Patents
Literature
36 results about "Effective stiffness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Effective stiffness is a function of the applied loading and detailing of the component. Reinforced concrete components behave differently under different loading conditions (e.g. tension, compression, flexure), as well as different rates of loading (impact, short term, long term).
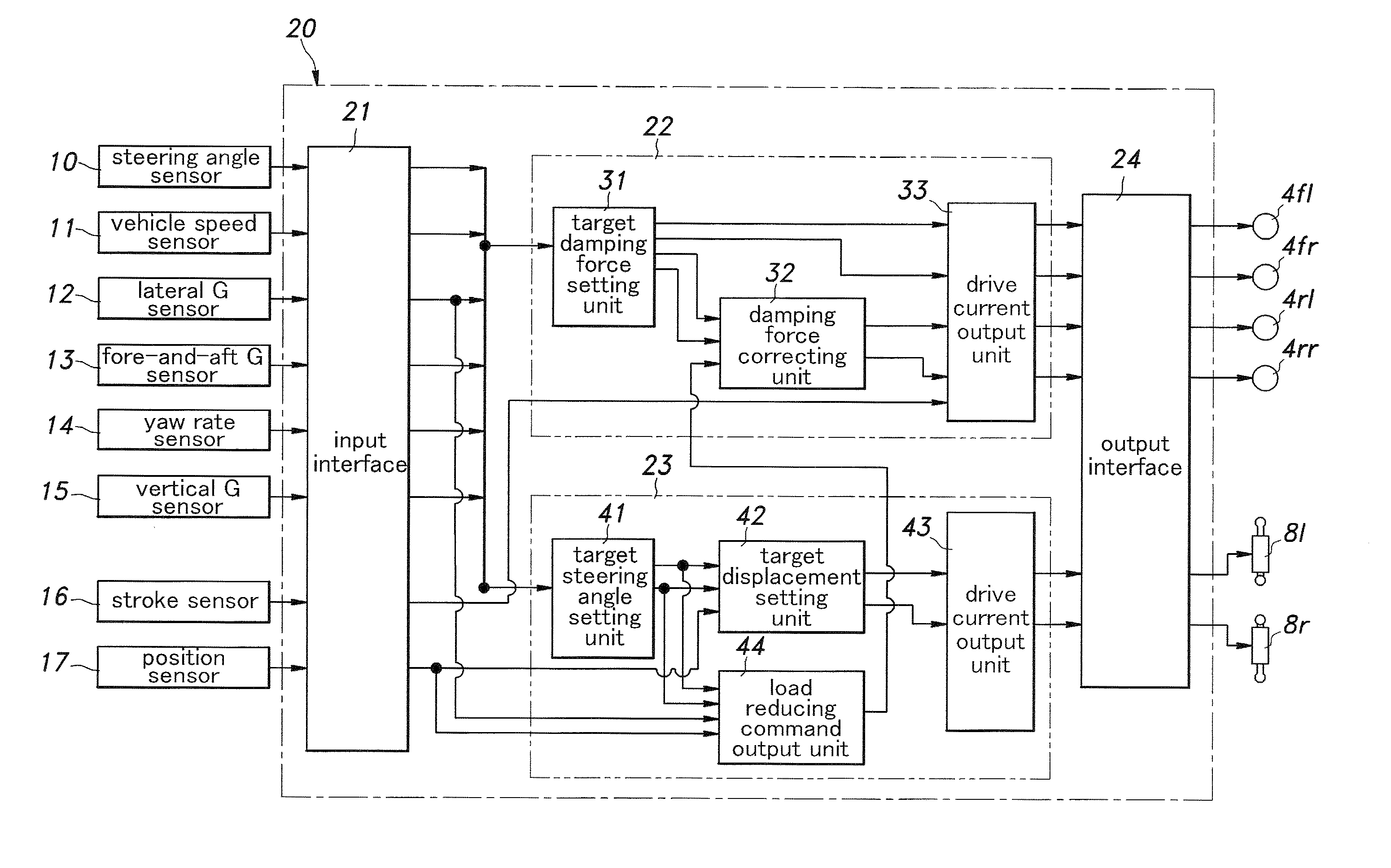
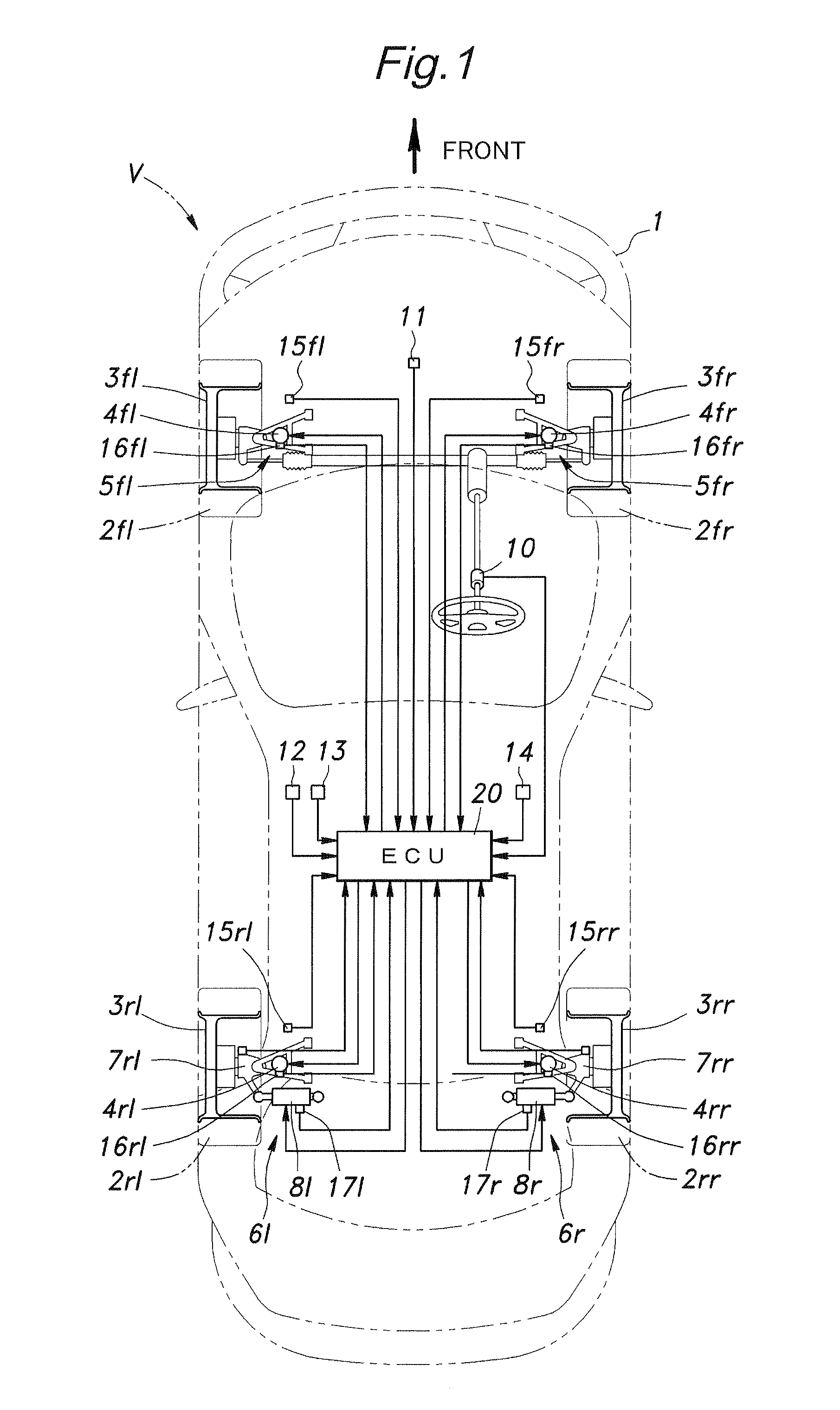
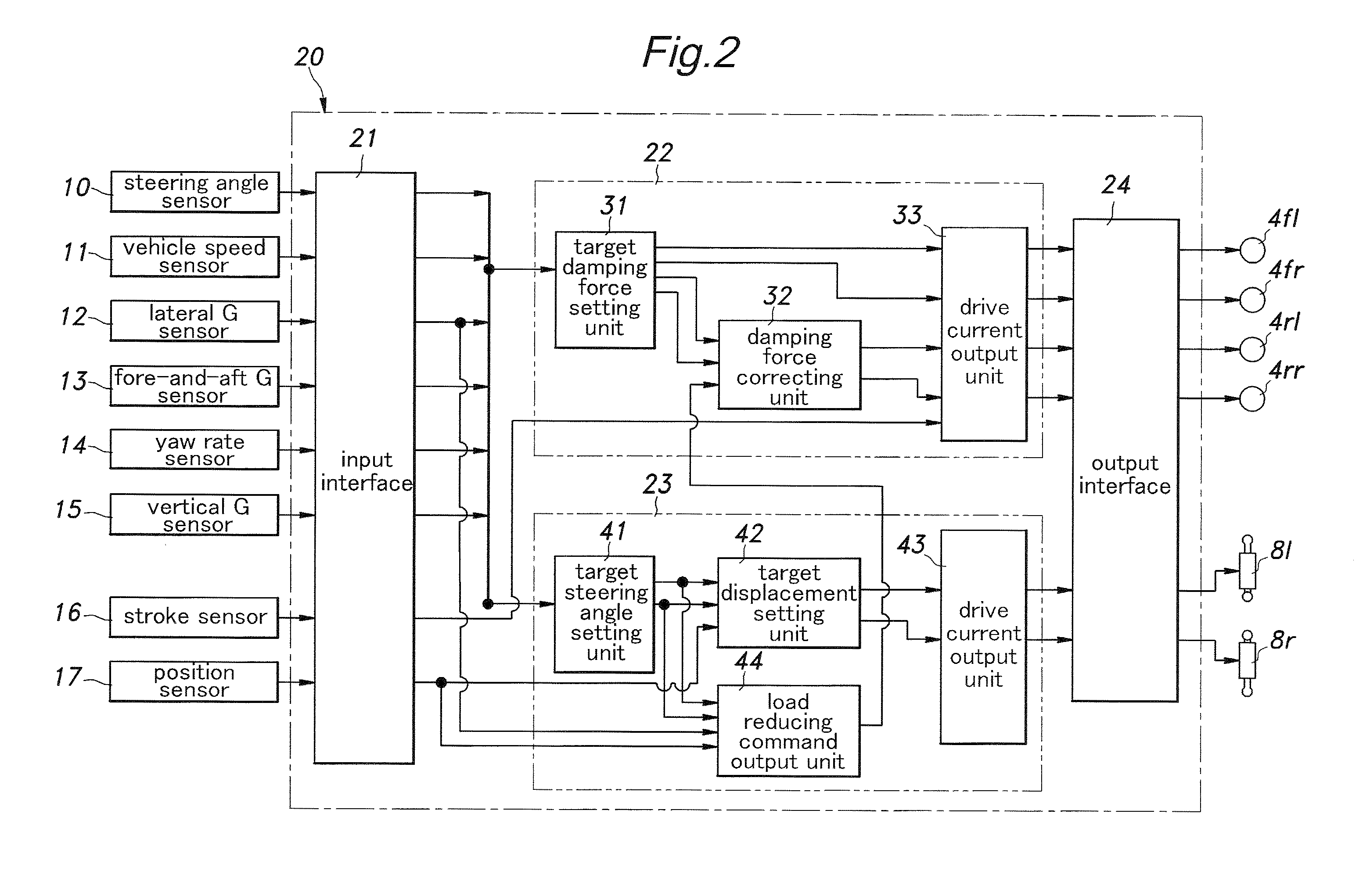
Vehicle behavior control system
InactiveUS20100211261A1High response rateReduced torque outputDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesBehavior controlVehicle behavior
Provide is a vehicle behavior control system that can achieve a rear wheel steering control demonstrating a high rate of response at all times without requiring the actuator for the rear wheels to be steered to be unduly increased. A control unit (20) for controlling the rear wheel steering angle is configured to reduce the effective stiffness of the rear wheel suspension systems while increasing the effective stiffness of the front wheel suspension systems when an increase in the road contact load of one of the rear wheels is detected or estimated. Thereby, an actuator (8) for the rear wheel is enabled to steering the rear wheels without involving any undue time delay with a minimum power requirement.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
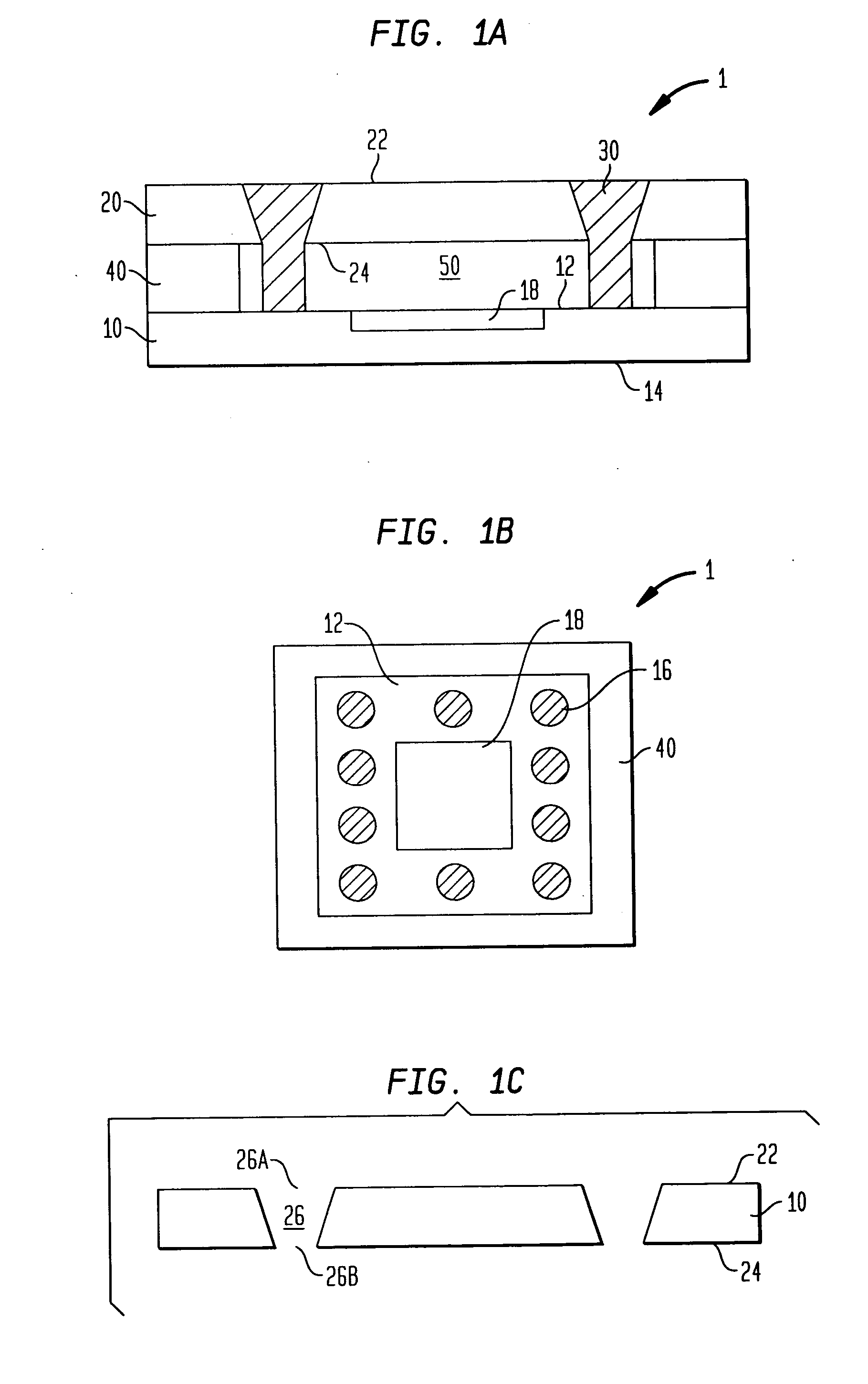
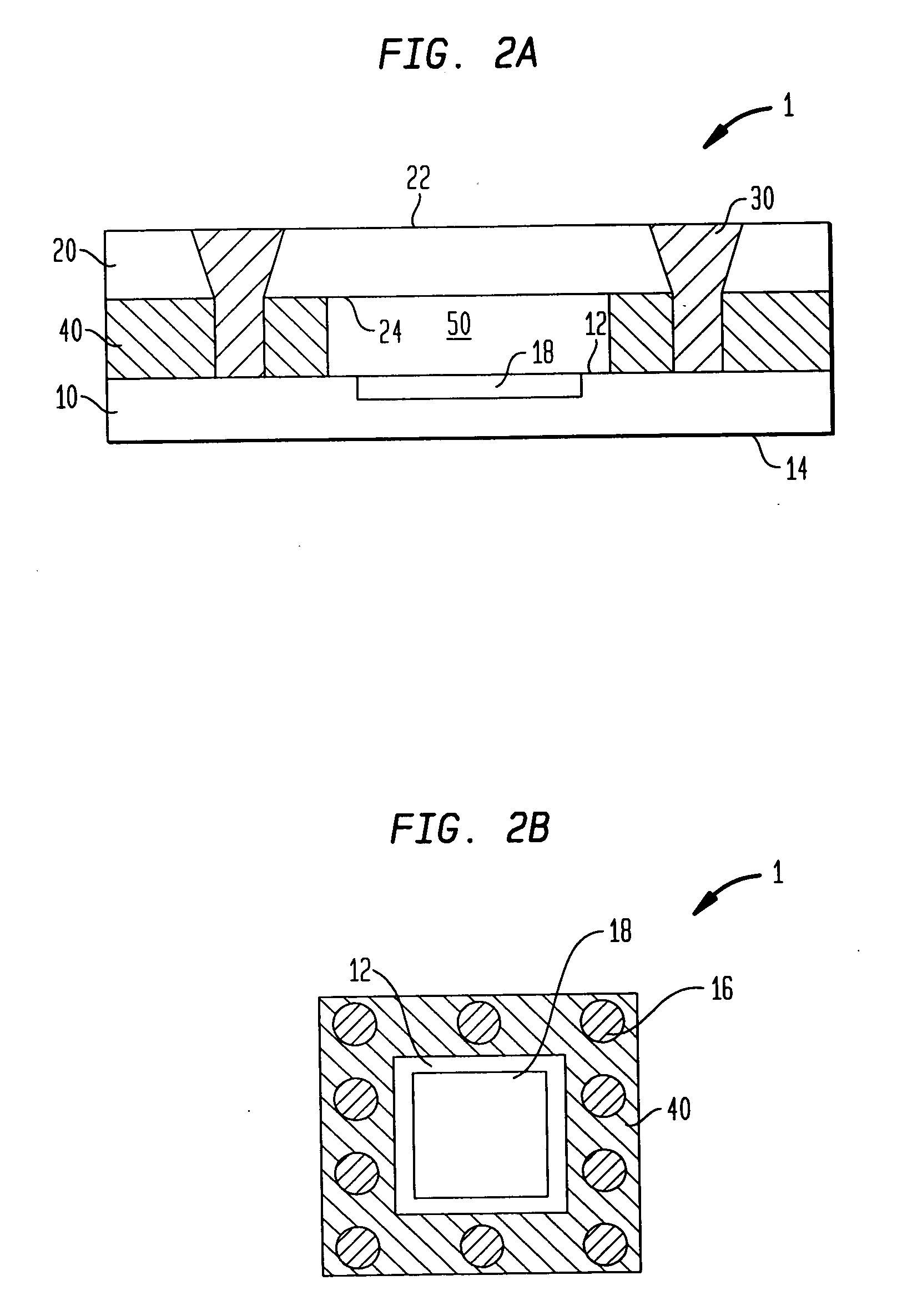
Microelectronic package optionally having differing cover and device thermal expansivities
InactiveUS20070042527A1Different coefficientEffective stiffnessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal expansionElectronic packaging
A microelectronic package is provided that includes a microelectronic device and a cover. The device and the cover are typically substantially immobilized relative to each other. The cover typically has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion while the device has a higher effective stiffness. The package may be formed in wafer-level processes.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Noise isolating underlayment
ActiveUS20080236097A1Improve performanceImproved impact noise isolating propertyConstruction materialCovering/liningsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
A noise-reducing substrate for use in a flooring system, the flooring system having a subfloor and a decorative upper layer. The substrate comprises a series of edge butted panels, each of which has a bottom surface, a top surface and side surfaces. Each panel's top surface and oppositely facing bottom surface are parallel to each other and are spaced apart by the thickness of the substrate. A profile in the bottom surface of the substrate changes the substrate's effective stiffness and improves the noise isolation of the substrate compared to the stiffness and noise isolation of the panel without the profile. Additionally, the profile reduces the weight of the panel, thereby reducing manufacturing and installation costs. When the substrate is positioned between the subfloor and the decorative top layer, the material hardness and the flat profile of the upper surface provide a platform with the strength and texture required to allow for installation of the decorative floor layer without the need for an additional rigid backing material. Such a system greatly improves the impact noise reduction on a variety of floor / ceiling systems while keeping the installation cost low and the adding very little to the total system thickness.
