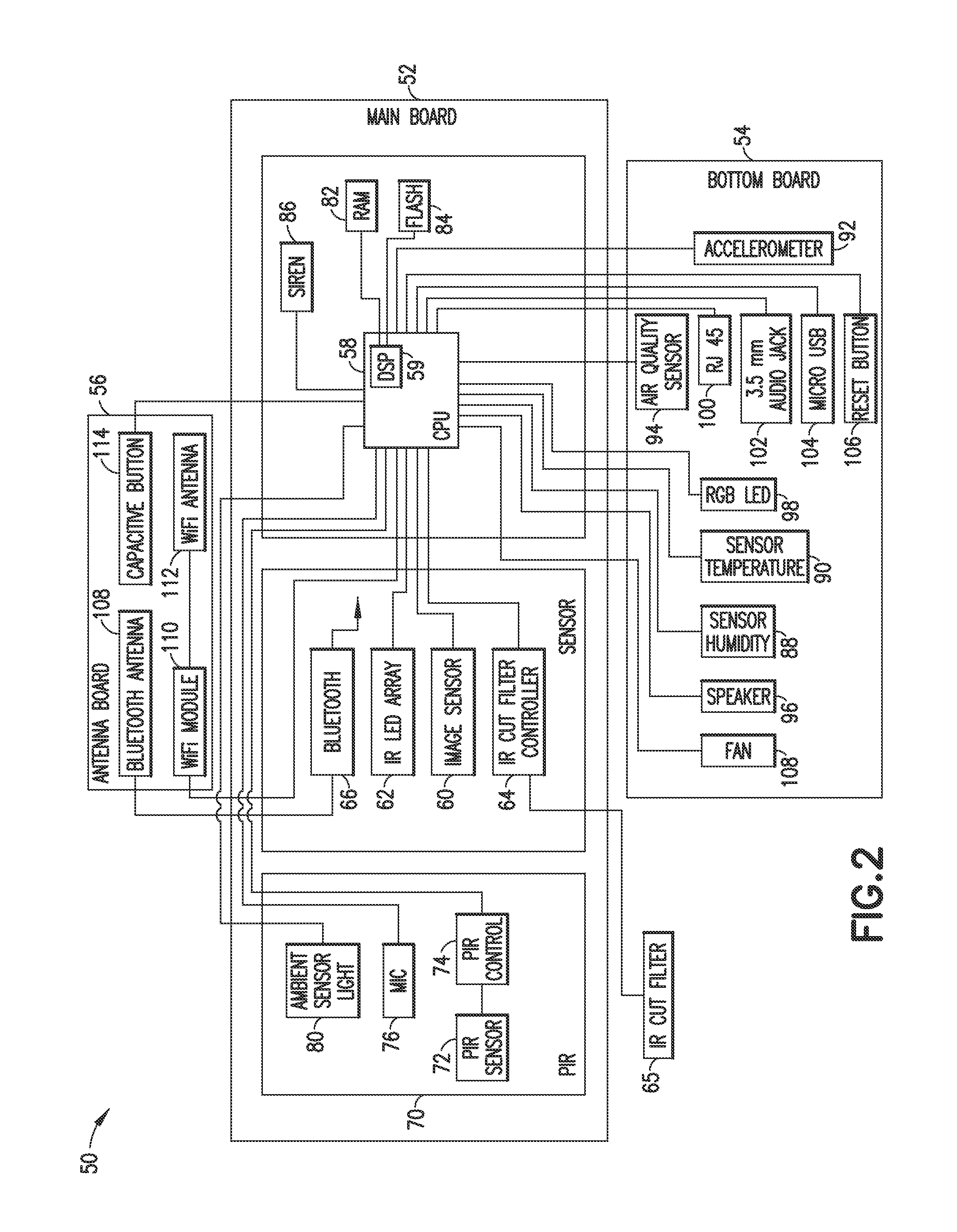
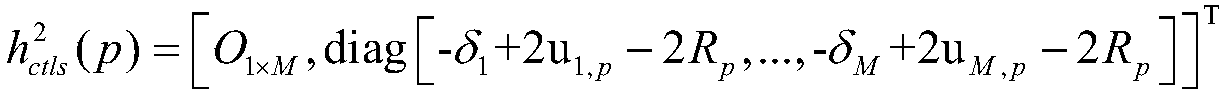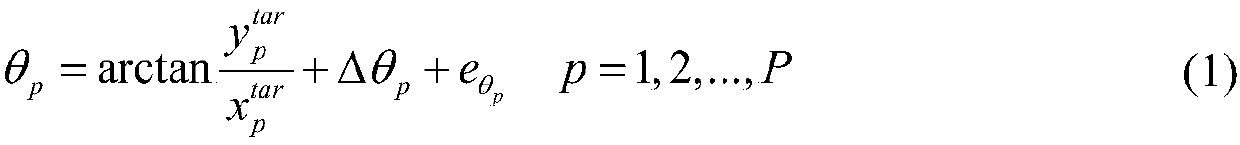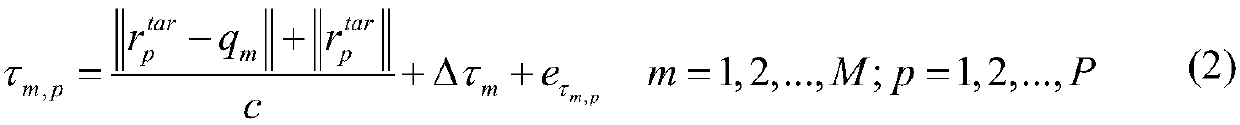Patents
Literature
262 results about "Location status" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
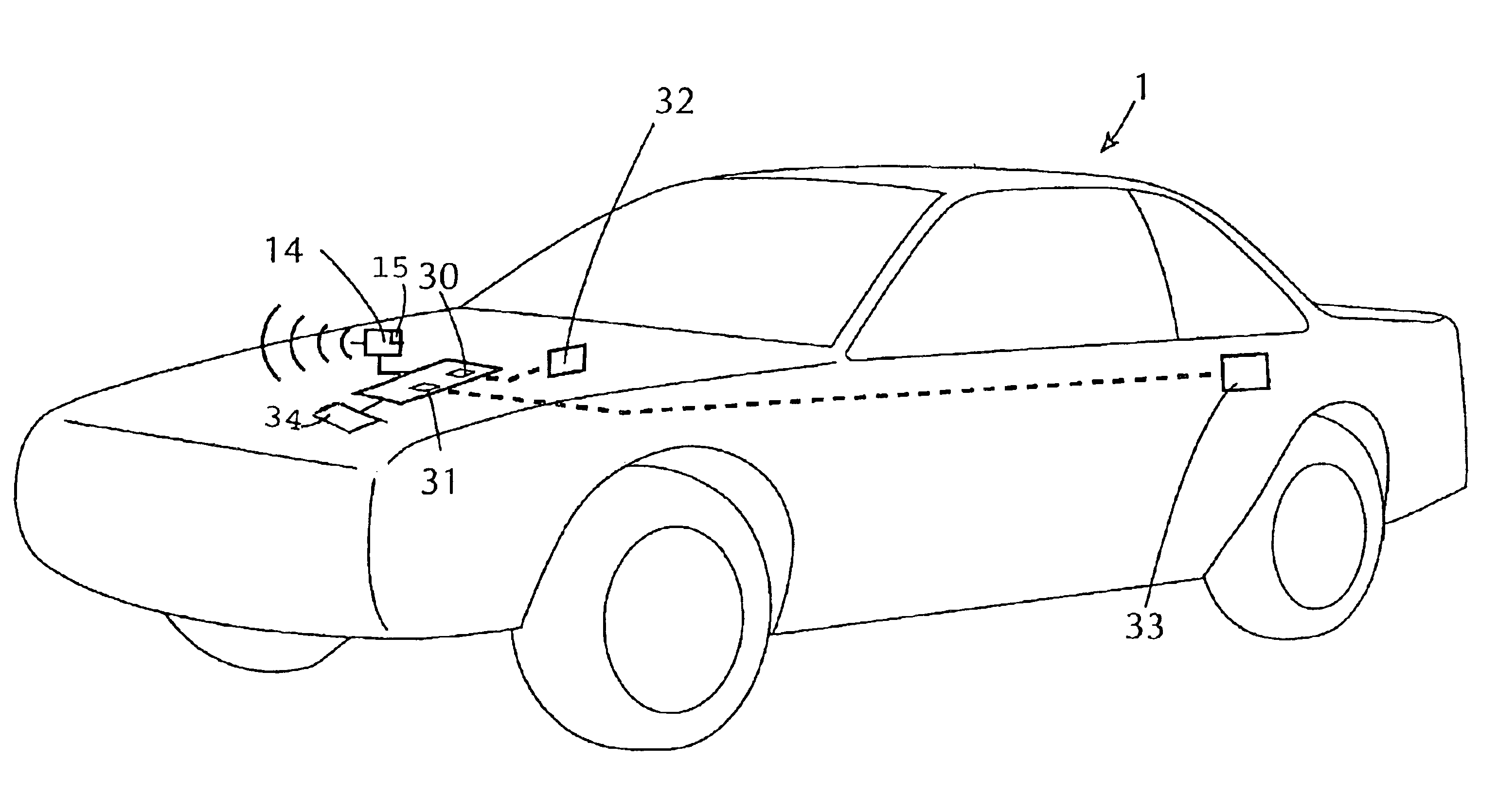
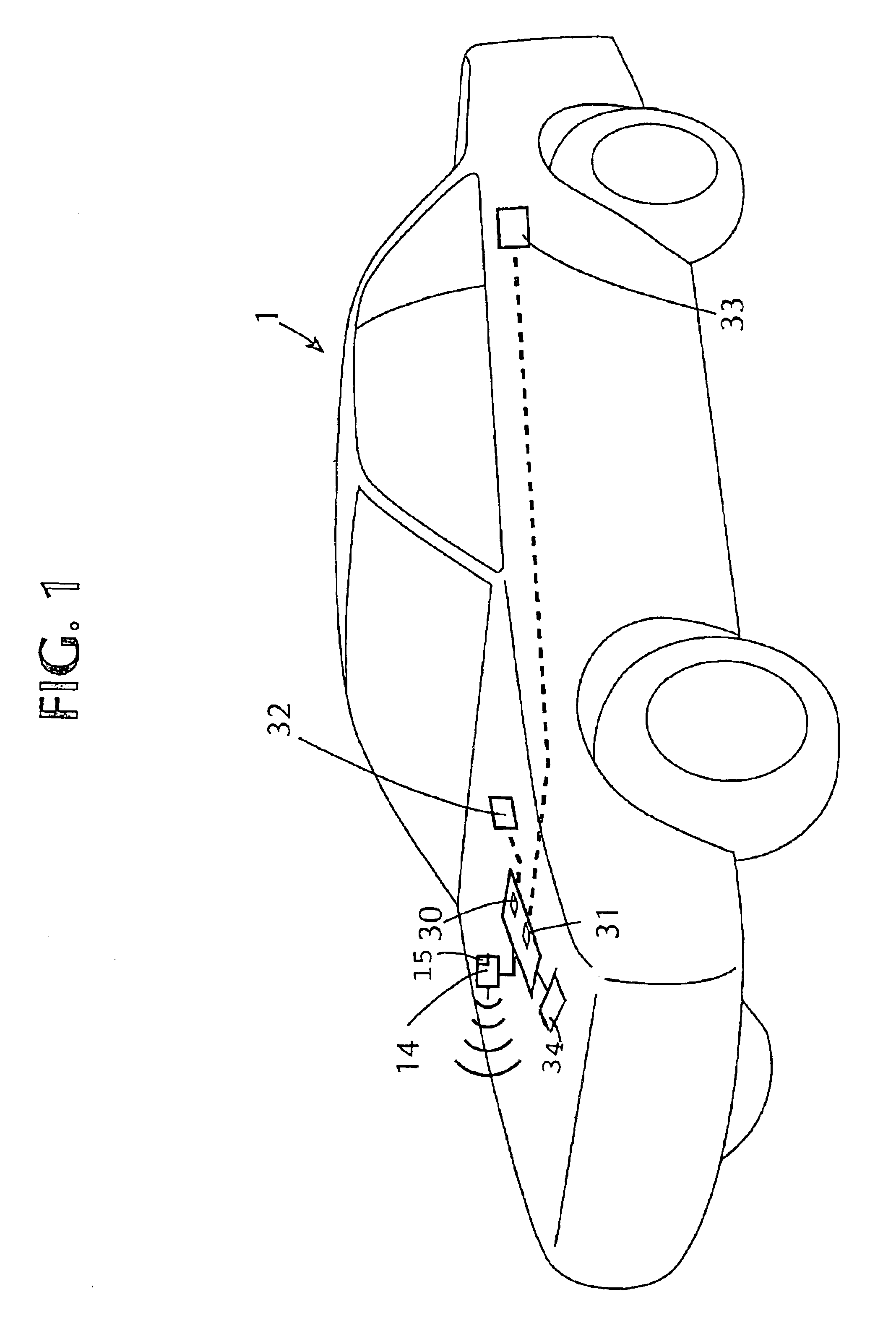
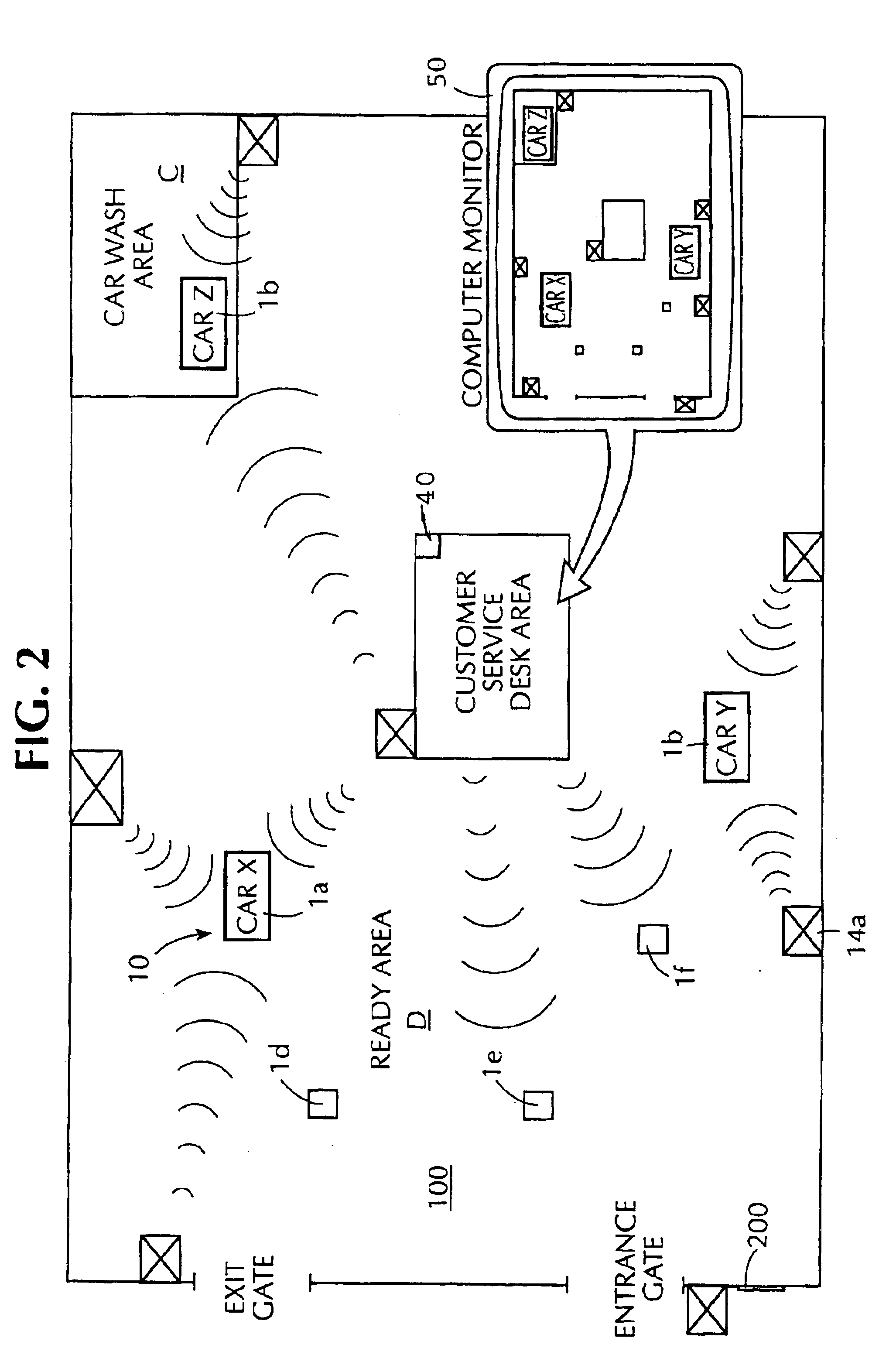
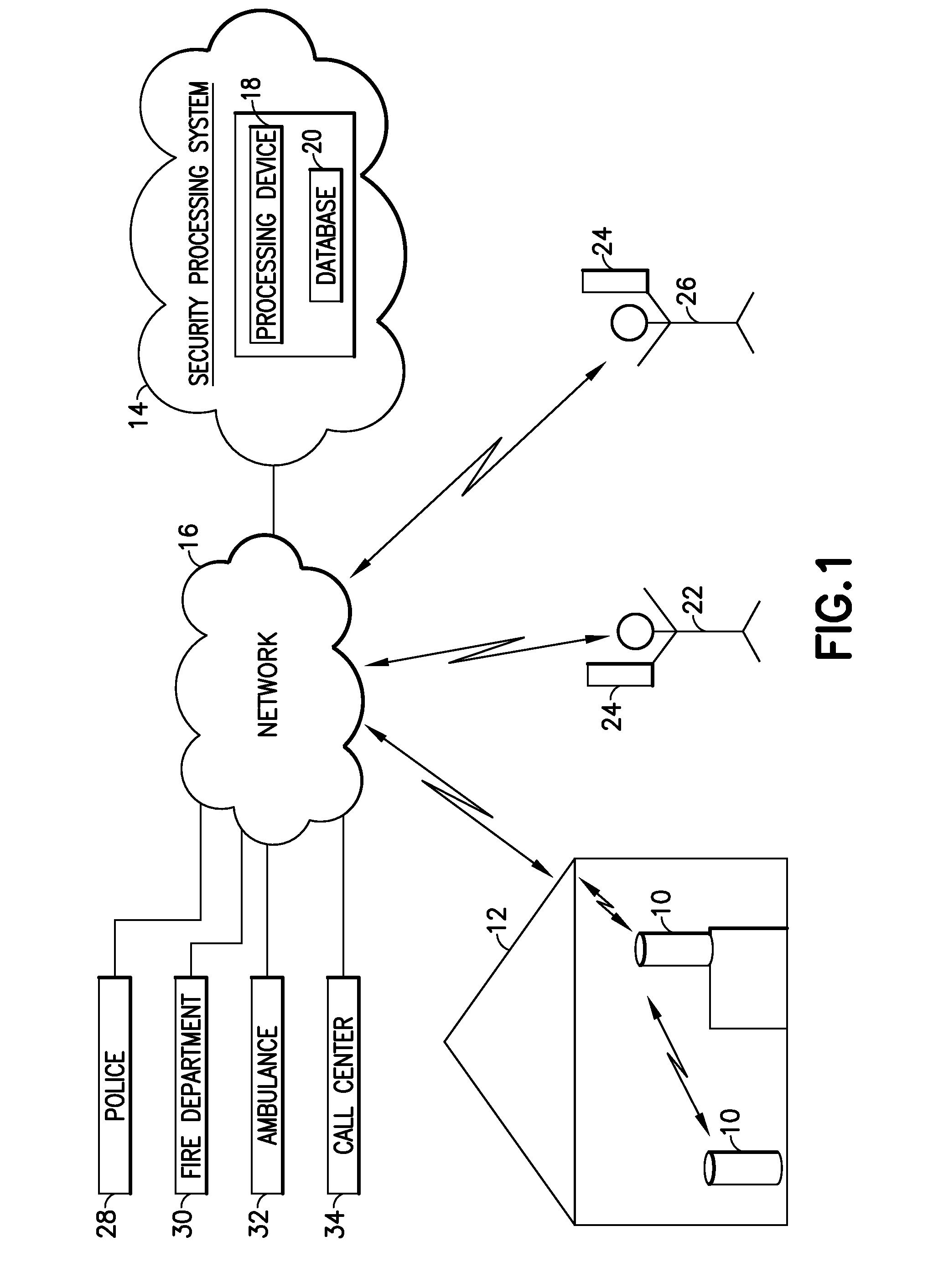
Fully automated vehicle rental system
InactiveUS6898493B2Accurate calculationVehicle testingTicket-issuing apparatusLocation statusIn vehicle
An automated vehicle rental system with individual vehicle transmitting sensors for keeping track of vehicle mileage, fill state of vehicle fuel tank, and localized position status in a rental lot. Sensors are linked to the vehicle odometer reading and to the vehicle fuel tank float sensor with compensation for types of driving and fuel fill-ups which affect float level readings. The sensors are integrated with or are linked with communicating tags operable in a defined site for ultimate communication of stored vehicle related sensor data, vehicle location and type to a central data base for automatically completely effecting check out, charges and state of vehicle readiness for renewed rental. The transmitting sensors are adapted to avoid interference between sensors of other vehicles during multiple transmissions. Also included is an in-vehicle check out and payment device operatively linkable to the transmitting sensor of the vehicle.
Owner:I D SYST
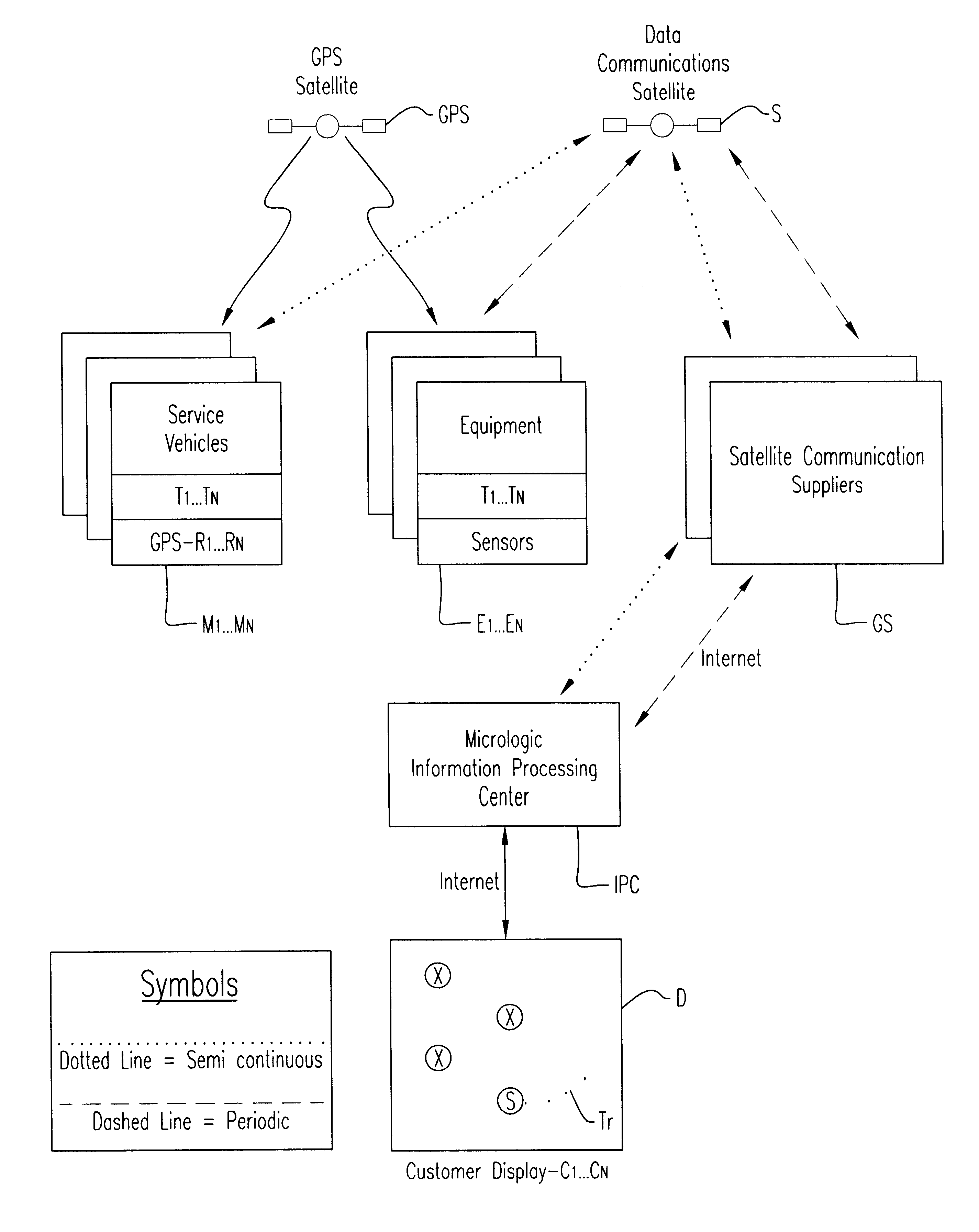
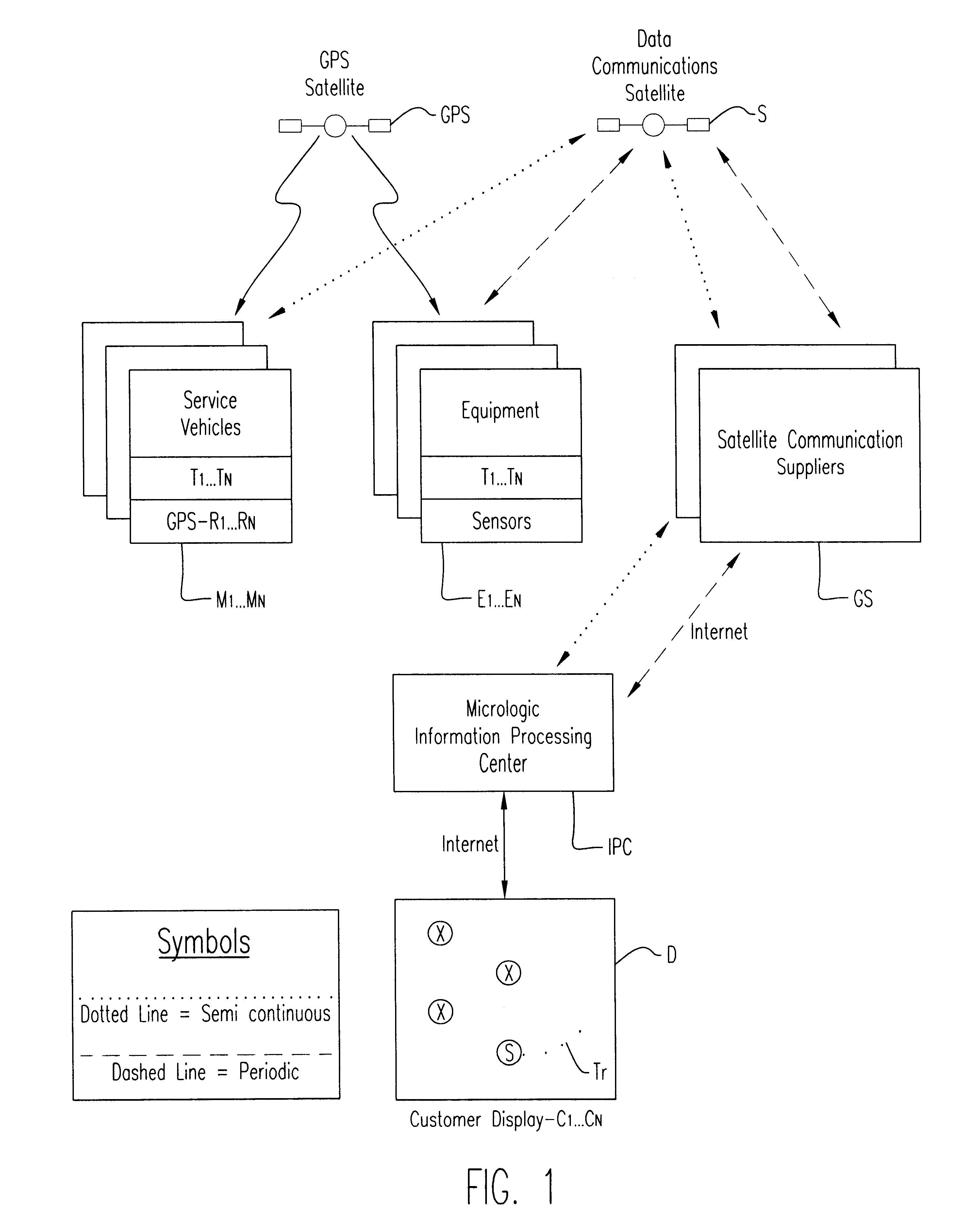
Method of and system and apparatus for integrating maintenance vehicle and service personnel tracking information with the remote monitoring of the location, status, utilization and condition of widely geographically dispersed fleets of vehicular construction equipment and the like to be maintained, and providing and displaying together both construction and maintenance vehicle information
InactiveUS6651001B2Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesService personnelIntegrated monitoring
An integrated monitoring system for integrating and displaying the location of widely dispersed construction vehicle equipments at their respective sites together with the present location and recent track of respective maintenance vehicles for servicing the equipments, through the use of satellite positioning, wireless data communication and Internet facilities for determining such locations.
