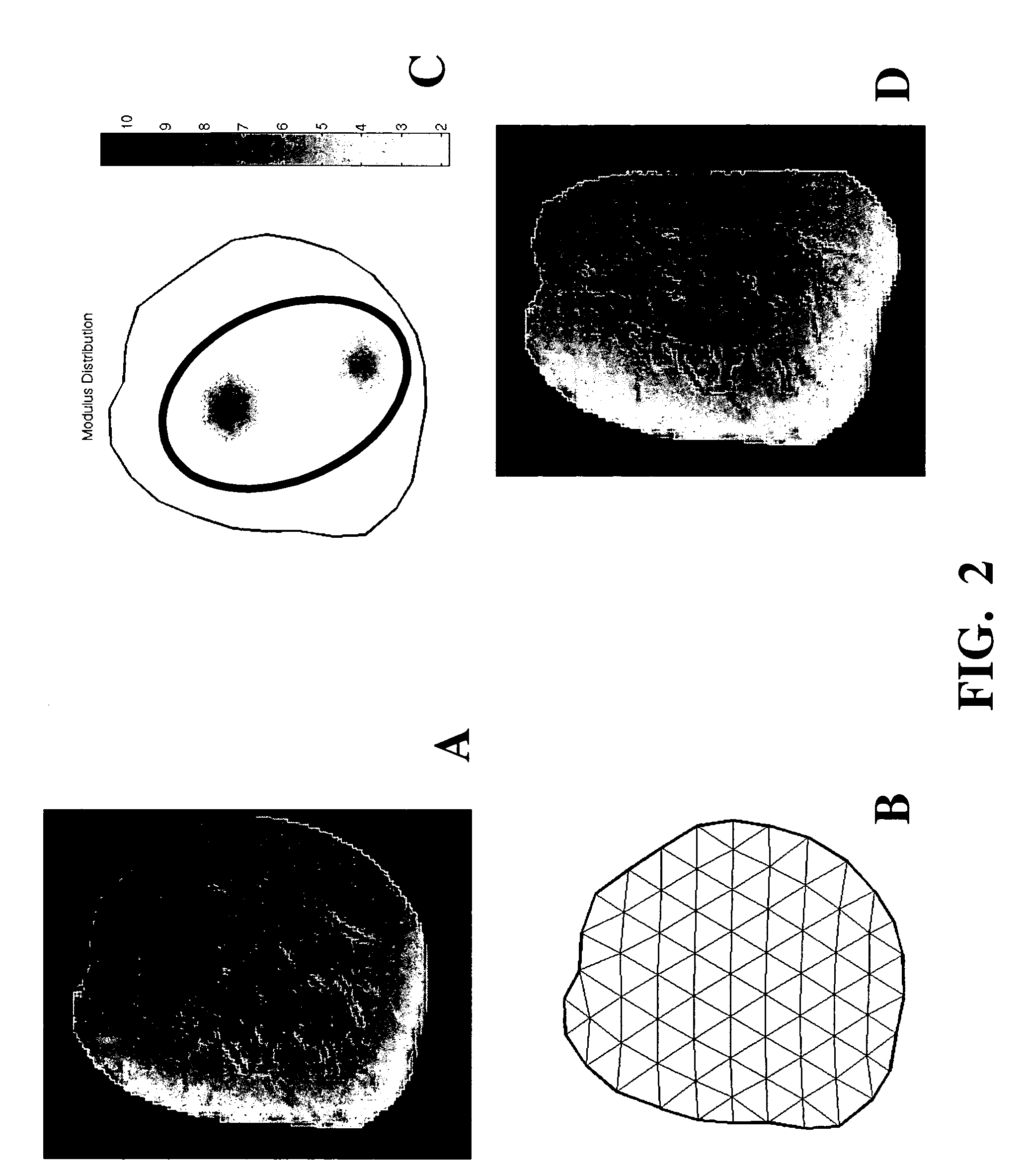
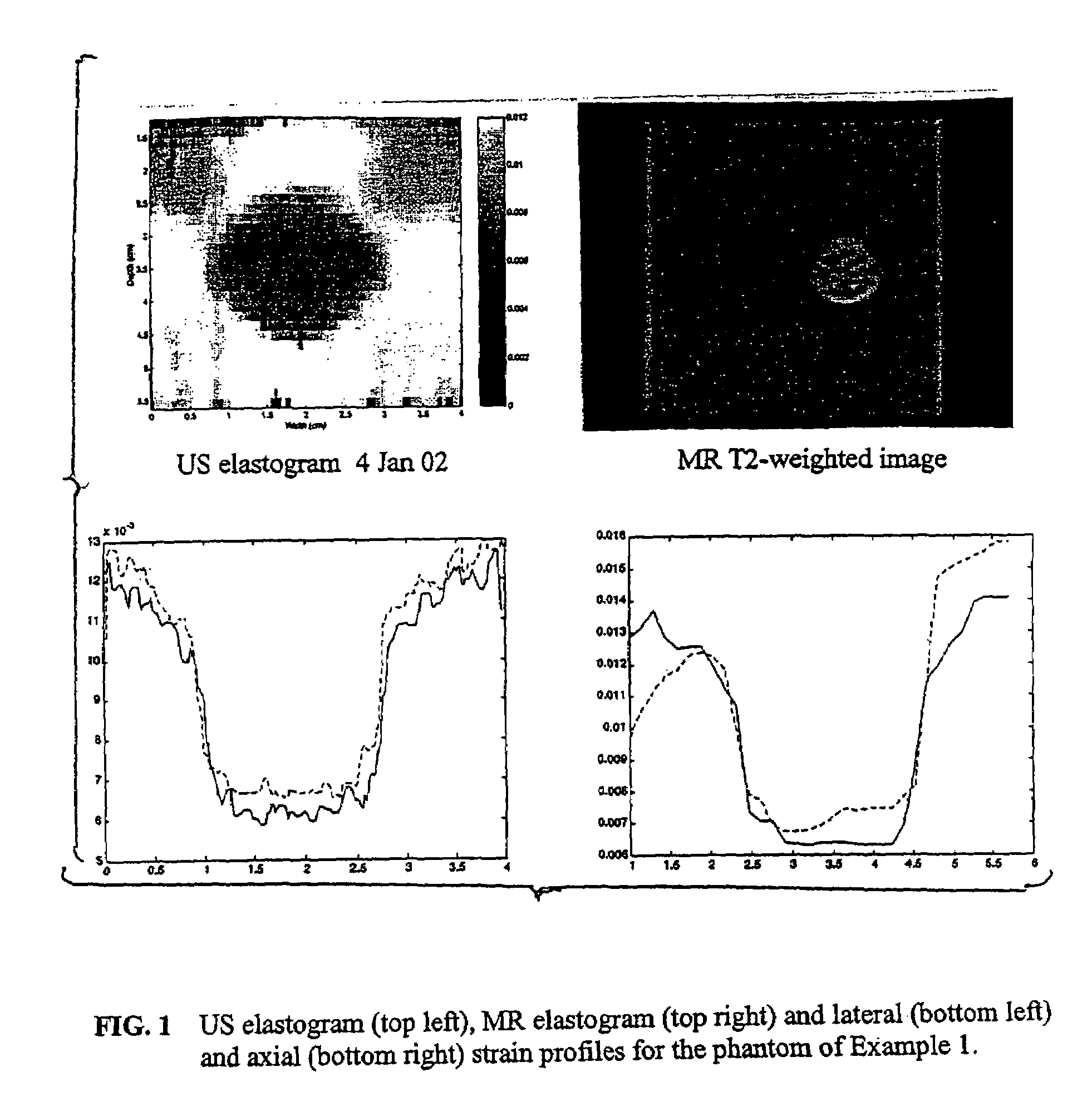
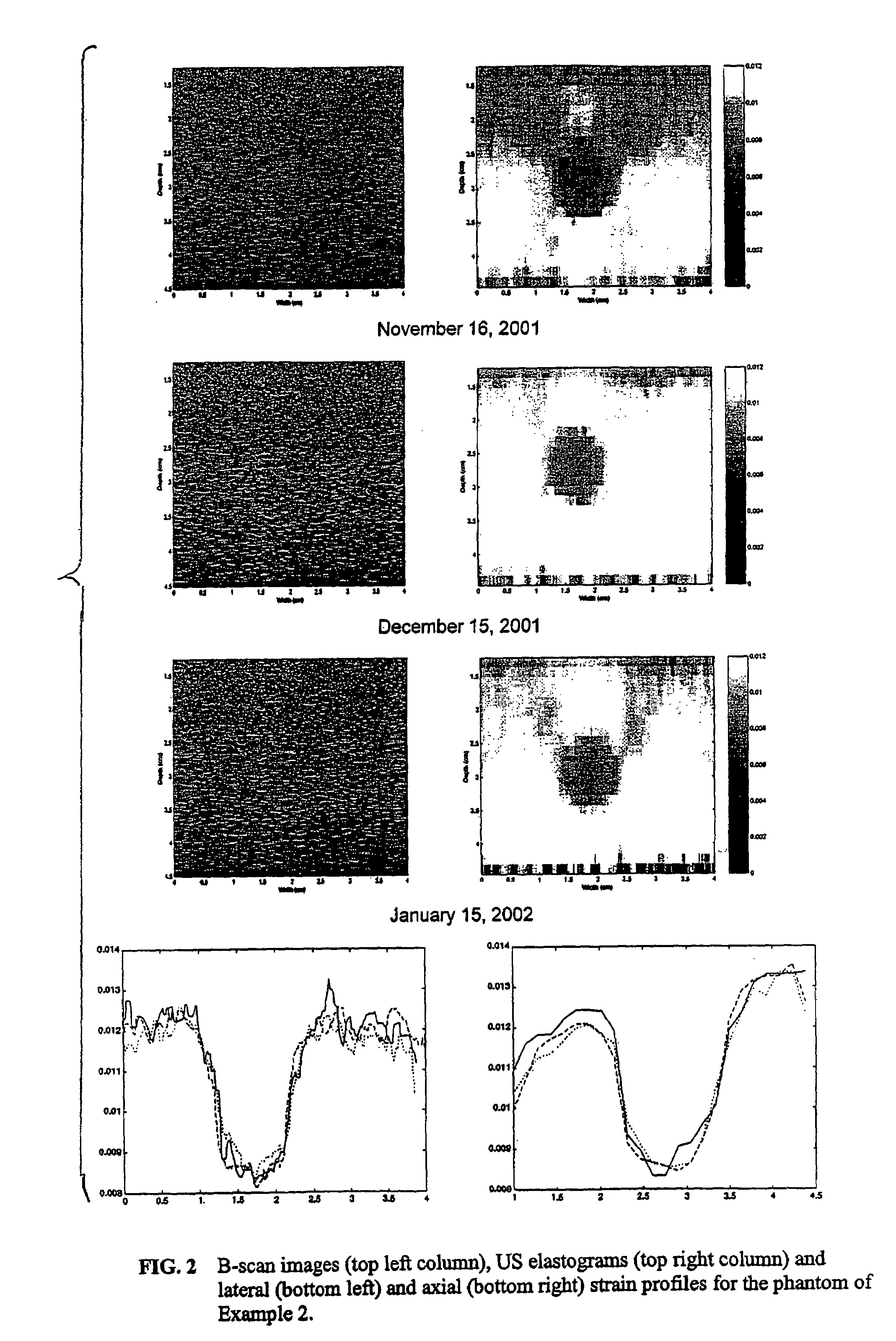
Patents
Literature
172 results about "Ultrasound elastography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
While not visible on conventional grayscale ultrasound (left), a strain elastography image (centre) of the prostate gland detects a cancer (dark red area at lower left).
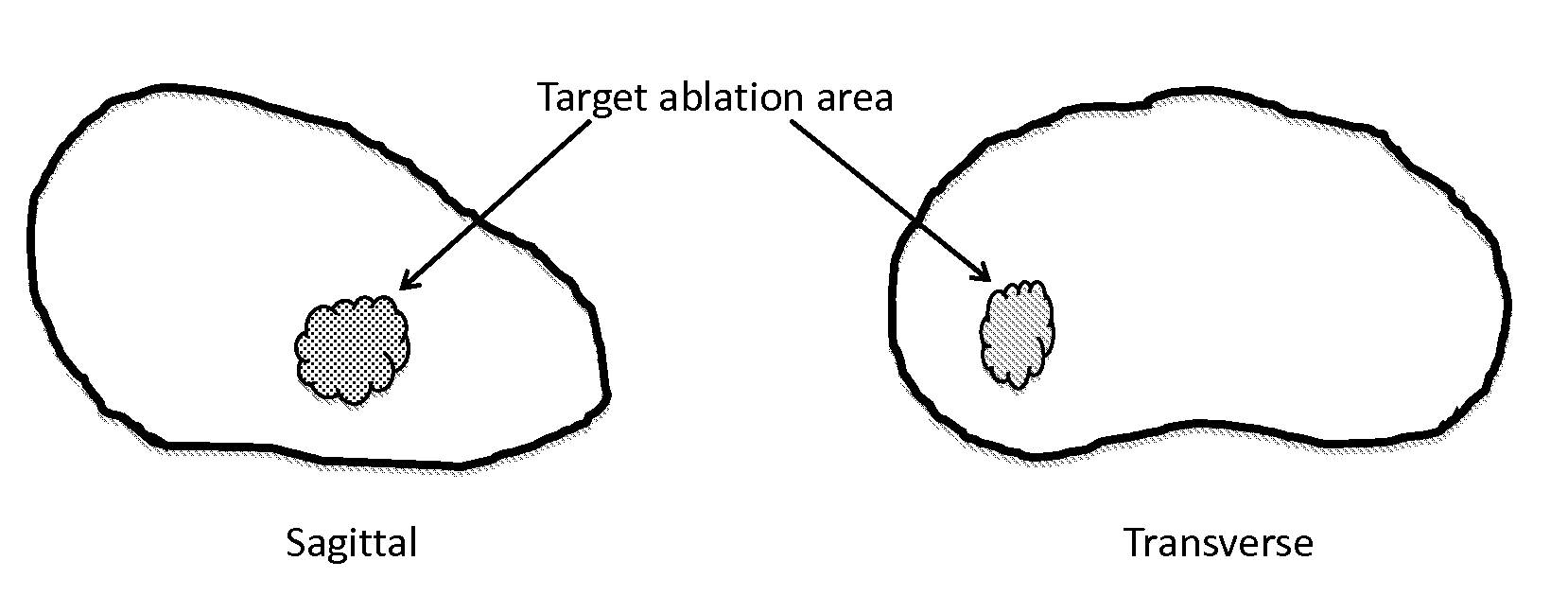
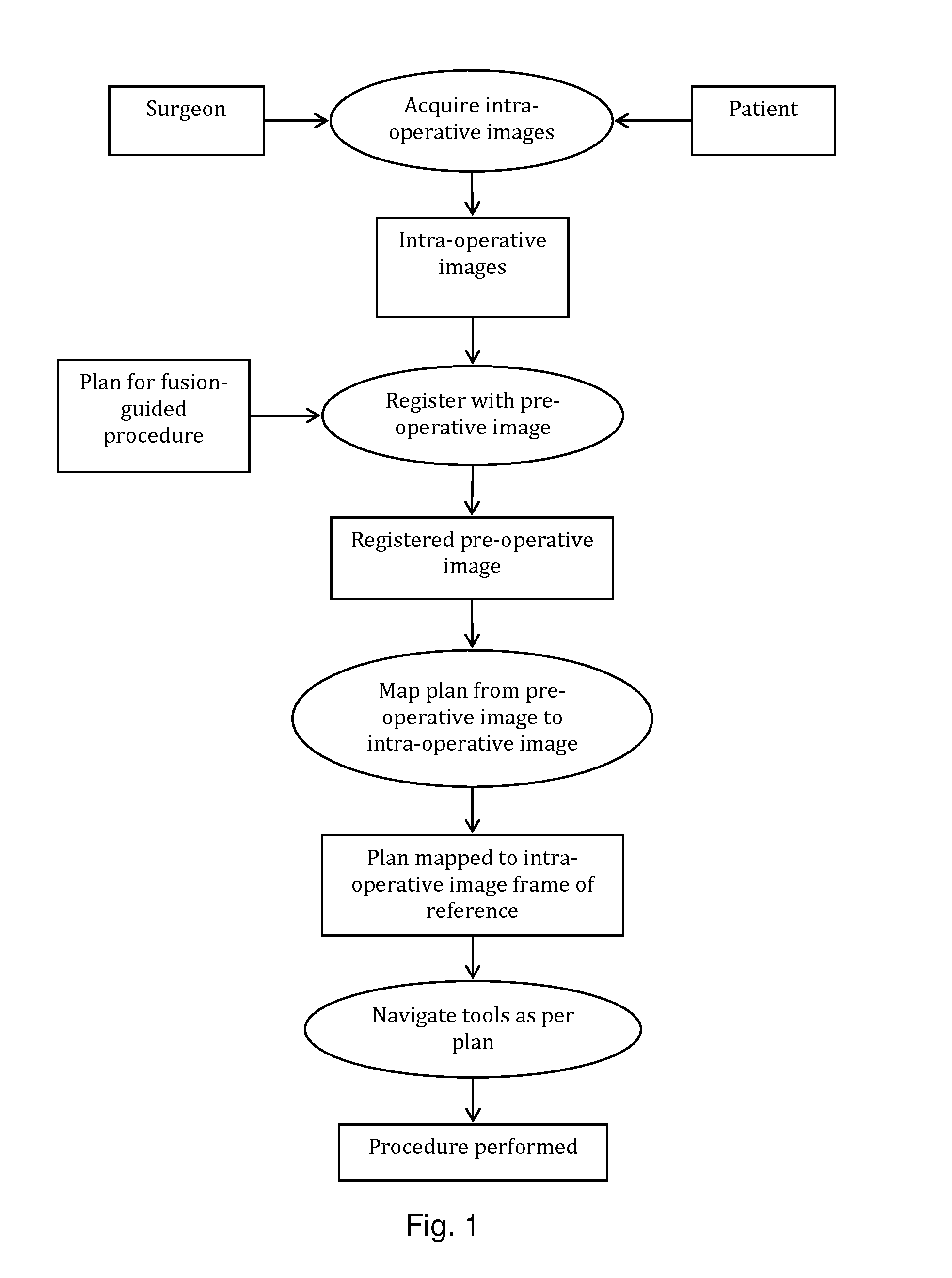
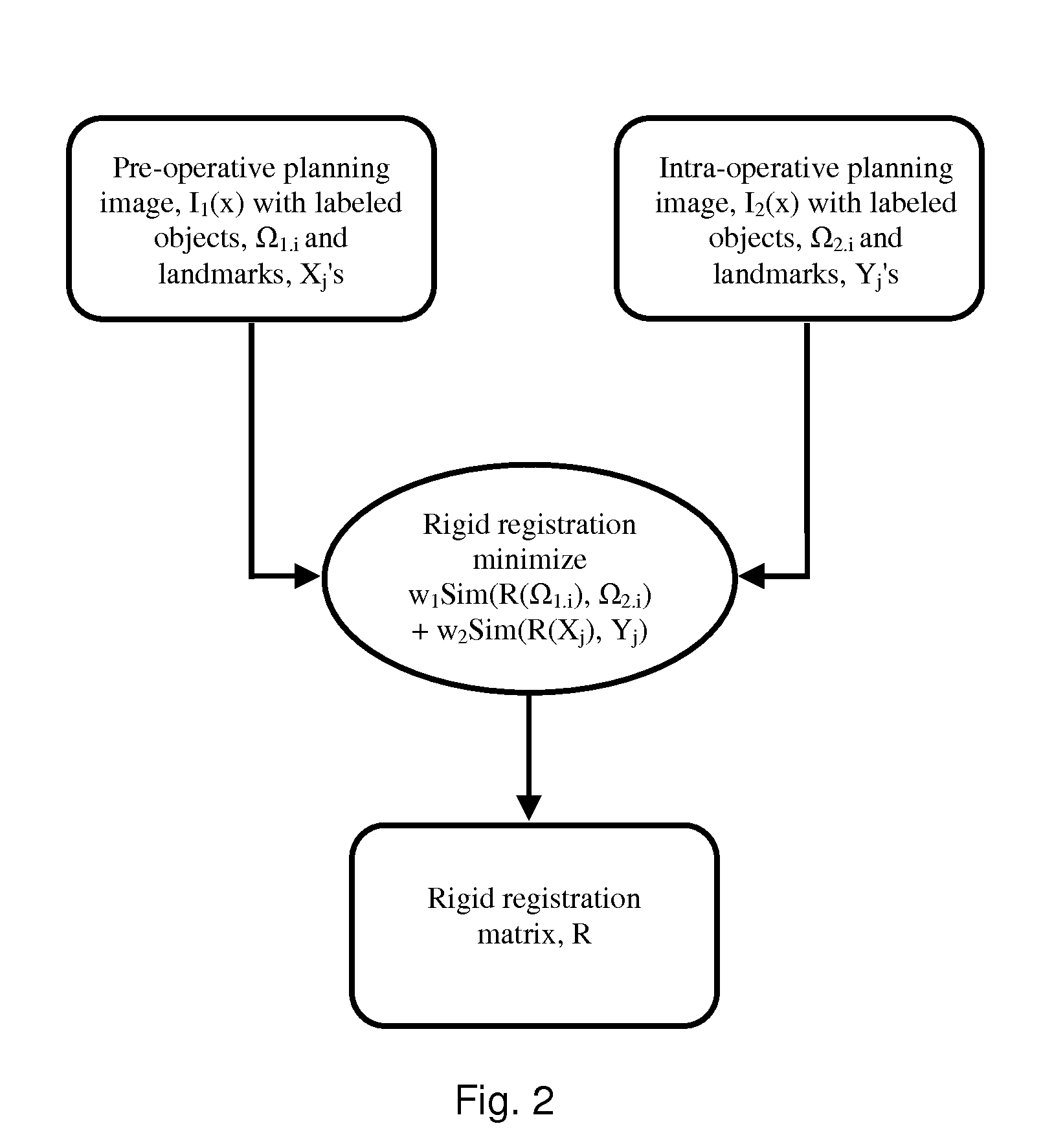
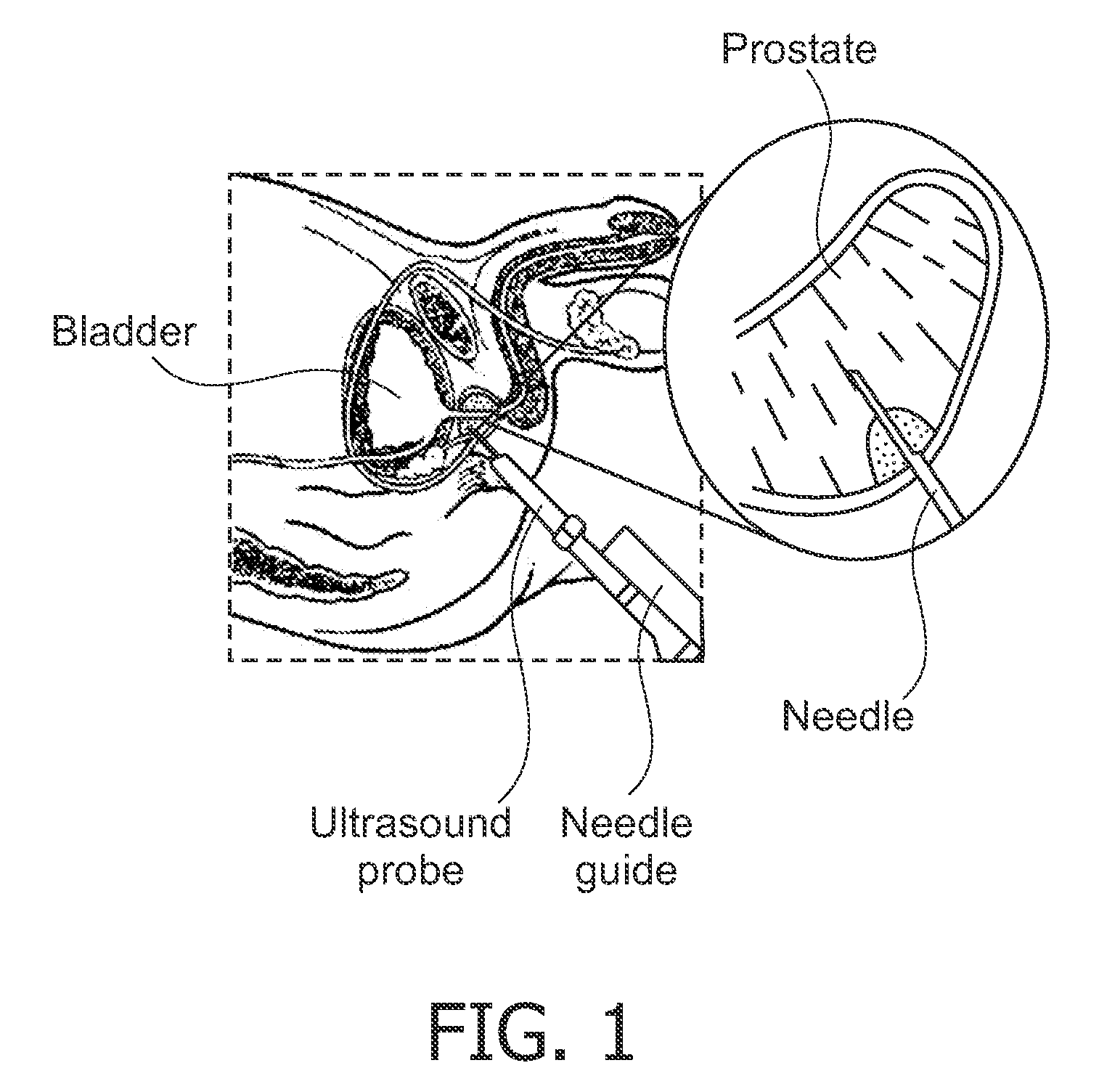
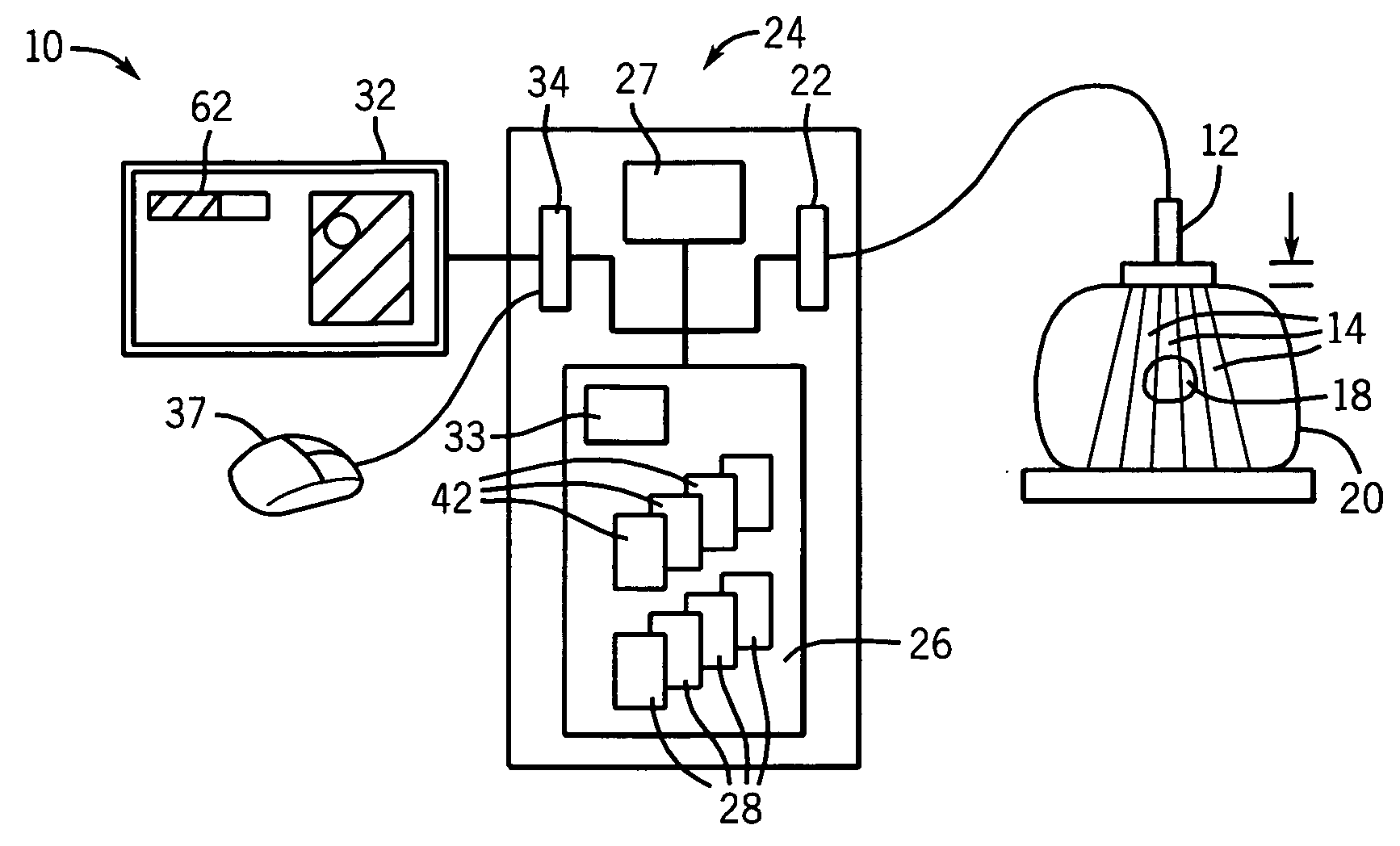
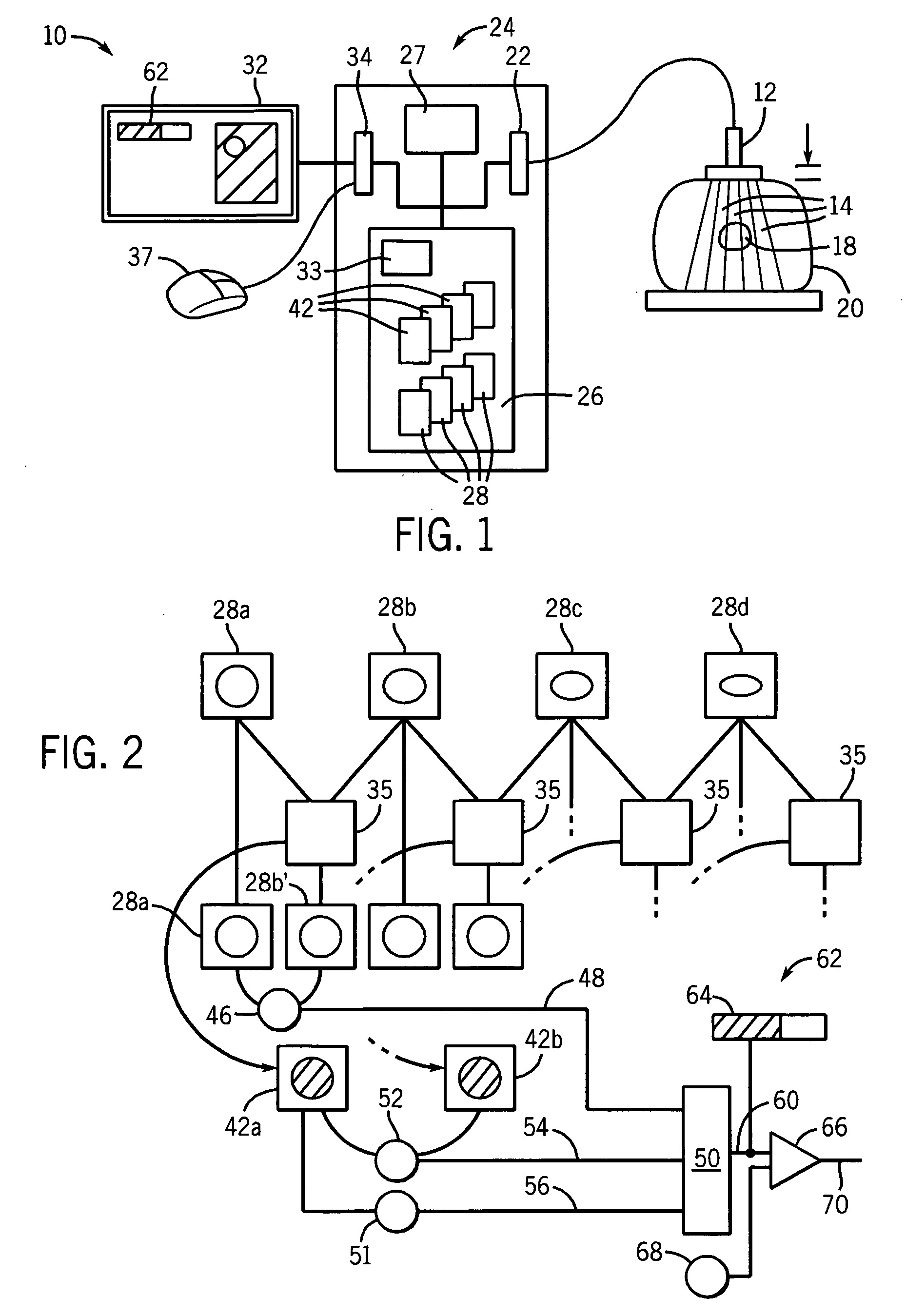
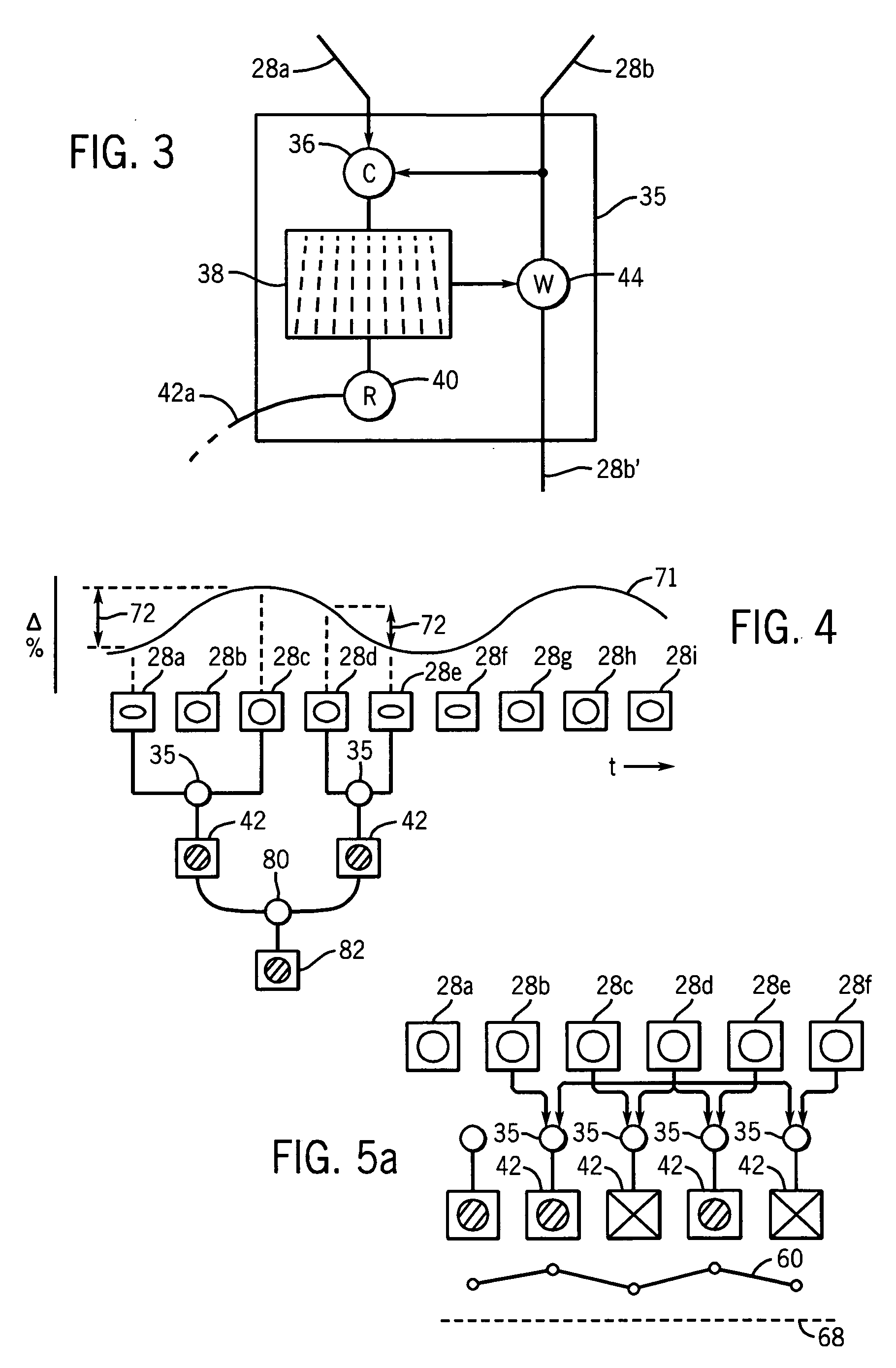
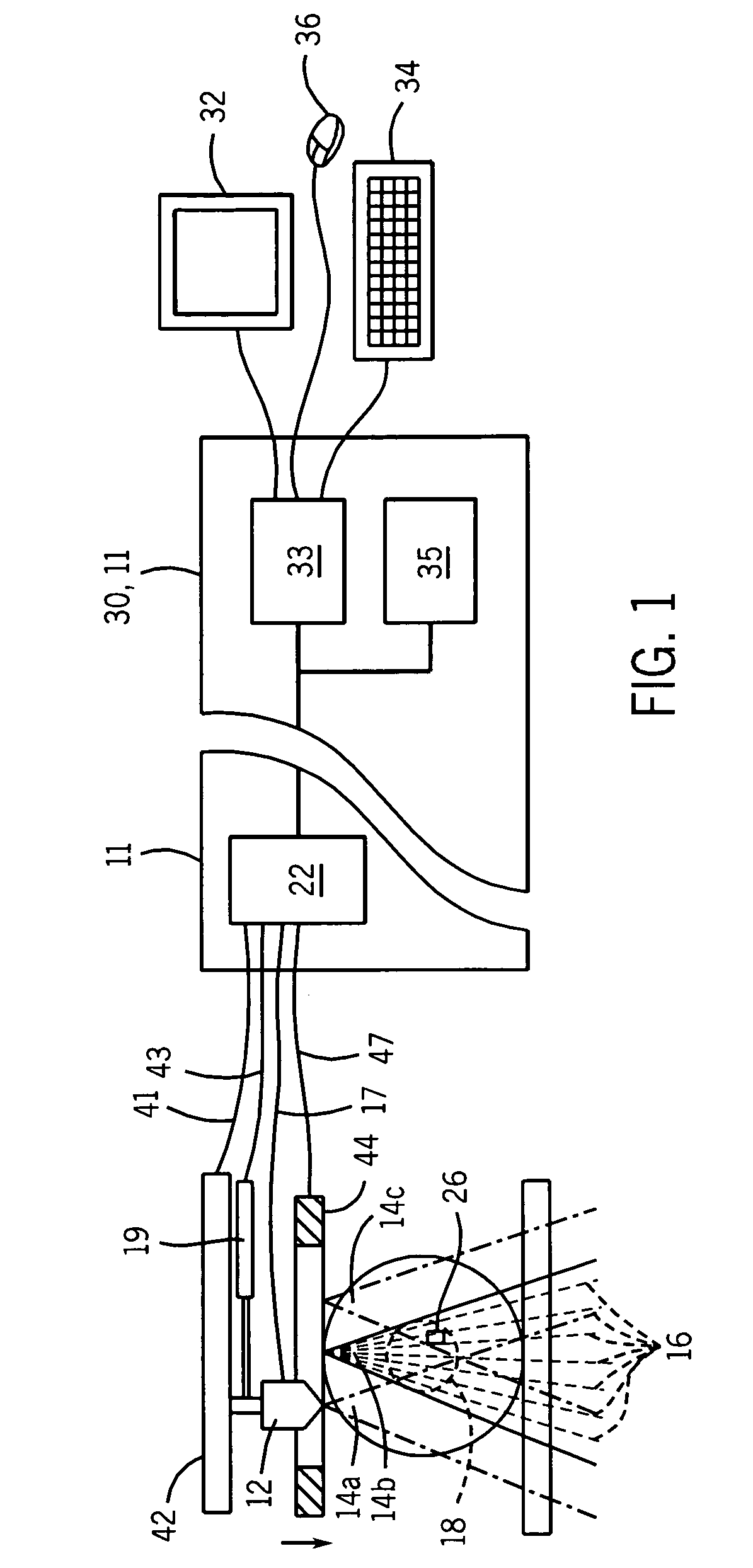
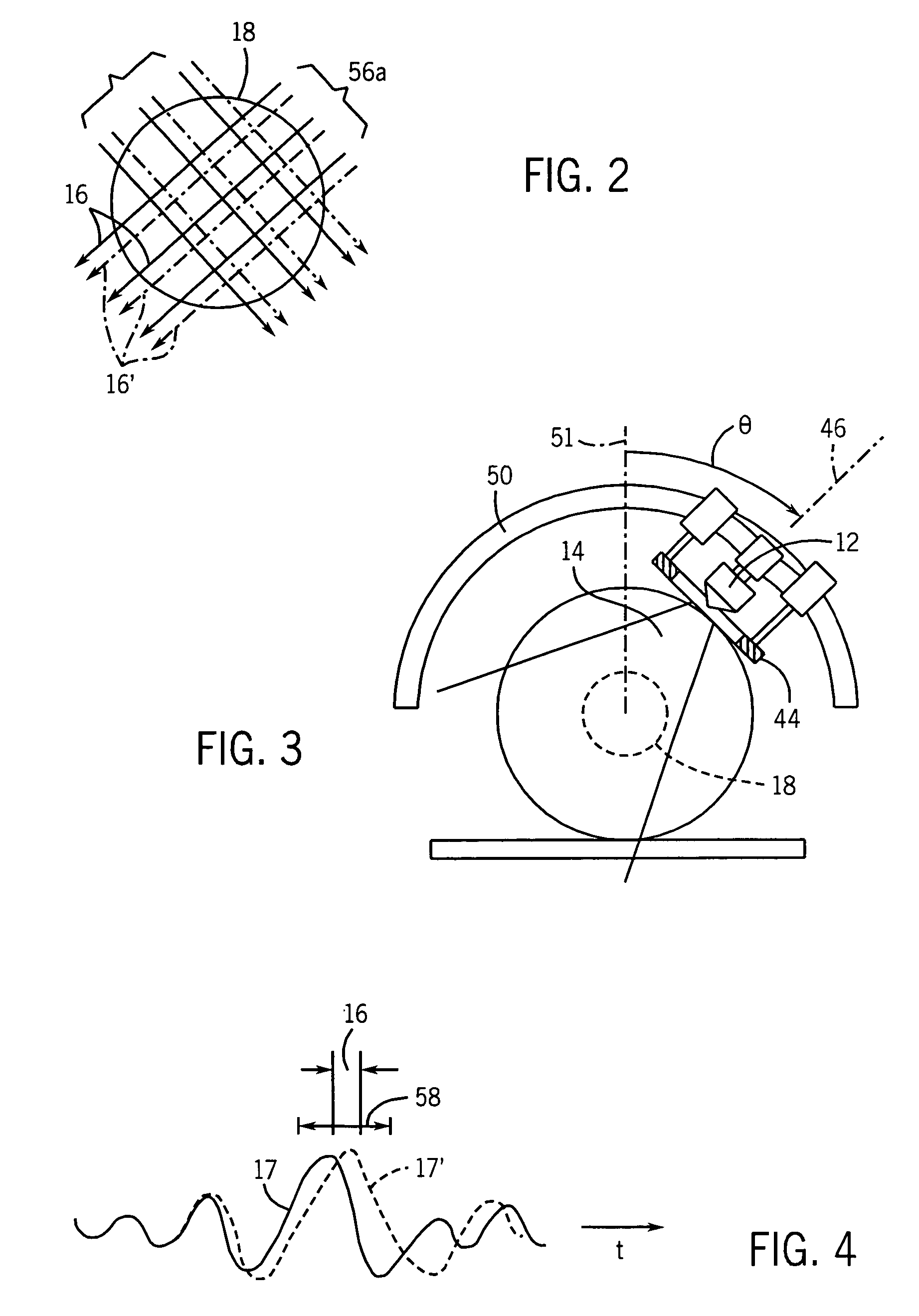
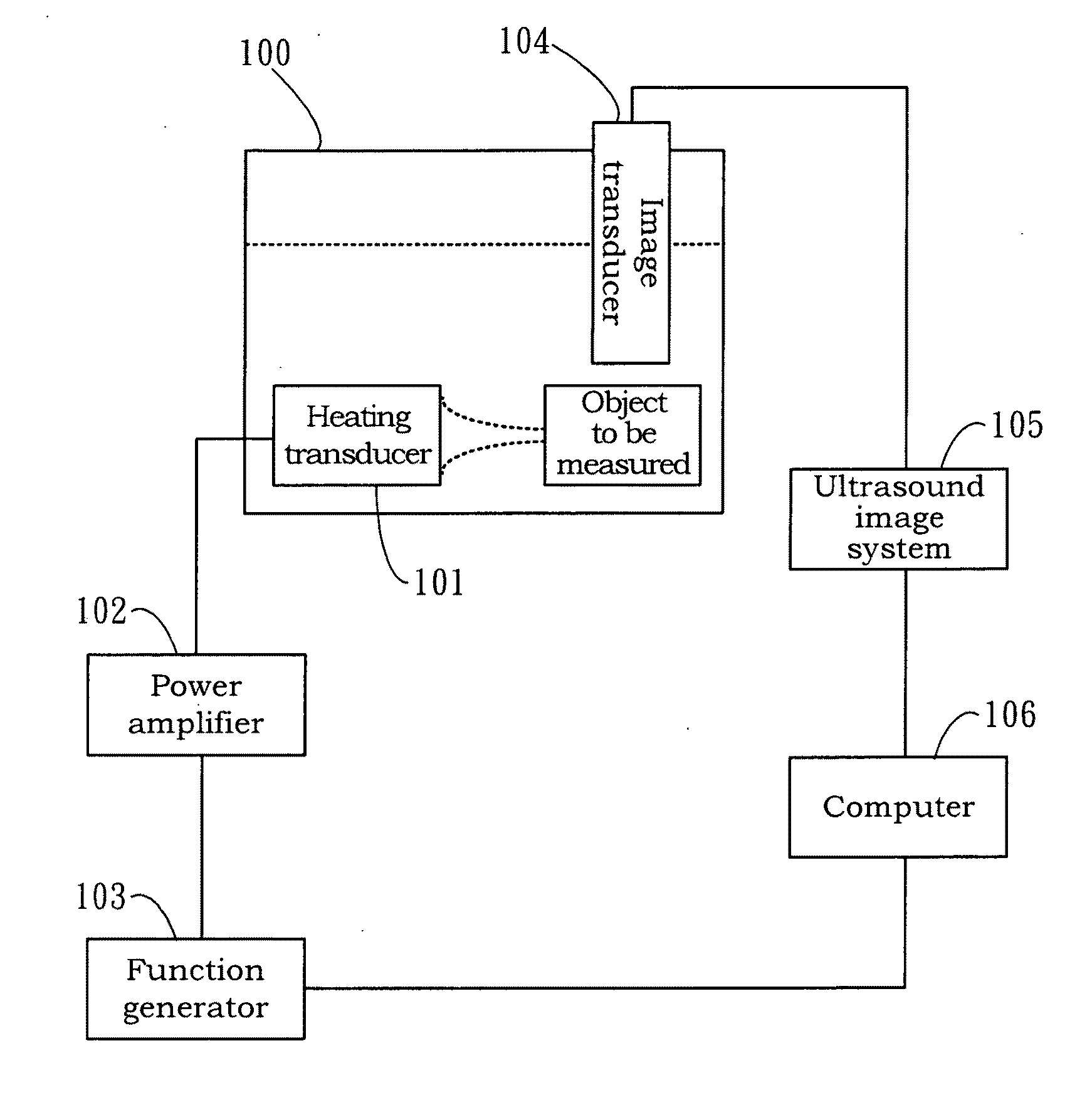
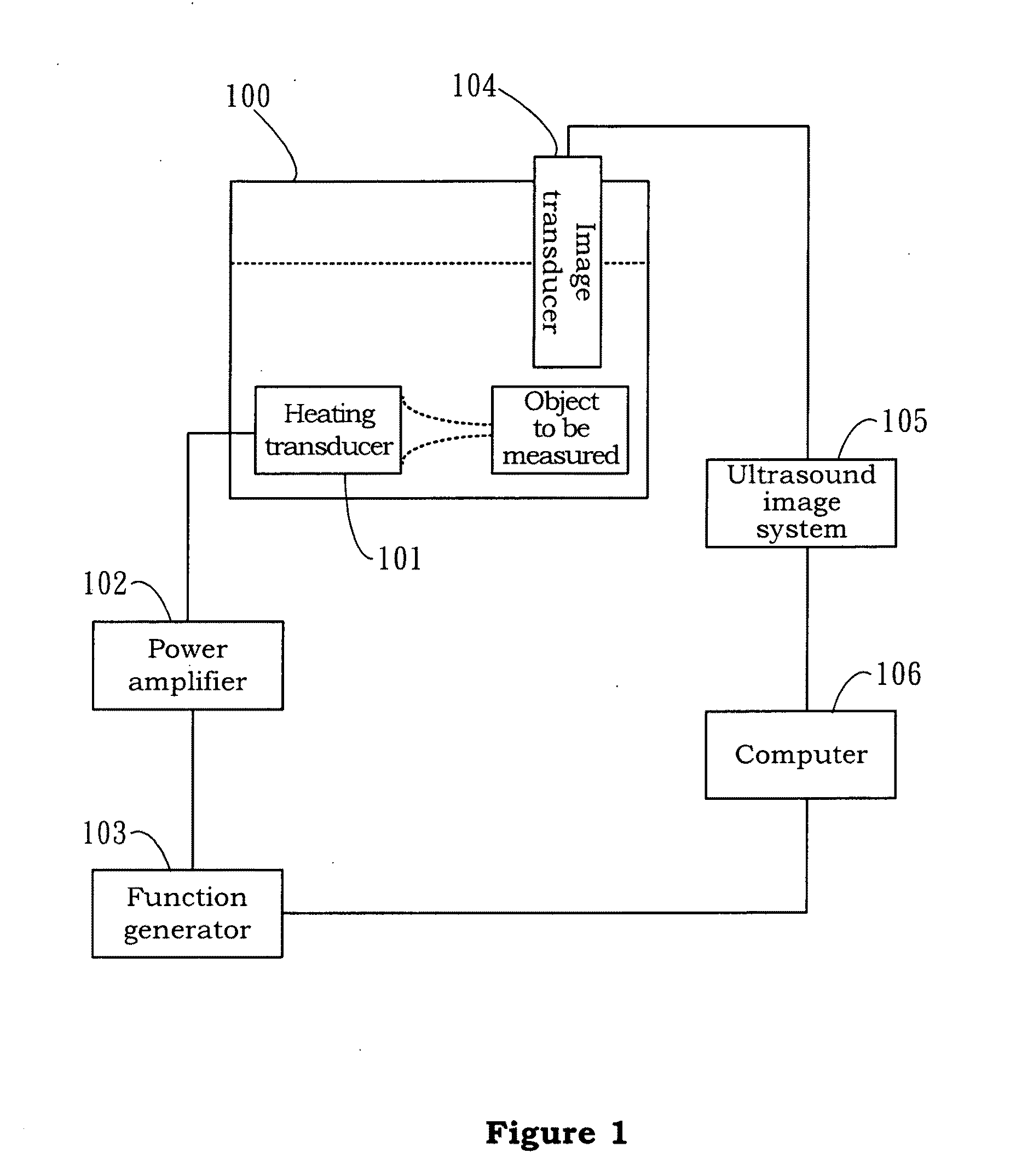
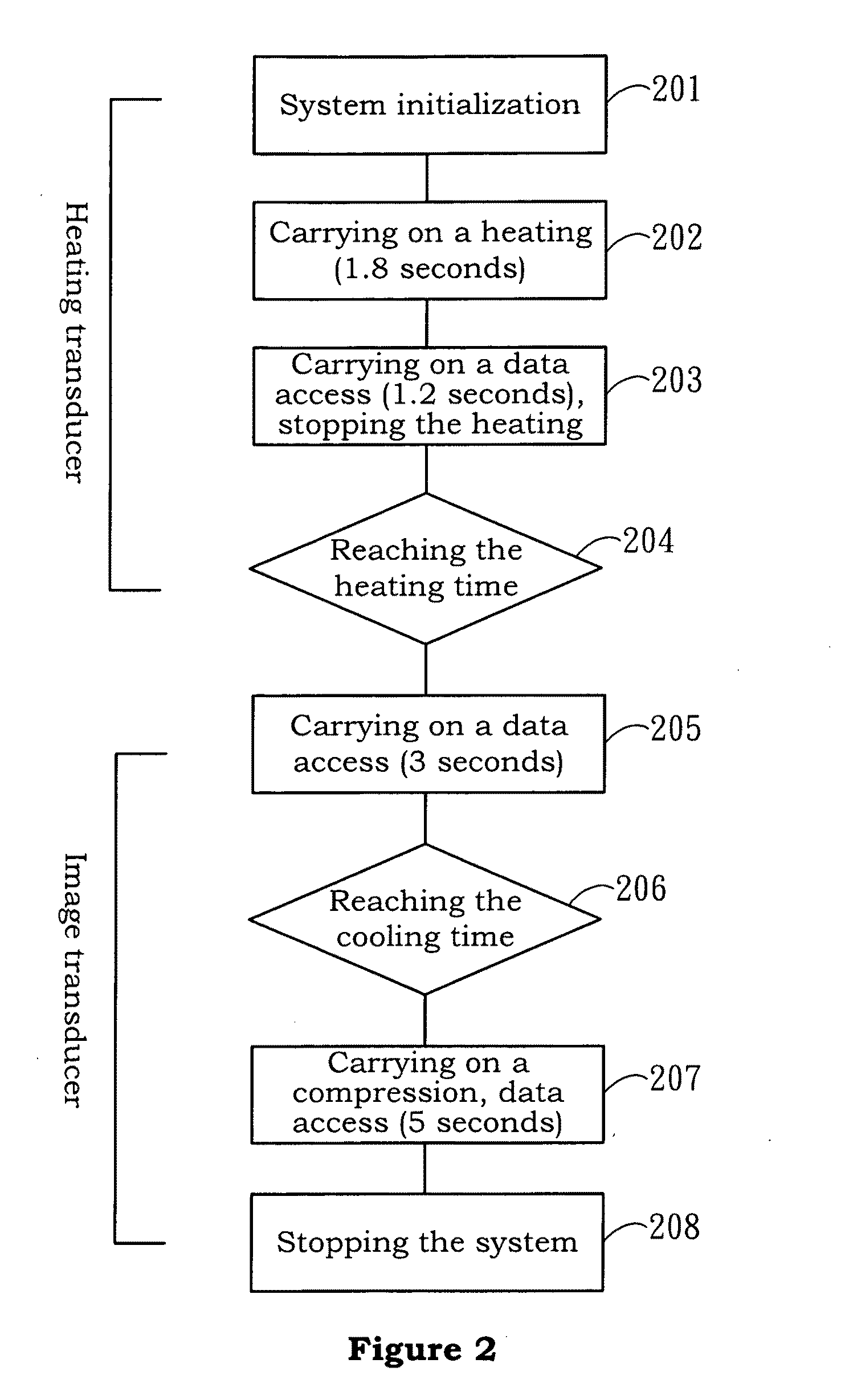
