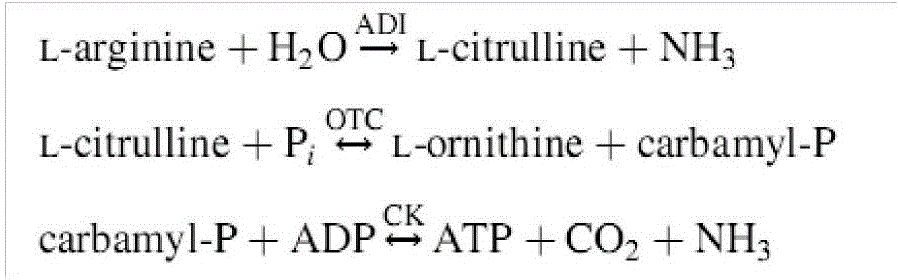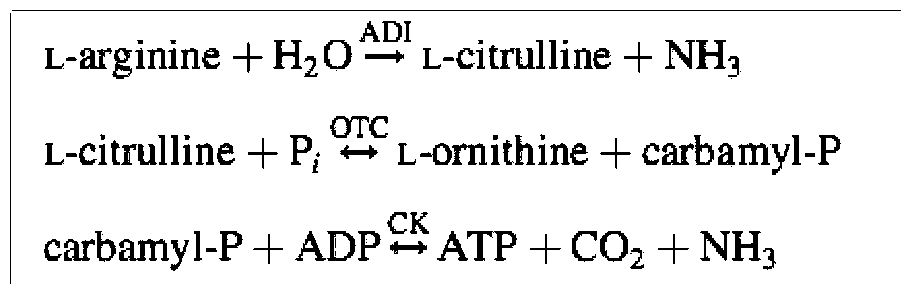Patents
Literature
30 results about "Multicopy gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multicopy Genes. Macrosatellites or variable number of tandem repeats (VNTRs), in certain cases, are known to carry functional components such as exons or sometimes even complete genes, resulting in what is known as multicopy genes.
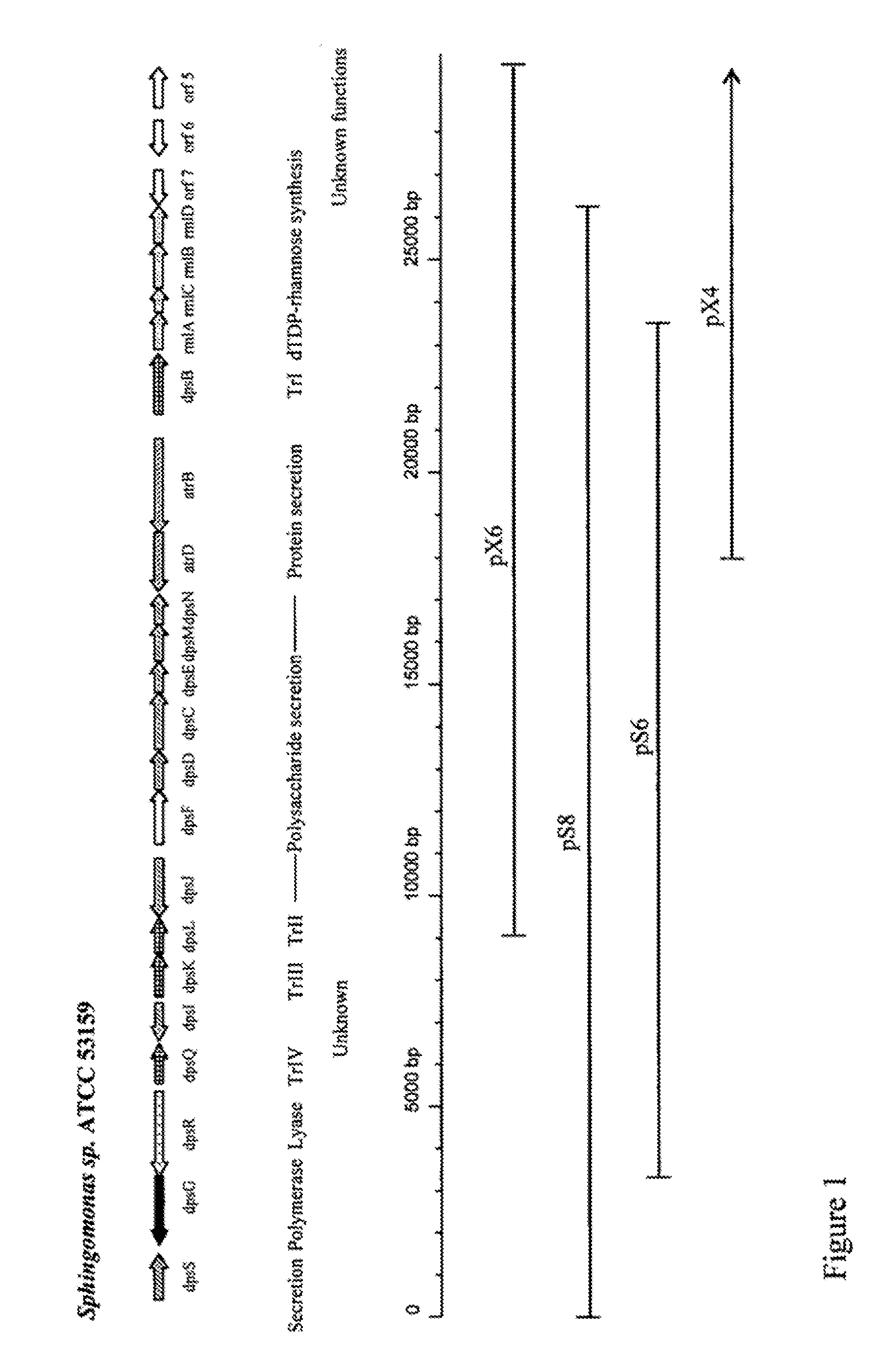
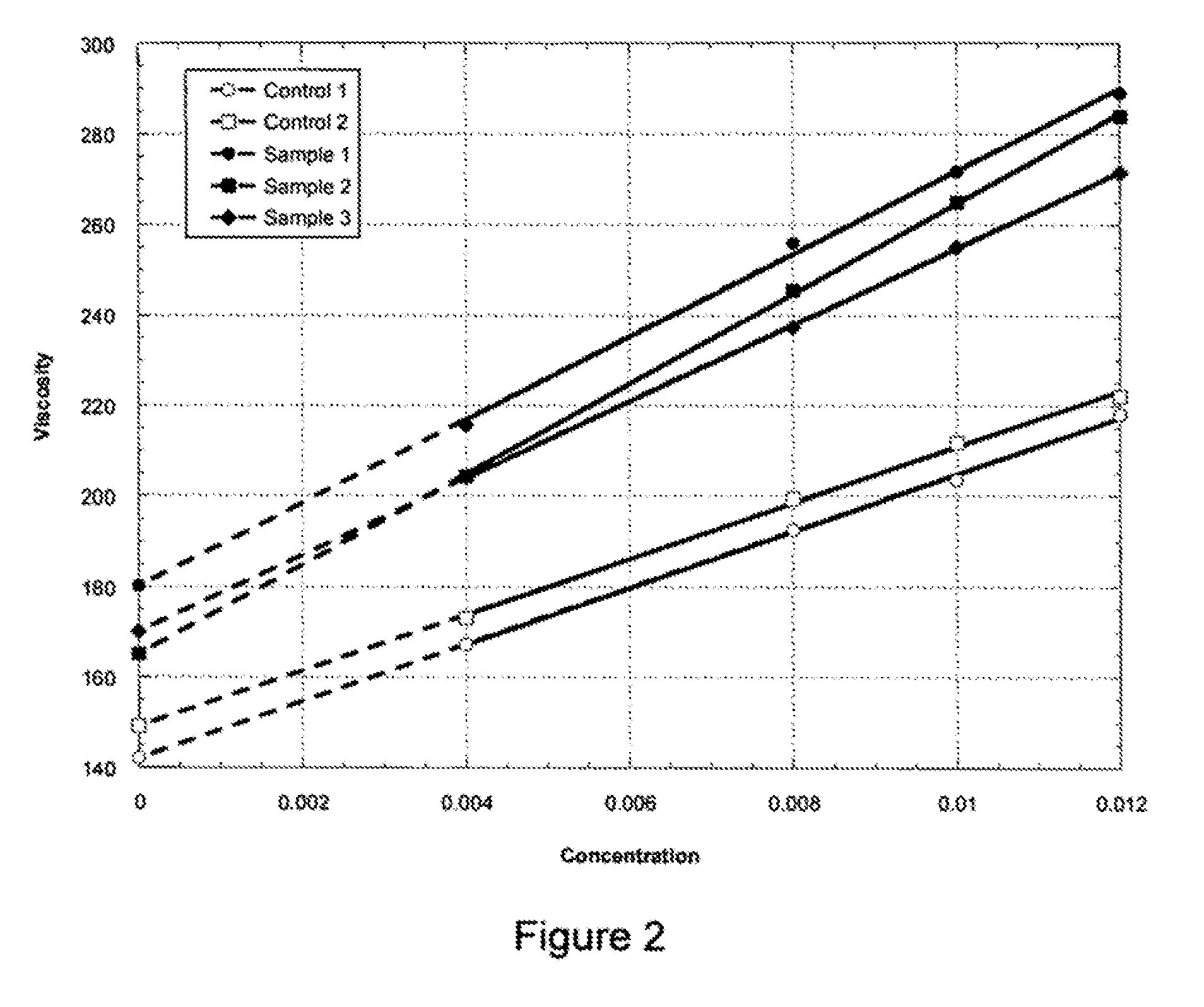
High viscosity diutan gums
ActiveUS7868167B2Increase productionImproved viscosity propertiesBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyPhysical property
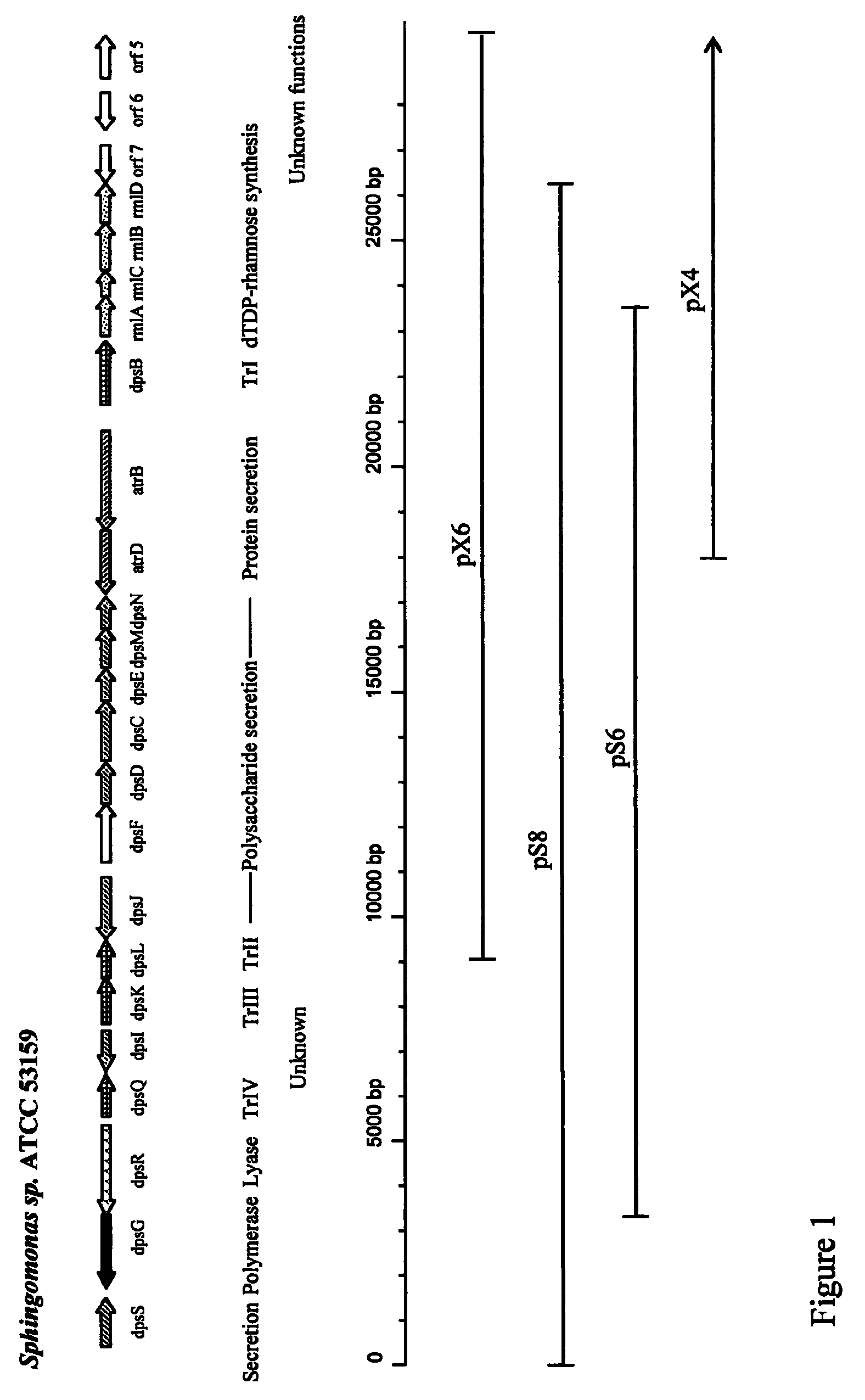
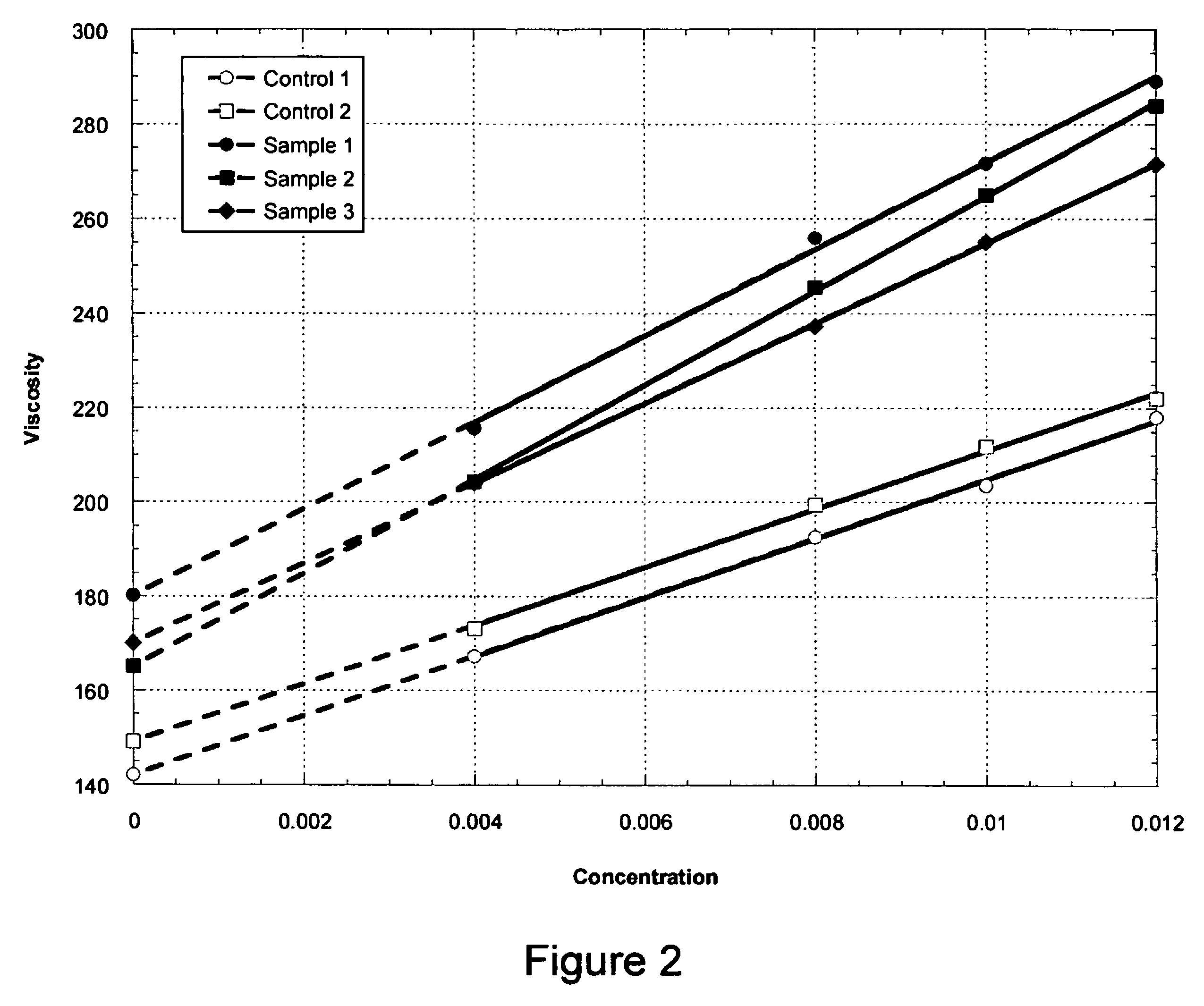
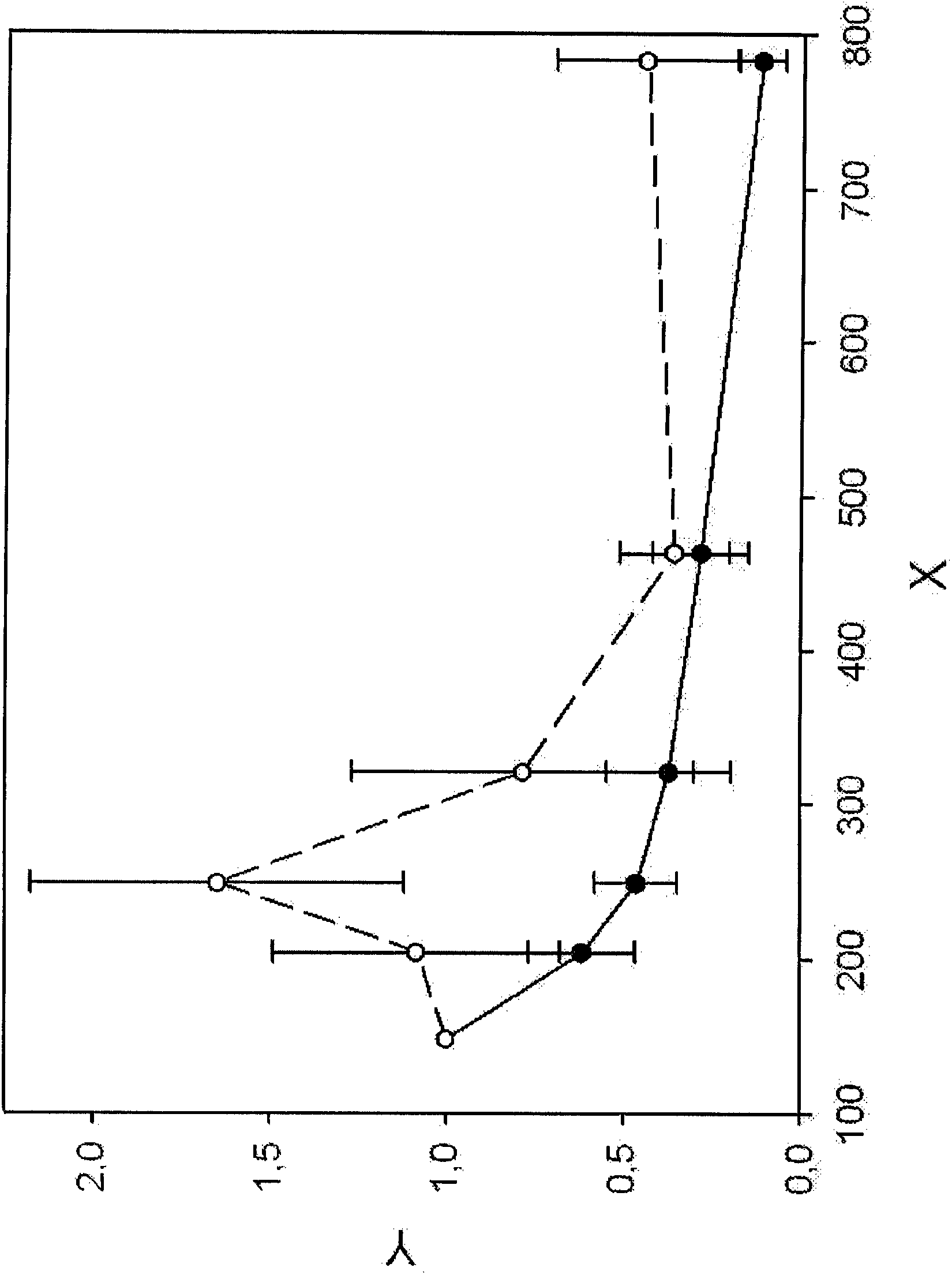
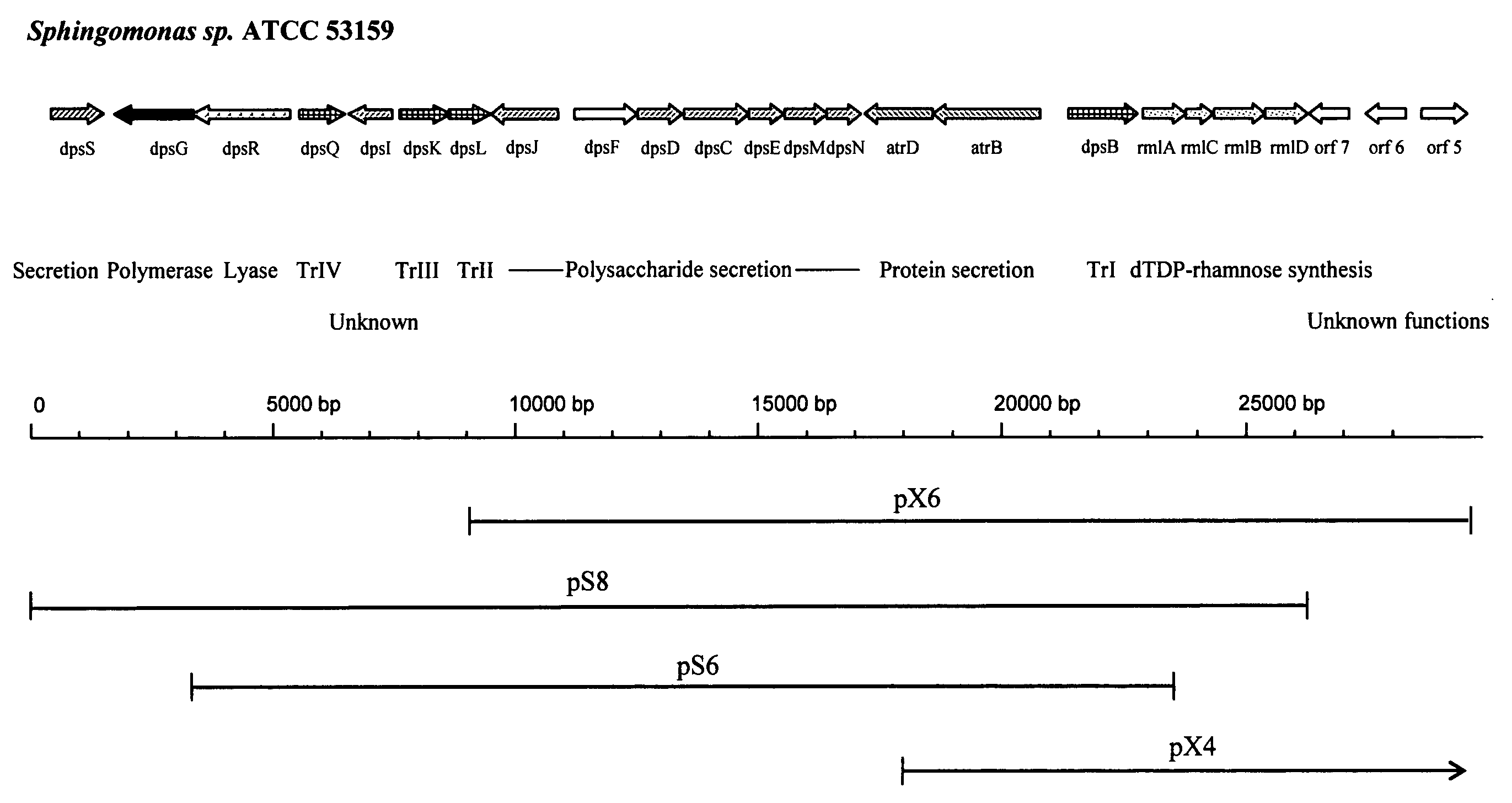
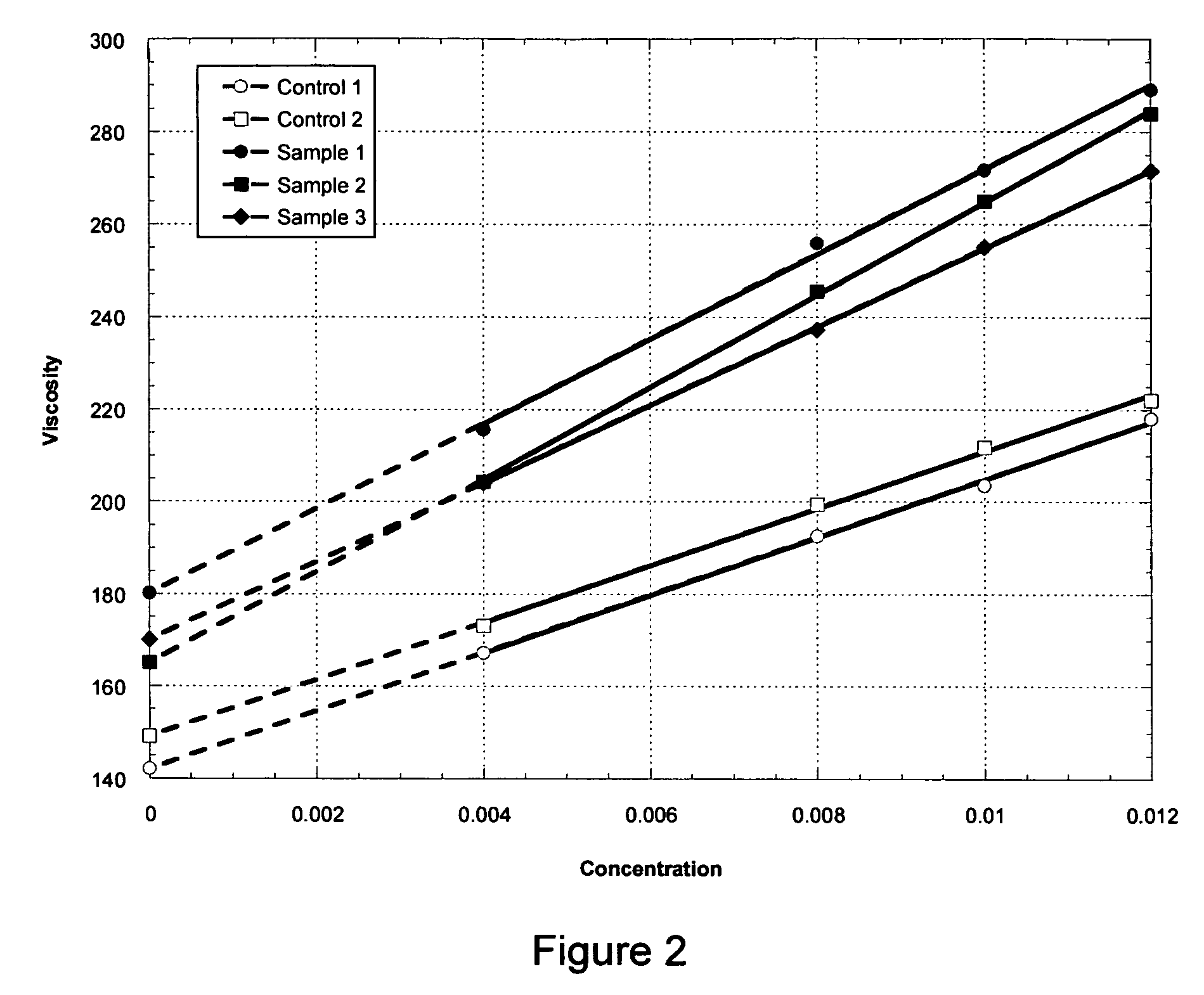
The production of a diutan polysaccharide exhibiting increased viscosity properties as compared with previously produced polysaccharide of the same type of repeating units. Such an improved diutan polysaccharide is produced through the generation of a derivative of Sphingomonas sp. ATCC 53159 that harbors a multicopy broad-host-range plasmid into which genes for biosynthesis of diutan polysaccharide have been cloned. The plasmid provides the capability within the host Sphingomonas strain to produce multiple copies of genes for such polysaccharide synthesis. In such a manner, a method of not just increased production of the target diutan polysaccharide, but also production of a diutan polysaccharide of improved physical properties (of the aforementioned higher viscosity) thereof is provided. Such a diutan polysaccharide has proven particularly useful as a possible viscosifier in oilfield applications and within cement materials. The inventive methods of production of such an improved diutan polysaccharide, as well as the novel cloned genes required to produce the improved diutan within such a method, are also encompassed within this invention. Additionally, the novel engineered Sphingomonas strain including the needed DNA sequence is encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Method for diagnosis of cancer and monitoring of cancer treatments
The present invention relates to a method for cancer diagnosis and for monitoring cancer treatments based on the analysis of the DNA fragmentation pattern of repetitive elements (preferably LINE1) or multi copy genes (preferably U1 RNA) identified in body fluid samples isolated from cancer patients.
