Patents
Literature
258 results about "Video projector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
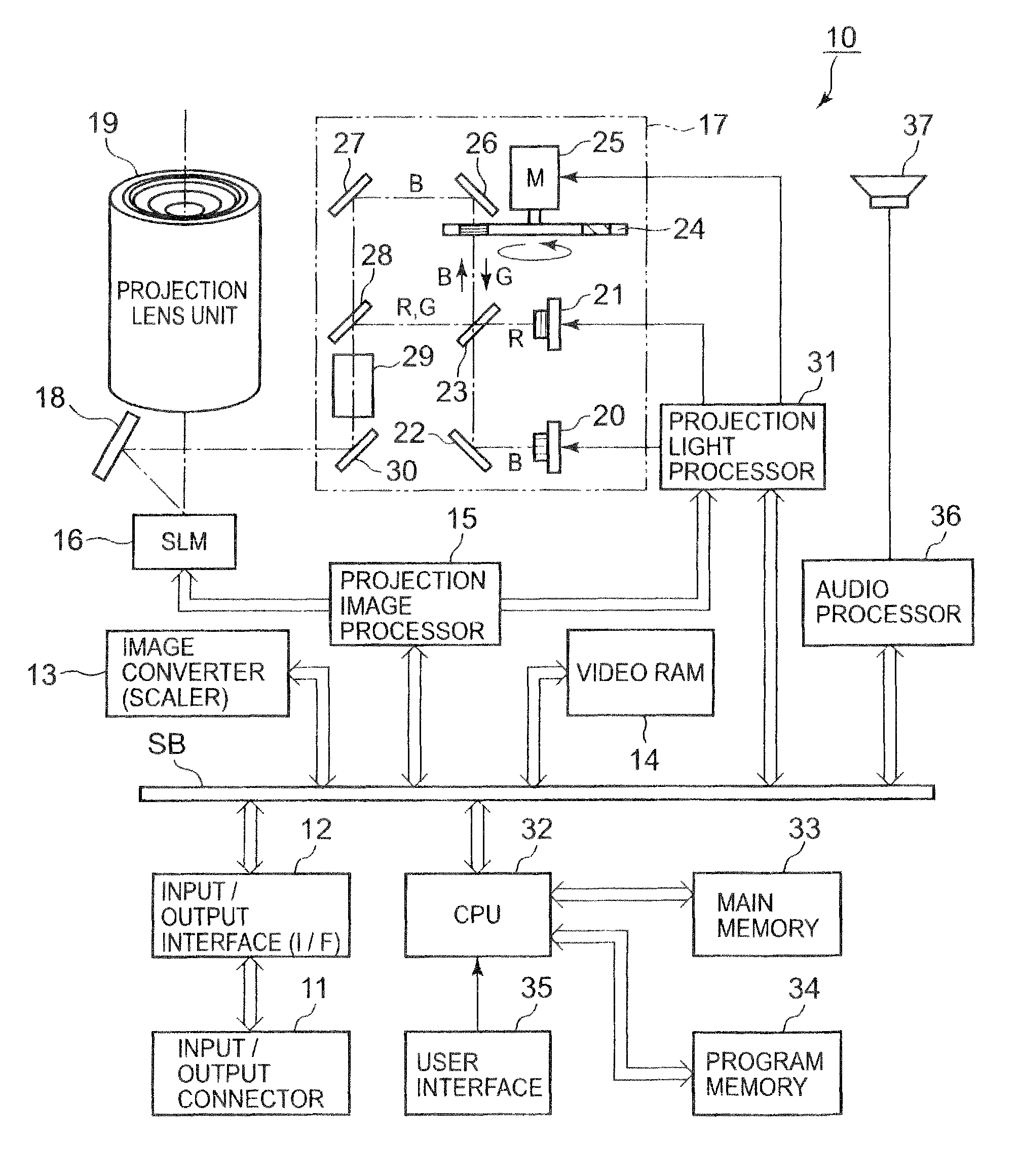
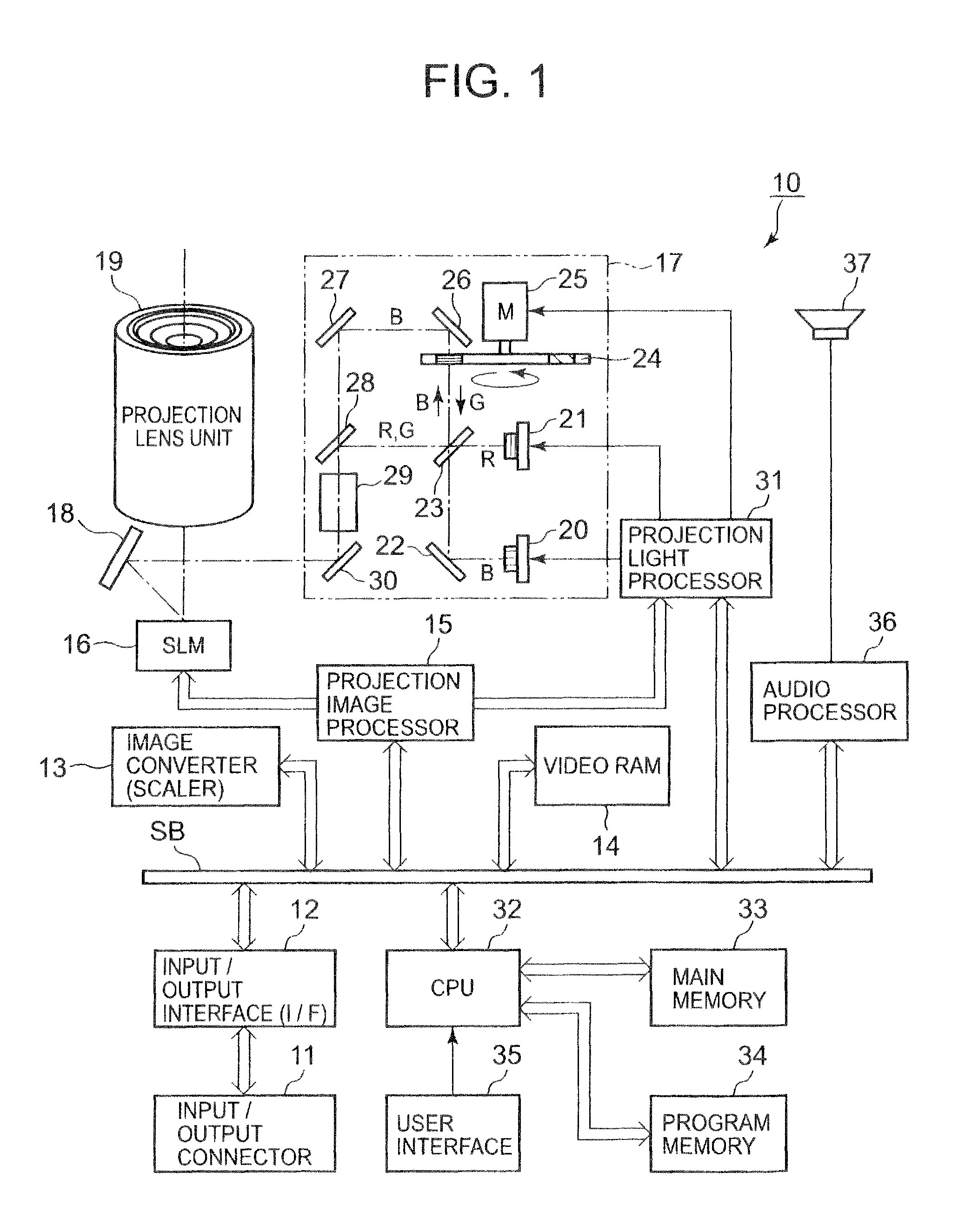
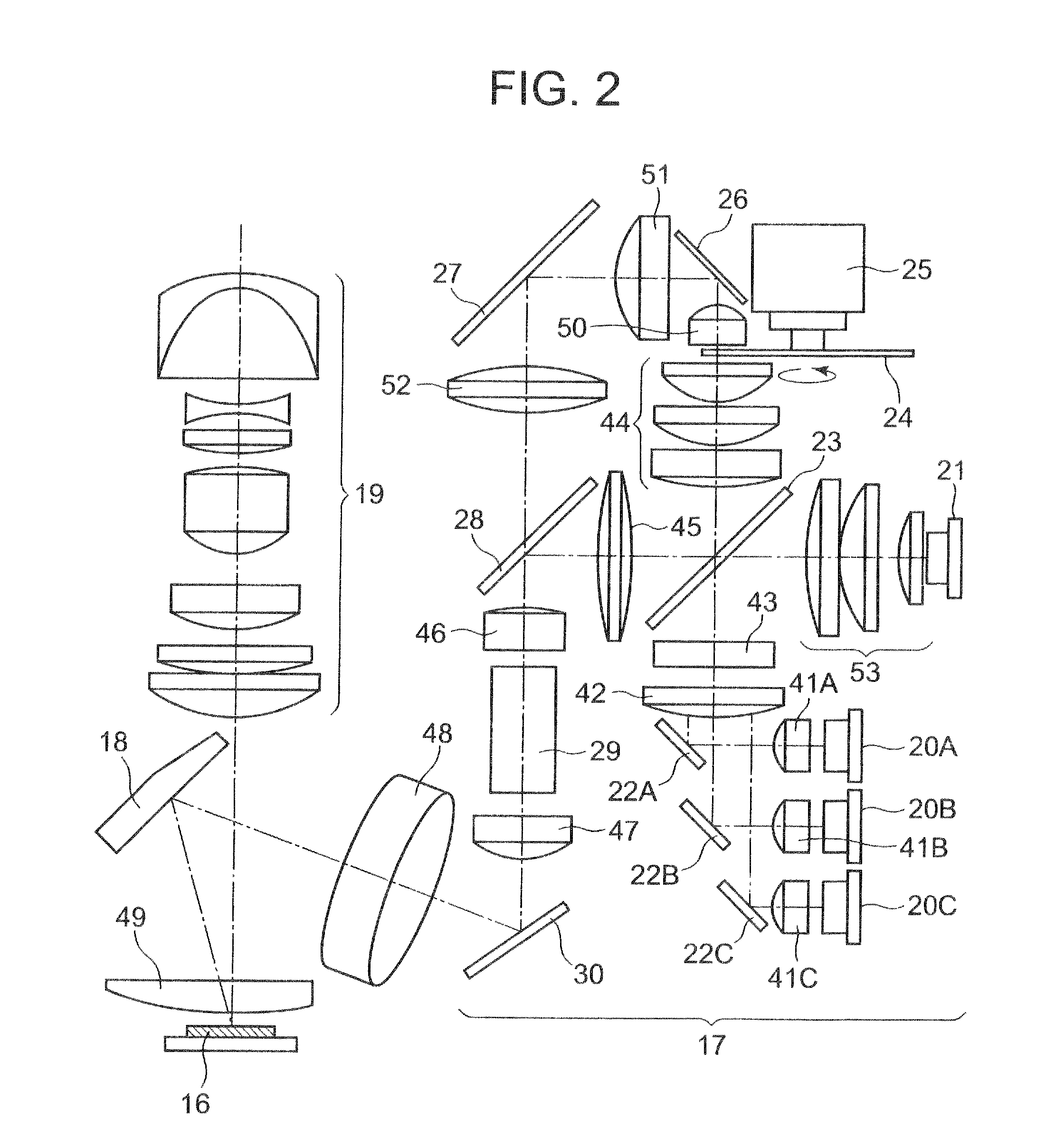
A video projector is an image projector that receives a video signal and projects the corresponding image on a projection screen using a lens system. All video projectors use a very bright ultra high pressure mercury lamp, LED or solid state blue or RGB laser to provide the illumination required to project the image, and most modern ones can correct any curves, blurriness, and other inconsistencies through manual settings. If a blue laser is used, a phosphor wheel is used to turn blue light into white light, which is also the case with white LEDs. (White LEDs do not use lasers.) A wheel is used in order to prolong the lifespan of the phosphor, as it is degraded by the heat generated by the laser diode.
Far-field display
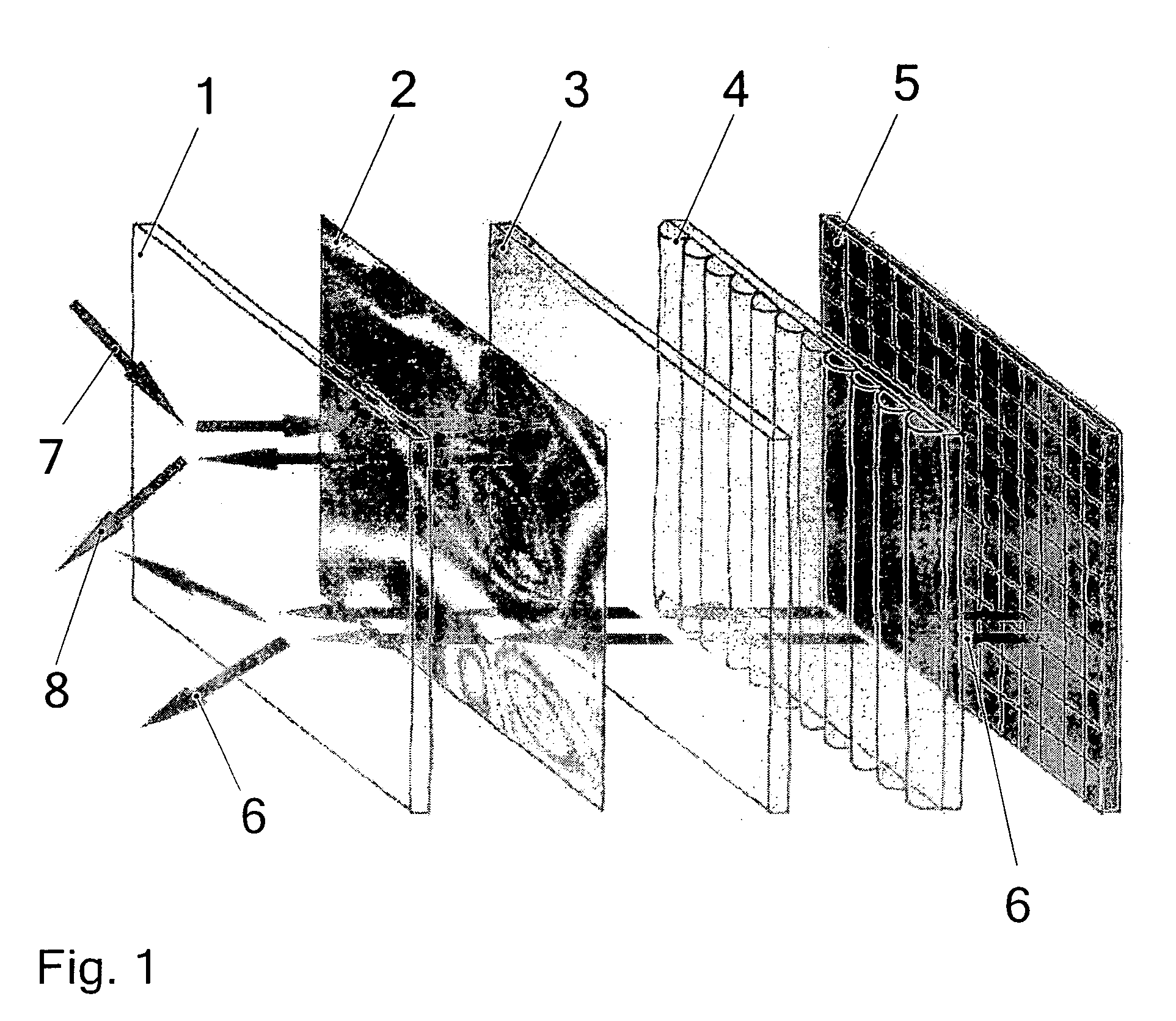
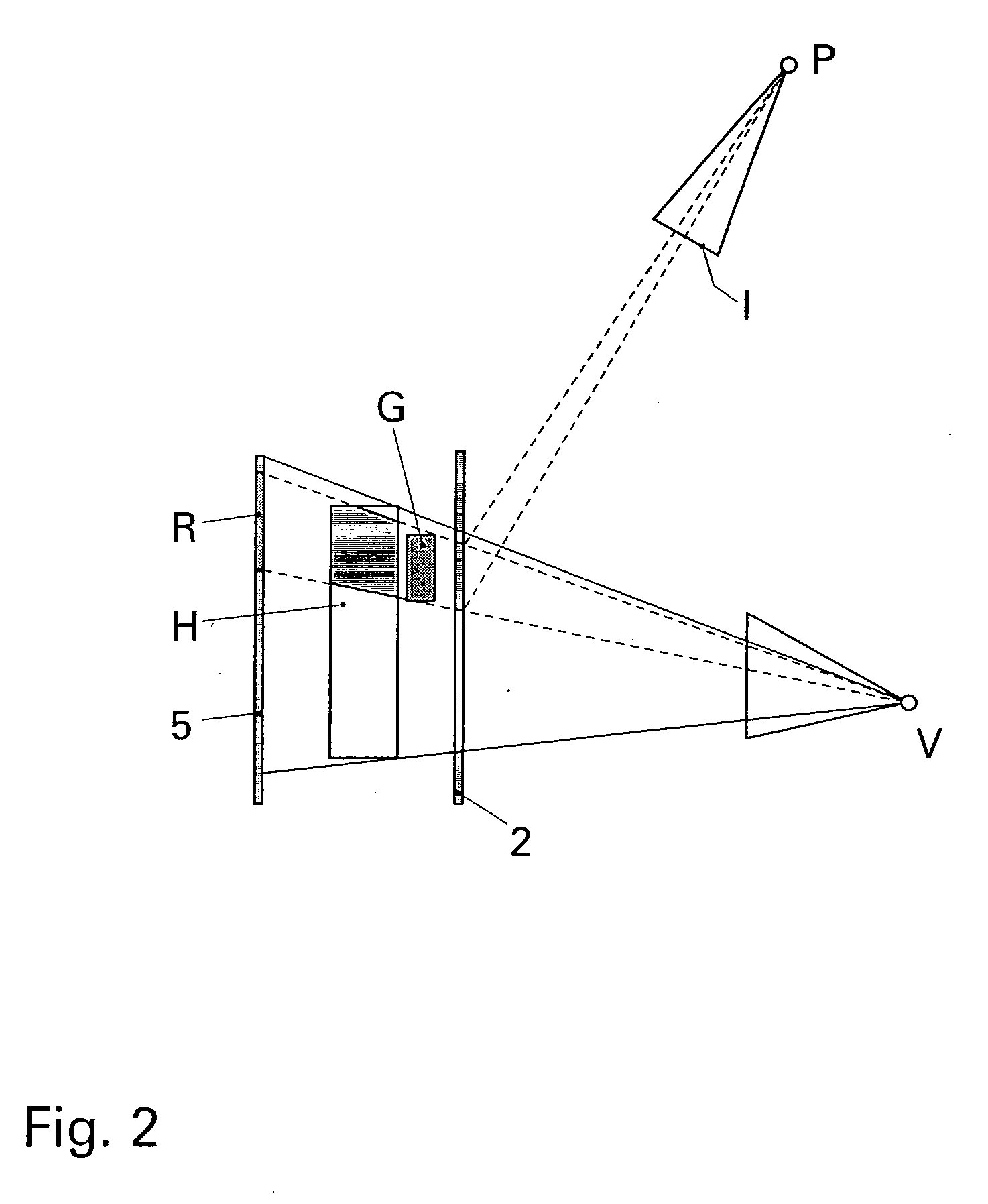
A flat-panel projection display comprises a transparent slab and integral area grating, a transparent rod with rectangular cross-section and integral linear grating, arranged along the edge of the slab, and a small video projector. The projector is arranged to direct a virtual image into the end of the rod, directly or via mirrors, the light travelling along the rod via total internal reflection. The linear grating diverts the light into the plane of the slab, and the area grating projects it out of the slab towards a viewer, so that the viewer sees an image at infinity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Flat-panel display using tapered waveguide
InactiveUS7410286B2Reduce blurIncrease contrastTelevision system detailsMechanical apparatusFlat panel displayWaveguide
A video display for two or three dimensions has a flat liquid-crystal screen which ejects light from the plane at a selectable line. One or, in the case of a 3-D display, several video projectors project a linear image into the plane from an edge. A complete image is written on the screen by addressing the line with appropriate images as it is scanned down the screen. To screen a three-dimensional image, the video projectors, each projecting an image as seen at a slightly different angle, combine to constitute a three-dimensional display which produces a three-dimensional image that is one line high.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
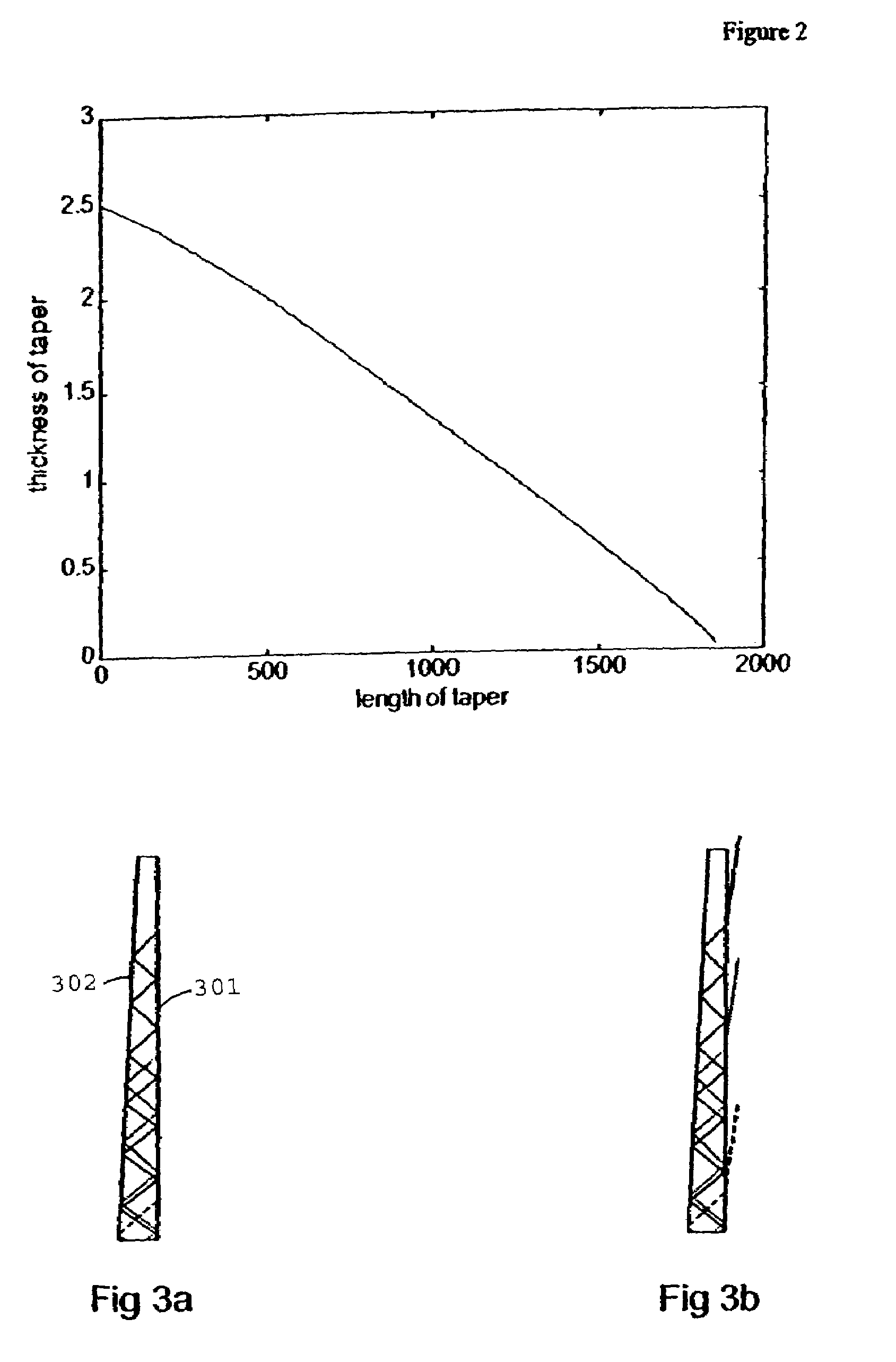
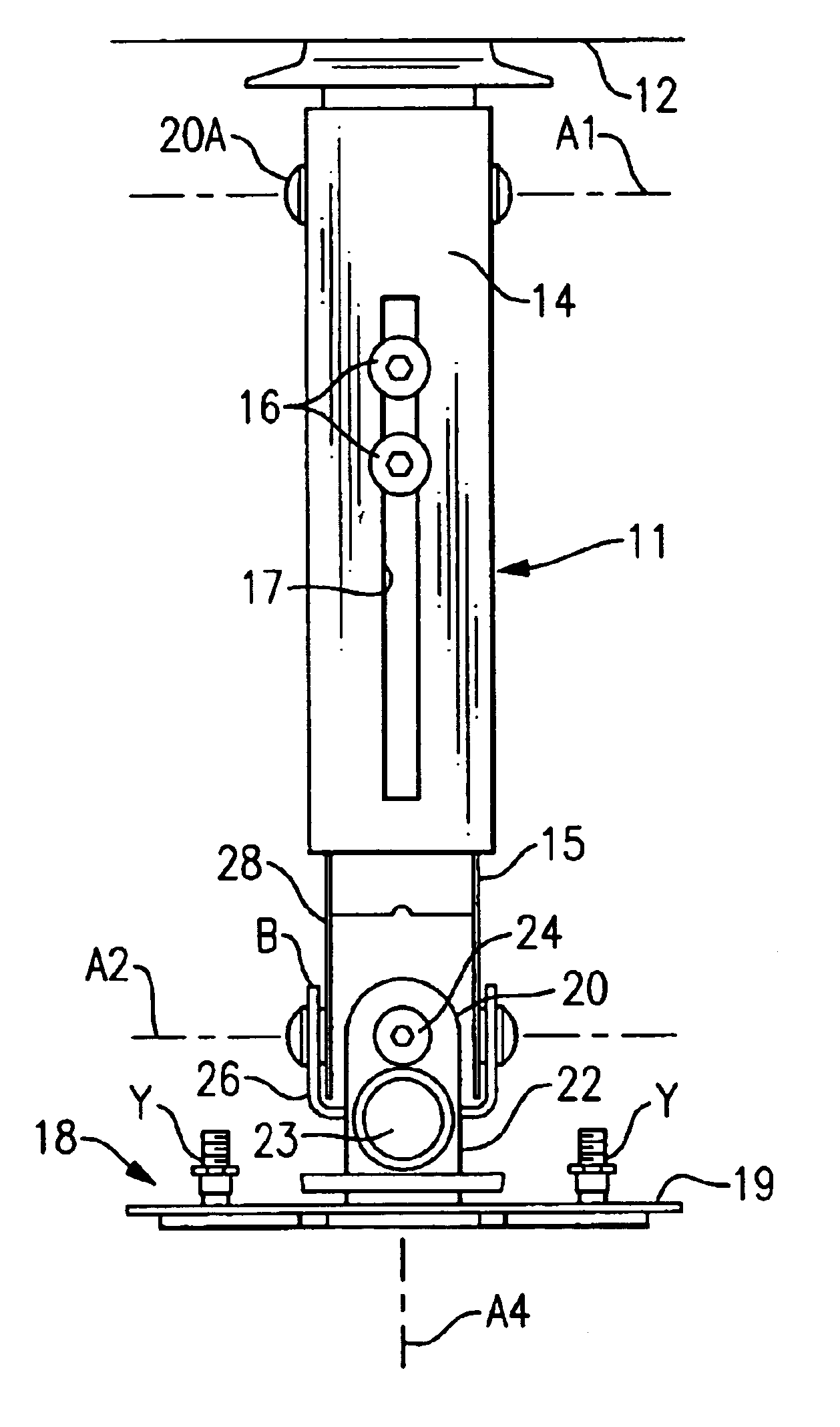
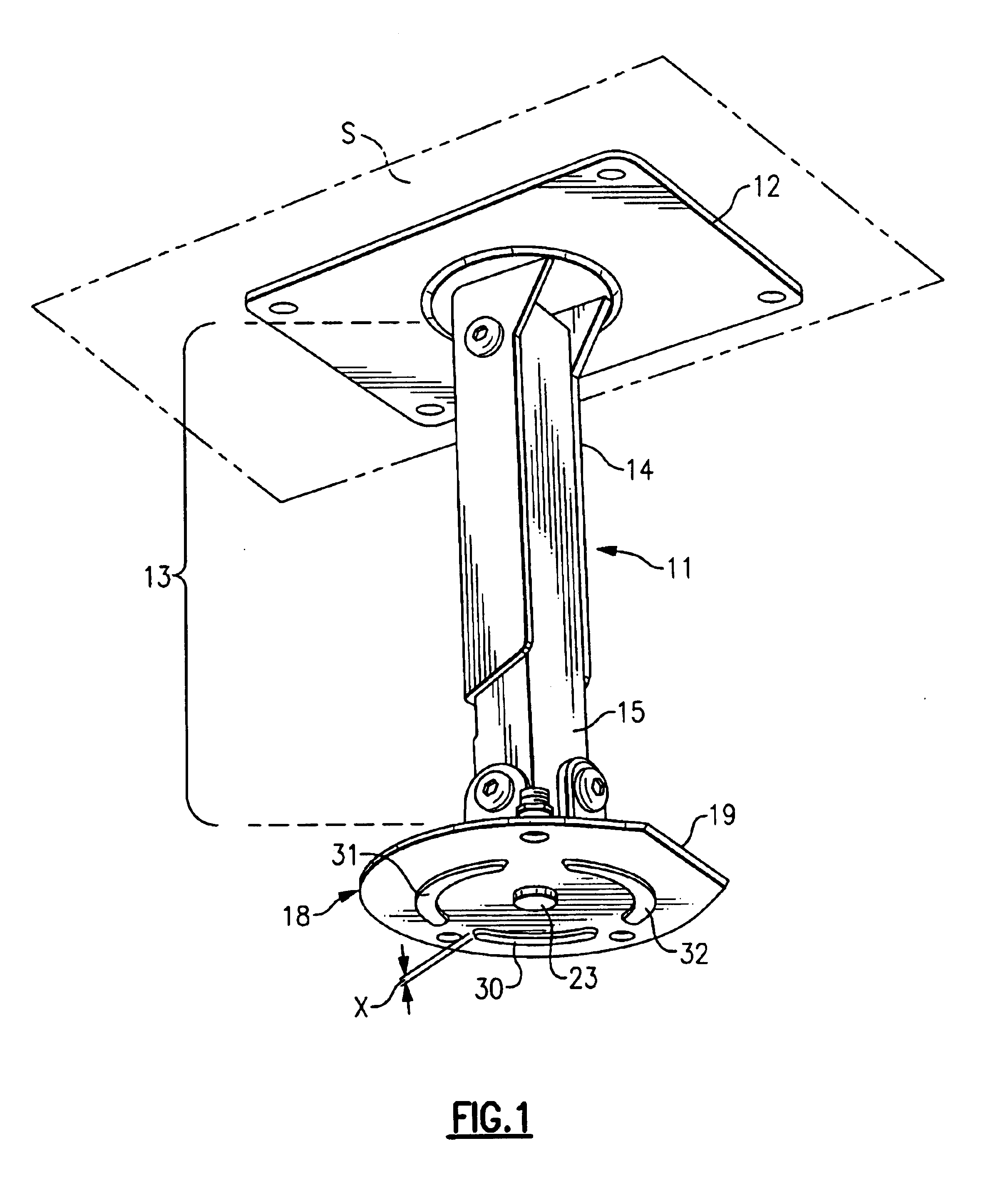
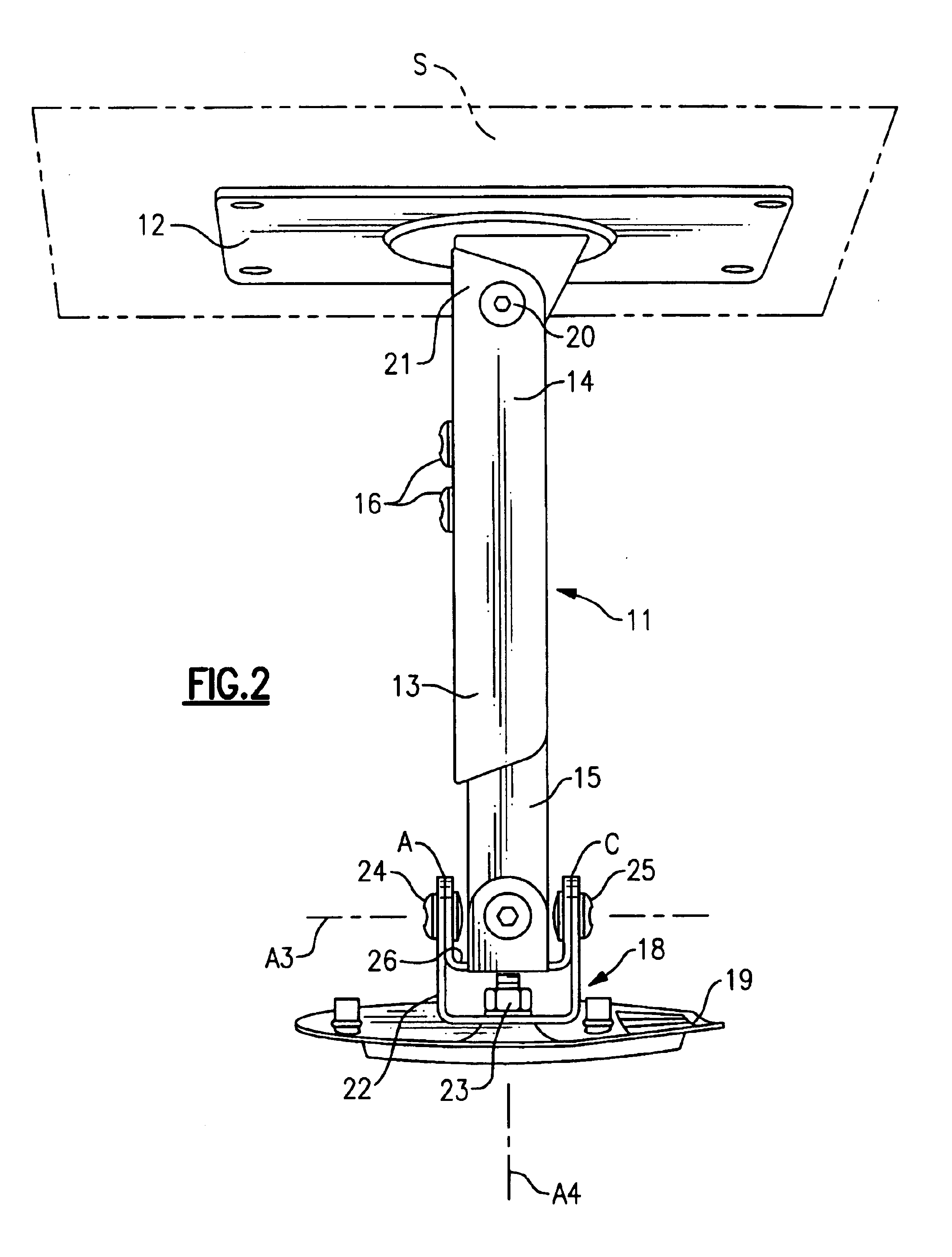
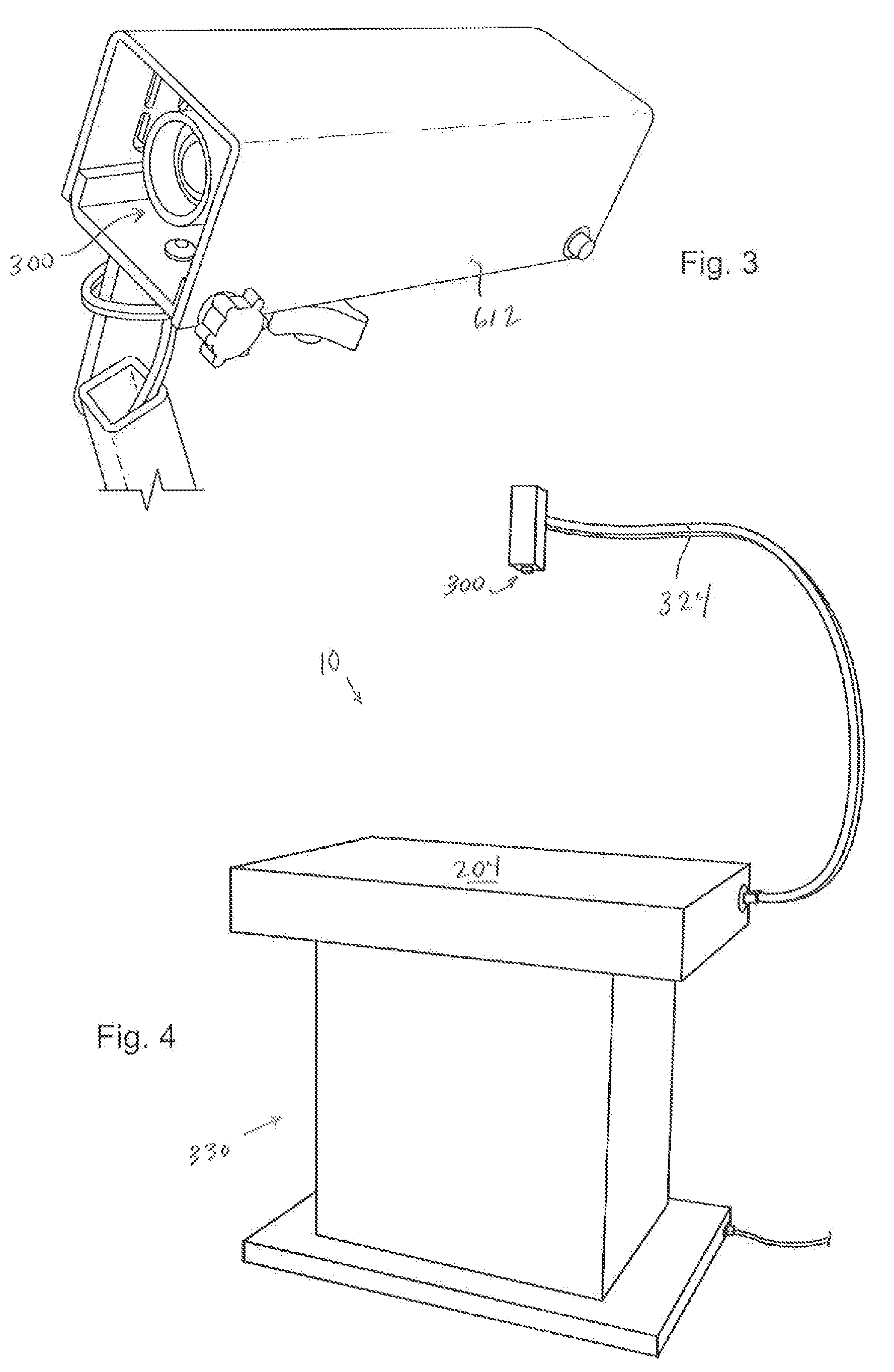
Mounting bracket
A mounting unit (11) for a attaching a working unit such as a video projector to a mounting surface which can be horizontal or vertical or at some angle intermediate the horizontal and the vertical comprising: an anchorage (12) whereby the unit can be attached to the mounting surface; a beam (13); a carrier (18) comprising in combination a holding plate (19) and a mounting plate; the carrier being adapted to provide for the attachment of a working unit to the mounting plate; a first pivot (20a) whereby a first end of the beam is pivotably attached to the anchorage to enable the beam to pivot about a first axis (a1); a second pivot whereby the other end of the beam to the first end is pivotably attached to the holding plate to enable the holding plate to pivot about a second axis (a2) parallel to the first axis; a third pivot (24) whereby the holding plate can pivot about a third axis perpendicular to the second axis; a fourth pivot (23) whereby the holding plate can pivot about a fourth axis (a4) perpendicular to the second and third axes; the carrier including mechanism whereby the mounting plate can be rotated about an fifth axis parallel to the holding plate.