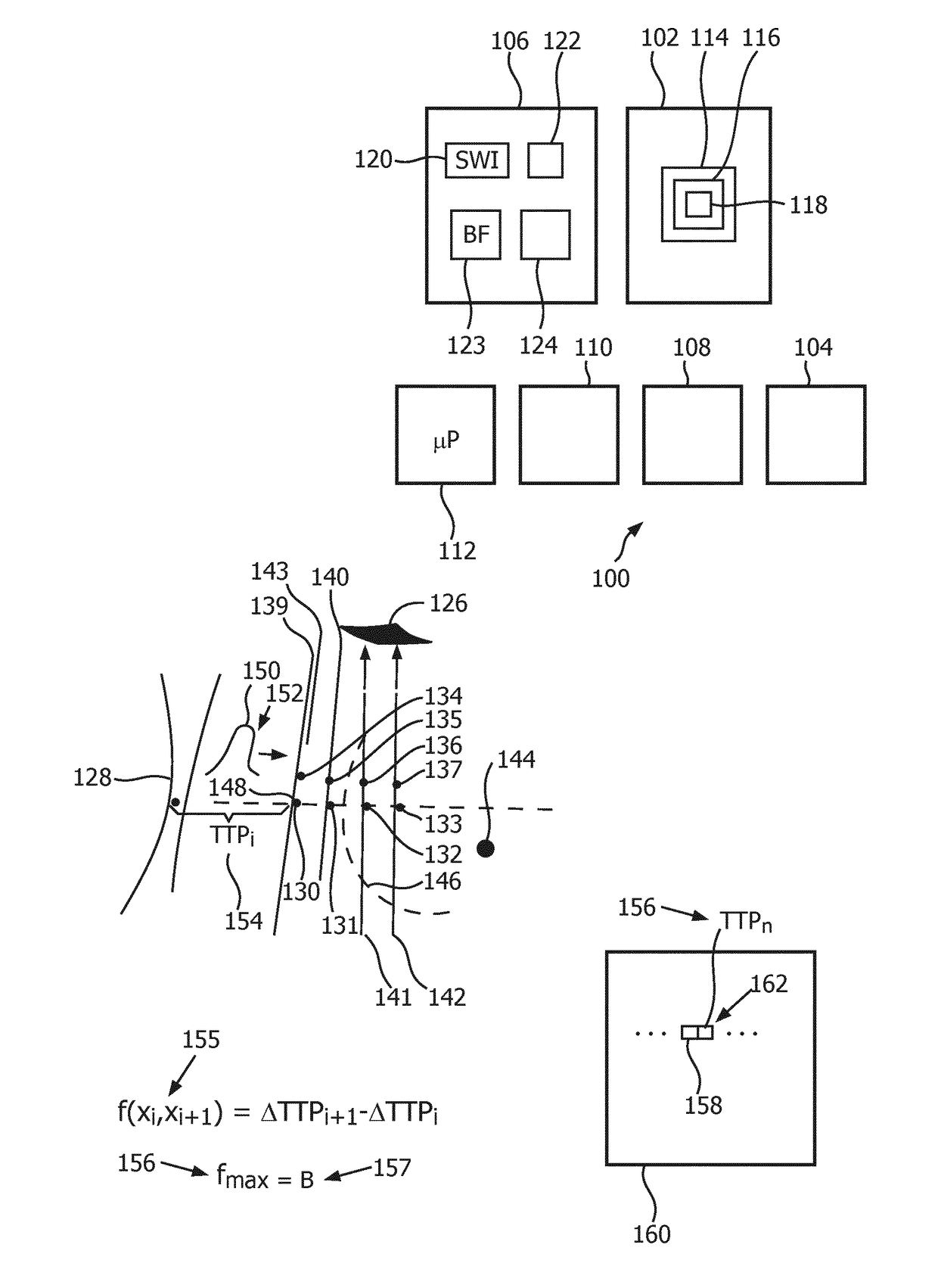
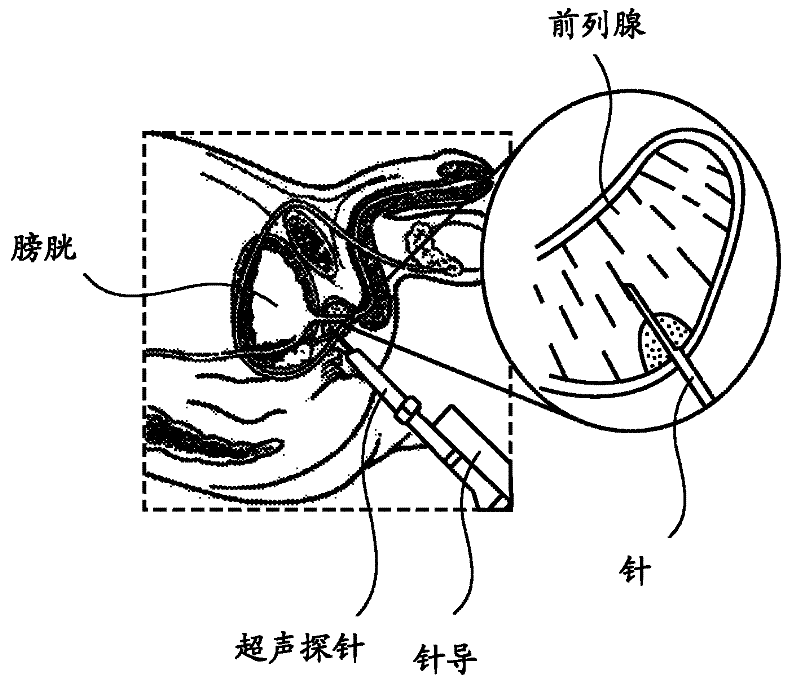
System and method for image guided medical procedures
InactiveUS20140073907A1Correction can be minimizedEasy to useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySoft tissue deformation
A system and method combines information from a plurality of medical imaging modalities, such as PET, CT, MRI, MRSI, Ultrasound, Echo Cardiograms, Photoacoustic Imaging and Elastography for a medical image guided procedure, such that a pre-procedure image using one of these imaging modalities, is fused with an intra-procedure imaging modality used for real time image guidance for a medical procedure for any soft tissue organ or gland such as prostate, skin, heart, lung, kidney, liver, bladder, ovaries, and thyroid, wherein the soft tissue deformation and changes between the two imaging instances are modeled and accounted for automatically.
