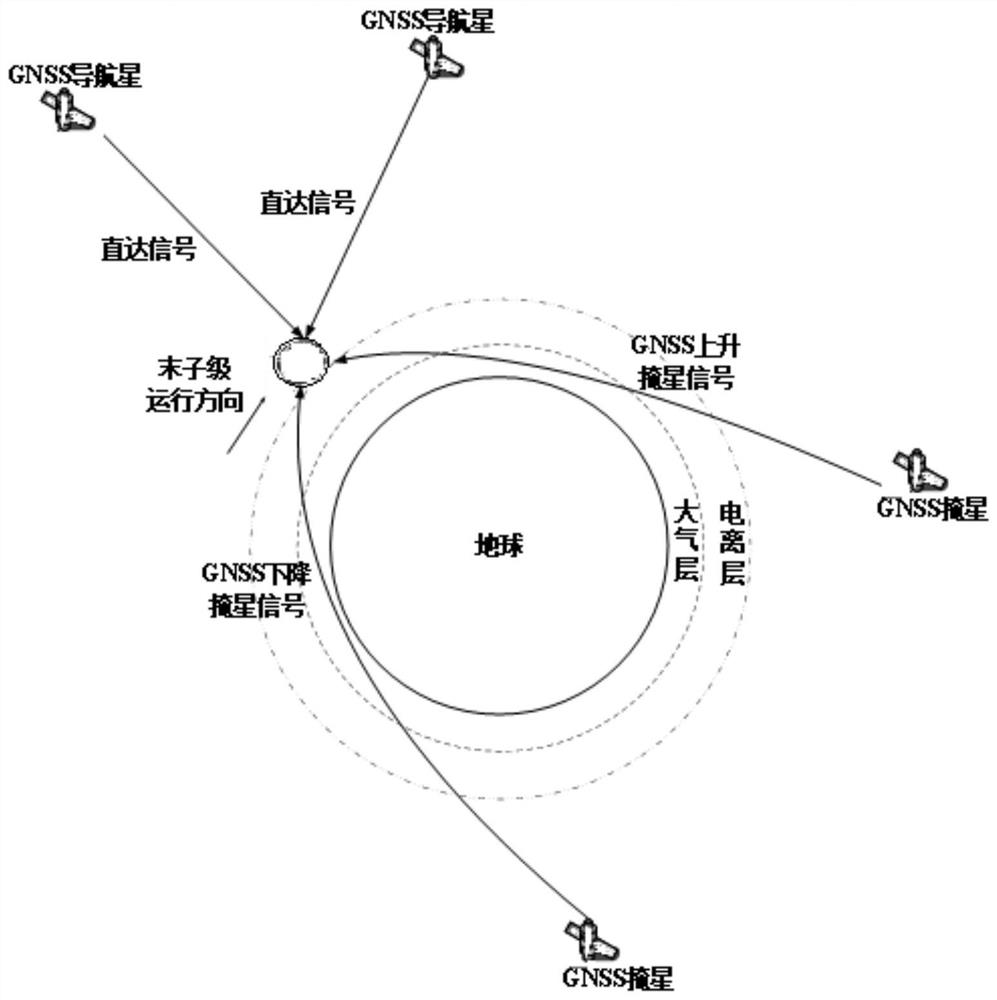
PendingCN114114328AImprove spatio-temporal resolutionImprove detection accuracySatellite radio beaconingDetection using electromagnetic wavesInclined orbitRefractive index
The invention discloses an occultation atmospheric detection system based on a tail sub-level cluster, and the system is characterized in that a GNSS occultation detection load is loaded on an orbit-remaining tail sub-level cluster provided with an orbit-remaining platform, and the orbit-remaining tail sub-level cluster comprises a plurality of orbit-remaining tail sub-levels on a sun-synchronous orbit task and an inclined orbit task; the orbit remaining tail sub-levels adjust the attitude through an orbit remaining platform, receive a direct signal of a GNSS navigational star and an ascending occultation signal and a descending occultation signal of GNSS occultation through a GNSS occultation detection load, and analyze parameter data including ionosphere electron density, atmospheric refractive index and temperature and humidity profile to realize atmospheric detection. The orbit remaining tail sub-level under high-density launch of a carrier rocket is fully utilized to carry out adaptive modification, the orbit remaining tail sub-level and an existing GNSS occultation detection satellite constellation form a giant hybrid detection network, and the temporal-spatial resolution and the detection precision of GNSS occultation atmosphere detection can be effectively improved.
Owner:NO 63921 UNIT OF PLA
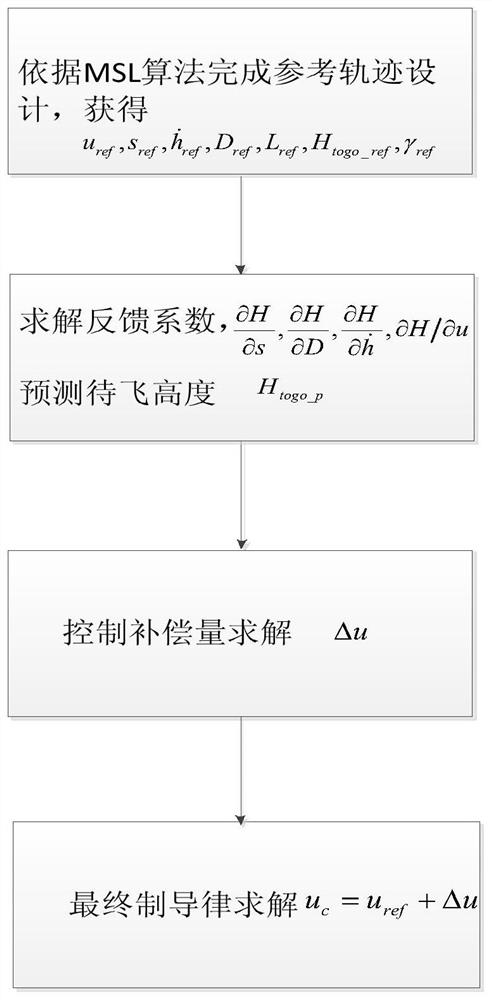
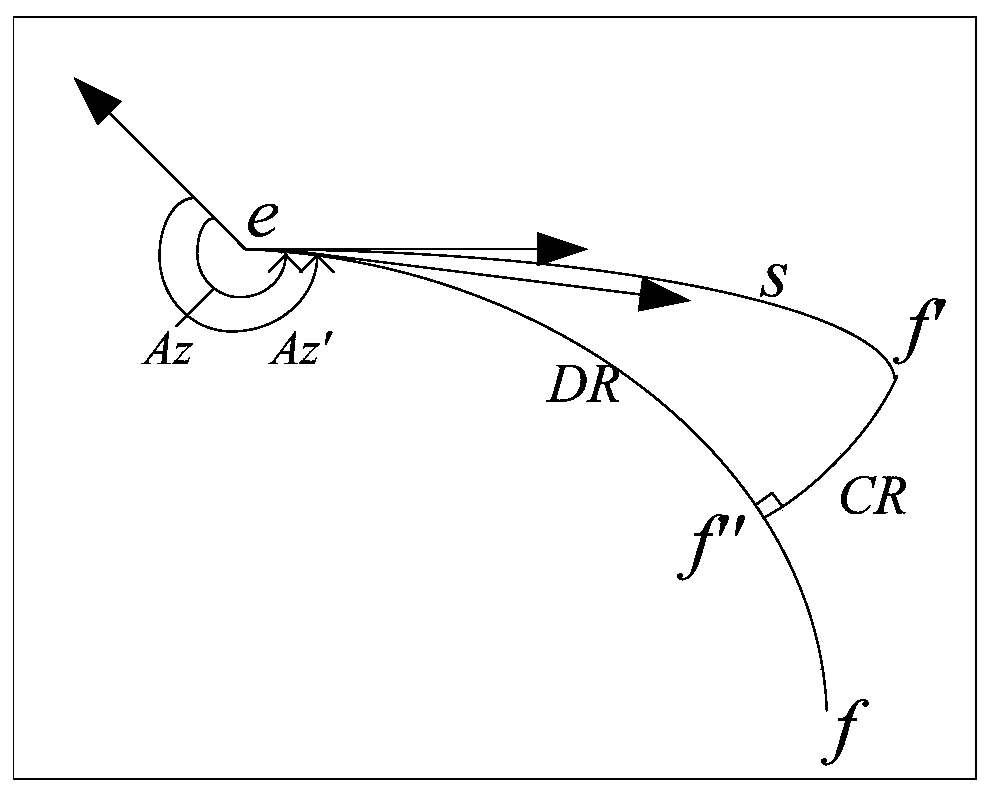
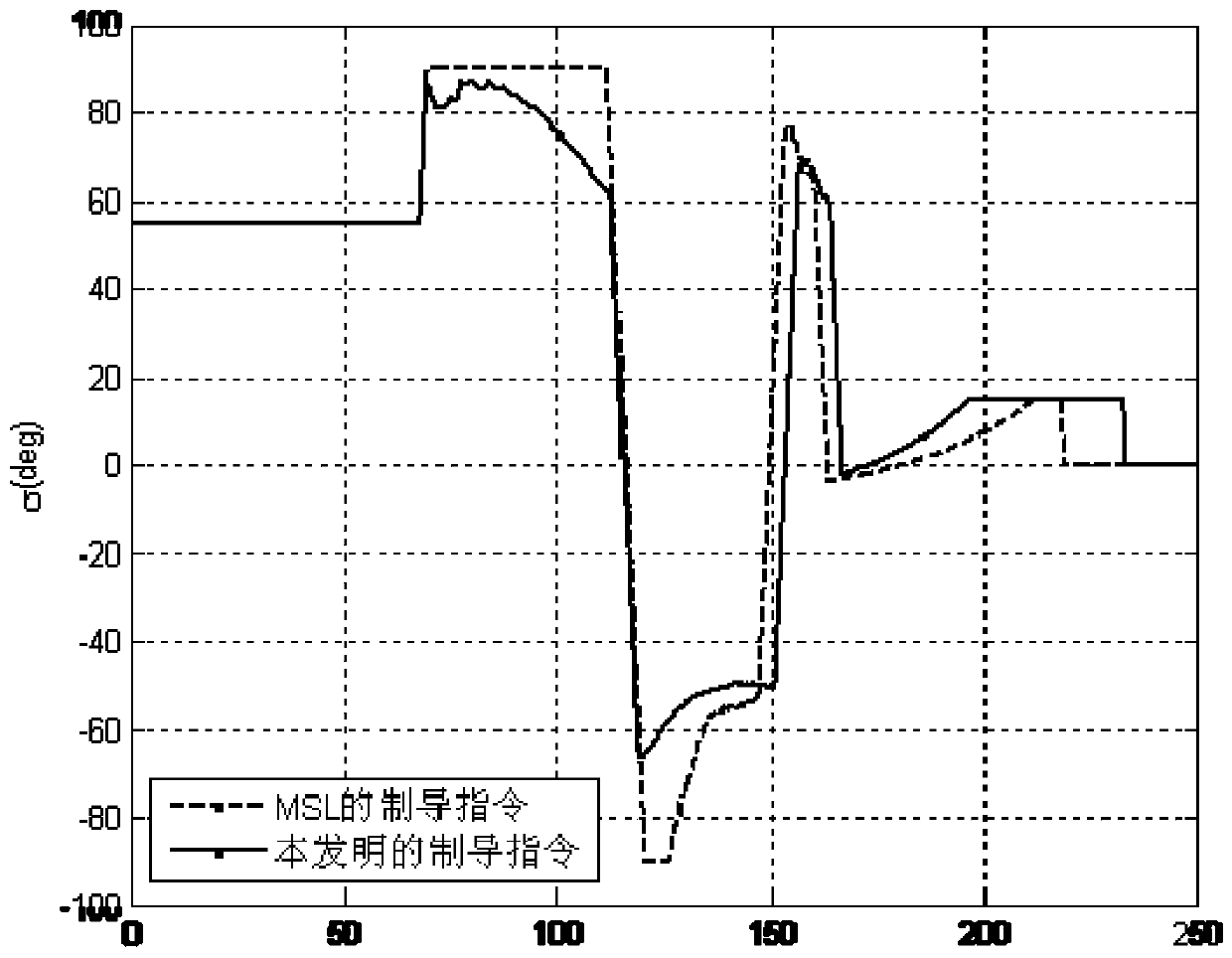
A Method of Atmospheric Entry Guidance with Parachute Opening Altitude as Control Target
ActiveCN108548541BEnsure safetyReduce spreadInstruments for comonautical navigationLoop controlControl objective
The invention relates to an atmosphere entry guidance method using a parachute-opening height as a control target. The atmosphere entry guidance method comprises: (1) completing nominal trajectory design to obtain nominal guidance law uref, nominal longitudinal range sref, nominal height change rate h<.>ref, nominal resistance acceleration Dref, nominal lift force acceleration Lref, nominal to-be-flying height Htogo_ref and nominal flight path angle [gamma]ref; (2) according to the deviation of the current flight longitudinal range s, the current resistance D and the current height change rateh<.> relative to the nominal longitudinal range sref, the nominal resistance acceleration Dref and the nominal height change rate h<.