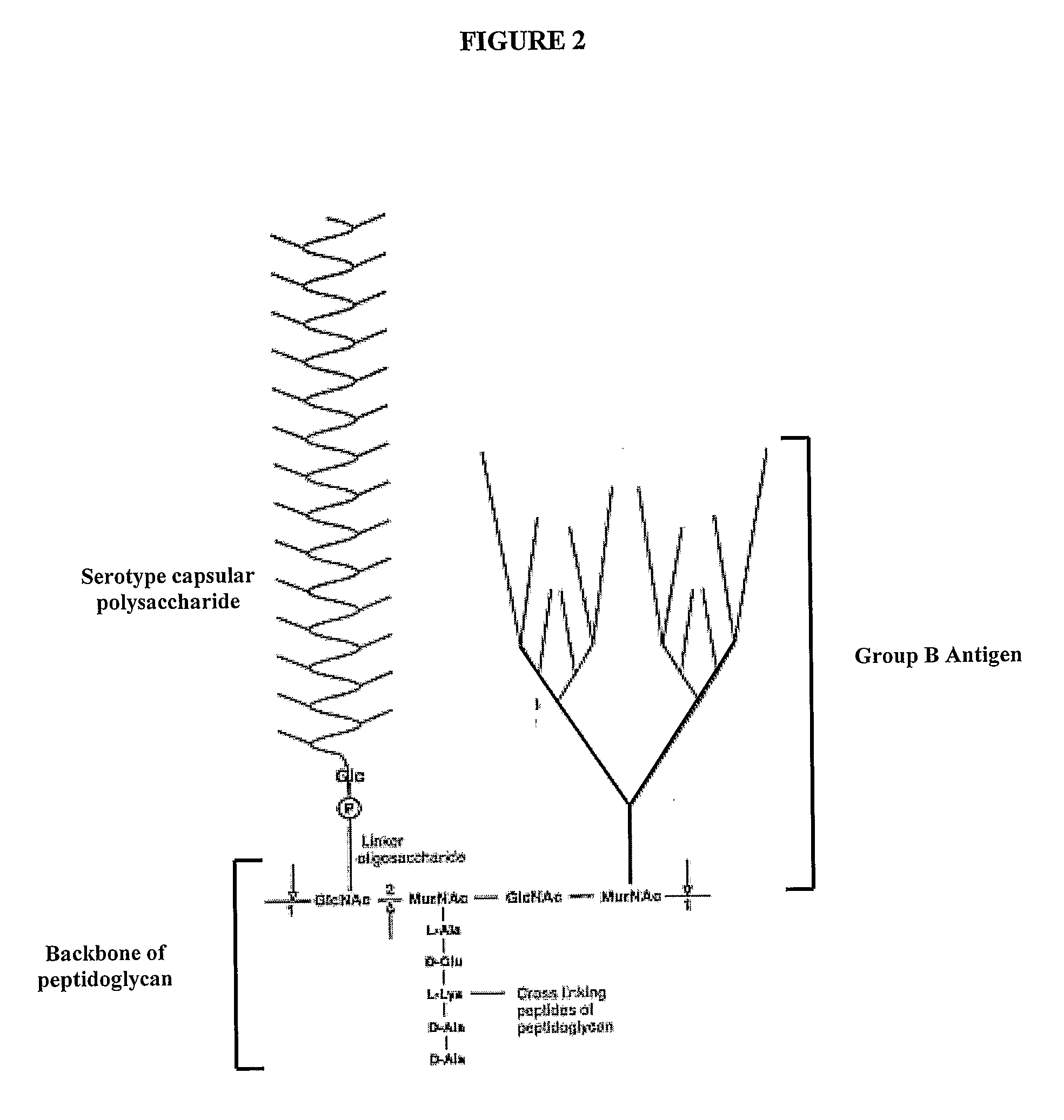
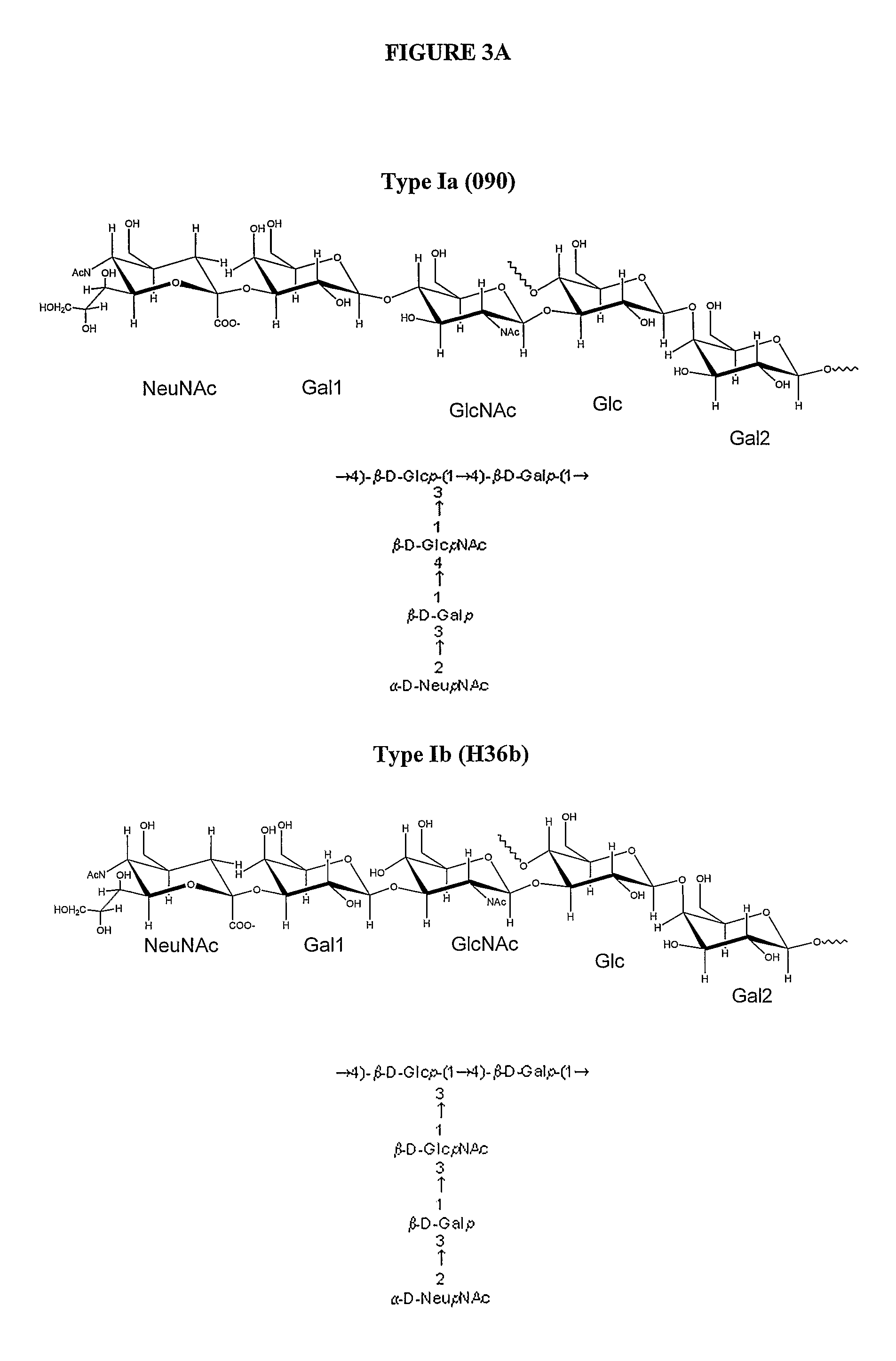
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Streptococcal strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antitumor and anticholesterol preparations containing a lipoteichoic acid from streptococcus
InactiveUS6214978B1Improve usabilityImprove liquidityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBackbone chainHyaluronidase
The invention concerns a new lipoteichoic acid which can be isolated from the new Streptococcus sp DSM 8747. The new LTA is called LTA-T. It has a lipid anchor, which is a galacto-furanosyl-beta-1-3-glycerol with different rests of fatty acids esterified in the two adjacent hydroxy groups in the glycerol moiety and a non-glycosylated, linear, unbranched GroP chain with an unusual short hydrophilic GroP chain. The hydrophilic backbone consists of only 10 glycerophosphate units esterified with D-alanine in an extent of 30%. The invention further concerns a pharmaceutical composition with the new LTA-T, optionally together with a monokine and / or hyaluronidase, a method of treating cancer comprising administration of an antitumor effective amount thereof, a method of producing the new compound and the new pharmaceutical composition, two degradation products of the new LTA-T and their use, and the new Streptococcus strain from which the new compound can be isolated.
Owner:LUNAMED
Fermentation processes for cultivating streptococci and purification processes for obtaining cps therefrom
ActiveUS20100272755A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesPurification methods
This invention is in the field of bacterial cultures and specifically relates to the optimization of culture conditions to improve the production of bacterial capsular polysaccharides from Streptococcus strains in fed batch culture and to novel purification methods suitable for production scale purification of bacterial capsular polysaccharides from Streptococcus strains resulting in higher levels of purity than previously obtained for production scale.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Microarray for monitoring gene expression in multiple strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae
InactiveUS20110177960A1Understanding of genetic expression patternRapid and accurate and discriminable detectionNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementStreptococcus pneumoniaeStreptococcus mitis
The present invention features an array capable of monitoring gene expression patterns of multiple strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae including a substrate having a plurality of addresses, each of which has a probe disposed thereon.