Owner:奥里迪斯生物标记有限责任公司
High viscosity diutan gums
ActiveUS20080319186A1Increased biosynthetic productionHigh viscosity propertySugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyPhysical property
The production of a diutan polysaccharide exhibiting increased viscosity properties as compared with previously produced polysaccharide of the same type of repeating units. Such an improved diutan polysaccharide is produced through the generation of a derivative of Sphingomonas sp. ATCC 53159 that harbors a multicopy broad-host-range plasmid into which genes for biosynthesis of diutan polysaccharide have been cloned. The plasmid provides the capability within the host Sphingomonas strain to produce multiple copies of genes for such polysaccharide synthesis. In such a manner, a method of not just increased production of the target diutan polysaccharide, but also production of a diutan polysaccharide of improved physical properties (of the aforementioned higher viscosity) thereof is provided. Such a diutan polysaccharide has proven particularly useful as a possible viscosifier in oilfield applications and within cement materials. The inventive methods of production of such an improved diutan polysaccharide, as well as the novel cloned genes required to produce the improved diutan within such a method, are also encompassed within this invention. Additionally, the novel engineered Sphingomonas strain including the needed DNA sequence is encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
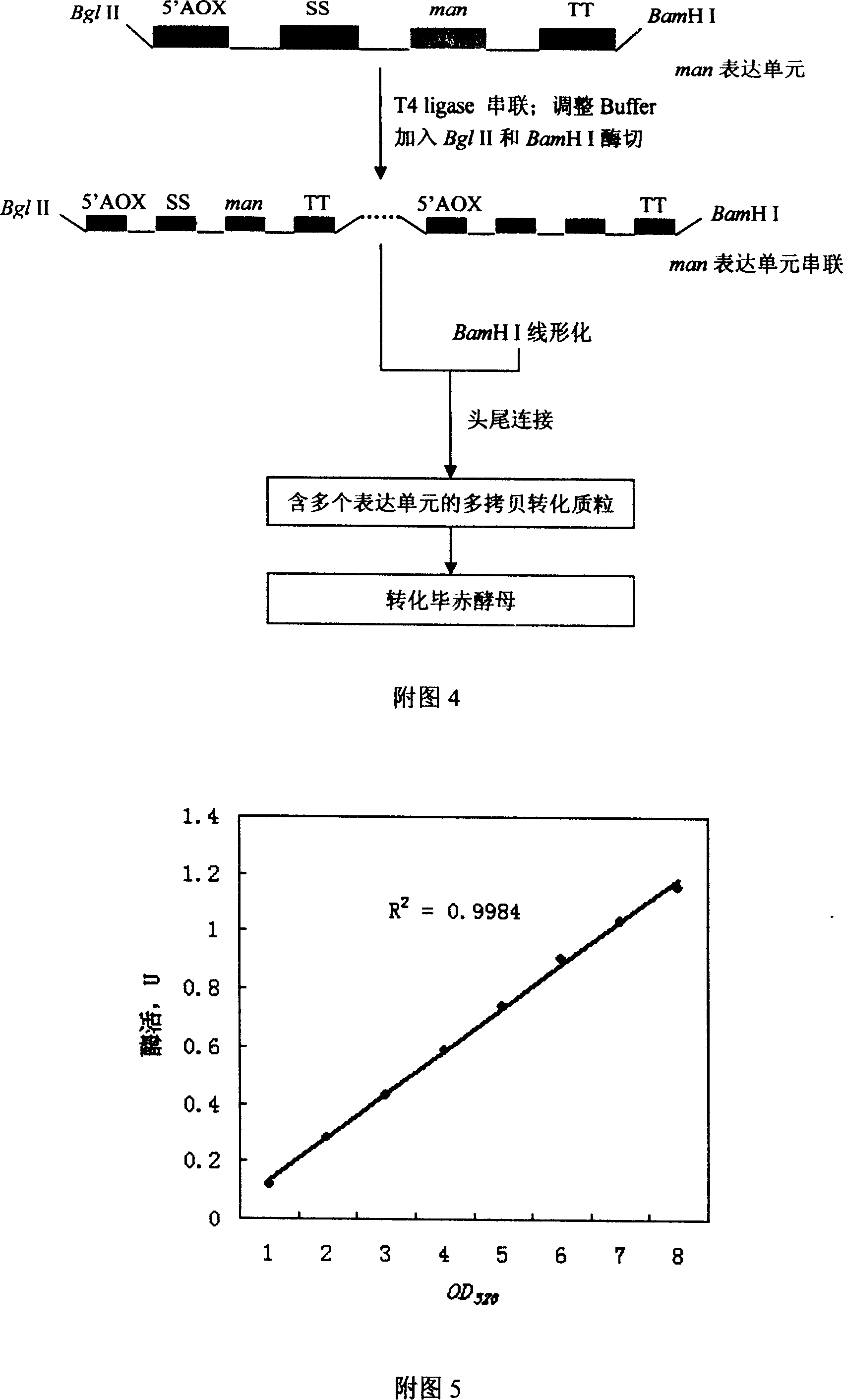
Multi-copy gene carrier of high efficient expression mannanase
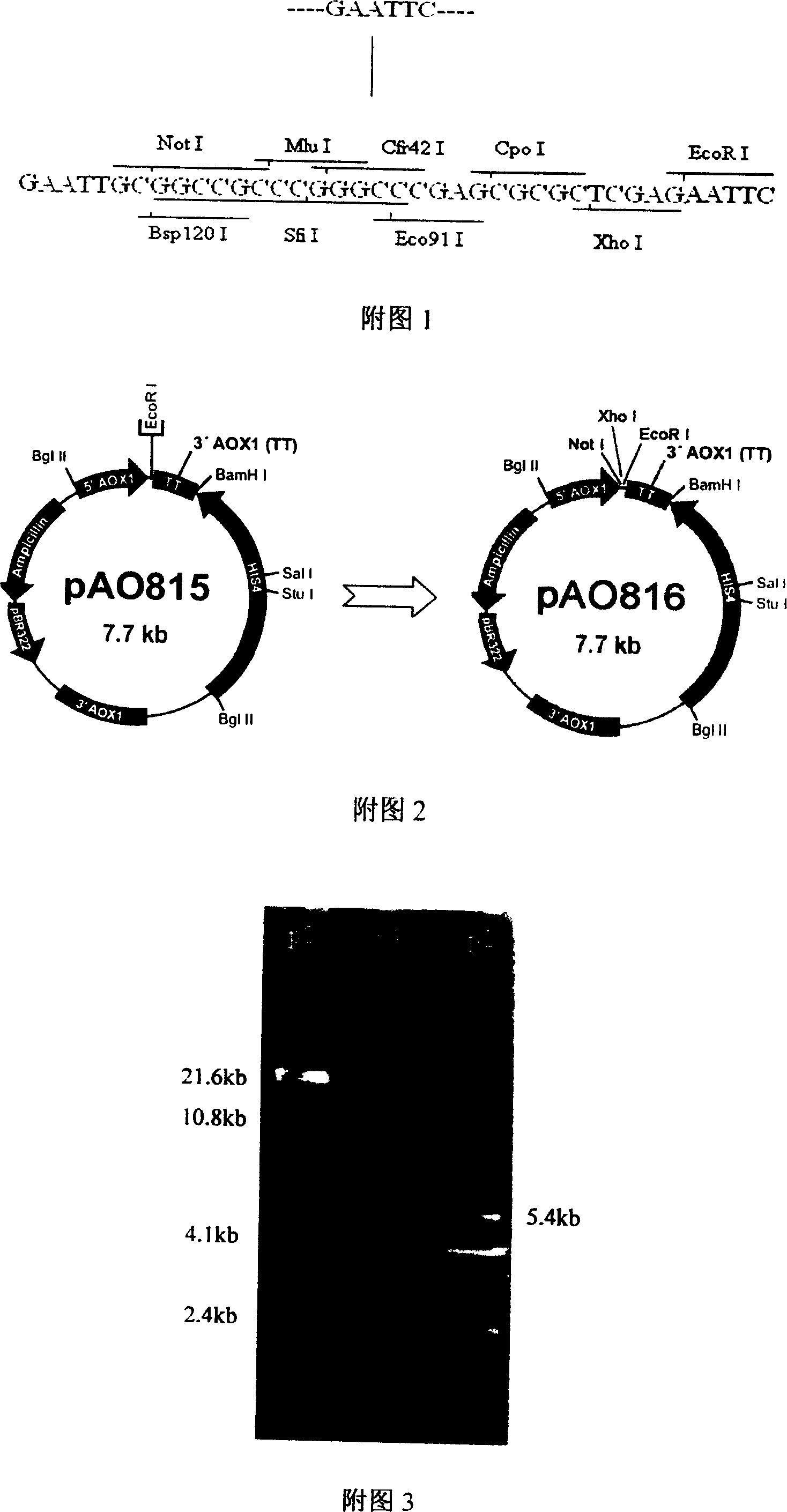
The present invention relates to gene engineering bacteria, and is especially one expression vector for high efficiency secreting expression on mannase gene and its multicopy body. Primer is designed according to the cloning site of Pichia yeast pAO815, the polyclonal site region of the target expression vector is replaced into Not I, XhoL I and EcoR I to form polyclonal sites for easy cloning, the alpha-factor signal peptide and the target gene are fused and connected to the expression vector for the expression vector containing the target gene to secrete and express mannase, and the restriction enzymes Bgl II and BamH I with complementary sticky ends are cleaved, linked and converted to obtain multicopy expression unit plasmid containing mannase gene. The multicopy body after transforming Pichia yeast can express mannase in high efficiency and is used to prepare mannase from konjaku meal.
