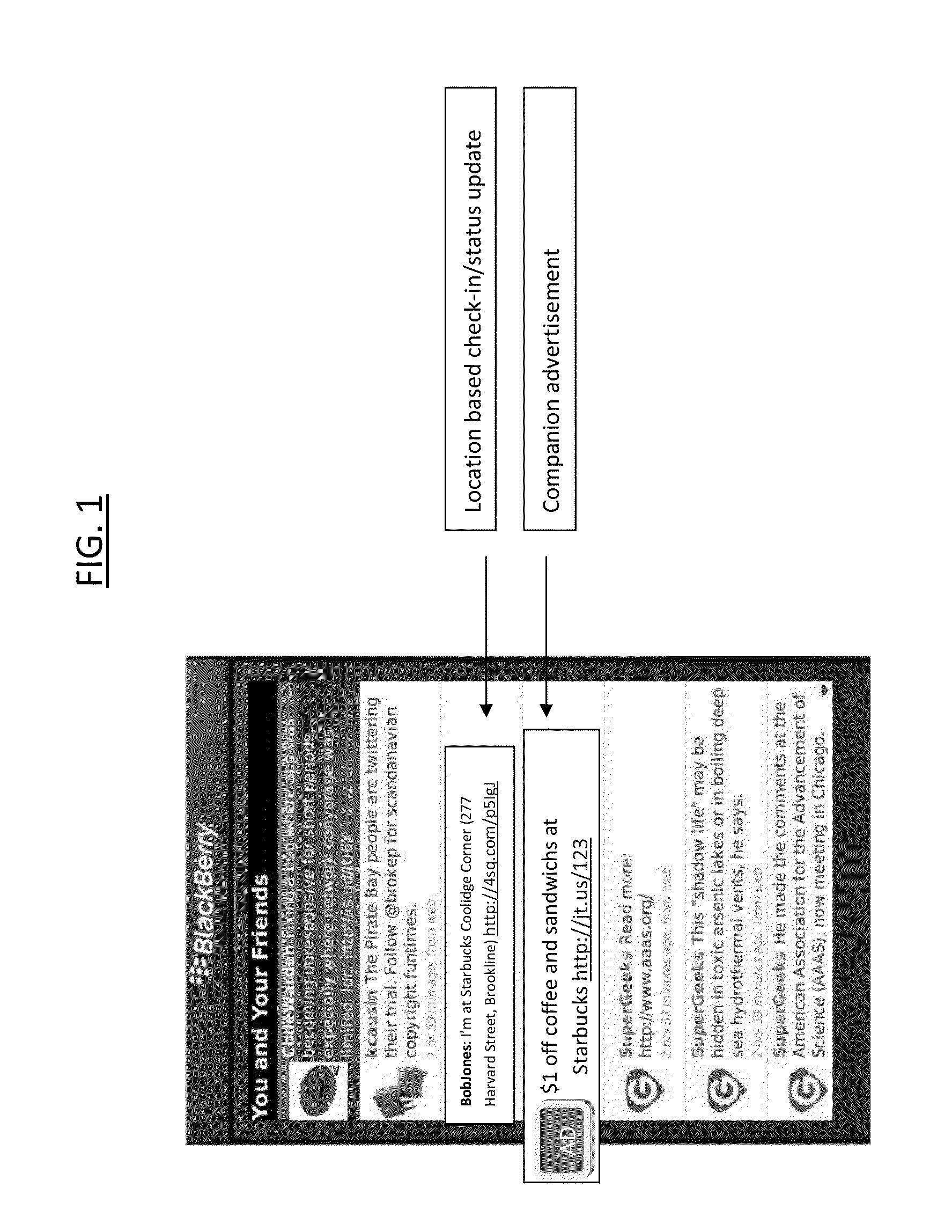
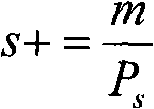Patents
Literature
55 results about "Probabilistic estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glossary:Probabilistic estimate. The probabilistic (risk weighted) approach of estimating recognizes that, in the real world, there are uncertainties associated with each project component. As such, for each component, there exists probabilities of occurrence within a range of possible values.
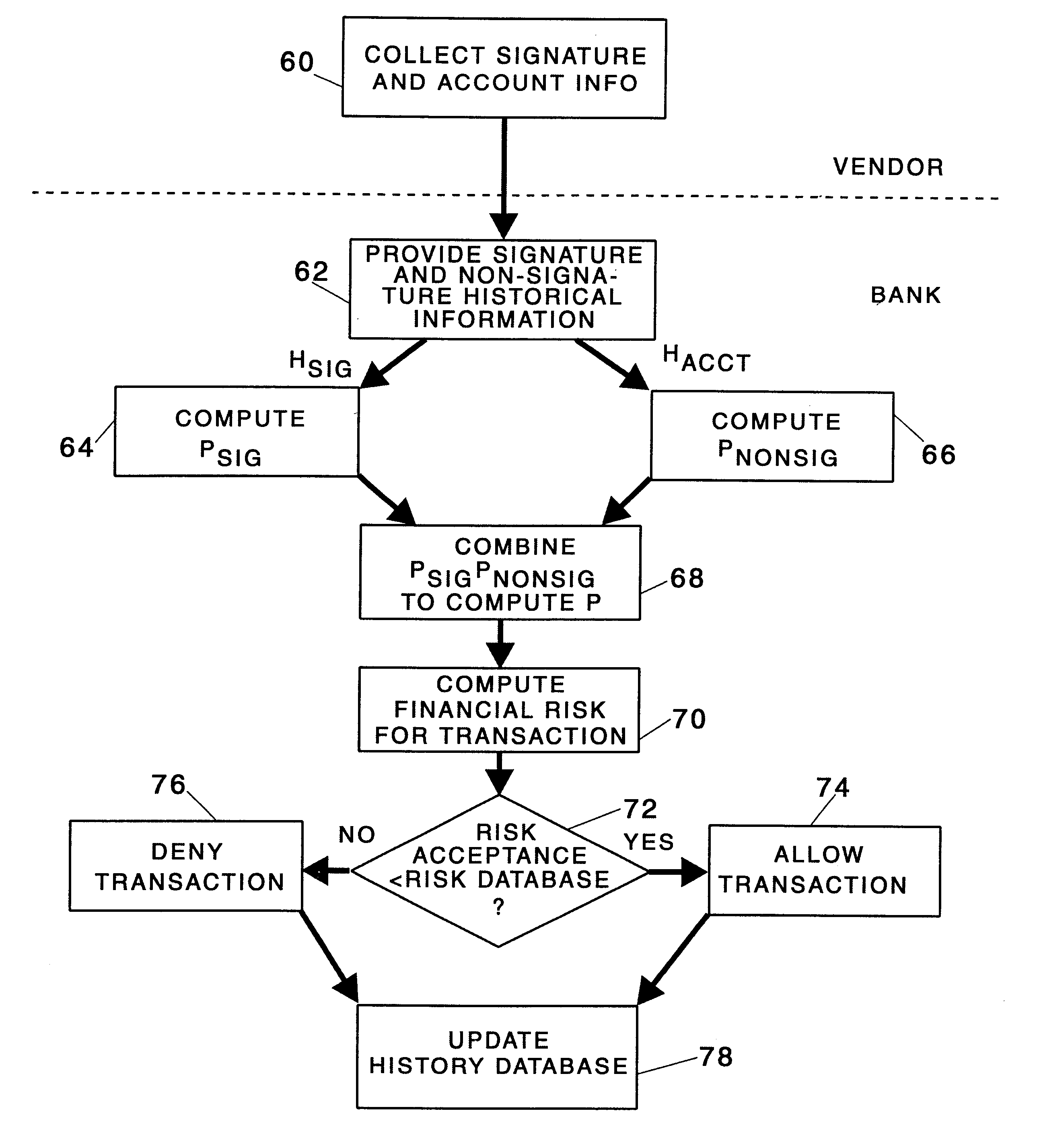
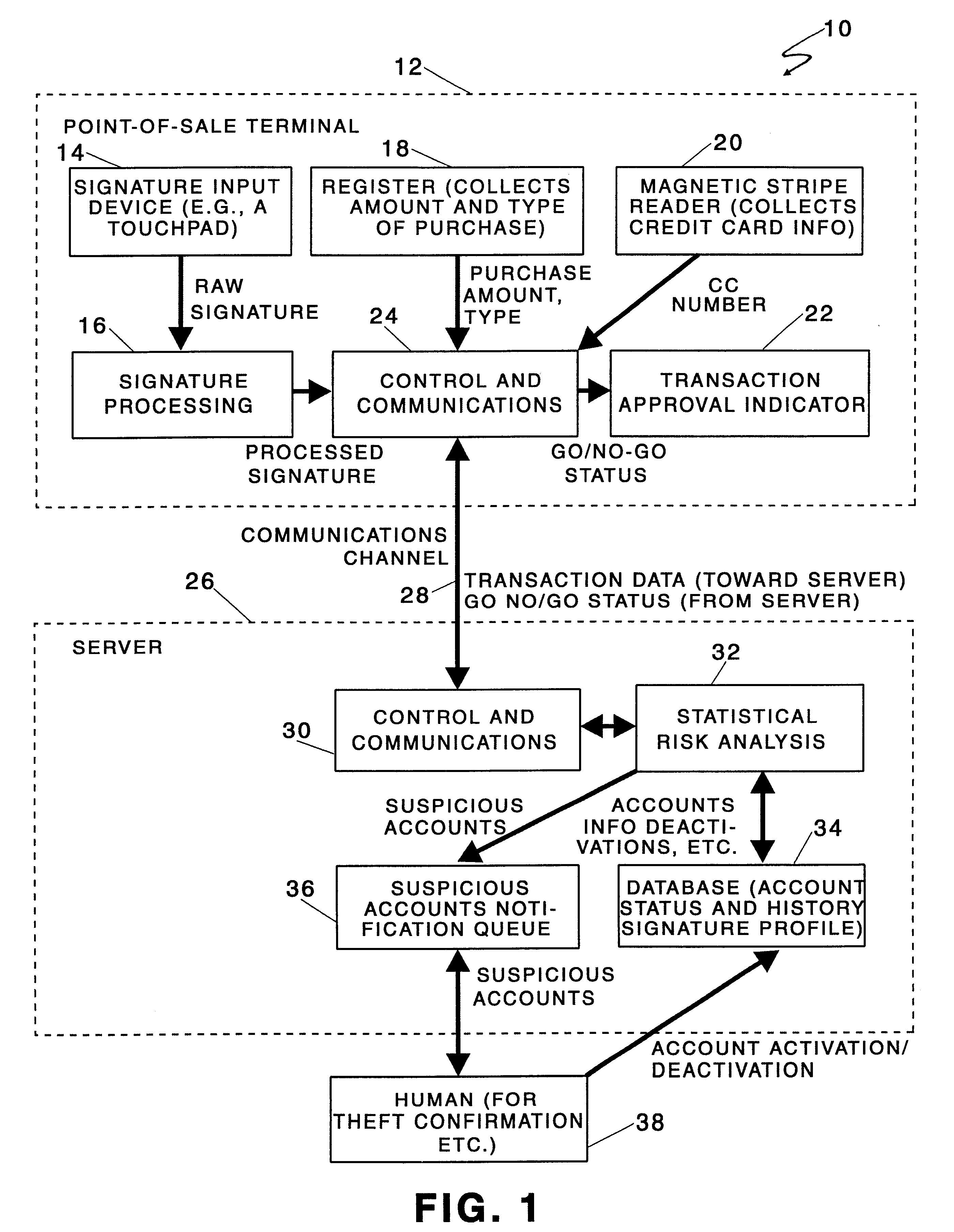
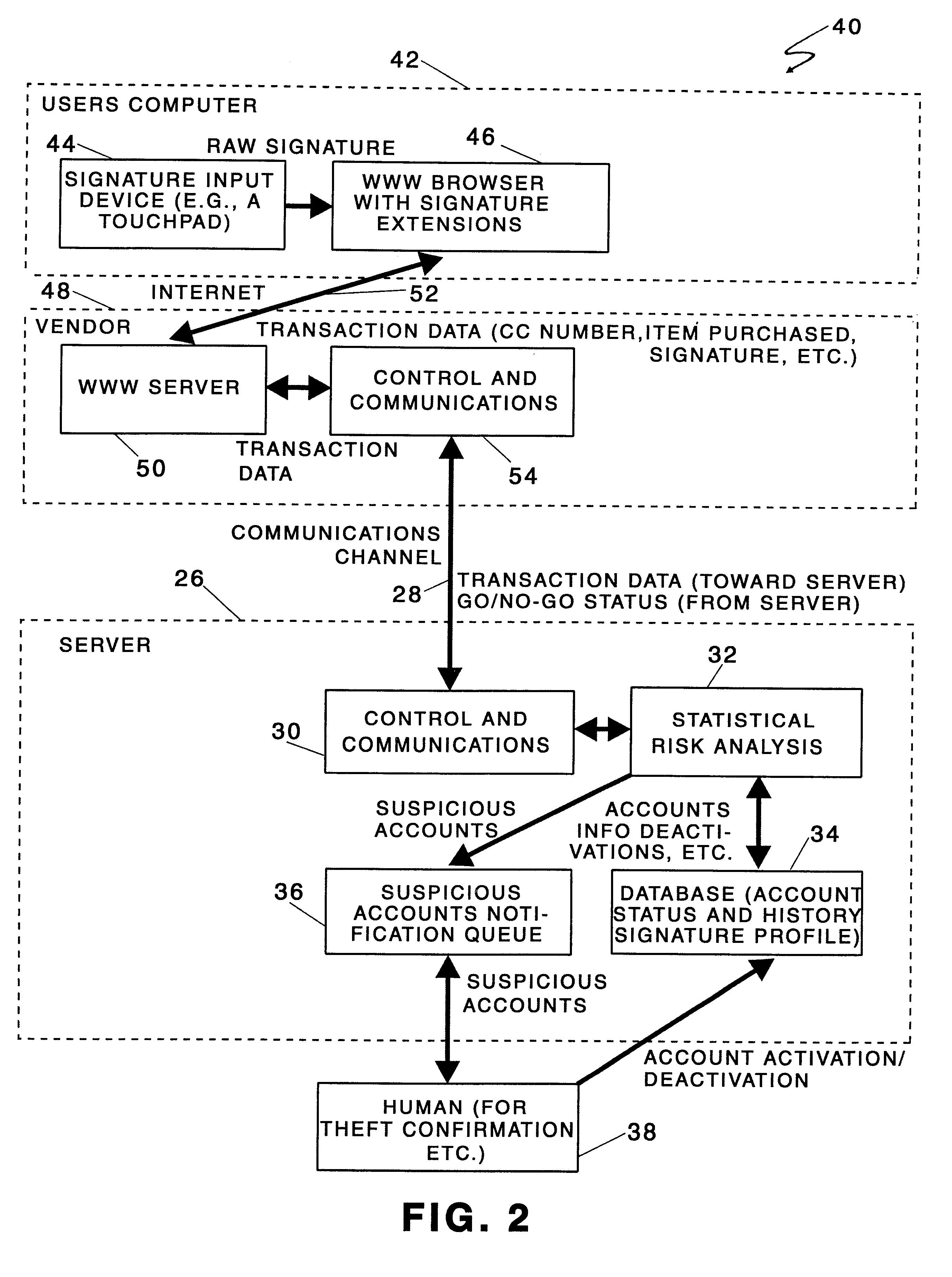
Identity verification methods
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
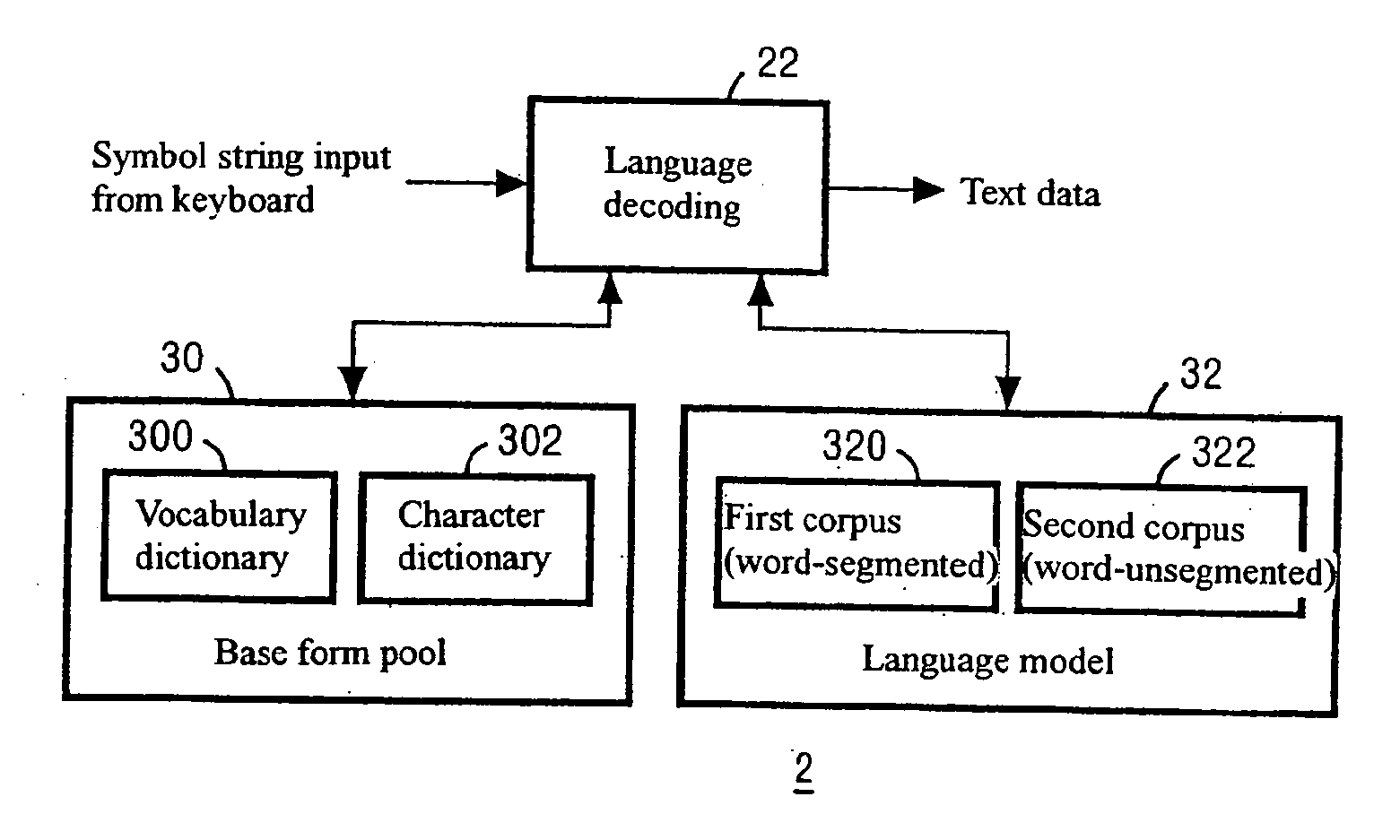
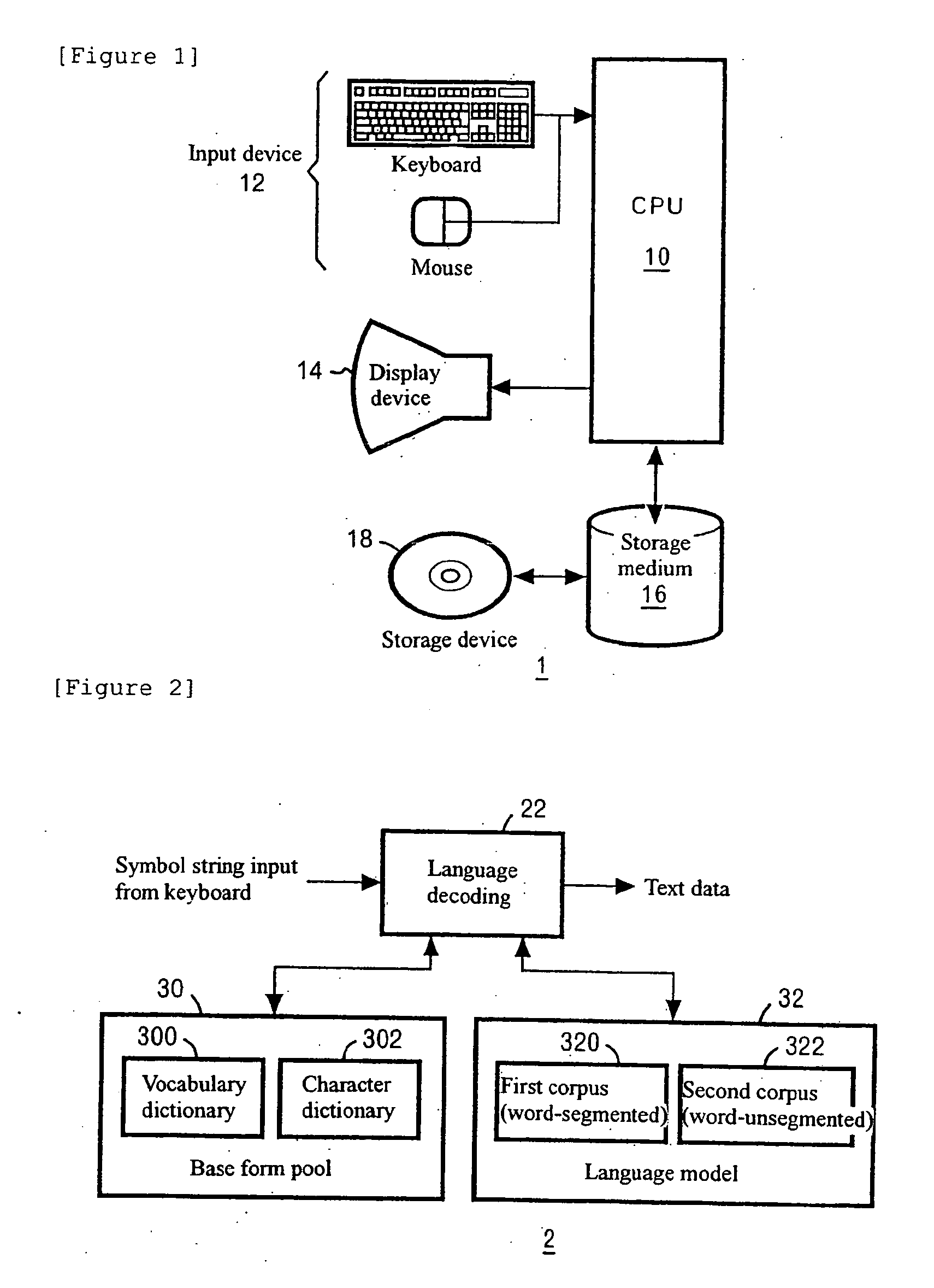
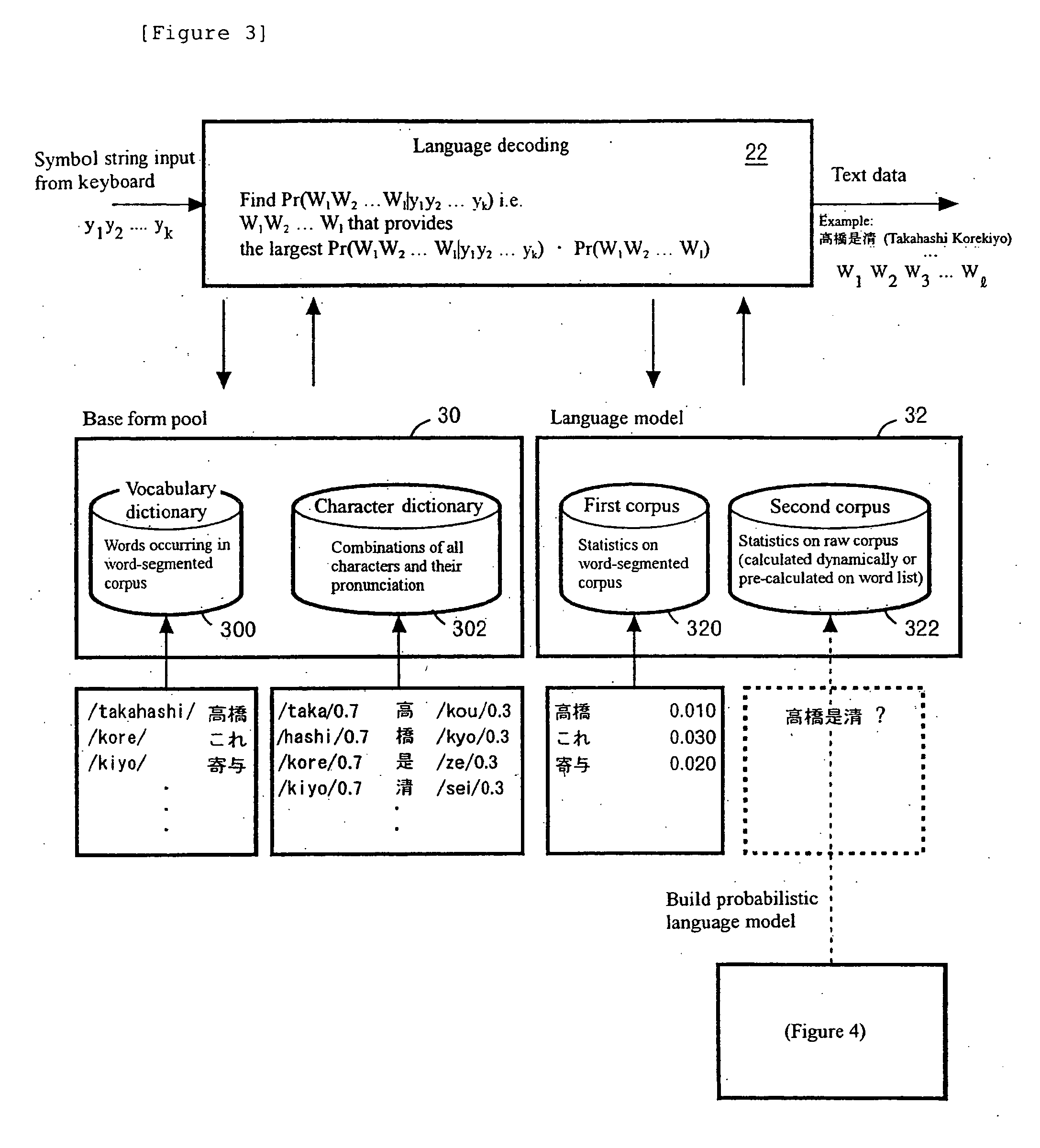
Word boundary probability estimating, probabilistic language model building, kana-kanji converting, and unknown word model building
InactiveUS20080228463A1Accuracy of recognitionImprove abilitiesNatural language translationSpeech recognitionCorpus restiformeWord model
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
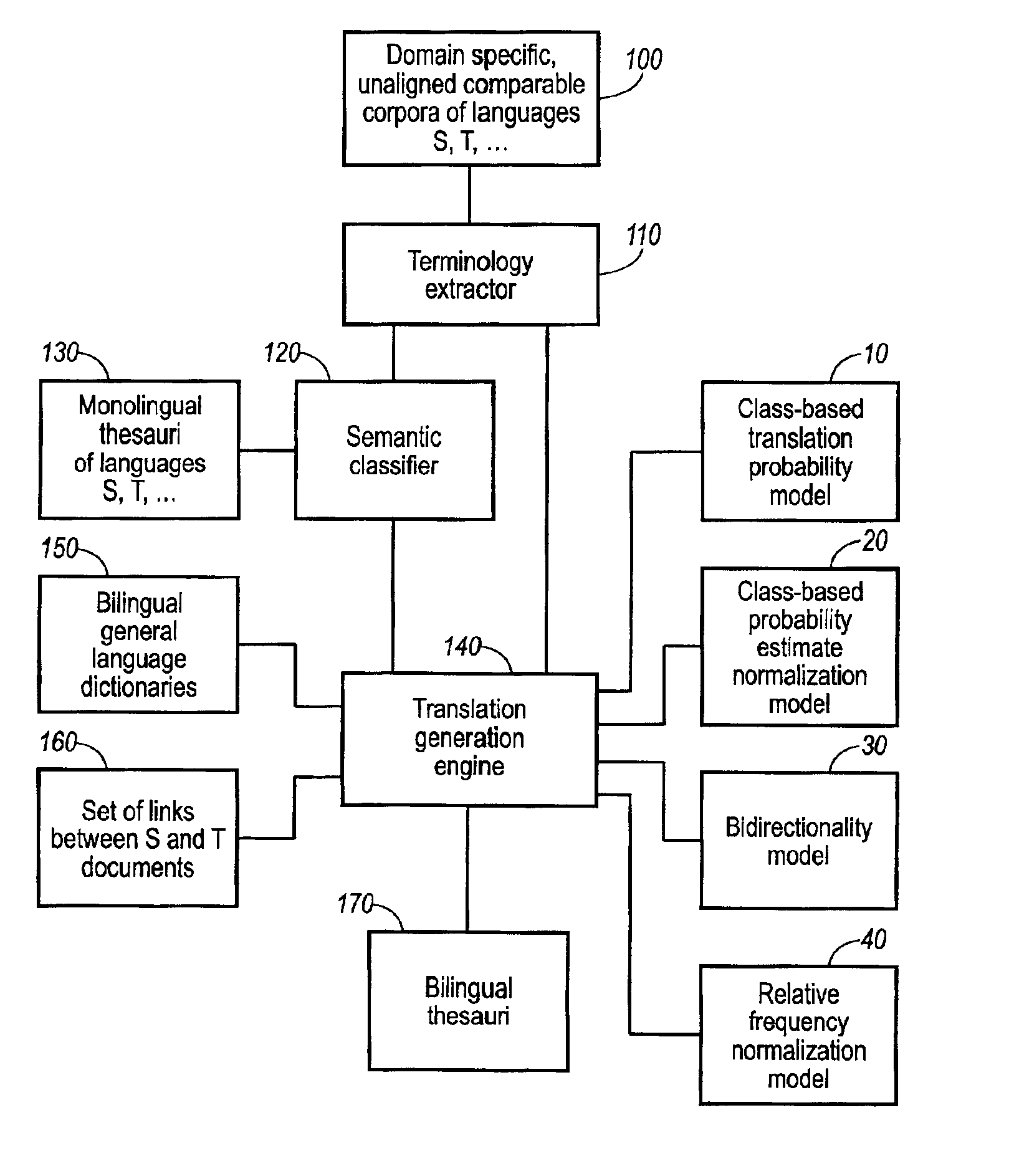
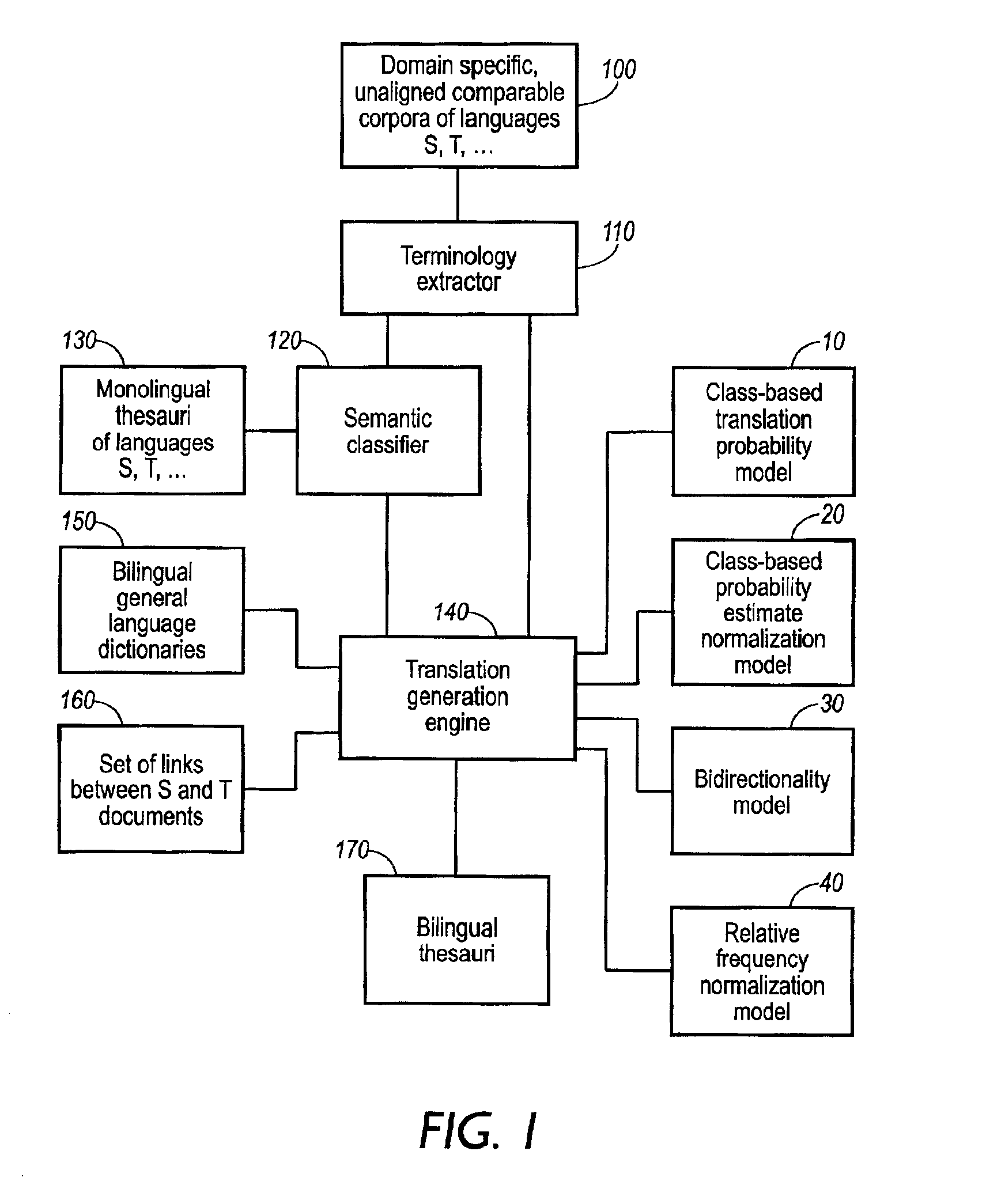
Terminology translation for unaligned comparable corpora using category based translation probabilities
InactiveUS6885985B2Quality improvementRankingNatural language translationSpeech analysisSemi automaticDocument preparation
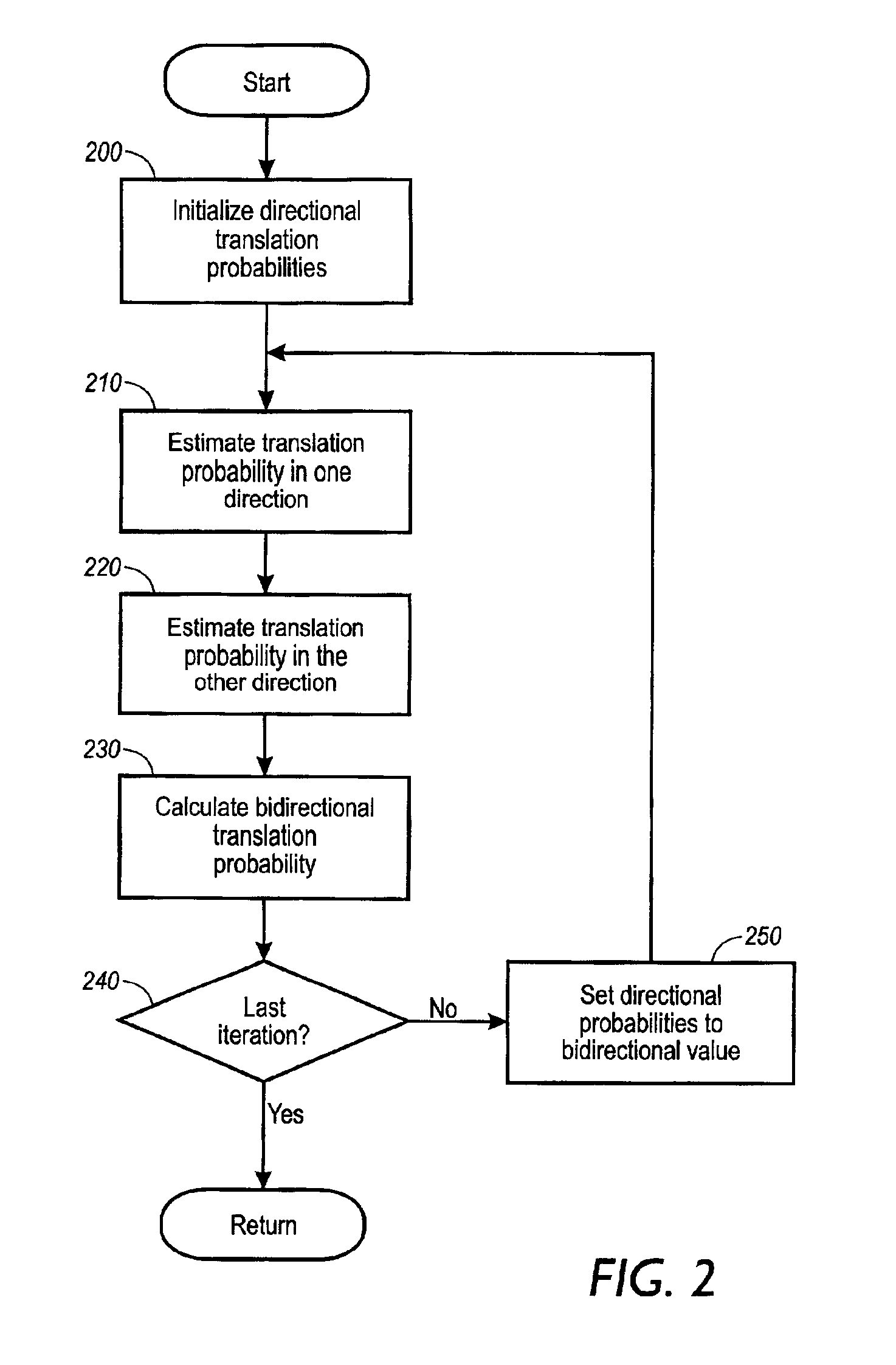
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for generating translations of natural language terms from a first language to a second language. A plurality of terms are extracted from unaligned comparable corpora of the first and second languages. Comparable corpora are sets of documents in different languages that come from the same domain and have similar genre and content. Unaligned documents are not translations of one another and are not linked in any other way. By accessing monolingual thesauri of the first and second languages, a category is assigned to each extracted term. Then, category-to-category translation probabilities are estimated, and using said category-to-category translation probabilities, term-to-term translation probabilities are estimated. The invention preferably exploits class-based normalization of probability estimates, bi-directionality, and relative frequency normalization. The most important applications are cross-language text retrieval, semi-automatic bilingual thesaurus enhancement, and machine-aided human translation.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Classification using probability estimate re-sampling
