Patents
Literature
542 results about "Anti-lock braking system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
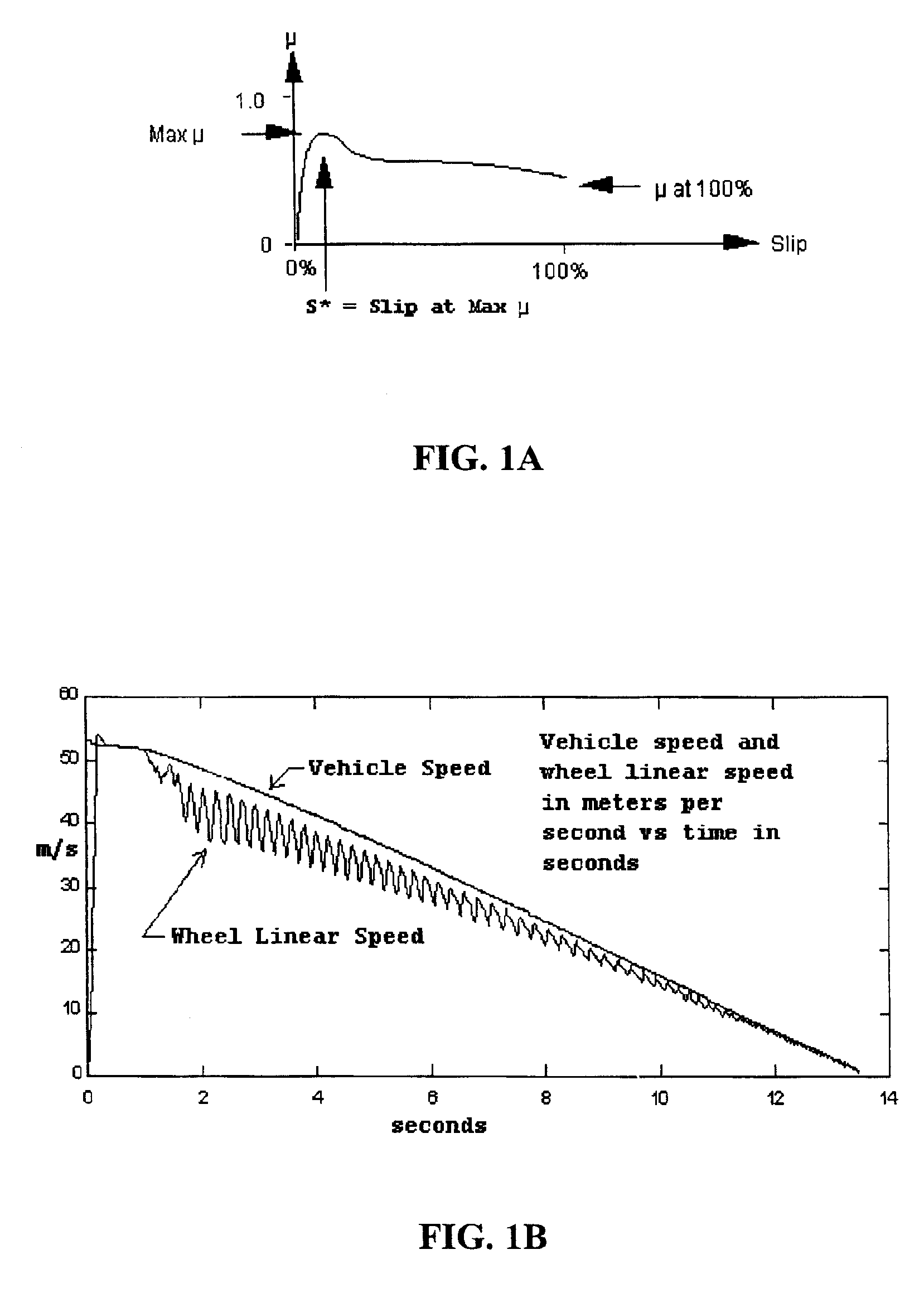
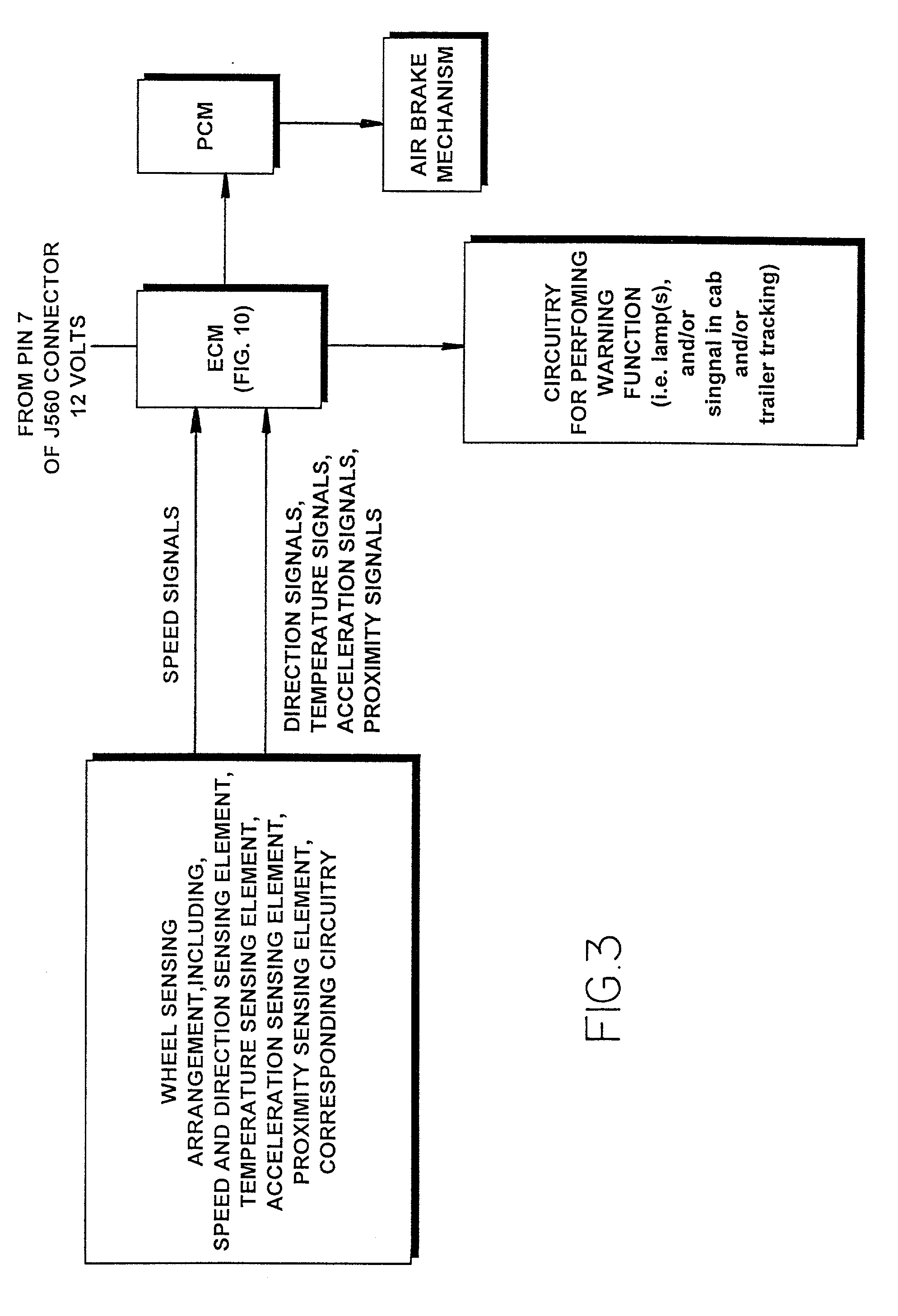
An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety anti-skid braking system used on aircraft and on land vehicles, such as cars, motorcycles, trucks, and buses. ABS operates by preventing the wheels from locking up during braking, thereby maintaining tractive contact with the road surface.
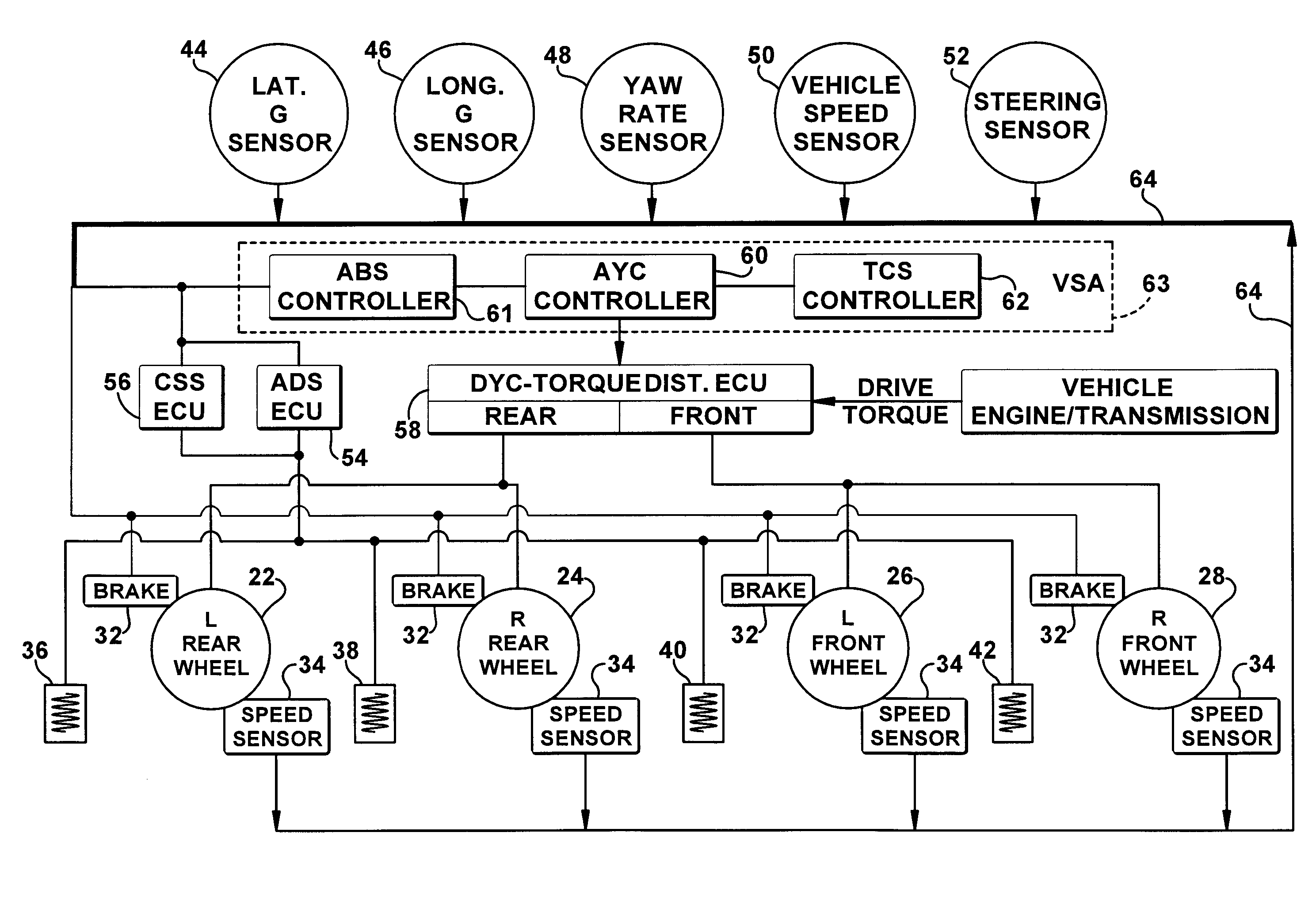
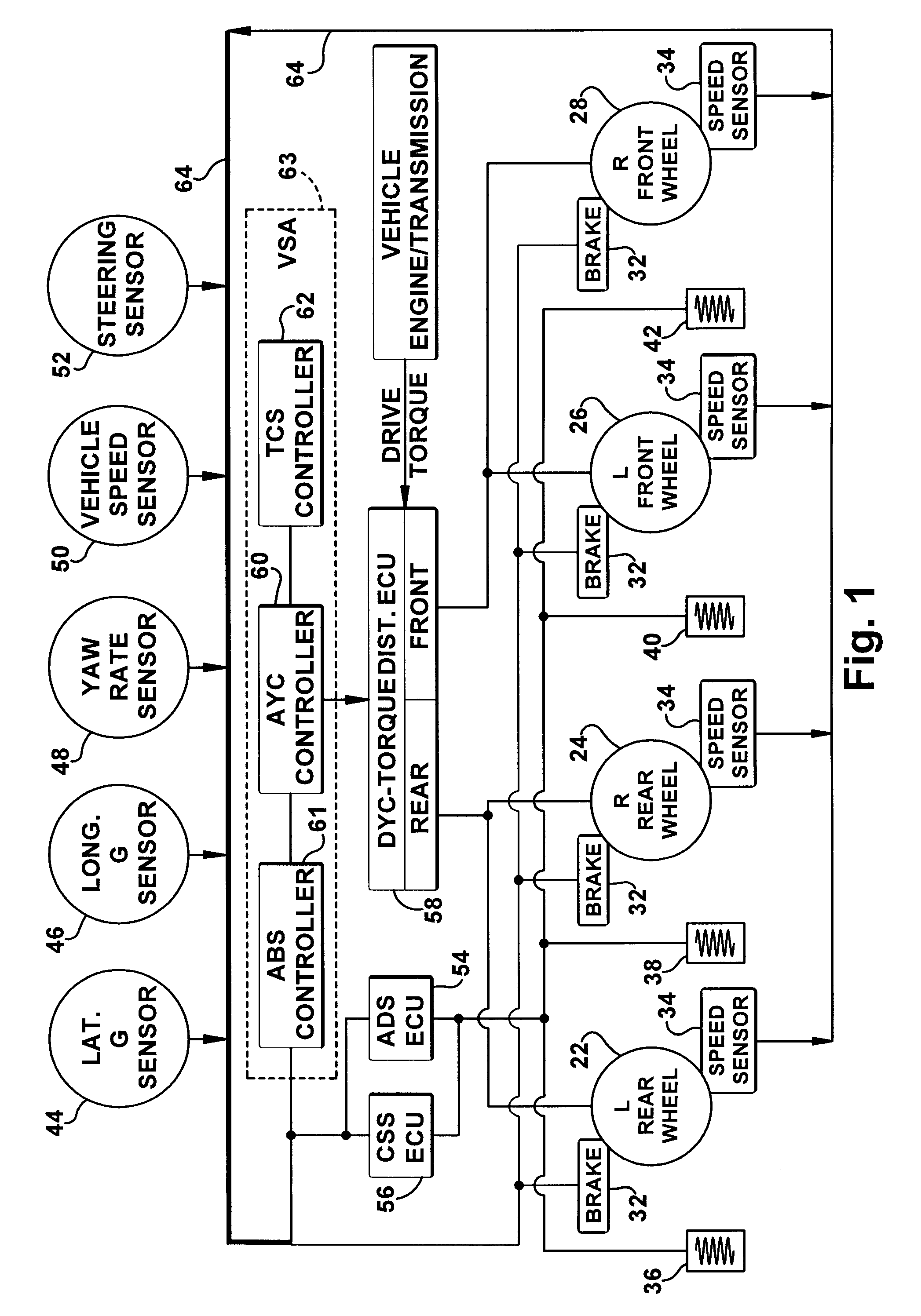
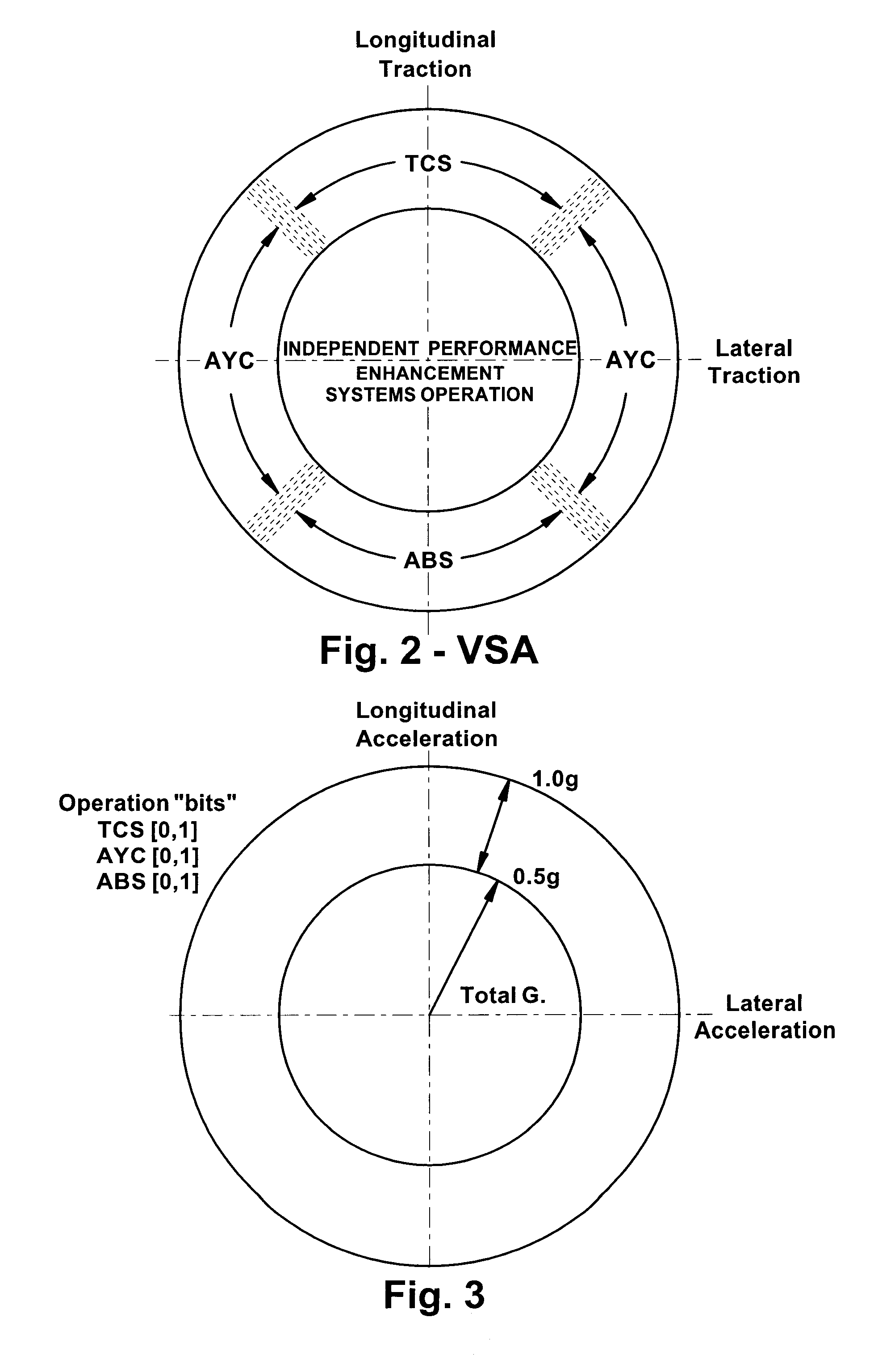
Vehicle systems control for improving stability
InactiveUS20080183353A1Improve vehicle stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesControl systemTraction control system
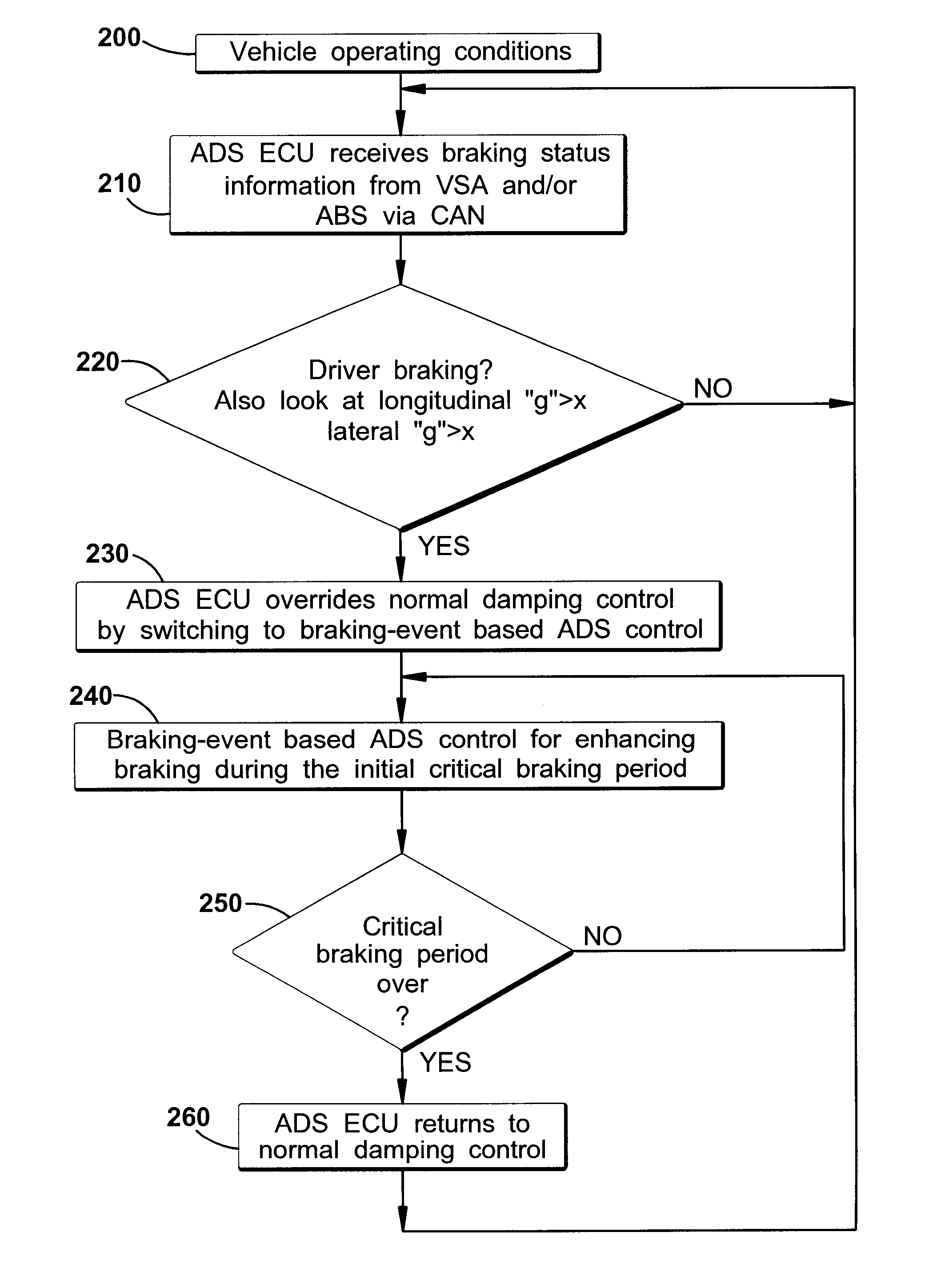
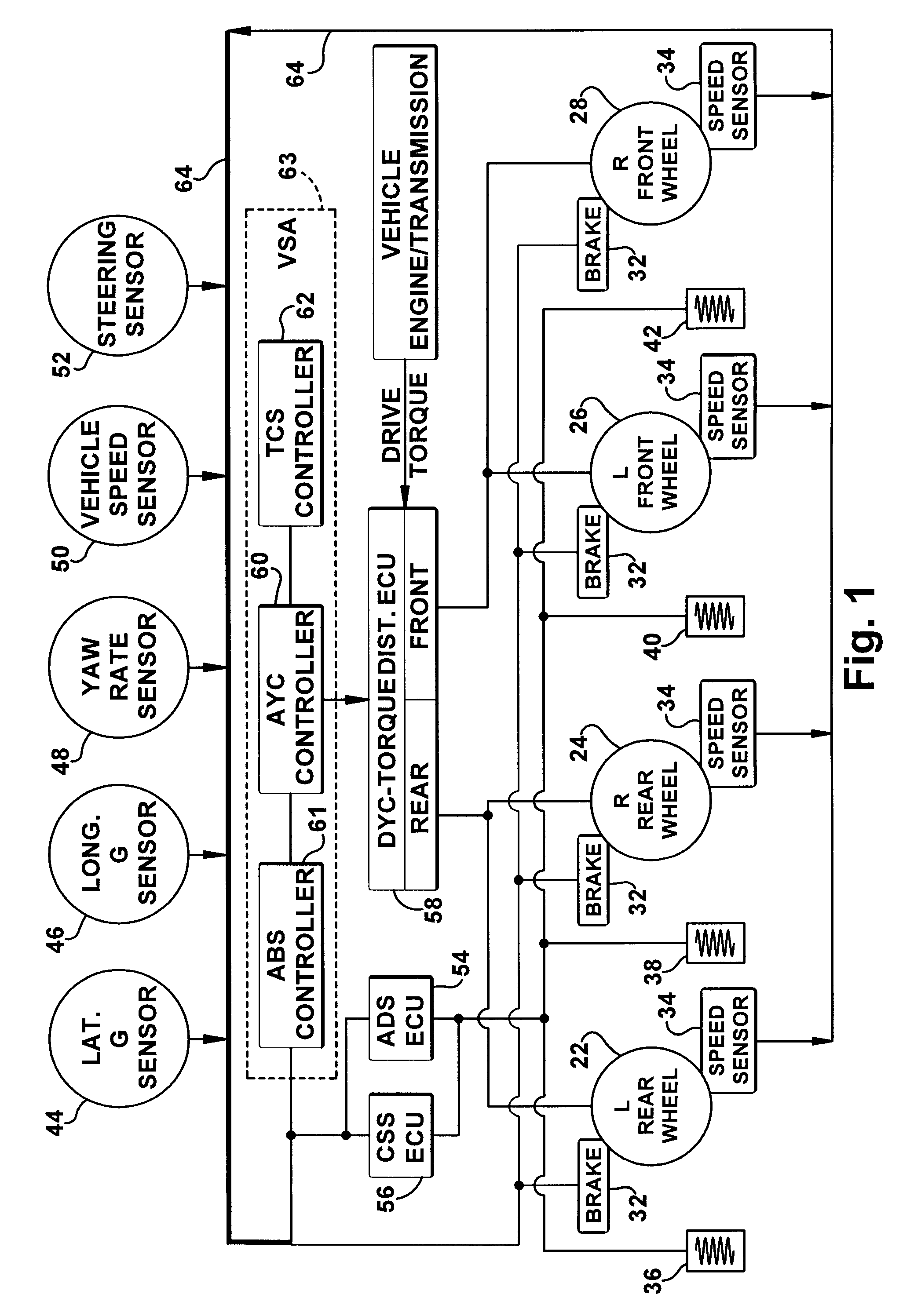
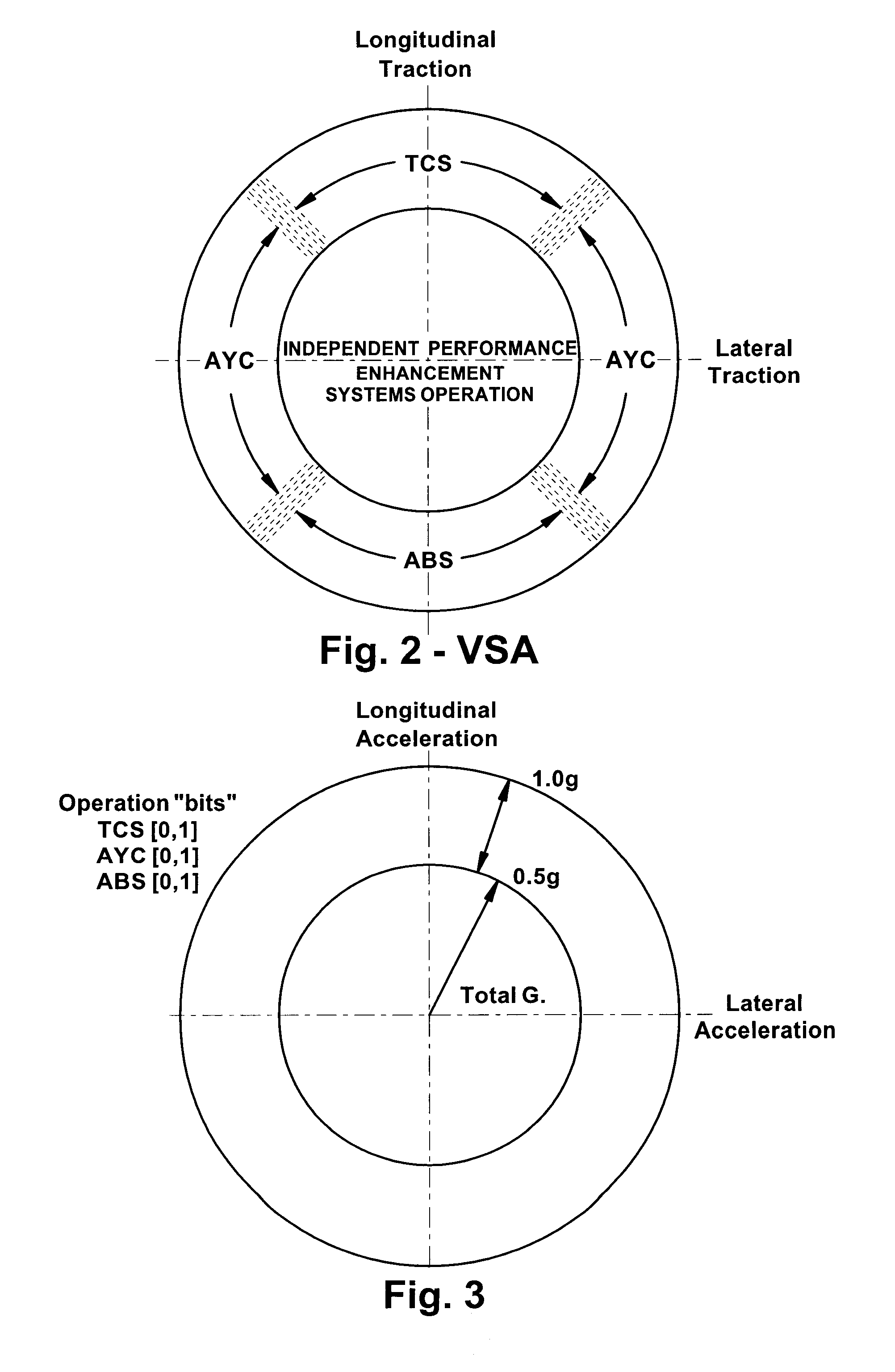
Improved methods of controlling the stability of a vehicle are provided via the cooperative operation of vehicle stability control systems such as an Active Yaw Control system, Antilock Braking System, and Traction Control System. These methods use recognition of road surface information including the road friction coefficient (mu), wheel slippage, and yaw deviations. The methods then modify the settings of the active damping system and / or the distribution of drive torque, as necessary, to increase / reduce damping in the suspension and shift torque application at the wheels, thus preventing a significant shift of load in the vehicle and / or improving vehicle drivability and comfort. The adjustments of the active damping system or torque distribution temporarily override any characteristics that were pre-selected by the driver.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for responding to driver behavior
Methods of assessing driver behavior include monitoring vehicle systems and driver monitoring systems to accommodate for a driver's slow reaction time, attention lapse and / or alertness. When it is determined that a driver is drowsy, for example, the response system may modify the operation of one or more vehicle systems. The systems that may be modified include: visual devices, audio devices, tactile devices, antilock brake systems, automatic brake prefill systems, brake assist systems, auto cruise control systems, electronic stability control systems, collision warning systems, lane keep assist systems, blind spot indicator systems, electronic pretensioning systems and climate control systems.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
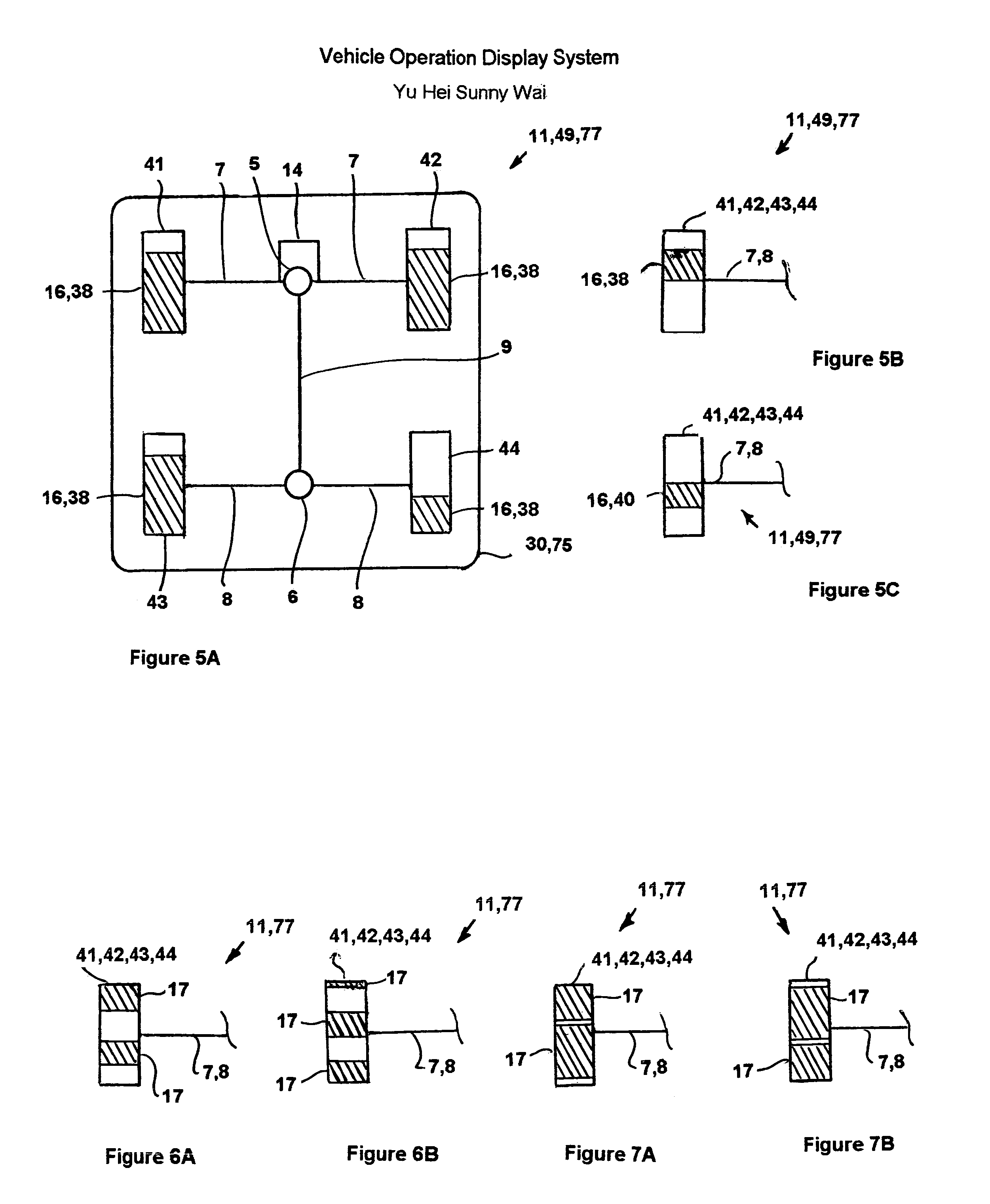
Vehicle operation display system
InactiveUS7145442B1Accurate visual displayRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesOptical signallingMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
An apparatus, method, system and / or image editing process for presenting visual displays to the driver of a motor vehicle regarding the real time operating condition of the vehicle systems and components. These include the anti-lock braking system, the stability of the vehicle as to proximity to rolling over, the power consumed by vehicle components such as the heating system and lights and / or, for four-wheel drive vehicles, the torque and / or braking forces delivered to the wheels. The information is acquired from sensors and / or from signals generated by the vehicle and it processed by the vehicle CPU or, in another embodiment, by a display CPU, the information being presented in black and white or in color using an LED, LCD, vacuum fluorescent means, numerical display, gauge, meter or PDA.