>ref, and the nominal to-be-flying height Htogo_ref correspondingto the current speed, predicting the current to-be-flying height Htogo_p; (3) according to the predicted to-be-flying height Htogo_p, calculating a control compensation amount [delta]u to eliminate the deviation between the predicted to-be-flying height and the reference to-be-flying height; (4) determining the final guidance law uc by using the guidance law compensation amount [delta]u and the nominal guidance law uref obtained in the step (1); and (5) real-timely obtaining the longitudinal range s, the height change rate h<.> and the resistance acceleration D of a landing device from an atmosphere entry point to parachute-opening, generating guidance law uc, and transmitting to a landing patrol device so as to carry out closed-loop control.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Distributed autonomous navigation method for Mars entry phase based on covariance cross fusion
ActiveCN106441309BImprove stabilityImprove fault toleranceNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationFault toleranceAutonomous Navigation System
The present invention proposes a distributed autonomous navigation method for the Mars entry section based on covariance cross-fusion. The steps are: establishing a three-degree-of-freedom dynamic model of the Mars atmosphere entry section navigation system; establishing a measurement model for the Mars atmosphere entry section; Establish a distributed fault-tolerant autonomous navigation system; discrete and linearized three-degree-of-freedom dynamic model and measurement model of the distributed fault-tolerant autonomous navigation system; establish a sub-filter based on the EKF navigation filter algorithm; establish information based on the covariance cross-fusion algorithm Fusion. The present invention uses a distributed information fusion method with strong fault tolerance for autonomous navigation, which is beneficial to improving the utilization efficiency of radio communications, reducing the calculation amount of autonomous navigation filtering, improving the fault tolerance of the autonomous navigation system in the Mars atmosphere entry section, and enhancing This improves the stability of the navigation filter and effectively improves the autonomous navigation accuracy of the detector during the Martian atmosphere entry phase.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
An Adaptive Estimation Method of Martian Atmosphere Entry Based on Model Perturbation
ActiveCN106525055BReduce the number of uncertain parameter itemsGuaranteed stabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationModel dynamicsAlgorithm
The invention discloses an adaptive estimation method of Mars atmosphere entry based on model perturbation and belongs to the technical field of deep-space exploration. A coupling relation between uncertain parameters and an aerodynamic model of a Mars entry section is analyzed and perturbation on a dynamic system, caused by the uncertain parameters, is converted into aerodynamic model deviation so as to reduce the number of the uncertain parameters; according to a change