Owner:STARTRAK INFORMATION TECH
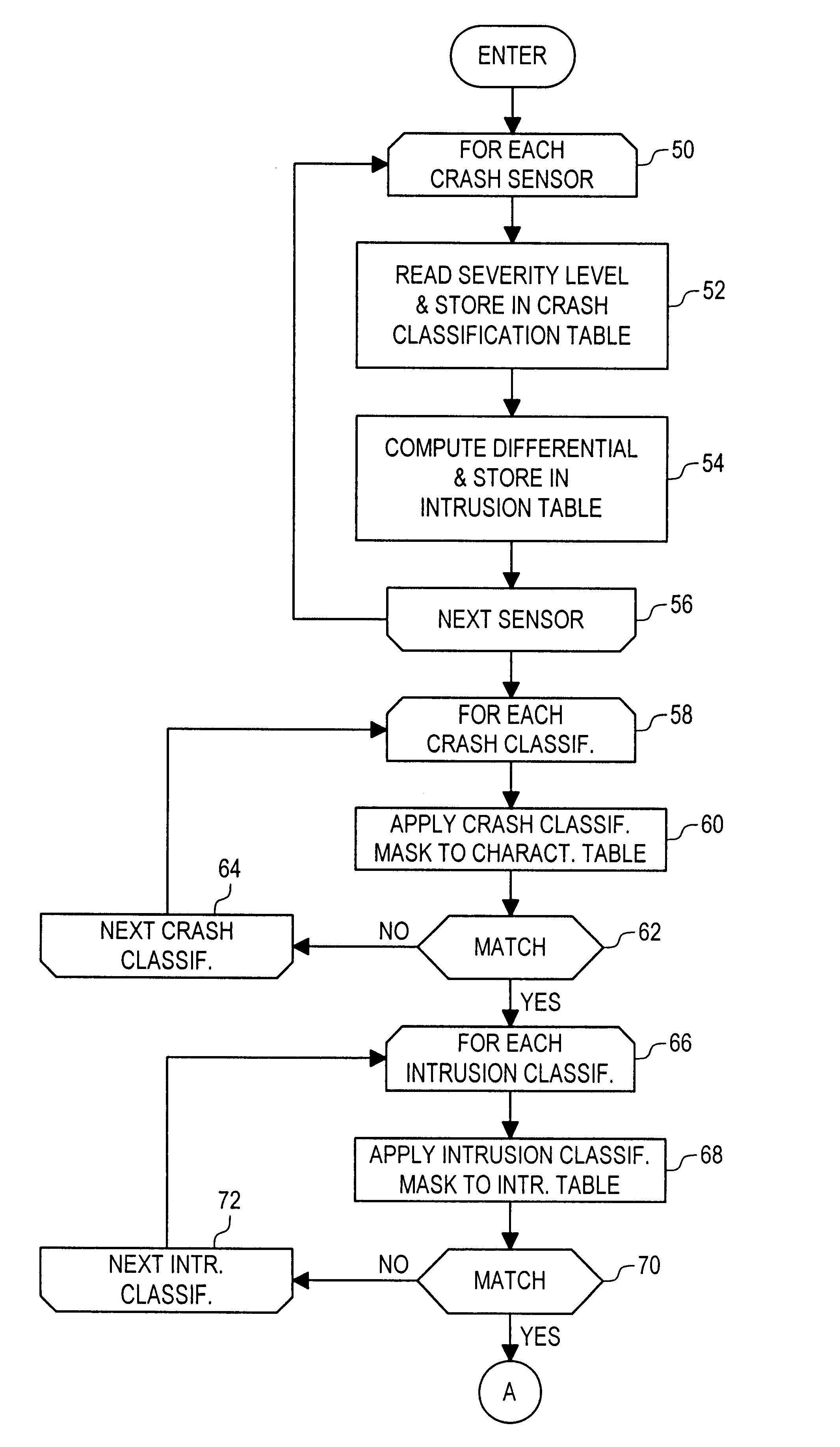
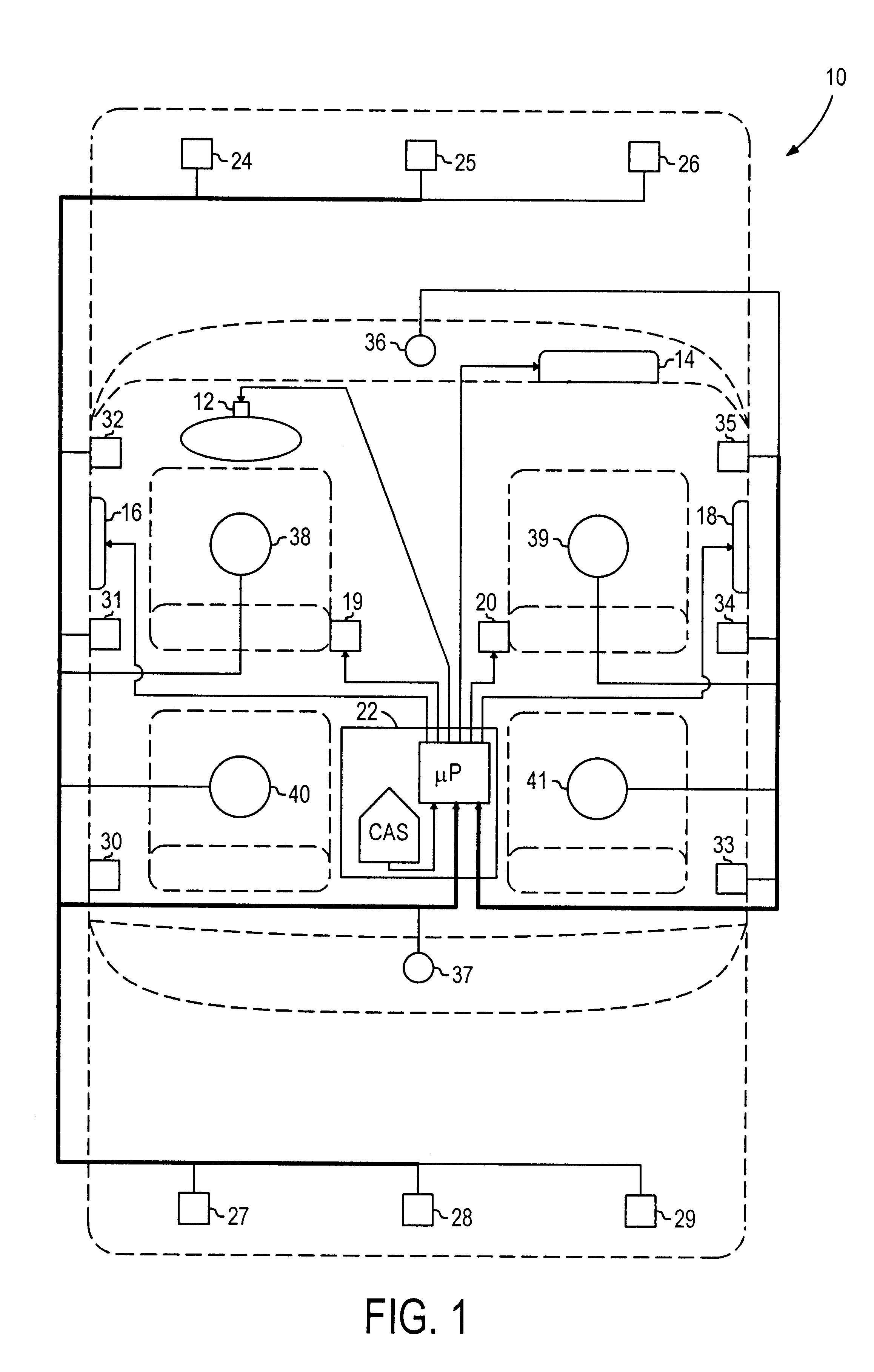
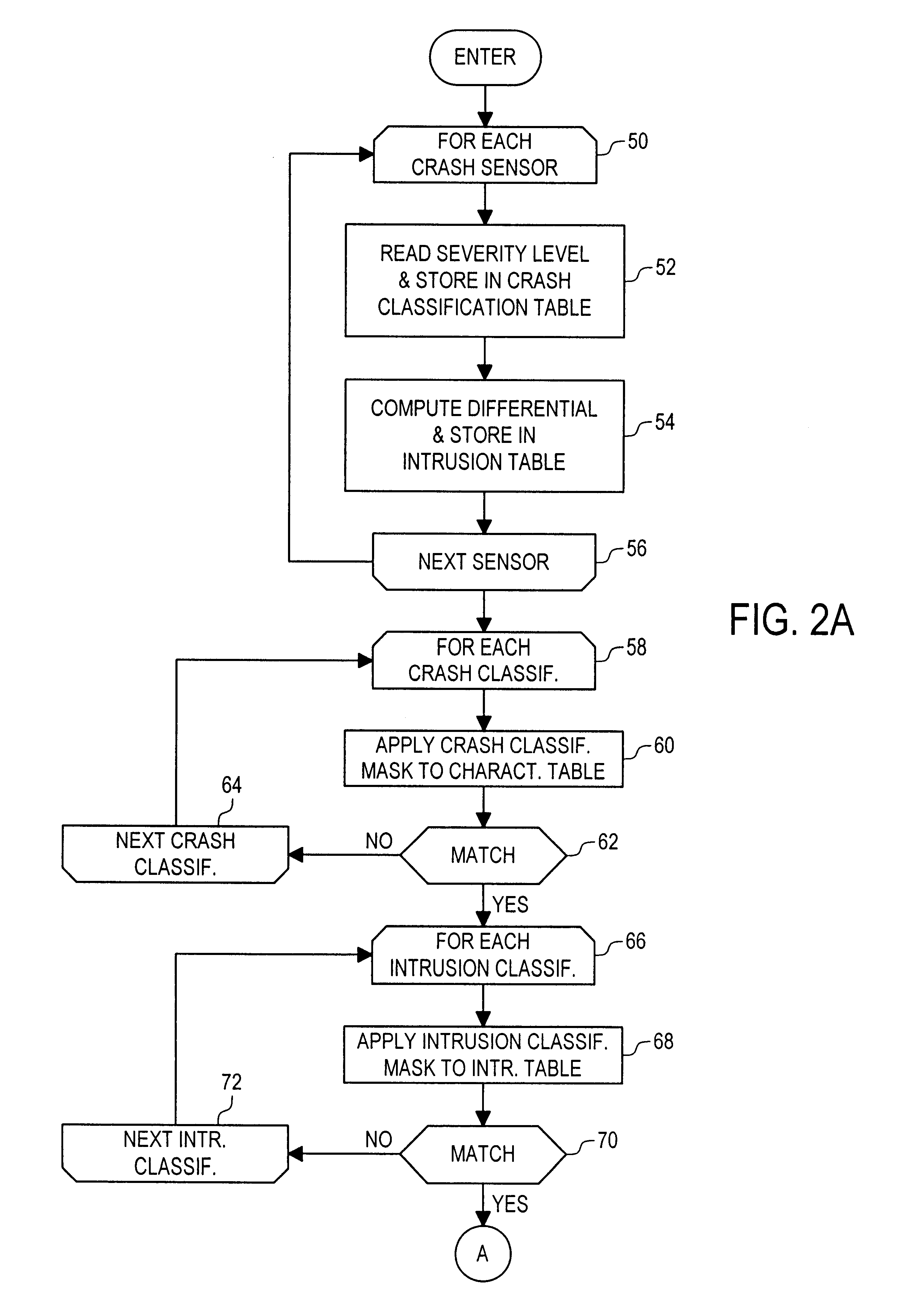
Crash classification method and apparatus using multiple point crash sensing
An improved method of using multiple point crash sensing and multiple sensor occupant position sensing for classifying a crash event and determining which restraints should be deployed. A central controller collects crash data from multiple crash sensors and combines severity characterization data from each of the multiple sensors to construct a characterization table or matrix for the entire system. Each possible crash event classification is represented by a characterization value mask, and the various masks are sequentially applied to the system characterization table until a match is found, with a match identifying the appropriate crash event classification. The classification decision, in turn, is used to determine which, if any, of the restraint devices should be deployed based upon the crash severity. Similarly, the controller collects data from various occupant position sensors to construct a characterization table or matrix for the occupant position detection system. Each possible occupant position sensor classification is represented by a characterization value mask, and various masks are sequentially applied to the table until a match is found, with a match identifying the appropriate occupant position status. The occupant position status, in turn, is used to determine which, if any, of the restraints may be deployed. The system also includes a centrally located crash sensor, and the controller constructs an intrusion table based on differences between the remote and central sensors. The intrusion classification is determined and combined with the crash classification and occupant position status to determine which restraints should ultimately be deployed.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Video processing method and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN106303690AImprove experienceImage enhancementImage analysisLocation statusComputer graphics (images)
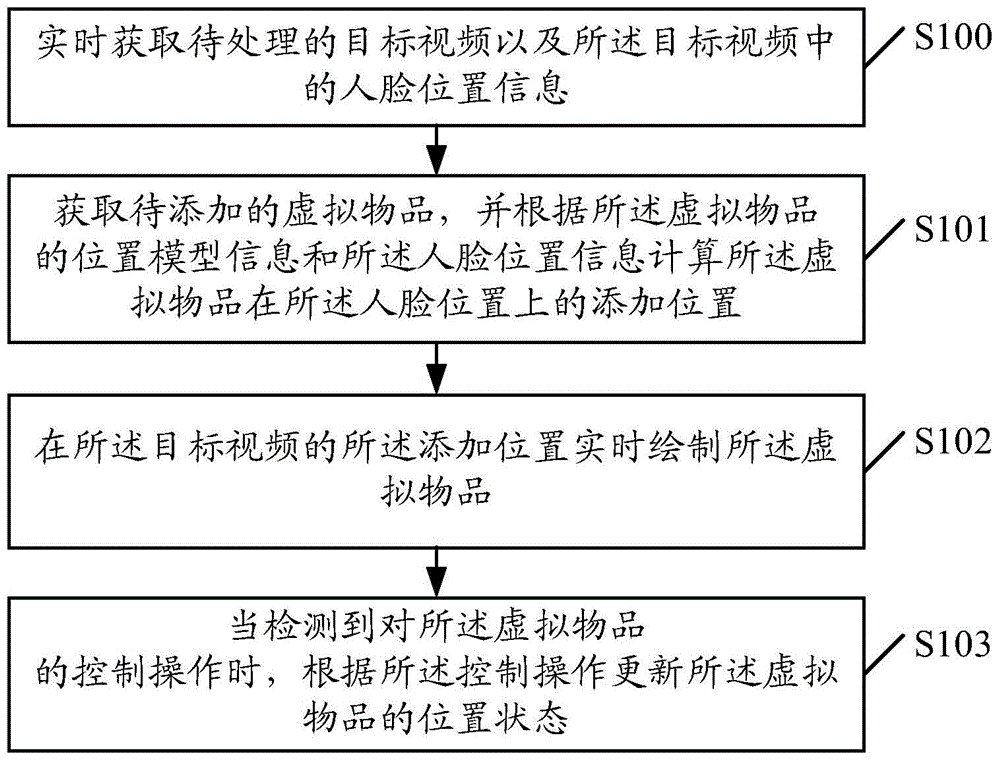
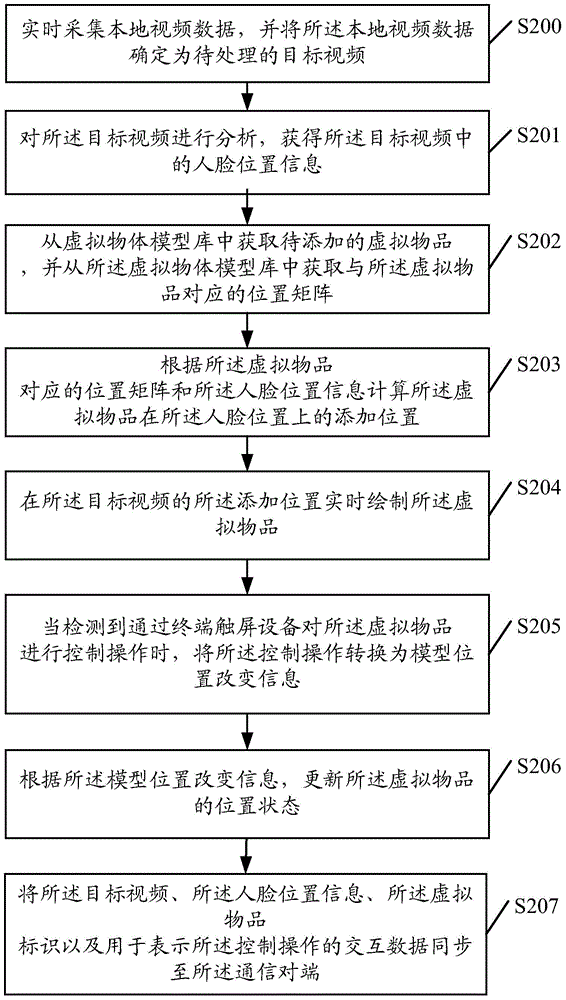
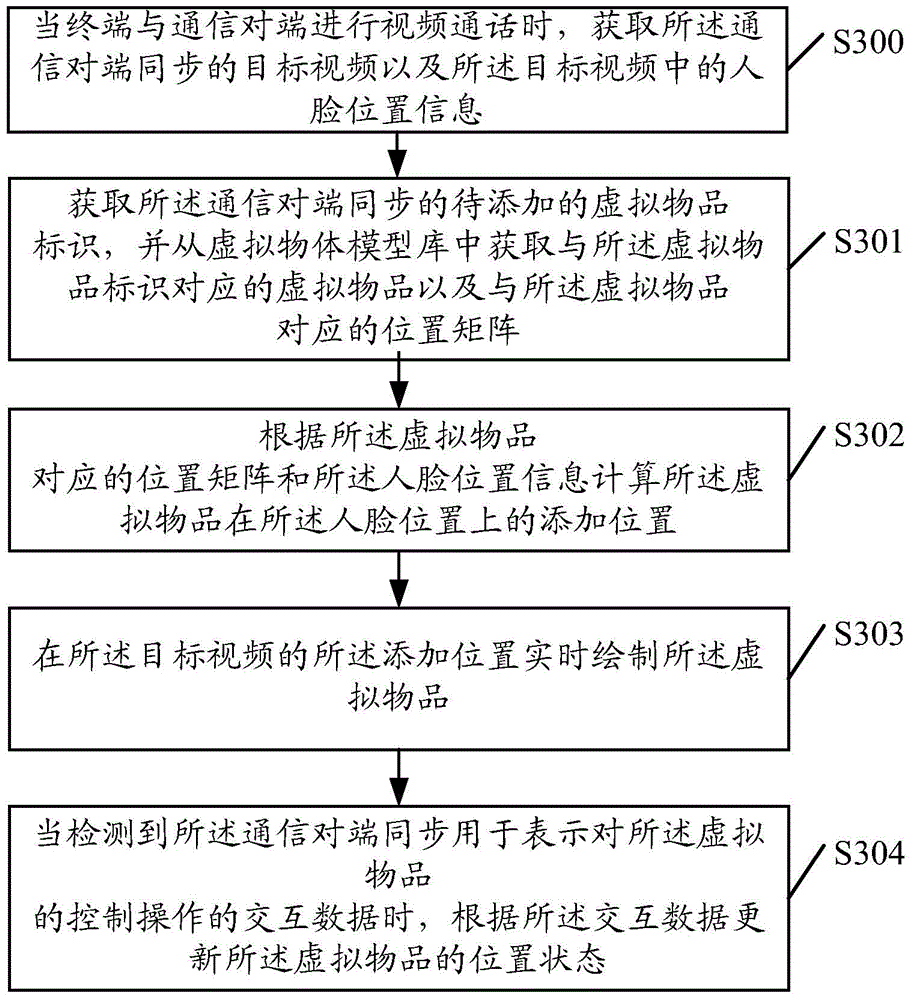
An embodiment of the invention provides a video processing method and an apparatus thereof. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring a target video to be processed and face position information in the target video in real time; acquiring a virtual article to be added, and calculating an adding position of the virtual article on a face position according to position model information of the virtual article and the face position information; drawing the virtual article at the adding position of the target video in real time; and when control operation to the virtual article is detected, according to the control operation, updating a position state of the virtual article. In the invention, the virtual article can be added to the face position in the target video and a user can operate the virtual article so that there are various kinds of video processing modes and a user experience is increased.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
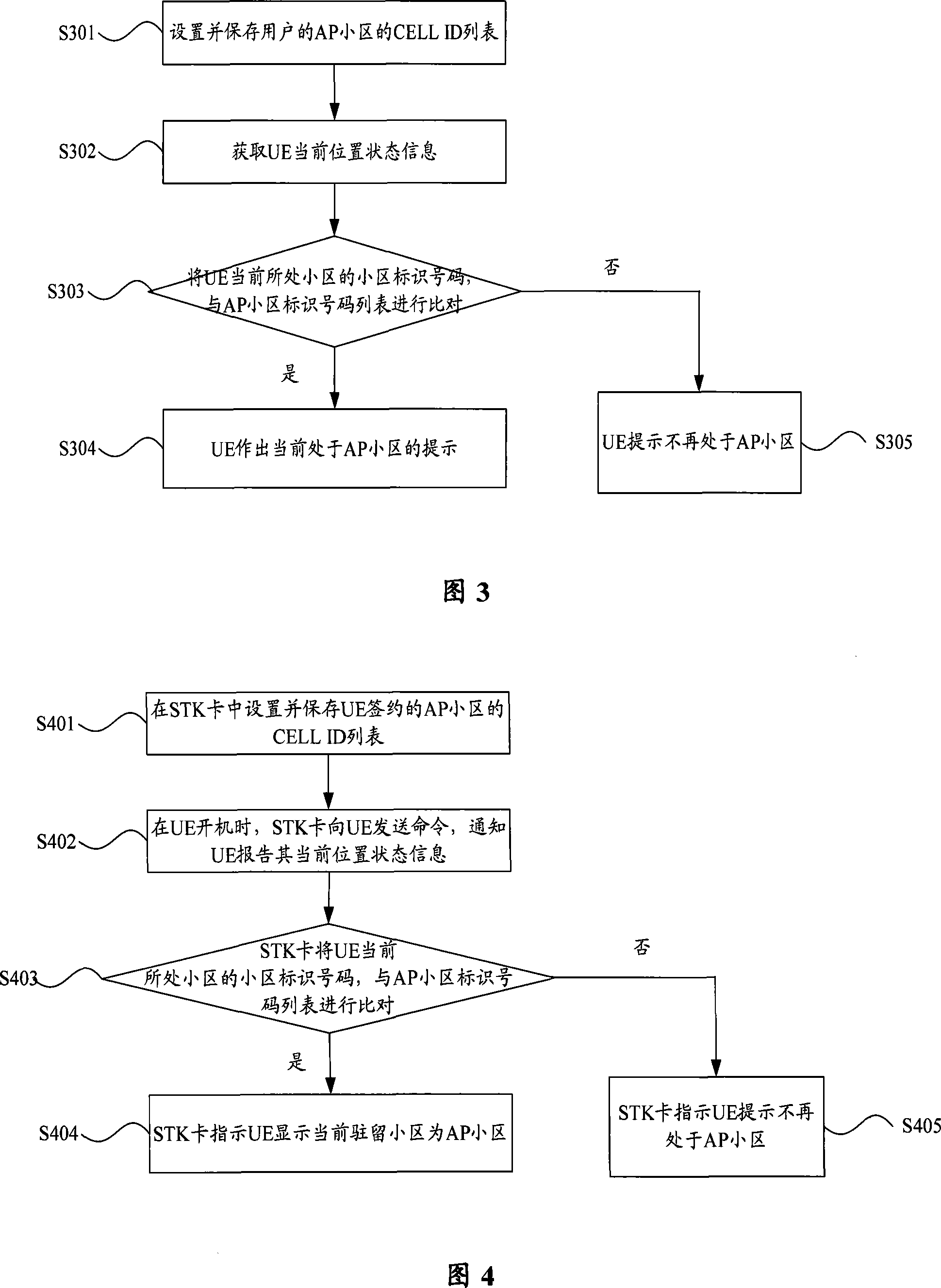
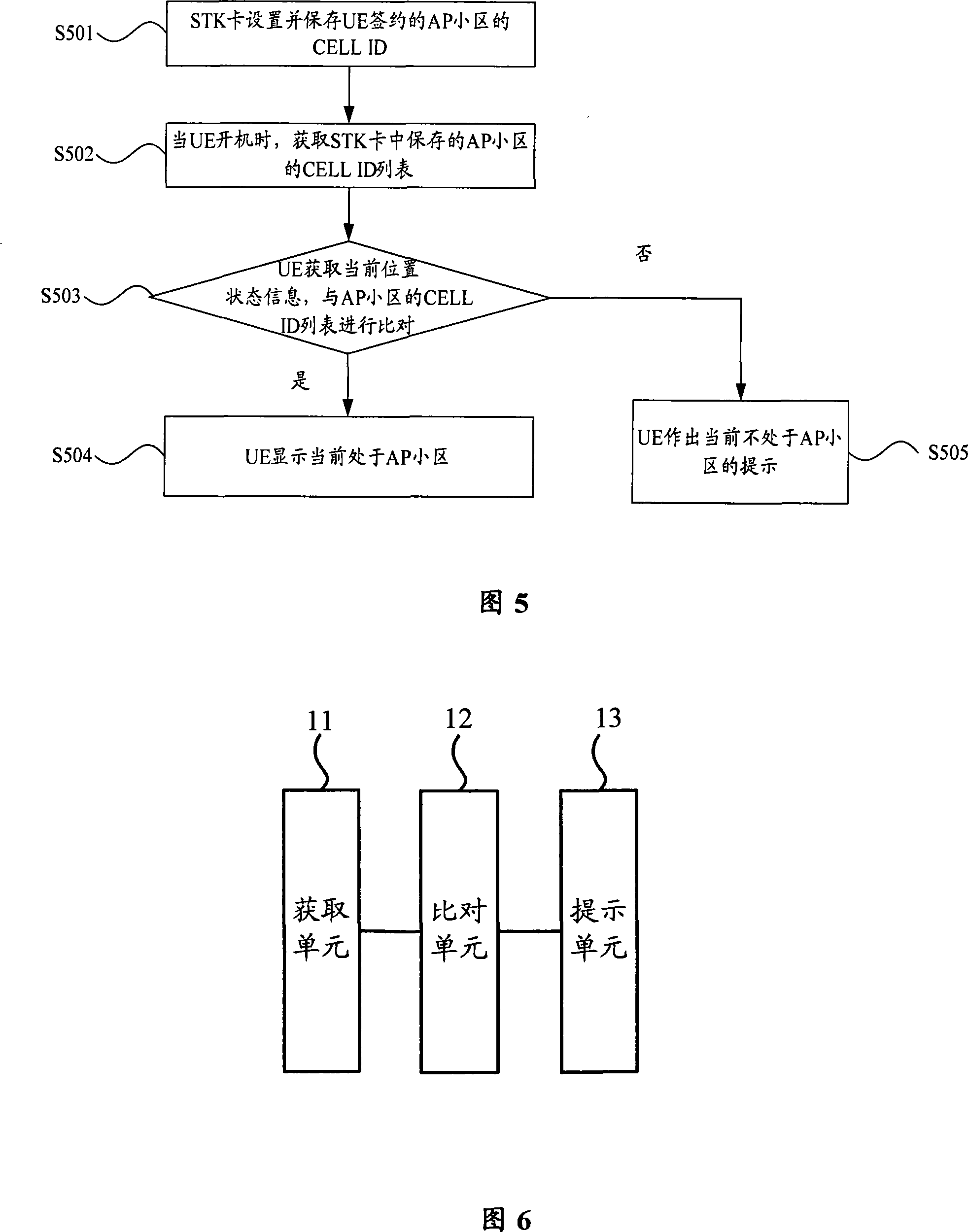
Method and device for reminding subscriber terminal of being in AP subdistrict
InactiveCN101175333APrompt is accuratePrompt in timeRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsLocation statusTelecommunications
The present invention discloses a method and a device, which are used for instructing that a user terminal is located at an AP district. The steps of the method are: the current location status message of a user terminal UE is gained, the current location status message comprises the district mark number of the district, in which the UE currently is located. The district mark number of the UE currently located district is compared with the AP district mark number list of the wireless access point signed by the UE. If the AP district mark number list includes the district mark number of the UE currently located district, the instruction that the UE is located at the AE district is made by the UE. With the technical proposal of the present invention, whether the UE is located at the AP district currently can be accurately and timely instructed.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Postural state attitude monitoring, caution, and warning systems and methods
InactiveUS8436737B1Inflated body pressure measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsLocation statusAccelerometer
A postural state attitude monitoring, caution, and warning system includes a multiple axis accelerometer carried by a node for generating output signals that are a function of positional orientation of the node along a path of attitude displacement of the node extending from a reference position of the node to a caution position of the node, and from the caution position of the node to a warning position of the node, and a signal device operatively coupled to the multiple axis accelerometer for issuing a caution signal in response to a caution positional state of the node at the caution position of the node and distally therebeyond to inside of the warning position of the node, and for issuing a warning signal different from the caution signal in response to a warning positional state of the node at the warning position of the node and distally therebeyond.