Owner:WYETH LLC
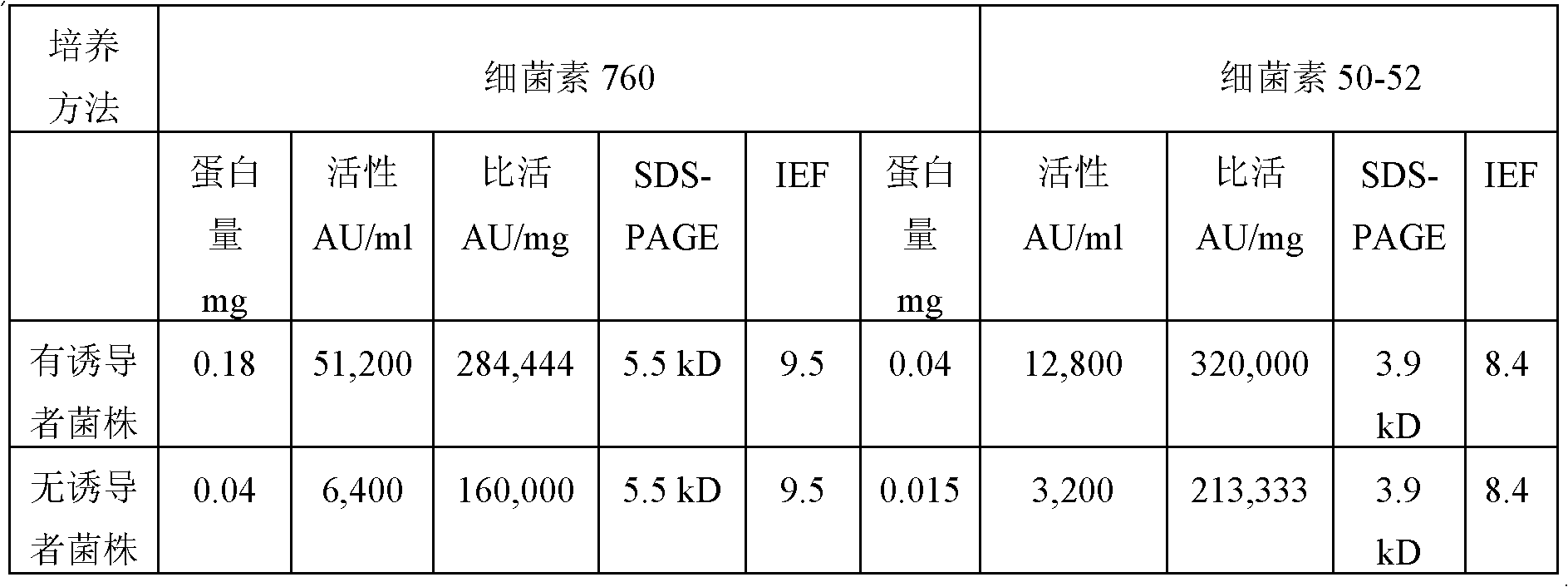
Novel enterococcus and streptococcus strains and bacteriocins
InactiveUS20060223161A1Lower Level RequirementsIncrease productionBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsColonizationBacteriocin
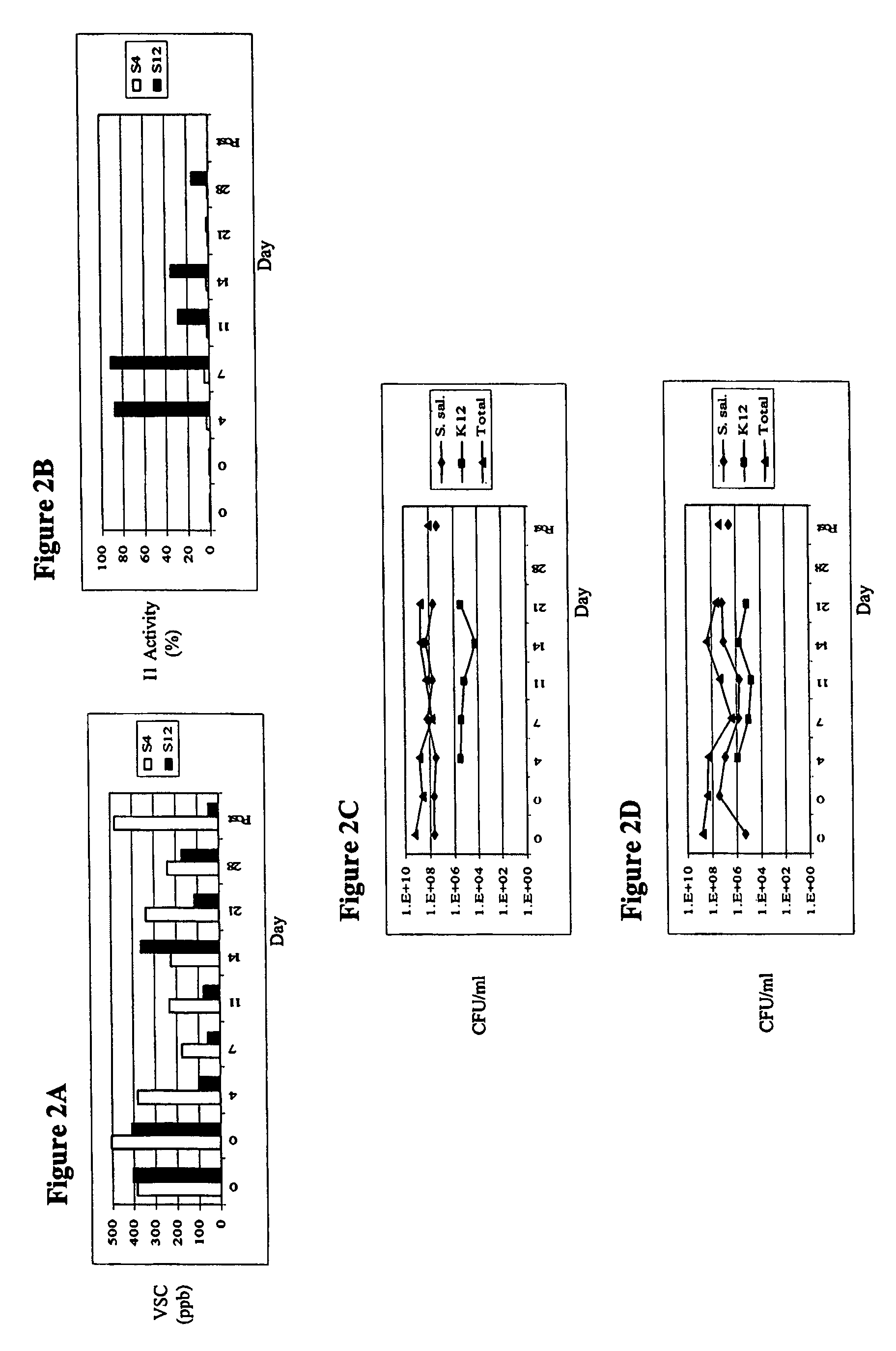
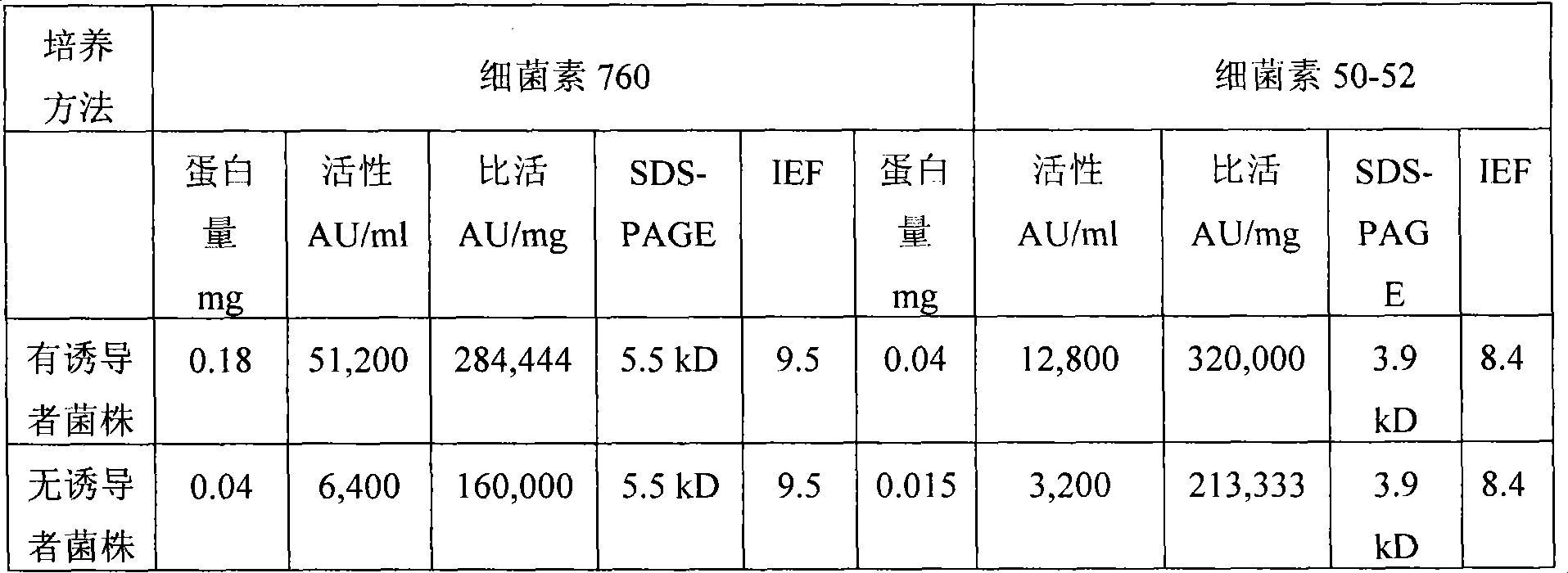
Novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus bacteriocins produced by novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains are used for at least reducing the levels of colonization by at least one target bacteria in animals, especially poultry.
Owner:STATE RES CENT FOR APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY & BIOTECH MINIST OF HEALTH & SOCIAL DEV RF AS REPRESENTED BY THE DIRECTOR OF THE STATE RES CENT FOR APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY & BIOTECH MINIST OF HEALTH & SOCIAL DE +1
Antimicrobial composition
This invention provides novel Streptococcus salivarius, compositions containing same, and use of S. salivarius strains as antimicrobial agents. The strains are bacterial inhibitors with respect to at least S. mutans and / or MS and therefore have a number of therapeutic applications. The applications include but are not limited to forming part of therapeutic formulations for use in controlling, treating, or preventing dental caries.
Owner:BLIS TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Attenuated Streptococcus suis Vaccines and Methods of Making and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20140004144A1Reduced virulenceLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStreptococcus suisStreptococcus mitis
The present invention provides attenuated S. suis strains that elicit an immune response in animal S. suis, compositions comprising said strains, methods of vaccination against S. suis, and kits for use with such methods and compositions. The invention further provides novel, mutagenically-induced mutations in S. suis genes, which are useful in the production of novel attenuated S. suis bacterial strains.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM ANIMAL HEALTH USA INC
Lactic Acid Bacteria for Coeliac Disease
The present invention discloses strains of Lactobacillus and Streptococcus which have a capacity to degrade gliadin peptides involved in coeliac disease and which peptide degrading activity is stable under low pH and in the presence of mammalian digestive enzymes. These strains are suitable in a product for use in prevention and / or treatment of celiac disease.
Owner:DANONE
Compositions and methods for the maintenance of oral health
The invention provides compositions comprising one or more isolated LDH-deficient mutans streptococcus strains and one or more isolated S. oralis strains and / or one or more isolated S. uberis strains. Compositions of the invention are useful to maintain oral health, by for example treating and / or preventing one or more symptoms of dental caries, periodontitis and / or other oral cavity diseases or wounds.
