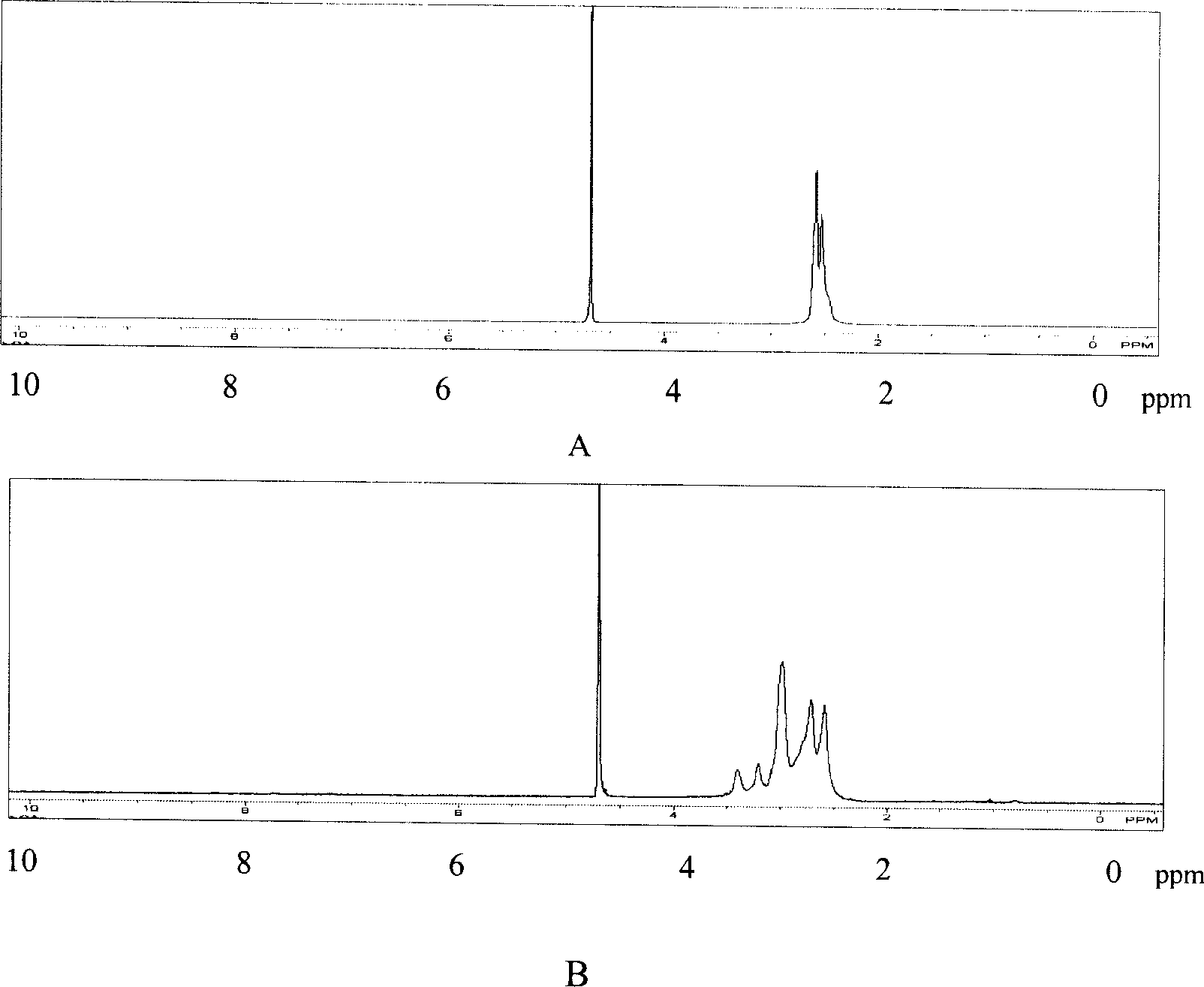
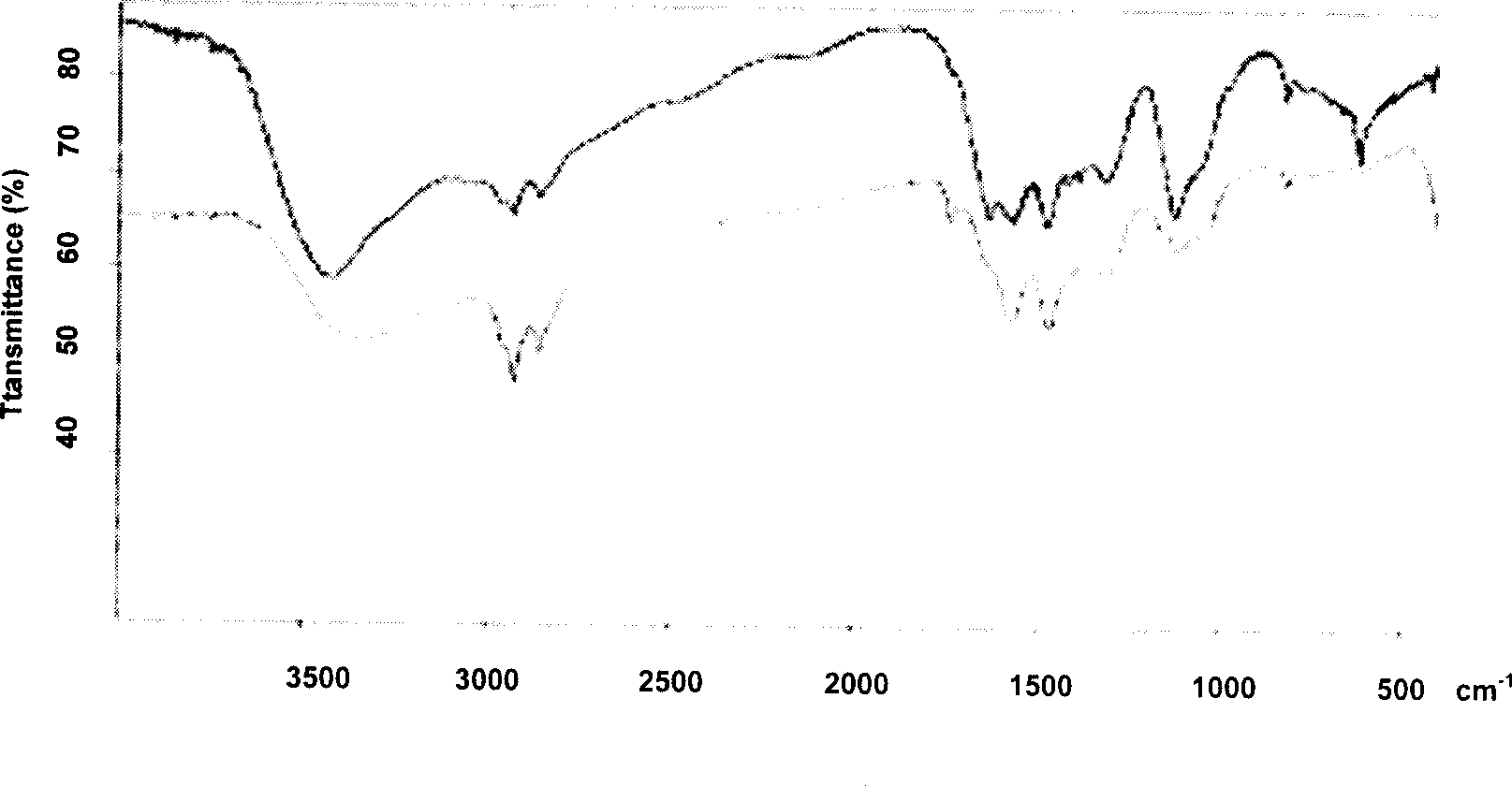
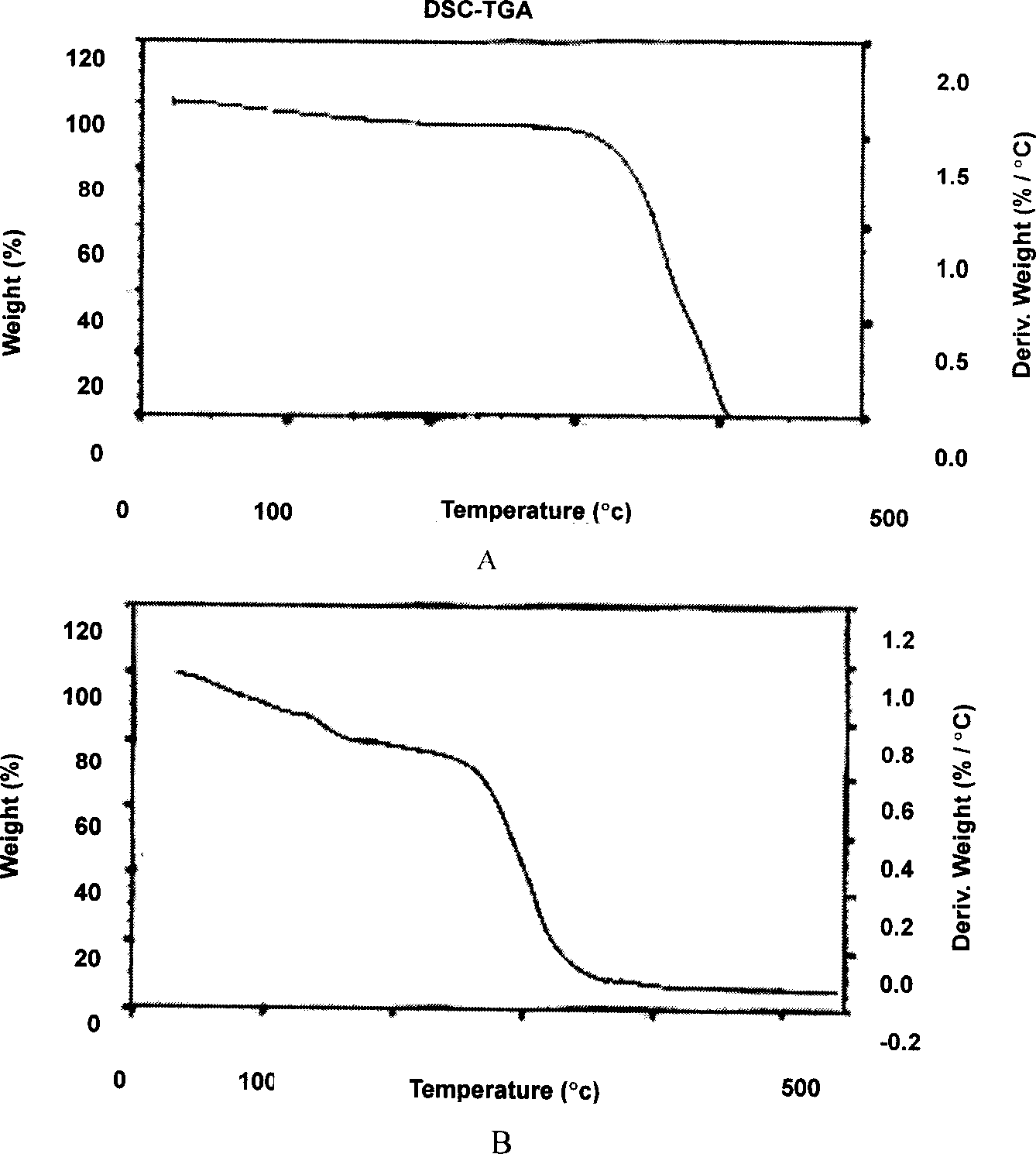
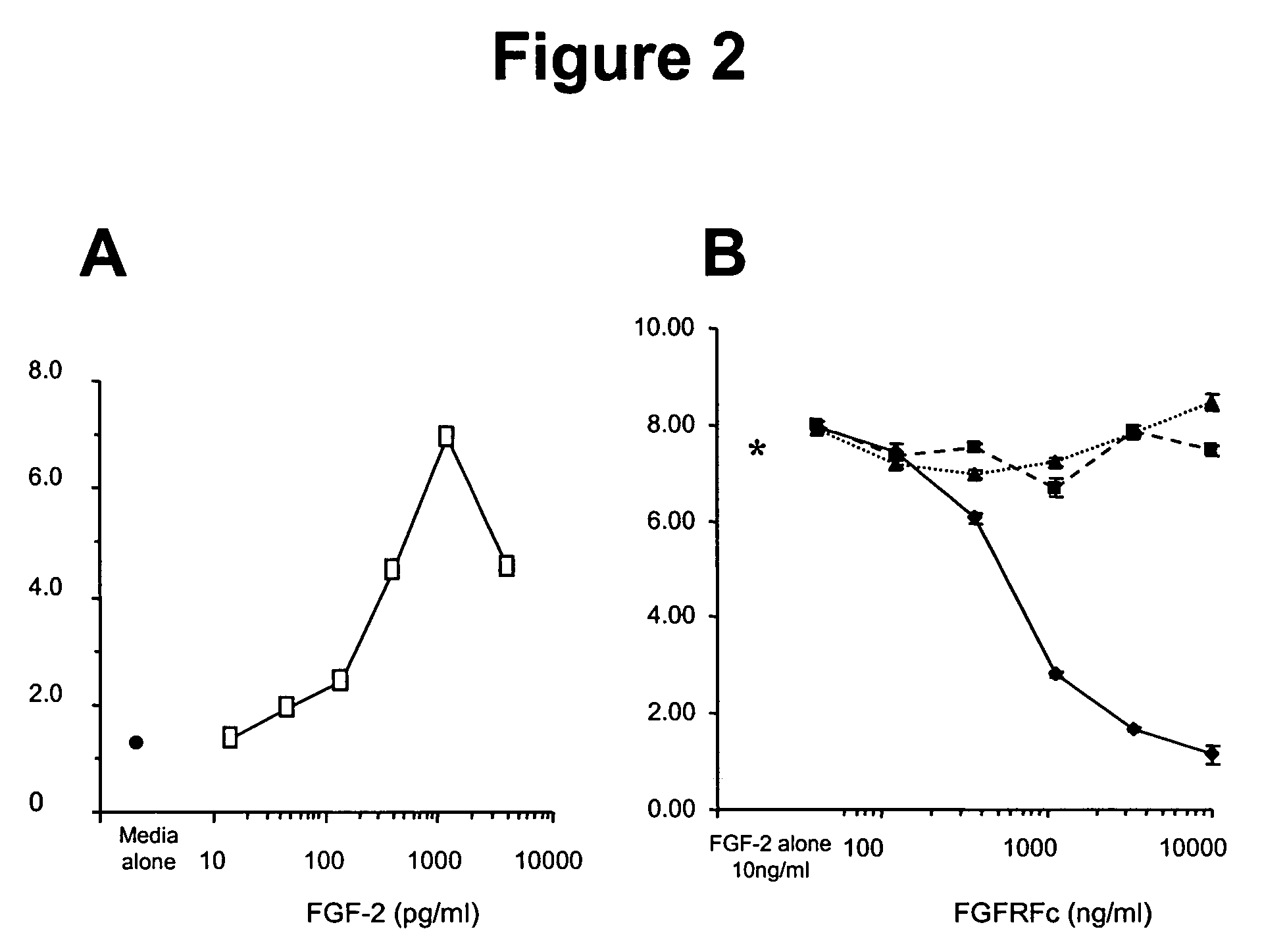
Patents
Literature
59 results about "Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
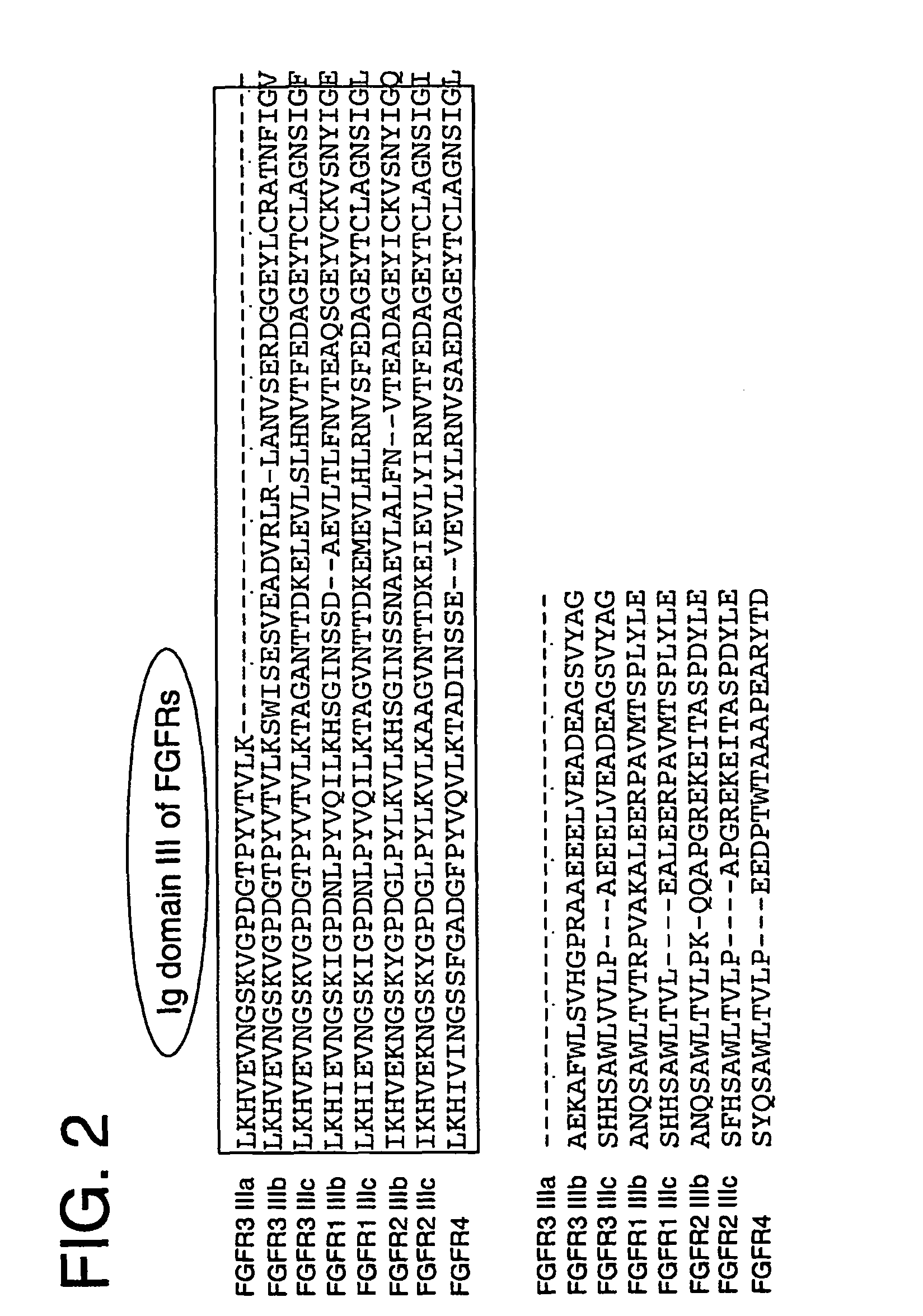
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGFR4 gene. FGFR4 has also been designated as CD334 (cluster of differentiation 334). The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, where amino acid sequence is highly conserved between members and throughout evolution. FGFR family members differ from one another in their ligand affinities and tissue distribution. A full-length representative protein would consist of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin-like domains, a single hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion of the protein interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and differentiation. The genomic organization of this gene, compared to members 1-3, encompasses 18 exons rather than 19 or 20. Although alternative splicing has been observed, there is no evidence that the C-terminal half of the IgIII domain of this protein varies between three alternate forms, as indicated for members 1-3. This particular family member preferentially binds acidic fibroblast growth factor and, although its specific function is unknown, it is overexpressed in gynecological tumor samples, suggesting a role in breast and ovarian tumorigenesis.
