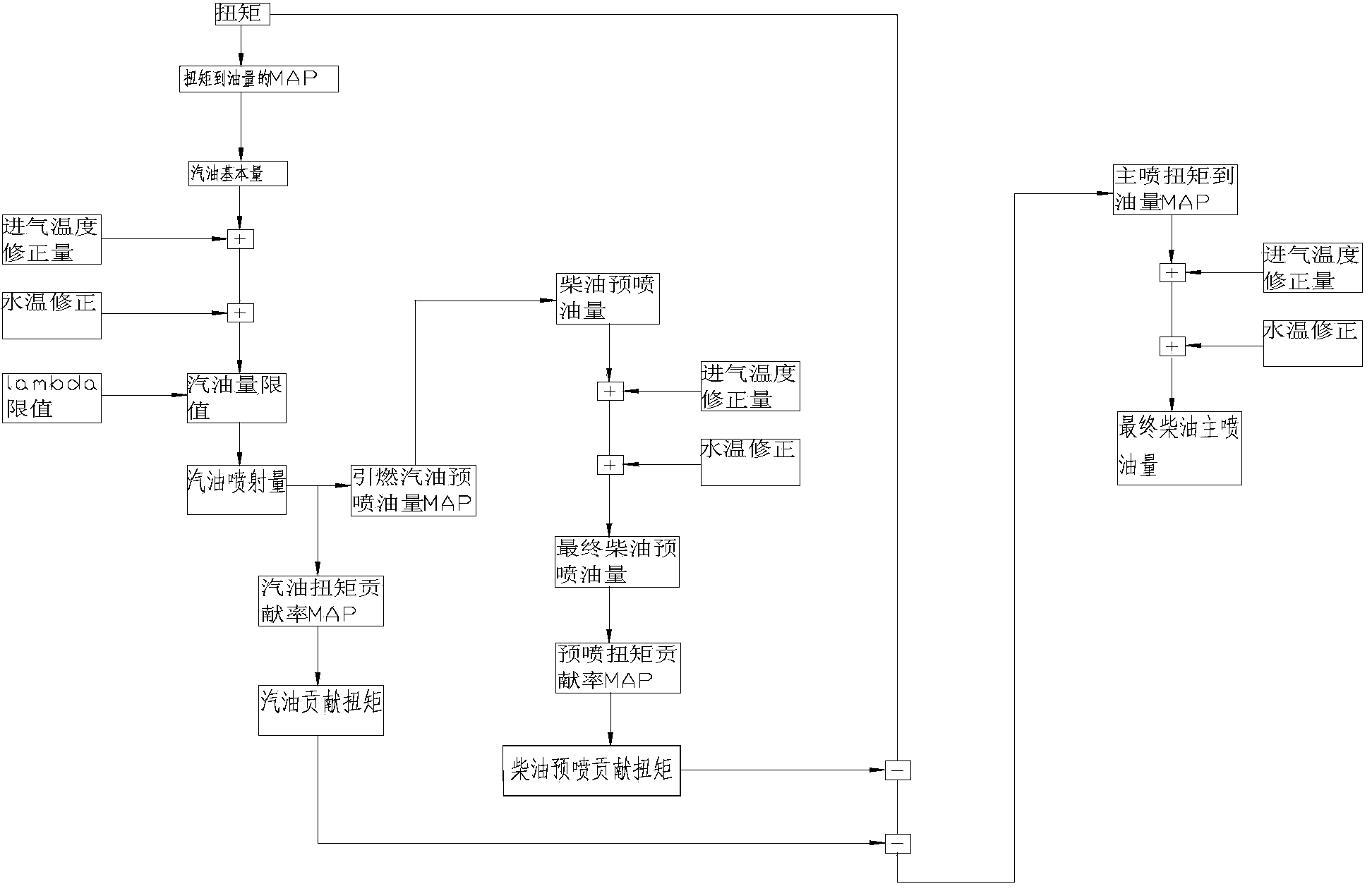Patents
Literature
206 results about "Pilot injection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
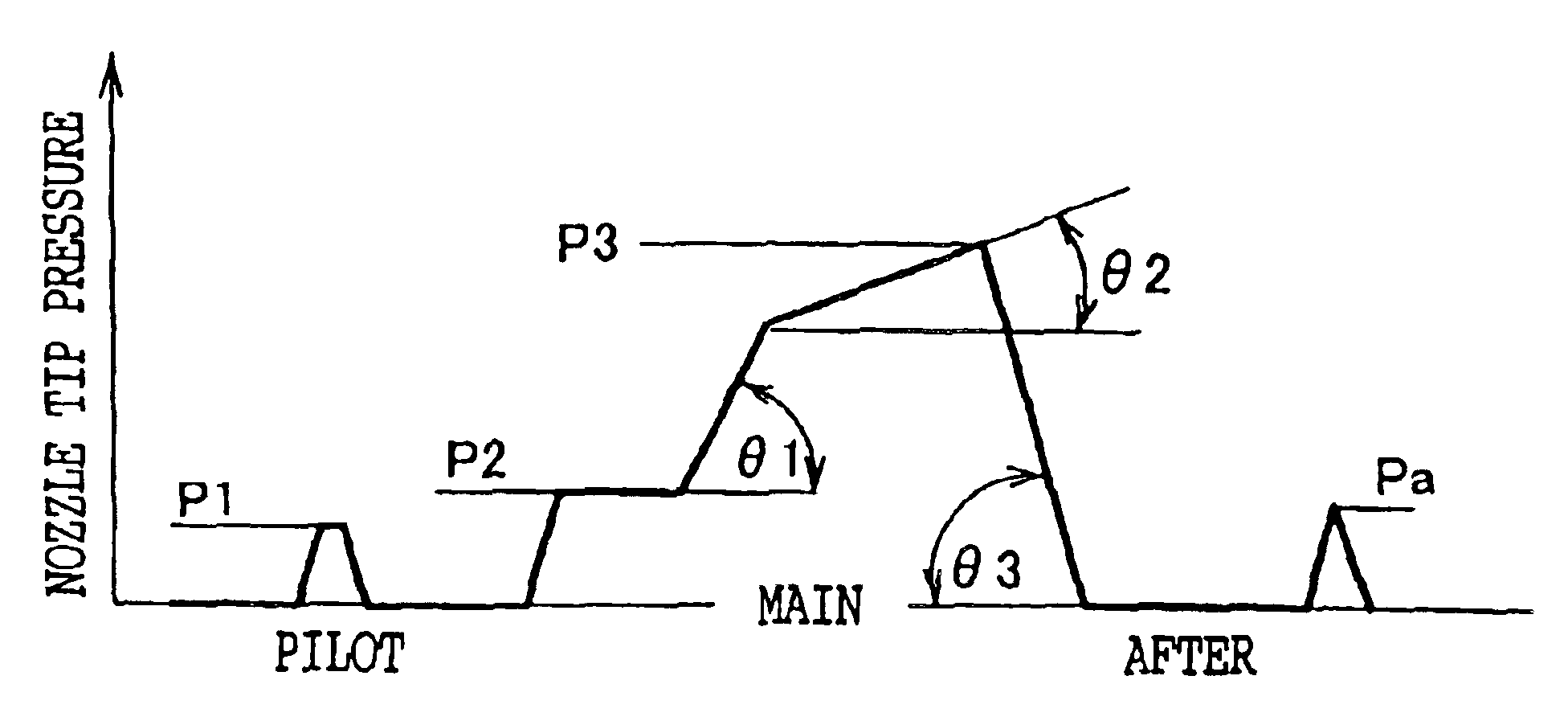
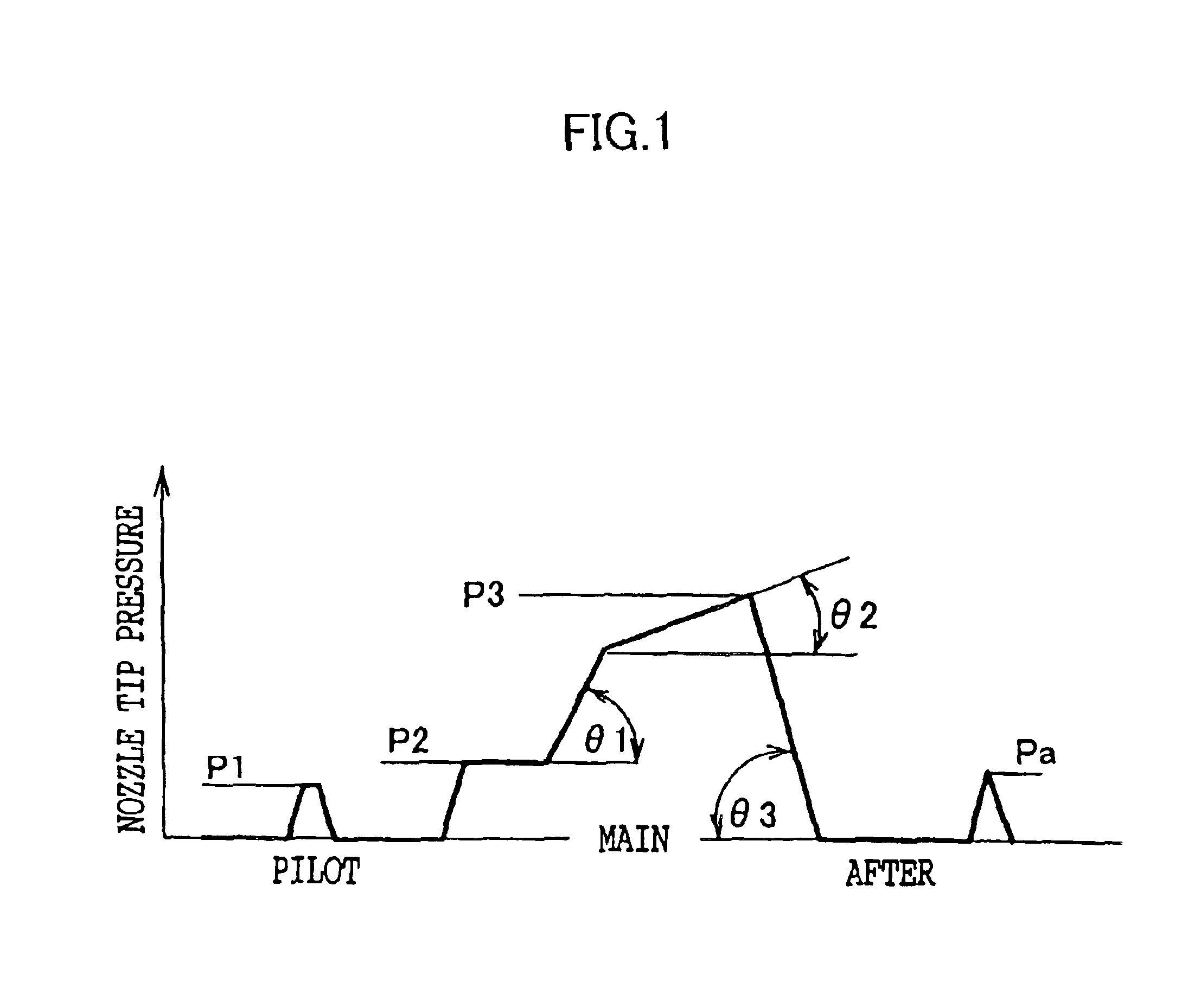
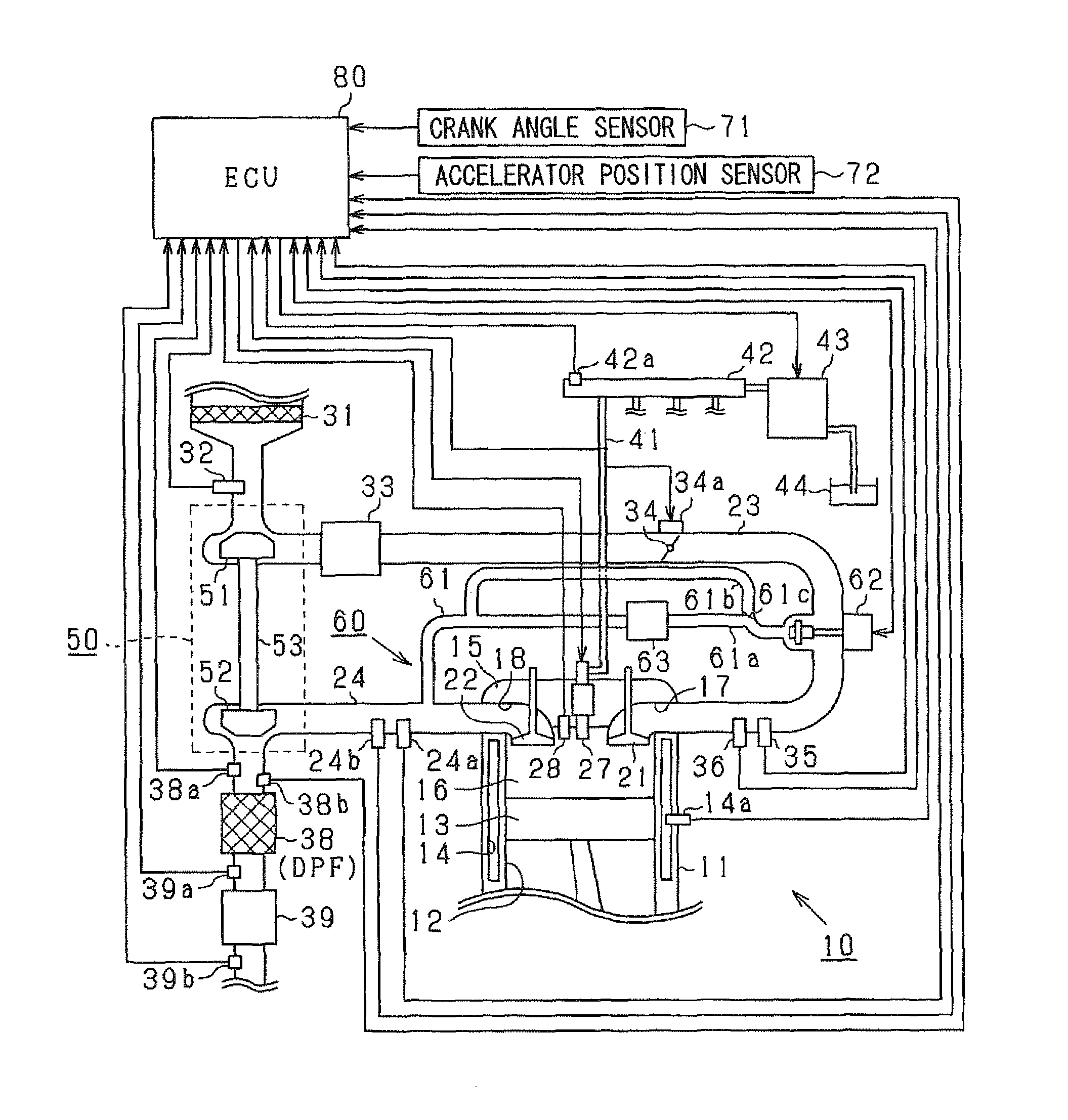
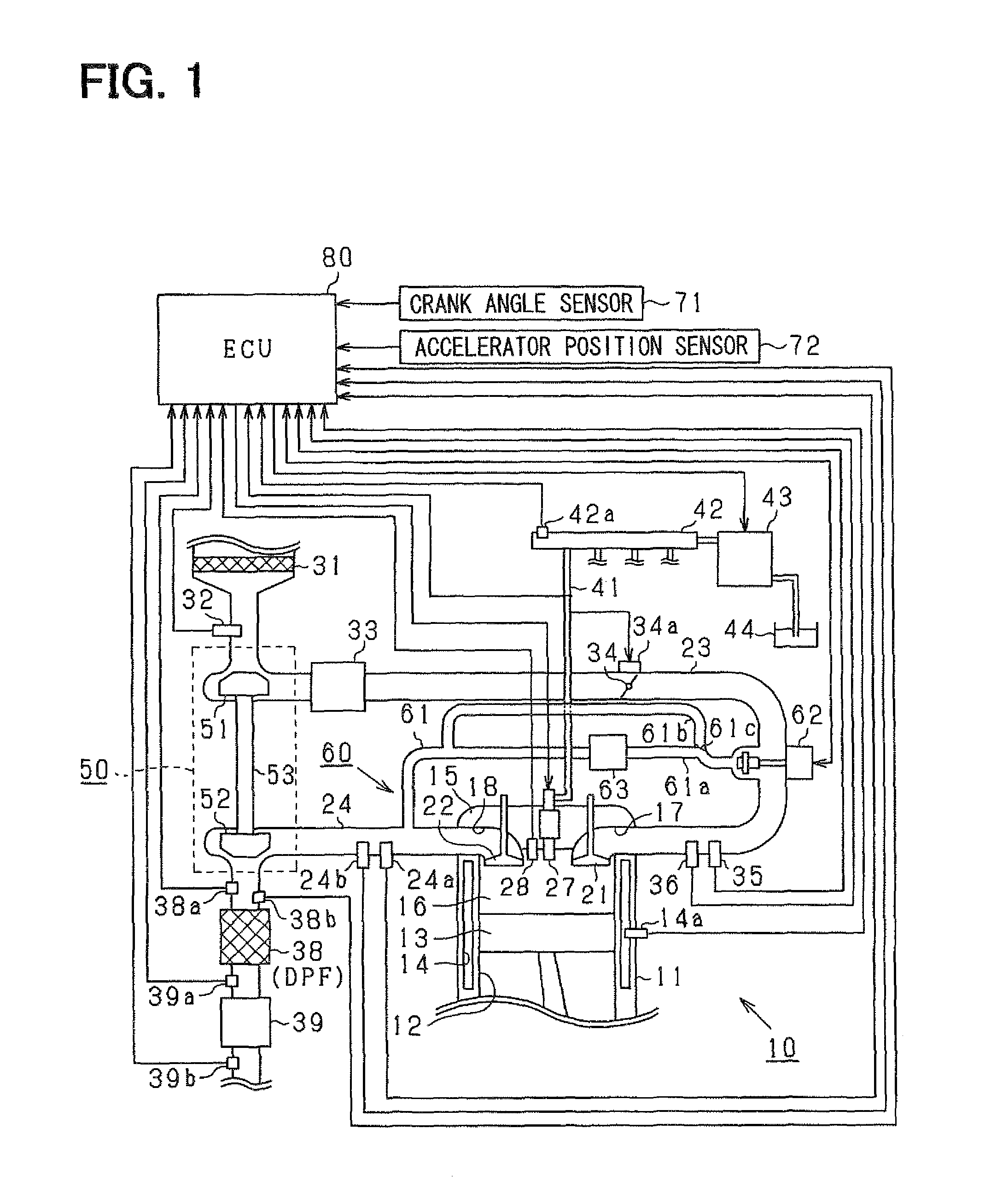
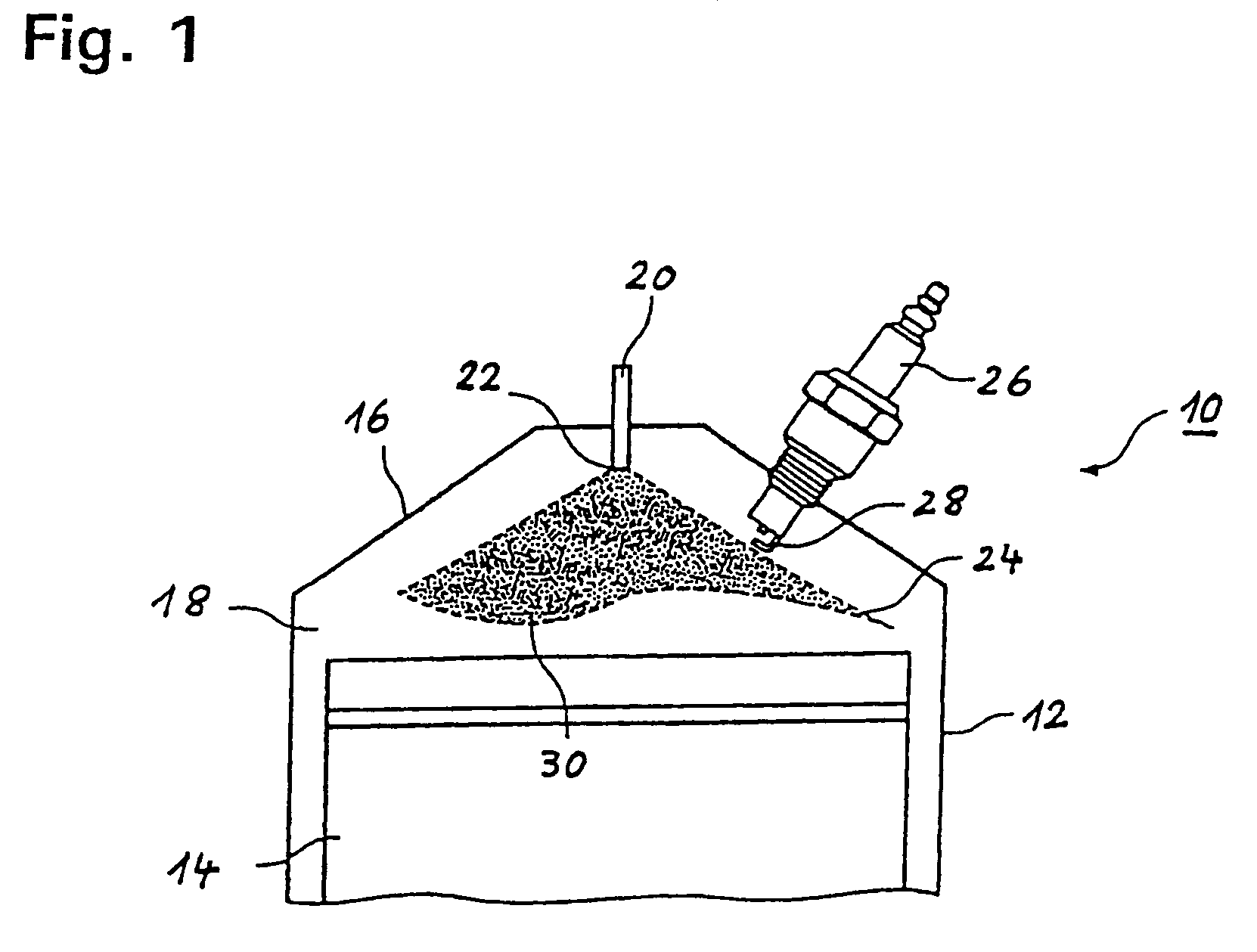
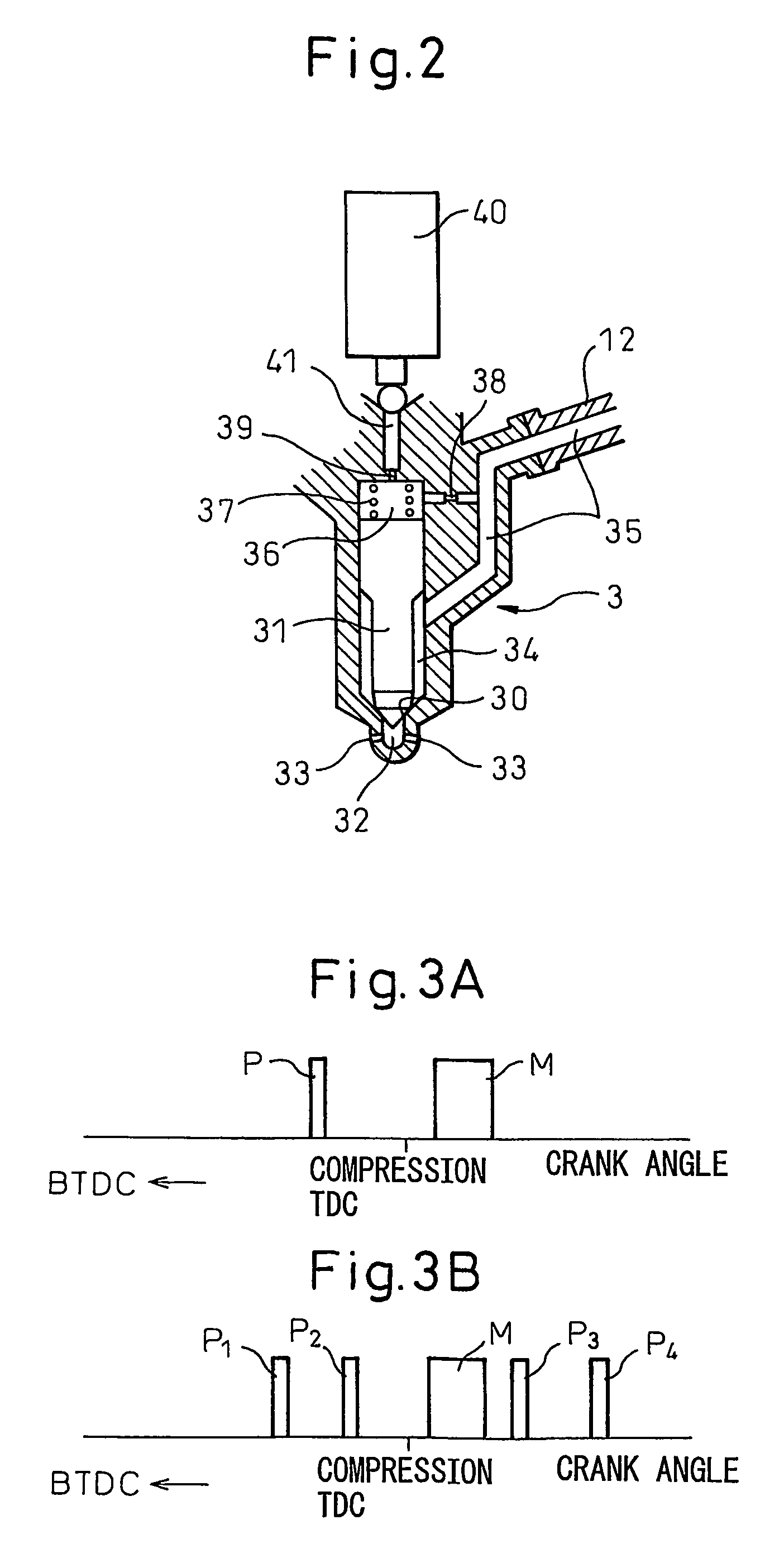
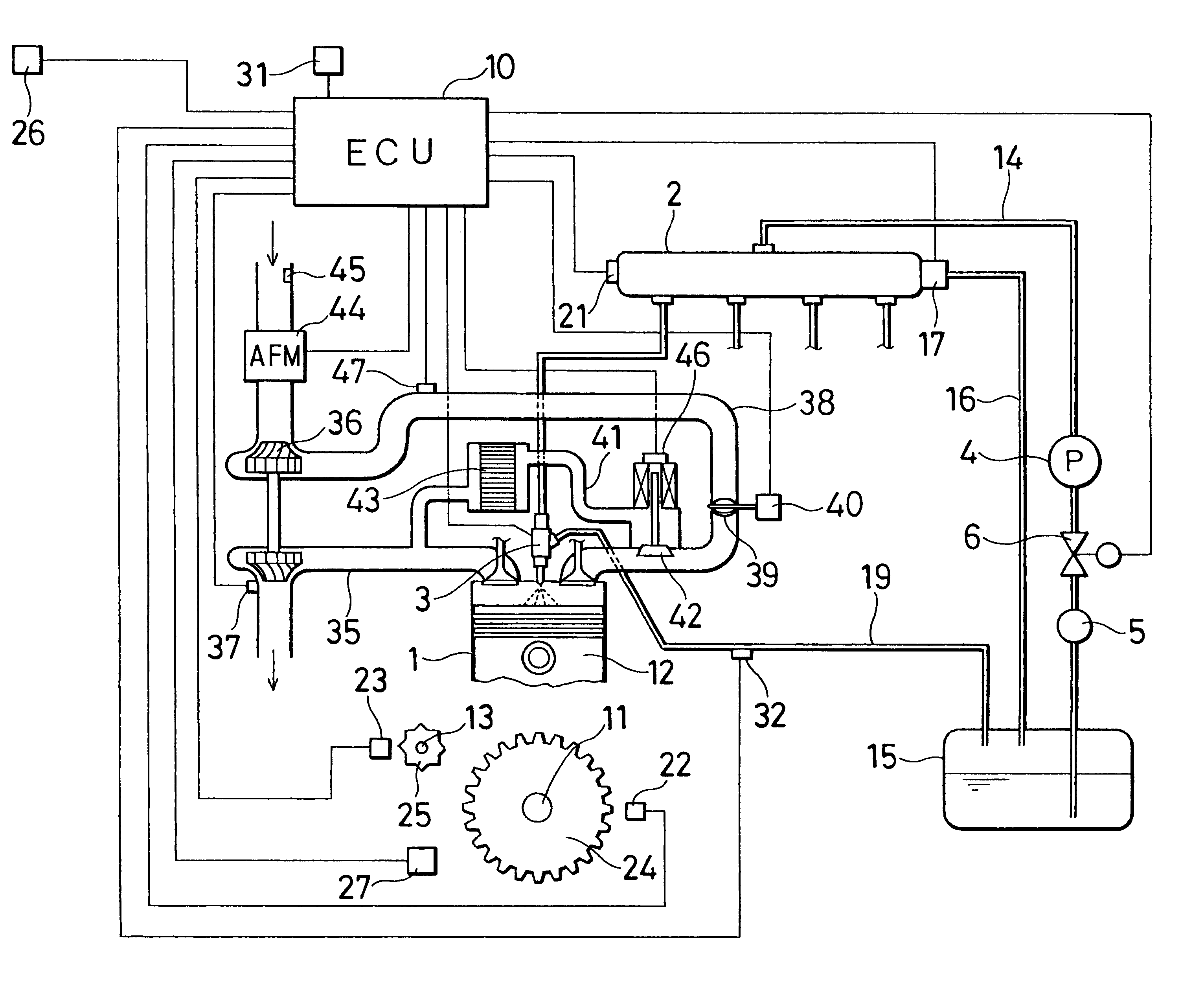
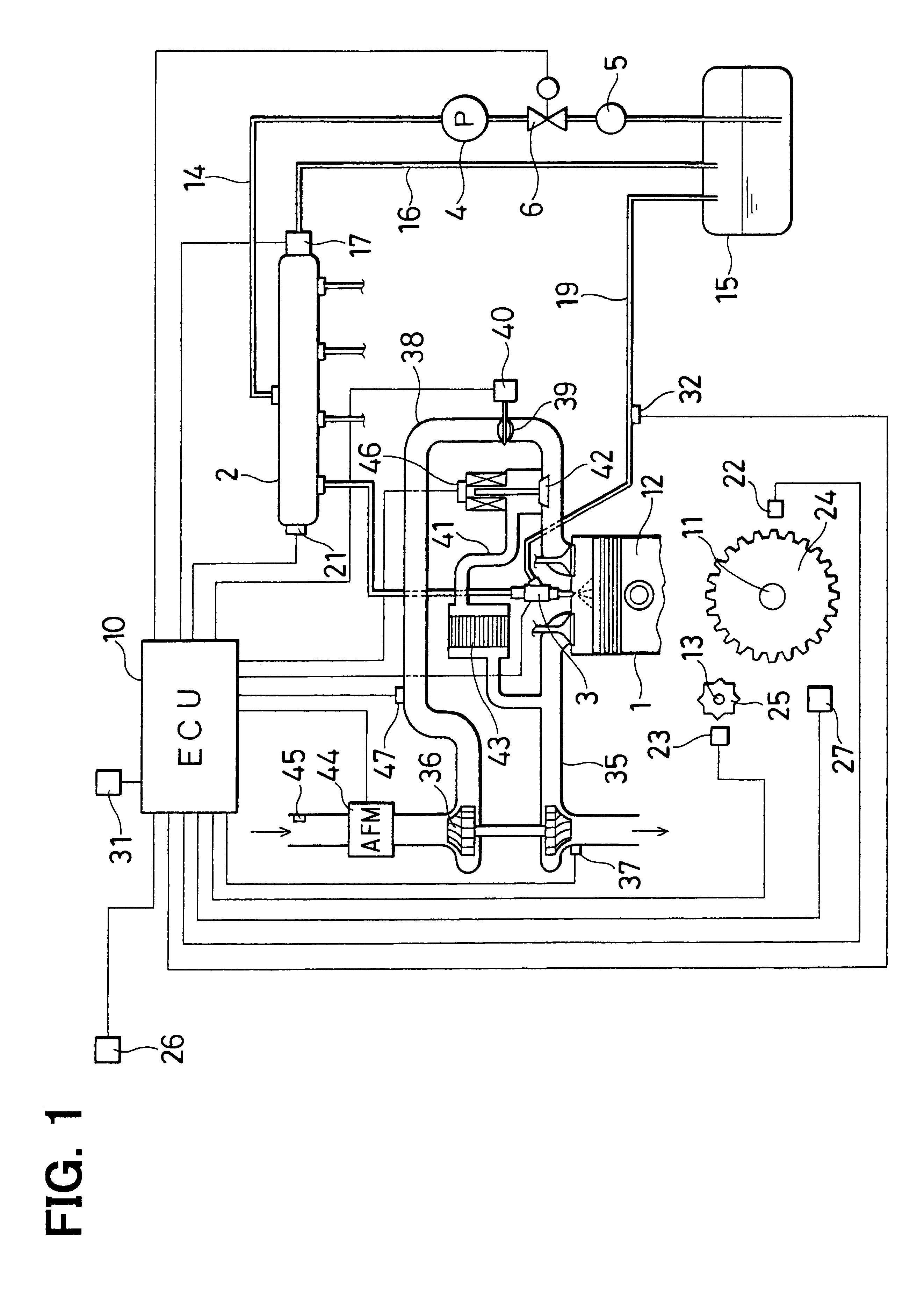
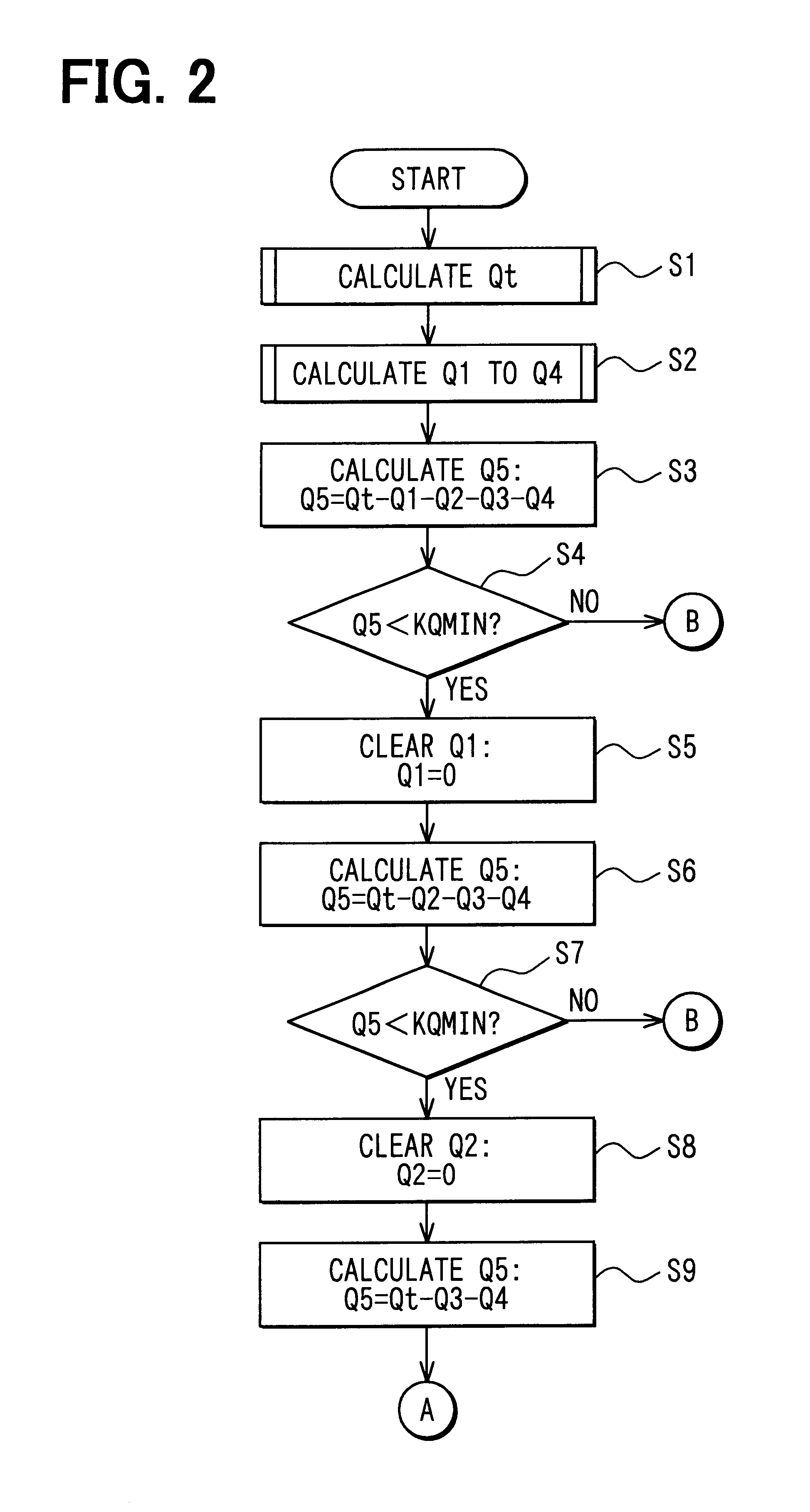
