Patents
Literature
189 results about "Ride quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
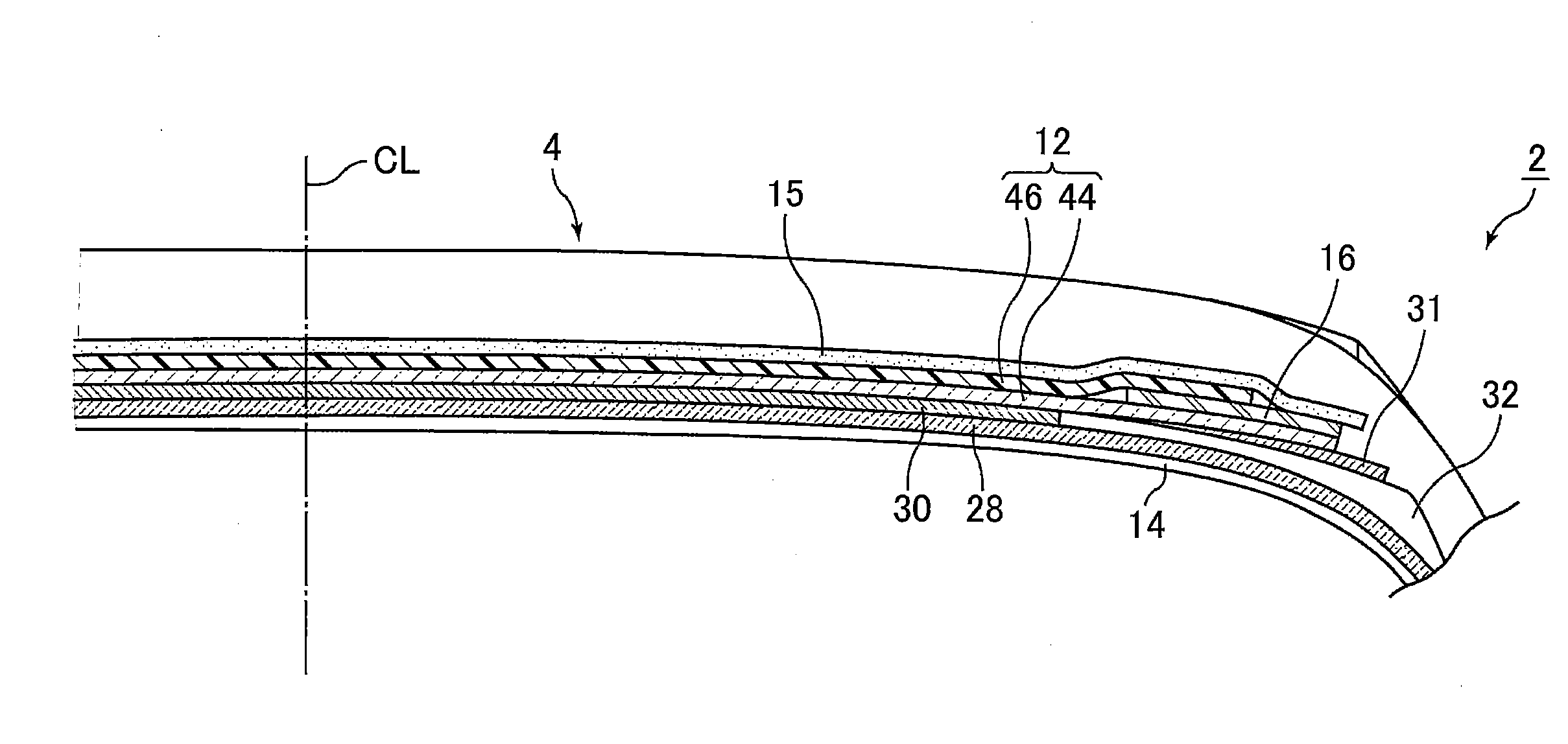
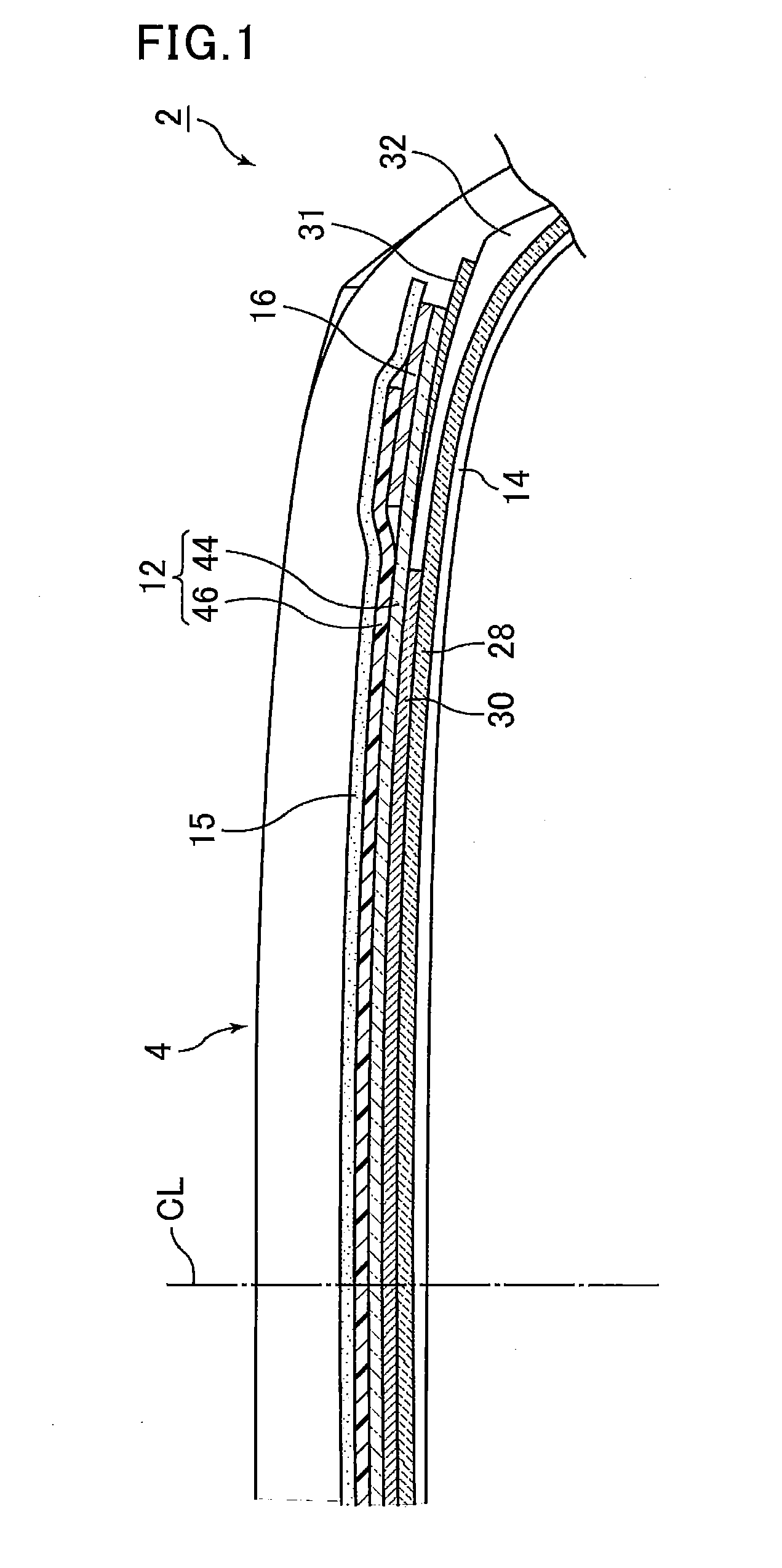
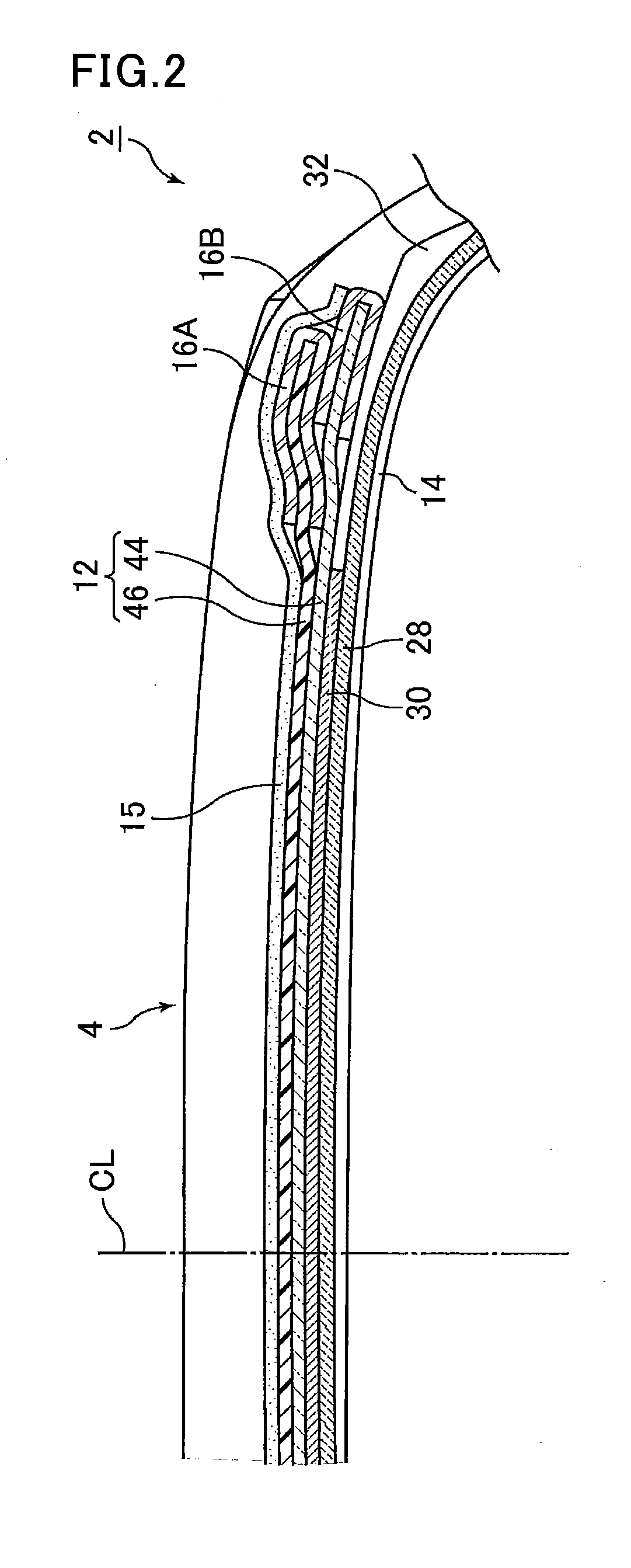
Ride quality refers to a vehicle's effectiveness in insulating the occupants from undulations in the road surface (e.g., bumps or corrugations). A vehicle with good ride quality provides a comfort for the driver and passengers.
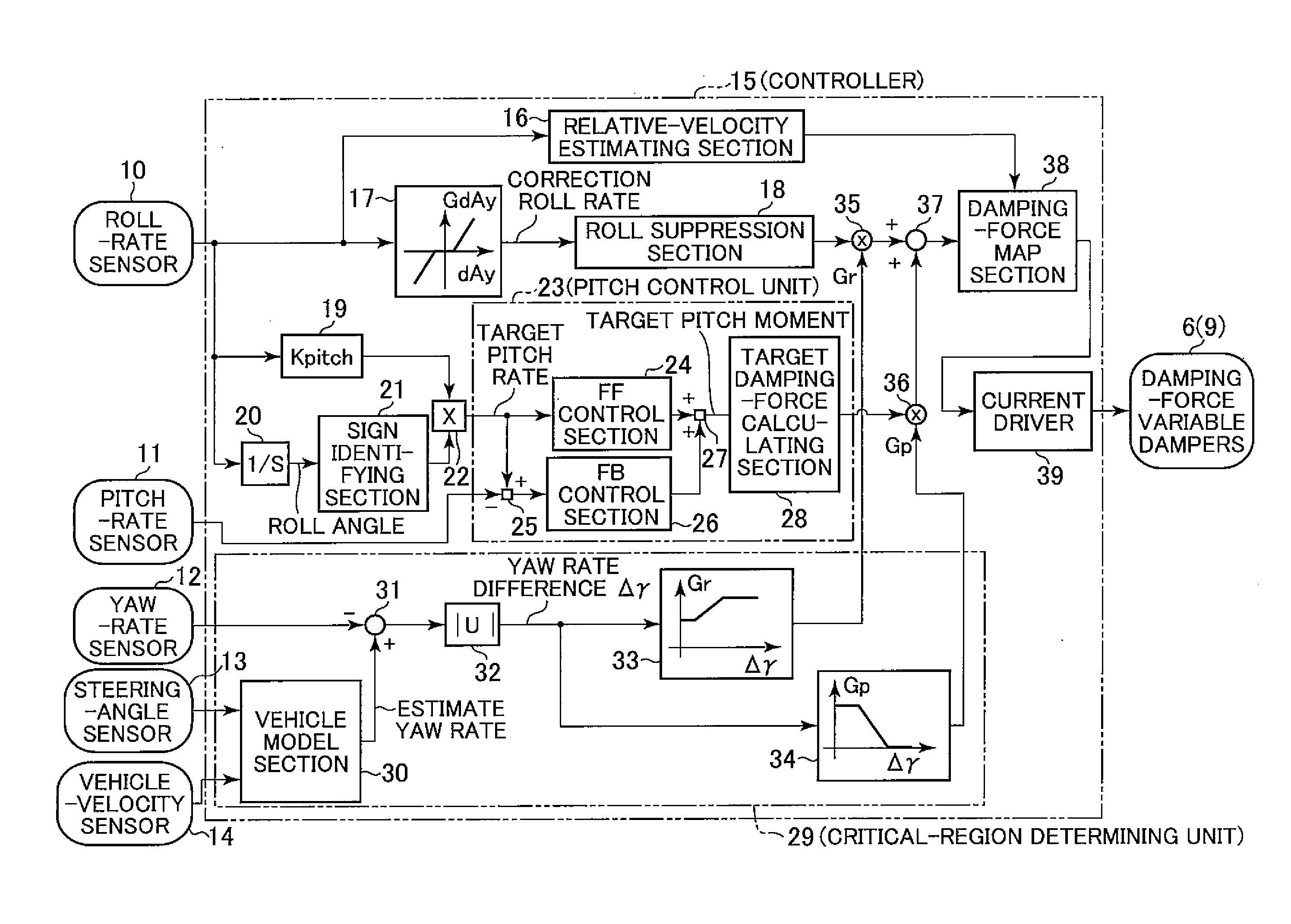
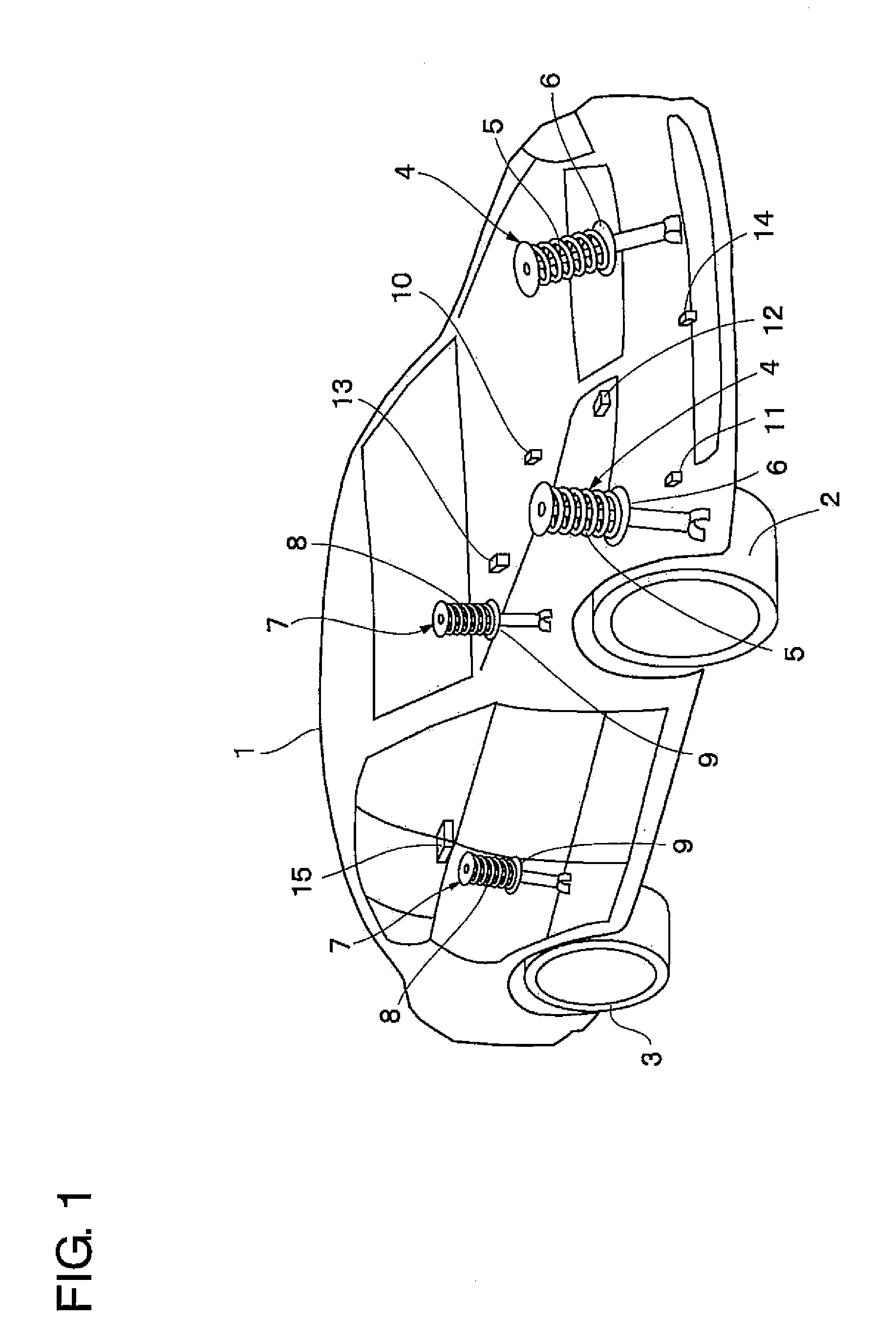
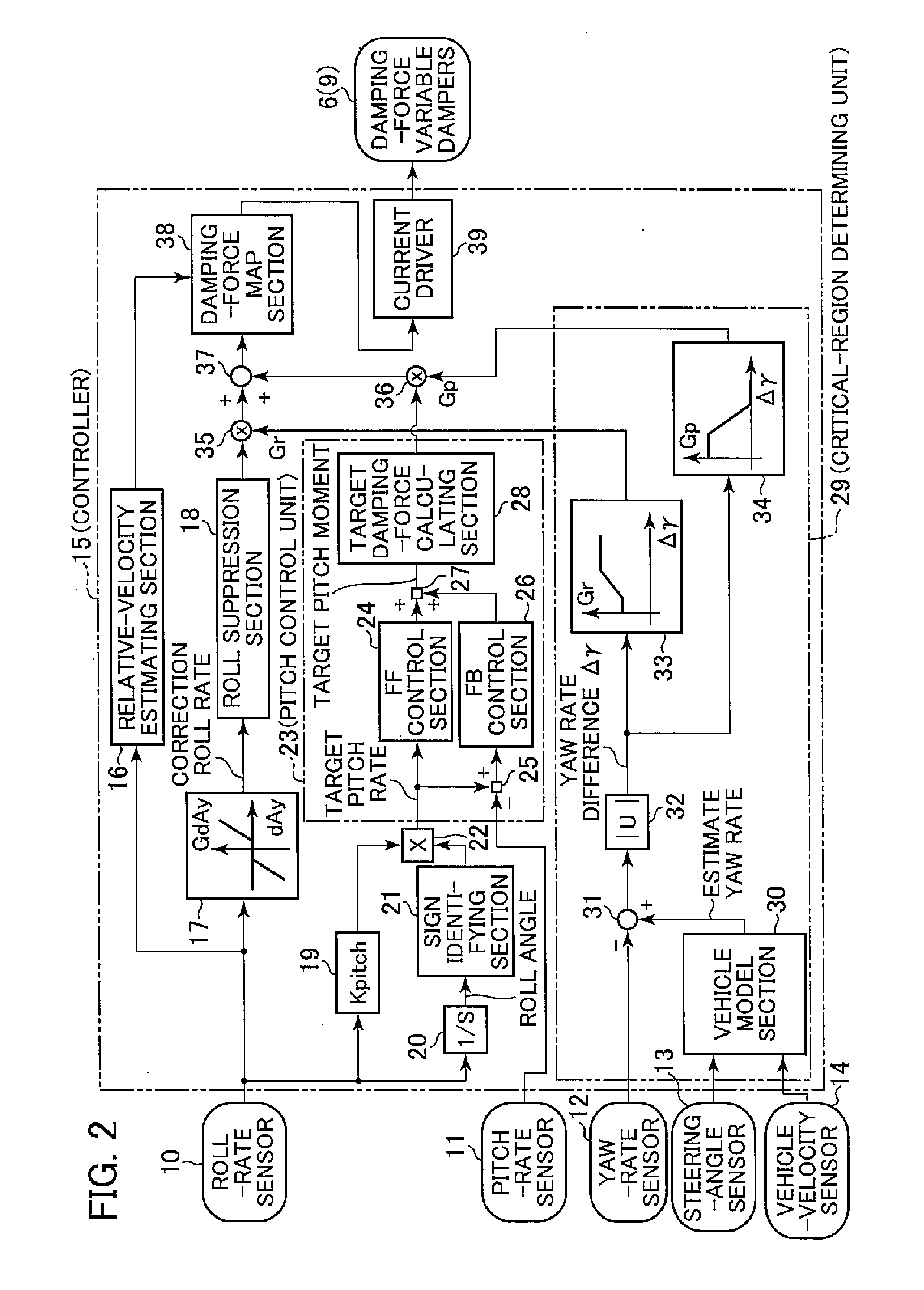
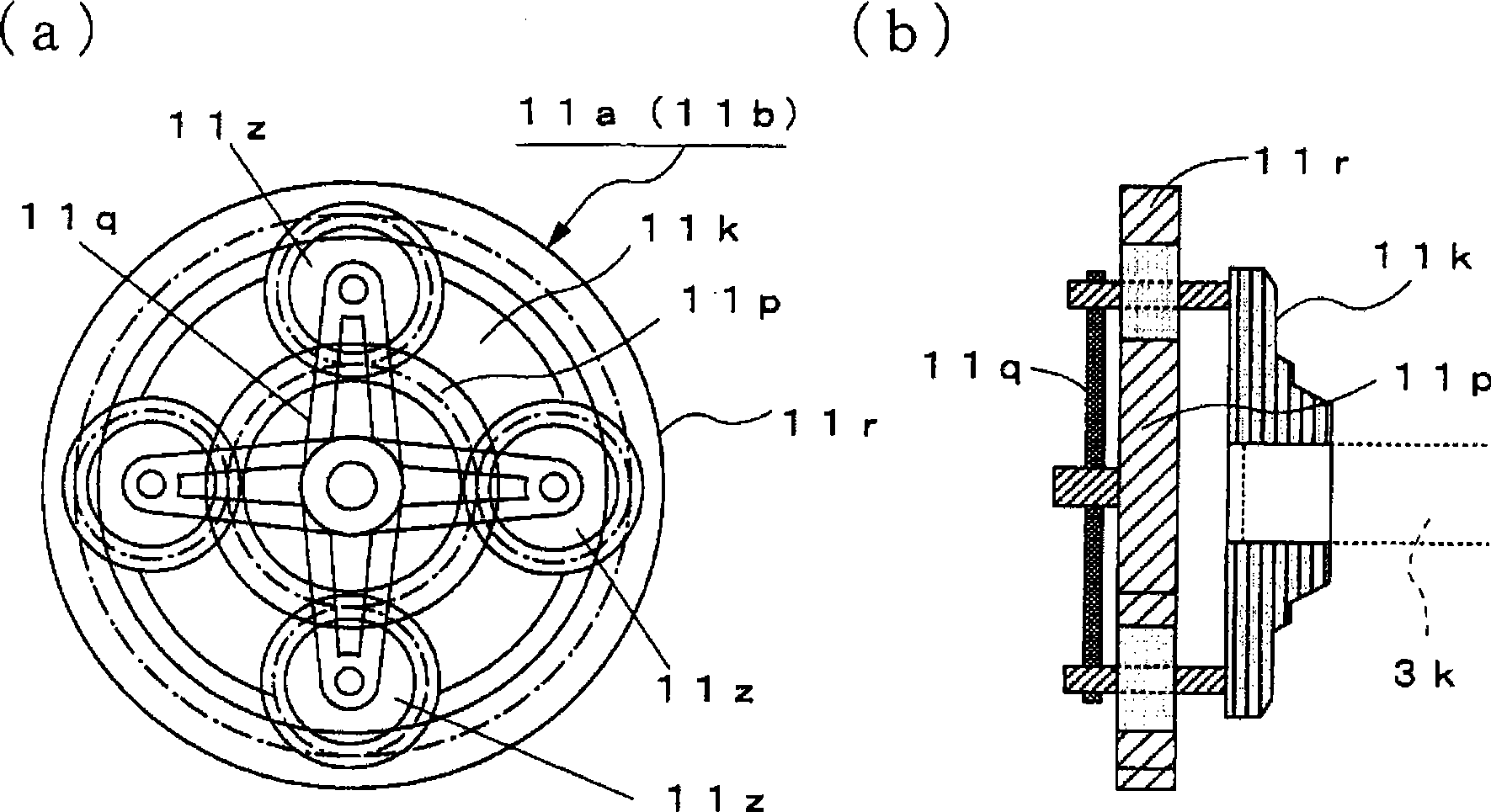
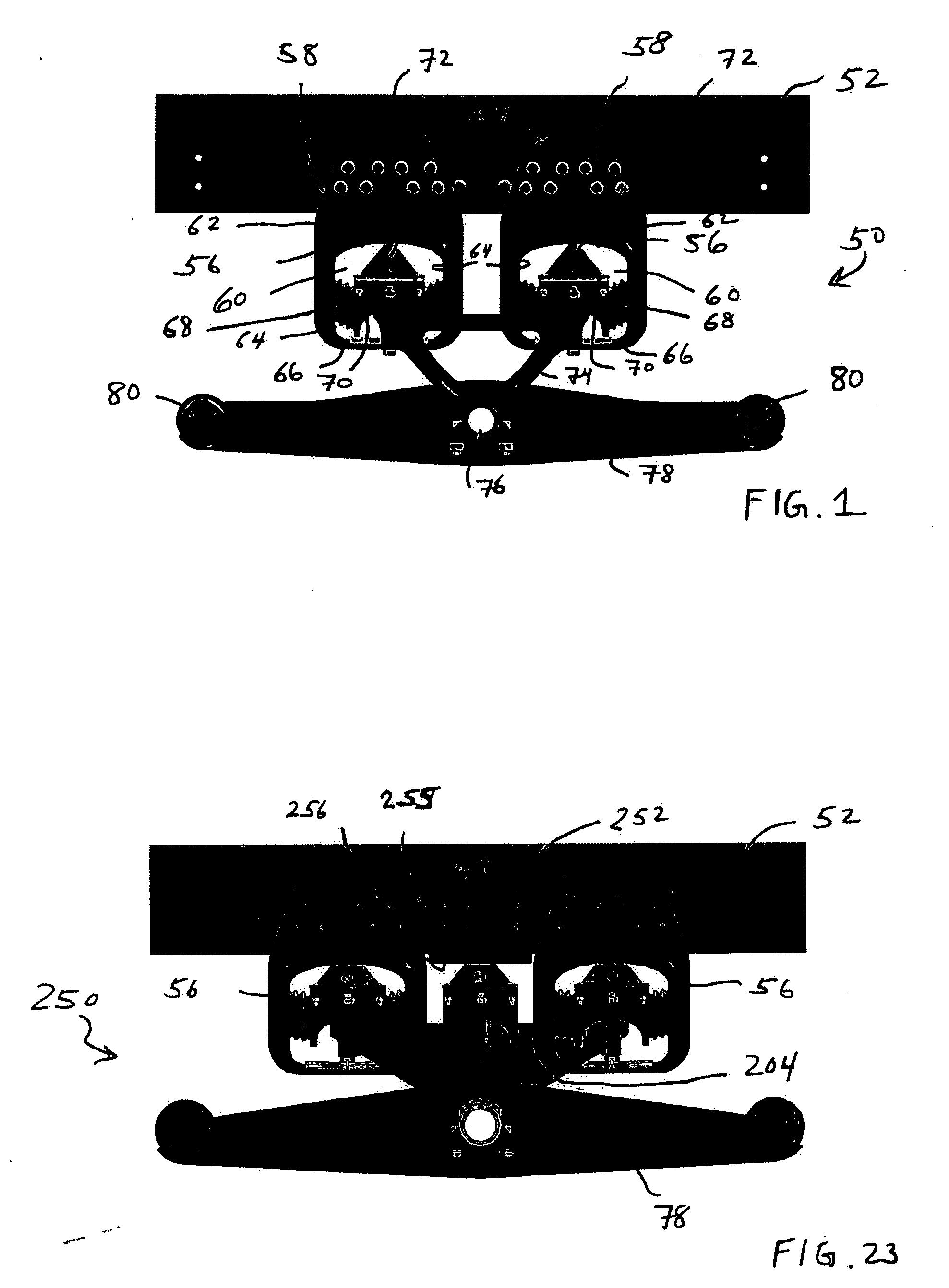
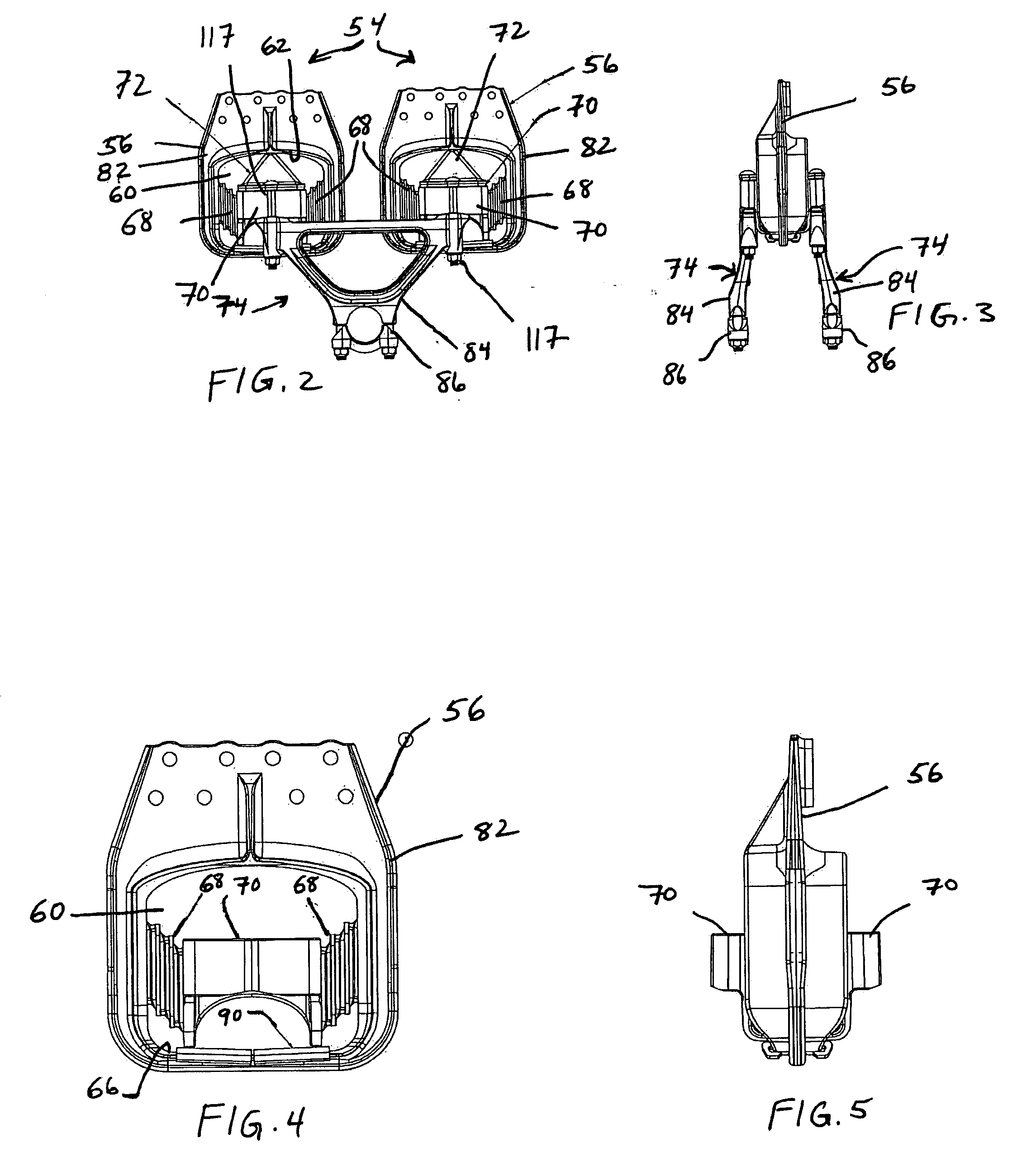
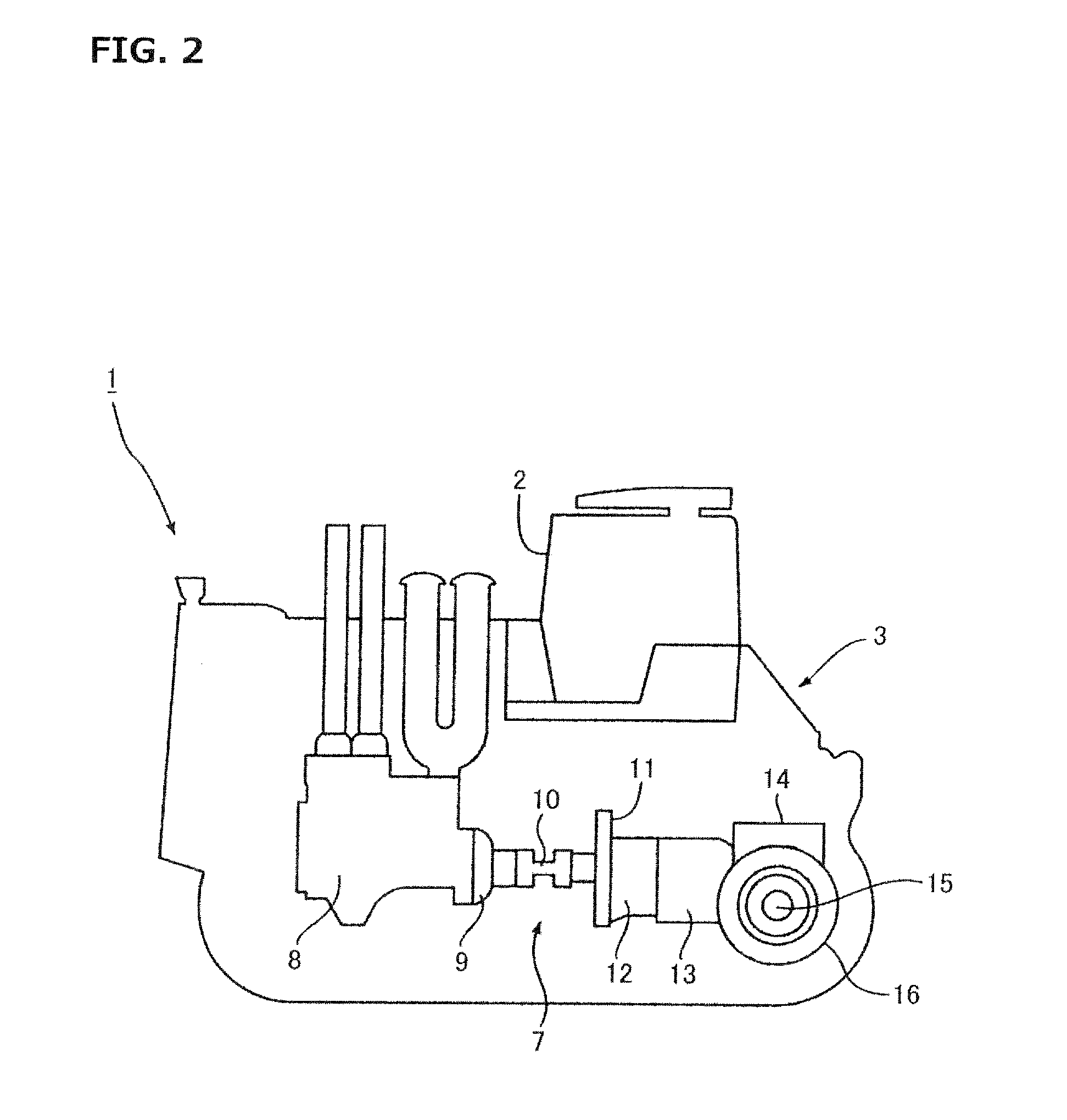
Vehicle attitude controller
ActiveUS20120078470A1Guaranteed uptimeFeel goodDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesAttitude controlSnubber
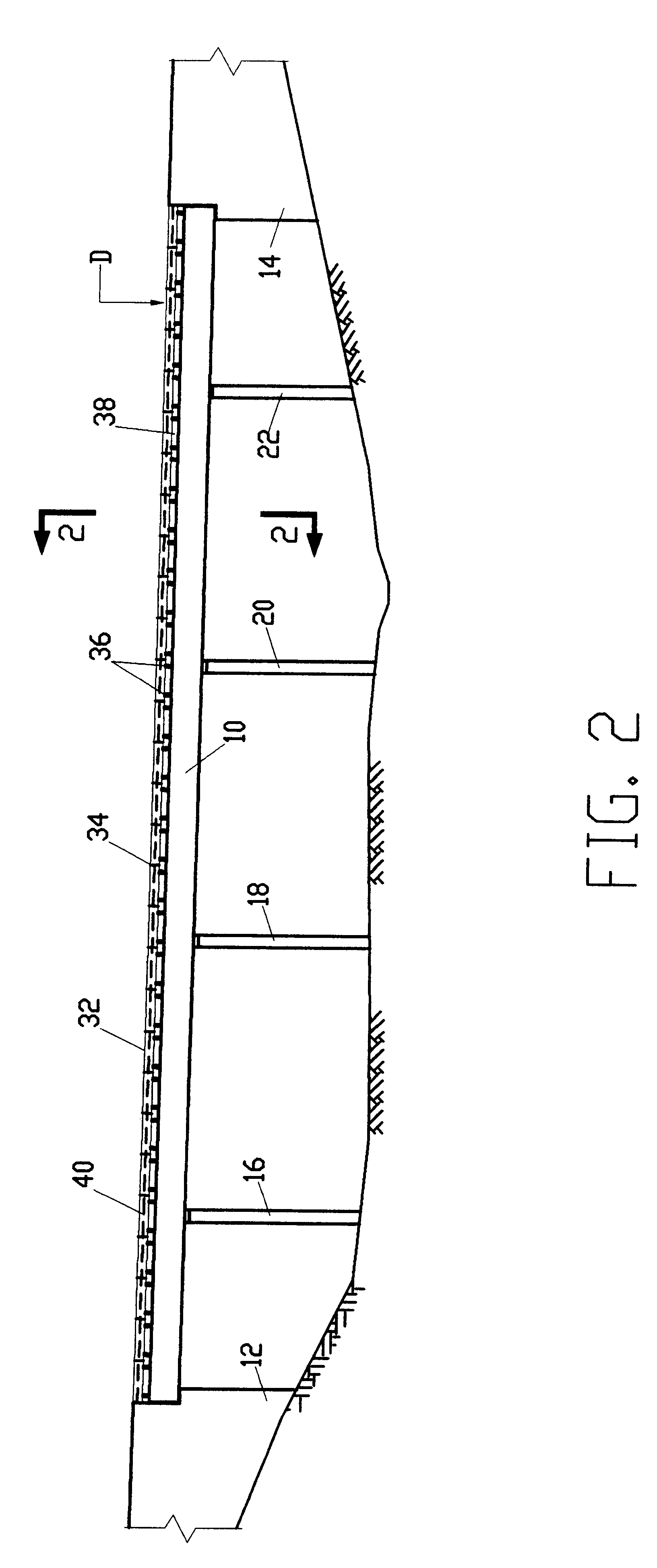
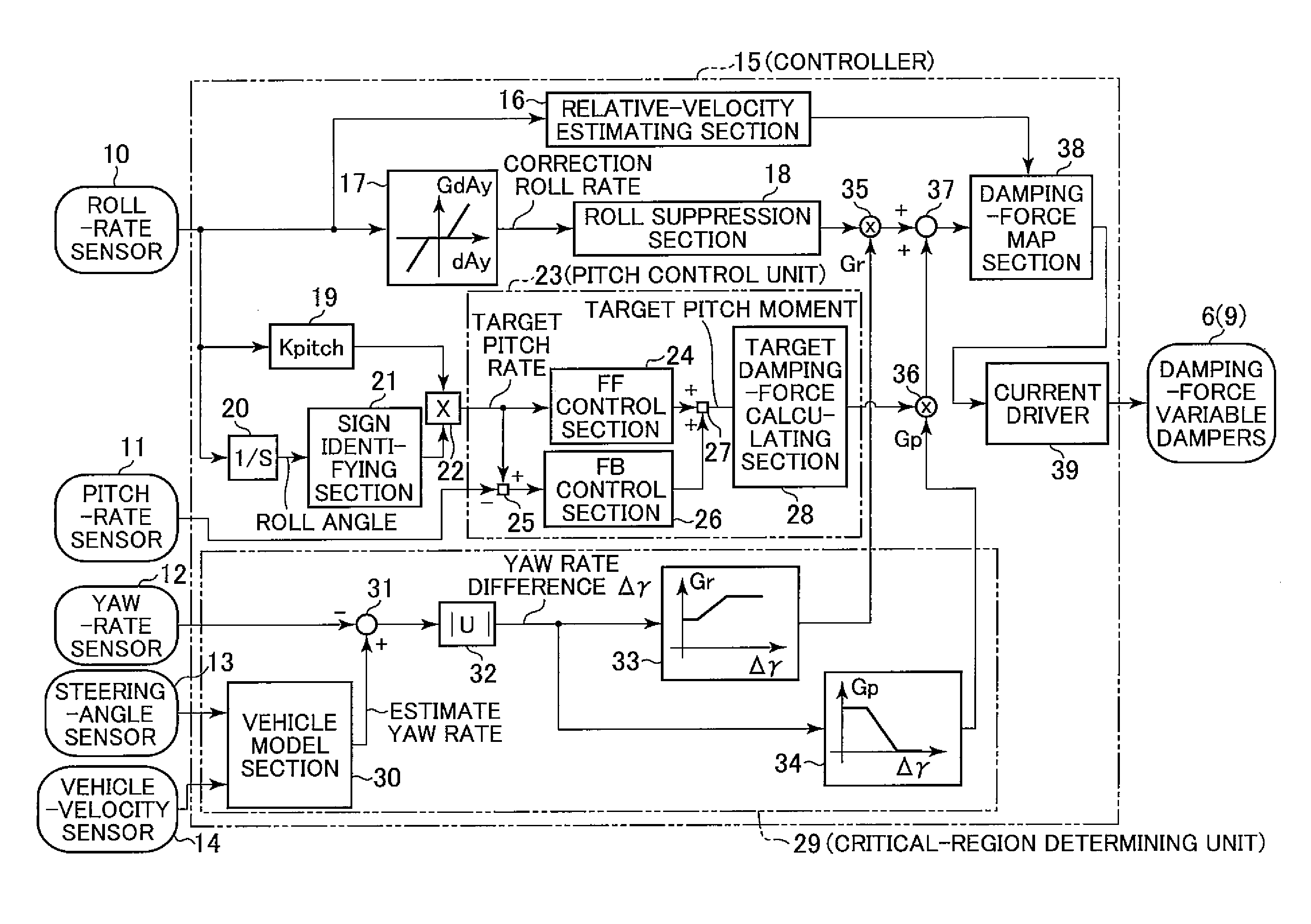
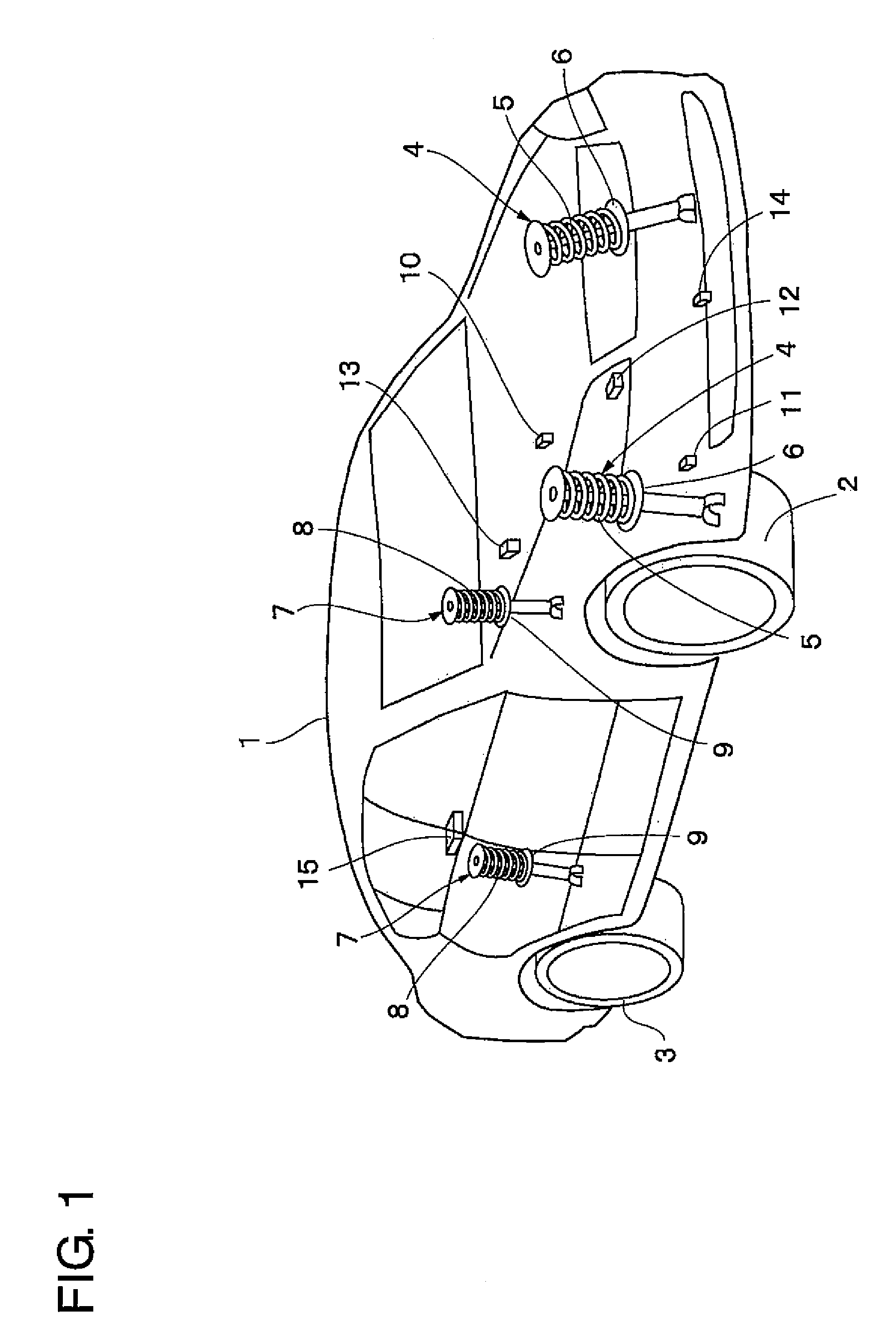
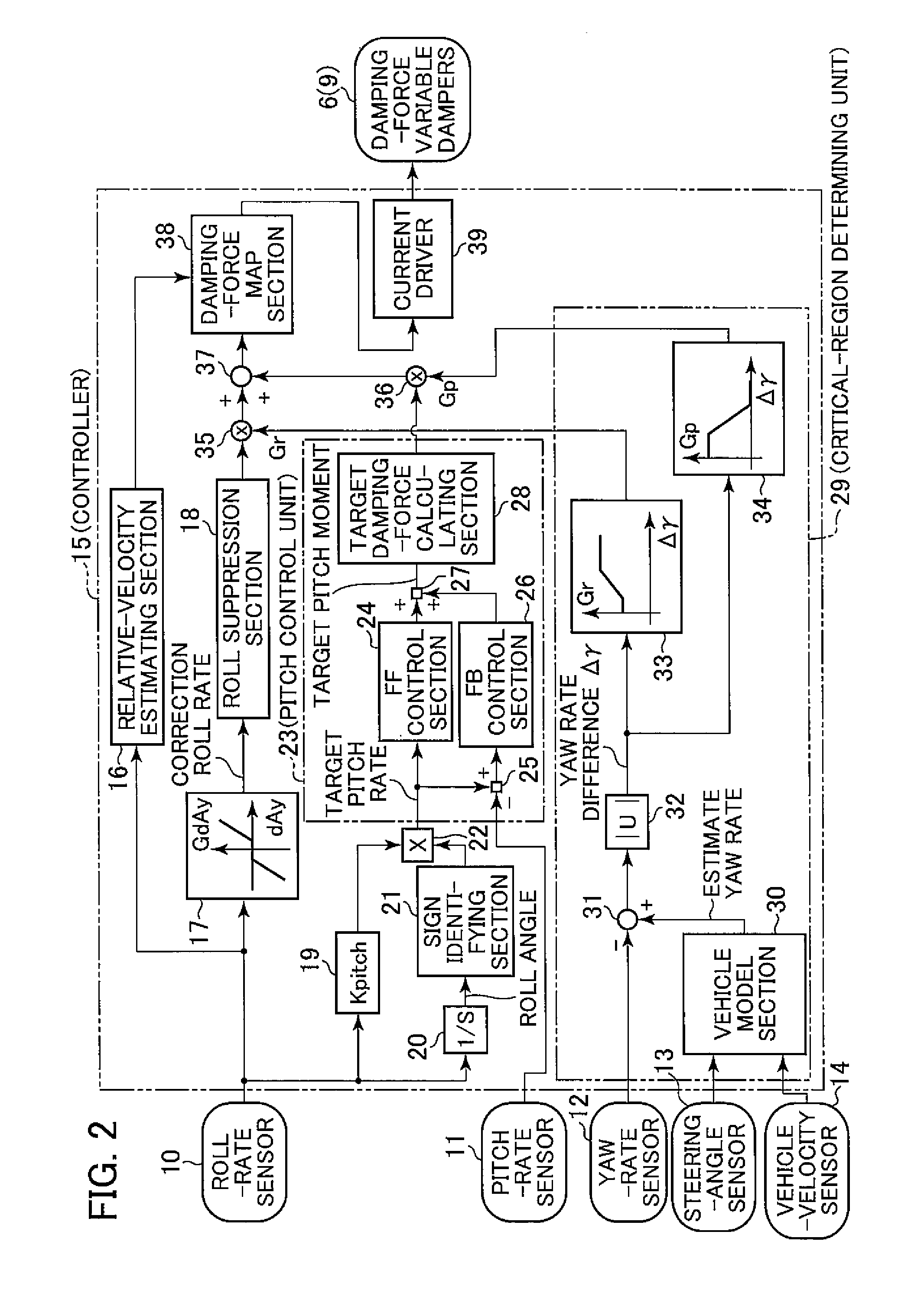
A vehicle attitude controller capable of improving turning operability, steering stability, and ride quality of a vehicle. In a normal-operation region, a pitch control unit for calculating a target pitch rate in accordance with a roll rate performs control in priority to a roll suppression section. In this case, a