Patents
Literature
64 results about "Dorsal parts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
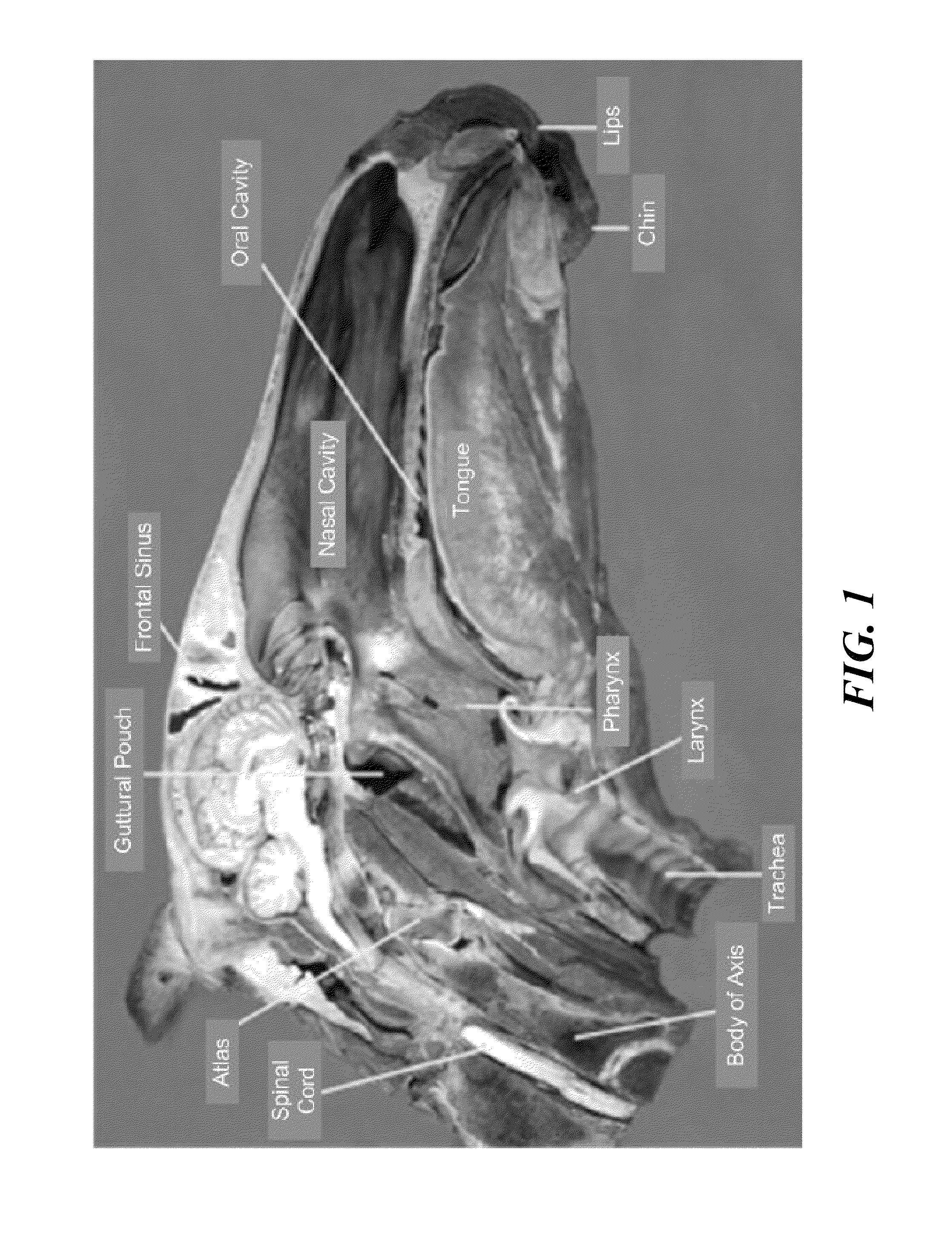
Dorsal is an anatomical term used to refer to the position of a body part in an organism (plant or animal). It is used in contrast to the term ventral. In vertebrates, the dorsal part of the animal usually is where the backbone is located.
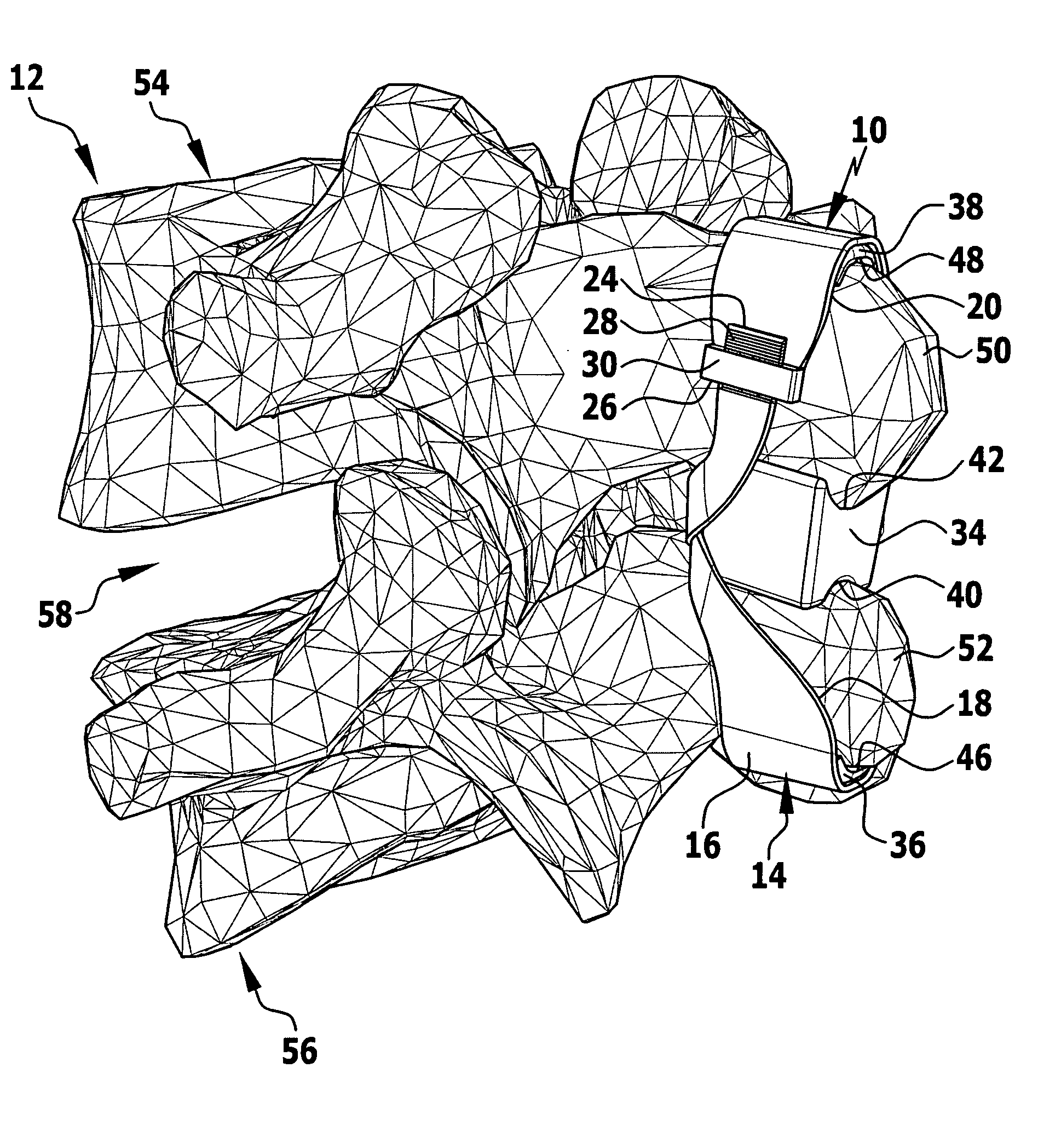
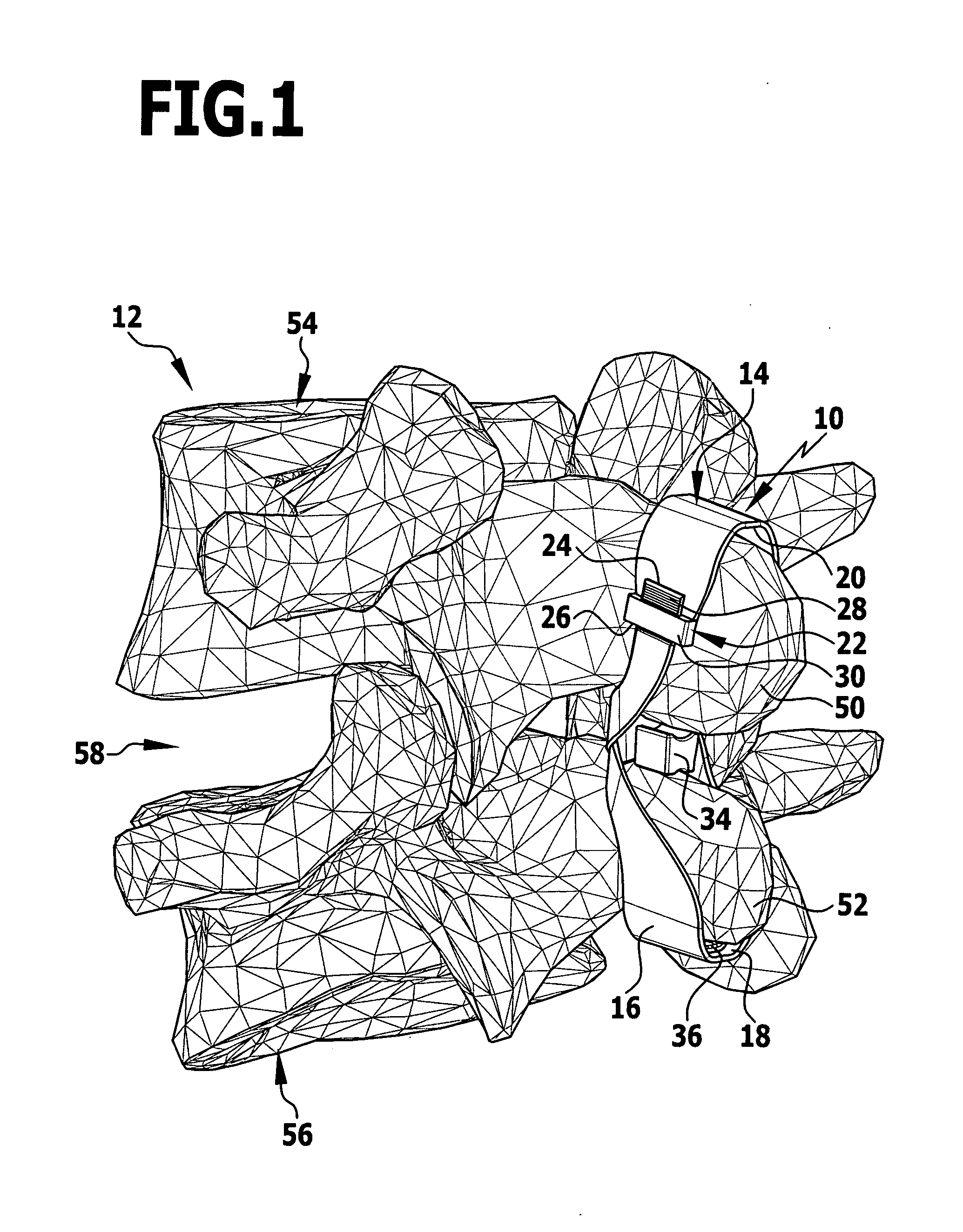
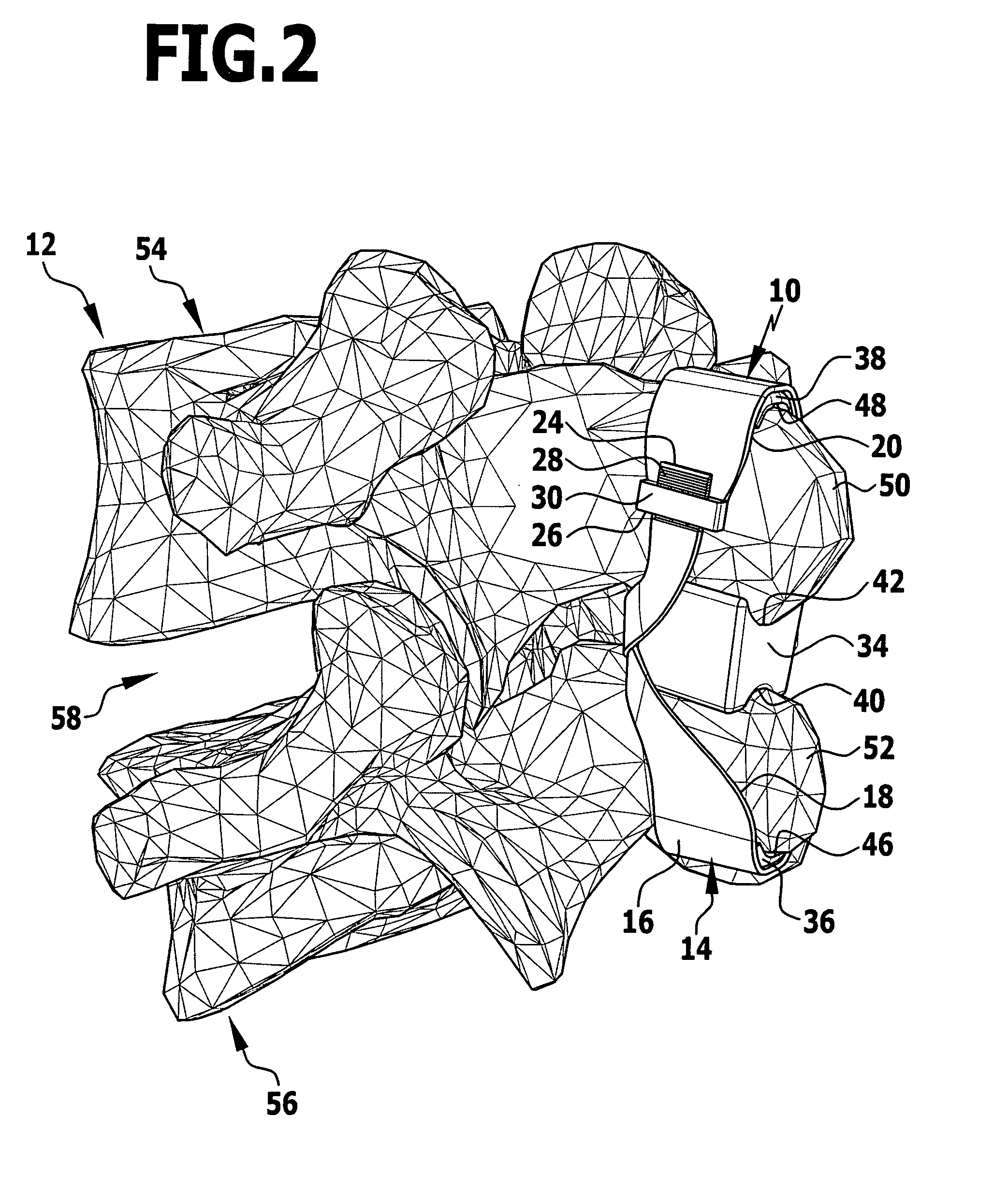
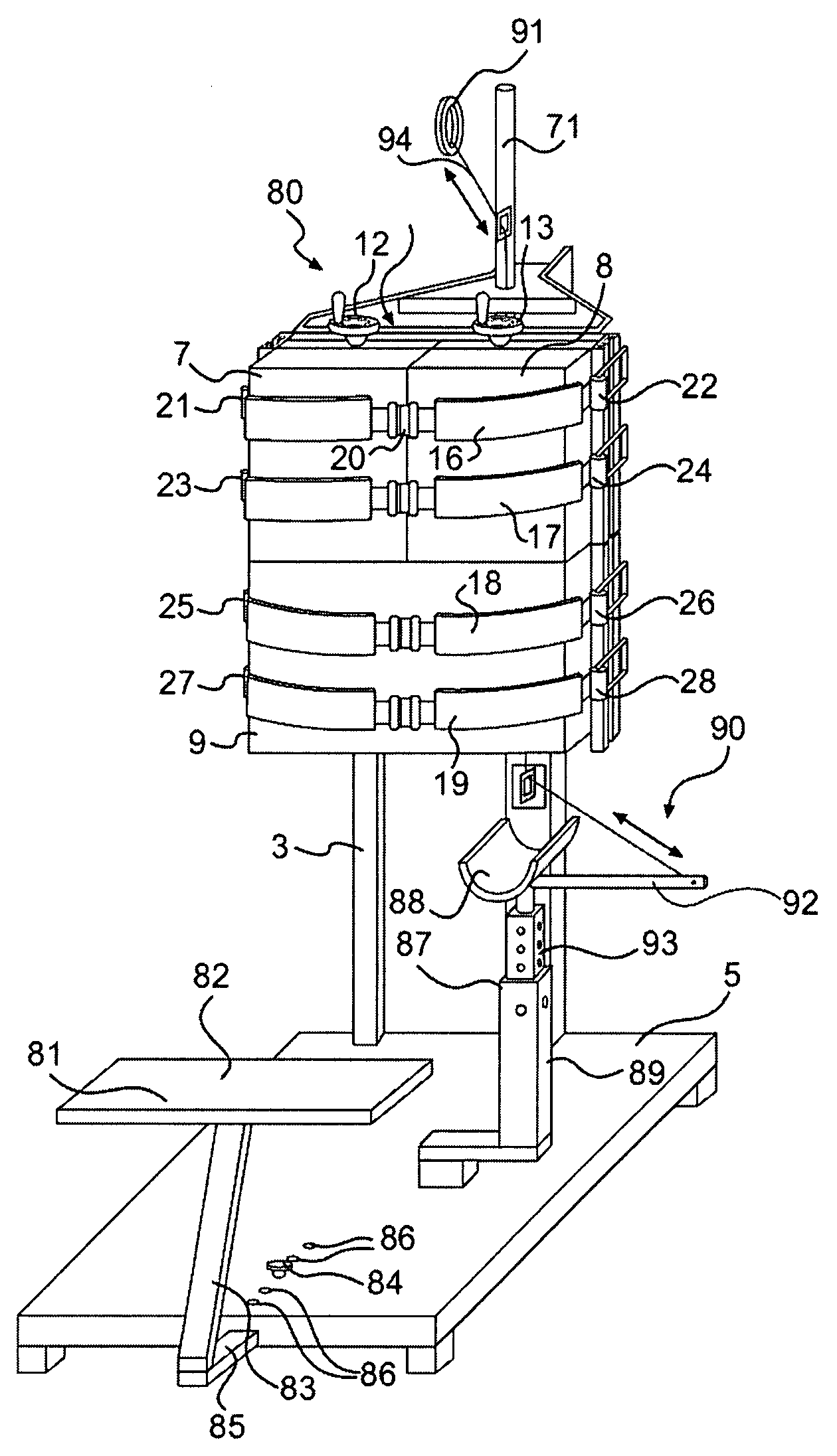
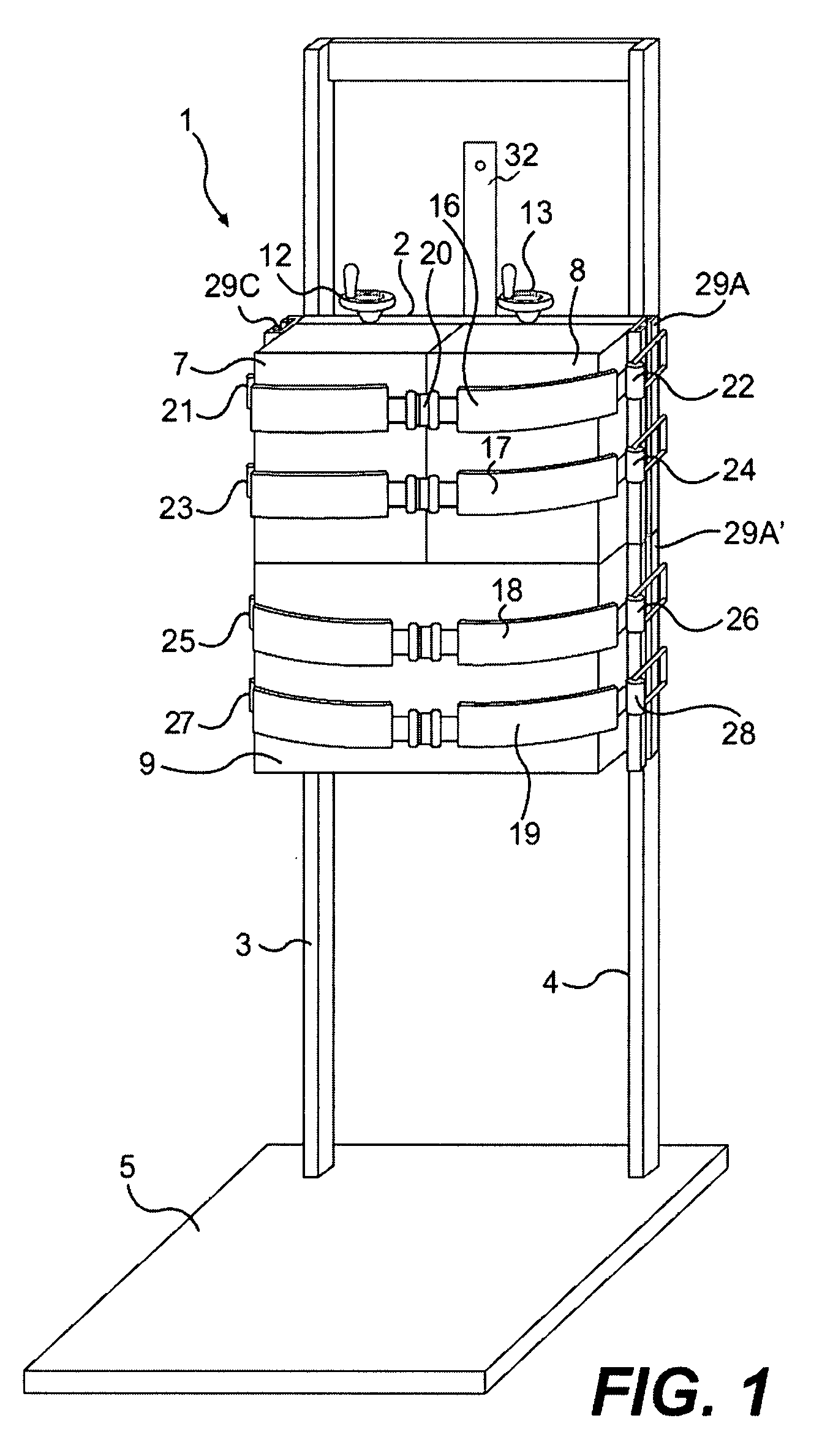
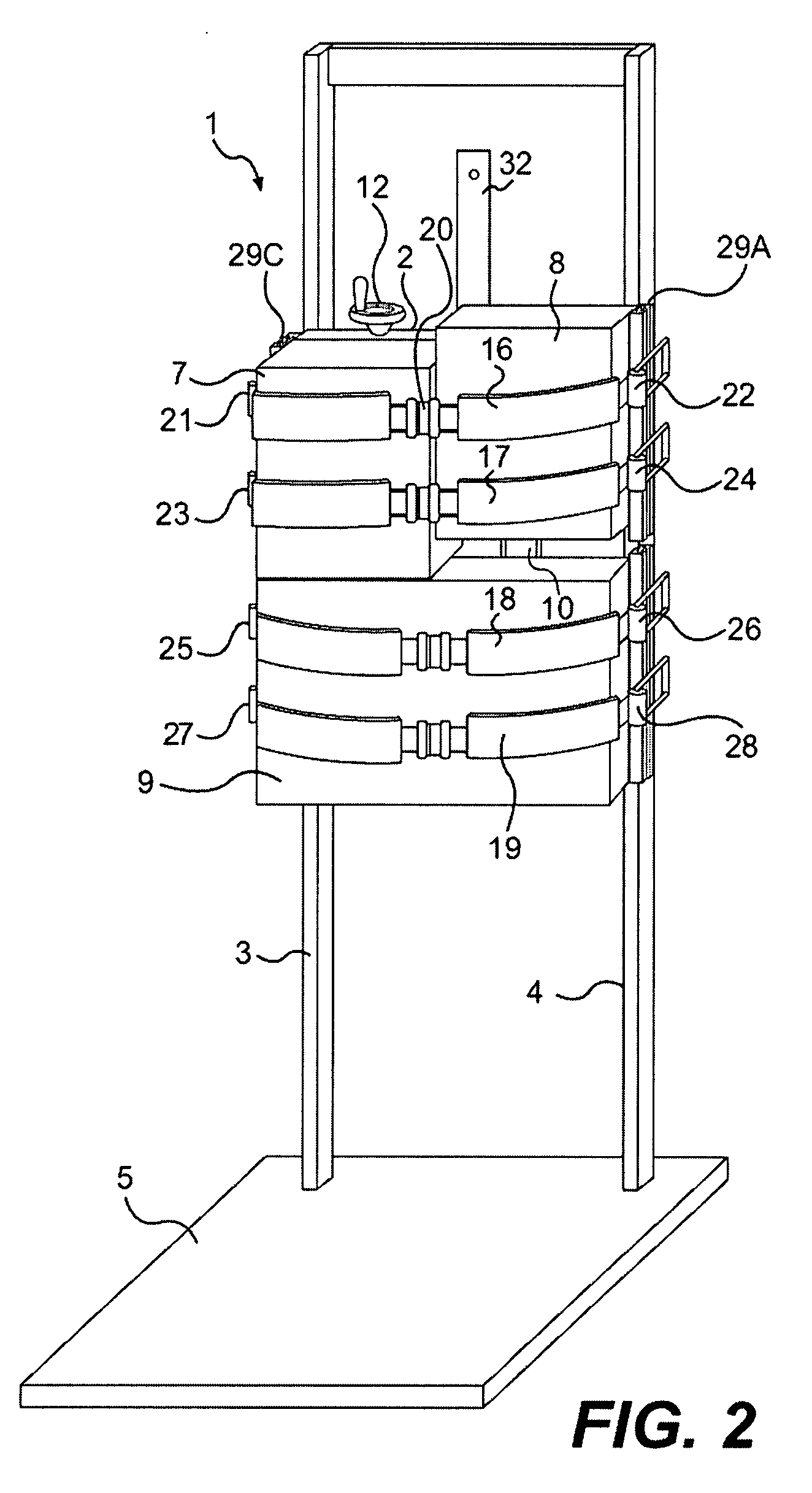
Implant and implant system
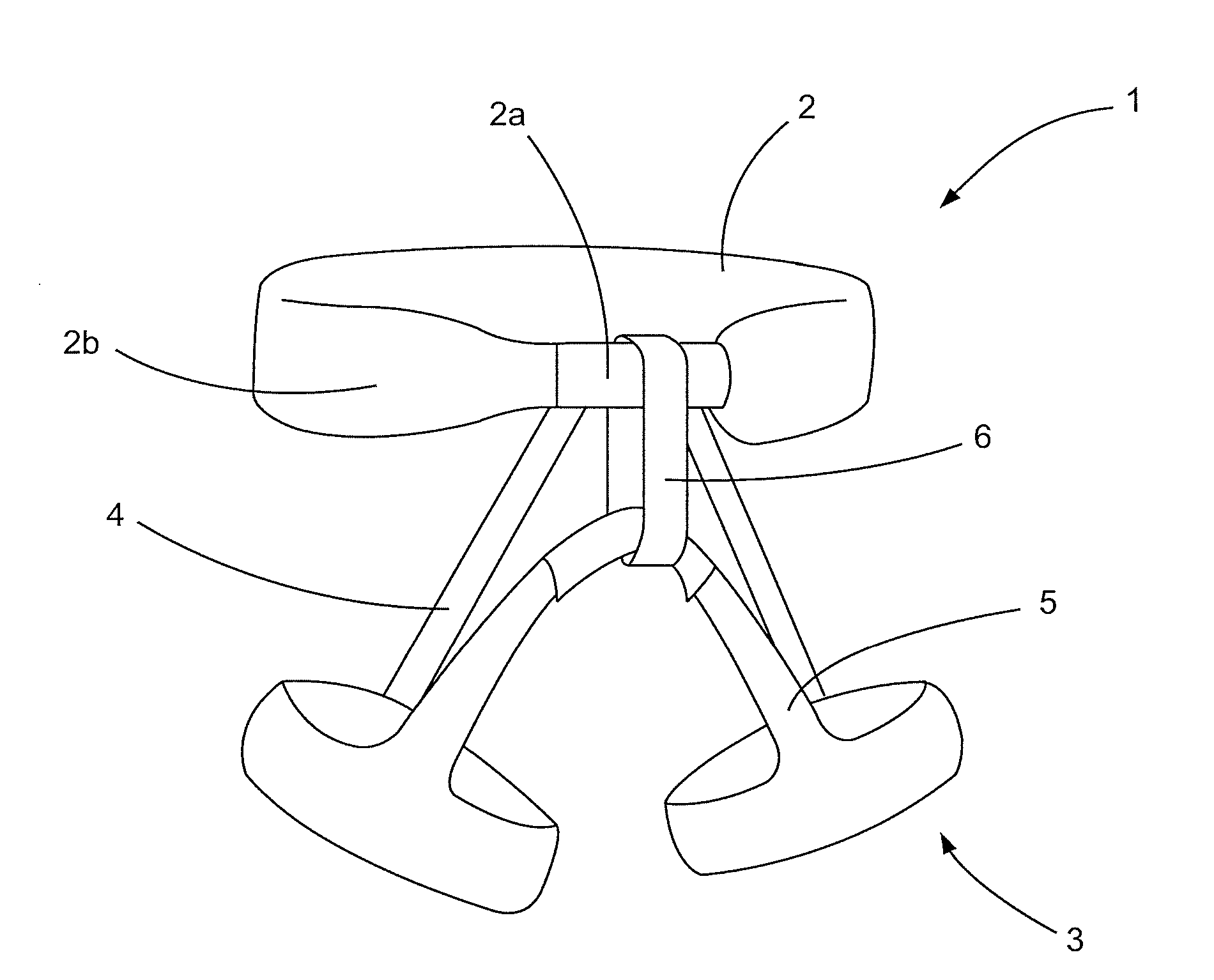
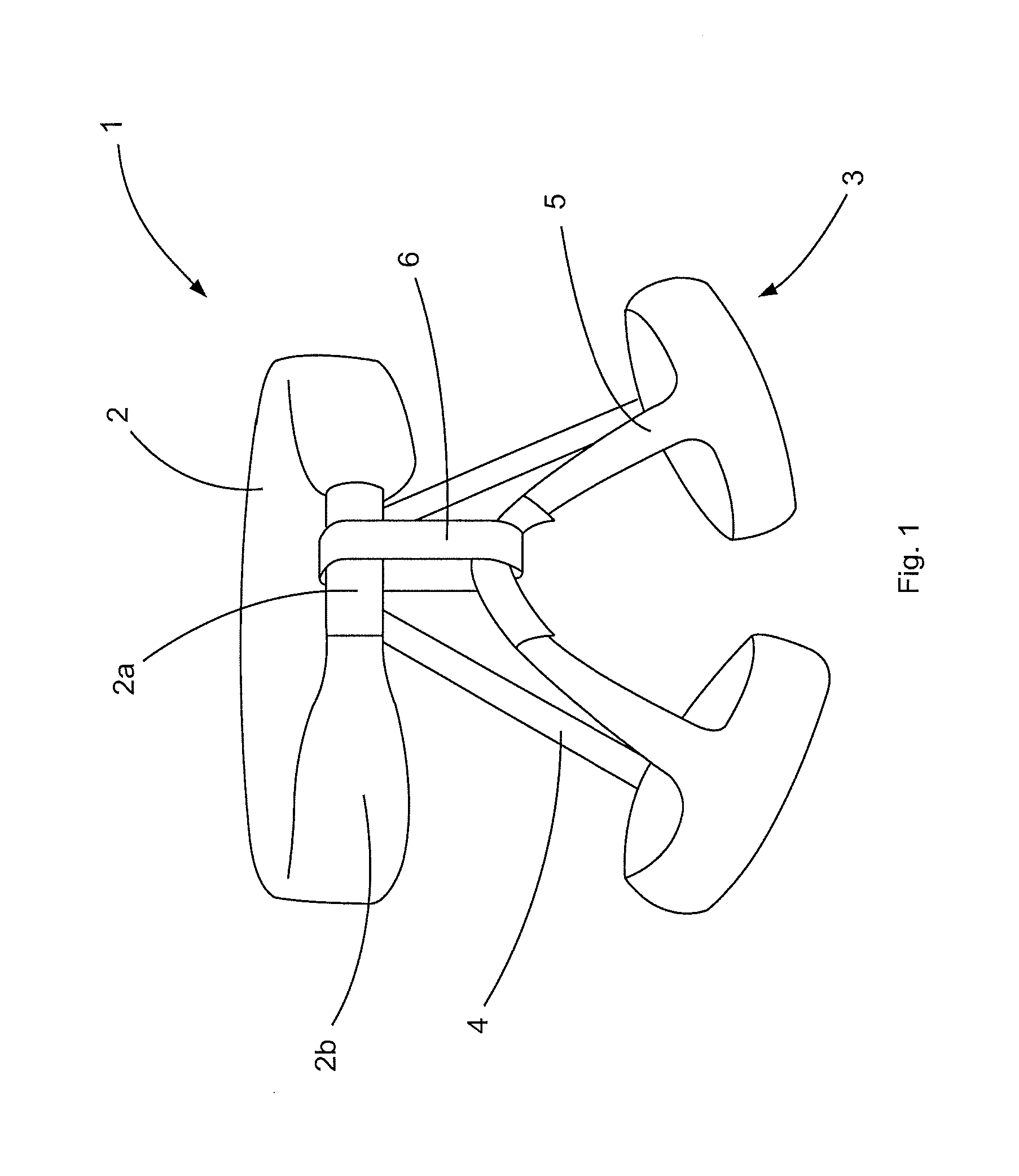
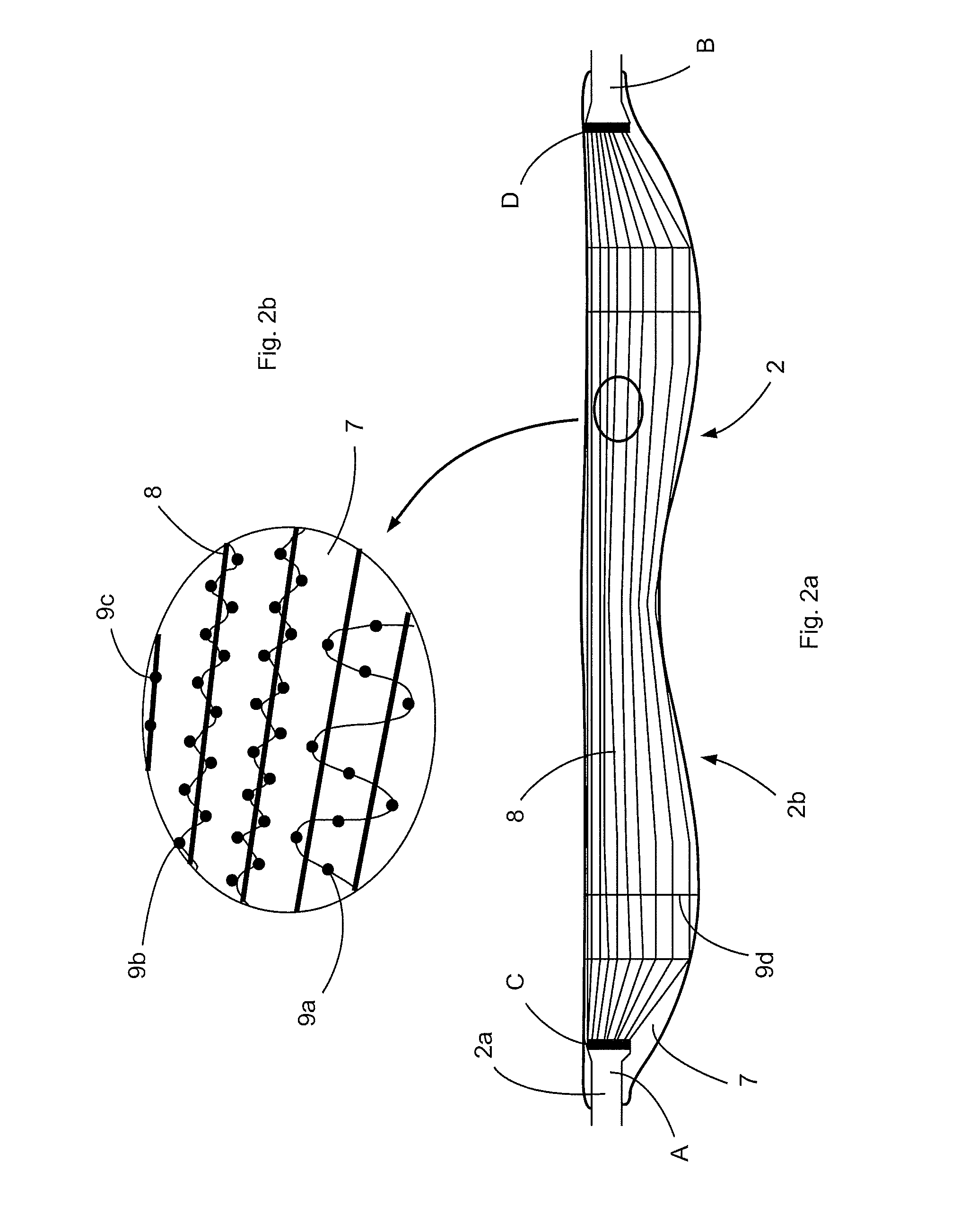
In order to improve an implant for the dorsal stabilization of a human or animal spinal column, comprising an attachment device for placing in position against and / or fixing to spinous processes of adjacent vertebrae of the spinal column, such that it can be used for the dynamic dorsal stabilization of the spinal column, it is suggested that the implant comprise at least one spacer element which is associated with the attachment device and designed in such a manner that it alters its external shape and / or its elastic properties as a result of a change in ambient conditions and / or forces acting on it.Furthermore, an improved implant system for the dorsal stabilization of a human or animal spinal column is suggested.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
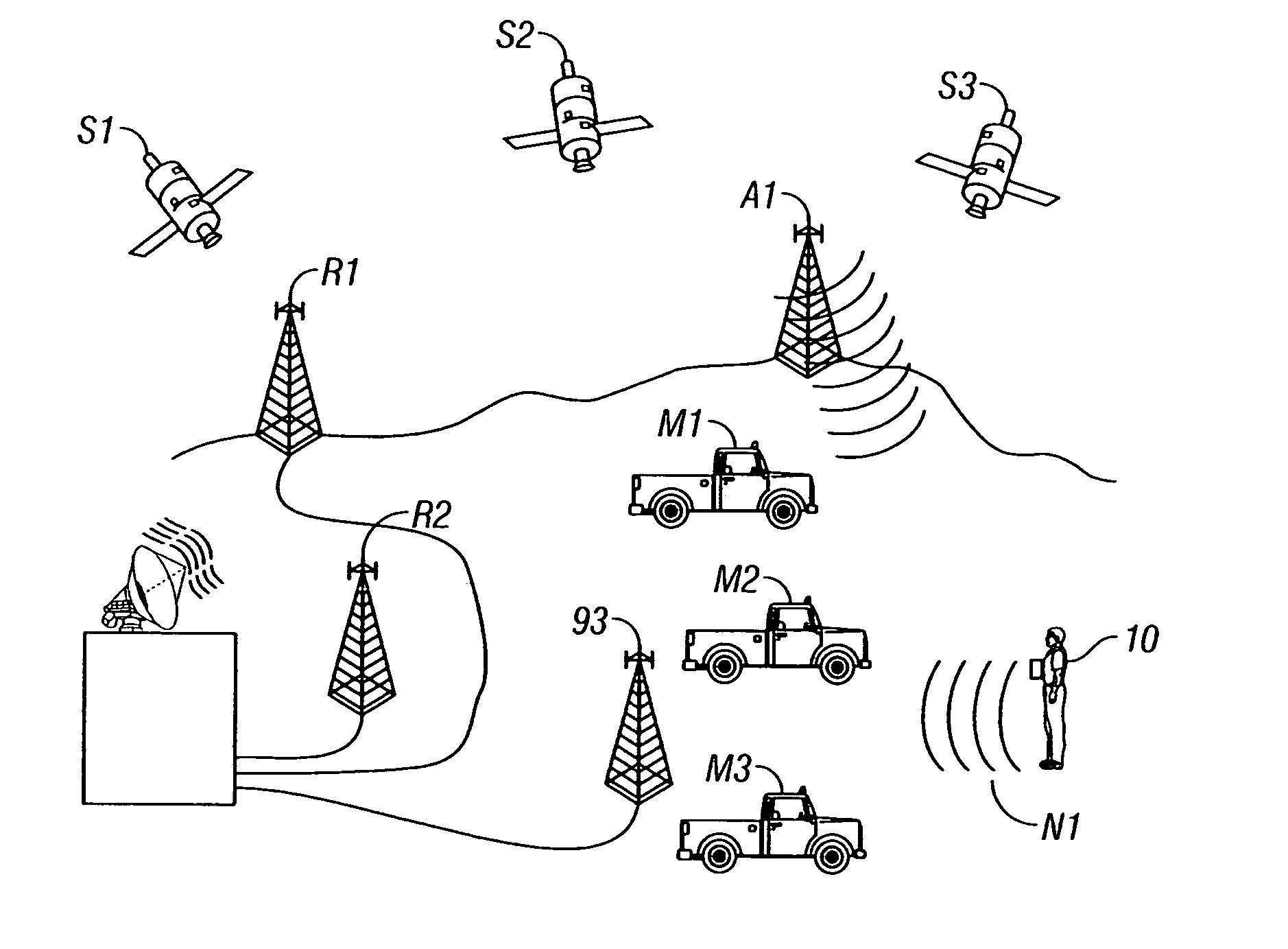
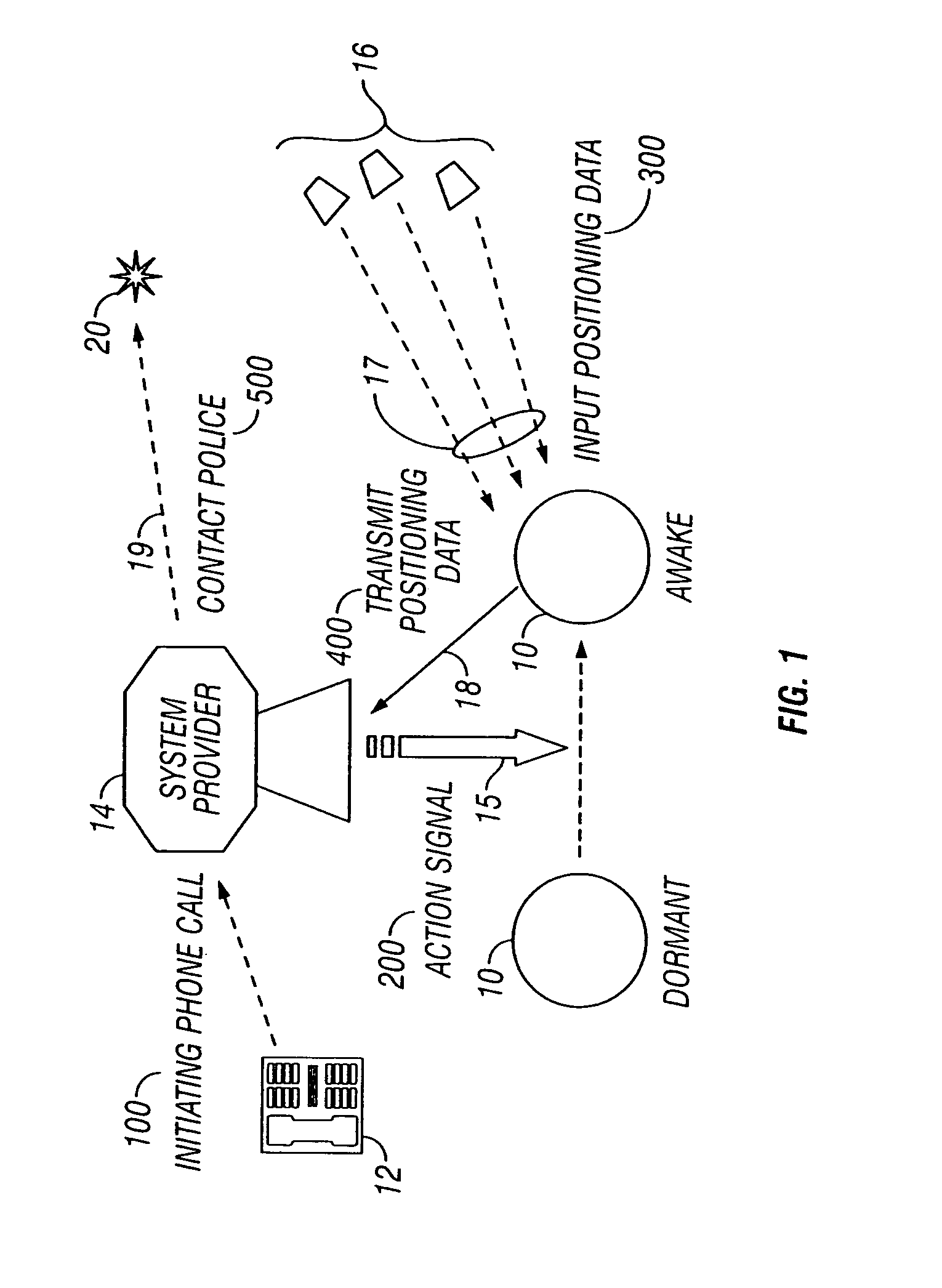