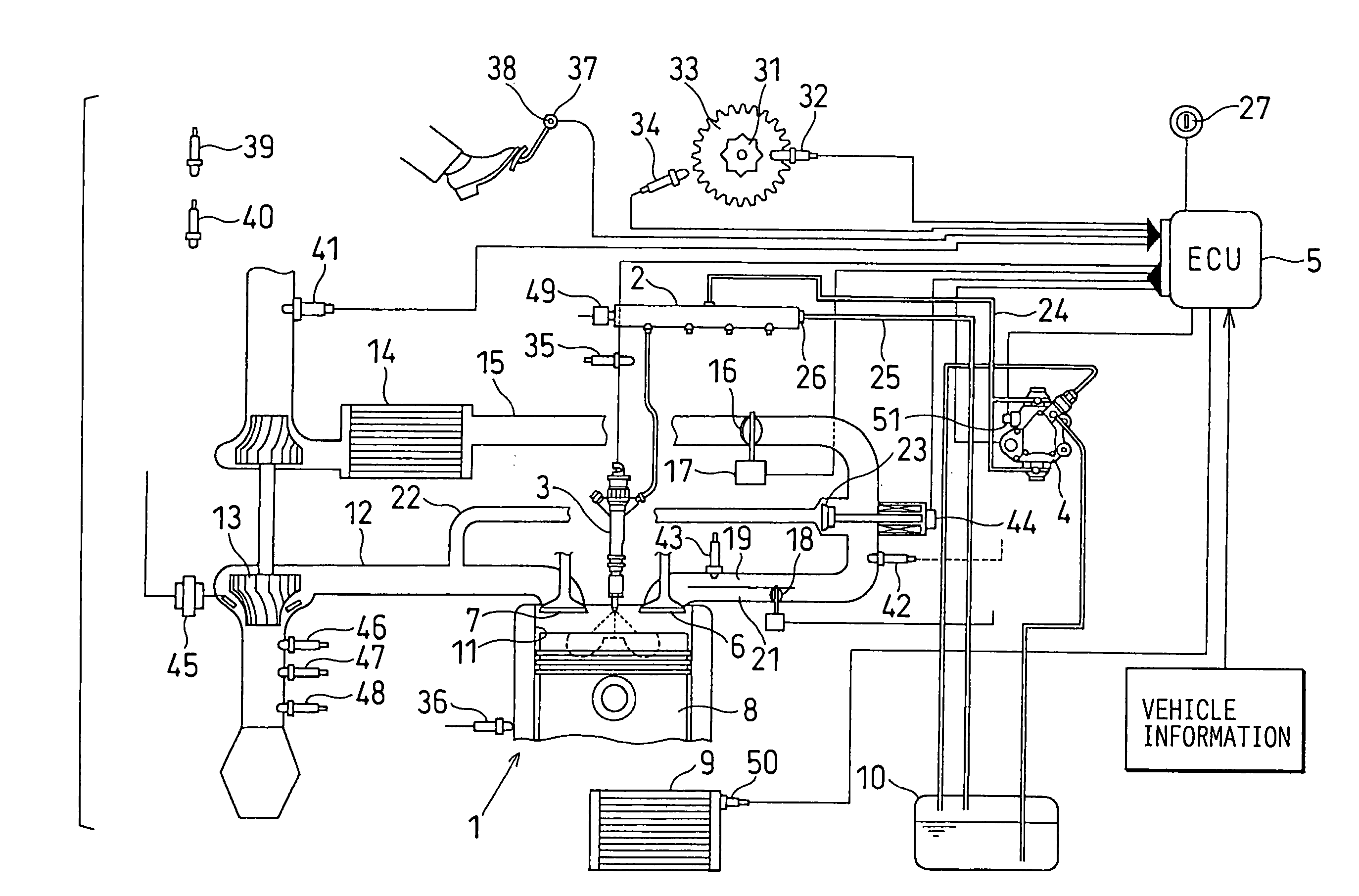
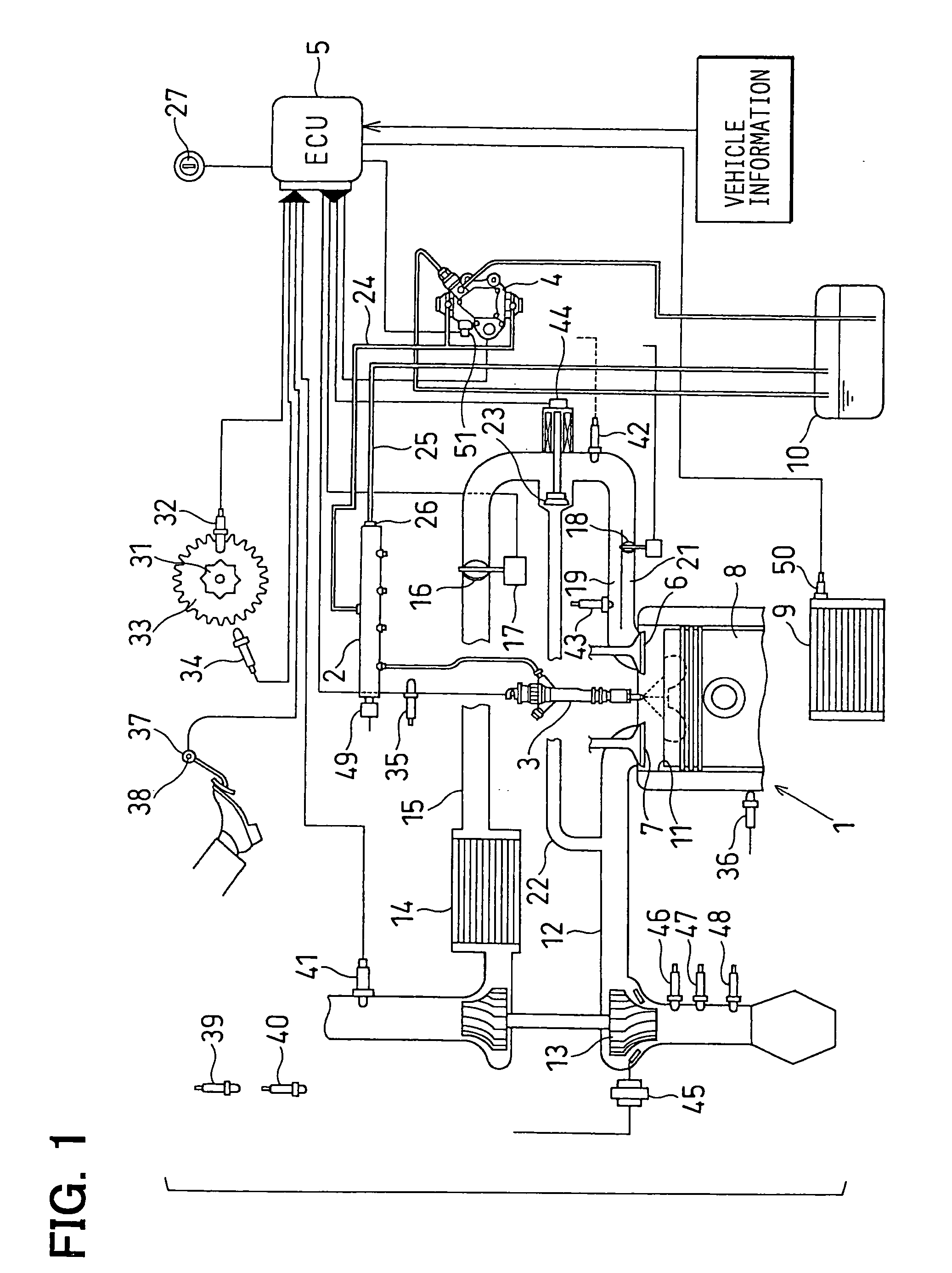
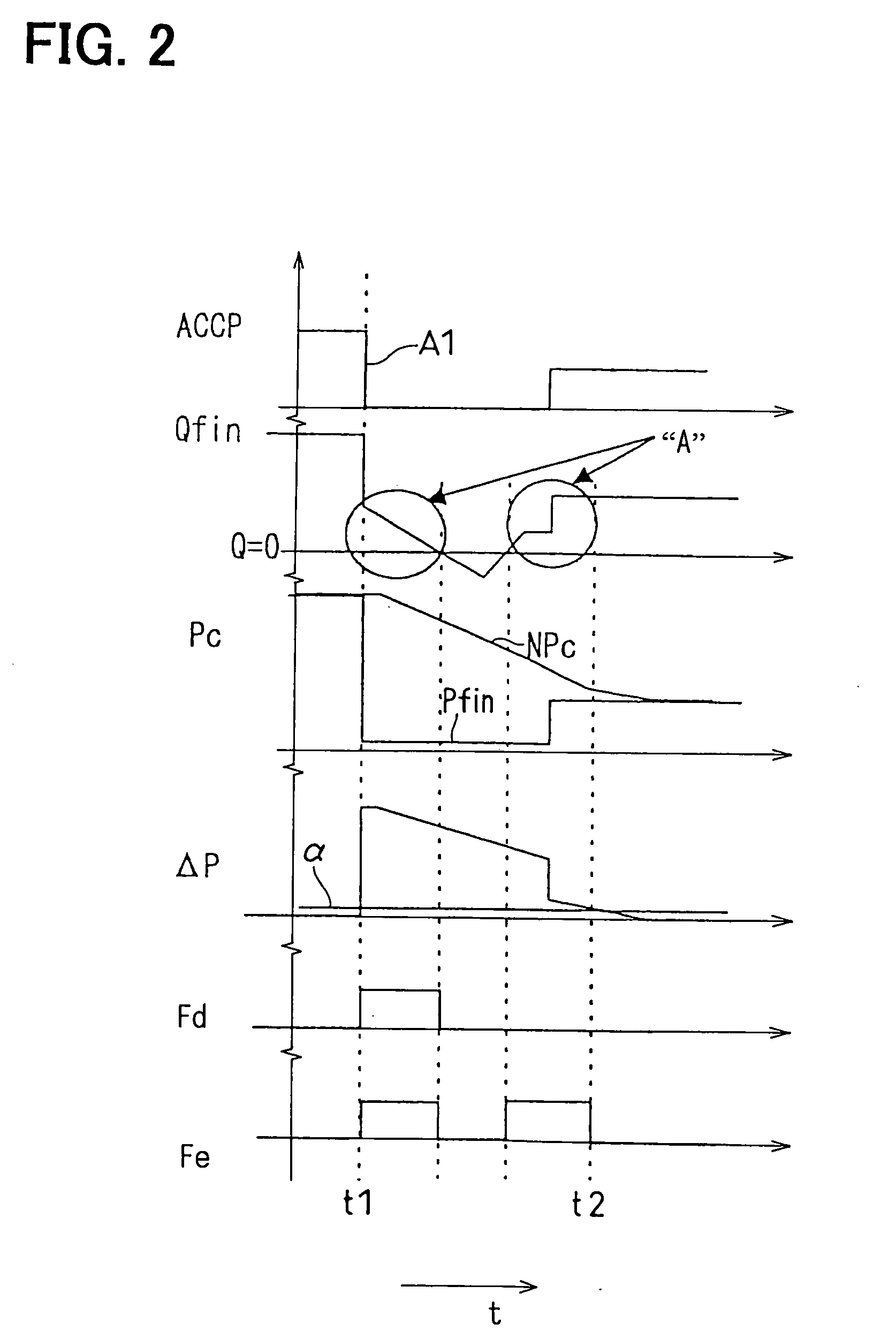
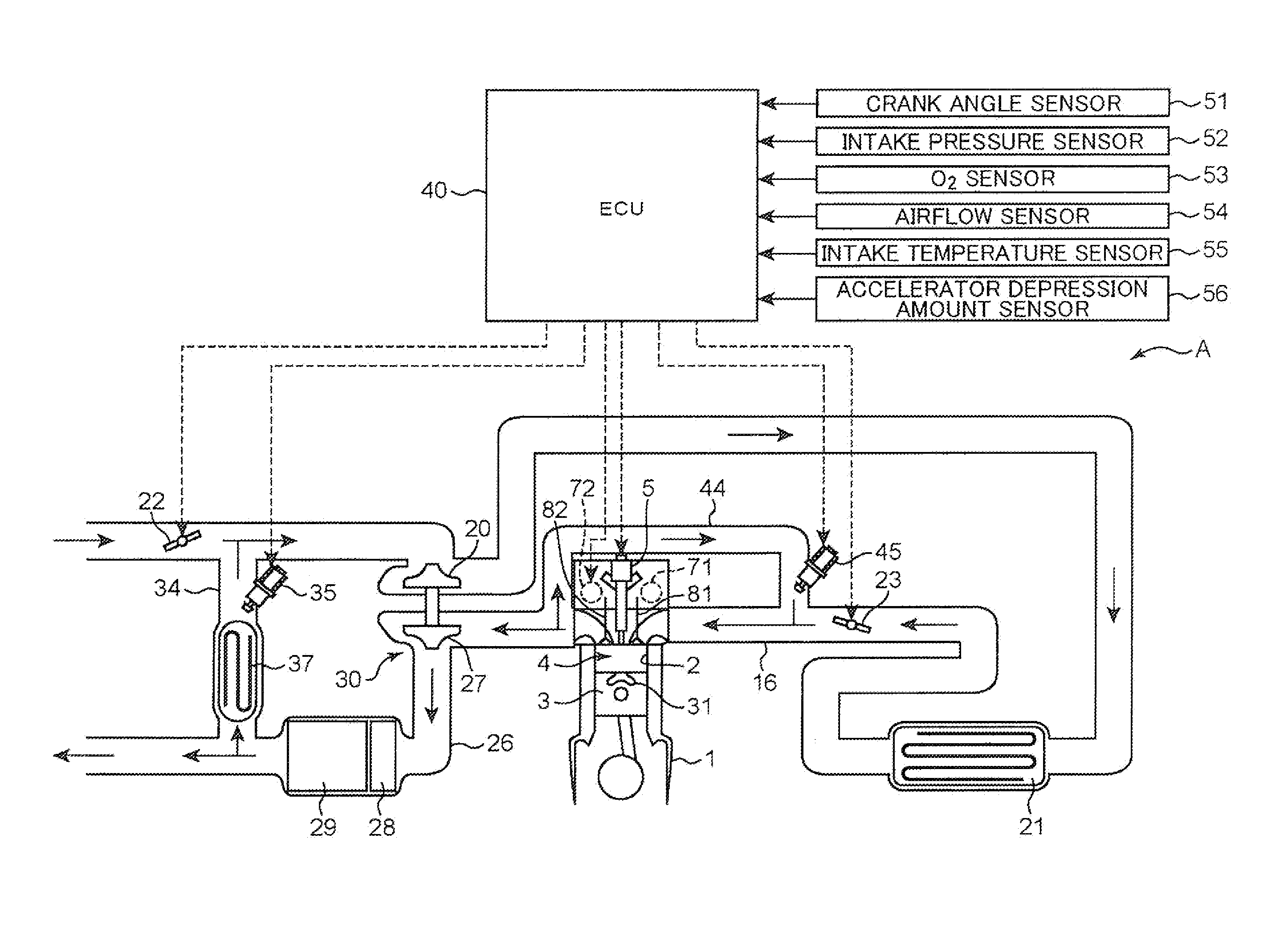
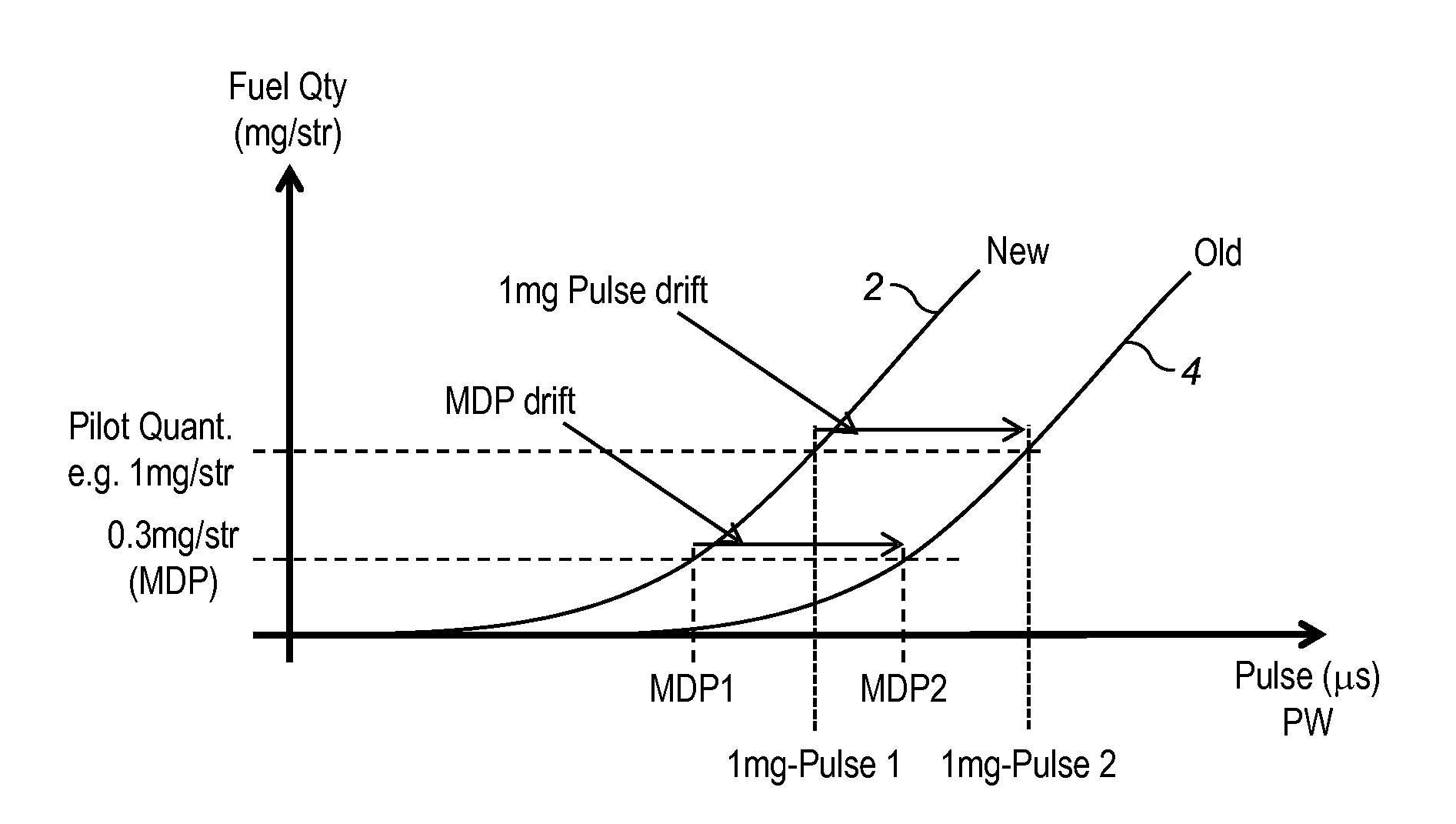
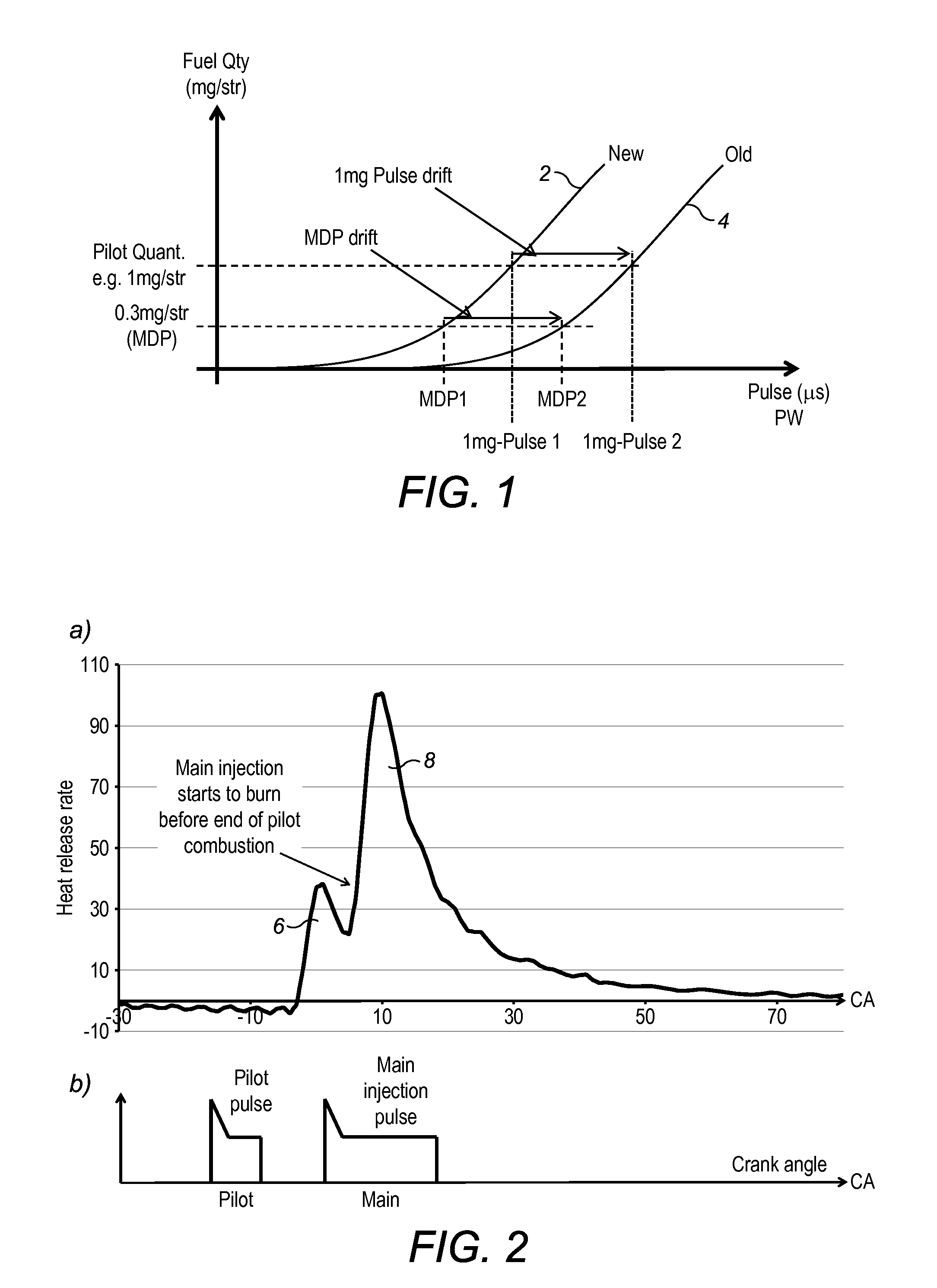
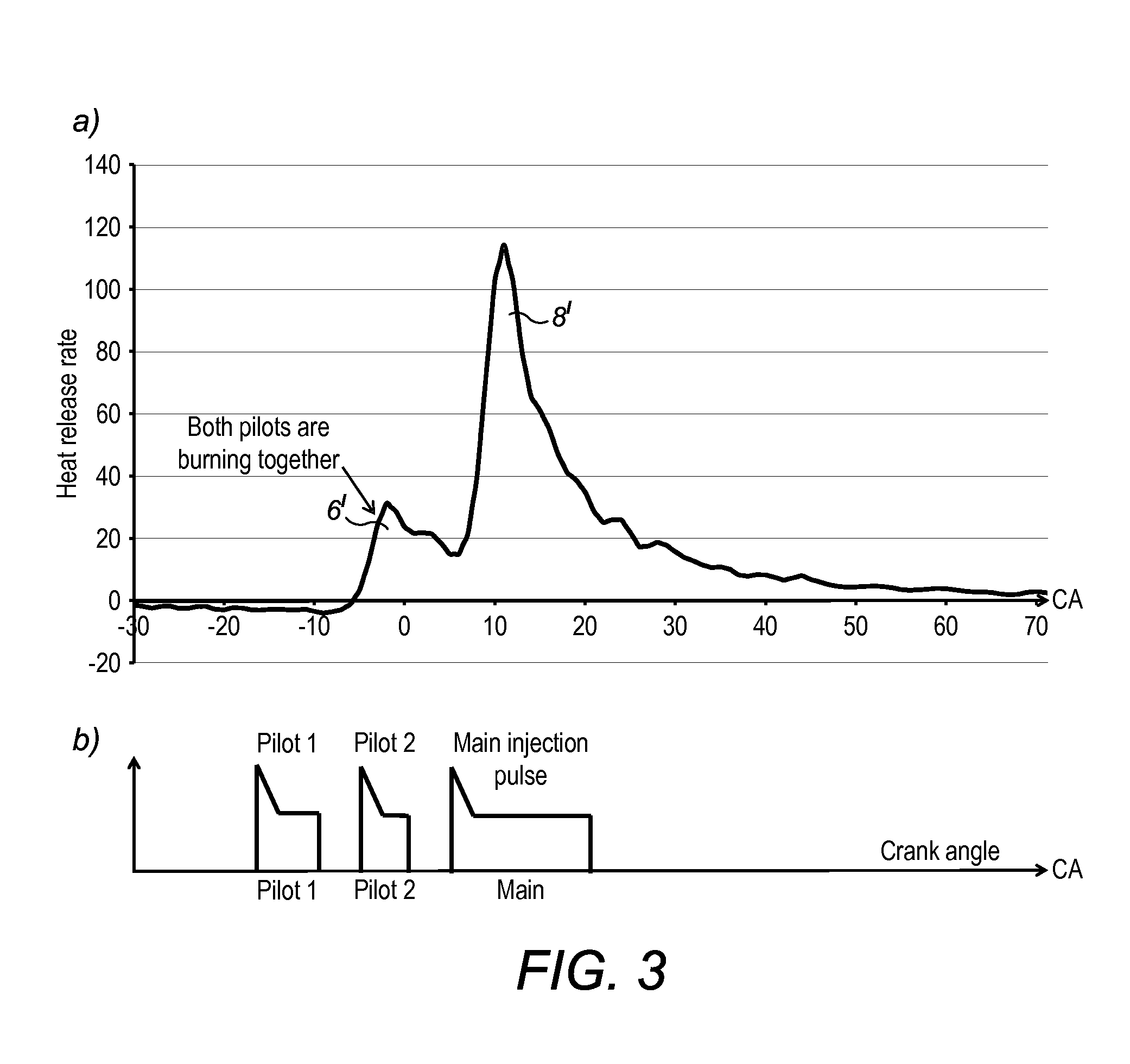
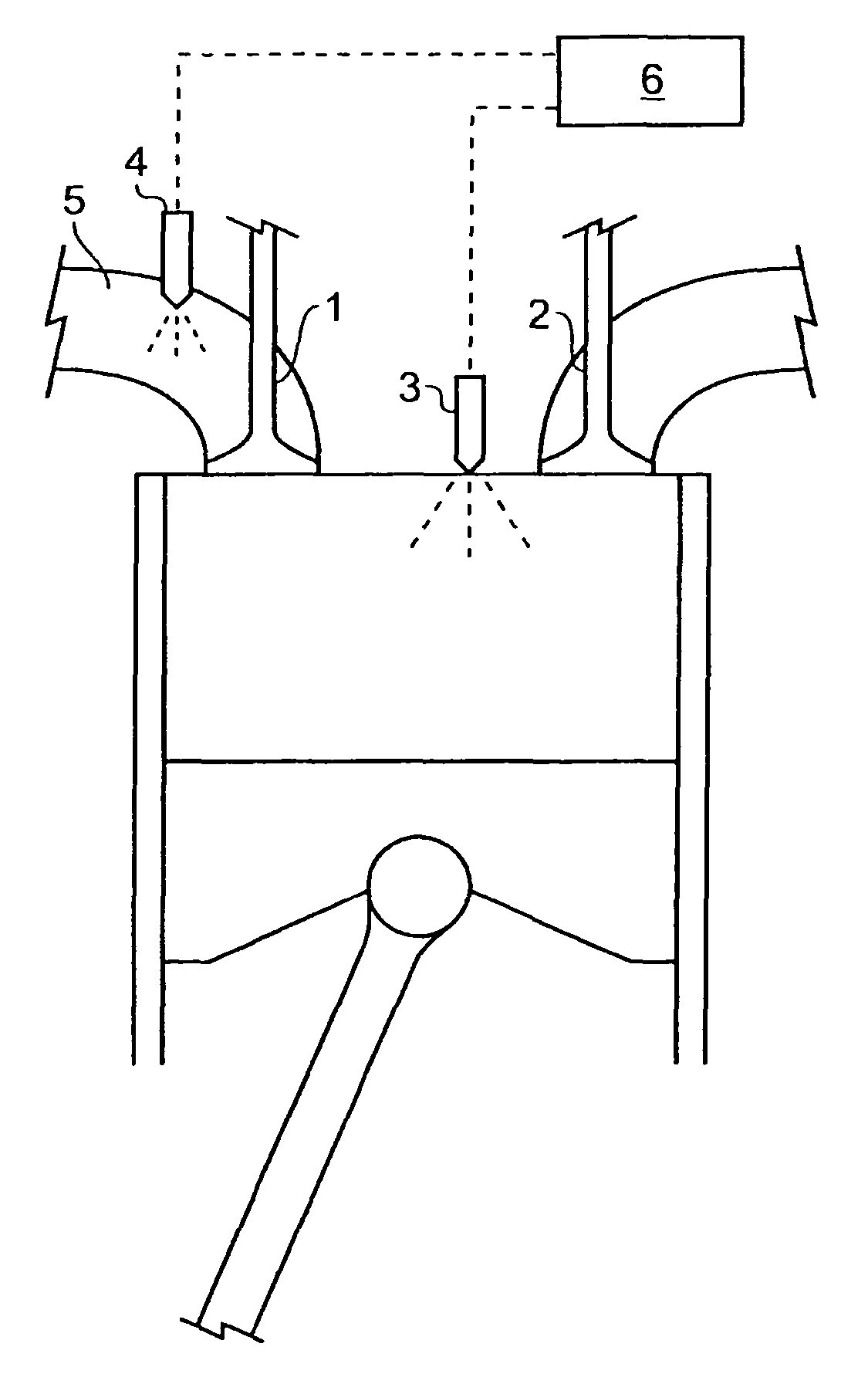
Pilot fuel injection is defined as a pre-injection of a small quantity of fuel 5 to 20 crankshaft degrees before the main fuel injection. This pre-injection softens the main injection pressure rise and reduces combustion noise.