Owner:VEHICLE OPERATION TECH
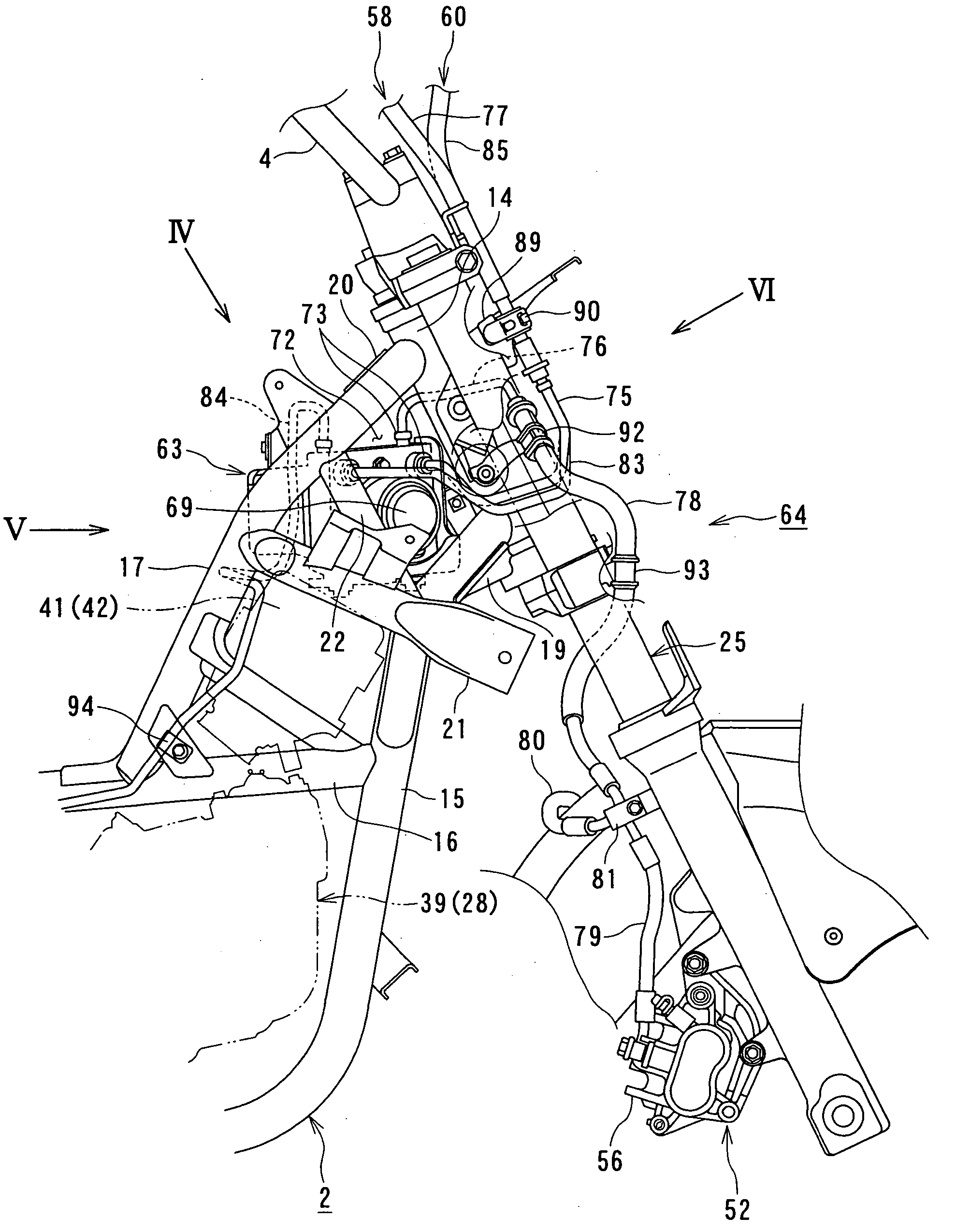
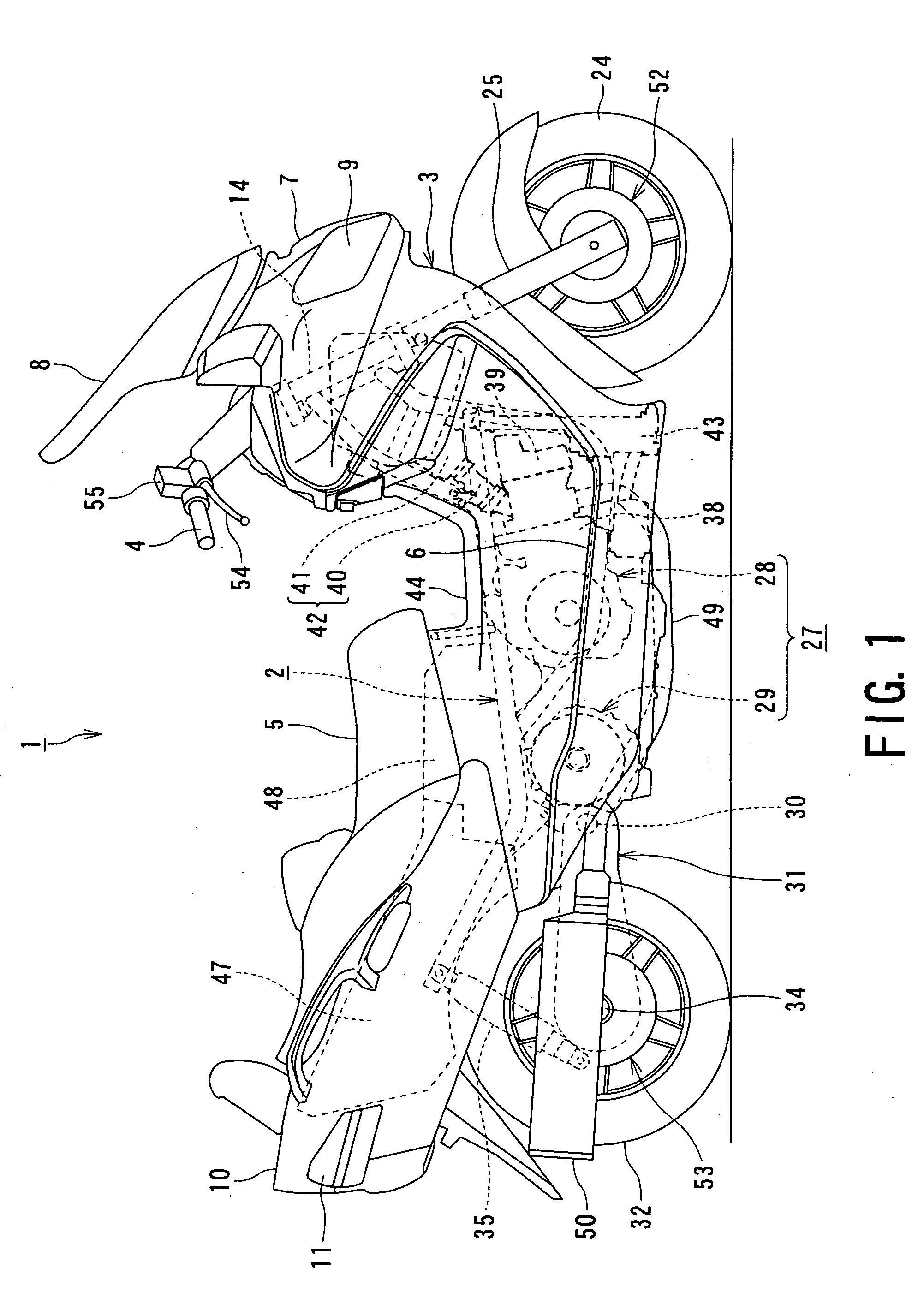
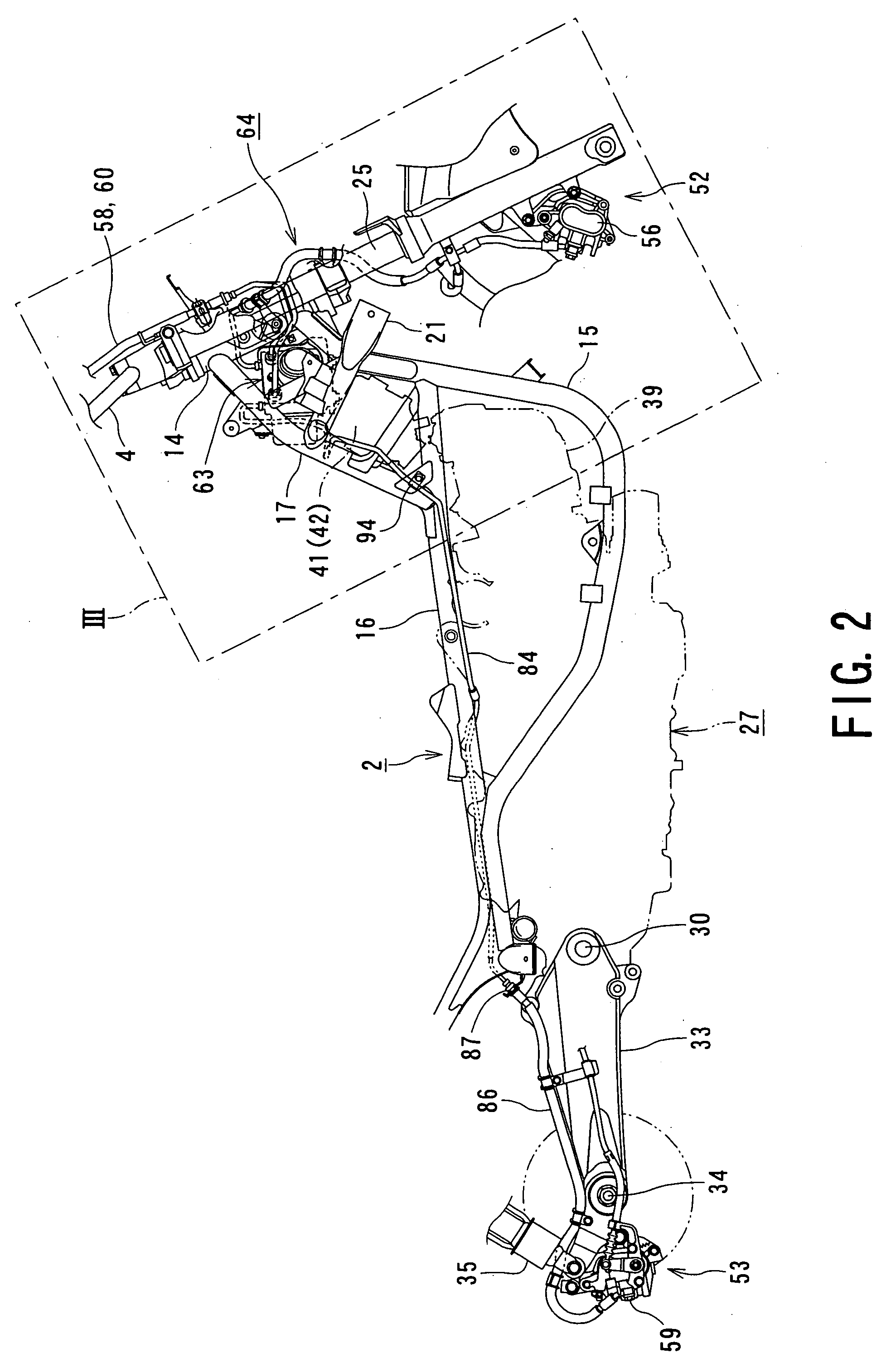
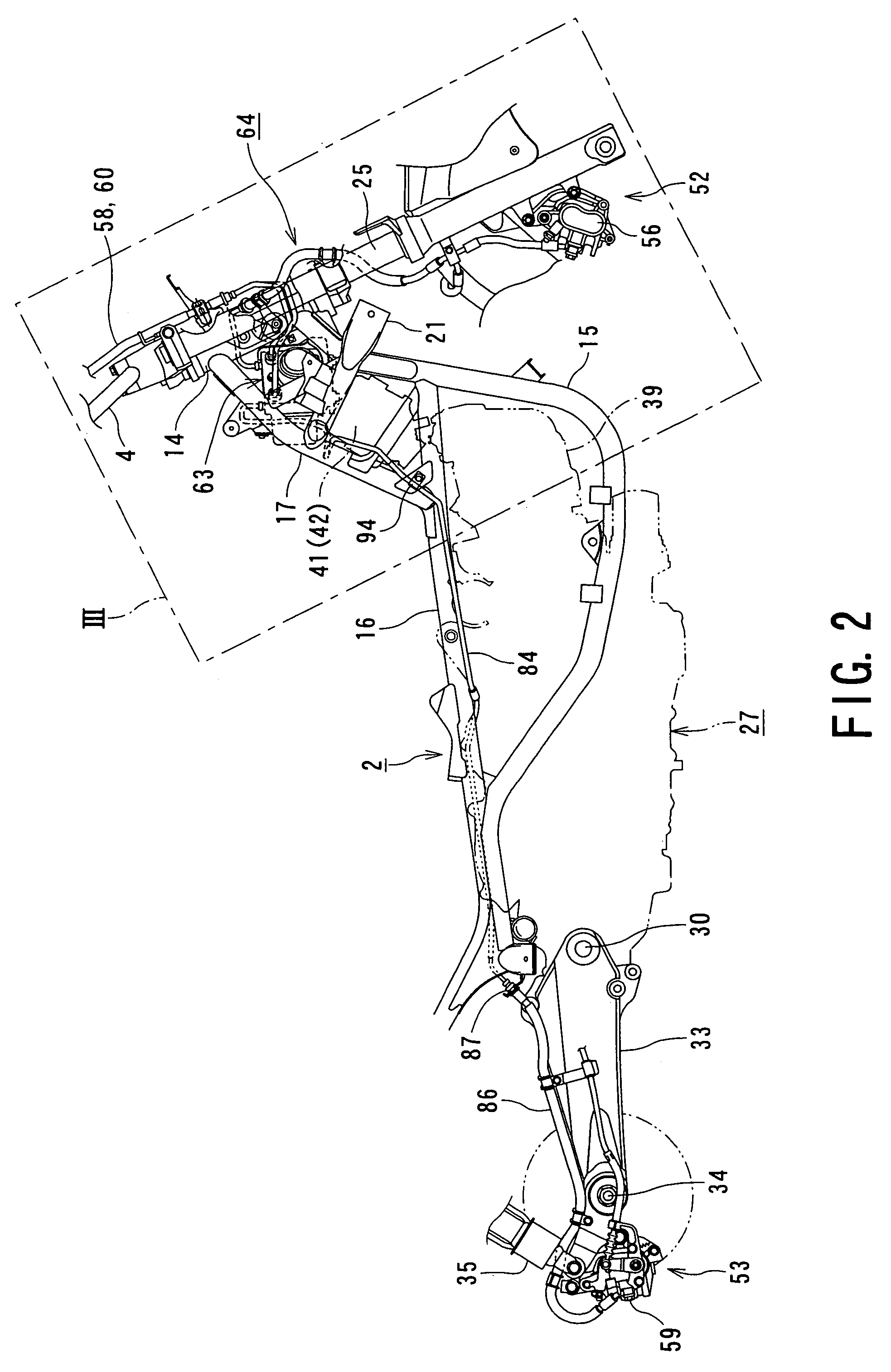
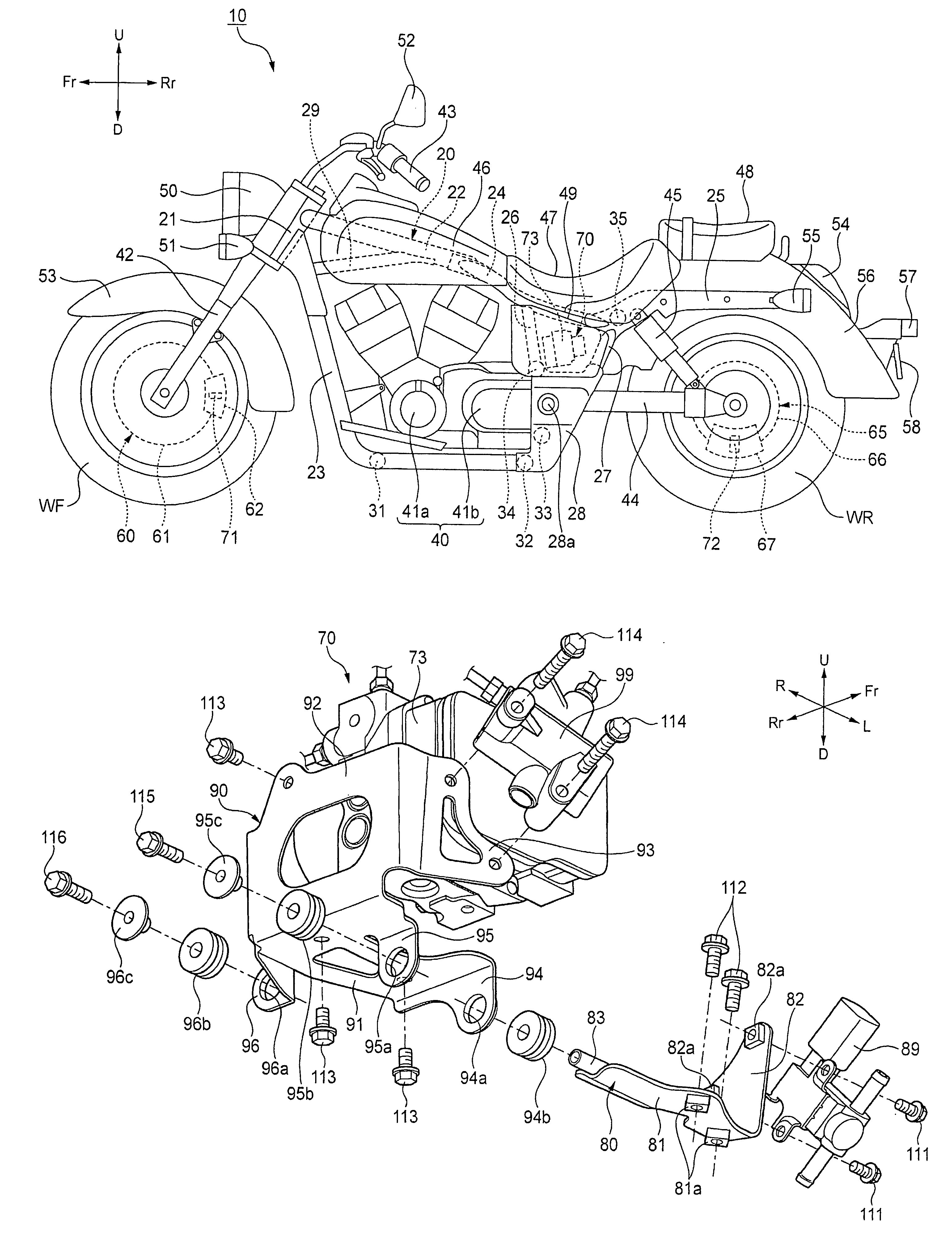
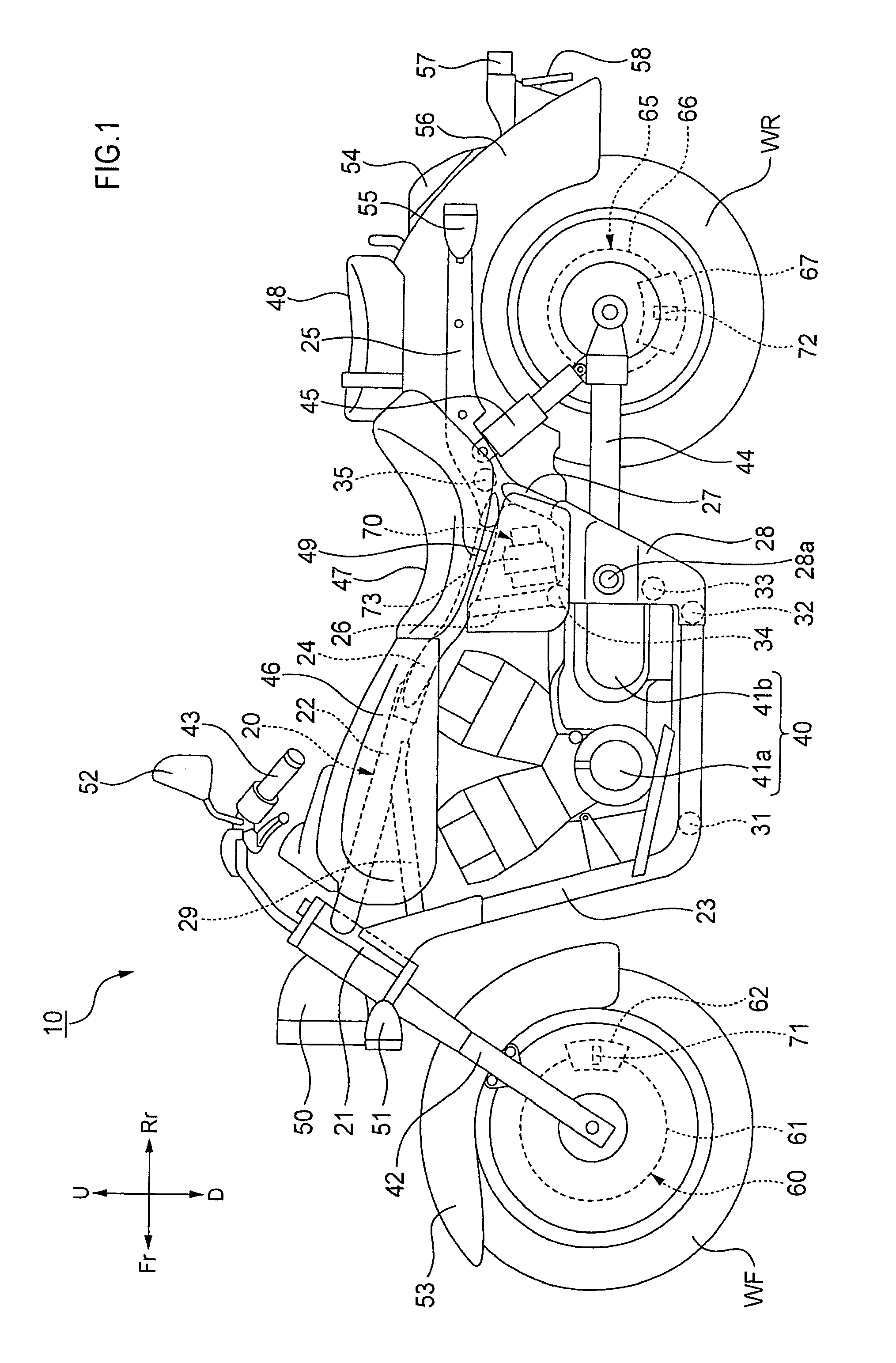
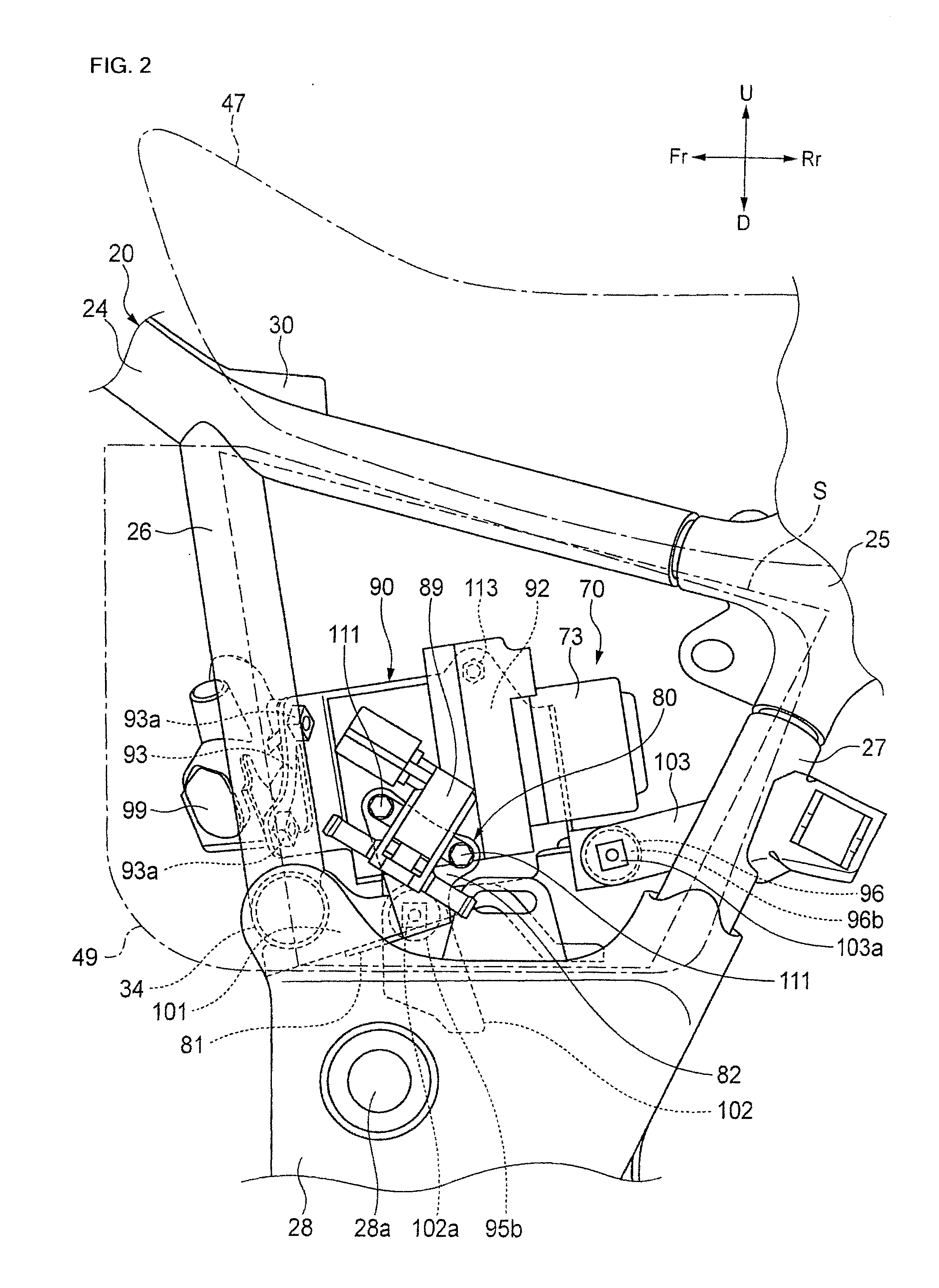
Motorcycle with antilock brake system
ActiveUS20050134114A1Improve braking performanceImprove engine performanceElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingMaster cylinderEngineering
In a motorcycle provided with an antilock brake system, a front fork supporting a front wheel of a motorcycle is supported to be rotatable by a head pipe which is located at the front end portion of a body frame of a motorcycle, a handle-bar is secured to an upper end portion of the head pipe, master cylinders attached to the handle-bar are connected to hydraulic wheel brakes, respectively, via brake pipes. An antilock brake system includes an ABS-unit for antilock control disposed in an intermediate portion of the brake pipes. The ABS-unit is disposed immediately behind the head pipe and between a pair of body frame components disposed on both lateral sides of the motorcycle body and extending, from the head pipe, obliquely downward and backward, while extending outward in directions opposite to each other in the width direction of the motorcycle body.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Anti-lock braking system based on an estimated gradient of friction torque, method of determining a starting point for anti-lock brake control, and wheel-behavior-quantity servo control means equipped with limit determination means
An anti-lock braking system includes a friction torque gradient estimating unit for estimating, from a small number of parameters, the gradient of friction torque with respect to a slip speed, and controls a braking force acting on wheels on the basis of the friction torque gradient estimated by the friction torque gradient estimating unit. The friction torque gradient estimating unit may employ several types of estimating methods; e.g., a method of estimating the gradient of friction torque from only time-series data concerning a wheel speed; a method of estimating the friction torque gradient from time-series data concerning wheel deceleration as well as from braking torque or time-series data concerning physical quantities associated with the braking torque; or a method of estimating the friction torque gradient from micro-gains which are obtained when brake pressure is excited in a very small amount at the resonance frequency of a vibration system comprising a vehicle, wheels, and a road surface and which represent the characteristics of the vibration system. Further, there is also disclosed a method of determining, from the thus-estimated friction torque gradient, the limit of the characteristics of friction torque developed between the wheels and the road surface.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Electronic intelligent turn signal control system
InactiveUS6876300B2Low costSmall sizeSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsDriver/operatorWheel speed sensor
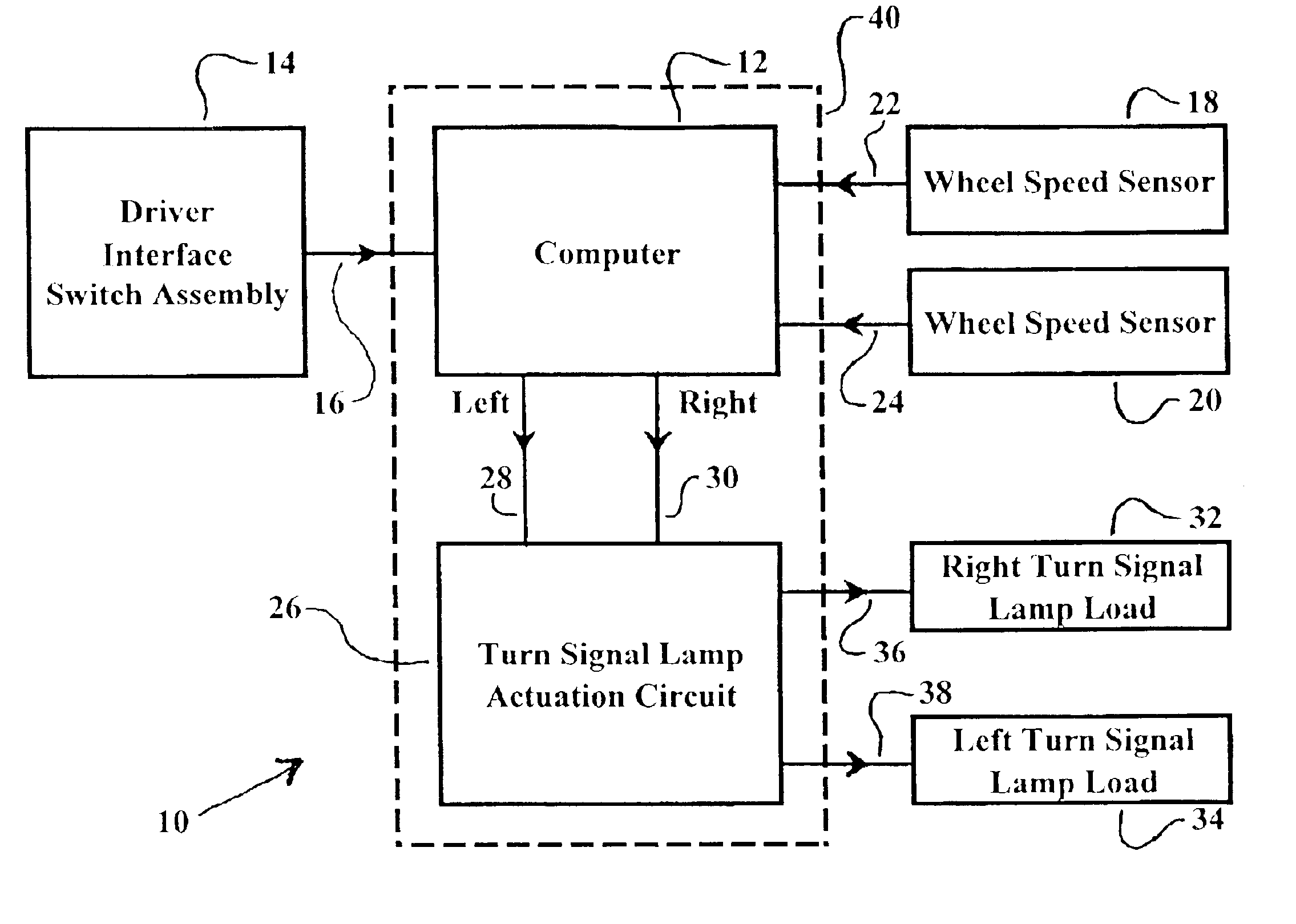
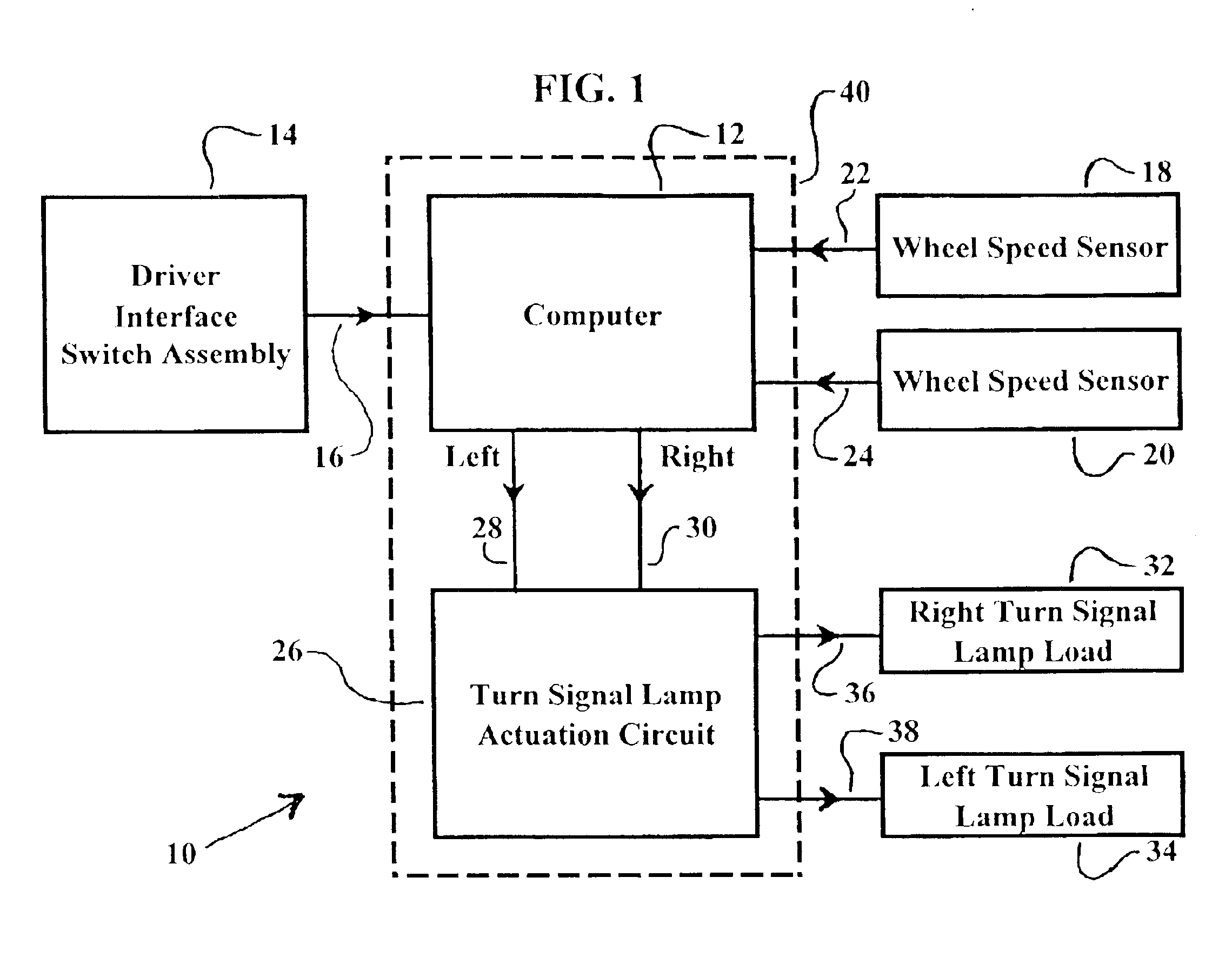
An intelligent turn signal control system for turning on and off left and right turn signals in a vehicle includes a computer, such as an antilock braking system computer, with programmed software operably disposed on a vehicle, a driver interface switch assembly as input to the computer. Two or more wheel speed sensors transmit differential wheel movement data as input to the computer, a circuit drives turn signal indicator lamps from conditionally computed output data from the computer to turn on and off turn signals in a situation-appropriate manner. Upon turn signal indication intent data input from the driver, extensive travel and turn data is computed, including yaw rotation and steering system position to turn off or cancel the turn signal at the appropriate point.