Owner:广州伯凯生物技术有限公司
Method For Identification Of Novel Physical Linkage Of Genomic Sequences
InactiveUS20090263798A1Rapidly and economically identifyingMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomeComputational biology
The invention is directed to methods to identify the location in a genome of a nonfixed or multicopy genomic element using microarrays or sequencing.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +2
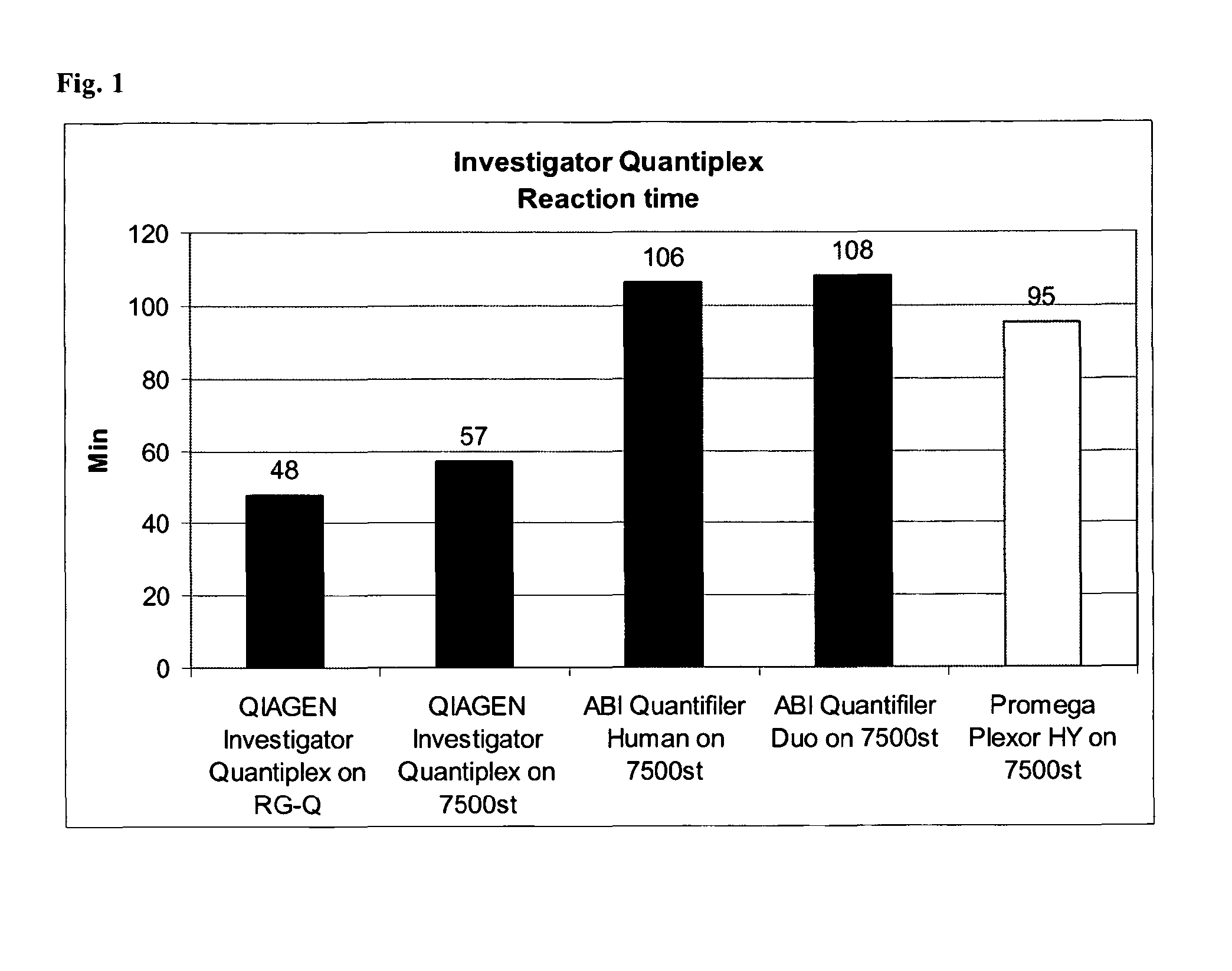
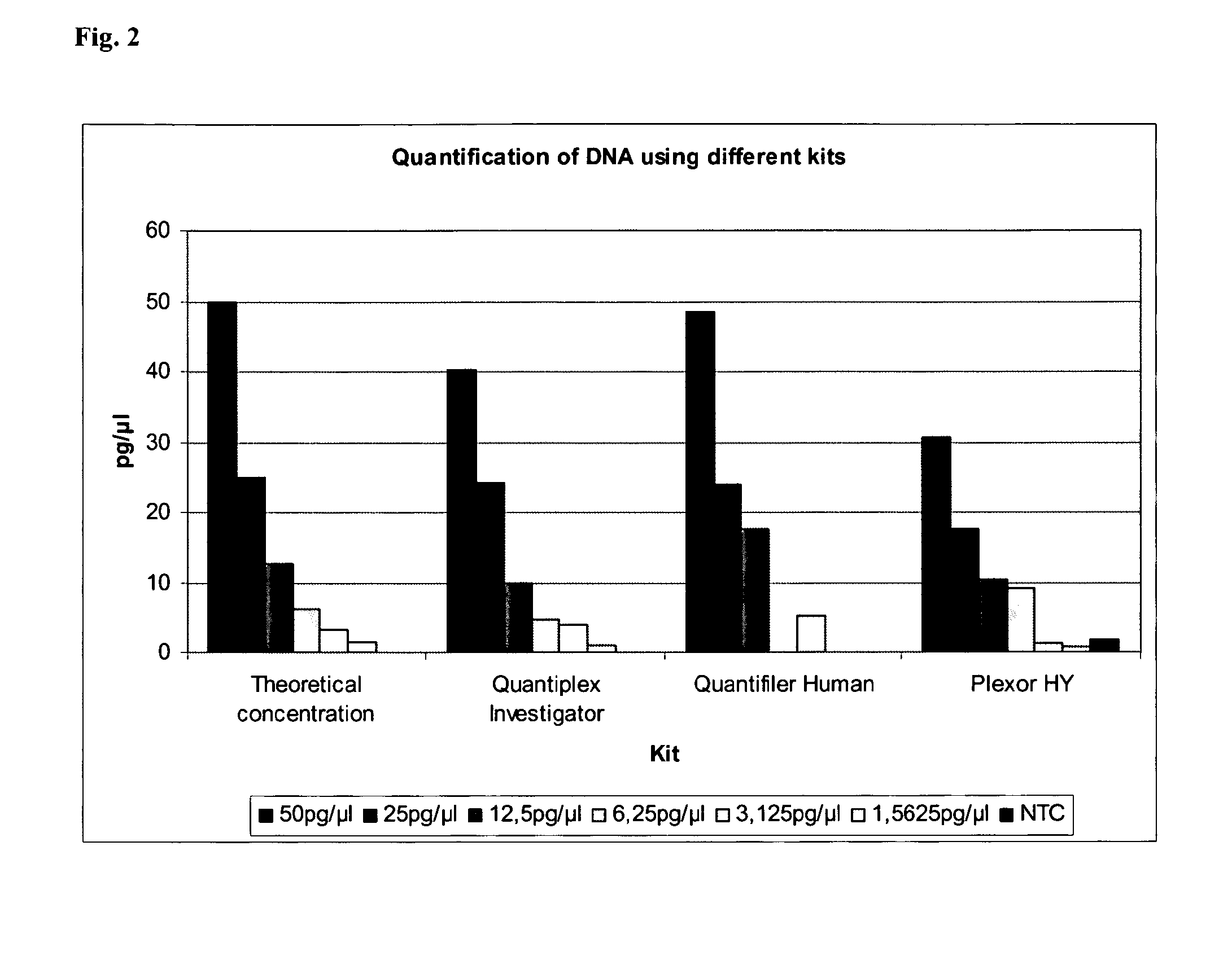
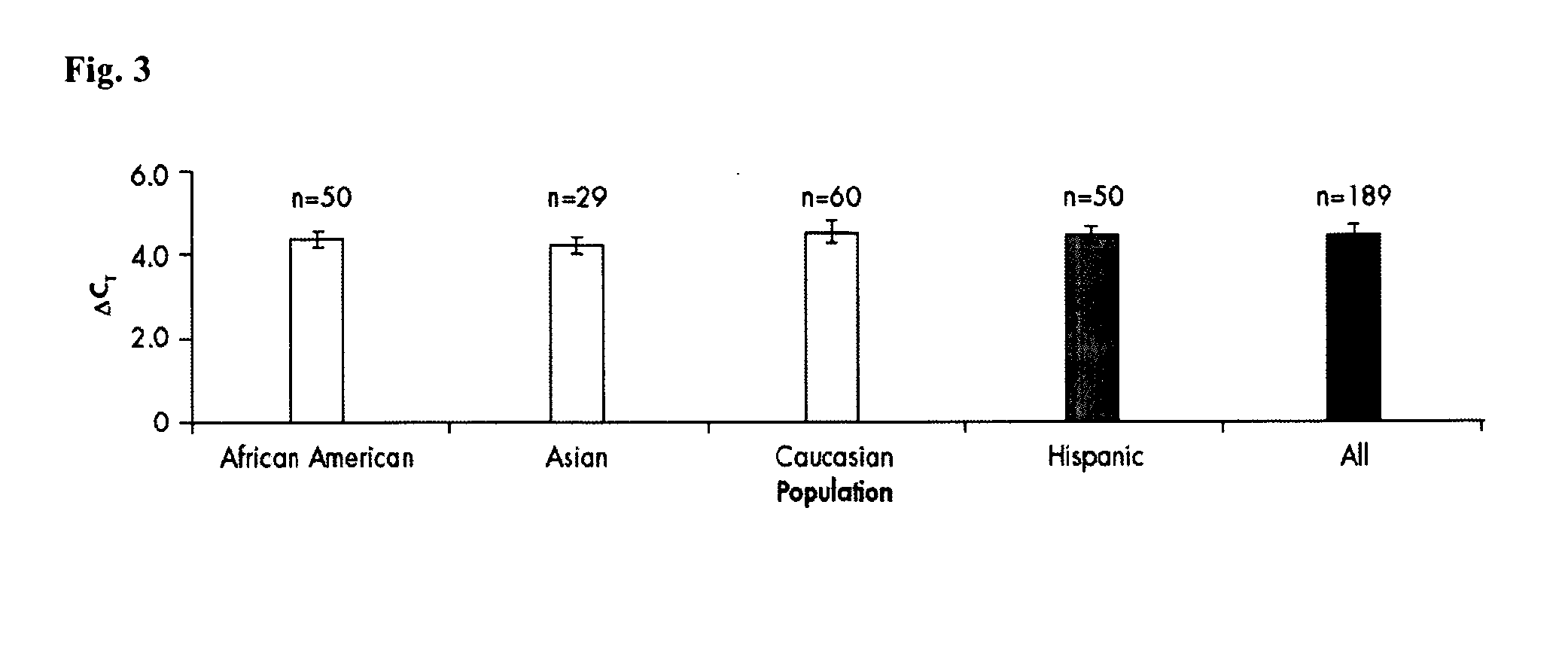
Method for quantifying human DNA using an internal control
ActiveUS20140147843A1High sensitivityHigh success rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomeBase pair
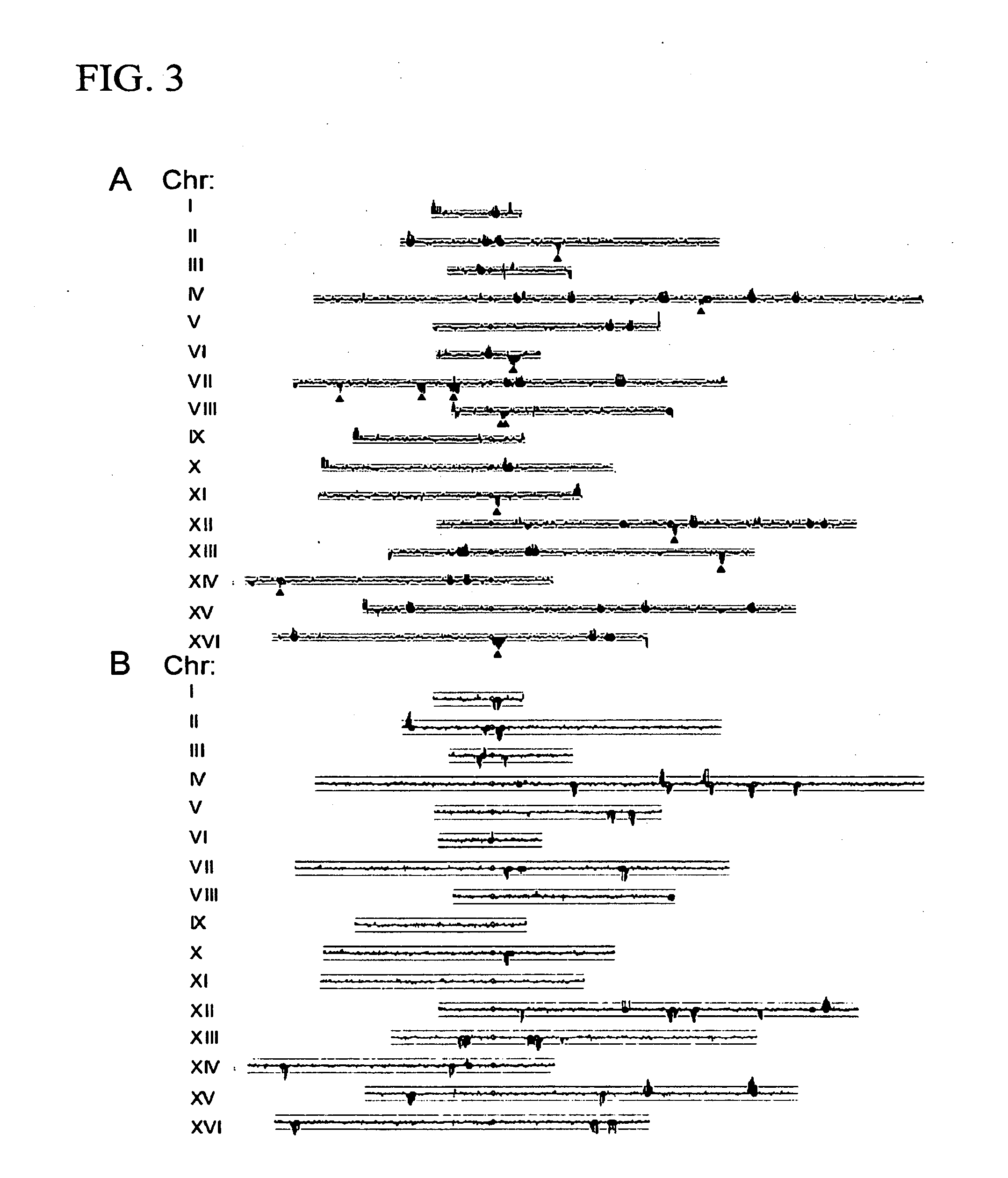
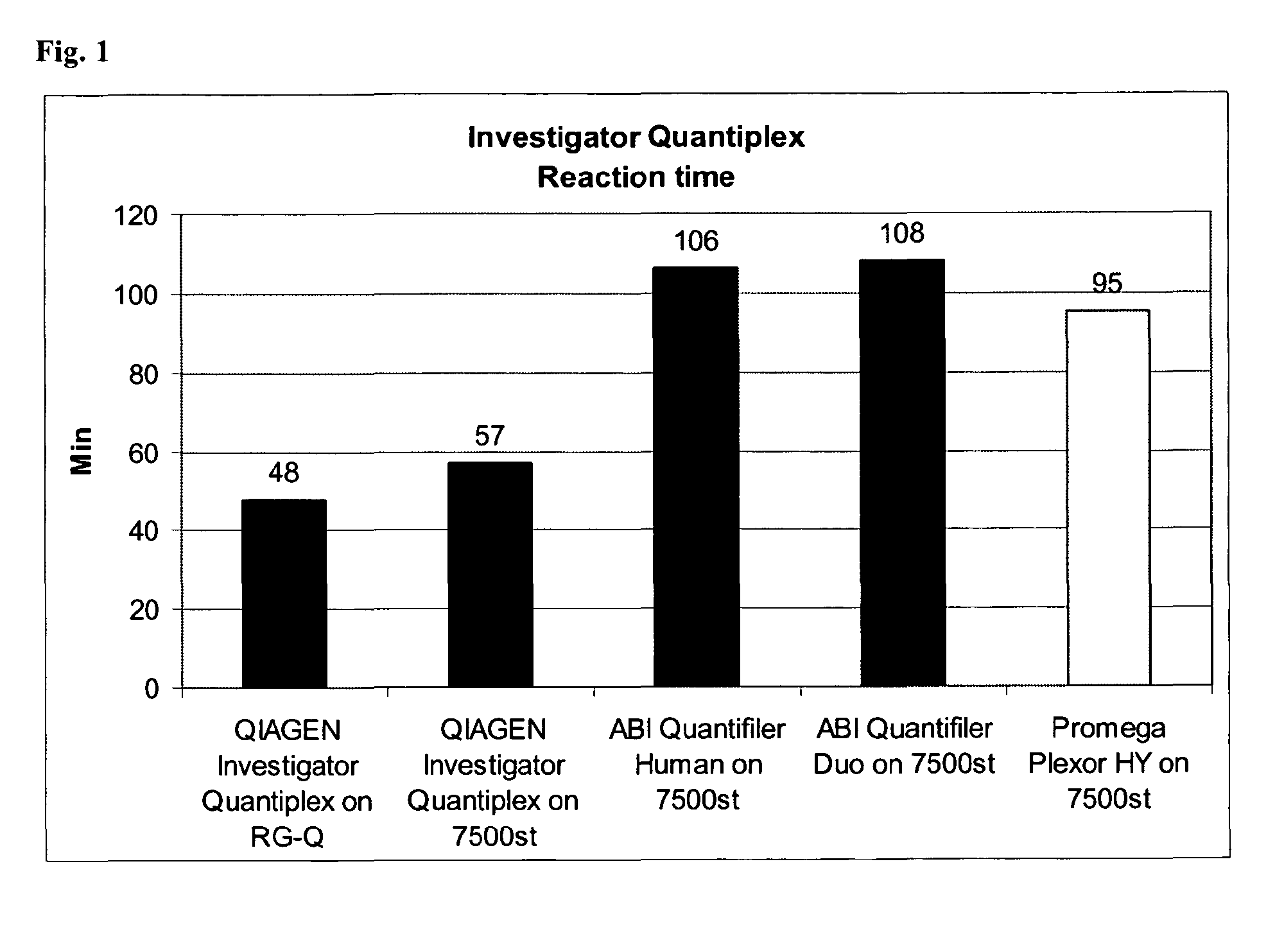
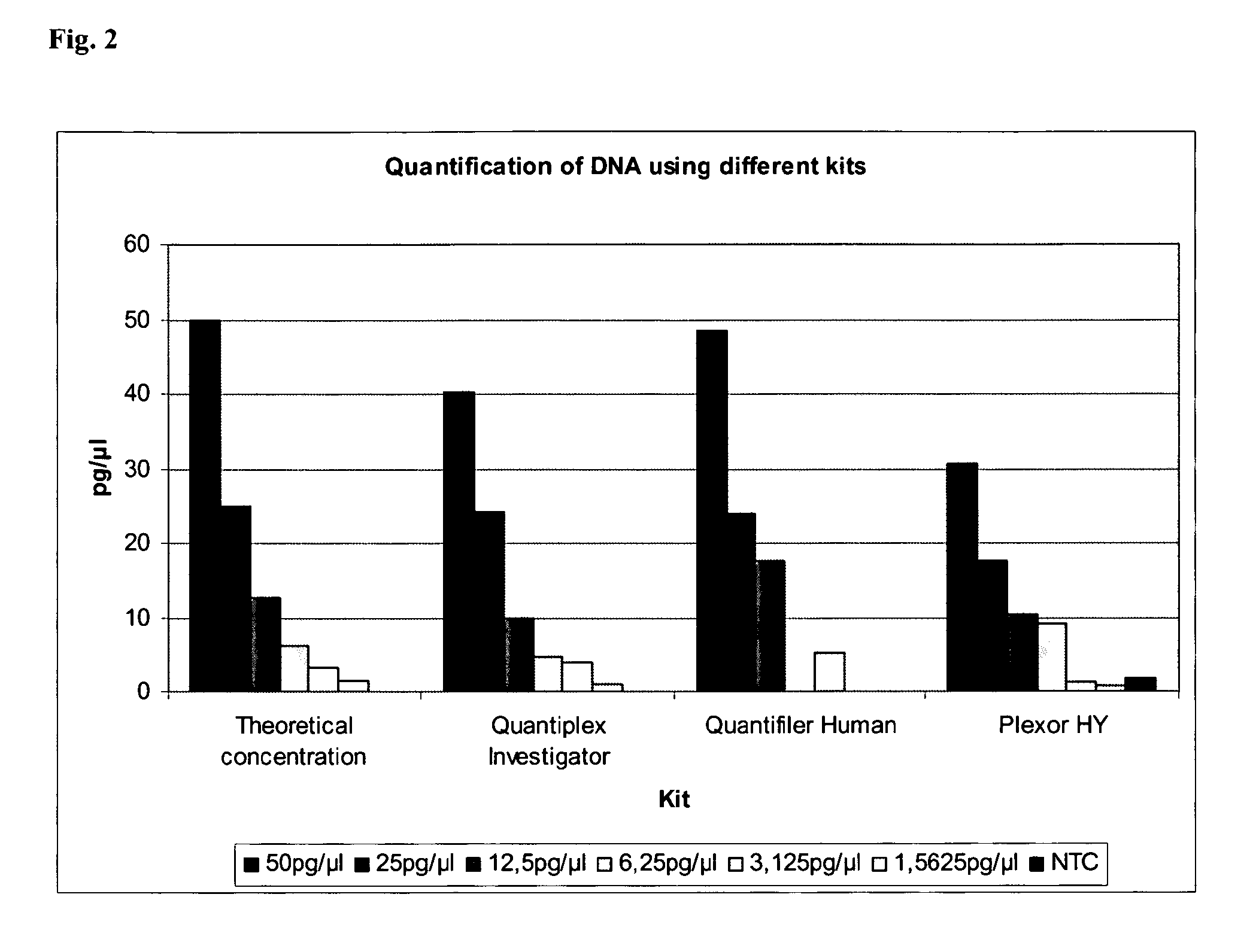
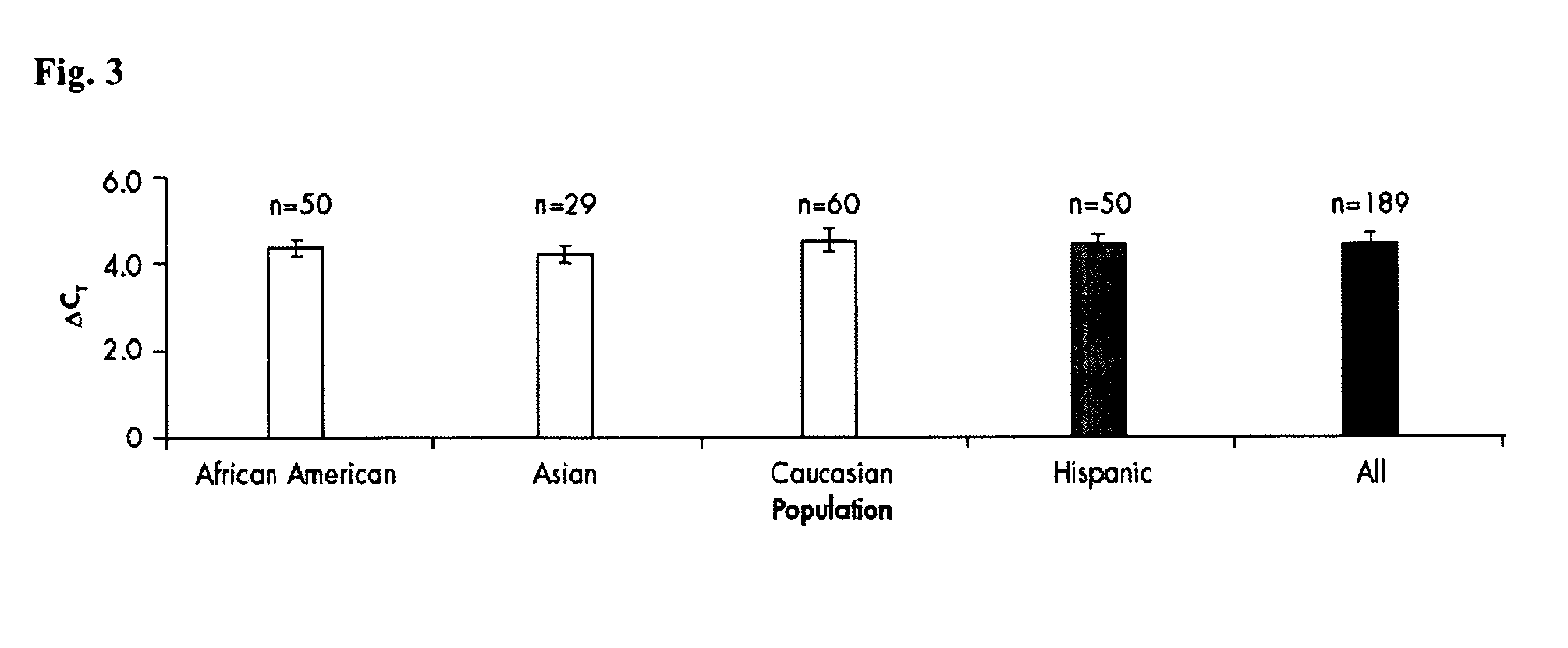
The present invention relates to a method for quantifying and / or detecting one or more nucleic acids of a genome in a sample, wherein in an amplification reaction, (i) a first nucleic acid is amplified, the locus that is amplified is a multicopy locus (MCL) within the genome, wherein the locus shares at least 80% sequence identity to a sequence according to SEQ ID NO. 1 over a stretch of 80 base pairs, and wherein the multicopy locus has copies on at least two different chromosomes, (ii) a second nucleic acid that has been added as an internal control (IC) is also amplified, and (iii) the amount of amplification product from the amplification of the first nucleic acid is determined.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH +1
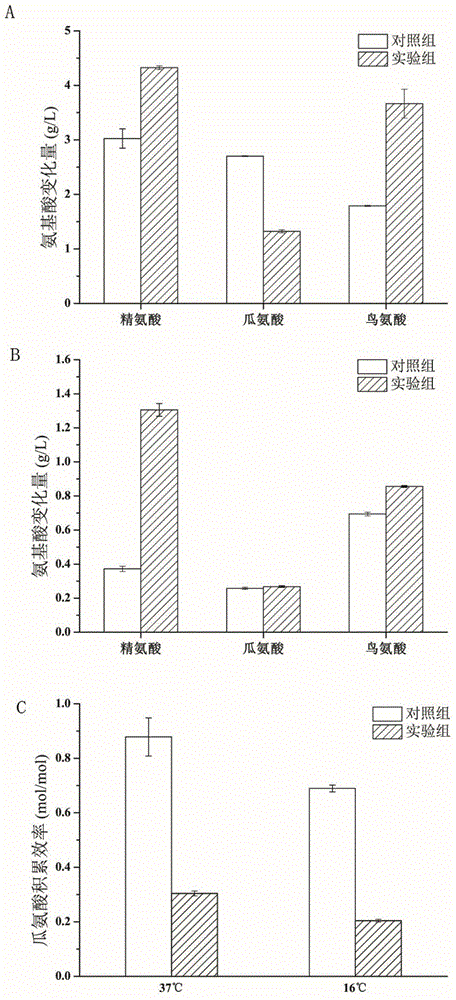
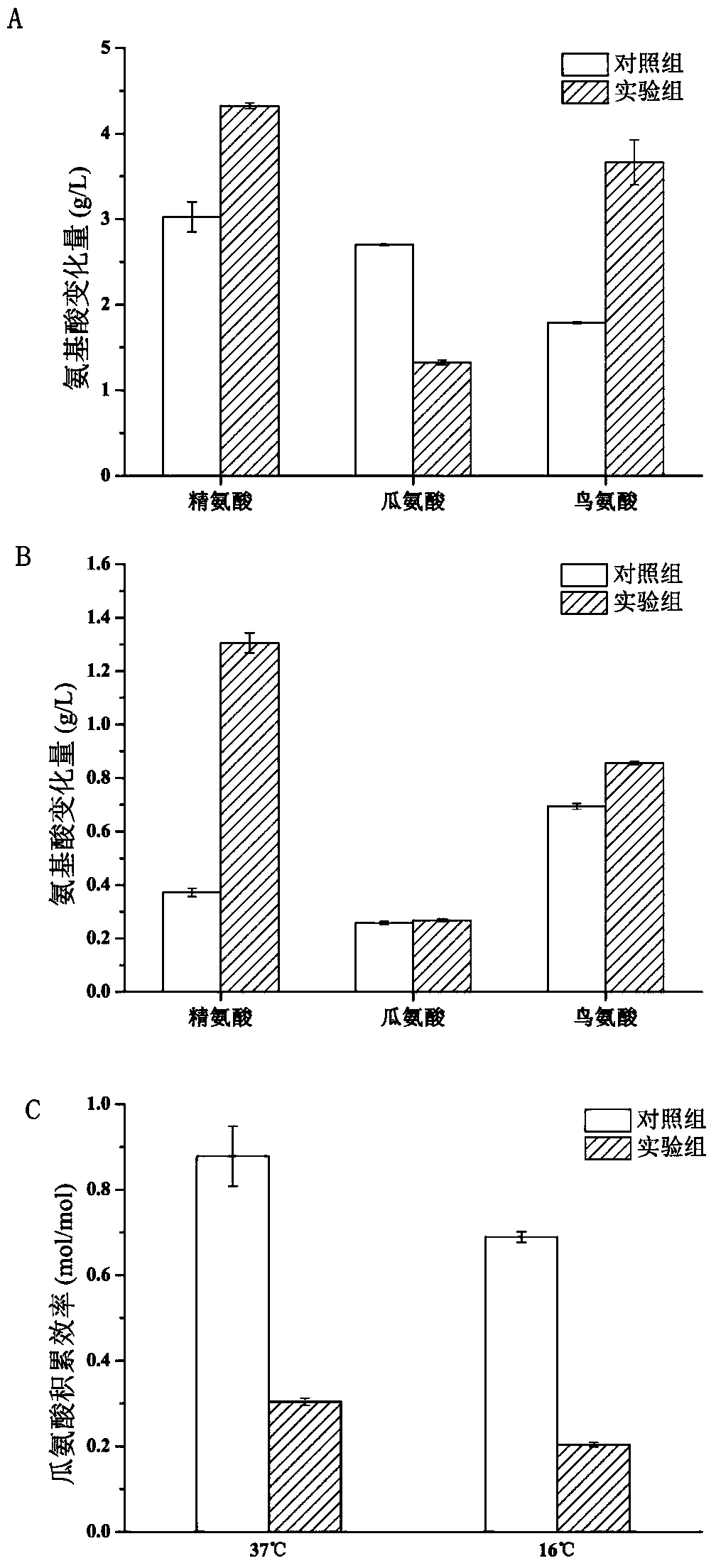
Method for efficiently screening lactic acid bacteria capable of sufficiently utilizing citrulline
ActiveCN104312953AReduce contentBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLactobacillusMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for efficiently screening lactic acid bacteria capable of sufficiently utilizing citrulline, belonging to the field of microorganisms. The method comprises the steps of starting with a genotype to screen bacteria with multicopy genes, inspecting the capability of metabolizing citrulline, and furthermore screening lactic acid bacteria capable of sufficiently utilizing citrulline. The content of citrulline is reduced through co-culture.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
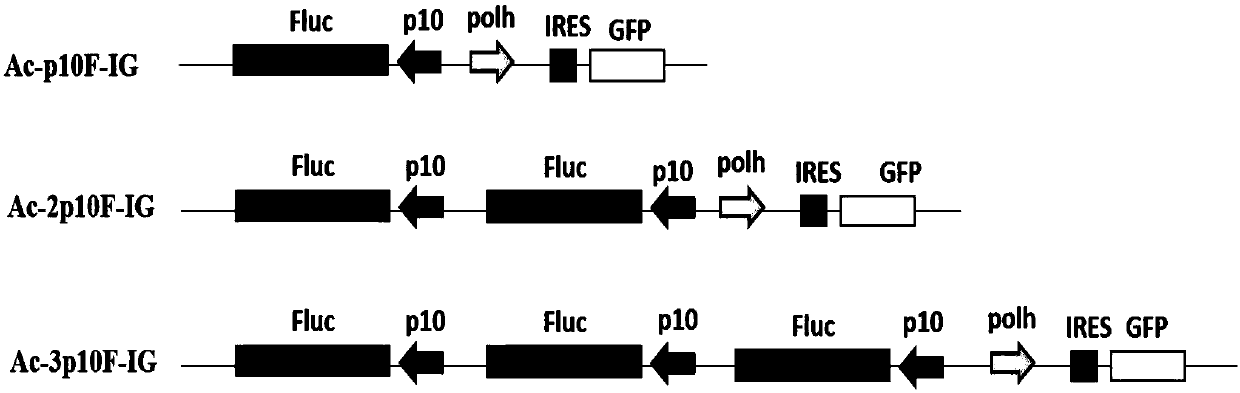
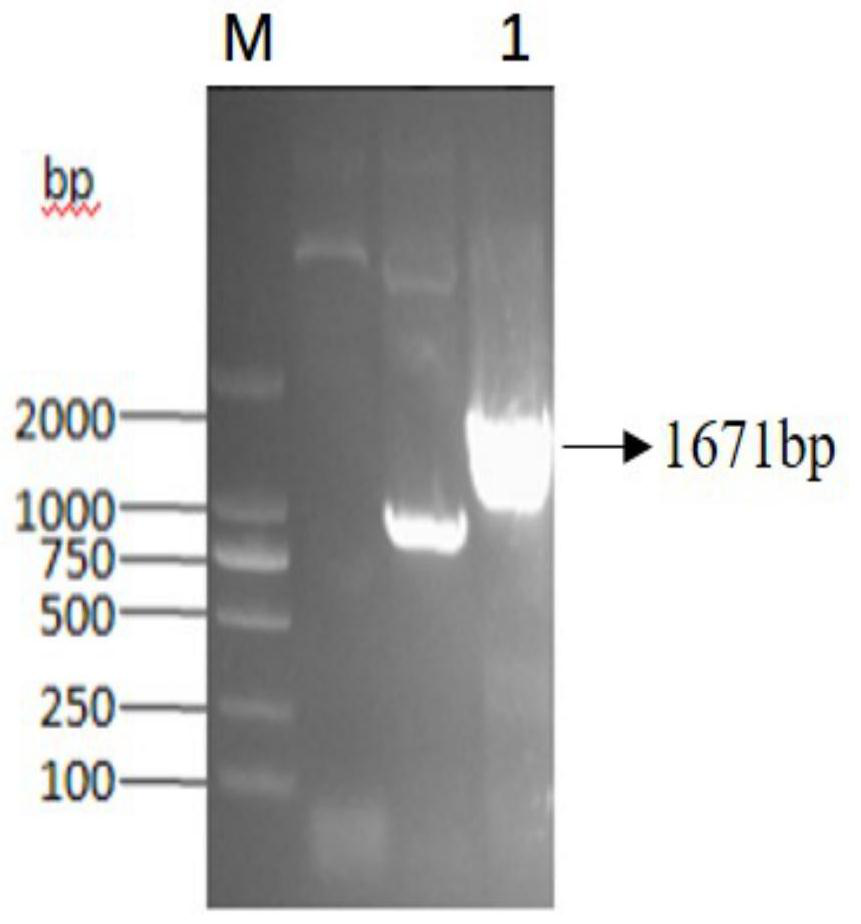
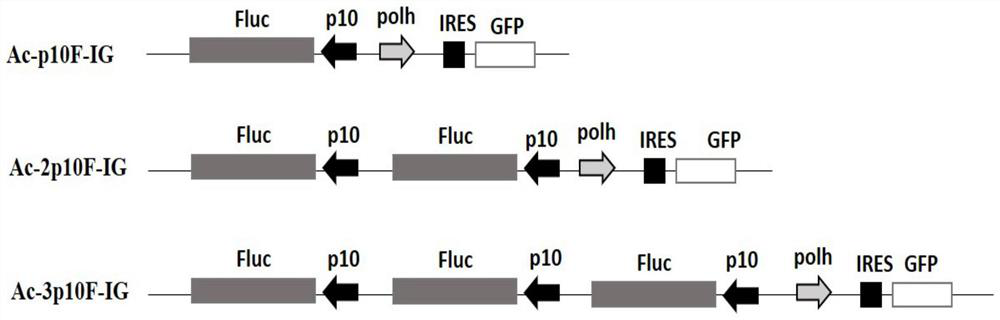
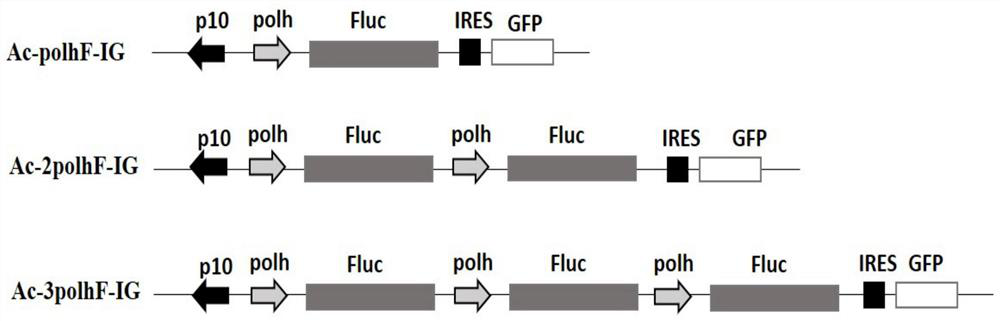
Method for constructing and expressing multicopy gene co-expressing baculovirus exogenous protein
ActiveCN108018264AHigh expressionEfficient expressionOxidoreductasesFermentationBafinivirusExogenous protein
The invention discloses a method for constructing and expressing a multicopy gene co-expressing baculovirus exogenous protein. The method comprises constructing recombinant baculovirus having 1-3 genecopy numbers and controlled by polyhedrin polh promoters polh and p10 through a firefly luciferase Fluc gene as a desired gene, infecting a SF9 cell line, then collecting cells and detecting the activity of the firefly luciferase. A detection result shows that compared with the unimproved baculovirus, the baculovirus improved by the method has the firefly luciferase gene expression quantity significantly increased by 2-5 times. The method significantly improves the expression quantity of the exogenous gene in the baculovirus system, is suitable for production of proteins with natural activity, has a great significance, provides a novel recombinant virus construction strategy for the baculovirus multi-gene expressing system and realizes the efficient expression of the exogenous gene in thebaculovirus multi-gene expressing system.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Method for detecting and/or quantifying human DNA