Owner:PACIFIC COAST BUILDING PRODS
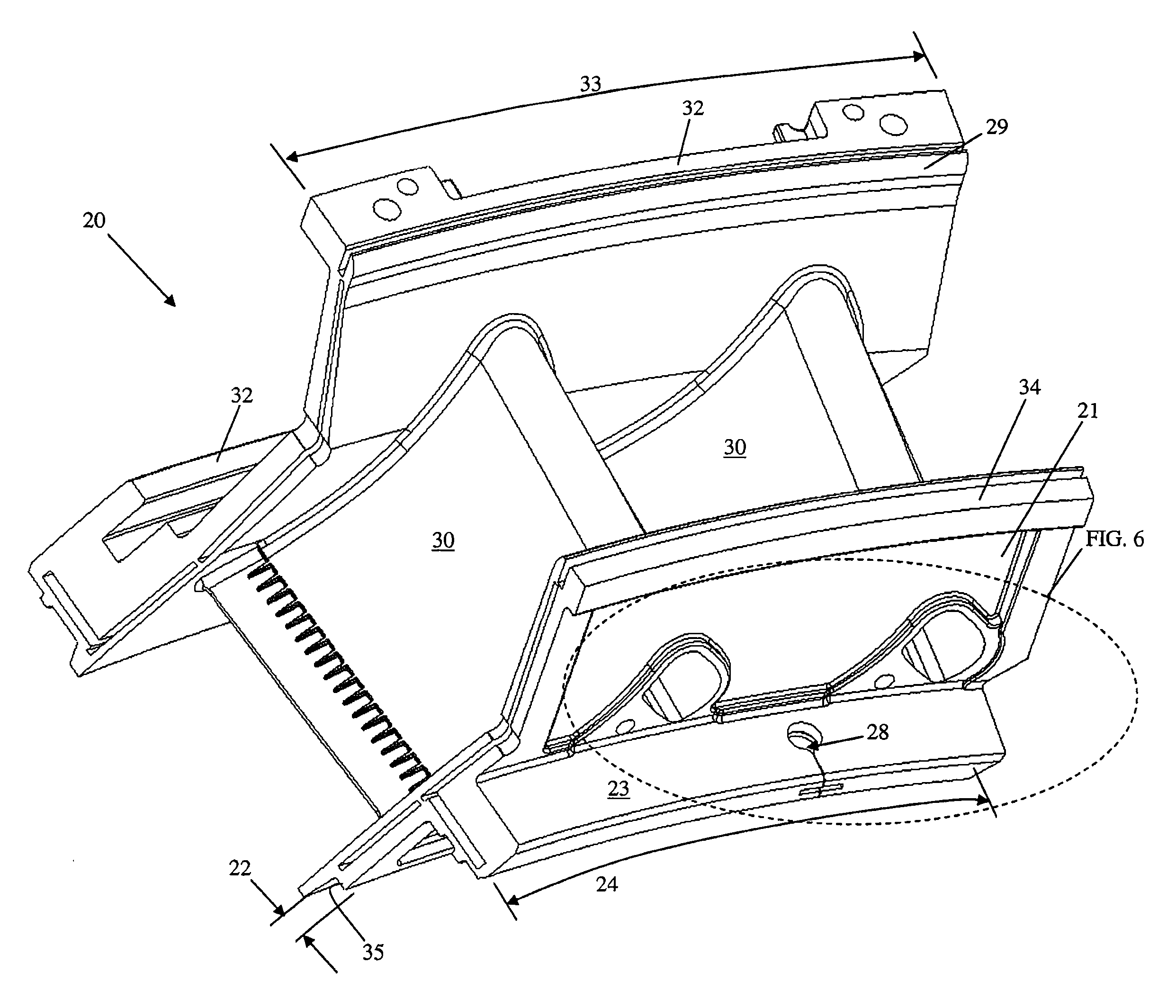
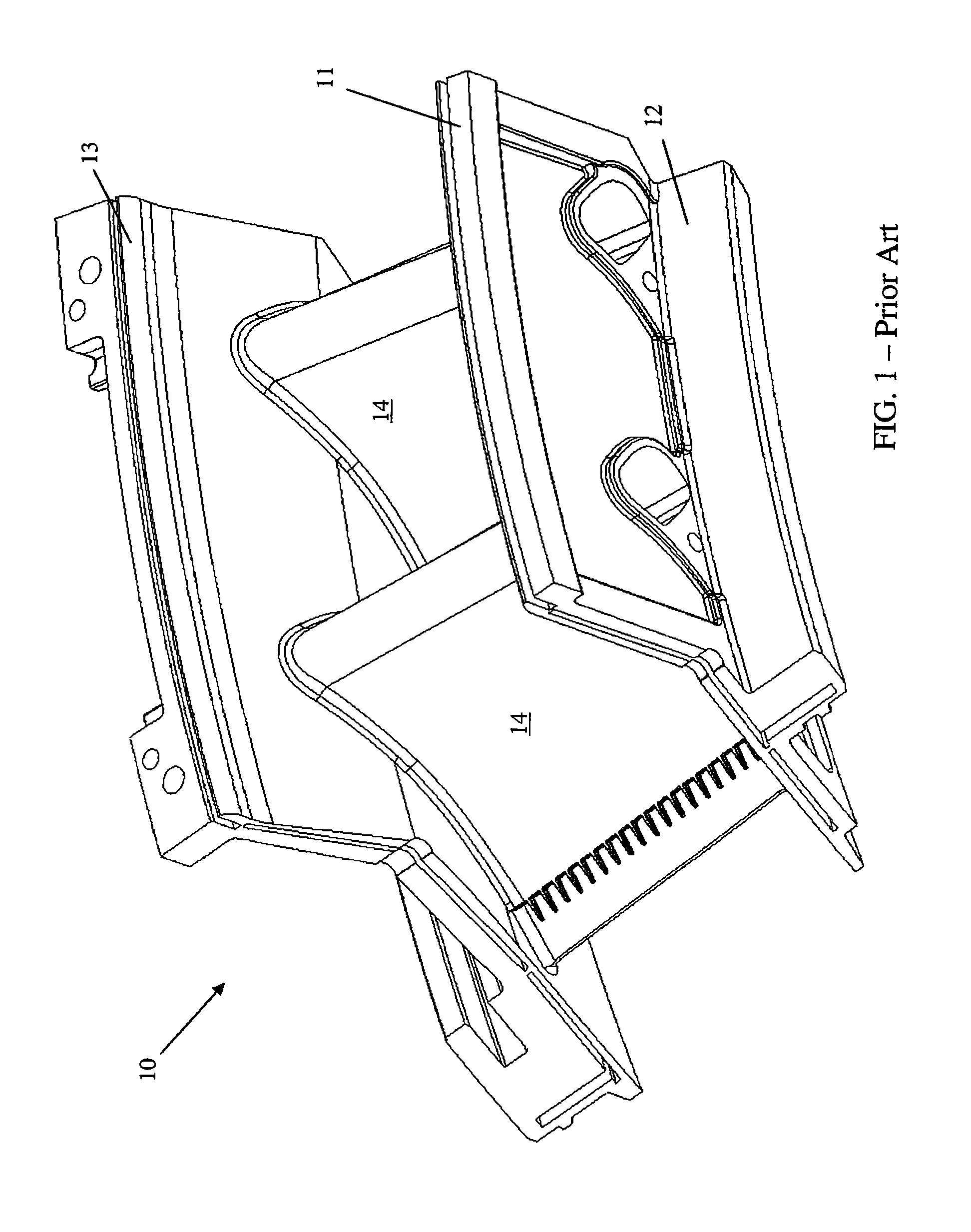
Vane platform rail configuration for reduced airfoil stress
ActiveUS20060013685A1Lower thermally induced stressImproved component durabilityPump componentsEngine fuctionsEngineeringGas turbines
A vane assembly for a gas turbine engine is disclosed having lower thermally induced stresses resulting in improved component durability. The stresses in the vane assembly airfoils are lowered by increasing the flexibility of the vane platform and reducing their resistance to thermal deflection. This is accomplished by placing an opening along the vane assembly rail that reduces the effective stiffness of the platform, thereby lowering the operating stresses in the airfoils of the vane assembly. A removable seal is then placed in the opening in order to prevent undesired leakages, while maintaining the benefit of the increased platform flexibility.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
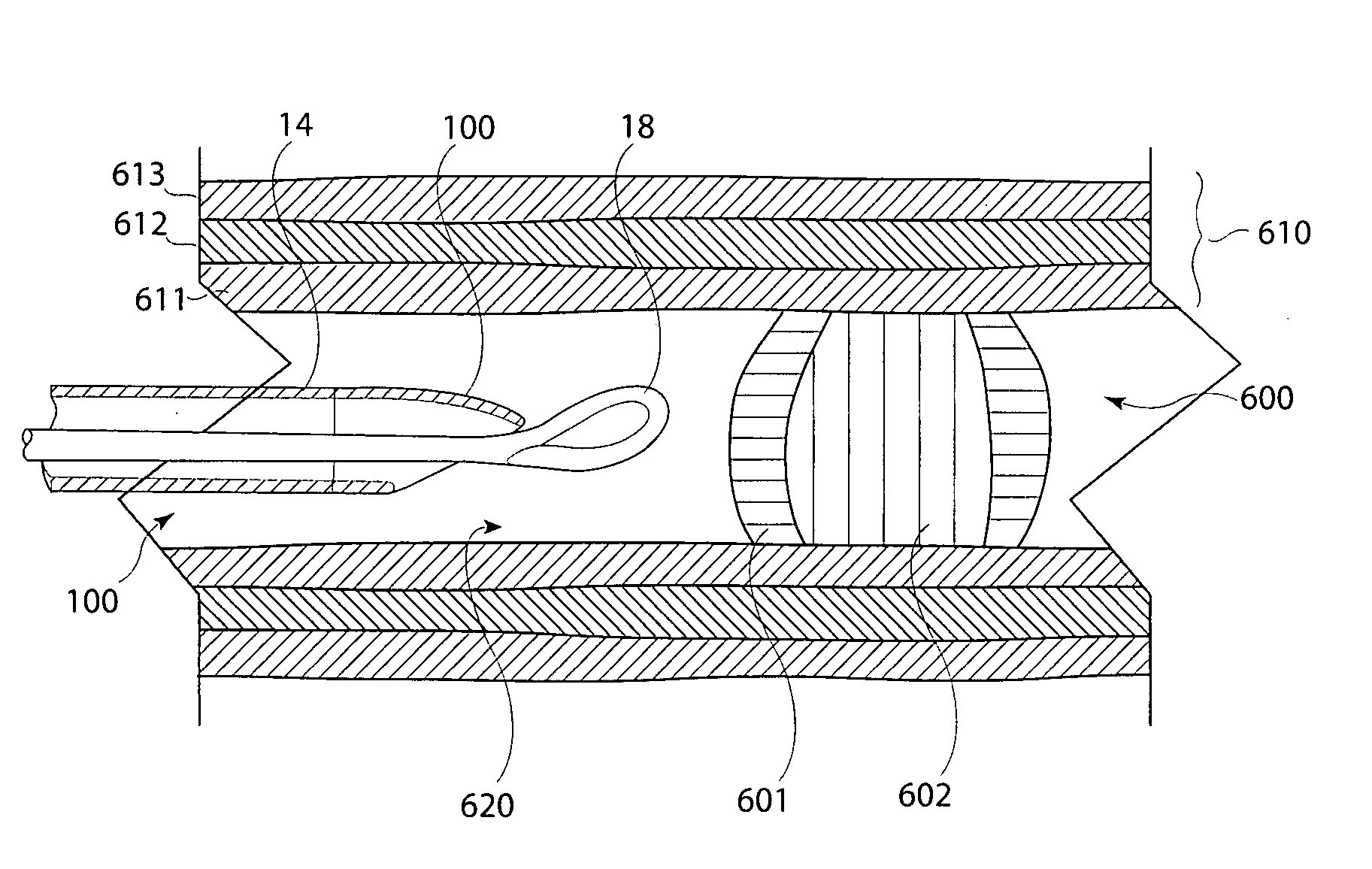
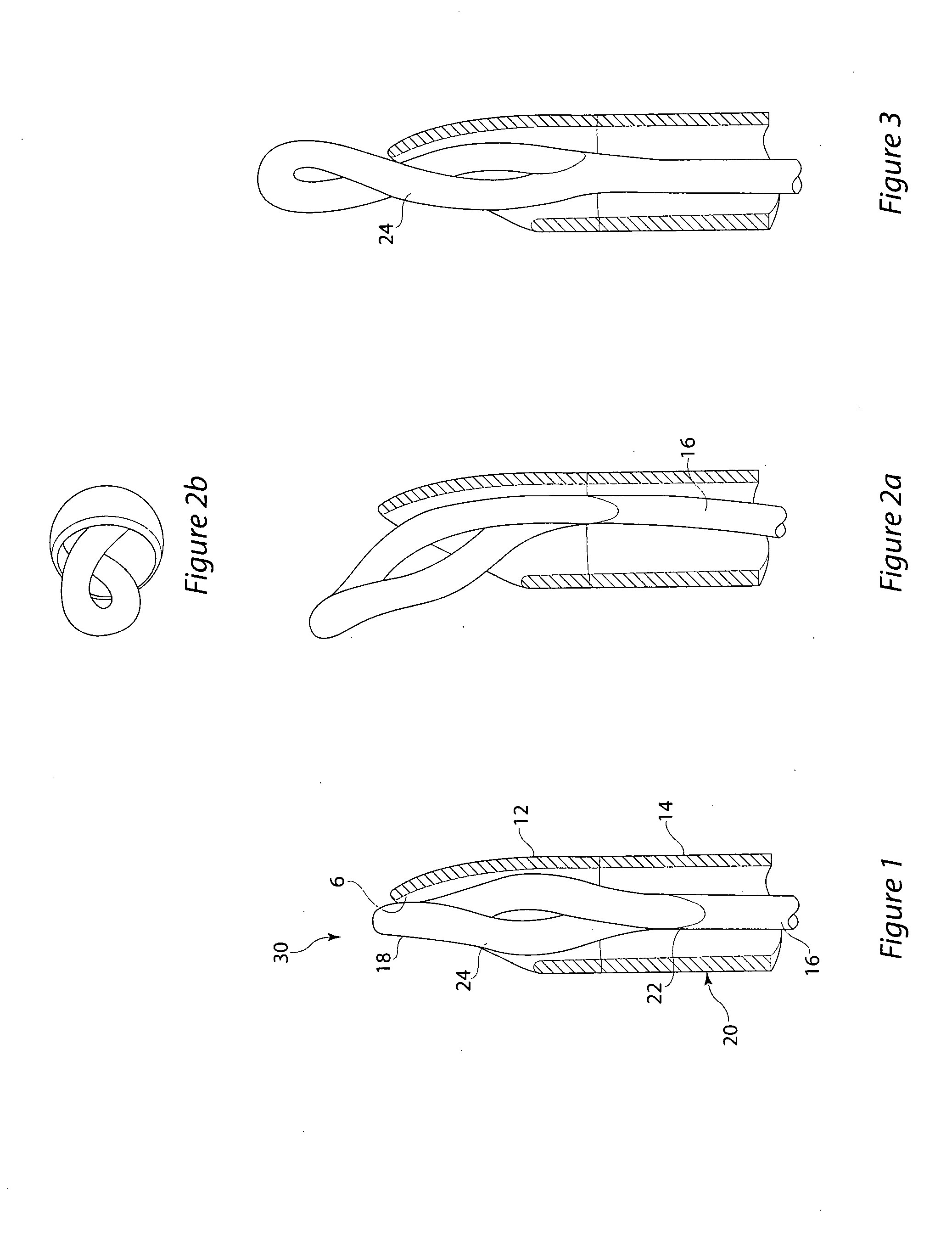
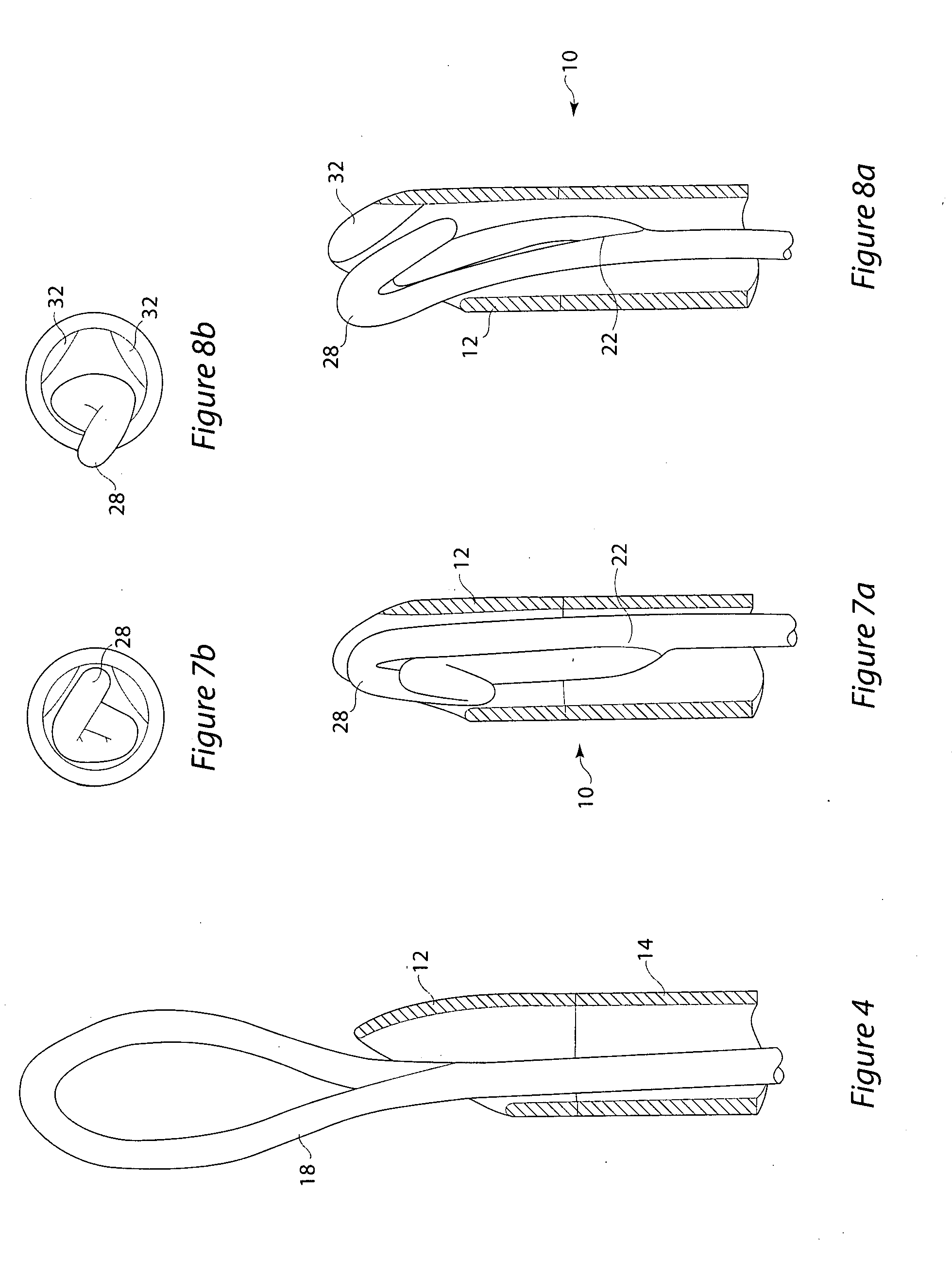
Chronic total occlusion (CTO) removal device
InactiveUS20090093829A1Increase effective stiffnessReduce stiffnessCannulasExcision instrumentsTotal occlusionThree vessels
There is disclosed a device for removing chronic total occlusions (CTO) from blood vessels or other body lumens. In one embodiment the device has a loop at a distal end connected by a shaft to a proximal end. The shaft is provided inside a catheter that has an opening at the distal end and a handle at the proximal end. By manipulating the position of the loop relative to the opening, the effective stiffness of the loop may be changed. This allows a physician to vary the loop stiffness so as to be appropriate with regard to the toughness of a CTO (some CTOs have a relatively tough exterior but a relatively soft interior). The loop may have a single turn or may comprise two or more turns.
