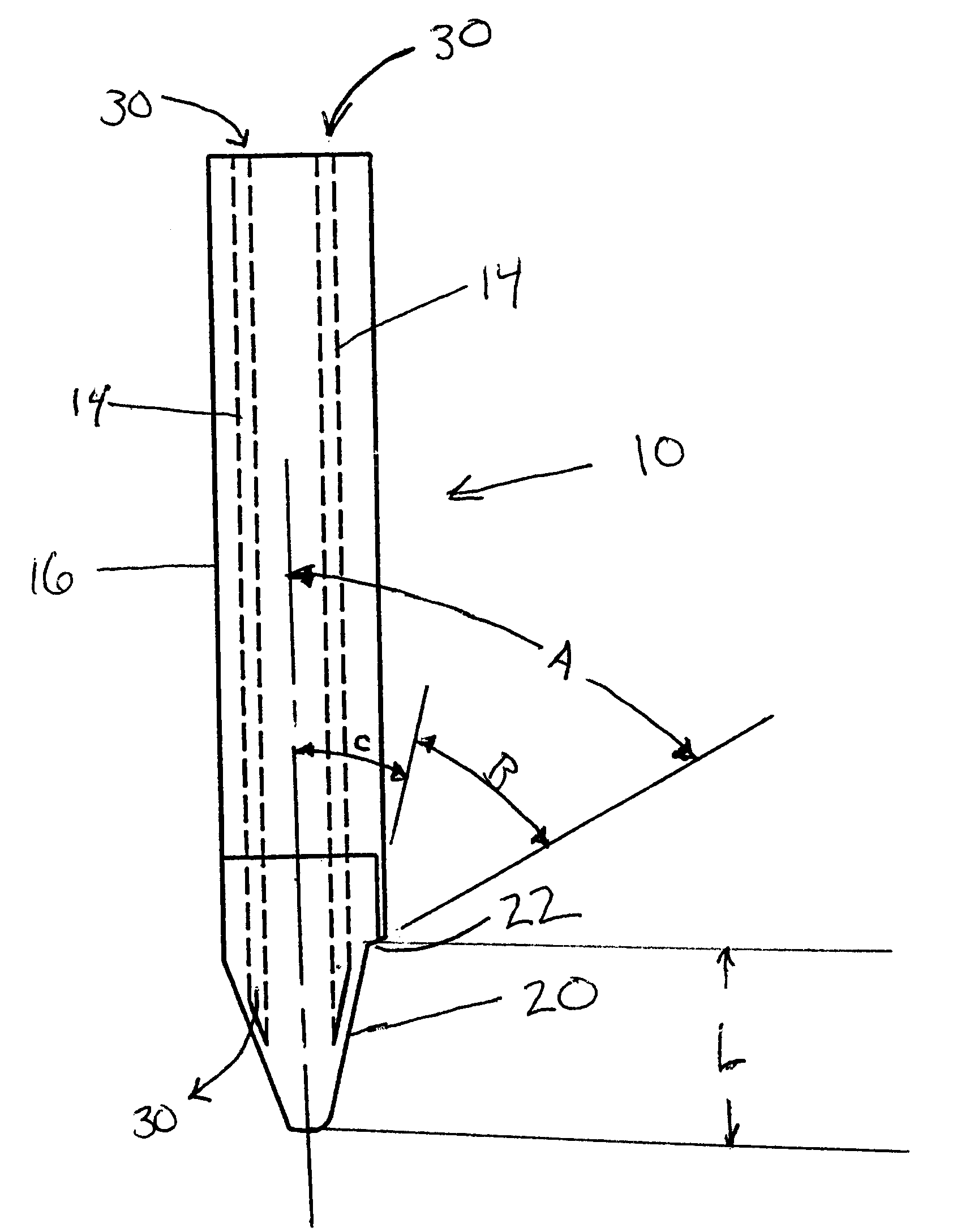
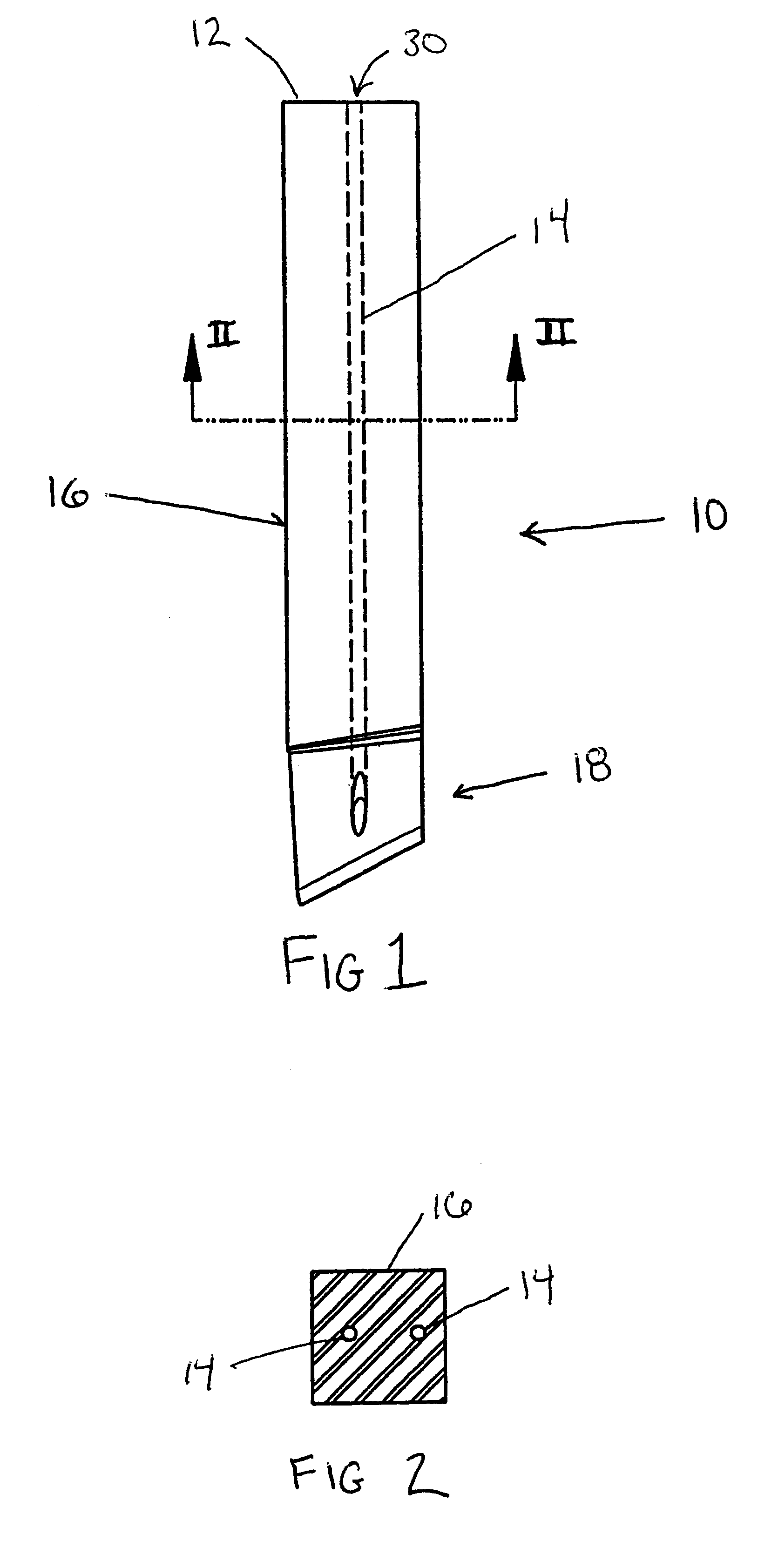
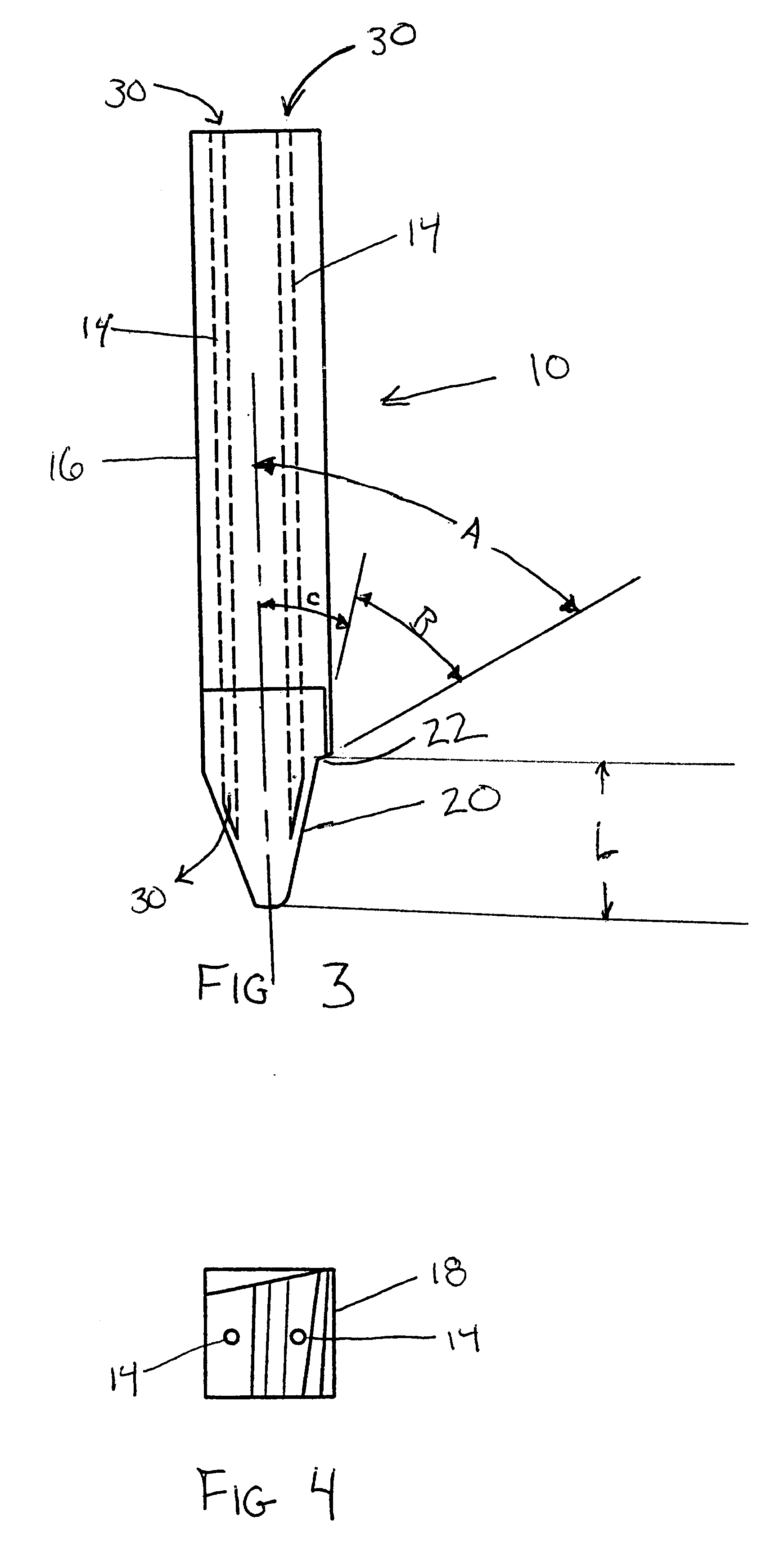
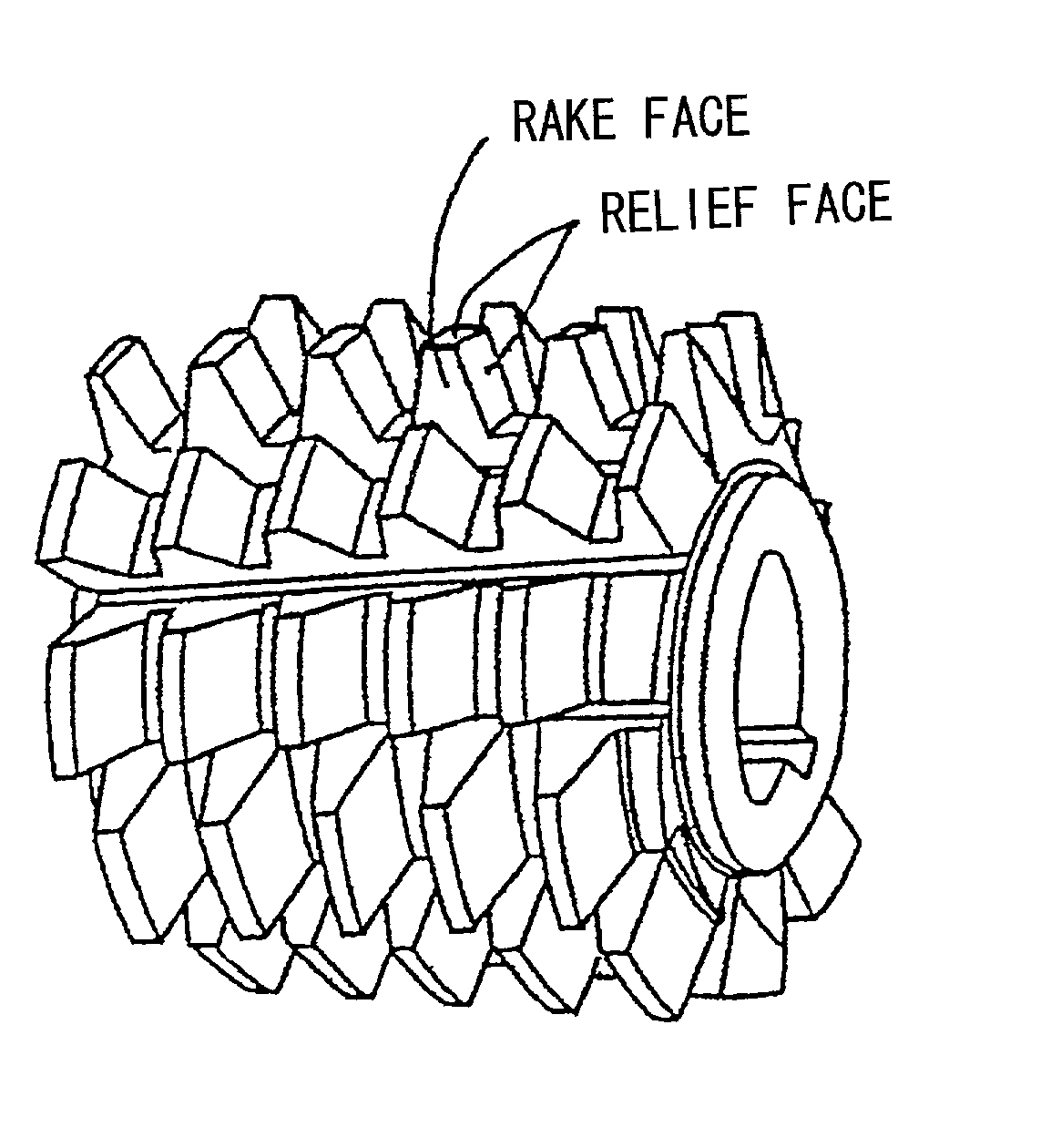
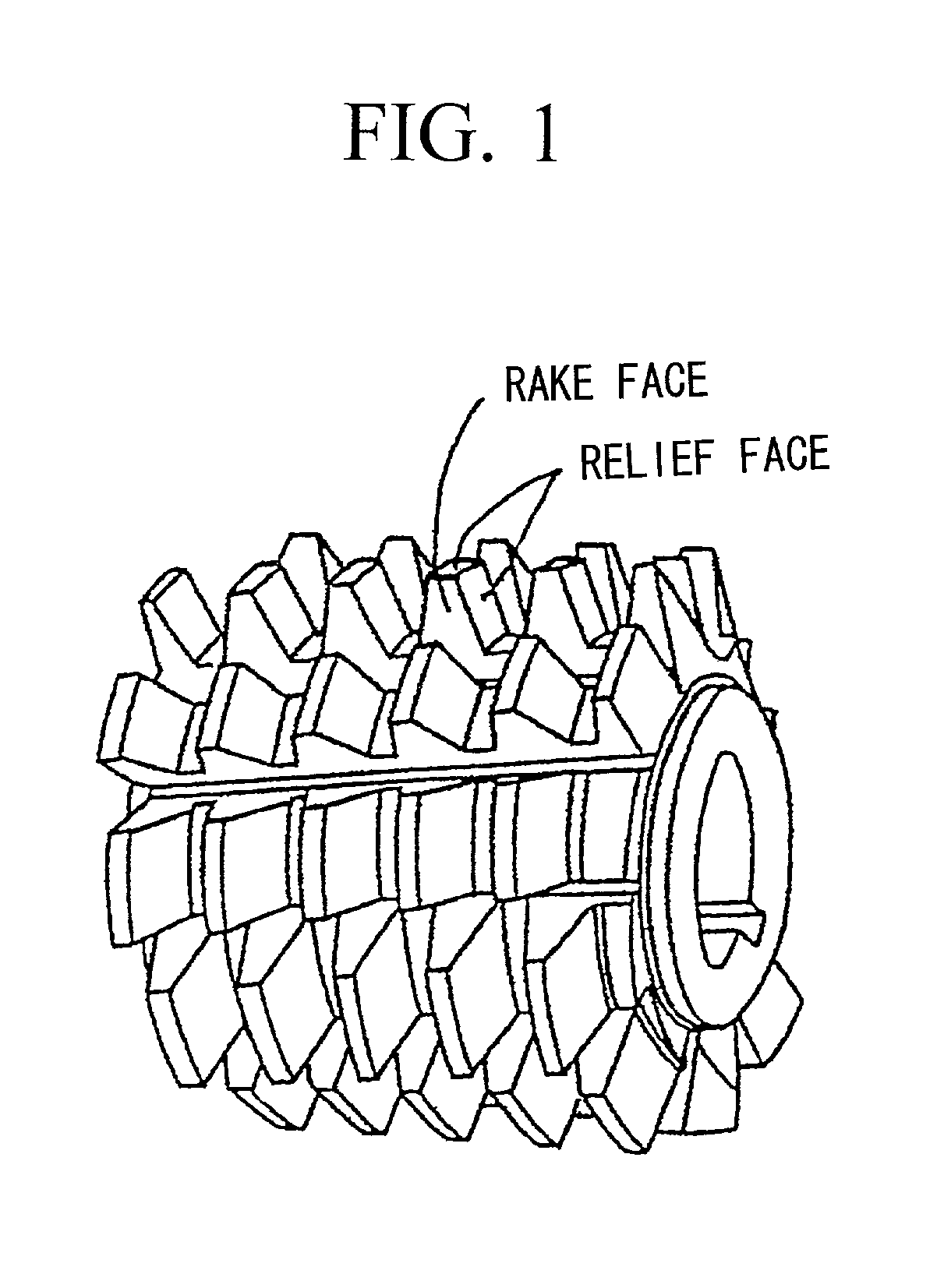
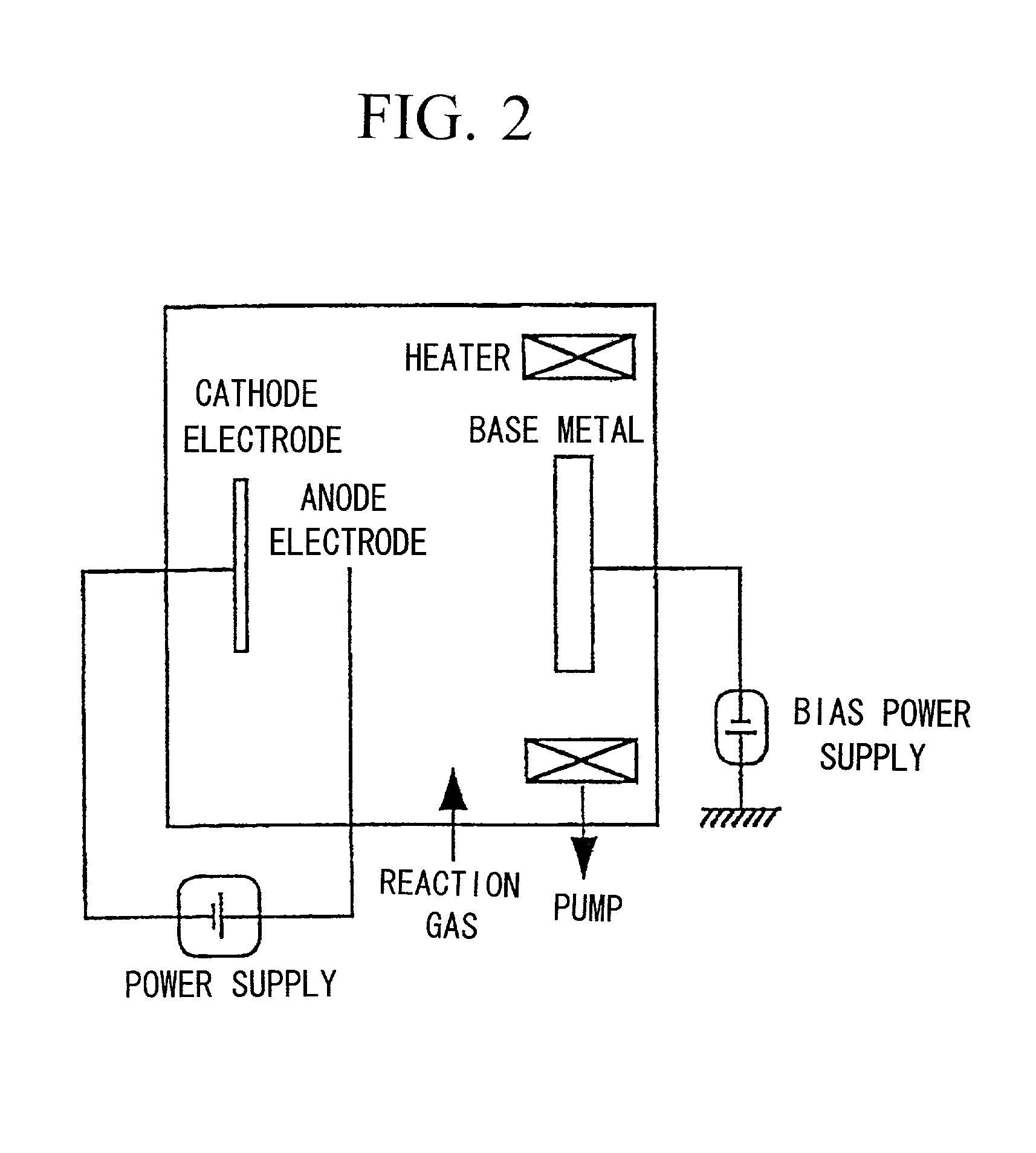
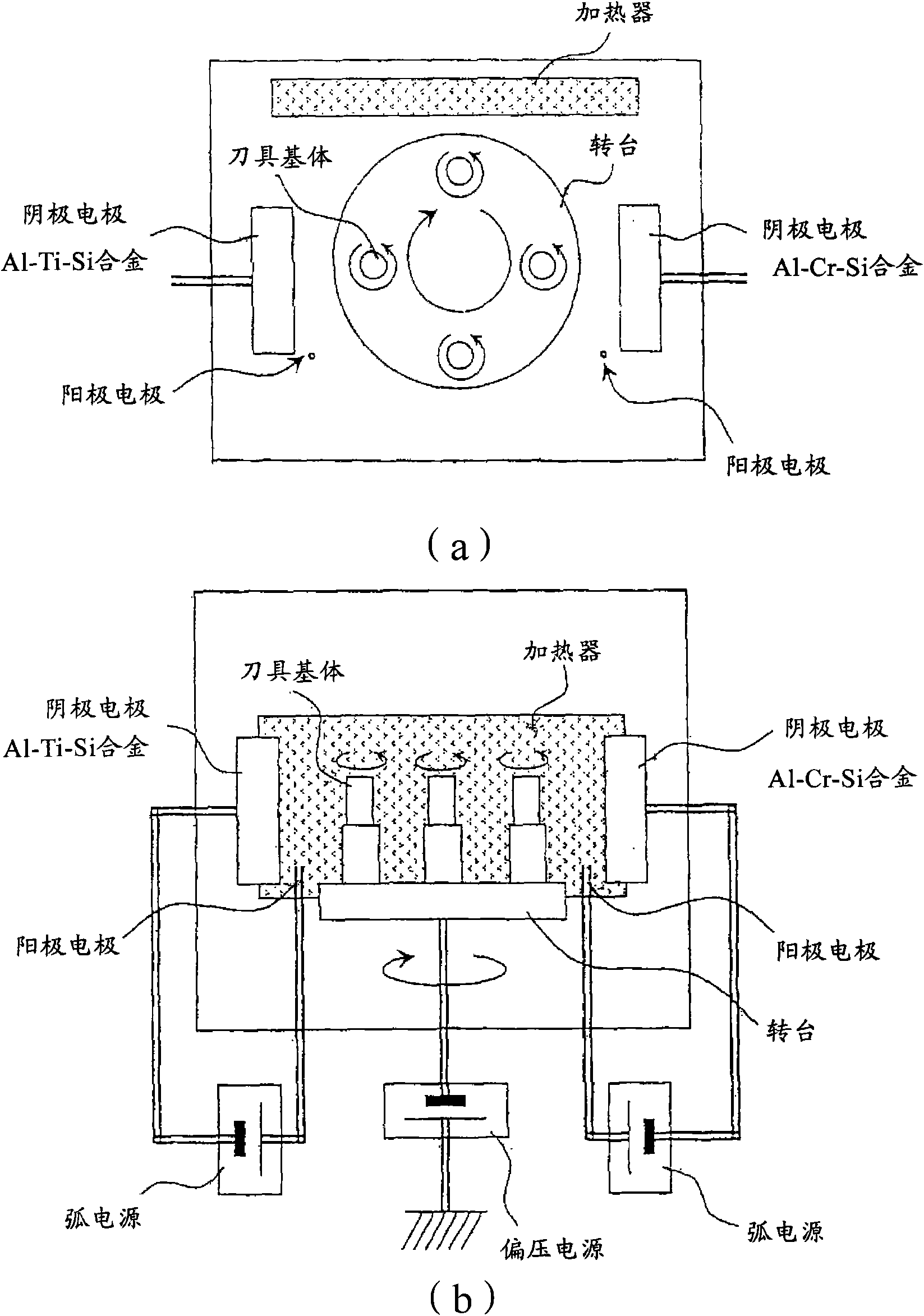
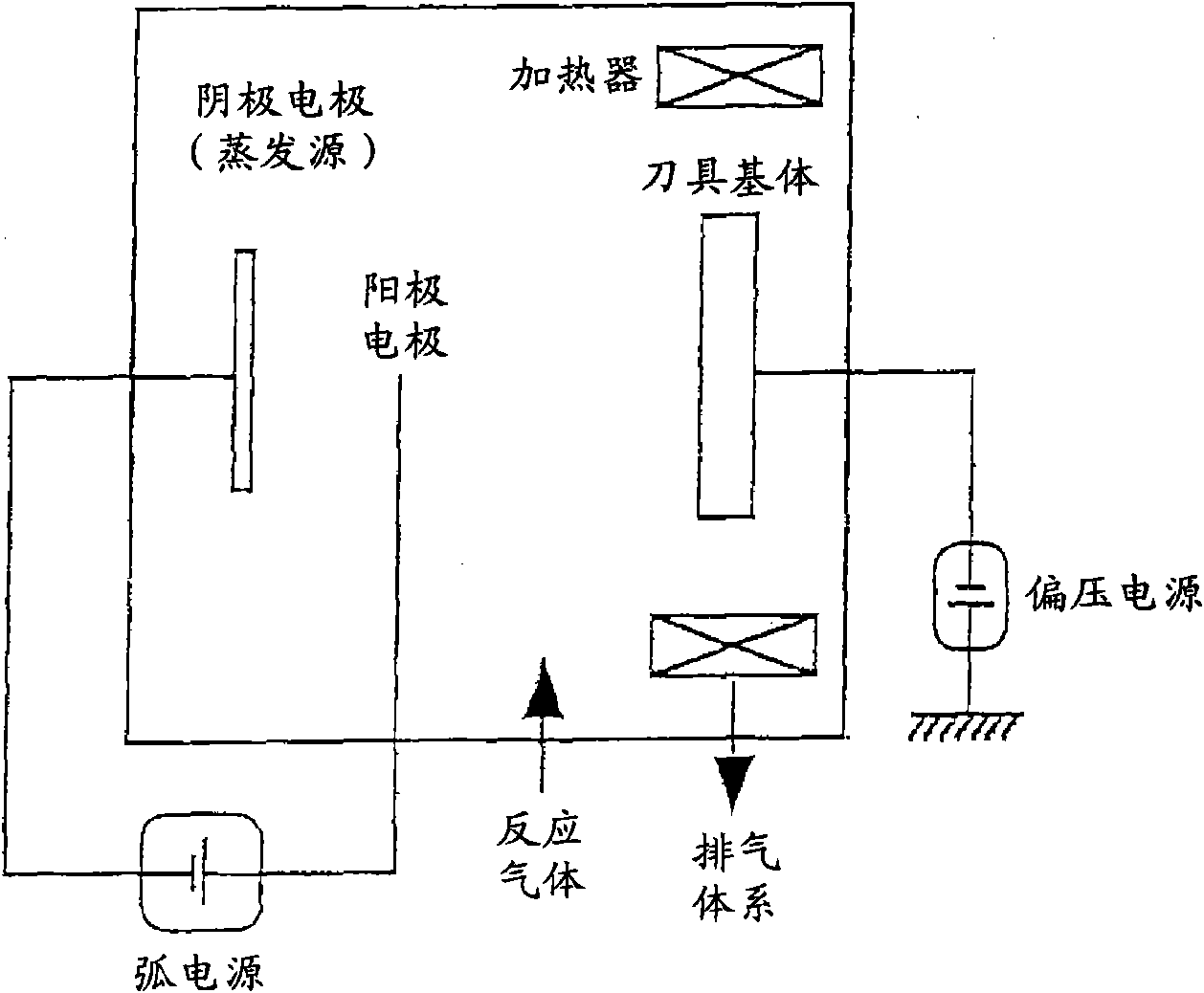
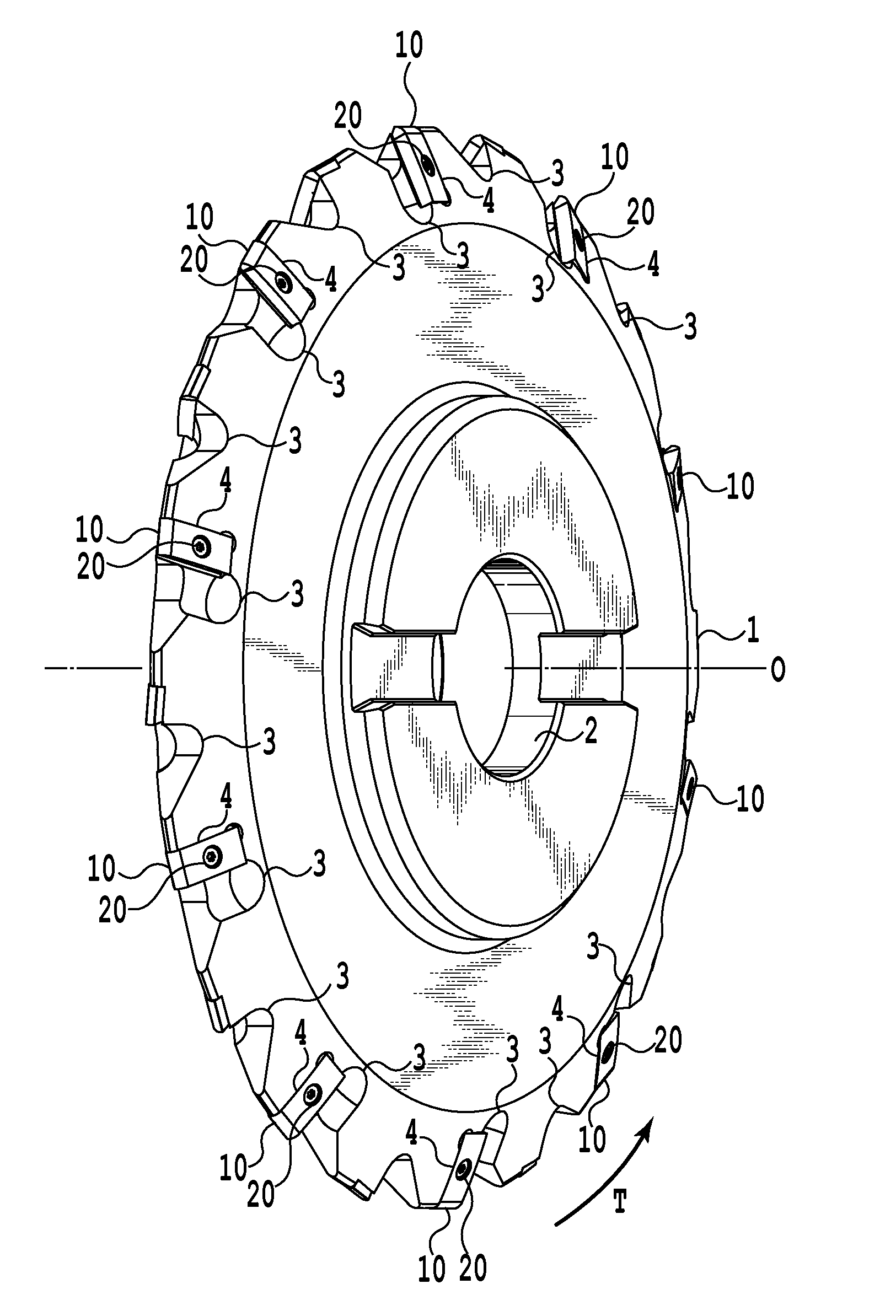
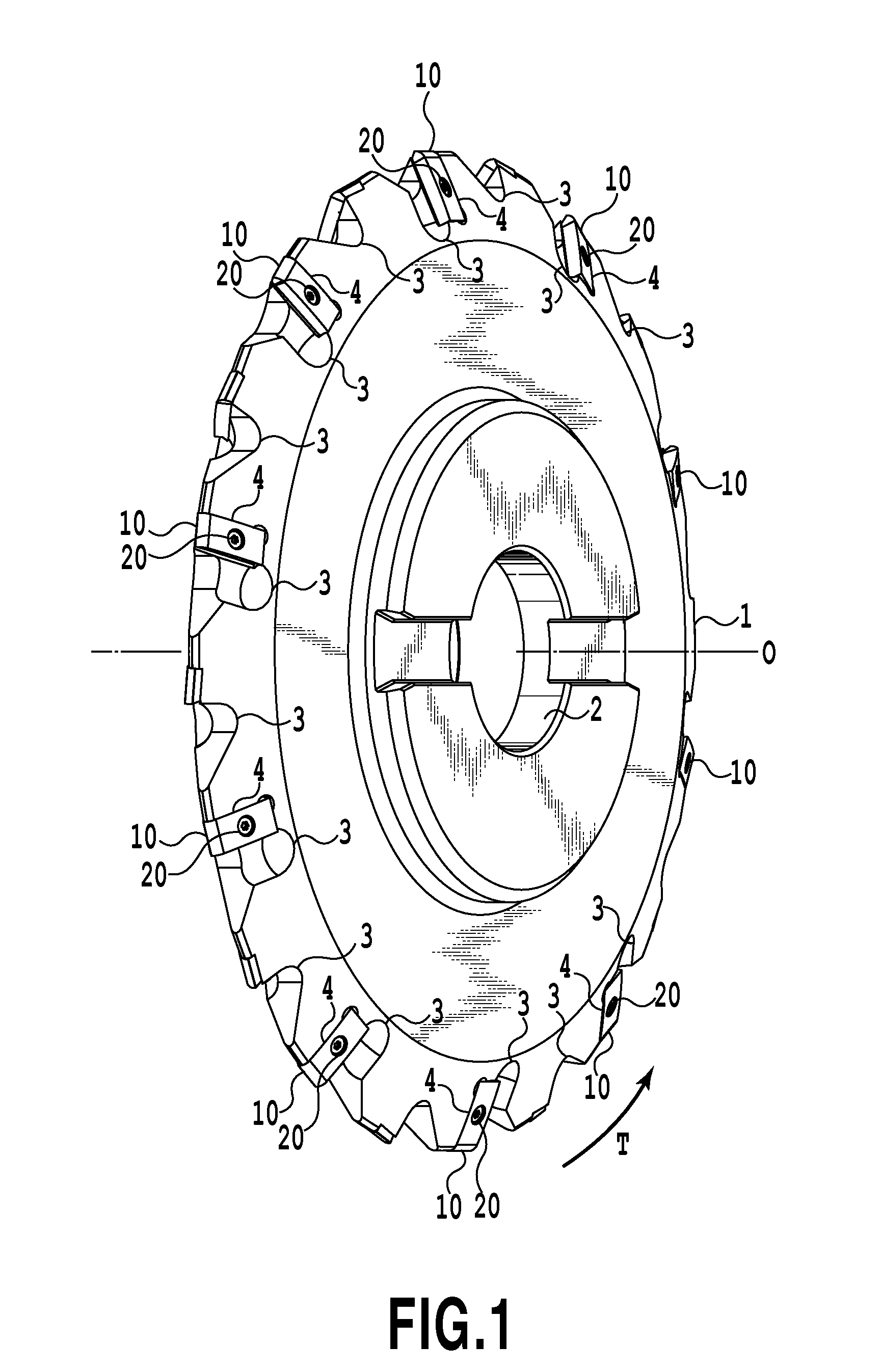
