Patents
Literature
109 results about "Prefix code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A prefix code is a type of code system distinguished by its possession of the "prefix property", which requires that there is no whole code word in the system that is a prefix (initial segment) of any other code word in the system. It is trivially true for fixed-length code, so only a point of consideration in variable-length code.
Method for compressed data with reduced dictionary sizes by coding value prefixes
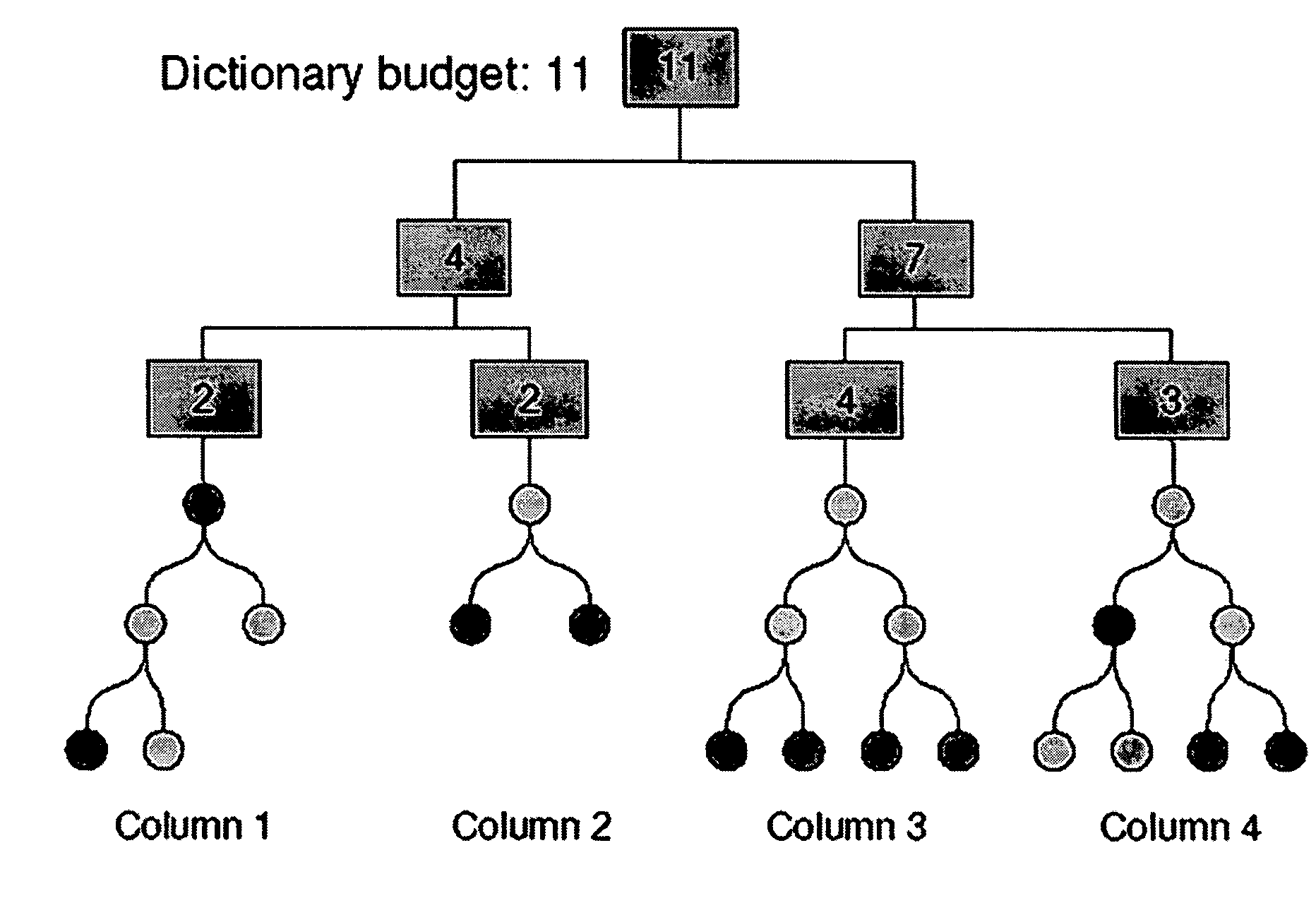
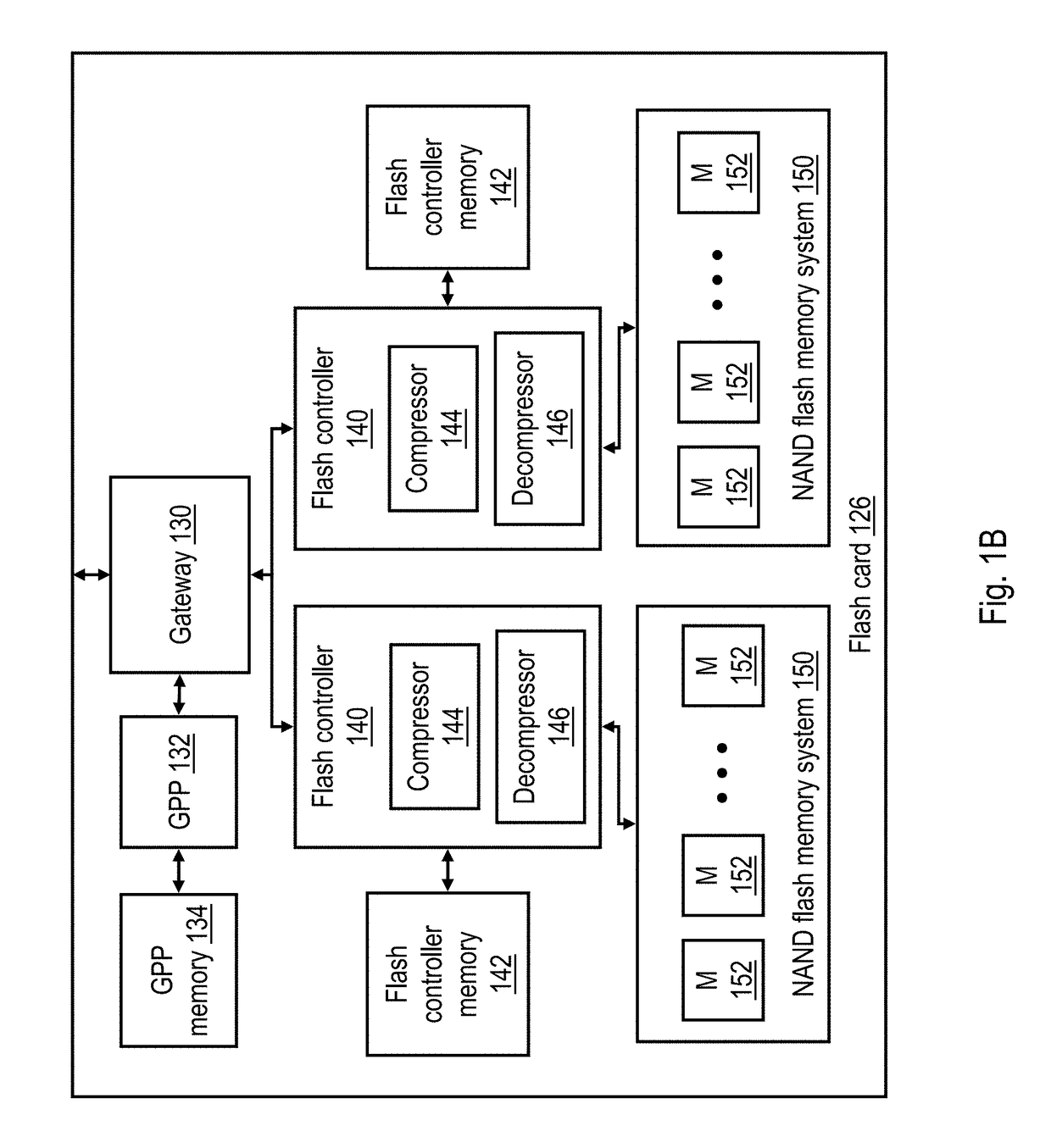
The speed of dictionary based decompression is limited by the cost of accessing random values in the dictionary. If the size of the dictionary can be limited so it fits into cache, decompression is made to be CPU bound rather than memory bound. To achieve this, a value prefix coding scheme is presented, wherein value prefixes are stored in the dictionary to get good compression from small dictionaries. Also presented is an algorithm that determines the optimal entries for a value prefix dictionary. Once the dictionary fits in cache, decompression speed is often limited by the cost of mispredicted branches during Huffman code processing. A novel way is presented to quantize Huffman code lengths to allow code processing to be performed with few instructions, no branches, and very little extra memory. Also presented is an algorithm for code length quantization that produces the optimal assignment of Huffman codes and show that the adverse effect of quantization on the compression ratio is quite small.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
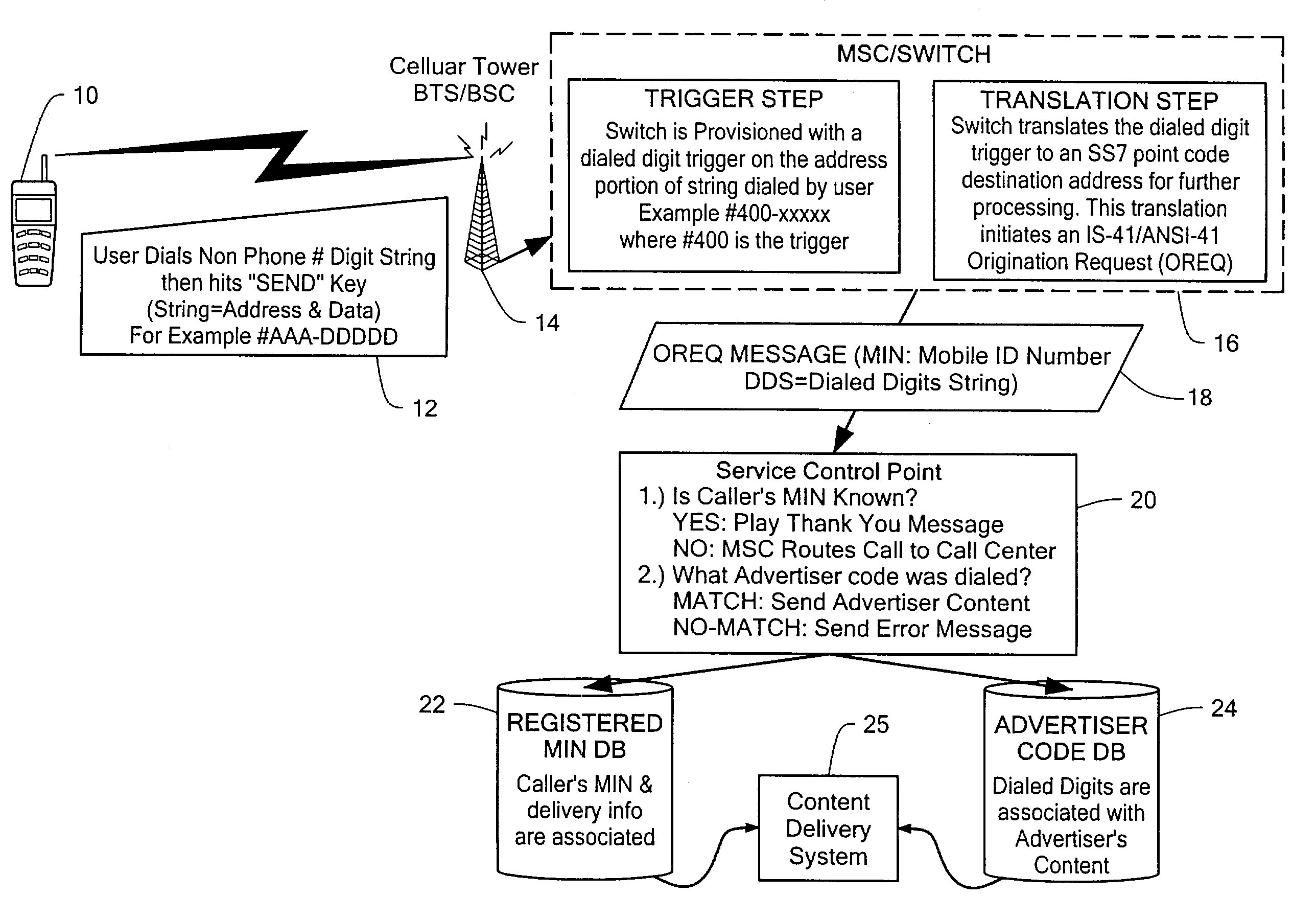
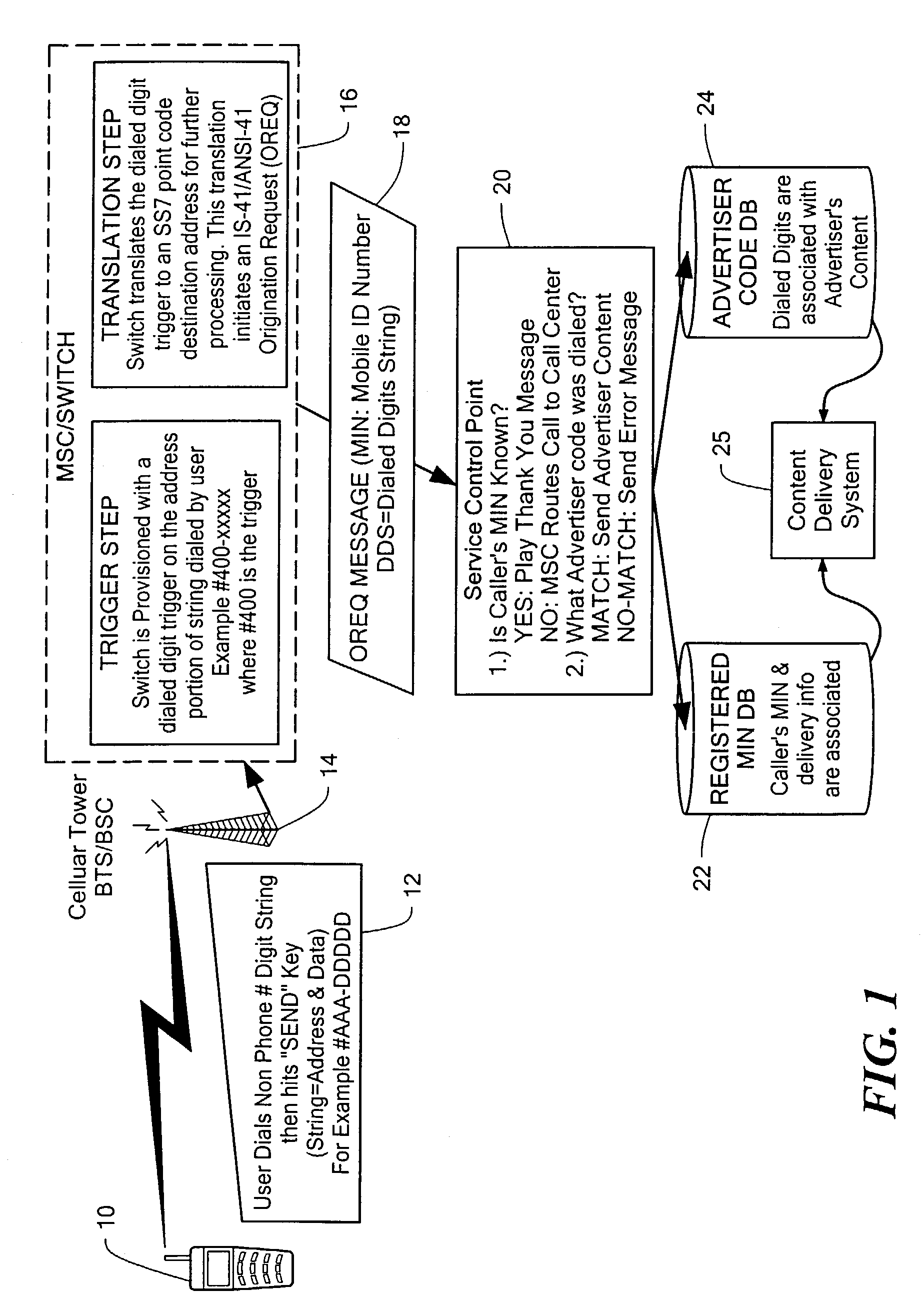
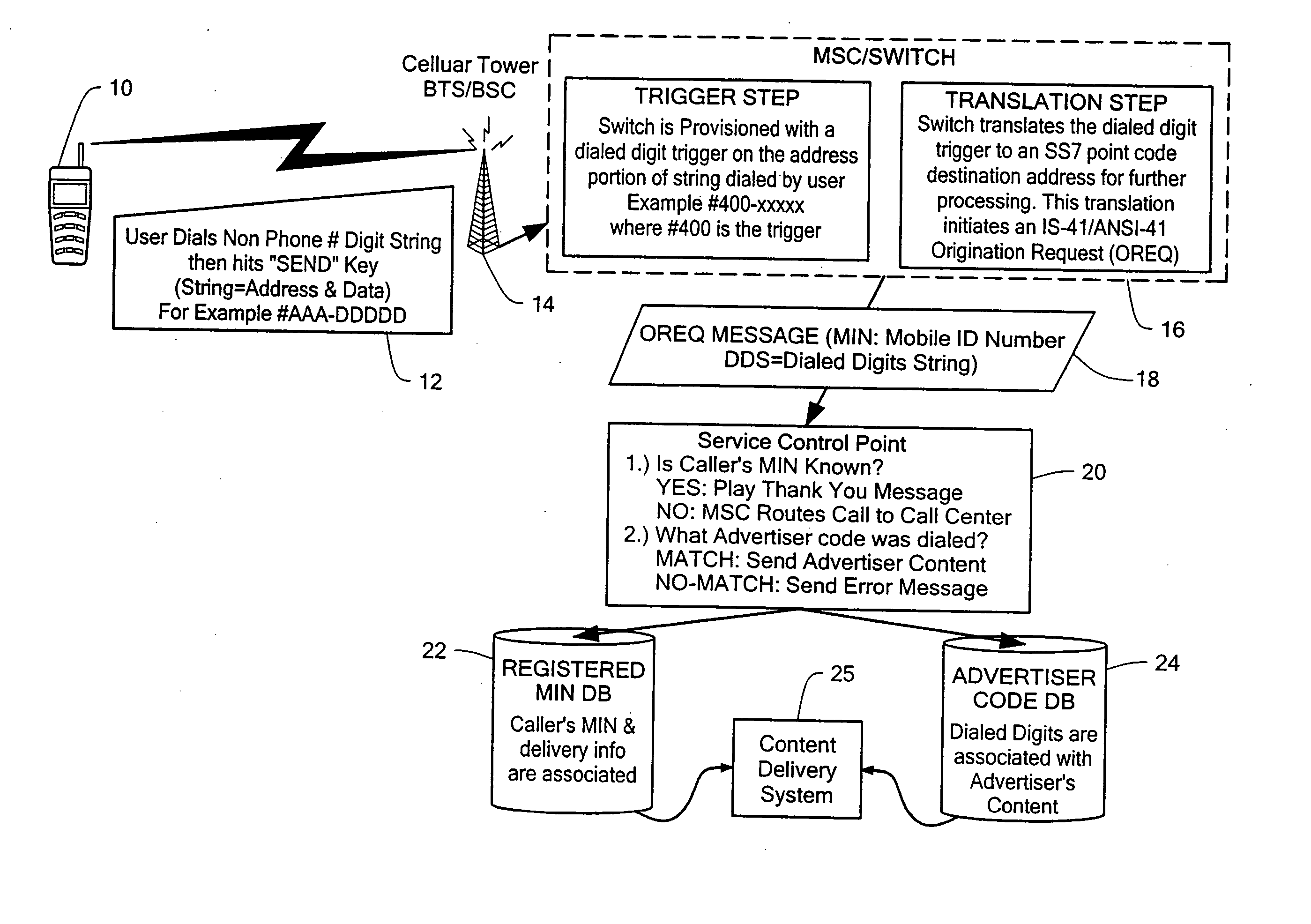
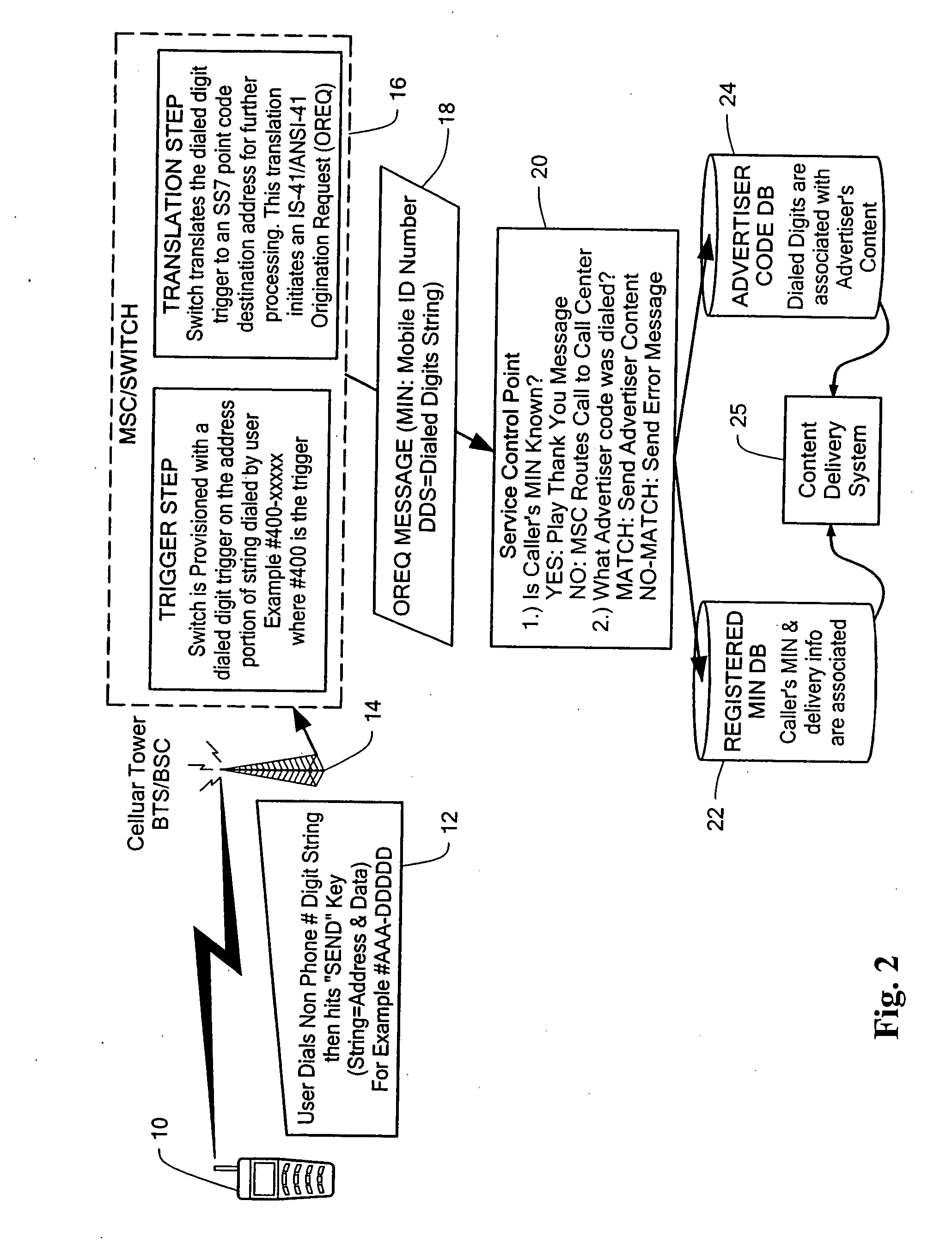
Wireless data system
ActiveUS7257391B2Small sizeIncrease contentAdvertisementsSpecial service for subscribersEmail addressUser input
A system and method for enabling a user to request and receive product information, participate in voting or polling activities, reprint an article or other publication, request and authorize a purchase of a magazine subscription, music sound clip, or other product, and / or share personal information with other users. The service request and information delivery may provided over a mobile phone. The user dials a series of digits into their phone and enters them into the disclosed system, for example by pressing the send key on a mobile phone. The digits entered by the user include a prefix or routing code, and a data code. The dialed digits are transferred to a call switching system, which determines, based on the prefix code, a processing system to which a message is sent including the originally dialed digits as well as identification of the user or phone that placed the call. The processing system may then determine, based on the identification of the mobile phone that placed the call, a user account. The processing system further determines, based on the data code of the dialed digits, the product information or other service such as entry of a polling response, vote, or product purchase, that is to be provided. The user account information may then be used to determine a delivery technique, such as electronic mail using an electronic mail address associated with the phone that made the call, SMS / MMS / EMS Text messaging, or WAP push, through which the product information associated with the data code may be forwarded to the requesting user.