Method and apparatus for locating and tracking persons
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for locating and tracking persons by use of an implantable device. The described invention is an implant able device composed of biocompatible materials in all areas where contact with organic tissue occurs. The gross anatomic siting of the device includes any limb, the torso, including back and perineum, the neck, and the head. The surgical anatomic siting of the device includes: (1) Supramuscular: for example, deep to the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat, on or attached to muscle and / or muscle fascia. Such a location is currently used for implantation of commercially available buried intravenous access ports, which are positioned on, and attached to, the pectoralis major muscle fascia; (2) Intramuscular: for example, within or between the muscles of a limb; (3) Submuscular: for example, deep to a large muscle. Such a location is currently used for implantation of commercially available artificial urethral and anal sphincter reservoirs, which are positioned deep to the rectus abdominus muscles, within the pre-peritoneal Space of Retzius; (4) Intraluminal: for example, within the lumen of an organ which has a naturally occurring orifice. Such a location is currently used for implantation of commercially available ingested video endoscopy capsule devices, i.e. gastrointestinal tract lumen, and intrauterine contraceptive devices, i.e. uterus lumen; and (5) Intracavitary: for example, intrathoracic or intraperitoneal. Such an intraperitoneal location is currently used for implantation of commercially available intraperitoneal dialysis catheters.