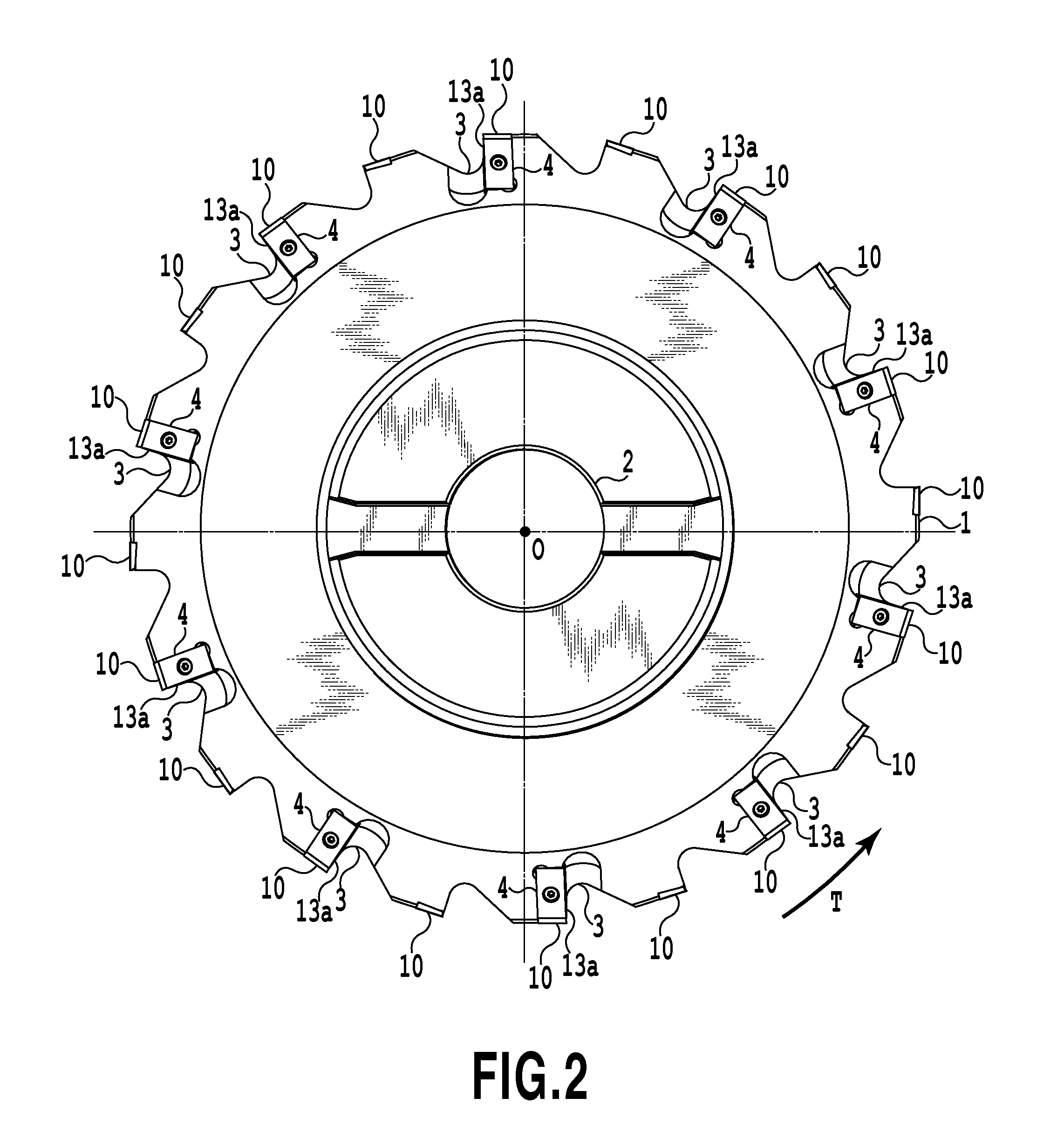
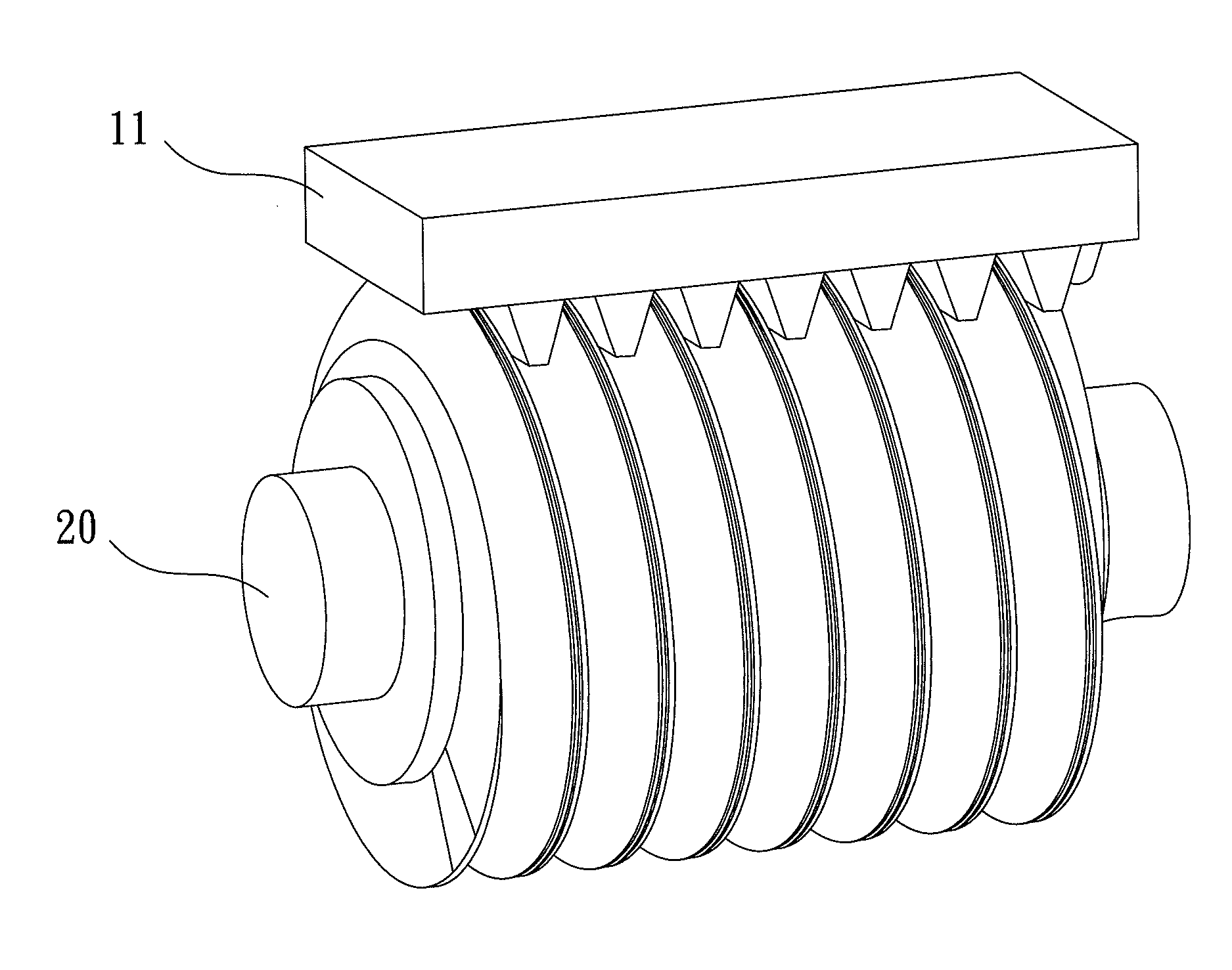
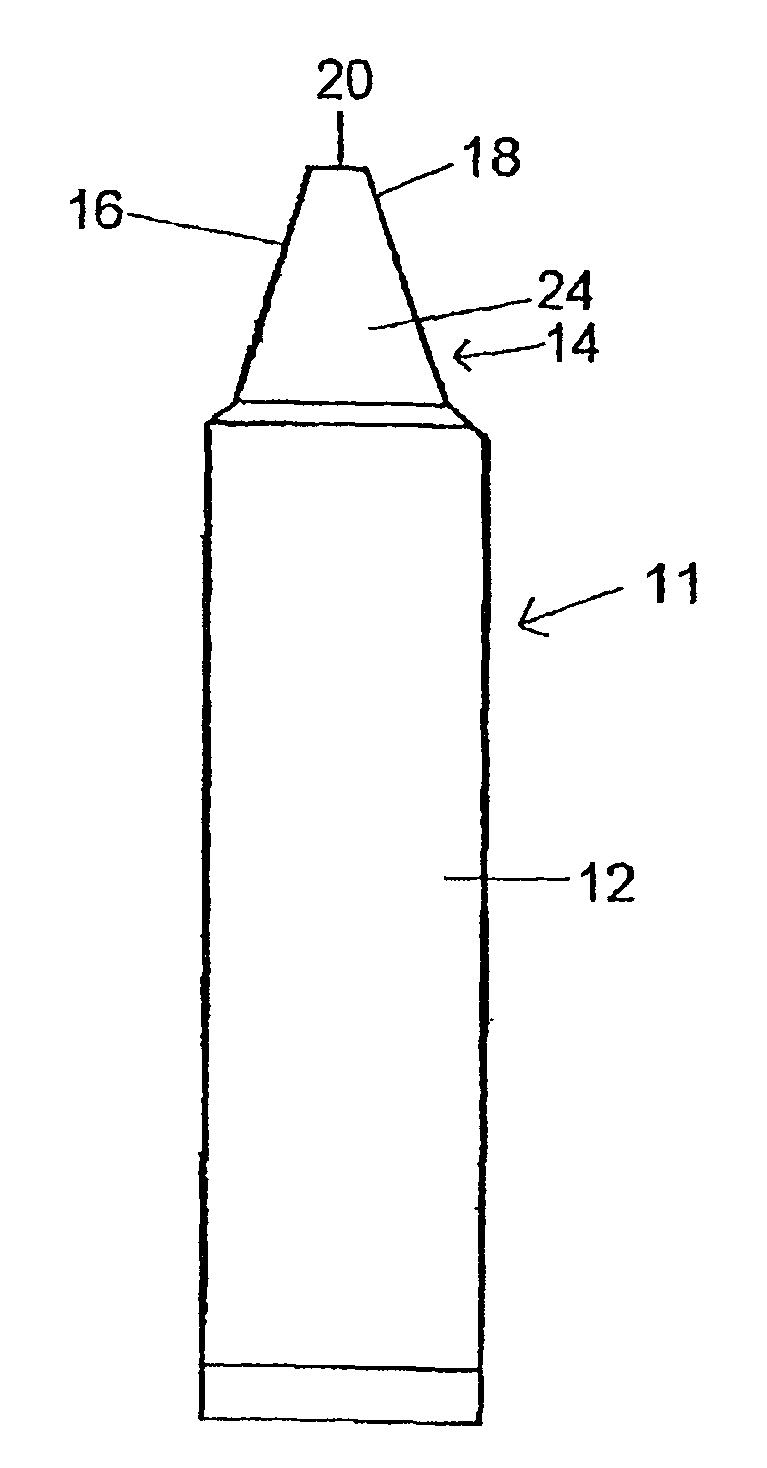
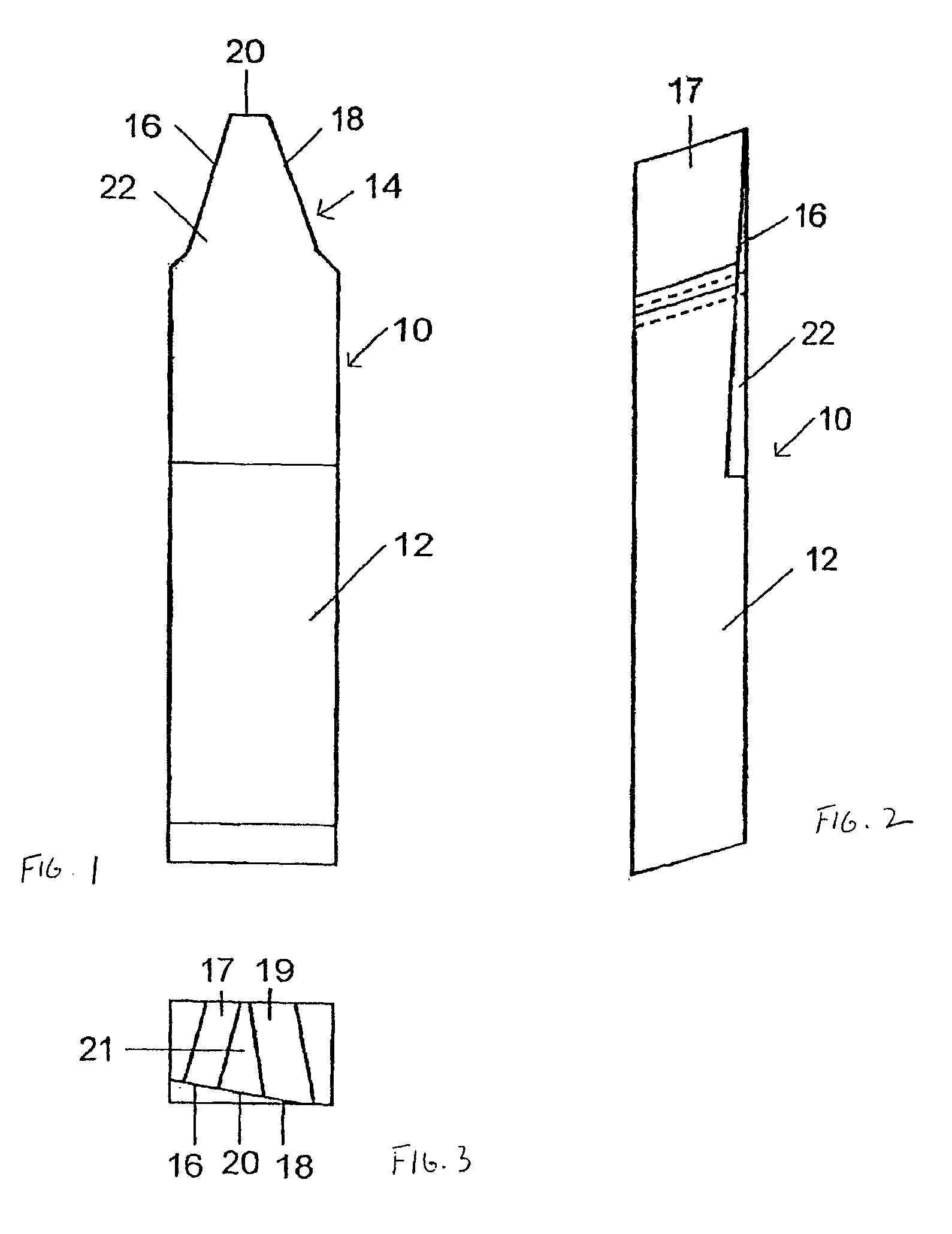
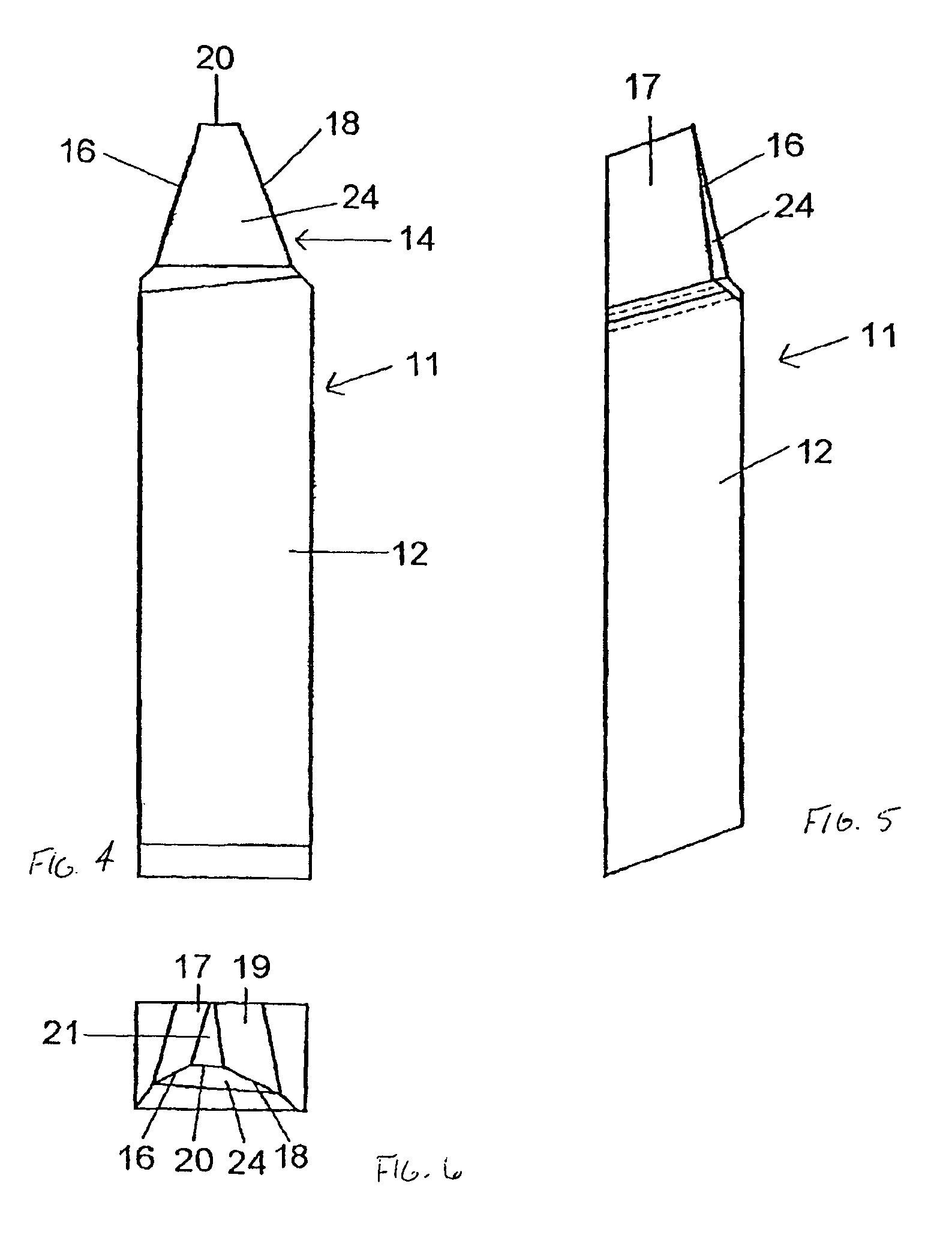
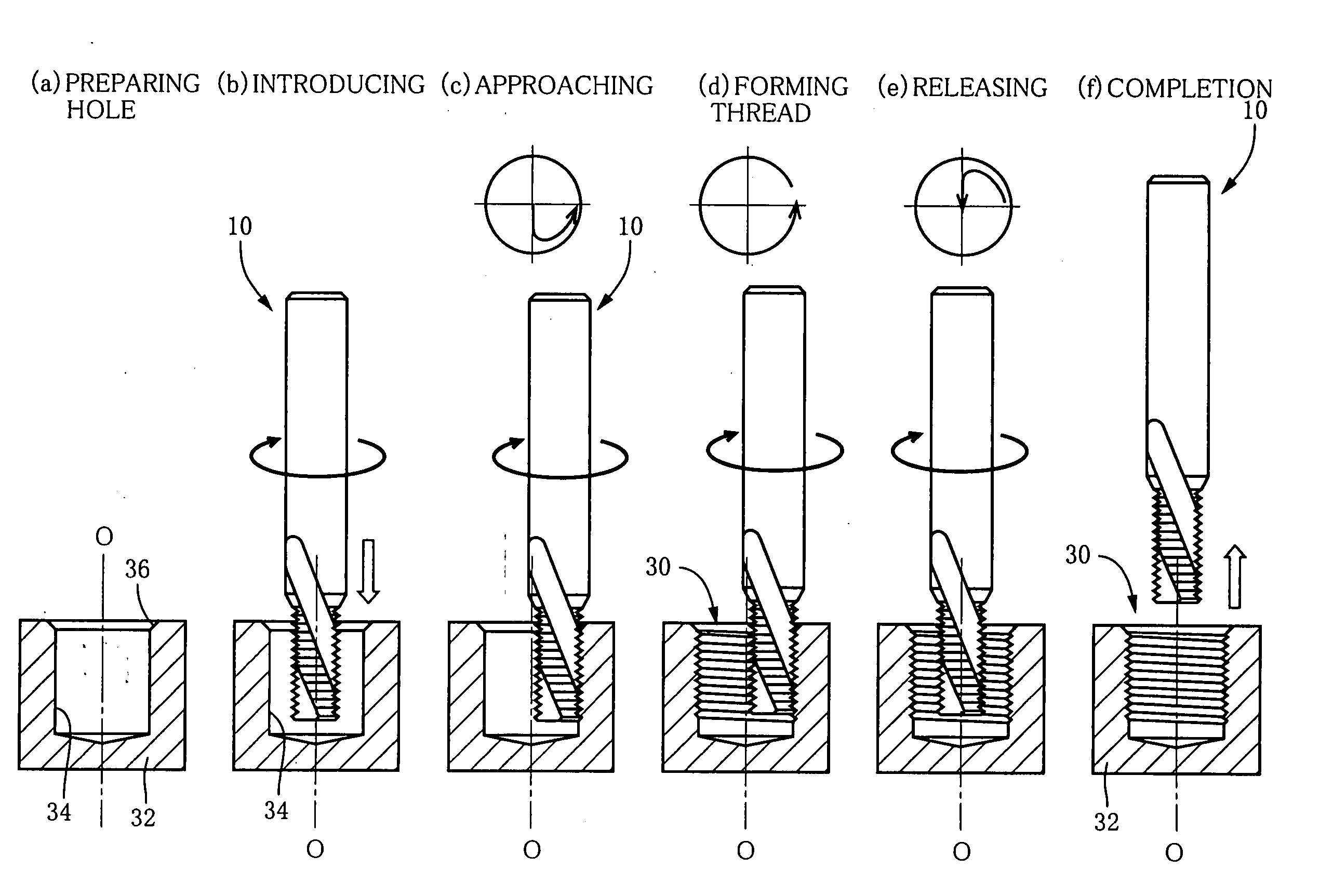
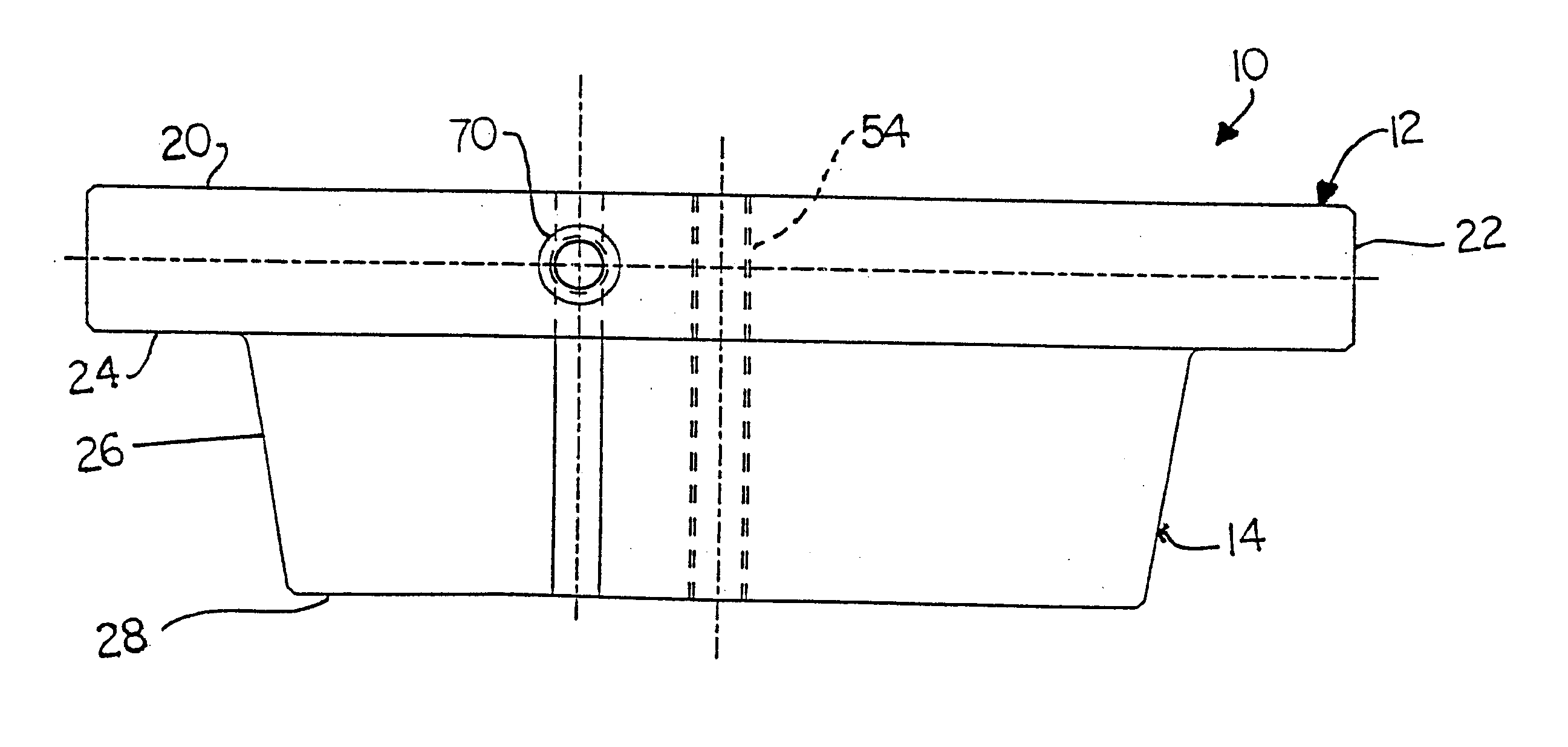
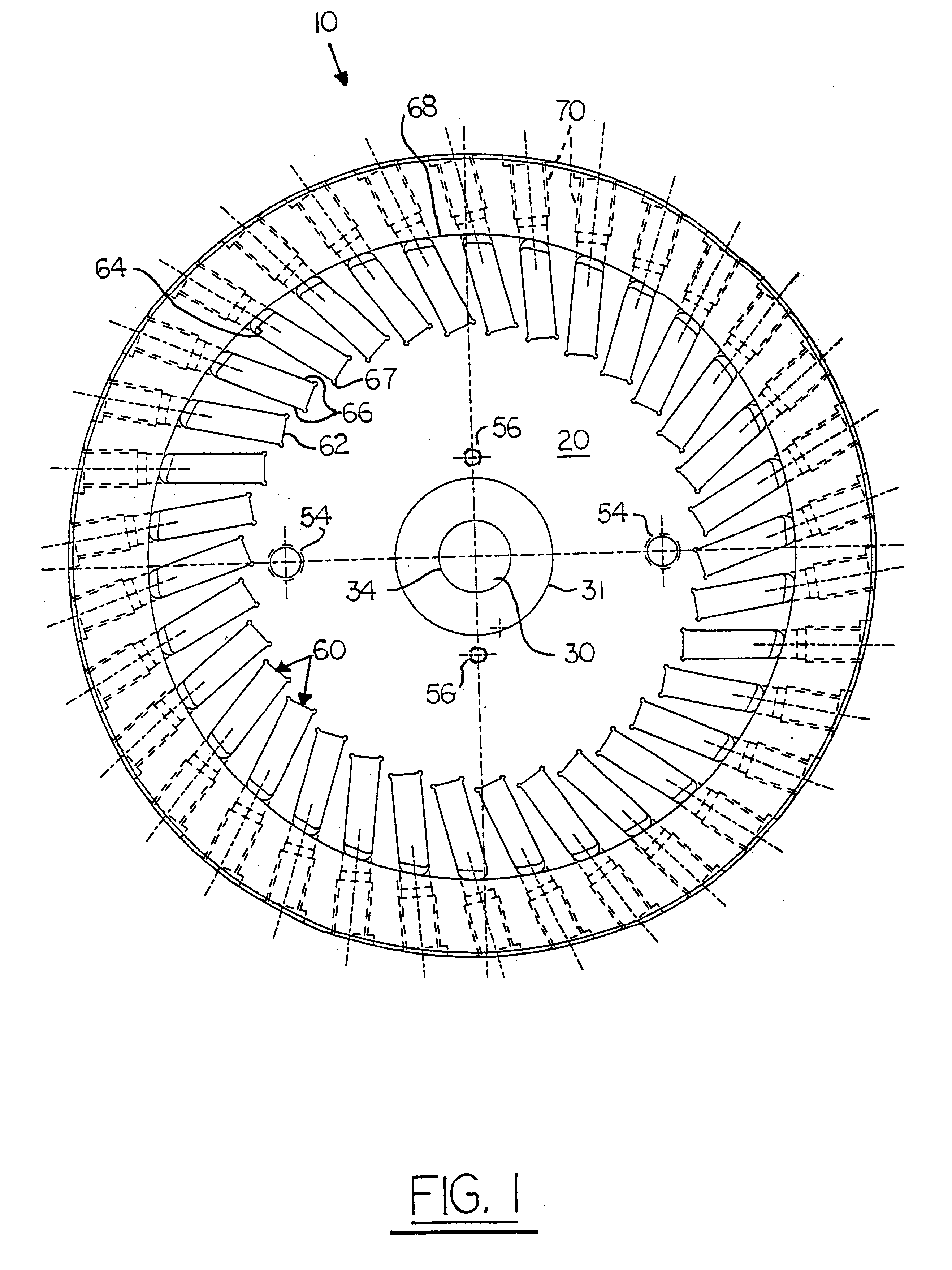
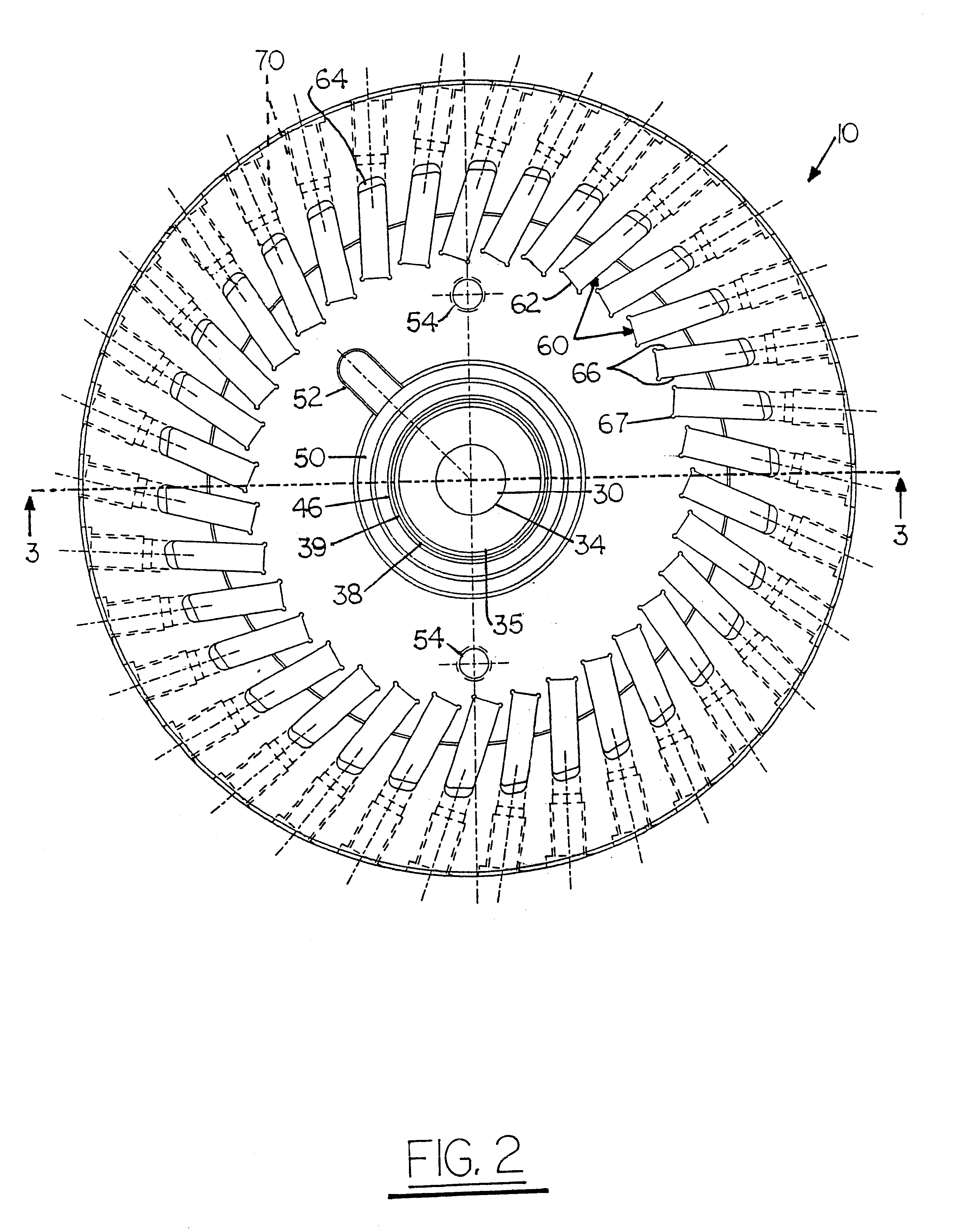
Patents
Literature