Owner:PROBIORA HEALTH LLC
Pharmaceutical preparation comprising a combination of streptococcus strains and lactobacillus strains
InactiveUS20110256179A1Reduce eliminateAntibacterial agentsBacteriaInduced infectionsLactobacillus rhamnosus
A pharmaceutical preparation for prophylaxis against and treatment of Staphylococcus induced infections or conditions in humans and animals, is disclosed, wherein it comprises a combination of a) one or more viable α-Streptococcus strains chosen from the group consisting of the Streptococcus sanguis II strains having the accession numbers NCIMB 40104, NCIMB 40105, NCIMB 40106, and NCIMB 40873, the Streptococcus mitis strains having the accession numbers NCIMB 40107, and NCIMB 40874, the Streptococcus oralis strains having the accession numbers NCIMB 40875 and NCIMB 40876, the Streptococcus lactis strain L1A having the accession number NCIMB 40157, and one or more variants thereof having the same or essentially similar effect; and b) one or more viable Lactobacillus strains chosen from the group consisting of the Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain LB21 having the accession number NCIMB 40564, the Lactobacillus plantarum strain LB3 having the accession number DSM 17852, and the Lactobacillus plantarum strain LB7 having the accession number DSM 17853, and one or more variants thereof having the same or essentially similar effect; in at least one pharmaceutically acceptable medium in which said strains maintain their viability, as well as a kit for and a method of prophylaxis and treatment of Staphylococcus induced infections and conditions, and use
Owner:ESSUM
Streptococcus pneumoniae pilus antigens
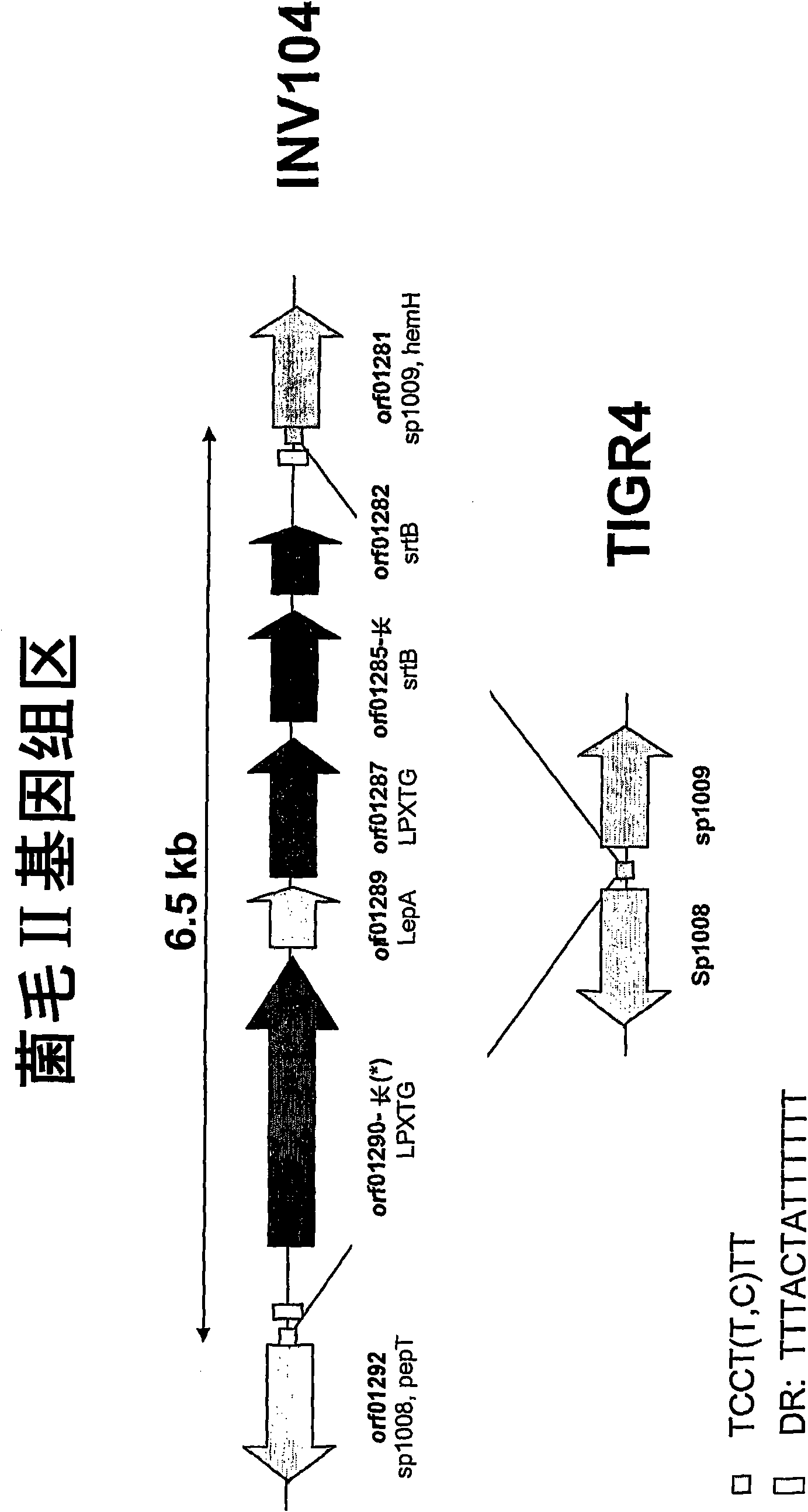
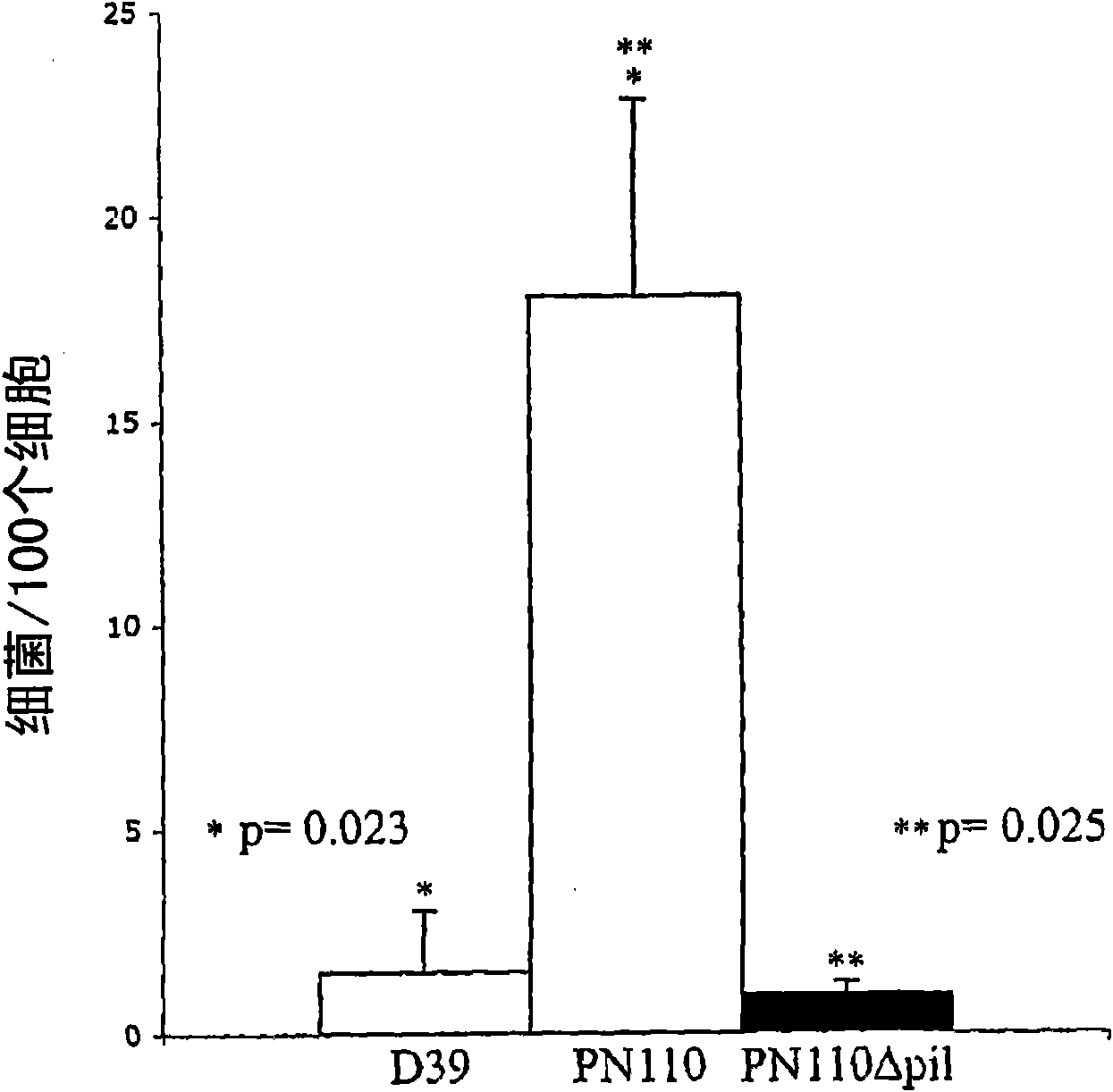
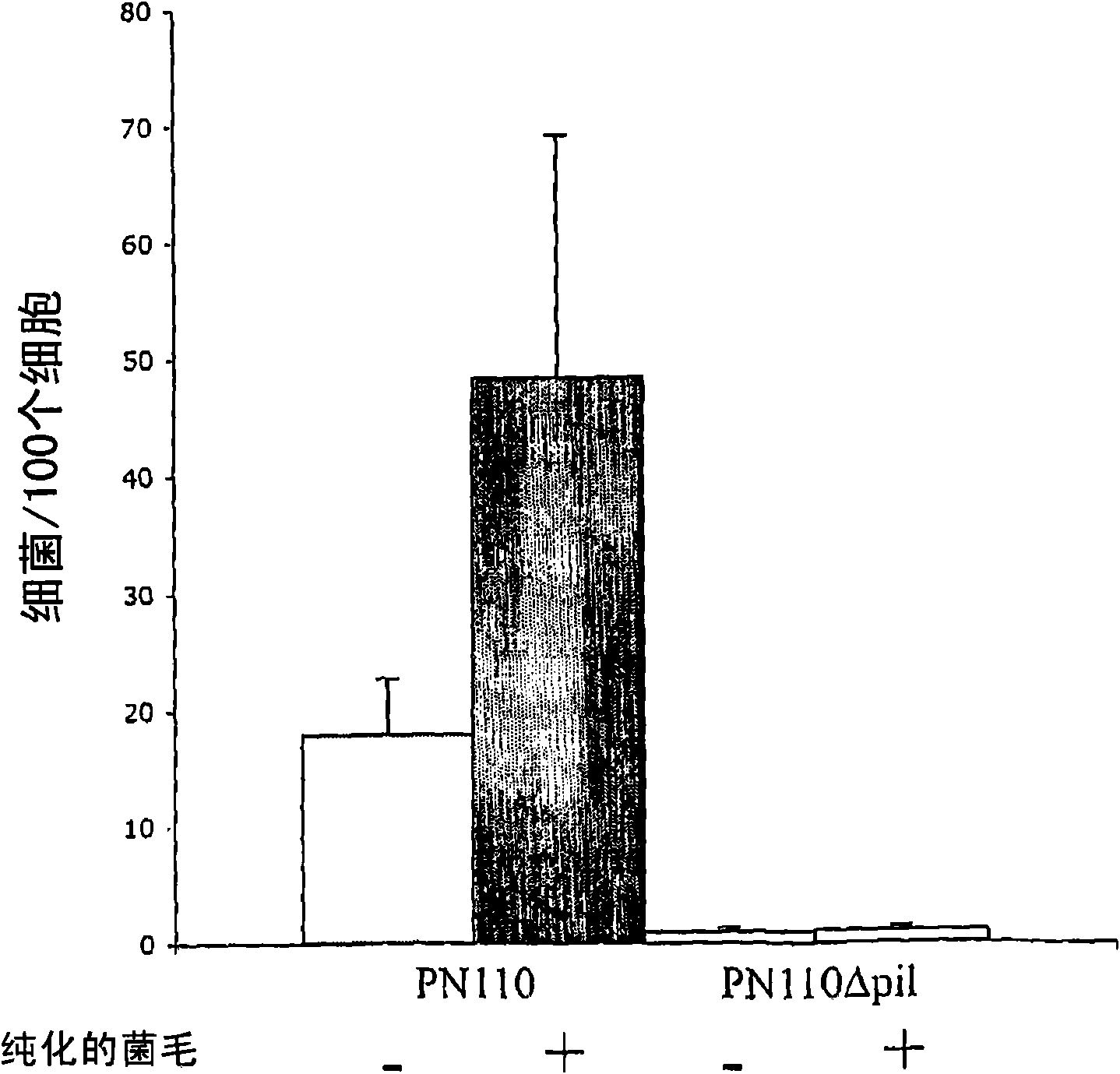