Owner:PERSEPHONE
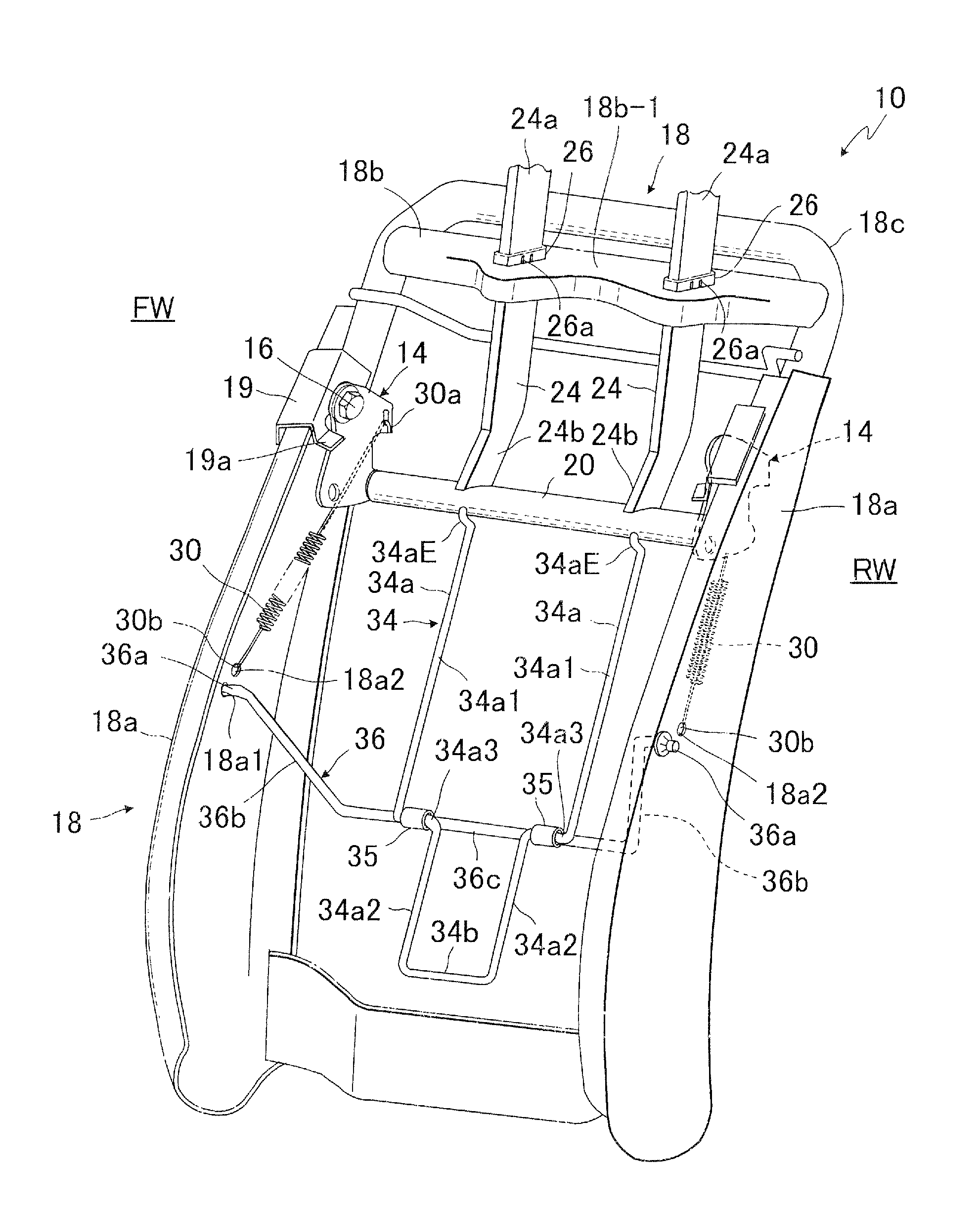
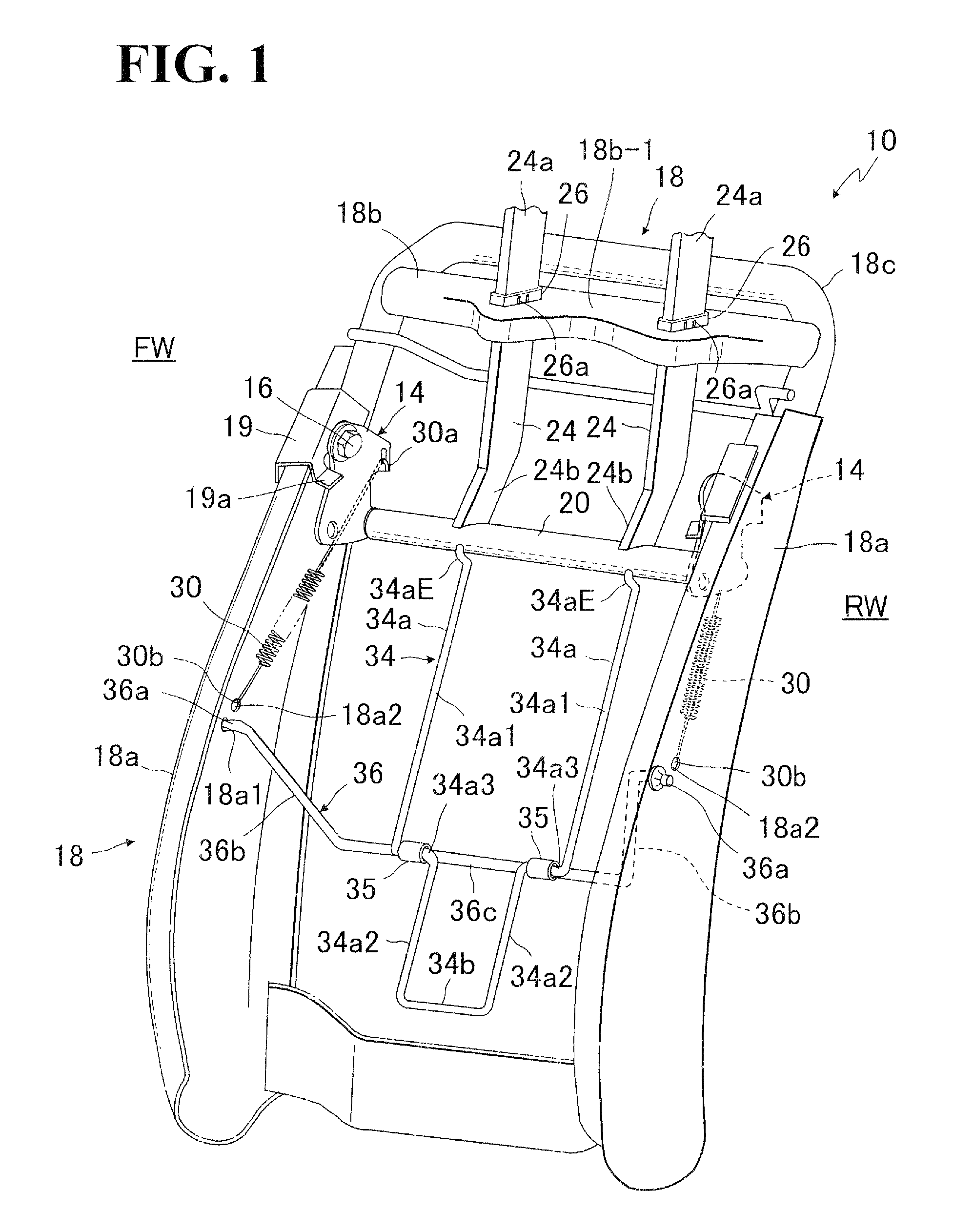
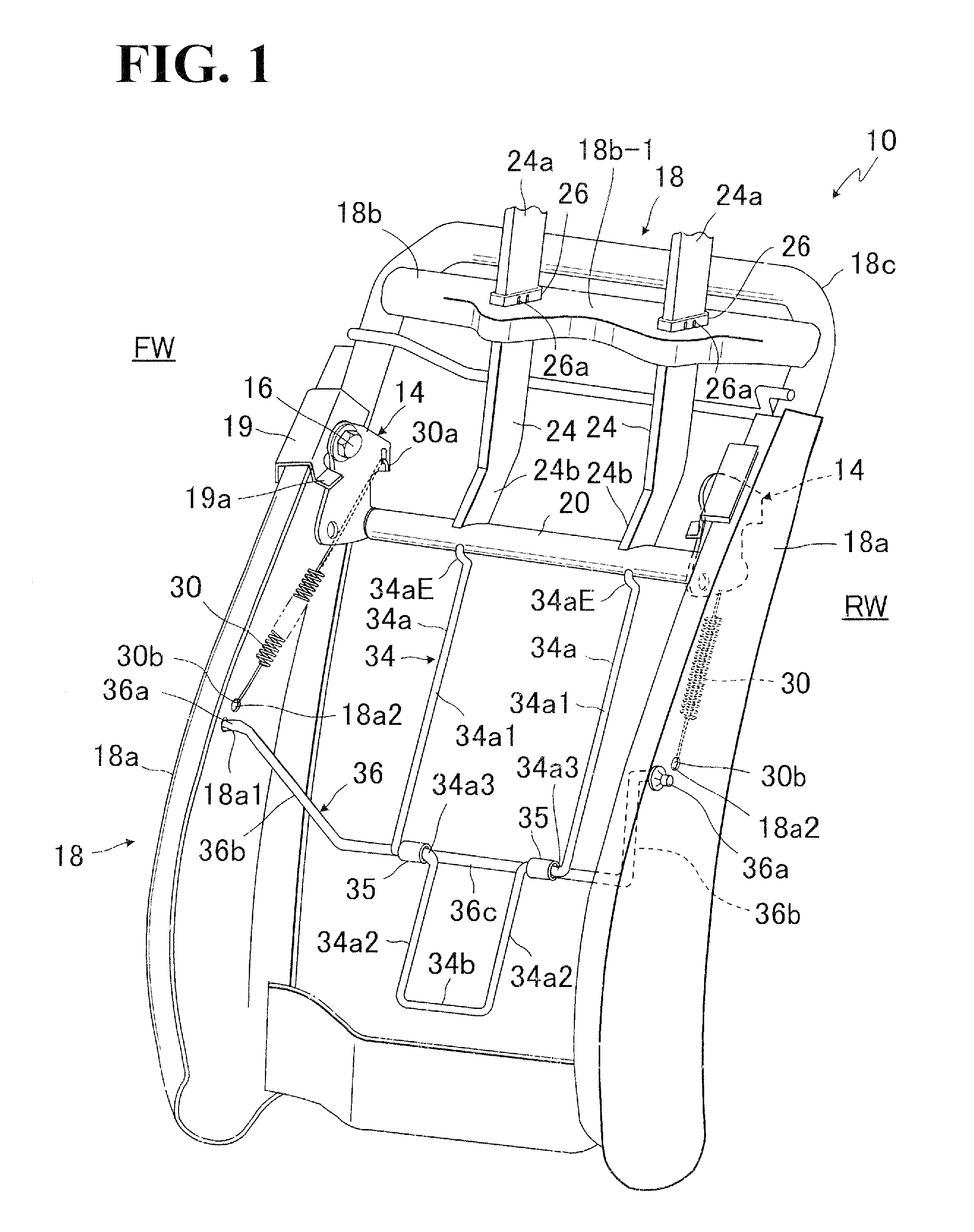
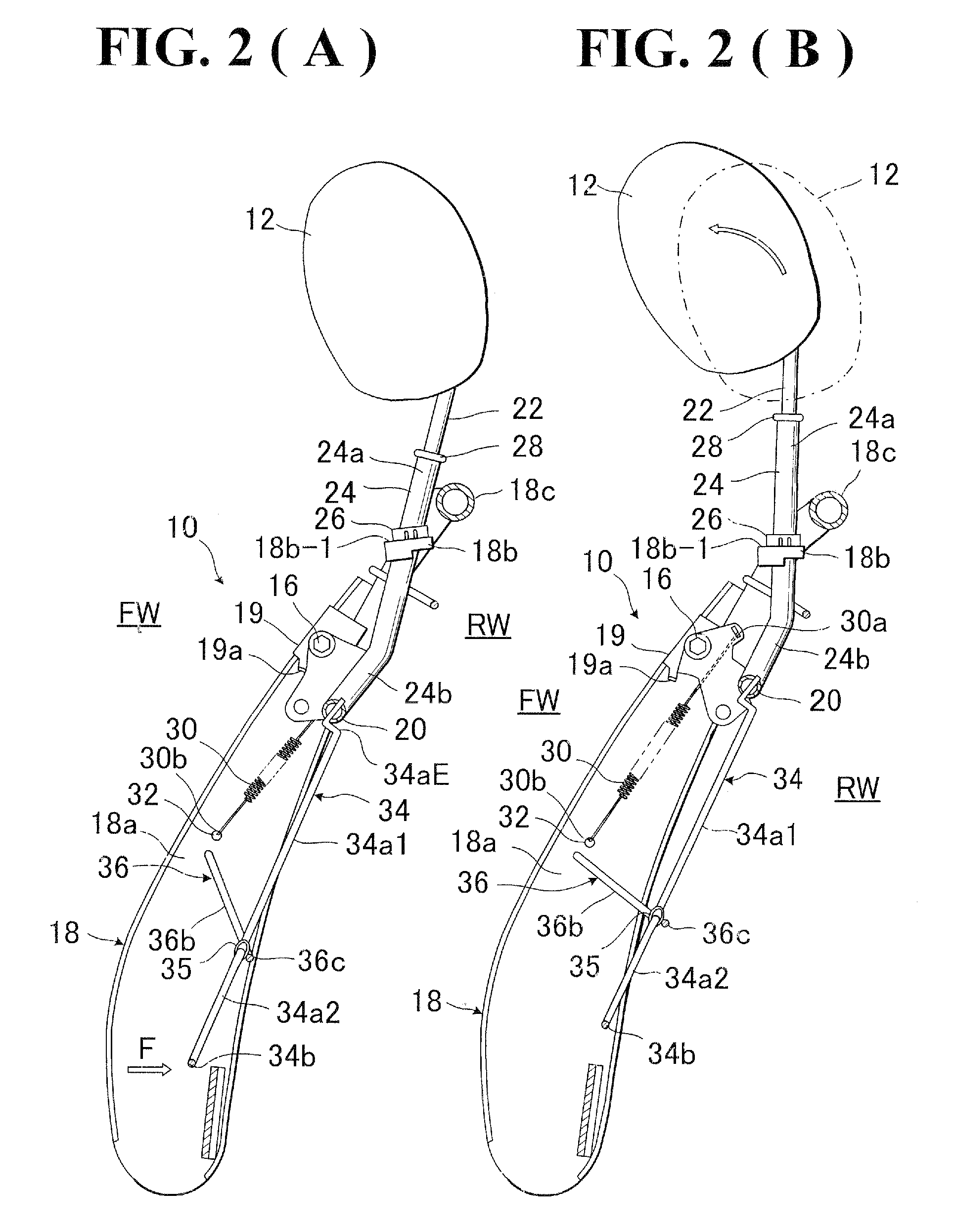
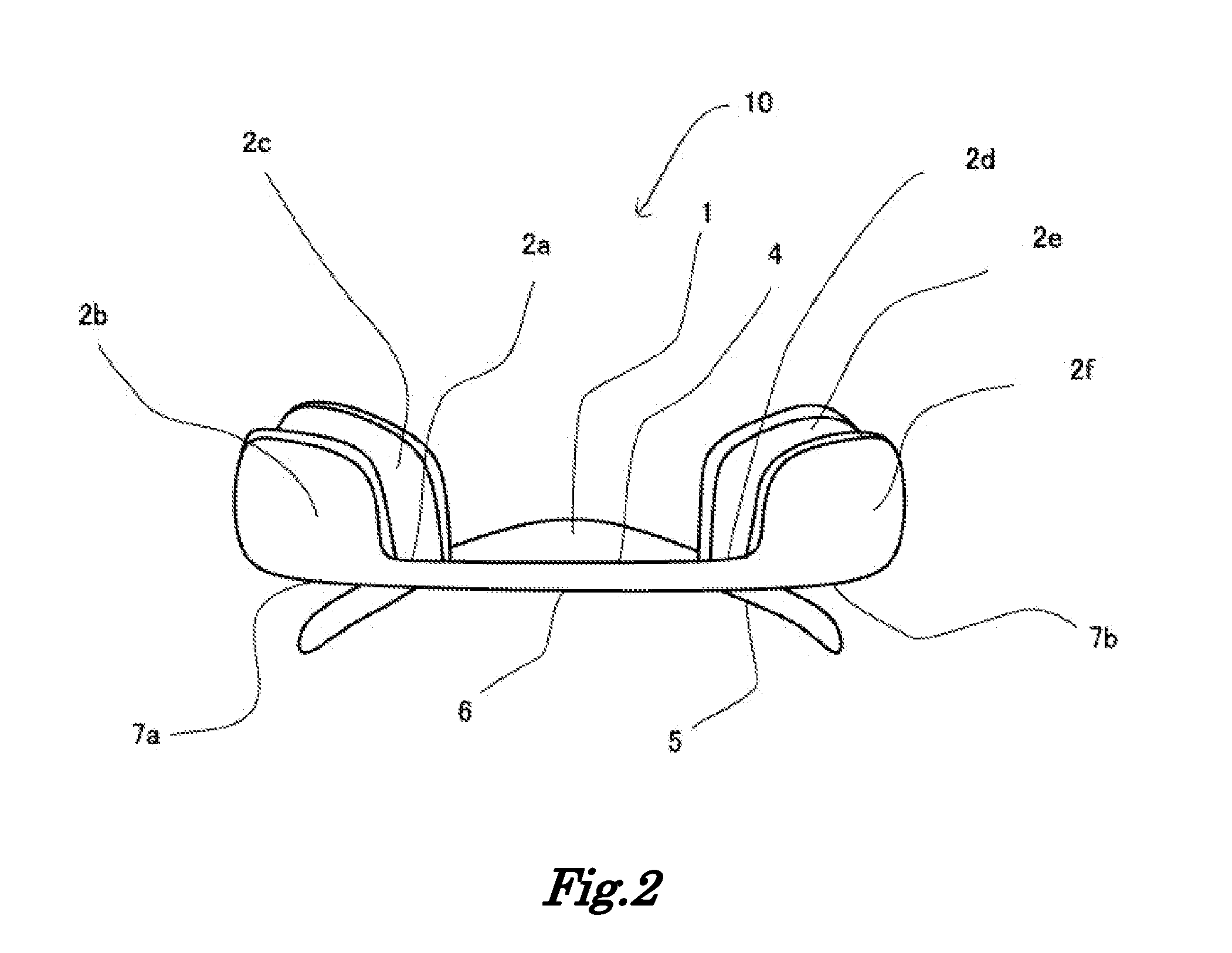
Seat back structure of vehicle seat
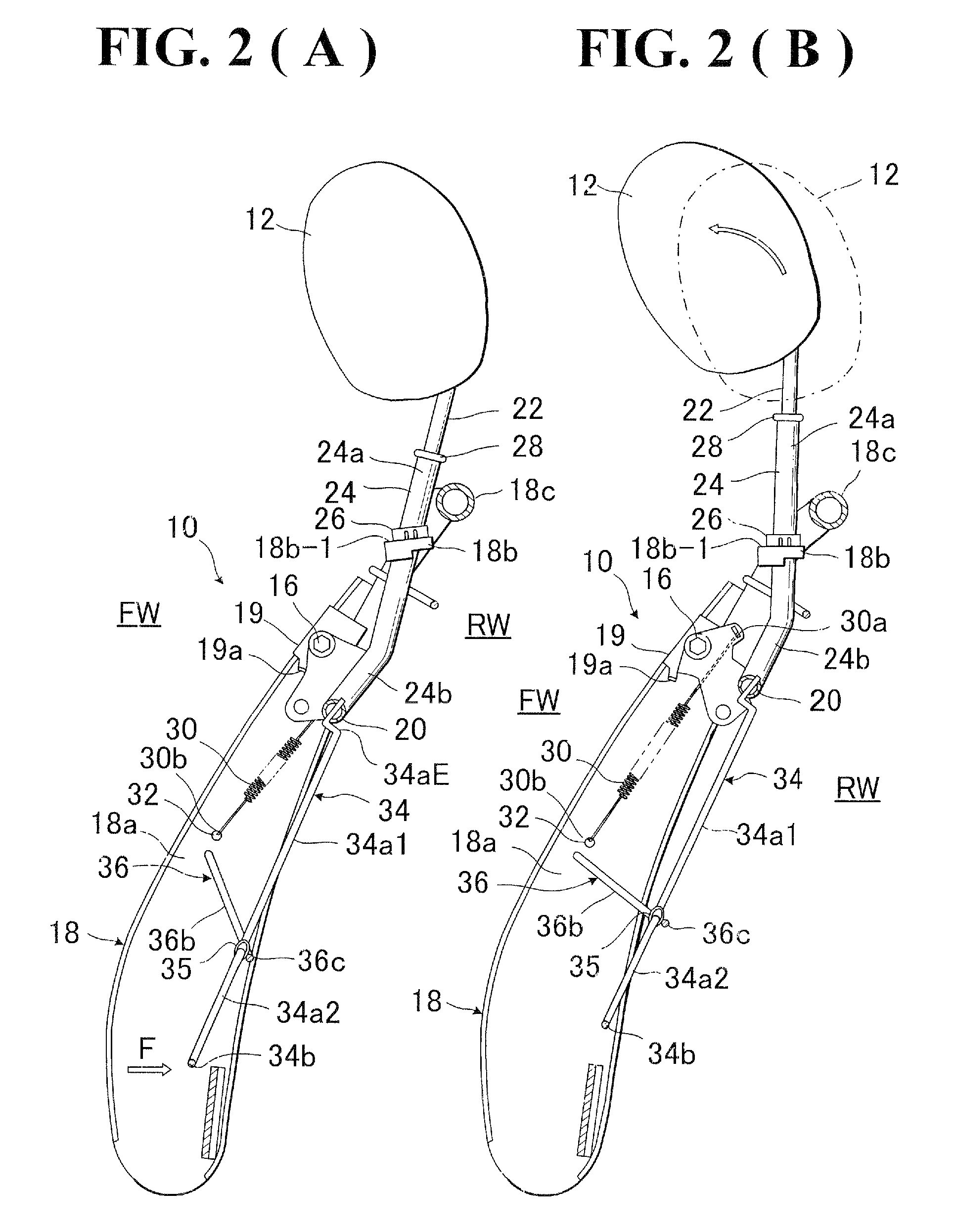
InactiveUS7758114B2Avoid excessive impactSimple structureVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementDorsal partsBack structure
In a seat back with movable headrest, a pressure receiving element is movably provided, which includes pressure receiving regions for receiving loads applied from lumber and dorsal parts of seat occupant. The pressure receiving element is movably connected with a crank member which is movably provided between two lateral frame members of seat back frame. Further, that pressure receiving element is connected with a support shaft extended between a par of rotating links rotatably arranged on the respective afore-said two lateral frame members. A biasing element is provided to normally bias the headrest to a home position.
Owner:TACHI S CO LTD
Peripheral nerve field stimulator curved subcutaneous introducer needle with wing attachment specification
An apparatus for use in peripheral nerve field stimulation (PNFS) whereby a plurality of curved introducer needles, of varying curvatures, are provided to permit the physician to best locate the region of oligodendrocytes that contain the A Beta fibers by matching the lumbar lordosis. A wing device is also provided that is attachable to the hub of the curved needle introducer which gives the physician better ability to maneuver the needle during insertion as well as permitting tenting of the skin. The invention benefits a large number of painful disorders arising from pathology in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine. In addition, this invention can also help a large number of other conditions including but not limited to failed back surgery syndrome / post-laminectomy pain, occipital / suboccipital headaches, scar pain, post herpetic neuralgia pain, mononeuritis multiplex, and pain following joint surgery (e.g., knee, hip, shoulder).
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Closure element for absorbent sanitary products, manufacturing process, process of use, and product thus obtained
InactiveUS20050113793A1Keep properlyReduce riskBaby linensAdhesivesDorsal partsMechanical engineering
A fastening element for absorbent sanitary products which can be worn like a pair of pants, the products having a waist line and end parts which can be connected together at edges so as to close the waist line of the product and the flaps located on the sides. The fastening element comprises two parts that are symmetrical with respect to an intermediate plane, each of these parts comprising in turn a base branch that can be connected to the first of said end parts, and a distal branch that can be connected to the second of said end parts. The base branch and the distal branch are connected together according to a general book-like configuration. The dorsal parts of the book-like configurations for connection between the base branch and the distal branches are set at a distance from said intermediate plane, the base branch connects together the two symmetrical parts so as to form a single body, each of which is able to connect together mutually facing edges of the end parts of a respective absorbent sanitary product and to ensure the fastening of the flaps set on the sides. Alternatively, the fastening element is made in such a way as to enable the function of releasing and refastening of the product to be performed, with the further possibility of selectively adjusting the fit of the product to the wearer's body.
Owner:FAMECCANICA DATA SPA
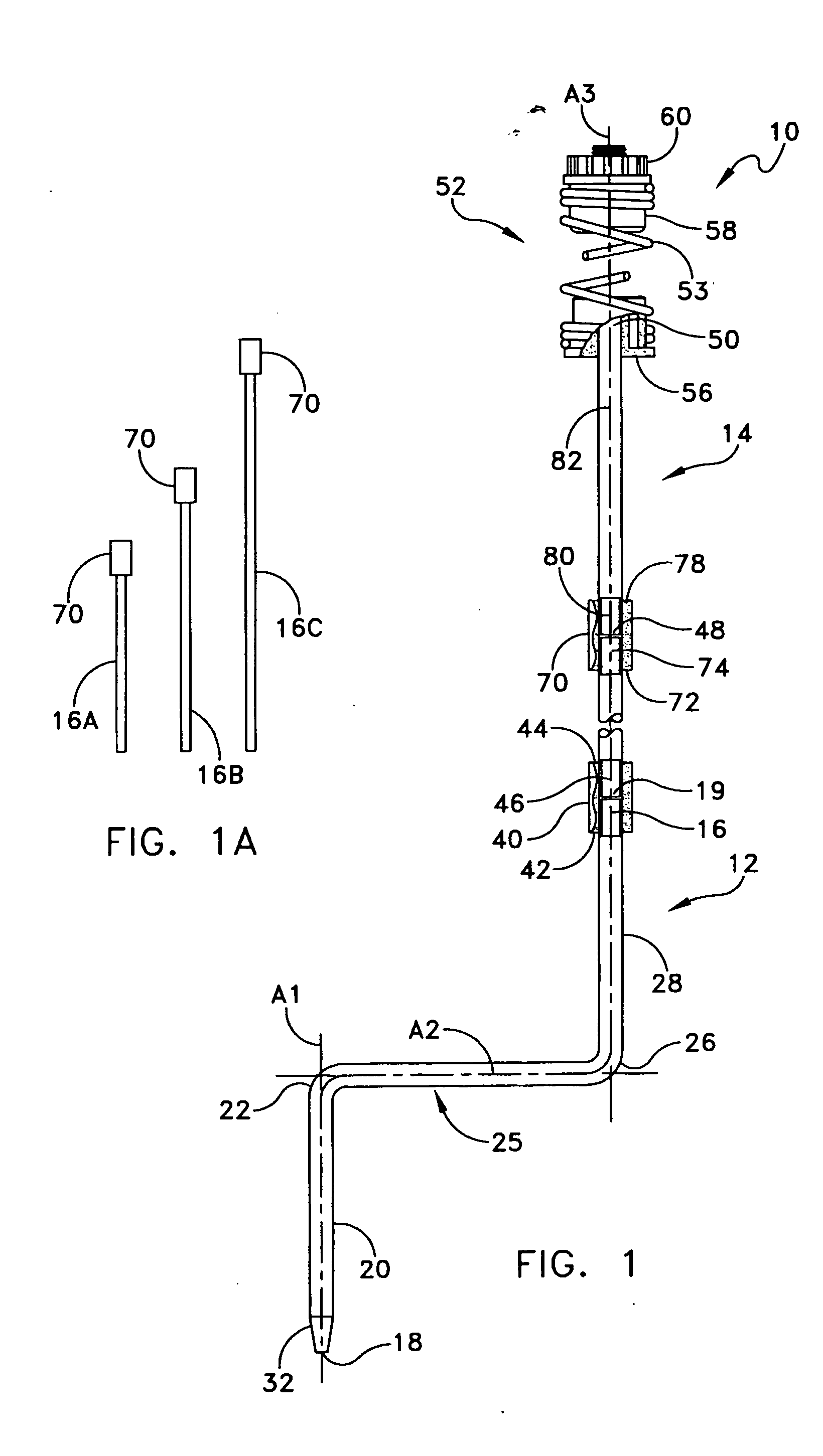
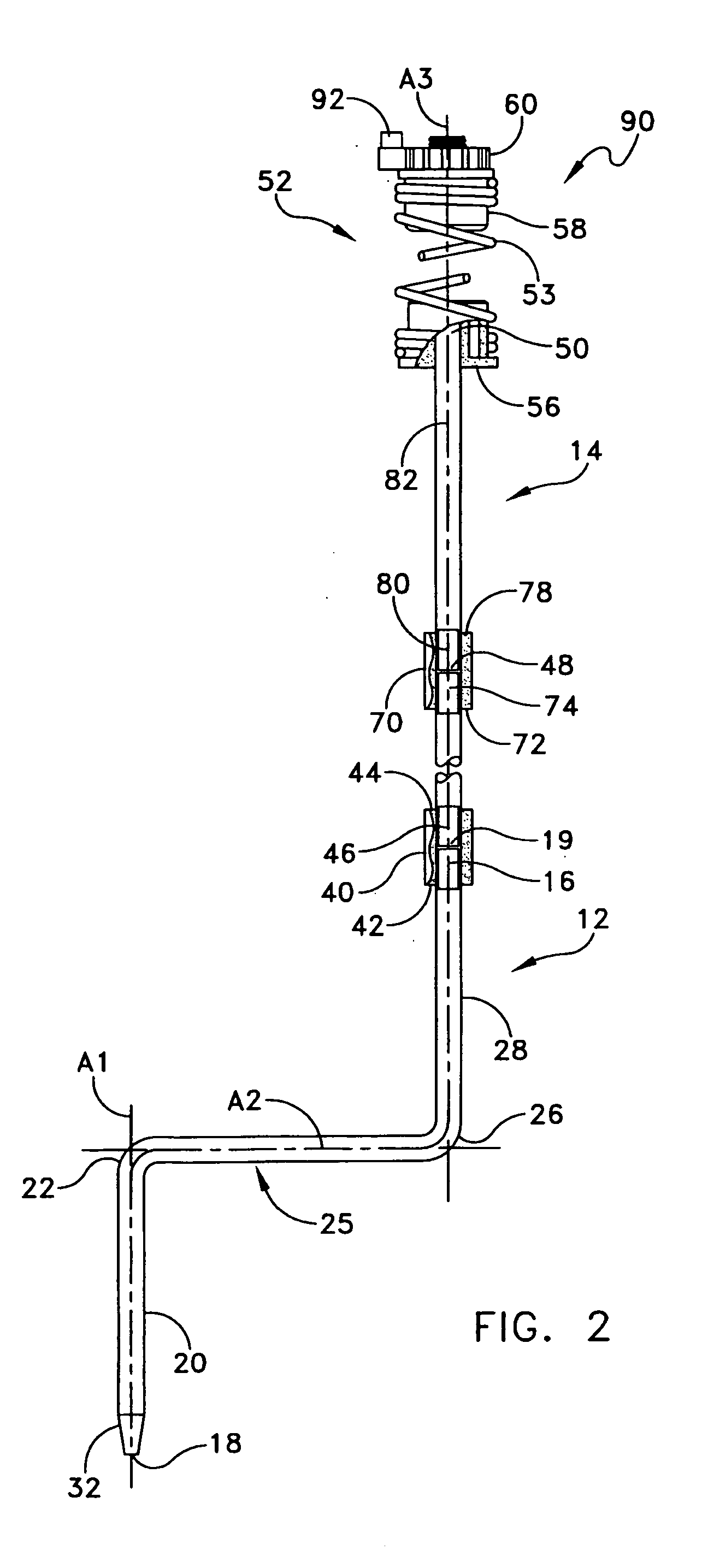
Adjustable stake for a decoy
A hunting decoy, for example simulating a wild turkey, is structured for lifelike motion in the field, and can be quickly deployed and adjusted in height. In one arrangement, freedom of body and head movement is provided to simulate natural movement in a limited range. Spring mounts including helical spring couplings between a vertical post and the dorsal part of a torso portion of the body, and also between the vertical post and a head / neck diverted support. These couplings allow the body and the head to move relative to one another both in a limited bobble-head motion and also bobble-body motion that is akin to a waddle. The spring couplings also minimize unnatural appearance if the decoy is deployed out of vertical alignment. The spring mountings permit limited movement in rotation on the vertical axis, and also damp the extent of free motion permitted. The vertical post can be provided with a step section, and can be length extensible by selection of intermediate extension lengths to place the decoy body at an optimal height in grass or brush.