Owner:PONZIANI RICHARD L
Vehicle and glide feedback control method thereof
ActiveCN104494599AIncrease the operating modeEnsure driving comfortHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesCruise controlFeedback control
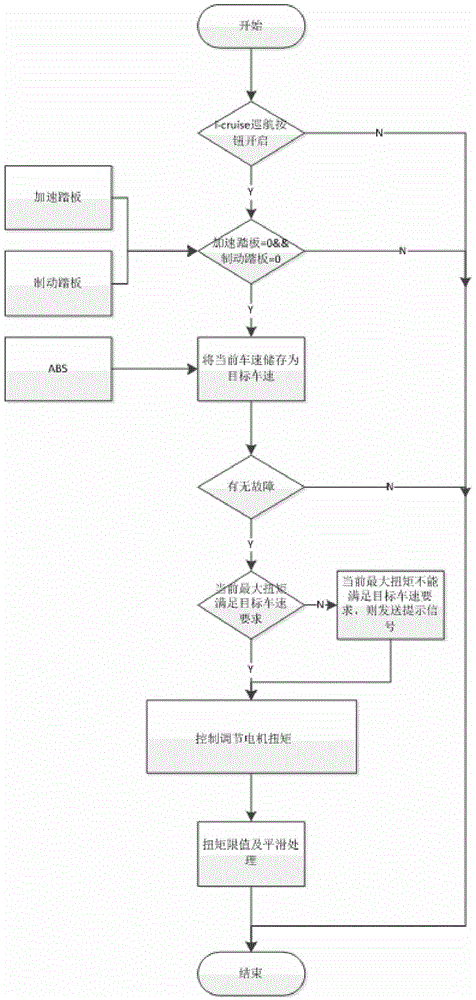
The invention discloses a vehicle and a glide feedback control method thereof, wherein the glide feedback control method comprises the following steps: the present speed of the vehicle, the depth of a brake pedal of the vehicle and the depth of an accelerator pedal are detected; and when the present speed of the vehicle is greater than the preset vehicle speed, the depth of the brake pedal and the depth of the accelerator pedal are both 0, the present gear of the vehicle is D gear, the vehicle is not in a cruise control mode, and an anti-locking braking system of the vehicle is in a unworking state, the vehicle is controlled to enter a glide feedback control mode, wherein when the vehicle is in the glide feedback control mode, the glide feedback torque of a first electric generator and the glide feedback torque of a second electric generator are distributed according to the selected glide feedback torque curve of the vehicle. The glide feedback control method of the vehicle can recover the energy to the greatest extent under the precondition of guaranteeing the driving comfort of the vehicle, so that the energy feedback efficiency is improved.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
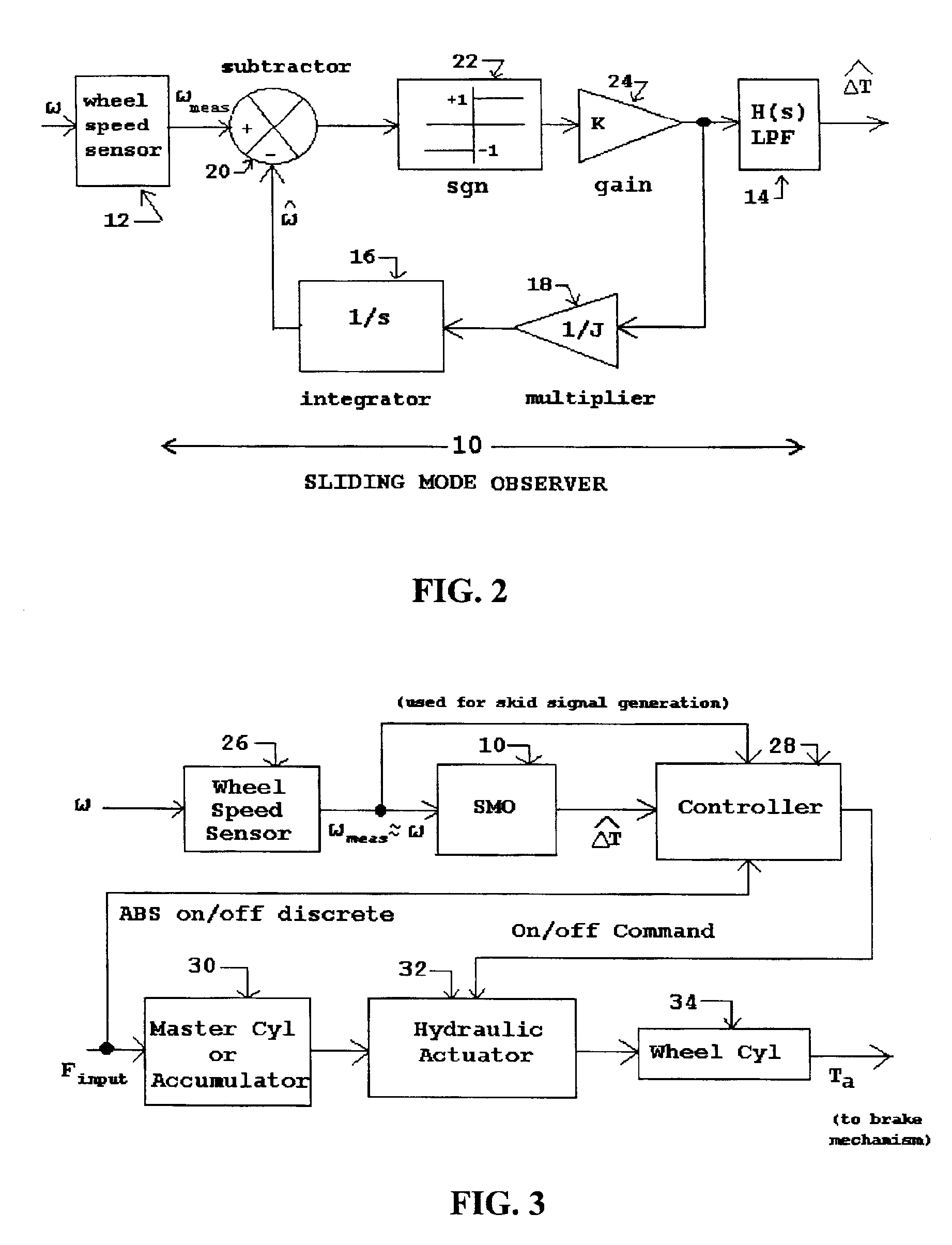
Antilock brake systems employing a sliding mode observer based estimation of differential wheel torque
InactiveUS6890041B1Easy to implementOptimize wheel slip during brakingBraking action transmissionBrake regulatorsAccelerometerControl signal
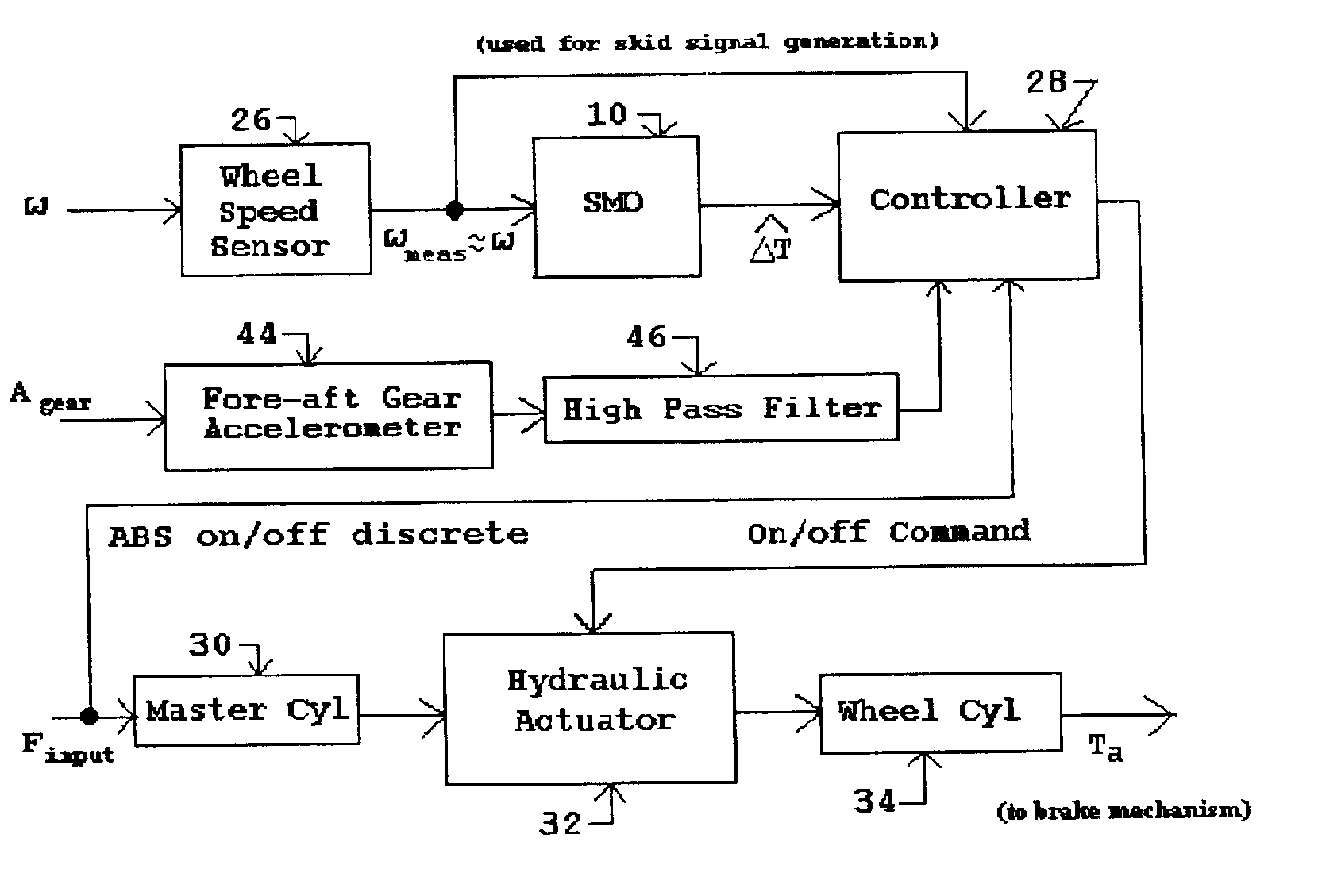
Improved methods and systems for controlling hydraulically or electrically actuated anti-lock brake systems (ABS) on air and land vehicles requiring only measurement of wheel angular speed although brake torque measurements can also be employed if available. A sliding mode observer (SMO) based estimate of net or different wheel torque (road / tire torque minus applied brake torque) derived from the measured wheel speed is compared to a threshold differential wheel torque derived as a function of a “skid signal” also based on wheel speed only to generate a braking control signal. The braking control signal can be employed to rapidly and fully applying and releasing the brakes in a binary on-off manner and, as an additional option, possibly modulating the maximum available brake hydraulic pressure or electrical current when the brakes are in the “on” state in a continuous manner. In the case of the basic on-off component of braking, the brakes are released when the estimate of differential wheel torque is less than the threshold differential wheel torque (i.e. for relatively high values of brake torque), and the brakes are applied fully when the estimate of differential wheel torque is greater than or equal to the threshold differential wheel torque. For aircraft landing gear applications, a fore-aft accelerometer mounted on the landing gear can be used to suppress nonlinear gear displacement oscillations commonly called gear walk in the direction of wheel roll.