Muteins of fibroblast growth factor 21
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor 21 with improved pharmaceutical properties. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and in reducing the mortality and morbidity of critically ill patients.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Muteins of fibroblast growth factor 21
ActiveUS7622445B2Reduce sensitivityReduced O-glycosylationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMutated proteinNucleic acid sequence
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor-21 with reduced susceptibility for proteolytic degradation when expressed in yeast. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Muteins of fibroblast growth factor 21
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor 21 with reduced capacity of O-glycosylation when expressed in yeast compared to wild-type human FGF-21. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Muteins of fibroblast growth factor 21
InactiveUS7655627B2Reduced deamidationReduce capacityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderADAMTS ProteinsWild type
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor 21 with reduced deamidation compared to wild-type human FGF-21. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Methods of monitoring the modulation of the kinase activity of fibroblast growth factor receptor and uses of said method
InactiveUS20110045511A1Useful predictionOrganic active ingredientsBiological material analysisFibroblast growth factor receptor 2Biomarker (petroleum)
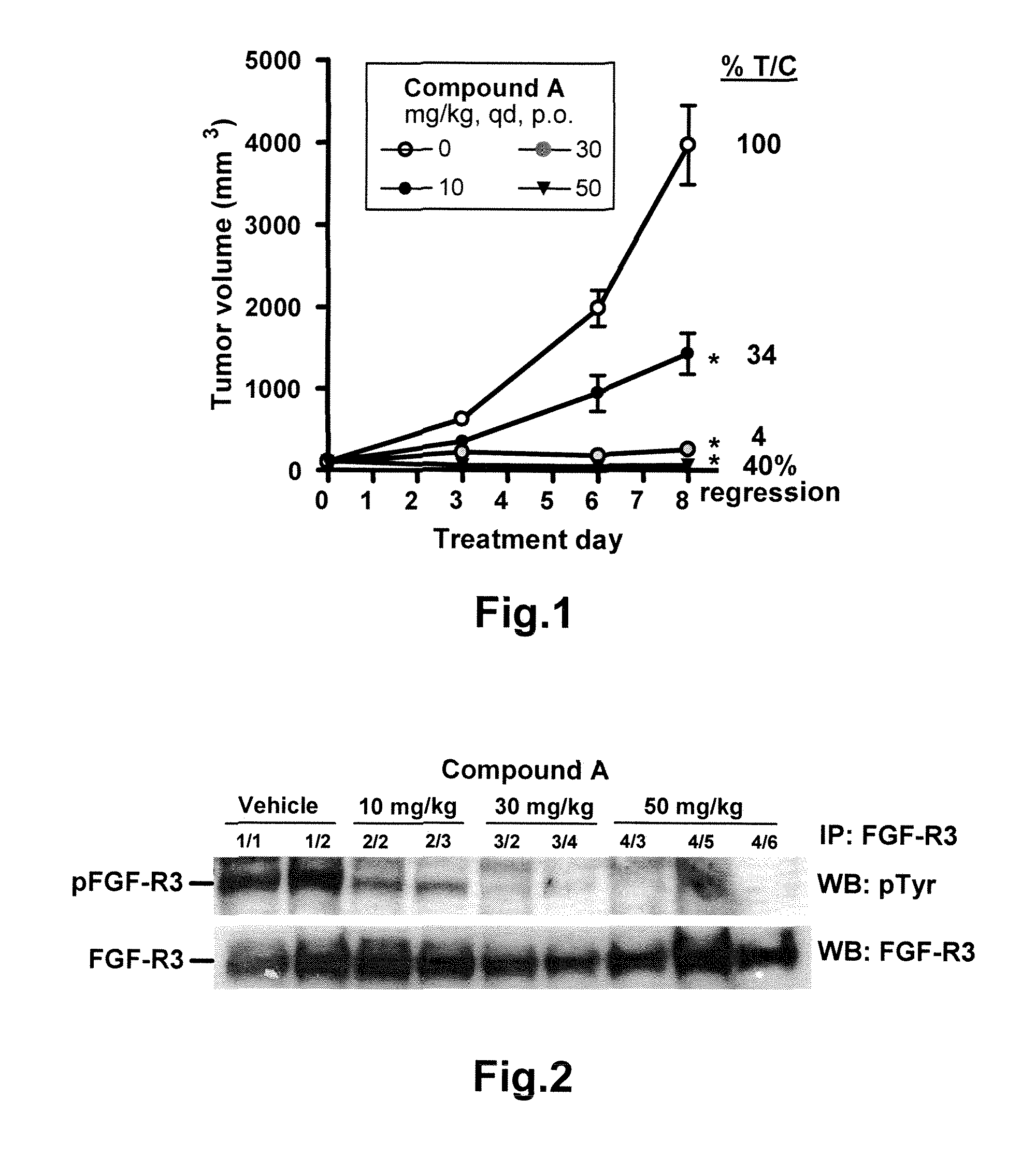
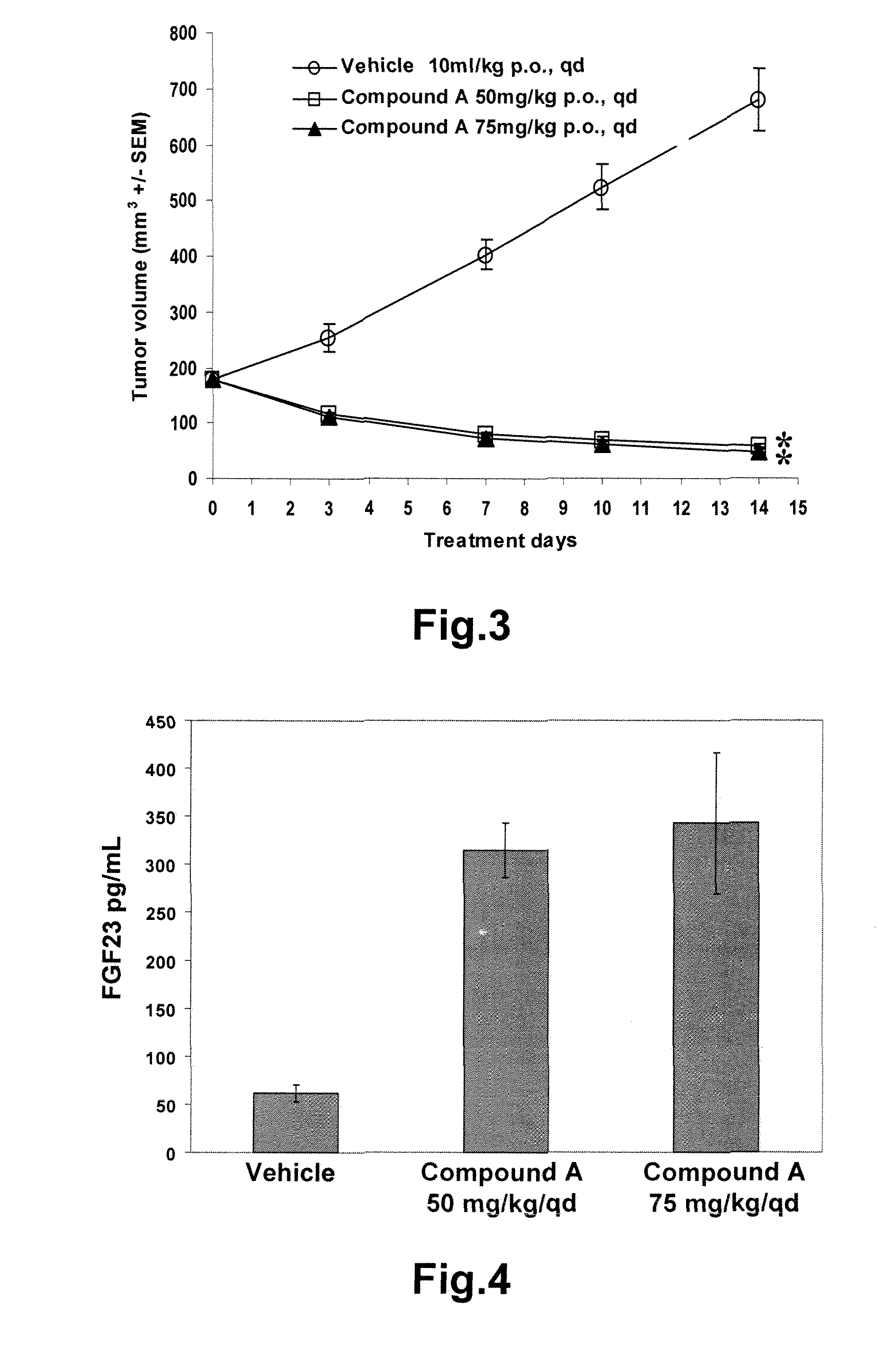
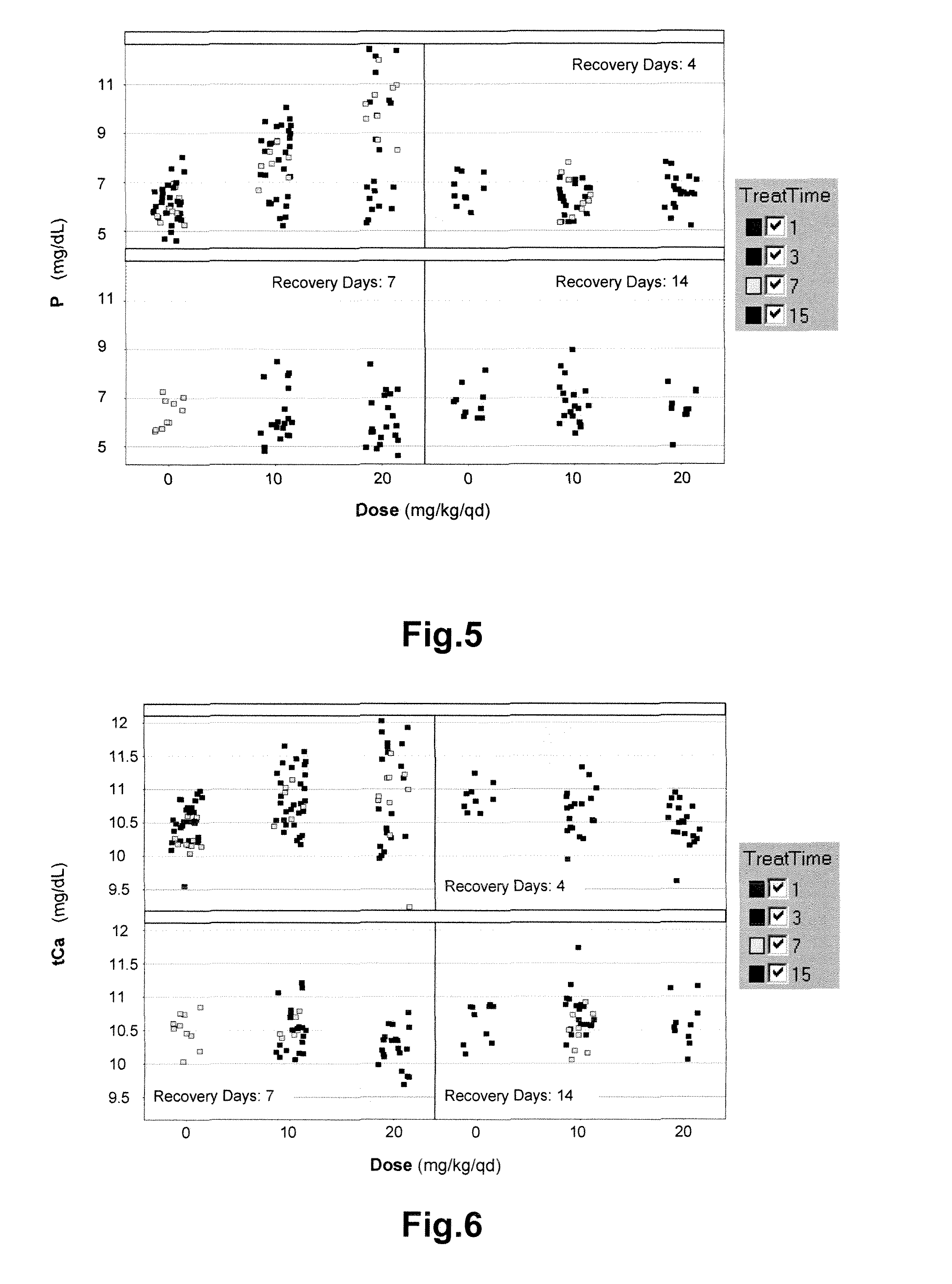
The present invention relates generally to methods of in vitro diagnostics, in particular the use of a compound selected from the group consisting of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), inorganic phosphorus (P), the product of inorganic phosphorus and total calcium (P×tCa), osteopontin (OPN) and parathyroid hormone (PTH) as biomarker. Said biomarkers can be used to monitor the modulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) kinase activity, in particular its inhibition, and / or the occurrence of secondary effects of FGFR inhibition. The invention further provides methods and kits relating to these uses.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Antibodies blocking fibroblast growth factor receptor activation and methods of use thereof
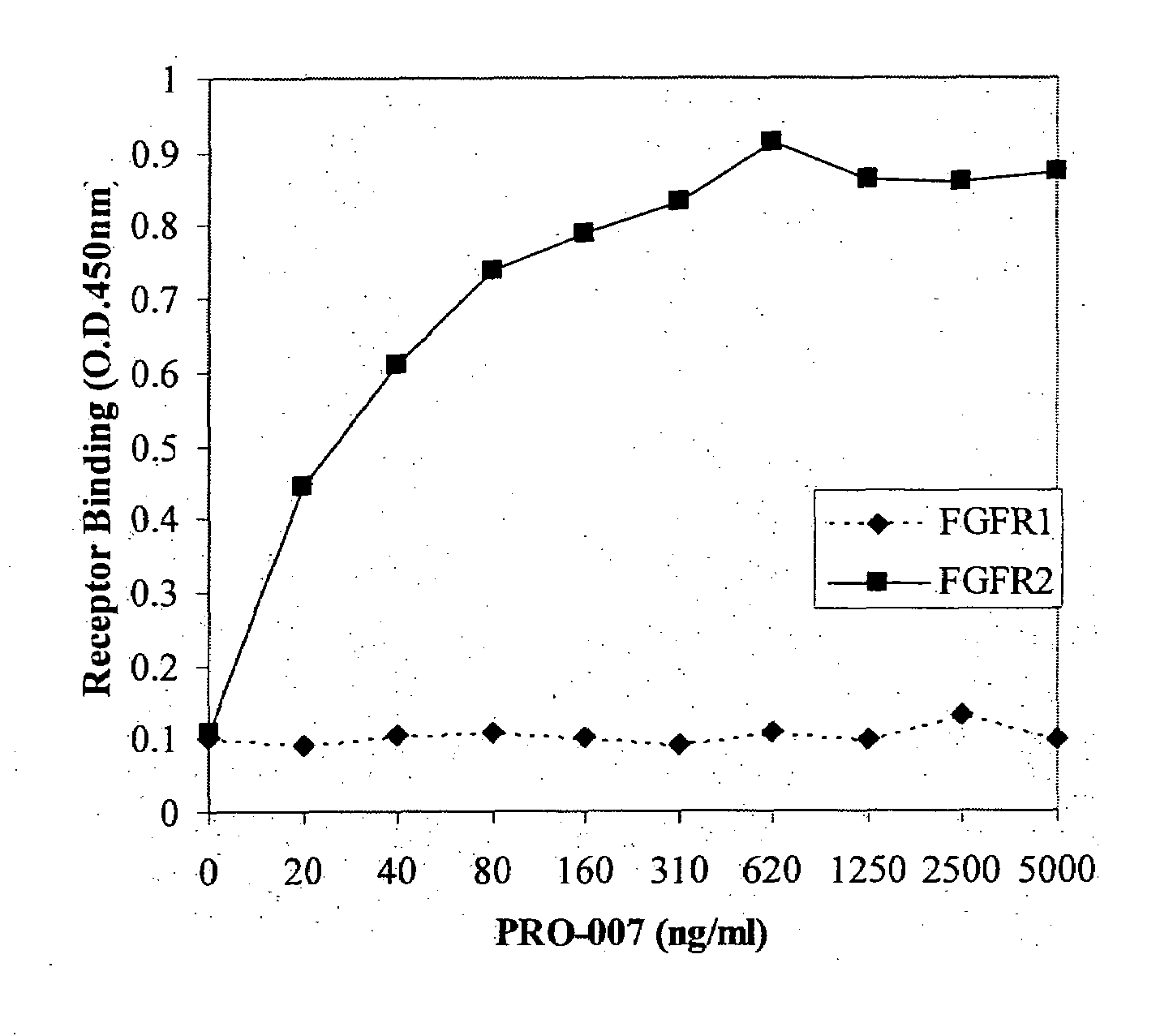
ActiveUS20100047251A1Strong specificityHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntibody ingredientsFGF ReceptorReceptor activation
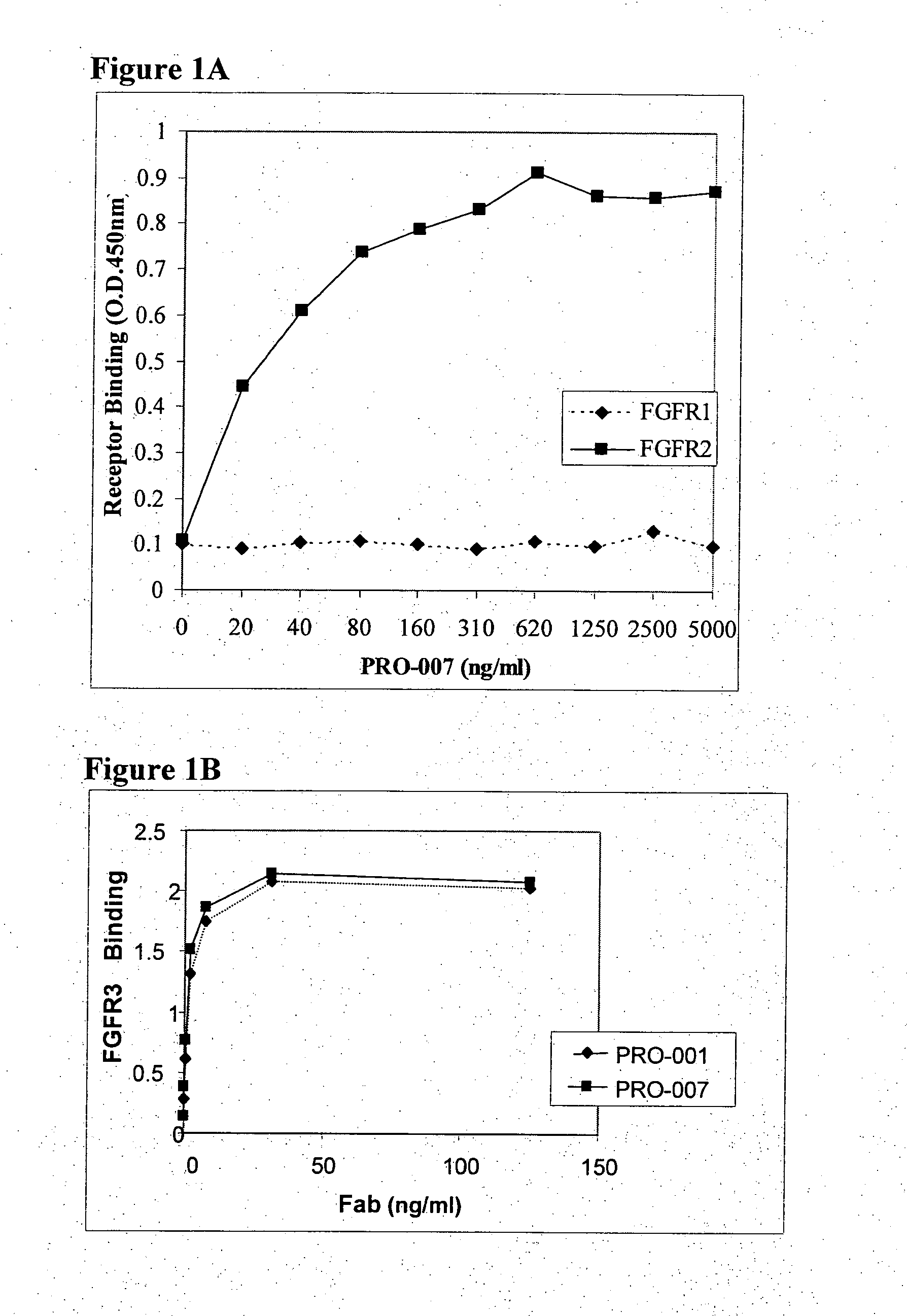
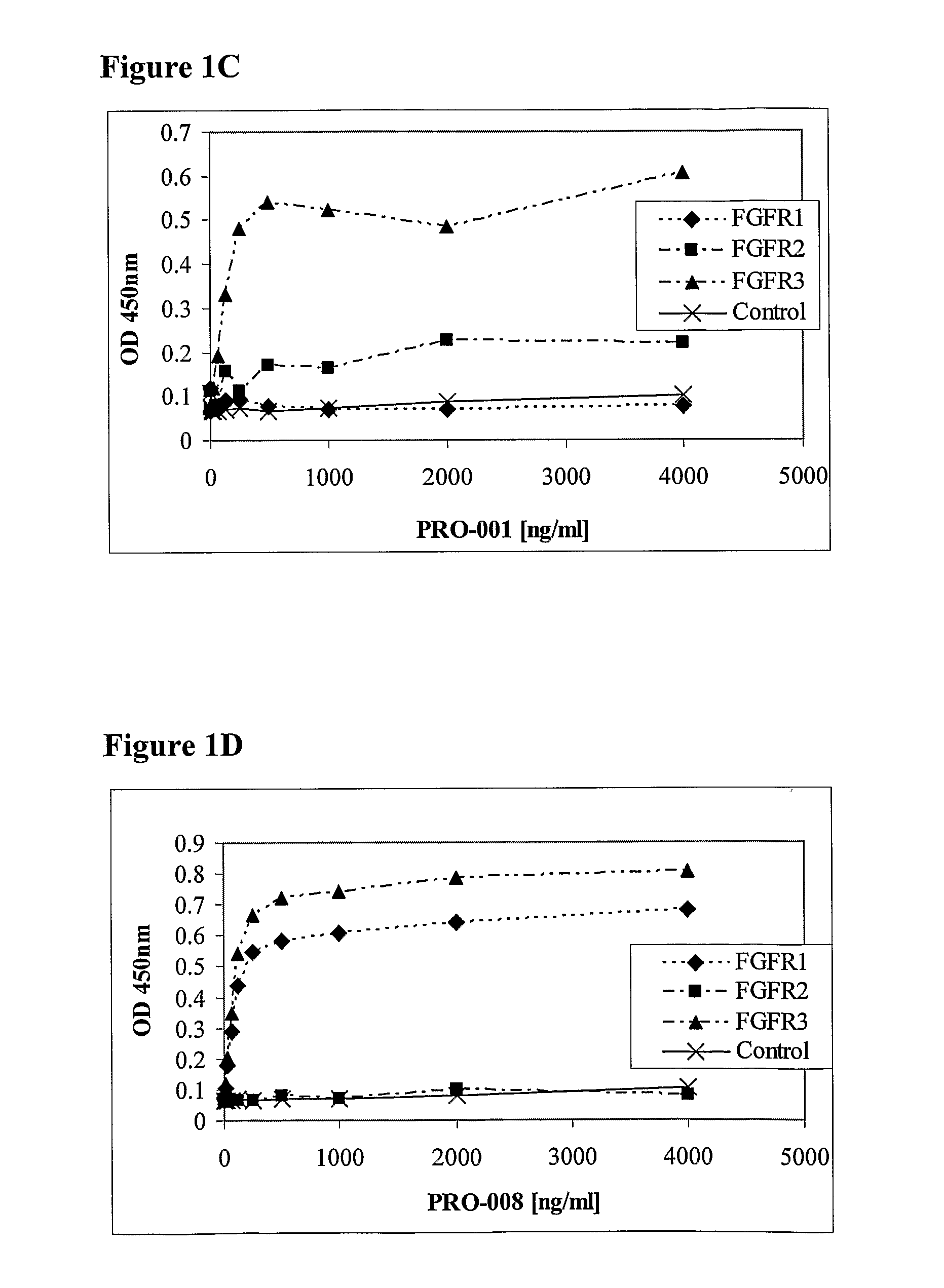
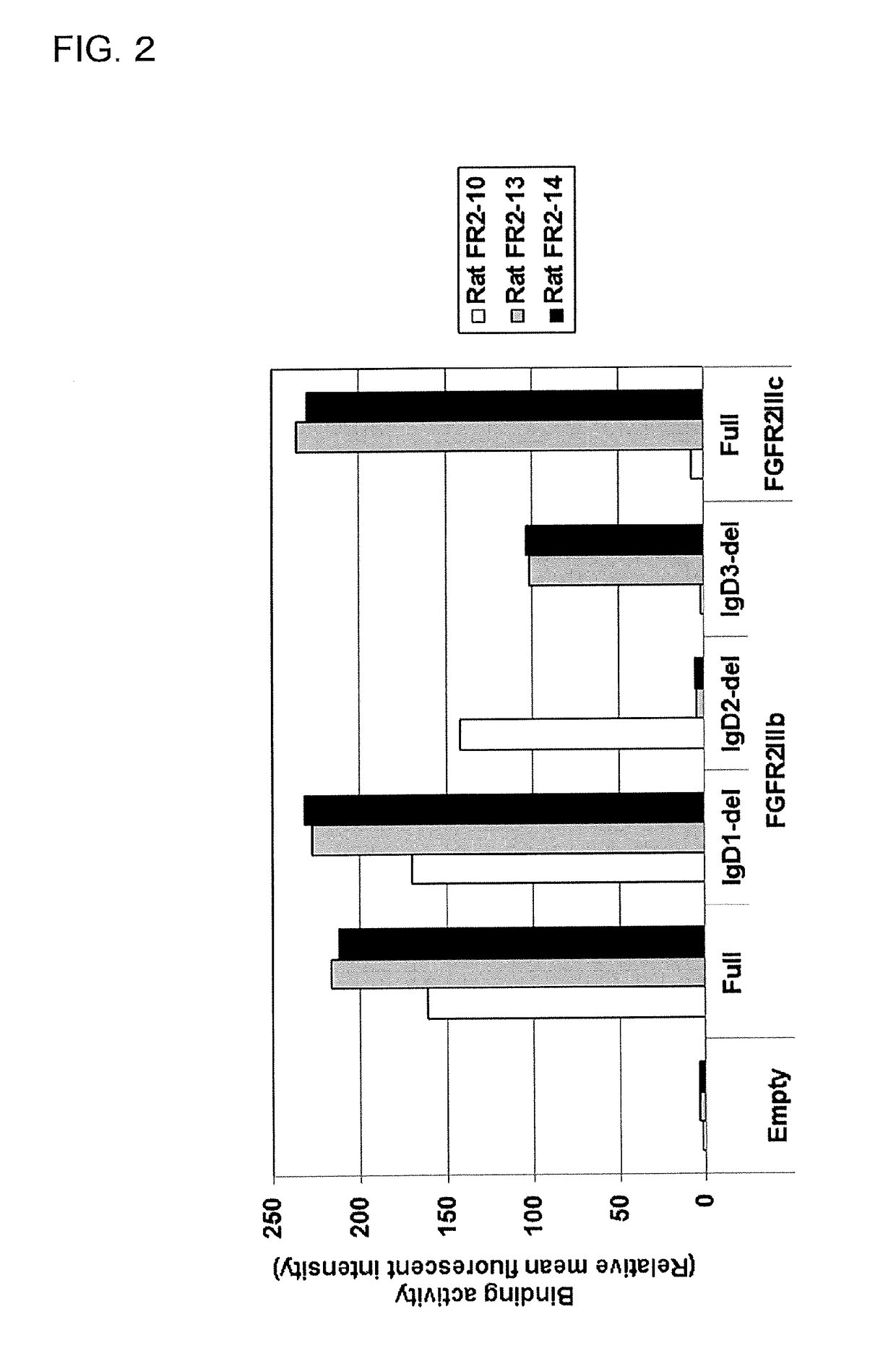
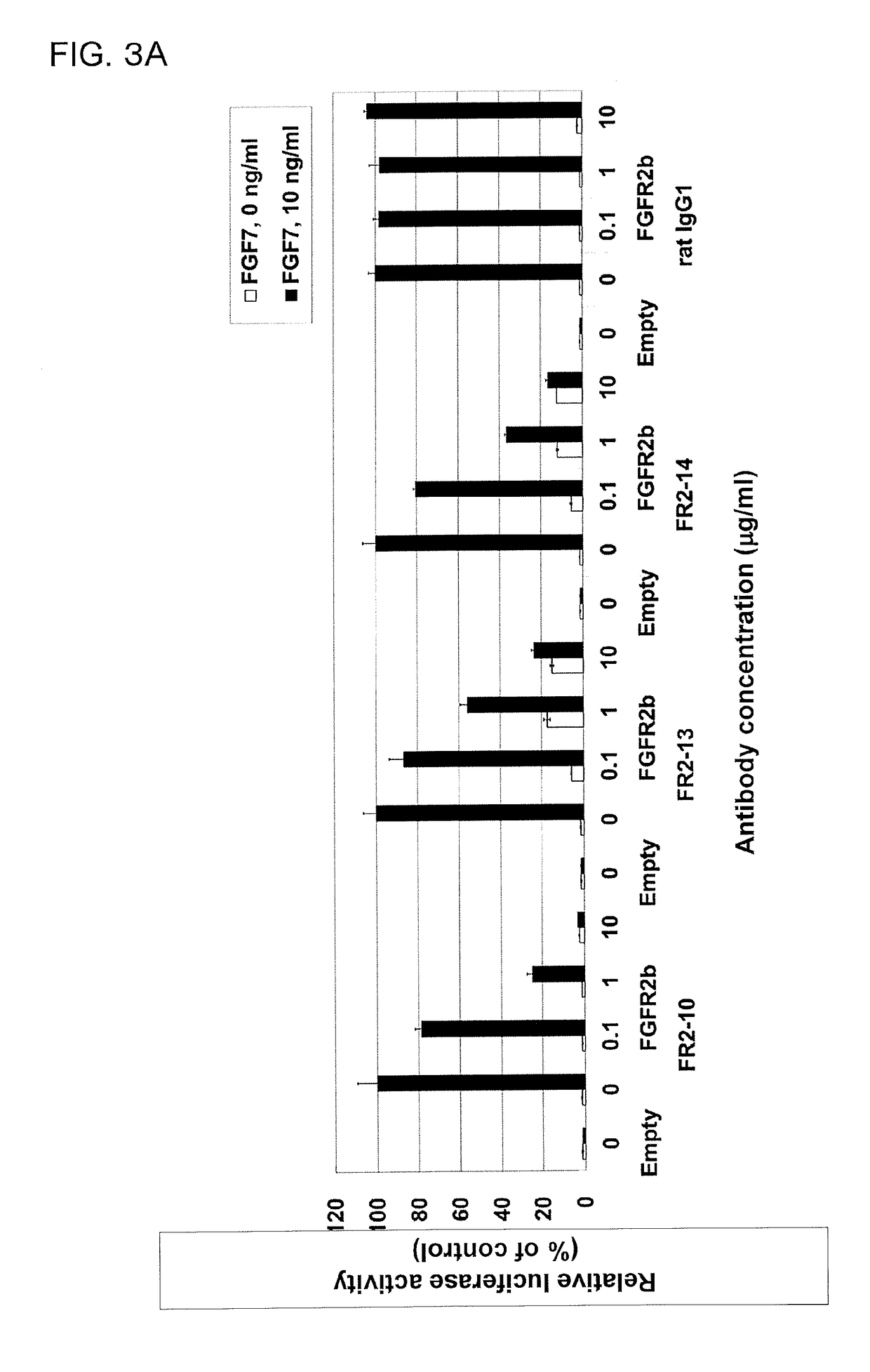
The present invention is related to antibodies with binding affinity to fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) optionally with binding affinity to other FGF receptors, which block both ligand-dependent and constitutive ligand independent receptor activation. Specifically, the present invention relates to antibodies with high affinity to more than one FGF receptor subtype, and fragments thereof, useful in treating disorders including cell proliferative diseases.