Owner:CONVERGENT LIFE SCI
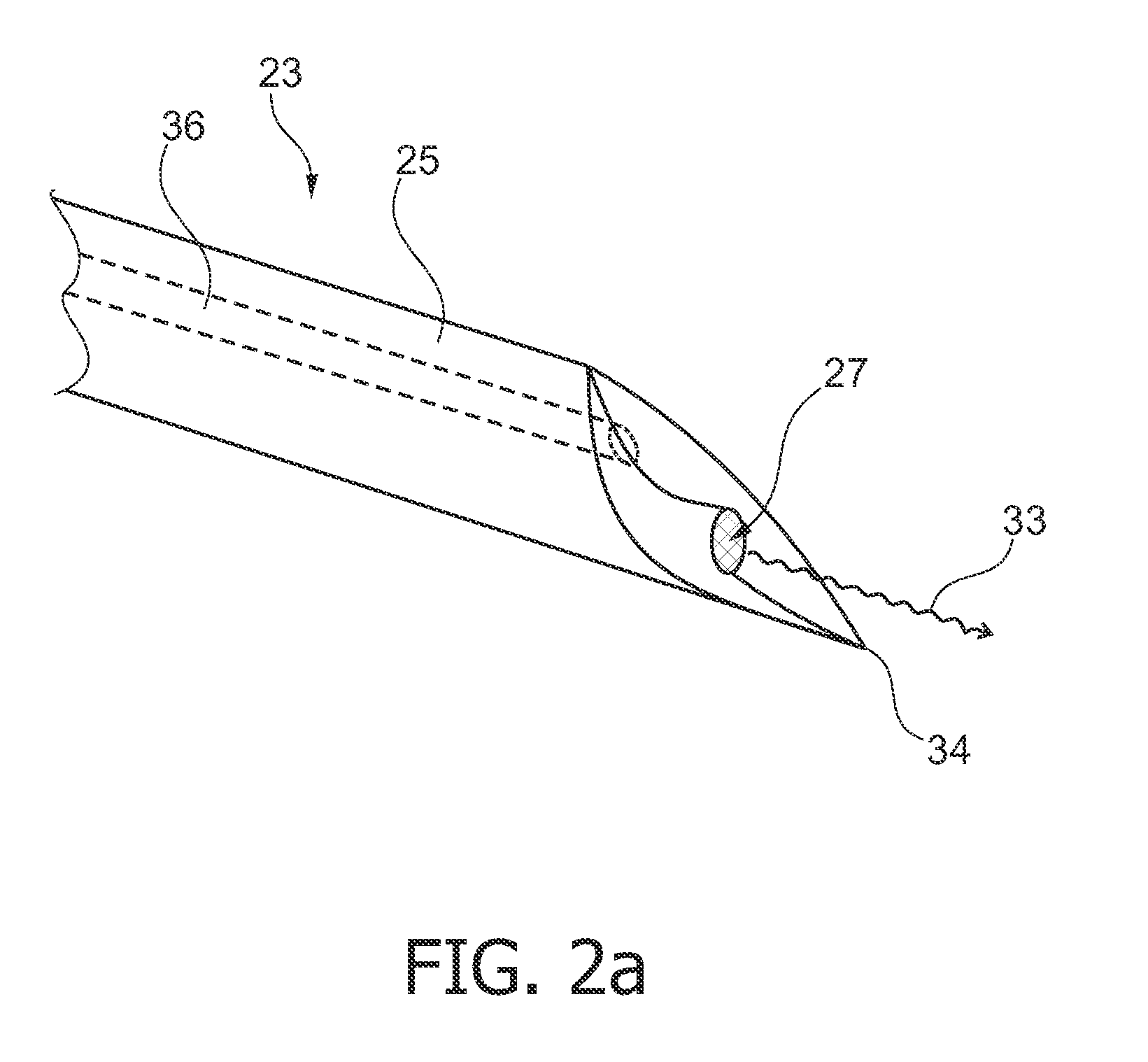
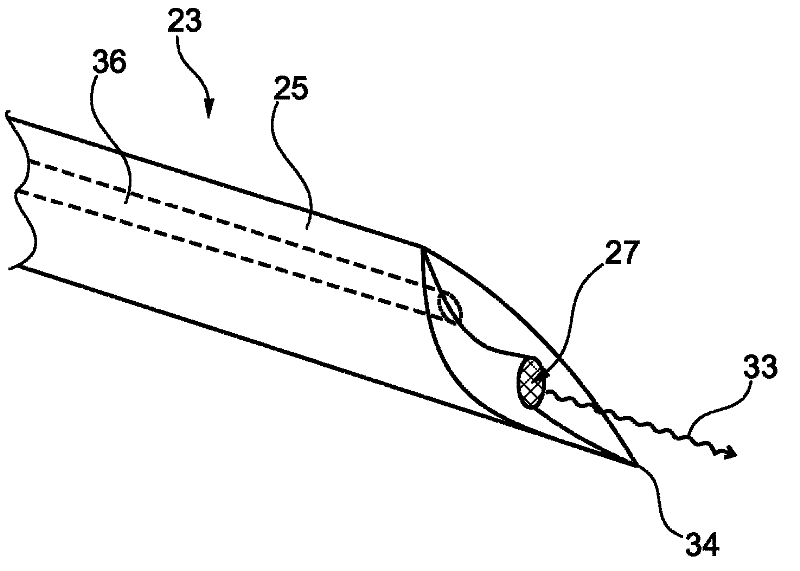
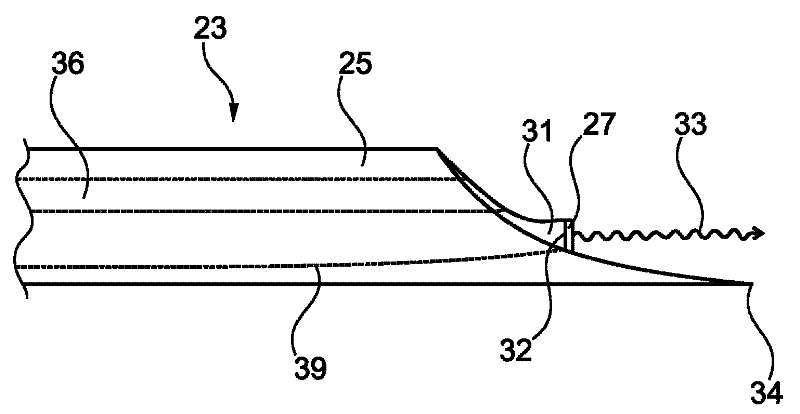
Biopsy device with acoustic element
InactiveUS20110066073A1Continuous measurementStrong absorption capacitySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsRadiologyTransducer
The invention relates to a biopsy device, particularly a biopsy device comprising a shaft with a transducer element for providing information about acoustic properties of a material to be analysed, a system of positioning a biopsy device and a method for positioning a biopsy device. The biopsy device may be adapted to take biopsies of different regions of the 5 human body for excluding or detecting abnormalities as cancerous lesions. The biopsy device may be used to measure acoustic properties of the material while inserting the tip portion of the biopsy device into the material to be analysed. The biopsy device may further allow measurement based on elastography.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
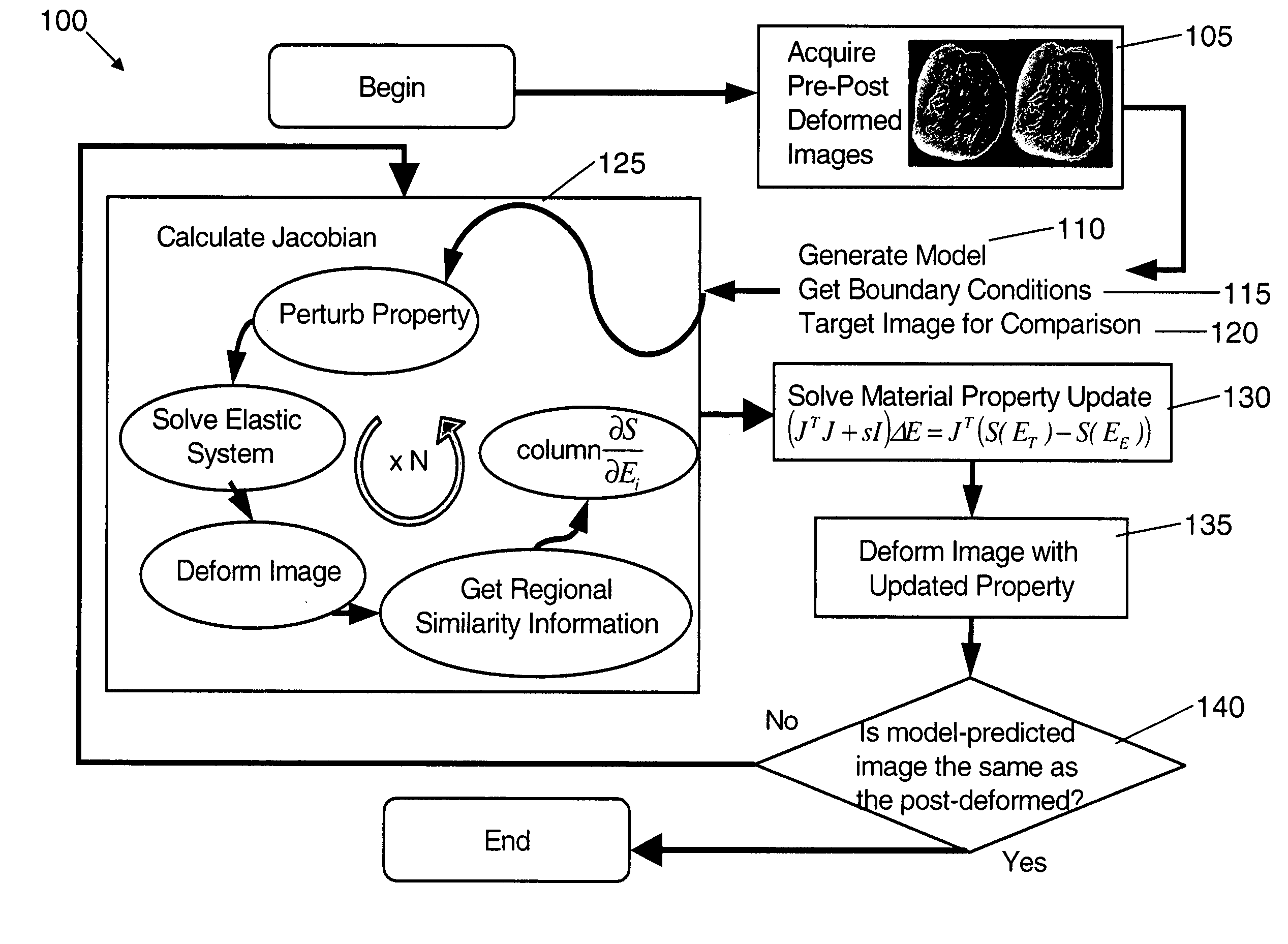
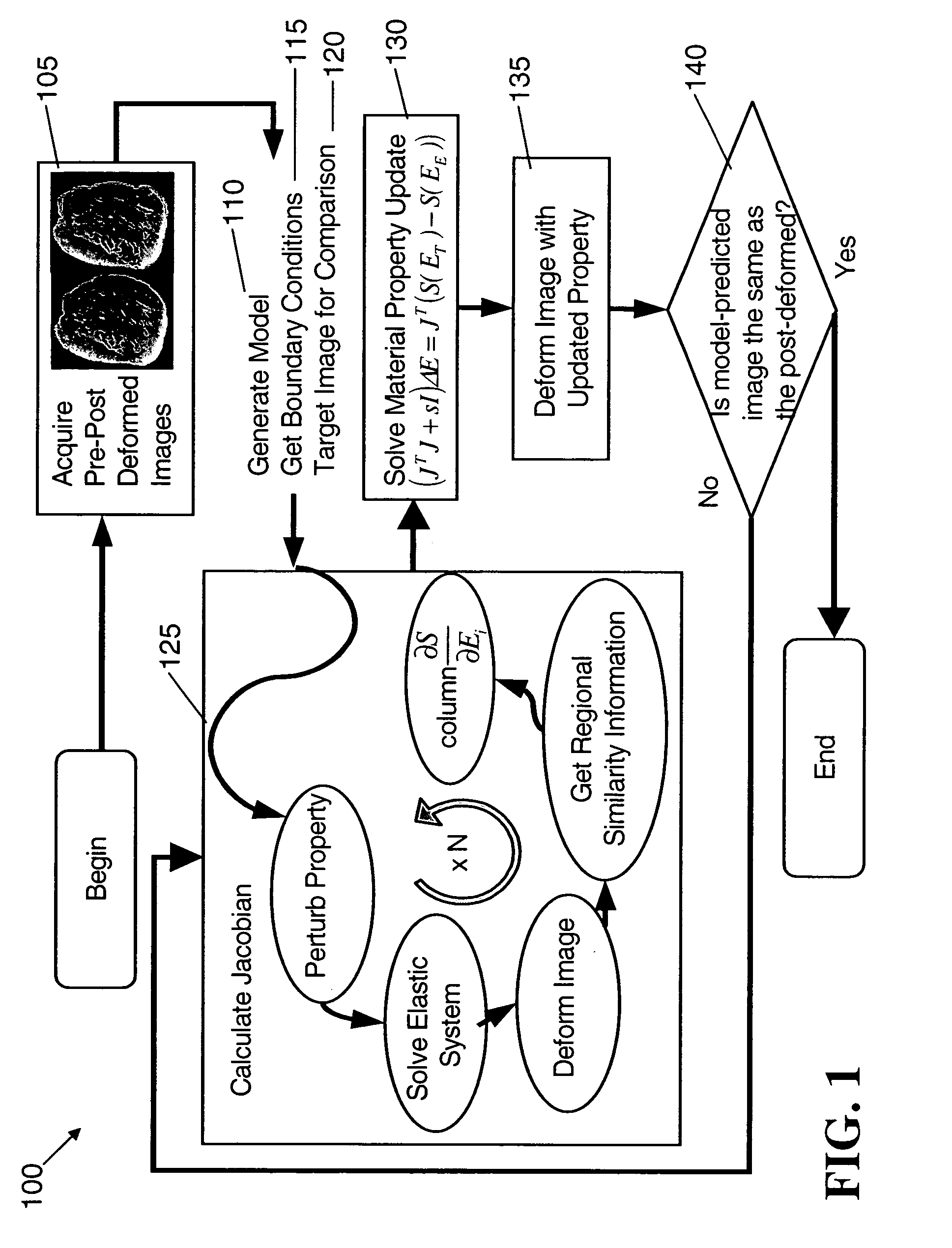
Elastography imaging modalities for characterizing properties of tissue
An image reconstruction algorithm begins with an initial acquisition of a preoperative imaging volume followed by a second imaging sequence subsequent to an applied deformation. A computational domain (model) is generated from the preoperative image series and boundary conditions are derived from a pre-post deformation comparison, as well as from information gathered from deformation source application (i.e., displacement and / or force). Using boundary conditions, a series of model-based image deformations is accomplished while varying model material properties. A calculation of a Jacobian matrix relating the change in regional mutual information is performed with respect to the change in material properties. Upon completion of this process, matrix regularization techniques are used to condition the system of equations and allow for inversion and subsequent delivery of model-property adjustments.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Tissue mimicking elastography phantoms
ActiveUS7462488B2Enhanced ultrasound backscatterImprove stabilityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceSonificationResonance
Tissue mimicking materials for elastography phantoms have elastic, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance characteristics that are characteristic of human soft tissues and well suited for the calibration and performance assessment of elastography imaging systems. In one embodiment, the material is formed from a base material containing an oil dispersed within a gel matrix and at least one inclusion formed from a gel. In another embodiment, the material is formed from a gel-forming material suffused throughout an open-cell reticulated mesh matrix.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Ultrasonic diagnostic device
