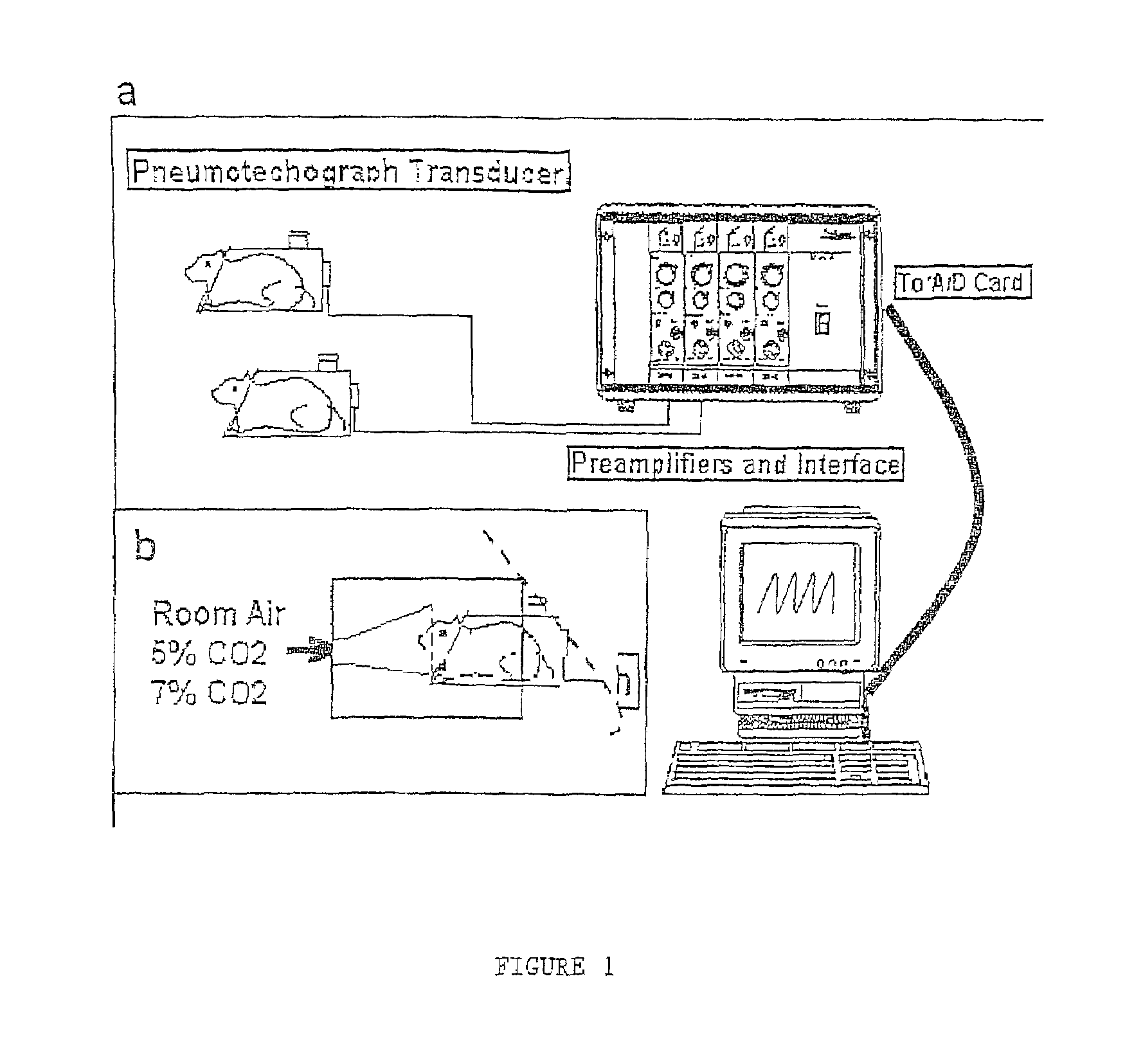
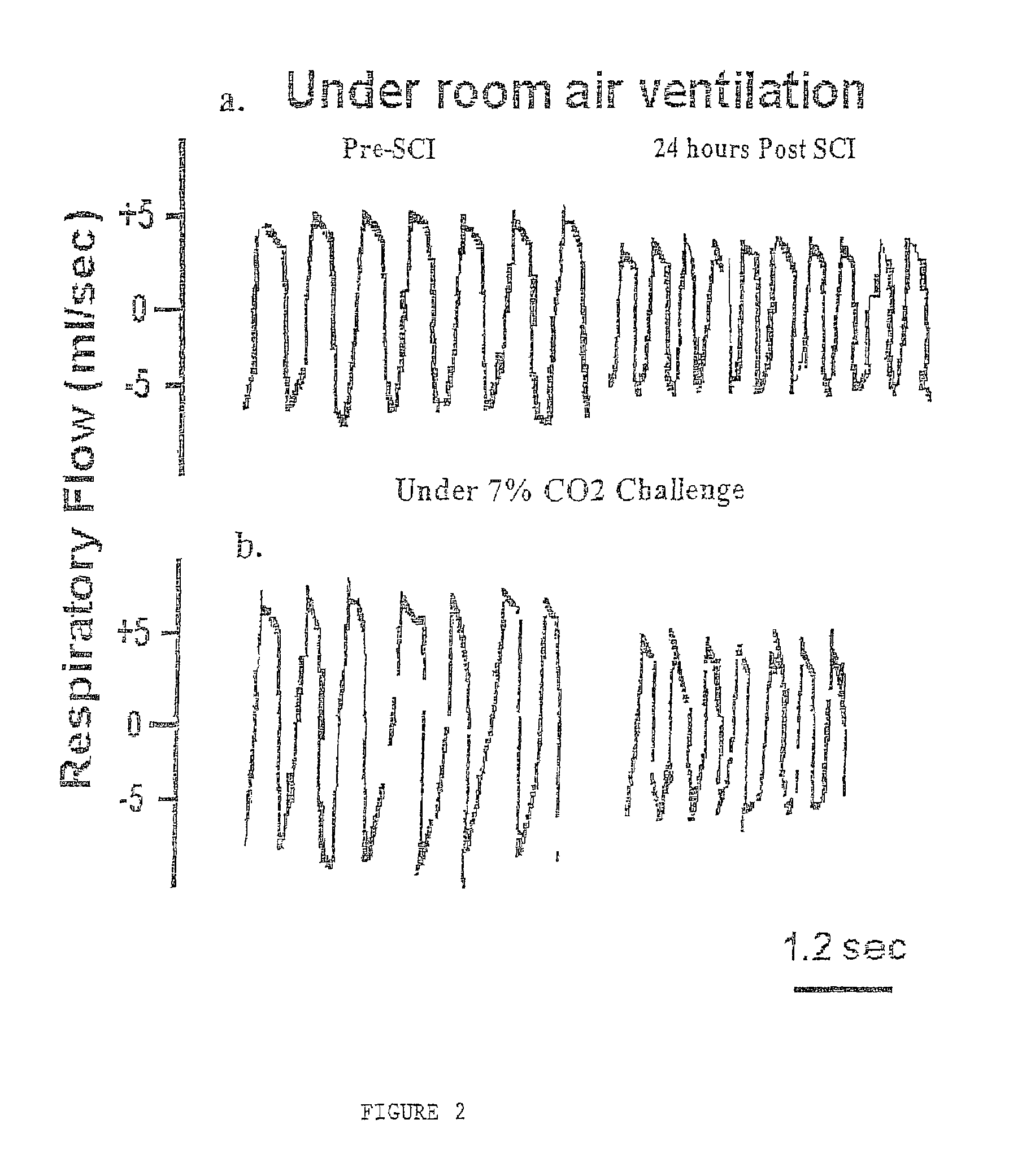
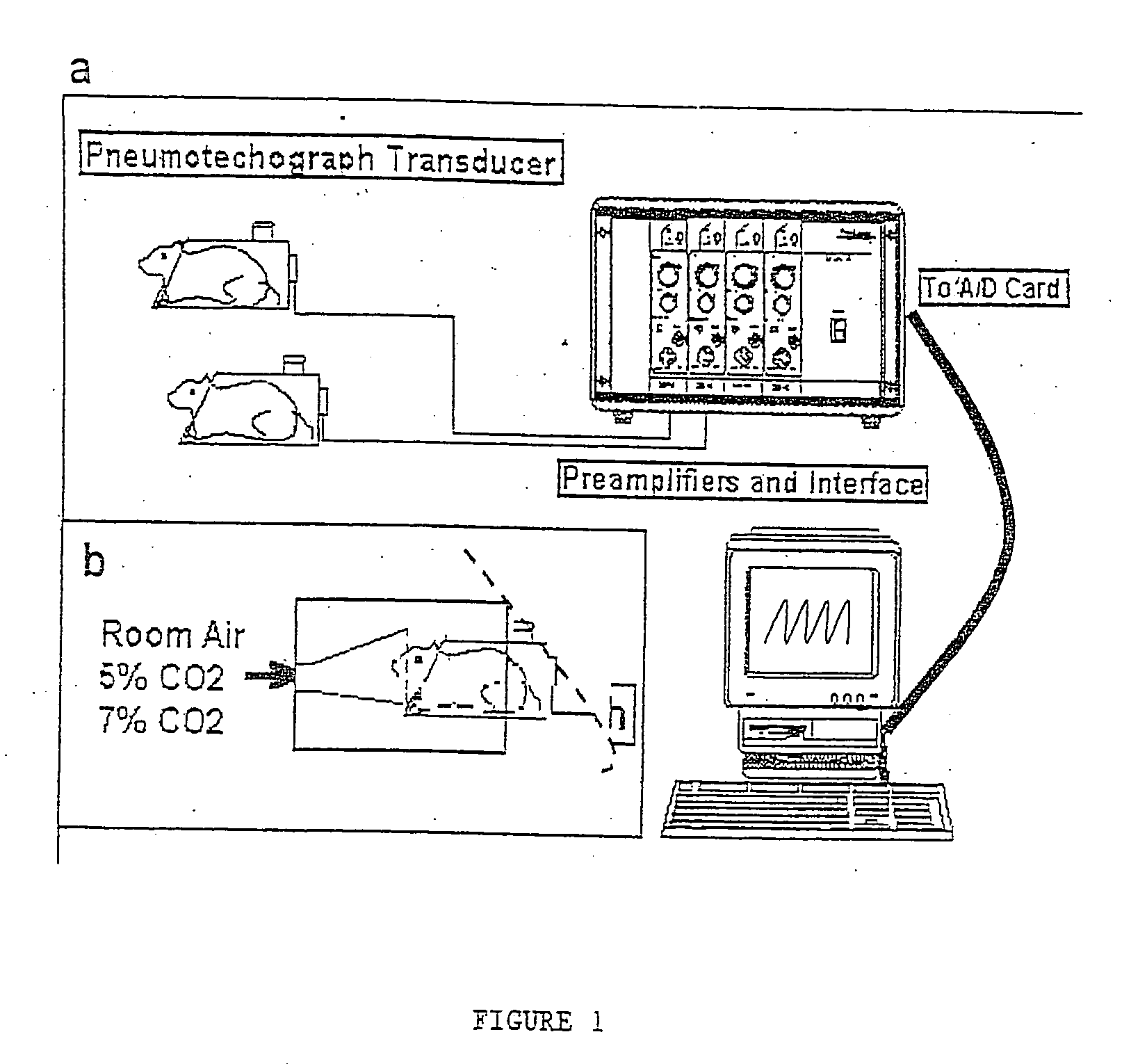
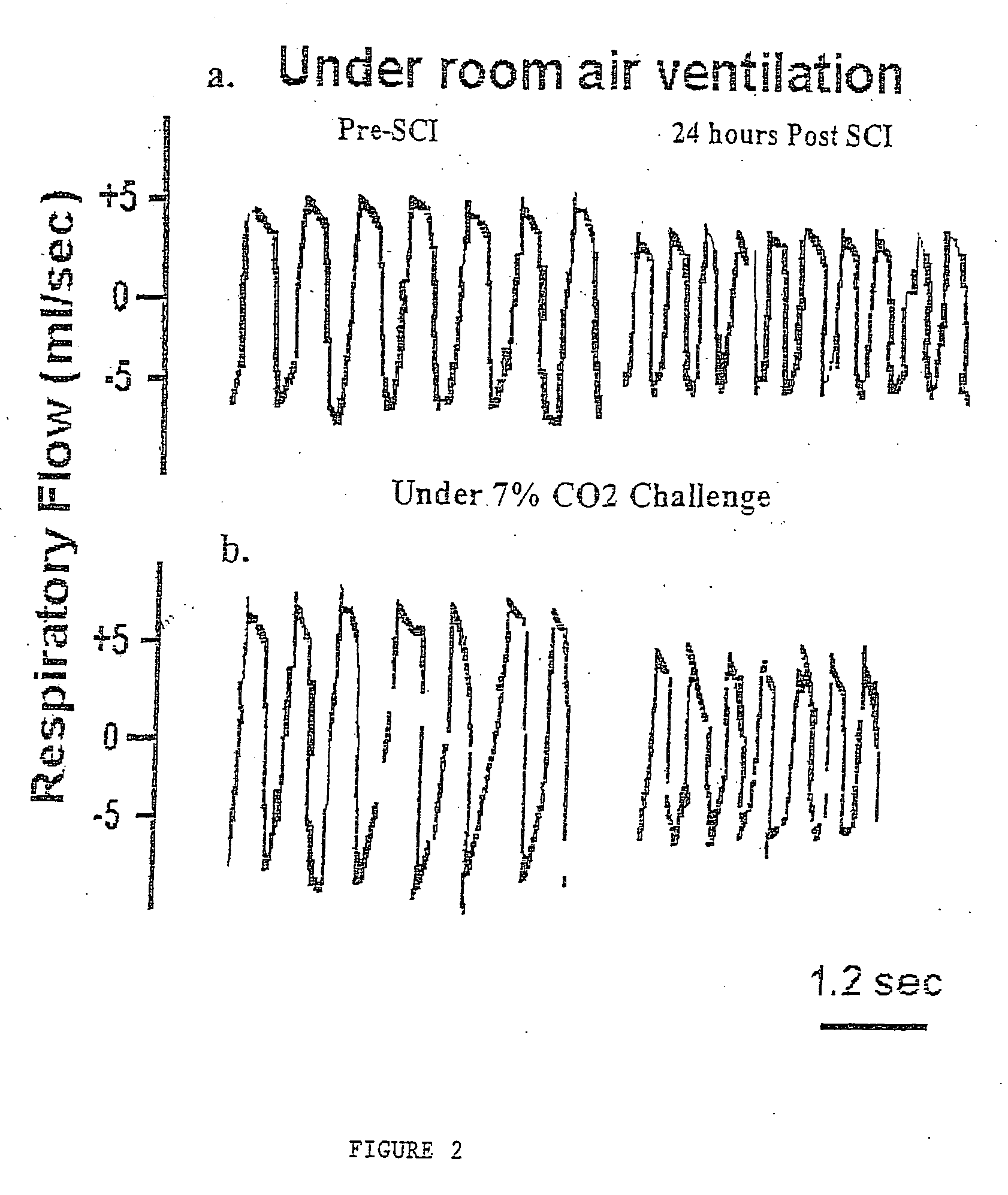
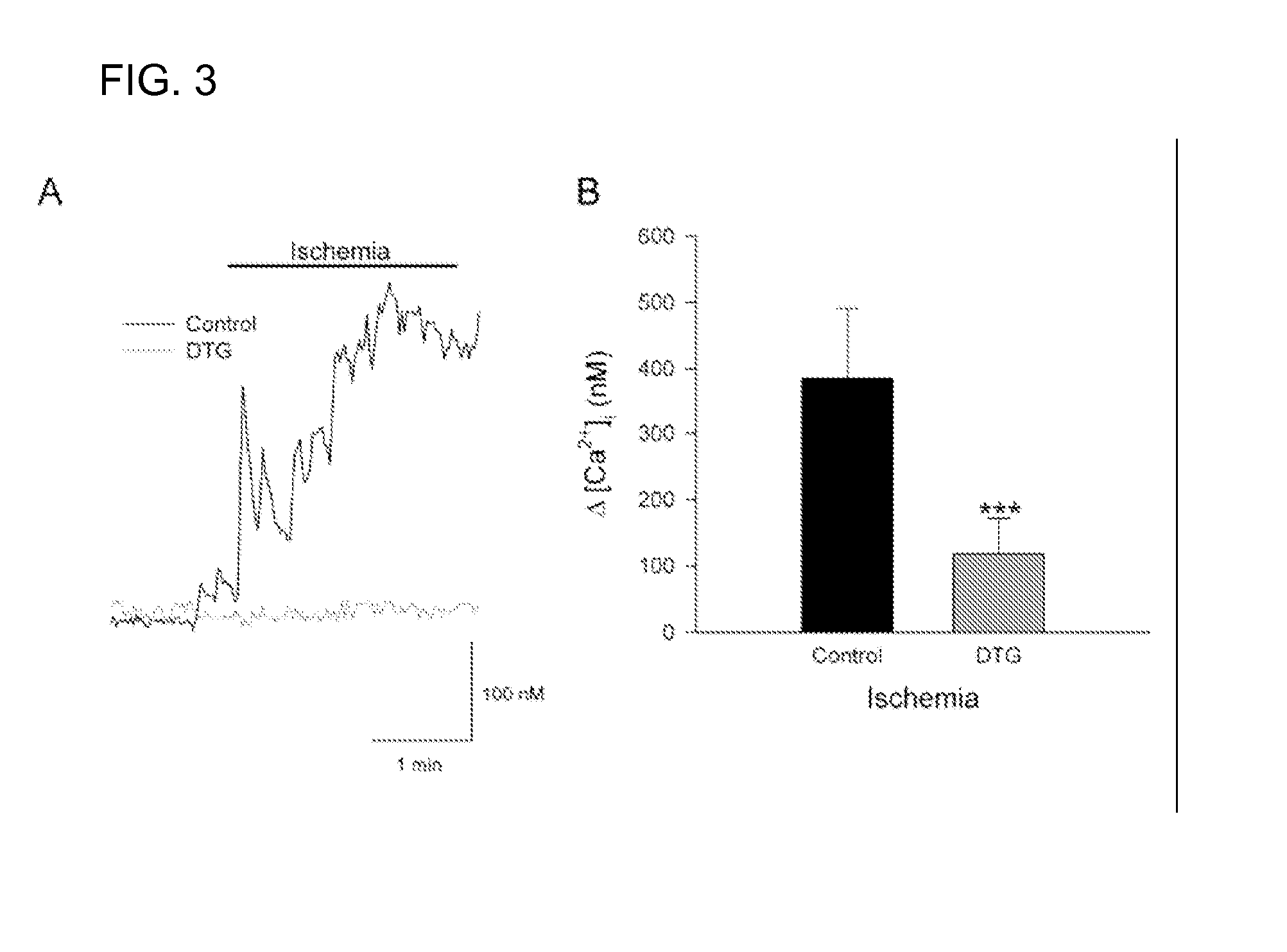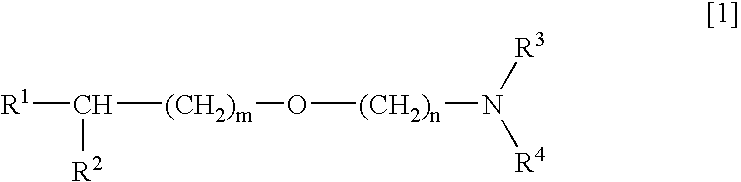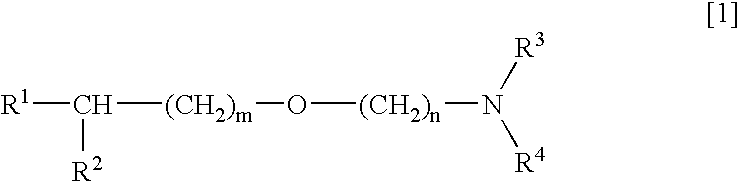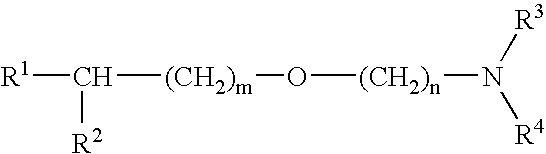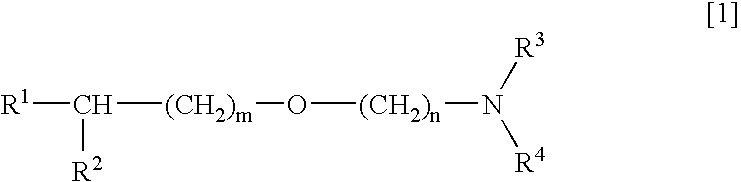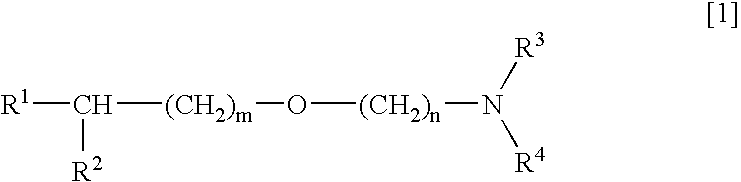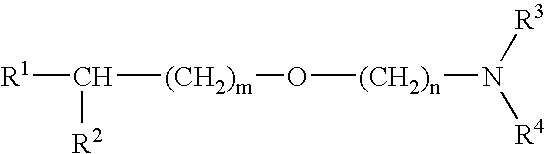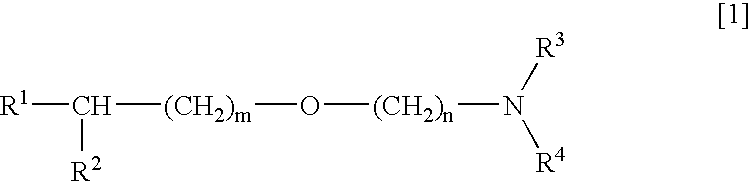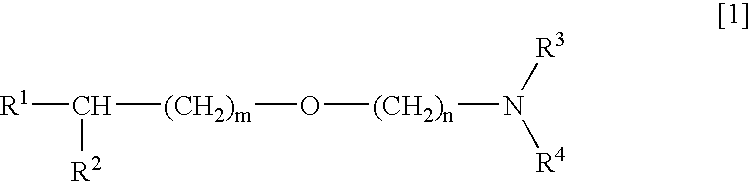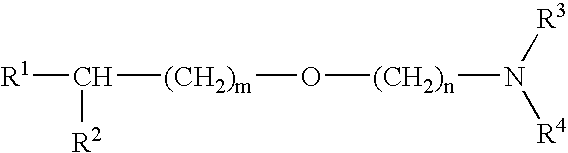Patents
Literature
87 results about "Neuron death" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mechanisms of cell death in neuronal cells. Although it is recognized that neurons die in neurodegenerative diseases, the mode of cell death is often unclear. There are a number of recognized ways in which neuronal cells can die, including apoptosis, necrosis, autophagic cell death (ACD) and excitotoxic-ity.