Owner:LIGERTWOOD PETER
Method And Apparatus For Generating 3D Images
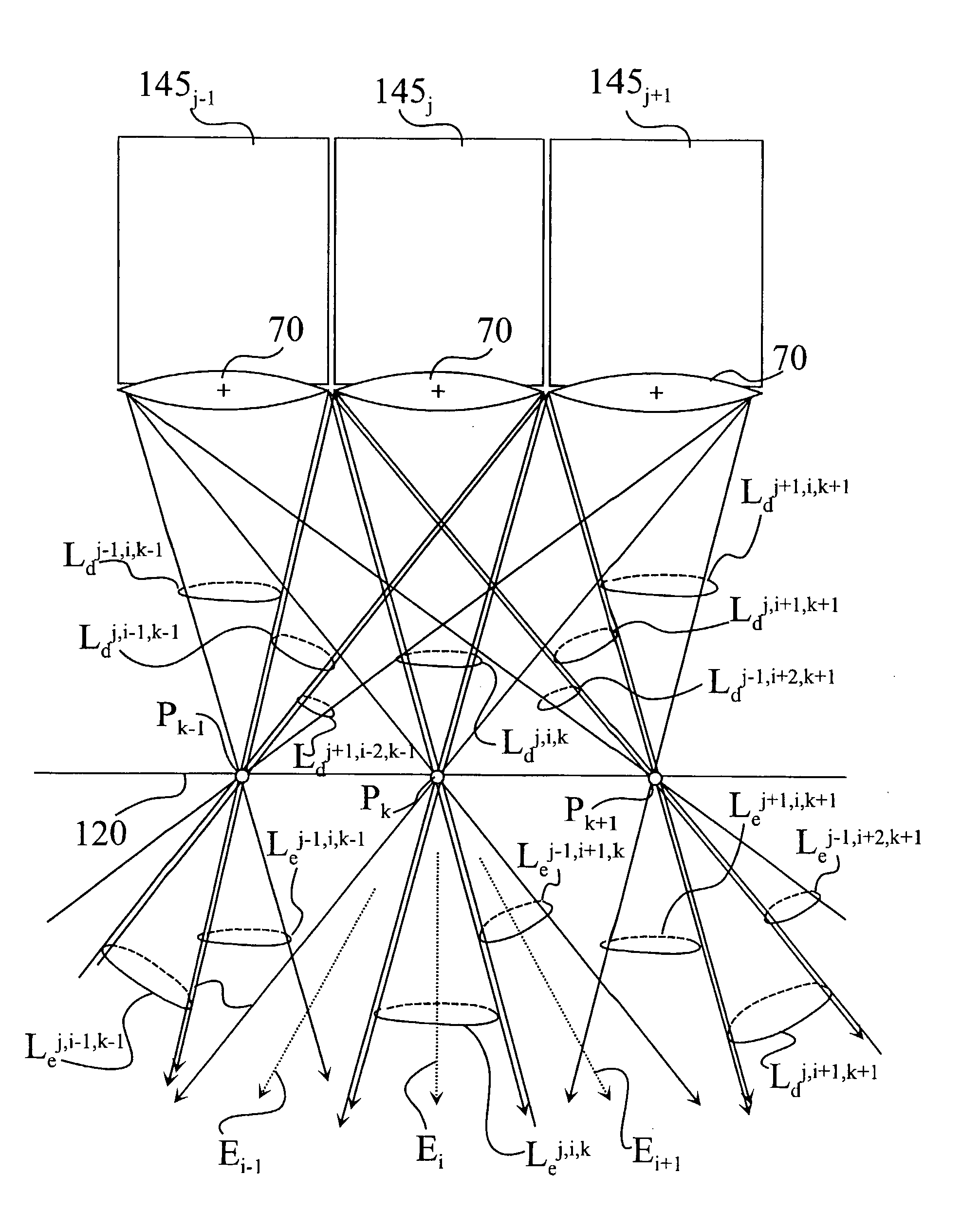
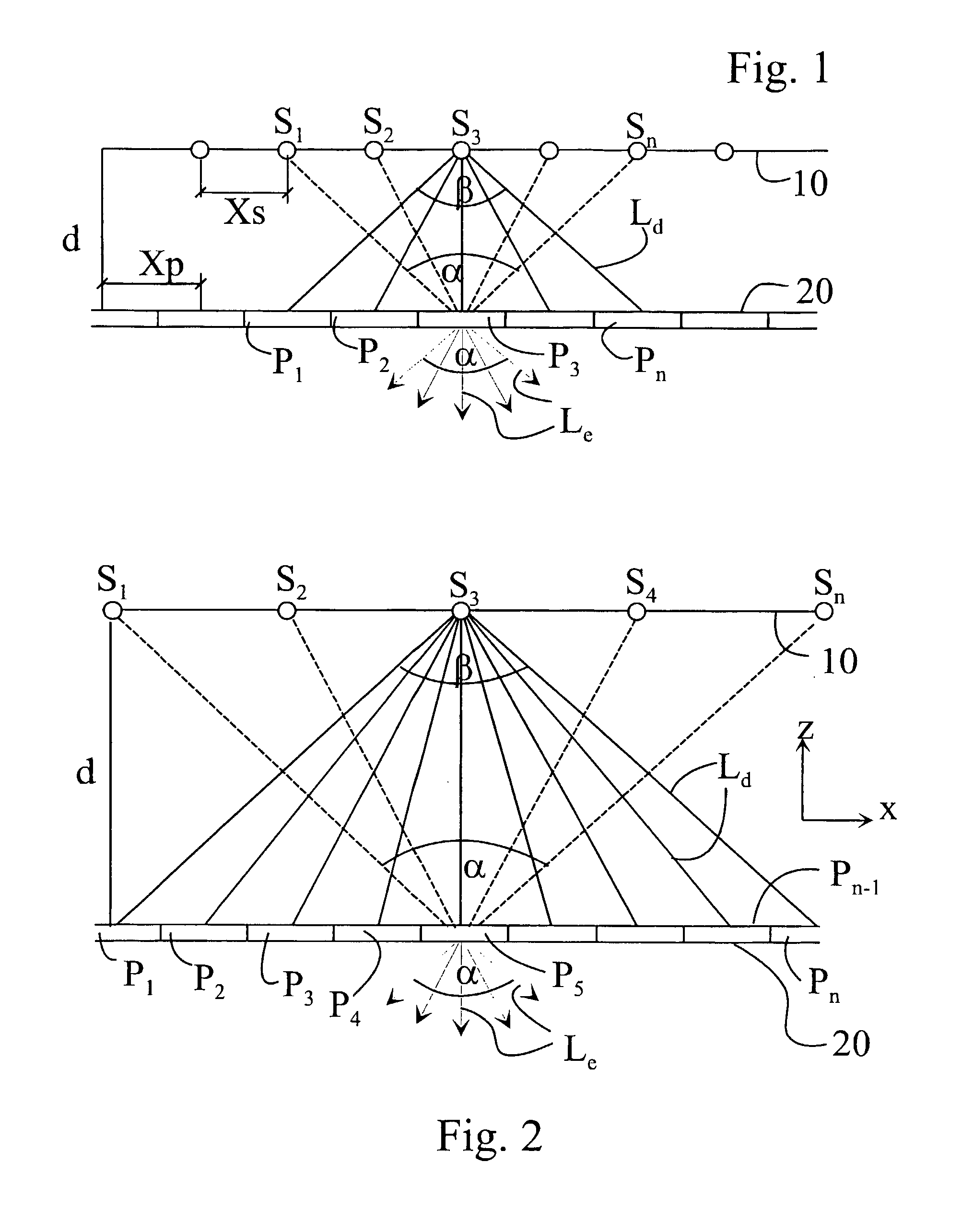
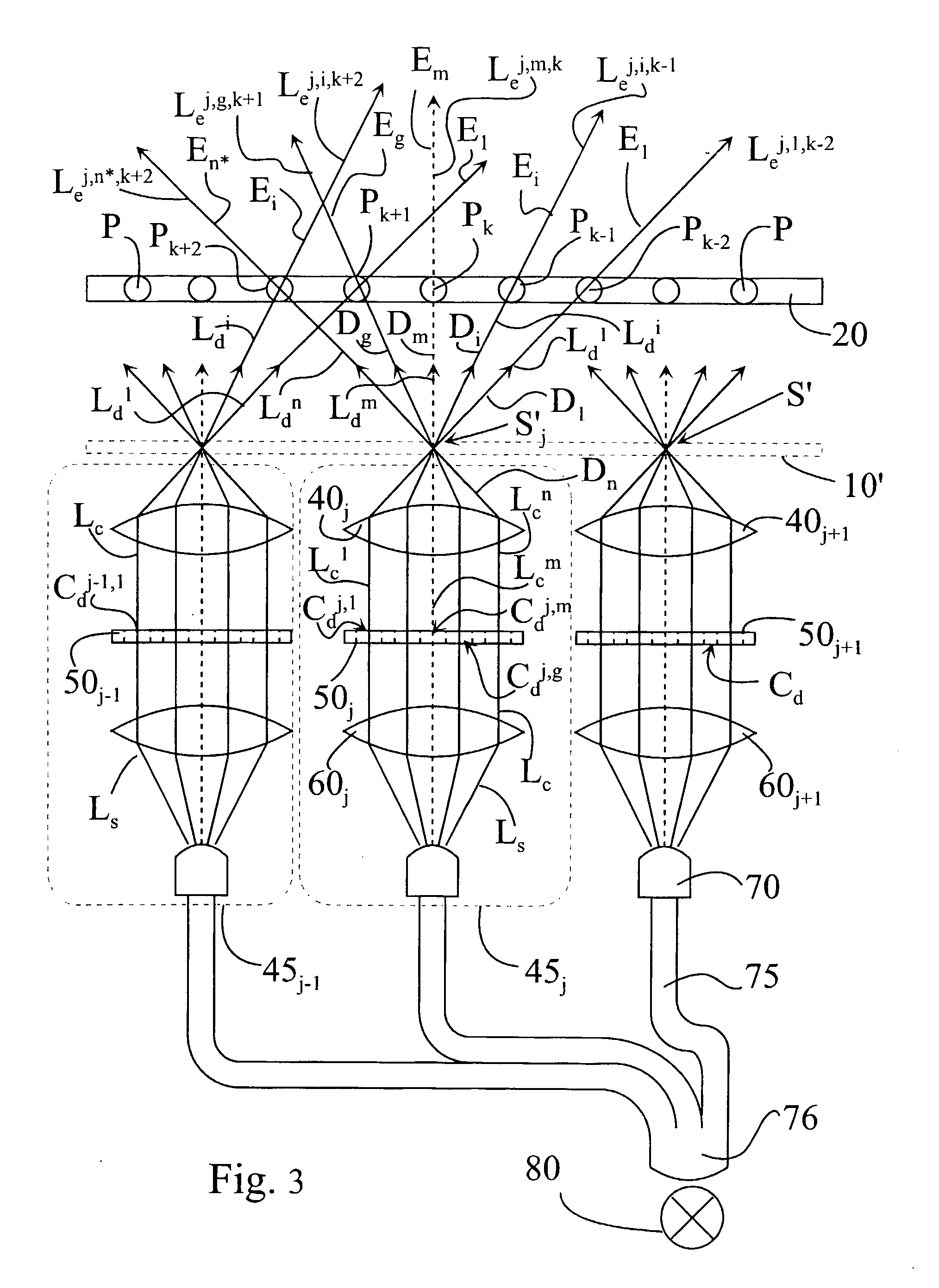
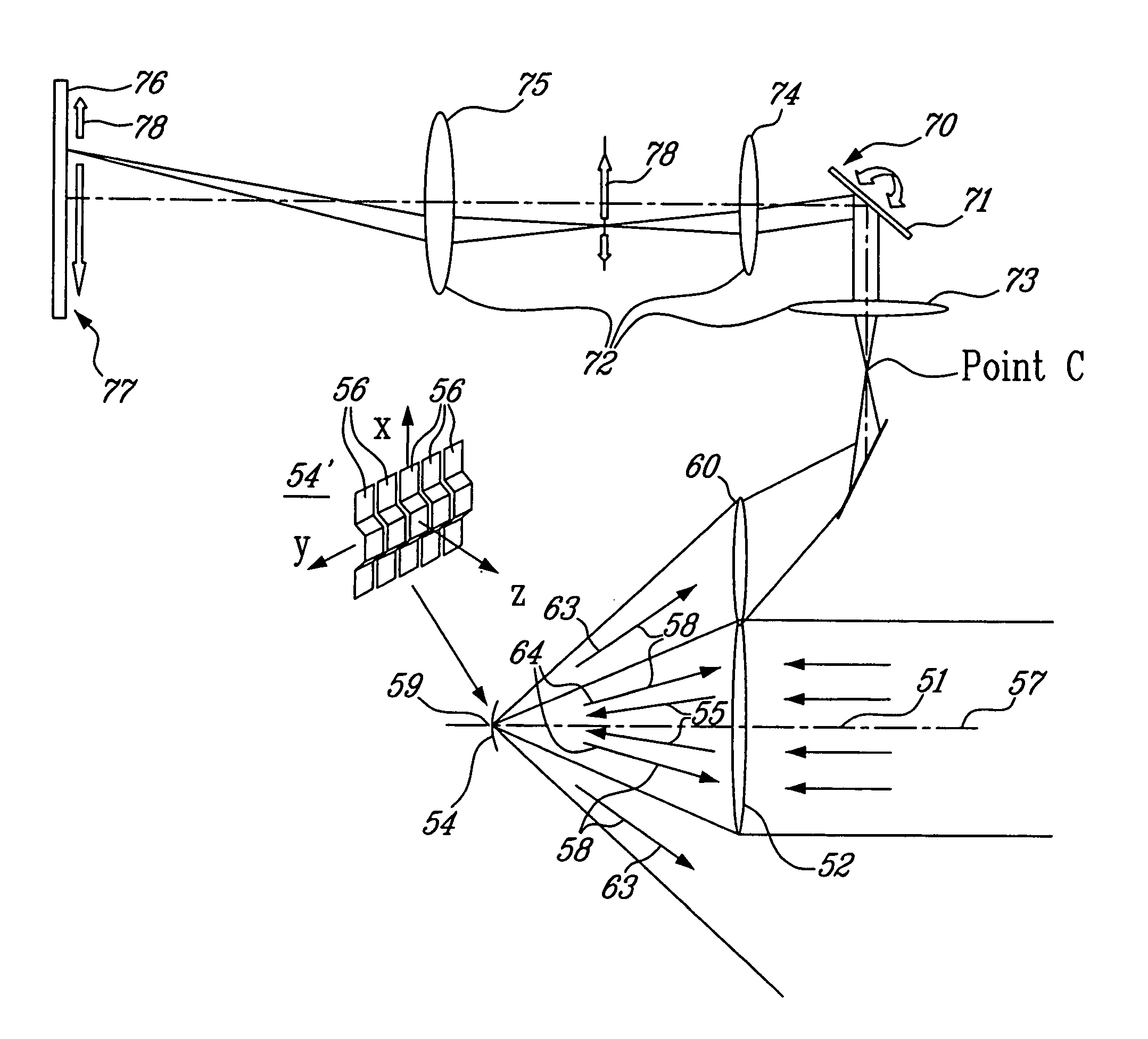
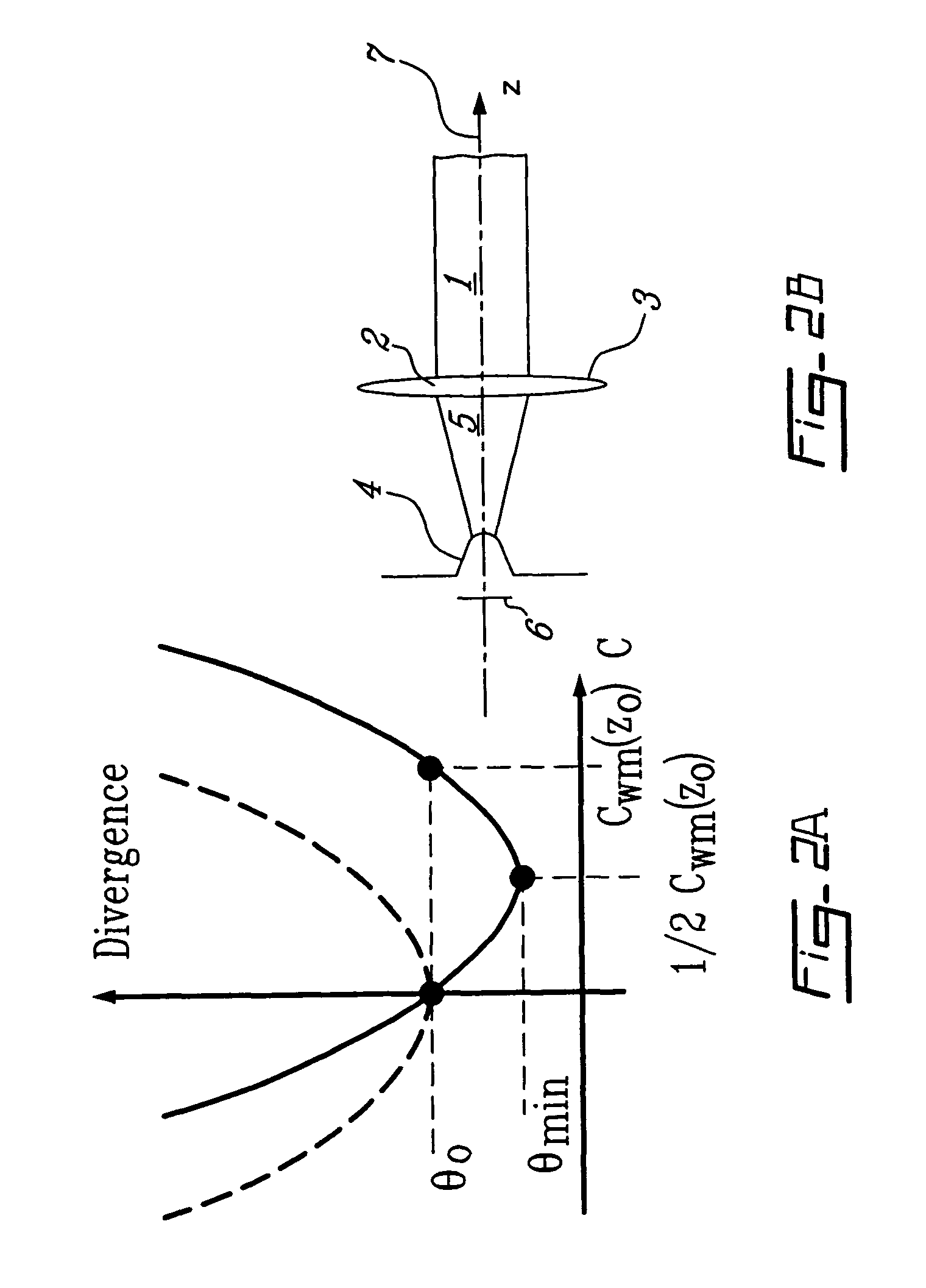
The present invention is directed to an apparatus and method for displaying 3D images. The apparatus comprises: a) a screen with angular dependent diffusion characteristics for direction selectively forwarding light; b) a screen illuminating system, the screen illuminating system comprising multiple modules for generating multiple light beams incident on points of the screen, the modules being arranged so that each point of the screen is illuminated by multiple modules, and the incident light beams generated by one module are projected into multiple different directions from the module towards multiple different points of the screen, and further the different incident light beams generated by one module are forwarded towards different emitting directions from the screen, means for coding each incident light beam with the image information of a single image point in the module, where the 3D image perceived by an observer being generated by multiple modules; c) a control system to control the modules; and d) means for imparting an exit divergence to the exiting light beams being transmitted through or reflected from the screen, the measure of the exit divergence substantially corresponding to the angle between neighbouring emitting directions associated with the optically neighbouring modules, go as to provide a substantially continuous motion parallax in the 3D image perceived by an observer. The apparatus according to the invention comprises imaging means for generating the incident light beams with a convergent section converging substantially towards a point of the screen, where a convergence of the incident light beams is substantially equal to the exit divergence of the light beams exiting the screen. The modules can be video projectors, LED projectors, the optical engines of these, or the like, arranged periodically shifted, preferably in the horizontal direction and the diffuser screen is realised as a holographic screen, arrays of diffractive or refractive elements, retroreflective surfaces, or any combination thereof, for imparting a larger divergence to the exit light beams along at least one, preferably in the vertical direction, while in the other direction the angle of divergence provided by the screen is smaller than the angle between the neighbouring emitting directions associated with the optically neighbouring modules. The invention is also directed to a method implemented by the apparatus according to the invention.
