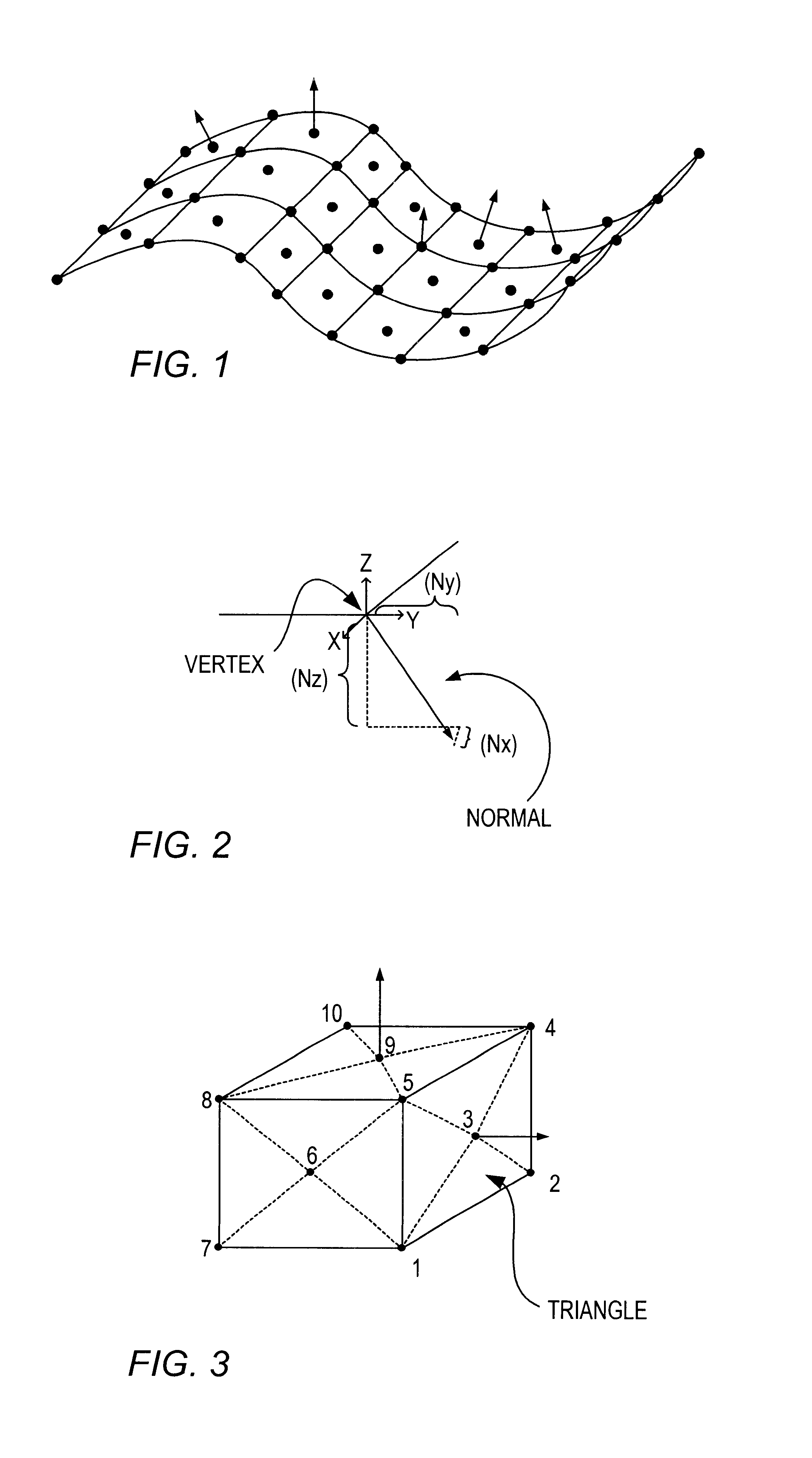
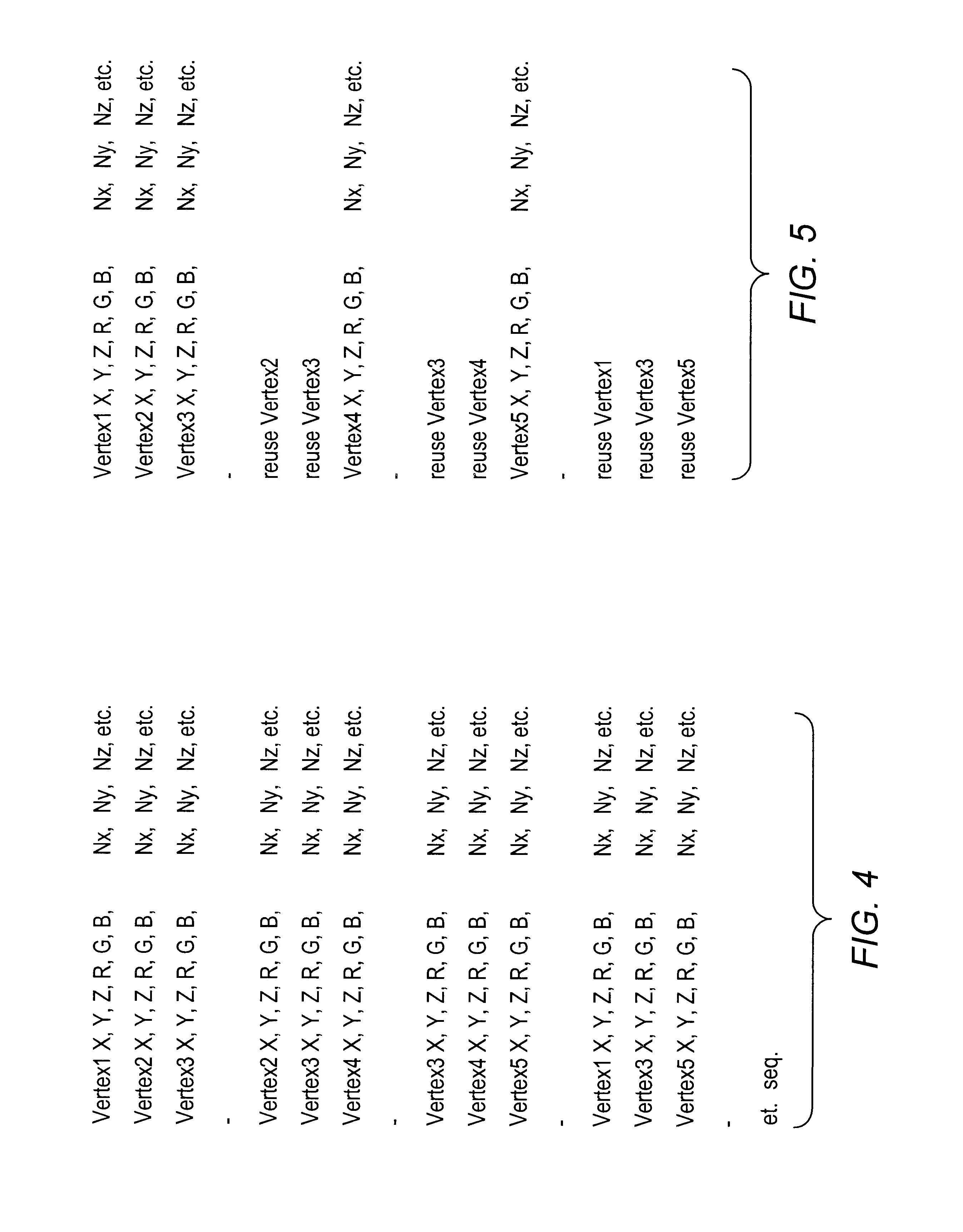
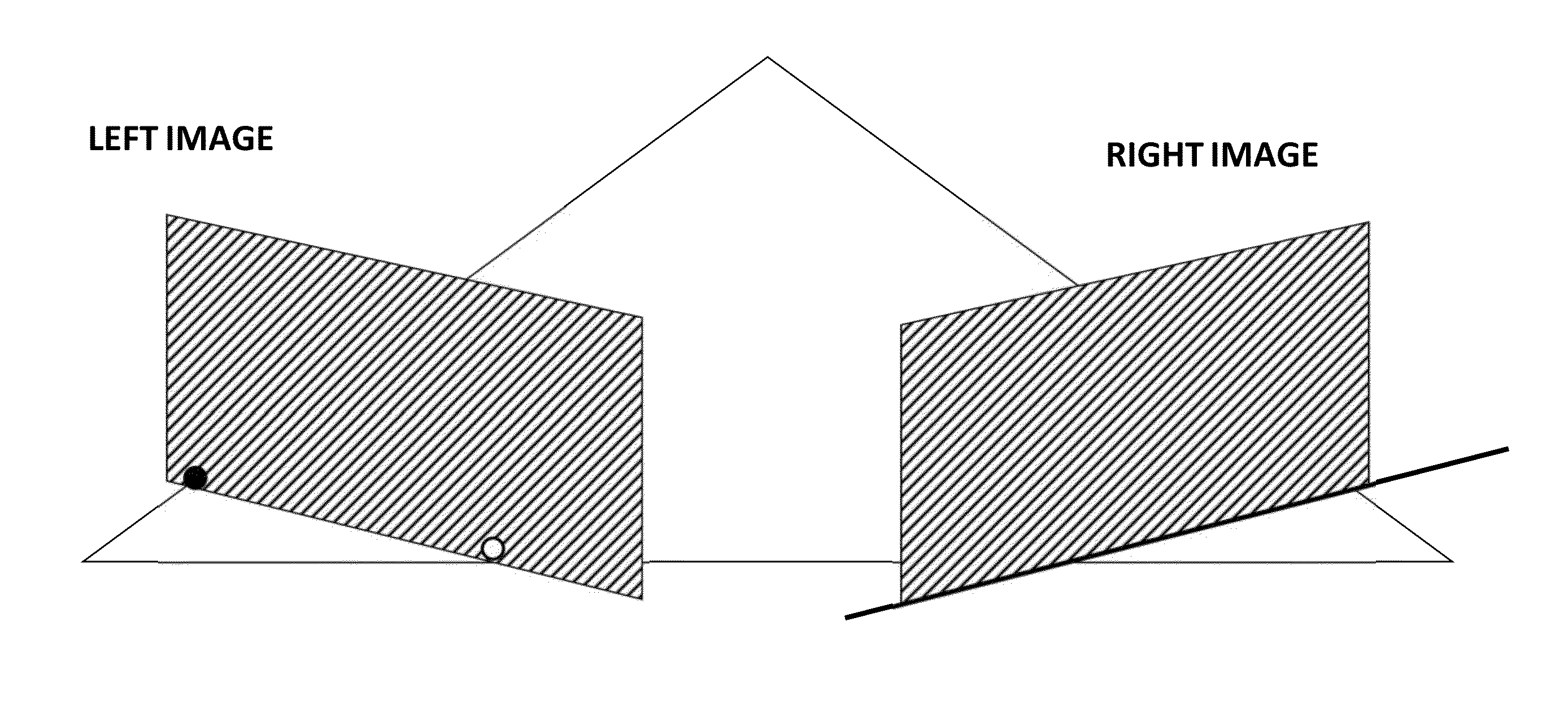
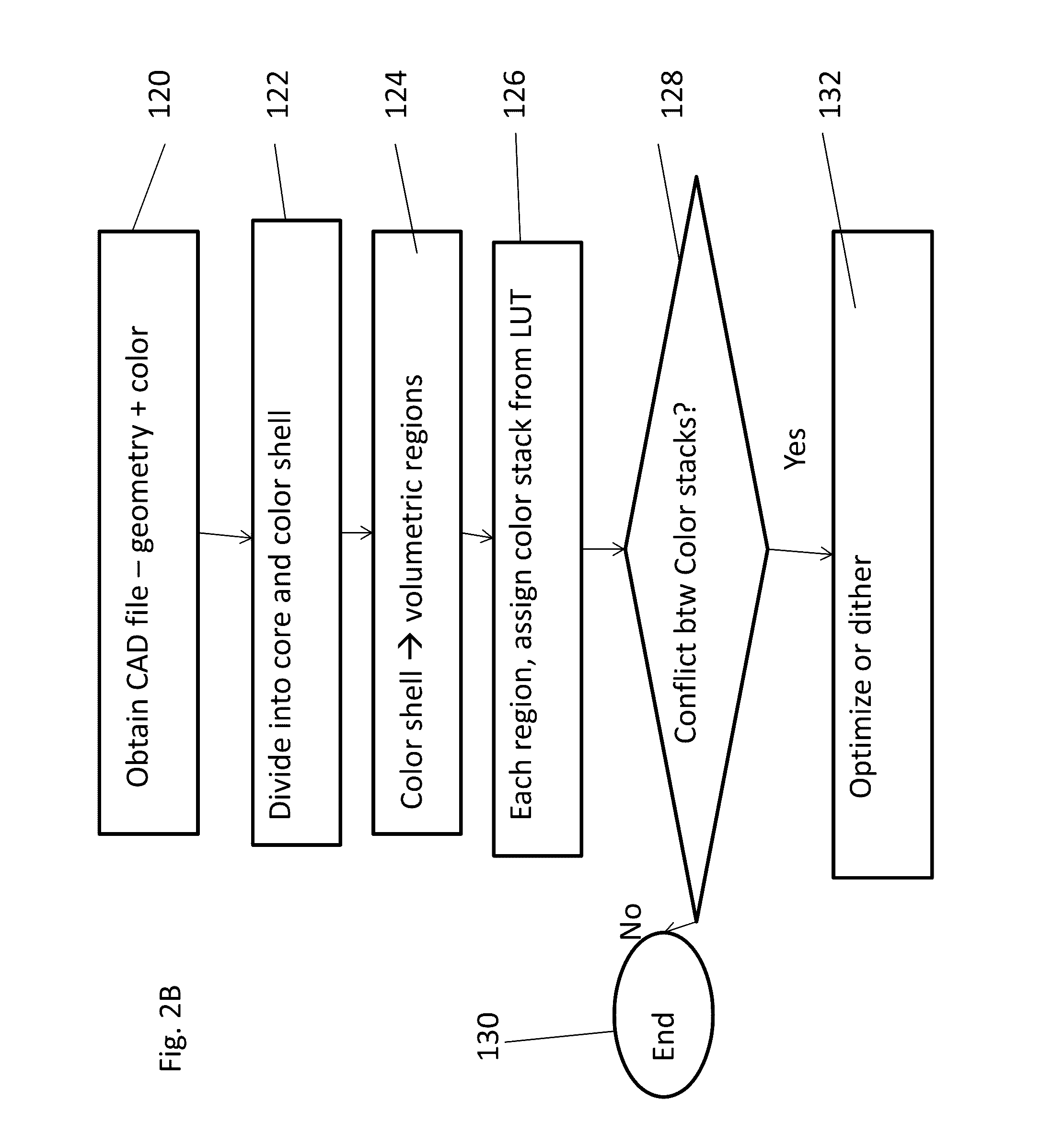
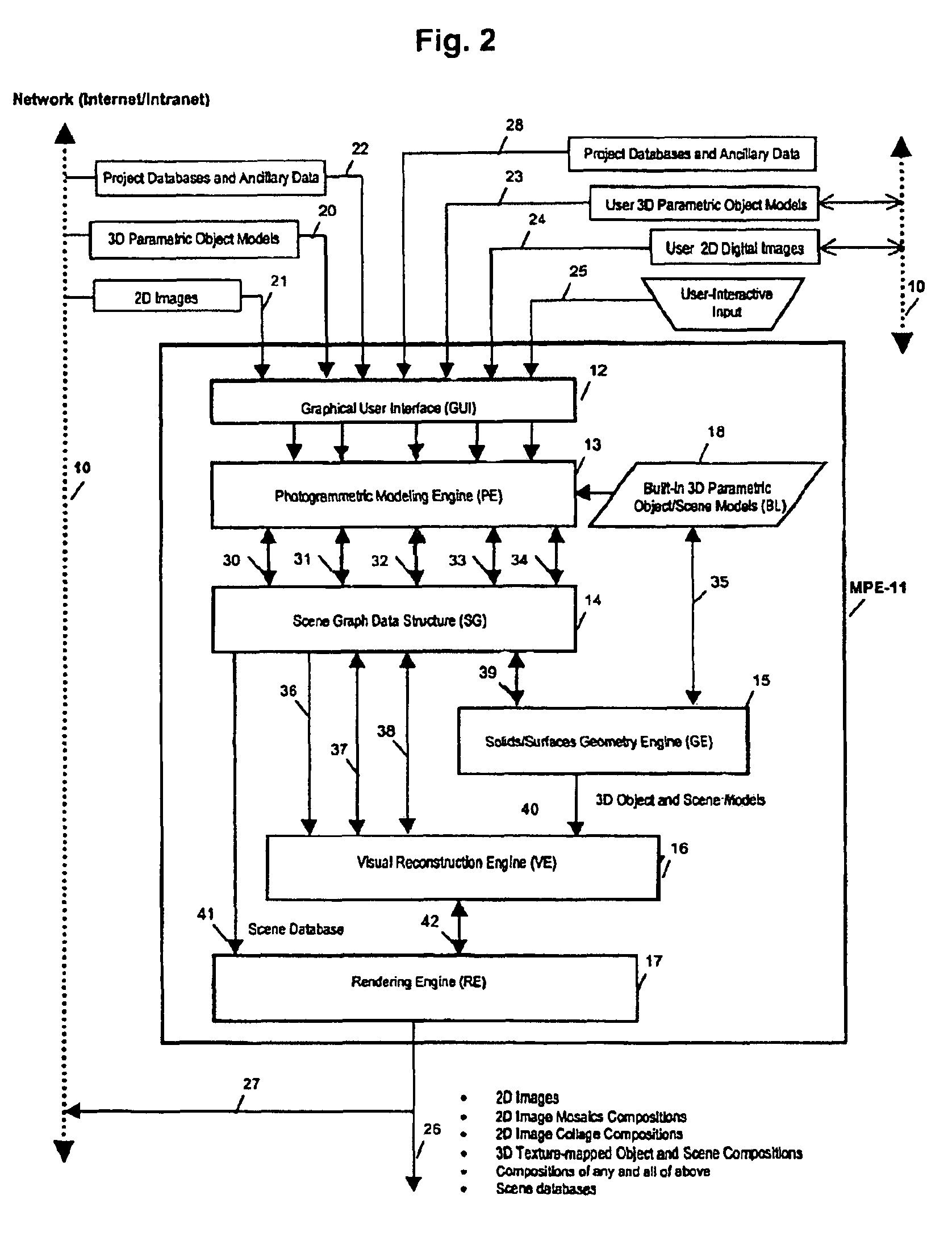
Patents
Literature
170 results about "3d geometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
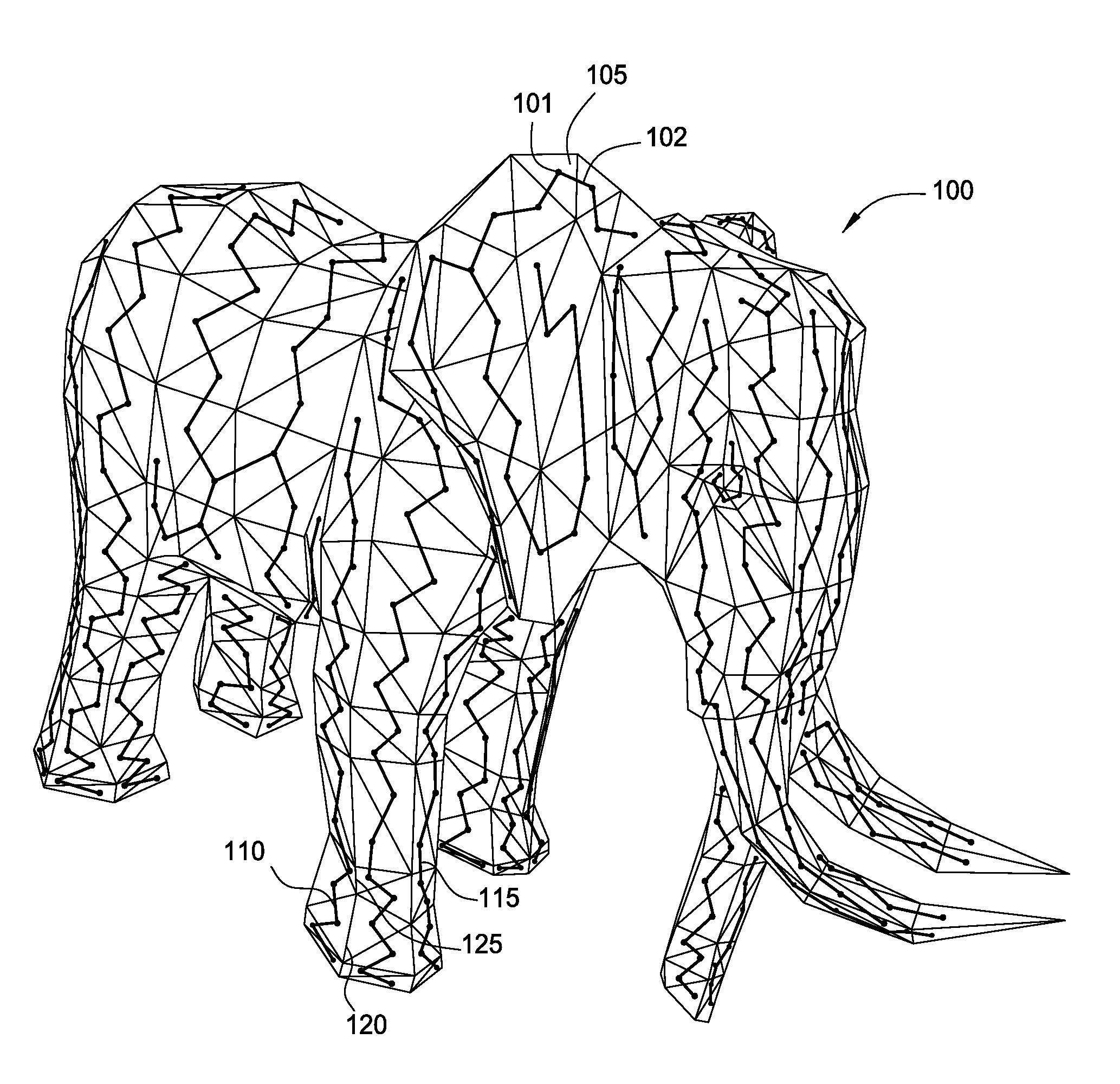
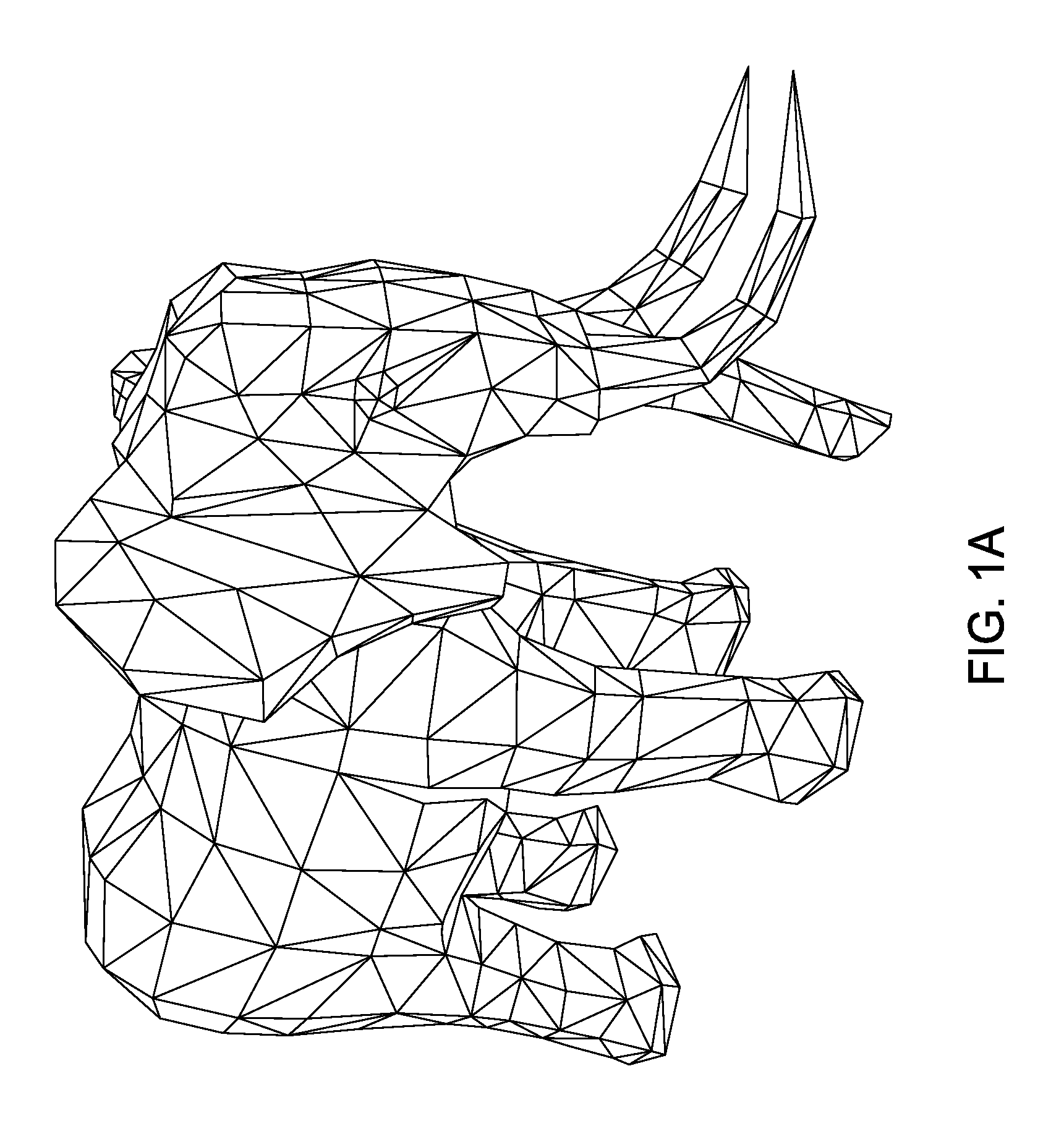
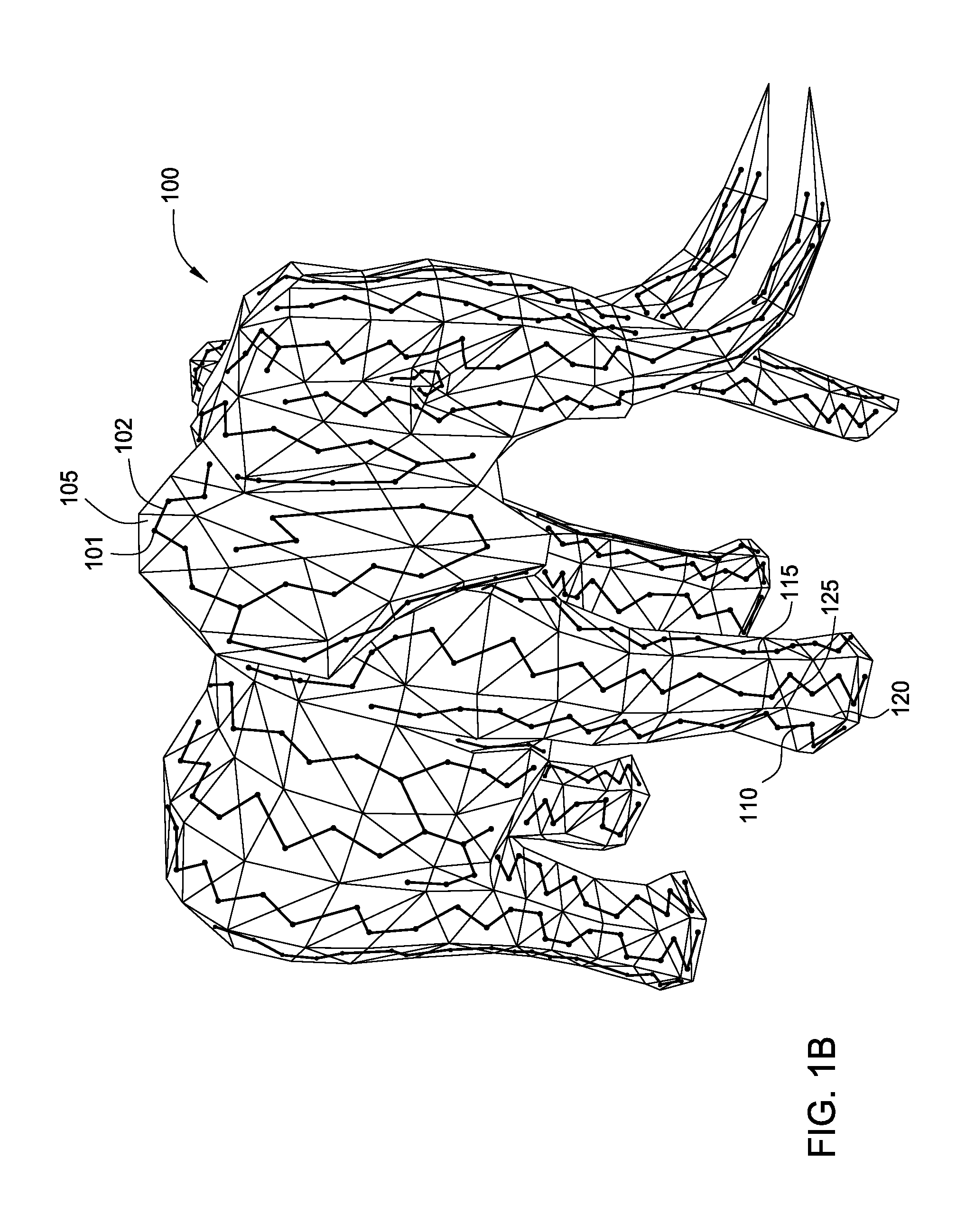
3D Geometric Modeling And Motion Capture Using Both Single And Dual Imaging
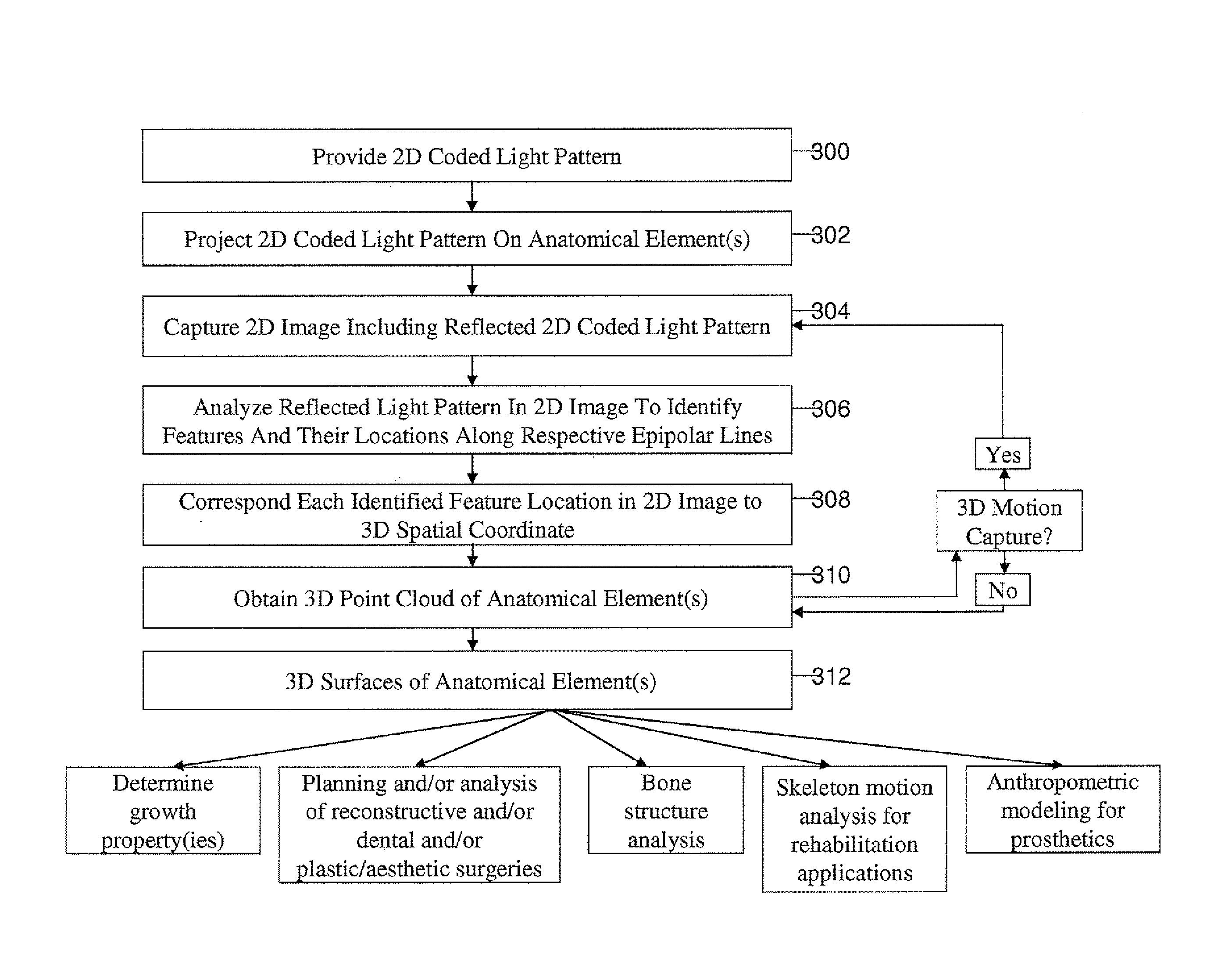
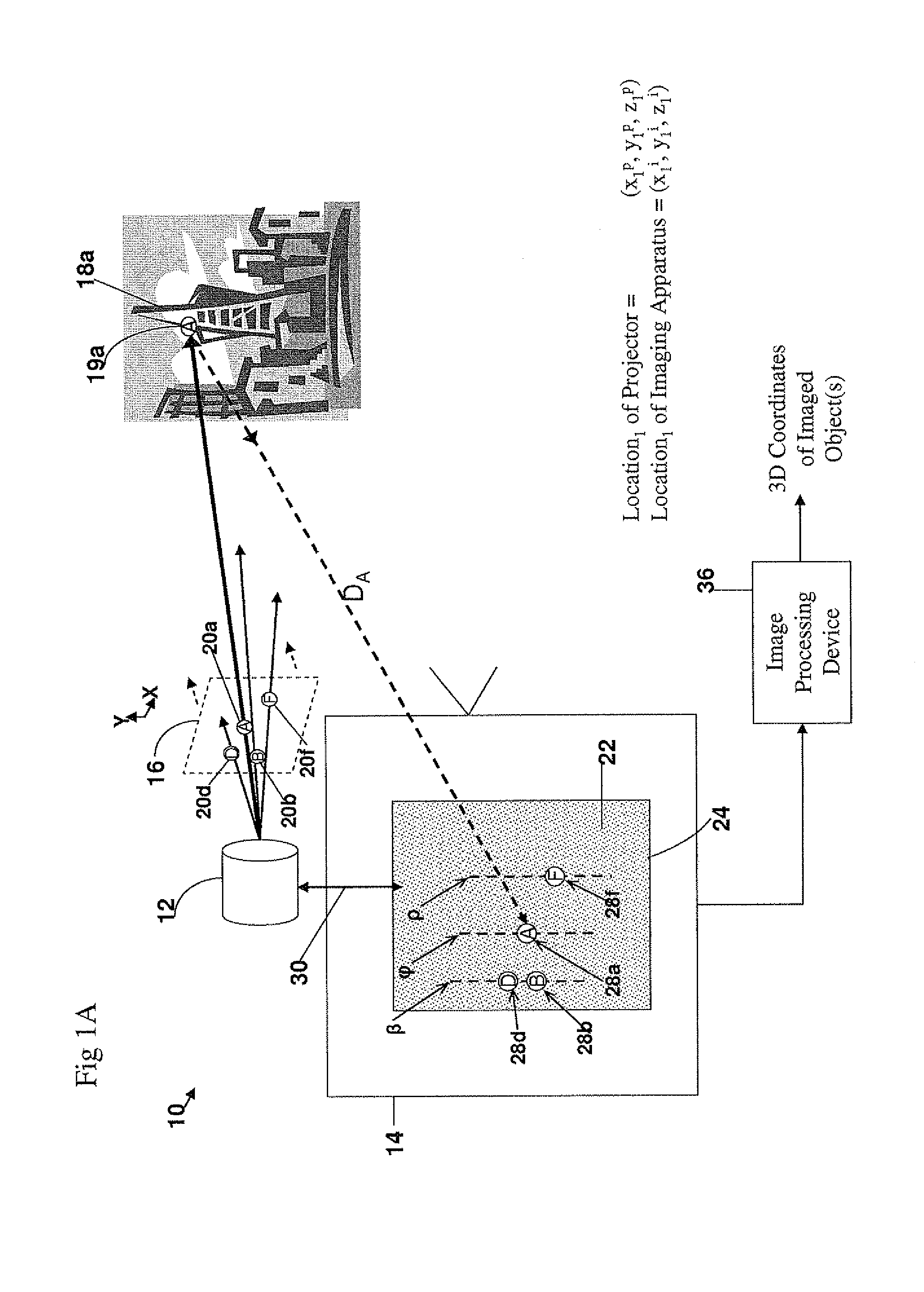
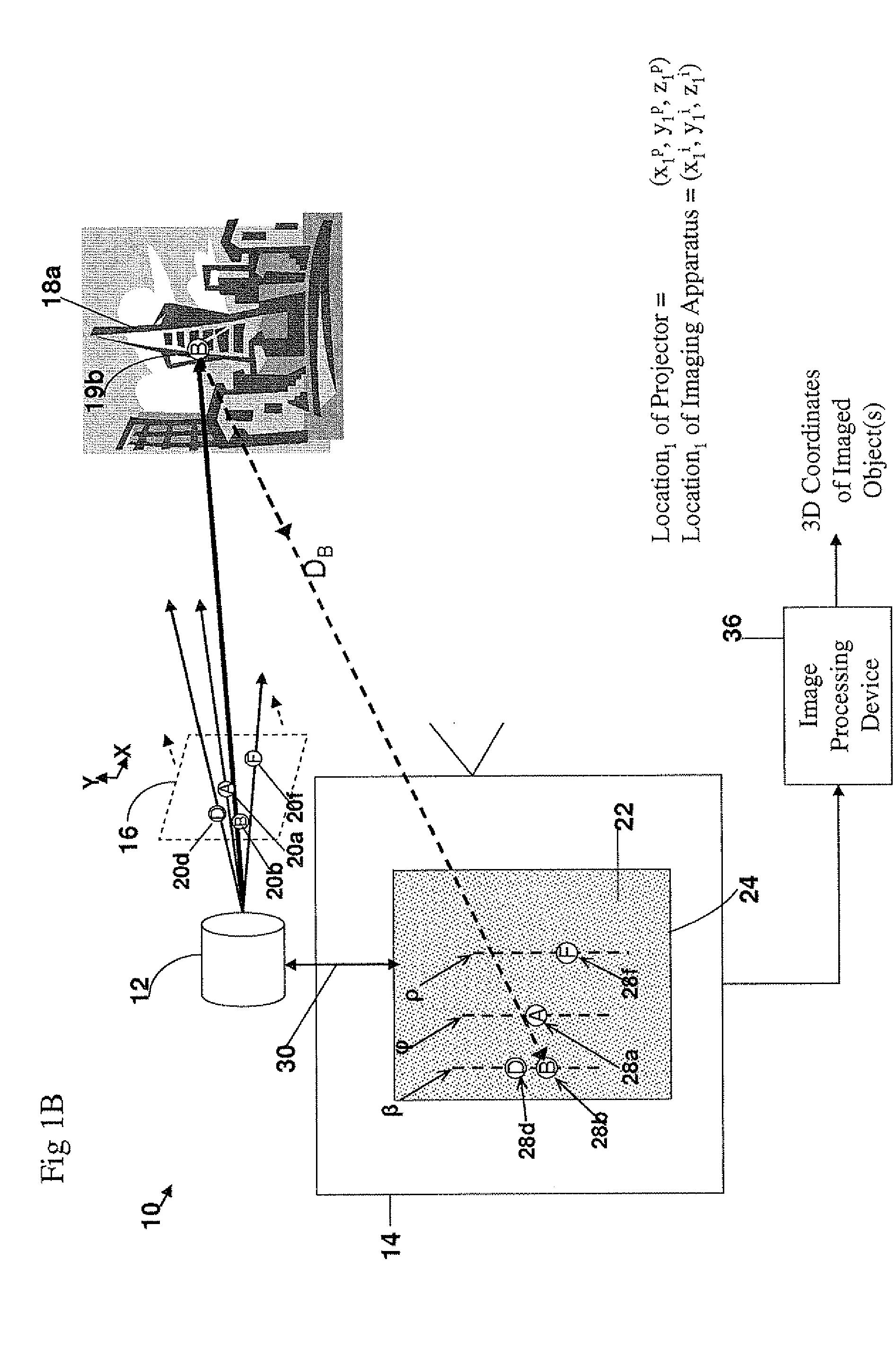
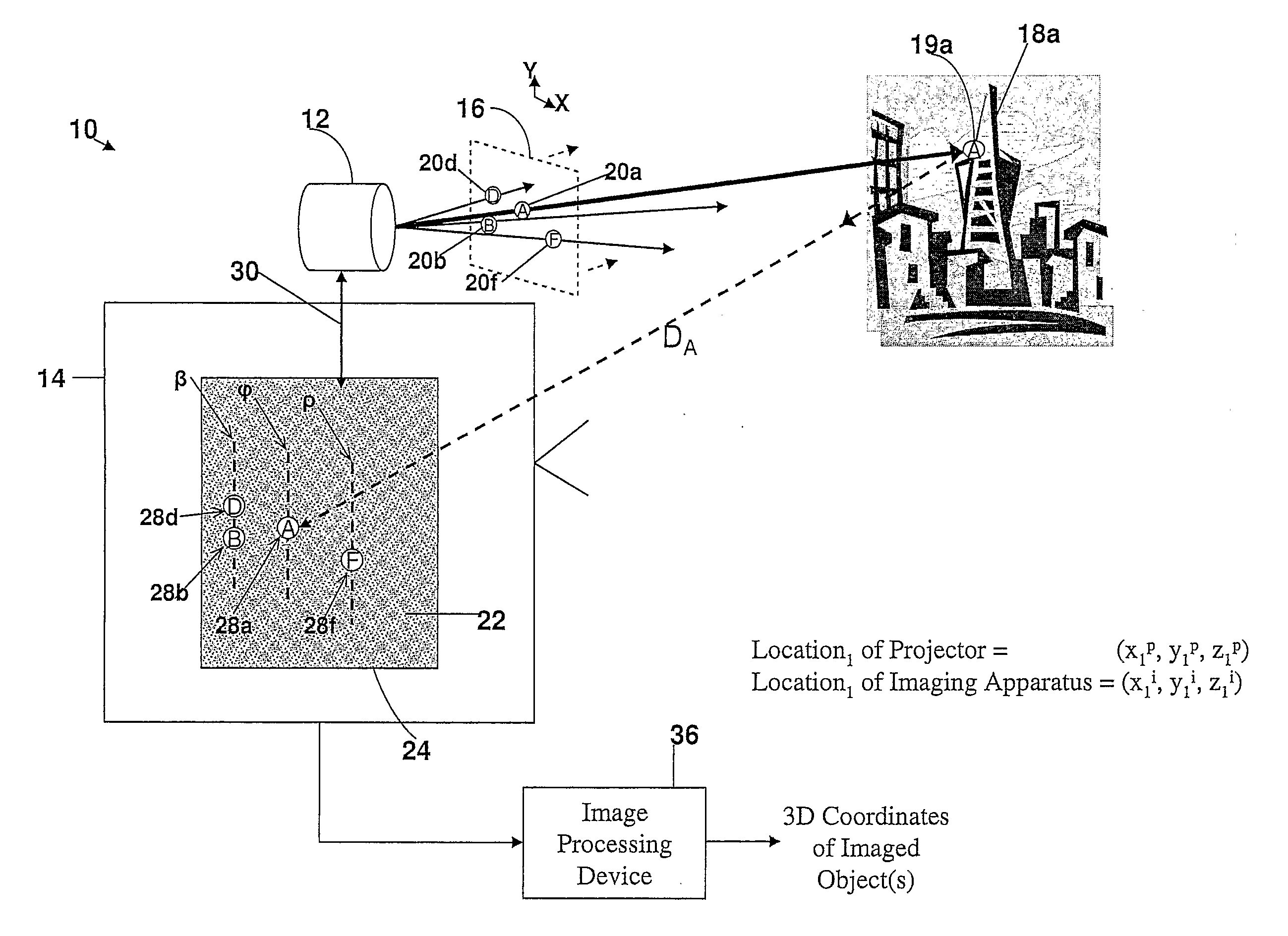
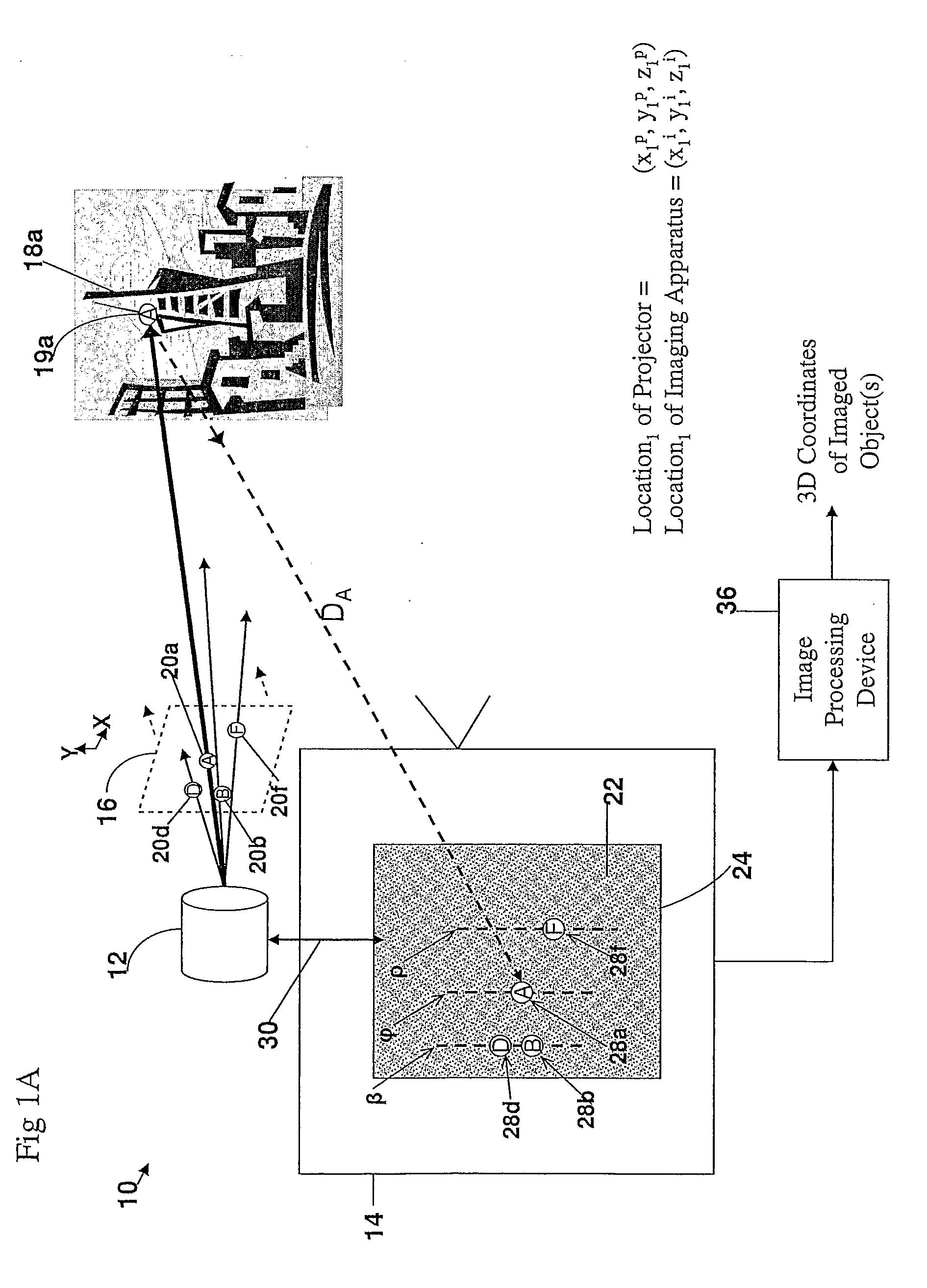
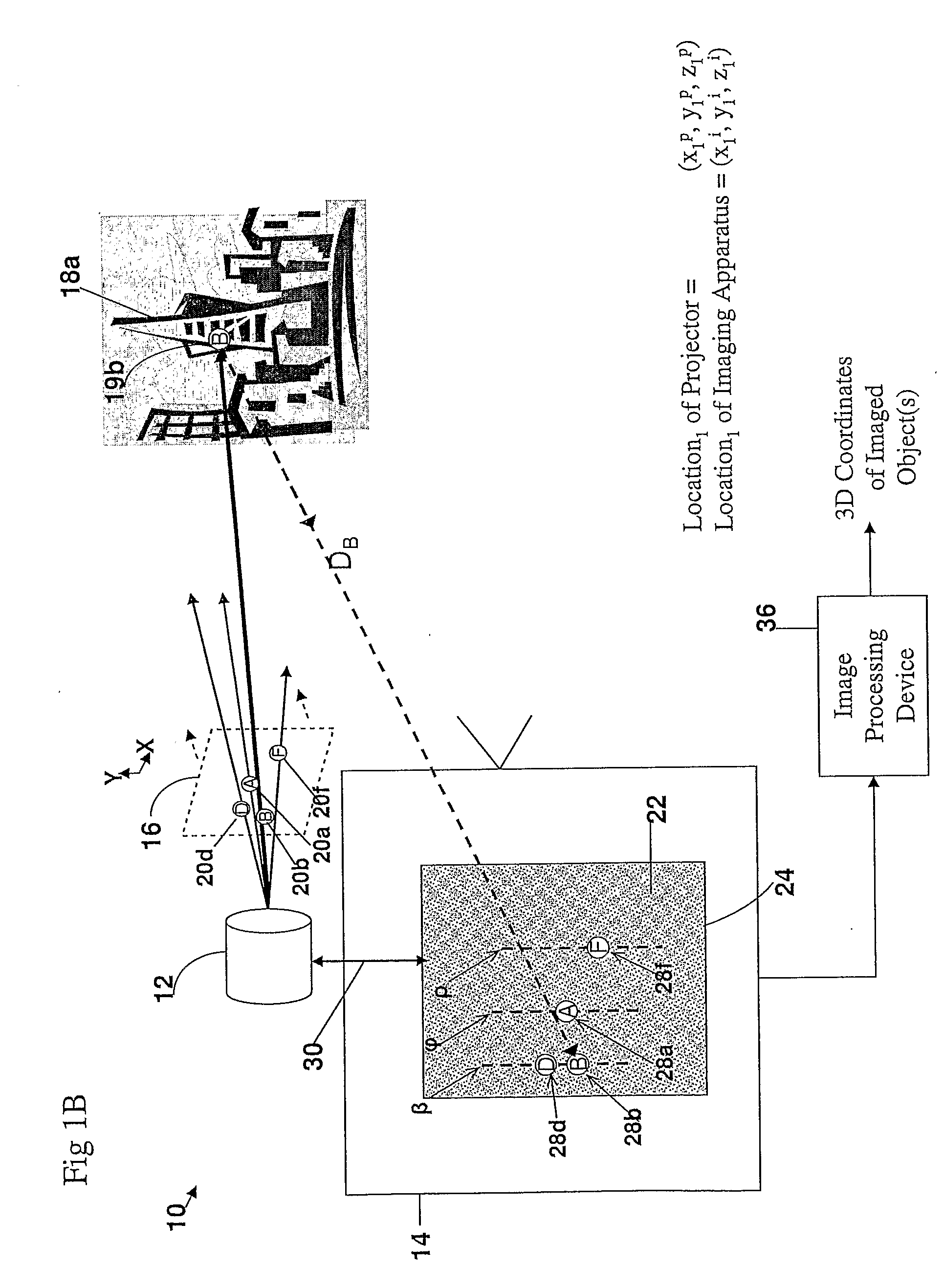
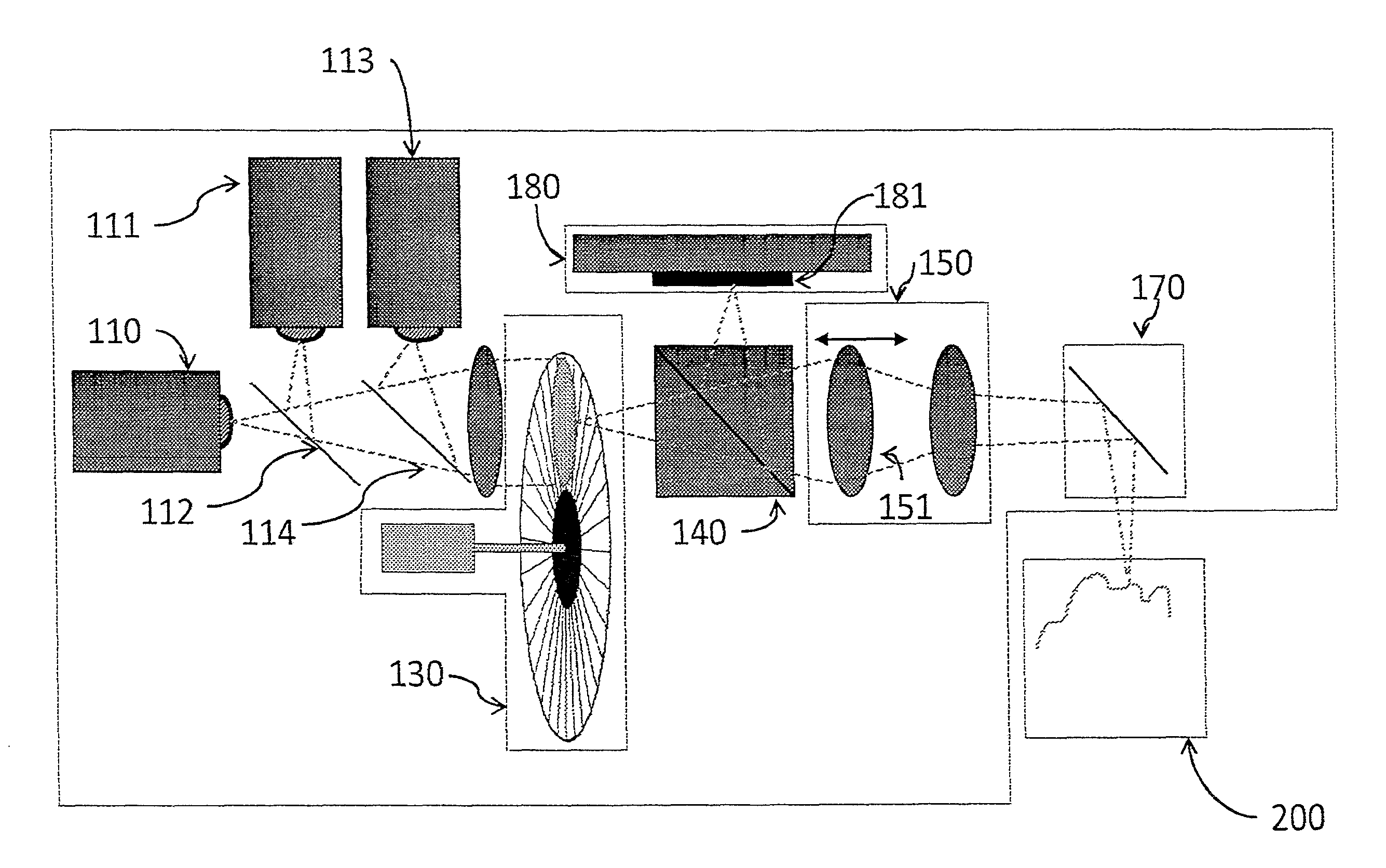
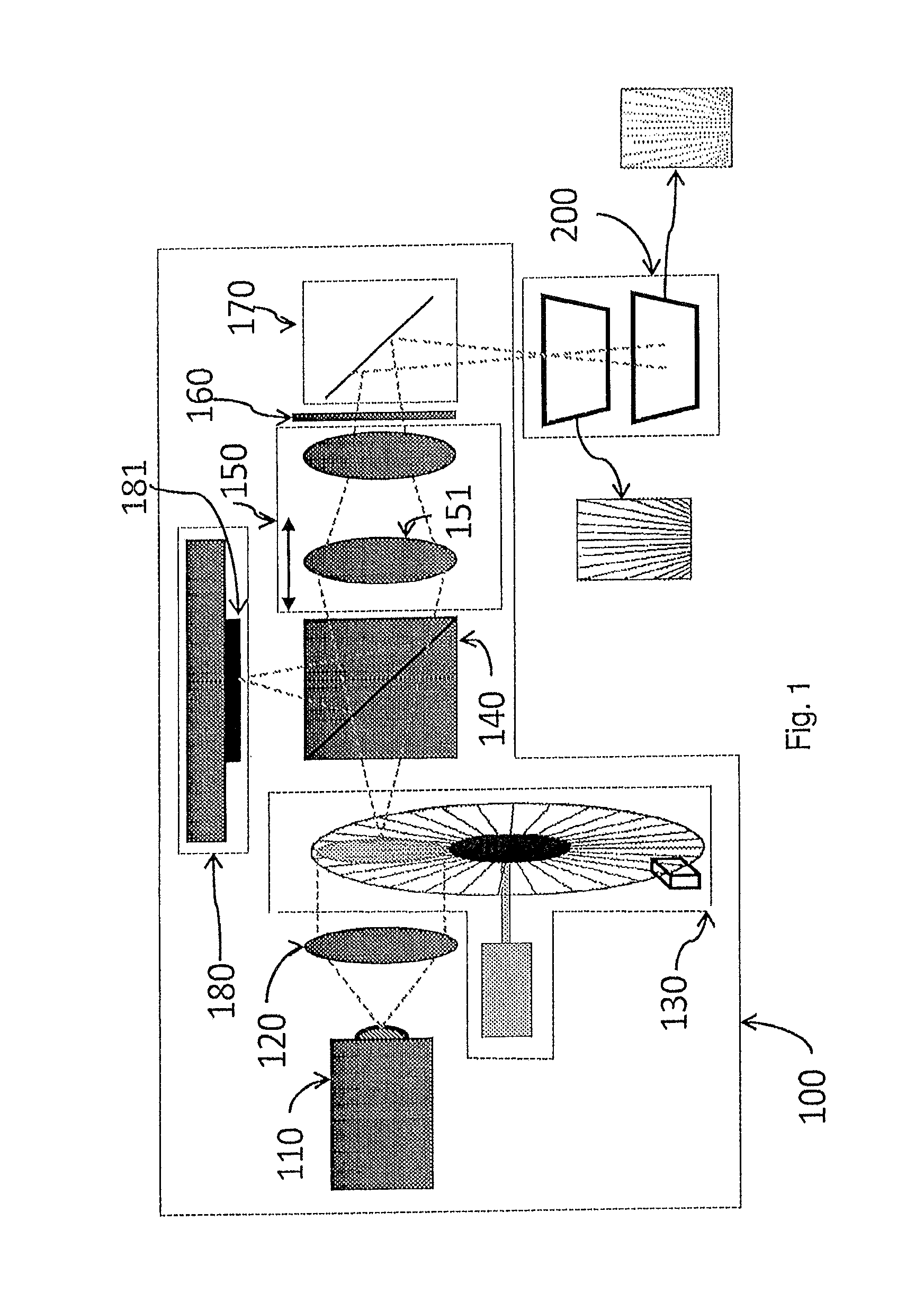
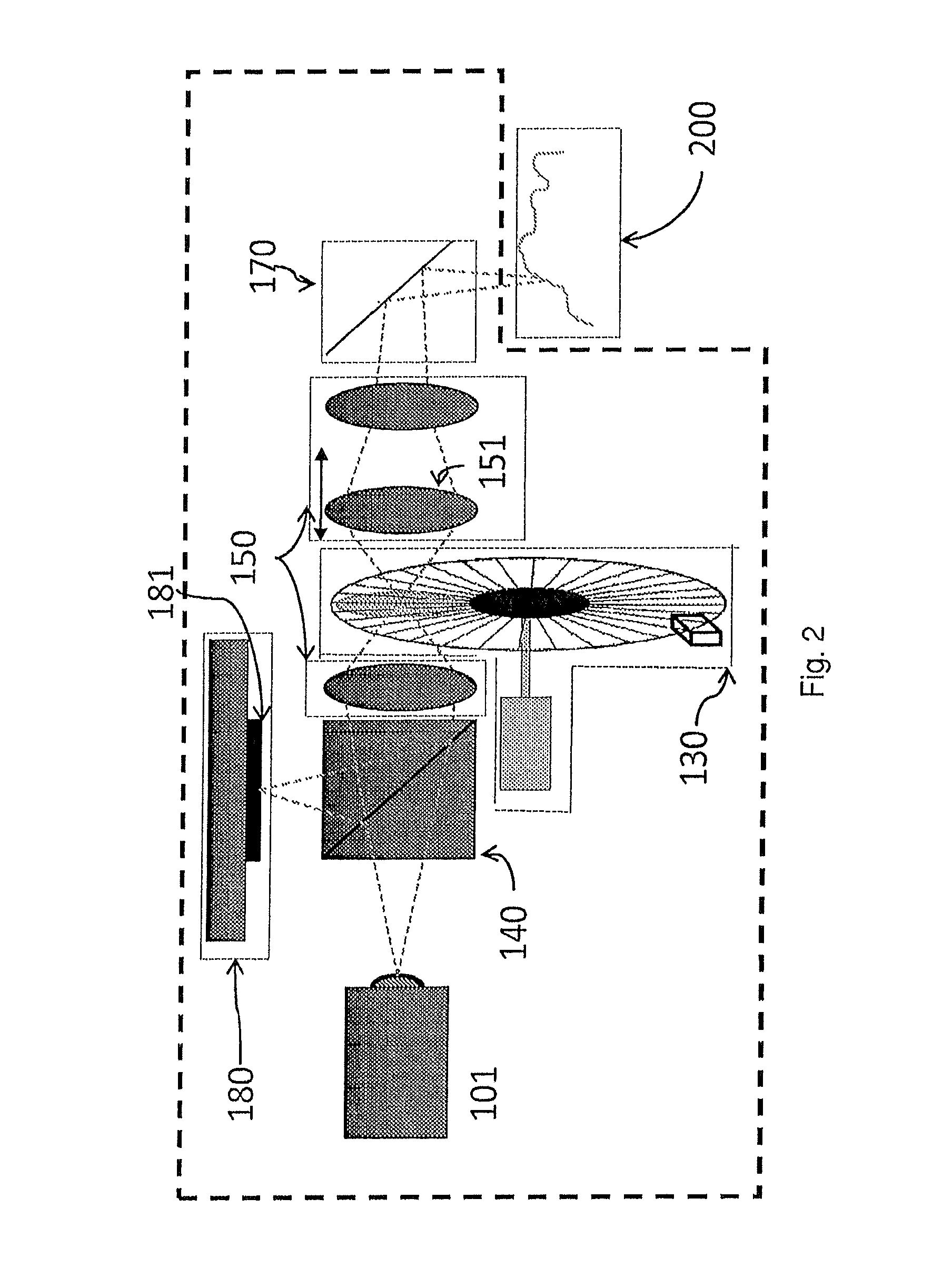
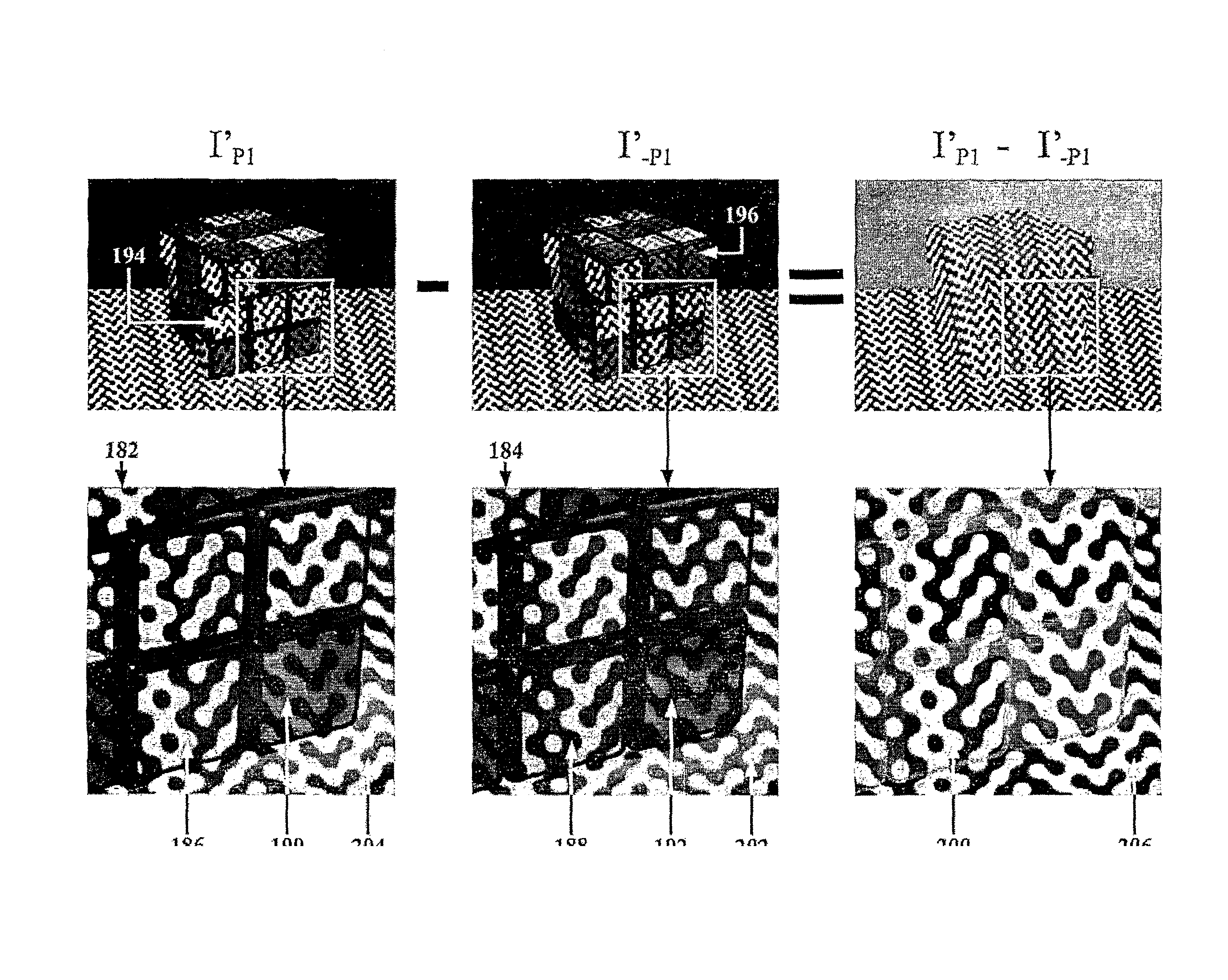
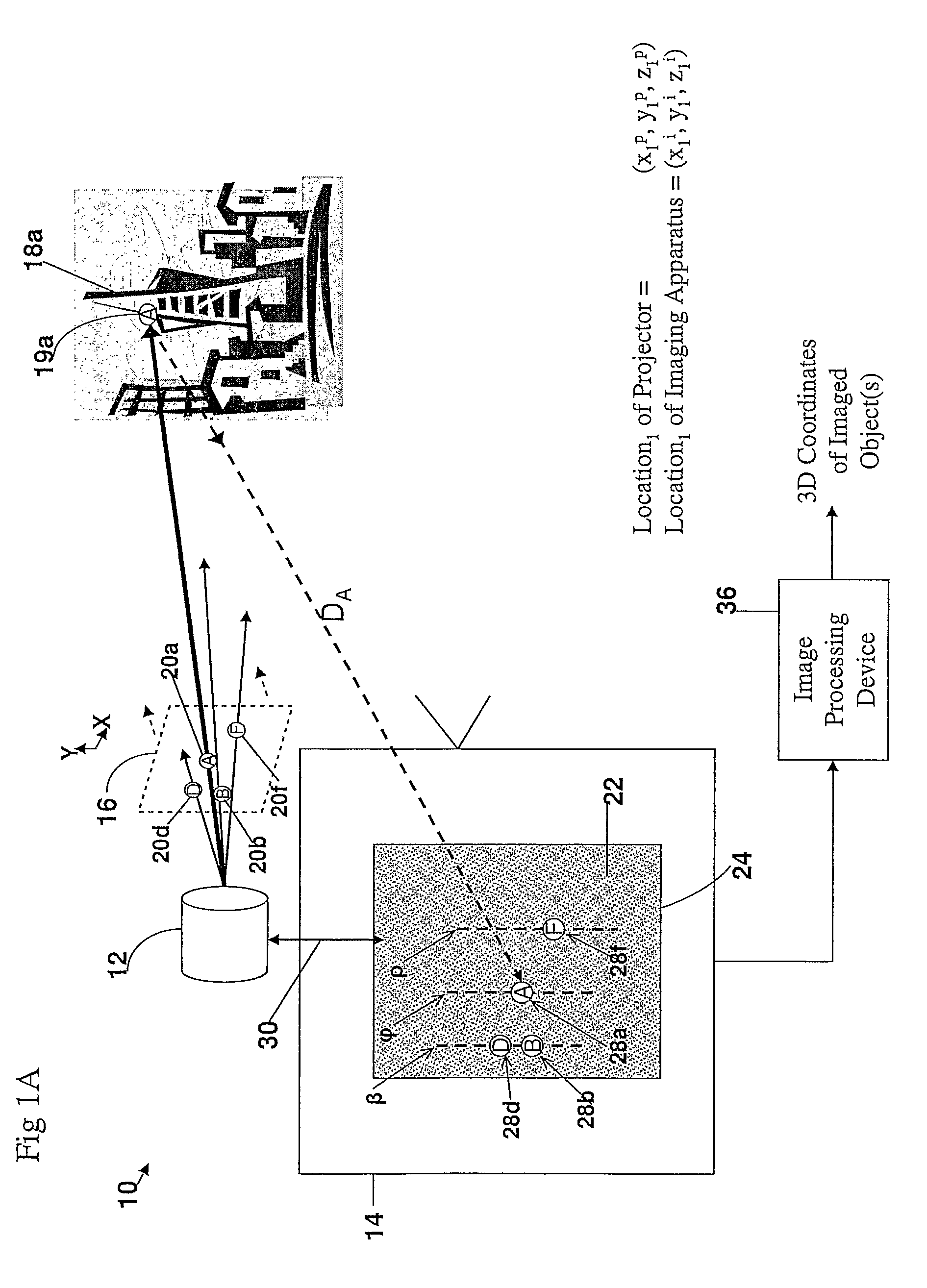
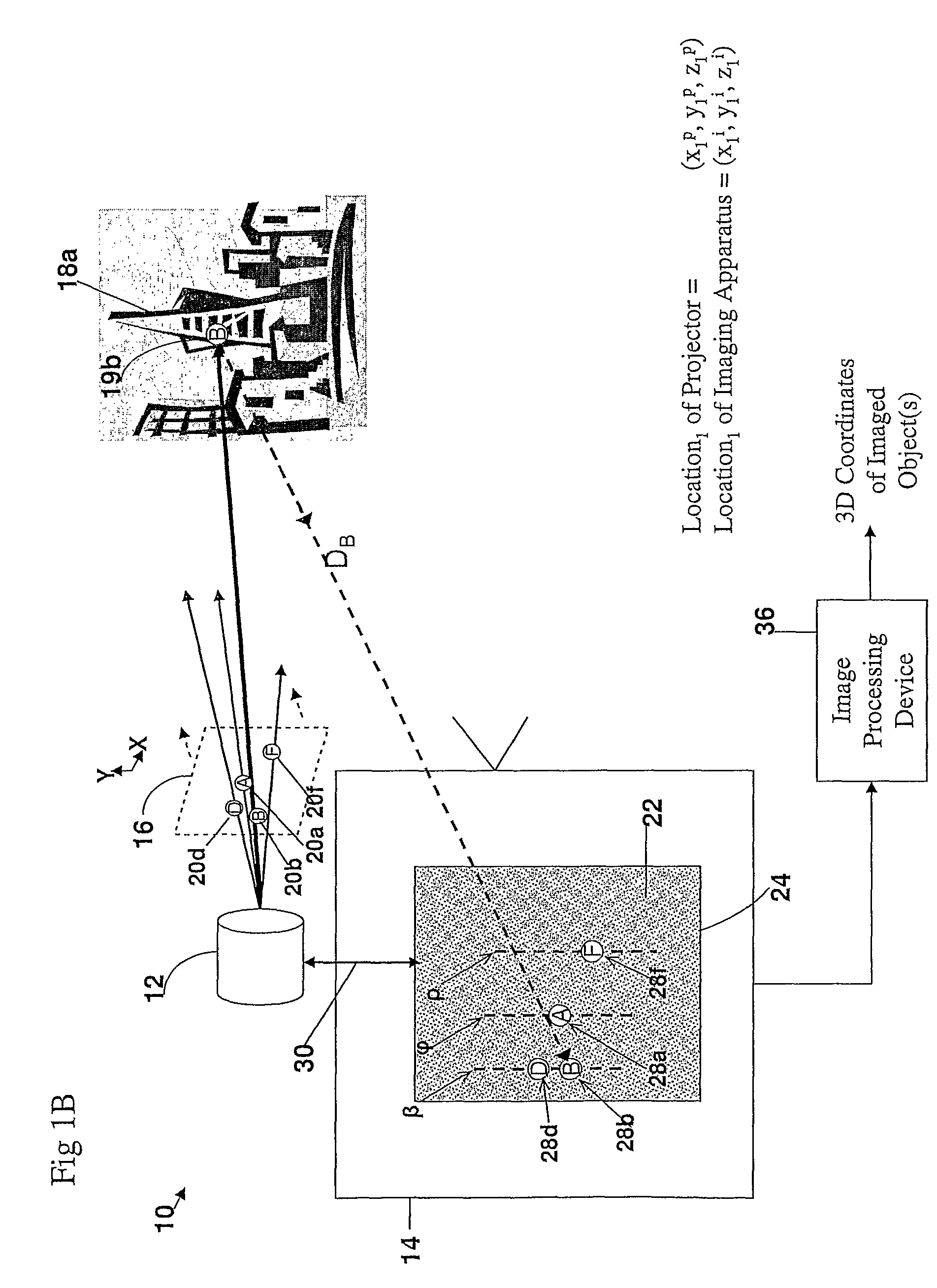
A method and apparatus for obtaining an image to determine a three dimensional shape of a stationary or moving object using a bi dimensional coded light pattern having a plurality of distinct identifiable feature types. The coded light pattern is projected on the object such that each of the identifiable feature types appears at most once on predefined sections of distinguishable epipolar lines. An image of the object is