Administration of growth factors for the treatment of CNS disorders
ActiveUS20070254842A1Prevents and delay onsetReduce severityHeavy metal active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseNervous system
A method and system that is directed to the local delivery of growth factors to the mammalian CNS to treat CNS disorders associated with neuronal death and / or dysfunction is described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for improving respiratory function and inhibiting muscular degeneration
InactiveUS7071194B2Improve respiratory functionInhibiting muscular degenerationBiocideAmmonia active ingredientsAtrophyNeuron death
The present invention provides a method for improving respiratory function and inhibiting muscular degeneration (e.g., dystrophy and atrophy). Alternative embodiments of the invention provide a method of inhibiting motor neuron apoptosis and the subsequent muscular degeneration associated with the denervation of muscular tissue resulting from neuron death.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Method for improving respiratory function and inhibiting muscular degeneration
InactiveUS20060258667A1Improve respiratory functionPrevent degradationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAtrophyNeuron death
The present invention provides a method for improving respiratory function and inhibiting muscular degeneration (e.g., dystrophy and atrophy). Alternative embodiments of the invention provide a method of inhibiting motor neuron apoptosis and the subsequent muscular degeneration associated with the denervation of muscular tissue resulting from neuron death.
Owner:TENG YANG D
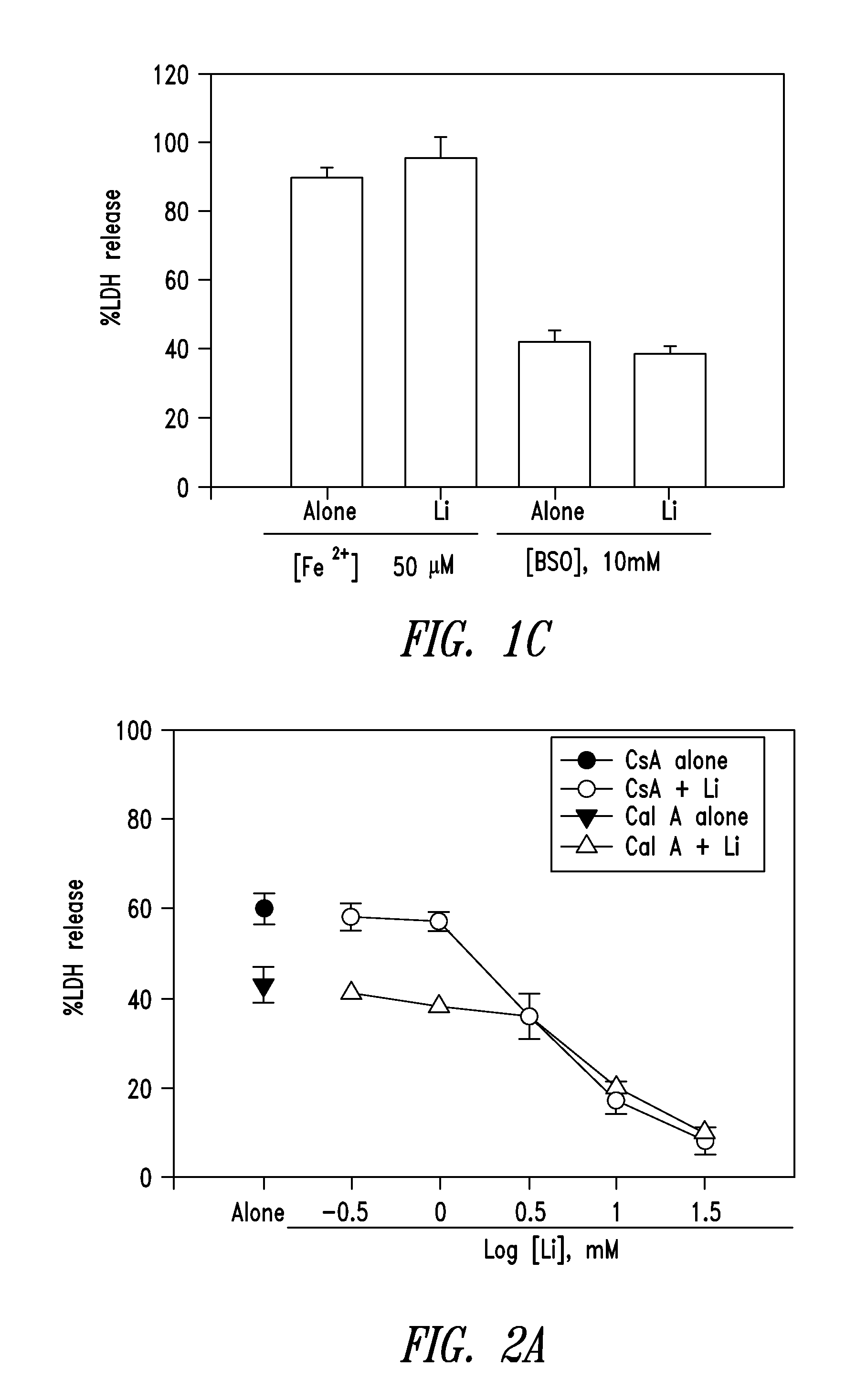
Combination of cell necrosis inhibitor and lithium for treating neuronal death or neurological dysfunction
InactiveUS20070049565A1Salicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideDiabetic retinopathyHuntingtons chorea
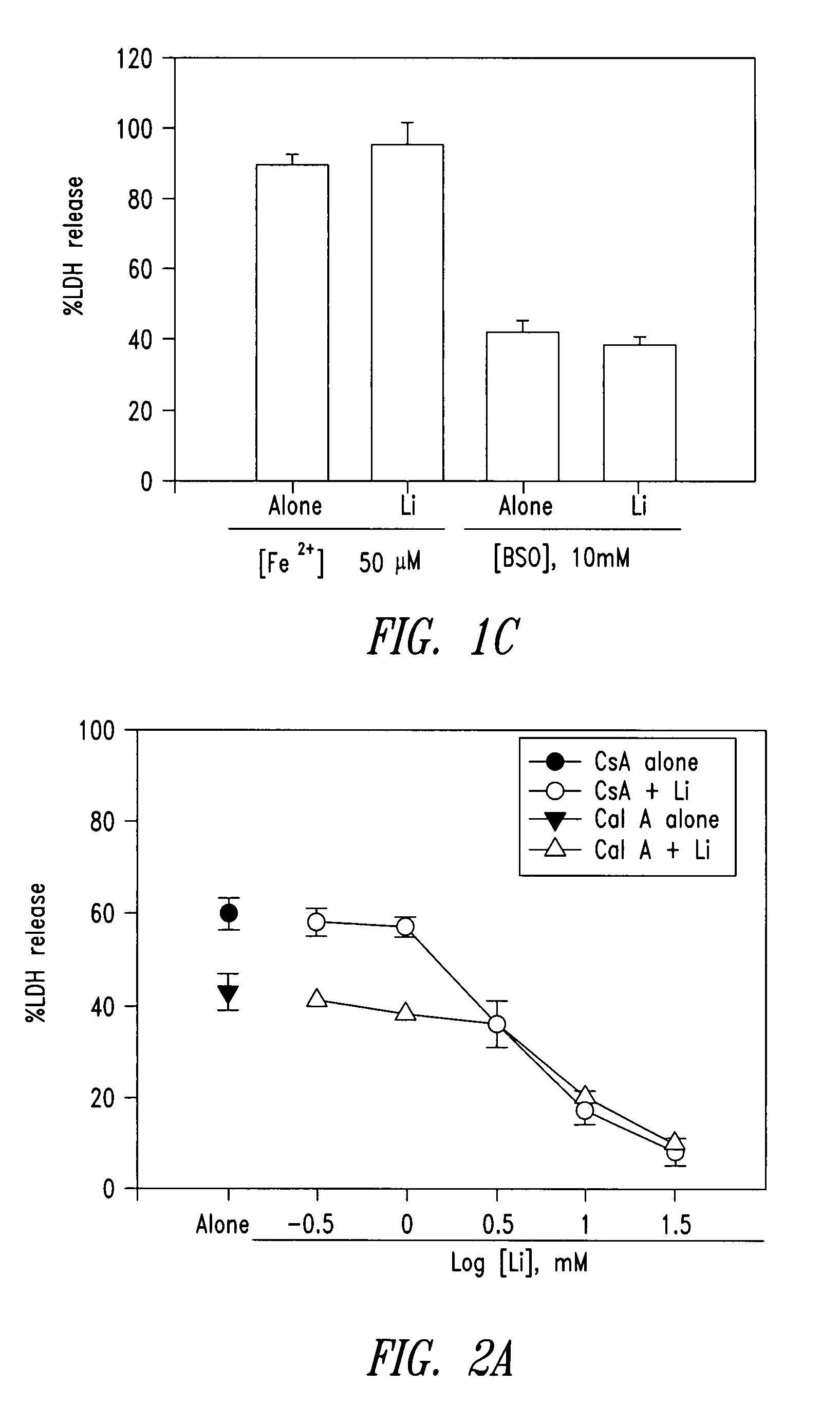
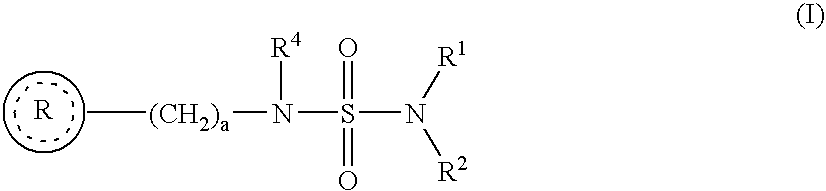
The present invention relates to a combination of cell necrosis inhibitor and lithium, process for the preparation of the combination, pharmaceutical formulation containing the combination and use of the combination by either concomitant or sequential administration for improvement of treatment of neuronal death or neurological dysfunction. The combination of the present invention shows a synergic effect and thus is useful for treating neurological diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Lou Gehrig's disease), Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, stroke, traumatic brain injury or spinal cord injury; and for treating ocular diseases such as glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy or macular degeneration.
Owner:NEUROTECH PHARMA
Methods of neuroprotection by cyclin-dependent kinase inhibition
InactiveUS20080182853A1Inhibiting neuronal degenerationPrevent degenerationOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCyclinKinase inhibition
The present invention relates to methods of suppressing neuronal death, such as is observed with ischemia-related diseases and disorders, including neuronal and cardiac conditions arizing from a sudden loss of oxygen and / or energy loss, and degenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease to name just one. The methods involve the use of inhibitors that act primarily in a simultaneous manner on the cyclin-dependent kinases, CDK4 and CDK6.
Owner:PANACEA PHARMA
Administration of growth factors for the treatment of CNS disorders
ActiveUS7922999B2Increased growth factor mobilityAvoid delayHeavy metal active ingredientsSenses disorderNeuron deathNeuron
A method and system that is directed to the local delivery of growth factors to the mammalian CNS to treat CNS disorders associated with neuronal death and / or dysfunction is described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
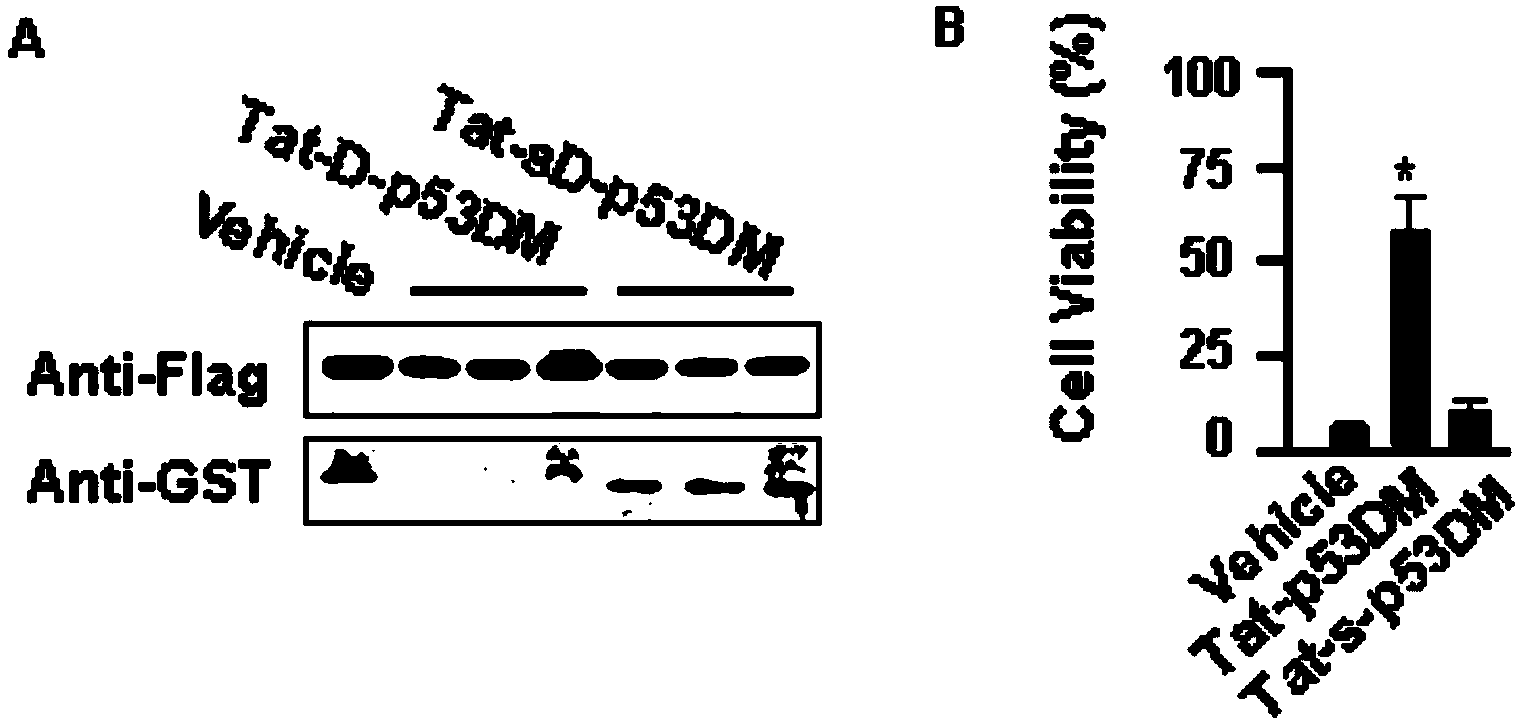
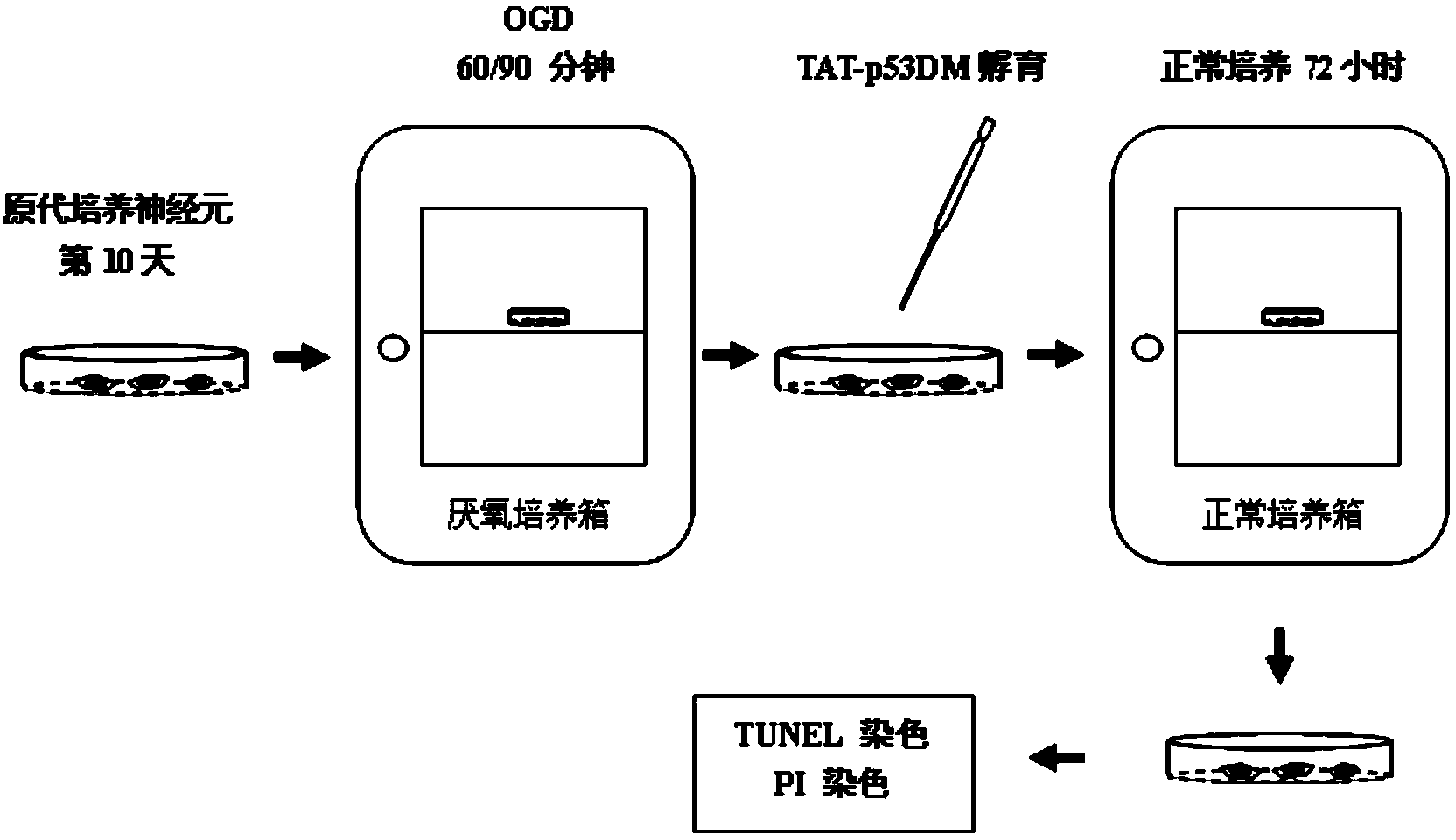
Micro-molecule polypeptide TAT-p53DM and application thereof to preparing medicine for treating or preventing ischemic stroke
ActiveCN103936838ASynthetic high purityNo side effectsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderInjury brainNerve cells
The invention discloses a micro-molecule polypeptide TAT-p53DM and an application thereof to preparing a medicine for treating or preventing ischemic stroke. A fusion protein polypeptide TAT-p53DM of a TAT protein transduction domain and p53DM is artificially synthesized; TAT carries p53DM protein polypeptide to pass through a blood brain barrier through blood so as to be taken by nerve cells; used in an in-vitro and in-vivo ischemic stroke model, the micro-molecule polypeptide TAT-p53DM is capable of effectively playing a biological role in blocking binding between death domain of death associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1DD) and tumor suppression protein p53DNA binding motifs (p53DM), inhibiting signals capable of causing neuronal apoptosis and necrosis at DAPK1 downstream, and reducing ischemic stroke brain injury; moreover, molecular targets are provided for further developing medicines for clinically treating ischemic stroke.