rule of the perturbation of the aerodynamic model, filtering models aiming at perturbation amount deviation in the dynamic system are established; the perturbation amount in each filtering model dynamic system corresponds to a deviation value; a measurement residual error is predicated through each filtering module and a weight value of each model is self-adaptively updated based on measurement residual error information; and iterative approximation is close to real model perturbation so that influences of the aerodynamic model deviation on state estimation precision are inhibited. By adopting the self-adaptive estimation method disclosed by the invention, influences of the aerodynamic model perturbation on the state estimation precision in a Mars entry section combined navigation method can be reduced, and the state estimation precision of a detector in an entering process and the stability of a navigation system are guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
An Adaptive Trajectory Planning Method for Atmospheric Entry Guidance
ActiveCN108534785BReduce spreadIncrease success rateInstruments for comonautical navigationAdaptive controlGround trackSelf adaptive
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
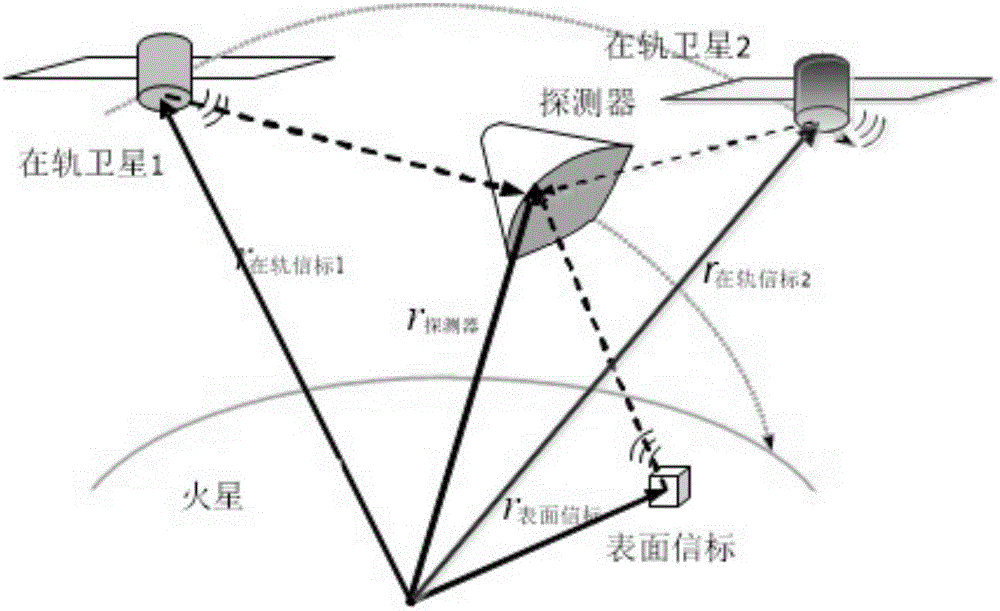
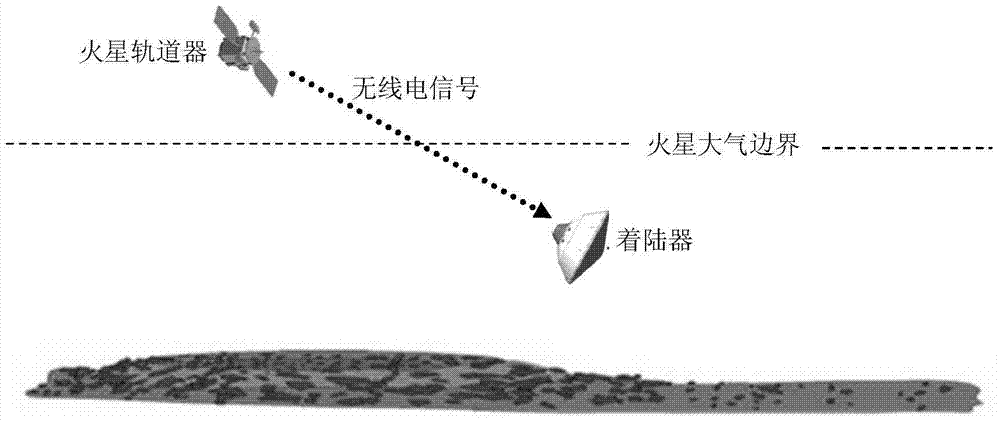
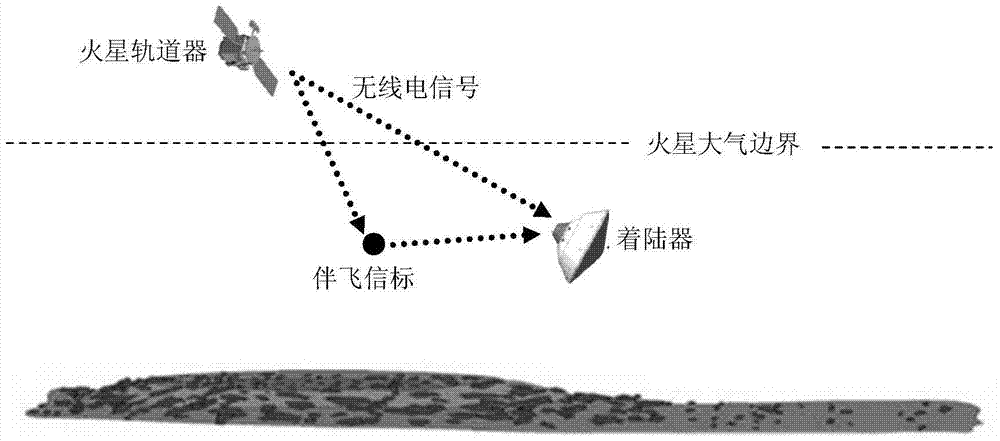
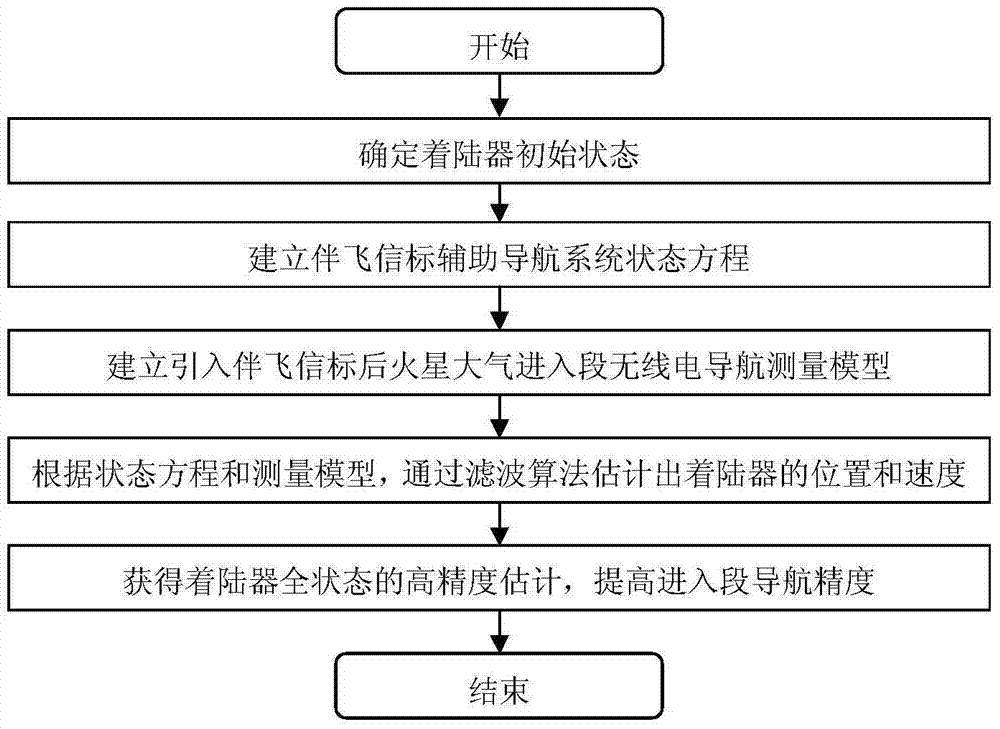
A method for assisting navigation with beacons during Martian atmosphere entry
InactiveCN105203112BOptimize geometryAchieving High-Precision EstimationInstruments for comonautical navigationObservational errorDeep space exploration
The invention discloses a Mars atmosphere entry section accompanying flight beacon auxiliary navigation method, relates to a beacon auxiliary navigation method, and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. According to the method, on the basis of the Mars atmosphere entry section inertial navigation, an accompanying flight beacon is introduced; by adding the radio distance measurement and speed measurement among a landing device, a rail device and the accompanying flight beacon as a measuring quantity, an initial state deviation is corrected; a geometrical configuration during the radio navigation of the landing device and the rail device is improved; the entry section navigation precision is further improved. The Mars atmosphere entry section accompanying flight beacon auxiliary navigation method disclosed by the invention can solve the problems of the inertial navigation that the initial state deviation cannot be corrected during inertial navigation, and the measurement errors are accumulated along with time. The geometrical configuration of the radio navigation can be improved; the high-precision estimation of a full state of the landing device is obtained; the entry section navigation precision is further improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Intelligent Predictive Control Entry Guidance Method for Spacecraft