107results about "Gear cutting tool" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
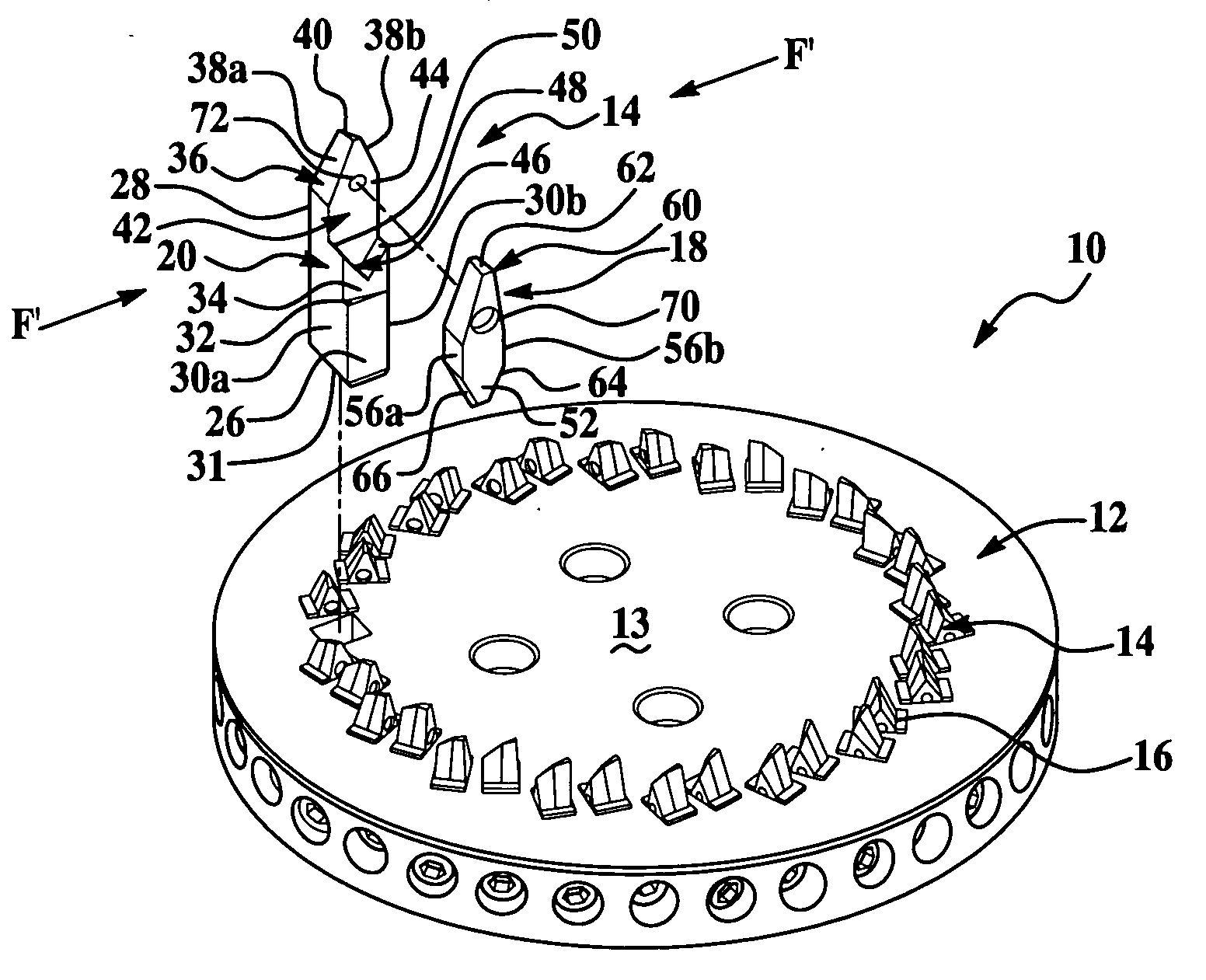
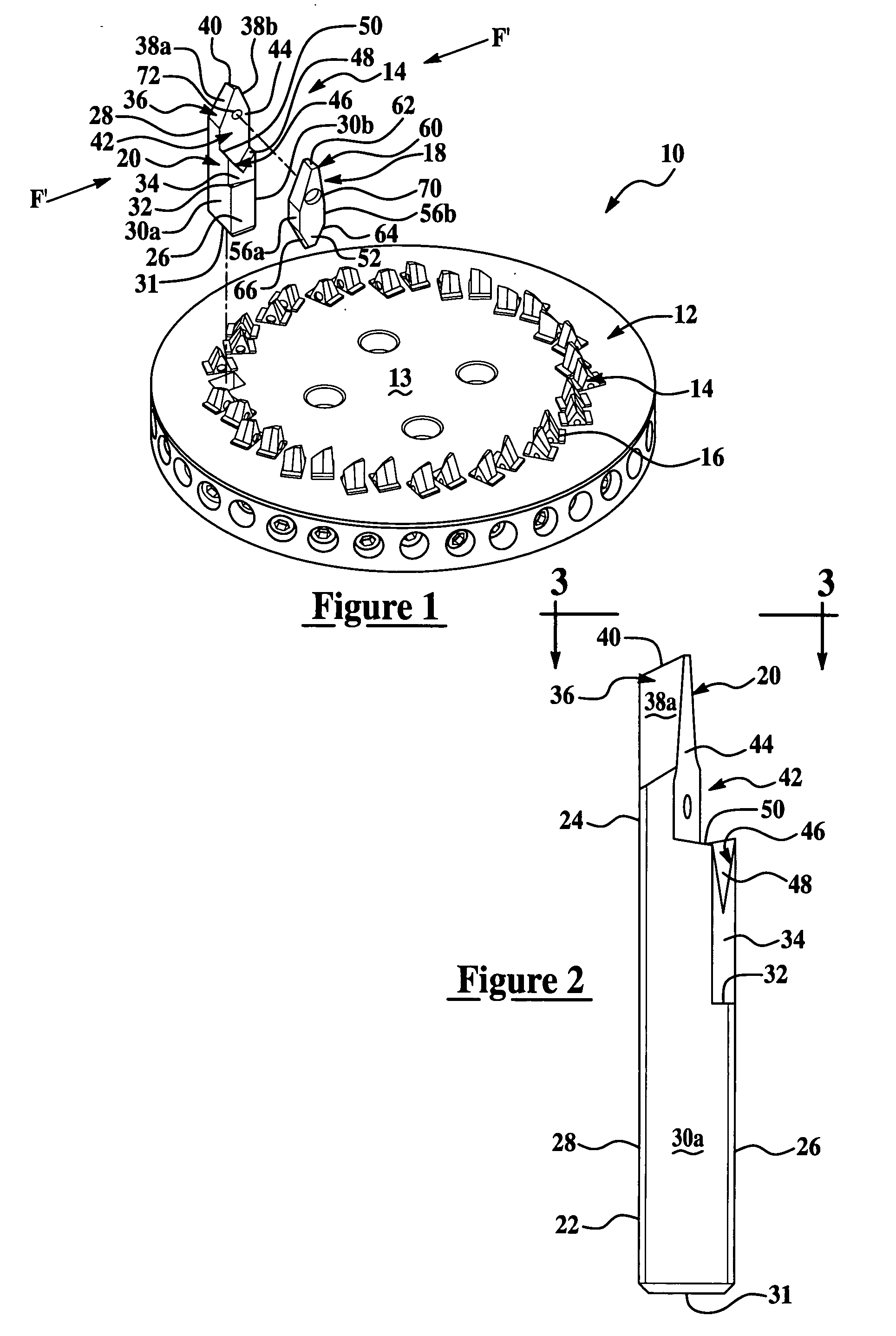
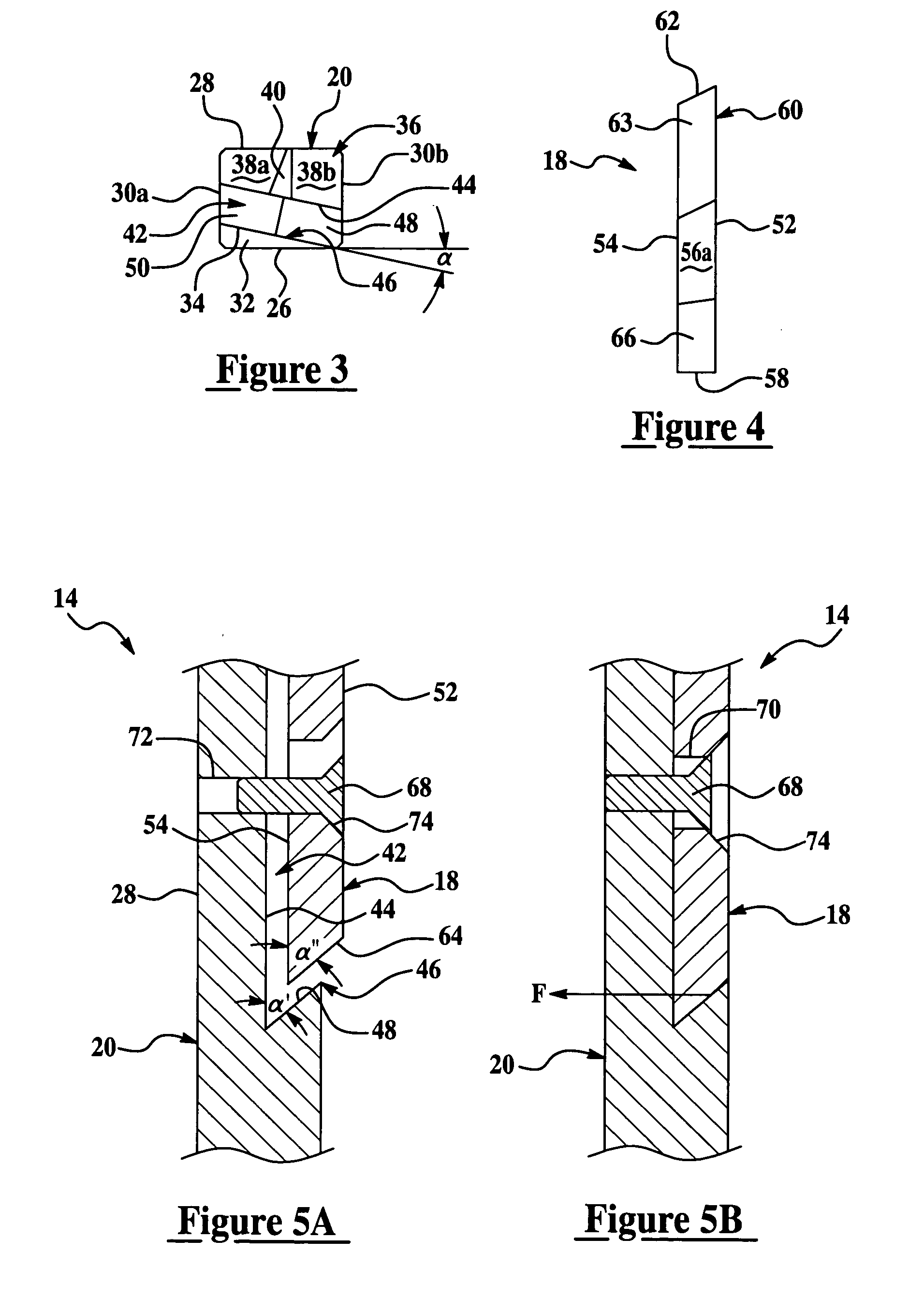
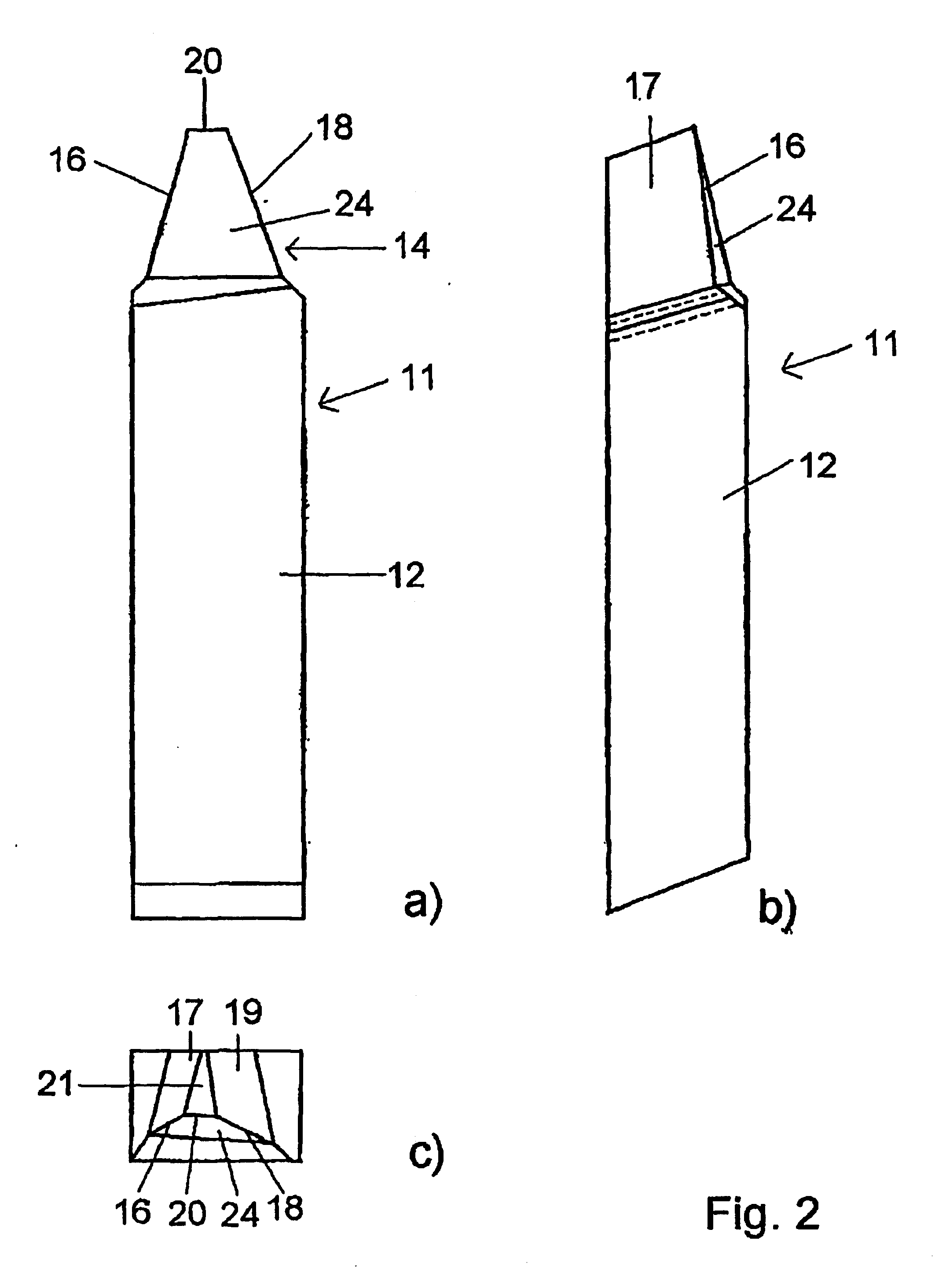
Cutter blade with integral coolant passages
InactiveUS6634835B1Low heat generationHeat dissipationMetal working apparatusGear teeth manufacturing toolsHobbingCarbide
A hob type cutter blade for use in a hobbing process. The cutter blade is formed with at least one cooling passage that permits the flow of coolant through the cutter blade to the contact surface reducing the heat generation as well as dissipating any heat already produced during the hobbing operation. During manufacturing, the cooling passage is sintered into the carbide cutter blade without the addition of separate operation.