ActiveUS7194380B2Improve fitEffective calculationMathematical modelsFinanceAlgorithmClass membership
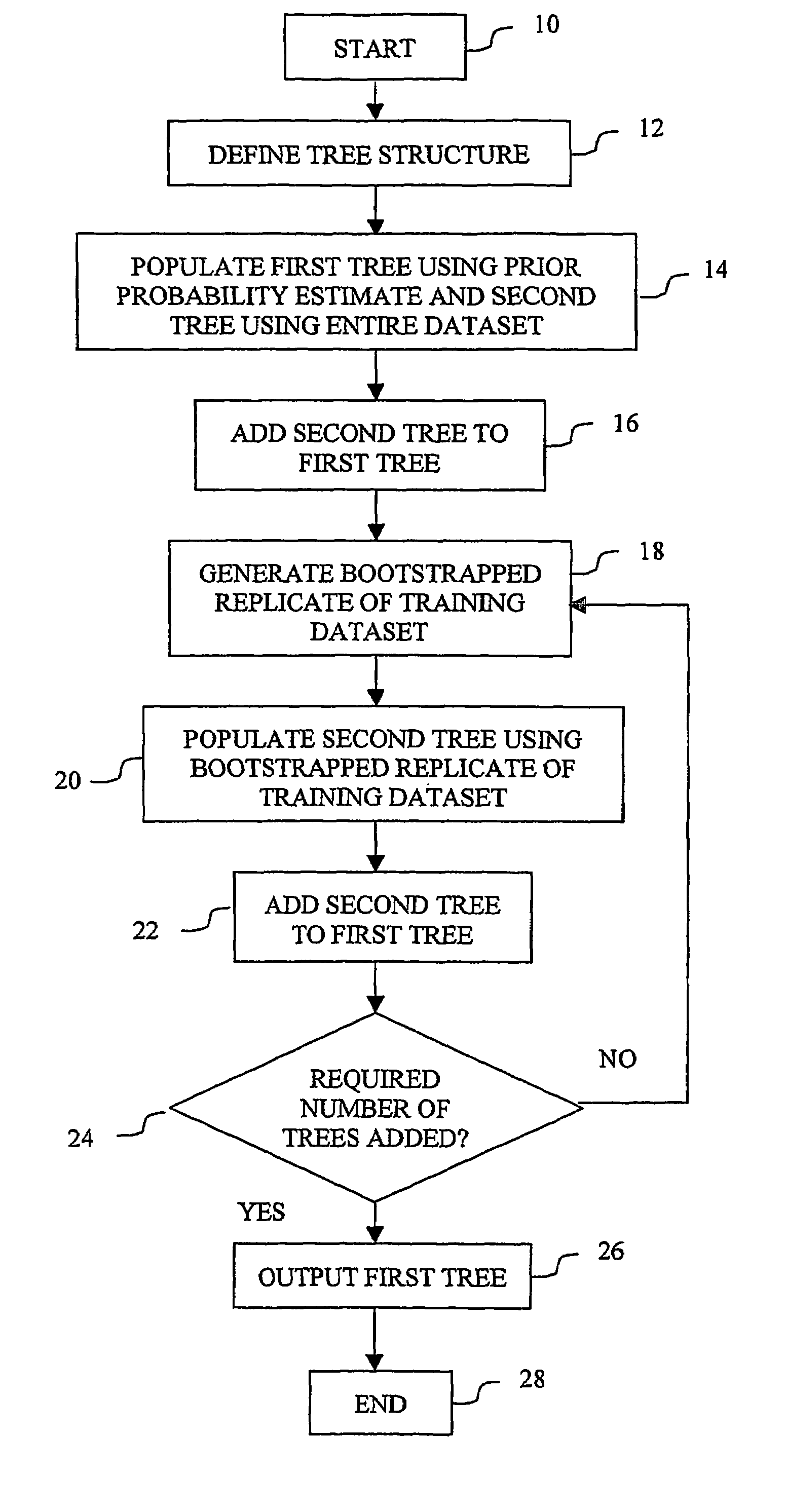
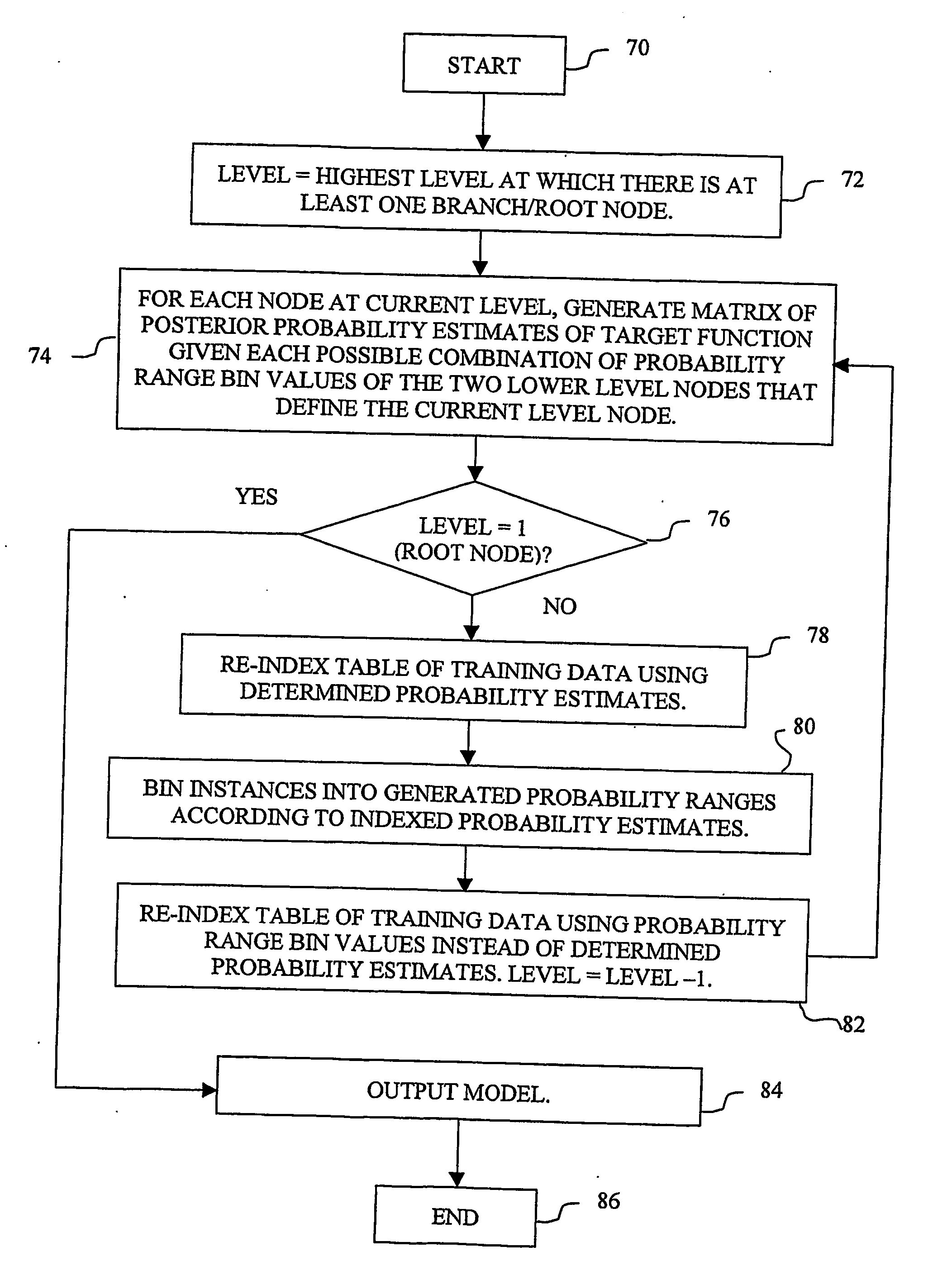
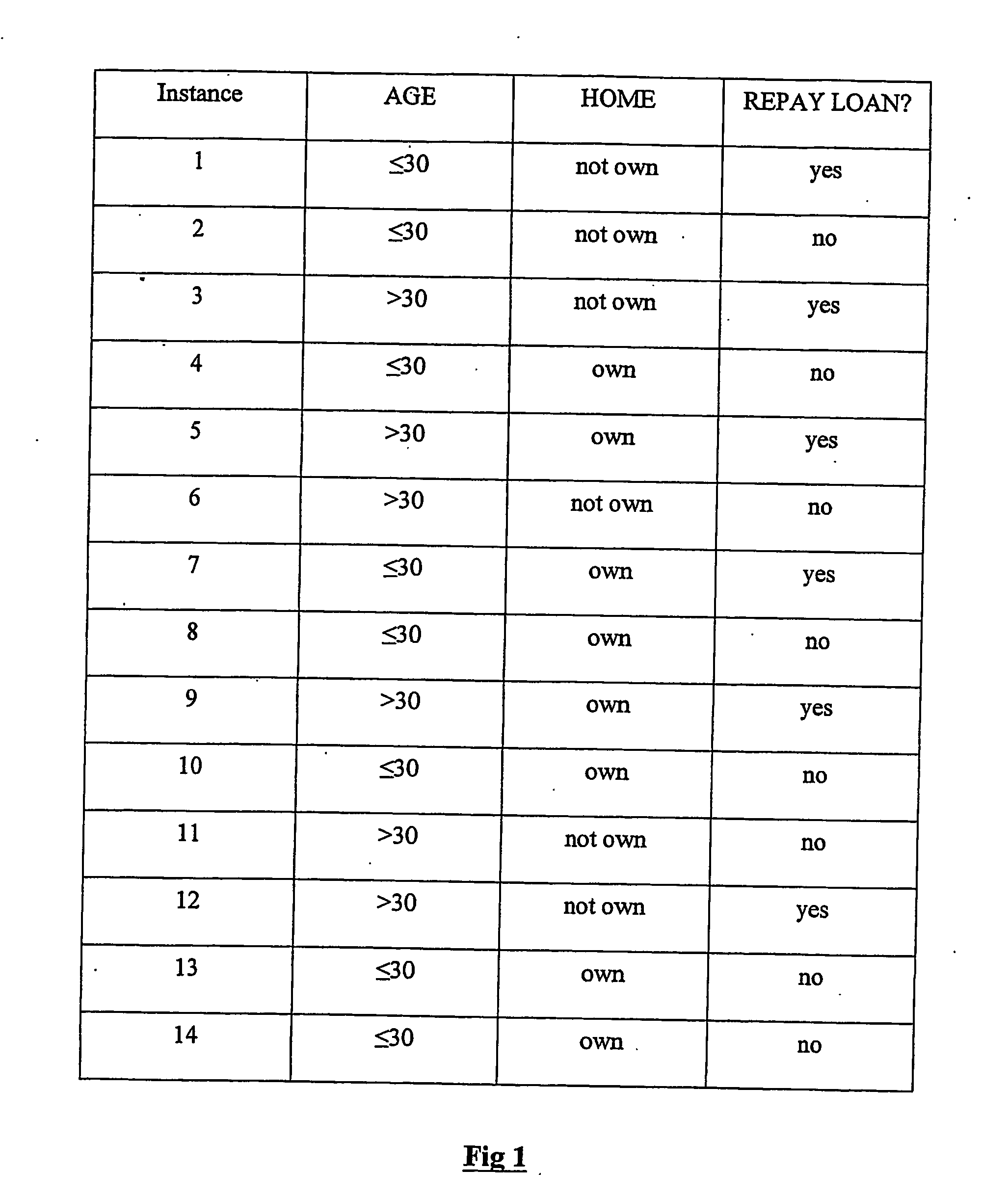
Embodiments of a computer-implemented method of calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership given combinations of attribute values of a pair of attributes are disclosed. The calculating is performed on the basis of data representing a training set of a plurality of instances defined by attribute values for a plurality of attributes together with a class membership outcome. Embodiments of the method comprise calculating first and second estimates of a posterior probability of class membership given attribute values of a first and second attribute of the pair, respectively, and binning the first and second estimates into a respective plurality of first and second probability range bins. Instances of the training set are mapped to combinations of one of each of the first and second pluralities of probability range bins, and on the basis of the mapping, calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership.
Owner:CHORDIANT SOFTWARE INT
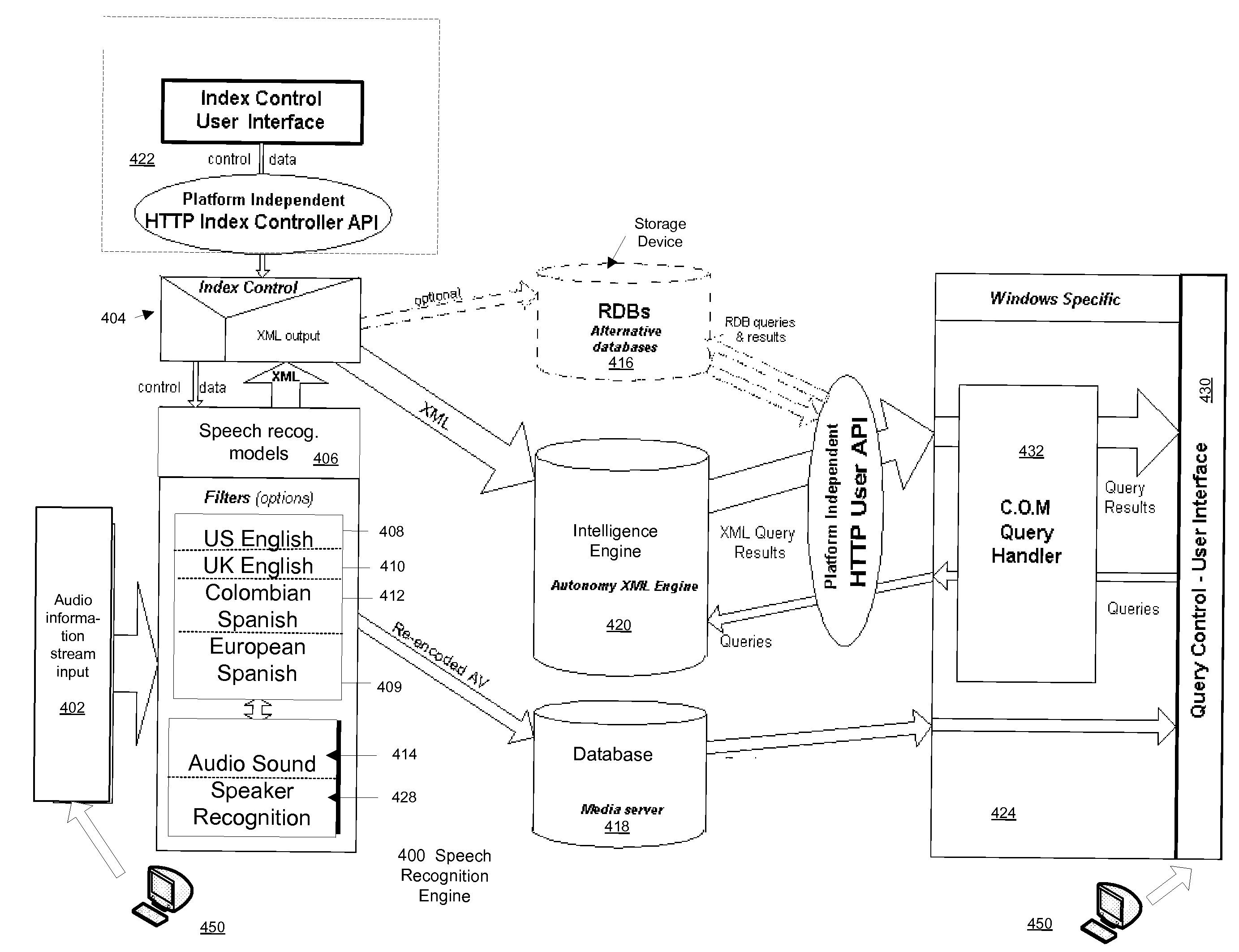
Speech recognition system
Various methods and apparatus are described for a speech recognition system. In an embodiment, the statistical language model (SLM) provides probability estimates of how linguistically likely a sequence of linguistic items are to occur in that sequence based on an amount of times the sequence of linguistic items occurs in text and phrases in general use. The speech recognition decoder module requests a correction module for one or more corrected probability estimates P′(z|xy) of how likely a linguistic item z follows a given sequence of linguistic items x followed by y, where (x, y, and z) are three variable linguistic items supplied from the decoder module. The correction module is trained to linguistics of a specific domain, and is located in between the decoder module and the SLM in order to adapt the probability estimates supplied by the SLM to the specific domain when those probability estimates from the SLM significantly disagree with the linguistic probabilities in that domain.