InactiveUS20120136250A1Increase displacementImprove securityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsWide areaSonification
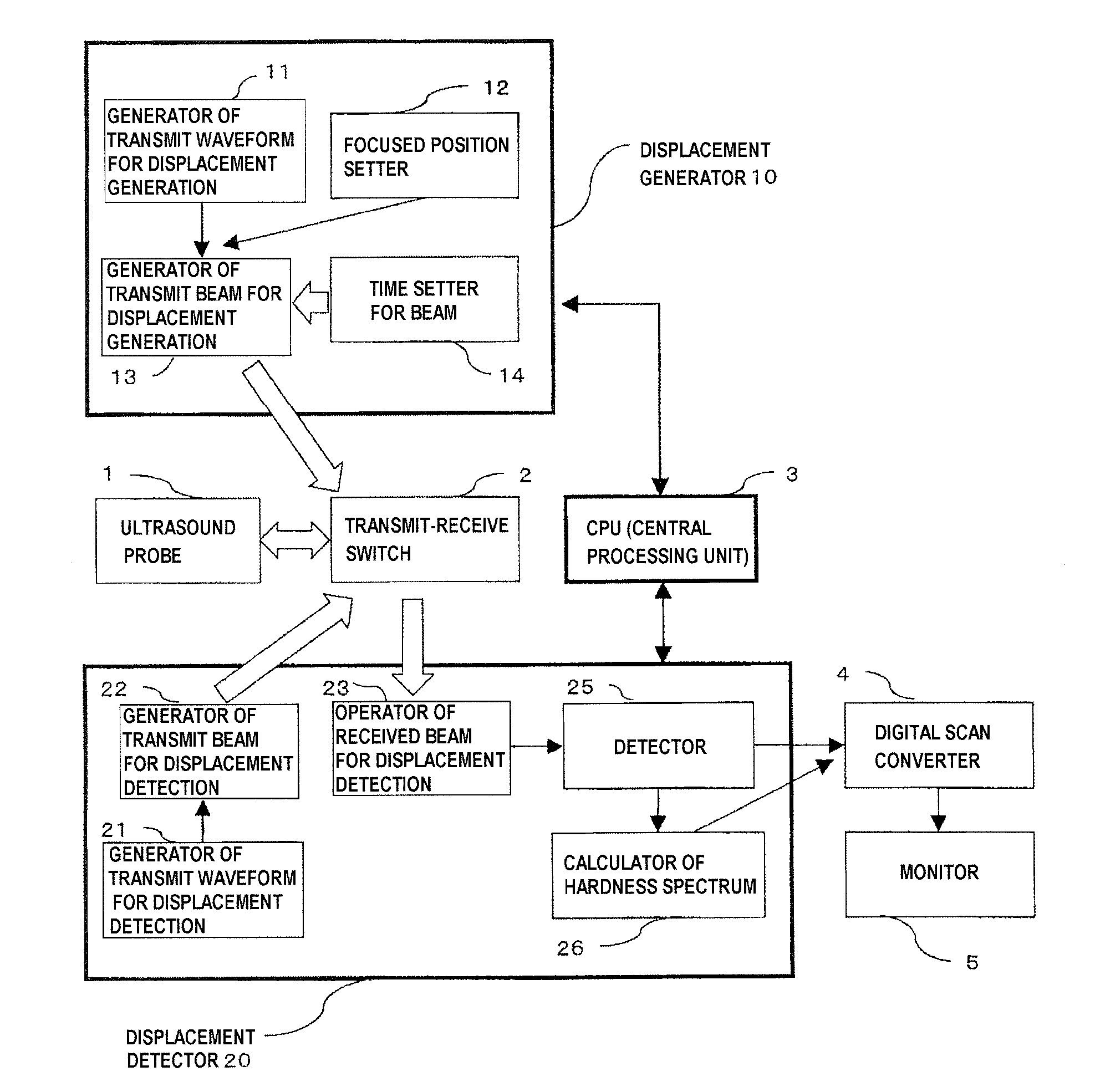
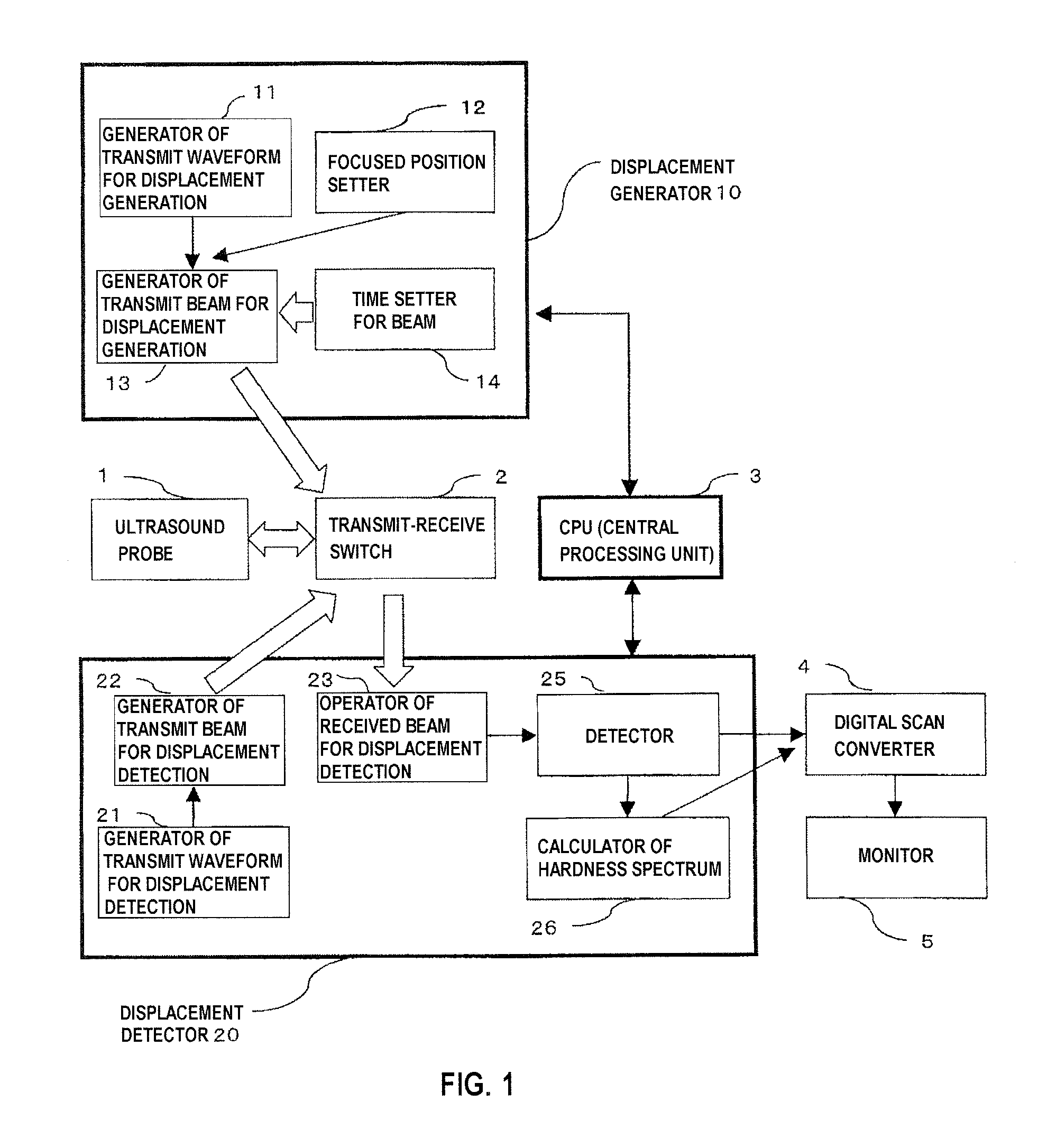
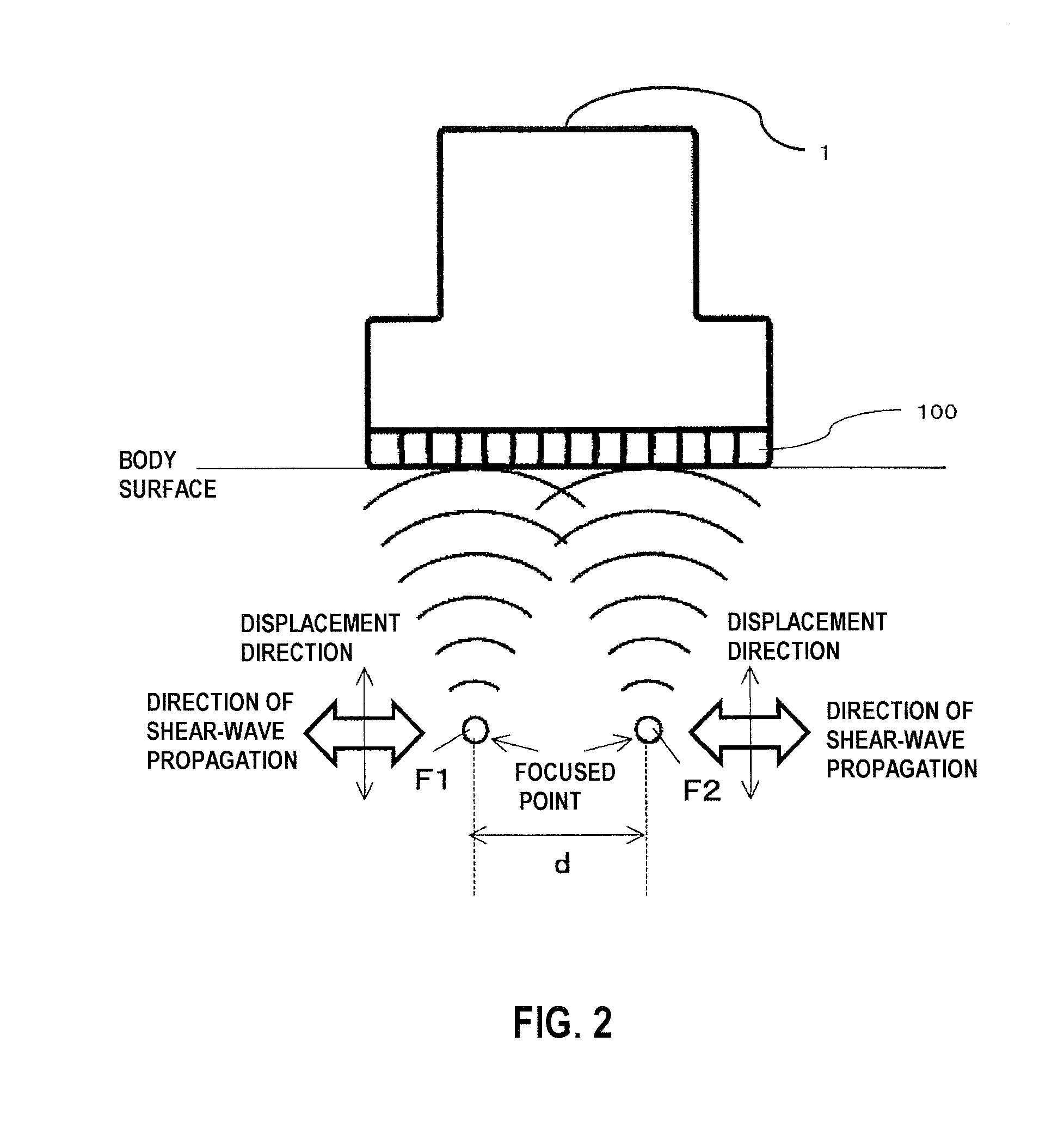
In a radiation-pressure elastography technique for transmitting a ultrasound focused beam into a test object body and diagnosing the hardness thereof, it is required to consider high sensitivity and safety.In the present invention, the focused beam is transmitted to two positions as a means for displacing a tissue and exciting a shear wave. In addition, time control is performed in such a manner that a transmit beam serves as a burst-chirp signal, and ultrasound waves are transmitted and received while sweeping a transmit frequency. On this occasion, when the distance between the two focused points and the transmit frequency become integral multiple of the wavelength, two waves interfere with each other, thereby obtaining a large amplitude. Furthermore, when the transmit frequency becomes equal to a resonance frequency peculiar to the tissue, the amplitude also becomes larger. Accordingly, a small intensity of transmit waveform enhances sensitivity. In addition, transmission using the burst-chirp signal facilitates widening of a bandwidth of the transmit frequency, enabling usage of a frequency highly sensitive for a target measurement site. Optional number of focused points and arbitrary positions thereof allow a wide area to be covered.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
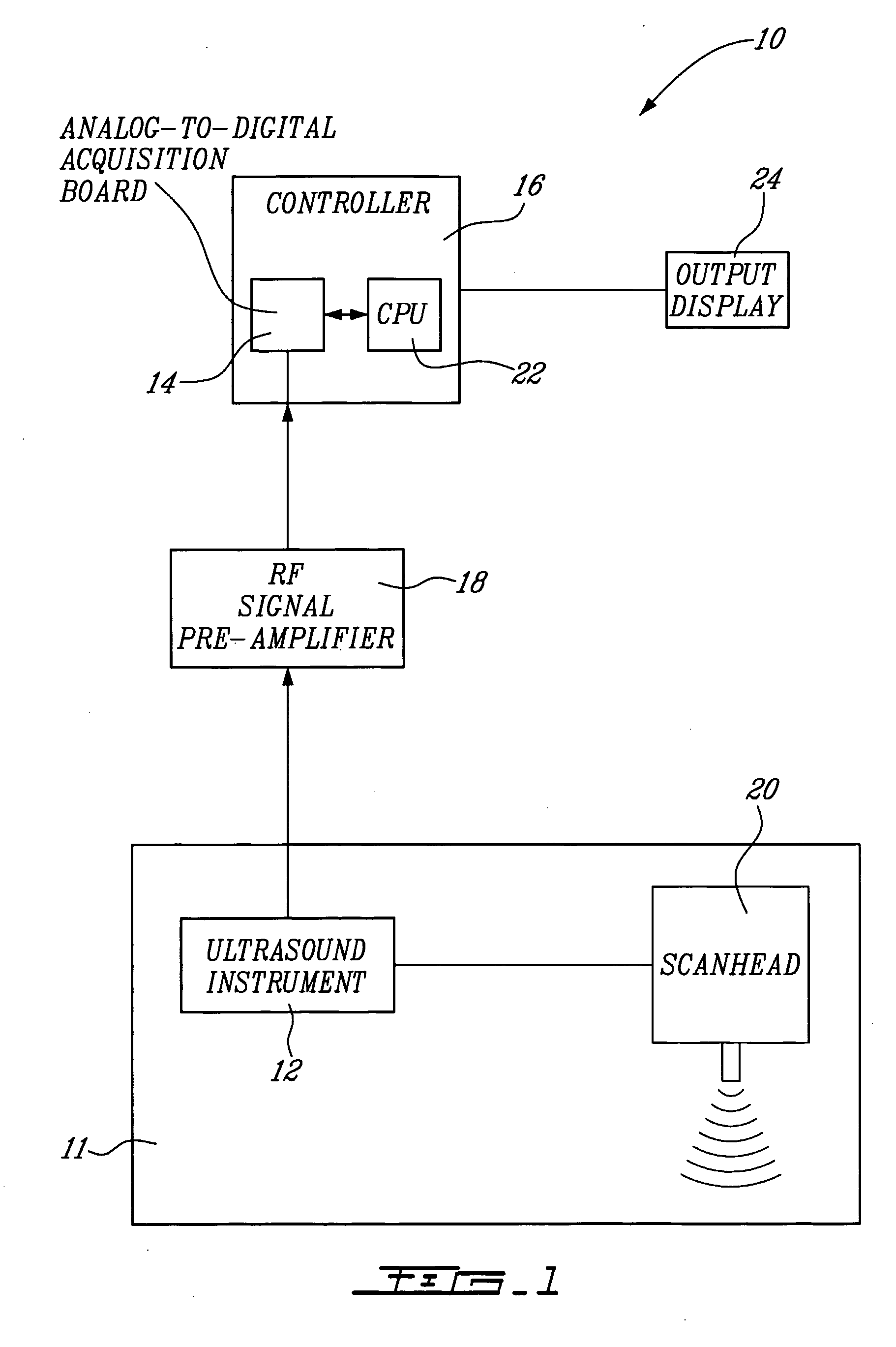
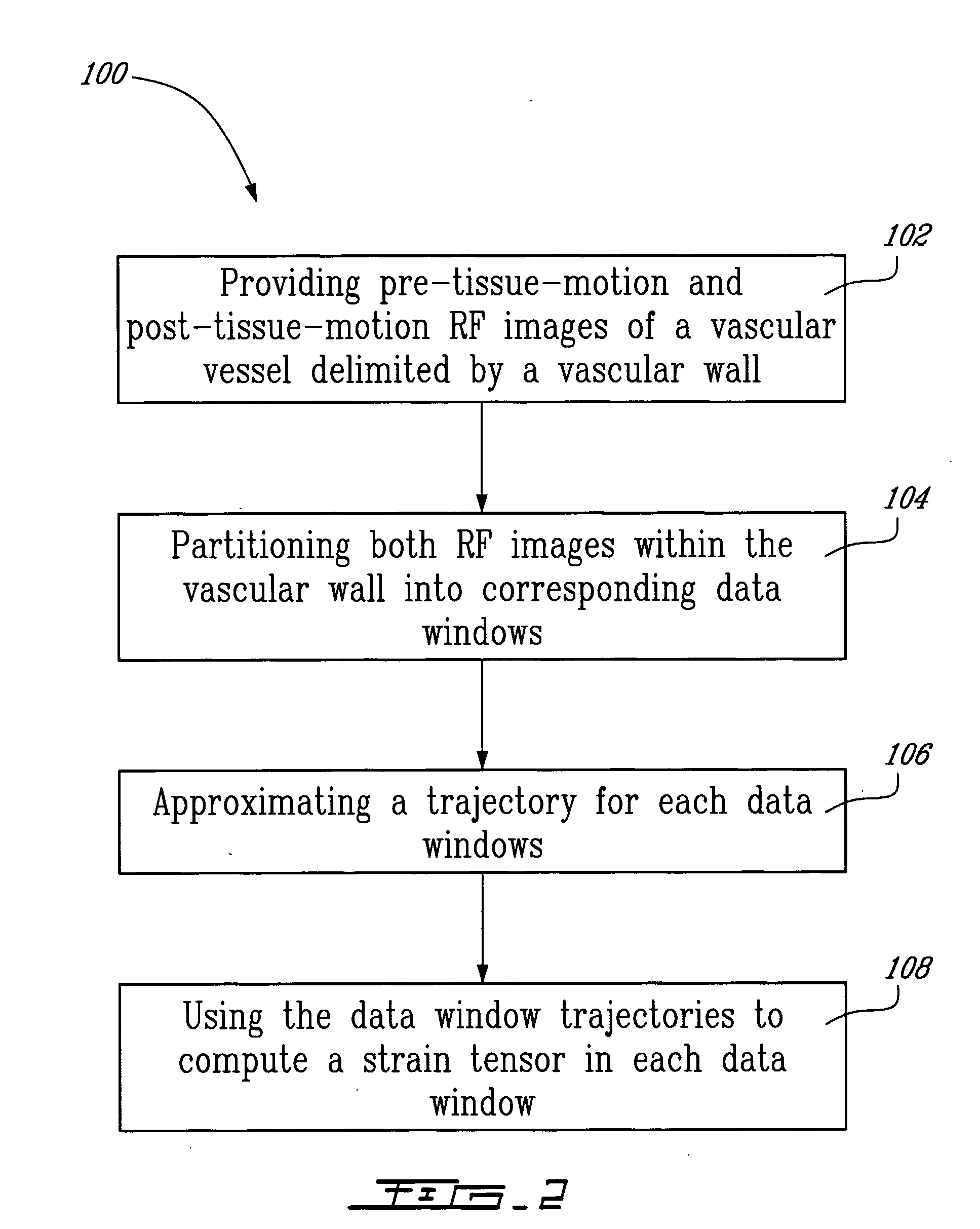
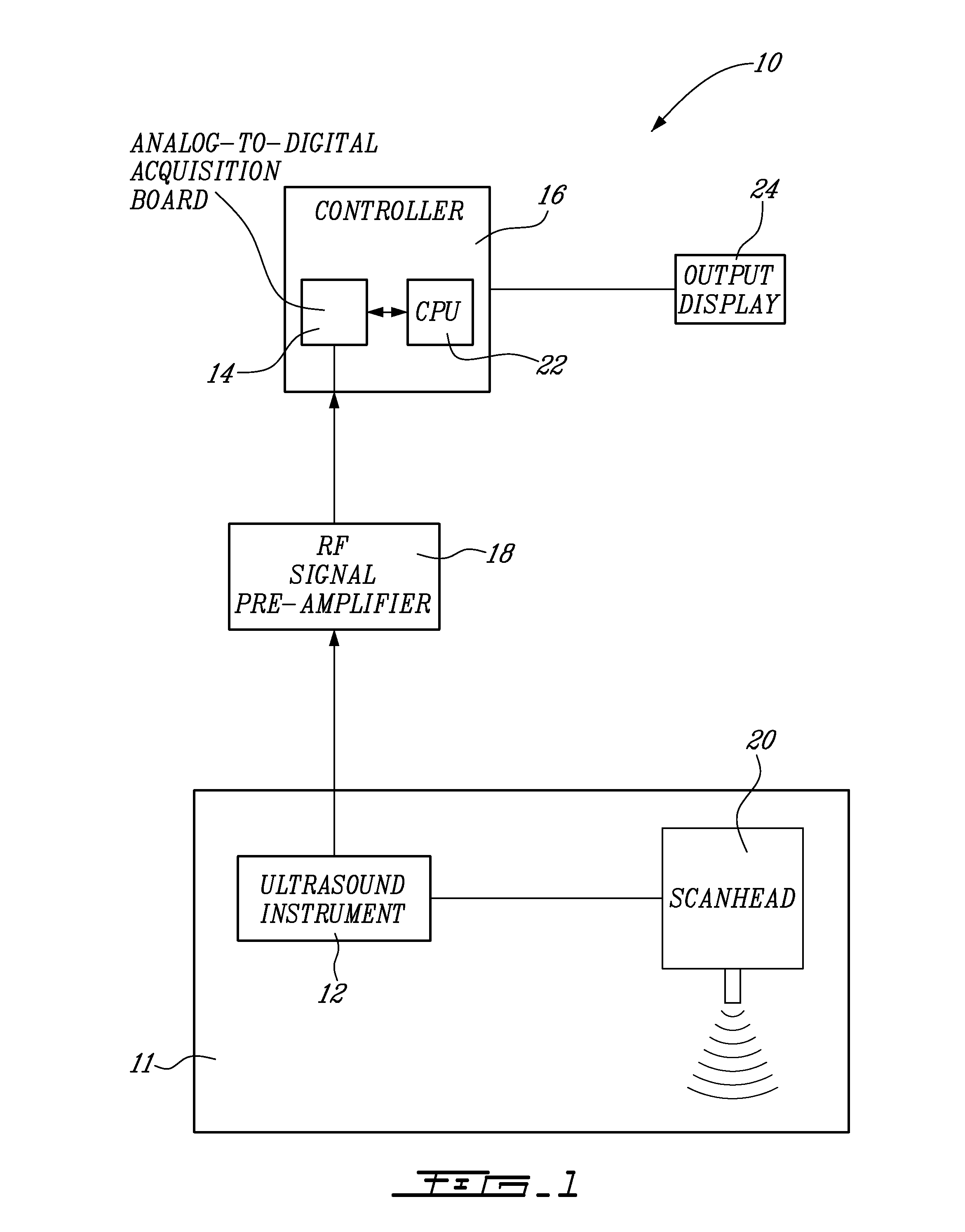
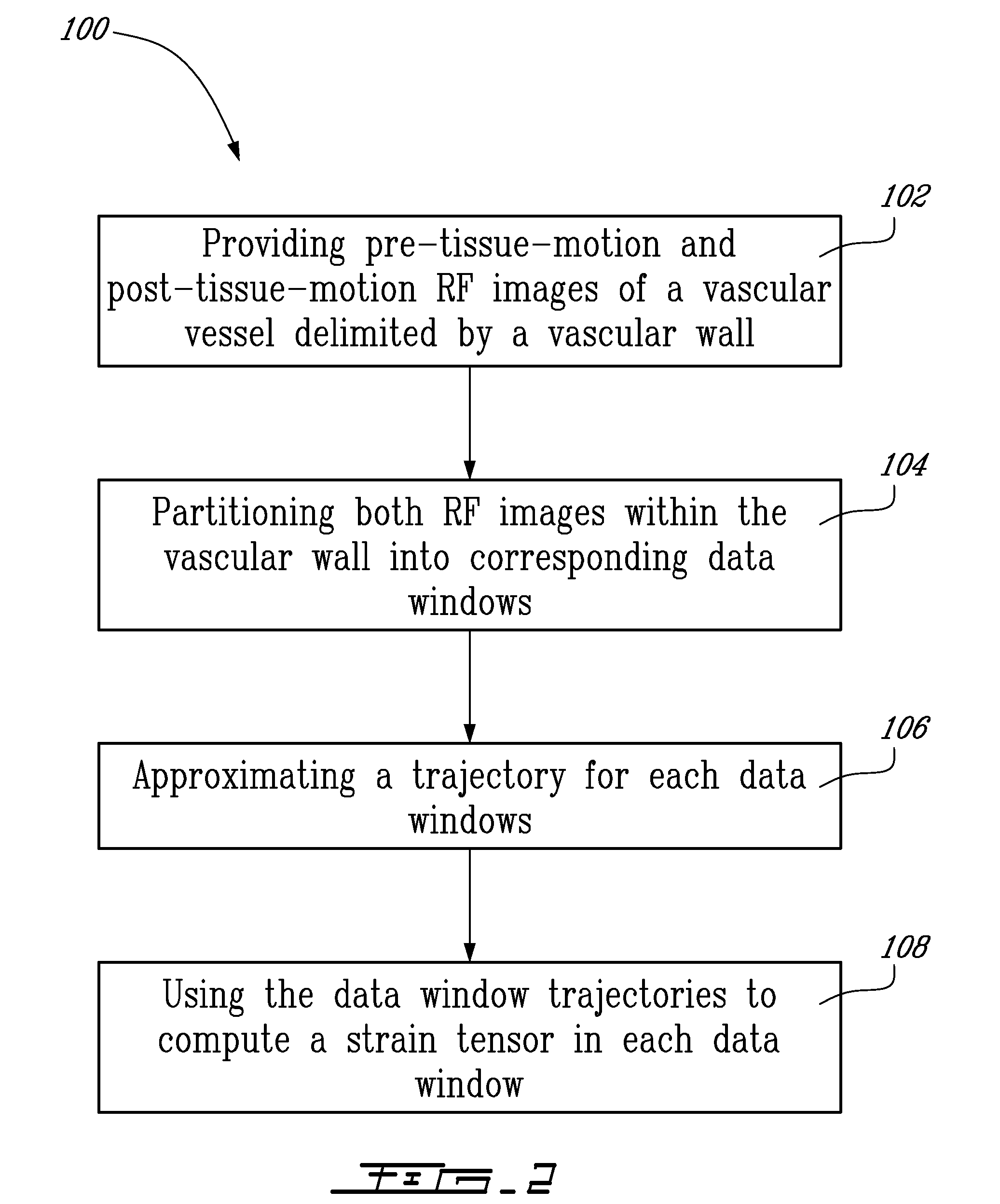
Method And System For Vascular Elastography
The method for vascular elastography comprises: i) obtaining a sequence of radio-frequency (RF) images including pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images in digital form of a vessel delimited by a vascular wall; the pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images being representative of first and second time-delayed configuration, of the whole vessel; ii) partitioning both the pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images within the vascular wall into corresponding data windows; approximating a trajectory between the pre- and post-tissue-motion for corresponding data windows; and using the trajectory for each data window to compute the full strain tensor in each data window, which allow determining the Von Mises coefficient. The method can be adapted for non-invasive vascular elastography (NIVE), for non-invasive vascular micro-elastography (MicroNIVE) on small vessels, and for endovascular elastography (EVE).