Owner:FIBRON
Remodeling and glycopegylation of fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
ActiveUS20120172300A1Cost effectiveImprove pharmacokineticsSenses disorderNervous disorderFibre cellMutant
The present invention relates to mutants of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF), particularly FGF-20 and FGF-21, which contain newly introduced N-linked or O-linked glycosylation site(s). The polynucleotide coding sequences for the mutants, expression cassettes comprising the coding sequences, cells expressing the mutants, and methods for producing the mutants are also disclosed. Further disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the mutants and method for using the mutants.
Owner:89BIO LTD
Mutant polypeptides of fibroblast growth factor 1
ActiveUS7595296B1Good effectFacilitated DiffusionPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesWild typeX-ray
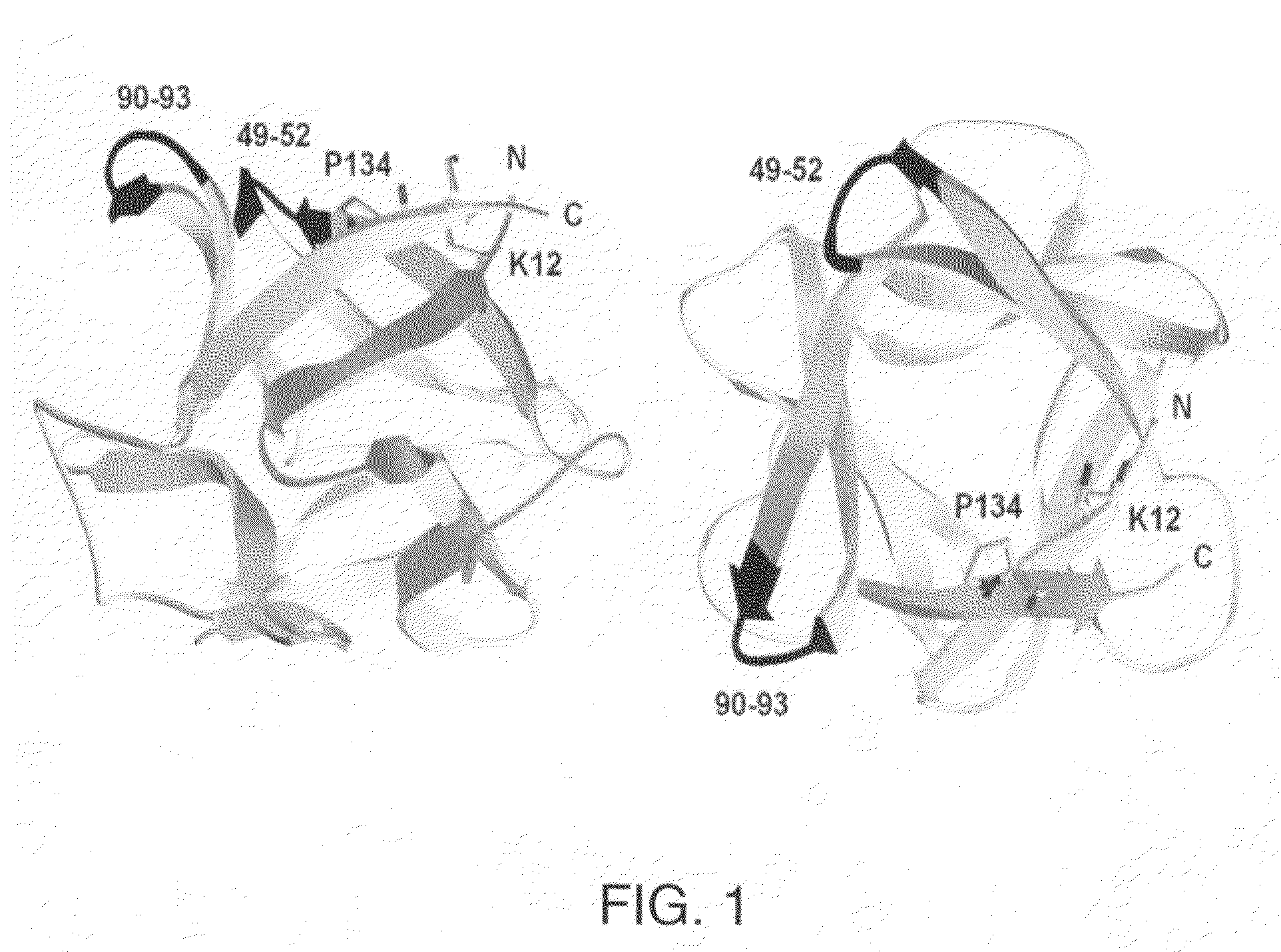
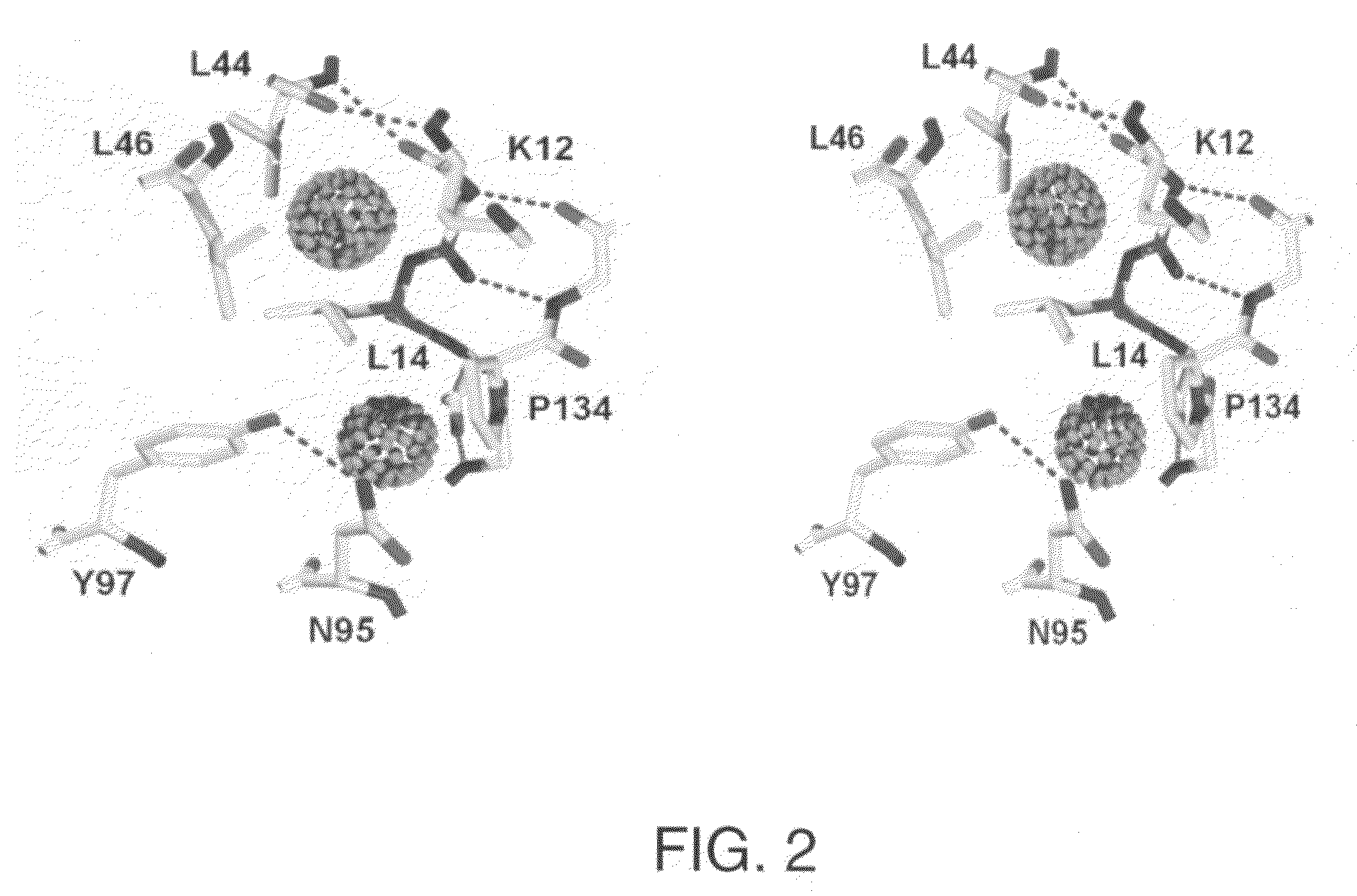
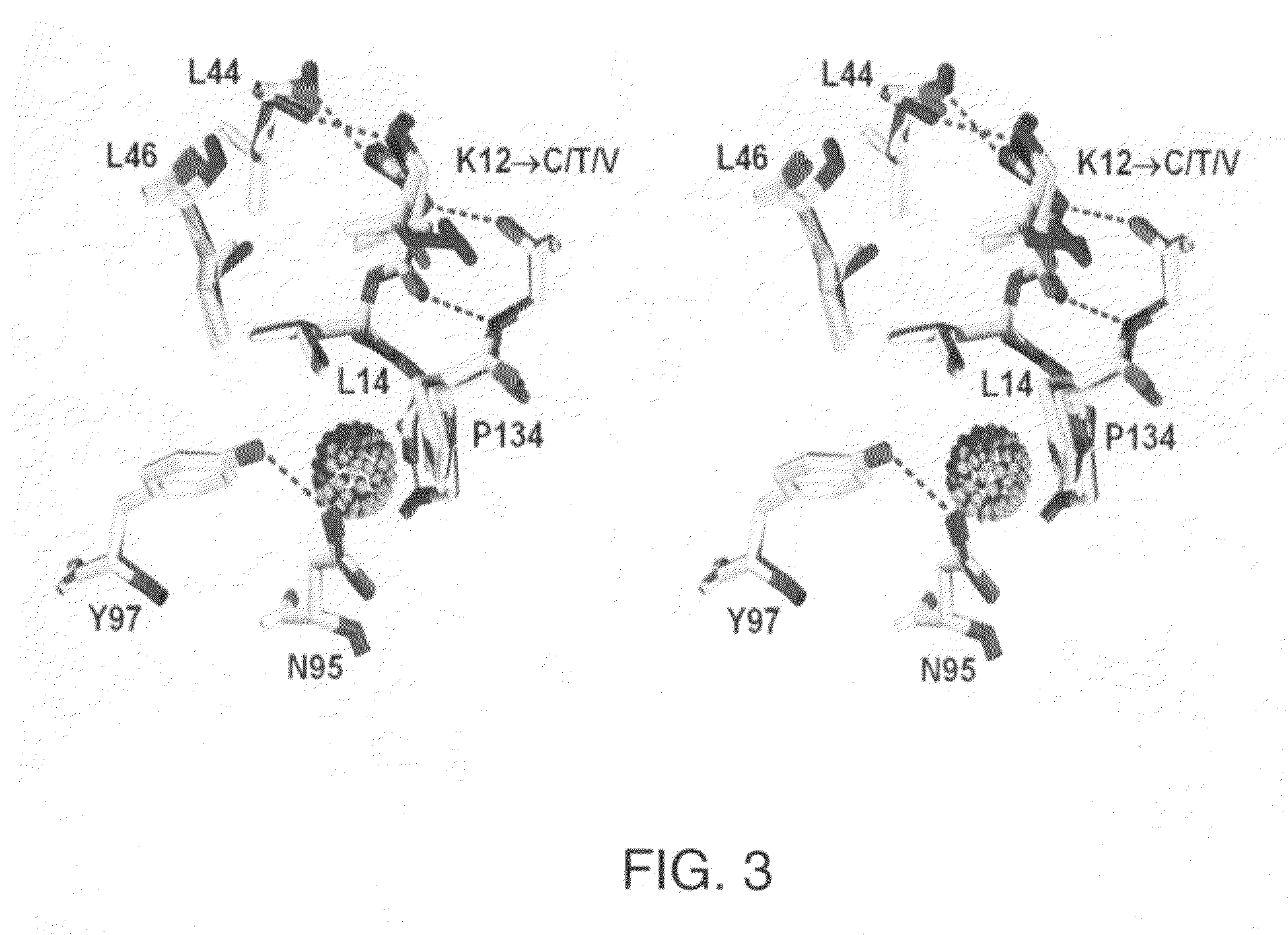
The β-trefoil protein human fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF-1) is made up of a six-stranded anti-parallel β-barrel closed off on one end by three β-hairpins, thus exhibiting a three-fold axis of structural symmetry. The N- and C-termini β-strands hydrogen bond to each other and are postulated from both NMR and X-ray structure data to represent a structurally-weakened region of the β-barrel. Val mutations within the N- and C-termini β-strands are shown to stabilize the structure and to increase van der Waals contacts by filling local cavities present within this region. Mutations that increase van der Waals contacts between both the N- and C-termini β-strands are generally associated with significant reductions in the unfolding kinetics, and also increase the cooperativity of unfolding. Surprisingly, several mutant polypeptides herein disclosed greatly exceed the wild-type polypeptide in ability to stimulate human fibroblasts to proliferate.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Fibroblast growth factor 21 mutations
InactiveUS9023791B2Good biological propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiologyFGF21
The present invention provides novel polypeptide and protein variants of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) and pharmaceutical compositions comprising FGF21 polypeptide and protein variants.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
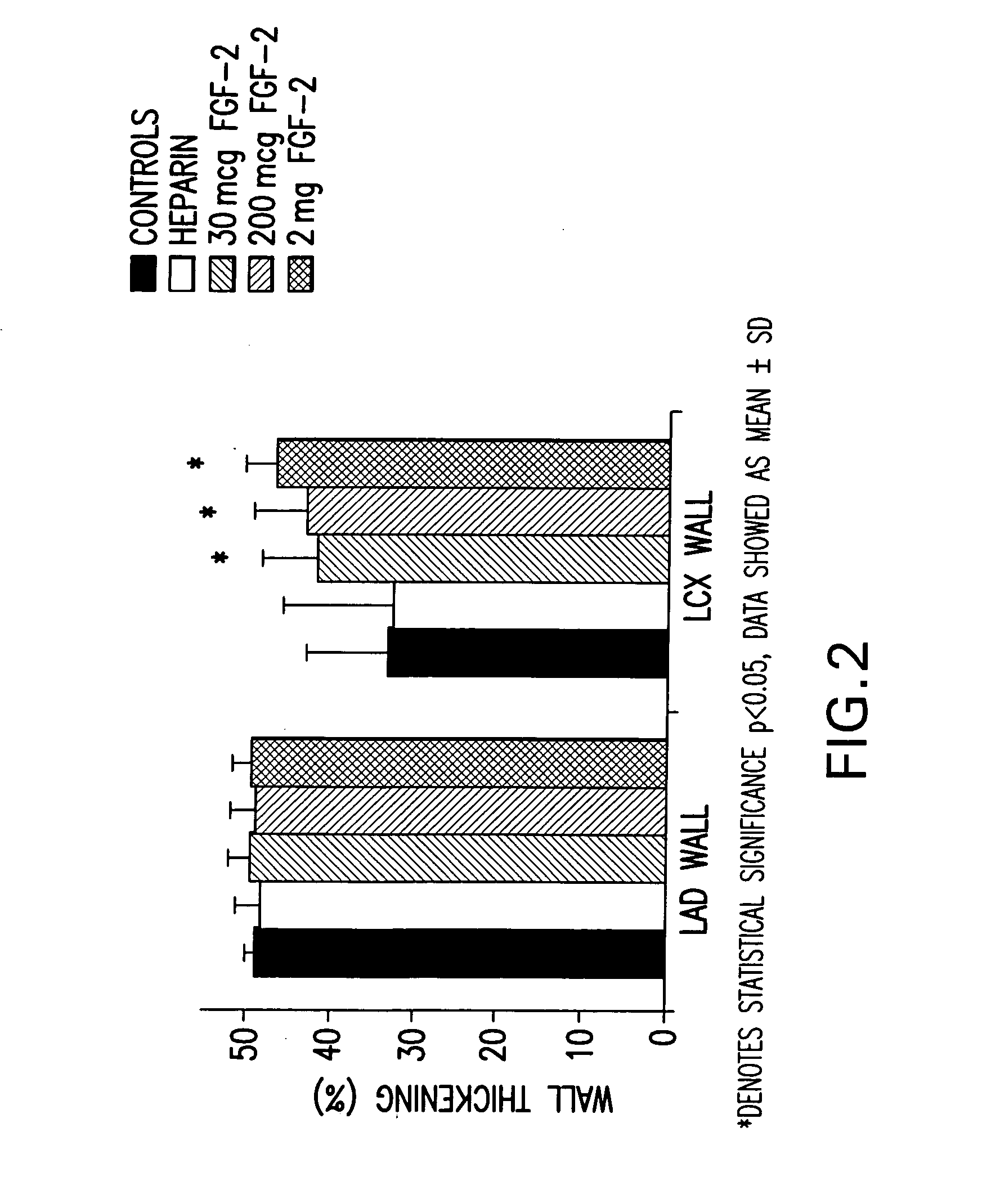
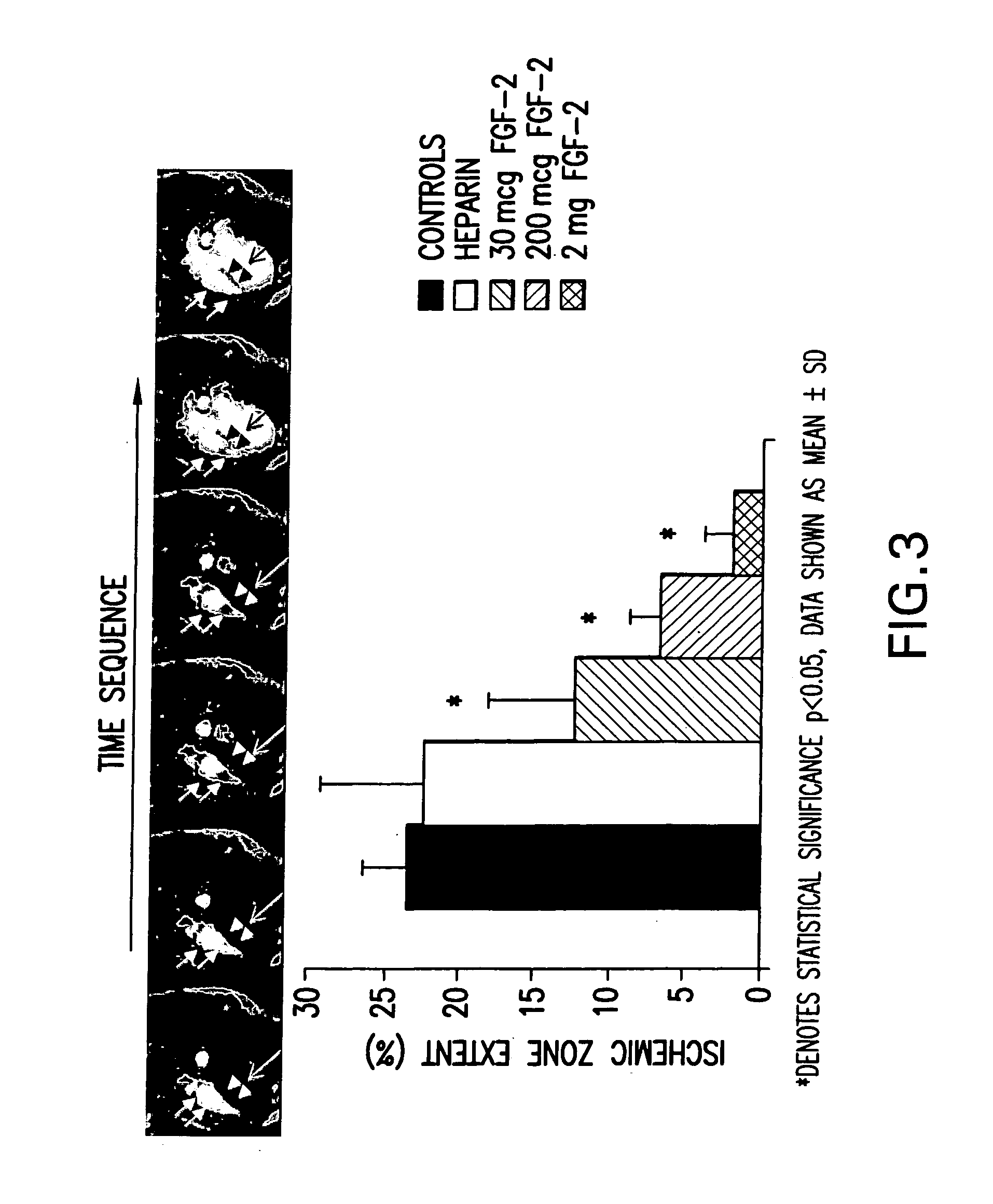
Methods of use of fibroblast growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor and related proteins in the treatment of acute and chronic heart disease
Disclosed herein is a rational, multi-tier approach to the administration of growth factor proteins in the treatment of heart disease. Also disclosed is a method to evaluate the effectiveness of the administration of growth factor proteins comprising the clinical assay of CPK-MB levels in a patient undergoing treatment with growth factor proteins. In addition, there is disclosed a method for treatment of heart disease comprising administration of a therapeutically effective amount of a growth factor protein by oral inhalation therapy.