ActiveUS20130224742A1High sensitivityRapid intrachromosomal homogenizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomeNucleic acid sequence
The present invention relates to a method, kit and use of various nucleic acid sequences for deleting and / or quantifying one or more nucleic acids of a genome in a sample. Wherein the nucleic acid is amplified and the locus that is amplified is a multi copy locus within the genome, the multicopy locus has copies on at least two different chromosomes and the amplification product is detected and / or quantified.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Quick and batch test method for copy number of multi-copy genes of genomes
InactiveCN103103280AImprove design requirementsImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiologyNucleic acid sequence
The invention discloses a quick and batch test method for the copy number of multi-copy genes of genomes by virtue of a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology. The method comprises the following steps of: respectively carrying out PCR amplification and product purification on some multi-copy genes and some known single-copy gene on a same tissue DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sample to test the mass concentration of each gene PCR purified product, converting the mass concentration into molar concentration according to the nucleotide sequence of the product, and preparing the standard curves of the genes by same RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) by taking the PCR product and the tissue DNA sample which are subjected to gradient dilution as a template, thus obtaining the concentration of each gene in the DNA sample. Under the same extraction efficiency, the copy number of the multi-copy genes is the number obtained by dividing the quantity of the multi-copy genes under the same volume by the quantity of the single-copy gene, so that the copy number of seven different multi-copy genes in same biont can be tested by once 96-pore RT-PCR reaction, and the copy number of eleven different multi-copy genes can be tested by once 384-pore RT-PCR reaction. Therefore, the quick and batch test efficiency can be realized.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for detecting and/or quantifying human DNA
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Method for quickly and quantitatively detecting mammalian cell deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA)
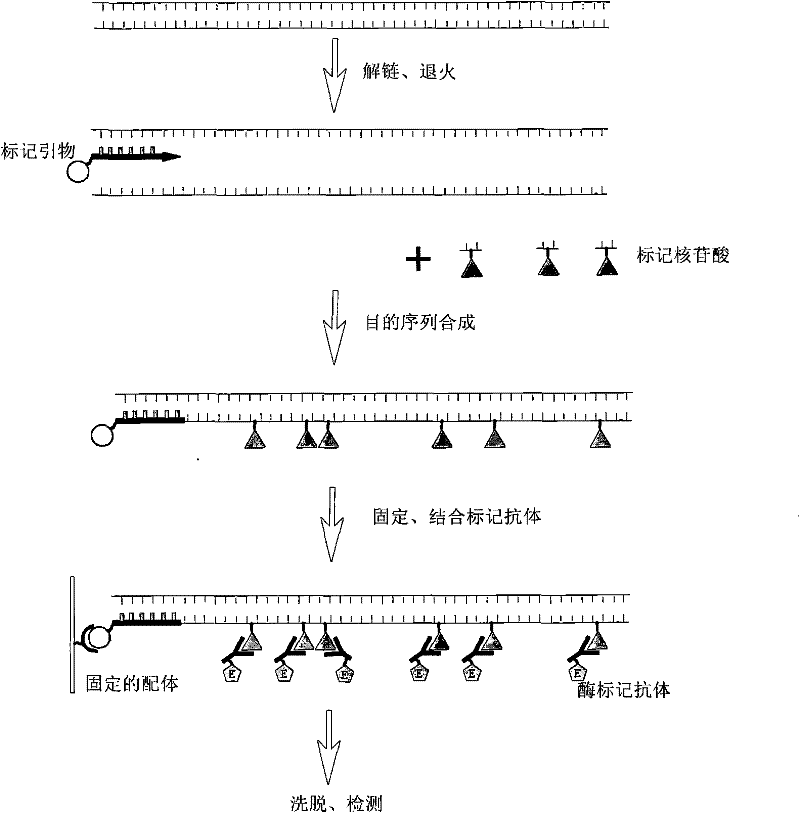
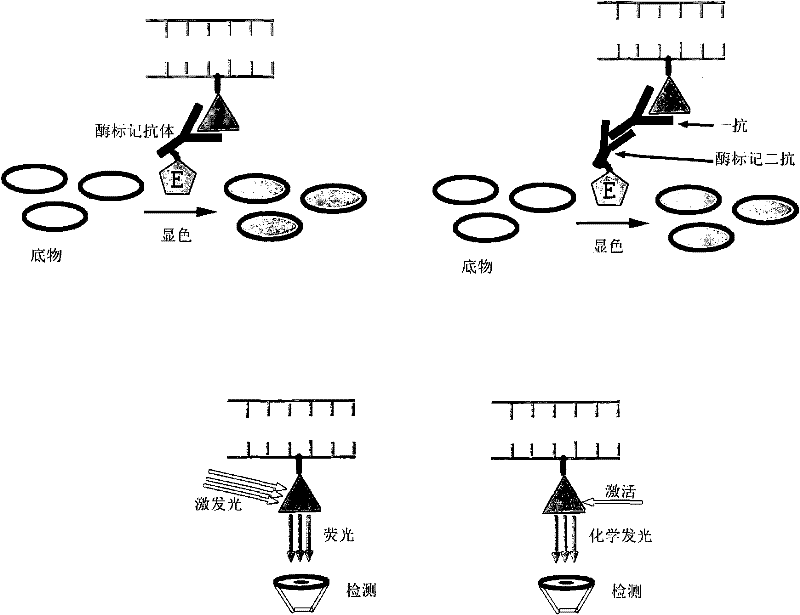
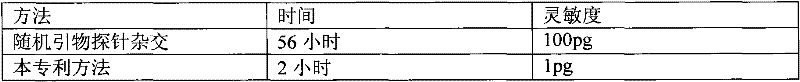
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively detecting mammalian cell deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA), which is used for detecting host cell DNA remained in a biological product which takes mammalian cells as matrixes. Multicopy genes in a mammalian cell genome are used as detection tag sequence templates, DNA polymerase, a molecular marker primer and molecular marker DNA are synthesized into a detection purpose sequence, and the detection purpose sequence is quantitatively analyzed. Compared with a molecular hybrid method, the method has the characteristics of short detection time (a detection process can be finished within two hours), stable detection results and high sensitivity.