target damping force calculated in the pitch control unit is weighed to control a damping-force characteristic of the dampers so that a pitch rate becomes equal to the target pitch rate. In a critical region in which a road-surface gripping state of the vehicle tires is bad, the roll suppression section performs control in priority to the pitch control unit so as to weigh a target damping force calculated in the roll suppression section. As a result, the damping-force characteristic of the dampers is controlled so as to increase the amount of roll suppression control.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
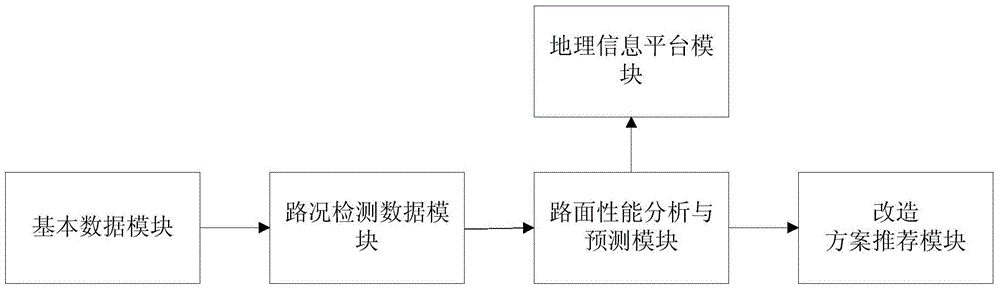
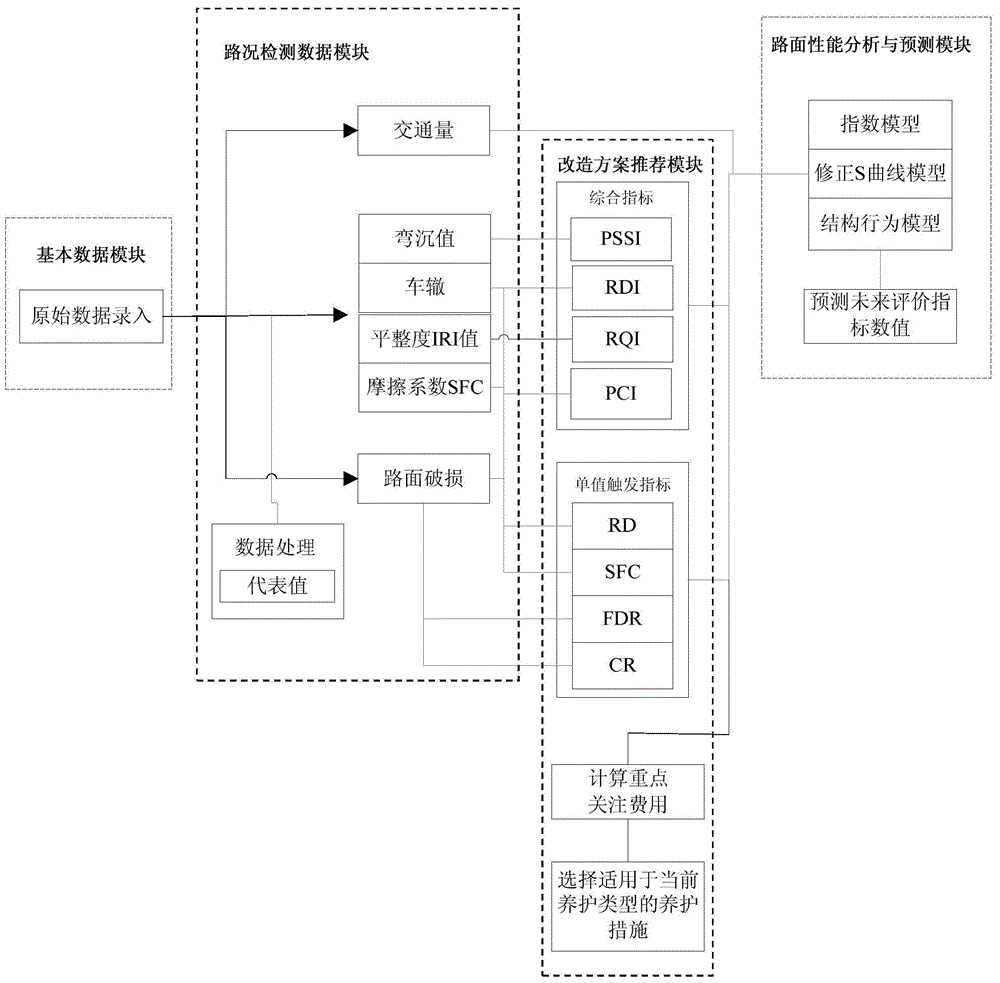
Modification scheme decision-making system and method for bituminous pavement
InactiveCN104463348AEasy to useSmall amount of calculationForecastingResourcesPavement maintenanceImage resolution
Owner:辽宁省交通科学研究院有限责任公司
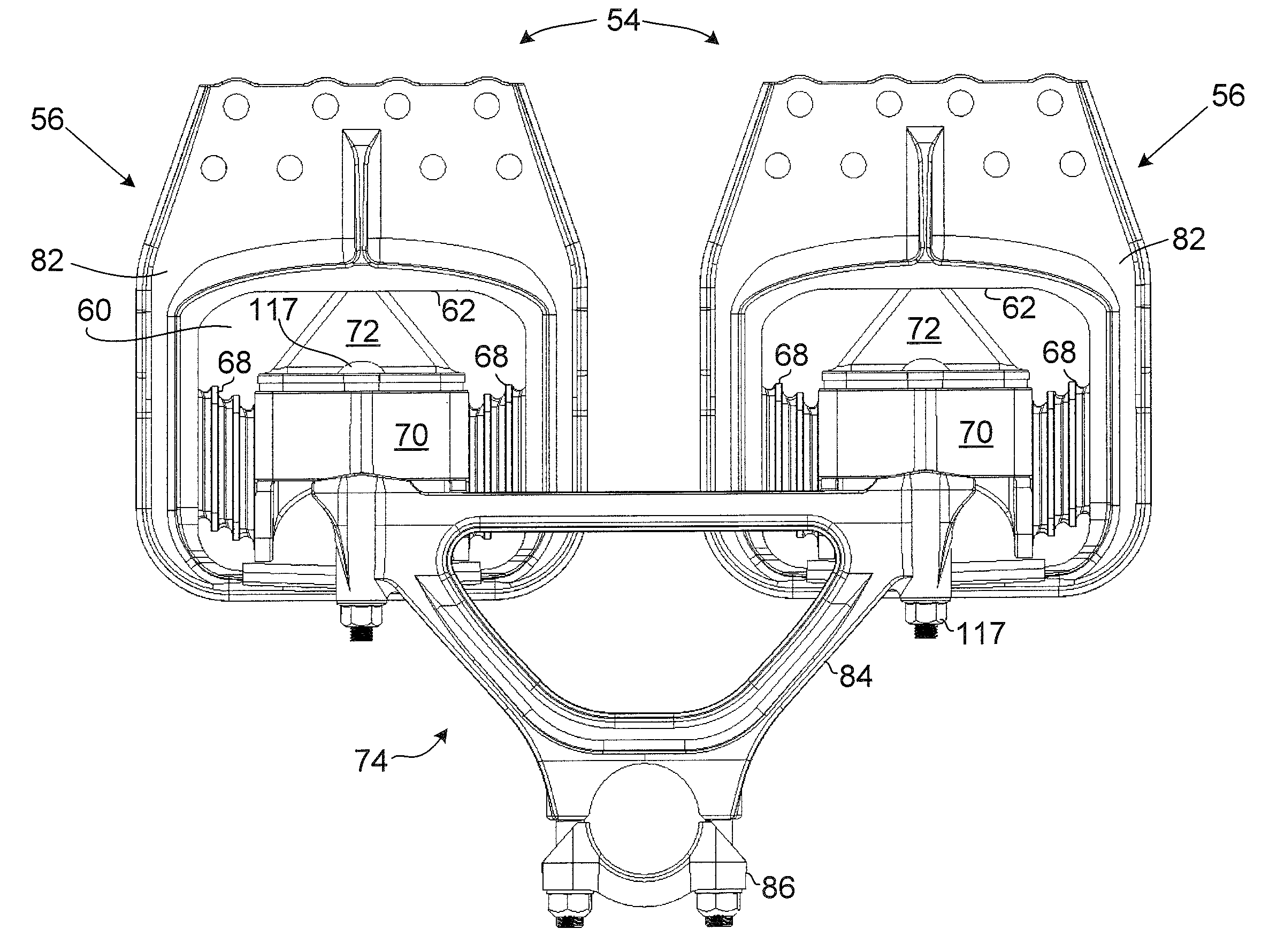
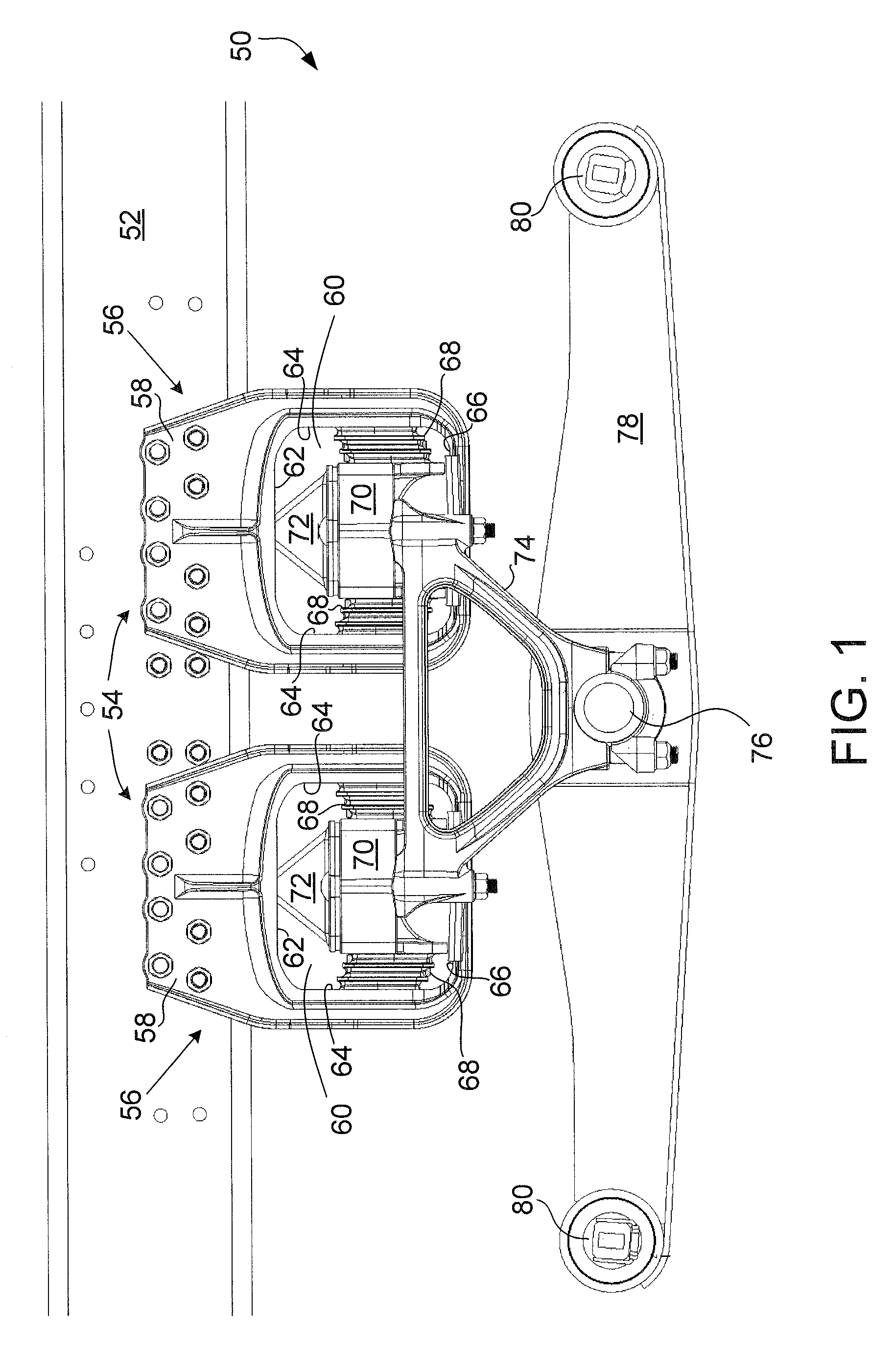
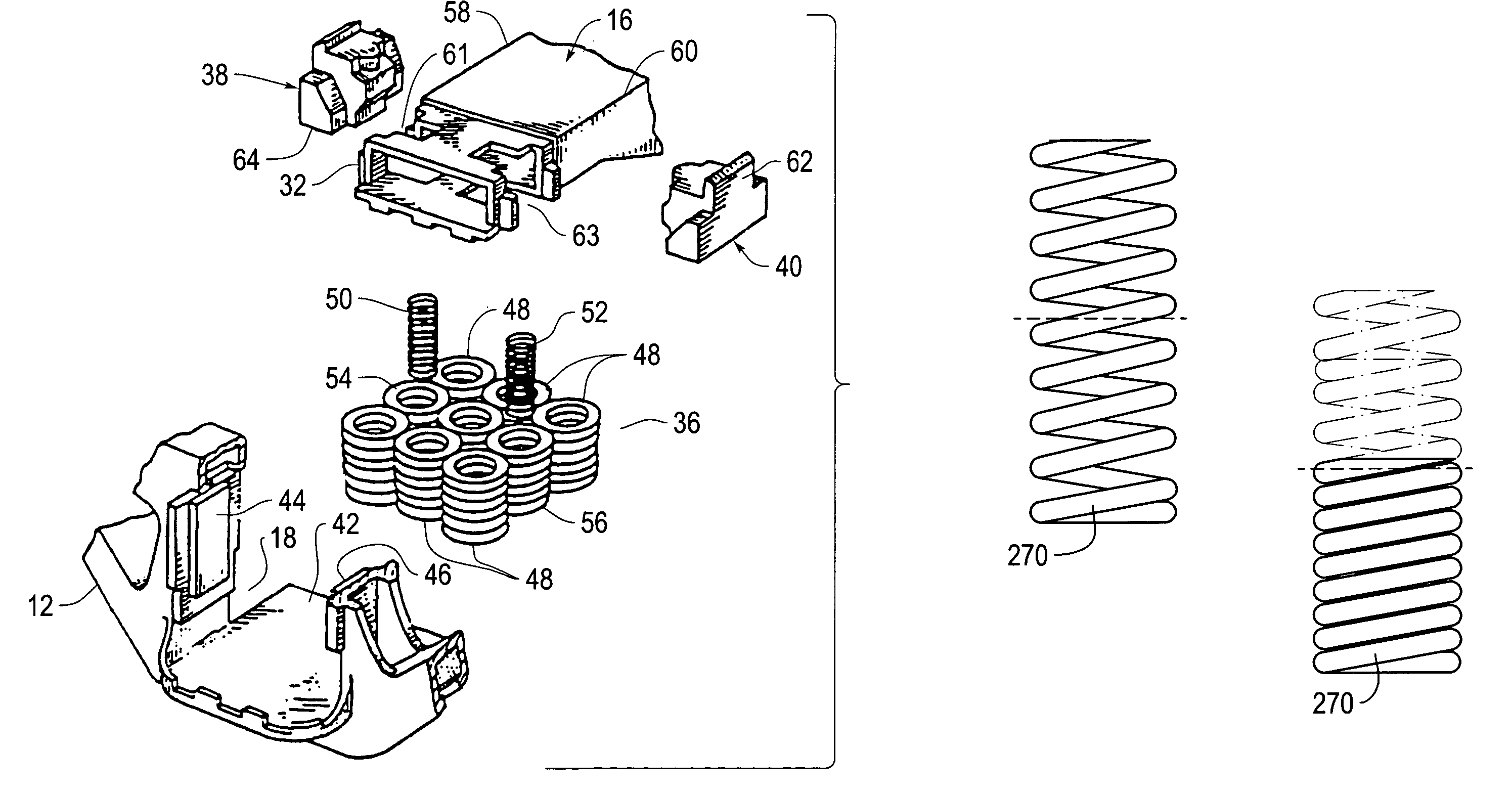
Elastomeric spring vehicle suspension
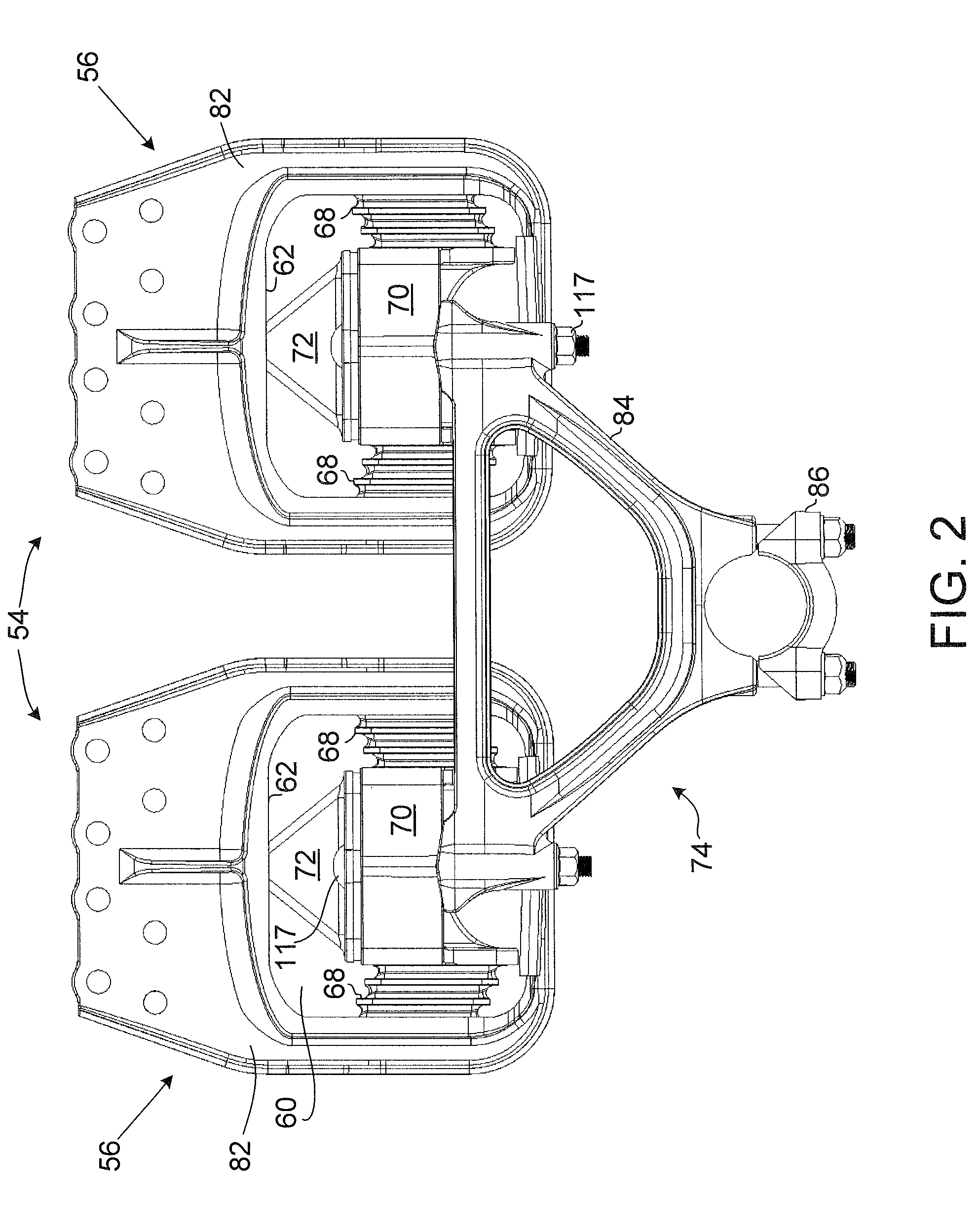
An elastomeric spring suspension is described for supporting a longitudinally extending vehicle frame rail above first and second axles forming a tandem axle configuration. The suspension includes a frame hanger assembly mounted to the vehicle