Owner:SMO GRP
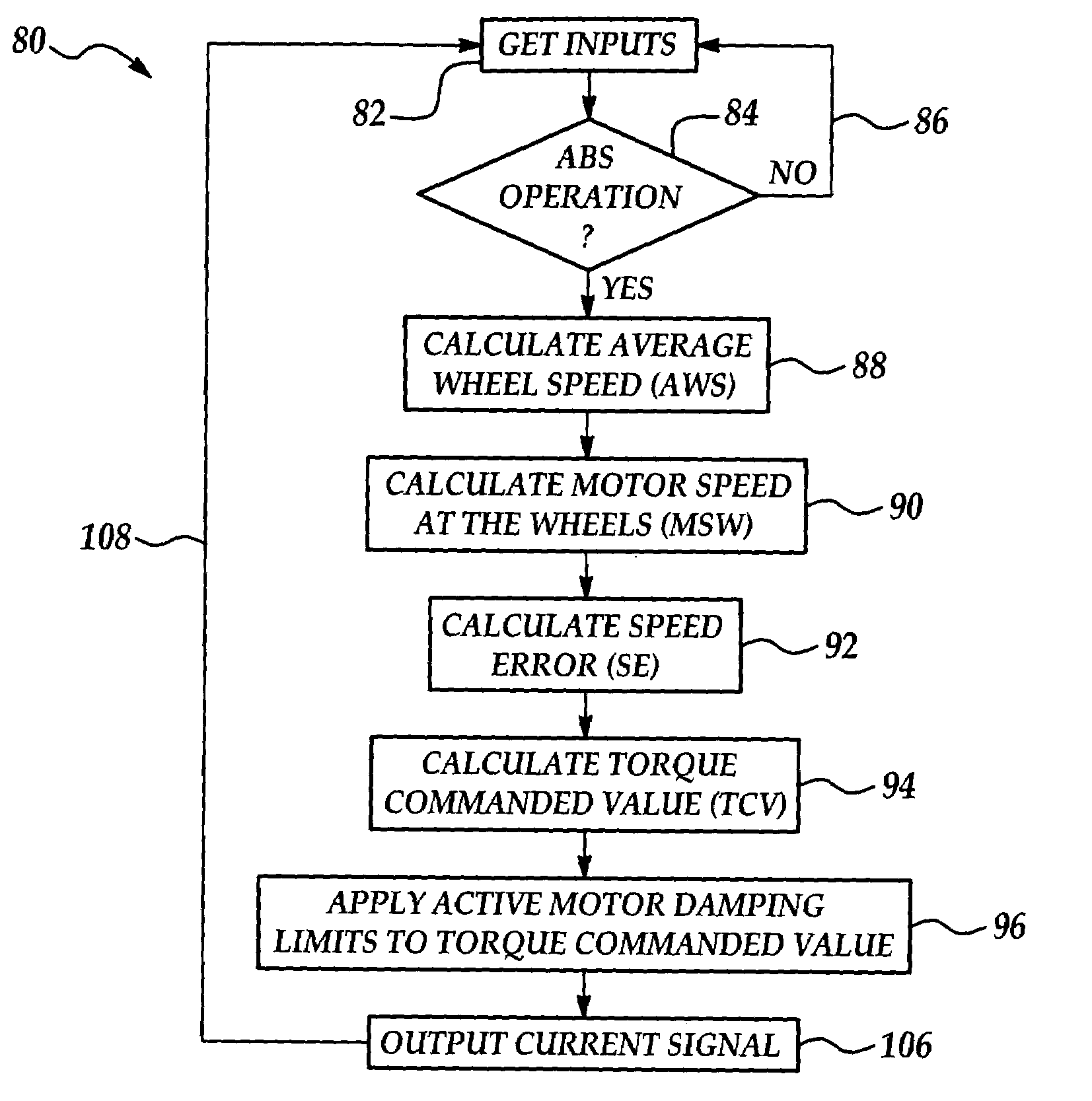
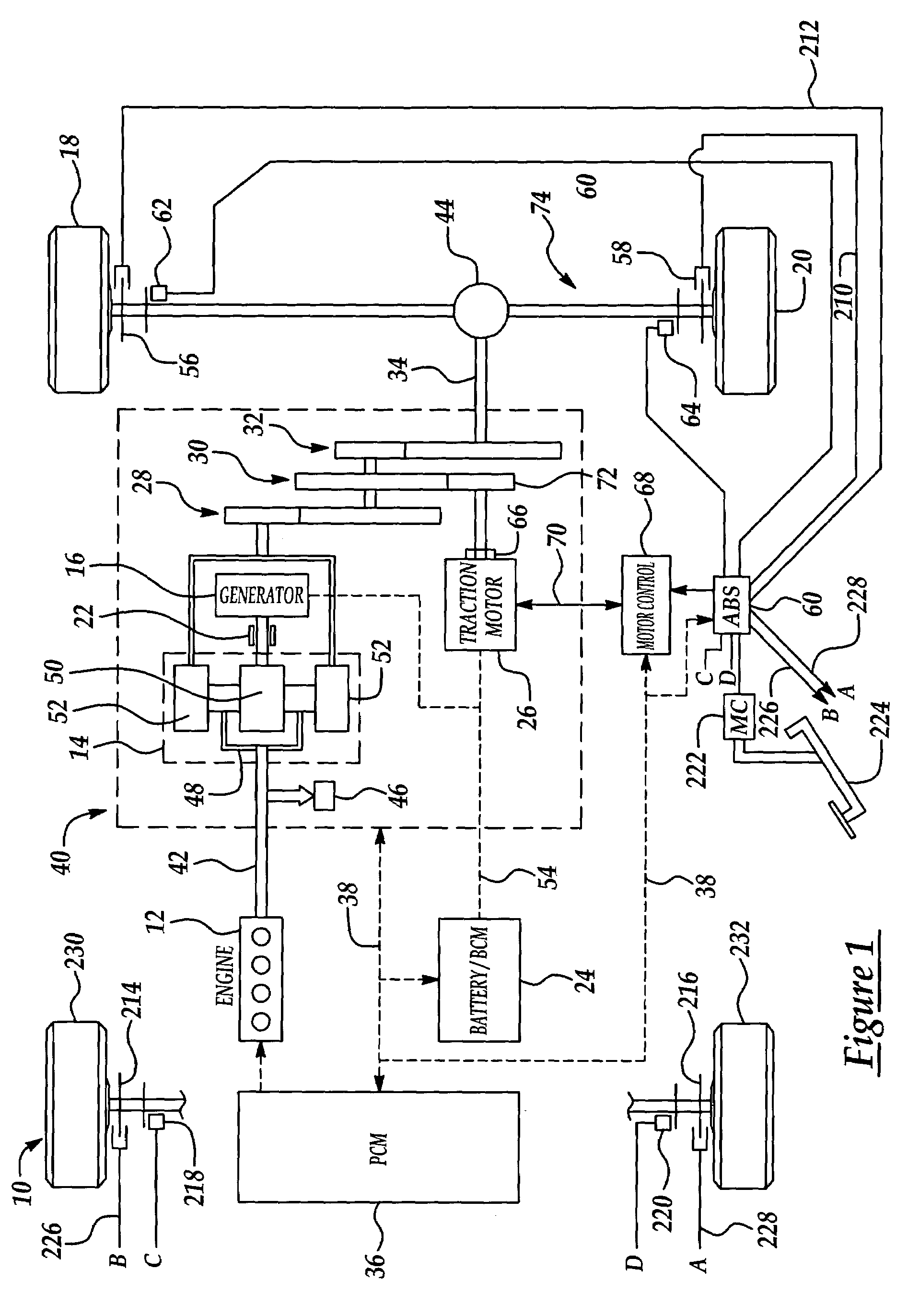
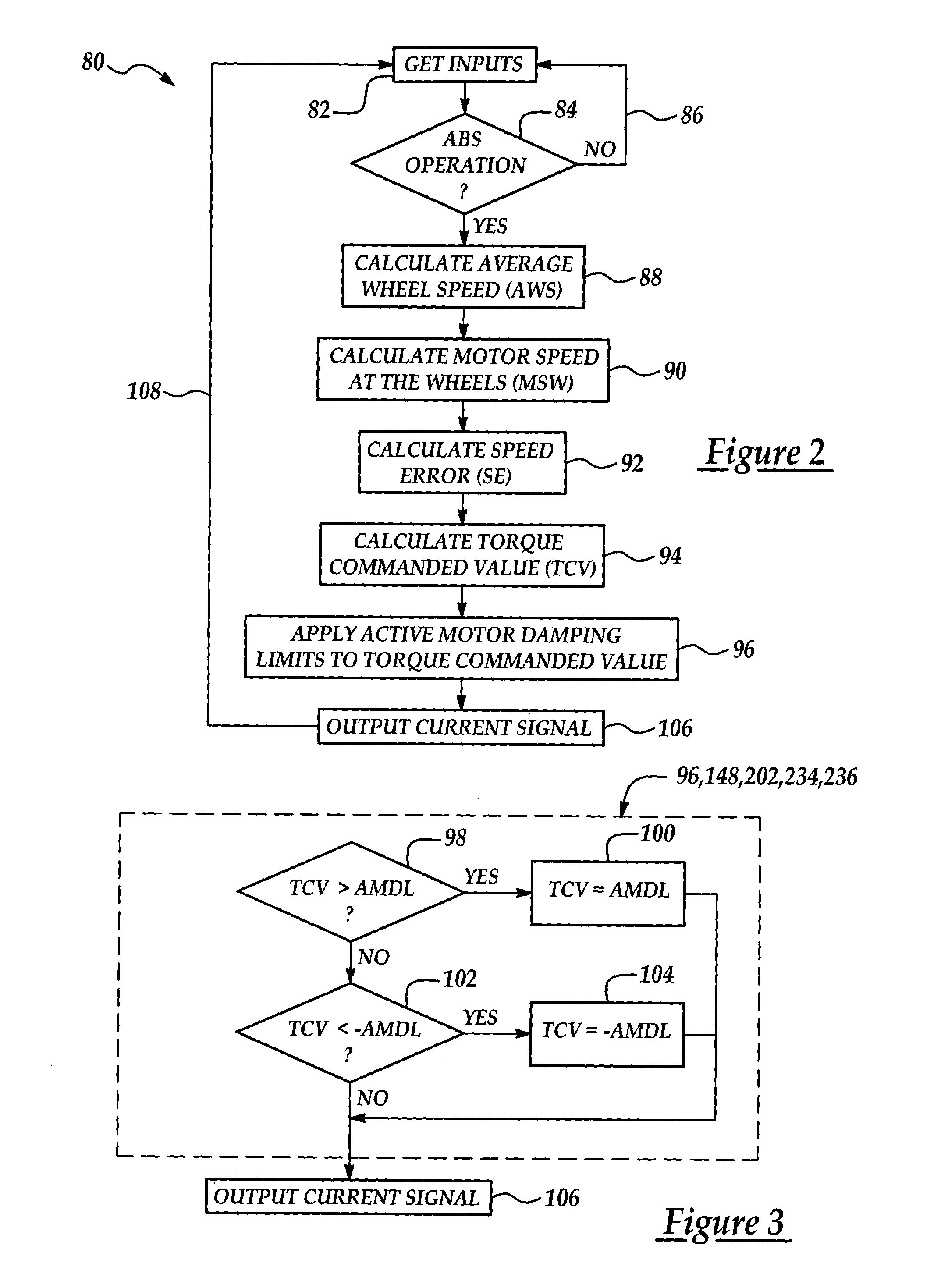
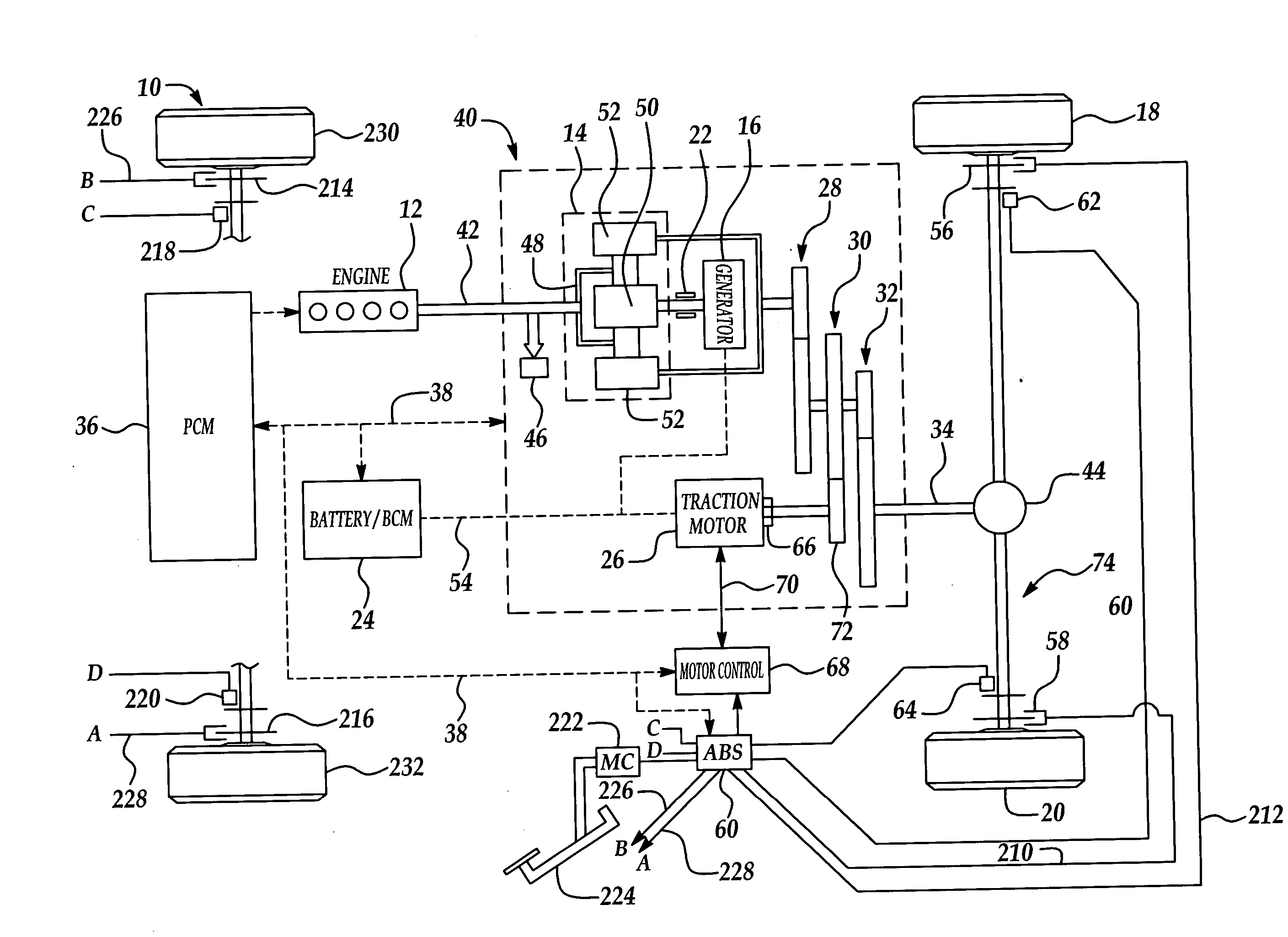
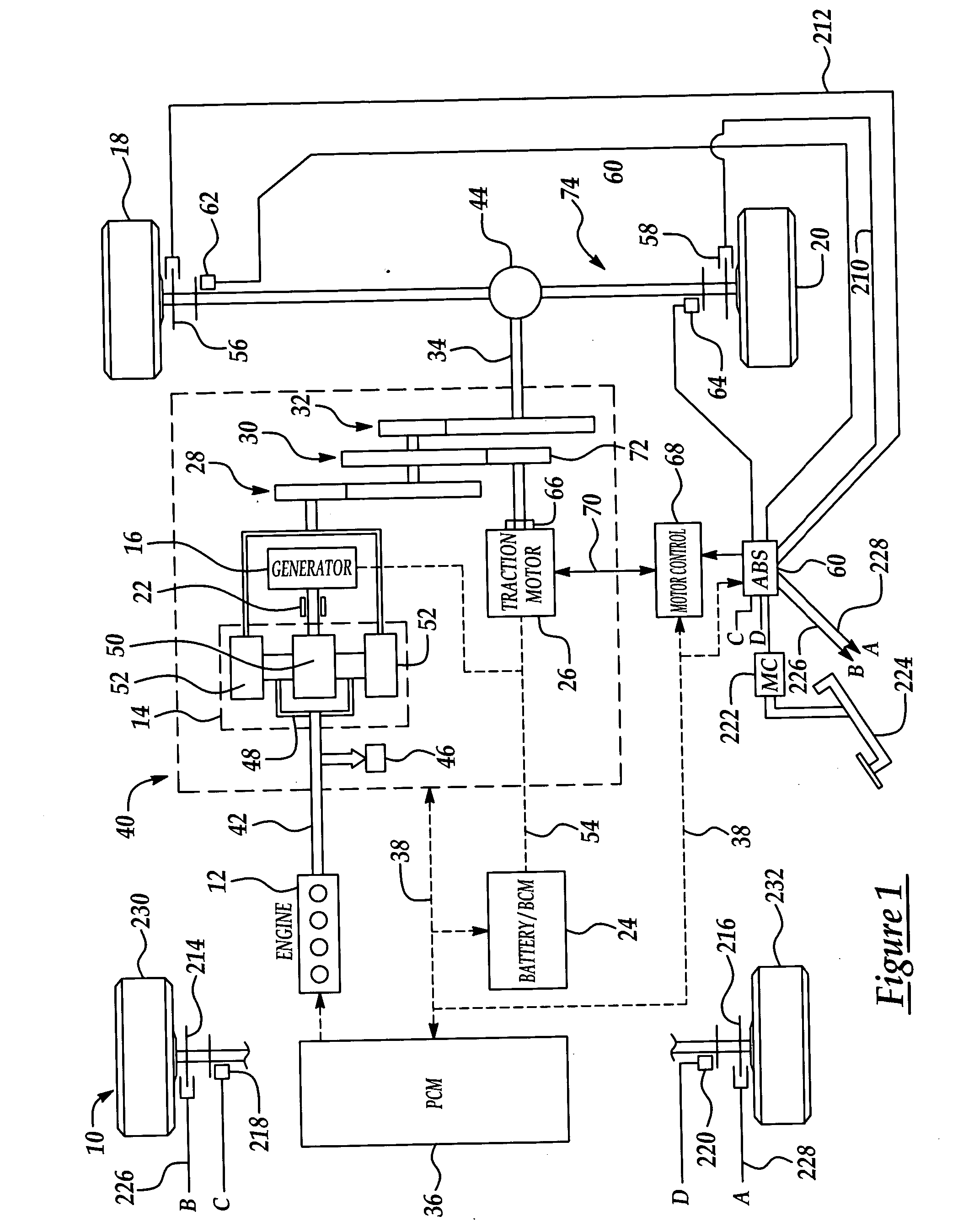
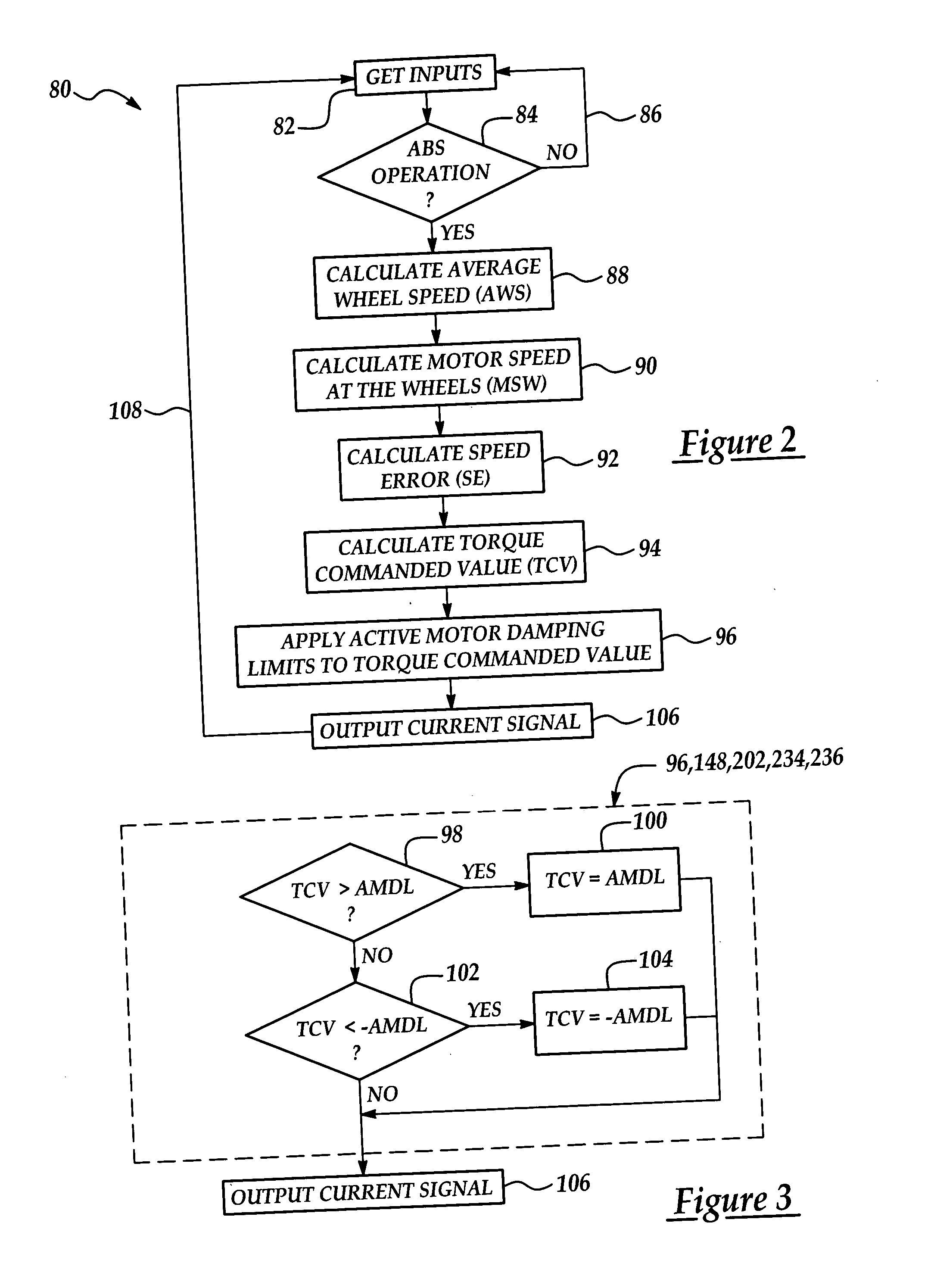
Active motor damping to mitigate electric vehicle driveline oscillations
ActiveUS7024290B2Reduce oscillationOscillation suppressionDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesMotor speedDrive wheel
A system and method for actively damping driveline oscillations in a motor vehicle having a traction motor to drive a vehicle's drive wheels and an antilock brake system (ABS). A traction motor controller controls a torque output signal of the motor to effectively to dampen driveline oscillations during an ABS operation. A proportional, a proportional derivative, or a derivative controller may be used to generate the torque output signal based on at least one of motor speed, an average of the drive wheel speeds, a difference in the two speeds, a motor angular acceleration, an average wheel angular acceleration, and a difference in the angular accelerations. Motor speed signals and average drive wheel speed signals may be filtered to eliminate high frequency components of each speed signal. Additionally, amplitude of the torque output signal may be limited within a positive upper and a negative lower active motor damping limit.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Active motor damping to mitigate electric vehicle driveline oscillations
ActiveUS20060025905A1Component can be removedReduce oscillationDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesMotor speedDrive wheel
A system and method for actively damping driveline oscillations in a motor vehicle having a traction motor to drive a vehicle's drive wheels and an antilock brake system (ABS). A traction motor controller controls a torque output signal of the motor to effectively to dampen driveline oscillations during an ABS operation. A proportional, a proportional derivative, or a derivative controller may be used to generate the torque output signal based on at least one of motor speed, an average of the drive wheel speeds, a difference in the two speeds, a motor angular acceleration, an average wheel angular acceleration, and a difference in the angular accelerations. Motor speed signals and average drive wheel speed signals may be filtered to eliminate high frequency components of each speed signal. Additionally, amplitude of the torque output signal may be limited within a positive upper and a negative lower active motor damping limit.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
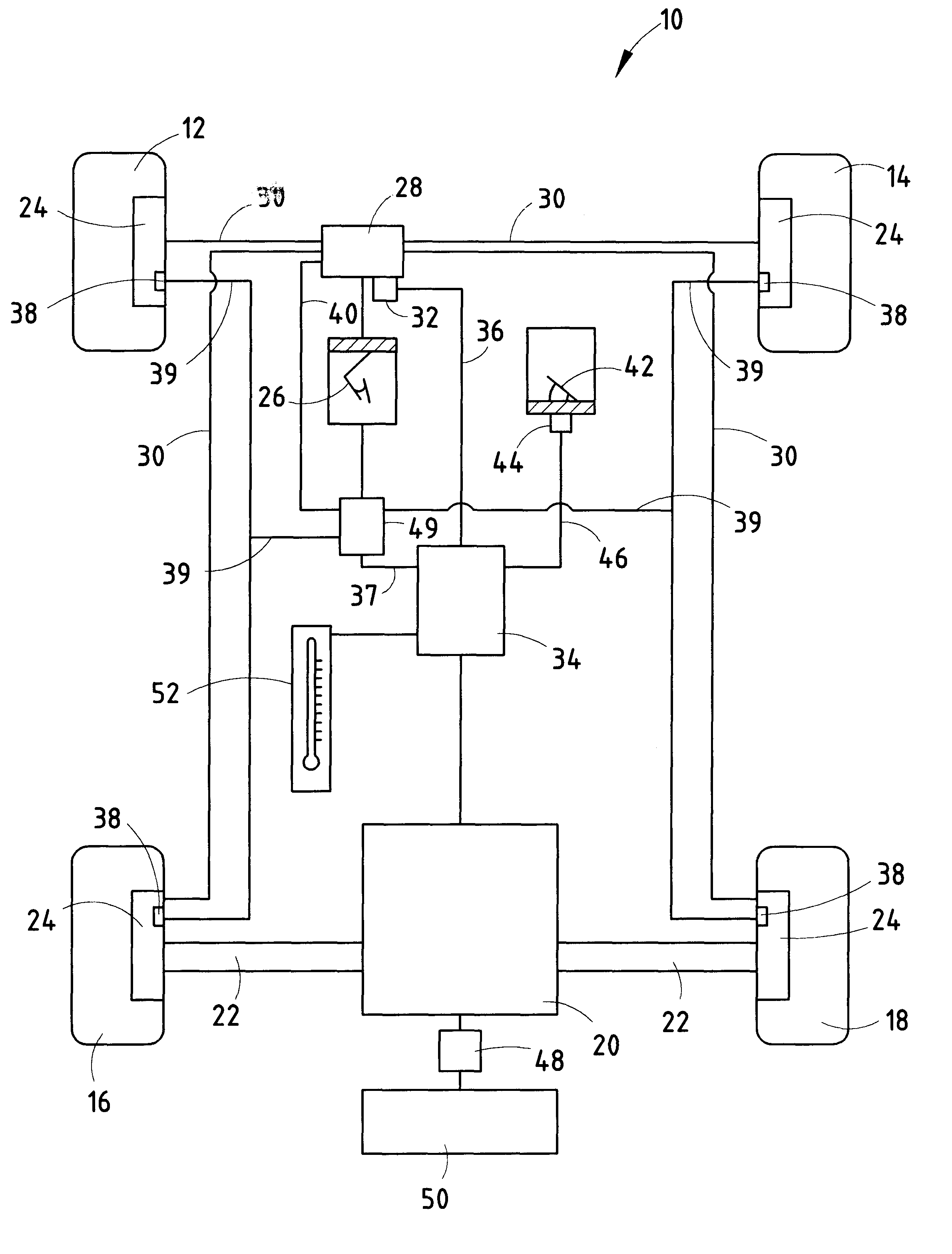
Temperature dependent regenerative brake system for electric vehicle
InactiveUS6275763B1Increase chanceReduce degradation rateAuxillary drivesBraking element arrangementsMobile vehicleRegenerative brake
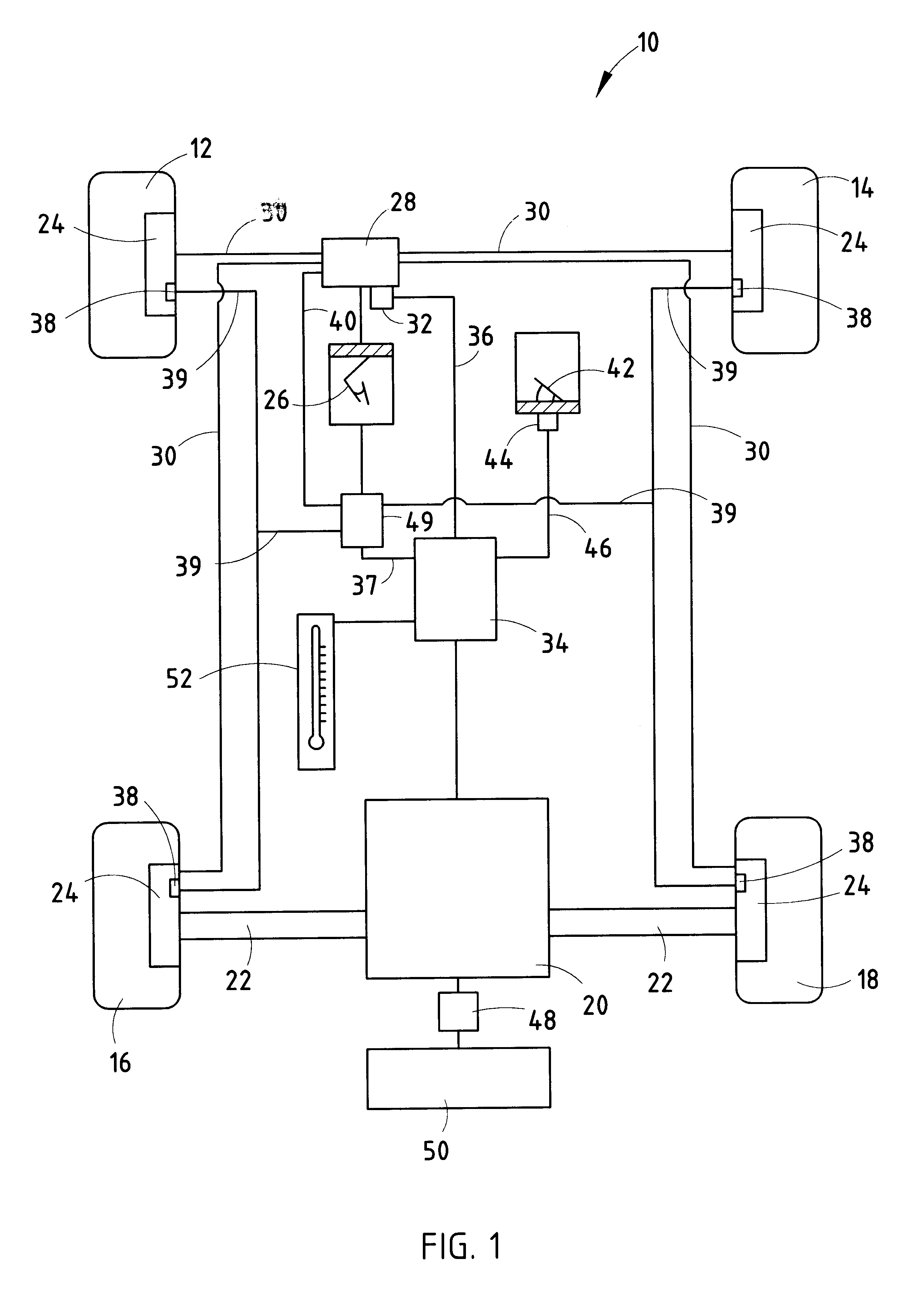
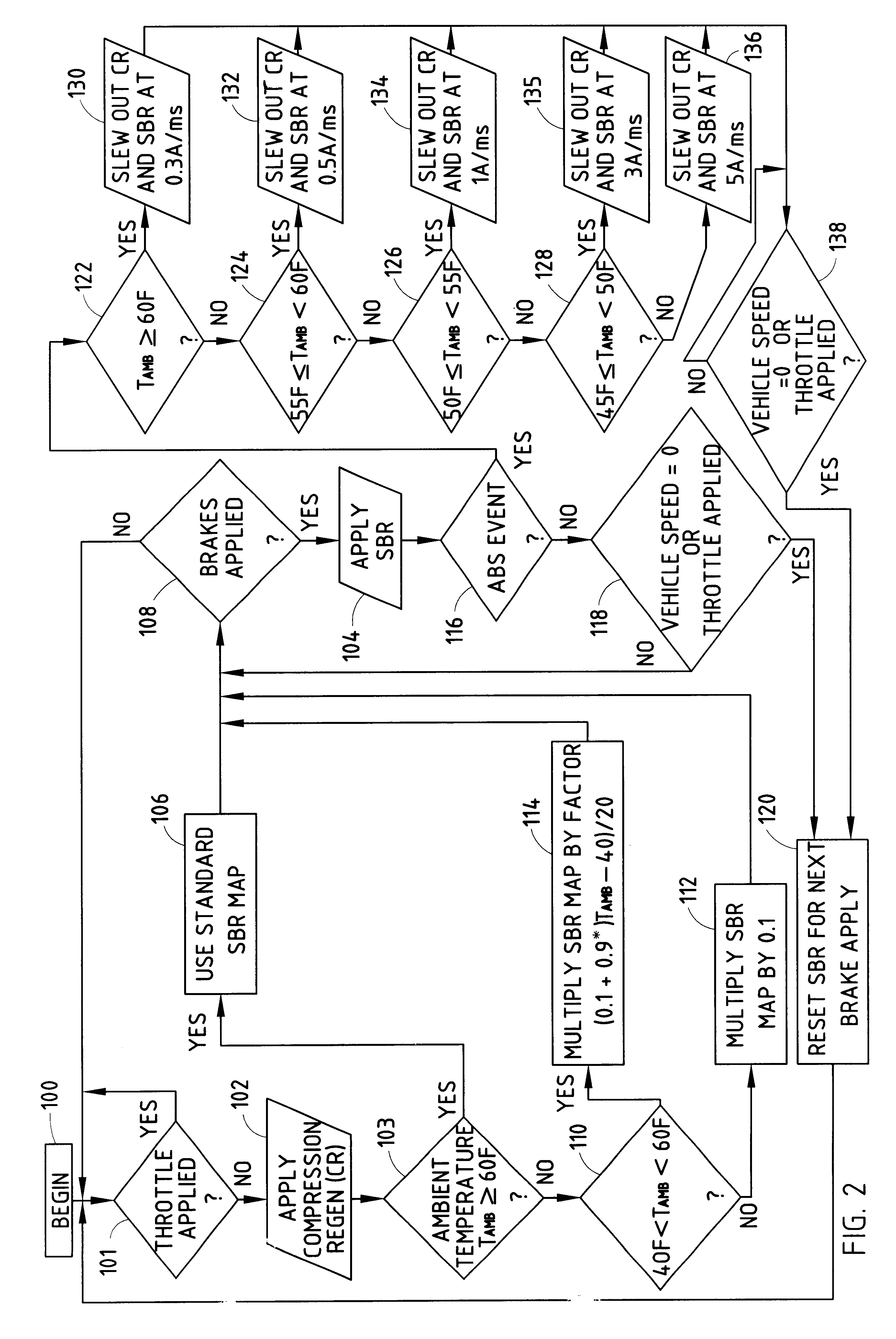
A braking system for a motor vehicle having braking wheels 16, 18, a service brake pedal, a friction braking system operative upon the braking wheels 16, 18 in response to actuation of the vehicle brake pedal 26, an anti-lock braking system cooperative with the friction braking system to control the friction braking force applied to the braking wheels 16, 18 upon detection of slippage of the braking wheels 16, 18, a regenerative braking system operative upon the braking wheels 16, 18 in response to actuation of the vehicle brake pedal 26 for selectively generating an applied regenerative braking force through the braking wheels 16, 18, and an ambient temperature