Owner:BALOGH
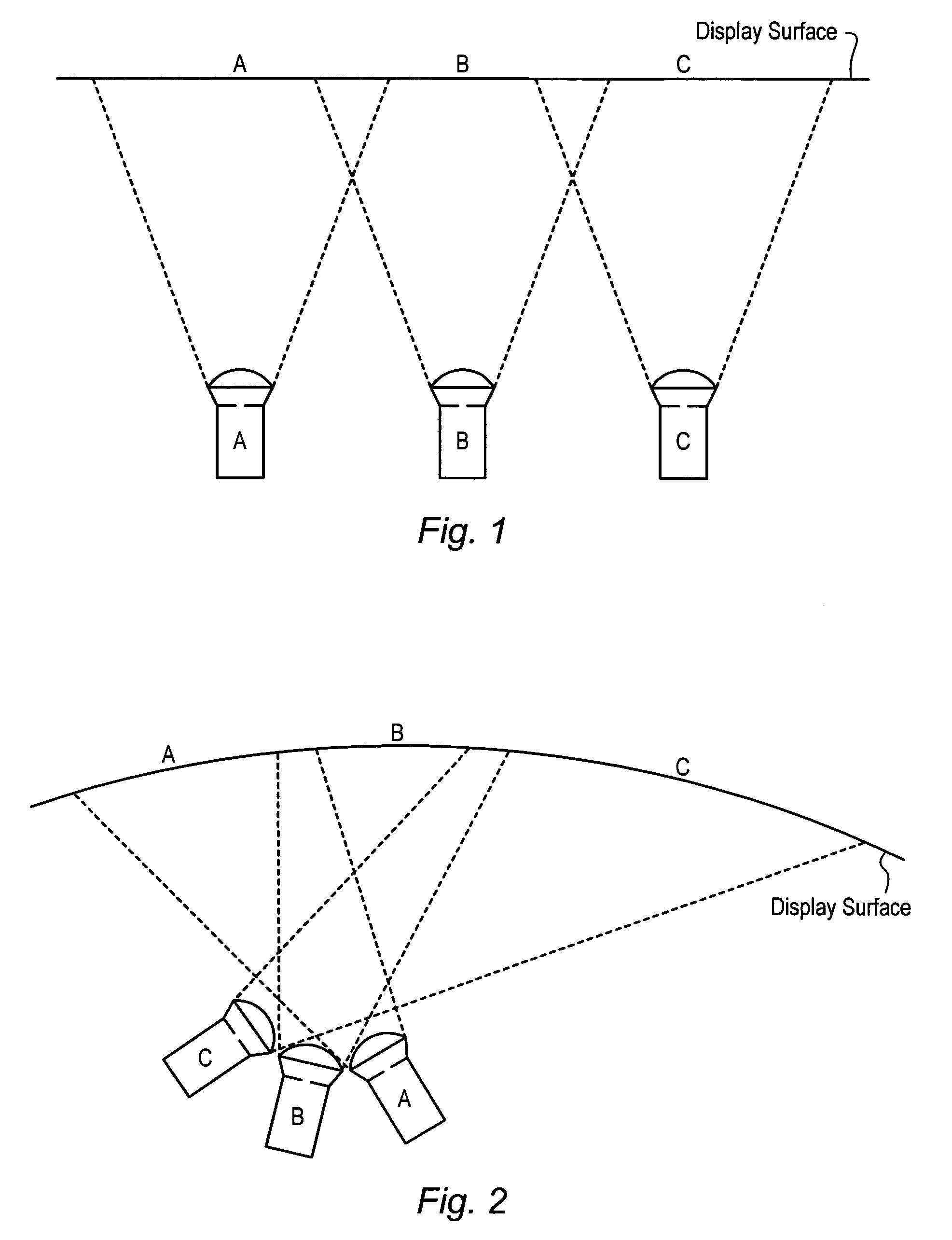
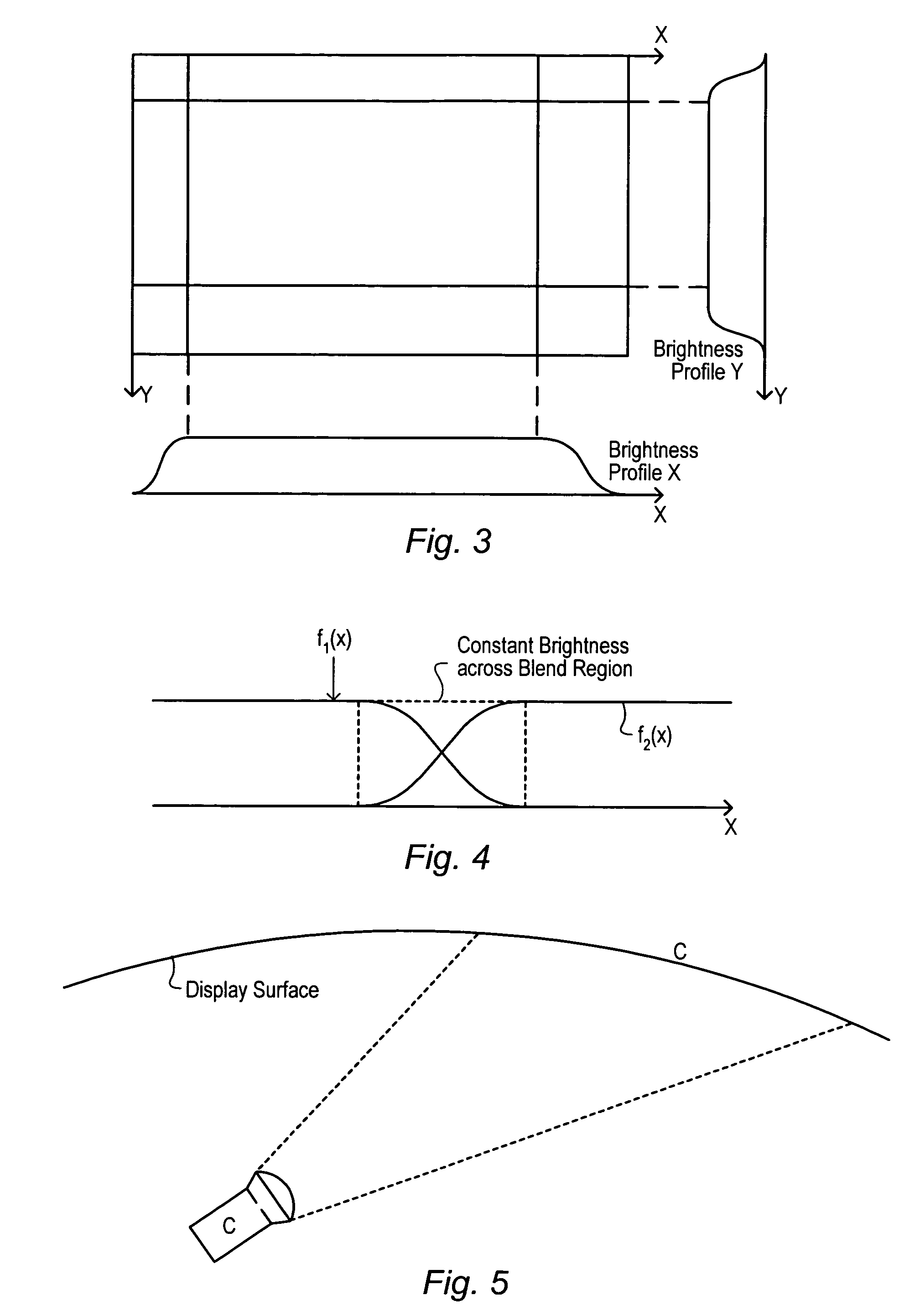
Computing blending functions for the tiling of overlapped video projectors
ActiveUS7292207B1Intensity PreciseColor television detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsBinary multiplierComputer vision
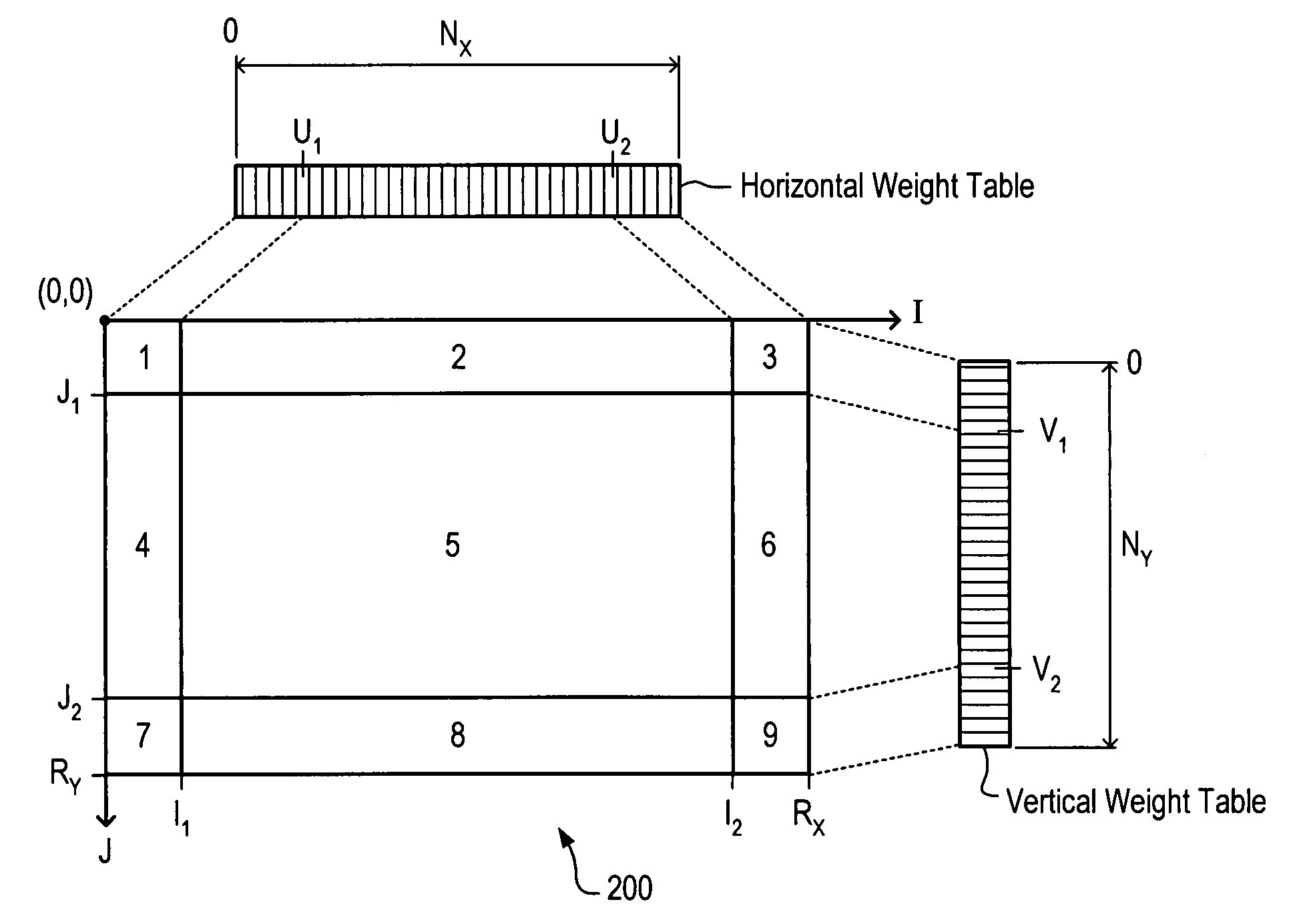
A system for correcting the intensities of pixels supplied to a projector. An image generated by the projector has a number of regions formed by the overlapping of the image with one or more other images generated by one or more other projectors. The system includes: a first unit configured to generate a horizontal scaling value; a second unit configured to generate a vertical scaling value; a first multiplier configured to multiply the horizontal scaling value and the vertical scaling value to obtain a scaling coefficient, and a set of one or more additional multipliers configured to multiply components of an input pixel by the scaling coefficient to determine components for an output pixel. The first unit and second unit compute their respective scaling values in a way that allows for regions whose boundaries non-aligned in the vertical direction.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Image projector with flexible reflective analog modulator
InactiveUS7835056B2Change shapeAltering divergenceProjectorsColor television detailsProjection opticsLight beam
An image projector comprises a plurality of flexible reflective analog modulators (FRAMs), an illumination optics for focusing at least one light source thereon, a conversion optics for converting the variations in divergence of the beams reflected therefrom into variations in intensity, and a scanning mechanism coupled to a projection optics for displaying an image, constructed of intensity modulated light dots or pixels, on a screen. FRAM curvatures, responsible for determining the divergence of the reflected beams, and ultimately the intensity of each pixel, are varied by an actuation voltage that can be modulated using waveforms that minimize the FRAM response times. For multicolor images, three laser light sources operating at different wavelengths are used in conjunction with three linear FRAM arrays.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT +1
System and method for theatrical followspot control interface
ActiveUS20110285854A1Television system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Display device
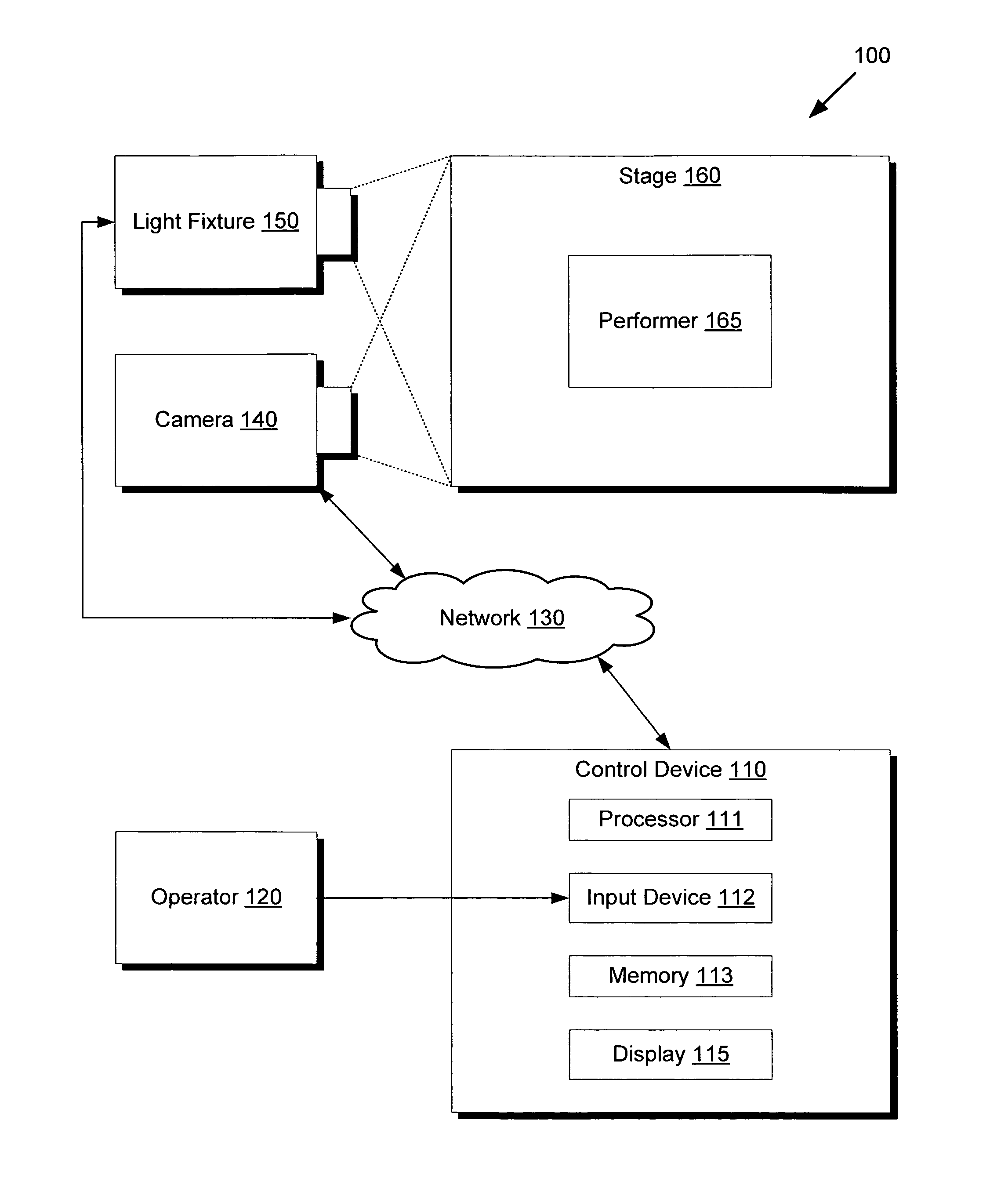
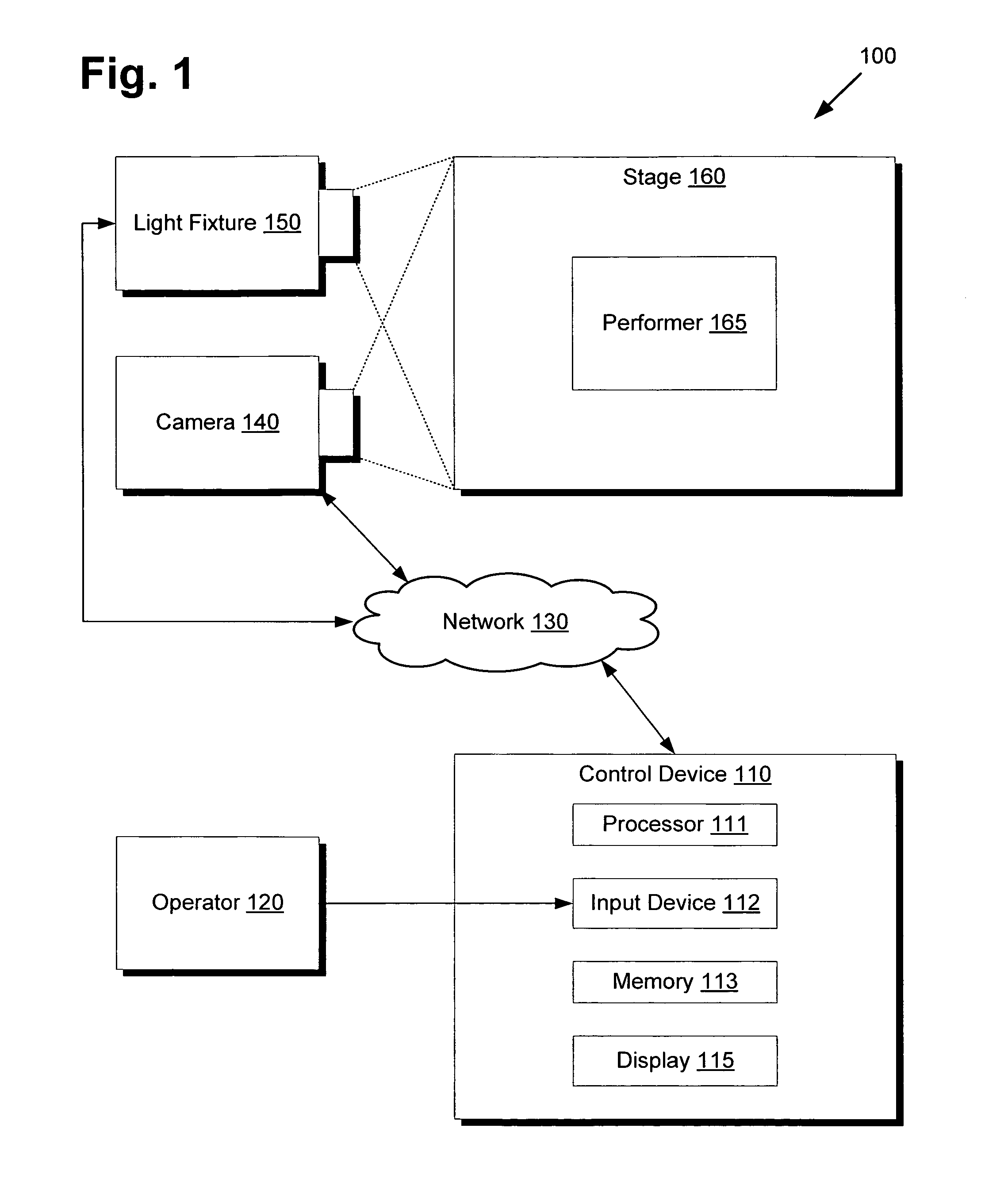
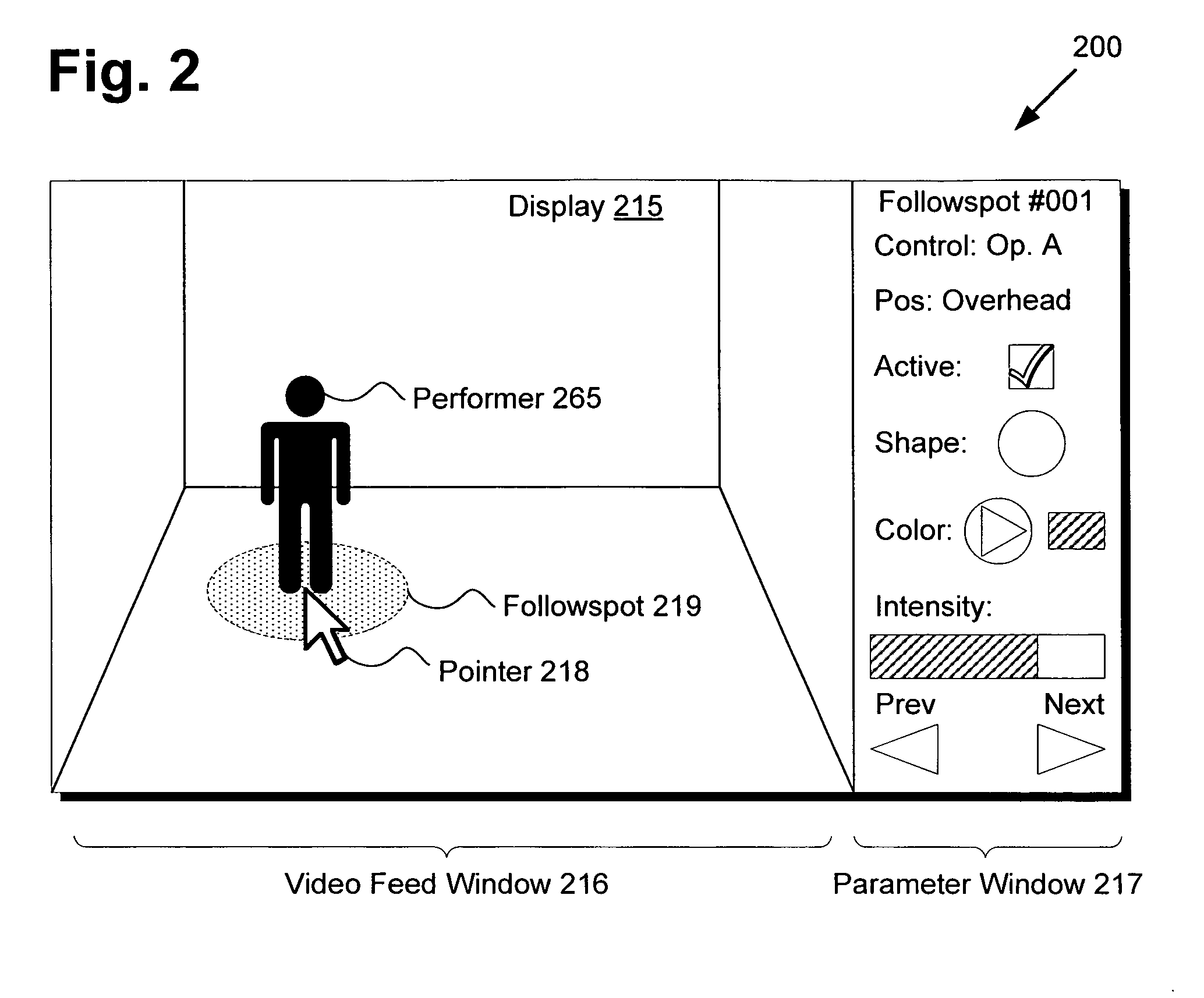
There is provided a system and method for controlling a tracking device to follow a location of a performer on a stage. The tracking device may comprise a lighting fixture such as a high output video projector or an automated mechanical moving light such as a DMX lighting fixture to provide a followspot, or a microphone to record audio from a particular performer. The method comprises capturing a video feed of the stage using a camera, presenting the video feed on a display of a control device, receiving input data indicating a position of the performer in the video feed, translating the input data into the location of the performer on the stage, and adjusting the tracking device to follow the location of the performer on the stage. The control device thereby provides lighting operators with an intuitive interface readily implemented using cost effective commodity hardware.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Light source device, video projector and video projection method
ActiveUS20100328554A1ProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesVideo projectorWavelength range
A light source device includes: a first light source configured to emit a first source light in a first wavelength range; a source light generator configured to generate, from the first light, a color-varying source light having time varying color; a second light source configured to emit a second source light in a second wavelength range that is different from the first wavelength range; and a light source controller configured to control driving timing for turning on and off each of the first light source and the second light source so as to cyclically select one of the color-varying source light and the second source light to be output as an output source light.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Illumination module for color display
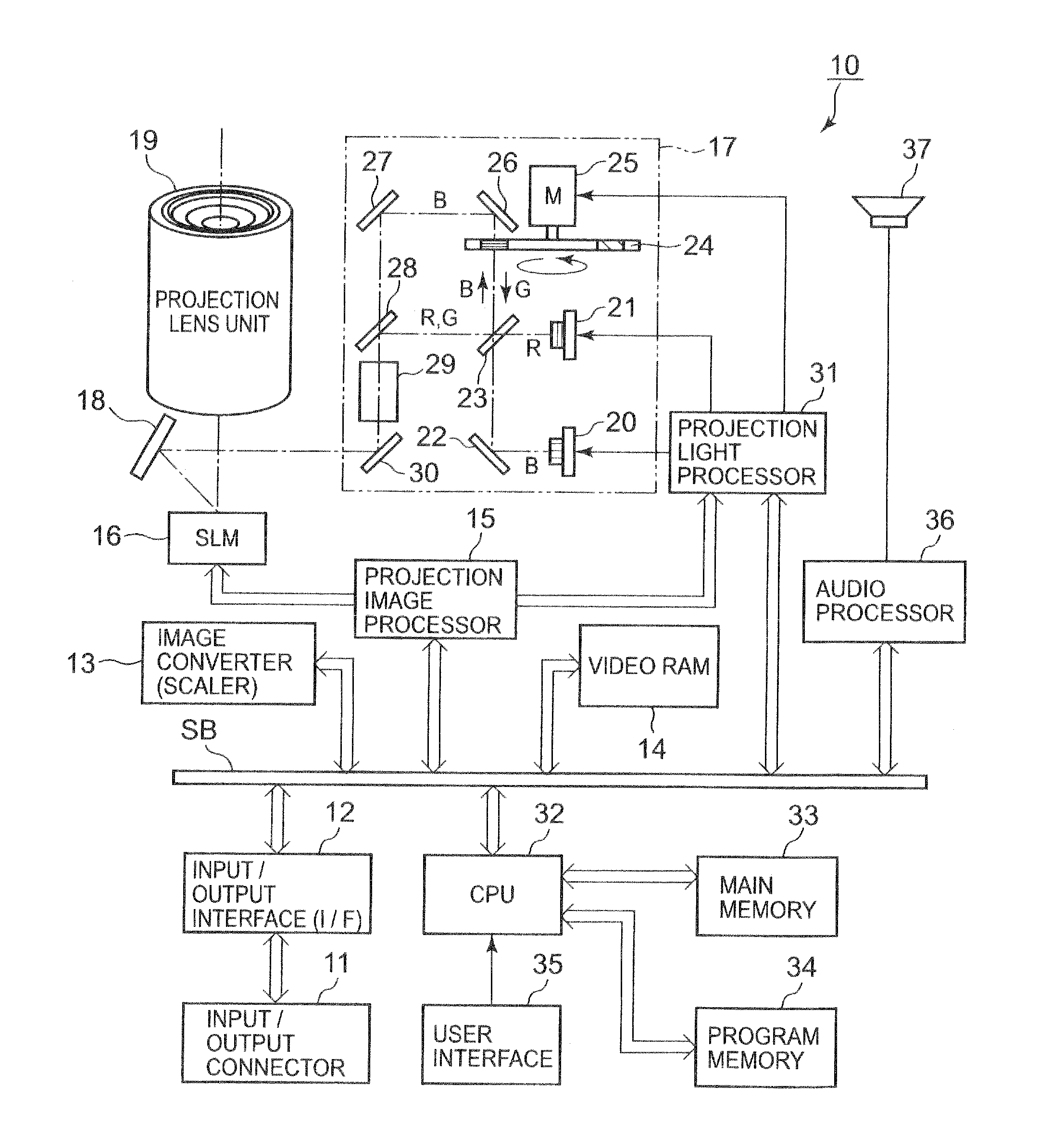
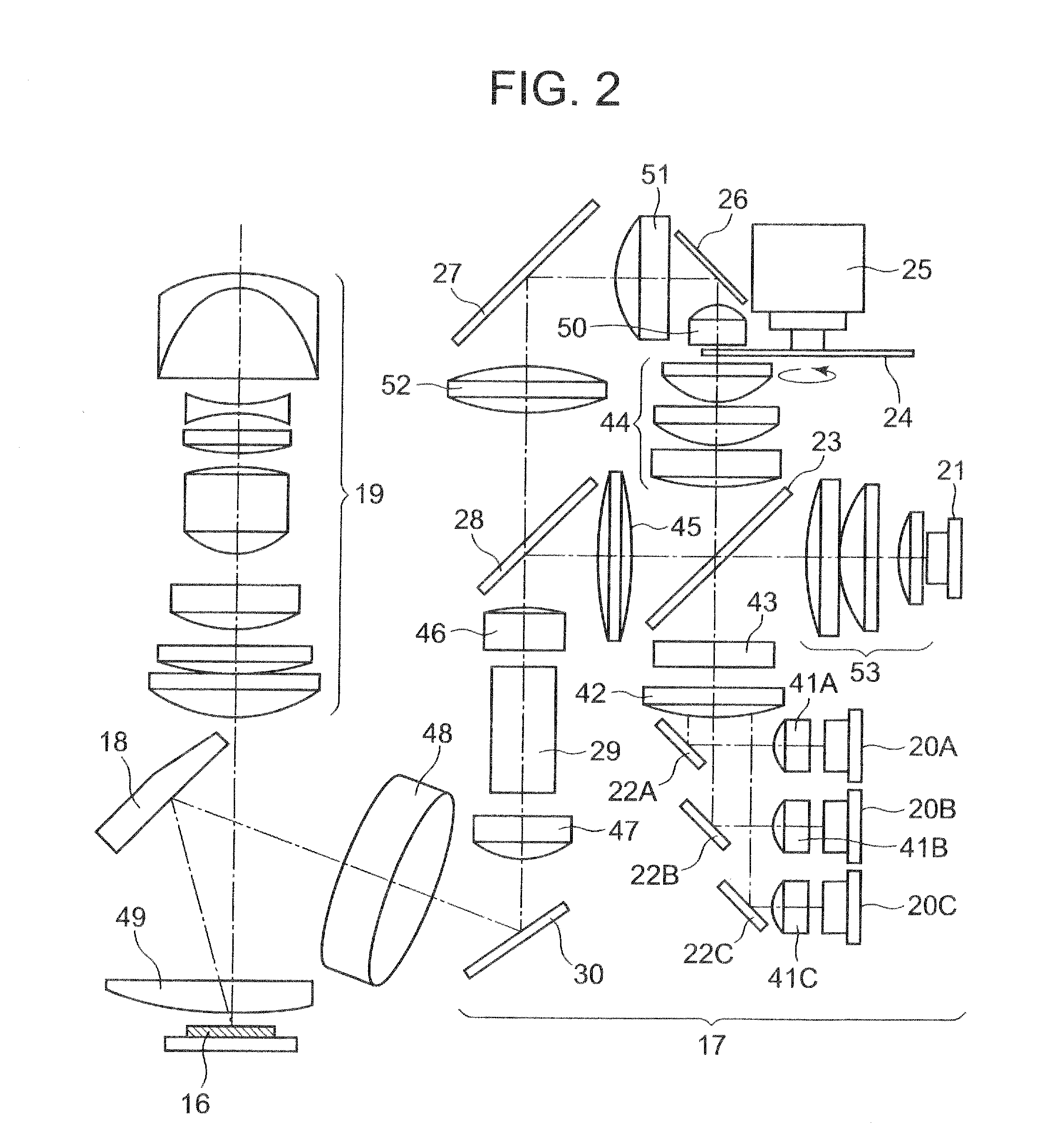
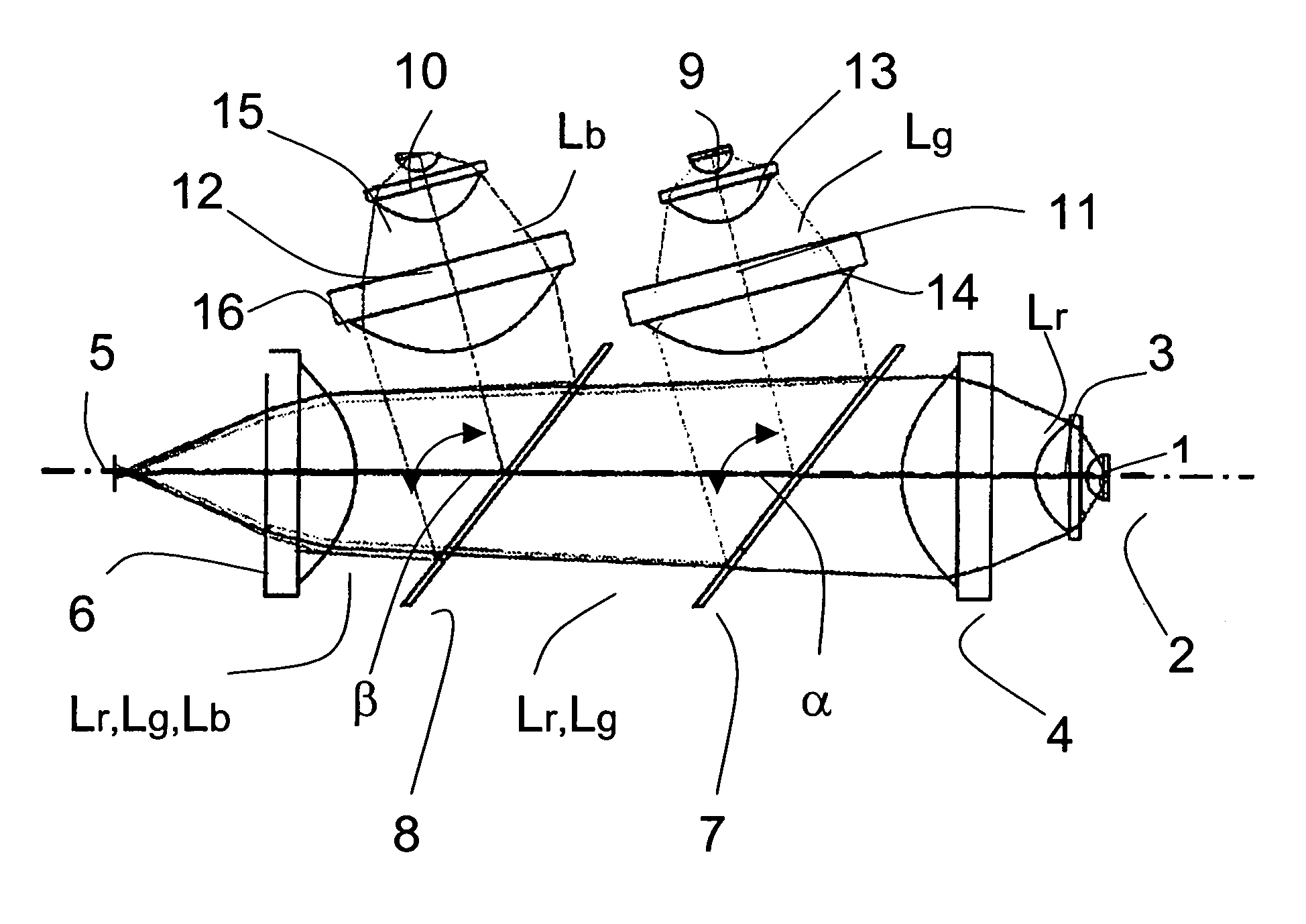
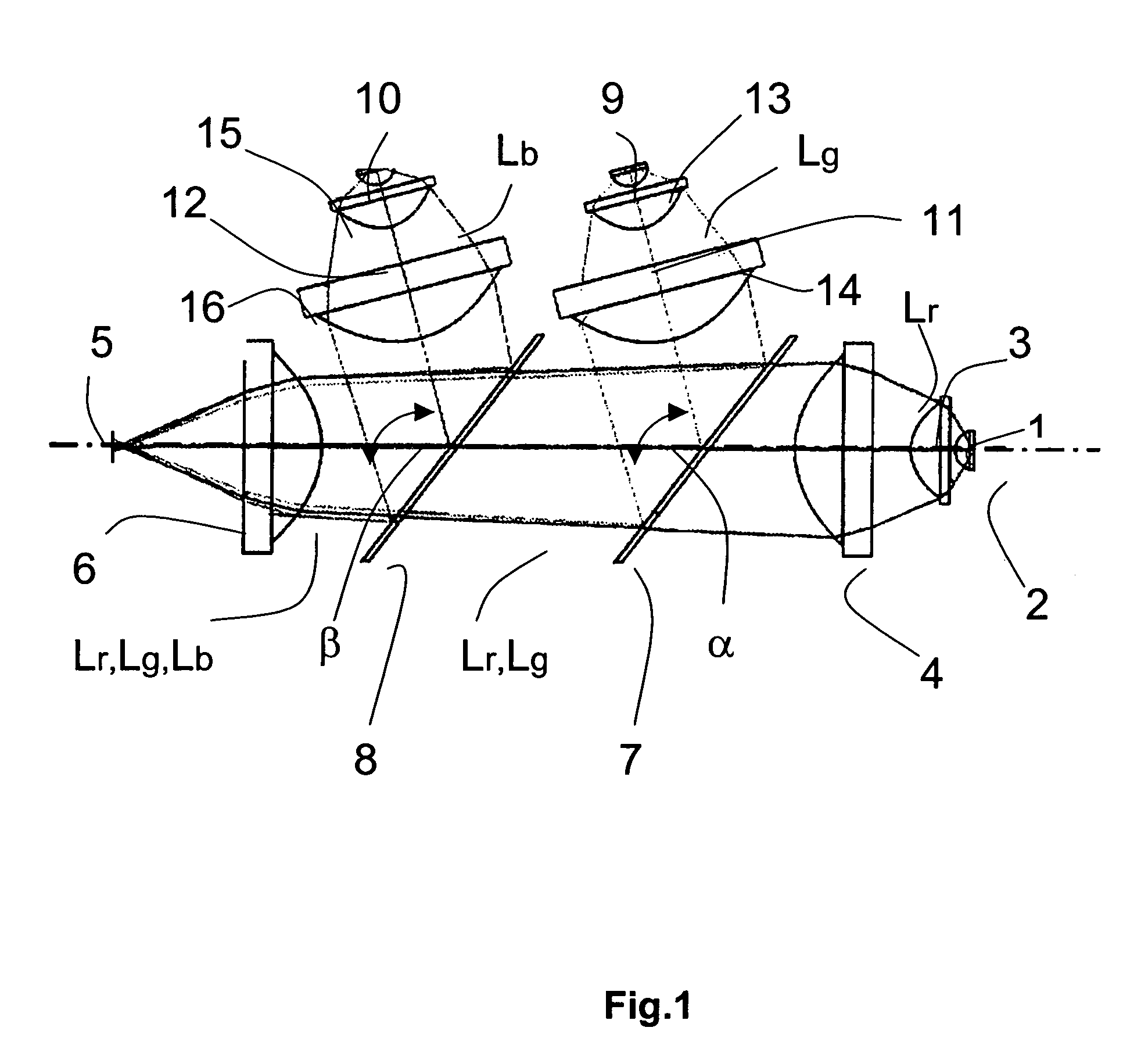
ActiveUS7239449B2Increasing the thicknessImprove input efficiencyTelevision system detailsProjectorsLed arrayOptical axis
The invention relates to an illumination module for color display, preferably for use in data or video projectors as well as rear projection television sets, in which the light from at least three luminescent diodes (LEDs) or LED arrays of the base colors red, green and blue is collimated at a point provided for connection to a display unit and ranged on an optical axis of the illumination module. An LED or an LED array of a base color with a beam path (Lr) oriented in the direction of the display unit is arranged on the optical axis of the illumination module. For the purpose of color mixing, the LEDs and LED arrays of the other base colors are attached in such a way tat their beam paths (Lg, Lb) are laterally input in sequence under input angles (α, β) of <90 degrees into the beam path (Lr) of the first base color.
Owner:SYPRO OPTICS
Voice-activated video projector
A voice-activated video display mechanism that projects or displays information on a screen during a presentation as controlled by a user's voice is disclosed. The preprogramed slides or pictures change in response to certain spoken words by the presenter. Such functionality permits seamless display of information that corresponds directly to the speaker's spoken word thus allowing for a presentation that is easier to comprehend and understand. Also, the projector has capabilities for the playback of DVD media, either as part of a presentation or as a separate standalone DVD viewer. A built in printer also allows for the production of hard copies of the displayed information.