captured and the reflected feature types are extracted along with their location on known epipolar lines in the captured image. Displacements of the reflected feature types along their epipolar lines from reference coordinates thereupon determine corresponding three dimensional coordinates in space and thus a 3D mapping or model of the shape of the object at any point in time.
Owner:MANTIS VISION LTD
3D geometric modeling and 3D video content creation
A system, apparatus and method of obtaining data from a 2D image in order to determine the 3D shape of objects appearing in said 2D image, said 2D image having distinguishable epipolar lines, said method comprising: (a) providing a predefined set of types of features, giving rise to feature types, each feature type being distinguishable according to a unique bi-dimensional formation; (b) providing a coded light pattern comprising multiple appearances of said feature types; (c) projecting said coded light pattern on said objects such that the distance between epipolar lines associated with substantially identical features is less than the distance between corresponding locations of two neighboring features; (d) capturing a 2D image of said objects having said projected coded light pattern projected thereupon, said 2D image comprising reflected said feature types; and (e) extracting: (i) said reflected feature types according to the unique bi-dimensional formations; and (ii) locations of said reflected feature types on respective said epipolar lines in said 2D image.
Owner:MANTIS VISION
Methods and apparatus for constructing virtual environments
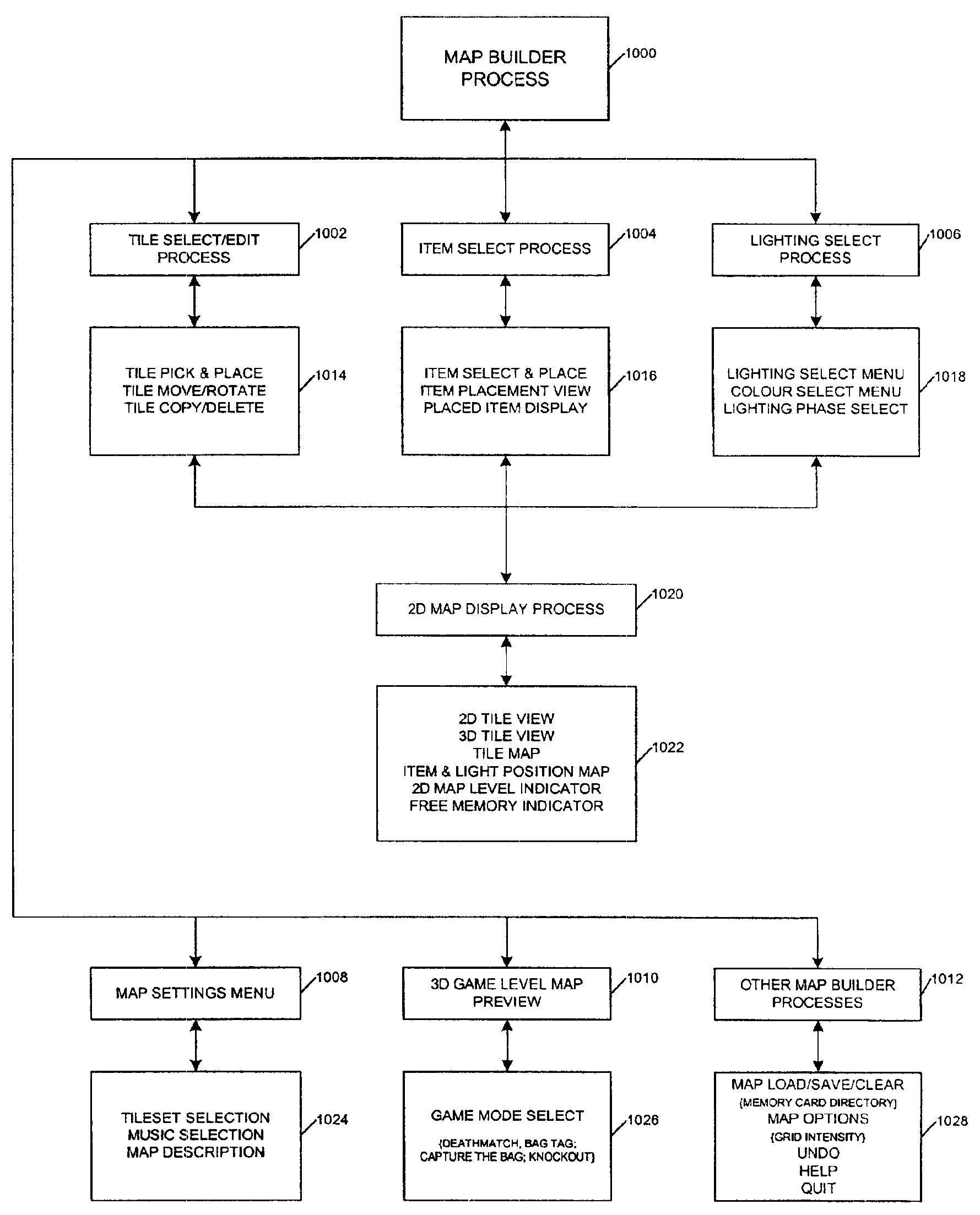
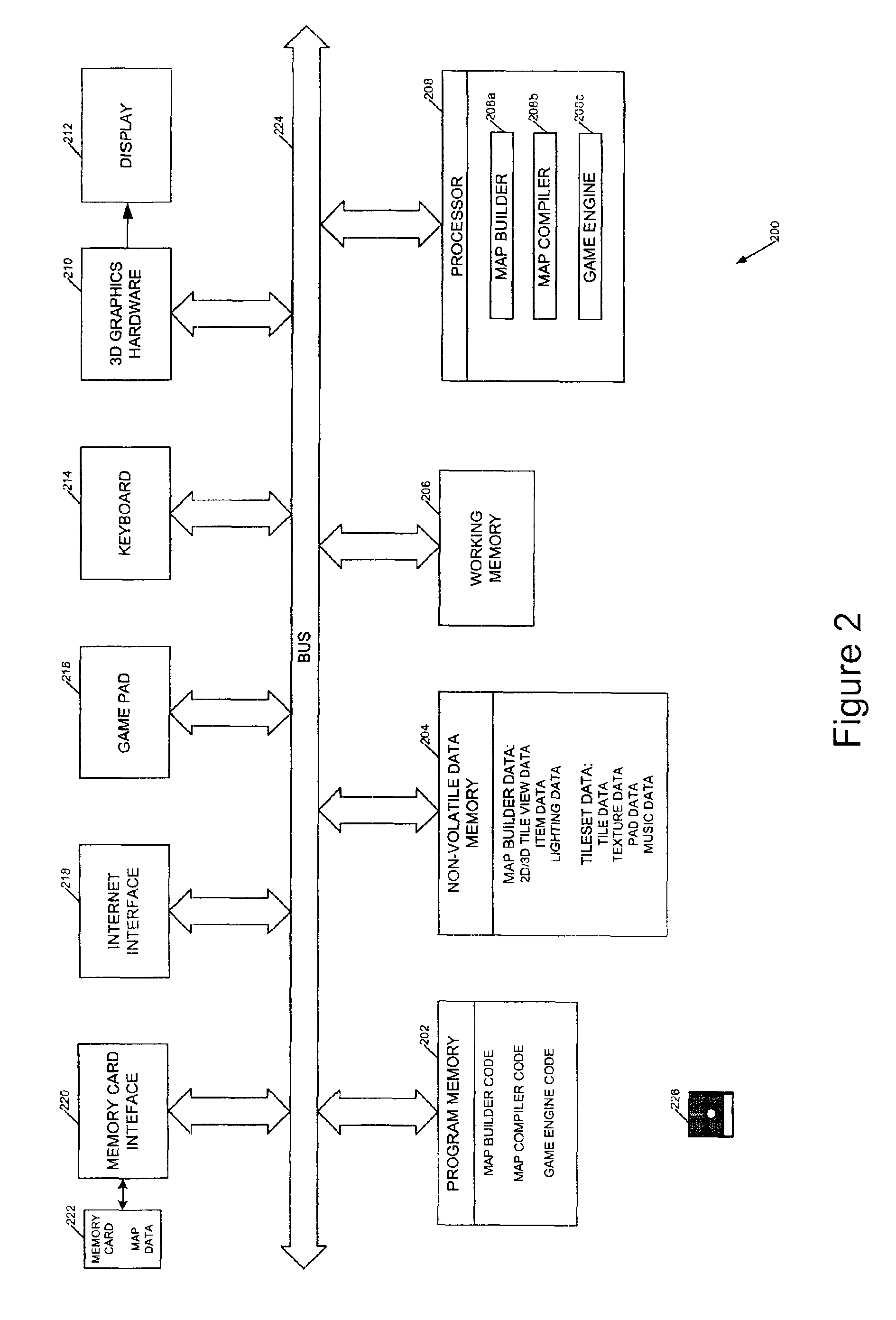
InactiveUS20030058238A1Multiple digital computer combinationsVideo gamesComputer graphics (images)3d geometry
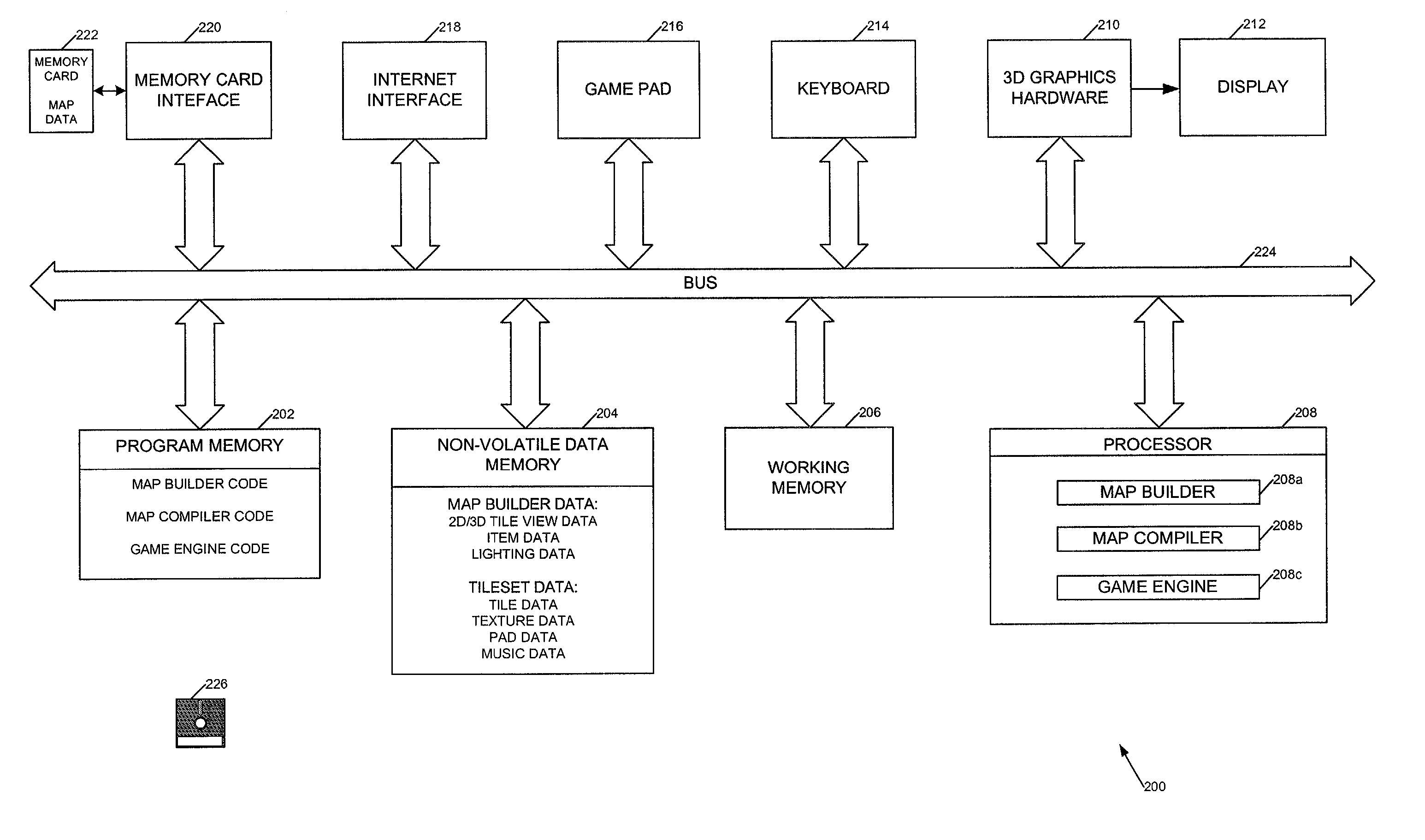
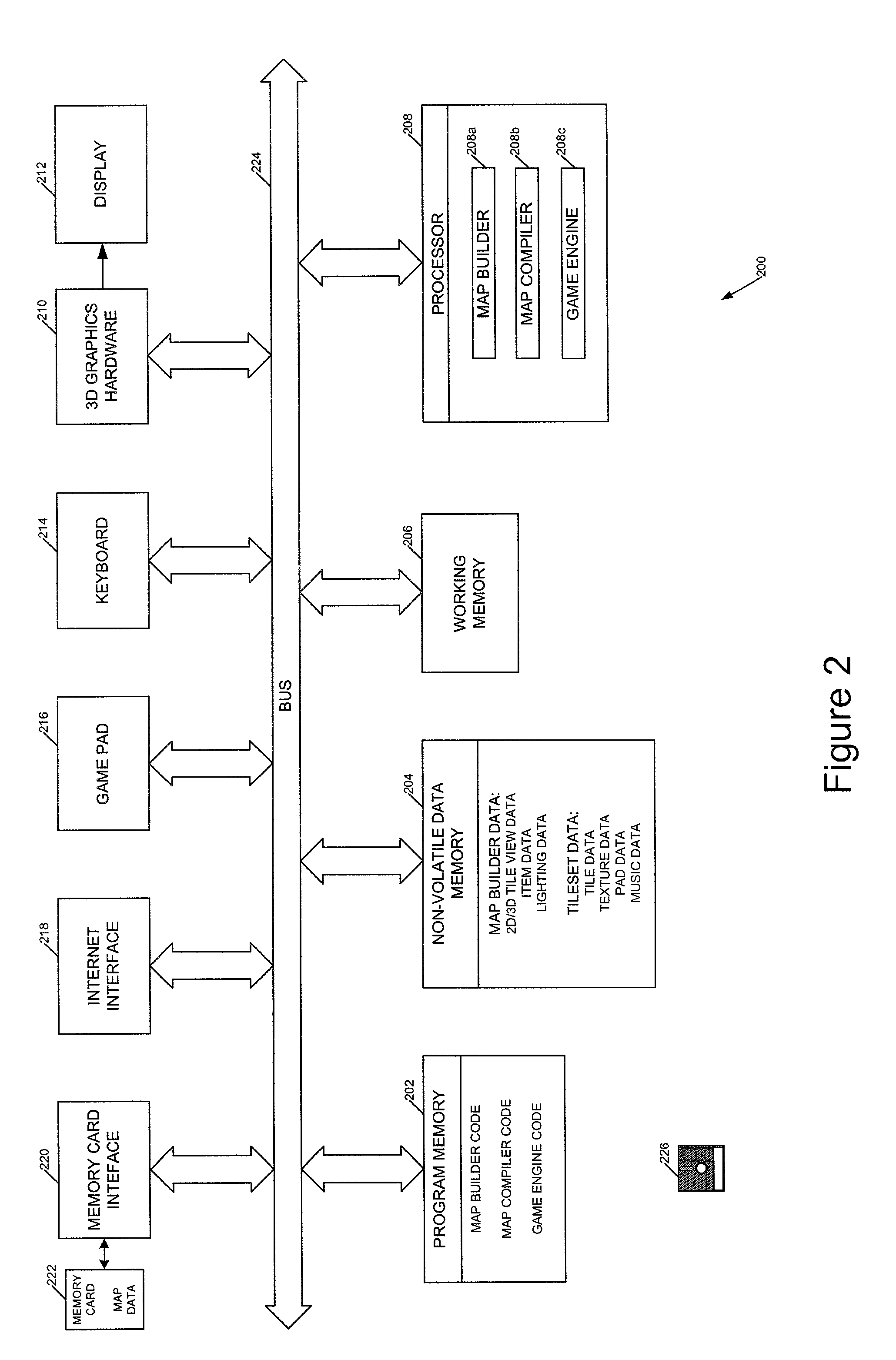
The invention relates to methods, apparatus, and software for designing and building virtual environments for playing computer games. A map builder is used to construct one or more two-dimensional maps comprised of tiles selected from a set of tiles, the map or maps representing the virtual environment for the computer game. Data describing the map is then combined with tile data providing 3D geometry to create the virtual environment. The tile data preferably also includes non-visible game-related data such as collision and navigation data, which is also combined to provide game data for the game's virtual environment. The tiles include interfaces for connecting one tile to another and, in a preferred embodiment, two versions of the interface geometry are provided for each tile, one with the interface open, the other with the interface closed. The invention facilitates the rapid construction of 3D virtual environments for playing games.