Owner:LONGSAND
Systems and methods for placing electronic advertisements
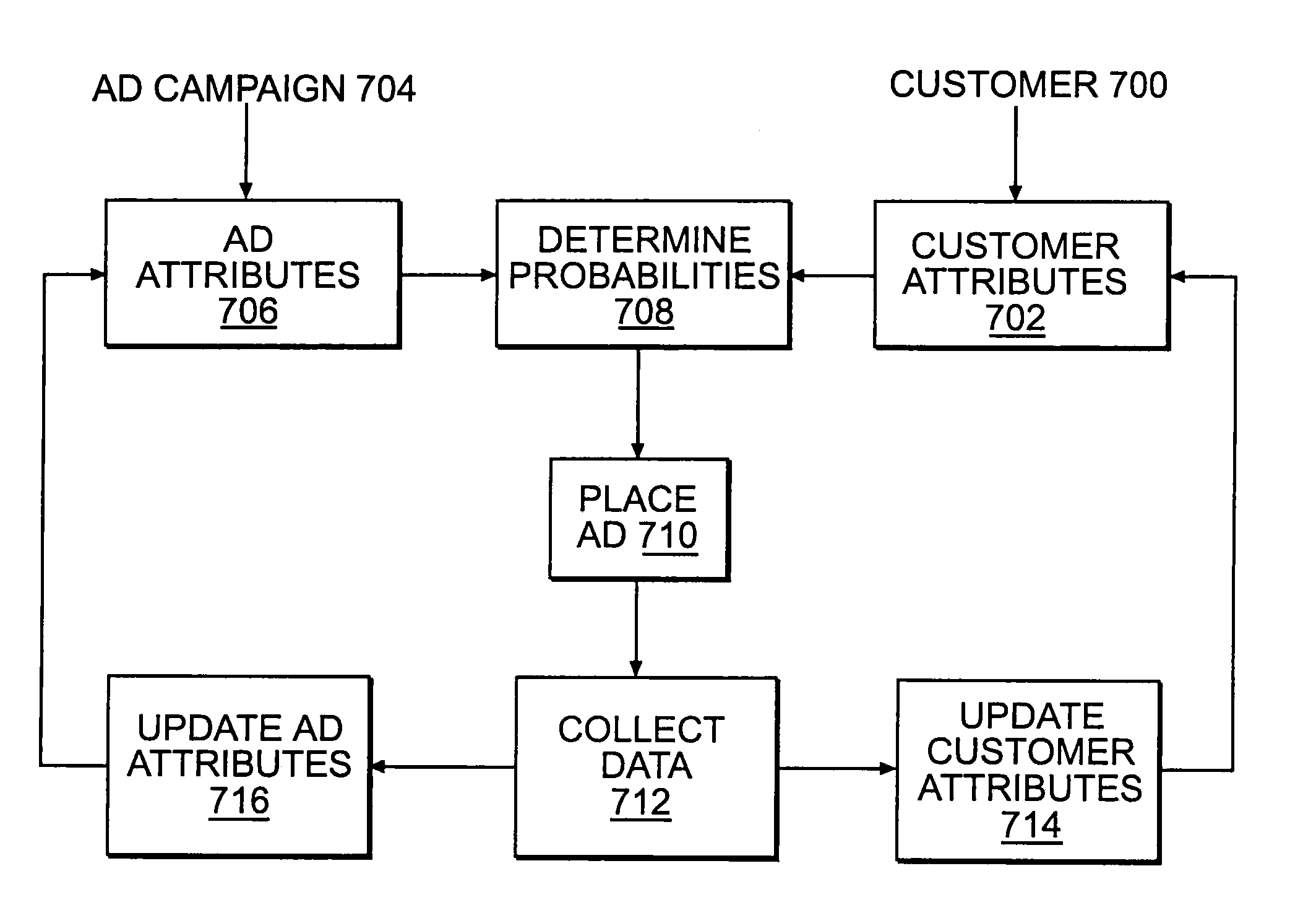
InactiveUS20100257053A1Improve click-through rateReduce deliveryAdvertisementsWeb pageInformation retrieval
This invention concerns optimal ad selection for Web pages by selecting and updating an attribute set, obtaining and updating an ad-attribute profile, and optimally choosing the next ad. The present invention associates a set of attributes with each customer. The attributes reflect the customers' interests and they incorporate the characteristics that impact ad selection. Similarly, the present invention associates with each ad an ad-attribute profile in order to calculate a customer's estimated ad selection probability and measure the uncertainty in that estimate. An ad selection algorithm optimally selects which ad to show based on the click probability estimates and the uncertainties regarding these estimates.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Classification using probability estimate re-sampling
ActiveUS20060167655A1Effective calculationImprove fitMathematical modelsFinanceAlgorithmClass membership
Embodiments of a computer-implemented method of calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership given combinations of attribute values of a pair of attributes are disclosed. The calculating is performed on the basis of data representing a training set of a plurality of instances defined by attribute values for a plurality of attributes together with a class membership outcome. Embodiments of the method comprise calculating first and second estimates of a posterior probability of class membership given attribute values of a first and second attribute of the pair, respectively, and binning the first and second estimates into a respective plurality of first and second probability range bins. Instances of the training set are mapped to combinations of one of each of the first and second pluralities of probability range bins, and on the basis of the mapping, calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership.
Owner:CHORDIANT SOFTWARE INT
Software bug predicting
InactiveUS20140033174A1Reliability/availability analysisSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware bugParallel computing
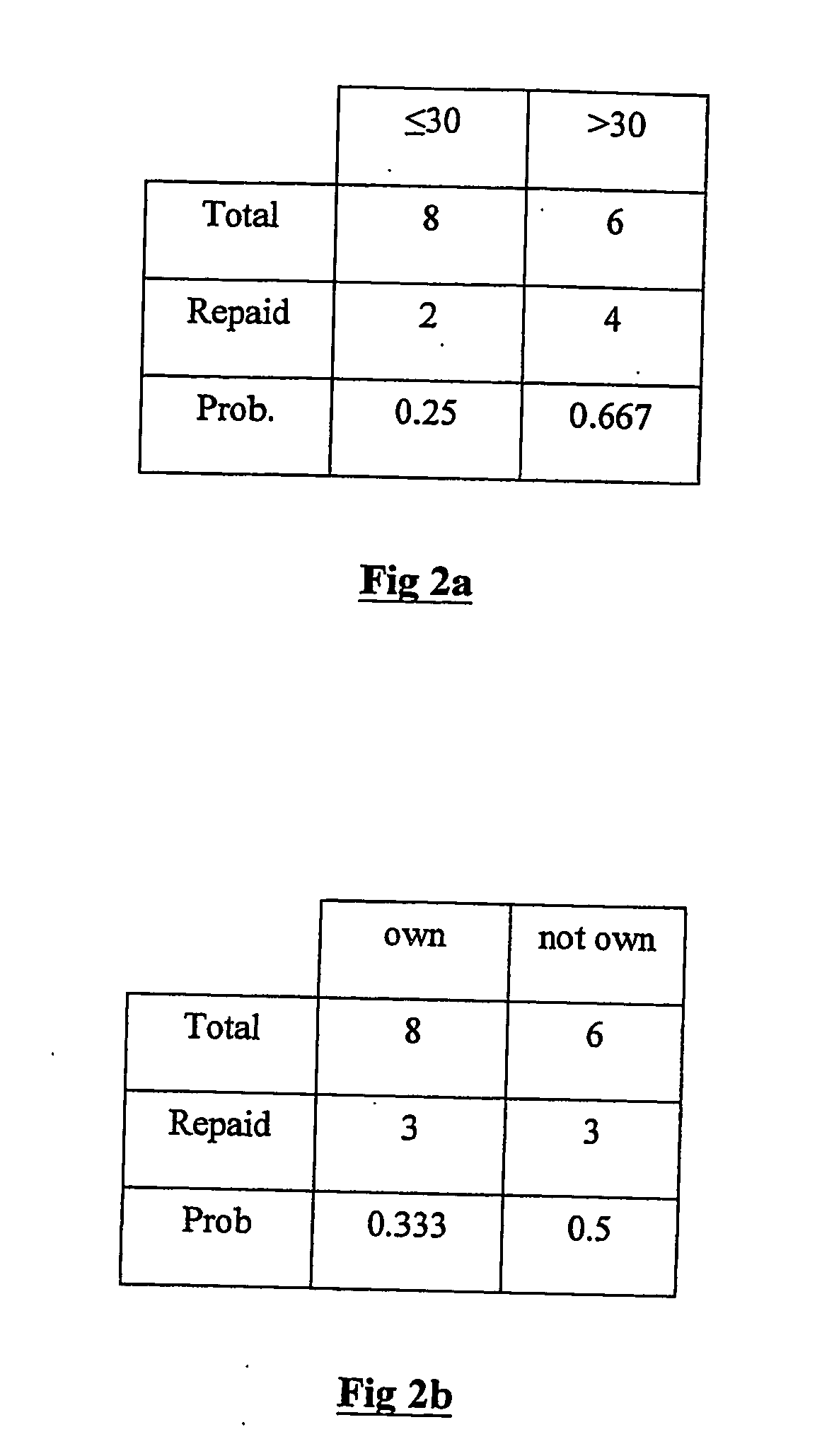
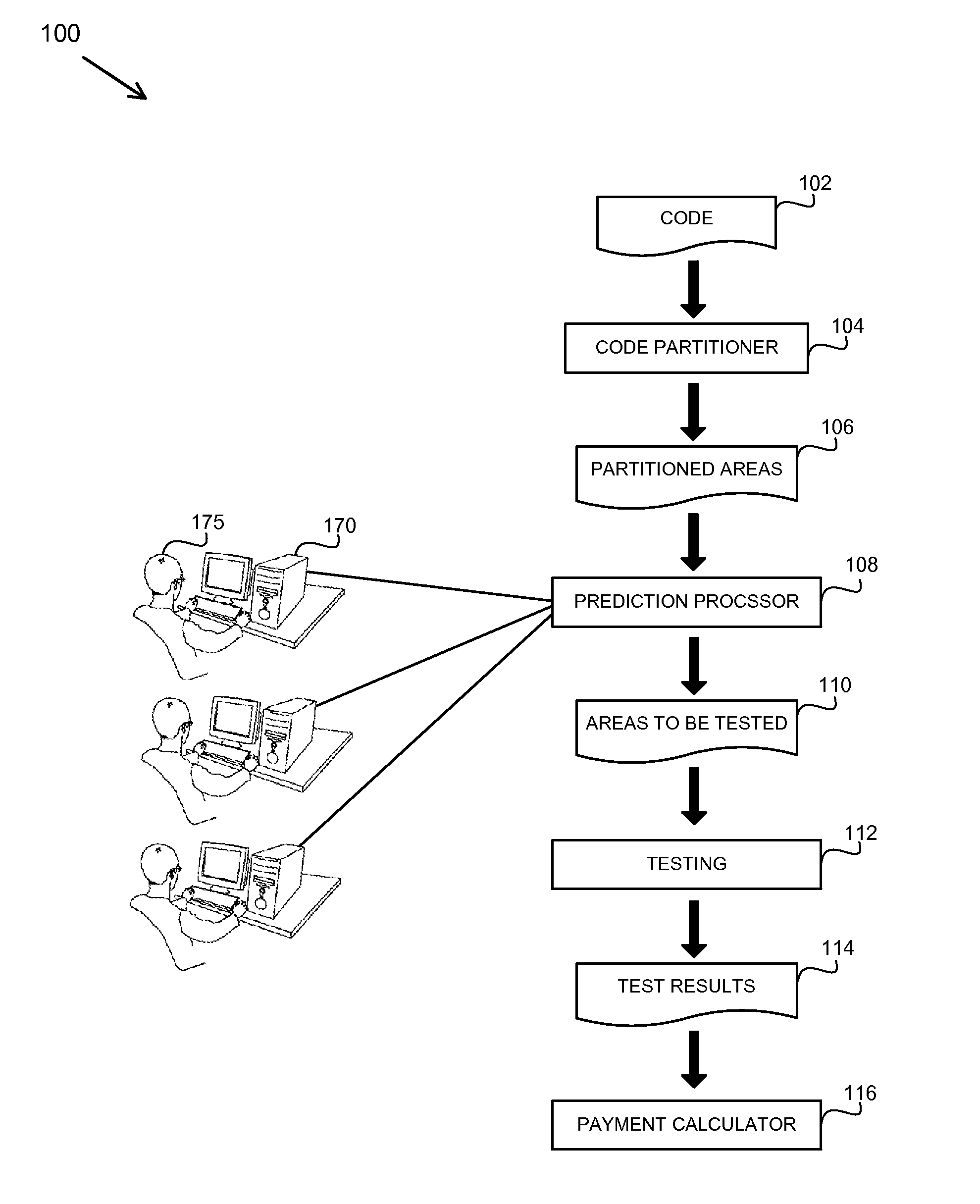
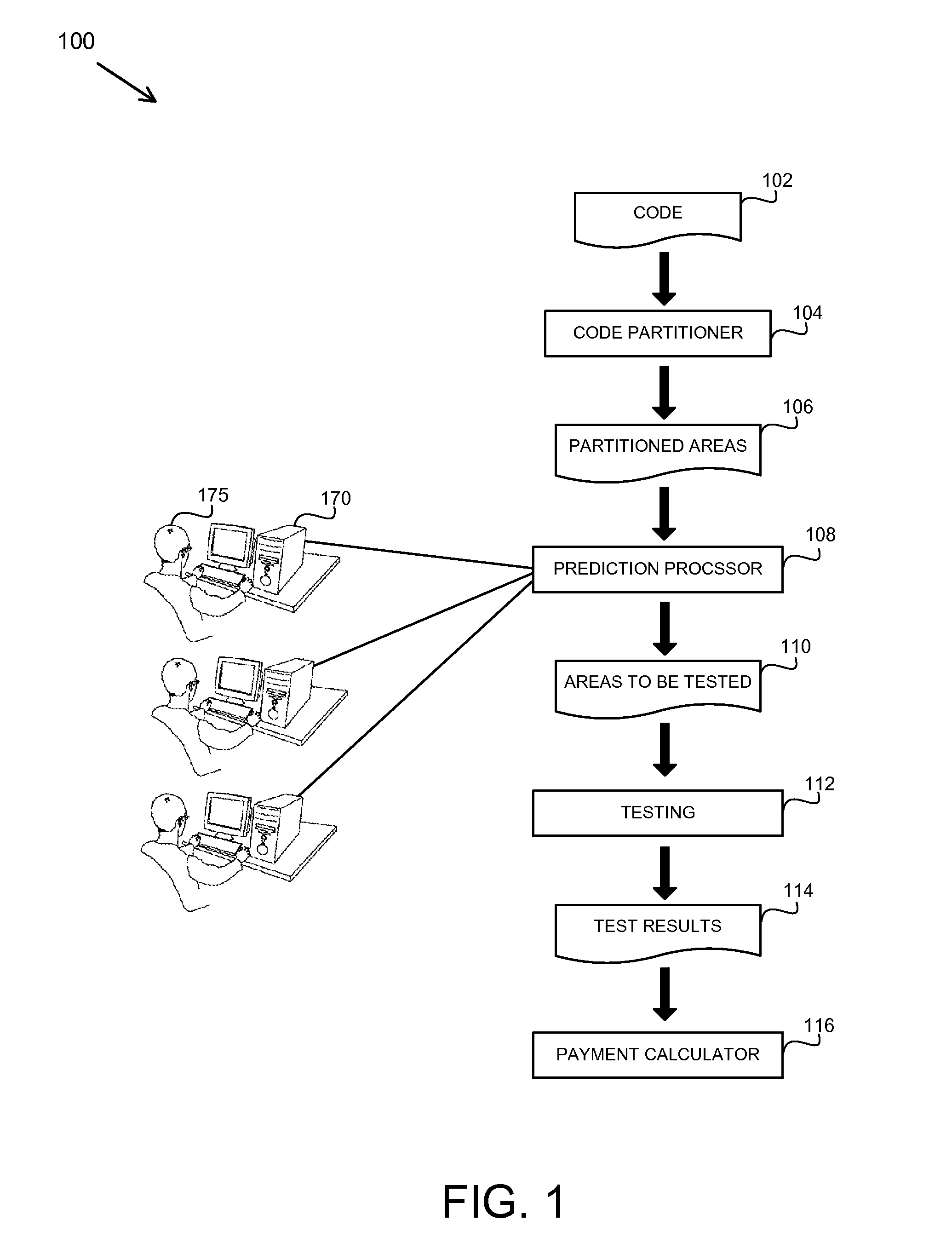
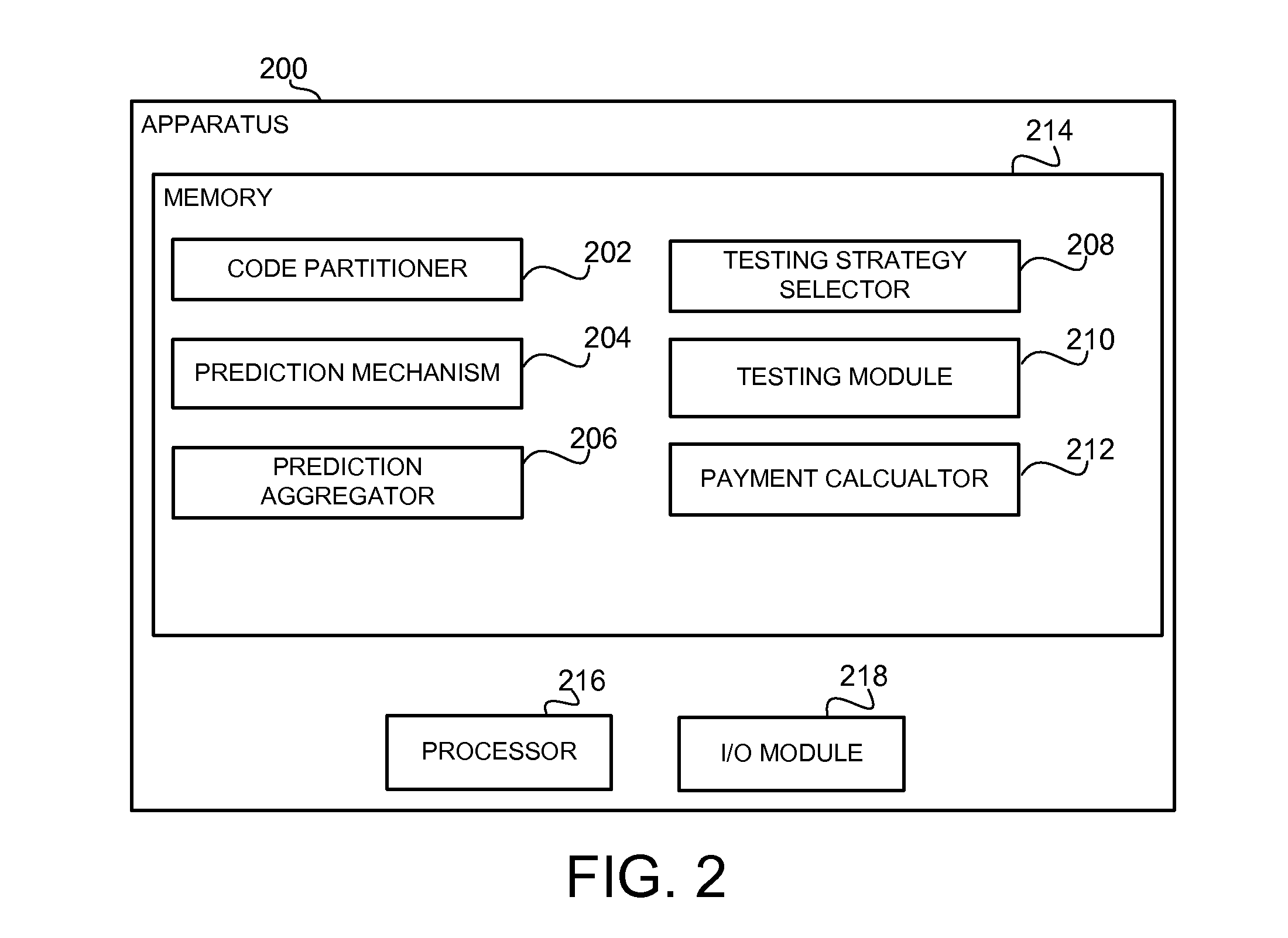
A method, apparatus and product for software bug prediction. The method comprising obtaining from a plurality of developers probability estimates to areas in a plurality of code partitioned areas of a code, wherein a probability estimate is representative of an estimated probability of the area having a software bug according to a developer of the plurality of developers; and determining a testing strategy of the plurality of code partitioned areas based on the probability estimates.
Owner:IBM CORP
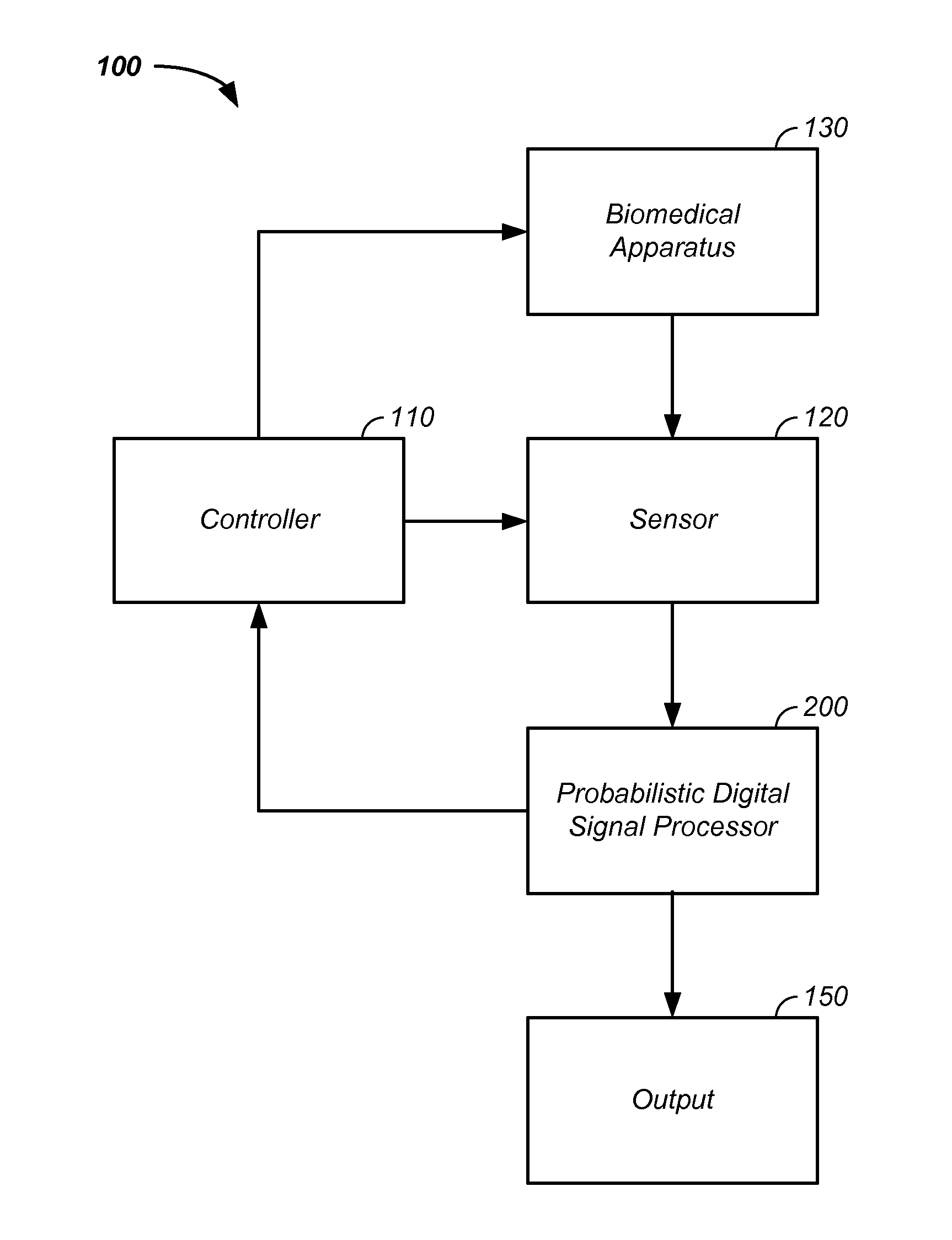
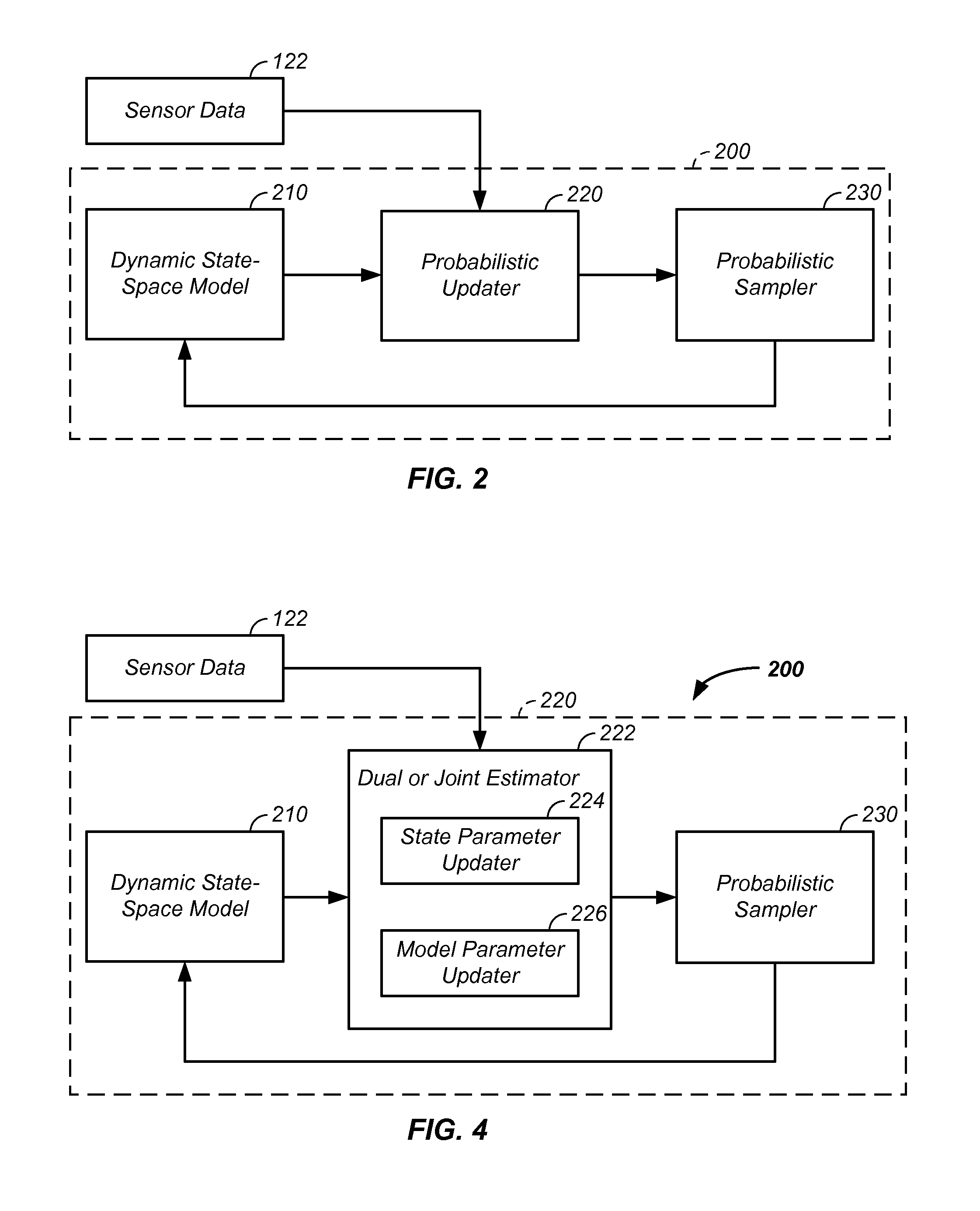
Biomedical parameter probabilistic estimation method and apparatus
A probabilistic digital signal processor is described. Initial probability distribution functions are input to a dynamic state-space model, which operates on state and / or model probability distribution functions to generate a prior probability distribution function, which is input to a probabilistic updater. The probabilistic updater integrates sensor data with the prior to generate a posterior probability distribution function passed (1) to a probabilistic sampler, which estimates one or more parameters using the posterior, which is output or re-sampled in an iterative algorithm or (2) iteratively to the dynamic state-space model. For example, the probabilistic processor operates using a physical model on data from a mechanical system or a medical meter or instrument, such as an electrocardiogram. Output of the physical model yields an enhanced output of the original data, an output to a second physical parameter not output by the medical meter, or a prediction, such as an arrhythmia warning.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