Owner:DANA AUTOMOTIVE SYST GRP LLC
High-speed tool steel gear cutting tool and manufacturing method therefor
The invention provides a high-speed tool steel gear cutting tool in which fracture or chipping does not occur at the cutting edge, and which realizes excellent cutting performance over long periods. Moreover, a method of manufacturing a gear cutting tool including: a step for quenching a tool material comprising high-speed tool steel and which has been rough processed to a shape corresponding to a final shape of a gear cutting tool, to transform a structure of the tool material into martensite, a step for temperling the tool material after quenching to transform any residual austenite dispersingly distributed throughout a matrix of the martensite structure formed by the quenching, into martensite, and a step for finishing the tool material after tempering to a final shape, is characterized in that the tool material after quenching is subjected to sub-zero treatment involving cooling and holding at a temperature of less than -150° C.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Surface-coated cutting tool
ActiveCN101678467AExcellent high temperature hardnessExcellent high temperature toughnessMilling cuttersVacuum evaporation coatingThin layerCemented carbide
A surface-coated cutting tool which has excellent chipping resistance and wearing resistance in high-speed cutting processing such as high-speed gear cutting processing, high-speed milling processing,and high-speed drilling processing. The surface-coated cutting tool comprises a tool base, e.g., a cemented carbide base, cermet base, or high-speed tool steel base, and at least a hard coating layerformed on a surface of the tool base and having a multilayer structure composed of a thin layer (A) and a thin layer (B) alternating therewith. The thin layer (A) is constituted of an (Al,Cr,Si)N layer satisfying the empirical formula ¢AlXCrYSiZ!N (wherein 0.2 <= X <= 0.45, 0.4 <= Y <= 0.75, 0.01 <=Z <= 0.2, and X+Y+Z=1 in terms of atomic ratio), and the thin layer (B) is constituted of an (Al,Ti,Si)N layer satisfying the empirical formula ¢AlUTiVSiW!N (wherein 0.05 <= U <= 0.75, 0.15 <= V <= 0.94, 0.01 <= W <= 0.1, and U+V+W=1 in terms of atomic ratio).
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
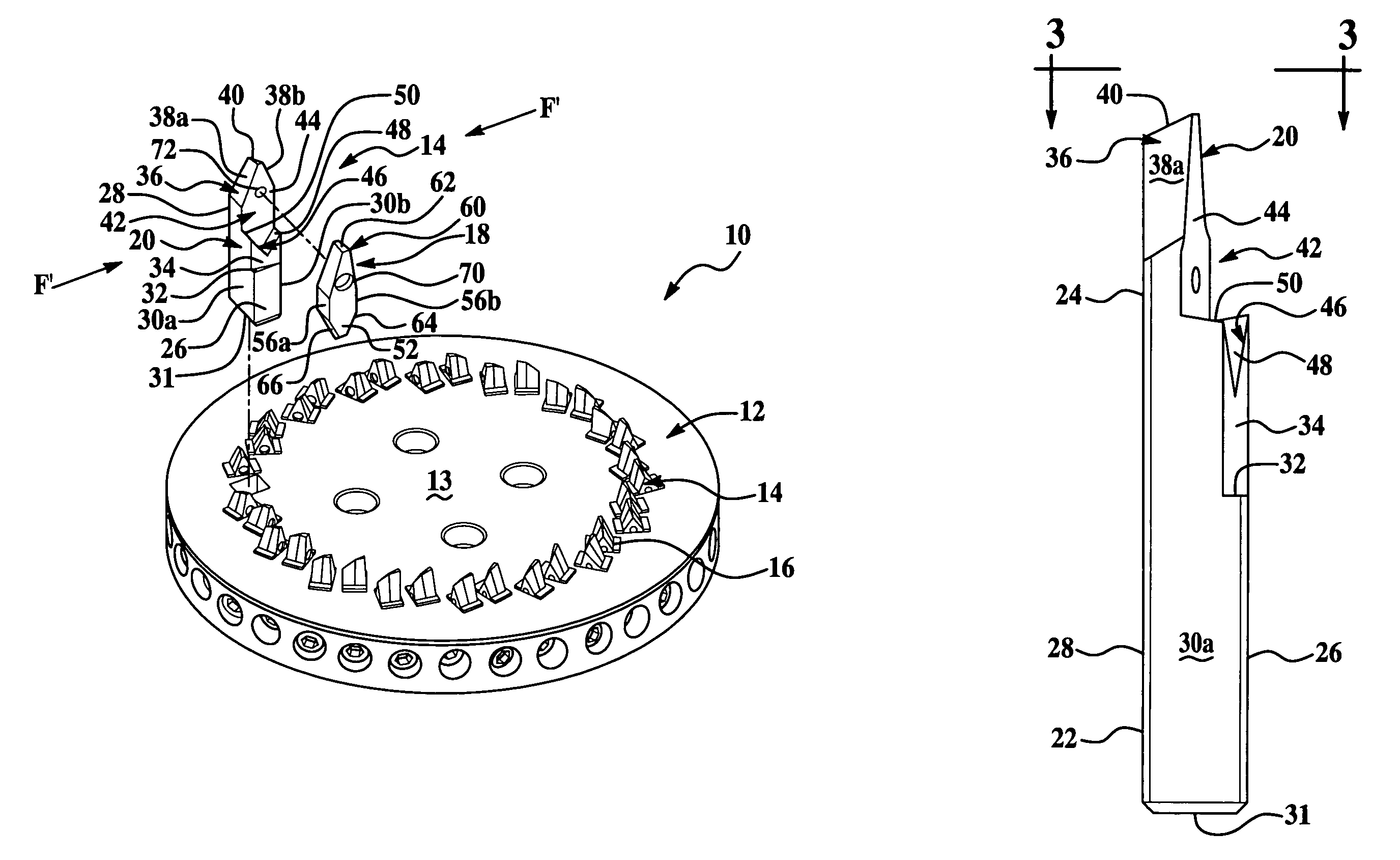
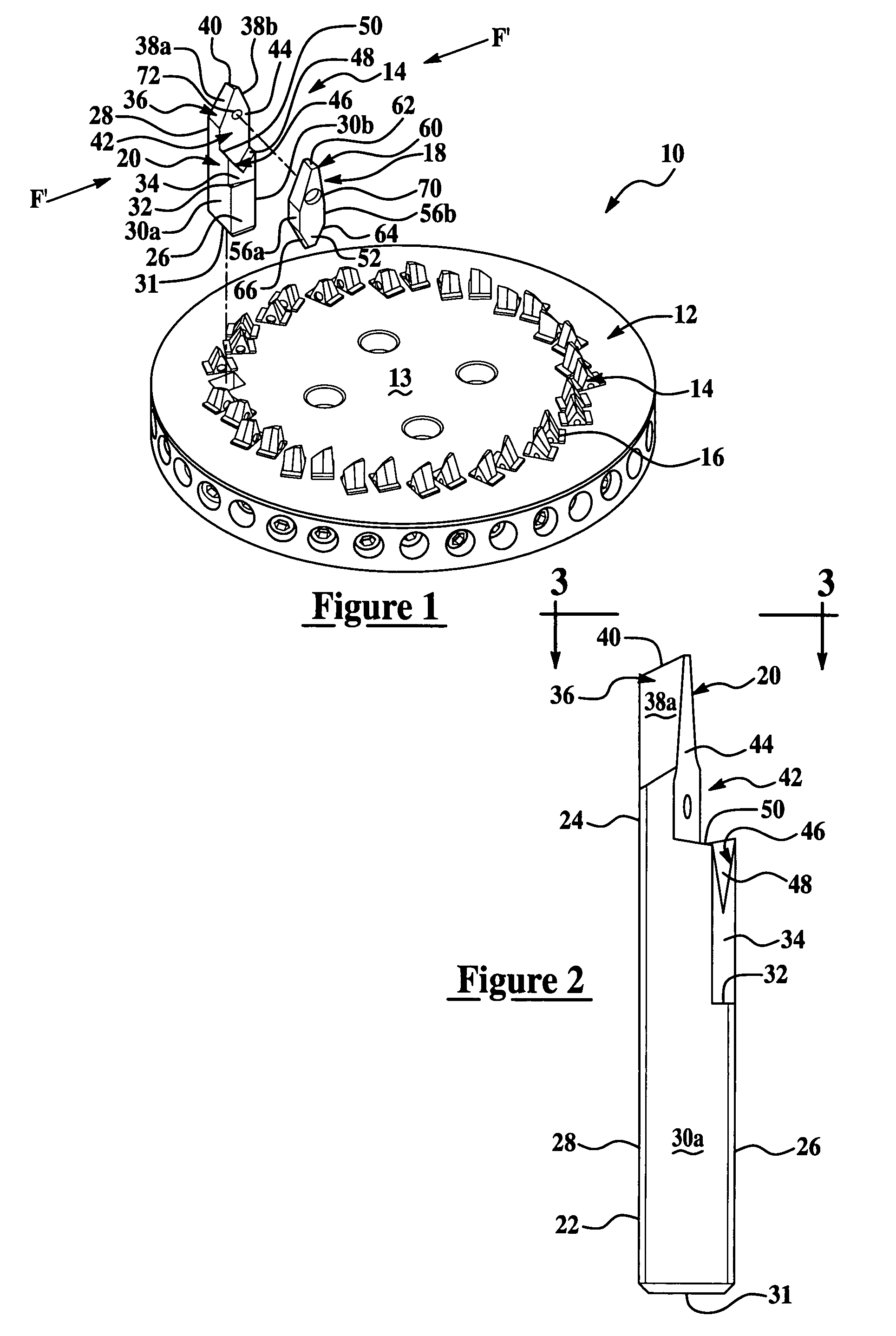
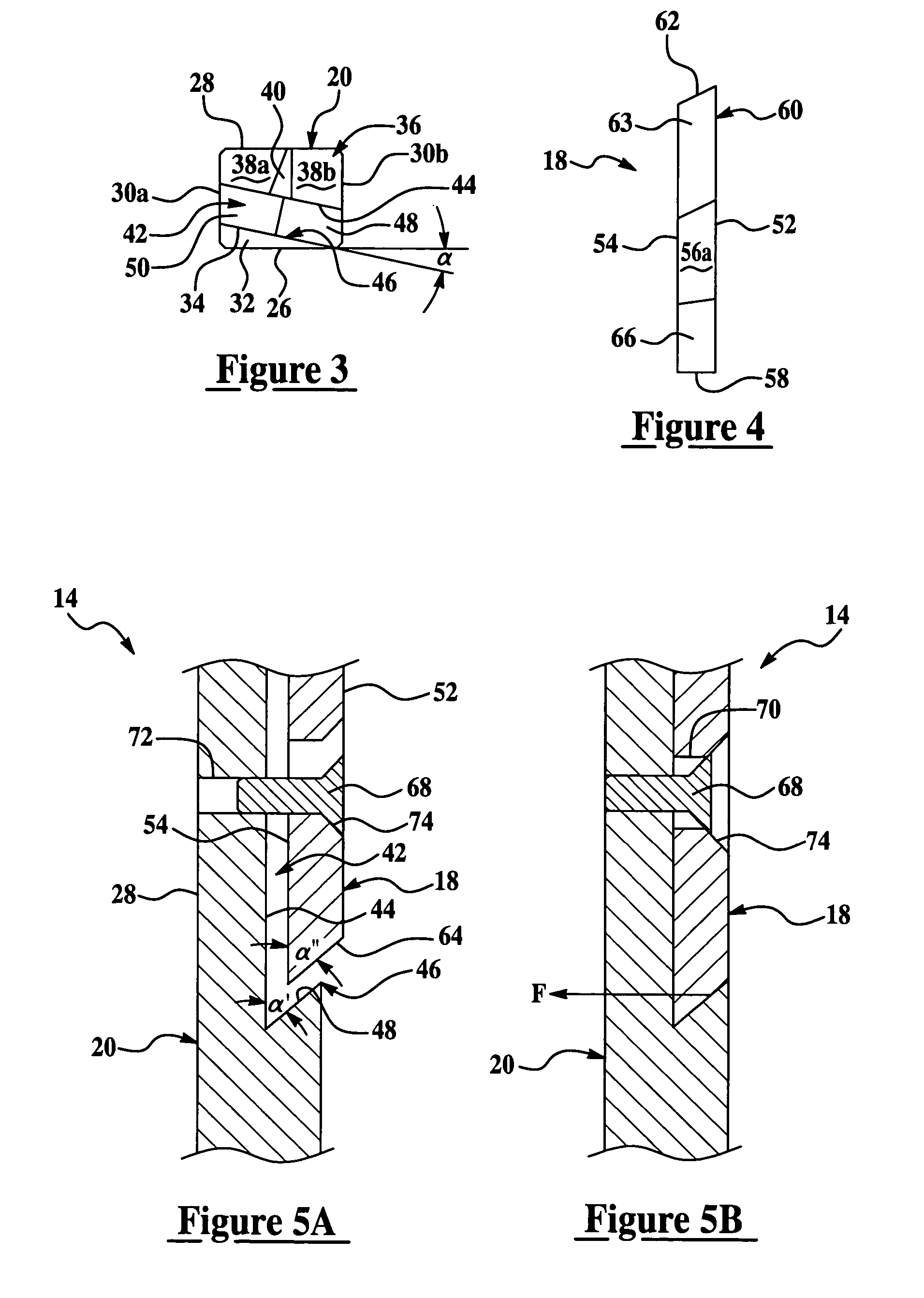
Gear milling tool with replaceable cutting inserts
A cutting tool assembly adapted to be coupled to a cutter head for manufacture of a gear. The cutting tool assembly includes a cutting insert and a holder adapted to couple the cutting insert to the cutting head. The holder includes a pocket defined by a back surface and at least one lip member that provides a force directed against the cutting insert toward the back surface to thereby retain the cutting insert within the pocket during cutting operations.
Owner:COLE CARBIDE IND
Gear shaping method and device and spiral bevel gear cutter
InactiveUS6416262B1Fast cutting speedNatural mineral layered productsGear teeth manufacturing toolsMilling cutterGear wheel
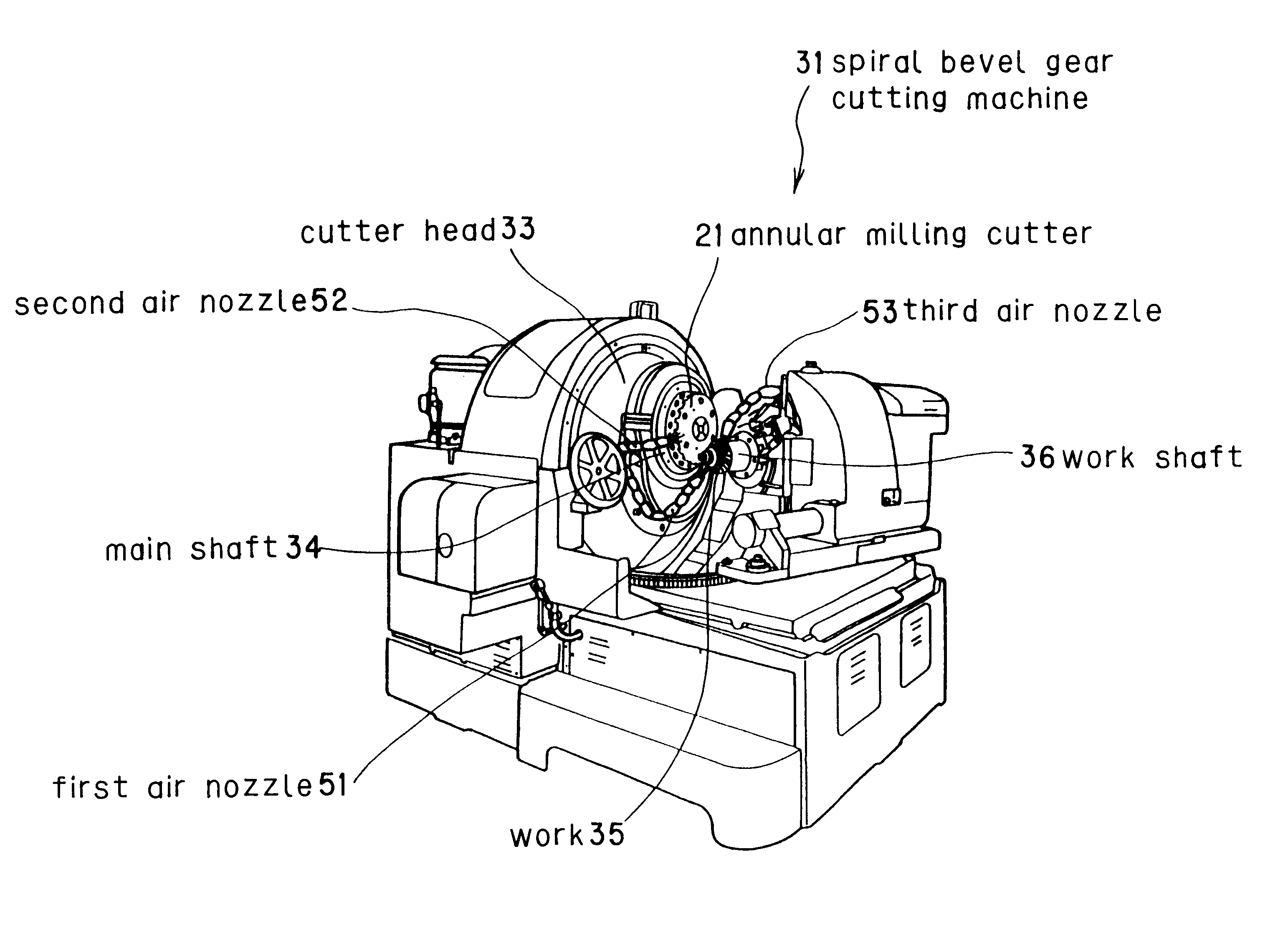
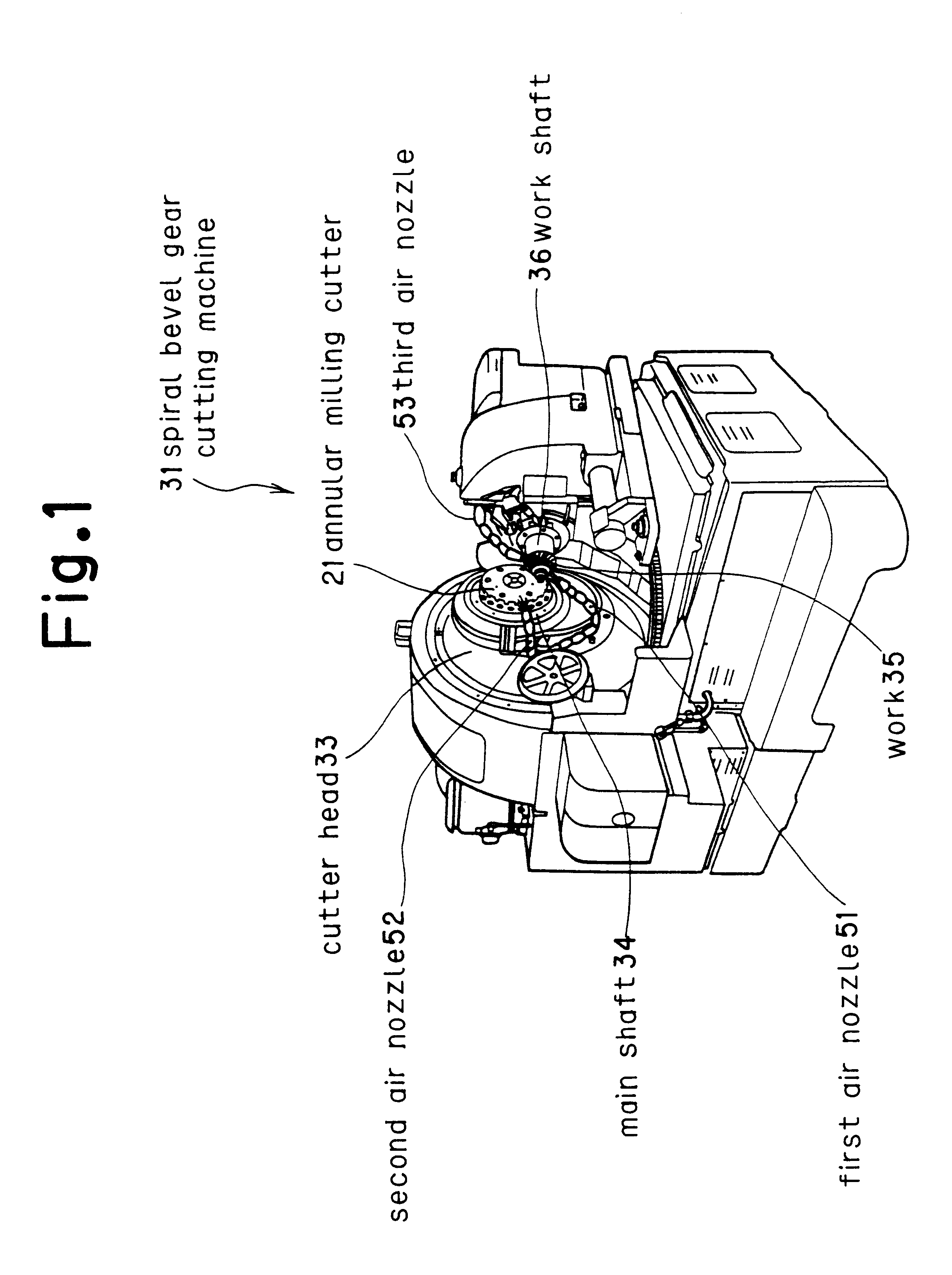
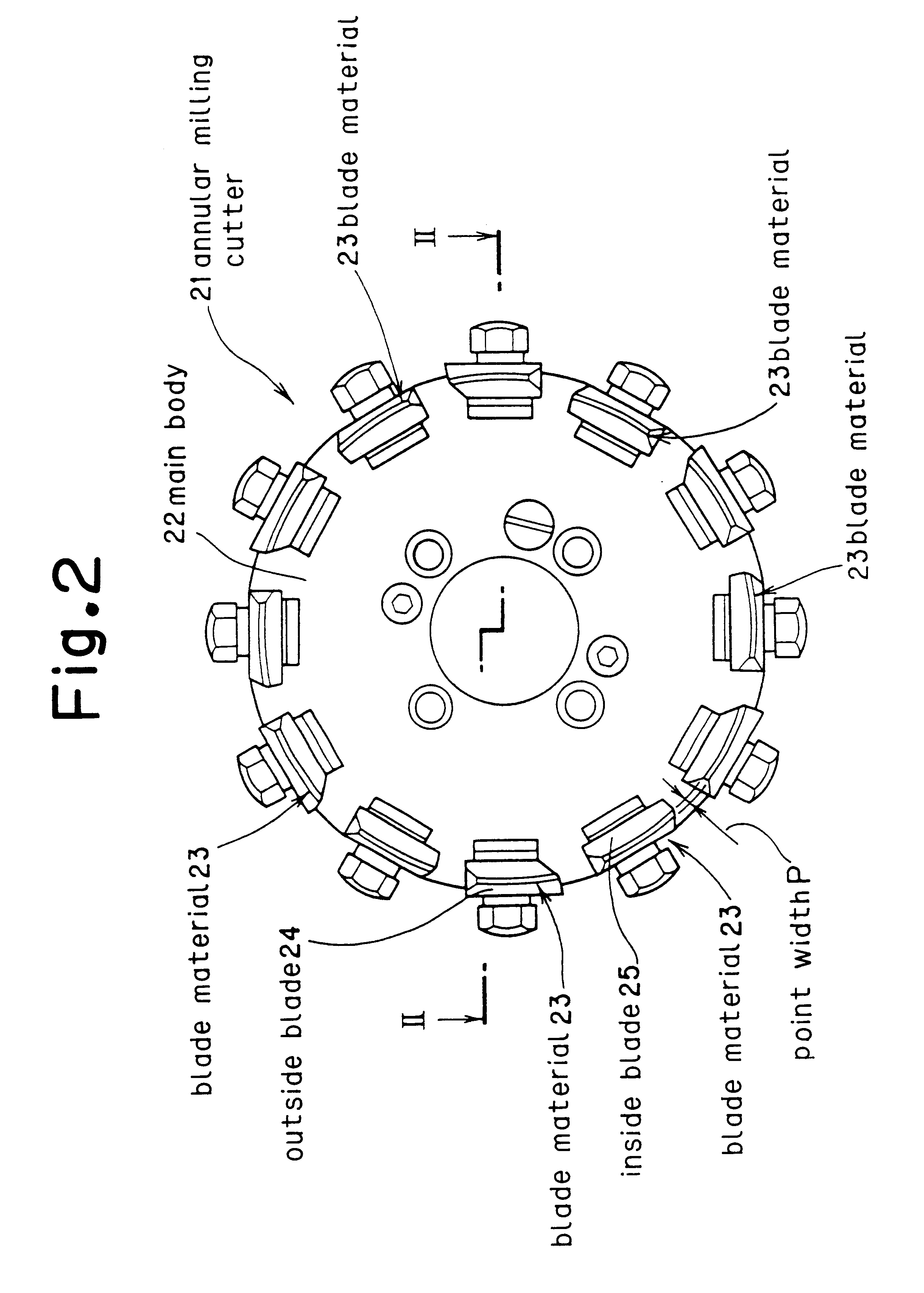
A bevel gear is generated using an annular milling cutter having a blade material made of a high-speed tool steel mounted to a main body, the blade material being coated with at least one layer of a film of a composition substantially comprising (Ti(1-x)Alx)(NyC(1-y)) (where, 0.2<=x<=0.85, 0.2<=y<=1.0), and dry cutting is performed at a cutting speed in the range from 20 to 400m / min without using a cutting oil. With this method, teeth can be generated at a greatly improved cutting speed without using any expensive tool such as cemented carbide, thereby realizing efficient production of a bevel gear at a reduced cost.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Chamfer hob and method of use thereof
Owner:ARVIN JOSEPH L
Drill thread milling cutter
InactiveUS20060216125A1Improve cutting effectGood chip breaking effectThread cutting toolsWood turning toolsMilling cutterEngineering
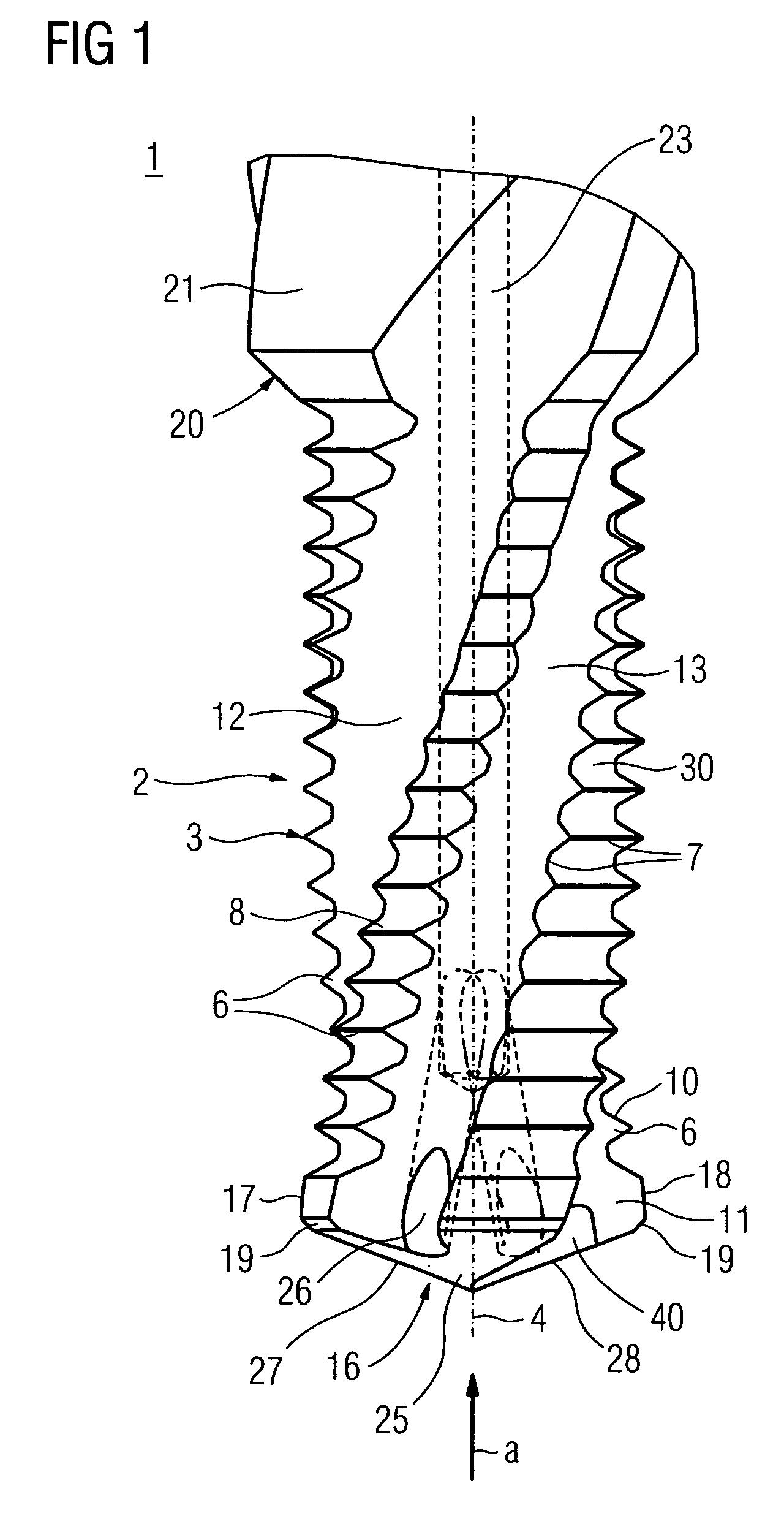
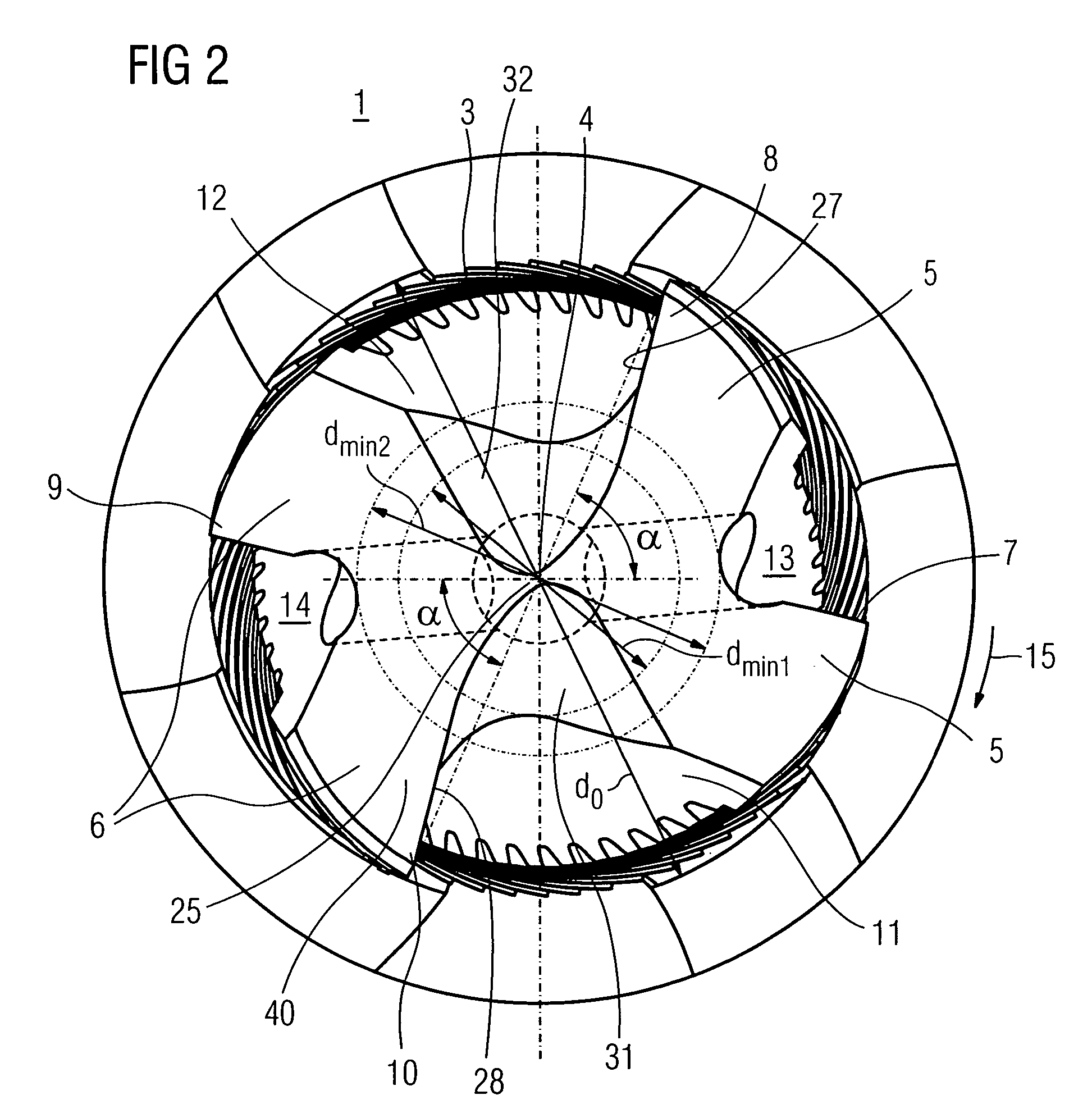
The invention relates to a drill thread milling cutter (1) for producing a bore and for the subsequent milling of a thread in the bore, said drill thread milling cutter (1) having a working region (2), on the circumference (3) of which a number of drilling and milling cutting edges are arranged. A number of milling cutting edges (7, 8, 9, 10) greater than the number of drilling cutting edges (17) by a factor greater than 2 are arranged or are effective in the direction of rotation.
Owner:EMUGE WERK RICHARD GLIMPEL & FAB FUR PRAZISIONSWERKZEUGE
Full traction differential with hybrid gearing
InactiveUS20080103008A1Improved tooth contactImprove efficiencyDifferential gearingsMetal working apparatusEngineeringHelix angle
The compact, all-gear full-traction differential includes meshing pairs of side-gear worms and worm-wheel balance gears having a “hybrid” design. Preferably, the teeth of each side-gear worm have an involute profile but are cut with only plunge feed, while the teeth of the worm-wheel portions of the balance gears are helicoid worms having tip and root modifications made by a convex-shaped cutter. The side-gear worm teeth have a helix angle equal to or greater than 45° and significantly chamfered ends, and the gears are designed to provide a gear ratio between 1.5:1 and 2.5:1. The numbers of teeth in the spur-gear portion and worm-wheel portion of each balance gear and in each side-gear worm are all divisible by 2 or by 3, preferably by both 2 and 3.
Owner:TORVEC INC
Gear milling tool with replaceable cutting inserts
A cutting tool assembly adapted to be coupled to a cutter head for manufacture of a gear. The cutting tool assembly includes a cutting insert and a holder adapted to couple the cutting insert to the cutting head. The holder includes a pocket defined by a back surface and at least one lip member that provides a force directed against the cutting insert toward the back surface to thereby retain the cutting insert within the pocket during cutting operations.
Owner:COLE CARBIDE IND
Gear tooth profile
A gear and method for producing the gear. The gear has a gear tooth profile conjugate to a gear basic-cutter tooth-profile having an addendum with a convex portion having an addendum point proximal to a pitch line and a dedendum with a concave portion having a dedendum point proximal to the pitch line. The convex portion is complementary with a corresponding portion of a mating-gear basic-cutter tooth-profile dedendum. The concave portion is complementary with a corresponding portion of the mating-gear basic-cutter tooth-profile addendum. A transition zone between the addendum point and the dedendum point has a predetermined width. The gear basic-cutter tooth-profile has a predetermined half pitch relief at the pitch line and continuity of profile and continuity of slope at the addendum point.
Owner:GEAR INNOVATIONS LLC
Skiving tool comprising cutter bars
InactiveUS20120282055A1Improve performanceSignificant potential in machining timeTurning machine accessoriesGear teeth manufacturing toolsHyperboloidEngineering