Polypeptides from Streptococcus pneumoniae are described. In some aspects the polypeptides include pili polypeptides from a second pili island (pilus II island (INVl 04B)) identified in Streptococcus pneumoniae isolate INVl 04. In other aspects the polypeptides include pili polypeptides and non-pilus polypeptides from Streptococcus pneumoniae strains 23F, INV200, and OXC141 that are absent from Streptococcus pneumoniae isolate INV104. The polypeptides, including fragments and variants thereof, may be used in immunogenic compositions for prophylactic or therapeutic immunization against Streptococcus pneumoniae. The polypeptides are also disclosed to be used in compositions useful for the production of antibodies and immunostimulants. Also presented are methods of inhibiting Streptococcus pneumoniae, methods of treating Streptococcus pneumoniae infection, methods of identifying inhibitors of Streptococcus pneumoniae and methods for diagnosing / detecting Streptococcus pneumoniae infection.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Lactic acid bacteria for preparing fermented food products with increased natural sweetness and high texture
ActiveUS20200260750A1Improve propertiesImproved texturizing propertyMilk preparationBacteriaLactic acid bacteriumGalactokinase
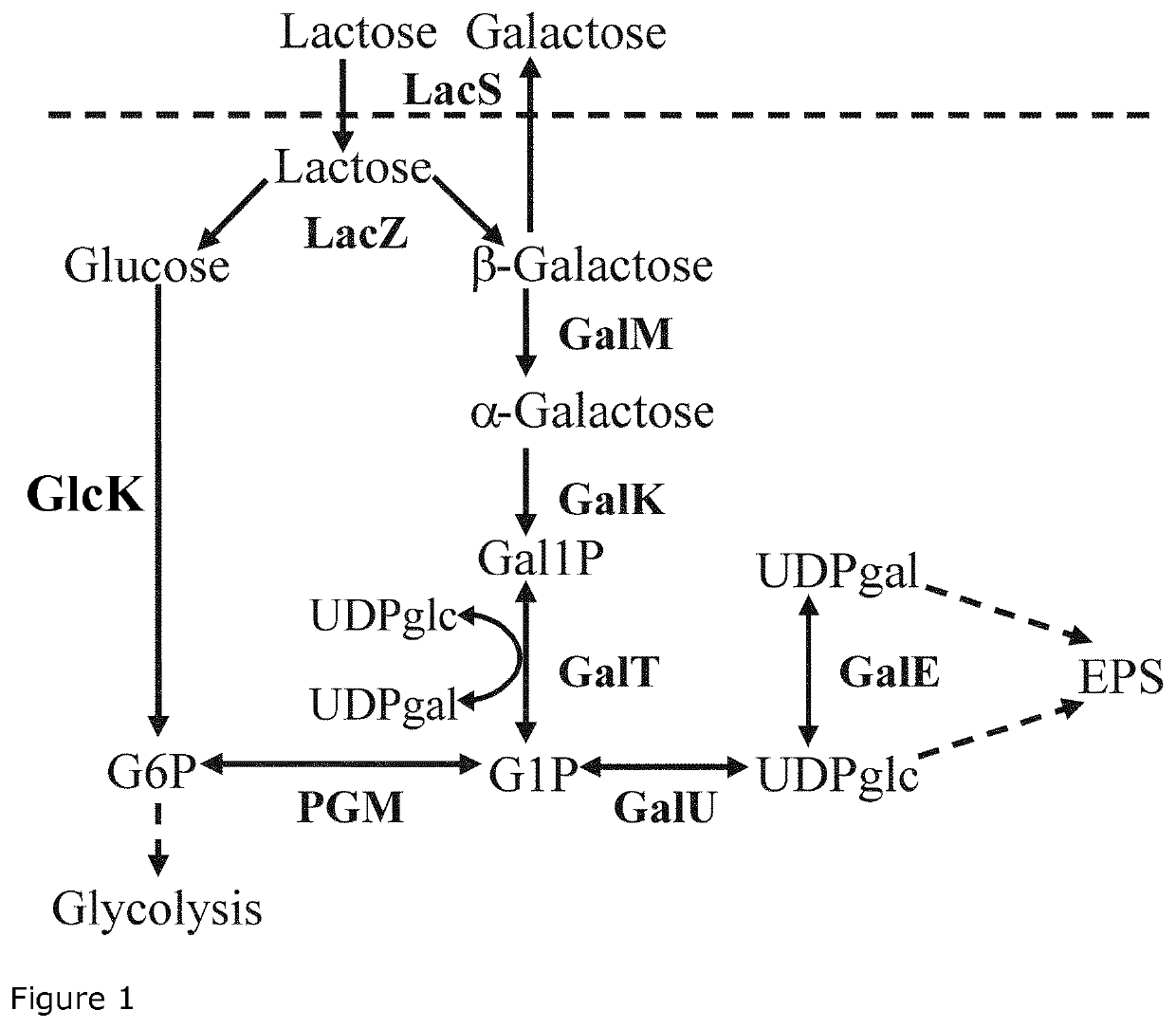
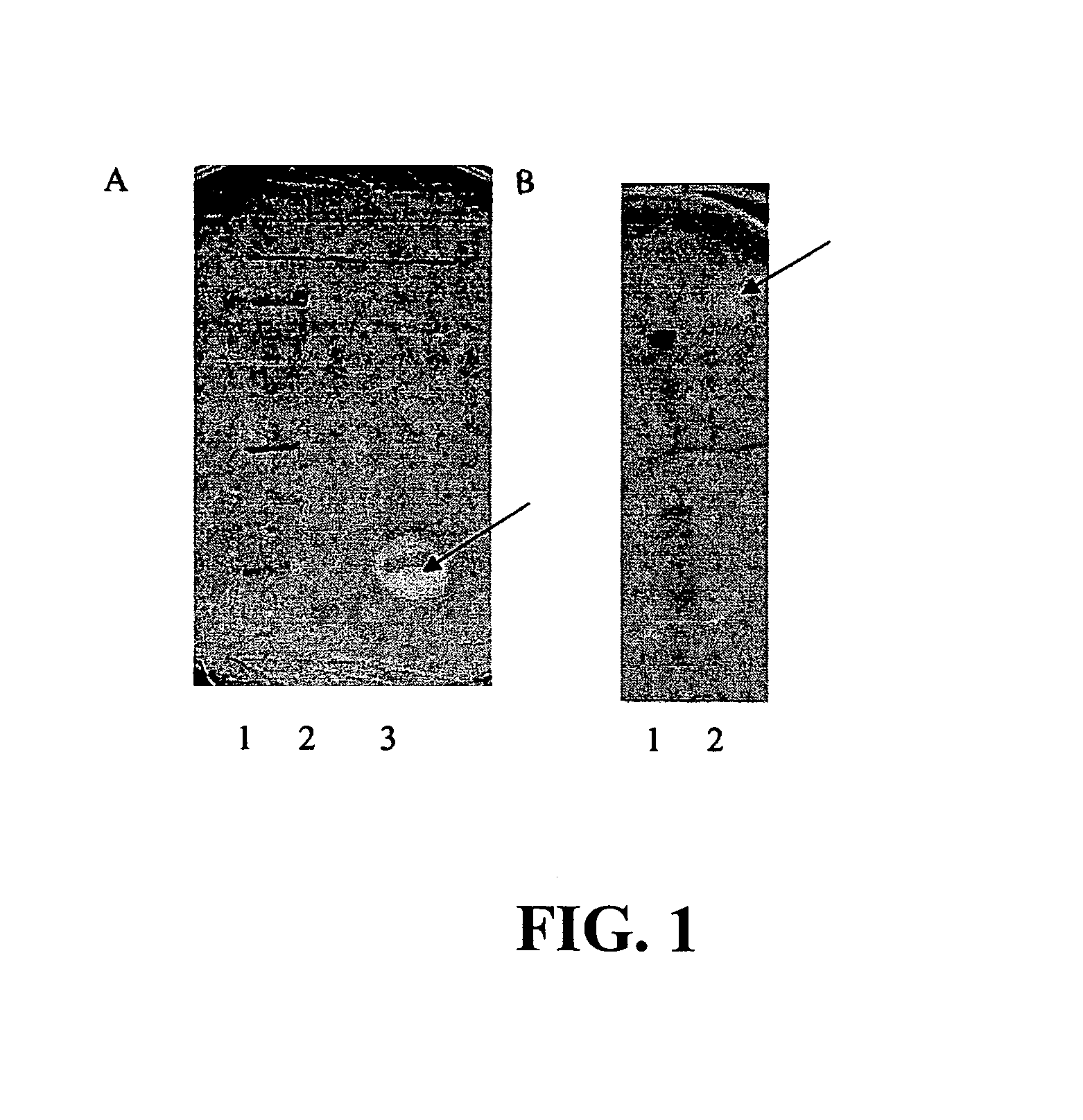
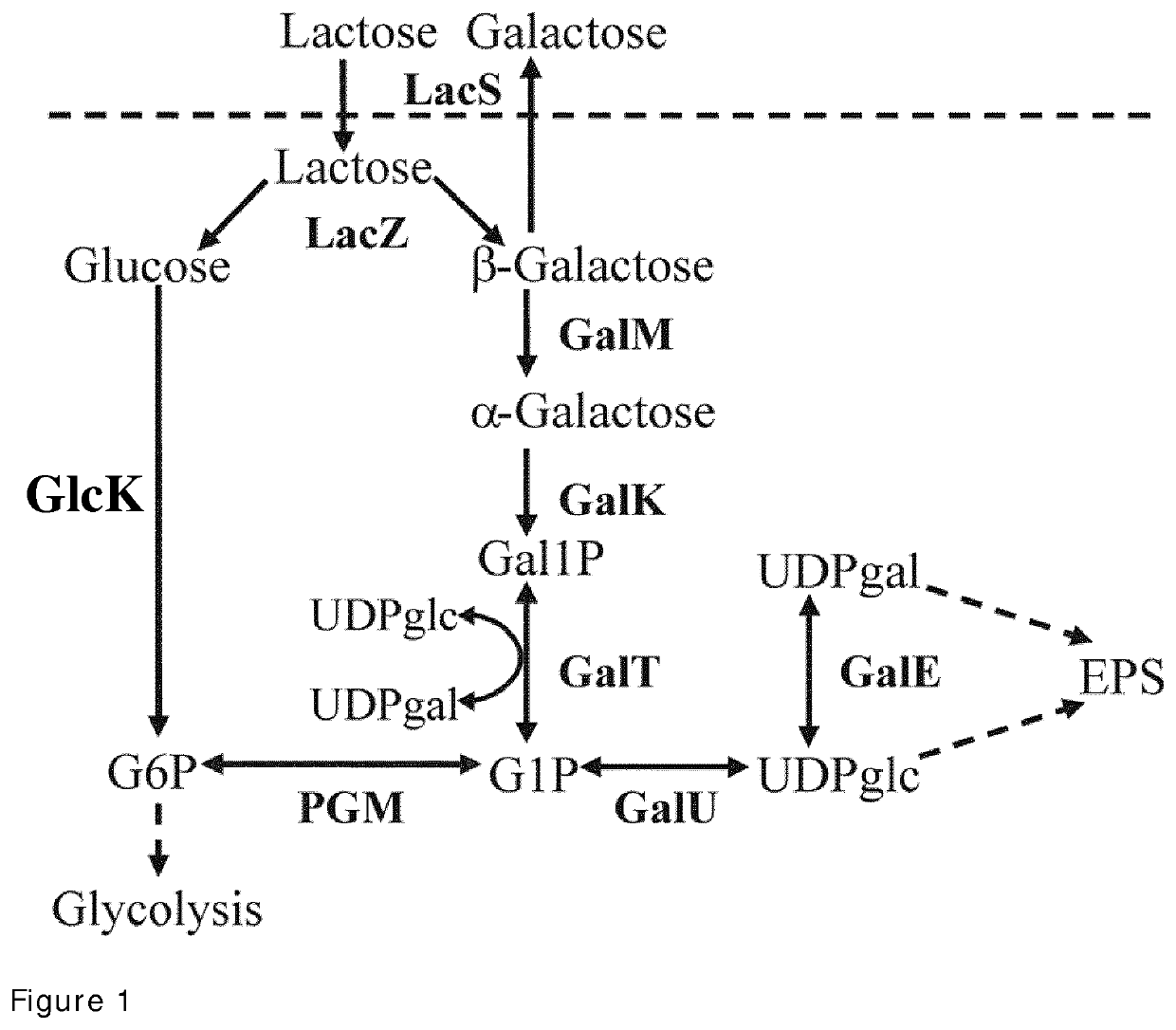
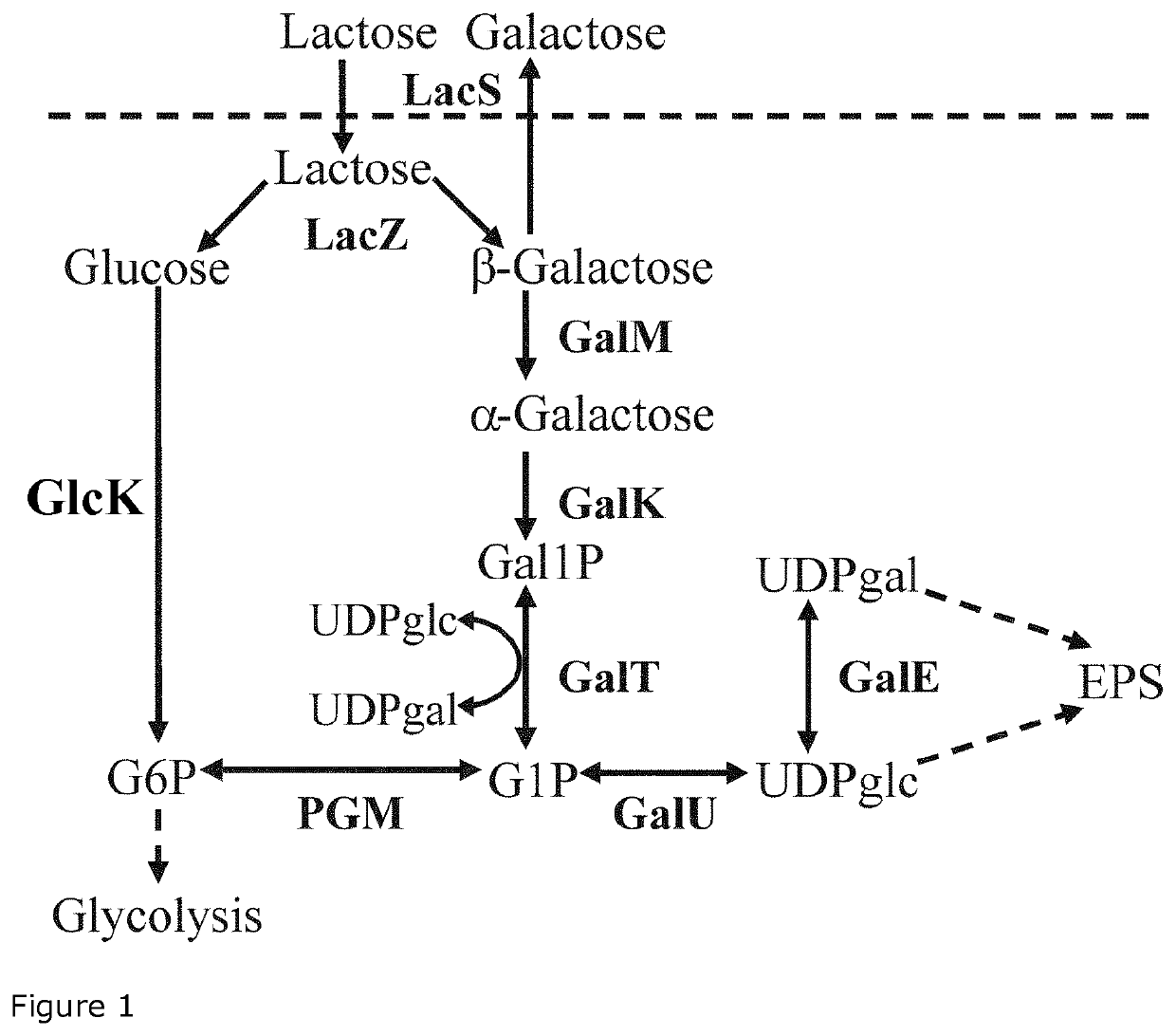
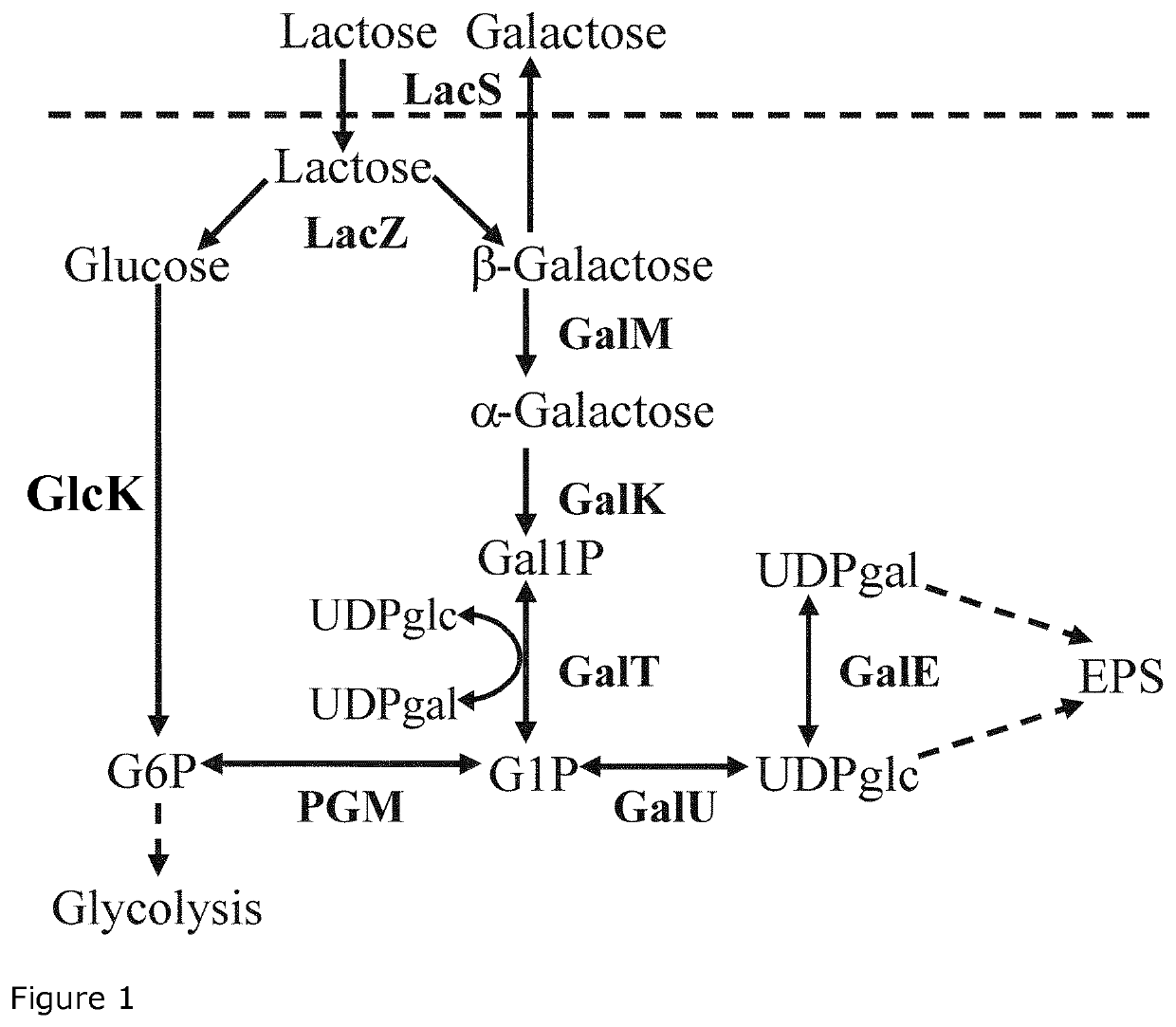
The present invention relates to a Streptococcus thermophilus strain, wherein the strain is galactose-fermenting, wherein the strain carries a mutation in the DNA sequence of the glcK gene encoding a glucokinase protein, wherein the mutation inactivates the glucokinase protein or has a negative effect on expression of the gene, and wherein the strain carries a mutation in the promoter region of the GalK gene encoding a galactokinase protein.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Method for breeding weak post-acidification streptococcus thermophilus strain