Owner:CRYTEK IP HLDG
Geometry compression for regular and irregular mesh structures
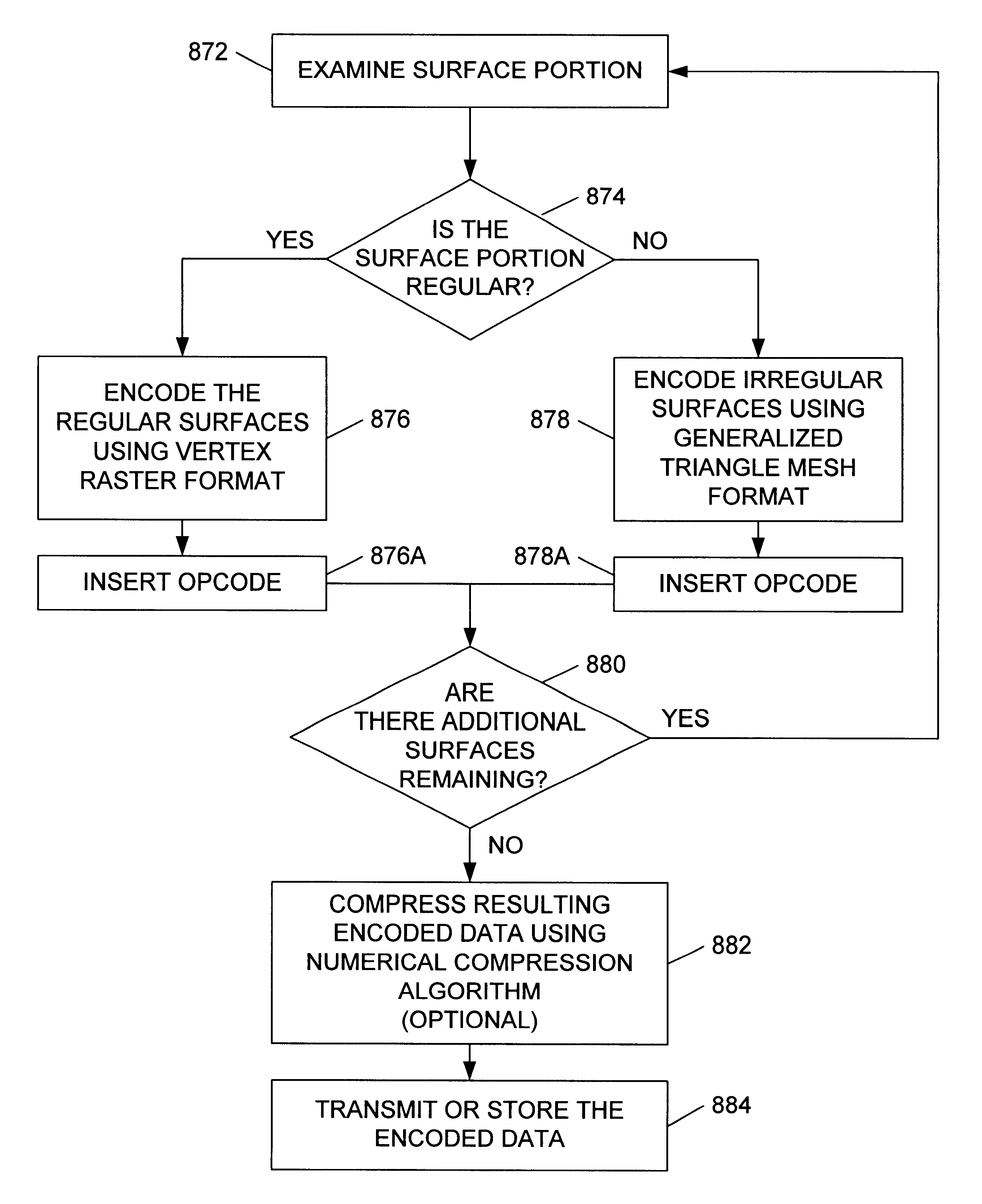
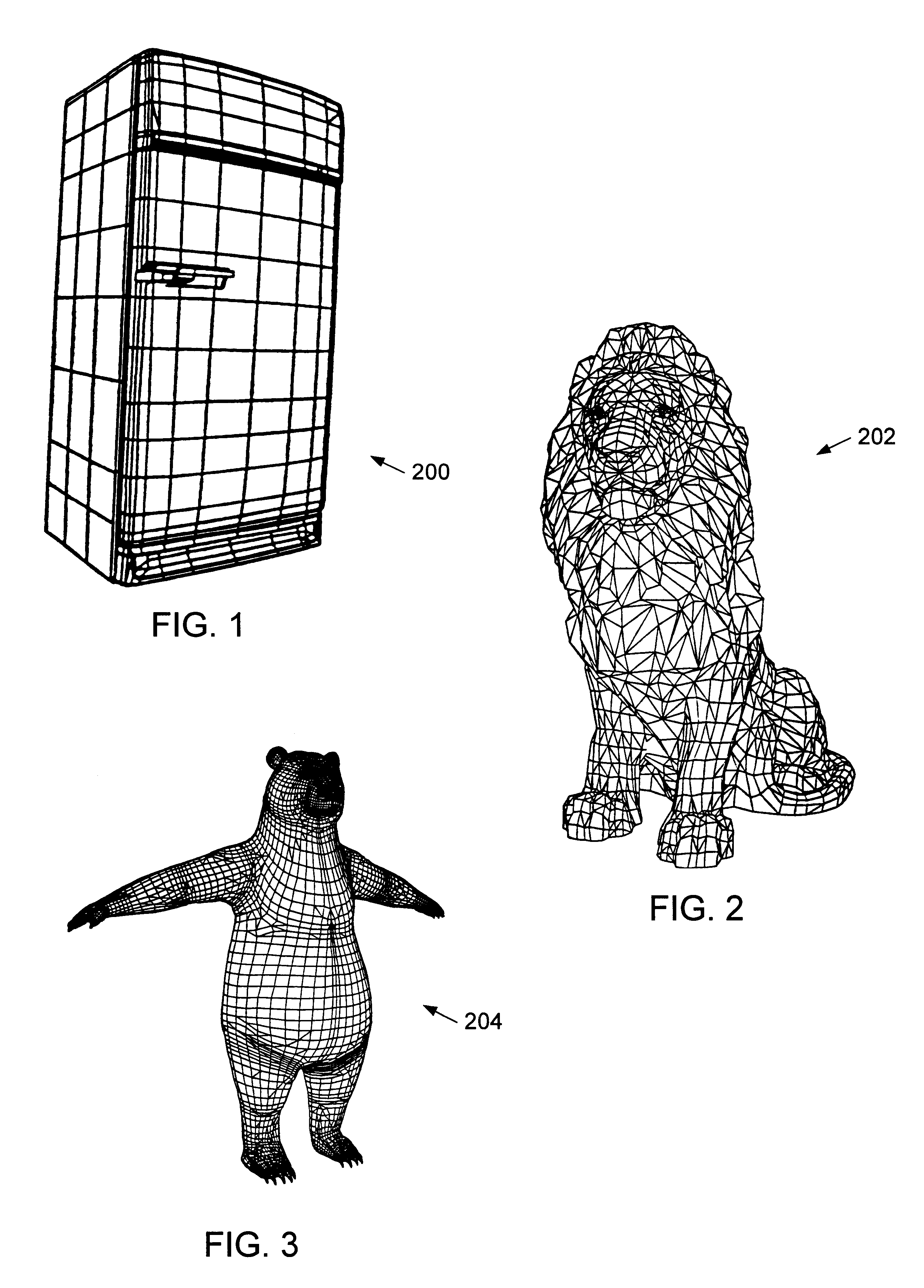
A method for compressing 3D geometry data that is capable of compressing both regularly tiled and irregularly tiled surfaces is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises examining 3D geometry data to detect the presence of regularly tiled surface portions. The 3D geometry data is then compressed by: (1) encoding any regularly tiled surface portion using a first encoding method, and (2) encoding any irregularly tiled surface portions using a second encoding method, wherein the second encoding method is different from the first encoding method. The first encoding method may encode the regularly tiled surface portions as vertex rasters, while the second method may encode the irregularly tiled surface portions by geometry compression using a generalized triangle mesh.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Segmenting compressed graphics data for parallel decompression and rendering
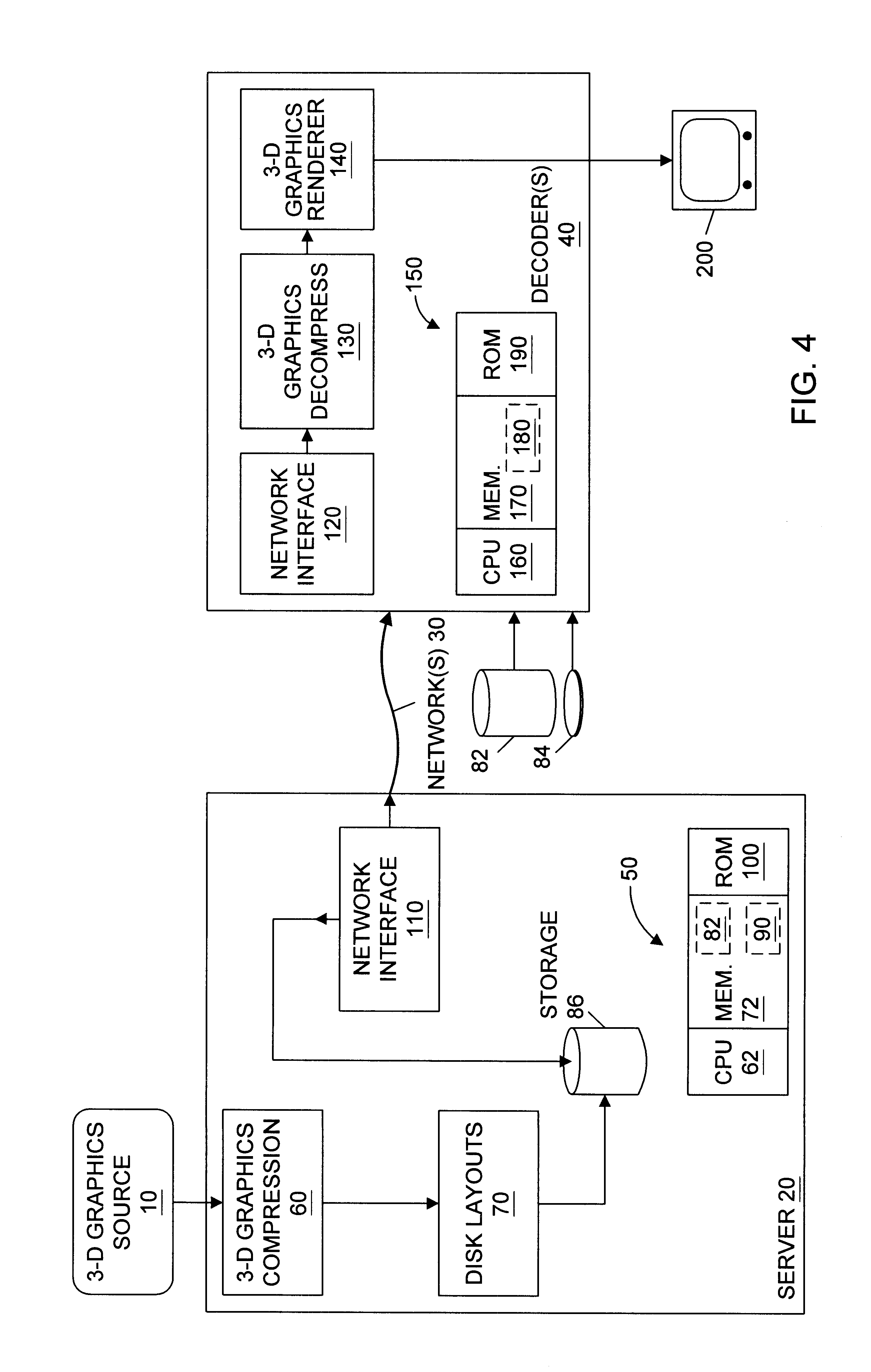
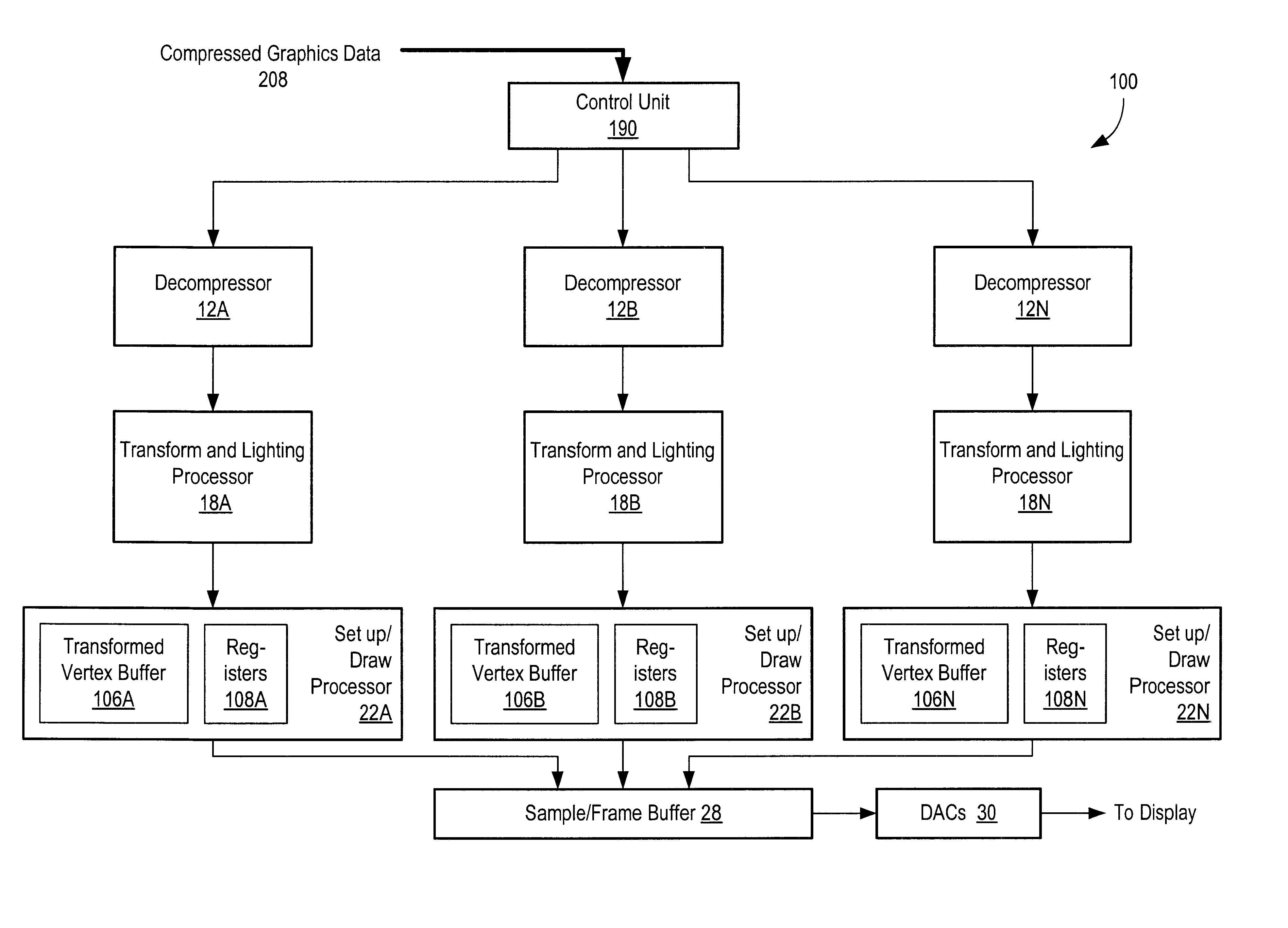
A graphics system and method for reducing redundant transformation and lighting calculations performed on vertices that are shared by more than one geometric primitive is disclosed. The amount of data transmitted in certain data blocks may be reduced by incorporating a multicast / unicast bit into each data block. This bit may then be set to instruct the control unit to use the current 3D geometry data or state information for subsequent vertices. This may increase efficiency by allowing subsequent vertices using the same 3D geometry data to transfer less data. Conversely, if a vertex has wholly independent 3D geometry data, then its multicast / unicast bit may be set to invoke use of the current 3D geometry data on the current vertex as opposed to all future vertices. The reduction in redundant calculations is accomplished by delaying the formation of geometric primitives until after transformation and lighting has been performed on the vertices. Transformation and or lighting are performed independently on a vertex-by-vertex basis without reference to which geometric primitives the vertices belong to. After transformation and or lighting, geometric primitives may be formed utilizing previously generated connectivity information. The connectivity information may include mesh buffer references, vertex tags, and or other types of information.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Mobile device with three dimensional augmented reality
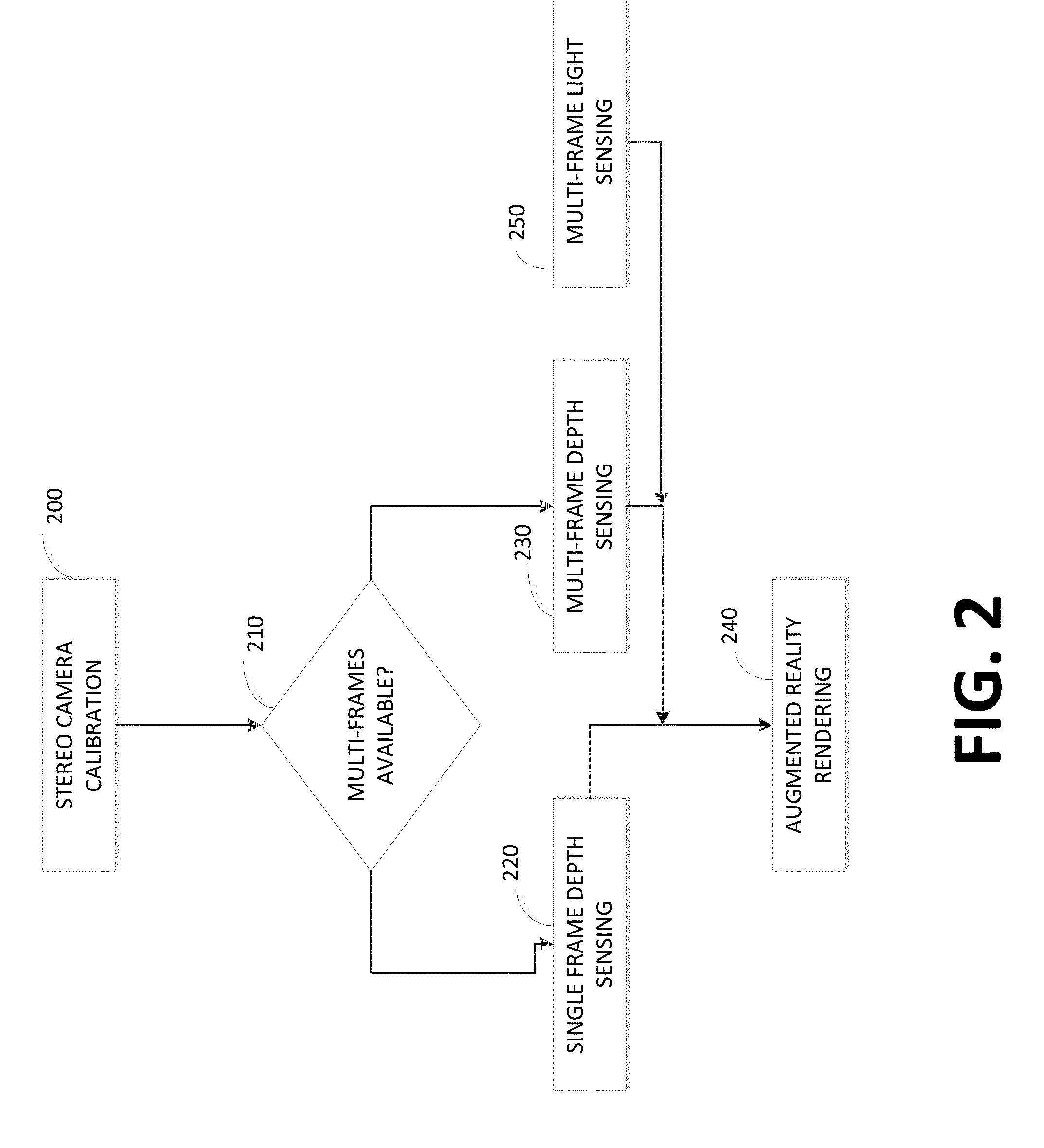
A method for determining an augmented reality scene by a mobile device includes estimating 3D geometry and lighting conditions of the sensed scene based on stereoscopic images captured by a pair of imaging devices. The device accesses intrinsic calibration parameters of a pair of imaging devices of the device independent of a sensed scene of the augmented reality scene. The device determines two dimensional disparity information of a pair of images from the device independent of a sensed scene of the augmented reality scene. The device estimates extrinsic parameters of a sensed scene by the pair of imaging devices, including at least one of rotation and translation. The device calculates a three dimensional image based upon a depth of different parts of the sensed scene based upon a stereo matching technique. The device incorporates a three dimensional virtual object in the three dimensional image to determine the augmented reality scene.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
Methods and apparatus for constructing virtual environments
InactiveUS6961055B2Constructed much more quicklyFast constructionCathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer graphics (images)Data combination
The invention relates to methods, apparatus, and software for designing and building virtual environments for playing computer games. A map builder is used to construct one or more two-dimensional maps comprised of tiles selected from a set of tiles, the map or maps representing the virtual environment for the computer game. Data describing the map is then combined with tile data providing 3D geometry to create the virtual environment. The tile data preferably also includes non-visible game-related data such as collision and navigation data, which is also combined to provide game data for the game's virtual environment. The tiles include interfaces for connecting one tile to another and, in a preferred embodiment, two versions of the interface geometry are provided for each tile, one with the interface open, the other with the interface closed.The invention facilitates the rapid construction of 3D virtual environments for playing games.
Owner:CRYTEK IP HLDG
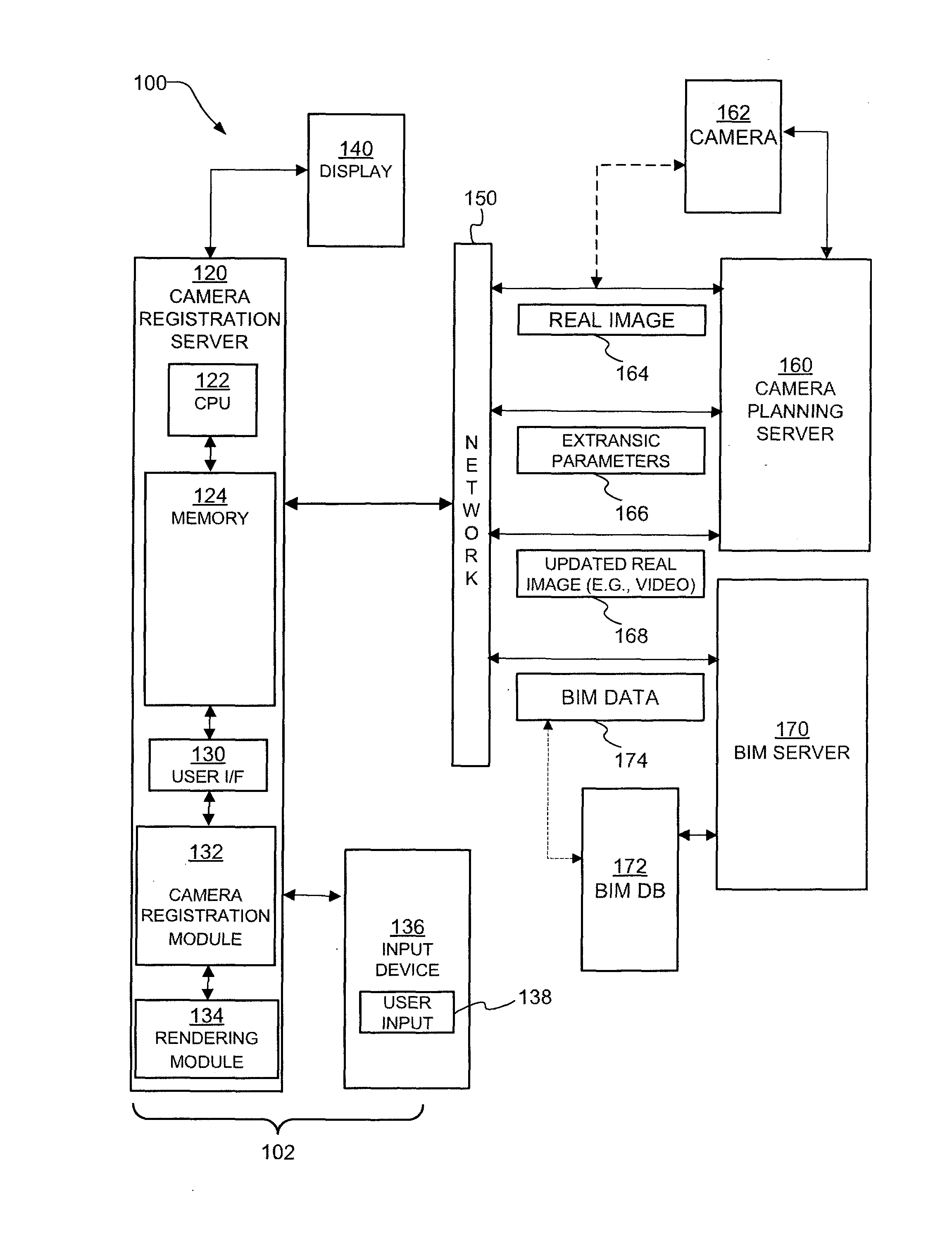
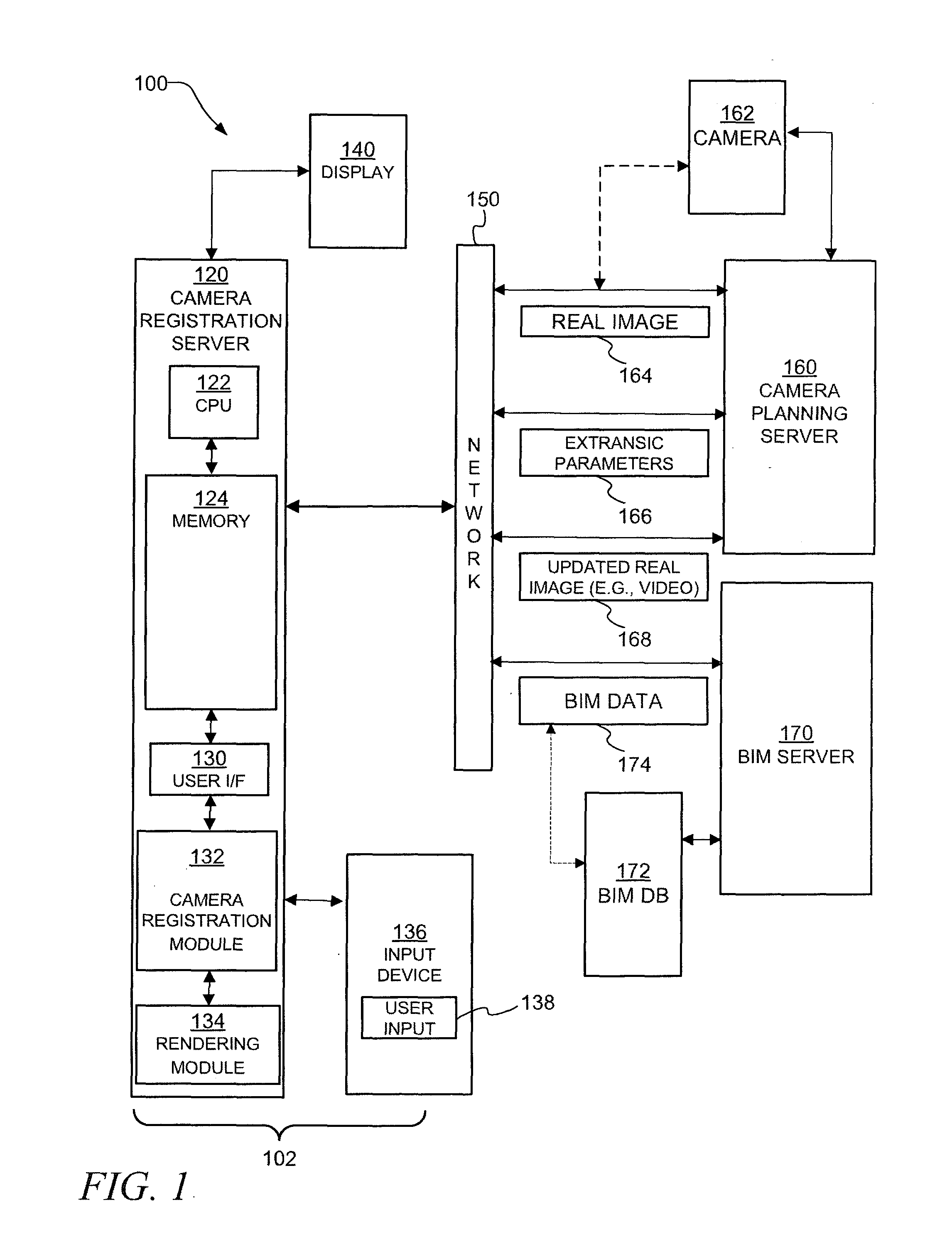
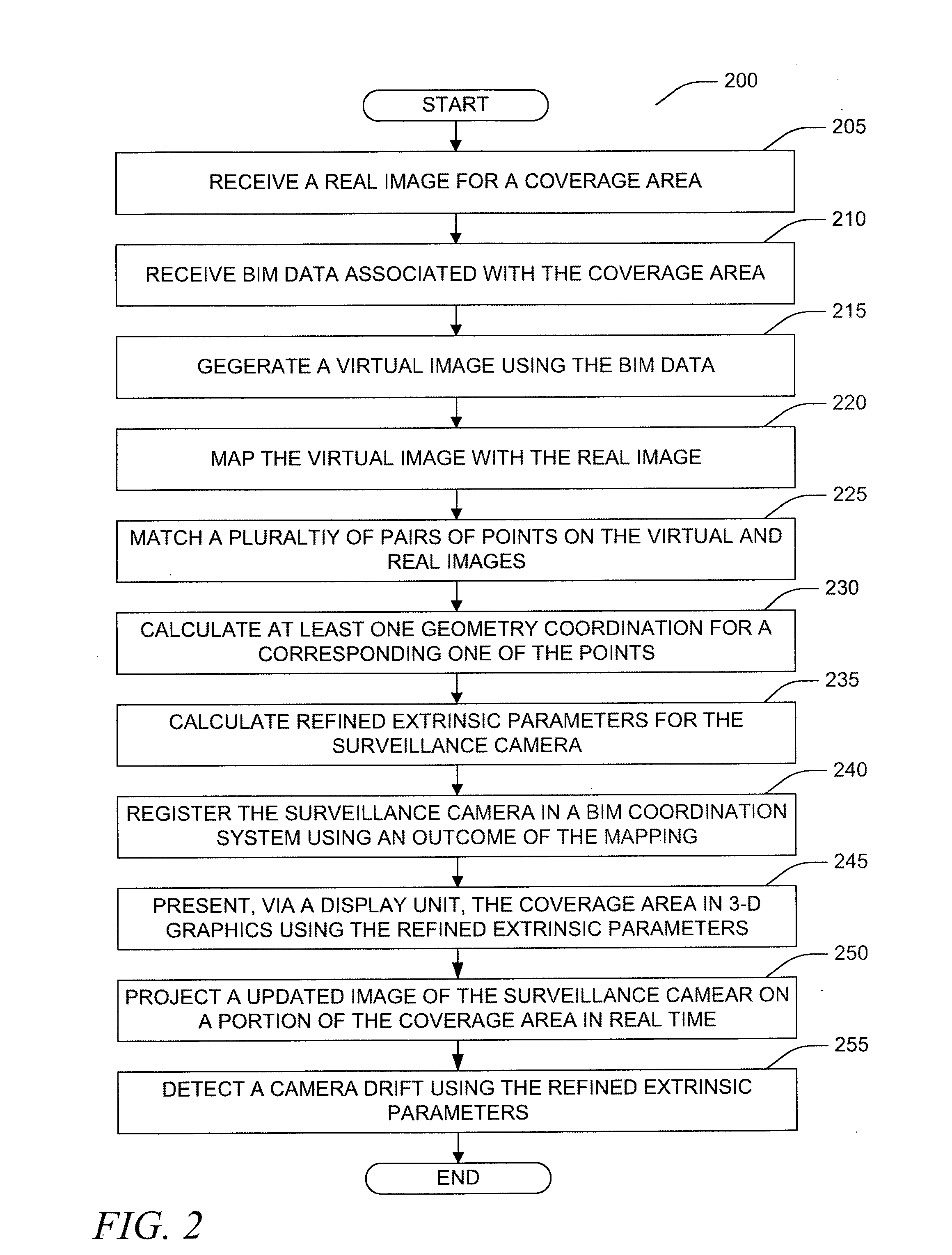
Camera registration and video integration in 3D geometry model
Apparatus, systems, and methods may operate to receive a real image or real images of a coverage area of a surveillance camera. Building Information Model (BIM) data associated with the coverage area may be received. A virtual image may be generated using the BIM data. The virtual image may include at least one three-dimensional (3-D) graphics that substantially corresponds to the real image. The virtual image may be mapped with the real image. Then, the surveillance camera may be registered in a BIM coordination system using an outcome of the mapping.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
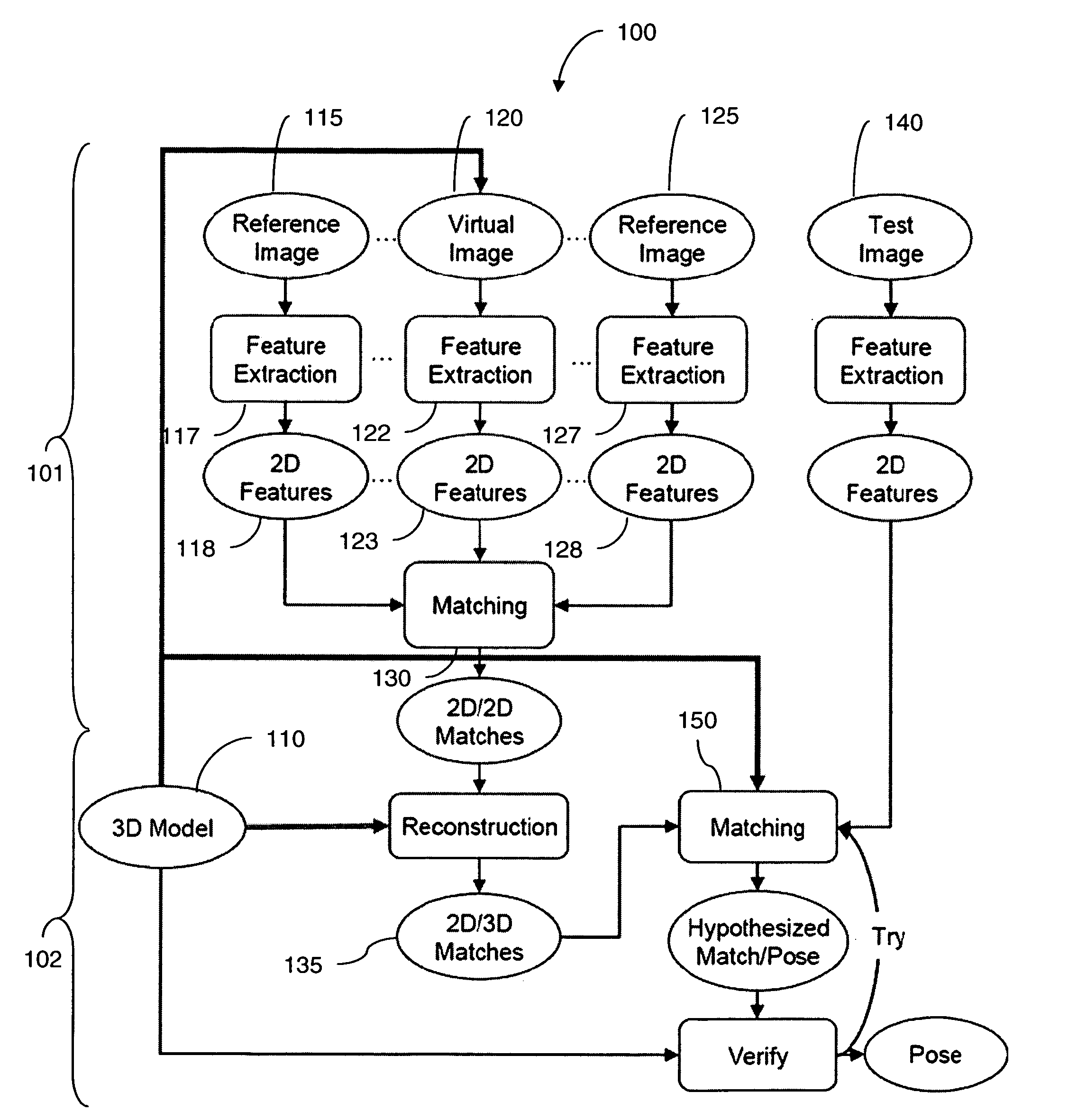
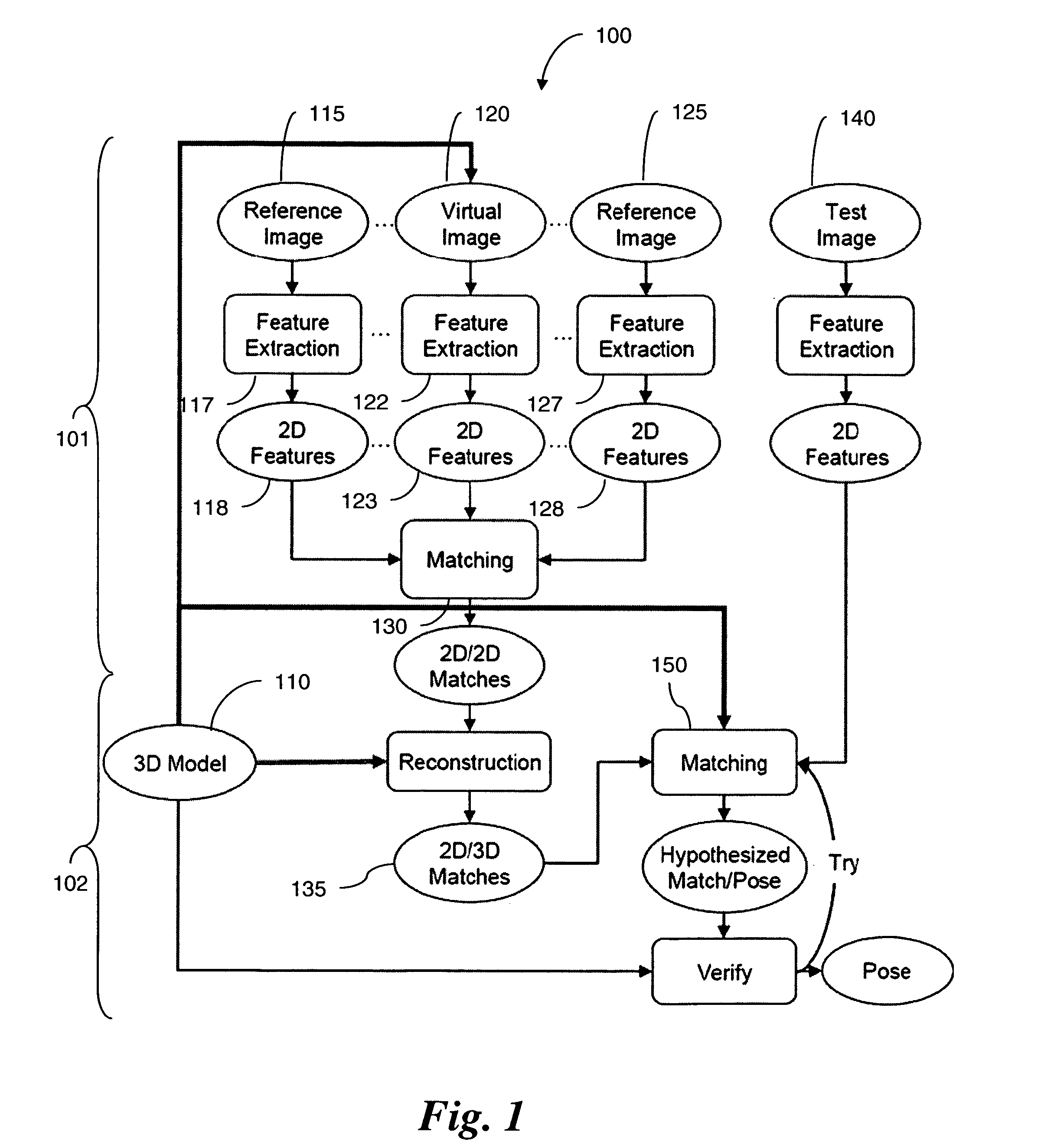
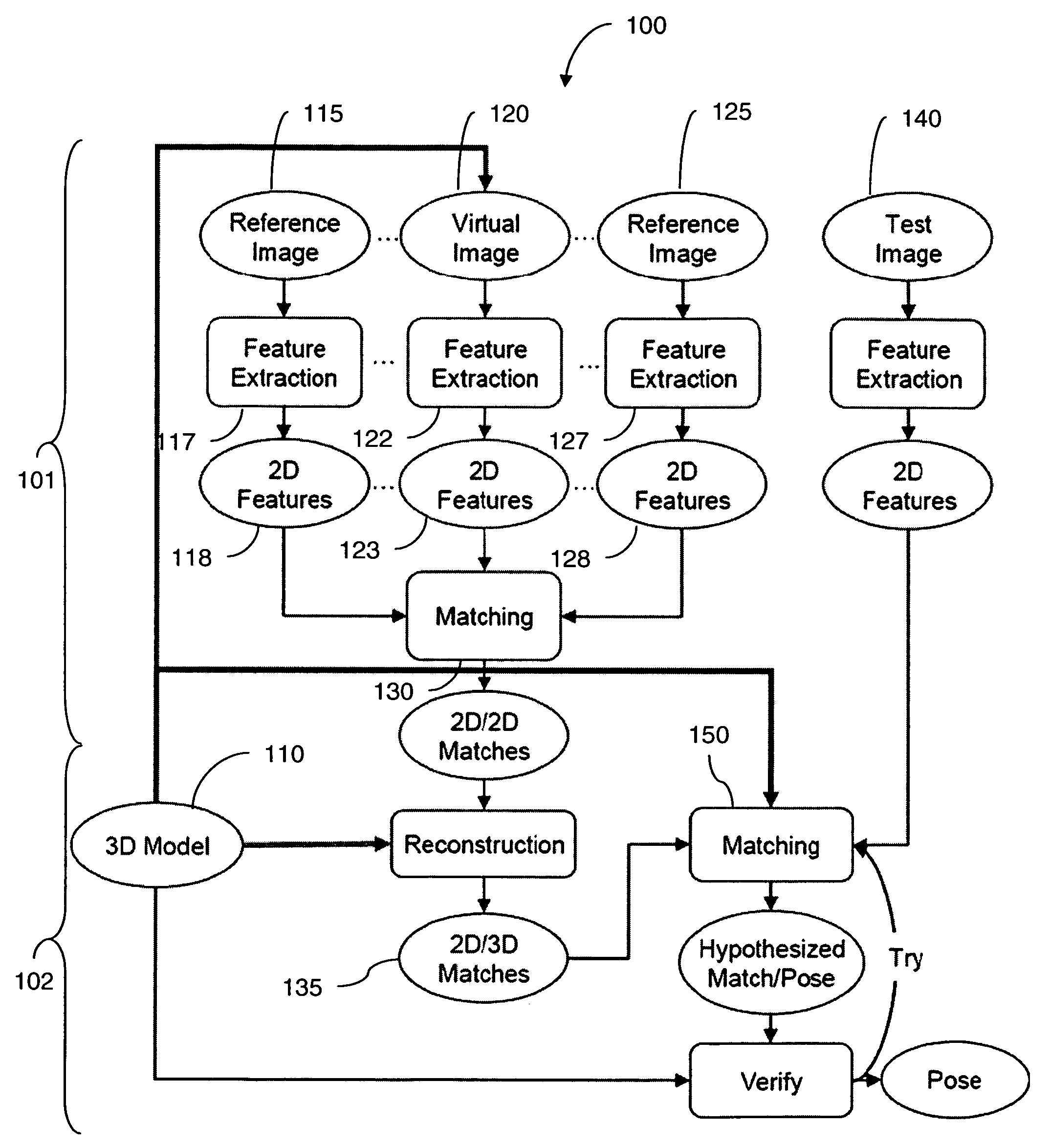
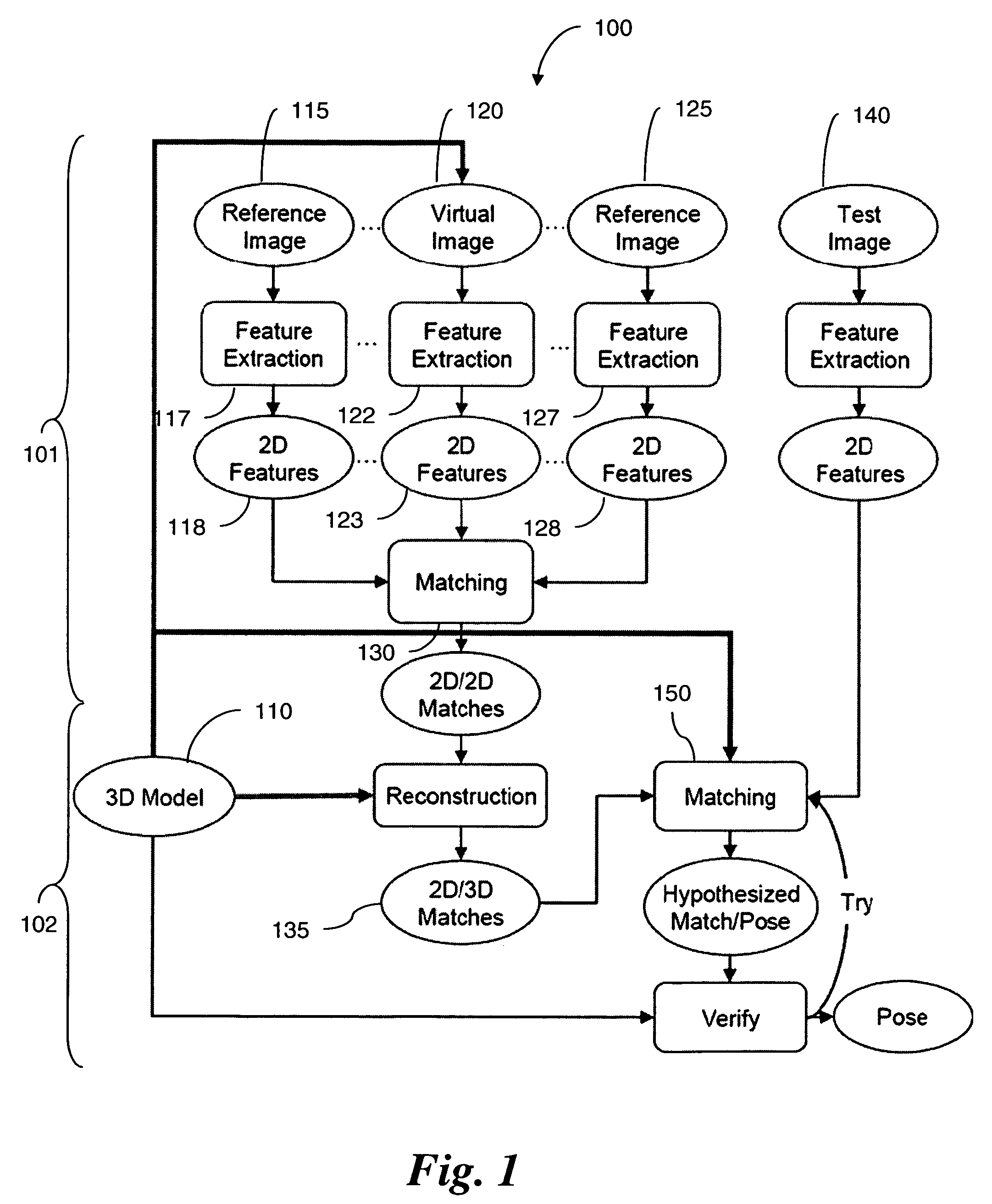