Owner:WUHAN QR SCI & TECH DEV +1
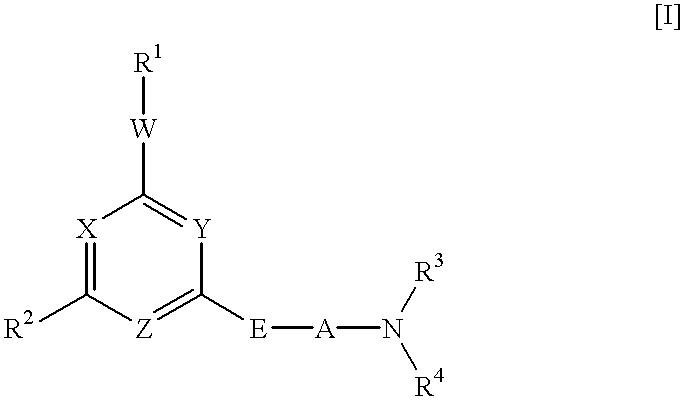
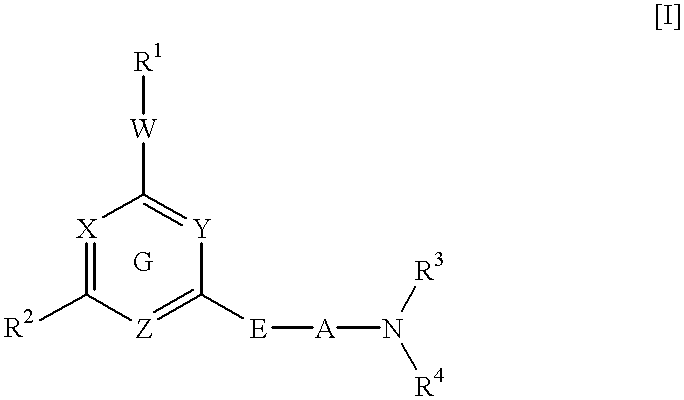
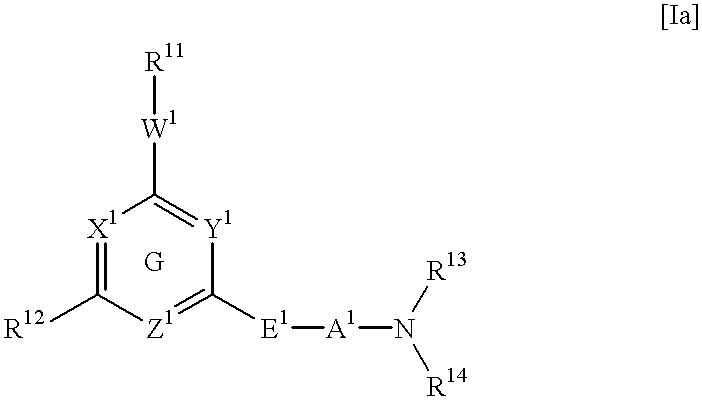
Heterocyclic derivative and medicine
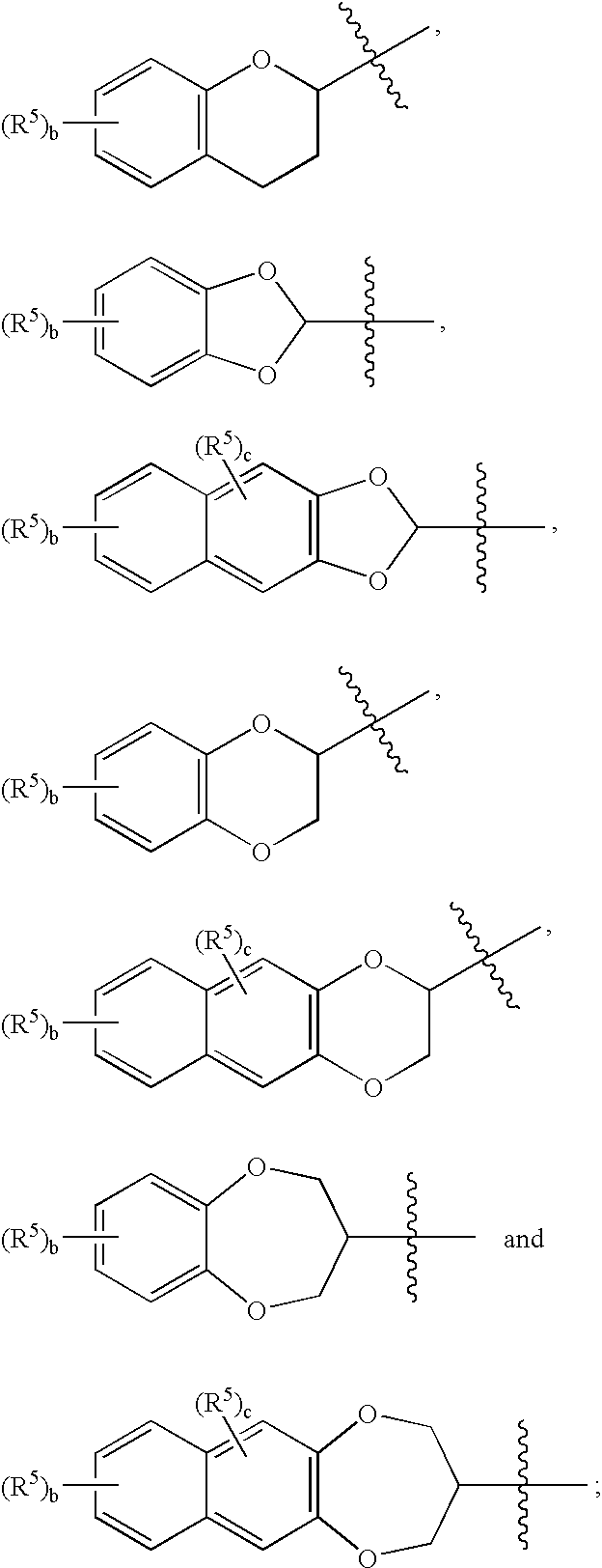
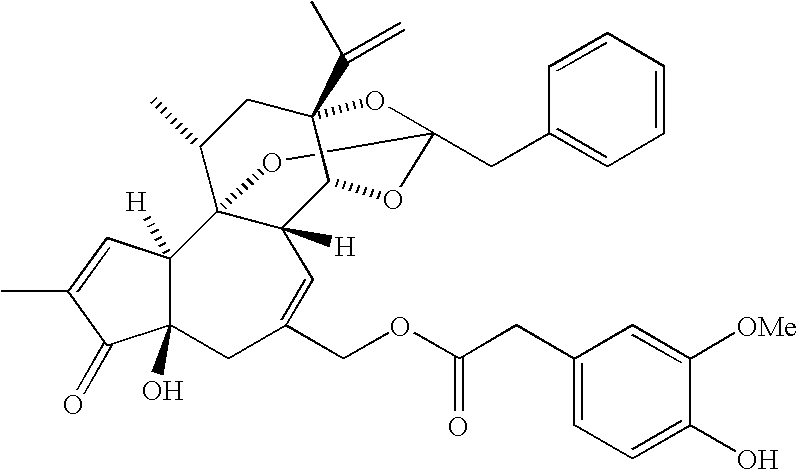
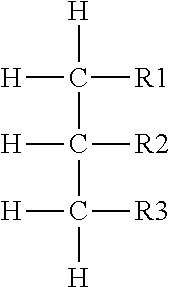
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of the following general formula [I] or its salt.wherein R1 represents aryl or a heteroaromatic group.R2 represents hydrogen, alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, hydroxyalkyl, haloalkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio, amino, monoalkylamino, dialkylamino, or phenyl. R3 and R4 independently represent hydrogen or alkyl or R3 and R4 taken together with the adjacent N atom represent a 5- through 7-membered cyclic amino group. A represents a single bond C2-10 alkylene. W represents O, S, or (CH2)n (where CH may be substituted by alkyl; n is an integer of 1 or 2). X, Y, and Z may be the same or different and each represents CH (which may be substituted by alkyl), or N. Provided, however, that the case in which X, Y, and Z concurrently represent CH is excluded. The compound of the invention has excellent neuronal death inhibitory activity and is useful as a therapeutic drug for cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:NIPPON SHINYAKU CO LTD
Use of GSK3 inhibitors in combination with radiation therapies
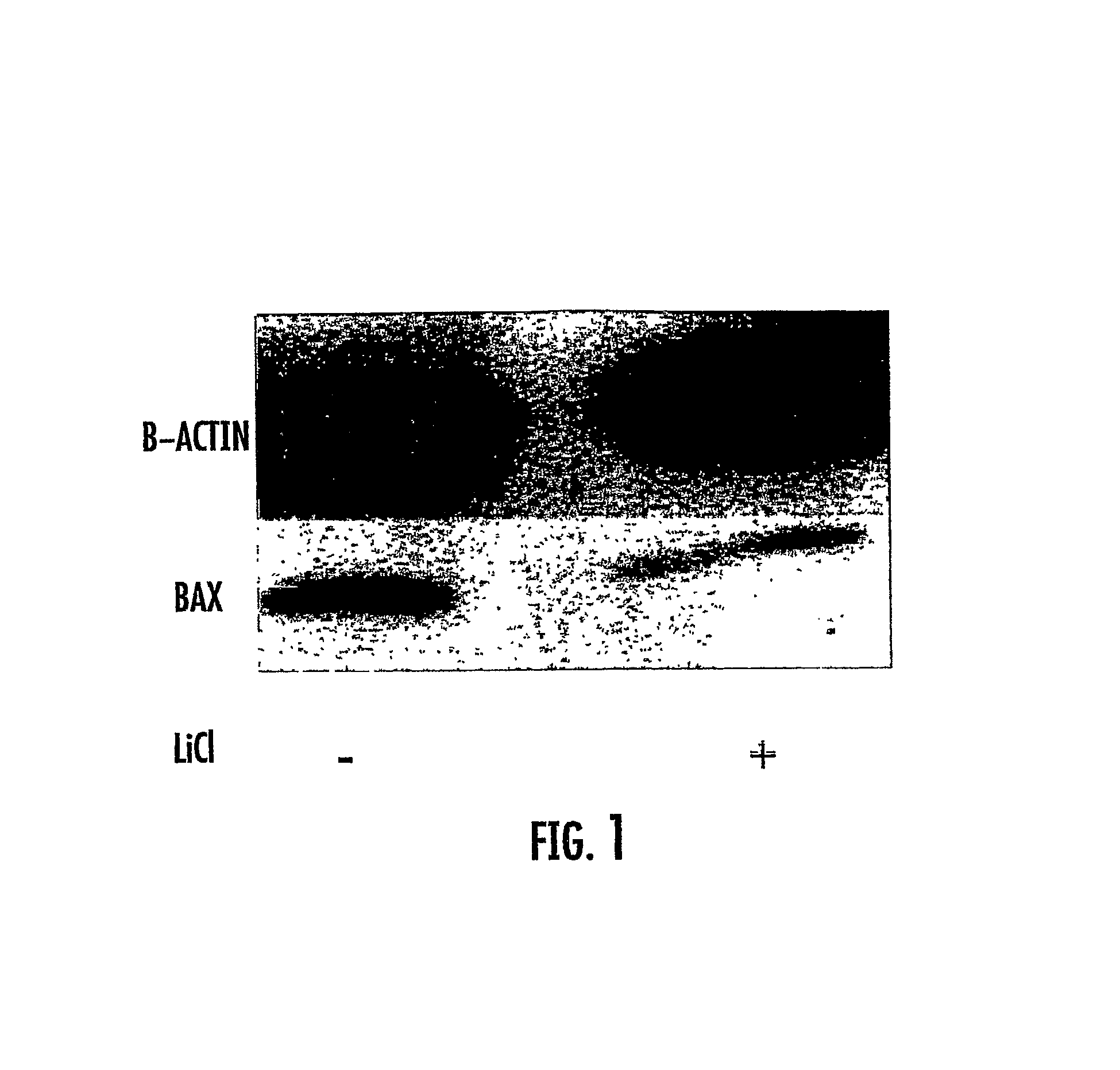
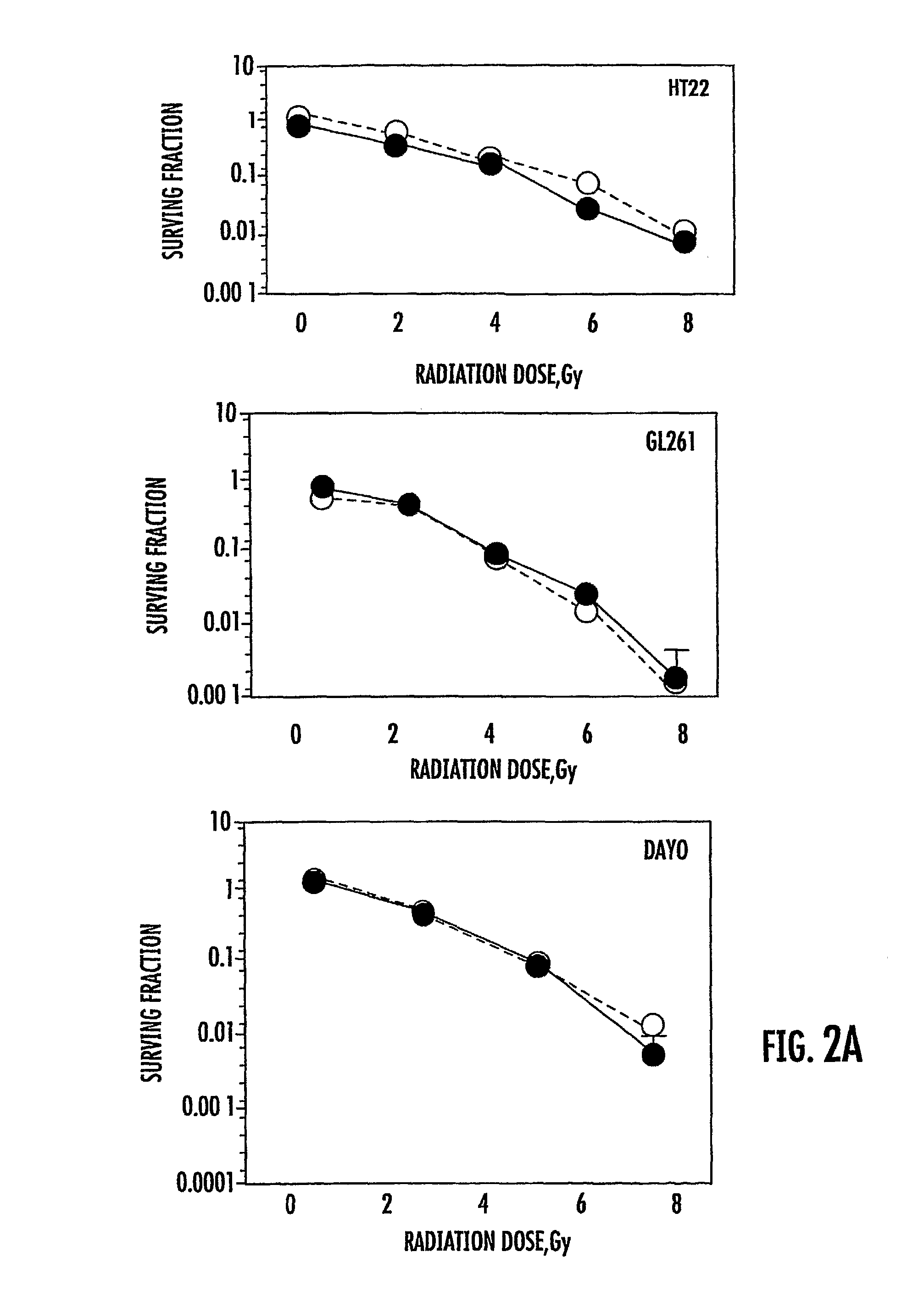
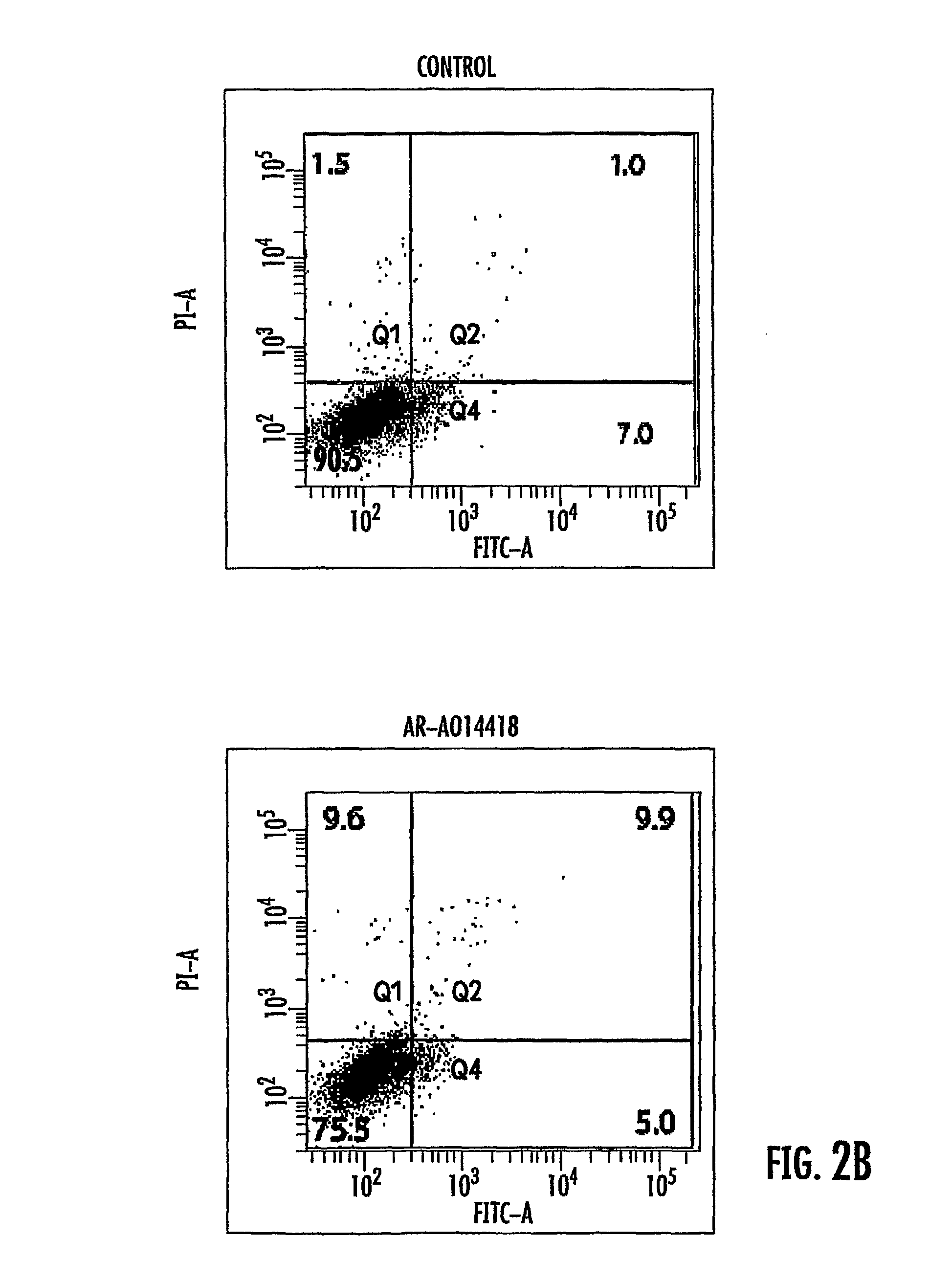
The presently disclosed subject matter relates generally to the fields of molecular biology and medicine. More particularly, it concerns methods involving the use of GSK3 inhibitors in combination with radiation therapies. In some embodiments, administration of a GSK3 inhibitor to a subject results in an amelioration of cognitive decline, toxicity to vascular endothelial cells, and / or neuron death associated with radiation therapy alone.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Compounds and compositions for treating neuronal death or neurological dysfunction
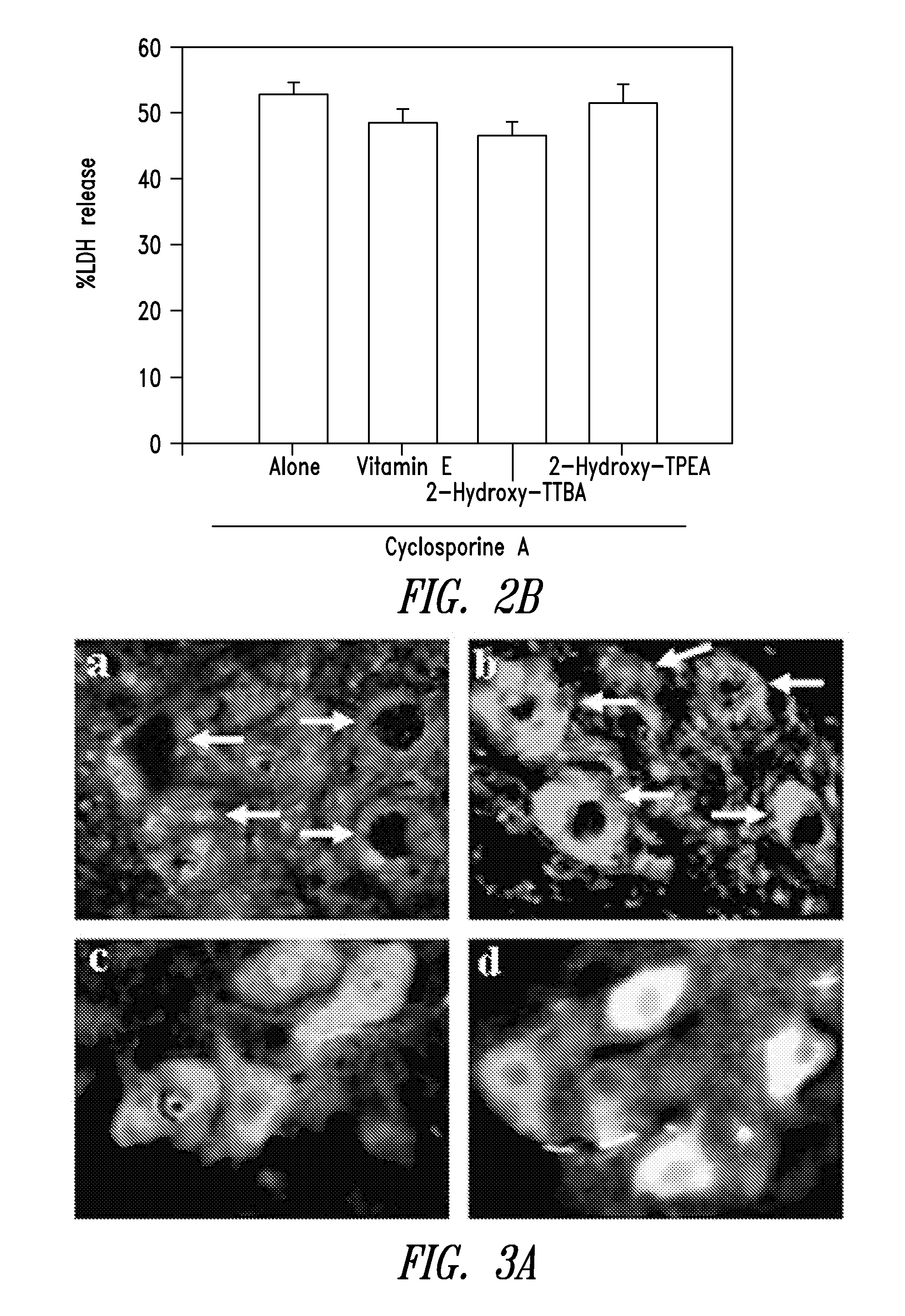
InactiveUS20070298129A1Avoid necrosisReduced infarct volumeBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsDiabetic retinopathyBenzoic acid
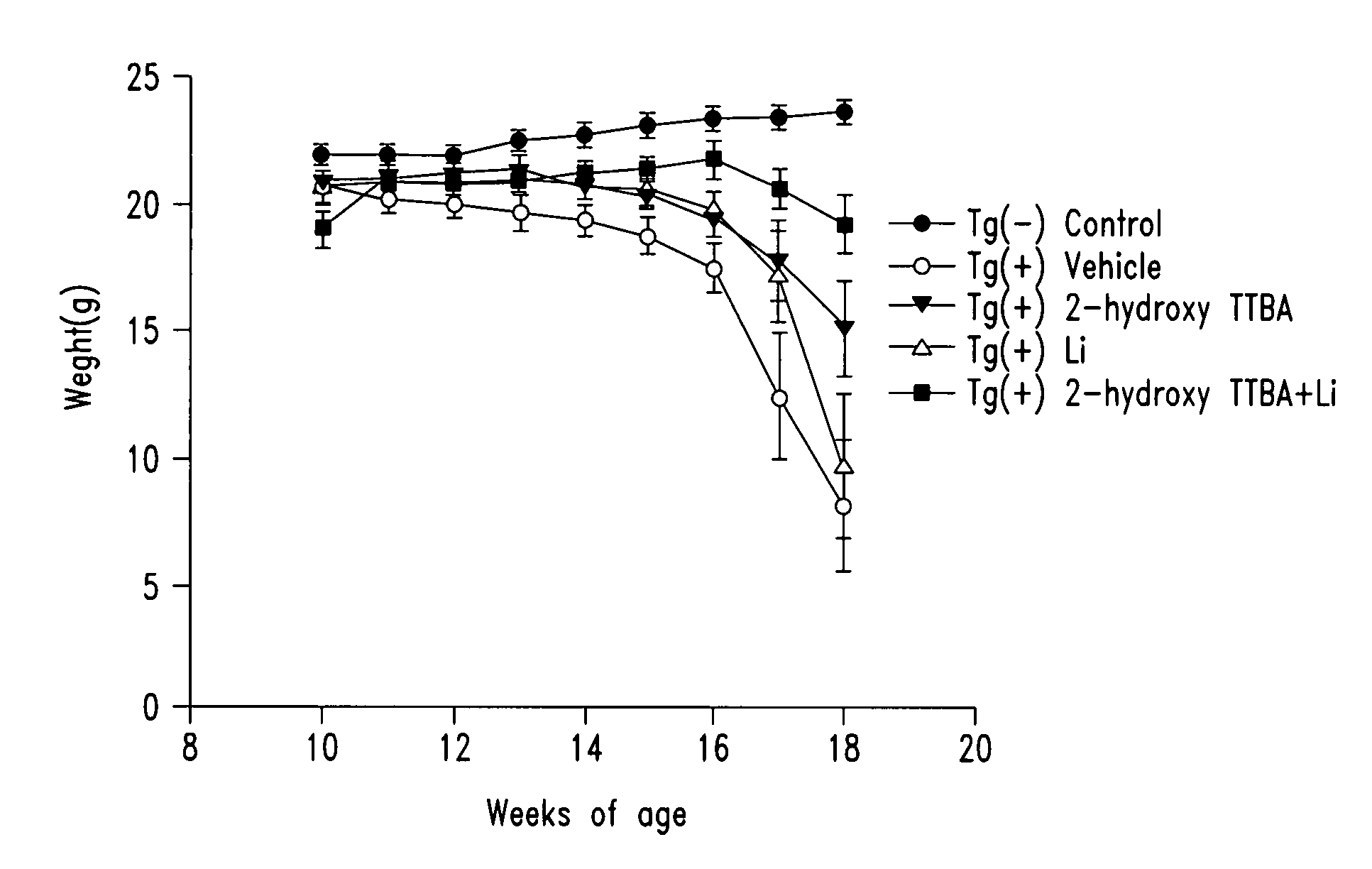
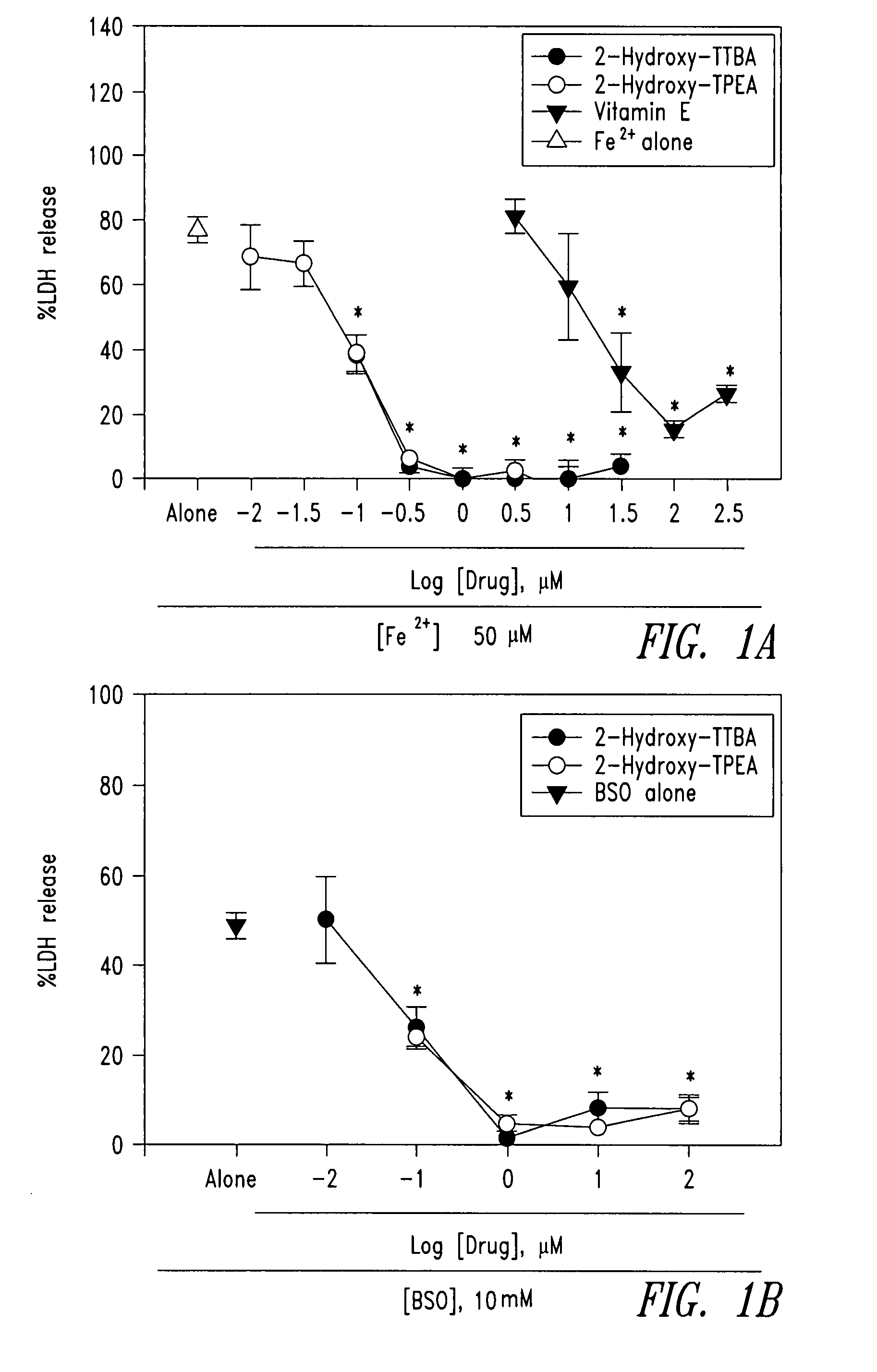
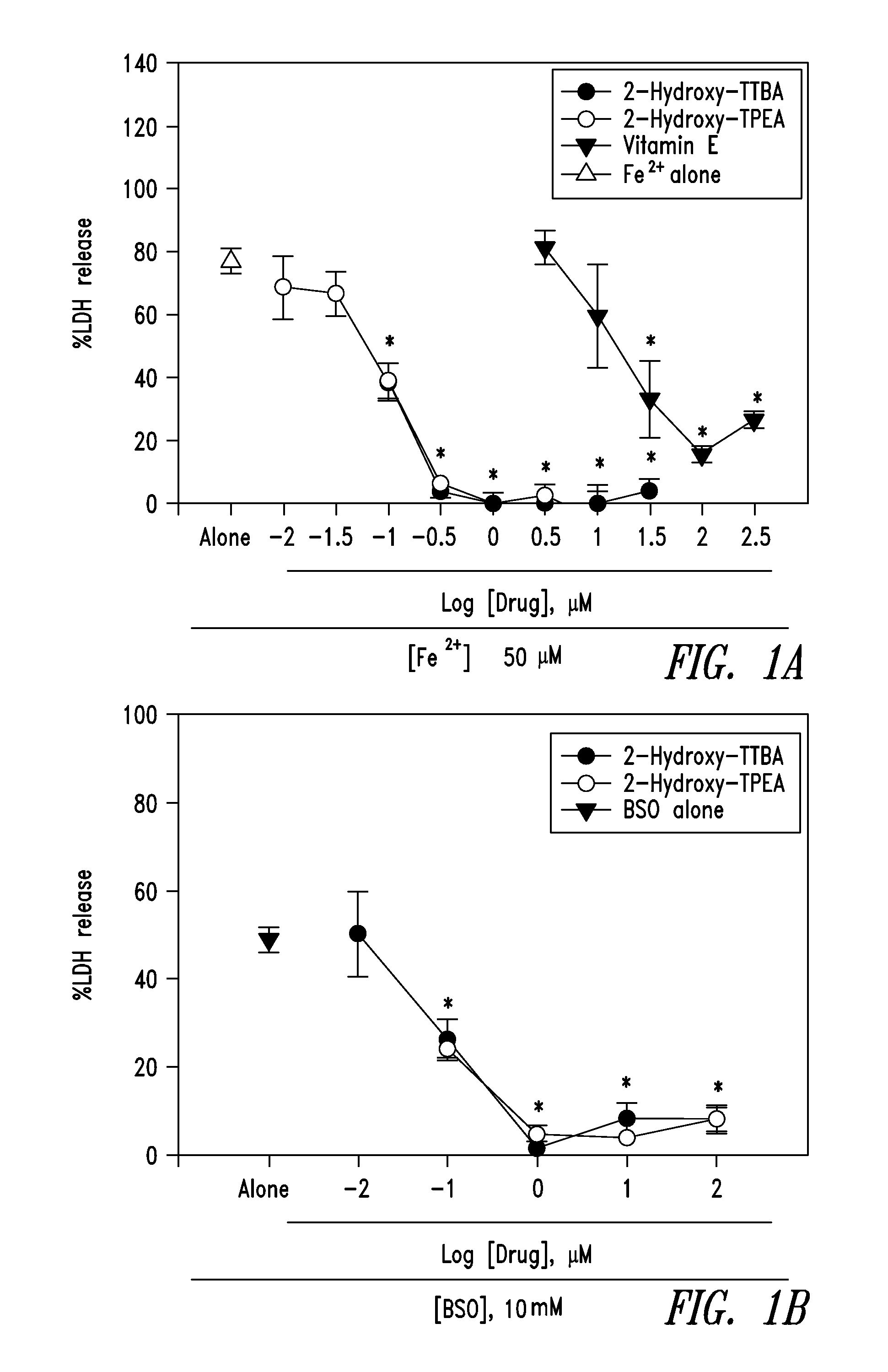
The present invention relates to 2-hydroxy-alkylamino-benzoic acid derivatives and to a combination of cell necrosis inhibitor and lithium, process for the preparation of the derivatives or the combination, pharmaceutical formulation containing the derivatives or the combination, and use of the derivatives or the combination by either concomitant or sequential administration for improvement of treatment of neuronal death or neurological dysfunction. The derivatives and the combination of the present invention are useful for treating neurological diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Lou Gehrig's disease), spinal muscular atrophy, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, stroke, traumatic brain injury or spinal cord injury; and for treating ocular diseases such as glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy or macular degeneration.
Owner:NEUROTECH PHARMA
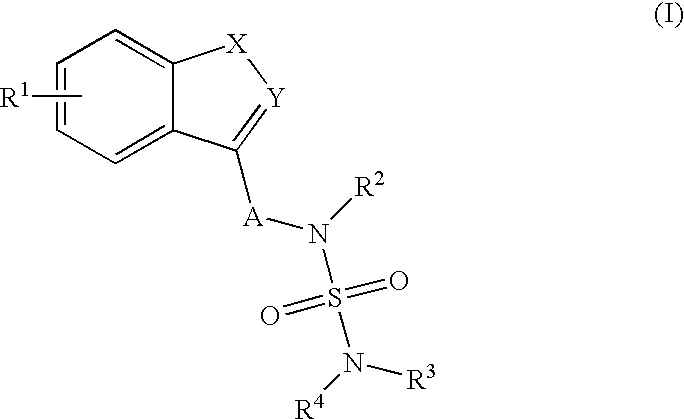
Use of benzo-fused heterocycle sulfamide derivatives as neuroprotective agents
InactiveUS20070155823A1Preventing neuron deathAvoid damageBiocideNervous disorderNeuron deathSpinal cord
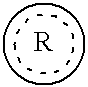
The present invention is a methods for neuroprotection, for treating an acute neurodegenerative disorder, for treating a chronic neurodegenerative disorder and / or for preventing neuron death or damage following brain, head and / or spinal cord trauma or injury comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of one or more novel benzo-fused heterocycle sulfamide derivatives of formula (I) and formula (II) as herein defined.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Selective ablation of pain-sensing neurons by administration of a vanilloid receptor agonist
The present invention provides methods and kits for the selective ablation of pain-sensing neurons. The methods comprise administration of a vanilloid receptor agonist to a ganglion in an amount that causes death of vanilloid receptor-bearing neurons. Accordingly, the present invention provides methods of controlling pain and inflammatory disorders that involve activation of vanilloid receptor-bearing neurons.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Agents for treating neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20070078144A1Prevent neuronal deathInhibit caspase cleavageBiocideAnimal repellantsHuntingtons choreaMedicine