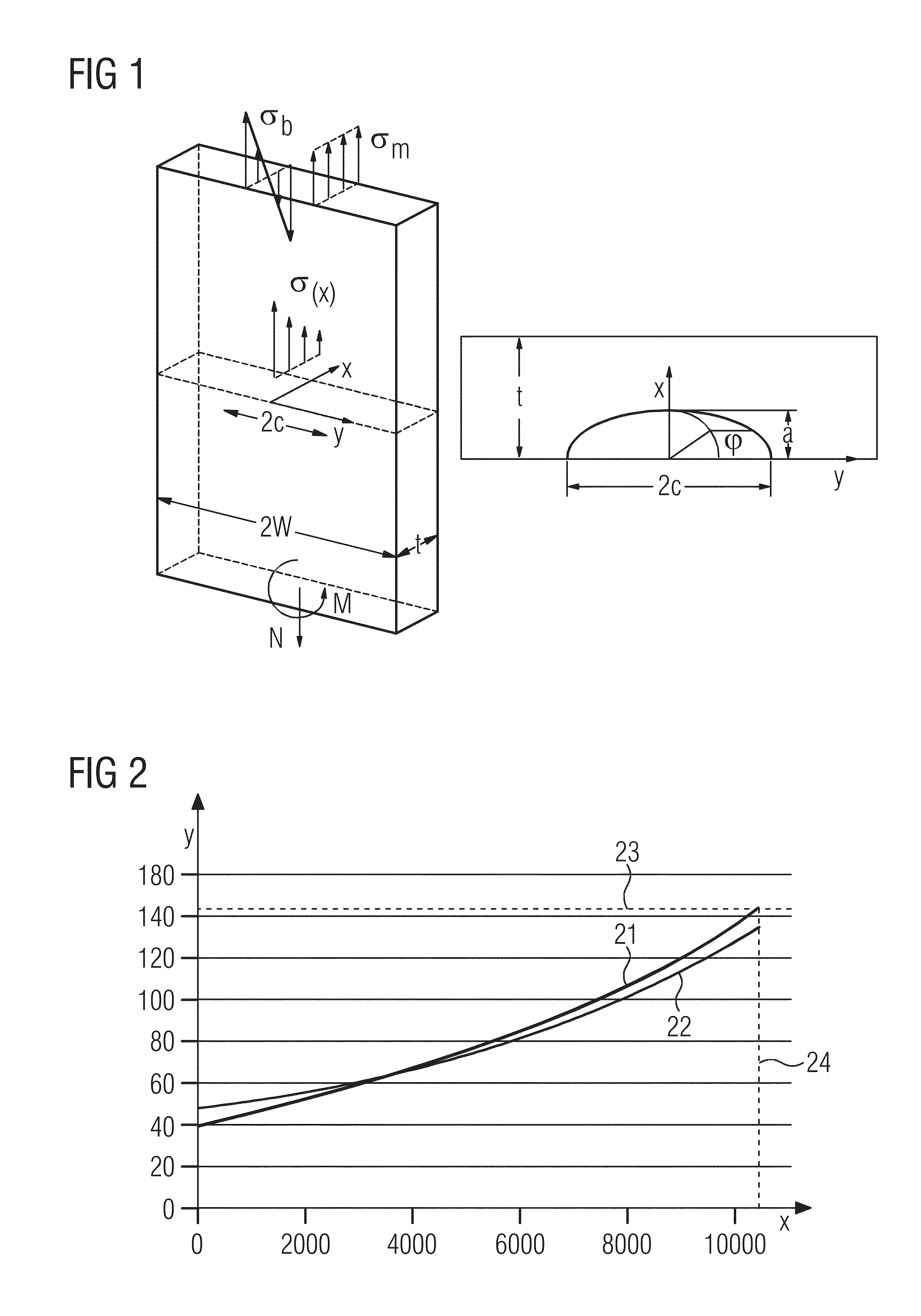
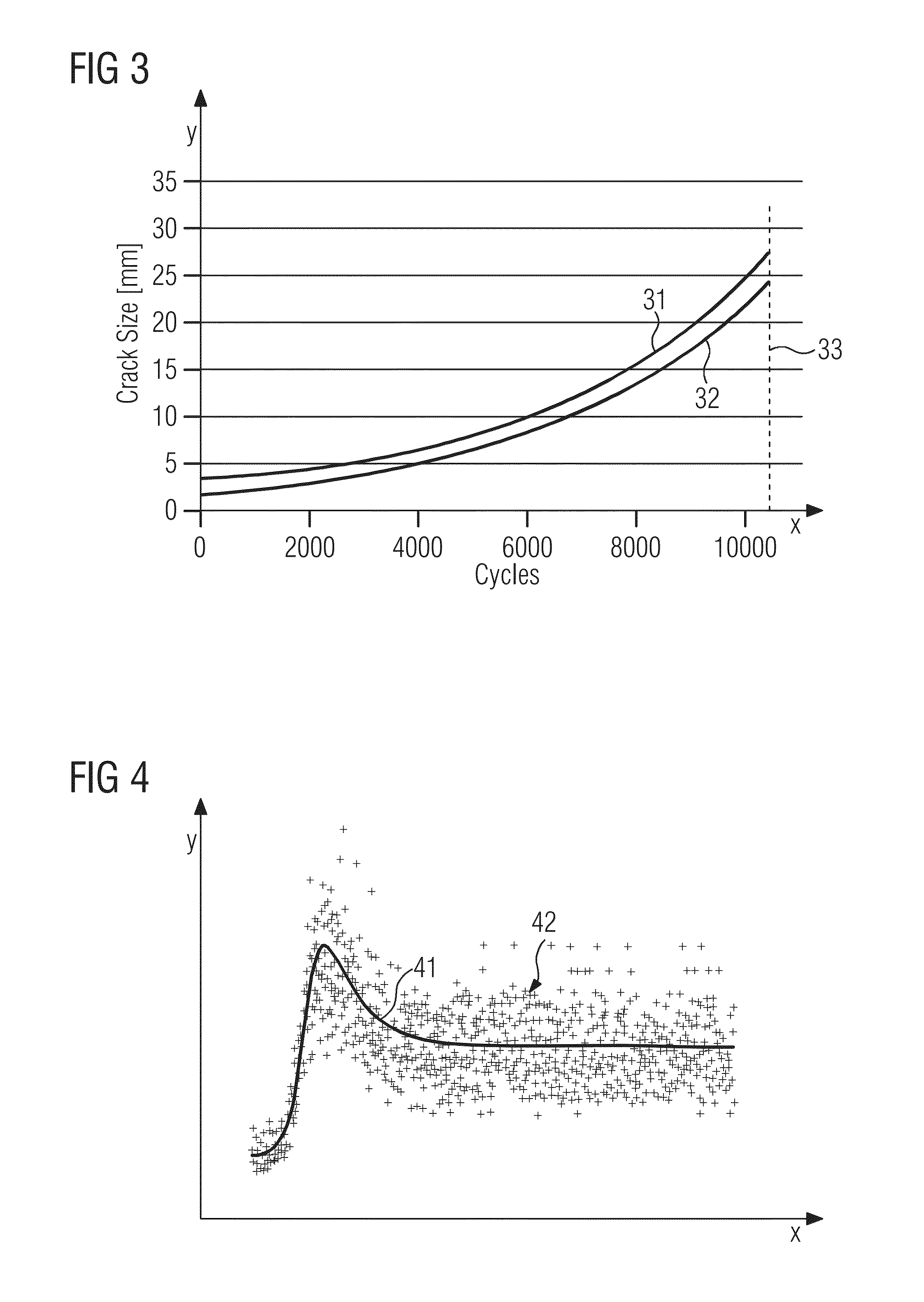
Method and system for probabilistic fatigue crack life estimation
ActiveUS20140107948A1Estimate conservativeReduce computing timeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer scienceFatigue cracking
A probabilistic estimation of fatigue crack life of a component is provided. A plurality of representations of the component is defined from material property scatter data and flaw-size scatter data, wherein each representation is defined by one possible material condition and flaw-size condition associated with the component. For each representation, a component location is selected and a determination is made whether said individual representation fails after a given number of cycles N, based on the calculation of a crack growth in the selected location. The crack growth is calculated on the basis of the material condition and the flaw-size condition in the selected location. Failure of the individual representation is determined if the crack growth is determined to be unstable. The sum total of the number of the representations that failed after N cycles is determined. A probability of failure of the component after N cycles is then determined.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Probability route improving method in delay-tolerance mobile sensor network based on node activeness
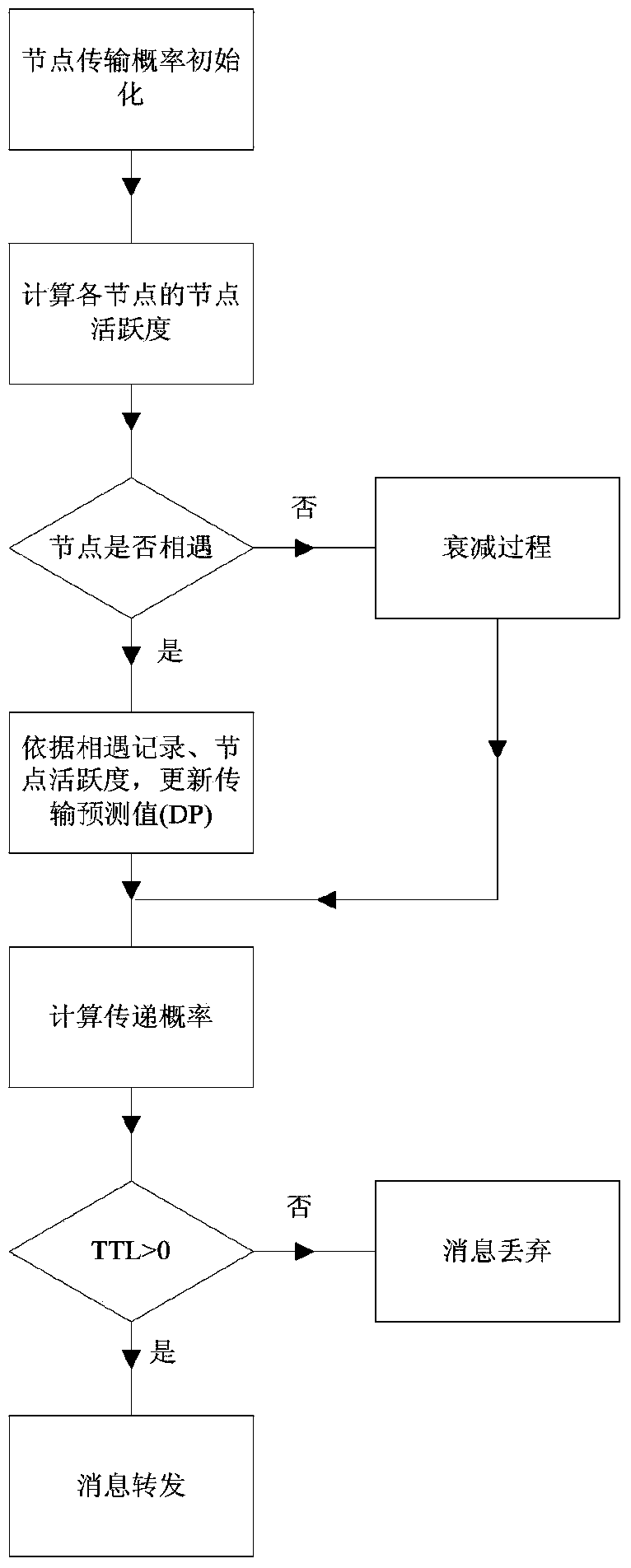
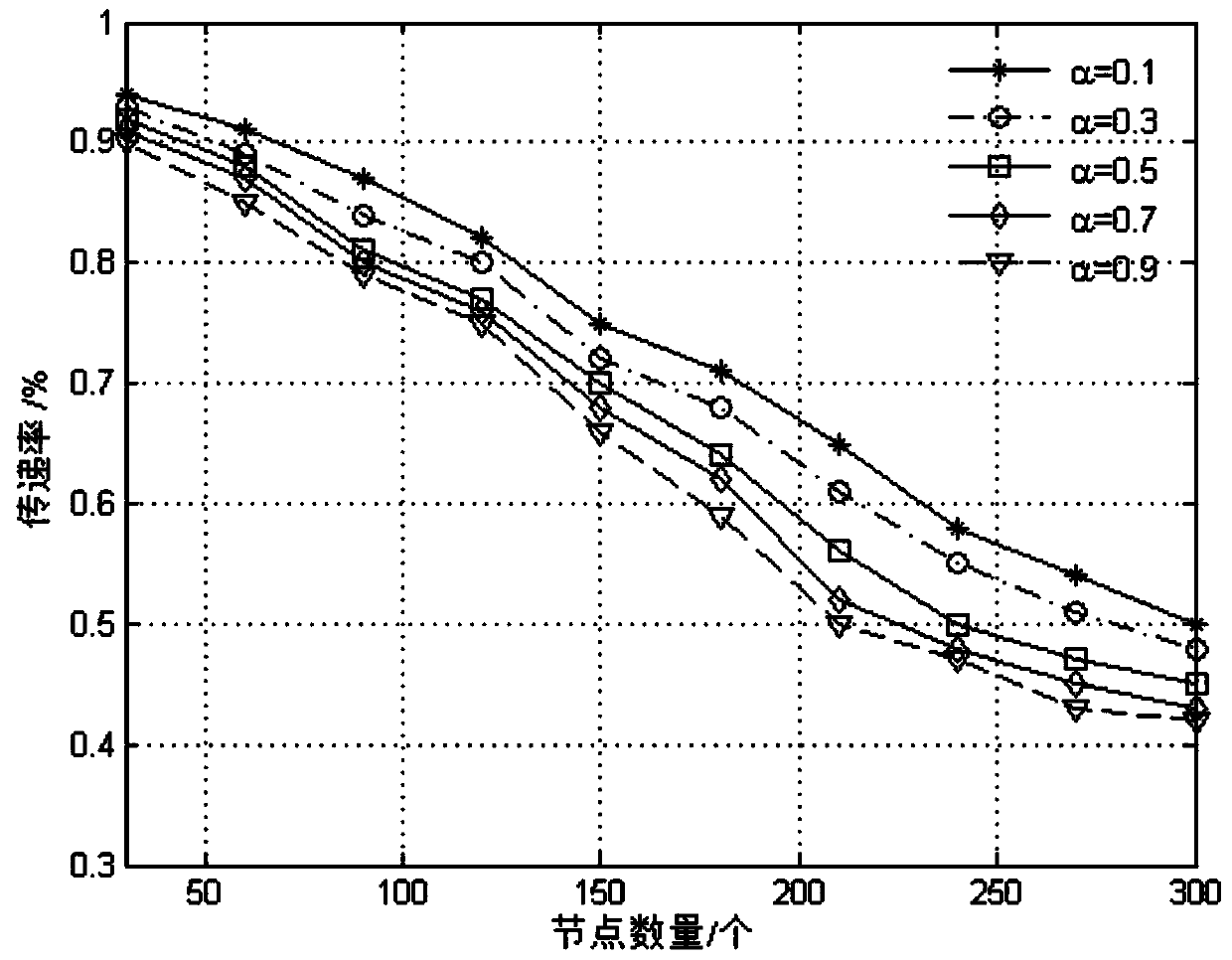
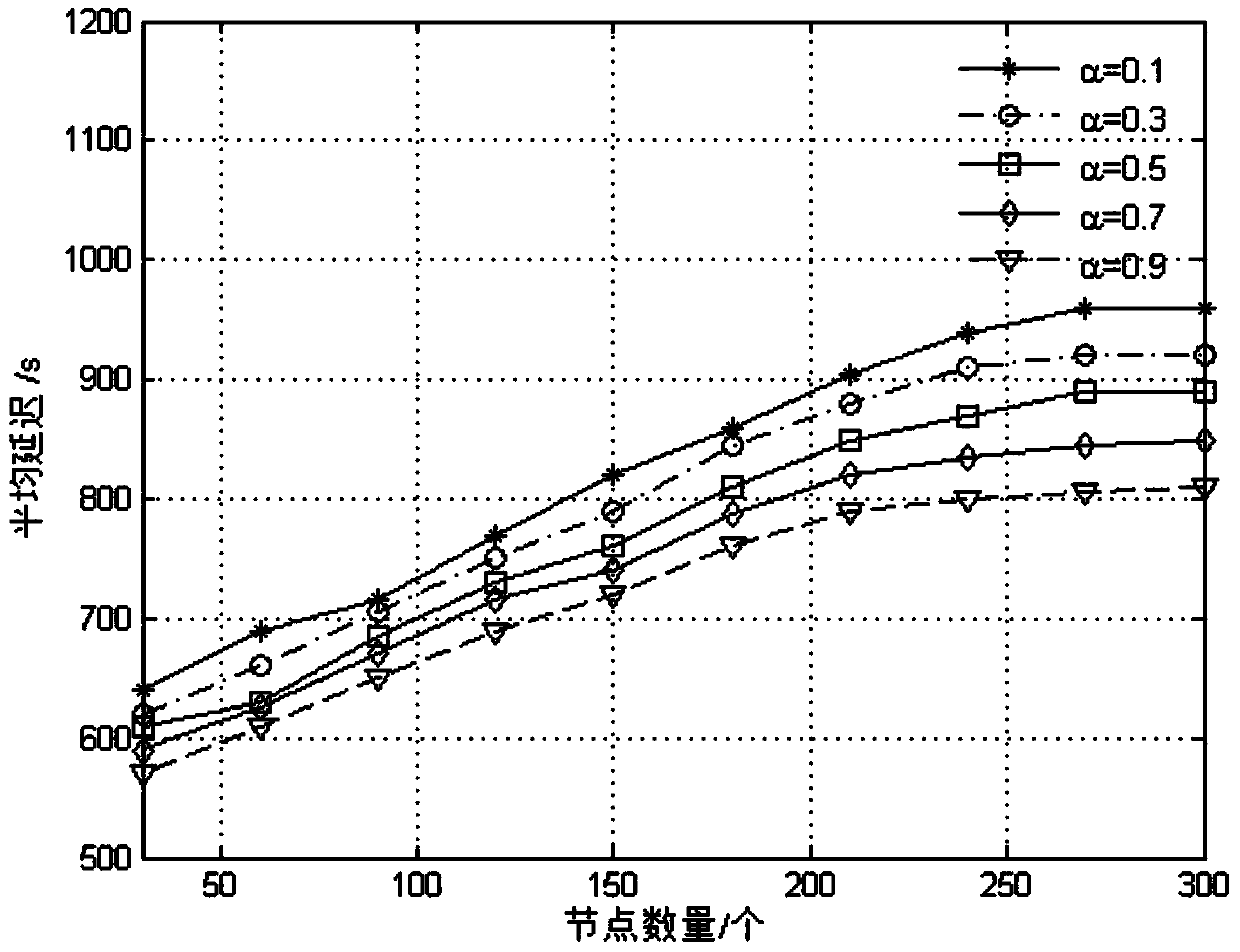
ActiveCN103561426AAverage delay increaseReduce overhead rateNetwork traffic/resource managementPrediction probabilityComputer science
The invention relates to a probability route improving method in a delay-tolerance mobile sensor network based on the node activeness. The method adds node activeness factors into prediction of the transmission probability to provide a calculating formula of the self node activeness NA, the NA and a transmission prediction probability value of an original PROPHET algorithm are weighed through a weight alpha, a new transmission prediction probability value is calculated according to node meeting history information and node activeness in the network, whether information is transmitted is decided by comparing transmission prediction probability values of nodes, and buffer memory is managed through a time to live TTL discarding strategy. Simulation results show that a probability estimating method of an NAPR algorithm is more comprehensive than a PROPHET algorithm, fewer copies are generated, the NAPR algorithm reduces the node overhead rate even though the average delay of the information is slightly increased, and the delivery rate of message is improved. In future work, the probability route improving method can be further used for solving the jam problem in the network.
Owner:王堃
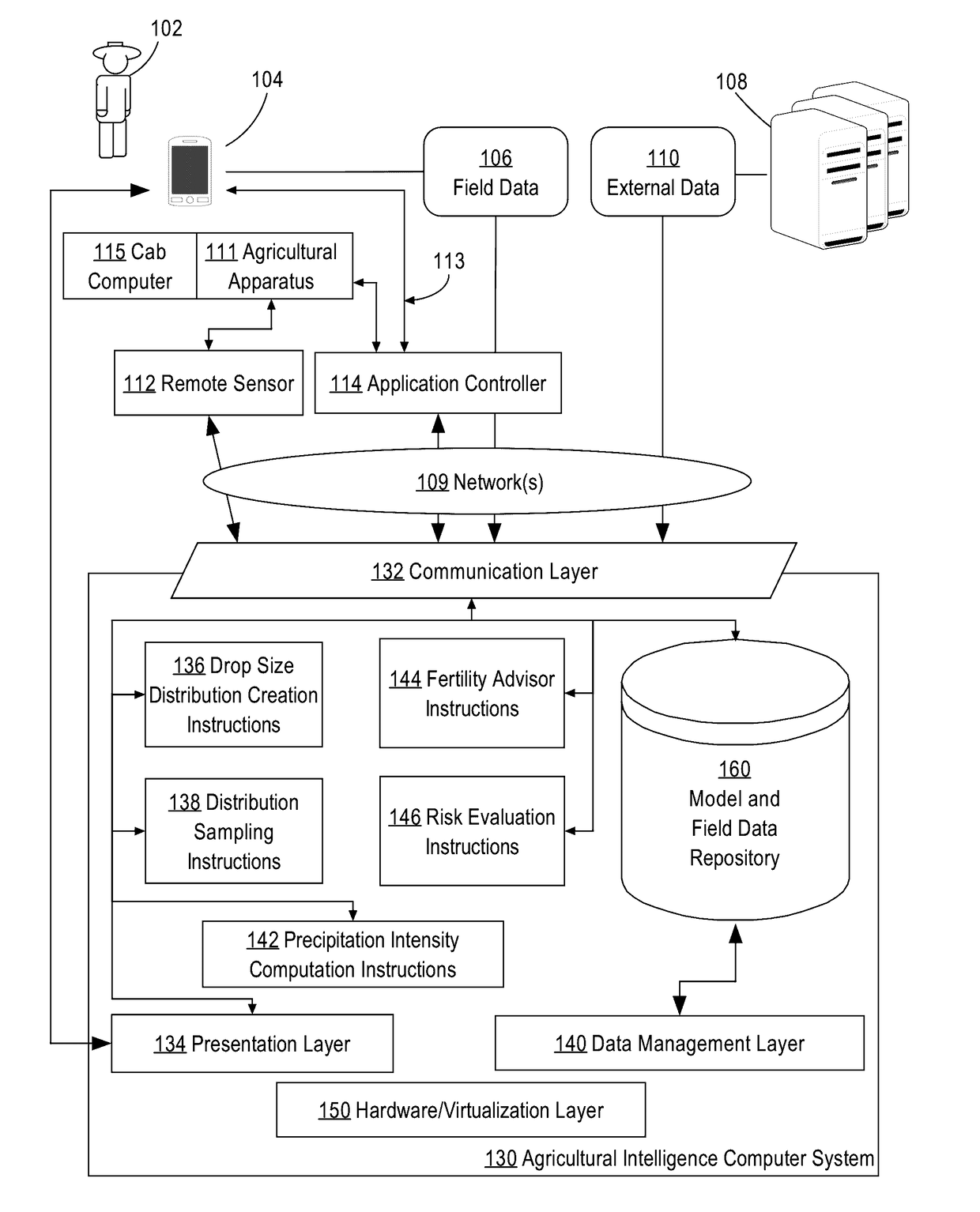
Generating probabilistic estimates of rainfall rates from radar reflectivity measurements
ActiveUS20170075034A1Rainfall/precipitation gaugesData processing applicationsExternal dataRadar reflectivity
A method and system for generating probabilistic estimates of precipitation intensity from radar reflectivity measurements is provided. In an embodiment, an agricultural intelligence computer system receives radar reflectivity measurements for a particular location from an external data source. The agricultural intelligence computer system constructs a probability distribution of drop sizes describing the probability that the precipitation included drops of various sizes based on the radar reflectivity measurements. The agricultural intelligence computer system samples a plurality of values from the probability of distribution of drop sizes and uses the plurality of values and the radar reflectivity measurements to compute a plurality of rainfall rates. Based on the plurality of rainfall rates, the agricultural intelligence computer system constructs a probability distribution of rainfall rates for the particular location.