PendingCN113151250AAchieve weakeningIncrease mutation frequencyMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLactic acid bacterium
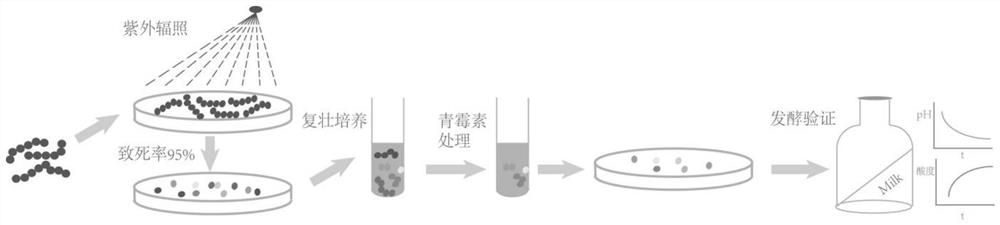
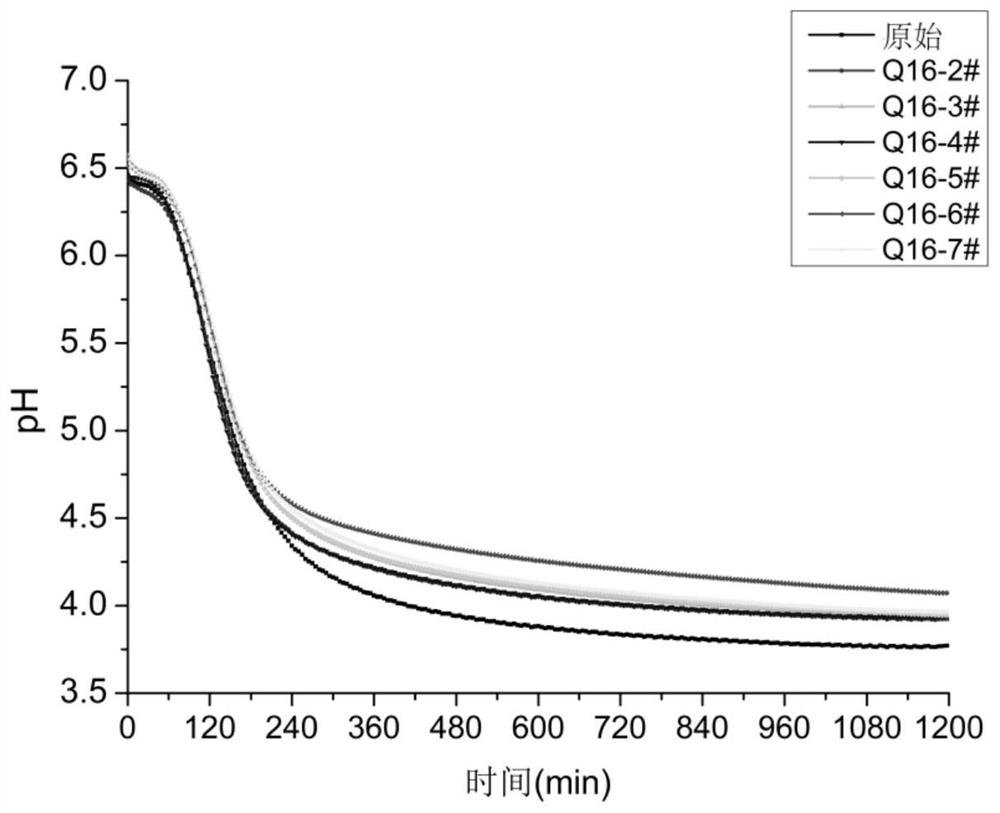
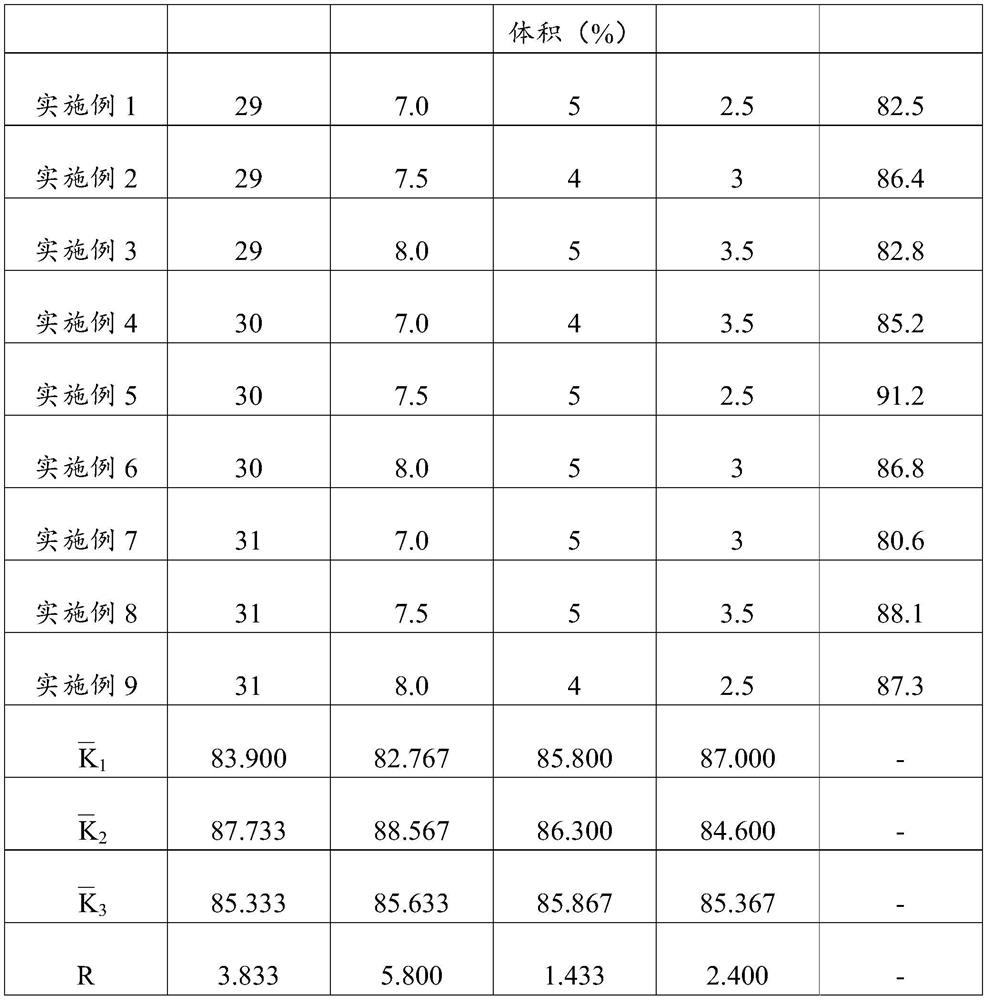
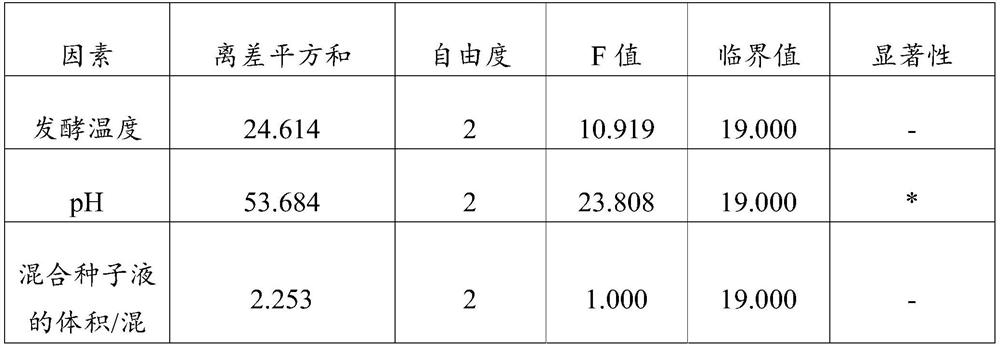
The invention relates to the technical field of mutation breeding of lactic acid bacteria, and provides a method for breeding weak post-acidification streptococcus thermophilus strains. The method comprises the following steps: S1, preparation of a bacterial suspension: culturing an original strain to obtain a bacterial solution, transferring and continuously culturing the bacterial solution to a logarithmic metaphase, centrifuging, washing and concentrating the bacterial solution to obtain the suspension, and placing the suspension in an empty plate for later use; S2, ultraviolet irradiation: placing the suspension under an ultraviolet lamp for irradiation; S3, rejuvenation culture: resuspending the bacteria obtained in S2 in a fresh culture medium for rejuvenation culture; S4, penicillin treatment: adding penicillin for treatment, performing dilution, and coating an MC culture medium with the solution for culture; and S5, screening weak post-acidification strains. According to the technical scheme, the problem that the weak post-acidification streptococcus thermophilus strain cannot be efficiently bred in the prior art is solved.
Owner:河北一然生物科技股份有限公司
Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains and bacteriocins
InactiveUS7988958B2Decrease in levelLower Level RequirementsBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesEnterococcus avium
Novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus bacteriocins produced by novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains are used for at least reducing the levels of colonization by at least one target bacteria in animals, especially poultry.
Owner:STATE RES CENT FOR APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY & BIOTECH MINIST OF HEALTH & SOCIAL DEV RF AS REPRESENTED BY THE DIRECTOR OF THE STATE RES CENT FOR APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY & BIOTECH MINIST OF HEALTH & SOCIAL DE +1
Lactic acid bacteria composition for preparing fermented food products with increased natural sweetness and flavor
PendingUS20210274800A1Increase the number of cellsMilk preparationMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacilli
The present invention relates to a composition for producing a fermented milk product comprising (i) at least one Streptococcus thermophilus (St) strain, wherein the St strain is galactose-fermenting, wherein the strain carries a mutation in the DNA sequence of the glcK gene encoding a glucokinase protein, wherein the mutation inactivates the glucokinase protein or has a negative effect on expression of the gene, and (ii) at least one Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus (Lb) strain, wherein the Lb strain is lactose-deficient and capable of metabolizing a non-lactose carbohydrate.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Streptococcus zooepidemicus strain and application thereof
The invention provides a streptococcus zooepidemicus strain. The glucokinase gene of the streptococcus zooepidemicus strain is overexpressed. After the streptococcus zooepidemicus strain disclosed by the embodiment of the invention is subjected to fermentation treatment, the yield of the obtained HA is obviously improved.
