Patents
Literature
33 results about "TRNA synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
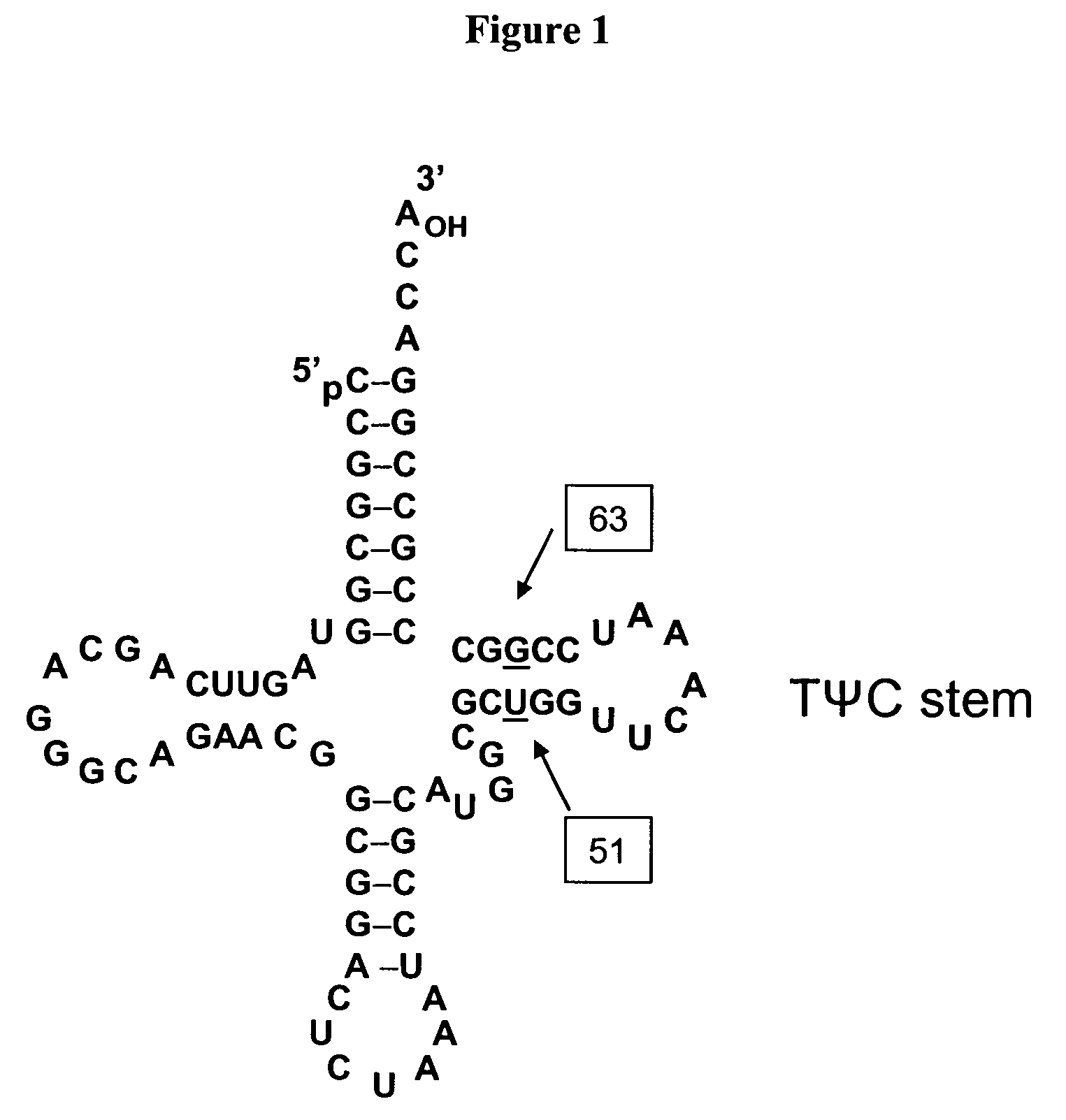
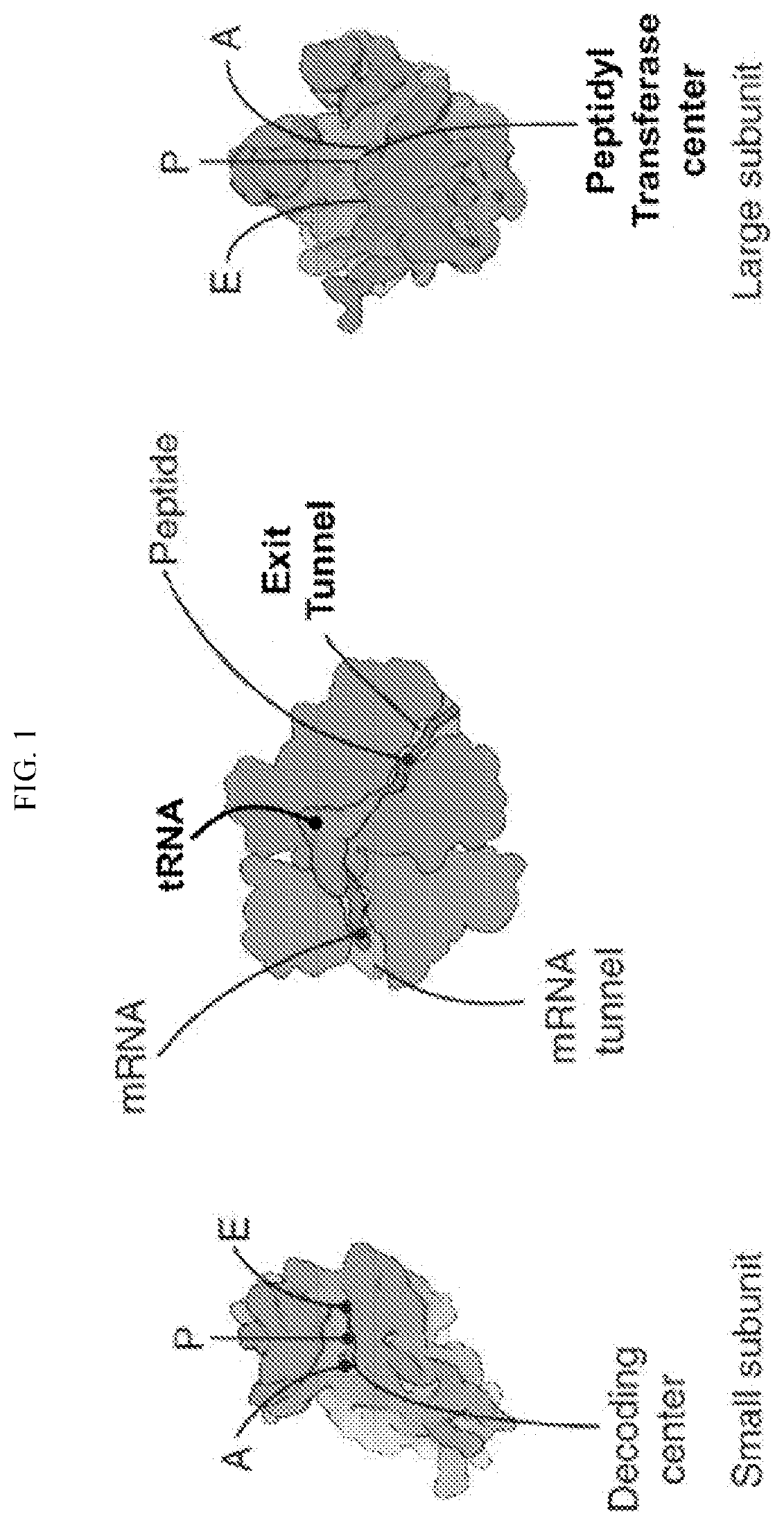
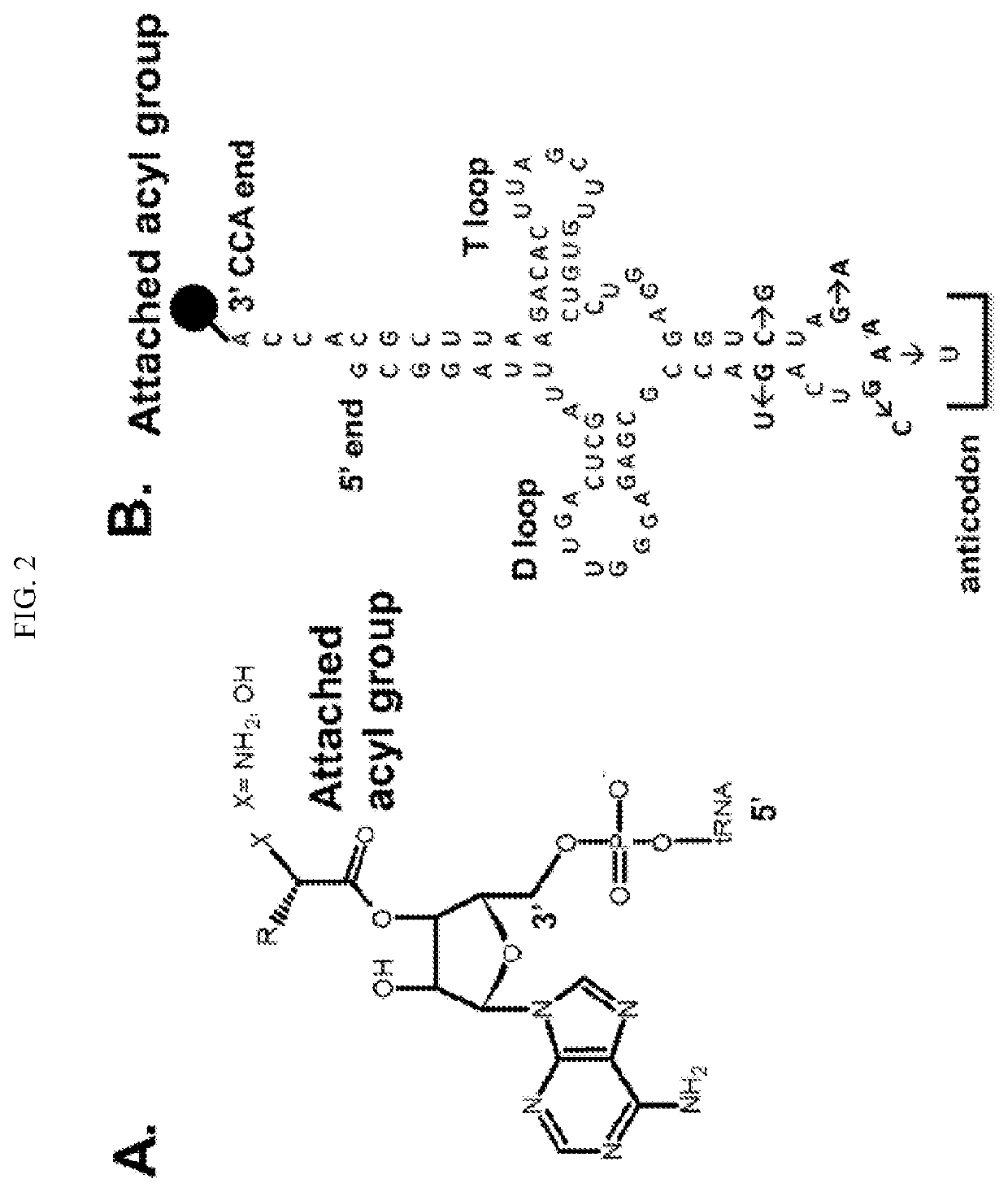
The interaction of tRNA and mRNA in protein synthesis. A transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length, that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins.
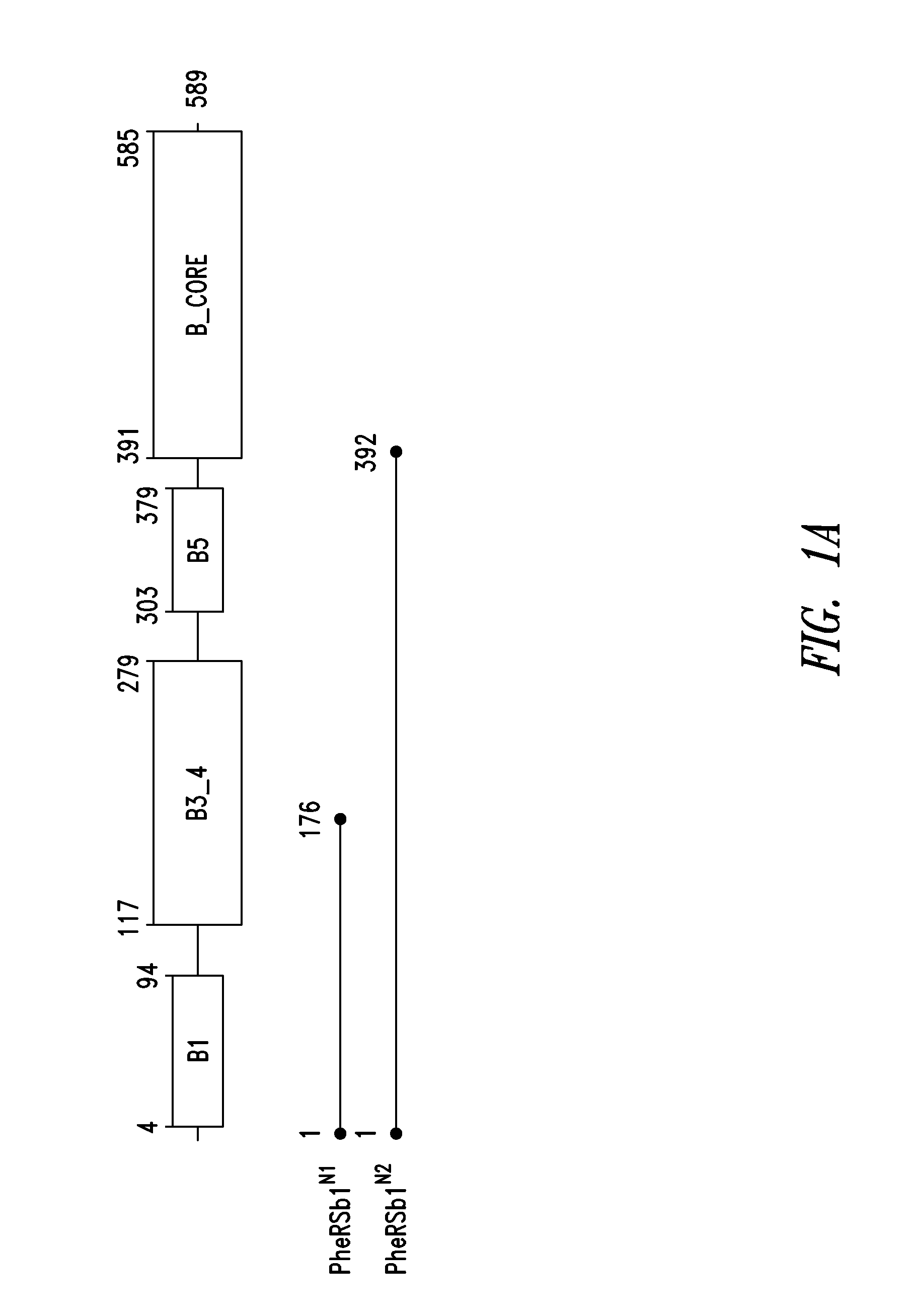
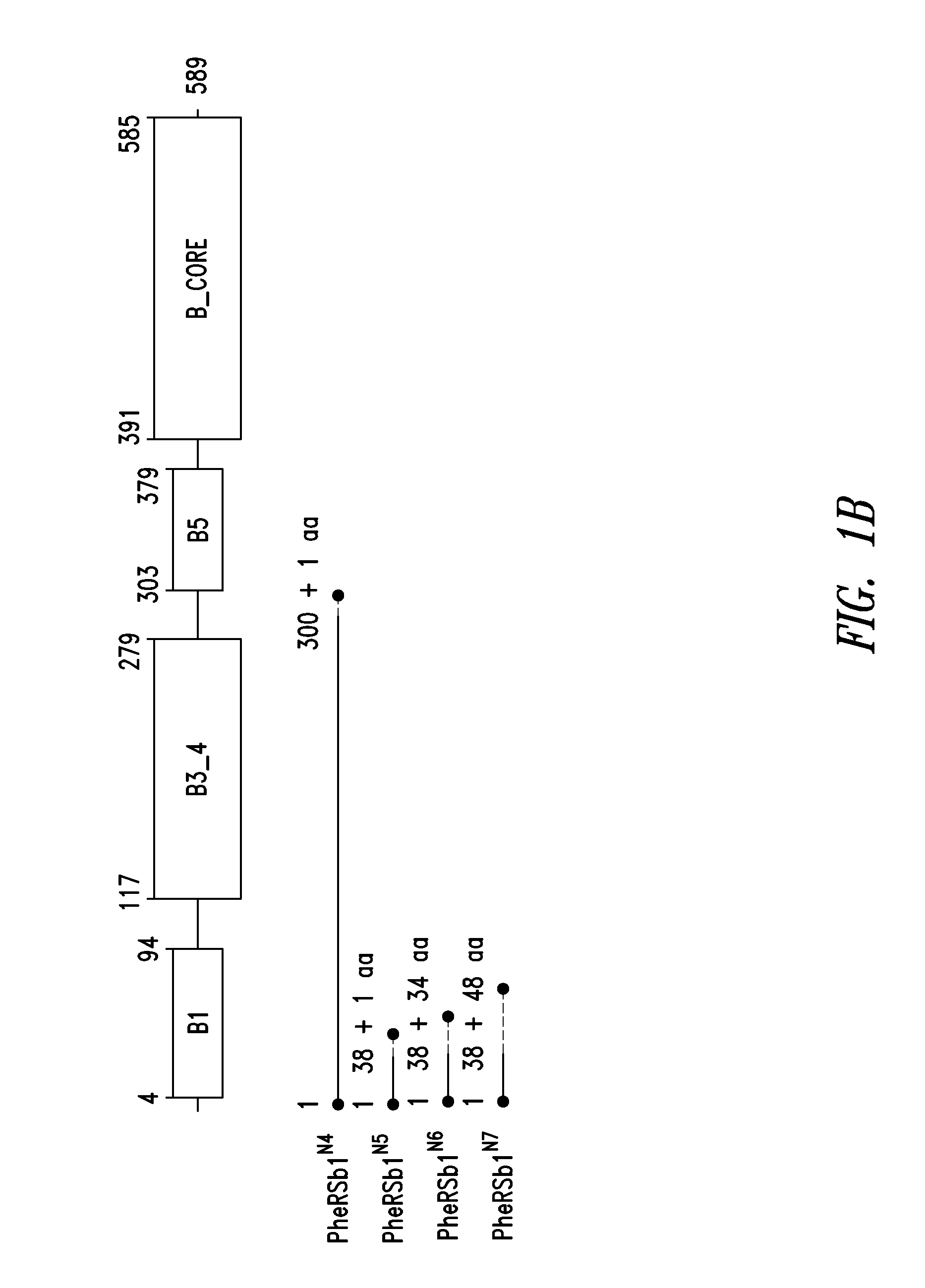
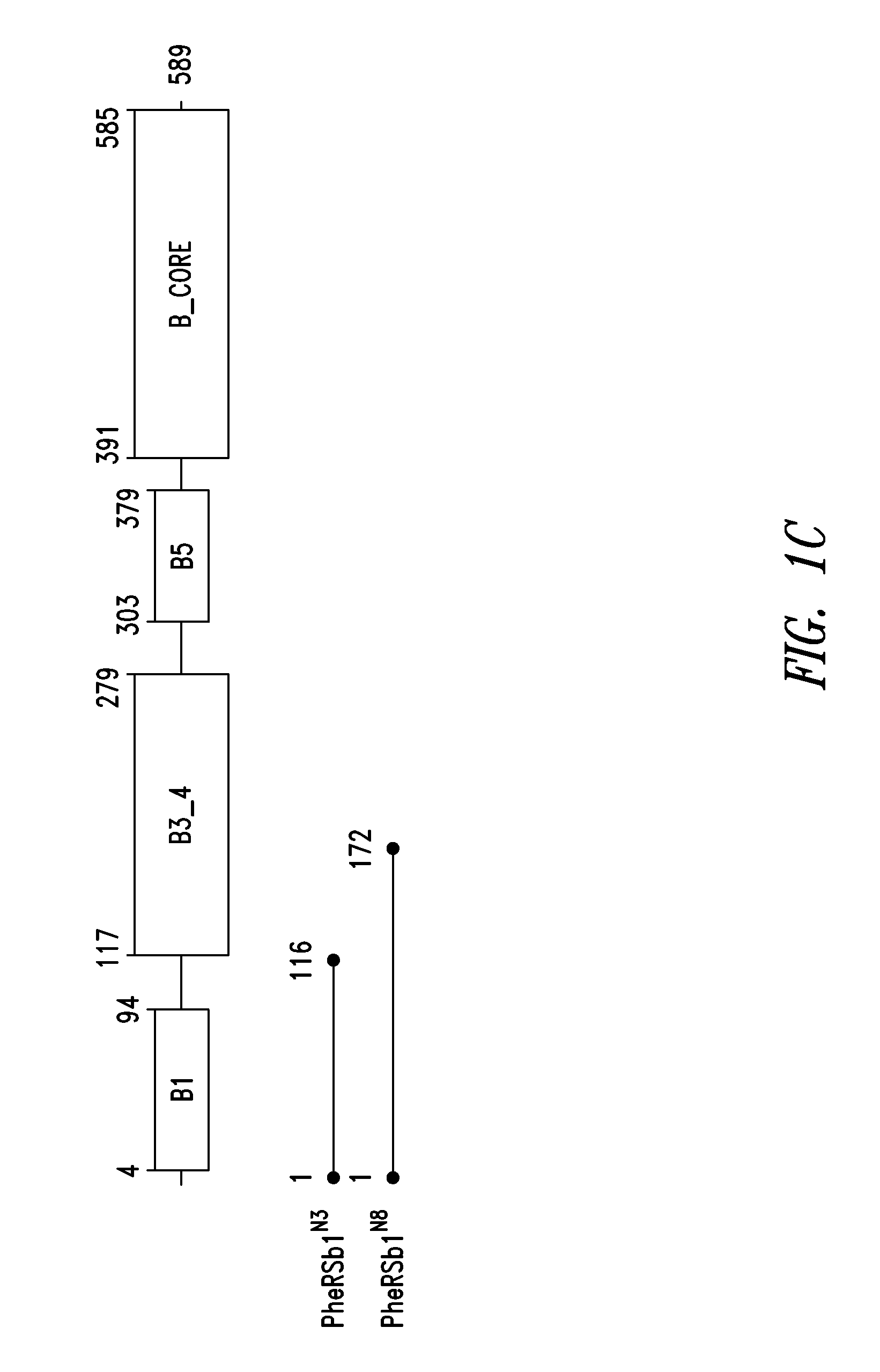
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of phenylalanyl-beta-trna synthetases
ActiveUS20130202575A1Altering abilityImprove purification effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticNucleotideNGAL Protein
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
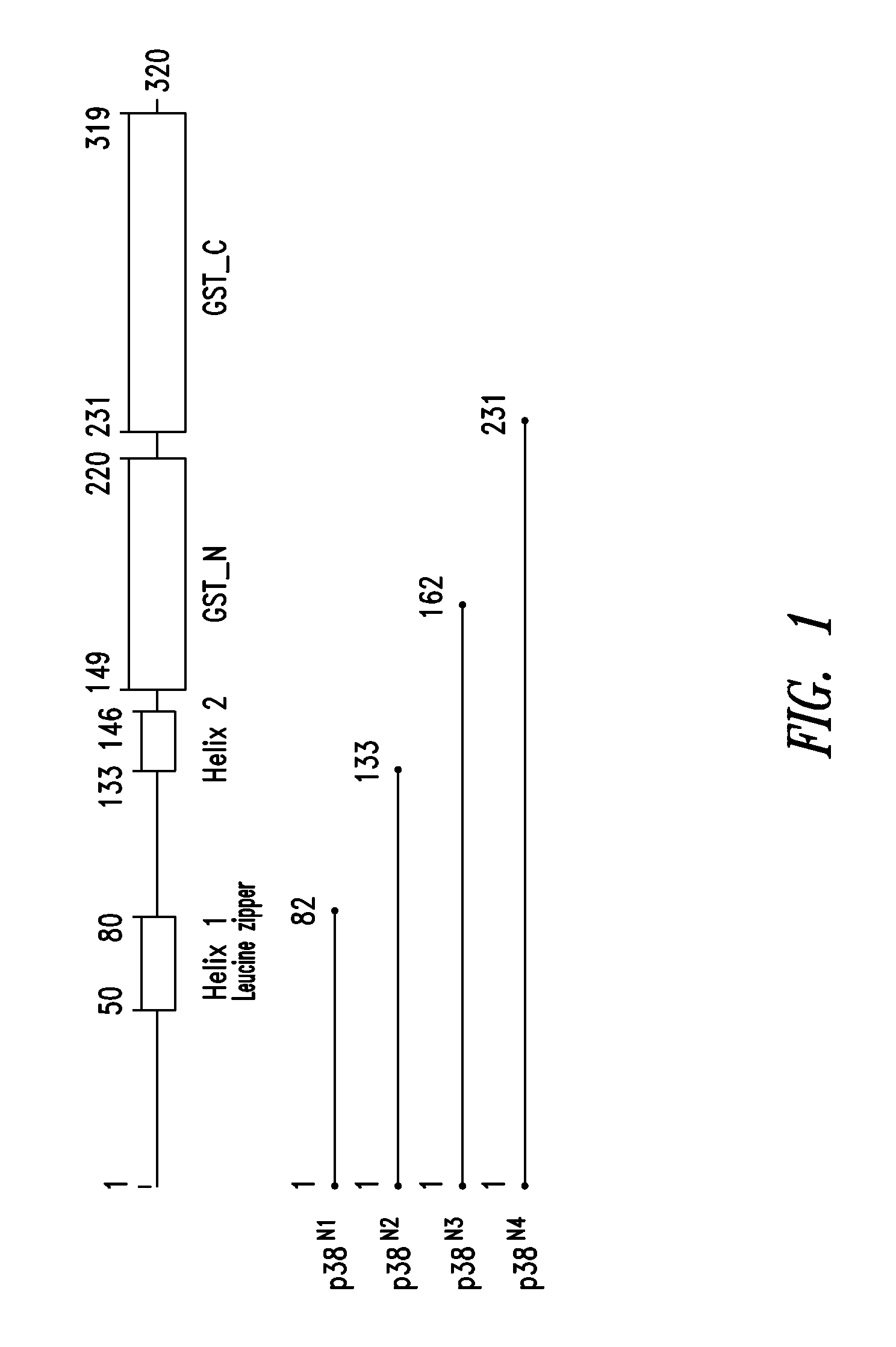
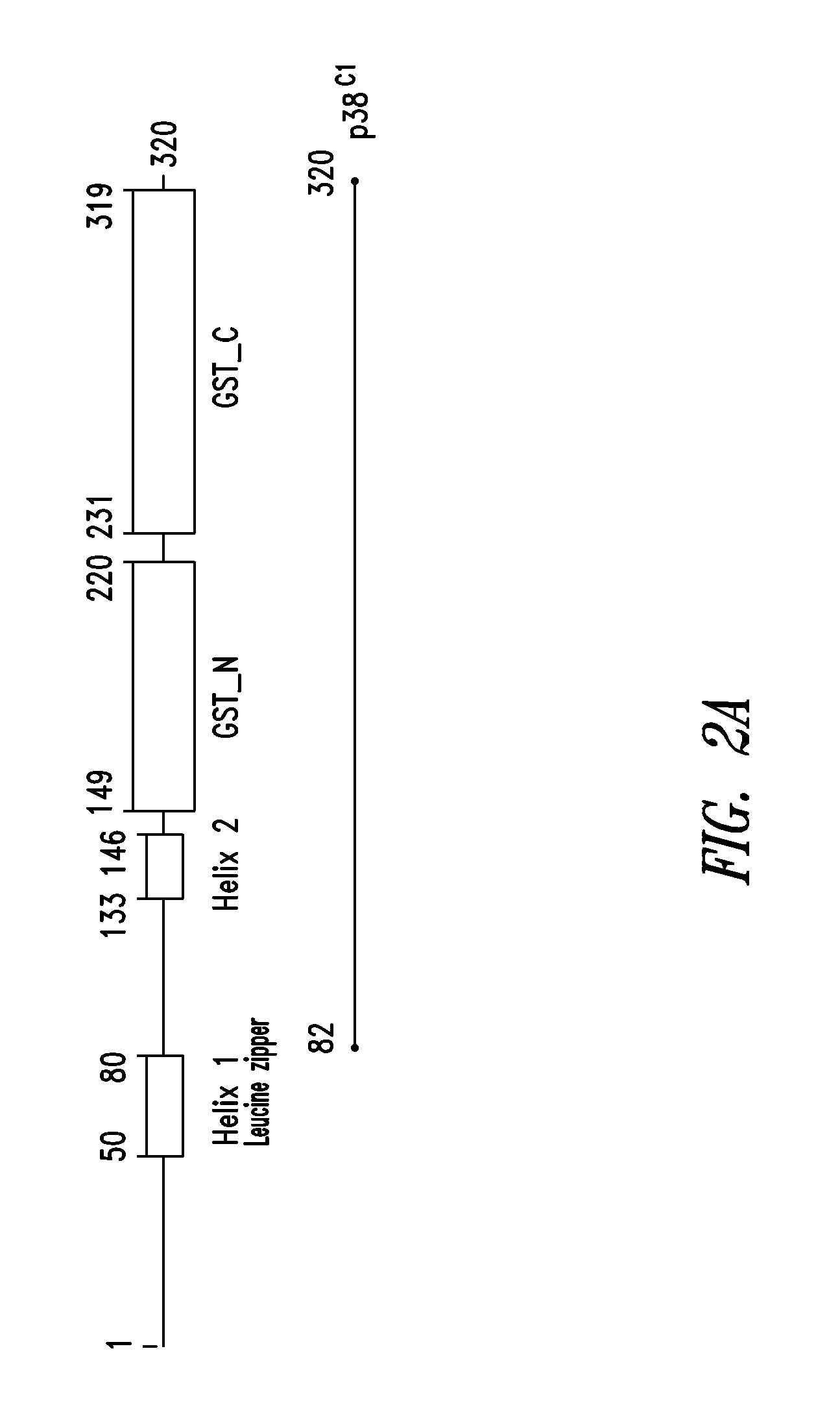
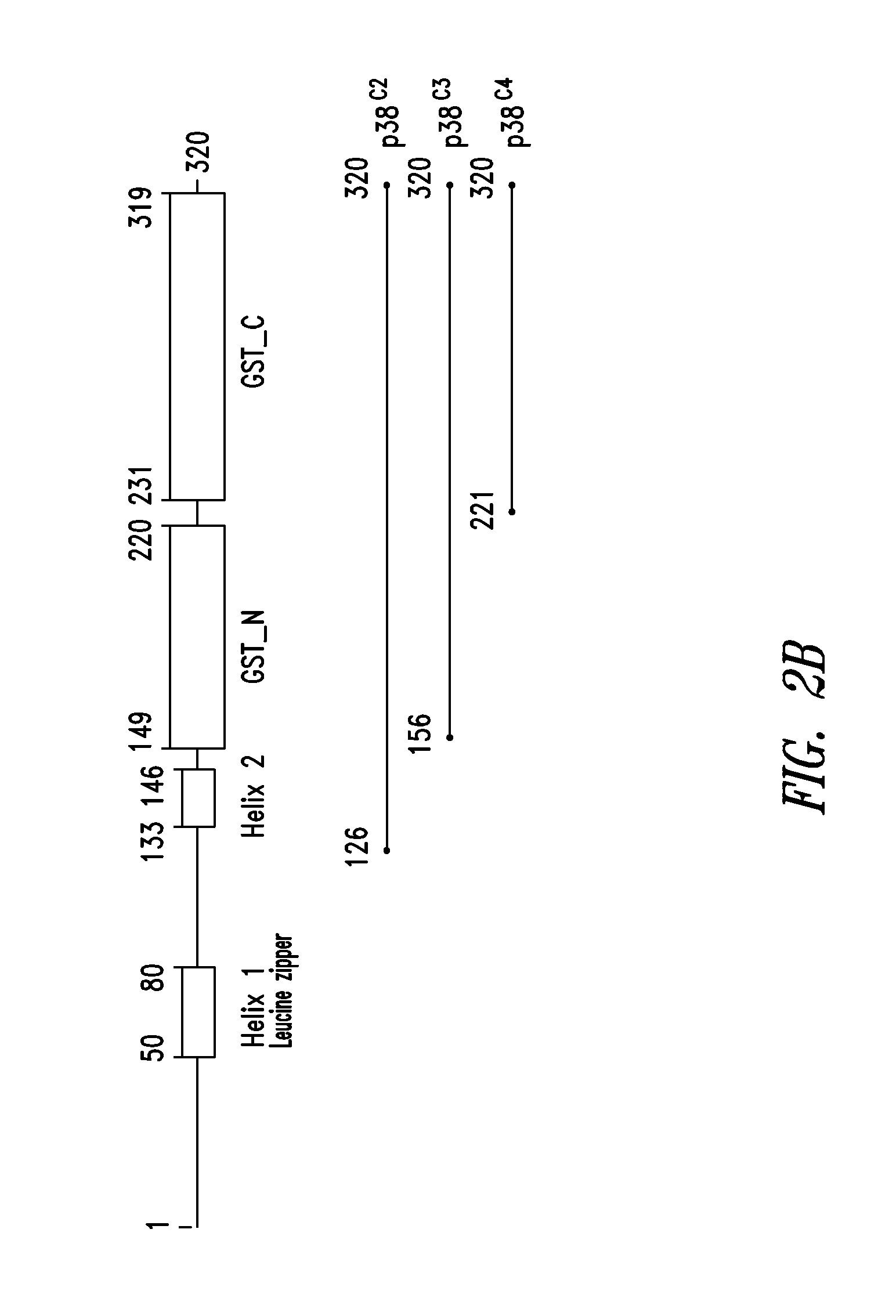
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of p38 multi-trna synthetase complex
ActiveUS20130230507A1Altering abilityImprove purification effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticNucleotideProtein Fragment
Owner:PANGU BIOPHARMA +1
Compositions of aminoacyl-TRNA synthetase and uses thereof
Compositions and methods of producing components of protein biosynthetic machinery that include orthogonal tRNA's, orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, and orthogonal pairs of tRNA's / synthetases are provided. Methods for identifying these orthogonal pairs are also provided along with methods of producing proteins using these orthogonal pairs.