Owner:THE CLIMATE CORP
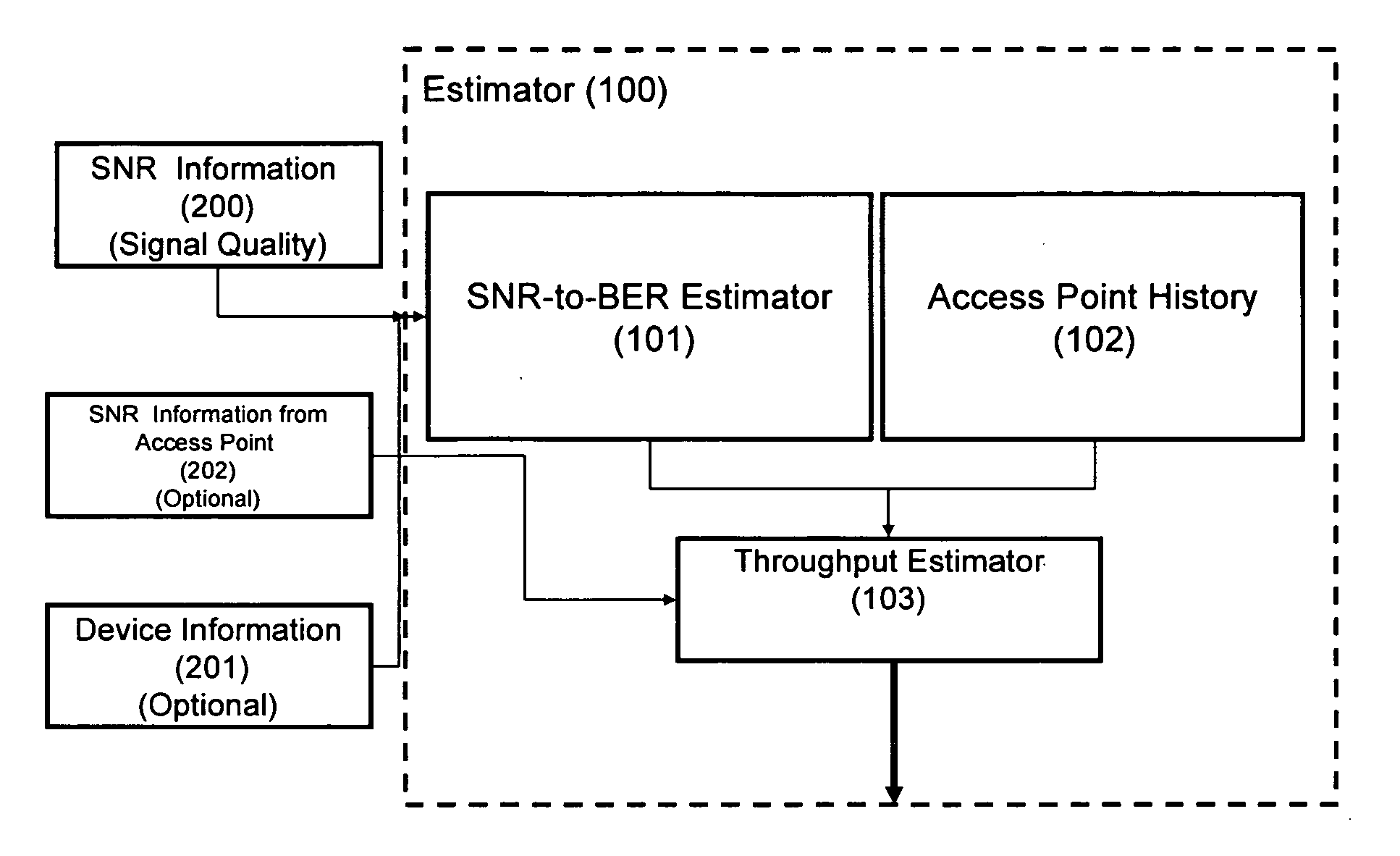
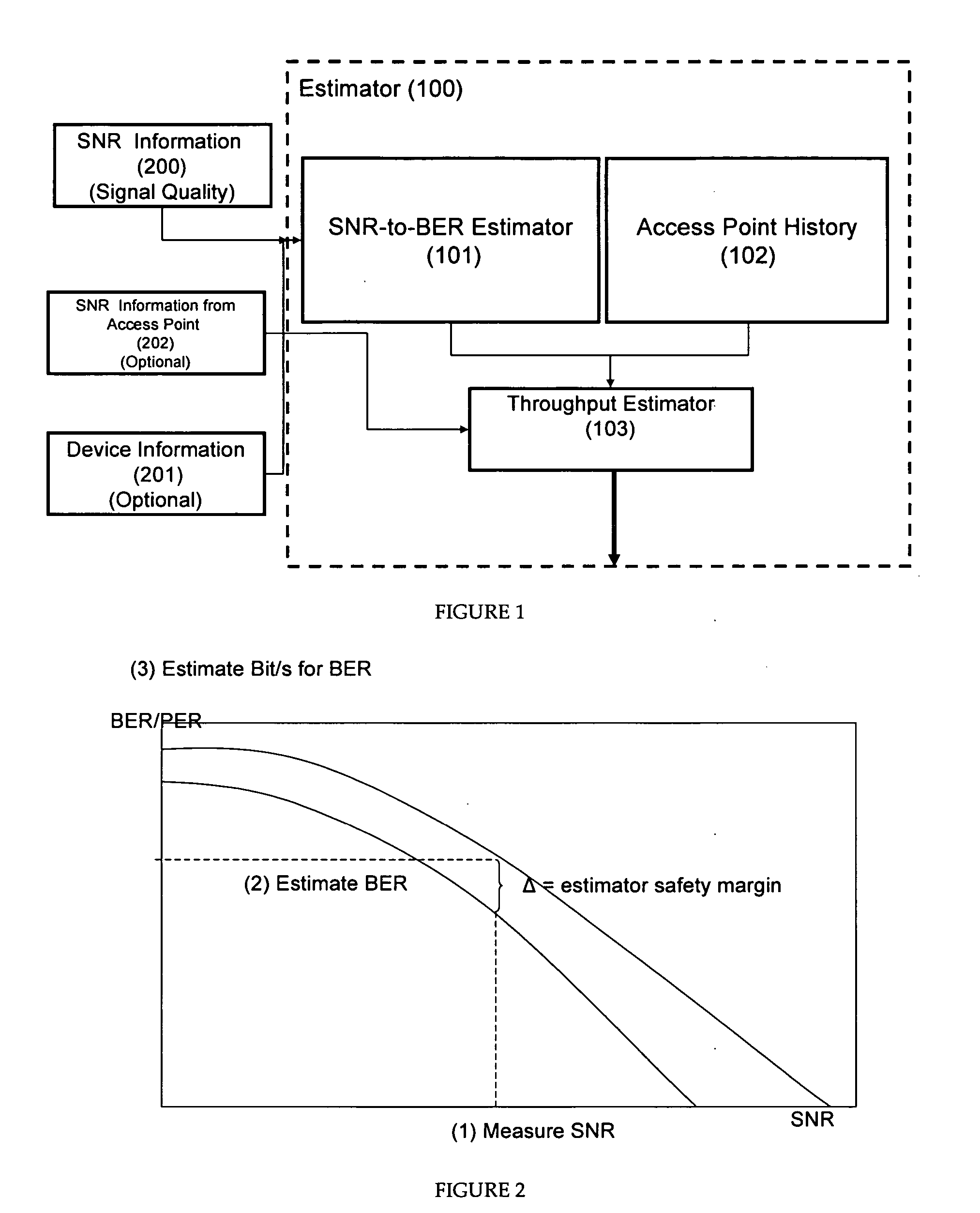
Probabilistic estimation of achievable maximum throughput from wireless interface
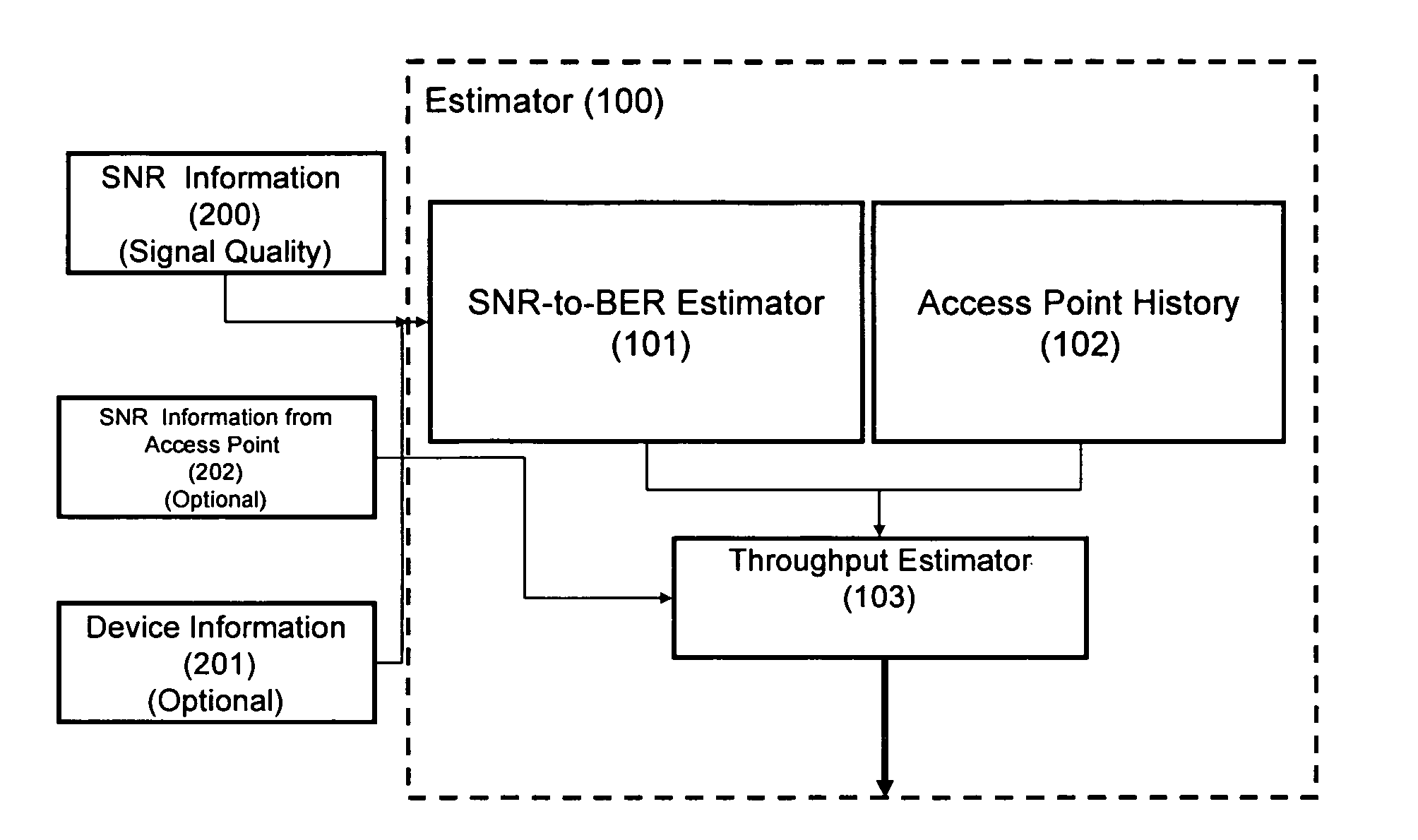
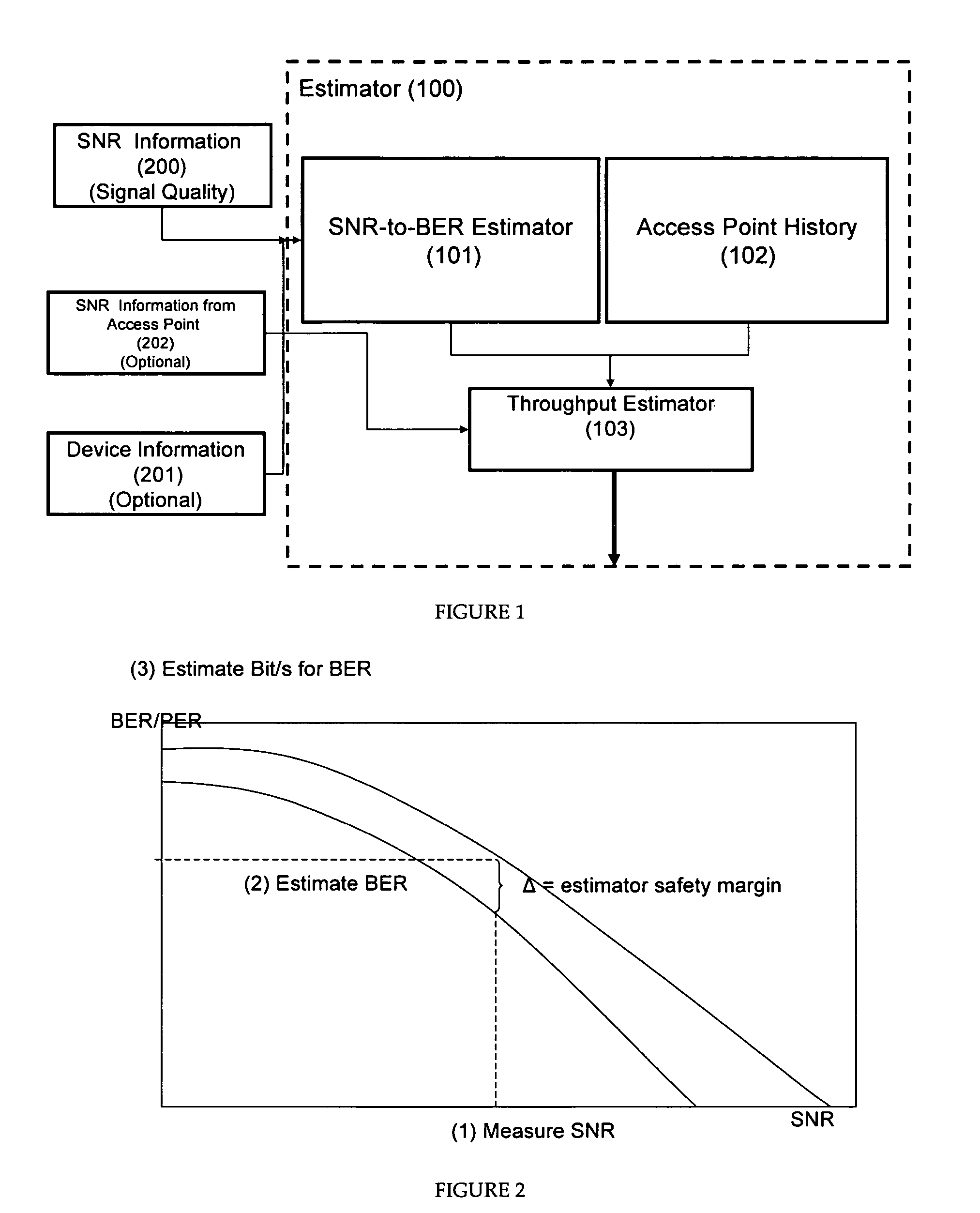
InactiveUS20070086353A1Estimation of bit-rate more accurate and robustExperienced-quality-of-connection better and more predictableTransmission systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementSignal qualityComputer science
A maximum achievable bit rate estimation for the expected bit rate between a wireless client and an access point is calculated in two phases. In the first phase, the maximum achievable bit rate is estimated using signal quality information and optionally congestion level information of the access point(s) of interest. In a second phase of the bit rate estimation, the first phase estimator output is corrected by using historical information relating the estimated bit rate values to the bit rates actually experienced. In the second phase of the estimation, a repository stores known signal quality behavior of the access points so as to provide an Access Point History (APH). The APH can be implemented as a simple memory (database) entity where a record is maintained on how accurate the previous bit-rate estimations turned out to be in practice. The actual physical embodiment of APH memory is implemented using any adequate memory technology such as FLASH, local hard disk, and the like. The APH is an ordered list where Access Point ID (SSID) and MAC address are combined with the data in an experimentally known relation between the SNR and the stable throughput. This two phase technique thus provides the implicit capability to include a rough bias to throughput estimation by congestion level of the access point as well as by historical bit rate averages.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
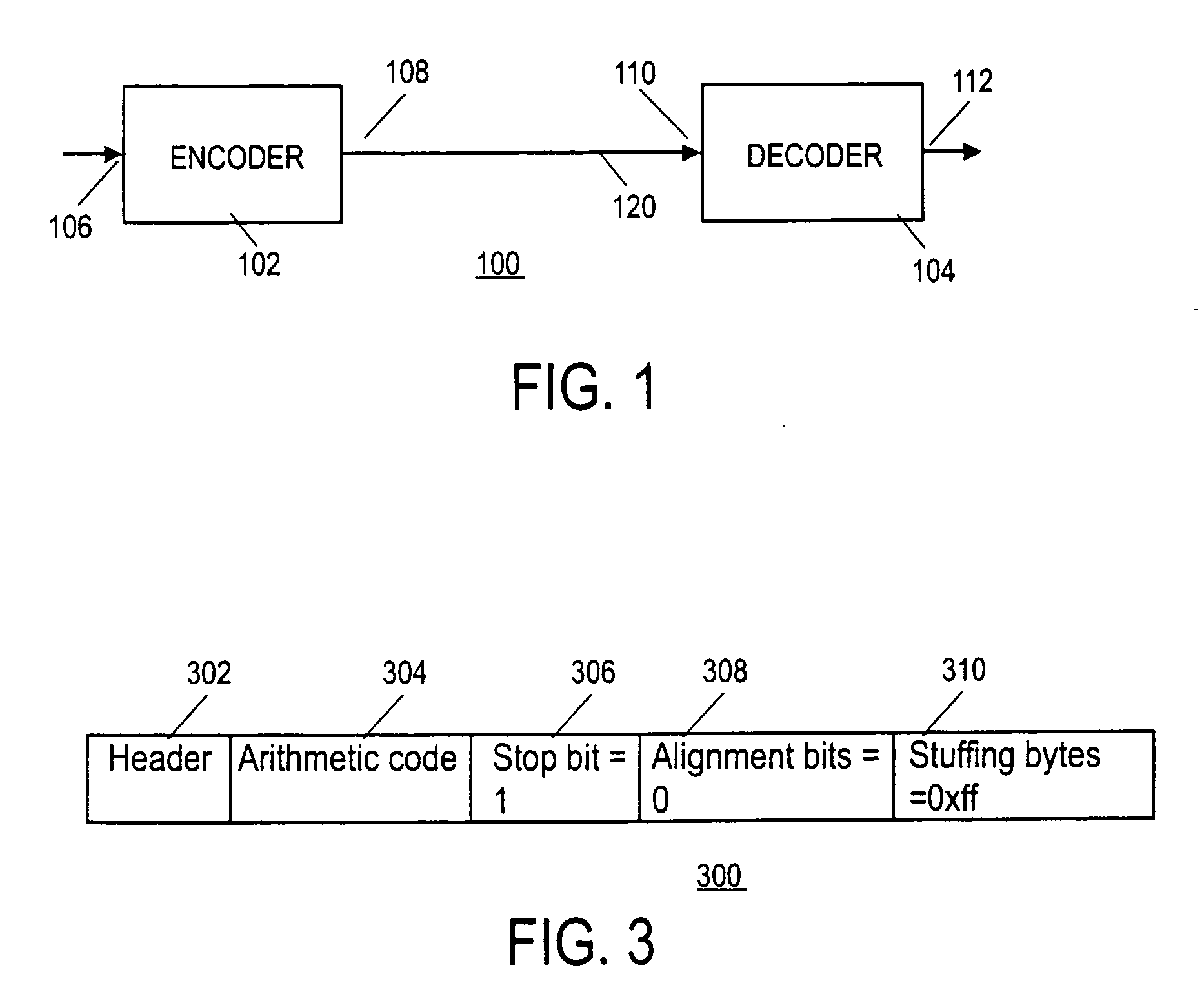
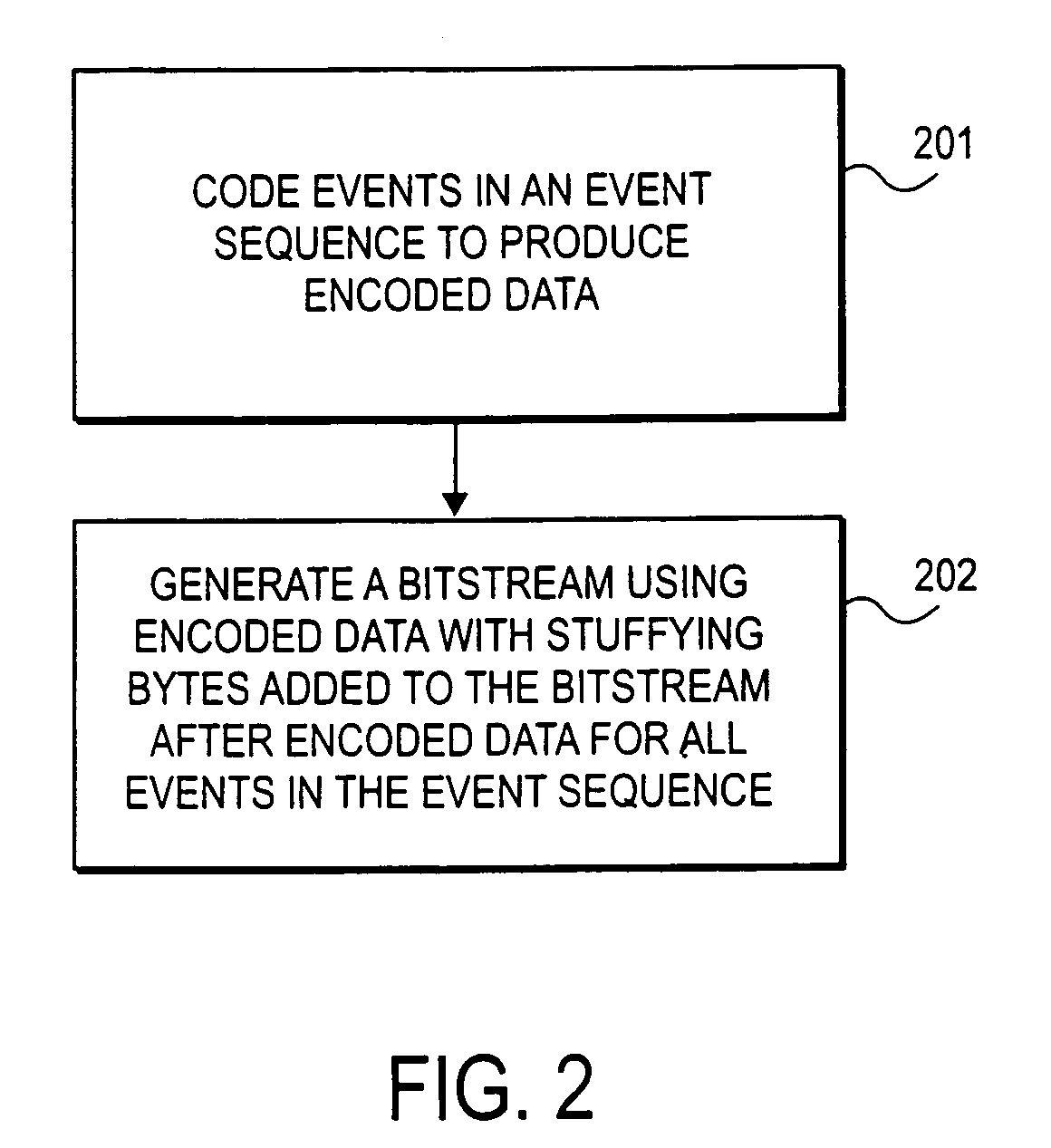
Method and apparatus for arithmetic coding and termination
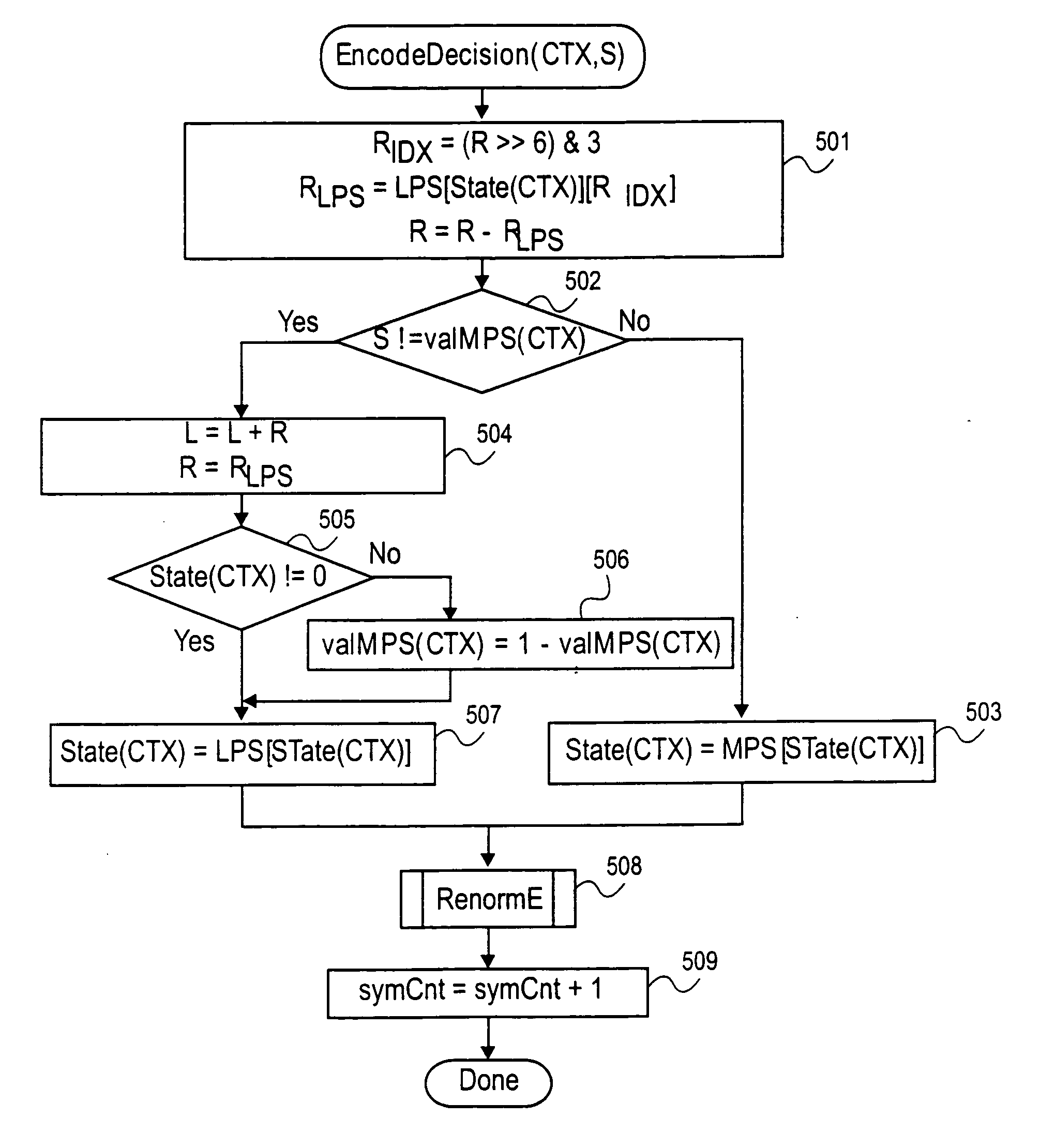
InactiveUS20060017591A1Code conversionError correction/detection using arithmatic codesArithmetic codingComputer science
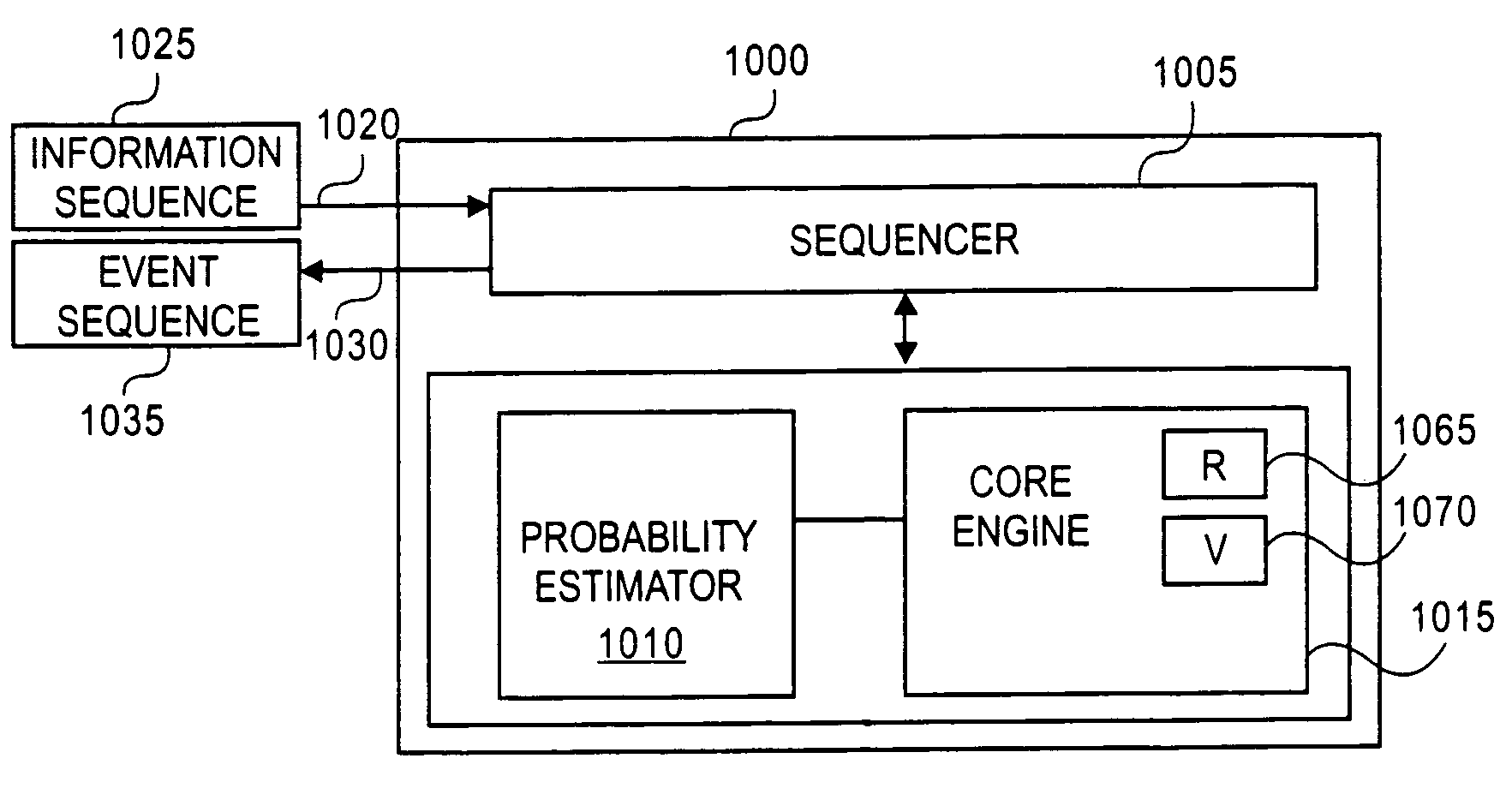
Methods and apparatuses for performing arithmetic encoding and / or decoding are disclosed. In one embodiment, an arithmetic decoder comprises a sequencer to generate a context identifier for an event of an event sequence, a probability estimator to determine a value for a LPS and a probability estimate for the LPS, and a decoding engine that includes a range register to assign a value to a range for the LPS. The value is based on the probability estimate, a value stored in the range register and the context identifier to a range for the LPS if the context identifier is not equal to an index and the value is not based on the value stored in range register if the context identifier is equal to the index. The decoding engine further determines a value of a binary event based on the value of the range for the LPS and bits from an information sequence.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
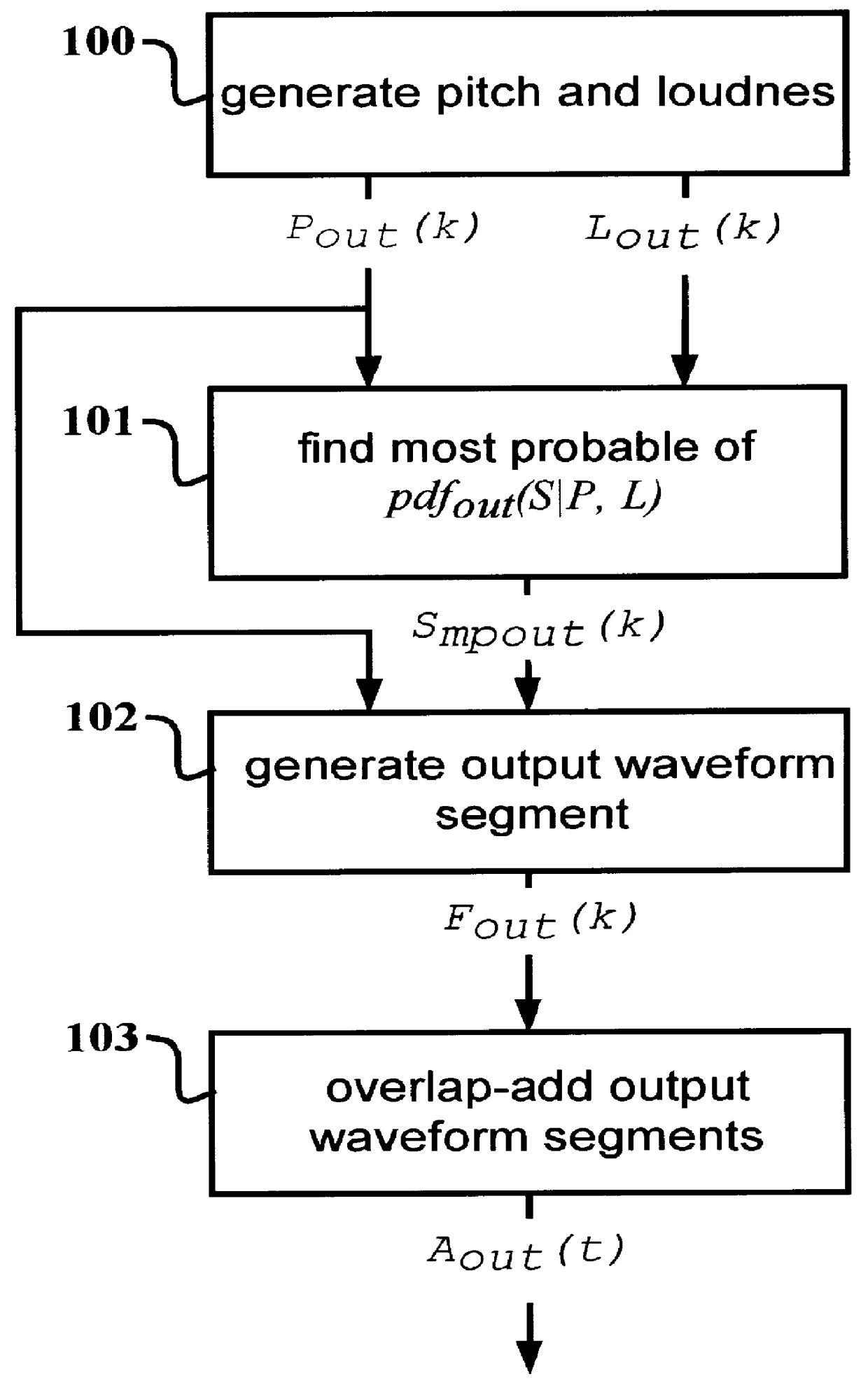
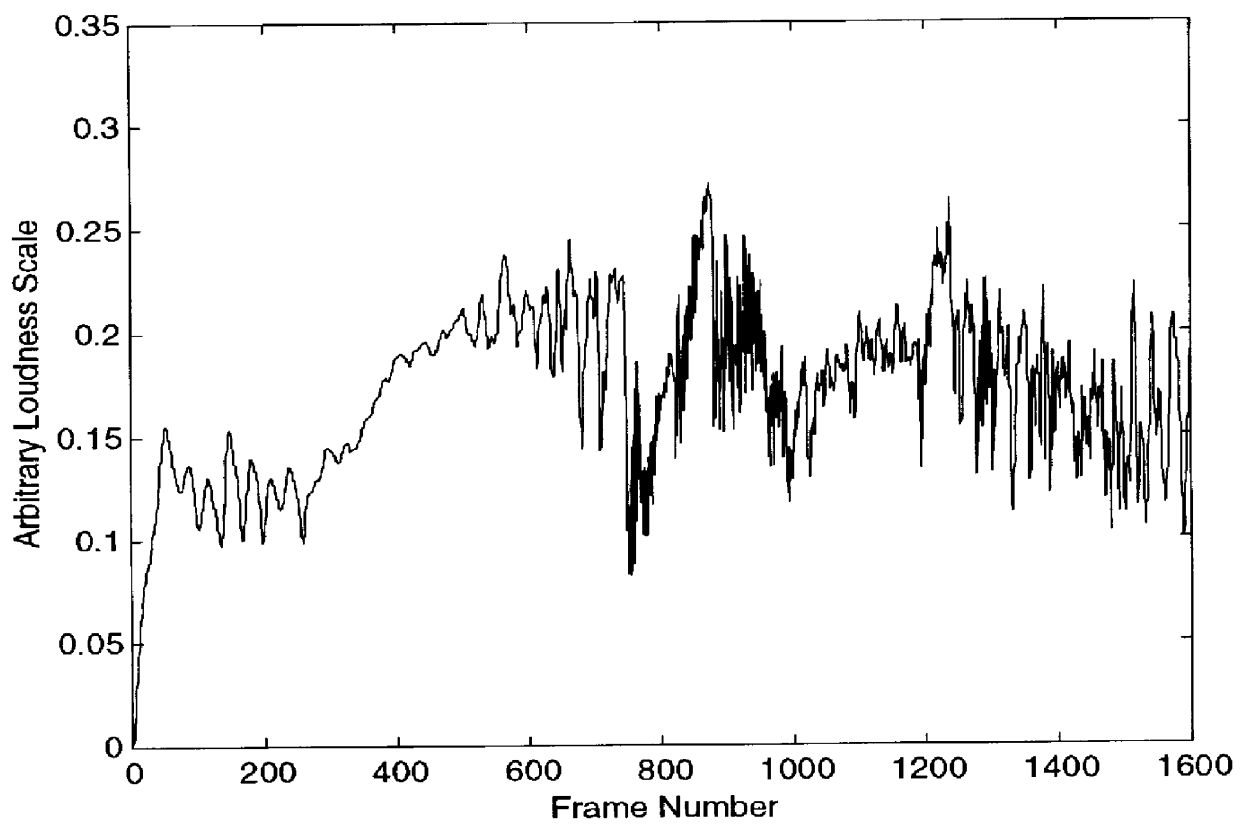
Audio signal synthesis system based on probabilistic estimation of time-varying spectra
InactiveUS6111183AReduce calculationImprove sound qualityMultiple-port networksElectrophonic musical instrumentsFrequency spectrumConditional probability
The present invention describes methods and means for estimating the time-varying spectrum of an audio signal based on a conditional probability density function (PDF) of spectral coding vectors conditioned on pitch and loudness values. Using this PDF a time-varying output spectrum is generated as a function of time-varying pitch and loudness sequences arriving from an electronic music instrument controller. The time-varying output spectrum is converted to a synthesized output audio signal. The pitch and loudness sequences may also be derived from analysis of an input audio signal. Methods and means for synthesizing an output audio signal in response to an input audio signal are also described in which the time-varying spectrum of an input audio signal is estimated based on a conditional probability density function (PDF) of input spectral coding vectors conditioned on input pitch and loudness values. A residual time-varying input spectrum is generated based on the difference between the estimated input spectrum and the "true" input spectrum. The residual input spectrum is then incorporated into the synthesis of the output audio signal. A further embodiment is described in which the input and output spectral coding vectors are made up of indices in vector quantization spectrum codebooks.