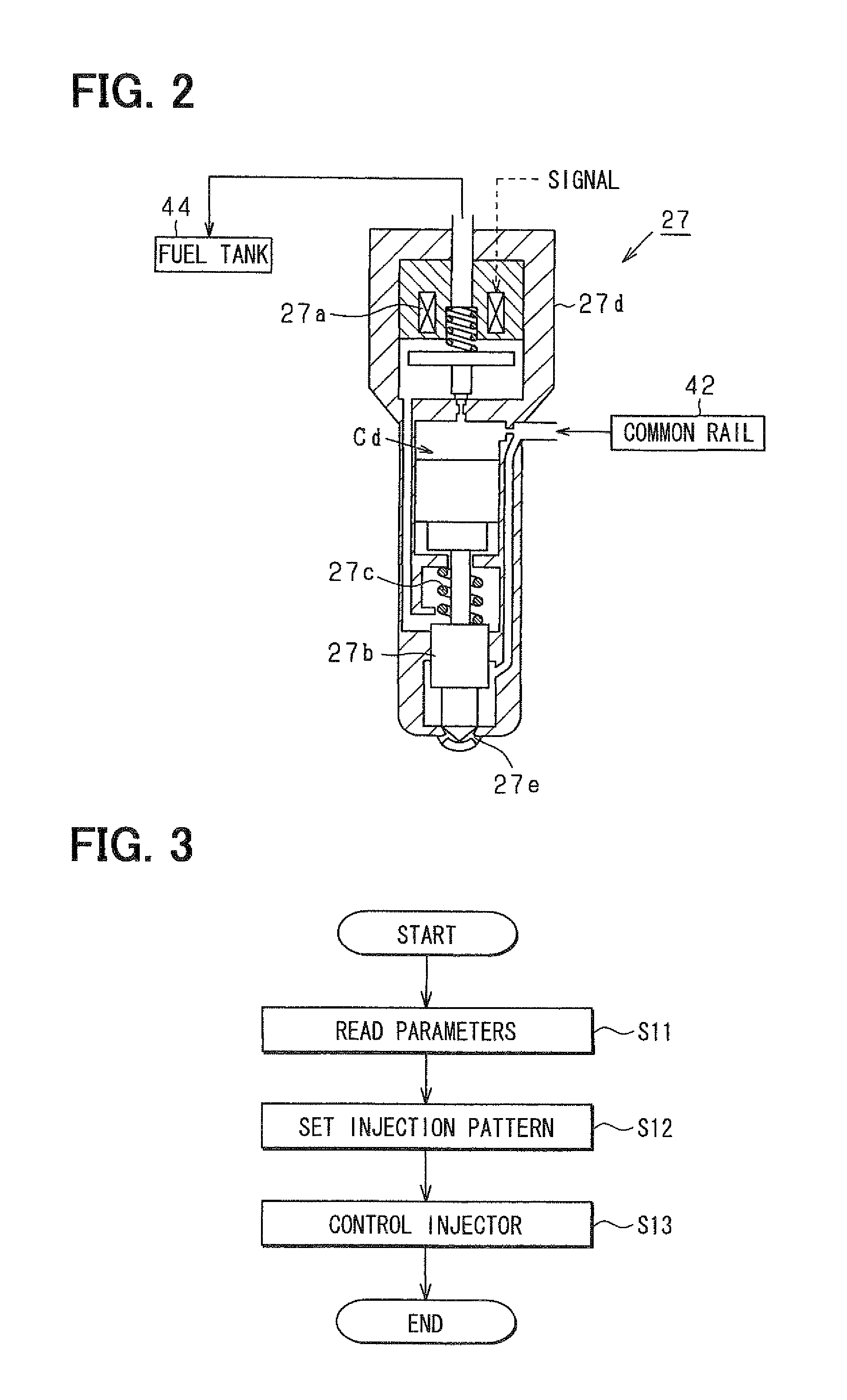
Fuel injection method in fuel injector
InactiveUS6904893B2Increase freedomRealize the structureElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesPhase differenceEngineering
In fuel injector including an accumulator and an intensifier, fuel is injected such that an injection control valve and a piston control valve are individually controlled, an operational phase difference therebetween is regulated, and at least one of a maximum injection pressure, a rate of increase of an injection pressure at the start of an increase of pressure, a rate of decrease of the injection pressure at the completion of injection, a pilot injection pressure, and an after injection pressure of fuel injected from a fuel injection nozzle is arbitrarily changed. Namely, a pressure during a movement from a base common rail pressure of the accumulator to a static maximum pressure statically determined by an operation of the intensifier is positively used as a control factor of injection, whereby a fuel injection pattern can be implemented with an extremely high degree of freedom.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
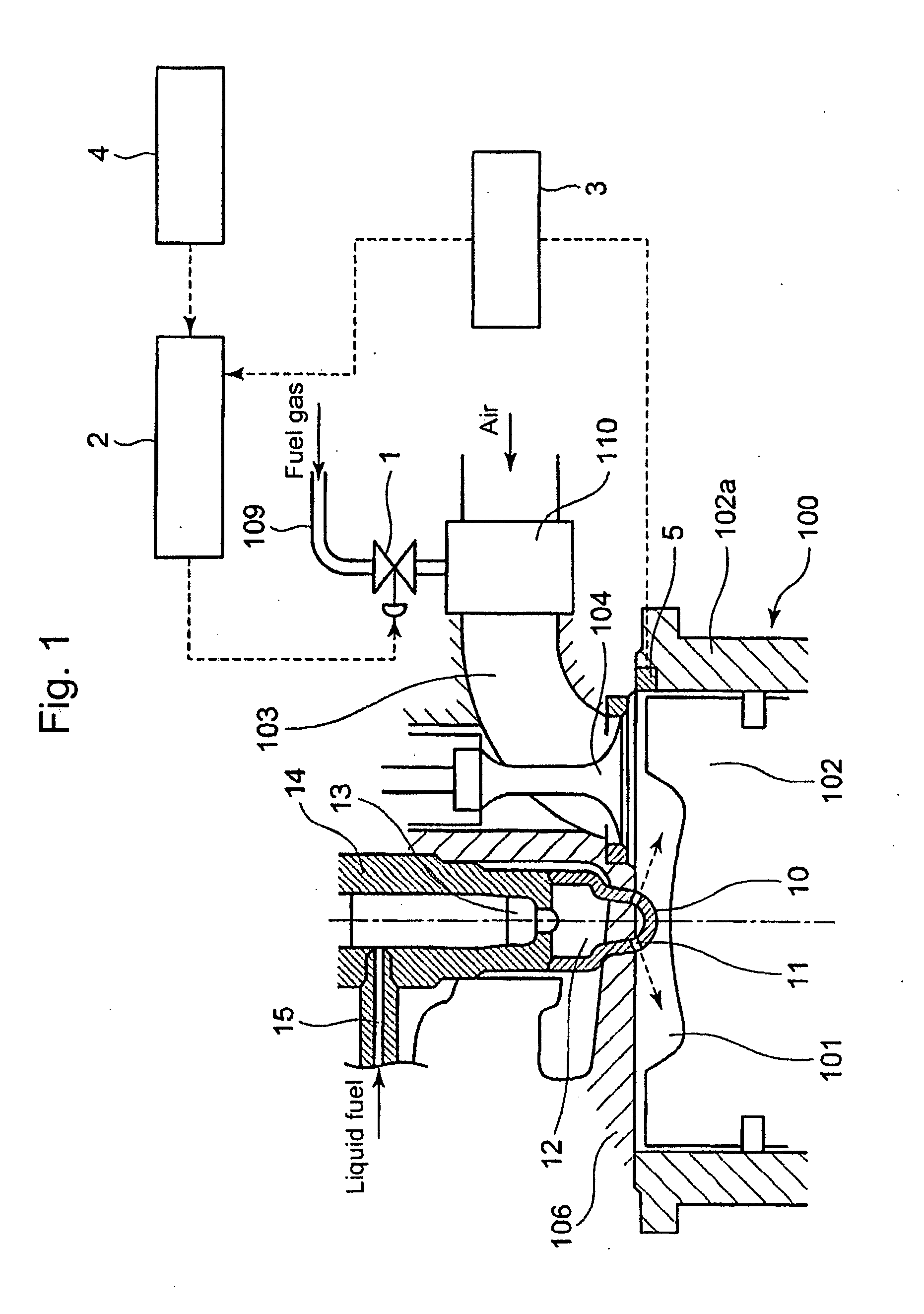
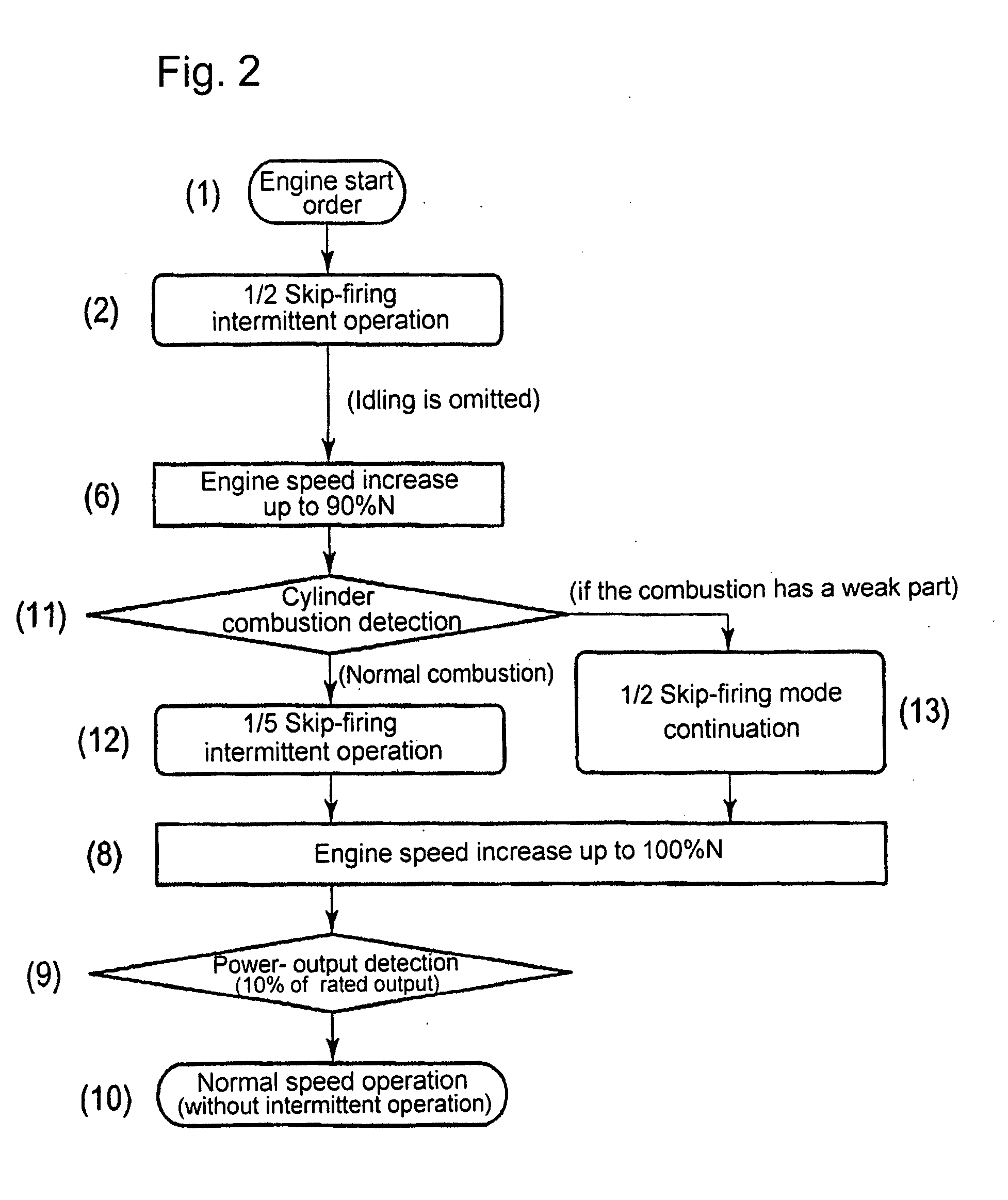
Micro-pilot injection ignition type gas engine
ActiveUS20100043744A1High precisionIdle timeValve arrangementsElectrical controlFuel supplyAir–fuel ratio
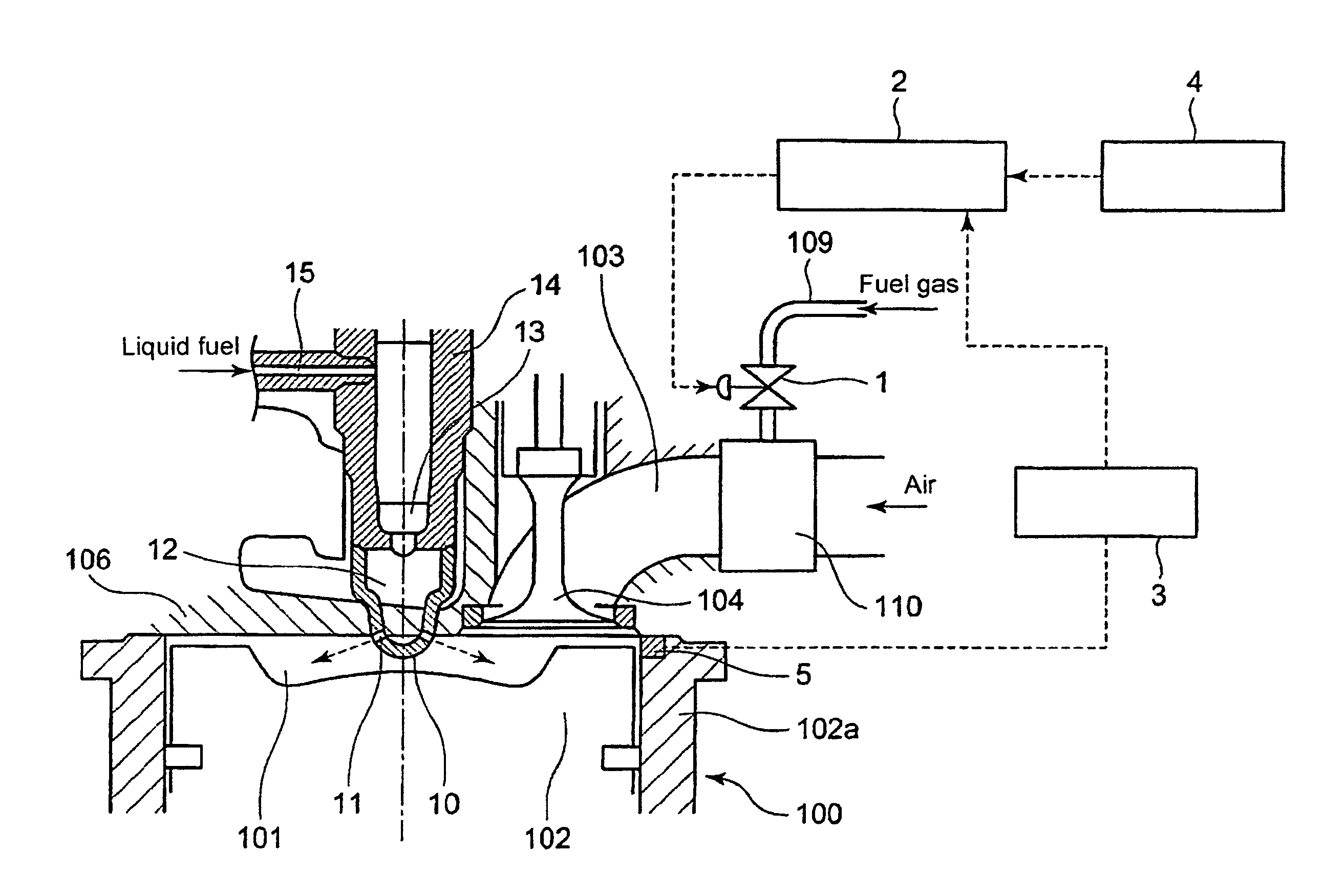
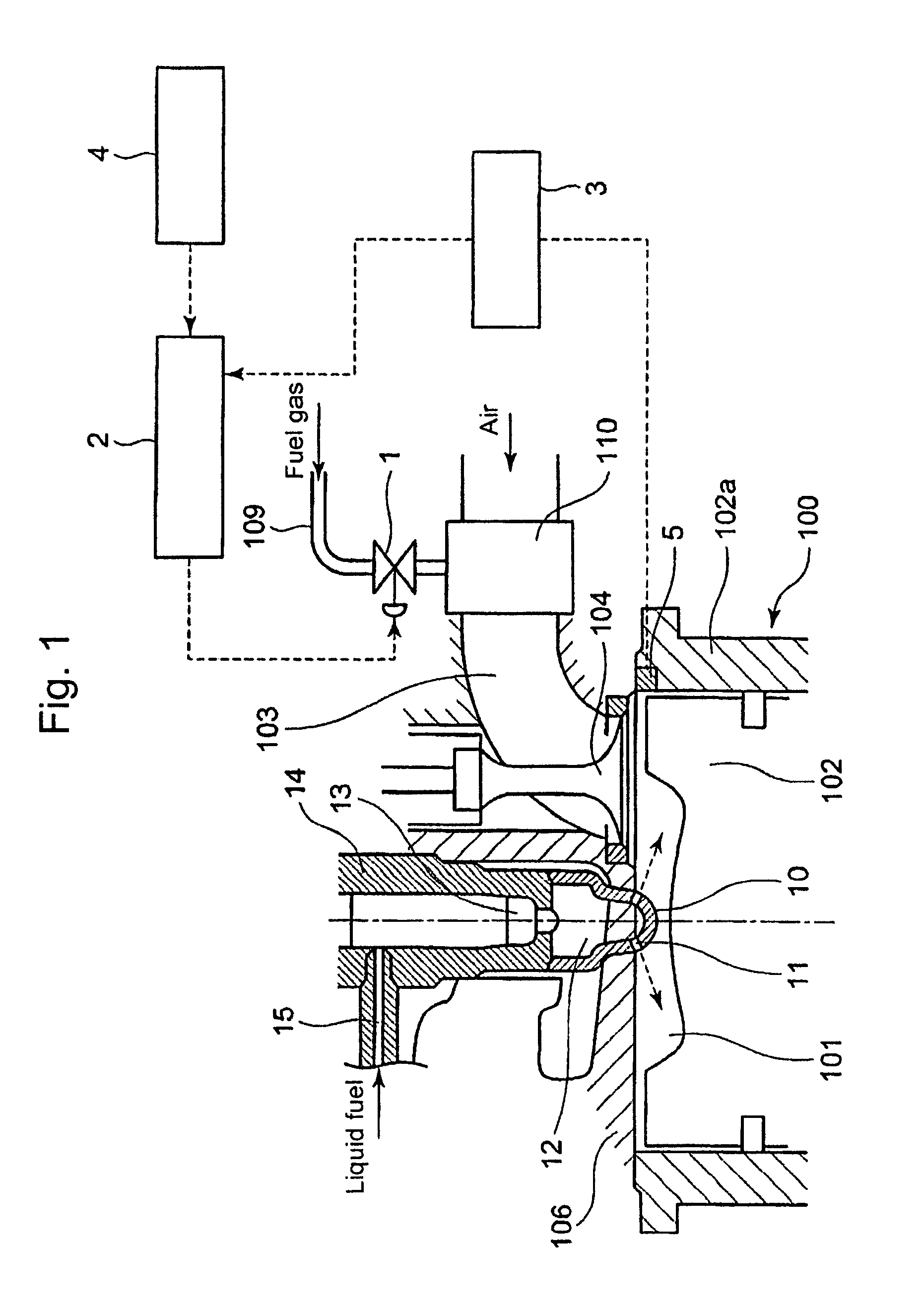
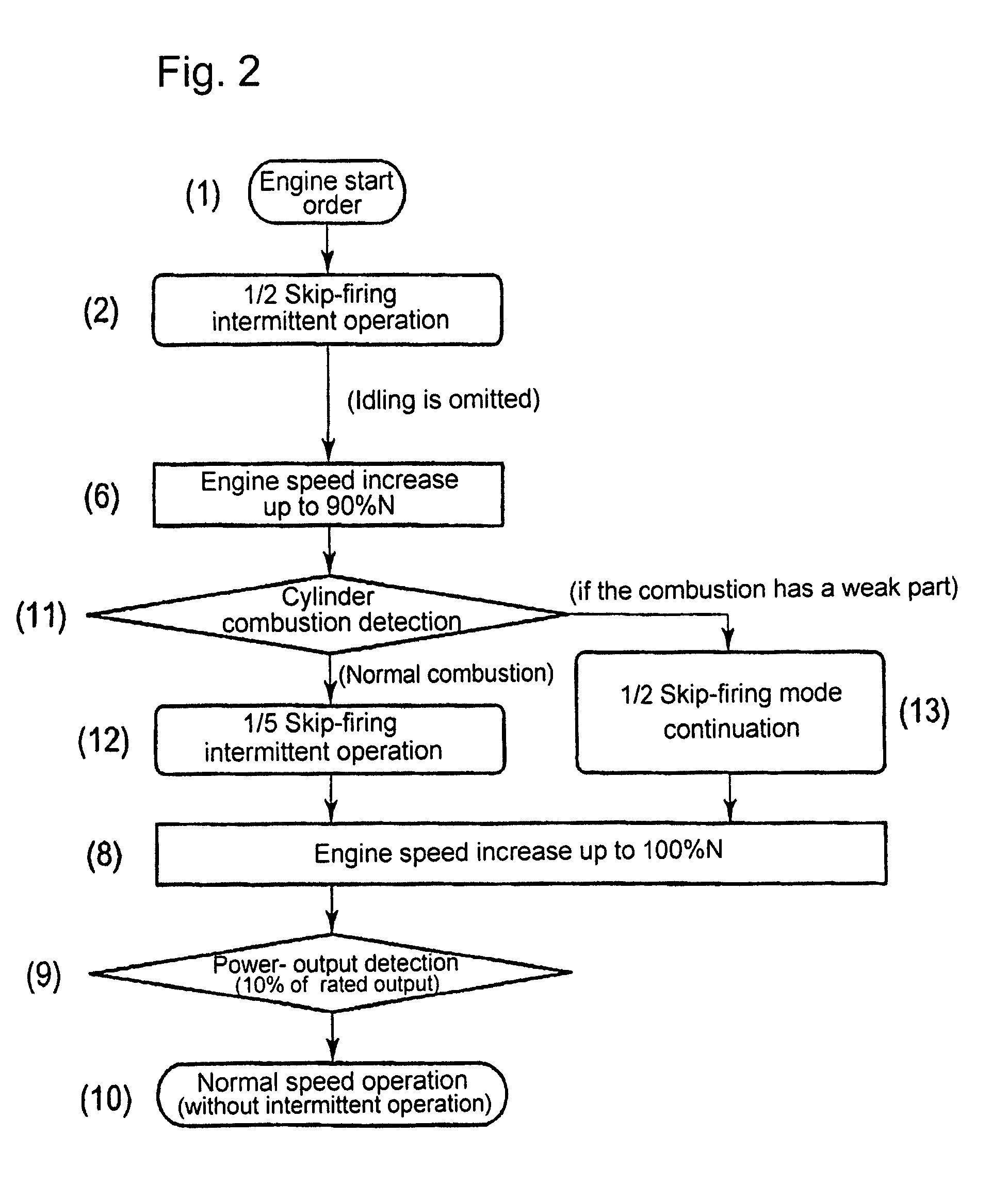
What is disclosed is a micro-pilot injection ignition type gas engine, whereby an air fuel ratio control in starting the engine is executed with enhanced precision, by means of introducing skip-firing intermittent operations which reflect the engine operation conditions, while an idling time span can be shortened or omitted.The engine includes: a gas valve that opens and closes a fuel-gas passage in front of each cylinder, so as to arbitrarily control the throat area as well as the opening-closing time span of the gas valve; an engine speed detecting unit to detect the engine speed; a combustion diagnosis unit to detect an engine combustion state through a cylinder pressure distribution along elapsed time, as to each cylinder; an opening-closing control unit as to the gas valve, so as to control the intermittent opening-closing of the gas valve according to the levels of the detected engine speed as well as the cylinder pressure distribution; whereby, in starting the engine, the intermittent opening-closing of the gas-valve enables at least one skip-firing mode that brings an enhanced fuel-supply pressure-pulsation with which a relatively large amount of fuel-gas is supplied per engine cycle with firing so that the air fuel-gas ratio of each cylinder reaches a prescribed target value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND ENGINE & TURBOCHARGER LTD