Owner:UNIV JOSEPH FOURIER +1
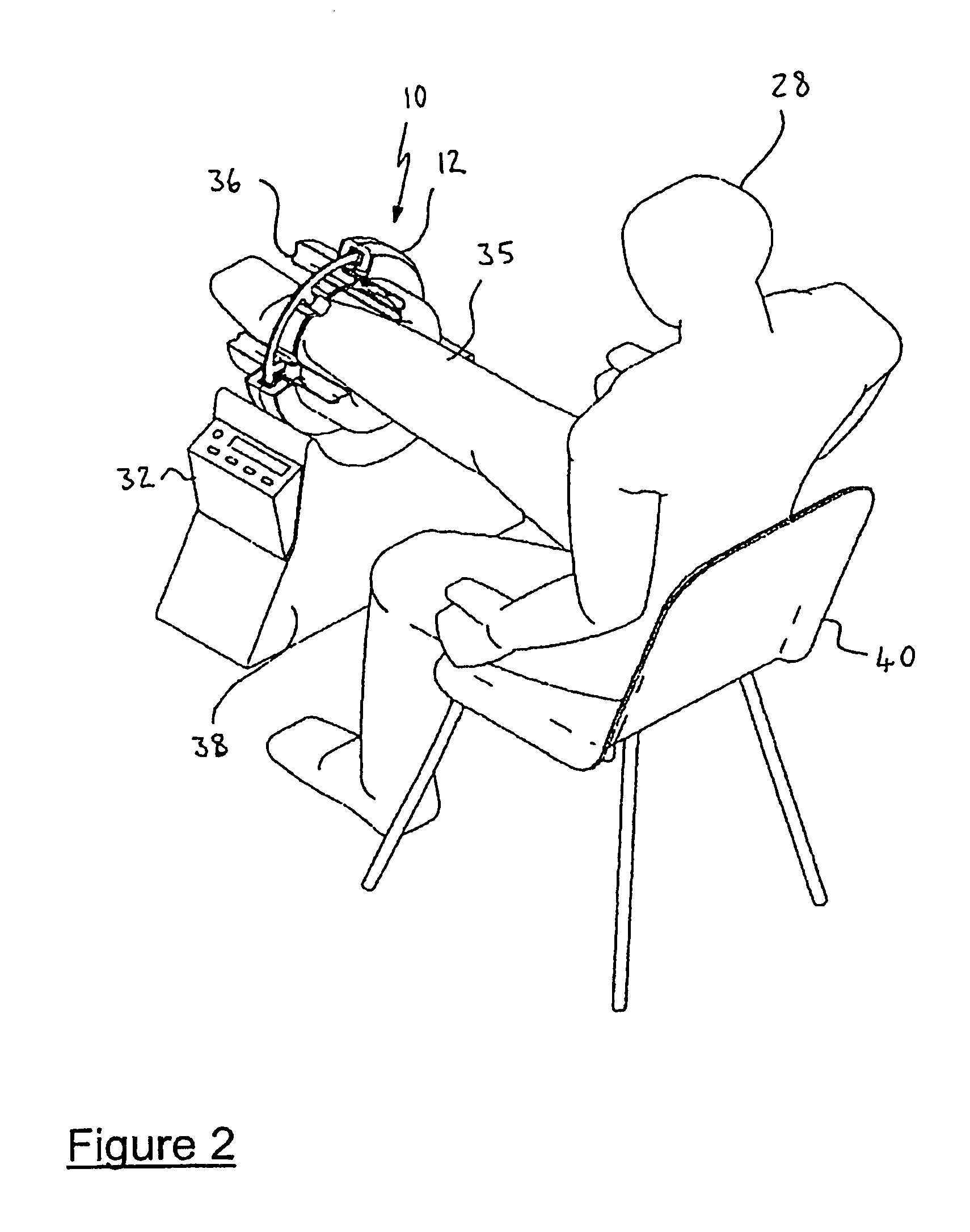
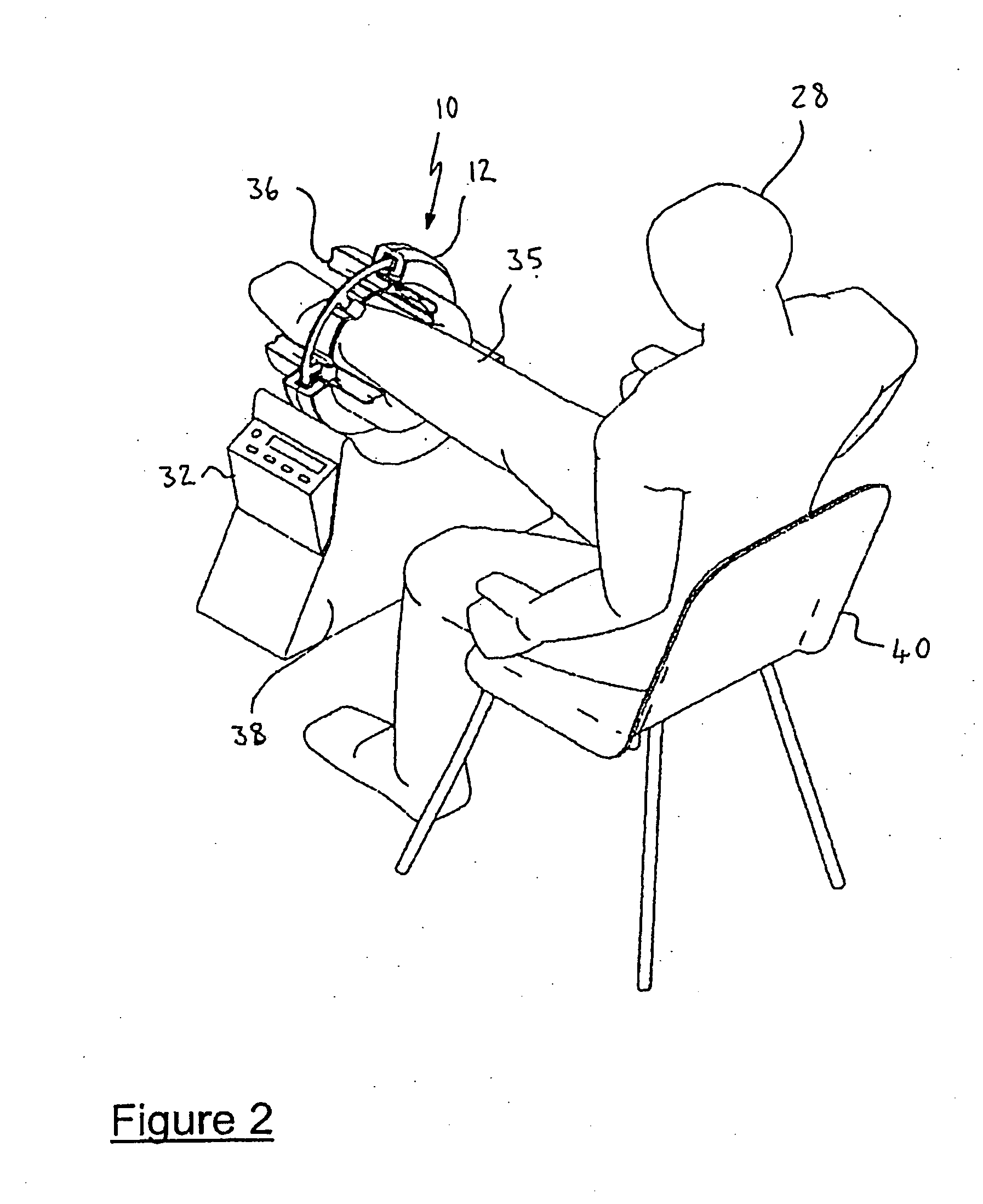
Medical apparatus, use and methods
InactiveUS7648471B2Maximize contact areaMove quicklyElectrotherapyChiropractic devicesTransducerBiomedical engineering
In accordance with one embodiment, a vibratory transducer has an armature suspended in a magnetic field. The armature has a plurality of electrical conductive paths to provide electrical current flow in said armature to react with said magnetic field and cause movement in the armature controlled by variation in the electrical current flow. A contact surface is secured to the armature, with a surface area for frictionally coupling to a corresponding surface area of a patient for example. Movement of the vibratory transducer induces movement in the patient, and the transducer can produce movement in the contact surface in at least two dimensions simultaneously. In one embodiment the contact surface is flat, while in alternative embodiments the contact surface is incorporated in a toroidal structure so as to surround part of the patient. Medical application can include treatment of bone fractures, oedema, and in elastography, amongst other applications.
Owner:MERLEX CORP PTY LTD
Automated ultrasonic elasticity image formation with quality measure
ActiveUS20060285731A1Operate quicklyEasy to operateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave based measurement systemsUltrasoundAnimation
Image data and E-mode images used in ultrasonic elasticity imaging may be automatically evaluated for quality to provide a single value used as operator feedback or for automatic selection of images for averaging or animation.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
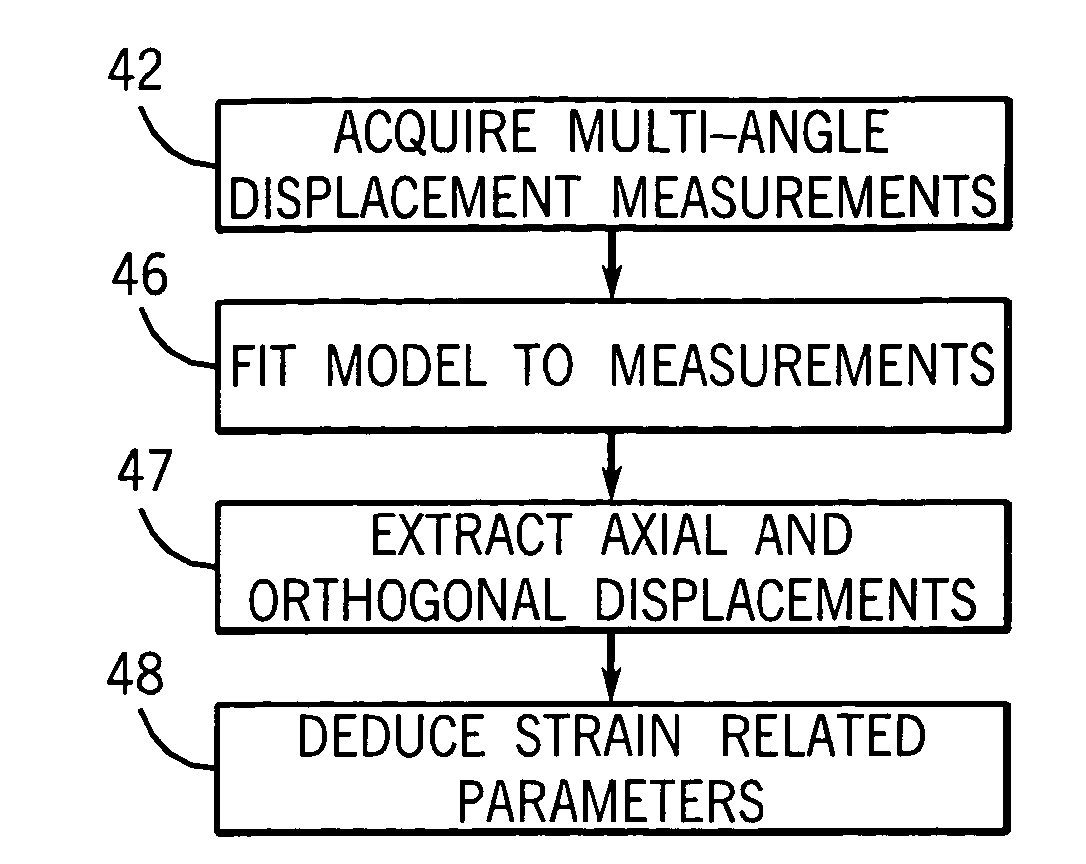
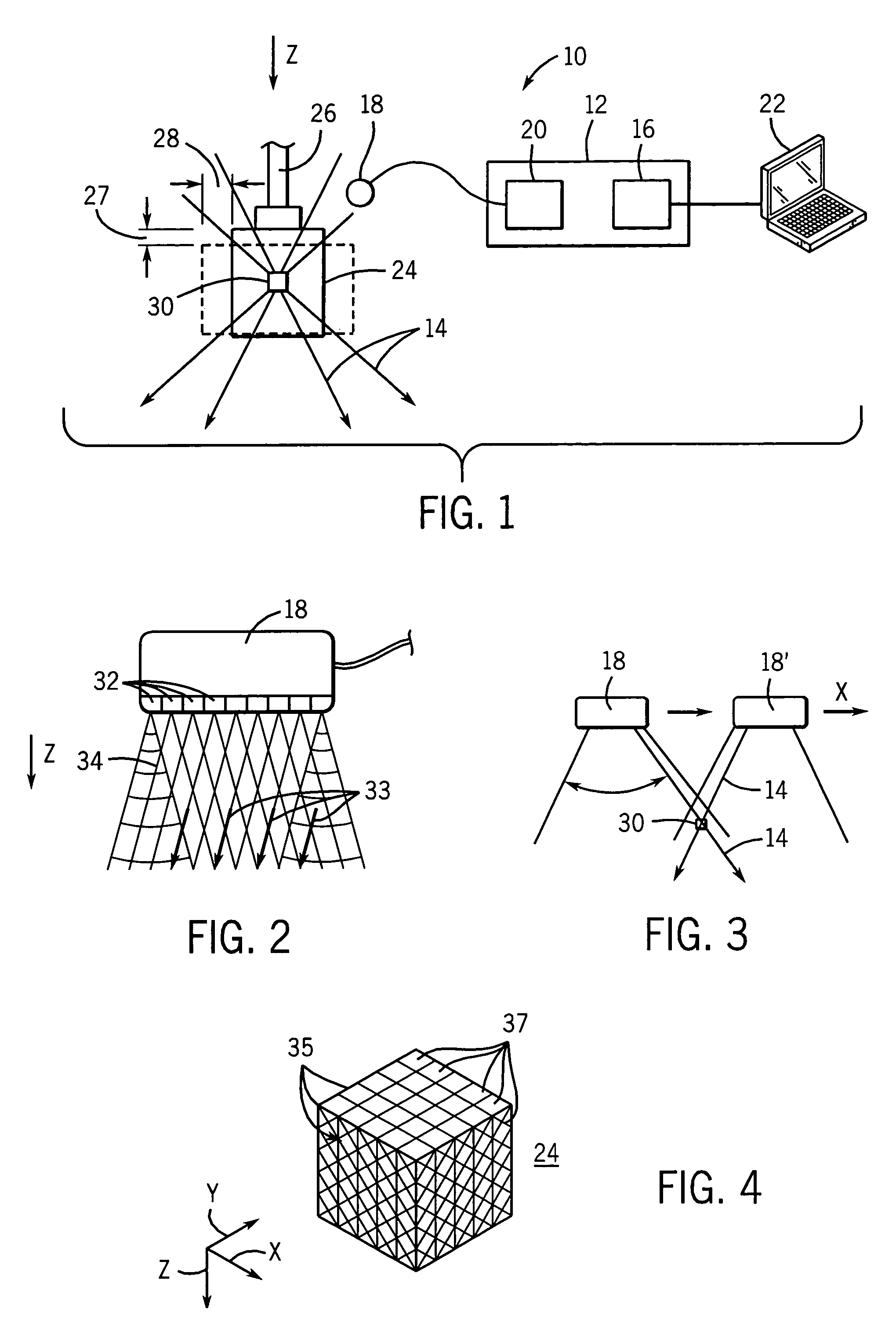
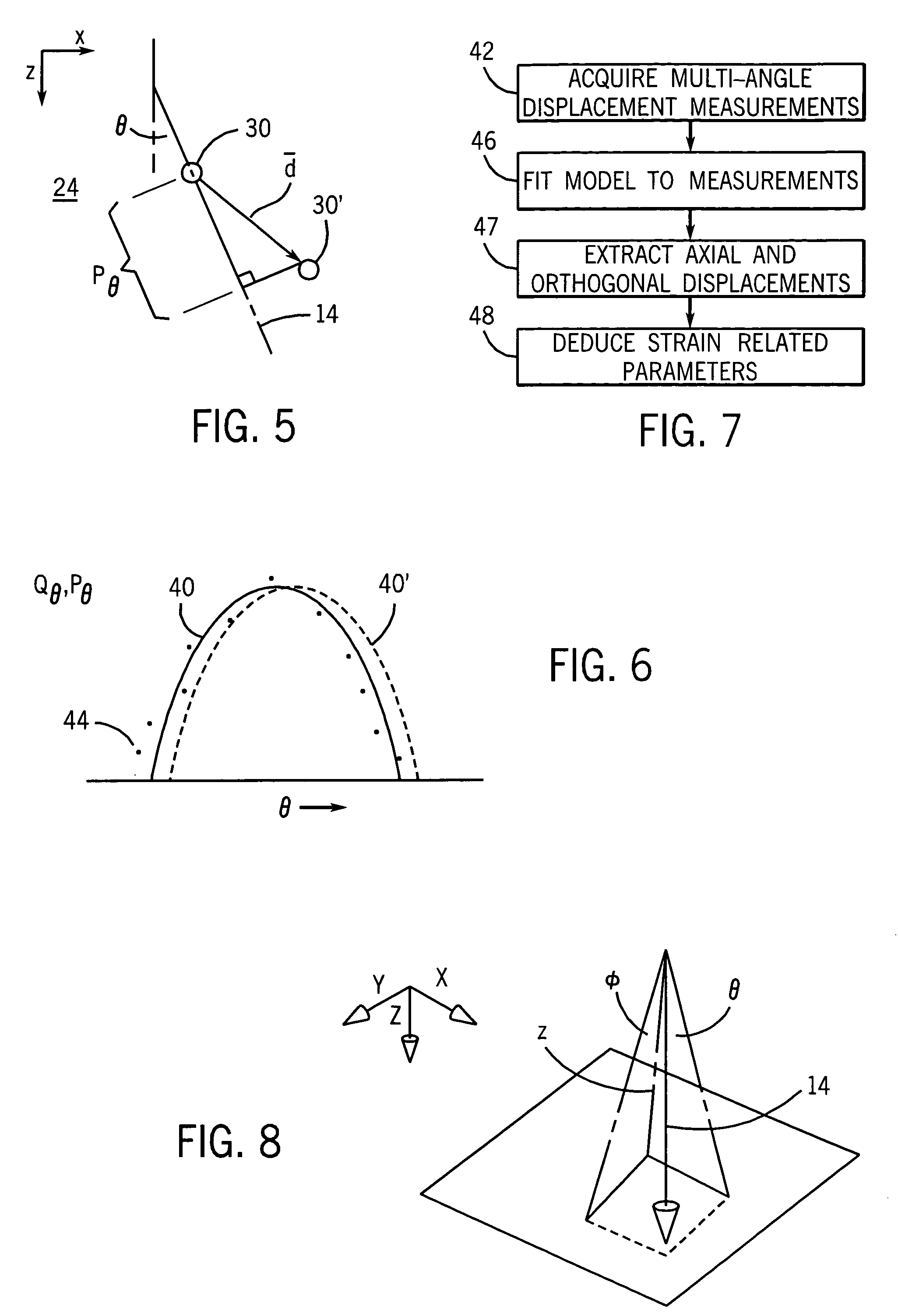
Ultrasonic elastography providing axial, orthogonal, and shear strain
ActiveUS7331926B2Reduce the impact of noiseOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationEngineering
Ultrasonic signals obtained at a range of angles are fit to a material independent model to derive both axial and lateral strain and thus parameters dependent on lateral strain including Poisson's ratio and shear strain.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Ultrasonic elastic imaging system and method
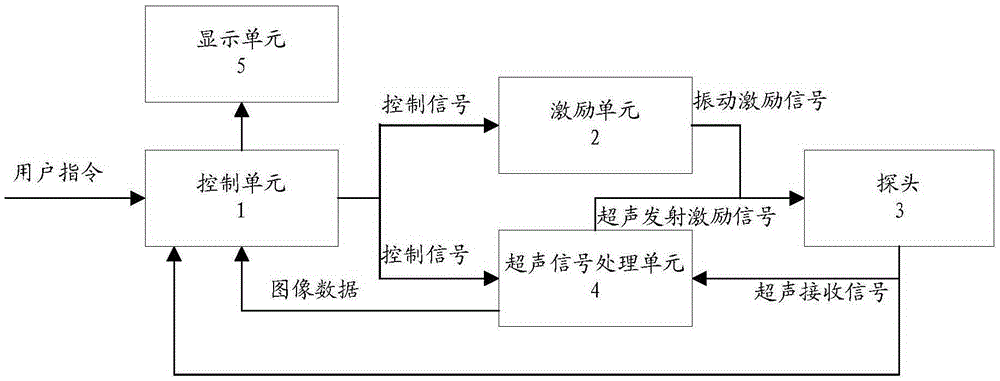
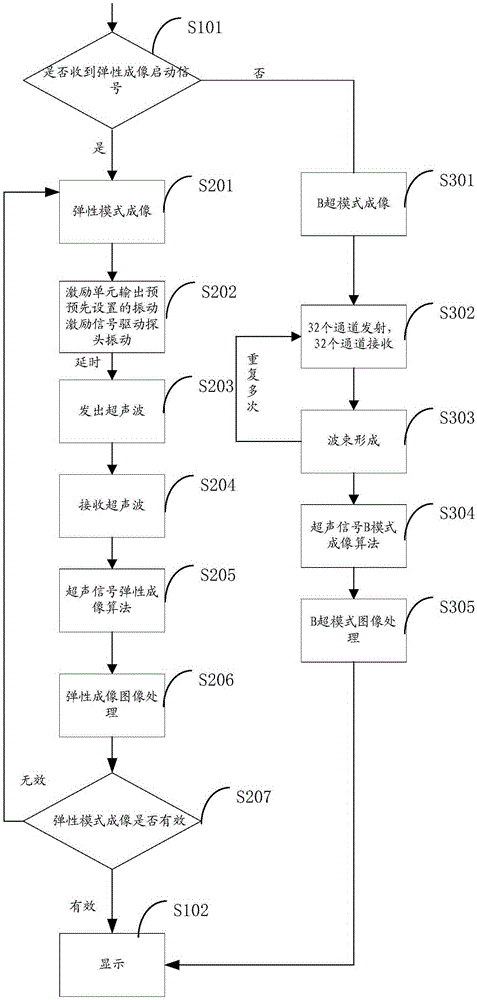
ActiveCN105395218ASolve the problem of inaccurate positioning of transient elastographyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic sensorControl signal
The invention relates to an ultrasonic elastic imaging system and method. The ultrasonic elastic imaging system comprises a control unit, an exciting unit, a probe and an ultrasonic signal processing unit. The probe comprises an ultrasonic sensor array, a vibration exciter and a pressure sensor. The control unit selects a work mode according to a received user instruction and converts the user instruction into a control signal. The exciting unit receives the controls signal and outputs a vibration exciting signal; the vibration exciter receives the vibration exciting signal and drives the probe to make periodical mechanical vibration; the ultrasonic signal processing unit receives the control signal, transmits and receives ultrasonic waves through the ultrasonic sensor array and performs signal processing on the received ultrasonic waves, and a processing result is sent to the control unit. An instantaneous elastic imaging probe and a B ultrasonic mode probe are combined. The B ultrasonic mode probe has the effects of transmitting and receiving ultrasounds and meanwhile has the function of vibrating an exciting source. Seamless switching of elastic imaging measurement and B ultrasonic mode measurement is achieved through the relevant imaging process and the relevant imaging algorithm. The problem that ultrasonic elastic imaging in the prior art is not accurate is solved.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Elastography Using Ultrasound Imaging of a Thin Volume
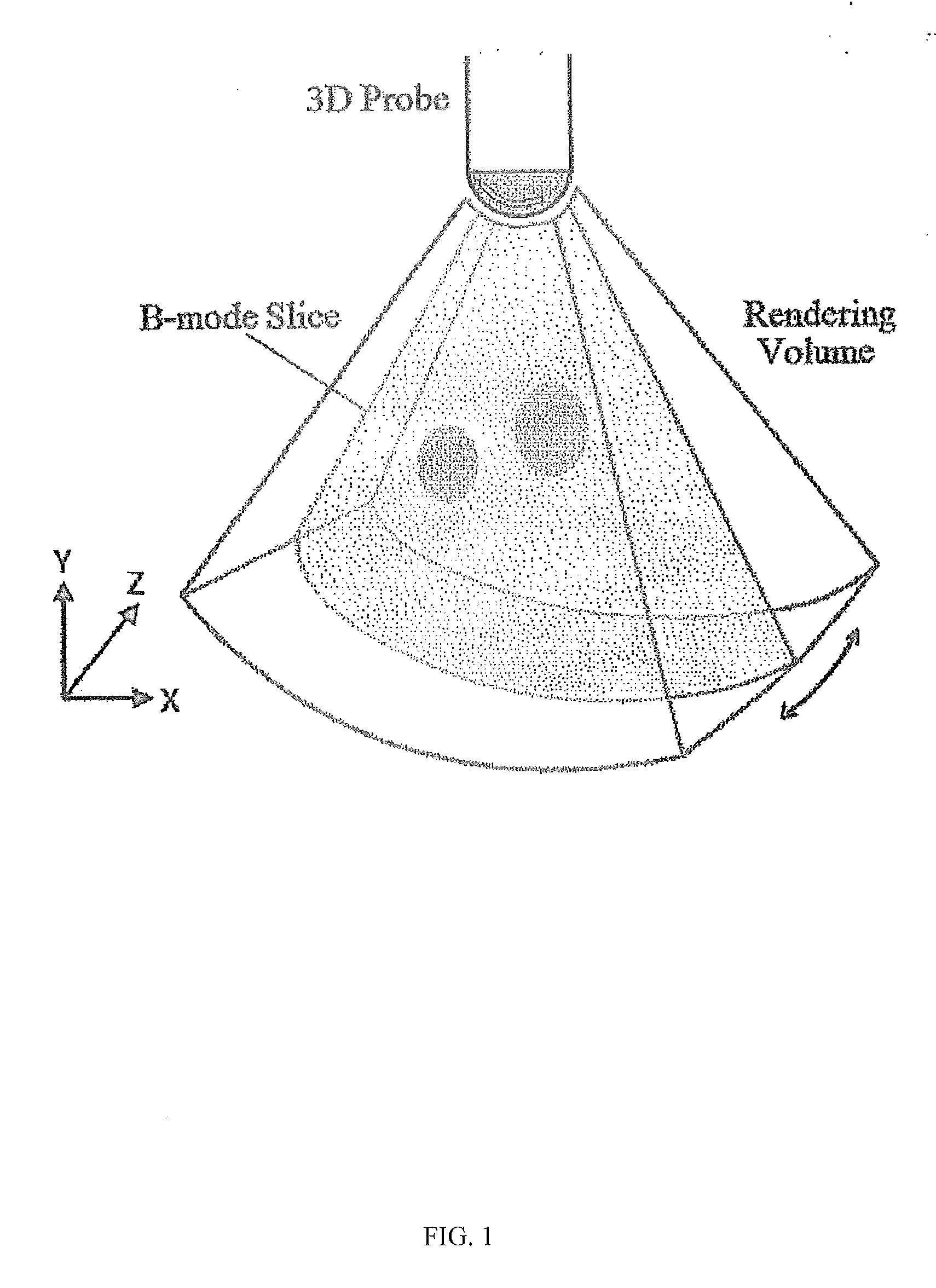
The embodiments described herein relate generally to an elastography method and system for obtaining ultrasound images of an excited tissue over a certain time period, then computationally determining one or more mechanical properties of the tissue within a real time refresh rate. This method can perform elastography in real time as only a thin volume of the excited tissue is imaged and processed. The thin volume includes a desired cross-sectional plane of the tissue and at least two adjacent planes that are adjacent to the desired cross-sectional plane. A maximum number of adjacent planes is selected so that a computer system is capable of computationally determining mechanical properties within a real time refresh rate.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Handheld volumetric ultrasound scanning
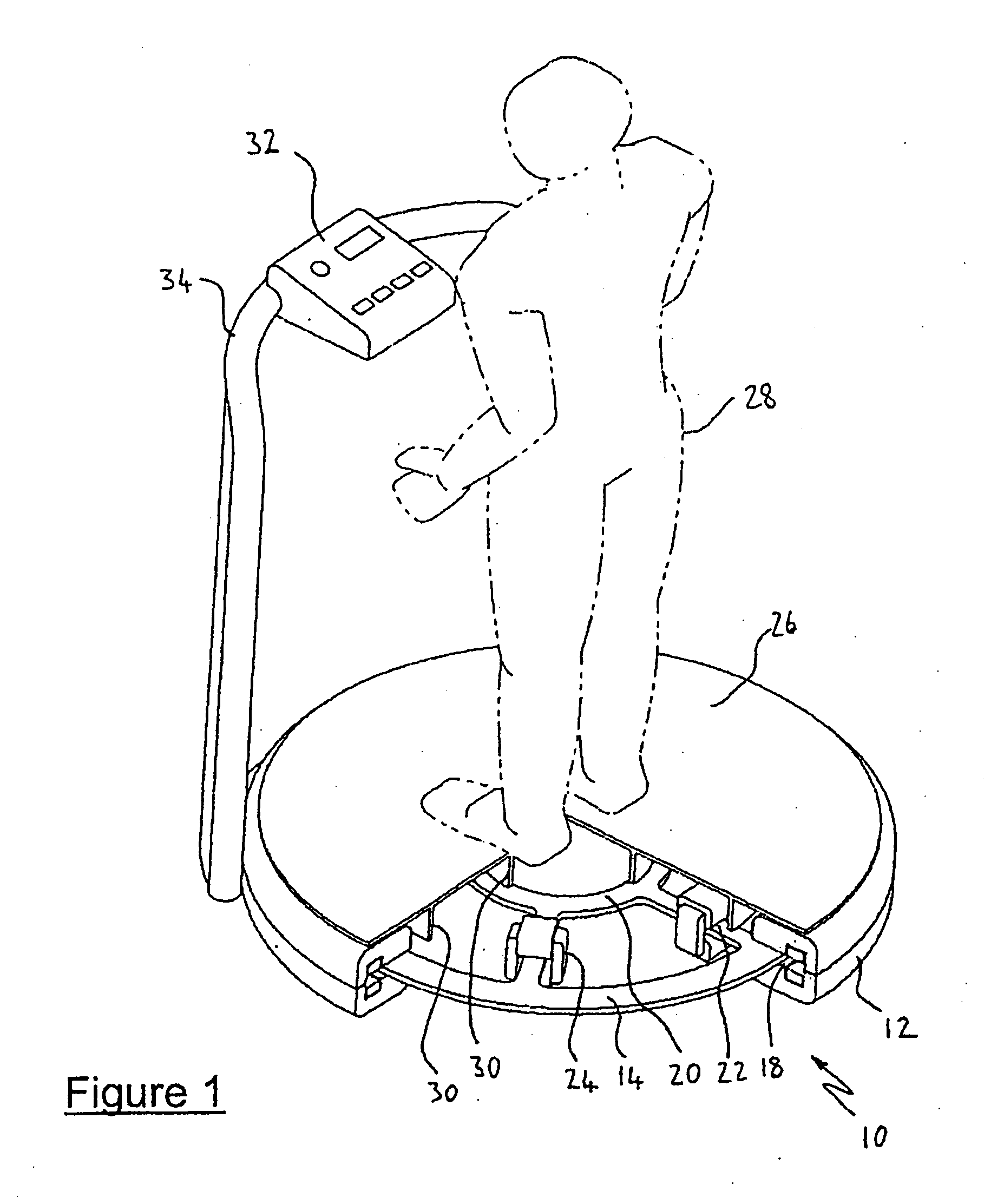
InactiveUS20100179429A1Improve positional stabilityProcess stabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationImaging quality
Systems, methods, and related computer program products for ultrasonic examination of a tissue volume, such as a human breast, are described. A handheld volumetric ultrasound scanning probe, which is characterized by a two-dimensional scan area with a substantially rigid cap extending across the two-dimensional scan area, is provided with a texturably couplant-porous material sheet covering the substantially rigid cap over at least a portion of the two-dimensional scan area. The texturably couplant-porous material sheet facilitates positional stability of the handheld volumetric ultrasound scanning probe while positioned against a skin surface of the tissue volume. Advantageously, while the texturably couplant-porous material sheet brings about a more stable physical interface at the skin surface, the texturably couplant-porous material sheet brings about little or no degradation in acquired image quality. Also described are systems and related methods for elastography imaging using the handheld volumetric ultrasound scanning probe.