Owner:COOK INC
Vane platform rail configuration for reduced airfoil stress
ActiveUS7293957B2Reduce stressReduced resistance to thermal deflectionPump componentsEngine fuctionsEngineeringGas turbines
A vane assembly for a gas turbine engine is disclosed having lower thermally induced stresses resulting in improved component durability. The stresses in the vane assembly airfoils are lowered by increasing the flexibility of the vane platform and reducing its resistance to thermal deflection. This is accomplished by placing an opening along the innermost vane assembly rail that reduces the effective stiffness of the platform, thereby lowering the operating stresses in the airfoils of the vane assembly. A removable seal is then placed in the opening in order to prevent undesired leakages, while maintaining the benefit of the increased platform flexibility.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
Vane platform rail configuration for reduced airfoil stress
ActiveUS7229245B2Reduce stressIncrease flexibilityPump componentsEngine fuctionsEngineeringGas turbines
A vane assembly for a gas turbine engine is disclosed having lower thermally induced stresses resulting in improved component durability. The stresses in the vane assembly airfoils are lowered by increasing the flexibility of the vane platform and reducing their resistance to thermal deflection. This is accomplished by placing an opening along the vane assembly rail that reduces the effective stiffness of the platform, thereby lowering the operating stresses in the airfoils of the vane assembly. A removable seal is then placed in the opening in order to prevent undesired leakages, while maintaining the benefit of the increased platform flexibility.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
Noise isolating underlayment
ActiveUS7987645B2Improve performanceImproved impact noise isolating propertyConstruction materialCovering/liningsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
A noise-reducing substrate for use in a flooring system which ha a subfloor and a floating floor upper layer. The substrate comprises a series of edge butted panels, each having a bottom surface, a top surface and side surfaces. A profile in the bottom surface of the substrate changes the substrate's effective stiffness improving the noise isolation of the substrate compared to the stiffness and noise isolation of the panel without the profile. Additionally, the profile reduces the weight of the panel, thereby reducing manufacturing and installation costs. Material hardness and profile flatness of the upper surface provide the strength and texture required to allow for installation of the floating floor layer without the need for an additional rigid backing material. Such a system greatly improves the impact noise reduction on floor / ceiling systems while keeping the installation cost low and adding little to the total system thickness.
Owner:PACIFIC COAST BUILDING PRODS
Vane platform rail configuration for reduced airfoil stress
ActiveUS20070166154A1Lower thermally induced stressImproved component durabilityPump componentsEngine fuctionsEngineeringGas turbines
A vane assembly for a gas turbine engine is disclosed having lower thermally induced stresses resulting in improved component durability. The stresses in the vane assembly airfoils are lowered by increasing the flexibility of the vane platform and reducing its resistance to thermal deflection. This is accomplished by placing an opening along the innermost vane assembly rail that reduces the effective stiffness of the platform, thereby lowering the operating stresses in the airfoils of the vane assembly. A removable seal is then placed in the opening in order to prevent undesired leakages, while maintaining the benefit of the increased platform flexibility.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
Microelectronic package optionally having differing cover and device thermal expansivities
InactiveUS7485956B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal expansionBiomedical engineering
A microelectronic package is provided that includes a microelectronic device and a cover. The device and the cover are typically substantially immobilized relative to each other. The cover typically has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion while the device has a higher effective stiffness. The package may be formed in wafer-level processes.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Torsional coupling
InactiveUS7335107B2Increase effective stiffnessIncrease rotation speedYielding couplingFluid couplingsCouplingRotation velocity
A torsional coupling includes a body having a circumference and defining a center axis. The body is rotatable about the center axis. The coupling also includes a ring including an inner diameter disposed about the circumference. The ring includes a ring contact surface having a first radius and the ring is configured to rotate about the center axis. A coupling element is associated with the body and is configured to apply a centrifugal force radially outwardly from the circumference of the body when the body rotates. The coupling element includes a coupling element contact surface having a second radius which is different than the first radius of the ring contact surface. The coupling element contact surface is in contact with the ring contact surface and is configured to apply a force against the ring contact surface to rotate the ring relative to the body and increase the effective stiffness of the torsional coupling as the rotational speed of the body increases.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Adjustable tine leaf rake
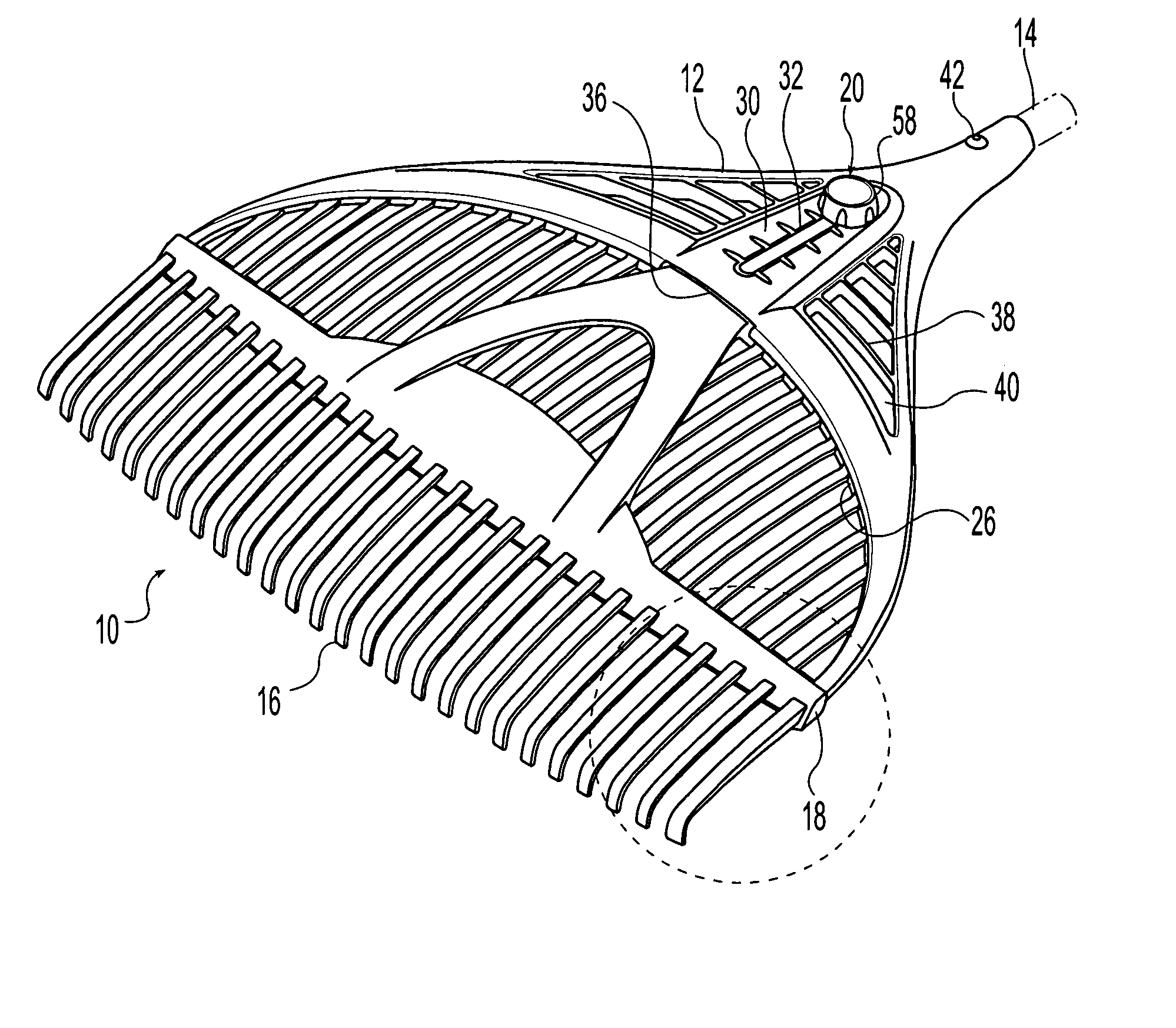
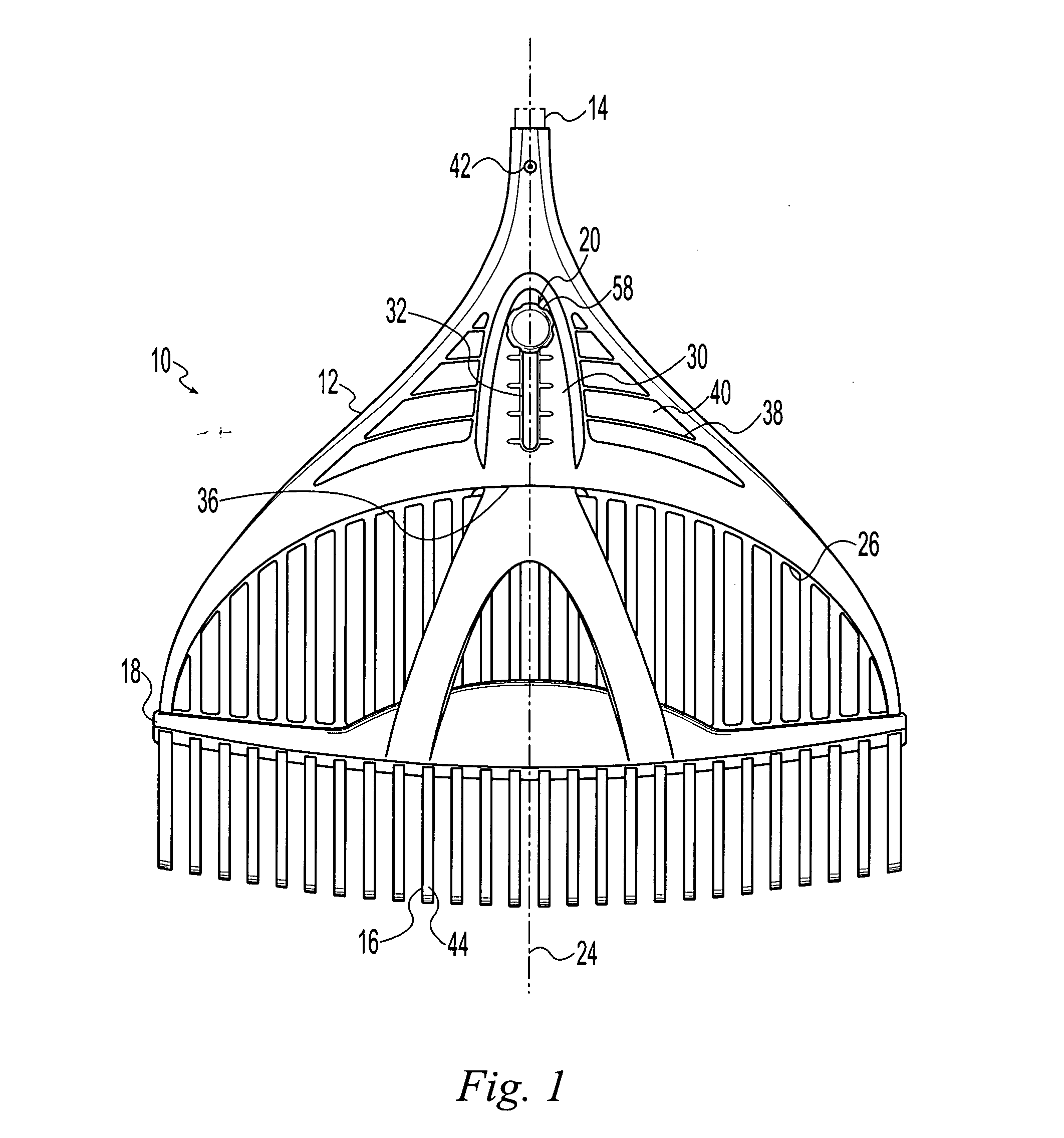
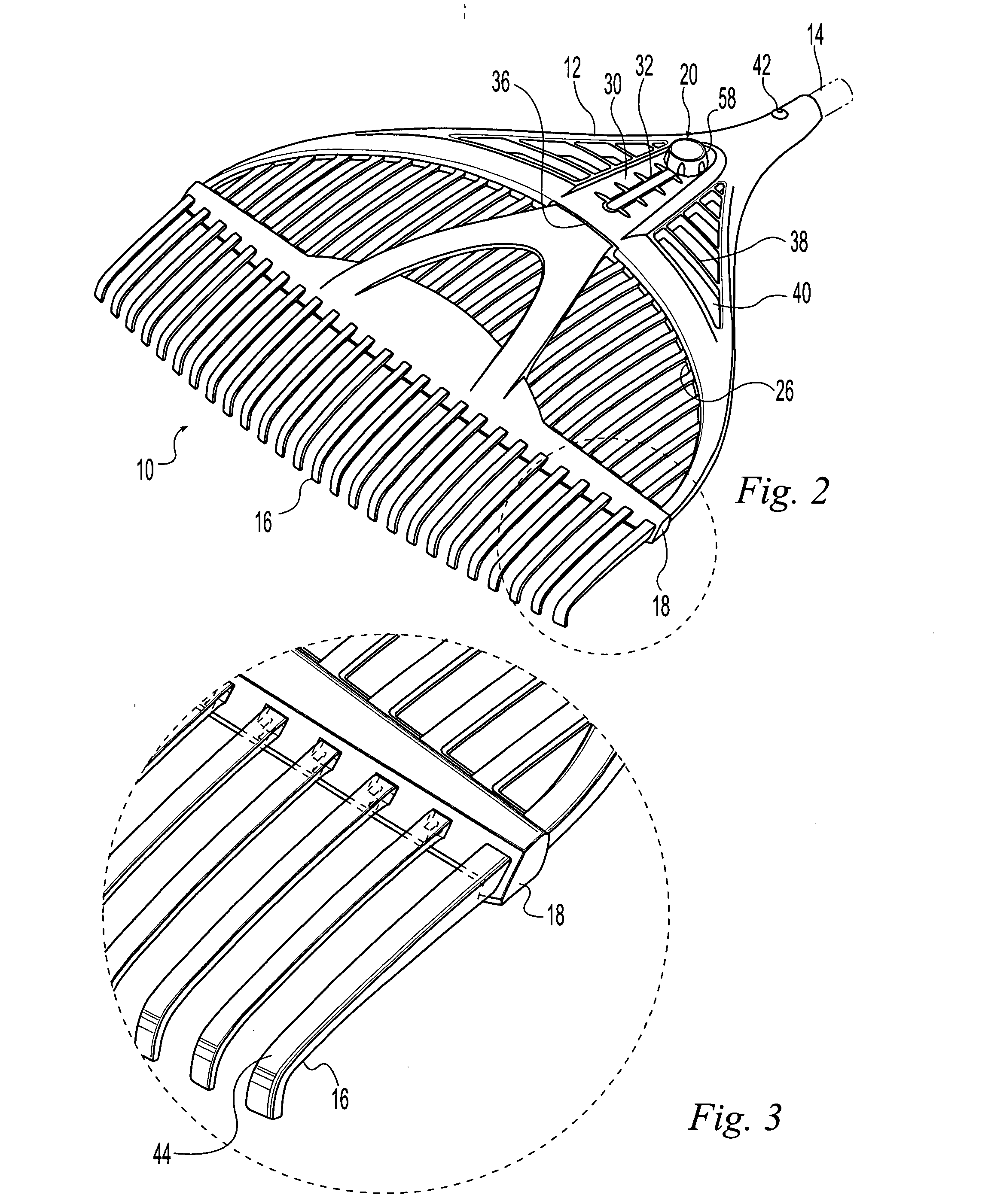
InactiveUS20050188671A1Improve business performanceQuality improvementRakesRange of motionEffective length
A rake including a head, an elongate handle extending from the head, and a plurality of parallel, spaced-apart, flexible tines extending from the head opposite the handle. A brace is movable along the tines between first and second positions and limits a range of motion of the tines to change the effective length and thus the effective stiffness of the flexible tines. A locking device releasably secures the brace to the head in the first and second positions and preferably at locations between the first and second positions. Spacing between the tines remains unchanged as the brace moves between the first and second positions. The handle extends past the head to the tines improving stiffness of the head so that the rake is lightweight with a low profile.