Owner:BEIJING XINYI YUANCHENG BIOLOGICAL TECH
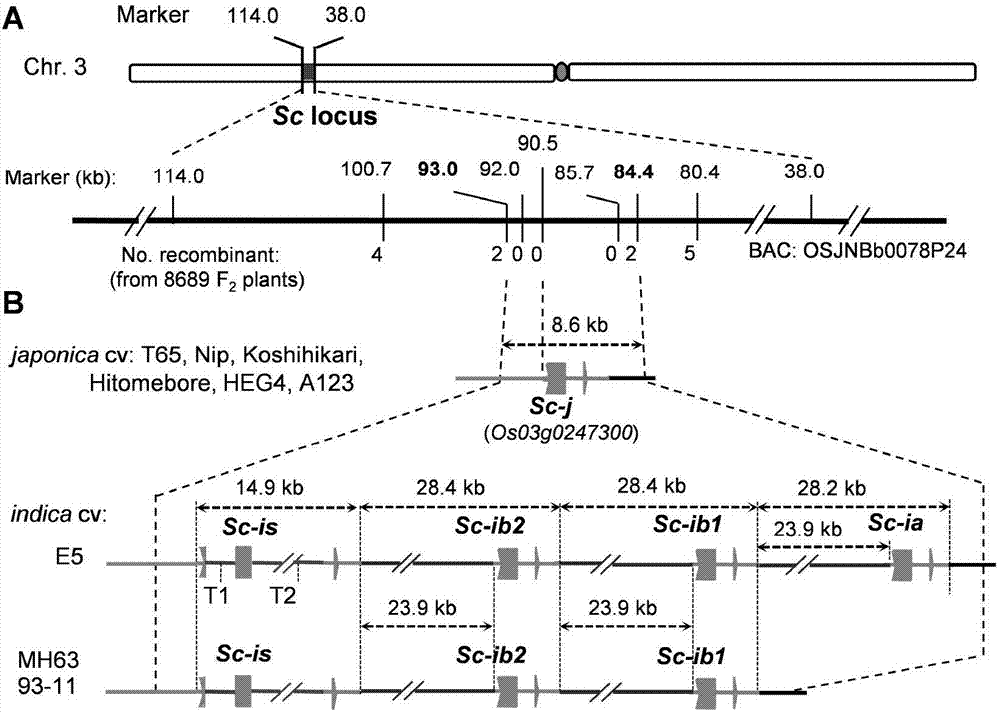
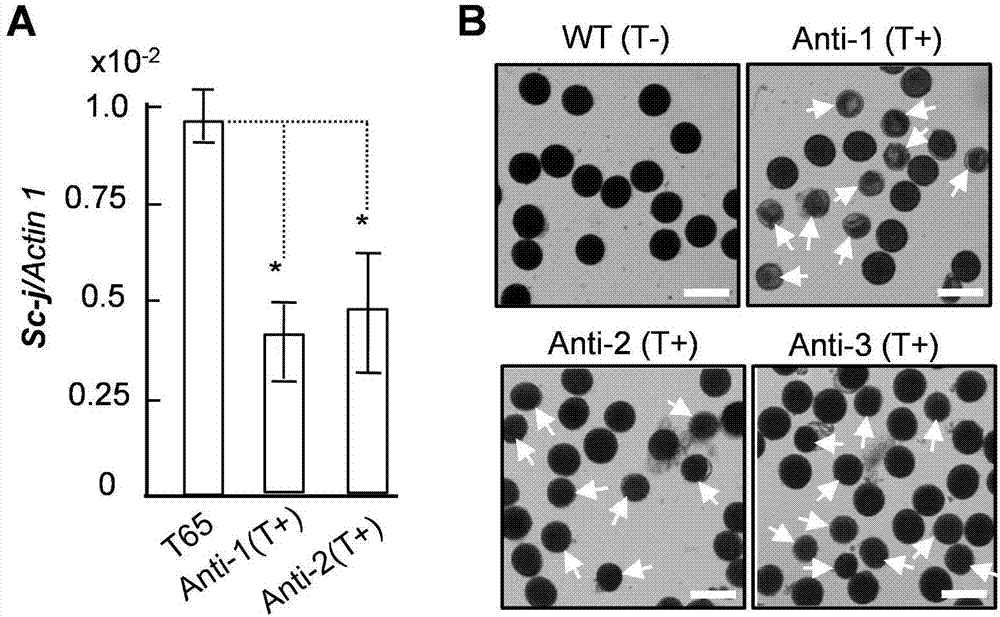
Separation and cloning of alleles Sc-j and Sc-i of pollen fertility gene loca Sc of paddy rice hybrids, and application in seed breeding
InactiveCN107164390AImprove fertilityOvercome infertilityPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceHigh level expression
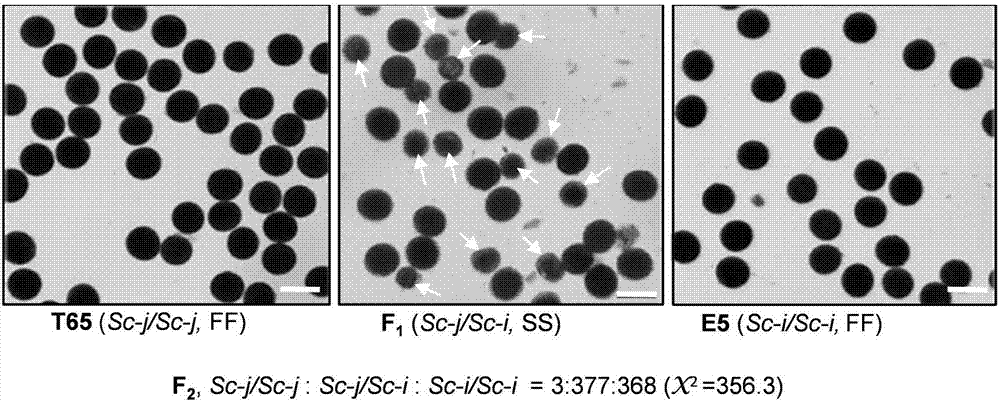
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering and particularly discloses separation and cloning of alleles Sc-j and Sc-i of a pollen fertility gene loca Sc of paddy rice hybrids, and an application in seed breeding. Sc-j encoding of japonica rice and Sc-i encoding of indica rice contain proteins in a DUF1618 structural domain, which are required in normal growth of pollen of paddy rice. The Sc-j only has one gene copy while the Sc-i, in different varieties, has two or three tandem gene copies. In a hybrid between the japonica rice and indica rice, high-level expression products of the Sc-i multi-copy gene can inhibit expression of the Sc-j, which causes hybrid pollen sterility. The invention discloses a hybridization seed breeding method, in which a part of copies of th Sc-i is mutated by utilizing a gene-editing technology, so that the gene dosage effect of the Sc-i is reduced and further fertility of Sc-j pollen in a japonica-indica paddy rice hybrid is recovered, thus overcoming male sterility of a japonica-indica paddy rice hybrid.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
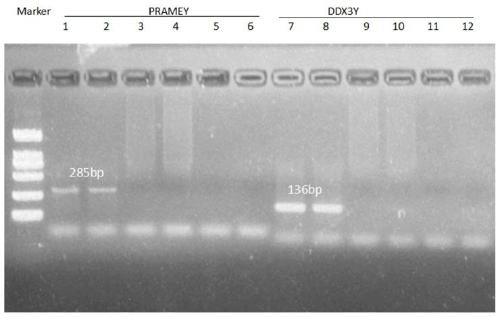
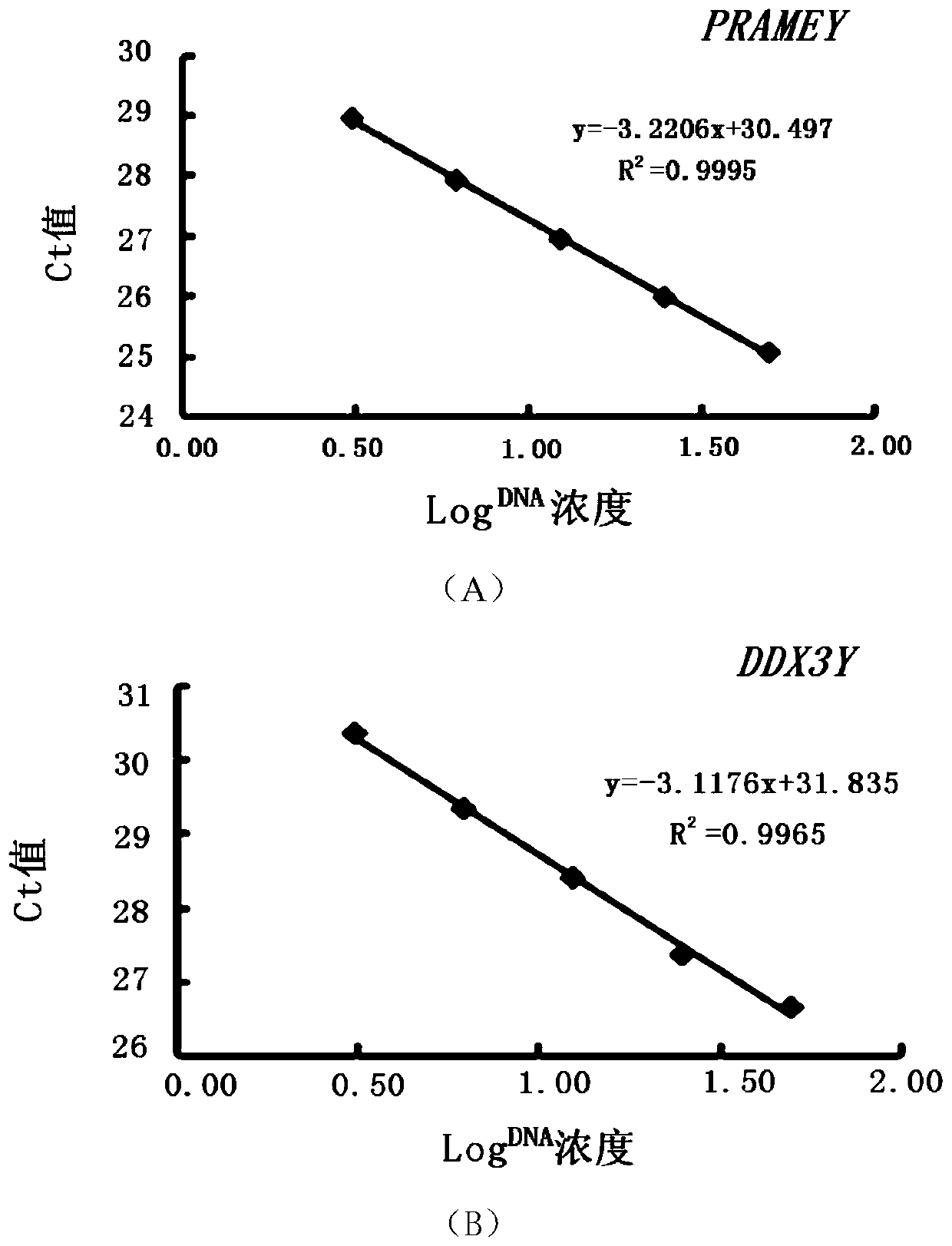
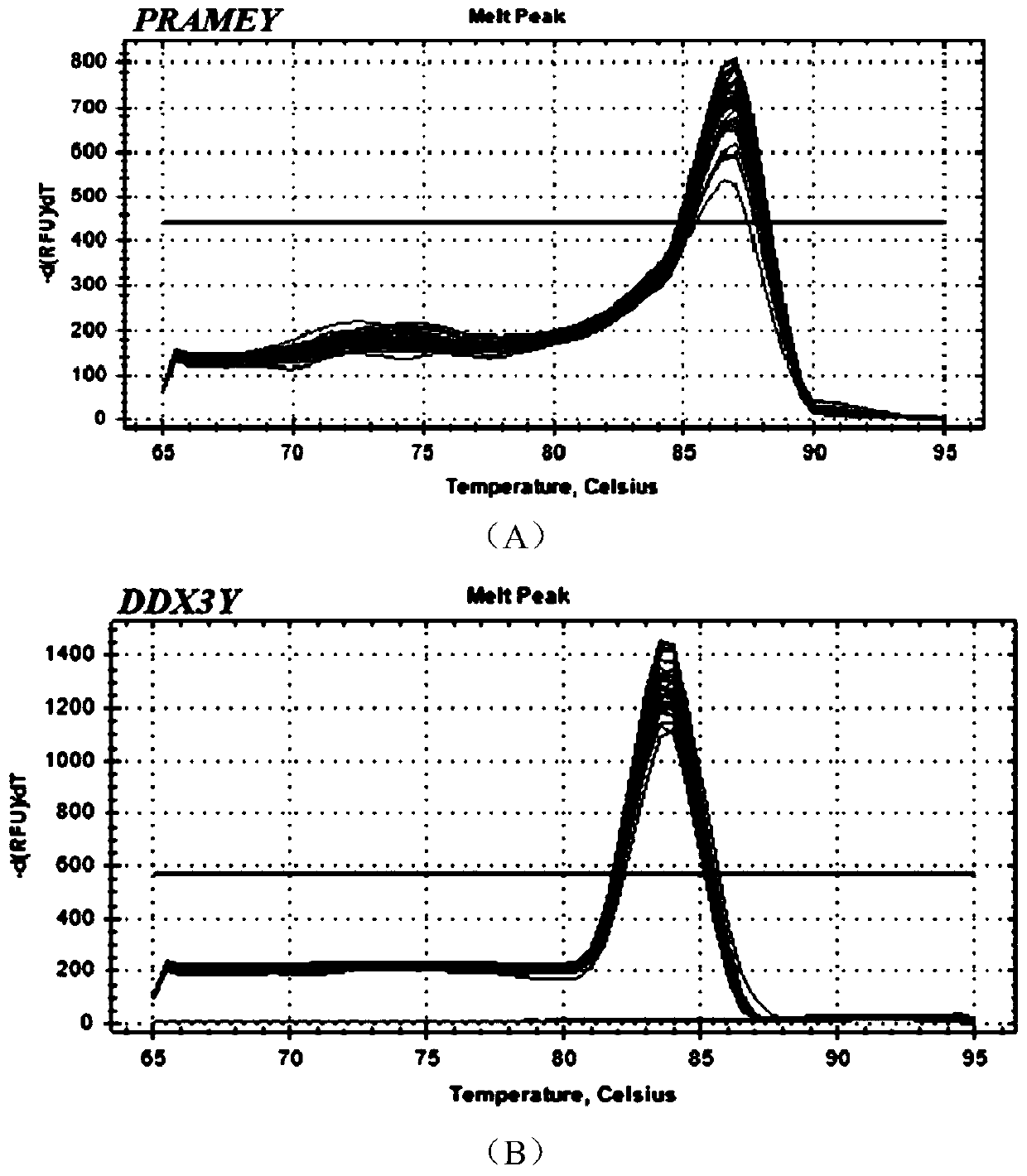
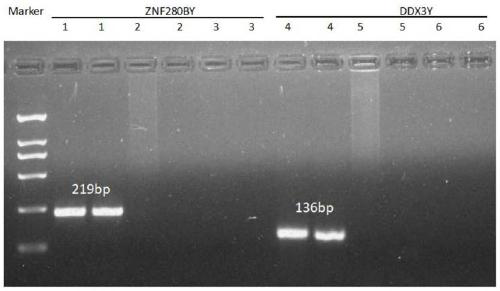
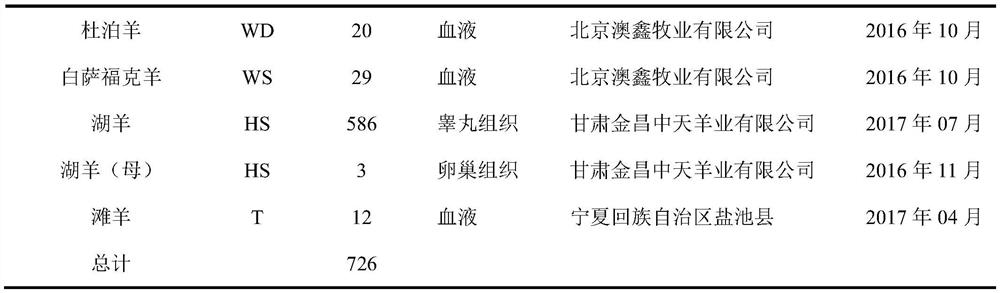
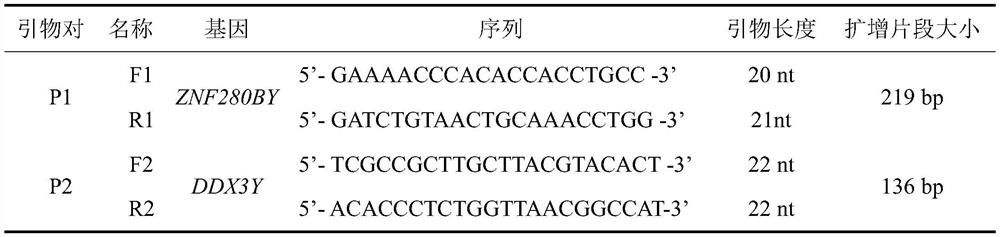
Method for detecting sheep PRAMEY gene copy number variation and application thereof
PendingCN111363831ABreeding for Accelerated FecundityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFood processingBiotechnologyReference genes
The invention discloses a method for detecting sheep PRAMEY gene copy number variation and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: taking whole genome DNA of a ram to be detected as a template, amplifying part of fragments of ram PRAMEY gene and DDX3Y gene through male specific qPCR primer pairs P1 and P2 respectively, serving the multi-copy PRAMEY gene as a detection gene and the single-copy DDX3Y gene as reference genes, and calculating the copy number of the ram PRAMEY gene according to a quantitative result. The method is simple, rapid and convenient to apply and popularize.