Owner:VHT STARSTAR LLC
Method and apparatus for faster-than-real-time lossless compression and decompression of images
InactiveUS20080219575A1Maximize compression ratioMinimized on demandCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationFrequency spectrumContext independent
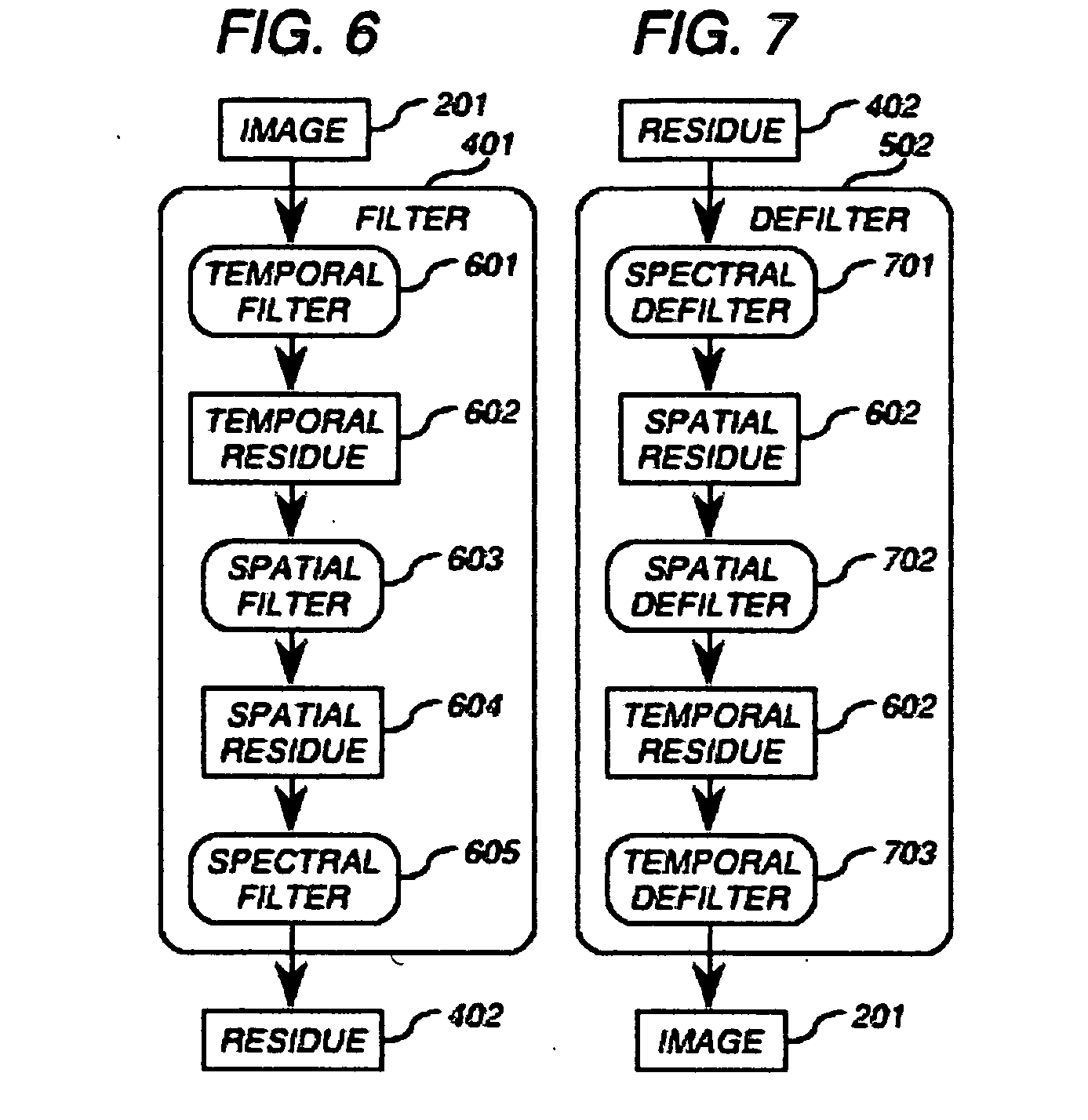
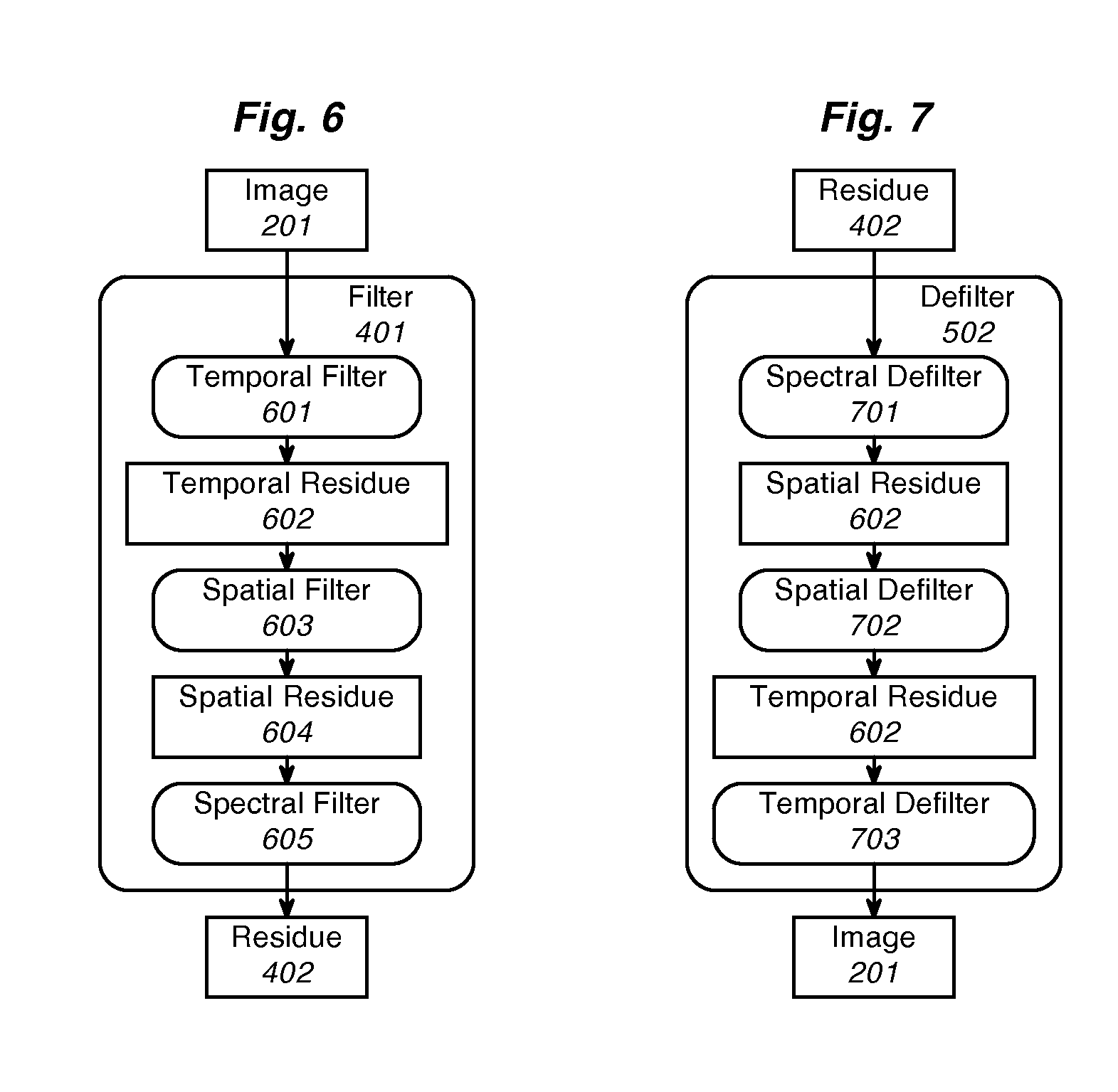
The present invention is a method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing data. In particular, the present invention provides for (de-)compressing naturalistic color-image and moving-image data, including high-precision and high-definition formats, with zero information loss, one-sample latency and in faster than real time on common computing platforms, resulting in doubled transmission, storage, and playback speed and doubled transmission bandwidth and storage capacity, and hence in doubled throughput for non-CPU-bound image-editing tasks in comparison with uncompressed formats. The present invention uses a nearly symmetrical compression-decompression scheme that provides temporal, spatial, and spectral compression, using a reversible condensing / decondensing filter, context reducer, and encoder / decoder. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the compression filter is implemented as a cascade of quasilinear feedforward filters, with temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral stages, where appropriate, in that order, whose support consists of adjacent causal samples of the respective image. The decompressor cascades quasilinear feedback inverse filters in the reverse order. The filters can be implemented with mere integer addition, subtraction, and either one-dimensional table lookup or constant multiplication and binary shifting, depending on the computing environment Tables permit the data precision to be constrained throughout to that of the image samples. The encoder uses a table of prefix codes roughly inversely proportional in length to their probability, while the decoder uses chunked decode tables for accelerated lookup. In the fastest and simplest mode, the code tables are context-independent. For greater power, at the cost of a reduction in speed, the code tables are based on the temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral adjacent causal residue samples, where contexts with similar probability distributions are incoherently collapsed by a context reducer using one-dimensional lookup tables followed by implicitly multidimensional lookup tables, to minimize the overall table size. The invention's minimal resource requirements makes it ideal for implementation in either hardware or software.
Owner:WITTENSTEIN ANDREAS
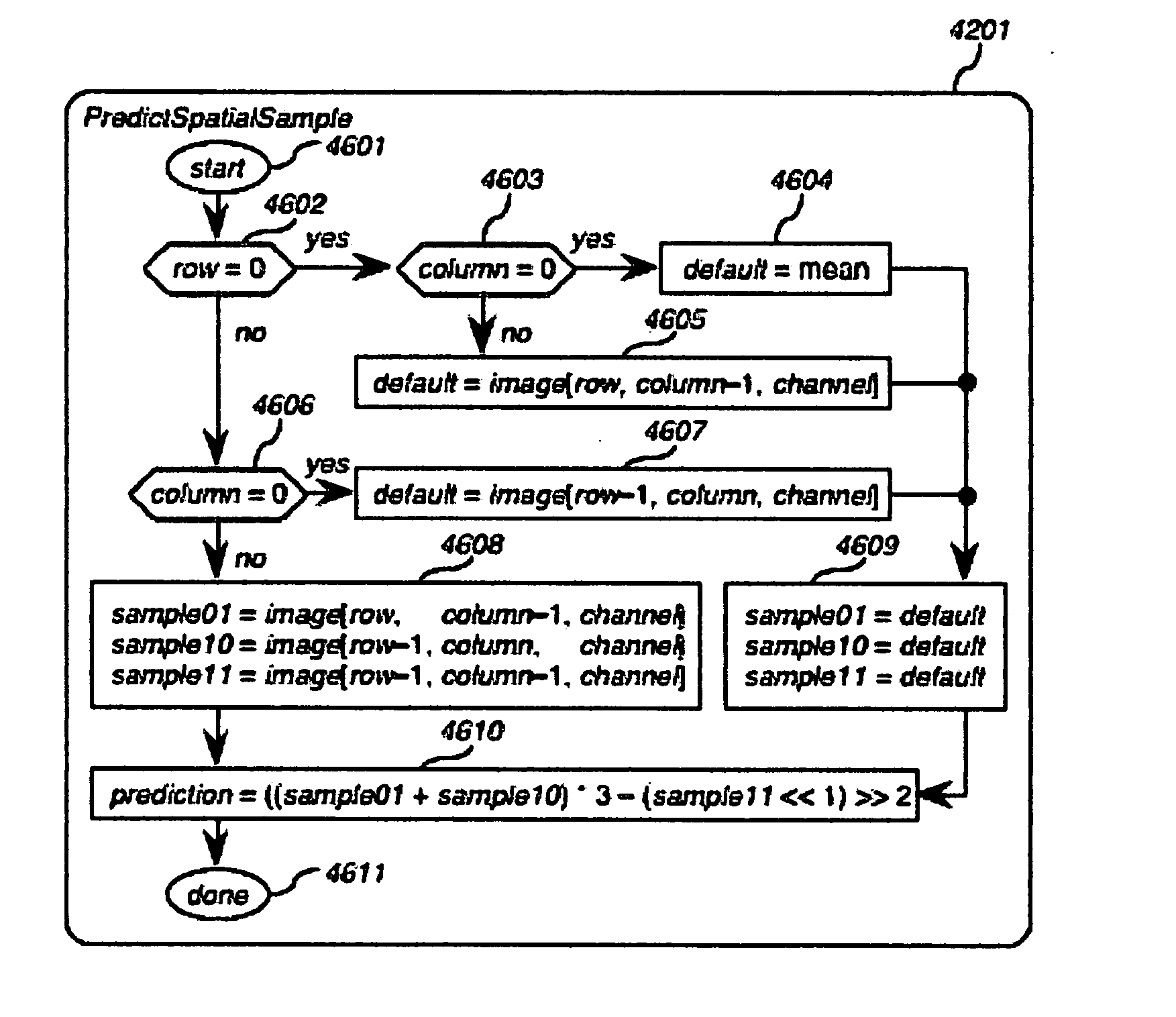
Method and apparatus for faster-than-real-time lossless compression and decompression of images
InactiveUS7693339B2Minimized on demandSame amount of timeCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationFrequency spectrumSpatial prediction
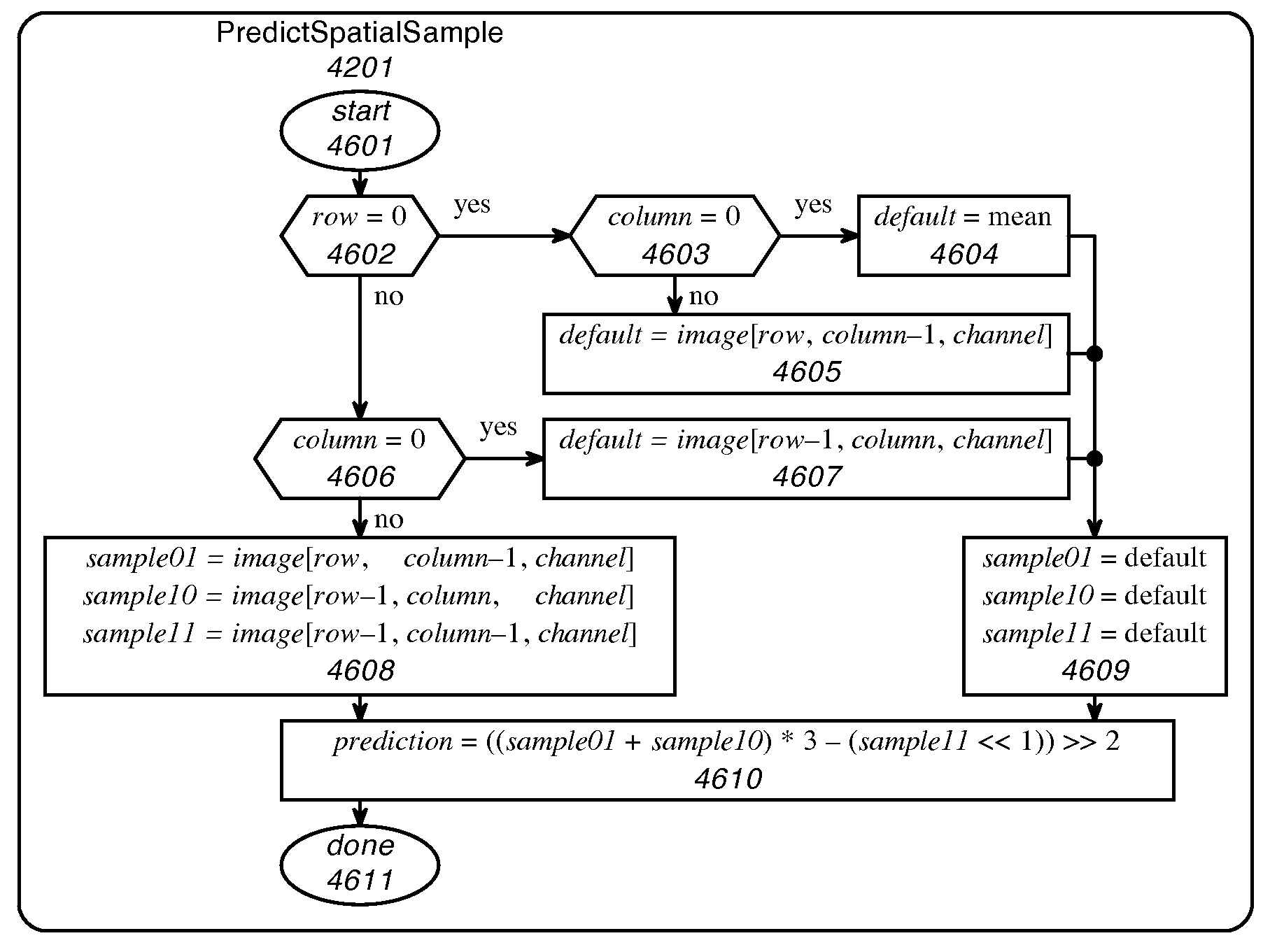
Image compression wherein a spatial prediction filter combines two adjacent samples and a corner sample in the proportion 3:3:−2, or wherein chunked decode tables are used to decode embedded prefix codes more than one bit at a time. A spectral prediction filter might be used in conjunction with the spatial prediction filter. Chunked decode tables might be used in combination with simple prediction filters.
Owner:WITTENSTEIN ANDREAS