Owner:AMBRX
Genetically Programmed Expression of Proteins
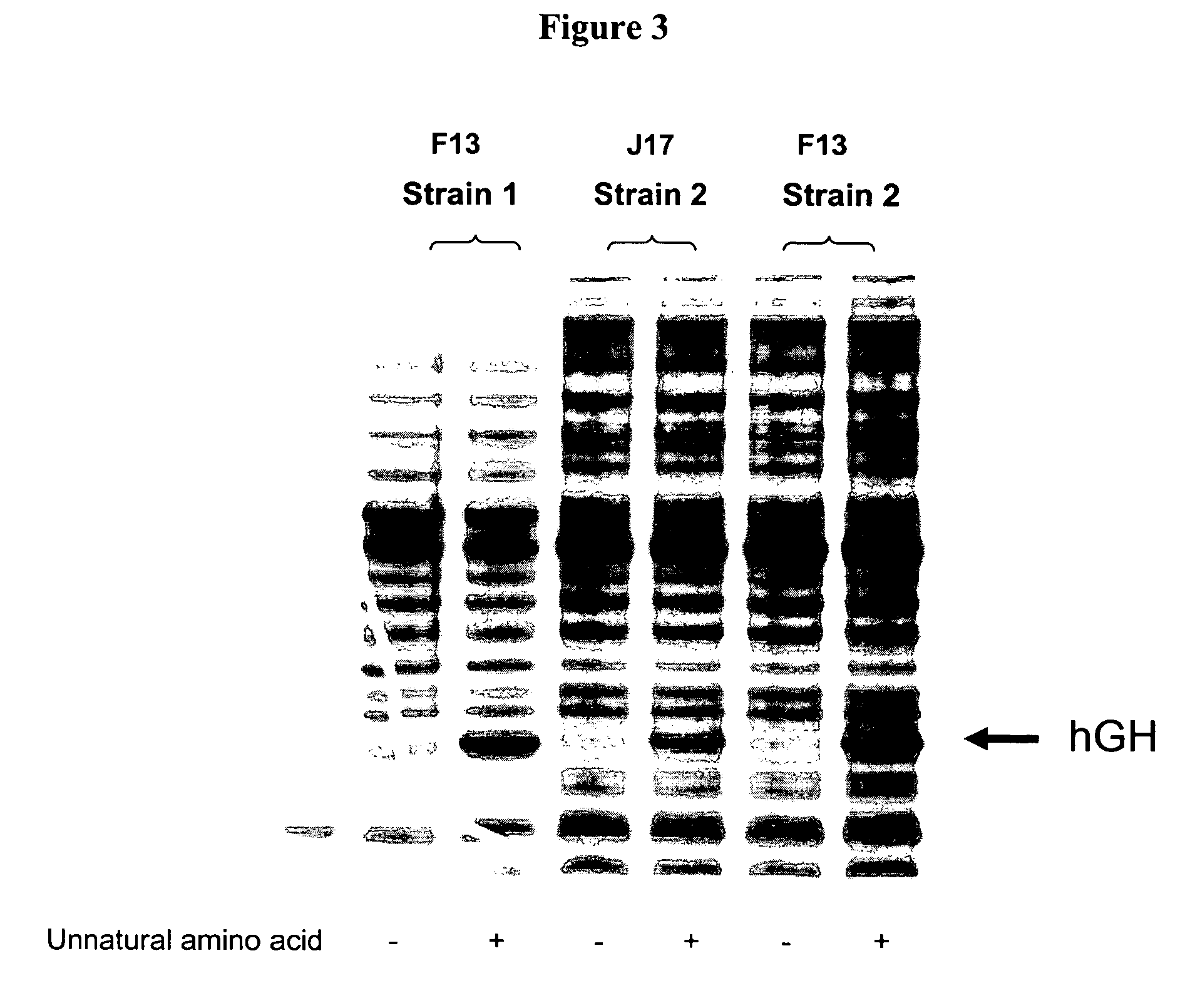
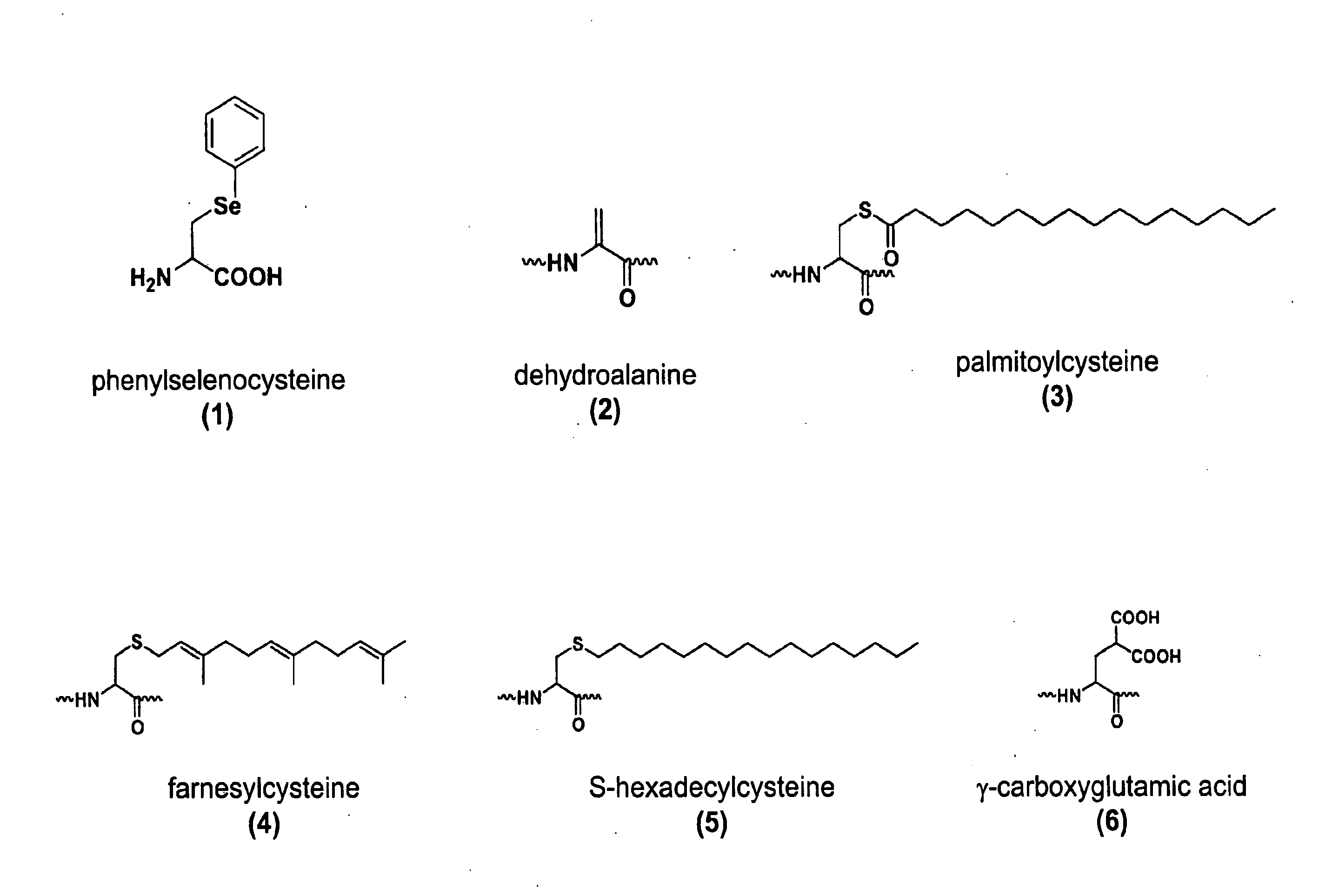
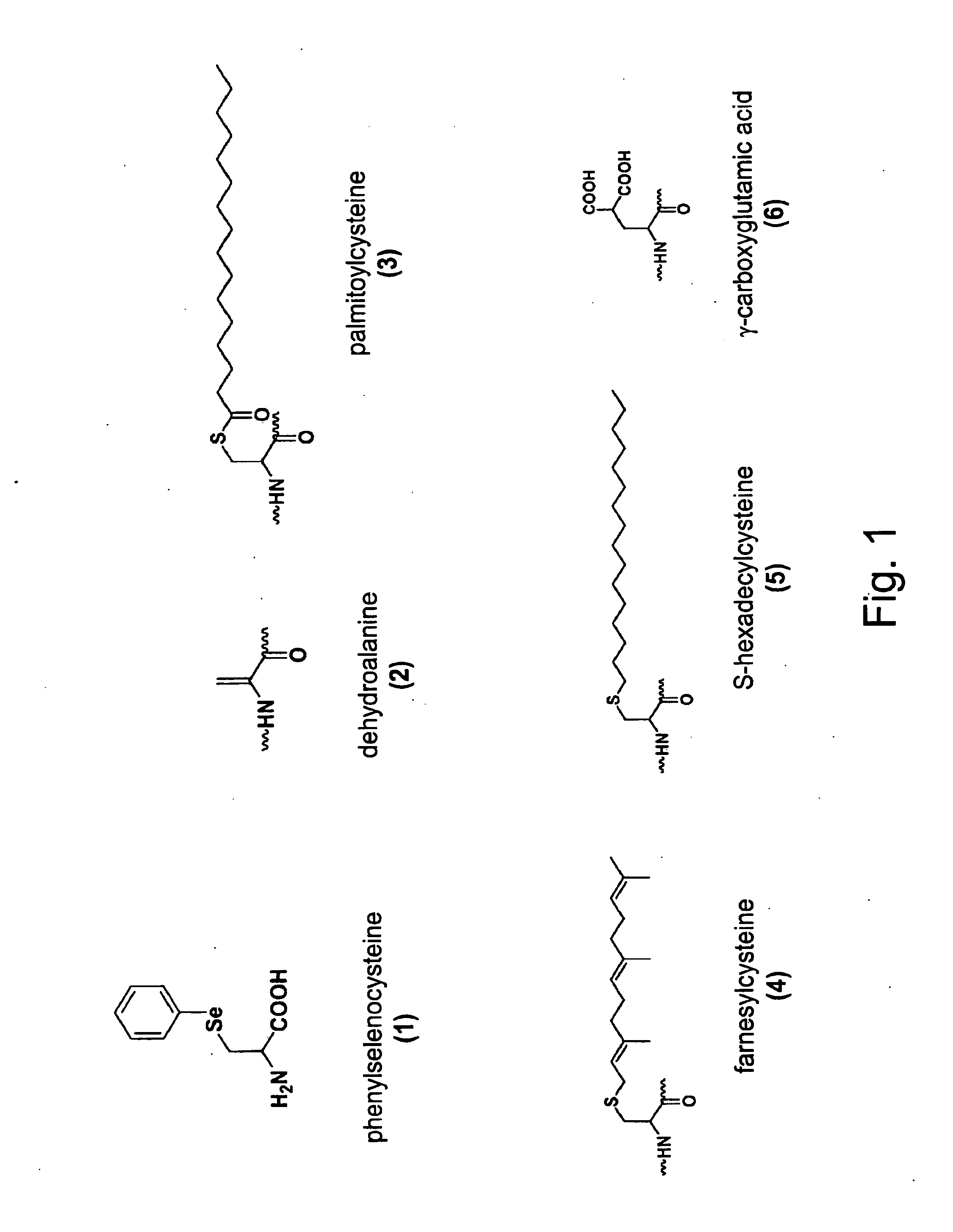
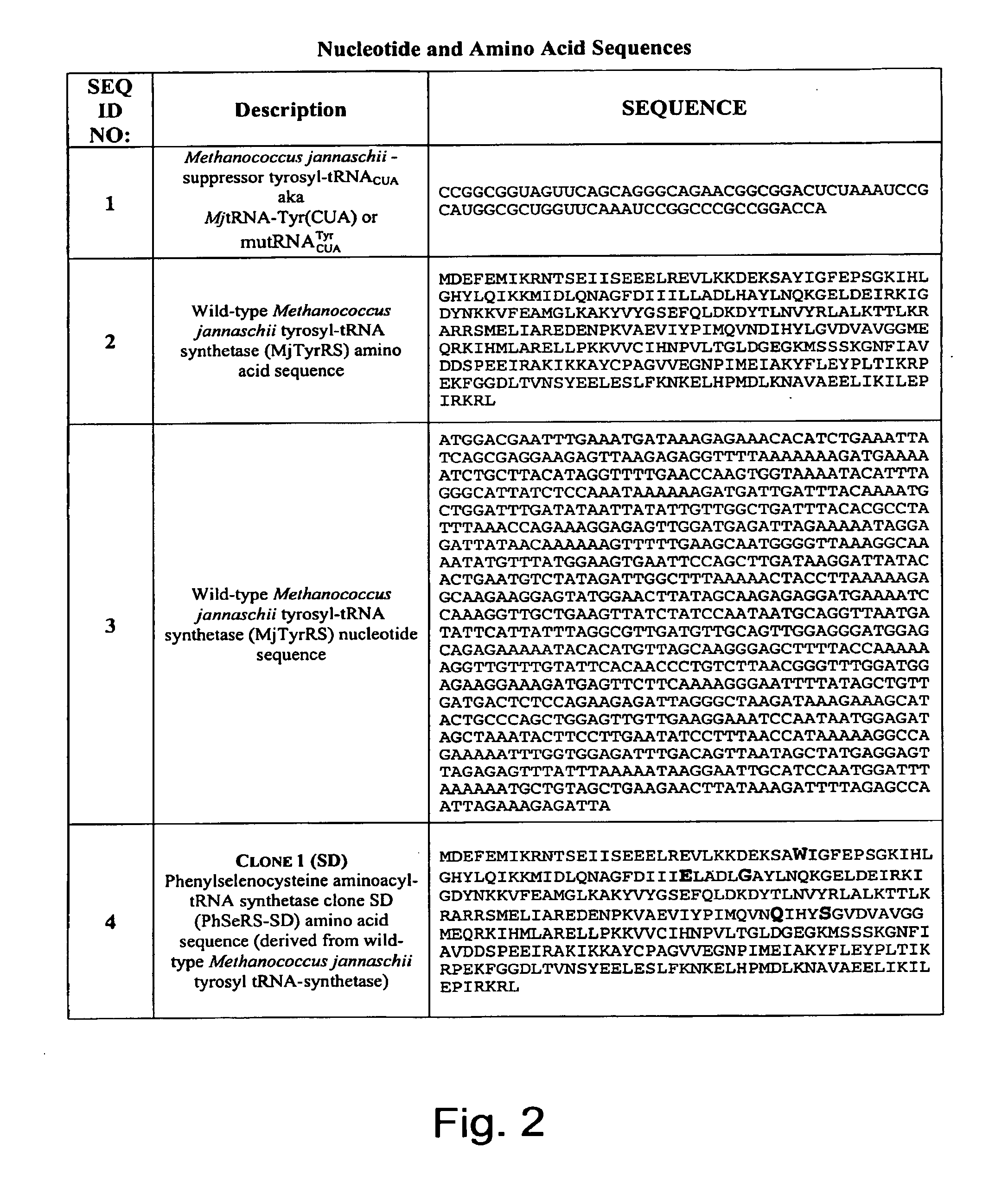
The invention relates to orthogonal pairs of tRNAs and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that can incorporate the unnatural amino acid phenylselenocysteine into proteins produced in eubacterial host cells such as E. coli. The invention provides, for example but not limited to, novel orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, polynucleotides encoding the novel synthetase molecules, methods for identifying and making the novel synthetases, methods for producing proteins containing the unnatural amino acid phenylselenocysteine and translation systems. The invention further provides methods for producing modified proteins (e.g., lipidated proteins) through targeted modification of the phenylselenocysteine residue in a protein.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
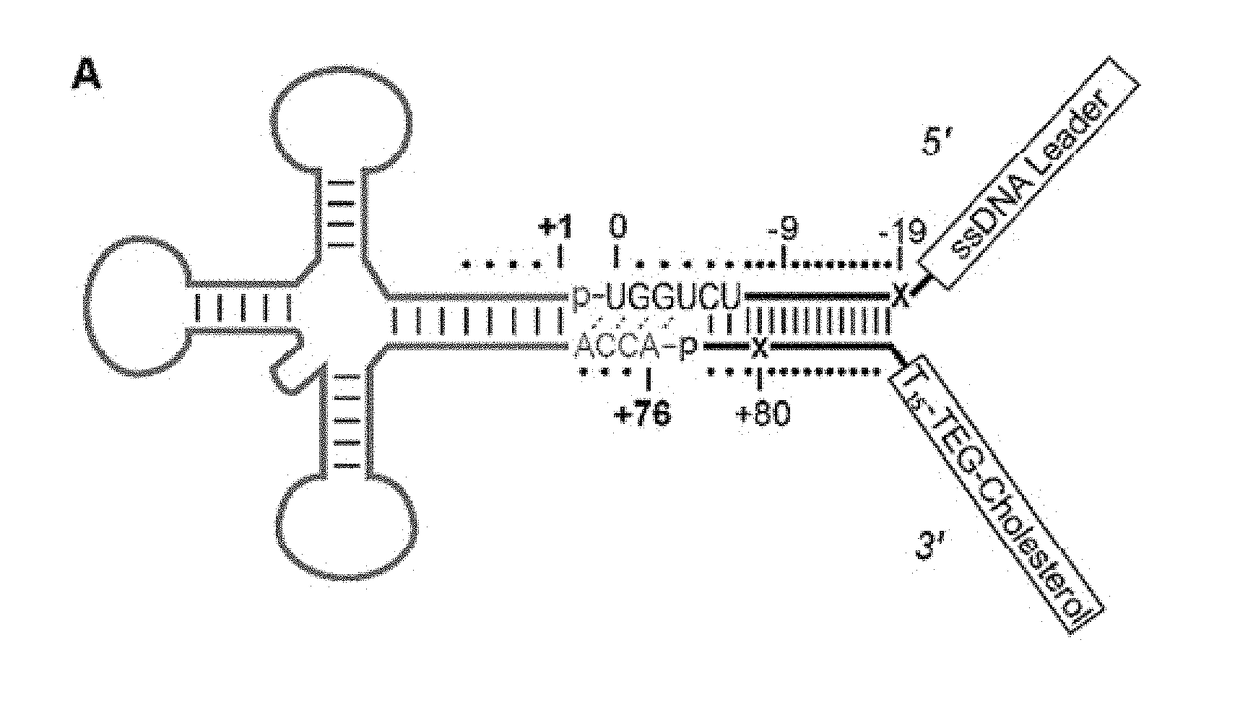
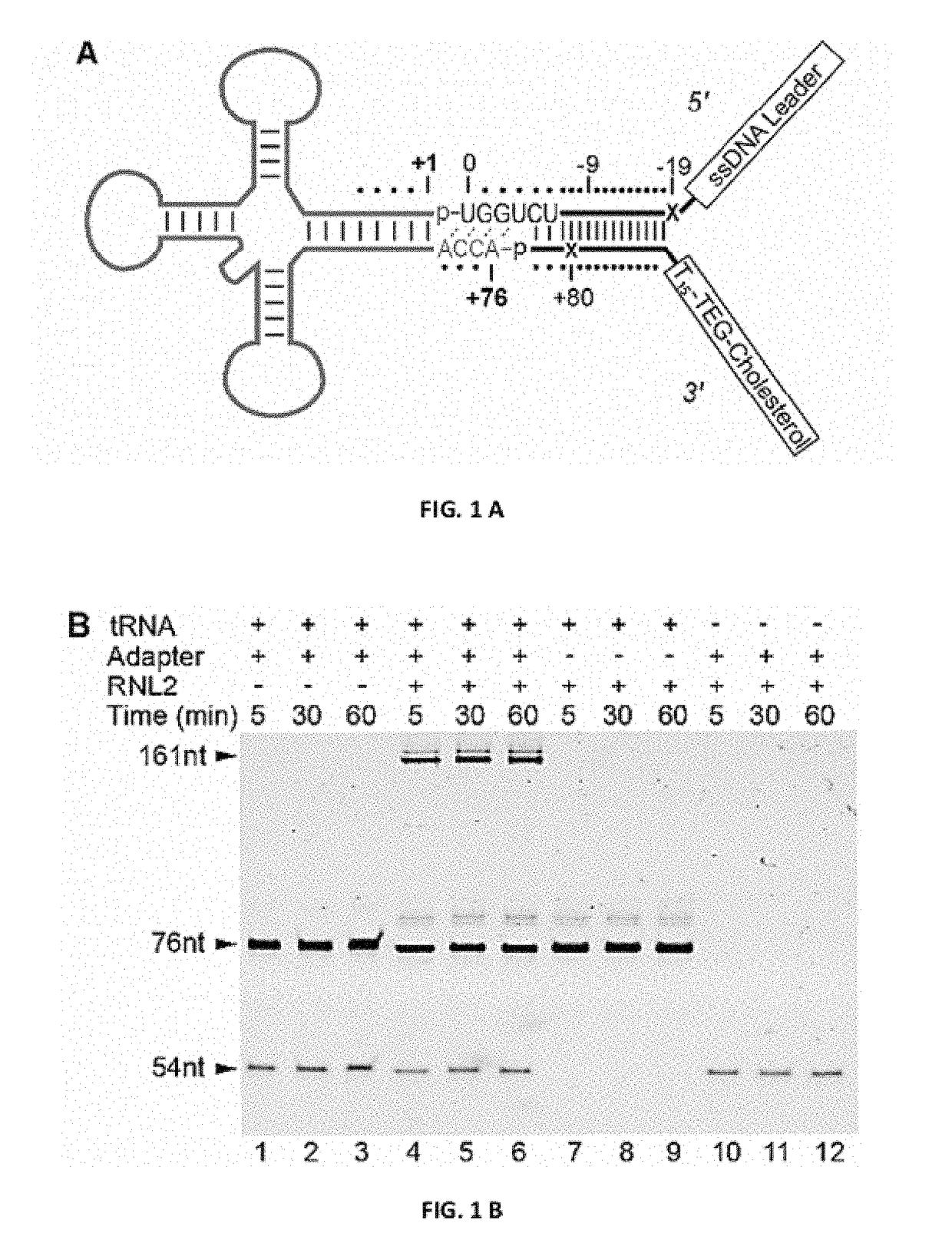
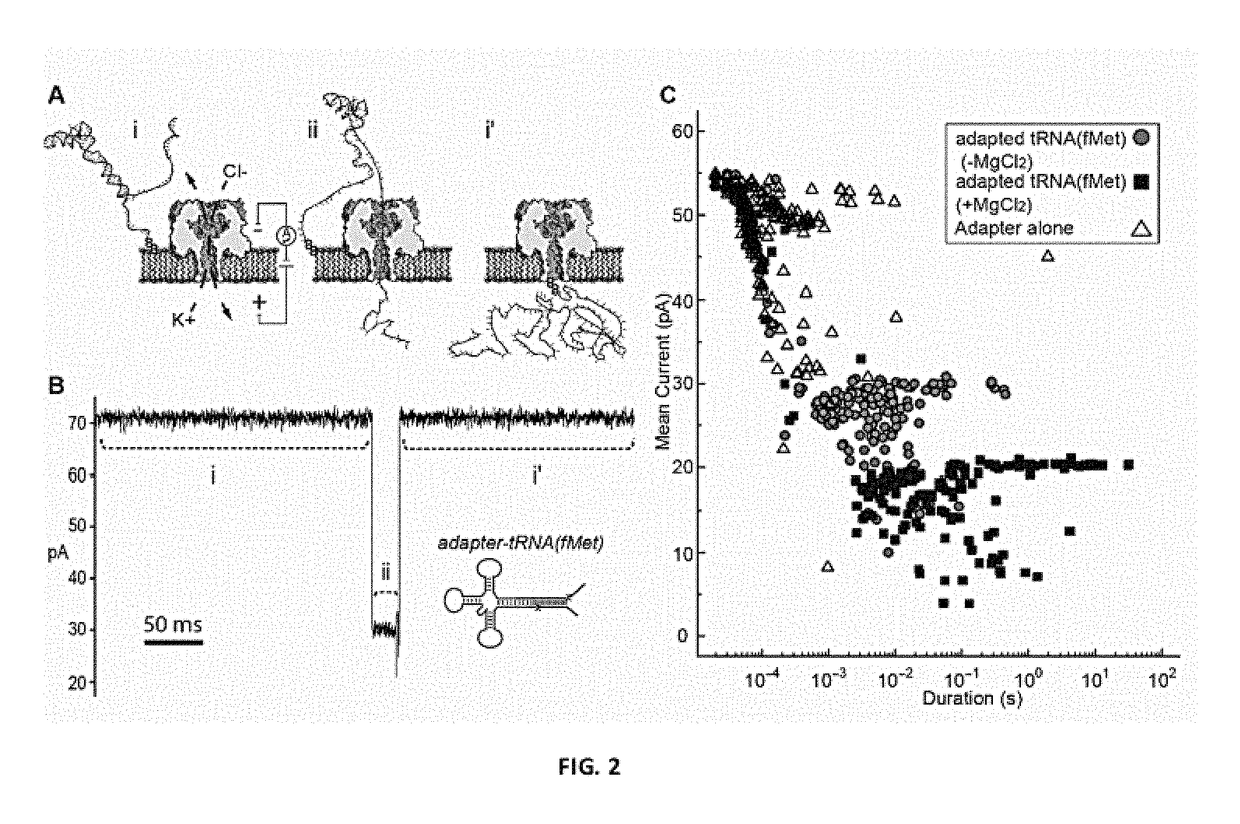
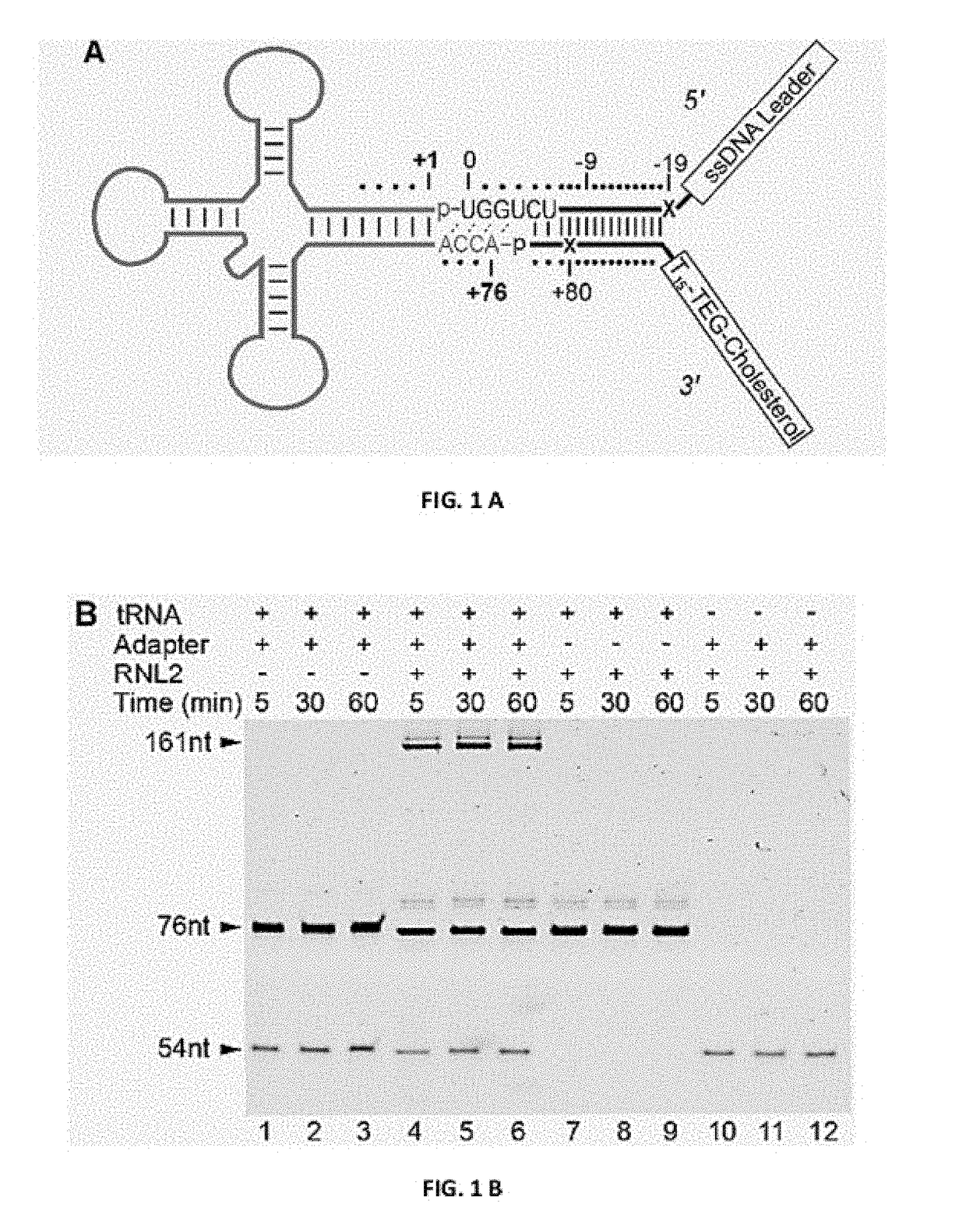
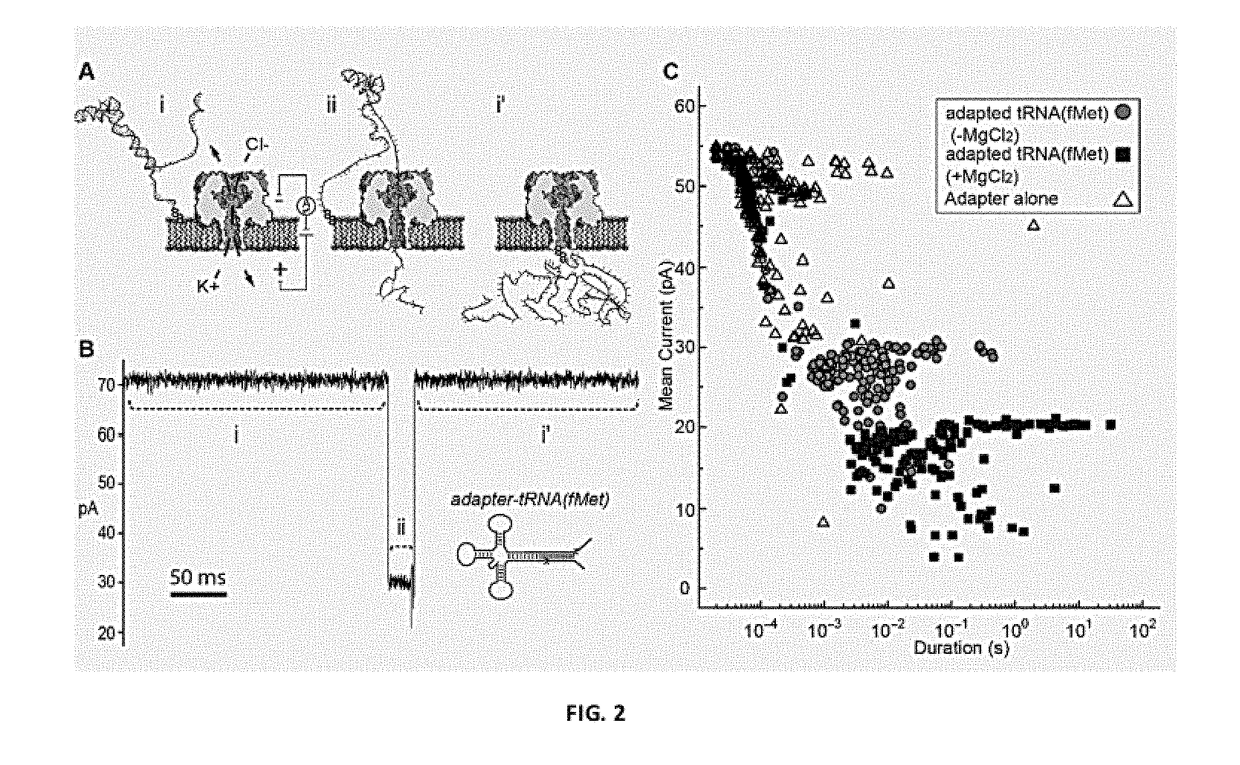
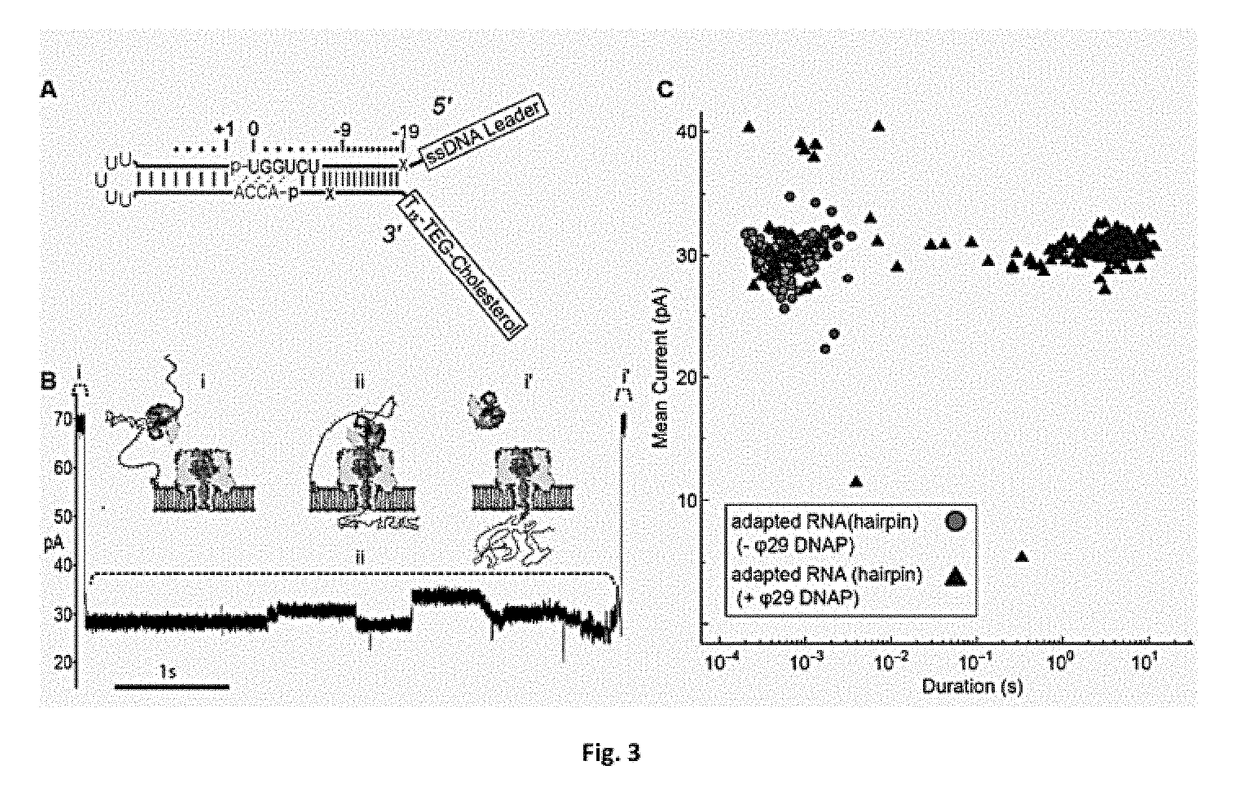
Molecular adapter for capture and manipulation of transfer RNA
ActiveUS10131944B2Easy to adaptSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCholesterolOligonucleotide
The invention also encompasses novel structures and methods comprising providing a molecular adapter for capture and manipulation of transfer RNA. The adaptor is bound to a tRNA molecule. The adaptor may be a cholesterol-linked DNA adapter oligonucleotide. The invention is useful in sequencing, identification, manipulation and modification of tRNA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
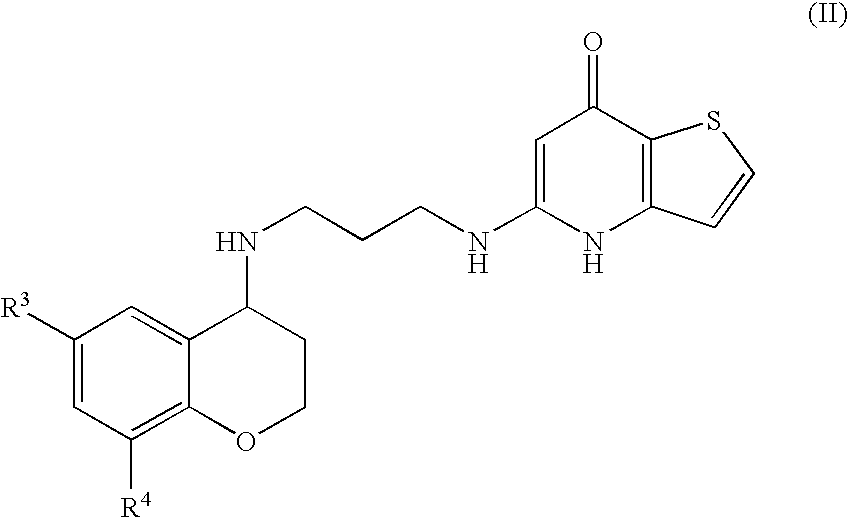
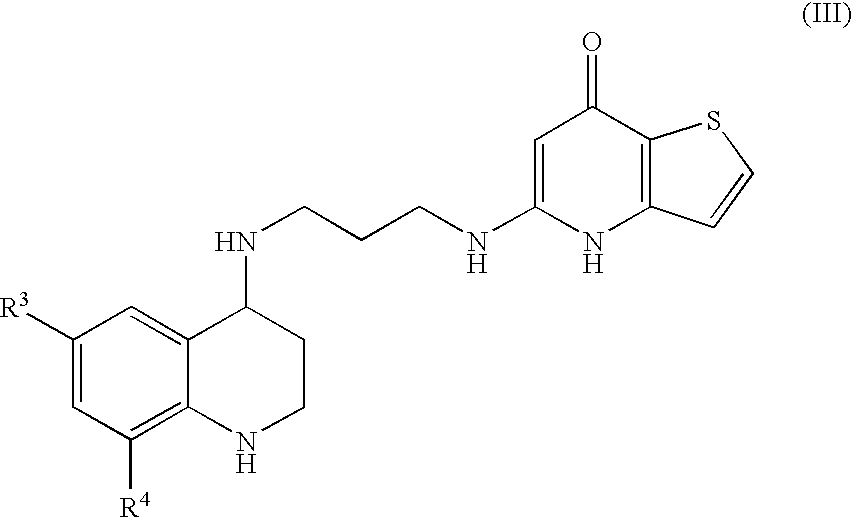
Substituted Thienopyridone Compounds With Antibacterial Activity
Novel bicyclic heteroaromatic compounds are provided that are inhibitors of bacterial methionyl tRNA synthetase (MetRS). Compounds of the invention generally have a left hand side chroman group or left hand side tetrahydroquinoline group and a right hand side thienopyridone group. Also disclosed are methods for their preparation and their use in therapy as antibacterial agents, particularly as anti-Clostridium difficile agents.
Owner:REPLIDYNE
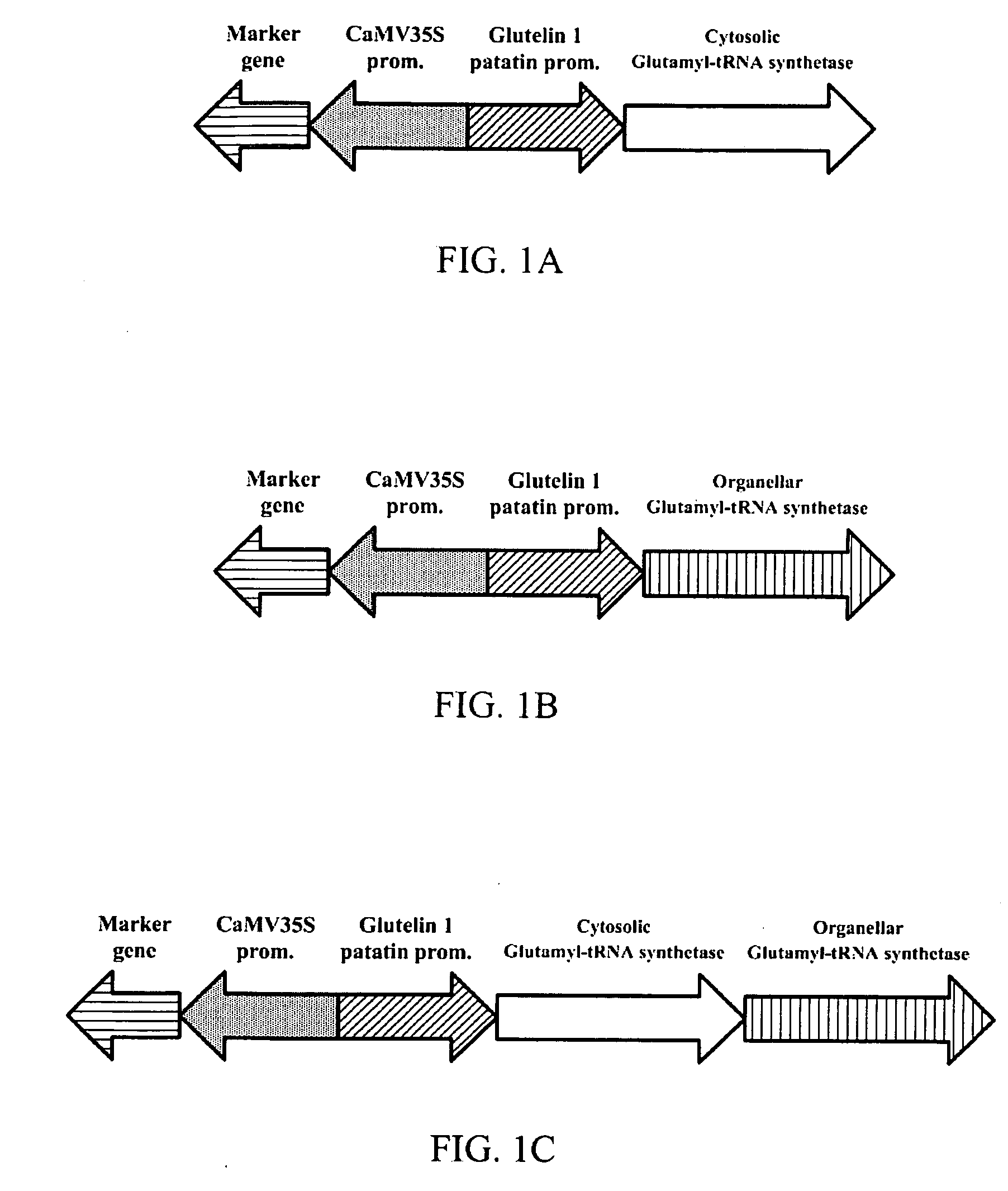
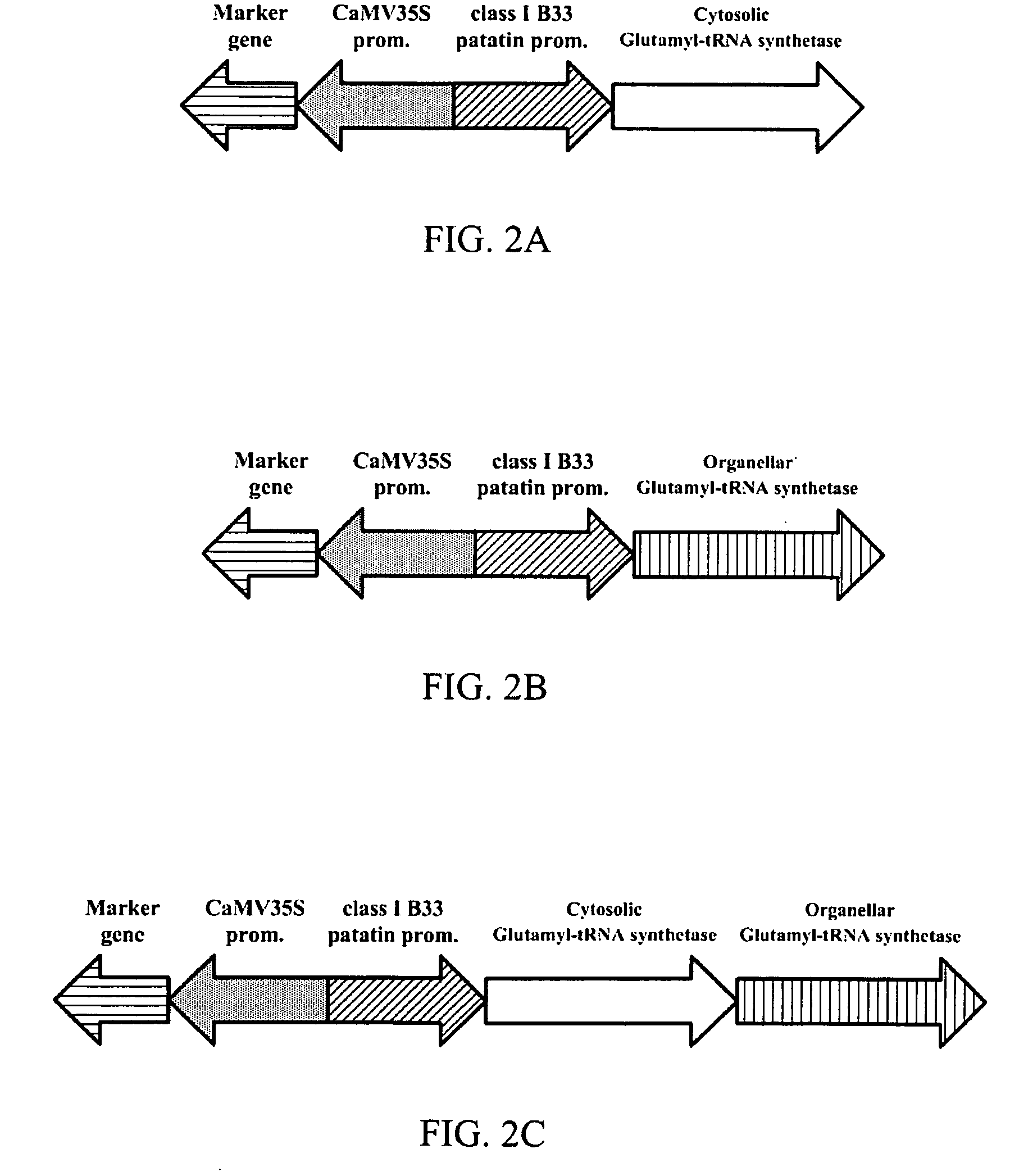
Transgenic plant expressing glutamyl-tRNA synthetase
InactiveUS20080307541A1Constant and high chlorophyll levelOther foreign material introduction processesLigasesDNA constructTransgene
The present invention provides a DNA construct which comprises glutamyl-tRNA synthetase. Additionally, transgenic plants and tissues for the expression of glutamyl-tRNA synthesis are also provided. Furthermore, the present invention also provides methods for utilizing the DNA construct to produce the transgenic plants and tissues.