Owner:甘肃润牧生物工程有限责任公司
Functional linked marker 0707-1 and application thereof to germplasm improvement of maize
The invention relates to a functional linked marker 0707-1 and application thereof to the germplasm improvement of maize. In the functional linked marker 0707-1, one major modifying factor of 27-kD[gamma]-zein is positioned for the first time, is located in the range of 100kb near of the 120Mb of a No. 7 chromosome, and is the multicopy of the 27-kD[gamma]-zein. According to the application, a molecular marker and an identification method for identifying a gene of the multicopy are also established; therefore, an effective approach is provided for identifying quality protein maize.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Method for quantifying human DNA using an internal control
ActiveUS9328385B2High sensitivityHigh success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomeBiology
The present invention relates to a method for quantifying and / or detecting one or more nucleic acids of a genome in a sample, wherein in an amplification reaction, (i) a first nucleic acid is amplified, the locus that is amplified is a multicopy locus (MCL) within the genome, wherein the locus shares at least 80% sequence identity to a sequence according to SEQ ID NO. 1 over a stretch of 80 base pairs, and wherein the multicopy locus has copies on at least two different chromosomes, (ii) a second nucleic acid that has been added as an internal control (IC) is also amplified, and (iii) the amount of amplification product from the amplification of the first nucleic acid is determined.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH +1
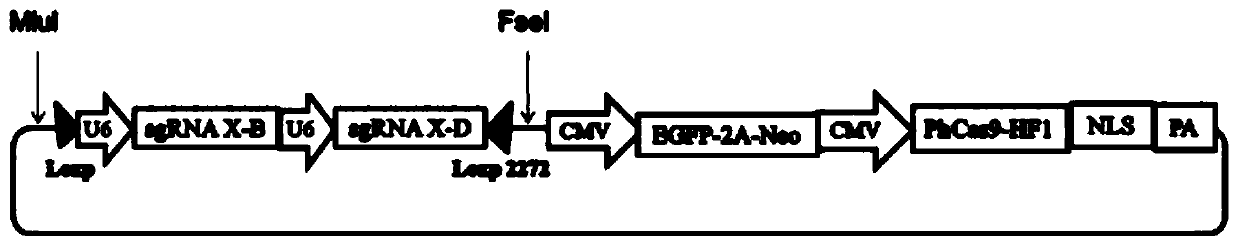
Method for realizing animal sex control by editing X chromosome multi-copy genes
ActiveCN111549070AIncrease birth rateImprove cutting efficiencyStable introduction of DNAVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal scienceX chromosome
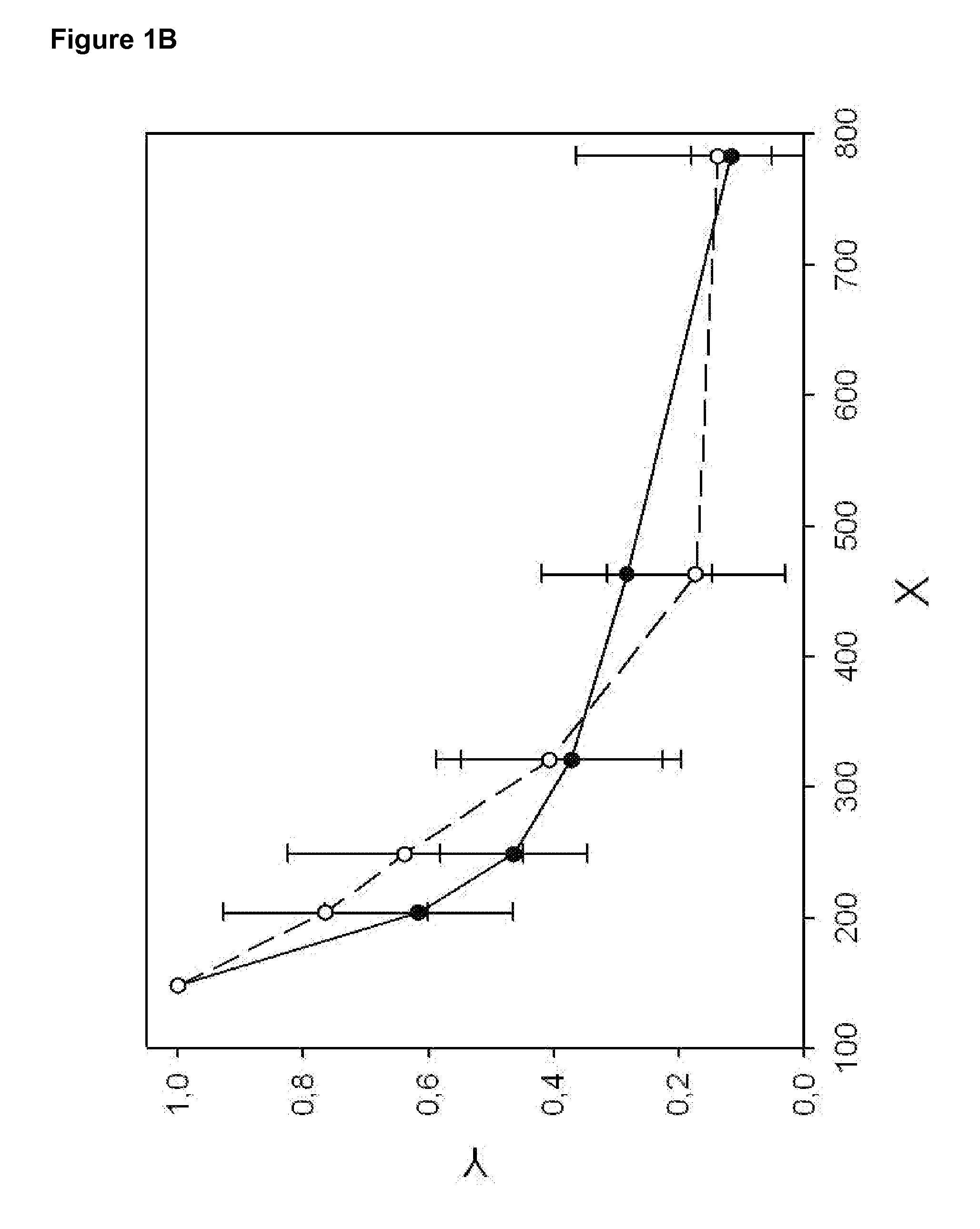
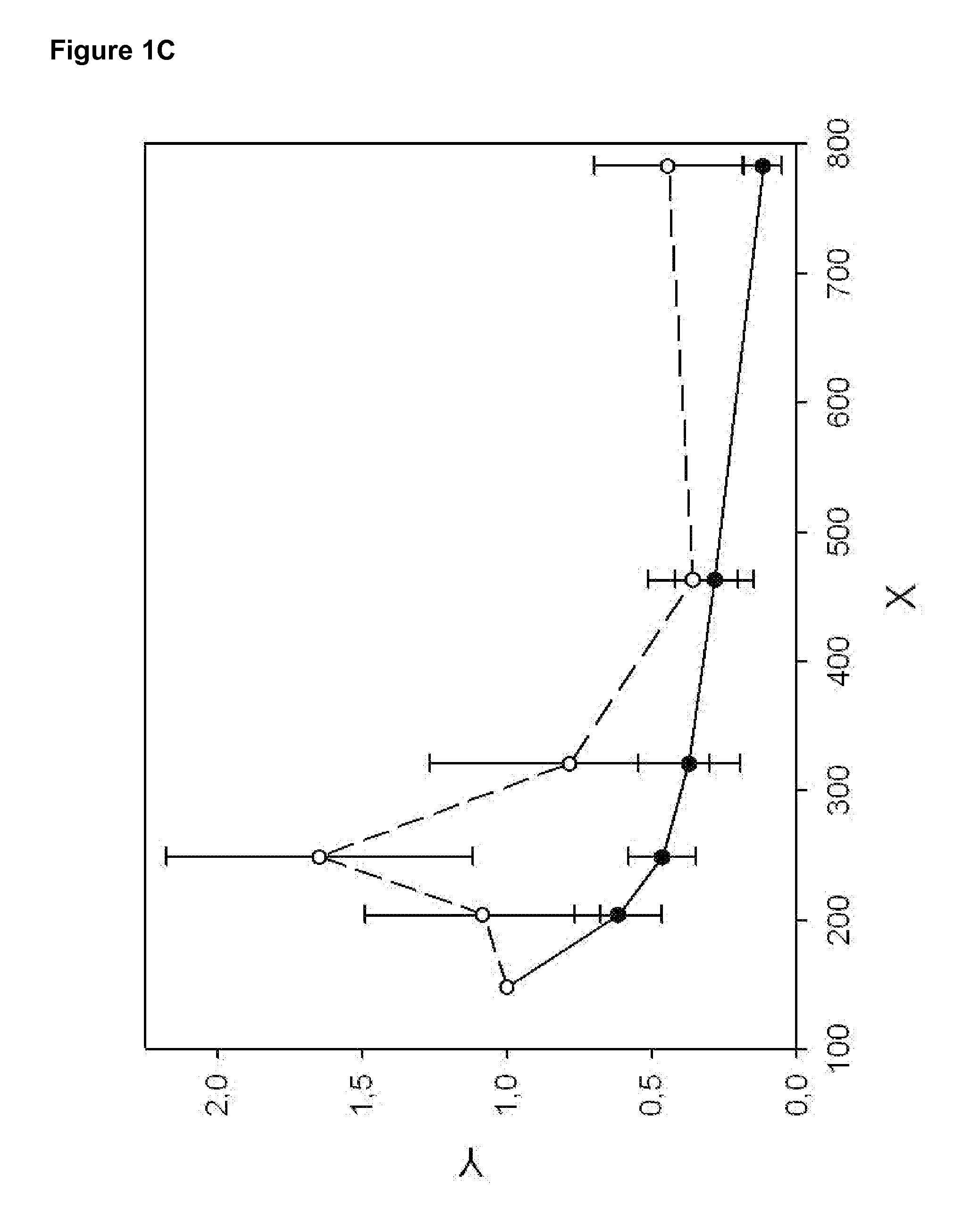
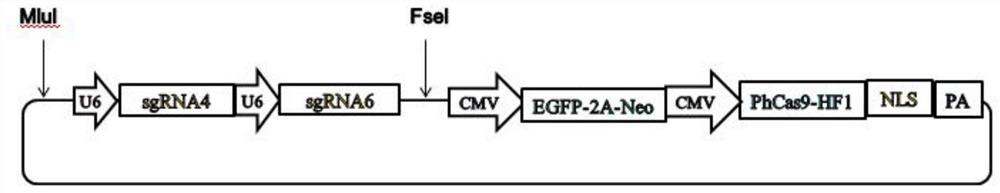
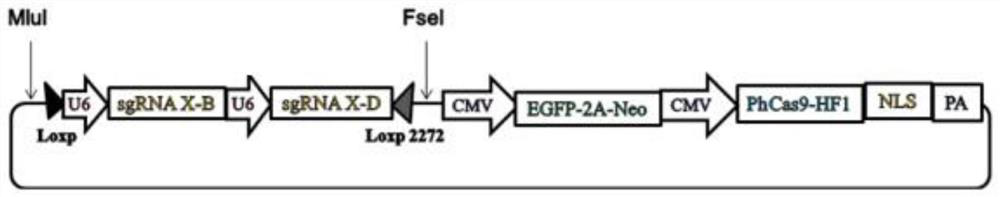
The invention discloses a method for realizing animal sex control by performing gene editing on X chromosome multi-copy genes. The method comprises the following steps: screening and selecting one ormore multi-copy genes on an X chromosome of a mammal as target sites, and designing and synthesizing corresponding sgRNA; then, constructing a CRISPR / Cas9 expression system of a targeted X chromosomemulti-copy gene to cut the X chromosome in sperms or fertilized eggs of mammals; according to the method, the whole X chromosome can be inactivated, X sperms can be killed, the birth rate of male mammals can be increased, or XY type embryos can be killed, and the birth rate of female mammals can be increased. According to the method provided by the invention, the X chromosome cutting efficiency ishigh, the off-target rate is low, and a good sex control effect is achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
High Viscosity Diutan Gums
ActiveUS20110282051A1Increase productionImproved viscosity propertiesSugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyPhysical property
The production of a diutan polysaccharide exhibiting increased viscosity properties as compared with previously produced polysaccharide of the same type of repeating units. Such an improved diutan polysaccharide is produced through the generation of a derivative of Sphingomonas sp. ATCC 53159 that harbors a multicopy broad-host-range plasmid into which genes for biosynthesis of diutan polysaccharide have been cloned. The plasmid provides the capability within the host Sphingomonas strain to produce multiple copies of genes for such polysaccharide synthesis. In such a manner, a method of not just increased production of the target diutan polysaccharide, but also production of a diutan polysaccharide of improved physical properties (of the aforementioned higher viscosity) thereof is provided. Such a diutan polysaccharide has proven particularly useful as a possible viscosifier in oilfield applications and within cement materials. The inventive methods of production of such an improved diutan polysaccharide, as well as the novel cloned genes required to produce the improved diutan within such a method, are also encompassed within this invention. Additionally, the novel engineered Sphingomonas strain including the needed DNA sequence is encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
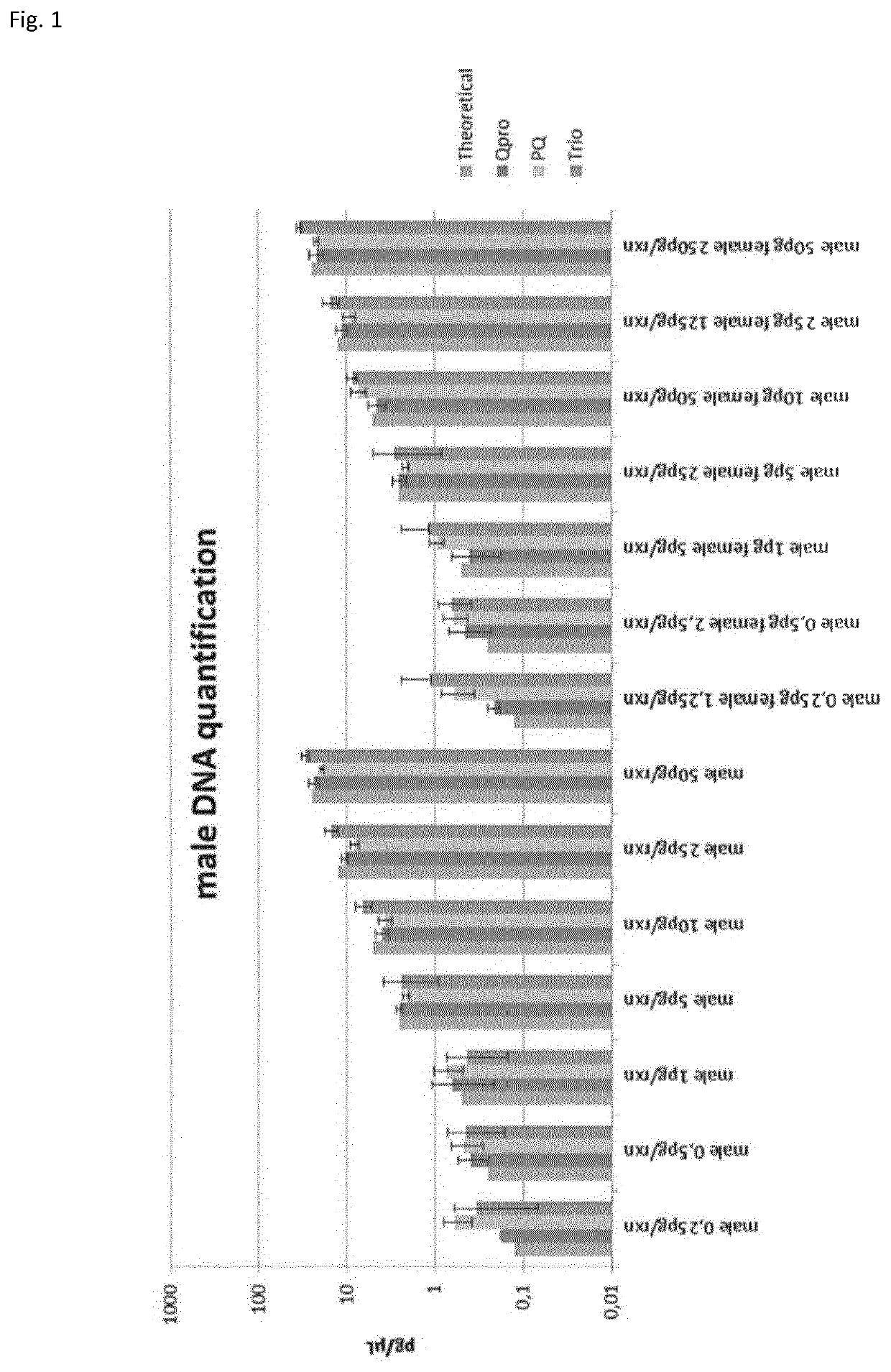
Method for quantifying and/or detecting human male DNA
ActiveUS11078527B2Reduce riskAids in identification of fetalMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicineGenomic DNA
According to a first aspect of the present invention, a method is provided for detecting and / or quantifying male genomic DNA in a sample, wherein the method comprises the step of amplification of a multicopy locus within the human Y-chromosome (MCL-Y), wherein said locus shares at least 80% sequence identity to a sequence according to SEQ ID NO. 3 over a stretch of at least 60 base pairs (bp). A second aspect of the present invention relates to a primer or primer pair which hybridizes under stringent conditions to a sequence according to SEQ ID NO. 3 and / or any of 4 to 11. The invention also relates to a kit.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Method for editing x-chromosome multi-copy genes to realize animal sex control
ActiveCN111549070BLow miss rateAsymmetricalStable introduction of DNAVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal scienceX chromosome
The invention discloses a method for gene editing of X chromosome multi-copy genes to realize animal sex control. By screening and selecting one or more multi-copy genes on the X chromosome of mammals as target sites, designing and synthesizing corresponding sgRNAs, and then By constructing a CRISPR / Cas9 expression system targeting multiple copies of the X chromosome to cut the X chromosome in mammalian sperm or fertilized eggs, the entire X chromosome can be inactivated, the X sperm can be killed, and the birth rate of male mammals can be improved. , or lethal XY embryos, increase the birth rate of female mammals. The method provided by the invention has high cutting efficiency of X chromosome, low off-target rate, and good sex control effect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Functional Linkage Marker 0707-1 and Its Application in Maize Germplasm Improvement
The invention relates to a functional linked marker 0707-1 and application thereof to the germplasm improvement of maize. In the functional linked marker 0707-1, one major modifying factor of 27-kD[gamma]-zein is positioned for the first time, is located in the range of 100kb near of the 120Mb of a No. 7 chromosome, and is the multicopy of the 27-kD[gamma]-zein. According to the application, a molecular marker and an identification method for identifying a gene of the multicopy are also established; therefore, an effective approach is provided for identifying quality protein maize.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
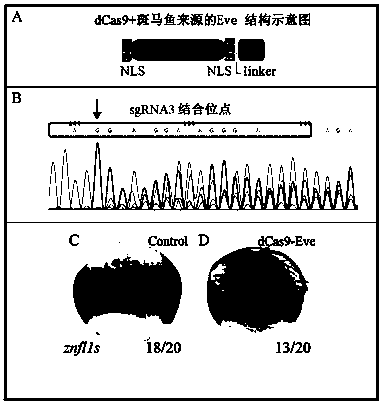
A method for targeted knockdown of multiple copies of genes in the zebrafish genome
ActiveCN106636197BInhibit expressionAvoid the effects of non-specific phenotypesVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsEmbryoProtein C
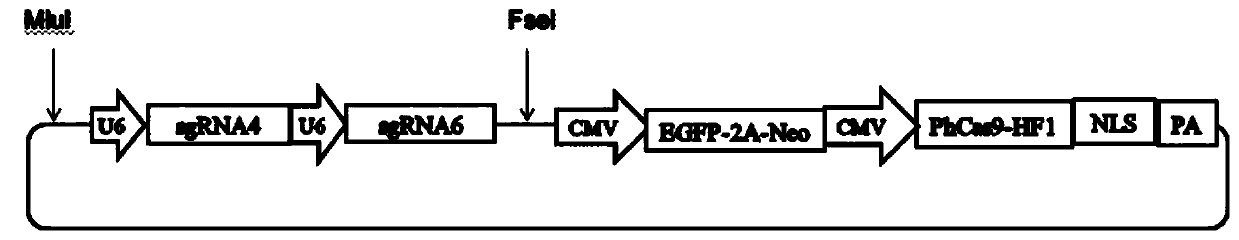
The invention discloses a method for directional knockdown of a multi-copy gene in zebrafish genome. The method comprises the following steps: I, preparing a zebrafish embryo; II, constructing an expression vector of dCas9-Eve fusion protein; III, conducting in-vitro transcription of sgRNA, dCas9-Eve, Cas9 and gene, and purifying the sgRNA, dCas9-Eve, Cas9mRNA and gene mRNA, which are synthesized through the in-vitro transcription, by virtue of RNeasy Mini Kit; IV, identifying activity of the sgRNA; and V, knocking out expression of the multi-copy gene znfl1s by virtue of a dCas9-Eve method, and judging the situation that the gene expression is knocked out by detecting the expression of the gene by virtue of an embryo whole-mount in situ hybridization method. The method provided by the invention, by virtue of the dCas9-Eve, can specifically knock down the transcription of the gene under the circumstance of implementing the effective targeted identification of sgRNA existence of a gene promoter, so that the researched gene is prevented from being affected by MO toxicity or non-specific phenotype caused by target missing; and moreover, since an Eve inhibiting transcription structural domain is derived from zebrafish, the dCas9-Eve is applicable to knockdown of any zebrafish genes at a transcription level.