frame rail. The frame hanger assembly has two full spring modules, each of which includes two elastomeric shear springs, an elastomeric progressive spring rate load cushion having a pyramidal shape with a flattened top surface and a spring mount for mounting the springs. A saddle assembly is connected to the spring mount, and an equalizing beam is connected to the saddle assembly and further connected to the axles. The spring rate for the suspension increases almost linearly as a function of sprung load, resembling a pneumatic suspension. Accordingly, the suspension exhibits excellent ride quality, without sacrificing roll stability.
Owner:HENDRICKSON USA L L C
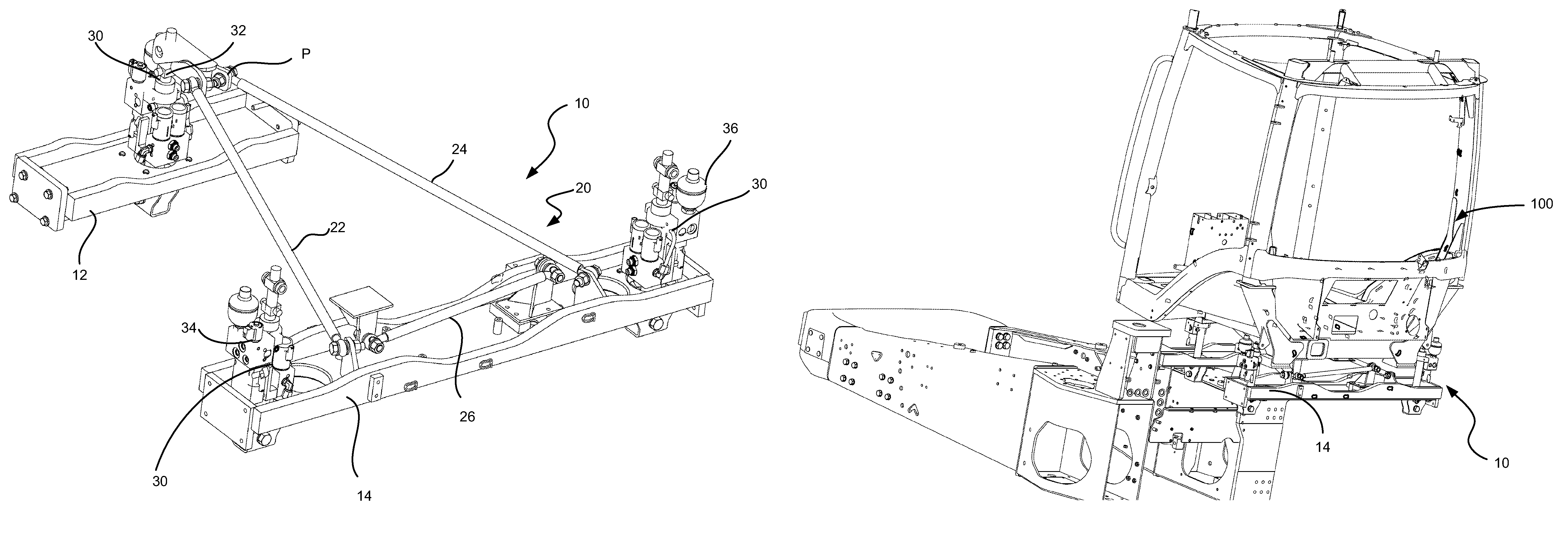
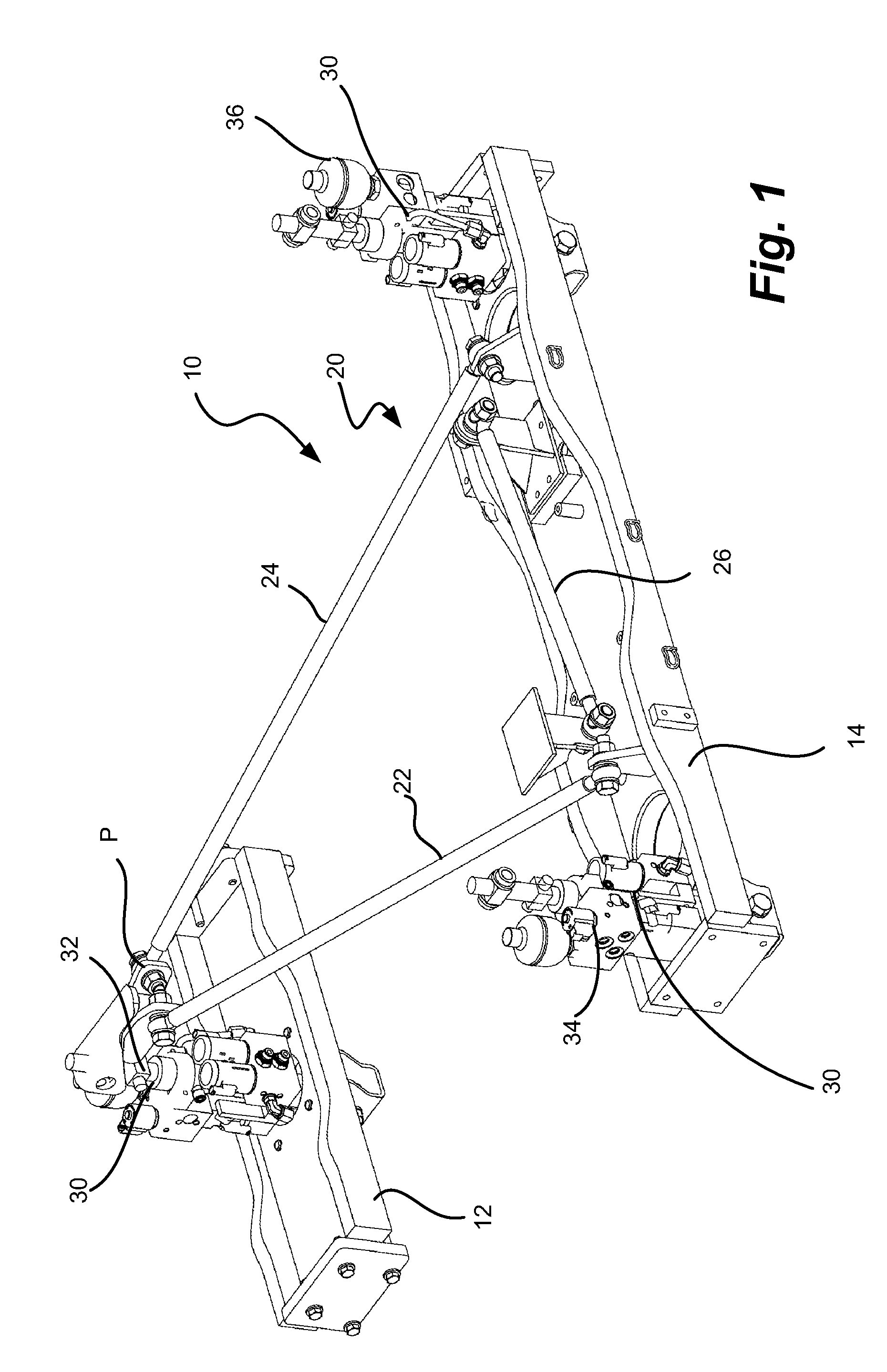
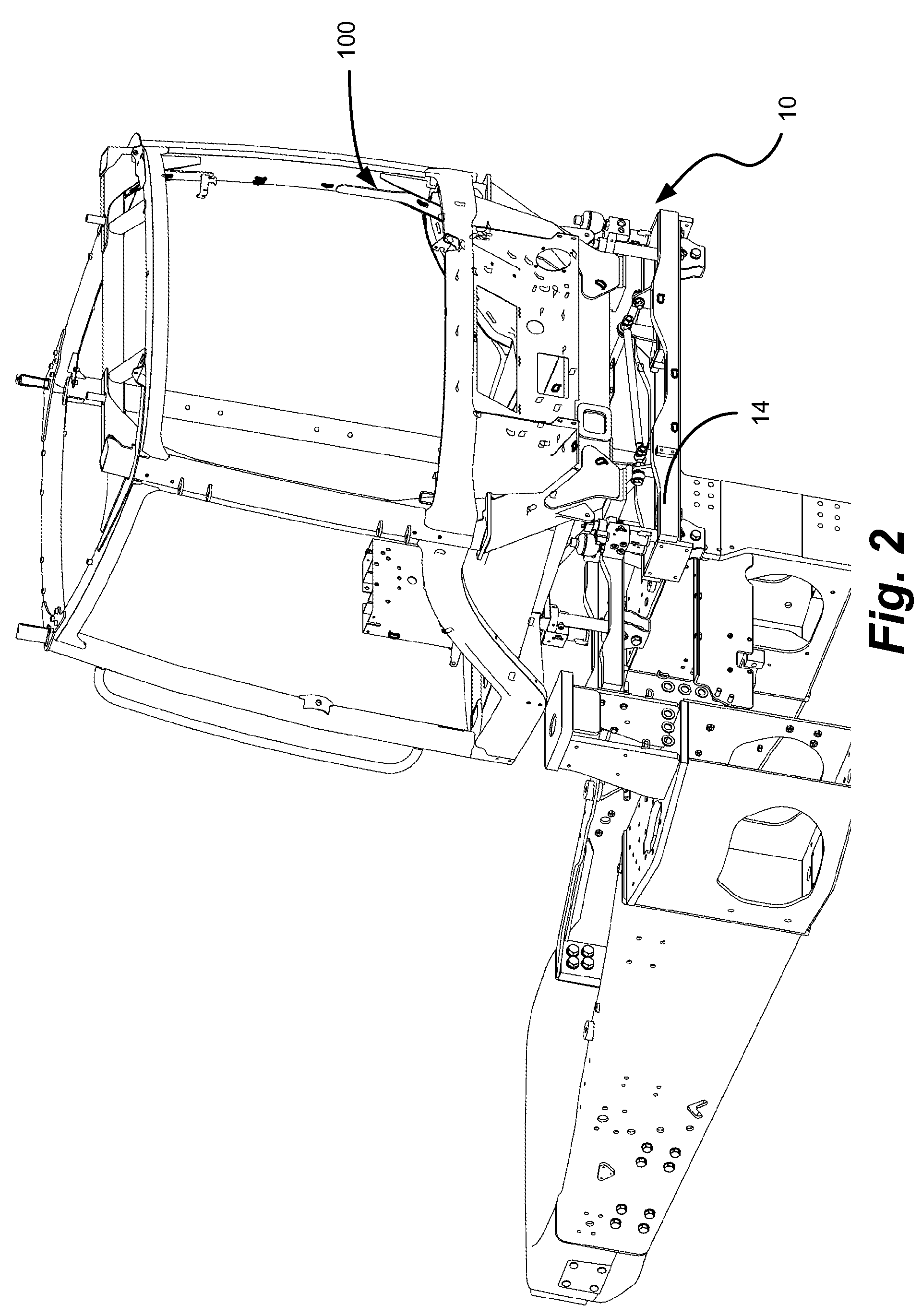
Cab suspension linkage system
InactiveUS7744149B2Reduce the overall heightImprove ride qualityVehicle seatsDashboardsVehicle frameRide quality
An agricultural vehicle is described having a chassis and a cab mounted on the chassis. A suspension system for reducing the accelerations transmitted from the vehicles tires or tracks through the frame, into the cab, and ultimately through to the operator is provided. By reducing the accelerations, the ride quality is greatly improved, allowing operators to operate a vehicle for longer periods of time without excessive fatigue.