The present invention relates to compounds effective in preventing neuronal cell death, which may be used in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that particular compounds were effective in preventing neuronal death in model systems of Huntington's Disease.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Treatment with Sigma Receptor Agonists Post-Stroke
InactiveUS20070123556A1Decrease in infarction areaHigh affinityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHippocampal regionGlial fibrillary acidic protein
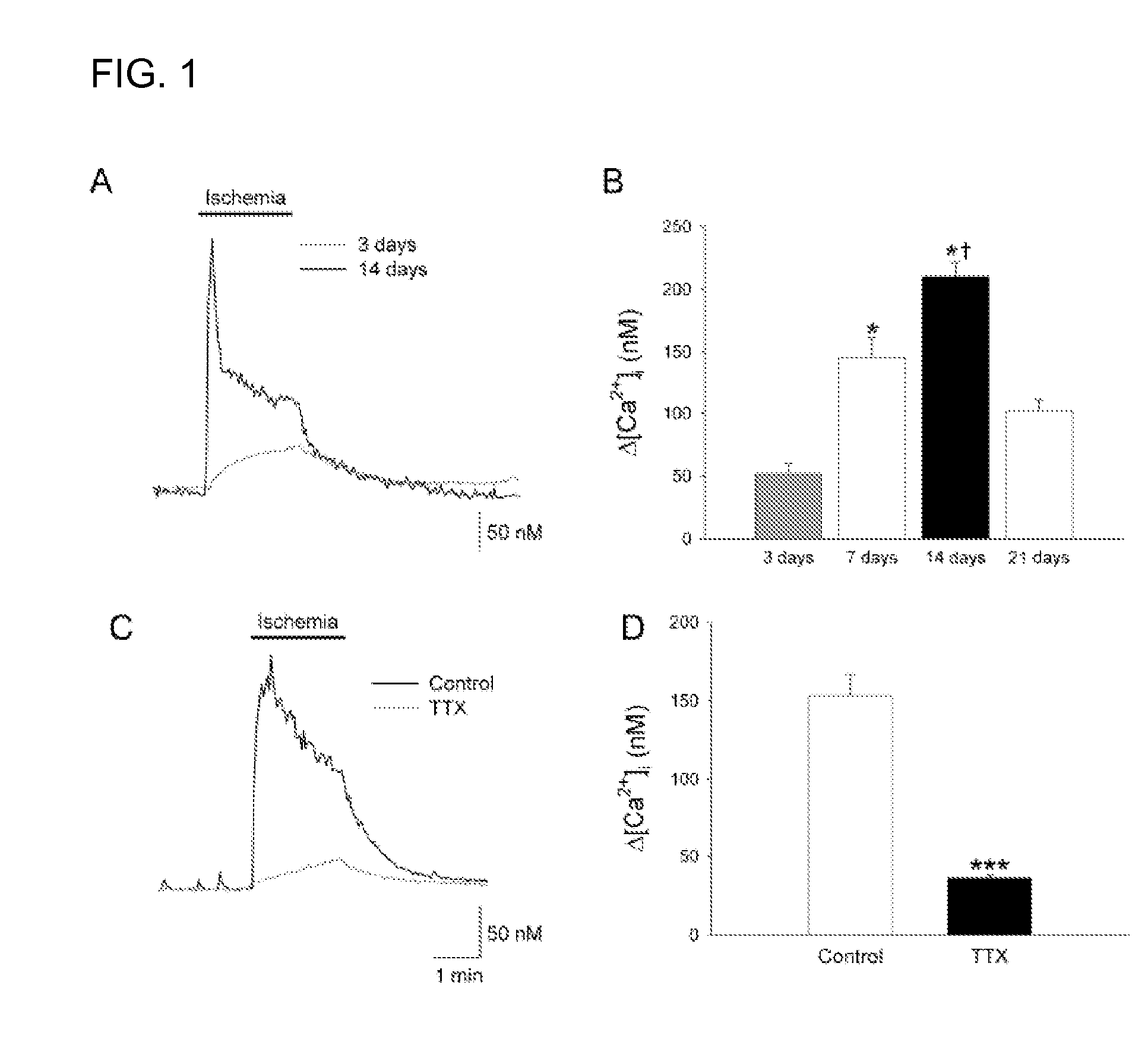
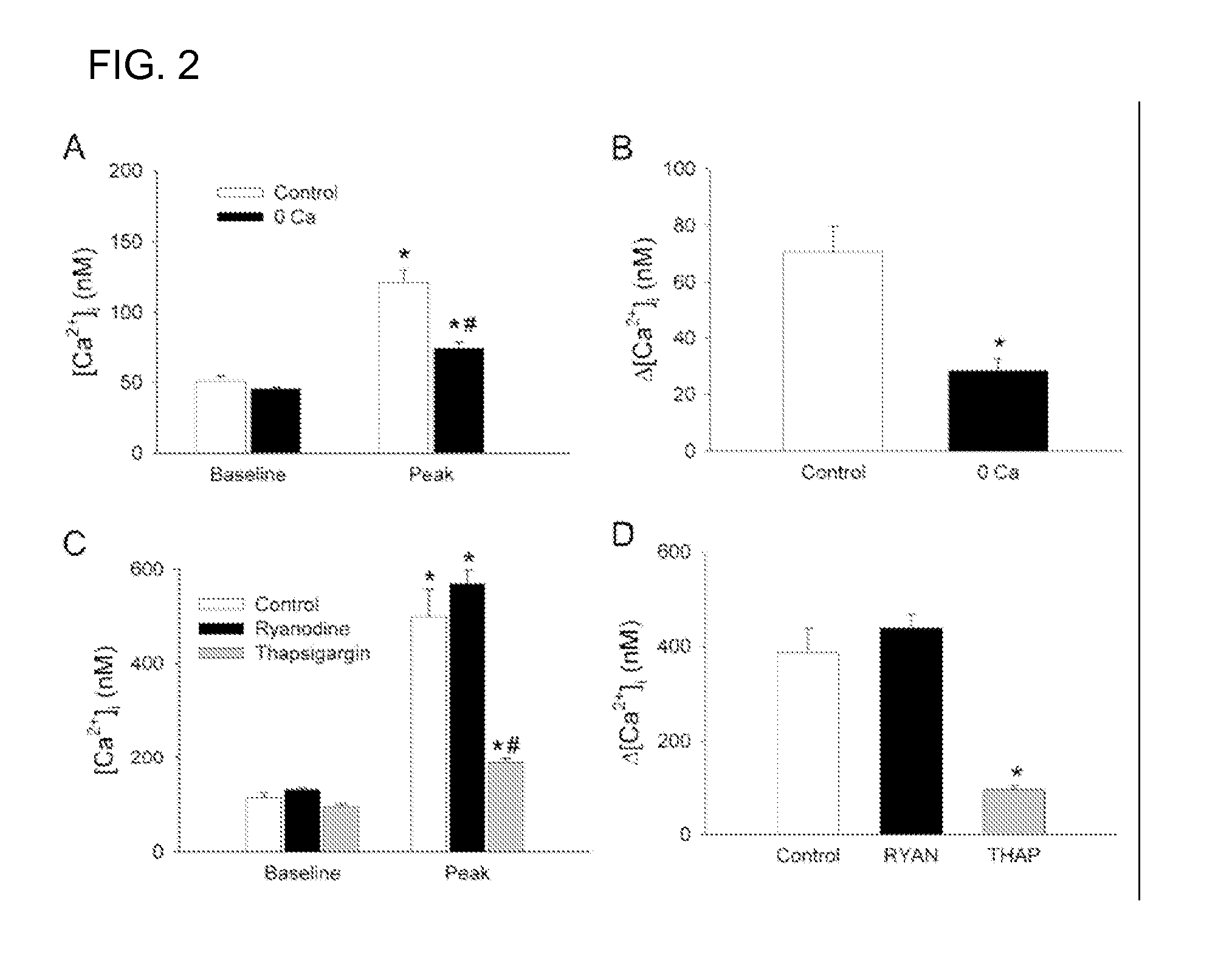
A method of post-stroke treatment at delayed timepoints with sigma receptor agonists. Sigma receptors are promising targets for neuroprotection following ischemia. One of the key components in the demise of neurons following ischemic injury is the disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis. The sigma receptor agonist, DTG, was shown to depress [Ca2+]i elevations observed in response to ischemia induced by sodium azide and glucose deprivation. Two sigma receptor antagonists, metaphit and BD-1047, were shown to blunt the ability of DTG to inhibit ischemia-evoked increases in [Ca2+]i. DTG inhibition of ischemia-induced increases in [Ca2+]i was mimicked by the sigma-1 receptor-selective agonists, carbetapentane, (+)-pentazocine and PRE-084, but not by the sigma-2 selective agonist, ibogaine, showing that activation of sigma-1 receptors is responsible for the effects. Activation of sigma receptors can ameliorate [Ca2+]i dysregulation associated with ischemia in cortical neurons, providing neuroprotective properties. The effects of 1,3-di-o-tolyguanidine (DTG), a high affinity sigma receptor agonist, as a potential treatment for decreasing infarct area at delayed time points was further examined in rats. DTG treatment significantly reduced infarct area in both cortical / striatal and cortical / hippocampal regions by >80%, relative to control rats. These findings were confirmed by immunohistochemical experiments using the neuronal marker, mouse anti-neuronal nuclei monoclonal antibody (NeuN), which showed that application of DTG significantly increased the number of viable neurons in these regions. Furthermore, DTG blocked the inflammatory response evoked by MCAO, as indicated by decreases in the number of reactive astrocytes and activated microglia / macrophages detected by immunostaining for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and binding of isolectin IB4, respectively. Thus, the sigma receptor-selective agonist, DTG, can enhance neuronal survival when administered 24 hr after an ischemic stroke. In addition, the efficacy of sigma receptors for stroke treatment at delayed time points is likely the result of combined neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties of these receptors.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Method for preventing and treating at a superacute phase, against neurological deficits or neuronal death in brain ischemia and pathological conditions
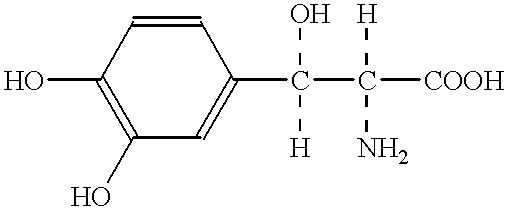
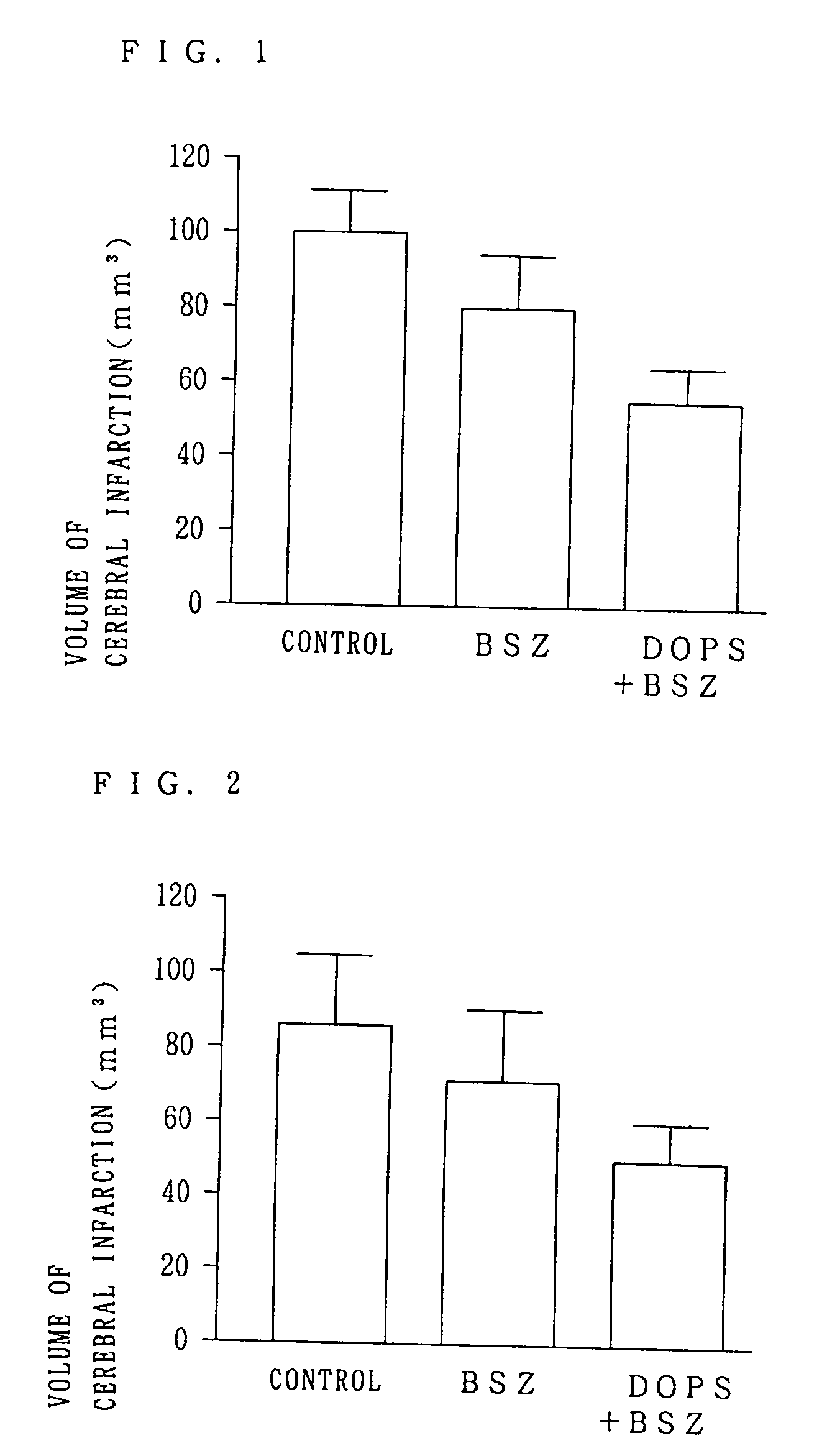
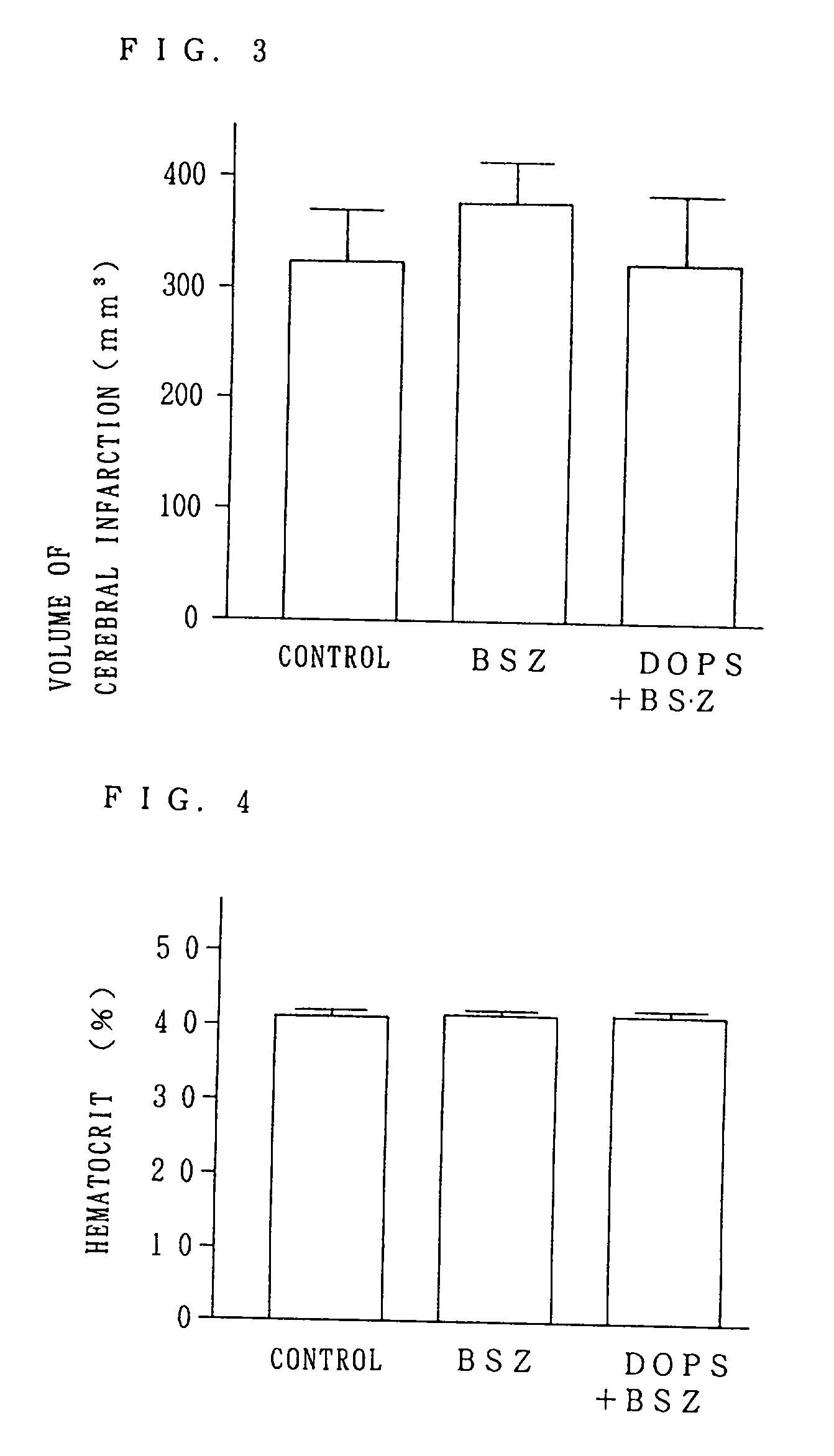
A neuroprotective pharmacological method in cerebral ischemic insult comprising administration of L- or DL-threo-DOPS or a pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salt thereof to a patient. Threo-DOPS directly acts on neurons to exert an effect to protect against neuronal death due to brain ischemia, an antilethal effect, and an anti-edema effect due to excessive polarization of neuronal membrane potential caused by an increase in Na-K-ATPase activity. renaline.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Medicinal compositions improving brain function and method for improving brain function
An alkyl ether derivative represented by the formula: wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, m and n are as defined in the specification, or salts thereof exhibits synergistically improved anti-hypoxic activity when combined with a compound having an acetylcholine esterase inhibitory activity. Therefore, the combination according to the present invention is useful as a method for improving cerebral function. Further, a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound relating to the combination according to the present invention is useful for treatment and prevention of dysfunction of cerebral acetylcholine neurons in the sequelae of cerebrovascular dementia, senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease and ischemic cerebral lesion and in the cerebral apoplexy or the memory impairment caused by selective neuronal death.