Owner:NANJING MATERNITY & CHILD HEALTH CARE HOSPITAL +2
A method for efficiently screening lactic acid bacteria that can fully utilize citrulline
ActiveCN104312953BReduce contentBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismLactobacillus
The invention discloses a method for efficiently screening lactic acid bacteria capable of sufficiently utilizing citrulline, belonging to the field of microorganisms. The method comprises the steps of starting with a genotype to screen bacteria with multicopy genes, inspecting the capability of metabolizing citrulline, and furthermore screening lactic acid bacteria capable of sufficiently utilizing citrulline. The content of citrulline is reduced through co-culture.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
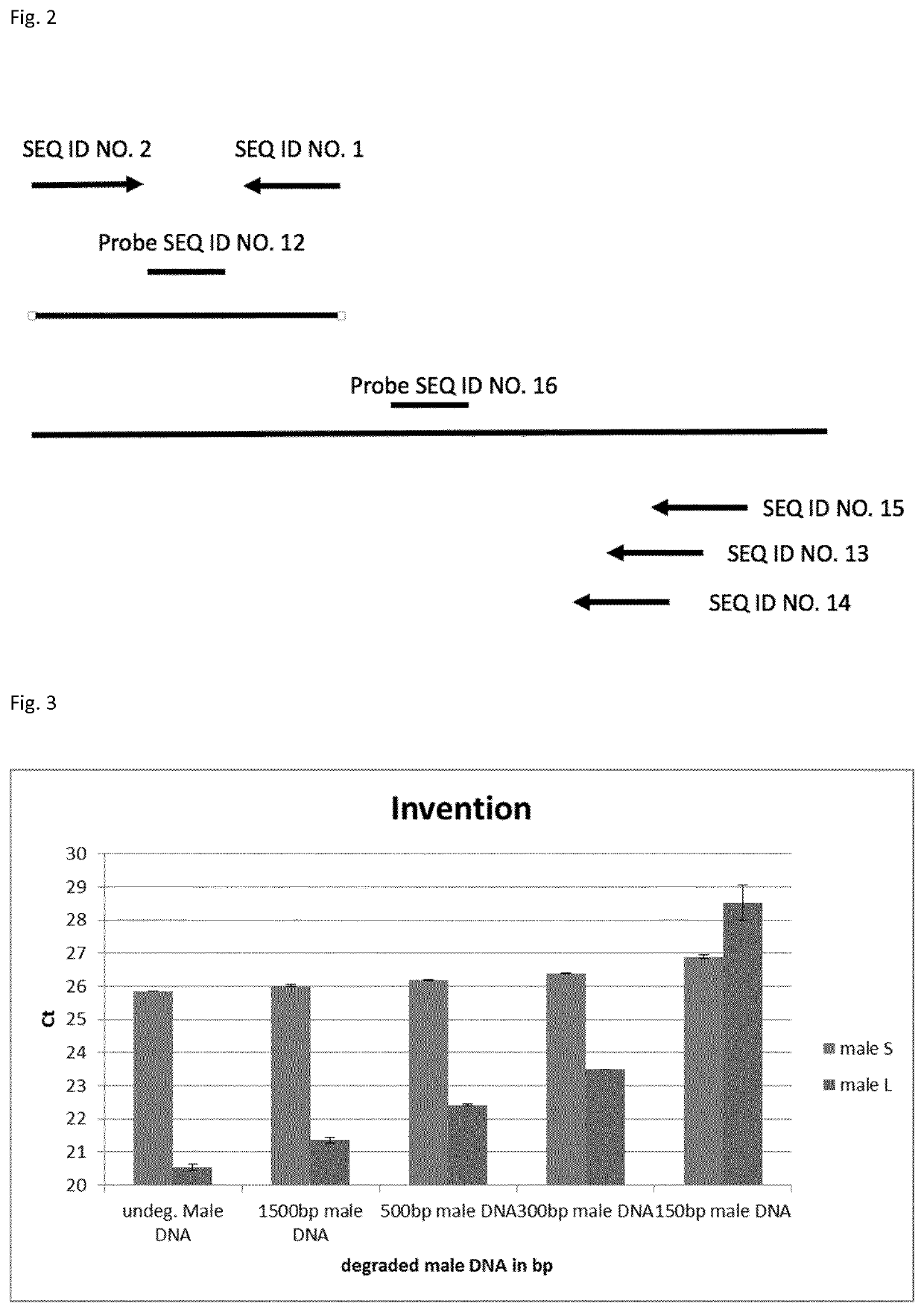
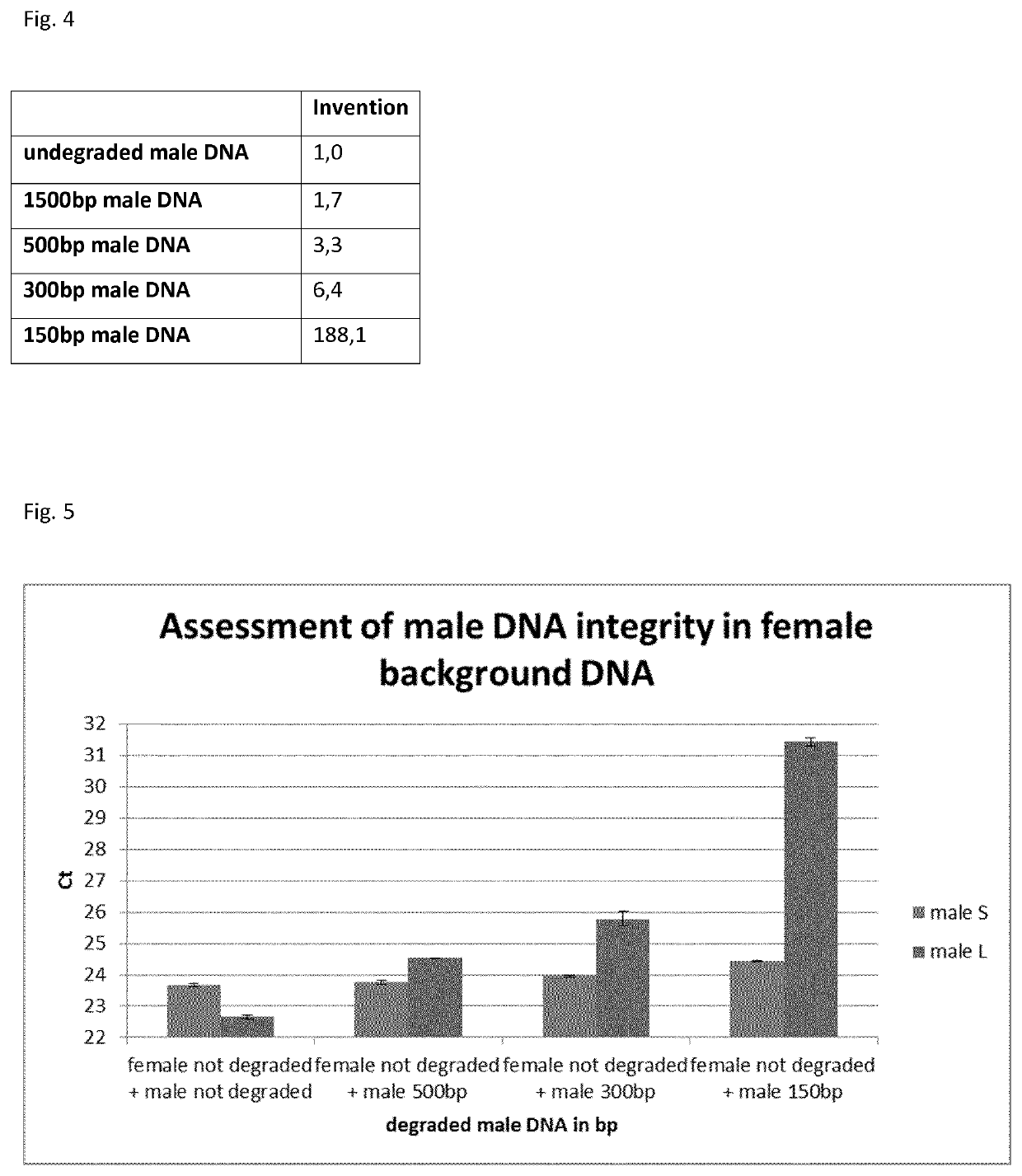
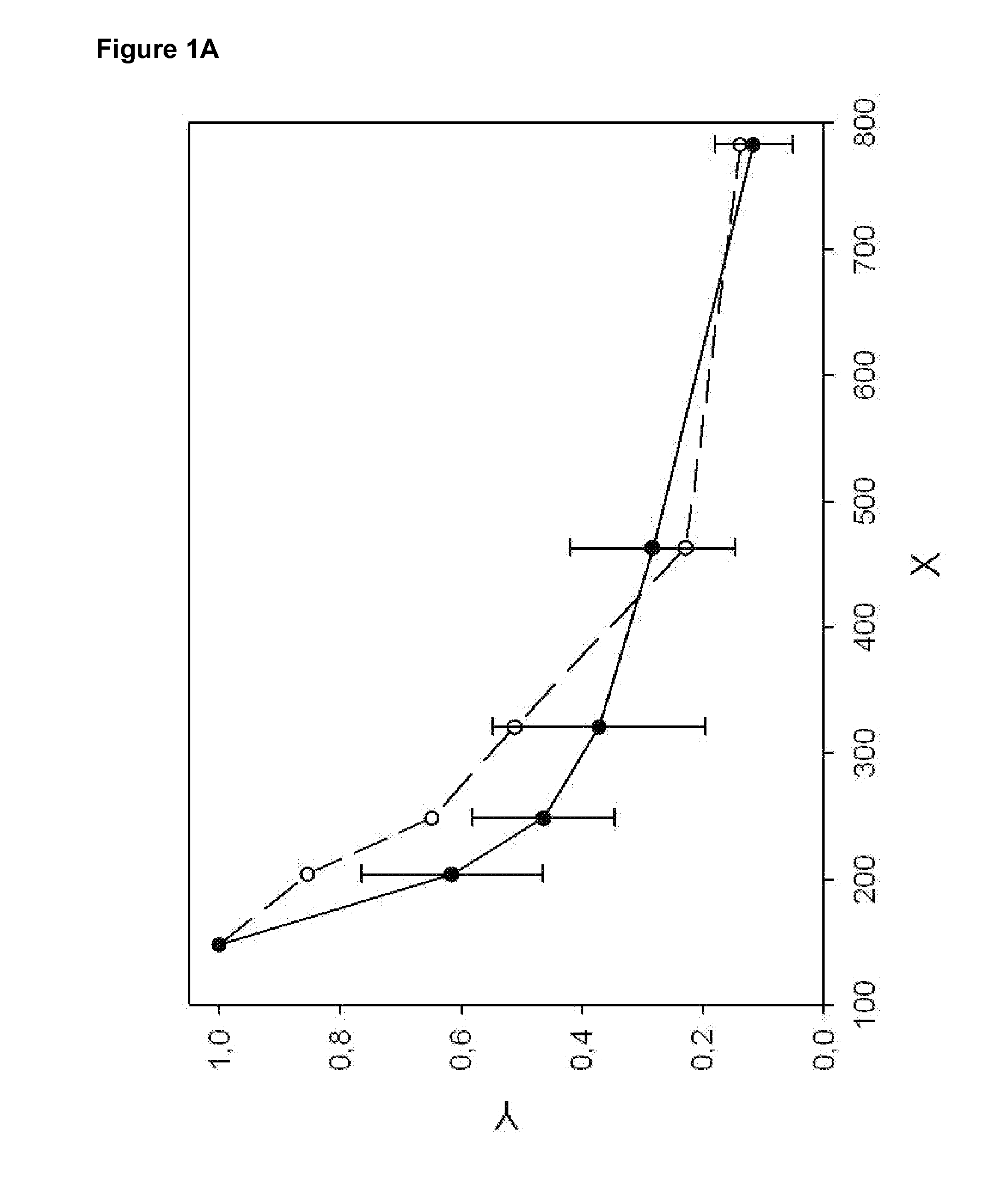
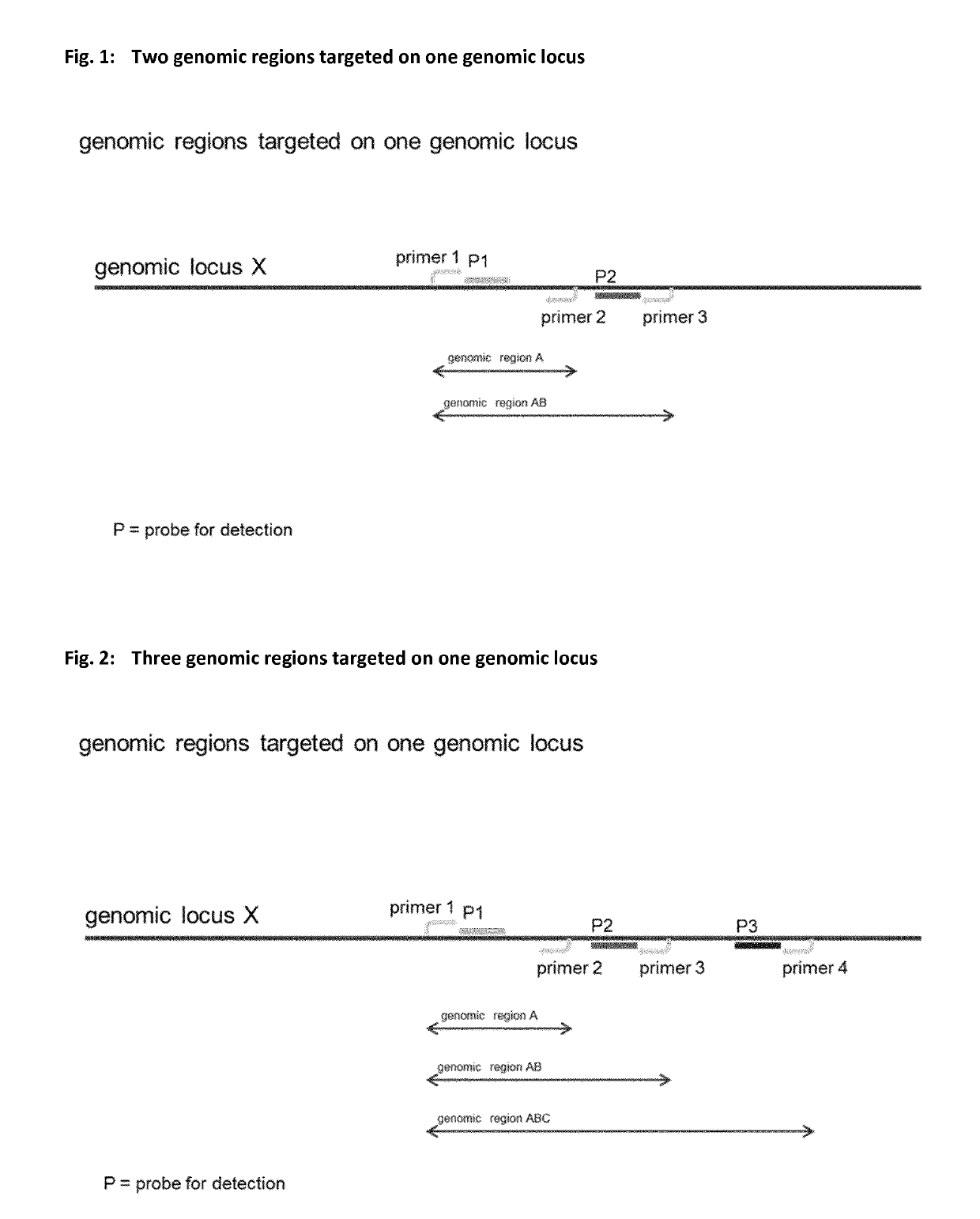
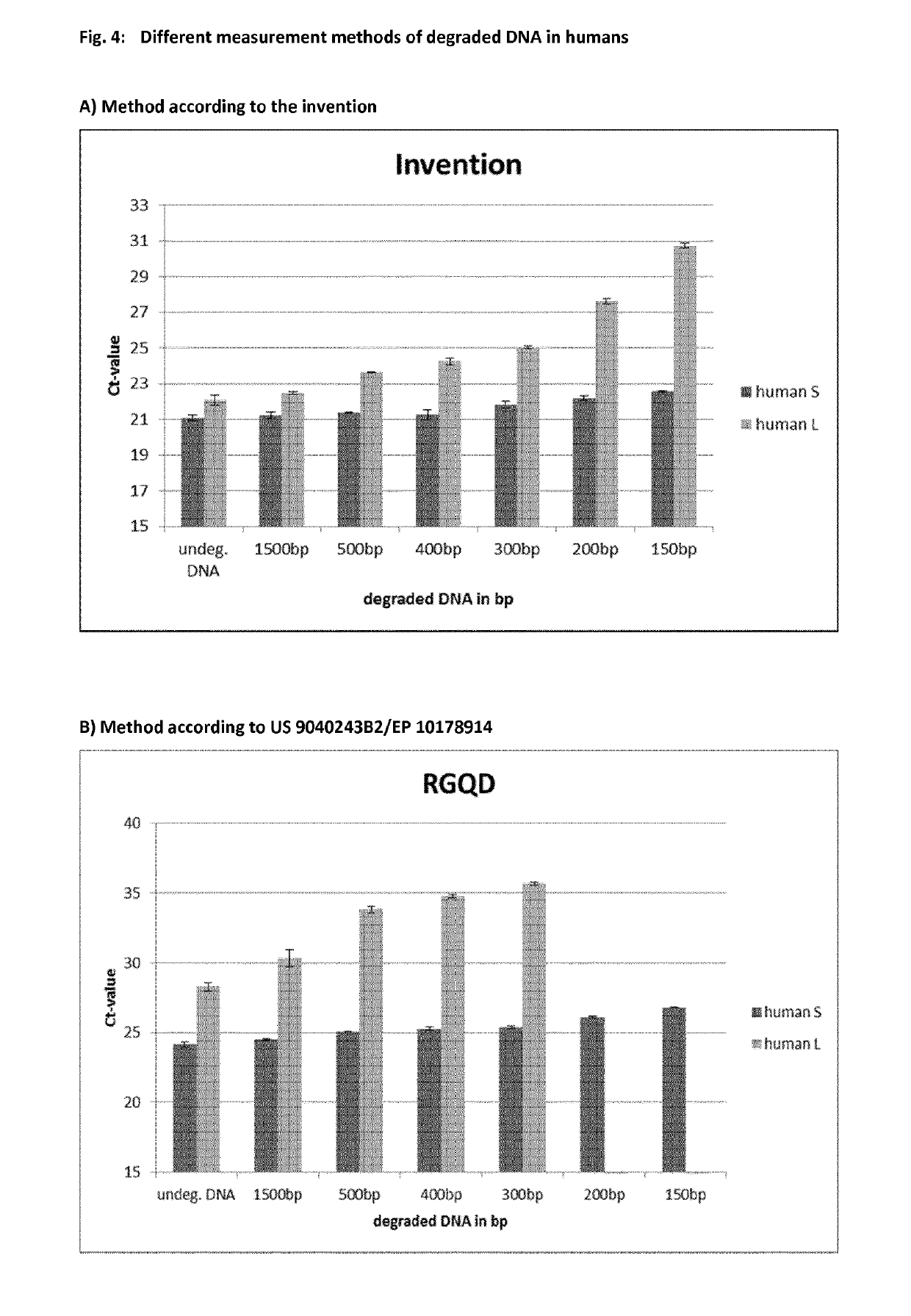
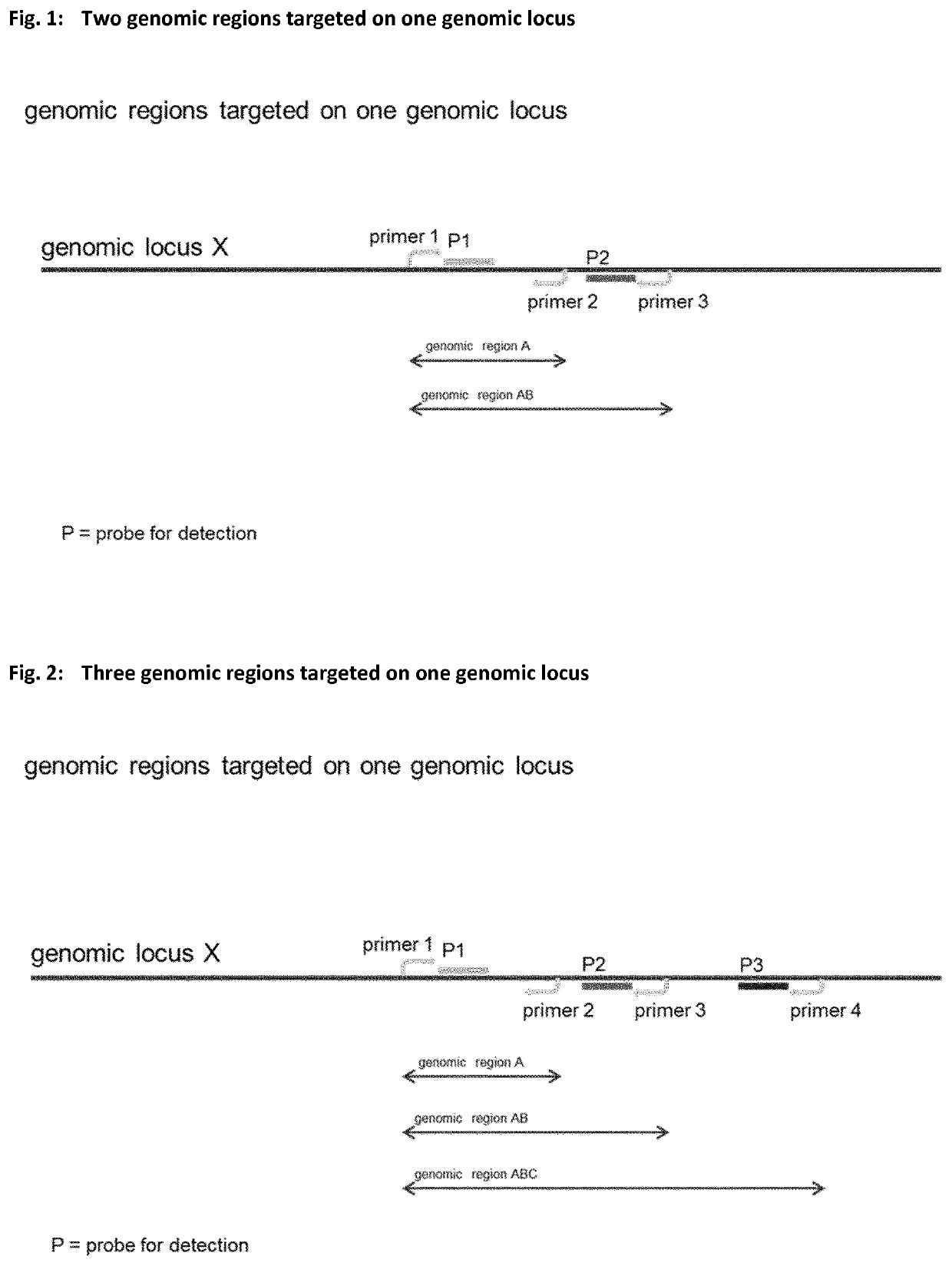
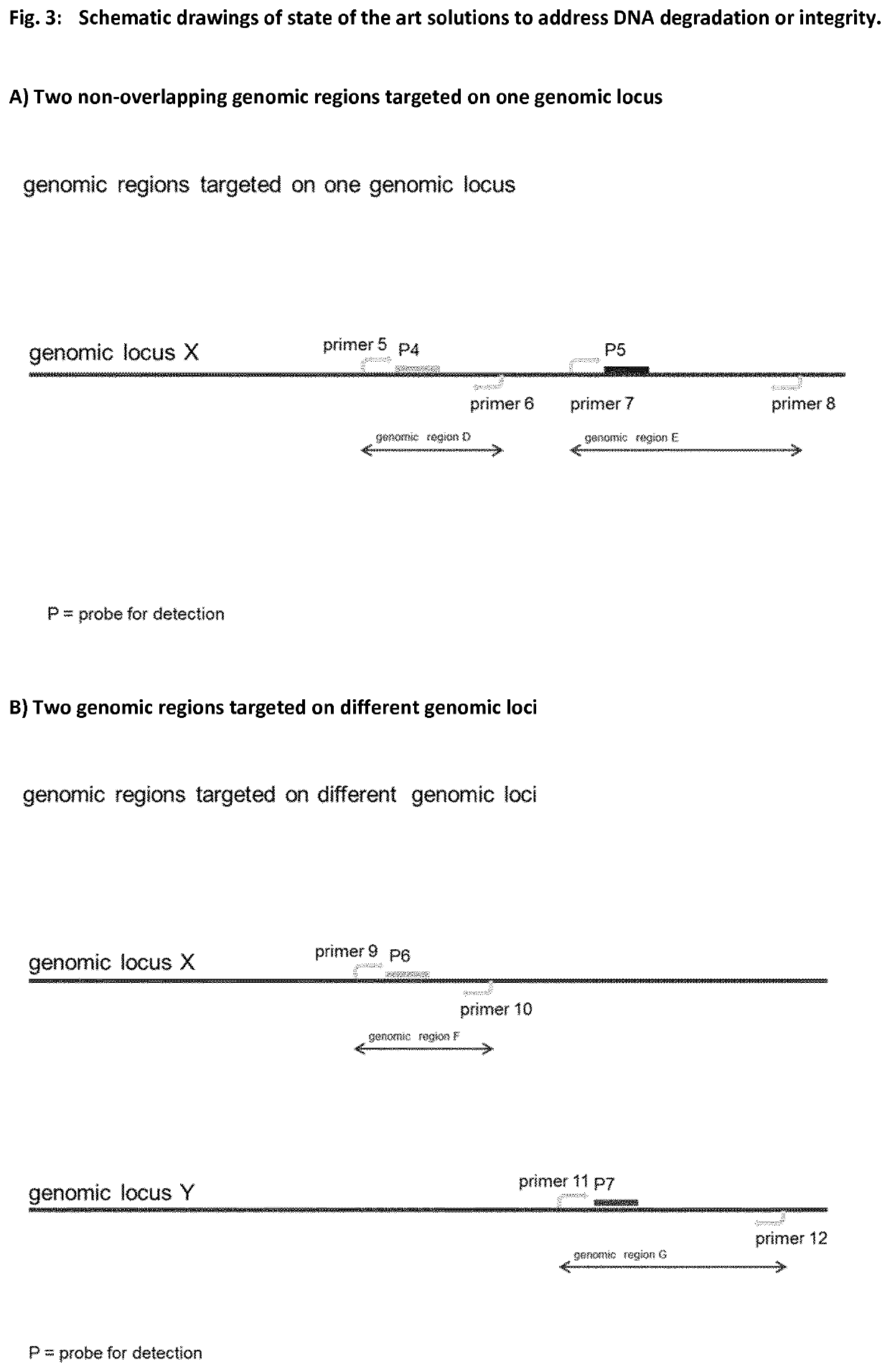
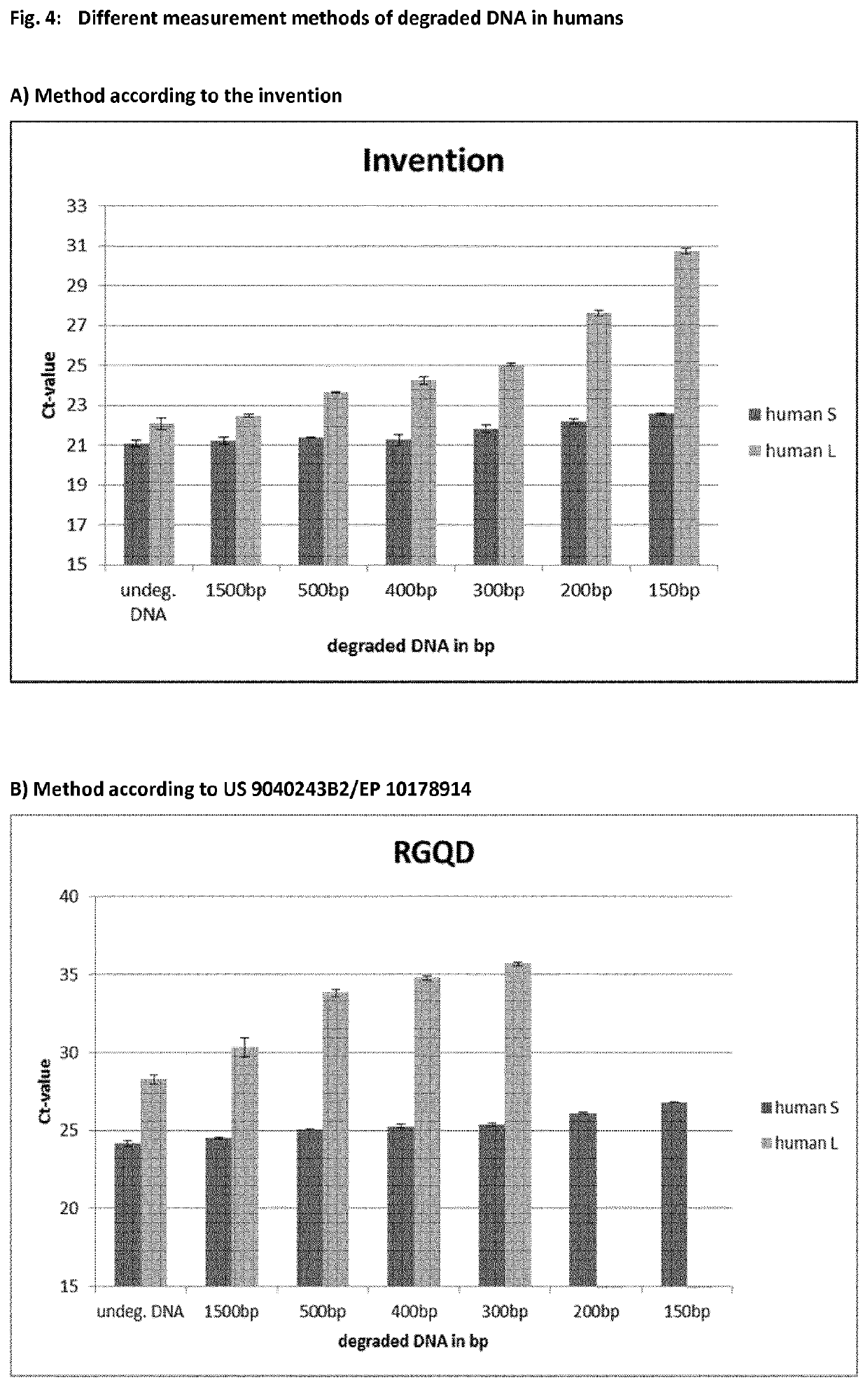
Method for determining nucleic acid degradation in a sample in which at least two overlapping amplicons are produced and two probes are used in the method
The present invention relates to a method for assessing the status of nucleic acid degradation and / or integrity of one or more nucleic acids in a sample, comprising the steps amplifying at least two overlapping regions within at least one locus (e.g. by heminested or nested PCR), and detecting the amount of the at least two amplification products through the use of at least two probes, wherein one probe binds to the region of overlap and the at least one other probe binds to a non-overlapping region. The invention further relates to a method of designing primers and / or probes for amplifying at least two overlapping regions within at least one locus, wherein the locus that is amplified is a single copy locus (SCL) or multicopy locus (MLC). The invention also relates to a primer and a primer pair for amplifying at least two overlapping regions from one nucleic acid template which is a multicopy locus present in 21 loci in the human genome. These primers and probes may be in a kit. Hence, the invention also relates to a kit for assessing the status of nucleic acid degradation and / or integrity of one or more nucleic acids in a sample.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Method for determining nucleic acid degradation in a sample in which at least two overlapping amplicons are produced and two probes are used in the method
The present invention relates to a method for assessing the status of nucleic acid degradation and / or integrity of one or more nucleic acids in a sample, comprising the steps amplifying at least two overlapping regions within at least one locus (e.g. by heminested or nested PCR), and detecting the amount of the at least two amplification products through the use of at least two probes, wherein one probe binds to the region of overlap and the at least one other probe binds to a non-overlapping region. The invention further relates to a method of designing primers and / or probes for amplifying at least two overlapping regions within at least one locus, wherein the locus that is amplified is a single copy locus (SCL) or multicopy locus (MLC). The invention also relates to a primer and a primer pair for amplifying at least two overlapping regions from one nucleic acid template which is a multicopy locus present in 21 loci in the human genome. These primers and probes may be in a kit. Hence, the invention also relates to a kit for assessing the status of nucleic acid degradation and / or integrity of one or more nucleic acids in a sample.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
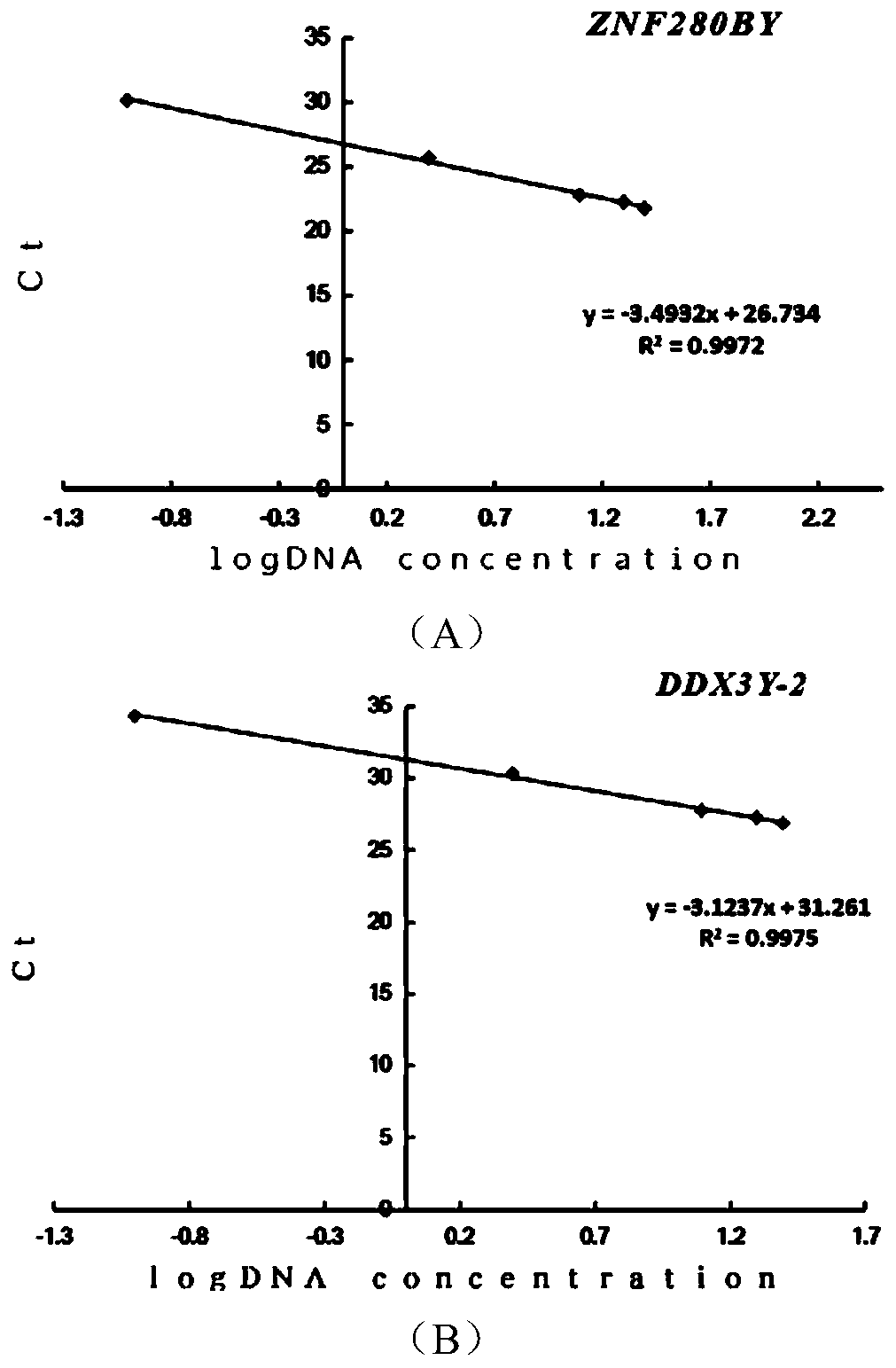
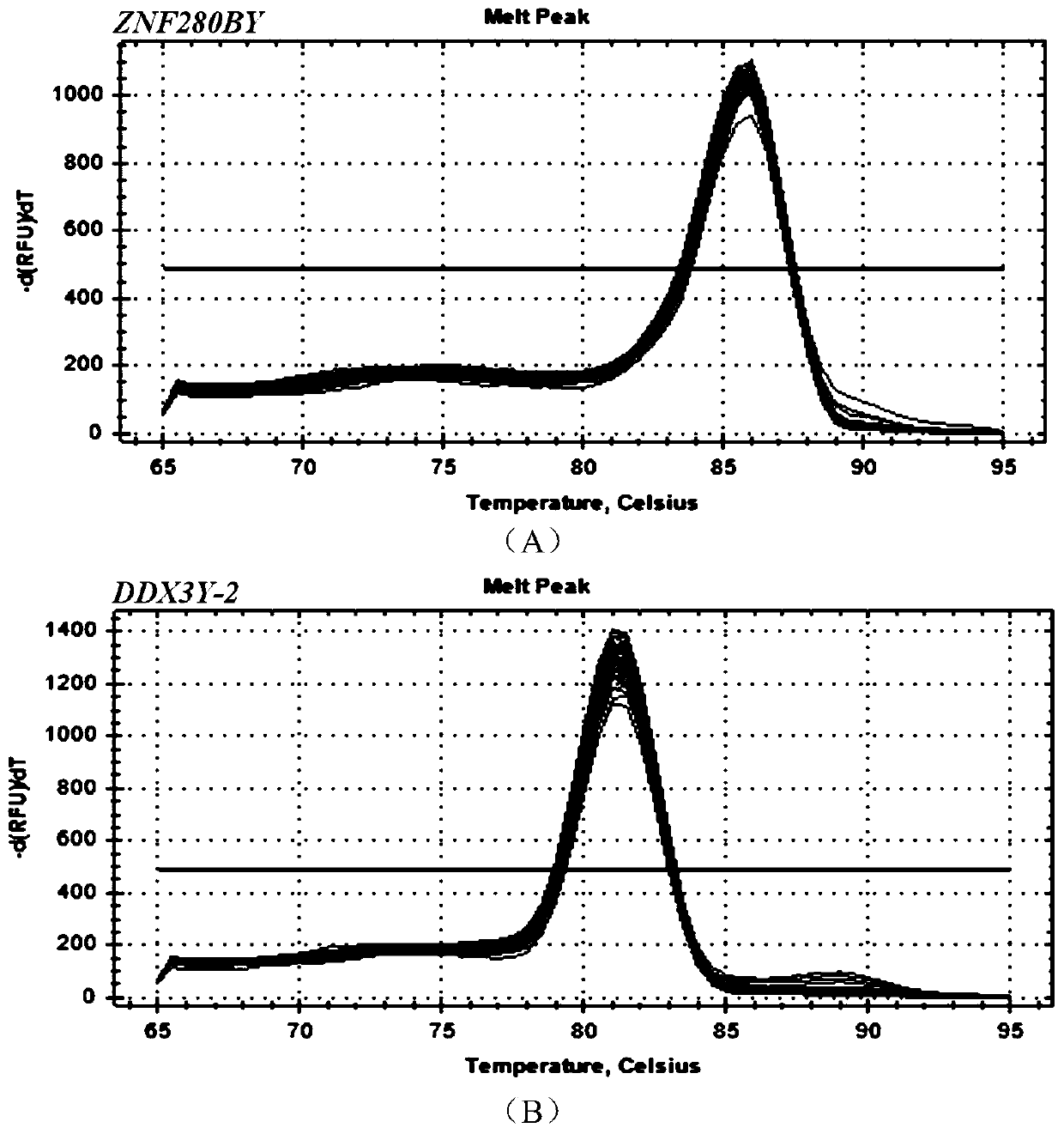
Method for detecting copy number variation of sheep ZNF280BY gene, and application of method
ActiveCN111349707AHigh sensitivityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyReference genes