Owner:STEELHEAD INNOVATIONS
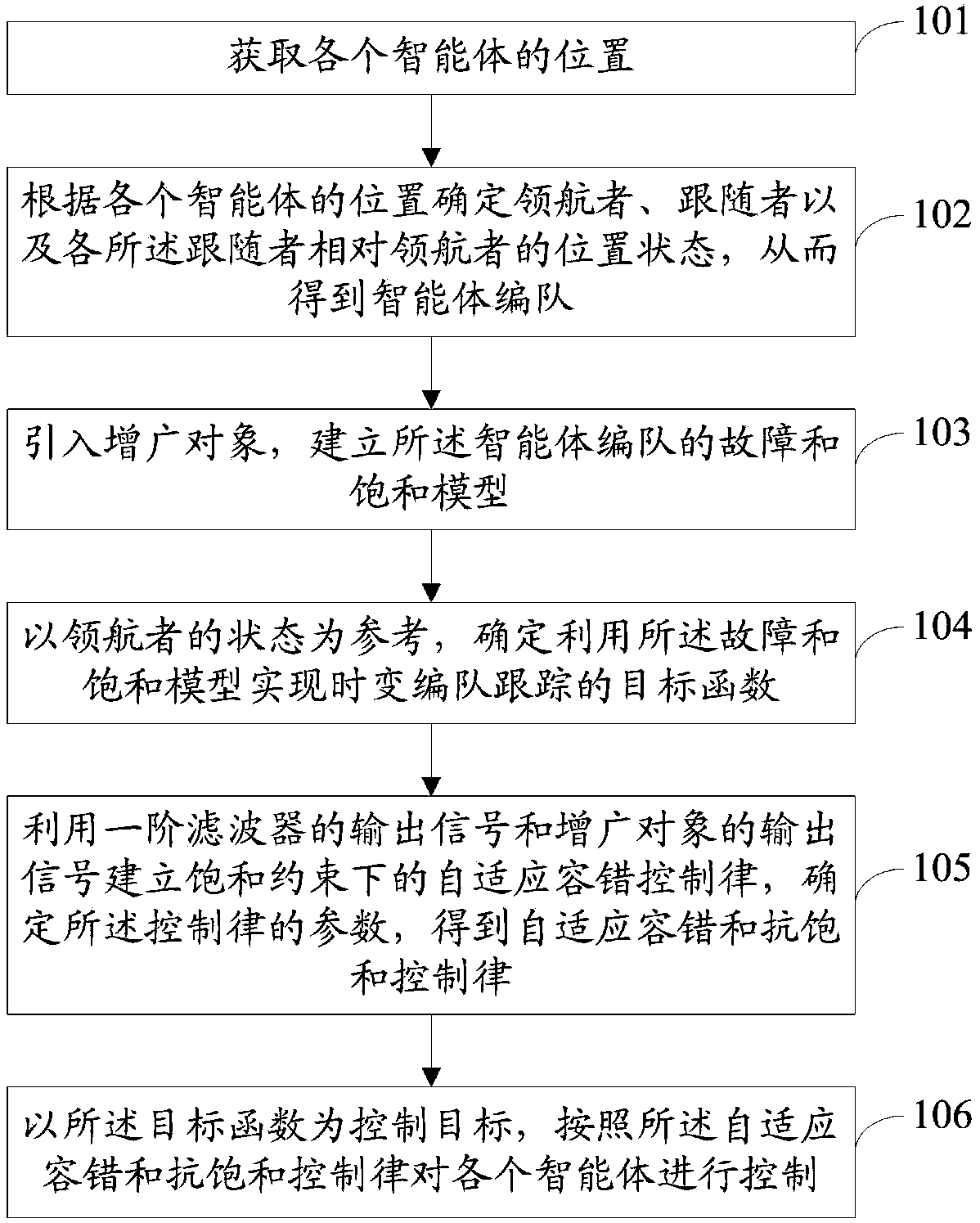
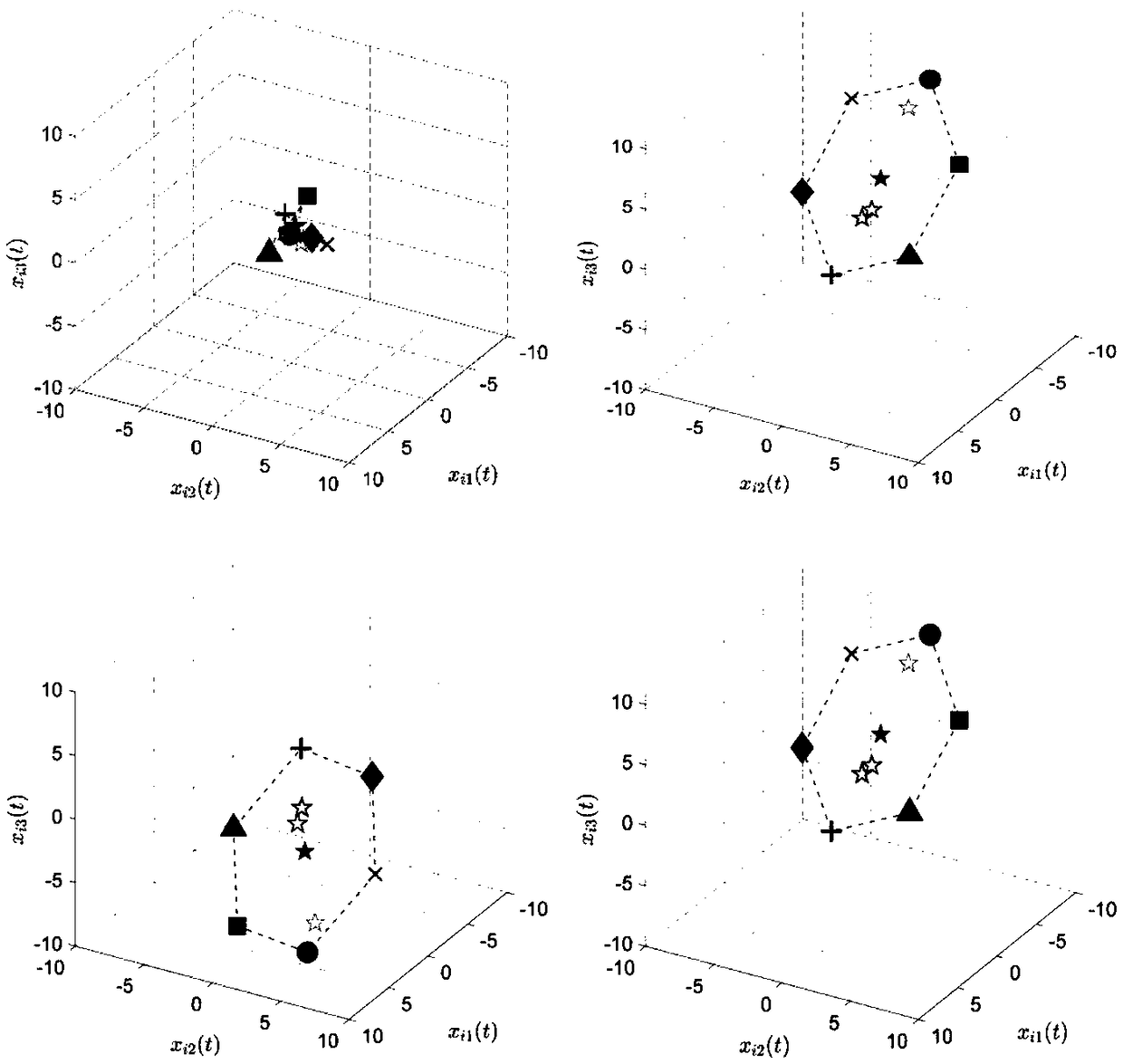
Multi-agent formation tracking control method and system
ActiveCN109445447AGuaranteed convergencePosition/course control in three dimensionsPosition/course control in two dimensionsLocation statusControl objective
The invention discloses a multi-agent formation tracking control method and system. The method comprises the steps that the position of each agent is obtained; according to the position of each agent,the position status of a navigator, the position statuses of followers and the position status of each follower relative to the navigator are determined, thereby obtaining an agent formation; an augmented object is introduced, and a fault and saturation model of the agent formation is established; the status of the navigator is taken as reference to determine an objective function of time-varyingformation tracking based on the fault and saturation model; an adaptive fault-tolerant control law under saturation constraints is established by using an output signal of a first-order filter and anoutput signal of the augmented object, a parameter of the control law is determined, and an adaptive fault-tolerant and anti-saturation control law is obtained; the objective function is taken as a control target, and each agent is controlled according to the adaptive fault-tolerant and anti-saturation control law. The multi-agent formation tracking control method and system have the advantages that the convergence of the multi-agent formation tracking error is ensured, and even if in the case of the fault, a control signal is within the saturation boundary of an actuator.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
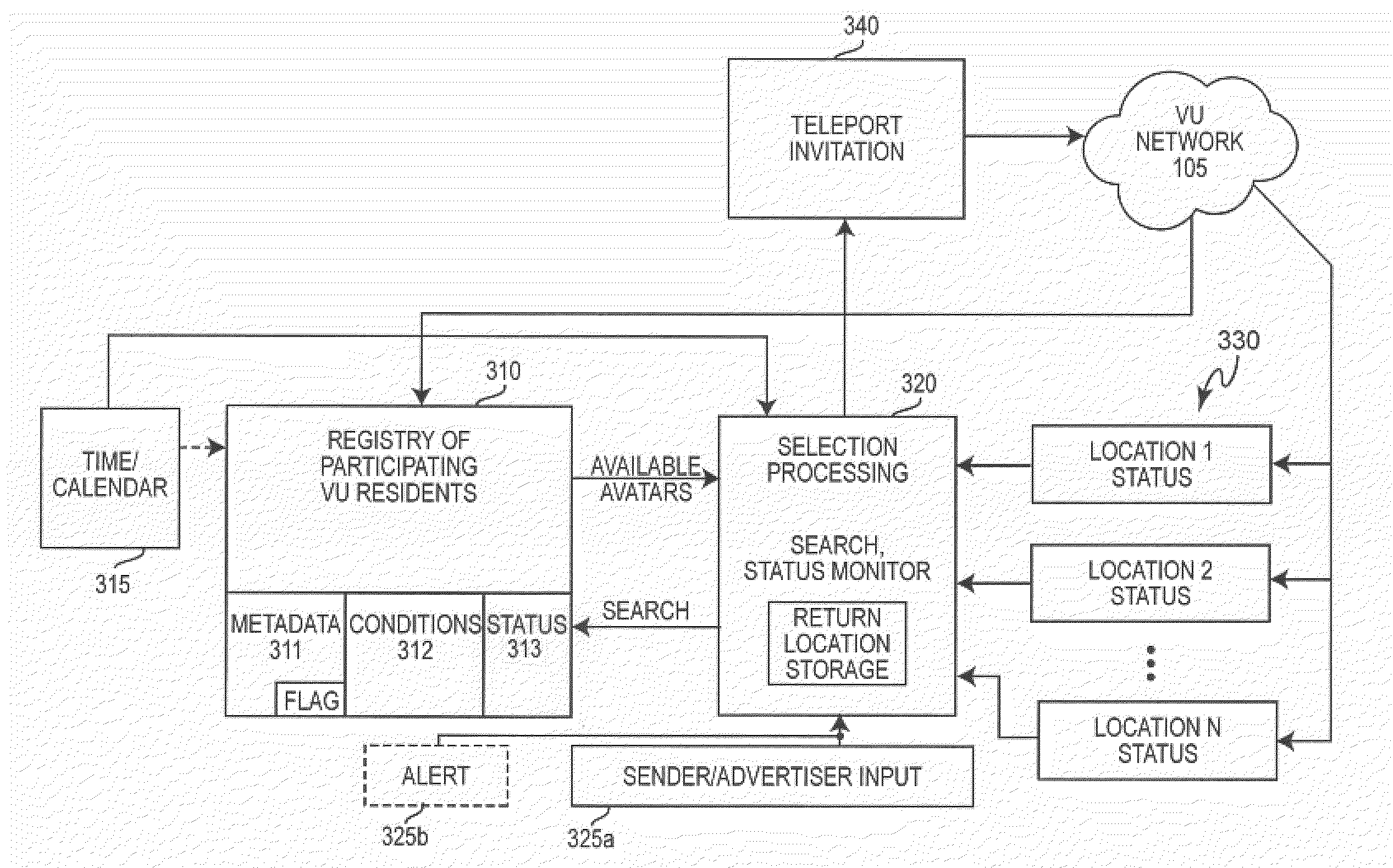
Relocation Between Virtual Environments Based Upon Promotional and Alert Conditions
InactiveUS20110055136A1Enhancing advertisingEnhancing promotional potentialArtificial lifeKnowledge representationLocation statusVirtual universe
Awards of value are awarded to residents of a virtual universe for consenting to be teleported in response to invitations for teleportation. The consent can he made conditional upon any of a variety of circumstances which can be specified by a resident of the virtual universe for a corresponding avatar and which form rules for auto-teleportation. These conditions can be stored and searched and avatar and location status monitored and compared to the conditions to control issuance of invitations to increase the likelihood that an invitation will be automatically accepted. A delay before acceptance is also preferably provided to provide for graceful conclusion or termination of current avatar activity.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
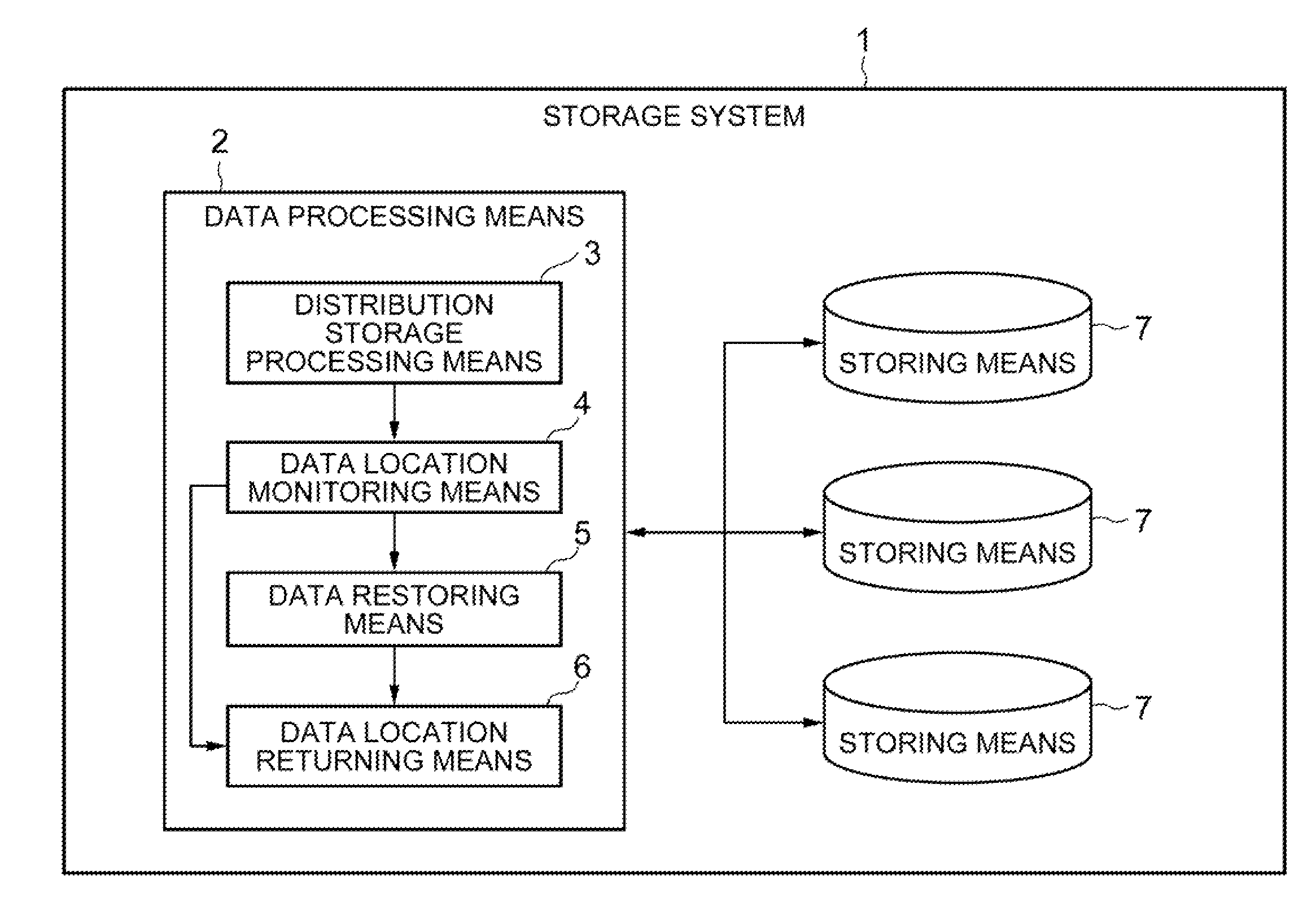
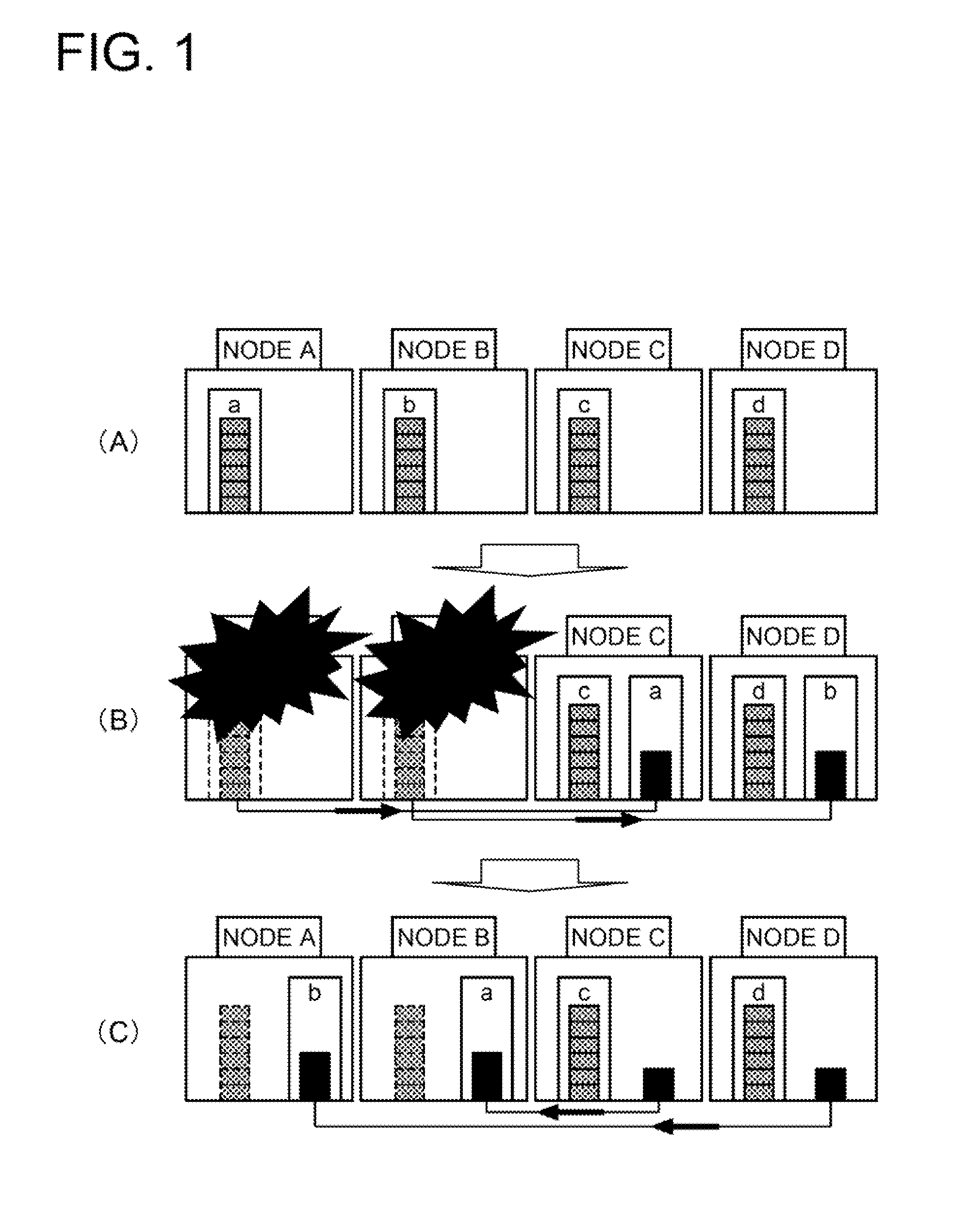
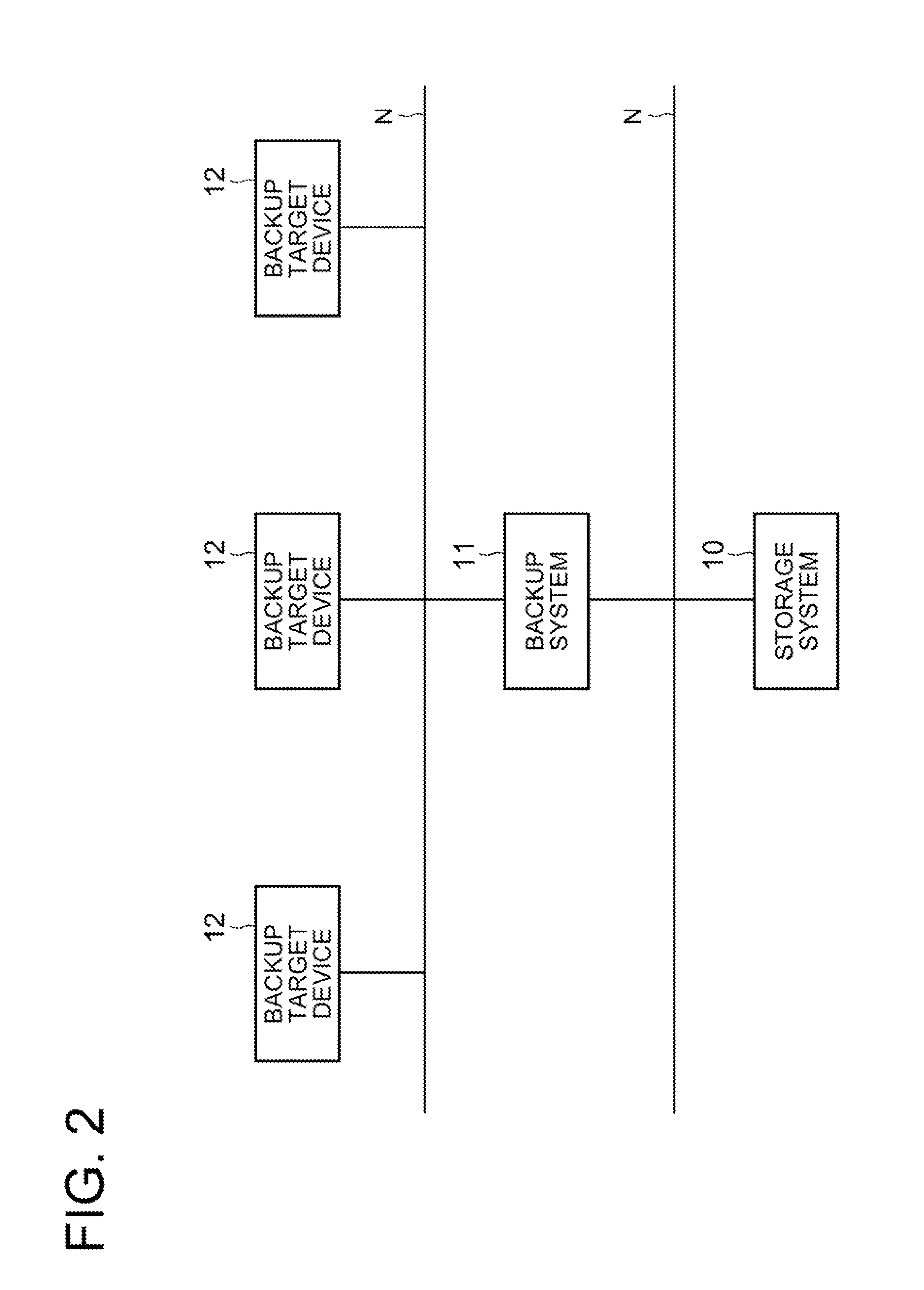
Storage system
InactiveUS20110296104A1Efficient and quick data restorationImprove processing efficiencyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionLocation statusData location
A storage system includes: a distribution storage processing means configured to distribute and store a plurality of fragment data into a plurality of storing means; a data location monitoring means configured to monitor a data location status of the fragment data and store data location information representing the data location status; and a data restoring means configured to, when the storing means is down, regenerate the fragment data having been stored in the down storing means based on the fragment data stored in the other storing means. The storage system also includes: a data location returning means configured to, when the down storing means recovers, return a data location of the fragment data by using the fragment data stored in the storing means having recovered so that the data location status becomes as represented by the data location information stored by the data location monitoring means.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
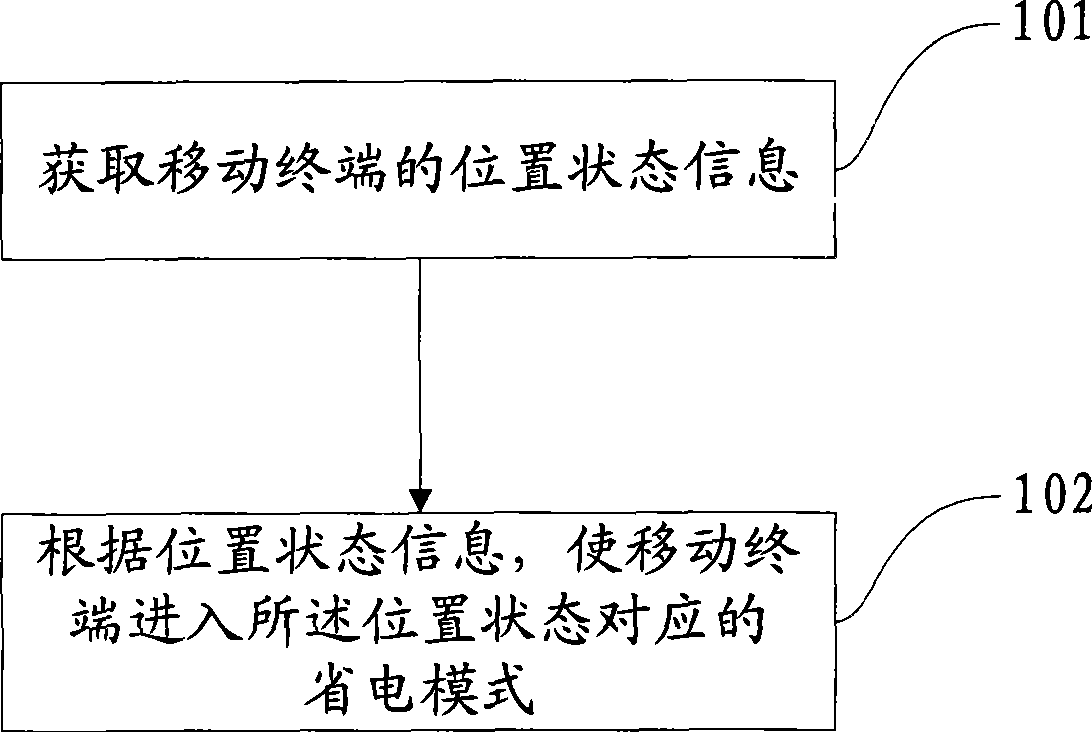
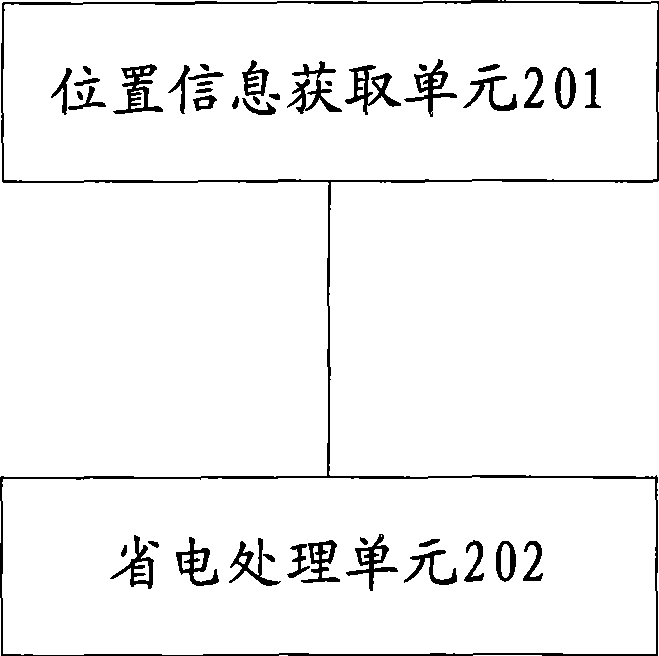
Method and apparatus for managing mobile terminal status
InactiveCN101442589AExtend standby timeSave powerCurrent supply arrangementsSubstation equipmentLocation statusComputer engineering
The invention discloses a method and a device for managing a state of a mobile terminal, and relates to the field of communication. Through acquiring position state information of the mobile terminal, the method makes the mobile terminal enter a power saving mode corresponding to a position state according to the position state information, can further optimize power utilization property of the mobile terminal, and improves power saving effect. The method and the device are suitable for the mobile terminal.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Application program control method and device based on mobile terminal and mobile terminal
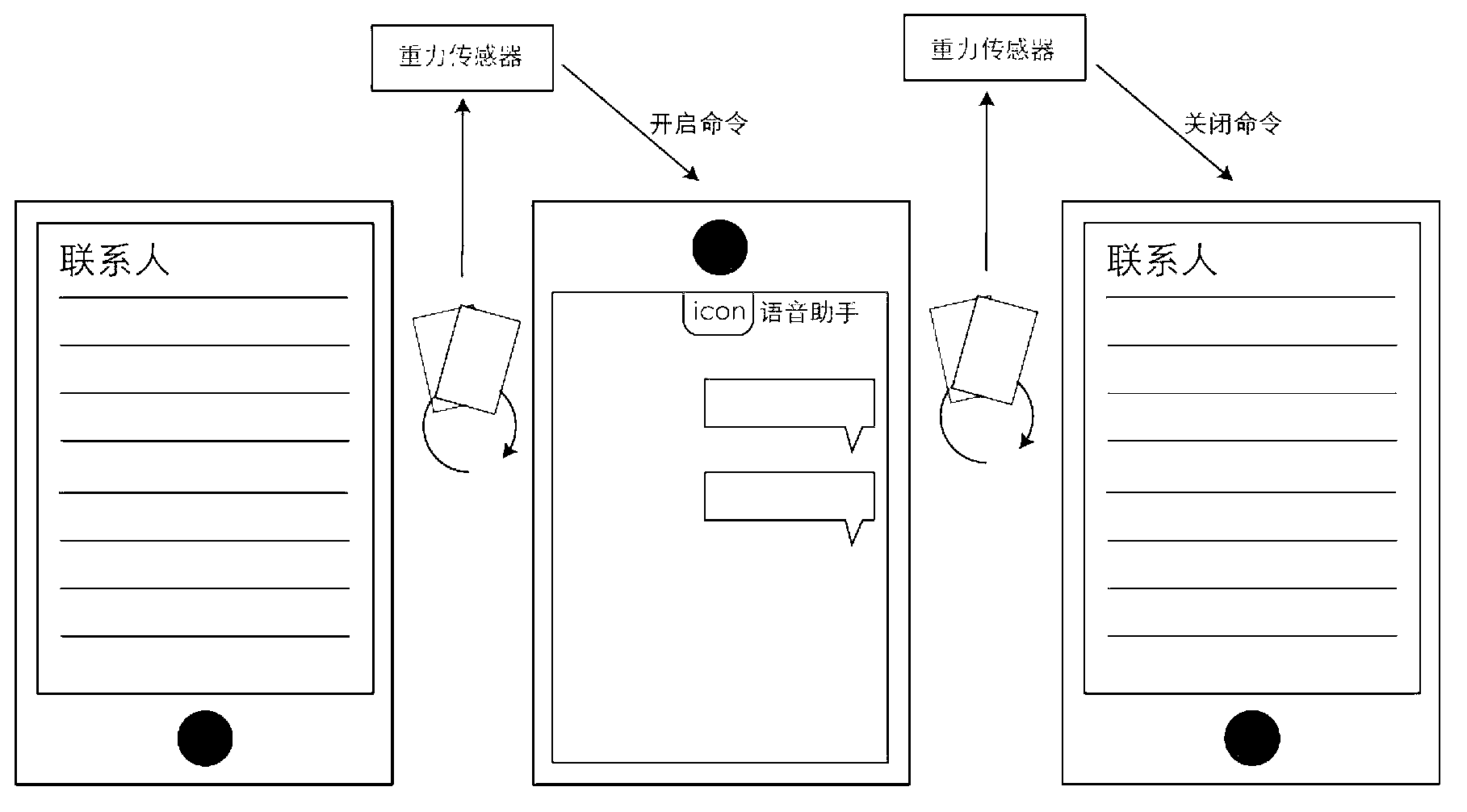
ActiveCN102937863AEasy to operateProgram loading/initiatingInput/output processes for data processingLocation statusAccelerometer
The invention provides an application program control method and a device based on a mobile terminal and the mobile terminal. The problem that the operation of a prior technical control application program is complex is solved. The method comprises that an included angle which is formed between gravitational acceleration of the mobile terminal and a longitudinal coordinate axis in a accelerometer of the mobile terminal is detected; a current position of the mobile terminal under gravity induction is determined through the included angle; when the current position meets a preset state control requirement for starting of the application program, a starting command is sent to a corresponding application program, and the application program is started and executed; and when the current position meets a preset state control requirement for closing of the application program, a closing command is sent to a corresponding application program which is being executed, and the application program is closed. Whether a position state belongs to the position state for control of a preset corresponding application program is determined through detection, the application program is controlled through the position state, and operation steps in which the corresponding application program is controlled are simplified.