Owner:TOYAMA CHEM CO LTD
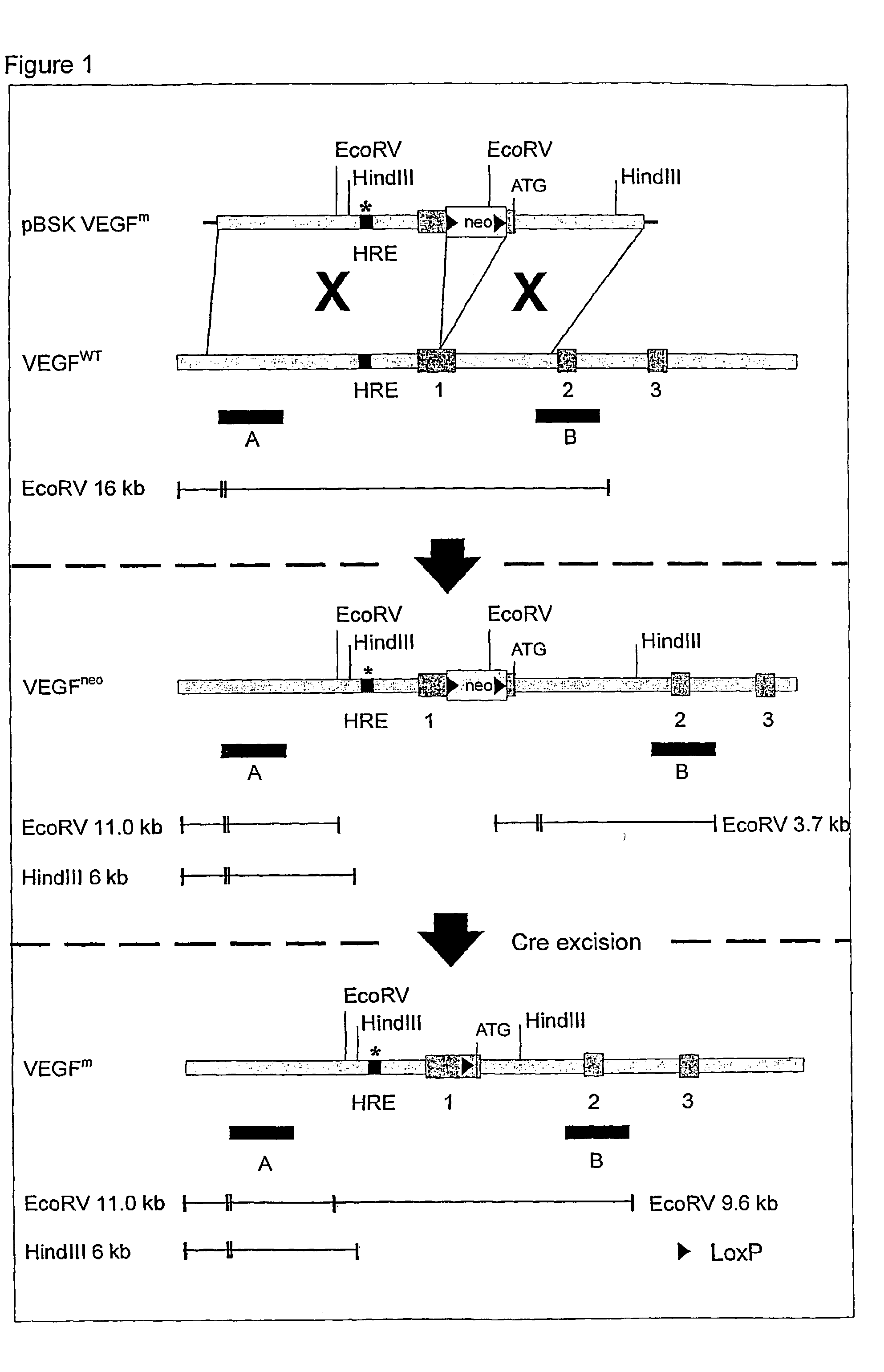
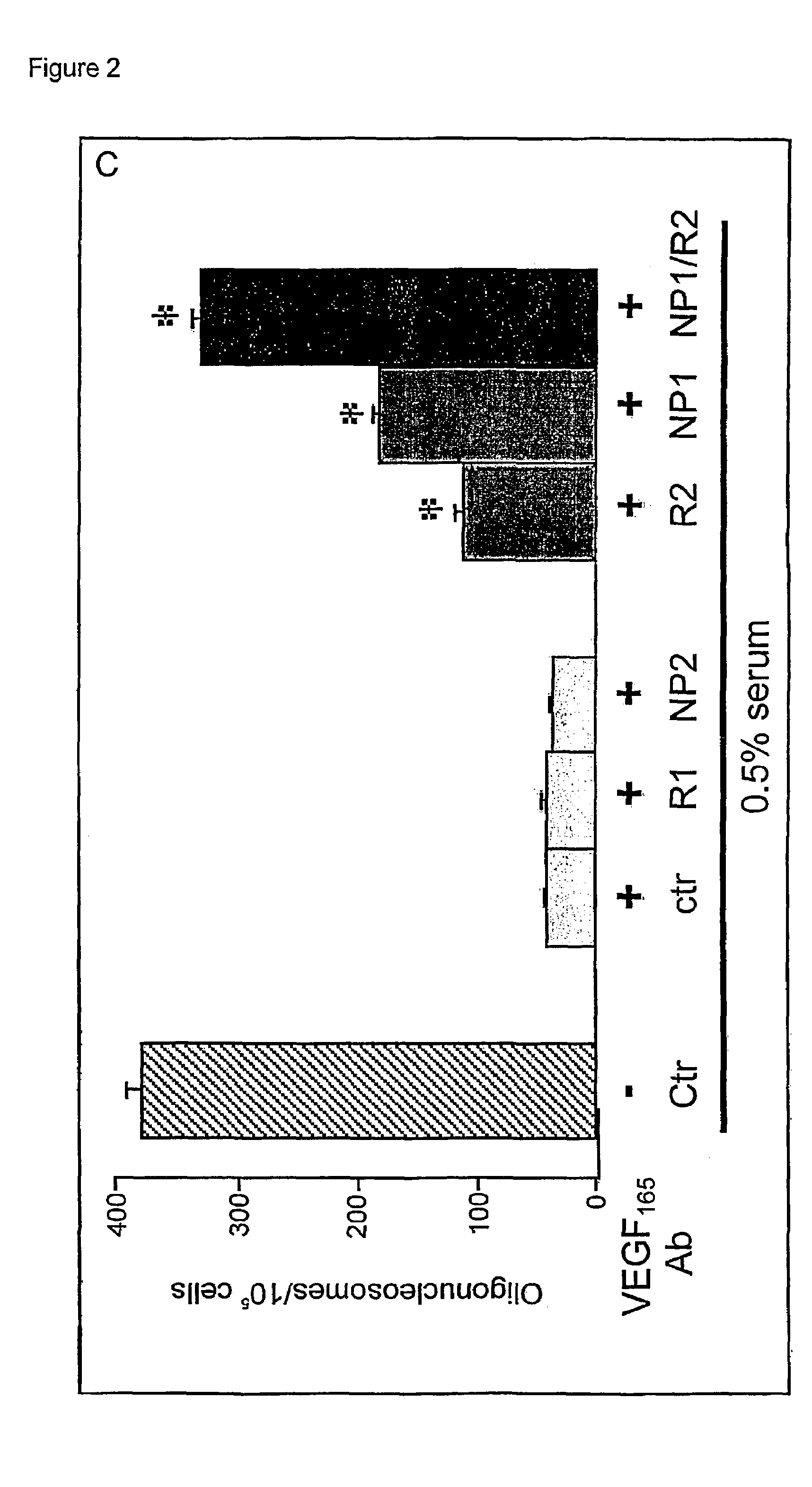
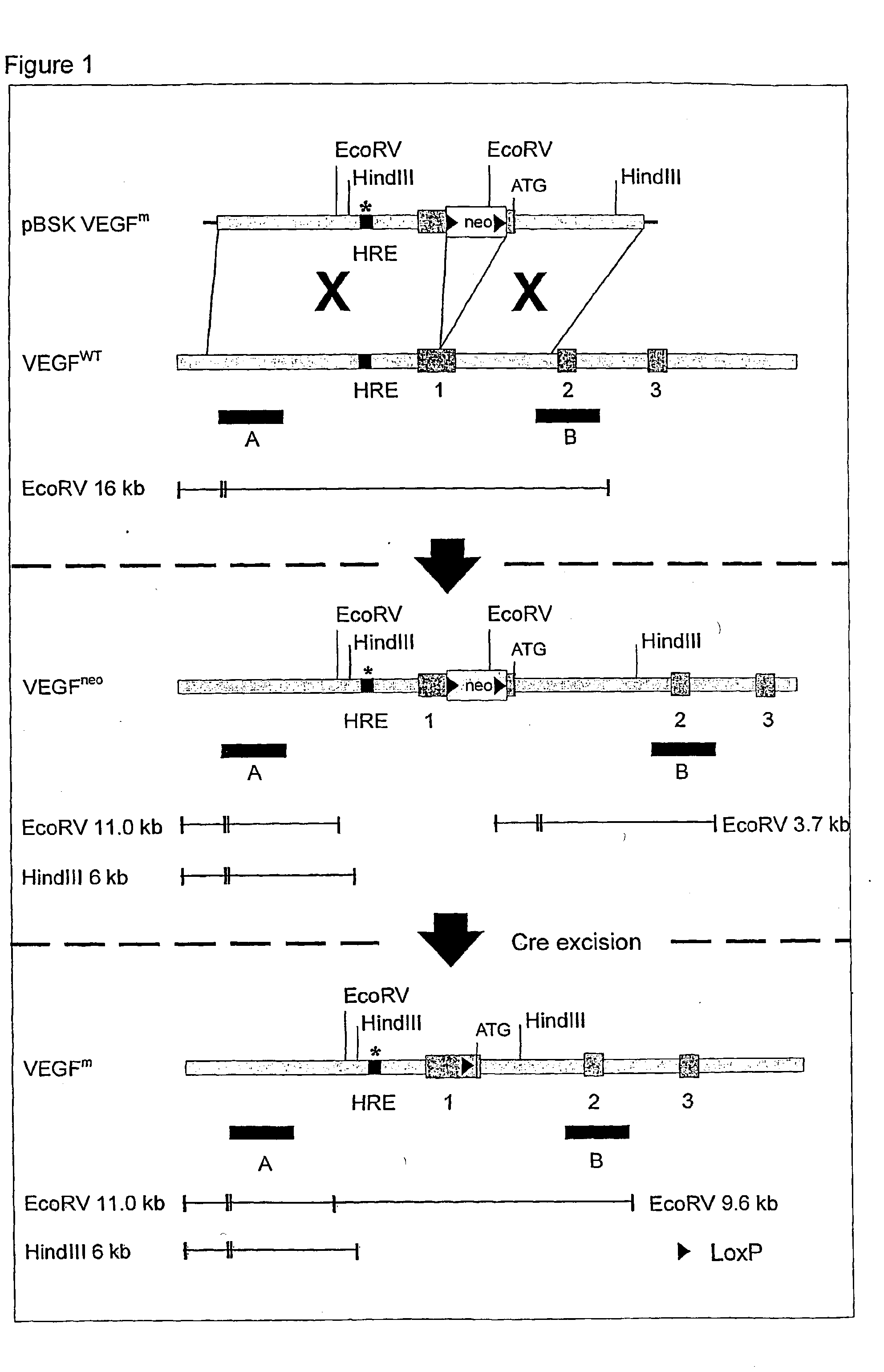
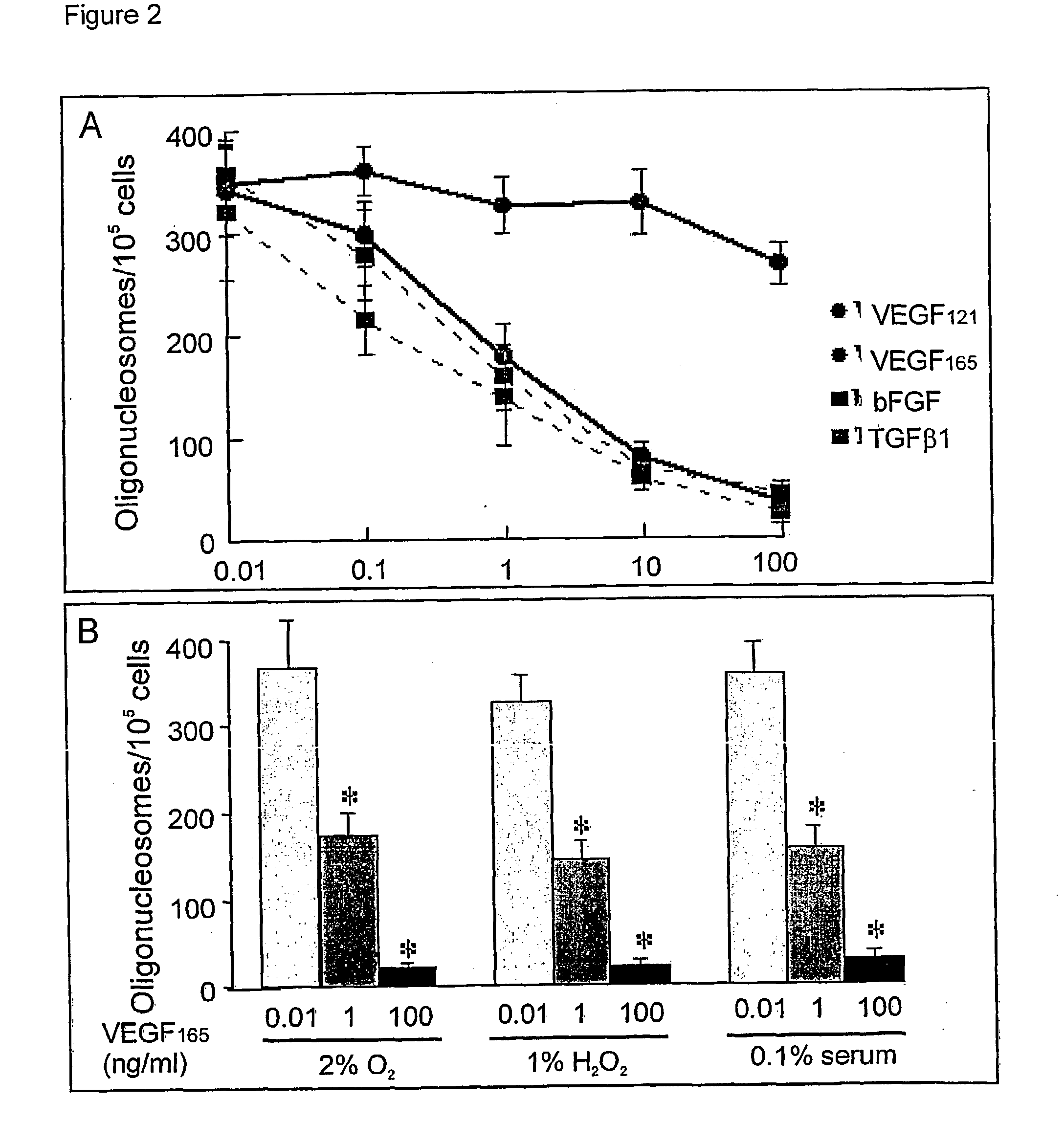
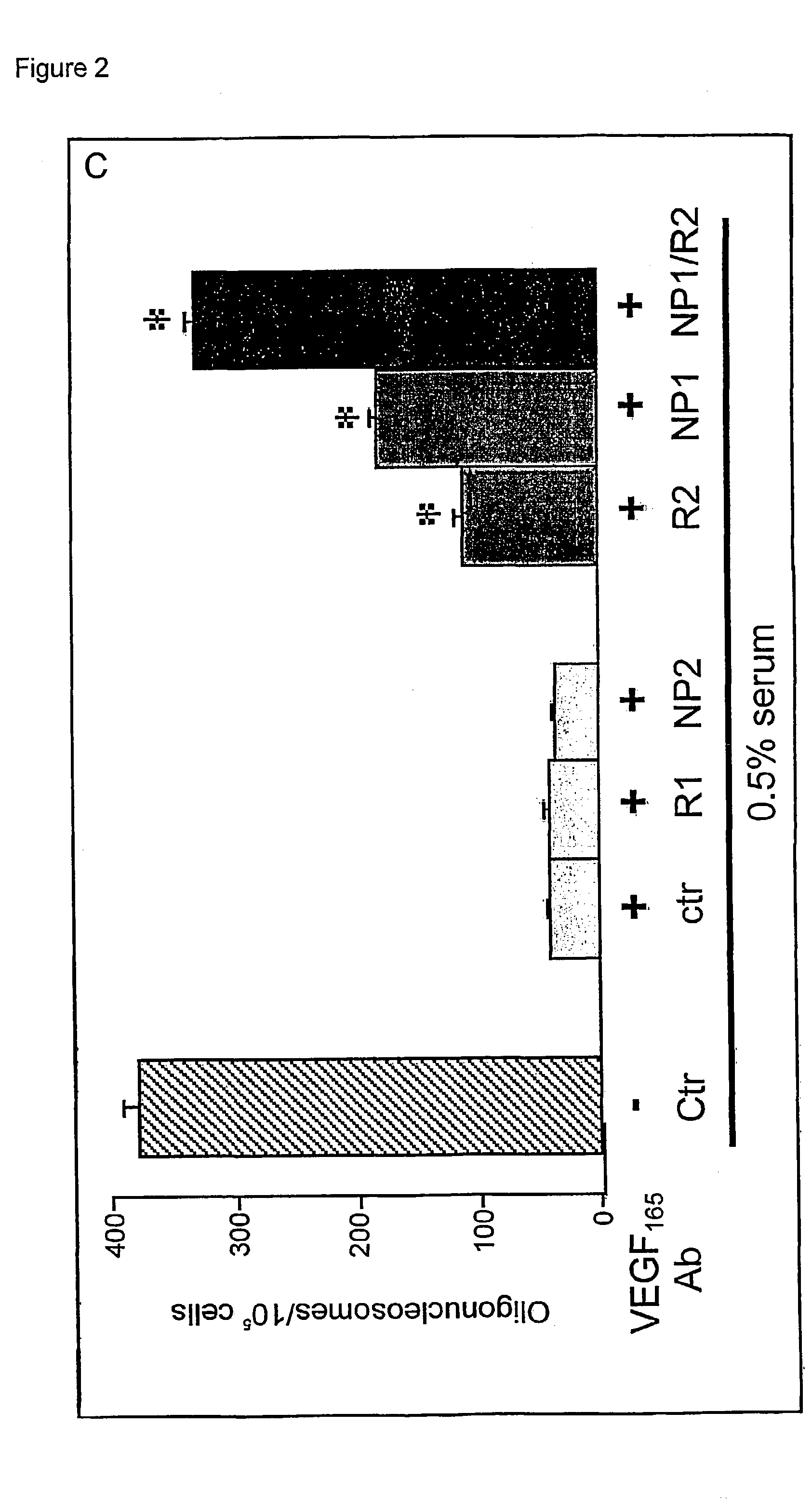
Use of VEGF and homologues to treat neuron disorders
InactiveUS7226908B2Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsTruncal muscle weaknessSurvival of motor neuron
The present invention relates to neurological and physiological dysfunction associated with neuron disorders. In (particular, the invention relates to the involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and homologues in the aetiology of motor neuron disorders. The invention further concerns a novel, mutant transgenic mouse (VEGFm / m) with a homozygous deletion in the hypoxia responsive element (HRE) of the VEGF promoter which alters the hypoxic upregulation of VEGF. These mice suffer severe adult onset muscle weakness due to progressive spinal motor neuron degeneration which is reminiscent of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)—a fatal disorder with unknown aetiology. Furthermore, the neuropathy of these mice is not caused by vascular defects, but is due to defective VEGF-mediated survival signals to motor neurons. The present invention relates in particular to the isoform VEGF165 which stimulates survival of motor neurons via binding to neuropilin-1, a receptor known to bind semaphorin-3A which is implicated in axon retraction and neuronal death, and the VEGF Receptor-2. The present invention thus relates to the usage of VEGF, in particular VEGF165, for the treatment of neuron disorders and relates, in addition, to the usage of polymorphisms in the VEGF promotor for diagnosing the latter disorders.