Owner:BUCKWING PRODS
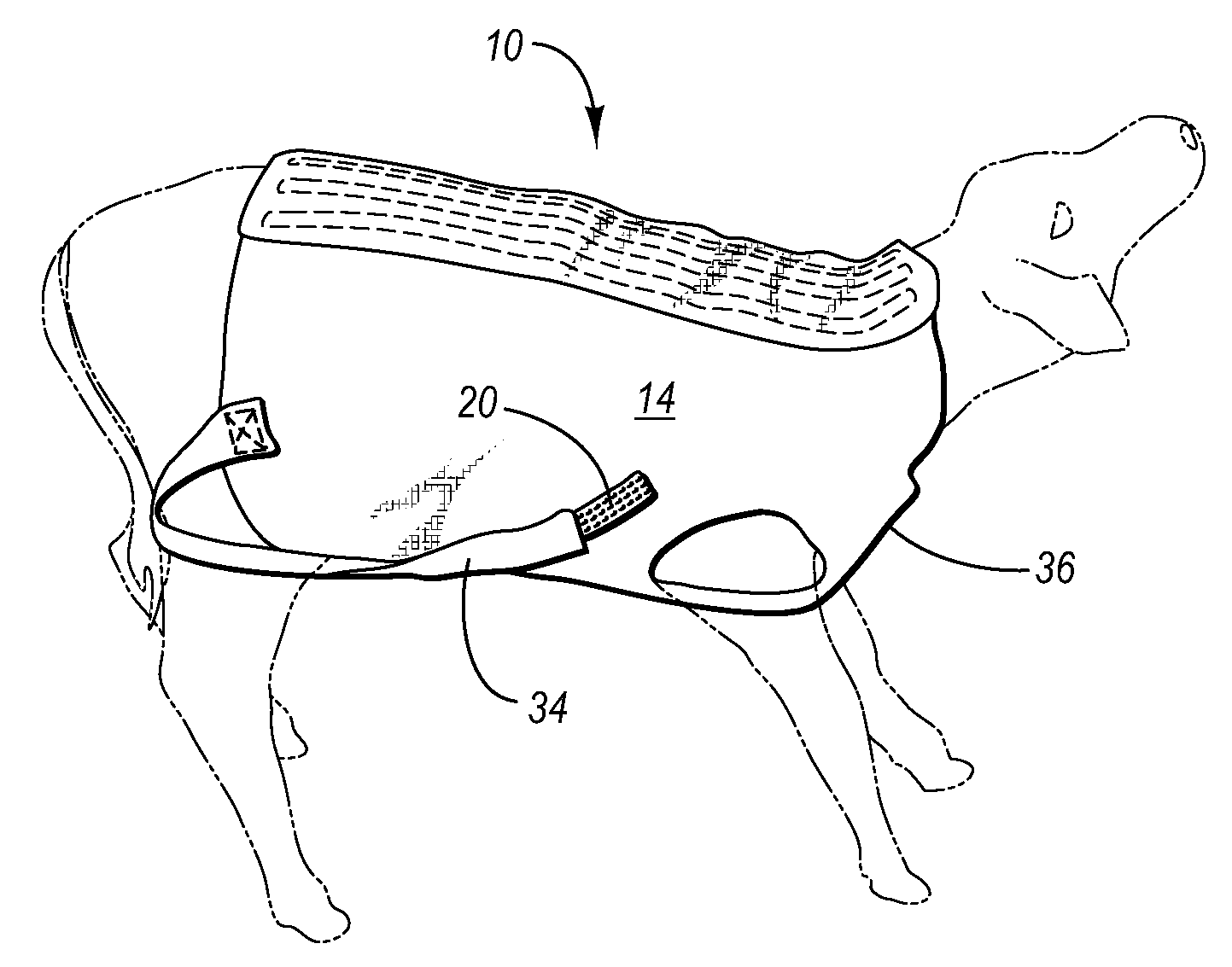
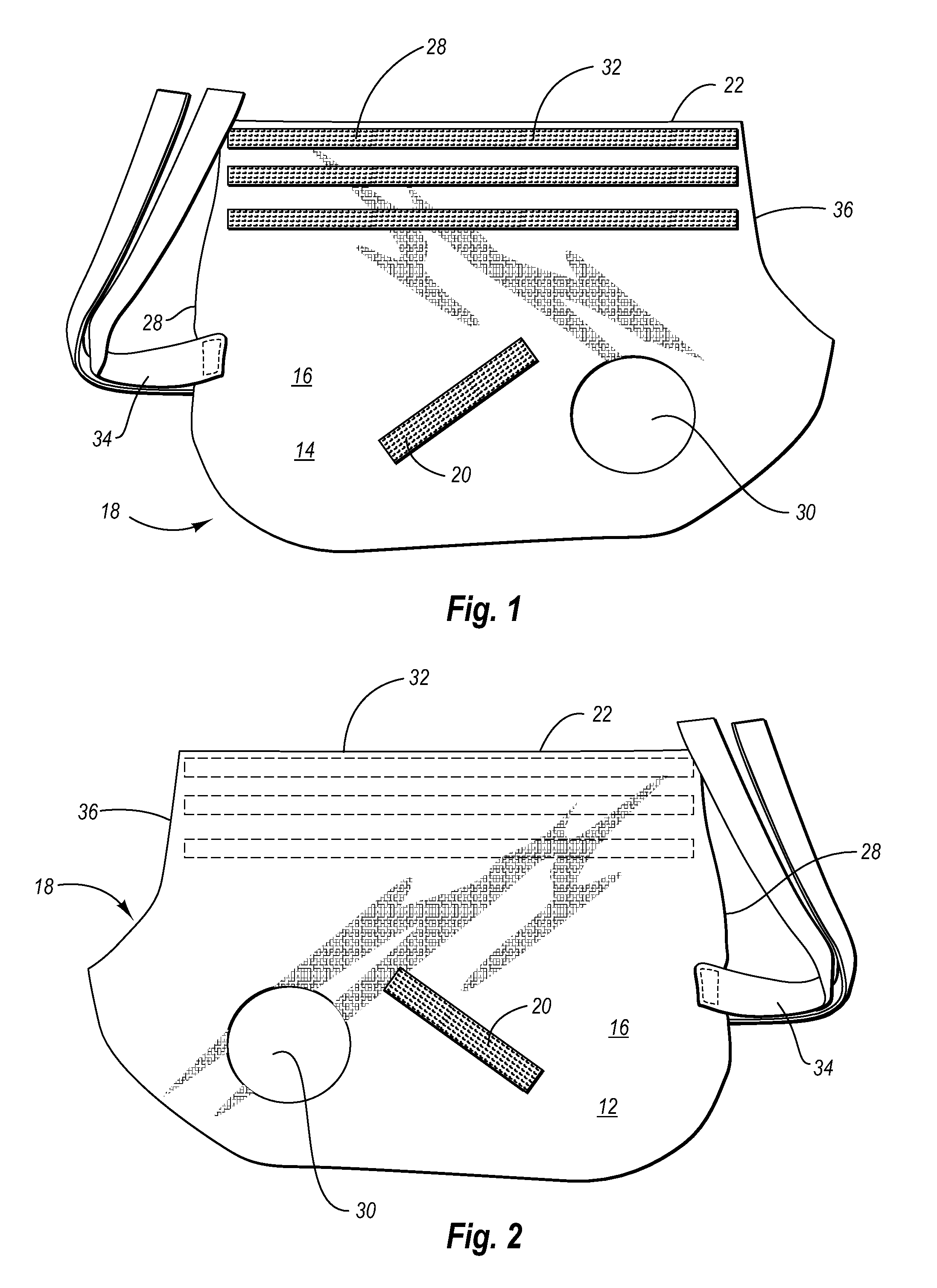
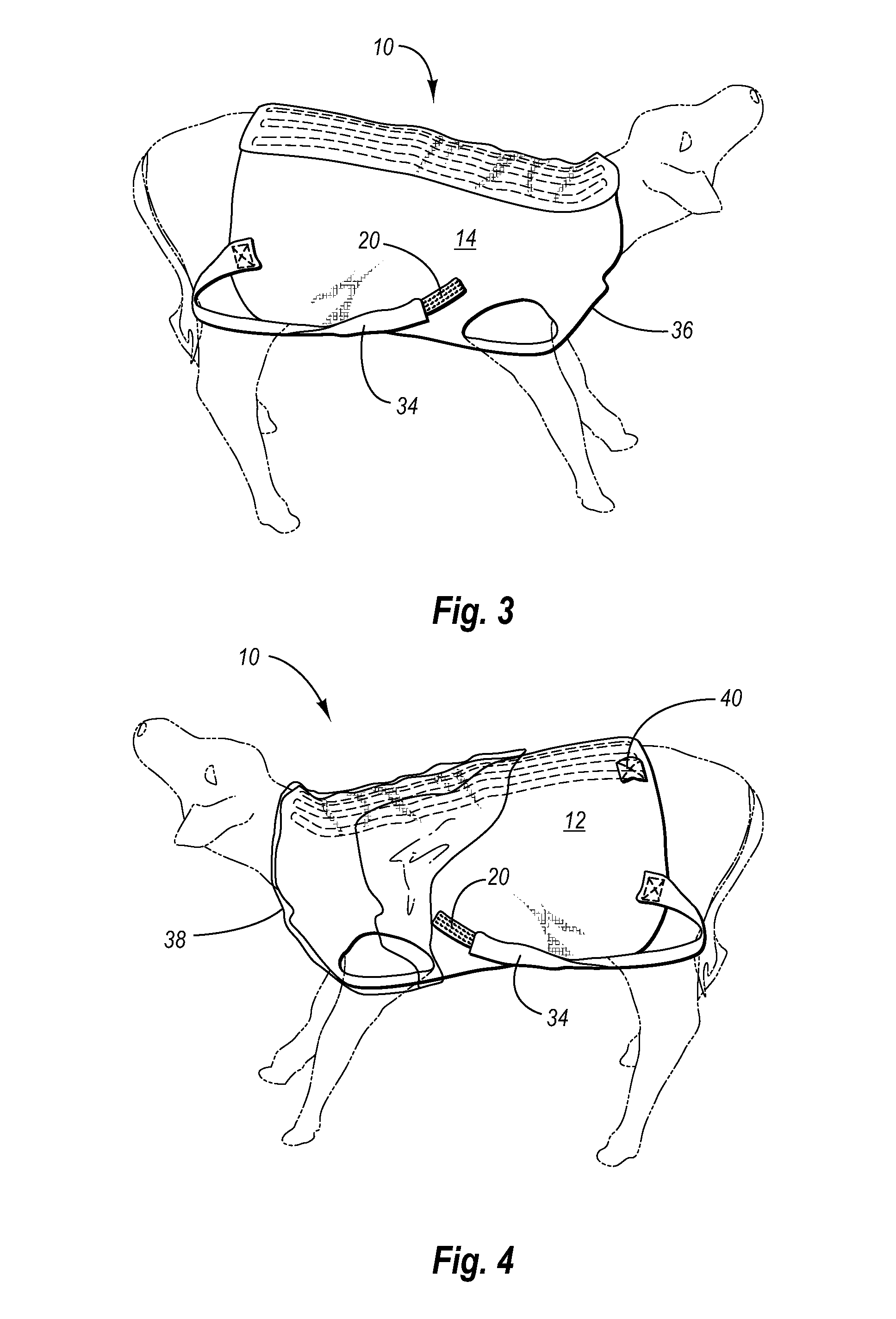
Animal garment
An animal garment for four-legged animals to protect such animals such as lambs and calves from cold and wet and to enhance their survivability. The garment is made up of connected halves and is adjustable along a portion that covers the back of the animal so as to allow for accommodation of the device to fit animals of different sizes or as an animal grows. The device includes holes for forelegs and detachable straps for hind legs, which hold the device in a secure position.
Owner:GERDES JANICE
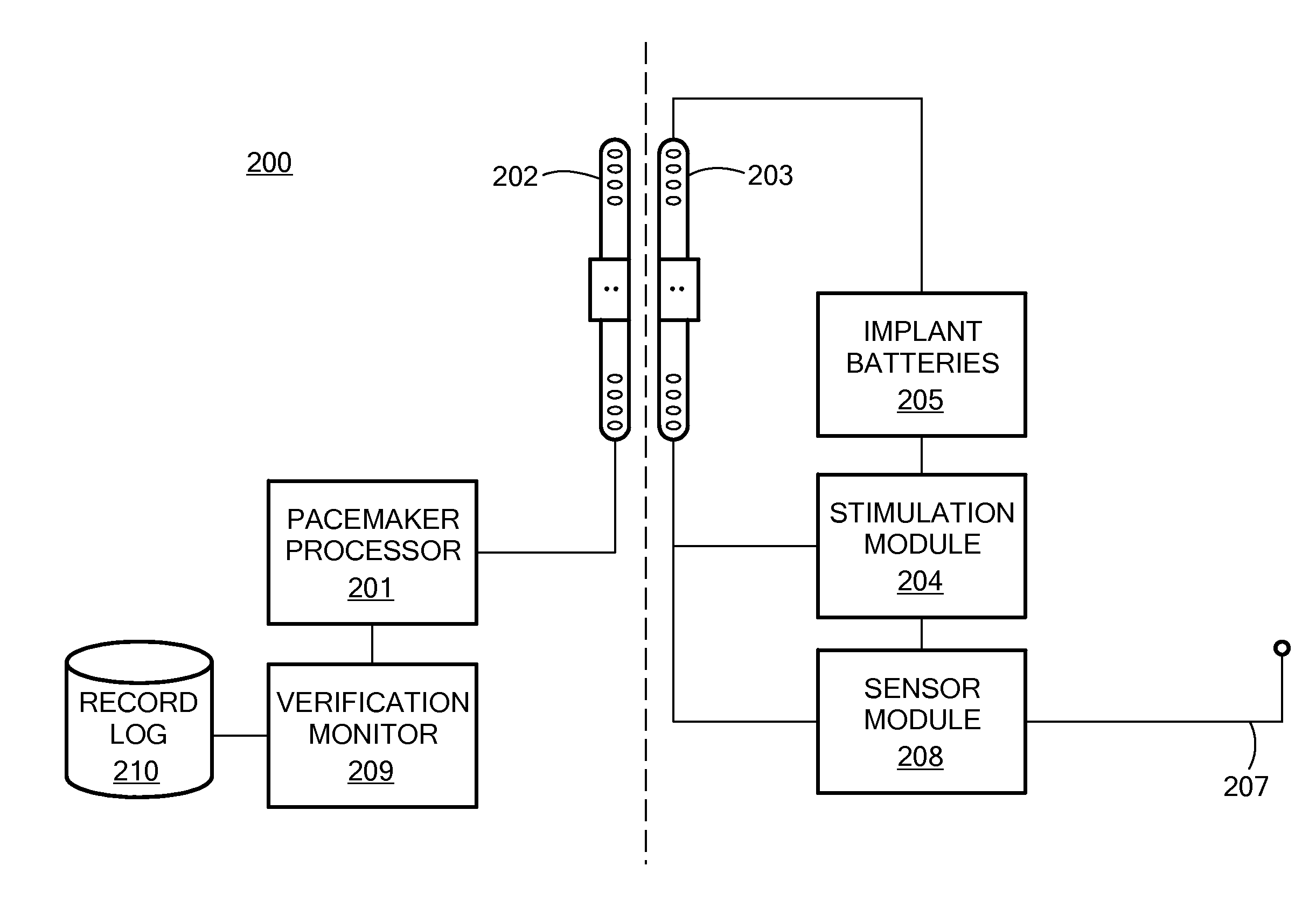
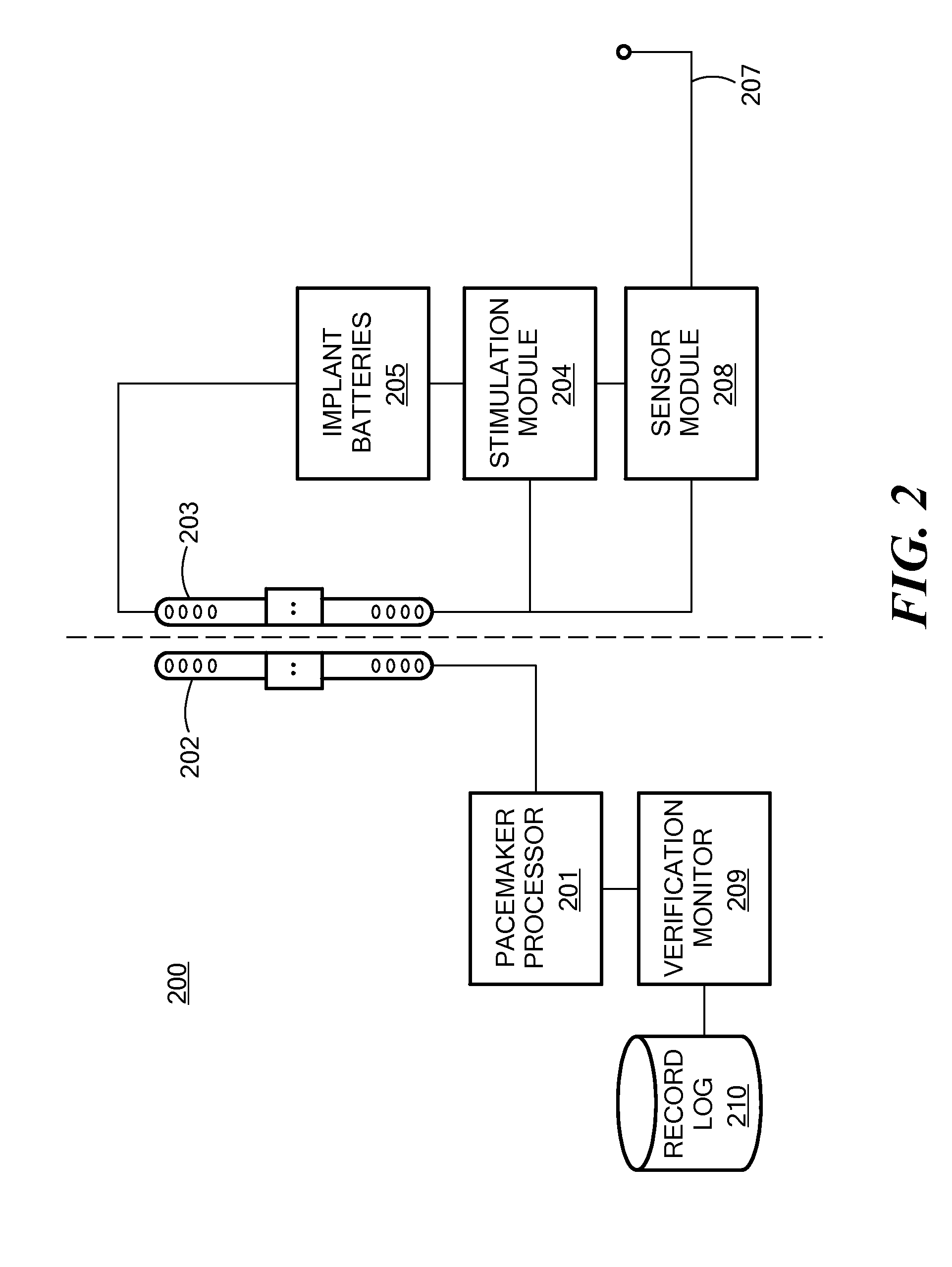
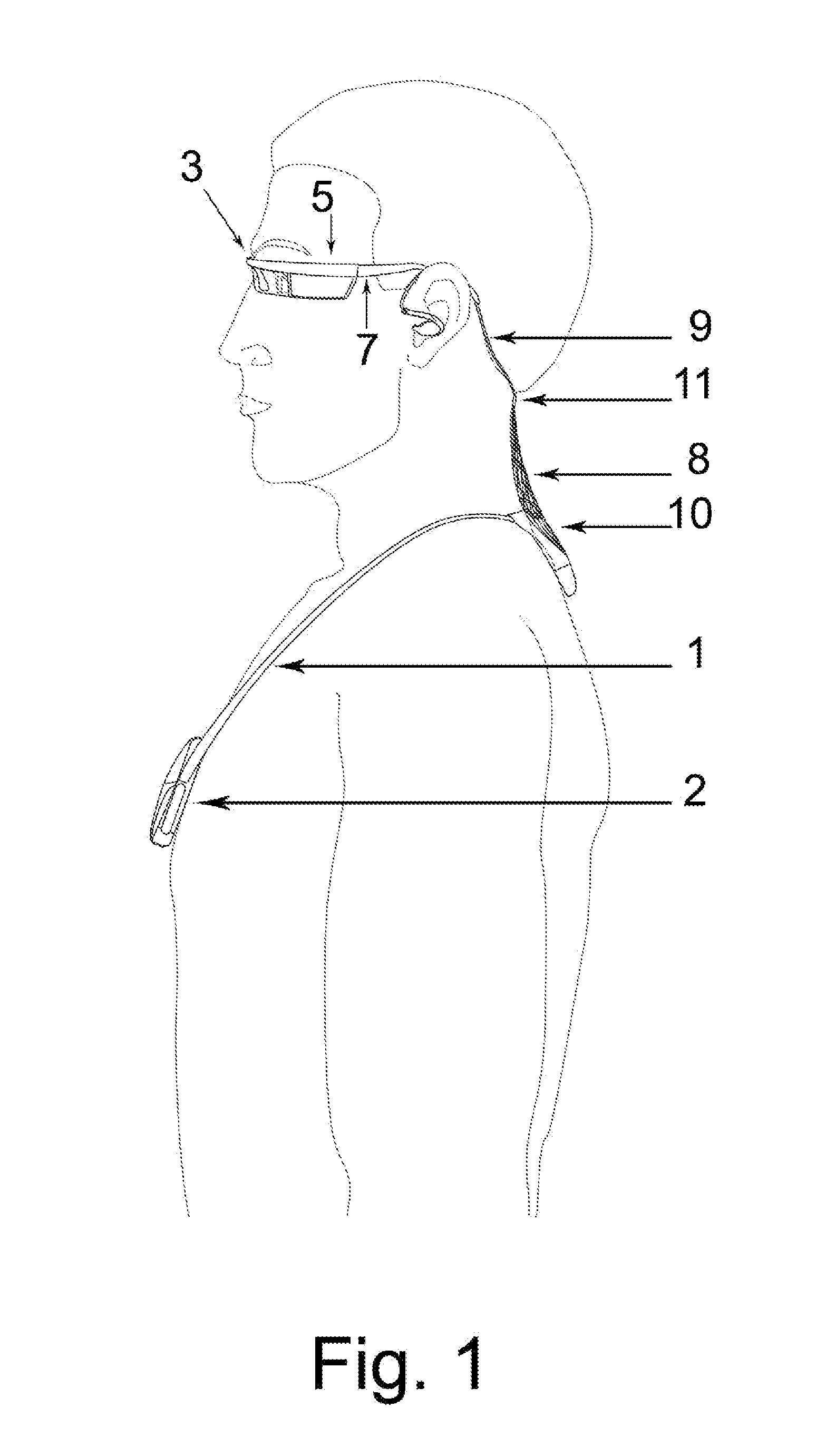
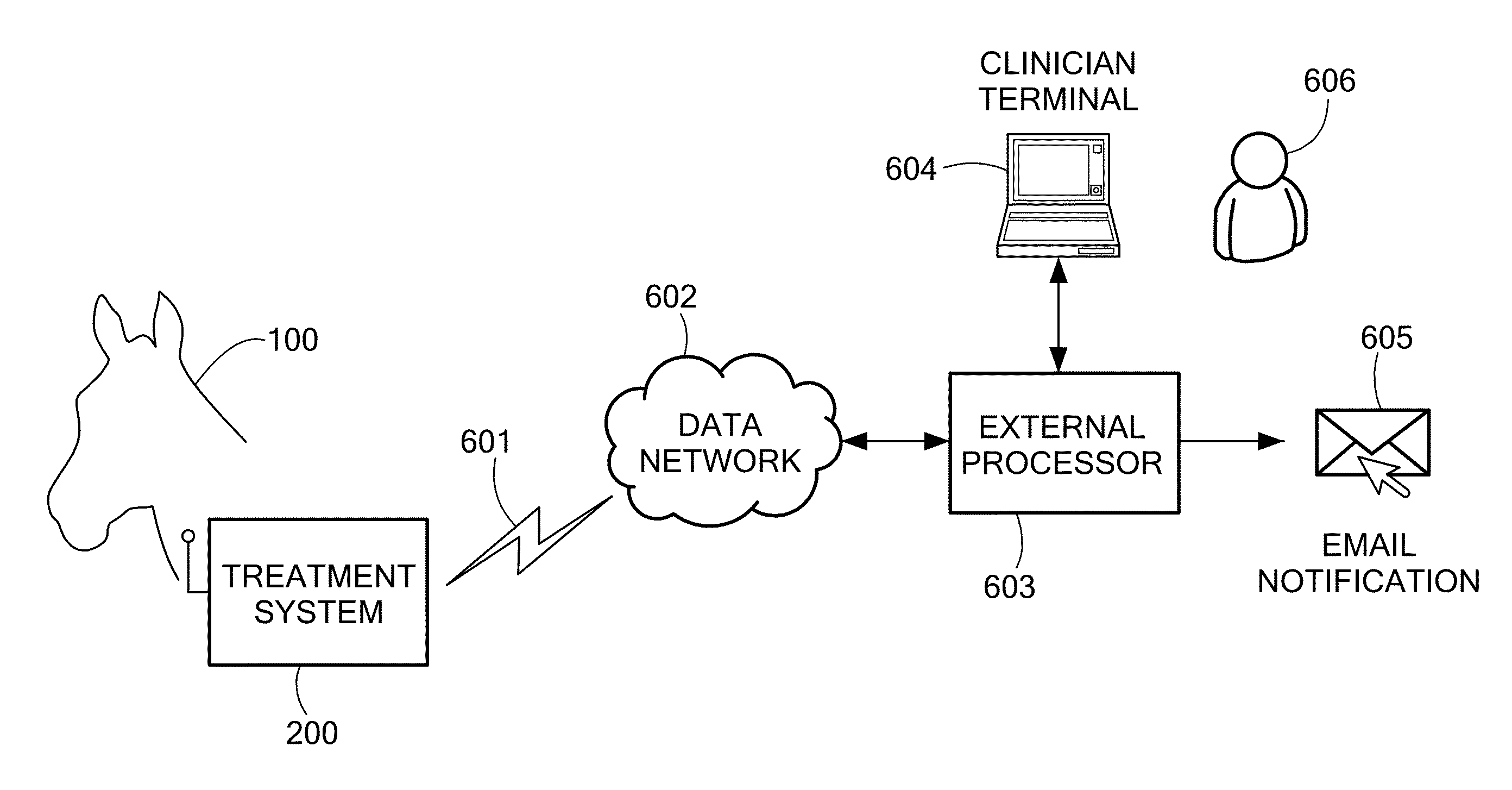
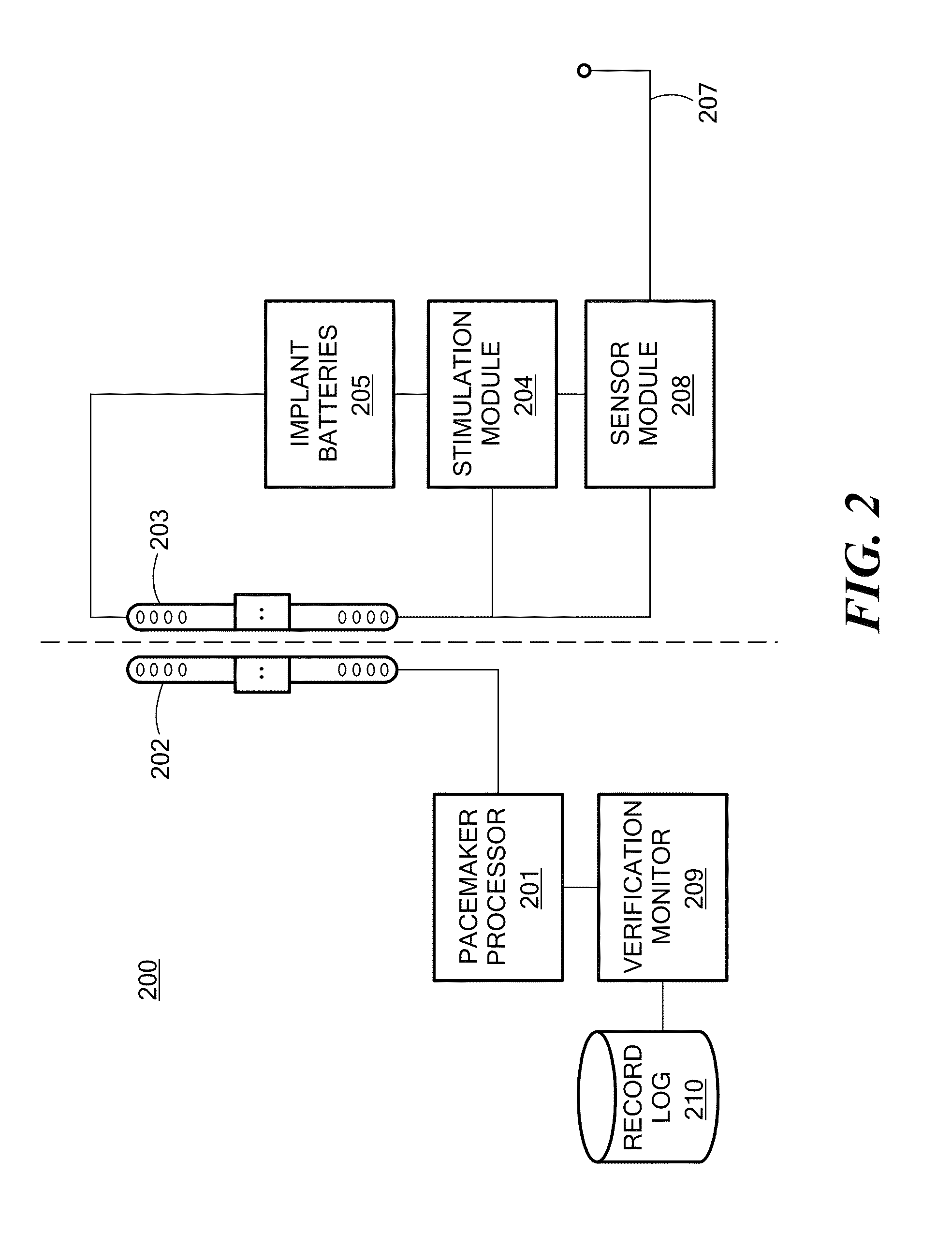
Adaptive Airway Treatment of Dorsal Displacement Disorders in Horses
An adaptive airway treatment system is described for treating a dorsal displacement disorder in a horse. A pacemaker processor generates a dorsal displacement disorder treatment signal as a function of at least one therapy parameter. One or more stimulation electrodes are adapted to interface with tissue of the horse for delivering the treatment signal to continuously or intermittently stimulate soft palate tissue of the horse during an entire period of increased activity of the horse or for training prior to exercise.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
Restraint, reposition, traction and exercise device and method
ActiveUS20080269030A1Maintain positionOperating chairsChiropractic devicesDorsal partsPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Owner:BACKPROJECT
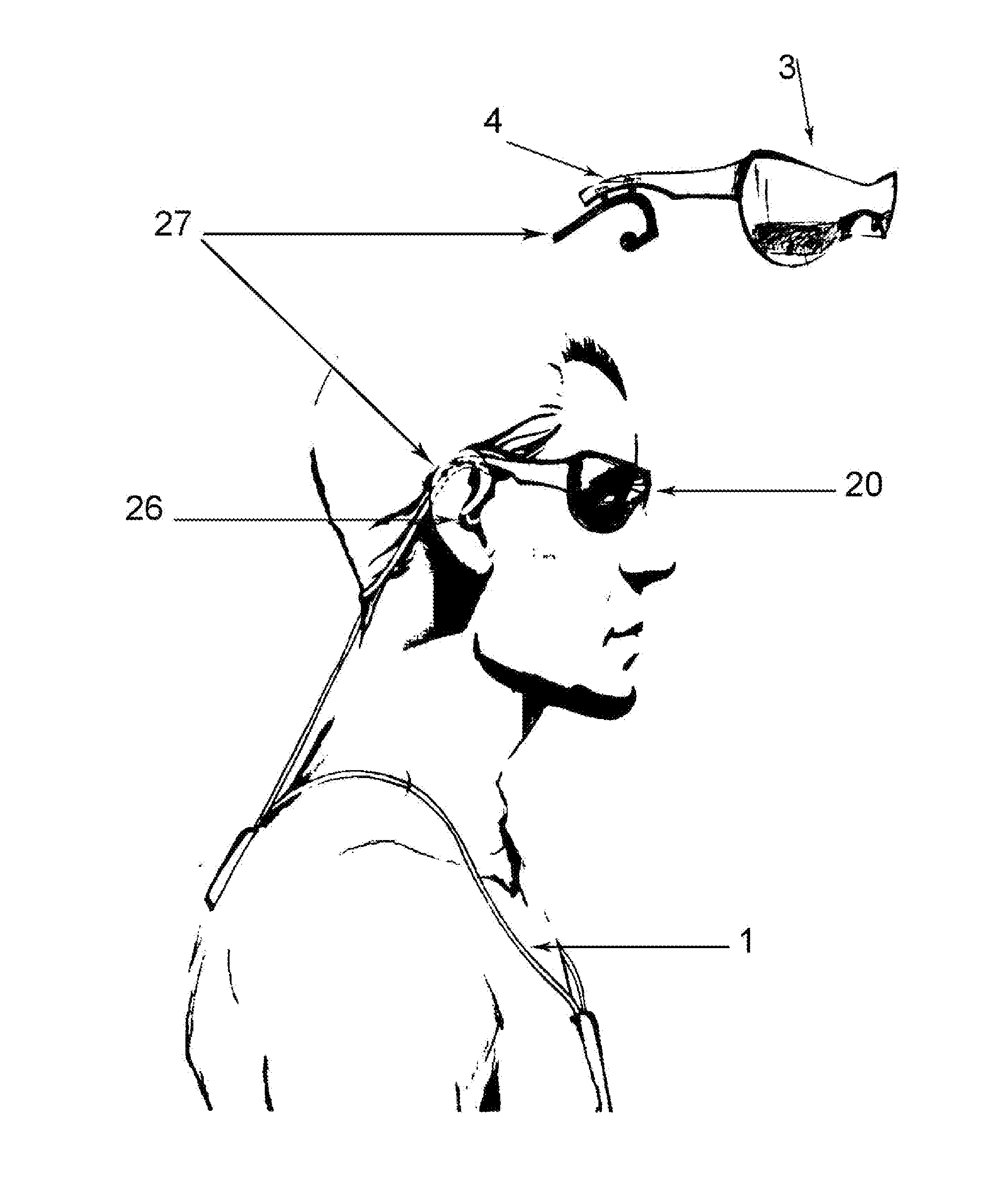
Composite wearable electronic communication device
InactiveUS20160070110A1Shorten the lengthAvoid breakingTelevision system detailsTransmission systemsElectricityDorsal parts
A composite wearable electronic communication device comprising a neck loop configured to bear electronic components and control means, a spectacle frame configured to bear display and videocamera, a flexible adapter comprising two wires, wherein at least one of the wires is electrically connected the neck loop and the spectacle frame, wherein the two wires of the flexible adapter are connected to the neck loop in close proximity to each other and form a dorsal wire joint disposed on the lower dorsal part of the user's neck while wearing the device, wherein in addition, the two wires are mechanically connected to each other in the wire portions between the spectacle frame and the dorsal joint, thus forming a suboccipital wire joint disposed below the user's occiput while wearing the device.Said composite method of coupling a wearable communication device allows to reduce the overall length of the connecting wires, organizing their mobility to compensate the user's head turns, and in some embodiments, when the device comprises winding mechanisms and storage pockets, extra batteries, microphone—array microphones, the method allows to use the wearable communication device for a long time and to wear it on the body under the clothing in operating and non-operating state.
Owner:USHAKOV ALEXEY LEONIDOVICH
Adaptive airway treatment of dorsal displacement disorders in horses
An adaptive airway treatment system is described for treating a dorsal displacement disorder in a horse. A pacemaker processor generates a dorsal displacement disorder treatment signal as a function of at least one therapy parameter. One or more stimulation electrodes are adapted to interface with tissue of the horse for delivering the treatment signal to continuously or intermittently stimulate soft palate tissue of the horse during an entire period of increased activity of the horse or for training prior to exercise.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
Method for predicting contact stress between human body and mattress
InactiveCN108897930ALow costPredict and analyze contact stressDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman bodyDorsal parts
The invention discloses a method for predicting the contact stress between a human body and a mattress. The contact stress between the human body and an arenga engleri mattress is predicted and analyzed by adopting a method integrating a three-dimensional scanning technology and a finite element method; sensing cameras Kinect are used and are arranged on four columns respectively, a tester standsin a scanning range and keeps double arms slightly open, then point clouds on the surface of the human body can be scanned, a scanned human body model is processed by using Geomagic Studio to obtain asolid model of a subject; the obtained human body model is imported into grid generation software, material parameters of the mattress and the skin and muscles of the human body are input, and the contact stress between the human body and the mattress is predicted. Different users can select suitable mattresses according to the body pressure distribution situations on the mattresses made from different materials, accordingly back pain is effectively relieved, and the quality of sleep is improved.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for conducting a targeted training and a corresponding training device
InactiveUS20050245365A1Change loadEasy to useMovement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesHuman bodyDorsal parts