Owner:QUORI KENYA
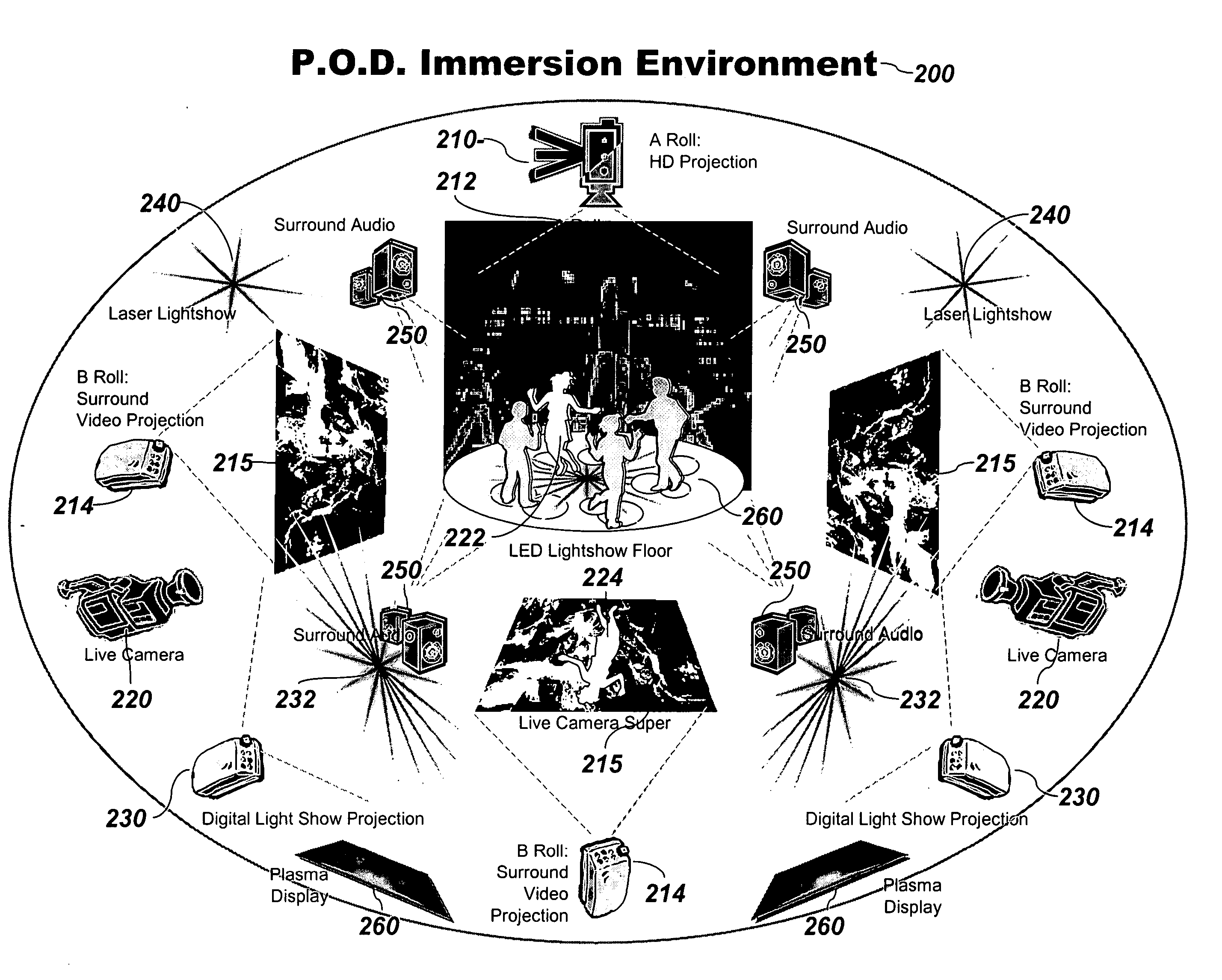
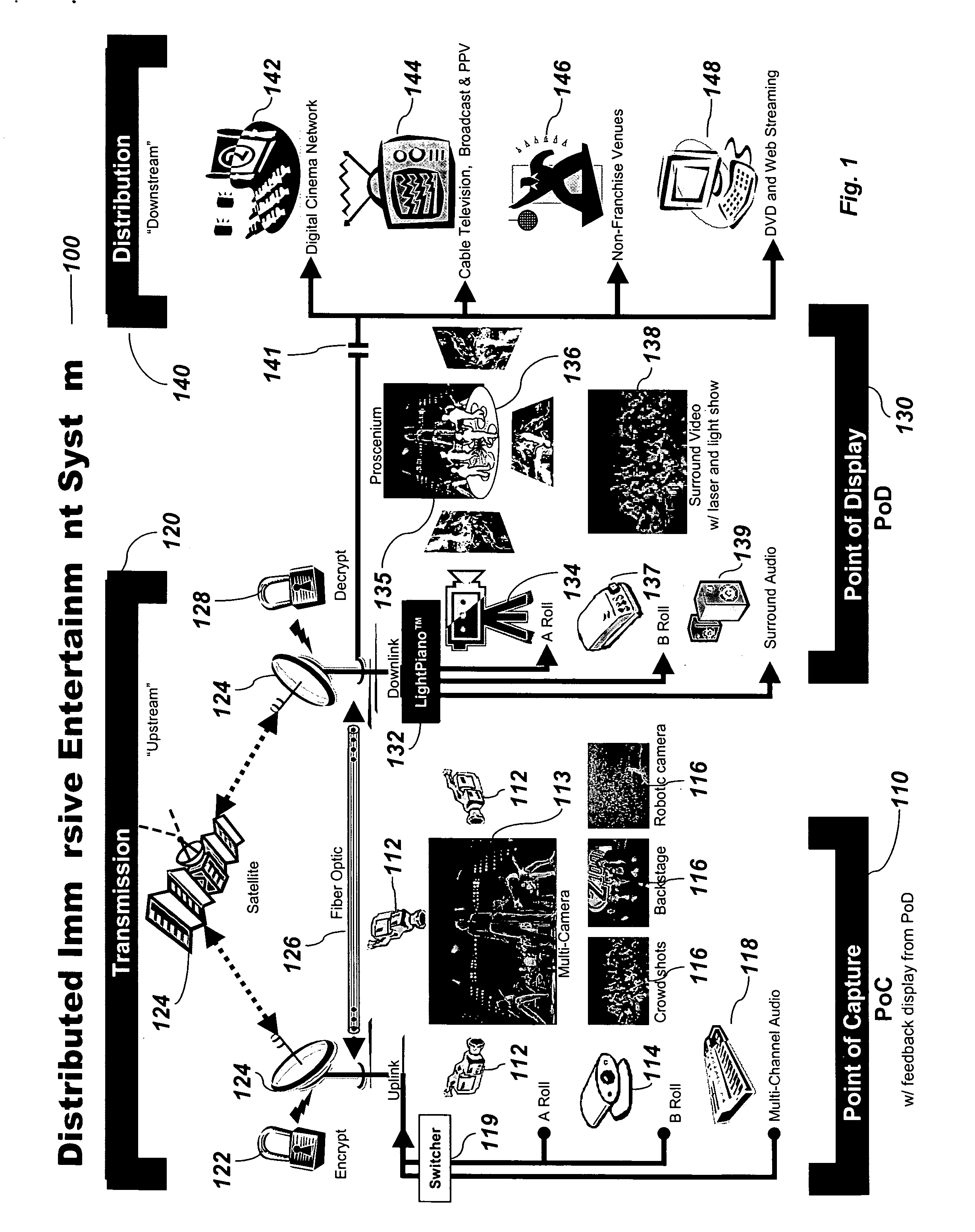
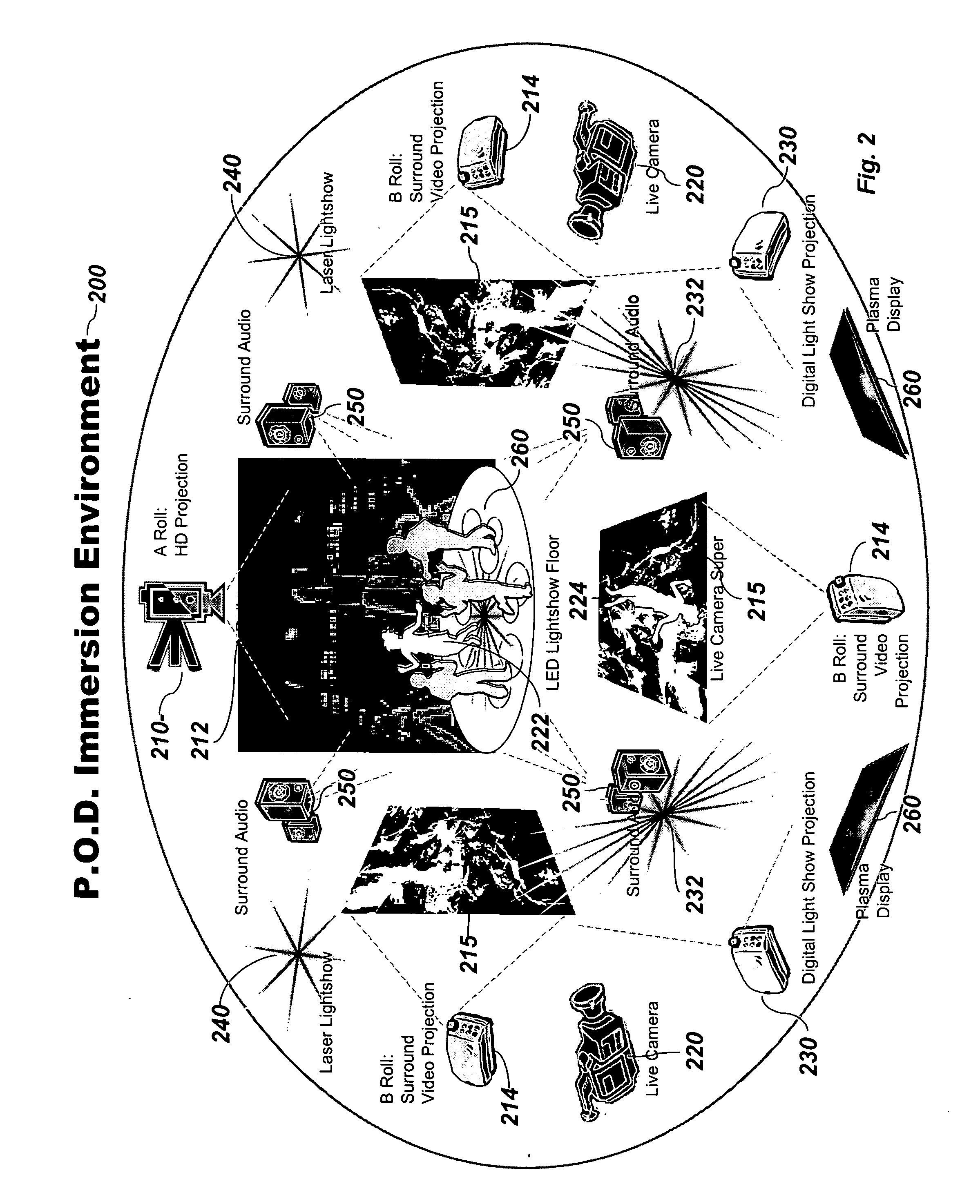
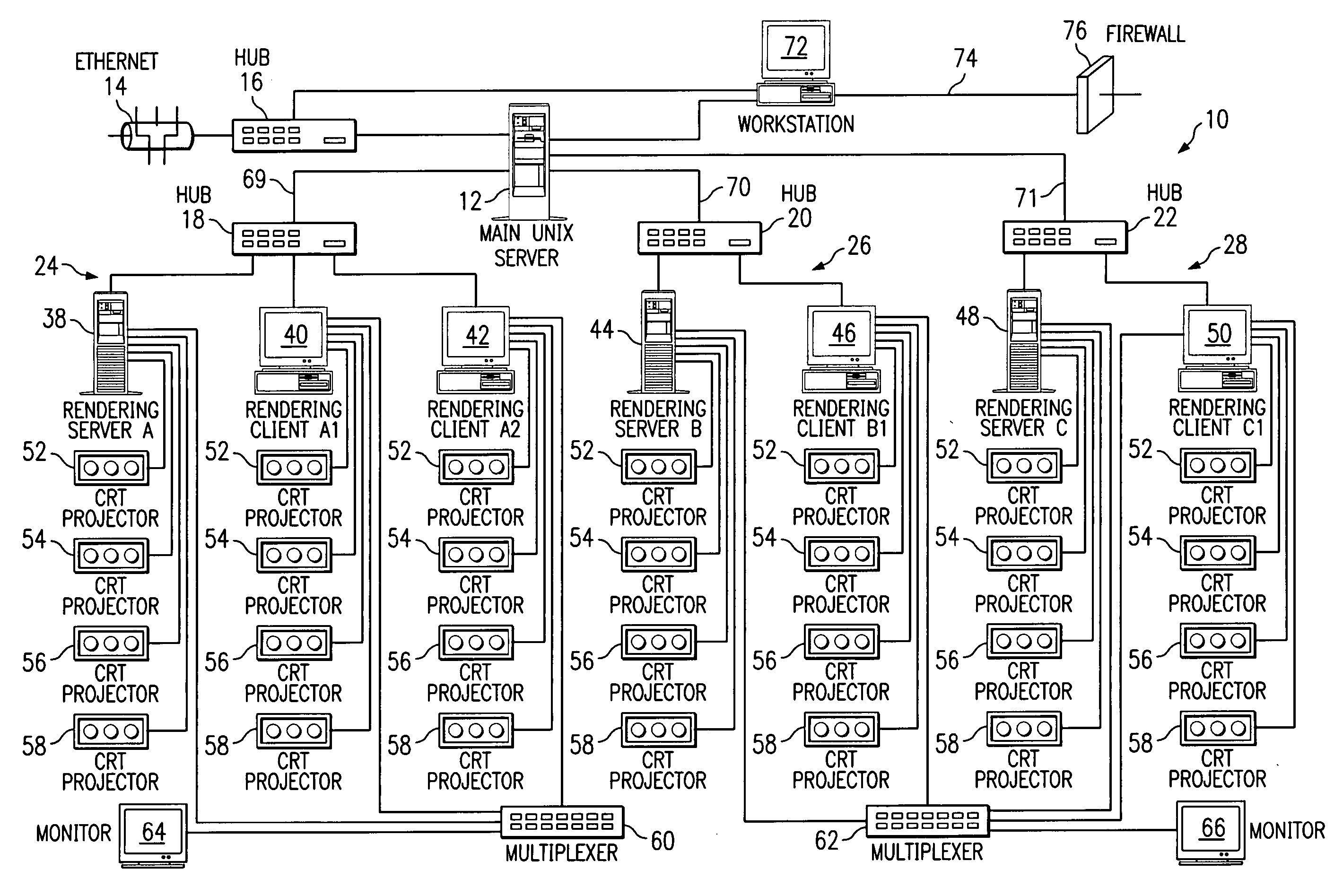
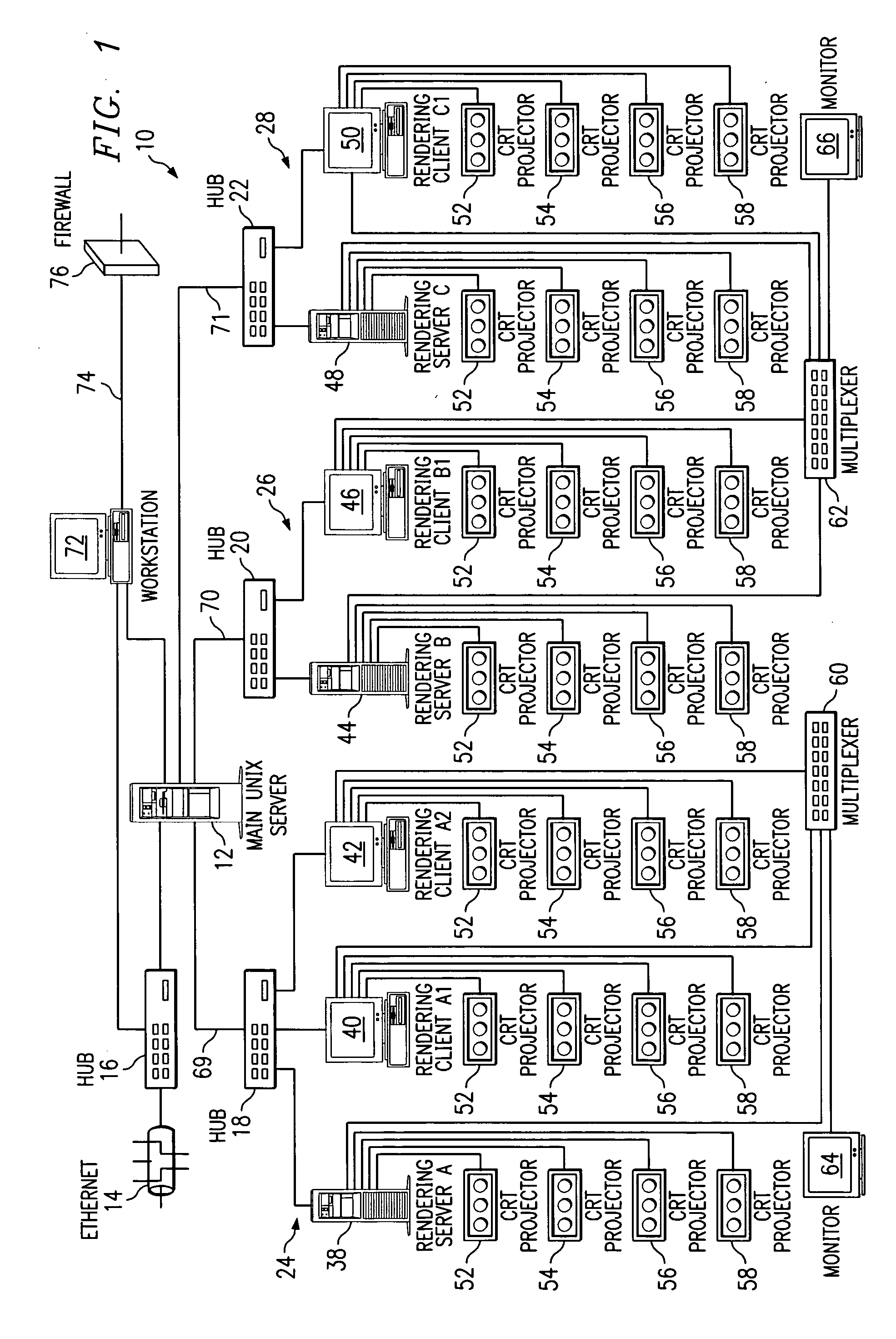
Distributed immersive entertainment system
InactiveUS20050024488A1Reduce deliveryEasy to integrateTelevision system detailsTelevision conference systemsMulti cameraDisplay device
A multi-camera high-definition or standard-definition switched video signal is distributed from the Point of Capture (POC) using industry standard technology for broadband distribution such as fiber optic or satellite, to a Point Of Display (POD) where multiple video projectors or displays integrated with a digital light show and high-end audio are utilized to provide a totally immersive entertainment environment. That environment is controlled using a graphically based tool called the LightPiano™, and is then extended through the festival atmosphere in the Club Annex, where licensed merchandise, auctions, and swap meets are located. Online Instant Messaging, Short Message System (SMS) text messaging, Chat, and Fan Clubs generate additional content, which is sent back to the POD. There is extensive use of the Worldwide Web for both local and remote access to the chat, fan clubs, SMS and instant messaging systems, as well as for online access for customers to view scheduling, and purchase ticketing, webcasts and archive access. The Web is also used by the venue owner to manage the entire system for booking, data mining, scheduling, ticketing, webcasting, and facilities management. The Web interface combined with the power of the LightPiano makes this complex interrelated system relatively easy and intuitive to operate. It significantly lowers the cost of operation and makes the system scalable to a large network of POCs and PODs. It allows one POC to feed many PODs, enabling a truly global distributed, immersive entertainment environment.
Owner:BORG ANDREW S
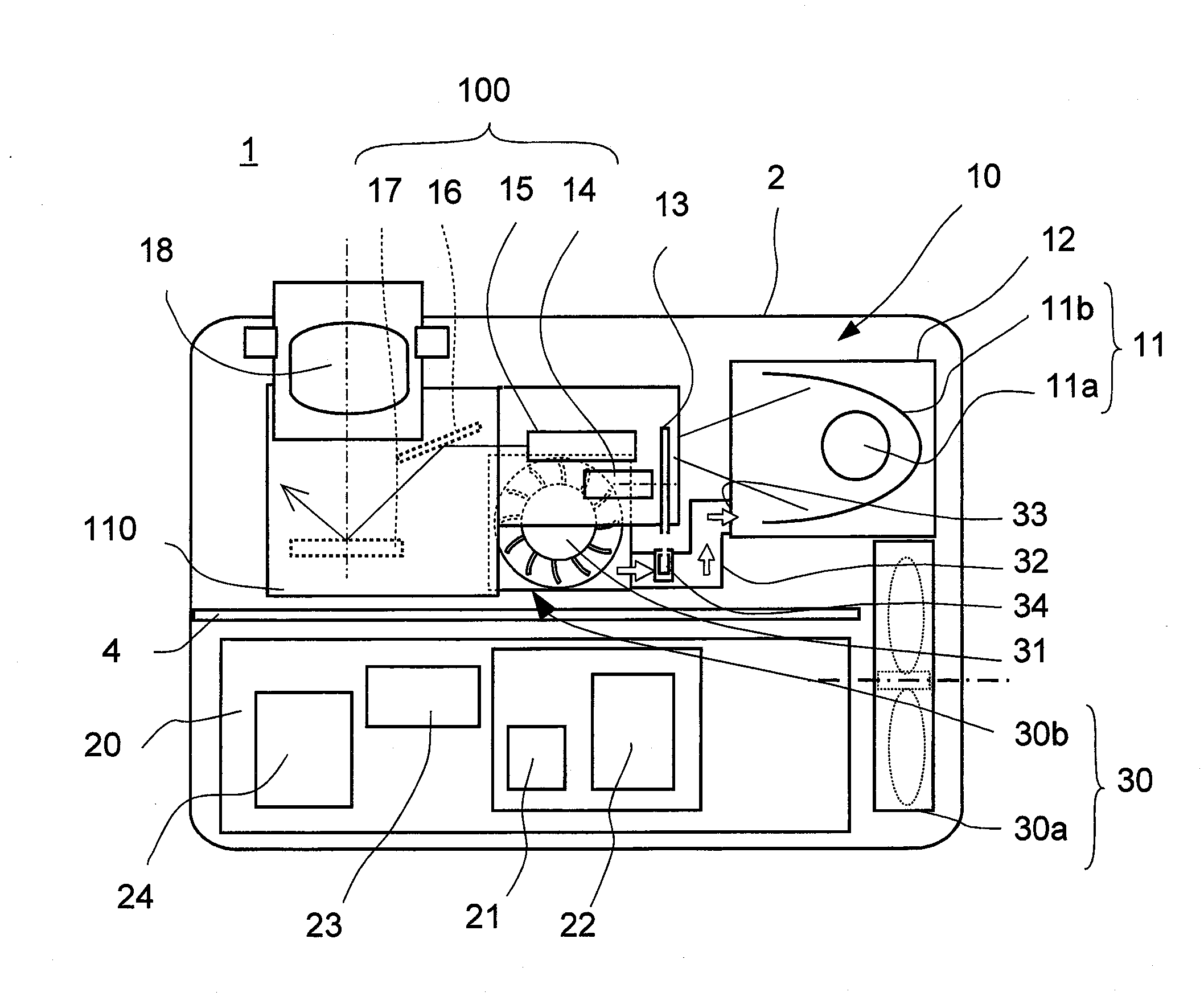
Video Projector
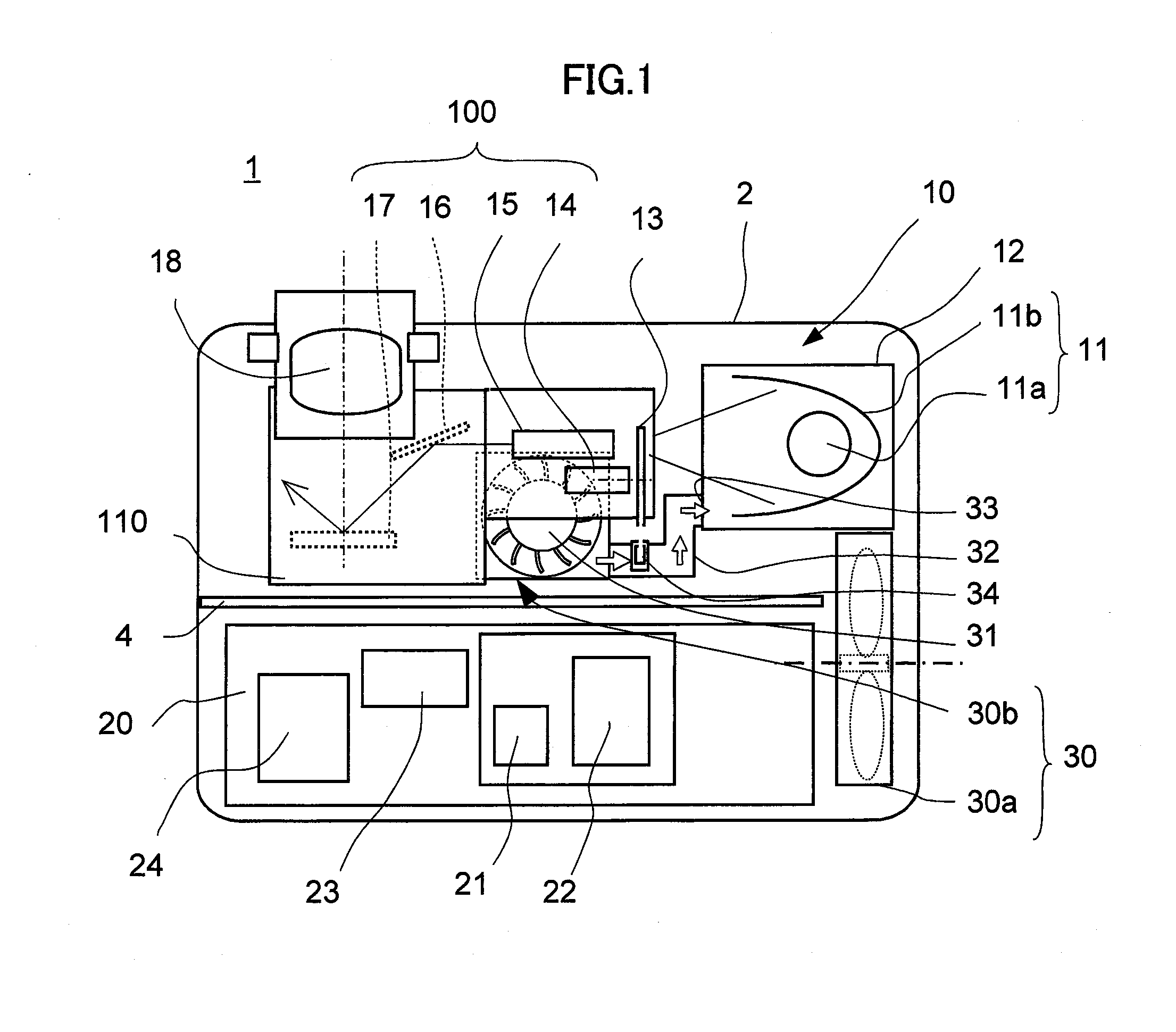
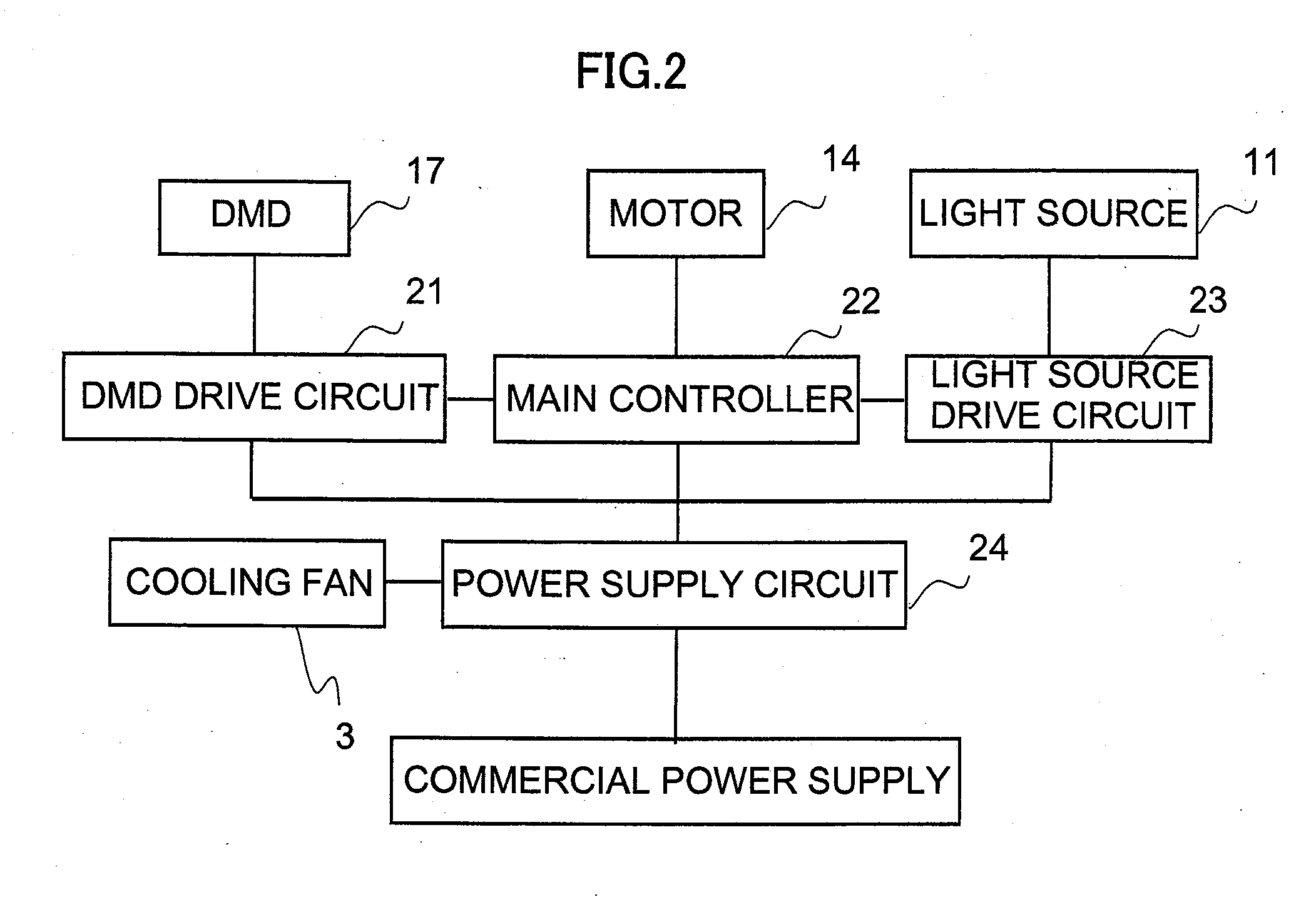
InactiveUS20070273839A1Increase the number ofReduce manufacturing costProjectorsDigital micro mirror deviceEngineering
A video projector (1) comprises a light source (11) enclosed in a lamp box (12), an optical engine (100) including a color wheel (13), an optical tunnel (15), a mirror (16) and a DMD (Digital Micro-mirror Device) (17), and a blower fan (30a) disposed in the vicinity of the light source (11) and below the optical engine (100). The blower fan (30b) sucks air through a portion of the optical engine (100) where the optical tunnel (159 and so an are provided except the color wheel (13), generates a cooling air and exhausts a part of the cooling air toward the color wheel (13) and the rest of the cooling air toward the light source (11), so that the elements of the optical engine (100) and the light source (11) are cooled by the blower fan (30b) simultaneously.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and device for controlling a video projector in a video projection system comprising multiple video projectors
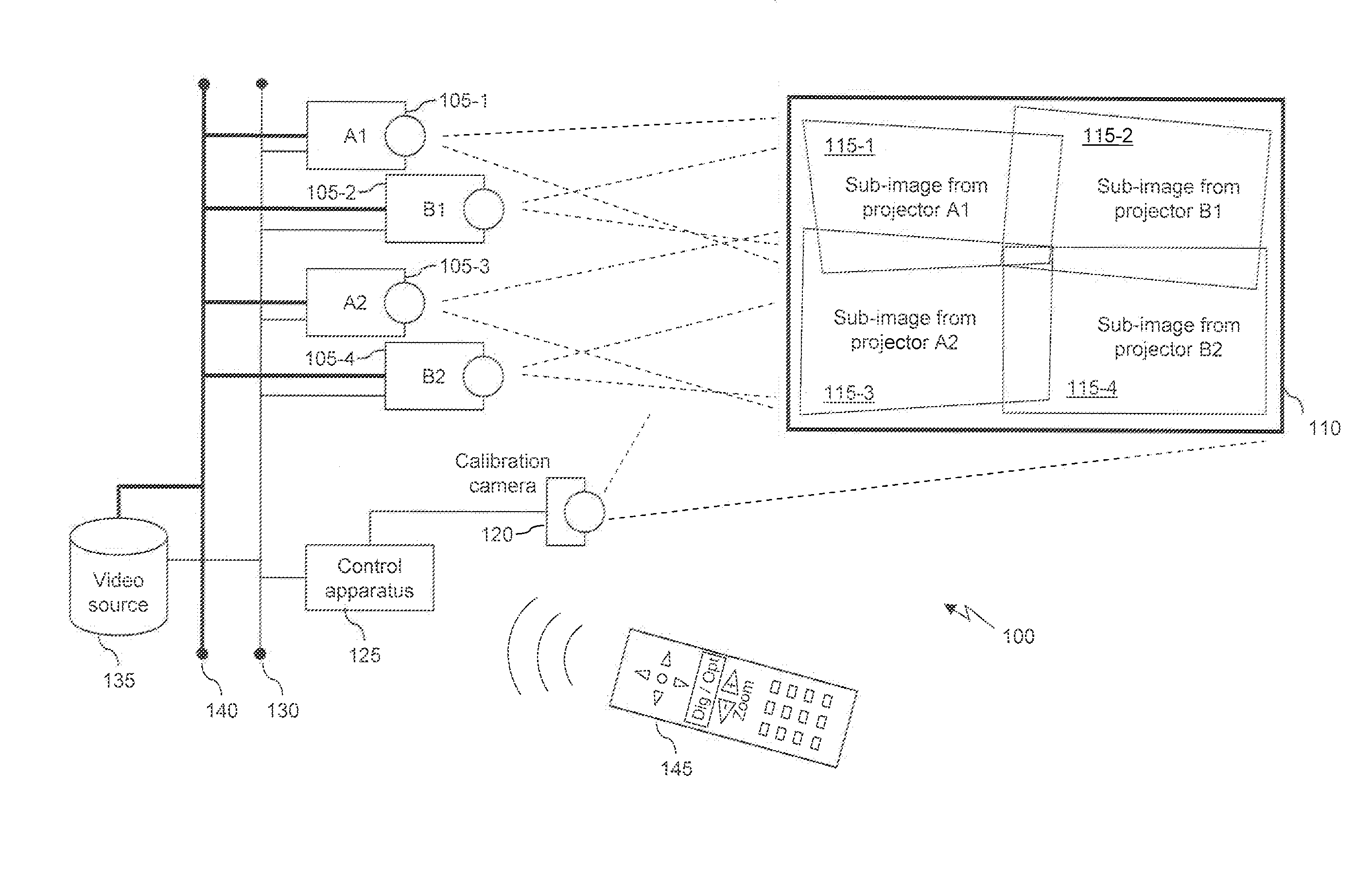
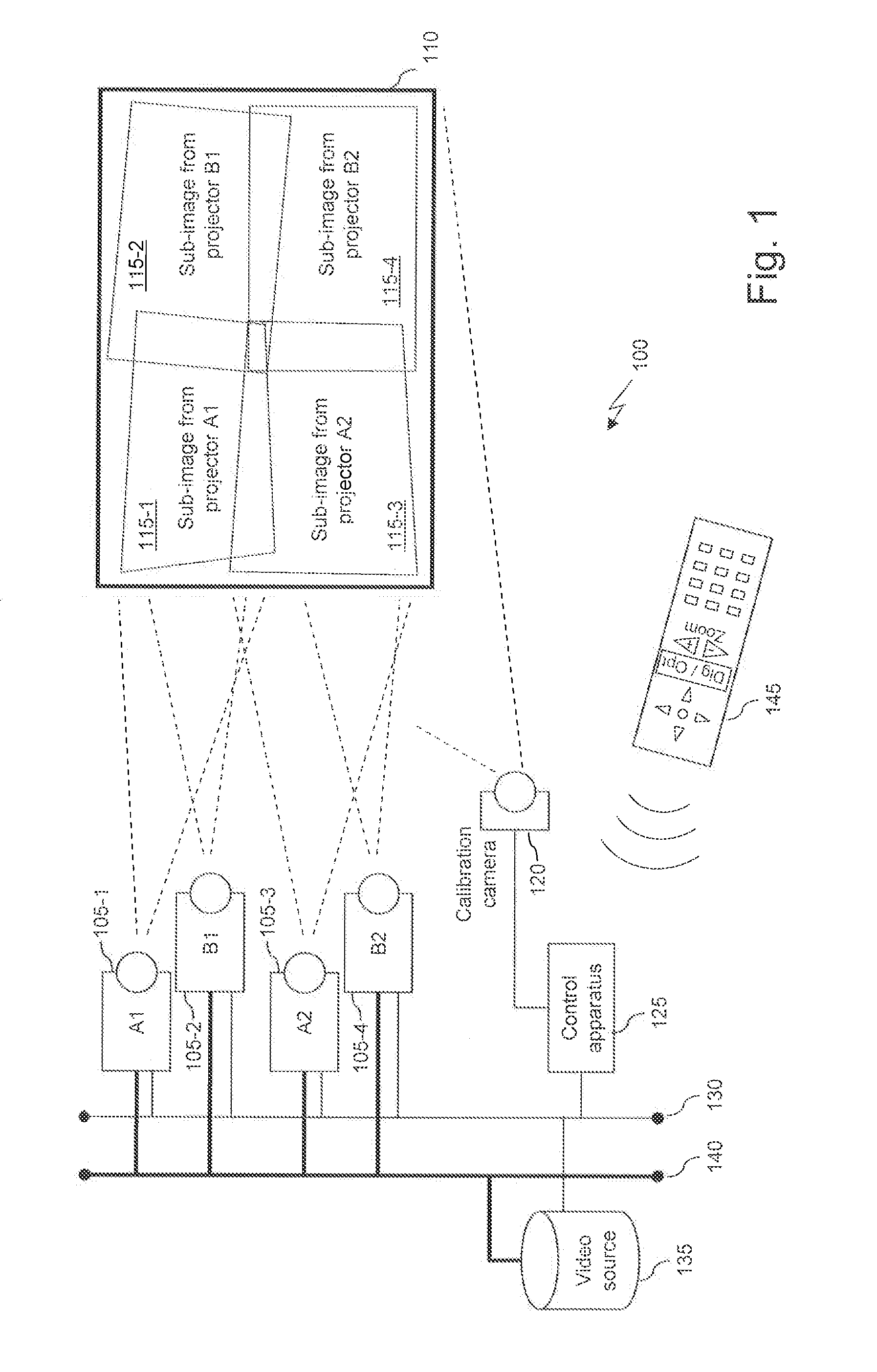
InactiveUS20130169888A1Easy to identifyHigh precisionTelevision system scanning detailsPulse generatorProjection systemVideo projector
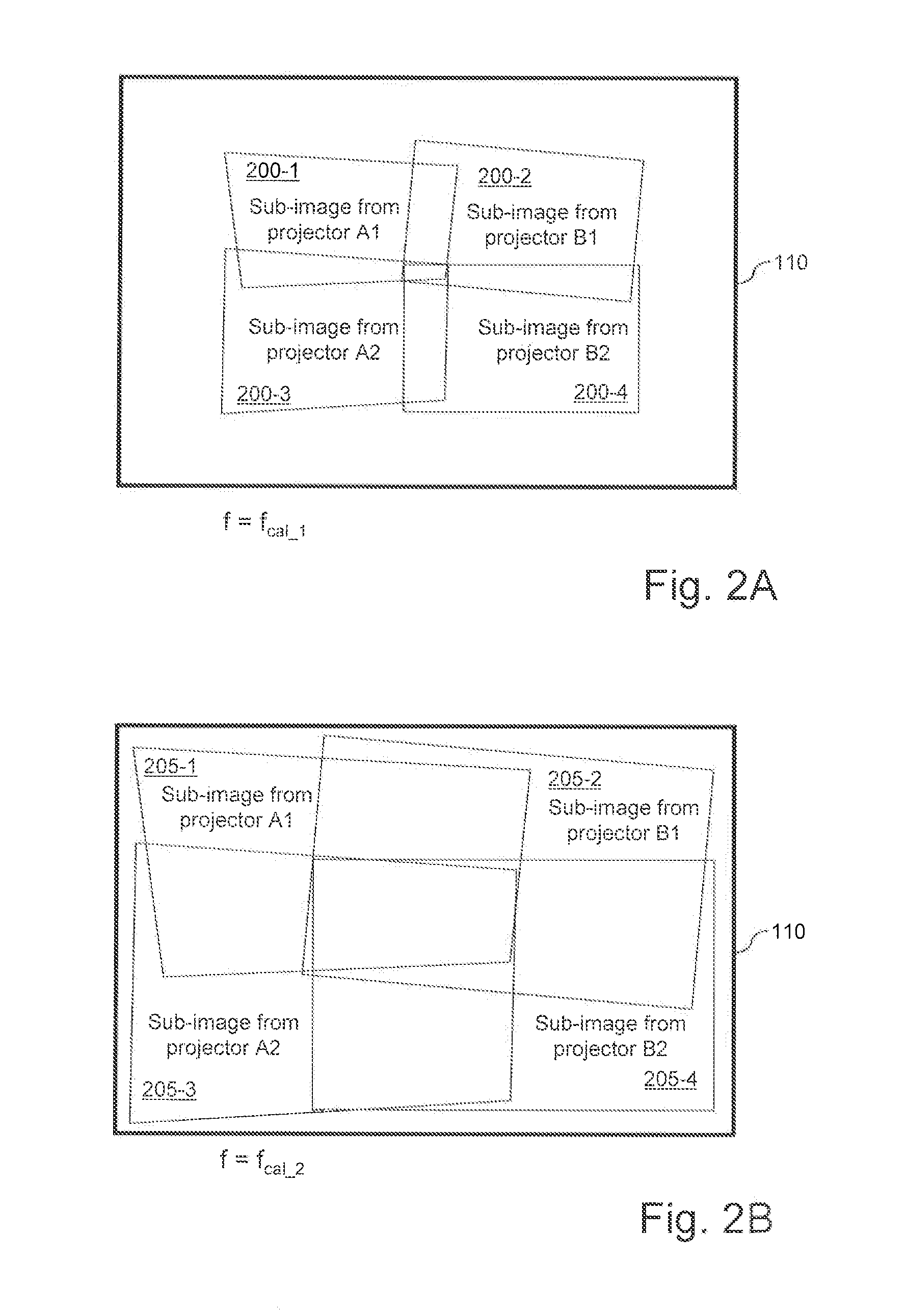
Controlling at least one video projector of a video projection system comprising multiple video projectors having a modifiable focal length and adapted to project sub-images. After determining a first calibration parameter associated with a first predetermined focal length of the video projectors, a second calibration parameter corresponding to a second predetermined focal length of the video projectors is computed, the second calibration parameter computed as a function of the first calibration parameter and the second predetermined focal length different from the first one. A display parameter is computed for a video projector, the display parameter being computed as a function of second calibration parameter, and a sub-image to be projected by the video projector is calculated according to the computed display parameter. Necessary display parameters are determined during an initial calibration step and used during a projection session whenever the user issues an “optical zoom” command, without repeating the calibration.