Owner:AMES TRUE TEMPER
Torsional coupling
InactiveUS20060046859A1Increase effective stiffnessIncrease rotation speedYielding couplingFluid couplingsCouplingEngineering
A torsional coupling includes a body having a circumference and defining a center axis. The body is rotatable about the center axis. The coupling also includes a ring including an inner diameter disposed about the circumference. The ring includes a ring contact surface having a first radius and the ring is configured to rotate about the center axis. A coupling element is associated with the body and is configured to apply a centrifugal force radially outwardly from the circumference of the body when the body rotates. The coupling element includes a coupling element contact surface having a second radius which is different than the first radius of the ring contact surface. The coupling element contact surface is in contact with the ring contact surface and is configured to apply a force against the ring contact surface to rotate the ring relative to the body and increase the effective stiffness of the torsional coupling as the rotational speed of the body increases.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
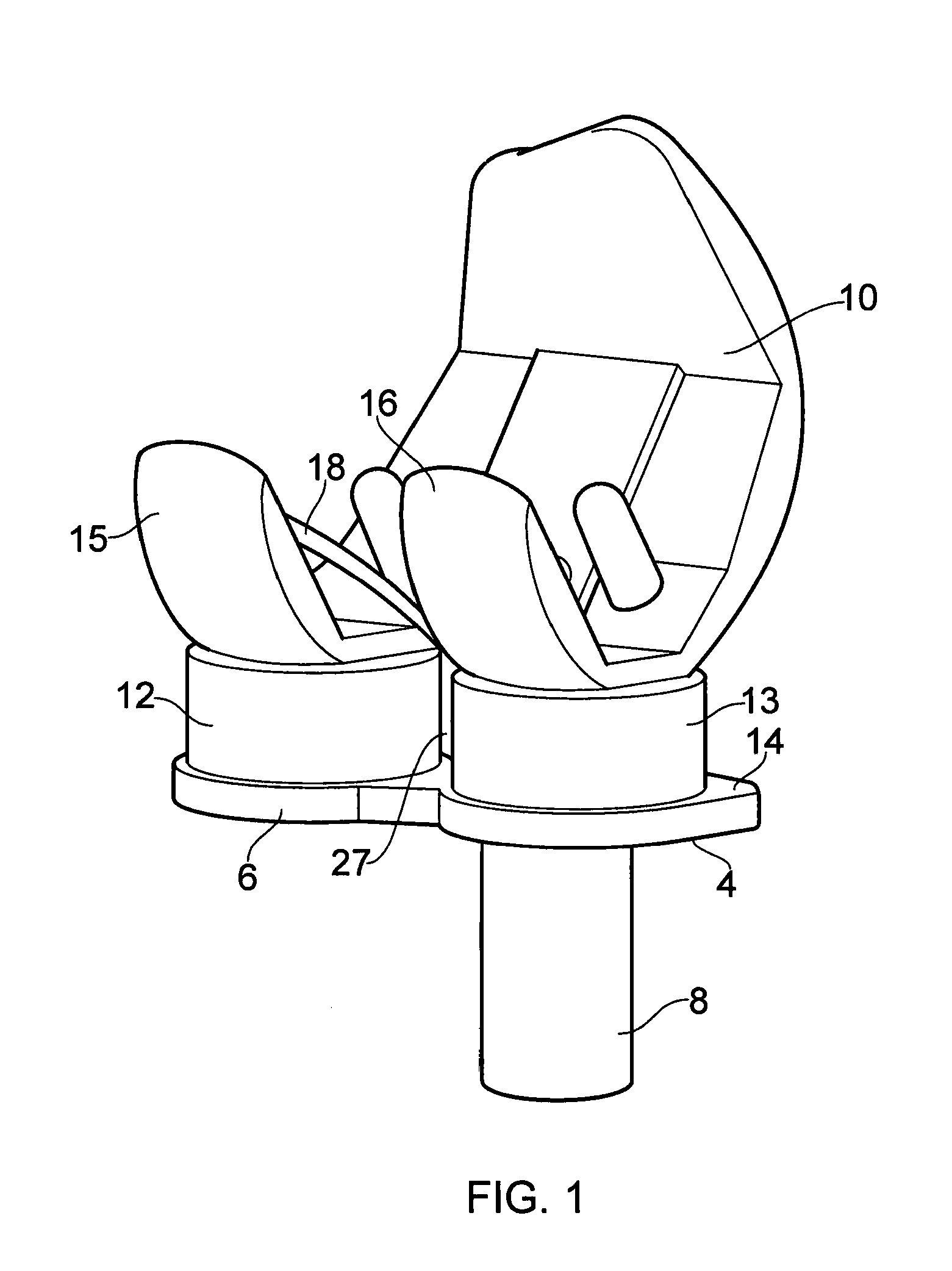
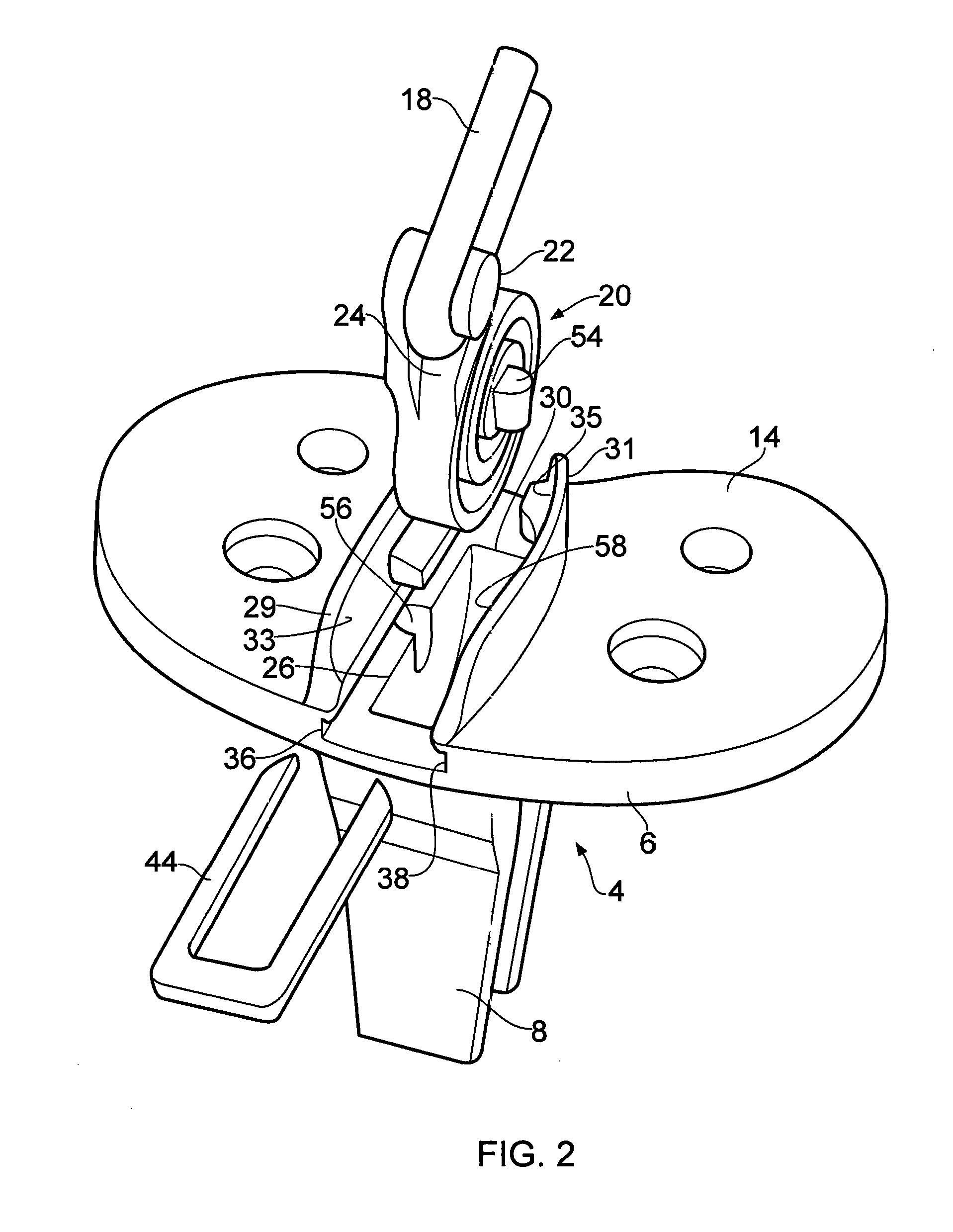
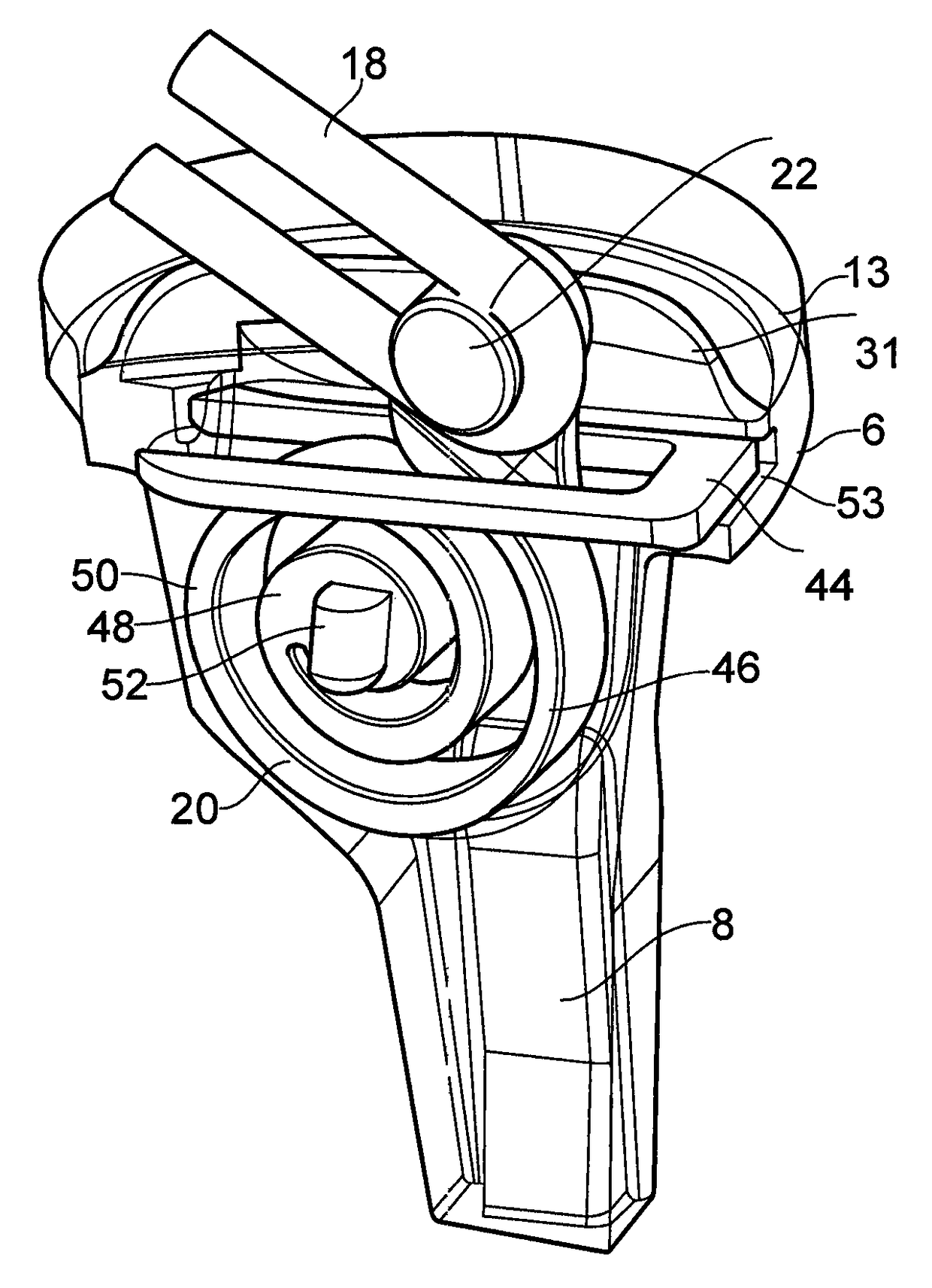
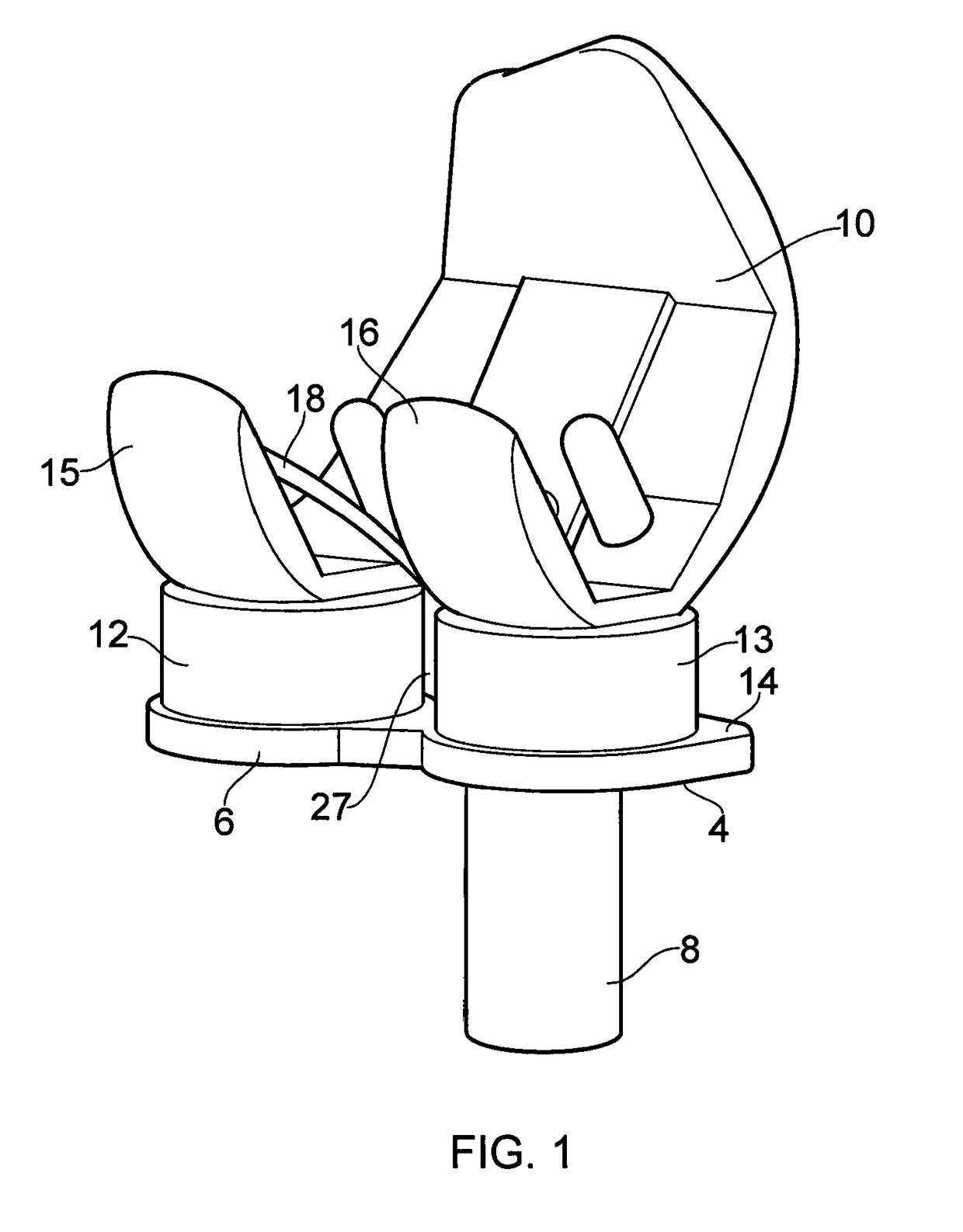
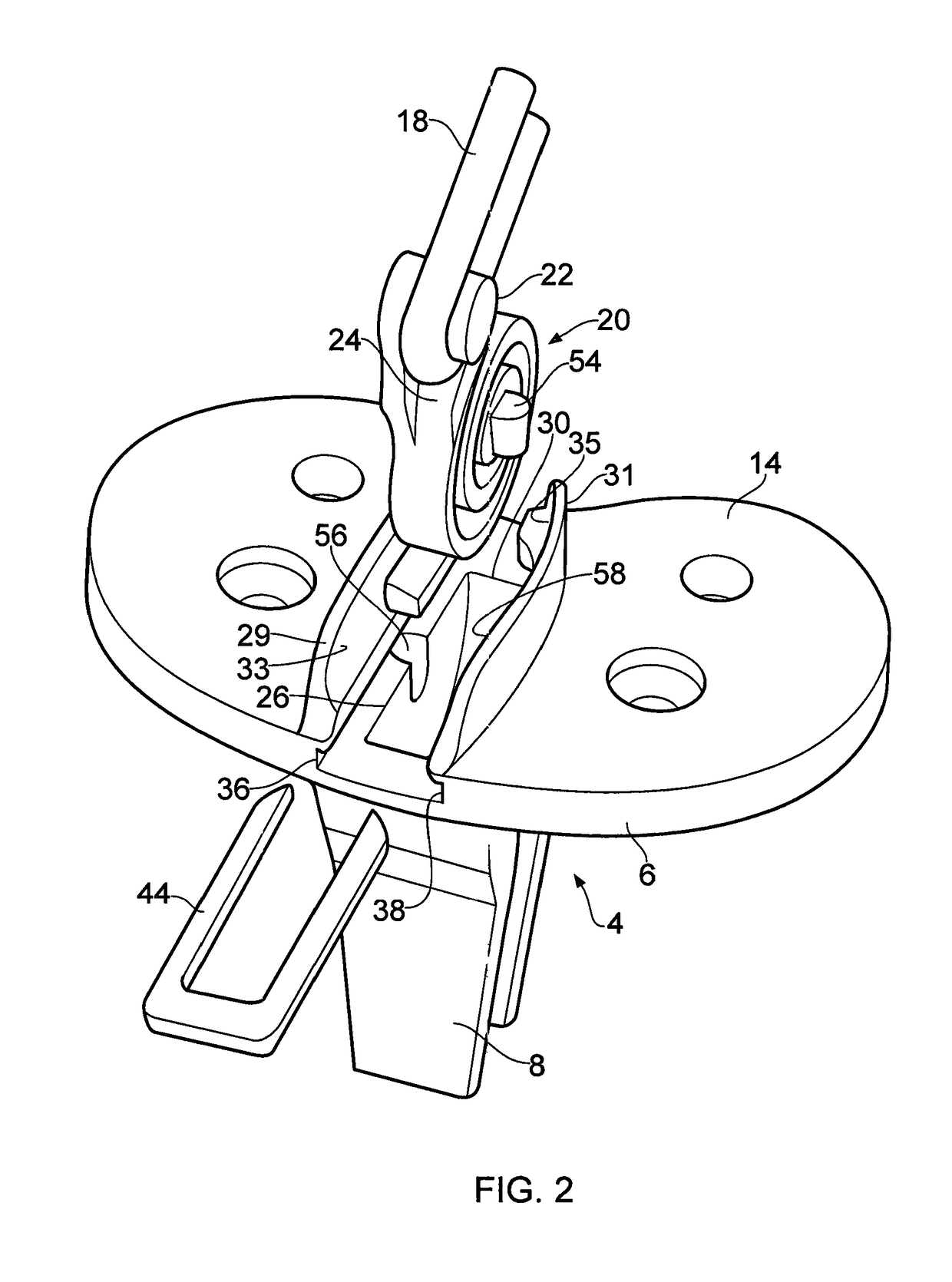
Ligament assembly
A ligament assembly (2) comprising a resilient element (20) connected to a bone anchor (4) and a ligament (18), the resilient element (20) acting m a cantilever and resisting toads transmitted between the bone anchor (4) and the ligament (18) by virtue of the resistance to bending of the resilient element. The ligament (18) may comprise an artificial ligament (18) which is adapted to replace a human or animal ligament. The resilient element (20) may comprise a spiral spring and may act as a biasing element / shock absorber operatively coupled to the artificial ligament (18) to control the effective stiffness of the artificial ligament (18). Consequently, the resilient element (20) enables an effective stiffness of the artificial ligament (18) to be achieved that more closely approximates the stiffness of a natural ligament.