Owner:LIFE SCI RES PARTNERS VZW +1
Medicinal compositions improving brain function and method for improving brain function
An alkyl ether derivative represented by the formula:wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, m and n are as defined in the specification, or salts thereof exhibits synergistically improved anti-hypoxic activity when combined with a compound having an acetylcholine esterase inhibitory activity. Therefore, the combination according to the present invention is useful as a method for improving cerebral function. Further, a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound relating to the combination according to the present invention is useful for treatment and prevention of dysfunction of cerebral acetylcholine neurons in the sequelae of cerebrovascular dementia, senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease and ischemic cerebral lesion and in the cerebral apoplexy or the memory impairment caused by selective neuronal death.
Owner:TOYAMA CHEM CO LTD
Use of vegf and homologues to treat neuron disorders
InactiveUS20030105018A1Impaired hypoxic upregulationDeterioration progressNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsTruncal muscle weaknessSurvival of motor neuron
The present invention relates to neurological and physiological dysfunction associated with neuron disorders. In (particular, the invention relates to the involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and homologues in the aetiology of motor neuron disorders. The invention further concerns a novel, mutant transgenic mouse (VEGFm / m) with a homozygous deletion in the hypoxia responsive element (HRE) of the VEGF promoter which alters the hypoxic upregulation of VEGF. These mice suffer severe adult onset muscle weakness due to progressive spinal motor neuron degeneration which is reminiscent of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-a fatal disorder with unknown aetiology. Furthermore, the neuropathy of these mice is not caused by vascular defects, but is due to defective VEGF-mediated survival signals to motor neurons. The present invention relates in particular to the isoform VEGF165 which stimulates survival of motor neurons via binding to neuropilin-1, a receptor known to bind semaphorin-3A which is implicated in axon retraction and neuronal death, and the VEGF Receptor-2. The present invention thus relates to the usage of VEGF, in particular VEGF165, for the treatment of neuron disorders and relates, in addition, to the usage of polymorphisms in the VEGF promotor for diagnosing the latter disorders.
Owner:LIFE SCI RES PARTNERS VZW +1
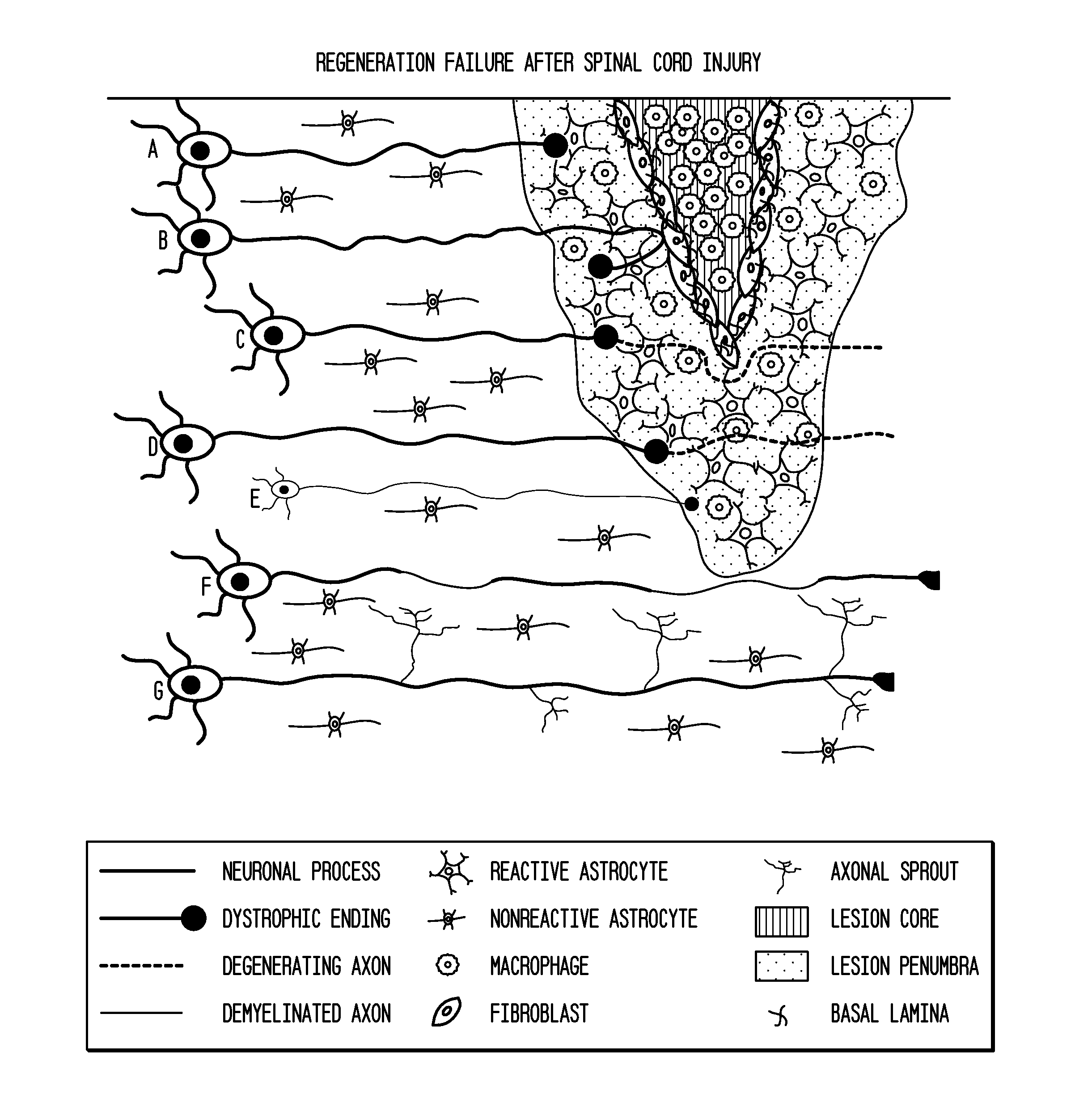
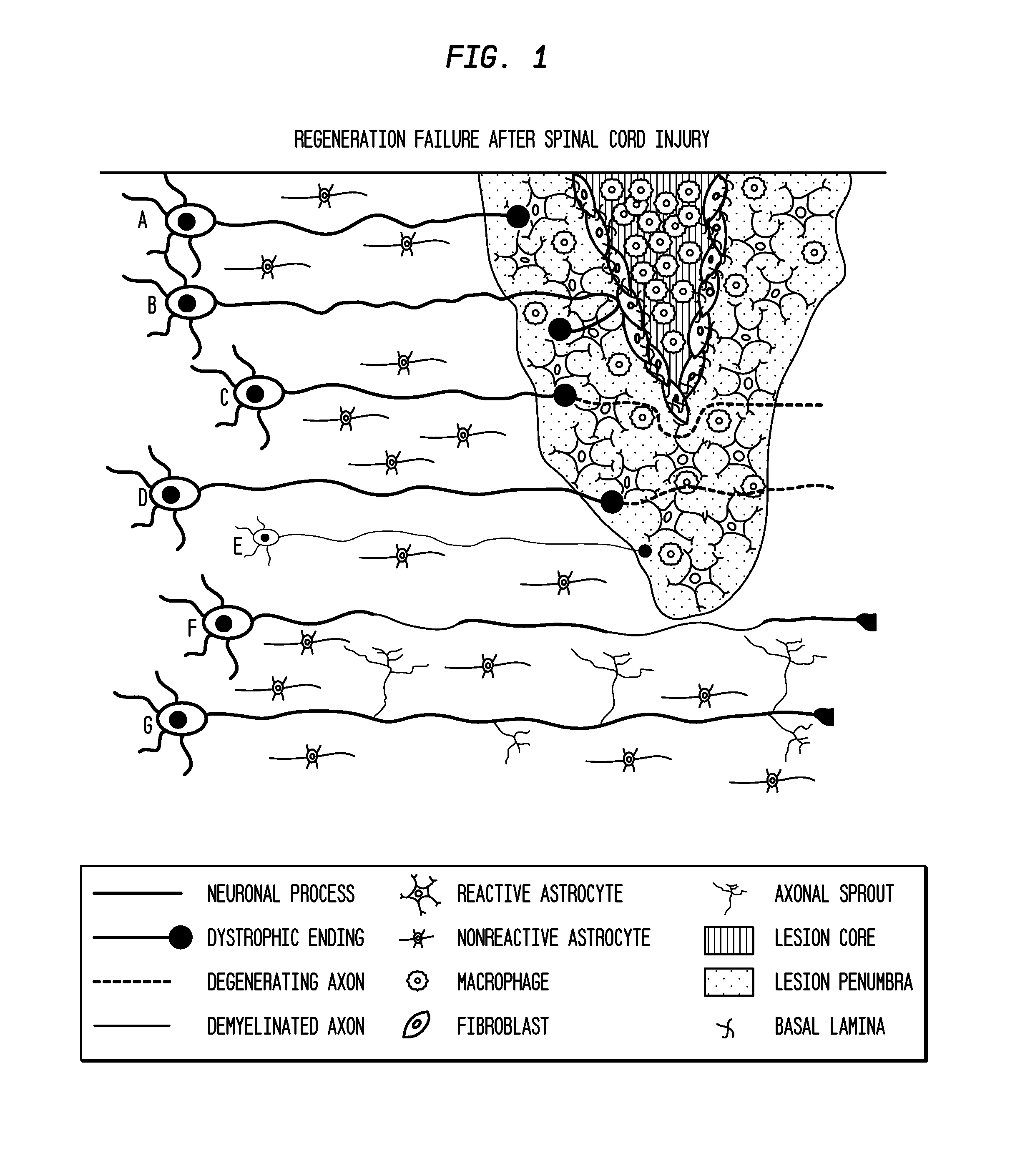
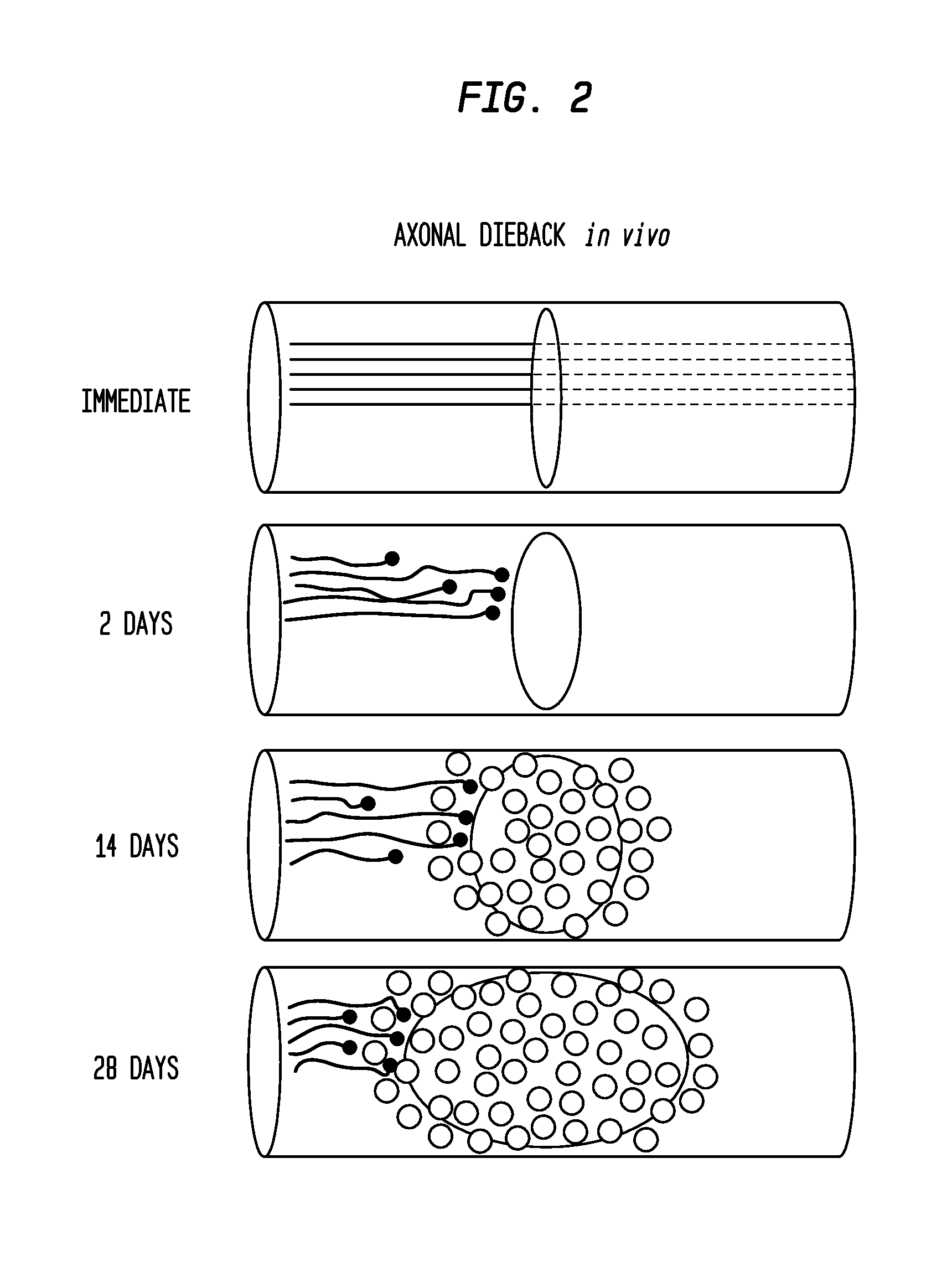
Use of Stem Cells to Prevent Neuronal Dieback
PendingUS20110293578A1Reduce retractionReduce harmBiocideNervous disorderNervous systemNeuronal damage
The invention is generally directed to treatment of neuronal injury. In particular, the invention is directed to reducing axonal retraction (“dieback”) that occurs as a result of the interaction of activated macrophages with dystrophic axons that are produced during nervous system acute or chronic injury. The invention is also directed to promoting axonal growth / regeneration. The invention is specifically directed to using stem cells or their secreted cellular factors, such as would be produced in conditioned cell culture medium, to ameliorate or prevent axonal dieback and / or promote growth / regeneration of axons.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY +1
Use of GSK3 inhibitors in combination with radiation therapies
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
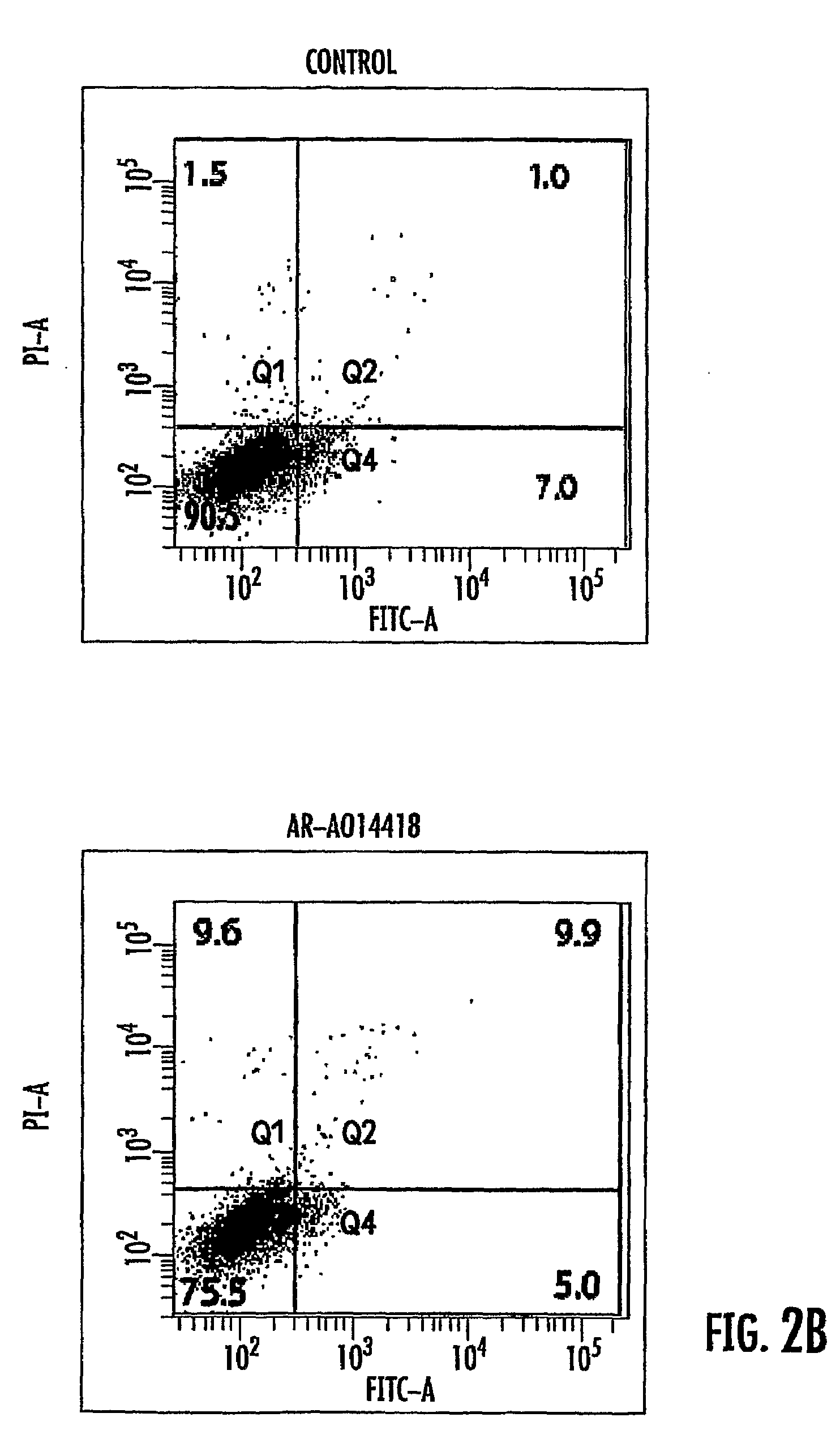
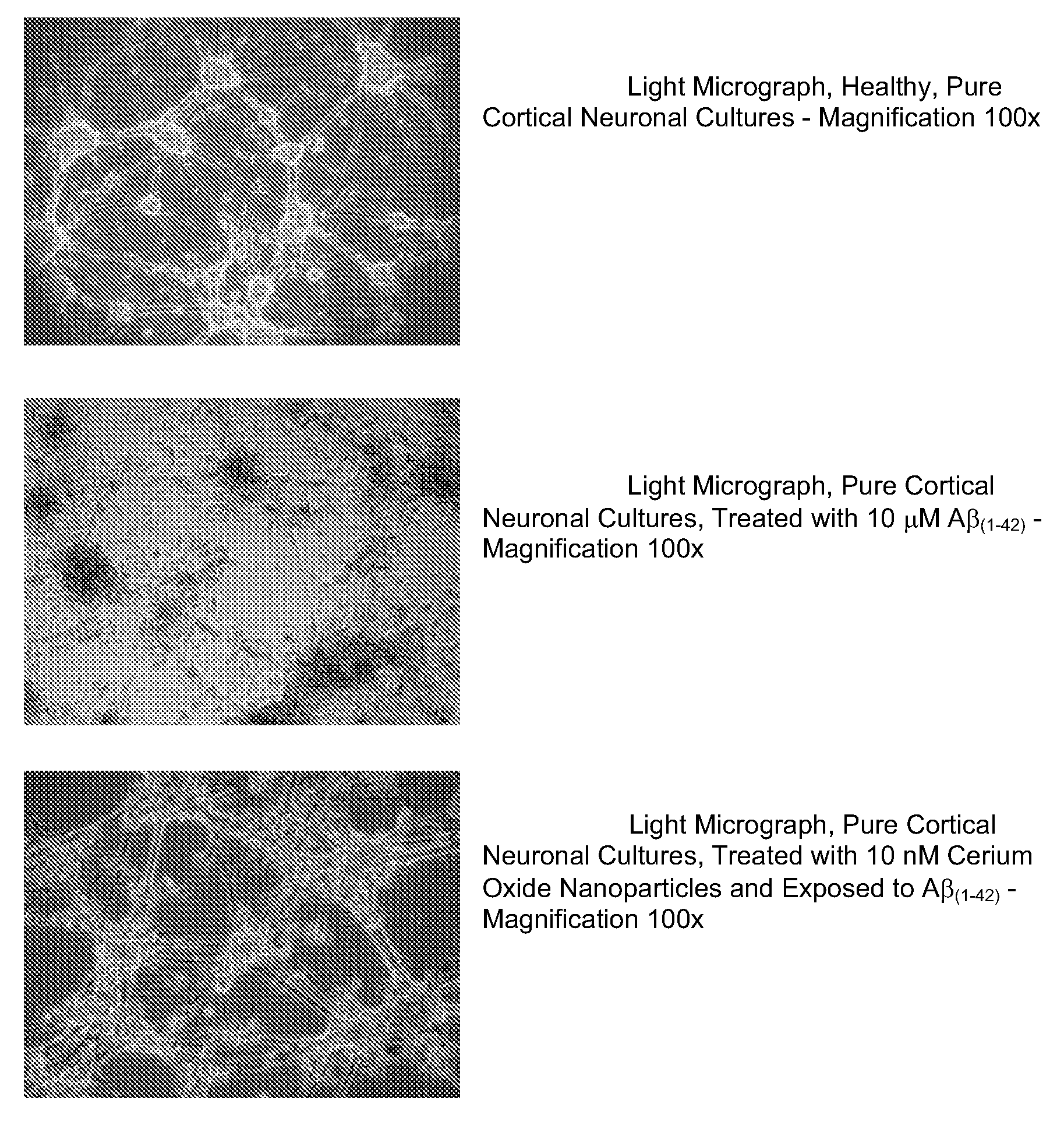
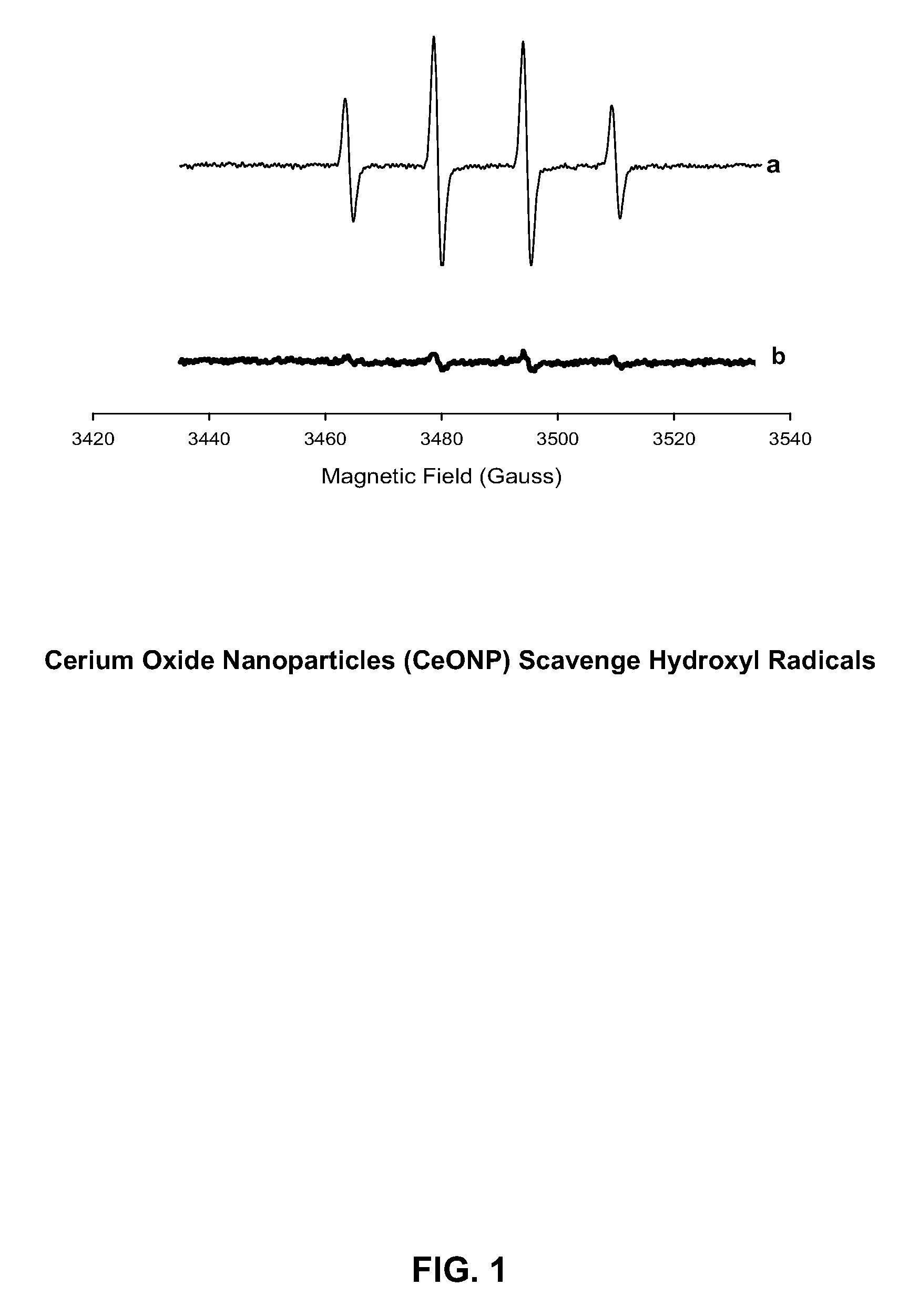