Owner:HSIEH HSU LIANG
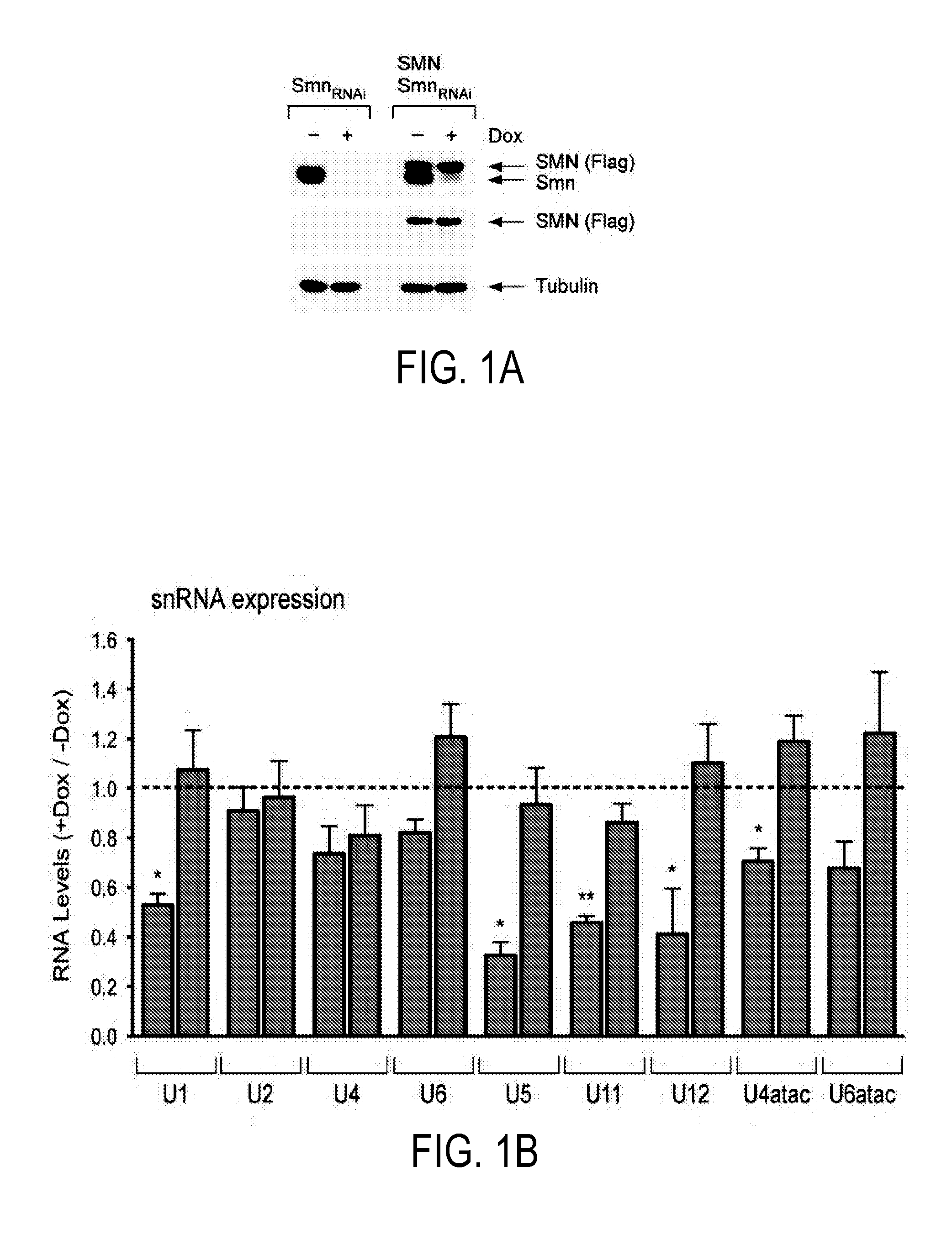
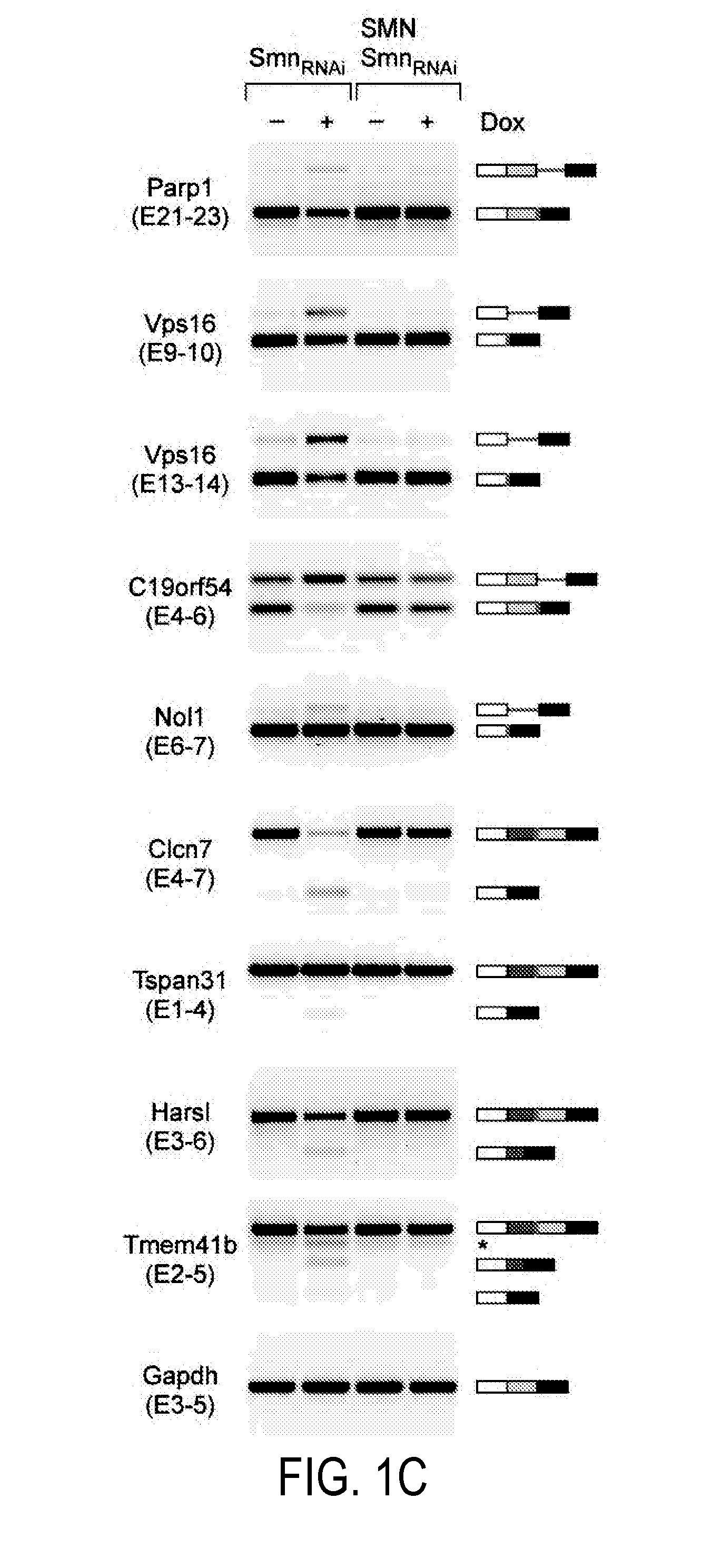
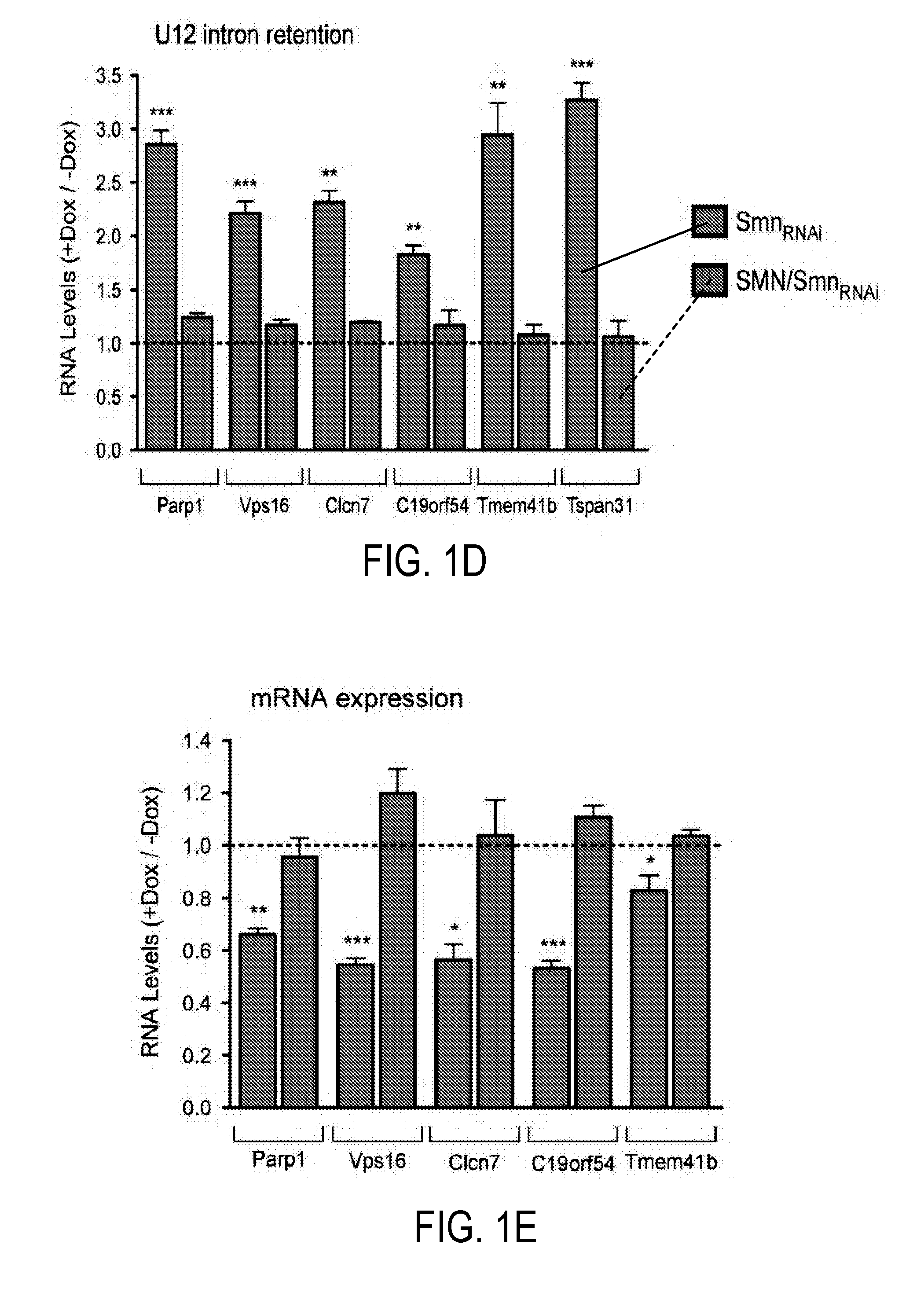
Diagnosis and Treatment of SMA and SMN Deficiency
The present invention provides for methods for diagnosing and treating a motor neuron disease. More specifically, the present invention offers new methods for diagnosing and treating SMA or SMN deficiencies and monitoring treatment. It is possible to identify a subject having a symptom of the disease, and then administer to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of one or more proteins or a gene delivery vehicle or pharmaceutical composition comprising one or more genes selected from the group consisting of Transmembrane protein 41B (Stasimon), Chromosome 19 open reading frame 54 (Rashomon), Tetraspanin 31, Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 1, Histidyl-tRNA synthetase-like, Chloride channel 7, and Nucleolar protein 1.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of phenylalanyl-alpha-tRNA synthetases
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
Genetically expanded cell free protein synthesis systems, methods and kits
InactiveUS20170292139A1Convenience to mergeImprove translationLigasesFermentationEscherichia coliBiological body
This invention relates to methods of producing a rare amino acid- or non-natural amino acid-containing protein in a cell free protein synthesis system and kits for use in and for accomplishing same. Specifically, the methods comprise the steps of expressing at least one orthogonal suppressor tRNA (o-tRNA) / aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS) pair or derivatives thereof specific for incorporation of a rare amino acid- or non-natural amino acid in an E. coli organism; preparing a lysate of said E. coli organism expressing said orthogonal suppressor tRNA (o-tRNA) / aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS) pair; and contacting said lysate with a template DNA containing a mutant gene in which at least one amino acid codon at a given site of the protein-encoding gene has been mutated into an amber or ochre mutation and further providing a cognate rare amino acid or non-natural amino acid and other factors necessary for protein synthesis; wherein protein synthesis occurs following said contact to produce a protein containing said at least one rare amino acid or said non-natural amino acid. Kits for use are described, as well.
Owner:B G NEGEV TECH & APPL LTD
Compositions and methods for treatment of neovascular diseases
InactiveUS20060003933A1Good synergistic effectBiocideSenses disorderAbnormal tissue growthTryptophan
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treating neovascular diseases, such as a retinal neovascular diseases and tumors, by administering to a patient suffering from a neovascular disease or tumor a vascular development inhibiting amount of a combination of the angiogenesis suppressing drugs comprising an angiostatic fragment of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (TrpRS) and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling inhibitor and an integrin signaling inhibitor. Compositions for use in the methods include an admixture of an angiostatic fragment of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (TrpRS) and at least one of a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling inhibitor and an integrin signaling inhibitor, together with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method for production of protein having non-natural type amino acid integrated therein
This invention provides a method for producing proteins into which non-natural amino acids have been incorporated at desired positions involving the use of either prokaryote-derived or eukaryote-type aaRS* and prokaryotic cells or eukaryote-type as host cells, the method comprising steps of: (a) introducing genes encoding prokaryote-derived aminoacyl tRNA synthetase mutants having enhanced specificity to non-natural amino acids similar to given natural amino acids (compared with specificity to the natural amino acids) and tRNA genes for non-natural amino acids capable of binding to the non-natural amino acids in the presence of the prokaryote-derived aminoacyl tRNA synthetase mutants into prokaryotic cells that express genes encoding eukaryote-type aminoacyl tRNA synthetase having specificity to the given natural amino acids and tRNA genes capable of binding to the natural amino acids in the presence of eukaryote-type aminoacyl tRNA synthetase; and (b) knocking out genes encoding aminoacyl tRNA synthetase having specificity to the natural amino acids, which are inherent in the prokaryotic cells, and inherent tRNA genes capable of binding to the natural amino acids in the presence of the inherent aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.
Owner:RIKEN
Application of T3 DNA ligase and T4 RNA ligase 2 in detection of N6 methyladenine
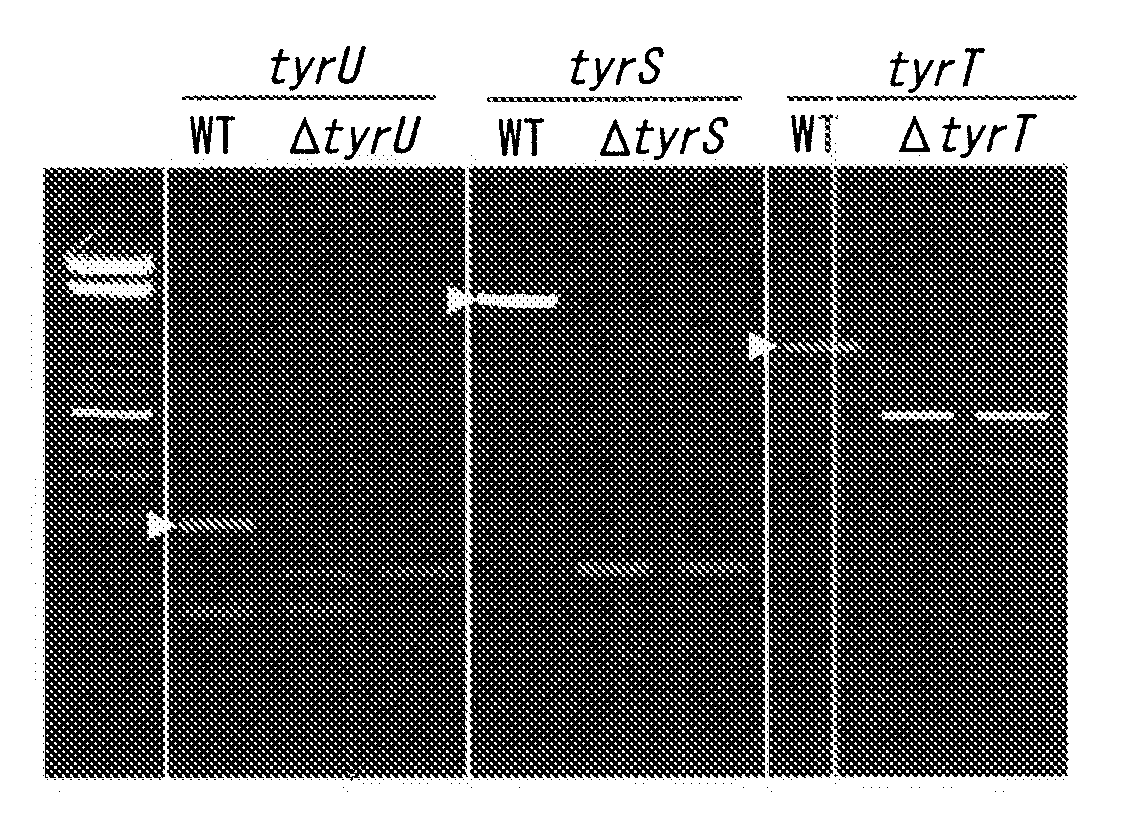
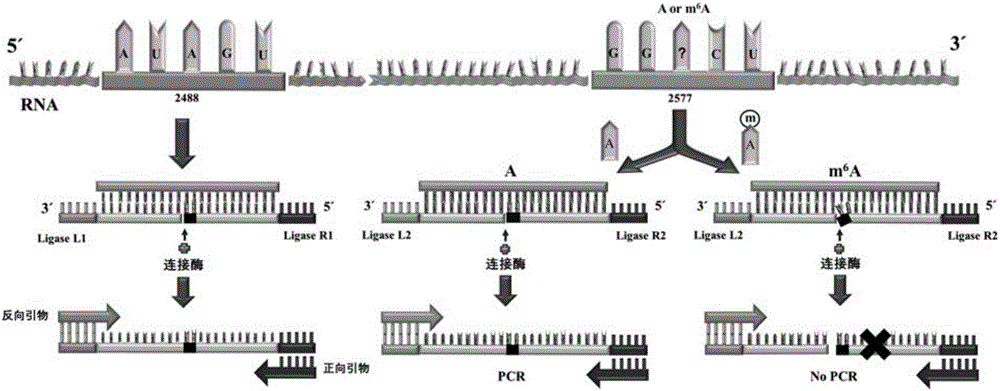
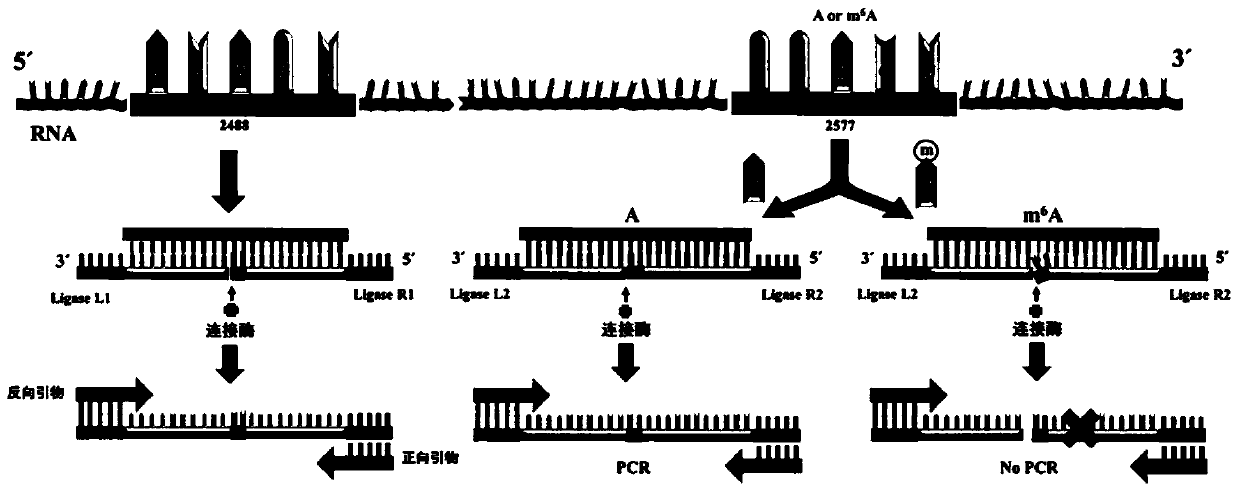
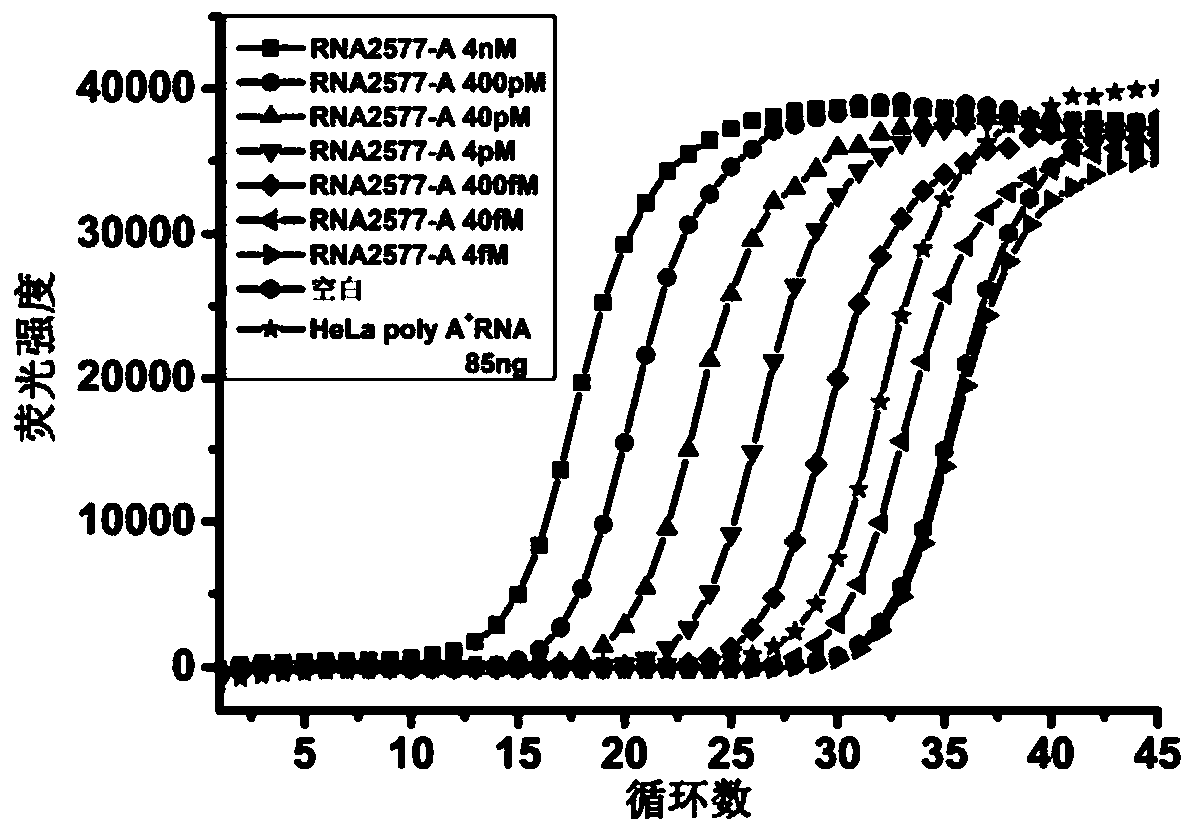
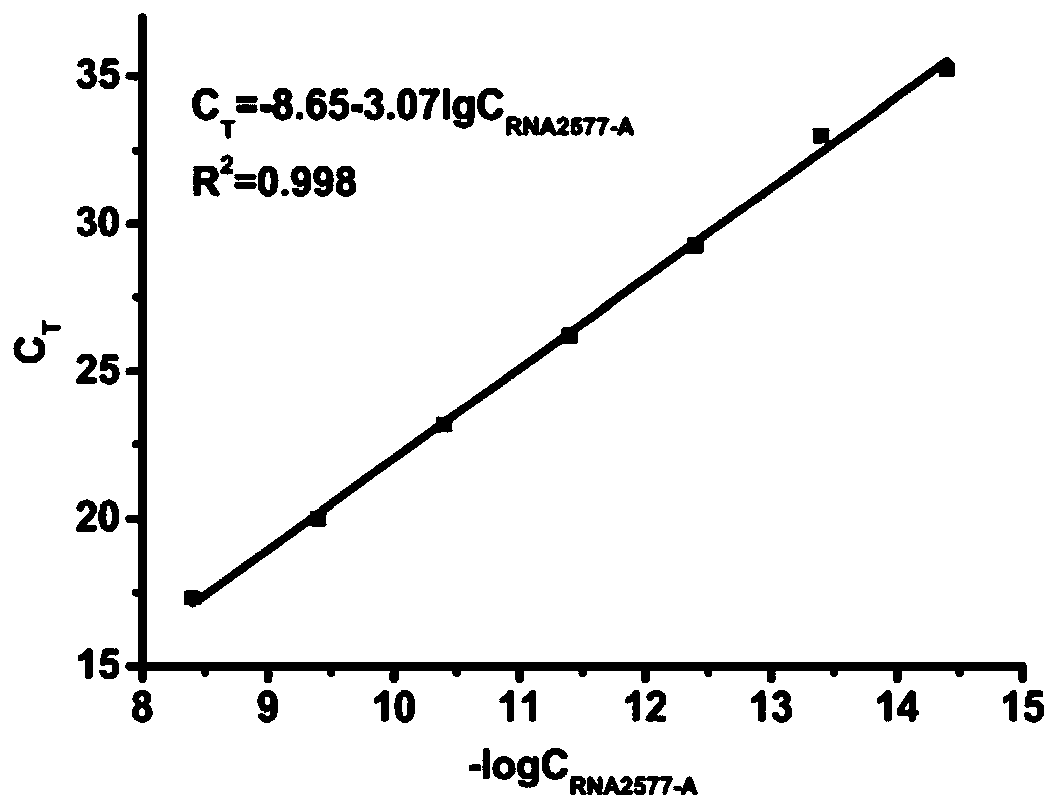
ActiveCN106755306AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMessenger RNABiology
The invention discloses an application of ligase in detection of N6 methyladenine, wherein the ligase is T3 DNA ligase or the T4 RNA ligase 2. The invention firstly discovers that the N6 methyladenine (m6A) can inhibit the connection activity of the T3 DNA ligase and the T4 RNA ligase 2 in comparison with adenine (A), based on the characteristic, the RNA (the RNA containing A and the RNA containing m6A) is taken as a template to establish a method for quantitatively determining the m6A percent content based on the ligase-polymerase chain reaction. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in operation, high in sensitivity and good in specificity, the m6A percent content in each of messenger RNA, long non-coding RNA, ribosome RNA, transfer RNA and small RNA and other RNA can be determined.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Transfer RNA ligand adduct libraries
InactiveUS20210054018A1Easy to identifyHigh sensitivityPeptide librariesSugar derivativesRibosomeAdduct
The present invention is drawn to, among other things, compositions of matter and methods for producing an aminoacyl-tRNA analogue comprising an adaptor tRNA and modified amino acid for ribosome-directed translation in vitro.