Entropy coding using adaptable prefix codes
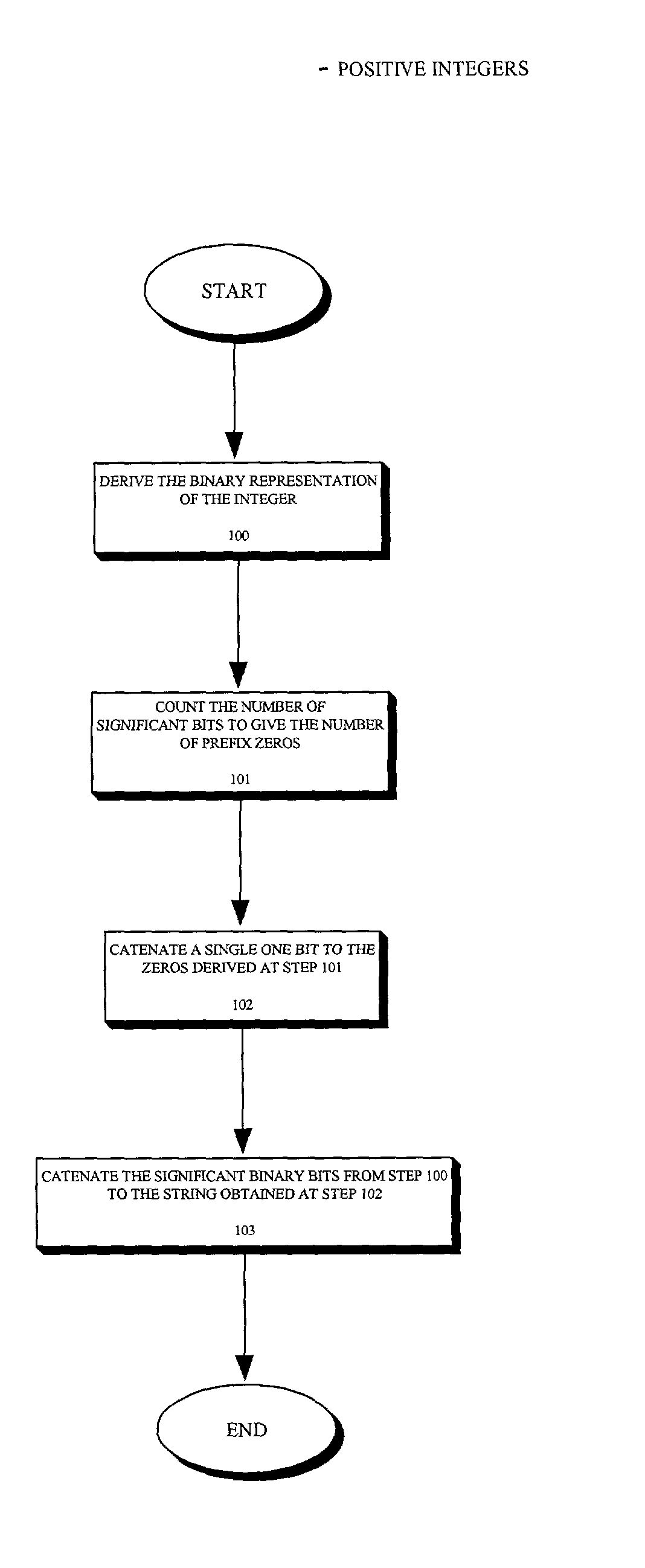
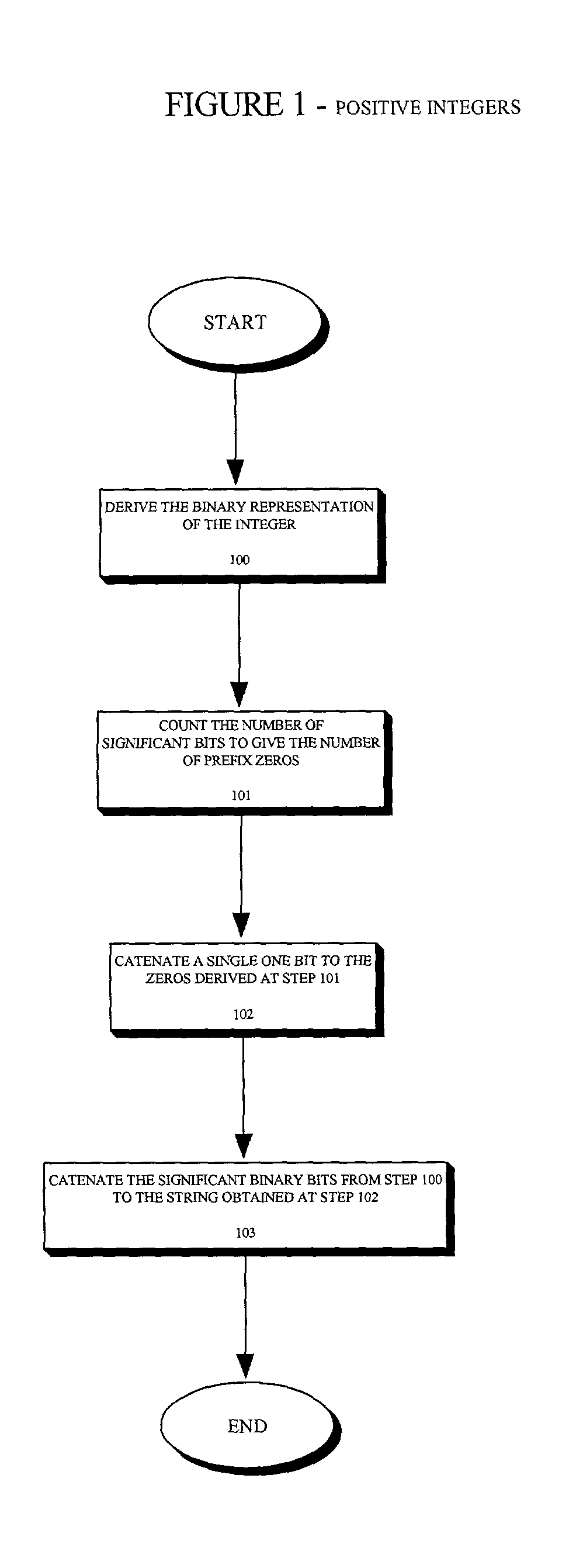
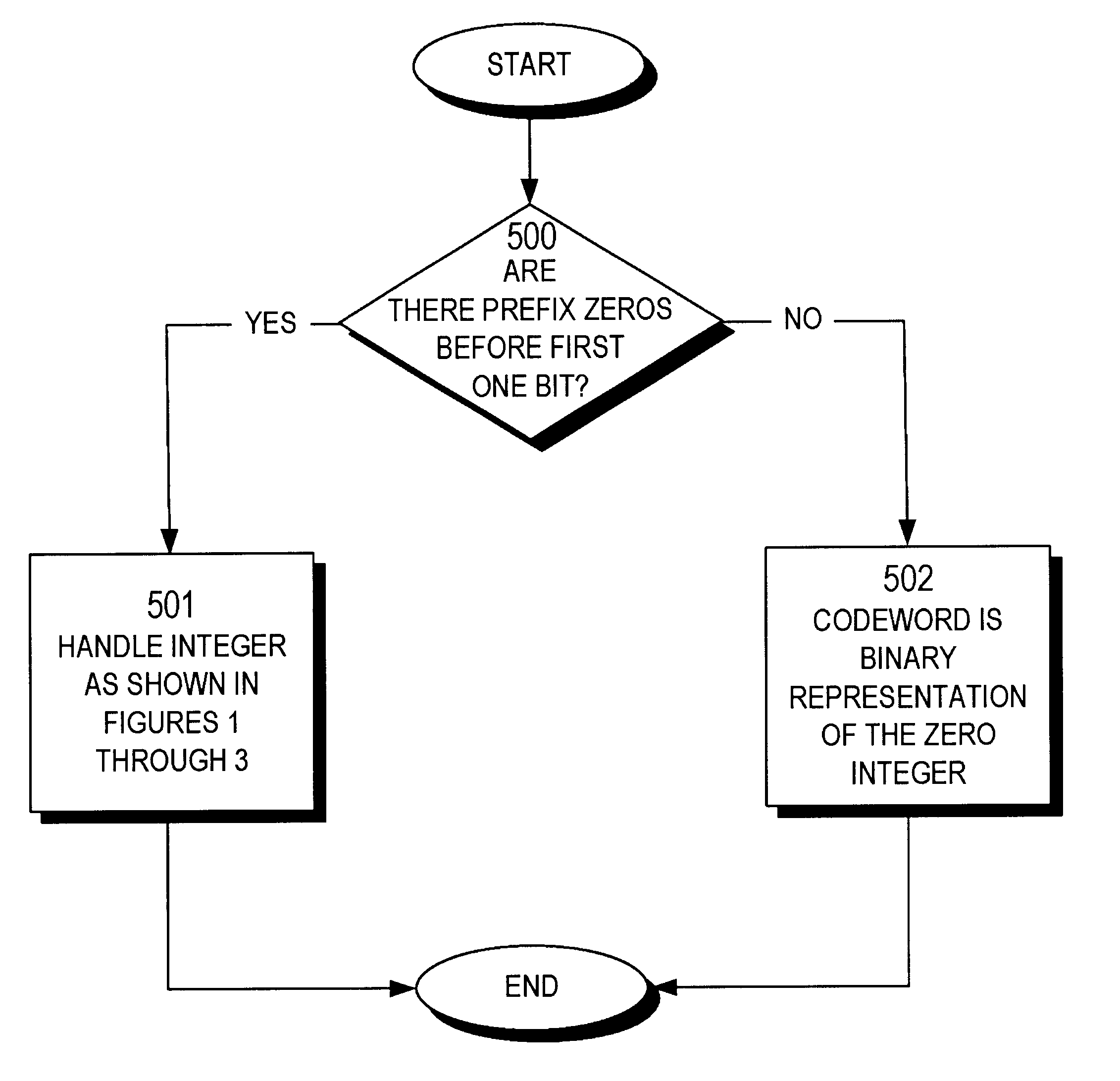
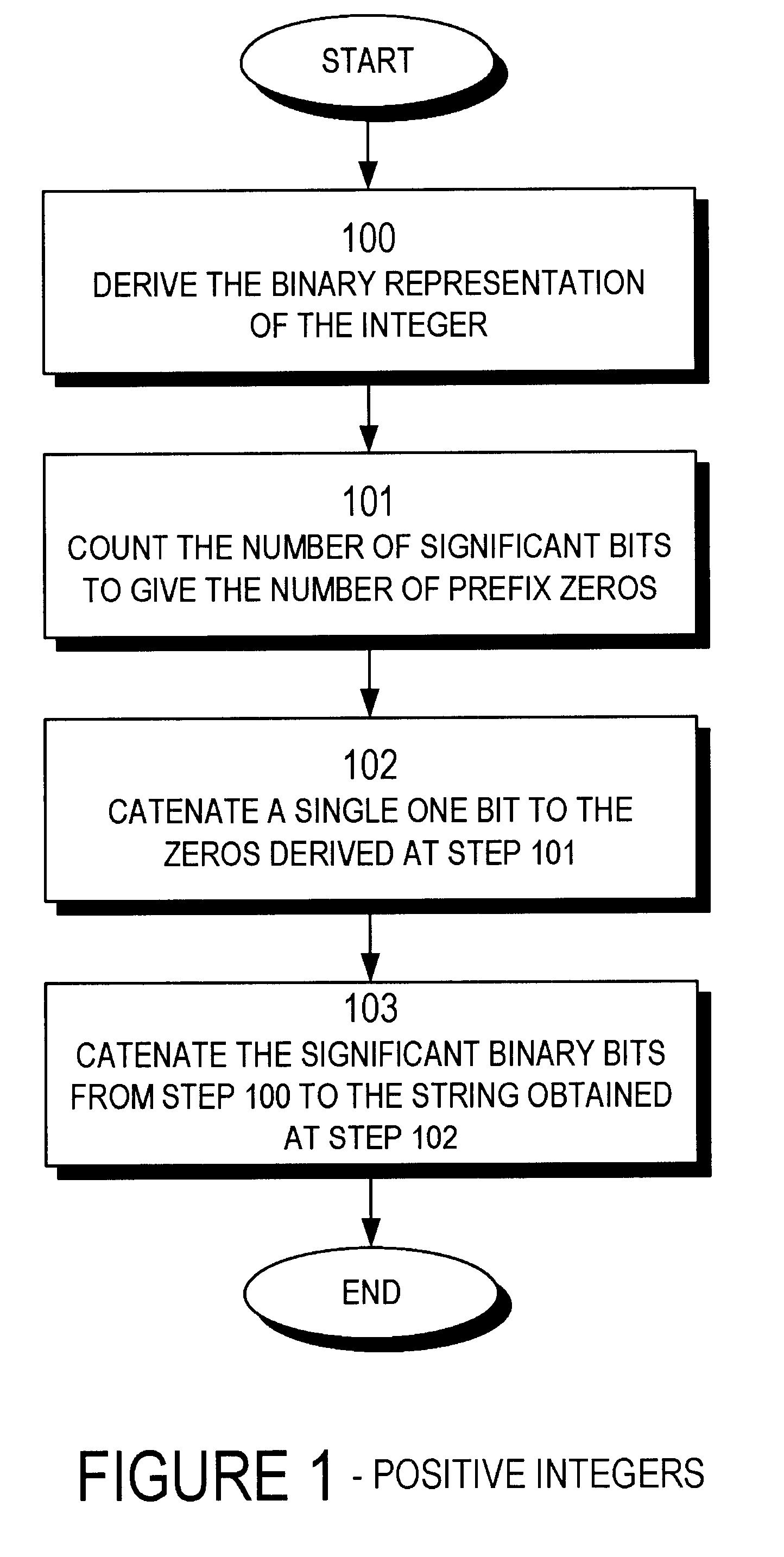
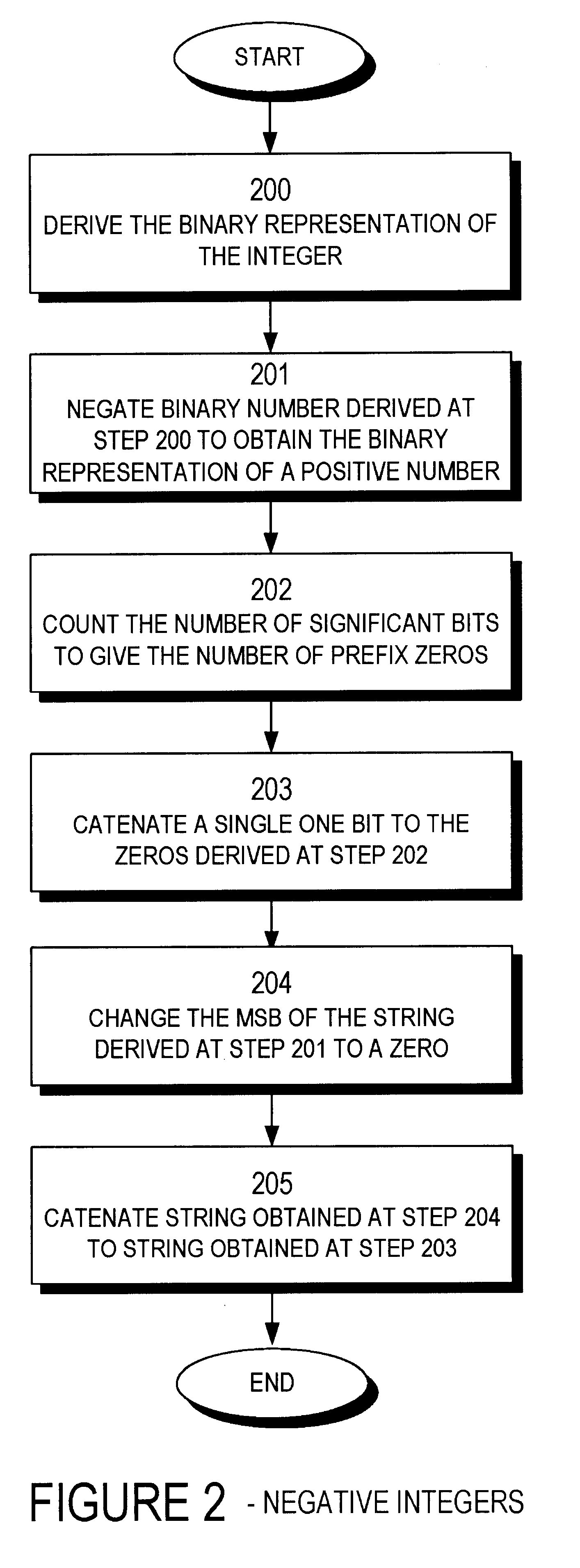
The present invention provides an entropy coding scheme using an adaptable prefix code. The prefix code is a binary representation of the algorithm used to compress and decompress the data. There are prefix zeros that represent the number of significant binary digits that follow the first one. According to one embodiment, this scheme works on both positive and negative integers and encodes lower order integers with a smaller length of codeword. In another embodiment, the zero integer is encoded as a special case with the shortest codeword. In yet another embodiment, the present scheme is preferred by data sets that are clustered about zero, such as image data sets that have been transformed via a wavelet transform or a discrete cosine transform.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
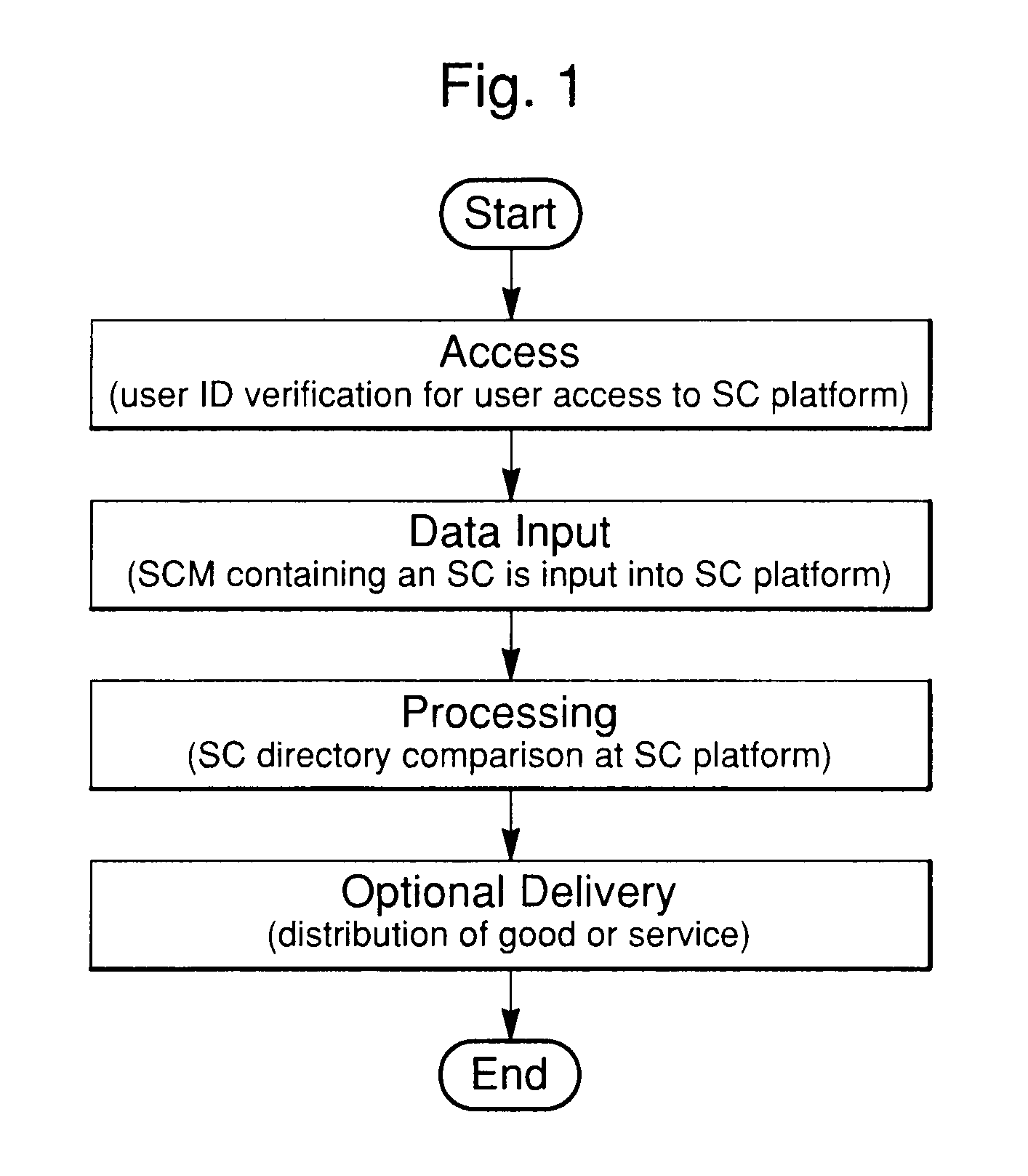
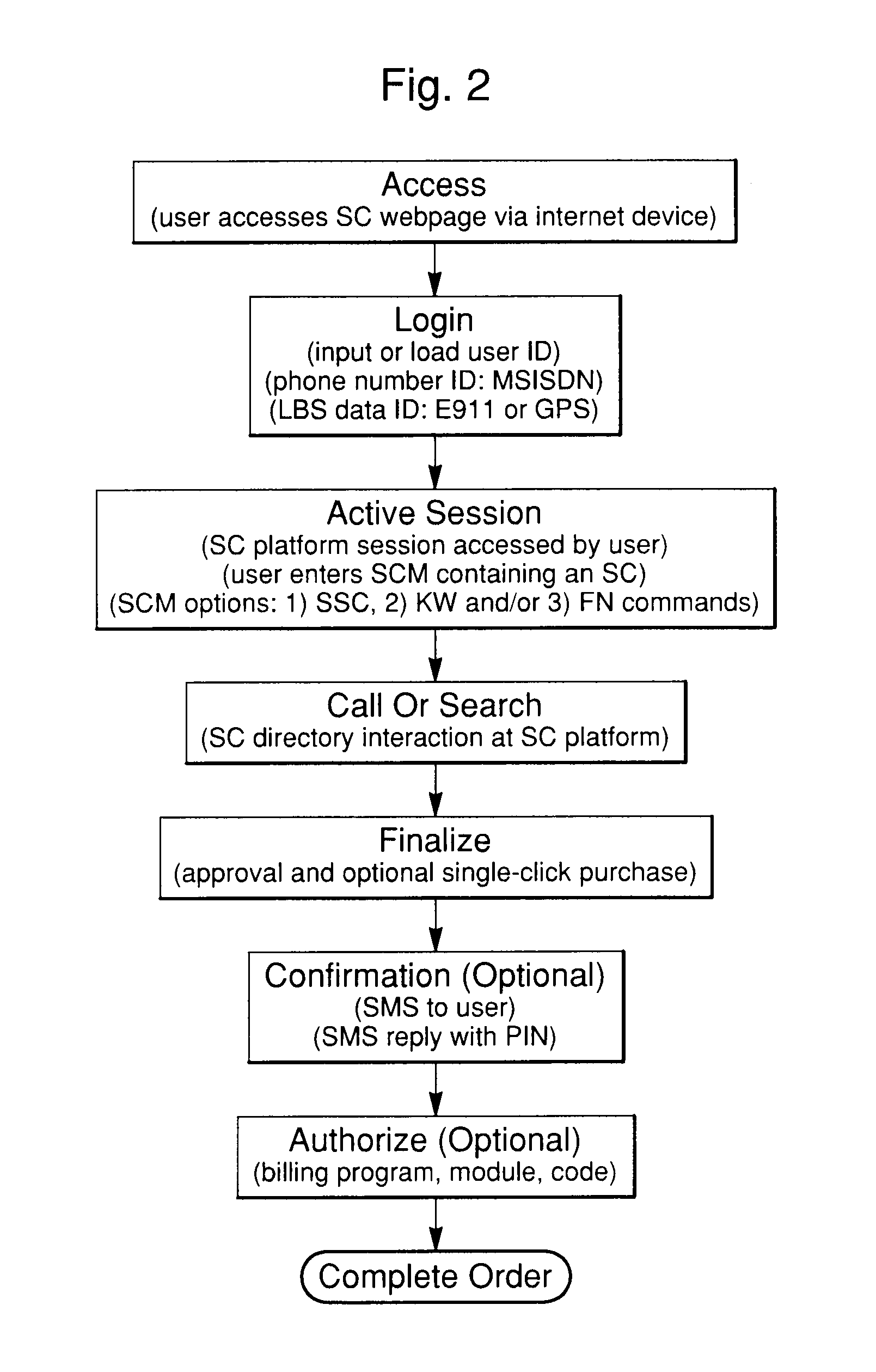
System and method for using symbol command language within a communications network via SMS or internet communications protocols
ActiveUS20110093949A1FunctionalWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareThe Country Code
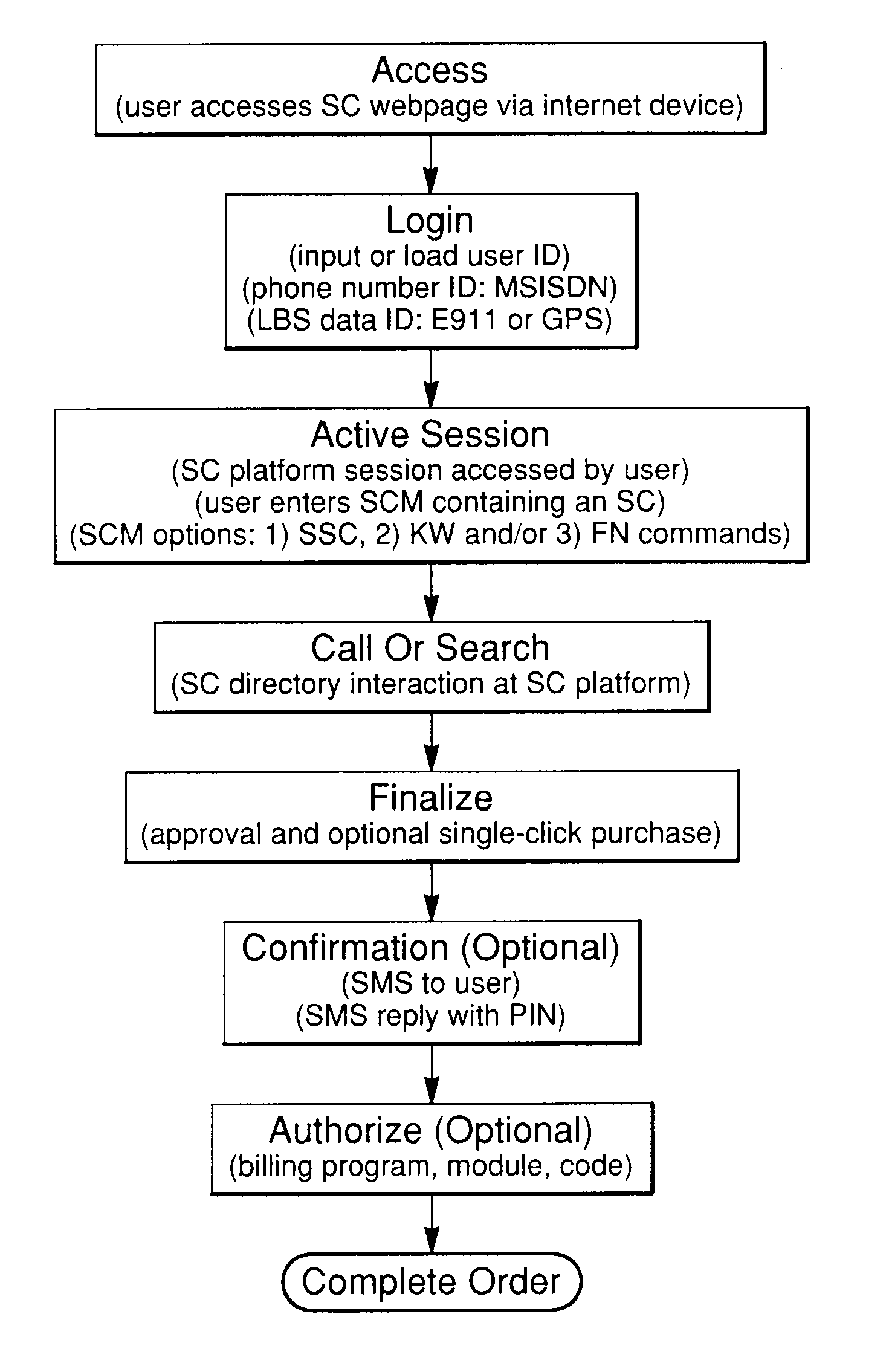
A system and method for generating actions utilizing predefined commands within a communications network comprises predefined commands called symbol commands. These are character strings entered into a platform during an internet or SMS communications protocol session. The method and system can be used via the internet or a GSM network and is well-suited for mobile use. In addition, utilization of keywords and alpha-numeric or other character symbols to form symbol commands allows for complex command structuring. A search process is used in combination with a symbol command and a symbol command directory to identify specific goods and services, or related symbol commands. In addition, a platform performs specific predetermined actions in response to the symbol command such as making product purchases or providing services such as location-based services, coupon delivery or travel ticketing. The symbol command structure and platform will also utilize identification information associated with an individual user. Furthermore, the platform may implement a response using location information associated with the user from the country code, area code or prefix code of a user's telephone number, or use GPS location information associated with the user's internet device. The symbol command system and method provide an improved form of access to products and services via the internet or SMS.
Owner:MESSAGE4U
Updating prefix codes for pseudo-dynamic data compression
In a data storage system, a prior set S of prefix codes for pseudo-dynamic compression as well as data compressed utilizing prior set S are stored. While data compressed utilizing prior set S are stored in the data storage system, the number of prefix codes utilized by the data storage system for pseudo-dynamic compression are augmented. Augmenting the number of codes includes determining a new set S′ of prefix codes for pseudo-dynamic compression from a training data set selected from a workload of the data storage system and storing the new set S′ in the data storage system with the prior set S.