Owner:U SYST
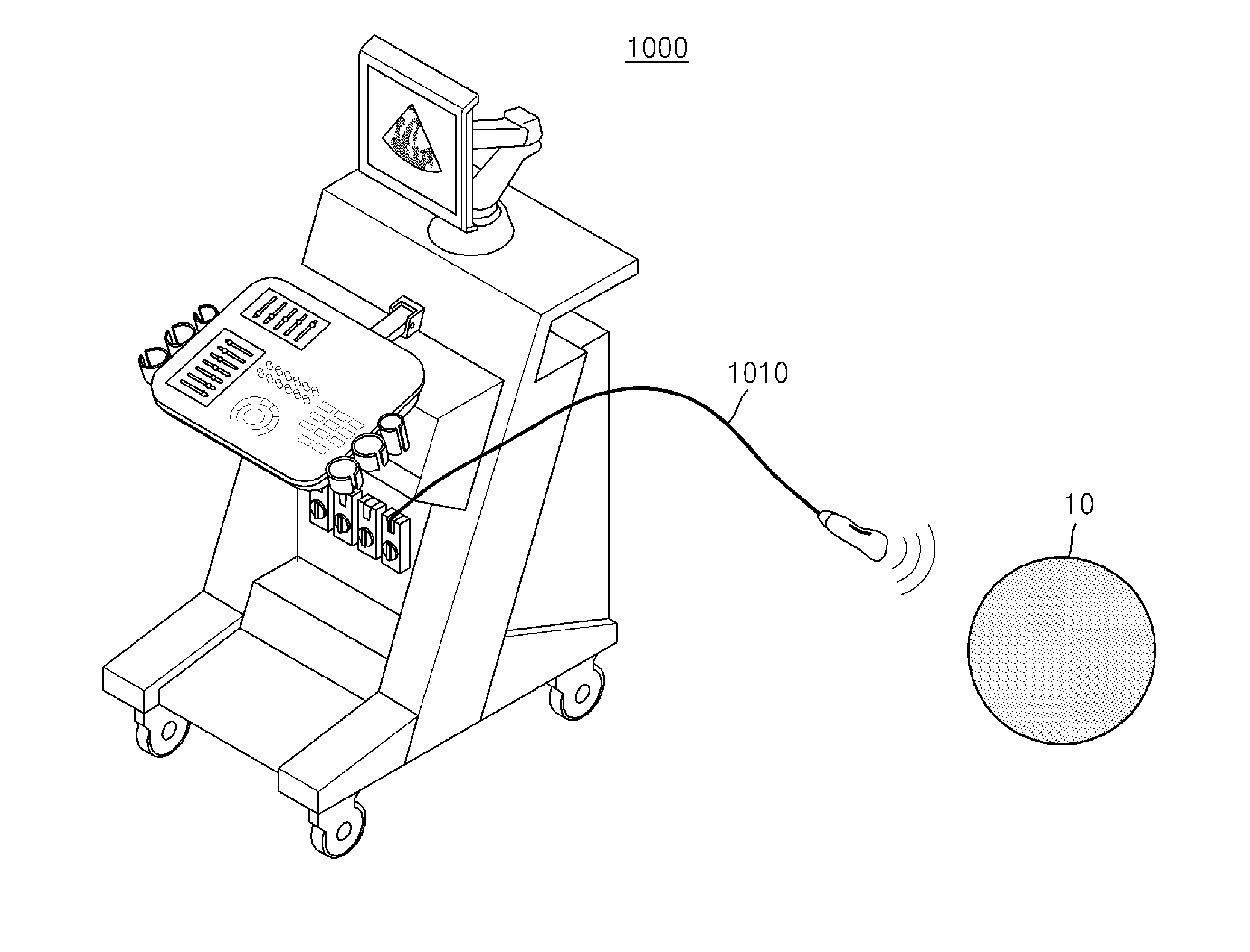
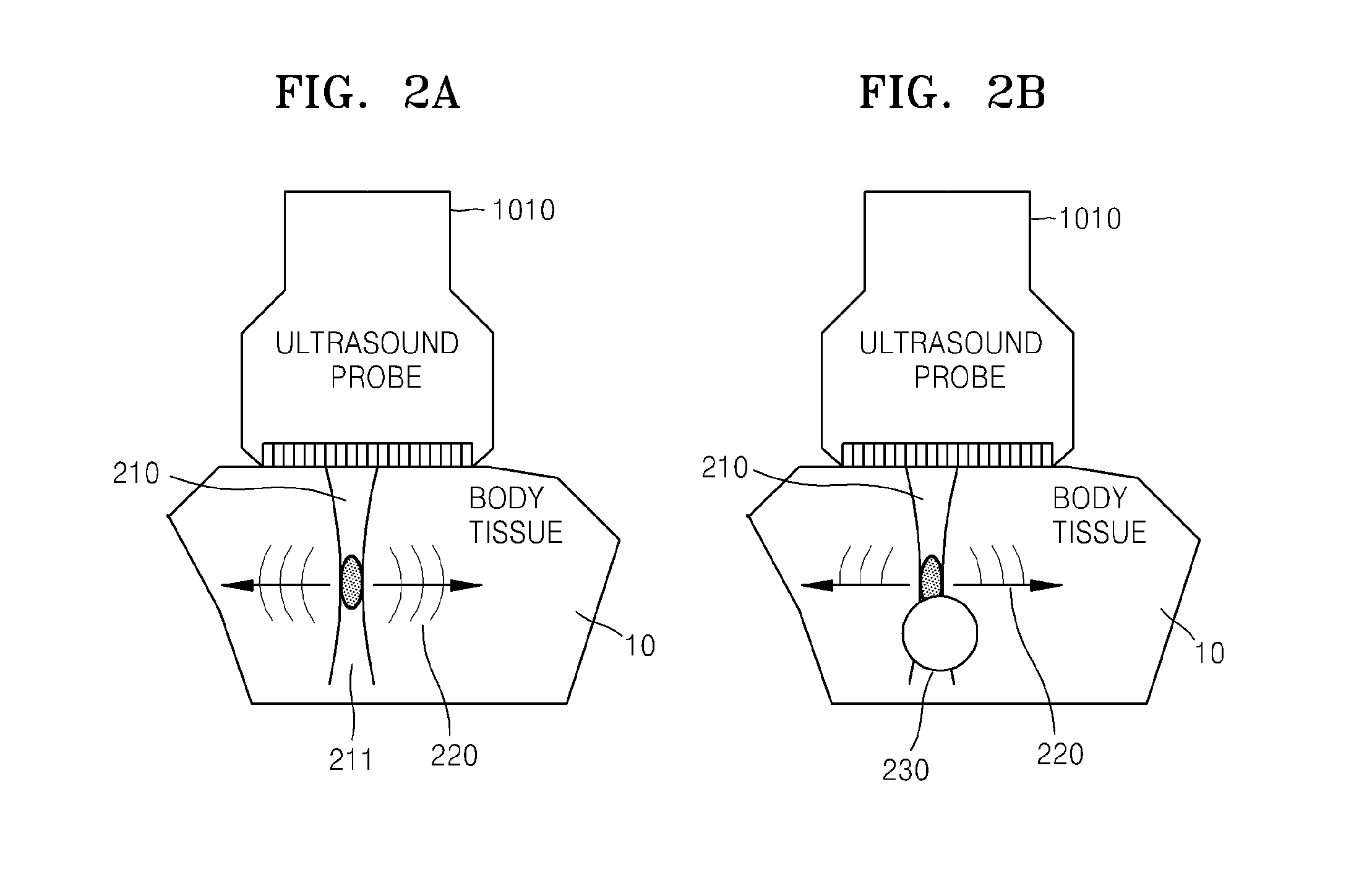
Method and ultrasound apparatus for providing ultrasound elastography image
ActiveUS20150148674A1Improve accuracyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationComputer science
A method of providing an ultrasound elastography image that includes inducing a shear wave by transmitting a first ultrasound signal pushing an object to the object, transmitting a second ultrasound signal tracing the shear wave to the object to receive a response signal to the second ultrasound signal from the object; acquiring an elastography image of the object, based on the response signal, and providing the elastography image of the object and transmission position information of the first ultrasound signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
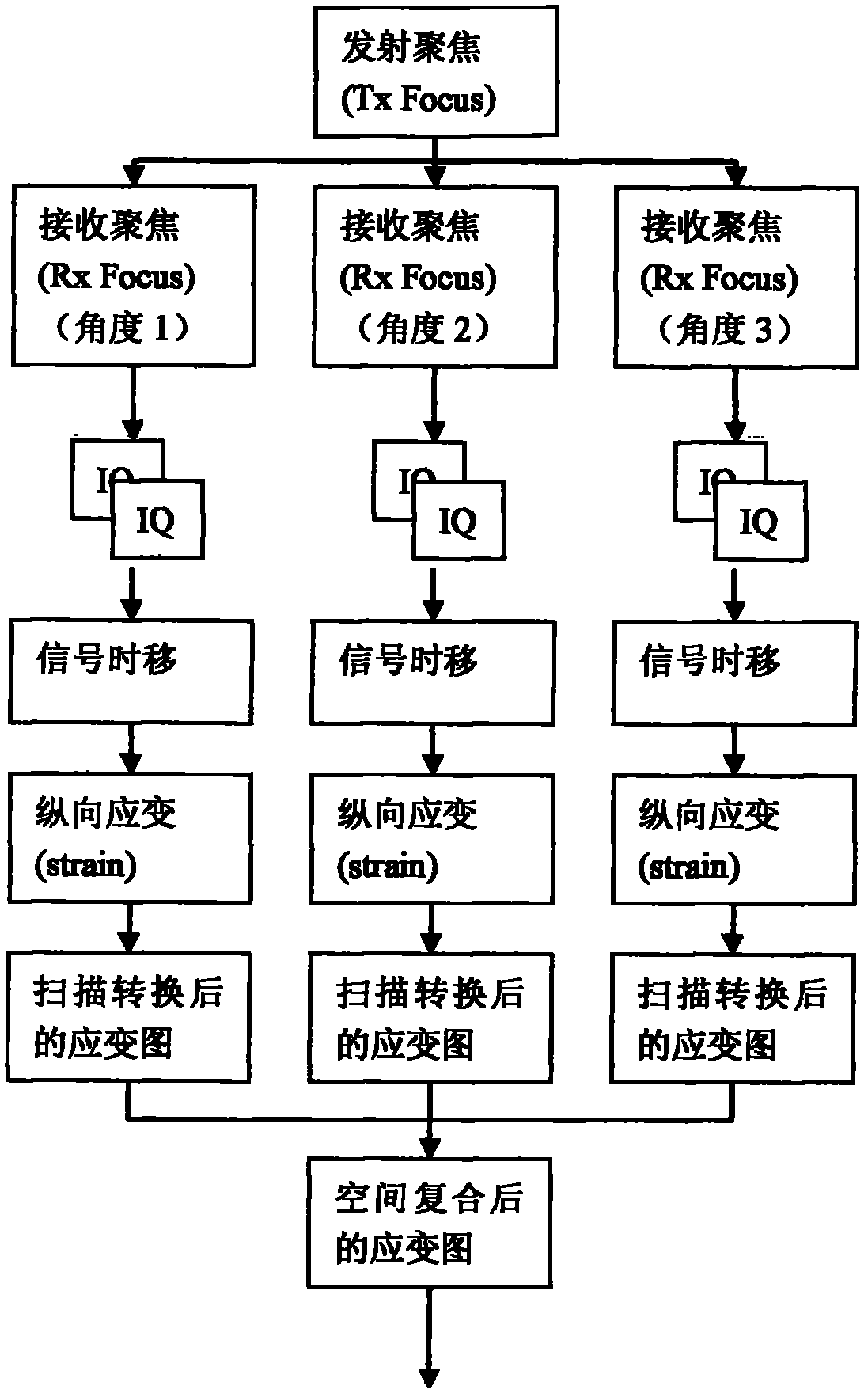
Ultrasonic elastography with angular compounding
ActiveUS7601122B2Reduce Image ArtifactsReduce image noiseOrgan movement/changes detectionPerson identificationSonificationMultiple echo
Ultrasonic strain measurements, which characterize the structure of tissue, may be obtained by combining multiple echo signals acquired at different compressions and at different angles. Such angular compounding may improve the quality of the elastic signal and provide at one time both an axial and lateral strain measurement.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
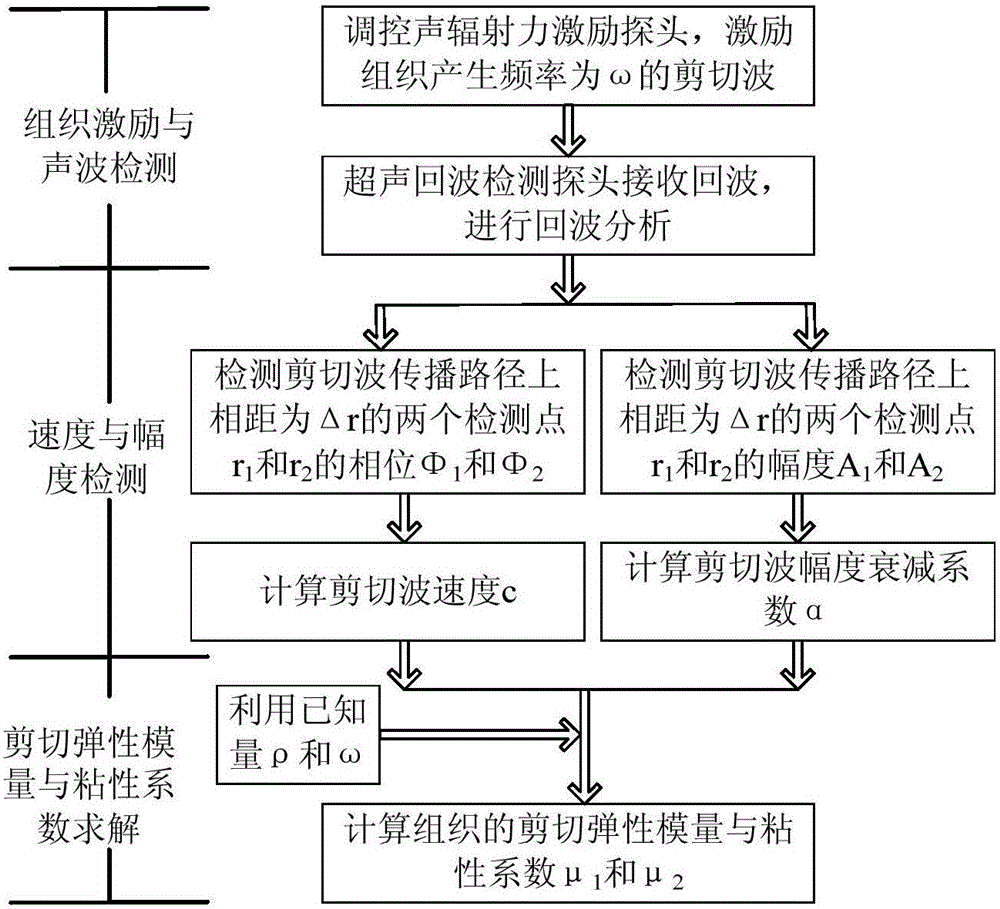
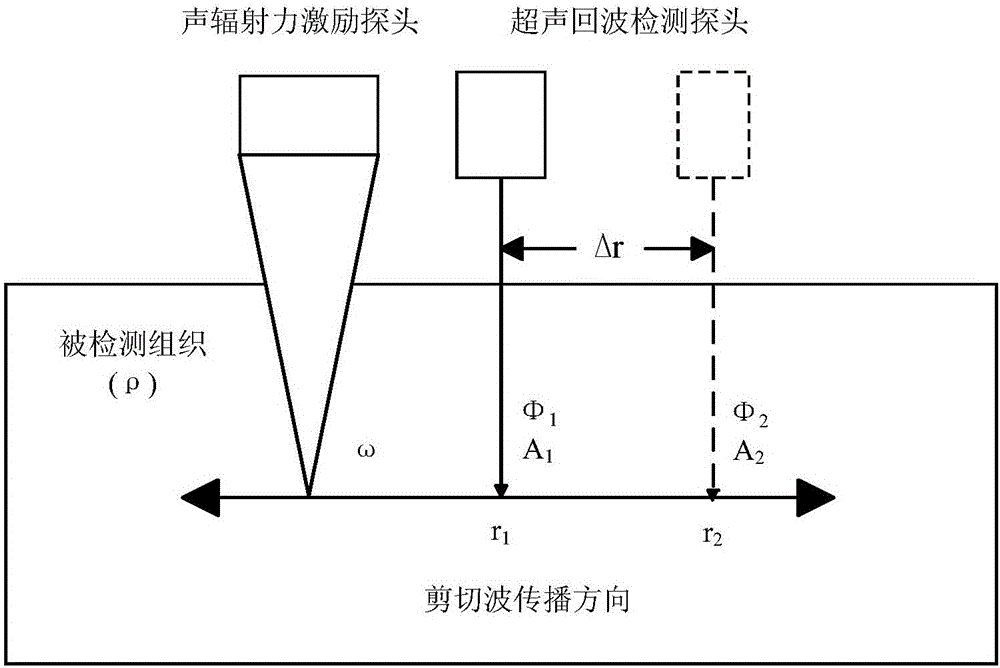
Tissue viscoelasticity measuring method based on shear wave amplitude and phase detection
ActiveCN106175831AGood for expanding the scopeGood for leveling upOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseViscoelasticity
The invention provides a tissue viscoelasticity measuring method based on shear wave amplitude and phase detection. An acoustic radiation force excitation probe and an ultrasonic echo detection probe are used for detection at the same time, the acoustic radiation force excitation probe generates push wave beams, tissue generates shear waves at certain frequency, the ultrasonic echo detection probe generates detection wave beams to detect amplitude attenuation and phase change of the shear waves on a propagation path, the elasticity modulus and viscosity coefficient of the tissue are estimated through an amplitude attenuation coefficient and a speed detection value, in other words, the elasticity modulus and viscosity coefficient of the tissue can be quantitatively detected at the same time, precise and rich mechanical parameter information is provided for diagnosis of multiple diseases, the clinical application range of ultrasonic elastography can be widened, and the level of ultrasonic elastography can be improved. The method can carry out detection through the shear waves at one frequency, the system complexity and design cost are reduced, detection efficiency is improved, phase detection noise caused by high-frequency shear waves is avoided, and the accuracy of mechanical tissue parameter detection is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
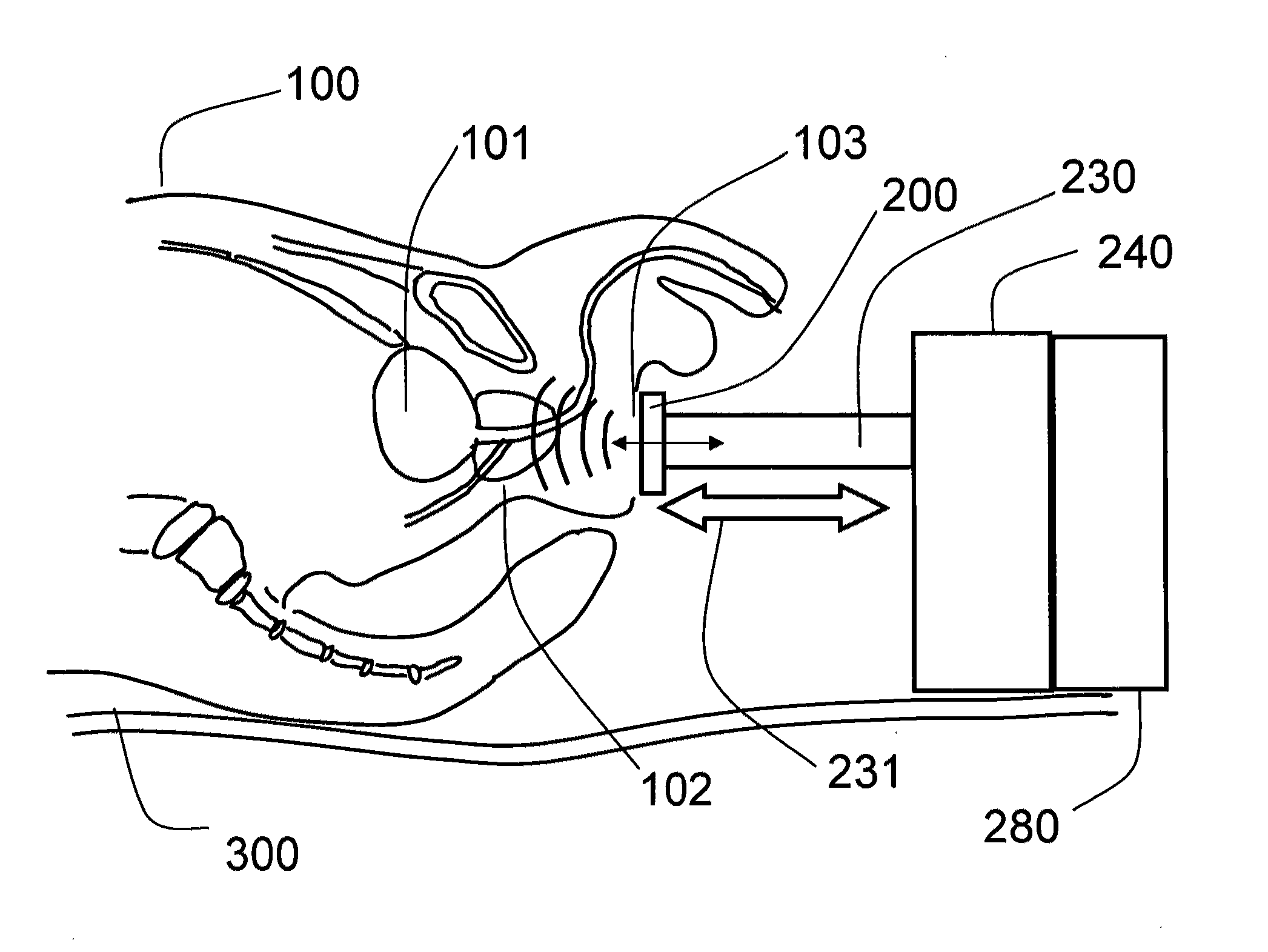
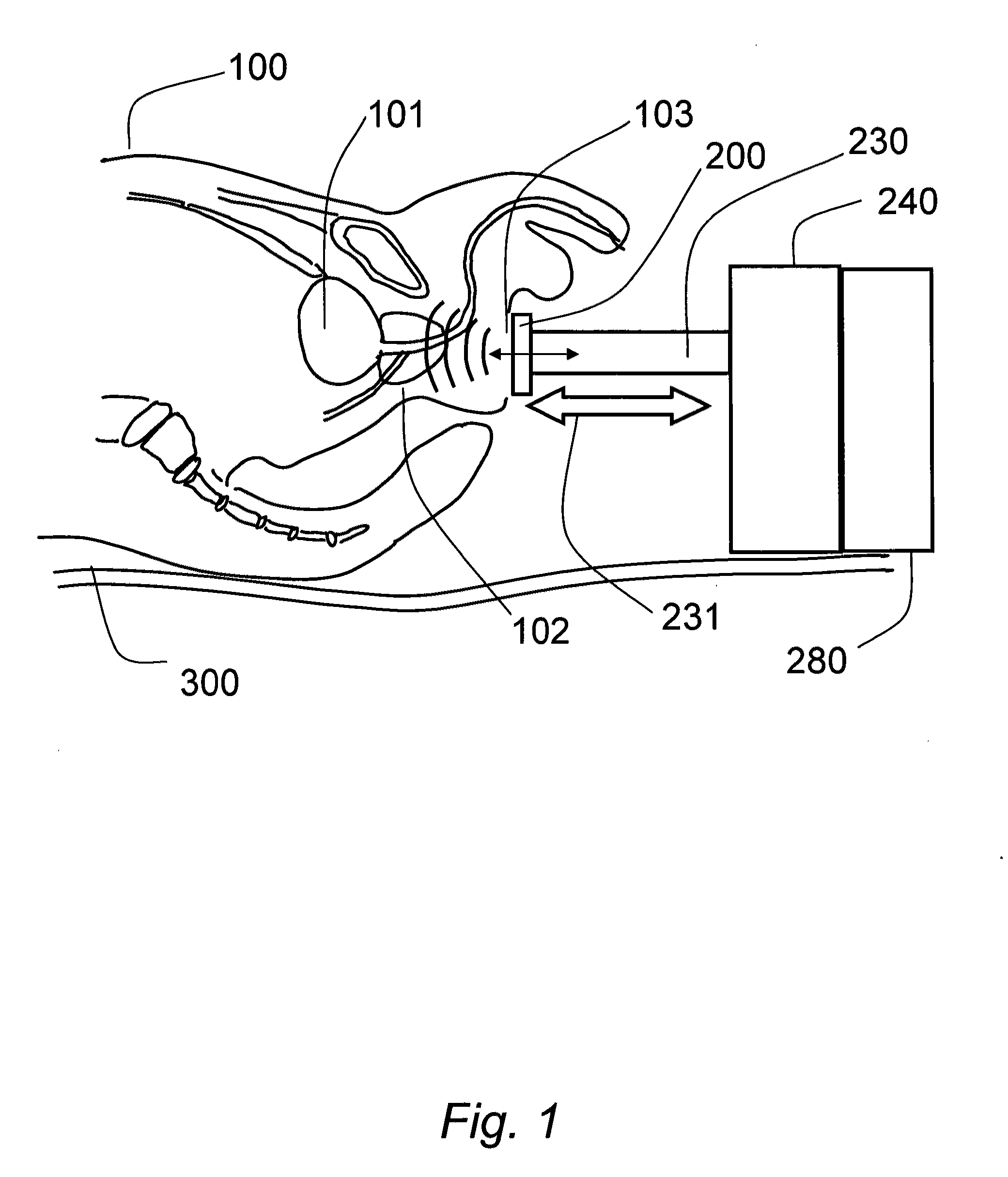
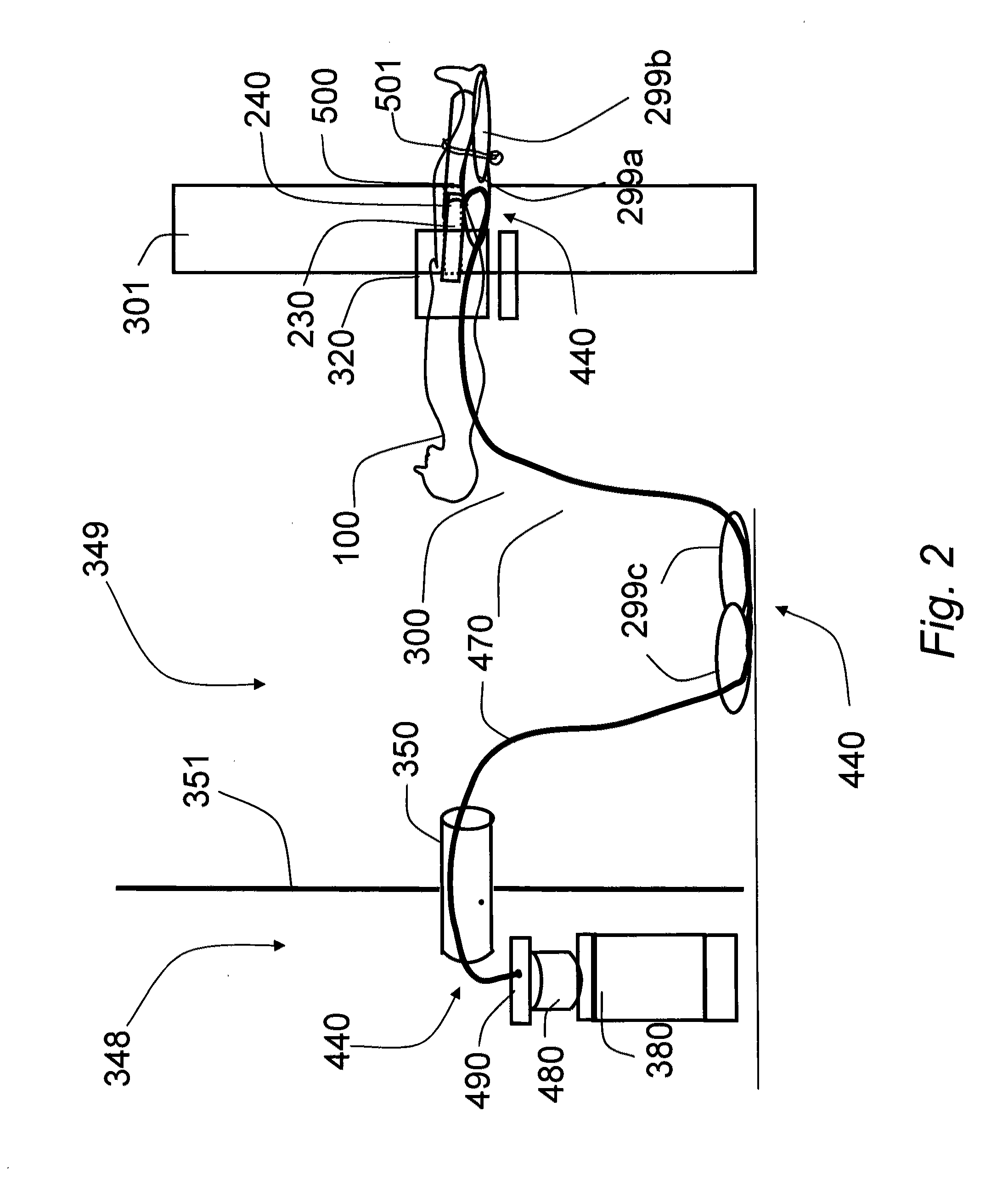
System and method for intracorporeal elastography
ActiveUS20100045289A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using vibrationsRadiologyMechanical energy
A system and method for intracorporeal elastography include an intra-luminal vibratory member configured to be positioned within a lumen of an imaging subject and configured to impart mechanical energy into tissue of the lumen. In a preferred embodiment, an external piezoelectric energy source is included and coupled to the vibratory member and configured to cause the vibratory member to longitudinally vibrate, thereby generating shear waves for use with magnetic resonance elastography.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
High-intensity focused ultrasound thermal ablation apparatus having integrated temperature estimation and elastography for thermal lesion determination and the method thereof
ActiveUS20110306881A1Image obtainedImprove accuracyUltrasound therapyHealth-index calculationSonificationRadiology
The invention disclosed a high-intensity focused ultrasound thermal ablation apparatus having integrated temperature estimation and elastography for thermal lesion determination and the method thereof, using the different power to burn by the same focused ultrasound transducer, and then using the apparatus to measure the temperature and elasticity estimating by the relevant analysis method.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Calibration of ultrasonic elasticity-based lesion-border mapping
ActiveUS20180168552A1Great potential in ablation monitoringReduce displacementUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionReference mapPropagation delay
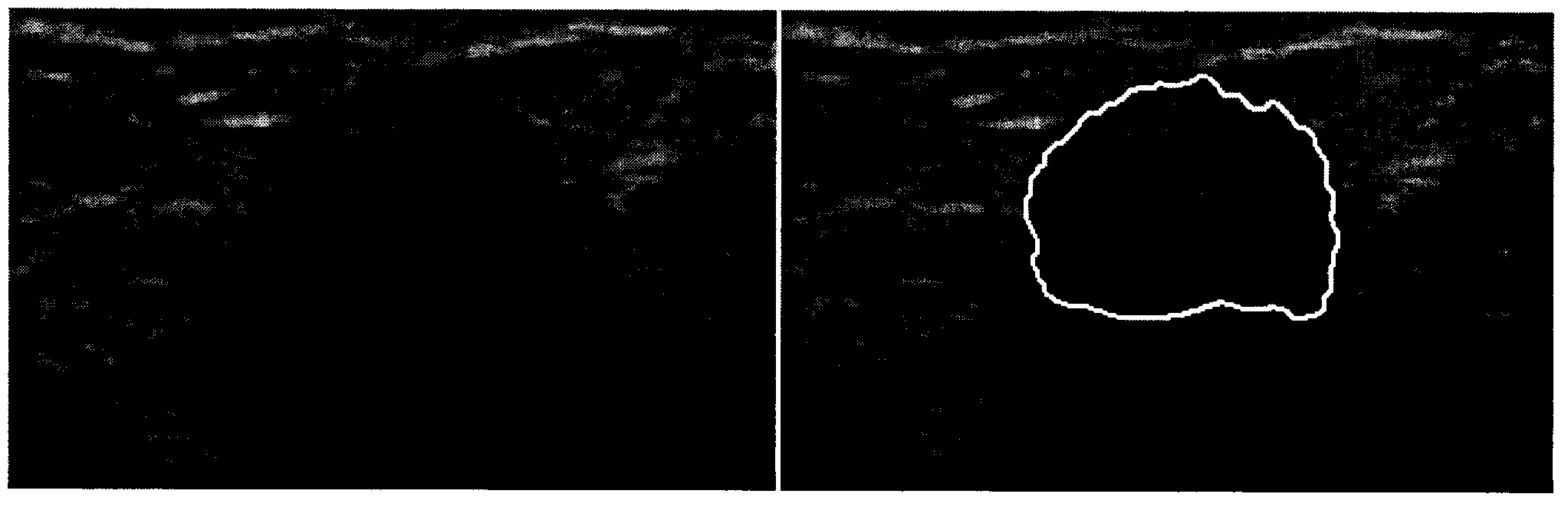
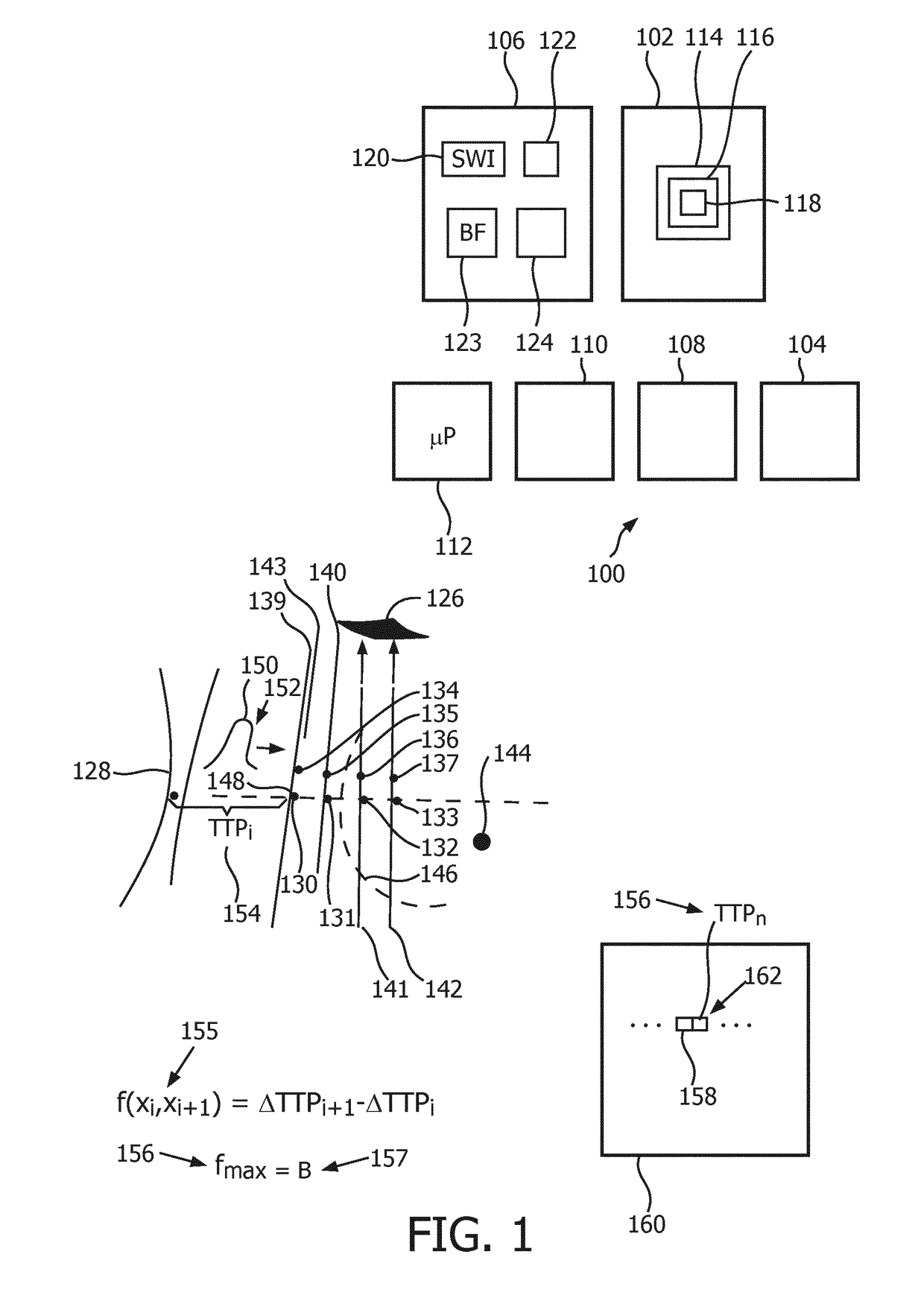
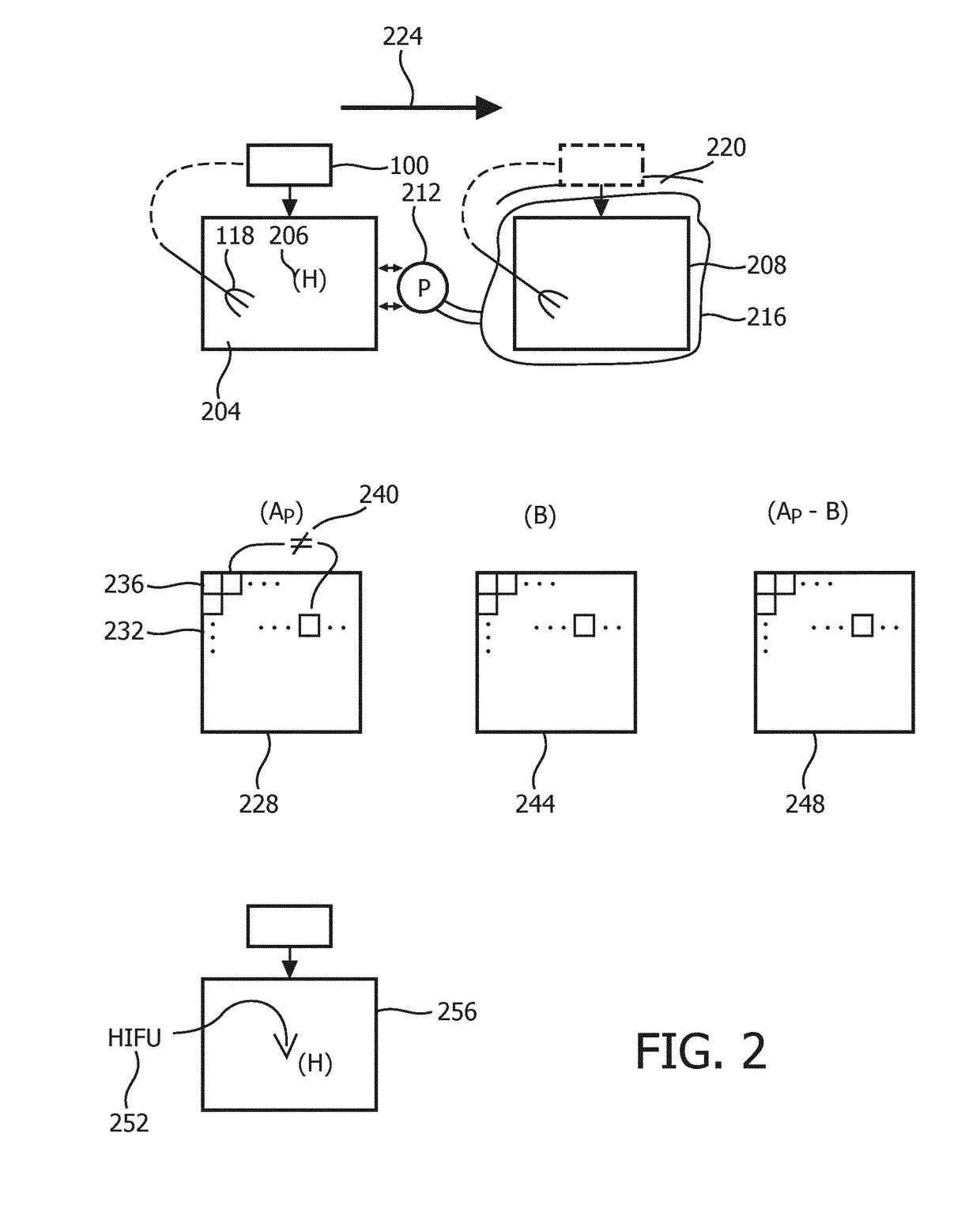