ActiveCN112114521BMeet real-time requirementsImprove robustnessForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionGuidance systemData set
The invention discloses a spacecraft intelligent predictive control entry guidance method. Firstly, considering the constraint conditions of the spacecraft's atmospheric entry, the guidance system is designed using the nonlinear model predictive control method, and the attenuation memory filter is introduced, and a prediction model correction method based on error information estimation is proposed. The robustness of the control system to model errors is enhanced. Then, using the guidance system as a guidance template, a sample data set is generated and a multi-layer neural network is trained offline to approximate the mapping relationship between the spacecraft's real-time flight status and guidance instructions. Finally, in the process of entering guidance, the trained neural network is used to replace the process of solving complex optimization problems and integral prediction, which reduces the time for online solution of guidance instructions. The simulation results show that the guidance method proposed by the present invention can meet the mission requirements in both accuracy and real-time performance of the guidance method in the presence of errors such as large model uncertainties.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
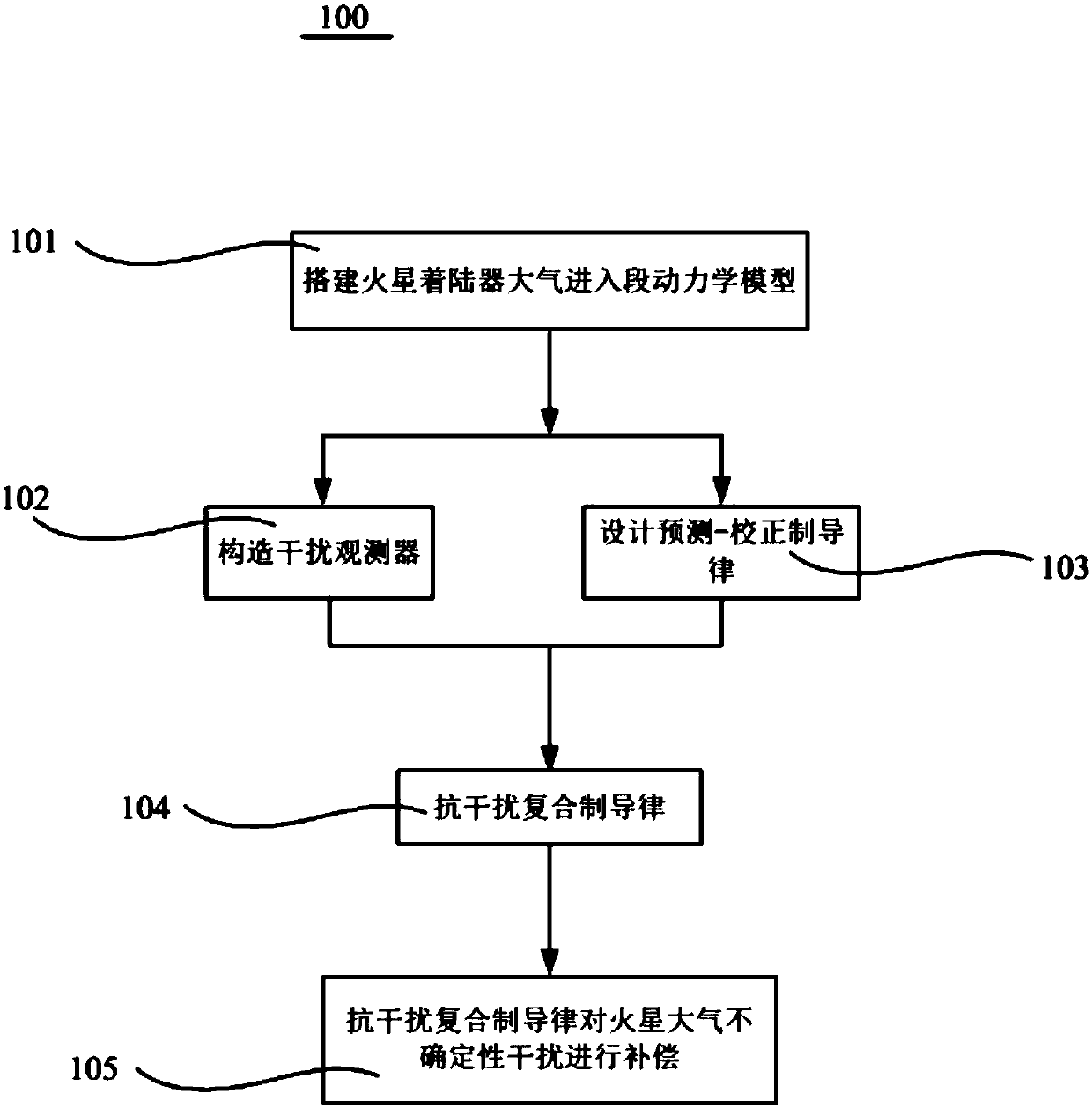
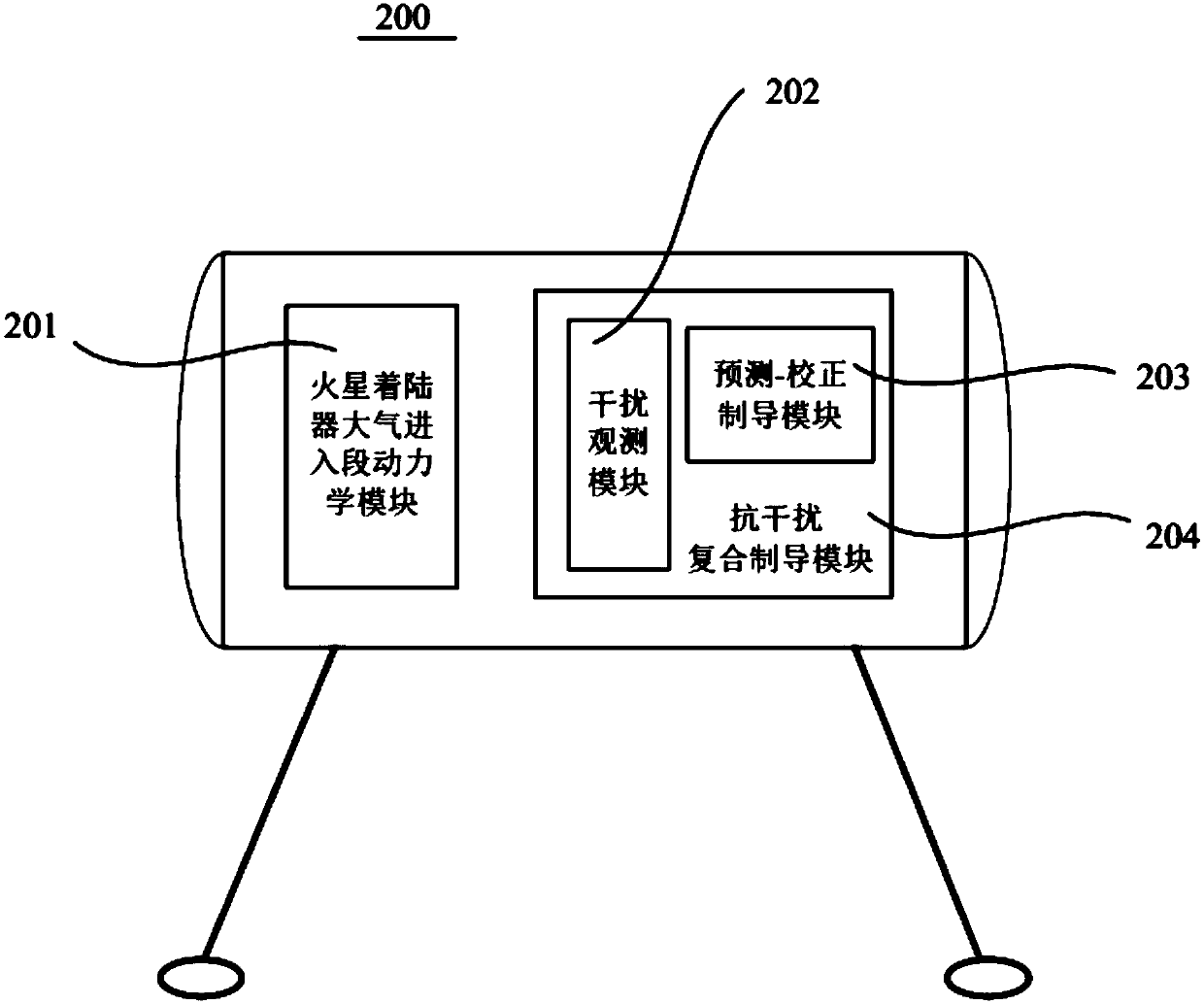
An Anti-jamming Composite Online Guidance Method for Mars Lander Atmospheric Entry Section
ActiveCN105867402BStrong autonomyImprove anti-interference abilityCosmonautic vehiclesSystems for re-entry to earthDynamic modelsEngineering
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
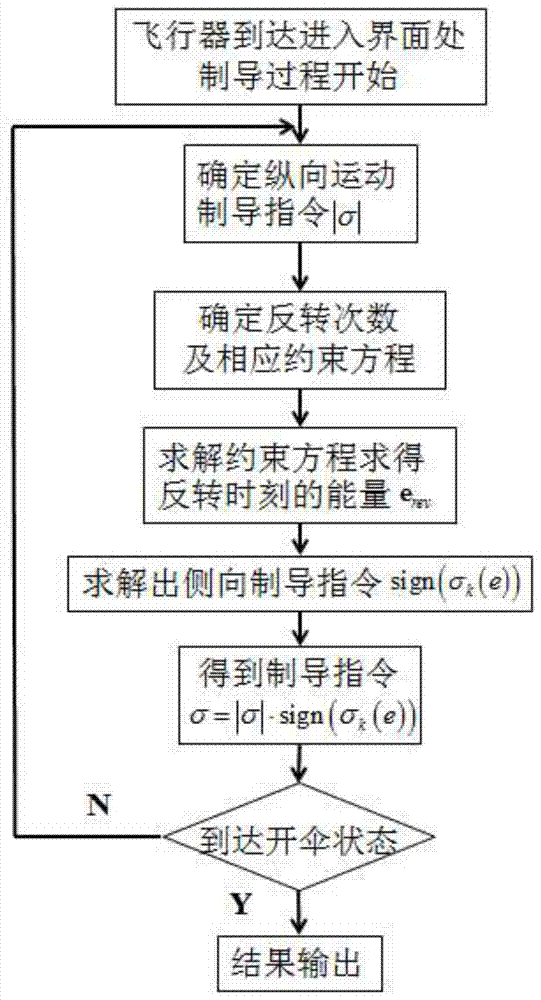
A lateral prediction and correction guidance method for Mars atmosphere entry section
InactiveCN105115512BGuaranteed accuracyFlexible planningInstruments for comonautical navigationDeep space explorationOrbit
The invention discloses a method for lateral prediction correction guidance in the stage of entering mars atmosphere, relates to a lateral prediction correction guidance method and belongs to the technical field of deep-space exploration. On the basis of a conventional longitudinal prediction correction guidance method, the prediction correction method is introduced into design of a detector lateral motion guidance law. Firstly, lateral motion constraint conditions required by a landing detection task are determined, so as to determine heeling angle inversion frequency required by a detector at the entering stage; then, lateral motion constraint conditions are solved to determine energy of the detector