The invention relates to a method for a targeted training of the human body as well as a corresponding training device for realizing said method. The training device is used for the training of the body region (vertebral column) between shoulder girdle and pelvic girdle (back region) by using the limbs, arms and legs, such that the body region of the shoulder girdle is turned (twisted) in the opposite direction as the body region of the pelvic girdle, thereby resulting in a relative turning movement between the respective vertebras of the vertebral column.
Owner:ROLLI ENGELBERT
Spinal puncture training stimulation standard patient
InactiveCN101877192ATactile realAppearance image simulationEducational modelsHuman anatomyPolyvinyl chloride
The invention relates to the technical teaching of clinical puncture, in particular to a stimulation standard patient for lumbar puncture operation training of doctors and students in hospitals and medical schools. The invention relates to techniques of human anatomy, stimulation materials, moulds and the like in medicine. The lumbar puncture standard patient stimulation adult male mould is made of PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), is stimulated in appearance. The body of the stimulation standard patient lies on a bed, the back is perpendicular to a bed surface, the head bends forward, double knees bend towards the belly, the trunk forms an arc shape, and the waist can move. An operator draws the head part of the stimulation standard patient with one hand and draws the double lower fossa with the other hand so that the spine is backward protruded as far as possible to increase the intervertenral space, and then the lumbar puncture can be carried out. During the process of carrying out the lumbar puncture, needle feed is blocked and the needle touches nothing when reaching the target part, and man-made cerebrospinal fluid can flow out. The standard patient can be used for stimulating cerebrospinal fluid drawing, intravaginal medicine injection, epidural anesthesia and lumbar anesthesia in the operation of lumbar puncture.
Owner:营口巨成教学科技开发有限公司
Seat back structure of vehicle seat
InactiveUS20100013275A1Avoid excessive impactSimple structureVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementDorsal partsBack structure
In a seat back with movable headrest, a pressure receiving element is movably provided, which includes pressure receiving regions for receiving loads applied from lumber and dorsal parts of seat occupant The pressure receiving element is movably connected with a crank member which is movably provided between two lateral frame members of seat back frame. Further, that pressure receiving element is connected with a support shaft extended between a par of rotating links rotatably arranged on the respective afore-said two lateral frame members. A biasing element is provided to normally bias the headrest to a home position.
Owner:TACHI S CO LTD
Device for strengthening tongue muscle
ActiveUS20100184566A1Appropriate burdenSnoring preventionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesStress inducedPoor posture
To provide a tongue muscle-strengthening device which can prevent or recover a poor posture that is attributed to no development of lingual adhesion in the mandible to the skull due to the decreased function of tongue muscles, stress-induced disorder that is attributed to the hyperfunction of the masticatory muscle group and tongue muscles in the cerebral cortex motor area, as well as the dysfunction and an aesthetic impairment of the mouth and which can actualize lingual adhesion. The tongue muscle-strengthening device in the invention of this application is composed of the part of maxillary teeth contact that is in contact with the maxillary teeth, the parts of dorsum of tongue and palate contact that are respectively in contact with the dorsum of tongue and palate, as well as the part of connection that connects the part of maxillary teeth contact with the parts of dorsum of tongue and palate contact. The user brings the part of palate contact into contact with the palate by inserting the part of maxillary teeth contact into the maxillary teeth, by bringing the part of dorsum of tongue contact into contact with the dorsum of tongue, by bringing the lingual apex into contact with the part of lingual apex contact, and by elevating the dorsum of tongue, and maintains the condition for a while. The elasticity of the part of connection places a sustained and strong burden on tongue muscles and strengthens tongue muscles. Furthermore, the tongue muscle-strengthening device in the invention of this application has good usability because it is an intraoral device.
Owner:MUNEHIRO MOTONORI
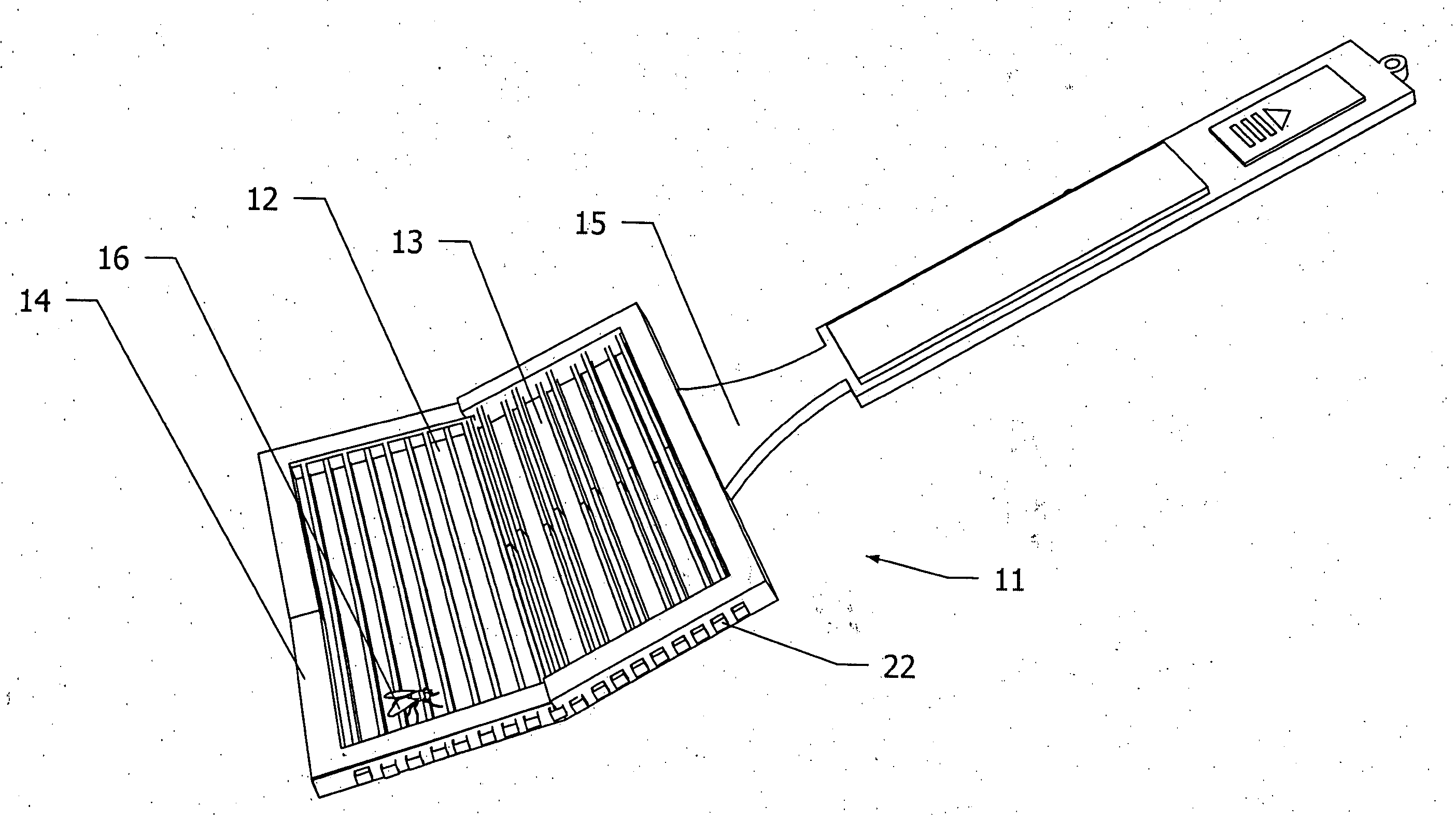
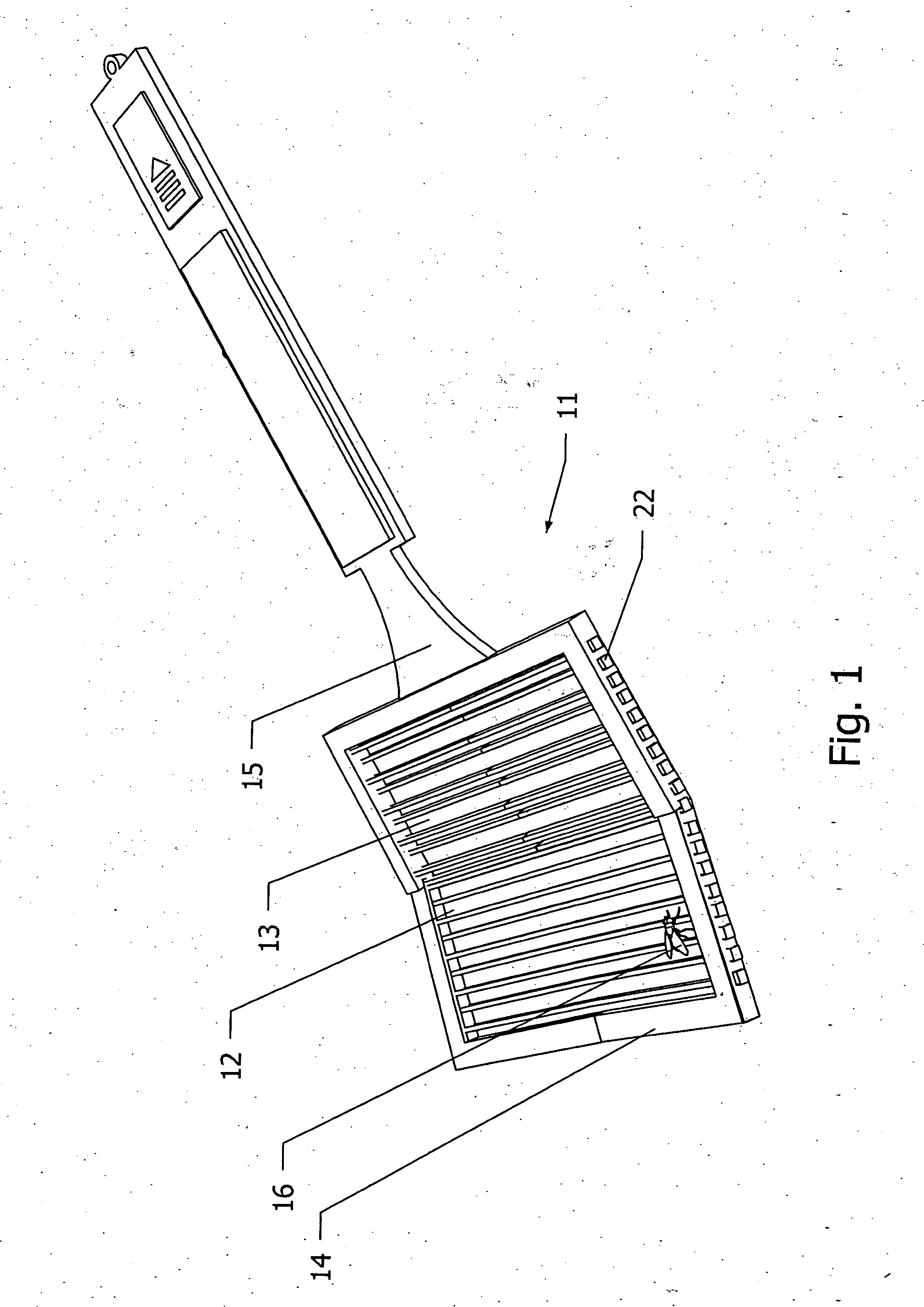
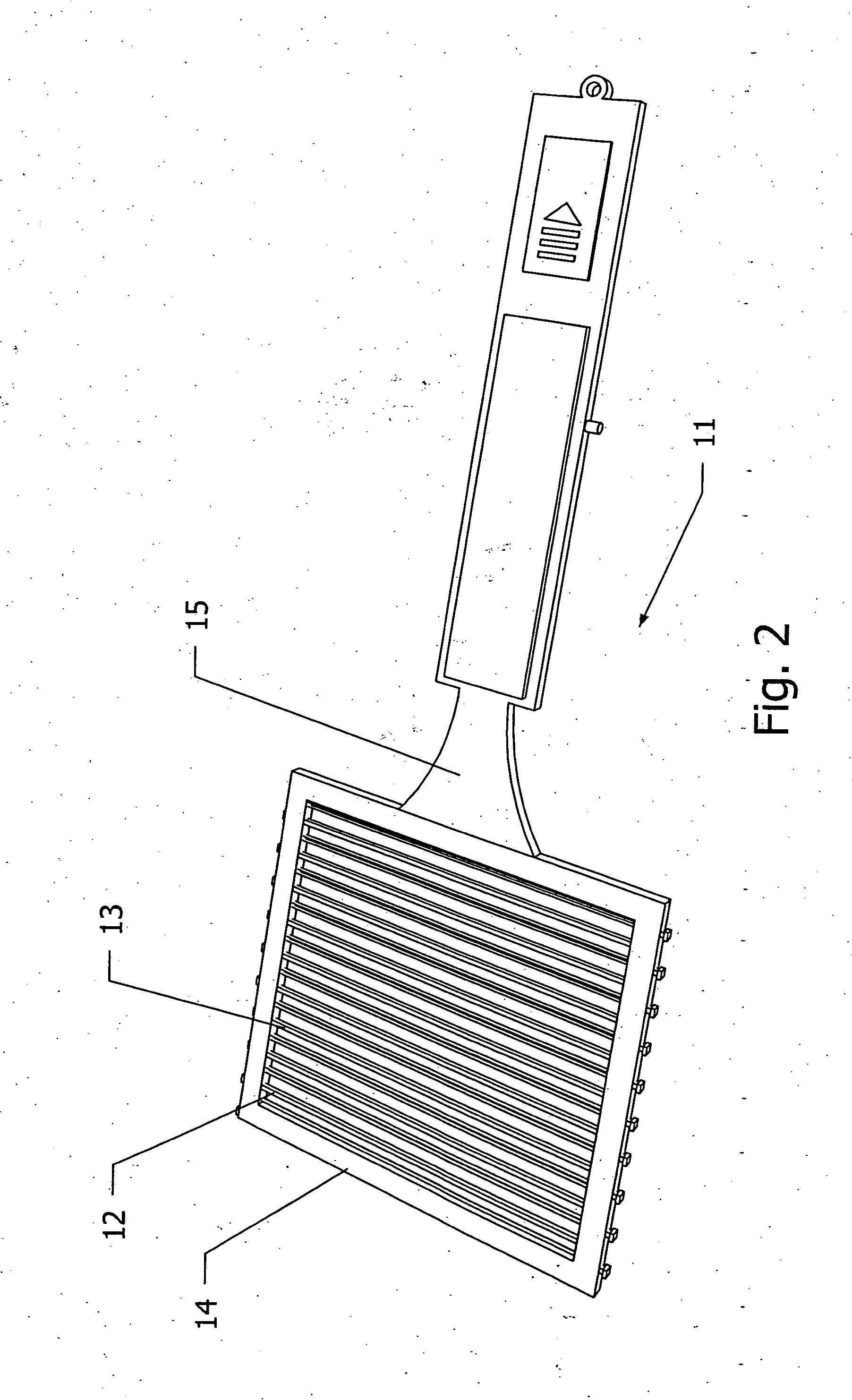
Flexible electric flyswatter with shape memory capabilities
A flexible electric fly swatter comprising a grid of electrically conducting shape memory materials encased within a flexible frame for striking against and electrocuting a fly on a surface or in the air. The single layer grid has odd and even rods oppositely charged where both the frame and the grid return back to their original shape after being struck. An alternate embodiment of this invention is a flexible electric fly swatter comprising two or more meshes in parallel of electrically conducting shape memory materials that are fastened together with connecting-spacers to allow a gap between the top mesh and the bottom meshes such that when a fly touches the meshes the circuit is completed and the fly is electrocuted. Also included in this invention is a spring-pivot-hinge fastened between the dorsal part of the handle to the proximal part of the frame or meshes.