Owner:XIAOMI INC
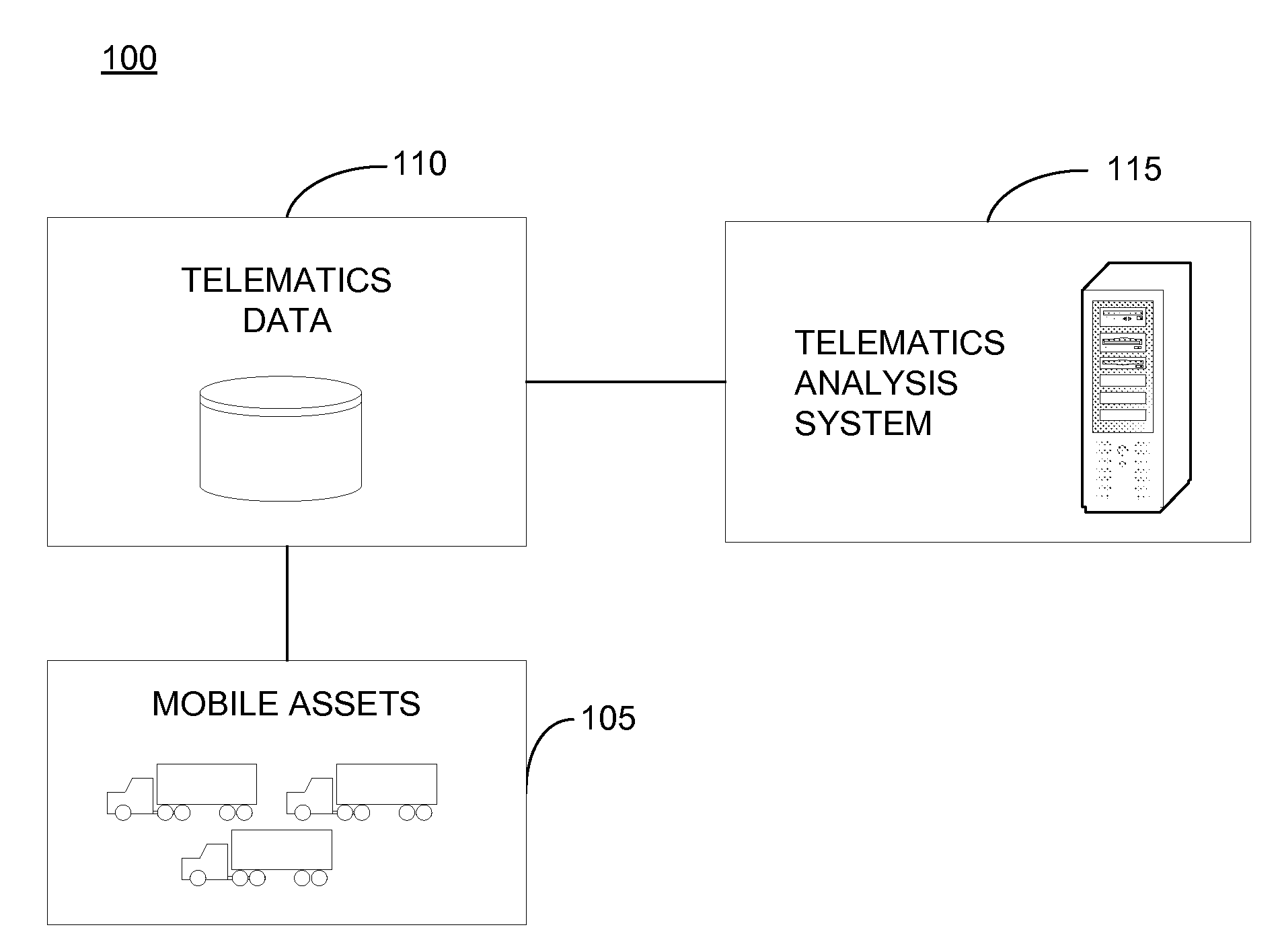
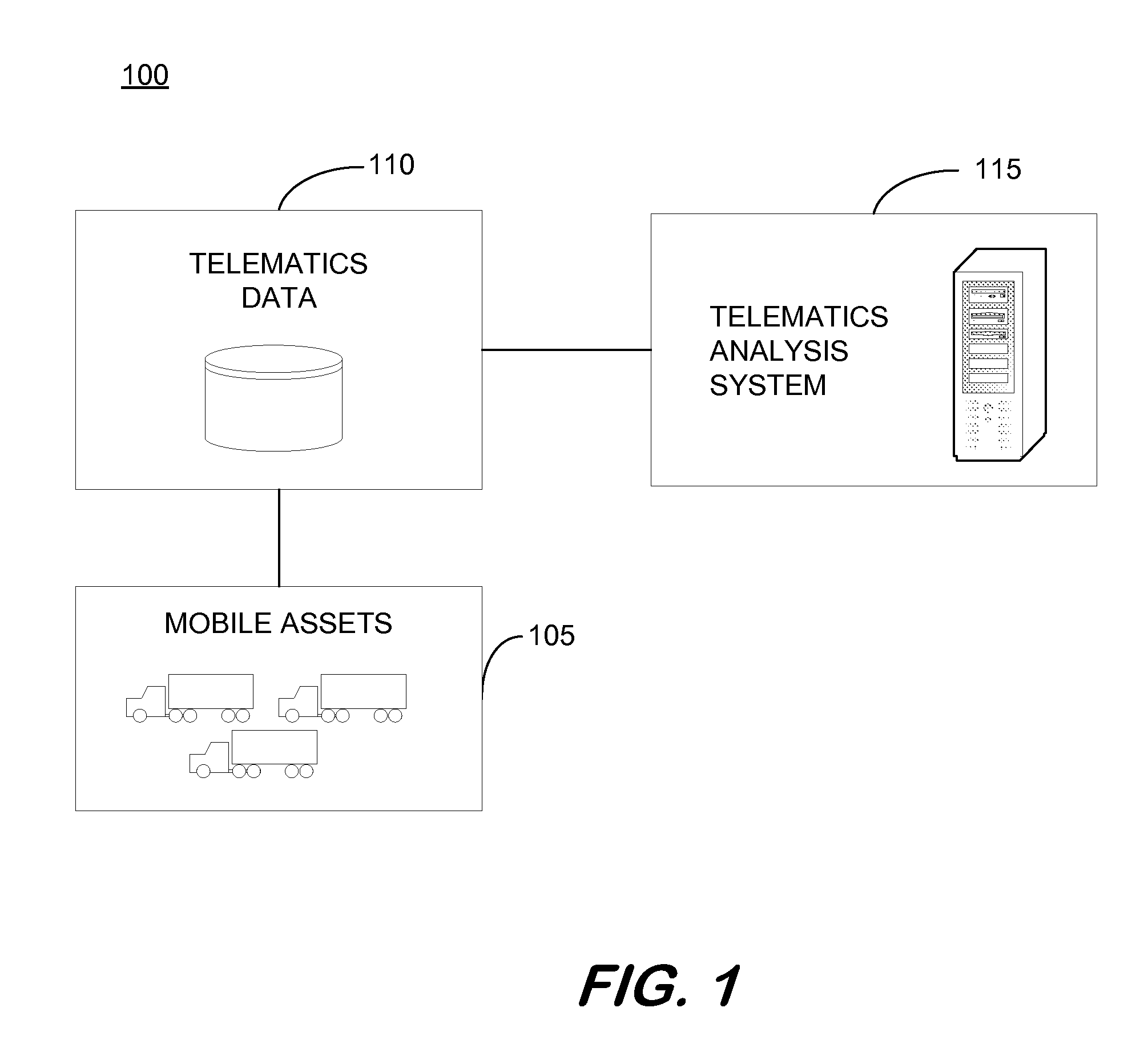
Method and system for mobile asset management
InactiveUS20100262450A1Improve analysisEfficient managementRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesLocation statusEvent data
A method and system related to managing mobile assets, the method including receiving asset event data associated with a plurality of mobile assets including information indicative of location status, motion status, and cargo status of the plurality of mobile assets; determining asset segment data defined by the asset event data of the plurality of mobile assets during a time interval based on the asset event data; determining turn time data for each of the plurality of mobile assets; calculating a set of metrics for the plurality of mobile assets based on the asset segment data and the turn time data; determining an optimal asset pool size for a location to be serviced by the plurality of mobile assets; and providing an output of the determined optimal asset pool size for the location.
Owner:ASSET INTELLIGENCE
Digital device configuration and method
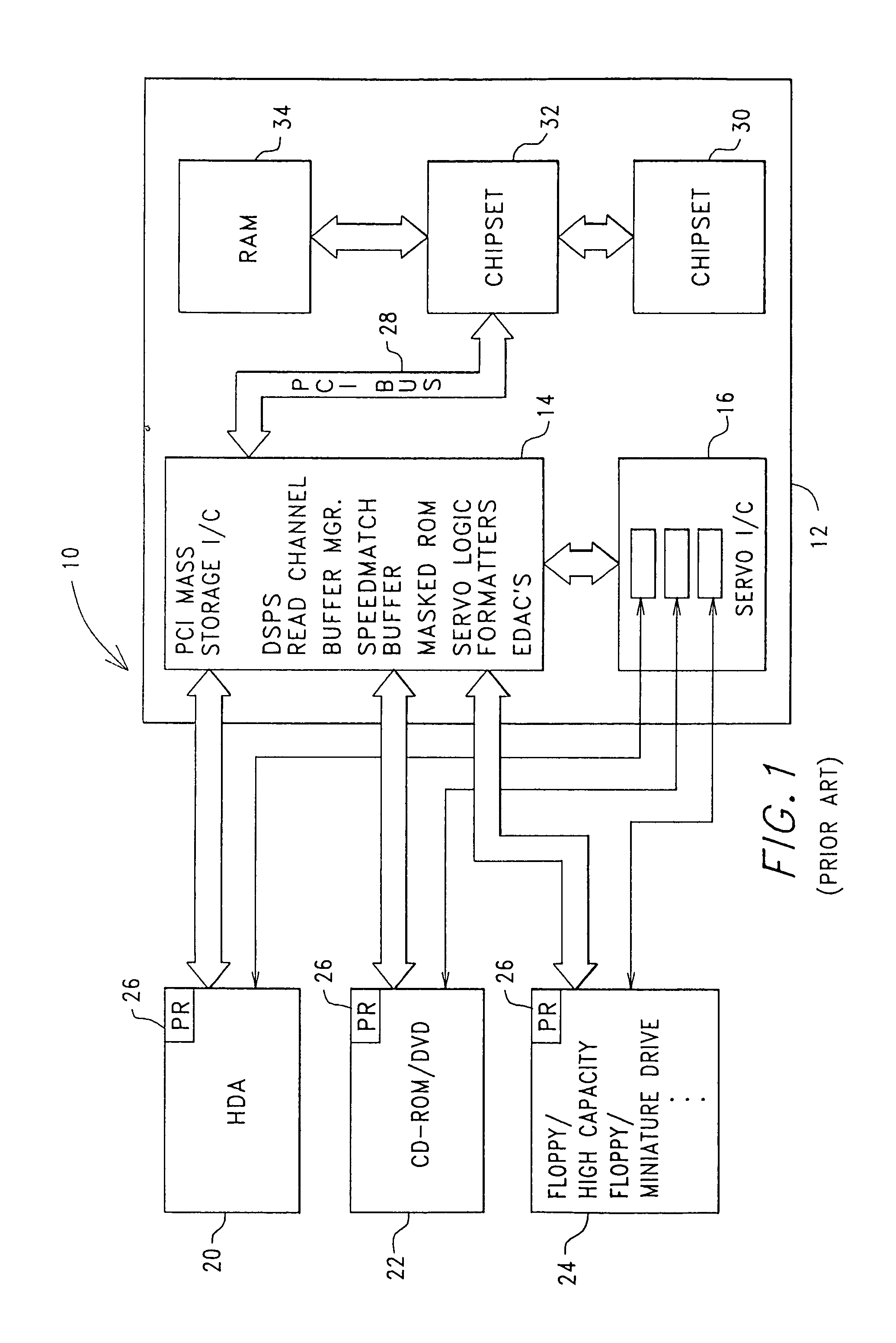
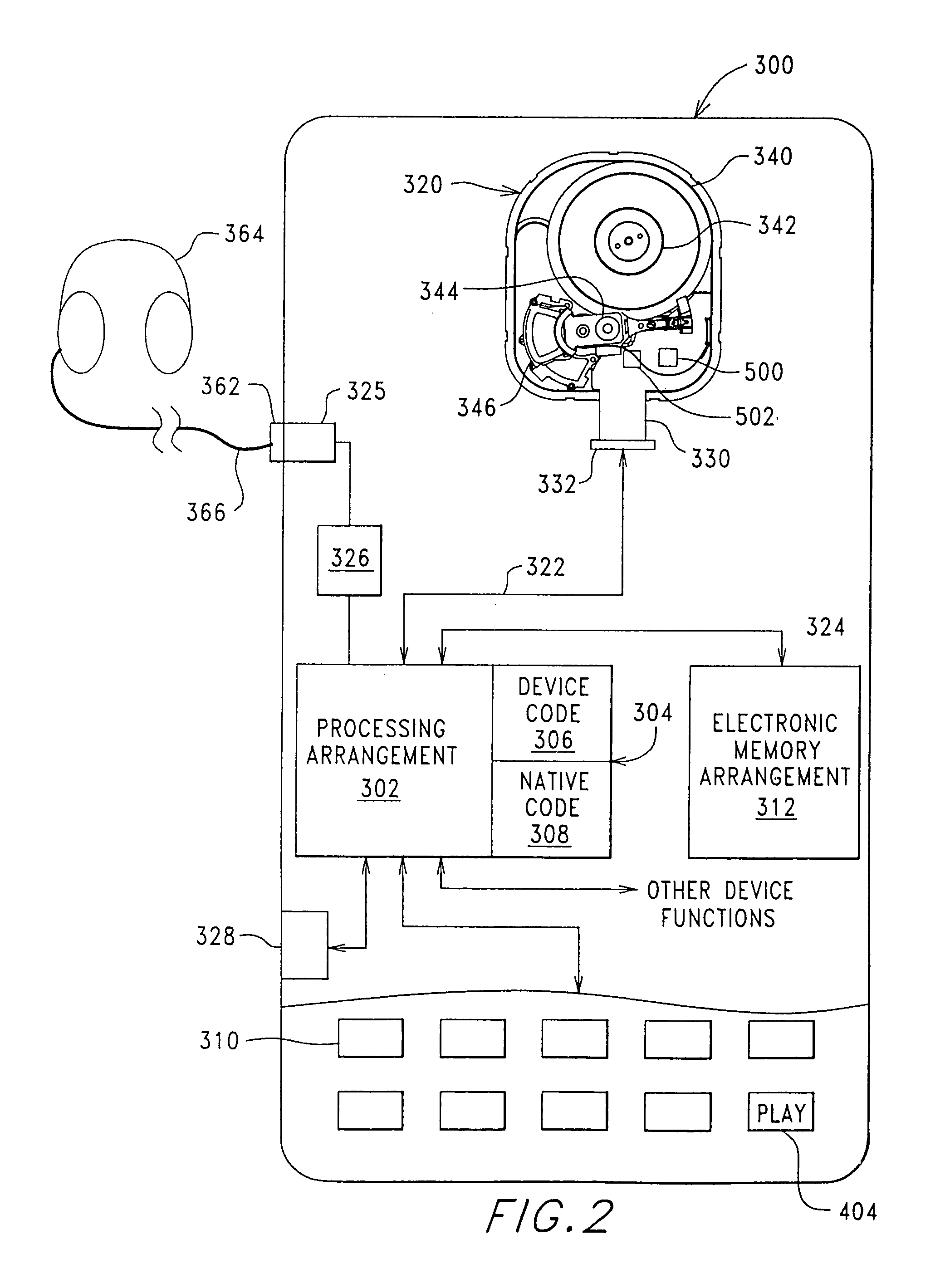
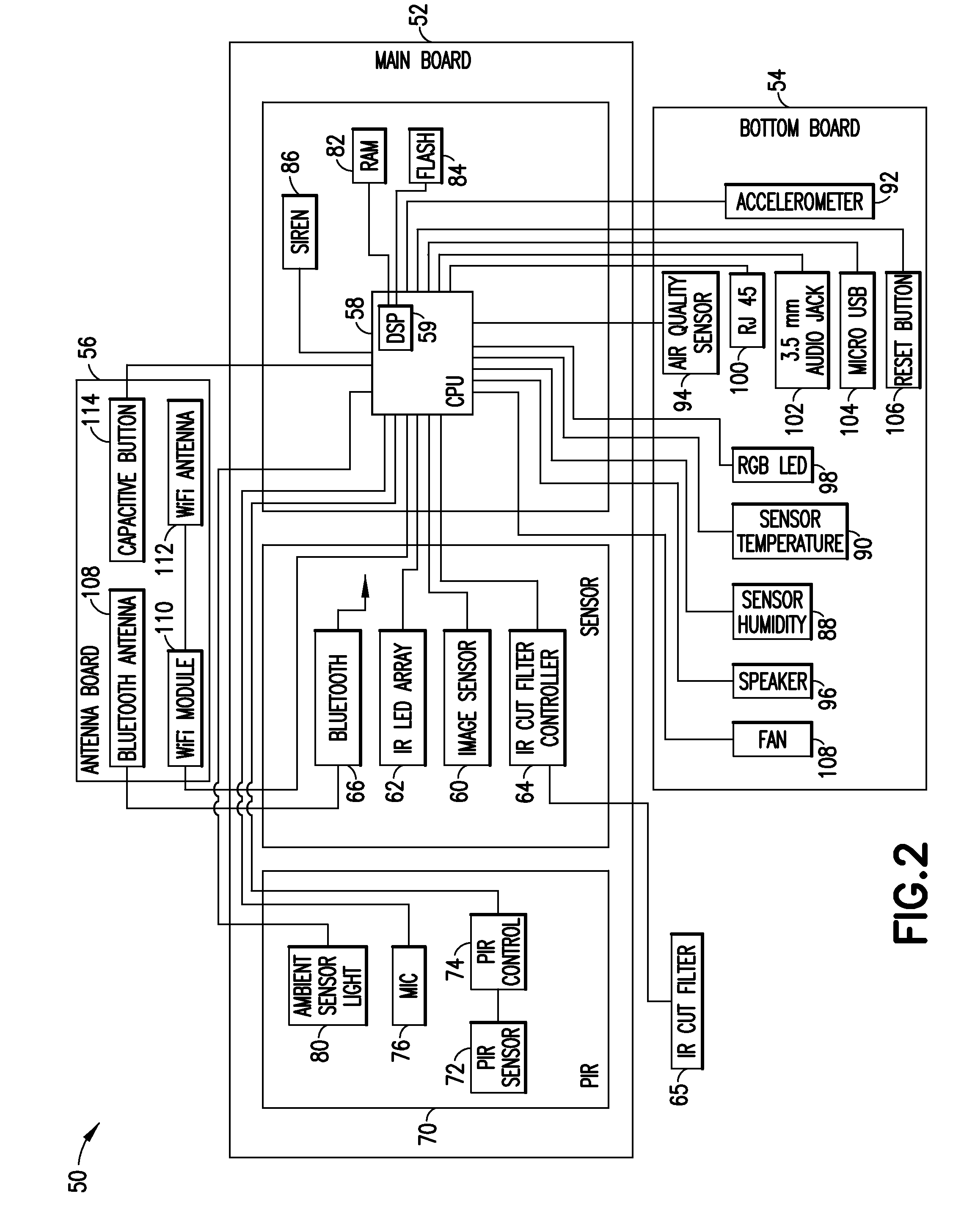
InactiveUS7106541B2Energy efficient ICTElectrical connection between head and armLocation statusSoftware engineering
A digital Storage Element is described. A device is configured including a Storage Element for access by a user responsive to a native control code. A processing arrangement executes a control program for controlling the overall device and executing at least a portion of the native control code as part of the control program for interfacing with the Storage Element. A programming arrangement is provided separate from the device for customizing a read channel within the Storage Element. Command, user interaction and data transfer execution are discussed for mitigation of potential mechanical shock effects. Status indications relating to the Storage Element are provided including head position and mechanical shock. Calibration, test and operational monitoring procedures, for using head position status, are described. Failure configuration monitoring is provided in tracking overall performance and design considerations.