sensor 52. The regenerative braking system operates at a first effective rate of applied regenerative braking force upon application of the brake pedal 26 at an ambient temperature above a desired temperature, and the regenerative braking system operates at a second, lower effective rate of applied regenerative braking force at an ambient temperature below a desired temperature. Upon activation of the anti-lock braking system, the applied regenerative braking force is reduced at a first predetermined rate when the ambient temperature is above a desired temperature and the regenerative braking force is reduced at a second, faster predetermined rate when the ambient temperature is below a desired temperature.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
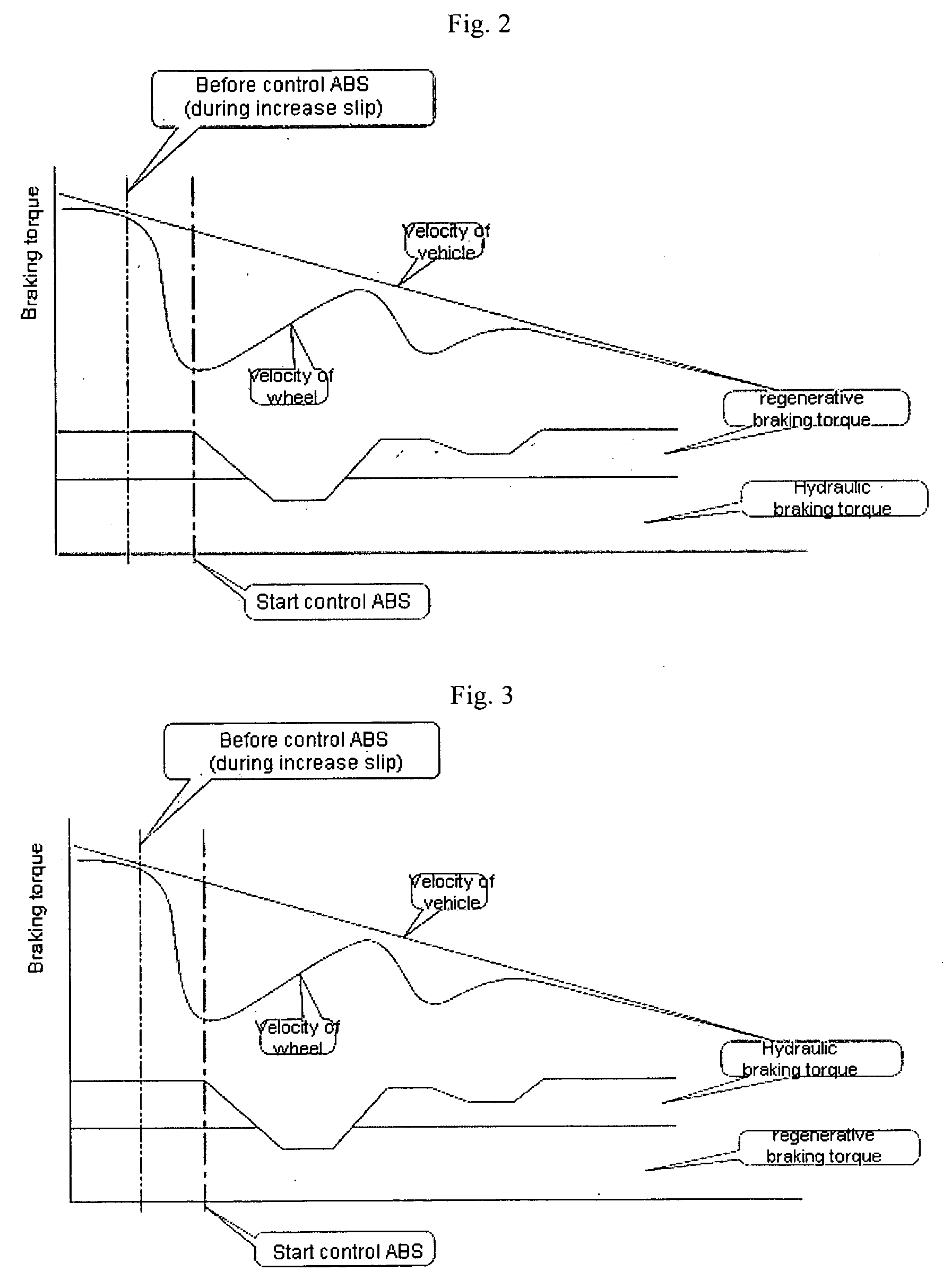
Method for control regenerative braking of electric vehicle
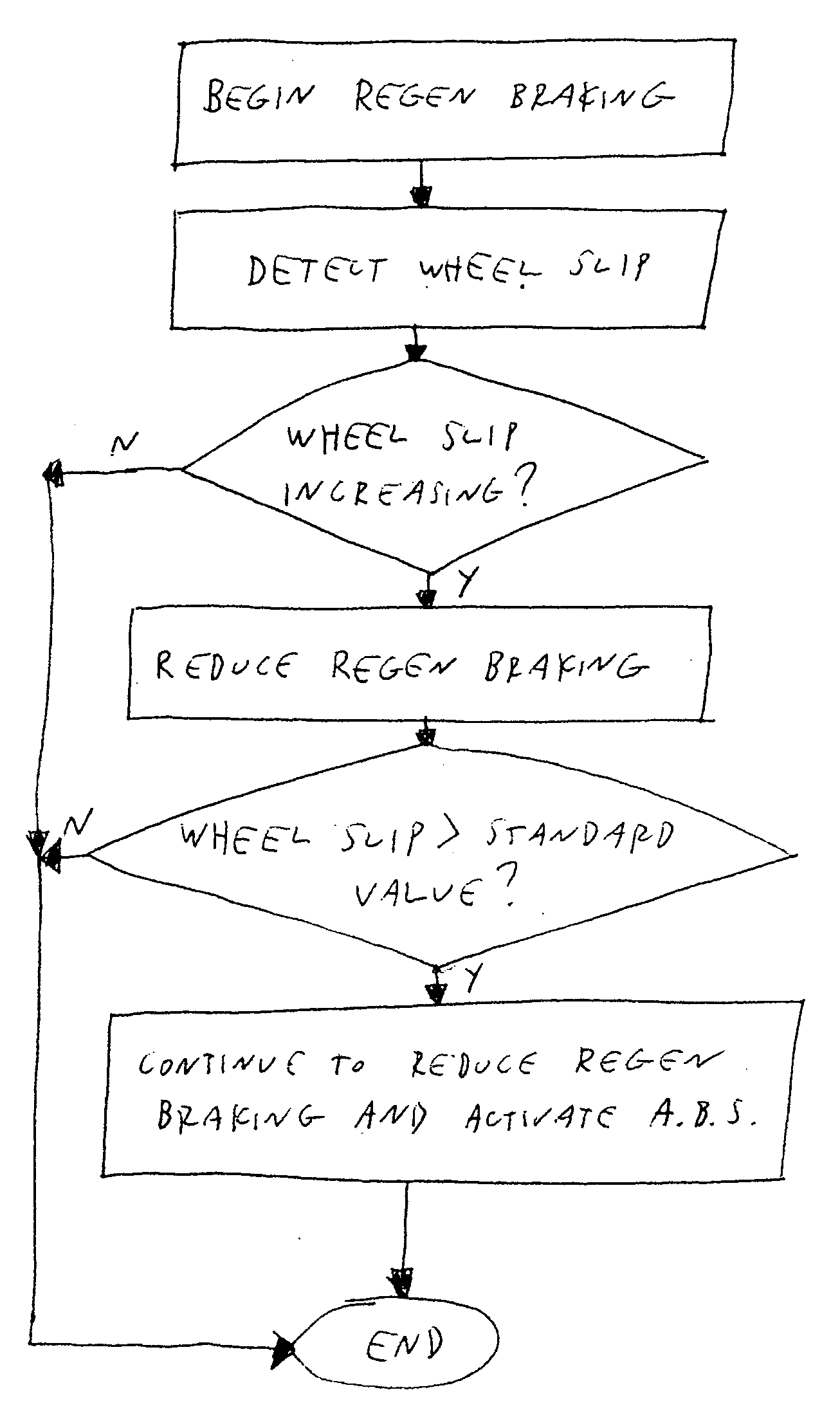
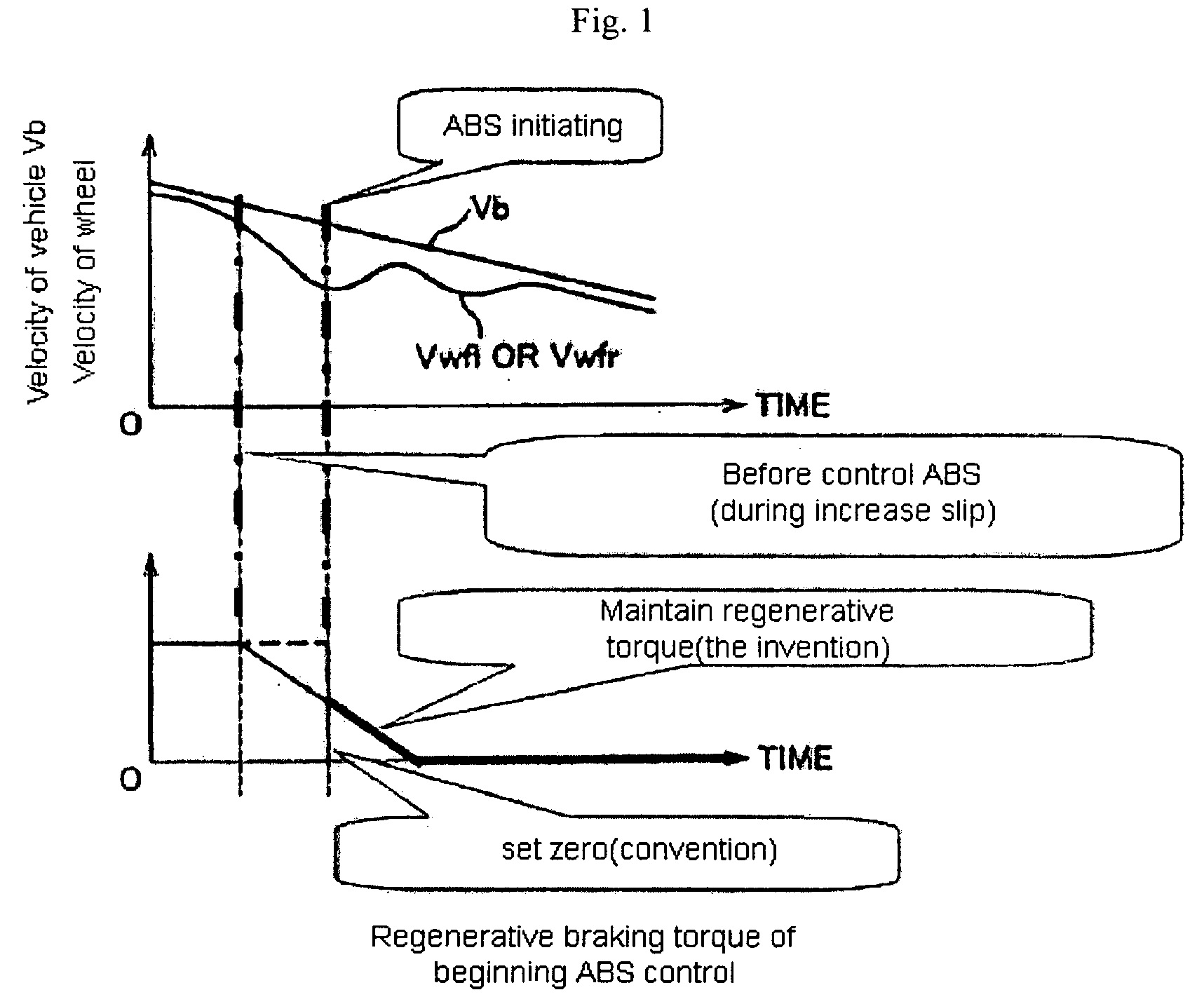
A method for controlling regenerative braking of a vehicle includes: initiating the regenerative braking; detecting an amount of slip of a wheel during the regenerative braking; if the amount of slip is increasing, reducing a regenerative braking torque; and if the amount of slip is greater than a set value, actuating an antilock brake system and reducing the regenerative braking torque or a hydraulic braking torque continuously until the vehicle is stopped. Alternatively, if the amount of slip is increasing, the regenerative braking torque is not reduced.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Vehicle systems control for improving stability
InactiveUS8229642B2Improve vehicle stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesTraction control systemControl system
Improved methods of controlling the stability of a vehicle are provided via the cooperative operation of vehicle stability control systems such as an Active Yaw Control system, Antilock Braking System, and Traction Control System. These methods use recognition of road surface information including the road friction coefficient (mu), wheel slippage, and yaw deviations. The methods then modify the settings of the active damping system and / or the distribution of drive torque, as necessary, to increase / reduce damping in the suspension and shift torque application at the wheels, thus preventing a significant shift of load in the vehicle and / or improving vehicle drivability and comfort. The adjustments of the active damping system or torque distribution temporarily override any characteristics that were pre-selected by the driver.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
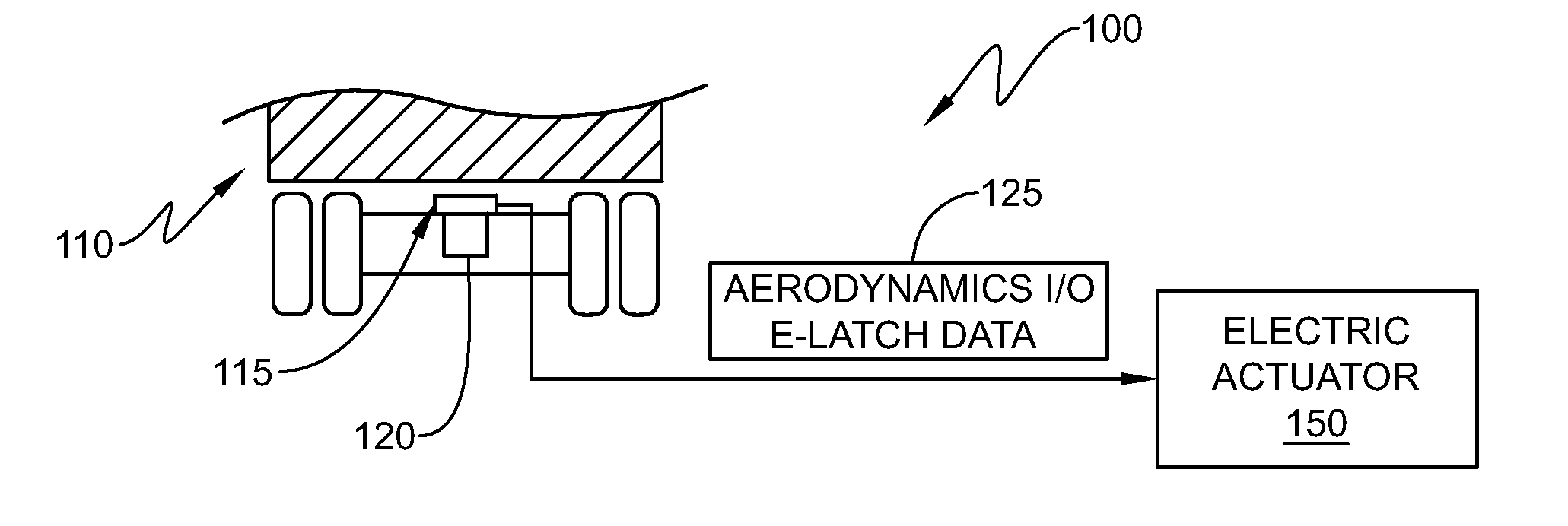
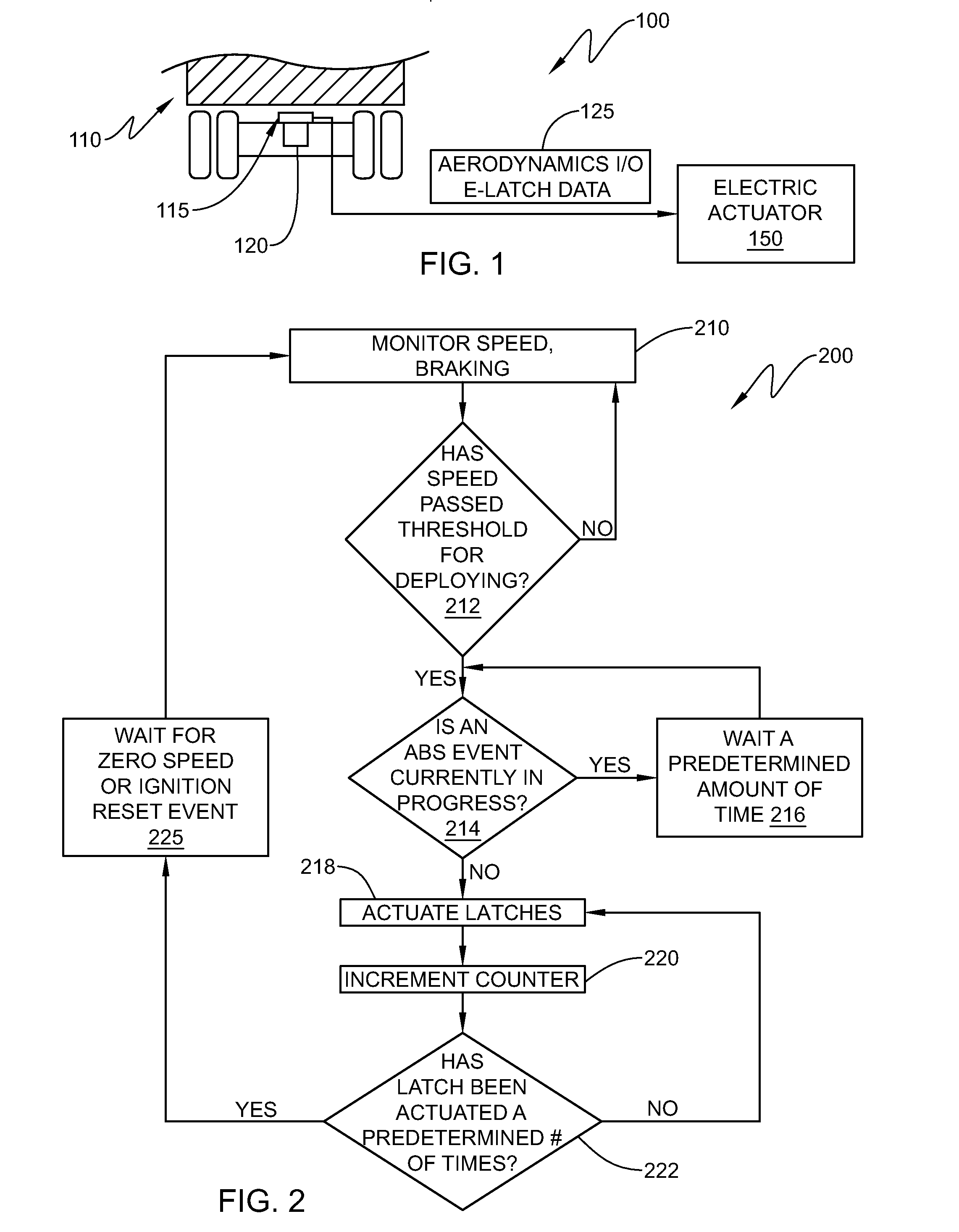
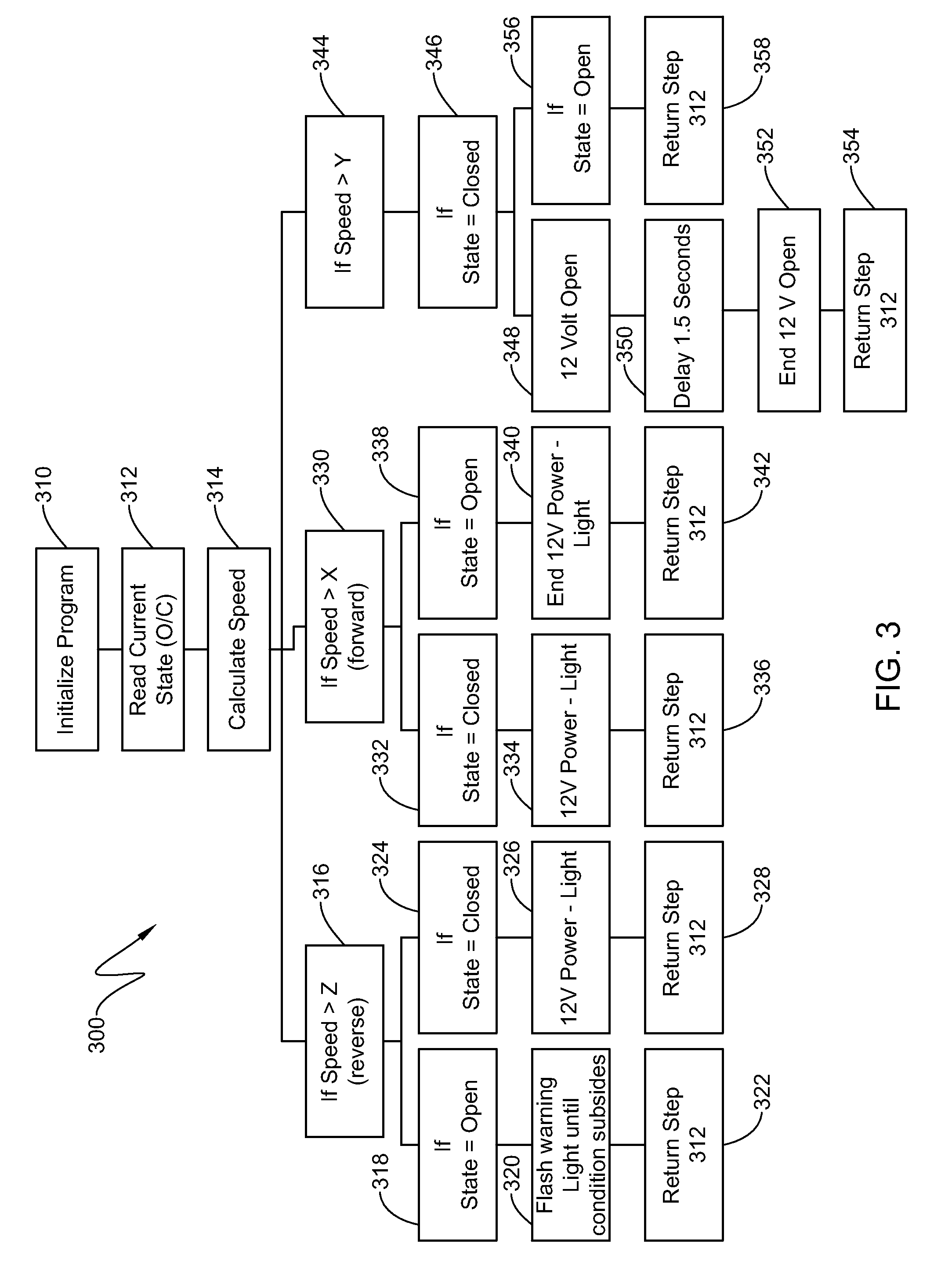
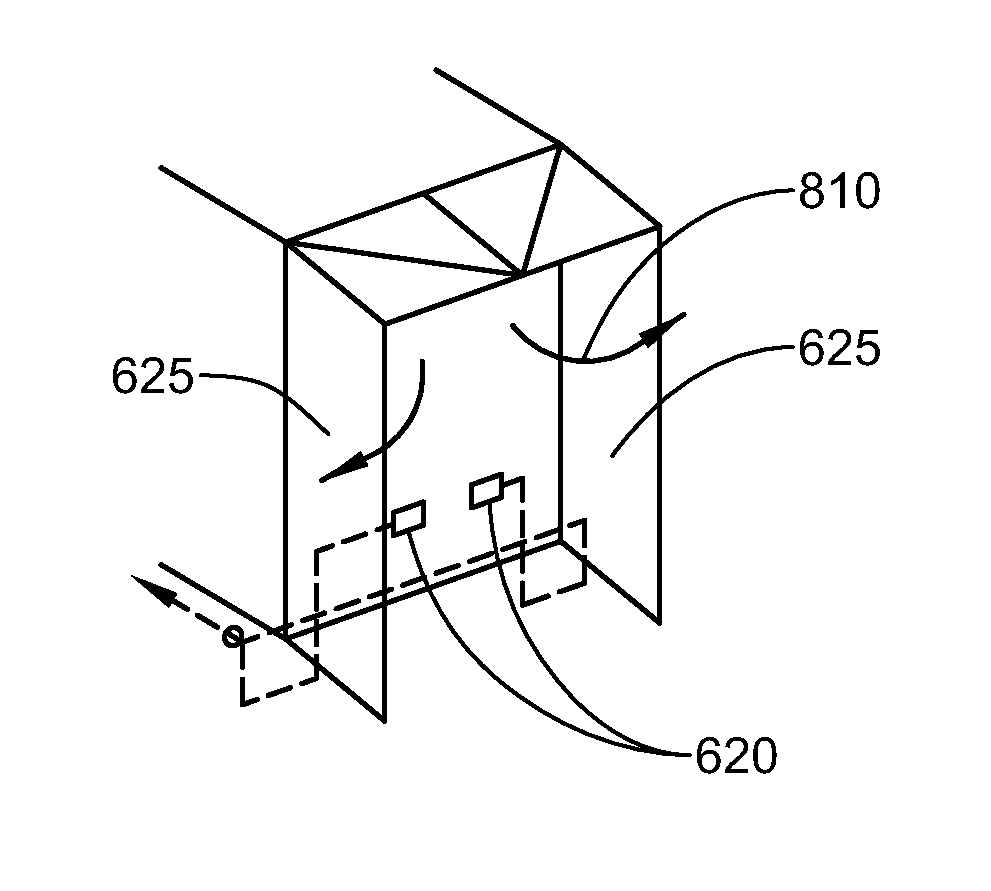
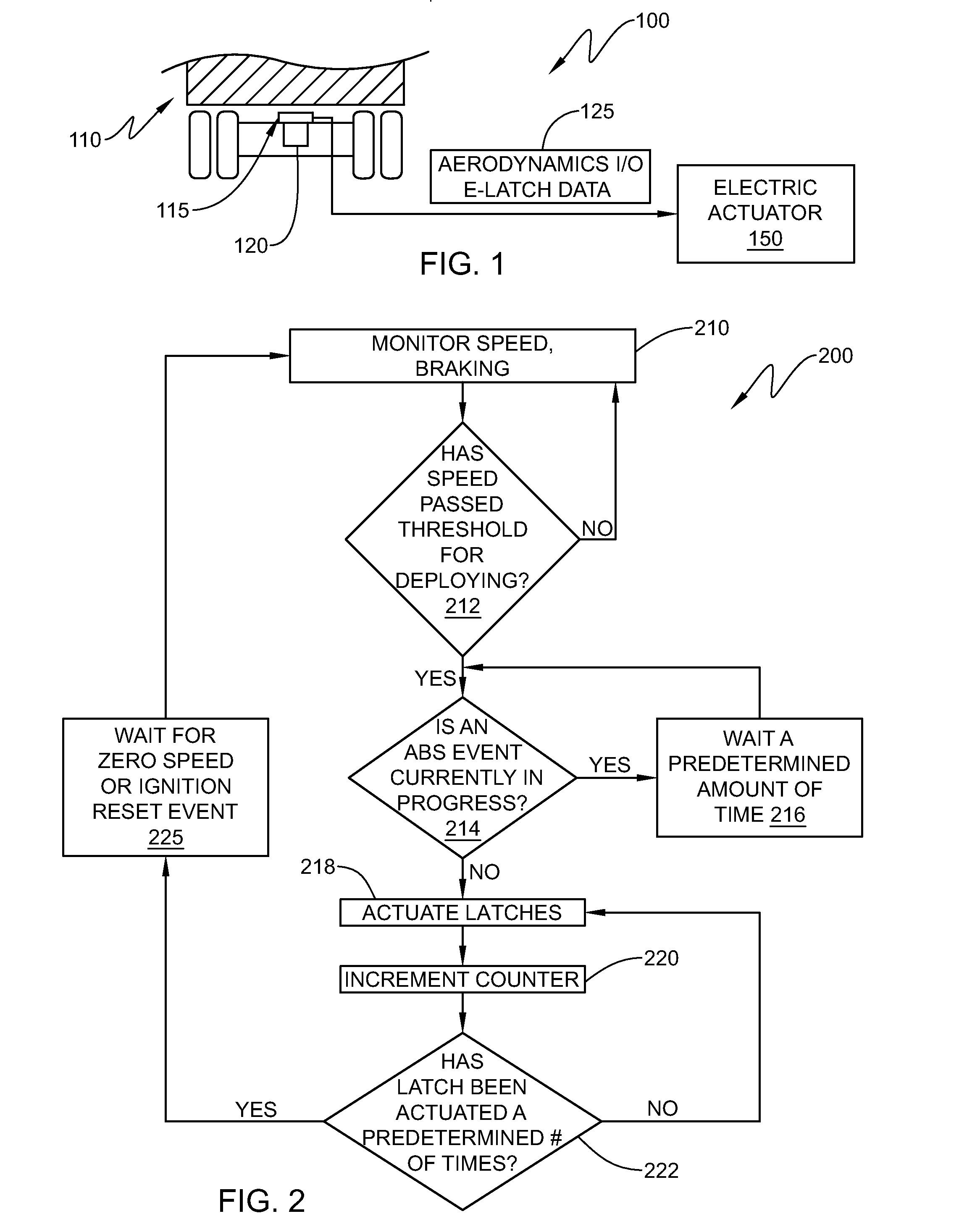
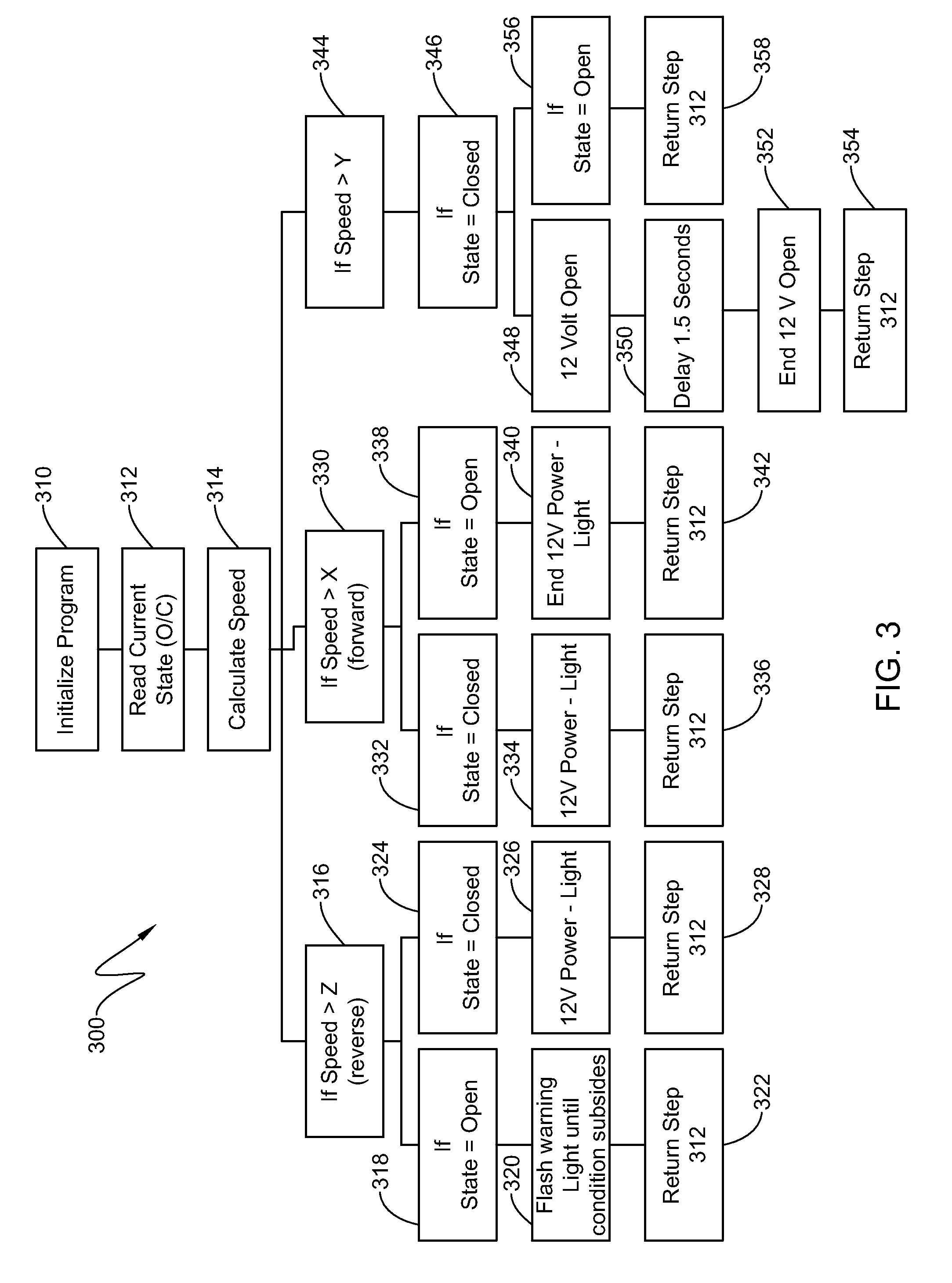
Retractable aerodynamic structures for cargo bodies and methods of controlling positioning of the same
ActiveUS20140019010A1Overcome disadvantagesDigital data processing detailsPower-operated mechanismEngineeringControl theory
A system that has electrically or electro-pneumatically actuated aerodynamic structures. An electric or electro-pneumatic actuator is employed, which receives signals from an existing anti-lock braking system (ABS) controller to determine when actuation occurs. Other systems are also provided that feature electric or electro-pneumatic actuation, including underbody skirts and scoops, as well as inflatable tractor-trailer gap sealing devices, adjustable tractor-trailer gap sealing flaps and inflatable trailer upper streamlining devices. Electronic control units (ECUs) for aerodynamic system control interfacing with alternate sensors for calculating speed are also provided. Satellite navigation, platooning awareness and managed pressure reserve capability can be employed with the aerodynamics ECU.