Owner:LINDEMANN ERIC
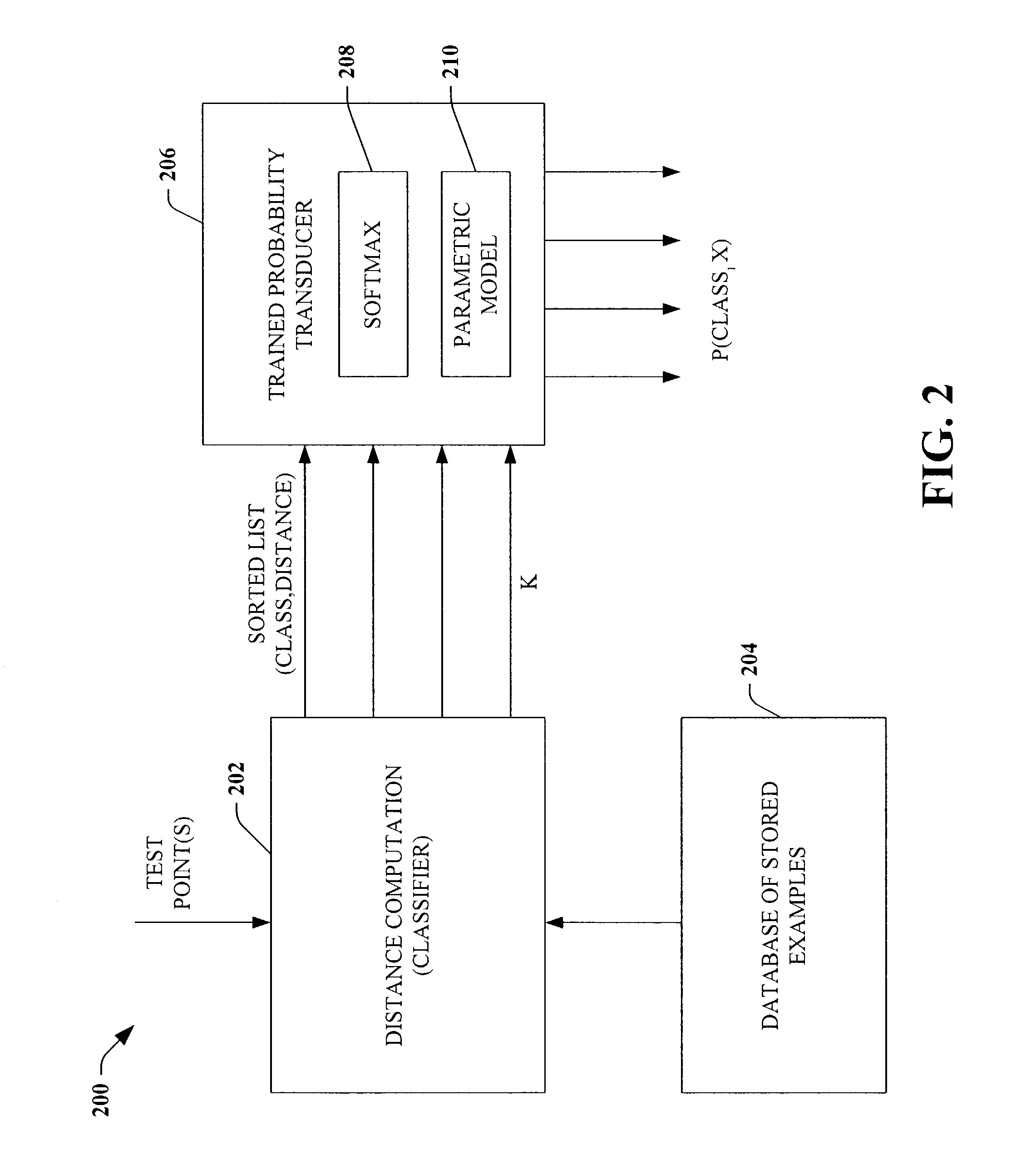
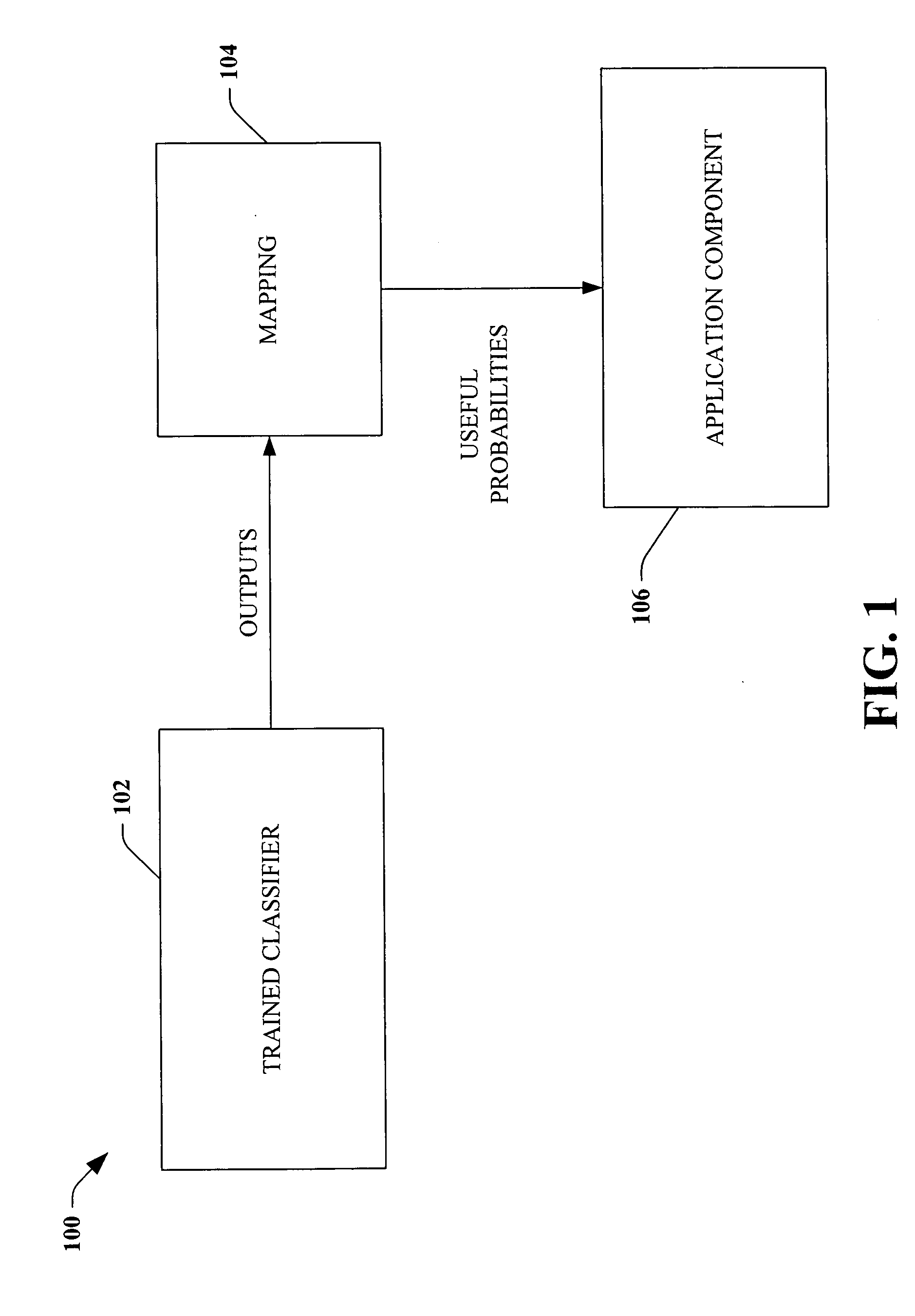
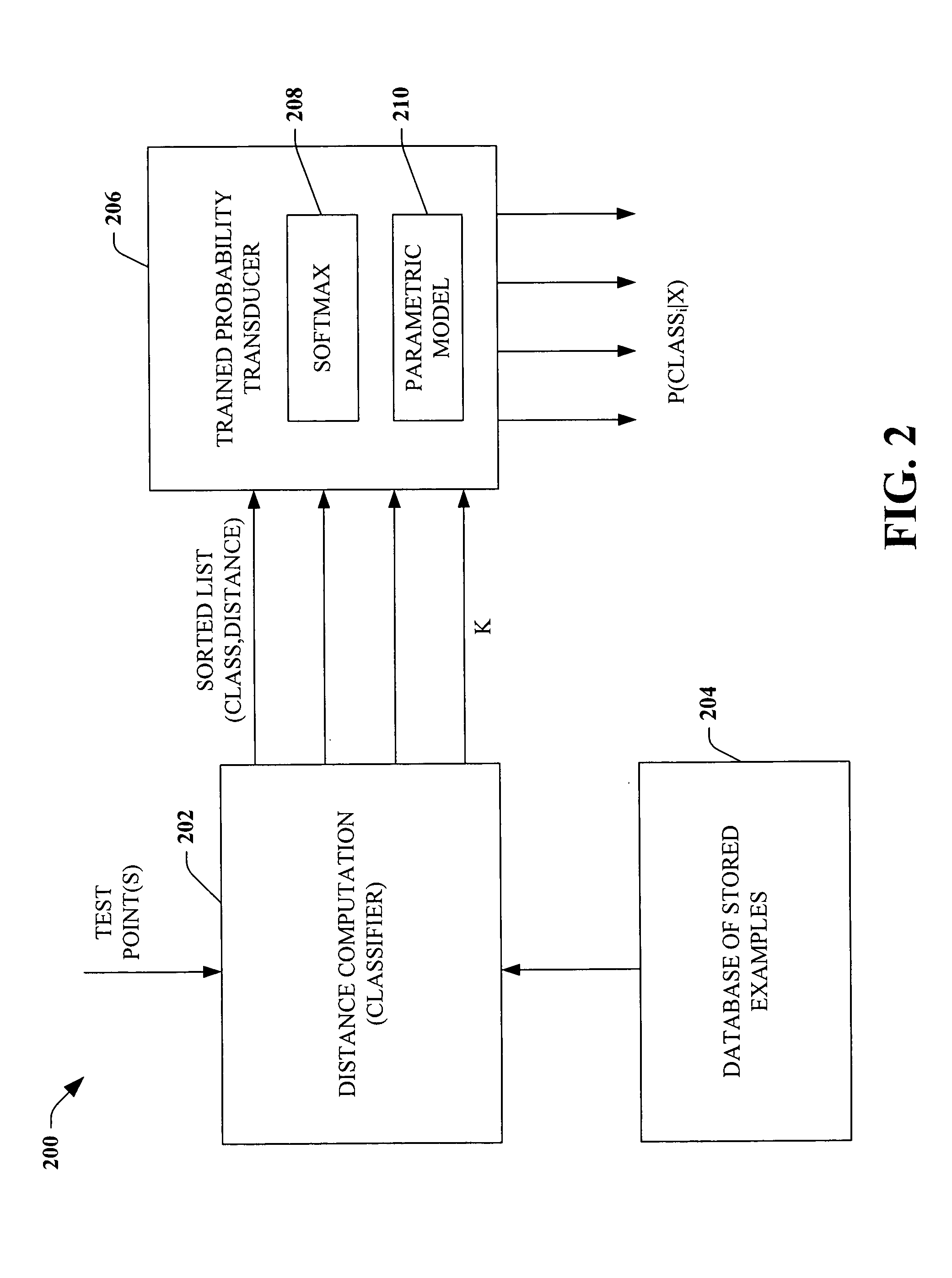
Probability estimate for K-nearest neighbor
ActiveUS7016884B2Reduce the possibilityFacilitate producing probabilistic outputsDigital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsAlgorithmNear neighbor
Systems and methods are disclosed that facilitate producing probabilistic outputs also referred to as posterior probabilities. The probabilistic outputs include an estimate of classification strength. The present invention intercepts non-probabilistic classifier output and applies a set of kernel models based on a softmax function to derive the desired probabilistic outputs. Such probabilistic outputs can be employed with handwriting recognition where the probability of a handwriting sample classification is combined with language models to make better classification decisions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for arithmetic coding and termination
InactiveUS7183951B2Code conversionError correction/detection using arithmatic codesProcessor registerArithmetic coding
Methods and apparatuses for performing arithmetic encoding and / or decoding are disclosed. In one embodiment, an arithmetic decoder comprises a sequencer to generate a context identifier for an event of an event sequence, a probability estimator to determine a value for a LPS and a probability estimate for the LPS, and a decoding engine that includes a range register to assign a value to a range for the LPS. The value is based on the probability estimate, a value stored in the range register and the context identifier to a range for the LPS if the context identifier is not equal to an index and the value is not based on the value stored in range register if the context identifier is equal to the index. The decoding engine further determines a value of a binary event based on the value of the range for the LPS and bits from an information sequence.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Probability estimate for K-nearest neighbor
InactiveUS20060112042A1Reduce the possibilityFacilitate producing probabilistic outputsDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmNear neighbor
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
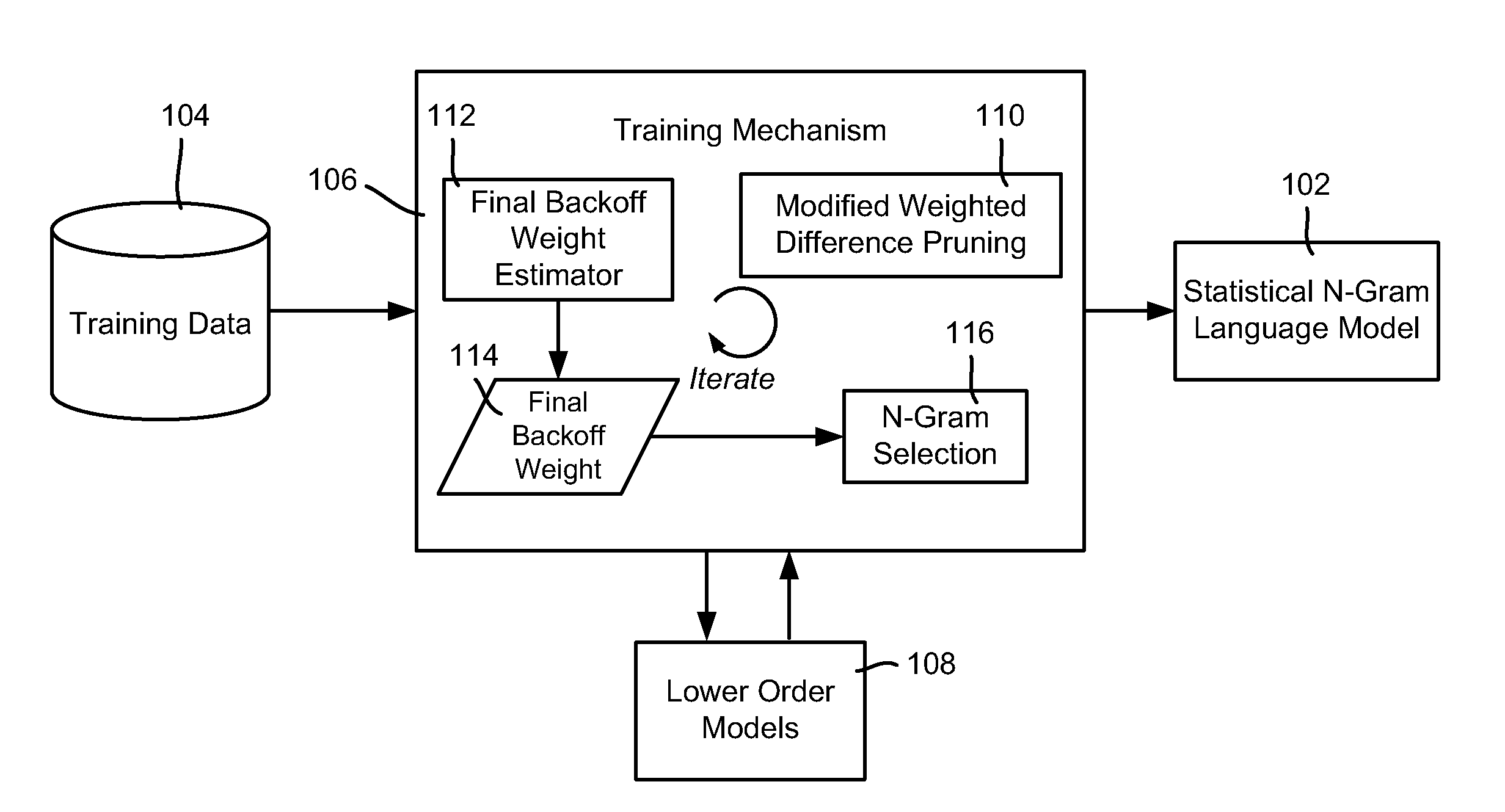
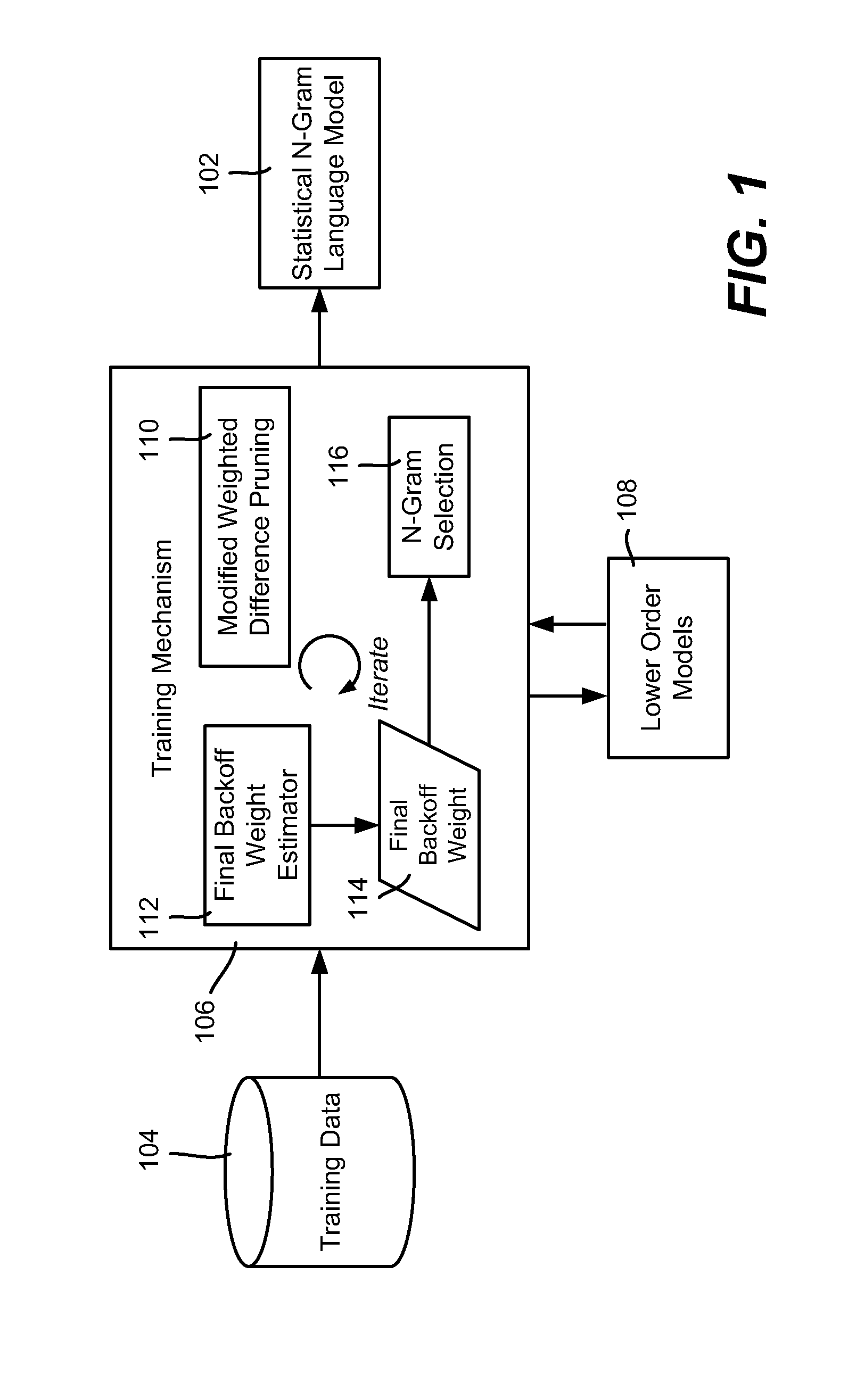
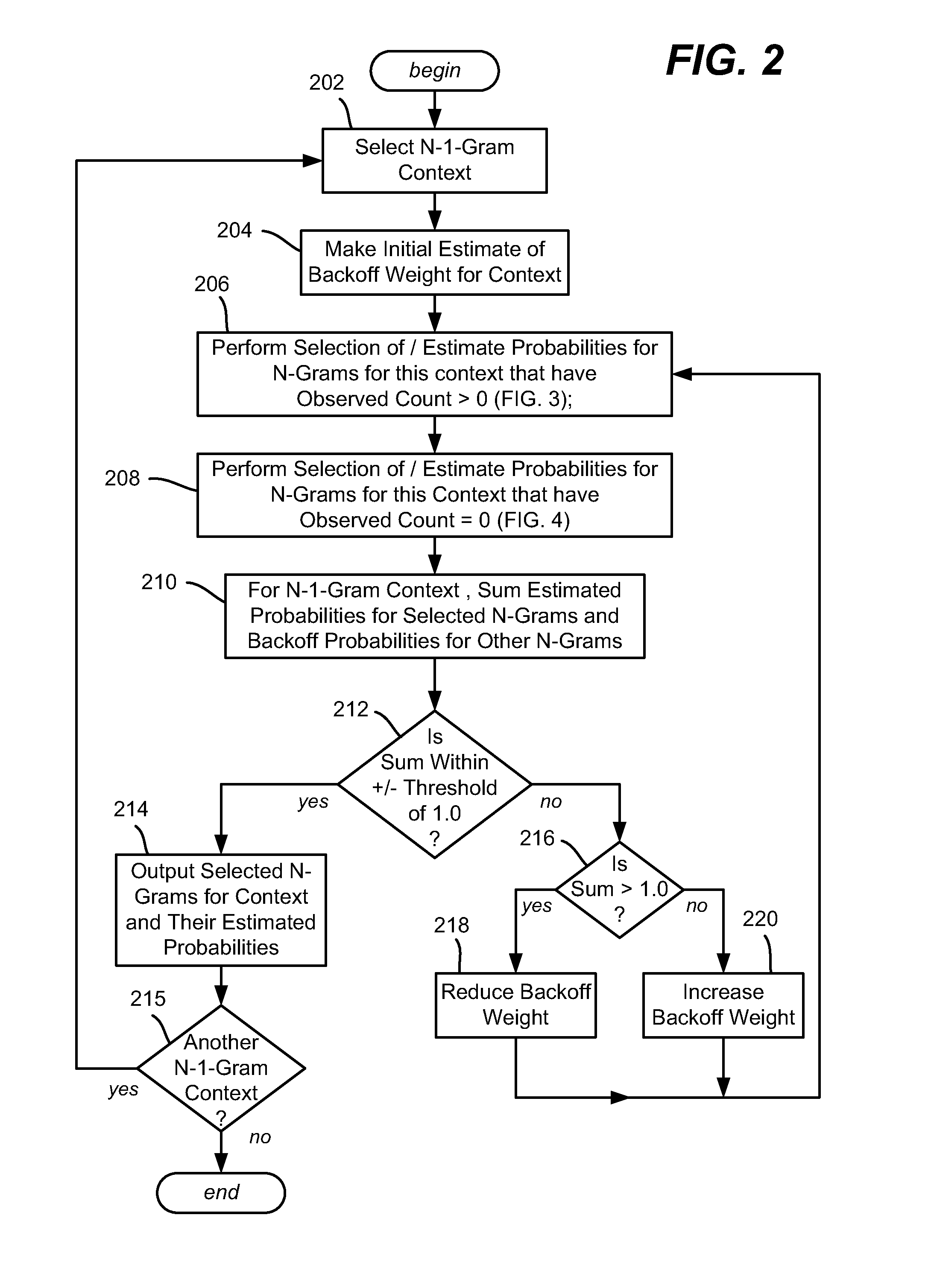
N-Gram Selection for Practical-Sized Language Models
ActiveUS20110224971A1Well formedNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmHuman language
Described is a technology by which a statistical N-gram (e.g., language) model is trained using an N-gram selection technique that helps reduce the size of the final N-gram model. During training, a higher-order probability estimate for an N-gram is only added to the model when the training data justifies adding the estimate. To this end, if a backoff probability estimate is within a maximum likelihood set determined by that N-gram and the N-gram's associated context, or is between the higher-order estimate and the maximum likelihood set, then the higher-order estimate is not included in the model. The backoff probability estimate may be determined via an iterative process such that the backoff probability estimate is based on the final model rather than any lower-order model. Also described is additional pruning referred to as modified weighted difference pruning.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
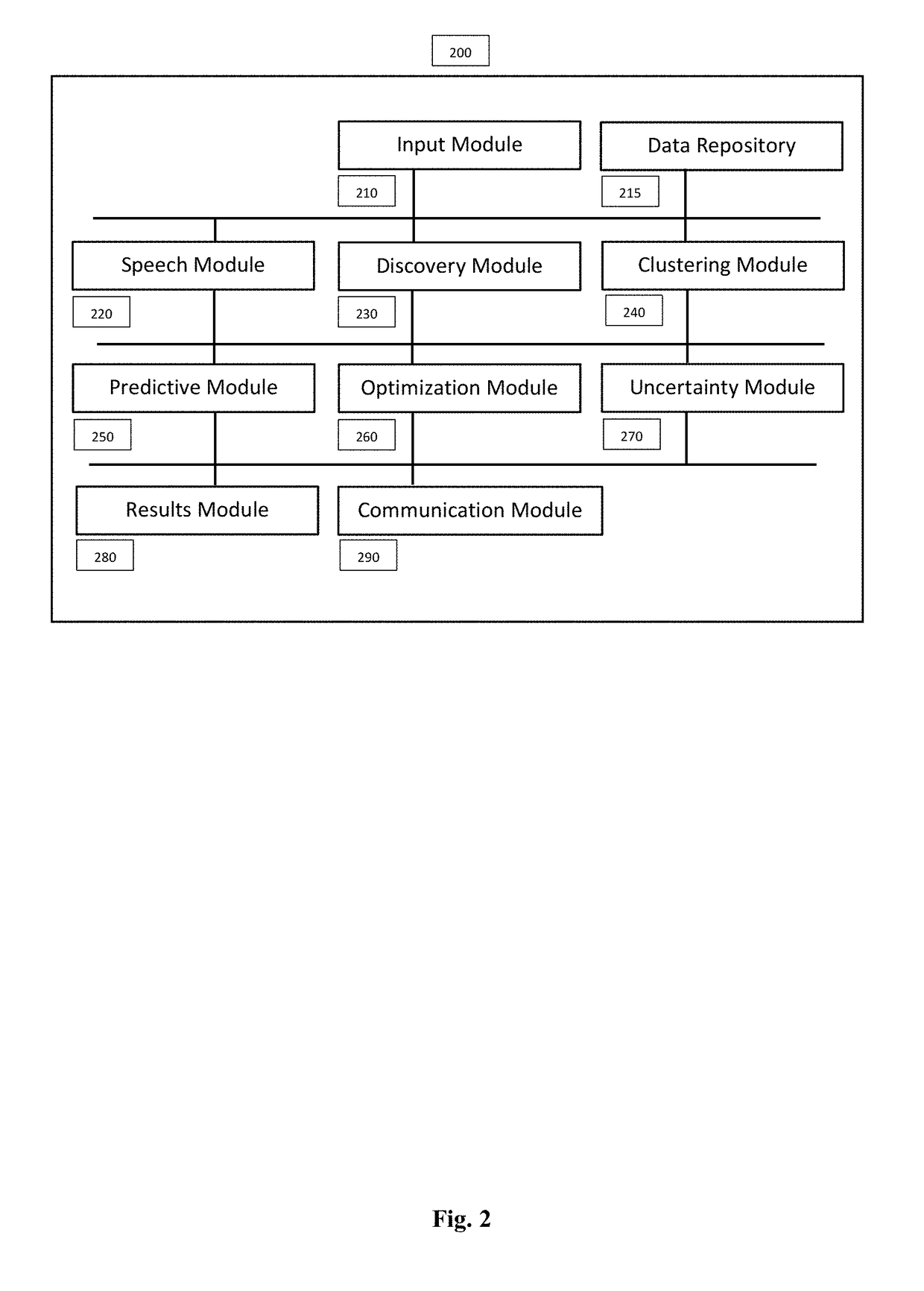
Method and System for Innovation Management and Optimization under Uncertainty
InactiveUS20170220928A1Well formedKernel methodsDigital computer detailsInnovation managementIntelligent machine
An integrated and comprehensive method and system is disclosed for management and optimization of innovation and associated processes under uncertainty. A first embodiment of the invention consists of a data mining and clustering module to compare a new innovation submission with existing internal and external entries and databases, identify similarities and group similar entries together. A second embodiment of the invention is directed towards an intelligent machine learning module to learn from the available data of previous innovation projects and provide estimates of outputs or target values for new innovation submissions or entries. In a third embodiment of the invention, an uncertainty quantification method and system is introduced to handle uncertain inputs of innovation entries and provide probabilistic estimates of outputs by generating a plurality of solutions and scenarios. In a fourth embodiment of the invention, a multiobjective optimization module is used to simultaneously optimize multiple competing objectives.