Owner:AGCO CORP
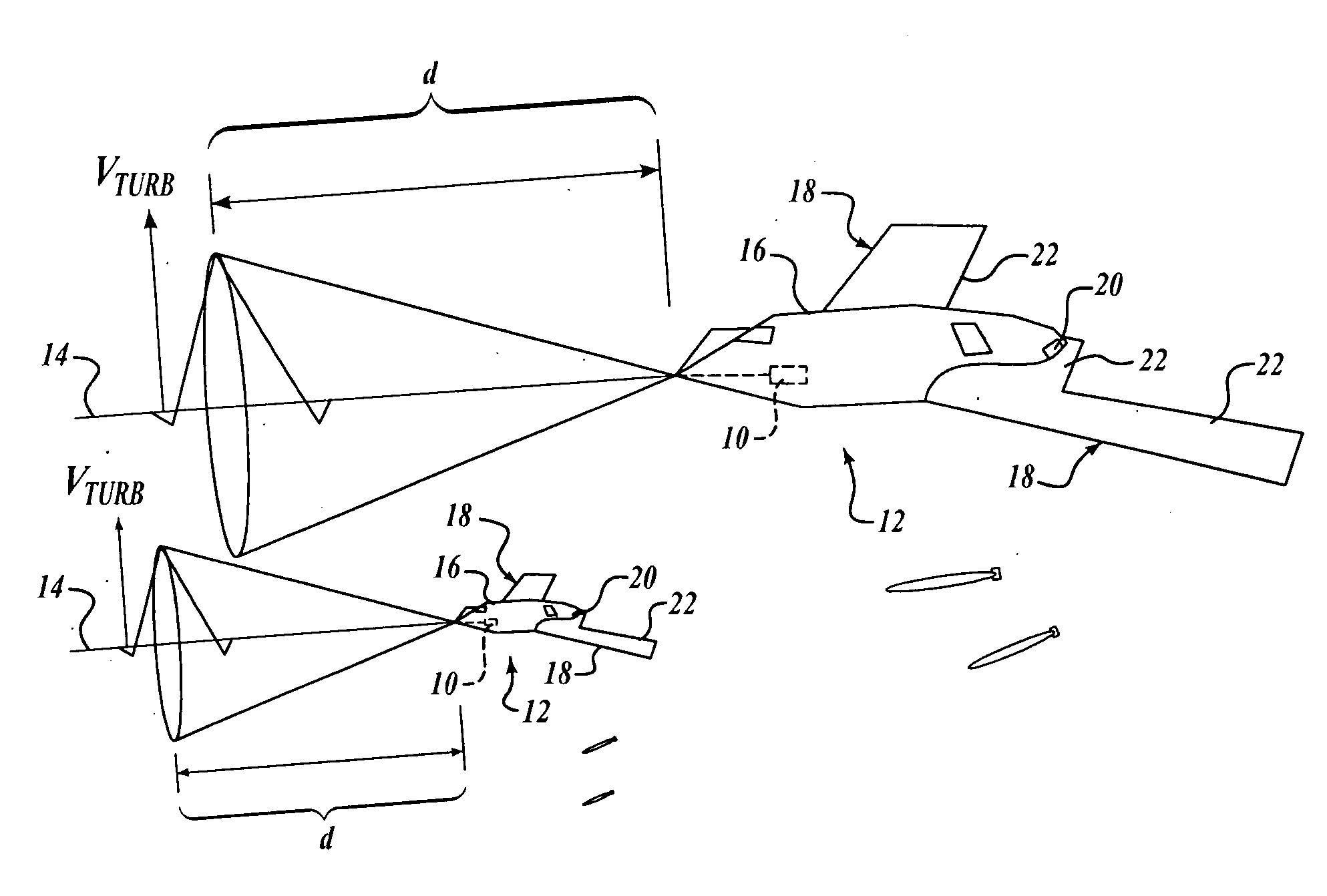
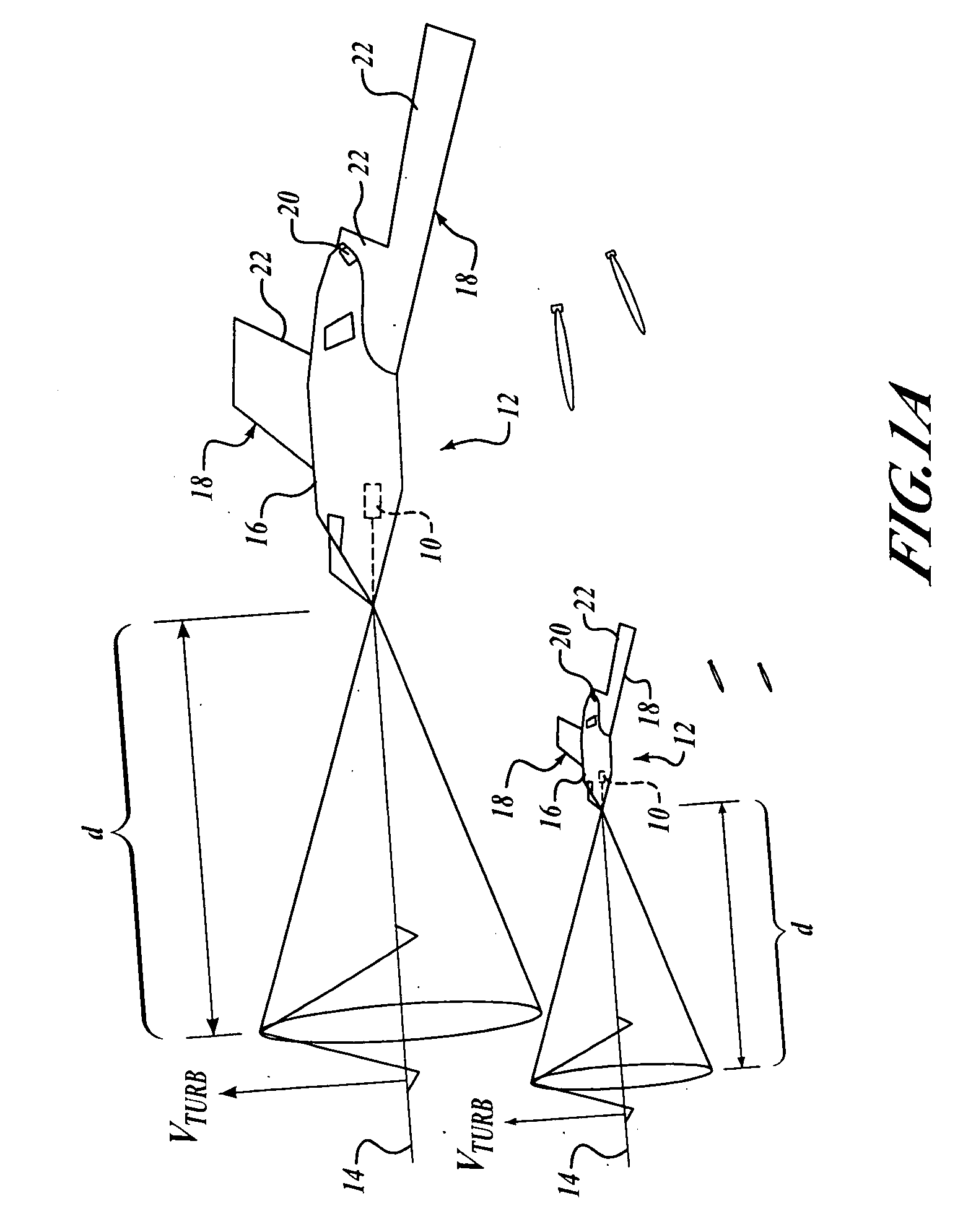
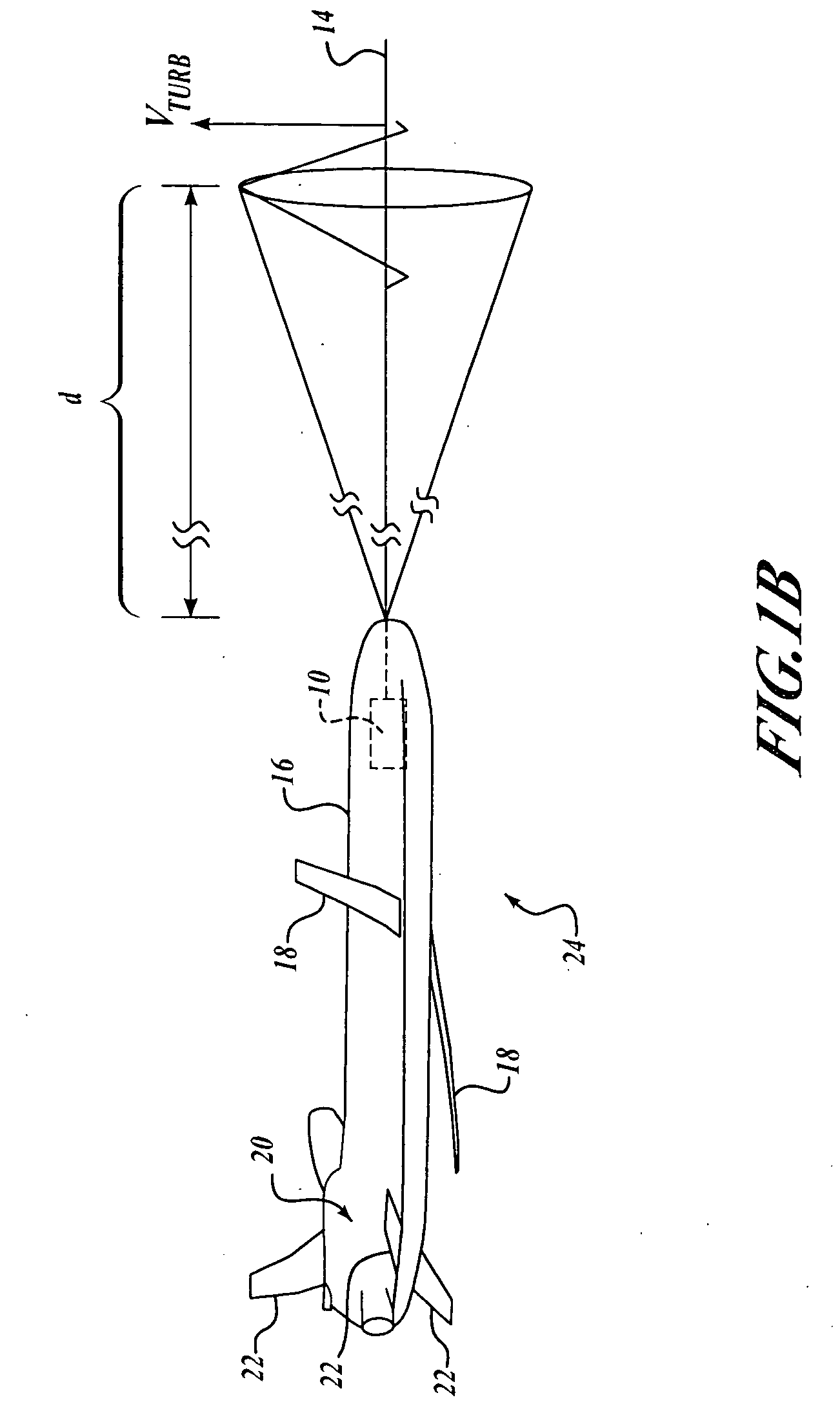
Proactive optical wind shear protection and ride quality improvement system
InactiveUS20090048723A1Improve ride qualityImprove flight safetyAircraft power plantsDirection controllersFlight vehicleControl signal
Embodiments of the present invention automatically compensate control of an aircraft for an environmental condition, such as turbulence or wind shear. A sensor is configured to sense speed of air relative to an aircraft at a predetermined distance in front of the aircraft. A processor is coupled to receive the sensed speed of air from the sensor. The processor includes a first component configured to determine whether the speed of the air at the predetermined distance is indicative of an environmental condition, such as turbulence or wind shear. A second component is configured to automatically generate control signals for controlling the aircraft such that the environmental condition is automatically compensated by a time the aircraft enters the environmental condition.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
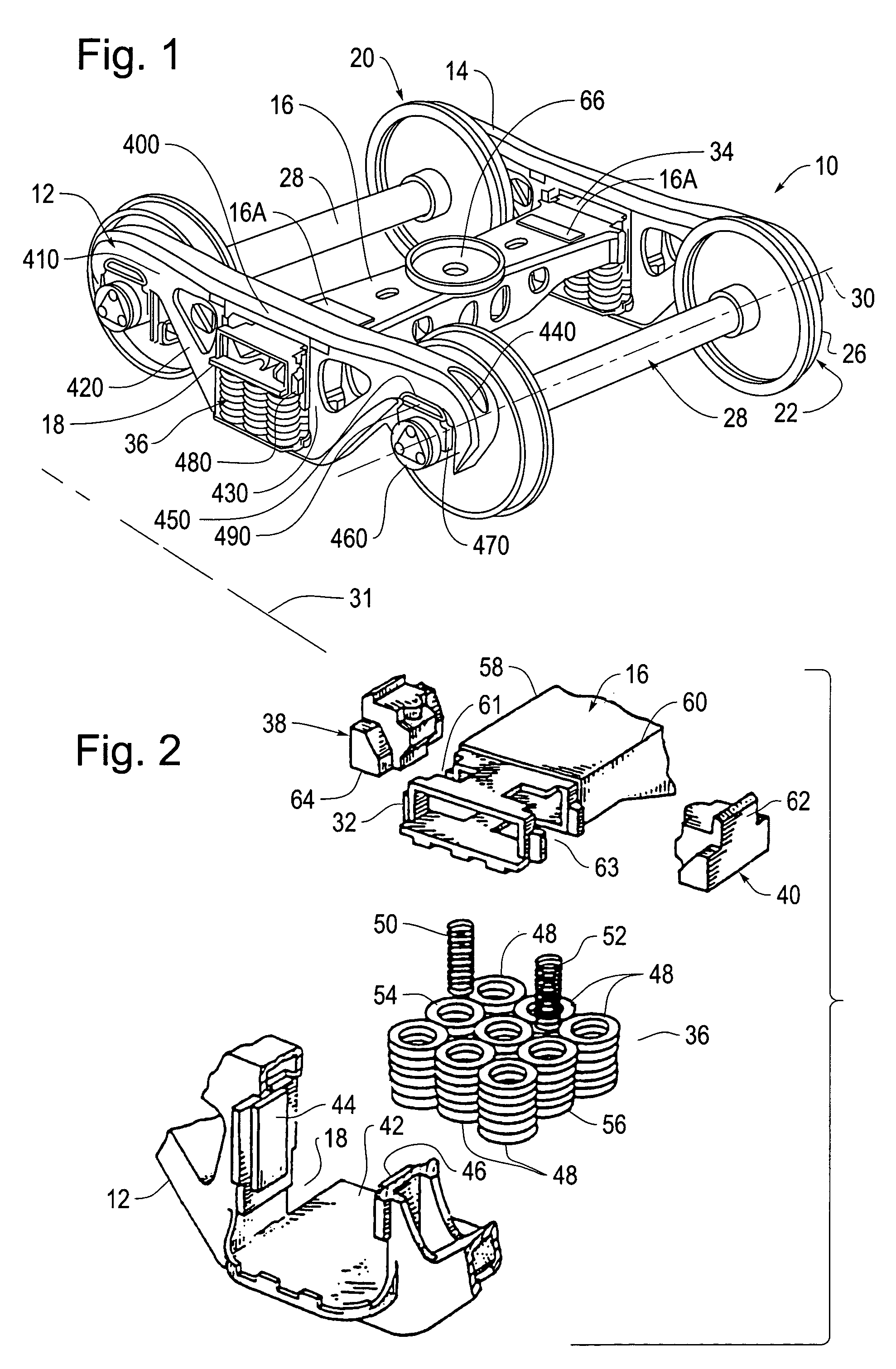
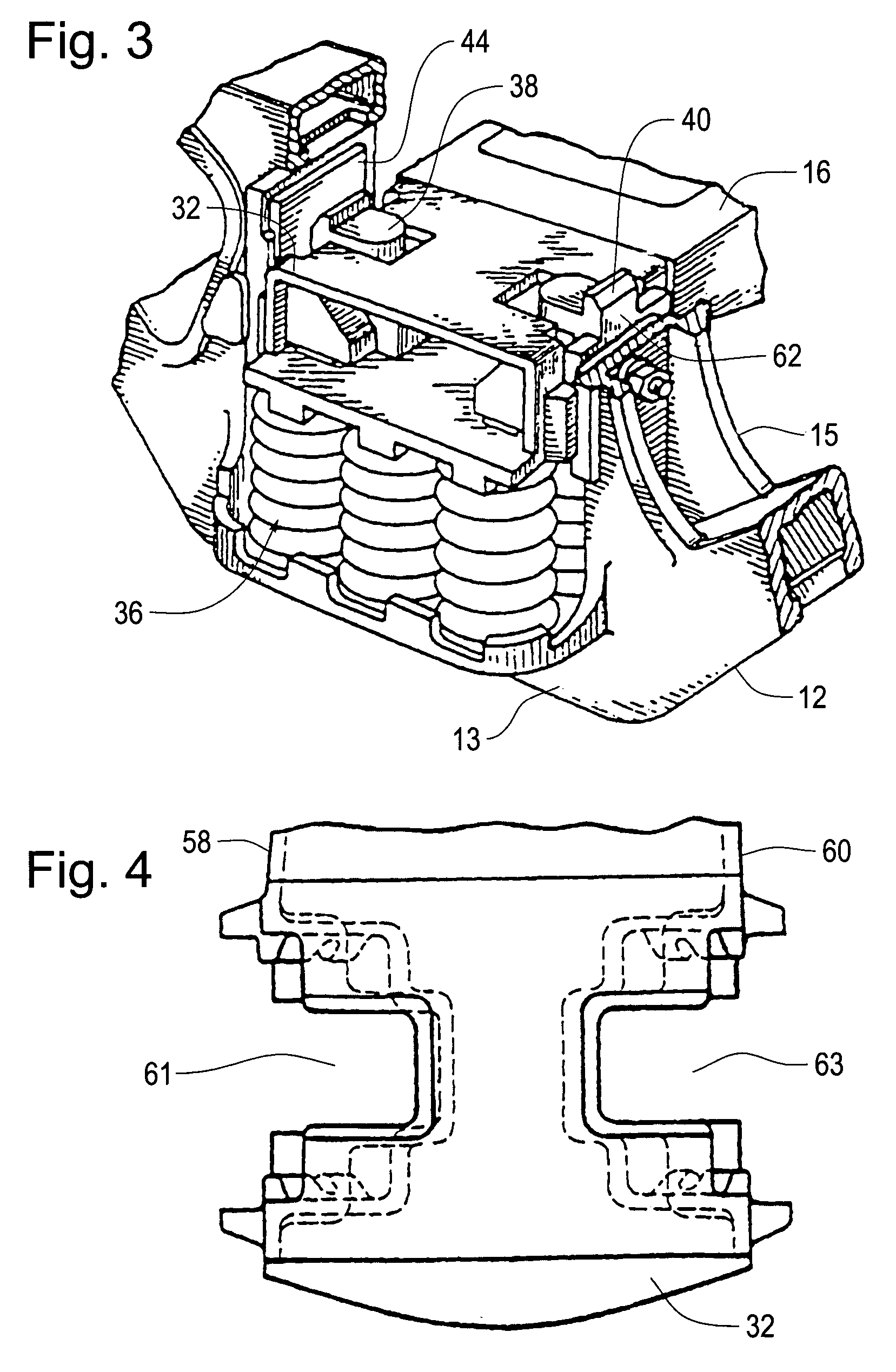
Three-piece motion control truck system
An improved three-piece truck system for railroad cars provides long travel side bearings for improved stability, a “wide” friction shoe design or equivalent to improve sideframe and bolster squareness, a resilient pedestal pad for improved curving performance and enhanced wear resistance, and a suspension system tuned and optimized for rail cars to have a minimum reserve capacity of less than 1.5 to improve motion control and ride quality, increase resistance to suspension bottoming, and increase hunting threshold speed. Such a motion control truck system is able to meet recent, more stringent American Association of Railroads standards, such as M-976, for railcars having a 286,000 lb. gross rail load rating.
Owner:AMSTED RAIL CO INC
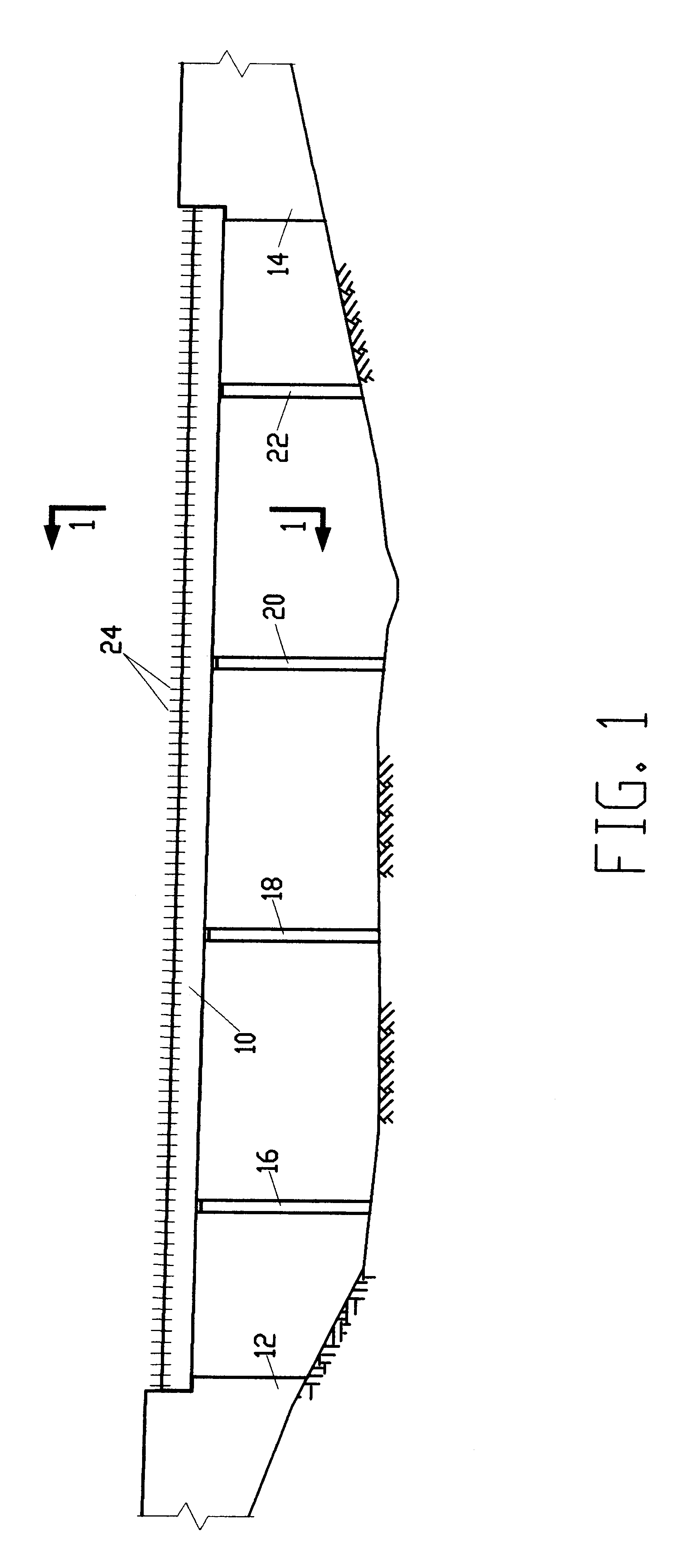
Composite bridge superstructure with precast deck elements
InactiveUS6470524B1Good ride qualitySaving maintenance costBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblyPre stressCrack free
A method for constructing a composite bridge superstructure of simple precast elements. According to the method, the bridge superstucture is comprised of one or more prestressed beams aligned substantially parallel to the bridge longitudinal axis. On top of the prestressed beams, there is placed a plurality of full width, precast deck slabs forming the bridge deck, with the precast deck slabs being transversely disposed side by side, with adjacent slabs attached by joints to complete the bridge deck structure. The deck slabs are spaced from the beams by spacing devices, such that a gap is left between the beams and the deck slabs and the bridge deck structure is prestressed separately from the beams. Subsequent to the prestressing of the deck structure and the beams, the bridge deck structure is connected to the beams by a concrete layer cast in situ in the gap between the bottom face of the precast deck slabs and the top face of the prestressed beams. The concrete is preferably of the low shrinkage type but normal shrinkage concrete may also be employed. The connection is further reinforced by a plurality of shear stirrups. The method is characterized by separate prestressing of the deck structure and the beams and by natural compression of the connecting concrete layer resulting in significant savings of construction time and costs. The construction sequence according to the method enables the deck structure as well as the cast in place concrete layer connecting the deck structure to the beams to undergo a natural compressing process due to time dependent creep and shrinkage contraction of the beams relative to the connecting layer and the deck structure, thereby eliminating the need to apply additional prestressing. In addition, the substantially separate longitudinal prestressing of the deck structure and the beams is highly effective, achieving considerable saving of prestressing steel. The natural compressing of the deck structure and the cast-in-place concrete layer result in crack-free condition and better riding quality of the deck, thereby eliminating the well known drawbacks of additional prestressing, and saving maintenance costs.
Owner:MAIRANTZ BENJAMIN
Vehicle attitude controller
ActiveUS8718872B2Feel goodDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesAttitude controlSnubber
A vehicle attitude controller capable of improving turning operability, steering stability, and ride quality of a vehicle. In a normal-operation region, a pitch control unit for calculating a target pitch rate in accordance with a roll rate performs control in priority to a roll suppression section. In this case, a target damping force calculated in the pitch control unit is weighed to control a damping-force characteristic of the dampers so that a pitch rate becomes equal to the target pitch rate. In a critical region in which a road-surface gripping state of the vehicle tires is bad, the roll suppression section performs control in priority to the pitch control unit so as to weigh a target damping force calculated in the roll suppression section. As a result, the damping-force characteristic of the dampers is controlled so as to increase the amount of roll suppression control.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
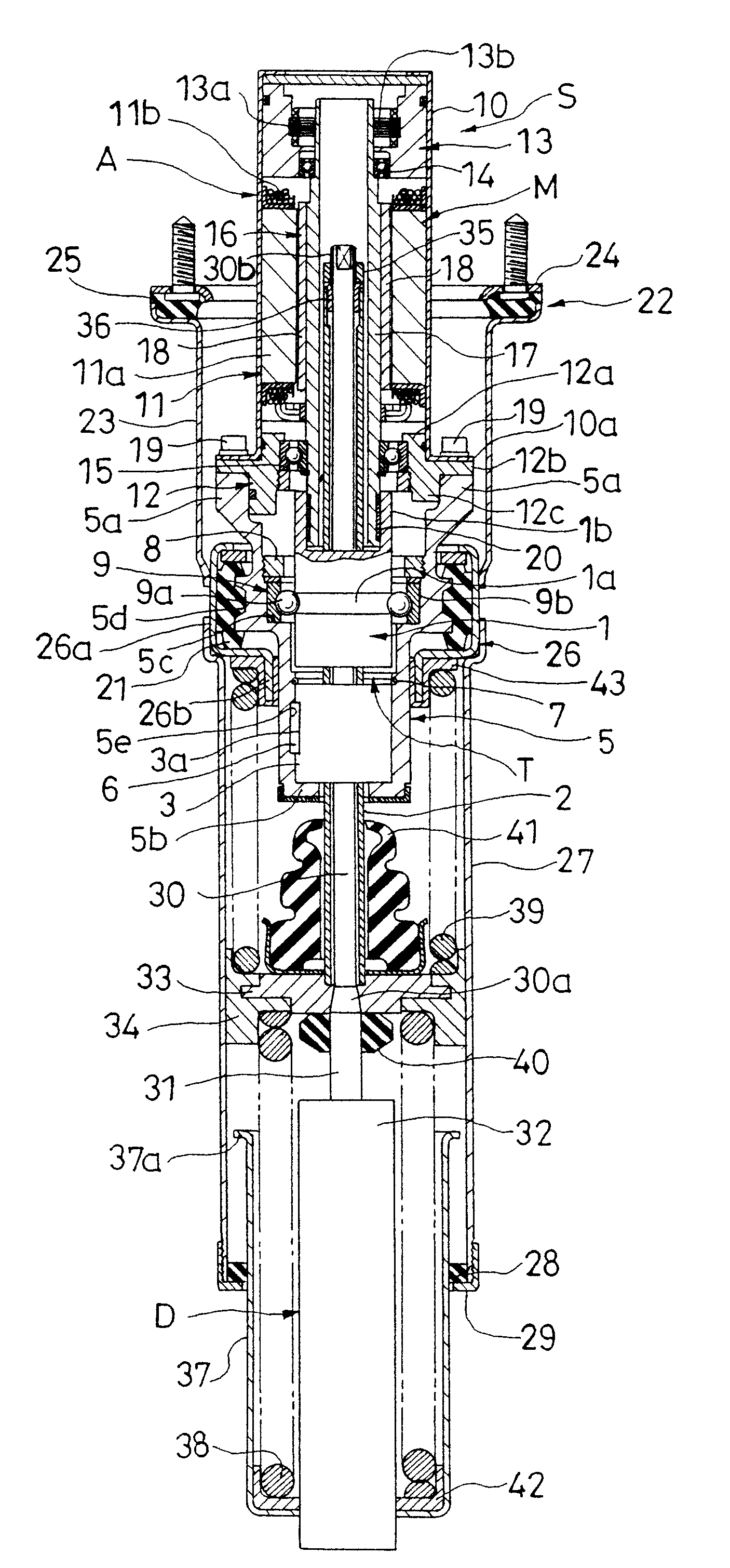
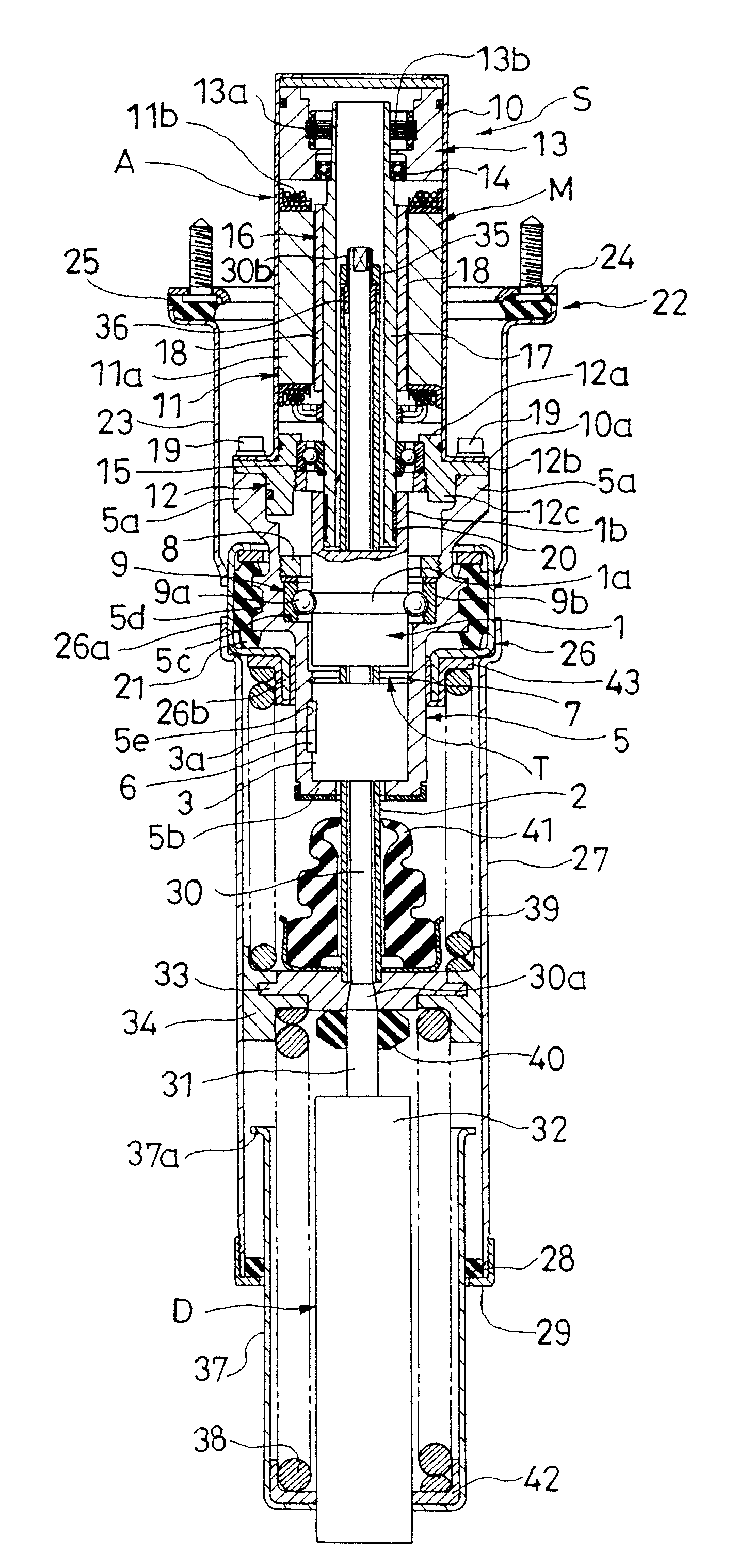
Suspension device
InactiveUS8490761B2Improving reliability and vehicle ride qualityImprove ride qualitySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionLinear motionEngineering
A suspension device (S) comprises: an actuator (A) including a motion conversion mechanism (T) for converting a linear motion to a rotational motion and a motor (M) connected to a rotary member (1) which performs the rotational motion in the motion conversion mechanism (T); a fluid pressure damper (D) connected to a linear motion member (2) which performs the linear motion in the motion conversion mechanism (T); an outer cylinder (27) connected to the actuator (A); and a bearing (34) attached to a rod (31) or a cylinder (32) connected to the linear motion member (2) of the fluid pressure damper (D) and slidably contacting with the inner circumference of the outer cylinder (27). This suspension device can improve reliability and vehicle ride quality.