Owner:CORNICE
Combined DOA and TOA single-station passive positioning method based on error correction
ActiveCN108717184AImprove targeting performanceGuaranteed estimated performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLocation statusRadar systems
The invention discloses a combined DOA and TOA single-station passive positioning method based on error correction. According to measurement information obtained by a receiving station of an externalradiation source radar system, by introducing an auxiliary variable, a nonlinear equation is converted into a pseudo-linear equation, a pseudo-linear model between the state of a target position and the state of an observation station position is established, an iterative least square method is adopted for estimation, a constrained total least square estimation model is constructed, a constrainedoptimization problem is converted into an unconstrained optimization problem, a Newton iteration method is used for optimization and solution, and the correlation between the auxiliary variable and the target position is used for constructing a correlation least square estimation model, so that the target positioning performance is further improved. The target positioning accuracy is improved through combined estimation of the target position and system errors. Convenience is provided for improving the target positioning performance, the complexity of error registration under the premise of ensuring the estimation performance is reduced, and good positioning performance in the case of large measurement noise is achieved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
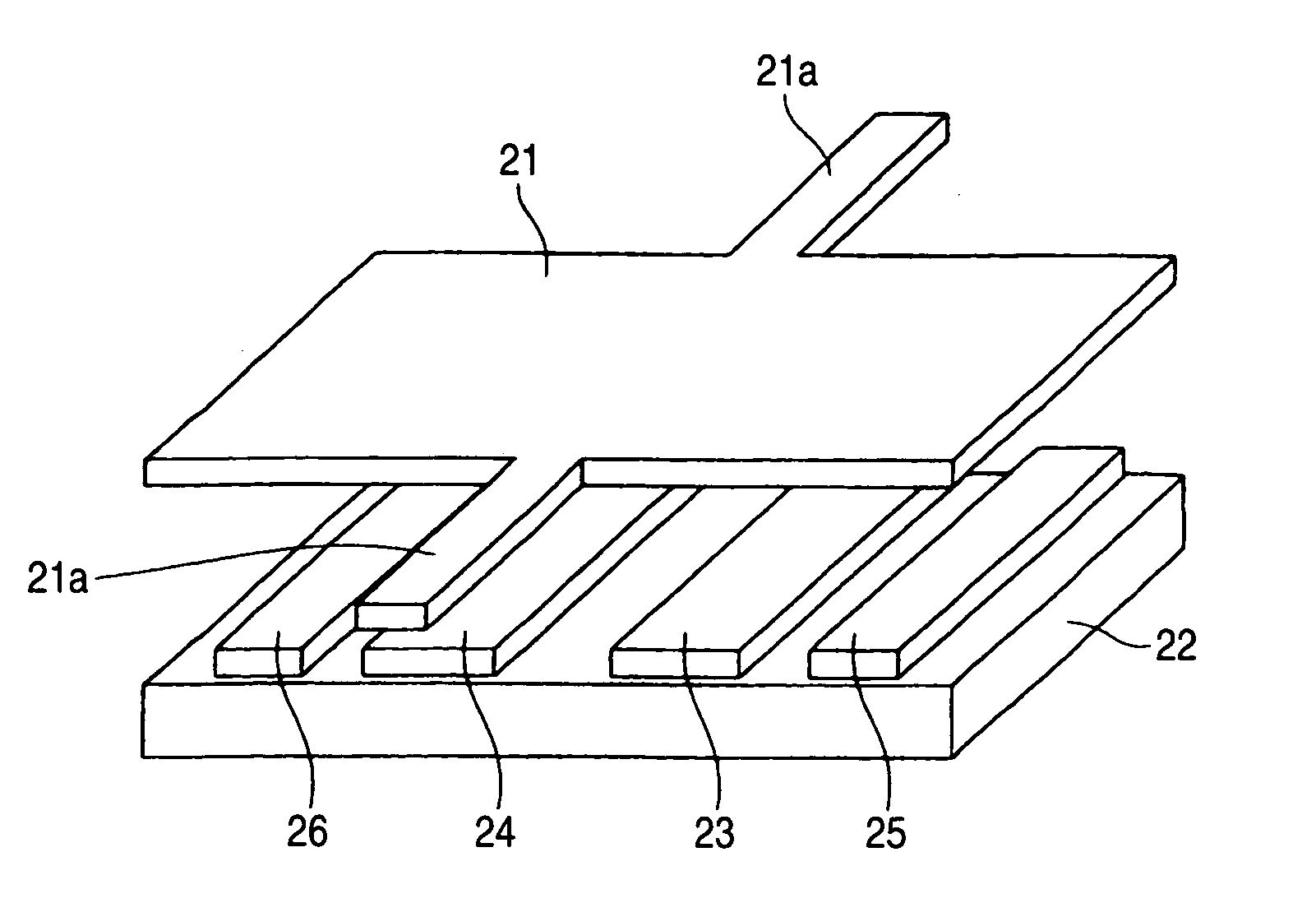
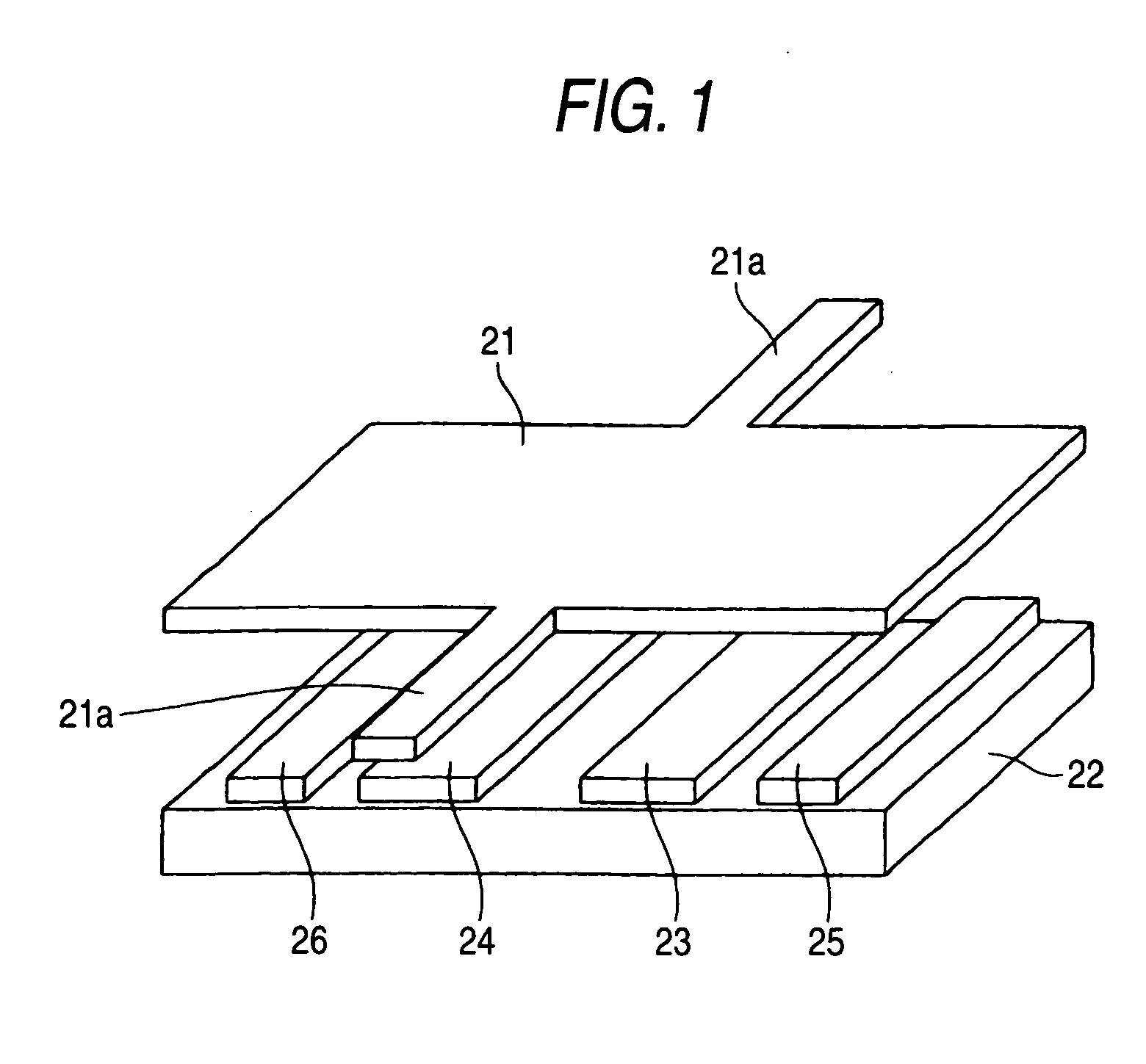
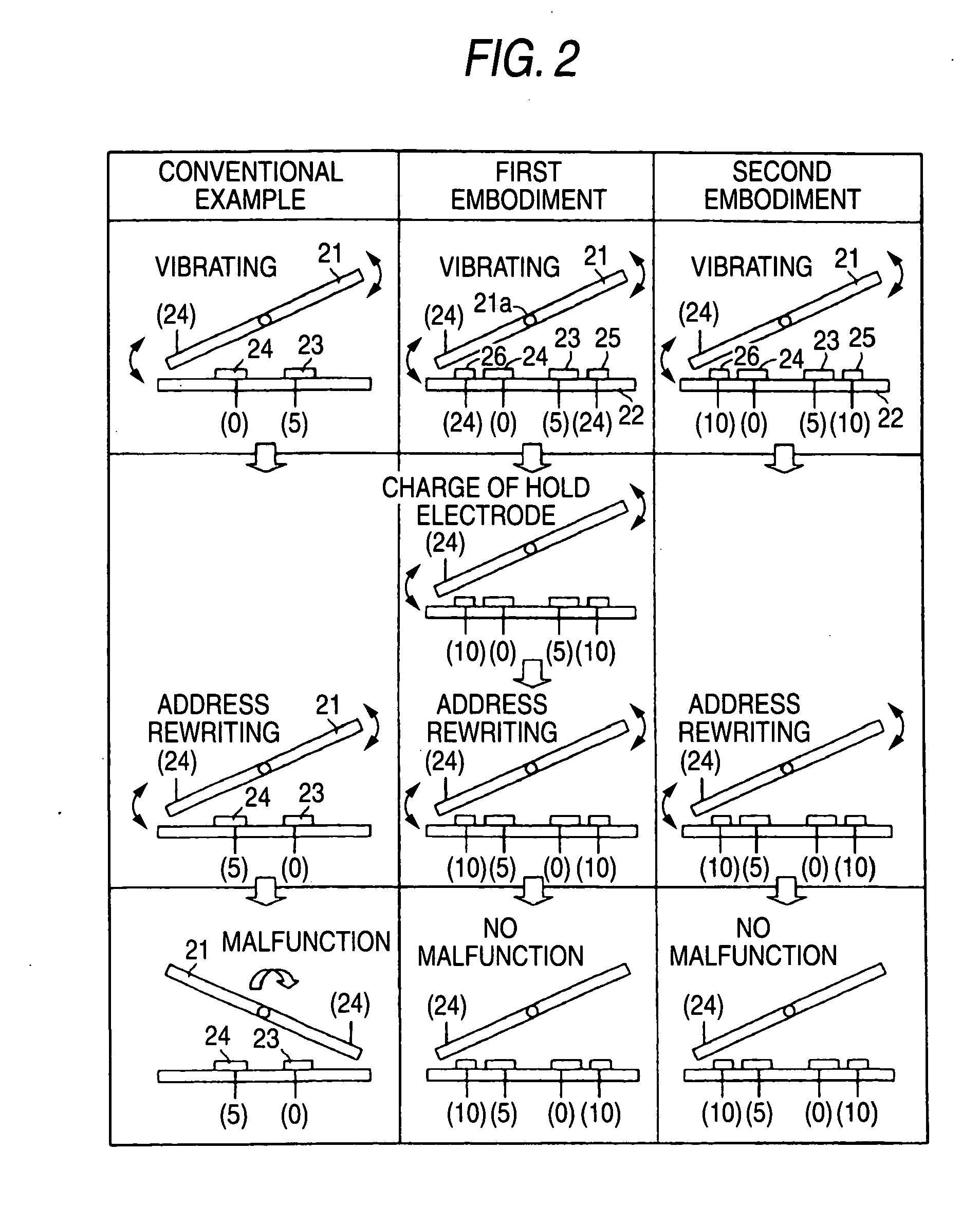
Microelectromechanical device array and method for driving the same
InactiveUS20060279496A1Increase speedRun at high speedStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLocation statusVoltage
In a microelectromechanical device array including an array of devices arranged at least one of one-dimensionally and two-dimensionally each of which includes a movable portion that is supported to be elastically deformed and that has a movable electrode on at least one part thereof and fixed electrodes that are disposed to face the movable portion and by which the movable portion is moved to one of at least two different positions, hold electrodes are disposed beside the fixed electrodes, and a hold voltage is applied to the hold electrodes and before rewriting an address voltage that is applied to the fixed electrodes so as to fix the position state of the movable portion.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Method and system for controlling plurality of mobile robots to operate in parallel manner
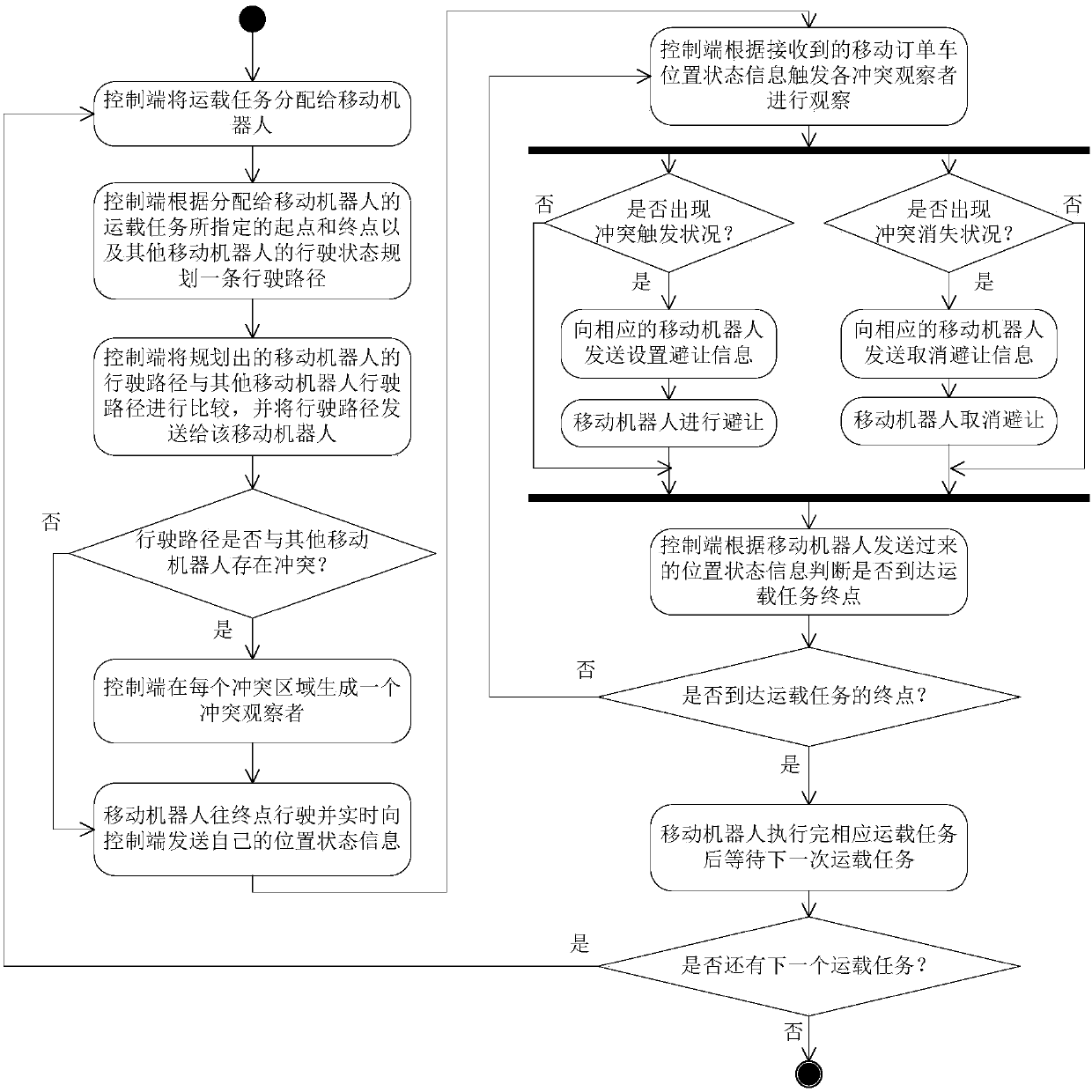
InactiveCN107703943AAvoid stateful interactionsReduce trafficPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesLocation statusControl system
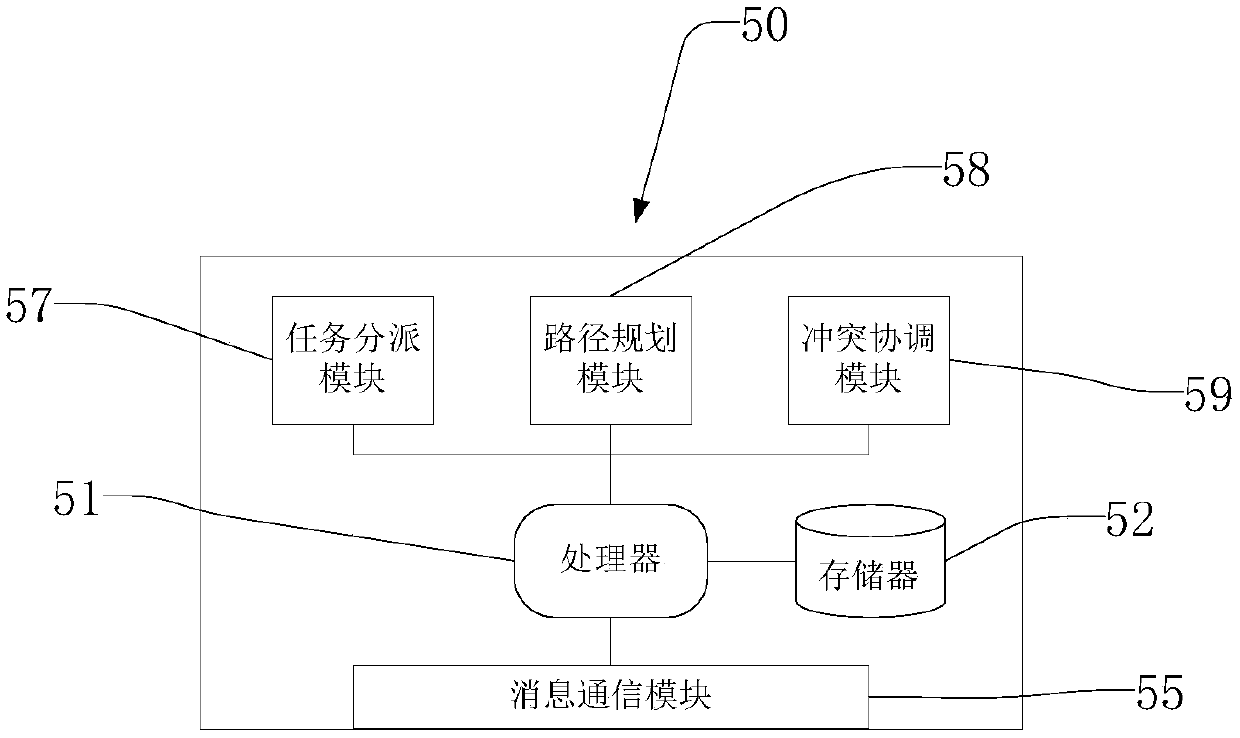
The invention discloses a method and system for controlling a plurality of mobile robots to operate in a parallel manner and belongs to the technical field of automation and intelligentization of a warehousing system. The control method comprise the following steps: carrying tasks are distributed via a control end, path planning operation is performed for the mobile robots to which the tasks are distributed, path planning results are sent to the mobile robots, real time position state information is reported by the mobile robots, the position state information reported by all the mobile robotsis processed comprehensively via the control end, possible conflict conditions are determined, conflict evasion information is generated in real time and sent to the mobile robot, and the mobile robots evade each other in real time during operation according to the evasion information till terminal points are reached. The control system comprises a task assigning module, a path planning module, aconflict coordination module, a message communication module, a processor and a storage device. Via the method and system disclosed in the invention, stateful interaction between the mobile robots and the control system is prevented as much as possible, message communication traffic is effectively reduced, and overall operation efficiency of the system is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
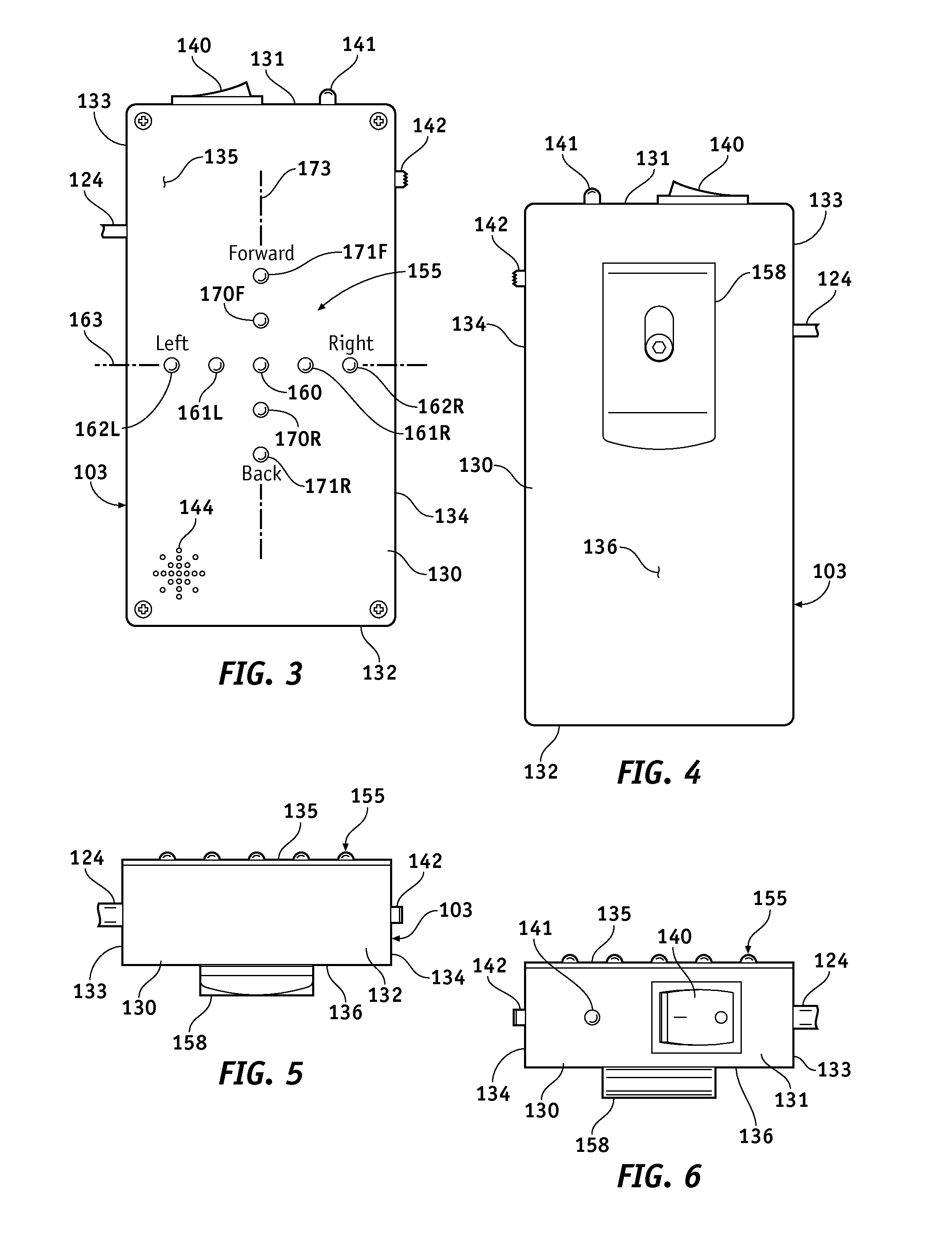
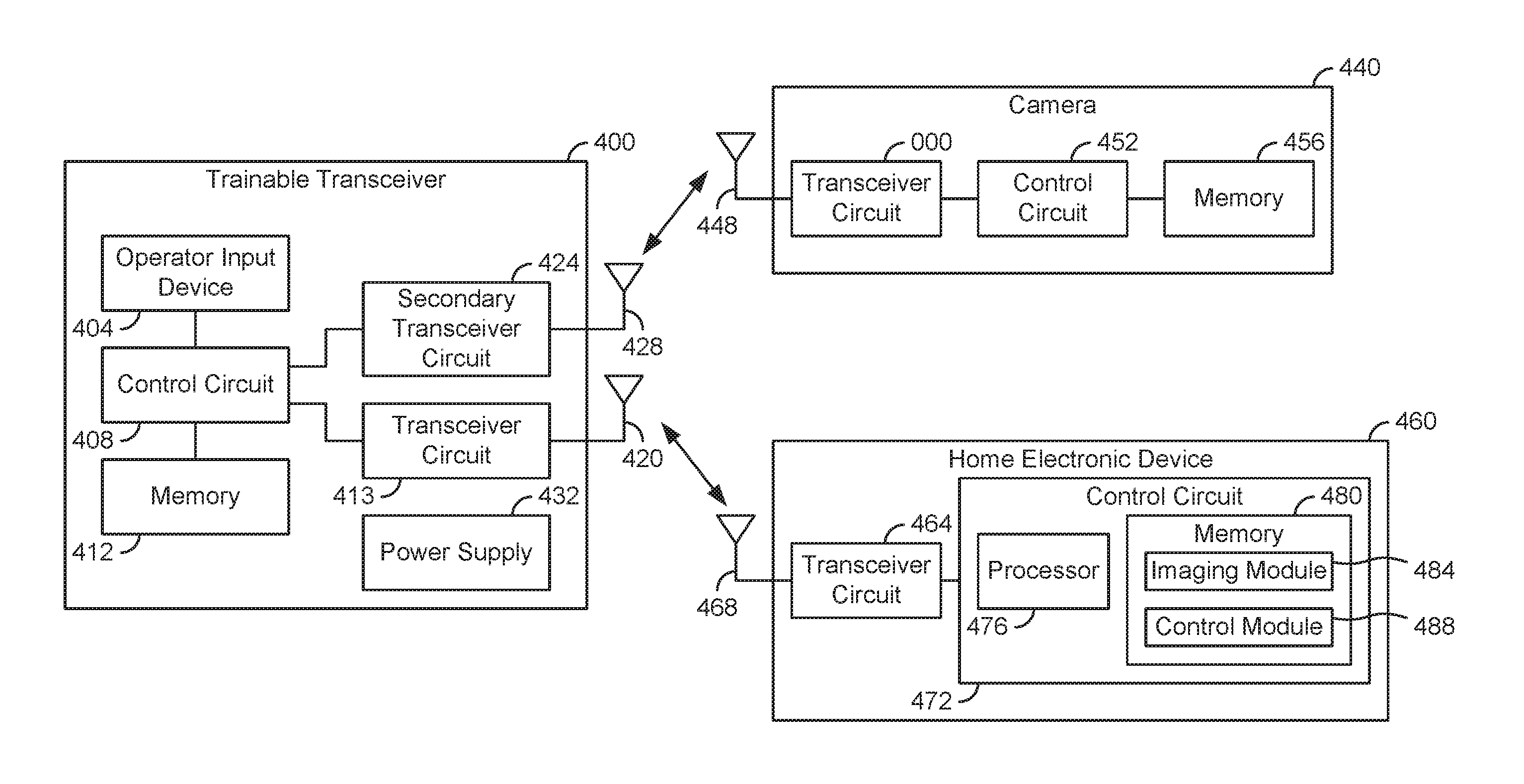
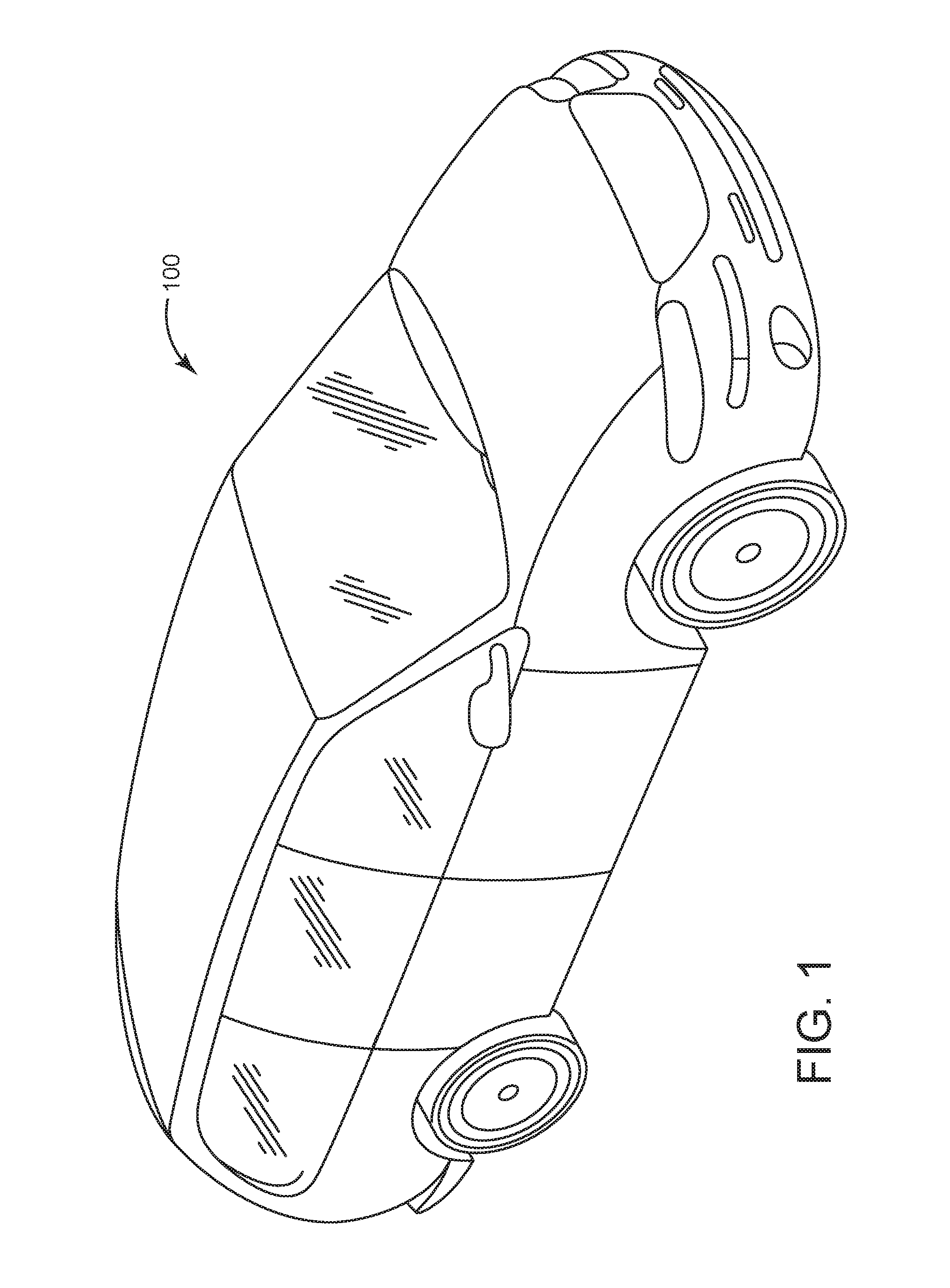
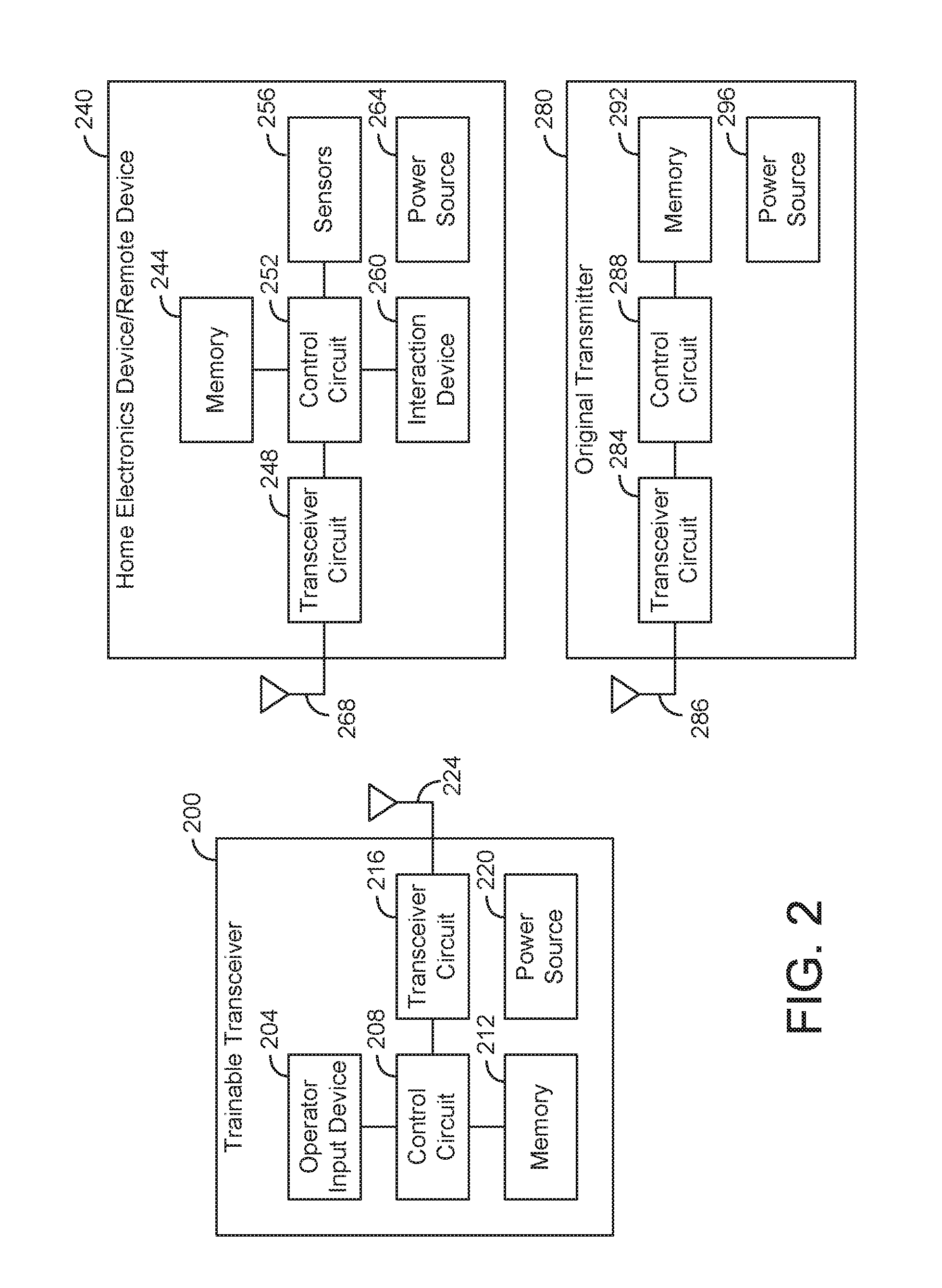
Trainable transceiver with single camera park assist
A trainable transceiver for controlling a device and providing vehicle position information to a vehicle occupant includes a transceiver circuit, an output device, and a control circuit coupled to the transceiver circuit and the output device. The control circuit is configured to receive, using the transceiver circuit or a secondary transceiver, image data corresponding to a position of the vehicle. The control circuit is further configured to determine a vehicle position status based on the image data and to control the output device to convey information to the vehicle occupant based on the vehicle position status.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
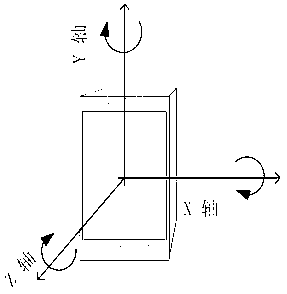
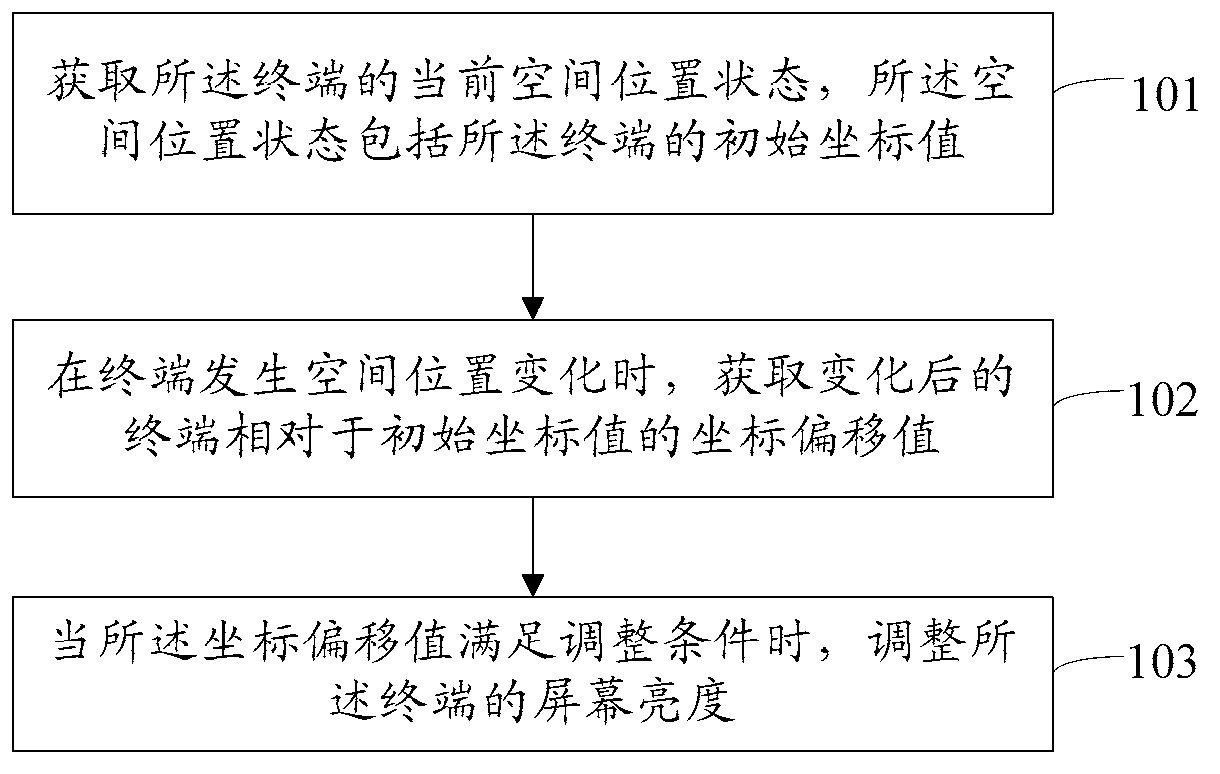
Method and device of adjusting of screen luminance of terminal and terminal
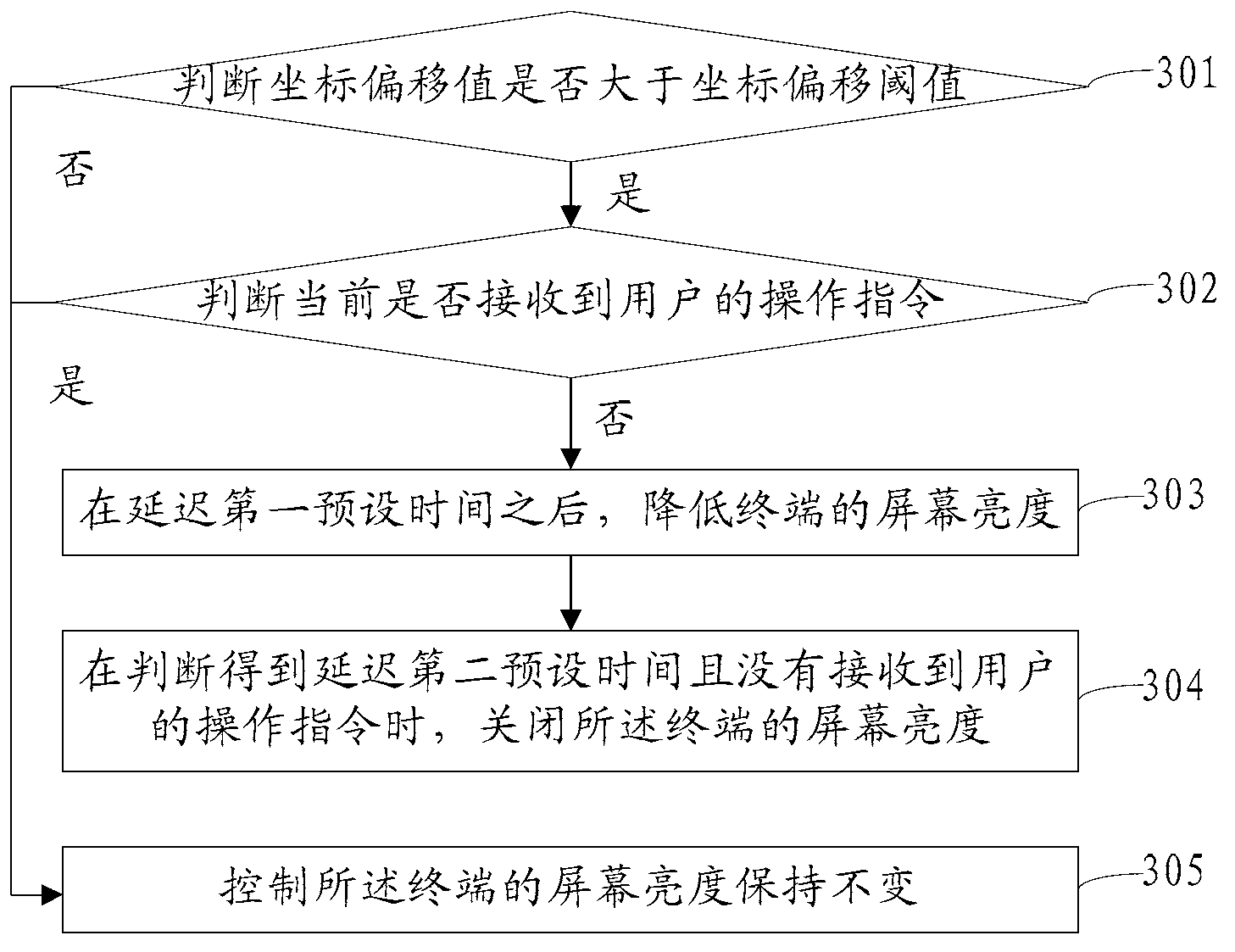
ActiveCN102984352ASave powerWill not hang up by mistakePower supply for data processingSubstation equipmentElectricityLocation status
The invention discloses a method and a device of adjusting of screen luminance of a terminal and a terminal. The method comprises that the current spatial position state of the terminal is acquired, and the spatial position state comprises the initial coordinate value of the terminal. When the spatial position of the terminal changes, the coordinate offset value of the terminal relative to the initial coordinate value after changing is acquired. When the coordinate offset value meets an adjusting condition, the screen luminance of the terminal is adjusted. By using the method and the device of adjusting of the screen luminance of the terminal and the terminal, not only electricity is further saved in a using process of the terminal, but also the phenomenon that the user hangs up by mistake caused by mis-turning on a background light of the screen can be prevent from occurring.