Owner:HAJIZADEH YASIN
Predicted value based measurement conversion and sequential filtering maneuvering target tracking method
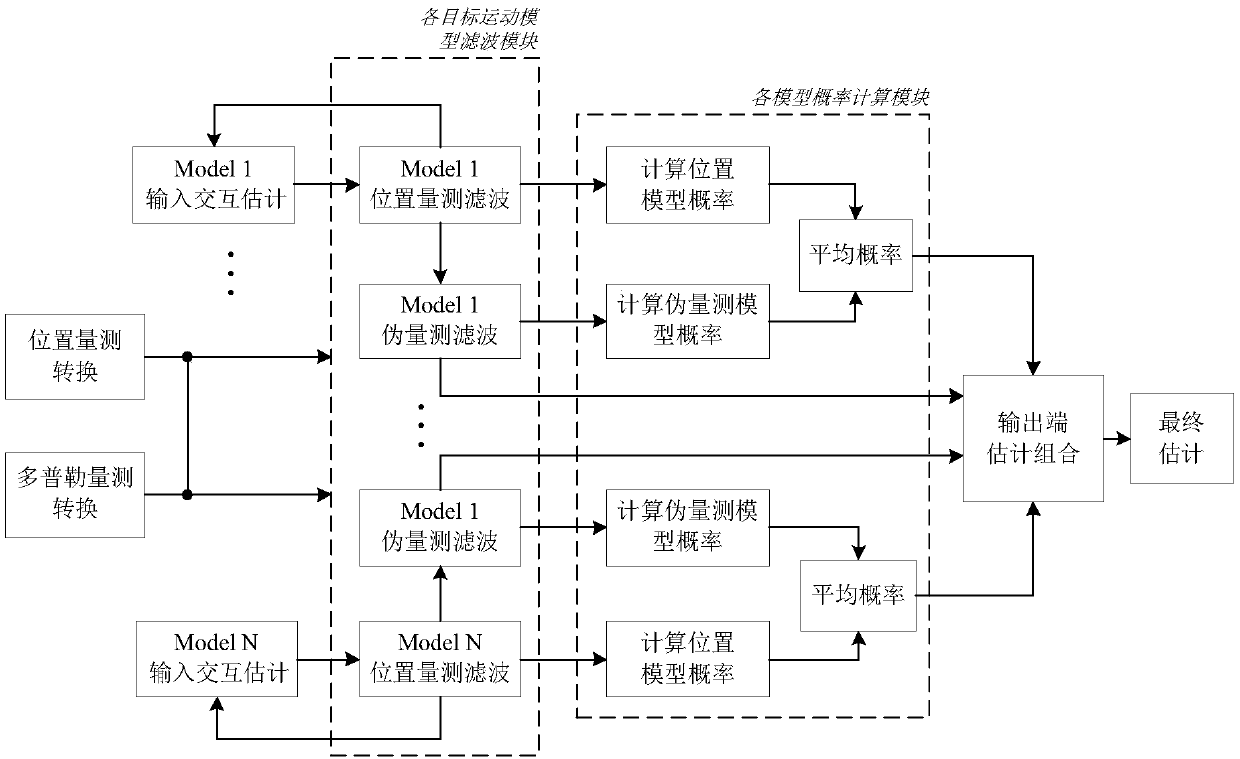
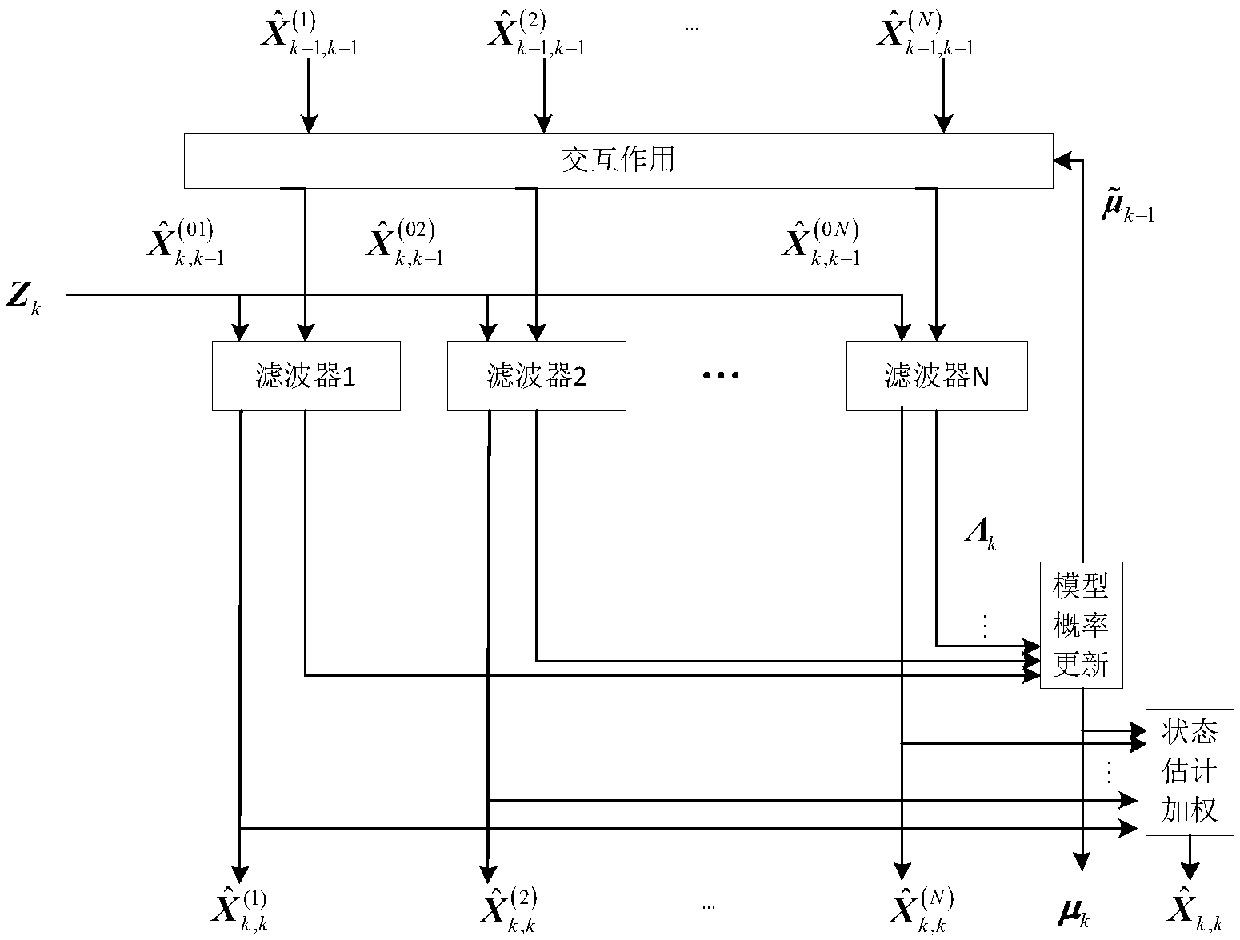
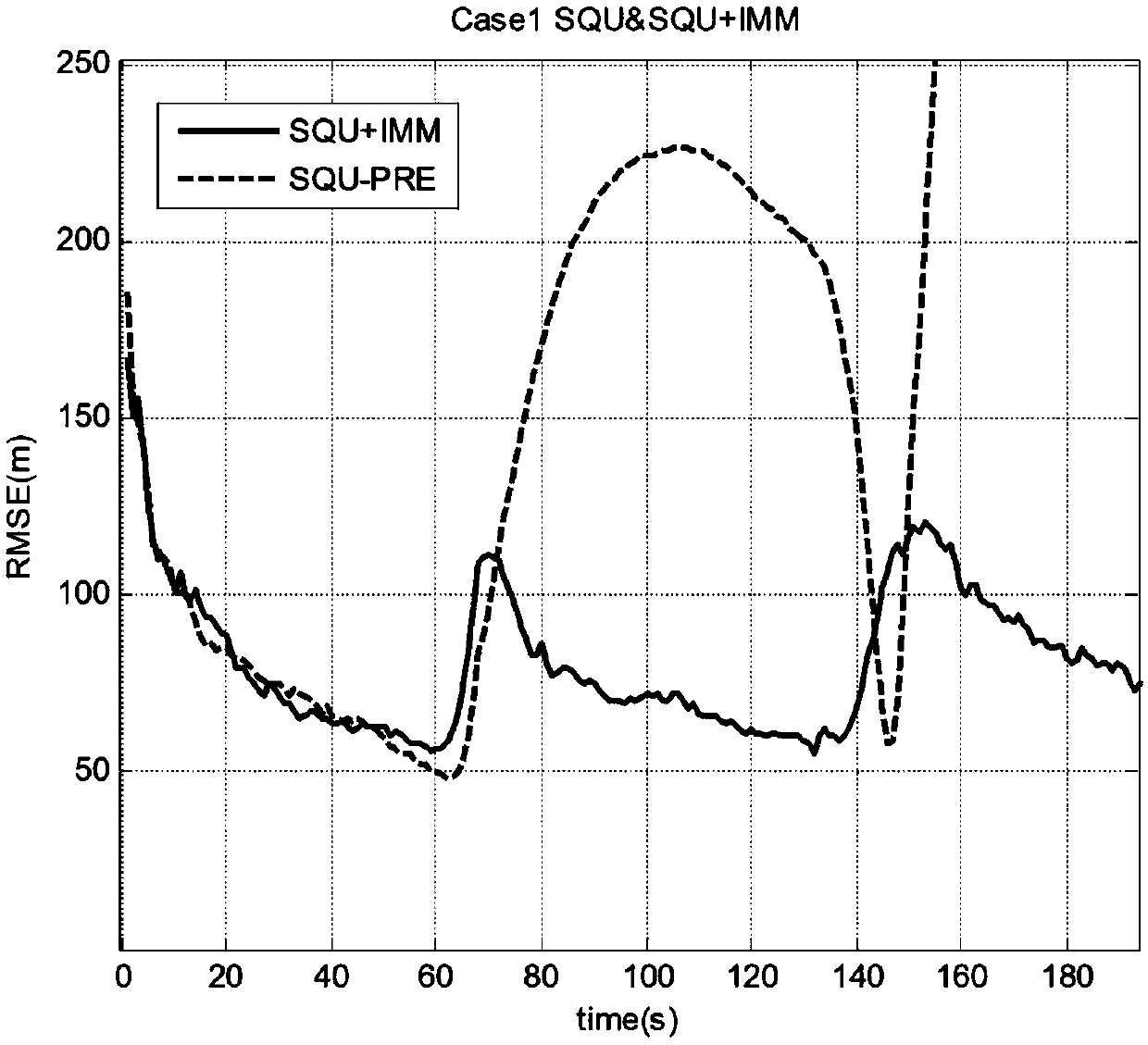
The invention discloses a predicted value based measurement conversion and sequential filtering maneuvering target tracking method, relates to the field of radar target tracking, and mainly aims at the field of Doppler radar tracking under maneuvering target tracking. A predicted value based sequential filtering method is combined under the framework of an interactive multi-model algorithm to realize target tracking. The model probability is decided by both a position model probability and a Doppler model probability, and the model probability is estimated more accurately; and measurement conversion based on the predicted value can be used to eliminate the correlation between an error statistical characteristic and a measuring value of the measurement conversion error. The method can be used for maneuvering target tracking of Doppler measurement effectively at the same time.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
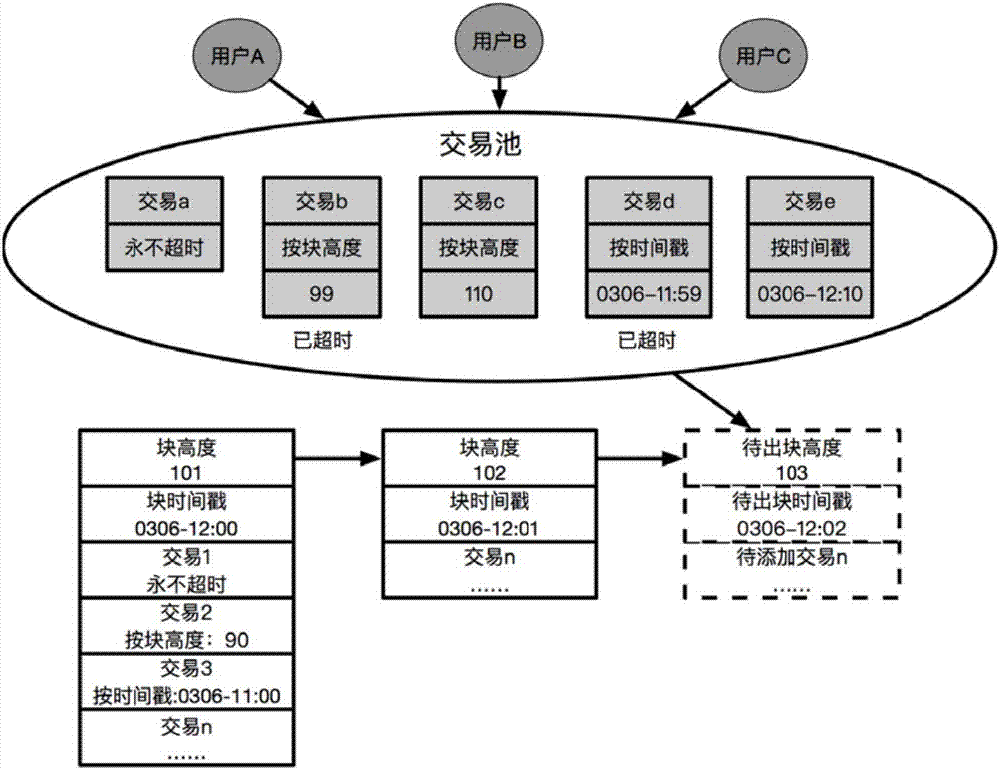
Block chain based transaction timeout control method
The invention discloses a block chain based transaction timeout control method, which is characterized in that a user needs to set a timeout limit for a transaction when initiating a transaction, the timeout limit can be a timestamp or a block height, a node firstly judges the timeout limit when packaging the transaction, the transaction is packaged if the transaction does not exceed the timeout limit, the transaction is discarded if the transaction exceeds the timeout limit, the user monitors a block chain in real time, the transaction is regarded to be failed if the transaction of the user is not packaged into a block after the timeout limit is exceeded, and the user needs to initiate the transaction again and does not need to wait any longer. According to the invention, a clear timeout mechanism is set for a transaction of the user on the block chain, and probabilistic estimation on whether the transaction can be on the chain or not is not required any longer, thereby being convenient for the user to perform a timeout processing operation on a client.
Owner:HANGZHOU RIVTOWER TECH CO LTD
System for determining interests of users of mobile and nonmobile communication devices based on data received from a plurality of data providers
InactiveUS20130124330A1Broadcast characteristics identification/recognitionMarketingData setData provider
A system for determining interests of users of mobile and non-mobile communication devices based on data received from a plurality of data providers, wherein the system is configured to perform the steps of: (a) obtaining multiple datasets, wherein each dataset comprises at least one user and at least one corresponding attribute for the at least one user; (b) creating a first cluster comprising a first user from at least one dataset and the at least one corresponding attribute for the first user; (c) creating a second cluster comprising a second user from the at least one dataset and the at least one corresponding attribute for the second user; (d) merging the first cluster with the second cluster; and (e) assigning values to previously unknown attributes based on probabilistic estimations.
Owner:MILLENNIAL MEDIA
Probabilistic estimation of achievable maximum throughput from wireless interface
InactiveUS7515538B2Estimation of bit-rate more accurate and robustGood serviceFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementSignal qualityData combination
A maximum achievable bit rate estimation for the expected bit rate between a wireless client and an access point is calculated in two phases. In the first phase, the maximum achievable bit rate is estimated using signal quality information and optionally congestion level information of the access point(s) of interest. In a second phase of the bit rate estimation, the first phase estimator output is corrected by using historical information relating the estimated bit rate values to the bit rates actually experienced. In the second phase of the estimation, a repository stores known signal quality behavior of the access points so as to provide an Access Point History (APH). The APH can be implemented as a simple memory (database) entity where a record is maintained on how accurate the previous bit-rate estimations turned out to be in practice. The actual physical embodiment of APH memory is implemented using any adequate memory technology such as FLASH, local hard disk, and the like. The APH is an ordered list where Access Point ID (SSID) and MAC address are combined with the data in an experimentally known relation between the SNR and the stable throughput. This two phase technique thus provides the implicit capability to include a rough bias to throughput estimation by congestion level of the access point as well as by historical bit rate averages.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of decoding a signal implementing a progressive construction of a decoding tree, corresponding computer program and decoding device
ActiveUS20110122004A1Control complexityReduce complexityError preventionCode conversionStructure of Management InformationData signal
A method of decoding a data signal includes progressively constructing a decoding tree, implementing at least two iterations of the following steps: selecting at least one child node of a current node belonging to a selection interval; storing the child nodes in a first stack; deleting the current node from the first stack; selecting a new current node from the first stack; and if the new current node is a leaf node, storing the path between the root node and the leaf node, in the second stack, and deleting the leaf node from the first stack; otherwise, return to the step of selecting a child node for the new current node. Moreover, the method assigns a probability of likelihood to the bits of at least one symbol of the data signal, taking account of the paths stored in the second stack, and determines a probabilistic estimation of the signal.