Owner:KYB CORP
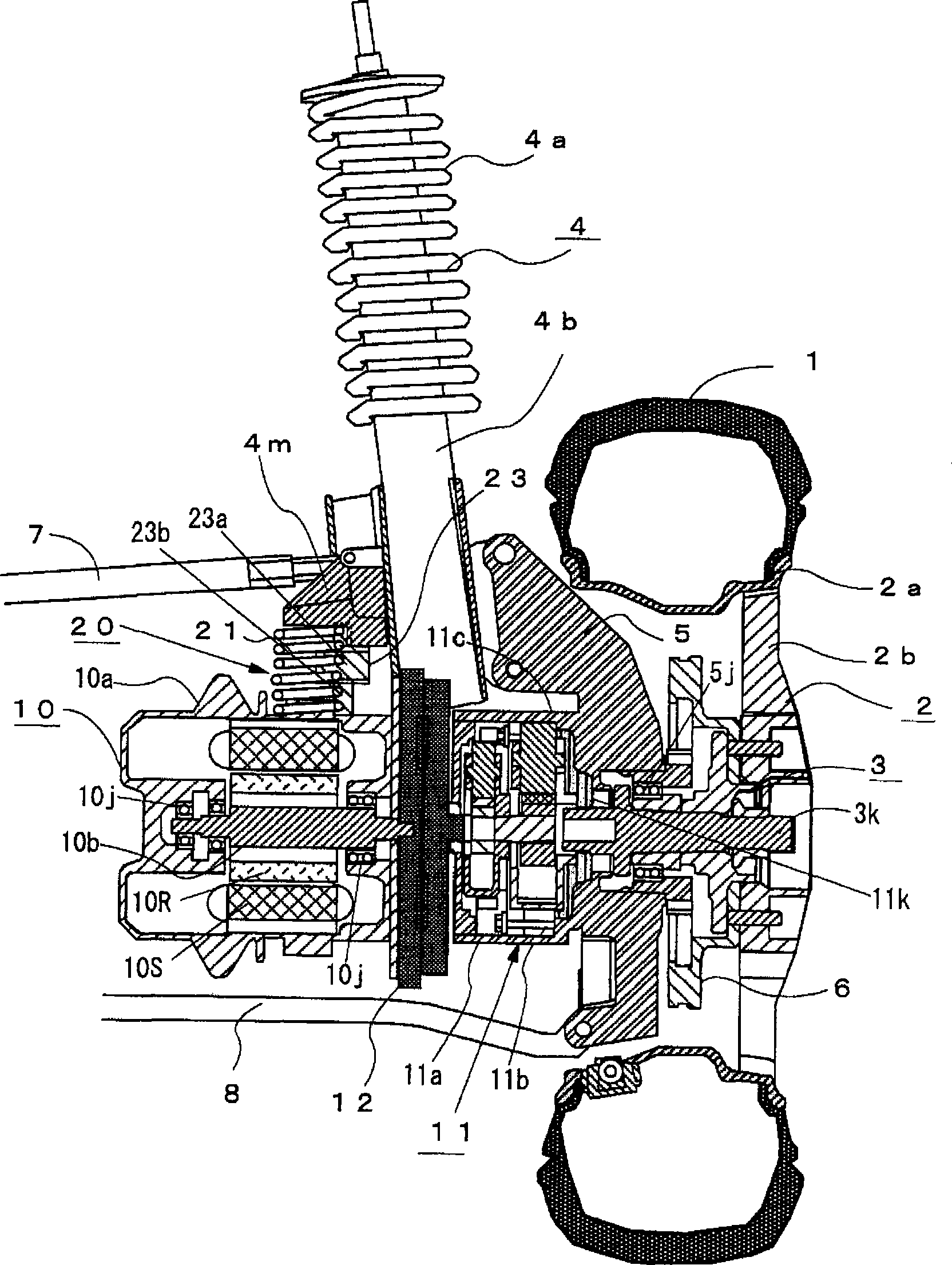
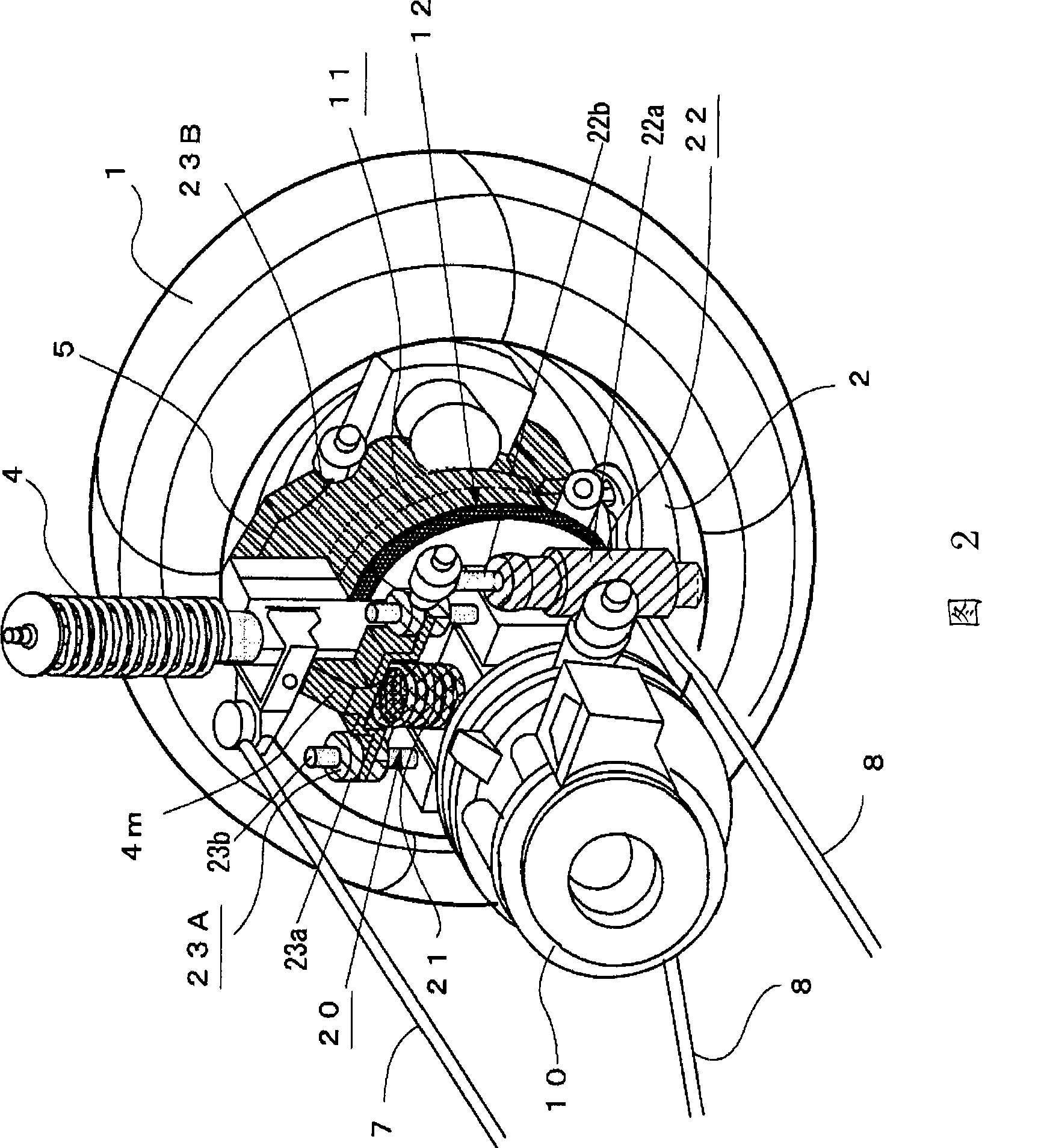
In-wheel motor system
InactiveCN101370678AGood grounding effectImprove durabilitySpeed controllerElectric devicesGround contactCoupling
An electric motor (10) and a speed reduction gear mechanism (11) are coupled by a flexible coupling (12) that is a power transmission mechanism such as an Oldham's coupling. A casing (11c) of the speed reduction gear mechanism (11) is formed integrally with a knuckle (5) as a component of vehicle's unsprung portion, or alternatively, is attached to the knuckle (5). Further, a motor case (10a) of the electric motor (10) is attached to a motor installation member (4m) via a shock absorbing mechanism (20), the motor installation member (4m) being provided on the lower side of a strut (4) for supporting the knuckle (5). The shock absorbing mechanism (20) has a spring member (21), a damper, and two guide members (23) for guiding the direction of operation of the spring member (21) and the damper. The construction allows the mass of the motor (10) to act as the mass of a dynamic damper. An in-wheel motor system thus obtained improves ground contact performance and ride quality of a vehicle traveling on a bad road and has good space efficiency.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
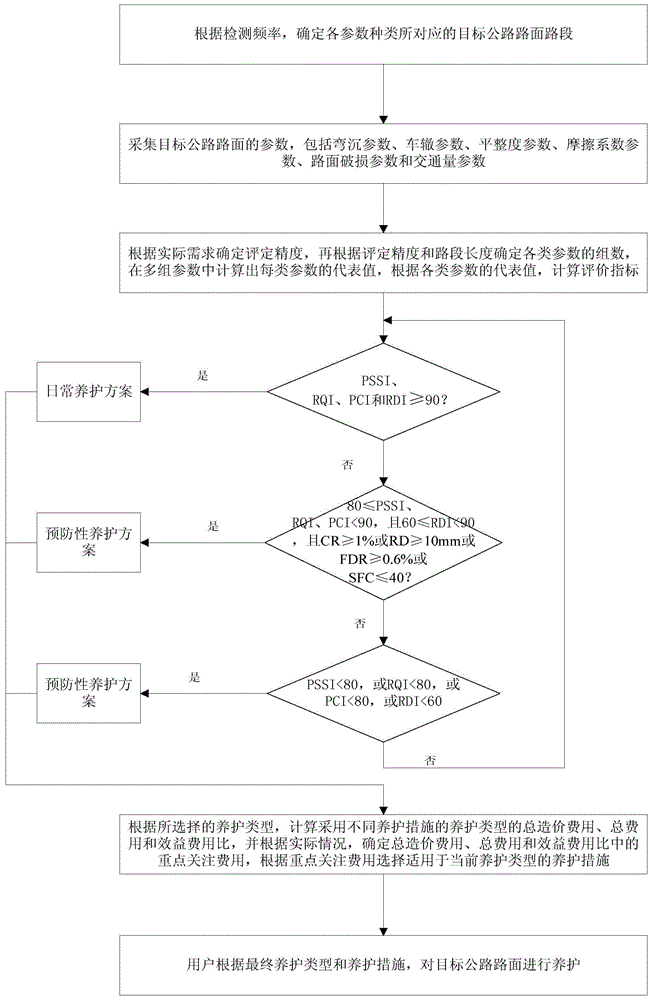
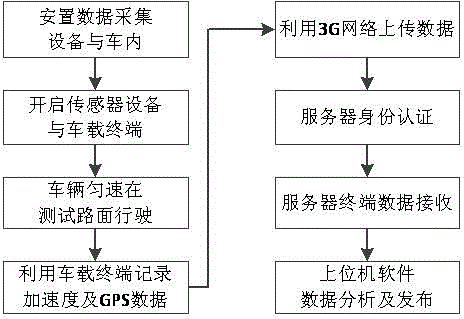
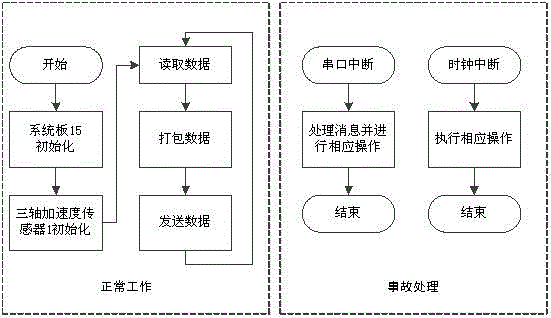
Quick road surface roughness detection system based on vehicle-mounted accelerometer
ActiveCN104790283AHigh precisionRealize real-time monitoringRoads maintainenceInformation processingAccelerometer
The invention relates to a quick road surface roughness detection system based on a vehicle-mounted accelerometer. The system comprises a three-axis acceleration sensor, an angular velocity sensor, a Zigbee short-range wireless communication module, a touchable vehicle-mounted terminal, a GPS (global positioning system) and a central computer information processing system, wherein the Zigbee short-range wireless communication module and the three-axis acceleration sensor are integrated to form data acquisition equipment, and the data acquisition equipment is used for acquiring acceleration values produced during riding of a vehicle and performs internal short-range wireless transmission; the GPS, the angular velocity sensor and a 3G remote module are used for recording geographic coordinates of the riding vehicle and turn angle conditions of the riding vehicle and transmit packed files to a server; the touchable vehicle-mounted terminal is used for acquiring acceleration sensor data and matching the acceleration sensor data with GPS data and angular velocity data by using a time sequence to generate initial data; the central computer information processing system is used for directionally receiving data sent by the to-be-detected vehicle and processing the data to acquire an estimated IRI (internal roughness index) / RQI (riding quality index) to be displayed on an electronic map. The system is used for solving problems that traditional detection methods are time-consuming, labor-consuming, low in efficiency, high in price and the like and monitors the road surface roughness in real time.
Owner:上海祎个科技有限公司
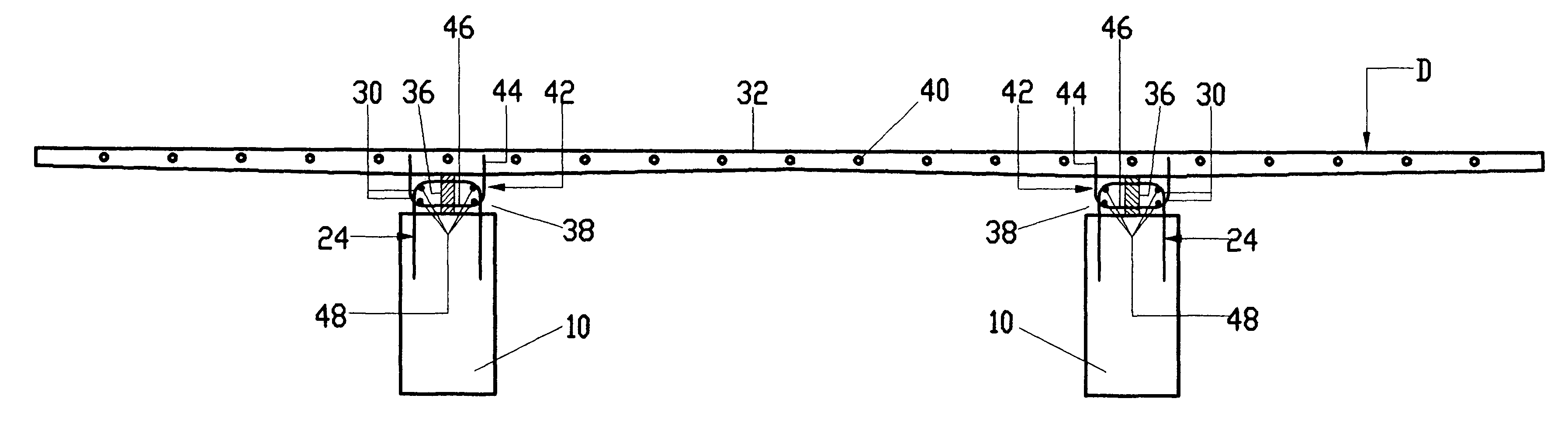
Elastomeric spring vehicle suspension
ActiveUS20090224504A1Increase the spring rateMultiple spring combinationsInterconnection systemsElastomerVehicle frame