Owner:IBM CORP
Entropy coding using adaptable prefix codes
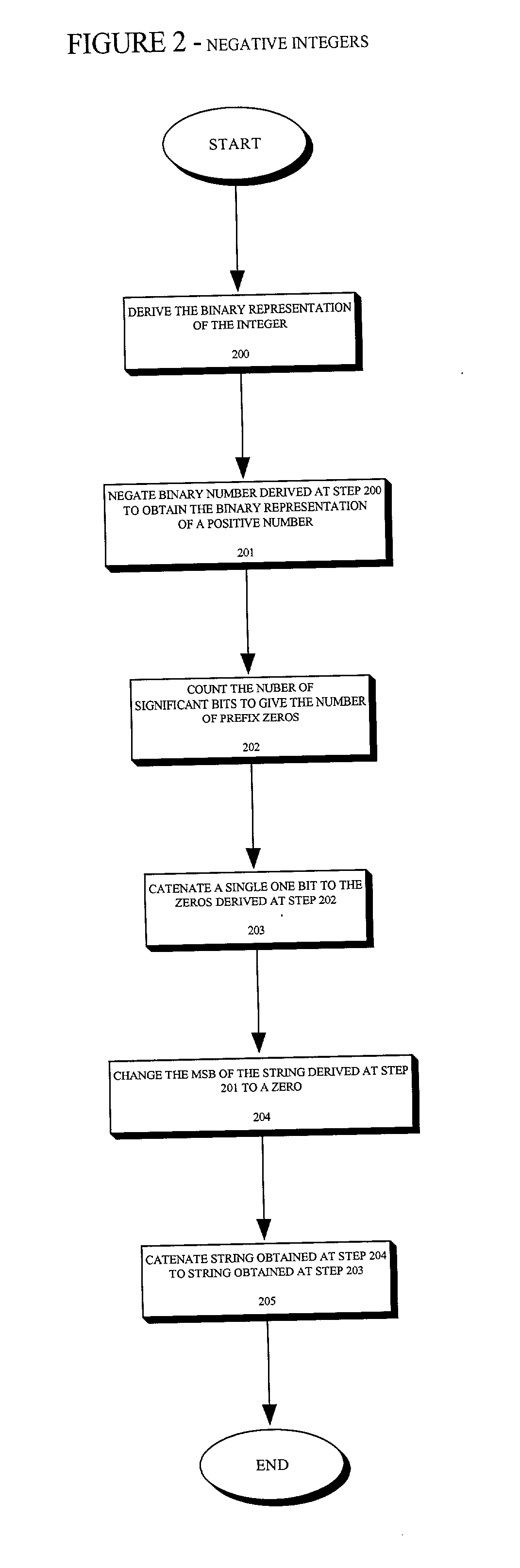
The present invention provides an entropy coding scheme using an adaptable prefix code. The prefix code is a binary representation of the algorithm used to compress and decompress the data. There are prefix zeros that represent the number of significant binary digits that follow the first one. According to one embodiment, this scheme works on both positive and negative integers and encodes lower order integers with a smaller length of codeword. In another embodiment, the zero integer is encoded as a special case with the shortest codeword. In yet another embodiment, the present scheme is preferred by data sets that are clustered about zero, such as image data sets that have been transformed via a wavelet transform or a discrete cosine transform.< / PTEXT>
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
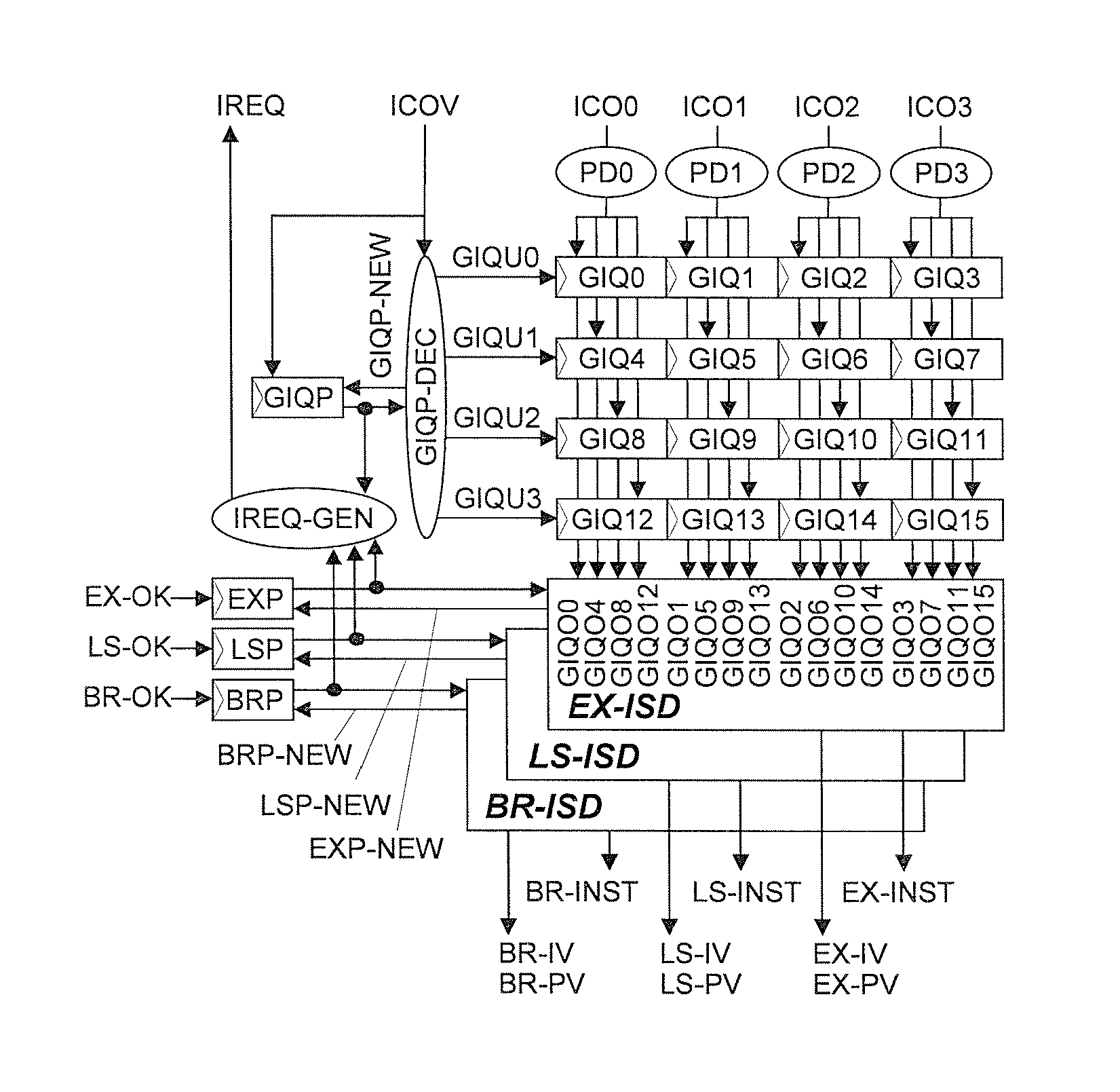
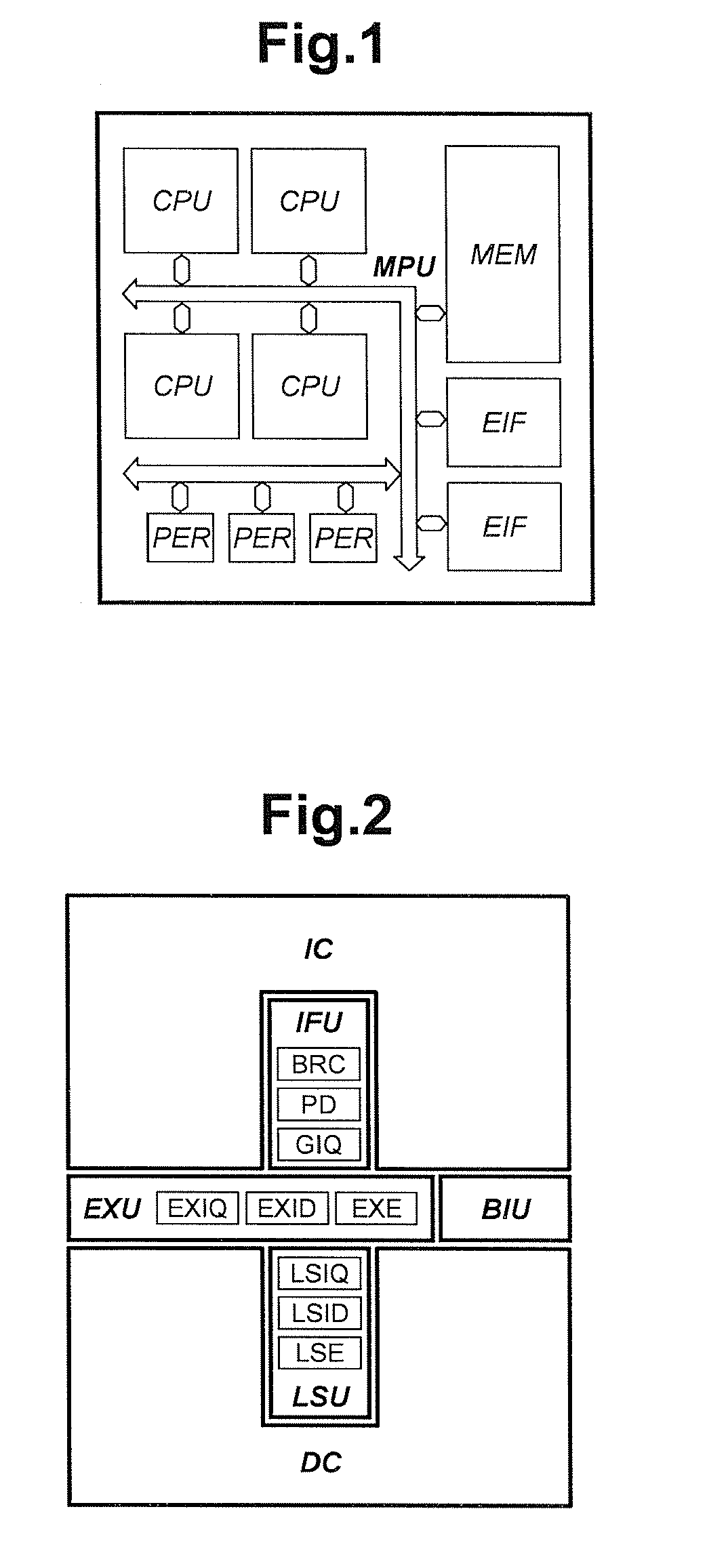
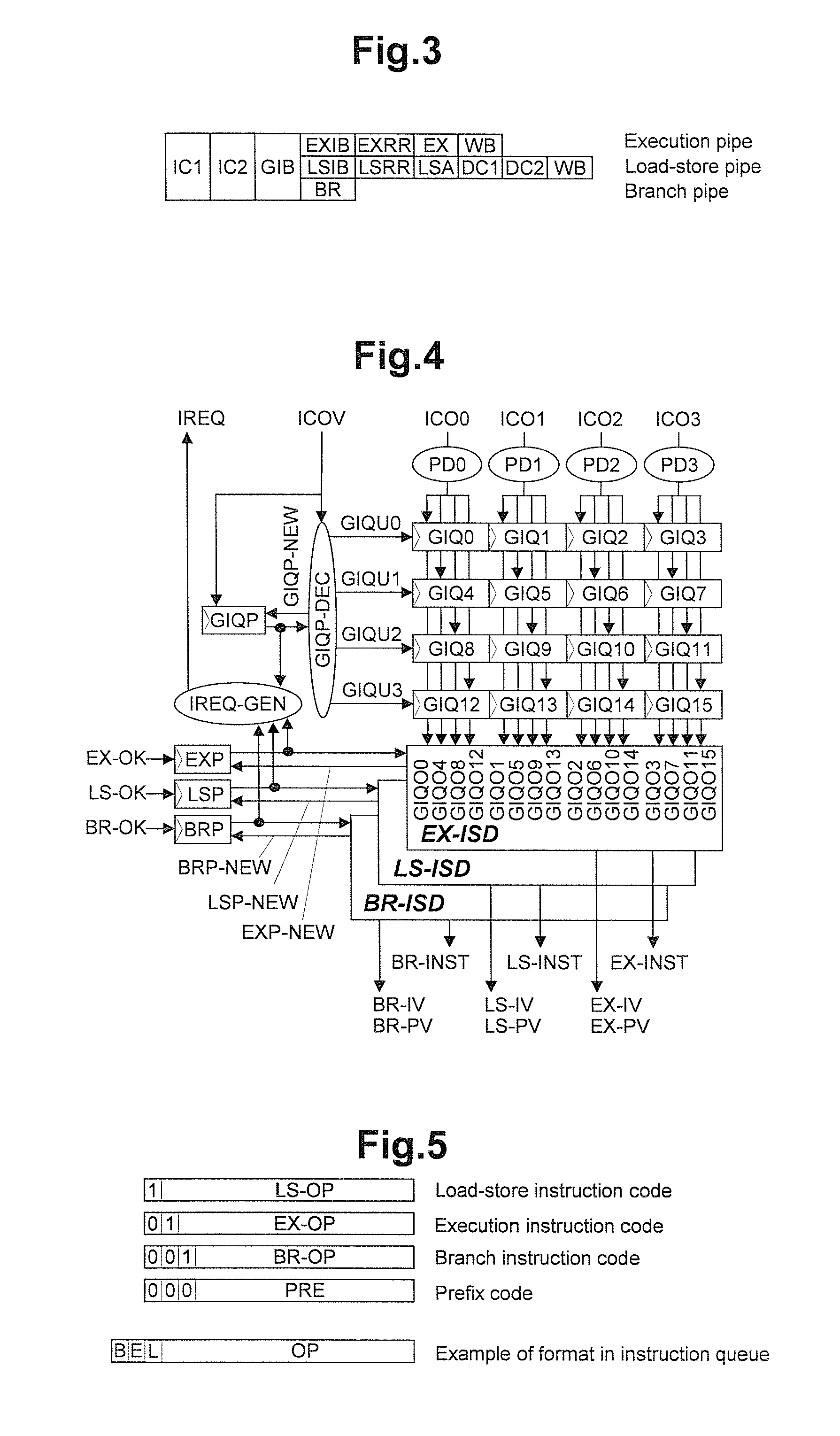
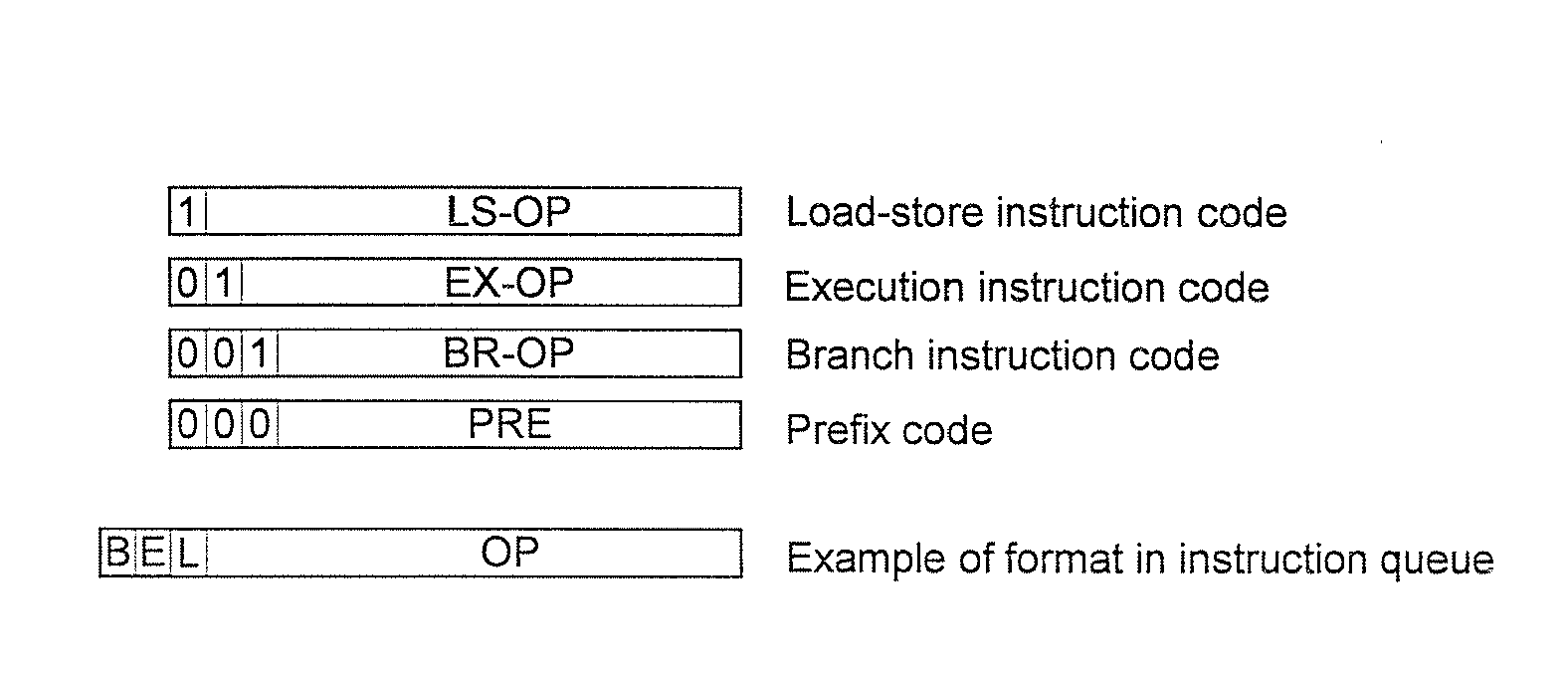
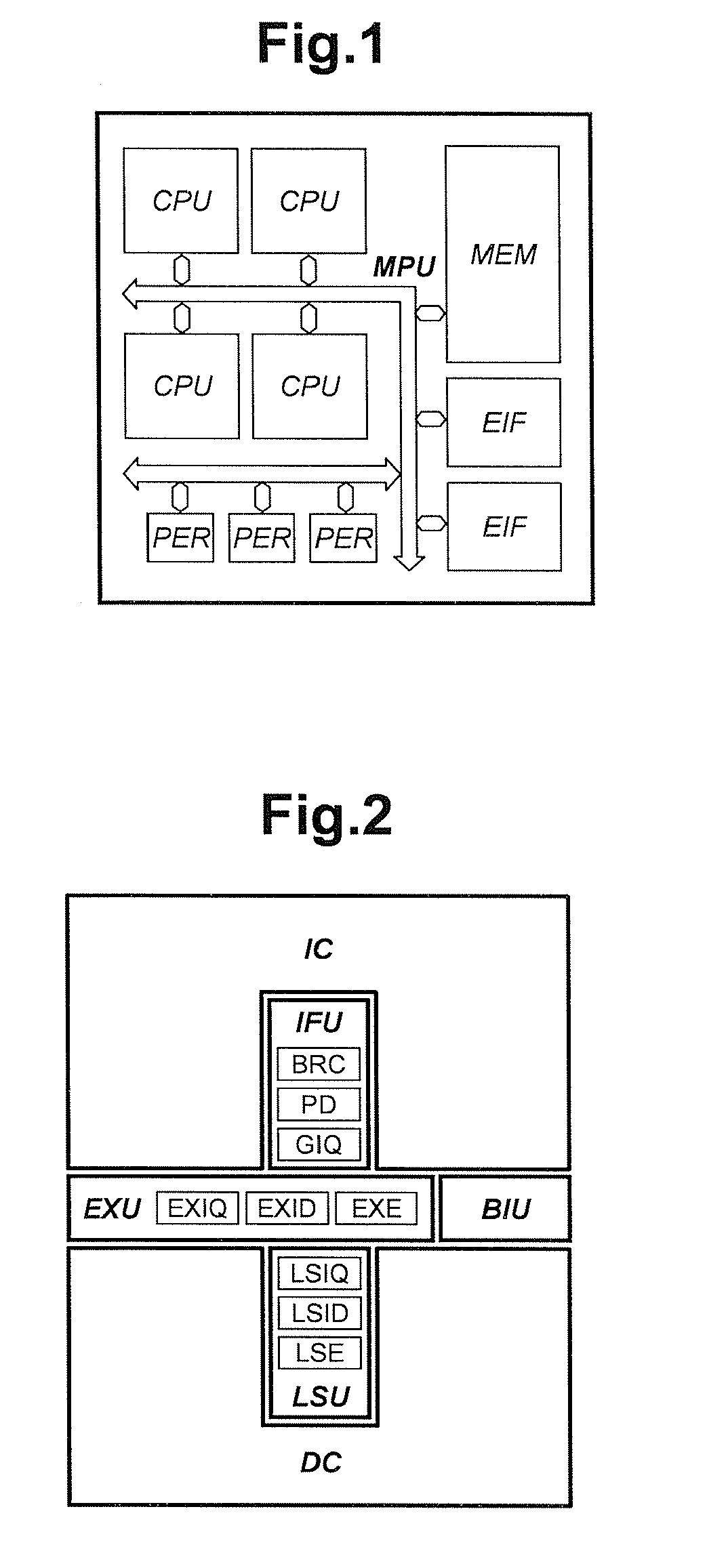
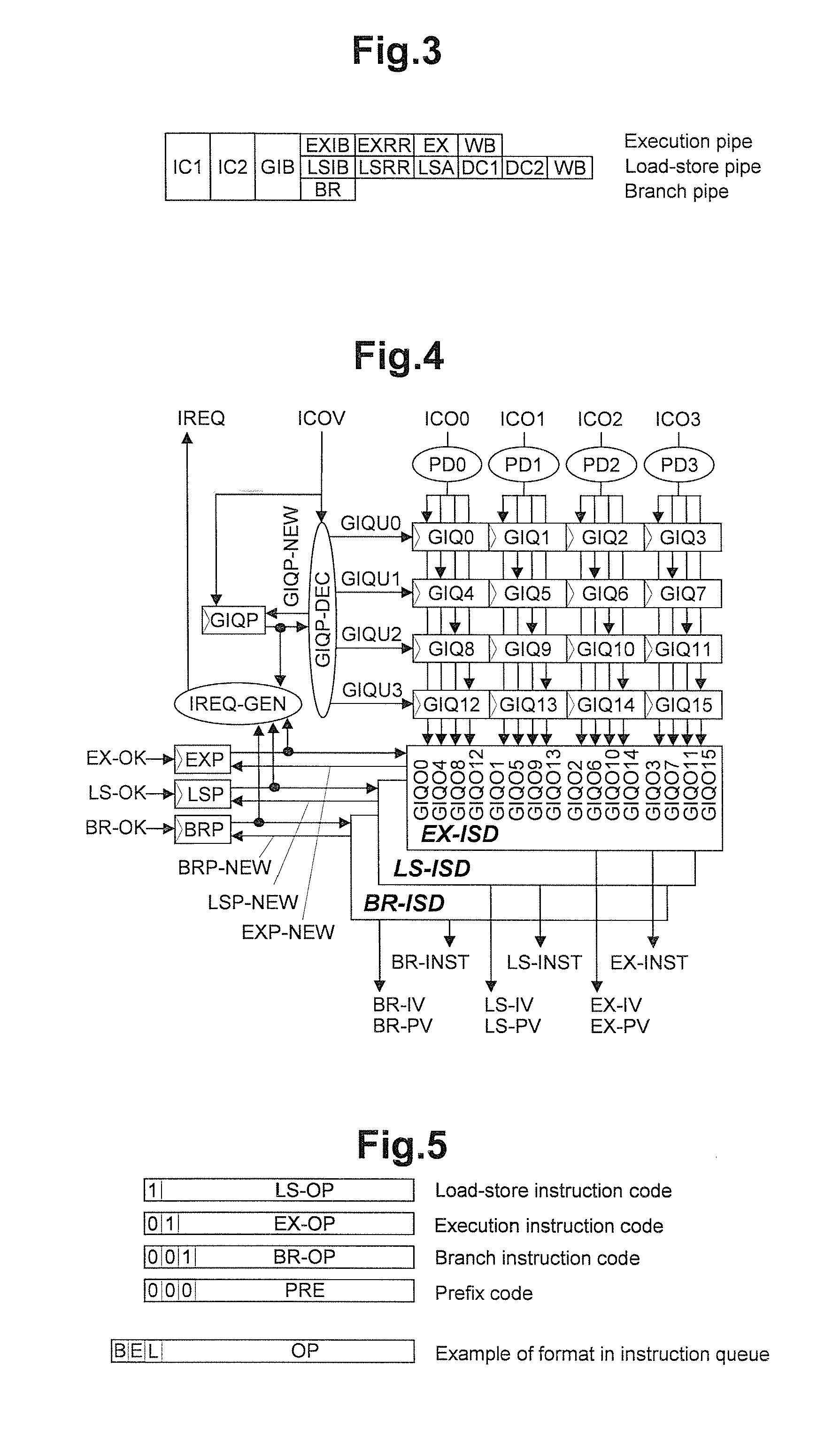
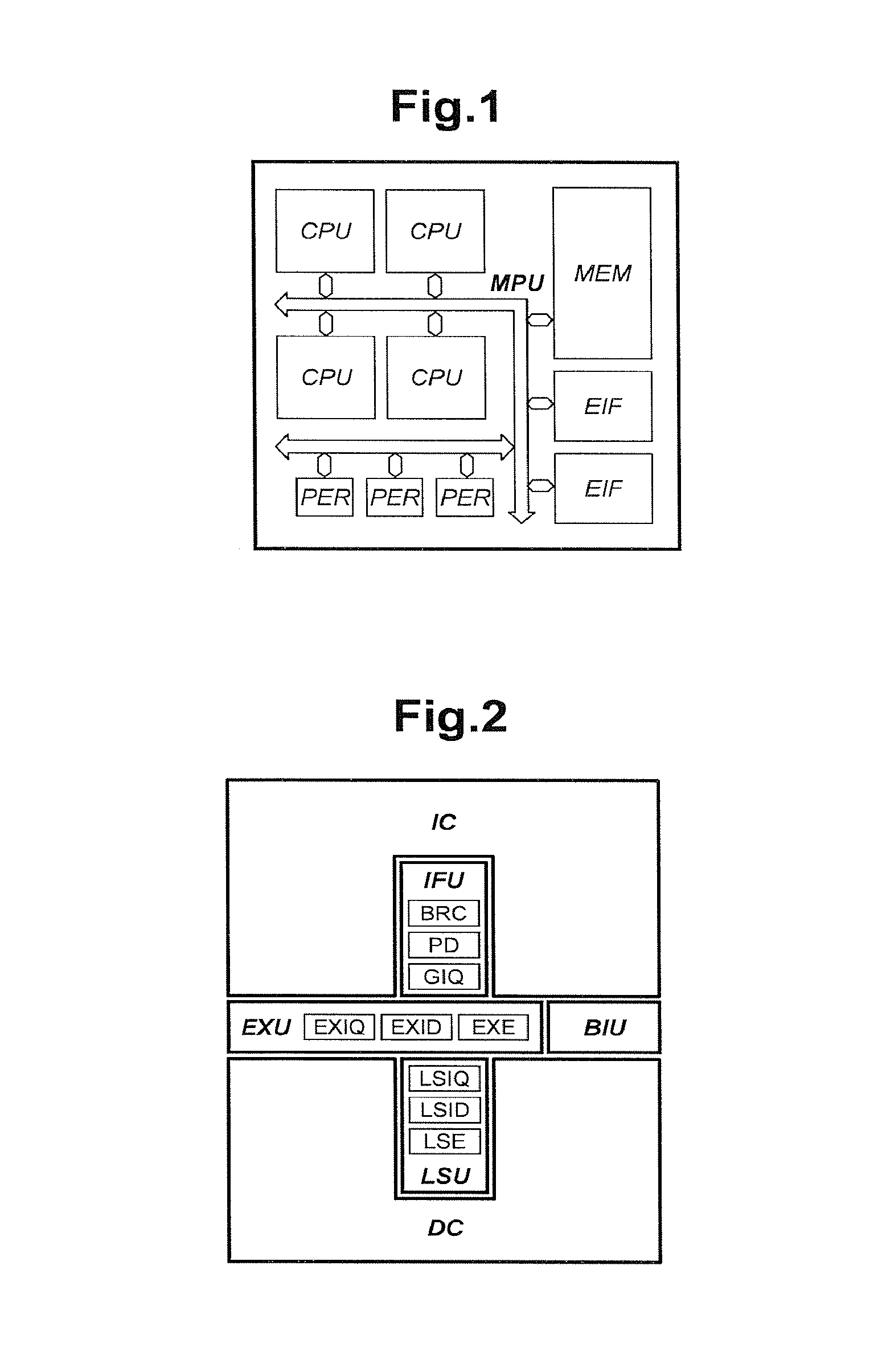
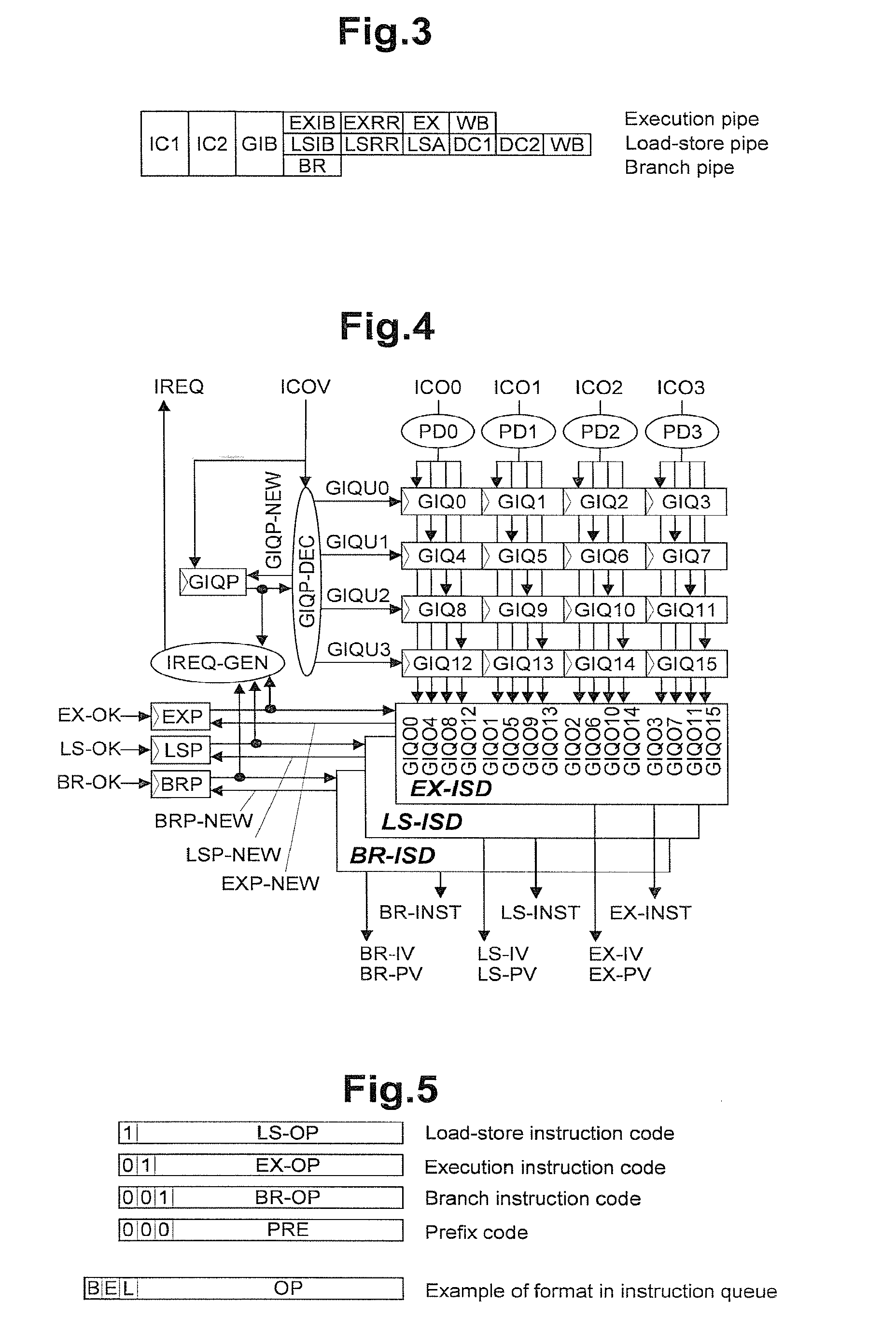
Processing prefix code in instruction queue storing fetched sets of plural instructions in superscalar processor
InactiveUS8402256B2Improve performanceIncrease powerInstruction analysisRuntime instruction translationInstruction unitScalar processor
The present invention is directed to realize efficient issue of a superscalar instruction in an instruction set including an instruction with a prefix. A circuit is employed which retrieves an instruction of each instruction code type other than a prefix on the basis of a determination result of decoders for determining an instruction code type, adds the immediately preceding instruction to the retrieved instruction, and outputs the resultant to instruction executing means. When an instruction of a target instruction code type is detected in a plurality of instruction units to be searched, the circuit outputs the detected instruction code and the immediately preceding instruction other than the target instruction code type as prefix code candidates. When an instruction of a target instruction code type cannot be detected at the rear end of the instruction units to be searched, the circuit outputs the instruction at the rear end as a prefix code candidate. When an instruction of a target instruction code type is detected at the head in the instruction code search, the circuit outputs the instruction code at the head.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Data processor
InactiveUS20100064119A1Improve performanceIncrease powerInstruction analysisRuntime instruction translationInstruction unitPrefix code
The present invention is directed to realize efficient issue of a superscalar instruction in an instruction set including an instruction with a prefix. A circuit is employed which retrieves an instruction of each instruction code type other than a prefix on the basis of a determination result of decoders for determining an instruction code type, adds the immediately preceding instruction to the retrieved instruction, and outputs the resultant to instruction executing means. When an instruction of a target instruction code type is detected in a plurality of instruction units to be searched, the circuit outputs the detected instruction code and the immediately preceding instruction other than the target instruction code type as prefix code candidates. When an instruction of a target instruction code type cannot be detected at the rear end of the instruction units to be searched, the circuit outputs the instruction at the rear end as a prefix code candidate. When an instruction of a target instruction code type is detected at the head in the instruction code search, the circuit outputs the instruction code at the head.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