Owner:CANON KK
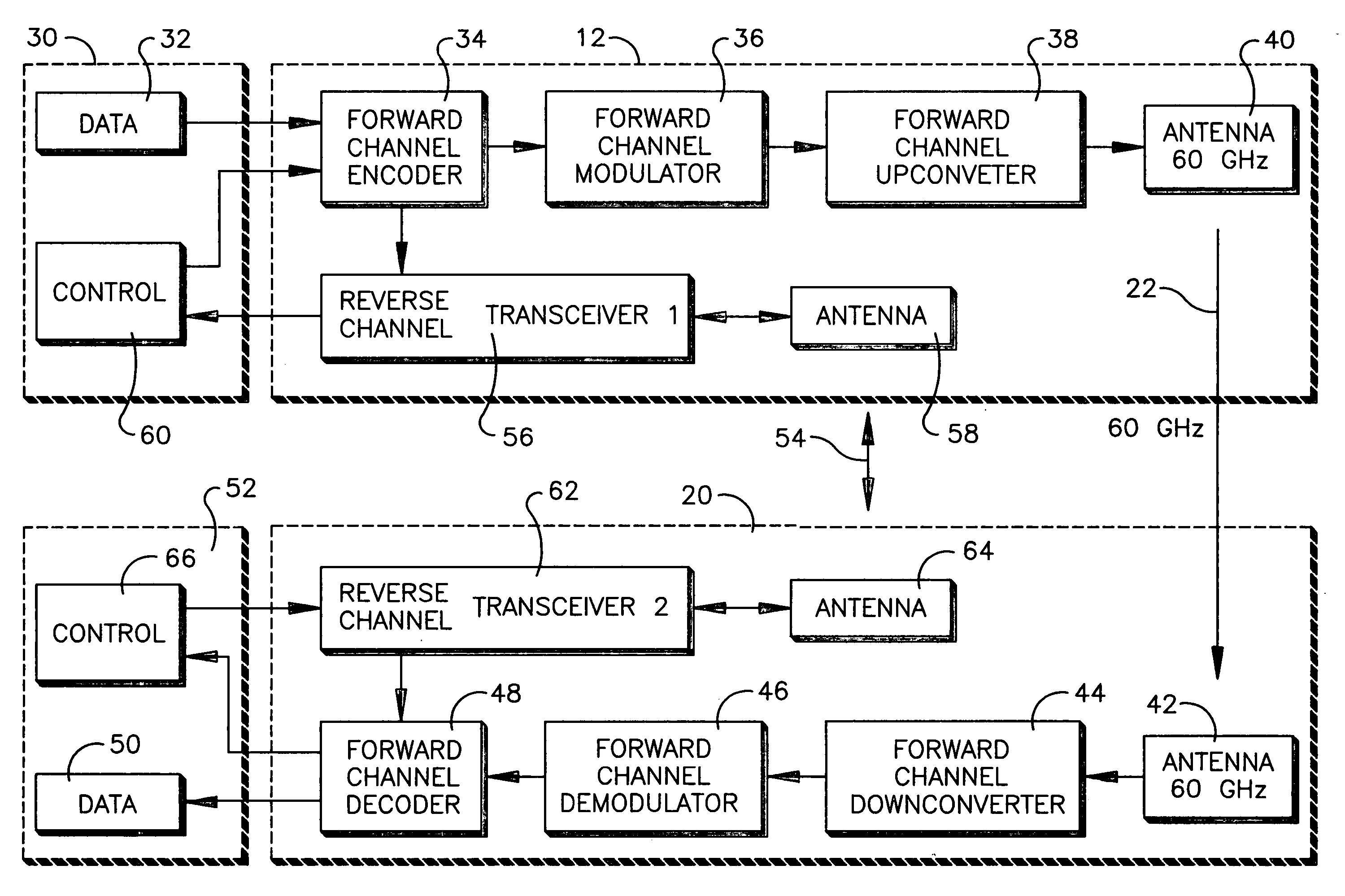
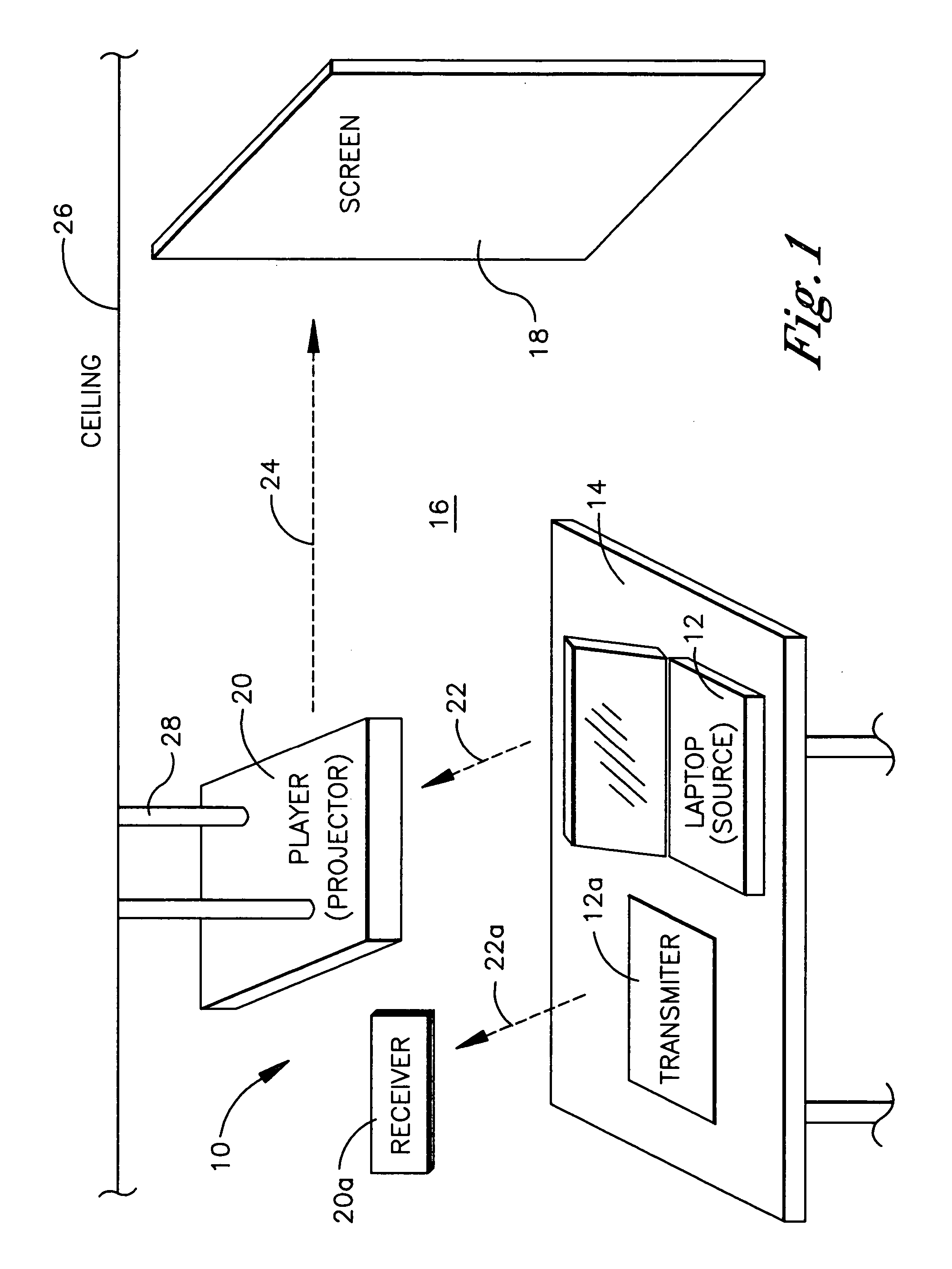
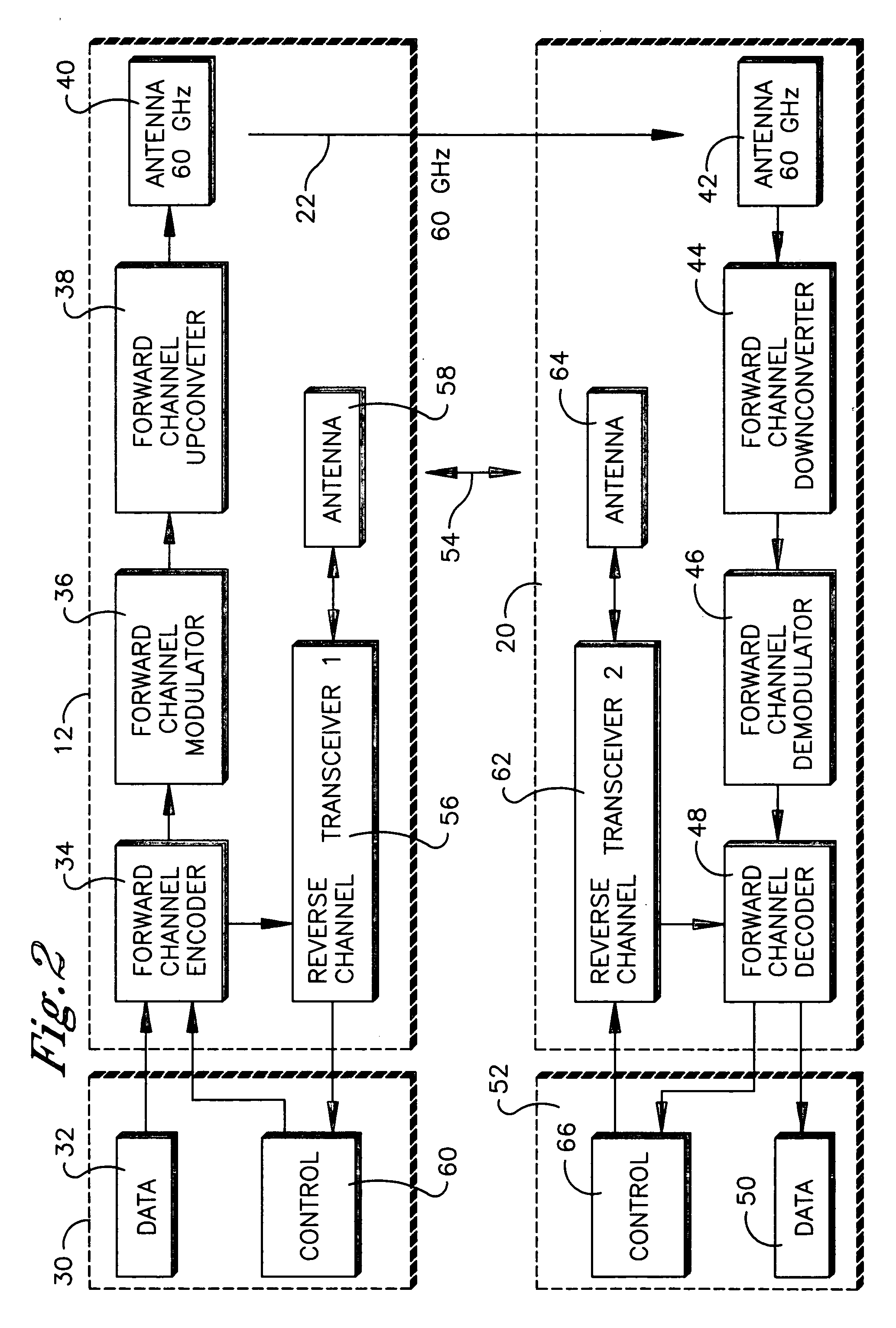
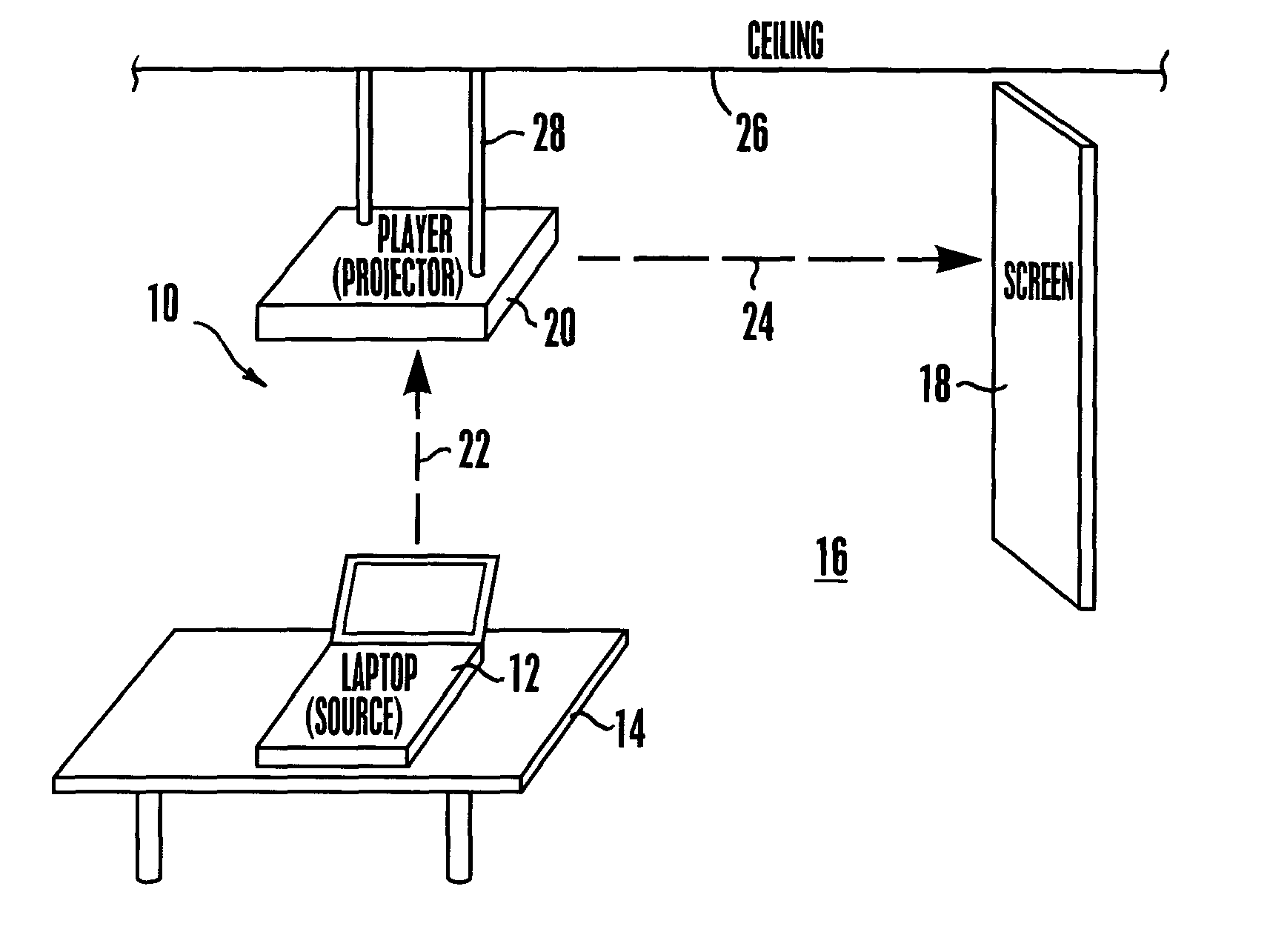
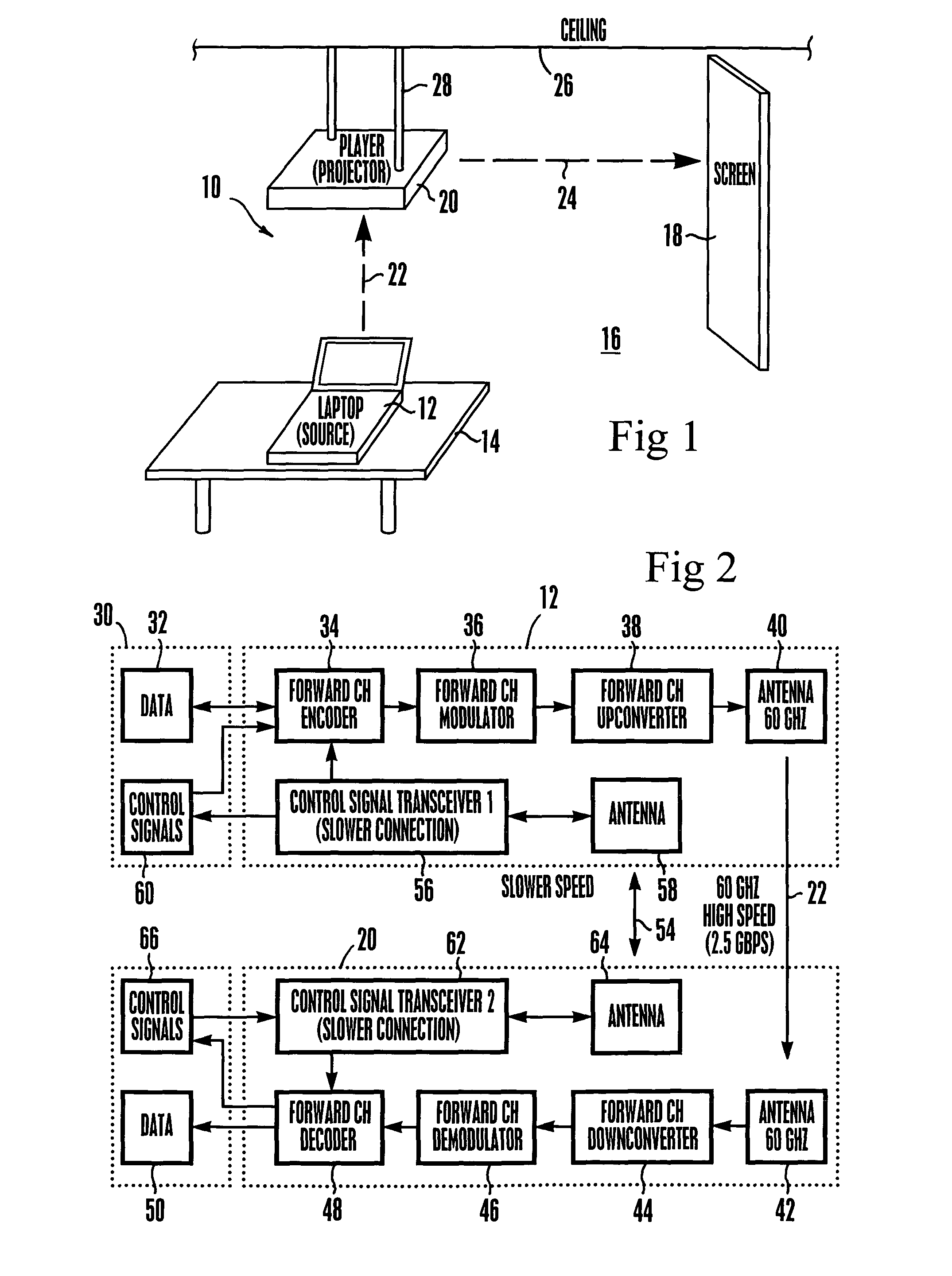
Method and system for wireless digital communication
Data such as high definition (HD) video may be sent from a transmitter such as a laptop computer to a receiver such as a video projector using a 60 GHz (and, hence, inherently directional, short range, and thus secure) forward channel wireless link. Encryption information such as encryption keys are also exchanged over the forward channel link. The encryption information is used to encrypt control signals that can be exchanged over a reverse channel link that may operate at a frequency of 2.4 GHz.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Image projection system
InactiveUS20090015548A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingProjection systemVideo projector
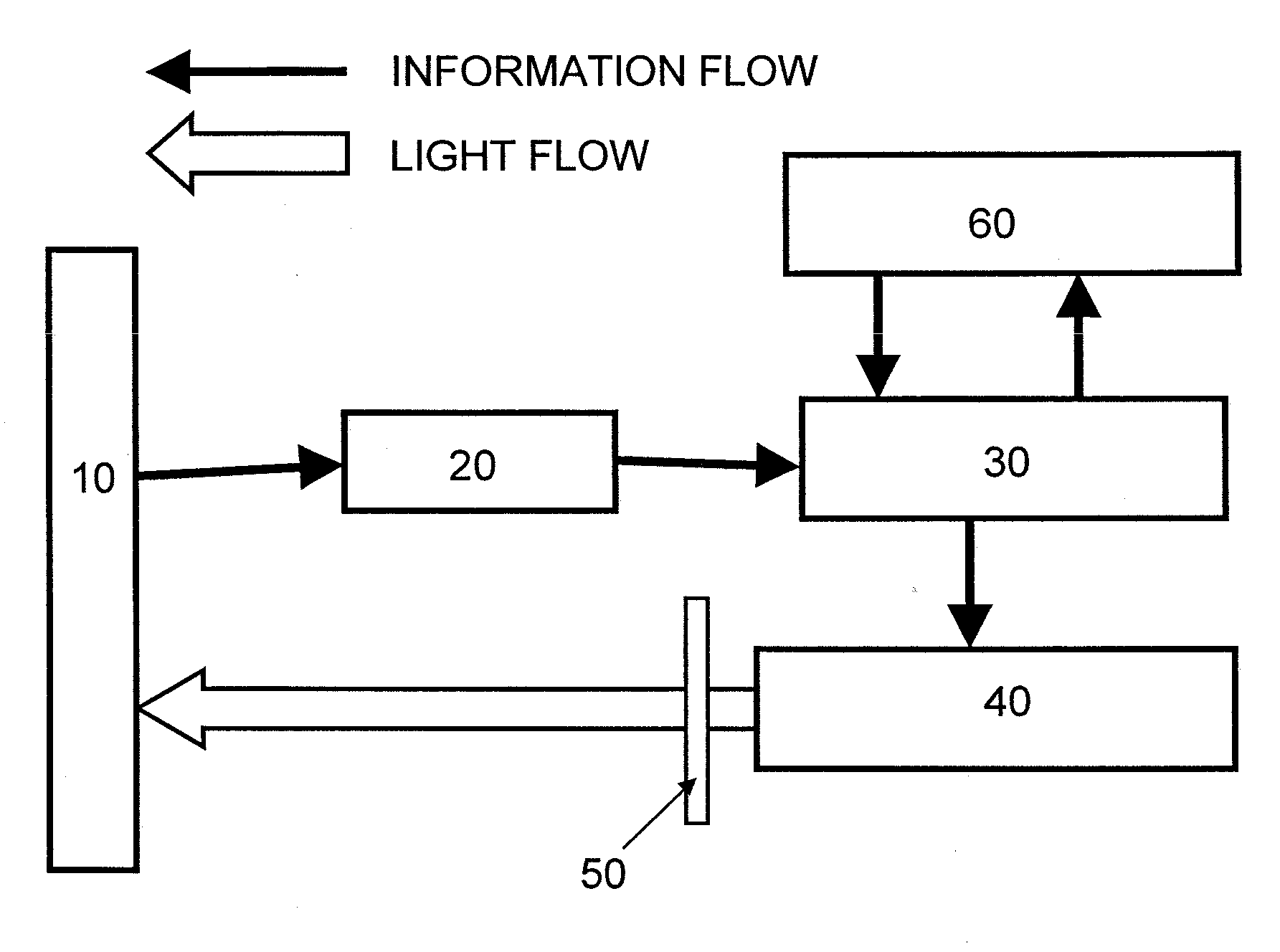
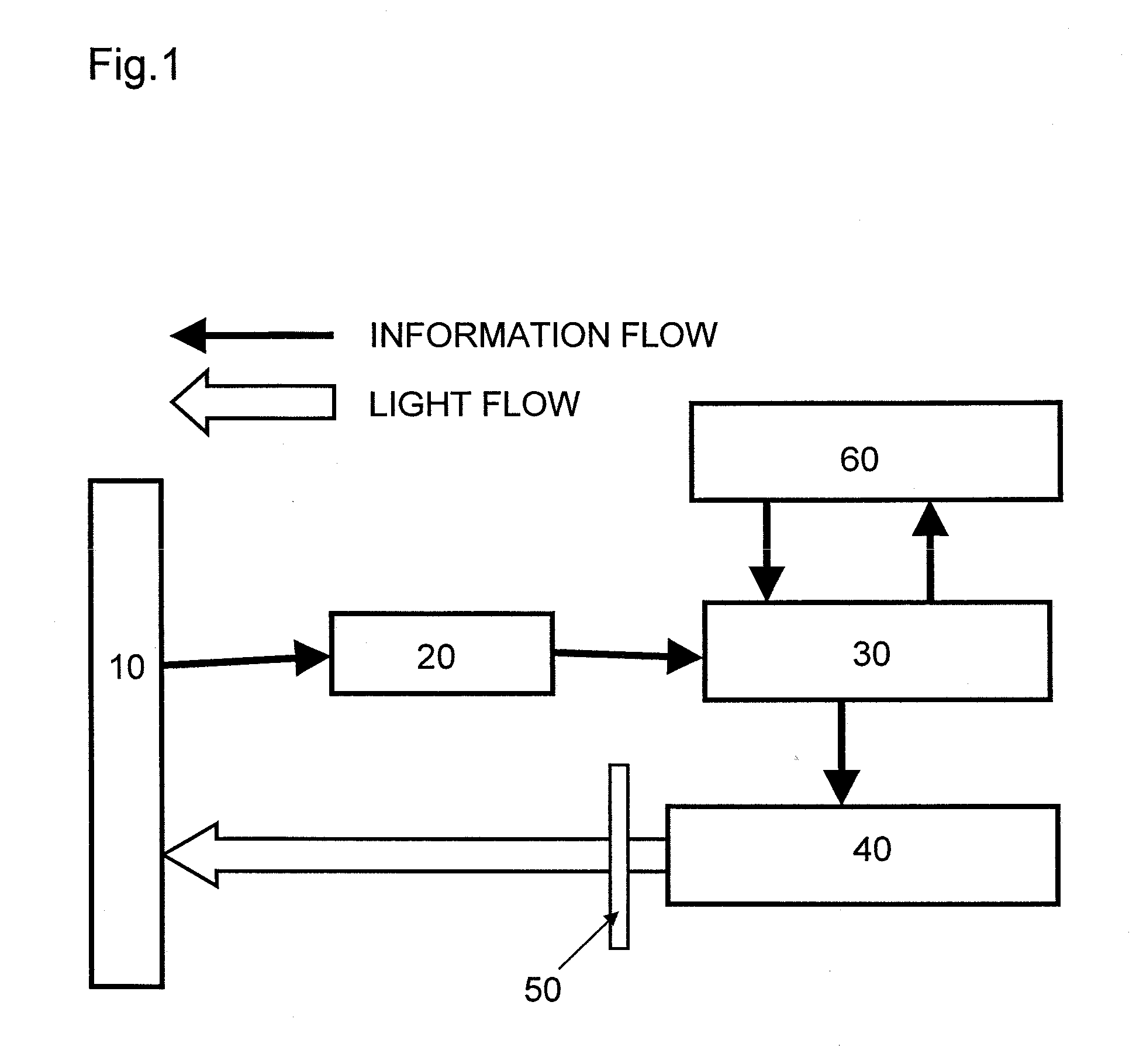
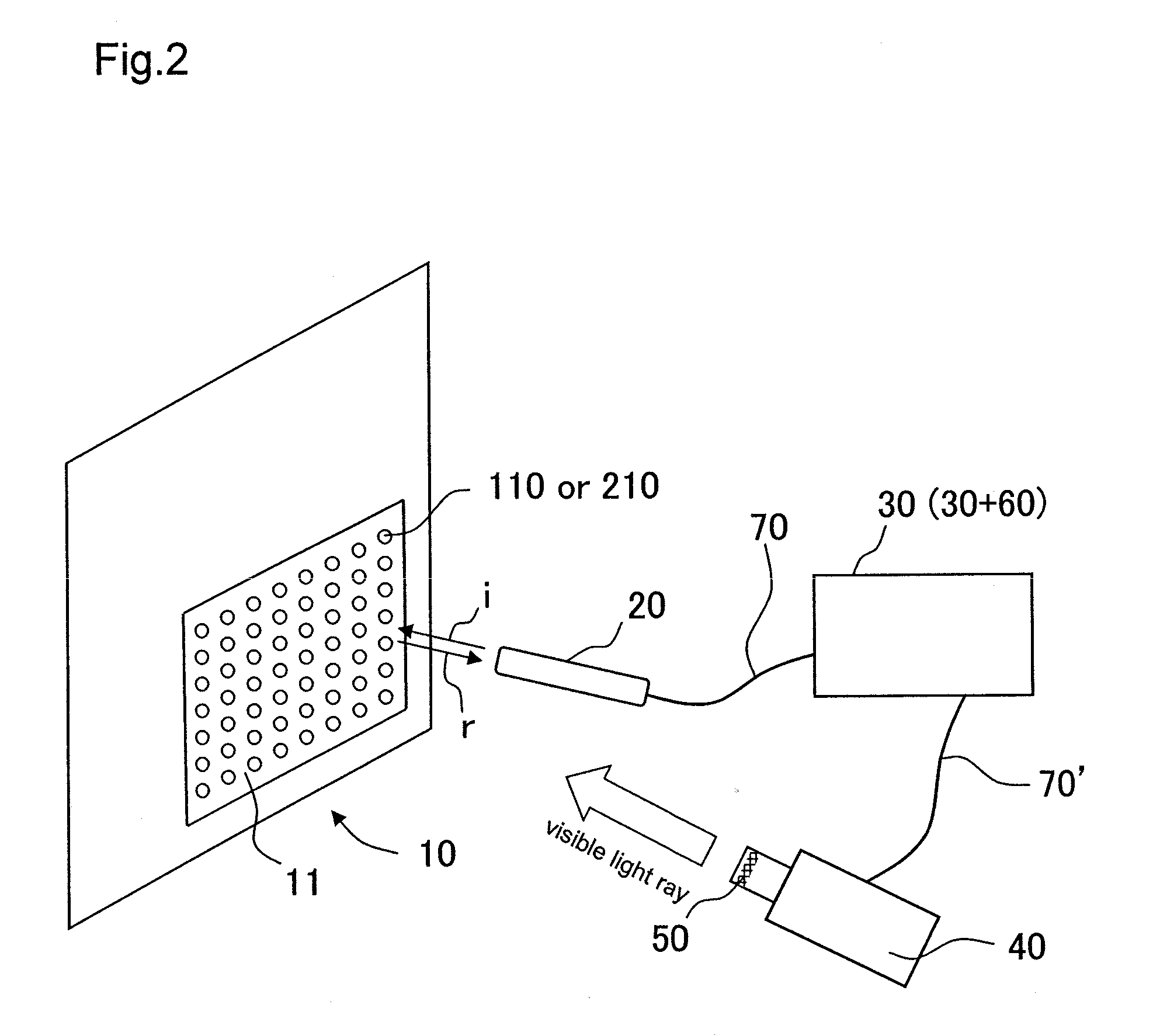
Provided is an image projection system including a screen, an input terminal, an image processing unit, an image projector, and invisible light ray-shielding member, characterized in that: the screen has a pattern-printed sheet having reflection patterns for transmitting positional information by reflecting invisible light rays or absorption patterns for transmitting positional information by absorbing invisible light rays; the input terminal has an invisible light ray-applying portion, detects a reflected light ray of an invisible light ray, which is applied from the invisible light ray-applying portion and reflected from a specific site of the pattern-printed sheet, reads positional information of any one of the reflection patterns or any one of the absorption patterns, and outputs the positional information to the image processing unit; the image processing unit converts the positional information input from the input terminal into image information A, and transfers the image information A to the image projector; the image projector converts the image information A transferred from the image processing unit into visible light rays, and projects the visible light rays on the screen; and the invisible light ray-shielding means is placed in front of or inside the image projector, and removes the invisible light ray from the visible light rays to be projected. The present invention can provide the image projection system in which, even when a screen is large, the positional information of the screen can be simply input in a non-contact fashion with high accuracy, and image information converted from the input positional information can be further converted into visible light rays to be projected.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Method and arrangement for combining holograms with computer graphics
InactiveUS20070081207A1Reduce risk of damageReduce riskHolographic optical componentsDigital holography electronic componentGraphicsVideo projector
The aim of the invention is to provide a method and an arrangement for carrying out said method, by which means optical holograms and interactive computer graphics can be harmoniously and uniformly combined, so that all components can be recognised in an optically sharp and separate manner and the holograms can be represented in a modified manner, especially also partially accentuated. According to the invention, the hologram is illuminated by an illumination image projected by the video projector, a holographic wave front that can be seen by the observer is reconstructed therefrom, and computer graphics are simultaneously displayed on the screen. The invention also relates to a method for combining computer graphics with an optical hologram having a virtual content, using a partially transparent, optical element, a hologram, a monitor located on the side of the partially transparent element opposing the observer, and a video projector, the 3D holographic image of the hologram superimposing the image of the monitor.