An elastomeric spring suspension is described for supporting a longitudinally extending vehicle frame rail above first and second axles forming a tandem axle configuration. The suspension includes a frame hanger assembly mounted to the vehicle frame rail The frame hanger assembly has two full spring modules, each of which includes two elastomeric shear springs, an elastomeric progressive spring rate load cushion having a pyramidal shape with a flattened top surface and a spring mount for mounting the springs. A saddle assembly is connected to the spring mount, and an equalizing beam is connected to the saddle assembly and further connected to the axles. The spring rate for the suspension increases almost linearly as a function of sprung load, resembling a pneumatic suspension. Accordingly, the suspension exhibits excellent ride quality, without sacrificing roll stability.
Owner:HENDRICKSON USA L L C
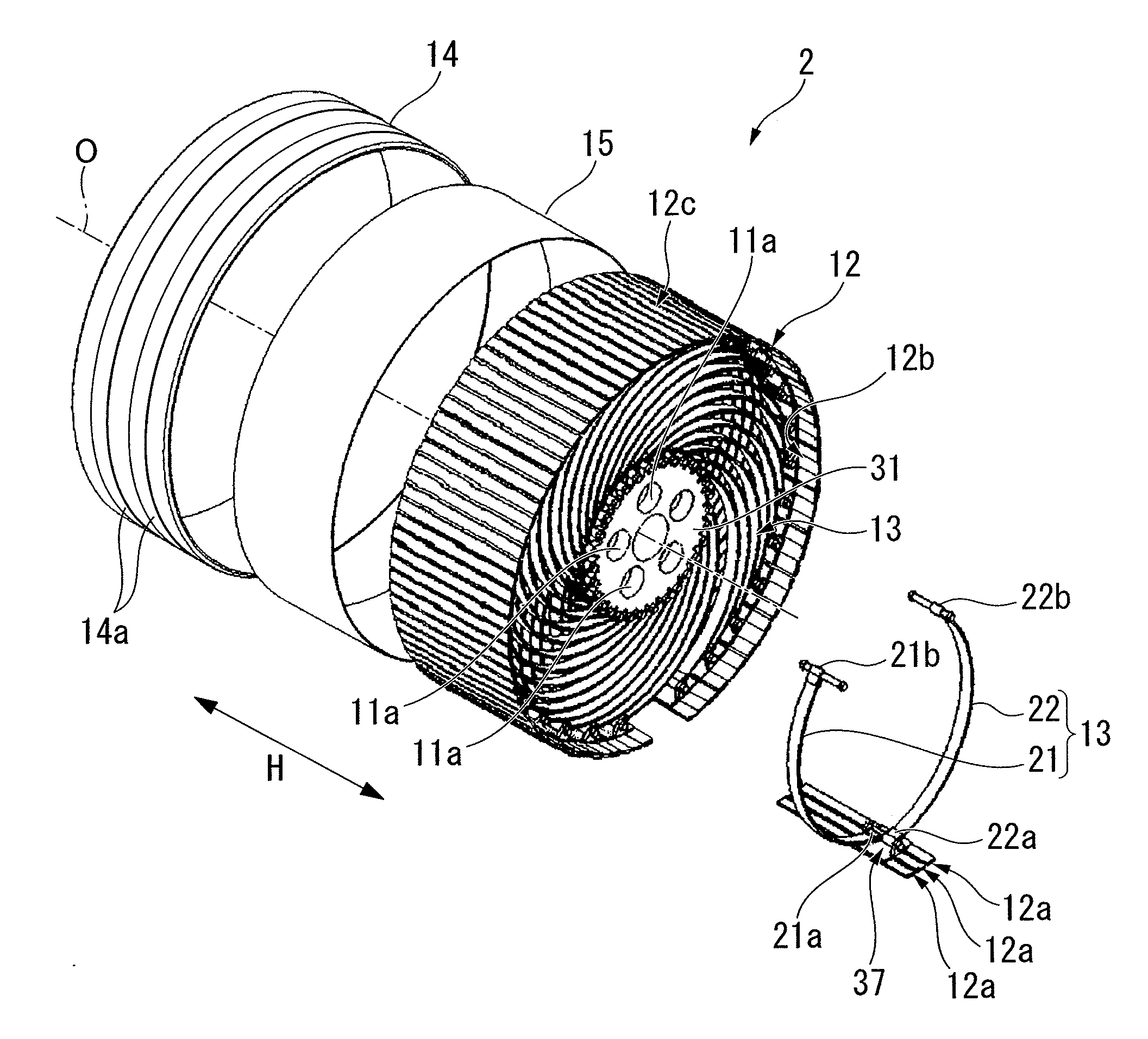
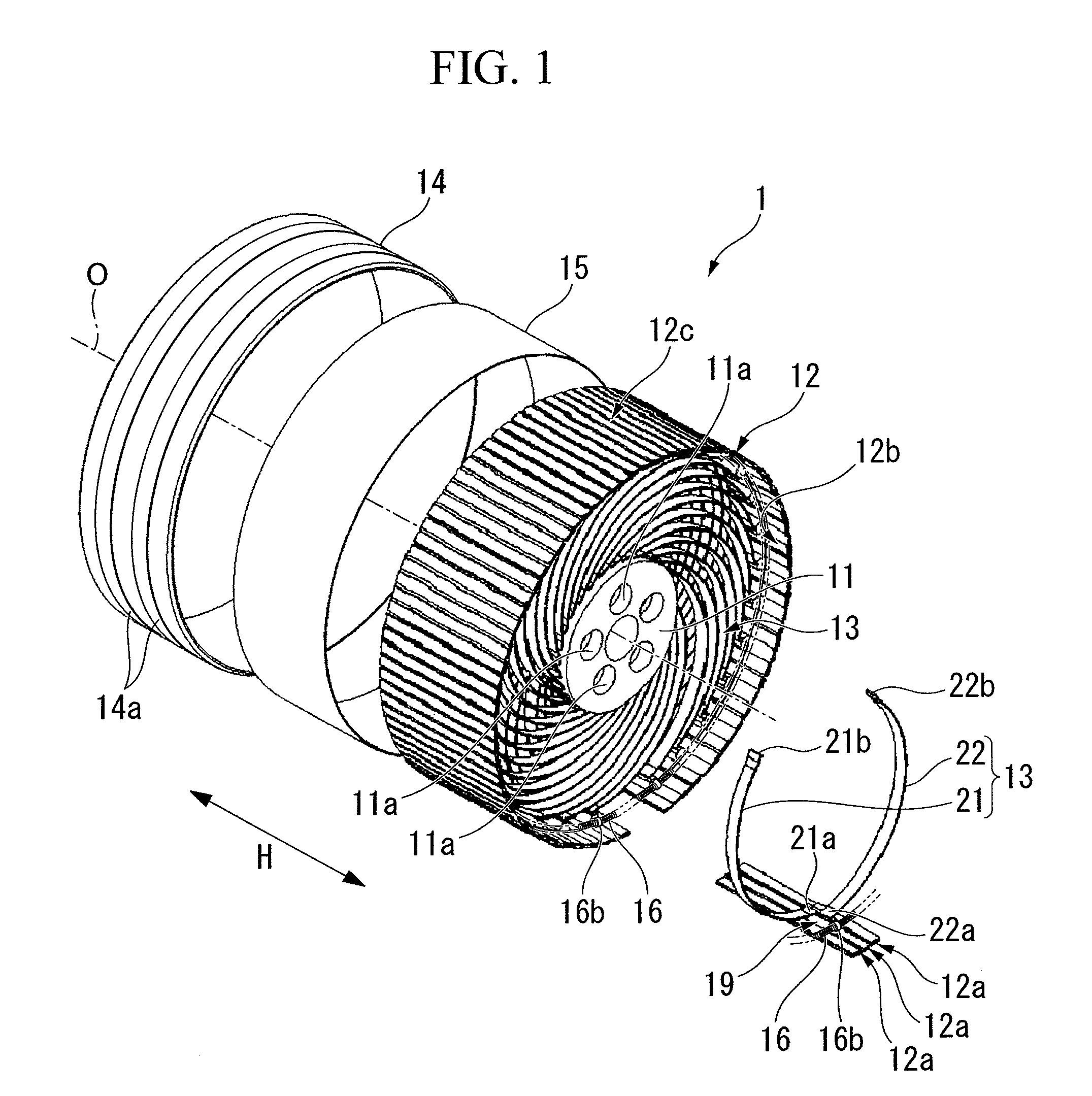
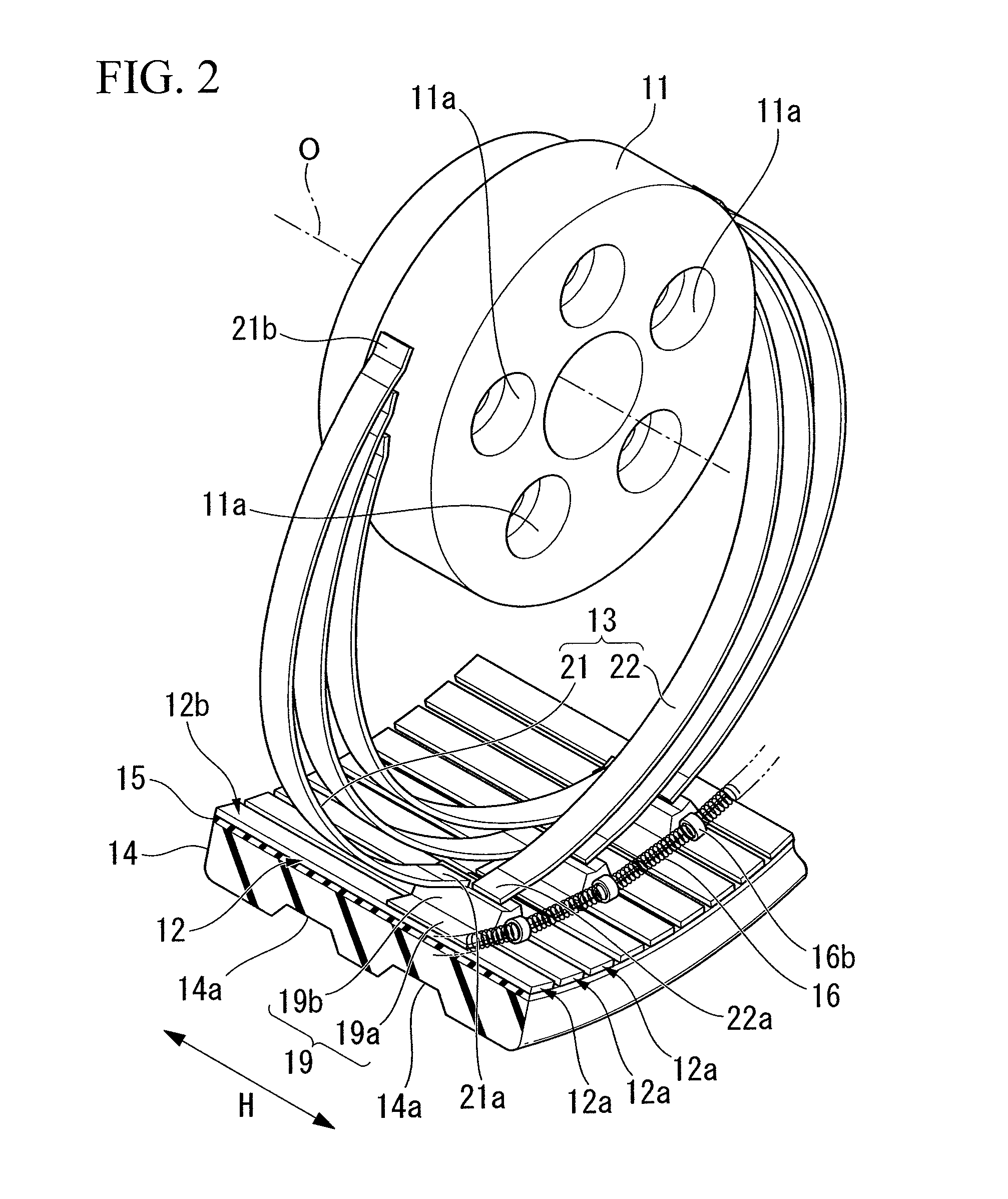
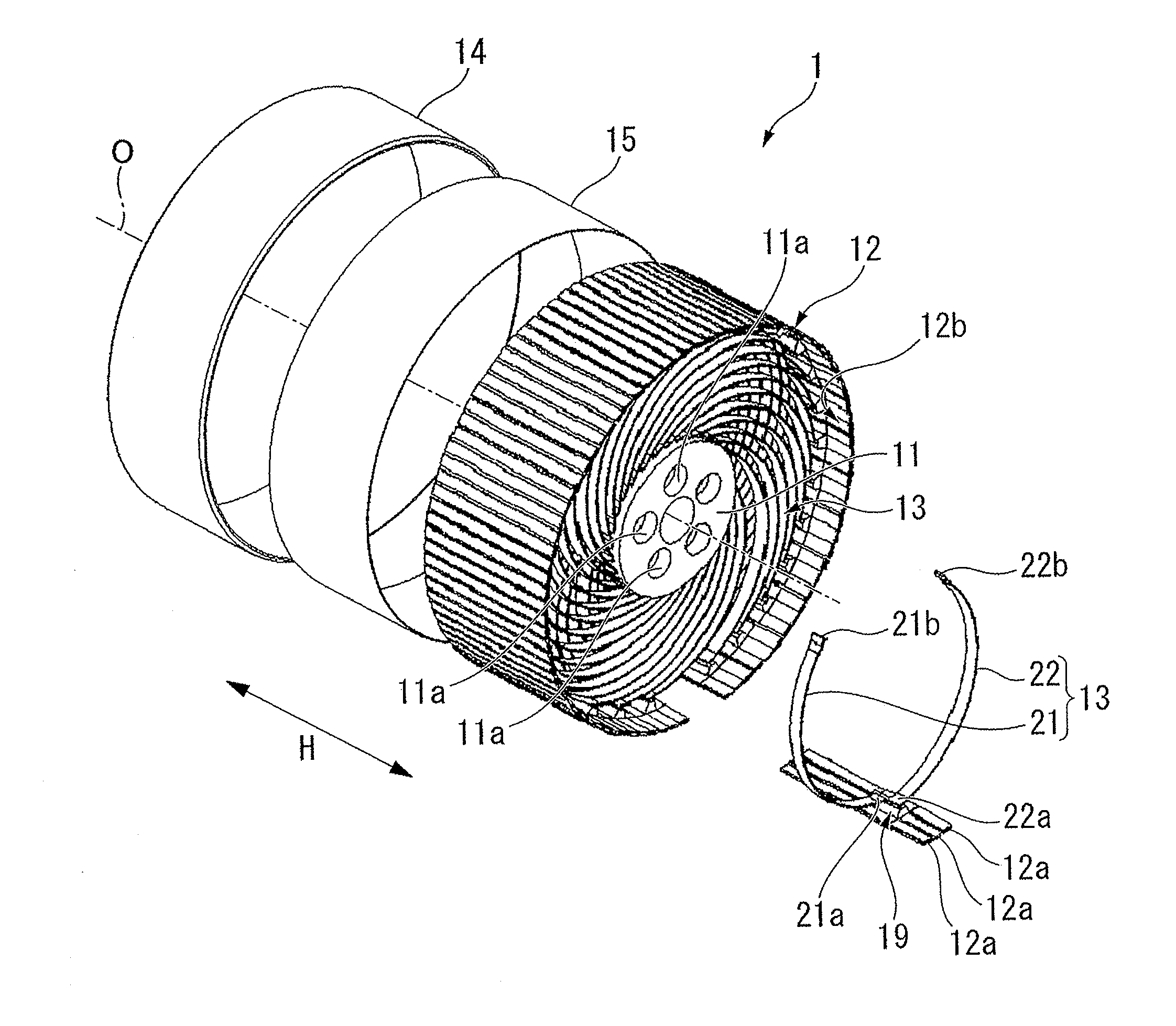
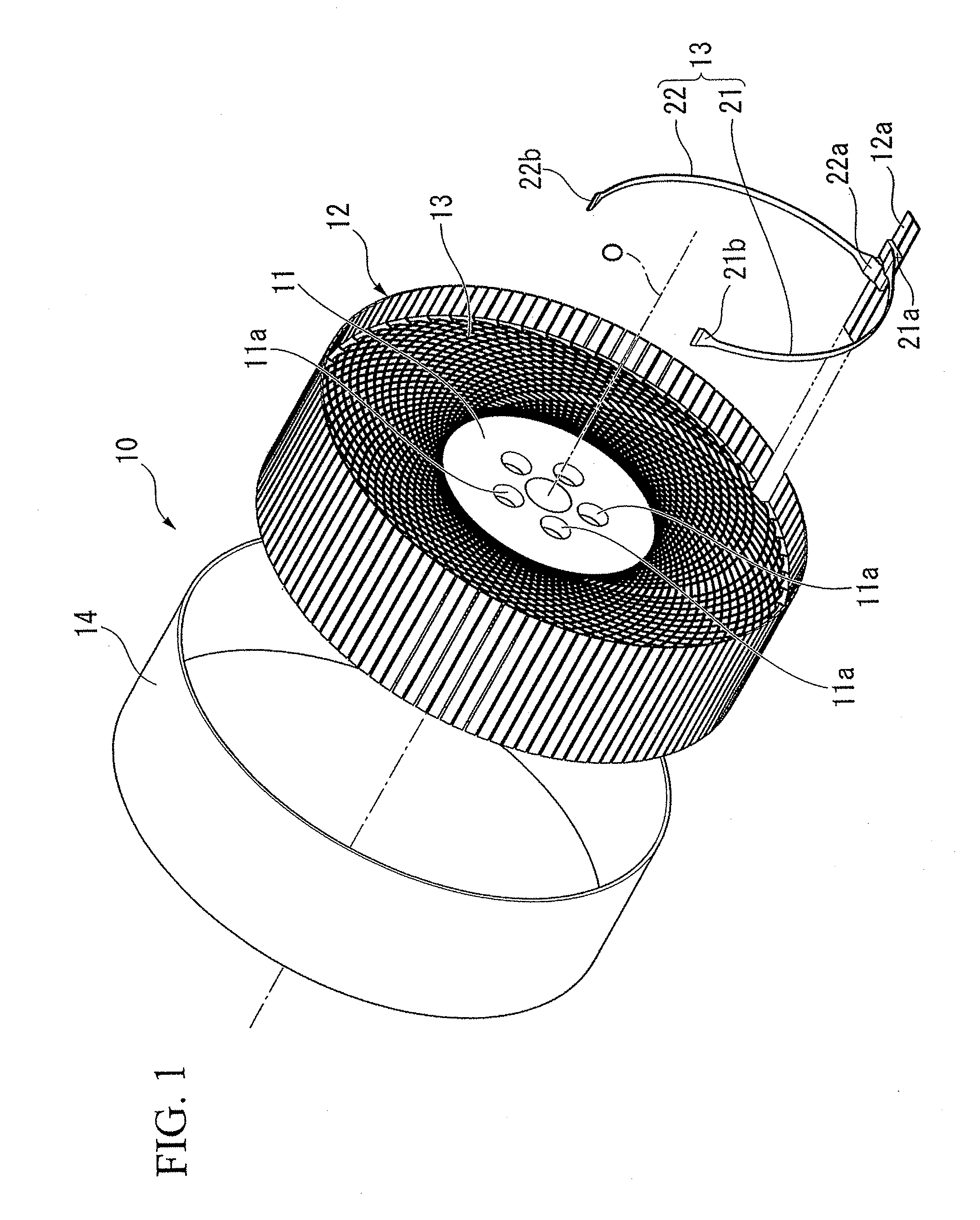
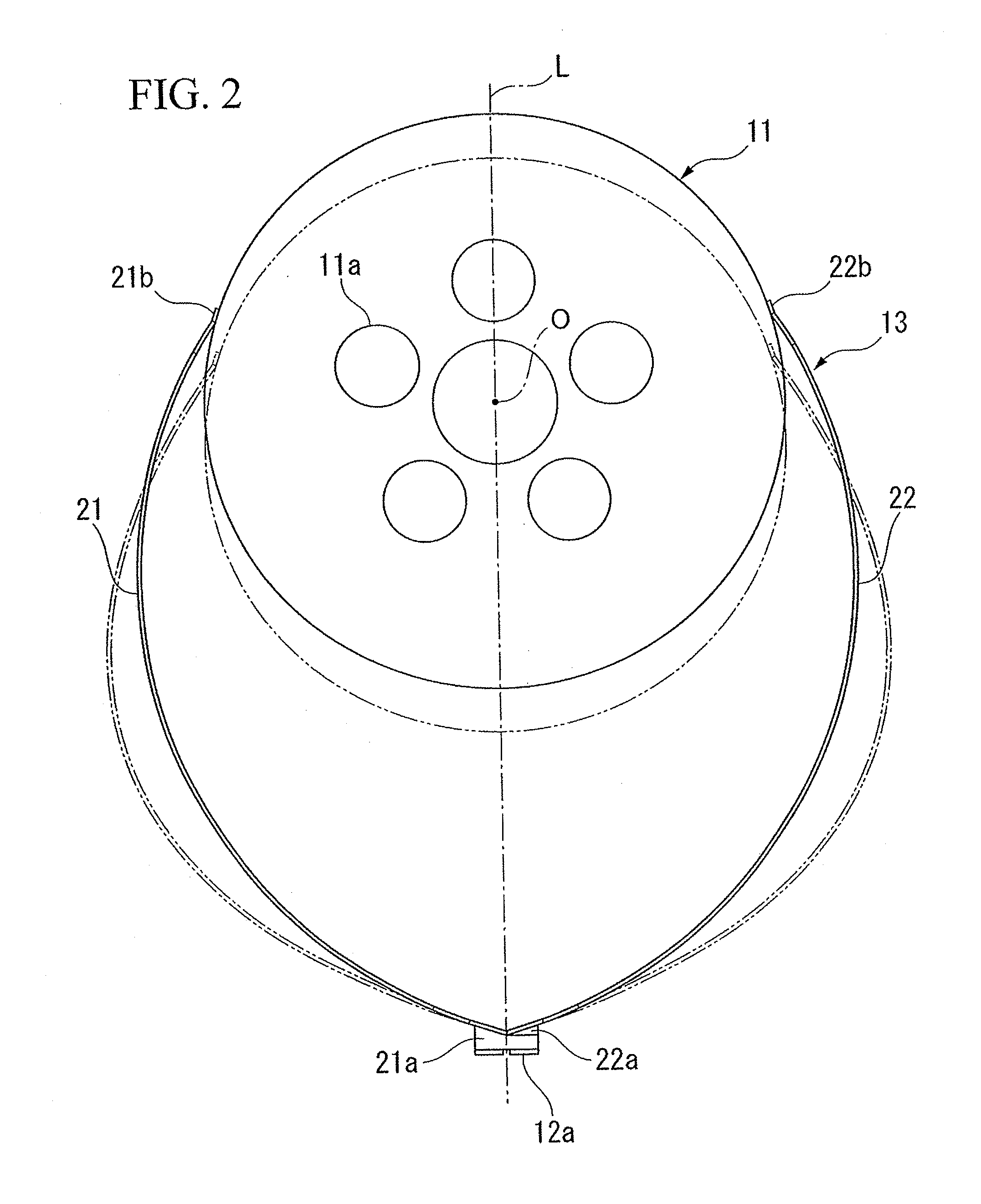
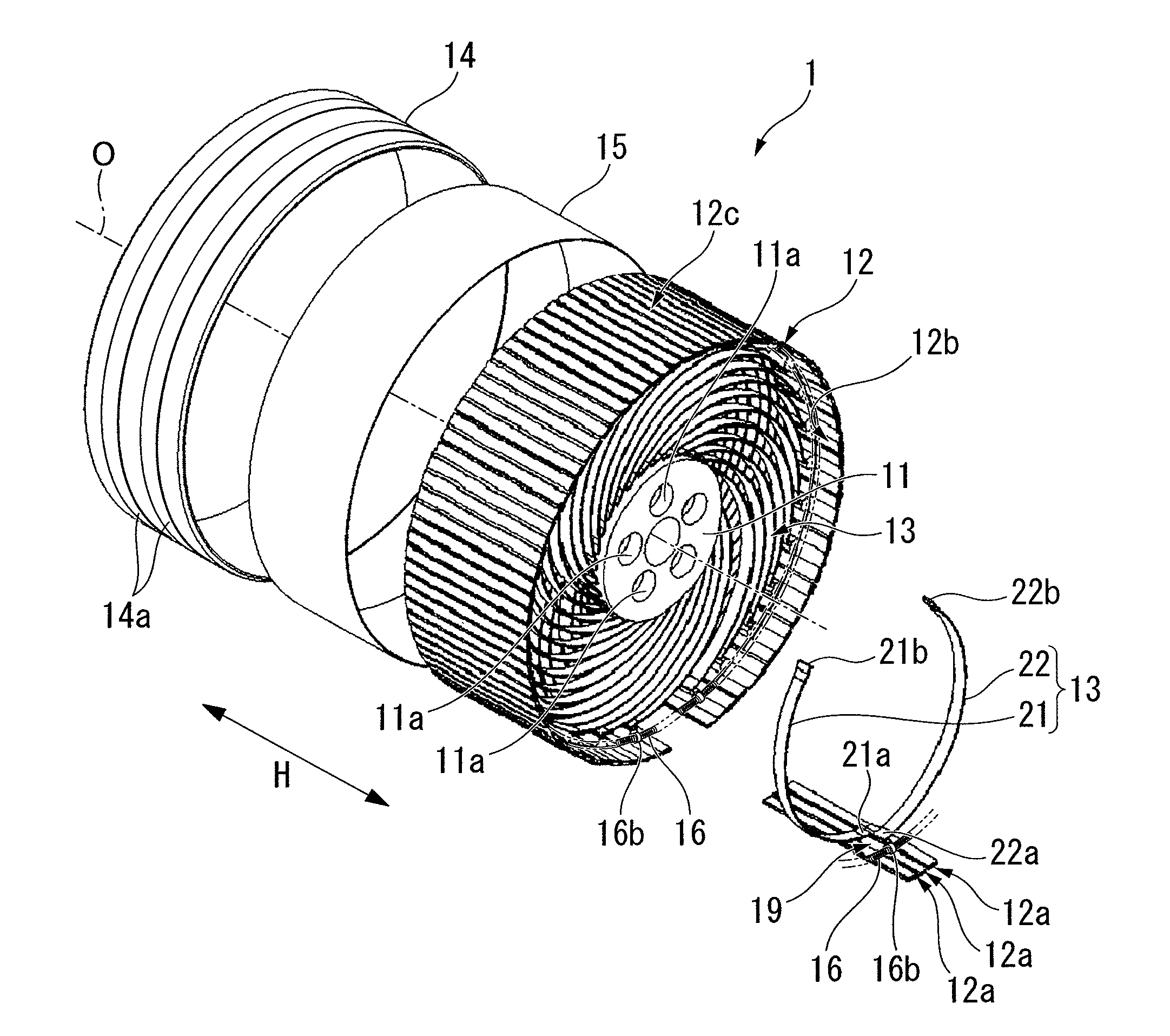
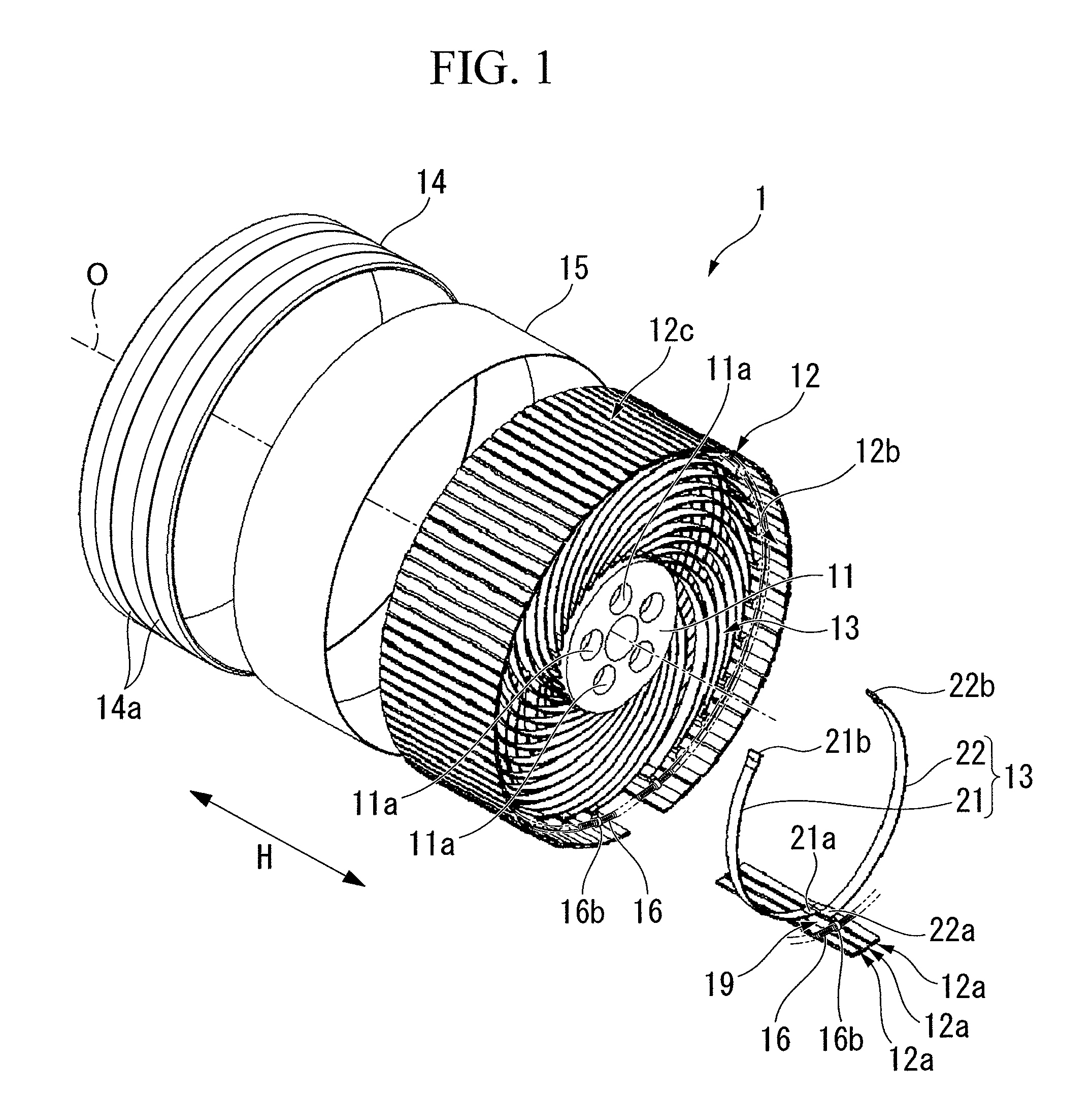
Non-pneumatic tire
InactiveUS20110108173A1Satisfactory ride qualitySatisfactory maneuverabilityNon-inflatable tyresTyre tread bands/patternsContact pressureRolling resistance
In a non-pneumatic tire (1), a plurality of connecting members (13) that connects a mounting body (11) and an annular body (12) are provided along a tire-circumferential direction. The annular body is split into a plurality of split bodies (12a) along the tire-circumferential direction. A resilient member (16) that is extended along the tire-circumferential direction and connects the plurality of split bodies in the tire-circumferential direction is provided in the annular body. This non-pneumatic tire (1) secures satisfactory ride quality, maneuverability and durability by suppressing increase in weight, hardness and rolling resistance, ensures uniform contact-pressure distribution, and prevents the occurrence of a puncture.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Non-pneumatic tire
ActiveUS20100218869A1Increase in hardnessSuppression of resistance riseNon-inflatable tyresHigh resiliency wheelsRolling resistanceHardness
A plurality of connection members 13 connecting an installation disk 11 to a ring-shaped body 12 are formed, in a side view of the non-pneumatic tire, to be axisymmetrical about an imaginary line connecting the respective first ends 21a and 22a of first connection plates 21 and second connection plates 22 to an axial line O and extending in a tire-radial direction. The connection members 13 are arranged in a tire-circumferential direction such that the first connection plates 21 are arranged at a first tire-widthwise position in the tire-circumferential direction and that the second connection plates 22 are arranged at a second tire-widthwise position in the tire-circumferential direction. According to the invention, it is possible to suppress an increase in the weight, hardness, and rolling resistance to secure satisfactory ride qualities and handling qualities, and it is possible to prevent a blowout from occurring.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Suspension system with optimized damping response
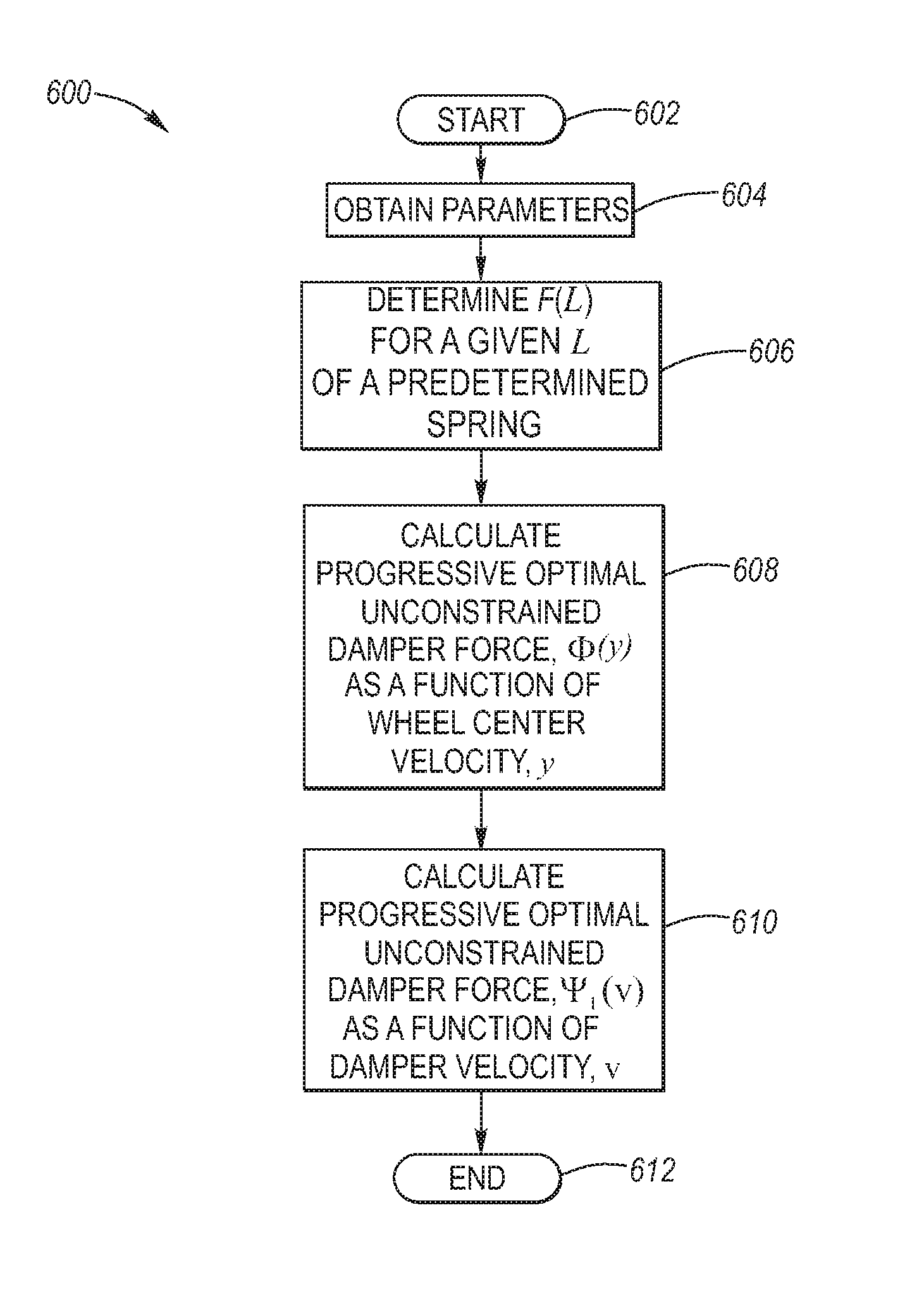
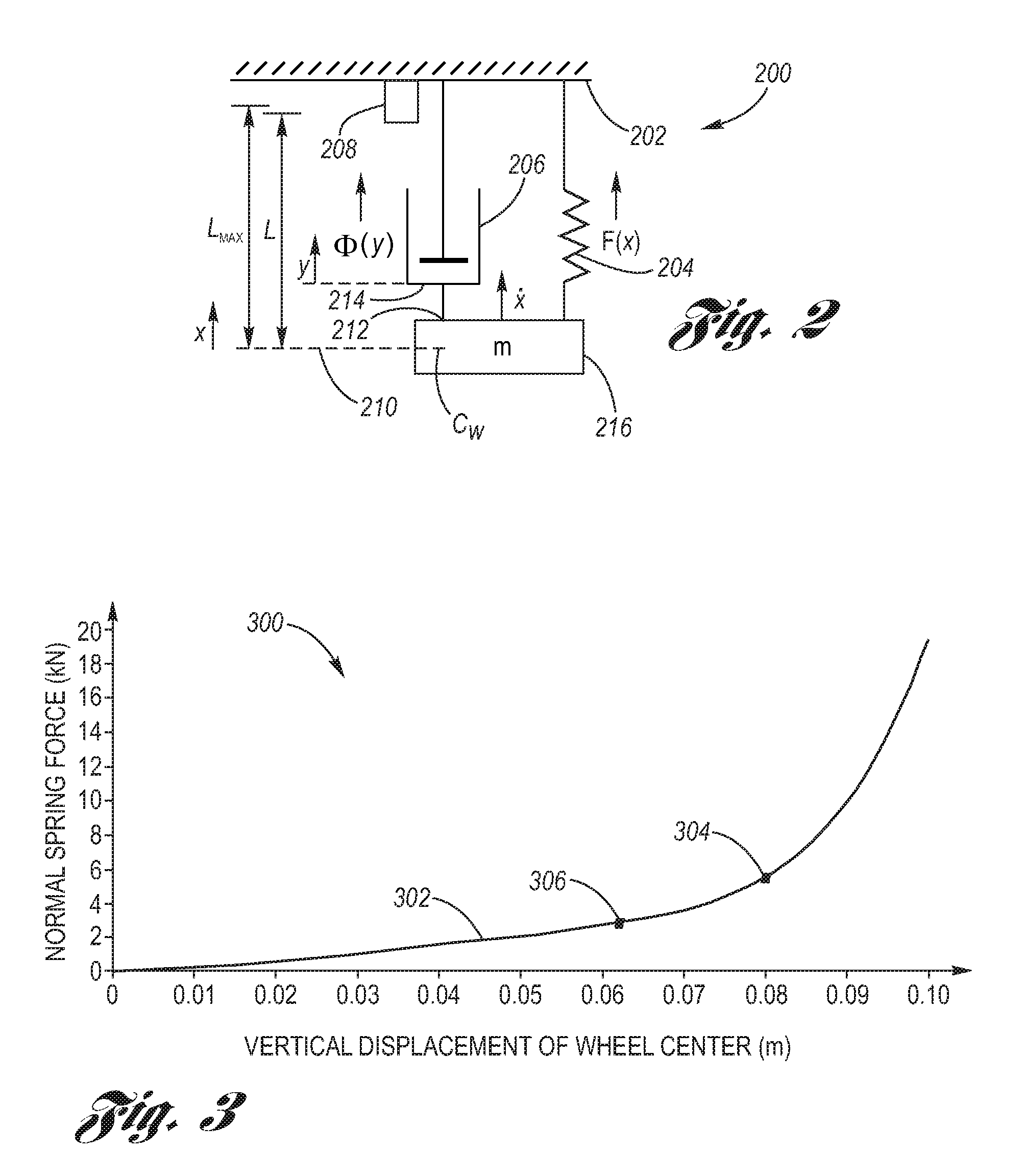
InactiveUS8457841B2Reduce roughnessAcceptable ride qualitySpringsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringAnalysis method
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
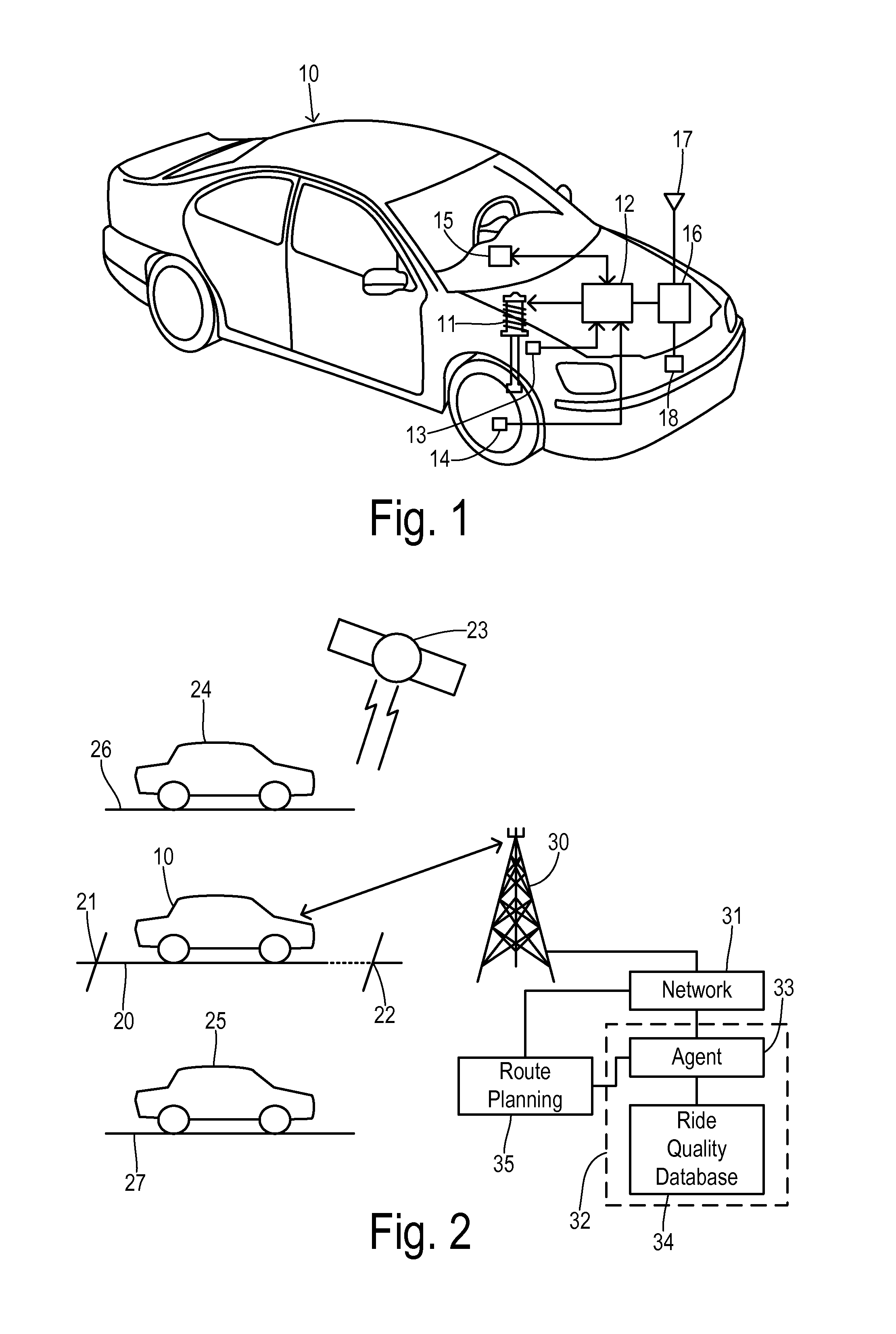
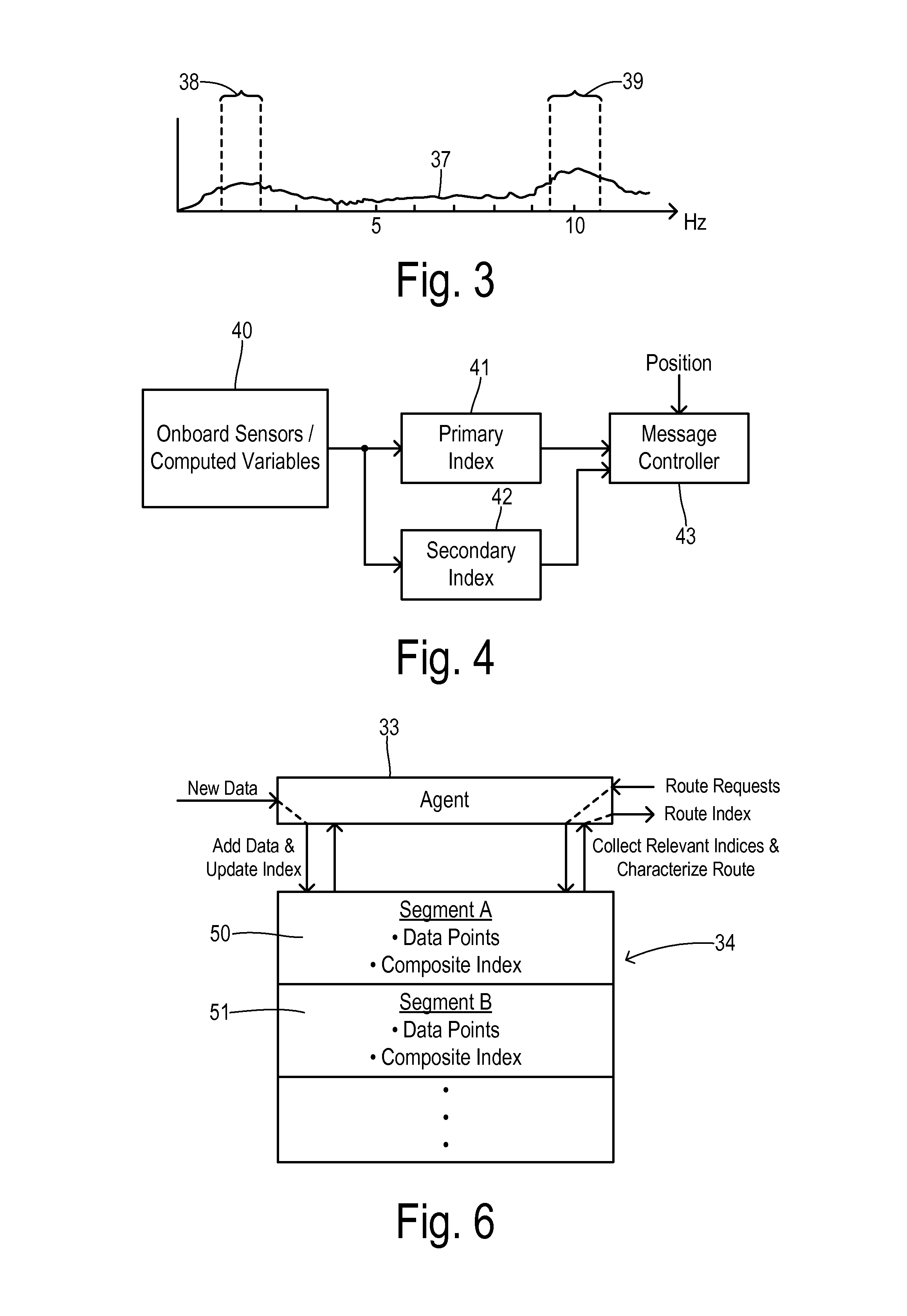
Roadway-induced ride quality reconnaissance and route planning
ActiveUS20150094948A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlRoute planningRide quality