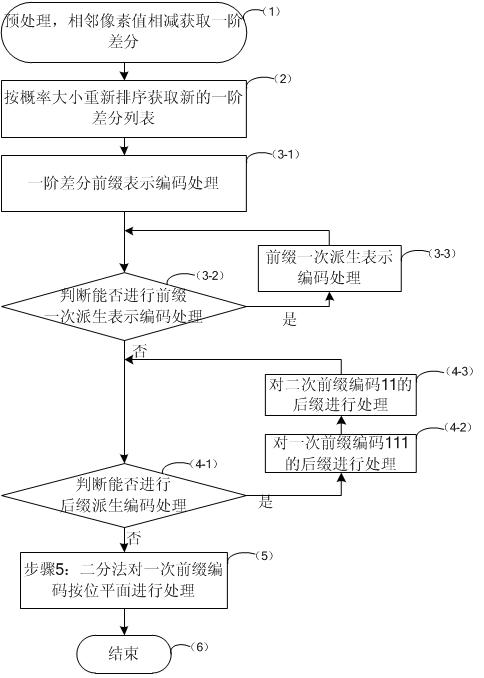
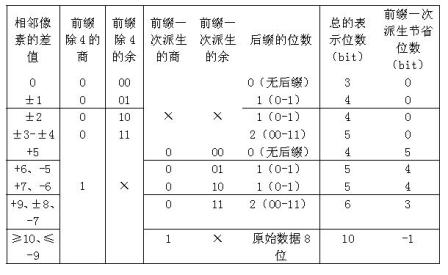
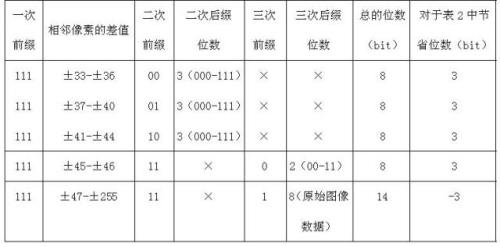
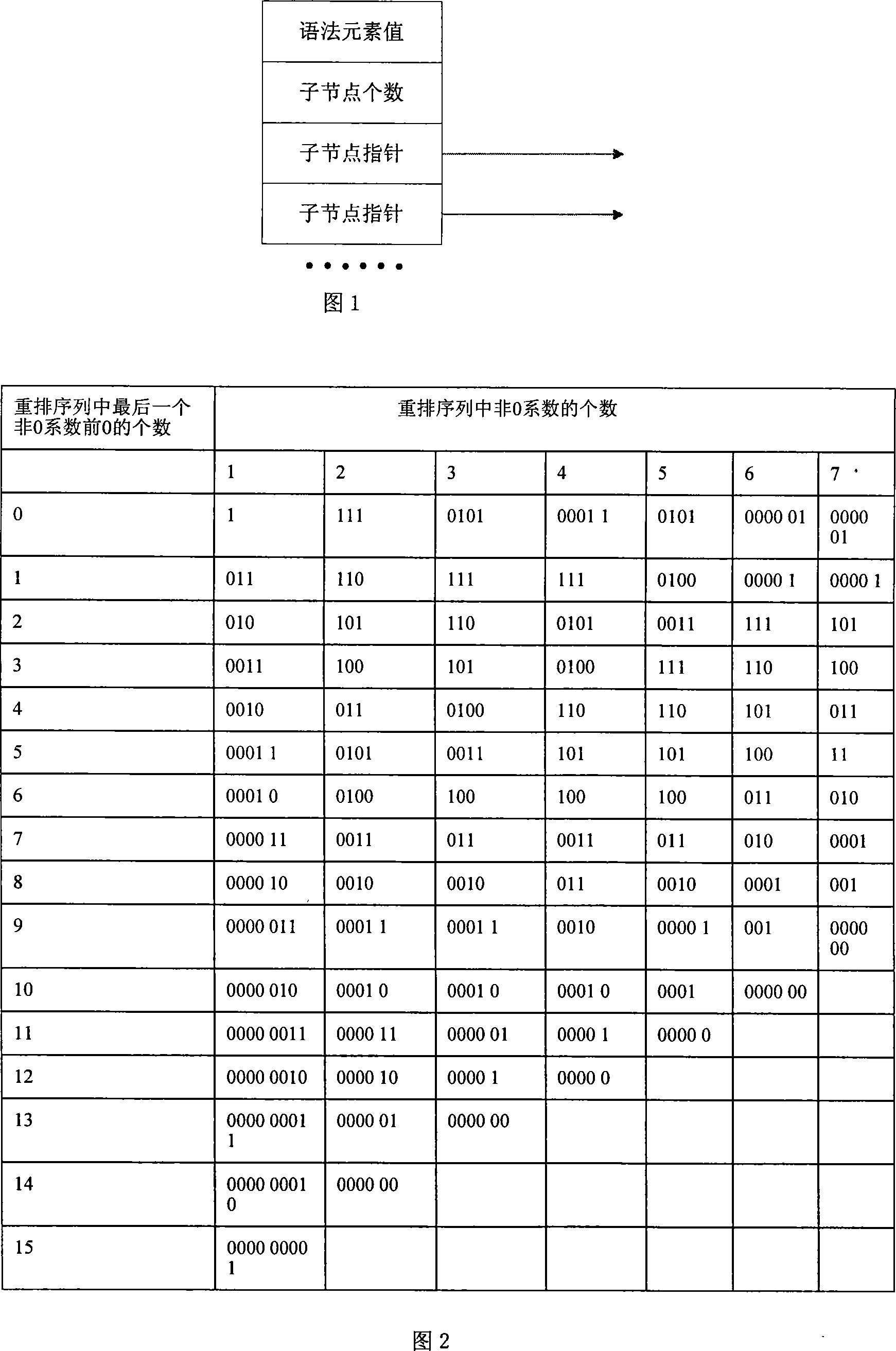
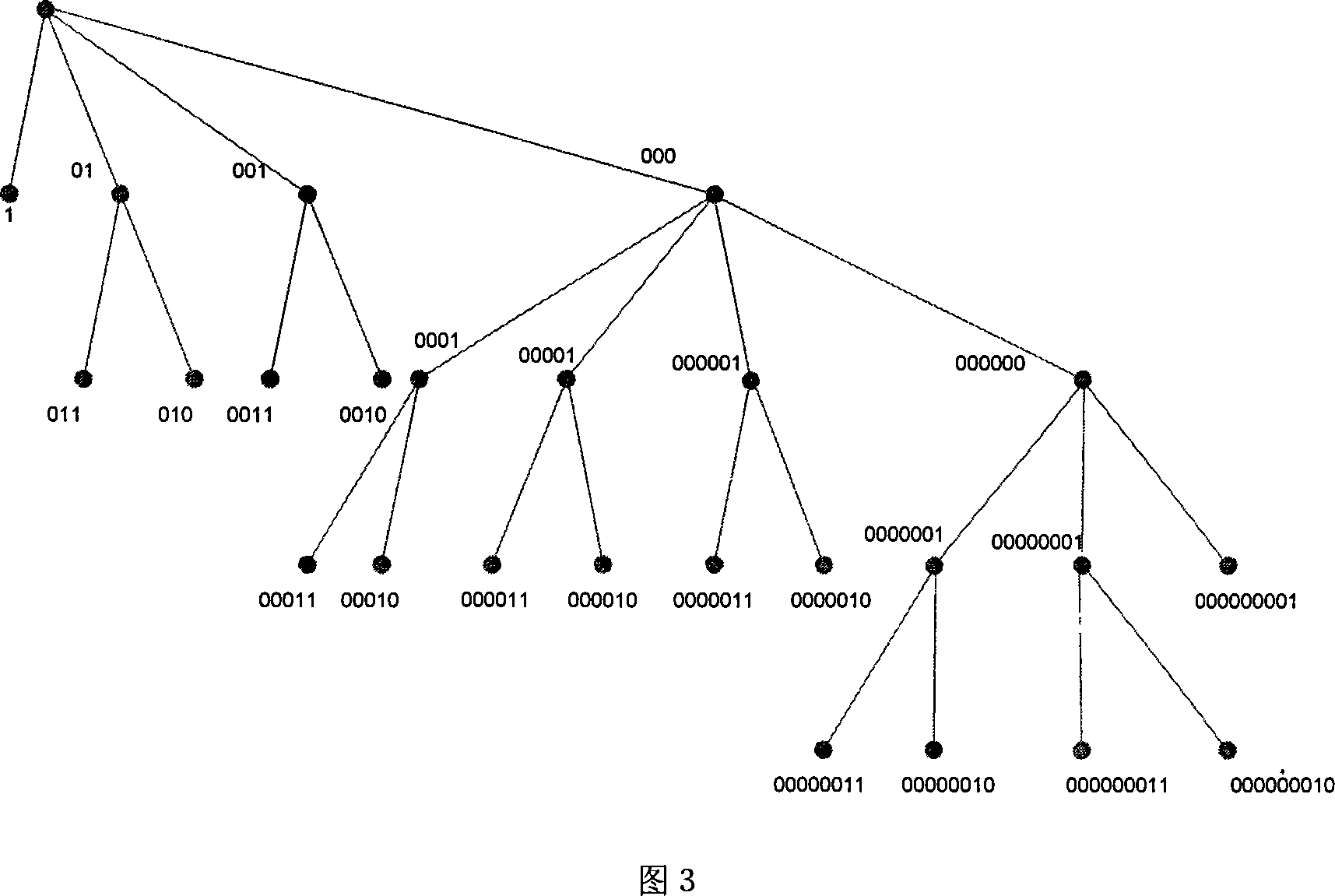
First-order difference prefix notation coding method for lossless compression of image data
InactiveCN102014283AReduce computational complexitySimple codingTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationLossless compression algorithmComputation complexity
The invention discloses a first-order difference prefix notation coding method for the lossless compression of image data, which comprises the following steps of: 1, pre-processing original image data to obtain first-order differences between adjacent pixel values; 2, counting the probabilities of occurrence of each first-order difference, and re-sequencing the first-order differences from higher probabilities to lower probabilities to obtain new first-order differences; 3, performing first-order difference prefix notation coding processing on the new first-order differences obtained by the step 2 to obtain a prefix code table and a suffix code table; 4, performing order-reduction processing on suffix codes in the step 3 by adopting a suffix derivation method; and 5, performing coding processing on primary prefix codes in the step 4 according to bit planes by adopting dichotomy. The method ensures relatively lower computational complexity, simple coding, high coding and decoding efficiency remarkably higher than that of JPEG2000, and no need of adopting special compression and decompression chips, and compared with a conventional lossless compression algorithm, remarkably increases a compression ratio to be equivalent to that of the international standard JPEG2000.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
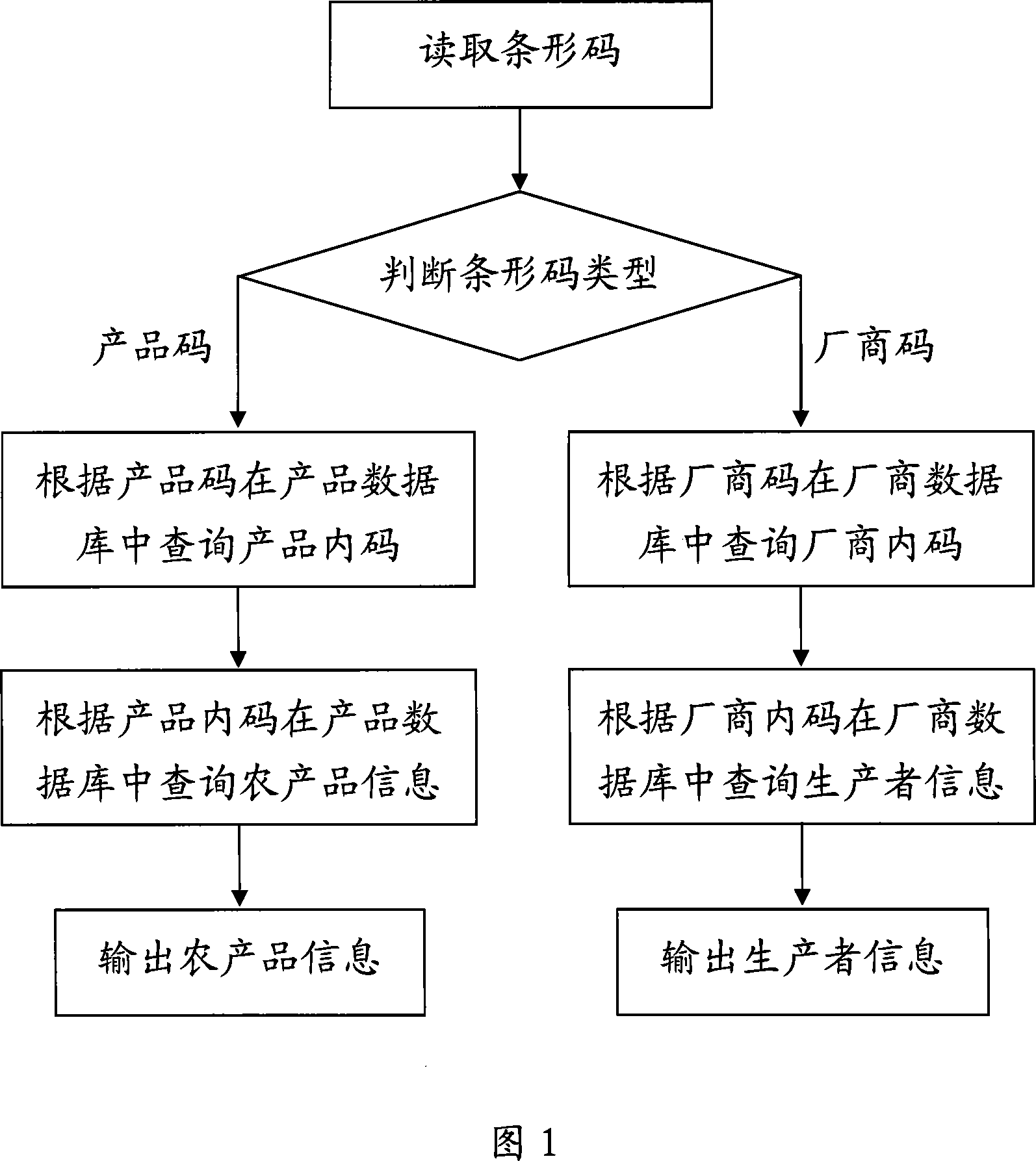
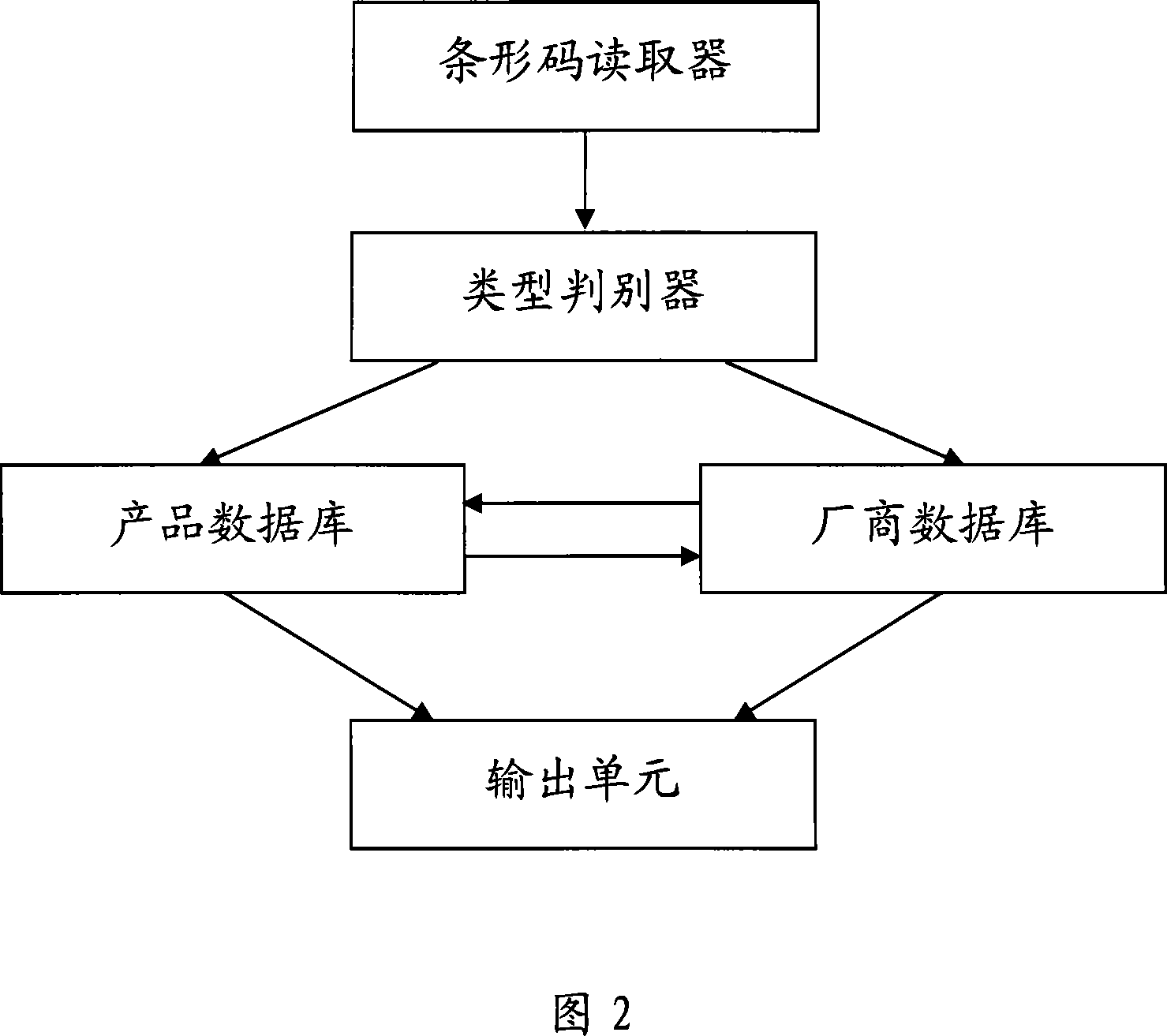
Method and system for identifying agricultural product by code bar
InactiveCN101055614AUnable to solveSolve the real problemSensing record carriersSpecial data processing applicationsBarcodePrefix code
The invention relates to a method and system for identifying agricultural products using bar code. The method comprises: (1) reading the bar code which is associated with the agricultural products and has 13 code bits including prefix code, sequence code and check code; (2) judging the type of bar code according to prefix code; (3) if bar code being product code, inquiring corresponding information of agricultural products in the product database according to product code; (4) outputing the inquired information of agricultural products. The system and method, not only can solves the problem that the current bar code is not popularized in the agricultural products in our country, also can use product code to bring the contact with the whole process for producing and managing the entire agricultural products, accordingly the efficiency of production and management can be improved greatly; while carrying out coding based on the biology classfication of agriculture products and the agricultural normalized process, each aspect associated with agricultural production can be contacted, and the scientific system for information circulation and service can be formed.