Owner:GORDON IV NATHAN LOUIS
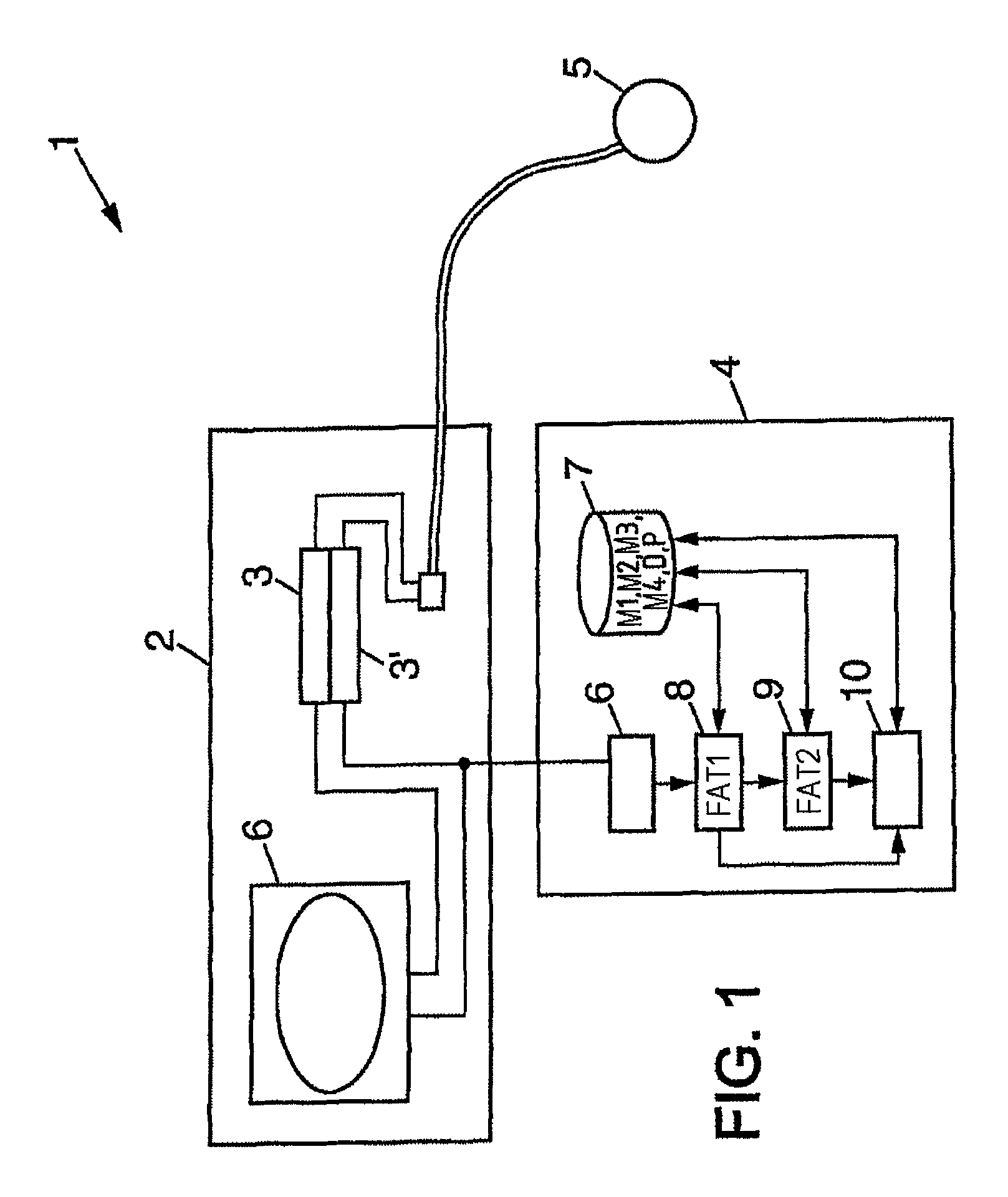
Method and system for determining total body fat, and method and system for determining body composition
InactiveUS7918794B2Quick implementationAvoid traumaOrgan movement/changes detectionPerson identificationDorsal partsThigh
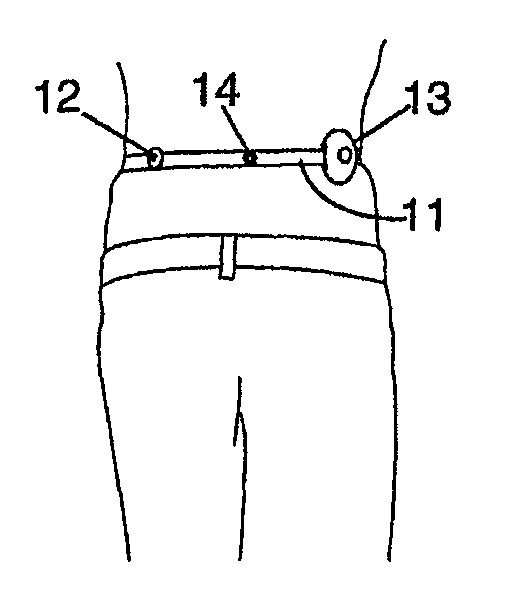
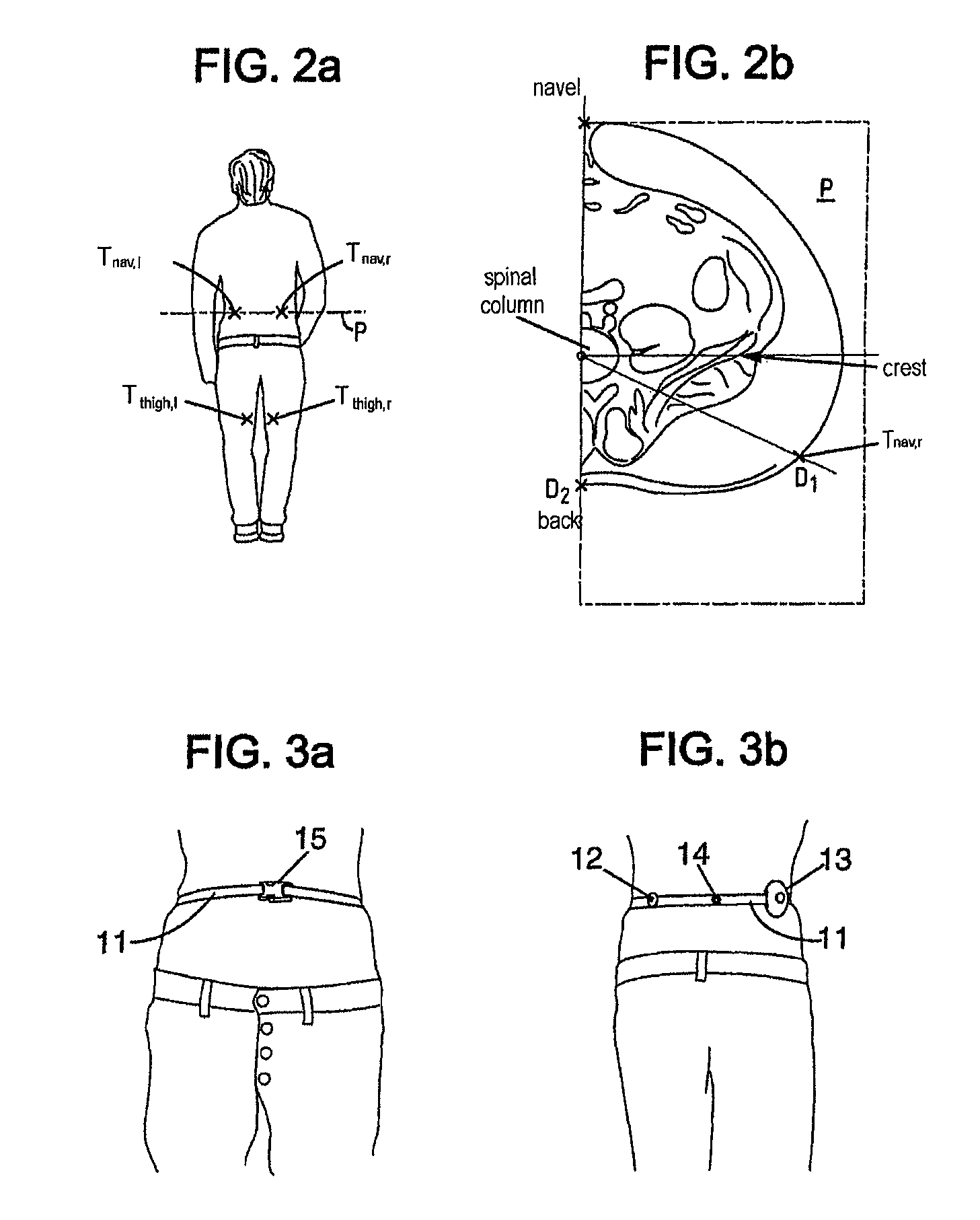
A method of determining the total body fat of a person comprising measuring a subcutaneous fat thickness at four points on the person's body, located in the right anterior part of the left mid-thigh, in the left anterior part of the right mid-thigh, in the right dorsal part navel level and in the left dorsal part at navel level, respectively, and determining a first estimate of the person's total body fat as a function of these measurements.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
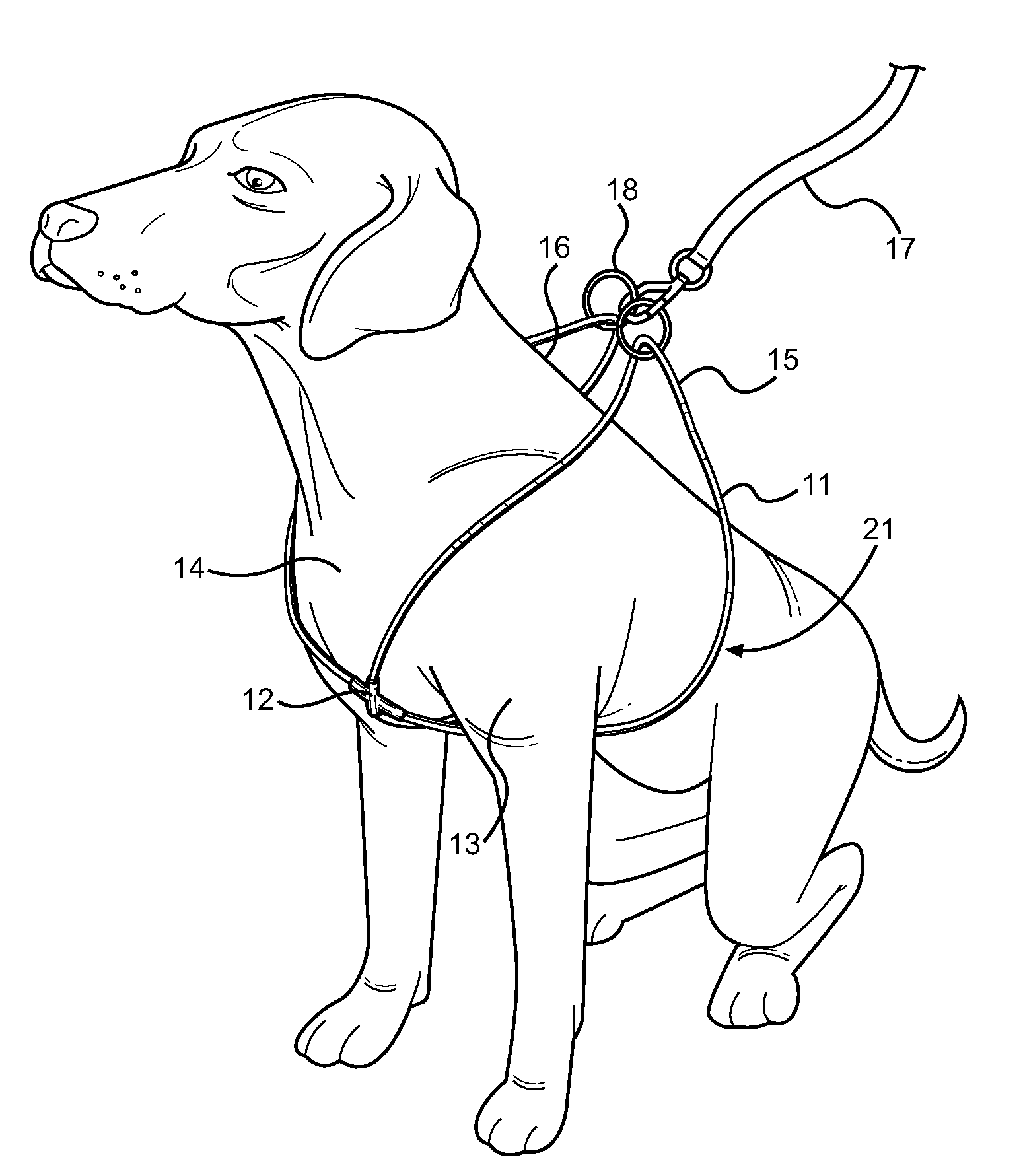
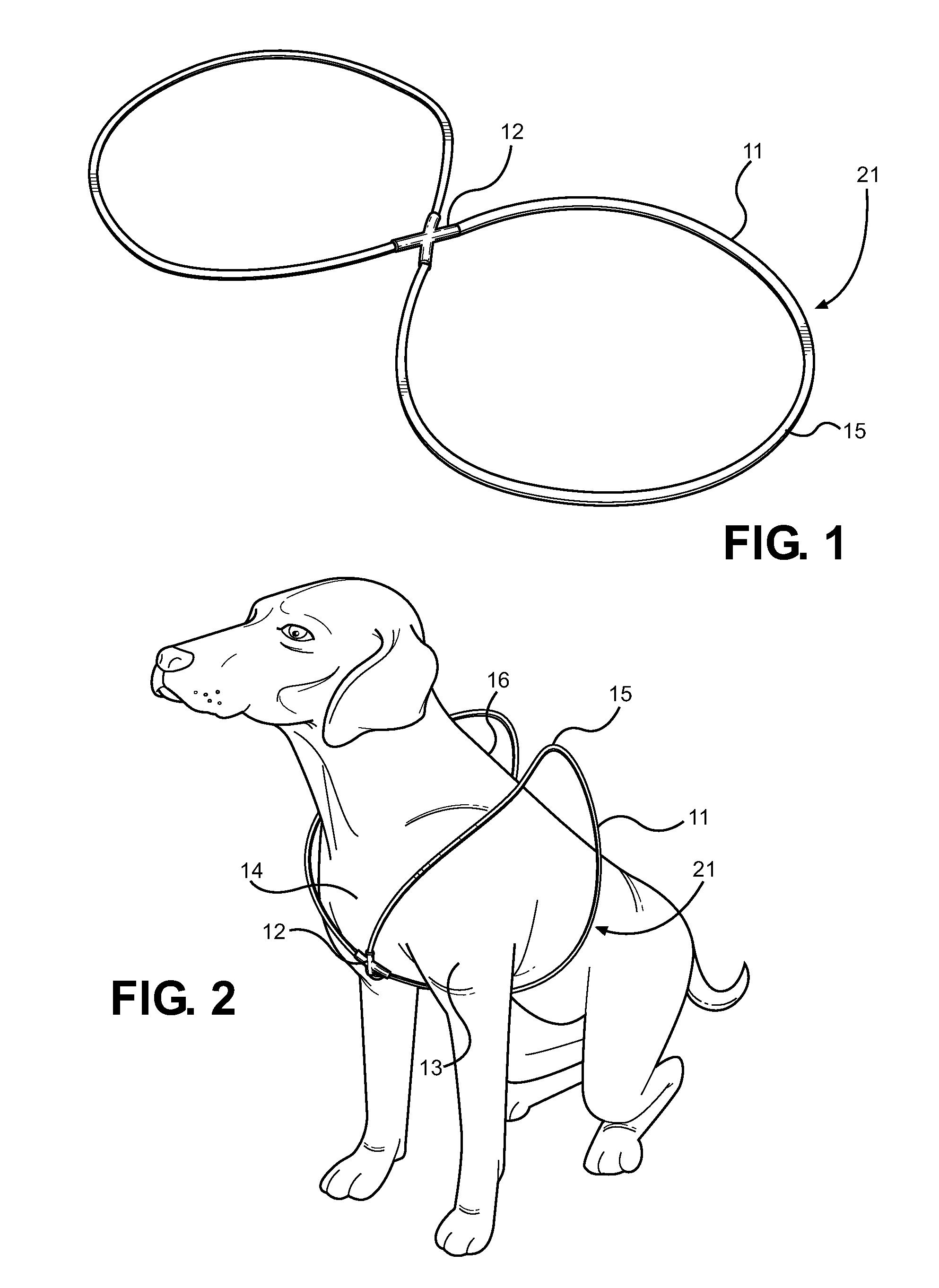
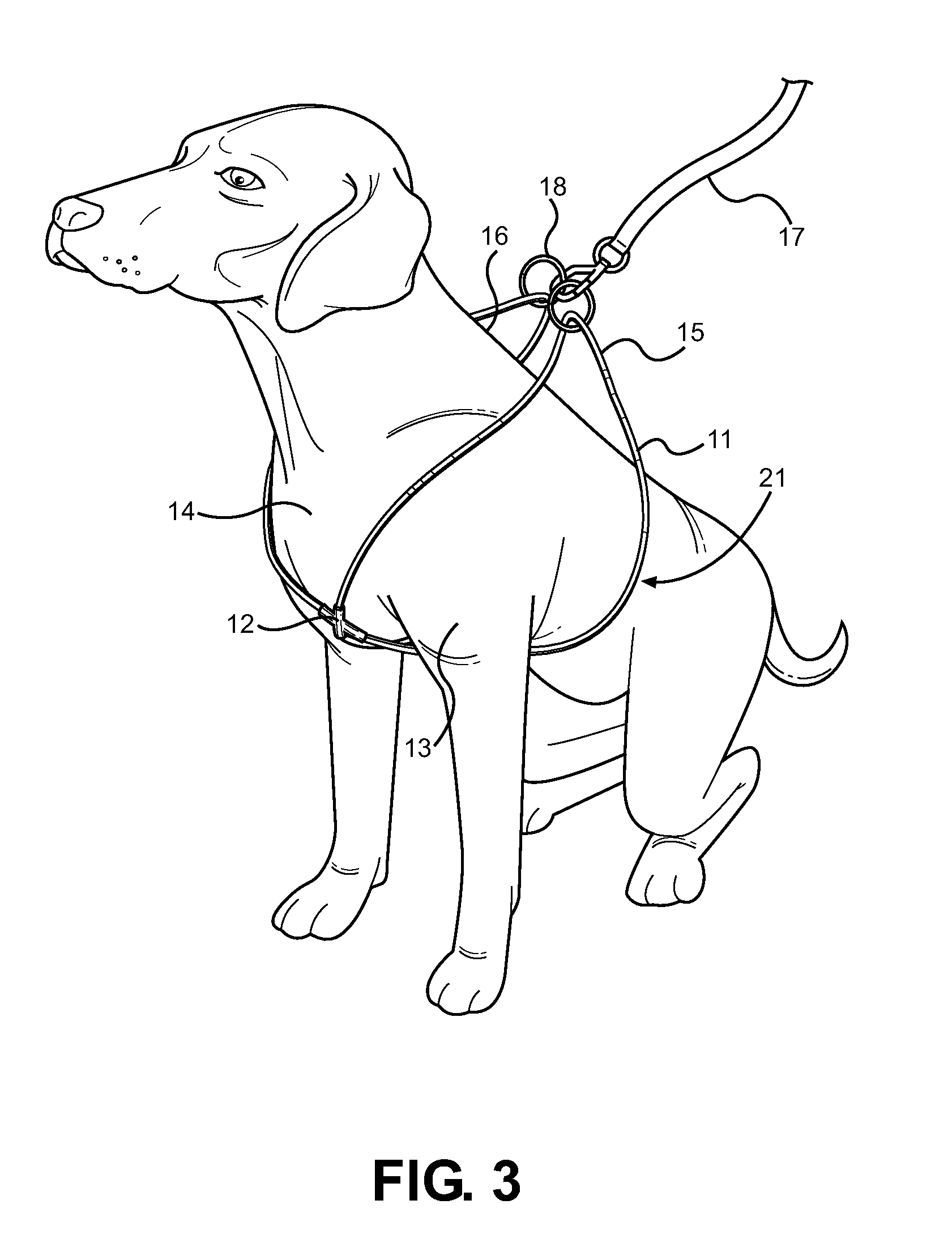
Looped Dog Walking Harness
InactiveUS20120234261A1Quickly and easily secured to and removedAvoid suffocationTaming and training devicesDorsal partsCross connection
Disclosed is an improved harness for a quadruped animal, comprising a length of material forming a first and second closed loop, along with a connector means for forming the loops into a figure eight shape. The animal's forelegs are places through the first and second loops of the figure eight, while the intersecting connector is positioned centrally against the animal's chest. The outer ends of each loop are wrapped around the animal's shoulders and secured along the animal's back via a securing means such as a leash clasp. A leading strap can be attached to the harness for use when walking the animal, wherein the connector bears against the animal's chest and the position of the loops provides improved control over the actions of the animal. The harness prevents choking or twisting of the animal's neck, while allowing the user to have better over control.