Owner:XIAOMI INC
Method and system automatic monitoring and real-time blocking false calling of communication network
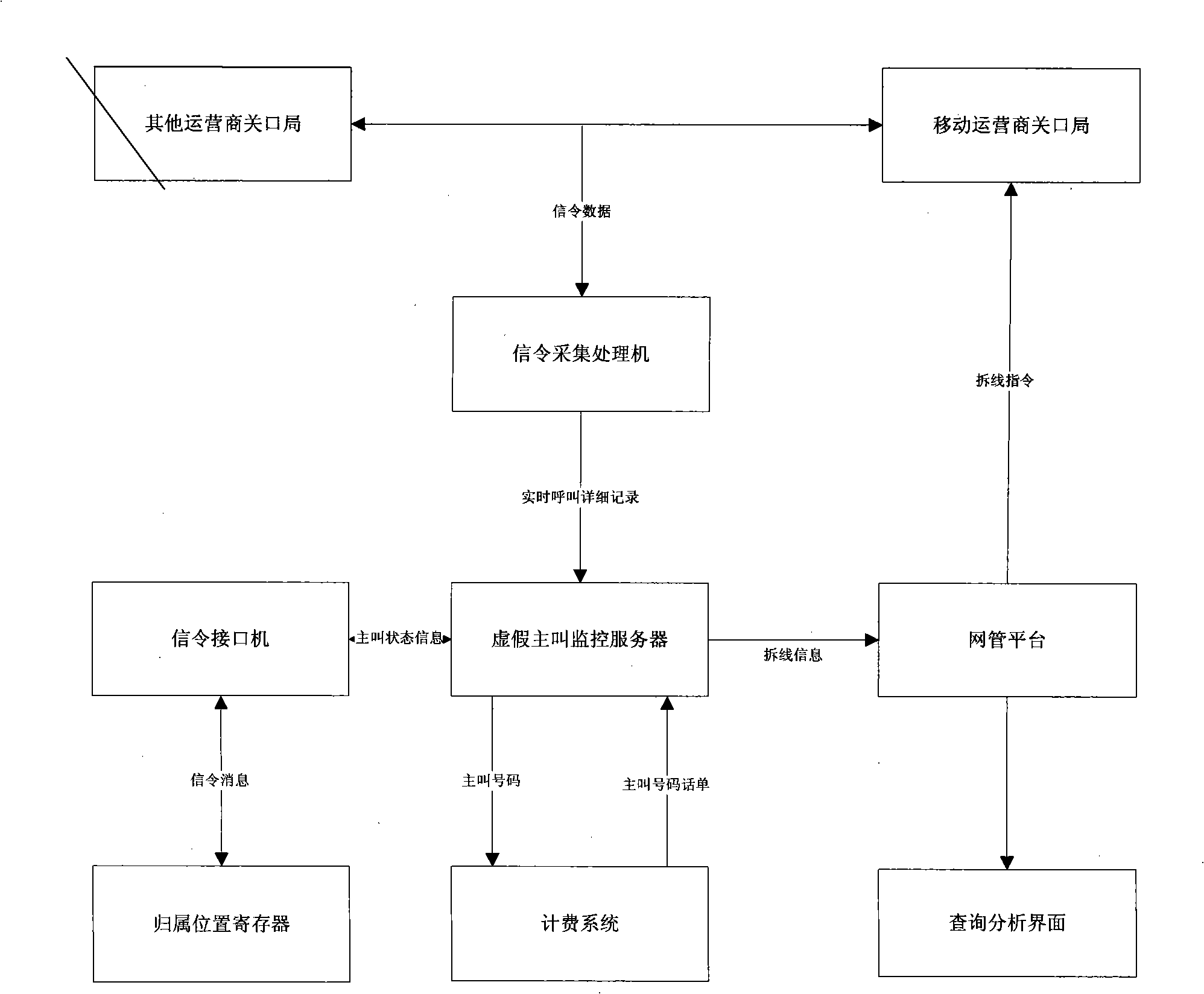
ActiveCN101345795ACall for accurate and comprehensive judgmentCall judgmentSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsLocation statusProcessor register
A communication network false call automatic monitoring and real time interception method includes the following steps: a front-end signaling acquisition and processing step, for performing event synthesizing to signaling data on the monitored chain, generating detailed record of real-time calls, and then transmitting it to a false call monitoring server; a false call judging step, taking user position state information (the number of the mobile switching centre the user located and the busy / idle state of the user's mobile phone) from a home location register in the communication network through a false call monitoring server, automatically inter-comparing the user position state information with the call association information in the call detailed record according to a false call real time criterion rule, and then submitting the intercomparison result to a network management platform; a false call real-time interception step, in which the false call monitoring server send out a rewirable information to the network management platform for realizing false call real-time interception function.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP SHANDONG
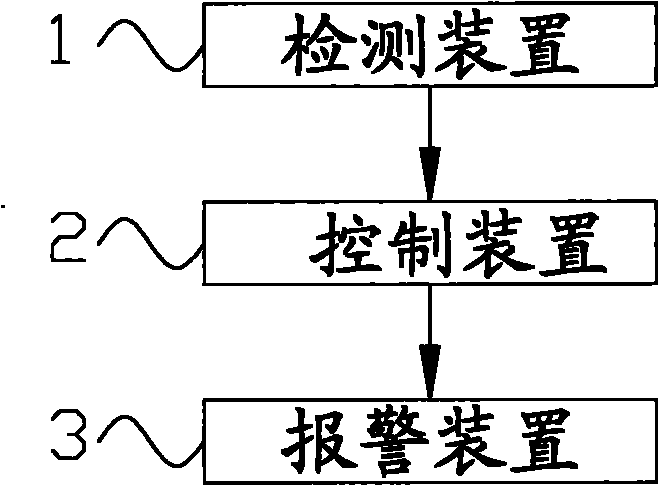
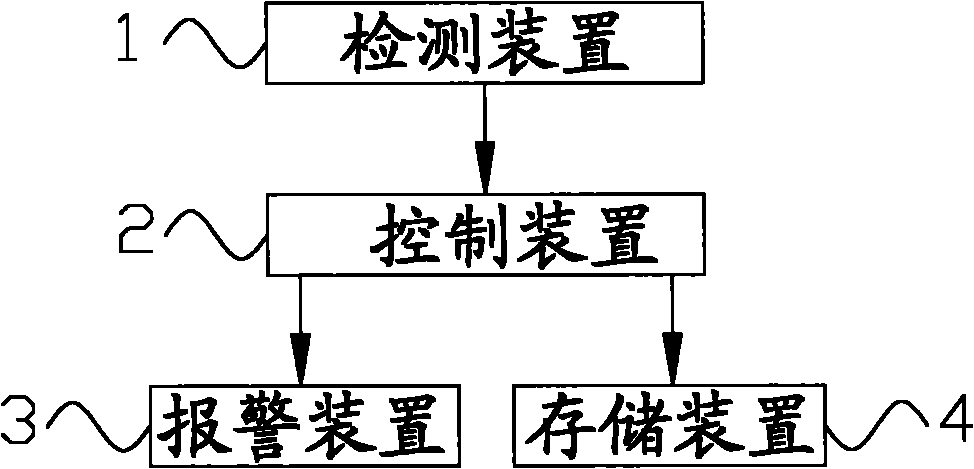
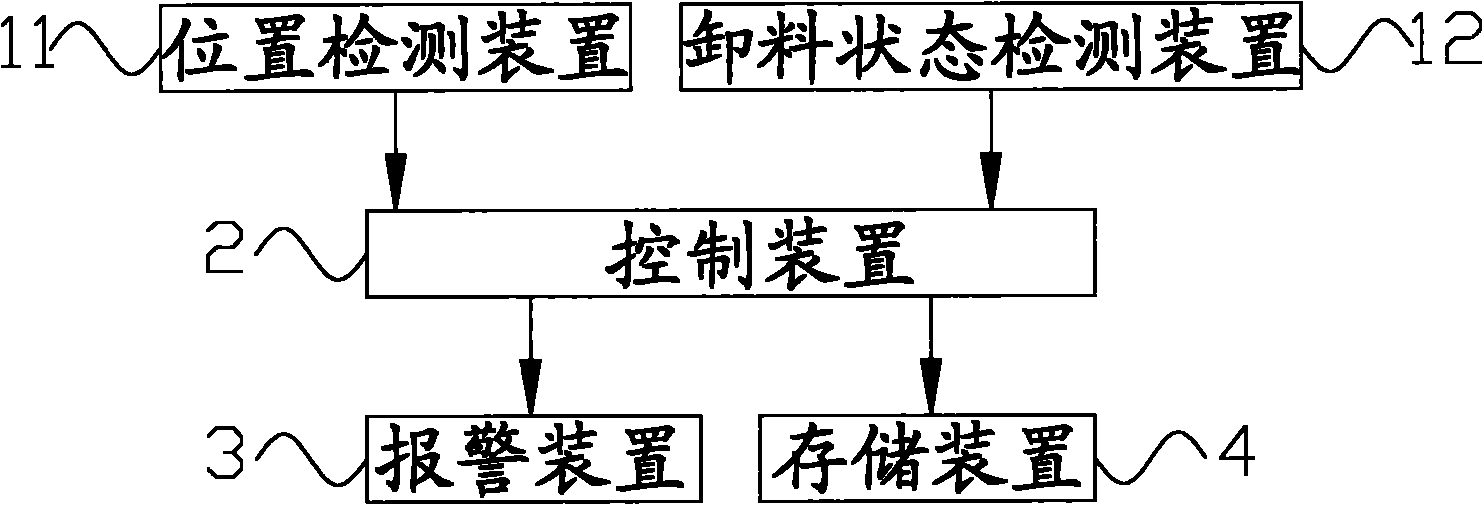
Mixing station and mixing vehicle state monitoring system and method thereof
The invention discloses a mixing vehicle state detecting system which comprises a detecting device (1), a control device (2) and an alarm device (3), wherein the detecting device (1) is mounted on a mixing vehicle and used for detecting the position and the unloading state of the mixing vehicle and obtaining a position signal and an unloading state signal; and the control device (2) is used for receiving the position signal and the unloading state signal and respectively comparing with a pre-stored target position signal and an unloading signal, when the position signal is different with the target position signal and the unloading state signal is the same with the unloading signal, the control device (2) is used for controlling the alarm device (3) to alarm. The mixing vehicle state monitoring system can monitor the position state and the unloading state of the mixing vehicle during the way of transporting concrete to a target site, effectively prevent the occurrence of phenomena of material stealing and the like and provide the guarantee to a third party with interest relationship. The invention further discloses the mixing vehicle including the mixing vehicle state monitoring system and a mixing vehicle state monitoring method.
Owner:SANY HEAVY IND CO LTD (CN)
System and method of sending notifications prior to service arrival
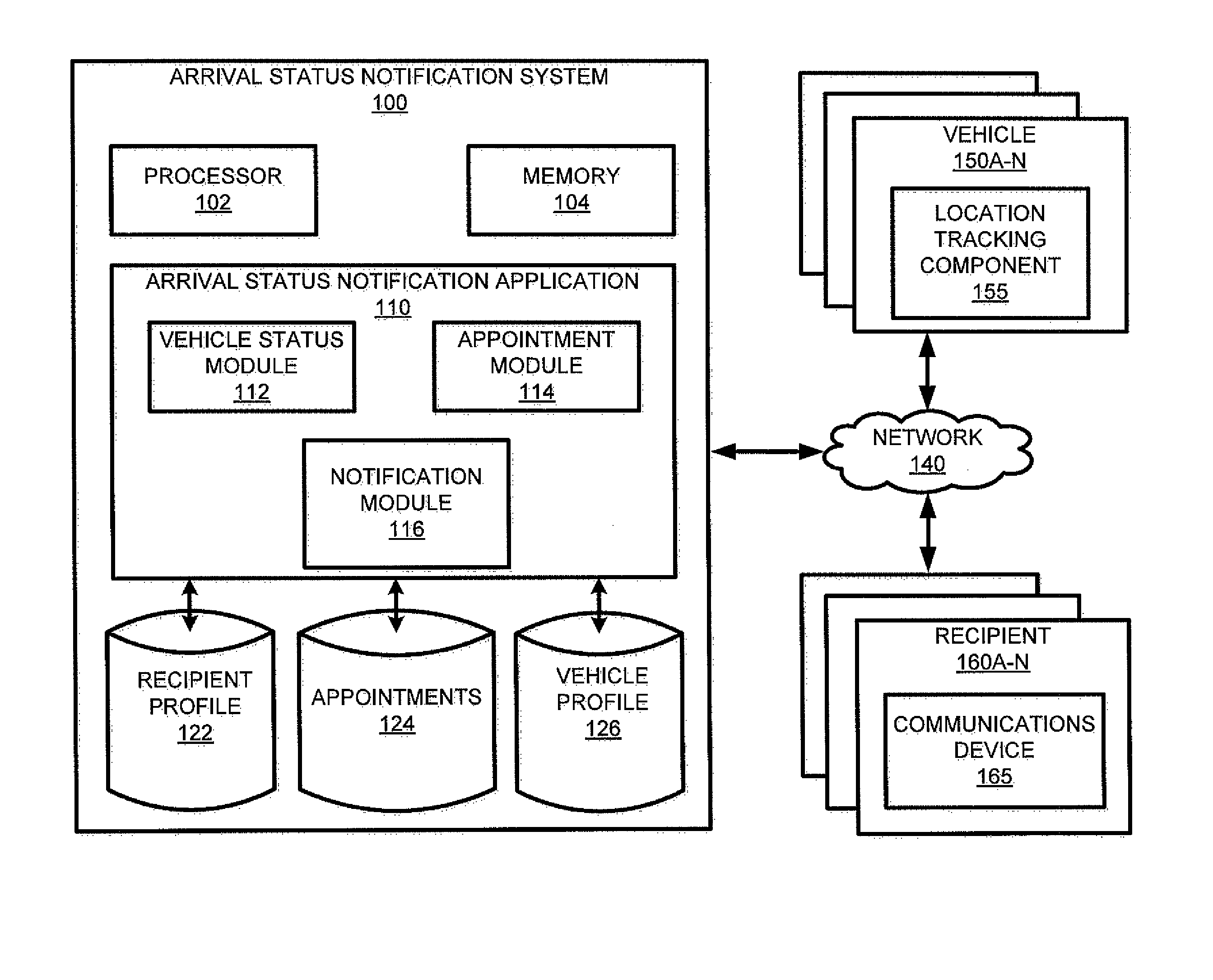
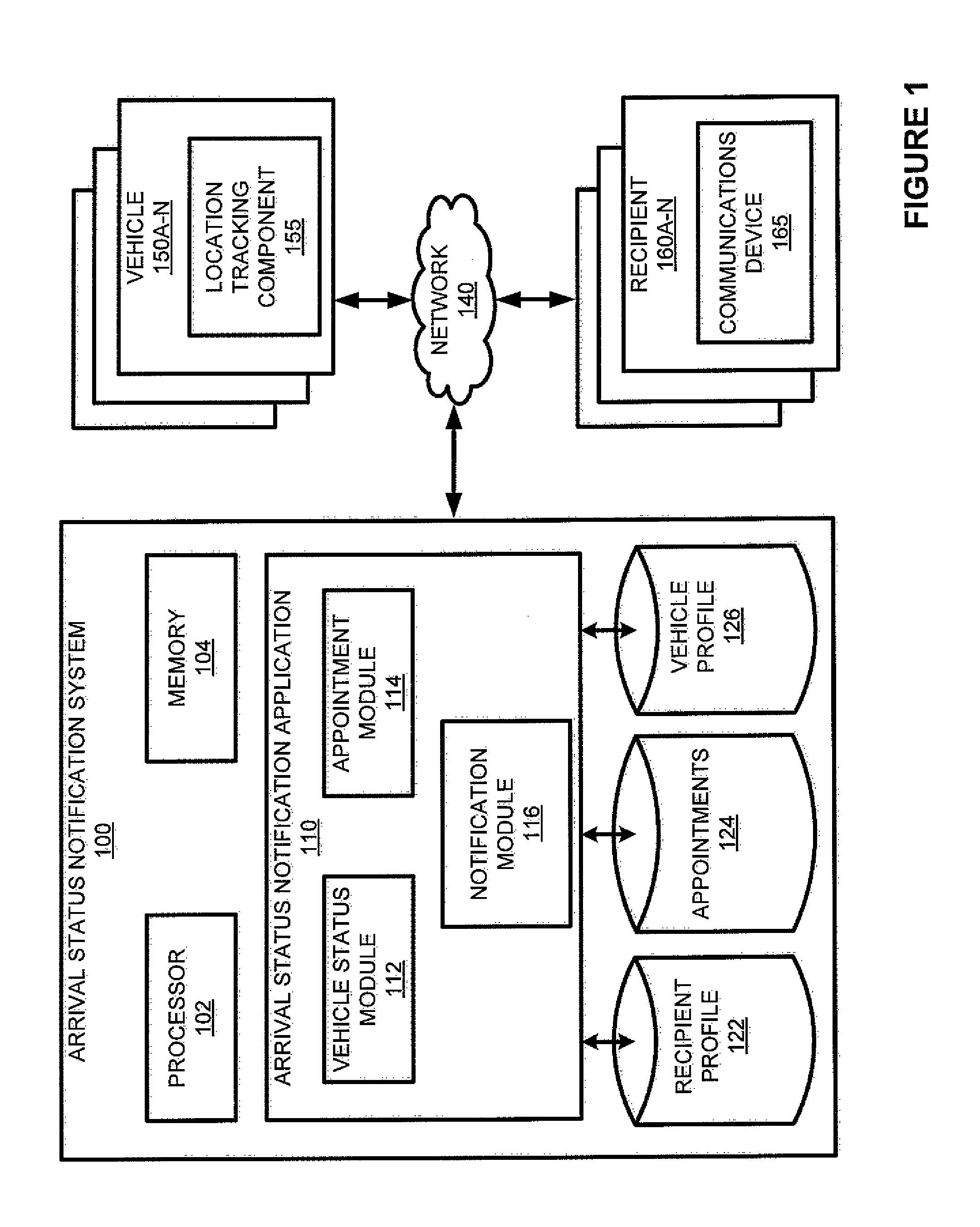
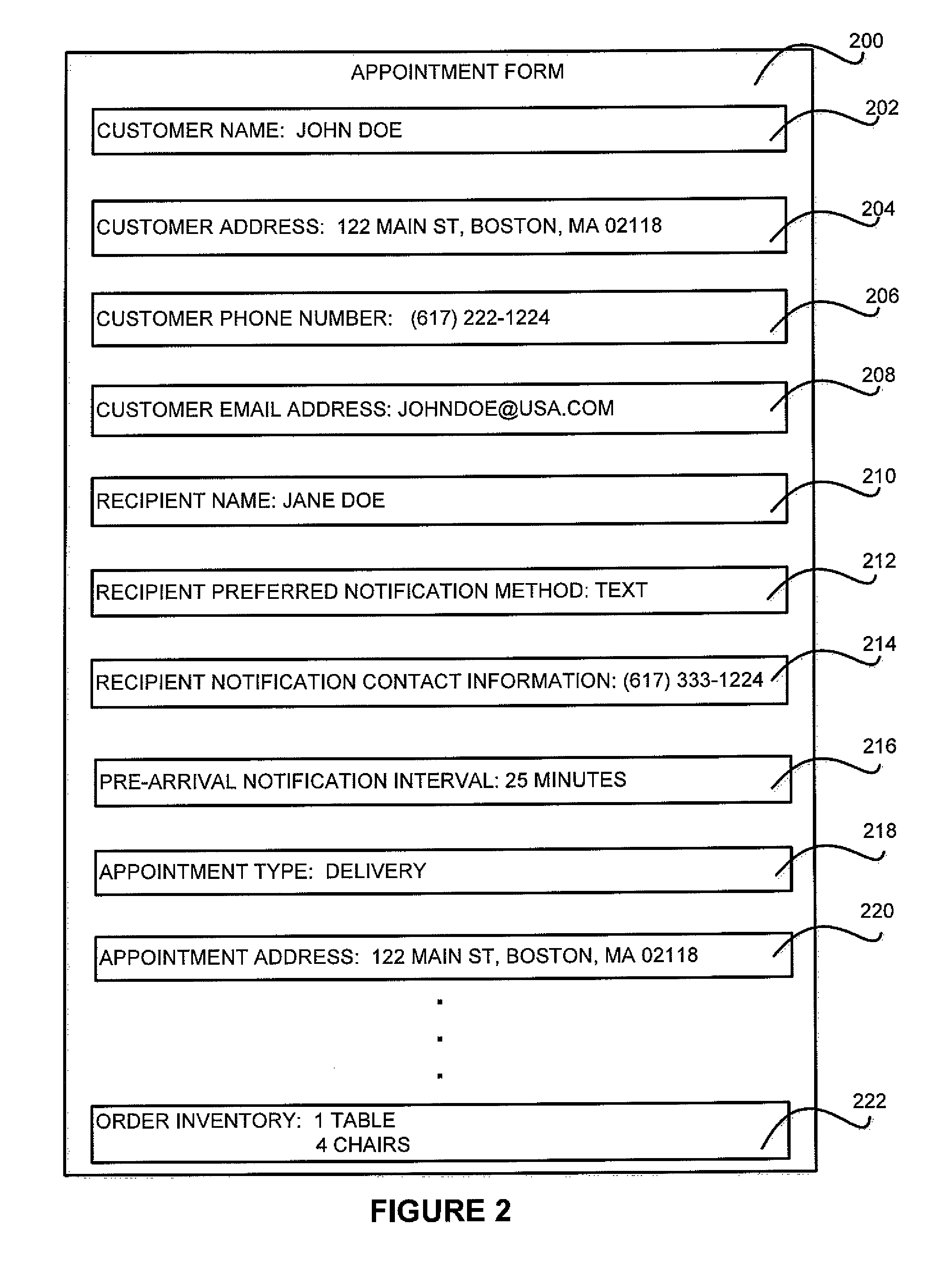
ActiveUS8682363B1Wireless commuication servicesLocation information based serviceLocation statusReal-time computing
A system and method for providing notification to a recipient of an arrival of a vehicle at an instant when the vehicle's estimated time to a destination corresponds to a recipient-defined pre-arrival notification interval is disclosed. In one embodiment, a system includes a location status module that determines the location of the vehicle. An appointment module determines the vehicle's estimated time to a destination and then determines if the estimated time to destination corresponds to a recipient-defined pre-arrival notification interval. If the vehicle's estimated time to destination corresponds to the recipient-defined pre-arrival notification interval, the appointment module sends a notification to the recipient. According to embodiments, the appointment module determines if the vehicle's estimated time to destination equals a pre-arrival notification interval. If the estimated time to destination equals the pre-arrival notification interval, a notification is sent to the recipient.