at the heeling angle inversion moment, and when the energy of the detector exceeds energy at the heeling angle inversion moment, heeling angle inversion is carried out. After the constraint conditions are met, next heeling angle inversion energy is determined; finally, a current guidance cycle is determined by combing energy at the heeling angle inversion moment and the longitudinal guidance law and output is guided finally. By adopting the method provided by the invention, while parachute-opening point position accuracy is ensured, lateral motion of the detector entering an orbit can be flexibly planned according to task needs and fuel is saved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
An Accelerometer Calibration Method Based on Attitude Information
InactiveCN105606846BGuaranteed autonomous navigation performanceImprove calibration accuracyTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesNonlinear filterGyroscope
The invention discloses an accelerometer calibration method based on attitude information, relates to an accelerometer calibration method, and belongs to the technical field of deep space detection. In order to calibrate the accelerometer in the absence of position measurement information, the present invention adopts the gyroscope-free inertial navigation method, derives the accelerometer output model, uses the attitude determination system output, and combines the nonlinear filtering method to estimate the accelerometer drift and recalculate Accelerometer drift and corresponding error variance matrix, the accelerometer drift and corresponding error variance matrix are input into the nonlinear filter, the accelerometer drift is estimated, the accelerometer calibration is completed, the calibration accuracy is improved, and the autonomous navigation performance of the atmospheric entry section is guaranteed. The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to improve the calibration accuracy of the accelerometer in the approaching section of the planet in the absence of position measurement information, and ensure the autonomous navigation performance in the atmospheric entry section.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
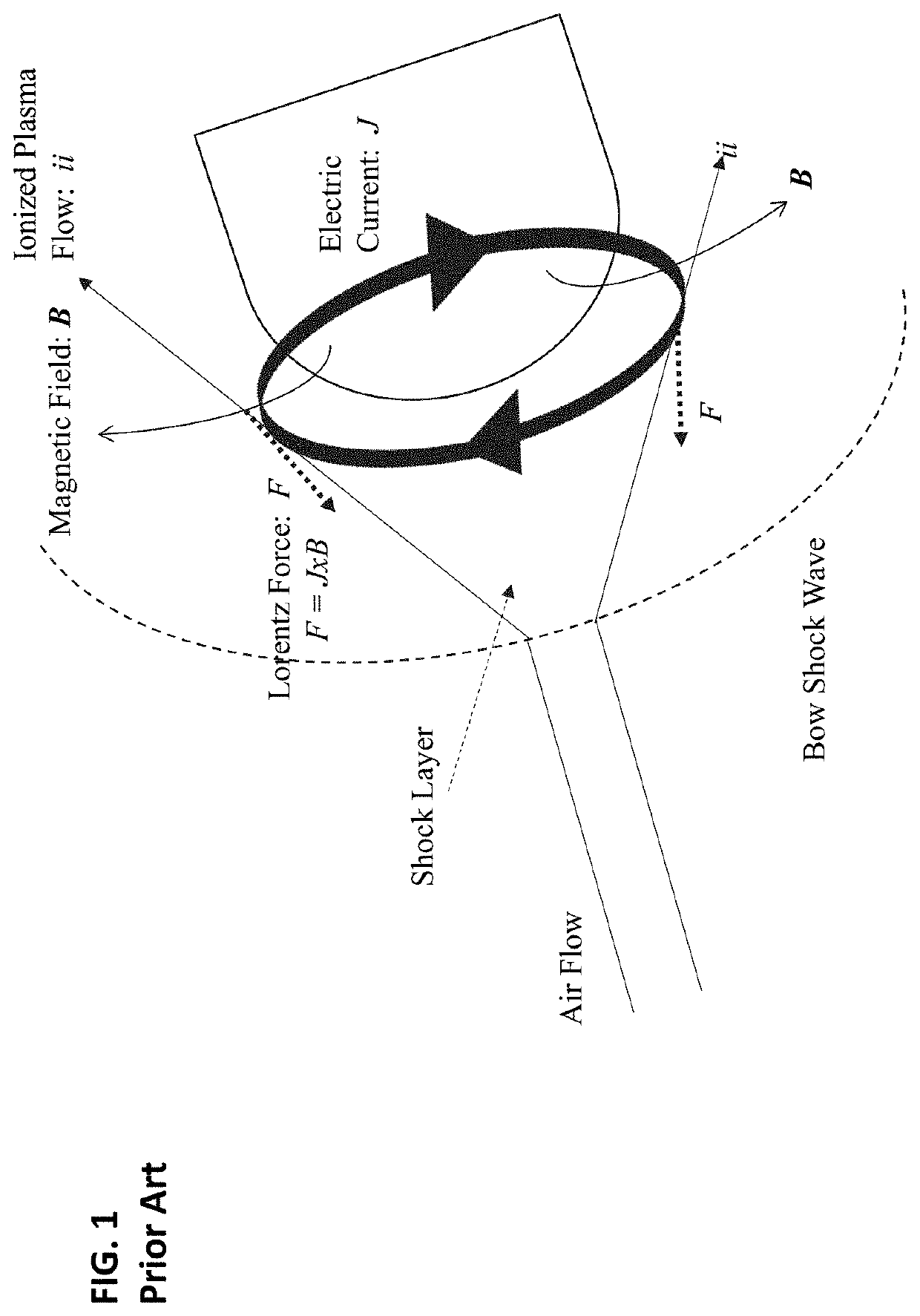
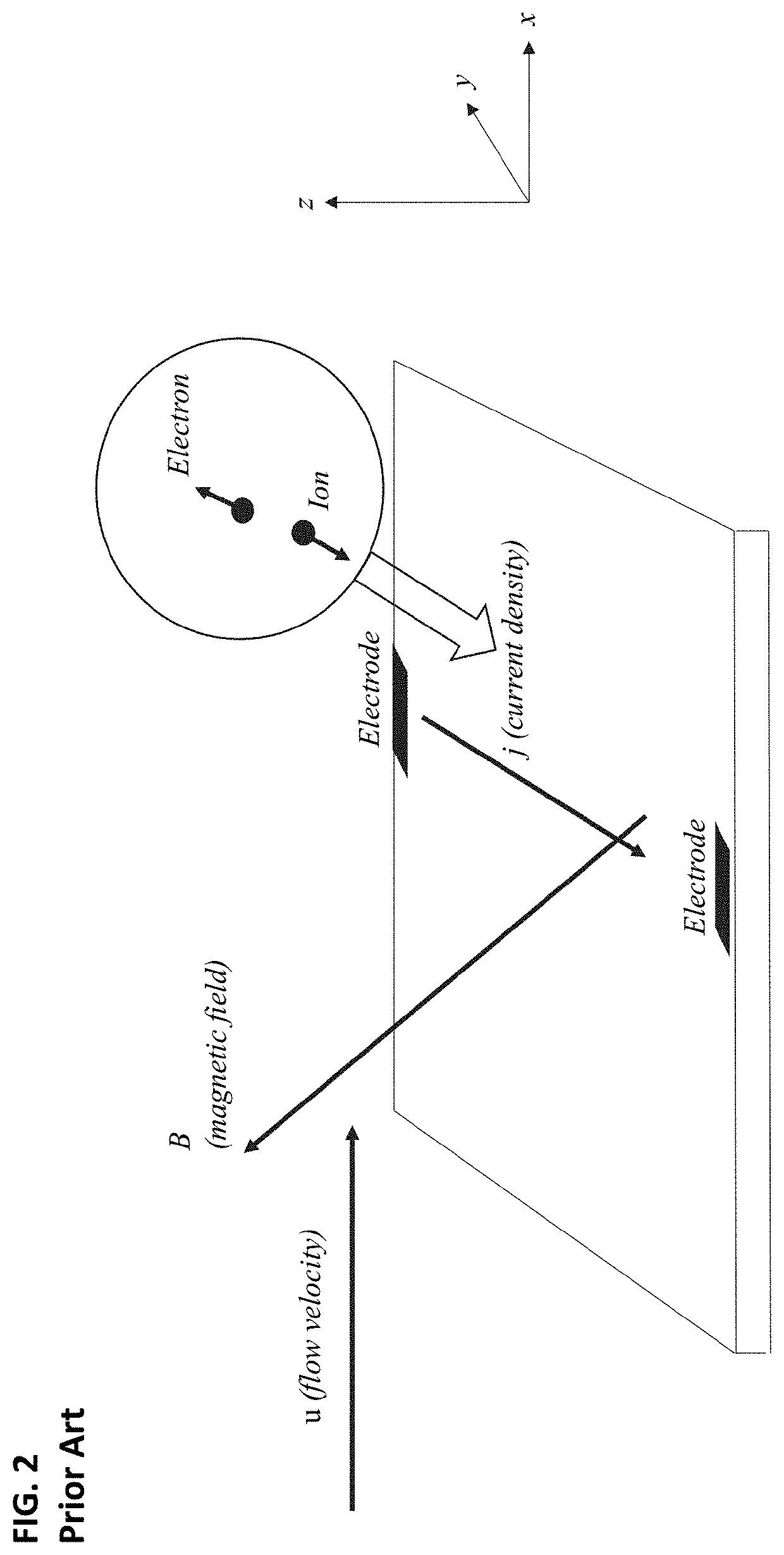
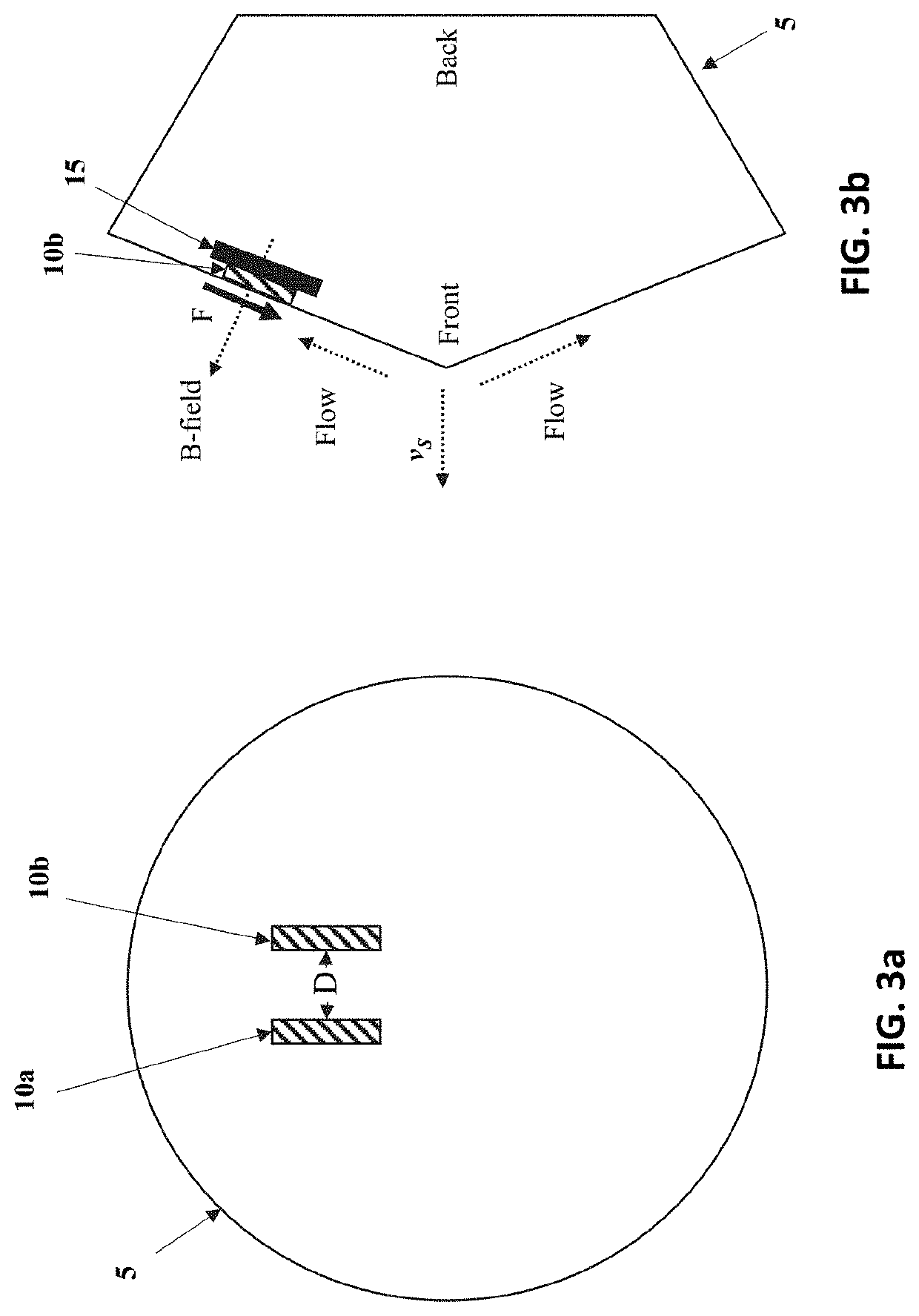
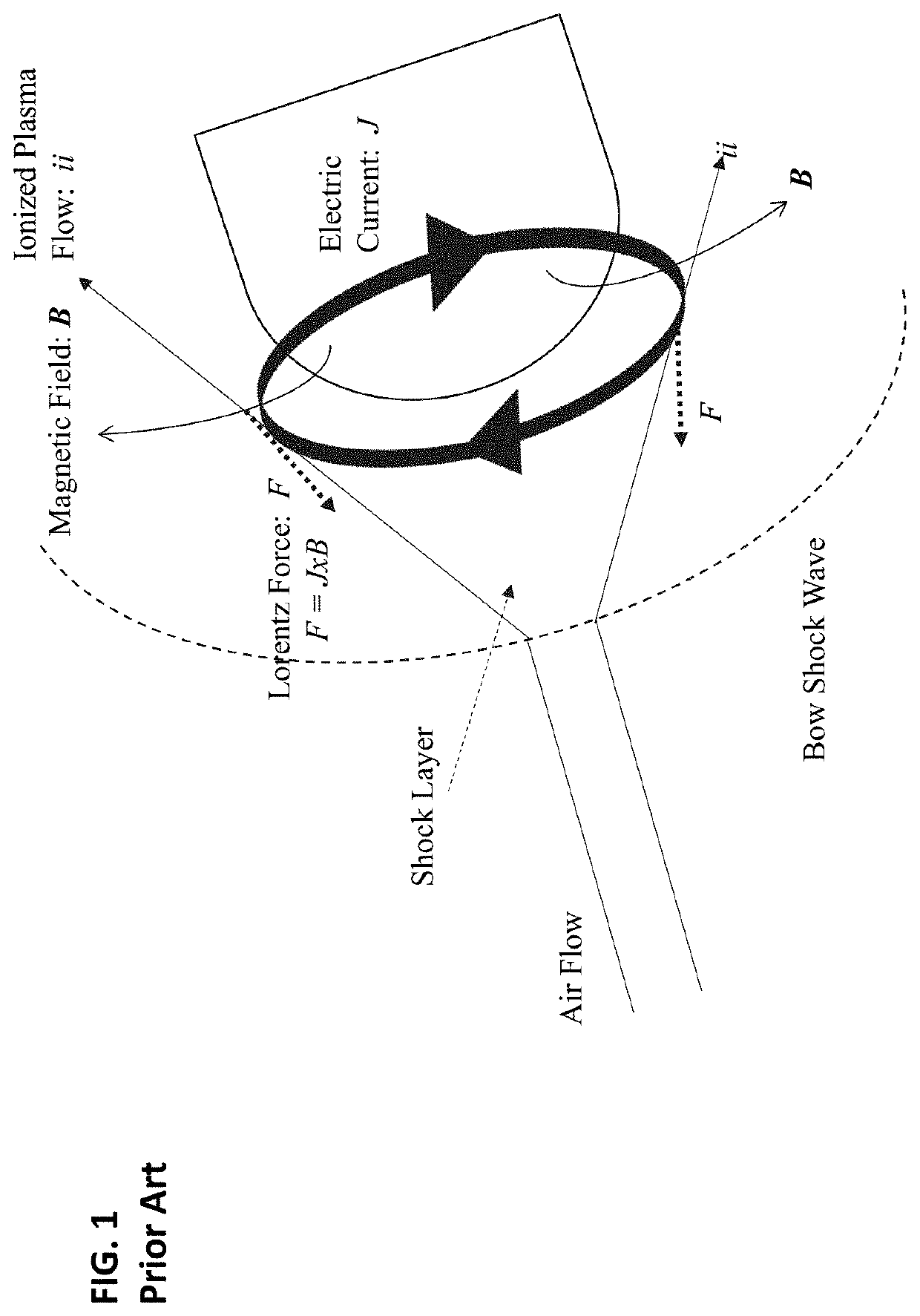
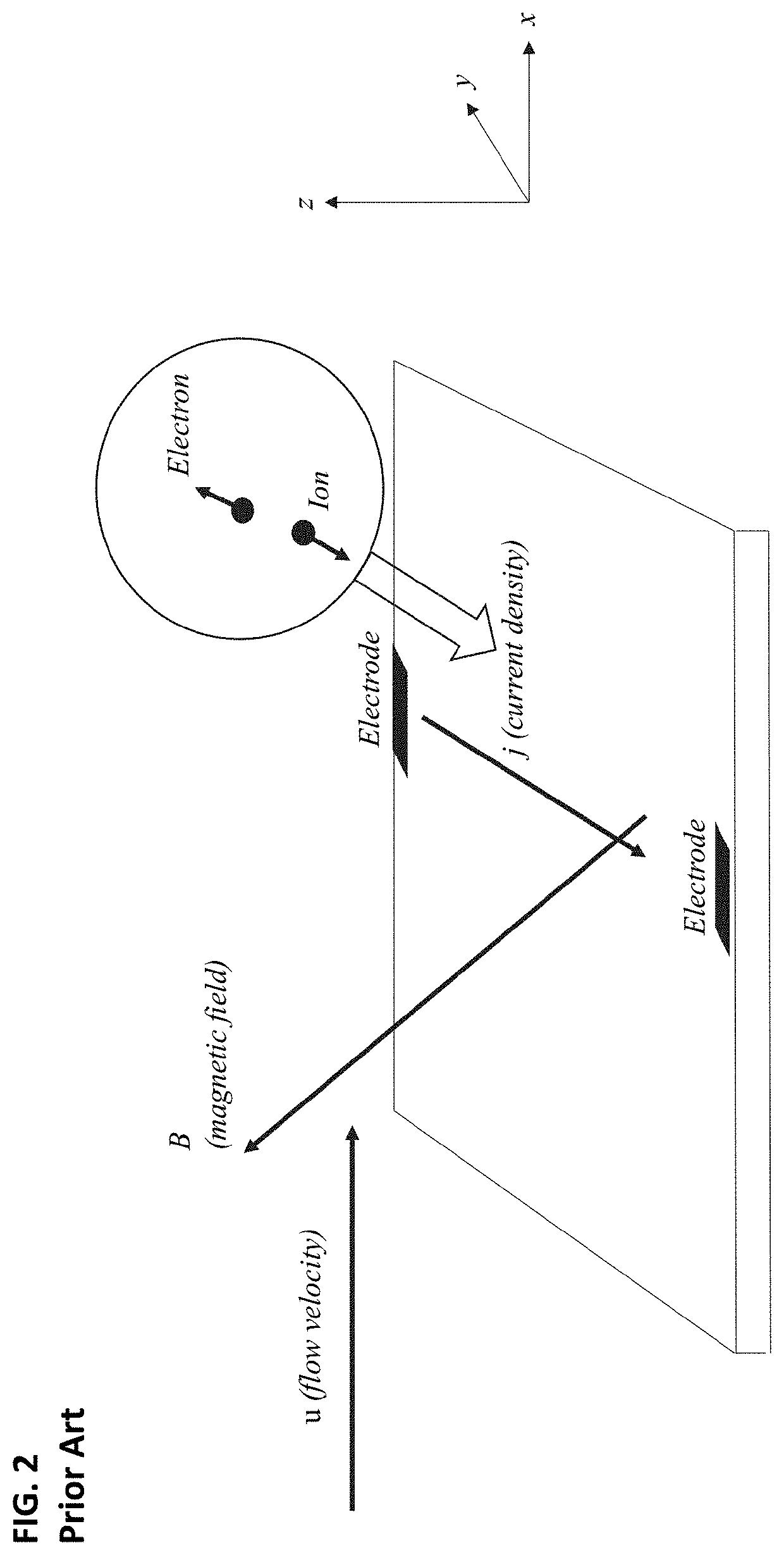
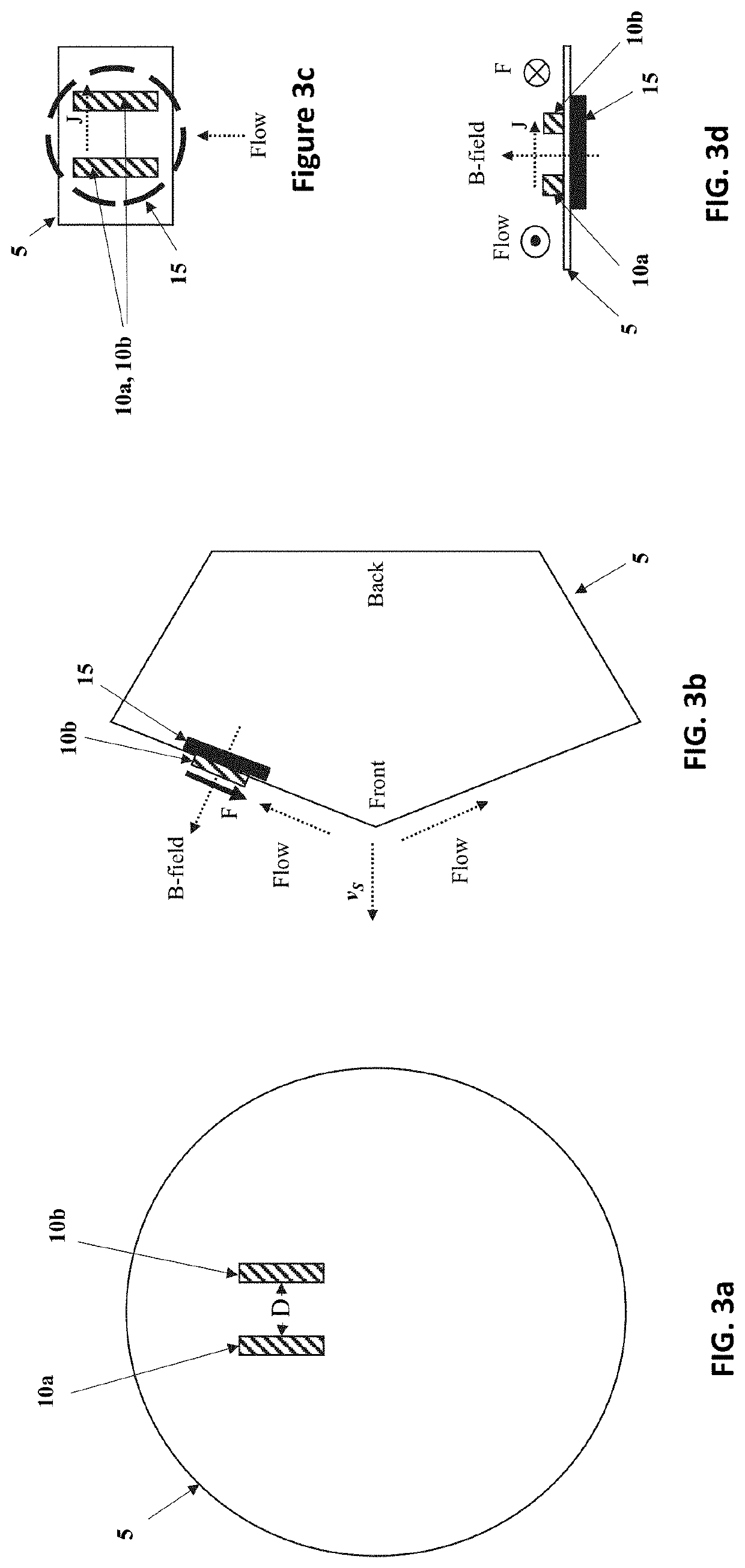
Electrode design for lift augmentation and power generation of atmospheric entry vehicles during aerocapture and entry, descent, and landing maneuvers
A magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow control mechanism is described which substantially improves the existing processes in that smaller magnetic fields, requiring far less mass, may be placed away from the forebody of the spacecraft to produce Lorentz forces that augment the lift and the drag forces for guidance, navigation, and control of the spacecraft. The MHD flow control mechanism may also be configured to provide additional thermal protection of the electrodes therein.