Owner:STEMCO PROD INC
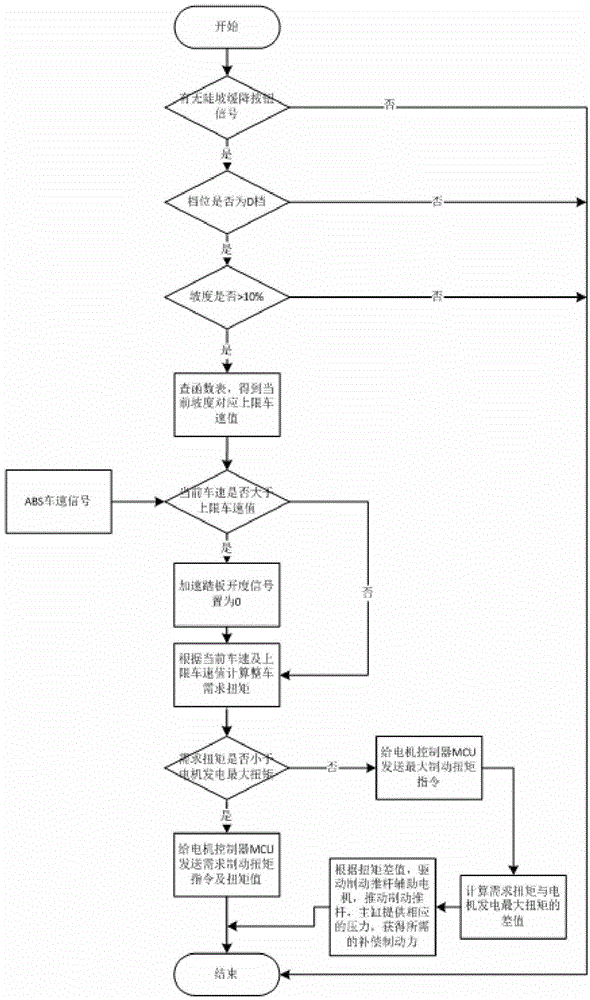
Hill descent control system of pure electric vehicle and control method thereof
The invention provides a hill descent control system of a pure electric vehicle and a control method of the hill descent control system. The hill descent control system comprises a vehicle signal unit, a hill descent unit, a vehicle control unit, an anti-lock braking system, a driving motor and an active brake unit. The vehicle signal unit, the hill descent unit and the anti-lock braking system are connected with the vehicle control unit. The vehicle control unit is connected to the driving motor through a motor controller. The vehicle control unit is also connected with the active brake unit. According to the hill descent control system, different slopes correspond to different vehicle speed intervals, and preferably the motor is used for generating power and recovering energy; especially down a slope along a long ramp, the burden of the braking system is relieved, and potential accidents caused by thermal failure due to an overheated brake are eliminated.
Owner:BEIJING ELECTRIC VEHICLE
Retractable aerodynamic structures for cargo bodies and methods of controlling positioning of the same
InactiveUS9145177B2Vehicle body streamliningPosition/direction controlControl theoryAnti-lock braking system
A system that has electrically or electro-pneumatically actuated aerodynamic structures. An electric or electro-pneumatic actuator is employed, which receives signals from an existing anti-lock braking system (ABS) controller to determine when actuation occurs. Other systems are also provided that feature electric or electro-pneumatic actuation, including underbody skirts and scoops, as well as inflatable tractor-trailer gap sealing devices, adjustable tractor-trailer gap sealing flaps and inflatable trailer upper streamlining devices. Electronic control units (ECUs) for aerodynamic system control interfacing with alternate sensors for calculating speed are also provided. Satellite navigation, platooning awareness and managed pressure reserve capability can be employed with the aerodynamics ECU.
Owner:STEMCO PROD INC
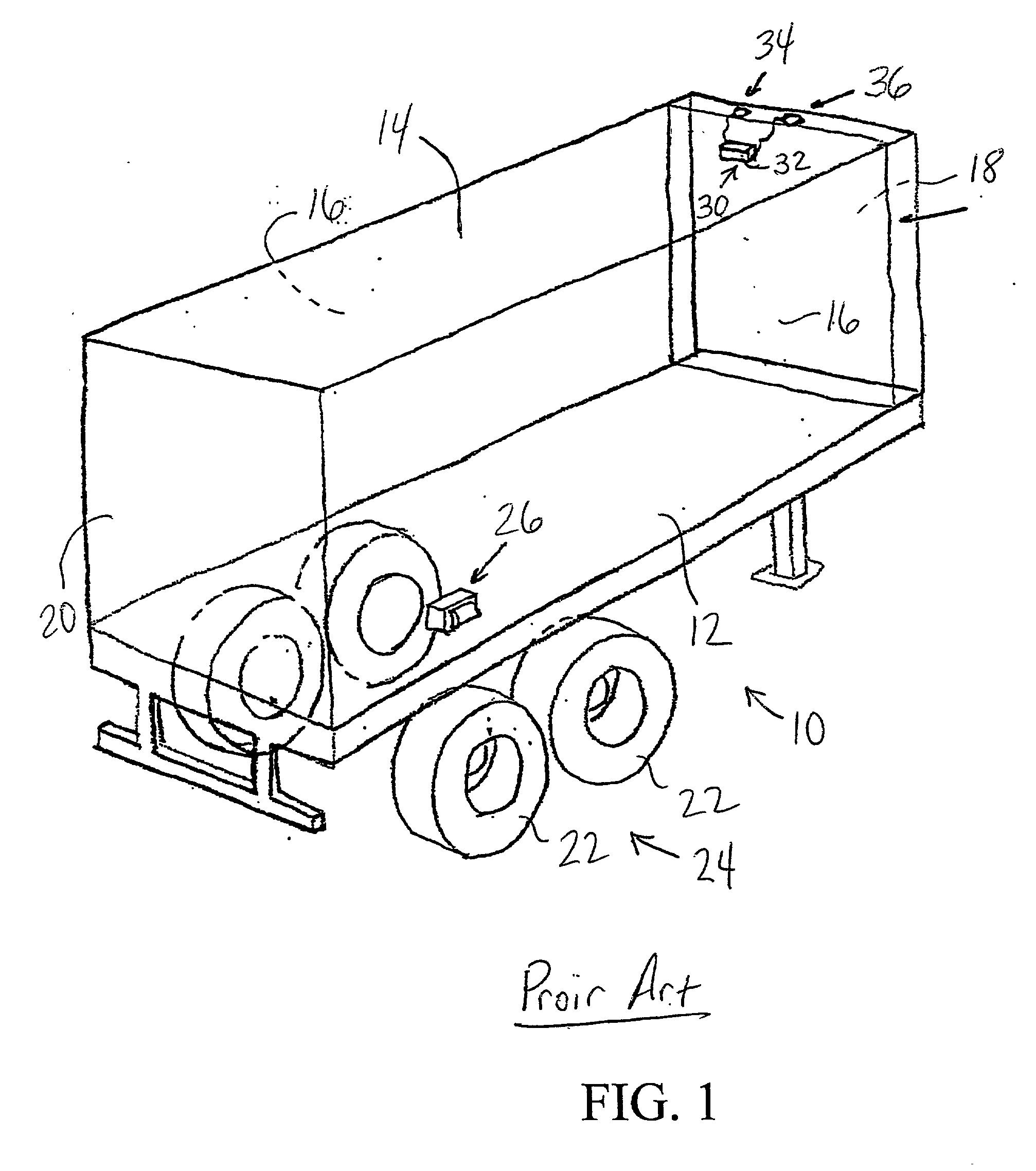
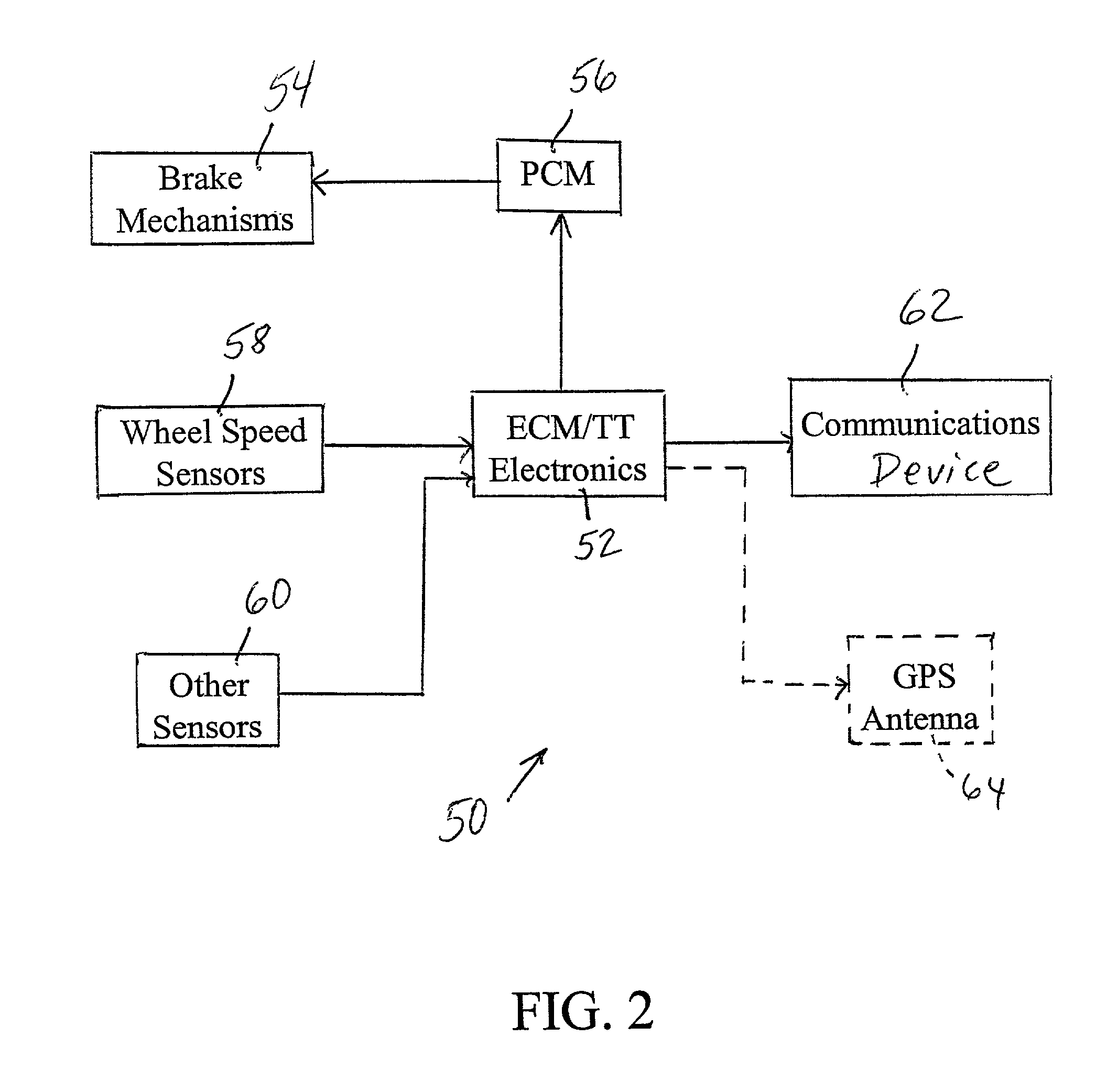
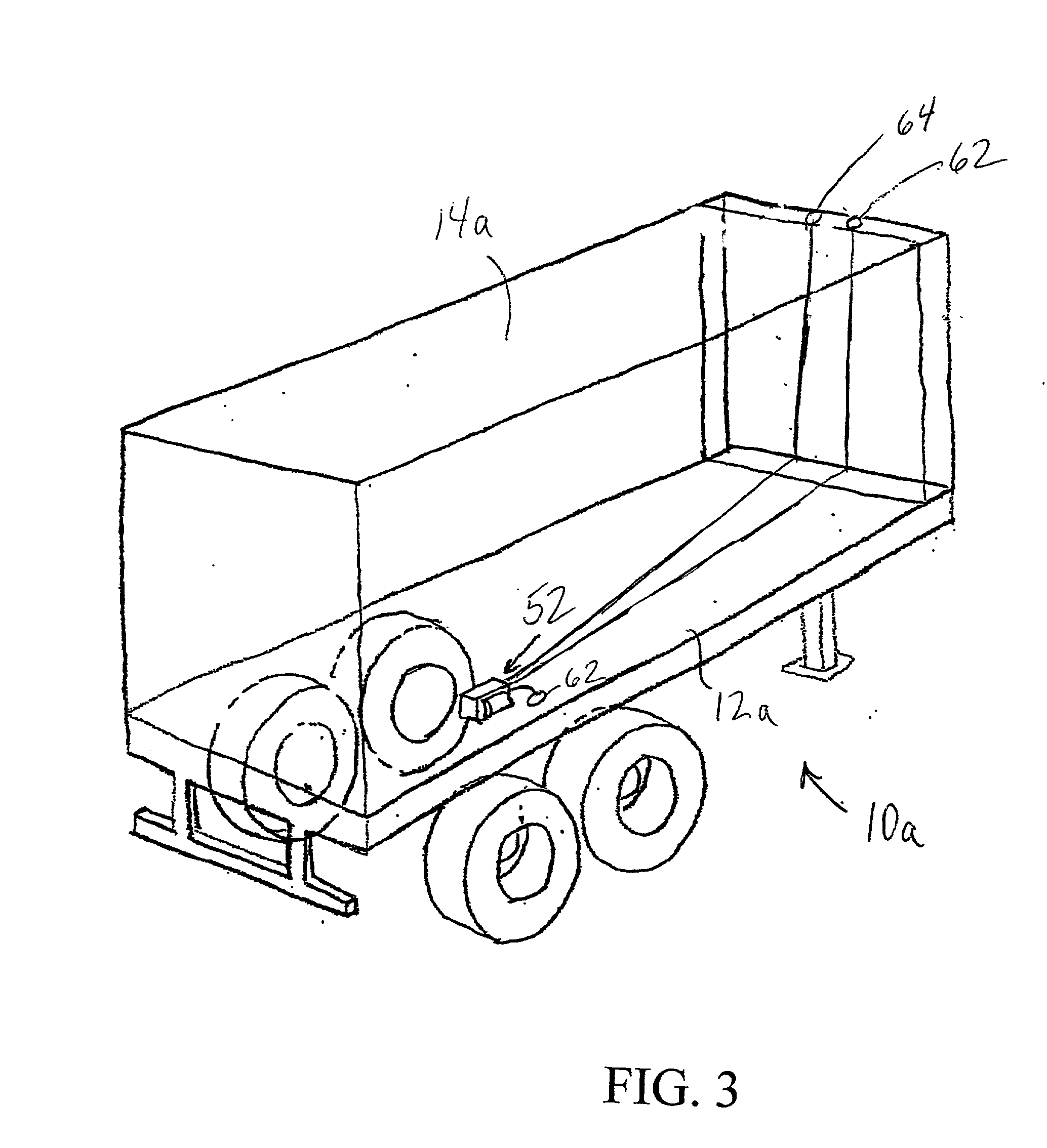
Braking system with wireless communication capability and trailer including same
InactiveUS20010038239A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesBraking action transmissionInformation transmissionWireless transmission
A braking system, such as an Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) or Electropneumatic Braking System (EBS), which is configured to communicate information in a wireless transmission to a remote location. The braking system may be provided on a trailer, and may be configured to communicate the information to a fleet base. The information which is communicated to the fleet base may include information regarding tire pressure and bearing health, as well as other information about the trailer. The braking system includes an Electronic Control Module, and the Electronic Control Module may be connected to a communications antenna for transmitting the information to the fleet base, or may be in communication with a Trailer Tracking system on the trailer, where the Trailer Tracking system is configured to transmit the information to the fleet base.