Owner:HEC PHARM
Preparation method of whey protein
InactiveCN113068762AAllergenicity reductionReduce allergiesProtein composition from milkMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyWhey protein
The invention discloses a preparation method of whey protein, and relates to the technical field of microbial fermentation. The preparation method of the whey protein comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a mixed seed solution, specifically, respectively taking a bifidobacterium lactis strain and a streptococcus acidophilus strain, firstly performing constant-temperature culture, then inoculating the bifidobacterium lactis strain and the streptococcus acidophilus strain into a seed culture medium for amplification culture, then performing shake culture to respectively obtain a bifidobacterium lactis seed solution and a streptococcus acidophilus seed solution, and mixing the bifidobacterium lactis seed solution with the streptococcus acidophilus seed solution to obtain the mixed seed solution; and (2) performing fermentation, specifically, mixing the mixed seed solution obtained in the step (1) with a fermentation substrate, and performing fermentation to obtain the whey protein, wherein the fermentation substrate is a whey protein solution.
Owner:广州金酮医疗科技有限公司
Novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains and bacteriocins
Novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus bacteriocins produced by novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains are used for at least reducing the level of colonization of at least one target bacteria in animals, particularly poultry.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI (US) +1
Treatment of malodour
Owner:BLIS TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Replacement therapy for dental caries
The invention provides recombinant Streptococcus mutans strains that can be used to improve oral health. An embodiment of the invention provides a method of reducing the incidence or severity of dental caries in a dental caries-susceptible host comprising administering orally to the host an isolated recombinant S. mutans strain of the invention in an amount effective for replacement of dental caries-causing S. mutans host strains in the oral cavity of the host. The isolated recombinant S. mutans strain 10 can be contained in a mouthwash, toothpaste, chewing gum, floss, chewable tablet, food, or beverage.
Owner:ORAGENICS +2
Novel enterococcus and streptococcus strains and bacteriocins
Novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus bacteriocins produced by novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains are used for at least reducing the levels of colonization by at least one target bacteria in animals, especially poultry.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI (US) +1
Use of lactic acid bacteria for preparing fermented food products with increased natural sweetness
ActiveUS20200093149A1Low in lactoseHigh sweetnessMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyProbiotic bacterium
The dairy industry today faces a problem of providing an alternative to adding sweeteners to fermented milk products in order to achieve the desired sweet taste without the added calories. Furthermore, it would be highly advantageous to establish a method for reducing lactose in fermented milk products to a level which is acceptable for lactose-intolerant consumers. The above problems have been solved by providing mutant Streptococcus thermophilus strains and mutant Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus strains that excrete glucose to the milk when the milk is inoculated and fermented with such Streptococcus thermophilus strains and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp, bulgaricus strains. Thus, the present invention relates to strains of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp, bulgaricus which secrete glucose to the milk substrate during fermentation, as well as to mixed cultures comprising the Streptococcus thermophilus strains and the Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp, bulgaricus strains, starter cultures comprising the strains and dairy products manufactured with the cultures. The present method also relates to use of the strains for decreasing the lactose content of a fermented food product and for boosting growth of the probiotic BB-12®.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
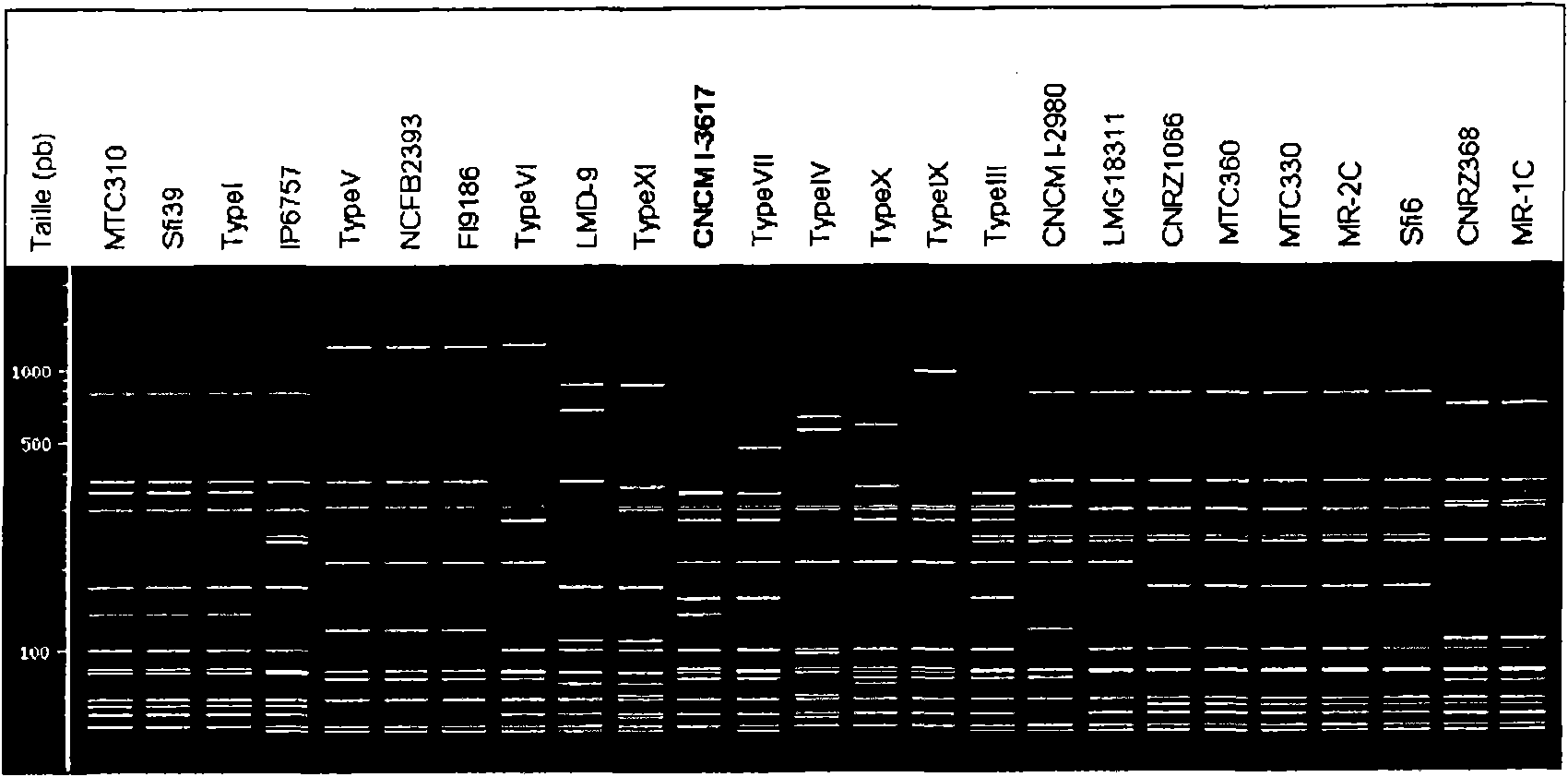
Genetic cluster of strains of streptococcus thermophilus having appropriate acidifying and texturizing properties for dairy fermentations
The invention relates to a genetic cluster of strains of Streptococcus thermophilus, which have a lysotype distinct from that of the strains currently used. Within this cluster novel acidifying and lexturizing strains have been identified.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Streptococcus-pneumoniae-toxicity-reducing live vaccine
InactiveCN101612394BSimple production processLow costAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStreptococcus pneumoniaePneumonia mrsa
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
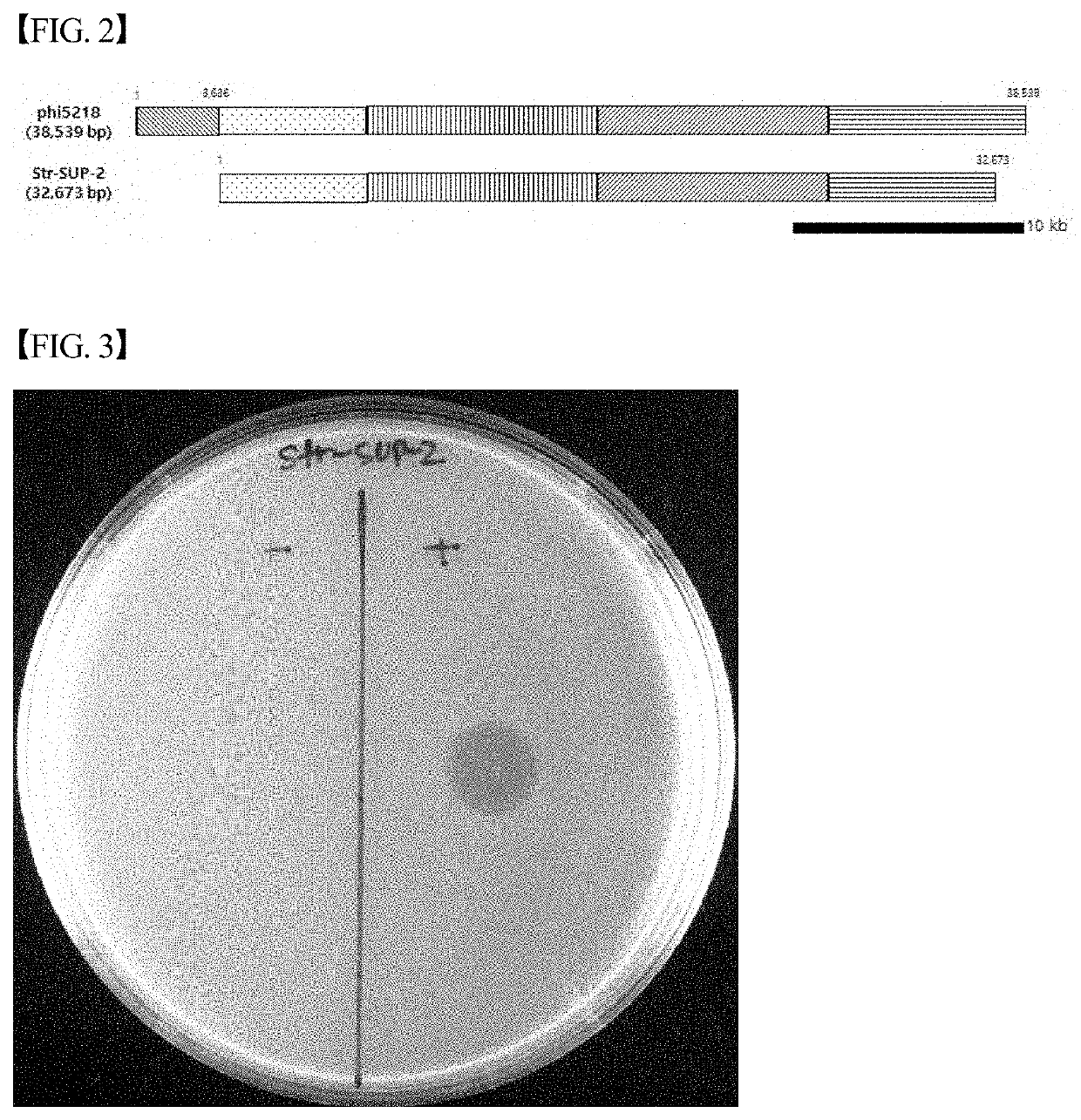
Novel streptococcus suis bacteriophage str-sup-2, and use thereof for inhibiting proliferation of streptococcus suis strains
PendingUS20210163897A1Strong specificityWeakened immunityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicrobiologySiphoviridae
The present invention relates to a Siphoviridae bacteriophage Str-SUP-2 (Accession number: KCTC 13515BP) isolated from nature and characterized by having the ability to kill Streptococcus suis and having the genome represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, and a method for preventing and treating diseases caused by Streptococcus suis using the composition containing the Siphoviridae bacteriophage Str-SUP-2 as an active ingredient.