Engine control apparatus
ActiveUS20080167786A1Accelerate emissionsImprove fuel economyAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlEngineeringControl variable
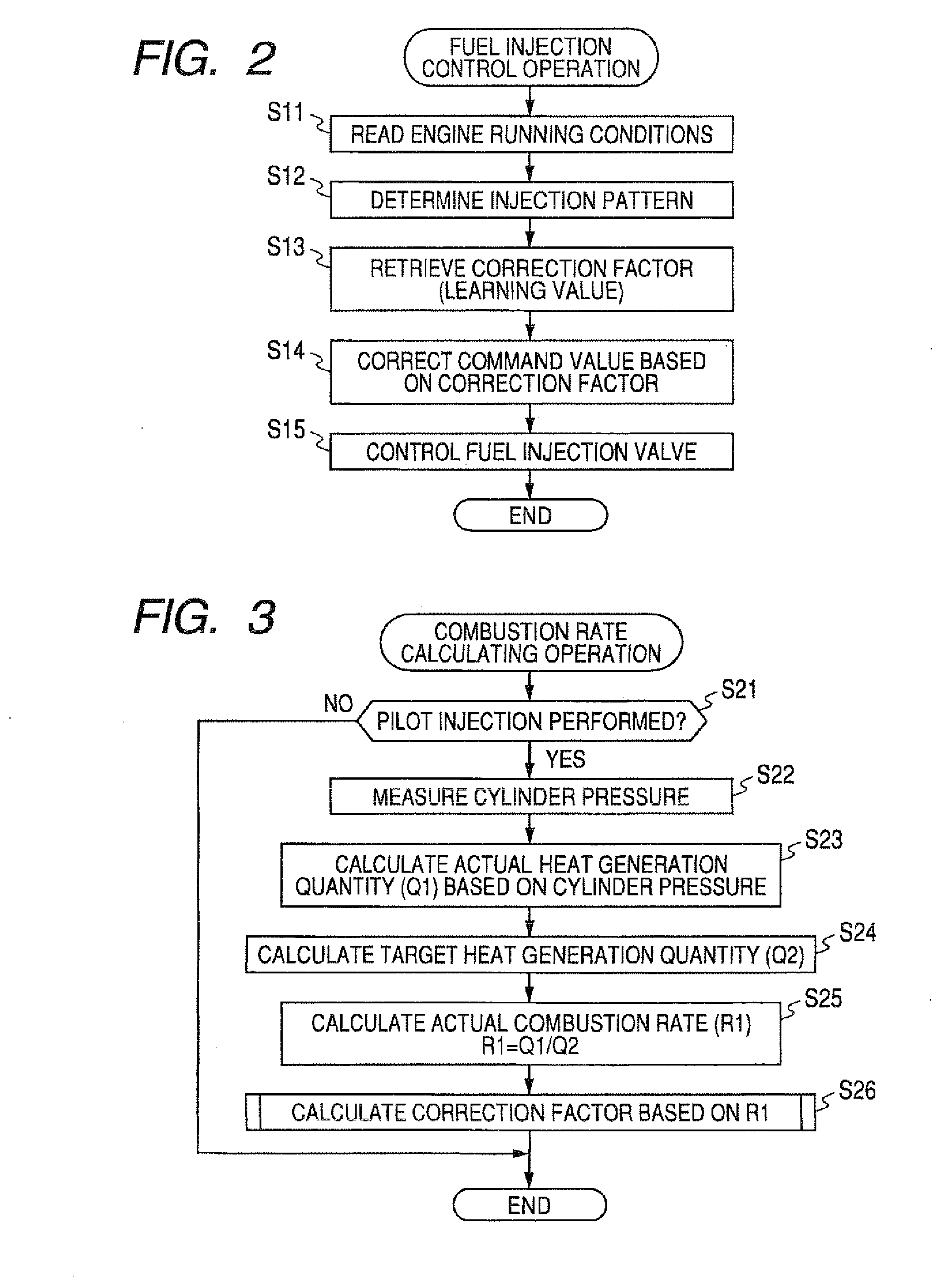
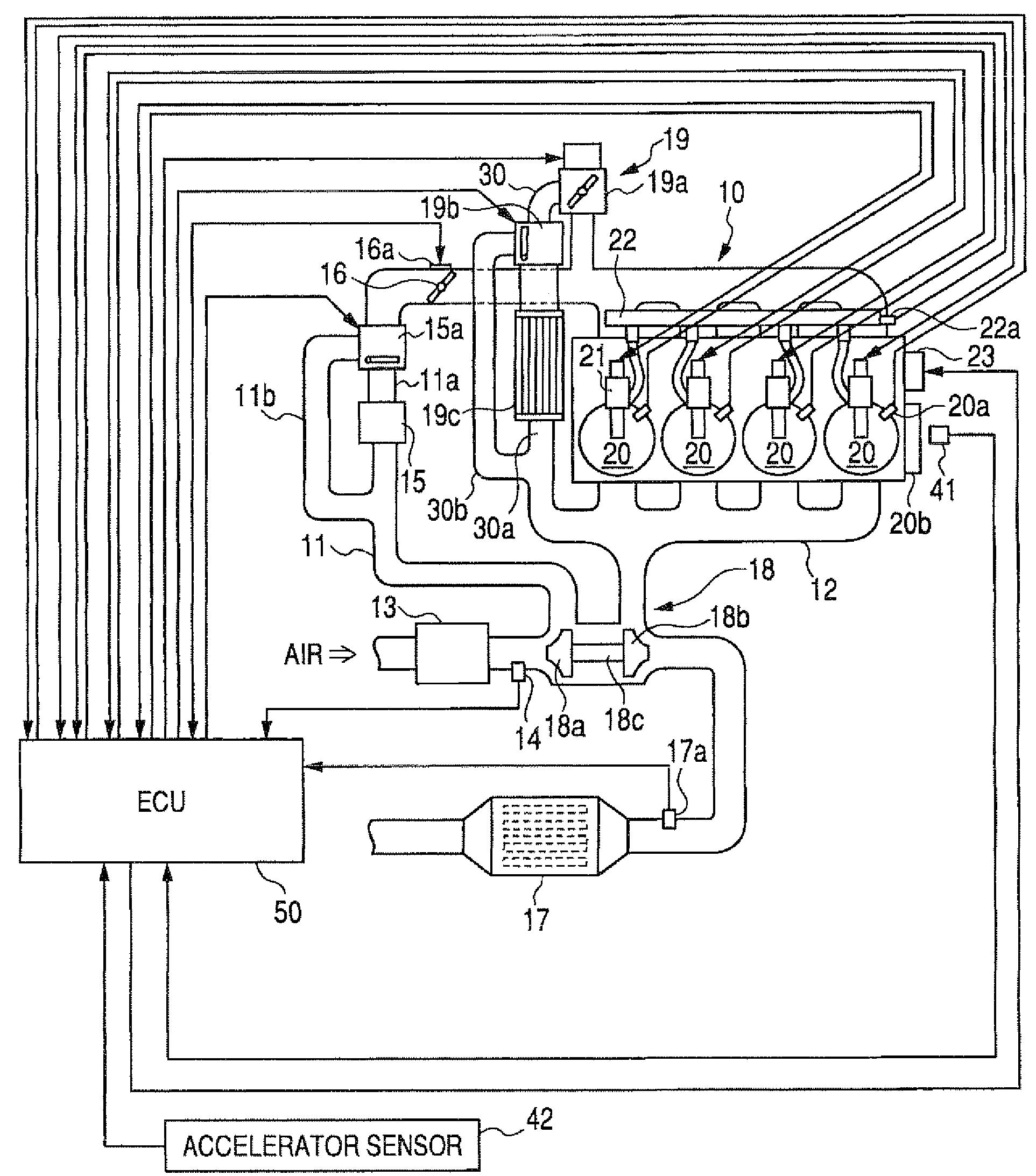
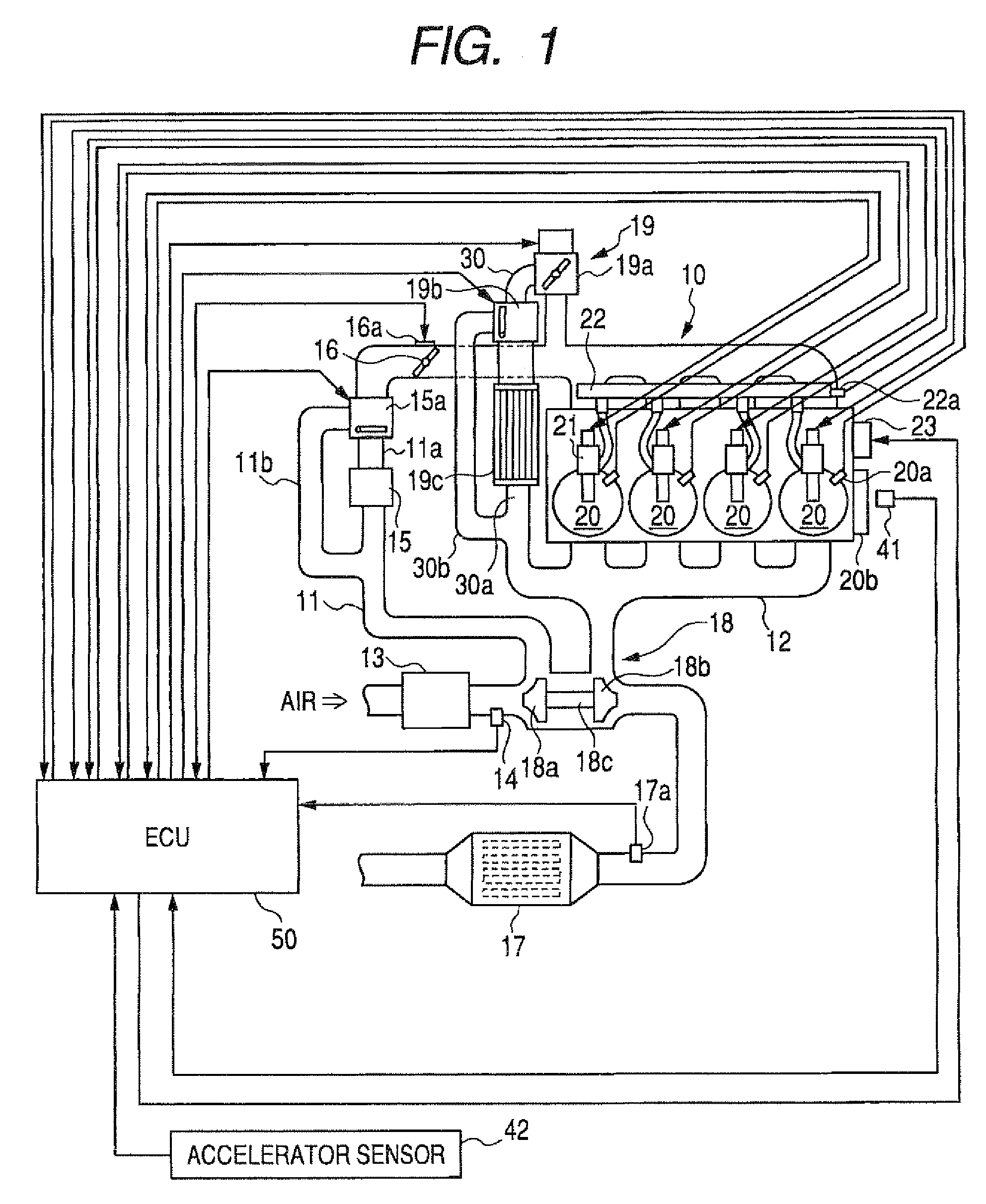
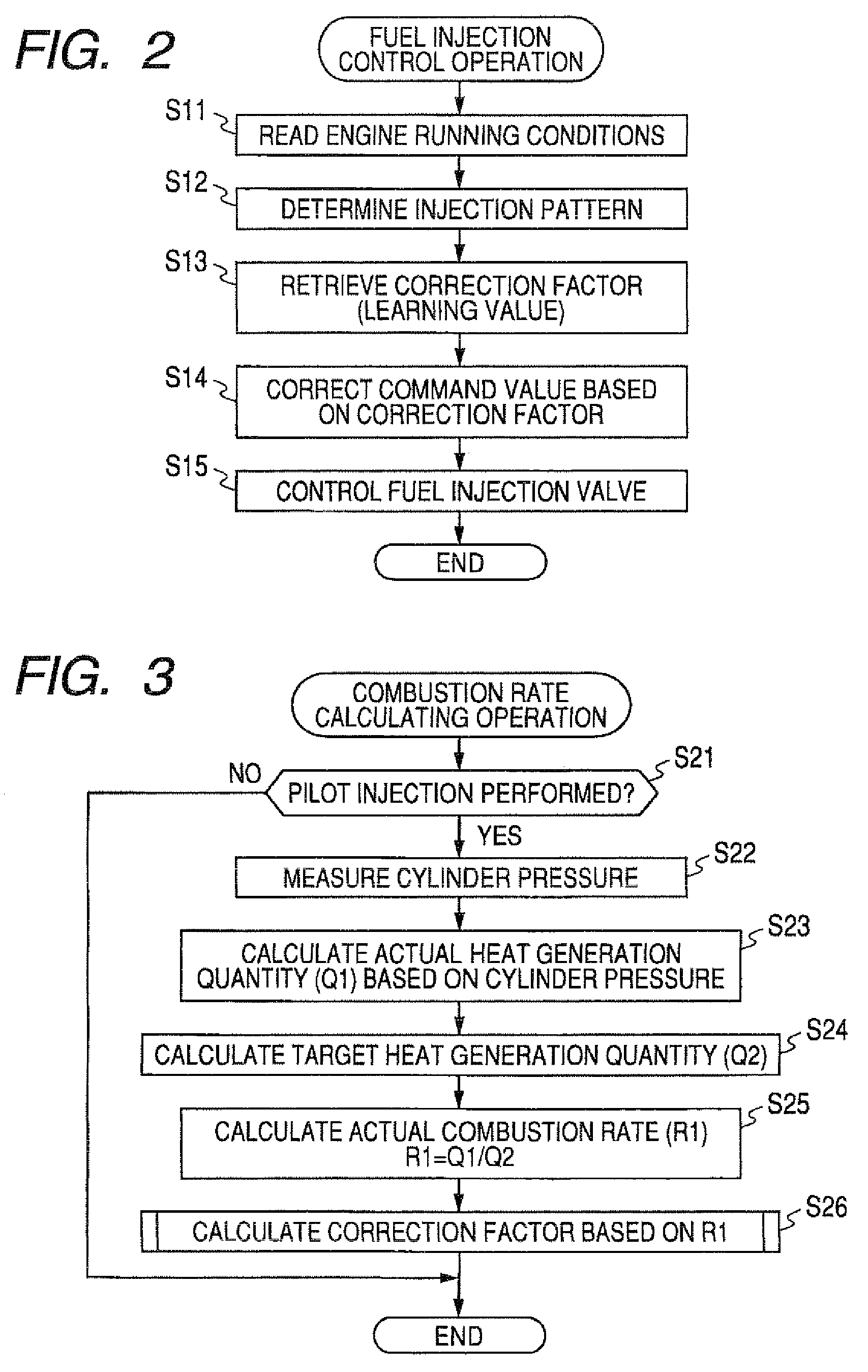
An engine control apparatus comprised of an engine control ECU has a program preloaded therein for determining a combustion rate (actual combustion rate) corresponding to the ratio of an ideal heat generation quantity (target heat generation quantity) estimated to be generated from a fuel supply quantity, and an actual heat generation quantity actually generated by the fuel supply quantity. The engine control apparatus controls pilot injection timing with a controlled variable corresponding to the thus determined combustion rate so as to increase the combustion rate.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Multi-fuelling an engine
InactiveUS20110088654A1Reduce NOxReduce soot emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesBiodieselCombustion chamber
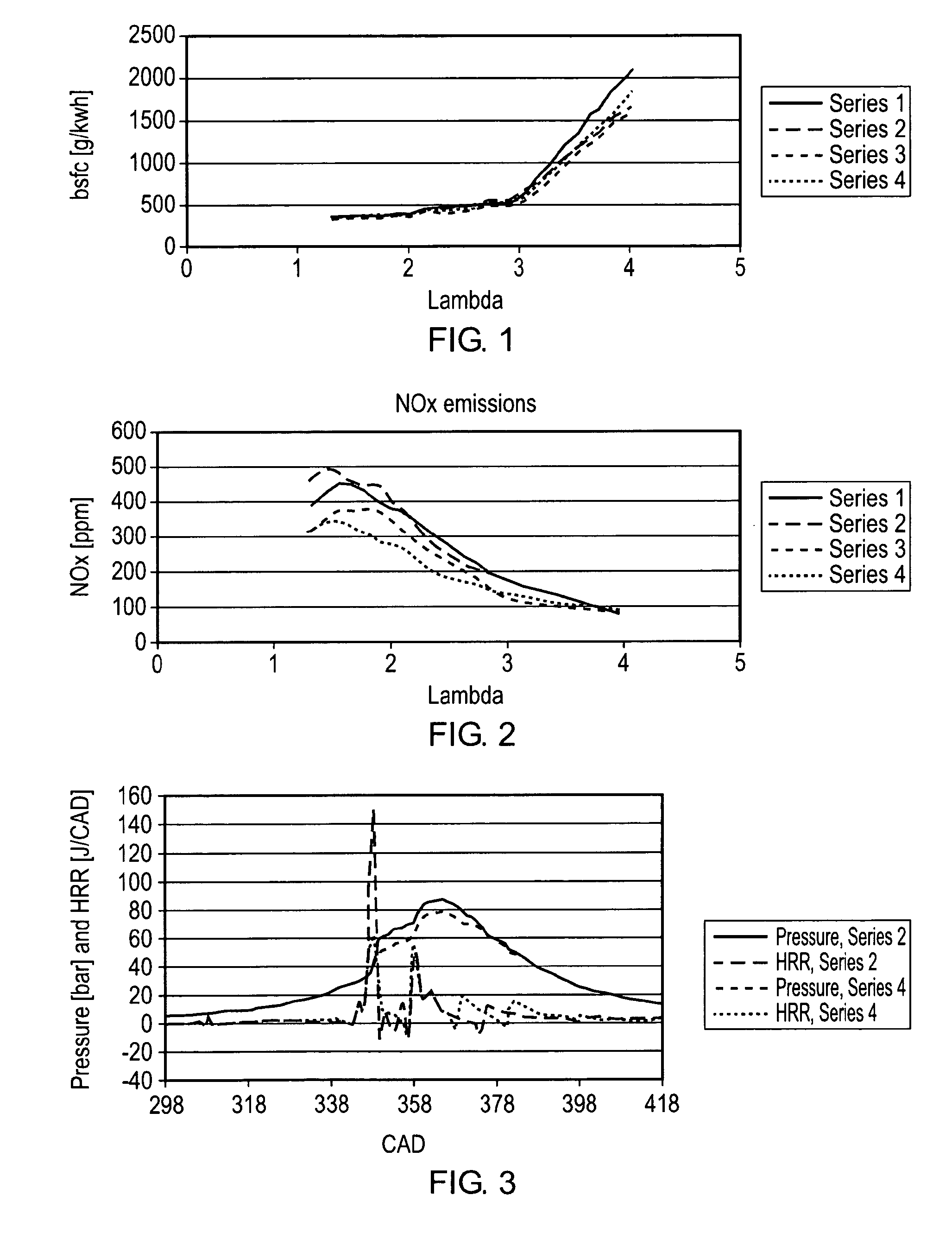
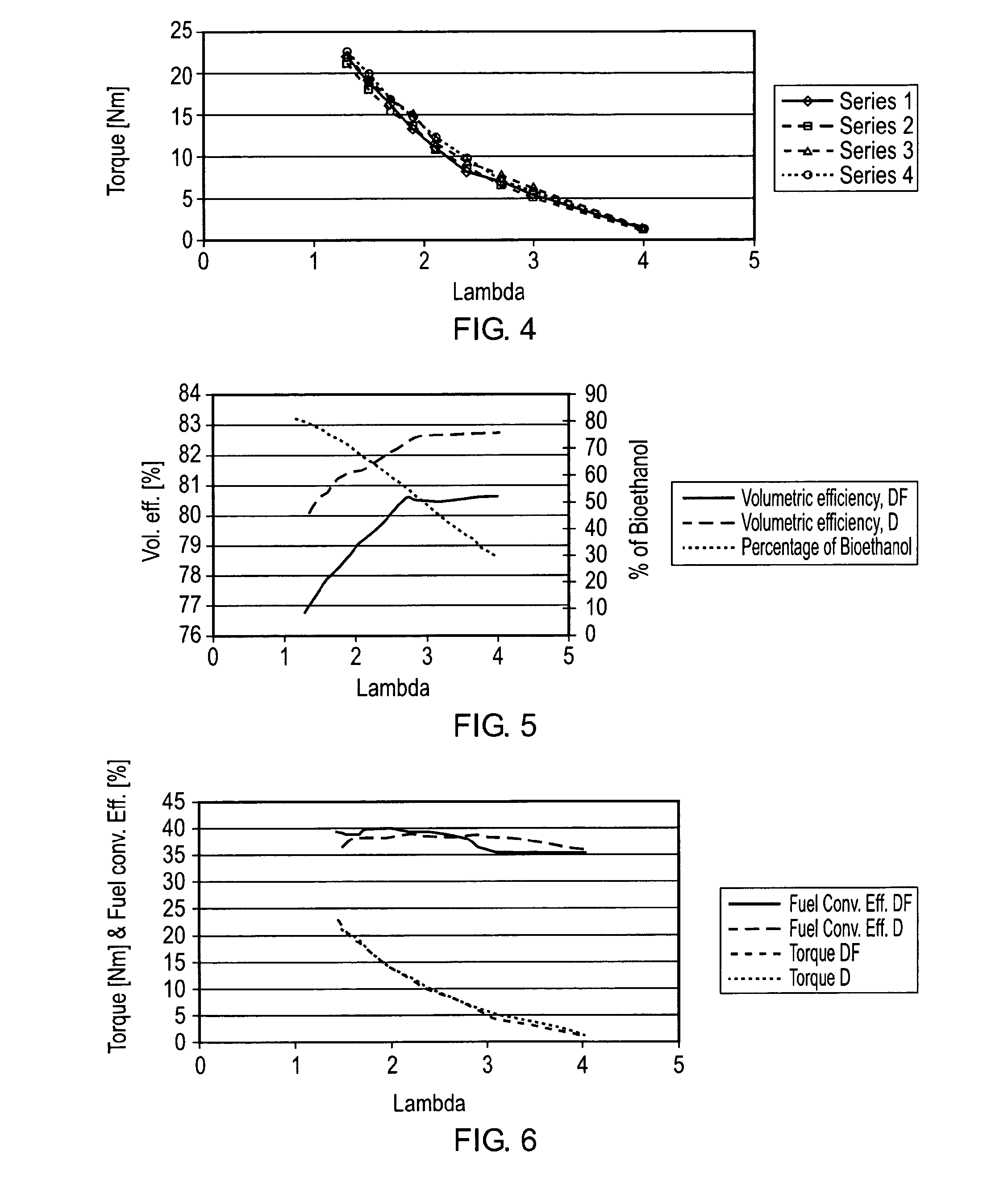
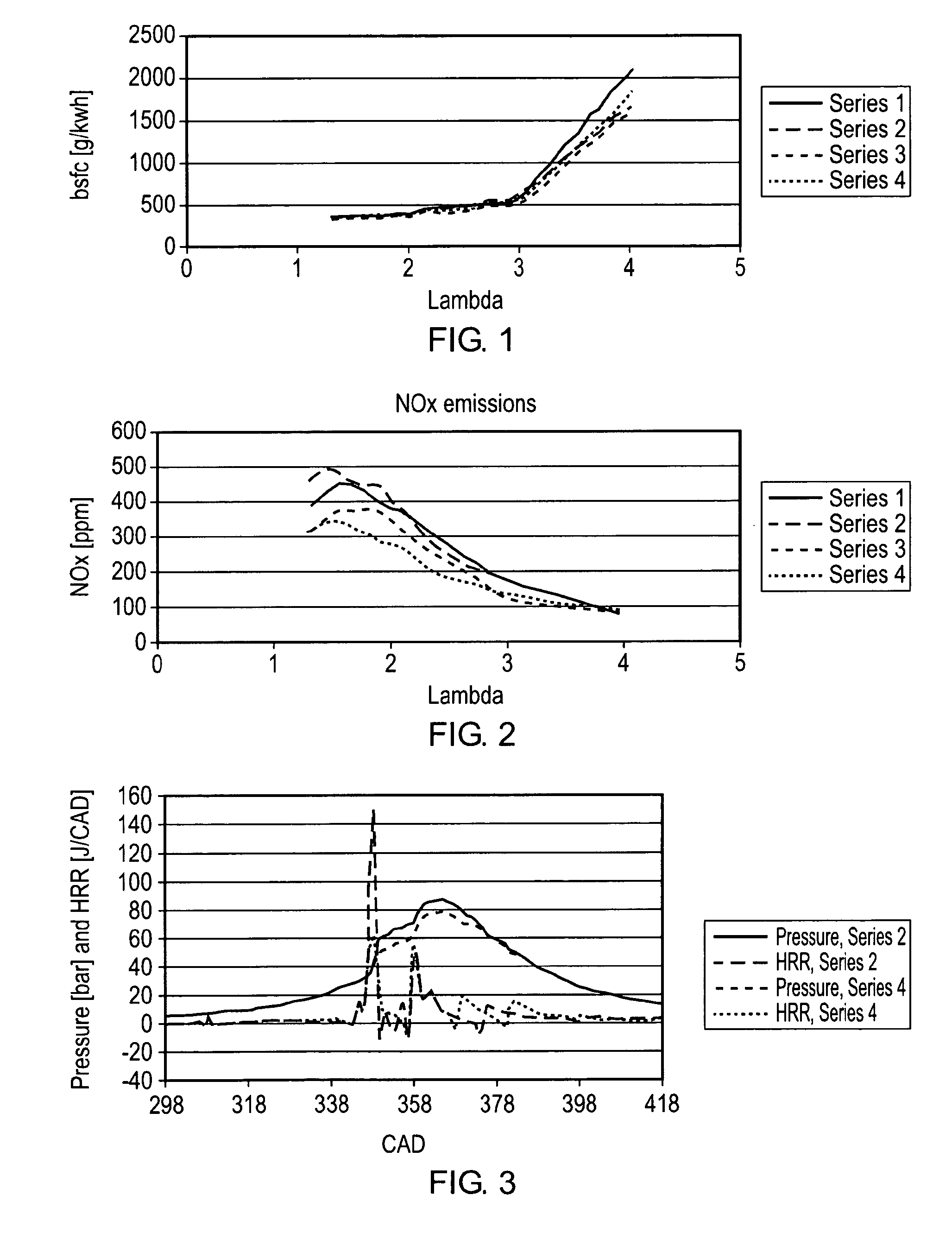
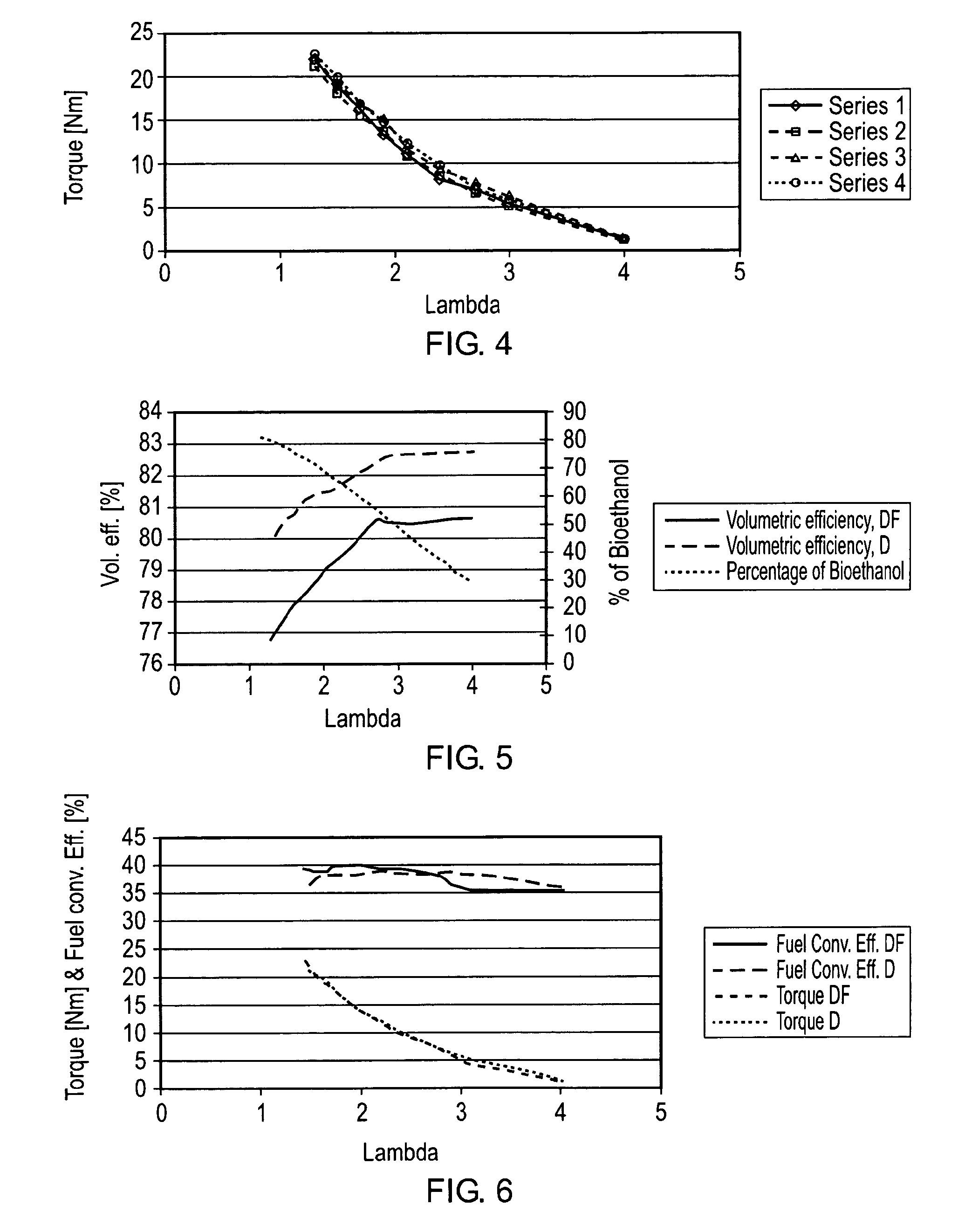
A compression ignition engine is supplied with a first fuel in a flow of air and a second fuel is injected into the combustion chamber. The first fuel comprises a more volatile fuel than diesel such as ethanol, LPG or other combustible gas; the second fuel comprises diesel or biodiesel; and the second fuel is injected in multiple pulses in each ignition cycle with the first pulse acting as a pilot pulse to trigger ignition, and the timing of the second pulse being such as to modify the temperature through evaporation of the second fuel and thereby reduce the combustion temperature and mitigate knock susceptibility. Preferably the pilot pulse is followed by a single further pulse of the second fuel in the ignition cycle. The engine may be controlled to operate in two different modes, one mode for light and medium load conditions when there is only a pilot pulse injection of the second fuel which reduces NOx and soot emissions, and the other mode for higher load conditions when there is a pilot pulse injection followed by a main pulse injection of the second fuel. The first fuel may comprise bioethanol and or one or more of the following: ethanol, butanol, propanol, lpg, natural gas, hydrogen.