Owner:BIOMET UK HEALTHCARE
Miniature non-directional microphone
InactiveUS7903835B2Improve responseHigh sensitivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesSolid state device transducersAir volumeMicrofabrication
A miniature microphone comprising a diaphragm compliantly suspended over an enclosed air volume having a vent port is provided, wherein an effective stiffness of the diaphragm with respect to displacement by acoustic vibrations is controlled principally by the enclosed air volume and the port. The microphone may be formed using silicon microfabrication techniques and has sensitivity to sound pressure substantially unrelated to the size of the diaphragm over a broad range of realistic sizes. The diaphragm is rotatively suspend for movement through an arc in response to acoustic vibrations, for example by beams or tabs, and has a surrounding perimeter slit separating the diaphragm from its support structure. The air volume behind the diaphragm provides a restoring spring force for the diaphragm. The microphone's sensitivity is related to the air volume, perimeter slit, and stiffness of the diaphragm and its mechanical supports, and not the area of the diaphragm.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Miniature non-directional microphone
InactiveUS20080101641A1Less stiffImprove responsePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesSolid state device transducersAir volumeSpring force
A miniature microphone comprising a diaphragm compliantly suspended over an enclosed air volume having a vent port is provided, wherein an effective stiffness of the diaphragm with respect to displacement by acoustic vibrations is controlled principally by the enclosed air volume and the port. The microphone may be formed using silicon microfabrication techniques and has sensitivity to sound pressure substantially unrelated to the size of the diaphragm over a broad range of realistic sizes. The diaphragm is rotatively suspend for movement through an arc in response to acoustic vibrations, for example by beams or tabs, and has a surrounding perimeter slit separating the diaphragm from its support structure. The air volume behind the diaphragm provides a restoring spring force for the diaphragm. The microphone's sensitivity is related to the air volume, perimeter slit, and stiffness of the diaphragm and its mechanical supports, and not the area of the diaphragm.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
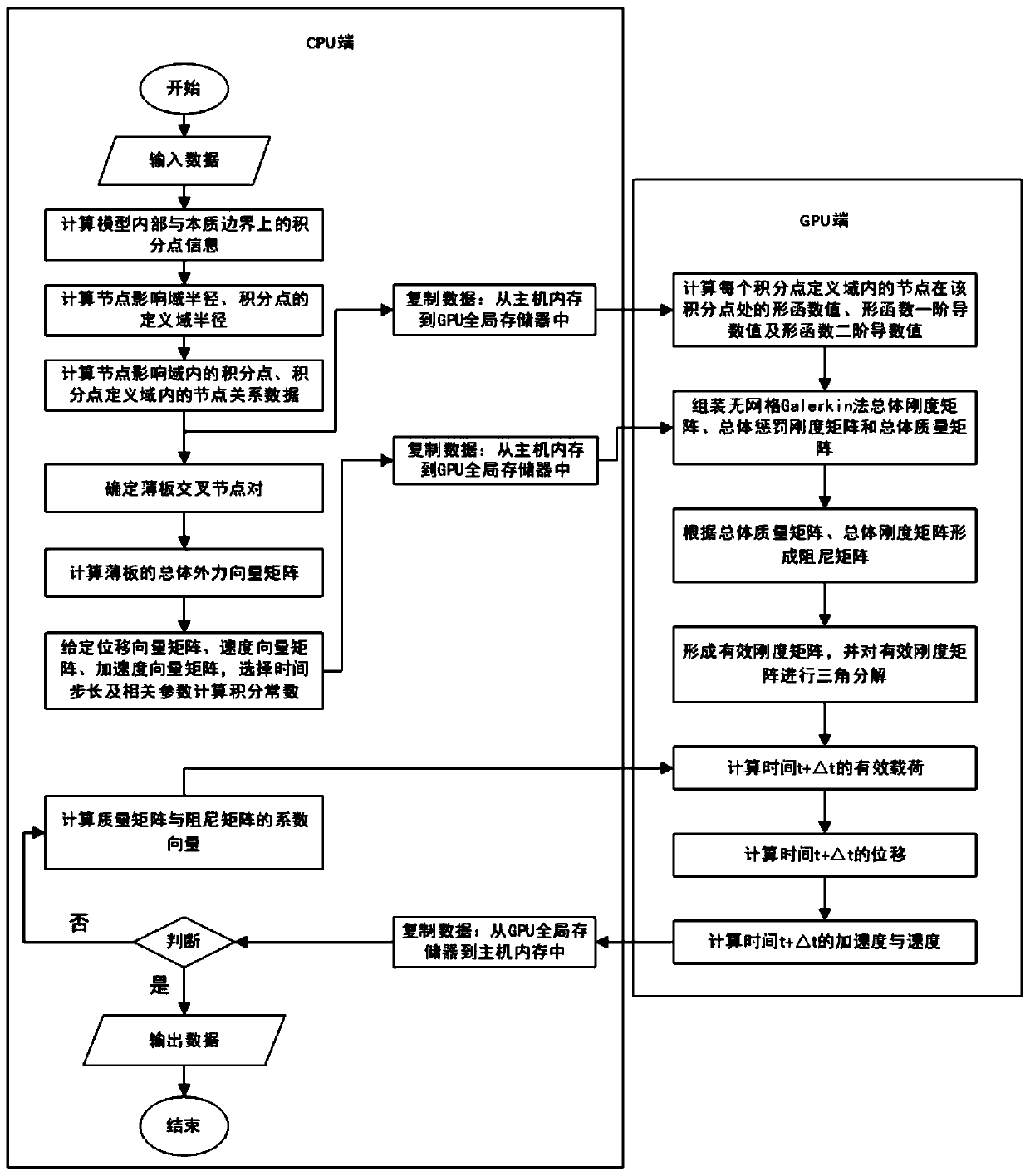
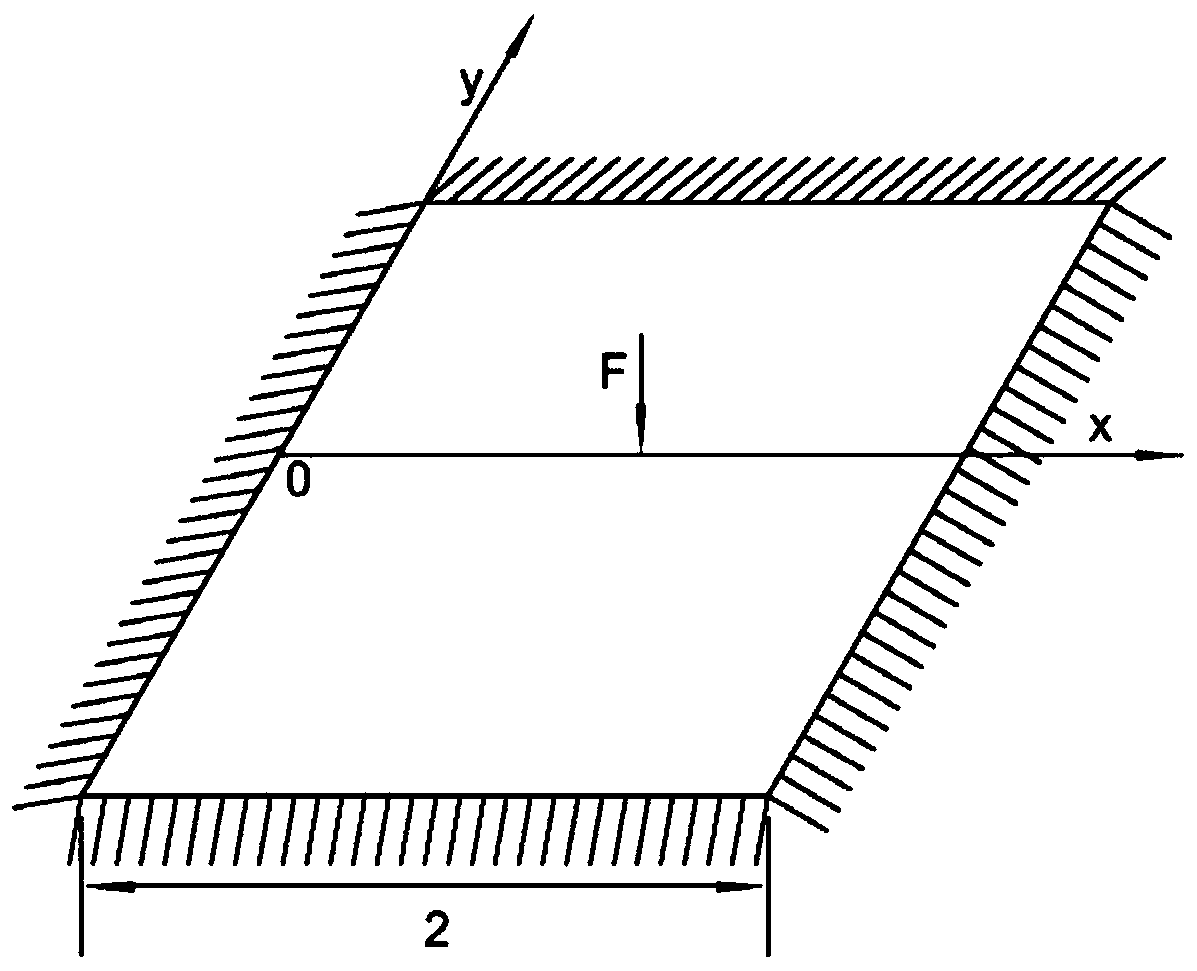
GPU acceleration method for dynamic response analysis of thin-plate gridless Galerkin structure
ActiveCN109960865AReduce assembly calculation timeRealize computingSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationHost memoryGraphics processing unit
The invention discloses a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) acceleration method for dynamic response analysis of a thin plate gridless Galerkin structure. The method comprises the following steps: reading sheet data into a host memory through a CPU (Central Processing Unit), calculating relevant data required by parallel processing of a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) according to input data, and copying the obtained data into a GPU global memory; setting the number of thread blocks and the number of threads on the GPU, performing parallel acceleration calculation on shape function values corresponding to the nodes, then establishing a one-to-one mapping mode of the thread blocks and the cross nodes of the GPU, and performing parallel acceleration assembly on an overall stiffness matrix and amass matrix of the thin plate; correcting the overall stiffness matrix on the GPU according to boundary conditions, then obtaining a damping matrix and an effective stiffness matrix through the mass matrix and the corrected stiffness matrix, and performing triangular decomposition on the effective stiffness matrix; and carrying out dynamic response analysis on the thin plate in a GPU by adopting aNewmark method, and finally outputting a result of solving the displacement, speed and acceleration. According to the method, the solving efficiency of dynamic response analysis is greatly improved.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Combination system of energy dissipation coupling beams and viscous dampers and design method of combination system
PendingCN107989226AAdditional damping ratio is largeHigh dynamic stiffnessWallsProtective buildings/sheltersDynamic stiffnessEarthquake resistance
The invention discloses a combination system of energy dissipation coupling beams and viscous dampers and a design method of the combination system, and belongs to the technical field of earthquake resistance and disaster prevention of building structures. The combination system consists of the multiple energy dissipation coupling beams and the multiple viscous dampers. The multiple energy dissipation coupling beams are arranged between adjacent two wall columns side by side. The position between the adjacent two wall columns is divided into a plurality of holes through the multiple energy dissipation coupling beams. Each hole is internally provided with at least one viscous damper. In the combination system, the energy dissipation coupling beams can provide effective stiffness and a certain damping ratio, the viscous dampers can provide high additional damping ratio and dynamic stiffness, in this way, the stiffness of a shear wall structure can be ensured, and meanwhile, seismic action can be reduced through the damping ratio, wall thickness is reduced, the cost is reduced, the building space is reduced, and good promoting prospects are achieved.
Owner:NANTONG LANKE DAMPING TECH CO LTD
Wedge loading mechanism for traction drives
InactiveUS7264567B2Low efficiencyReduced service lifeYielding couplingToothed gearingsWedge angleEngineering
A wedge loading mechanism for an eccentric planetary traction drive in which a roller having a flexibly mounted shaft is positioned between two raceways forming a convergent wedge. Rotation of either of the two raceways wedges the roller within the convergent wedge squeezing the roller between the two raceways thereby transmitting rotational motion and torque between the two raceways. The flexibly mounted shaft generates differences between an effective supporting stiffness of the roller and an contact effective stiffness at the points where the roller contacts the two raceways. The difference in the effective stiffness allow the roller to operate efficiently at smaller convergent wedge angles.
Owner:THE TIMKEN CO
Variable stiffness quadruped bionic quadruped robot flexible continuous body spine mechanism
The invention belongs to the field of robots and more specifically relates to a variable stiffness quadruped bionic quadruped robot flexible continuous body spine mechanism. According to the variable stiffness quadruped bionic quadruped robot flexible continuous body spine mechanism, two pairs of driving steel cables are symmetrically placed on the two sides of the transverse direction and the longitudinal direction of cross-shaped knuckle supports fixed on a square rubber strut in an equally paced manner; a differential driving spine is bent in the horizontal or vertical direction to realize flexible bending of the spine in the horizontal or vertical direction so that the motion flexibility and motion performance of a quadruped robot are improved; by oppositely placing two specially designed elastic elements with nonlinear force-deformation characteristics on the two sides of the longitudinal direction of the spine mechanism, a linear relation is established between an adjusting variable (steel cable telescopic amount) and the stiffness of a spine within an effective stiffness adjusting range; and therefore, the accurate stiffness control ability is obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Ligament assembly
A ligament assembly (2) comprising a resilient element (20) connected to a bone anchor (4) and a ligament (18), the resilient element (20) acting m a cantilever and resisting toads transmitted between the bone anchor (4) and the ligament (18) by virtue of the resistance to bending of the resilient element. The ligament (18) may comprise an artificial ligament (18) which is adapted to replace a human or animal ligament. The resilient element (20) may comprise a spiral spring and may act as a biasing element / shock absorber operatively coupled to the artificial ligament (18) to control the effective stiffness of the artificial ligament (18). Consequently, the resilient element (20) enables an effective stiffness of the artificial ligament (18) to be achieved that more closely approximates the stiffness of a natural ligament.
