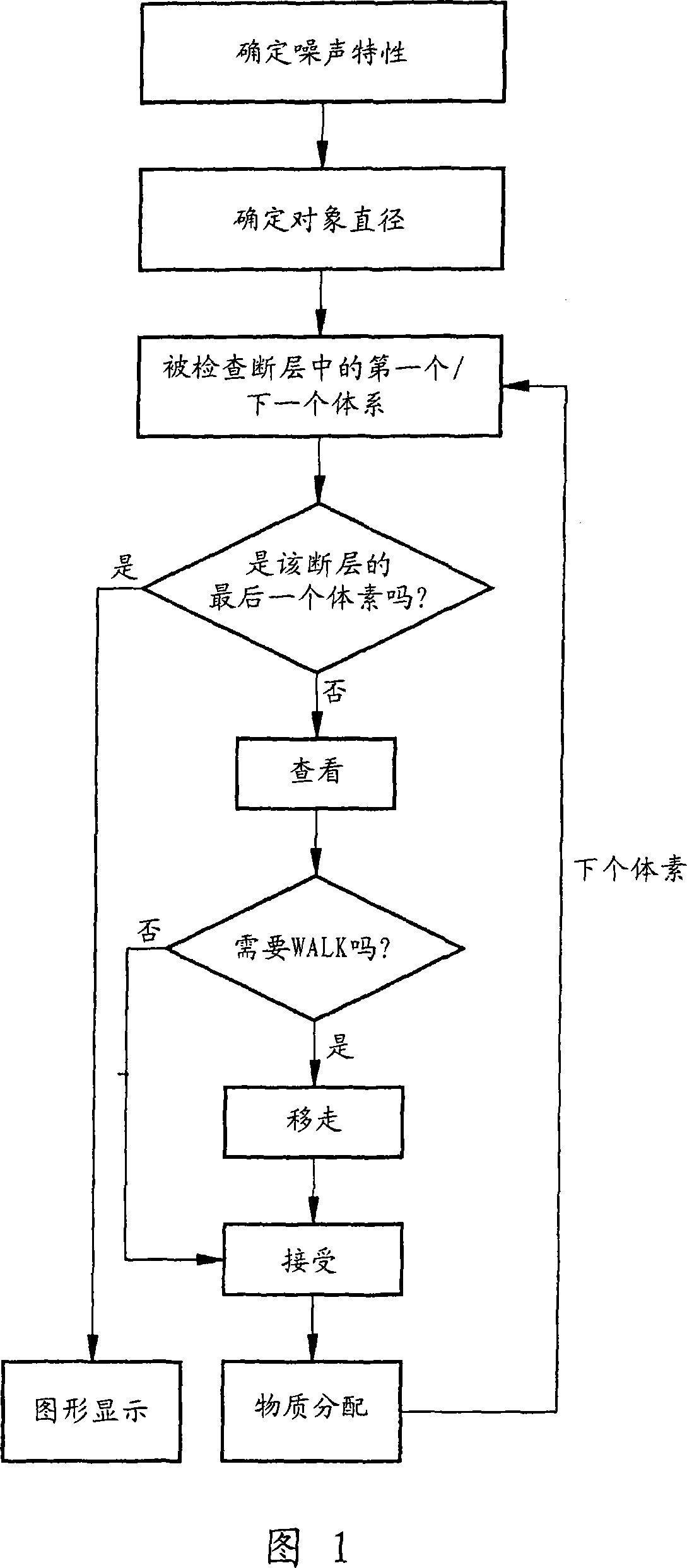
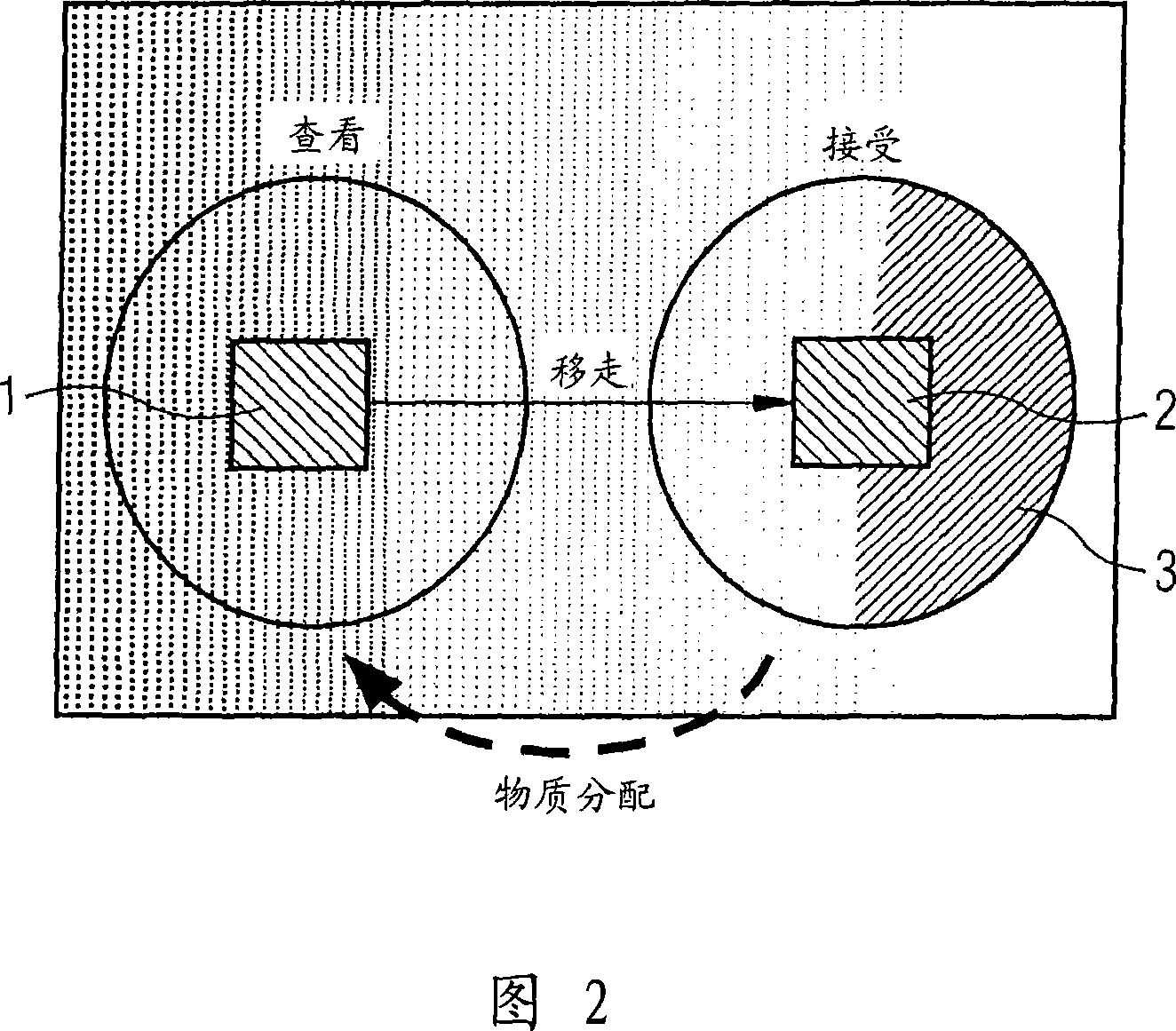
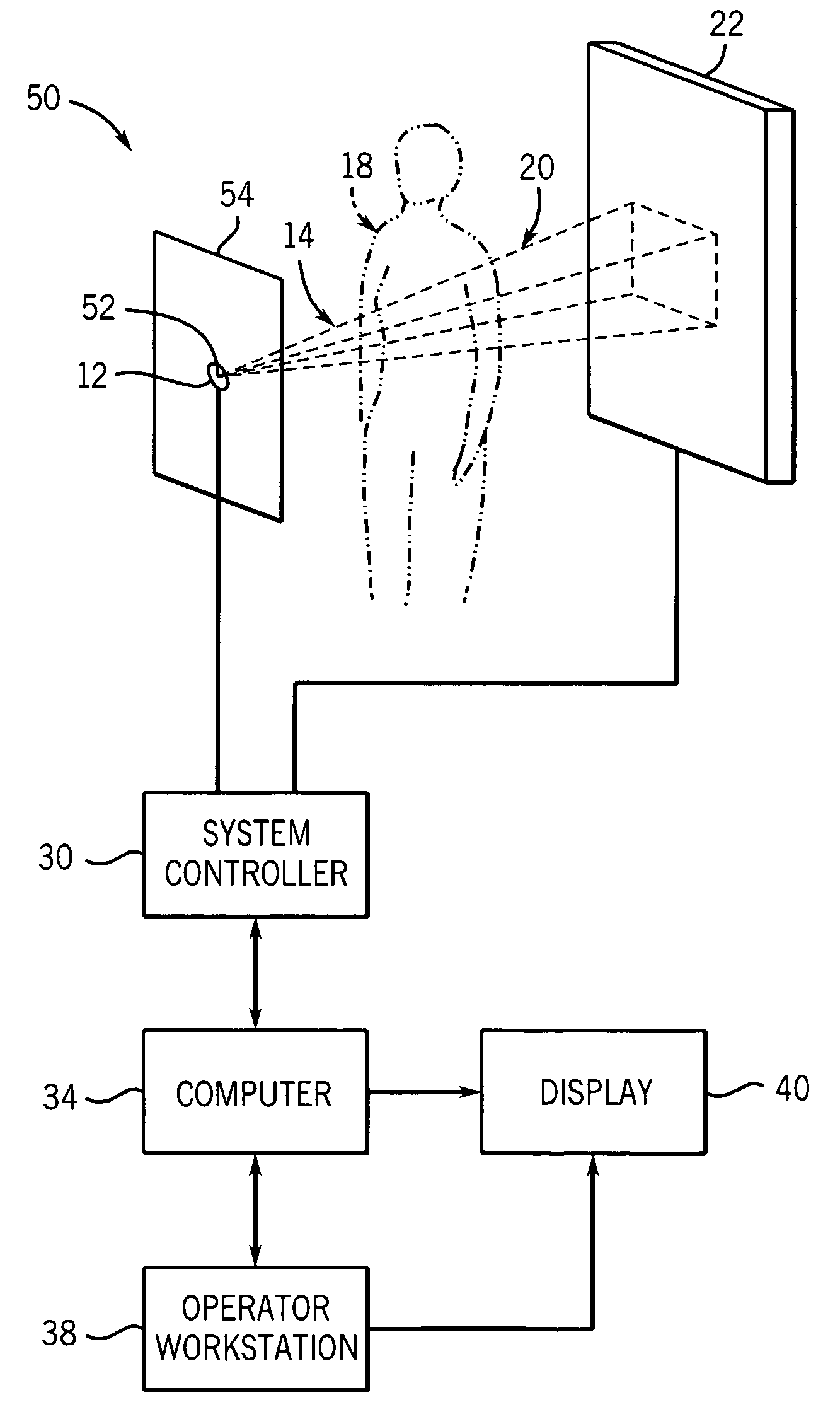
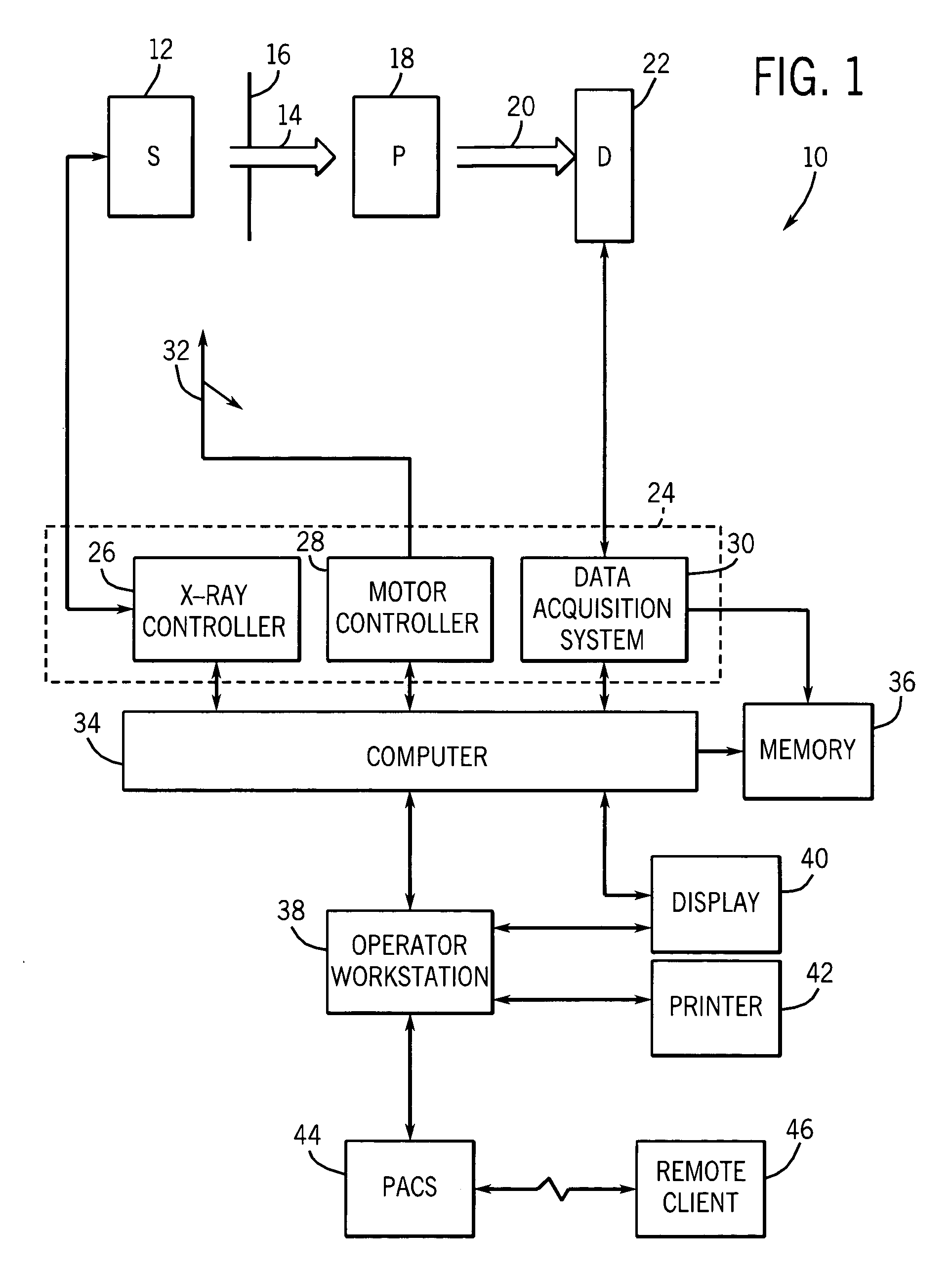
Patents
Literature
156 results about "X ray attenuation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The attenuation theory is valid for X-rays and gamma rays as well. It turns out that higher energy photons (hard X-rays) travel through tissue more easily than low-energy photons (i.e. the higher energy photons are less likely to interact with matter). Much of this effect is related to the photoelectric effect.