Owner:G VOLUTION
Fuel injection control apparatus of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20110005491A1Improve exhaust emissionsImprove stabilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineEngineering
In one embodiment, a total pilot injection amount is calculated from the difference between a compressed gas temperature in a cylinder and a fuel self-ignition temperature. As pilot injection, a plurality of instances of divided pilot injection are performed, and by setting the injection amount per one instance of divided pilot injection to an injector minimum limit injection amount, each divided pilot injection amount is suppressed, and the penetration of fuel is suppressed to a low level so that attachment of fuel to a wall face is avoided, and also, fuel is caused to accumulate in the center portion of the cylinder.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Directly controlled fuel injector with pilot plus main injection sequence capability
InactiveUS6910462B2Reduce pressureImprove accuracyElectrical controlCombustion enginesCommon railEngineering
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Accumulator fuel injection apparatus compensating for injector individual variability
InactiveUS7552709B2Inaccurate quantityElectrical controlCombustion enginesCommon railInternal combustion engine
Owner:DENSO CORP
System for controlling the combustion noise a motor vehicle diesel engine
InactiveUS20050005902A1Minimizes operating noiseNoise minimizationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultiple injectionCombustion noise
This system for controlling the combustion noise of a motor vehicle diesel engine of the type including means for feeding each of its cylinders with fuel by multiple injections of fuel, which means are adapted to trigger fuel feed into each cylinder in the form of at least one pilot injection and a main injection of fuel, comprises: means for determining pressure gradients in the engine cylinder while in operation, at least during the pilot and main injection stages; and means for determining the quantity of fuel to be injected into the cylinder during pilot injection for a predetermined quantity of fuel injected during main injection so as to optimize a criterion based on the ratio between the pressure gradients corresponding to the pilot and main injection stages, thereby optimizing the operating noise of the engine.
Owner:PEZHO SITROEN AUTOMOBILS SA +1
Combustion controller for compression-ignition direct-injection engine and engine control system for the same
ActiveUS8175789B2Improve featuresPromote combustionAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl systemEngineering
As a compression-ignition direct-injection engine combustion controller, a program for detecting ignition timing of a main injection Mn (main ignition timing), a program for correcting a command value of main injection execution timing in a direction to the side where a detection value is converged within a predetermined range, a program for determining whether or not the corrected command value is within a predetermined range, and a program for, when it is determined that the command value is not within the range, correcting a command value related to an injection amount of a pilot injection Pt based on whether or not the command value is on a delay side or an advance side of the range.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Fuel injection control system for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20130000606A1Facilitate fuel combustionImprove flammabilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesState parameterExternal combustion engine
A fuel injection control system for an internal combustion engine is provided which is designed to perform pilot injection of fuel into the engine through a fuel injector prior to main injection. The system monitors a combustion state parameter representing a combustion state of the fuel within a combustion chamber of the engine which has been sprayed in the event of the pilot injection. When the combustion state parameter is determined as lying out of a stable combustion range where the fuel is to burn stably, the system changes the number of pilot injections to be executed prior to the main injection and / or the quantity of the fuel to be sprayed in each pilot injection, thereby enhancing the ignitability of the fuel in the pilot injection.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Internal combustion engine control device
ActiveUS20100018187A1Fluctuation in moreReduce volatilityReciprocating combination enginesElectrical controlPtru catalystExhaust fumes
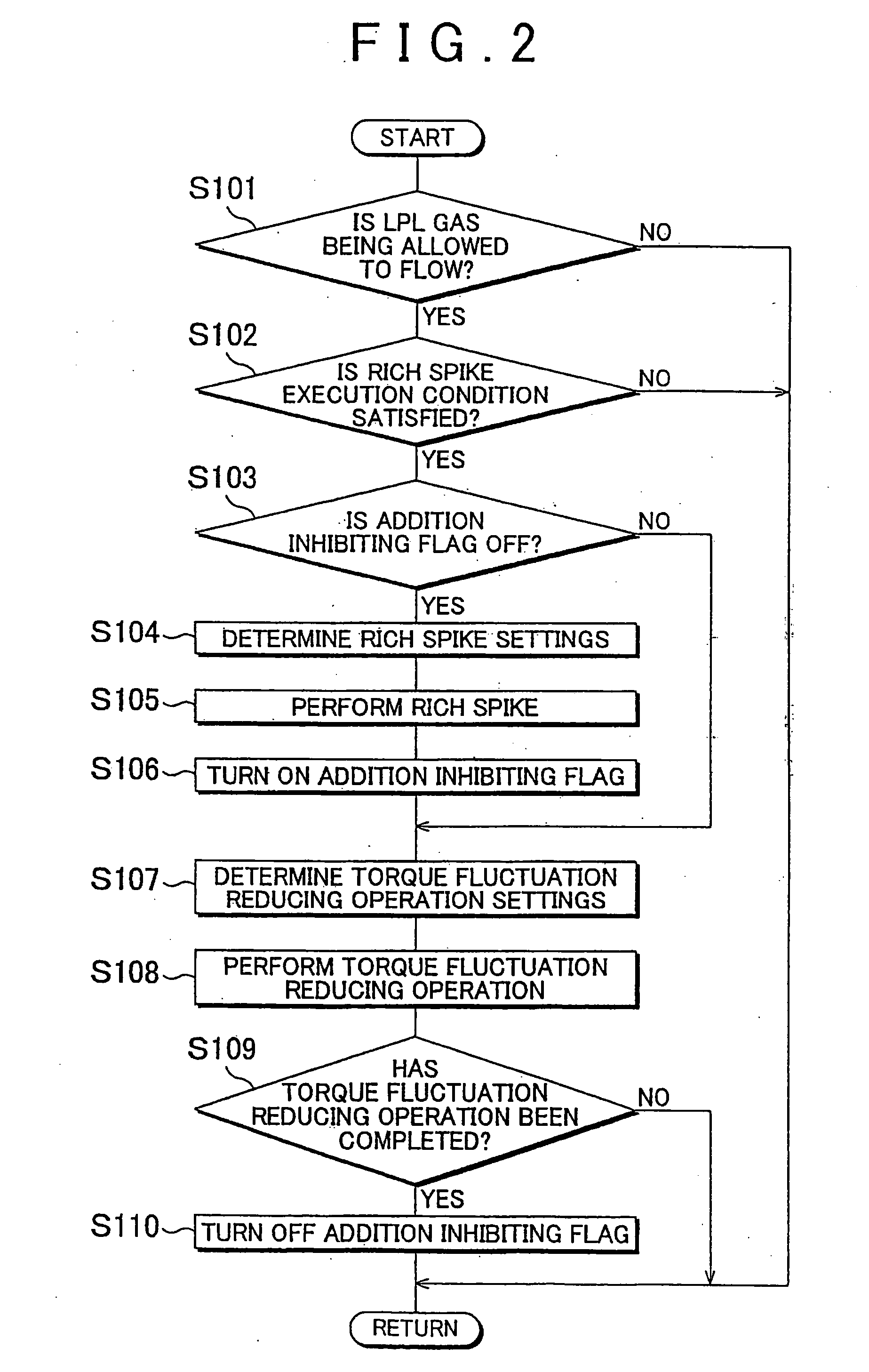
An internal combustion engine control device includes a NOx adsorber catalyst disposed in an exhaust passage, an EGR passage, a reducing agent adding device, a torque fluctuation reducing device, and a fuel injection device. The EGR passage draws a portion of exhaust gas from the exhaust passage downstream of the NOx adsorber catalyst and recirculates the exhaust gas into the intake passage. The reducing agent adding device adds a reducing agent to exhaust gas upstream of the NOx adsorber catalyst to reduce substances adsorbed by the NOx adsorber catalyst. When or after the reducing agent adding device adds the reducing agent, the torque fluctuation reducing device advances the timing of the fuel injection device or carries out a pilot injection to reduce a fluctuation in engine torque. The reducing agent adding device adds less reducing agent while the torque fluctuation reducing device is operating.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
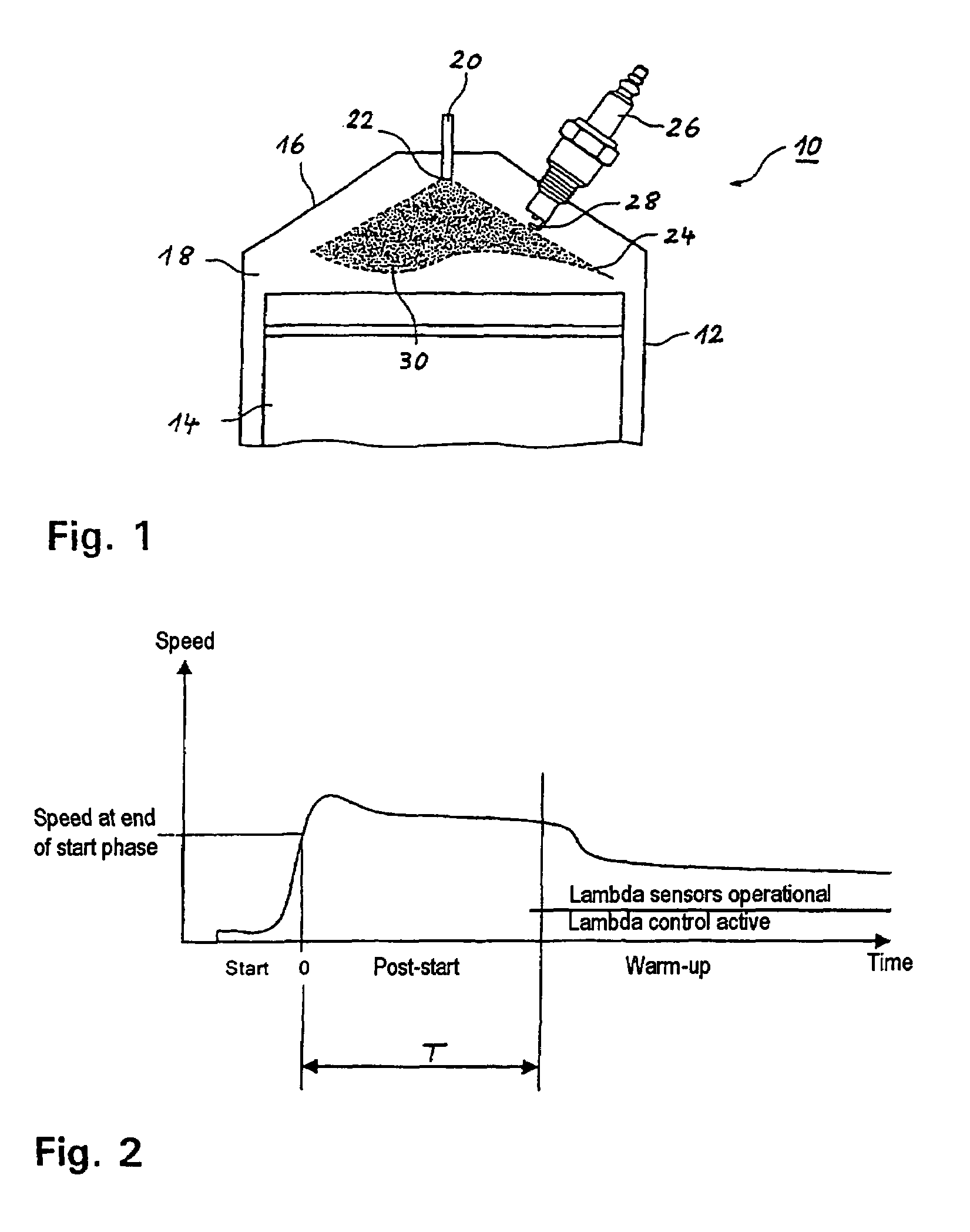
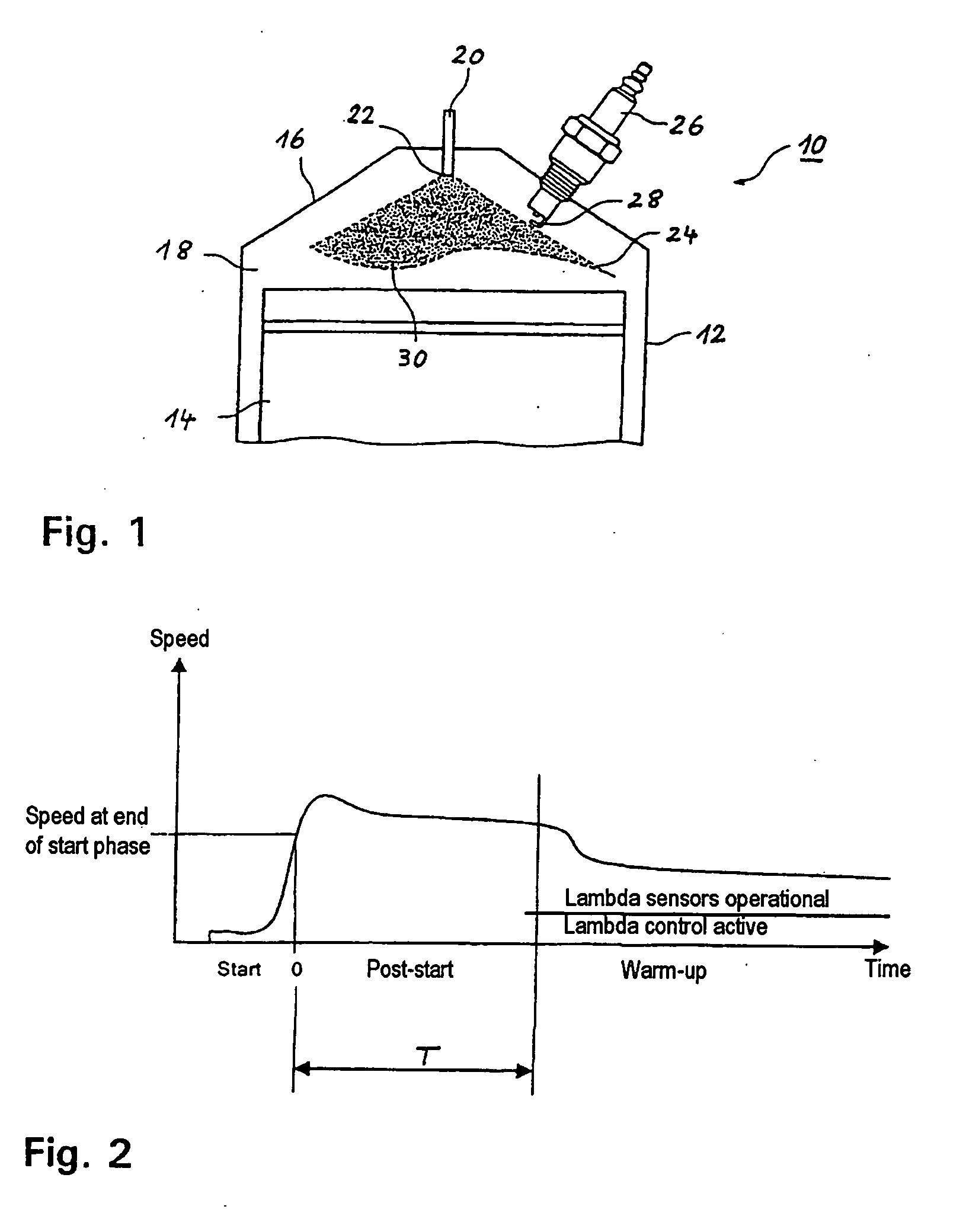
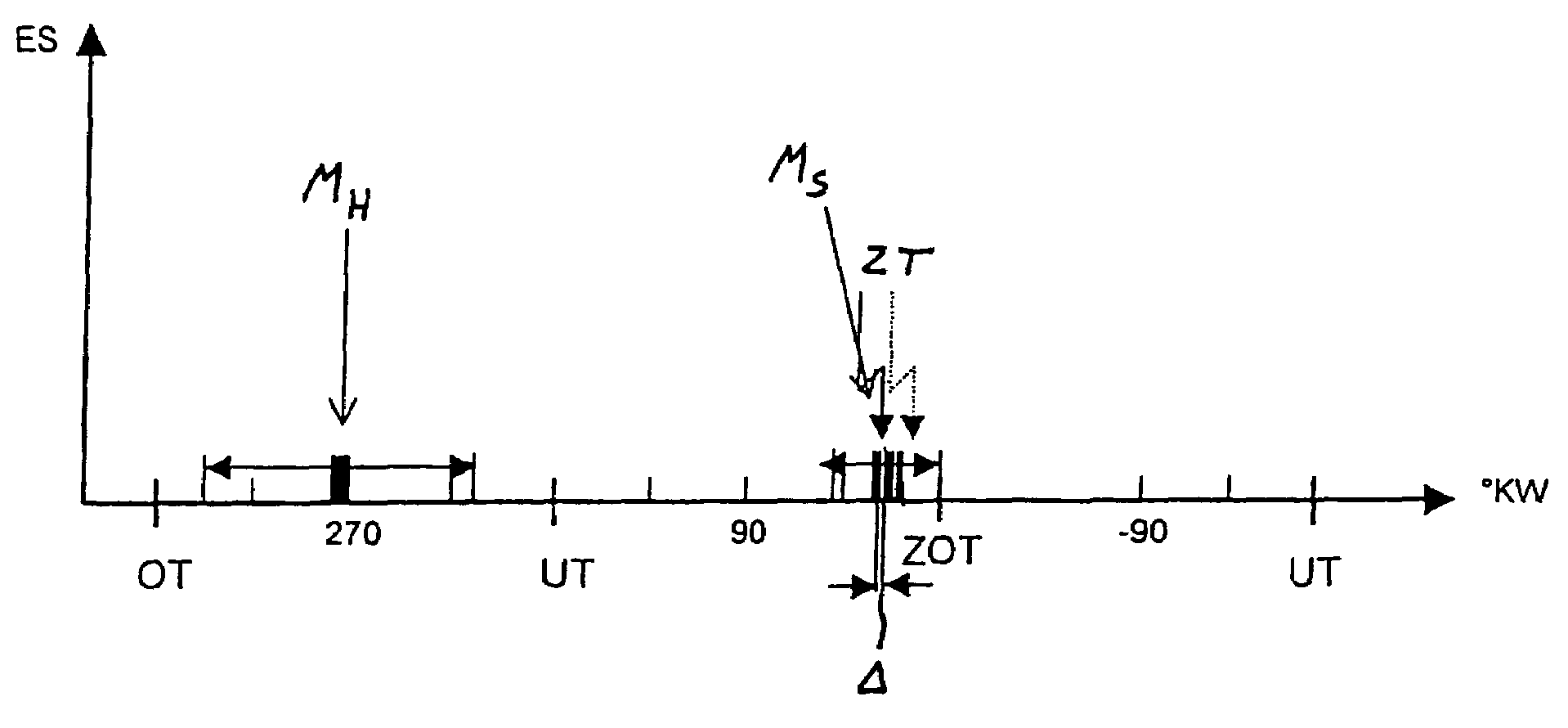
Method for operating an internal combustion engine with direct fuel injection during a post-start phase
ActiveUS7370629B2Reduce fuel consumptionEmission reductionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberInternal combustion engine
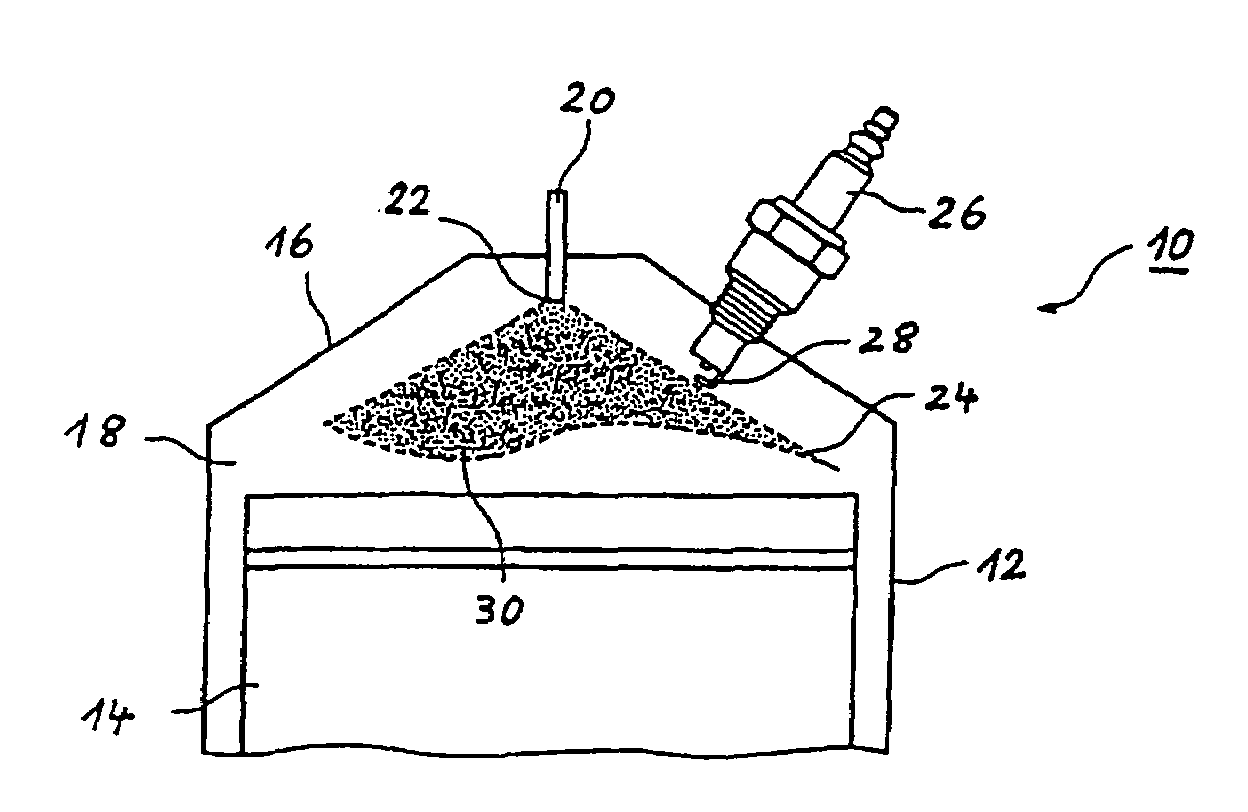
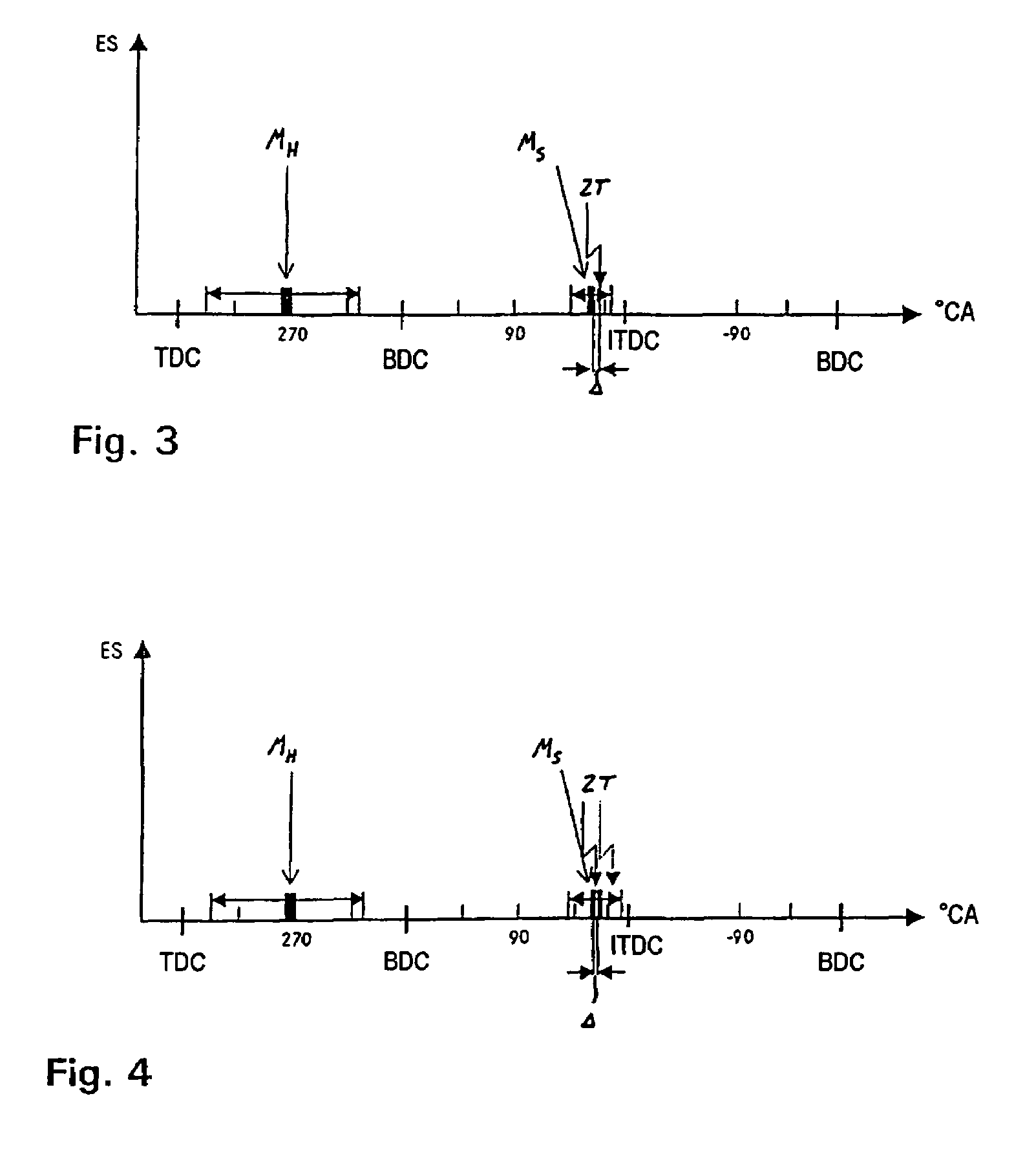
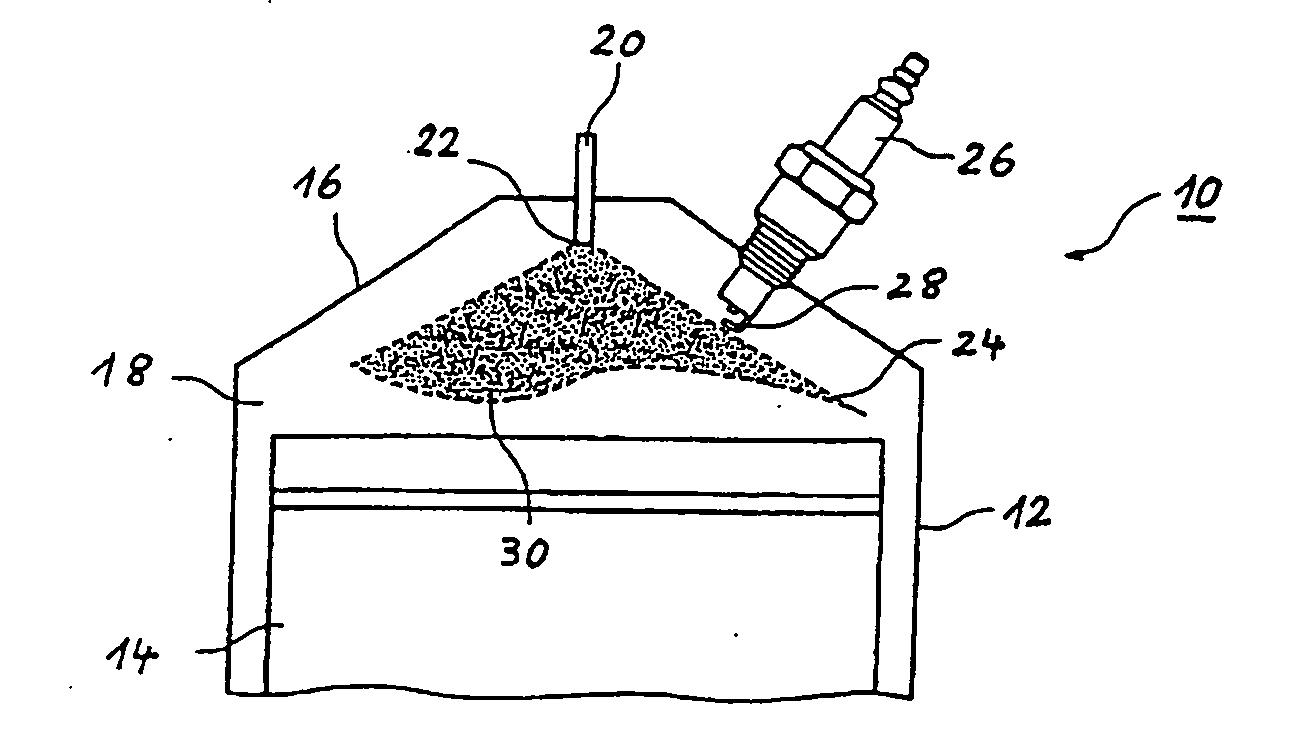
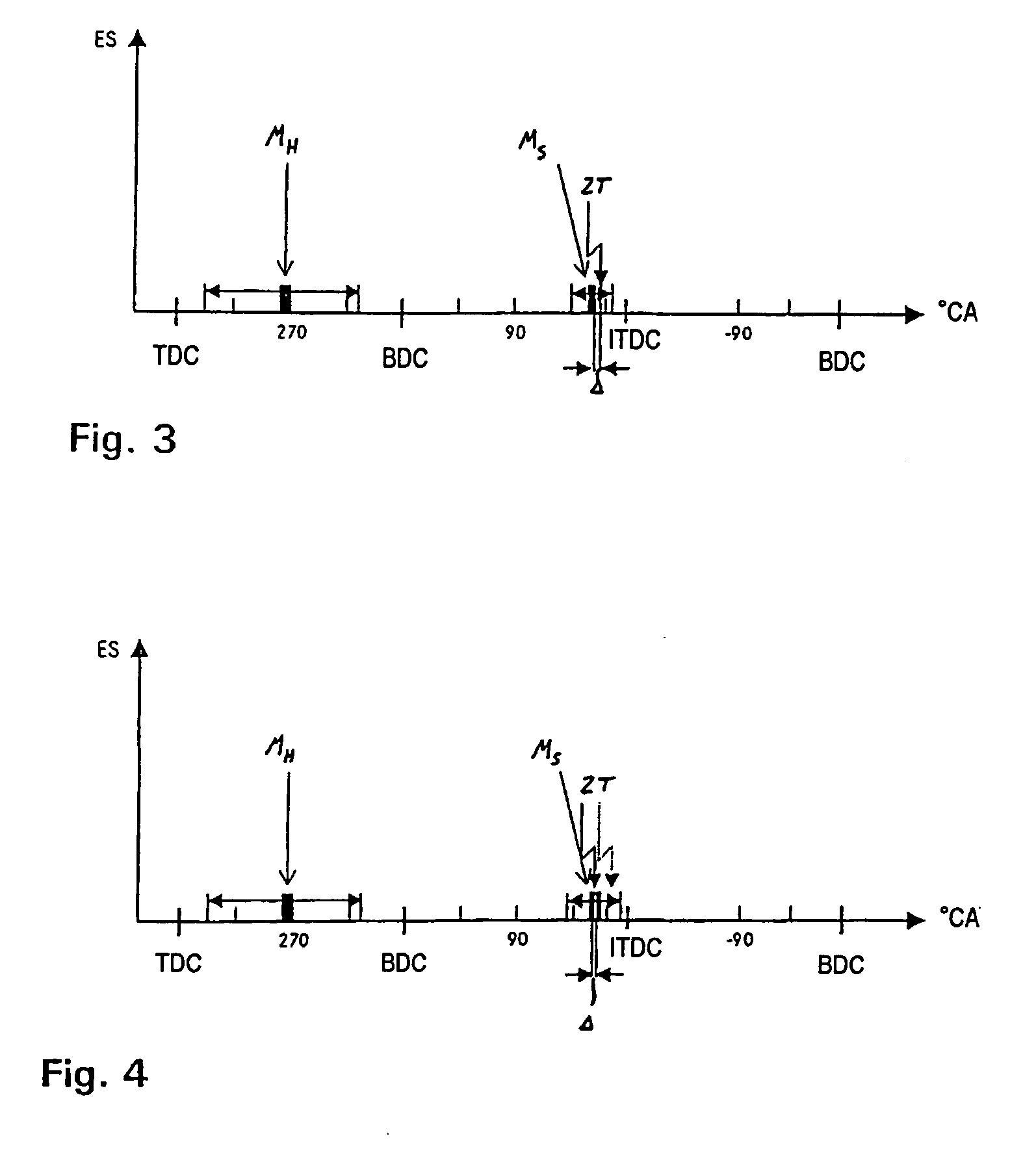
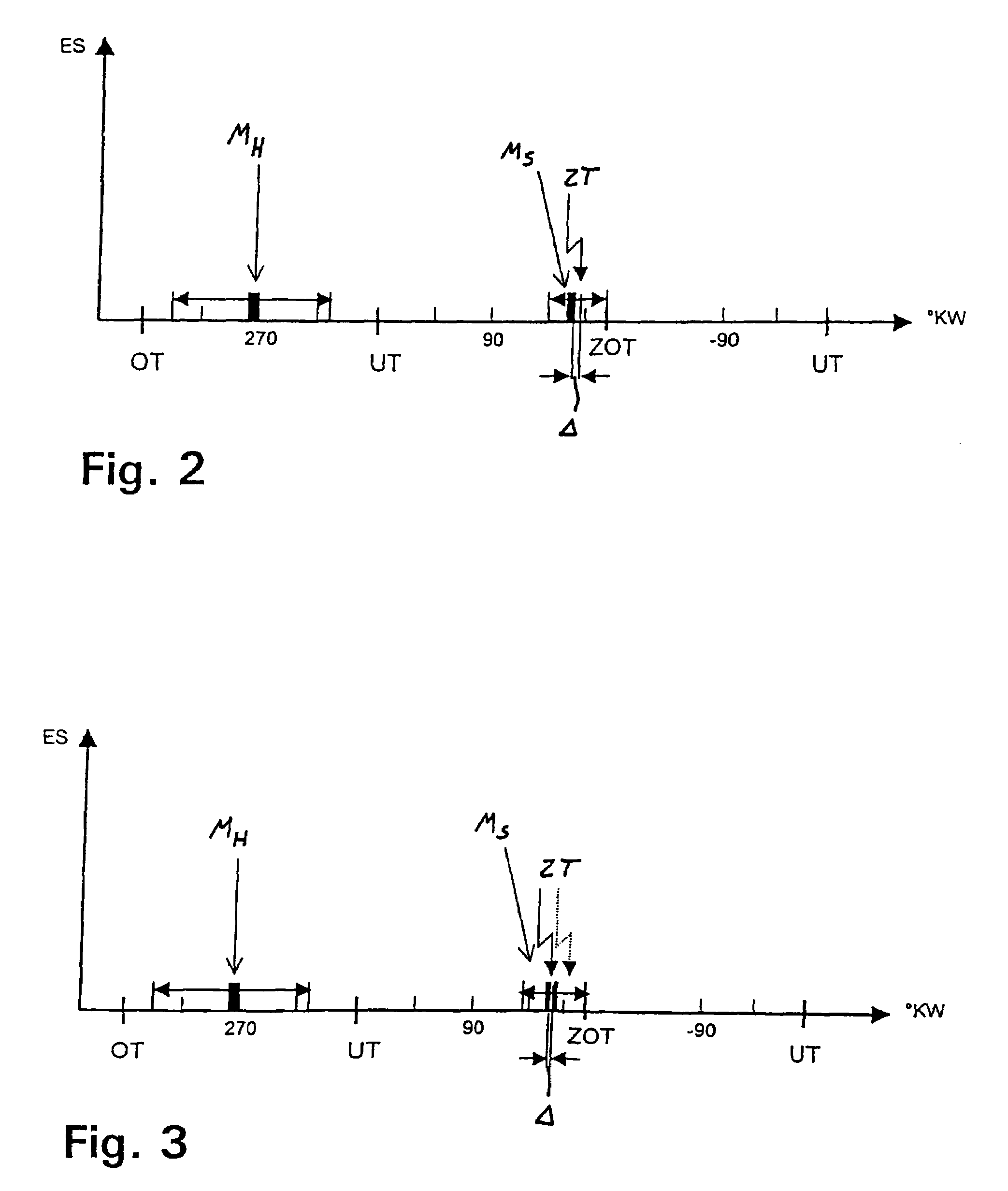
In a method for operating a spark-ignition internal combustion engine with direct fuel injection in the post-start phase at low temperatures, fuel is supplied to the combustion air in a pilot injection (MH) of a first fuel quantity during an intake stroke of the internal combustion engine such that the pilot injection (MH) forms a homogeneous, lean air / fuel mixture (λ>1) in substantially the entire combustion chamber, and a main injection (MS) of a second fuel quantity is subsequently injected into the combustion chamber during a compression stroke directly before the ignition time (ZT), said main injection (MS) forming in the region of the spark plug a stratified, rich air / fuel mixture (λ<1), which is then ignited by the spark plug.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Oil control system of diesel/natural gas dual-fuel internal combustion engine