Owner:GALEN BIOTECH LLC
Methods
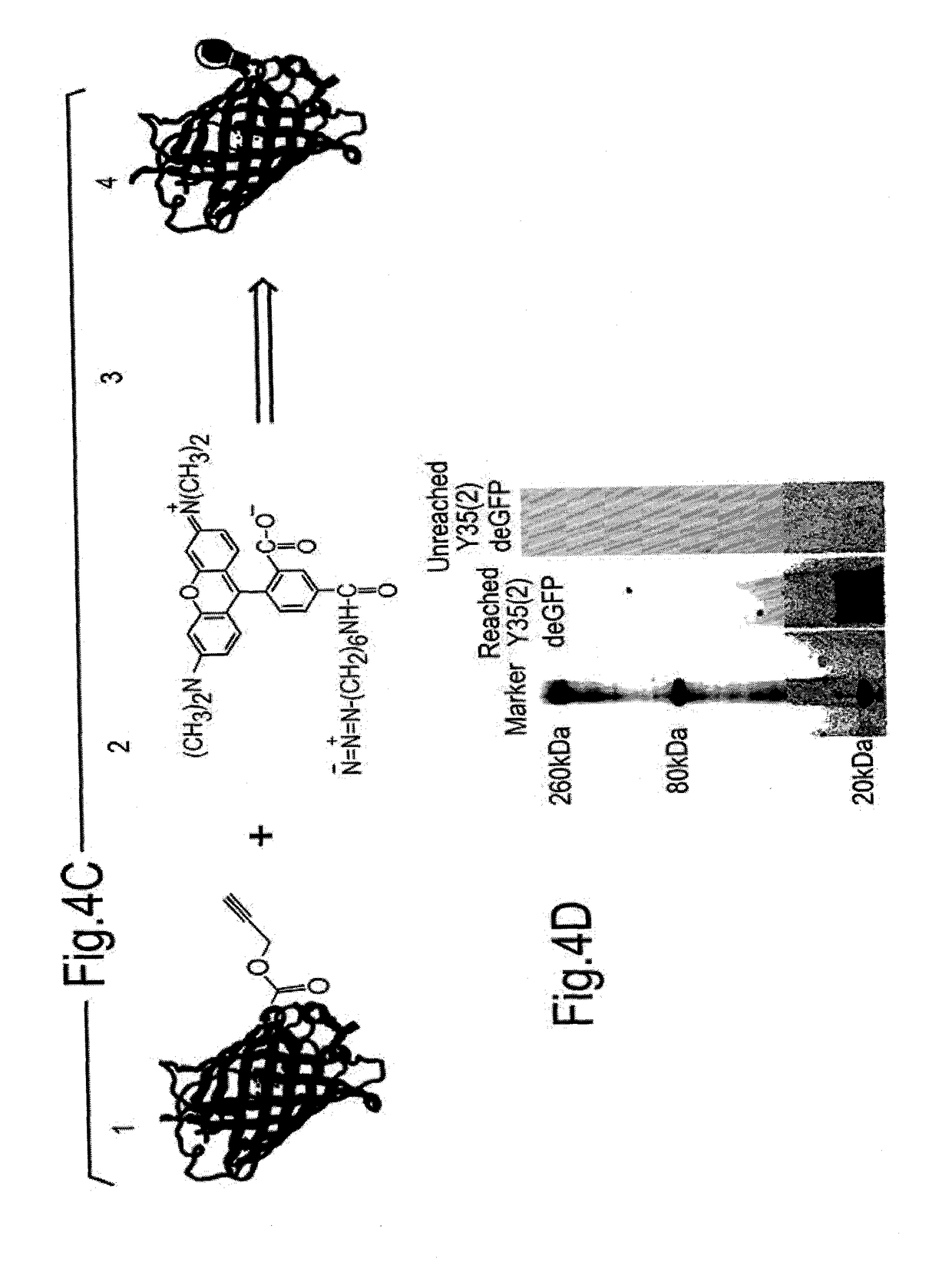
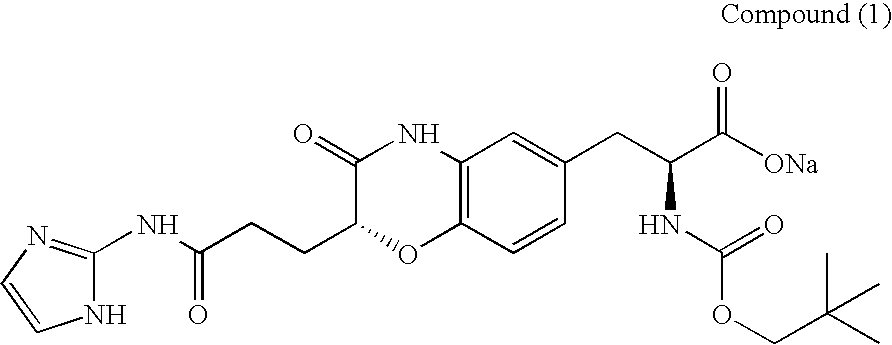
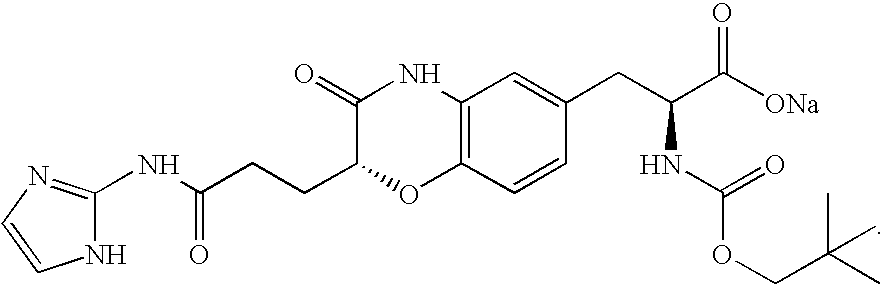
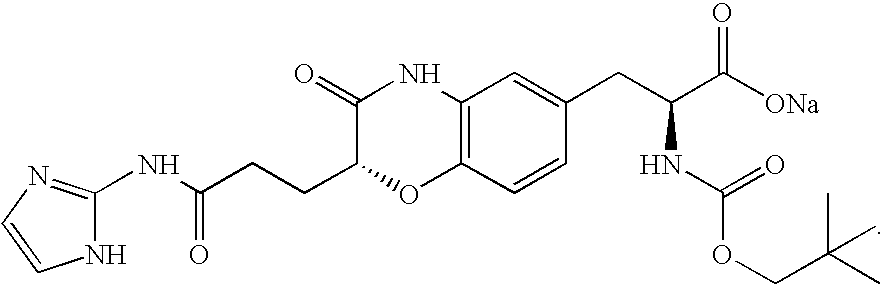
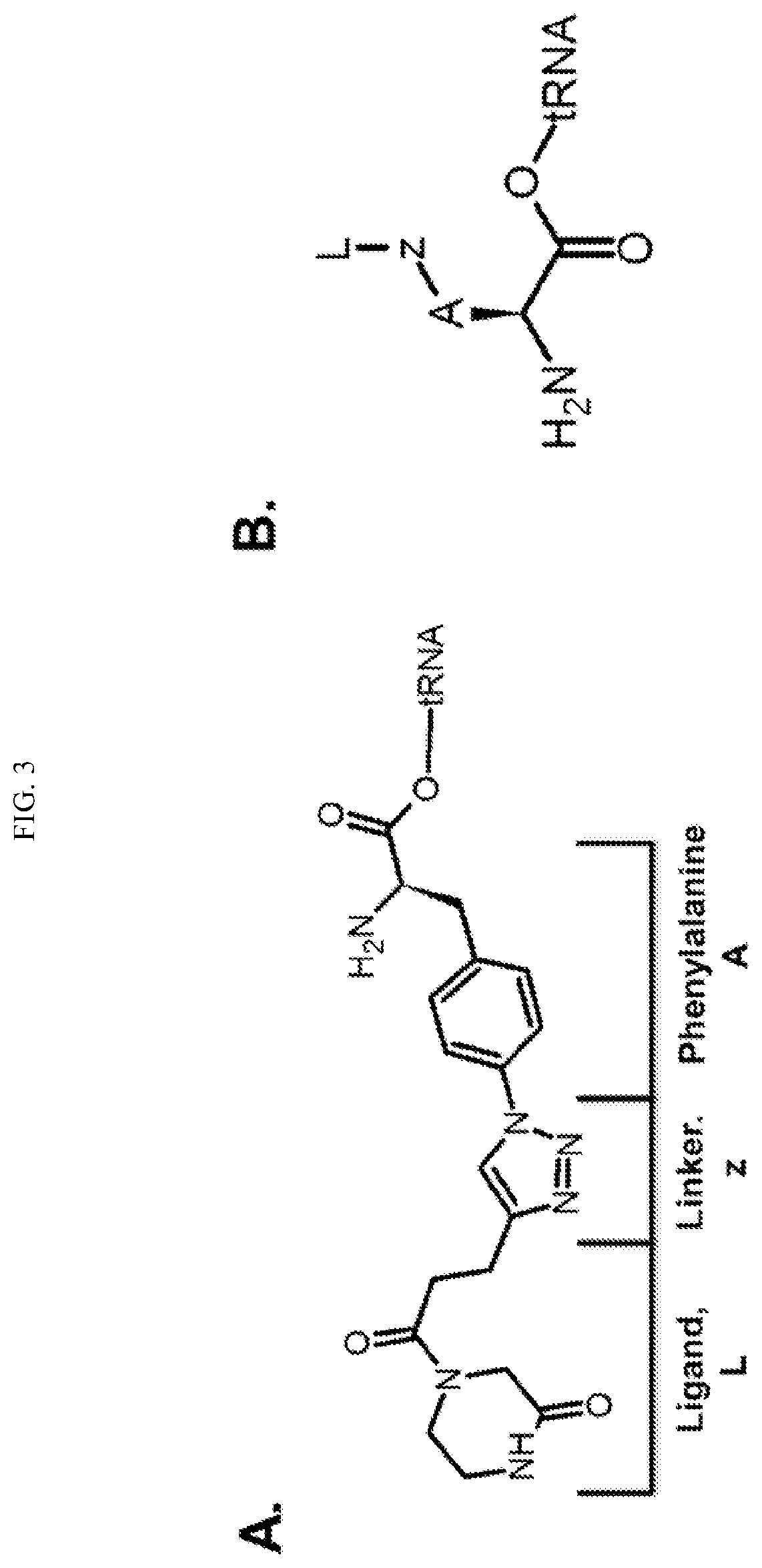
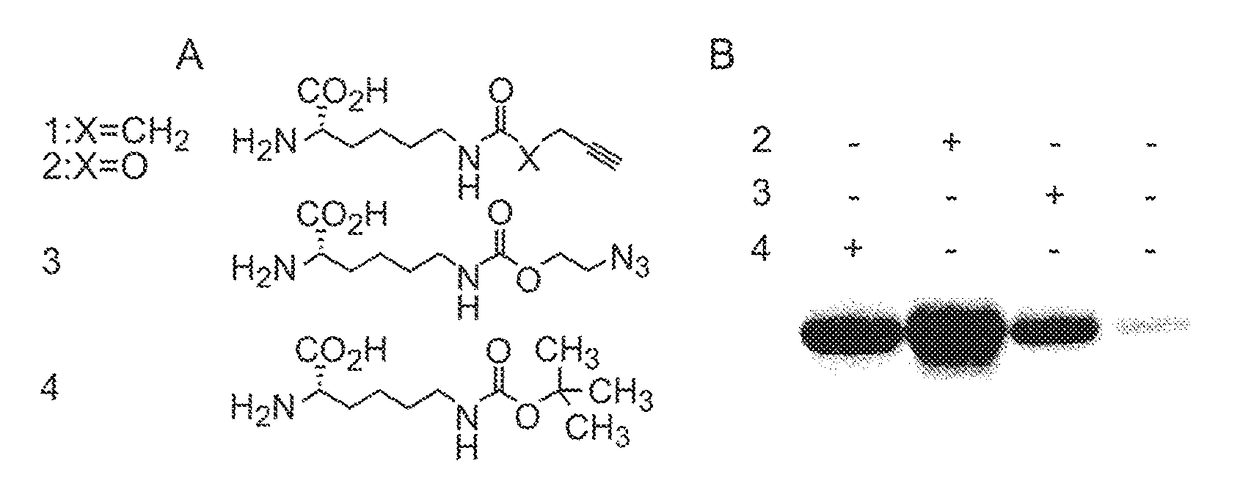
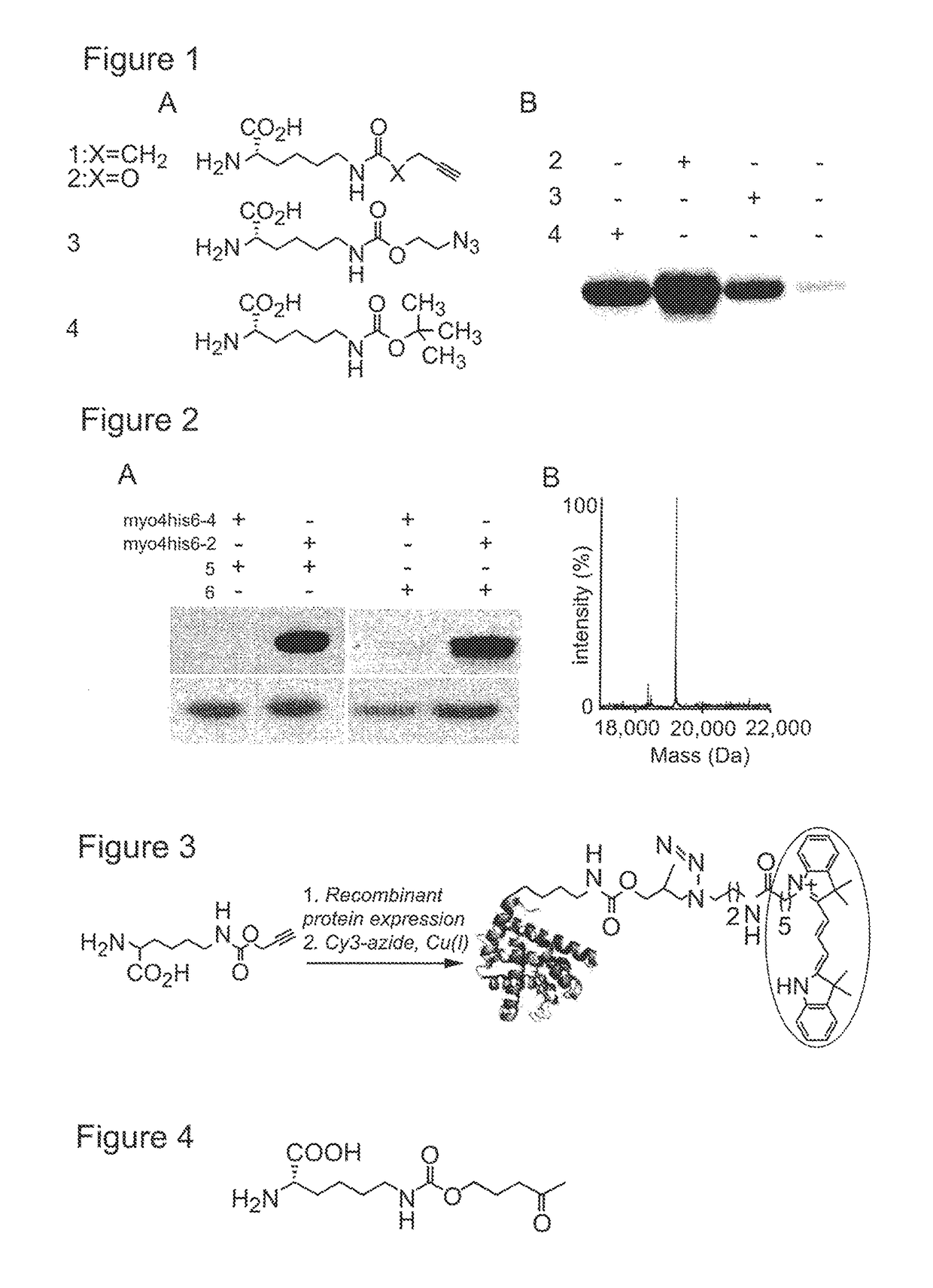
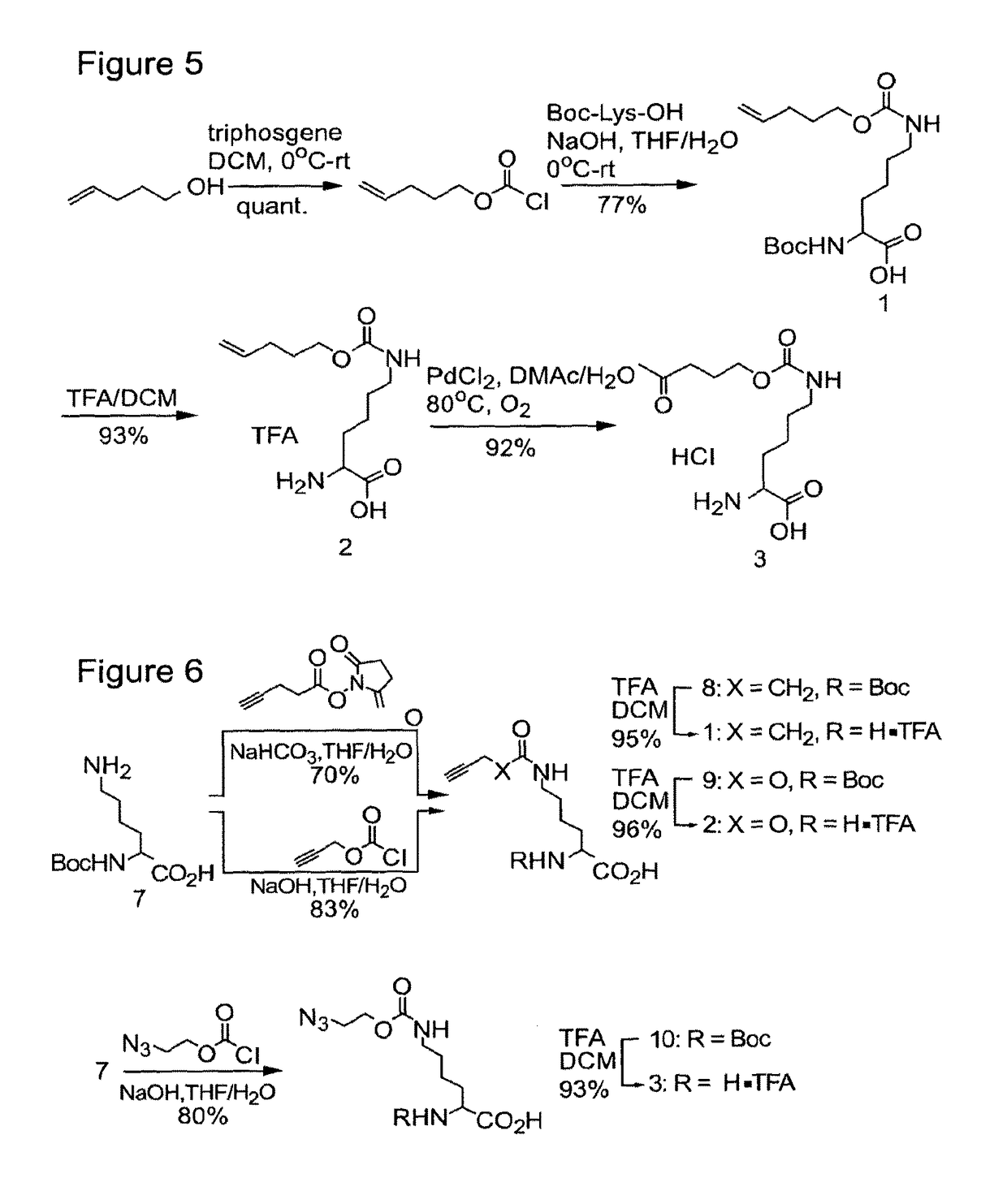
ActiveUS9868956B2Easy to usePrevent presentationCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationRNA synthetasesTRNA synthesis
The invention relates to a method of making a polypeptide comprising an orthogonal functional group, said orthogonal functional group being comprised by an aliphatic amino acid or amino acid derivative, said method comprising providing a host cell; providing a nucleic acid encoding the polypeptide of interest; providing a tRNA-tRNA synthetase pair orthogonal to said host cell; adding an amino acid or amino acid derivative comprising the orthogonal functional group of interest, wherein said amino acid or amino acid derivative is a substrate for said orthogonal tRNA synthetase, wherein said amino acid or amino acid derivative has an aliphatic carbon backbone; and incubating to allow incorporation of said amino acid or amino acid derivative into the polypeptide of interest via the orthogonal tRNA-tRNA synthetase pair. The invention also relates to certain amino acids, and to polypeptides comprising same.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD +1
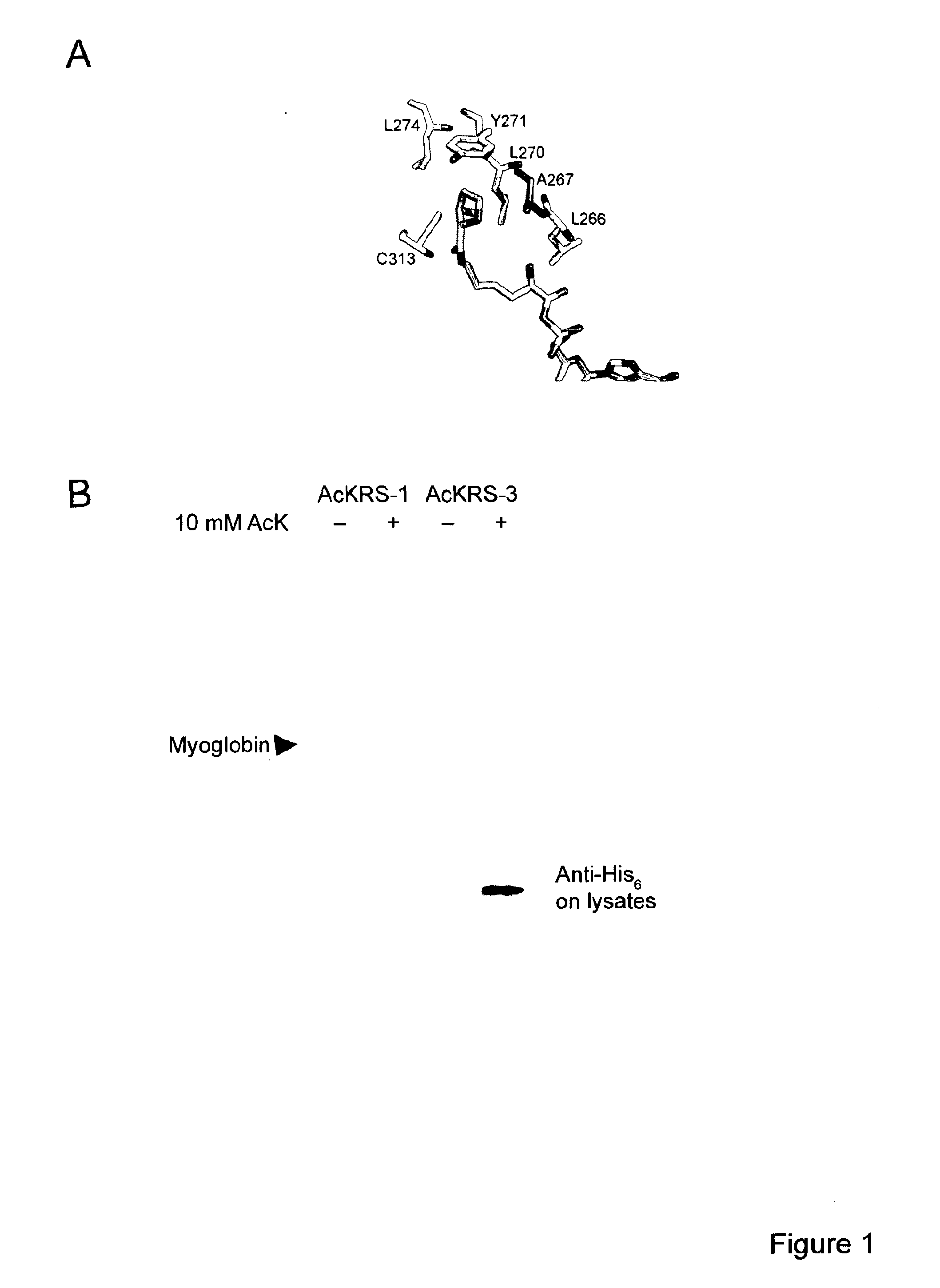
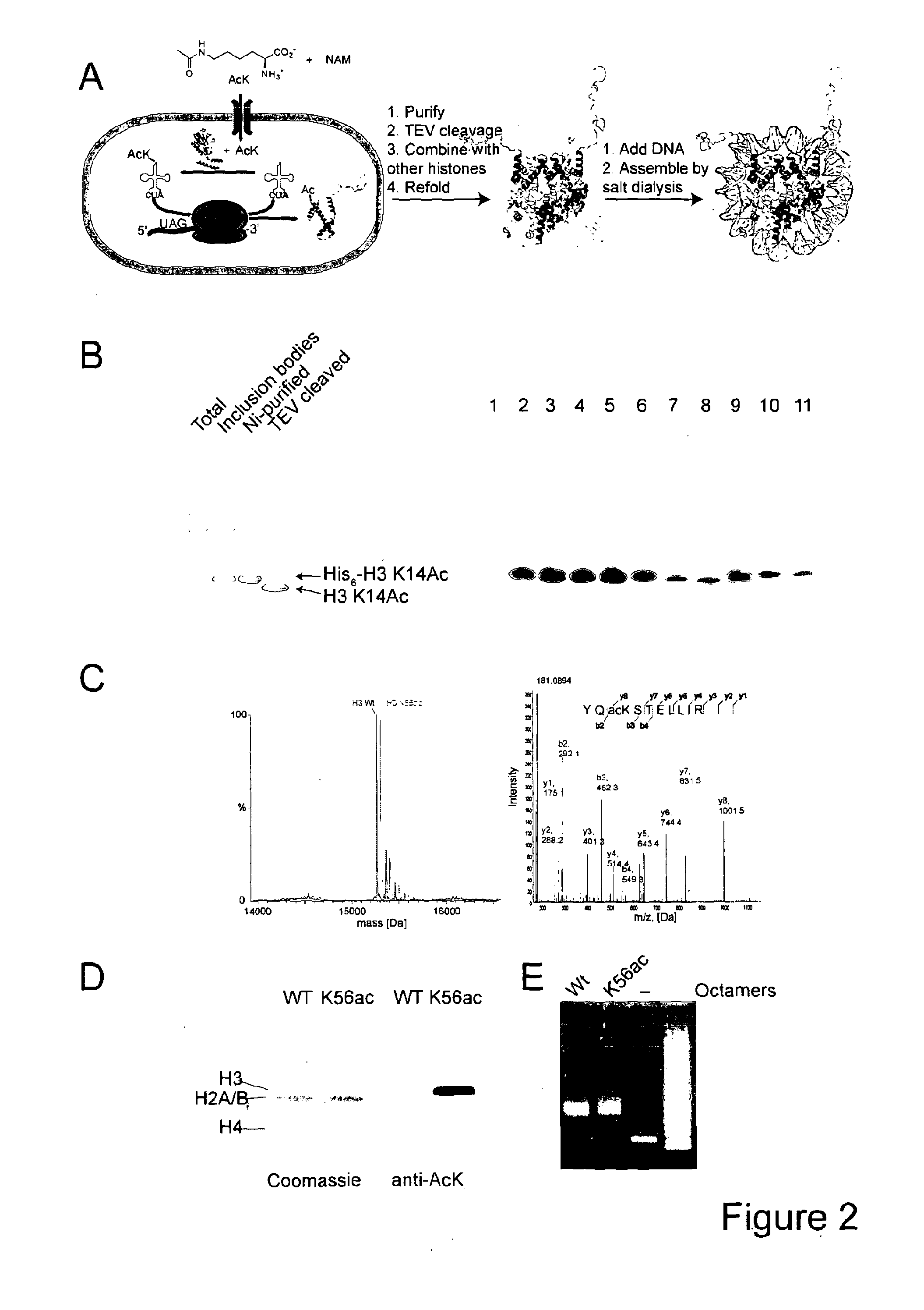
ACETYL LYSINE INCORPORATION WITH tRNA SYNTHETASE
The invention relates to a tRNA synthetase capable of binding Nε-acetyl lysine, wherein said synthetase comprises a polypeptide having at least 90% sequence identity to the amino acid sequence of MbPyIRS, and wherein said synthetase comprises a L266M mutation.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
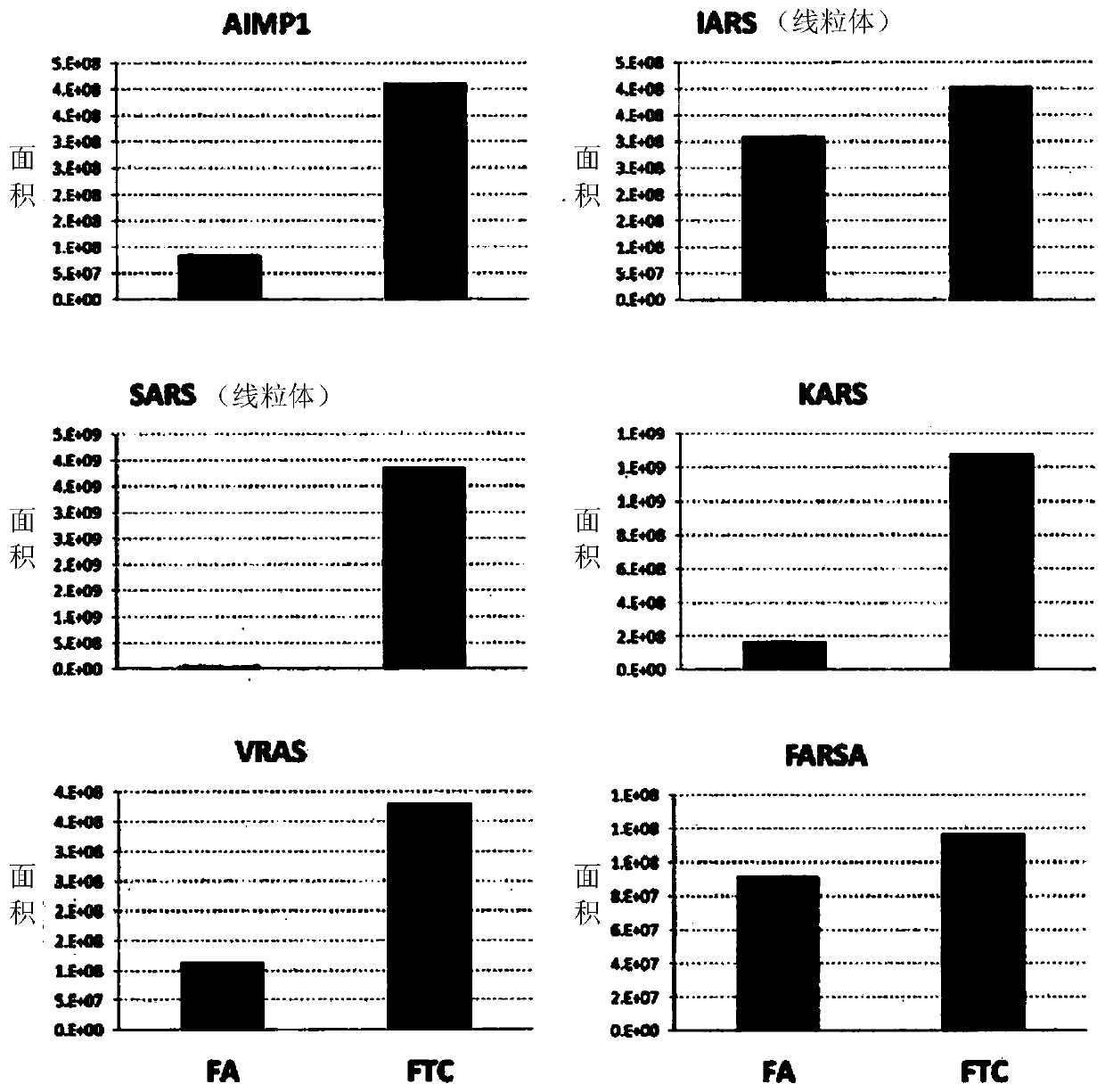
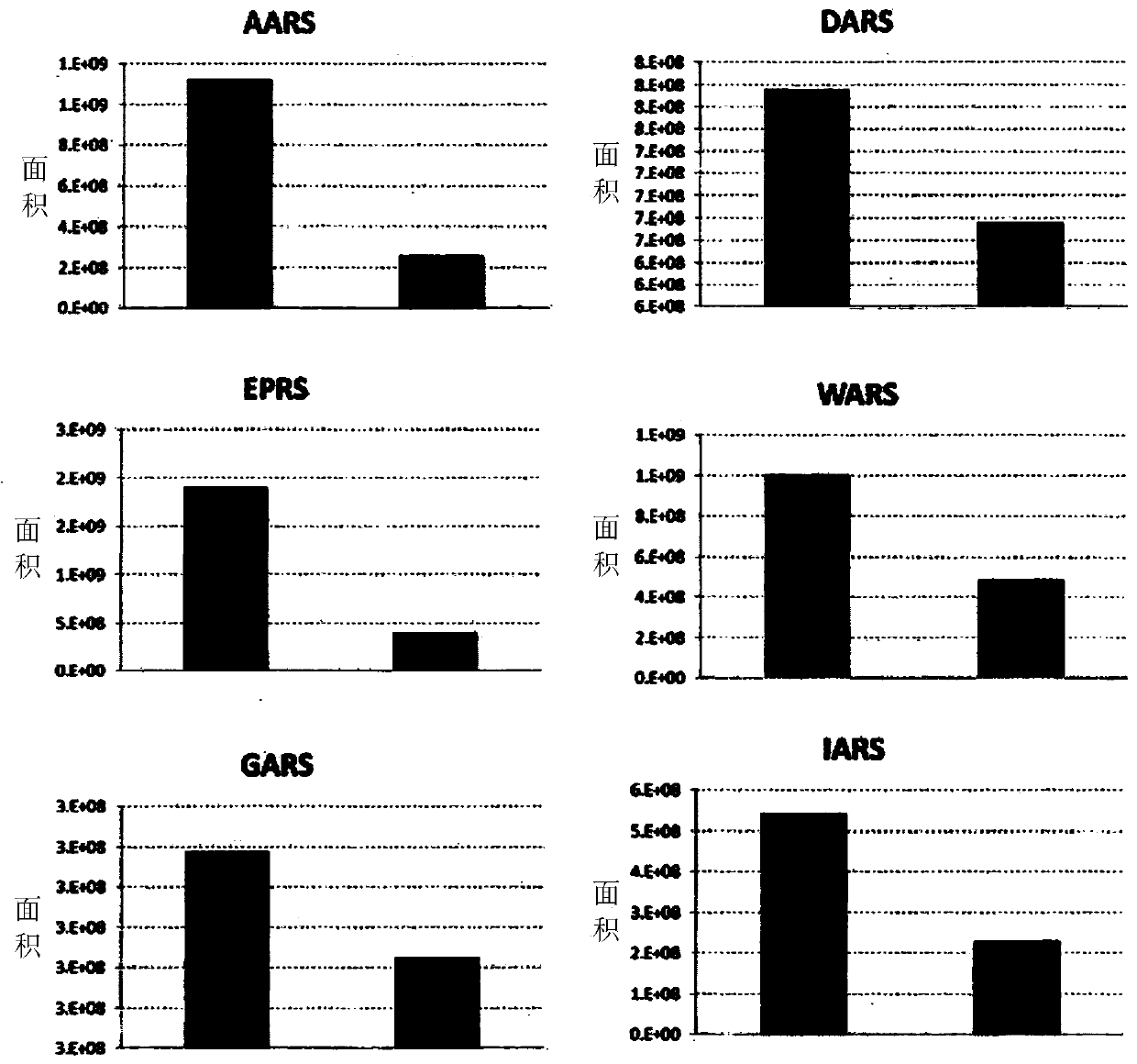
Method for detecting diagnostic marker of follicular thyroid carcinoma using expression level of aminoacyl-trna synthetase-related protein
InactiveCN109844535ASimple and accurate diagnosisHigh sensitivityBiological testingTrue positive rateProtein species
Owner:MEDICINAL BIOCONVERGENCE RES CENT +2
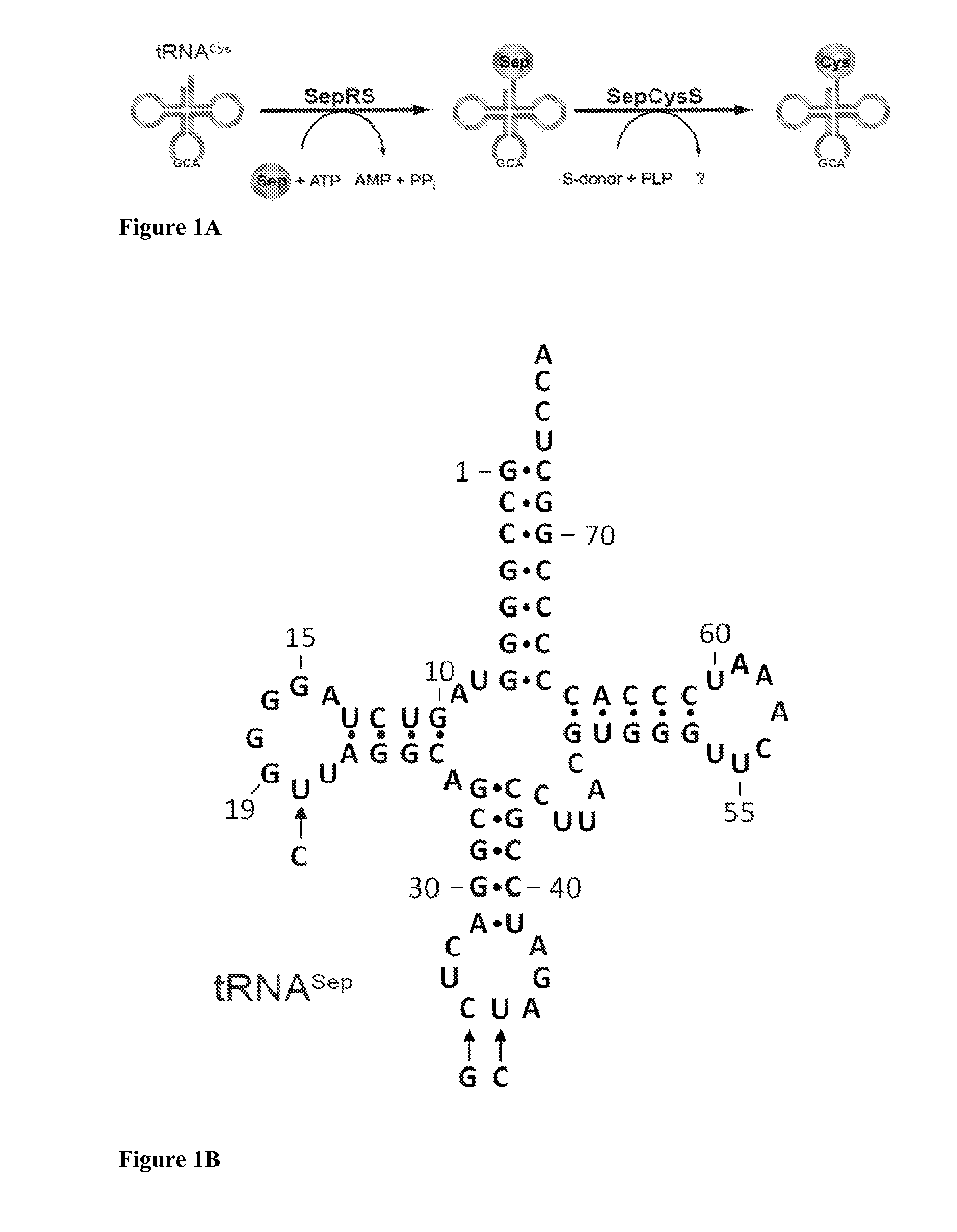
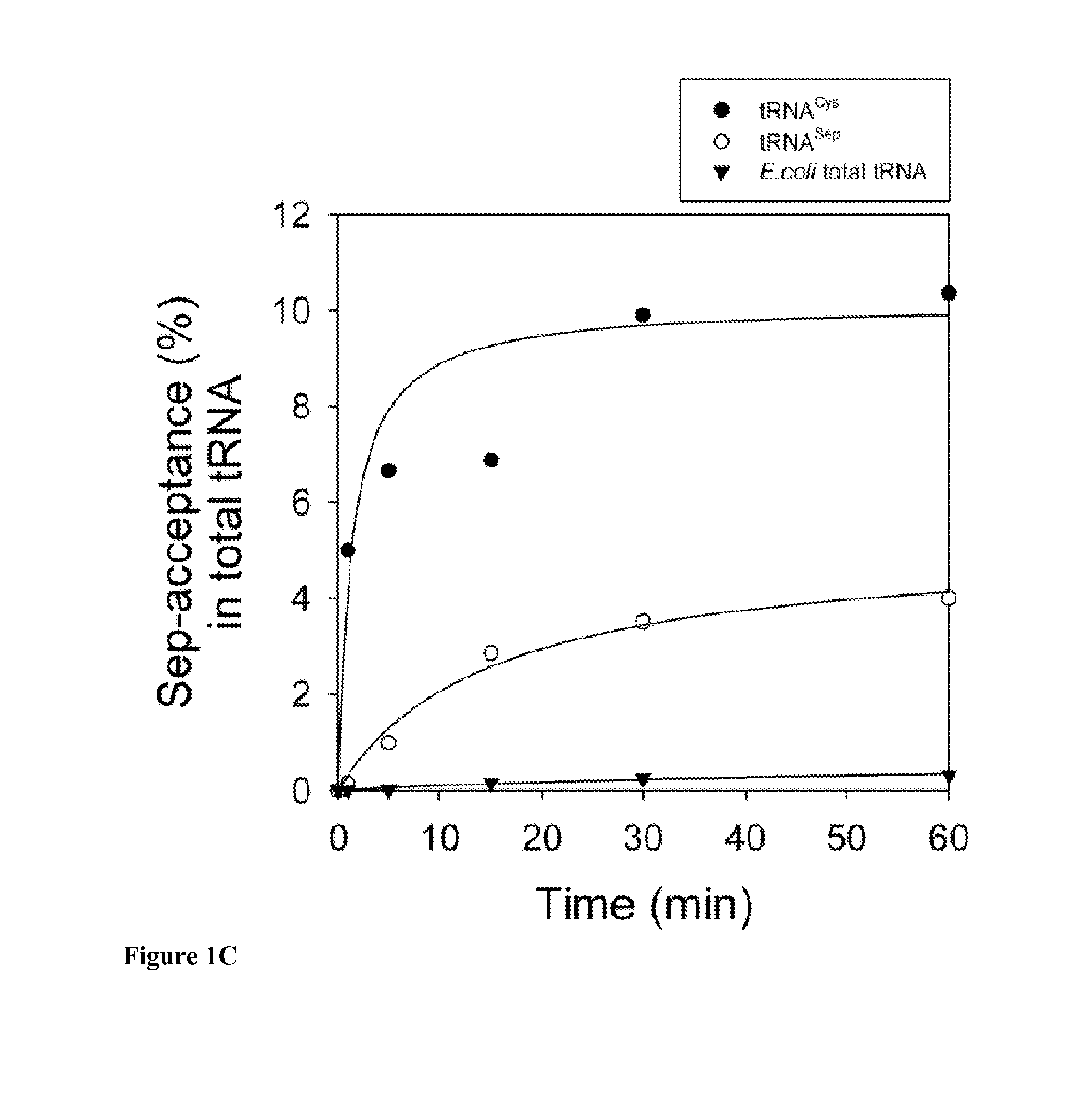
Site-Specific Incorporation of Phosphoserine Into Proteins in Escherichia Coli
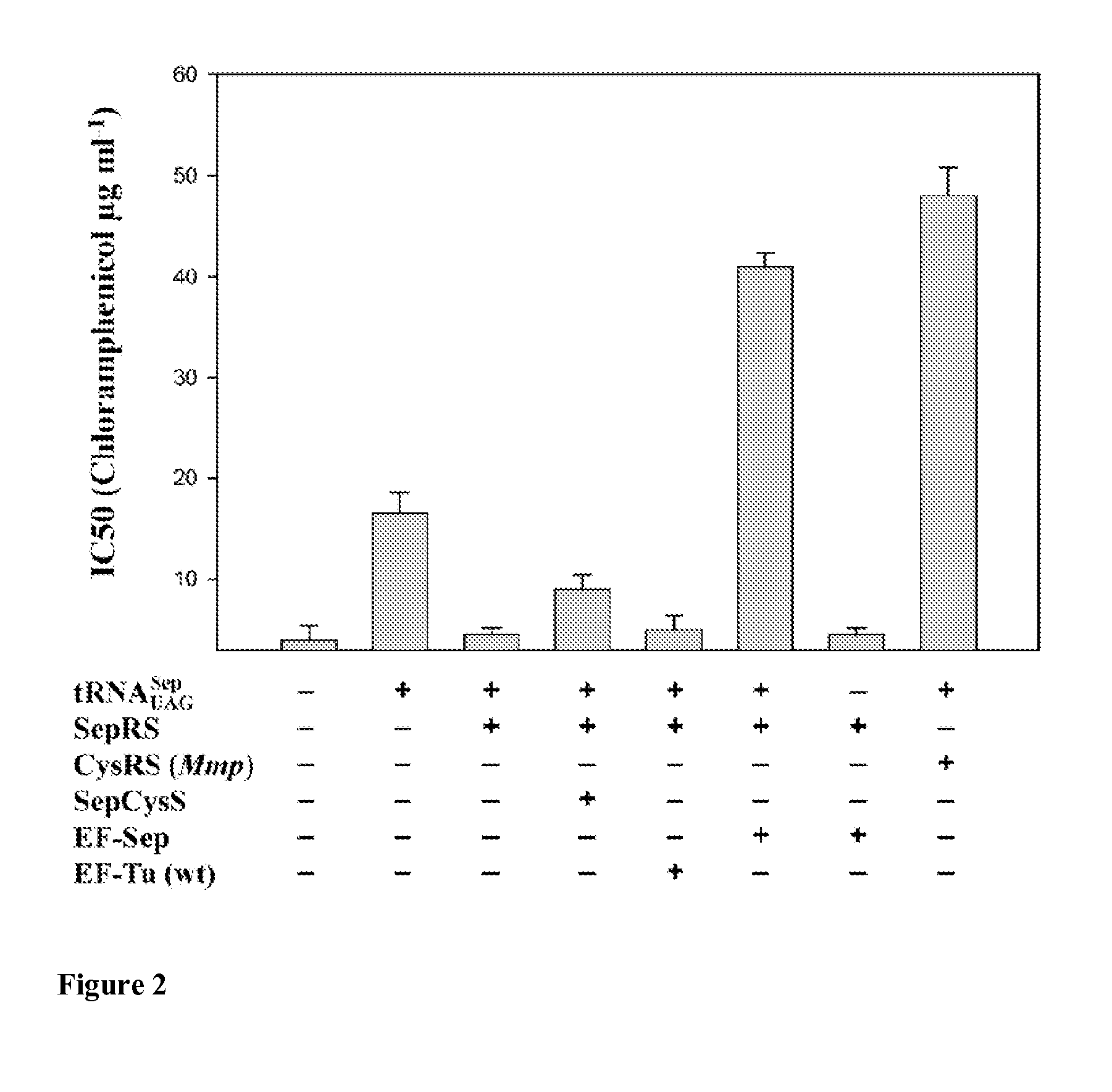
Nucleic acids encoding mutant elongation factor proteins (EF-Sep), phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase (SepRS), and phosphoseryl-tRNA (tRNASep) and methods of use in site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into a protein or polypeptide are described. Typically, SepRS preferentially aminoacylates tRNASep with O-phosphoserine and the tRNASep recognizes at least one codon such as a stop codon. Due to the negative charge of the phosphoserine, Sept-tRNASep does not bind elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu). However, mutant EF-Sep proteins are disclosed that bind Sep-tRNASep and protect Sep-tRNASep from deacylation. In a preferred embodiment the nucleic acids are on vectors and are expressed in cells such as bacterial cells, archeaebacterial cells, and eukaryotic cells. Proteins or polypeptides containing phosphoserine produced by the methods described herein can be used for a variety of applications such as research, antibody production, protein array manufacture and development of cell-based screens for new drug discovery.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Use of transfer rna molecules and fragments thereof for preventing or treating heart disease