A skiving tool for manufacturing a rotationally symmetrical periodical structure on a work piece by means of a power skiving method. The skiving tool comprises a base body comprising a central rotation axis and a plurality of receiving openings and a plurality of cutter bars, fewer than or equal to the number of receiving openings. Each of the receiving openings has an elongate shape having a longitudinal axis, and the receiving openings can be arranged uniformly around the central rotation axis. The longitudinal axes of the receiving openings are generators of a rotation hyperboloid, which is arranged rotationally symmetrical to the central rotation axis.
Owner:KLINGELNBERG AG
Hob
ActiveUS20110243671A1Easy to produceEasy to assembleMilling cuttersGear teeth manufacturing toolsDiagonalBiomedical engineering
A hob having a helically curved tooth profile. A plurality of segments covering only a limited angle range are attached to a base body for forming the tooth profile. The segments abut each other in the circumferential direction of the base body, and the segments form rows in the direction of the longitudinal axis of the base body. The segments each comprise a segment foot and a segment profile disposed diagonally thereon. The diagonal arrangement of the segment profile forms a coiled slope of the helically curved tooth profile in each segment and the tooth profile can be built up simply by arranging the segments in rows in the circumferential and the longitudinal directions.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Cutting Insert and Indexable Tooth Cutting Tool Using the Same
A cutting insert is removably mountable on an insert seat formed in a peripheral of a tool body rotated around an axis O and of substantial disc shape. The cutting insert includes a substantially planar insert body of a substantially square shape in plan view, a flank at an upper face of the body, a rake face at a side of the body intersecting with the flank, and a cutting edge at an intersection ridge between the rake face and the flank. The cutting edge is a substantial involute in side view of the body, the rake face is inclined to an inside of the body from an upper toward a lower face, and at least a front end arranged in a peripheral of the tool body is concave constituting a part of a substantially conical side face.
Owner:TUNGALOY CORP
Variable-Tooth-Thickness Worm-Type Tool and Method For Using The Same To Fabricate Gears
InactiveUS20130089386A1Reduce distortionEasy to controlGear teeth manufacturing toolsMetal working apparatusSpiral bladeDegrees of freedom
A variable-tooth-thickness worm-type tool comprises a main body and a spiral blade distributed on the main body and featuring variable tooth thickness. The main body and the spiral blade are respectively described with a rack cutter coordinate system and a tool coordinate system. The vector parameters based on the rack cutter coordinate system are transformed into vector parameters based on the tool coordinate system so as to simulate the main body with a rack cutter and develop the spiral blade to have variable tooth thickness. Thus, when a gear blank is tooled, the distance between the centers of the tool holder and the workpiece holder can be set as a constant, and the feed in the radial degree-of-freedom can be neglected, with twists of tooth flanks being inhibited.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Skiving tool comprising cutter bars
InactiveUS8950301B2Improve tool lifeReduce manufacturing costTurning machine accessoriesGear teeth manufacturing toolsHyperboloidEngineering
A skiving tool for manufacturing a rotationally symmetrical periodical structure on a work piece by means of a power skiving method. The skiving tool comprises a base body comprising a central rotation axis and a plurality of receiving openings and a plurality of cutter bars, fewer than or equal to the number of receiving openings. Each of the receiving openings has an elongate shape having a longitudinal axis, and the receiving openings can be arranged uniformly around the central rotation axis. The longitudinal axes of the receiving openings are generators of a rotation hyperboloid, which is arranged rotationally symmetrical to the central rotation axis.
Owner:KLINGELNBERG AG
Milling tool and insert, particularly thread milling cutter
InactiveUS20010018010A1Reduced stabilityTightly bondedThread cutting toolsMilling cuttersMilling cutterEngineering
Owner:VARGUS TOOL MFG
Method, bar blade, and use thereof for milling spiral bevel gears and hypoid gears
ActiveUS7775749B2Extended service lifeMetal working apparatusGear teeth manufacturing toolsGear wheelEngineering
In a method and a bar blade for milling spiral bevel gears and hypoid gears, a shaft of the bar blade has a blade profile that is formed by the cross-section of at least one cutting area, at least two free areas, and at least one top area. The blade profile is provided with a first cutting edge for a first flank, a second cutting edge for a second flank that faces the first flank, and a top cutting edge for the bottom of a tooth space. The first and the second cutting edge are embodied as principal cutting edges for completely cutting the first or second flank. The top cutting edge is configured for completely cutting the bottom of the tooth space such that the tooth space comprising the complete final geometry is created in one milling process by means of one and the same bar blade.
Owner:KLINGELNBERG AG
Thread mill having flute twisting in direction opposite to rotating direction
ActiveUS20060233623A1Good cutting sharpnessImprove accuracyThread cutting toolsThread cutting machinesFluteMilling cutter
A thread mill that is to be moved along a helical interpolation path while being rotated about an axis of the thread mill in a rotating direction, for forming a thread in a circumferential surface of a workpiece. The thread mill includes a cylindrical main body having (a) at least one spiral flute formed in an outer circumferential surface of the cylindrical main body, and (b) at least one cutting edge each provided by a rear-side one of widthwise opposite edges, as viewed in the rotating direction, of a corresponding one of the at least one spiral flute. Each of the at least one spiral flute extends in a direction opposite to the rotating direction as viewed in a direction away from a proximal end of the cylindrical main body toward a distal end of the cylindrical main body. Also disclosed is a method of forming the thread by using the thread mill.
Owner:OSG
Method, bar blade, and use thereof for milling spiral bevel gears and hypoid gears
In a method and a bar blade for milling spiral bevel gears and hypoid gears, a shaft of the bar blade has a blade profile that is formed by the cross-section of at least one cutting area, at least two free areas, and at least one top area. The blade profile is provided with a first cutting edge for a first flank, a second cutting edge for a second flank that faces the first flank, and a top cutting edge for the bottom of a tooth space. The first and the second cutting edge are embodied as principal cutting edges for completely cutting the first or second flank. The top cutting edge is configured for completely cutting the bottom of the tooth space such that the tooth space comprising the complete final geometry is created in one milling process by means of one and the same bar blade.