InactiveCN103498732ASimple structurePrecise and reliable controlElectrical controlMachines/enginesMicrocontrollerExternal combustion engine
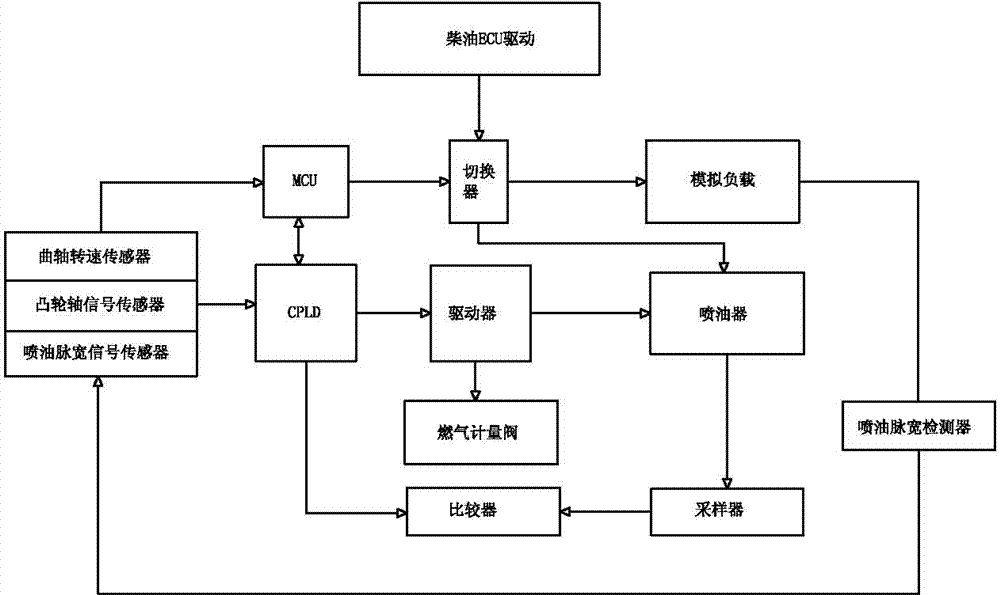
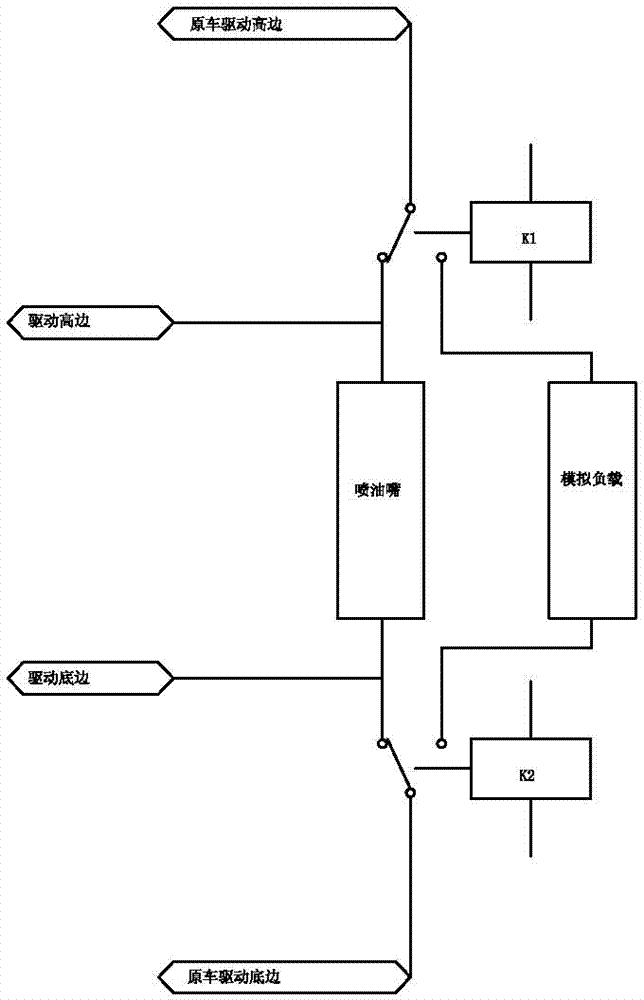
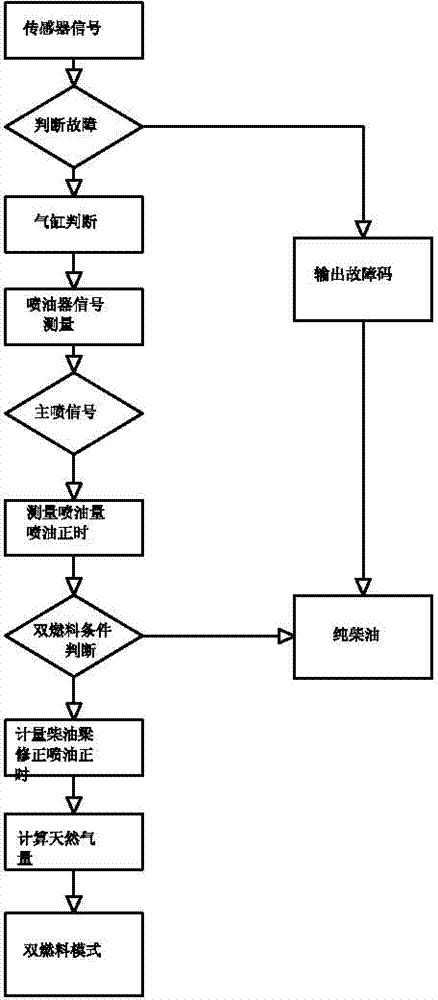
The invention relates to an oil control system of a diesel / natural gas dual-fuel internal combustion engine. The oil control system of the diesel / natural gas dual-fuel internal combustion engine can effectively solve the problem that control accuracy and refit effects are poor. According to the structure of the oil control system of the diesel / natural gas dual-fuel internal combustion engine, a microcontroller is connected with a programmable logic controller, a sensor is respectively connected with the input end of the microcontroller and the input end of the programmable logic controller, the output end of the microcontroller is connected with a switching circuit, the output end of the programmable logic controller is connected to an actuator, the switching circuit is respectively connected with diesel ECU driving signals, artificial loads and an oil atomizer, the oil atomizer is connected with the actuator and a sampling instrument, the sampling instrument is connected with a comparator, the comparator is connected to the programmable logic controller, and the artificial loads are connected with the sensor through a detector for detecting fuel injection pulse width. The oil control system of the diesel / natural gas dual-fuel internal combustion engine is simple, novel and unique in structure, and accurate and reliable in control, is effectively applied to dual-fuel diesel high pressure common rails, electronic controlled monoblock pumps and pump nozzle engines, can completely avoid influences of pilot injection, post injection and other multiple times oil injection signals of an original vehicle under a duel-fuel mode, reduces oil consumption of the system, and improves the substitution rate.
Owner:SHENZHEN GUOJU NATURAL GAS AUTOMOBILE TECH
Micro-pilot injection ignition type gas engine
ActiveUS8215284B2High precisionReduce stepsValve arrangementsElectrical controlGas engineFuel supply
What is disclosed is a micro-pilot injection ignition type gas engine, whereby an air fuel ratio control in starting the engine is executed with enhanced precision, by means of introducing skip-firing intermittent operations which reflect the engine operation conditions, while an idling time span can be shortened or omitted.The engine includes: a gas valve that opens and closes a fuel-gas passage in front of each cylinder, so as to arbitrarily control the throat area as well as the opening-closing time span of the gas valve; an engine speed detecting unit to detect the engine speed; a combustion diagnosis unit to detect an engine combustion state through a cylinder pressure distribution along elapsed time, as to each cylinder; an opening-closing control unit as to the gas valve, so as to control the intermittent opening-closing of the gas valve according to the levels of the detected engine speed as well as the cylinder pressure distribution; whereby, in starting the engine, the intermittent opening-closing of the gas-valve enables at least one skip-firing mode that brings an enhanced fuel-supply pressure-pulsation with which a relatively large amount of fuel-gas is supplied per engine cycle with firing so that the air fuel-gas ratio of each cylinder reaches a prescribed target value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND ENGINE & TURBOCHARGER LTD
Fuel injection controller of internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20070015630A1Sufficient learning frequencyAccurate calculationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesAutomatic transmissionStabilization control
A crankshaft of an internal combustion engine is connected to an automatic transmission mechanism through a torque converter. A difference in a load applied to the crankshaft between a D range and a P range is sensed based on a difference in a command fuel injection amount during idling stabilization control between the D range and the P range. A difference between a fuel amount required by learning control of pilot fuel injection in the D range and a standard command fuel injection amount required for performing the learning control under the load corresponding to the p range is reduced by a fuel injection amount difference caused by the difference of the load. A learning value of the pilot injection is learned based on the reduced difference.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method for operating an internal combustion engine with direct fuel injection during a post-start phase
ActiveUS20070056553A1Reduce fuel consumptionEmission reductionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberInternal combustion engine
In a method for operating a spark-ignition internal combustion engine with direct fuel injection in the post-start phase at low temperatures, fuel is supplied to the combustion air in a pilot injection (MH) of a first fuel quantity during an intake stroke of the internal combustion engine such that the pilot injection (MH) forms a homogeneous, lean air / fuel mixture (λ>1) in substantially the entire combustion chamber, and a main injection (MS) of a second fuel quantity is subsequently injected into the combustion chamber during a compression stroke directly before the ignition time (ZT), said main injection (MS) forming in the region of the spark plug a stratified, rich air / fuel mixture (λ<1), which is then ignited by the spark plug.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Engine control apparatus
ActiveUS7532971B2Improve economyAccelerate emissionsAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlFuel supplyControl variable
An engine control apparatus comprised of an engine control ECU has a program preloaded therein for determining a combustion rate (actual combustion rate) corresponding to the ratio of an ideal heat generation quantity (target heat generation quantity) estimated to be generated from a fuel supply quantity, and an actual heat generation quantity actually generated by the fuel supply quantity. The engine control apparatus controls pilot injection timing with a controlled variable corresponding to the thus determined combustion rate so as to increase the combustion rate.