Owner:WABASH TECH
Torque recycling control method and control system of pure electric vehicle
ActiveCN106627171ASolve the problem of accumulationSmooth transitionSpeed controllerElectrodynamic brake systemsControl systemRoad surface
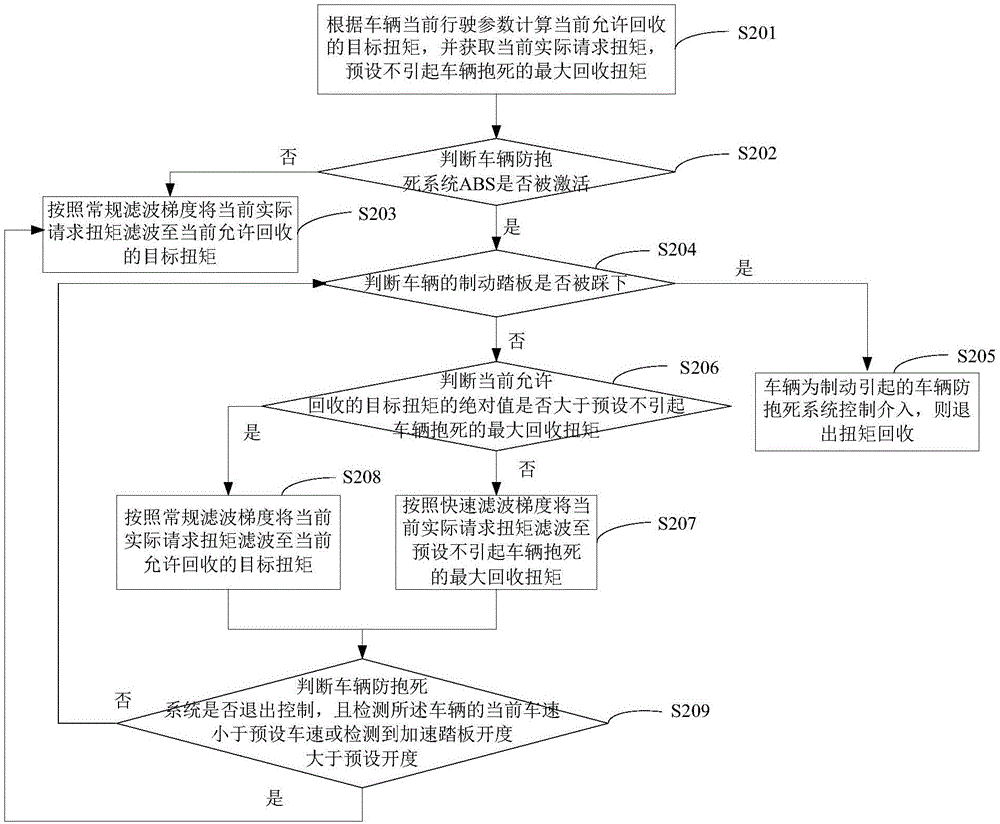
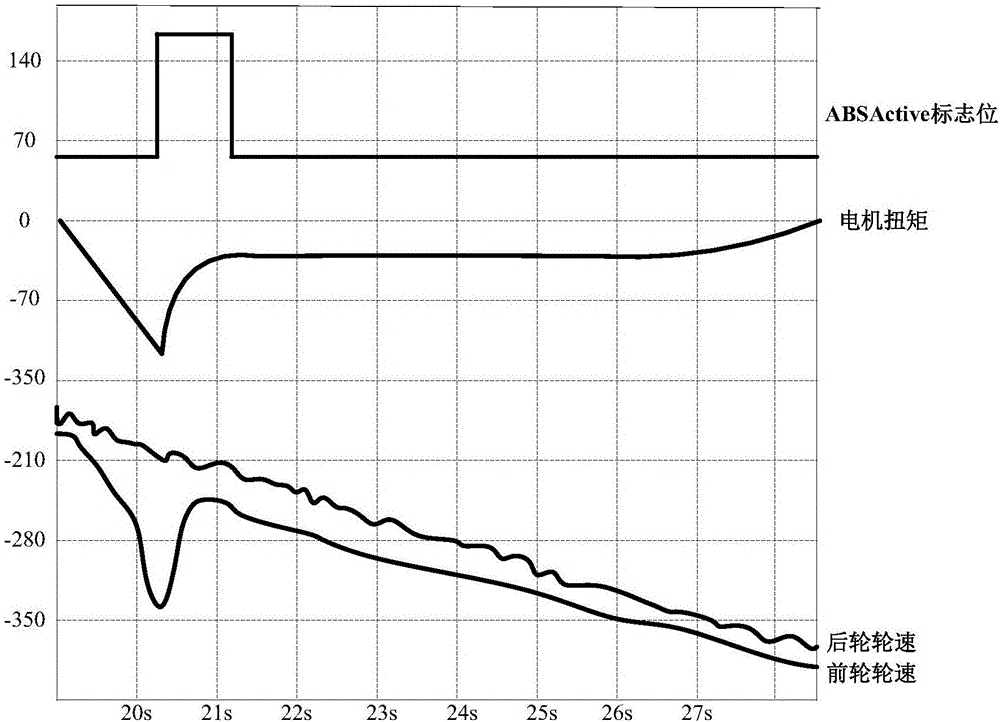
The invention discloses a torque recycling control method and control system of a pure electric vehicle. The method comprises the steps of calculating a current recyclable target torque according to current driving parameters of the vehicle, obtaining a current actual request torque, and presetting a biggest reclaimed torque not causing locking of the vehicle; when the anti-lock braking system ABS of the vehicle is activated and the brake pedal of the vehicle is not stepped on, determining to conduct filtering according to a fast filtering gradient or a regular filtering gradient based on the absolute value of the current recyclable target torque and the absolute value of the biggest reclaimed standardization torque. According to the torque recycling control method and control system of the pure electric vehicle, the vehicle can achieve steady transition before and after the interference of the ABS interference by controlling different filtering gradients, and it is guaranteed that the vehicle is provided with the corresponding reclaimed torque and meanwhile locking of vehicle wheels is not caused when the vehicle slides on a low attachment coefficient road; meanwhile, by setting the reset condition of a control state, the repeating interference of the ABS in the same reclaimed interval is avoided, and the problem of vehicle crowding is solved.
Owner:深蓝汽车科技有限公司
Motorcycle with antilock brake system
ActiveUS7350881B2Improve performanceEasy to installElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingMaster cylinderEngineering
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
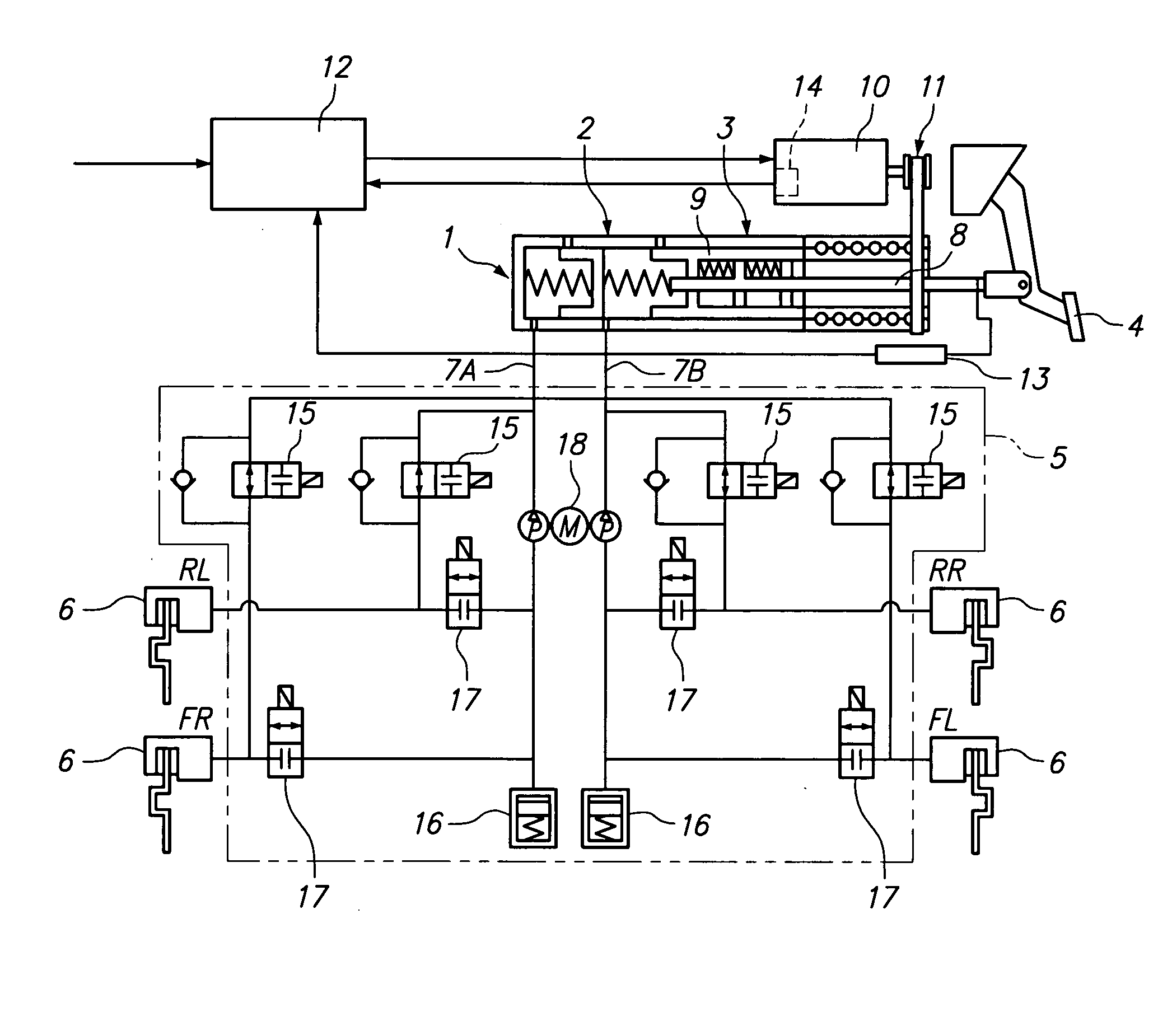
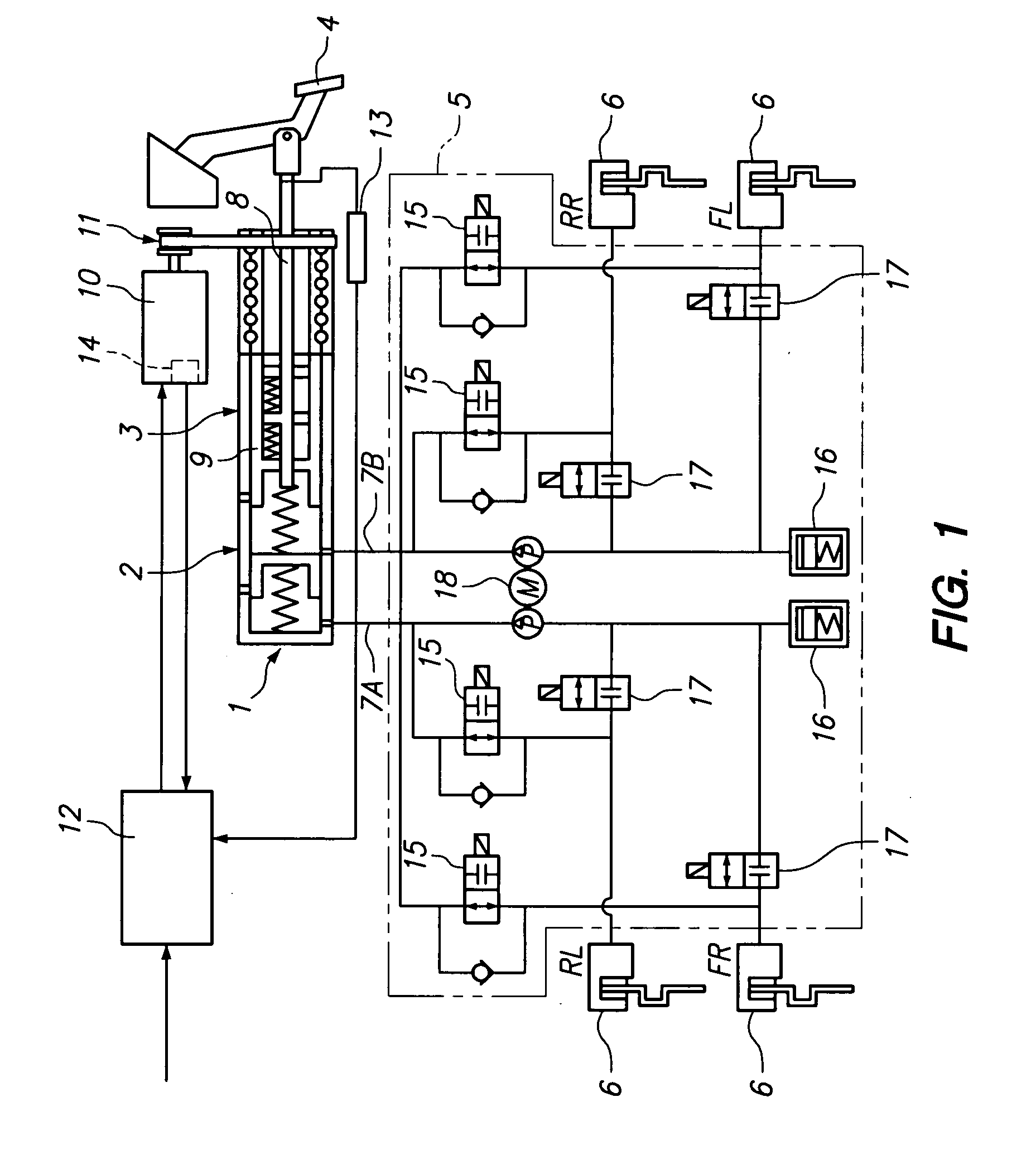
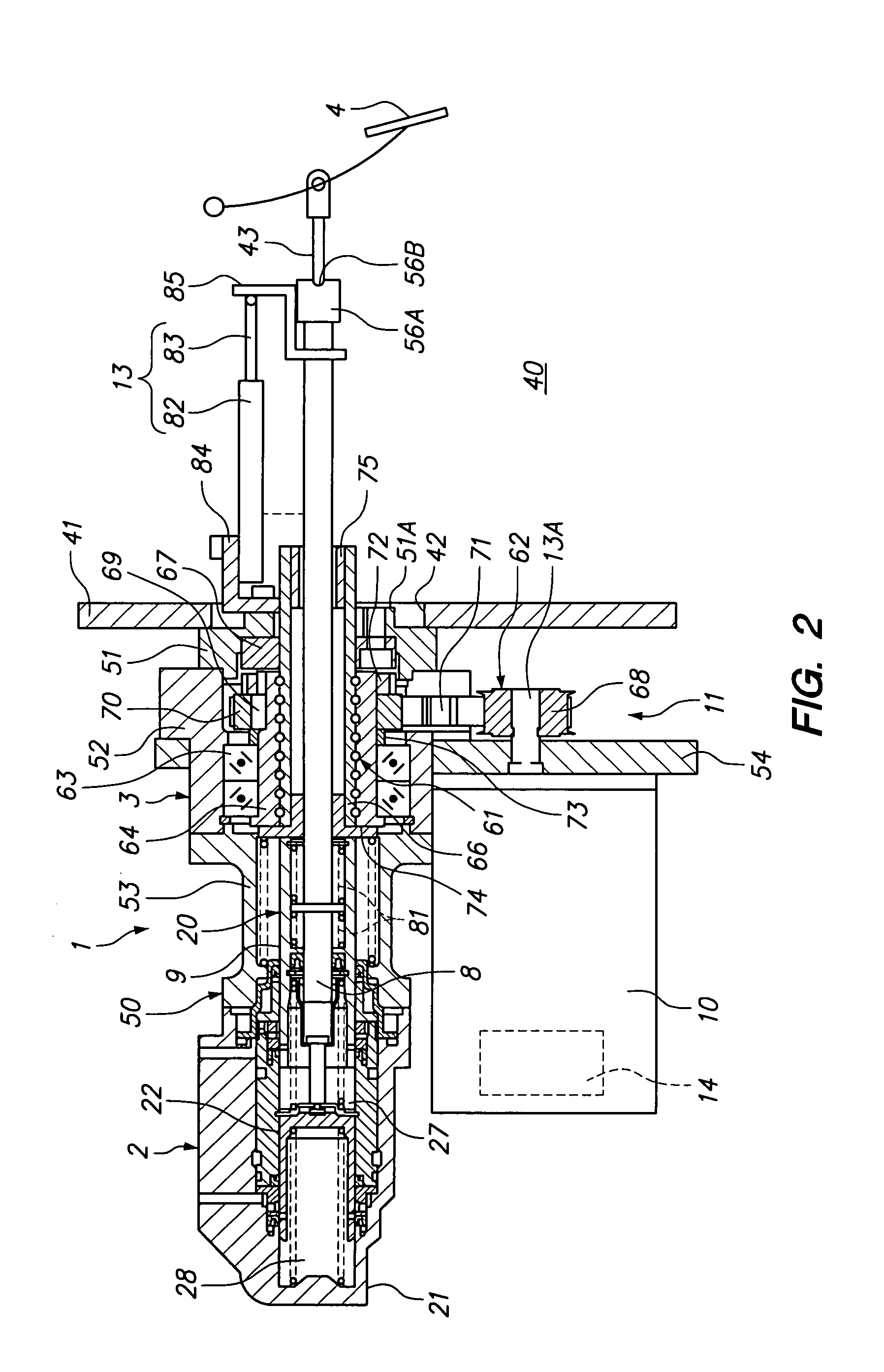
Brake apparatus
InactiveUS20080231109A1Improving pedal feelingPreventing hydraulic pressureBraking action transmissionApplication and release valvesWheel cylinderActuator
An object of the present invention is to provide a brake apparatus in which a hydraulic pressure in a master cylinder is prevented from being increasingly varied while an anti-lock brake system is in operation, and therefore a pedal feeling can be improved. The brake apparatus comprises an electric booster including an input member which moves forward or backward in response to an operation of a brake pedal, an assist member which moves forward or backward by being driven by an electric actuator using an electric motor as its driving source. The electric booster generates a boosted brake hydraulic pressure in the master cylinder under an input thrust provided to the input member through the brake pedal and an assist thrust provided to the assist member by the electric actuator. In the brake apparatus, the brake hydraulic pressure generated in the master cylinder is supplied to a wheel cylinder through a hydraulic pressure circuit of an anti-lock brake system, and, while the anti-lock brake system in operation, an operation of the assist member is restricted by a booster control, whereby a change in a hydraulic pressure in the master cylinder due to the operation of the assist member can be restrained.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for optimizing braking control during a threshold braking event
ActiveUS8062175B2Optimizing brake pressure controlMinimize such driveline disturbancesSpeed controllerElectrodynamic brake systemsDrive wheelRoad surface
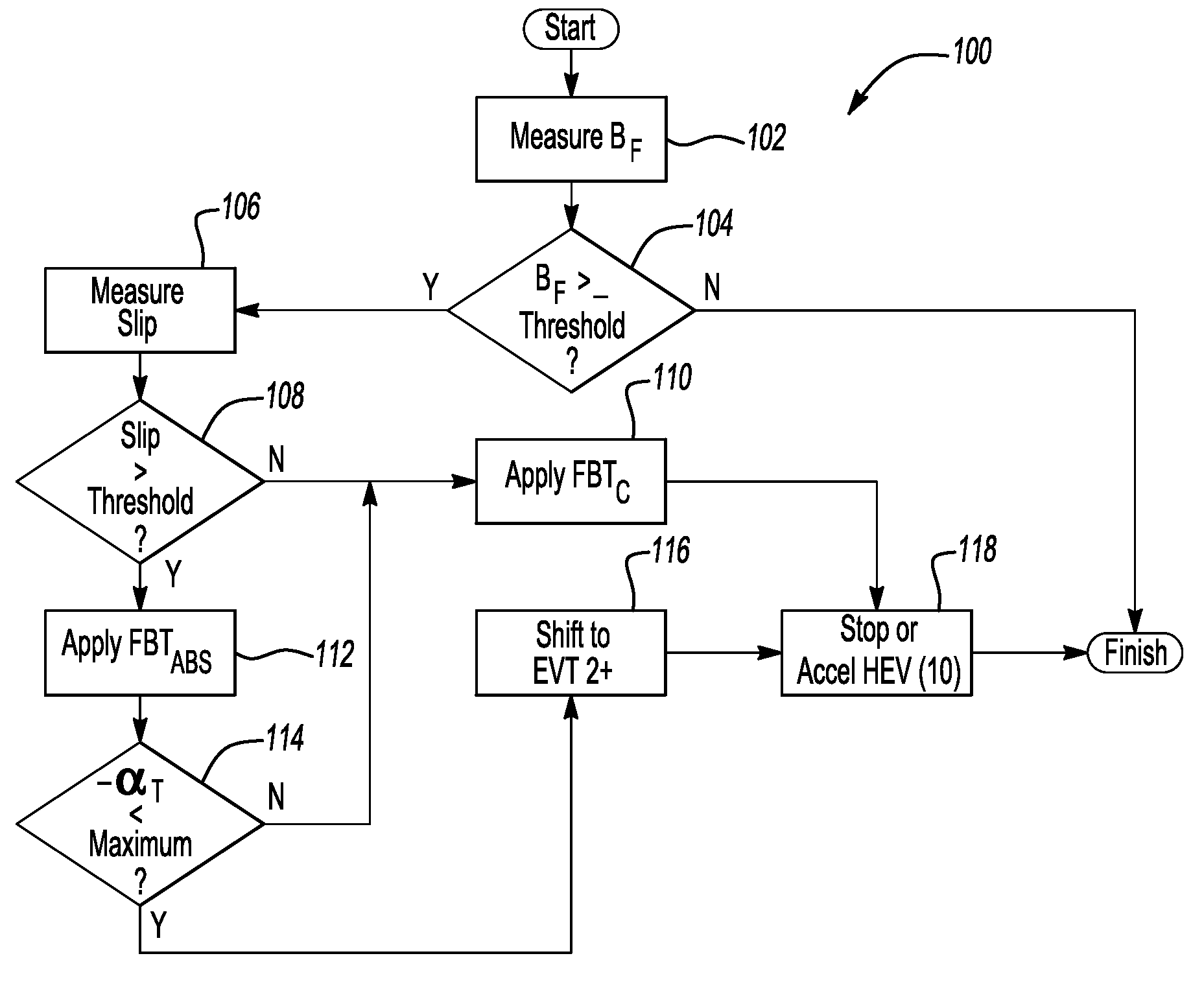
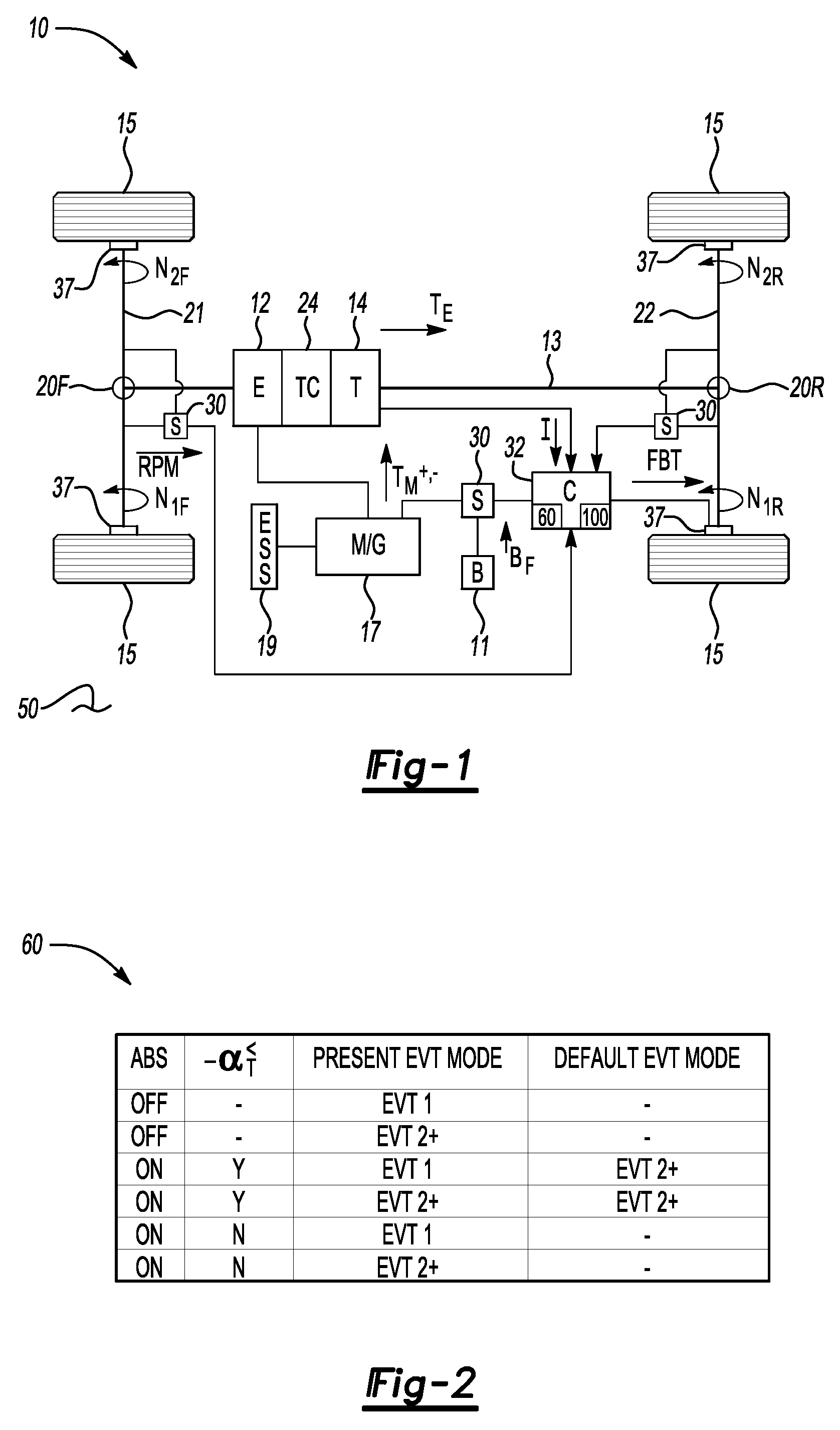
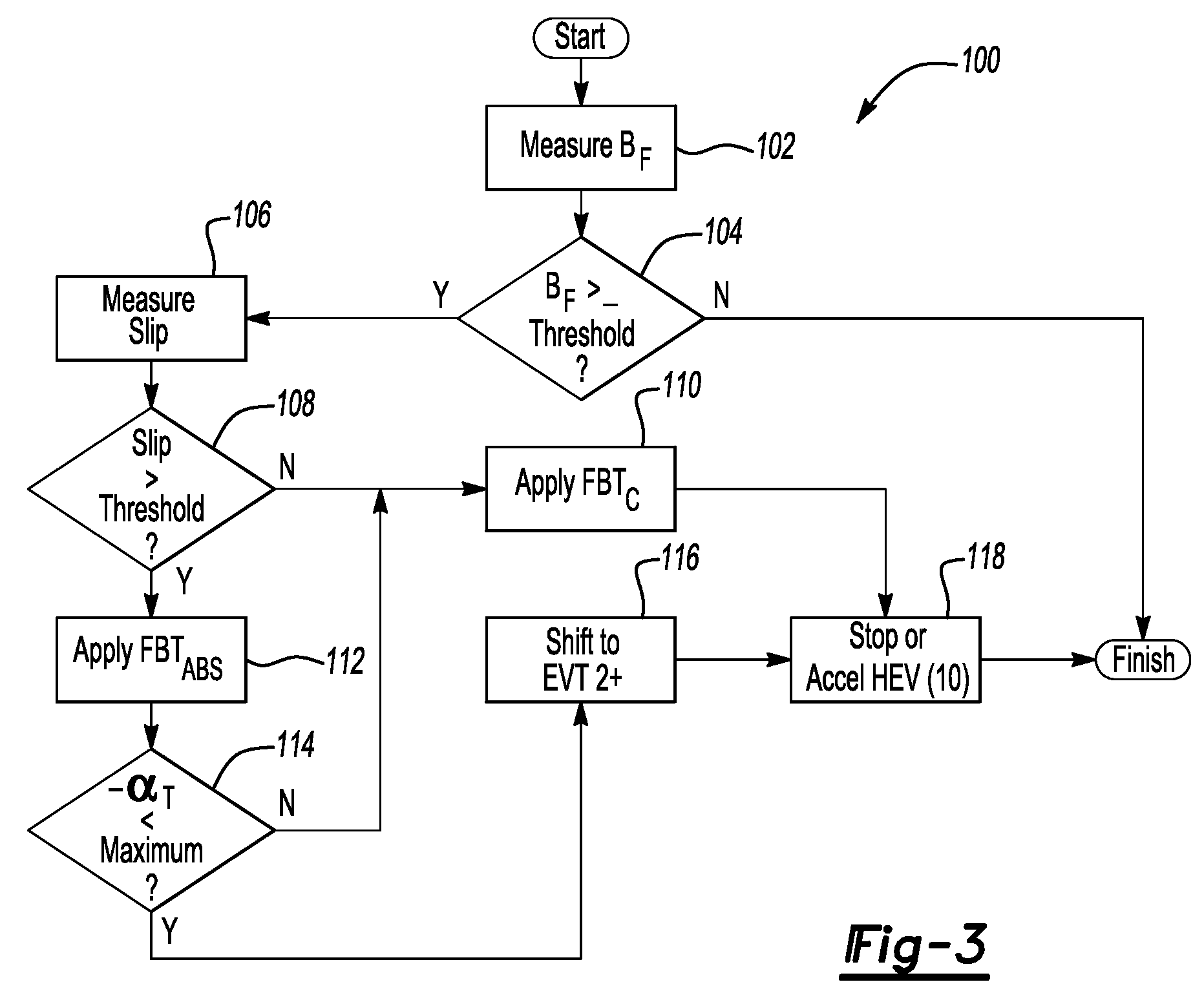
A method minimizes a driveline vibration and reduces stopping distances in a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) having a plurality of drive wheels, a friction braking system having antilock braking system (ABS) capability, and an electronically variable transmission (EVT) with two EVT modes. The method automatically shifts the EVT to a predetermined high speed / low torque EVT mode when the ABS is active and when a calibrated maximum deceleration rate is not exceeded. An HEV has a friction braking system with ABS capability and an EVT including a plurality of modes. A controller automatically activates the friction braking ABS in response to a threshold level of slip between the drive wheels and the road surface when the brake pedal is actuated. An algorithm automatically shifts the EVT into one of the high speed / low torque EVT modes when the ABS is activated and the calibrated maximum deceleration rate is not exceeded.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Anti-lock brake equipment solenoid valve
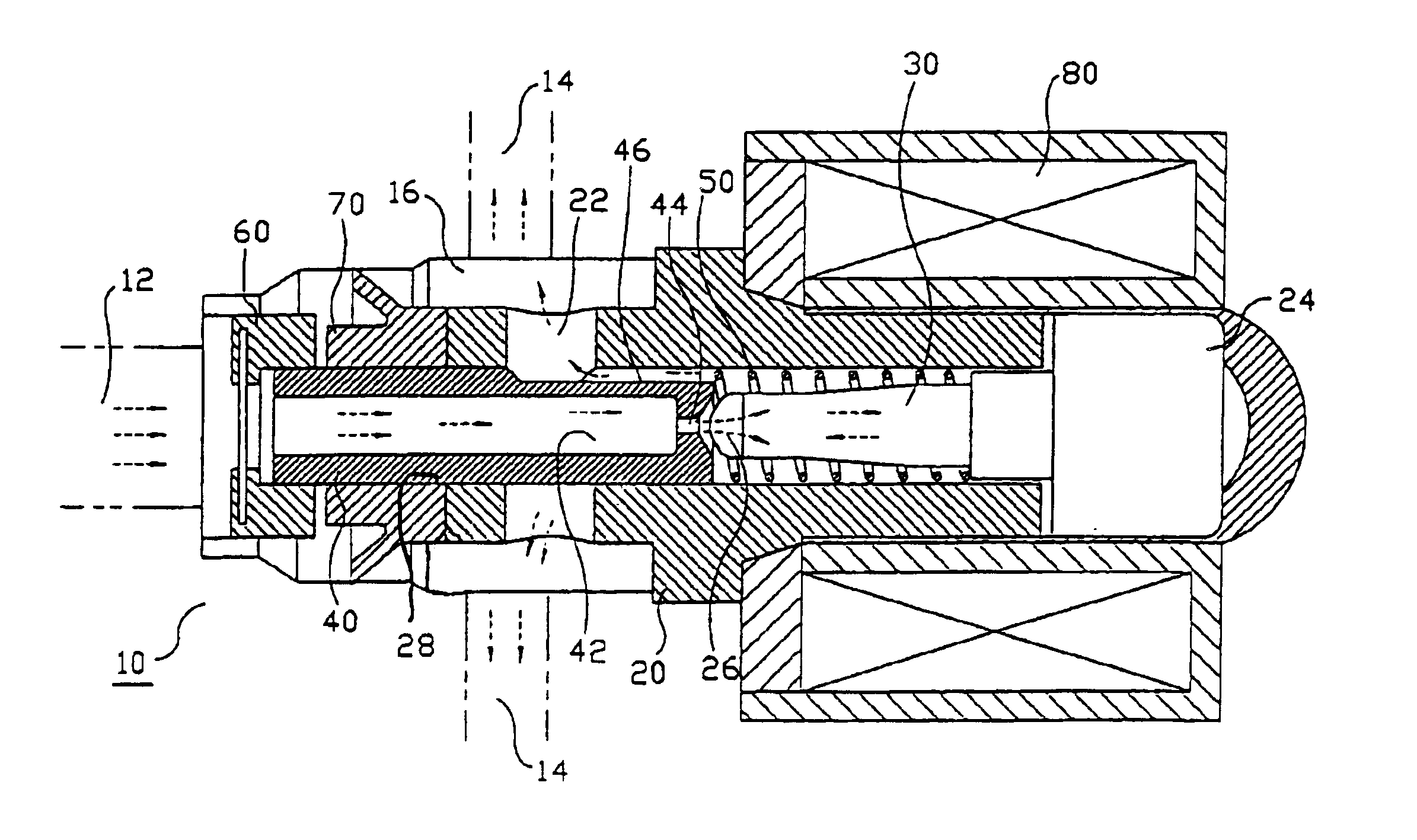
InactiveUS6918570B2Improve the preparation effectSpeed up the flowOperating means/releasing devices for valvesApplication and release valvesPower flowSolenoid valve
A hydraulic control valve for an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) includes a modulator block having at least a housing, an inlet port, a receiving unit, and an outlet port. The housing is coupled to at least a plunger, an armature, and a coil body. The housing also has a coupling hole to receive a valve seat. Upon application of a current, a coil generates a magnetic field causing a plunger coupled with the armature to perform a reciprocating motion in which a projection of the plunger moves in contact with and separates from an aperture in the valve seat to adjust fluid flow. The hydraulic control valve also comprises fluid flow paths, provided in a space between the valve seat and the housing, which communicate with an outlet port. The hydraulic control valve accommodates at least a filter and a seal cup on the outer periphery of the valve seat.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
Bearing condition monitor for a vehicle, such as a truck or a trailer
InactiveUS20010030466A1Axially engaging brakesMachine bearings testingWheel speed sensorMonitoring system
Owner:WABASH TECH
Vehicle and brake feedback control method thereof
ActiveCN104276050AIncrease mileageImprove riding performanceHybrid vehiclesPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingBrake torqueFeedback control
The invention discloses a vehicle and a brake feedback control method of the vehicle. The brake feedback control method comprises the following steps: detecting the current speed of the vehicle and the depth of a brake pedal of the vehicle; controlling the vehicle to enter a brake feedback control mode when the current speed of the vehicle is higher than a preset vehicle speed, the depth of the brake pedal is more than 0, and an anti-lock brake system of the vehicle stays at a non-work state, acquiring a needed brake torque corresponding to the vehicle according to the depth of the brake pedal when the vehicle stays at the brake feedback control mode, and allocating the brake torque of a first electric generator, the brake torque of a second electric generator and the brake torque for the basic brake of the vehicle according to the needed brake torque. By adopting the brake feedback control method of the vehicle, the energy can be reasonably allocated between the engine unit and the electric generators when the vehicle brakes, the brake feedback efficiency is improved, and high fuel economical performance, low emission and stable driving performance can be acquired.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Motorcycle frame configuration