Owner:BIOMET UK HEALTHCARE
Heat-static strong recovering type MEMS four-point support hanging beam structure
InactiveCN103552979AIncrease effective stiffnessEnhance resilienceTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a heat-static strong recovering type MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical System) four-point support hanging beam structure which comprises a substrate, static pull-down electrodes, anchor areas, a hanging main beam and bending support beams, wherein the top face of the substrate is coated with the static pull-down electrodes, the hanging main beam is hung above the substrate through the four anchor areas and the bending support beams; during the process that the hanging main beam switches from a pull-down state ('down' state) to a hanging state ('up' state), the bending support beams are subjected to ohmic heating to stretch the hanging main beam, so that the effective rigidity of the hanging main beam is improved, and the restoring force is strengthened; longitudinal beams of the bending support beams adopt the design of double parallel wide and narrow beams, so that the hanging main beam is more stable, and after being heated, the hanging main beam can recover from the 'down' state to the 'up' state more easily. The invention further discloses a specific operating manner for enhancing the restoring force, and the method is simple, convenient and feasible.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
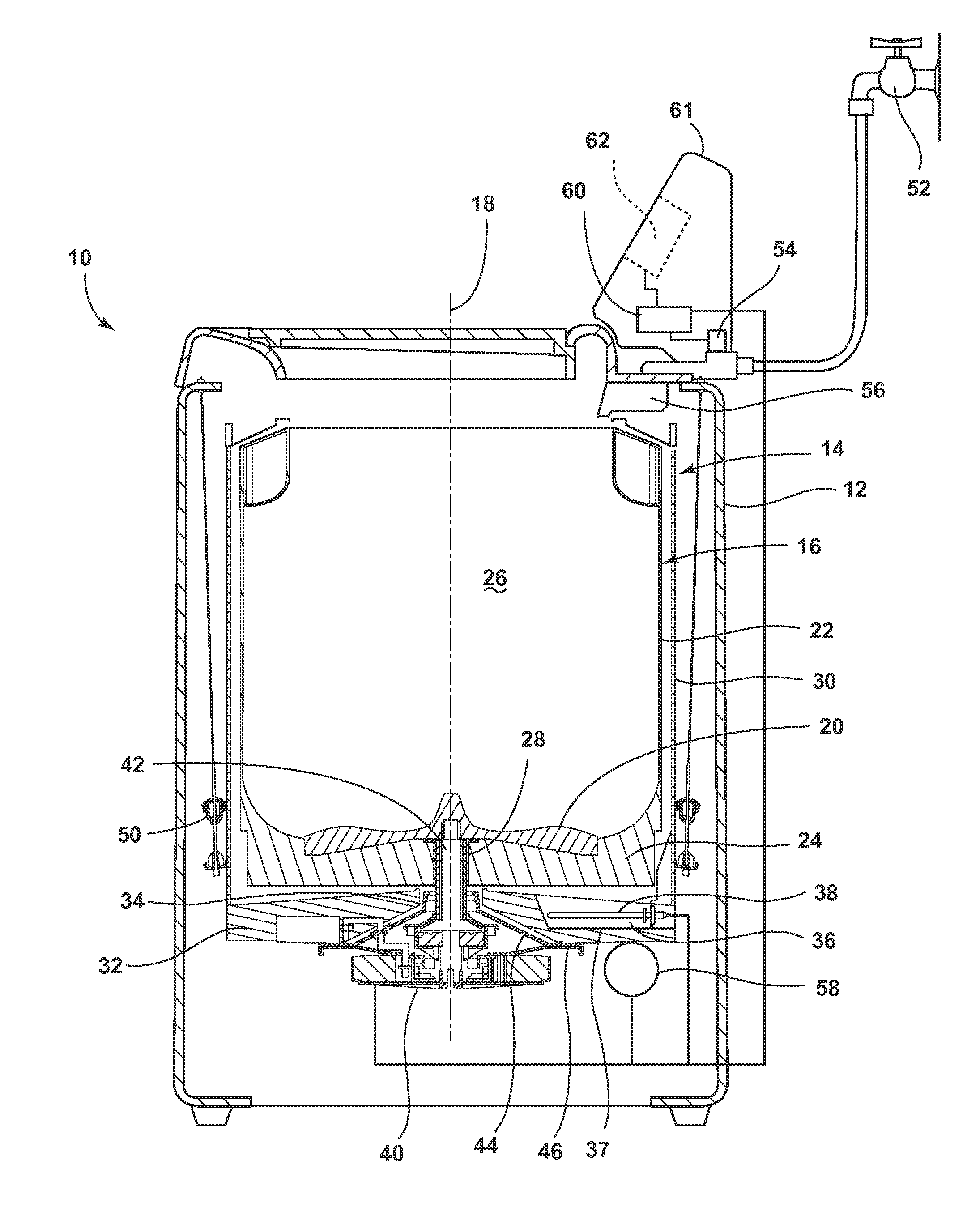
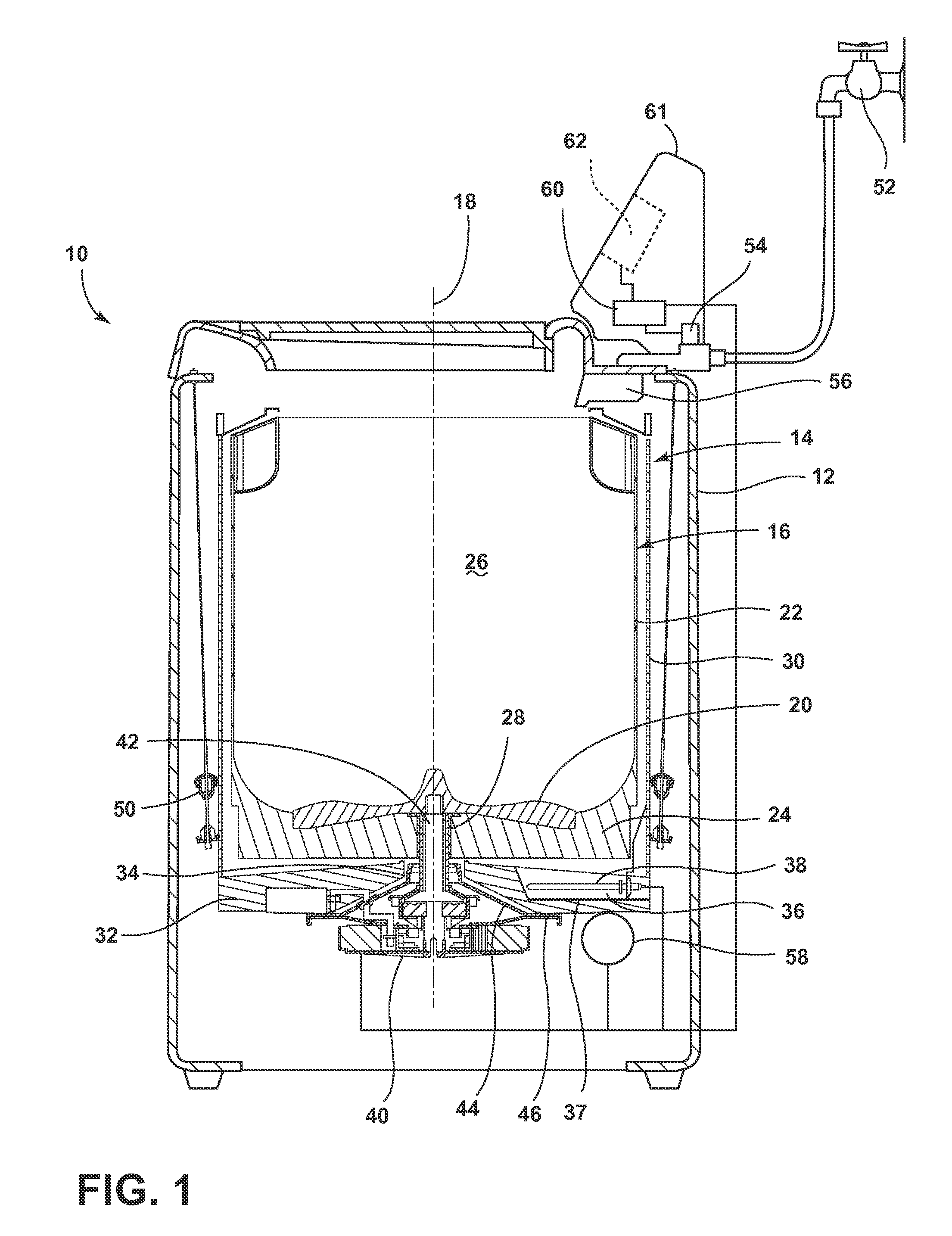
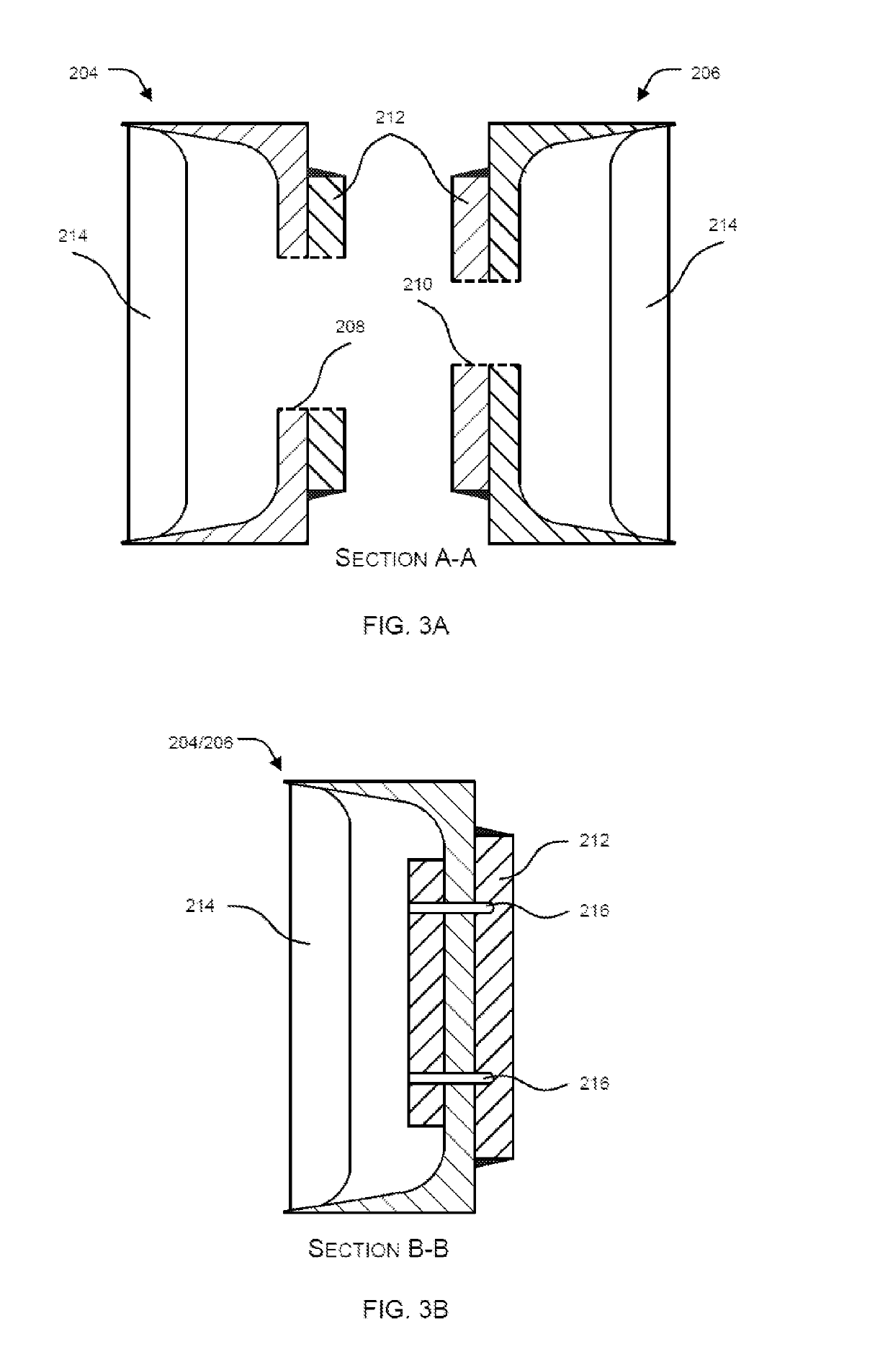
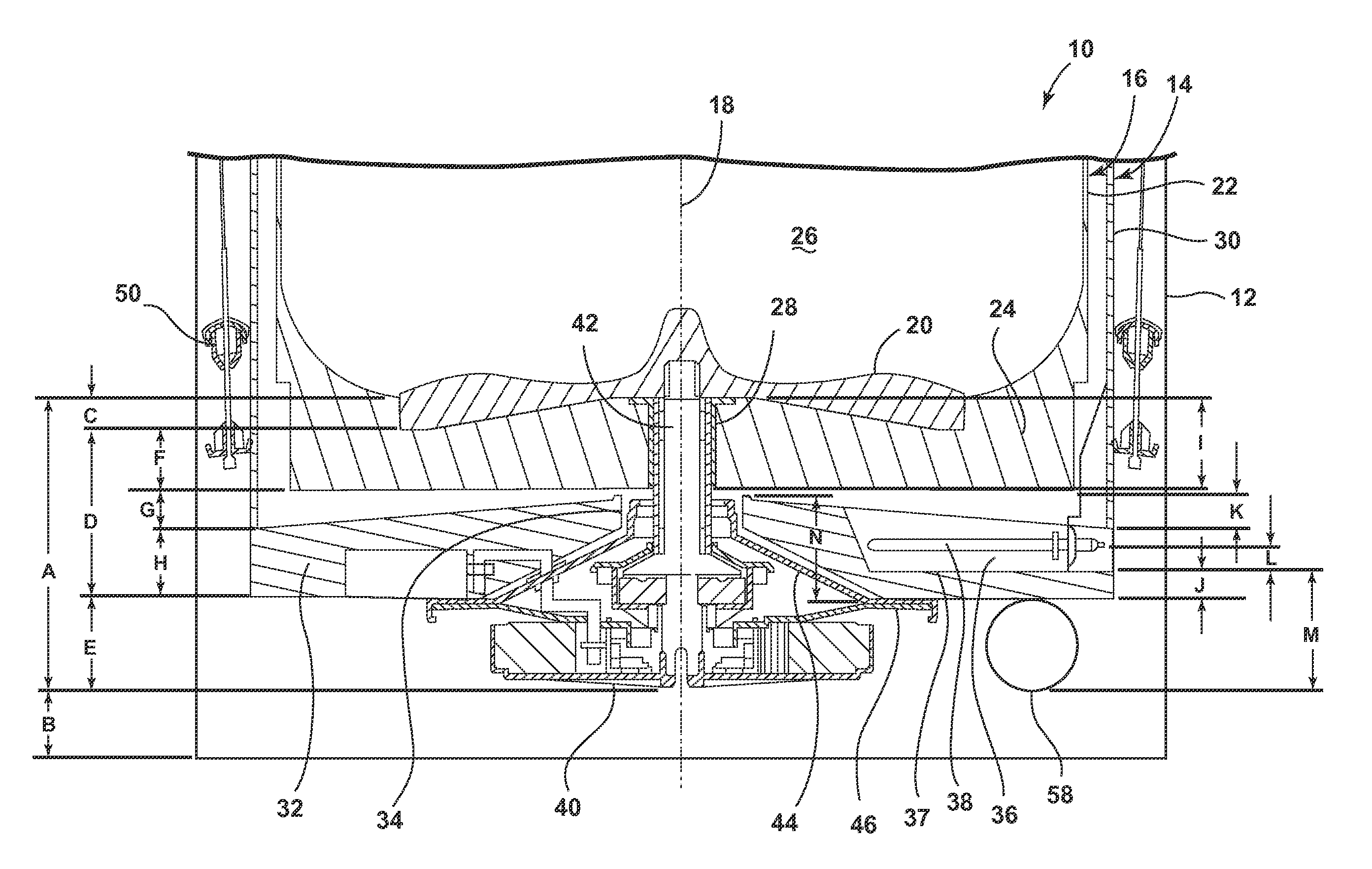
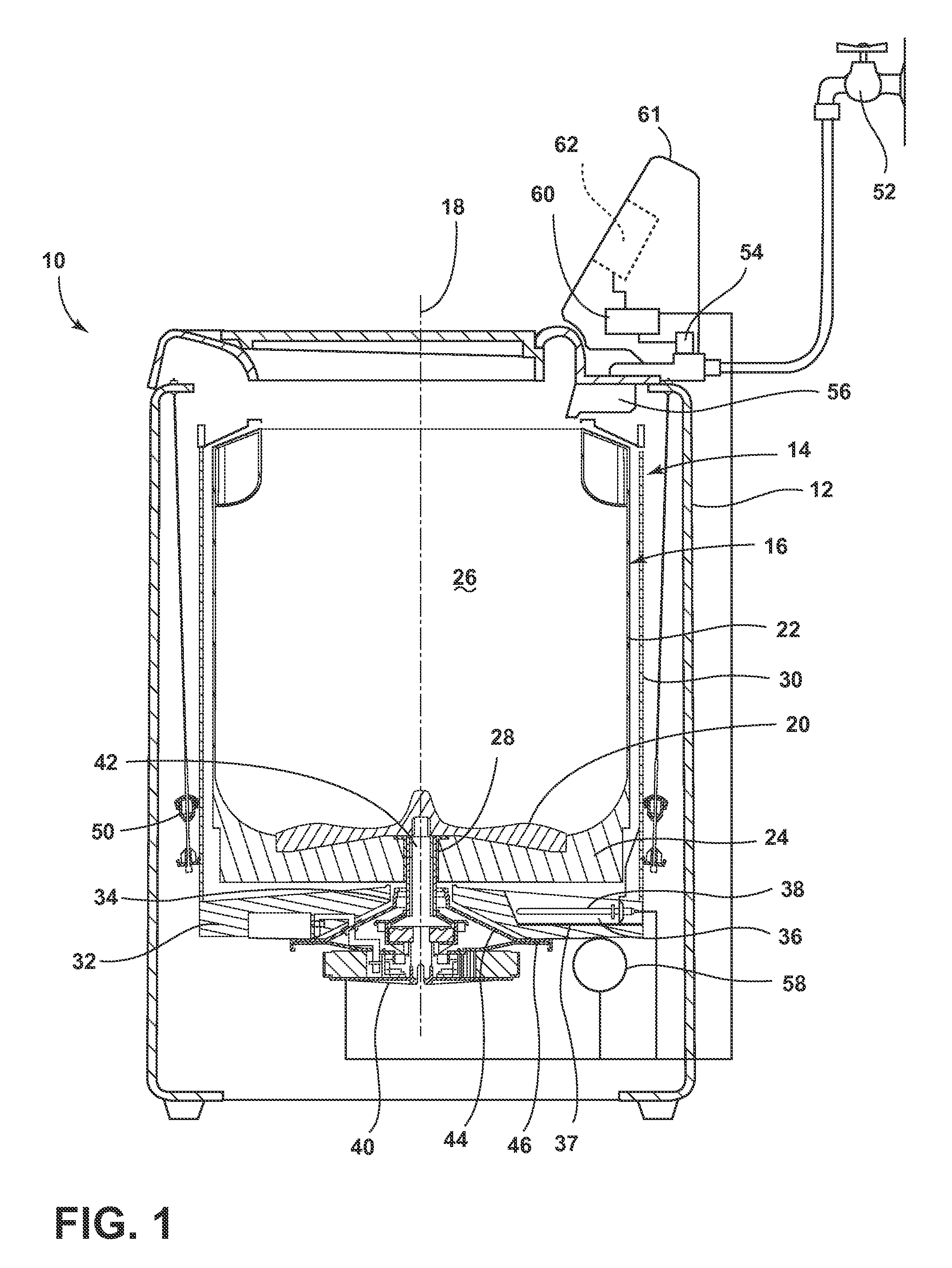
Laundry treating appliance
ActiveUS20150107308A1Other washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusRotational axisEngineering
A laundry treating appliance may include a tub and a basket located at least partially within the tub and at least partially defining a laundry treating chamber. A drive system may operatively couple the tub to the basket and may be operative to rotate the basket about a rotational axis. The tub and the basket may each have a base with an effective stiffness, and the effective stiffnesses may be matched.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Multilayer polymeric sheets and light weight laminates produced therefrom
InactiveCN105555528ASynthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsSound transmission classVolumetric Mass Density
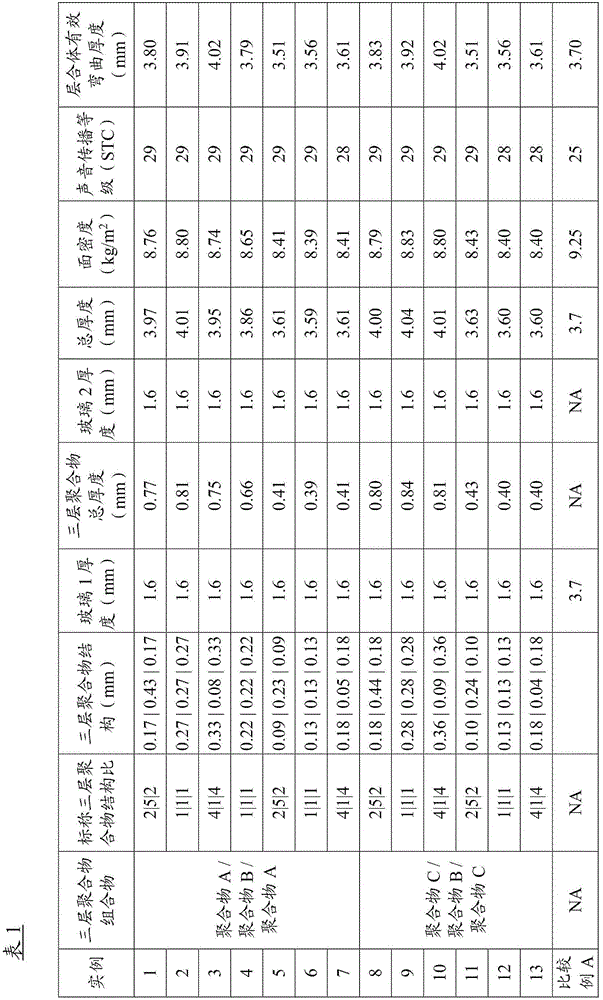
A multilayer polymeric sheet comprising three layers is provided. The two outer layers of the multilayer polymeric sheet comprise an ionomeric composition and are positioned on either side of the inner layer of the multilayer polymeric sheet, which comprises an ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) composition. Further provided is a laminate comprising the multilayer polymeric sheet, for example, a glass laminate. Preferred laminates exhibit a sound transmission class of greater than 25, as measured by ASTM E314, or an effective stiffness by bending of about 3.0 mm to about 5.0 mm, as measured by ASTM C158. Also preferably, the laminate has an areal density that is lower than that of a glass monolith of comparable thickness.