Owner:DENSO CORP
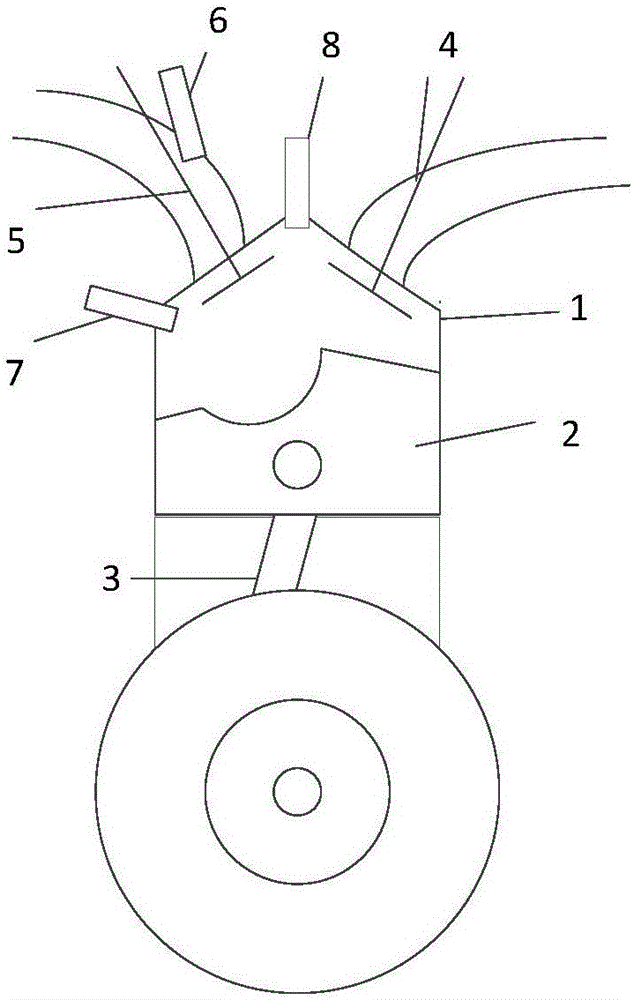
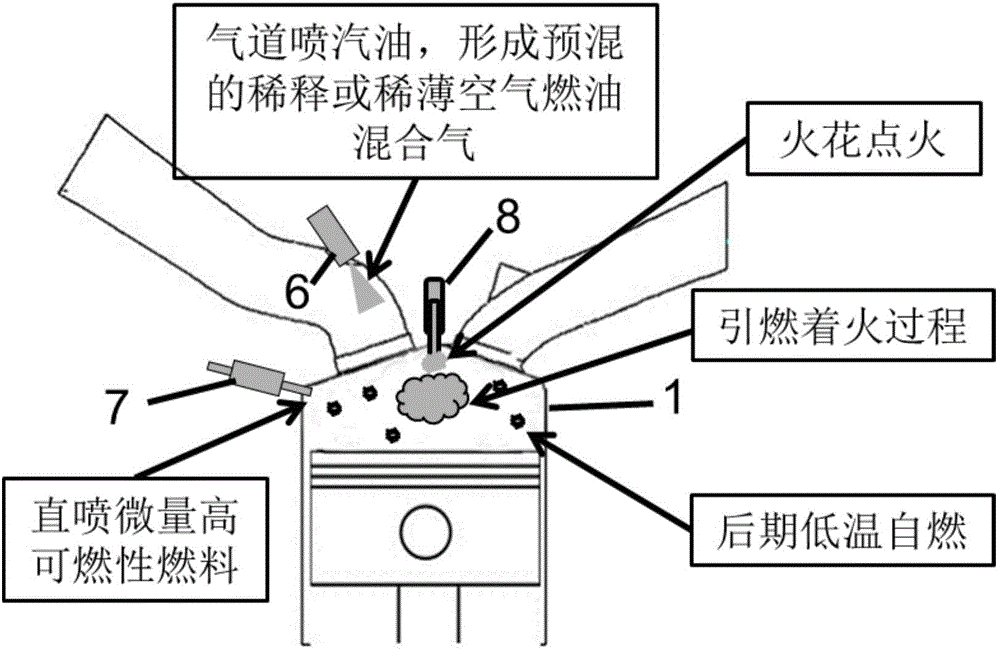
Method for controlling diluent or lean mixed gas burning and ignition through high-flammability fuel micro ignition
InactiveCN106321269AImprove economyExtended operating rangeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFlame propagationGasoline
The invention discloses a method for controlling diluent or lean mixed gas burning and ignition through high-flammability fuel micro ignition. The method comprises the steps that gasoline is ignited through spontaneous burning of a small amount of layered high-flammability fuel, and stable flame propagation is formed; the temperature inside a cylinder is increased through energy released by flame propagation and piston upward compression, meanwhile, multiple spontaneous burning points are formed in unburnt diluent or lean mixed gas under the assistance of a small amount of pilot injection high-flammability fuel, and then stable and rapid burning or multi-point spontaneous burning is formed. When an engine encounters knock or the largest explosion pressure exceeds limits, the burning process can be converted into rapid flame propagation type burning by introducing cooled burnt waste gas or excess air. When the heat state in the cylinder is not enough to form stable flame propagation or spontaneous burning heat release, the heat state in the cylinder is improved by introducing internal residual waste gas. The control problem in the ignition and burning process of premixed diluent or lean mixed gas can be solved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method of operating an internal combustion engine with direct fuel injection
ActiveUS7204228B2Optimize advantageIncreased turbulenceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultiple injectionCombustion chamber
In a method of operating a spark ignition internal combustion engine with direct fuel injection wherein combustion air is supplied to a combustion chamber, fuel is injected into the combustion air during an intake stroke via a fuel injector in a pilot injection using a first fuel quantity so as to from a homogeneous lean air / fuel mixture in substantially the entire combustion chamber, in a main injection subsequently a second fuel quantity is injected in multiple injection steps just before ignition time so as to form a stratified rich air / fuel mixture in the area of a spark plug and the stratified fuel charge is then ignited 2° CA to 10° CA after completion of the injection of the main stratified injection.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Electronic fuel injection apparatus
InactiveUS6192856B1Increased revolutionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesDriving currentEngineering
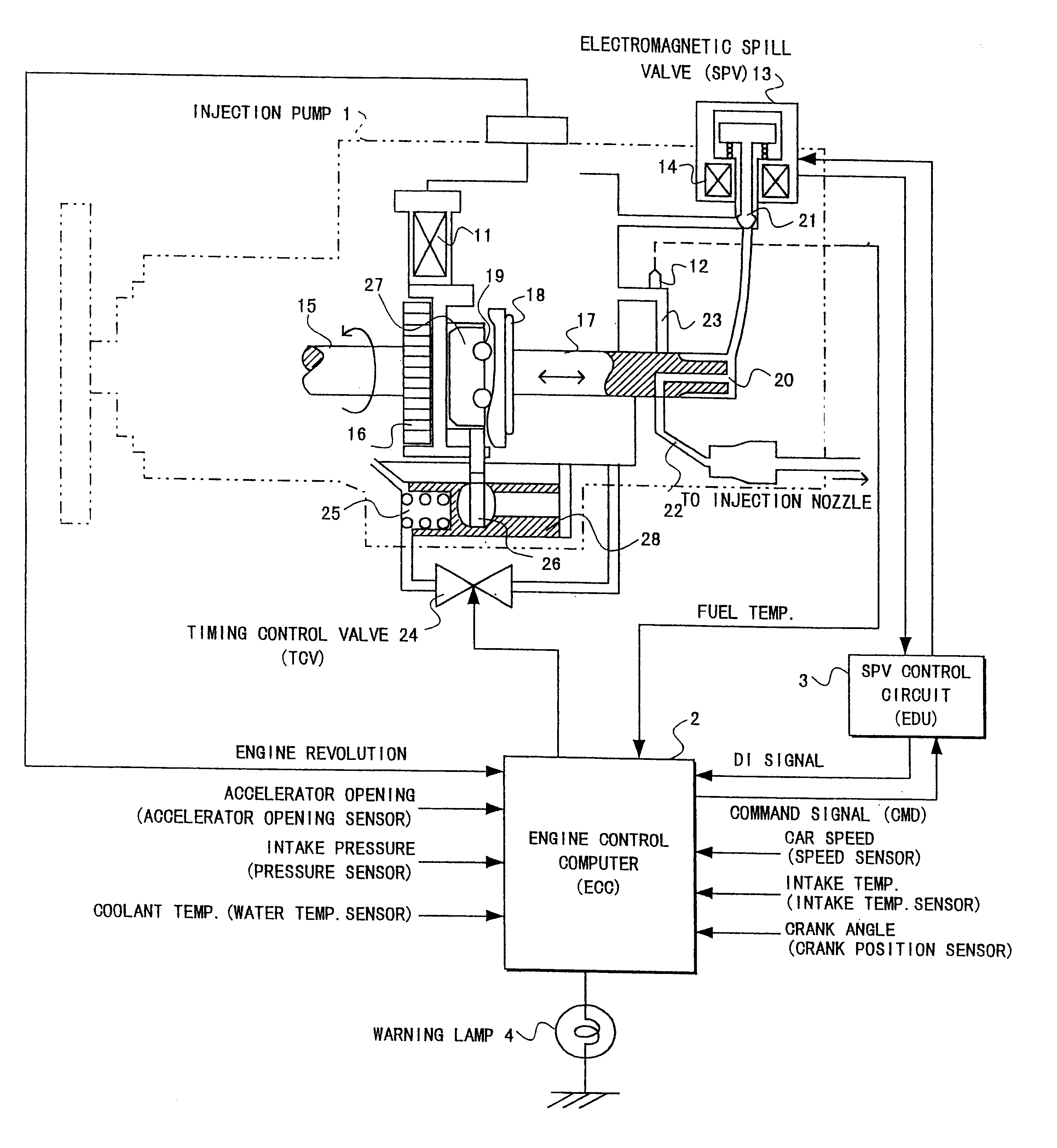
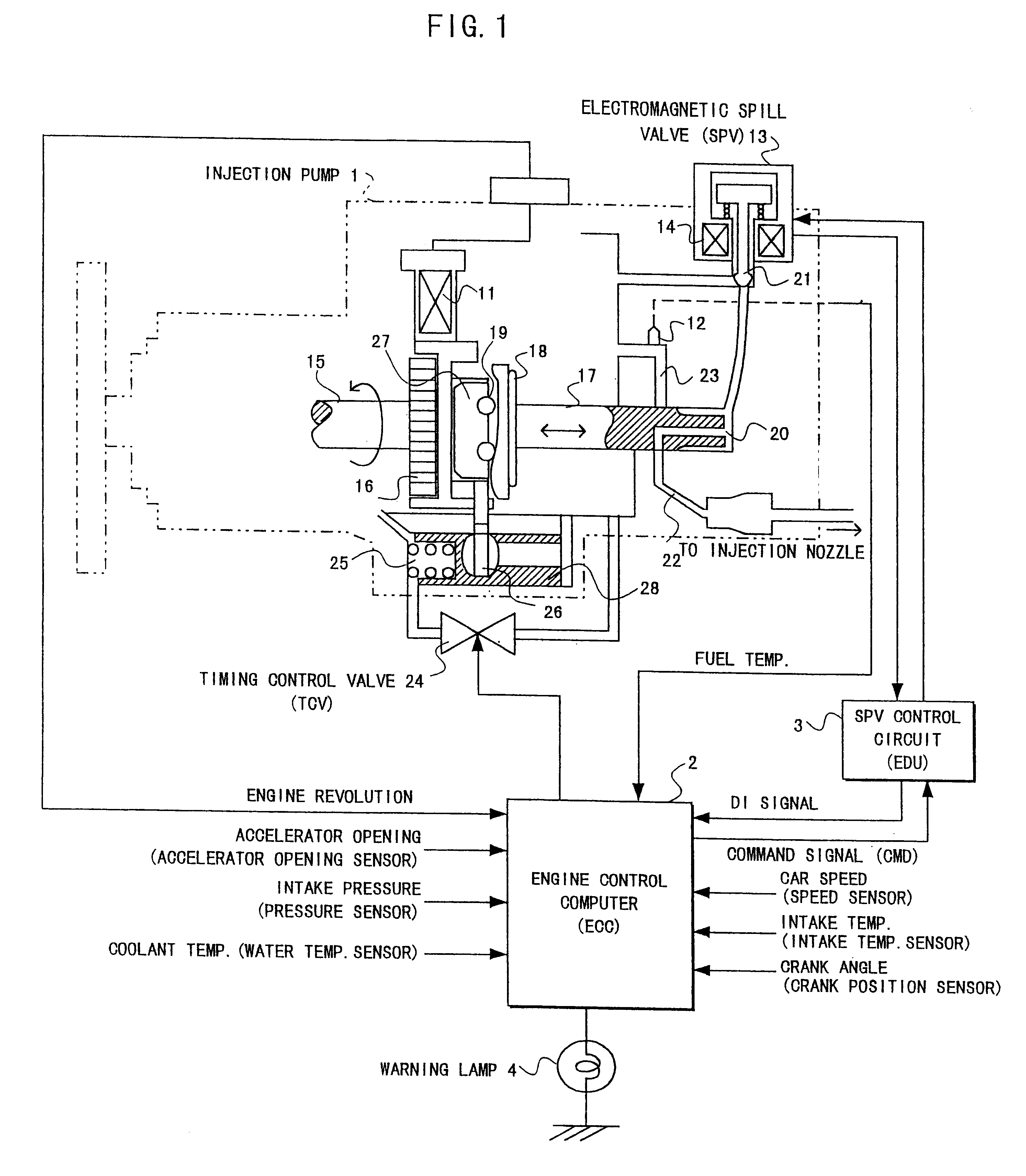
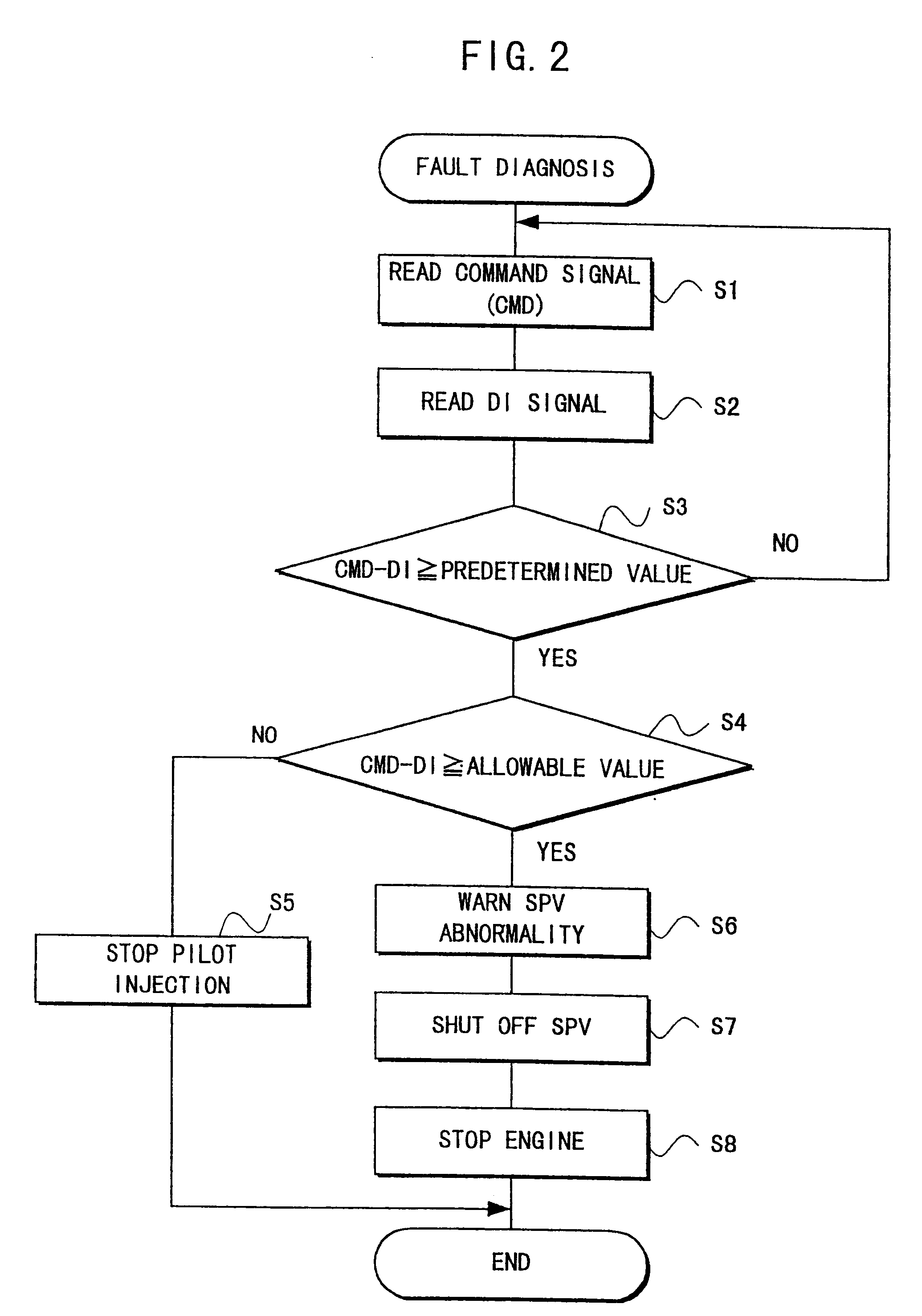
In an electronic fuel injection apparatus comprising a control circuit of an electromagnetic spill valve for adjusting a fuel injection quantity in a distribution-type fuel injection pump for a diesel engine, and a computing unit for providing a command signal to the control circuit, a driving current flowing through a solenoid of an electromagnetic spill valve is detected, a state where a delay time interval from a transit point of a command signal provided to the control circuit to a delay point at which the driving current crosses a threshold value is equal to or more than a predetermined value is determined as a slightly abnormal state to invalidate the command signal for a pilot injection, or a state where the delay time interval exceeds an allowable value further larger than the predetermined value is determined as a seriously abnormal state to stop the engine.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
Multi-transmitter communication system employing anti-phase pilot signals
InactiveUS7110739B2MinimizeResonant long antennasSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemEngineering
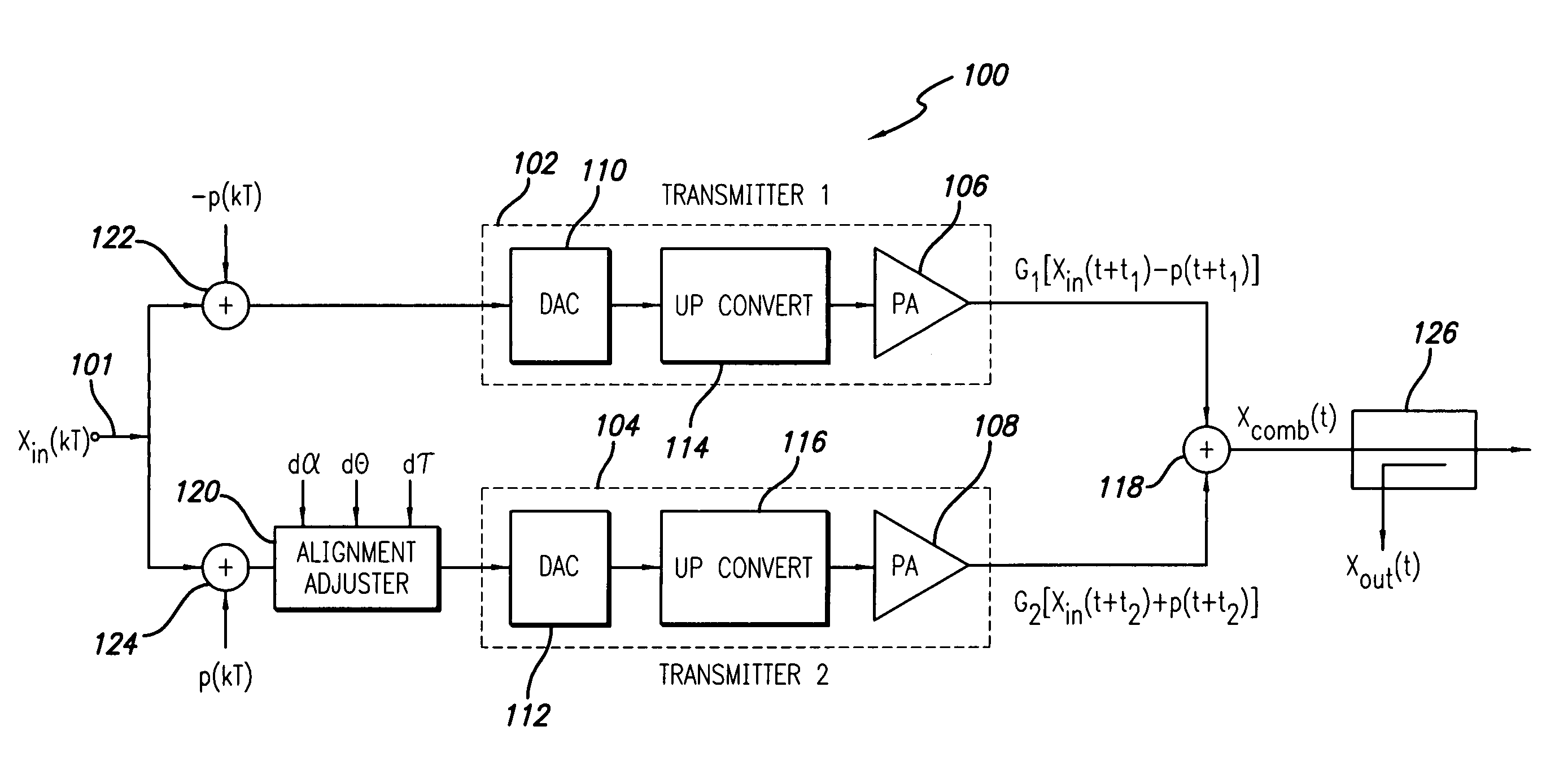
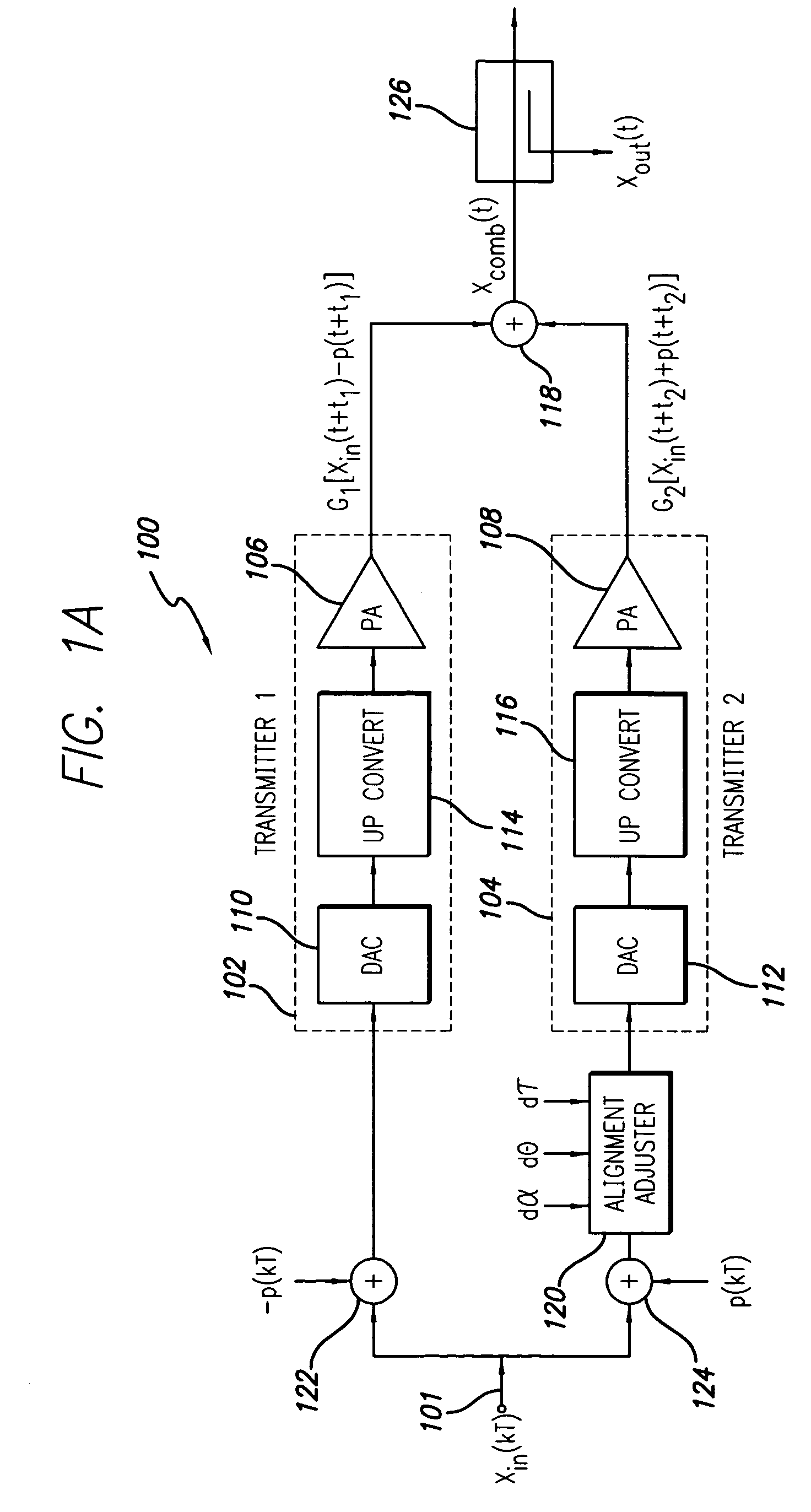
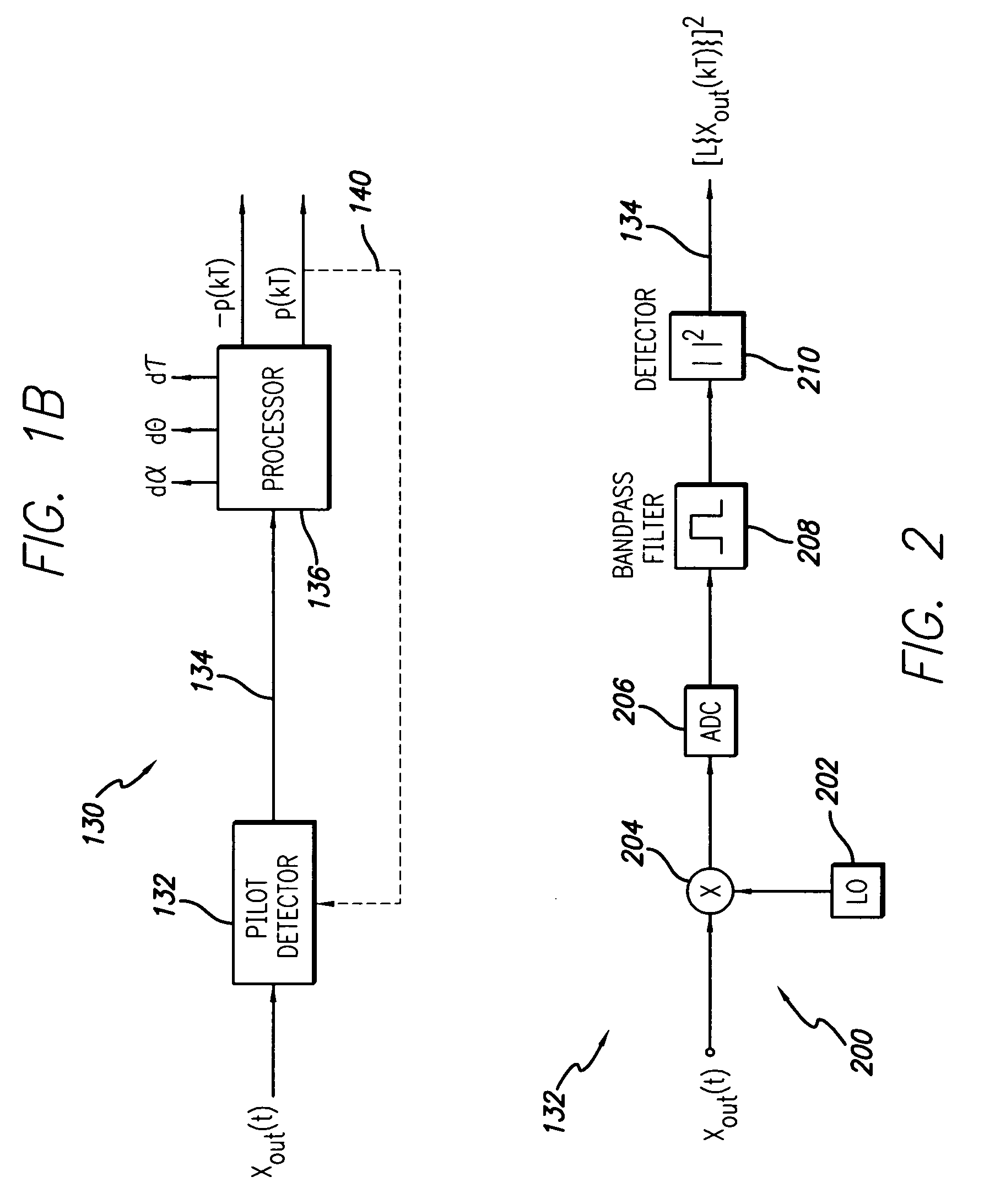
Base station transmitter signals are combined more effectively through the use of anti-phase pilots between pairs of transmission paths. At the combiner, the pilots will cancel when the amplitude, phase, and delay of the two transmission paths entering the combiner are matched. As a result, the pilots will not appear at the output except when the alignment is incorrect. By detecting the residual pilot at the combiner output, the information is used to adjust the alignment of one of the transmission paths to match the other. The adjustments to the amplitude, phase, and delay are performed on the input signal, after the pilot injection.