Owner:NELSON ROGER
Butchering processes for meat products
InactiveUS7503839B2Meat processing plantsPiercing-based meat tenderisingDorsal partsLongissimus dorsi
A method for mass-production butchering of a chuck roll of beef includes: sectioning the chuck roll anterior to and generally parallel to the first rib to separate a neck portion thereof from a remainder thereof, sectioning the remainder into a first portion and a second portion substantially along a natural seam, the first portion comprising rhomboideus, spinalis dorsi, and serratus ventralis muscles, and the second portion comprising multifidus dorsi, complexus, and longissimus dorsi muscles; sectioning the first portion to substantially remove the rhombolideus and the spinalis dorsi therefrom, leaving a denuded serratus ventralis; sectioning the serratus ventralis into a first set of separate portions. The method may further include: sectioning the second portion into a second set of separate portions, each separate portion in the second set including the multifidus dorsi, complexus, and longissimus dorsi muscles.
Owner:LOBELS ENTERPRISES
Method for conducting a targeted training and a corresponding training device
InactiveUS7691033B2Change loadEasy to useMovement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesHuman bodyDorsal parts
The invention relates to a method for a targeted training of the human body as well as a corresponding training device for realizing said method. The training device is used for the training of the body region (vertebral column) between shoulder girdle and pelvic girdle (back region) by using the limbs, arms and legs, such that the body region of the shoulder girdle is turned (twisted) in the opposite direction as the body region of the pelvic girdle, thereby resulting in a relative turning movement between the respective vertebras of the vertebral column.
Owner:ROLLI ENGELBERT
Roping harness
Owner:ZEDEL CORP
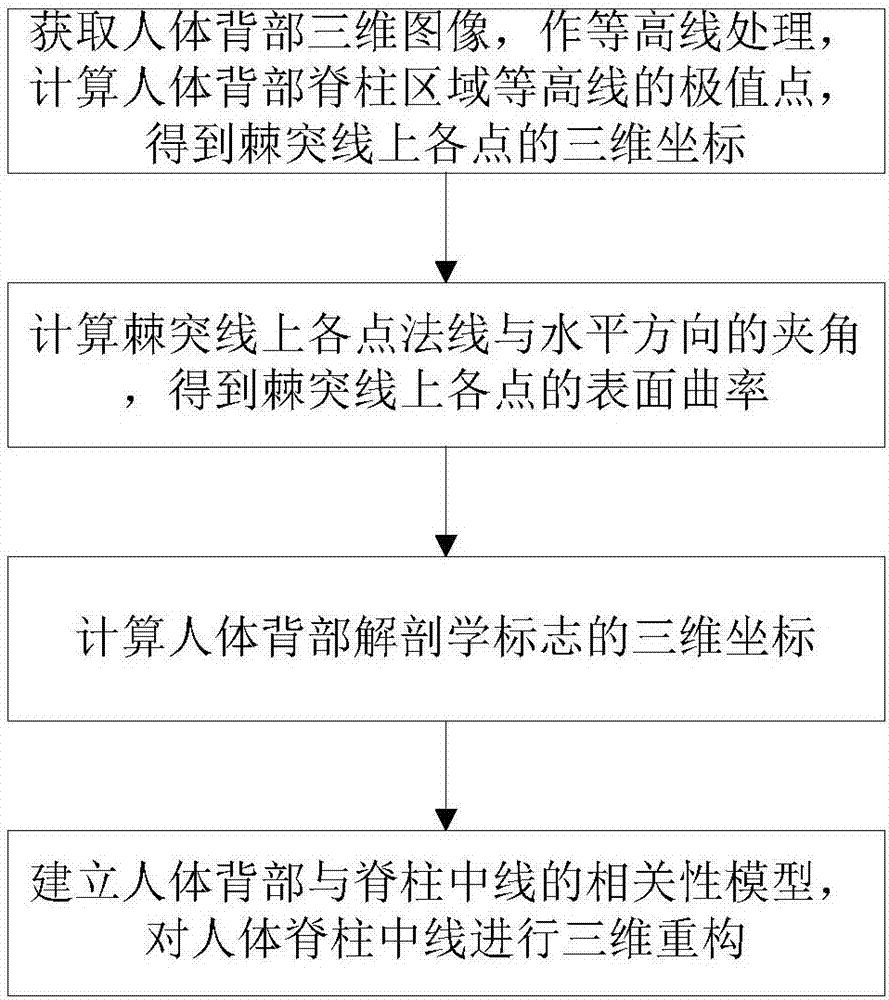
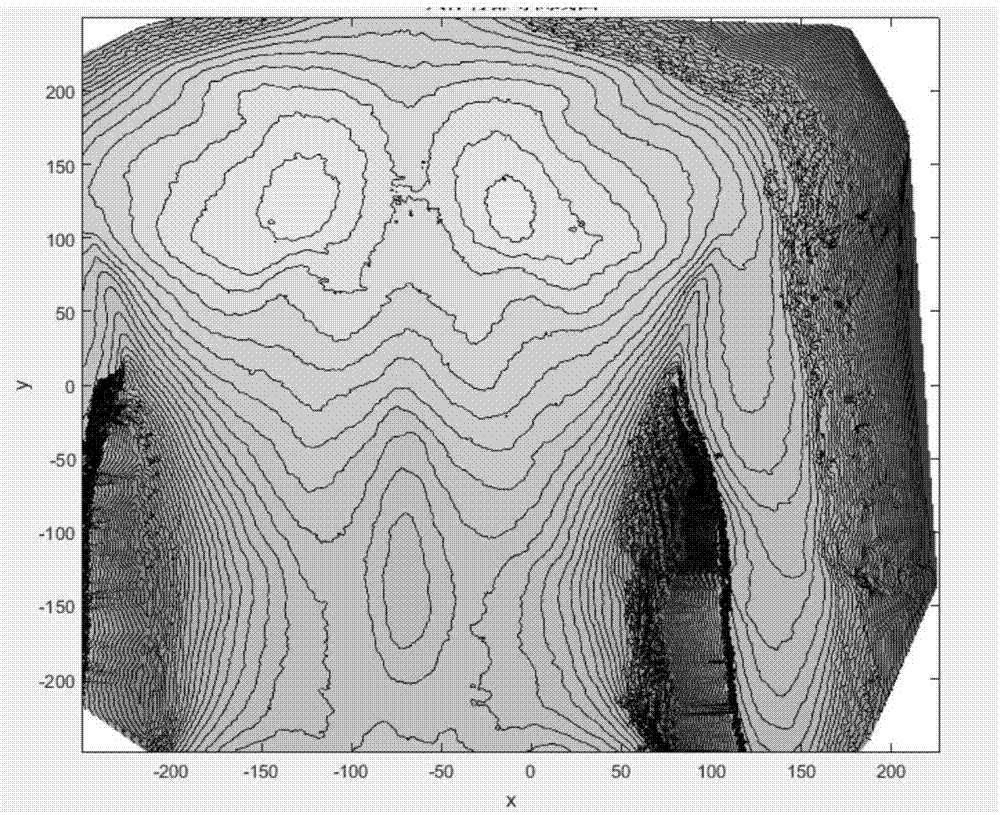
Three-dimensional reconstruction method of center line of spine of human body
InactiveCN107464275AImprove reconstruction accuracyPromote reconstructionImage rendering3D-image renderingDorsal partsHuman body
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method of the center line of the spine of a human body. According to the invention, the method comprises steps of by constructing a contour map of the curved face of the surface of the back of the human body, and combining related characteristics of the contour, finding the central line of the back of the human body; carrying out integer interpolation on the center line of the back to acquire the curvature of each point of the central line of the back; by use of sign points in the anatomy, solving the length of the spine main body and acquiring a spine main body length expression; and substituting the spine main body length expression into a correlation model to reconstruct the three-dimensional curve of the center line of the spine. Thus, reconstruction precision is greatly improved and reconstruction effects are good.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
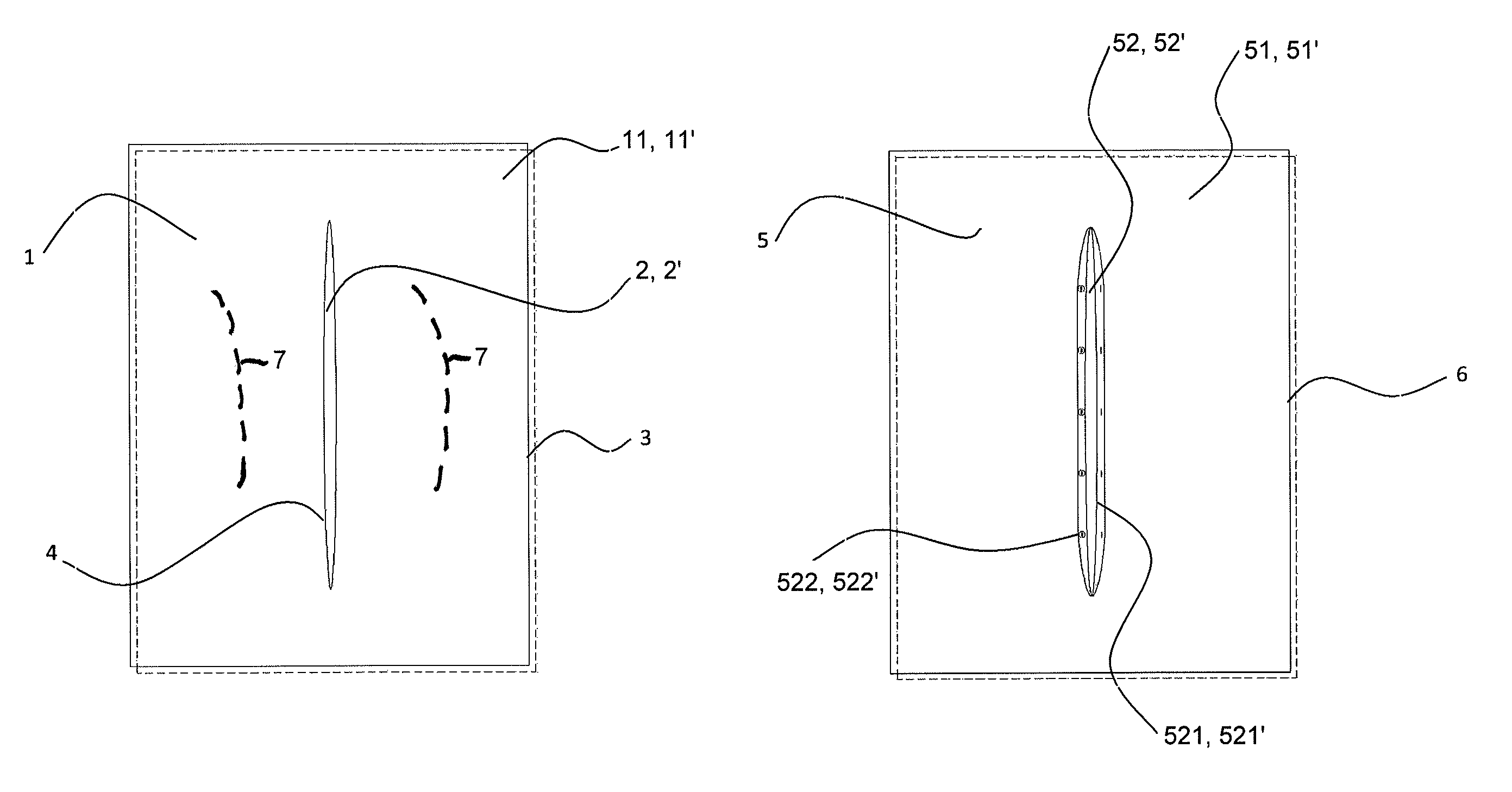
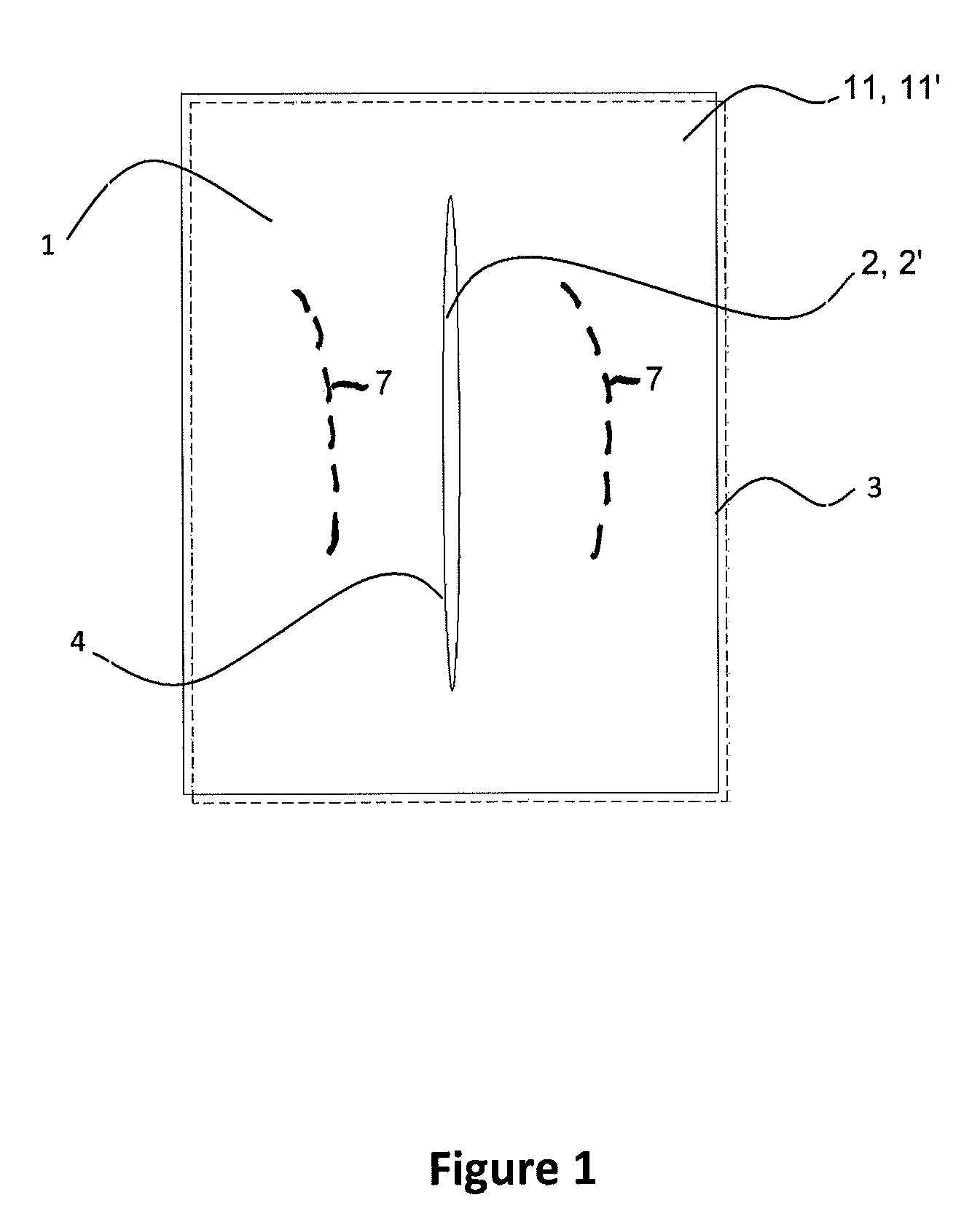
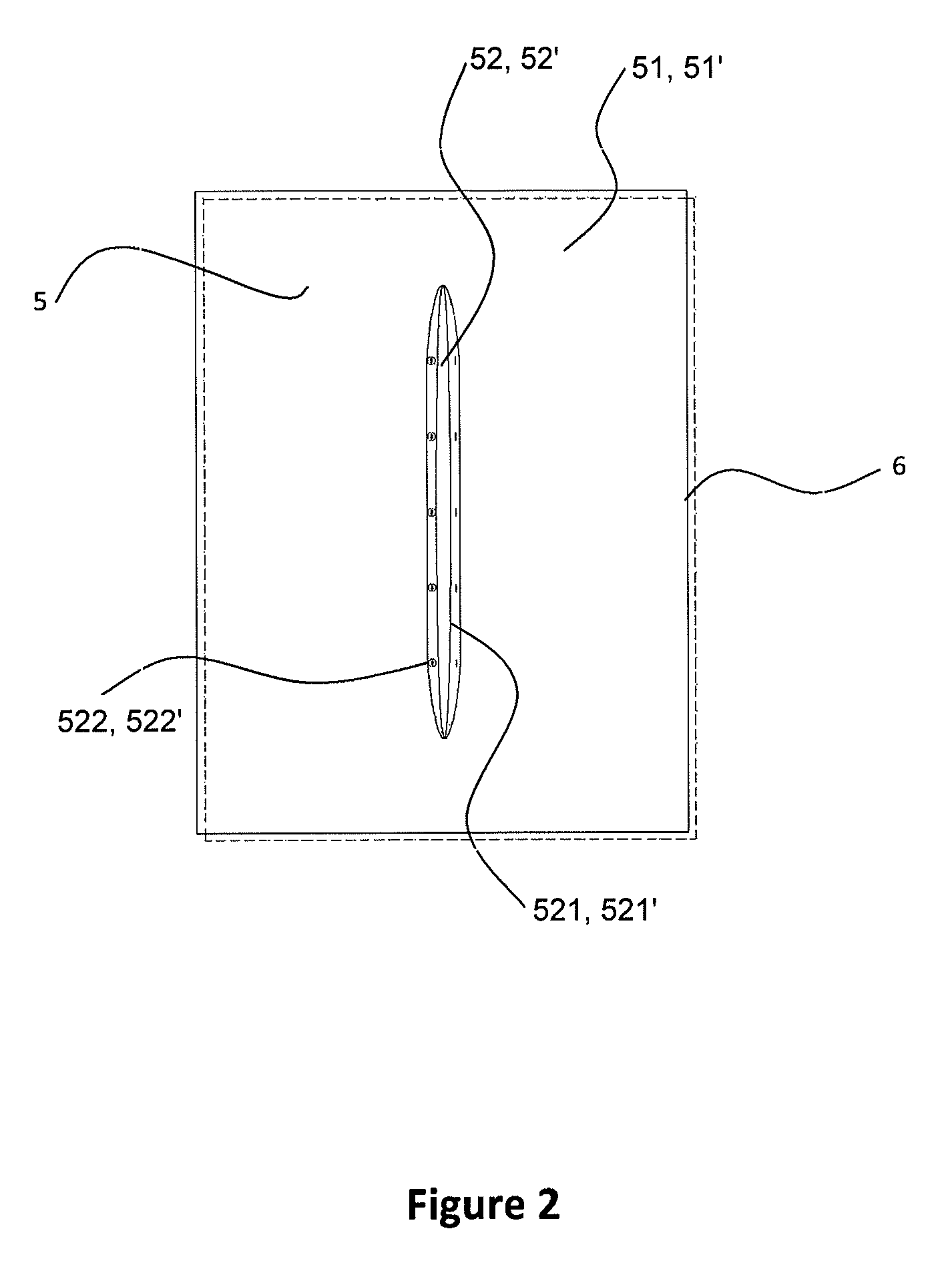
Blanket and blanket cover
Blanket with protective effect against dorsal parts of the human body becoming cold during sleep, with a composition of two textile layers (11, 11′) of the same size and shape that are equipped with identically located prolonged openings (2, 2′) of the same size and shape that are mutually firmly connected alongside their perimeters (3) and alongside the perimeter of the opening (4). A blanket cover is described, too, consisting of two textile layers of the same size and shape equipped with identically located prolonged openings of the same size and shape.