ActiveCN111419867BOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseaseHeart disease
Application of transfer RNA Molecules and their derived fragments for prevention or treatment of heart disease. The present invention provides a method of preventing or treating a subject suffering from heart diseases comprising administration of transfer RNA molecules and fragments derived from transfer RNA molecules or its functional variants or homologous to the subject, wherein the RNA molecules isolated from or derived from a plant of the genus Panax. The present invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention or treatment of heart diseases comprising said effective amount of RNA molecule and a pharmaceutically tolerable vector, virus or excipient. The present invention provides a method for the prevention or treatment of a subject suffering from a heart disease. It is found that transfer RNA molecules from ginseng are particularly effective in the treatment of heart diseases, and also have a restorative effect on the myocardial cytoskeleton after ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Owner:睿纳珠海横琴生物科技有限公司
Ribozyme with tRNA synthetase activity and methods of manufacturing and using the same
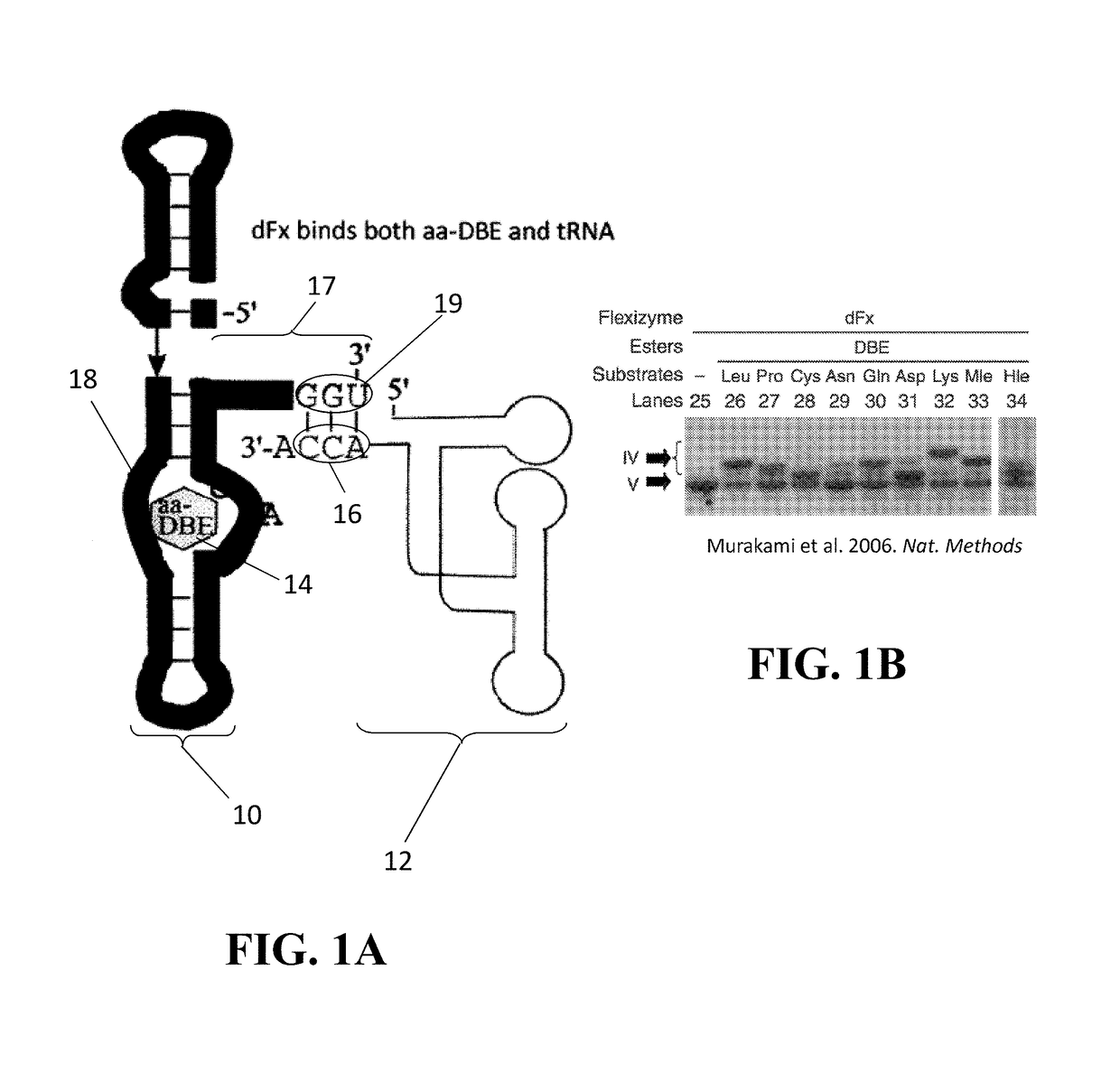
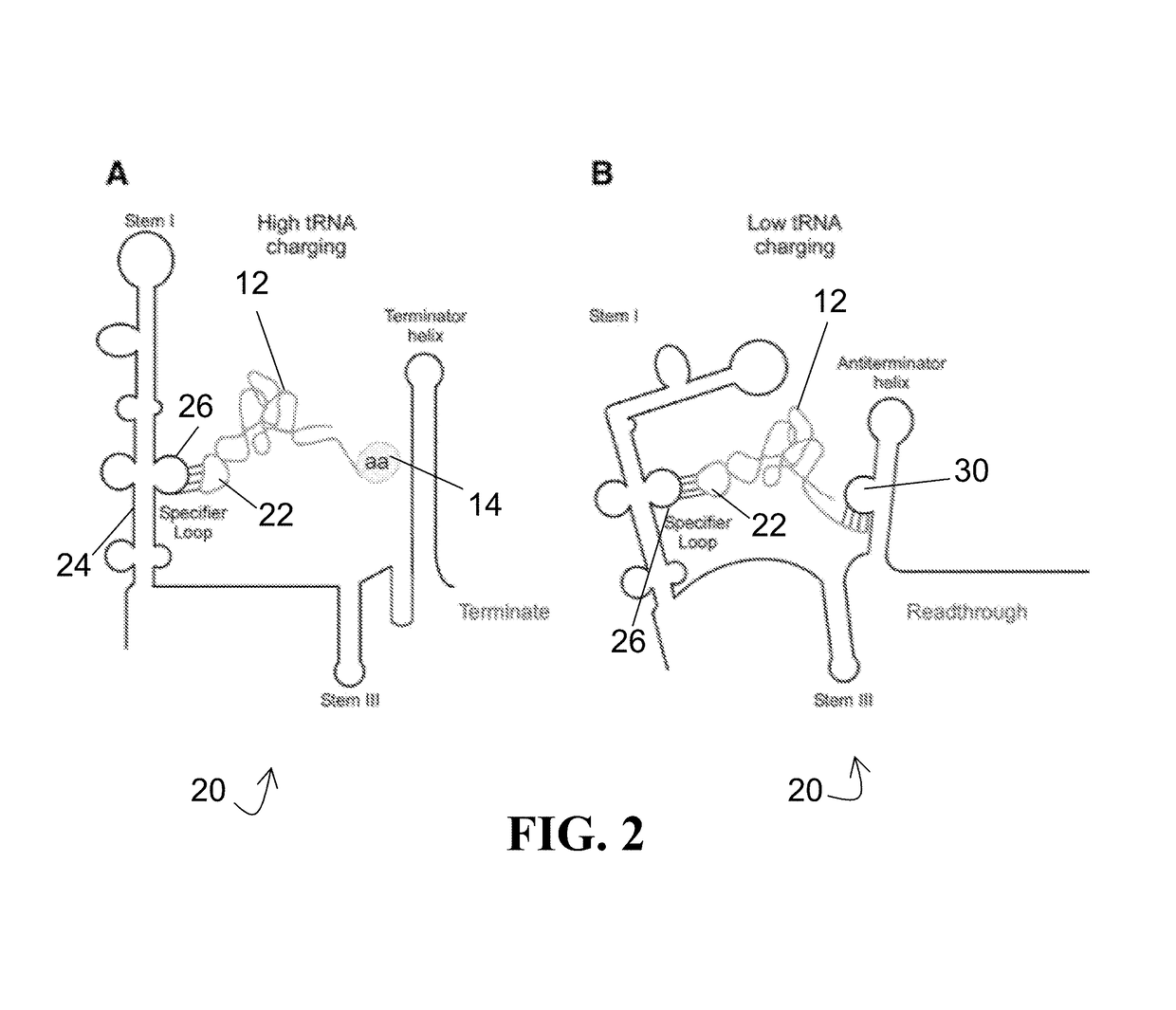
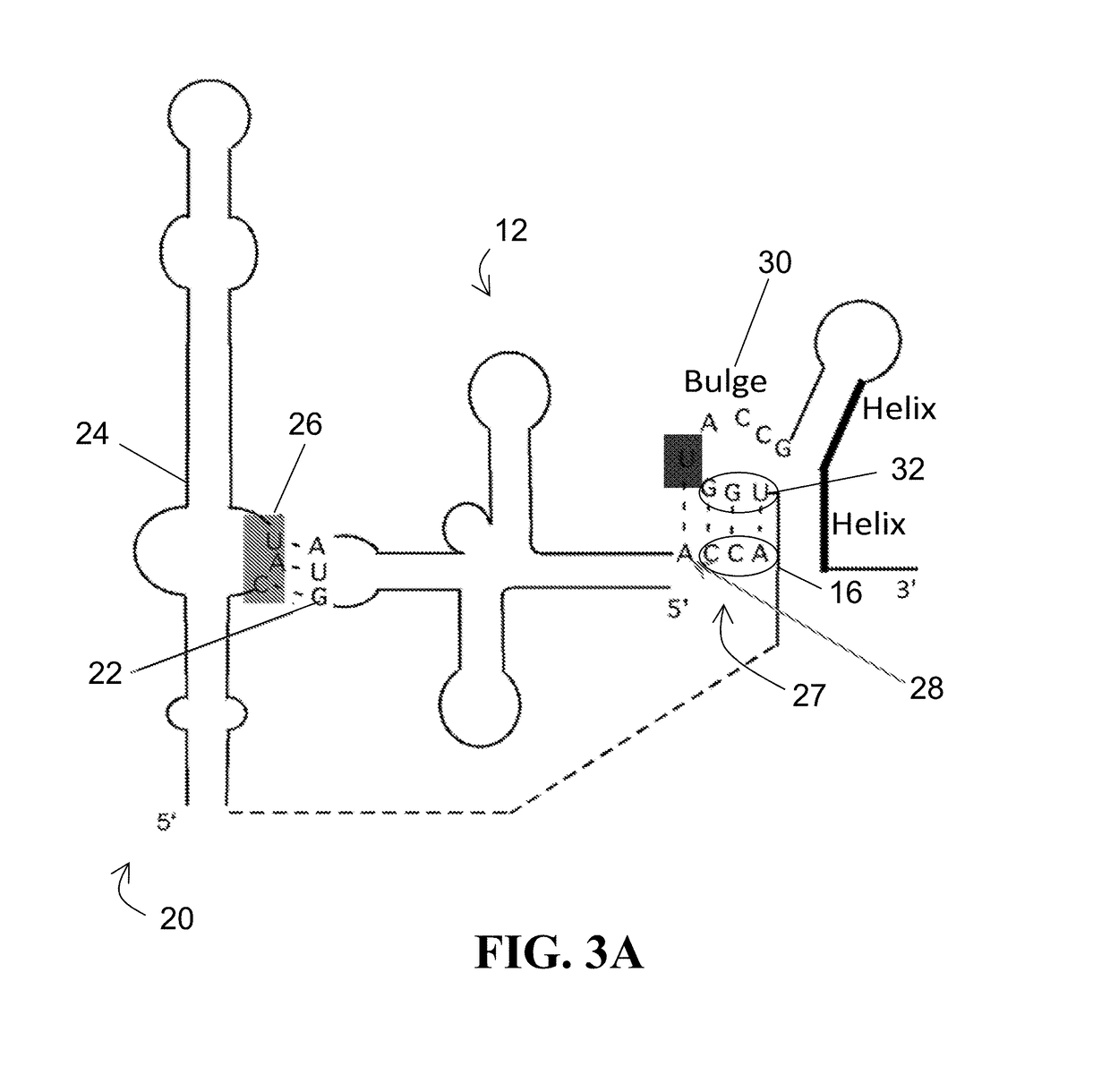
Ribozymes exhibiting tRNA synthetase activity and substrate specificity, as well as methods for engineering and producing the same, are disclosed. The ribozymes of the present disclosure comprise a T-box RNA module fused with a flexizyme module. The flexizyme module provides high promiscuity with respect to amino acid substrates and the T-box module provides tRNA substrate specificity. Systems are also described for aminoacylation of suppressor tRNAs with unnatural amino acids (uAAs), such systems comprising the ribozyme previously mentioned, suppressor tRNA, and the desired uAAs. Methods for incorporating a uAA into a growing polypeptide chain using the ribozyme hereof are also provided.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
Molecular adapter for capture and manipulation of transfer RNA
ActiveUS20170218439A1Easy to adaptElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementCholesterolOligonucleotide
The invention also encompasses novel structures and methods comprising providing a molecular adapter for capture and manipulation of transfer RNA. The adaptor is bound to a tRNA molecule. The adaptor may be a cholesterol-linked DNA adapter oligonucleotide. The invention is useful in sequencing, identification, manipulation and modification of tRNA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nanoparticles comprising aminoacyl trna synthetase and anticancer composition comprising same
ActiveUS20170072031A1Enhance immune functionPreventing and treating cancerPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsNanoparticleMedicine
The present invention relates to nanoparticles comprising aminoacyl tRNA synthetase and an anticancer composition comprising the same and, specifically, to nanoparticles which comprise glycyl-tRNA synthetase (GRS), leucyl-tRNA synthetase (LRS), and isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase (IRS), and have anticancer or immunostimulating activity; a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancer, comprising the nanoparticles as an active ingredient; a composition for immunostimulation; and a method for preparing the nanoparticles.
Owner:MEDICINAL BIOCONVERGENCE RES CENT
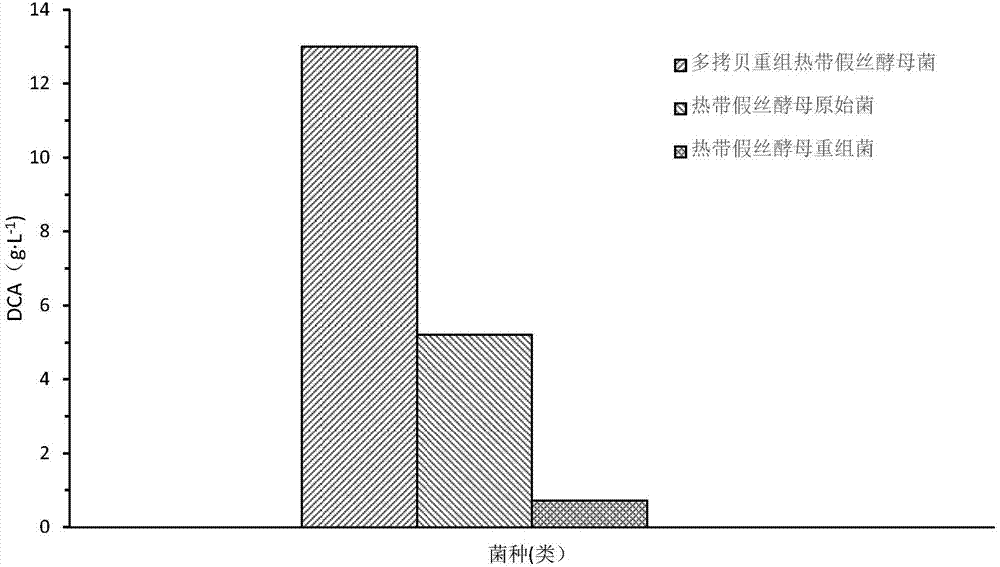