Fast object detection for augmented reality systems
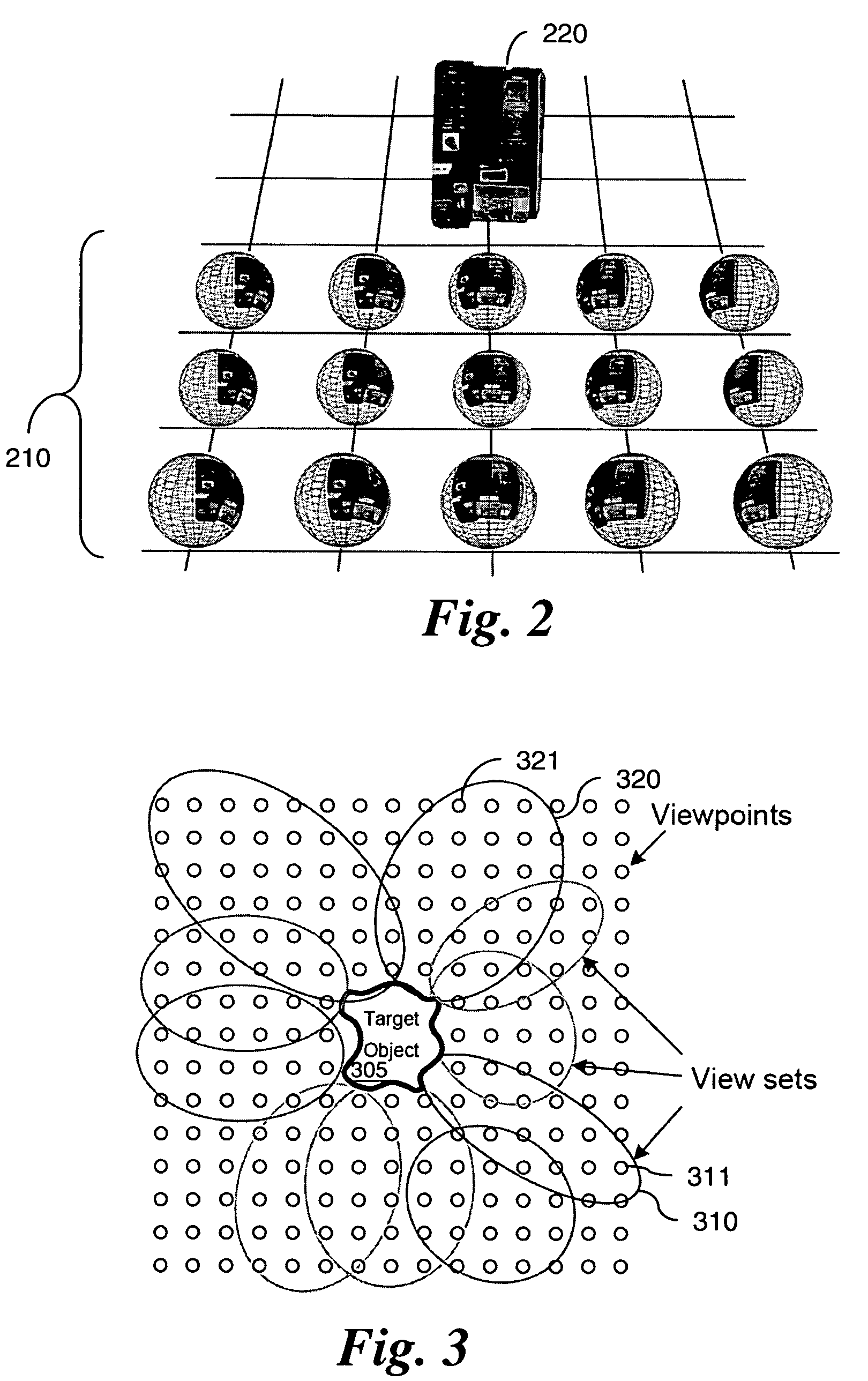
InactiveUS20060233423A1Reduce dimensionalityMinimize impactImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionVisibilityViewpoints
A detection method is based on a statistical analysis of the appearance of model patches from all possible viewpoints in the scene, and incorporates 3D geometry during both matching and pose estimation processes. By analyzing the computed probability distribution of the visibility of each patch from different viewpoints, a reliability measure for each patch is estimated. That reliability measure is useful for developing industrial augmented reality applications. Using the method, the pose of complex objects can be estimated efficiently given a single test image. In a fast method to detect objects in a given image or video sequence, a series of hierarchical feature descriptors permit balancing between the complexity of feature extraction and cost of combinatorial matching. The feature descriptors are derived from the 3D model of the object of interest along with the available calibrated real-life images or videos. The variability of the real-life images defines the granularity of the feature descriptors.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
3D geometric modeling and 3D video content creation
A system, apparatus and method of obtaining data from a 2D image in order to determine the 3D shape of objects appearing in said 2D image, said 2D image having distinguishable epipolar lines, said method comprising: (a) providing a predefined set of types of features, giving rise to feature types, each feature type being distinguishable according to a unique bi-dimensional formation; (b) providing a coded light pattern comprising multiple appearances of said feature types; (c) projecting said coded light pattern on said objects such that the distance between epipolar lines associated with substantially identical features is less than the distance between corresponding locations of two neighboring features; (d) capturing a 2D image of said objects having said projected coded light pattern projected thereupon, said 2D image comprising reflected said feature types; and (e) extracting: (i) said reflected feature types according to the unique bi-dimensional formations; and (ii) locations of said reflected feature types on respective said epipolar lines in said 2D image.
Owner:MANTIS VISION LTD
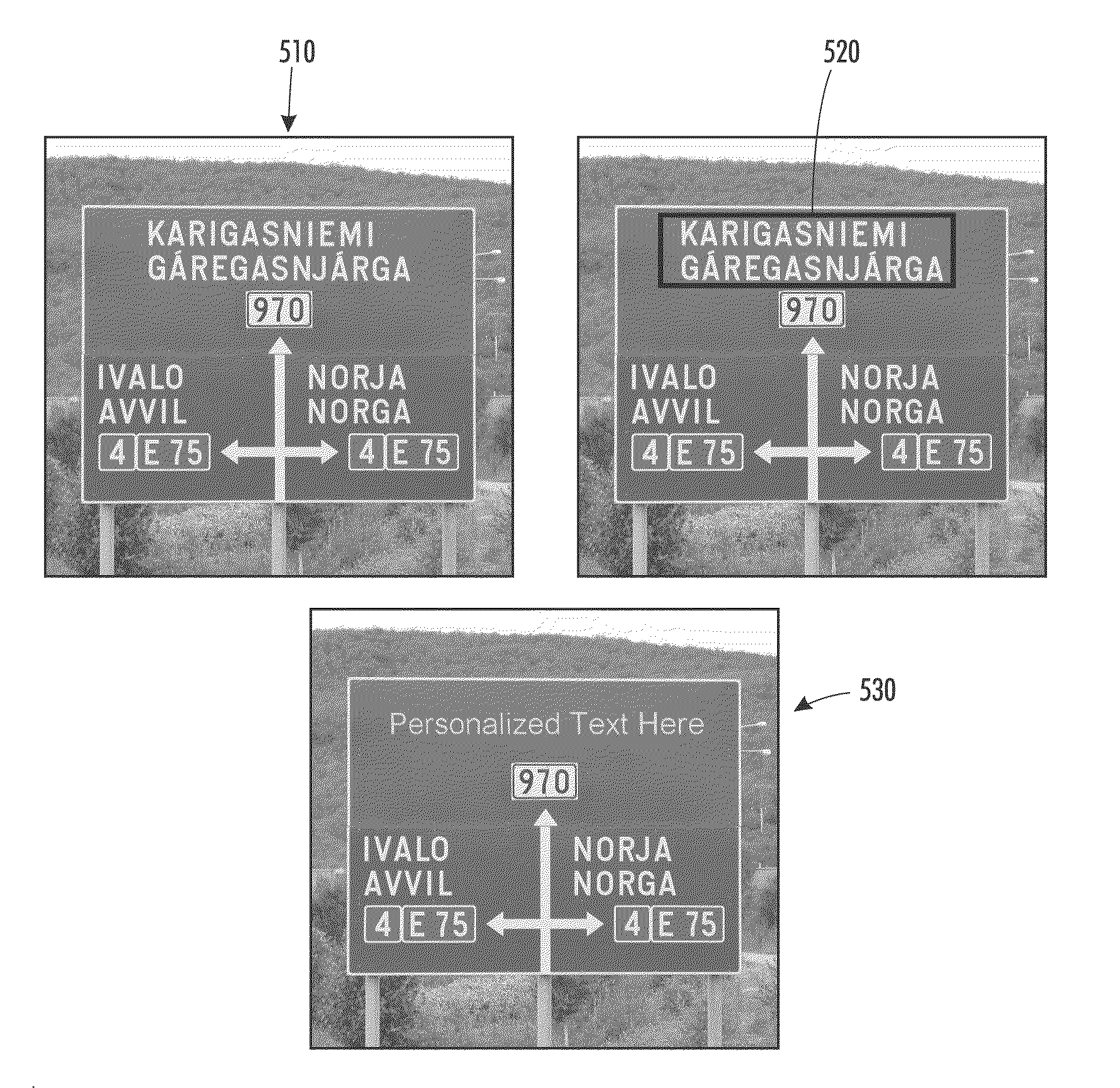
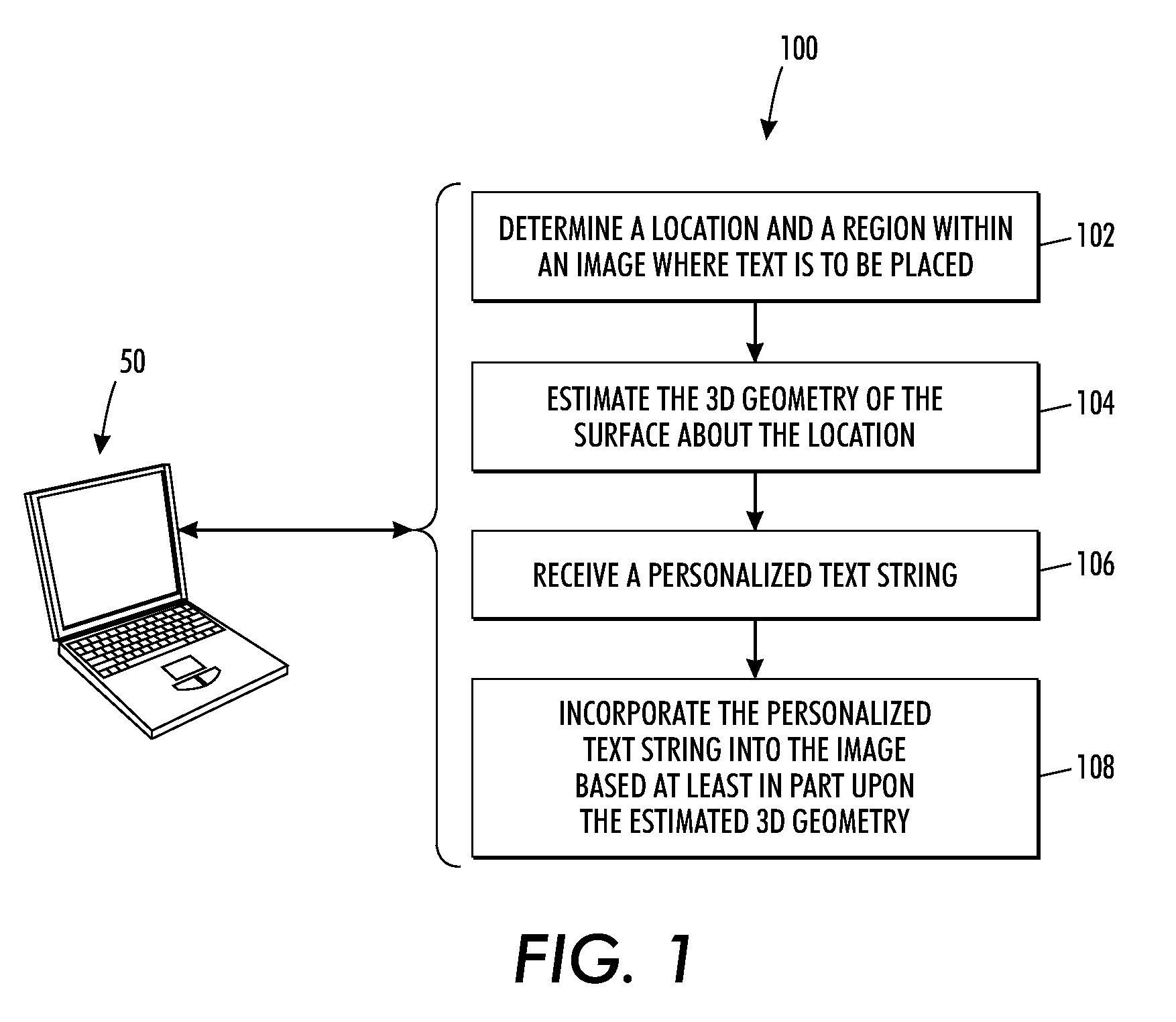
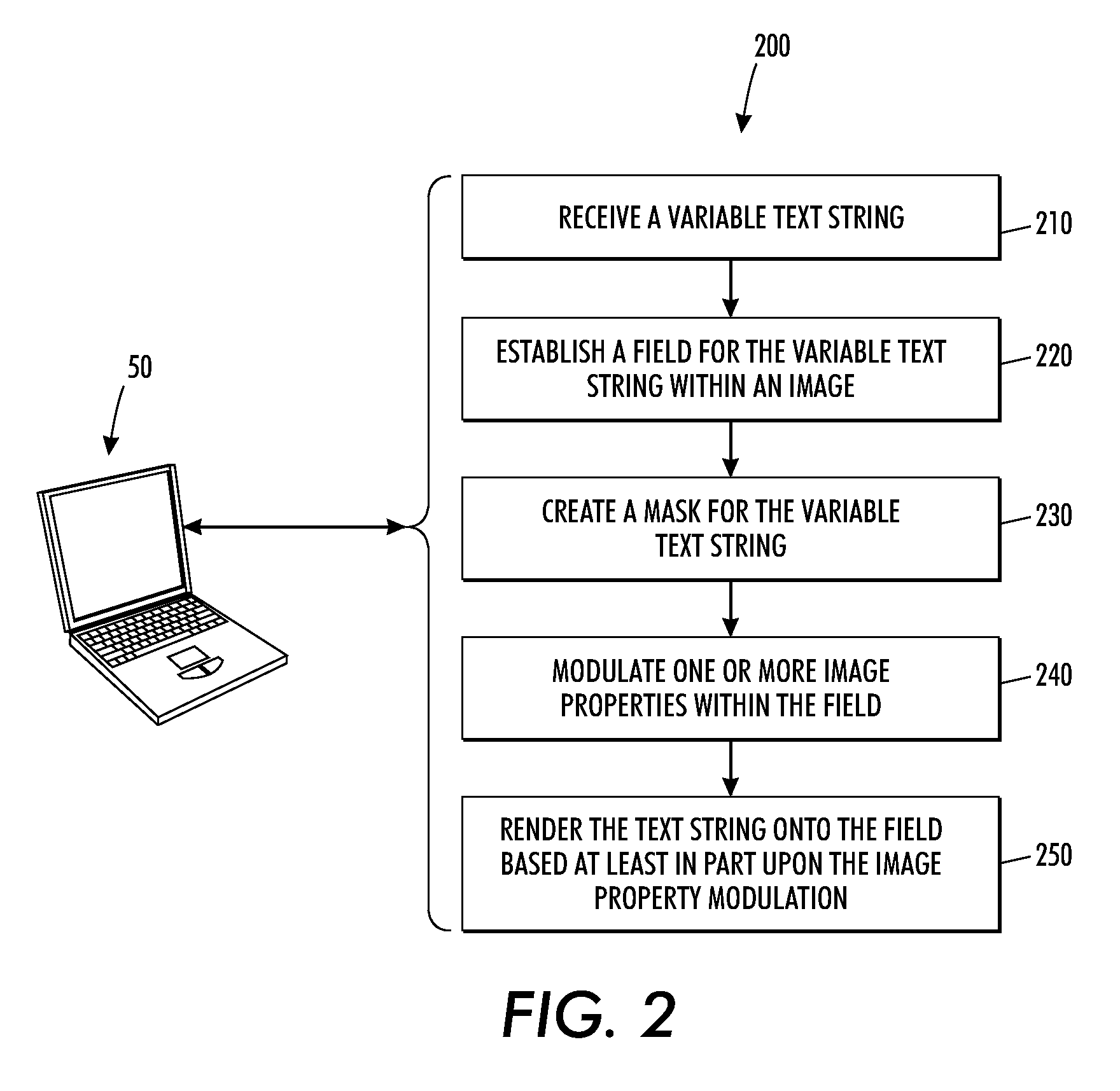
Systems and methods for text-based personalization of images
Owner:XEROX CORP
Cybernetic 3D music visualizer
InactiveUS20060181537A1Control inputImprove the level ofElectrophonic musical instrumentsAnimationFrequency spectrumInput control
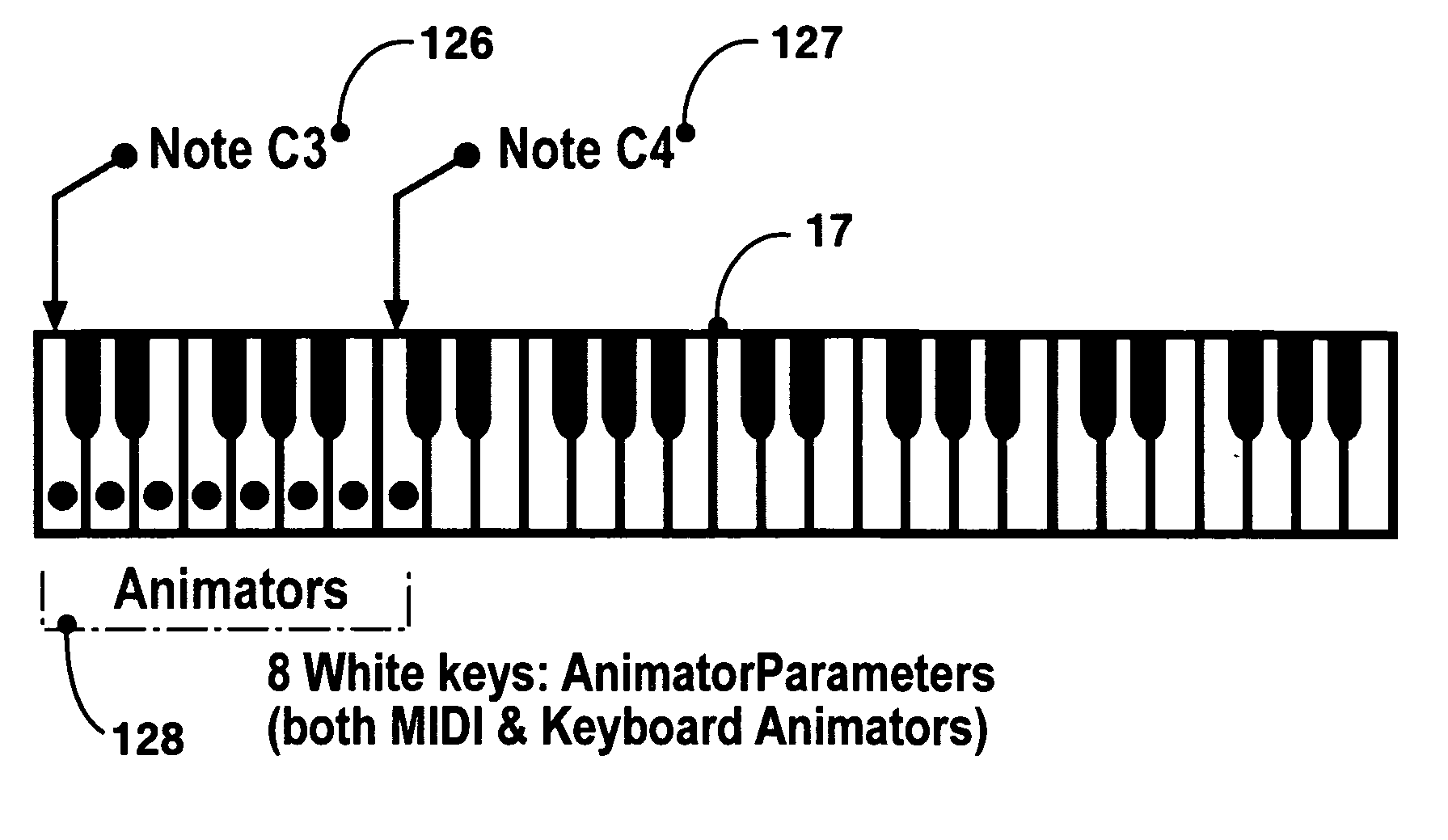
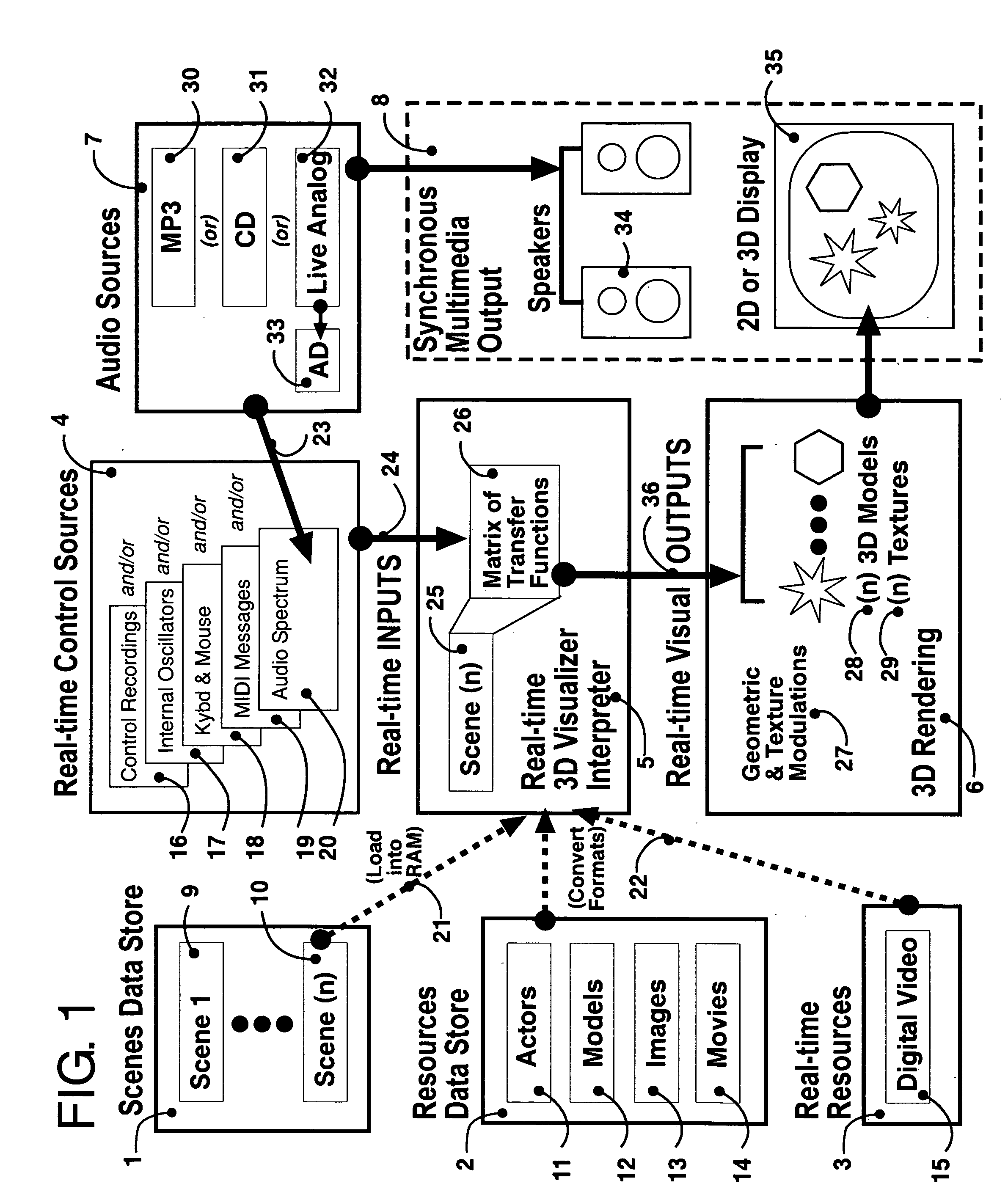
3D music visualization process employing a novel method of real-time reconfigurable control of 3D geometry and texture, employing blended control combinations of software oscillators, computer keyboard and mouse, audio spectrum, control recordings and MIDI protocol. The method includes a programmable visual attack, decay, sustain and release (V-ADSR) transfer function applicable to all degrees of freedom of 3D output parameters, enhancing even binary control inputs with continuous and aesthetic spatio-temporal symmetries of behavior. A “Scene Nodes Graph” for authoring content acts as a hierarchical, object-oriented graphical interpreter for defining 3D models and their textures, as well as flexibly defining how the control source blend(s) are connected or “Routed” to those objects. An “Auto-Builder” simplifies Scene construction by auto-inserting and auto-routing Scene Objects. The Scene Nodes Graph also includes means for real-time modification of the control scheme structure itself, and supports direct real-time keyboard / mouse adjustment to all parameters of all input control sources and all output objects. Dynamic control schemes are also supported such as control sources modifying the Routing and parameters of other control sources. Auto-scene-creator feature allows automatic scene creation by exploiting the maximum threshold of visualizer set of variables to create a nearly infinite set of scenes. A Realtime-Network-Updater feature allows multiple local and / or remote users to simultaneously co-create scenes in real-time and effect the changes in a networked community environment where in universal variables are interactively updated in real-time thus enabling scene co-creation in a global environment. In terms of the human subjective perception, the method creates, enhances and amplifies multiple forms of both passive and interactive synesthesia. The method utilizes transfer functions providing multiple forms of applied symmetry in the control feedback process yielding an increased level of perceived visual harmony and beauty. The method enables a substantially increased number of both passive and human-interactive interpenetrating control / feedback processes that may be simultaneously employed within the same audio-visual perceptual space, while maintaining distinct recognition of each, and reducing the threshold of human ergonomic effort required to distinguish them even when so coexistent. Taken together, these novel features of the invention can be employed (by means of considered Scene content construction) to realize an increased density of “orthogonal features” in cybernetic multimedia content. This furthermore increases the maximum number of human players who can simultaneously participate in shared interactive music visualization content while each still retaining relatively clear perception of their own control / feedback parameters.