Owner:FRANCO WAYNE P
Hair growth methods using fgfr4 extracellular domains
The present invention relates to a method of promoting hair growth comprising administering a fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) extracellular domain (ECD), including native FGFR4 ECDs, variants, fragments, and fusion molecules, to a subject in an amount sufficient to promote hair growth.
Owner:FIVE PRIME THERAPEUTICS
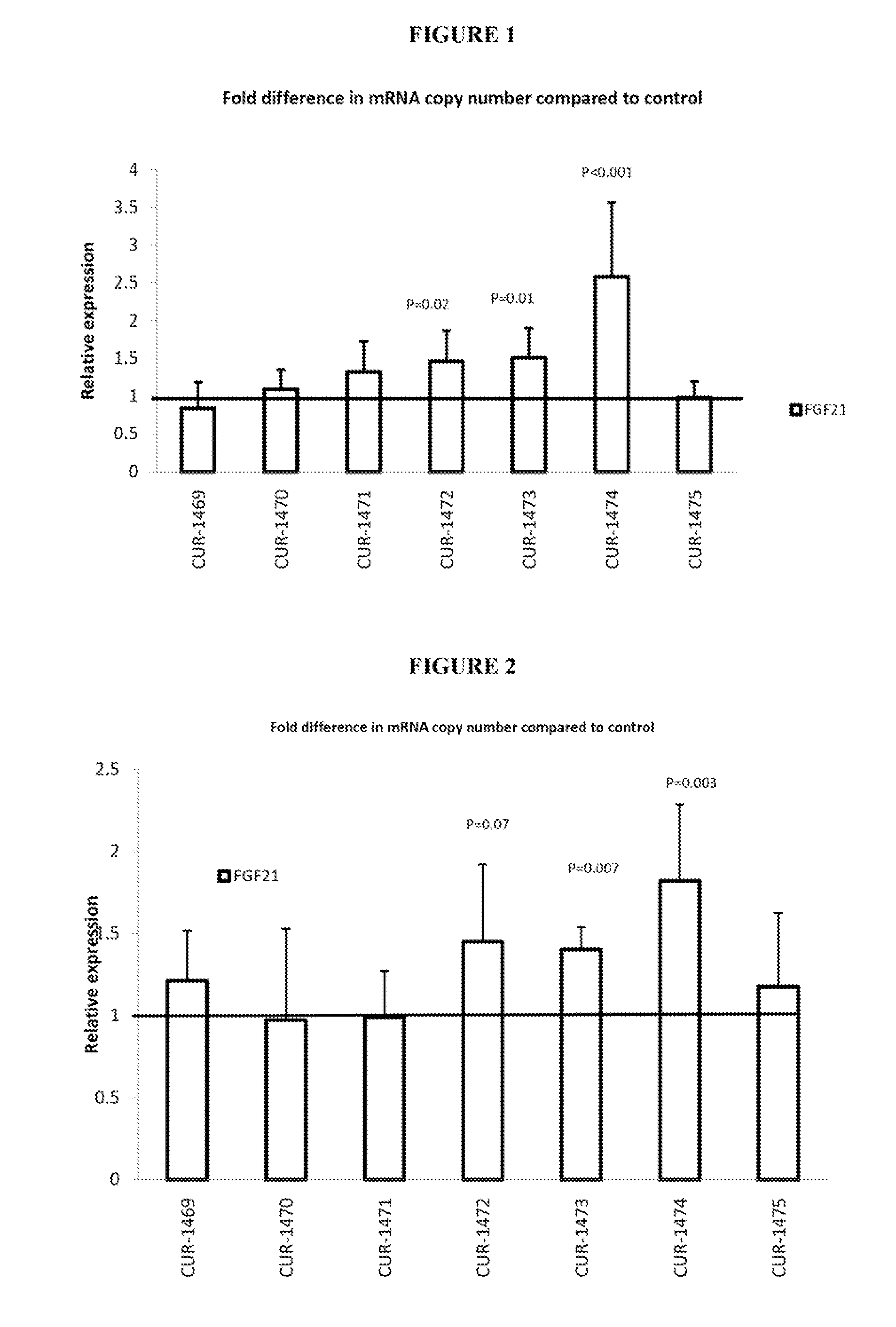
Treatment of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to fgf21
ActiveUS20130035373A1Modulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseasePolynucleotide
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of FGF21.
Owner:CURNA INC
Mutant polypeptides of fibroblast growth factor 1
ActiveUS7696171B1Good effectFacilitated DiffusionPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsStructural symmetryFibroblast
The β-trefoil protein human fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF-1) is made up of a six-stranded anti-parallel β-barrel closed off on one end by three β-hairpins, thus exhibiting a three-fold axis of structural symmetry. The N- and C-termini β-strands hydrogen bond to each other and are postulated from both NMR and X-ray structure data to represent a structurally-weakened region of the β-barrel. Val mutations within the N- and C-termini β-strands are shown to stabilize the structure and to increase van der Waals contacts by filling local cavities present within this region. Mutations that increase van der Waals contacts between both the N- and C-termini β-strands are generally associated with significant reductions in the unfolding kinetics, and also increase the cooperativity of unfolding. Surprisingly, several mutant polypeptides herein disclosed greatly exceed the wild-type polypeptide in ability to stimulate human fibroblasts to proliferate.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Bitarget fibroblast growth factor acceptor and transgene carrier of integrated element
InactiveCN1757738AGrowth inhibitionLow transfection efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsFermentationAbnormal tissue growthDisease
A transgenic carrier with deal targets (fibroblast growth factor receptor and integrant) is composed of the polypeptide CR16 specifically linked with alkaline fibroblast growth factor receptor, the polypeptide CP9 specifically linked with integrant, and the transgenic non-virus carrier system of CR16 / CP9 / cationic polymer PEI / exogenous DNA. Said carrier can effectively introduce the exogenous DNA to the tumor cell line and tumor tissue with high expression of FGFRs, so suppressing the growth of tumor. It can be used to preparation of the medicine for treating tumor and other diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
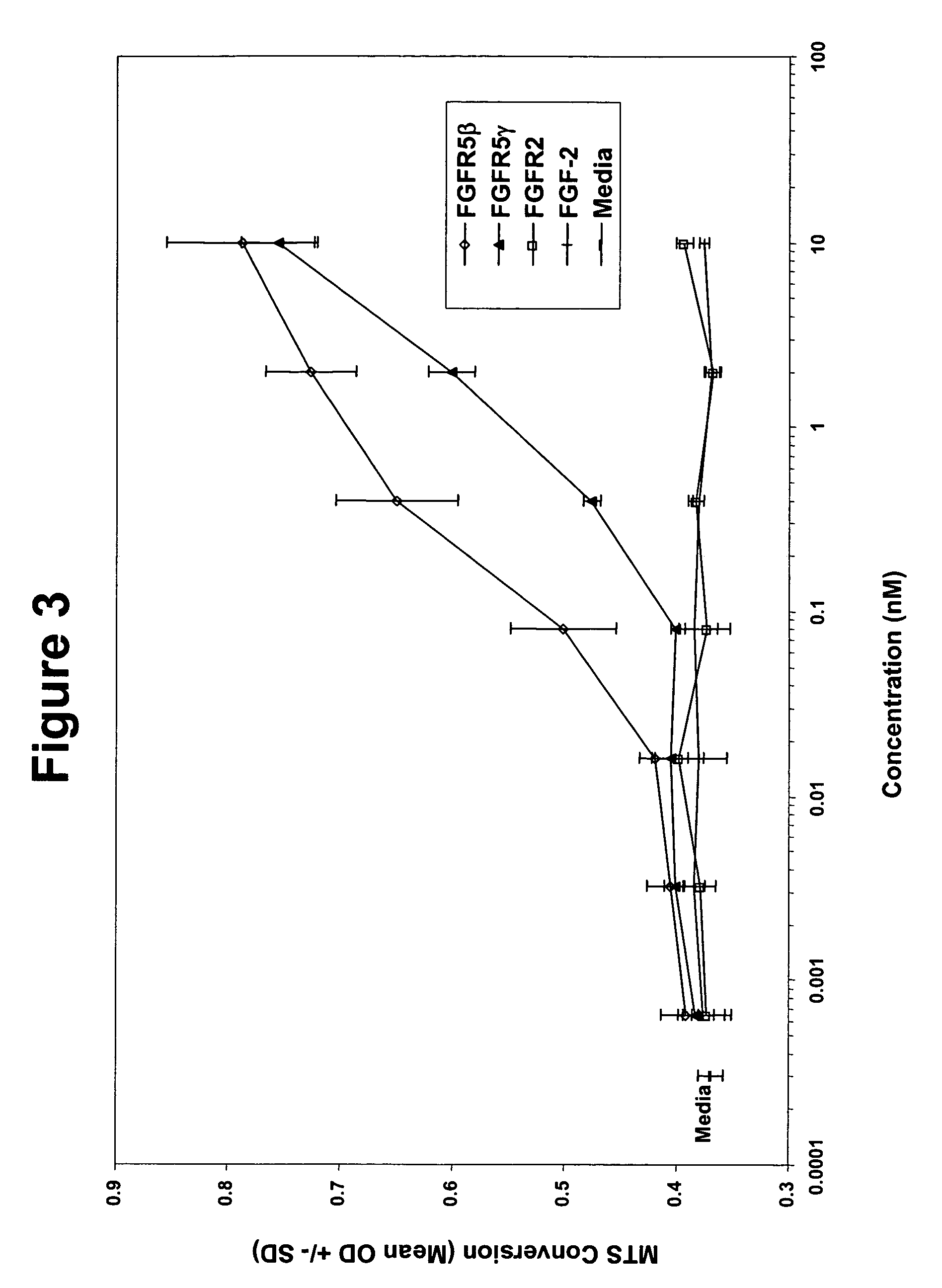
Methods for enhancing immune responses by fibroblast growth factor receptor 5 polypeptides
InactiveUS7083791B2Reduce decreaseDecreasing osteopontin gene expressionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHepatocellular carcinomaAutoimmune disease
Isolated fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR5) polypeptides and polynucleotides encoding such polypeptides are provided. Also provided are modulators of FGFR5 gene expression and binding molecules that specifically bind to and agonize or antagonize FGFR5 polypeptide function. Specific binding molecules include antibodies, functional fragments thereof, as well as scFv and Camelidae heavy chain IgG that specifically bind to FGFR5 thereby modulating the activity of FGFR5 and, thus, are effective agents suitable for the treatment of diseases such as osteopontin-mediated autoimmune disease, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, bone disorders including osteoporosis and osteopetrosis, and cancers, including cellular carcinomas such as hepatocellular carcinomas.
Owner:GENESIS RES & DEV
Keratinocyte growth factor-2
InactiveCN1372569AImprove biological activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologySolubility
The present invention relates to various newly identified polynucleotides, polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotides, uses of such polynucleotides and polypeptides, and production of such polynucleotides and polypeptides. More specifically, the polypeptide of the present invention is keratinocyte growth factor, sometimes referred to hereinafter as "KGF-2," and formerly referred to as fibroblast growth factor 12 (FGF-12). The present invention also relates to the therapeutic use of KGF-2 for promoting or accelerating wound healing. The present invention also relates to new mutant forms of KGF-2 which show enhanced activity, increased stability, higher yield or better solubility.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Methods for targeting cells that express fibroblast growth receptor-3 or -2
Fibroblast growth factor-18 (FGF-18) binds with FGF receptors-2 and -3. Compositions comprising an FGF-18 component can be used to target cells that express these receptors. Suitable targets include tumor cells that express constitutively activated forms of FGF receptors-2 and -3. For example, conjugates of FGF-18 and saporin can be used to target tumor cells that express FGF receptors-2 or -3, and to inhibit the proliferation of these cells.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
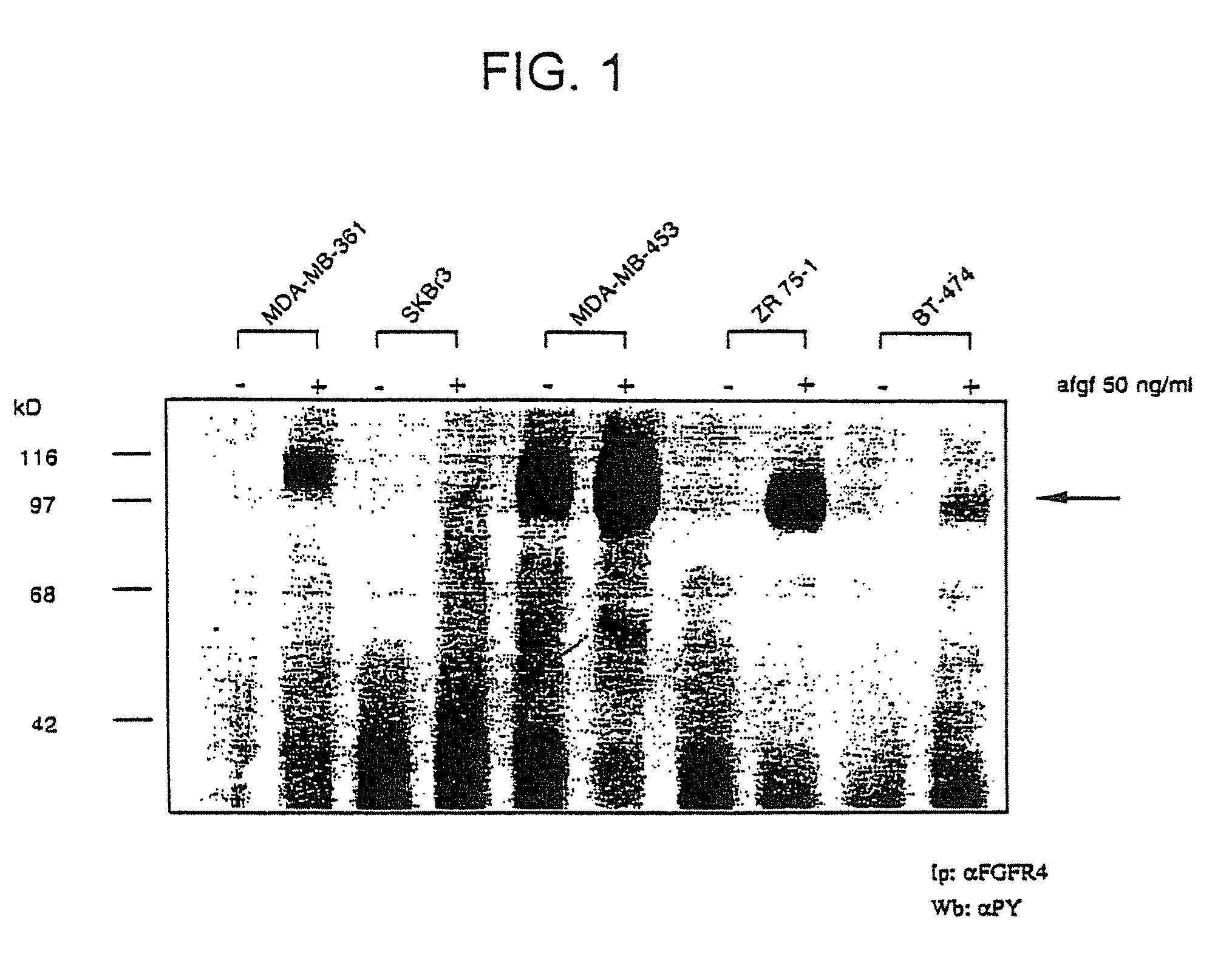
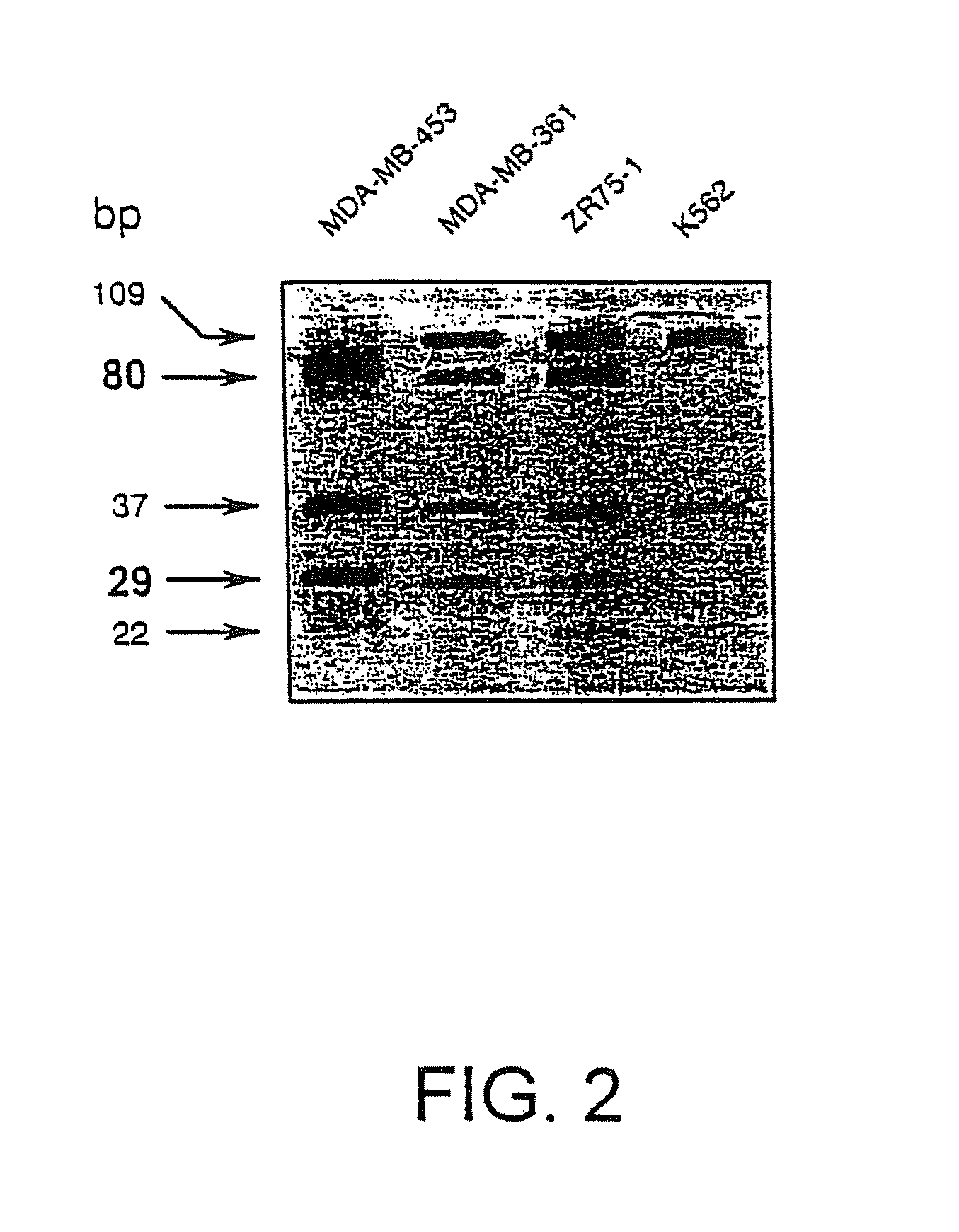
Method of diagnosing an RTK-hyperfunction-induced disorder
InactiveUS8043806B2Reduce overexpressionAltered activityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsGenetics predispositionHyperfunction
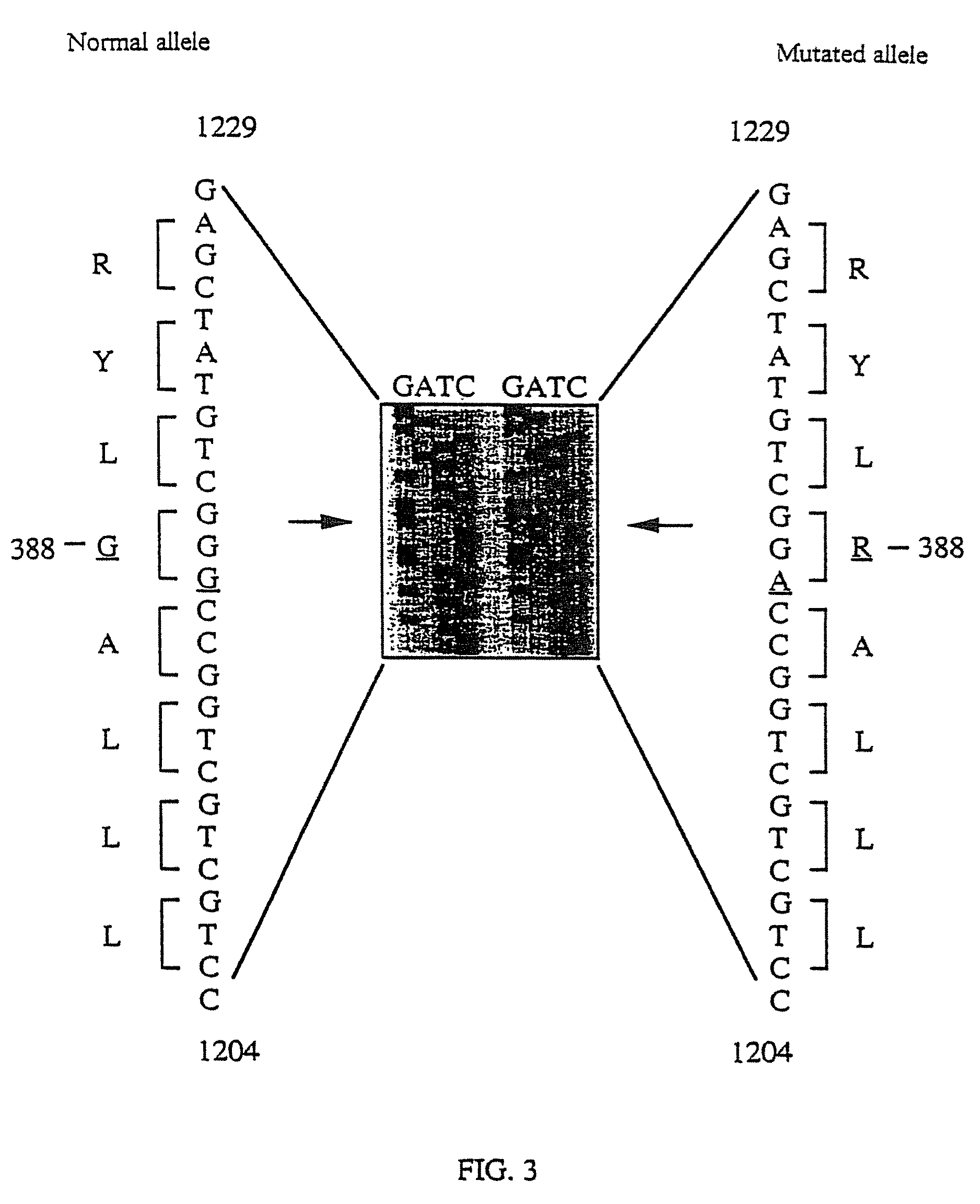
The invention provides method of diagnosing a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-hyperfunction-induced disorder or a genetic predisposition therefor in a mammal. The method comprises determining the presence of a nucleic acid encoding a mutated fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 (FGFR-4) protein in a nucleic acid sample from a mammal. The presence of a nucleic acid encoding a mutated FGFR-4 protein is indicative of an RTK-hyperfunction-induced disorder or a genetic predisposition therefor.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
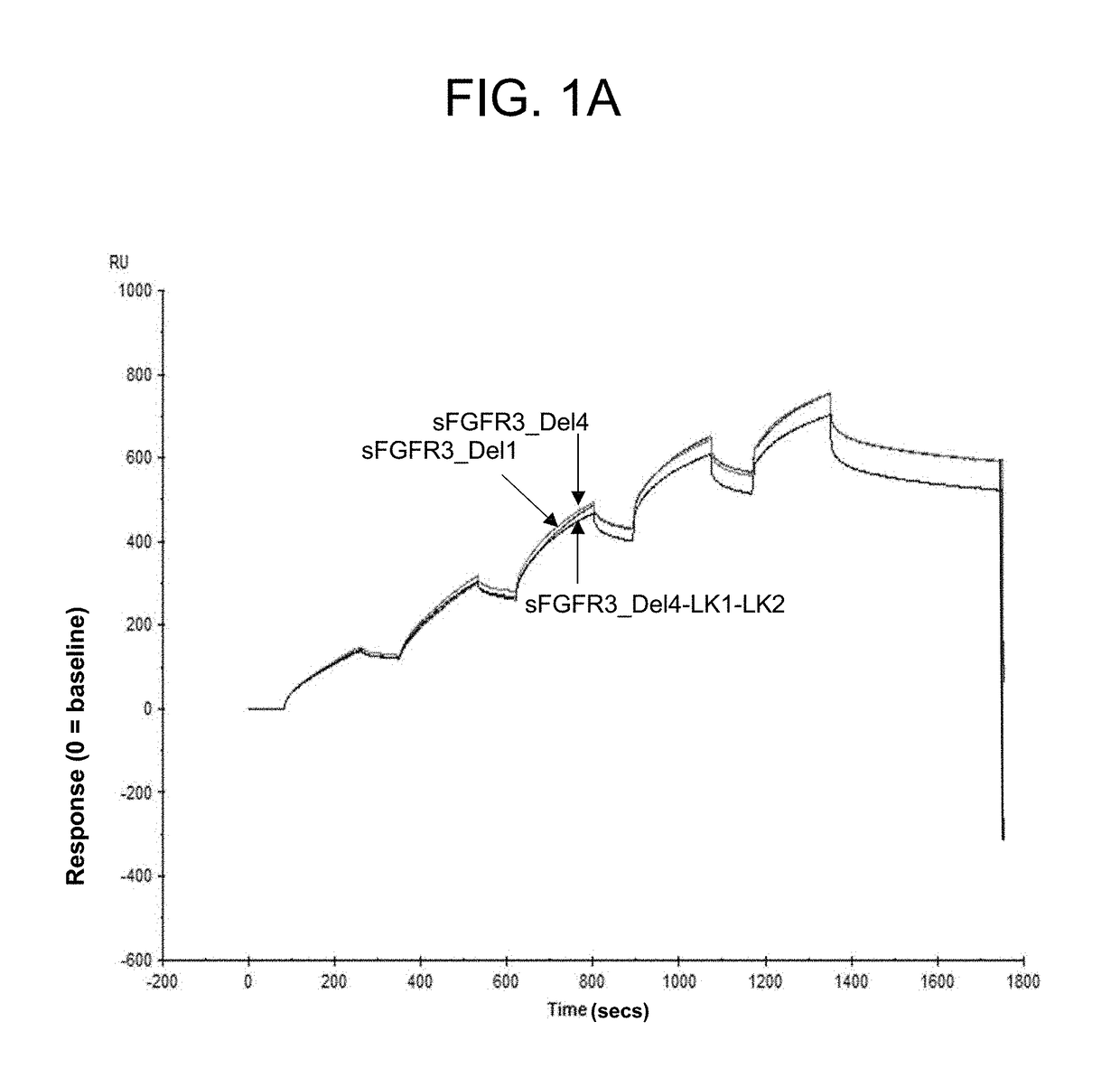
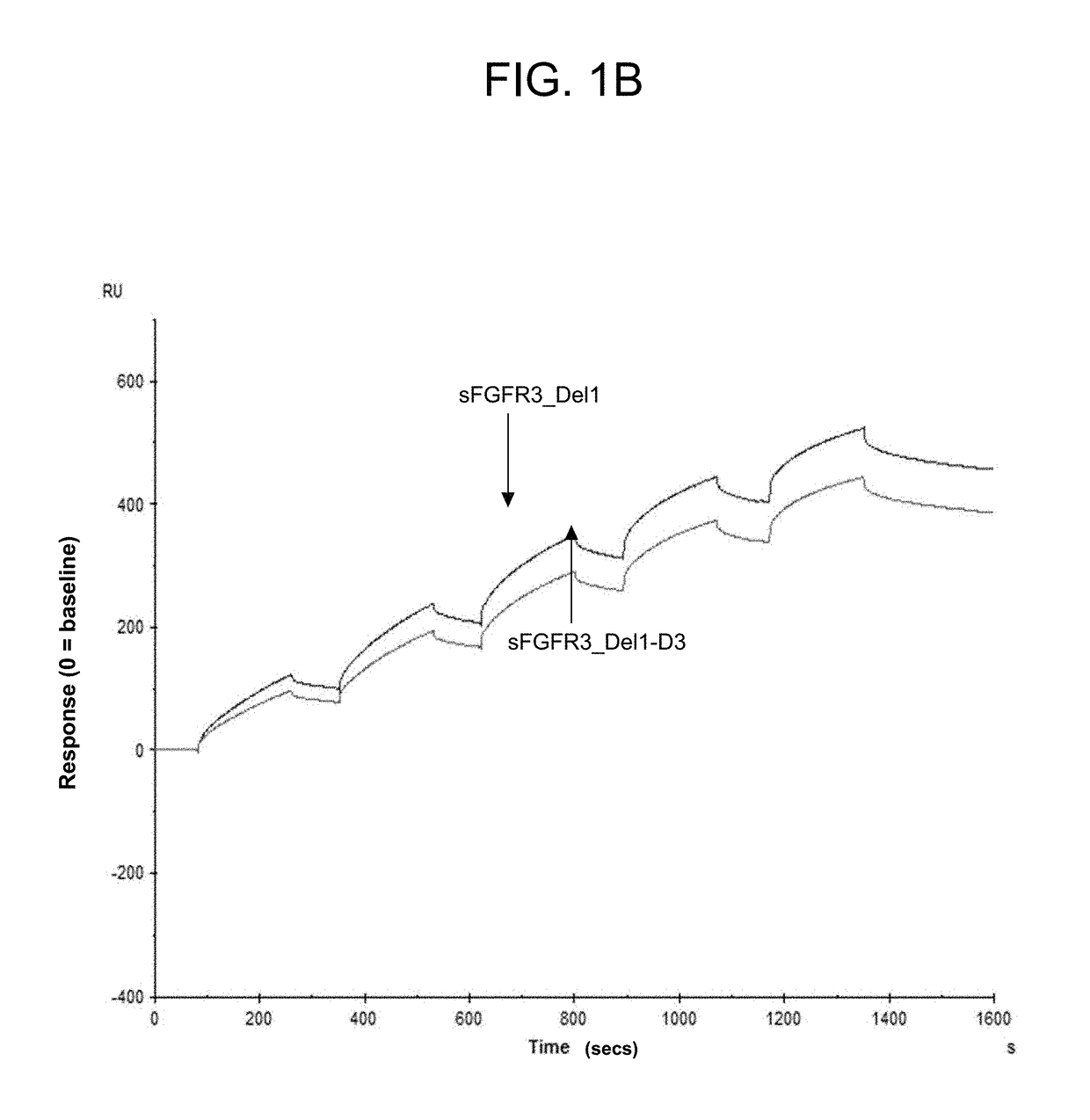
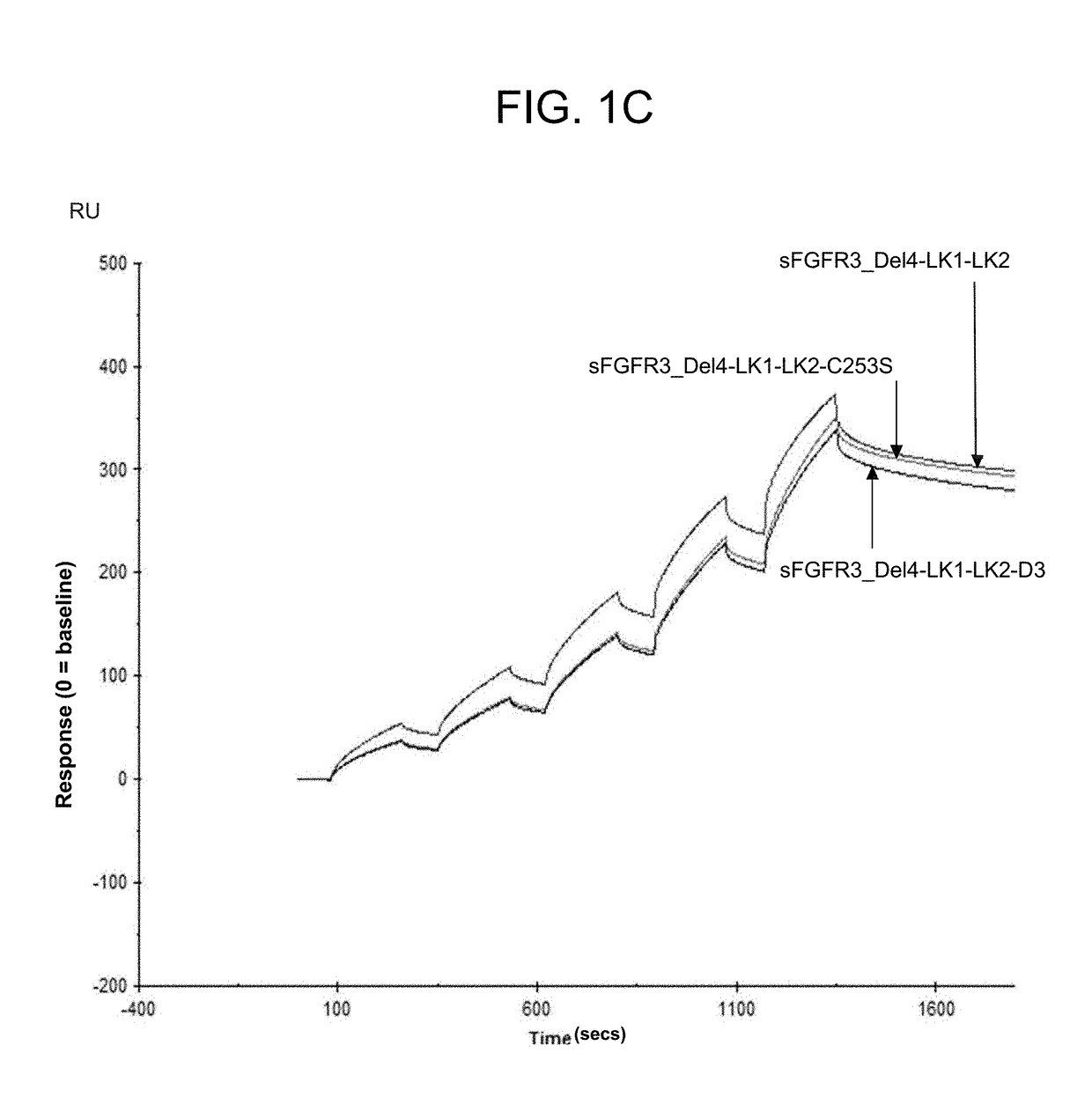
Soluble fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (sfgfr3) polypeptides and uses thereof
ActiveUS20180230197A1Improve survivalPromote sportsPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderFibroblast growth factor receptor 2Fibroblast Growth Factor 3 Gene
The invention features soluble fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (sFGFR3) polypeptides. The invention also features methods of using sFGFR3 polypeptides to treat skeletal growth retardation disorders, such as achondroplasia.
Owner:PFIZER INC +2
Hair growth methods using FGFR3 extracellular domains
InactiveUS8685931B2Cosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsHair streamsExtracellular Structure
The present invention relates to a method of promoting hair growth comprising administering a fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) extracellular domain (ECD), including native FGFR3 ECDs, variants, fragments, and fusion molecules, to a subject in an amount sufficient to promote hair growth.
Owner:FIVE PRIME THERAPEUTICS
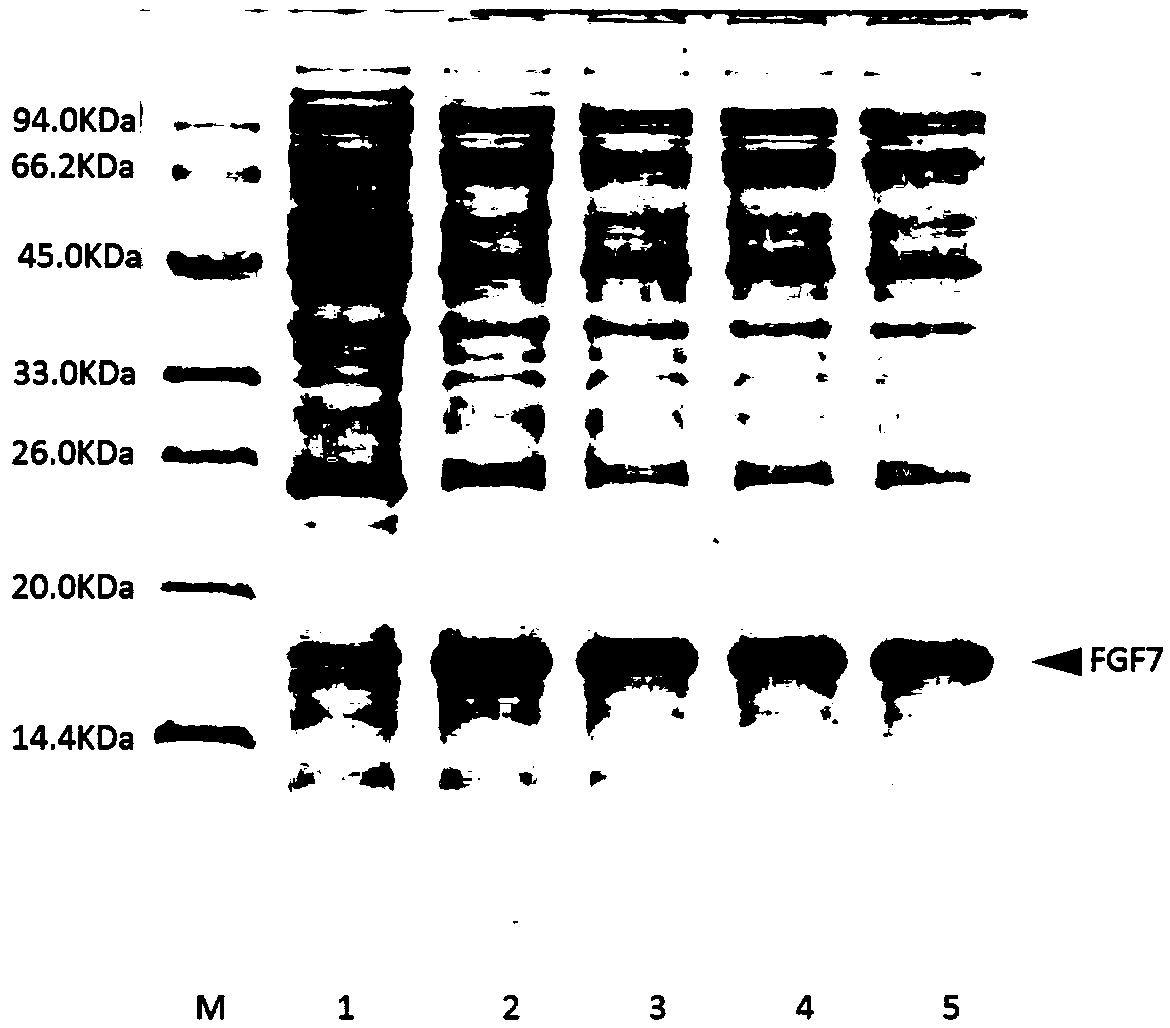
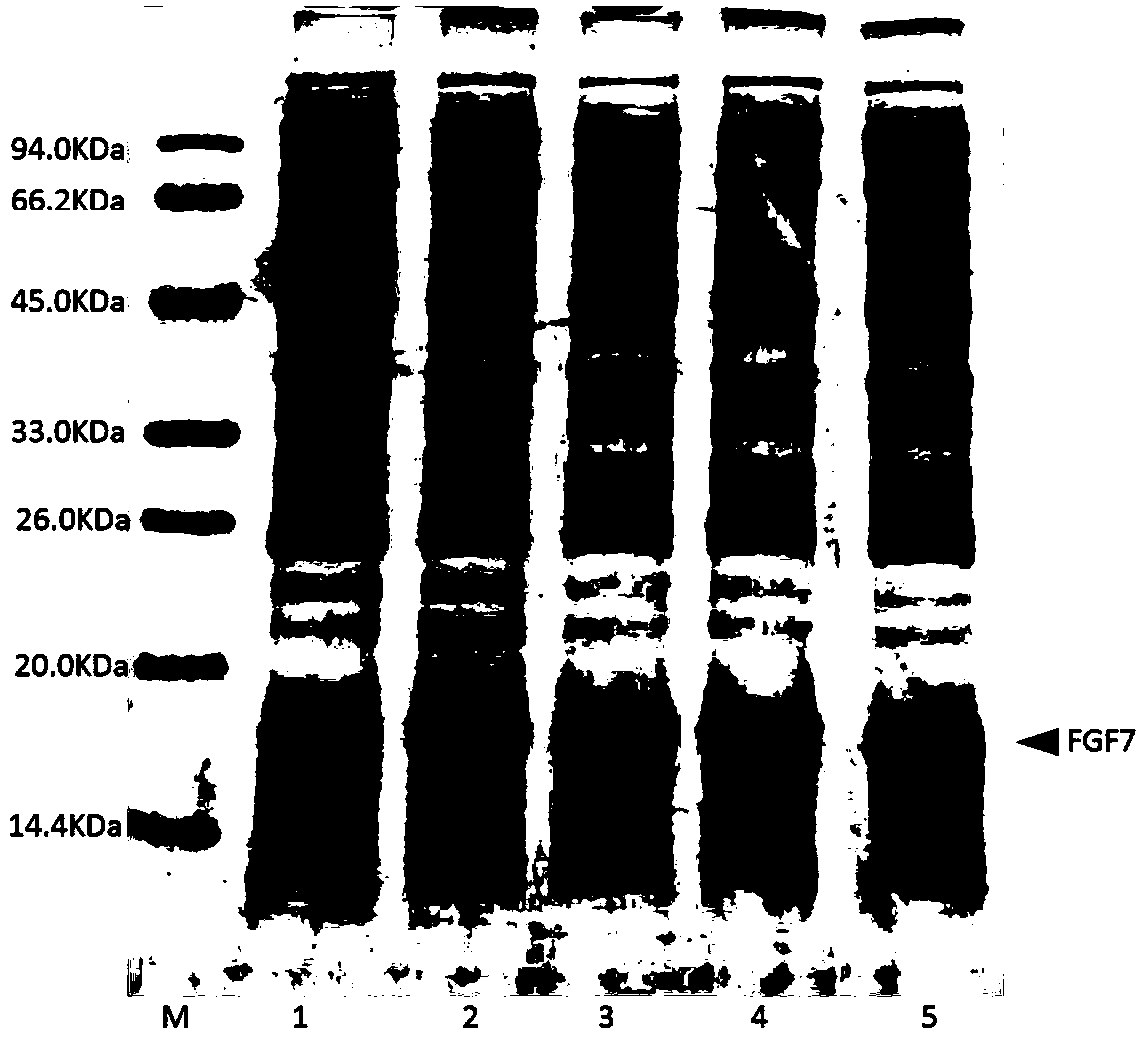
Solubleand efficient recombinant expression methodfor fibroblast growth factor protein
PendingCN109628533APromoting non-convergenceImprove economyMicroorganism based processesFibroblast growth factorEscherichia coliFGF4
The invention discloses a solubleand efficient recombinant expression methodfor fibroblast growth factor protein. In the method, as for an escherichia coli strain of a carrier containing coding-recombinant fibroblast growth factor family protein, expression of intracellularactive protein is promoted by adding a certain dosage of monosaccharide during induction.The fibroblast growth factor family protein comprises FGF1, FGF2, FGF4, FGF7, FGF8, FGF9, FGF11, FGF15, FGF18, FGF21, FGF23 and mutants of the fibroblast growth factor family protein. As for the process that the certain dosage of monosaccharide is added during induction, the monosaccharide is supplemented into before an inductive agent is added, or the monosaccharide is supplemented into while an inductive agent is added, or the monosaccharide is supplemented into after the inductive agent is added. The technology prejudice that expression of lac and araoperons is inhibited by glucose in escherichia colirecombinant is overcome inthe technical field, and the method capable of efficiently promoting expression of the fibroblast growth factor protein in escherichia coli is applied.