Gene for regulating transfer of long-chain diacid of candida tropicalis and application of gene
ActiveCN107488670AEasy to transportFacilitates transmembrane transportFungiBacteria peptidesCandida tropicalisLong-chain fatty acid transport
A gene for regulating transfer of long-chain diacid of candida tropicalis and an application of the gene are disclosed. Transfer gene ctlpA of long-chain diacid of candida tropicalis has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1. Transfer protein CtLpA of long-chain aliphatic acid has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The fact that transfer protein gene ctlpA of long-chain diacid in candida tropicalis is a key gene in a transmembrane transfer process of long-chain diacid is found for the first time in the invention. Expression of the transfer protein gene ctlpA can promote intracellular-to-extracellular transmembrane transfer of long-chain diacid, and a basis of synthesizing long-chain diacid through a new approach of taking grease as a raw material is founded.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for protein modification
PendingCN110468173AShort reaction timeLow costFermentationAnimals/human peptidesProtein targetProtein Fragment
The present invention discloses a method for protein modification. The method comprises the following steps: providing a vector comprising a target protein gene sequence, mutating codons encoding amino acids in the target protein gene sequence; constructing unnatural amino acids; respectively preparing Flexizyme and a tRNAsep; using the Flexizyme to ligate the unnatural amino acids to the above tRNAsep to obtain ThioAcX-tRNA; and adding the ThioAcX-tRNA and the codon-mutated target protein to a PURE EXPRESS protein expression system to conduct reaction to obtain a modified protein product. Byadding transfer RNA pre-assembled with the unnatural amino acids in an in vitro protein translation system and using a principle of codon suppression, the method can conduct modification of relativelylarge protein fragments, greatly shortens reaction time, reduces cost, and at the same time can complete synthesis of two or more proteins in the same system.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
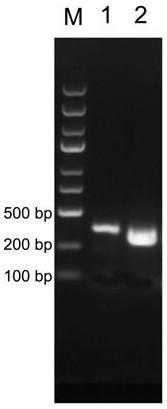
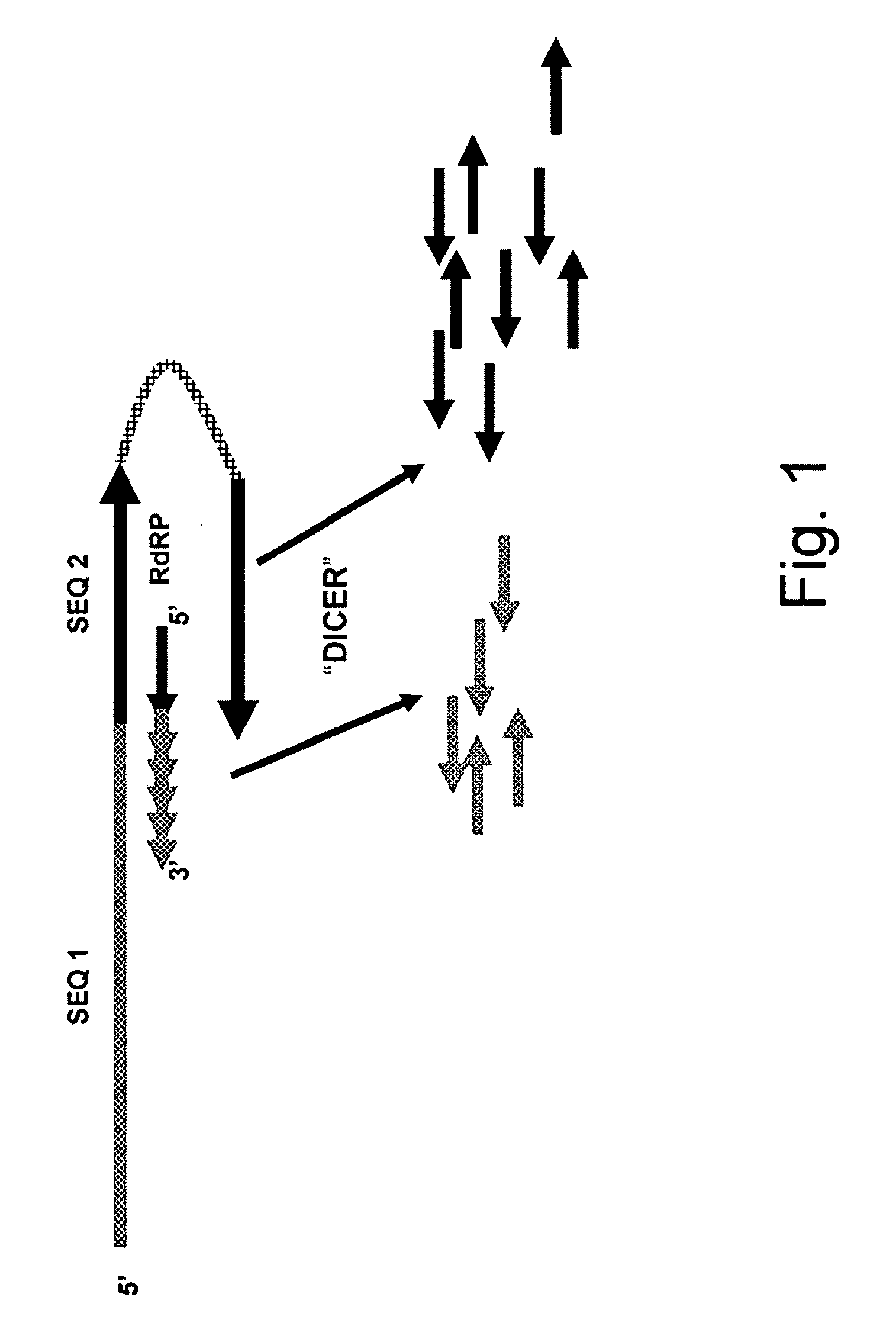
Methods of Eliminating or Reducing Expression of Genes in Filamentous Fungal Strains by Transitive RNA Interference
InactiveUS20100055755A1Reducing and eliminating expression of target geneExpression of one or more homologues of the target gene isFungiLigasesBiotechnologyTransitive RNA interference
The present invention relates to methods of reducing or eliminating expression of a target gene in a filamentous fungal strain by transitive RNA interference.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
In vivo incorporation of an unnatural amino acid comprising a 1,2-aminothiol group
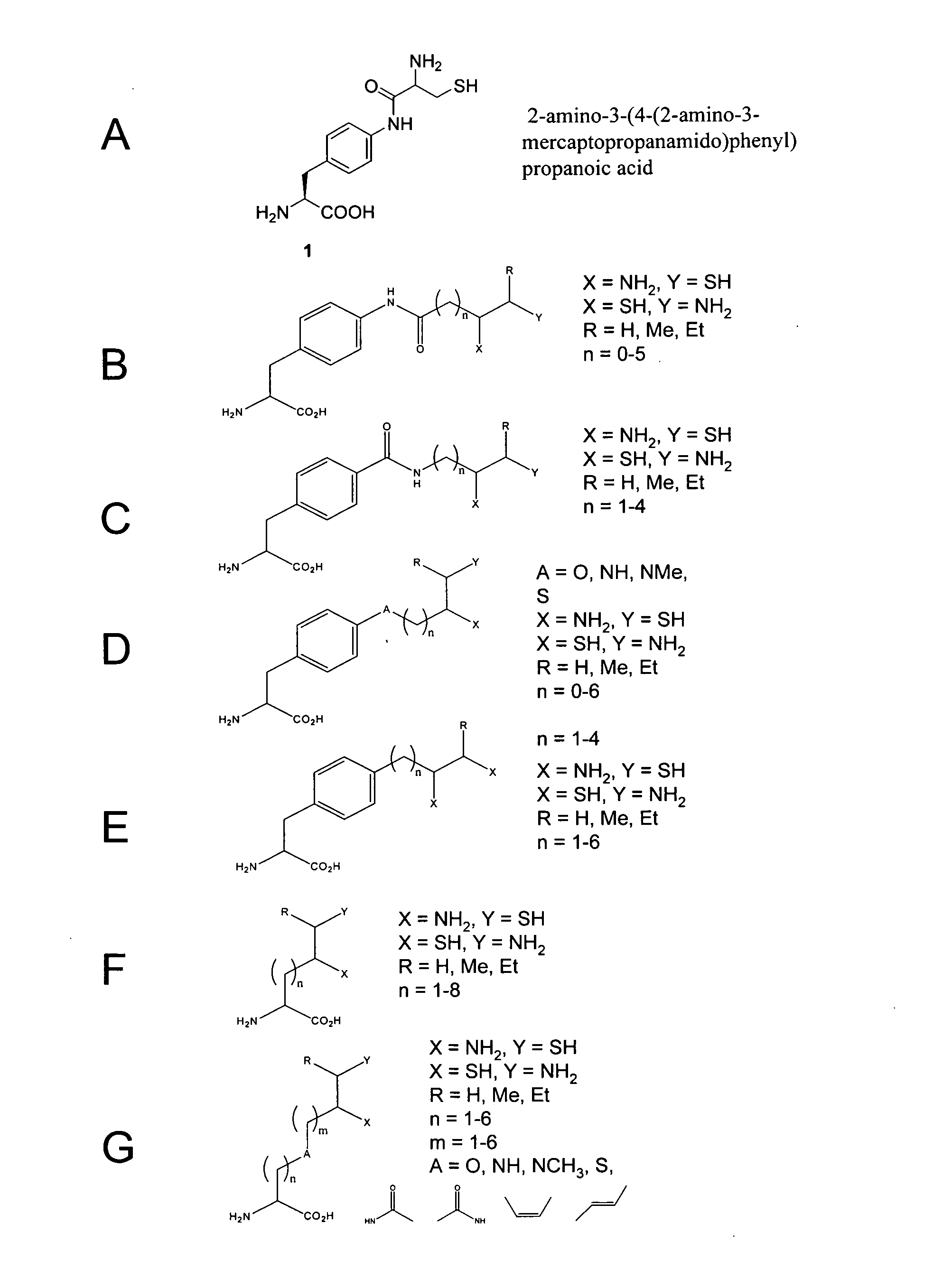
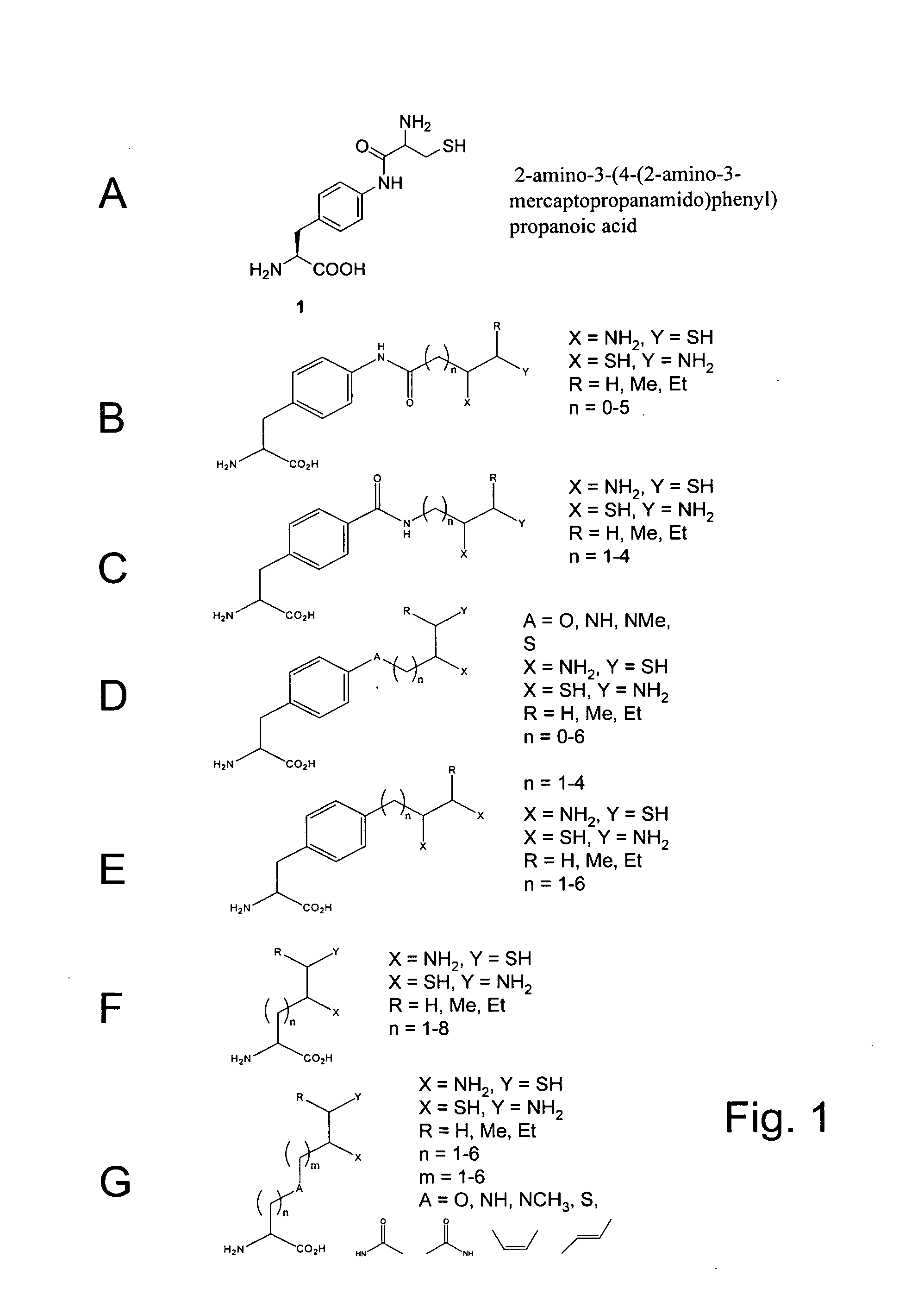
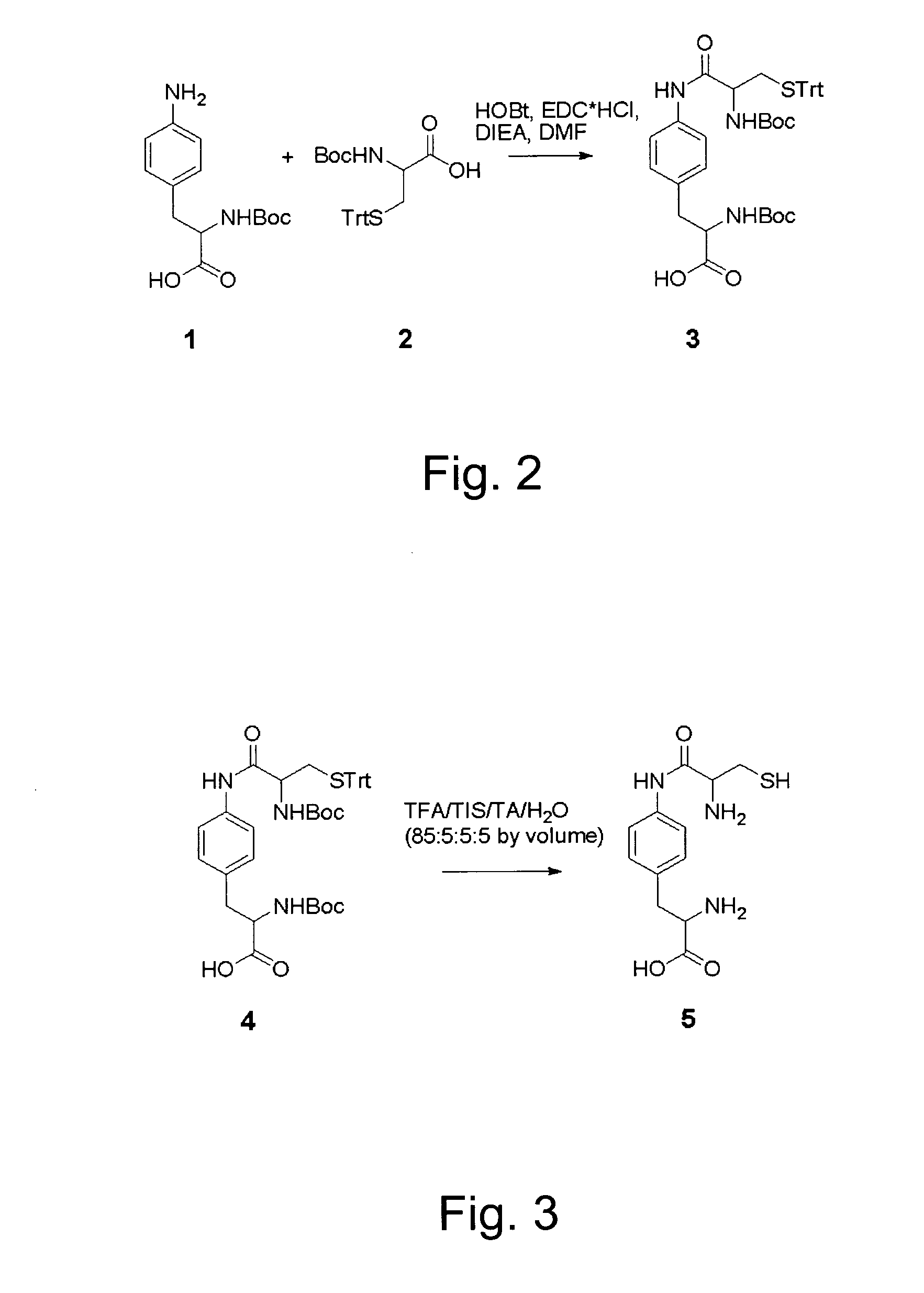
The invention relates to orthogonal pairs of tRNAs and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that can incorporate unnatural amino acids that comprise a 1,2 aminothiol group into polypeptides. The invention provides translation systems in which polypeptides comprising unnatural amino acids that comprise a 1,2 aminothiol group can be produced. The invention also provides methods for producing polypeptides containing unnatural amino acids that comprise a 1,2 aminothiol group. Also provided by the invention are compositions comprising orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that preferentially aminoacylate a cognate orthogonal tRNA with unnatural amino acids that comprise a 1,2 aminothiol group. The invention provides methods for the synthesis of the unnatural amino acid 2-amino-3-(4-(2-amino-3-mercaptopropan-amido)phenyl)-propanoic acid.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Transfer RNA fragments and their applications