The invention discloses a method for detecting copy number variation of a sheep ZNF280BY gene, and an application of the method. According to the method, full genome DNA of a ram to be detected is taken as a template, and partial fragments of a ZNF280BY gene and a DDX3Y gene of the ram are respectively amplified by using a male specific qPCR primer pair P1 and P2, wherein the multi-copy ZNF280BY gene is used as a detection gene, the single-copy DDX3Y gene is used as a reference gene, and the copy number of the ram ZNF280BY gene is calculated according to a quantitative result. The method can be used to detect a copy number variation molecular marker used for early identification of breeding capacity of rams, so that the breeding process of the rams is accelerated through molecular marker-assisted selection. The method is simple and rapid, and is convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:甘肃润牧生物工程有限责任公司
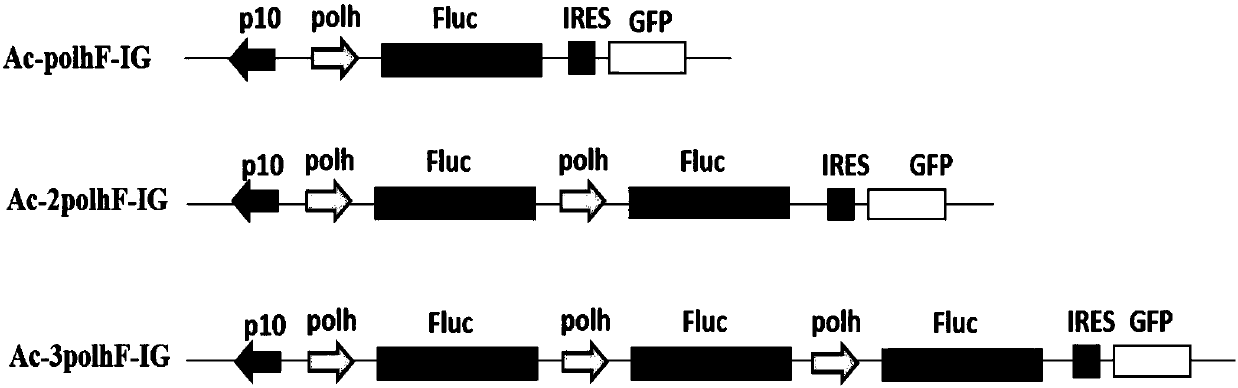
A construction and expression method for co-expressing foreign proteins of baculovirus by using multi-copy genes
ActiveCN108018264BHigh expressionEfficient expressionOxidoreductasesFermentationActive proteinSynexpression
The invention discloses a method for constructing and expressing foreign proteins of baculovirus co-expressed by using multi-copy genes. The firefly luciferase Fluc gene is used as the target gene to construct polyhedron polh promoter and p10 promoter controlled containing Recombinant baculoviruses with 1-3 gene copies were used to infect the SF9 cell line, and the cells were collected after infection to detect the activity of firefly luciferase. The beneficial effect of the present invention is: the method provided by the present invention, after detection, it is found that compared with the unmodified baculovirus, the expression of the firefly luciferase gene is significantly increased by 2-5 times, effectively improving the expression level of the exogenous gene in the baculovirus. The expression level in the virus system is suitable for the production of proteins with natural activity, which is of great significance. It provides a new strategy for constructing recombinant viruses for production using the baculovirus multi-gene expression system, realizing the realization of exogenous genes. High-efficiency expression in the baculovirus multi-gene expression system.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
A method for detecting variation in the copy number of sheep znf280by gene and its application
ActiveCN111349707BHigh sensitivityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesDDX3Y gene
The invention discloses a method for detecting the copy number variation of sheep ZNF280BY gene and its application. The invention uses the whole genome DNA of the ram to be tested as a template, and uses male-specific qPCR primer pairs P1 and P2 to amplify the ram ZNF280BY gene respectively. and a partial fragment of the DDX3Y gene, wherein multiple copies of the ZNF280BY gene are used as a detection gene, and a single copy of the DDX3Y gene is used as a reference gene, and the copy number of the ram ZNF280BY gene is calculated according to the quantitative results, and the present invention can detect copies used for early identification of ram fecundity The number of variant molecular markers can be used to speed up the breeding process of rams through molecular marker-assisted selection. The method of the invention is simple and fast, and is convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:甘肃润牧生物工程有限责任公司
Method for quantifying and/or detecting human male DNA
ActiveUS20190249233A1Reduce riskAids in identification of fetalMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAGenome
According to a first aspect of the present invention, a method is provided for detecting and / or quantifying male genomic DNA in a sample, wherein the method comprises the step of amplification of a multicopy locus within the human Y-chromosome (MCL-Y), wherein said locus shares at least 80% sequence identity to a sequence according to SEQ ID NO. 3 over a stretch of at least 60 base pairs (bp). A second aspect of the present invention relates to a primer or primer pair which hybridizes under stringent conditions to a sequence according to SEQ ID NO. 3 and / or any of 4 to 11. The invention also relates to a kit.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com