Owner:INTRON BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Compositions and methods of use of ORF1358 from beta-hemolytic streptococcal strains
InactiveUS7914798B2Antibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideStreptococcus hemolyticus
The present invention relates to polynucleotides encoding Streptococcus group C and G polypeptides and their use in immunogenic compositions. The invention also relates to immunogenic compositions comprising polypeptides encoded by those polynucleotides. In addition, the invention relates to methods of inducing an immune response in mammals against beta hemolytic Streptococcus or beta hemolytic Streptococcus infection using immunogenic compositions of the Streptococcus group C and G polypeptides and polynucleotides.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Use of lactic acid bacteria for preparing fermented food products with increased natural sweetness
ActiveUS11044920B2Low in lactoseHigh sweetnessMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyProbiotic bacterium
The dairy industry today faces a problem of providing an alternative to adding sweeteners to fermented milk products in order to achieve the desired sweet taste without the added calories. Furthermore, it would be highly advantageous to establish a method for reducing lactose in fermented milk products to a level which is acceptable for lactose-intolerant consumers. The above problems have been solved by providing mutant Streptococcus thermophilus strains and mutant Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus strains that excrete glucose to the milk when the milk is inoculated and fermented with such Streptococcus thermophilus strains and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp, bulgaricus strains. Thus, the present invention relates to strains of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp, bulgaricus which secrete glucose to the milk substrate during fermentation, as well as to mixed cultures comprising the Streptococcus thermophilus strains and the Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp, bulgaricus strains, starter cultures comprising the strains and dairy products manufactured with the cultures. The present method also relates to use of the strains for decreasing the lactose content of a fermented food product and for boosting growth of the probiotic BB-12®.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Compositions and methods of use of orf-1358 from beta-hemolytic streptococcal strains
The present invention relates to polynucleotides encoding Streptococcus group C and G polypeptides and their use in immunogenic compositions. The invention also relates to immunogenic compositions comprising polypeptides encoded by those polynucleotides. In addition, the invention relates to methods of inducing an immune response in mammals against beta hemolytic Streptococcus or beta hemolytic Streptococcus infection using immunogenic compositions of the Streptococcus group C and G polypeptides and polynucleotides.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Replacement Therapy for Dental Caries
ActiveUS20150044146A1Reduce incidenceReduce severityAntibacterial agentsBiocideOral healthTooth caries
The invention provides recombinant Streptococcus mutans strains that can be used to improve oral health. An embodiment of the invention provides a method of reducing the incidence or severity of dental caries in a dental caries-susceptible host comprising administering orally to the host an isolated recombinant S. mutans strain of the invention in an amount effective for replacement of dental caries-causing S. mutans host strains in the oral cavity of the host. The isolated recombinant S. mutans strain 10 can be contained in a mouthwash, toothpaste, chewing gum, floss, chewable tablet, food, or beverage.
Owner:ORAGENICS +2
Streptococcus thermophilus and application thereof
InactiveCN111826304AInhibition of adhesionReduce thicknessBacteriaDigestive systemBiotechnologyOral disease
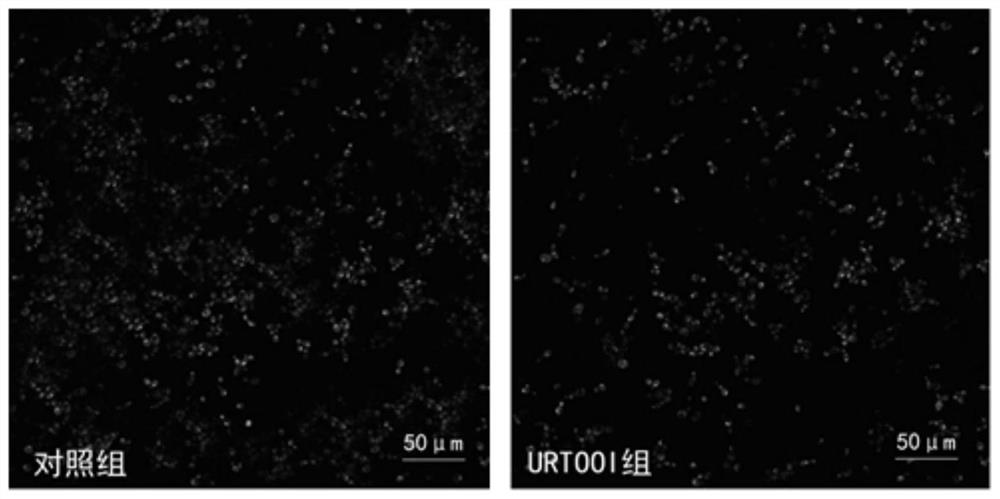
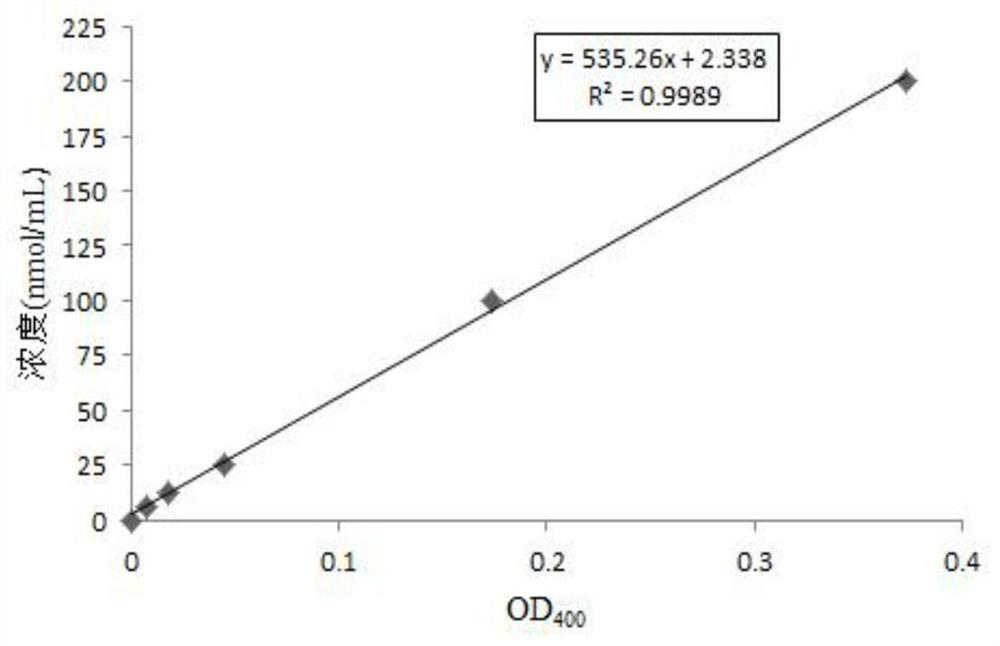
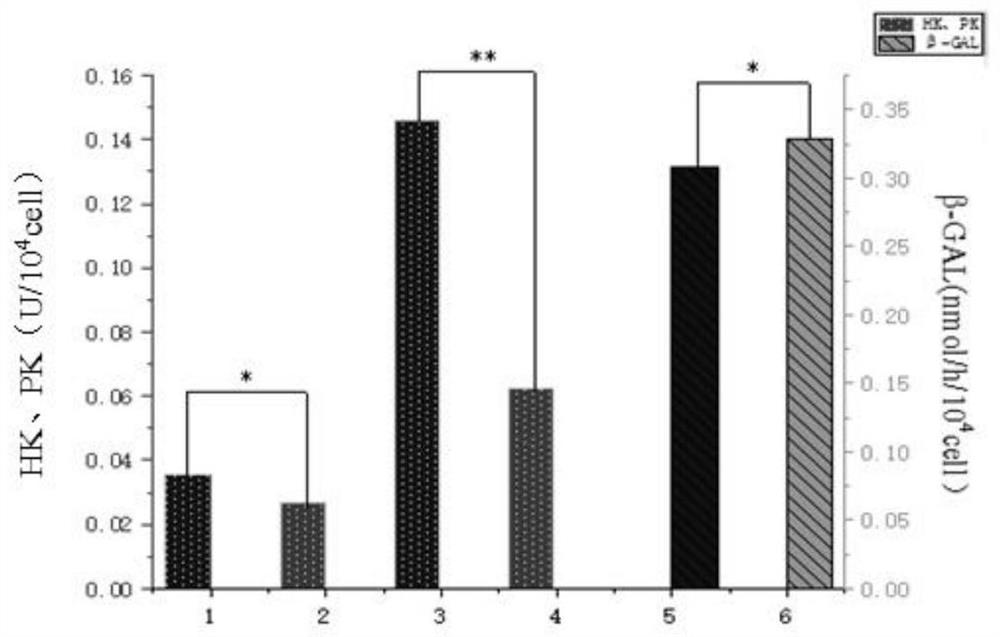
The invention relates to streptococcus thermophilus and application thereof. The streptococcus thermophilus is named as Streptococcus thermophilus URTOOI strain, wherein the preservation unit is ChinaGeneral Microbiological Culture Collection Center; the preservation time is April 13, 2020, the preservation number is CGMCC No.19575, and the address is No.3, Yard 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The streptococcus thermophilus strain has remarkable prevention and treatment effects on oral diseases, can remarkably inhibit adhesion of streptococcus gordonii or streptococcus mutans on hydroxyapatite, can remarkably reduce the thickness and density of a biological membrane formed by the streptococcus mutans on the hydroxyapatite, and can regulate oral flora. The strain is of great significance to prevention and control of oral health and oral diseases.
Owner:深圳迪健生物科技有限公司
Streptococcus thermophilus IMAU 80287Y strain and use thereof, and yoghourt and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113215053AExcellent fermentation performanceImprove water holding capacityMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyCow milking
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial fermentation, in particular to a streptococcus thermophilus IMAU80287Y strain and use thereof, and yoghourt and a preparation method thereof. The provided streptococcus thermophilus IMAU80287Y strain has the deposit number of CGMCC No.22260. The provided IMAU80287Y strain has a good fermentation performance and can metabolize galactose. The provided IMAU80287Y strain has improved metabolism capacity of lactose and galactose by 6.2% and 25% respectively in a cow milk fermentation period and a cow milk storage period compared with those of an original strain. The yoghourt obtained through fermentation by IMAU80287Y has water holding capacity obviously higher than that of original strain-fermented milk, and ha a good fermentation performance.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com