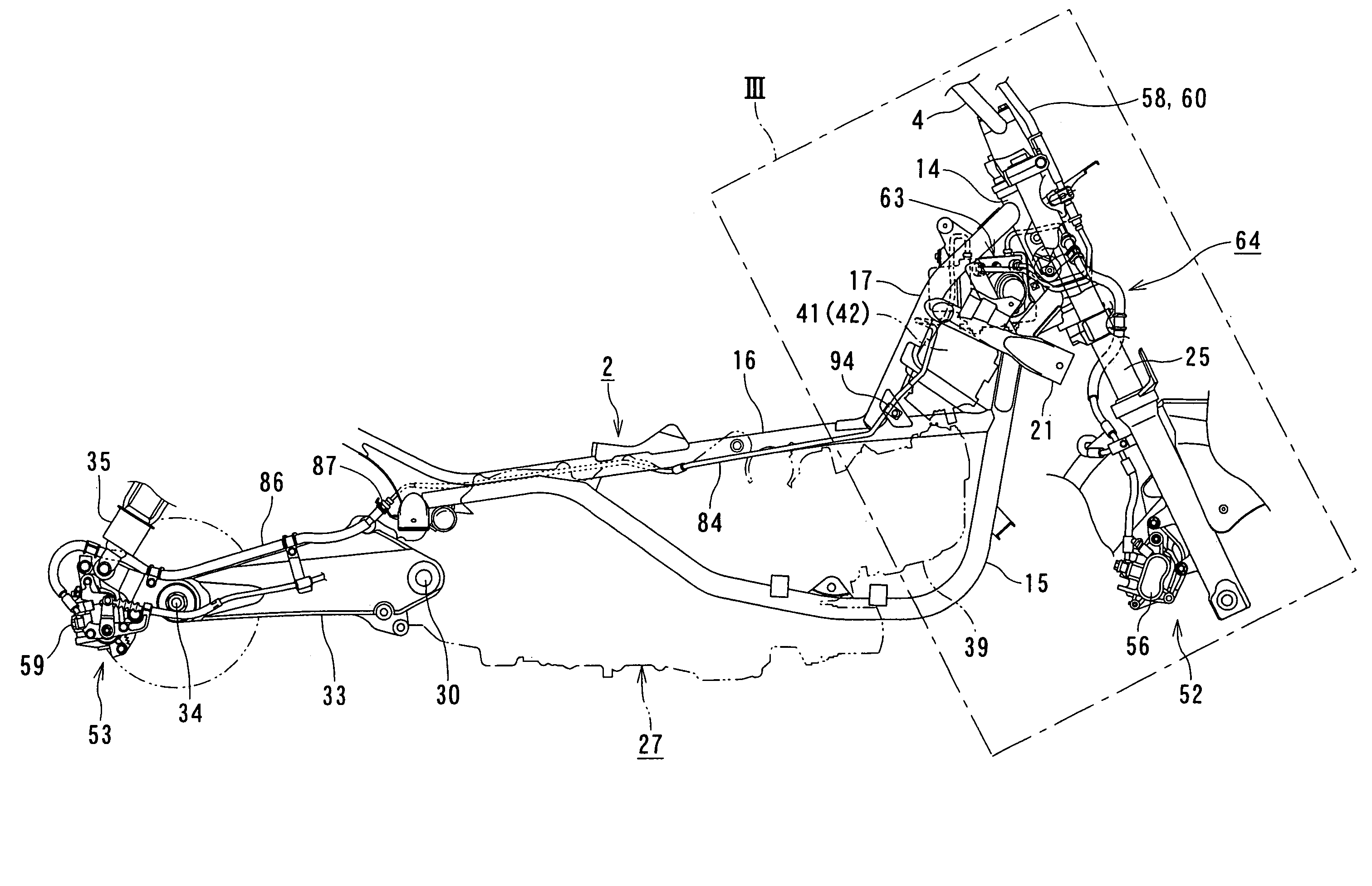
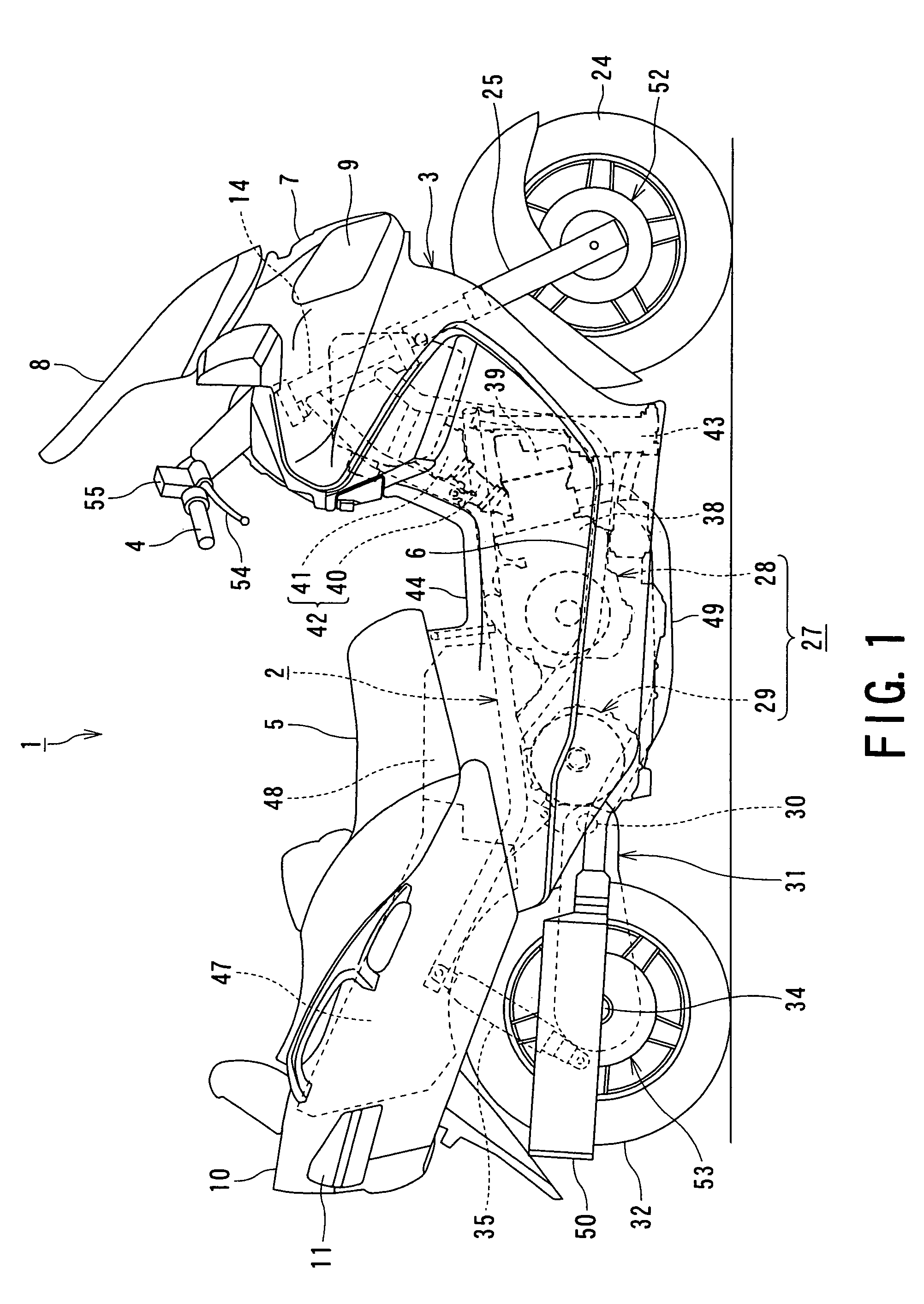
A motorcycle includes a seat configured to support a rider, and an antilock braking modulator disposed downwardly of the seat. The antilock braking modulator is configured to control an antilock braking system (ABS). A first control valve is configured to distribute a braking force between a front wheel and a rear wheel. A second control valve is configured to introduce fuel vapors into an intake system. A first bracket is fixed on a side of a vehicle body frame, and is mounted with the second control valve. A second bracket is supported by the first bracket and mounted with the antilock braking modulator and the first control valve.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
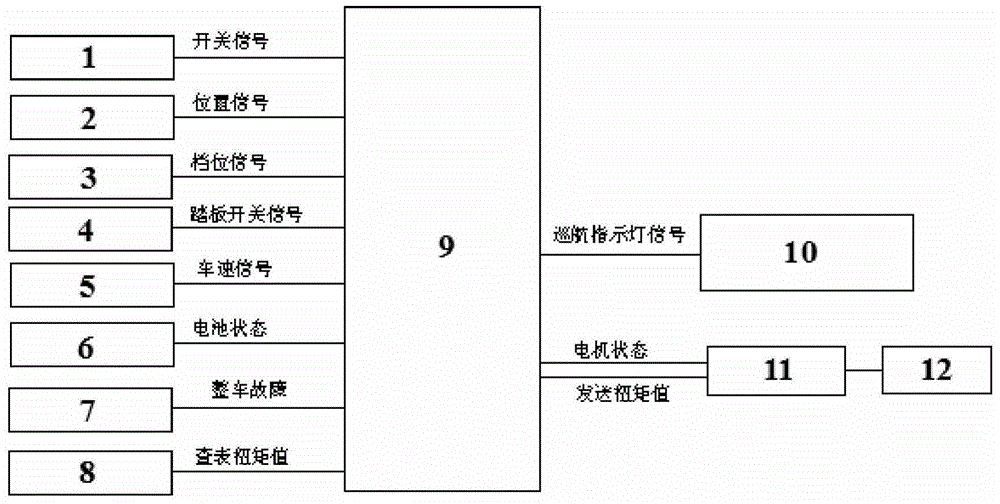
Semi-active cruise control system and method
The invention provides a semi-active cruise control system and method. The semi-active cruise control system comprises a signal input unit, a whole vehicle controller and a control feedback unit. The signal input unit is connected with the whole vehicle controller. The whole vehicle controller is connected with the control feedback unit. The signal input unit comprises a cruise switch, a key, a gear shifter, a braking pedal, an anti-lock braking system, a battery management system, a vehicle fault detecting module and an accelerator pedal. The current vehicle state can be judged by the whole vehicle controller on the basis of collected operation signals input by a driver to the signal input unit. The control feedback unit comprises a motor controller and a driving motor. The whole vehicle controller drives the driving motor to output corresponding control torque through the motor controller, so that the vehicle can be maintained to move at constant speed all the time. Cruising is carried out by the vehicle at stable speed under different conditions, so that the phenomenon that the driver frequently operates the two pedals is avoided.
Owner:BEIJING ELECTRIC VEHICLE
Electro-hydraulic brake system
InactiveCN104309599AQuick responsePrecise control of hydraulic braking forceBraking action transmissionBrake control systemsLiquid storage tankElectric control
The invention discloses an electro-hydraulic brake system driven by a motor for a vehicle. The electro-hydraulic brake system comprises a brake pedal, a pedal displacement sensor, a hydraulic sensor, a pedal simulator, a pedal push rod with two branches, an electric control unit, an electric control linear motion module, a brake main cylinder, a secondary main cylinder and an ABS (anti-lock braking system) / ESC (electronic stability control) module; one branch of the pedal push rod is abutted against the linear motion mechanism, and is positioned in the same axis as the piston of the brake main cylinder; the other branch of the pedal push rod is connected with the piston of the secondary main cylinder; the brake main cylinder sequentially comprises a front cavity, a first cavity and a second cavity for the brake main cylinder; the front cavity is connected with the secondary main cylinder and a liquid storage tank respectively through a decoupling valve and a liquid supply valve; the first cavity and the second cavity are connected with a vehicle wheel brake through the ABS / ESC module; the secondary main cylinder is connected with the liquid inlet of the pedal simulator. The electro-hydraulic brake system is used for recycling brake energy, improving system response time and accurately controlling hydraulic brake force, well feeds the braking force back to a driver, and realizes active control over hydraulic force and pedal force of the system.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Integrated electronic hydraulic brake system of automobile
The invention discloses an integrated electronic hydraulic brake system of an automobile. The integrated electronic hydraulic brake system comprises a brake master cylinder output unit with an oil storage cup, a hydraulic control unit (HCU), an electronic control unit (ECU) and a wheel brake. The integrated electronic hydraulic brake system has the advantages that a conventional brake condition and an ABS (anti-lock braking system) brake condition can be implemented, a power supply failure protection function can be realized when the ECU is powered down, in other words, normal braking can be guaranteed even when the system is in power supply failure, and the stability of the system is improved on the basis that brake functions are completed; various intelligent automobile auxiliary systems relevant to the brake system can be implemented by the aid of the hydraulic control unit (HCU).
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Electric and hydraulic combined braking test vehicle
InactiveCN102269658AMeet diverse needsRealize coordinated controlVehicle testingSteering linkagesElectric power steeringElectro hydraulic
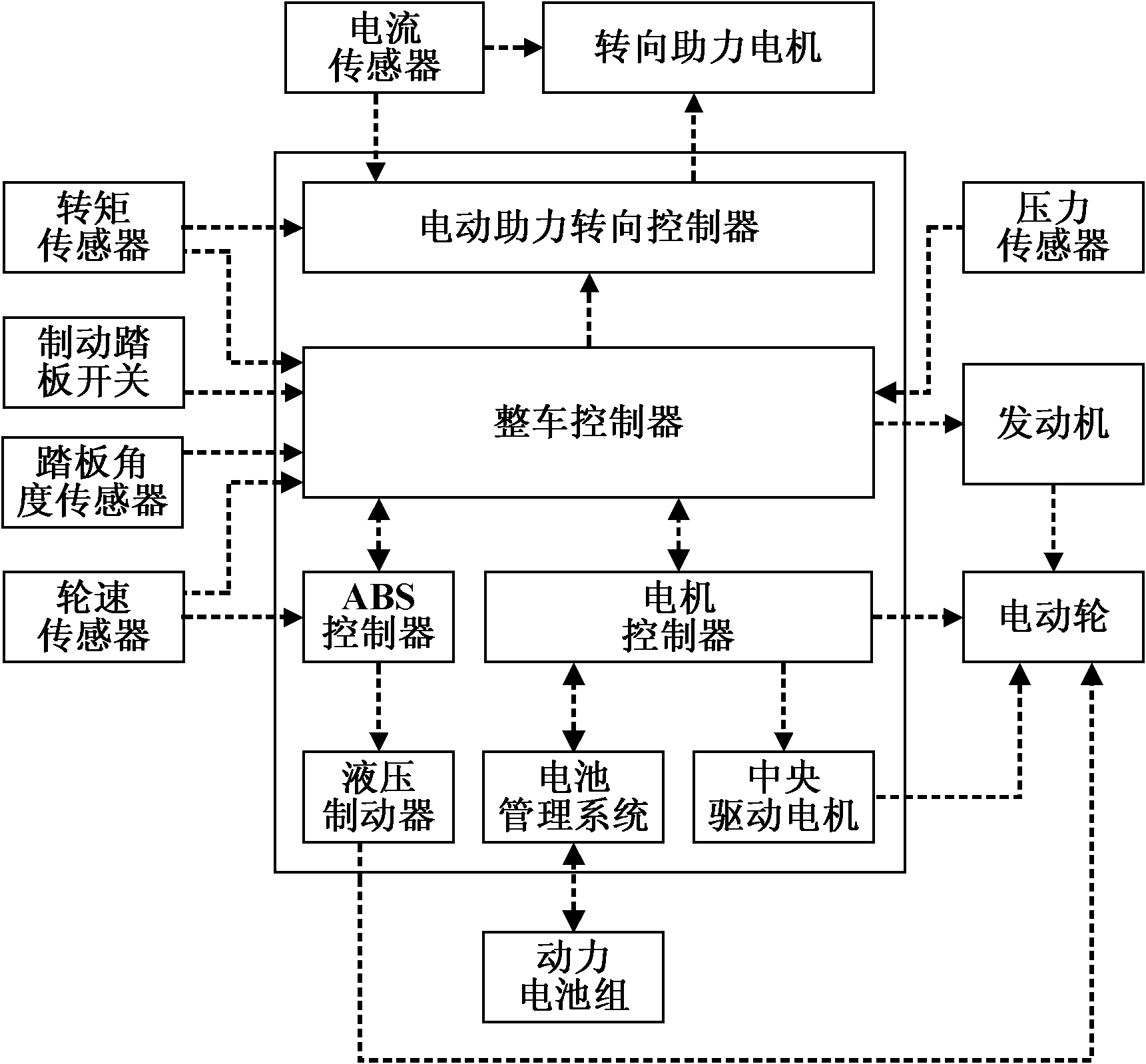
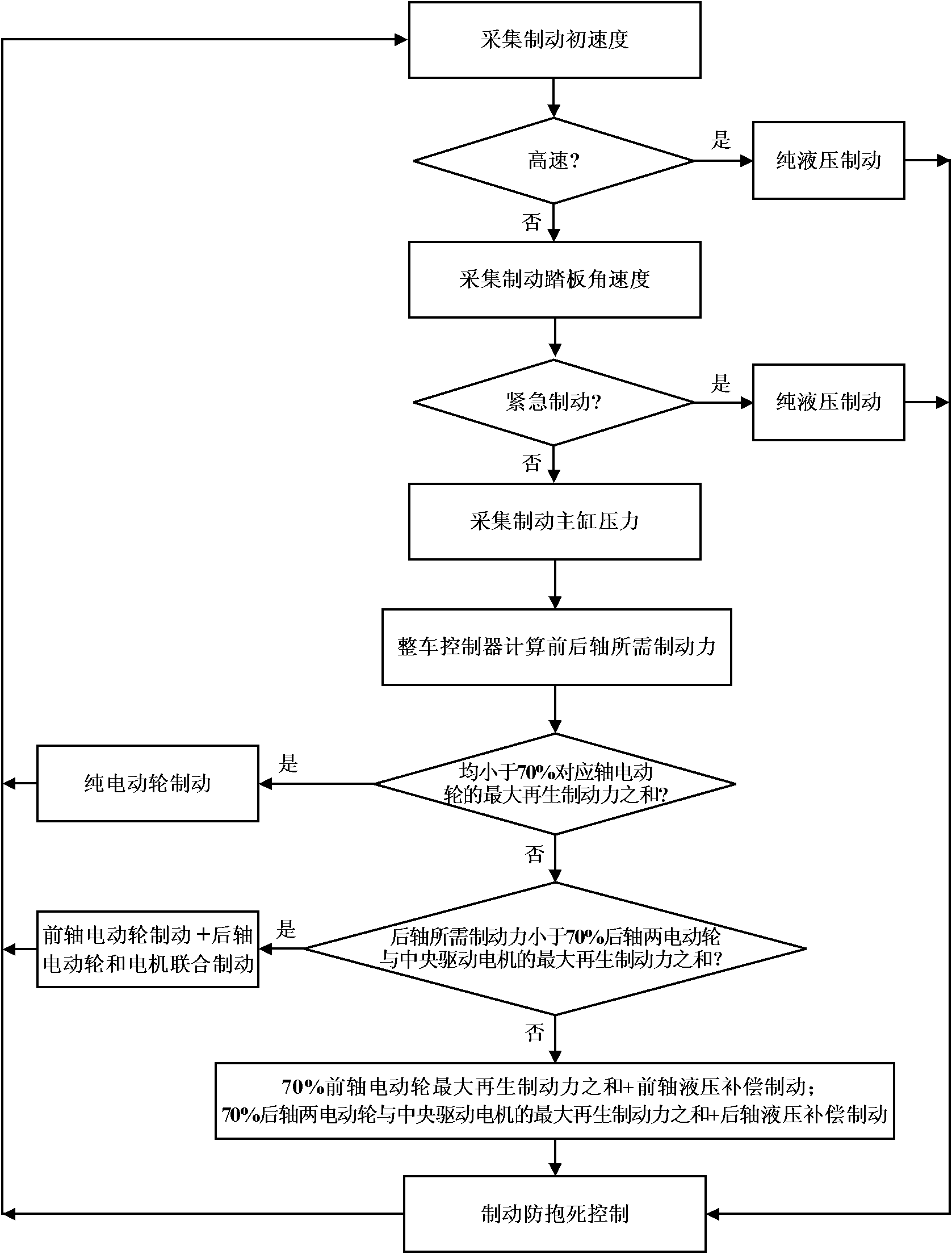
The invention discloses an electro-hydraulic combined brake comprehensive experiment vehicle, belongs to the field of dynamic performance testing of vehicles and relates to a comprehensive testing device which can simulate multiple driving modes, cooperative control on power-assisted steering and energy recovery. The electro-hydraulic combined brake experiment vehicle mainly comprises an electricwheel (5), a hydraulic brake (6), a steering power-assisted motor (29) and a whole vehicle controller (26); a motor controller (25) is used for controlling the electric wheel (5), an ABS (anti-lock braking system) controller (10) is used for controlling the hydraulic brake (6), and an electric power-assisted steering controller (27) is used for controlling the steering power-assisted motor (29); the motor controller (25), the ABS controller (10) and the electric power-assisted steering controller (27) are integrally controlled by the whole vehicle controller (26); and an engine (1) and a central driving motor (20) are integrally controlled by the whole vehicle controller (26). The device adopts multiple modern vehicle technologies and can provide a testing platform for the deep development of vehicles.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device for measuring action force of wheel and device for measuring stress of structure
InactiveUS6032520AEasy to measureShorter braking distanceAxially engaging brakesEngine testingSignal processing circuitsTraction control system
Action force of a wheel is measured in order to measure the road surface frictional force, vertical drag, road surface friction coefficient, etc. Means for making these measurements can be constituents of an antilock brake system, traction control system, etc. These constituents may also serve as devices for measuring stresses generated in other structures. In a specific example, axle of a vehicle is formed with a hole, a stress detection sensor is installed in the hole and secured in position with the aid of a spacer element, and a detection signal from the stress detection sensor is processed in a signal processing circuit.
Owner:JAPAN ELECTRONICS IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com