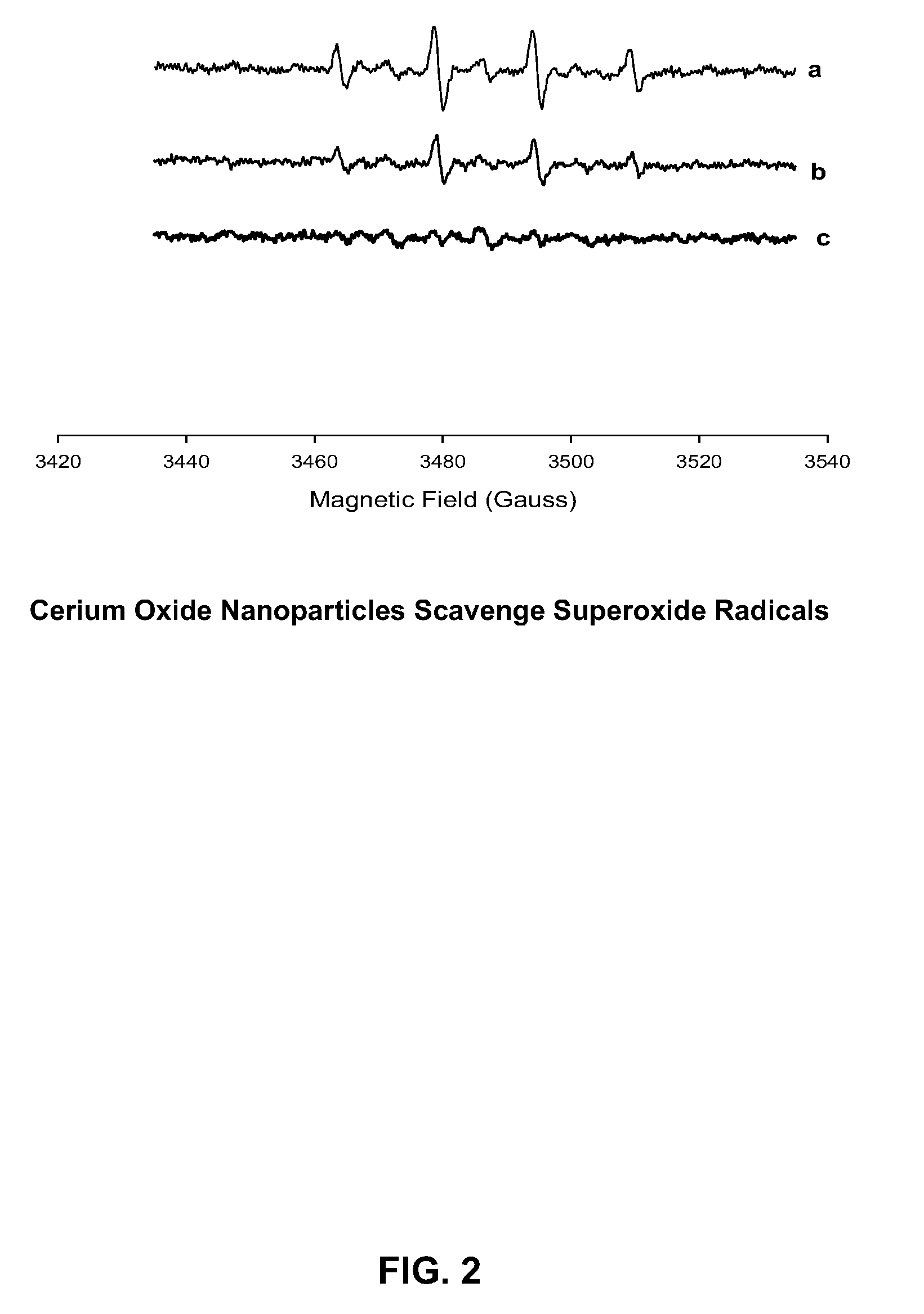
Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles for Treatment and Prevention of Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, and Disorders Associated with Free Radical Production and/or Mitochondrial Dysfunction
ActiveUS20090092671A1Reduce lossesDeter and prevent dopaminergic neuronal lossPowder deliveryBiocideMitochondrial diseaseLipid peroxidation
Cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeONP) can be used to treat or prevent neurodegenerative diseases, including for example Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, Huntington's Disease, AIDS-related dementia, ALS, progressive supranuclear palsy, and encephalitis, as well as mitochondrial diseases and diseases associated with mitochondrial damage. In particular, CeONP having an average size of about 2 nm to about 100 nm can be administered in an amount sufficient to block production of hydroxyl or superoxide radicals, block free radical production by Aβ(1-42), block Aβ(1-42)-induced neuronal death, block Aβ(1-42)-induced [Ca2+]i dysfunction in neurons, block Aβ(1-42)-induced lipid peroxidation, decrease loss of dopaminergic neurotransmission, or reduce mitochondrial dysfunction in a cell. CeONP can also be effective in treating conditions involving toxic exposures to compounds that induce mitochondrial dysfunction, such as rotenone, cyanide, carbon monoxide, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and other mitochondrial toxins.
Owner:EDWARD VIA VIRGINIA COLLEGE OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE
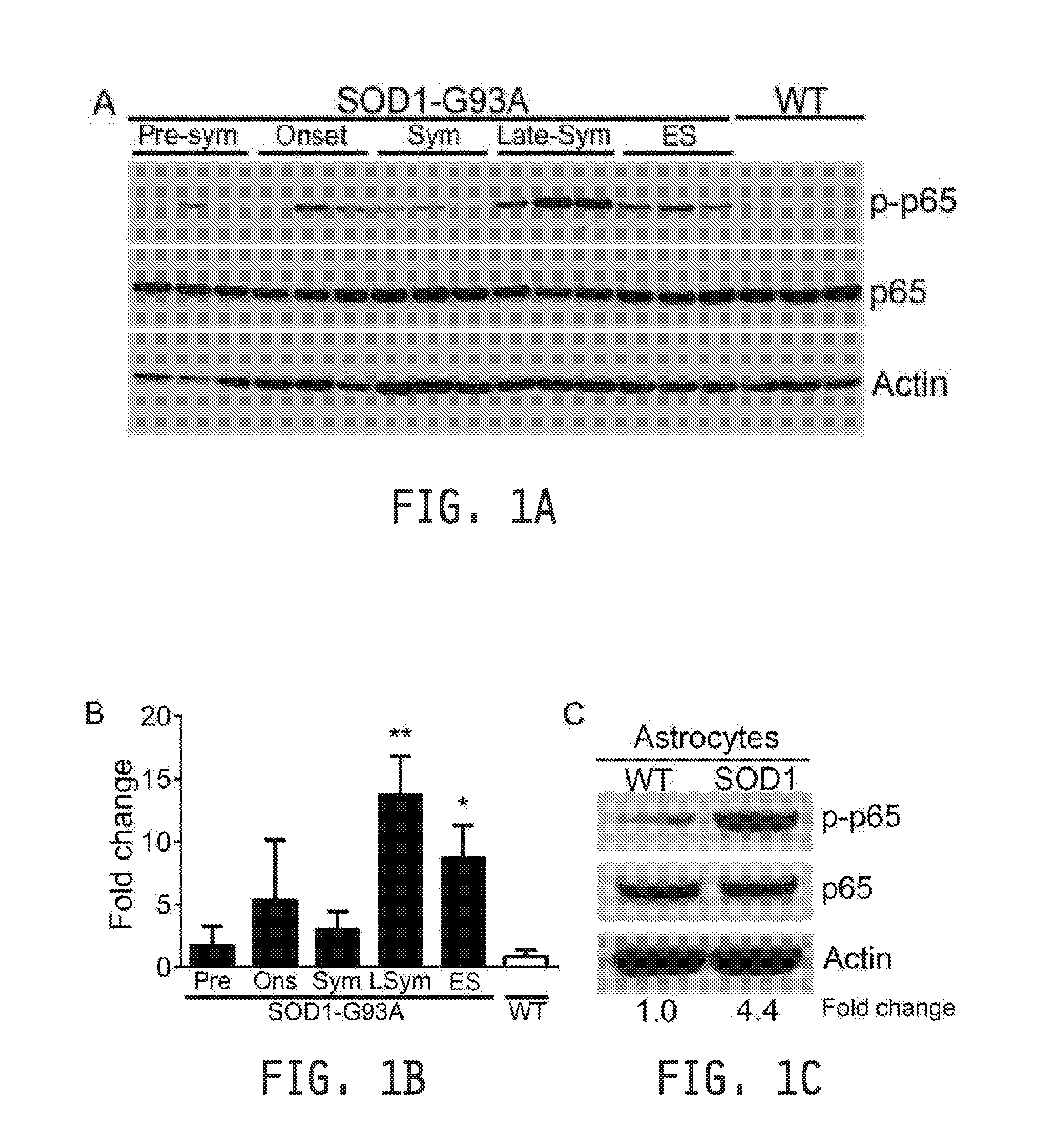
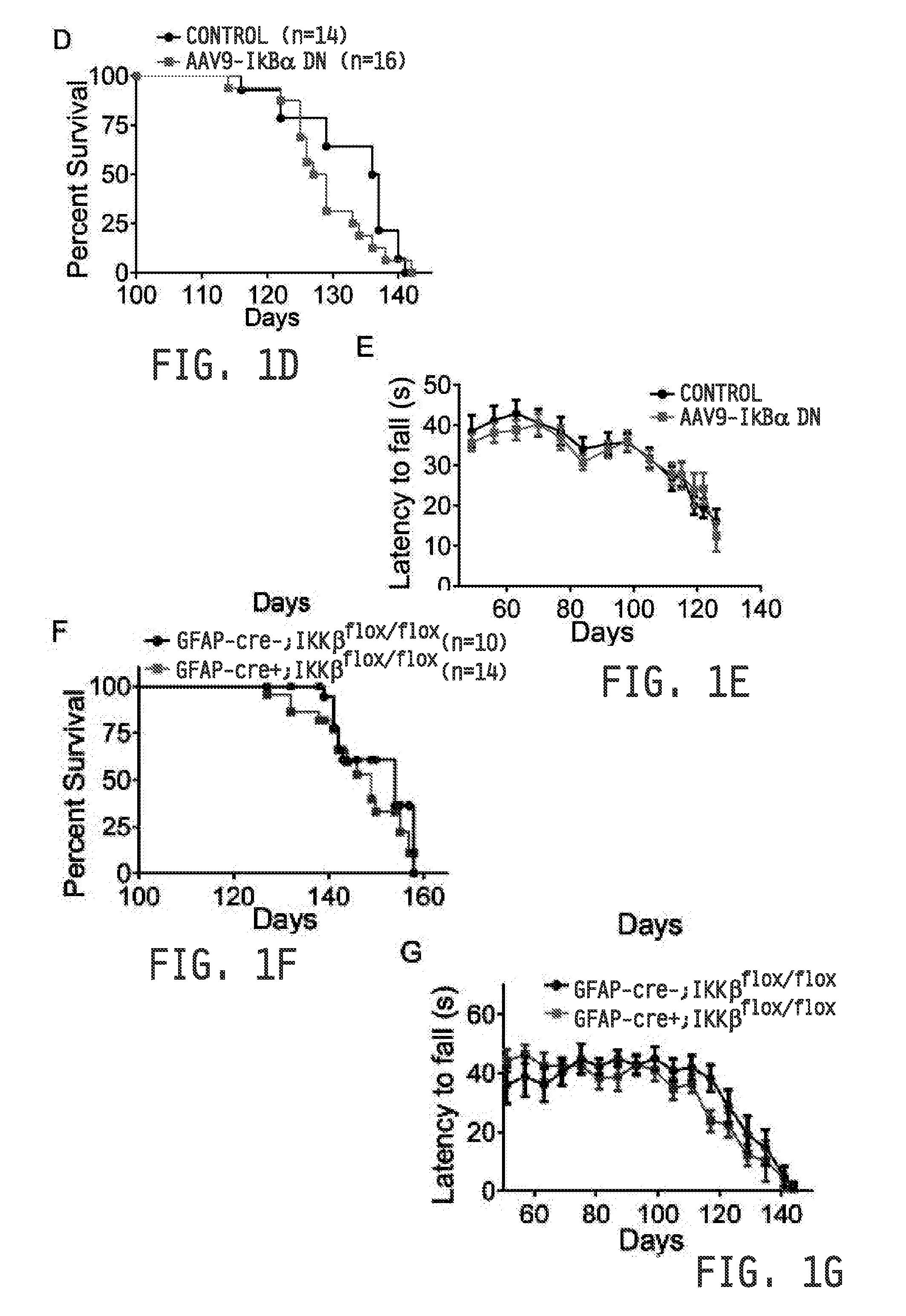
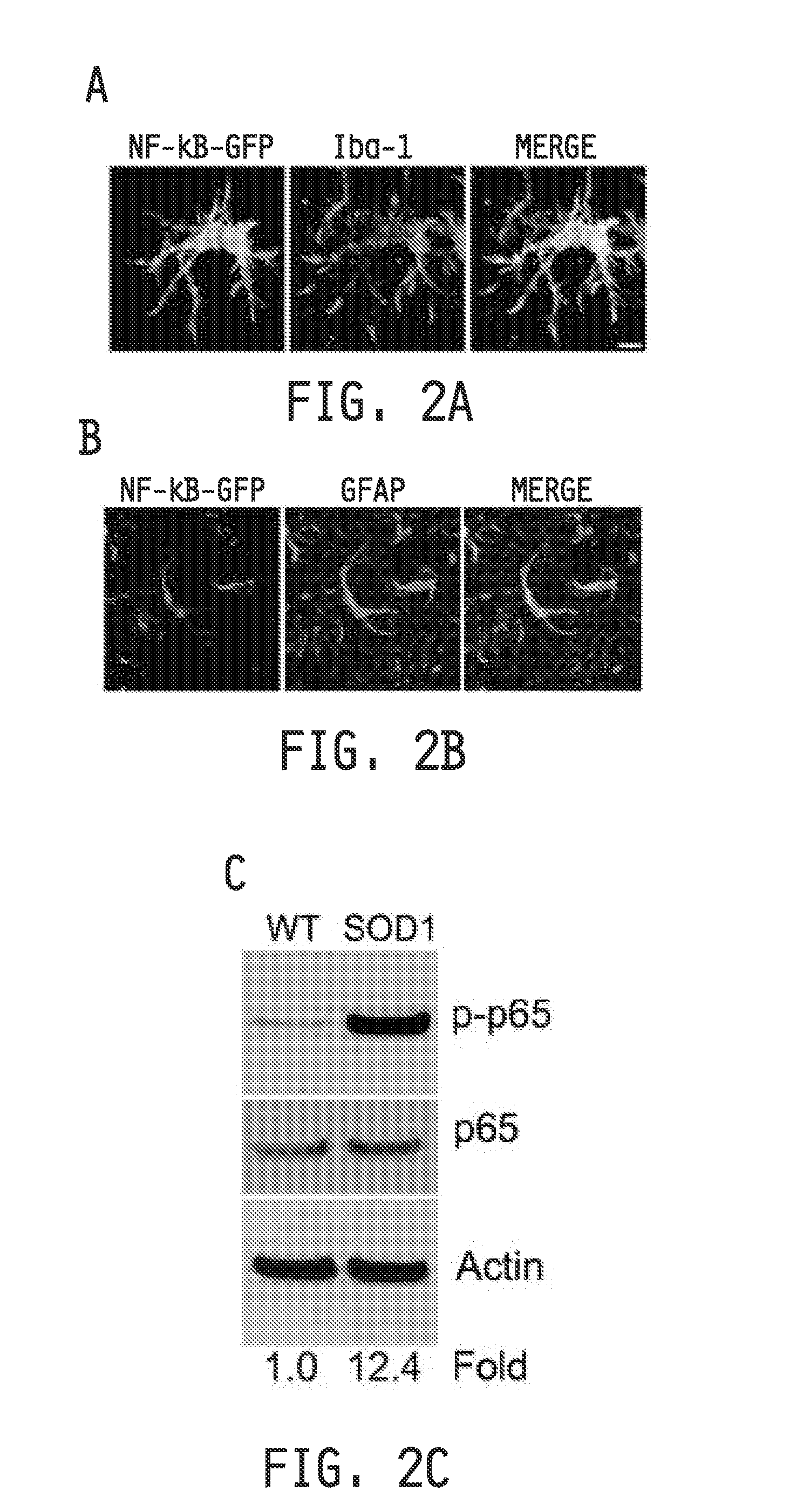
COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR INHIBITING NF- kB AND SOD-1 TO TREAT AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS
ActiveUS20160289676A1Improve survivalRelieve symptomsNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsAmyotrophic lateral sclerosisMedicine
The invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions, kits, methods, and uses for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In particular, the invention relates to compositions, kits, methods, and uses for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by inhibiting NF-κB in microglia or macrophages and by inhibiting motor neuron death. The invention further relates to compositions, kits, methods, and uses for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by inhibiting NF-κB in microglia in combination with inhibiting SOD-1 in astrocytes. The invention also relates to a method for inhibiting the expression or the activity of NF-κB in microglia or macrophages to inhibit motor neuron death, alone or in combination with inhibiting SOD-1 expression in astrocytes.
Owner:RES INST AT NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Medicinal compositions improving brain function and method for improving brian function
An alkyl ether derivative represented by the formula: wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, m and n are as defined in the specification, or salts thereof exhibits synergistically improved anti-hypoxic activity when combined with a compound having an acetylcholine esterase inhibitory activity. Therefore, the combination according to the present invention is useful as a method for improving cerebral function. Further, a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound relating to the combination according to the present invention is useful for treatment and prevention of dysfunction of cerebral acetylcholine neurons in the sequelae of cerebrovascular dementia, senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease and ischemic cerebral lesion and in the cerebral apoplexy or the memory impairment caused by selective neuronal death.