Route planning for road vehicles is performed taking into account a ride quality that results from the roadway conditions along road segments on a route. A plurality of vehicles equipped with controlled suspensions calculate ride quality indices as the vehicles move over a plurality of road segments. The plurality of vehicles transmit the ride quality indices tagged with respective geographic coordinates to an aggregating server. The aggregating server determines a composite ride quality index for each road segment. A subscriber generates a route planning request identifying an origin and a destination. At least one potential route is identified between the origin and the destination comprised of selected road segments. A route ride quality index is determined in response to the selected road segments, and the potential route and the route ride quality index are presented to the subscriber for selection.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Suspension device for a work vehicle
InactiveUS20120073843A1Improve ride qualityDriving force is stableAgricultural machinesSoil-shifting machines/dredgersTerrainRide quality
A suspension device for a work vehicle is capable of not only providing improved ride quality during nonoperational traveling such as on-site movement over uneven terrain, but also ensuring stable driving power during operational traveling such as an excavation operation on uneven terrain. The suspension device 60 has an equalizer bar 61 for coupling undercarriages 4, 4′ provided on both sides, respectively, of a vehicle body 3, the equalizer bar 61 being provided in the vehicle body 3 so as to be freely swingable up and down. This suspension device 60 has pitch angle change cylinders 65 as maximum pitch angle changing mechanism for changing the maximum pitch angle of the equalizer bar 61.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
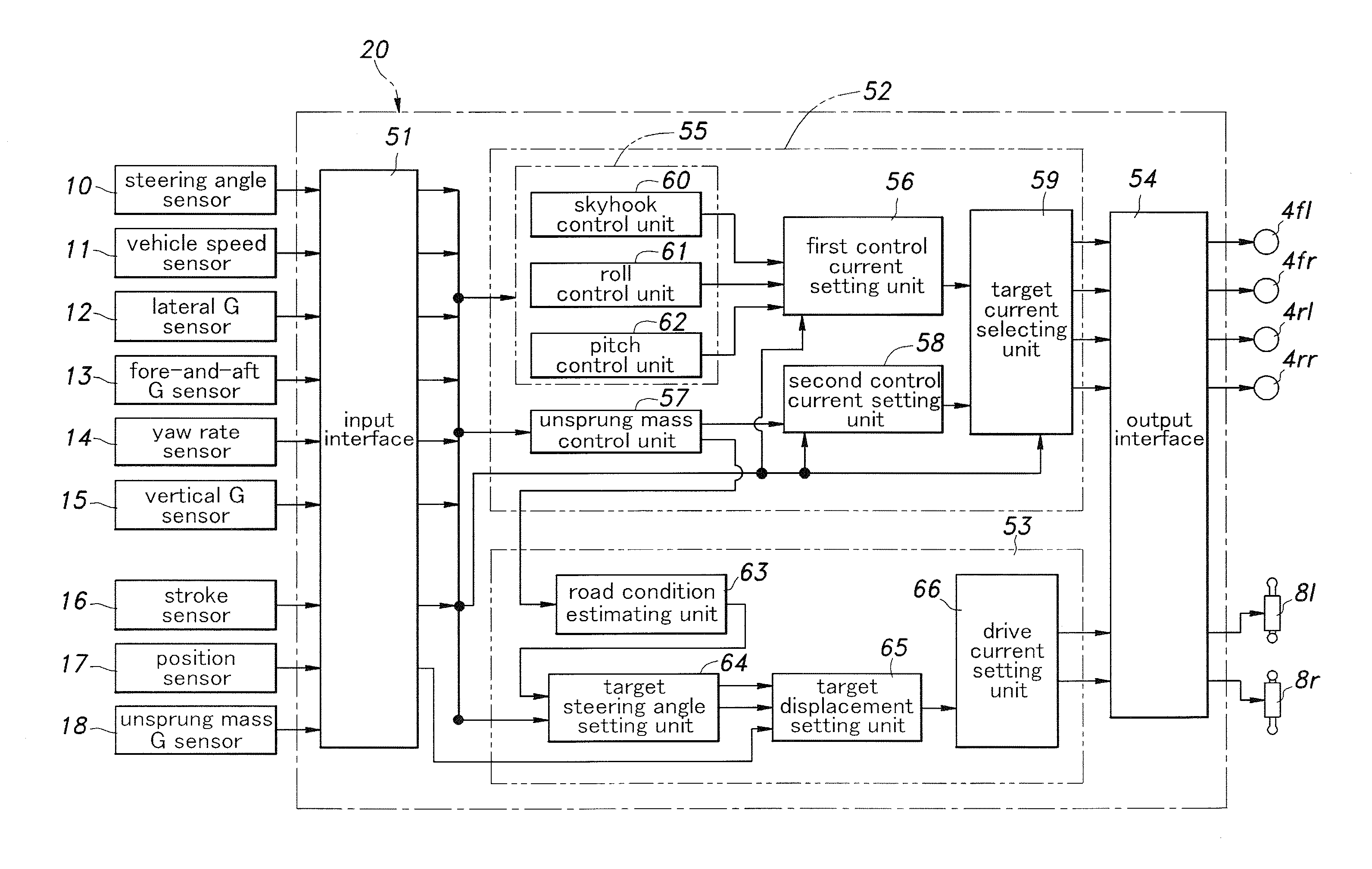
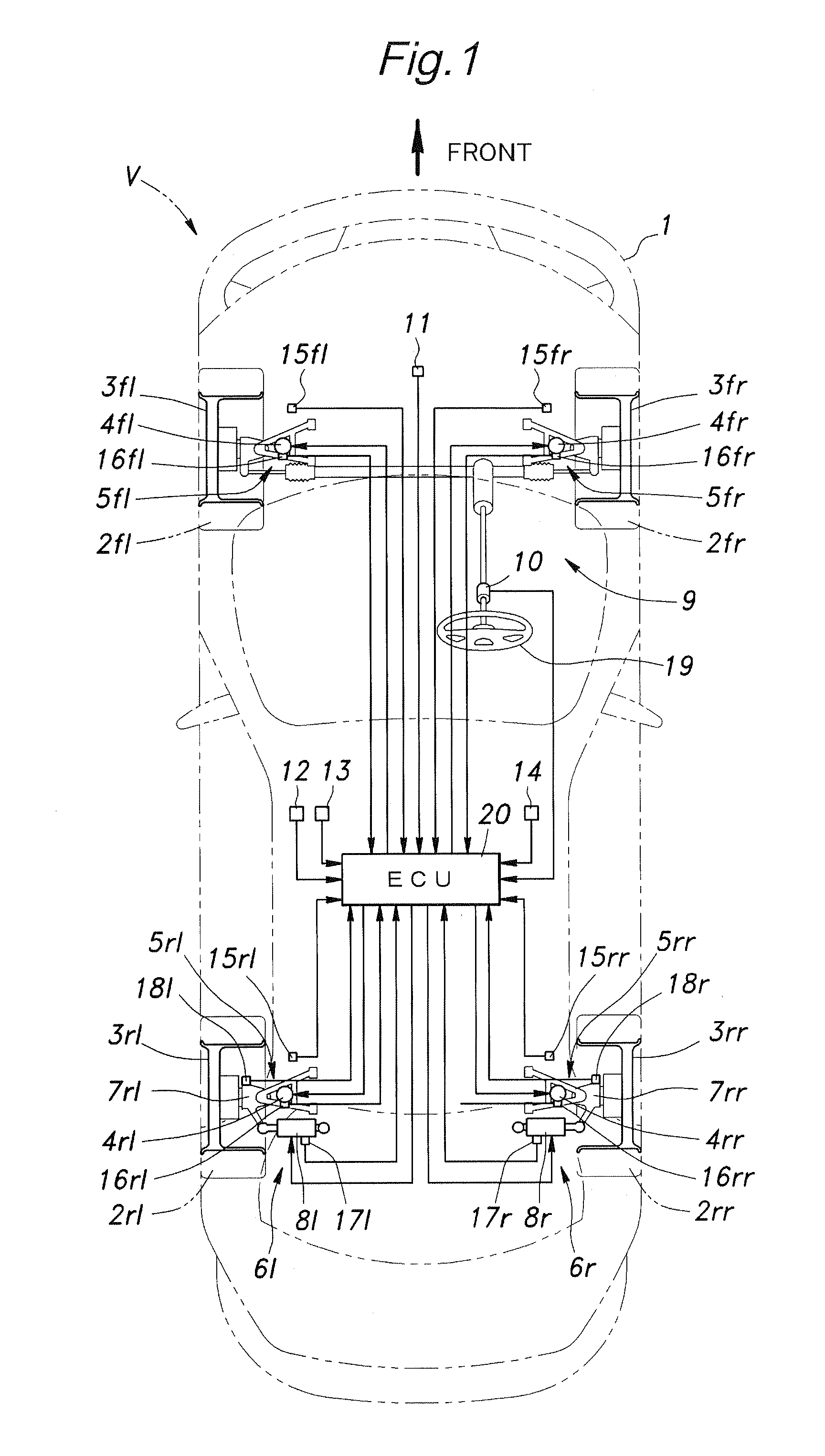
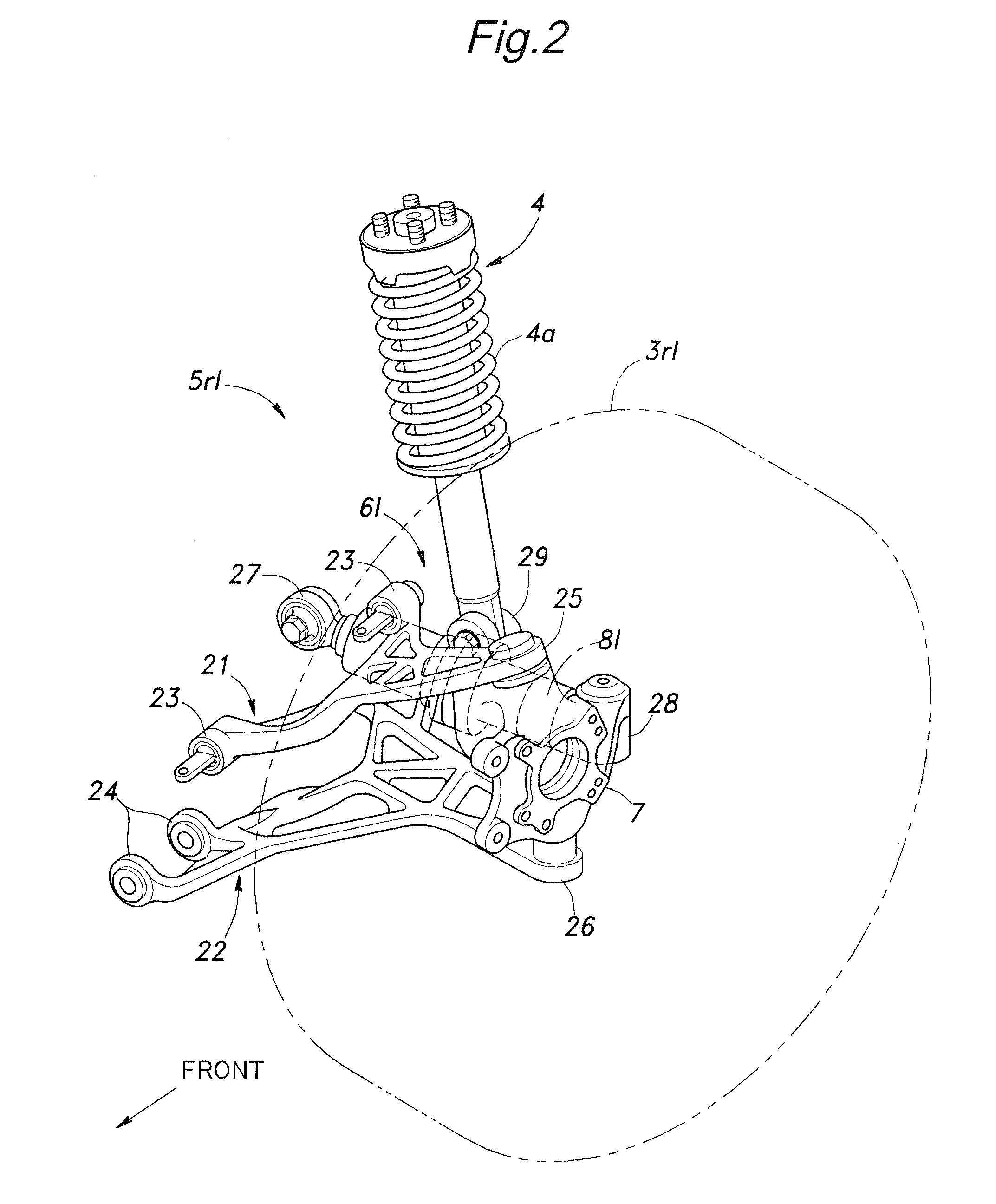
Rear wheel steering control system
InactiveUS20100204888A1Improve ride qualitySimple and compact structureDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsControl systemSteering control
In a rear wheel steering control system for a vehicle, a rear wheel steering control unit (53) forces the toe angle of each rear wheel (3rl, 3rr) to a substantially neutral position or a slightly toe-in position when a road condition estimating unit (63) has detected a rough road surface. Thereby, when the vehicle is traveling over a rough road surface, the actuator is forced to the neutral position, and the rear wheels are brought to a neutral position so that the changes in the wheel geometry (tread and / or alignment) of the rear wheels at the time of a bump or a rebound can be avoided. Therefore, the ride quality of a vehicle equipped with the rear wheel steering control system is favorably maintained even when the vehicle is traveling over a road surface, and the rear wheels undergo large vertical displacements.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Rubber composition for tire cord coating, breaker edge strip, breaker cushion or cord-adjoining strip, and pneumatic tire
ActiveUS20140228495A1Improve adhesionIncreased durabilityConductive materialSpecial tyresAlkylphenolEngineering
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
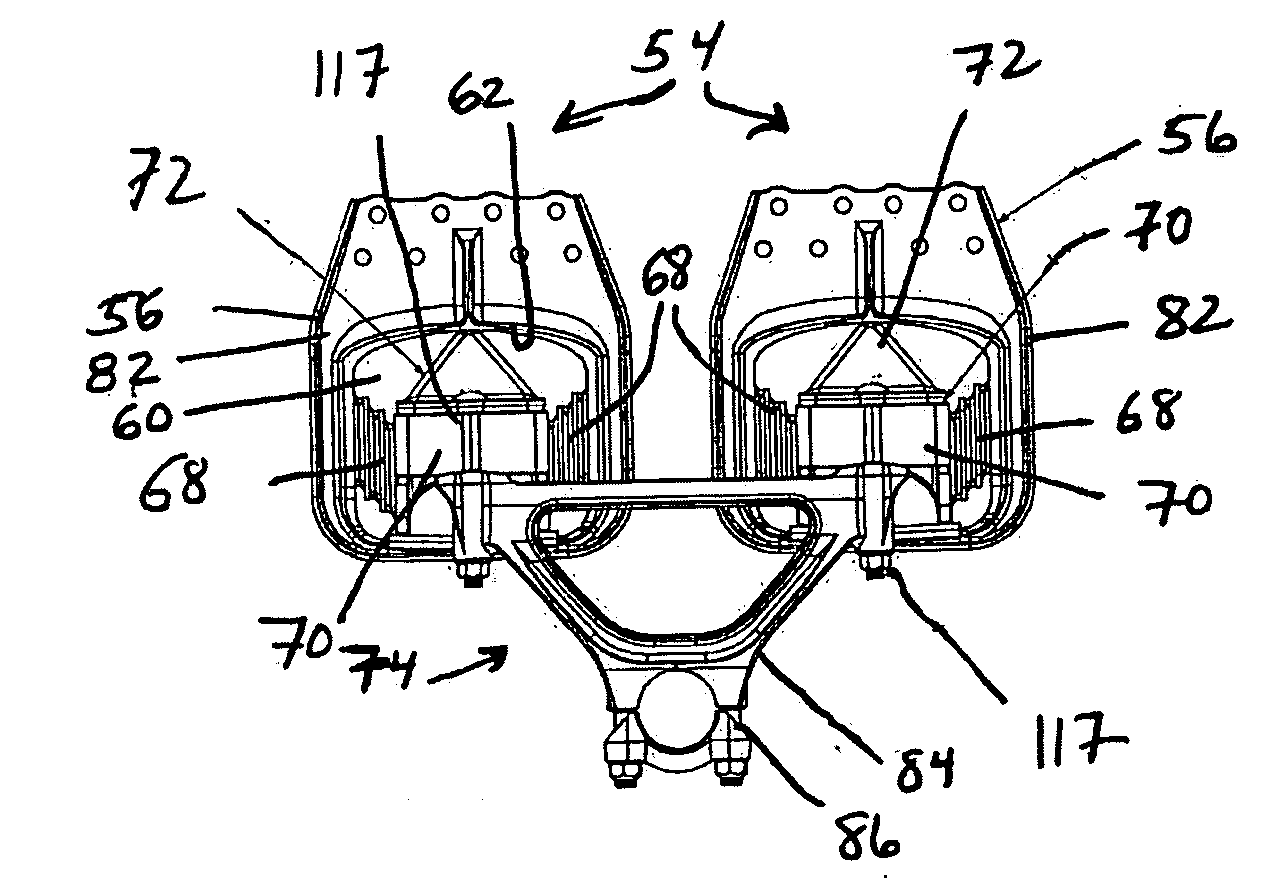
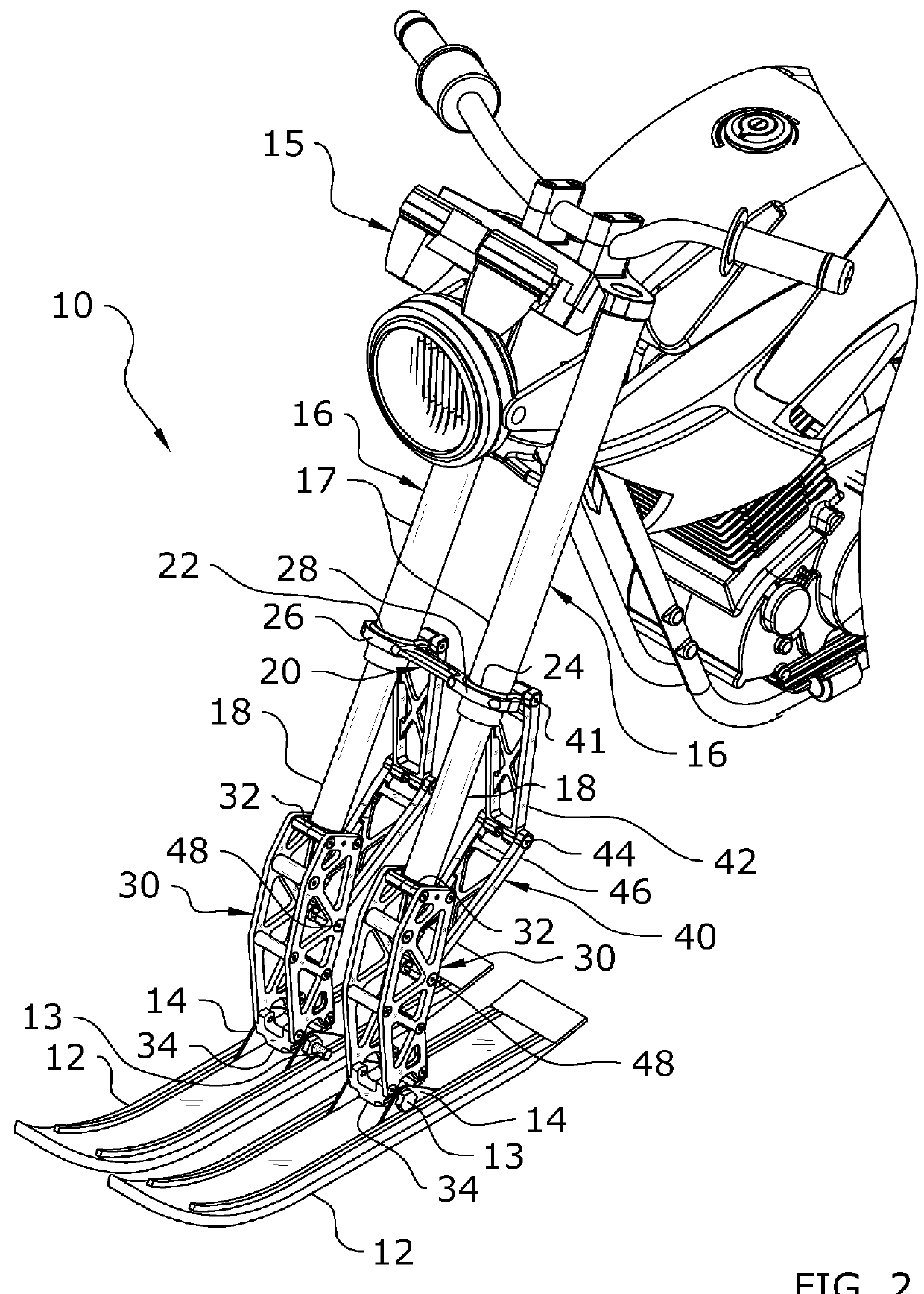
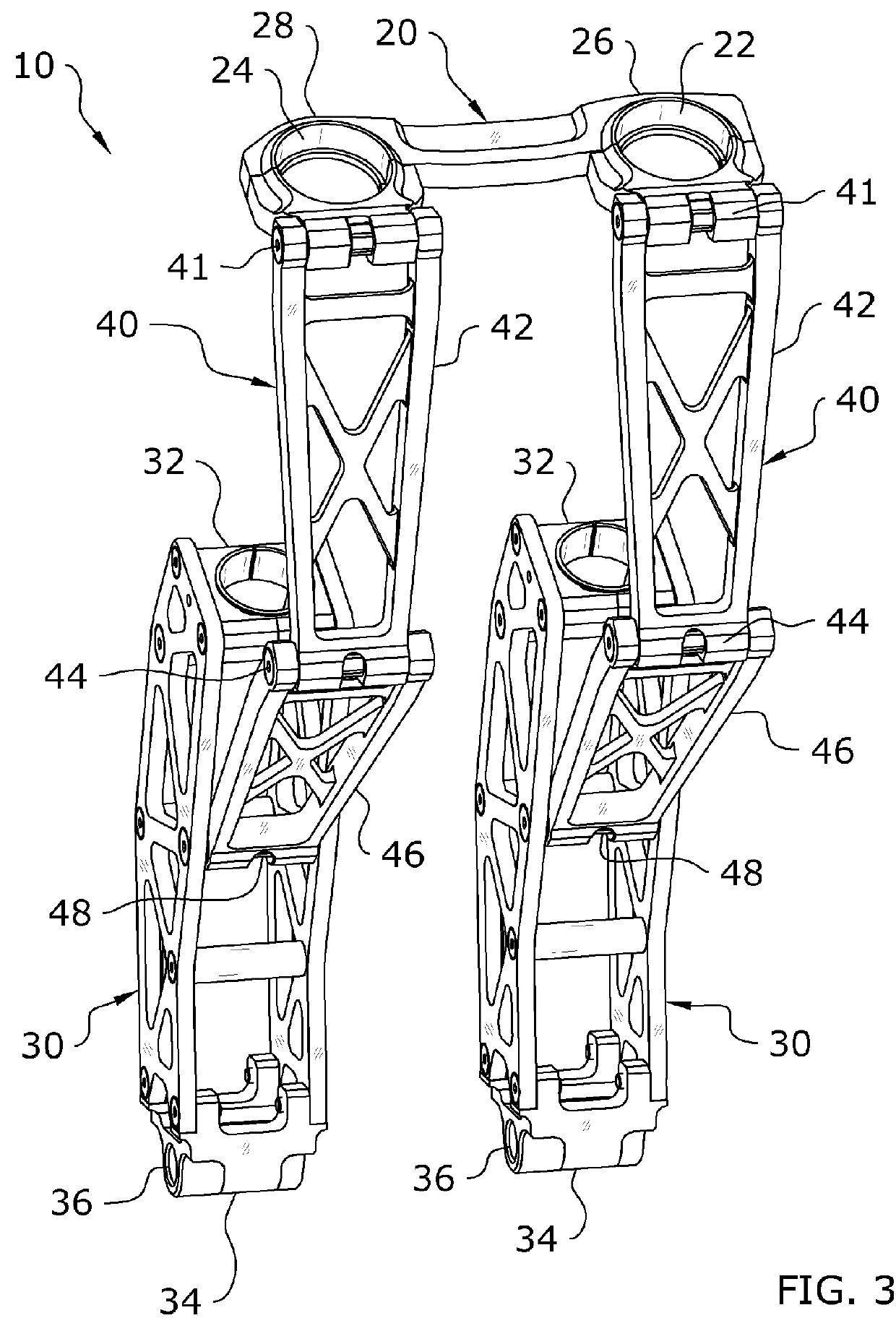
Snow Bike Front Suspension System
A snow bike front suspension system for improving the handling and ride quality for a snow bike. The snow bike front suspension system generally includes an upper bracket attached to the upper legs of a motorcycle's telescopic forks, at least one support arm attached to the lower leg of the telescopic forks and a guide arm pivotally connected between the upper bracket and the support arms to maintain the alignment of the support arms.