A medium of interest is interrogated according to ultrasound elastography imaging. A preliminary elasticity-spatial-map is formed. This map is calibrated against a reference elasticity-spatial-map that comprises an array (232) of different (240) elasticity values. The reference map is formed to be reflective of ultrasonic shear wave imaging of a reference medium. The reference medium is not, nor located at, the medium of interest, and may be homogeneous. Shear waves that are propagating in a medium are tracked by interrogating the medium. From tracking locations on opposite sides of an ablated-tissue border, propagation delay of a shear wave in the medium and of another shear wave are measured. The two shear waves result from respectively different pushes (128) that are separately issued. A processor decides, based on a function of the two delays, that the border crosses between the two locations. The calibrated map is dynamically updated and may include post-ablation border expansion (346) and time-annotated previous stages (344, 348).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Medical apparatus, use and methods
InactiveUS20060106313A1Move quicklyNot so rapidElectrotherapyChiropractic devicesTransducerBiomedical engineering
In accordance with one embodiment, a vibratory transducer has an armature suspended in a magnetic field. The armature has a plurality of electrical conductive paths to provide electrical current flow in said armature to react with said magnetic field and cause movement in the armature controlled by variation in the electrical current flow. A contact surface is secured to the armature, with a surface area for frictionally coupling to a corresponding surface area of a patient for example. Movement of the vibratory transducer induces movement in the patient, and the transducer can produce movement in the contact surface in at least two dimensions simultaneously. In one embodiment the contact surface is flat, while in alternative embodiments the contact surface is incorporated in a toroidal structure so as to surround part of the patient. Medical application can include treatment of bone fractures, oedema, and in elastography, amongst other applications.
Owner:MERLEX CORP PTY LTD
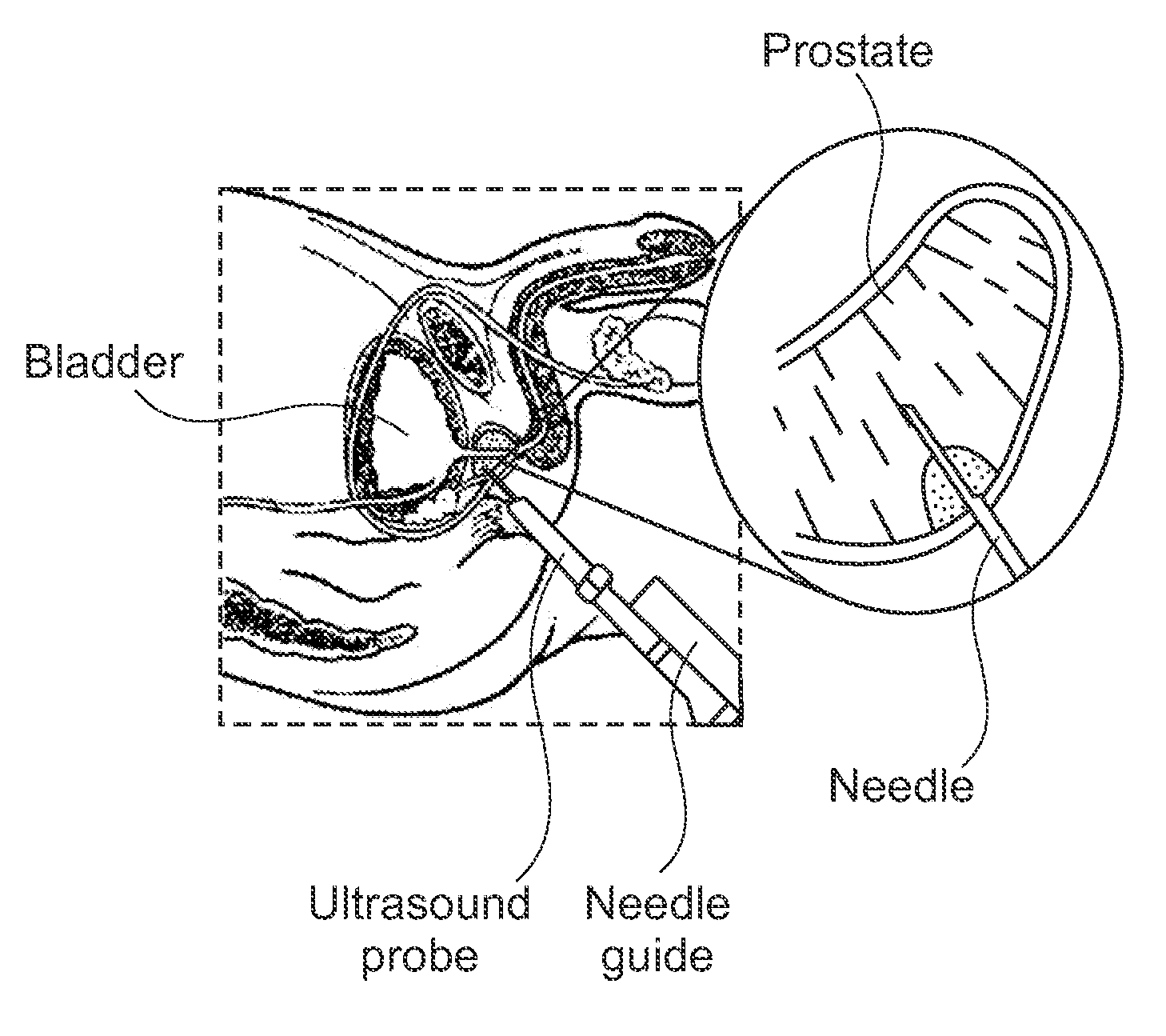
Trans-perineal prostate MR elastography
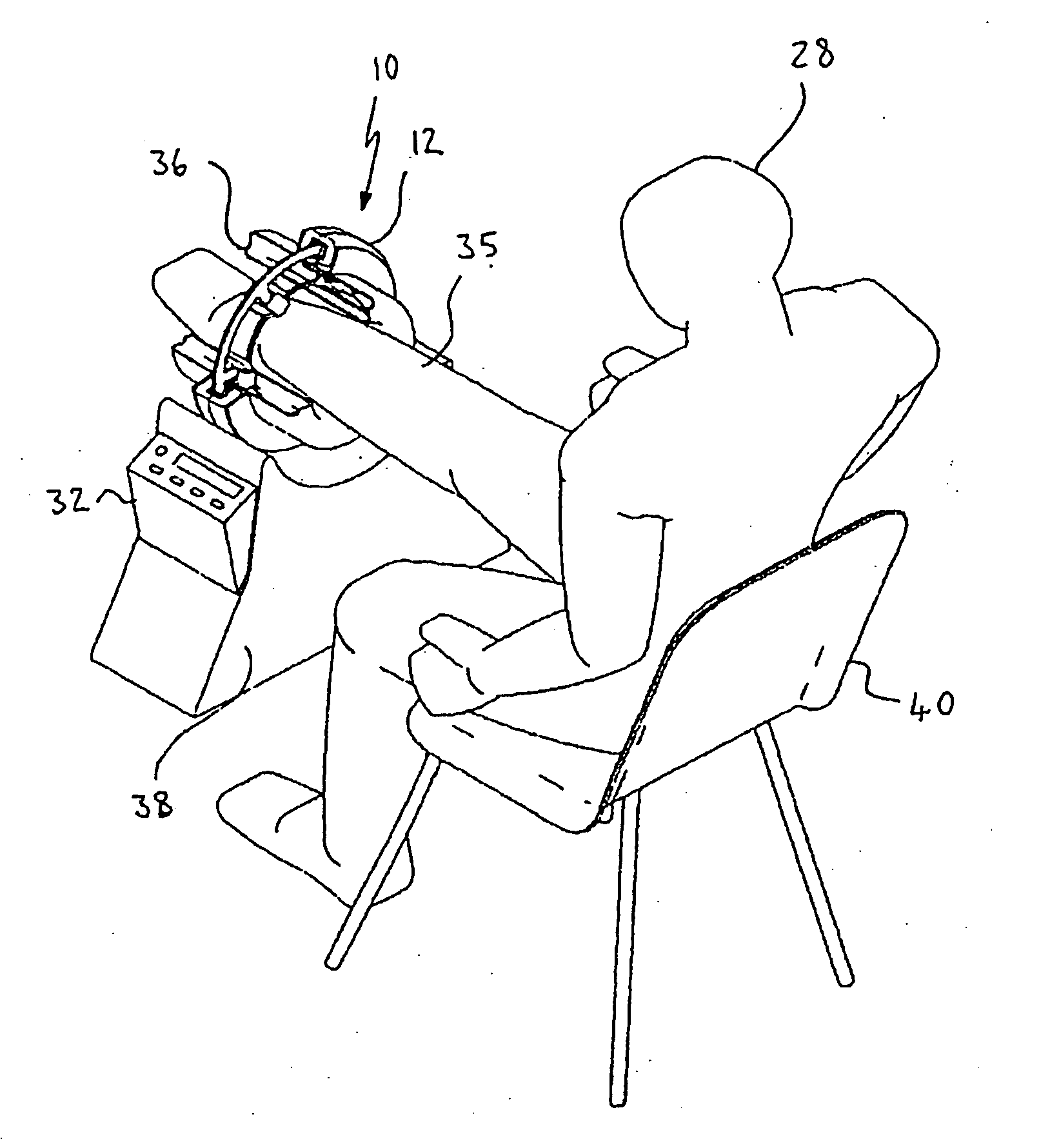
InactiveUS20120053450A1Travel efficientlyMagnetic measurementsDiagnostics using vibrationsRadiologyMagnetic resonance scanner
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for imaging the mechanical properties of the prostate of a patient non-invasively. The apparatus generally comprises a magnetic resonance scanner, a vibration assembly coupled to the perineal region of the patient, and a driver that drives the mechanical exciter. The method generally comprises positioning the vibration assembly against the perineal region of the patient, vibrating the mechanical exciter to cause deformational excitation of a tissue region contacted in the perineum, capturing a series of images in time (snapshots) of the tissue region using the MR scanner, and finally processing the displacement images to generate maps of mechanical properties of images tissue.
Owner:SALCUDEAN SEPTIMIU +2
Tissue mimicking elastography phantoms
ActiveUS20050227364A1Prevent slippingEnhanced ultrasound backscatterMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMedicineResonance
Tissue mimicking materials for elastography phantoms have elastic, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance characteristics that are characteristic of human soft tissues and well suited for the calibration and performance assessment of elastography imaging systems. In one embodiment, the material is formed from a base material containing an oil dispersed within a gel matrix and at least one inclusion formed from a gel. In another embodiment, the material is formed from a gel-forming material suffused throughout an open-cell reticulated mesh matrix.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method and system for vascular elastography
The method for vascular elastography comprises: i) obtaining a sequence of radio-frequency (RF) images including pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images in digital form of a vessel delimited by a vascular wall; the pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images being representative of first and second time-delayed configuration, of the whole vessel; ii) partitioning both the pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images within the vascular wall into corresponding data windows; approximating a trajectory between the pre- and post-tissue-motion for corresponding data windows; and using the trajectory for each data window to compute the full strain tensor in each data window, which allow determining the Von Mises coefficient. The method can be adapted for non-invasive vascular elastography (NIVE), for non-invasive vascular micro-elastography (MicroNlVE) on small vessels, and for endovascular elastography (EVE).