Owner:BAUHAUS UNIVERSITY
Simulator with fore and aft video displays
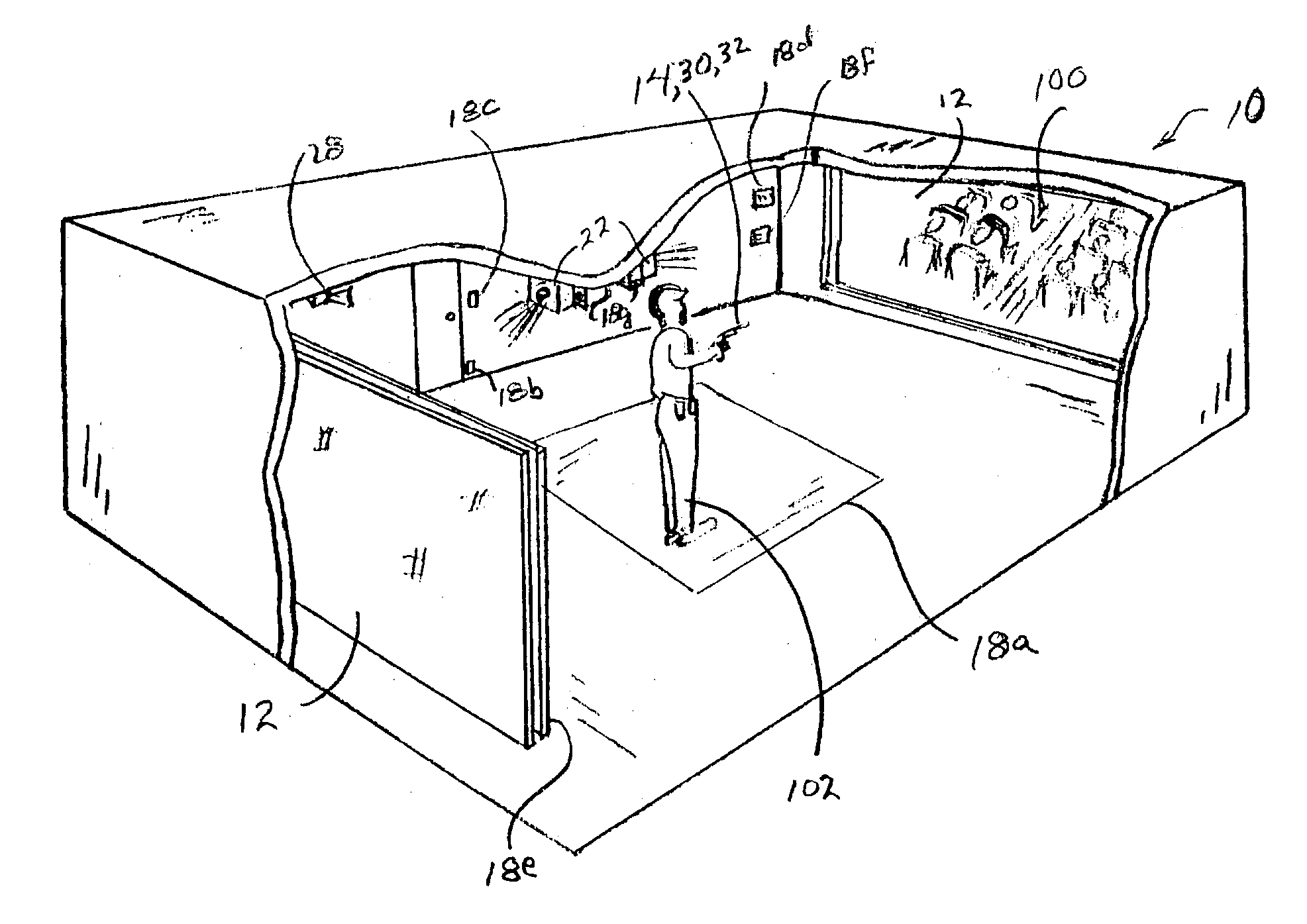
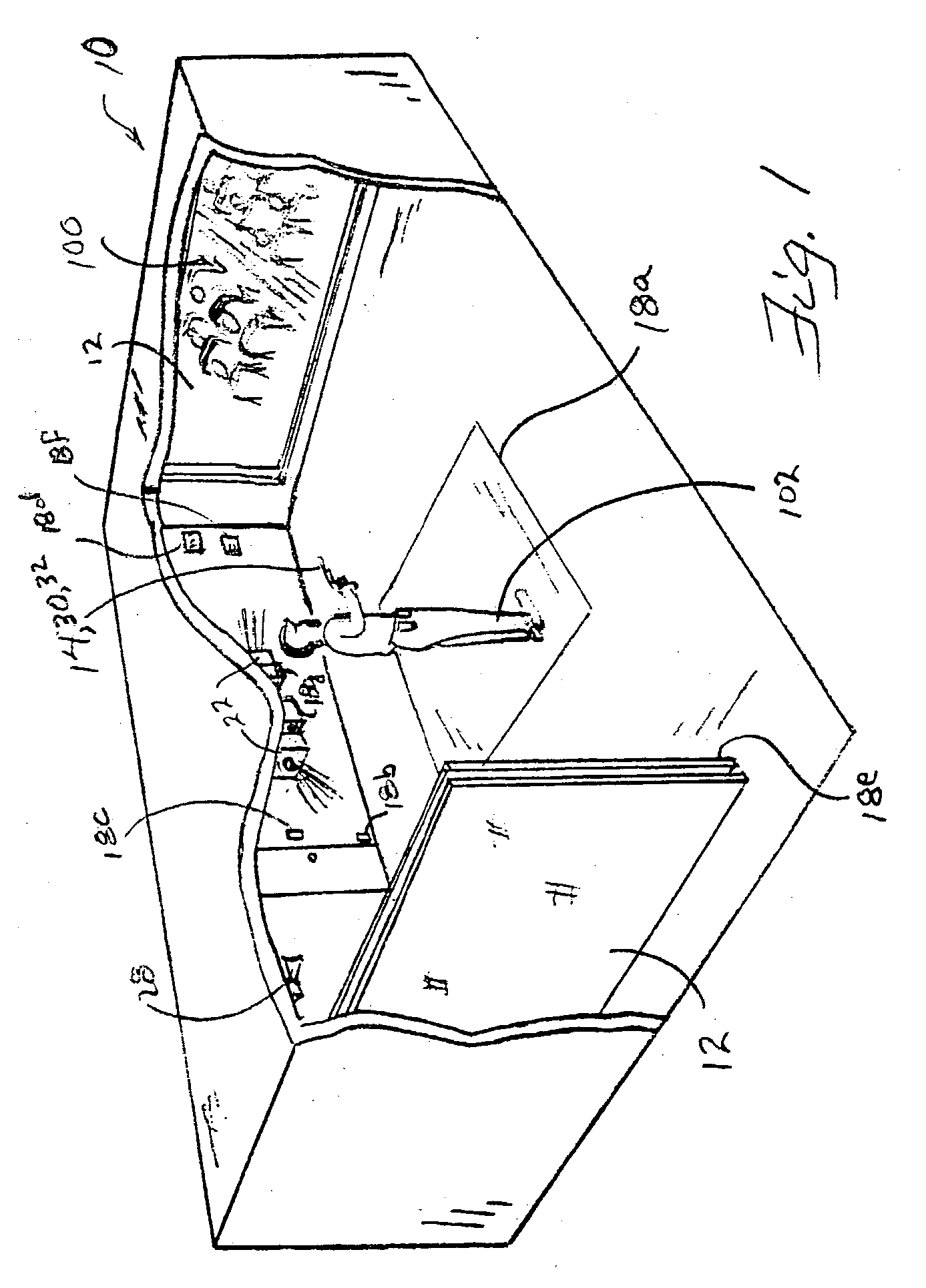
ActiveUS20040146840A1Improve the environmentAiming meansTraining adaptationComputer graphics (images)Taser
A simulated real-time environment employs a plurality of computer controlled video projectors and screens at least fore and aft of a participant-trainee to present life-size displays mutually coordinated to represent views of a same environment from a participant's perspective, each screen representing the participant's view looking in a different direction. In response to a participant's actions, the computer seamlessly changes a projected video to match the participant' actions and maintain a scenario consistent between the two screens. The participant uses a light-emitting simulated firearm or his own firearm loaded with a light-emitting cartridge and / or other equipment with which he is familiar, such as a modified or simulated flashlight, taser, chemical spray container or the like, tethered or untethered by a communication wire, to respond to a simulated situation, which response detected and interpreted by the computer to direct a branch in the projected videos and even shoot back a simulated bullet. He may also use verbal commands.
Owner:CUBIC CORPORATION
Systems and Methods for Displaying Three-Dimensional Images
InactiveUS20080309754A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using projection devices3d imageComputer graphics (images)
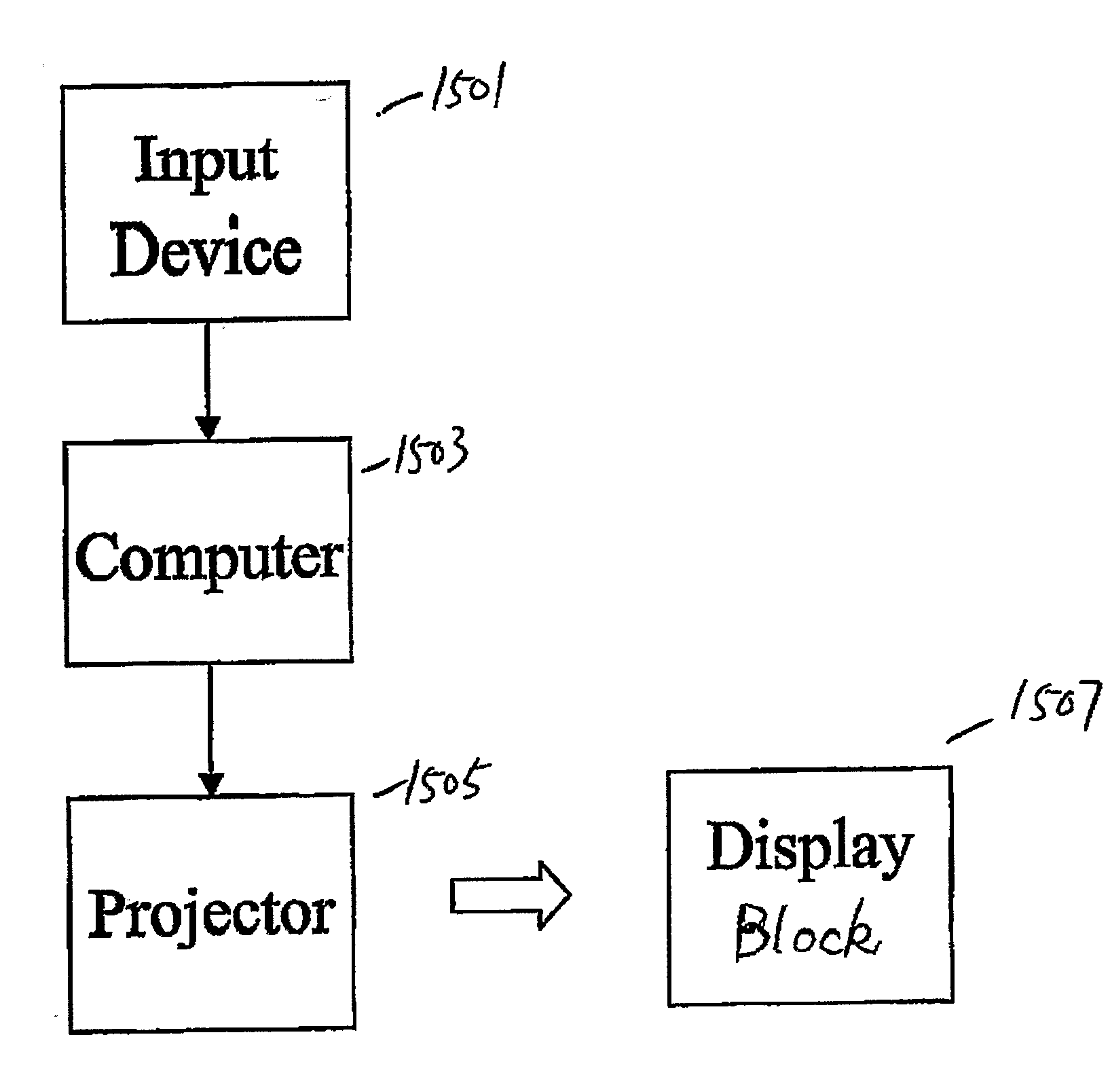
Systems and methods for displaying three-dimensional (3D) images are described. In particular, the systems can include a display block made from a transparent material with optical elements three-dimensional disposed therein. Each optical element becomes luminous when illuminated by a light ray. The systems can also include a computing device configured to generate two-dimensional (2D) images formatted to create 3D images when projected on the display block, by a video projector coupled to the computing device. The video projector is configured to project the 2D images on the block to create the 3D images by causing a set of the passive optical elements to become luminous. Various other systems and methods are described for displaying 3D images.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Screen and image projector using the screen
InactiveUS20050225687A1Improve viewing angleExcellent brightness characteristicsTelevision system detailsDiffusing elementsWide fieldProjection system
A projector screen having a simple configuration, which provides a wide field of view angle and can be used for both transmission and reflection projection is achieved. A screen according to the present invention is provided with a directional scattering layer that scatters incoming light within a specific angular range and transmits incoming light outside the specific angular range. Further, an image projection system can be made by combining the screen with an image projector that projects an image onto the screen.
Owner:YAMAUCHI NAOFUMI
Video Projector
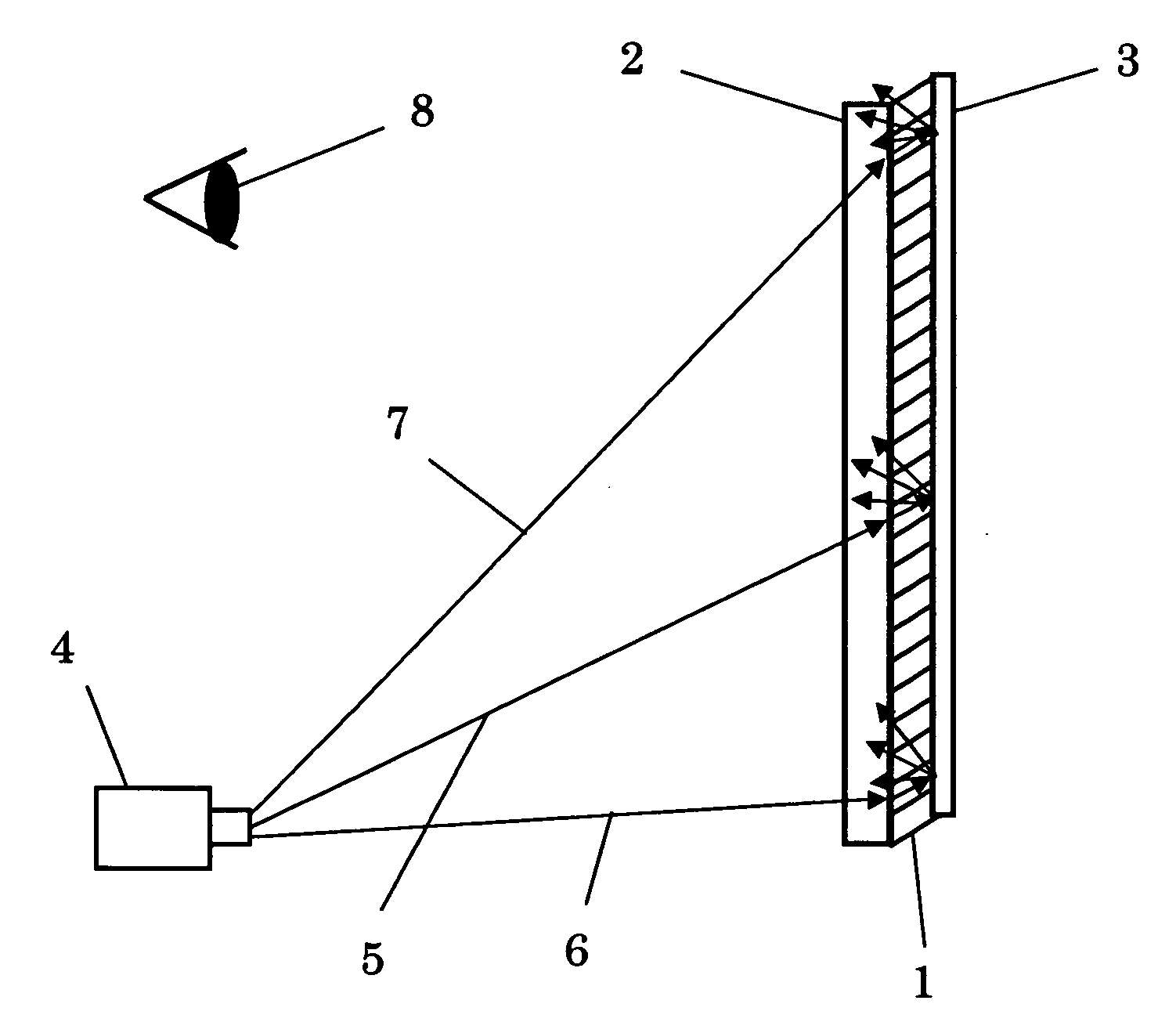
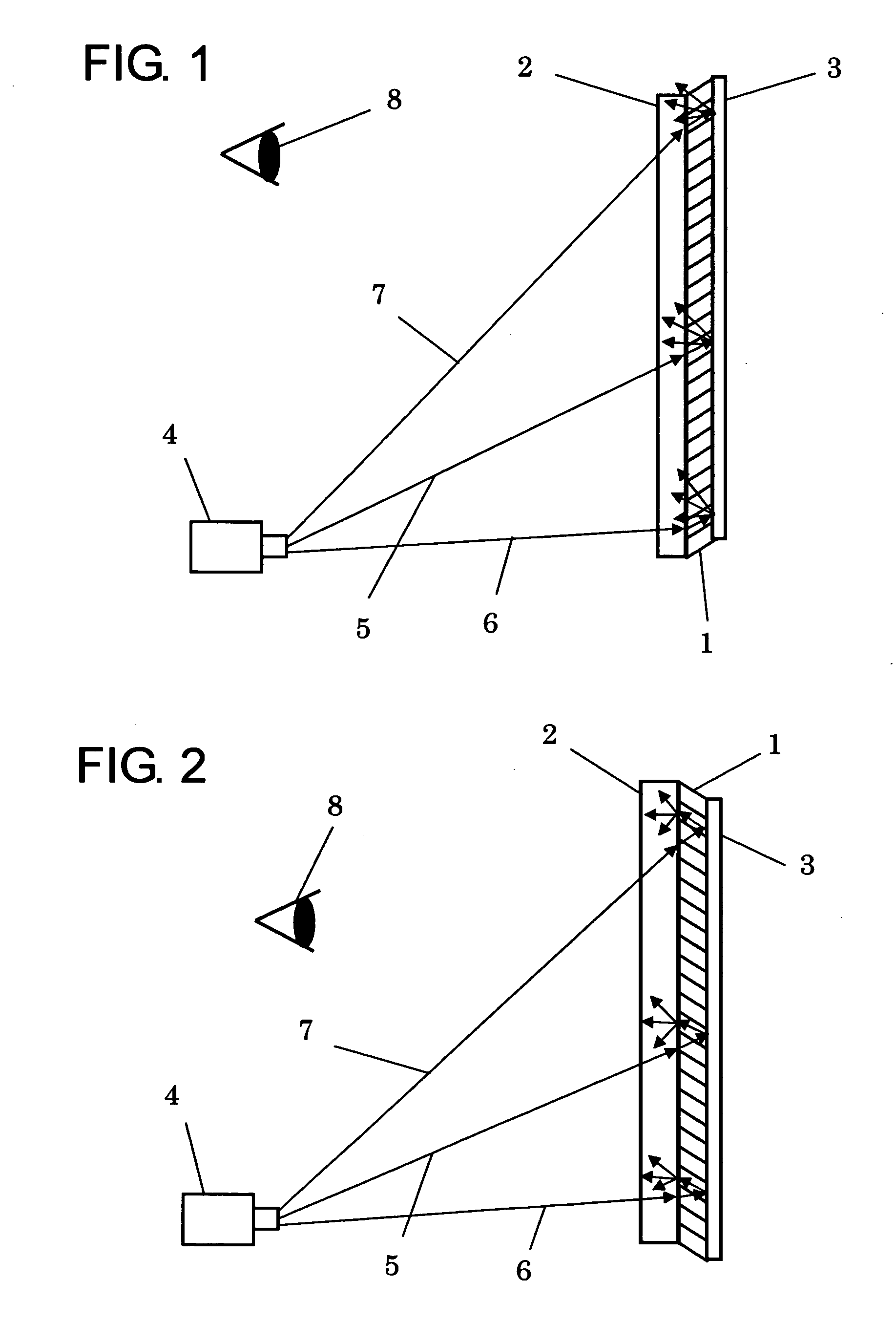
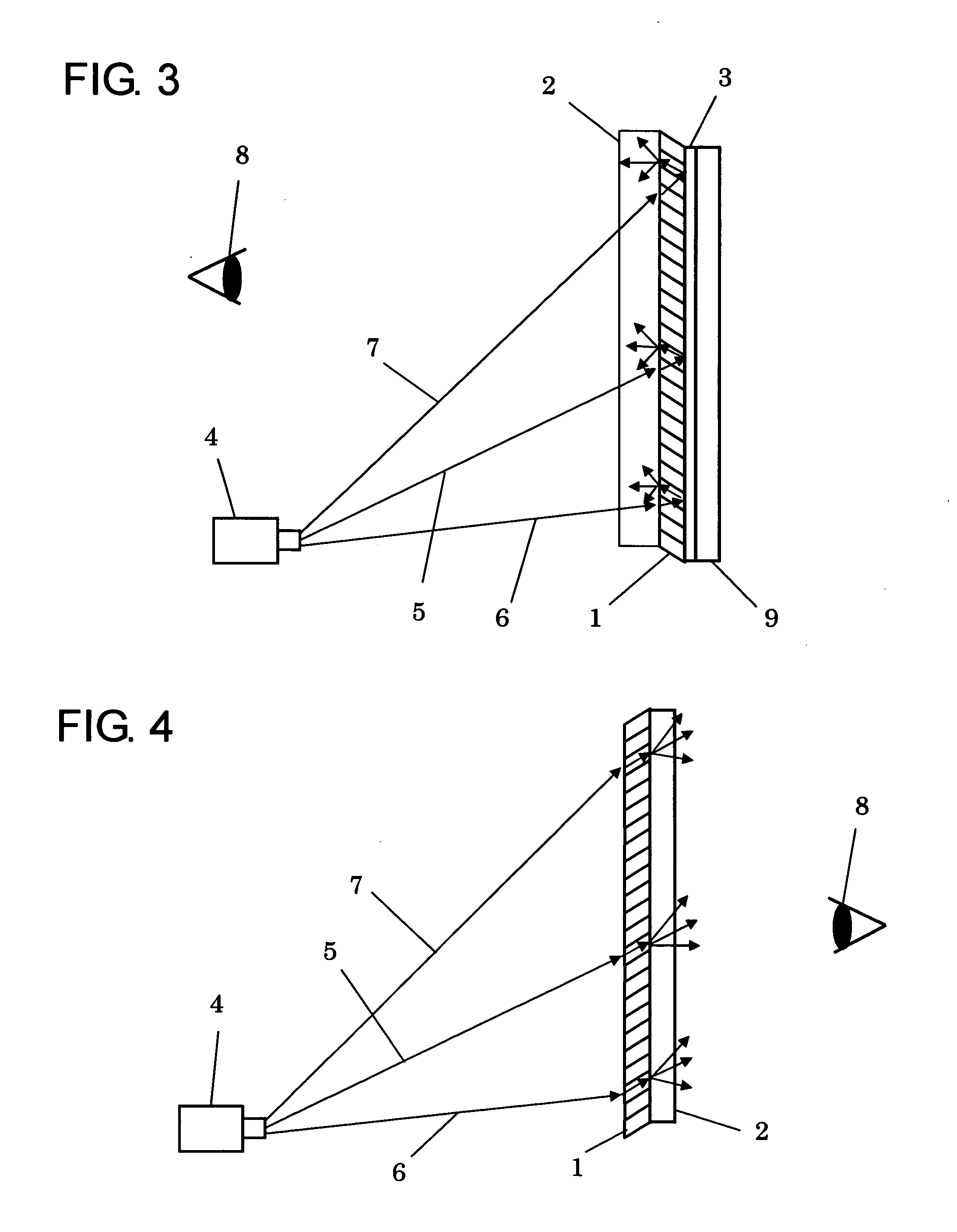
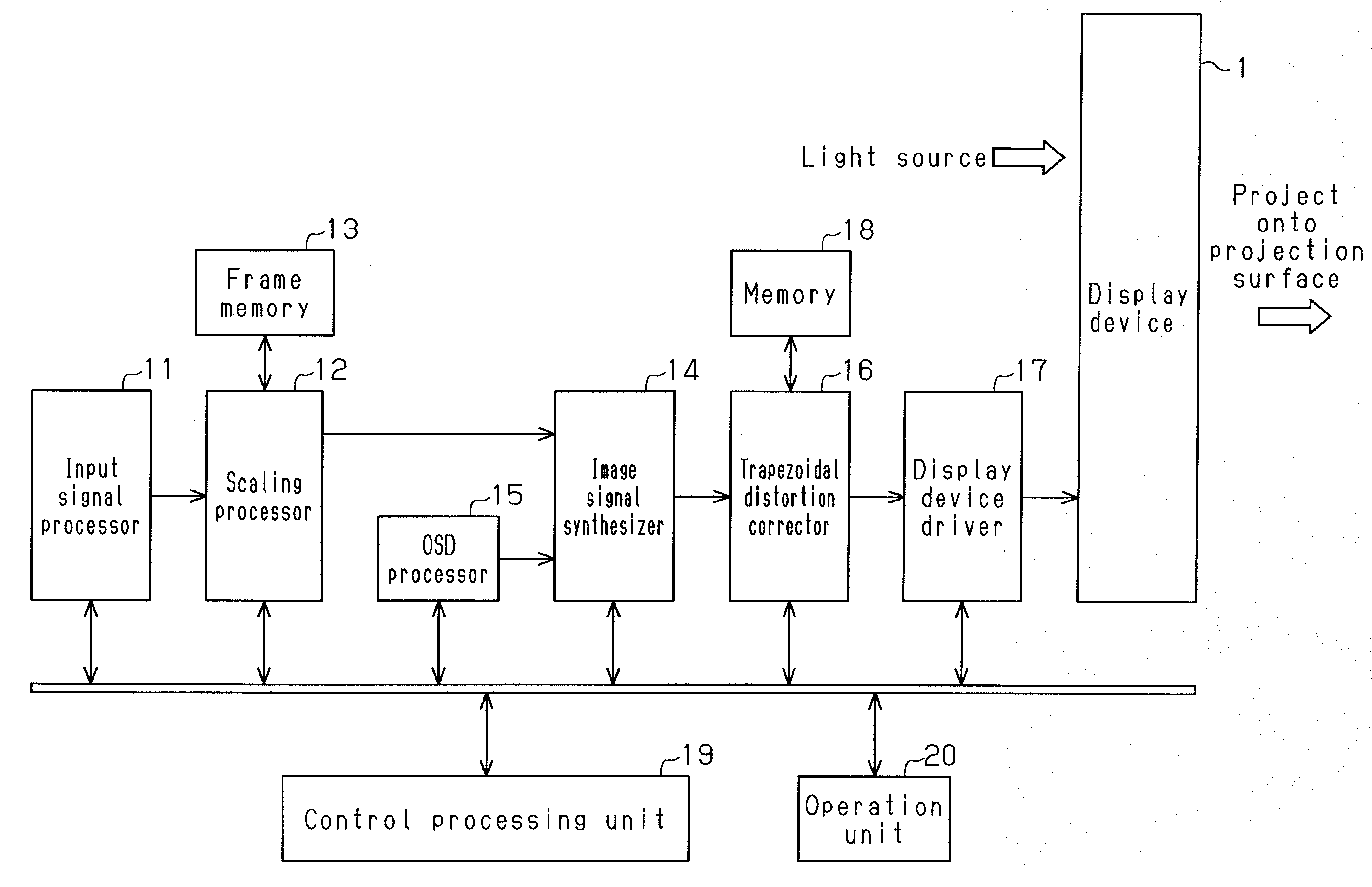
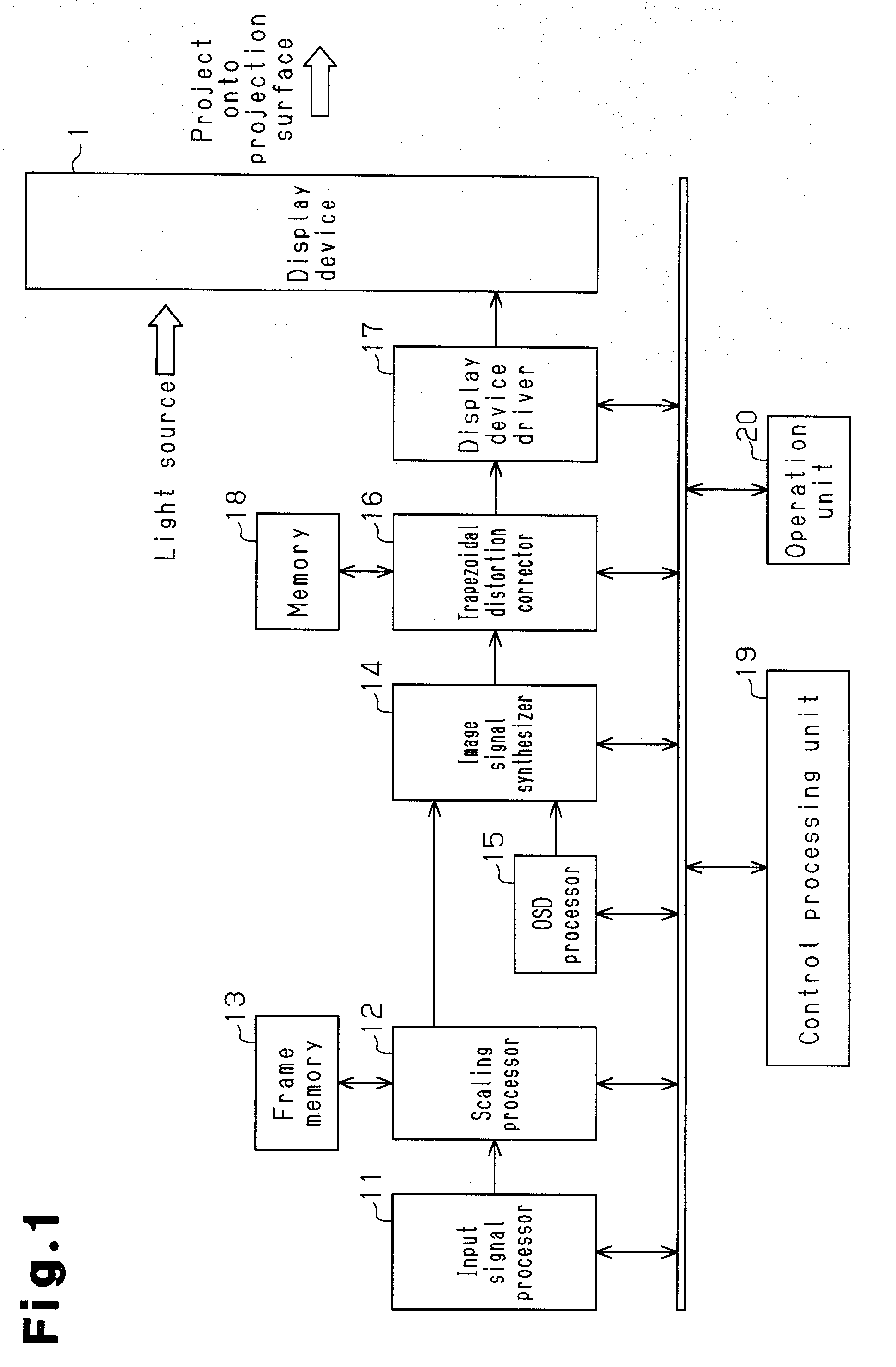
ActiveUS20090278999A1Improved trapezoidal distortion correction controlTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDisplay deviceVideo projector
A video projector includes a display device which receives an image signal and generates image light projected onto a projection surface. A scaling processor scales the input image signal. An OSD processor generates and corrects an adjustment pattern image in accordance with a correction instruction on the projection surface. An image signal synthesizer combines the image signal processed by the scaling processor with an OSD image signal generated and corrected by the OSD processor to generate a combined image signal. A trapezoidal distortion corrector performs trapezoidal distortion correction on the combined image signal from the image signal synthesizer based on the correction of the adjustment pattern image on the projection surface. The adjustment pattern image generated by the OSD processor includes a reference quadrangle pattern and downsized quadrangle patterns, which are reduced in size from the reference quadrangle pattern.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Interactive video presentation
A system in accordance with the invention includes an interactive video system that creates immersive multimedia experiences through responsive physical interaction and audience participation. The system transform floors, walls, screens, staging and other surfaces and video output devices into an interactive experience. Motion tracking and projection systems enable the combination of a background message to be manipulated in response to audience participation, including human body movements. Included within the system is a software application with a setup and programming user interface, used in conjunction with external hardware to which it is connected. External hardware includes, in one basic embodiment, one or more video projectors, one or more video cameras, and one or more computers. The computer receives input from the video cameras, and modifies the projected video based upon that input. A single system unit can be networked to other system units on a LAN, WAN, or global network.