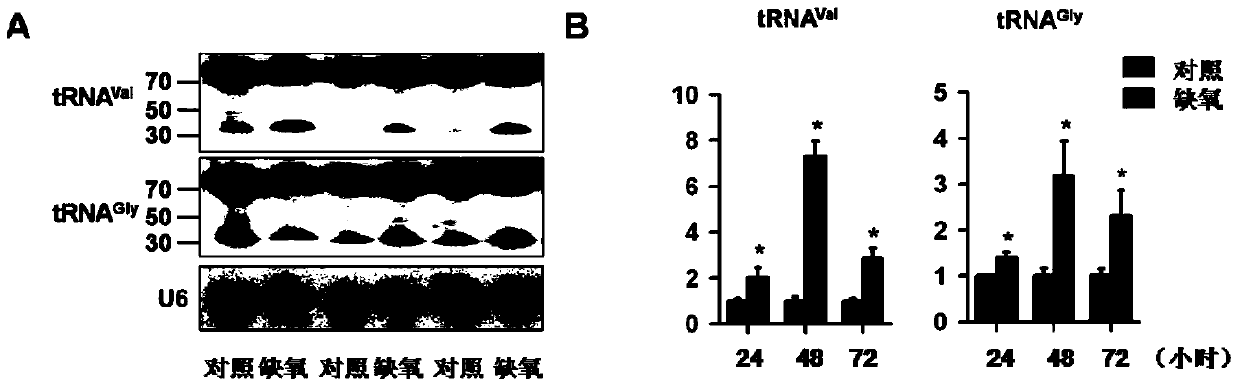
ActiveCN106978415BPrevent proliferationInhibit migrationOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryNucleotideAngiogenesis growth factor
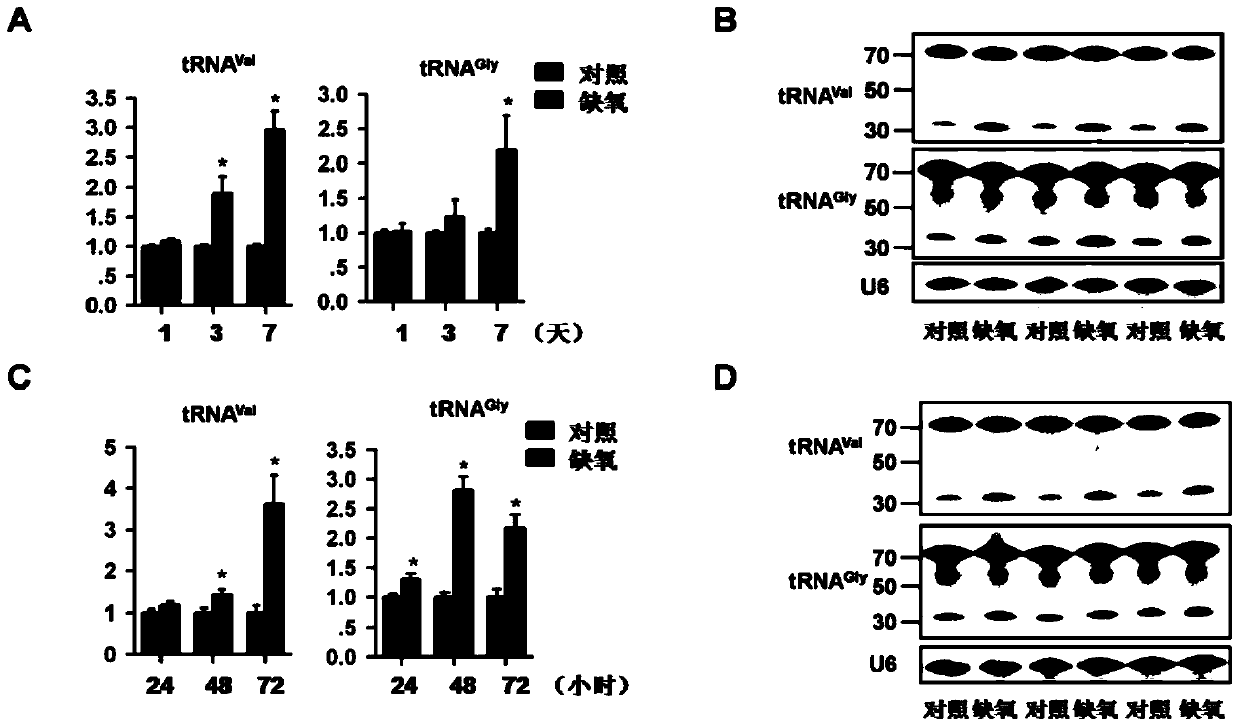
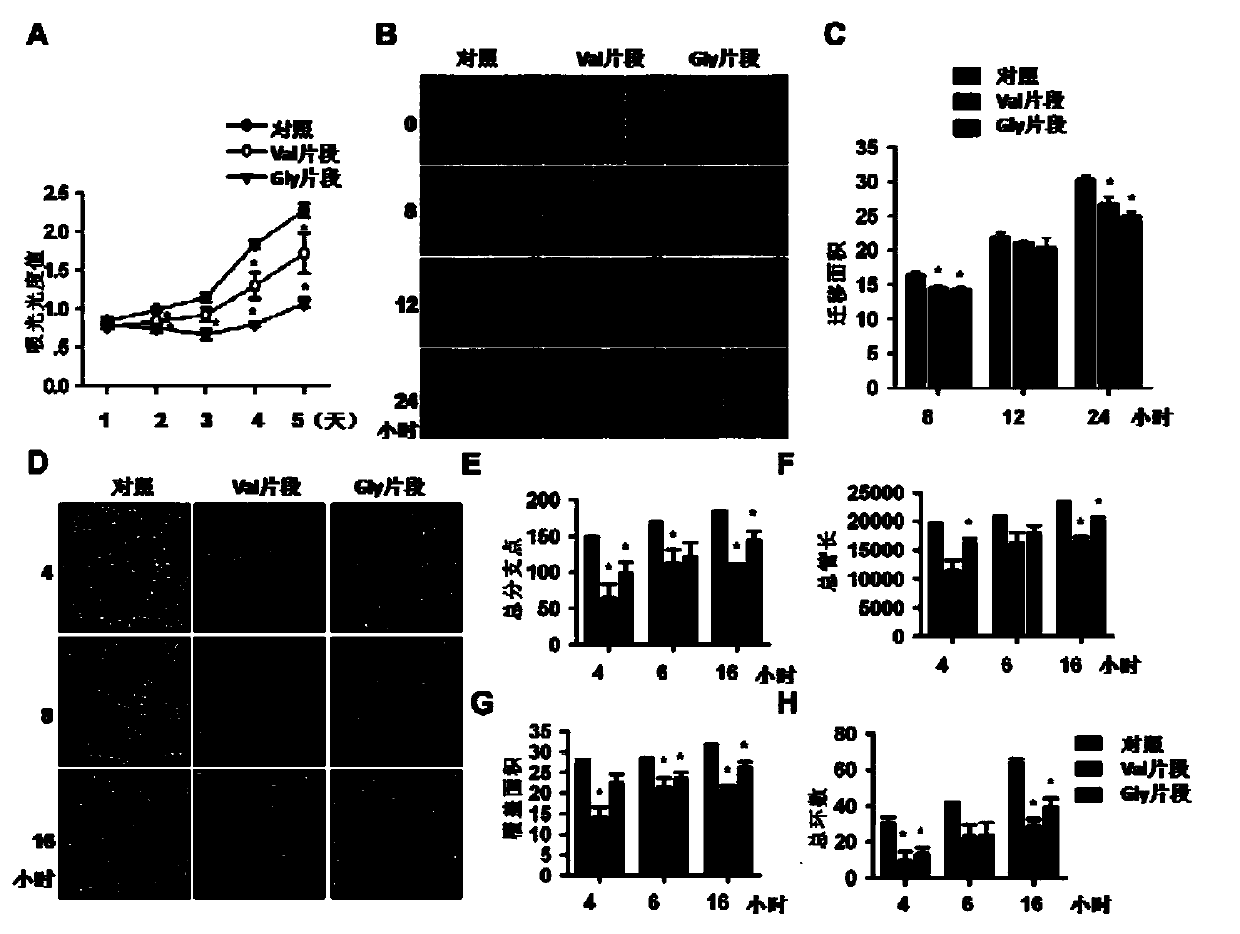
The invention discloses multiple transfer RNA fragments which derive from the following fragments with full-length sequences and containing 20-55 nucleotides: tRNA-val, tRNA-gly, tRNA-glu or tRNA-his, wherein the full-length sequence of tRNA-val is shown in SEQ ID NO 1, the full-length sequence of tRNA-gly is shown in SEQ ID NO 2, the full-length sequence of tRNA-glu is shown in SEQ ID NO 3, and the full-length sequence of tRNA-his is shown in SEQ ID NO 4. The transfer RNA fragments can be used for treating tumors and regulating angiogenesis.
Owner:上海市第六人民医院东院 +1
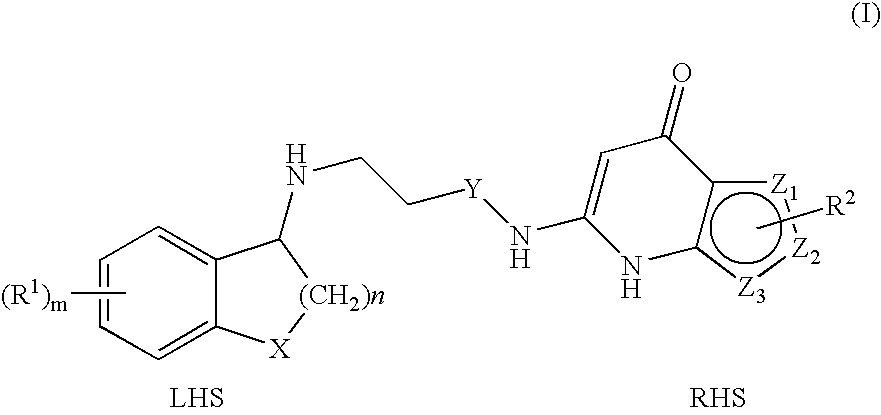
Novel heterocyclic compound, its preparation method, and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same
ActiveUS20190359617A1Inhibit PRS enzymatic activityEasy to useOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryProlyl tRNA synthetaseMedicinal chemistry
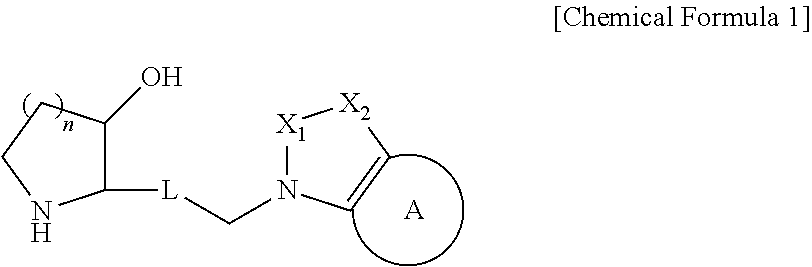
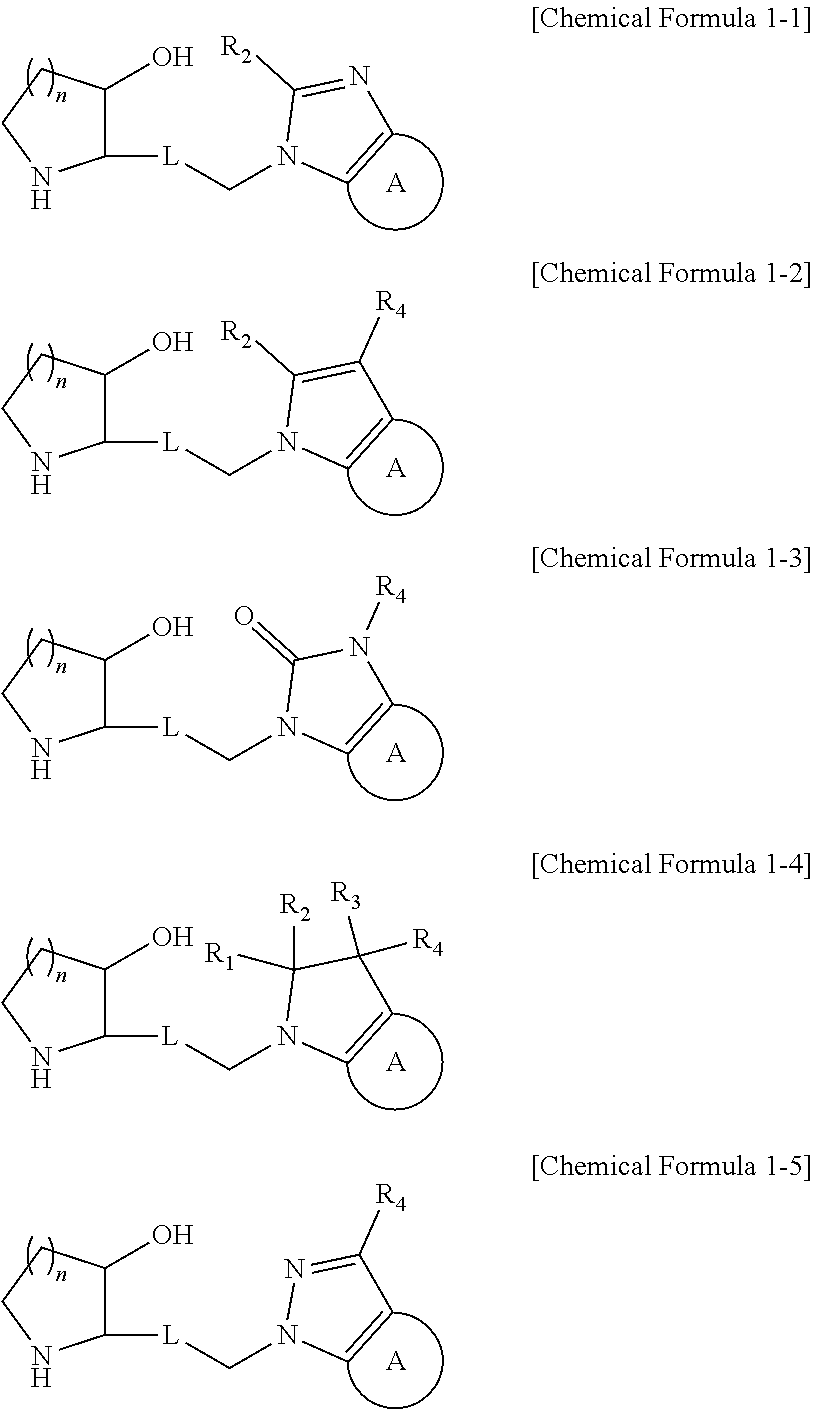
The present invention relates to a heterocyclic compound represented by Chemical Formula 1 that can be used for the prevention or treatment of diseases caused by abnormality in a PRS (prolyl-tRNA synthetase) activity, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a method for preparing the same, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same.
Owner:DAEWOONG PHARM CO LTD
Protein synthesis modulators
InactiveUS8428884B1Modulate activityMolecular designDigital data processing detailsRibosome SubunitsRna protein
The invention provides a high resolution three-dimensional structure of a deacylated transfer RNA protein synthesis modulator in association with a large ribosomal subunit. The protein synthesis modulator binds at least a portion of the E-site of a large ribosomal subunit. The invention provides methods for designing and / or identifying analogs of candidate molecules, for example, analogs or derivatives of the protein synthesis modulator, that bind and / or modulate the protein biosynthetic activity of the ribosome.
Owner:MELINTA SUBSIDIARY CORP
T3DNA ligase and T4RNA ligase 2 detect n 6 Application of methyladenine
ActiveCN106755306BEasy to operateHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMessenger RNABiology
The invention discloses an application of ligase in detection of N6 methyladenine, wherein the ligase is T3 DNA ligase or the T4 RNA ligase 2. The invention firstly discovers that the N6 methyladenine (m6A) can inhibit the connection activity of the T3 DNA ligase and the T4 RNA ligase 2 in comparison with adenine (A), based on the characteristic, the RNA (the RNA containing A and the RNA containing m6A) is taken as a template to establish a method for quantitatively determining the m6A percent content based on the ligase-polymerase chain reaction. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in operation, high in sensitivity and good in specificity, the m6A percent content in each of messenger RNA, long non-coding RNA, ribosome RNA, transfer RNA and small RNA and other RNA can be determined.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com