Owner:MAURICE ROCH LISTZ +3
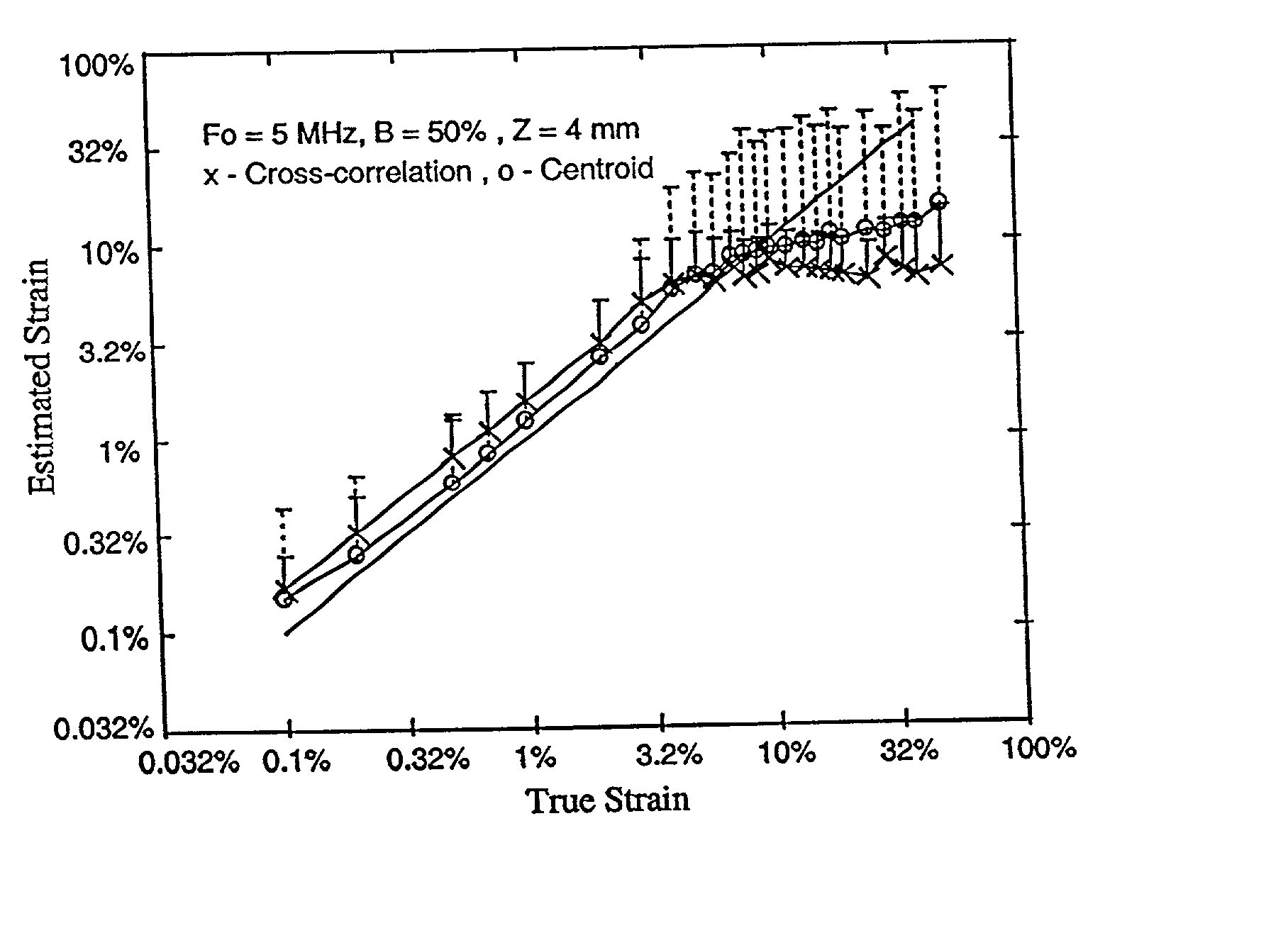
Power spectral strain estimators in elastography
InactiveUS20020010399A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionHand heldIn vivo
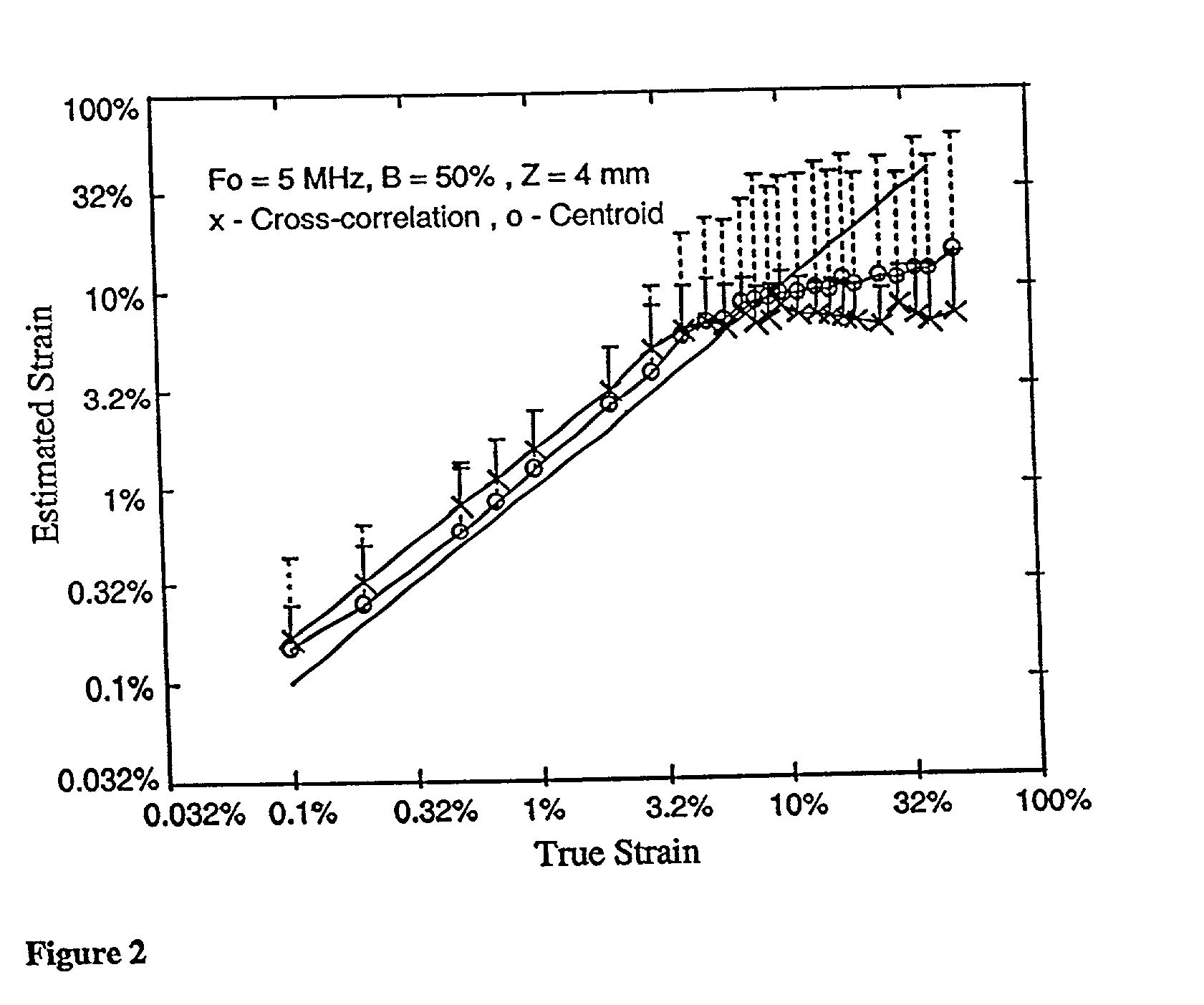
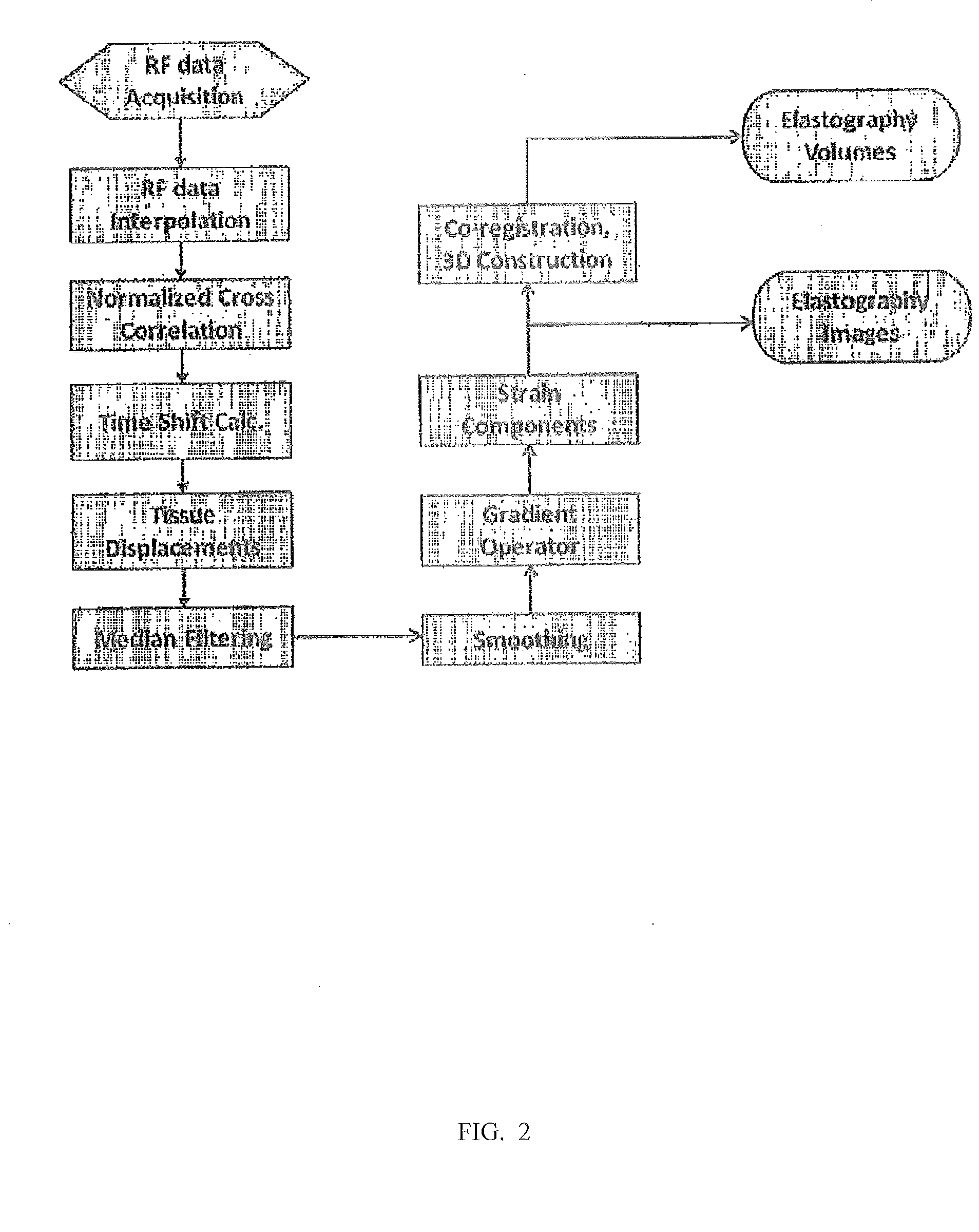
Elastography can produce quality strain images in vitro and in vivo. Standard elastography uses a coherent cross-correlation technique to estimate tissue displacement and tissue strain using a subsequent gradient operator. While coherent estimation methods generally have the advantage of being highly accurate and precise, even relatively small undesired motions are likely to cause enough signal decorrelation to produce significant degradation of the elastogram. For elastography to become more universally practical in such applications as hand-held, intravascular and abdominal imaging, the limitations associated with coherent strain estimation methods that require tissue and system stability, must be overcome. In this paper, we propose the use of a spectral shift method that uses a centroid shift estimate to measure local strain directly. Furthermore, we also show theoretically that a spectral bandwidth method can also provide a direct strain estimation. We demonstrate that strain estimation using the spectral shift technique is moderately less precise but far more robust than the cross-correlation method. A theoretical analysis as well as simulations and experimental results are used to illustrate the properties associated with this method.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
High resolution elastography using two step strain estimation
ActiveUS20070083113A1Reduce riskAvoid problemsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesImage enhancementStrain estimationComparison area
High-resolution elastography employs a multiple-step process in which successively finer samplings of data and smaller areas of data are evaluated to provide increasingly accurate displacement measurements, wherein each displacement measurement guides the determination of corresponding regions of comparison used in the next displacement evaluation.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
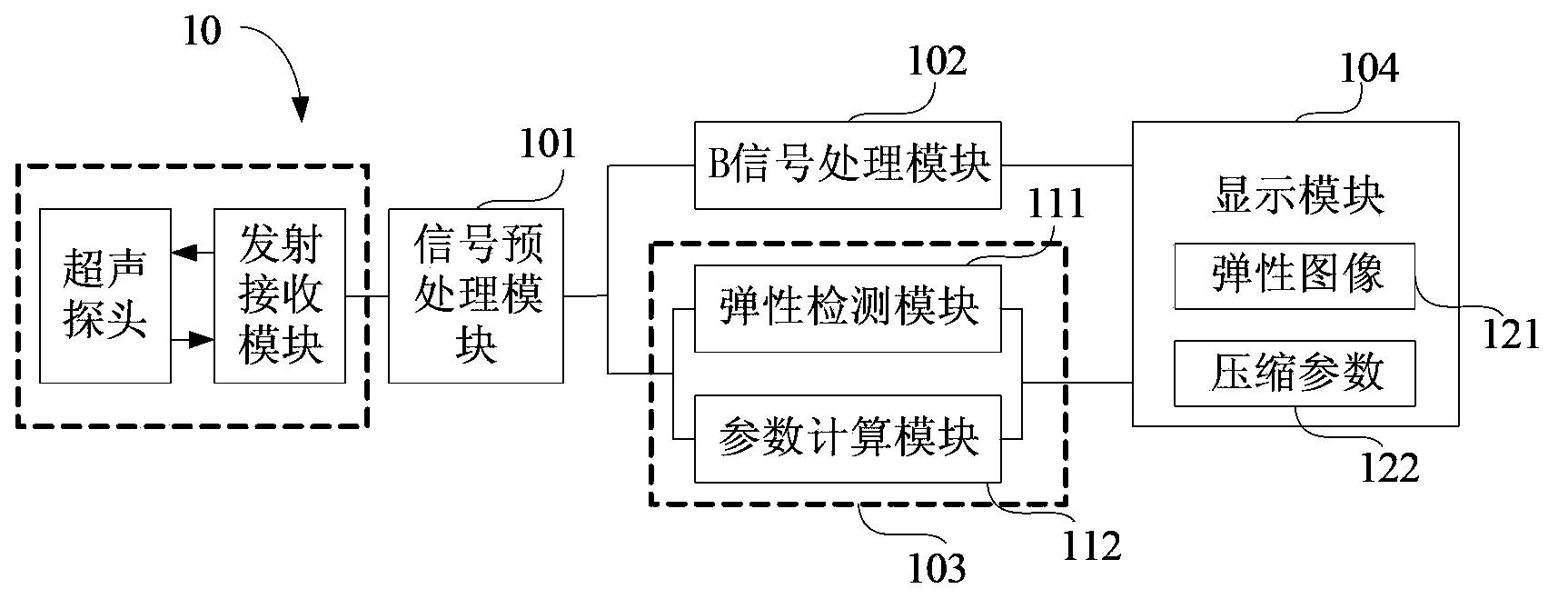
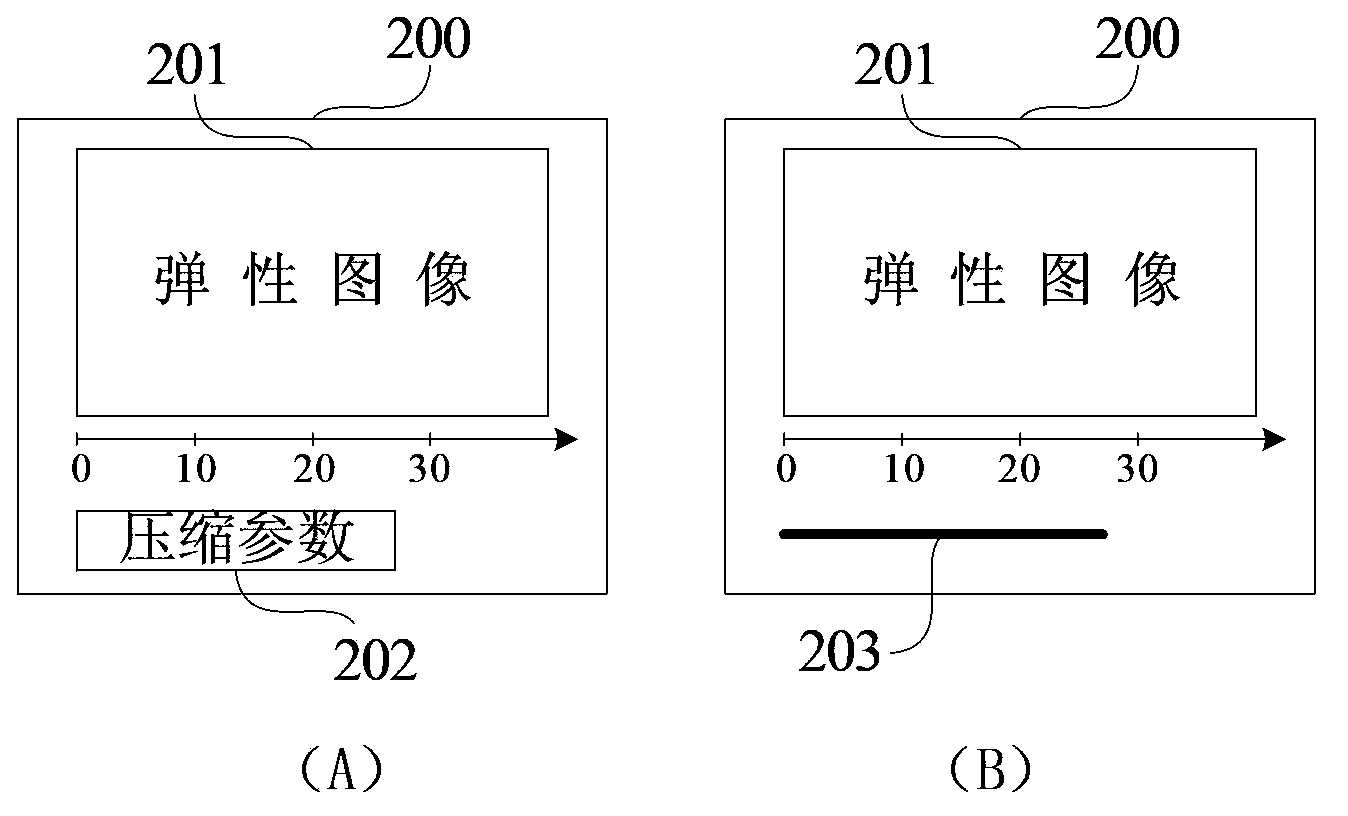
Ultrasonic elastography system and method
ActiveCN103845074ASimple and fast operationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationComputer module
The invention discloses an ultrasonic elastography system and method. The ultrasonic elastography system comprises an elastic detection module for processing a beam-forming output signal, calculating the elasticity physical quantity of a target to be detected and generating a corresponding elastic image according to the physical quantity, a parameter calculating module for calculating a compression parameter corresponding to the elastic image, a display module for displaying the elastic image and the corresponding compression parameter, wherein the compression parameter is used for reflecting the detected target compression degree of a probe. The ultrasonic elastography system can display the corresponding compression parameter while displaying the elastic image, a user can intuitively judge whether the compassion degree of the probe to the target to be detected is required to be adjusted or not, accordingly a certain guidance is provided for the user, especially for a user lack of operational experience, and the operation is simple and convenient.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
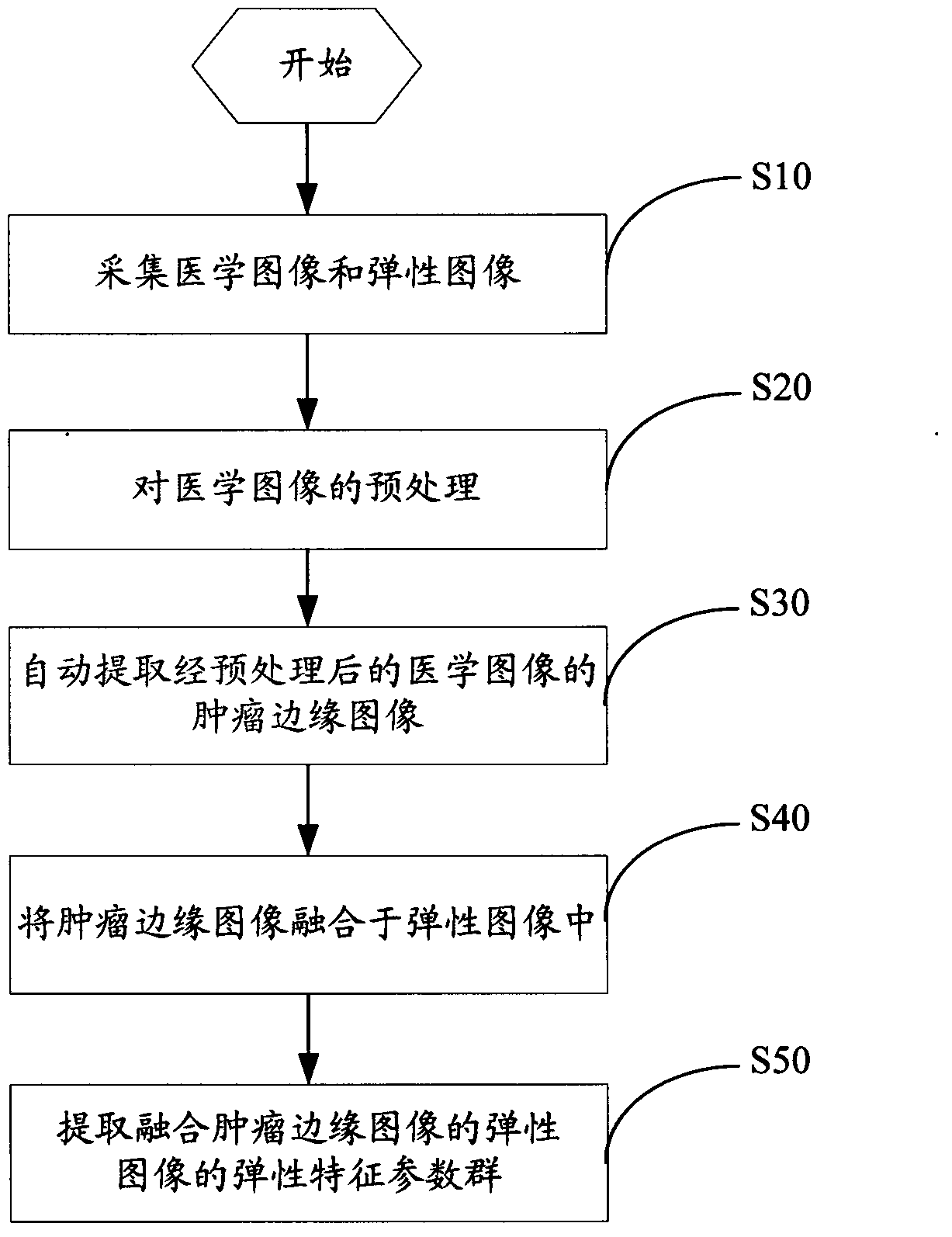
Method for extracting tumor elasticity characteristics based on ultrasonic elastography
ActiveCN103578099AEliminate subjective differencesAccurate and scientific diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationFeature extraction
The invention provides a method for extracting tumor elasticity characteristics based on ultrasonic elastography. The method comprises the following steps that medical images and elasticity images are collected; the medical images are preprocessed; the tumor marginal information of the preprocessed medical images is automatically extracted; the tumor marginal information is fused into the elasticity images; an elasticity characteristic parameter group, fused with the tumor marginal information, of the elasticity images is extracted. According to the method for extracting the tumor elasticity characteristics based on the ultrasonic elastography, the tumor marginal information is extracted through the medical images, meanwhile, the tumor marginal information is fused into the elasticity images, the elasticity characteristic parameter group based on the elasticity images is built and quantized and can describe the attributes of tumors from different angles, and therefore the subjective difference of clinicians is eliminated, and diagnosis is more accurate and more scientific.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Elastography device and method
ActiveCN102308207ADetermining viscoelastic propertiesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostic probe attachmentUltrasonic sensorUltrasound elastography
The present invention provides an elastography device (110) for quantitatively and / or qualitatively measuring the viscoelastic properties of any medium, said device being characterized in that it comprises a deformable tube (111) for positioning said ultrasonic transducer (104) located at the end of said deformable tube (111) and for holding it in position so as to ensure, during at least one measurement, perpendicularity and contact between said ultrasonic transducer (104) and the medium.
Owner:ECHOSENS SA
Biopsy device with acoustic element
The invention relates to a biopsy device, particularly a biopsy device comprising a shaft with a transducer element for providing information about acoustic properties of a material to be analysed, a system of positioning a biopsy device and a method for positioning a biopsy device. The biopsy device may be adapted to take biopsies of different regions of the 5 human body for excluding or detecting abnormalities as cancerous lesions. The biopsy device may be used to measure acousticproperties of the material while inserting the tip portion of the biopsy device into the material to be analysed. The biopsy device may further allow measurement based on elastography.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and Device for Tumor Characterization Using Nonlinear Elastography Imaging
ActiveUS20140288424A1Smoothly measuredHealth-index calculationOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorHuman tumor
The present invention provides a method and a device to image and characterize human tumors, and to classify the tumors as either malignant or benign. The method includes using a multi-compression technique upon the tissue or organ combined with a 3D ultrasound strain imaging of the compressed tissue or organ for acquiring raw data and analyzing the raw data using a computer processing unit equipped with a nonlinear biomechanical tissue model for tumor classification. A device is provided having a compression stage for delivering multi-compression with continuous force measurements, and a 3D ultrasound transducer strain imaging probe, wherein the imaging probe and the compression stage are in communication with a computer processing unit.
Owner:WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY
Ultrasonic elastography and pressure feedback method based on receive-side spatial-compounding
ActiveCN102626327AEasy to analyzeLow imaging noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Improved algorithm
The invention discloses an ultrasonic elastography andpressure feedback method based on receive-side spatial-compounding, namely, a medical ultrasonic elastography algorithm realized by an improved algorithm based on phase zero. When calculating displacement, the traditional algorithm carries out displacement calculation on a scanning line, which leads to large errors in the case that tissue movement contains a horizontal component; while, the window of noval algorithm covers a plurality of adjacent scanning lines, thereby reducing the errors brought by the horizontal component of tissue movement and improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the ultrasonic elastography. At the same time, the method provided in the invention also employs Receive-Side Spatial-Compounding technology in an elastography system, thereby further reducing the impact of elastography noise and further advancing the signal-to-noise ratio of the system. Finally, an average-strain-based elastography pressure feedback technology is provided to prompt current pressing strength and a normal pressing range for a doctor.
Owner:SASET CHENGDU TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com