Owner:王杰夫
Data processor
ActiveUS20130246765A1Improve performanceIncrease powerInstruction analysisRuntime instruction translationInstruction unitObject code
For efficient issue of a superscalar instruction a circuit is employed which retrieves an instruction of each instruction code type other than a prefix based on a determination result of decoders for determining instruction code type, adds the immediately preceding instruction to the retrieved instruction, and outputs the resultant. When an instruction of a target code type is detected in a plurality of instruction units to be searched, the circuit outputs the detected instruction code and the immediately preceding instruction other than the target code type as prefix code candidates. When an instruction of a target code type cannot be detected at the rear end of the instruction units, the circuit outputs the instruction at the rear end as a prefix code candidate. When an instruction of a target code type is detected at the head in the instruction code search, the circuit outputs the instruction code at the head.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
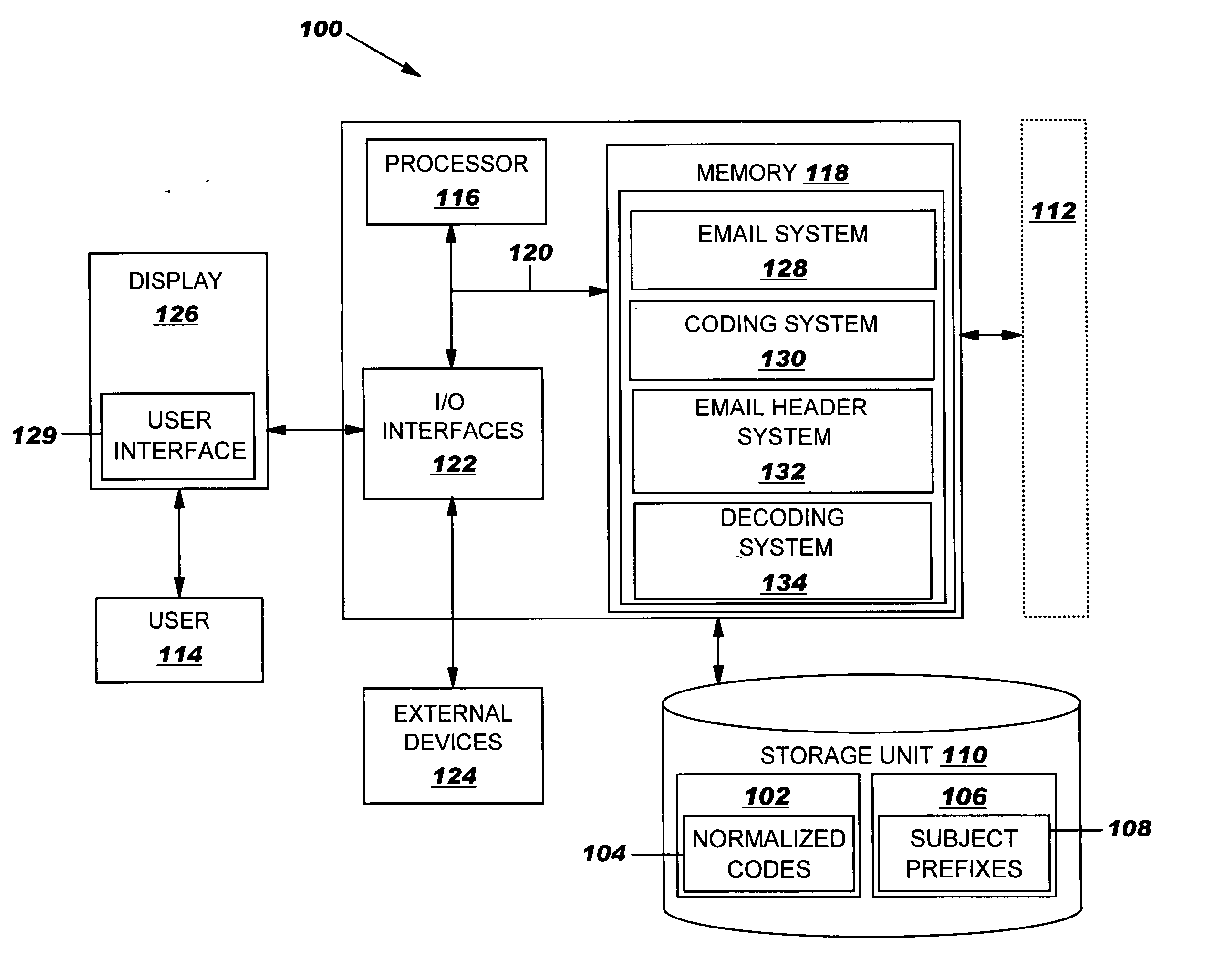
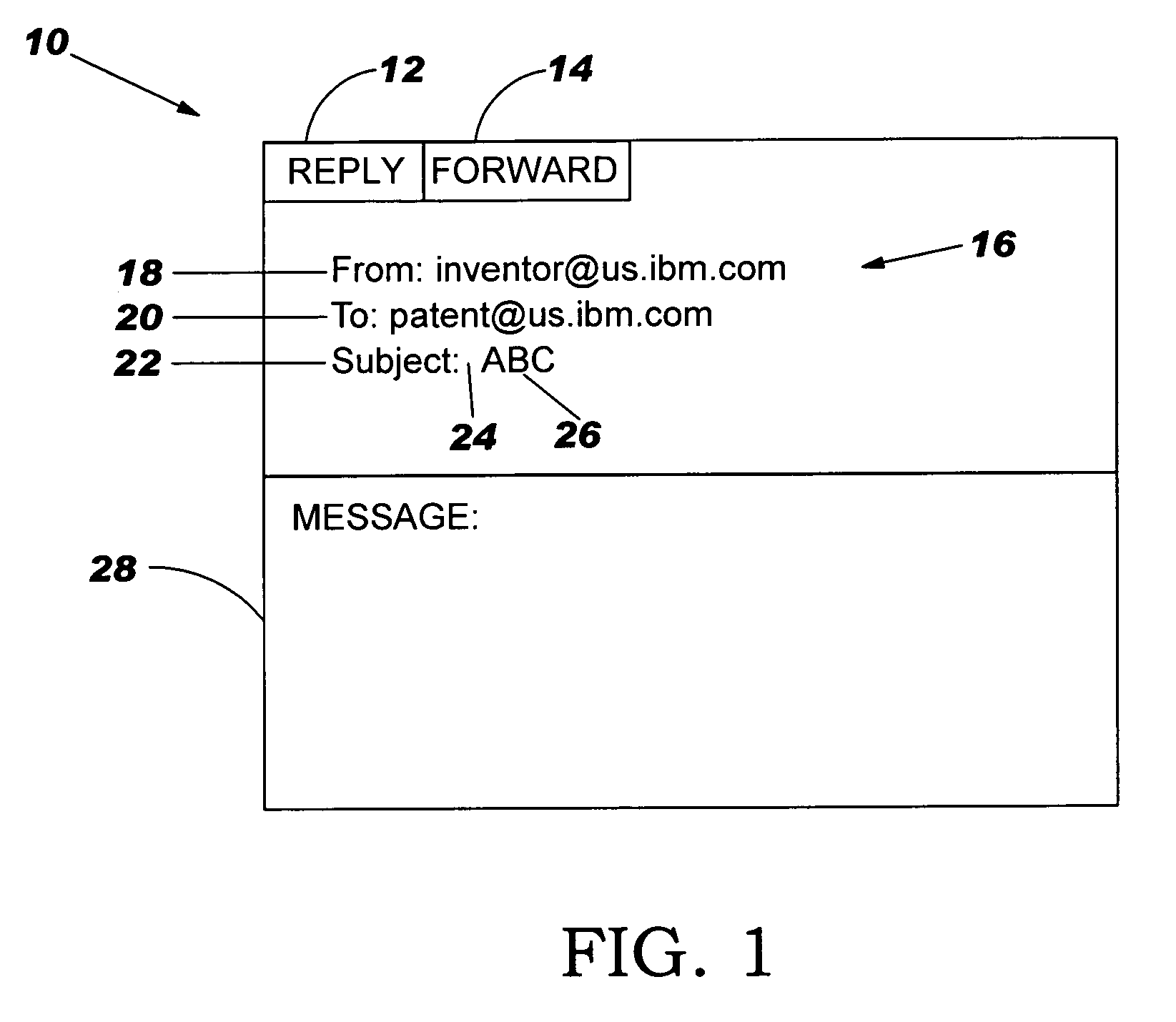
Method, system, and computer program product for displaying message genealogy
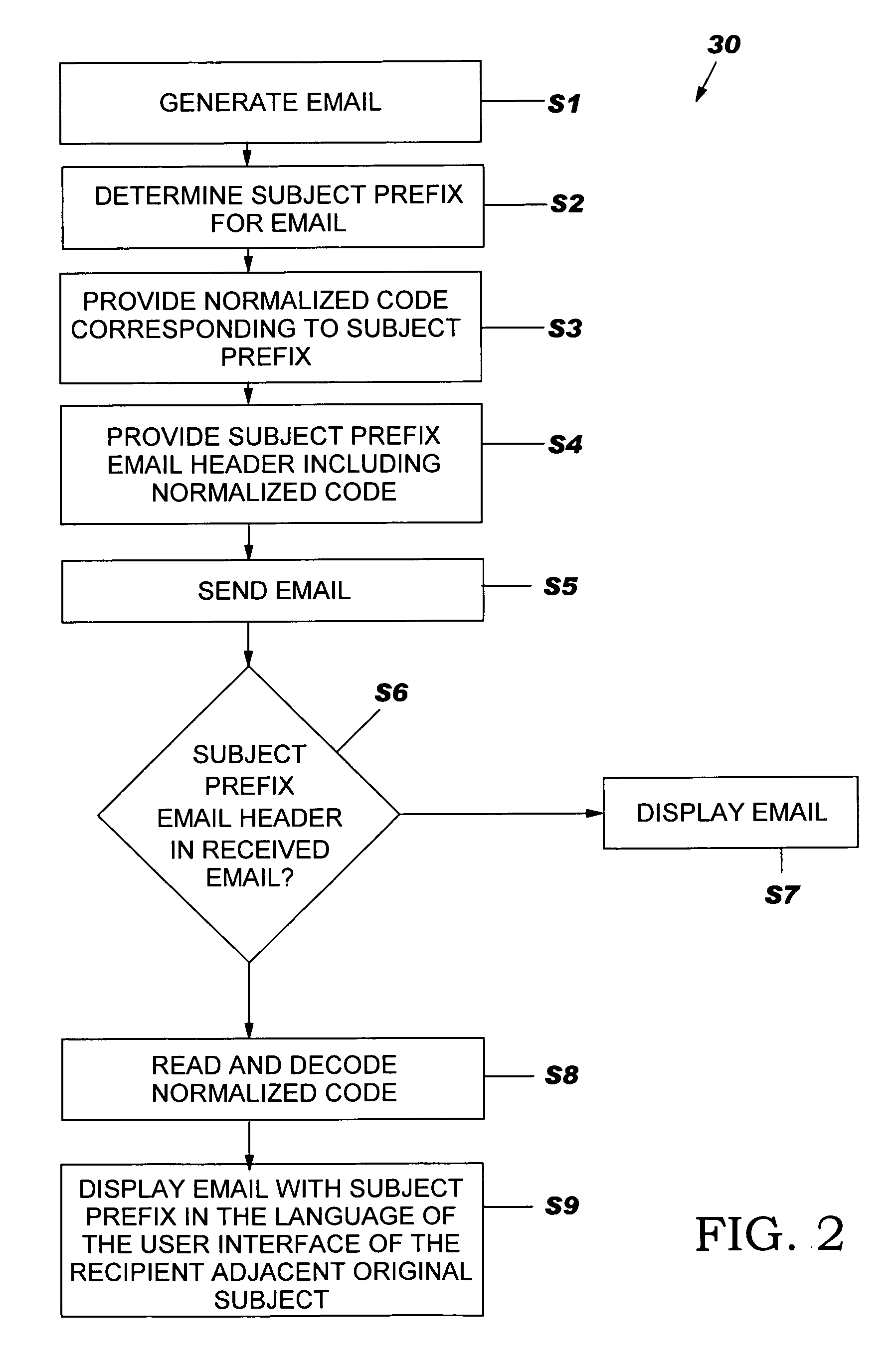
InactiveUS20060036691A1Multiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingSubject matterPrefix code
A method, system, and computer program product for displaying message genealogy in the language of the user interface of an email recipient using a normalized set of subject prefix codes. The method comprises: sending an email to a recipient, wherein the email has an original subject; sending a normalized code corresponding to a subject prefix for the email to the recipient; receiving and decoding at the recipient the normalized code to provide a subject prefix in a language of the user interface of the recipient; and displaying the subject prefix in the language of the user interface of the recipient adjacent the original subject of the email.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Short wave OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) channel estimating method in narrow band interference
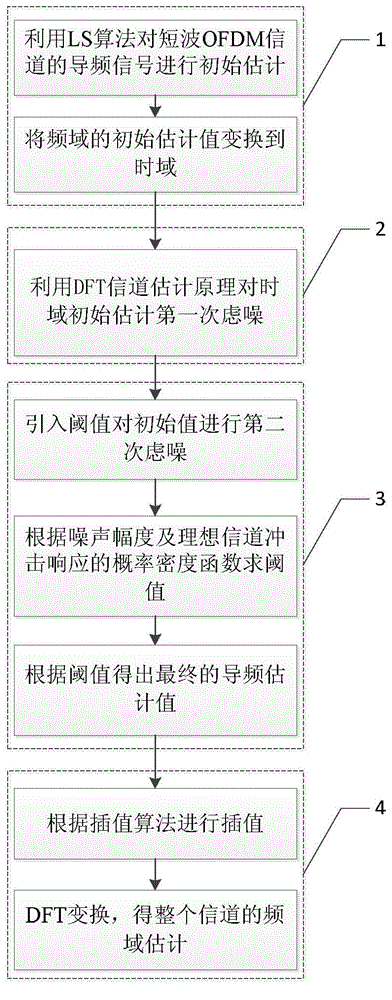
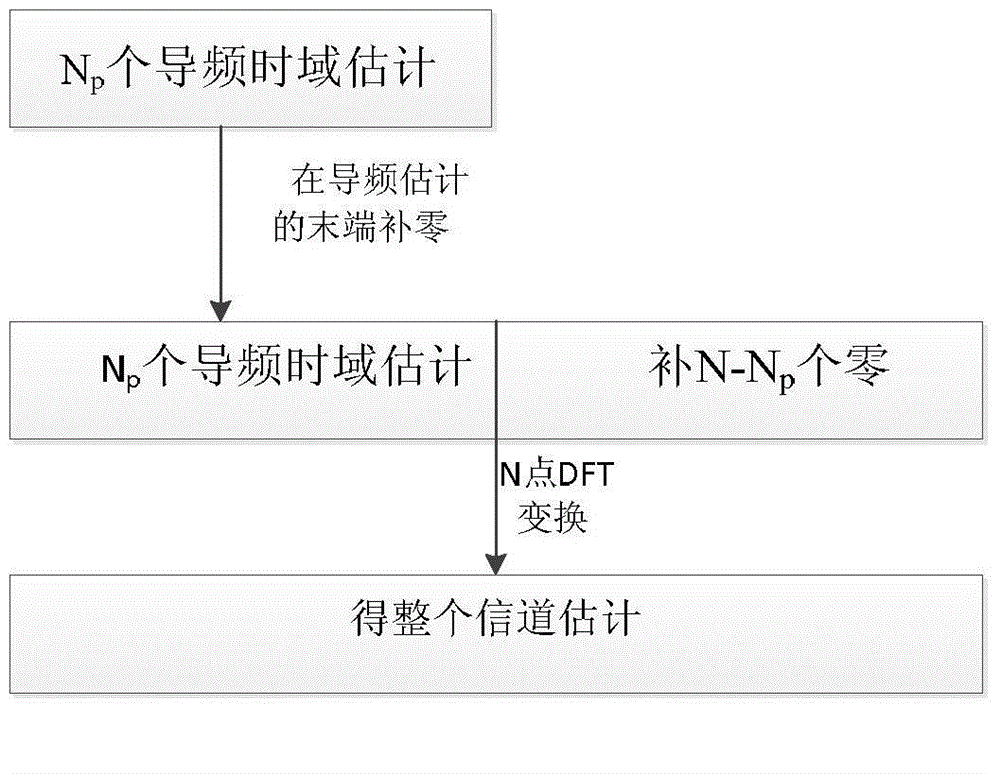
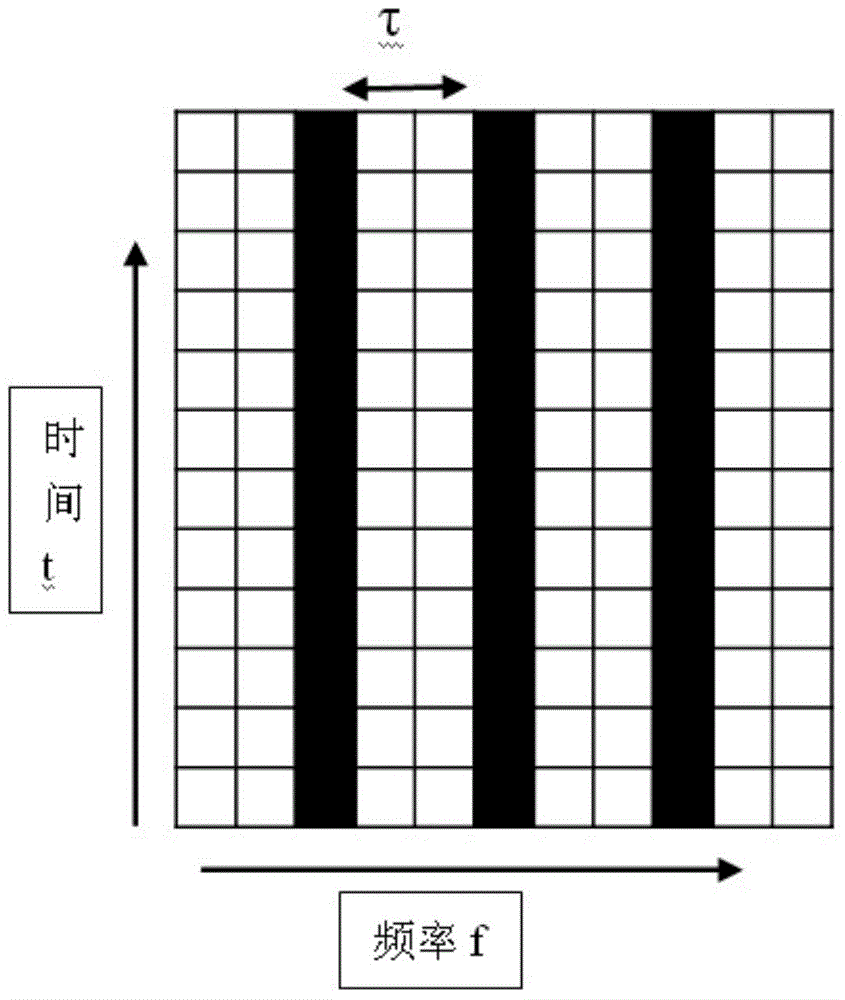
ActiveCN104618277AImprove estimation performanceMake up for the problem of incomplete noise filteringBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsFiltrationEngineering
The invention discloses a short wave OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) channel estimating method in narrow band interference. The method includes the steps: firstly, estimating an initial estimation value of a pilot frequency in a channel by the aid of an LS (list scheduling) algorithm, then performing a primary noise filtration for the initial estimation value by the aid of DFT (discrete Fourier transformation) channel estimation algorithm principle, namely, the length of a circulation prefix code is larger than channel impact response, filtering noise except a circulation prefix by the aid of a method that an estimation value larger than the length of the circulation prefix code is reset zero, finally, performing a secondary noise filtration for the initial estimation value by leading in a threshold value, acquiring a final estimation value at the pilot frequency by performing zero setting for signals smaller than the threshold value and keeping invariable for the portions larger than the threshold value, then performing interpolation for pilot frequency estimation according to interpolation modes to obtain estimation of the whole channel, and performing DFT for channel estimation of a time domain to obtain channel estimation of a frequency domain. The channel estimation perform is improved, the pilot frequency is of a comb-like pilot frequency structure, and rapid fading of short wave signals is effectively restrained.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
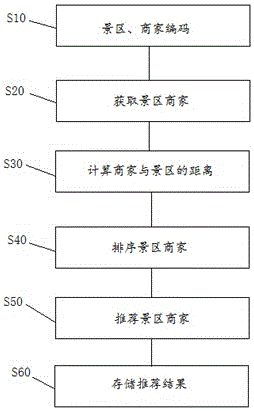
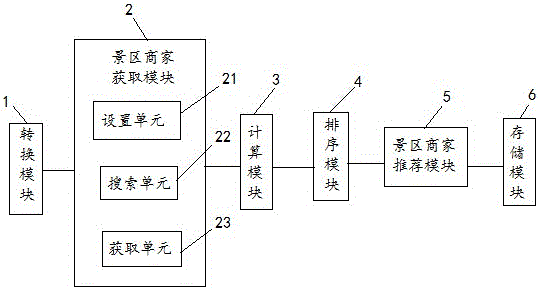
Scenic spot recommending method and system
InactiveCN106251164AImprove matching accuracyComplete business informationMarketingLongitudePrefix code
A scenic spot recommending method comprises the following steps: scenic spot and business encoding: acquiring the latitude and longitude information of scenic spots and businesses, converting the latitude and longitude information of businesses into business GeoHash codes, and converting the latitude and longitude information of scenic spots into scenic spot GeoHash codes; scenic spot business acquiring: acquiring scenic spot businesses by matching the prefix codes of the scenic spot GeoHash codes and the prefix codes of the business GeoHash codes; and scenic spot business recommending: recommending scenic spot businesses to users. The latitude and longitude of scenic spots and the latitude and longitude of businesses are encoded based on a GeoHash algorithm, matching is performed on the prefixes of the scenic spot GeoHash codes and the prefixes of the business GeoHash codes, and businesses belonging to a scenic spot and adjacent businesses thereof are acquired according to the matching result and recommended to users. Thus, even if there are different scenic spots and the scenic spots are close, complete and accurate business information can be obtained, and the matching accuracy of recommended businesses is improved.