Owner:ANDERSON JAKE R MR
Non-pneumatic tire
In a non-pneumatic tire (1), a plurality of connecting members (13) that connects a mounting body (11) and an annular body (12) are provided along a tire-circumferential direction. The annular body is split into a plurality of split bodies (12a) along the tire-circumferential direction. A resilient member (16) that is extended along the tire-circumferential direction and connects the plurality of split bodies in the tire-circumferential direction is provided in the annular body. This non-pneumatic tire (1) secures satisfactory ride quality, maneuverability and durability by suppressing increase in weight, hardness and rolling resistance, ensures uniform contact-pressure distribution, and prevents the occurrence of a puncture.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Vehicle
InactiveUS8985594B2Quality improvementImprove stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesDamping factorResonance
A spring constant of each of four suspension springs and a shared load on each of four wheels are adjusted so that a sprung resonance frequency corresponding to two front wheels and a sprung resonance frequency corresponding to two rear wheels are mutually different. From among the four shock absorbers, only two shock absorbers provided corresponding to two wheels of lowered sprung resonance frequency, from among the two front wheels and the two rear wheels have respectively damping coefficient modification mechanisms that modify a damping coefficient serving as a reference of the magnitude of the damping force generated by the two shock absorbers. The behavior of the entire vehicle body can be effectively curbed by controlling the damping force exerted on the comparatively large movement of sprung sections corresponding to the two wheels. Thus a vehicle having both enhanced steering stability and enhanced ride quality can be configured comparatively inexpensively.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Pneumatic tire
InactiveUS20110094648A1Improve quality stabilityImprove ride qualitySpecial tyresTyresEngineeringRubber sheet
In order to improve ride quality and steering stability, the present invention provides a pneumatic tire having a sidewall made of a rubber composition for a sidewall comprising at least a natural rubber and a diene rubber comprising a syndiotactic 1,2-polybutadiene, wherein rubber sheets obtained by extruding at a thickness of at most 1.5 mm the rubber composition for a sidewall with a complex modulus E*a in a tire circumferential direction measured at a temperature of 70° C. and a dynamic distortion of 2% of 3 to 15 MPa are laminated.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Pneumatic tire
InactiveUS20060272757A1Solve the lack of rigiditySolve the lack of hardnessSpecial tyresTyre tread bands/patternsRolling resistanceCrack resistance
A pneumatic tire which has a base tread having sufficient rigidity, hardness and crack resistance, and sufficiently satisfies the compatibility among steering stability, ride quality and lowering of rolling resistance is provided. A pneumatic tire having a base tread comprising a rubber composition containing 0.5 to 10 parts by weight of a thermosetting resin based on 100 parts by weight of a diene rubber, wherein complex elastic modulus E* of the rubber composition measured at a measurement temperature of 60° C. and dynamic strain of 1% is 8 to 15 MPa, tan δ is at most 0.15, and elongation at break EB of the rubber composition in a tensile test is at least 300%.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Low floor vehicle
InactiveUS20110239899A1Easily affectedReduce side pressureUnderframesPassenger carriagesBogieFront edge
A low floor vehicle reduces, when the vehicle enters a curved track, the lateral force of the vehicle, prevents occurrence of vibration and creaking sounds of the vehicle, improves riding quality of passengers, and reduces wear of wheel flanges. A low floor vehicle includes a bogie frame 9 of a bogie 7, a pair of bogie frame cross beams 9a arranged along a vehicle lateral direction in the middle of a vehicle longitudinal direction of the bogie frame 9 and arranged spaced apart from each other in the vehicle longitudinal direction, and a pair of wheels 8 provided in each of a vehicle front edge direction and a vehicle rear edge direction with respect to the pair of bogie frame cross beams 9a of the bogie frame 9 and configured to travel on a track 1. A pair of flexible traction rods 15 arranged along the vehicle longitudinal direction and configured to be capable of extending and retracting in the vehicle longitudinal direction are provided in the bogie 7, the pair of flexible traction rods 15 are arranged spaced apart from each other in a vehicle lateral direction, one ends 15b of the flexible traction rods 15 are attached to the bogie frame cross beams 9a, and the other ends 15c of the flexible traction rods 15 are attached to a receiving section 6c of in the vehicle body 6, and the bogie 7 is configured to be capable of turning with respect to the vehicle body 6.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Elevator with rollers having selectively variable hardness
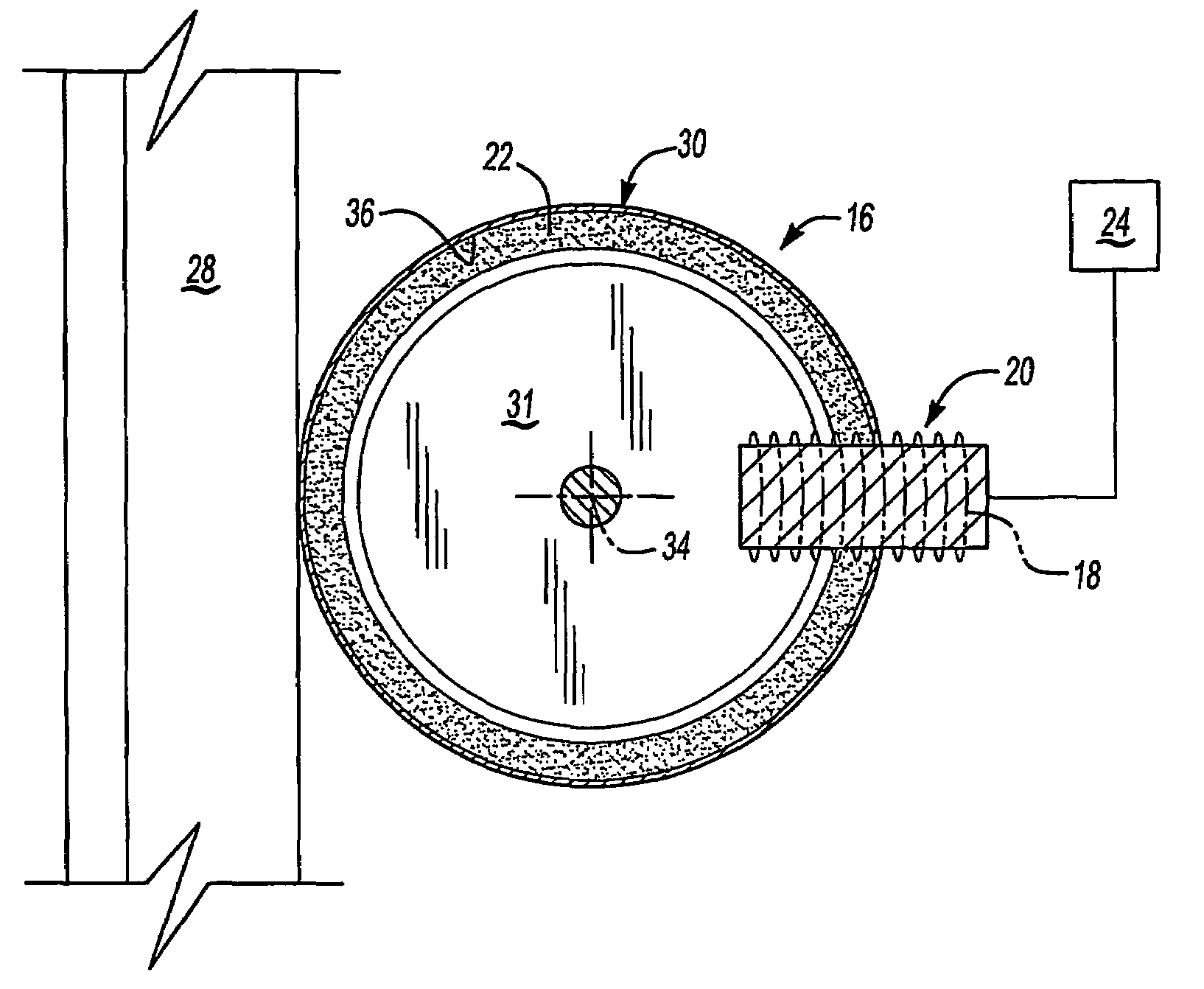
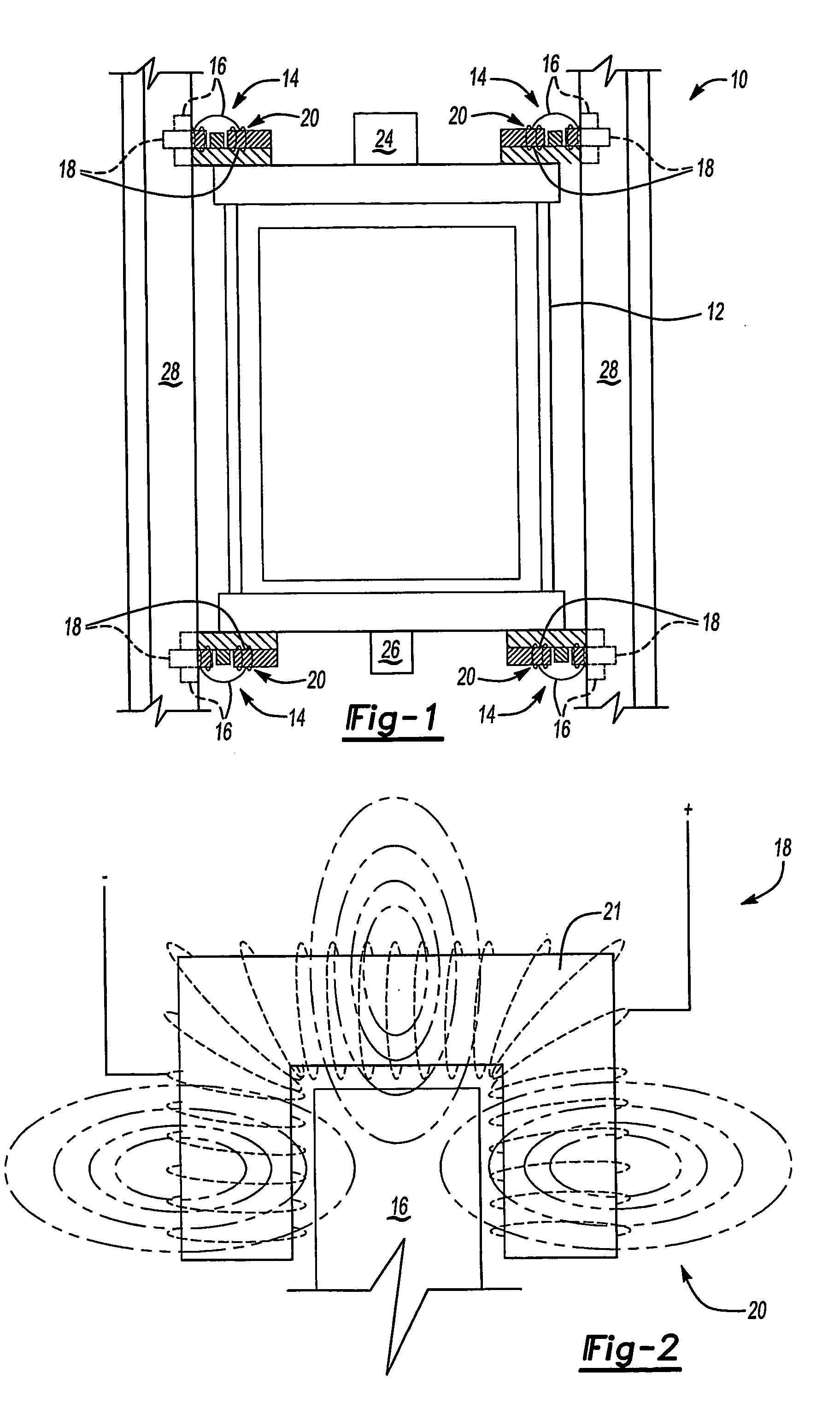
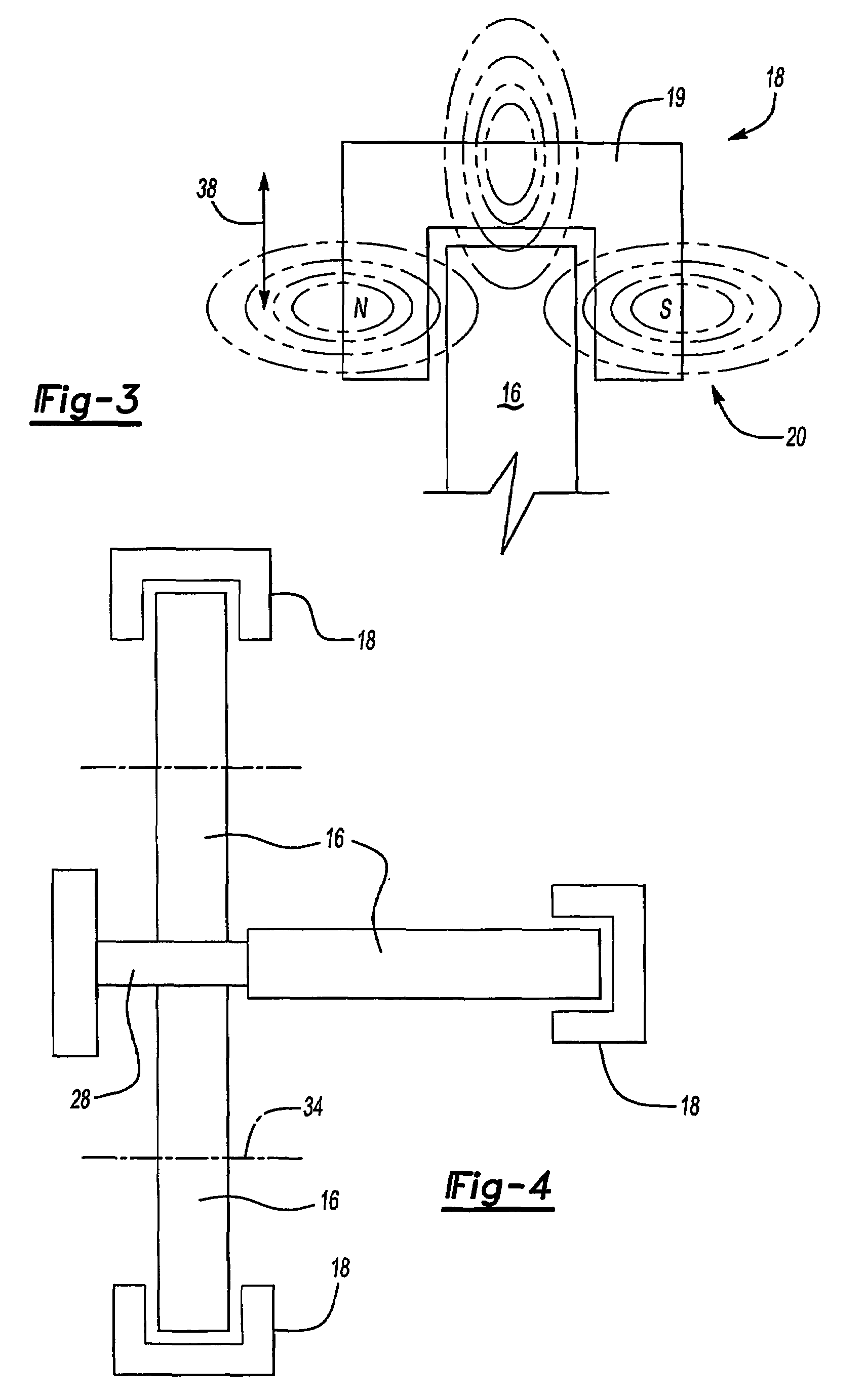
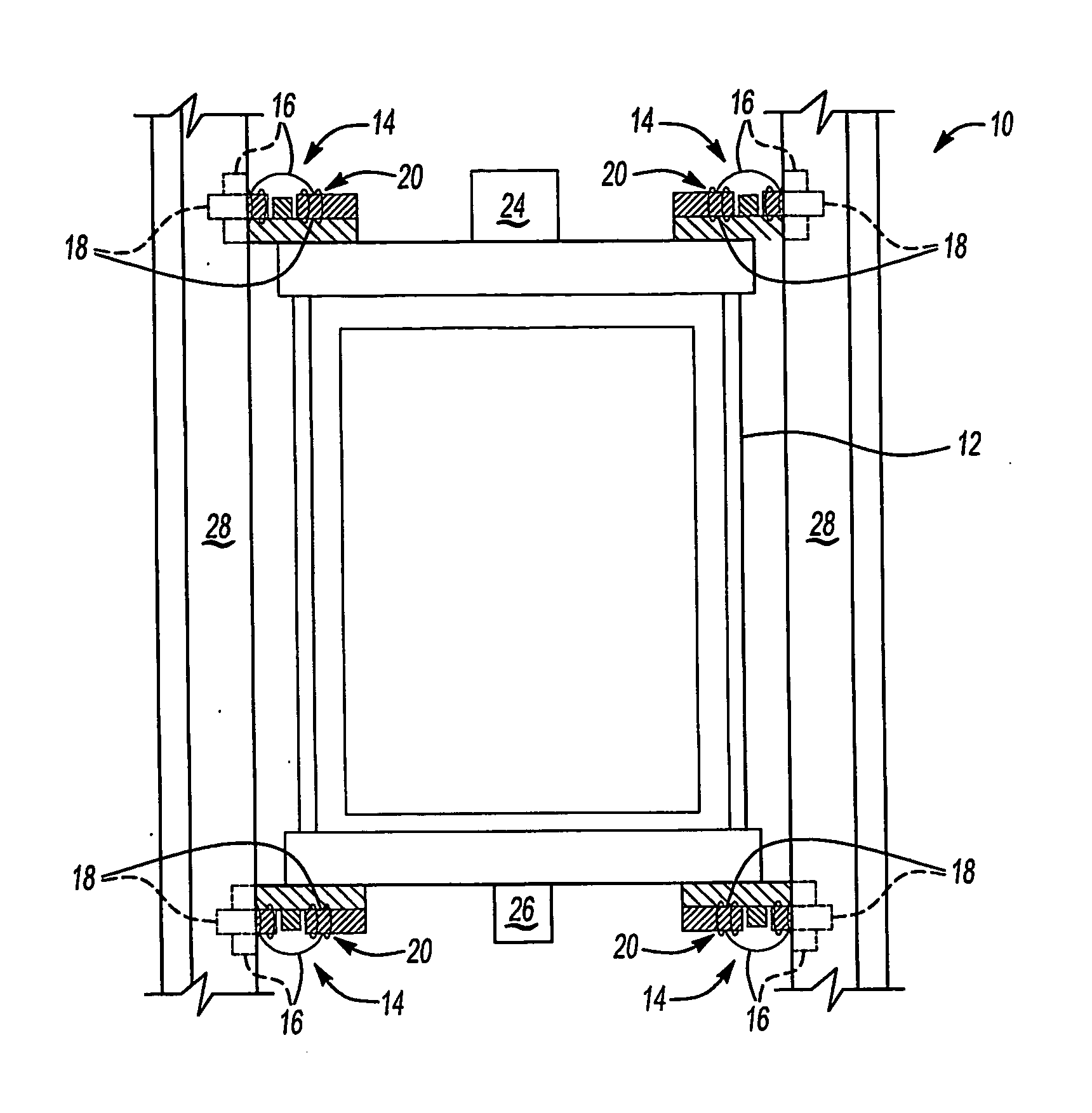
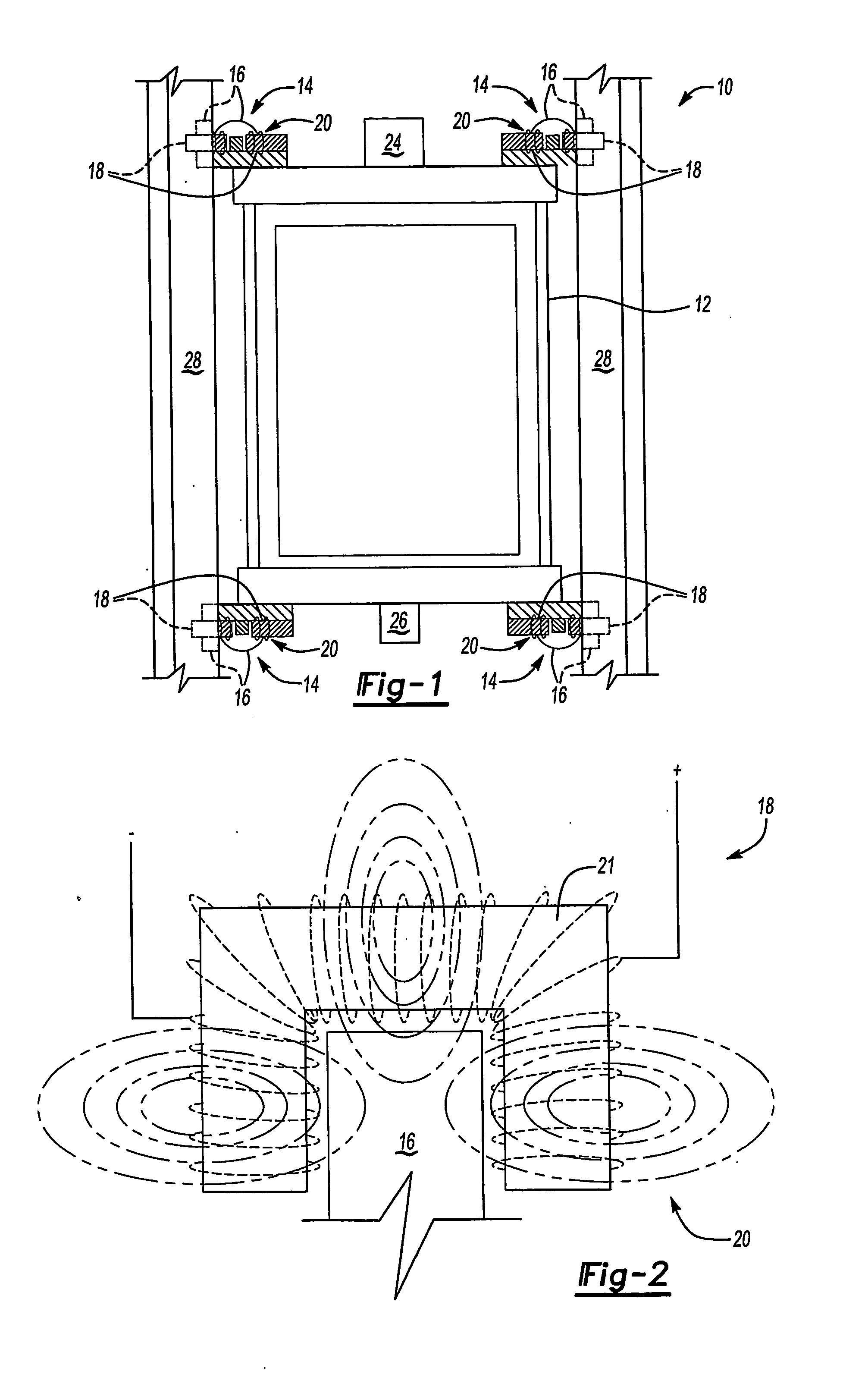
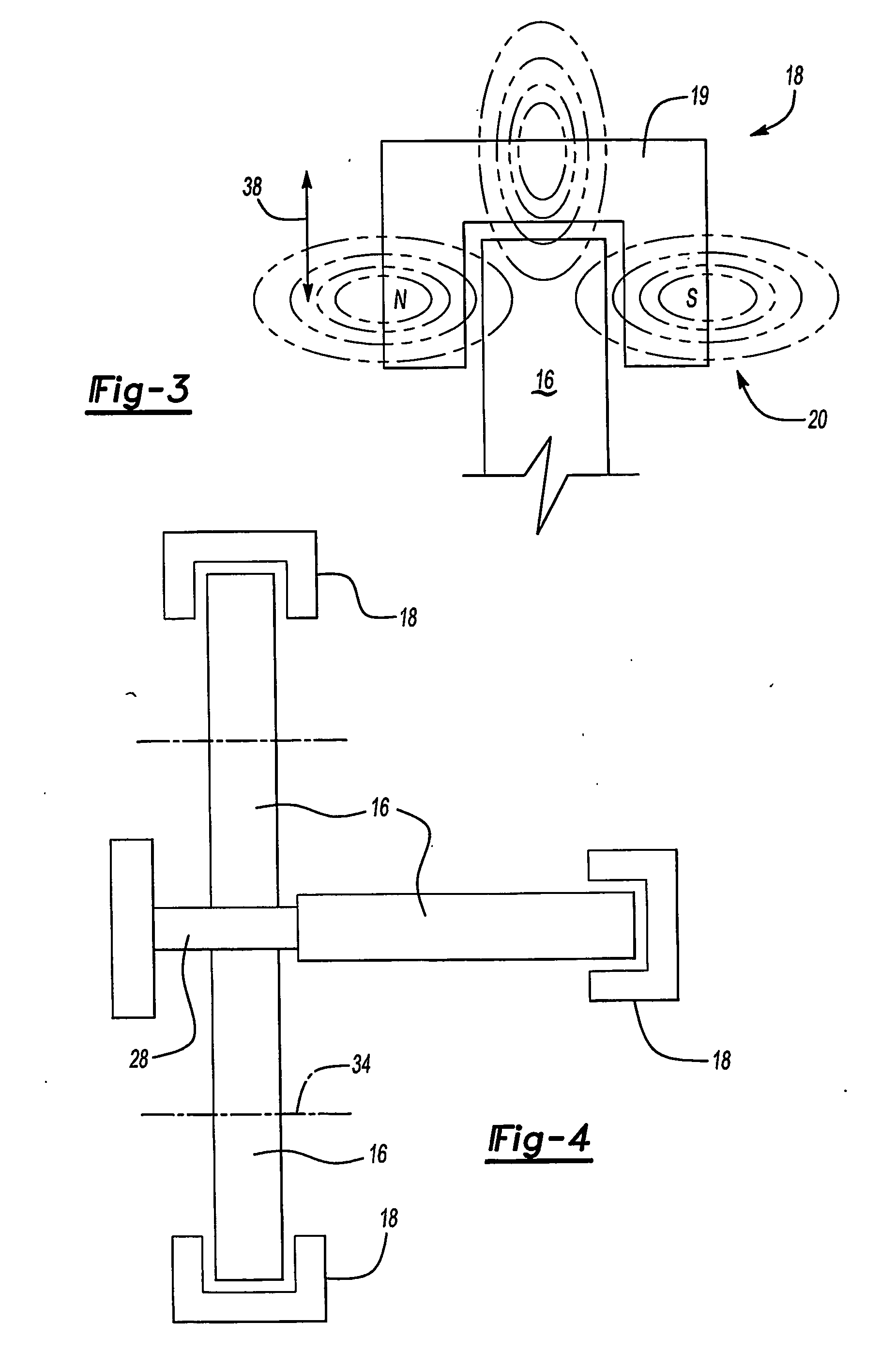
An elevator system includes a roller (16) having a hardness that varies responsive to a magnetic field (20). The roller (16) rolls along a guide rail (28) to maintain a desired orientation of the elevator car (12). In one example, the roller (16) includes a membrane (30) defining a generally annular chamber (36) containing fluid (22) that changes viscosity responsive to changes in the magnetic field (20). The rollers (16) are associated with at least one magnetic field generator (18) that generates a magnetic field (20) of a selected strength. Varying the magnetic field varies the hardness of each roller (16) to control vibrations of the elevator car (12) to improve ride quality.
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Conveyor apparatus
Owner:TOSHIBA ELEVATOR KK
Engine mount for vehicle
ActiveUS20170313171A1Easy to packImprove performanceSpringsJet propulsion mountingSemi activeEngine mount
A semi-active engine mount for a vehicle is provided to improve the NVH performance and ride quality. An engine mount for a vehicle includes a rubber module with a rubber having a core therein, and a case that surrounds an exterior circumference of the rubber and a fluid module with a module case coupled to the rubber module to define an upper and lower chamber and having straight and a bypass flow paths, a closure configured to open or close the straight flow path, and a diaphragm installed on the module case to close the lower chamber. A coil module has a coil embedded in the fluid module and configured to open and close the closure when a power source is turned on or off. In particular, a high loss factor when the vehicle travels is reduced, and decreasing dynamic characteristics when the vehicle idles is decreased.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
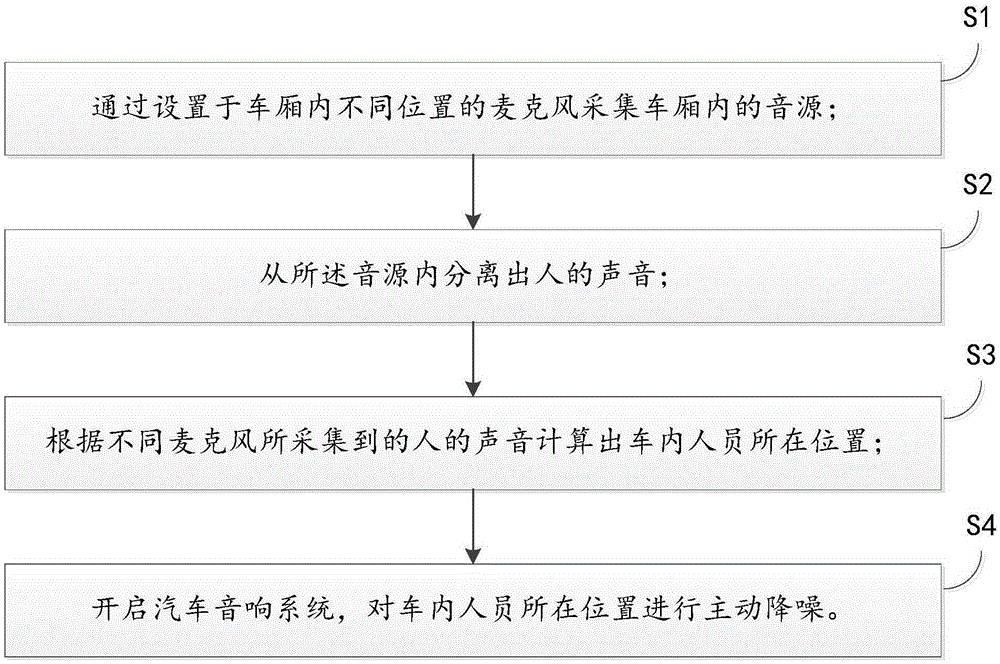
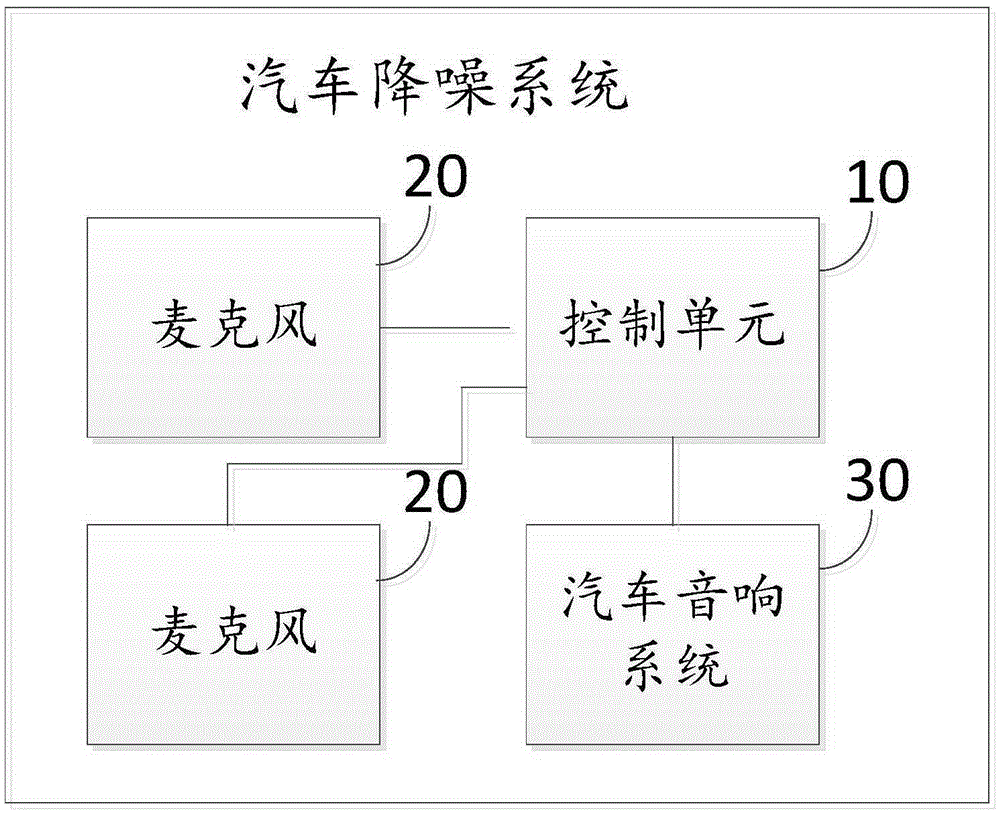
Automobile noise reduction method and system
ActiveCN105263088AImprove ride qualityReduce noiseTransducer acoustic reaction preventionSound sourcesEngineering
The invention discloses an automobile noise reduction method and system. The automobile noise reduction method comprises the steps of acquiring sound sources in a carriage through microphones arranged at different locations in the carriage; separating human voices from the sound sources; calculating locations of occupants in the automobile according to the acquired human voices by the different microphones; and opening an automobile voice box system for active noise reduction at the locations of the occupants. According to the invention, the automobile voice box system is used for active noise reduction, noises at the locations of the occupants in the carriage are effectively reduced, and the ride quality is improved.
Owner:FJ MOTOR GRP YUDO NEW ENERGY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Elevator with rollers having selectively variable hardness
InactiveUS20060207835A1Good damping propertiesImprove ride qualityElevatorsElevator systemEngineering
An elevator system includes a roller (16) having a hardness that varies responsive to a magnetic field (20). The roller (16) rolls along a guide rail (28) to maintain a desired orientation of the elevator car (12). In one example, the roller (16) includes a membrane (30) defining a generally annular chamber (36) containing fluid (22) that changes viscosity responsive to changes in the magnetic field (20). The rollers (16) are associated with at least one magnetic field generator (18) that generates a magnetic field (20) of a selected strength. Varying the magnetic field varies the hardness of each roller (16) to control vibrations of the elevator car (12) to improve ride quality.
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com