Method of estimating skeletal status
InactiveUS6411729B1Fast background correction of image dataReducing or preferably removing the low frequency informationImage enhancementImage analysisStatistical analysisState parameter
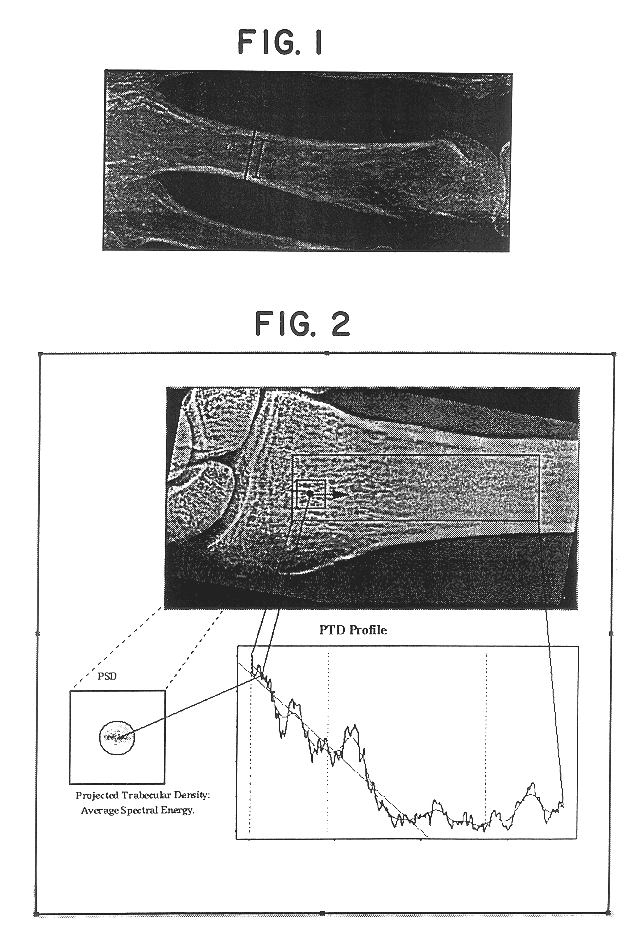
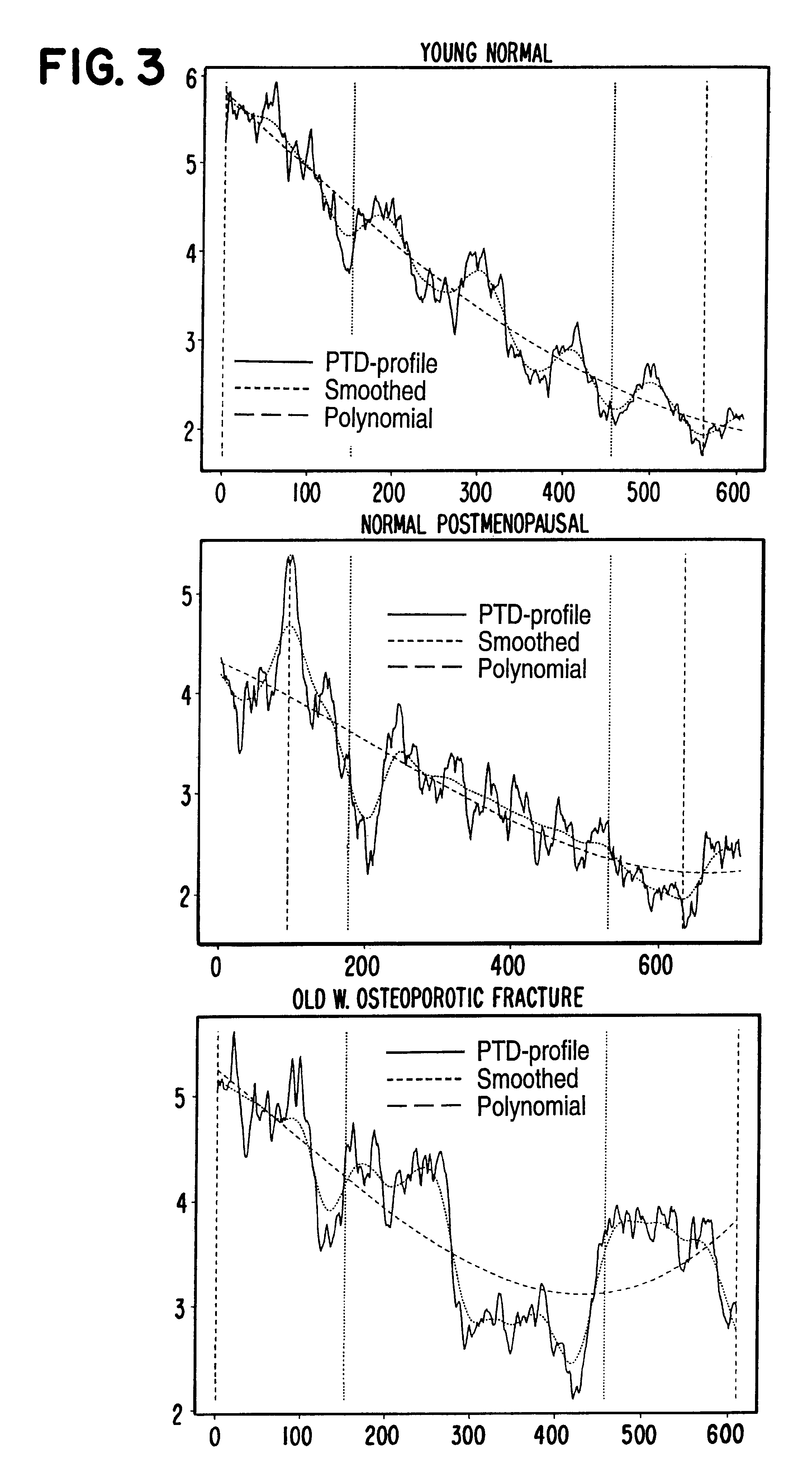
A method for estimating the skeletal status or bone quality of a vertebrate on the basis of two-dimensional image data comprising information relating to the trabecular structure of at least a part of a bone of the vertebrate, the image data being data obtained by exposing at least the part of the bone to electromagnetic radiation, such as X-rays, the method comprising subjecting the image data to a statistical analysis comprising a background correction procedure in which low frequency intensity variations not related to the trabecular structure of the bone are reduced relative to image data related to the trabecular structure of the part of the bone, a feature extraction procedure comprising (a) determining values reflecting the projected trabecular density in the image data, caused by the X-ray attenuating properties of cancellous bone in the part of the bone, for each of a number of locations or areas in the image data, (b) deriving one or more features from the variation of the determined PTD-values, preferably in the longitudinal direction of the bone, and an estimation procedure in which the skeletal status of the vertebrate is estimated on the basis of the one or more derived features and optionally other features related to the bone of the vertebrate and a predetermined relationship between the features and reference skeletal status parameters. Preferably, a profile describing the projected trabecullar density as a function of the distance along a line substantially at the center of the bone is determined, and information relating to skeletal status is derived from variations, fluctuations or other features of the profile.