Owner:INTEL CORP
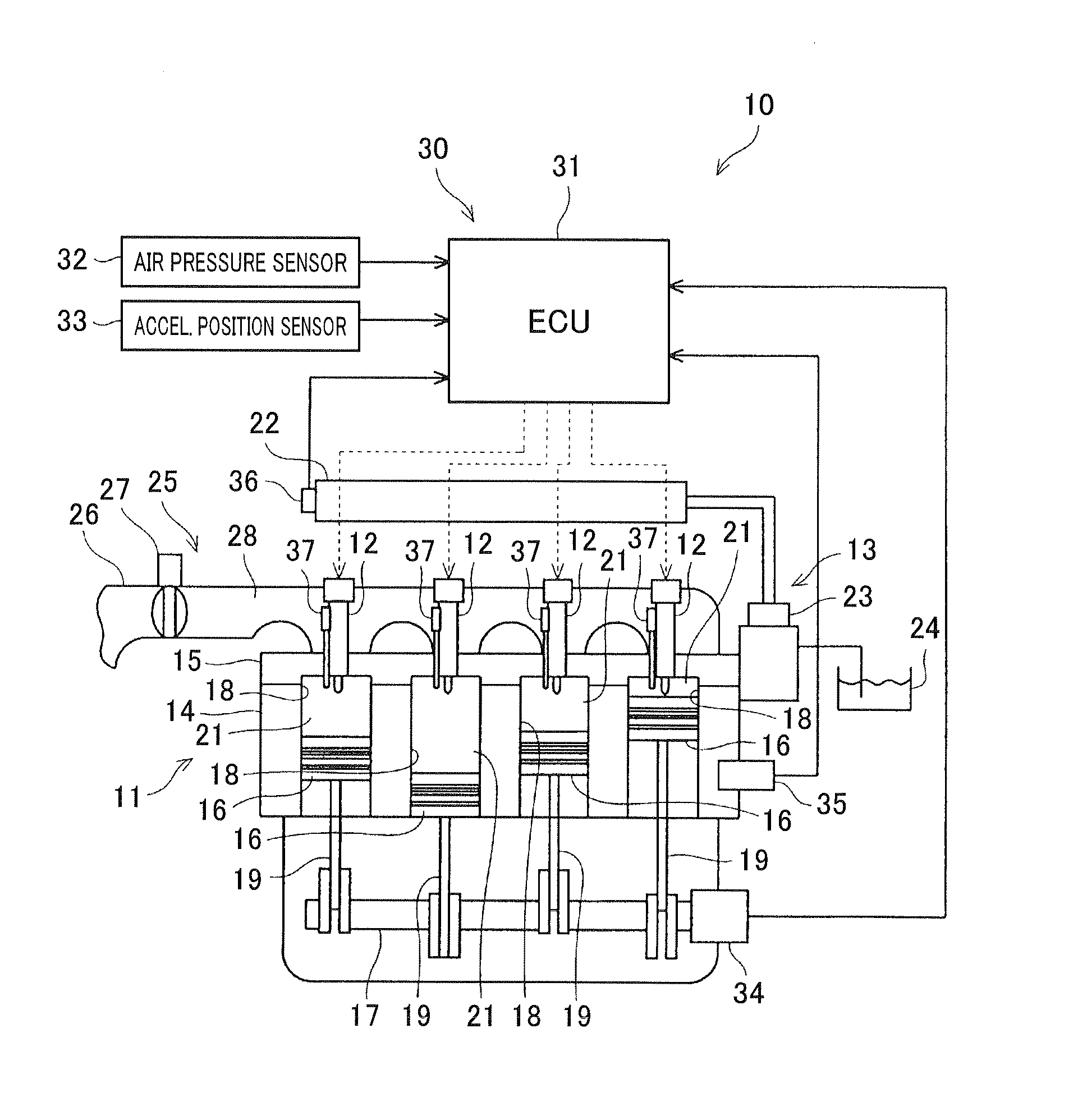
Fuel injection system of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7195002B2Easy dischargeEasy to operateElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInjection pressureCommon rail
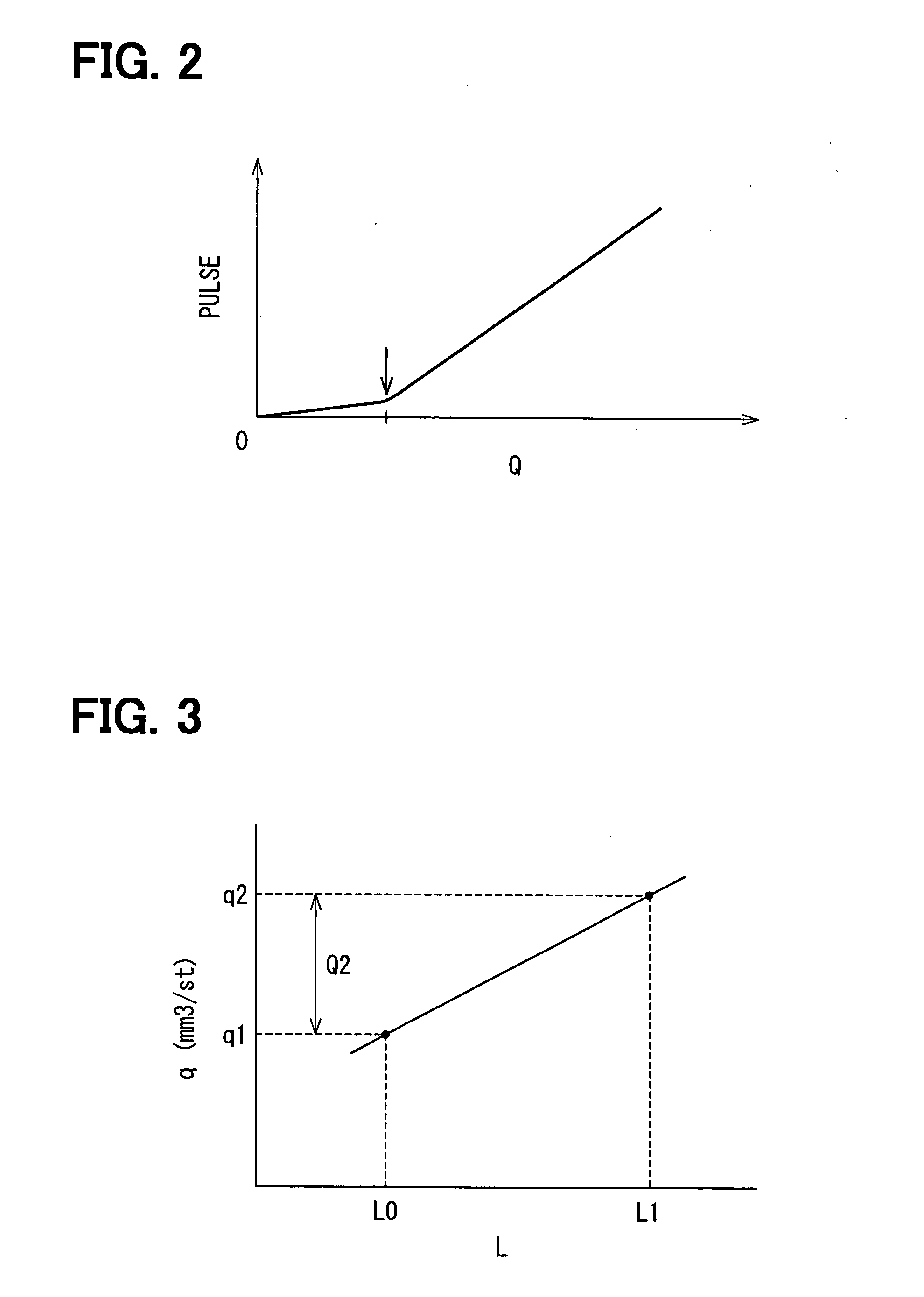
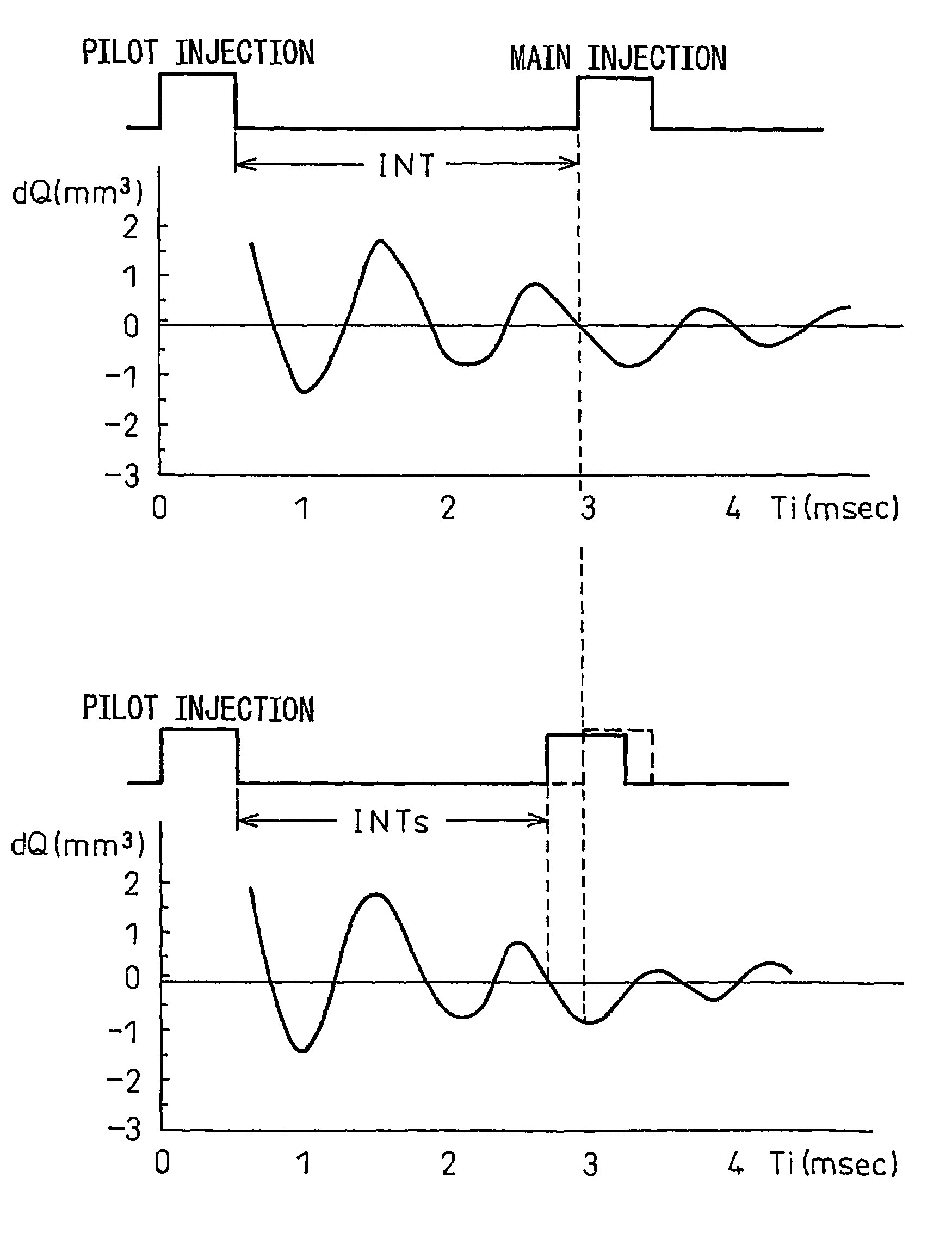
An internal combustion engine provided with a common rail (13) and fuel injectors (3) connected to the common rail (13). When pilot injection is performed, the injection pressure pulsates. At this time, the injection amount of the main injection fluctuates by a certain fluctuation pattern. If indicating on an abscissa a time interval from when pilot injection is started to when main injection is started and indicating on the ordinate a fluctuation amount of main injection, the fluctuation pattern of the injection amount of the main injection becomes a form contracted or expanded in the abscissa direction in accordance with the fuel properties. This characteristic is utilized to find the fluctuation amount of the injection amount of the main injection.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel injection system of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7267097B2Easy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInjection pressureRail pressure
An internal combustion engine provided with a common rail (13) and fuel injectors (3) connected to the common rail (13). When pilot injection is performed, the injection pressure pulsates. At this time, the injection amount of the main injection fluctuates by a certain fluctuation pattern. If indicating on an abscissa a time interval from when pilot injection is started to when main injection is started and indicating on the ordinate a fluctuation amount of main injection, the fluctuation pattern of the injection amount of the main injection becomes a form contracted or expanded in the abscissa direction and ordinate direction in accordance with the rail pressure. This characteristic is utilized to find the fluctuation amount of the injection amount of the main injection.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Injection ratio control system for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6748920B2Eliminate the effects ofSuppress mutationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMulti injectionControl system
Owner:DENSO CORP
Accumulation type fuel injection system
ActiveUS20040099248A1Reduce noiseElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMulti injectionPressure difference
An electronic control unit of an accumulation type fuel injection system increases a number of injections performed by an injector in one injection period from a normal injection number if a pressure difference provided by subtracting target pressure from actual pressure is greater than a determination threshold and conditions for performing the injection are established, or if high-temperature combustion is predicted. If a normal injection mode is a main injection mode, it is changed to a pilot injection mode or a multi-injection mode. If the normal injection mode is the pilot injection mode, it is changed to the multi-injection mode. If the normal injection mode is the multi-injection mode, a number of minute injections is increased. Thus, combustion is slackened and noise caused by the high-temperature combustion can be alleviated.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Diesel engine for automobile, control device and control method
ActiveUS20130073186A1Shorten ignition delaySlow down main combustionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesLow speedTop dead center
A geometric compression ratio in an engine main body 1 is set to 15 or less. Injection control means (ECU 40) performs a main injection of injecting fuel near a compression top dead center, and a preceding injection prior to the main injection at a specific region of predetermined load within an operating region on a relatively low-speed side. The injection control means performs, as the preceding injection, a pilot injection of performing injection at a timing such that at least part of a fuel spray reaches outside a cavity 31 on a top face of a piston, and a pre-injection of injecting fuel at a predetermined timing after the pilot injection, to suppress thereby ignition of the fuel injected by the pilot injection and shorten an ignition delay of the fuel injected by the main injection.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Method and system for controlling double-fuel engine
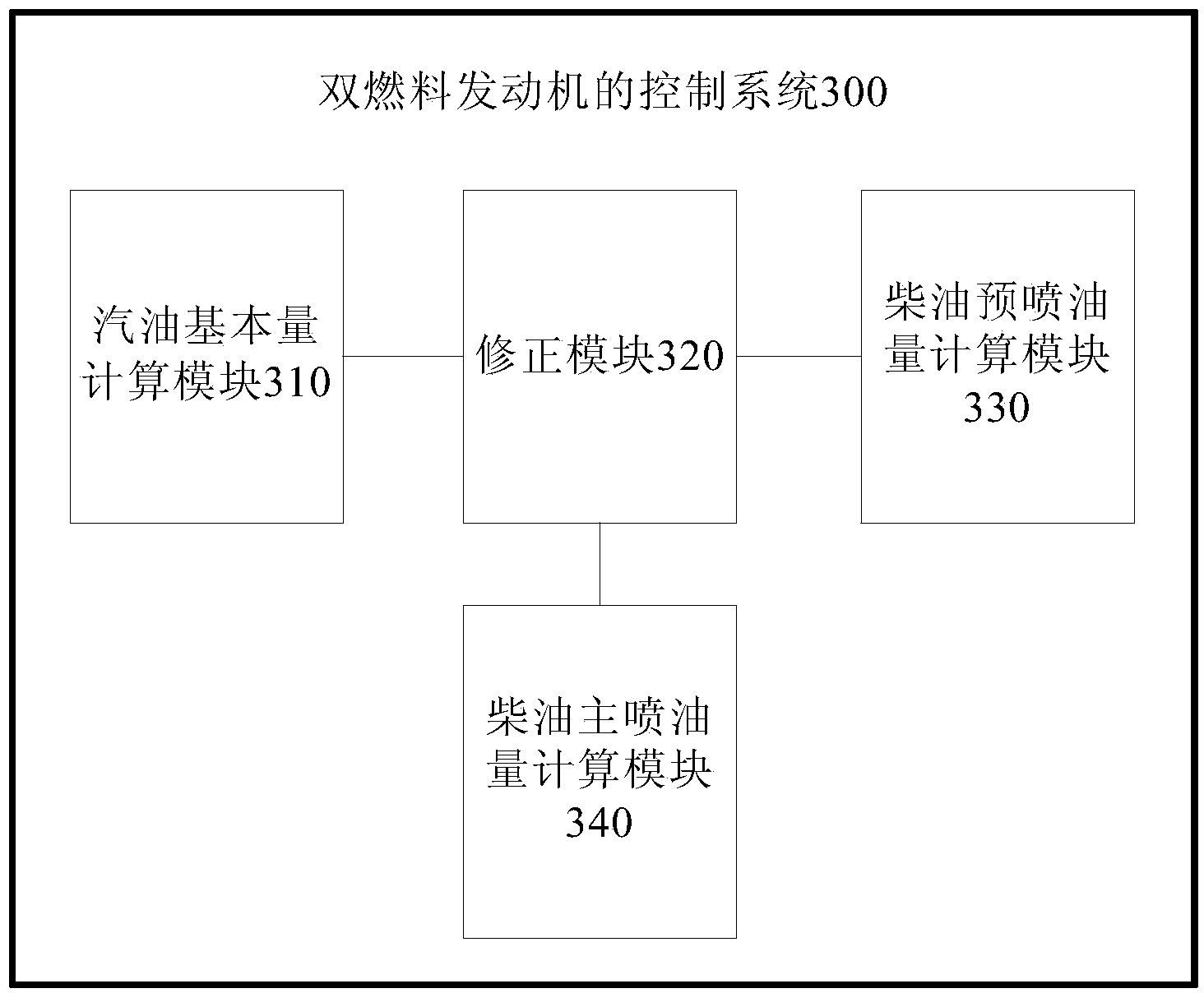
ActiveCN104033257AImprove work efficiencyMeet Torque DemandsEngine controllersMachines/enginesControl systemGasoline
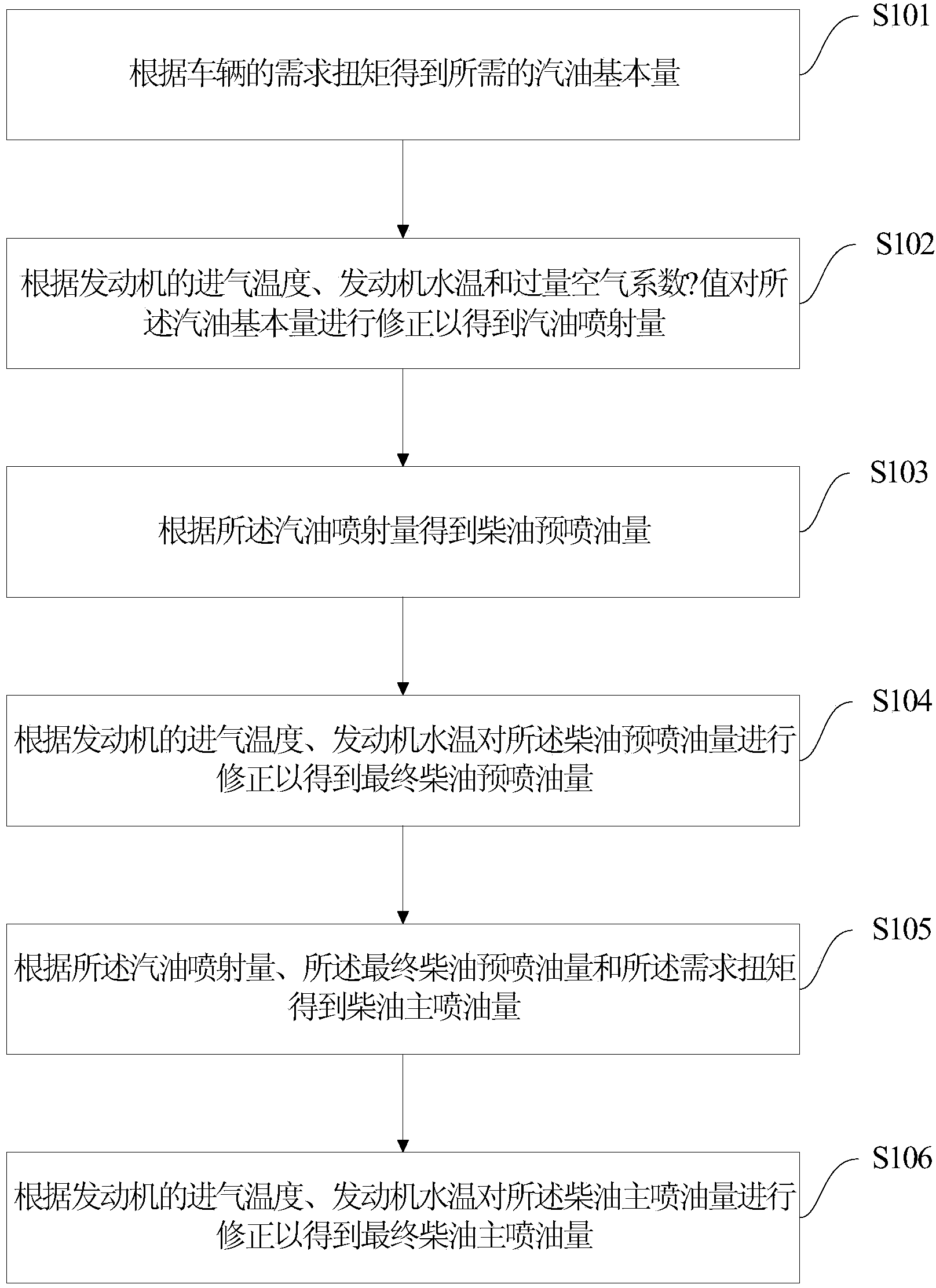
The invention provides a method for controlling a double-fuel engine. The method includes acquiring needed basic gasoline quantity according to needed torque of a vehicle; correcting the basic gasoline quantity according to air incoming temperature of the engine, water temperature of the engine and excess air coefficient lambda value to acquire gasoline injection quantity; acquiring diesel pilot-injection quantity according to the gasoline injection quantity; correcting the diesel pilot-injection quantity to acquire final diesel pilot-injection quantity; acquiring diesel main-injection quantity according to the gasoline injection quantity, the final diesel pilot-injection quantity and the needed torque; correcting the diesel main-injection quantity to acquire final diesel main-injection quantity. The method has the advantage that oil consumption and emission of the engine can be lowered. The invention further provides a system for controlling the double-fuel engine.
Owner:GREAT WALL MOTOR CO LTD
Fuel injection amount compensating method
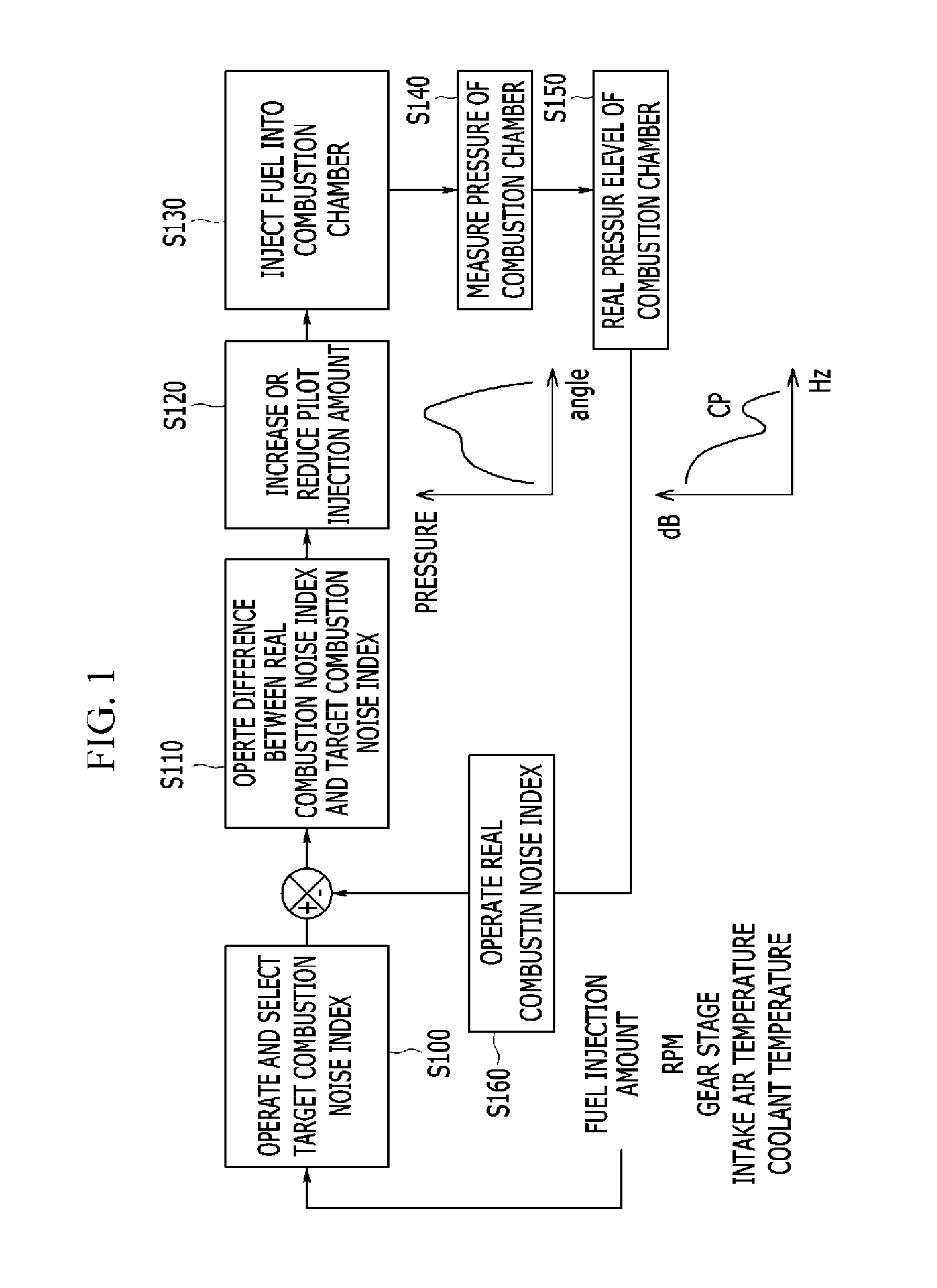
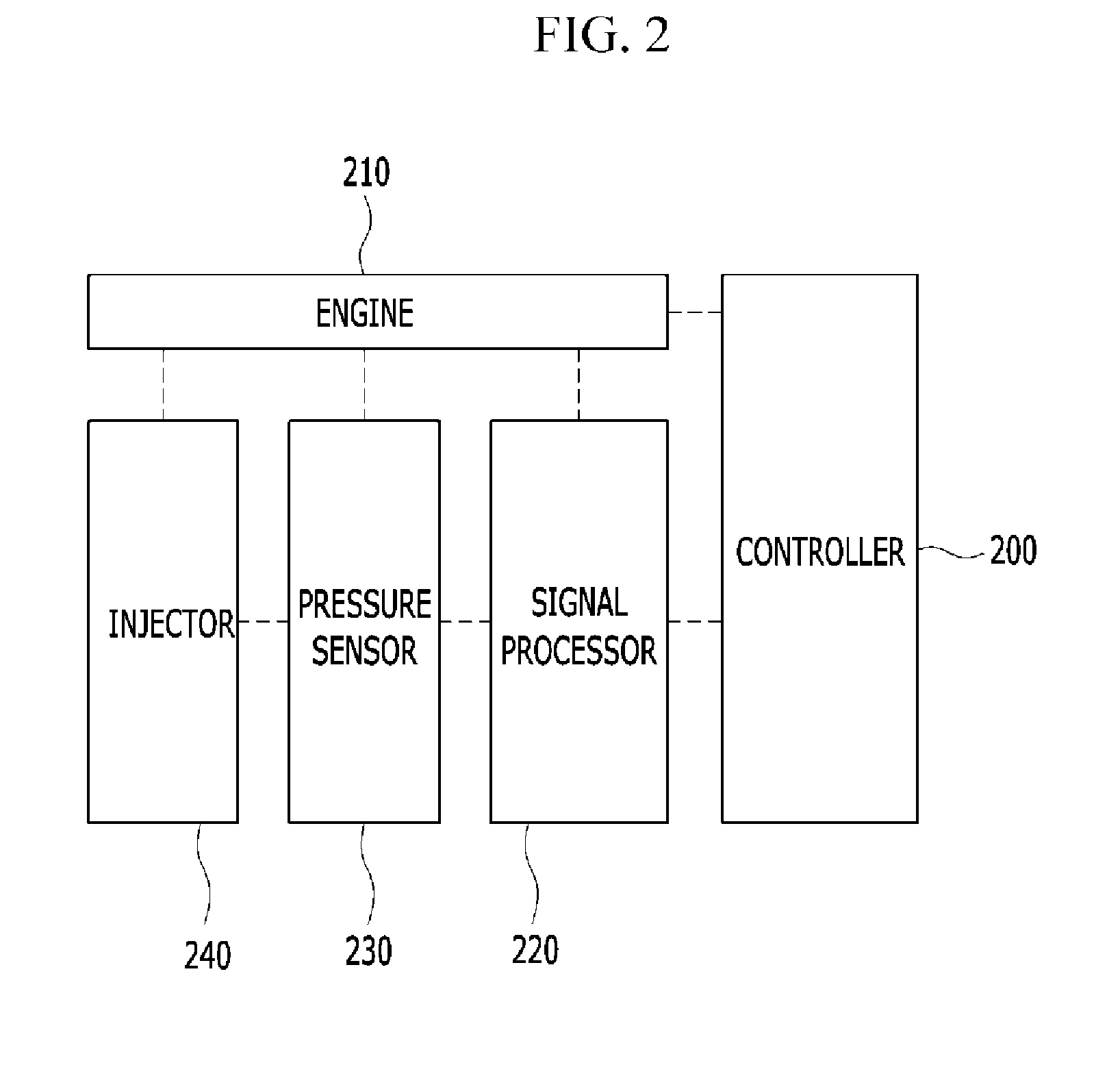
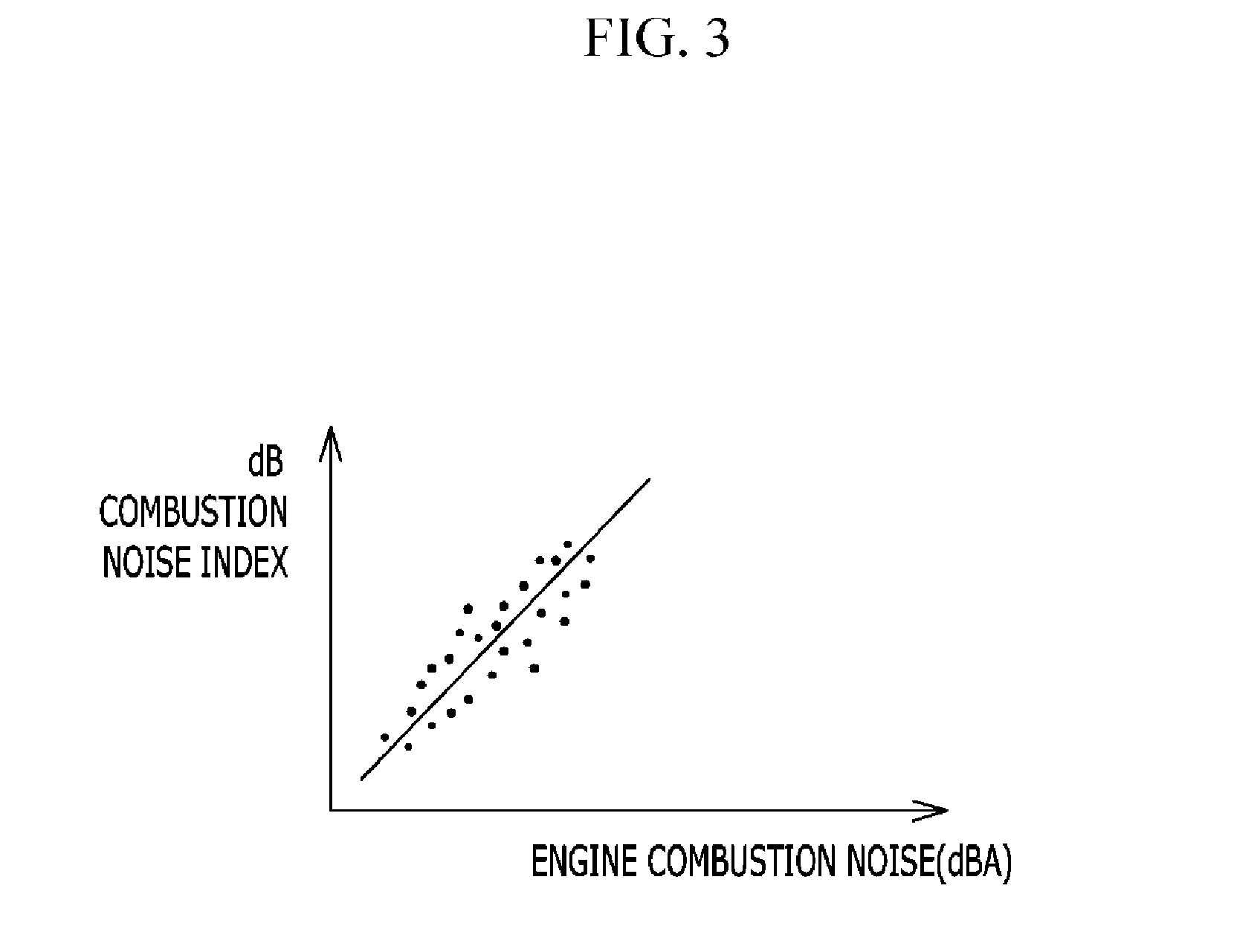
ActiveUS20140172276A1Reduce noiseReduce vibrationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberCombustion noise
Disclosed is a fuel injection amount compensating method that may include measuring a real pressure of a combustion chamber, calculating a real pressure level of the combustion chamber based on the real pressure, calculating a real combustion noise index based on the real pressure level of the combustion chamber, calculating a target combustion noise index based on a driving condition, calculating a difference between the real combustion noise index and the target combustion noise index, and increasing or reducing a pilot injection amount of a fuel injector in accordance with the difference. Also disclosed is a fuel injection amount compensating system.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Method of operating an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20140109873A1Accurate calculationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
A method of operating an internal combustion engine, wherein the engine is operated in an injector learning mode in which an injection parameter associated with a nominal fuel quantity of a pilot injection is learned, includes performing a learning pilot injection based on a candidate value for the injection parameter to influence injection of the nominal fuel quantity and determining a parameter indicative of the actually injected fuel quantity based on the in-cylinder pressure during combustion of the learning pilot injection. The learning pilot injection is operated at an early timing such that combustion thereof complete occurs within a learning window positioned before combustion TDC and before the next combustion starts. The pressure is measured over the learning window, so that the determination of the parameter indicative of the actually injected fuel quantity takes into account essentially the entire combustion event of the learning pilot injection.
Owner:DELPHI INT OPERATIONS LUXEMBOURG S A R L +1
Multi-fuelling an engine
InactiveUS8327823B2Reduce the temperatureReduce susceptibilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesBiodieselCombustion chamber
A compression ignition engine is supplied with a first fuel in a flow of air and a second fuel is injected into the combustion chamber. The first fuel comprises a more volatile fuel than diesel such as ethanol, LPG or other combustible gas; the second fuel comprises diesel or biodiesel; and the second fuel is injected in multiple pulses in each ignition cycle with the first pulse acting as a pilot pulse to trigger ignition, and the timing of the second pulse being such as to modify the temperature through evaporation of the second fuel and thereby reduce the combustion temperature and mitigate knock susceptibility. Preferably the pilot pulse is followed by a single further pulse of the second fuel in the ignition cycle. The engine may be controlled to operate in two different modes, one mode for light and medium load conditions when there is only a pilot pulse injection of the second fuel which reduces NOx and soot emissions, and the other mode for higher load conditions when there is a pilot pulse injection followed by a main pulse injection of the second fuel. The first fuel may comprise bioethanol and or one or more of the following: ethanol, butanol, propanol, lpg, natural gas, hydrogen.
Owner:G VOLUTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com