Owner:CHONGQING PEG BIO BIOTECH CO LTD
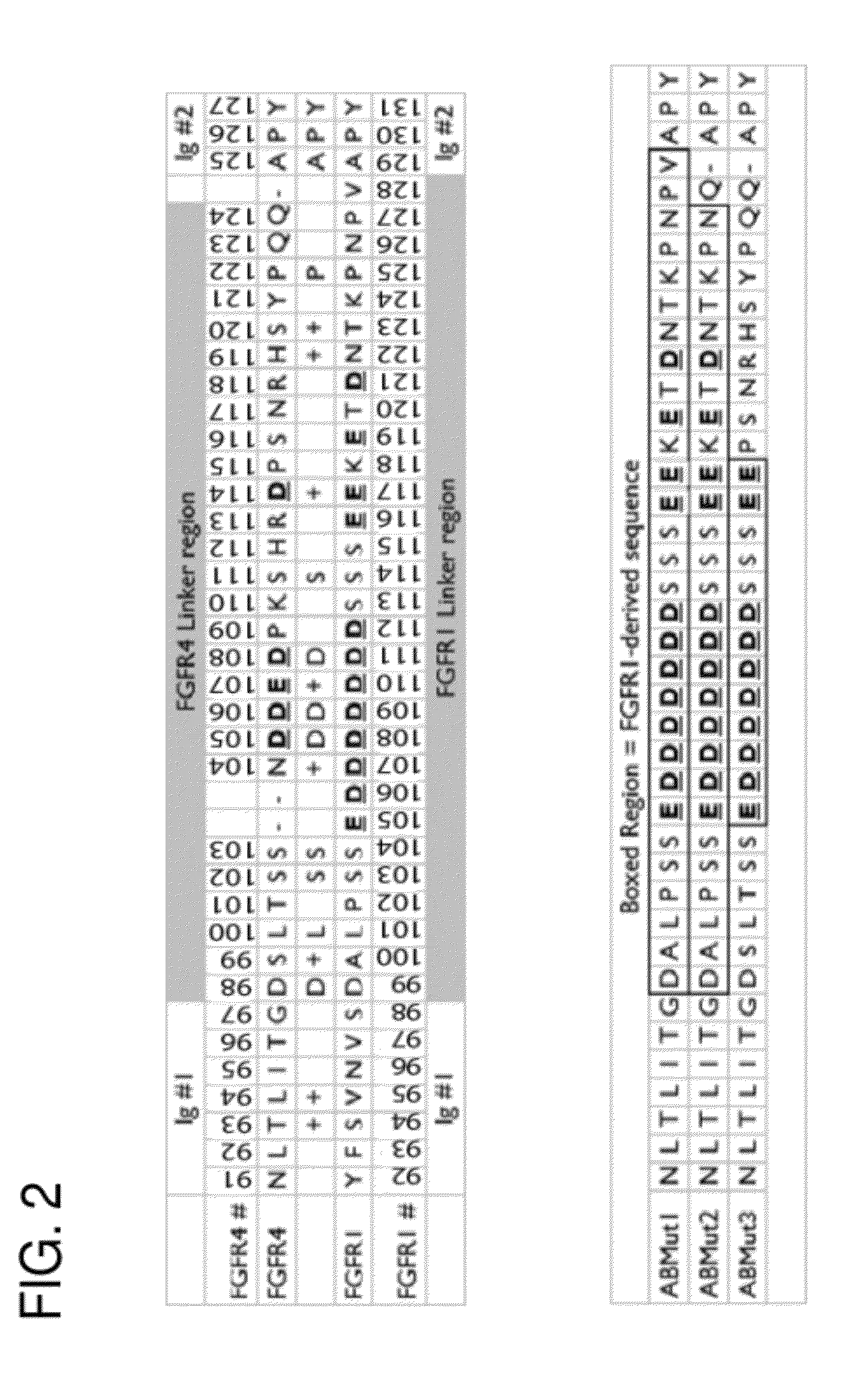
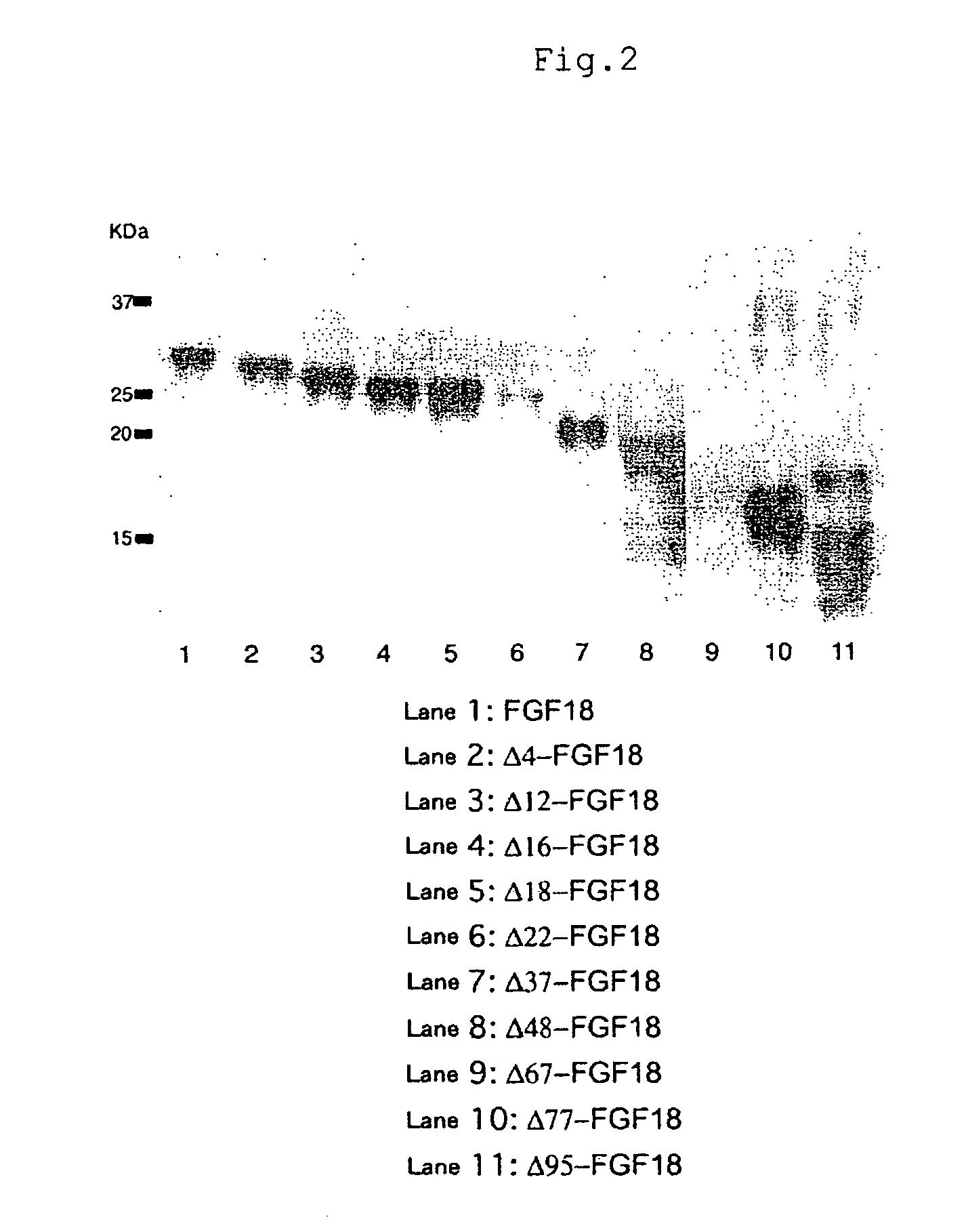
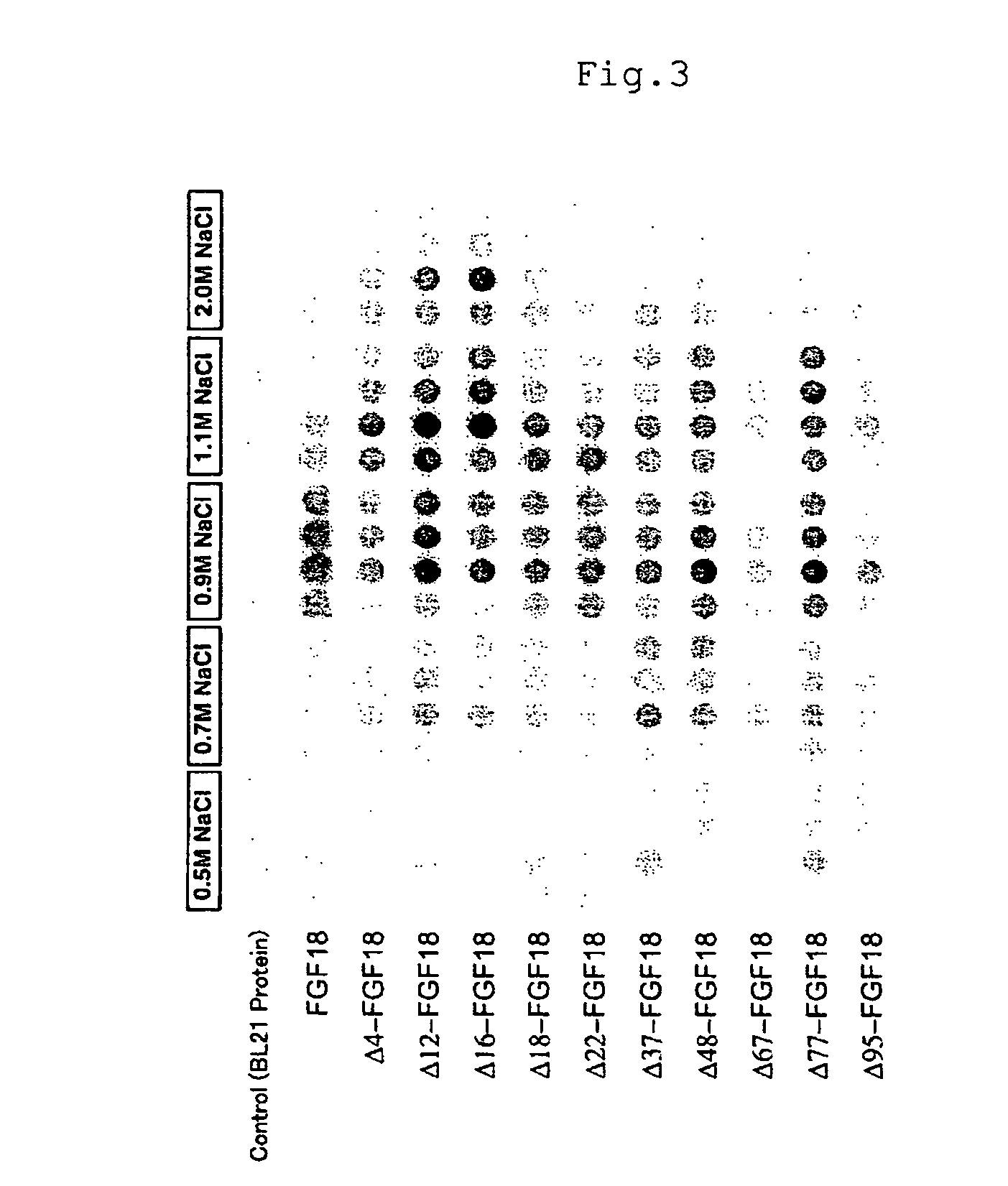
Mutant growth factors with altered receptor specificities and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same
InactiveUS20090286965A1Regulate a physiological activityCosmetic preparationsNervous disorderMutated proteinReceptor for activated C kinase 1
Disclosed is a mutant protein having an altered fibroblast growth factor receptor specificity, which is produced by deleting one or more amino acid residues from the N-terminus of the amino acid sequence of naturally secreted fibroblast growth factor 18. The protein mutant can be used in a pharmaceutical composition for regulating hair regeneration or growth or a pharmaceutical composition for regulating bone or cartilage formation.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
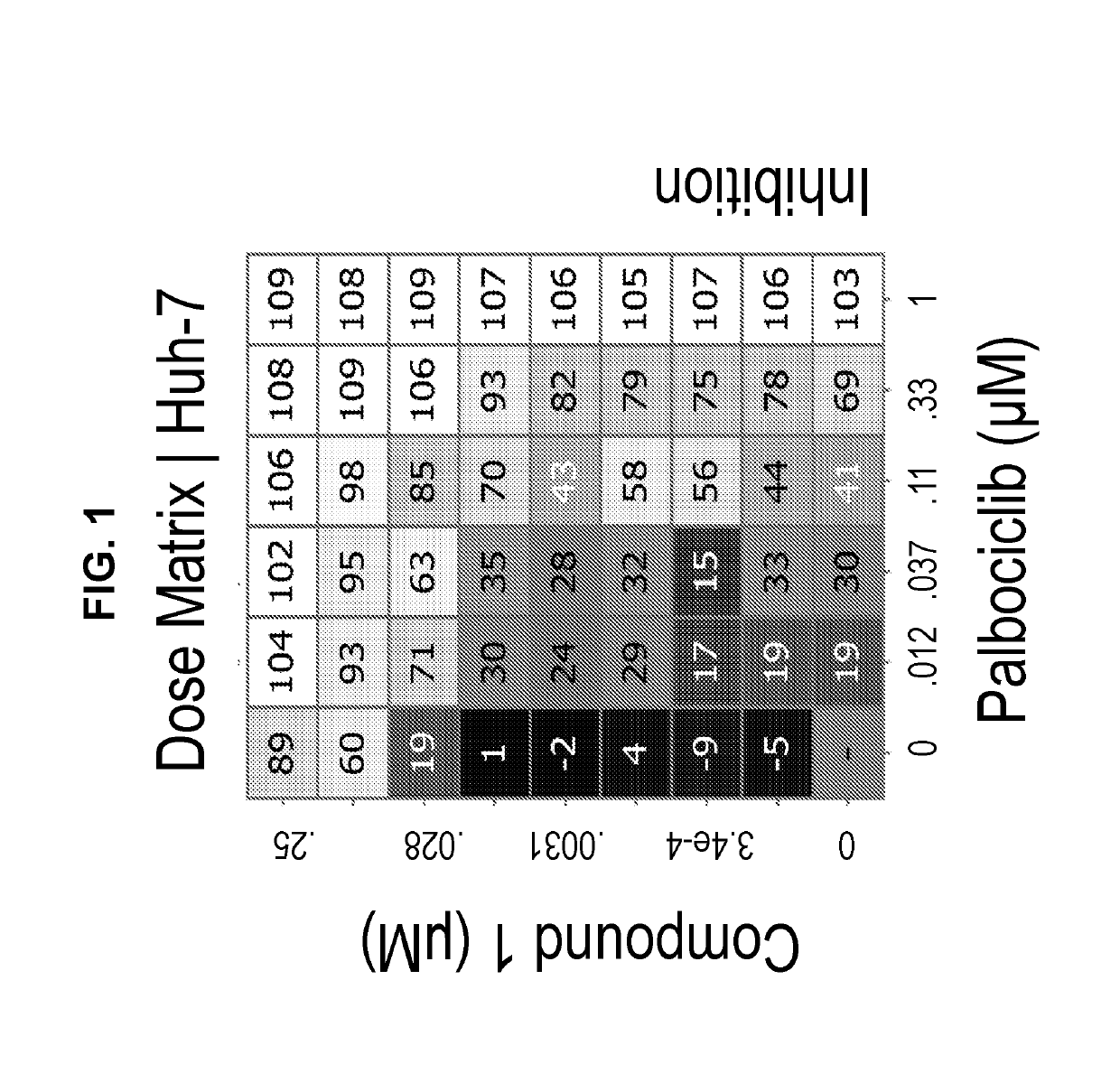
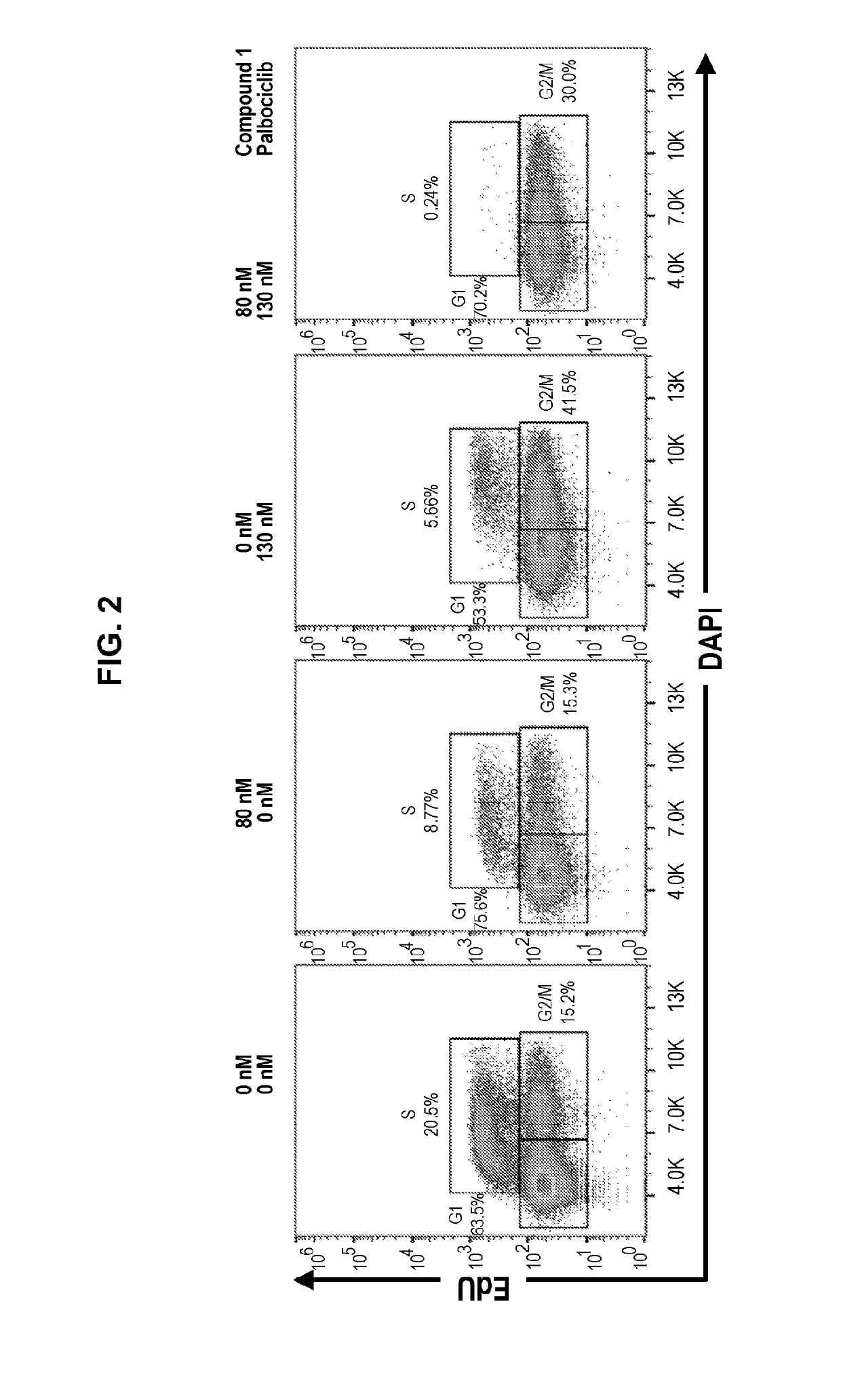
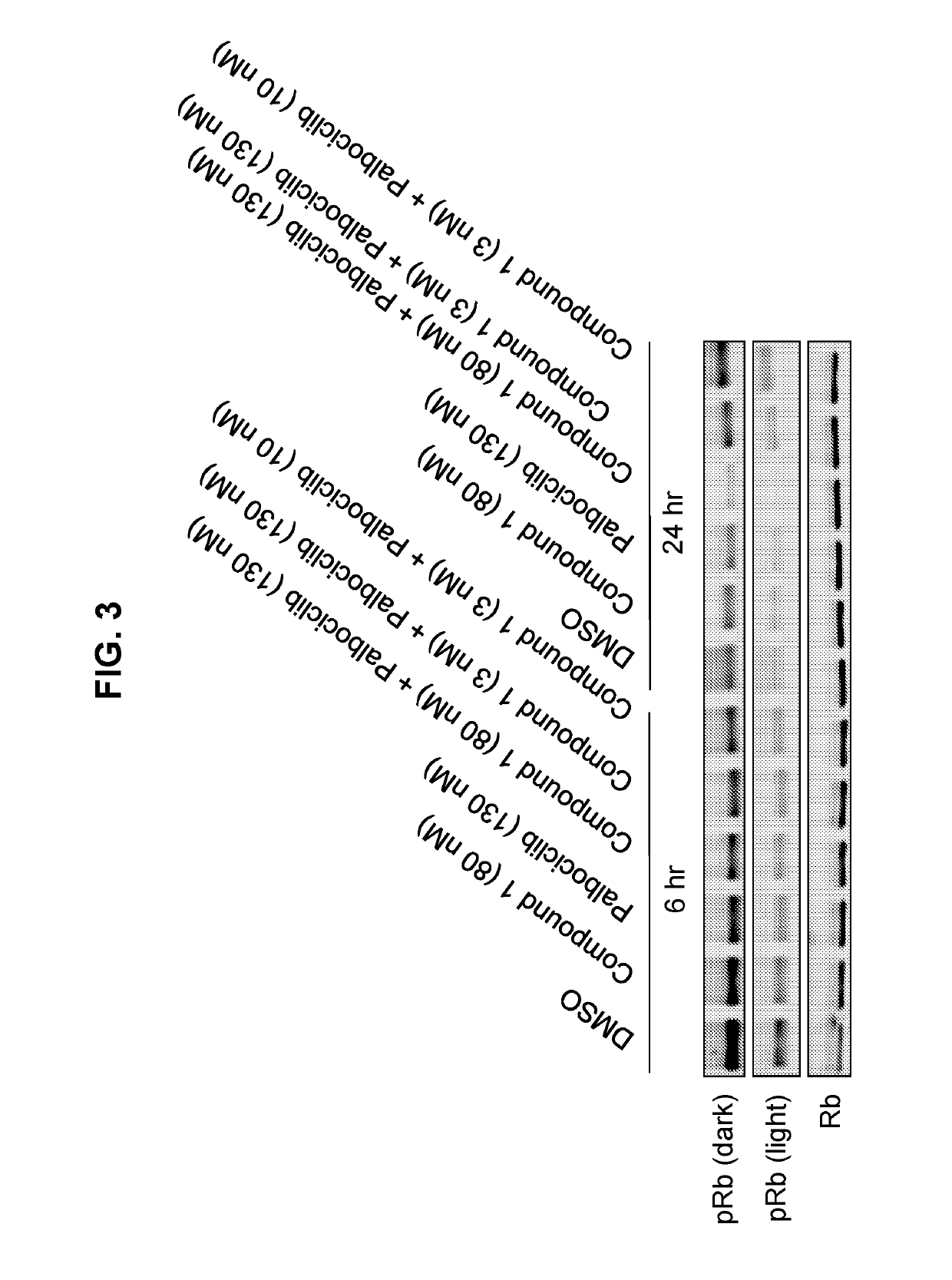
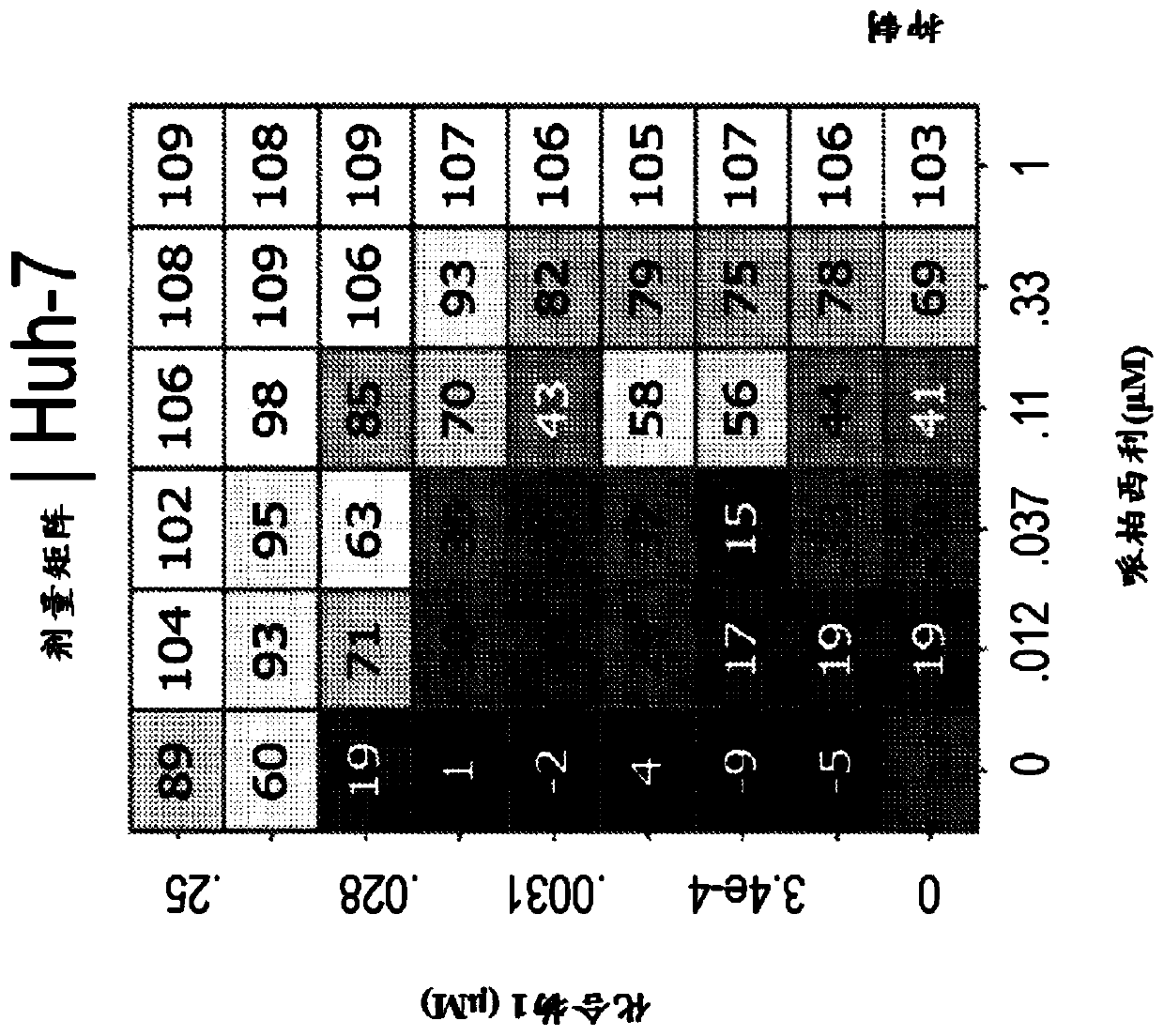
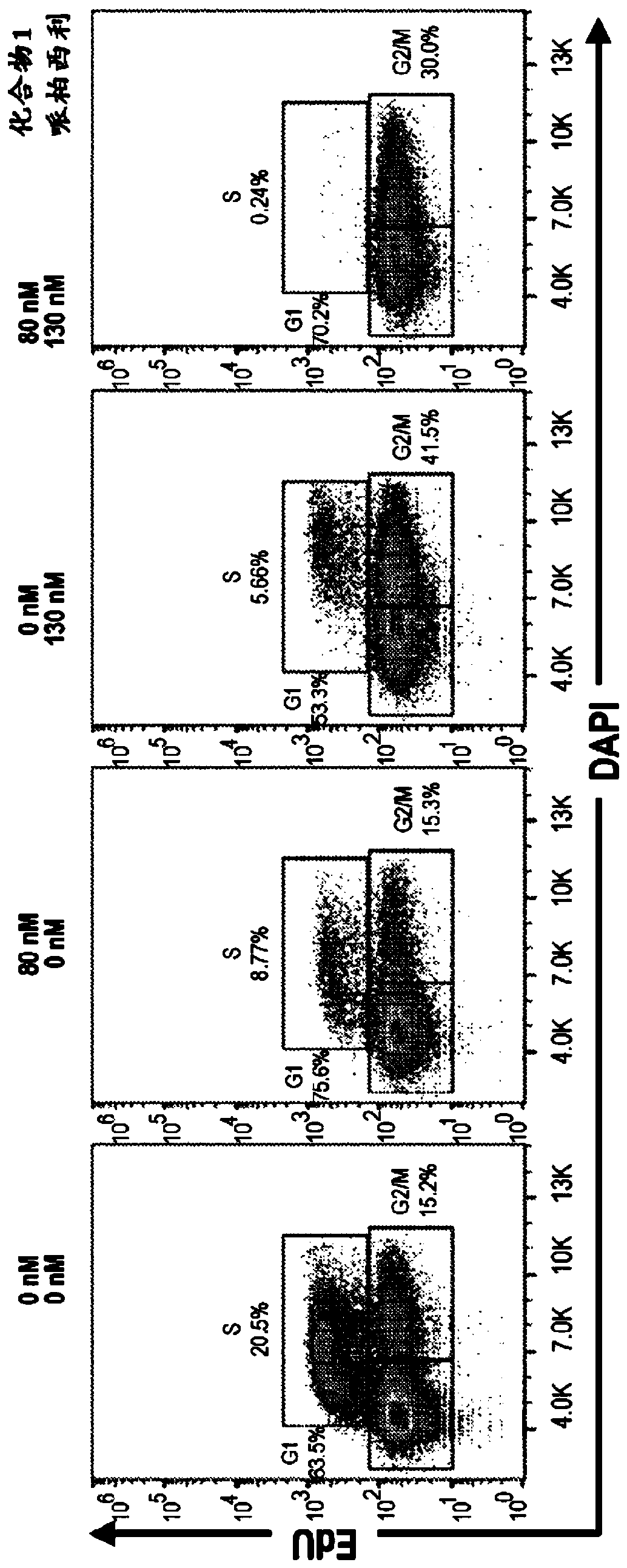
Inhibitors of the fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 in combination with cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS20190192522A1Inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryCDK inhibitorCyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors
Owner:BLUEPRINT MEDICINES
Inhibitors of the fibroblast growth factor receptor in combination with cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
InactiveCN110022900AOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBiochemistryCyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors
Owner:BLUEPRINT MEDICINES
Mutated fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 1 and methods of use
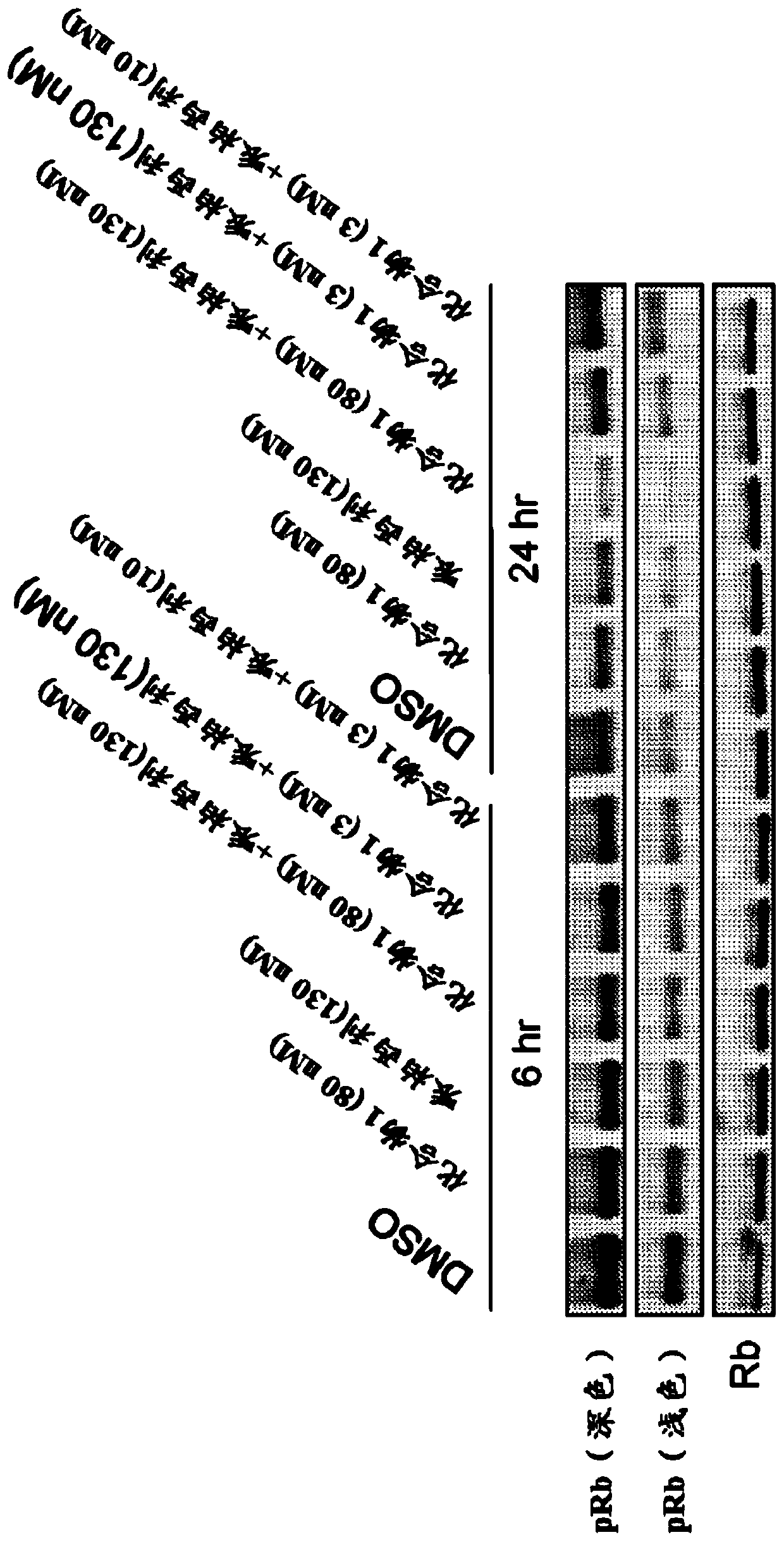
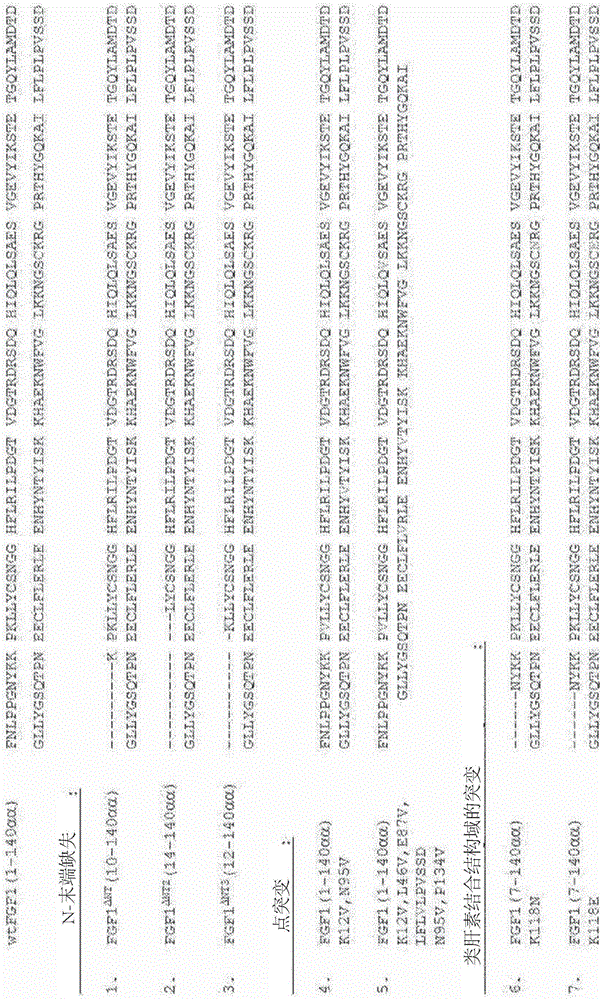
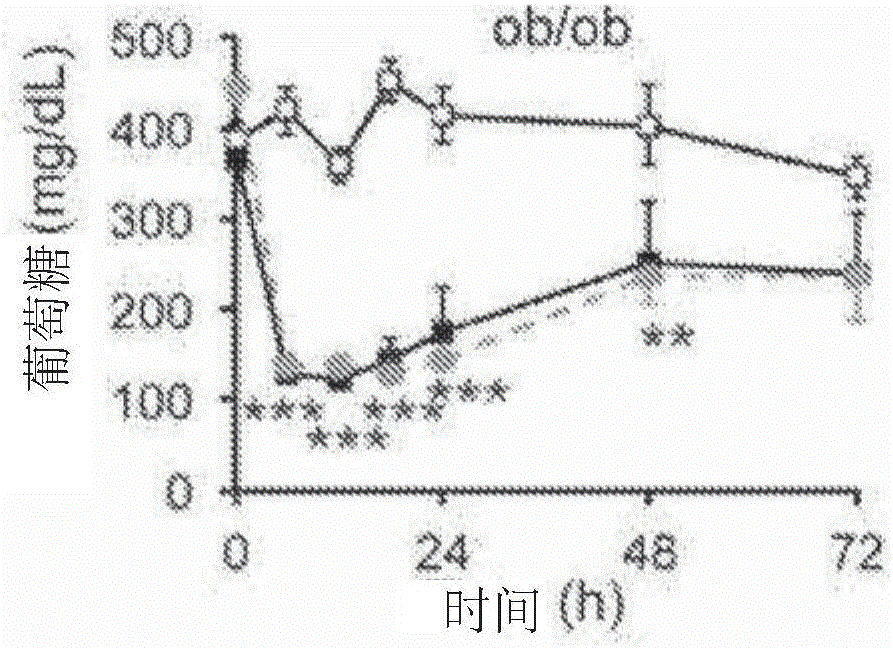
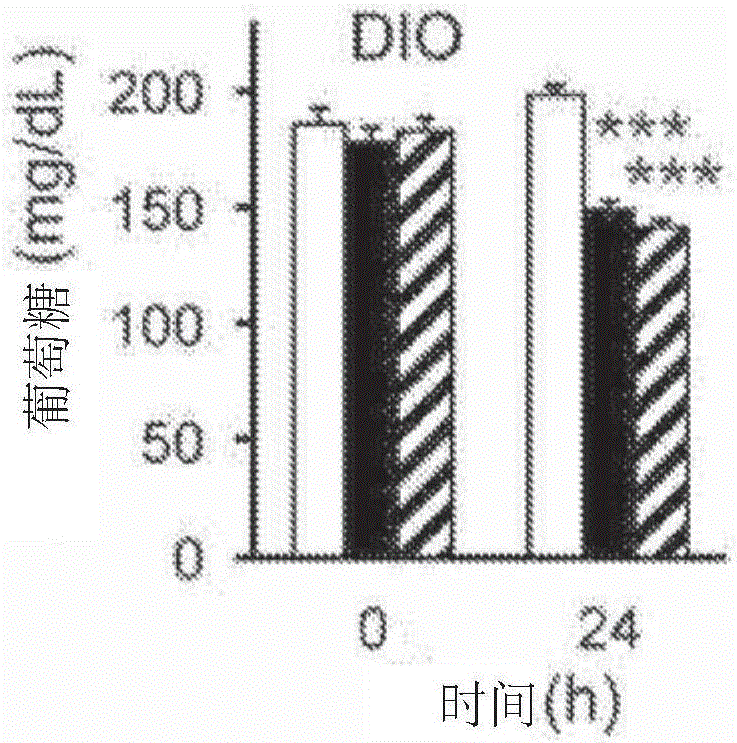
The invention discloses a mutated fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 1 and methods of use. The present disclosure provides FGF1 mutant proteins, such as those having an N-terminal deletion, point mutation(s), or combinations thereof, which can reduce blood glucose in a mammal. Such mutant FGF1 proteins can be part of a chimeric protein that includes a [Beta]-Klotho-binding protein, an FGFRlc-binding protein, a [Beta]-Klotho-binding protein and a FGFRlc-binding protein, a C-terminal region from FGF 19 or FGF21. In some examples, mutant FGF1 proteins have reduced mitogenic activity. Also provided are nucleic acid molecules that encode such proteins, and vectors and cells that include such nucleic acids. Methods of using the disclosed molecules to reduce blood glucose levels are also provided.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
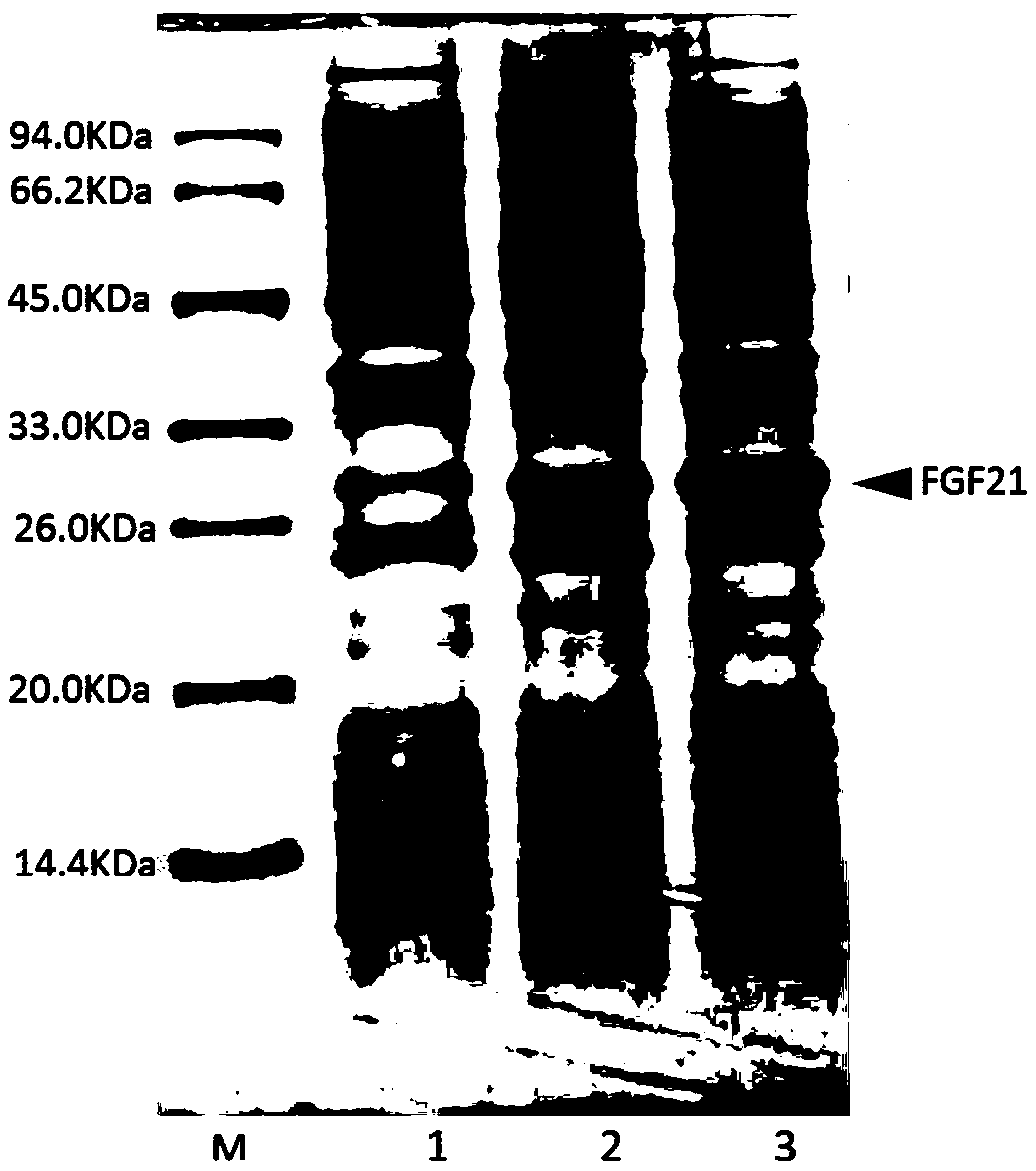