Owner:EPORIN
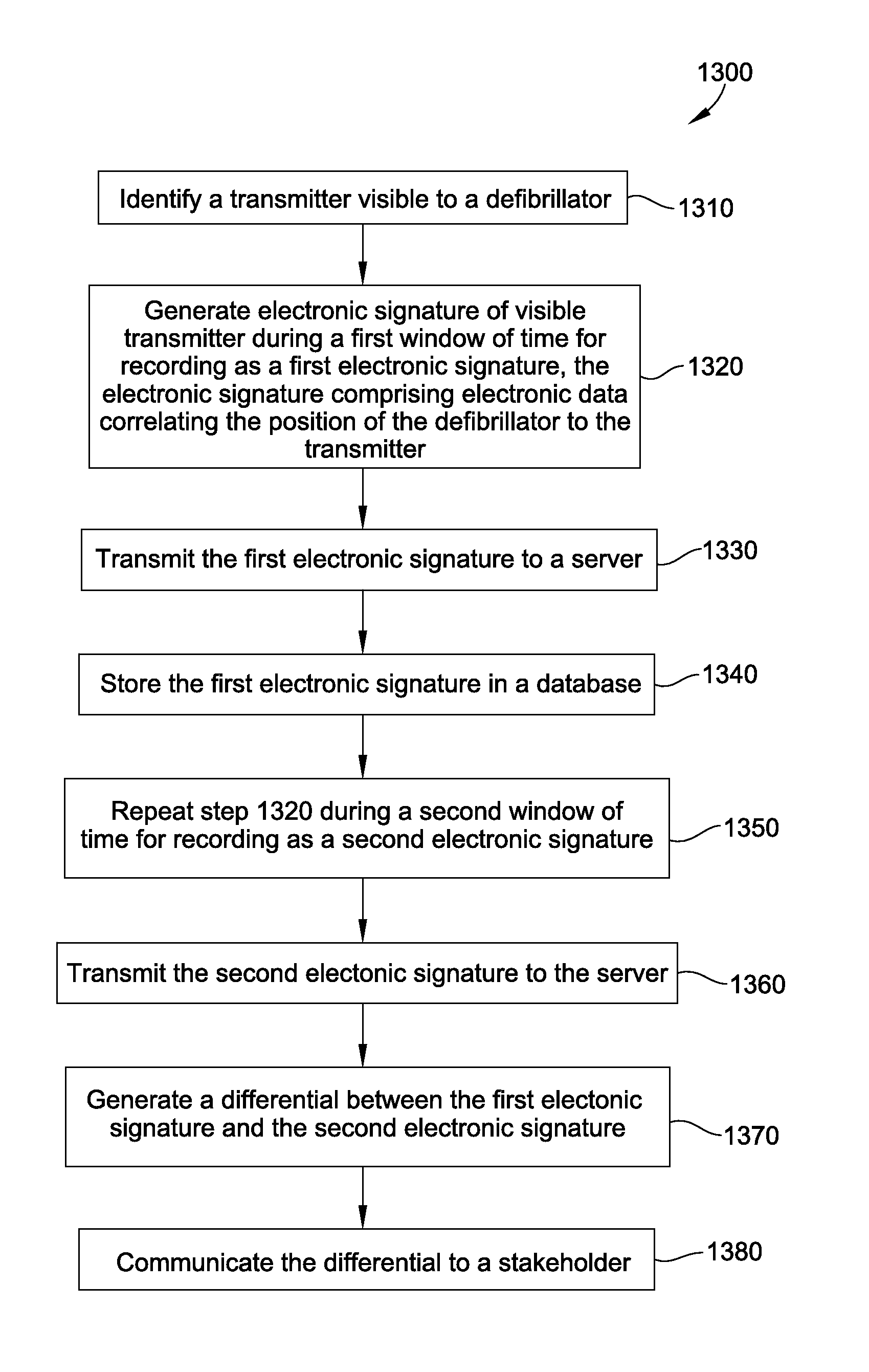
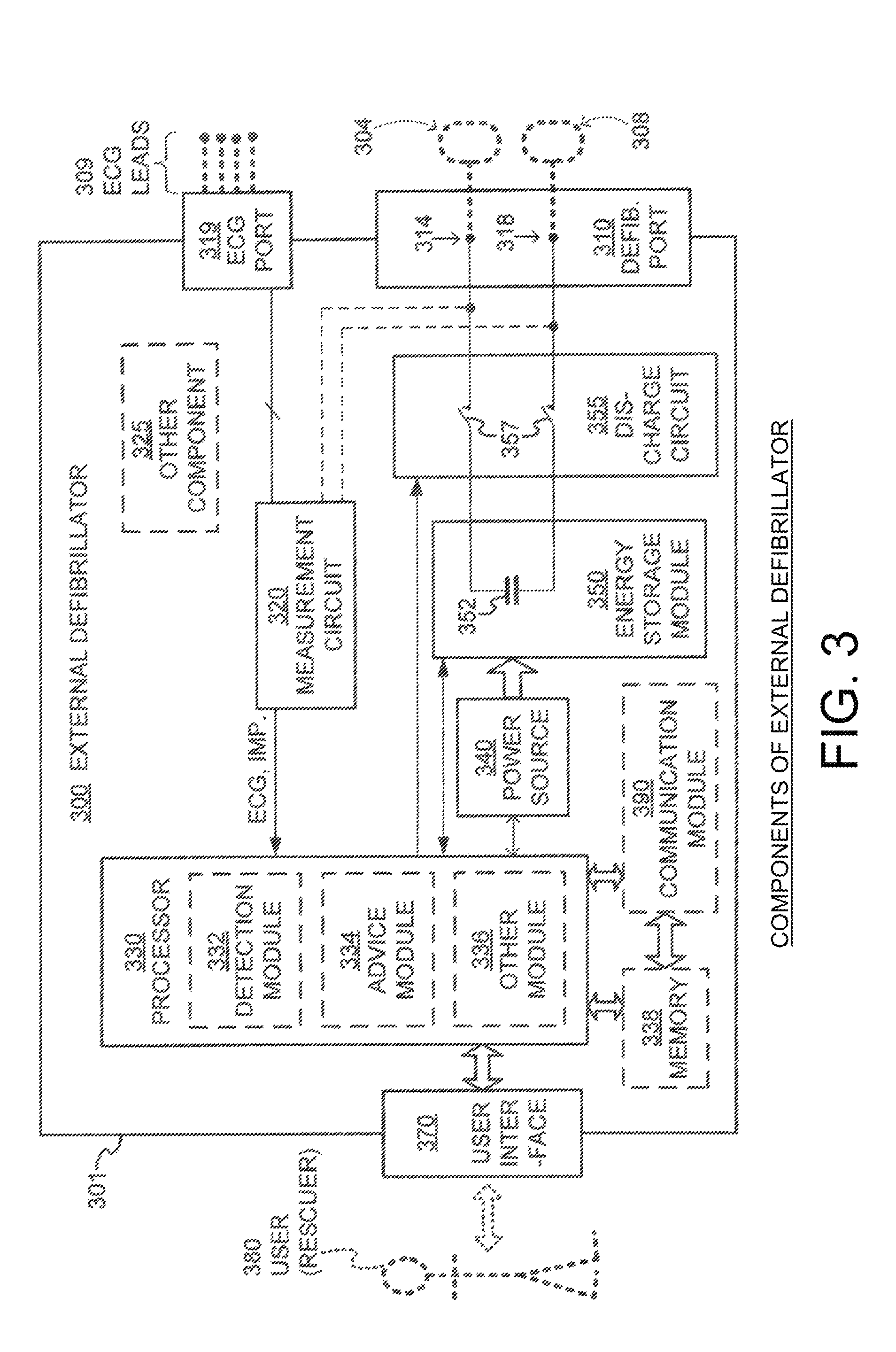
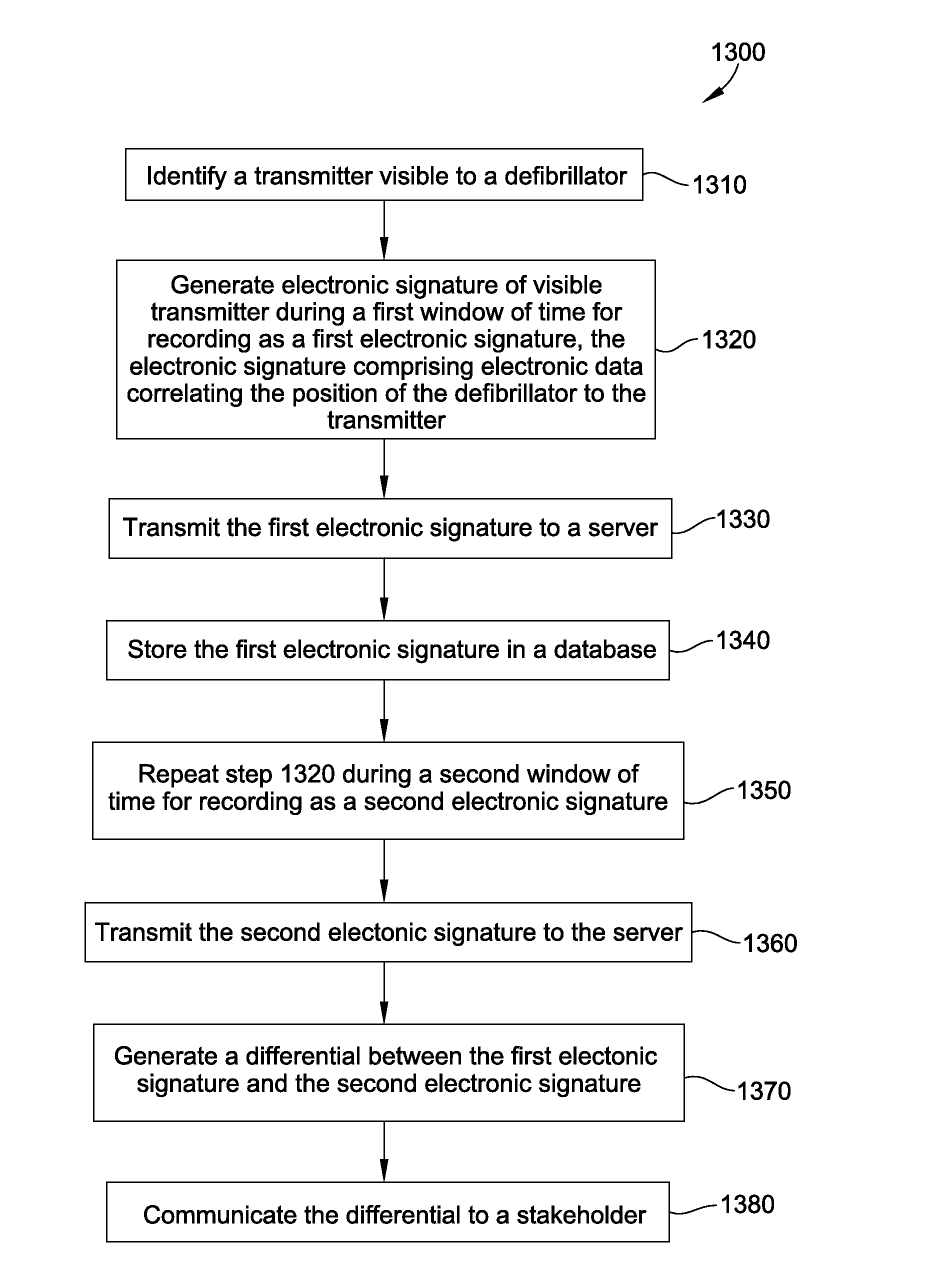
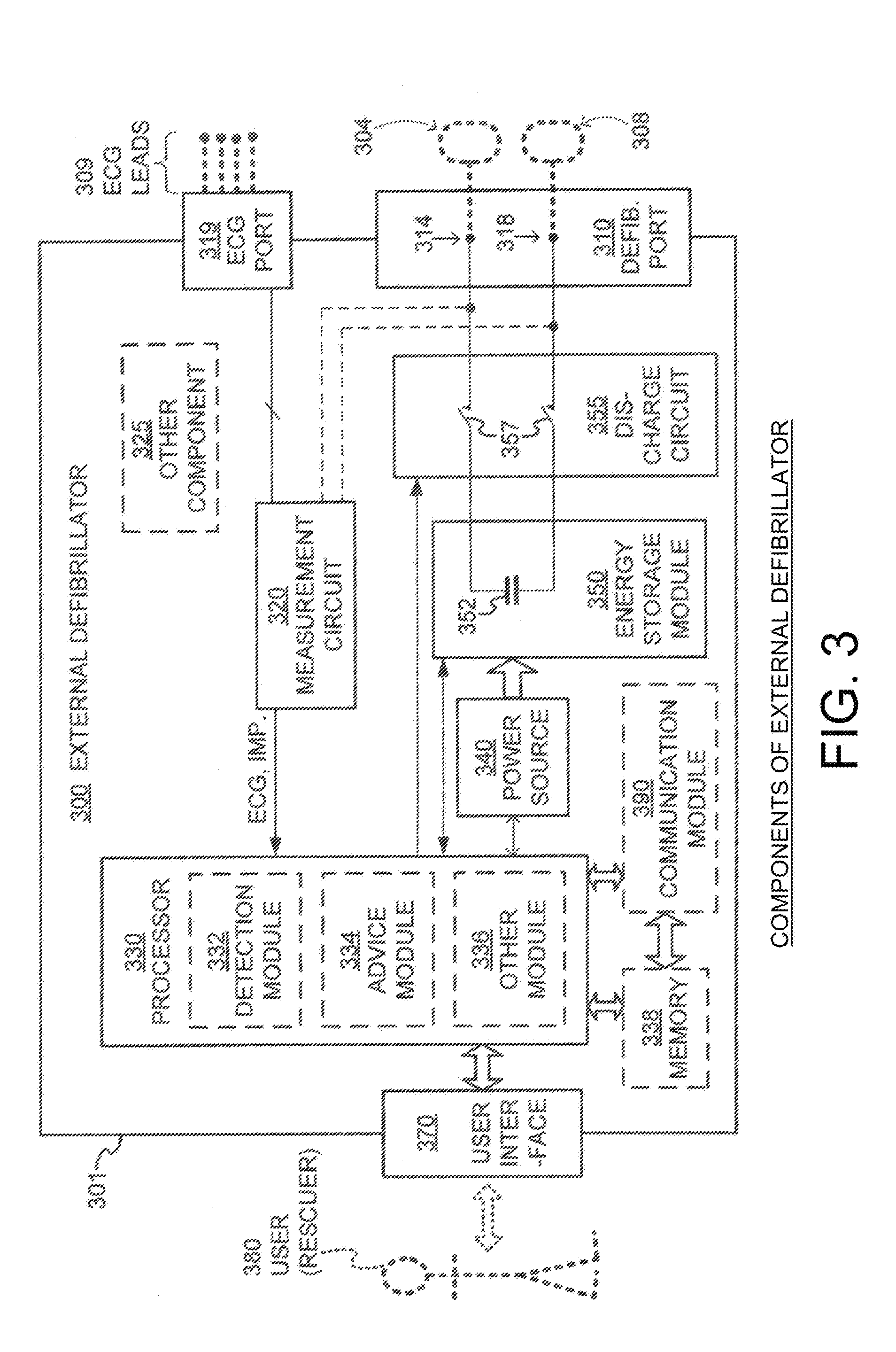
Defibrillator location tracking device
A defibrillator is disclosed for communication with a transmitter associated with a location. The defibrillator is configured to generate an electronic signature for determining a position of the defibrillator within the location. The electronic signature includes electronic data correlating the position of the defibrillator to the transmitter. The electronic data may include GPS data. The defibrillator is configured to generate the electronic signature during a first and a second window of time to define a first and a second electronic signature. A differential between the first and the second electronic signatures corresponds to a positional state of the defibrillator, indicating movement within or between two locations. In a disclosed system, the first electronic signature is stored in a database and a server is configured to generate the differential and to communicate the positional state of the defibrillator to a stakeholder. Methods of use are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
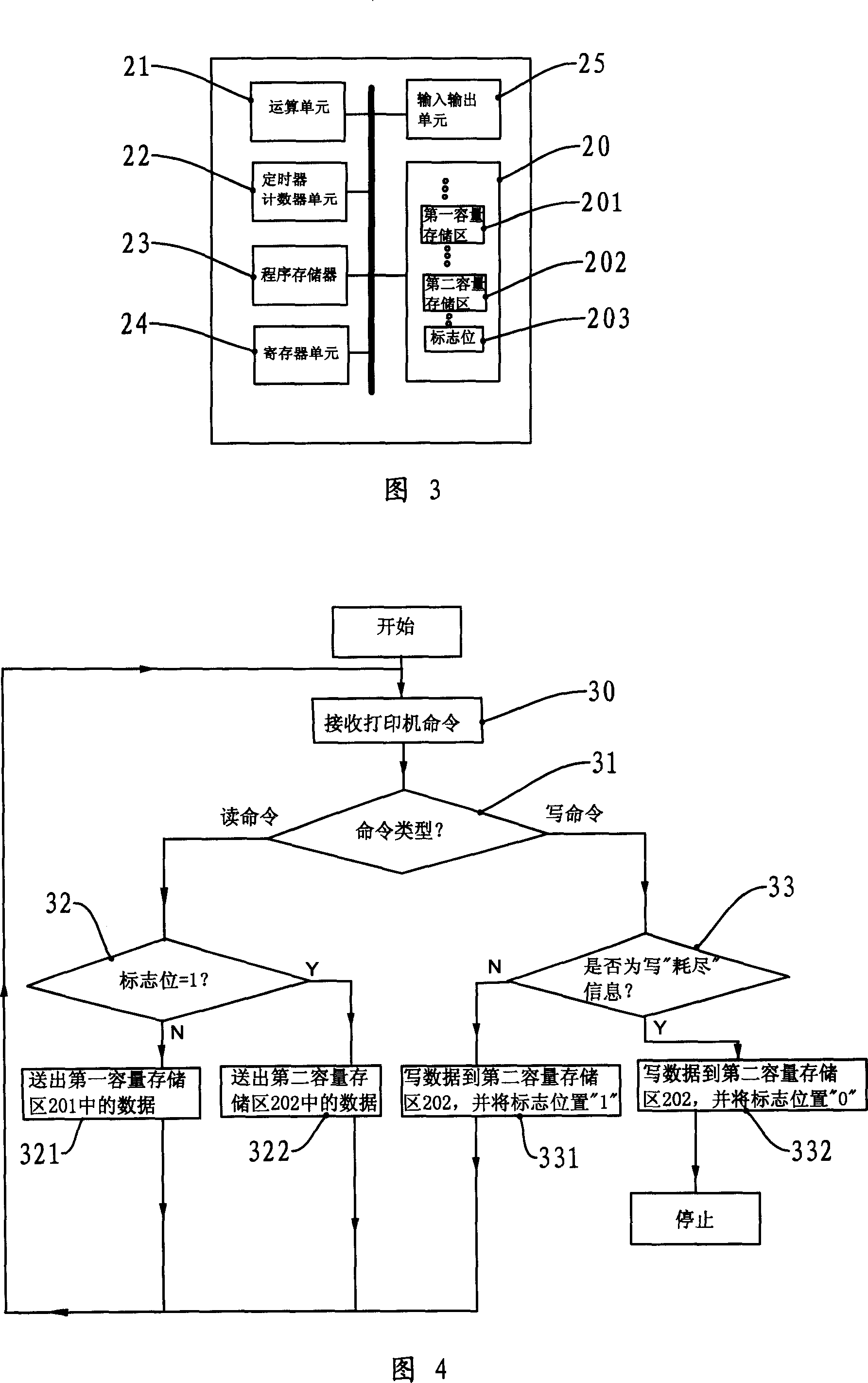
Intelligent chip and information processing method thereof
InactiveCN101082796AUse repeatElectrographic process apparatusPrintingInformation processingCapacitance
The invention discloses an intelligent chip and its information processing method, wherein the intelligent chip contains MCU and signal processing circuit, wherein the MCU concludes memory unit to communicate with imaging device through signal processing circuit; the memory unit contains first capacitance memory area to store a group of non-updated non-zero capacitance data, second capacitance memory area to reserve the capacitance data updated by imaging device, marking position to control the imaging device to read the data of first and second capacitance memory areas. The information processing method of intelligent chip comprises the following steps: judging whether the order pattern from imaging device is reading order or writing order; transmitting data according to the condition of marking position if the order pattern is reading order; changing the condition of marking position according to the content of order if the order pattern is writing order. The invention can control data reading of memory area through marking position with two capacitances, which makes the intelligent chip be used repeatedly.
Owner:ZHUHAI TIANWEI TECH DEV CO LTD
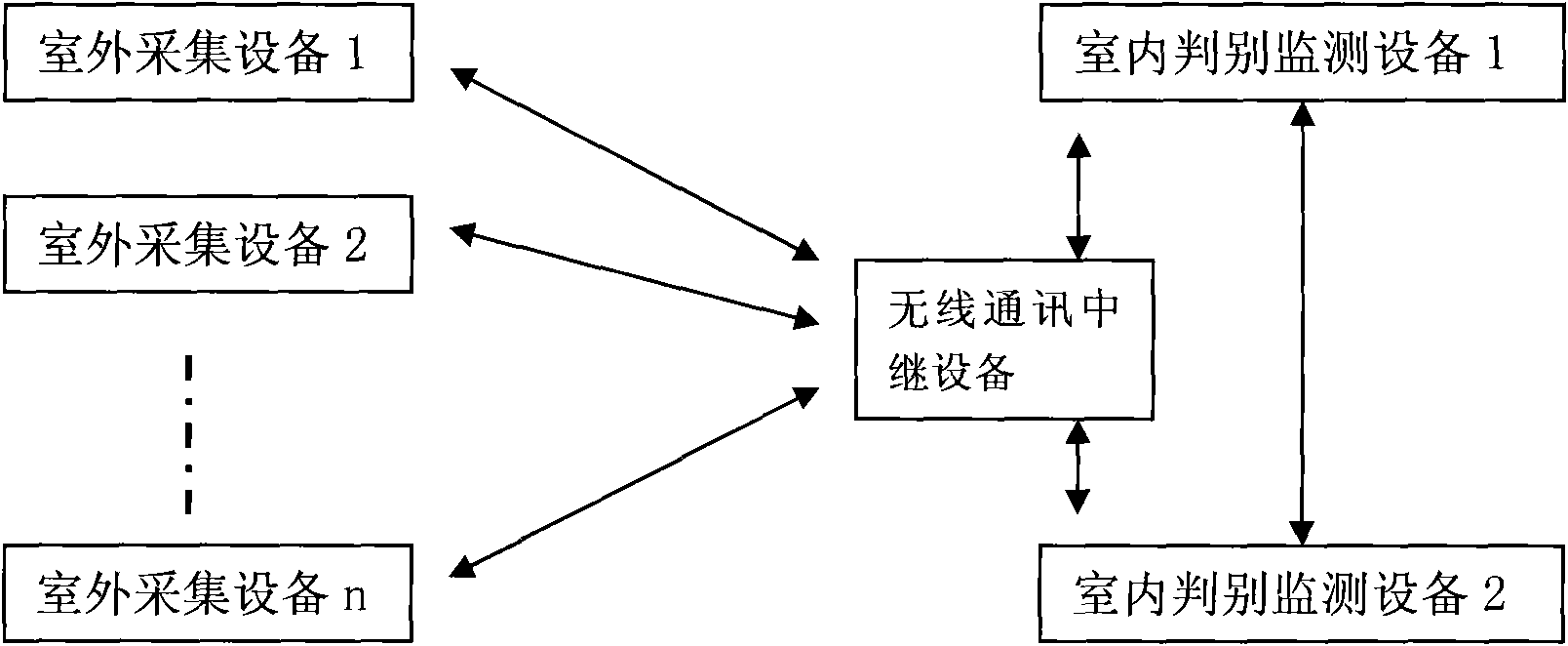
Monitoring system of railway derailer state
InactiveCN101590863APrecise positioningAccurately locate the fault locationRailway signalling and safetyLocation statusMonitoring system
The invention discloses a monitoring system of railway derailer state, which is characterized in that the monitoring system comprises an outdoor acquisition device and an indoor discriminating and monitoring device which are connected with each derailer, wherein, the indoor discriminating and monitoring device successively inquires the outdoor acquisition device in a railway station via a radio path; after receiving inquiry instruction, the outdoor acquisition device encodes according to derailer position state information collected by a sensor and sends the information back to the indoor discriminating and monitoring device; and the indoor discriminating and monitoring device discriminates, treats and displays signals. Thus, loaders and operation rooms can know the derailer state of each loading and unloading line of each railway station in time so as to ensure safe loading and unloading operation and shunting operation of freight stations.
Owner:北京人和路通科技有限公司
Defibrillator location tracking device
ActiveUS20140087762A1Readily apparentPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingLocation statusLocation tracking
A defibrillator is disclosed for communication with a transmitter associated with a location. The defibrillator is configured to generate an electronic signature for determining a position of the defibrillator within the location. The electronic signature includes electronic data correlating the position of the defibrillator to the transmitter. The electronic data may include GPS data. The defibrillator is configured to generate the electronic signature during a first and a second window of time to define a first and a second electronic signature. A differential between the first and the second electronic signatures corresponds to a positional state of the defibrillator, indicating movement within or between two locations. In a disclosed system, the first electronic signature is stored in a database and a server is configured to generate the differential and to communicate the positional state of the defibrillator to a stakeholder. Methods of use are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
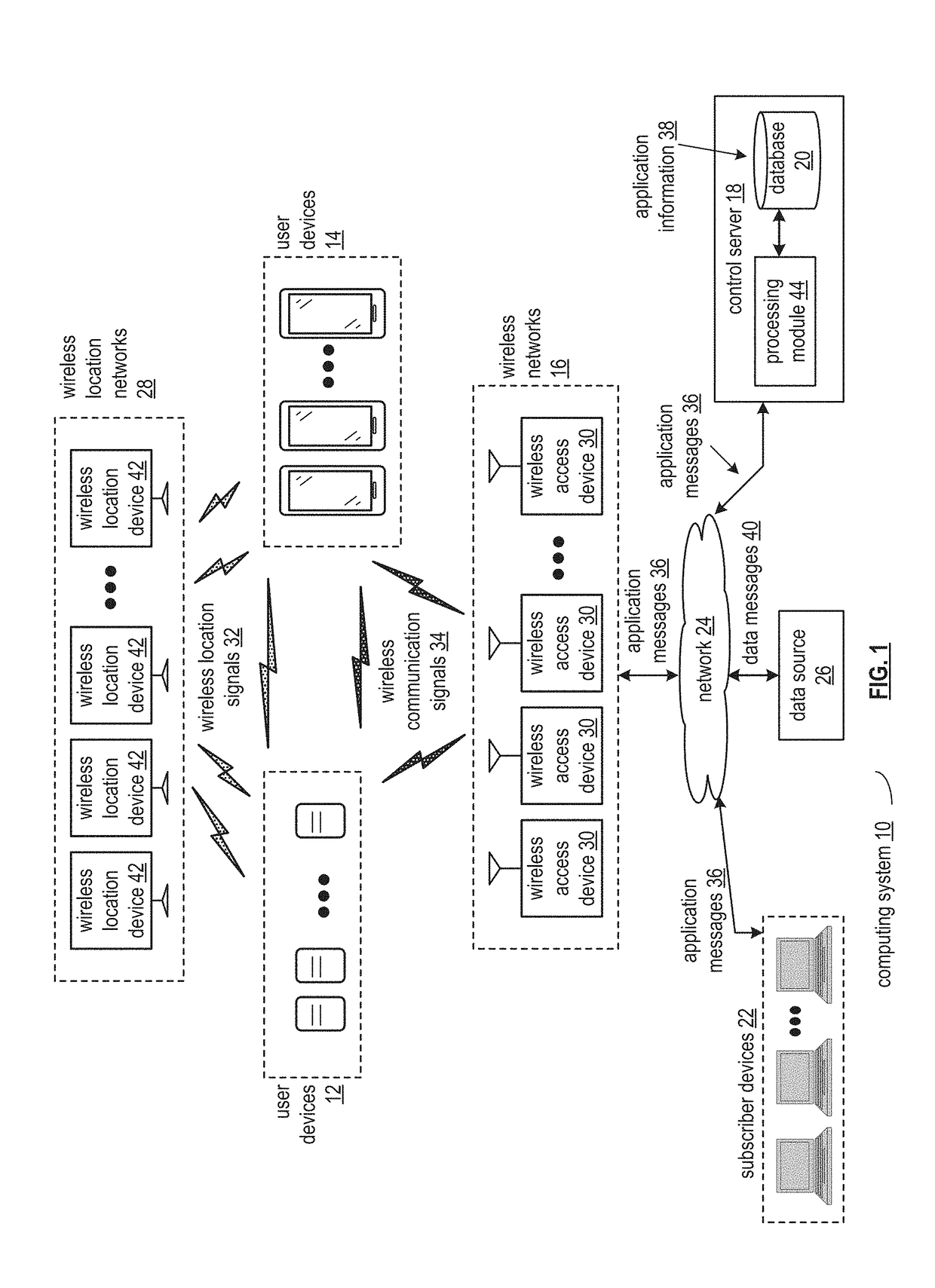
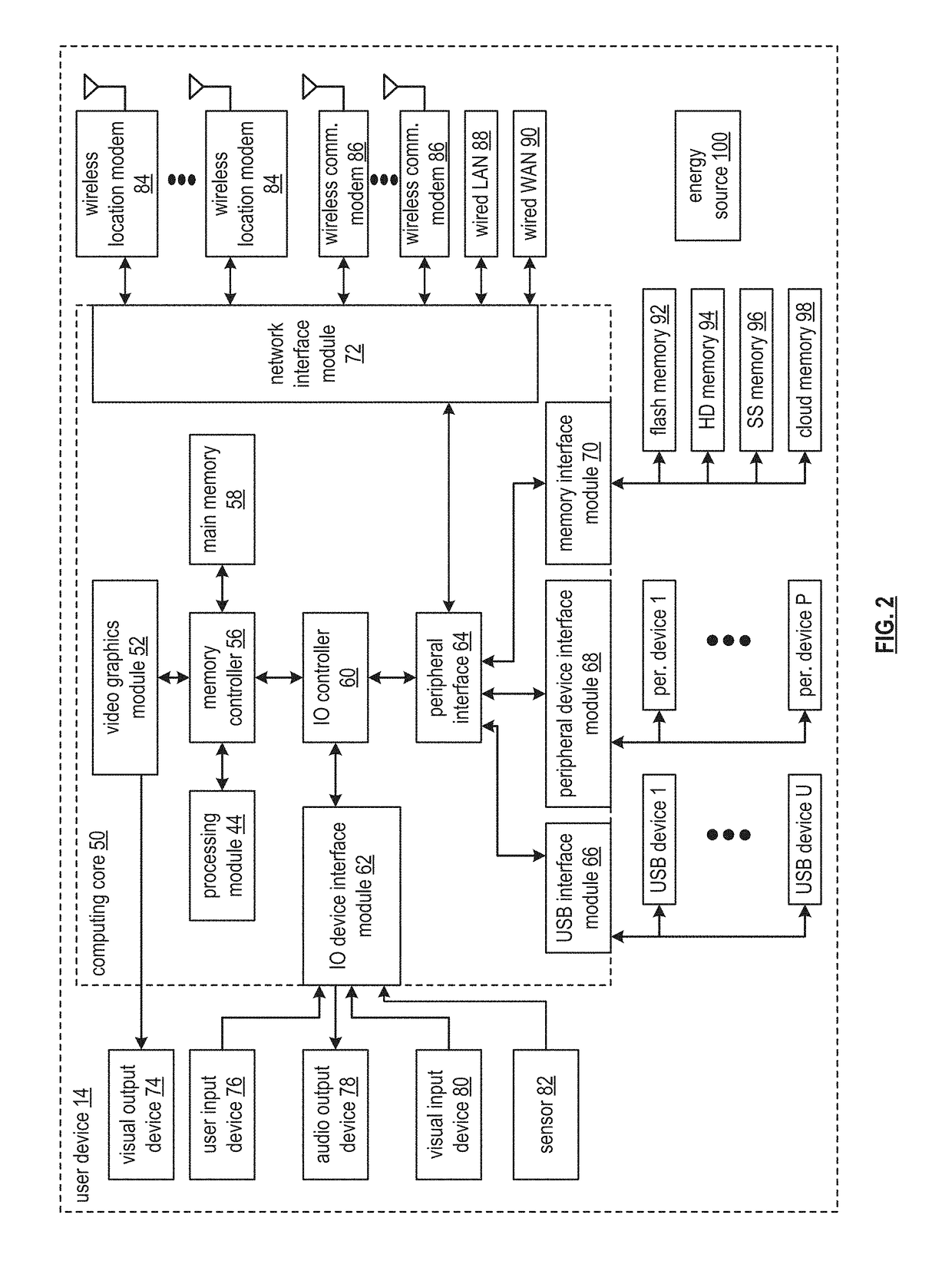
Synchronizing location status information in a computing system
A method includes obtaining, by a user computing device of one or more computing devices of a computing system, a location synchronization approach. The method further includes determining a location determination approach based on the location synchronization approach and availability of location assets. The method further includes generating location synchronization information utilizing the location determination approach. For each of one or more synchronization entities of the computing system, the method further includes identifying a communication path for communication of the location synchronization information. The method further includes facilitating communication of the location synchronization information to the each of the one or more synchronization entities utilizing the communication path in accordance with the location synchronization approach.