Owner:RESPONDR
Method and system for wireless digital video presentation
InactiveUS7965837B2High frequencyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoData rate
High definition (HD) video may be sent from, e.g., a laptop computer on a table in a room to a video projector mounted on the ceiling using a 60 GHz high capacity (2.5 Gbps) wireless link. At this frequency and data rate, the signal is so short range and directional that low power may be used and the video may be transmitted in an uncompressed form such that so much data is transmitted each second that bootlegging the content is essentially untenable. No wiring between the HD video source and the HD video display is necessary.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Method and system for producing and displaying visual presentations which inhibit off-screen duplication
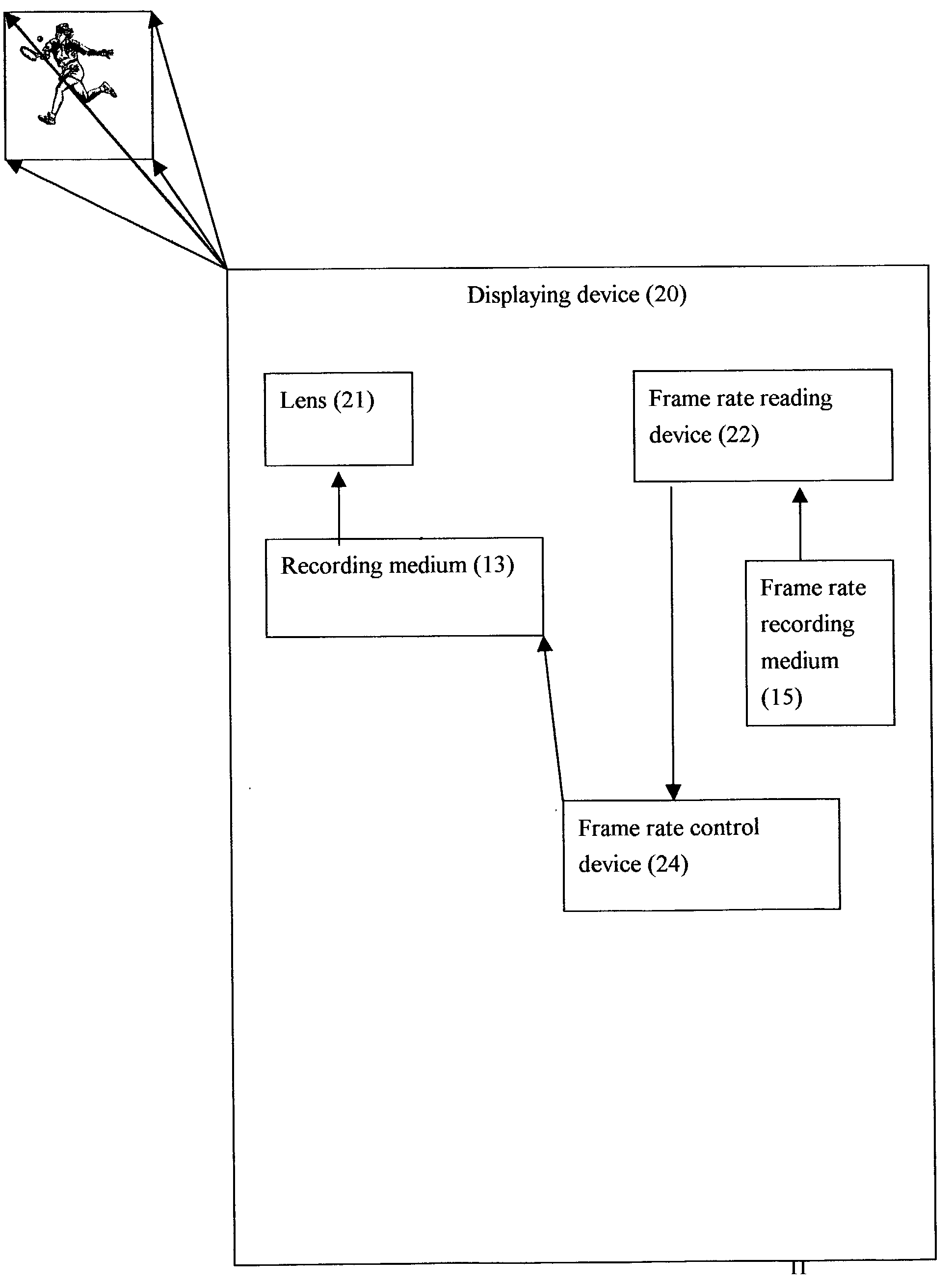
InactiveUS20040033051A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVideo projectorCathode Ray Tube Display
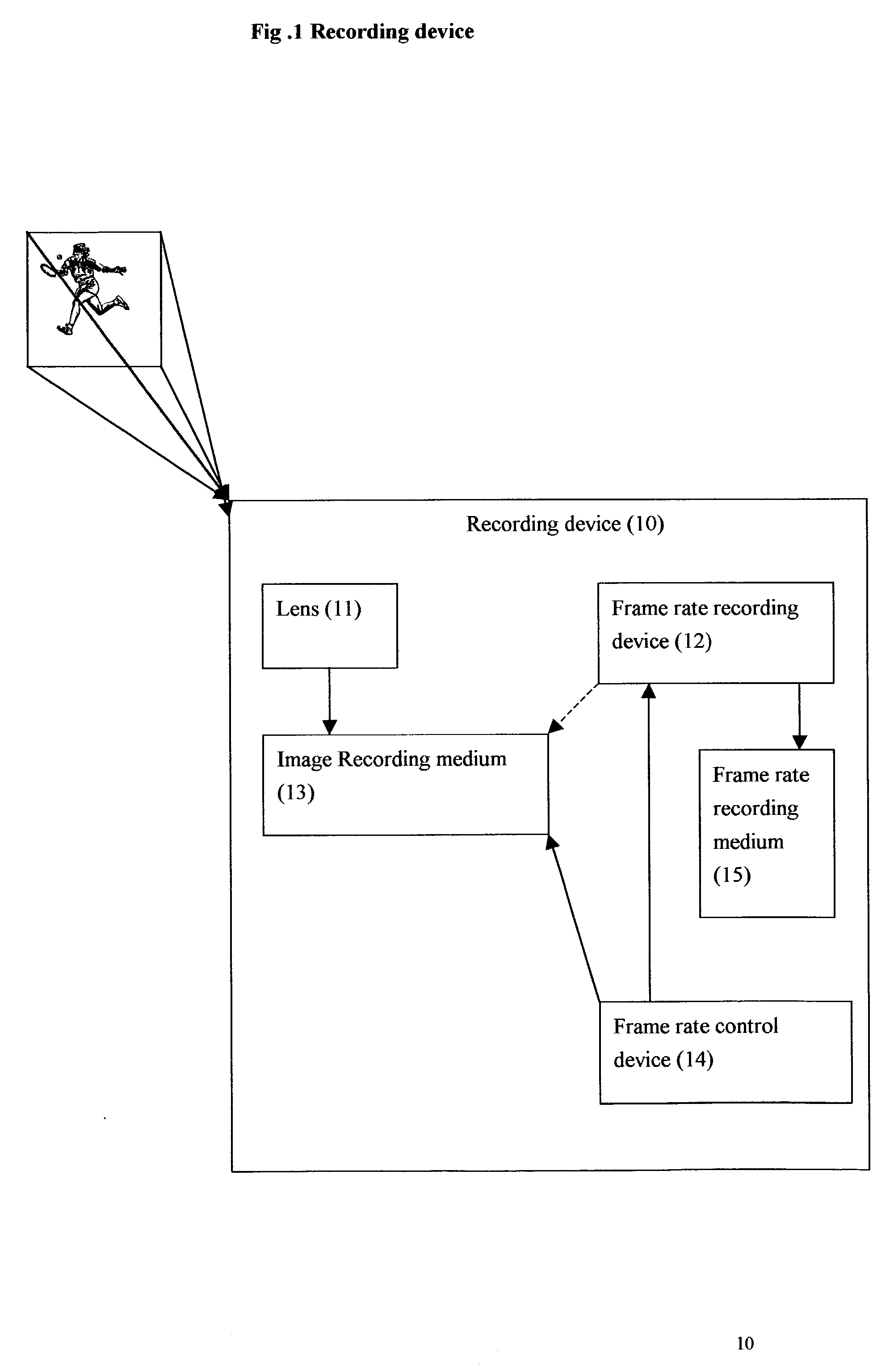
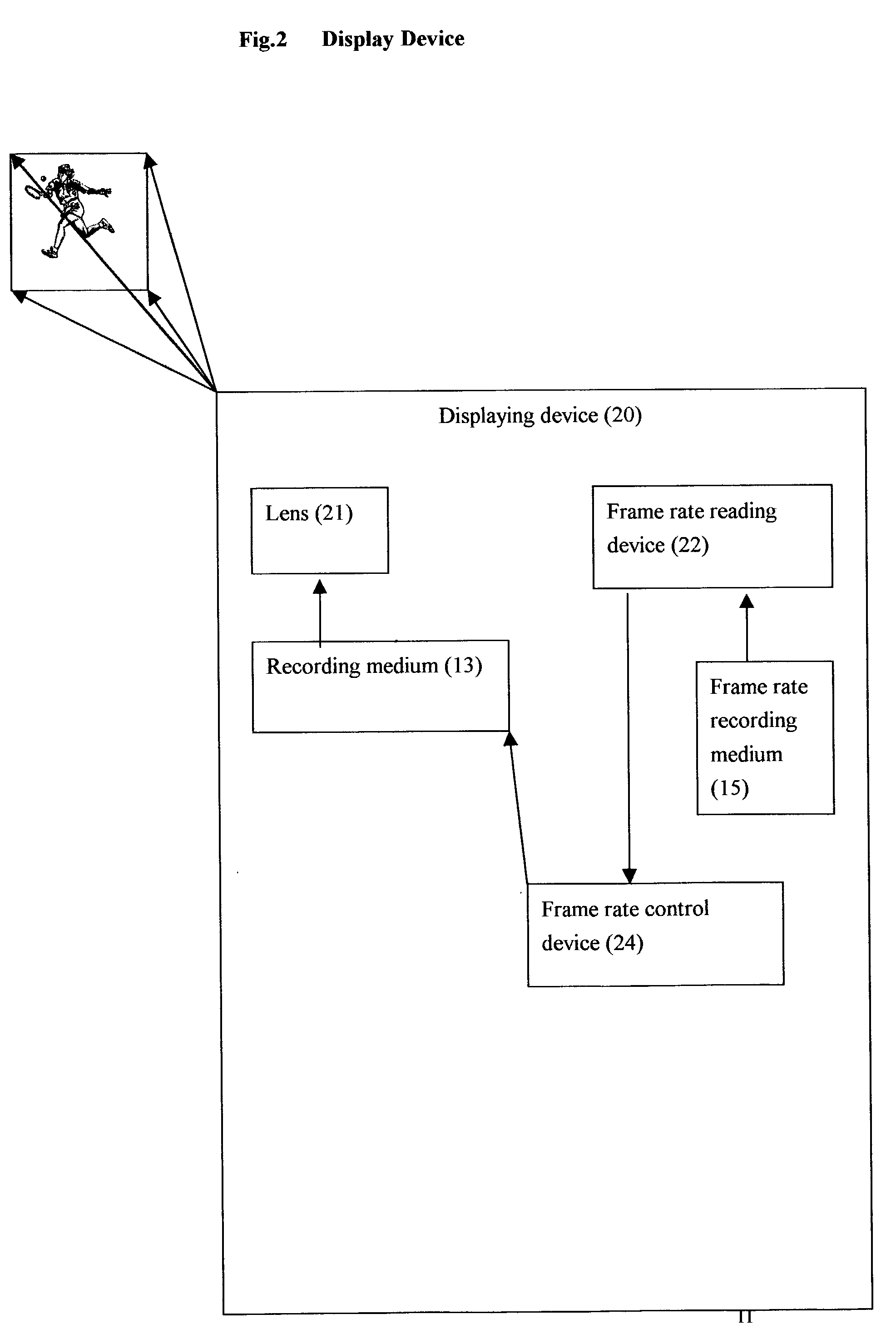
A method and system for preventing a visual video copy being made of a projected image on a screen. In a theater or television or computer screen environment, an image is displayed on a screen by a film projector or a video projector or by the cathode ray tube or the LCD screen. A form of piracy is accomplished by copying the image on the screen with a video camcorder or camera. This invention seeks to produce visual presentations which invention inhibits off-screen copying by camcorders or cameras. A preferred embodiment of the invention comprises of recording means which records images at variable frame rates which rates are either pre-programmed or decided by the user of the means. The variation of the frame rates forms a rate sequence which is recorded simultaneously when the images are recorded. The rate sequence will be read by the display device when the recorded images are displayed such that the images are displayed at the frame rates at which they are recorded. An unauthorized attempt to record the image sequence off the screen without the rate sequence will only record images displayed at unsynchronized rates. It will be extremely difficult if not impossible for an unauthorized person to attempt to synchronize his recording means to the various frame rates of display when the frame rate variation is large. This will make the unauthorized duplicated copy virtually unwatchable.
Owner:IP KIRIL KUN WAN
Method, device, computer program and information storage means for transmitting a source frame into a video display system
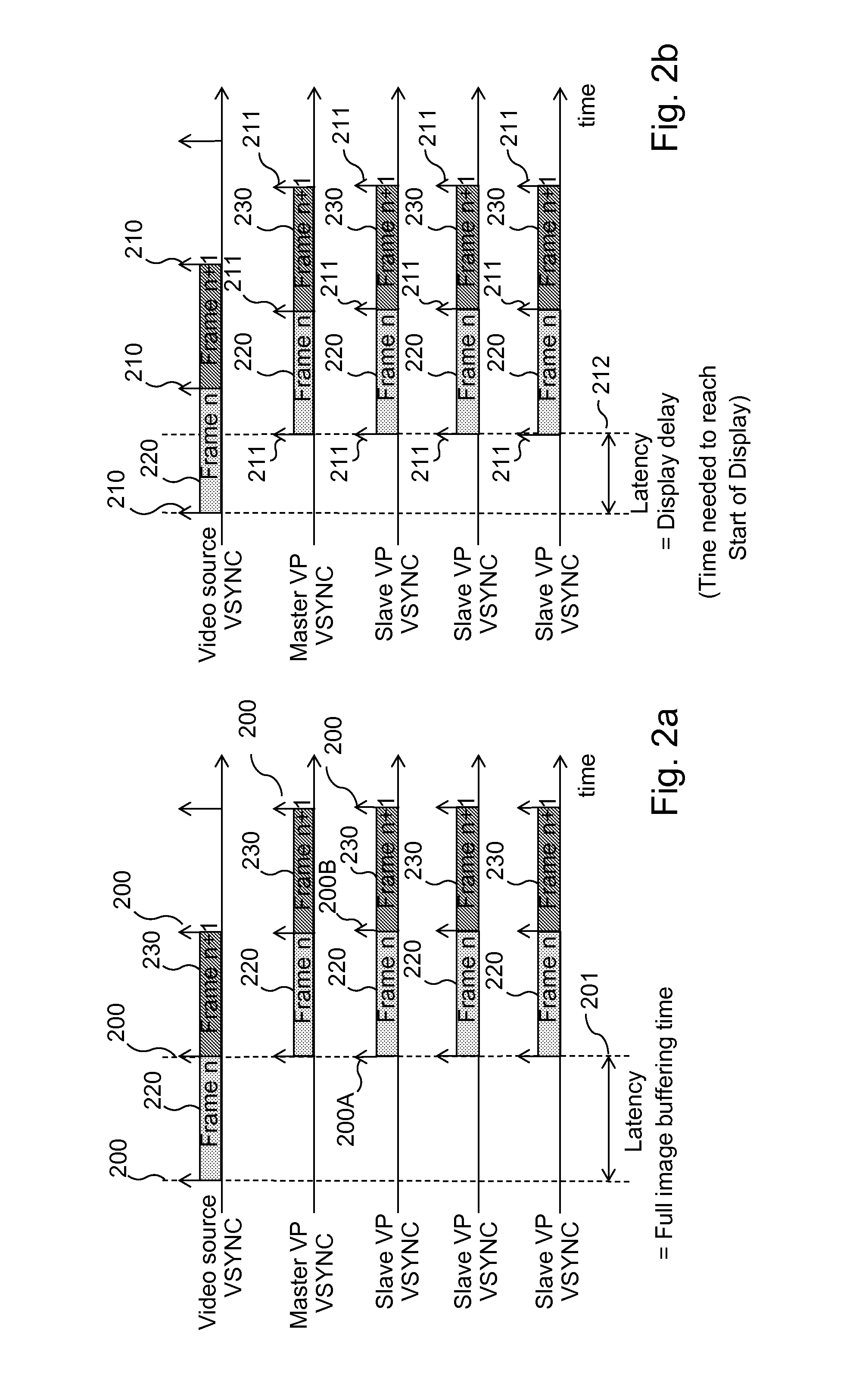
InactiveUS20130321701A1Eliminate delaysLatency is optimizedTelevision system detailsProjectorsComputer graphics (images)Video projector
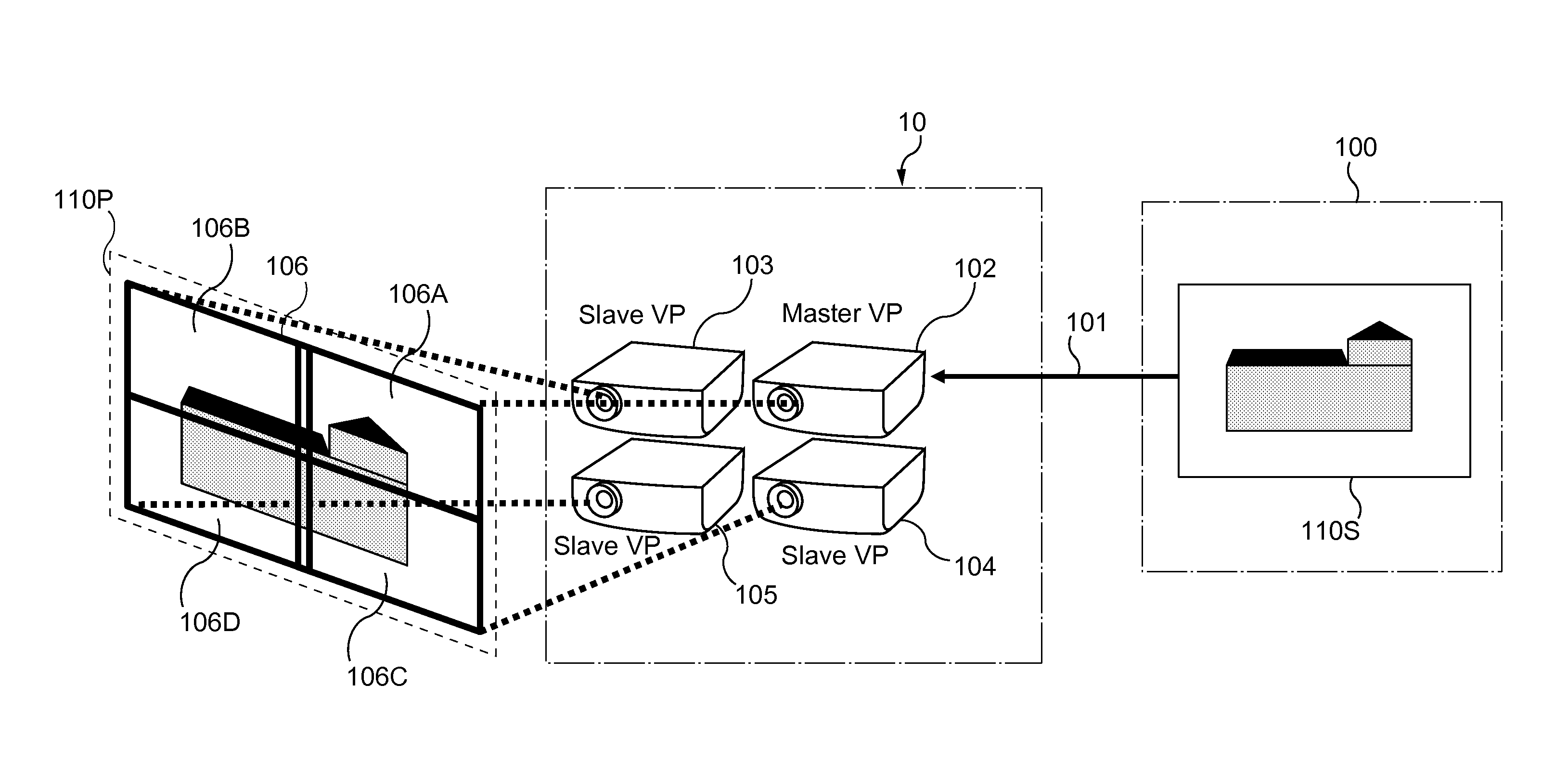
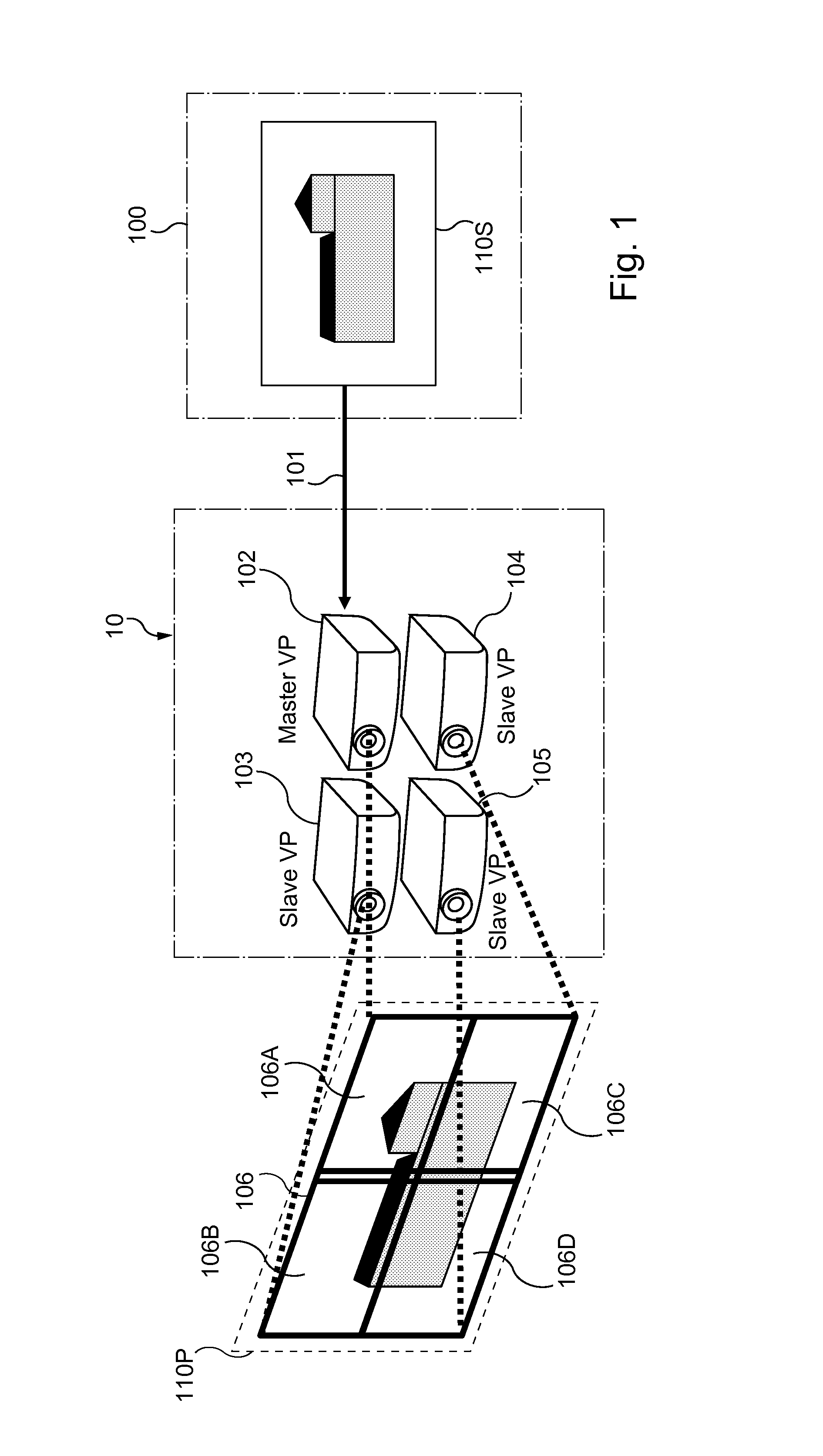
Method, device, computer program and information storage means for transmitting a source frame into a video display system, the video display system (10) comprising a plurality of projectors, the video display system (10) further arranged to produce a projected image (106) from the source frame (100), each projector (102, 103, 104, 105) arranged to display a sub-frame (106A, 106B, 106C, 106D) of the projected image (106). The video display system further comprises capability to arrange a display delay, equal to a delay between reception of a source frame synchronization signal and a sub-frame display synchronization signal, dependent on the positions and the orientations of the video projectors, such that display of the projected image begins before at least one projector has received an associated complete sub-frame.
Owner:CANON KK
Light source device, video projector and video projection method
ActiveUS8403492B2ProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesVideo projectorWavelength range
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Training simulator for sharp shooting
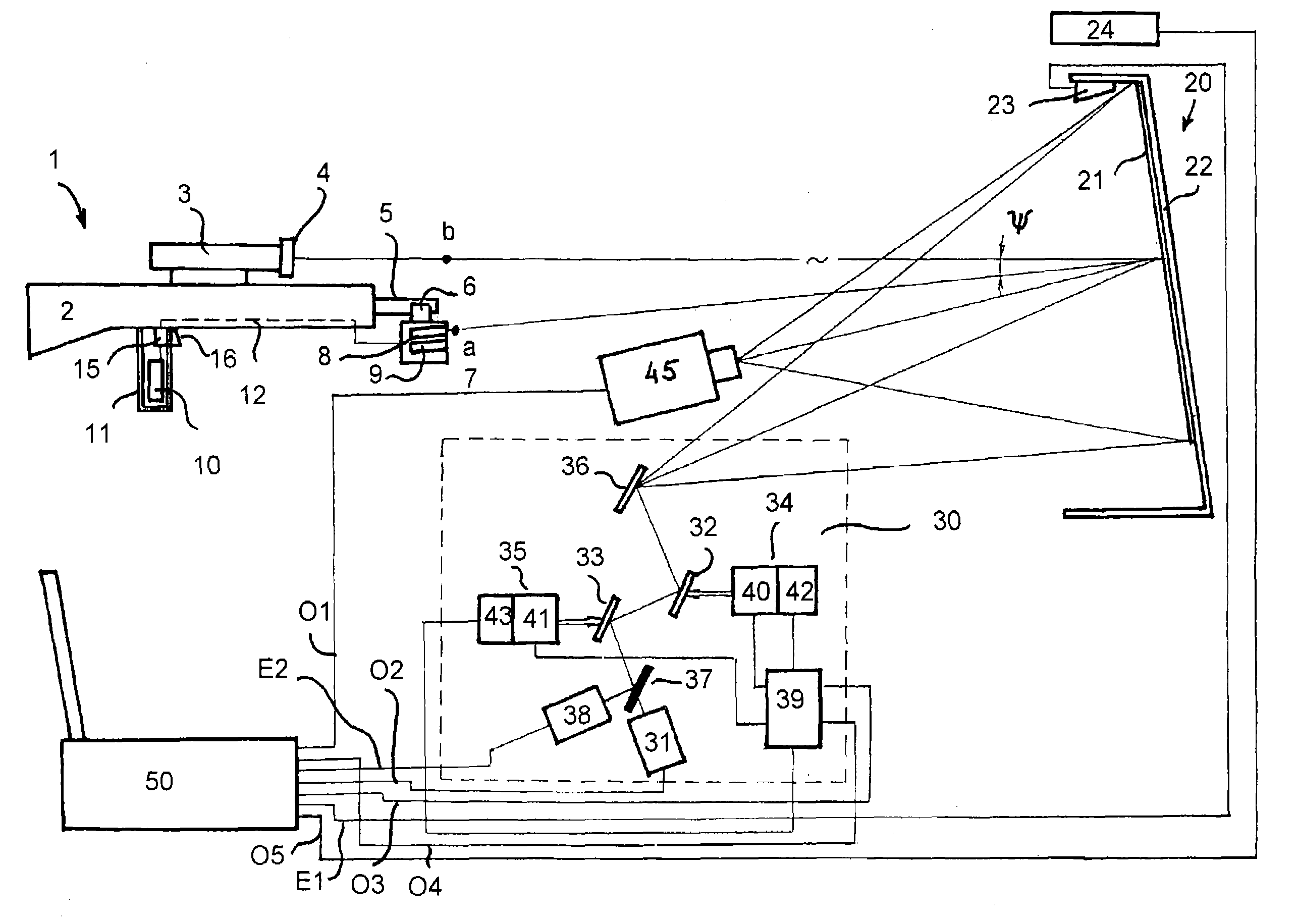
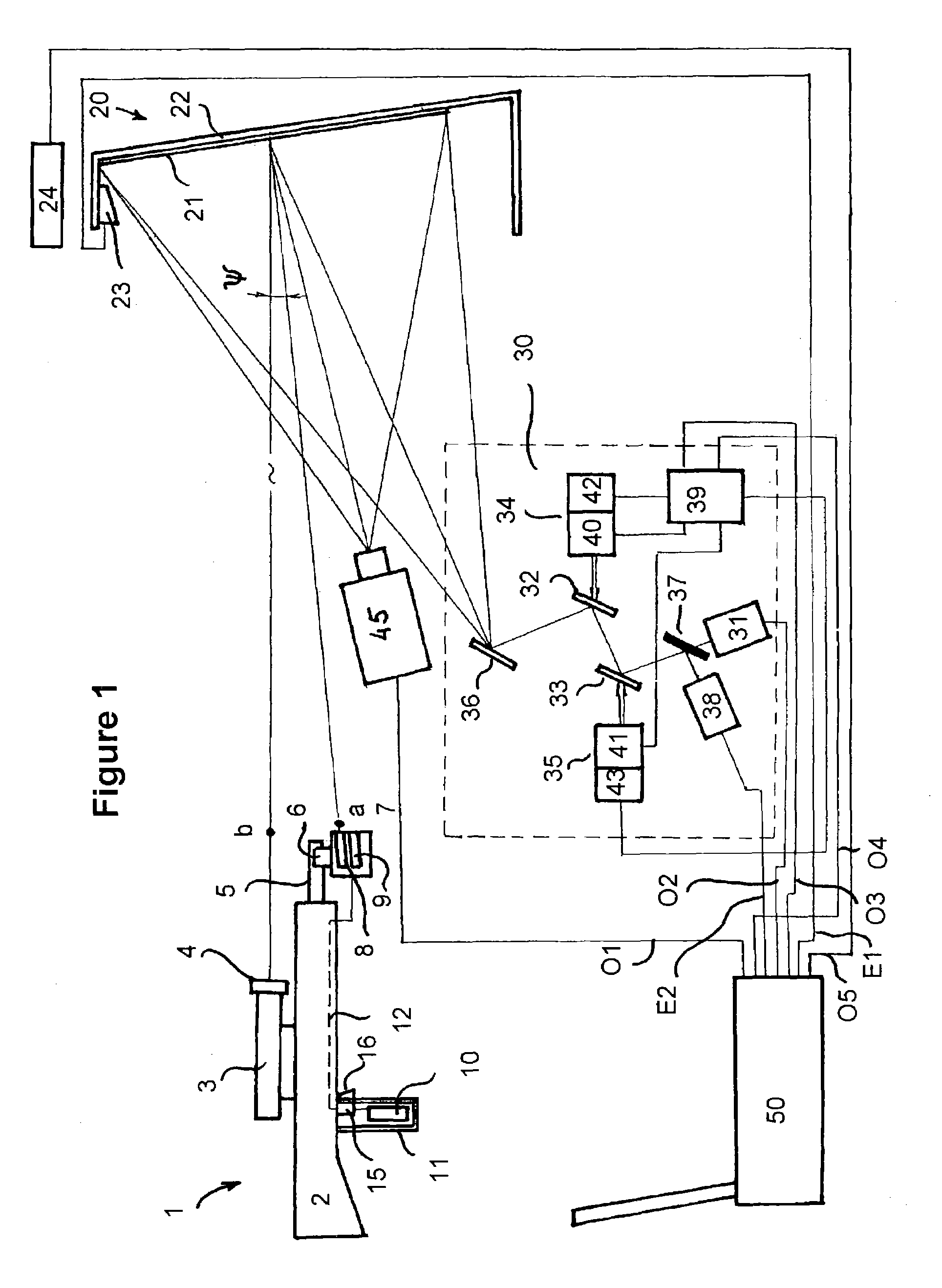
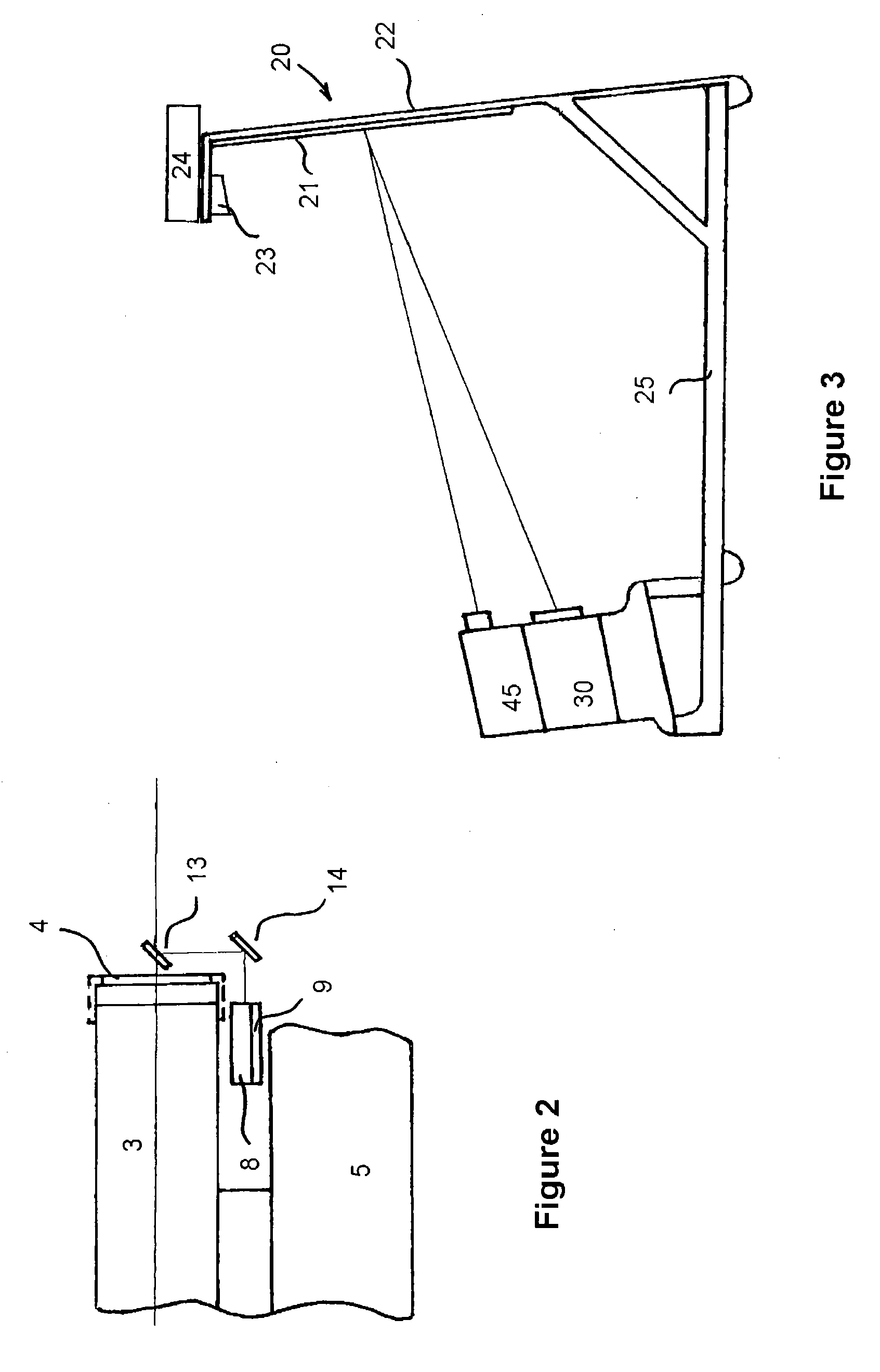
The simulator of the invention is based on a number of functional units connected directly or remotely to the central computer for controlling the operation and recording the shooting results. The weapon unit is untethered and includes a real hand gun equipped with a snap-on emitter unit to send simultaneously two beams of light upon pulling the trigger—a wide angle infrared beam and a narrowly focused and aimed at the target light beam. The infrared beam is registered by the sensor near the screen and a signal indicating a firing event is sent to the computer. The light beam, preferably from a laser source is sent towards the screen, reflected therefrom towards the optical block and travels through a number of fixed and rotating mirrors and through a light divider to the light sensor. That sensor when activated sends the HIT or MISS signal to the computer. Importantly, the optical travel path of the reflected from the screen light beam coincides with the travel path of the light beam generating the target of the screen. Controlled by the computer, rotation of the rotating mirrors both places the target at a specific area of the screen as well as allows accepting of the light beam from the screen by the light sensor. The target generator allows to position the target on the screen in any desirable area or to move it with constant or variable speed along a predetermined complex path on the screen. A video projector allows adding of the pre-recorded of virtual computer-generated surrounding scene onto the screen to increase the degree of realism of the shooting exercise.