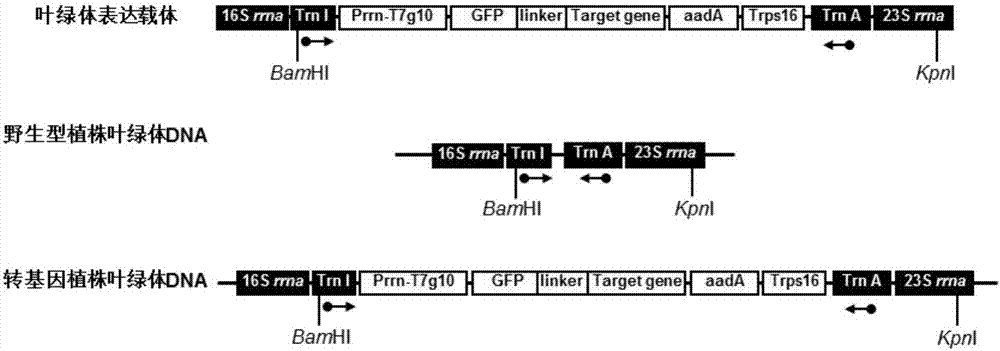
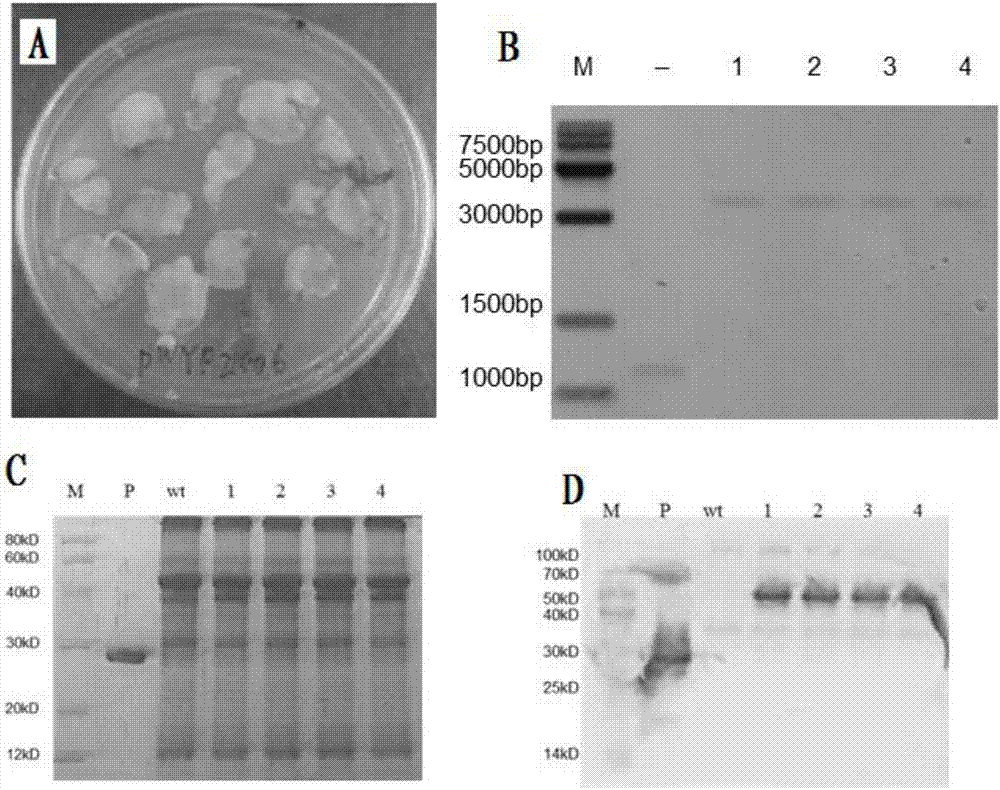
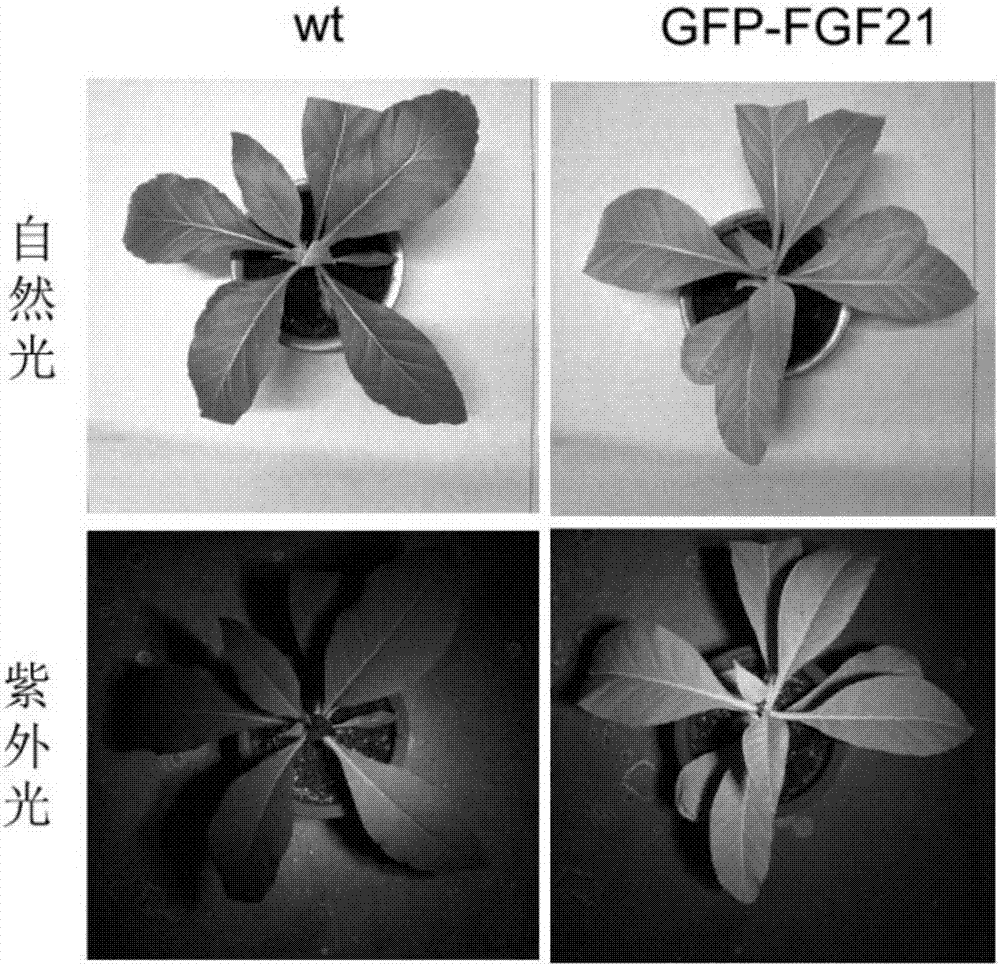
Chloroplast expressed fibroblast growth factor 21 protein and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107987151AEligible for commercial productionNucleic acid vectorPeptide preparation methodsNicotiana tabacumFactor ii
The invention discloses chloroplast expressed fibroblast growth factor 21 protein and a preparation method thereof. The amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. The preparation method of the protein comprises the following steps: constructing a tobacco leaf chloroplast expression vector pWYP23406; converting tobacco leaf chloroplast of a fibroblast growth factor 21 gene and carrying out homogenization screening to obtain a homogenized plant of the tobacco leaf chloroplast converted fibroblast growth factor 21 gene; analyzing an expression amount of the fibroblast growth factor 21 in chloroplast transgenic tobacco leaf plants; purifying the fibroblast growth factor 21 to obtain the chloroplast expressed fibroblast growth factor 21. According to the chloroplast expressed fibroblast growth factor 21 protein and the preparation method thereof, GFP fusion protein of the fibroblast growth factor 21 is efficiently expressed in the tobacco leaf chloroplast and commercial production conditions are provided.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Combination comprising anti-fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) antibody and a tyrosine kinase inhibitor
ActiveUS9931401B2Hybrid cell preparationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFibroblast growth factor receptor 2Tyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The present invention provides a combination of an antibody binding to a fibroblast growth factor receptor, and another agent.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors and application thereof
ActiveCN109384790ASure easyRelieve symptomsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseInhibitory effect
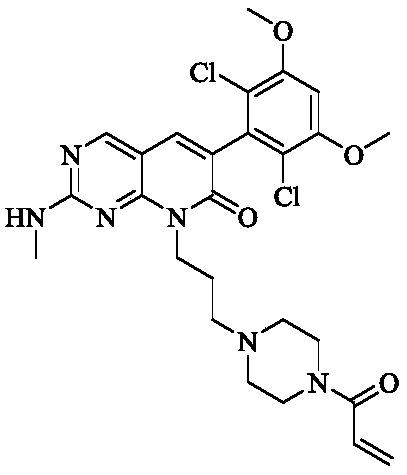
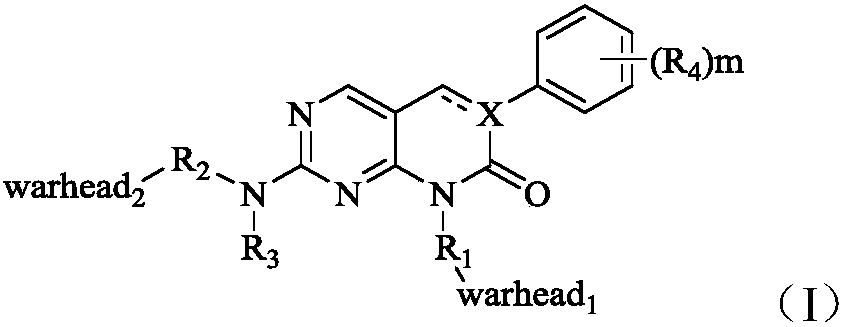
The invention specifically relates to irreversible inhibitors used for the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) and represented by a formula I which is described in the specification and pharmaceutically acceptable salts and stereoisomers thereof, and pharmaceutical preparations, pharmaceutical compositions and application of the compounds, belonging to the field of medical technology. R1, R2,R3, R4, m, X, warhead1 and warhead2 in the formula I are as defined in the specification. The compounds of the invention have high-efficiency high-selectivity inhibitory effects on the fibroblast growth factor receptor and can be applied to the treatment of related diseases mediated by FGF / FGFR abnormalities, especially to the treatment of cancer diseases.