Owner:上海驴徒电子商务有限公司
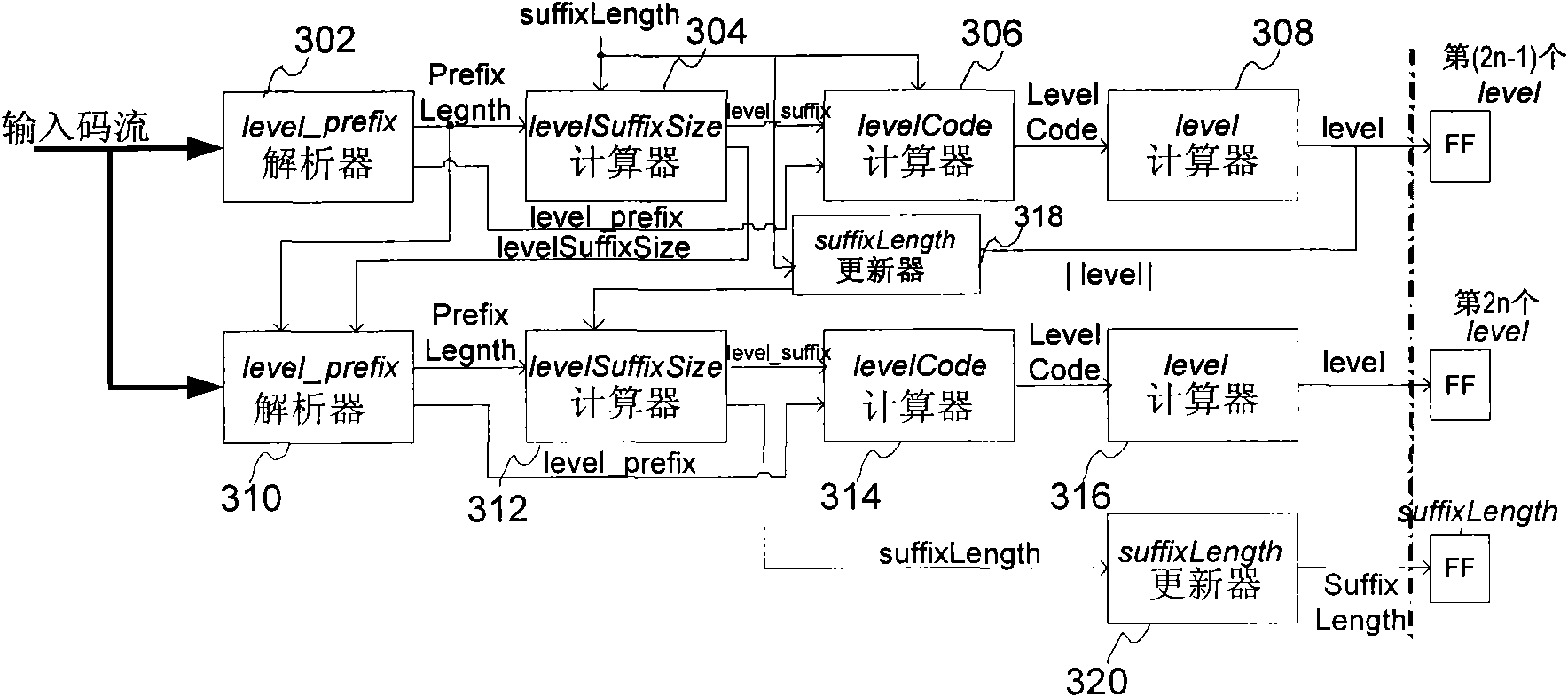
CAVLC decoding method and system
InactiveCN102740066AFast decodingTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsLookup table
The invention discloses a CAVLC decoding method and a system. The method completes decoding of two successive Level syntactic elements in one clock period through the following processes: finding out the prefix length and the prefix code of the (2n-1)th Level syntactic element by using a lookup table used for syntactic element Level, acquiring an amplitude code of the (2n-1)th Level syntactic element by using the prefix code, the suffix code and the suffix length of the (2n-1)th Level syntactic element, and acquiring a coefficient amplitude corresponding to the (2n-1)th Level syntactic element according to the amplitude code of the (2n-1) Level syntactic element; and finding out the code initial position of the (2n)th Level syntactic element by using the prefix length and the actual suffix length of the (2n-1)th Level syntactic element, finding out the prefix length and the prefix code of the (2n)th Level syntactic element by using the lookup table used for the syntactic element Level, acquiring an amplitude code of the (2n)th Level syntactic element according to the prefix code, the suffix code and the suffix length of the (2n)th Level syntactic element, and acquiring a coefficient amplitude corresponding to the (2n)th Level syntactic element according to the amplitude code of the (2n)th Level syntactic element.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
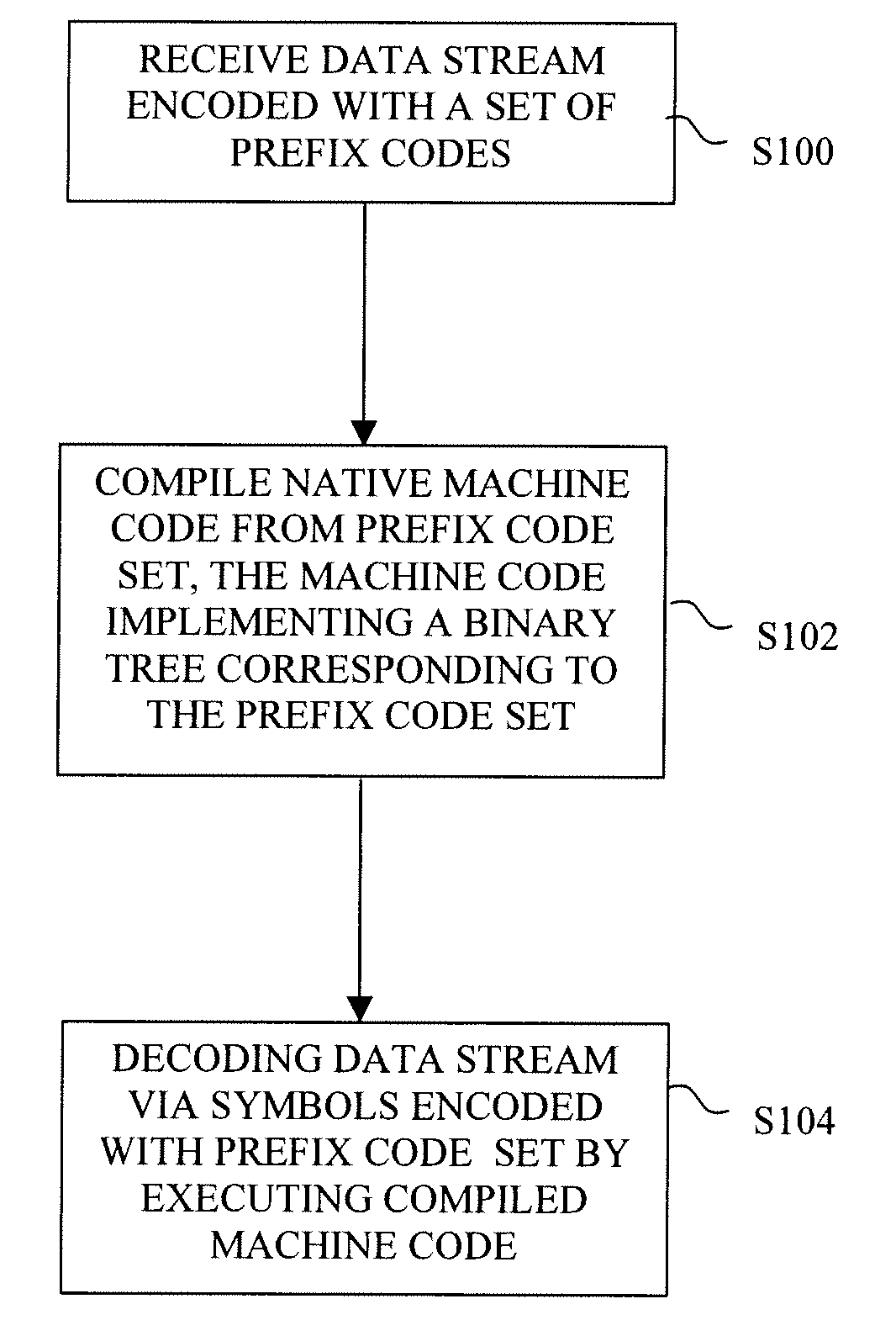
Method of decoding entropy-encoded data
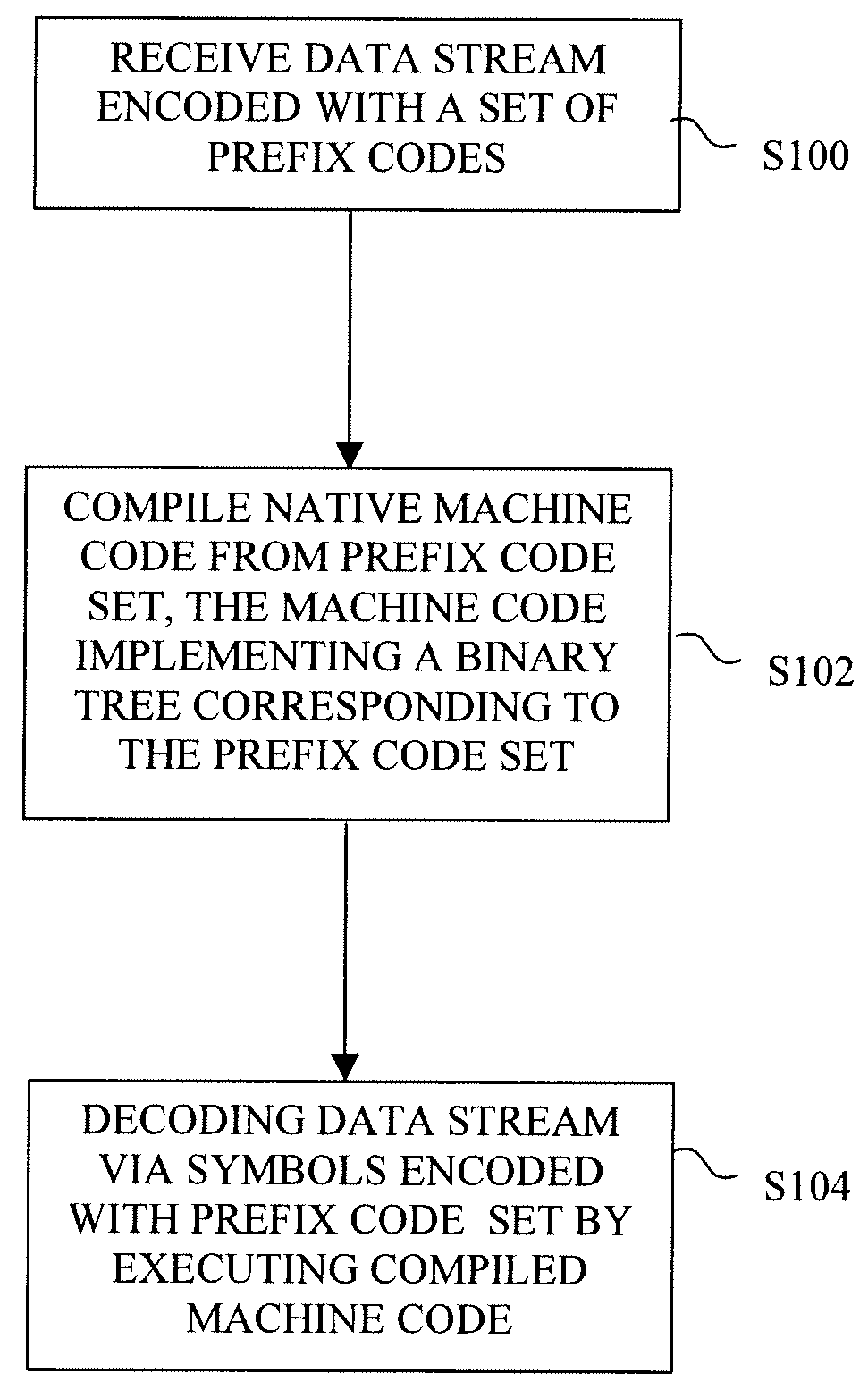
ActiveUS20080253668A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsTheoretical computer scienceBinary tree
A method of decoding data that is encoded with a set of prefix codes begins by receiving the data at a computing device, and then compiling native machine code from the prefix code set for execution by a processing unit of the computing device. The machine code implements a binary tree of prefix codes that corresponds to the prefix code set. The data is decoded by traversing the prefix code tree, which is effected by executing the machine code with the processing unit.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Expandable fast discovery technology for multi-stage sequencing resources
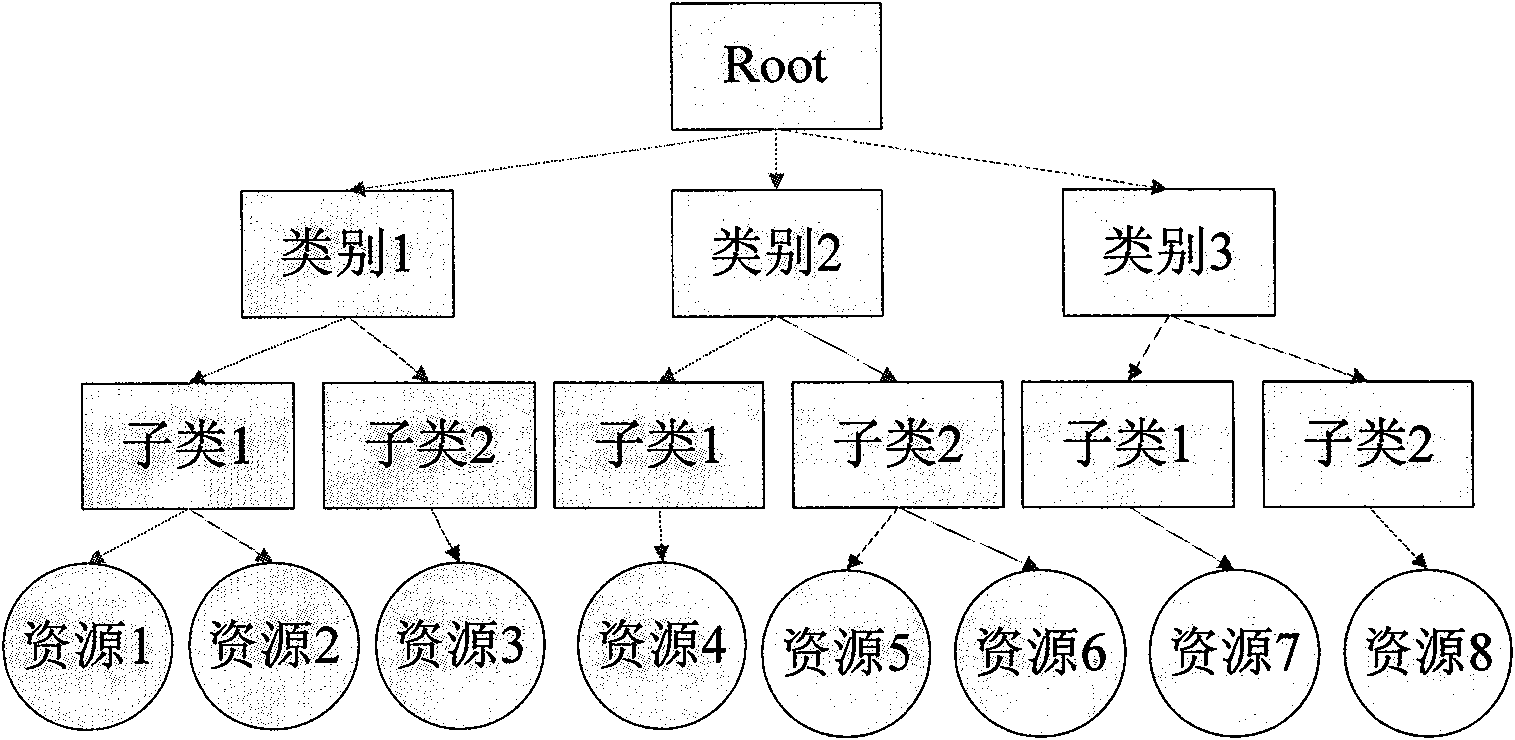
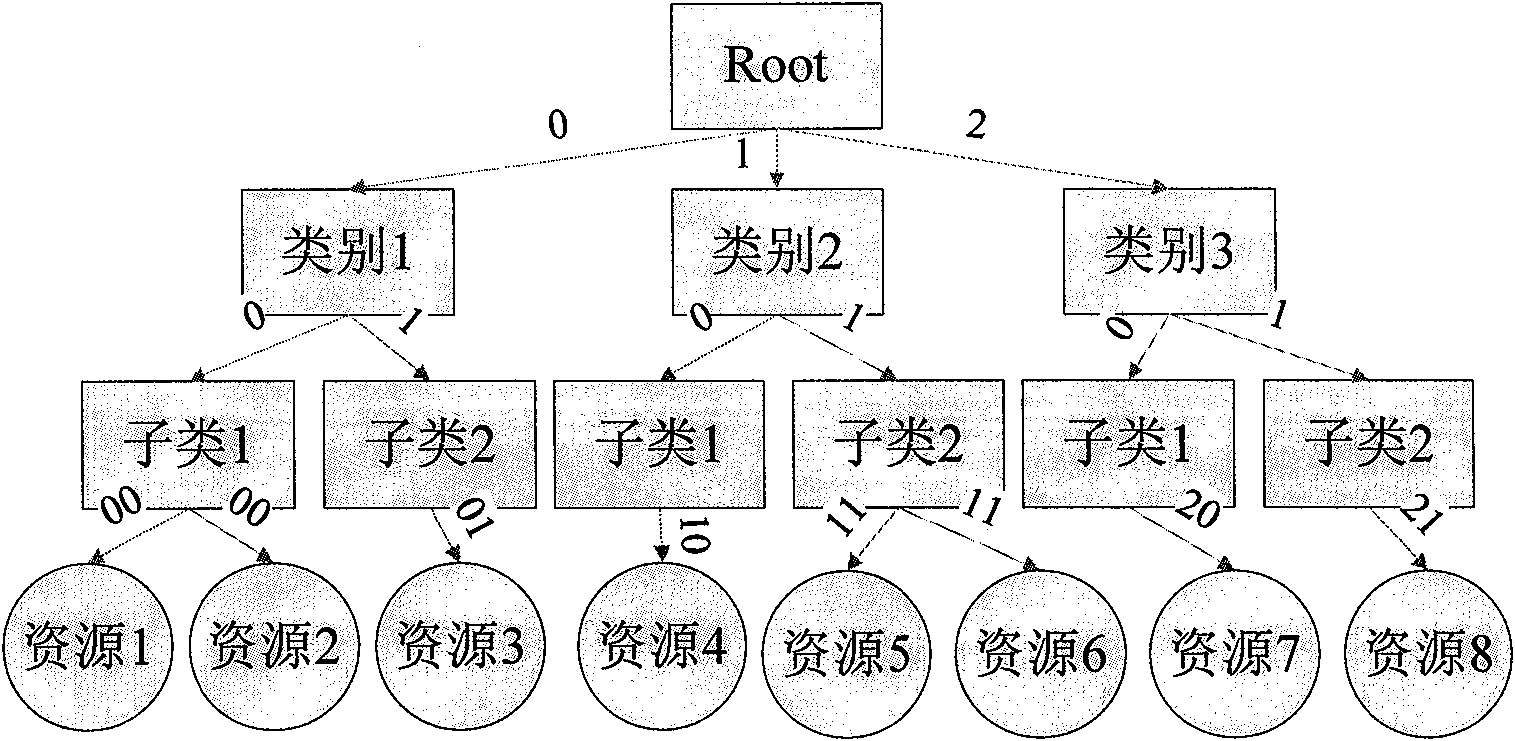
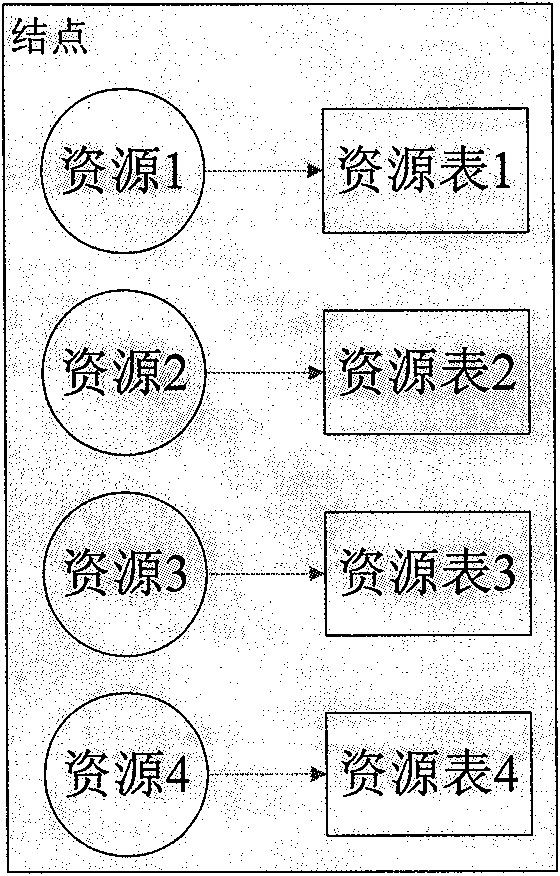
The invention provides an expandable fast discovery technology for multi-stage sequencing resources, comprising the following steps: as for a resource discovery problem for resource management in P2P application and grid technologies, classifying and organizing the resources in a system into a dendriform description form and giving prefix codes; establishing a resource routing table and storing the table in initial nodes in the system; carrying out resource discovery along the direction from root nodes to leaf nodes, and firstly searching the needed resources locally; if not found, searching the local resource routing table; if still not found, sending a query message to resource addresses of the same type; and repeatedly searching from next line of the newly found resource routing table, and completing dynamic maintenance of the resource routing table for new nodes or new resources during the discovery process. The expandable fast discovery technology has the characteristics of fast resource discovery speed, high efficiency and good expandability.
Owner:BEIJING FENGGE JIUZHOU CULTURAL DIFFUSION
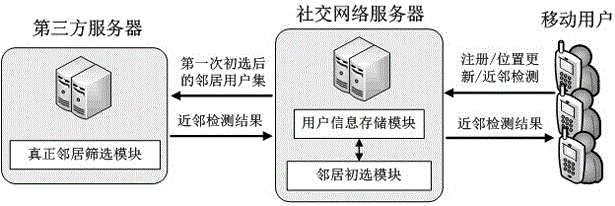
Neighbor detection method capable of protecting position privacy
ActiveCN106453049ASolve the problem of location privacy exposureEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesData switching networksThird partyInternet privacy
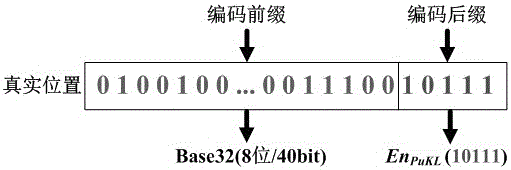
The invention relates to a neighbor detection method capable of protecting the position privacy. When a user updates a position, the position is encoded into two parts of a prefix code and a suffix code by adopting Geohash encoding, then the suffix code is encrypted to form a suffix ciphertext, and the prefix code and the suffix ciphertext are submitted to a social network server; when the user requests a neighbor detection service, the social network server carries out primary neighbor selection according to the prefix code of the position of the user and a neighbor query region designated by the user, and then a set of primarily-selected neighbors and corresponding suffix ciphertexts are forwarded to a third-party server; and the third-party server decrypts the suffix ciphertexts of the candidate neighbors, completes neighbor screening according to relative positions, and returns a result to the user by the social network server. According to the neighbor detection method disclosed by the invention, position information of the user is divided into two prefix and suffix parts, and the two parts are respectively processed by the social network server and the third-party server, so that the position privacy exposure problem of a conventional neighbor detection method is effectively solved, and the neighbor detection method disclosed by the inention has a wide practical prospect in the social network.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Method of decoding entropy-encoded data
ActiveUS8457419B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsTheoretical computer scienceBinary tree
A method of decoding data that is encoded with a set of prefix codes begins by receiving the data at a computing device, and then compiling native machine code from the prefix code set for execution by a processing unit of the computing device. The machine code implements a binary tree of prefix codes that corresponds to the prefix code set. The data is decoded by traversing the prefix code tree, which is effected by executing the machine code with the processing unit.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method for OFDM communication system to transmit and receive frame prefix
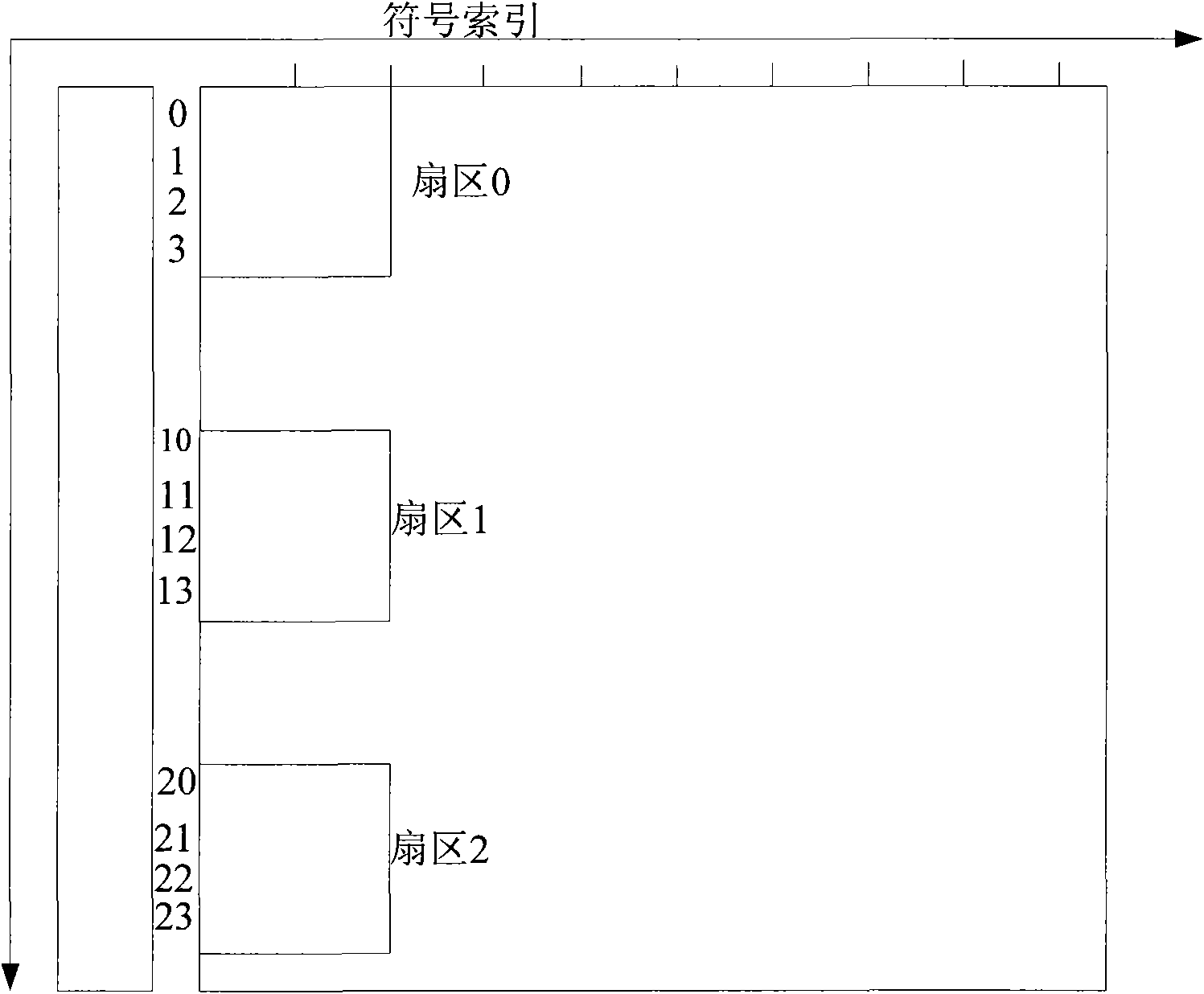
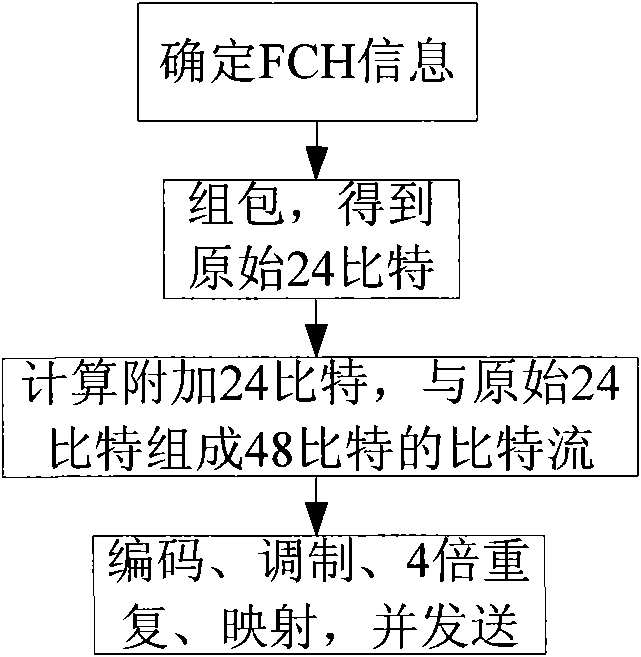
ActiveCN101686218ASave software and hardware resourcesSave resourcesError preventionMulti-frequency code systems24-bit48-bit
The invention relates to a method for OFDM system to transmit and receive frame prefix. The transmitting method includes that: a base station firstly assembles frame prefix information into package, so as to obtain original 24 bits; then additional 24 bits are calculated and forms 48 bits required by frame prefix coding with the original 24 bits; coding, modulating and four times repetition are carried out on the bit stream of the 48 bits, and the 48 bits are mapped into four sub channels to be transmitted; the receiving method includes that: a receiving terminal firstly extracts corresponding data in four channels, and demodulating, decoding and de-interlacing are carried out on the data to obtain bit stream of the 48 bits; then verification 24 bits are calculated; the verification 24 bits are compared with the rear 24 bits of the 48 bits, if coincident, decoding is correct, frame configuration information is reported to high layer; or else, decoding is error, and an error message isreturned to the base station. The invention can save system soft hardware resource while the receiving terminal analyzes error.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Variable-length code decoding method based on zero-prefix code
InactiveCN101022554AReduce accessImprove decoding efficiencyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDigital videoVariable-length code
A method for decoding variable length code based on zero prefix code includes generating a numbers of multiple fork trees based on zero prefix code and then carrying out variable length code decoding on code stream according to generated multiple fork tree. The structure of said multiple fork tree is also disclosed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
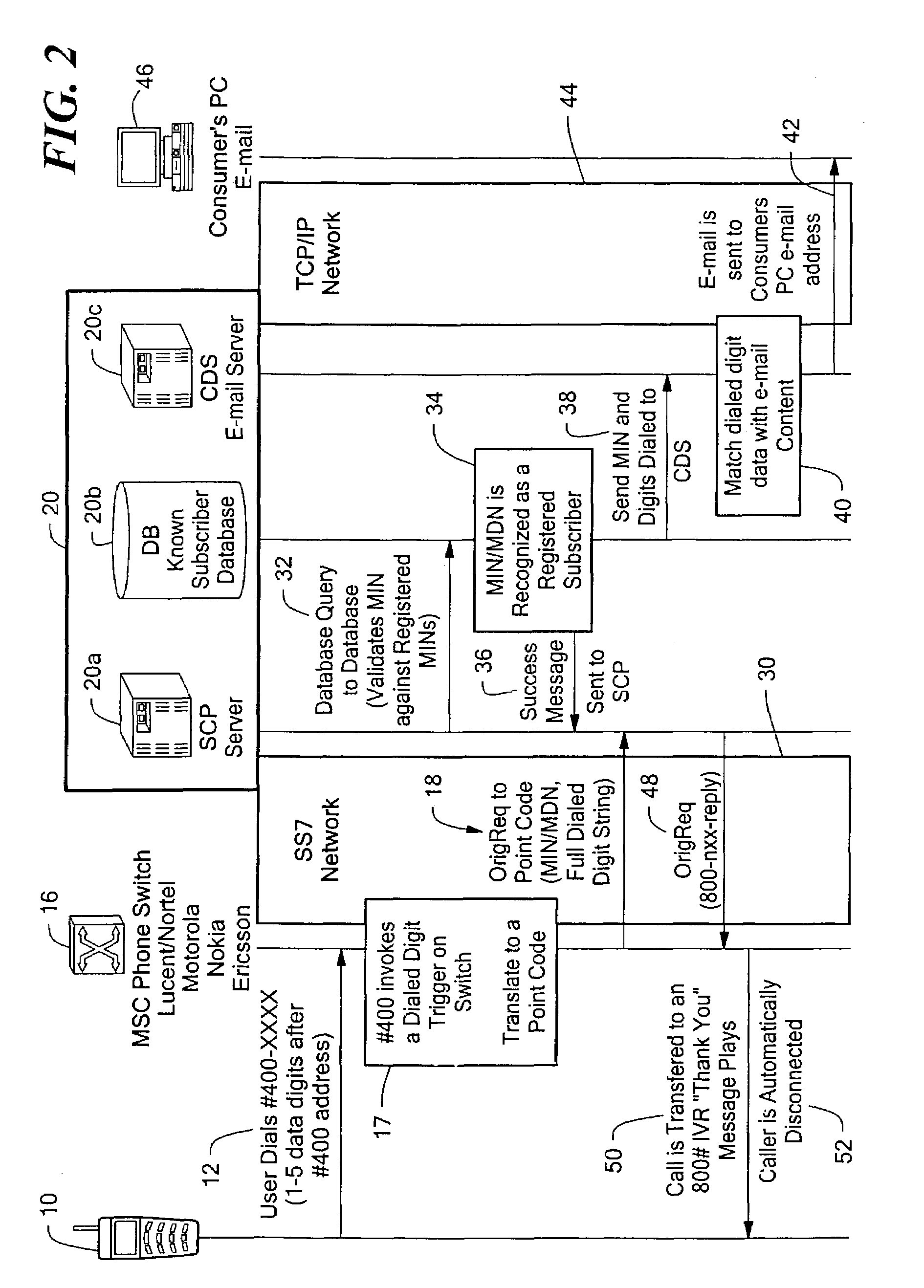
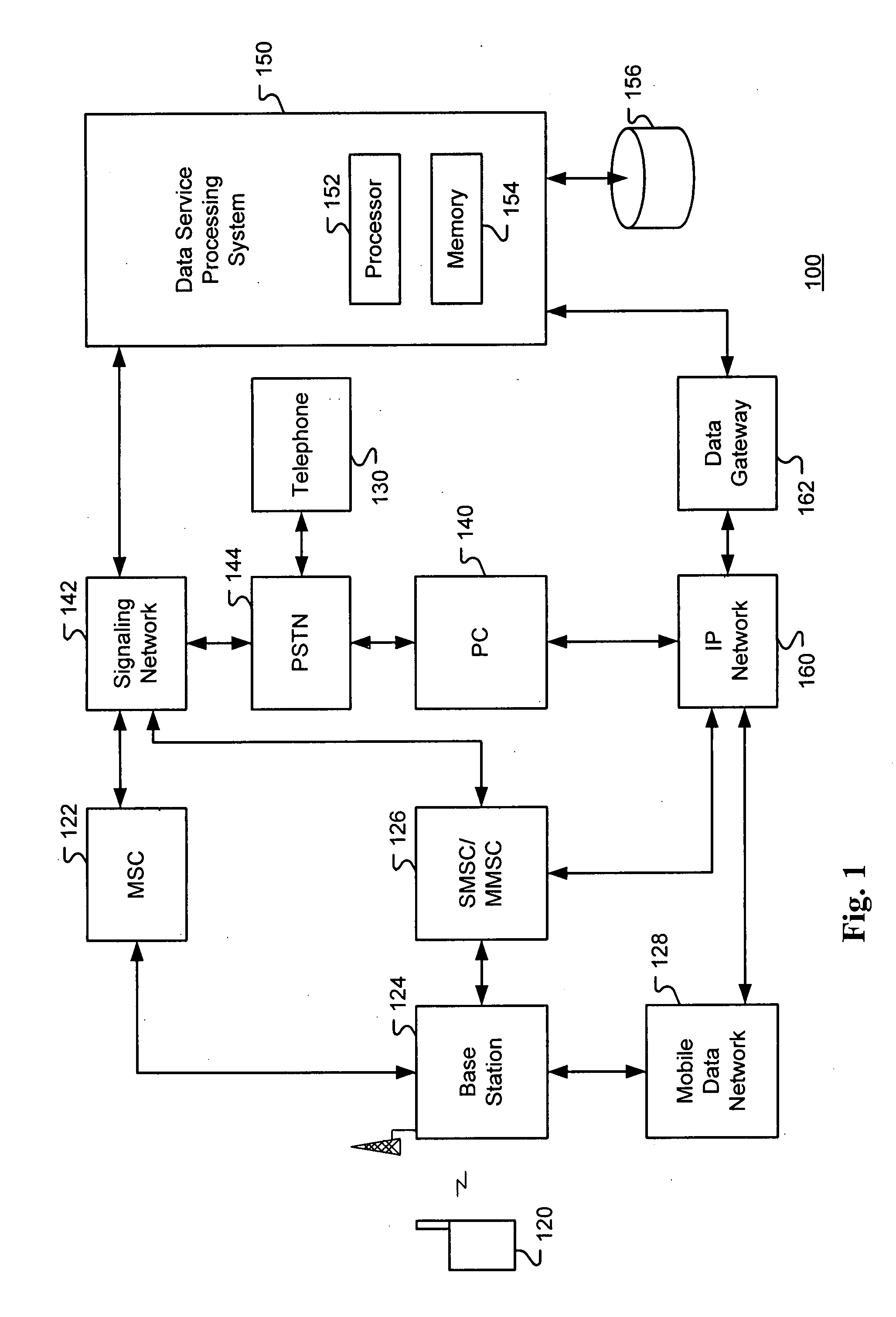
System and method for service invocation and response with a communication device
ActiveUS20080009273A1Increase contentPrivacy protectionSpecial service for subscribersConnection managementCommunications systemUser input
A system and method for enabling a user to invoke a service over a signaling channel in a communication system with a communication device such as a mobile phone. The user dials a series of digits into their phone and enters them into the disclosed system, for example by pressing the send key on a mobile phone. The digits entered by the user include a prefix or routing code, and a data code. The dialed digits are transferred to a call switching system, which determines, based on the prefix code, a processing system to which a message is sent. The processing system further determines, based on the data code of the dialed digits, the service to provide and how the service should be fulfilled. The service can be fulfilled by content over the signaling channel or a transport channel, or both.