Owner:VASAN SRINI +2
Computer system and method for generating a 3D geometric model
ActiveUS20100214291A1High resolutionImprove visual qualityGeometric CADCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerized systemDigital image
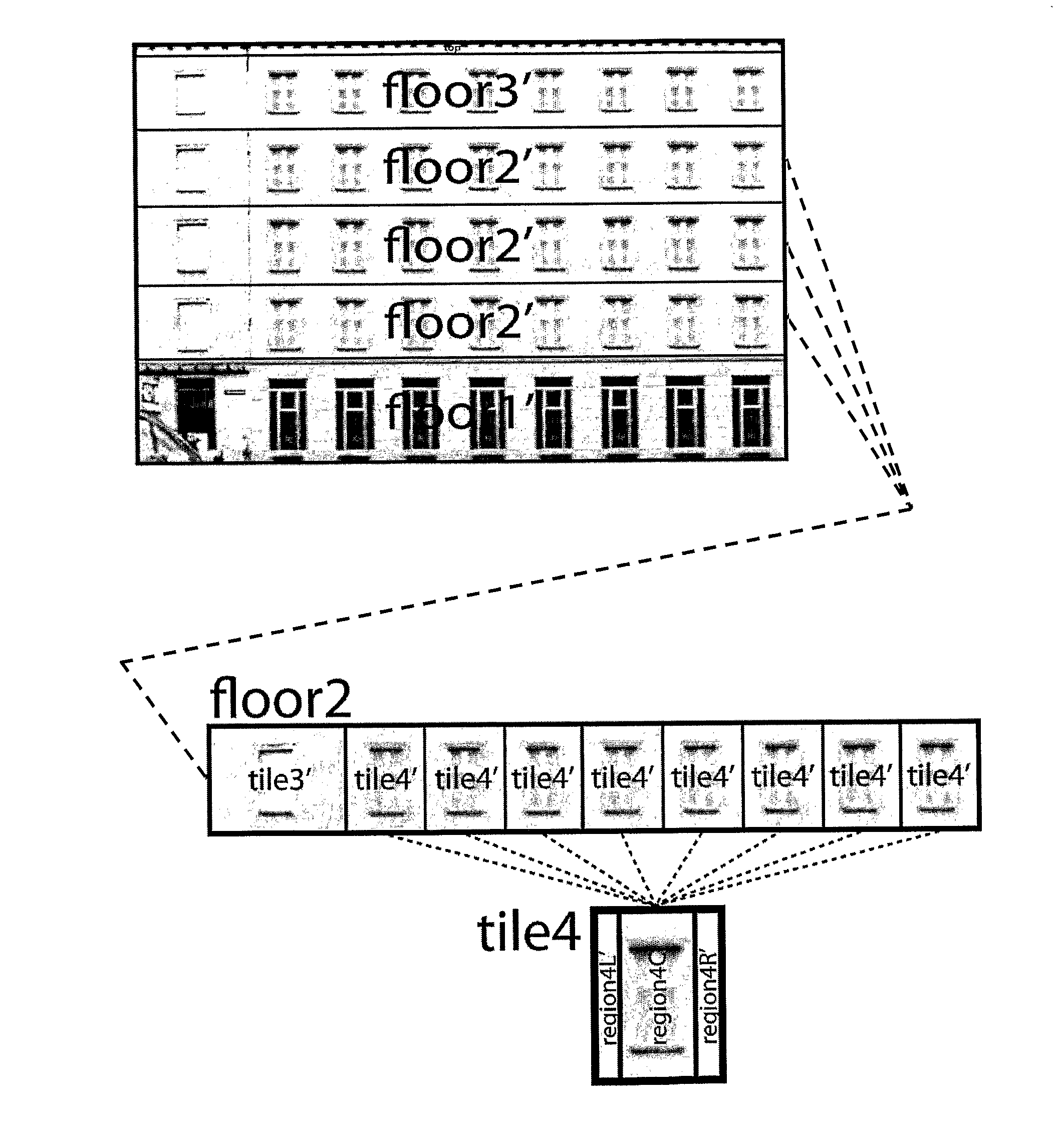
For generating a 3D geometric model (44) and / or a definition of the 3D geometric model from a single digital image of a building facade (4), a facade structure is detected from the digital image by dividing the facade (4) along horizontal lines into horizontal layers representative of floors (41), and by dividing the horizontal layers along vertical lines into tiles (42). The tiles (42) are further subdivided into a hierarchy of rectangular image regions (43). 3D architectural objects (45) corresponding to the image regions (43) are determined in an architectural element library. The 3D geometric model (44) or the definition of the 3D geometric model is generated based on the facade structure, the hierarchy and the 3D architectural objects (45). The library-based generation of the 3D geometric model makes it possible to enhance simple textured building models constructed from aerial images and / or ground-based photographs.
Owner:ESRI R&D CENT ZURICH AG
Three-dimensional printing preparation
ActiveUS20130297059A1Additive manufacturing apparatusComputer aided designMedial axisImage resolution
Embodiments disclosed herein provide systems and methods for preparing geometry for 3D printing. In one embodiment, a 3D printing preparation application receives 3D geometry and repairs non-manifold edges and non-manifold vertices, producing a topological manifold geometry. The 3D printing preparation application then welds coincident edges without coincident faces and fills holes in the geometry. The 3D printing preparation application may further perform resolution-aware thickening of the geometry by estimating distances to a medial axis based on distances to distance field shocks, and advecting the distance field using a velocity field. A similar approach may be used to perform resolution-aware separation enforcement. Alternatively, one component may be globally thickened and subtracted from another for separation enforcement. The 3D printing preparation application may also split large models and add connectors for connecting the split pieces after printing. In addition, the 3D printing preparation application may generate a 3D print preview.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Integration of graphical application content into the graphical scene of another application
InactiveUS20070211065A1Image data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingGraphics3d geometry
This application describes a system that captures 3D geometry commands from a first 3D graphics process and stores them in a shared memory. A second 3D environment process creates a 3D display environment using a display and display hardware. A third process obtains the 3D commands and supplies them to the hardware to place 3D objects in the 3D environment. The result is a fused display environment where 3D objects are displayed along with other display elements. Input events in the environment are analyzed and mapped to the 3D graphics process or the environment where they affect corresponding processing.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
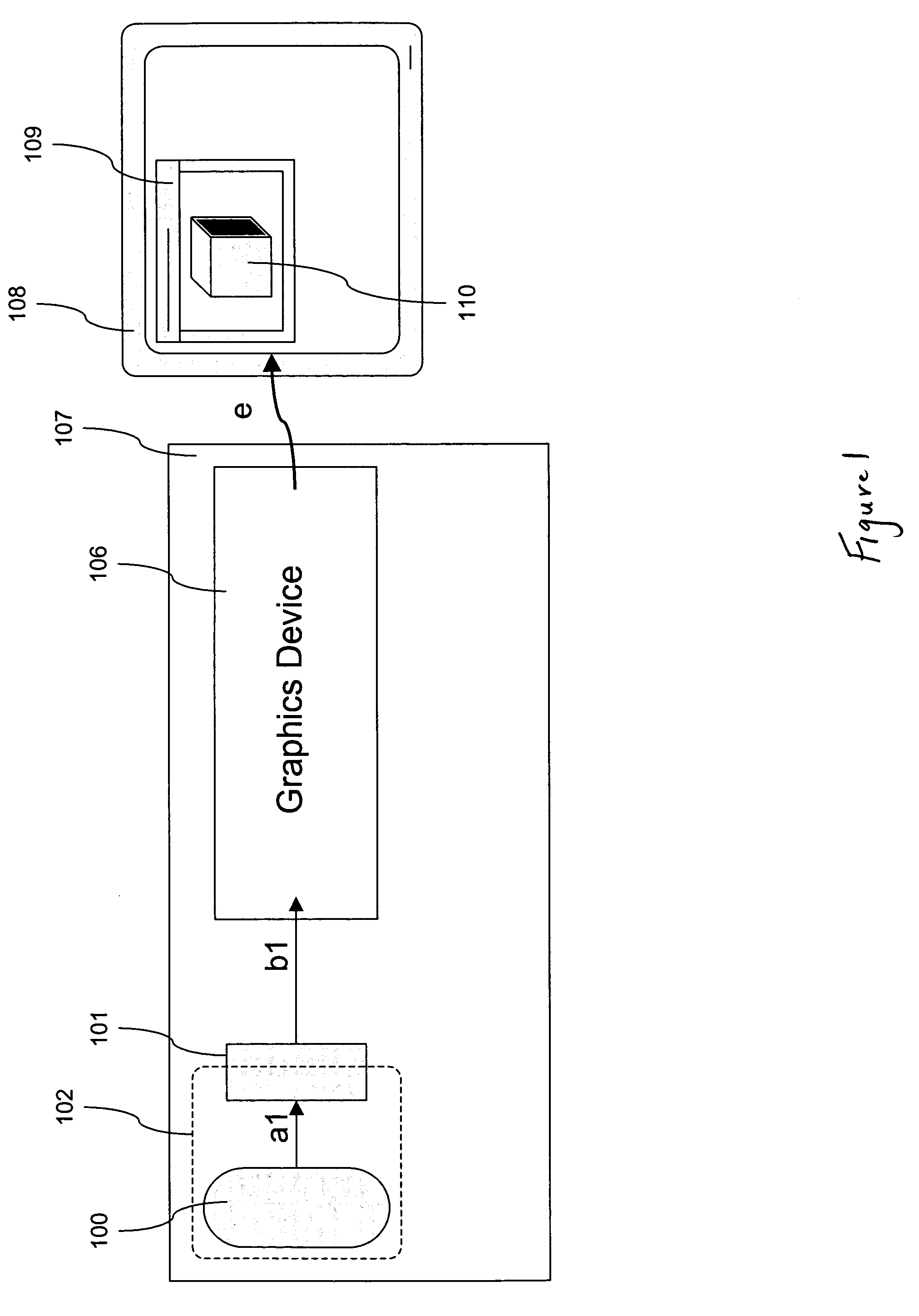
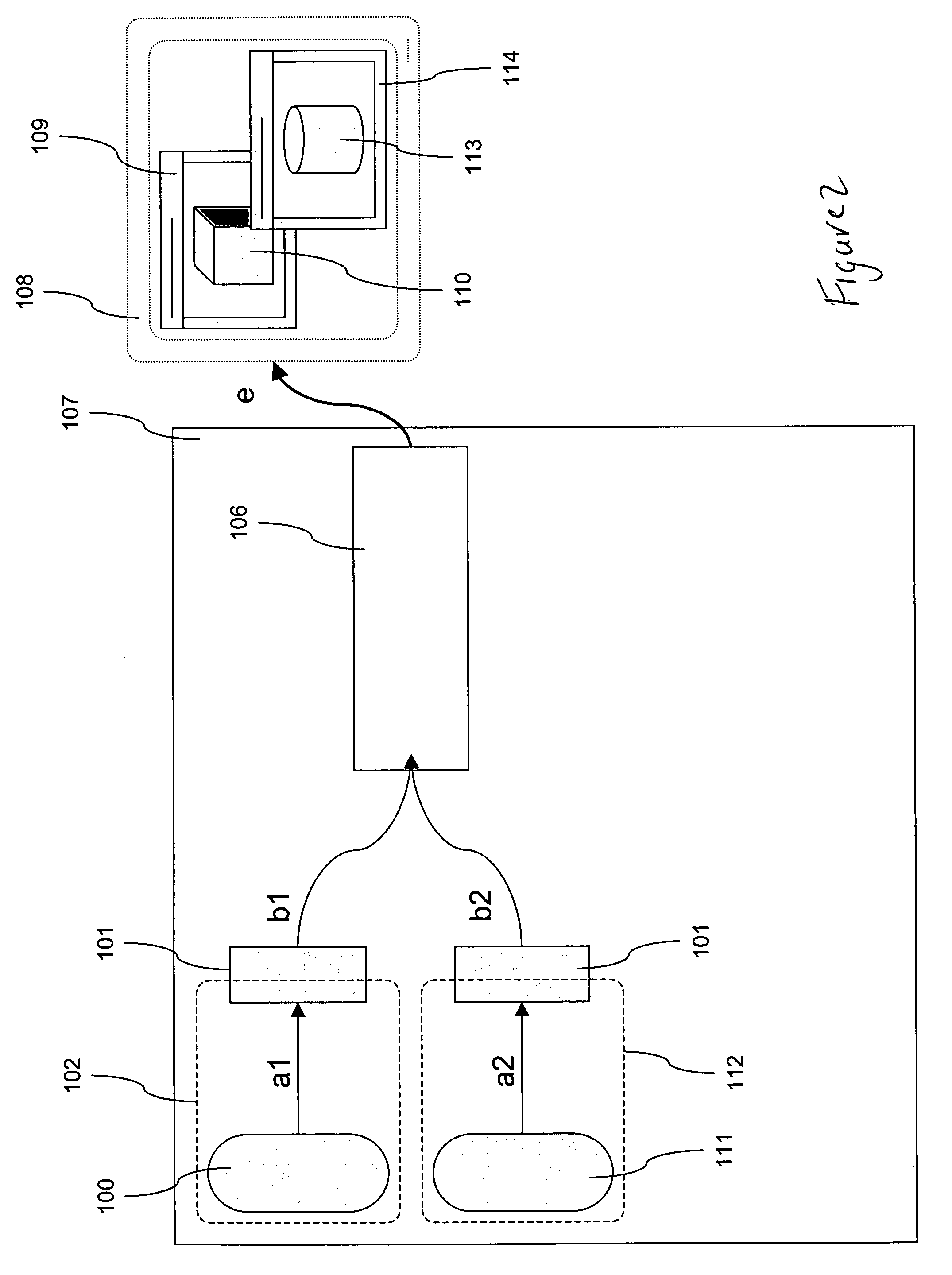
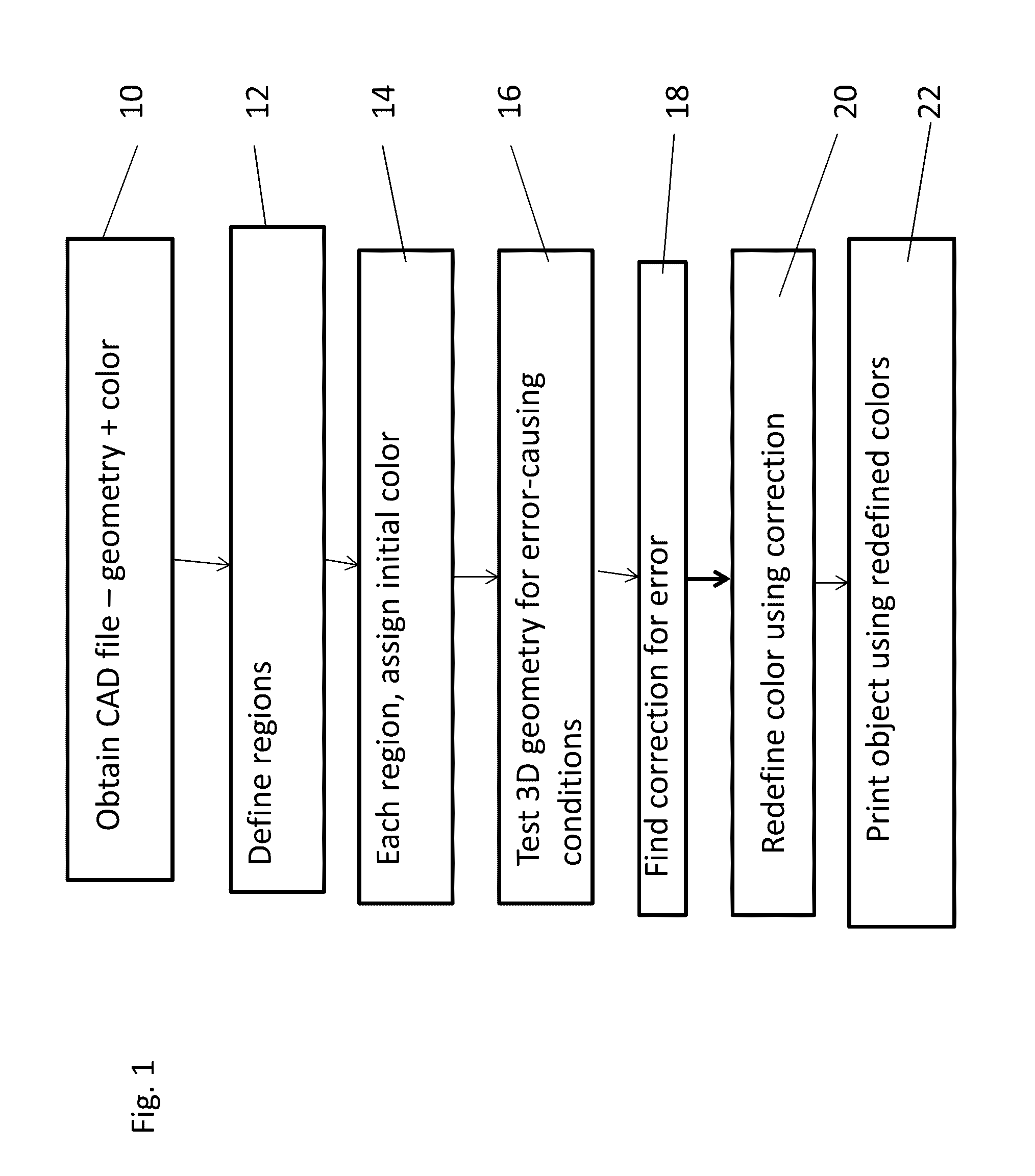
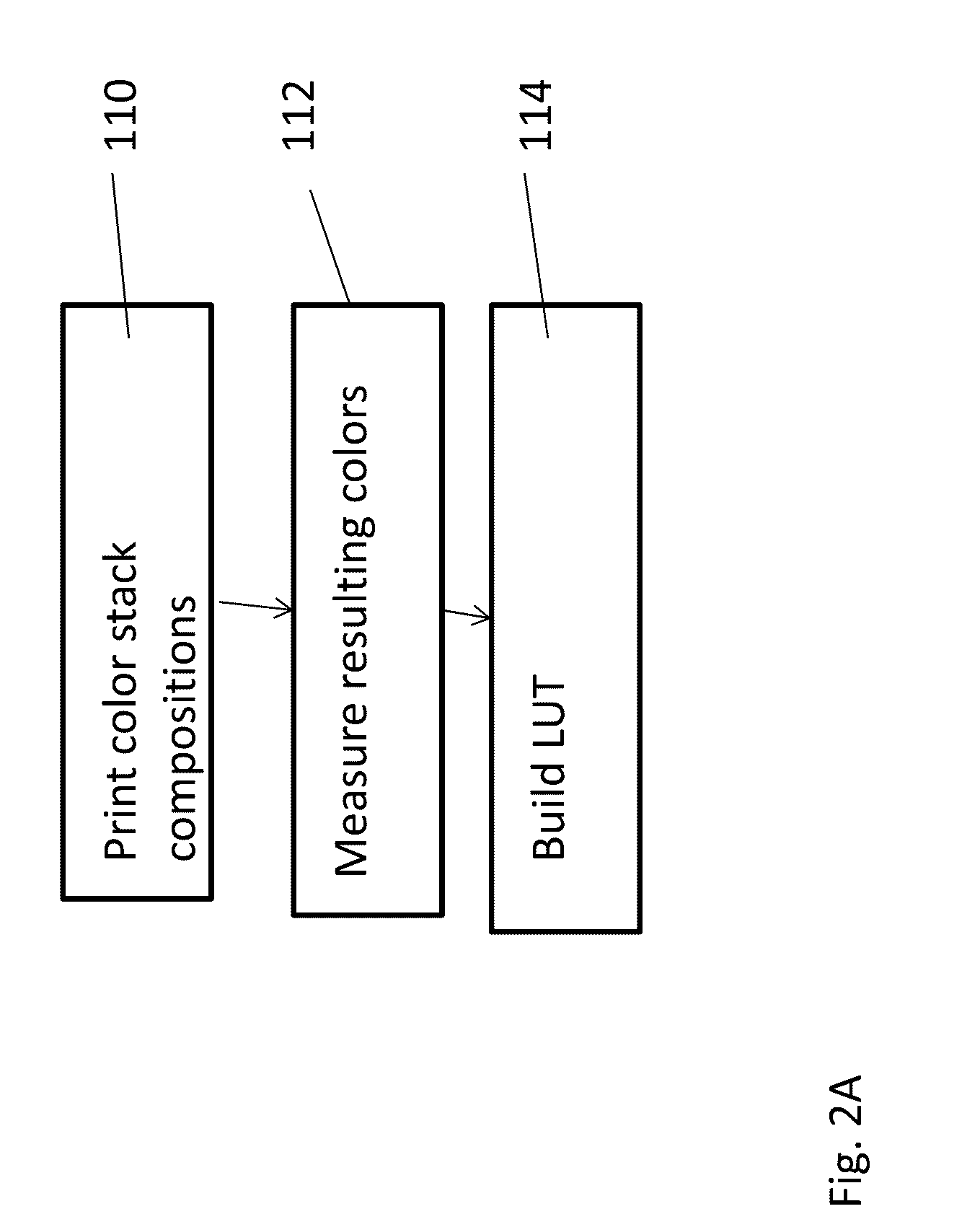
Coloring of three-dimensional printed objects
ActiveUS20160339643A1Additive manufacturing apparatusDuplicating/marking methodsComputer graphics (images)Color correction
Owner:STRATASYS LTD
Photogrammetry engine for model construction
InactiveUS7720276B1Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionThe InternetUser interface
Owner:KOROBKIN CARL P
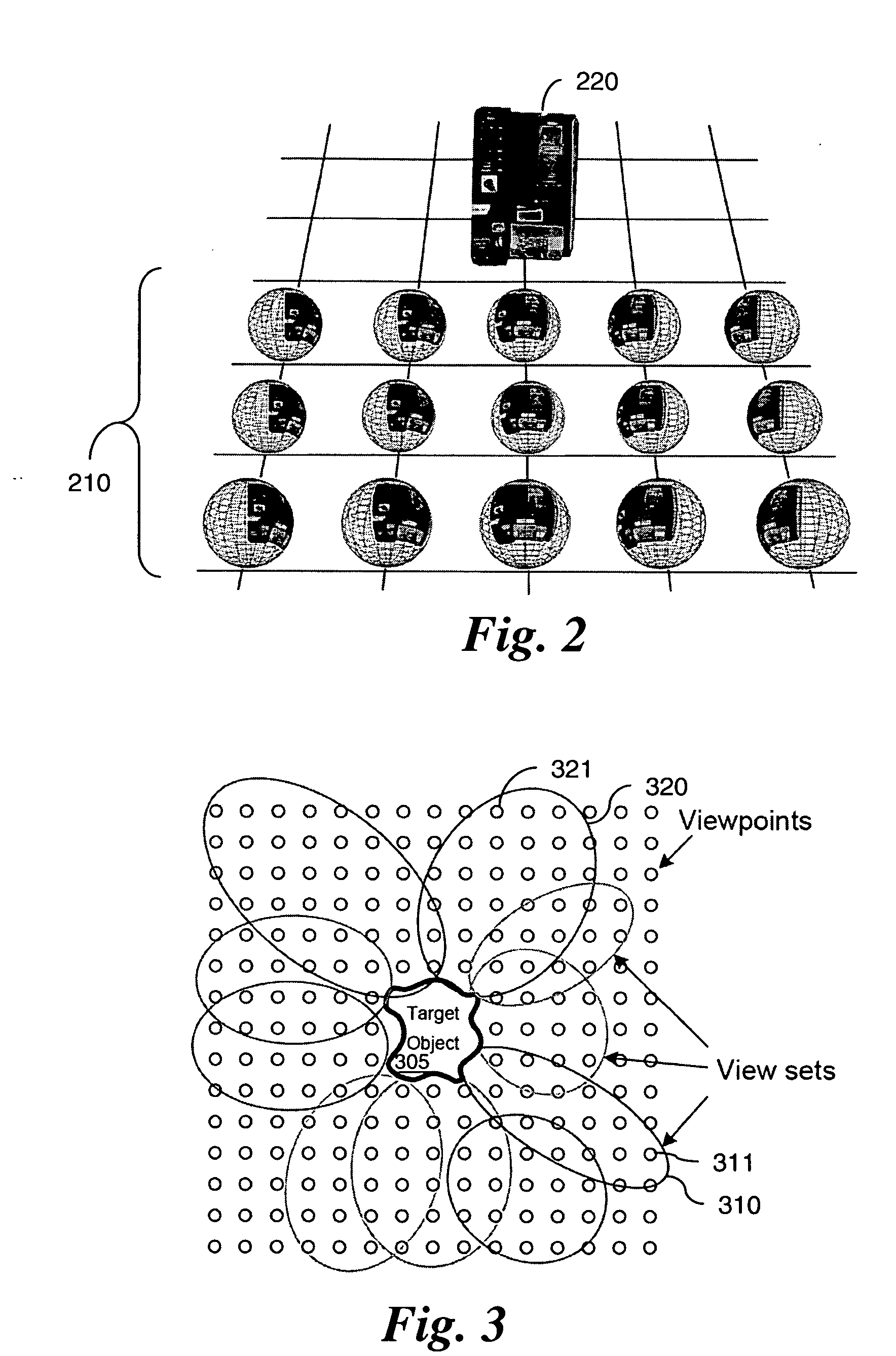
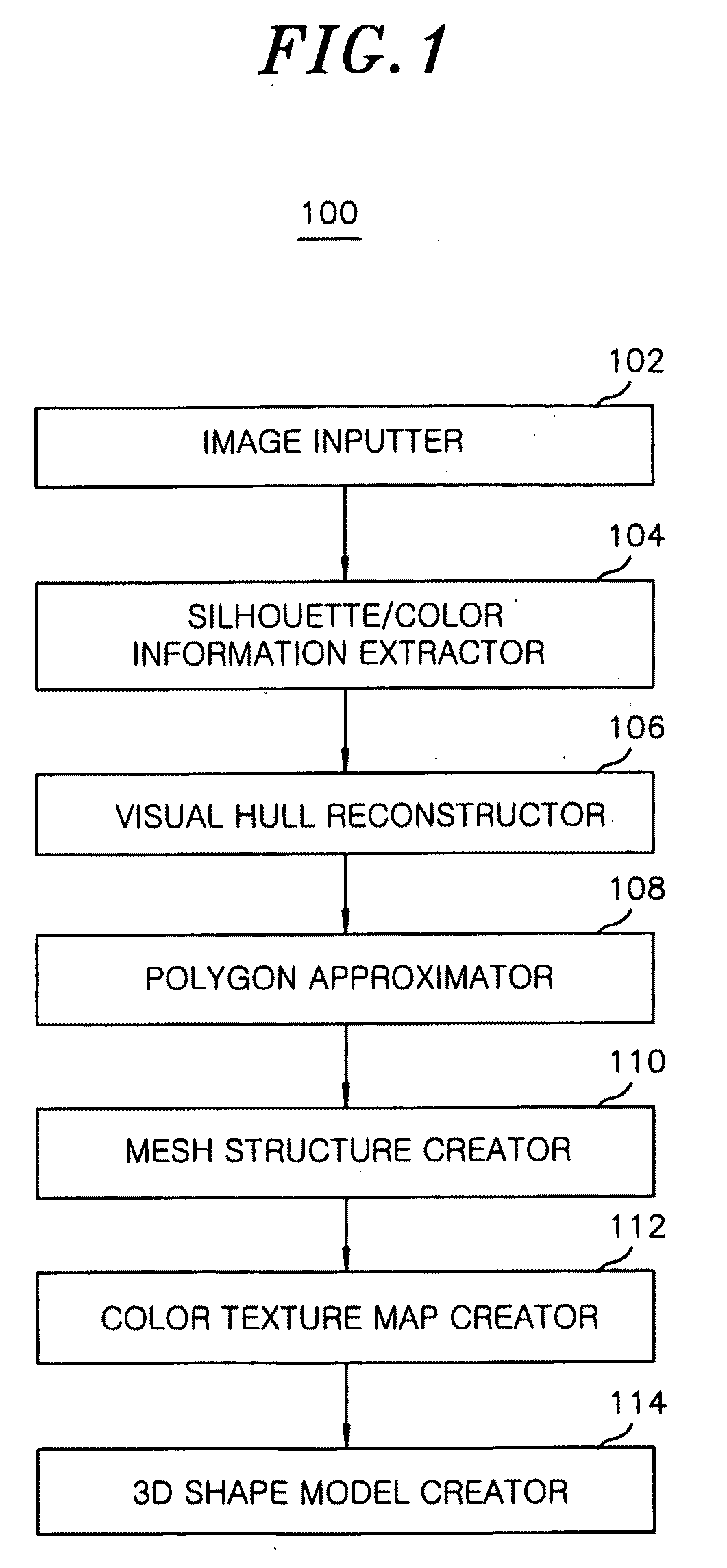
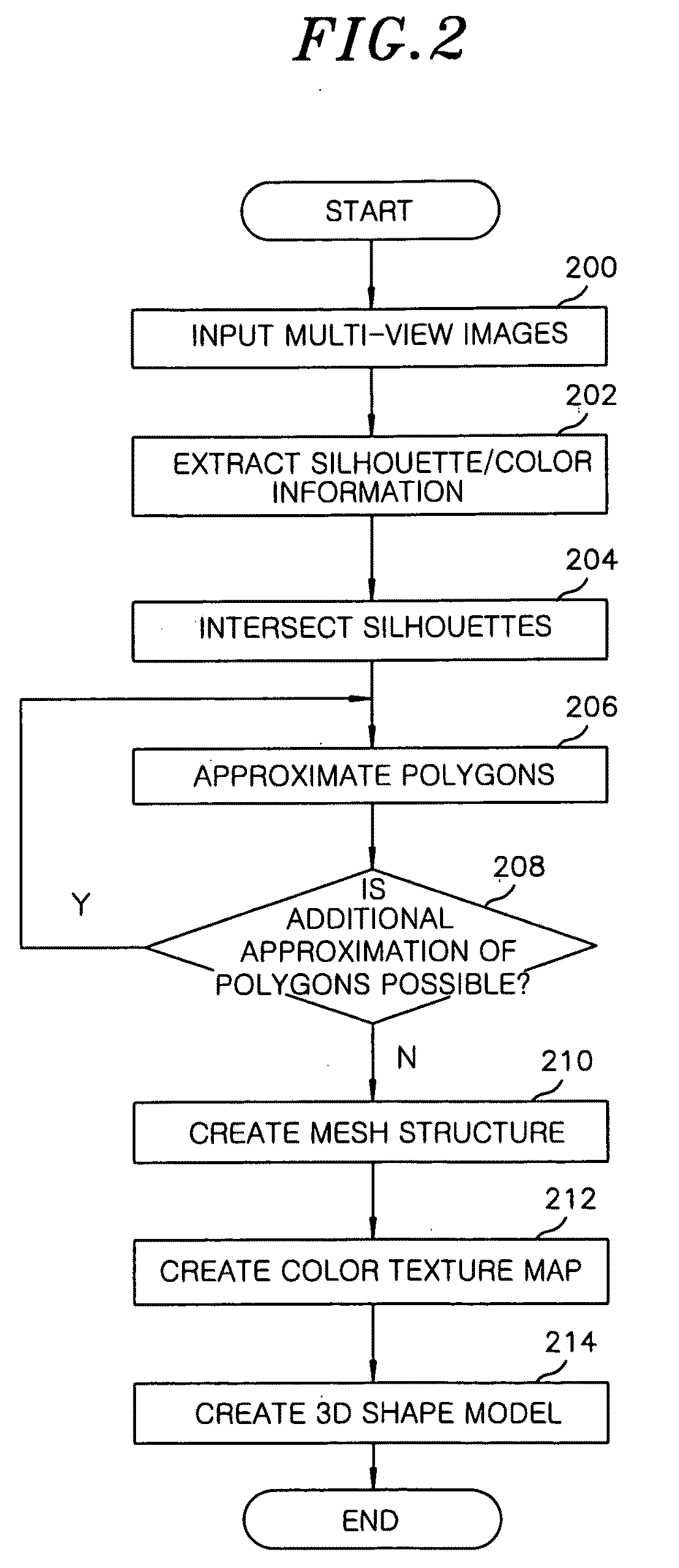
Method and apparatus for reconstructing 3D shape model of object by using multi-view image information
InactiveUS20090154794A1Improve reconstruction qualityQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systems3d shapesVoxel
A method for reconstructing a 3D shape model of an object by using multi-view image information, includes: inputting multi-view images obtained by photographing the object from multiple viewpoints in a voxel space, and extracting silhouette information and color information of the multi-view images; reconstructing visual hulls by silhouette intersection using the silhouette information; and approximating polygons of cross-sections of the visual hulls to a natural geometric shape of the object by using the color information. Further, the method includes expressing a 3D geometric shape of the object by connecting the approximated polygons to create a mesh structure; extracting color textures of a surface of the object by projecting meshes of the mesh structure to the multi-view image; and creating a 3D shape model by modeling natural shape information and surface color information of the object.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Fast object detection for augmented reality systems
InactiveUS7706603B2Reduce dimensionalityMinimize impactImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionVisibilityViewpoints
A detection method is based on a statistical analysis of the appearance of model patches from all possible viewpoints in the scene, and incorporates 3D geometry during both matching and pose estimation processes. By analyzing the computed probability distribution of the visibility of each patch from different viewpoints, a reliability measure for each patch is estimated. That reliability measure is useful for developing industrial augmented reality applications. Using the method, the pose of complex objects can be estimated efficiently given a single test image.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
Long bone fracture traction reduction navigation apparatus
InactiveCN101332137AHigh precisionImprove efficiencySurgeryFractureFracture reductionLONG BONE FRACTURE
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Surfacing algorithm for designing and manufacturing 3D models
ActiveUS20120158369A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)3d geometry
Techniques are described for decomposing three-dimensional (3D) geometry into an assemblable collection of two-dimensional (2D) panels. Importantly, the 3D geometry is automatically encoded into the 2D panels, allowing the 3D geometry to be recreated simply by joining the 2D panels at the appropriate seams and creating the appropriate bends / folds in each panel. Further, each panel has edges, vertices, and faces which can be encoded in the panelization, allowing assembly instructions to be algorithmically generated, Doing so allows users to be provided with a step-by-step instructions carried out to realize the 3D geometry encoded in the 2D panels.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Method And System For Determining Camera Parameters From A Long Range Gradient Based On Alignment Differences In Non-Point Image Landmarks
ActiveUS20130176392A1Improved calibration of cameraReduce errorsImage analysisSteroscopic systemsCamera imageComputer graphics (images)
A system and method improves a camera calibration. The method includes receiving a camera image, a planar template pattern, a 3D geometry of a surface on which the planar template pattern is embedded, and a set of parameter values. The method includes rendering the planar template pattern into a camera perspective based on the parameter values to generate a warped template image. The method includes generating an error image including at least one non-zero difference between the camera image and the warped template image. The method includes adjusting the parameter values to reduce an error between the camera image and the warped template image.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Interpretation of Real Time Compaction Monitoring Data Into Tubular Deformation Parameters and 3D Geometry
A method, apparatus and computer-readable medium for determining a deformation strain distribution of a member corresponding to a selected deformation mode is disclosed. Strain measurements are obtained at a plurality of sensors, wherein each strain measurement is related to a strain at a location of the member. A component of the strain related to a selected deformation mode for the obtained strain measurements is determined and a principal strain component and a secondary strain component for each of the determined components of the strain is determined. The determined principal strain component and secondary strain component are mapped to a surface of the member to determine the deformation strain distribution.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
System and method for non-contact measurement of 3D geometry
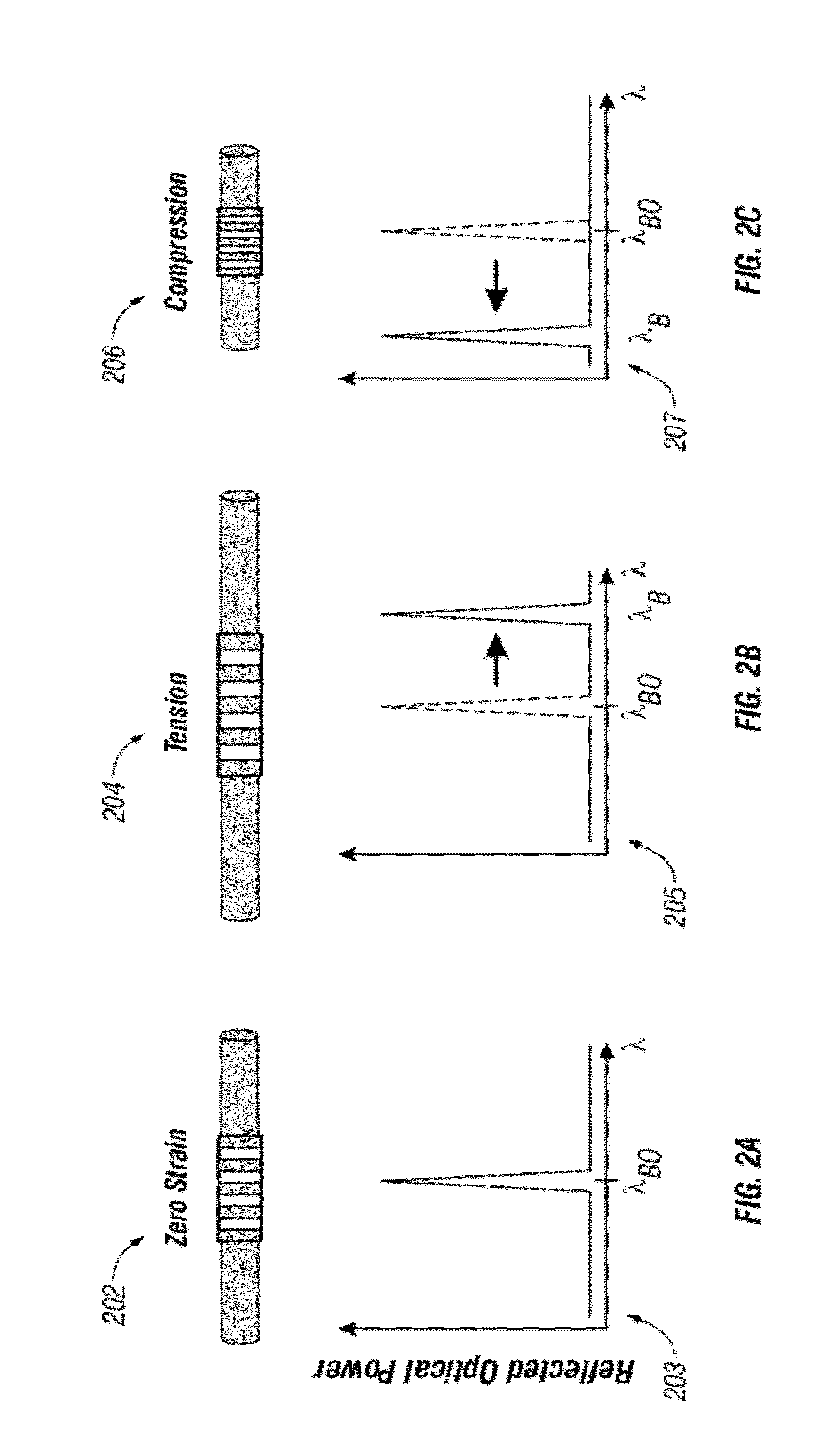
InactiveUS20150103358A1Advantageously effectiveRisk minimizationUsing optical meansStereo matchingElectrical polarity
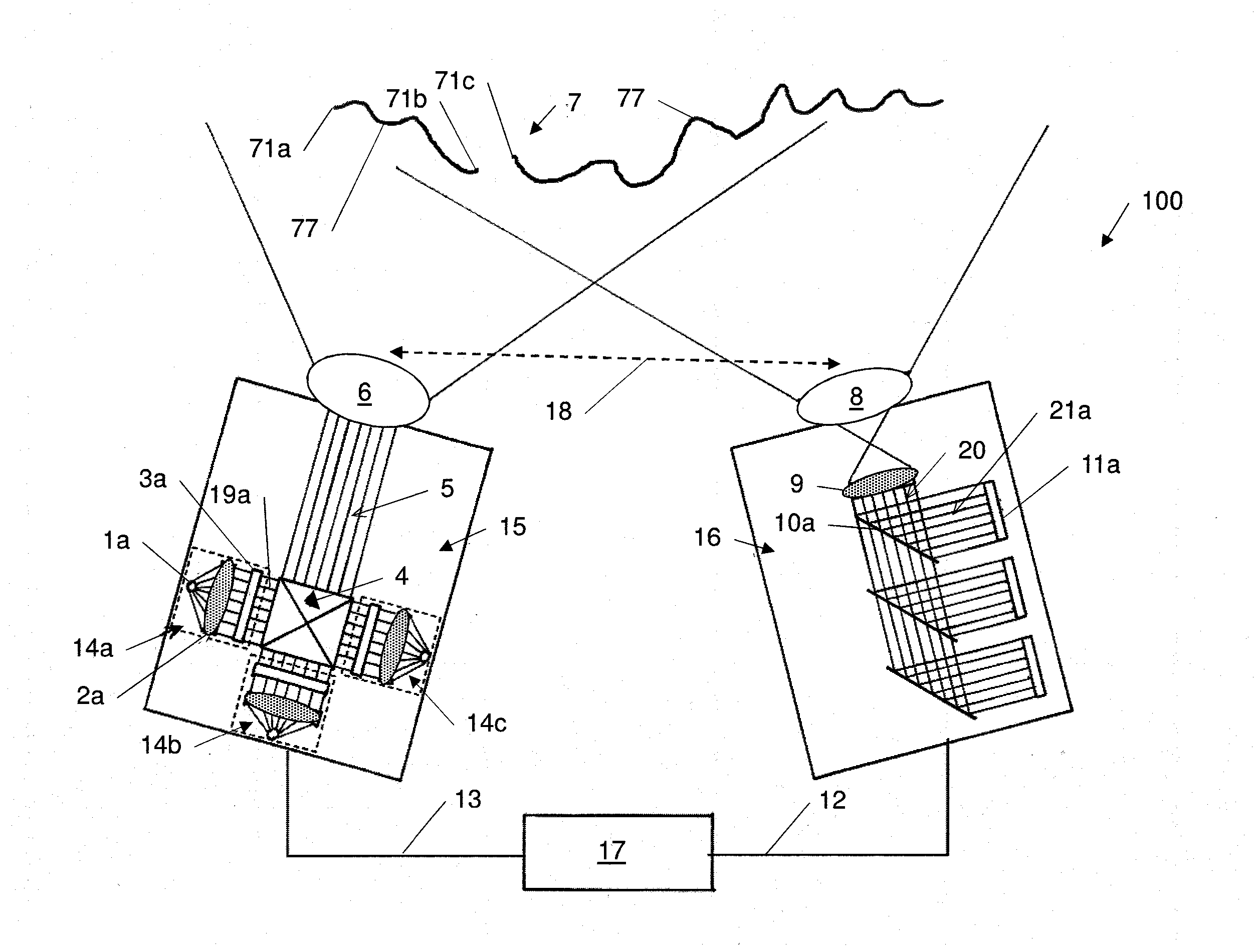
A method for the non-contact measurement of a scene's 3D geometry is based on the concurrent projection of multiple and overlapping light patterns of different wavelengths and / or polarity onto its surfaces. Each location in the overlapping light patterns is encoded (code-word) by the combined arrangements of code elements (code-letters) from one or more of the overlapping patterns. The coded light reflected from the scene is imaged separately for each wavelength and / or polarity by an acquisition unit and code-letters are combined at each pattern location to yield a distinct code-word by a computing unit. Code-words are then identified in the image, stereo-matched, and triangulated, to calculate the range to the projected locations on the scene's surface.
Owner:GALIL SOFT
Image Coding And Decoding Method And Apparatus For Efficient Encoding And Decoding Of 3D Light Field Content
InactiveUS20130242051A1Reduce storage capacityEfficient executionImage codingTelevision systemsMotion vectorComputer graphics (images)
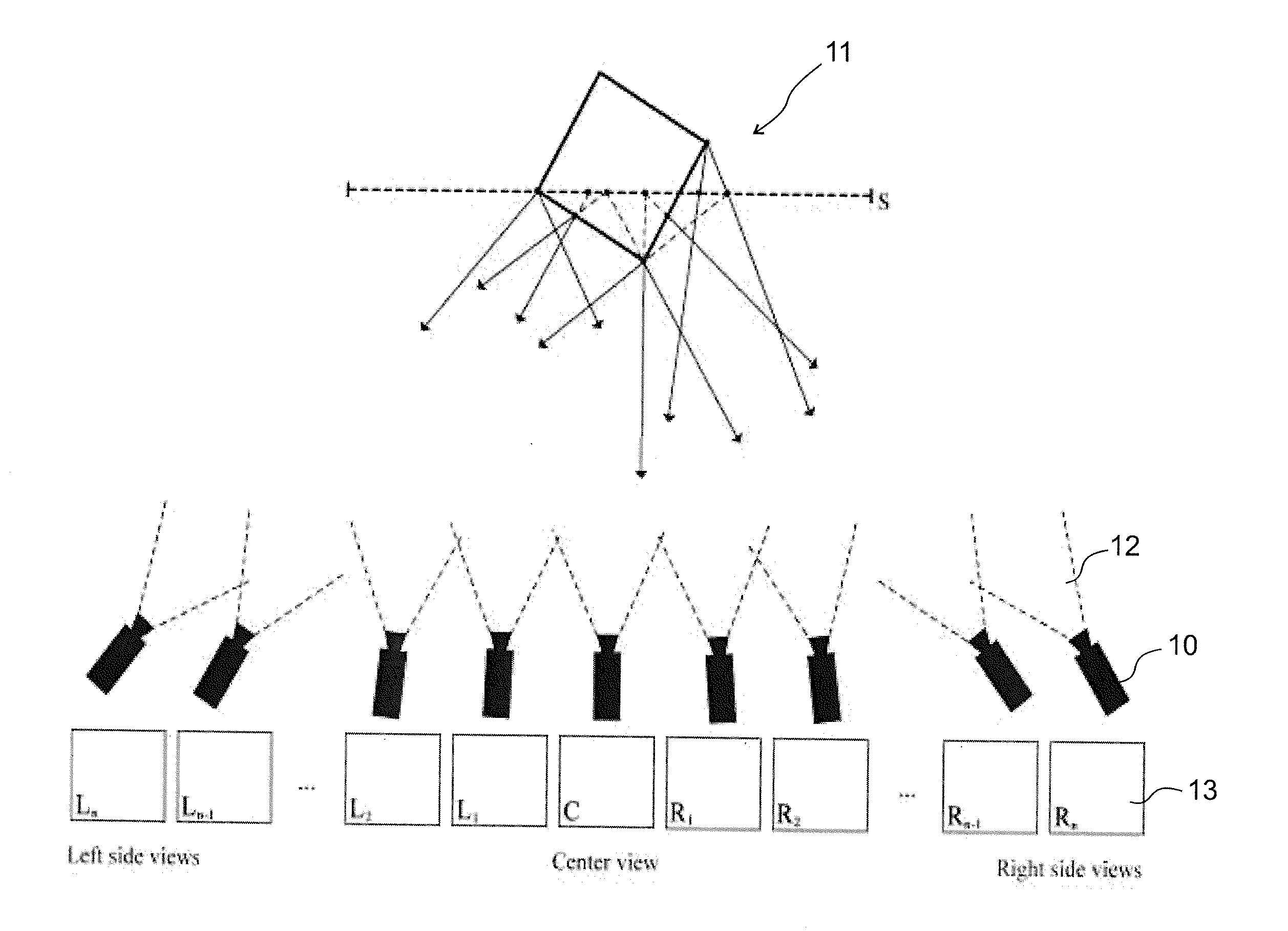
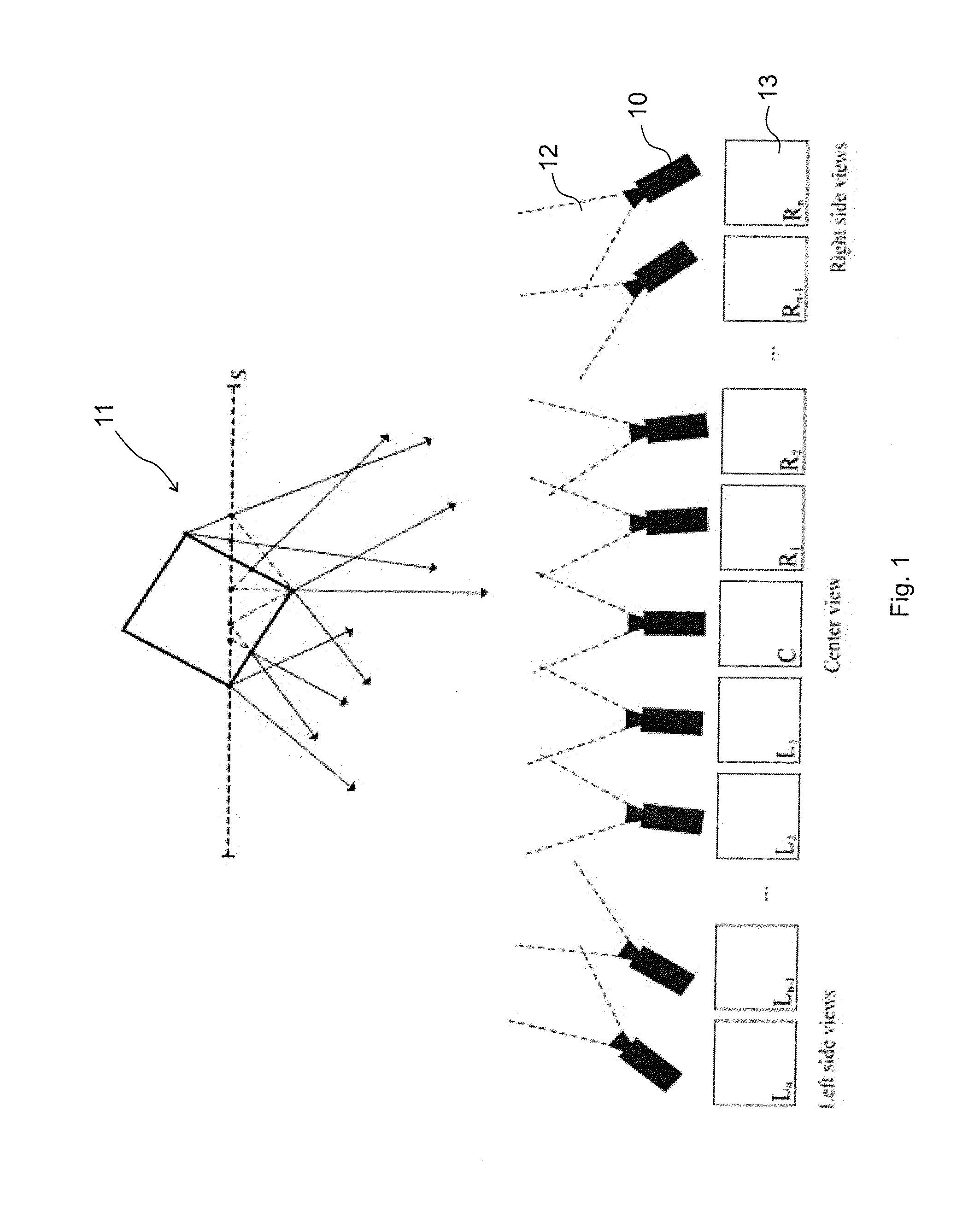
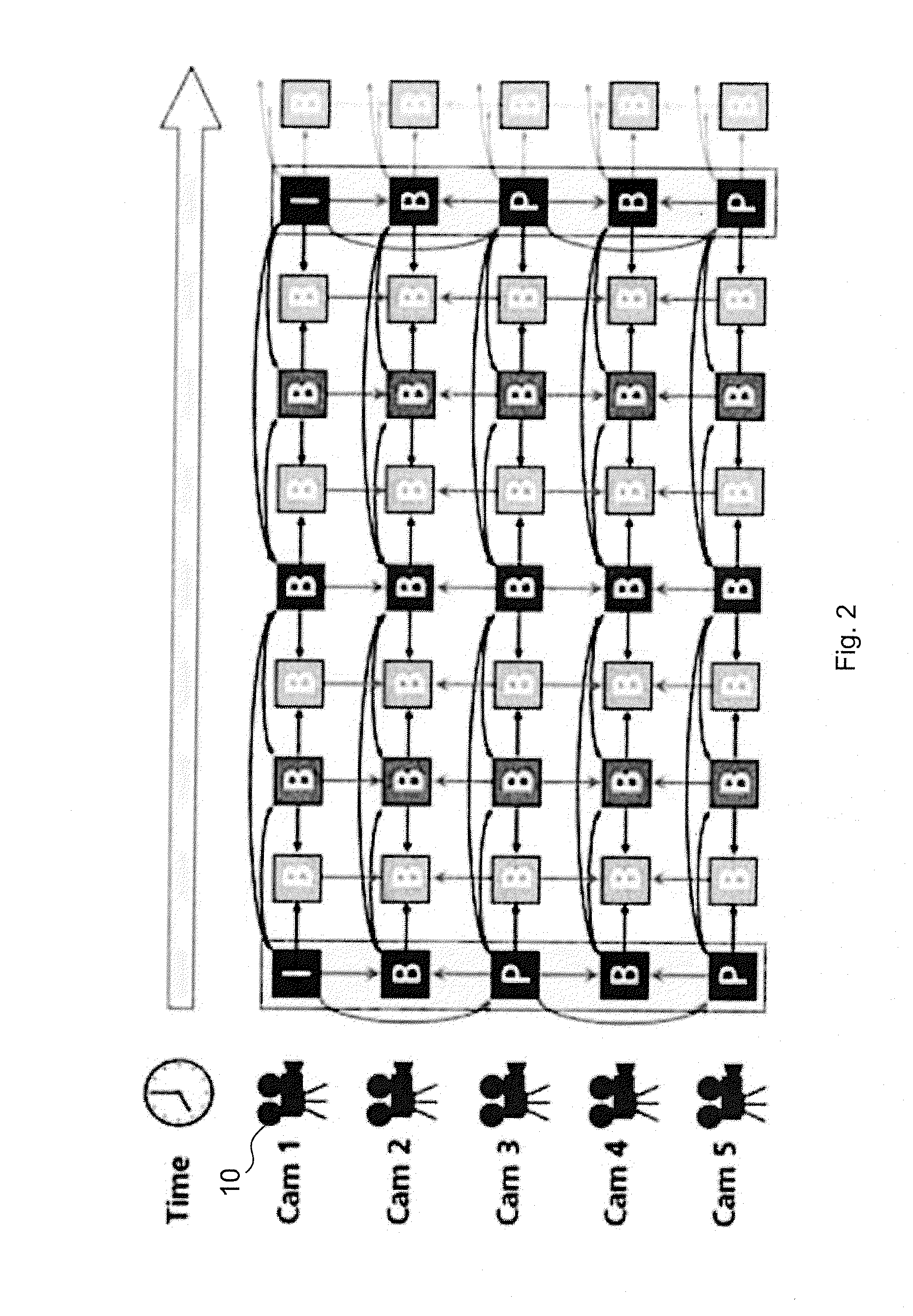