Owner:PERFORMANCE MATERIALS NA INC
Variable diffuser
ActiveUS9182097B2Easy constructionProduced cost-effectivelyPoint-like light sourceDiffusing elementsElastomerEngineering
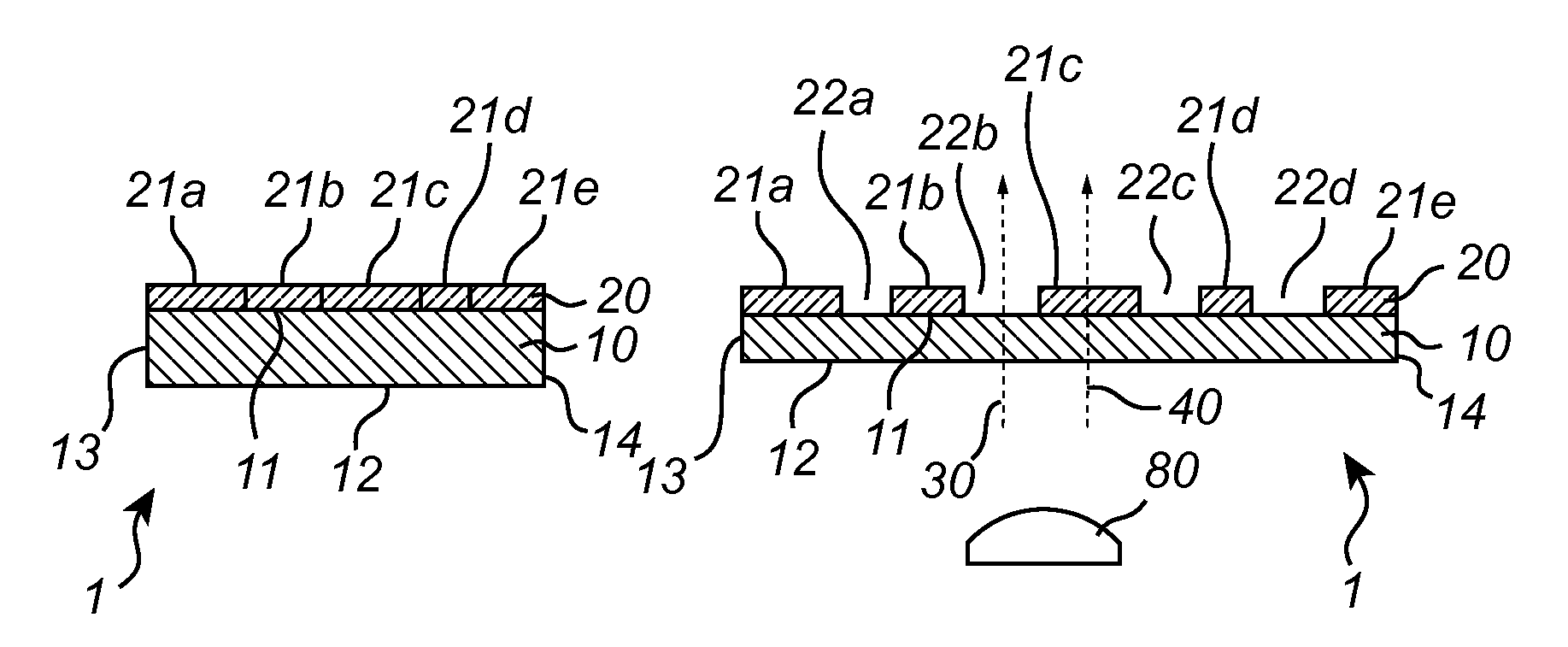
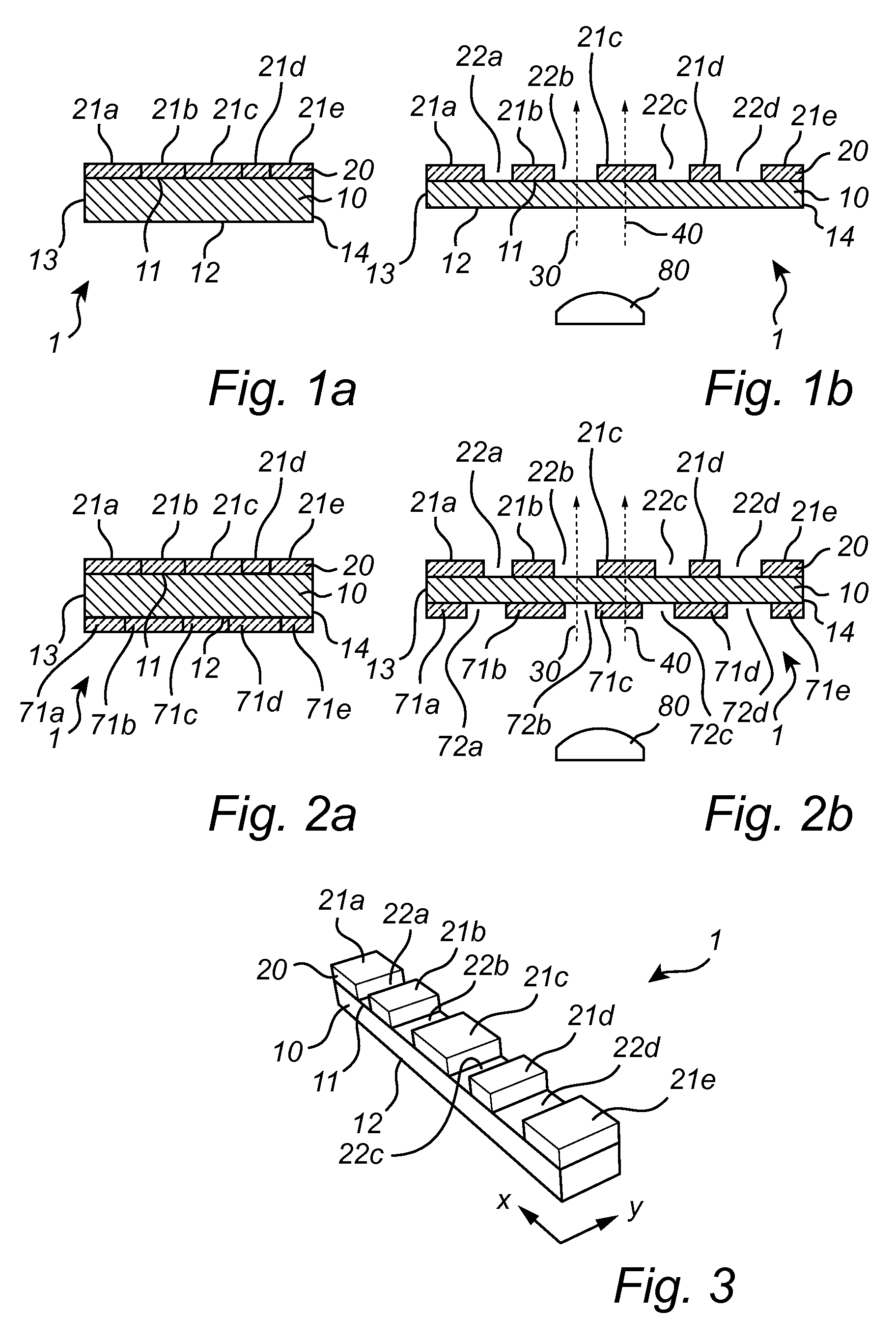
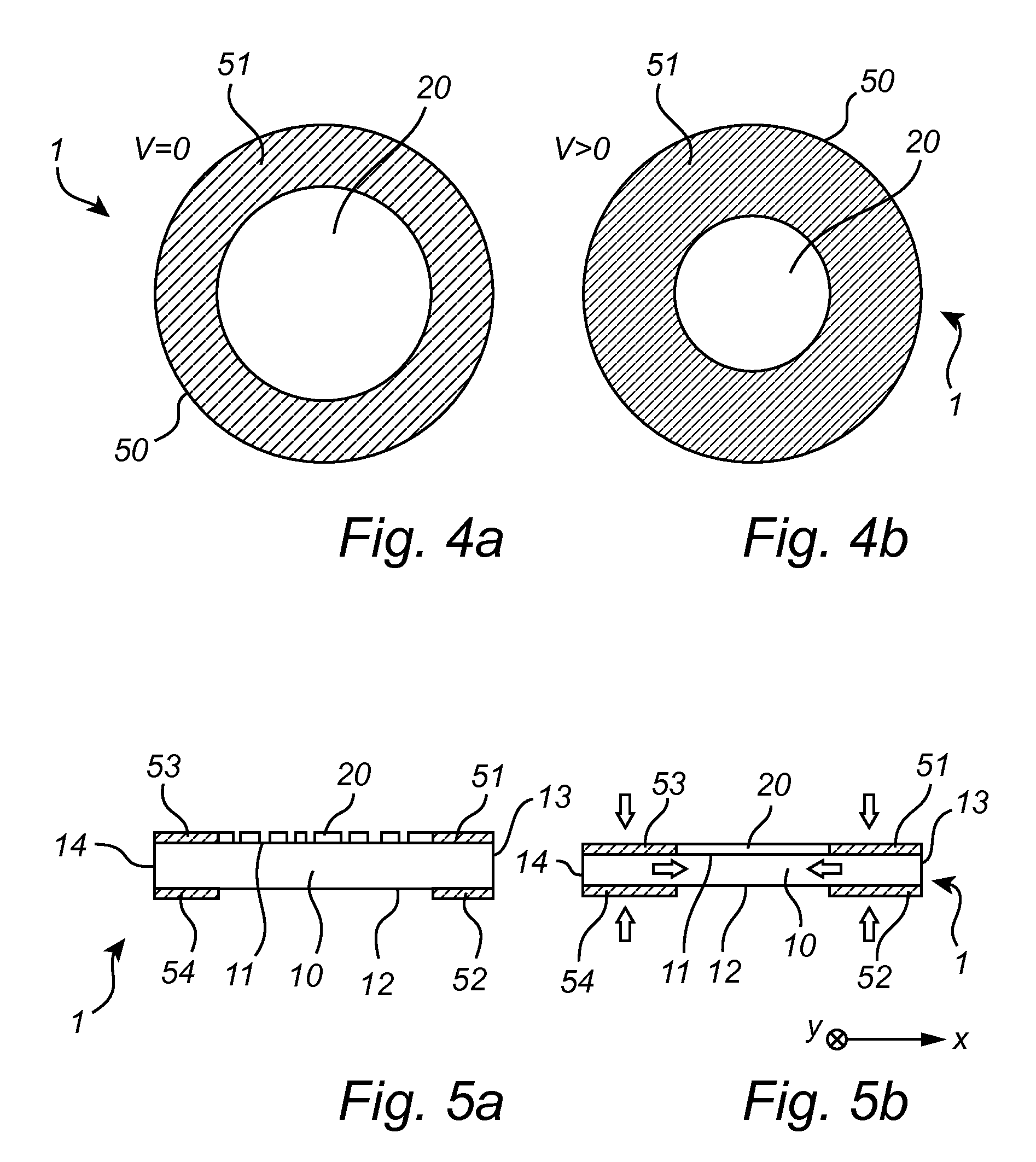
The invention relates to a diffuser (1) for use in a lighting device. The diffuser (1) comprises an at least partially transparent first layer (10) and an adjoining at least partially transparent second layer (20), the first layer being continuous and comprising a stretchable elastomer, the second layer being a segmented layer comprising a material with a high effective stiffness measured as the product of the thickness of the material and the elastic modulus of the material. The second layer (20) comprises a non-periodic pattern of segments (21a, 21b, 21c, 21d, 21e) having different dimensions. The diffuser is stretchable between a first position in which the first layer is in a non-stretched state and the segments of the second layer are arranged adjacent each other such as to form a substantially continuous layer, and a second position in which the first layer is stretched out and the segments of the second layer are separated from each other such that part of the first layer is exposed.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Improved elevator releveling control
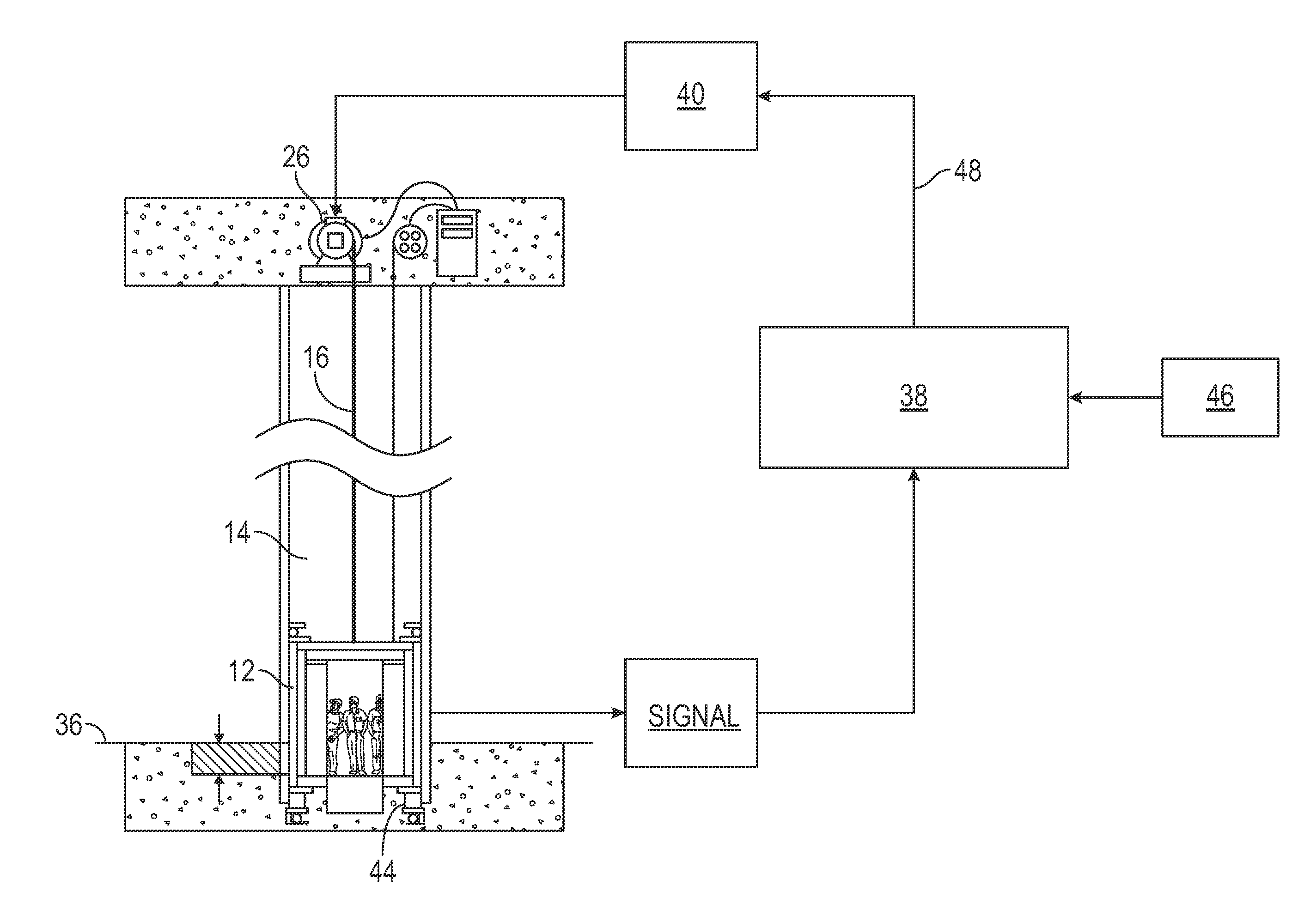
InactiveUS20170057782A1Improving reduction of position mismatchReduce mismatchElevatorsBuilding liftsAutomotive engineeringEffective stiffness
A system for releveling an elevator car floor with a landing floor includes a load weight sensor to sense a load weight of an elevator car at a landing floor, and a releveling controller operably connected to the load weight sensor to calculate a corrective velocity for the elevator car based on the load weight and estimates of the effective stiffnesses at the landing floor. A machine is operably connected to the releveling controller with both feedback and feedforward control and the elevator car to apply the corrective velocity to the elevator car thereby reducing a mismatch between the elevator car and the landing floor.
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Wedge loading mechanism for traction drives
InactiveCN1685170AImprove efficiencyImprove dynamic stabilityFriction gearingsWedge angleMechanical engineering
A wedge loading mechanism for an eccentric planetary traction drive in which a roller having a flexibly mounted shaft is positioned between two raceways forming a convergent wedge. Rotation of either of the two raceways wedges the roller within the convergent wedge squeezing the roller between the two raceways thereby transmitting rotational motion and torque between the two raceways. The flexibly mounted shaft generates differences between an effective supporting stiffness of the roller and an contact effective stiffness at the points where the roller contacts the two raceways. The difference in the effective stiffness allow the roller to operate efficiently at smaller convergent wedge angles.