Owner:VHT STARSTAR LLC
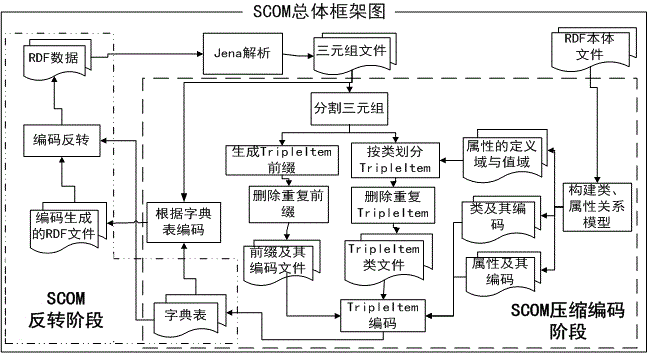
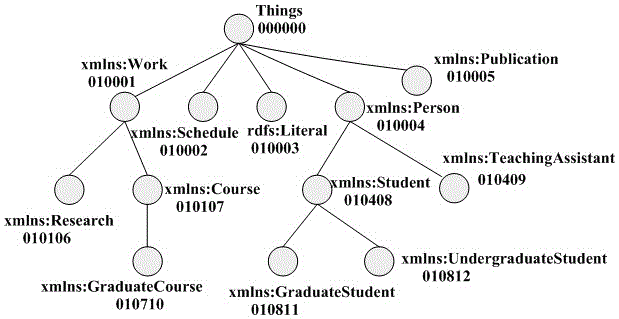
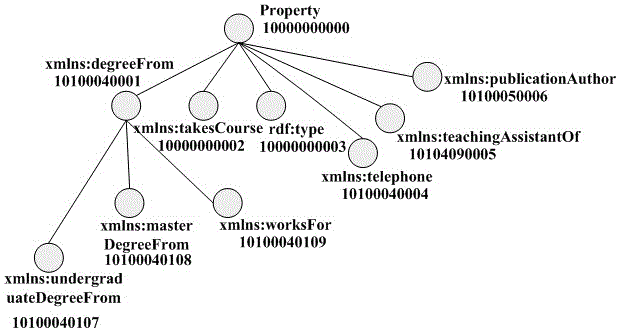
RDF data distributed parallel semantic coding method
ActiveCN105930419AAchieve reversalImprove reasoningSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsRelational modelData file
The invention relates to an RDF data distributed parallel semantic coding method. The method specifically comprises the following steps of S1: reading an RDF ontology file and constructing a class relation model and an attribute relation model; S2: reading an RDF data file, dividing a triple into triple items, classifying the triple items by class, deleting the repeated triple items, and generating prefix codes; filtering the triple items to ensure the consistency of RDF triple codes and enable the same triple item not to be allocated with different codes; S3: coding the triple items to generate a dictionary table; S4: coding the triple to generate a coded triple file; and S5: taking a result file in the step S4 as an input of the step S5, and performing inversion according to the dictionary table in the step S3 to generate an original RDF data file. According to the method, compressed coding and inversion of large-scale data can be efficiently realized in combination with ontology in a distributed environment.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Spatial-contiguity-considered vector space data coding method
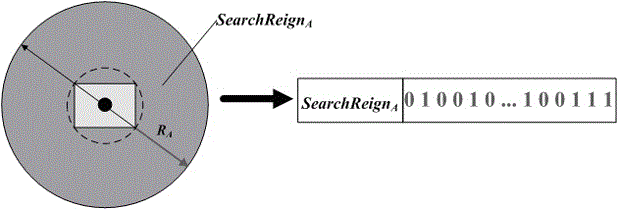
ActiveCN106649425AConsider spatial proximityAvoid repetitionSpecial data processing applicationsPoint objectHyperrectangle
The invention discloses a spatial-contiguity-considered vector space data coding method. The spatial-contiguity-considered vector space data coding method includes the steps that whether a given object P is a point object or not is judged; if the space object P is a non-point object, the maximum order k where a grid capable of completely containing a minimum external-containing hyperrectangle is obtained through calculation, and then k+1 pieces of ZG(P)<j*> from the zero order to the k order are calculated, wherein ZG(P)<j*> represents the coded value of the space object P in the j* order; the k+1 pieces of ZG(P)<j*> are coded according to the coding rule of a space filling curve, and Geocode(f.geometry)* is obtained; then coding is carried out according to the formula that Rowkey(f)* is equal to the sum of Geocode(f.geometry)* and FID(f)*. Based on the layered coding of the space filling curve, in the same space division, different space objects have same prefix codes, then unique sequence ID values are added to serve as postfix codes, the space proximity of the vector space objects is considered, and Rowkey can also be prevented from being repeated. In this way, Rowkey has the features of a spatial index, and direct spatial querying in a database becomes possible.
Owner:武汉兆图科技有限公司
Adaptive bifurcation query tree multi-label anti-collision method based on collision factor
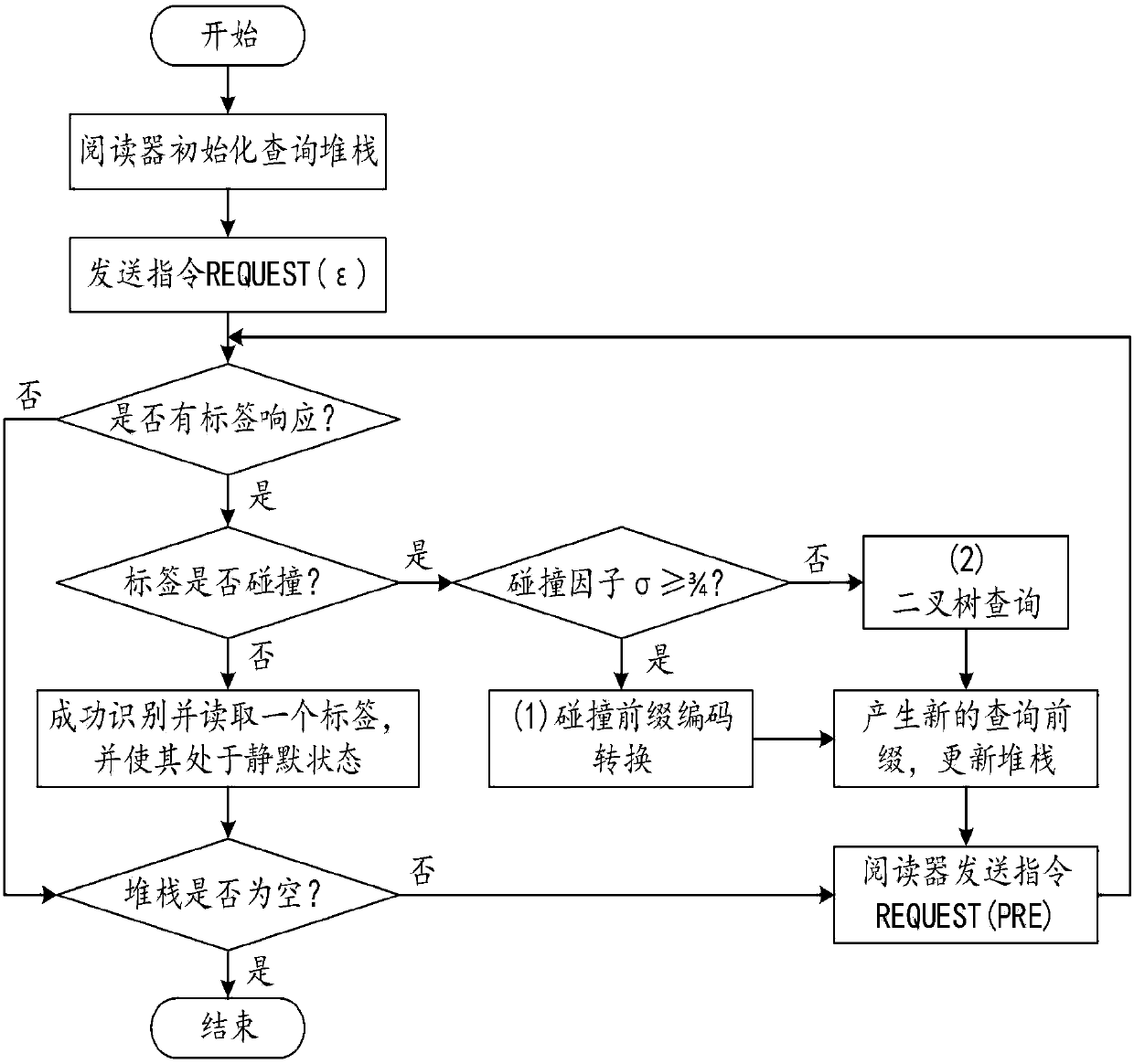
InactiveCN108537079AReduce the number of slotsAvoid idle time slotsSensing by electromagnetic radiationNODALIdle time
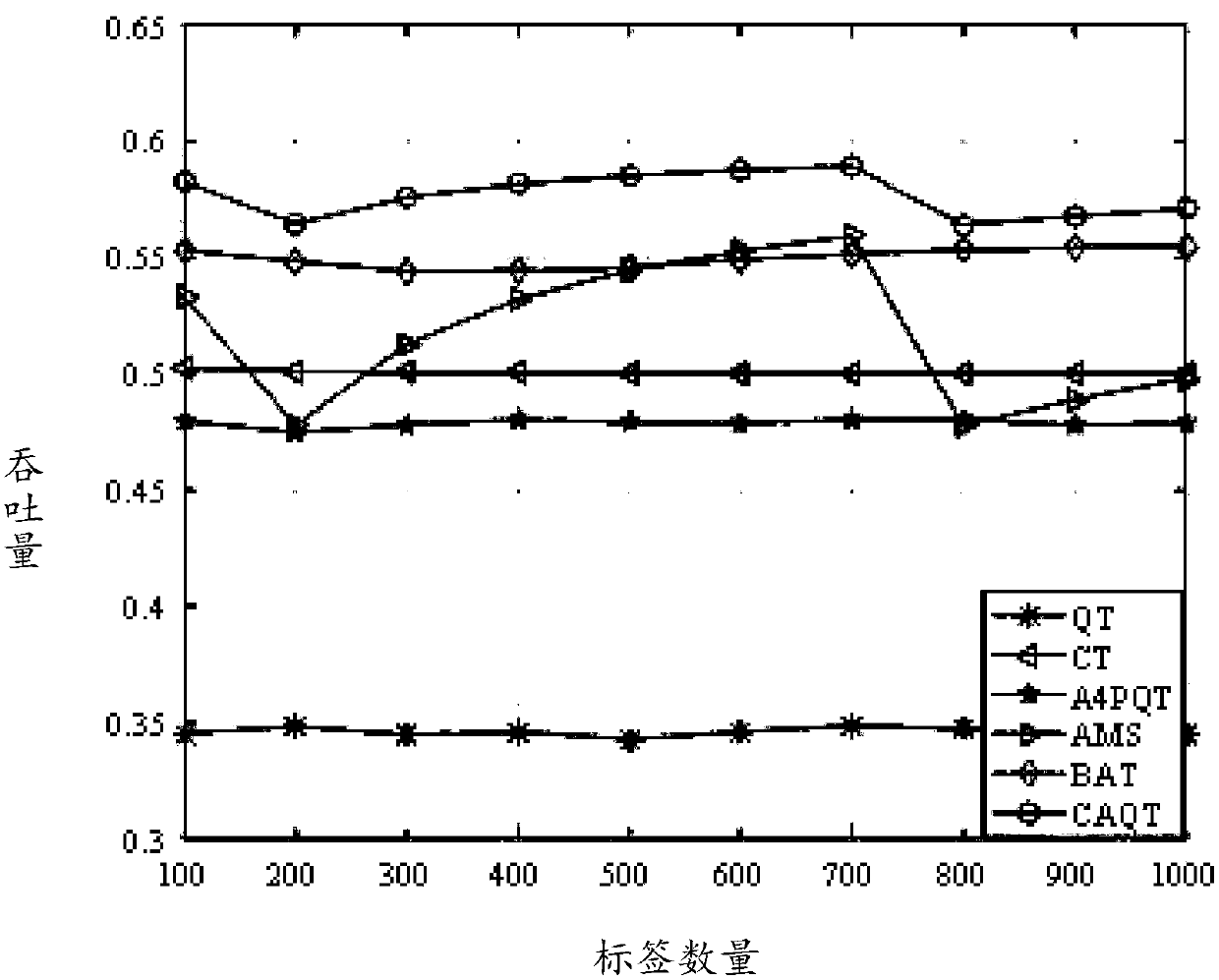
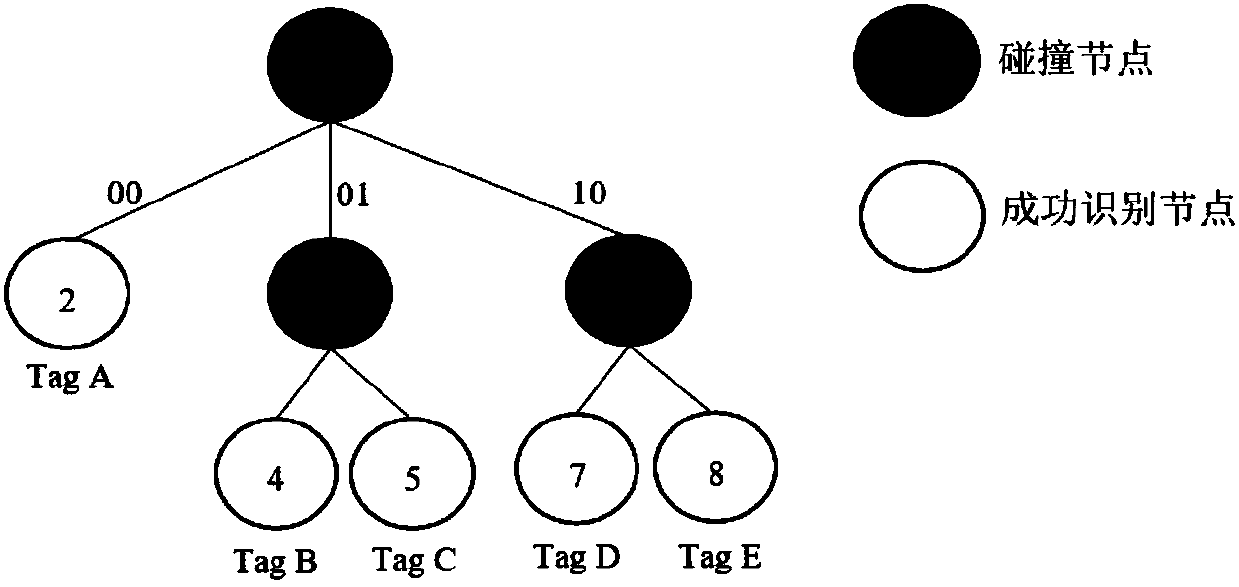
The invention discloses an adaptive bifurcation query tree multi-label anti-collision method based on a collision factor. The adaptive bifurcation query tree multi-label anti-collision method based ona collision factor includes the steps: in each query process, estimating the number of labels in a branch of the current query tree by calculating a collision factor; according to the estimated number of labels, selecting an appropriate bifurcation rule to perform adaptive bifurcation on the nodes of the query tree; and if the number of labels is bigger, performing query in a quadtree searching mode with no idle time slot for collision prefix code conversion, and if not, performing query in a binary tree searching mode. The invention provides an adaptive bifurcation query tree multi-label anti-collision method based on a collision factor. The adaptive bifurcation query tree multi-label anti-collision method based on a collision factor adaptively selects a bifurcation mechanism for the next query according to the size of the collision factor in each query, can completely avoid generation of the idle time slot and also reduce the total number of query time slots, and can improve the system throughput.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Commodity composite anti-fake code and symmetric test anit-fake method
The commodity anti-fake method includes two parts: method of creating composite commodity anti-fake code and method of verifying commodity anti-fake code. The composite commodity anti-fake code includes two digital codes of main commodity anti-fake code MZ and auxiliary commodity anti-fake code MF. The MZ consists of prefix code ZK0, function code ZK1 and base number code ZK2; and the MF consists of prefix code FK0 and calculation value code FK1. ZK1 corresponds to on unique function fZK1 (x) in the given function library CFDB, and FK1 belongs to function code library CFC and fZK1 (ZK2). The two anti-fake codes are printed on commodity before delivery; and during verification, MZ and MF are read out to distinguish ZK1, ZK2 and FK1, search fZK1 (x) and verify fZK1 (ZK2)=FK1 for checking the truth of the commodity.
Owner:刘普合
Commodity composite anti-fake code and symmetric test anit-fake method
The commodity anti-fake method includes two parts: method of creating composite commodity anti-fake code and method of verifying commodity anti-fake code. The composite commodity anti-fake code includes two digital codes of main commodity anti-fake code MZ and auxiliary commodity anti-fake code MF. The MZ consists of prefix code ZK0, function code ZK1 and base number code ZK2; and the MF consists of prefix code FK0 and calculation value code FK1. ZK1 corresponds to on unique function fZK1 (x) in the given function library CFDB, and FK1 belongs to function code library CFC and fZK1 (ZK2). The two anti-fake codes are printed on commodity before delivery; and during verification, MZ and MF are read out to distinguish ZK1, ZK2 and FK1, search fZK1 (x) and verify fZK1 (ZK2)=FK1 for checking the truth of the commodity.
Owner:刘普合
Device and method for selectivity controlling result write back
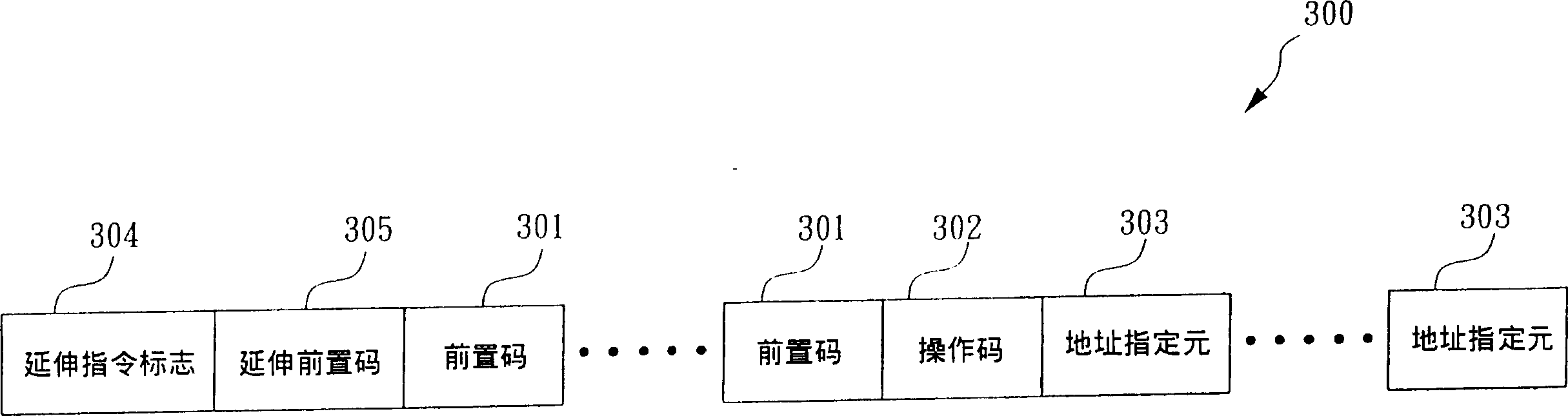
InactiveCN1414465AExclude writeback operationsDisable write backMicrocontrol arrangementsPrefix codeInstruction set
The invention relates to a microprocessor apparatus and method for selectively controlling write back of a result. The apparatus includes translation logic and extended execution logic. The translation logic translates an extended instruction into corresponding micro instructions. The extended instruction has an extended prefix and an extended prefix tag. The extended prefix disables write back of the result, where the result corresponds to execution of a prescribed operation. The extended prefix tag indicates the extended prefix, where the extended prefix tag is an otherwise architecturally specified opcode within an instruction set for a microprocessor. The extended execution logic is coupled to the translation logic. The extended execution logic receives the corresponding micro instructions, and executes the prescribed operation to generate the result, and precludes write back of the result.
Owner:IP FIRST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com