Owner:TOYAMA CHEM CO LTD
Compounds and compositions for treating neuronal death or neurological dysfunction
The present invention relates to 2-hydroxy-alkylamino-benzoic acid derivatives and to a combination of cell necrosis inhibitor and lithium, process for the preparation of the derivatives or the combination, pharmaceutical formulation containing the derivatives or the combination, and use of the derivatives or the combination by either concomitant or sequential administration for improvement of treatment of neuronal death or neurological dysfunction. The derivatives and the combination of the present invention are useful for treating neurological diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Lou Gehrig's disease), spinal muscular atrophy, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, stroke, traumatic brain injury or spinal cord injury; and for treating ocular diseases such as glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy or macular degeneration.
Owner:NEUROTECH PHARMA
Use of Thalidomide for Alzheimers Disease Treatment and Prevention
Owner:SHEN YONG +1
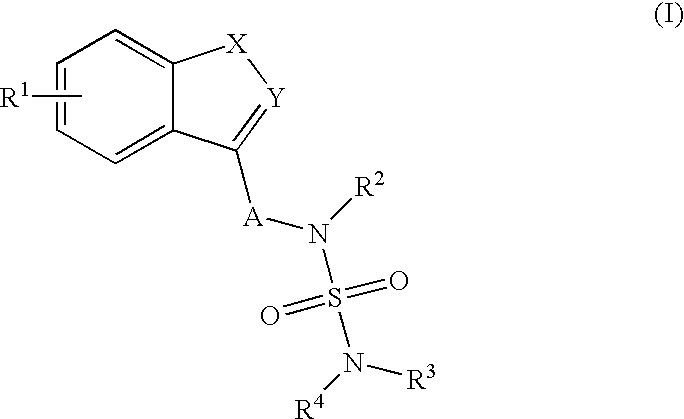
Use of benzo-heteroaryl sulfamide derivatives as neuroprotective agents
The present invention is a methods for neuroprotection, for treating an acute neurodegenerative disorder, for treating a chronic neurodegenerative disorder and / or for preventing neuron death or damage following brain, head and / or spinal cord trauma or injury comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of one or more novel benzo-heteroaryl sulfamide derivatives of formula (I) as herein defined.
Owner:SMITH SWINTOSKY VIRGINIA L
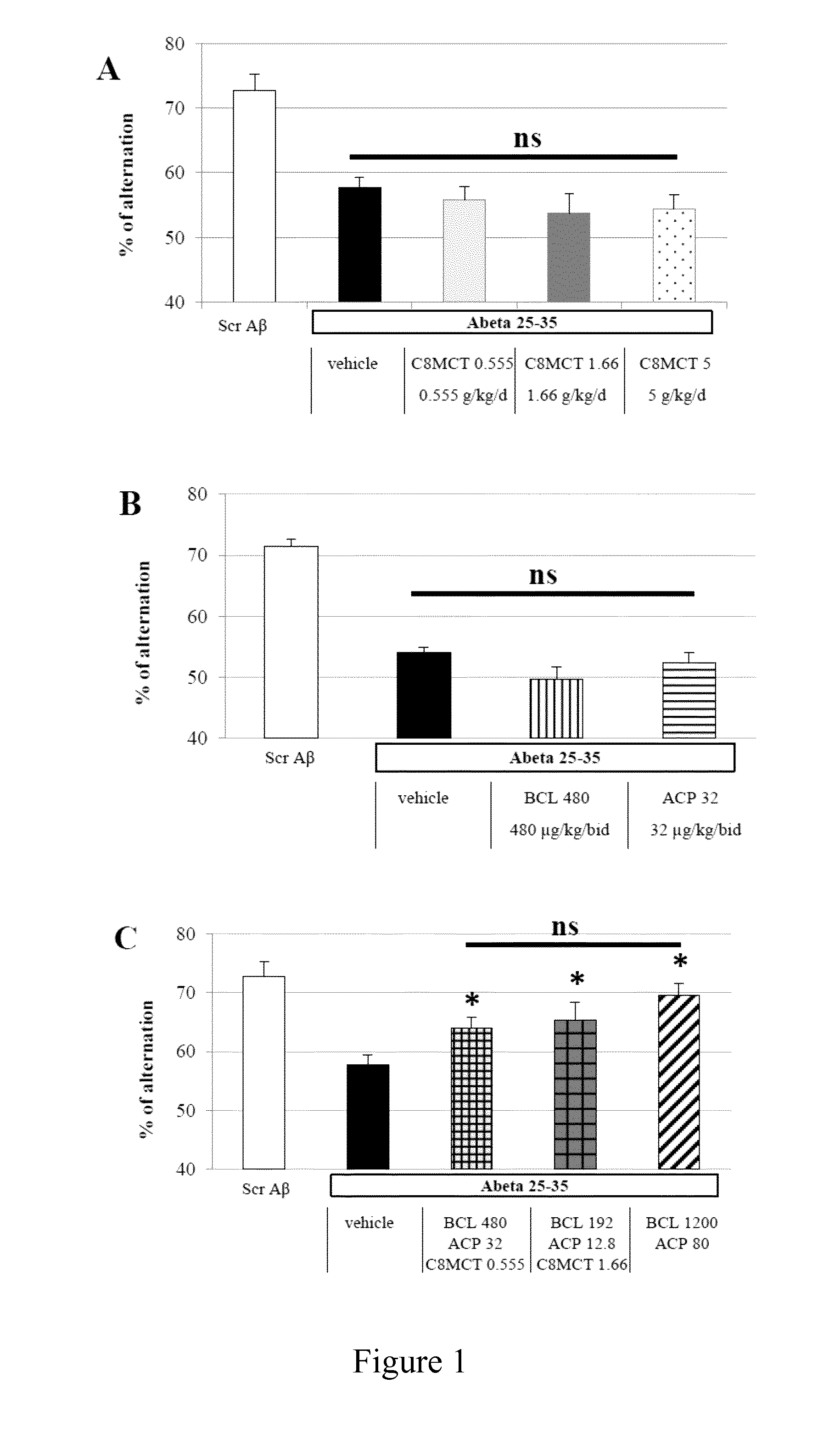
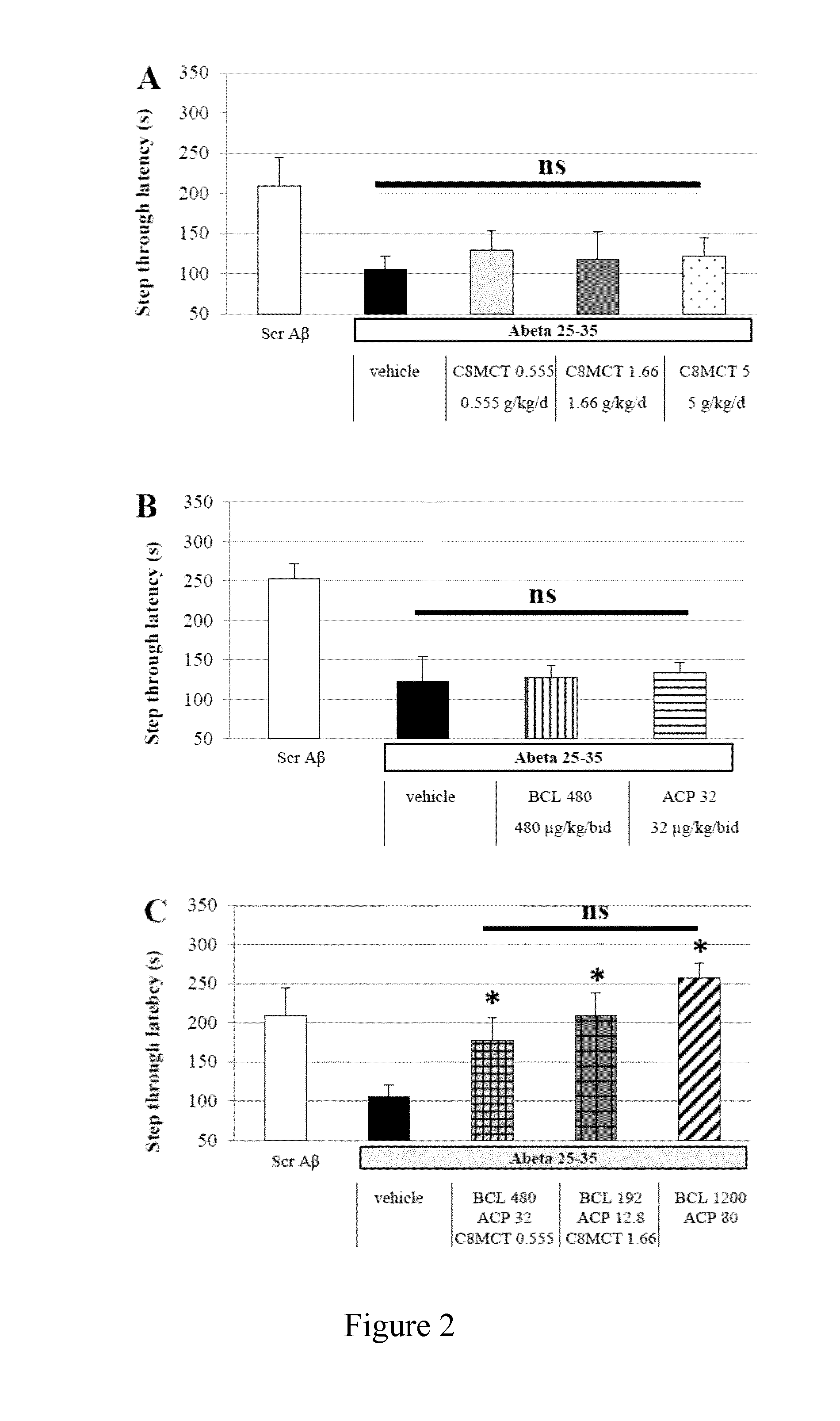
Combination of baclofen, acamprosate and medium chain triglycerides for the treatment of neurological disorders
ActiveUS20160354335A1Improve cognitive functionProtected growthNervous disorderMuscular disorderAlcoholismsHuntingtons chorea
The present invention relates to combinations and methods for the treatment of neurological disorders related Amyloid beta toxicity and / or neuronal death and / or glucose impaired neuronal metabolism. More specifically, the present invention relates to novel combinatorial therapies of Alzheimer's disease, Alzheimer's disease related disorders, frontotemporal dementia, Parkinson's disease, Lewy body dementia, Huntington's disease, peripheral neuropathies, alcoholism or alcohol withdrawal, neurological manifestations of drug abuse or drug abuse withdrawal, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, epilepsy, traumatic brain injury or brain ischemic events based on baclofen, acamprosate and at least one medium chain triglyceride.
Owner:PHARNEXT
Agents for treating neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20070027164A1Prevent neuronal deathInhibit caspase cleavageBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementHuntingtons choreaMedicine
The present invention relates to compounds effective in preventing neuronal cell death, which may be used in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that particular compounds were effective in preventing neuronal death in model systems of Huntington's Disease.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Neurodegenerative disease treatment using jak/stat inhibition
InactiveUS20150157597A1Alleviates HIV-associated dementiaEasily damagedBiocideNervous disorderCell cycleCell signaling
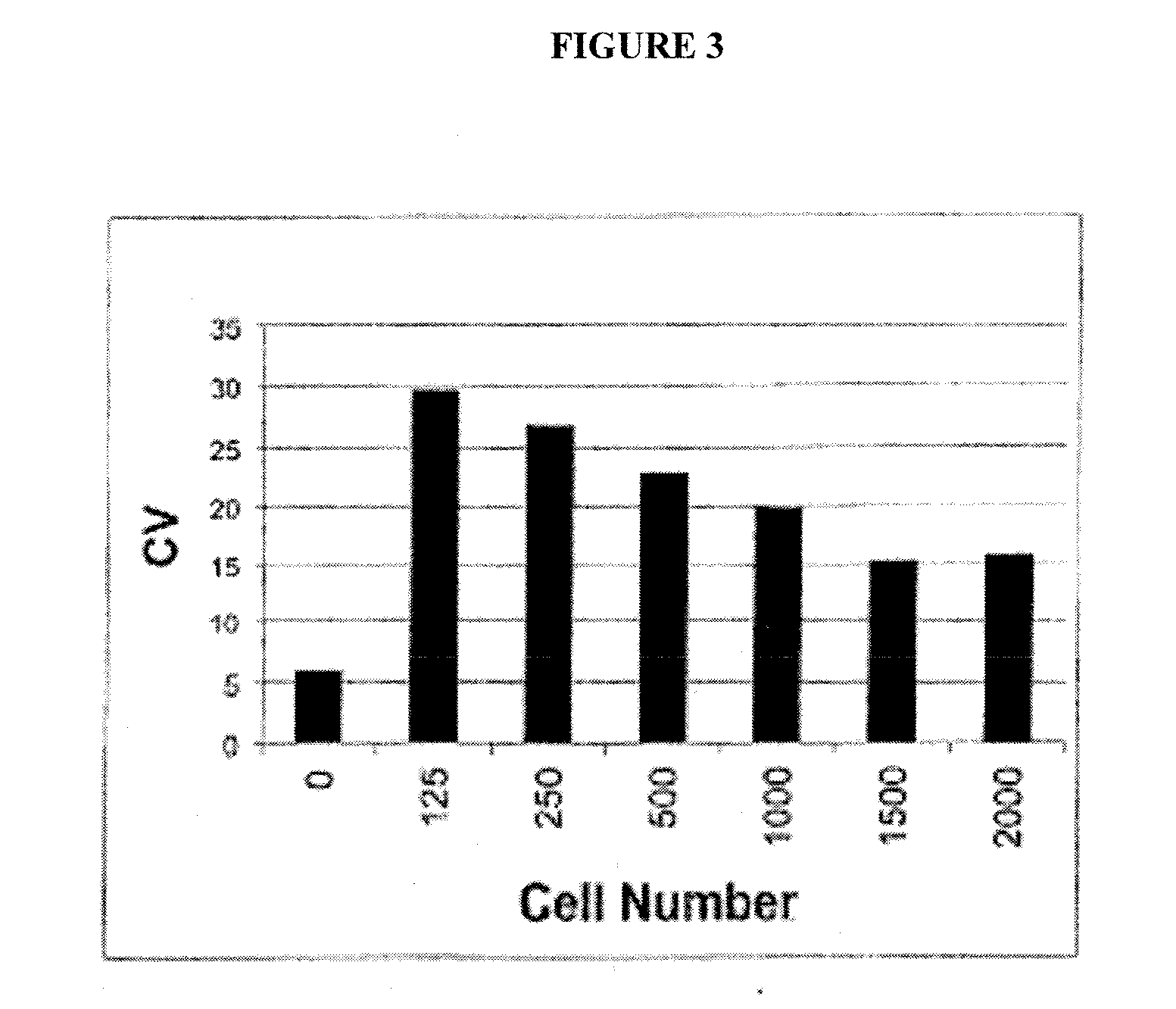
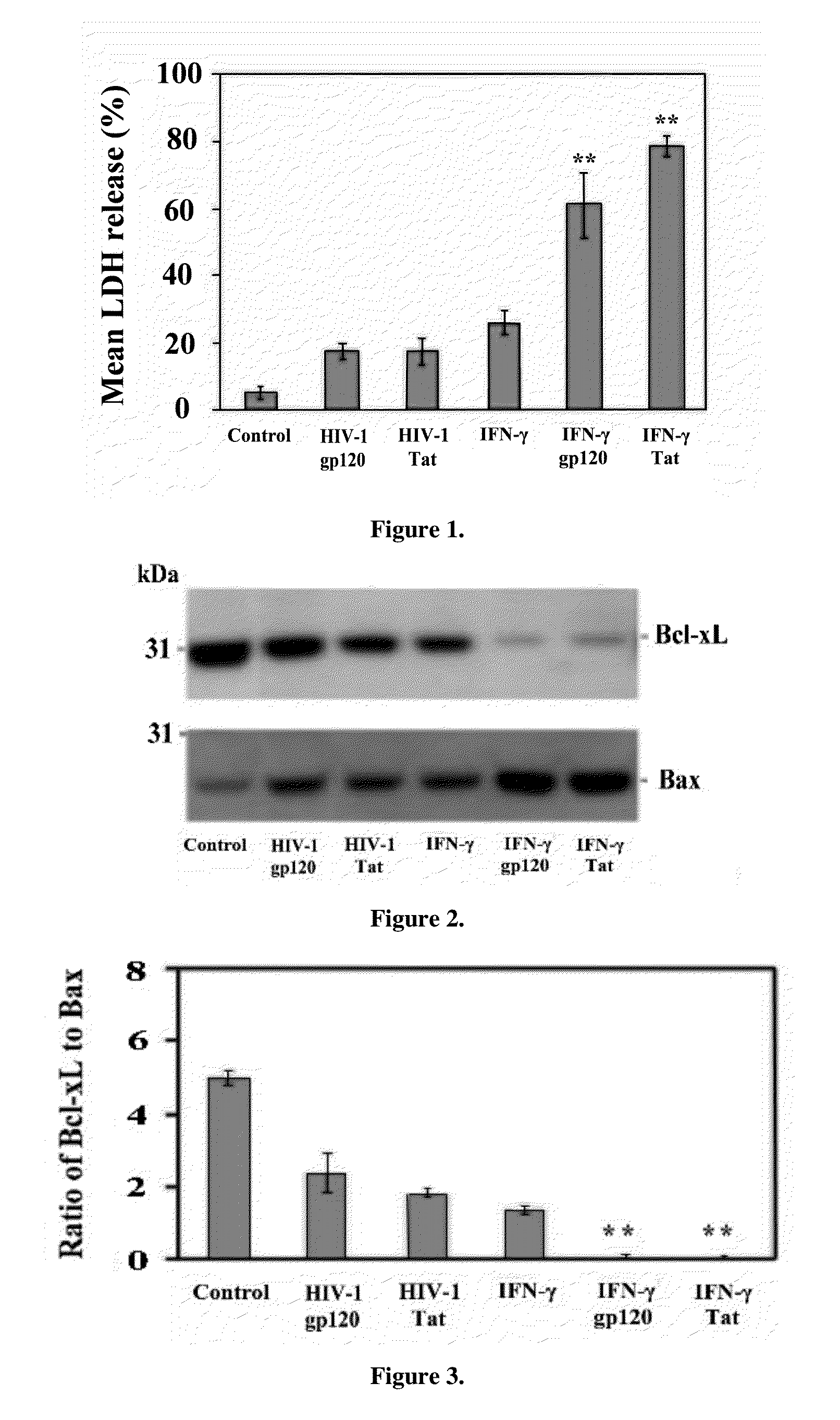
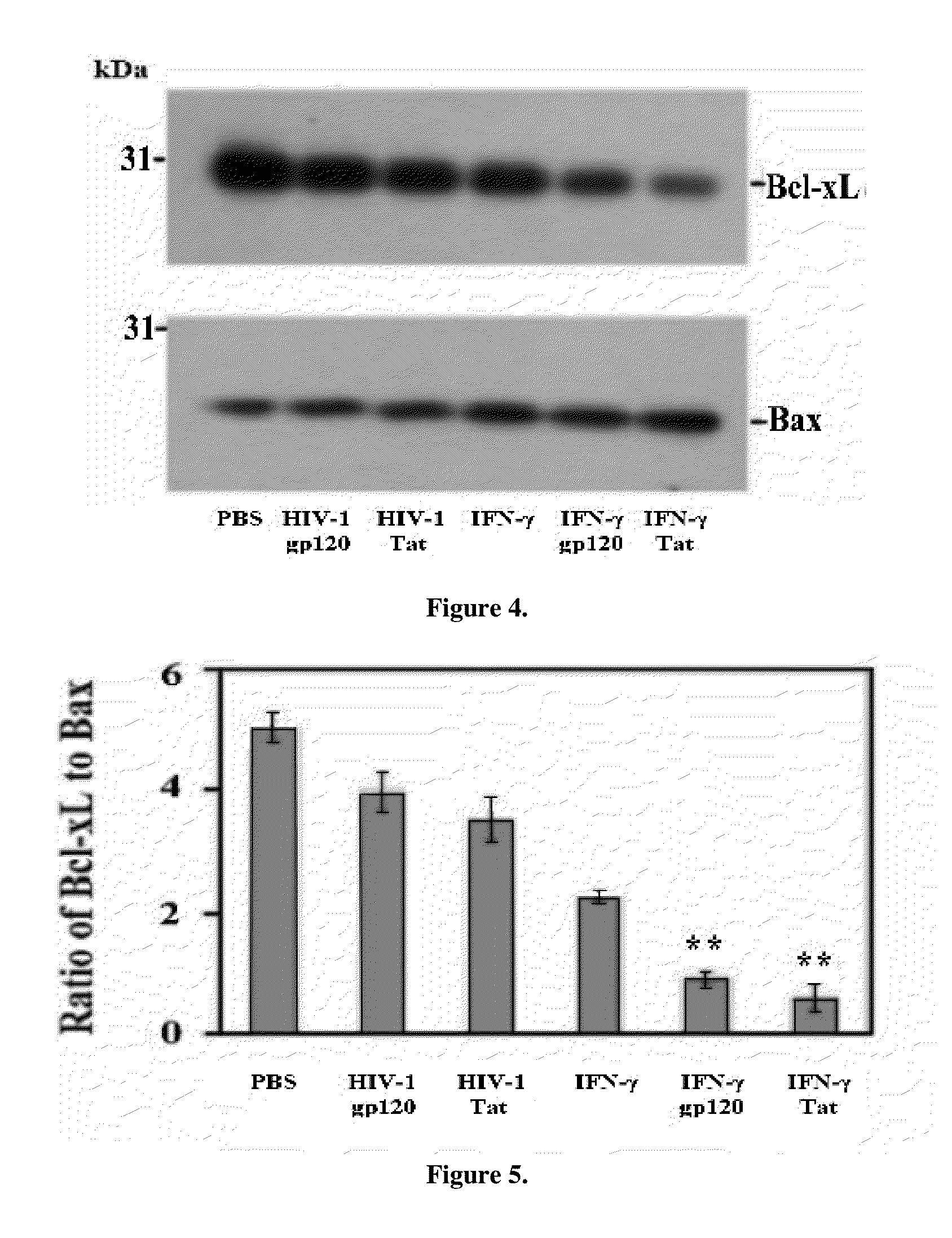
The invention relates to treatment of neurodegenerative diseases with JAK / STAT pathway inhibitors to eliminate extracellular cell signaling events leading to cell cycle abrogation and / or apoptosis. Primary neurons were administered neurotoxic proteins, such as gp120, Tat, or gp120 and Tat, with or without IFN-γ added, resulting in neuronal death, and simulated neurodegenerative diseases. The neurodegenerative disease is treated using a JAK / STAT pathway inhibitor, including (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), to modulate JAK1 or STAT1 phosphorylation, resulting in resistance to gp120 or Tat neurotoxicity. The invention may be used to treat neurons afflicted with HIV-associated Dementia, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or Pick's Disease, and may act in conjunction with antiviral treatment, like HAART.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com