Owner:NASA
System and method for lift augmentation of atmospheric entry vehicles during aerocapture and entry, descent, and landing maneuvers
PendingUS20220340308A1Electromagnets without armaturesCosmonautic vehiclesFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
A magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow control mechanism is described which substantially improves the existing processes in that smaller magnetic fields, requiring far less mass, are placed away from the forebody of the spacecraft to produce Lorentz forces that augment the lift and the drag forces for guidance, navigation, and control of the spacecraft.
Owner:NASA
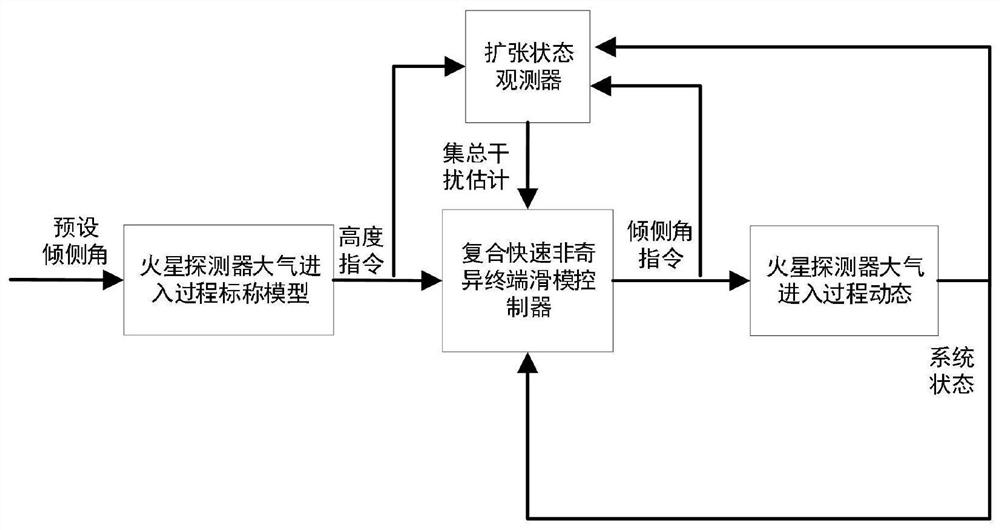
A composite fast non-singular terminal sliding mode control method for the atmospheric entry segment of the Mars rover
ActiveCN113359447BImprove anti-interference abilityFast convergenceAdaptive controlDynamic equationMotion dynamics
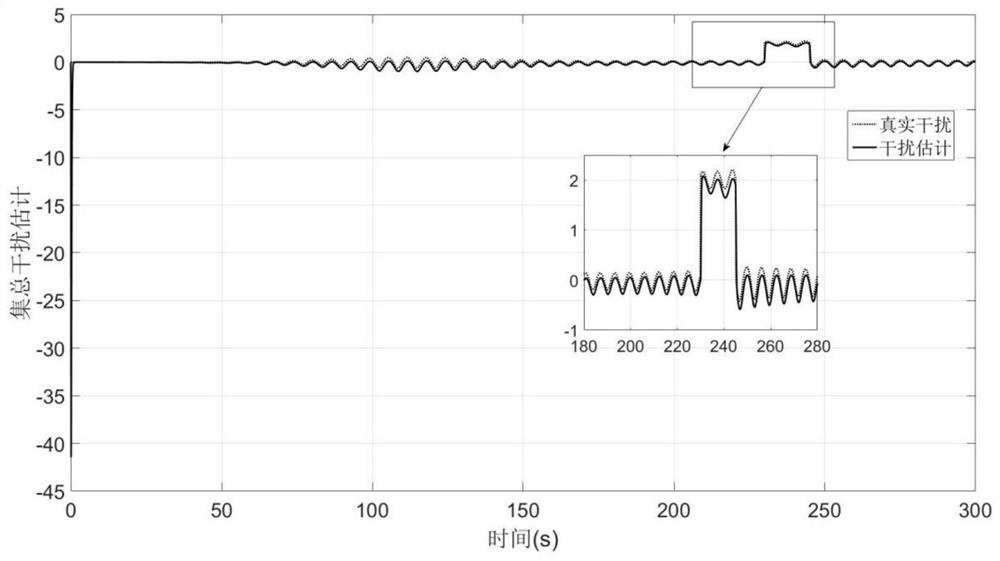
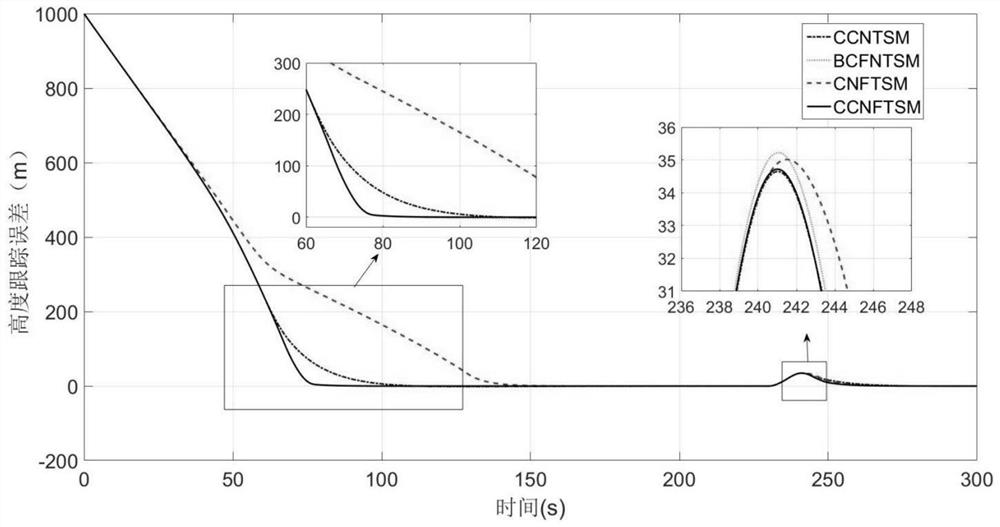
The invention discloses a composite fast non-singular terminal sliding mode control method for an atmospheric entry section of a Mars probe, which specifically includes the following steps: firstly establishing a longitudinal motion dynamic model of the atmospheric entry section of the Mars probe affected by multi-source interference, and establishing a height based on the model The dynamic equation of the command tracking error; secondly, aiming at the dynamics of the altitude command tracking error, an extended state observer is designed to realize the asymptotic estimation of multi-source interference; again, a fast non-singular terminal sliding mode surface is designed based on the altitude tracking error information; finally, the interference estimation information is combined Design a composite fast non-singular terminal sliding mode controller. The invention ensures the continuity of the control quantity, eliminates the chattering phenomenon, has a faster convergence speed, and significantly improves the anti-interference performance of the system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
A Mars Lander Navigation Method for Atmospheric Entry Segment Based on Sampling Point Inheritance Strategy
InactiveCN104266650BHigh state prediction accuracyImprove State Estimation AccuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationCovarianceAtmospheric sciences