Owner:TRANSTHERA SCIENCES (NANJING) INC
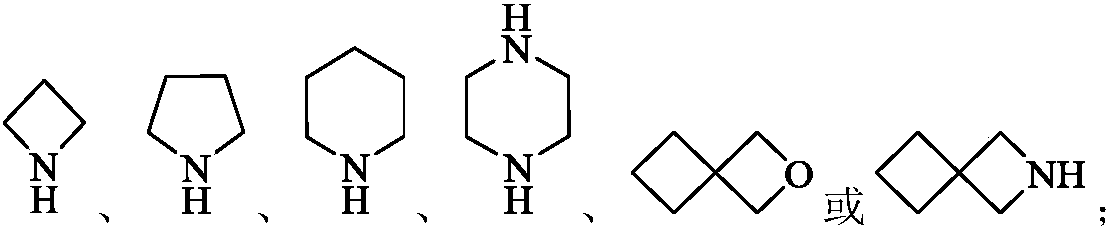
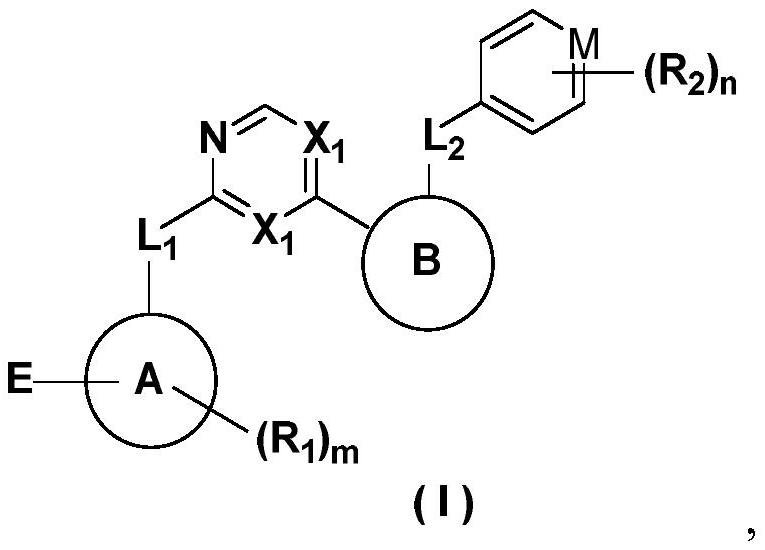
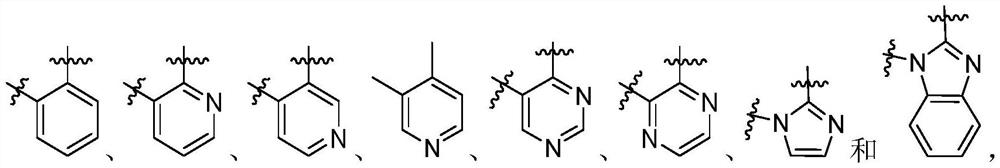
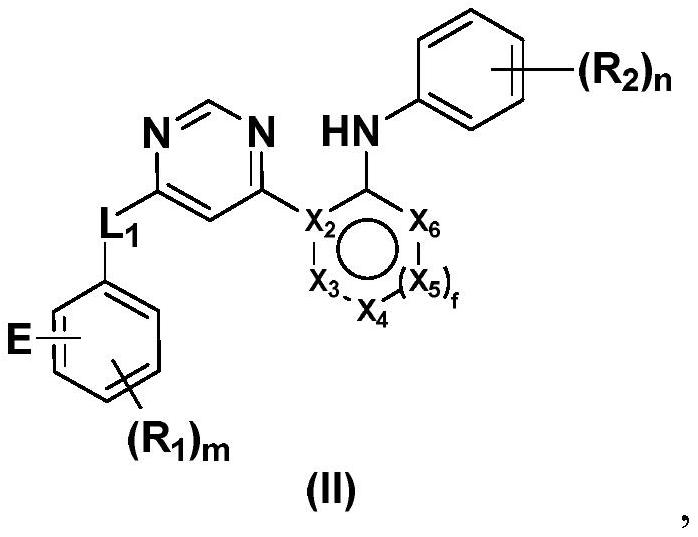
Heterocyclic compounds as FGFR4 inhibitors
InactiveCN112341431AStrong inhibitory activityStrong antiproliferative activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseasePharmaceutical drug
The present invention provides heterocyclic compounds as selective inhibitors of fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4), pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds, methods of preparingthe compounds, and methods of treating cell proliferative diseases, such as cancer, using the compounds of the invention.
Owner:QILU PHARMA
Novel splice variant of FGFR3 (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 3) in liver carcinoma tissue and application thereof
ActiveCN105294856APromote proliferationEasy transferBiological testingFermentationFibroblast growth factor receptor 2Biology
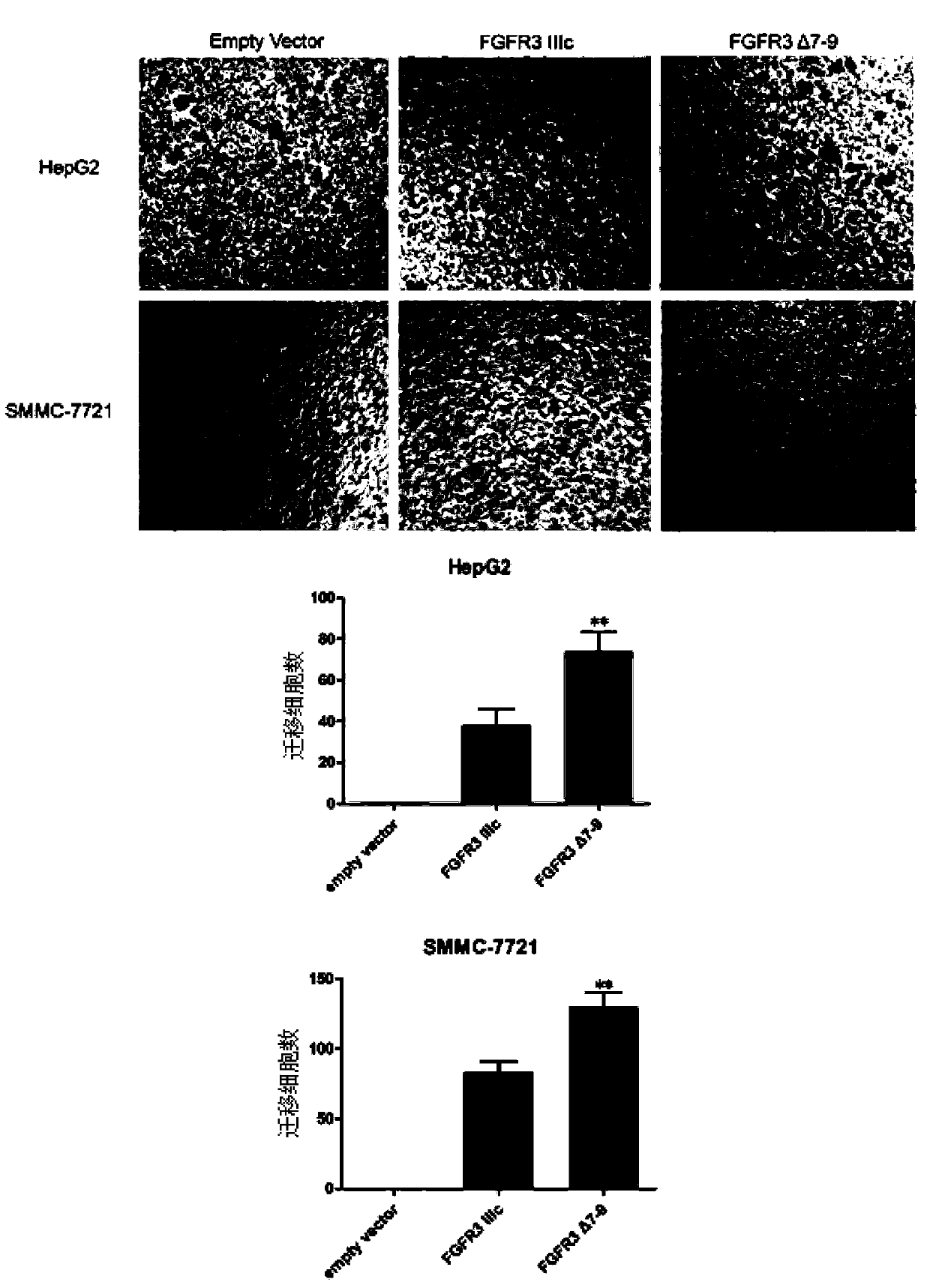
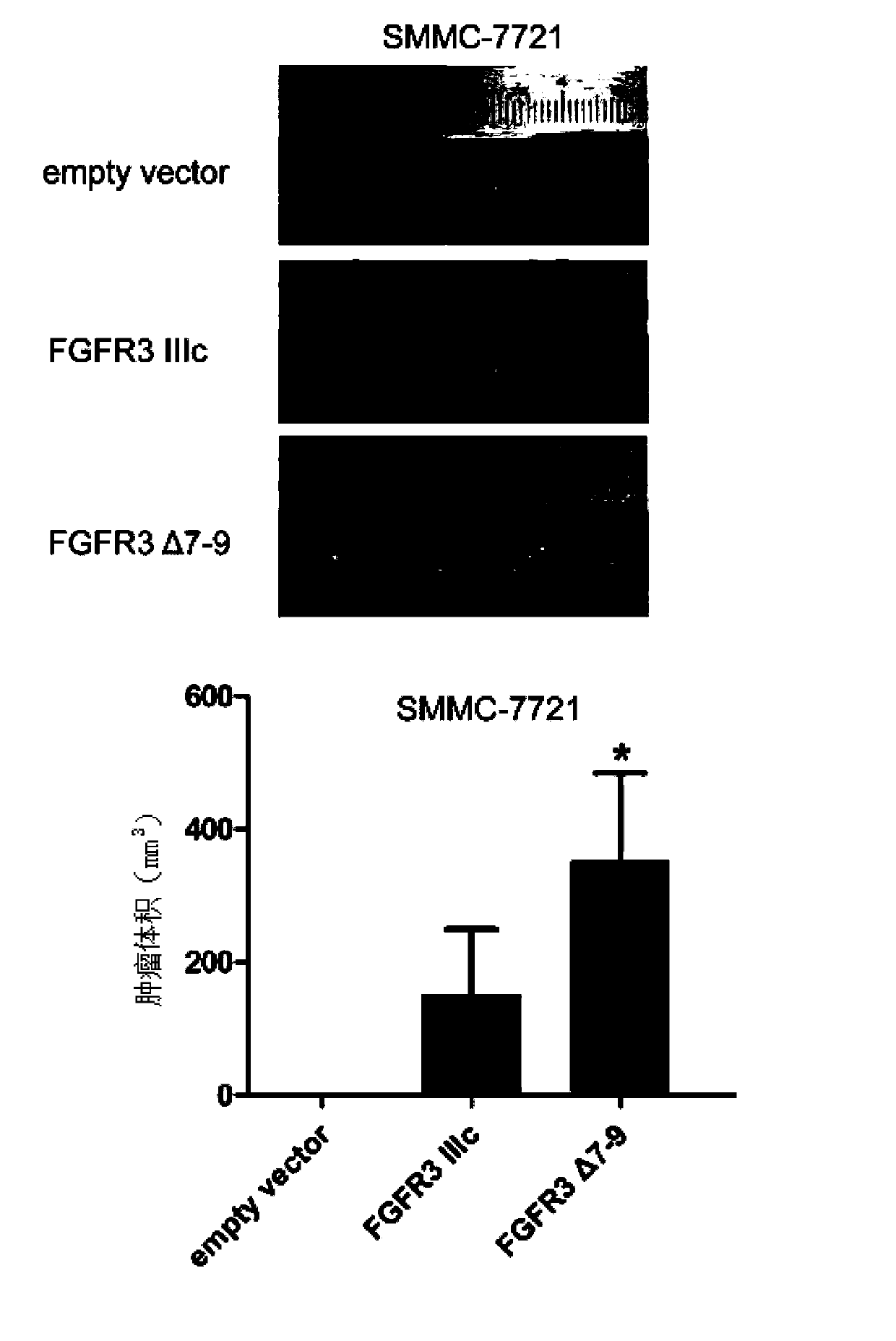
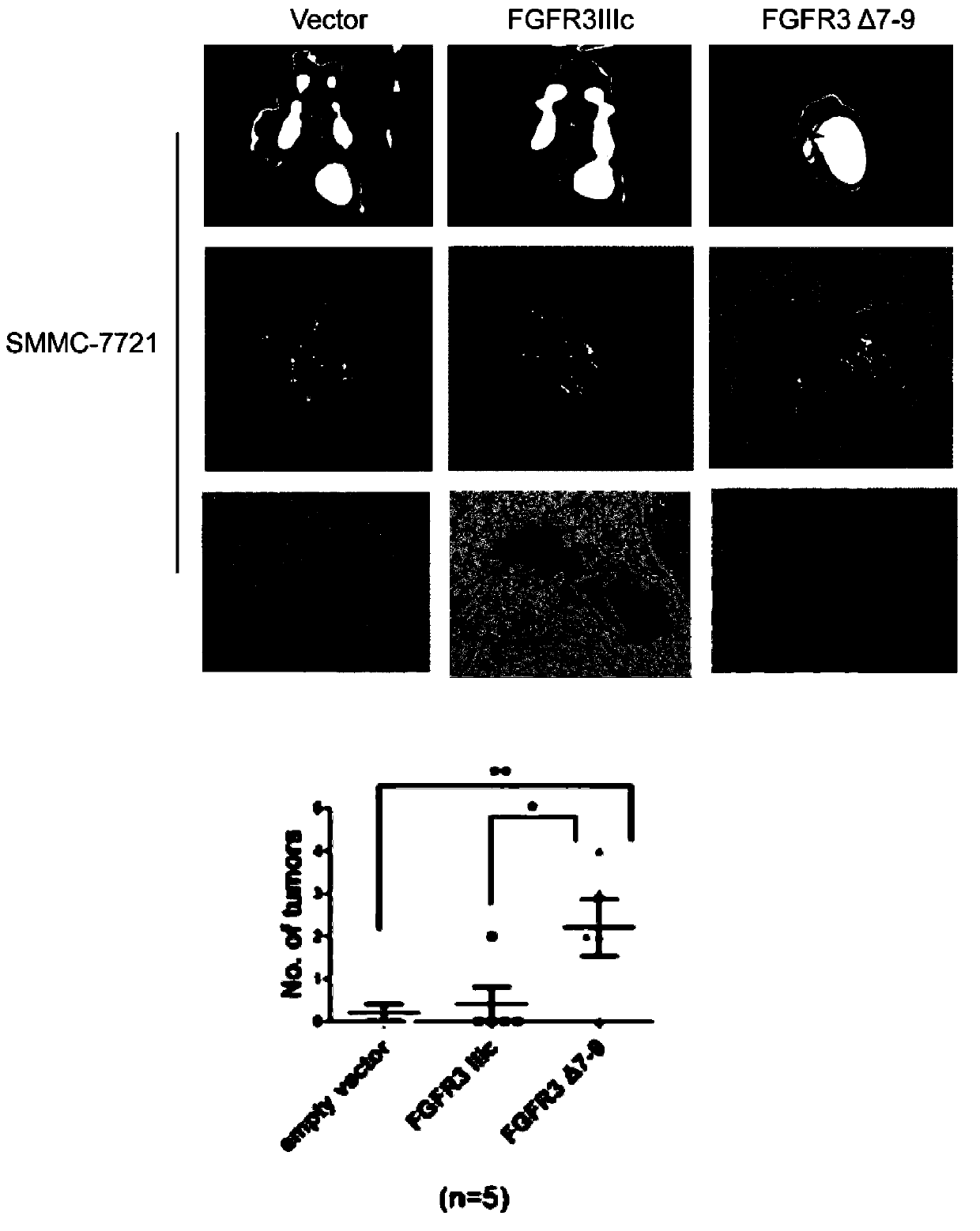
The invention discloses a novel splice variant of FGFR3 (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 3) in liver carcinoma tissue and application thereof. The novel splice variant is FGFR3 delta7-9, and the gene sequence of FGFR3 delta7-9 is CGCTGGACGTGCTGGCCGAGGAGGAGCTGG. According to the novel splice variant FGFR3 delta7-9, proliferation and transfer of hepatoma carcinoma cells are promoted, the growth of subcutaneous hepatoma carcinoma cell transplantation tumor of a naked mouse is further promoted; besides, the experimental result shows that FGFR3 delta7-9 can serve as the diagnostic marker of liver cancer, therefore whether the splice variant FGFR3 delta7-9 exists in the liver carcinoma tissues of patients has higher guiding significance on the judgment of prognosis in liver cancer.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com