Owner:THE TIMKEN CO
Tunable support frame structure for rotating machines
ActiveUS10288212B1Increase stiffnessPrevent rigid body modeMachine framesSpecial foundation layoutBraced frameEngineering
The present disclosure relates to a mounting assembly for supporting a machine. The mounting assembly comprises a support frame structure including a plurality of traverse members spaced apart from each other, each traverse member extending from a first longitudinal section to a second longitudinal section of the support frame structure, wherein each longitudinal sections and comprises a plurality of holes and respectively, and an attachment mechanism to increase effective stiffness of the support frame structure, the attachment mechanism comprising any or a combination of a plurality of attachments and a turnbuckle attachment to increase directional stiffness of the support frame structure, wherein the attachment mechanism arrests any or a combination of rolling mode of motion and pitching mode of motion of the support frame structure and the machine by increasing the effective stiffness of the support frame structure.
Owner:BHATTACHARYA MANTOSH ISANCHANDRA
Laundry treating appliance with tub and basket having matched characteristics
ActiveUS9284672B2Other washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusRotational axisEngineering
A laundry treating appliance may include a tub and a basket located at least partially within the tub and at least partially defining a laundry treating chamber. A drive system may operatively couple the tub to the basket and may be operative to rotate the basket about a rotational axis. The tub and the basket may each have a base with an effective stiffness, and the effective stiffnesses may be matched.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
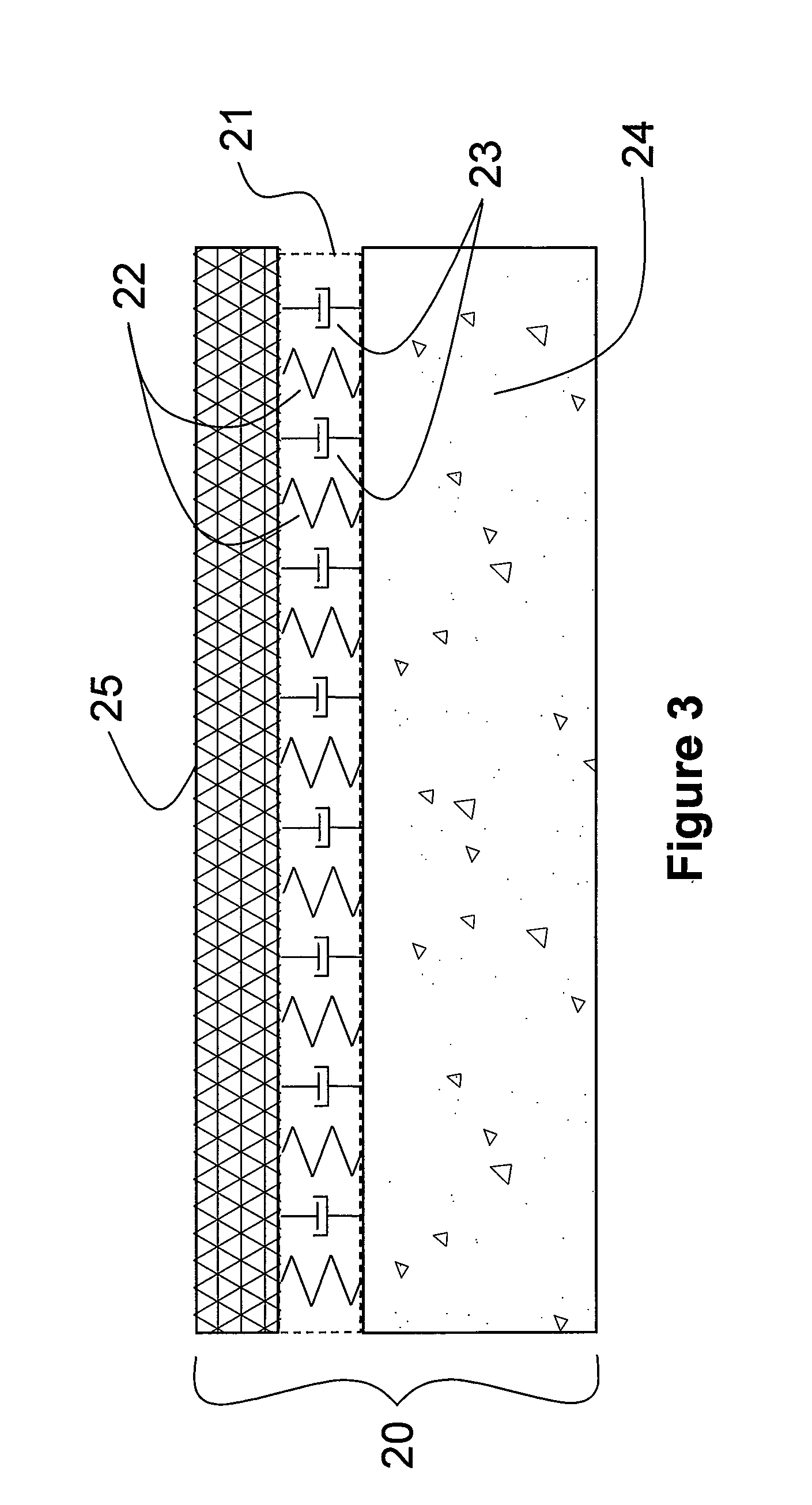
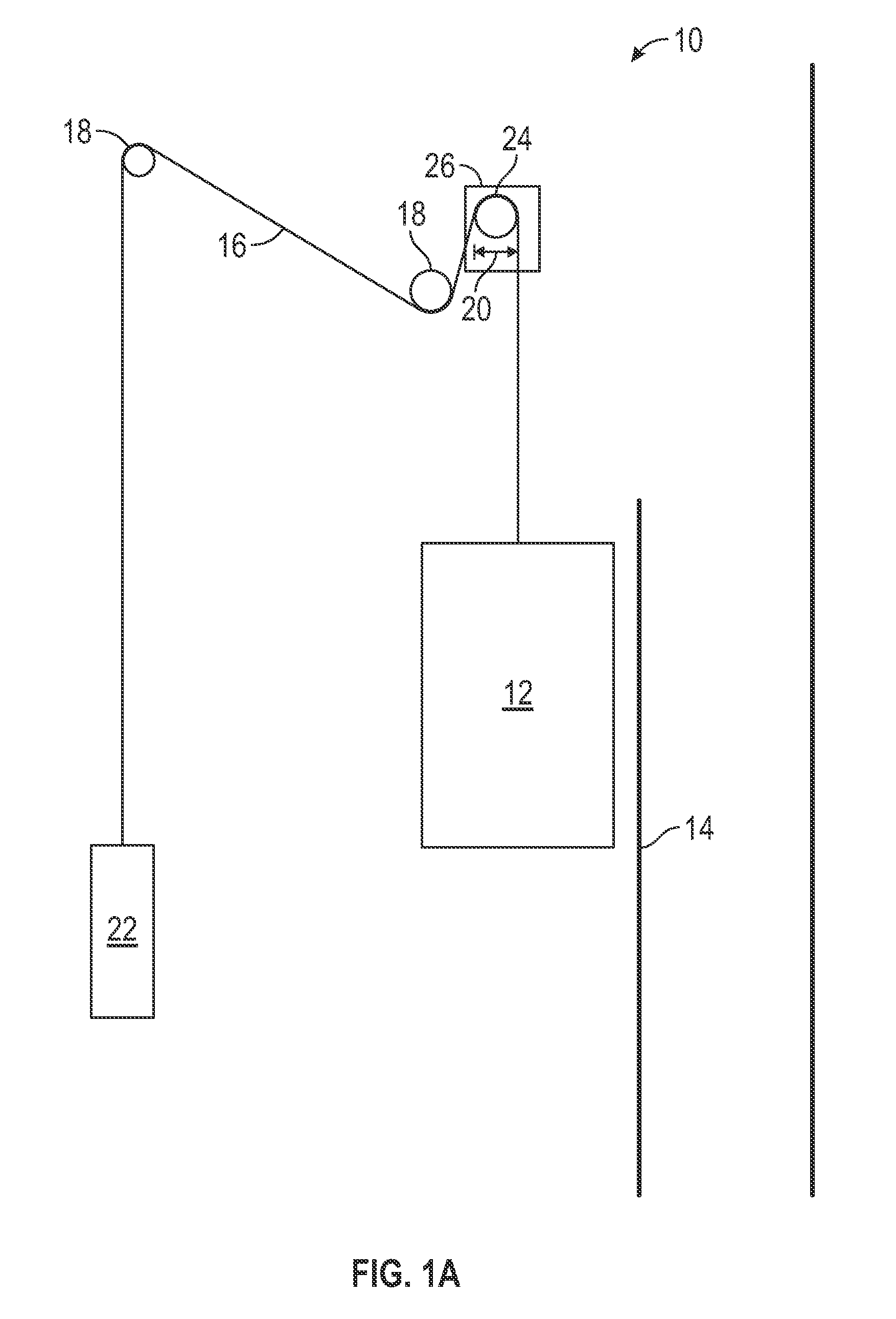
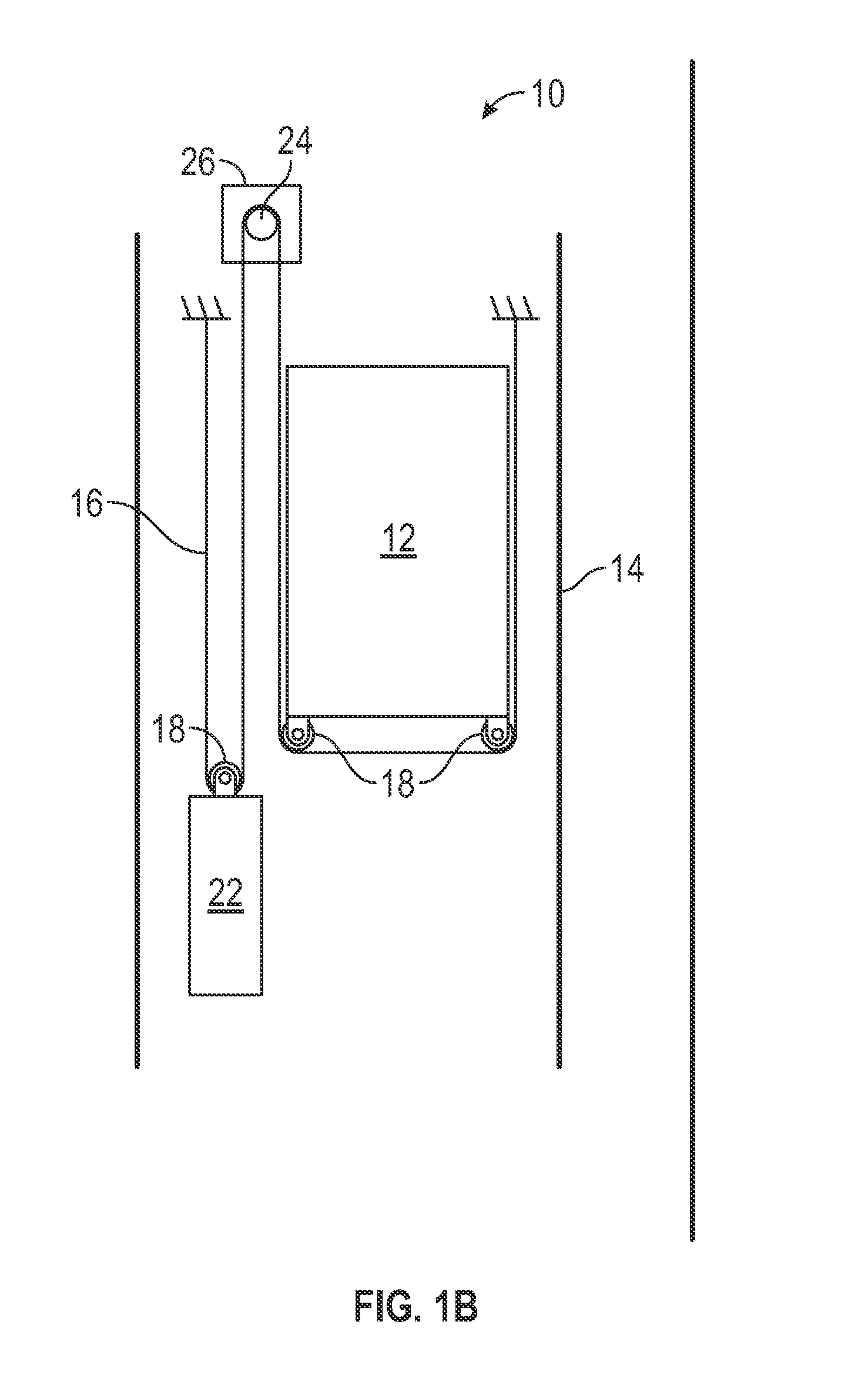
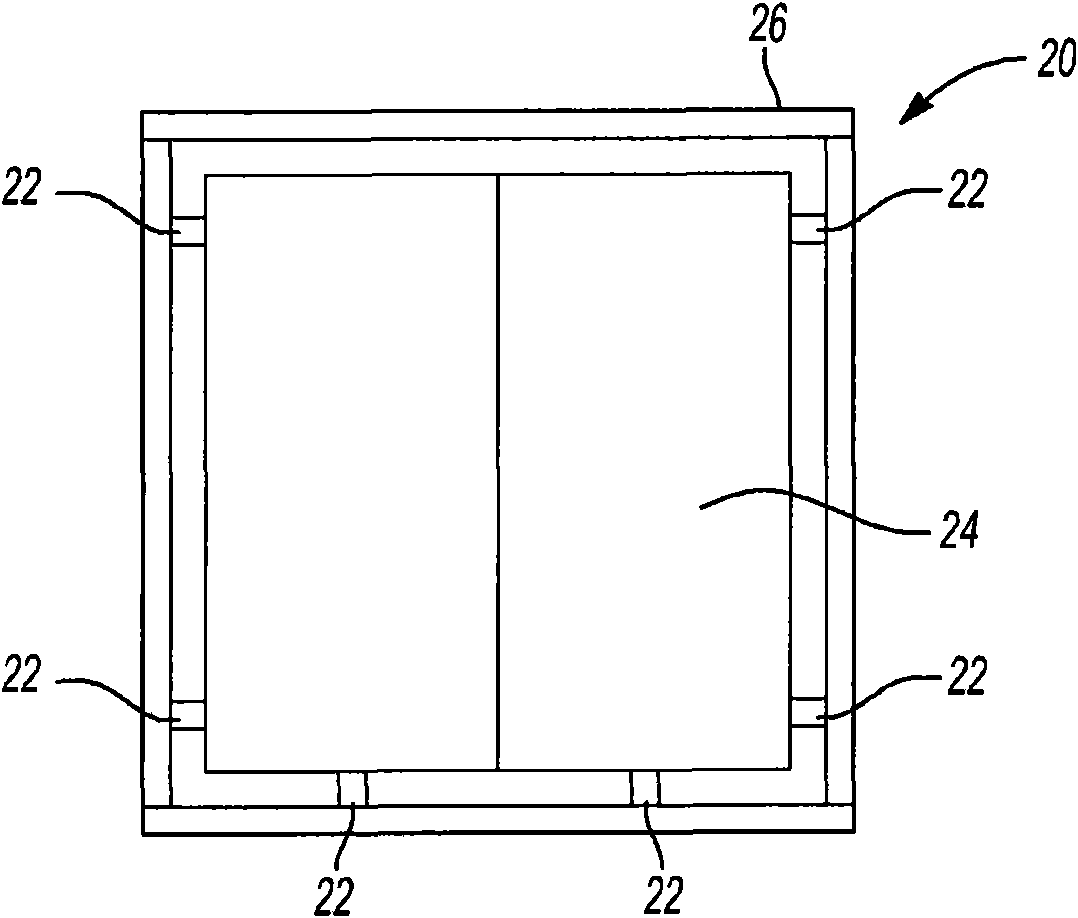
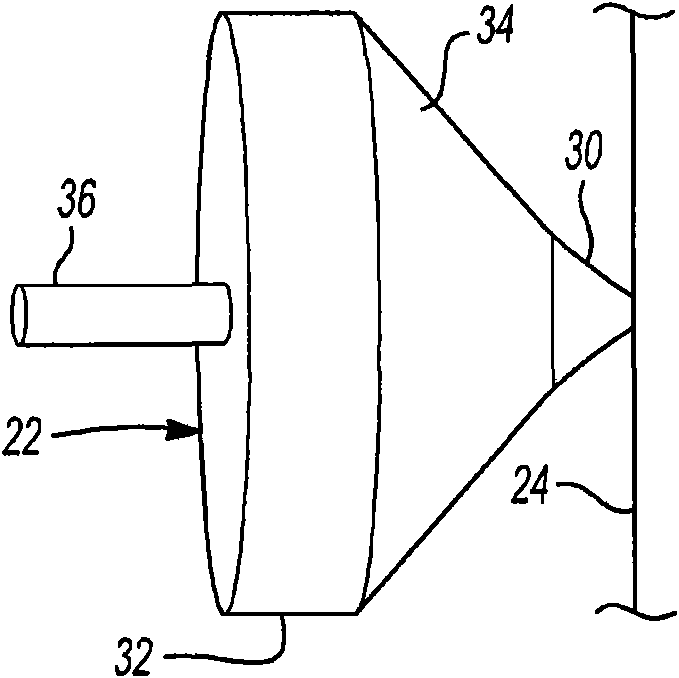
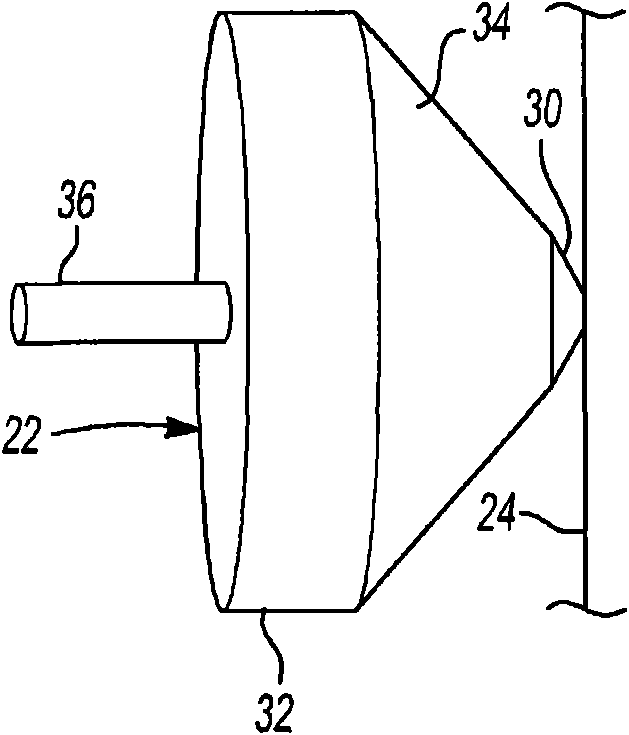
Elevator damper assembly
A damper assembly (22) is useful for controlling elevator ride quality. The damper assembly (22) includes a resilient member that deflects responsive to a load. An effective stiffness of the resilientmember is less than an associated rate of deflection of the resilient member. The resilient member includes a first portion (30, 40) that deflects prior to a second portion (32, 42) responsive to aninitial loading on the damper assembly (22).
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com