Owner:INST MINES TELECOM
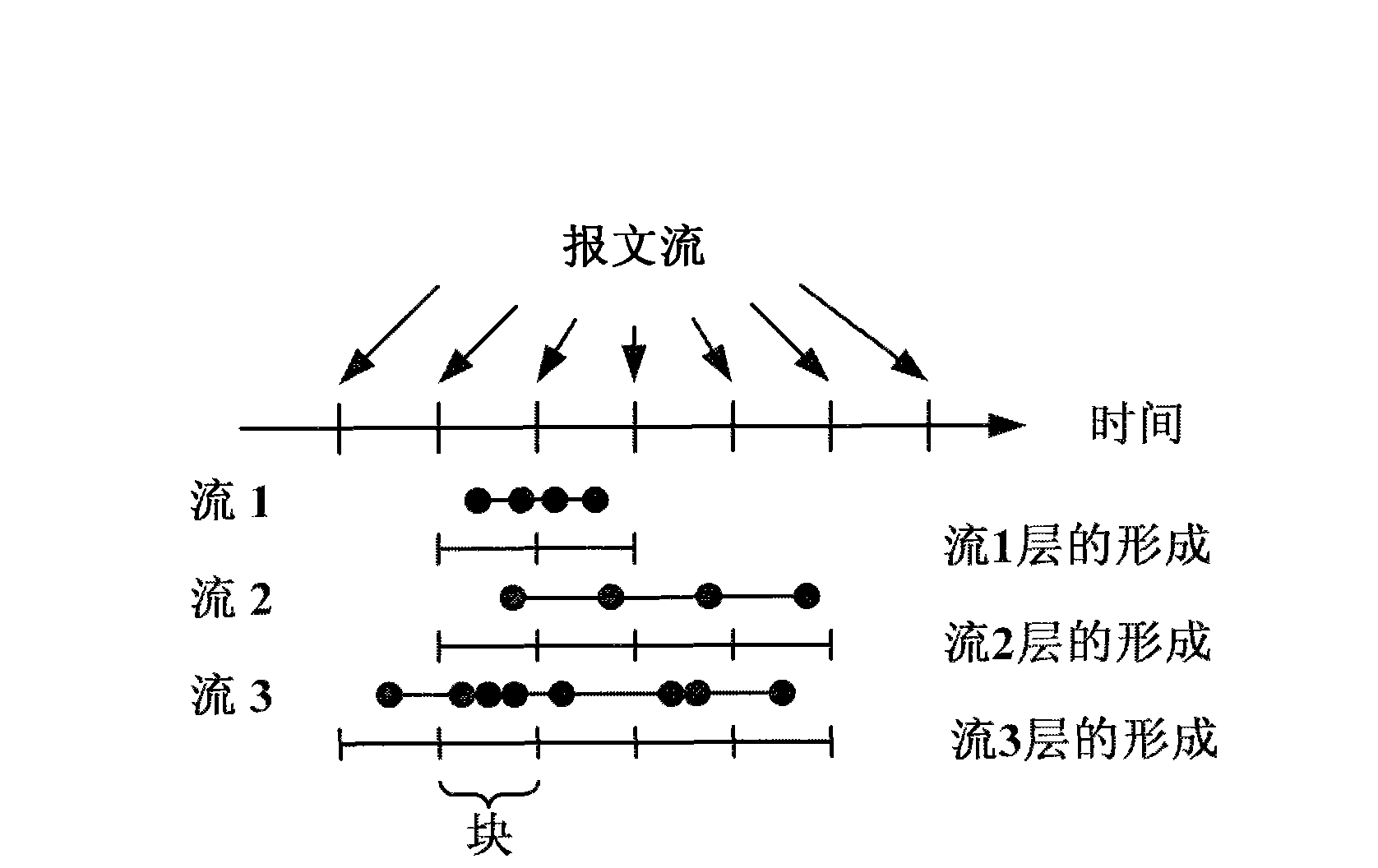
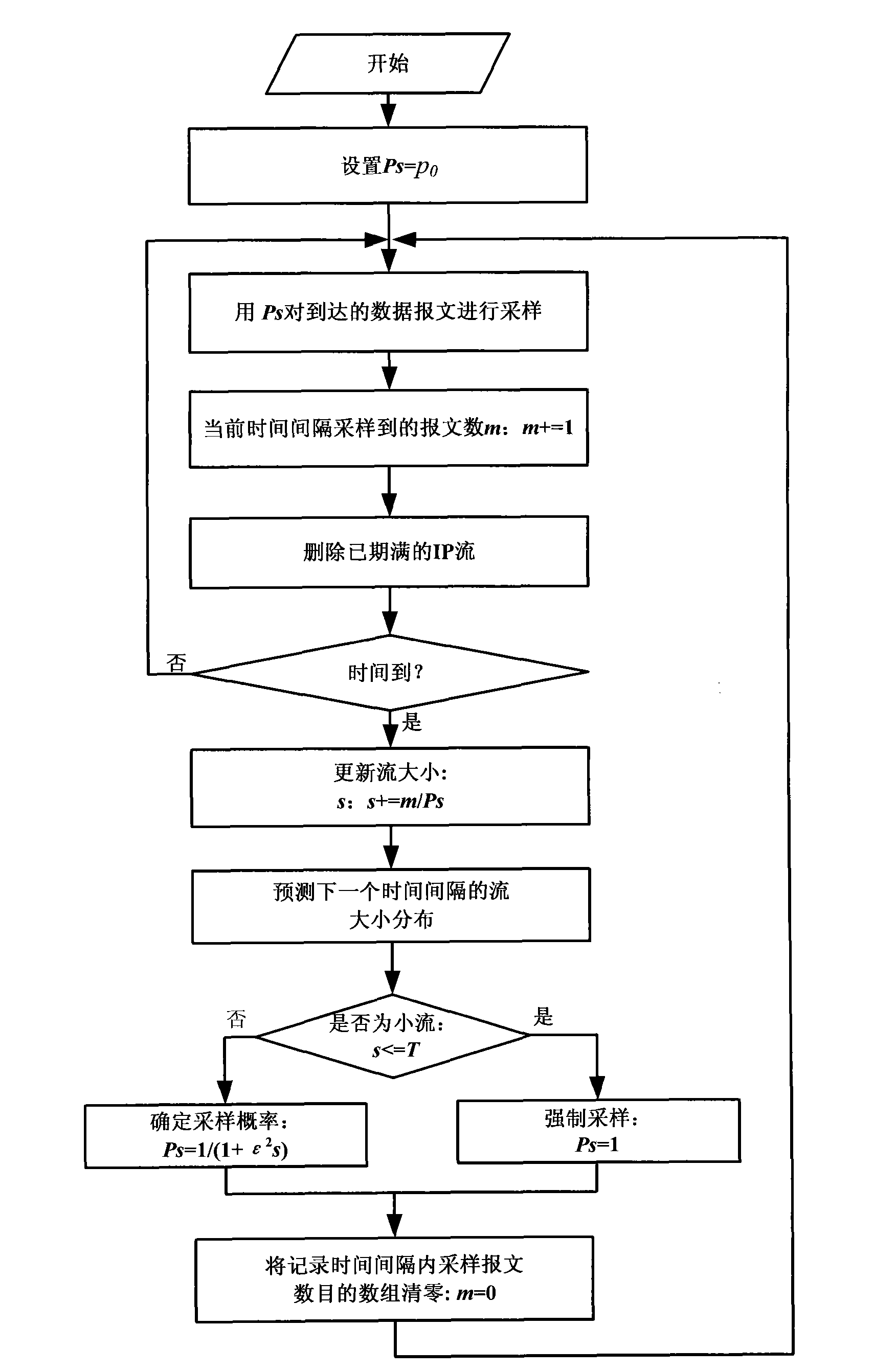
Self adaptive network traffic sampling method for anomaly detection
The invention provides a self adaptive network traffic sampling method for anomaly detection. Based on the ideal of time stratification, time is stratified into predefined non-overlapping intervals called as blocks or layers. In the same time interval, sampling is carried out on all data messages belonging to the same flow with the same probability, and whether the flow expires or not is detectedin real time. When the time interval ends, the flow is estimated with the number of the messages sampled in the current time interval and sampling probability, the flow distribution of the next time interval is predicted, then the predicted flow is taken as an important parameter for determining the sampling probability of the next time internal, and compulsory sampling is carried out on the datamessages of smaller flow by combining a compulsory sampling method. Compared with the prior art, the invention has simple and flexible algorithm, can provide a correct data source for anomaly detection, improve the high processing speed and save memory space.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method and System for Innovation Management and Optimization Under Uncertainty
Owner:HAJIZADEH YASIN
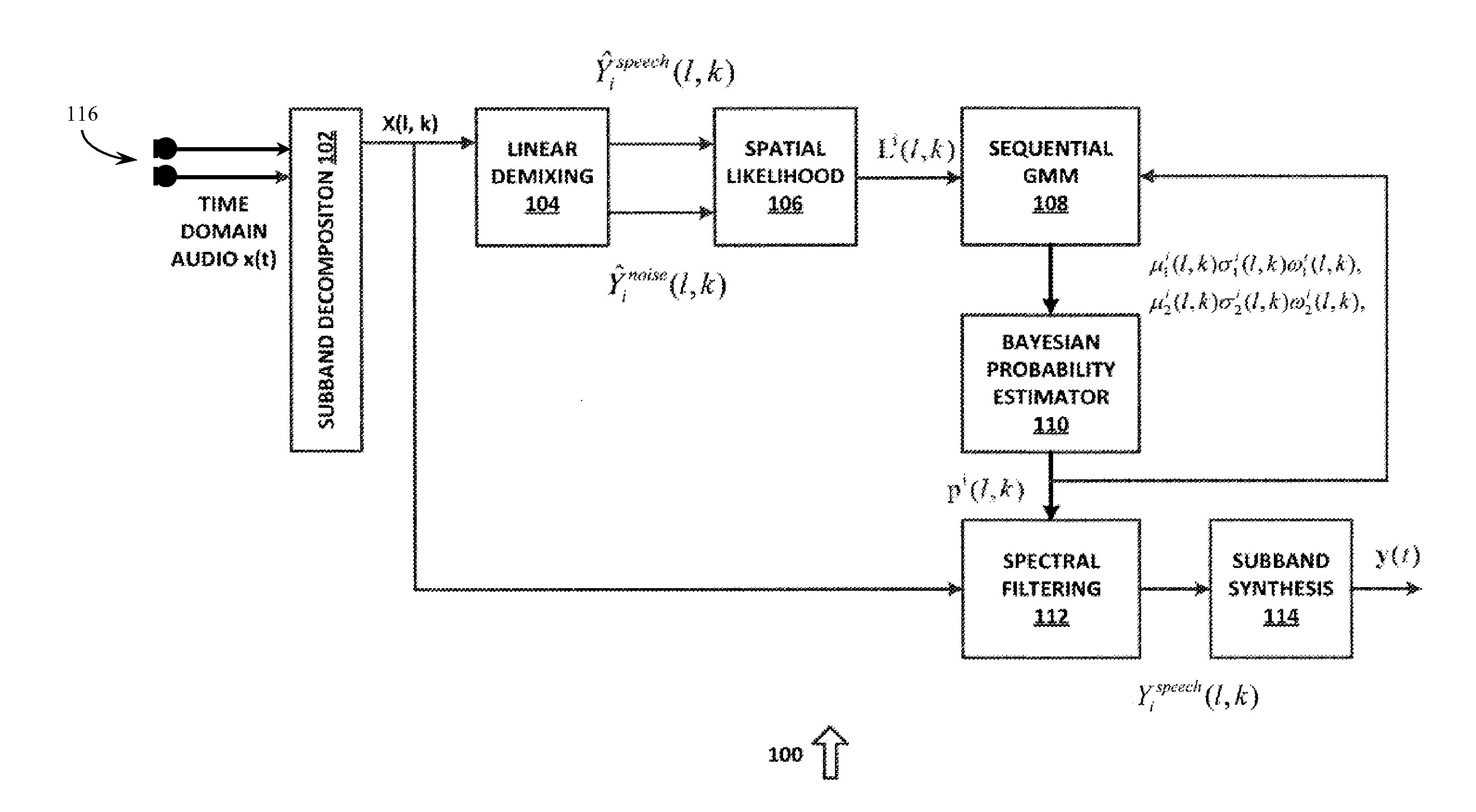
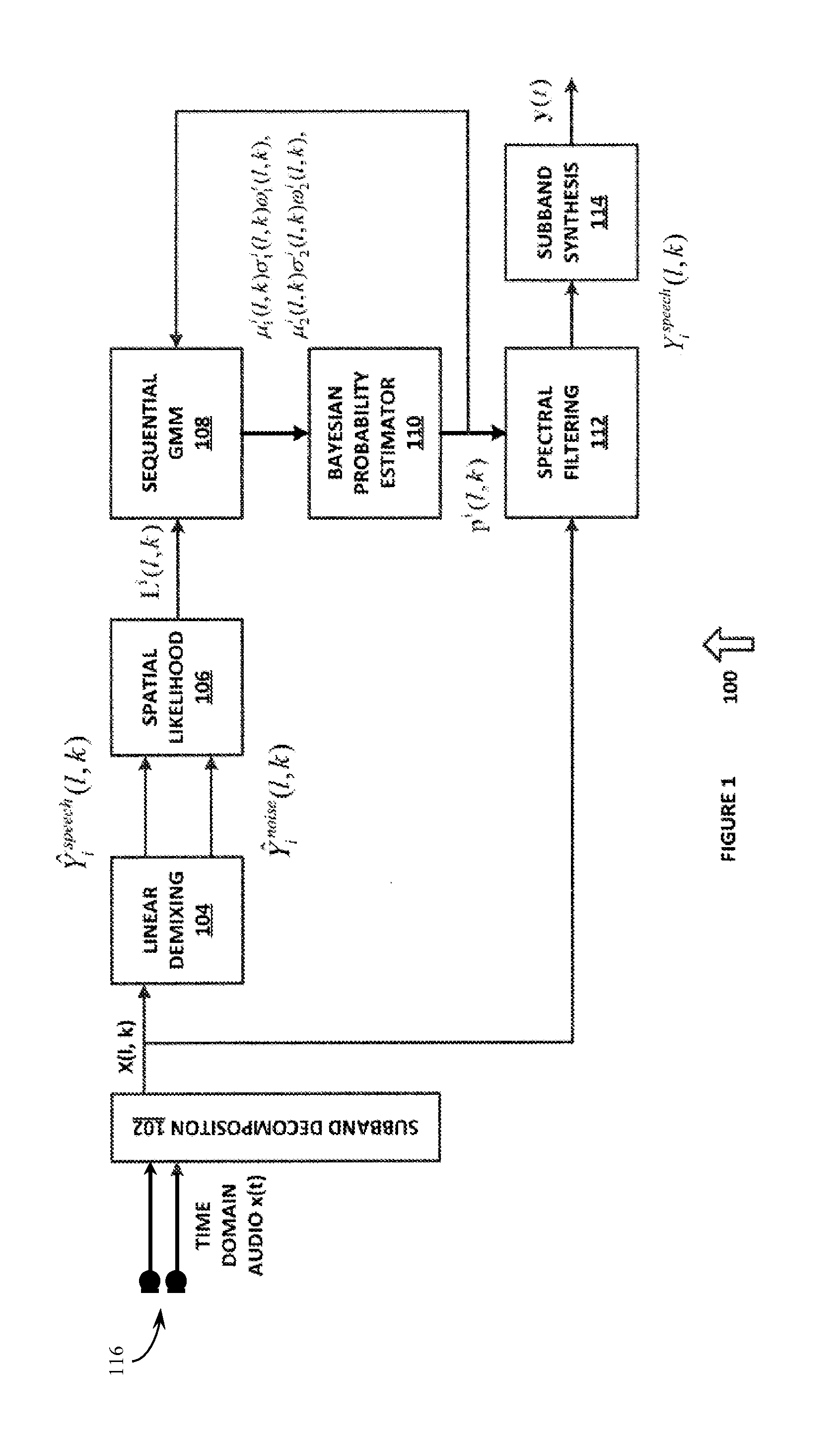
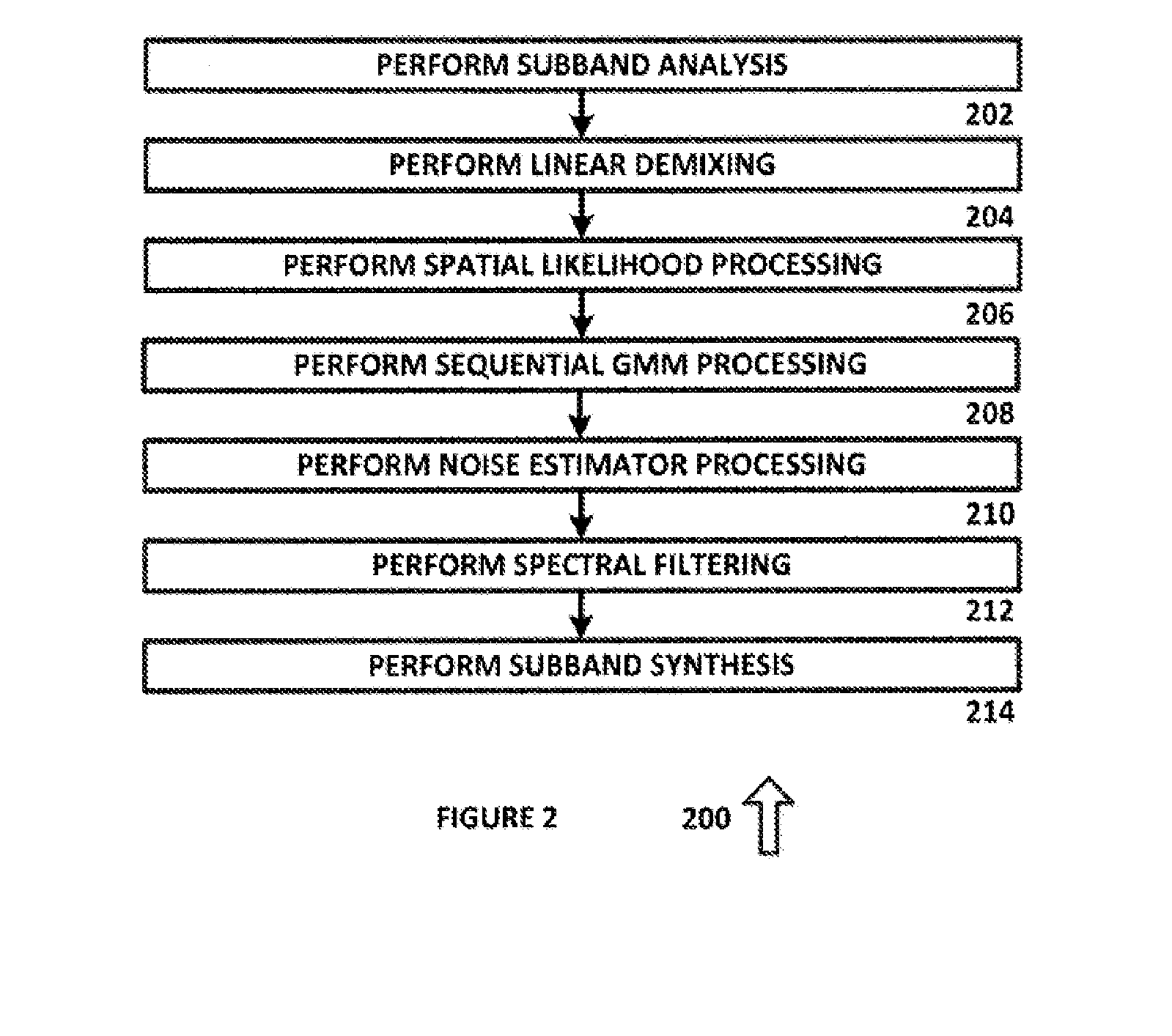
System and method for multichannel on-line unsupervised bayesian spectral filtering of real-world acoustic noise
A system for processing audio data comprising a linear demixing system configured to receive a plurality of sub-band audio channels and to generate an audio output and a noise output. A spatial likelihood system coupled to the linear demixing system, the spatial likelihood system configured to receive the audio output and the noise output and to generate a spatial likelihood function. A sequential Gaussian mixture model system coupled to the spatial likelihood system, the sequential Gaussian mixture model system configured to generate a plurality of model parameters. A Bayesian probability estimator system configured to receive the plurality of model parameters and a speech / noise presence probability and to generate a noise power spectral density and spectral gains. A spectral filtering system configured to receive the spectral gains and to apply the spectral gains to noisy input mixtures.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
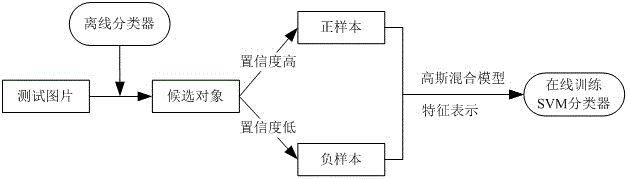
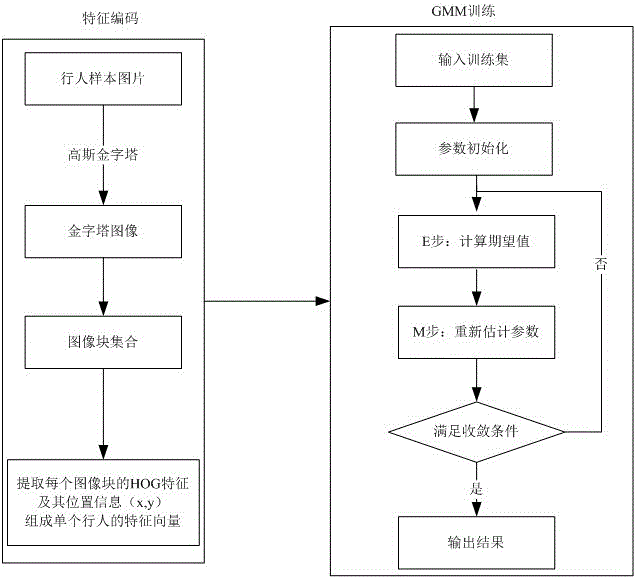
Pedestrian detection method based on self-learning
ActiveCN106845387ASolve the problem of not being able to adapt to specific scenariosImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionHistogram of oriented gradientsFeature coding
The invention discloses a pedestrian detection method based on self-learning. The method comprises the following specific steps that: firstly, training an AdaBoost-based cascade classifier as an off-line classifier, meanwhile, using one group of public pedestrian photos to train a Gaussian mixture model, and adopting HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradient) feature and position information for feature coding; then, adopting the off-line classifier of a low threshold value to carry out pedestrian detection on a specific scene, and outputting the confidence score of a candidate object; then, picking up a high confidence score as a positive sample and a low confidence score as a negative sample, and using a Gaussian mixture model to show the candidate detection object again; and finally, using a SVM (Support Vector Machine) classifier to train a pedestrian classifier with discriminating ability on line, predicting the candidate object again, and estimating an output probability. By use of the method, the problem that a traditional pedestrian detection method can not carry out adaptation on a specific scene is solved, and the method has a certain promoting effect on a pedestrian detection technology under the specific scene. Compared with a traditional pedestrian detection method, the pedestrian detection is characterized in that a recognition rate is obviously improved.
Owner:HEFEI NORMAL UNIV
System and method for probablistic WLAN positioning
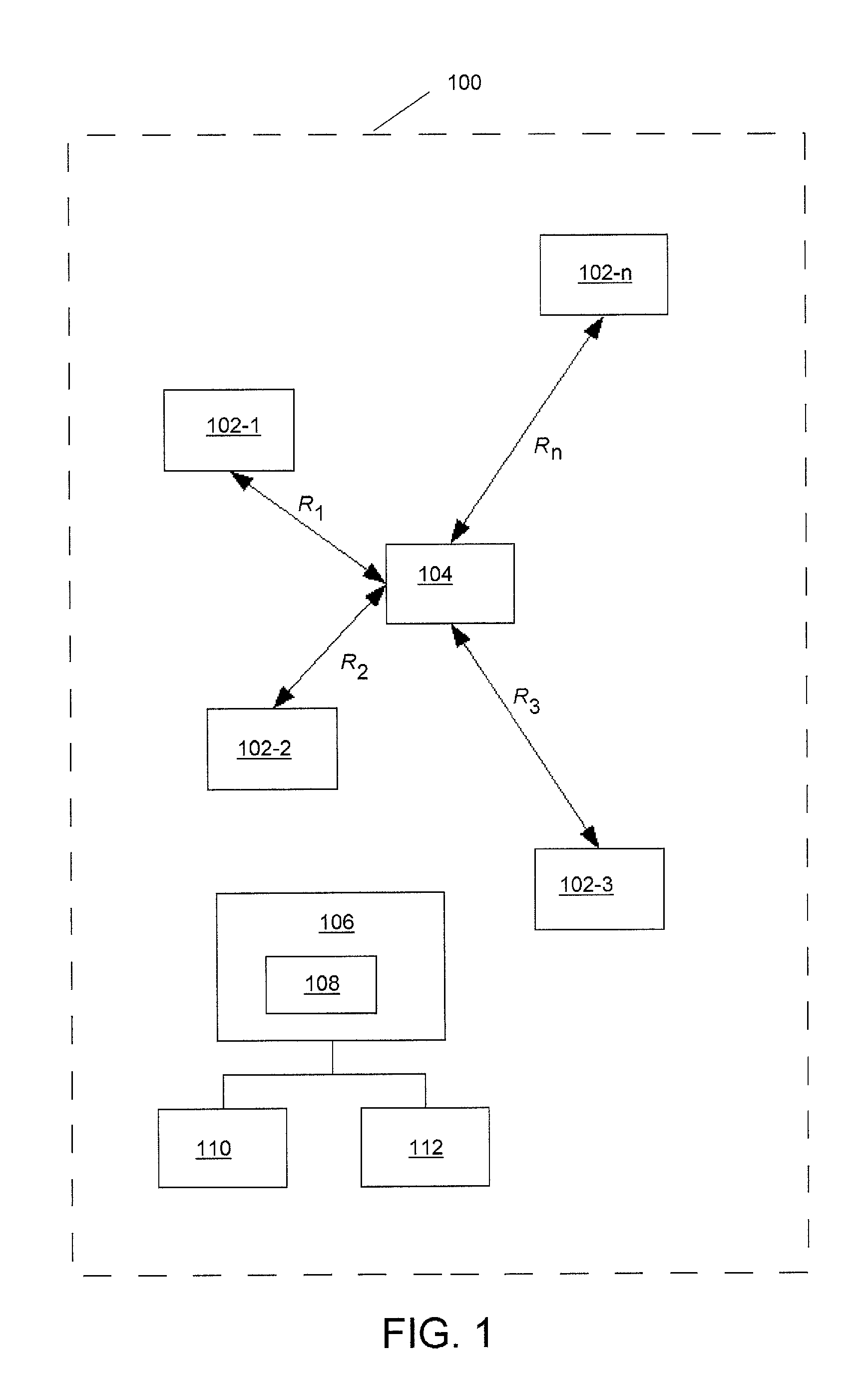
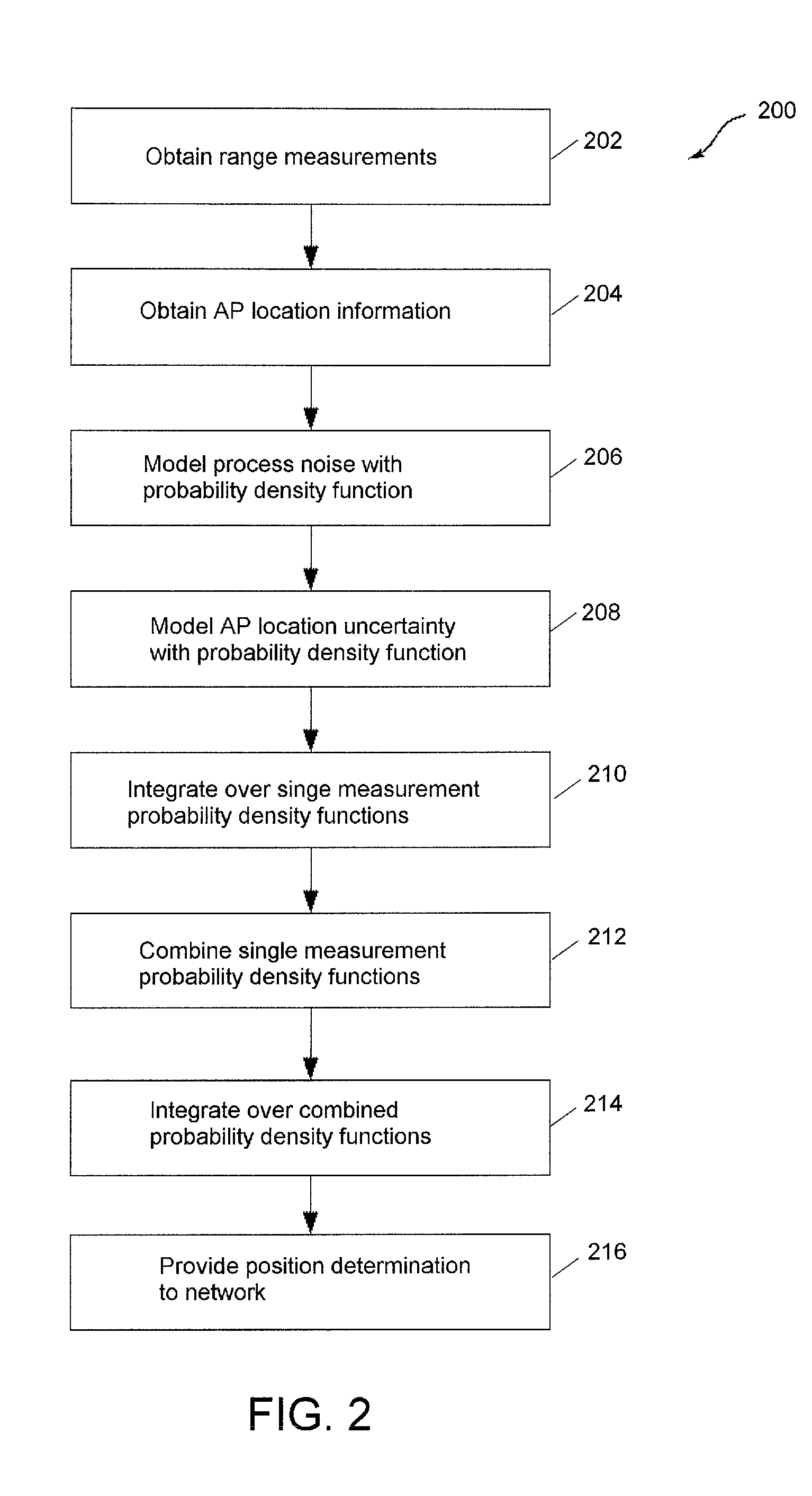
InactiveUS20130163448A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNormal densityRelative motion
This disclosure is directed to a wireless network node having position determination capabilities. The position of a node is determined using range measurements to other network nodes having known locations. Probability density functions modeling uncertainty factors are incorporated in the estimation algorithms to account for the dynamic nature of wireless network, including the relative motion of a node in the network. These probabilistic estimation techniques provide a solution in the form of an expectation value for the position of the network node and a variance that can be assessed to determine the validity of the position determination.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com