Owner:HOLEY QUILT
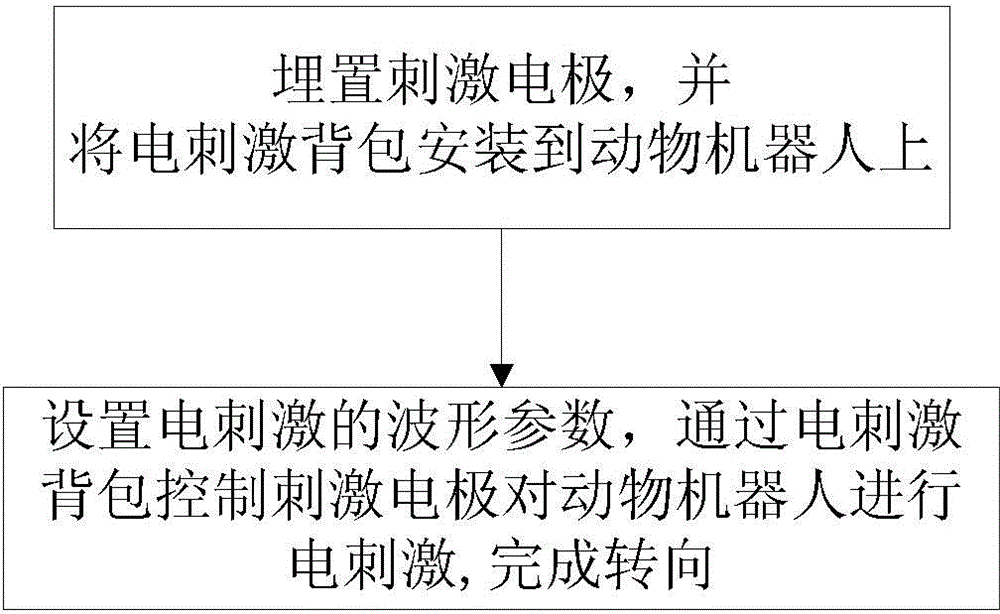
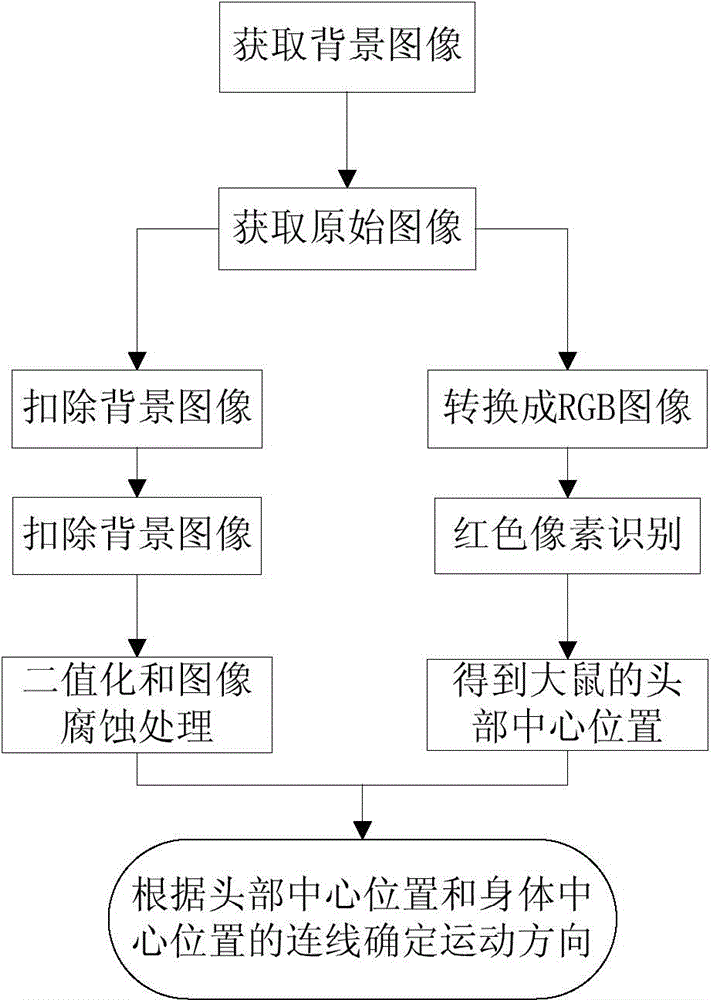
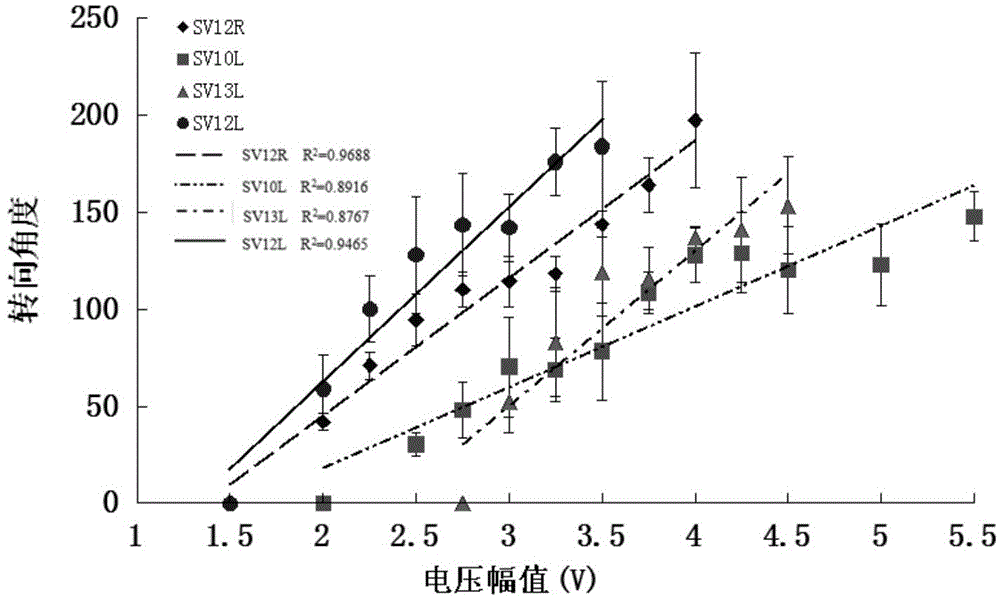
Method for controlling animal robot to turn on basis of ventral posterior medial nucleus electrical stimulation
InactiveCN104679028AControllable steering angleOmit training timeControl using feedbackControl animalThalamus
The invention relates to a method for controlling an animal robot to turn on the basis of ventral posterior medial nucleus electrical stimulation. The method comprises the steps that two stimulating electrodes are respectively imbedded into VPM (Ventral Posterior Medial Nucleus) regions on both sides of the animal robot, the electrodes are fixed on skulls with dental cement, and an electrical stimulation backpack is installed on the animal robot; waveform parameters of electrical stimulation are set by an upper computer and are transmitted to the electrical stimulation backpack at the back of the animal robot in a wireless mode, the stimulating electrodes are controlled by the electrical stimulation backpack, so as to perform electrical stimulation on the animal robot, and corresponding thalamus-cortex projection loops are activated, so that the animal robot generates a virtual feeling, so as to complete turning. According to the method, a traditional method that the animal robot learns to turn by reward training is eliminated, turning is realized directly through the electrical stimulation, the controllability over a turning angle is realized, a large amount of training time is saved, the working efficiency is high, and the method has good application prospects in the field of animal robot navigation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
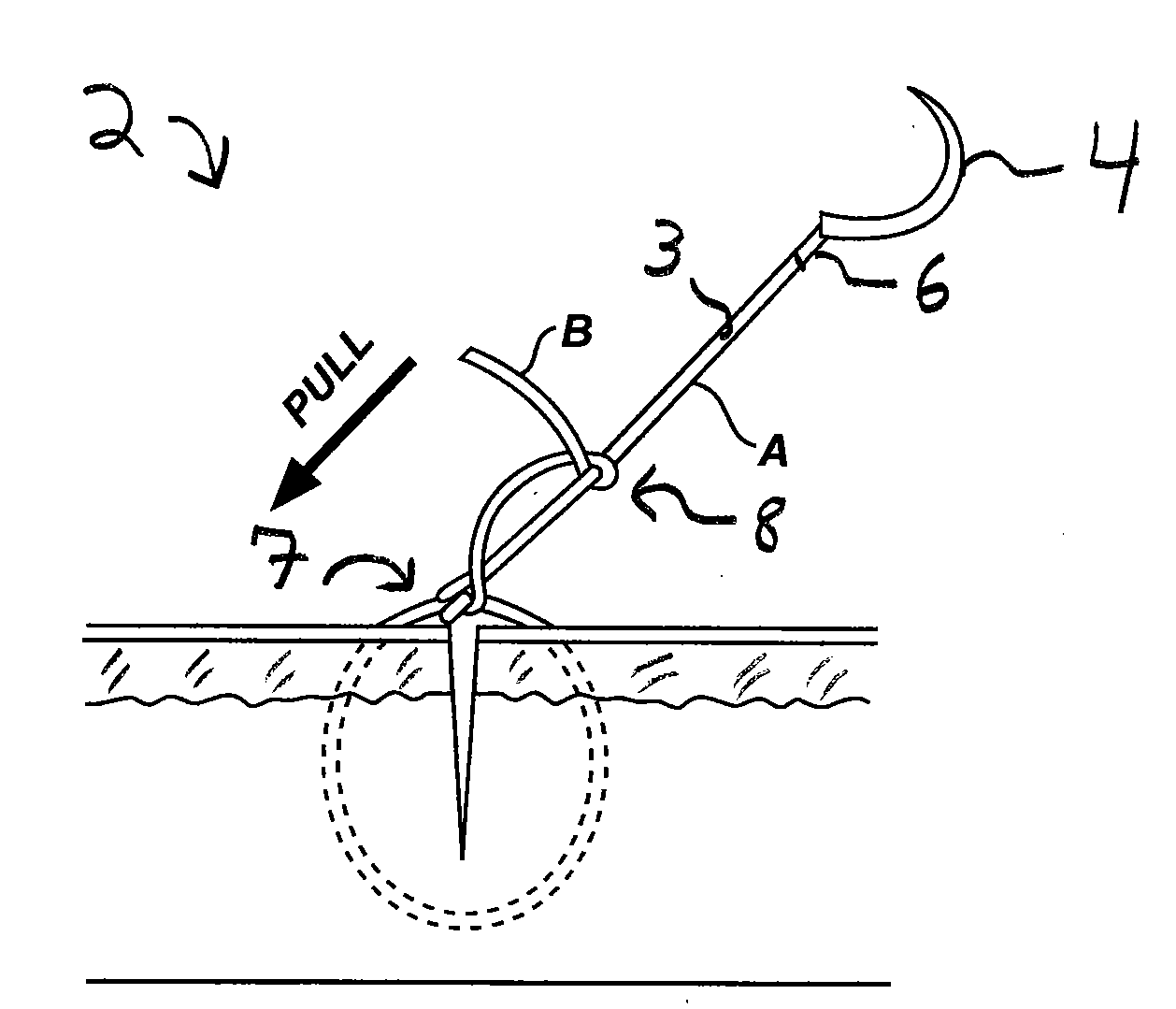
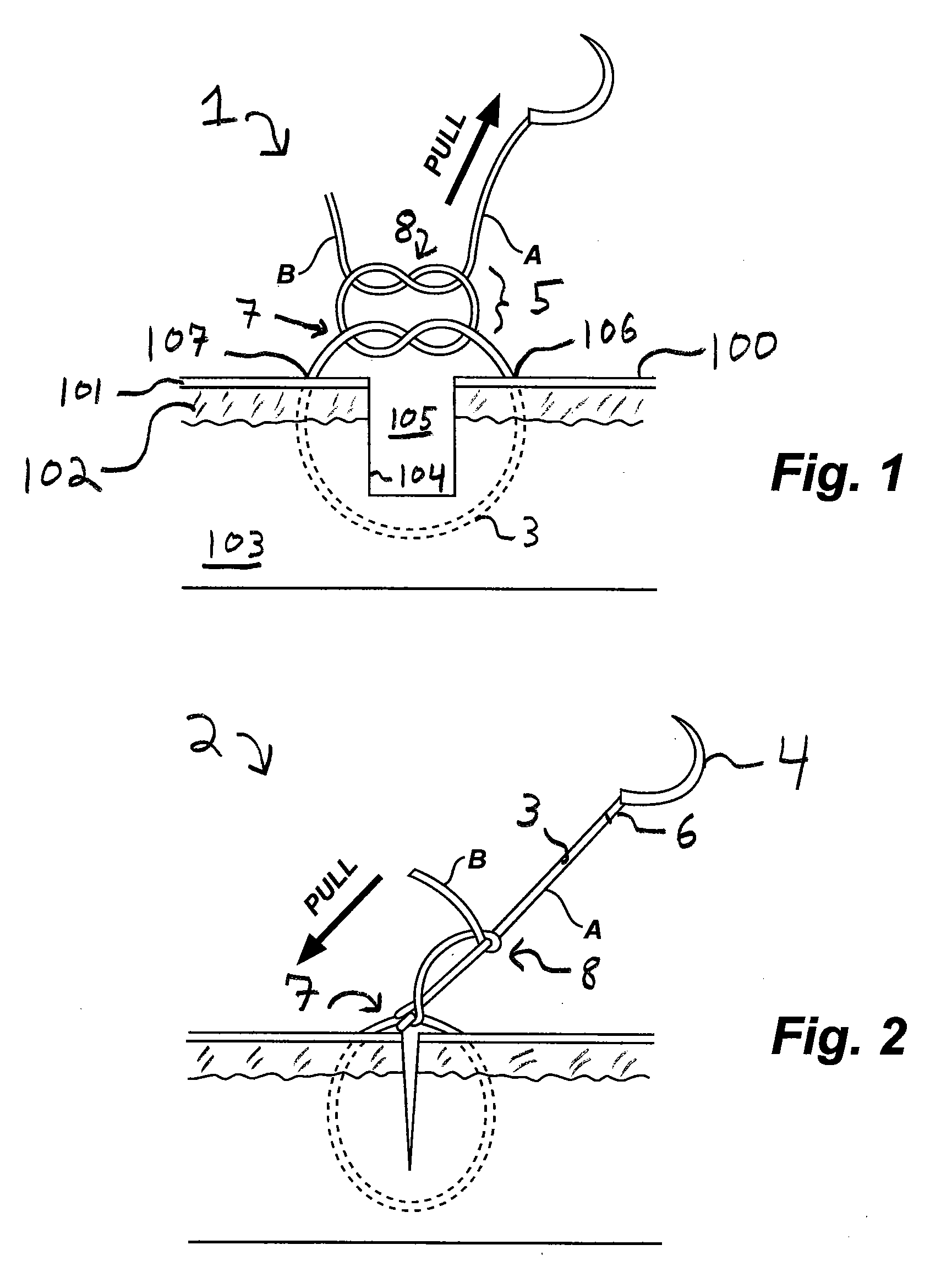
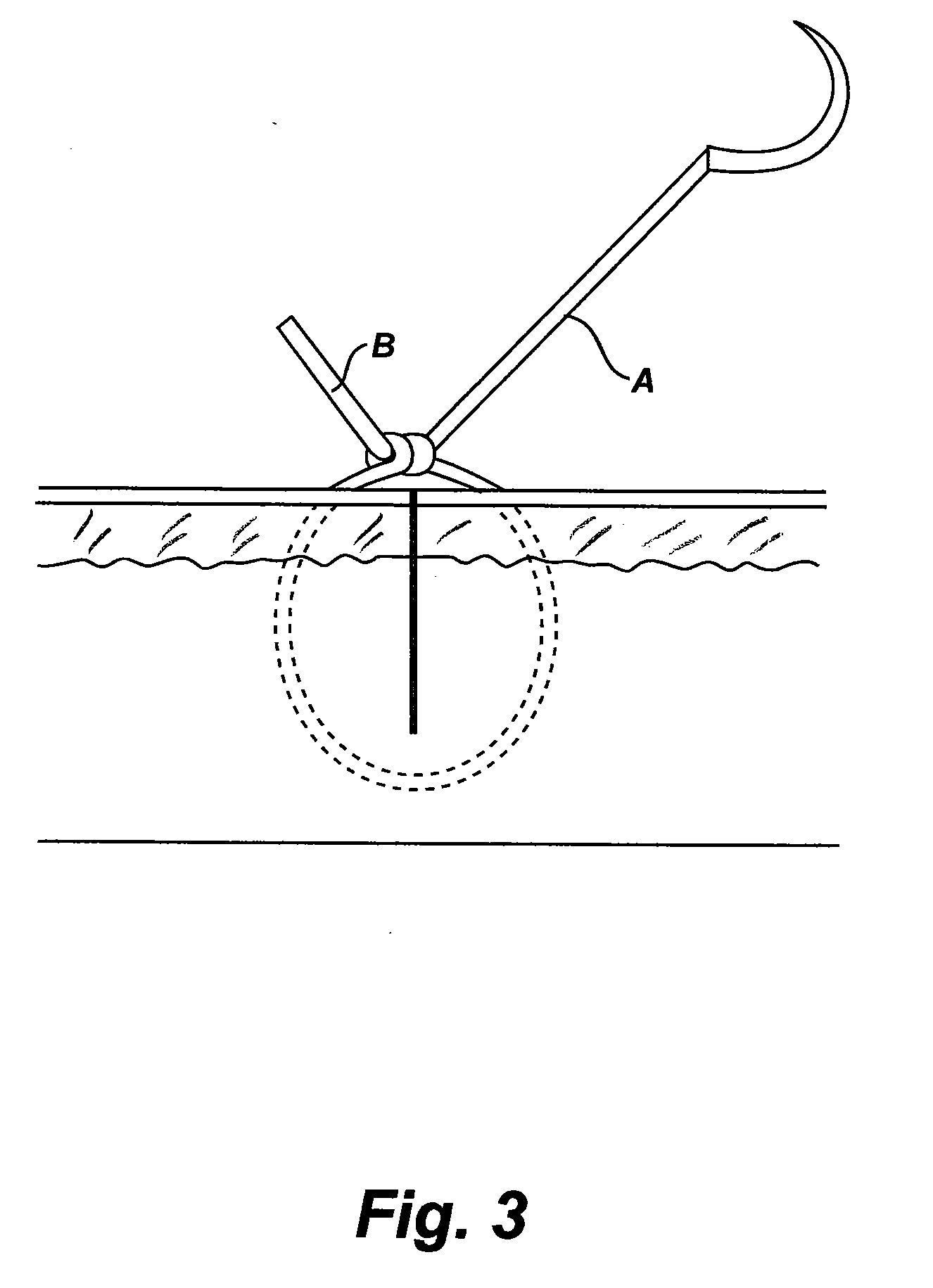
Gliding Stitch for Closing Wounds Under Tension
InactiveUS20090281569A1Efficient and effectiveOvercome deficienciesSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsClose woundsDorsal parts
A gliding stitch technique provides efficient and effective means to close a wound under tension. The gliding stitch is especially useful in treating wounds found within thick skin such as a scalp or back wound. The disclosed suture method may be used upon humans and other mammals.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
Closure element for absorbent sanitary products, manufacturing process, process of use, and product thus obtained
ActiveUS20080099124A1Keep properlyReduce riskSlide fastenersWood working apparatusDorsal partsEngineering
Owner:FAMECCANICA DATA SPA
Rotary torso exercise bench
InactiveUS7297095B2Safe and efficient and accurateEasy to implementStiltsWeightsExternal obliquesDorsal parts
A rotary torso exercise machine that isolates and targets the internal and external oblique muscles on both sides of the torso as well as providing conditioning to the rectus abdominis muscle. The machine supports a user's body in a generally supine position and includes five essential features, a frame, fixed feet stabilizing rollers, a fixed lower torso support or seat, a rotatable upper torso support, and a peg for holding free weights that impart resistance against the rotation of the upper torso support. The user may selectively vary the mount and direction of resistance as well as the degree of rotation. The machine may be easily converted for use as either a back or abdominal exercise.
Owner:ZACHARY KYRIACOS MARK
Hand protective device
InactiveUS20080263746A1Improve ergonomicsAvoid foldingGlovesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesDorsal partsAdhesive
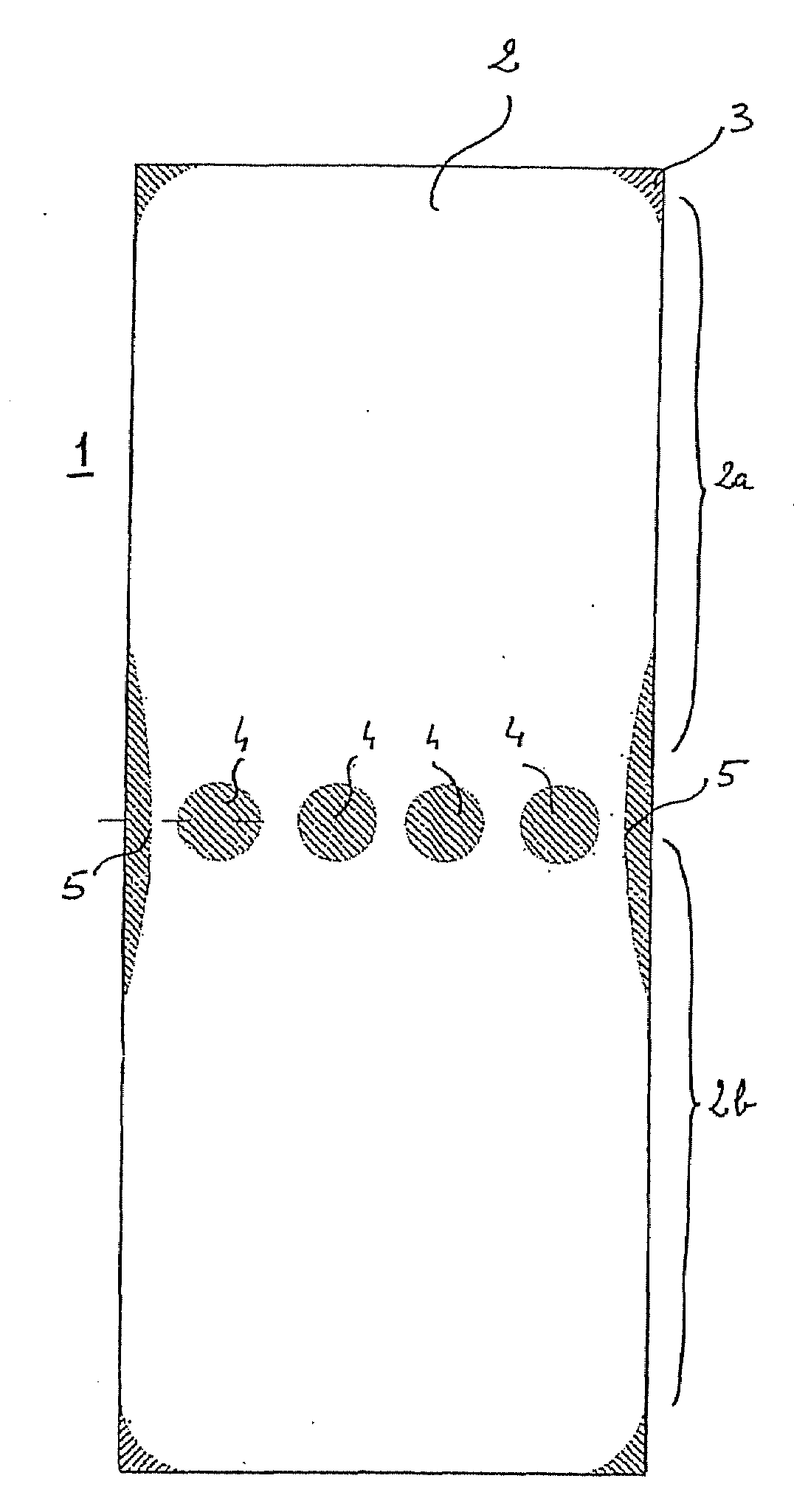
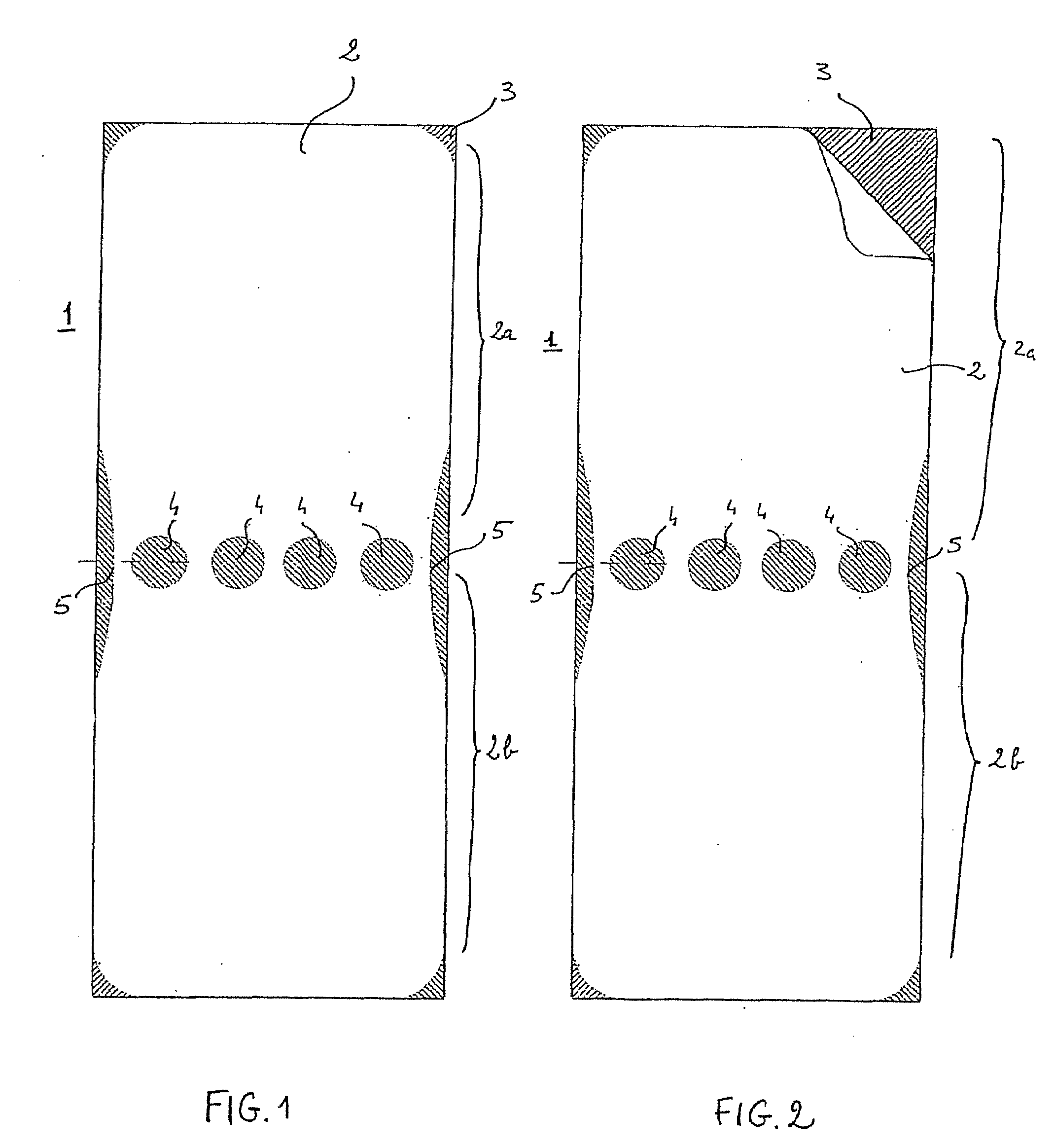
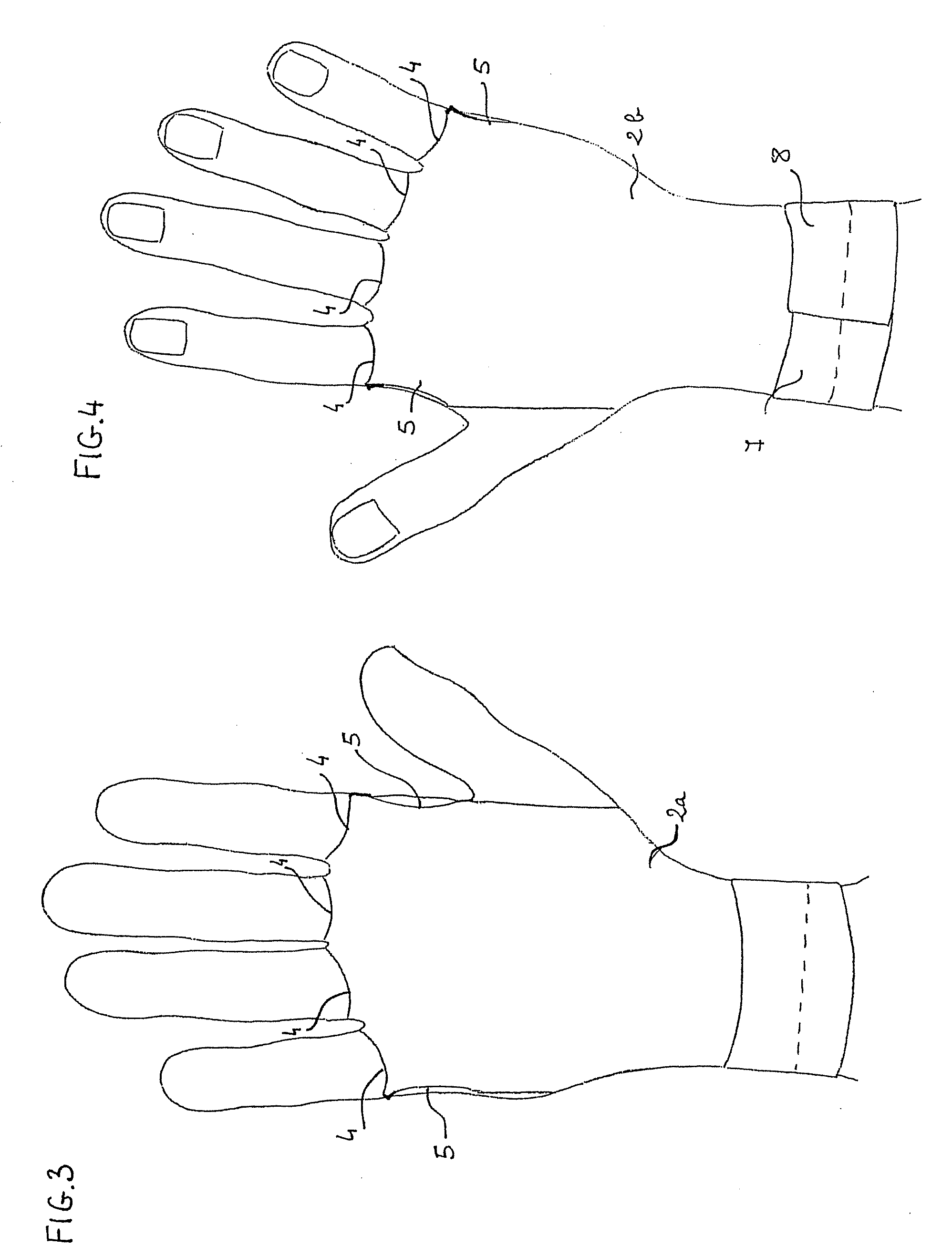
A protective device includinga protective sheet having a general rectangular shape, cut into which are four circular openings positioned in an aligned manner level with its transverse median axis which connects the middle of each of the lengths, the four openings separating the protective sheet into a first part known as the palmar part and a second part known as the dorsal part; the protective sheet being coated on one of its sides with a hypoallergenic adhesive; anda peelable film whose longitudinal and transverse dimensions are equal to those of the protective sheet superposed on the side of the protective sheet coated with the hypoallergenic adhesive.
Owner:ESTRADE DAVID
Protection element or attachment for safety glove fingers
Owner:SGOMBICH PEREZ JORGE RUBEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com