Owner:JIO INC
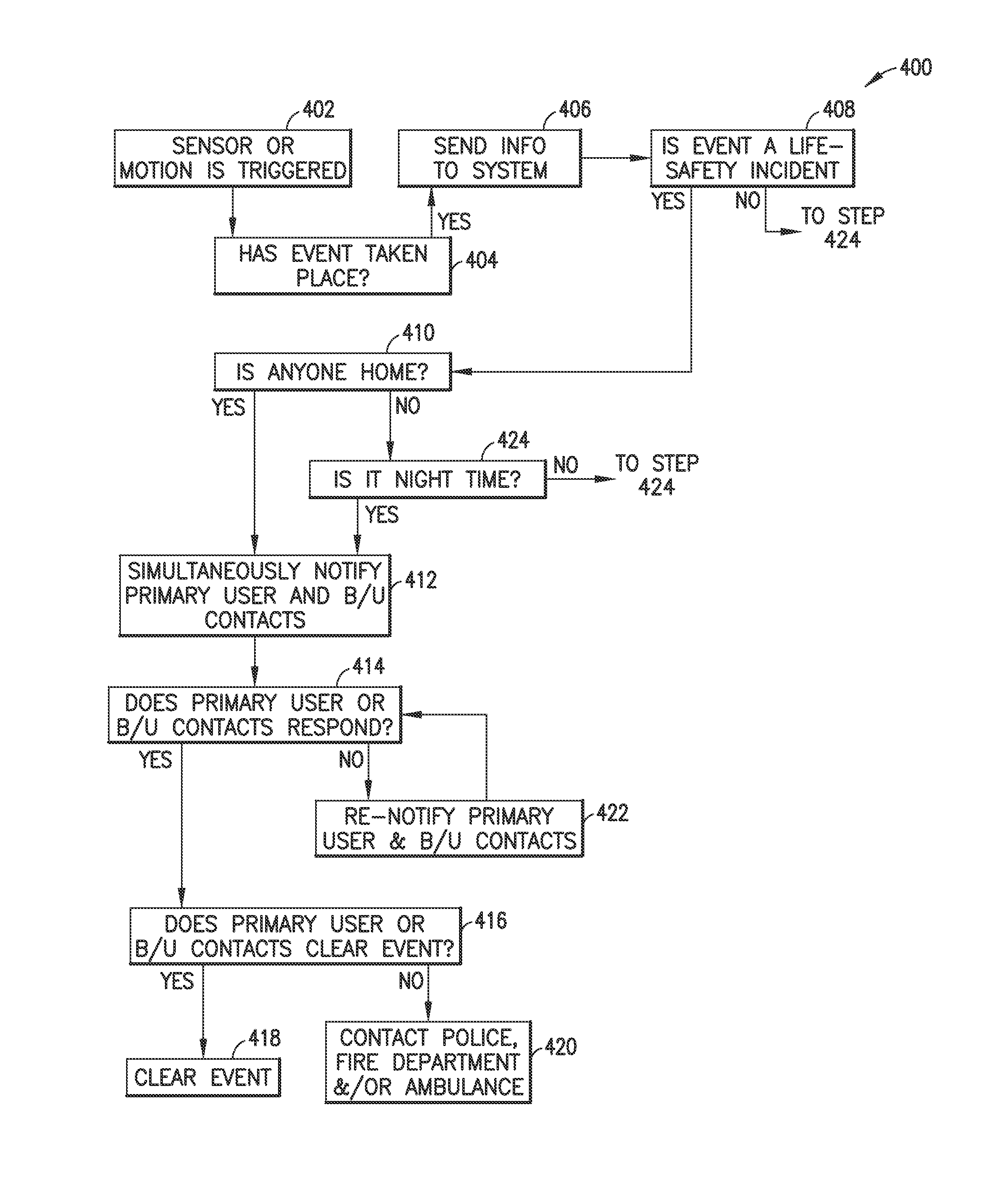
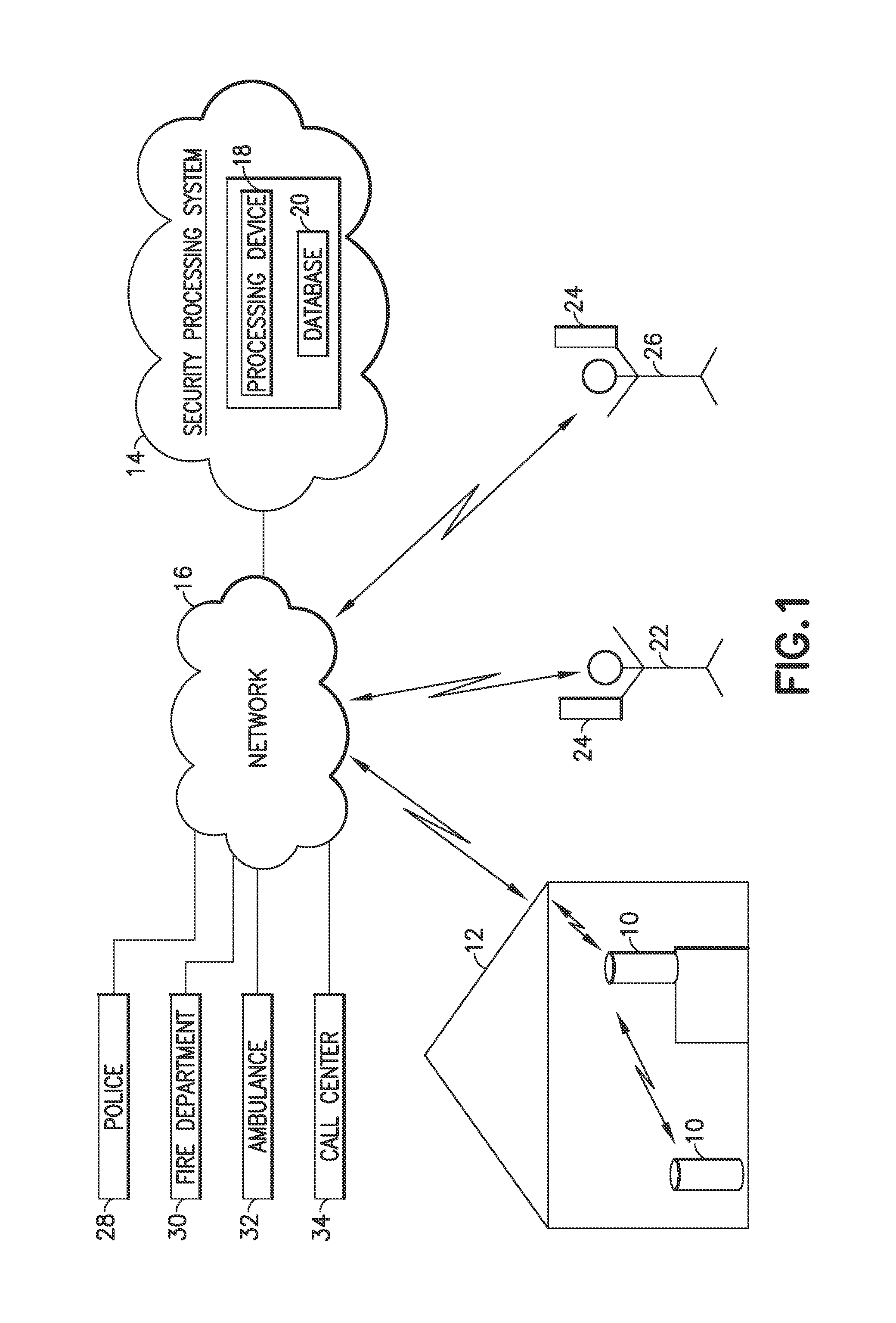
Method for arming and disarming a network enabled device using a user's geo-location
ActiveUS20140320280A1Accurate detectionAccurate impactThermometer detailsProgramme controlUser deviceLocation status
A method of controlling operation of a security device in a location by a mobile user device, comprises monitoring a region around a location of interest, via a mobile user device; providing at least one security device within the region, wherein the security device comprises at least one sensor to monitor a location. The user device recognizes that the user device has entered the region, and searches for a security device within the region. The security device is detected and at least certain security features and / or sensors are disarmed. Disarming may mean that at least certain notifications are not sent about the status of the location. When the user device recognizes that the device is leaving the region, security features and / or sensors may be armed.
Owner:WRV II LP
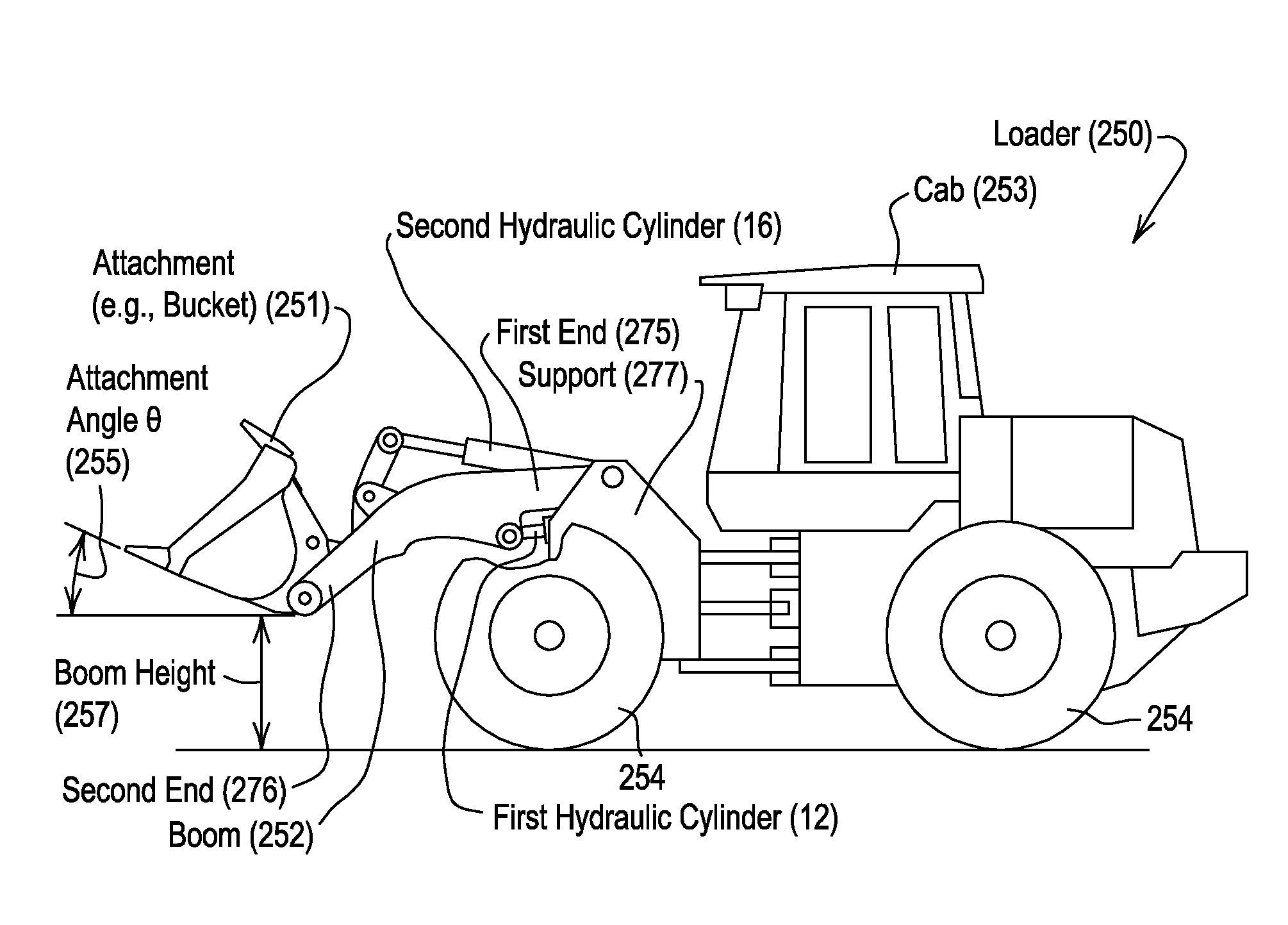
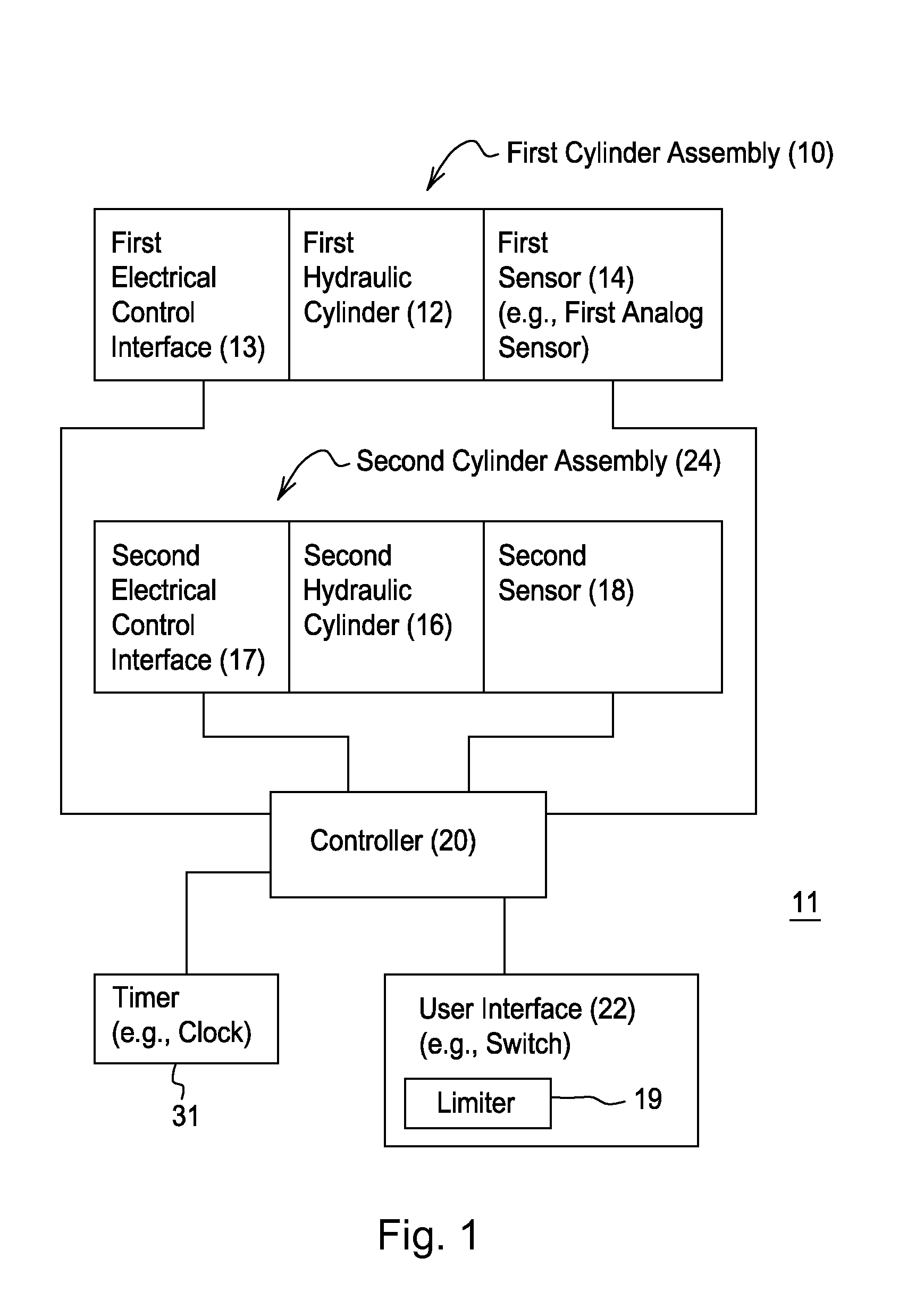
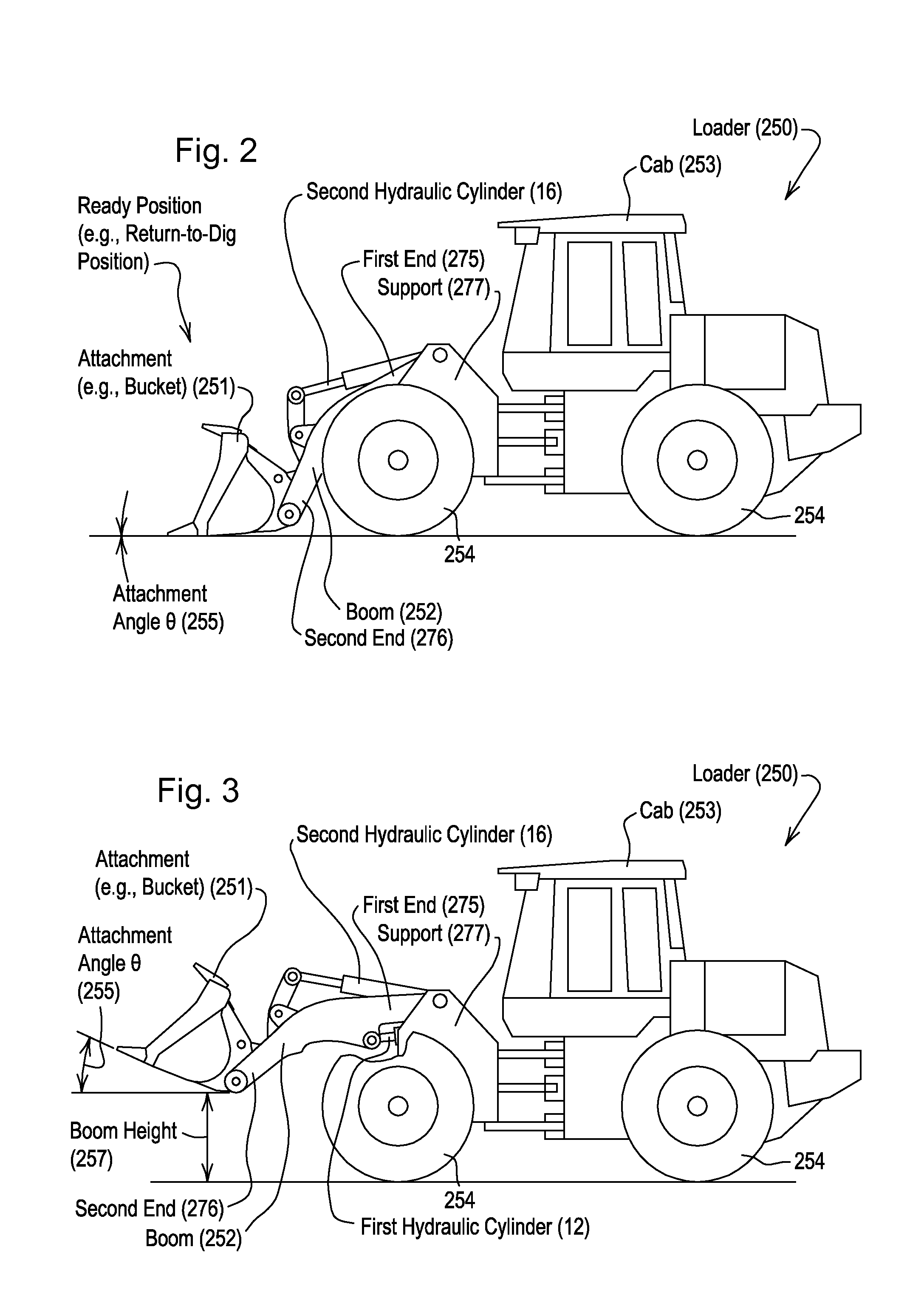
Automated control of boom and attachment for work vehicle
A method and system for automated operation of a work vehicle comprises a boom having a first end and a second end opposite the first end. A first hydraulic cylinder is associated with the boom. A first sensor detects a boom angle of a boom with respect to a support near the first end. An attachment is coupled to the second end of the boom. A second sensor detects an attachment angle of attachment with respect to the boom. A second cylinder is associated with the attachment. A switch accepts a command to enter a ready position state from another position state. A controller controls the first hydraulic cylinder to attain a boom angle within the target boom angular range and for controlling the second cylinder to attain an attachment angle within a target attachment angular range associated with the ready position state in response to the command.
Owner:DEERE & CO
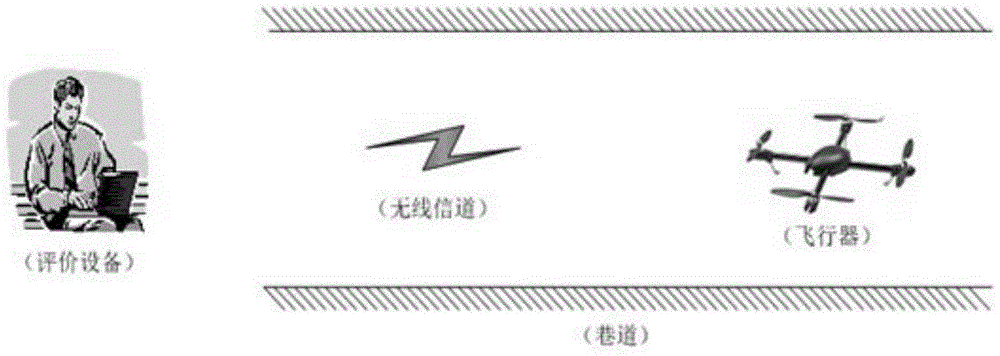
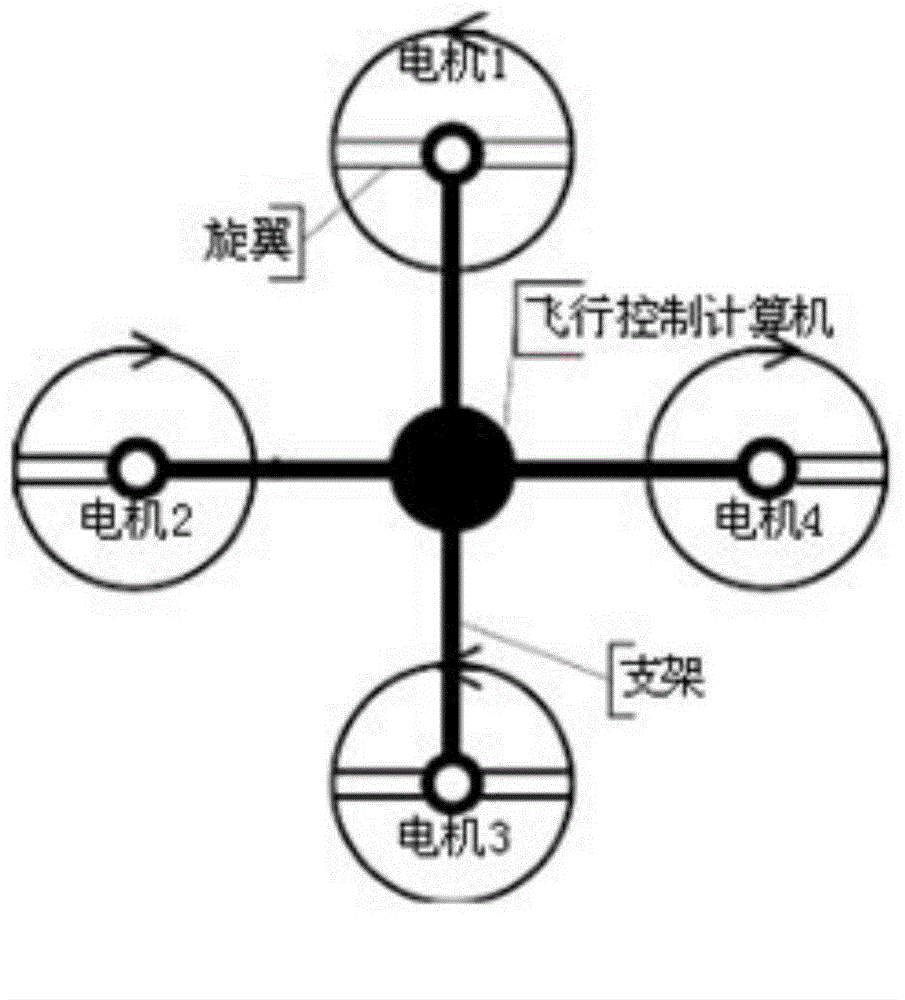
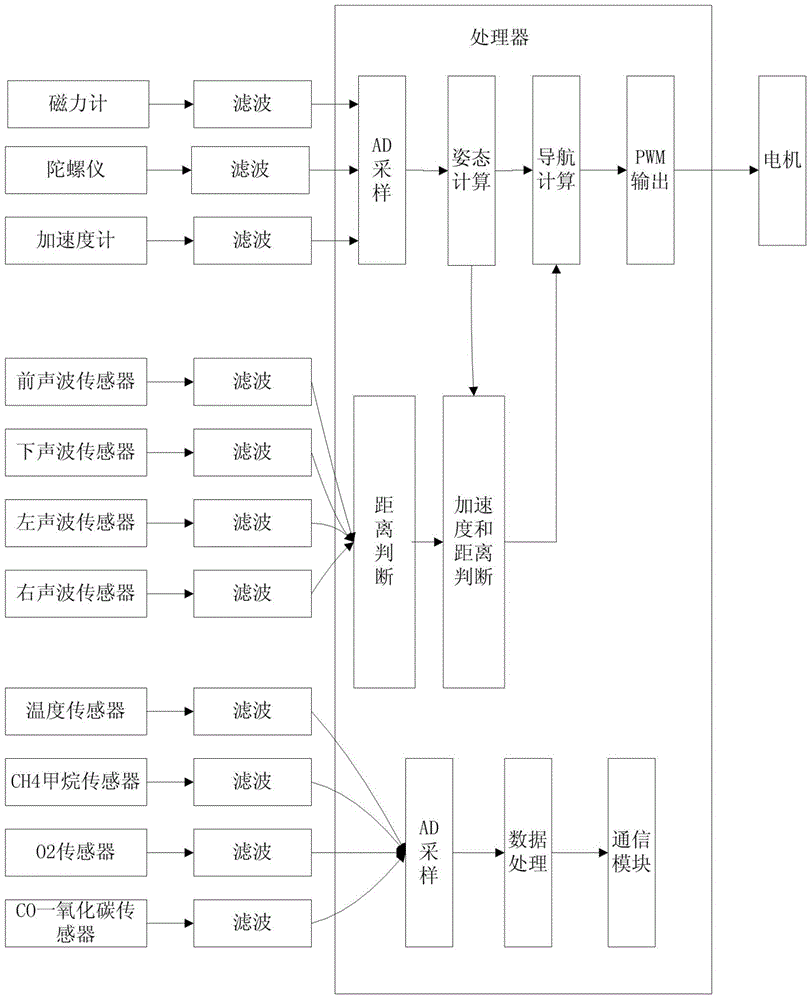
Self-flying method for mine emergent rescue aircraft
The invention provides a self-flying control method for a mine emergent rescue aircraft. By application of the method, the aircraft can fly automatically; in a hovering period, a eulerian angle and an acceleration value of the aircraft are calculated; distances between all the directions and an obstacle are tested by a distance measuring sensor; the current position state of the aircraft is judged according to the aircraft flying tendency and the distance, and a position signal is used as a control signal; then control on the attitude, the speed and the position of the aircraft is realized by adopting an algorithm of combining tendency judgment and fuzzy control, and reliable and stable self flying of the aircraft is guaranteed. By collecting environmental parameters in real time within a certain distance in an alley in the hovering period, and data information is transmitted to portable terminal equipment in real time by a wireless mode. A portable terminal can be used for evaluating the environment danger level in the alley in real time and carrying out displaying and alarming. A rescuer judges the safety within a certain distance according to an analysis result; under a safe condition, gradual promotion is realized until the rescuer reaches the disaster site.
Owner:陕西西科美芯电子科技有限公司
Remote User Interface & Display For Events For A Monitored Location
InactiveUS20140320648A1Accurate detectionAccurate impactProgramme controlThermometer detailsLocation statusUser device
Owner:CANARY CONNECT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com