Owner:KLINGELNBERG AG
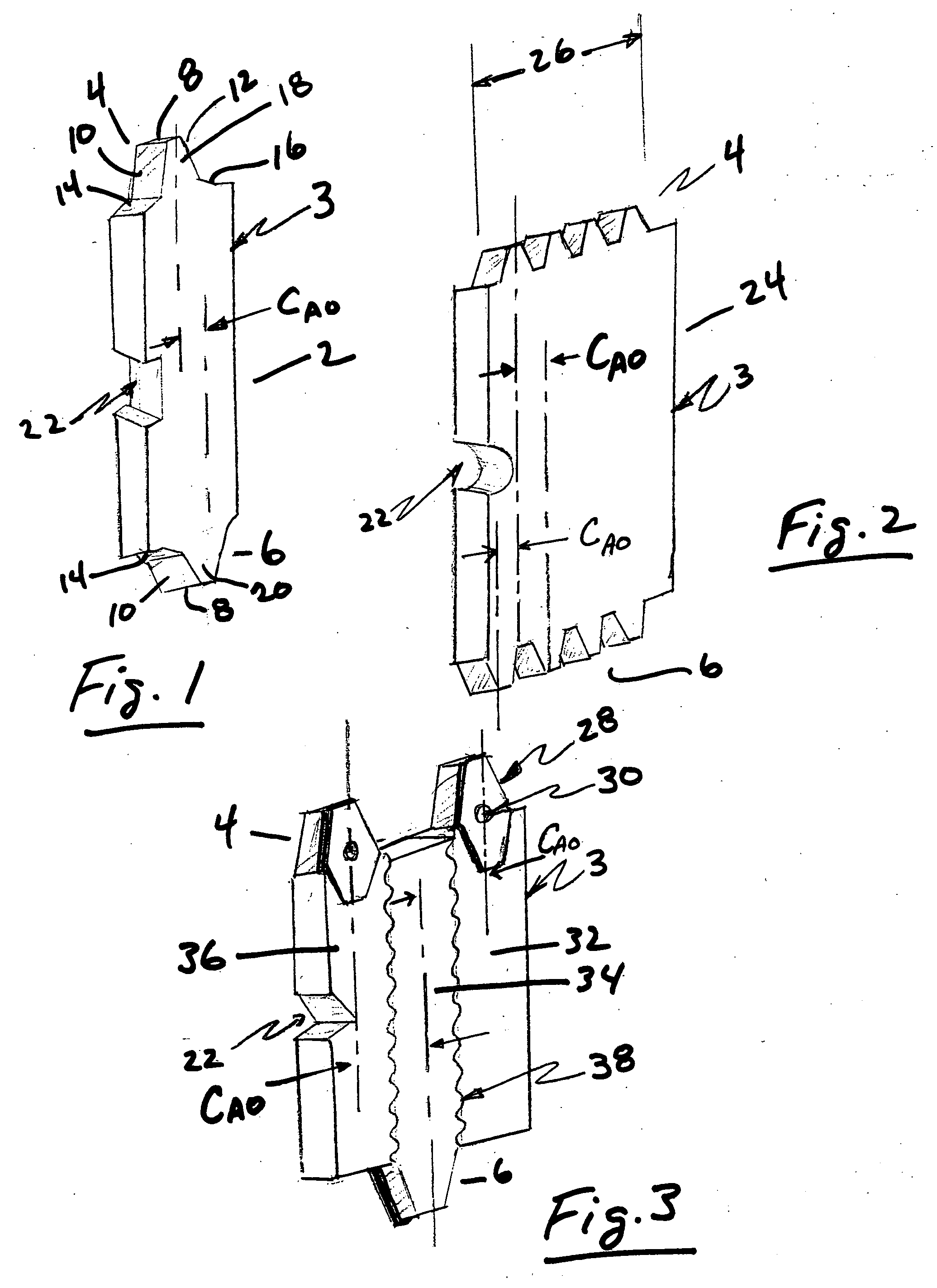
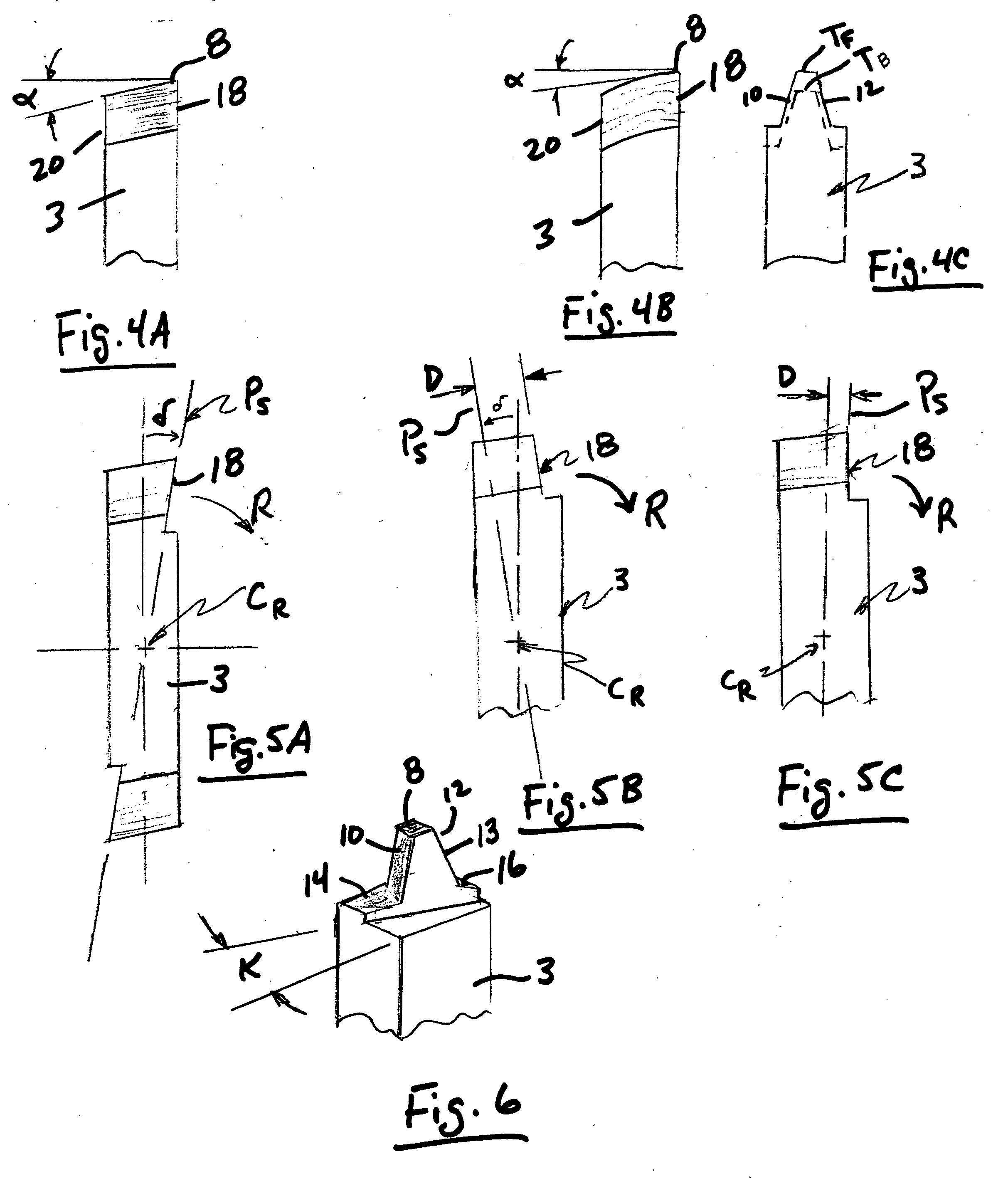
Cutting tool for gears and other toothed articles
InactiveUS20060133901A1Metal working apparatusGear teeth manufacturing toolsTooth surfaceTool holder
A cutting tool comprising a two-sided cutting blade positionable in a tool holder to form a blade hob. The inventive cutting tool can be used to duplicate the generation action of single or multi-threaded, multi-gashed hobs. The two-sided cutting blade comprises one or more tooth profile shaped cutting teeth located at each end of a cutting blade body. The cutting teeth on respective ends are axially offset from one another. The cutting blade is moved to a number of generating positions to generate the desired tooth surface on a workpiece.
Owner:GLEASON CUTTING TOOLS CORP
Deburring blade, device for mounting of deburring blades and bevel gear cutting machine for chamfering and/or deburring a bevel gear
ActiveUS7431544B2The degree of freedom becomes largerHandling device is simpleMilling cuttersLarge fixed membersEngineeringKnife blades
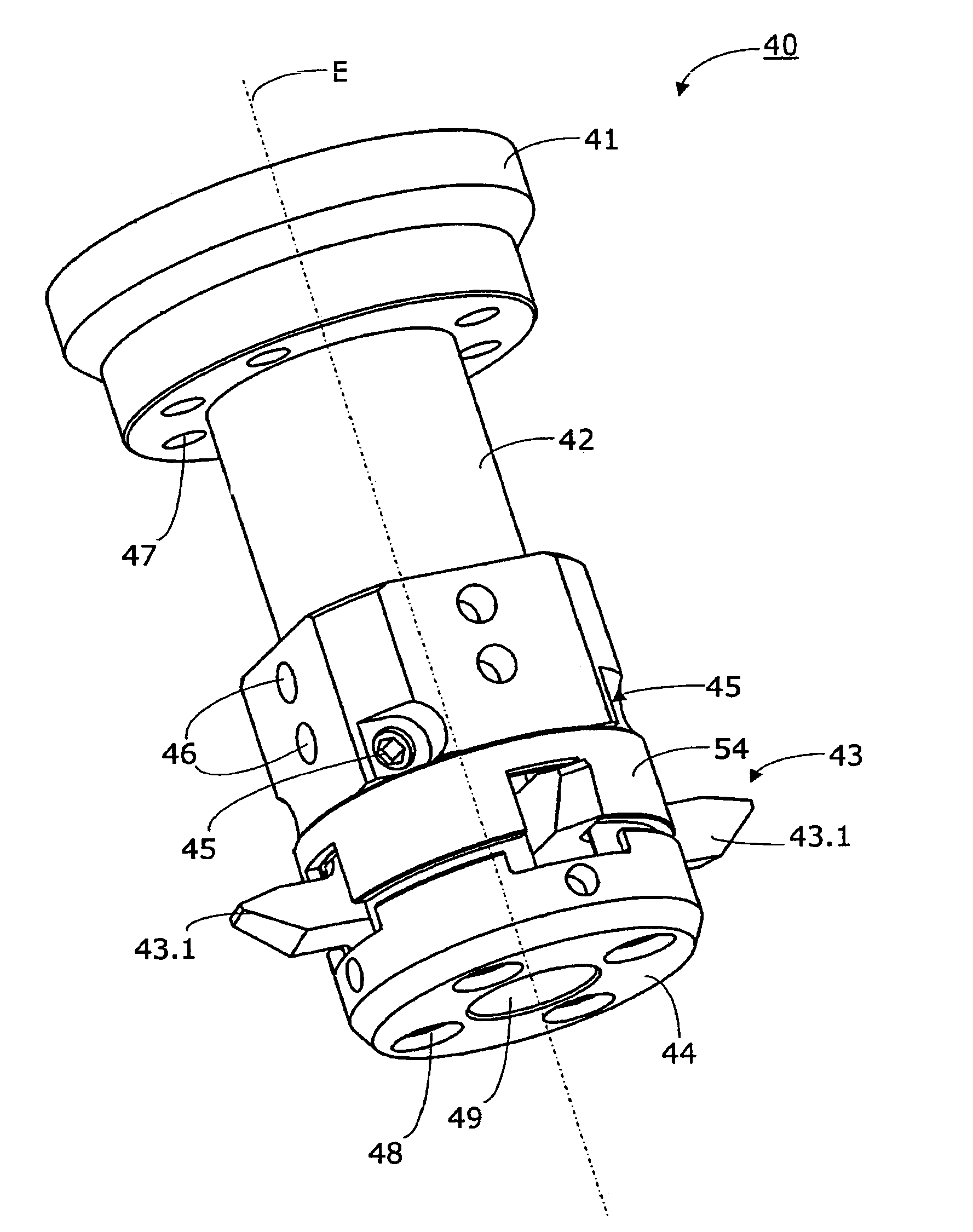
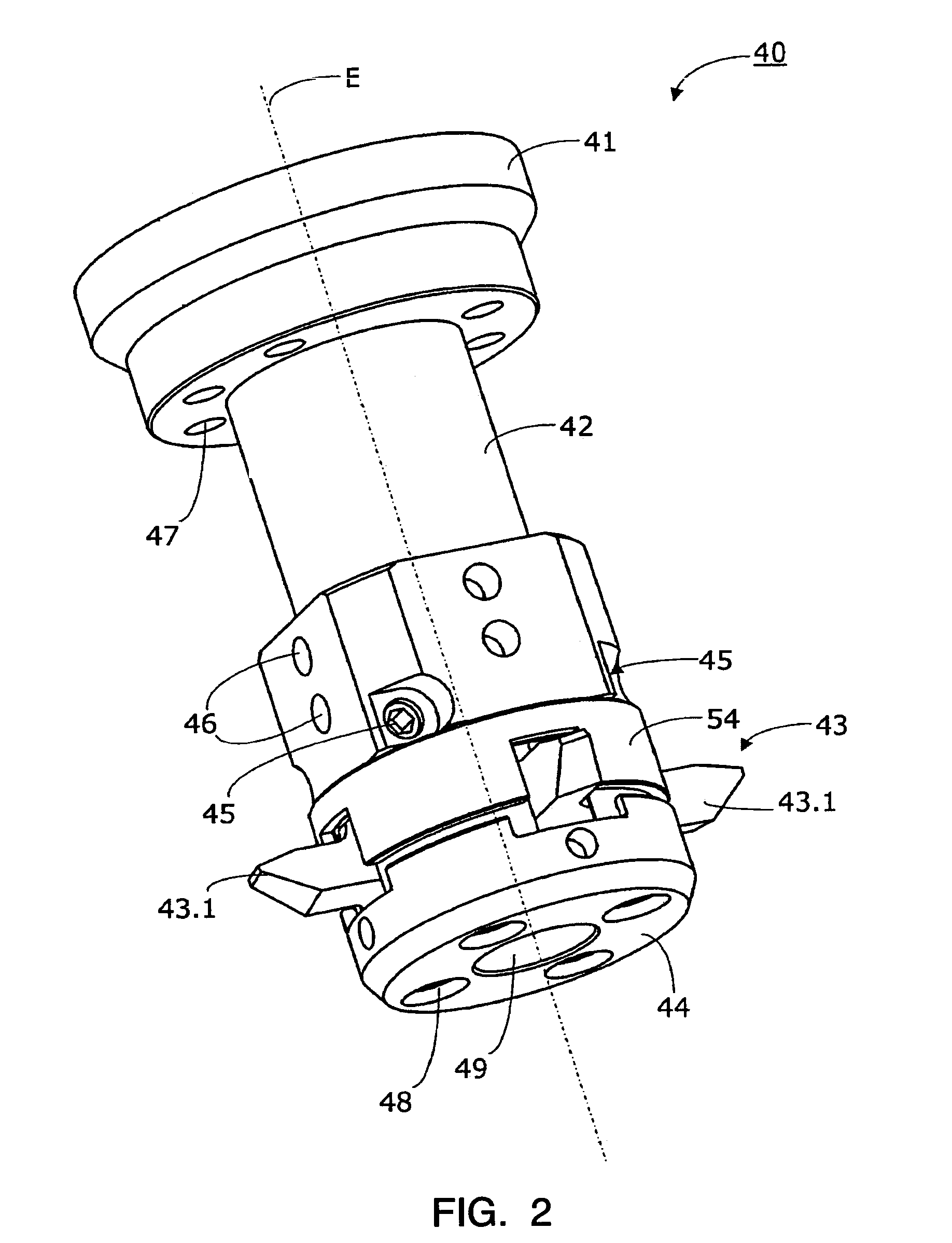
Bevel gear cutting machine for chamfering and / or deburring edges on the teeth of a bevel gear. The gear-cutting machine comprises a workpiece spindle, which receives the bevel gear coaxially of a spindle axis. Furthermore, a deburring spindle is provided for the receiving of a deburring tool and several numerically controllable axes are given. A deburring blade head with several blade cutter-like blade inserts serves as deburring tool, whereby the blade inserts are insertable in recesses of the deburring blade head essentially radially oriented to a deburring spindle axis (E) and comprise edges for chamfering and / or deburring.