The invention is an image coding method for video compression, especially for efficient encoding and decoding of true 3D content, without extreme bandwidth requirements, being compatible with the current standards serving as an extension, providing a scalable format. The method comprises of the steps of obtaining geometry-related information about the 3D geometry of the 3D scene and generating a common relative motion vector set on the basis of the geometry-related information, the common relative motion vector set corresponding to the real 3D geometry. This motion vector generating step (37) replaces conventional motion estimation and motion vector calculation applied in the standard (MPEG4 / H.264 AVC, MVC, etc.) procedures. Inter-frame coding is carried out by creating predictive frames, starting from an intra frame, being one of the 2D view images on the basis of the intra frame and the common relative motion vector set. On the decoder side large number of views are reconstructed based on dense, but real 3D geometry information. The invention also relates to image coding and decoding apparatuses carrying out the encoding and decoding methods, as well as to computer readable media storing computer executable instructions for the inventive methods. (FIG. 8)
Owner:BALOGH TIBOR
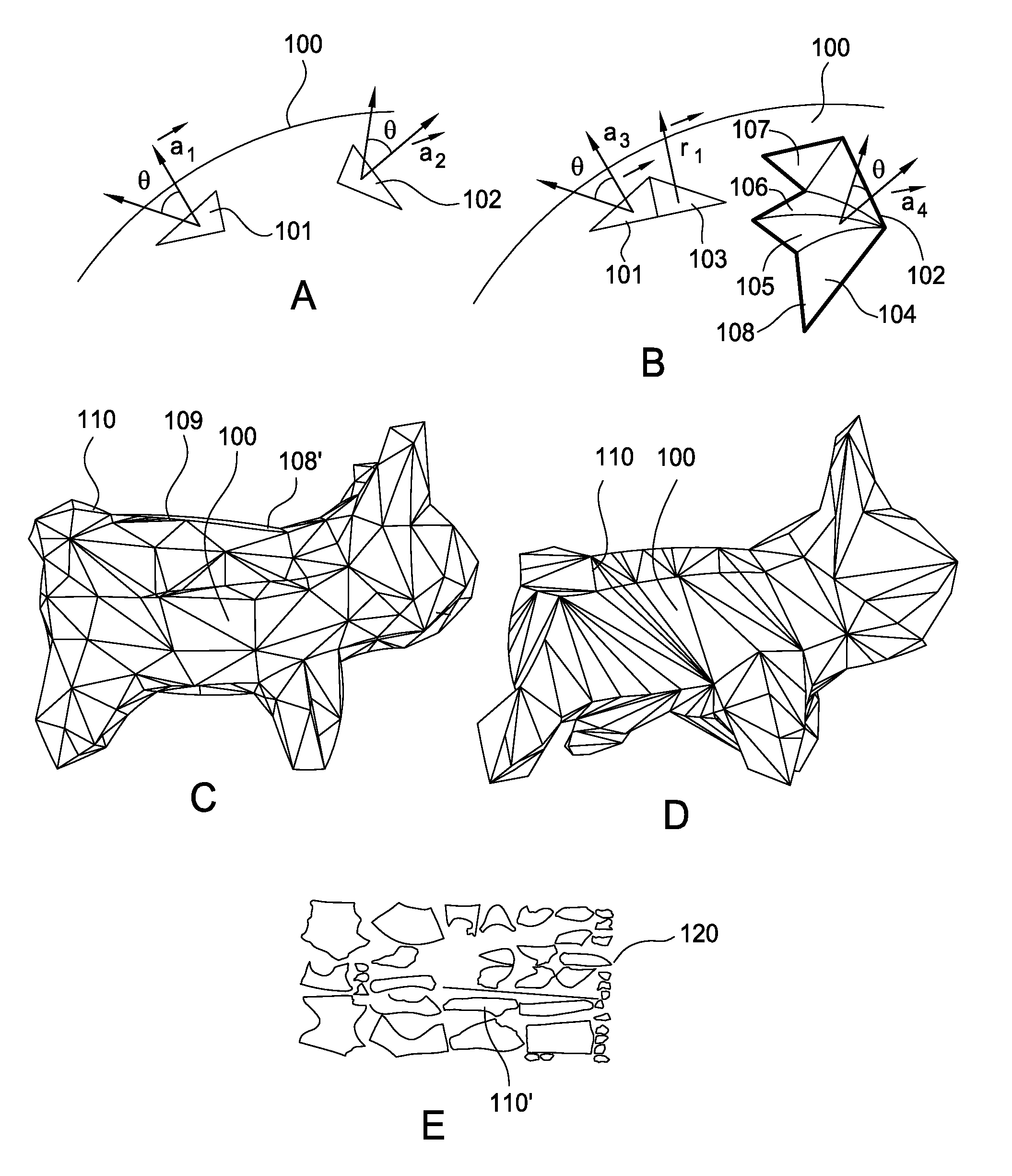
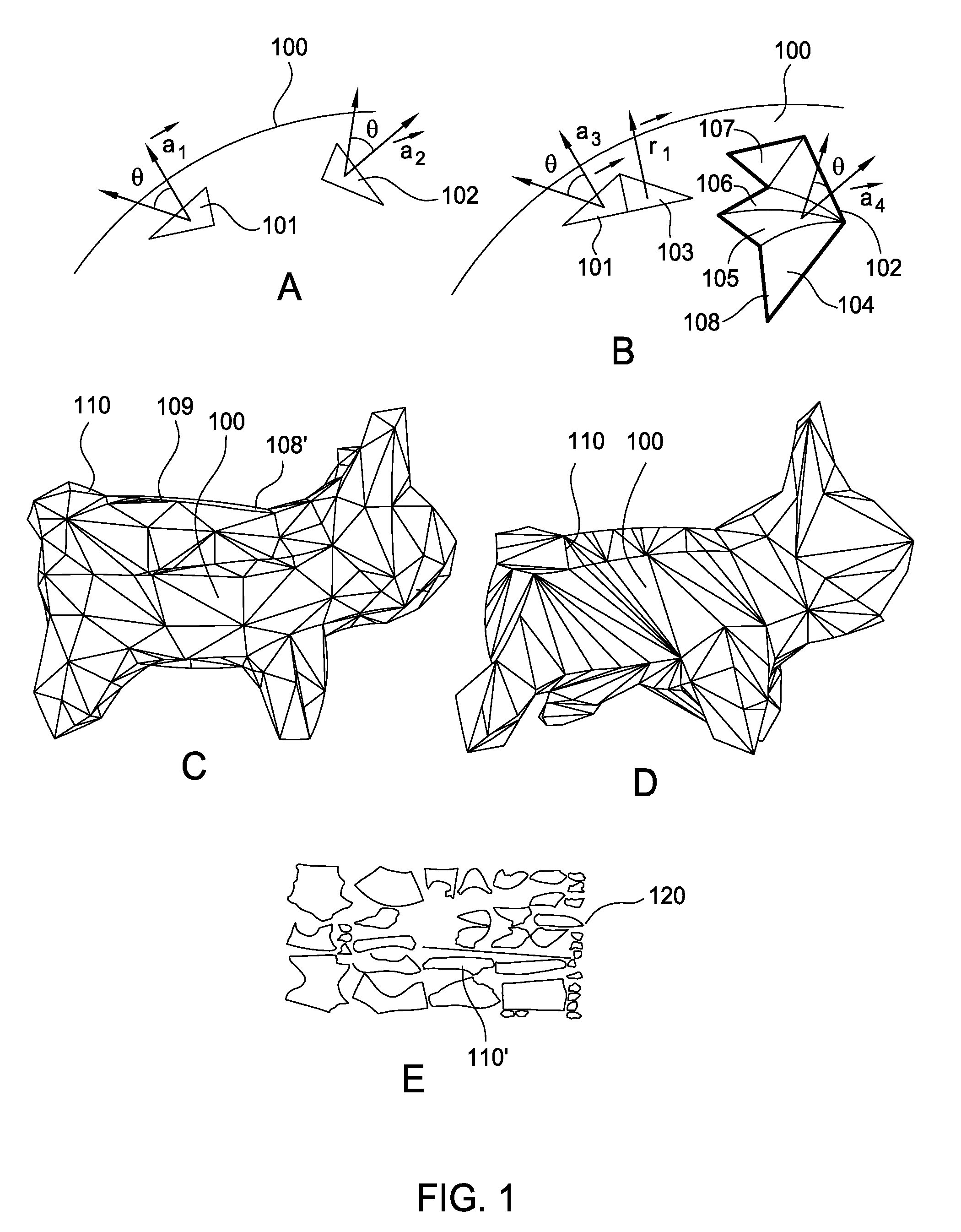
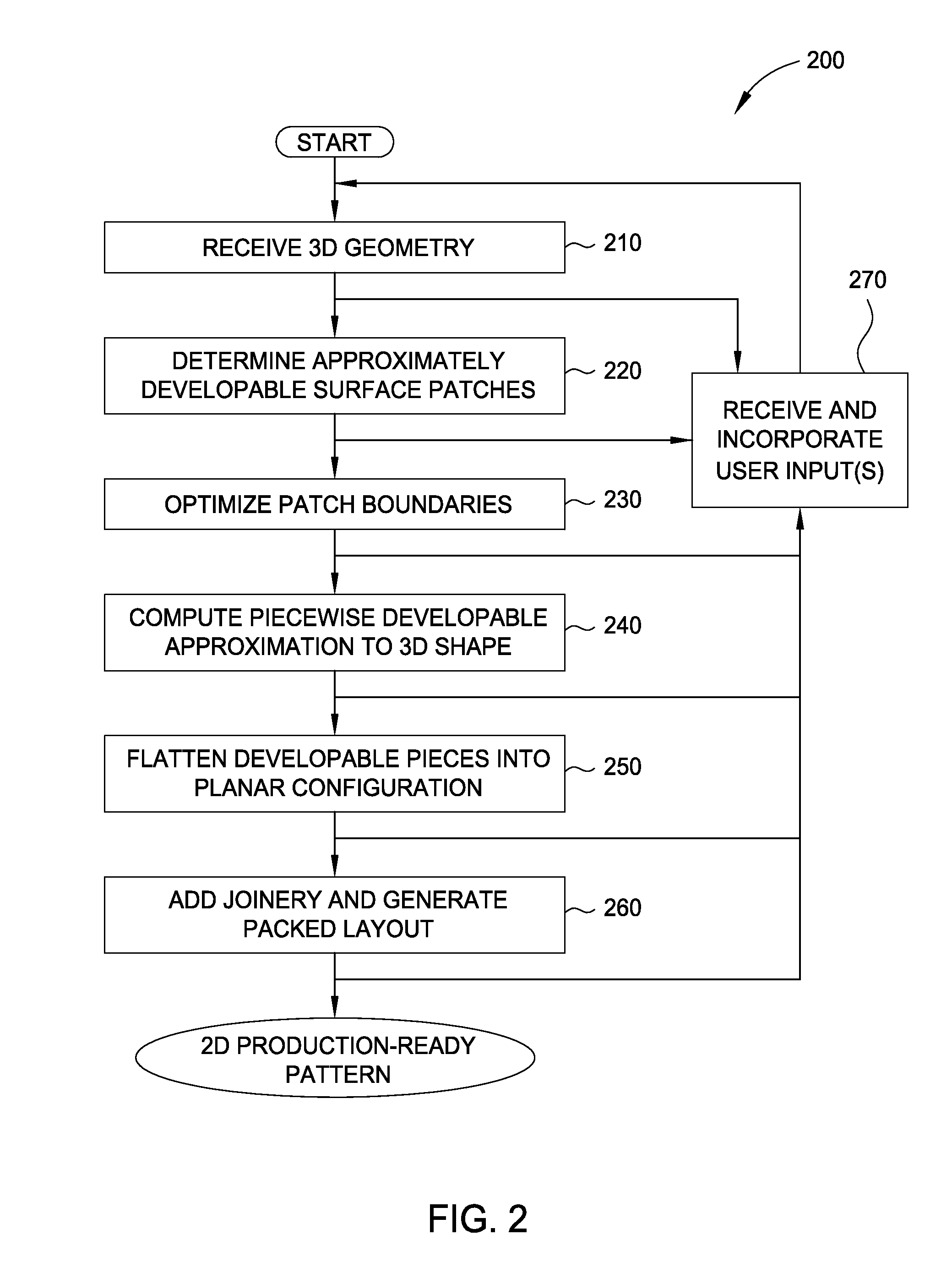
Decomposition of 3D geometry into developable surface patches and 2d cut patterns
ActiveUS20130297058A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)Decomposition
Embodiments disclosed herein provide techniques for decomposing 3D geometry into developable surface patches and cut patterns. In one embodiment, a decomposition application receives a triangulated 3D surface as input and determines approximately developable surface patches from the 3D surface using a variant of k-means clustering. Such approximately developable surface patches may have undesirable jagged boundaries, which the decomposition application may eliminate by generating a data structure separate from the mesh that contains patch boundaries and optimizing the patch boundaries or, alternatively, remeshing the mesh such that patch boundaries fall on mesh edges. The decomposition application may then flatten the patches into truly developable surfaces by re-triangulating the patches as ruled surfaces. The decomposition application may further flatten the ruled surfaces into 2D shapes and lay those shapes out on virtual sheets of material. A person, or machinery, may cut out those shapes from physical sheets of material based on the layout.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
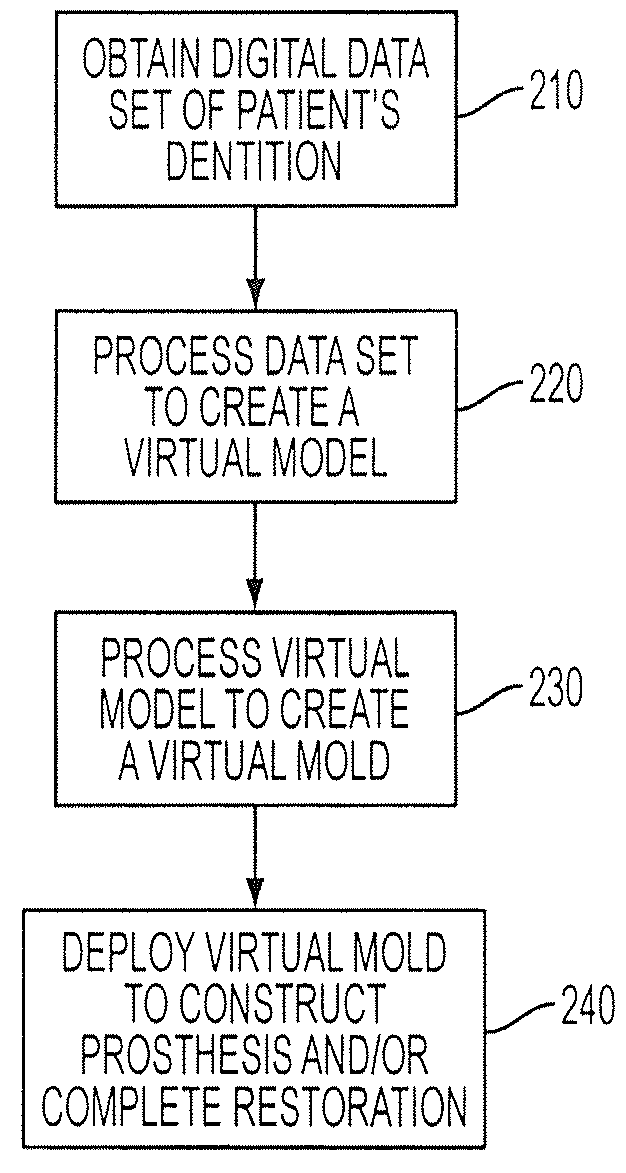
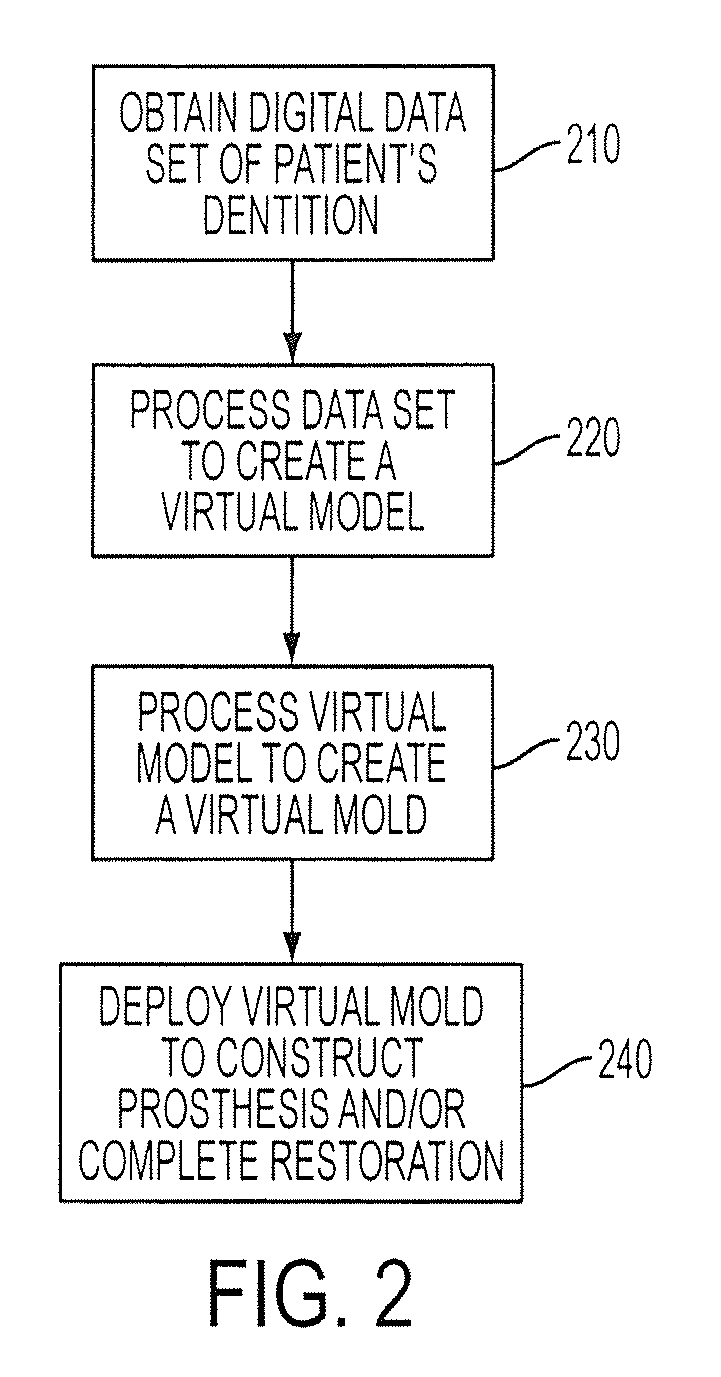
Method and system for forming a dental prosthesis
ActiveUS20100119996A1Additive manufacturing apparatusTooth crownsComputer graphics (images)Prosthesis
A system and method for use in constructing a prosthesis / complete restoration that obtains a digital dentition model, such as a 3D geometric surface model or a 3D volumetric image model, processes the digital dentition model to form a virtual model, forms a virtual mold including a digital prosthesis and / or complete restoration, and uses the virtual model to construct the prosthesis / complete restoration. Processing circuitry, such as a programmed server, can be used to obtain the digital dentition model and form the virtual mold. A rapid manufacturing device can be used to construct the prosthesis / complete restoration.
Owner:INNOVATIVE HEALTH TECH
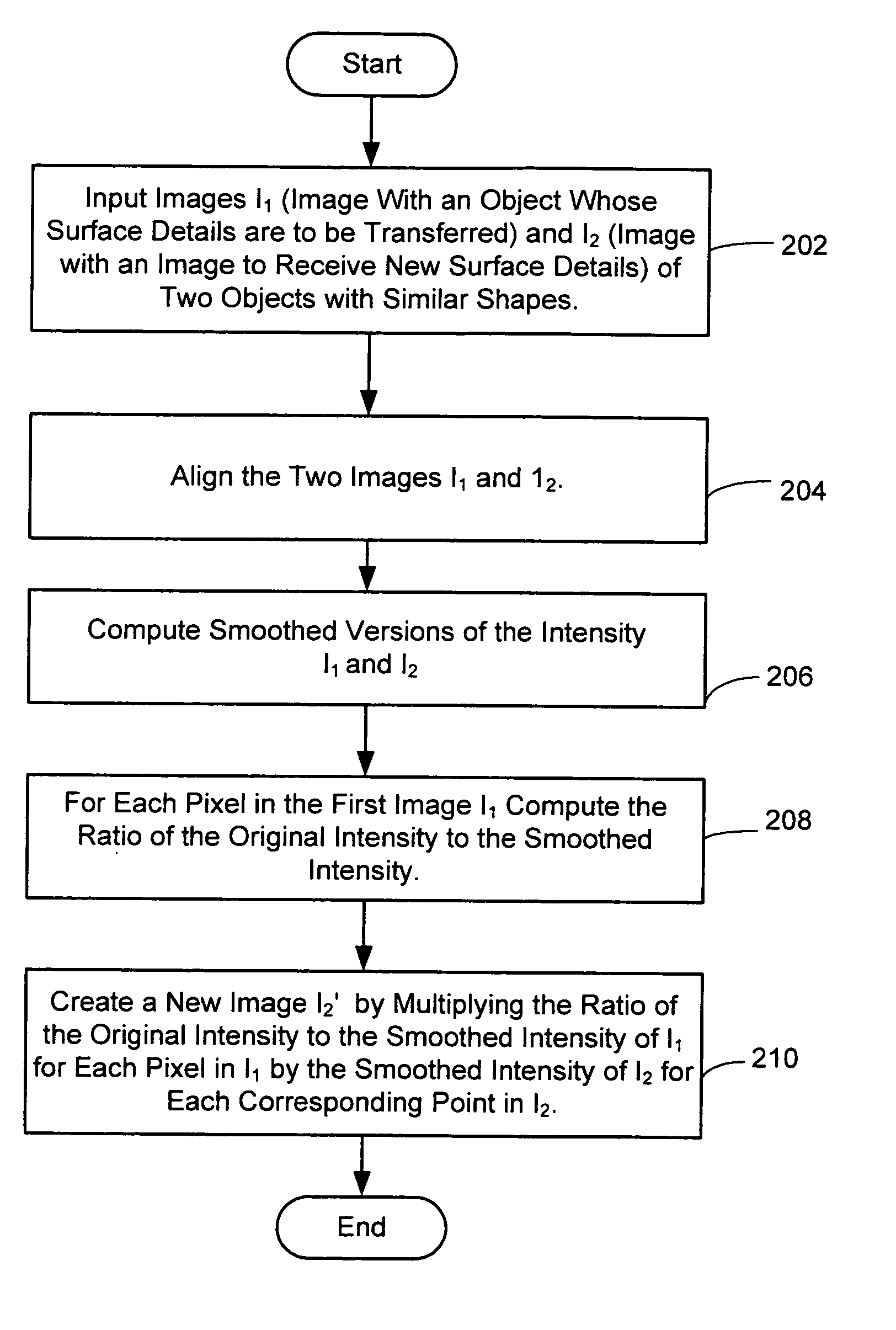
System and method for image-based surface detail transfer
InactiveUS20050180657A1Easy to implementPromote generationTexturing/coloringCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Single image
A system and method, called Image-Based Surface Detail Transfer, to transfer geometric details from one surface of an object in an image to another with simple 2D image operations. The basic observation is that, without knowing its 3D geometry, geometric details (local deformations) can be extracted from a single image of an object in a way independent of its surface reflectance, and furthermore, these geometric details can be transferred to modify the appearance of other objects directly in images. Examples are shown including surface detail transfer between real objects, as well as between real and synthesized objects.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Algorithm Enhancements for Haptic-Based Phased-Array Systems
InactiveUS20180310111A1Reduce complexityReduction in fidelityInput/output for user-computer interactionSpeech analysisSonificationPattern perception
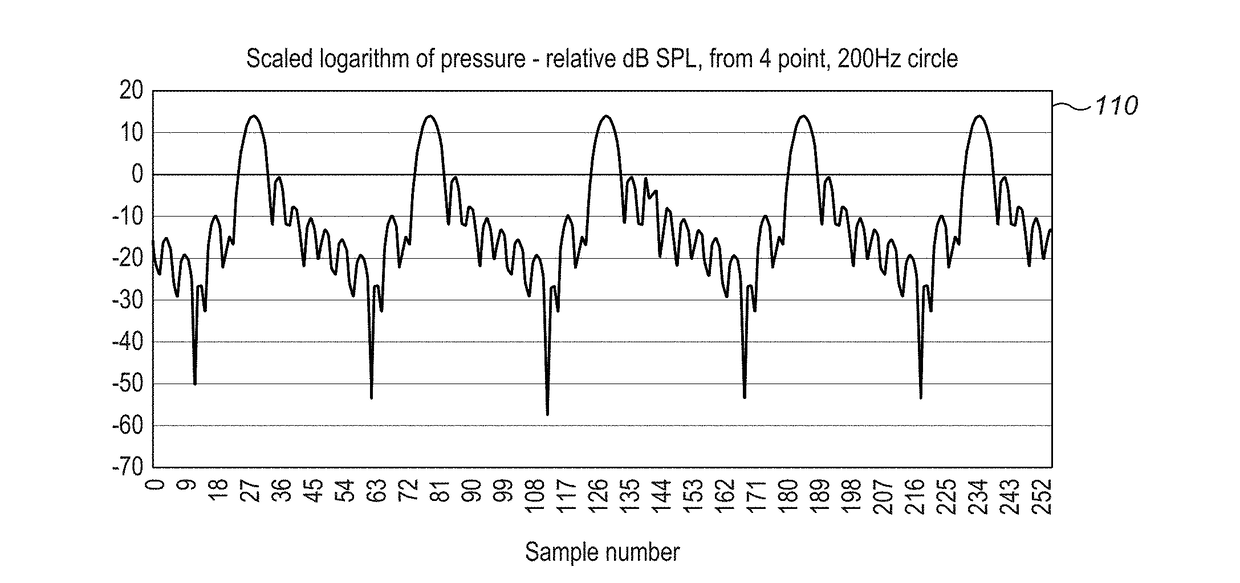
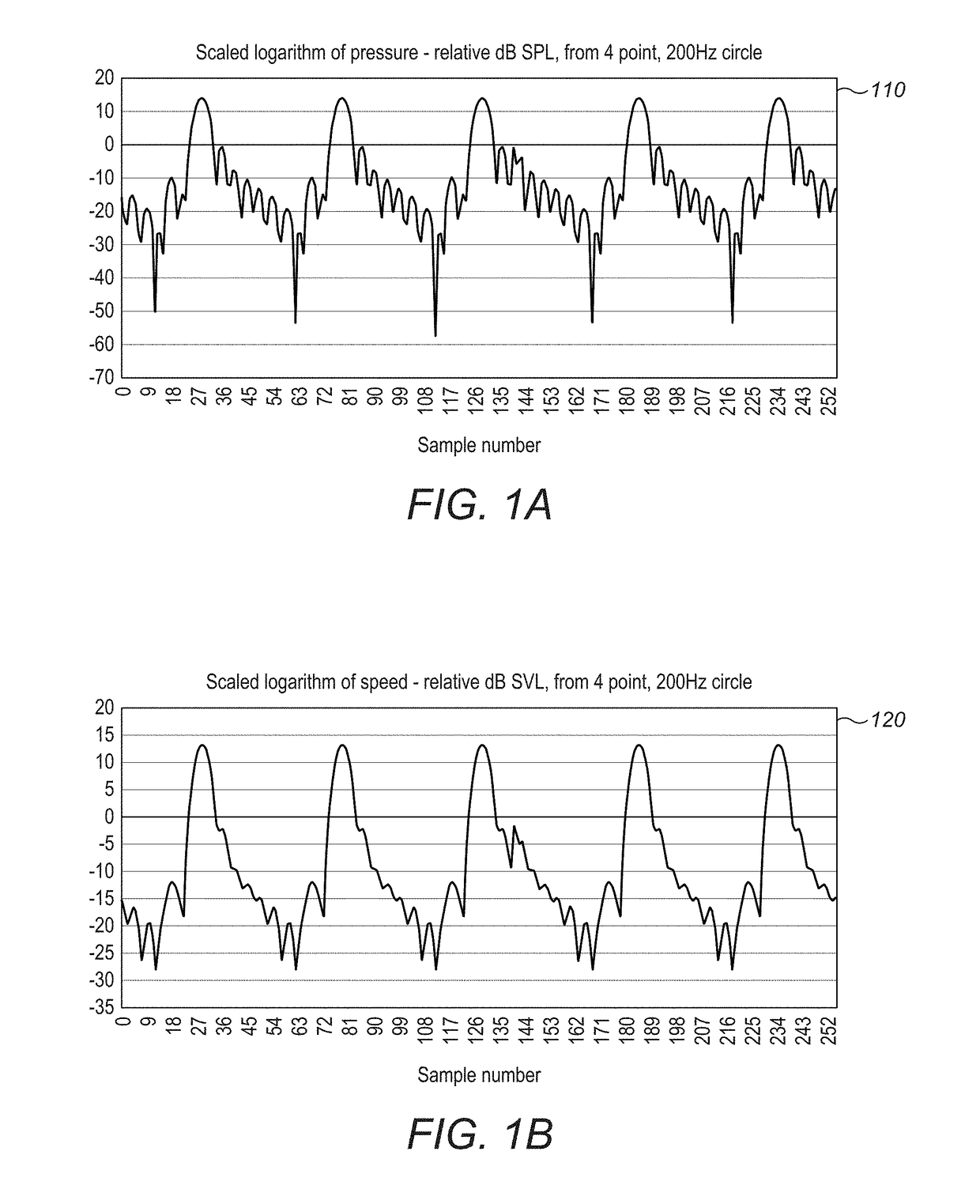
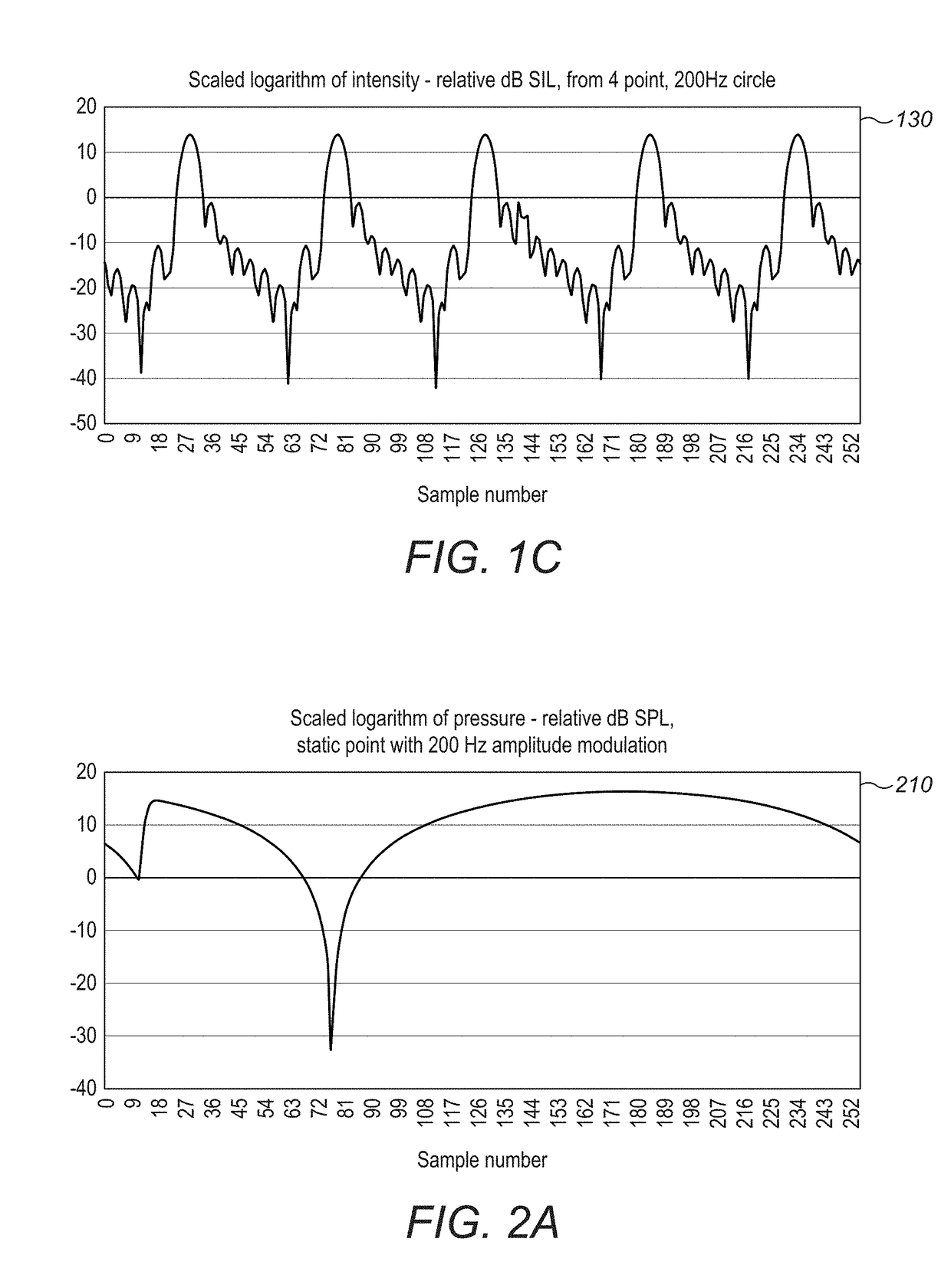
Improved algorithm techniques may be used for superior operation of haptic-based systems. An eigensystem may be used to determine for a given spatial distribution of control points with specified output the set of wave phases that are the most efficiently realizable. Reconstructing a modulated pressure field may use emitters firing at different frequencies. An acoustic phased-array device uses a comprehensive reflexive simulation technique. There may be an exchange of information between the users and the transducer control processors having the ability to use that information for optimal haptic generation shadows and the like. Applying mid-air haptic sensations to objects of arbitrary 3D geometry requires that sensation of the object on the user's hand is as close as possible to a realistic depiction of that object. Ultrasonic haptics with multiple and / or large aperture arrays have high-frequency update rates required by the spatio-temporal modulation. More efficient haptic systems require the prevention of a channel of audio unintentionally encoding phase information that may distort its perception.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com