A method for the atmospheric entry section navigation of a mars lander based on a sampling point inheritance strategy relates to the technical field of navigation guidance and control, in particular to a method for the atmospheric entry section navigation of the mars lander. The invention aims at solving the problem that the precision is low when the status of the lander is estimated according to the conventional filtering method. The method comprises the following steps: in a filtering beginning cycle, providing a sampling point and a sampling point weight according to sampling point generating rules of unscented Kalman filtering; providing a lander status predicted value x' and a lander status variance Px according to a transmitted sampling point and a generated weight; calculating a measurement predicted value y', a variance Py and a covariance Pxy according to unscented Kalman filtering rules; updating measurement and correcting the estimate value of the lander status; estimating x'<+> and a lander status variance Px<+> according to the lander status, correcting the transmitted sampling point Xi and obtaining the sampling point Xi<+> with the corrected value. The method has higher status estimate precision and is suitable for navigation in the atmospheric entry section of the mars lander.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
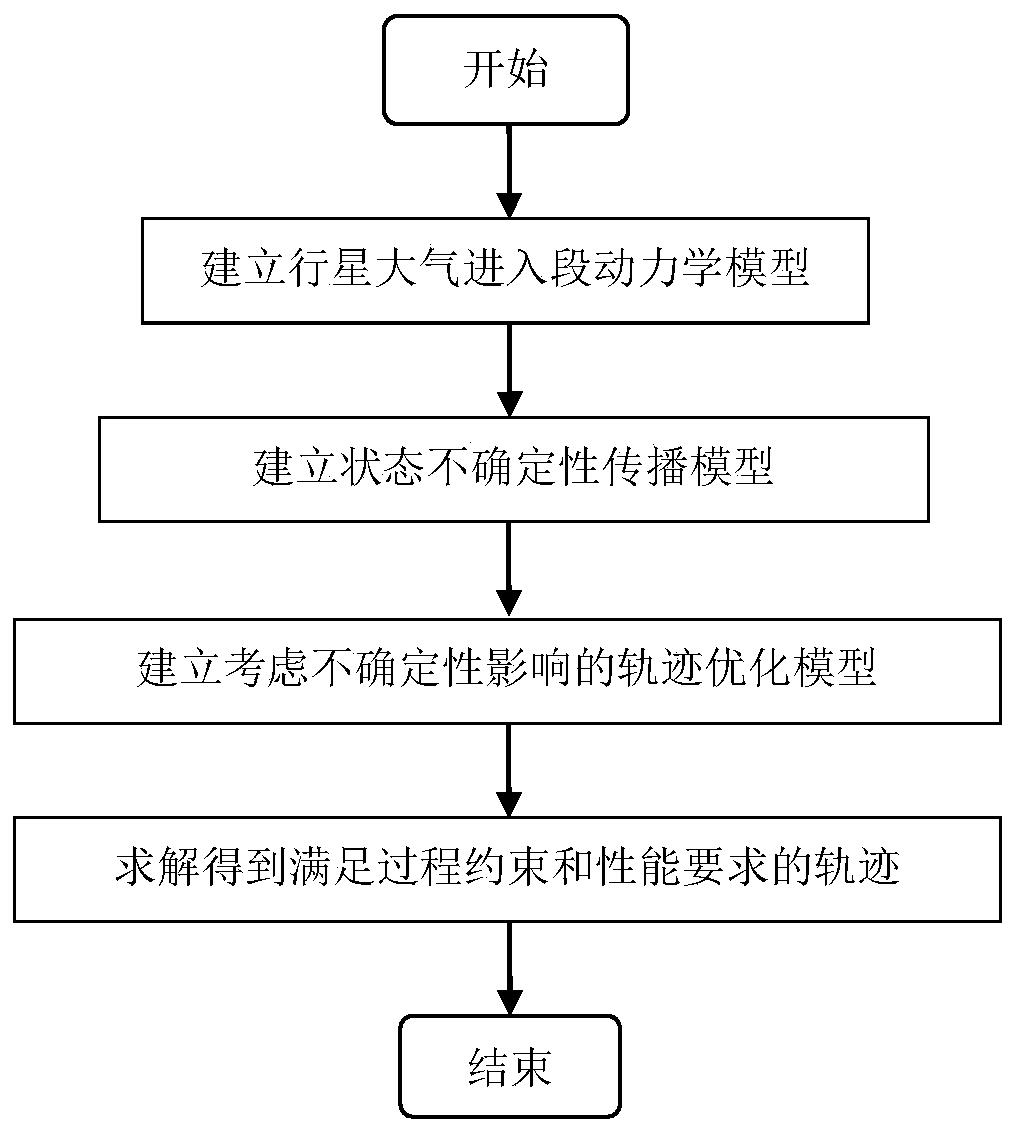
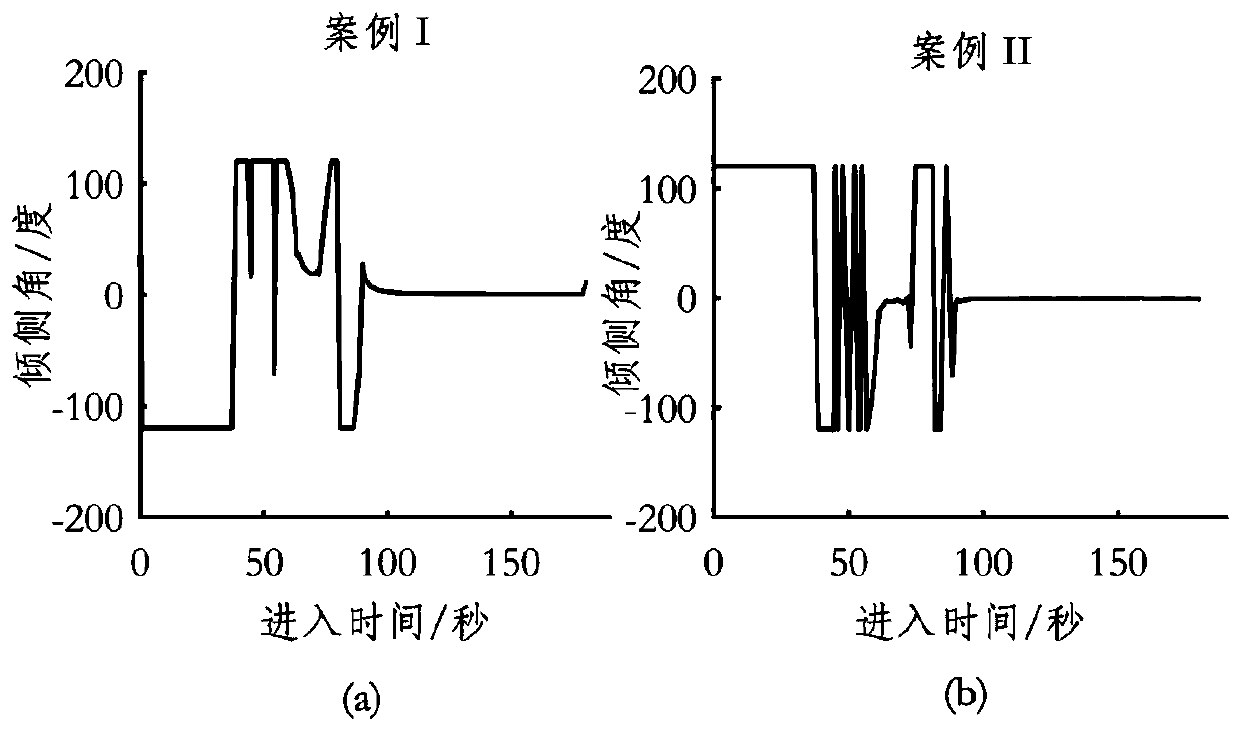
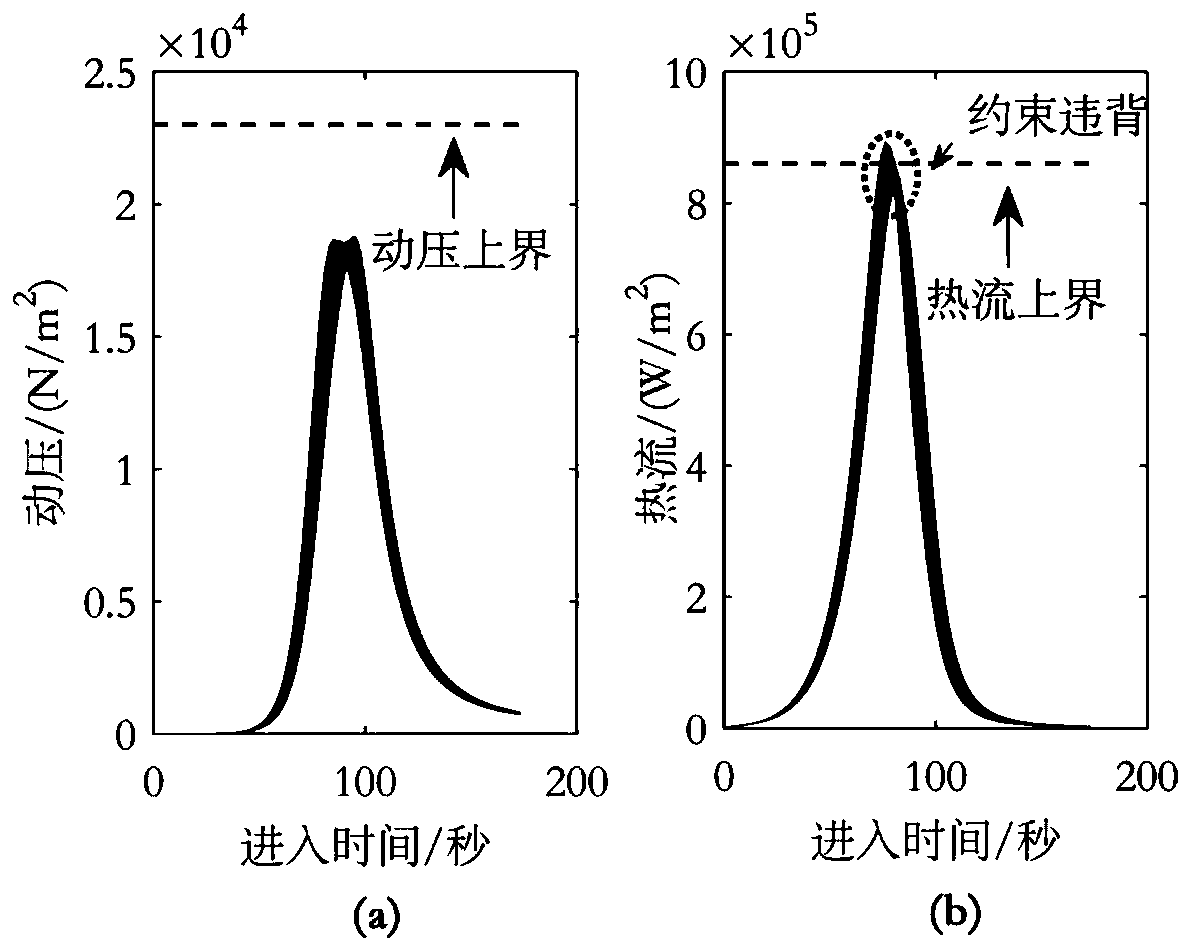
A Trajectory Optimization Method for the Entry Segment of the Martian Atmosphere Considering the Influence of Uncertainties
ActiveCN106295000BReduce the feasible regionReduce the probability of process violationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsDeep space exploration
The invention discloses a Mars atmosphere entrance section trajectory optimization method considering uncertainty effects, relates to Mars atmosphere entrance section trajectory optimization methods, and belongs to the field of deep-space exploration. The implementation method comprises steps as follows: a Mars atmosphere entrance section lander dynamic model is established; a state uncertainty propagation model under effects of uncertainty factors of initial state deviations and parameter modeling deviations is established; a trajectory optimization model considering the uncertainty effects is established, an optimization performance index is reconstructed into the weighed form of the mean value and a standard deviation of an optimized object, the nominal value and the dispersion performance of the optimized object are considered comprehensively, and the trajectory of the optimized object is met by adjusting the weight; besides, process constraint is reconstructed into the weighed form of the mean value and the standard deviation of constraint, the feasible region of the trajectory is reduced reasonably, the process violation probability of a lander when the lander flights in an uncertainty environment is decreased, and the flight safety is improved. The method is applicable to Mars atmosphere entrance section trajectory optimization in the field of deep-space exploration.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Optimal Tracking and Guidance Method for Martian Atmosphere Entry Trajectory