Owner:KLINGELNBERG AG
Milling tool, and milling insert kit
InactiveUS20120257935A1Improve accuracyExtended service lifeMilling cuttersGear teeth manufacturing toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Milling tool and milling insert kit are provided for the gash milling of a workpiece. The tool comprises a tool body that defines a rotation axis and has a first end, an opposite second end, and a peripheral surface that extends around the rotation axis between the first end and the second end. A large number of separated seats, which are arranged one after the other in the tool body along a line and receive one each of corresponding number of replaceable milling inserts, comprise a primary main cutting edge and a secondary main cutting edge that converge to each other. The milling inserts comprise outer milling inserts, which project from the tool body by a first length from the rotation axis, and inner milling inserts, which project from the tool body by a second length from the rotation axis. The first length is considerably greater than the second length.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
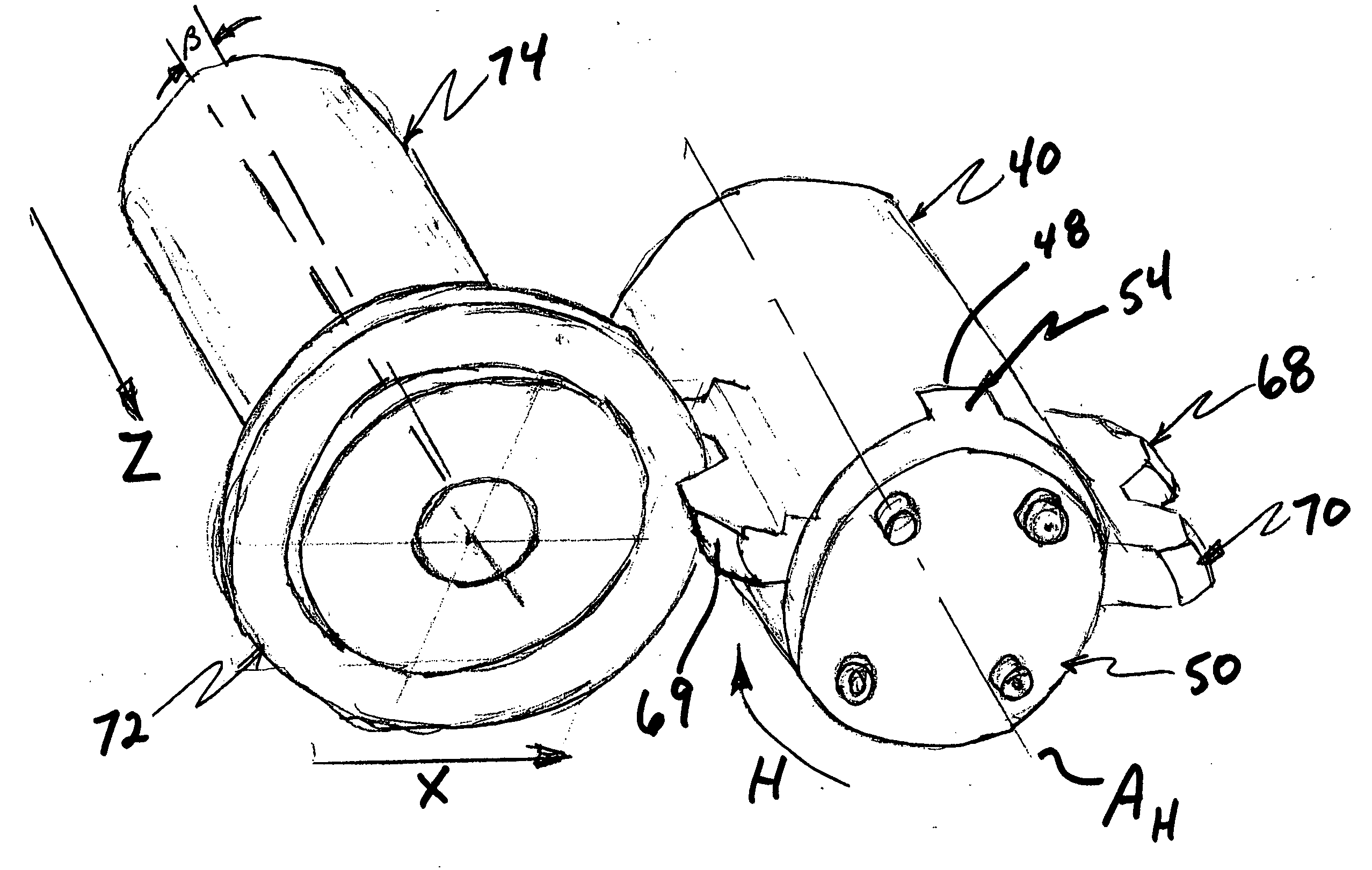
Milling tool for gear milling
ActiveCN102632303AExtended service lifeNo maintenanceThread cutting machinesMilling cuttersHelical lineHobbing
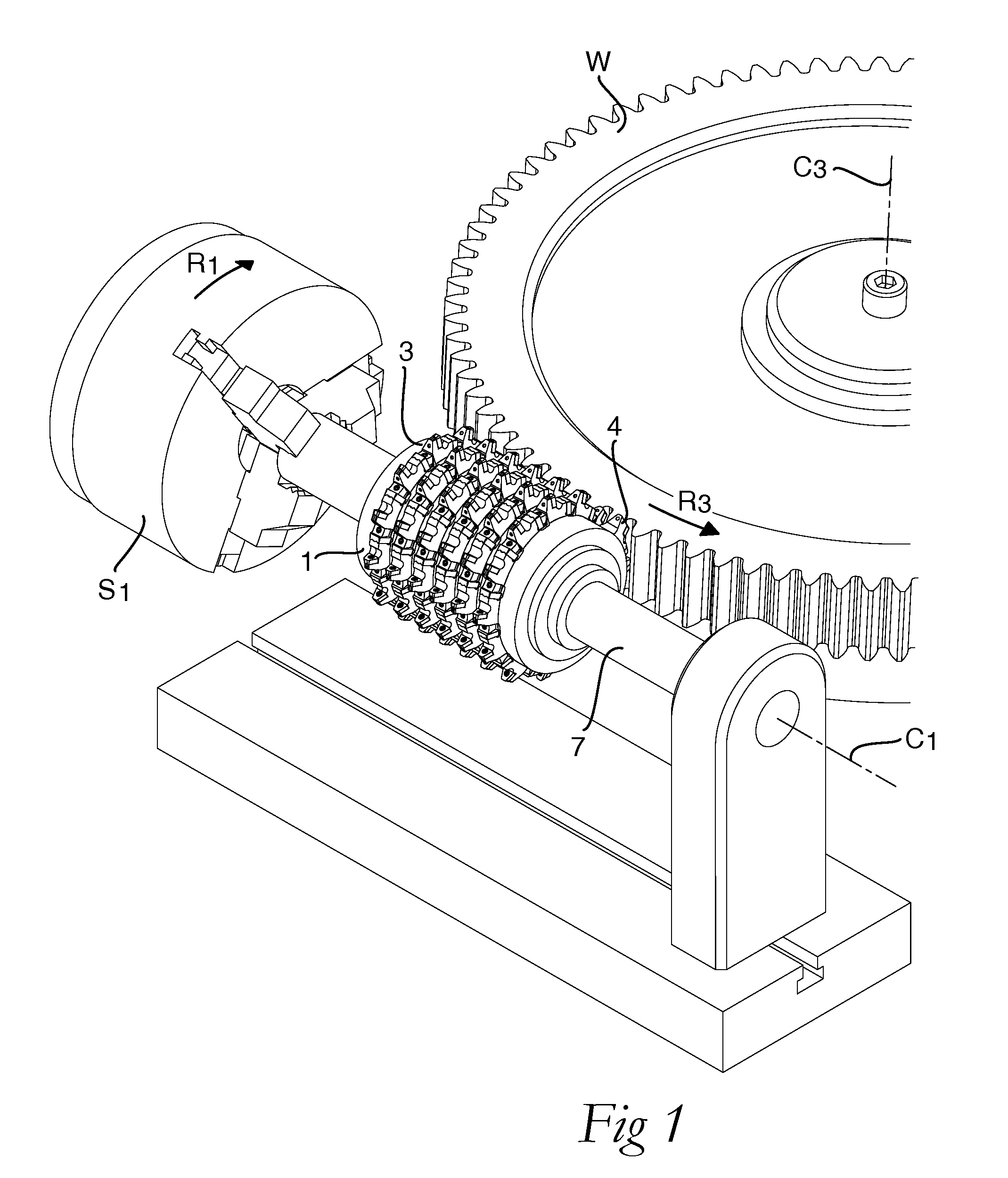
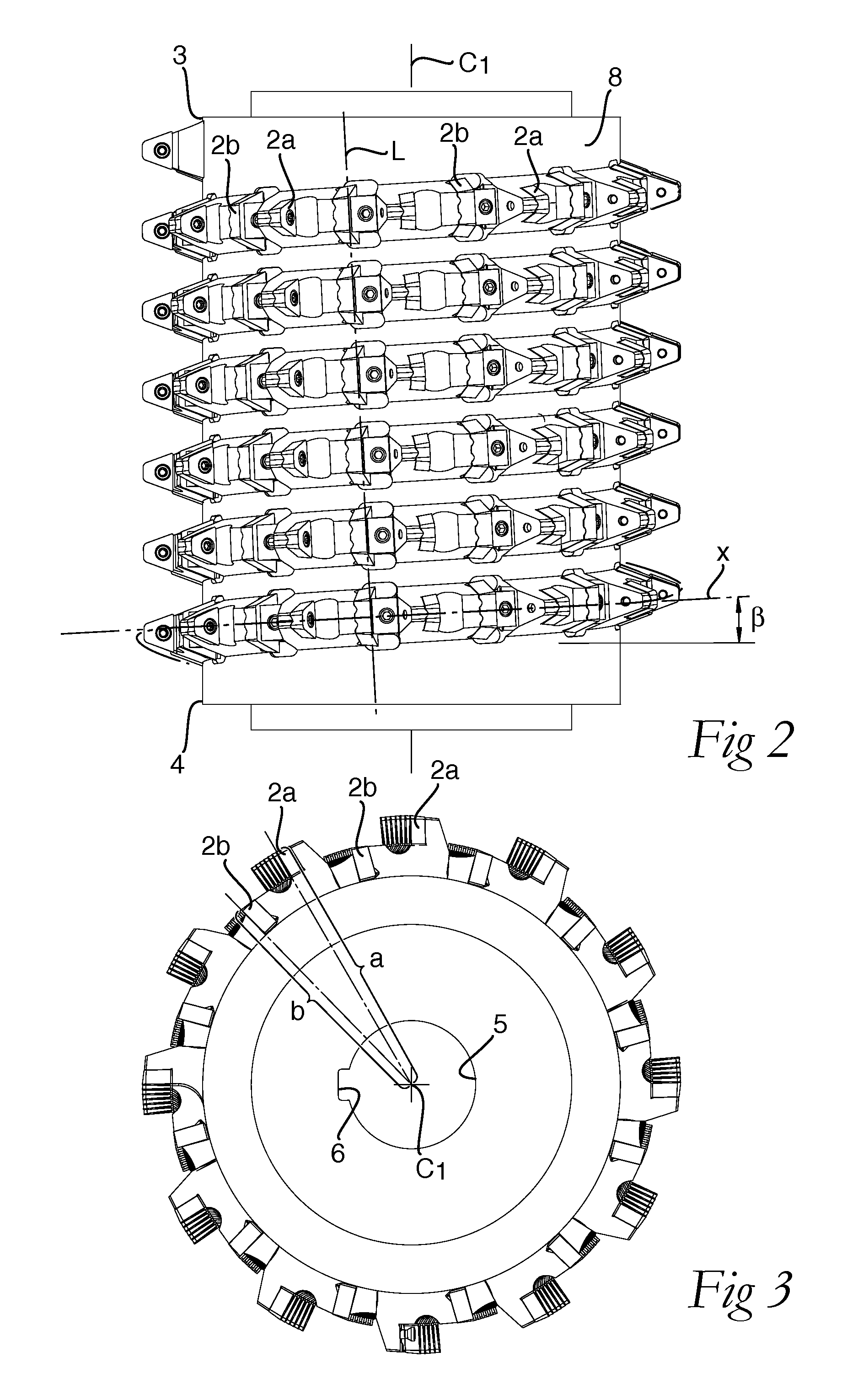
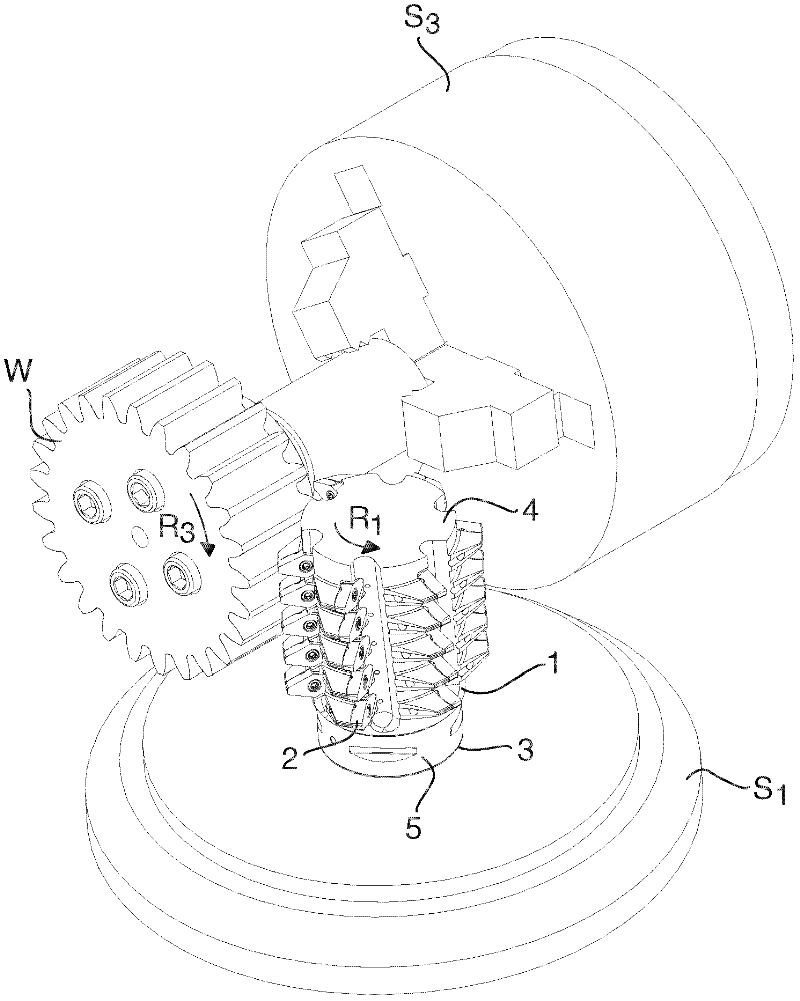
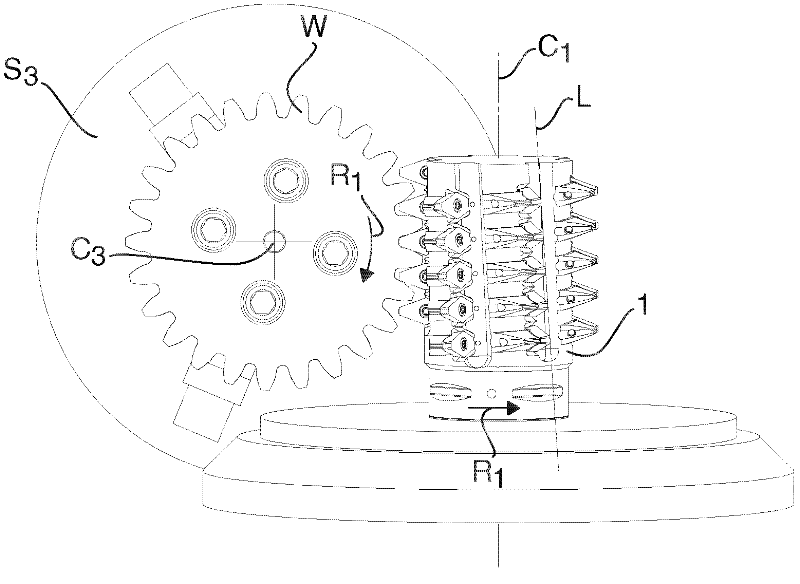
A milling tool, for the hobbing of a workpiece having cogs, comprises a tool body (1) that has a fixing end (3), an opposite outer end (4), and a peripheral surface (7). The tool body comprises a large number of separated seats (9) that are arranged at the peripheral surface (7) one after the other along a helix line (x) having a constant pitch. A corresponding large number of replaceable milling inserts (2) comprise an under side (21), an opposite upper side (22) that forms a chip surface (24), a circumferential edge side (23), two pairs of main cutting edges (25). The chip surface (24) extends in an extension plane that comprises the main cutting edges. Each seat is formed to receive one of the milling inserts and comprises a support surface that allows support to the milling insert projecting from the tool body for cutting engagement with a gash of the workpiece. The chip surface extension plane of each milling insert has a normal that is parallel to the tangent of the helix line where the same intersects the extension plane.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Universally usable bar cutter head and use thereof
ActiveUS20100111629A1Flexible usePrecise maintenanceGear teeth manufacturing toolsMetal working apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
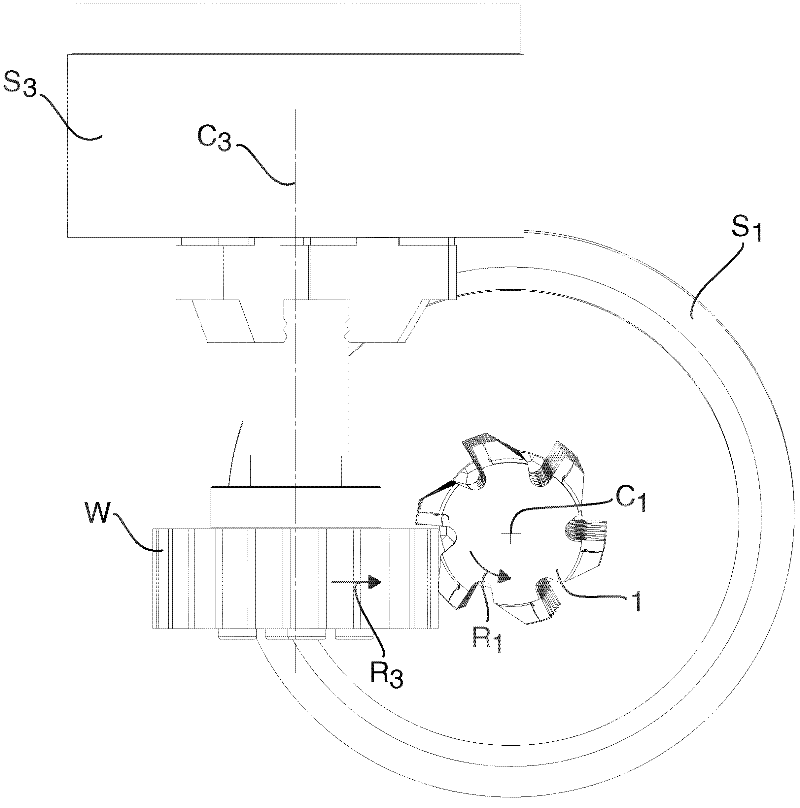
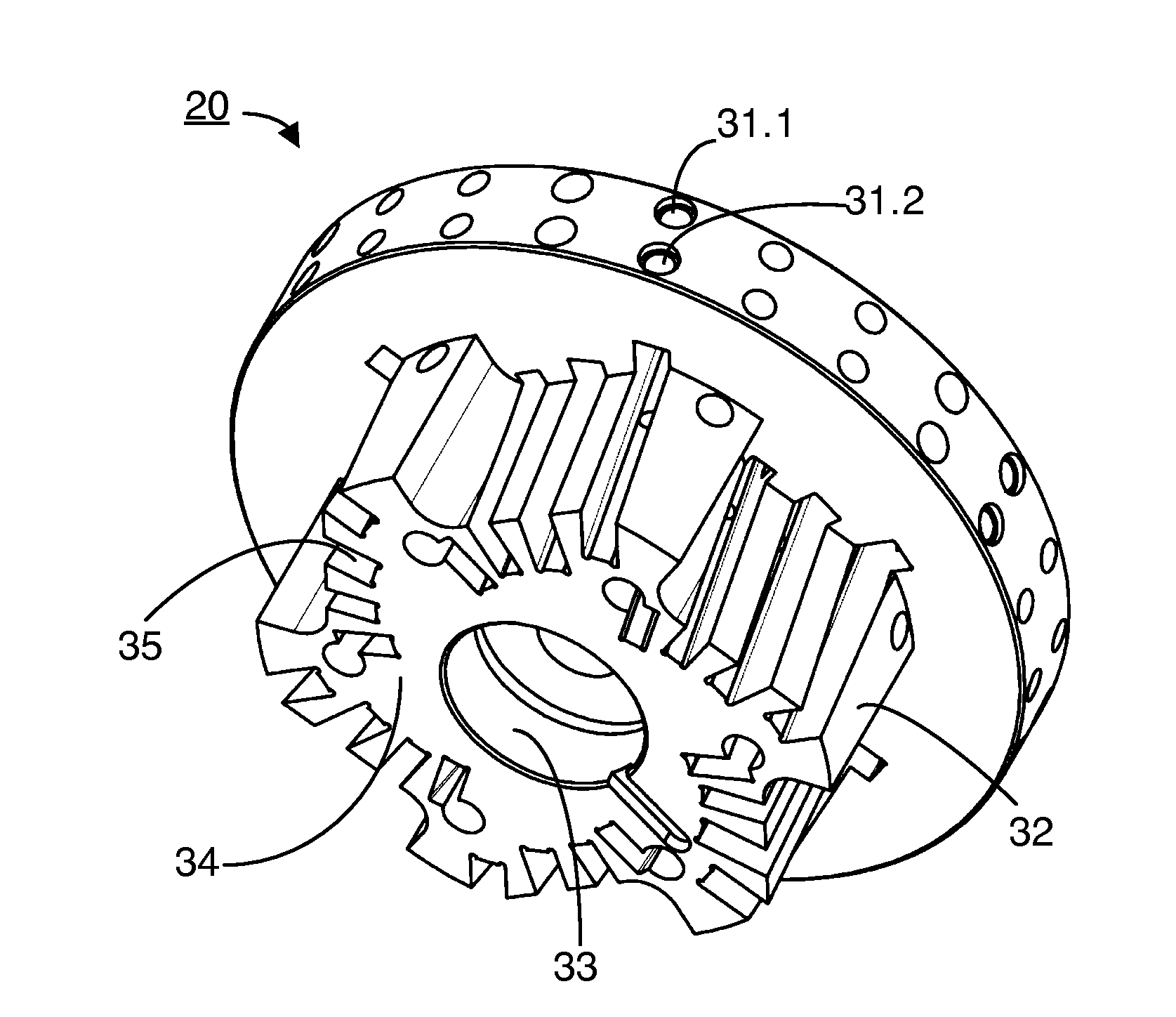
Bar cutter head (20) for receiving multiple bar cutters of a first bar cutter set, the bar cutter head (20) having n receptacle openings (25.1-25.6) for receiving n bar cutters of the first bar cutter set, which are all situated along a first concentric cutter head nominal circle having a first cutter head nominal radius (r1). A first spiral-toothed bevel gear (11) can be milled in the single-indexing method in this configuration. The bar cutter head (20) additionally has m receptacle openings (26.1-26.6) for receiving m bar cutters of a second bar cutter set, which are all situated along a second concentric cutter head nominal circle having a second cutter head nominal radius (r2). A second spiral-toothed bevel gear can be milled in the configuration having the m bar cutters. It is thus a universally-usable cutter head (20).
Owner:KLINGELNBERG AG
One piece cutter body
InactiveUS6398467B1Metal working apparatusGear teeth manufacturing toolsNumerical controlEngineering
One-piece cutter body for gear cutting operations. The one-piece cutter body has a plurality of circumferentially spaced slots for receipt of gear cutting blade. The slots are formed by a heatless electroerosive process, preferably electron-discharge machining (EDM) process utilizes computer numerical control (CNC) methods. A cutter body having outstanding strength and durability with highly precise slot configurations is obtained.
Owner:DANA CORP
Gear cutting machine, end mill and method of form milling
InactiveUS20130101367A1Reduce wear and tearFast cutting speedMilling cuttersMetal working apparatusMilling cutterEnd mill
The present disclosure relates to a gear cutting machine for gear cutting a workpiece, in particular a toothed wheel, by form milling having at least one cutter head for mounting at least one end mill, wherein the cutter head or the end mill and / or the workpiece mount are adjustable and the end mill axis can be aligned approximately parallel to the machined tooth flank of the clamped workpiece, and wherein the cutter axis can be applied to the flank contour and the end mill has an outer contour corresponding to the flank contour.
Owner:LIEBHERR VERZAHNTECHNIK GMBH
Combination gear hobber, chamfer/debur and shaver apparatus and method
An apparatus is provided for manufacturing a gear component. The apparatus includes a plurality of tooling stocks movable relative to a base. The tooling stocks function to retain a component, as well as operably driving a combination hob / shaver tool and a combination chamfer / debut tool. The apparatus reduces the number of machines required to complete the gear component as well as reducing the cycle time for complete component manufacture. In this way, a more efficient manufacturing system is provided, whereby capital investment and operational costs are reduced.
Owner:MAGNA DRIVETRAIN OF AMERICA
Face hobbing or gear cutting head for cutting gears, such as spiral, bevel, spiral-bevel, and hypoid gears
InactiveUS20080170915A1Accurate fitEasy constructionGear teeth manufacturing toolsGear cutting toolHobbingTrademark
A face hobbing or gear cutting head for cutting gears, such as spiral, bevel, and hypoid gears which has a blade carrier for holding cutter blades. The abstract of the disclosure is submitted herewith as required by 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b). As stated in 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b): A brief abstract of the technical disclosure in the specification must commence on a separate sheet, preferably following the claims, under the heading “Abstract of the Disclosure.” The purpose of the abstract is to enable the Patent and Trademark Office and the public generally to determine quickly from a cursory inspection the nature and gist of the technical disclosure. The abstract shall not be used for interpreting the scope of the claims. Therefore, any statements made relating to the abstract are not intended to limit the claims in any manner and should not be interpreted as limiting the claims in any manner.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Thread mill having flute twisting in direction opposite to rotating direction
ActiveUS7377732B2Good cutting sharpnessImprove accuracyThread cutting toolsThread cutting machinesFluteEngineering
A thread mill that is to be moved along a helical interpolation path while being rotated about an axis of the thread mill in a rotating direction, for forming a thread in a circumferential surface of a workpiece. The thread mill includes a cylindrical main body having (a) at least one spiral flute formed in an outer circumferential surface of the cylindrical main body, and (b) at least one cutting edge each provided by a rear-side one of widthwise opposite edges, as viewed in the rotating direction, of a corresponding one of the at least one spiral flute. Each of the at least one spiral flute extends in a direction opposite to the rotating direction as viewed in a direction away from a proximal end of the cylindrical main body toward a distal end of the cylindrical main body. Also disclosed is a method of forming the thread by using the thread mill.
Owner:OSG
Drill thread milling cutter
InactiveUS7419339B2Improve cutting effectGood chip breaking effectThread cutting toolsWood turning toolsMilling cutterDrill bit
The invention relates to a drill thread milling cutter (1) for producing a bore and for the subsequent milling of a thread in the bore, said drill thread milling cutter (1) having a working region (2), on the circumference (3) of which a number of drilling and milling cutting edges are arranged. A number of milling cutting edges (7, 8, 9, 10) greater than the number of drilling cutting edges (17) by a factor greater than 2 are arranged or are effective in the direction of rotation.
Owner:EMUGE WERK RICHARD GLIMPEL & FAB FUR PRAZISIONSWERKZEUGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com