Owner:LVOVSKY MIKHAIL
Autostereoscopic display system
InactiveUS20050062678A1Reduce the amount requiredCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
An autostereoscopic display system includes a lenticular lens display screen that projects a plurality of views of a scene from its front surface. A plurality of video projectors are disposed to the rear of the display screen and focus on a convergence point of the display screen's rear surface. Imaging computers drive the video projectors, each having a memory storing a scene to be displayed on the display screen. Each computer renders the scene from a preselected viewpoint that may be different from the viewpoints of the other imaging computers.
Owner:MARK RESOURCES
Projection method
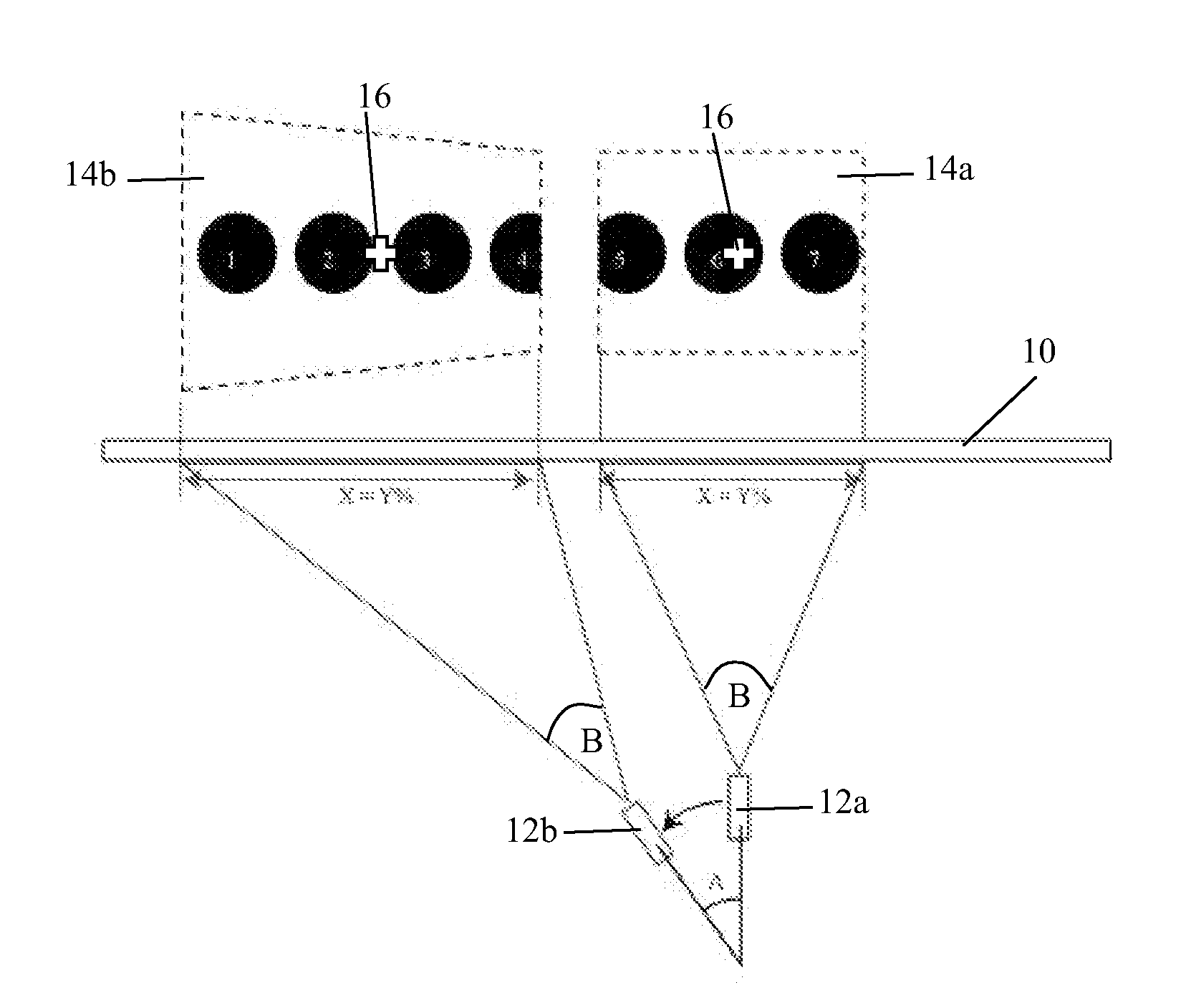
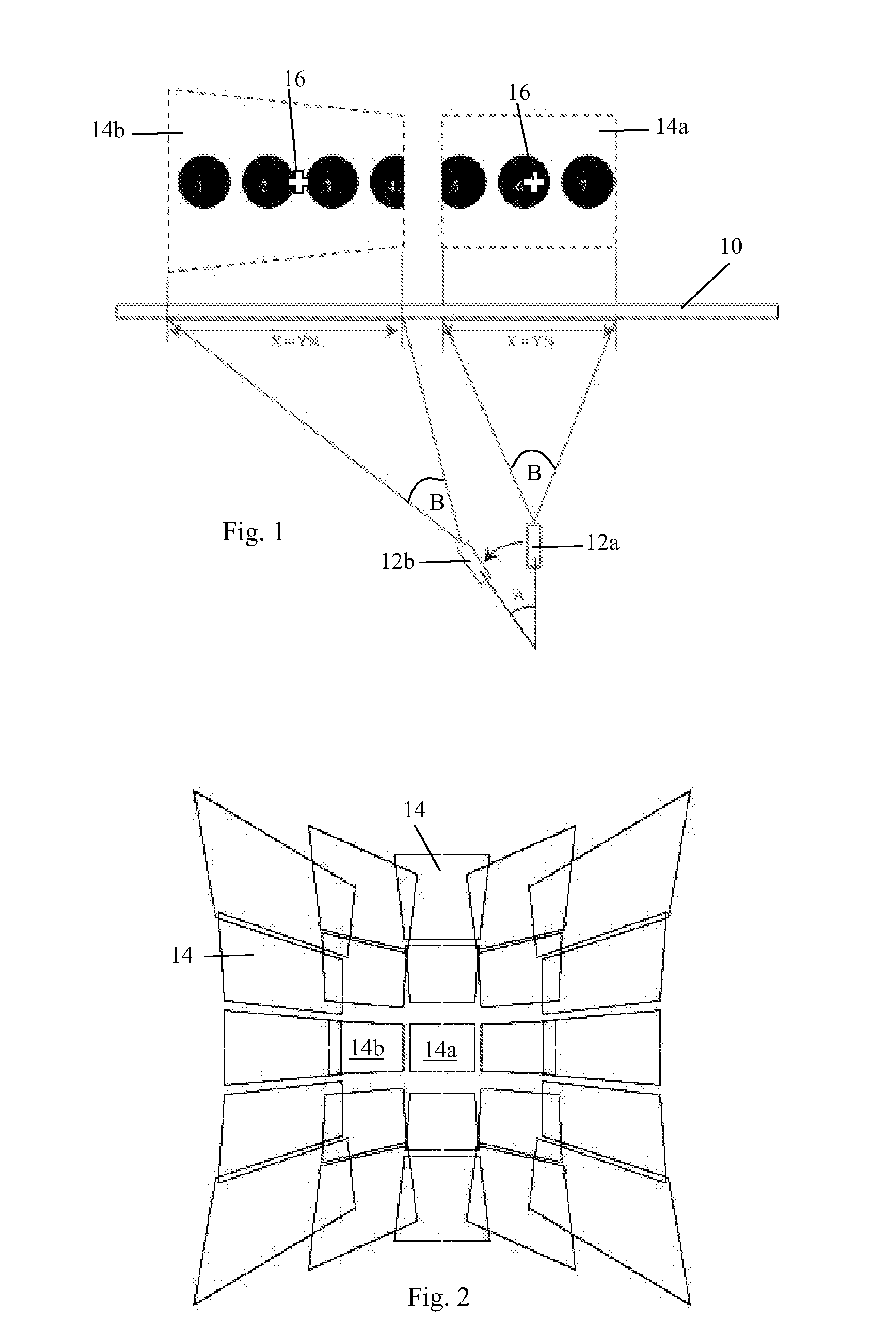
InactiveUS20100188587A1Small sizeSmall weightTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using projection devicesComputer graphics (images)Digital image
There is disclosed a method of displaying a visual image, such as a digital image, on a display surface (10), such as a screen or wall, using a video projector (12). The total area occupied by the complete visual image on the display surface (10) is larger than the area of the projected image (14) produced by the video projector (12). The method comprises determining the location (14a,14b) on the display surface (10) of the projected image produced by the video projector (12). Subsequently, a part of the complete visual image is selected which corresponds in position within the visual image to the location of the projected image (14a,14b) on the display surface (10). The image part is displayed as the projected image (14a,14b). The method has the advantage that all of the projected image (14) can be used to display the visual image, in parts. The video projector (12) can be moved to display any desired region of the complete visual image.
Owner:ASHLEY KALMAN
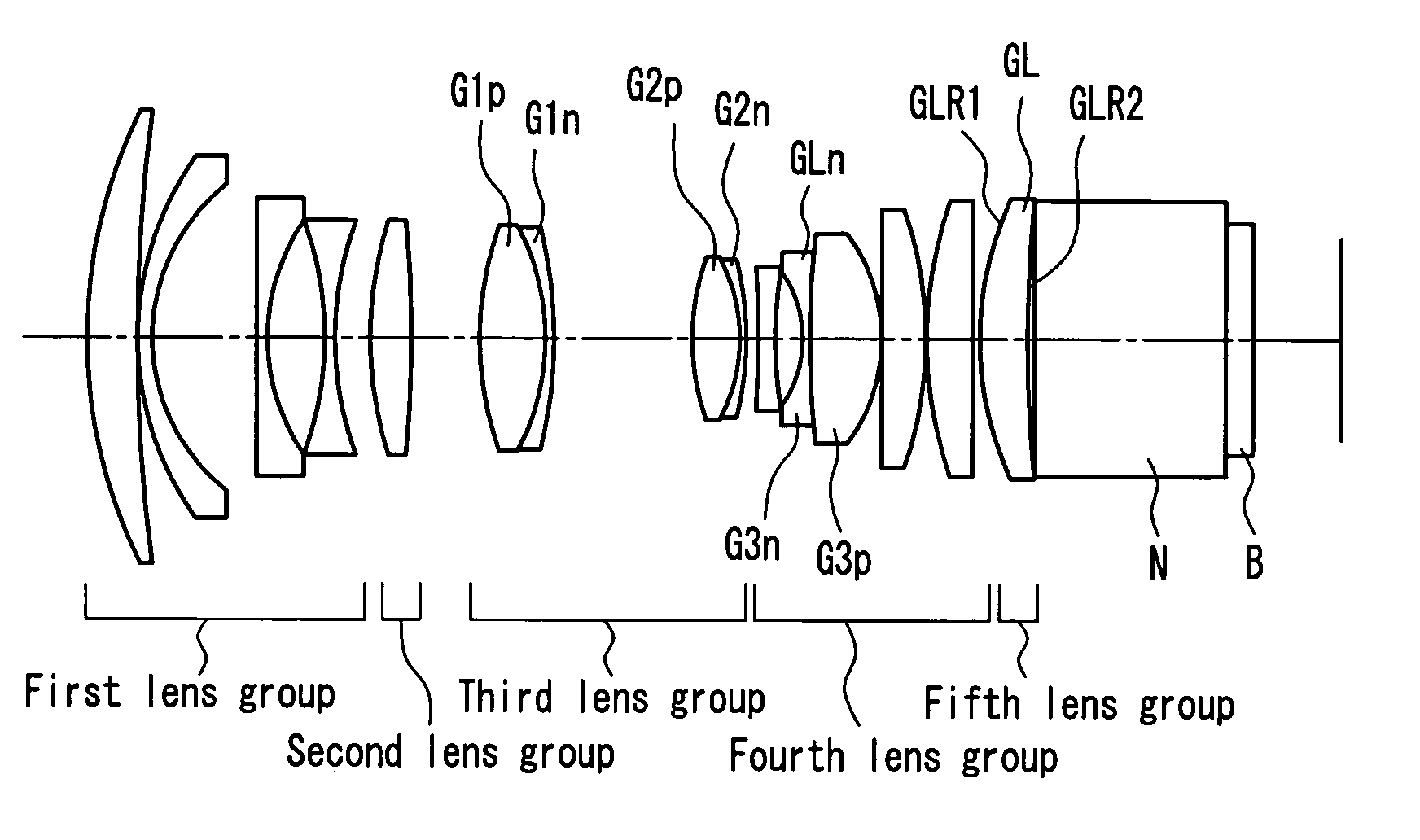
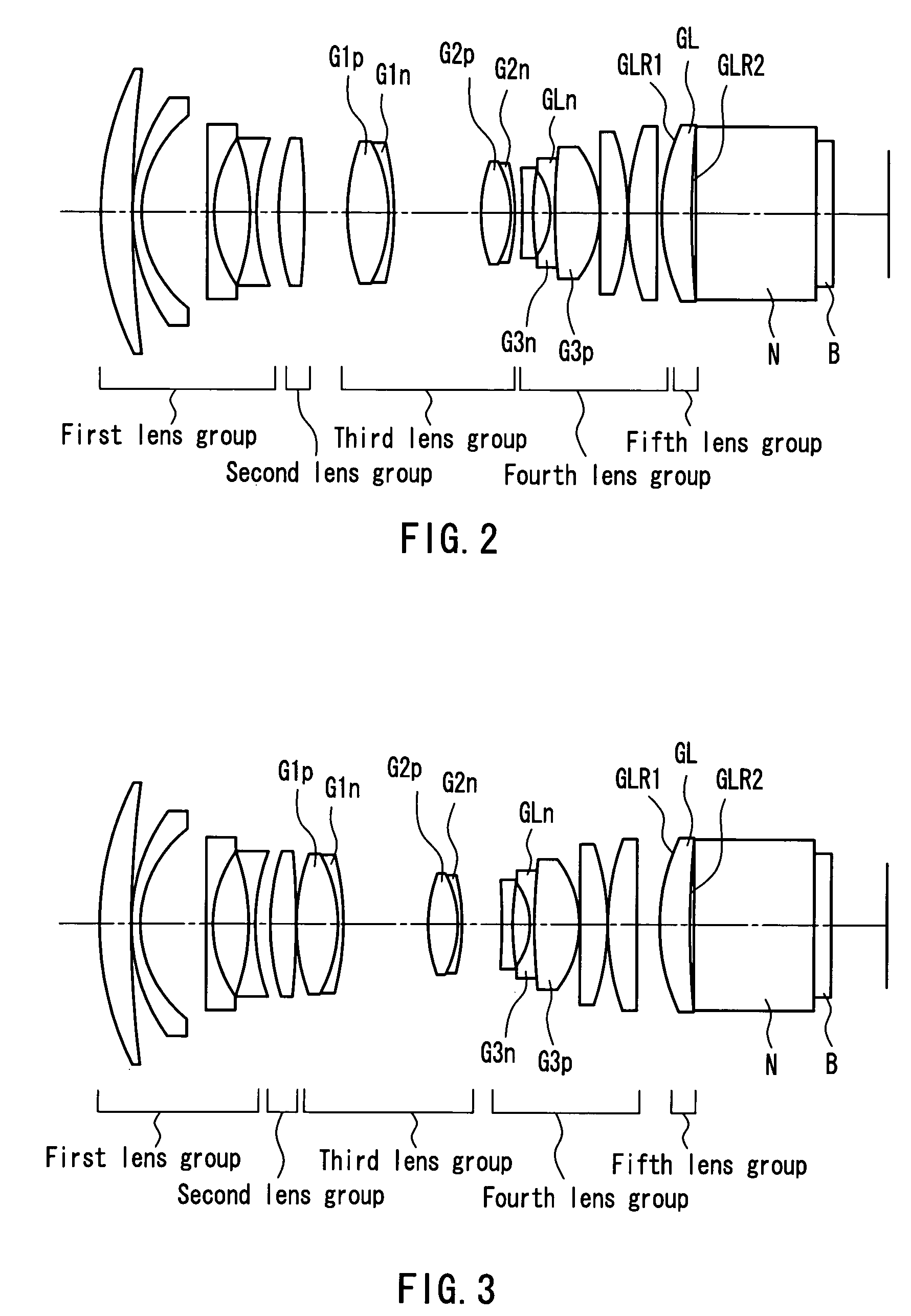
Zoom lens, image magnification projection system and video projector using the zoom lens and rear projector and multi-vision system using the video projector
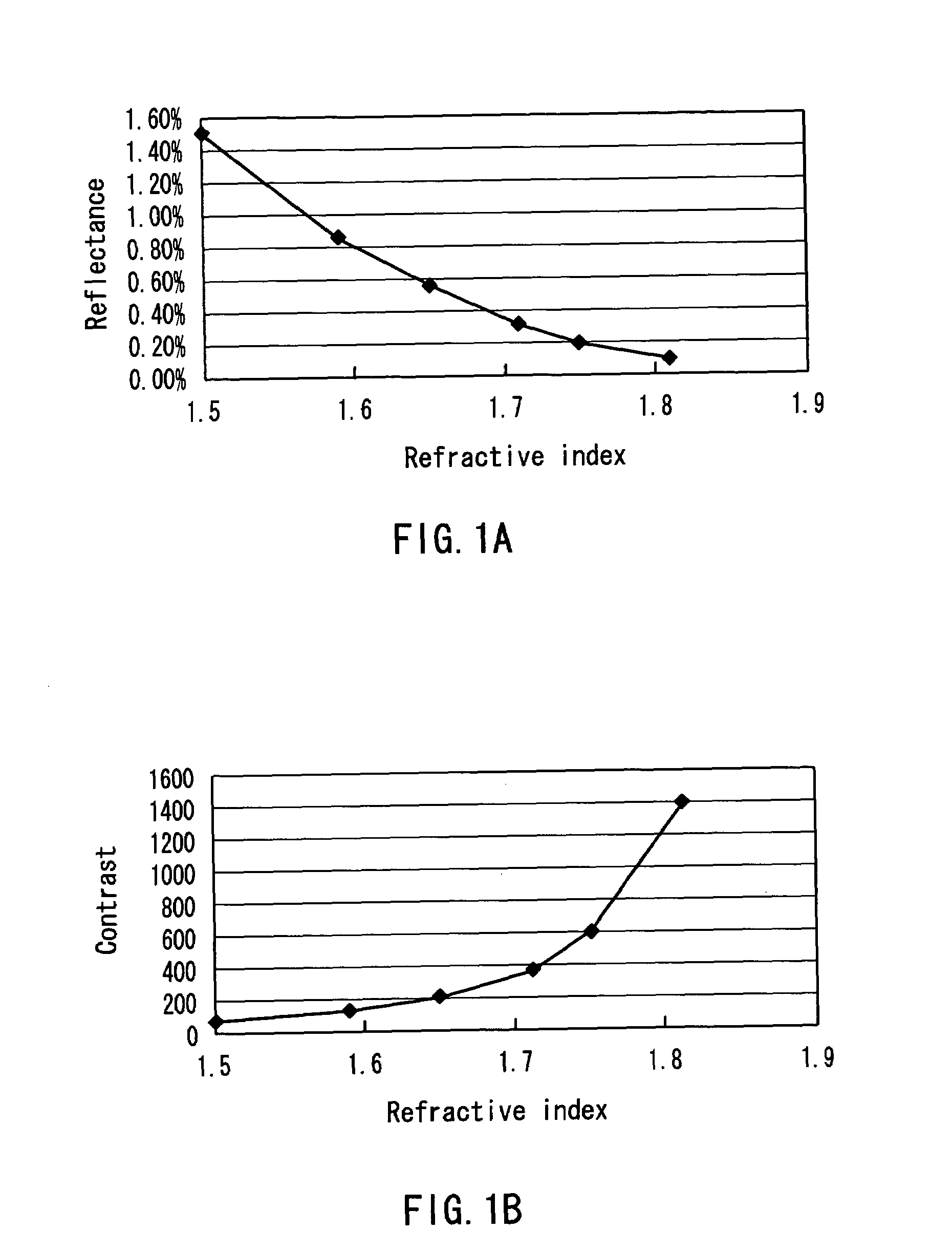
ActiveUS7173766B2Back focal lengthAberration suppressionProjectorsDiffraction gratingsOphthalmologyRefractive index
The present invention provides a zoom lens that suppresses the generation of unnecessary light and is suitable for a projection lens. The zoom lens is used as a projection lens of a projector in which a prism is located between the projection lens and a spatial optical modulating element B. A lens closest to the spatial optical modulating element B is a meniscus positive lens whose convex surface faces a screen. A refractive index of the meniscus positive lens is 1.75 or more.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
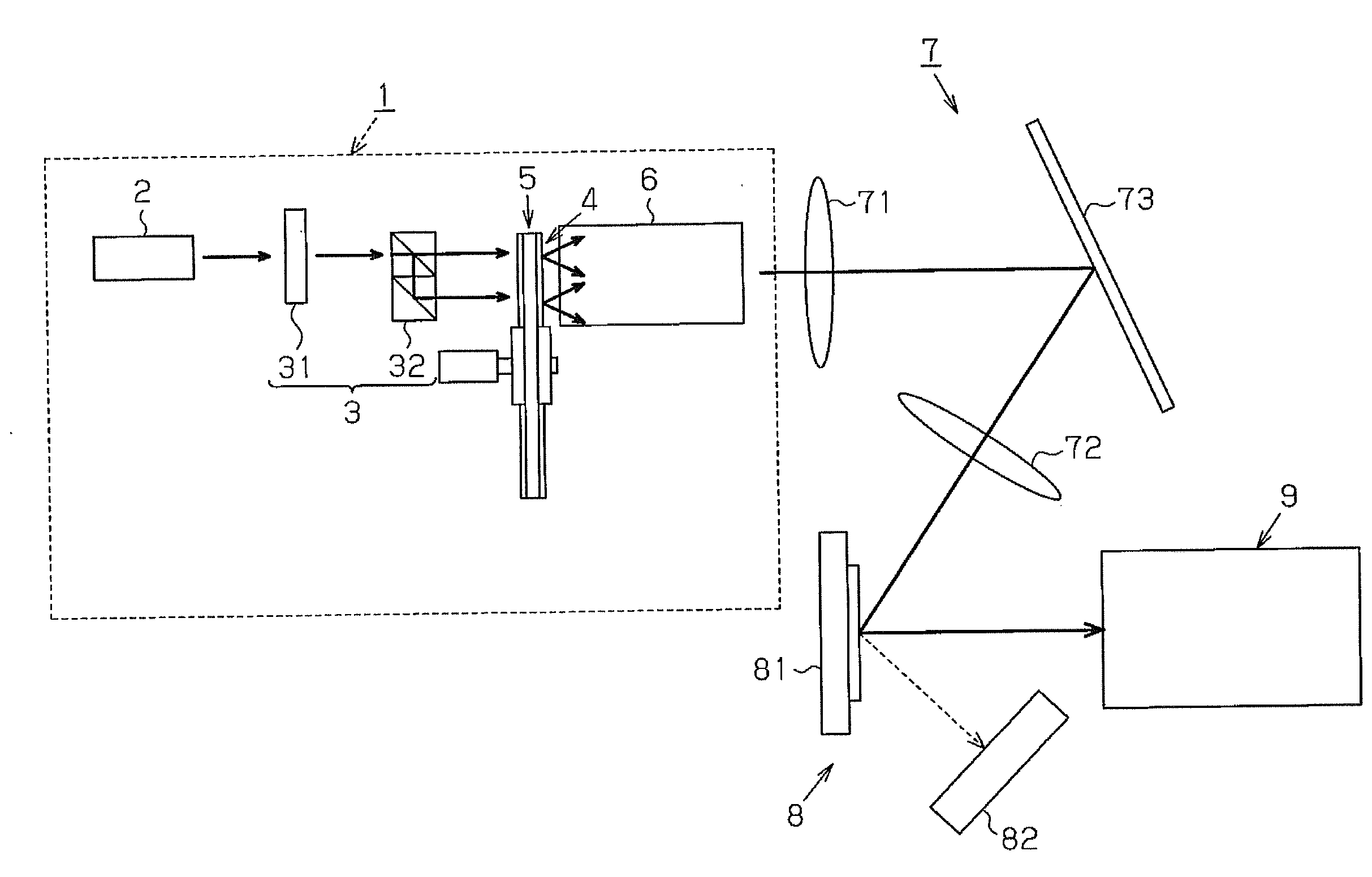
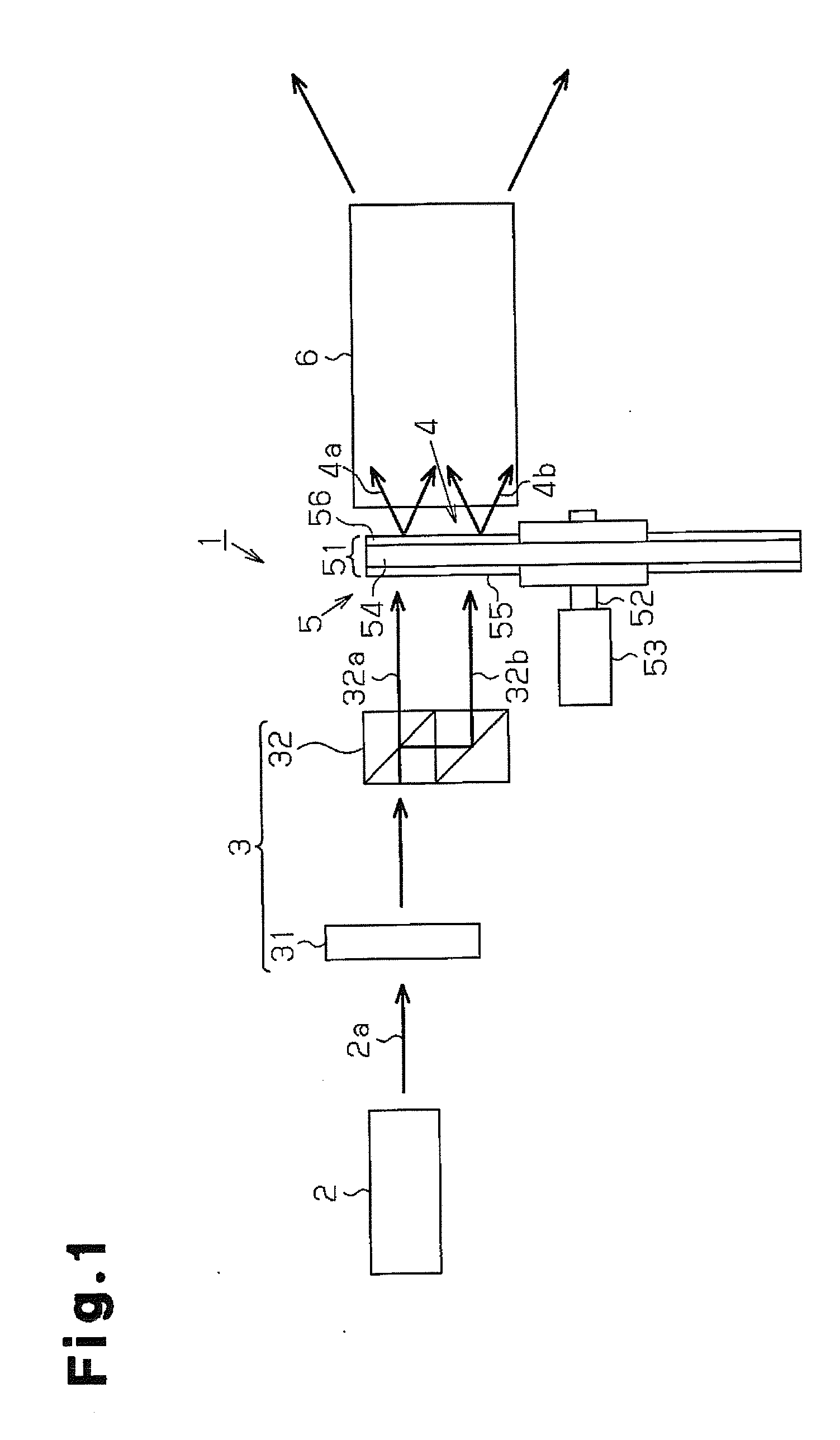
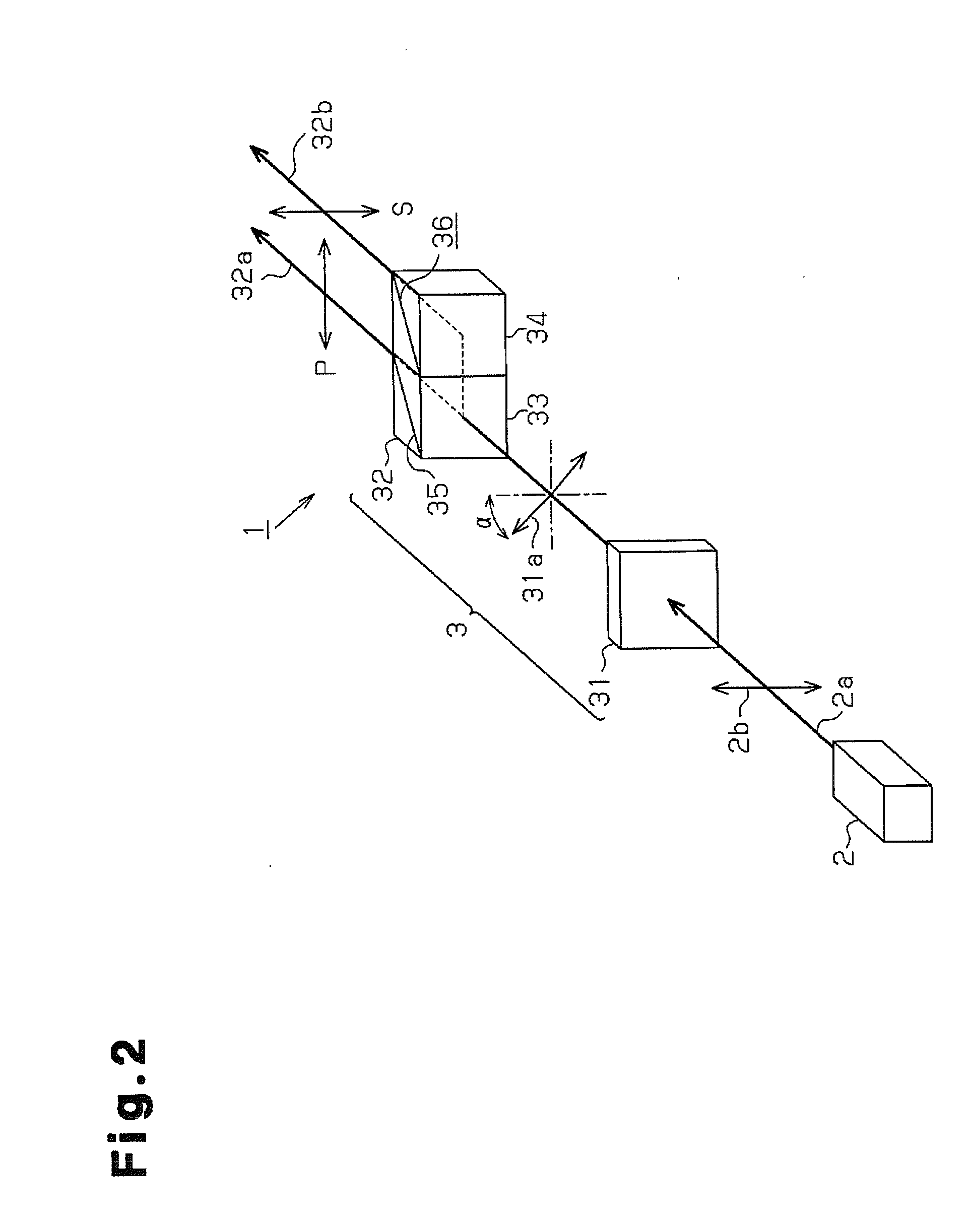
Illumination device and video projector
InactiveUS20120133846A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using projection devicesLight equipmentBeam splitting
An illumination device includes a light source, which emits light polarized in a single direction, and a beam splitting unit, which splits the polarized light into beams of polarized light at a given ratio. A switching unit switches light converters to convert the polarized light, which is split into a plurality of beams, into beams of colored light. The beams of colored light are combined to change the balance of color purity and light amount of the polarized light.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com