ActiveCN109250153BFor quadratic programming problemsImprove solution efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusDynamic modelsInterior point method
The invention discloses an optimal trajectory tracking guidance method for Mars atmospheric entry phase, belonging to the field of deep space exploration. The realization method of the invention comprises the follow steps: (1) establishing a longitudinal dynamic model of a Mars atmospheric entry stage probe; (2), performing convexification processing on the path constraint and the control constraint, and selecting the quadratic performance index to establish a trajectory optimal trajectory tracking problem model; (3), discretizing that trajectory optimal tracking problem model in the step (2),converting the model into a quadratic programming problem, so that the problem can be solved in polynomial time by an interior point method, the discretized quadratic programming problem can be solved by a numerical method, the solution efficiency is improved, and the real-time online guidance of the Martian atmosphere entry section is realized. The invention converts the trajectory tracking guidance problem into an optimal control problem for solving, and the parachute opening accuracy can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
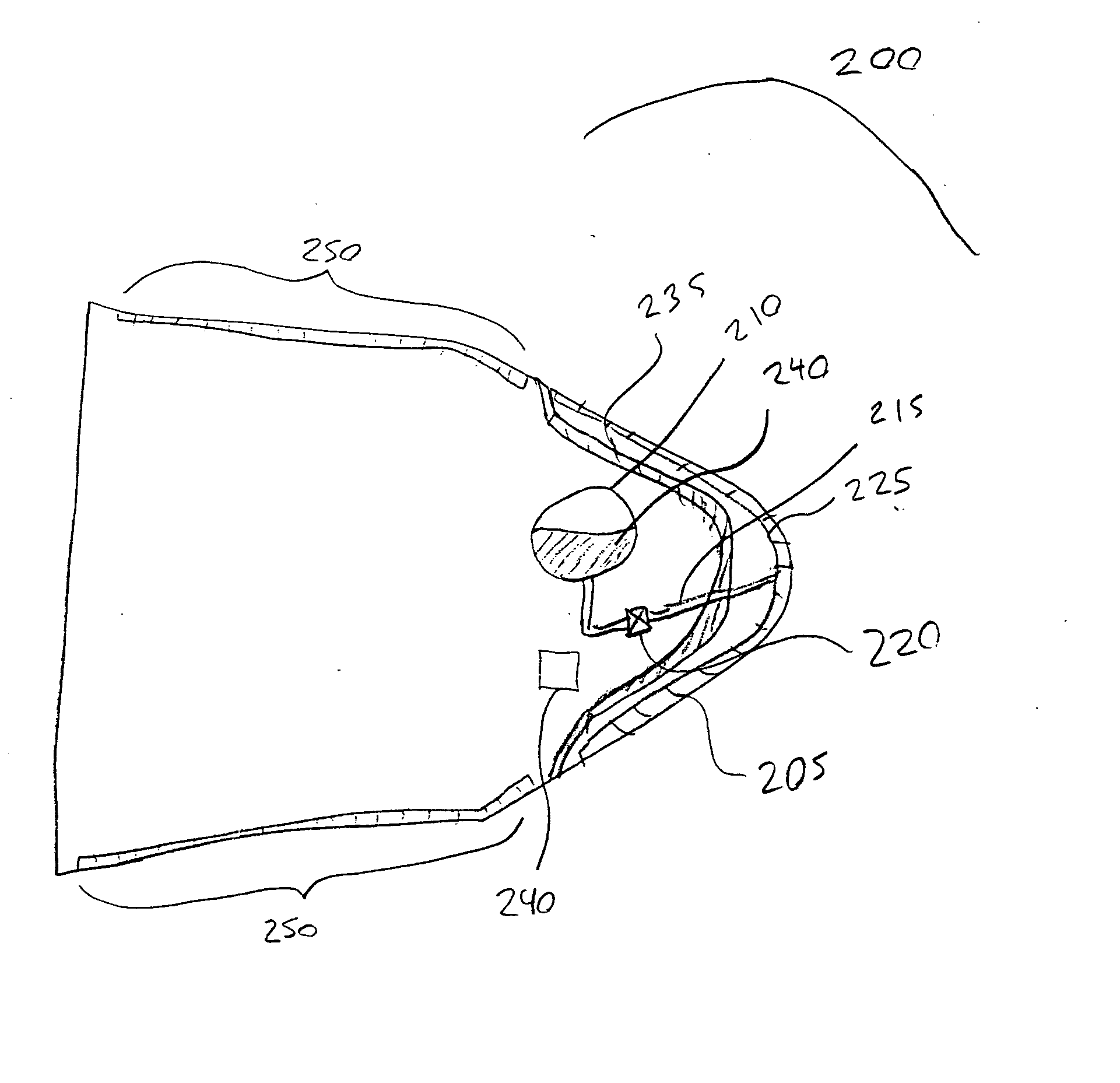
Systems and methods for autonomous deorbit of spacecraft
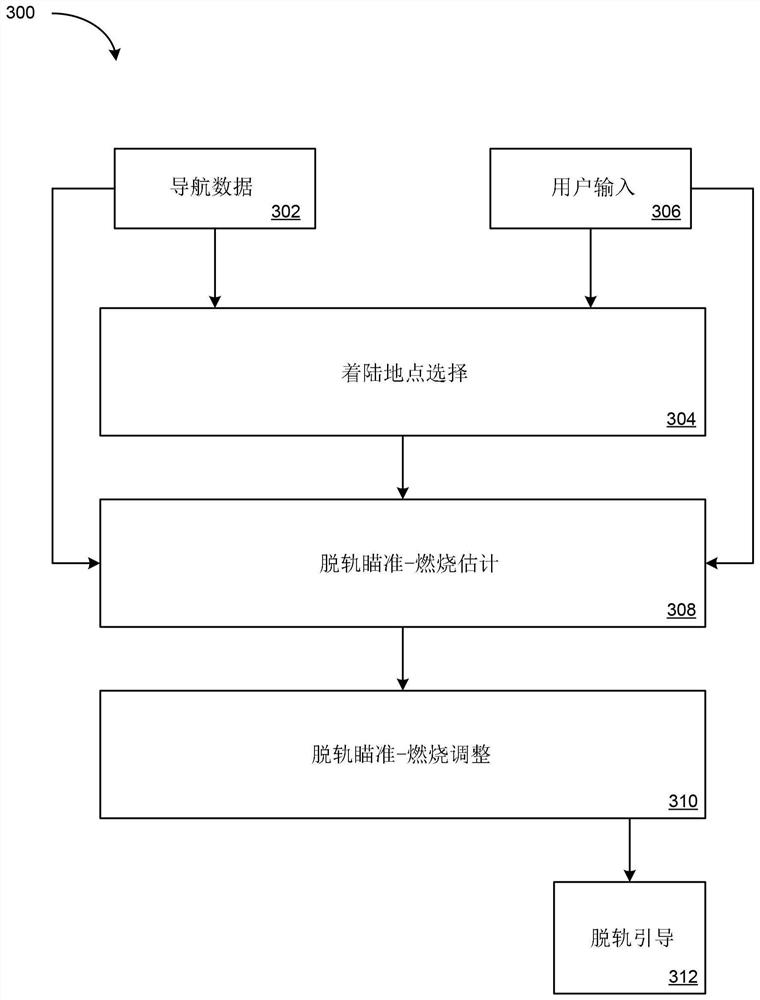
PendingCN112441260ACosmonautic vehiclesSystems for re-entry to earthClassical mechanicsAtmospheric entry
The invention relates to a system and a method for autonomous deorbital of a spacecraft. In an example, a method for deorbiting a spacecraft is described. The method includes selecting a target landing site for deorbiting the spacecraft. The method includes determining a range target and a velocity target for reaching a predicted atmospheric entry location. The method includes determining a back-propagated orbit state estimate of the spacecraft. The method includes comparing the back-propagated orbit state estimate to a known orbit state of the spacecraft to determine that the back-propagatedorbit state estimate has converged with the known orbit state. The method includes calculating based on determining that the back-propagated orbit state estimate has converged with the known orbit state, (a) an estimated time of ignition for a propulsion system of the spacecraft and (b) an estimated burn velocity vector of the propulsion system using the range target and the velocity target. The method includes performing a burn pulse by the propulsion system.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com