Owner:TORSANA OSTEOPOROSIS DIAGNOSTICS
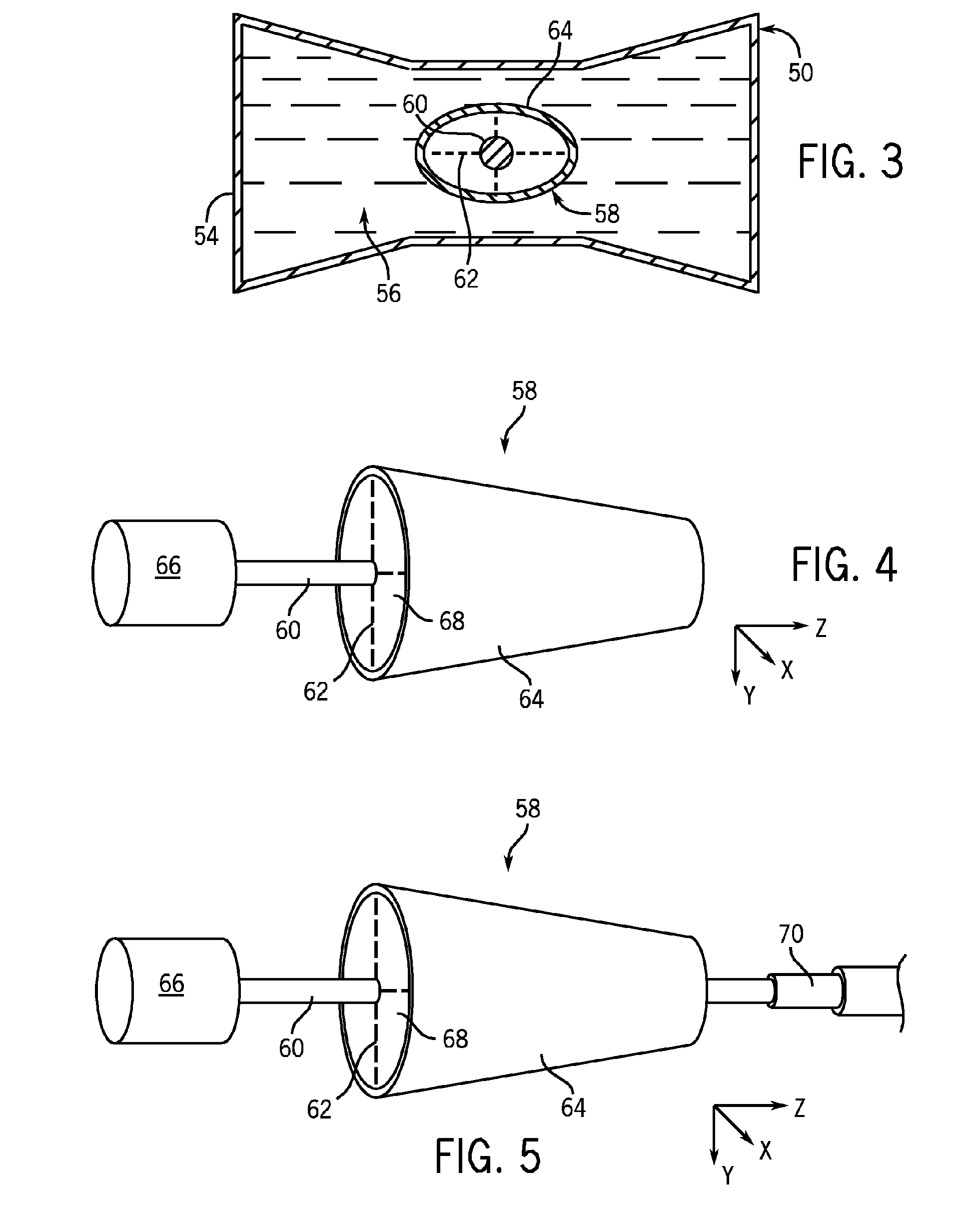
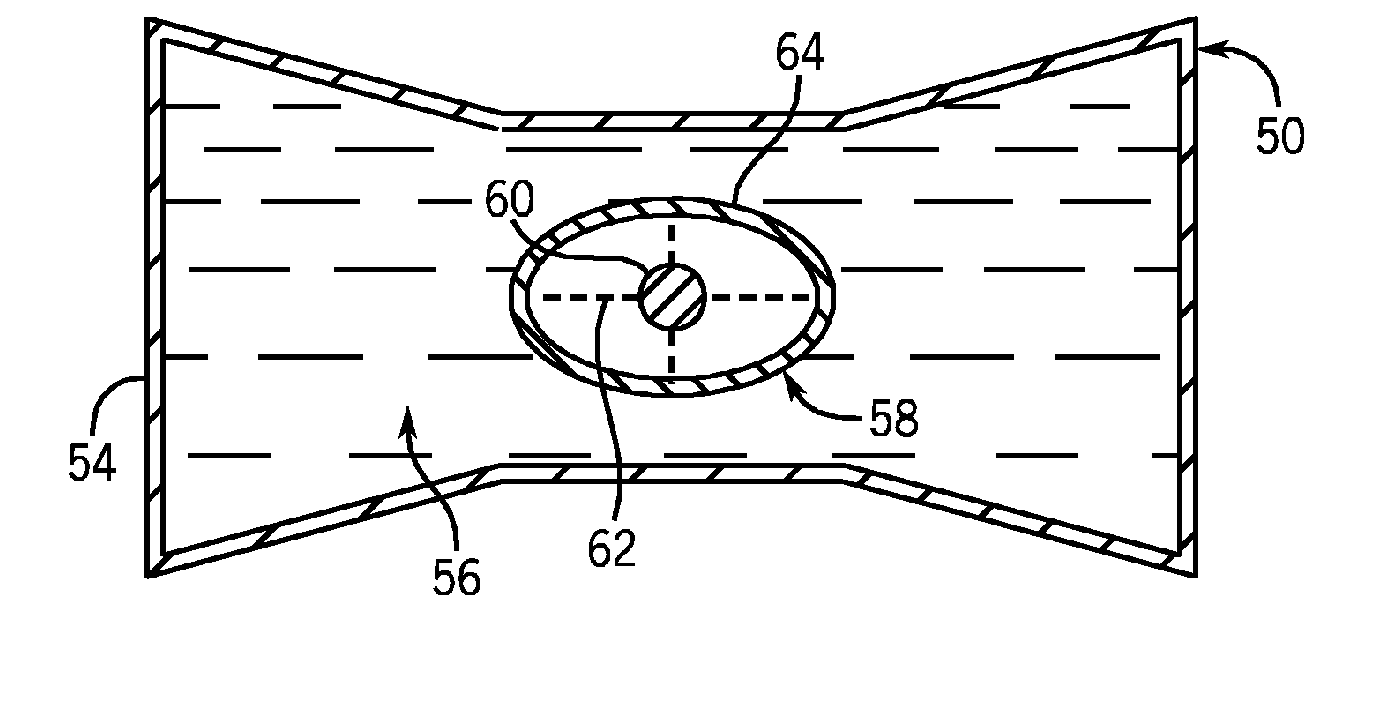
X-ray filter having dynamically displaceable x-ray attenuating fluid
InactiveUS7308073B2High rateLower levelMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray filter
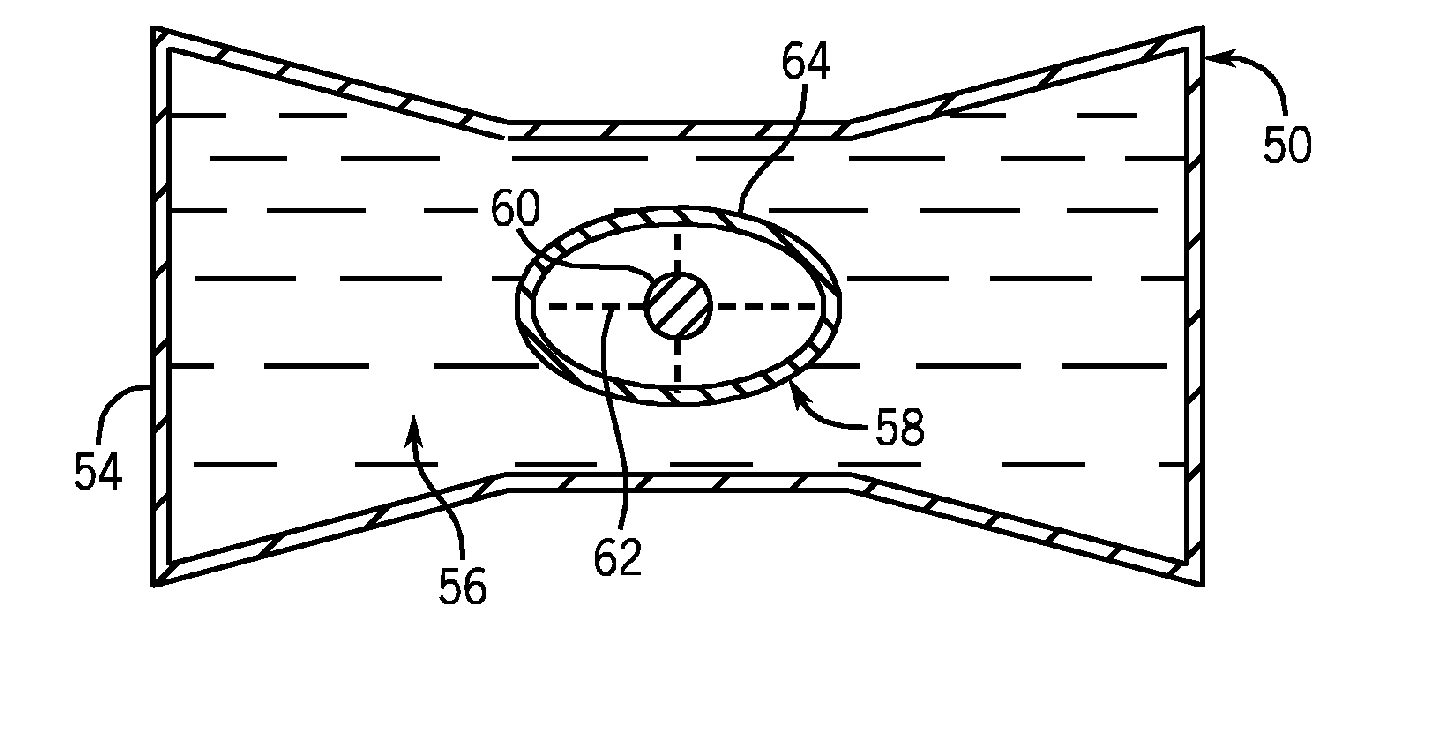
A bowtie filter is constructed to have a fluidic envelope filled with attenuating fluid and a displacement insert that can present various x-ray attenuation profiles during a scan. The insert is designed to displace the attenuating fluid to achieve a denied attenuating or filtering profile. The insert can be rotated, twisted, moved, and otherwise contorted within the fluidic envelope as needed during the course of a scan. As the angle, position and shape of the zombie is changed, the x-ray profile of the filter changes. The insert may have a default shape when at rest, but can have its shape changed when external forces are placed thereon. As x-ray filtering needs change during the course of the scan, the insert can be compressed, stretched, and / or contorted to achieve additional filtering profiles.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Real-time feedback for preventing high dose c-arch geometry positions
ActiveUS20140307855A1Reduce total usageSmall impactLocal control/monitoringRadiation safety meansSoft x rayImaging quality
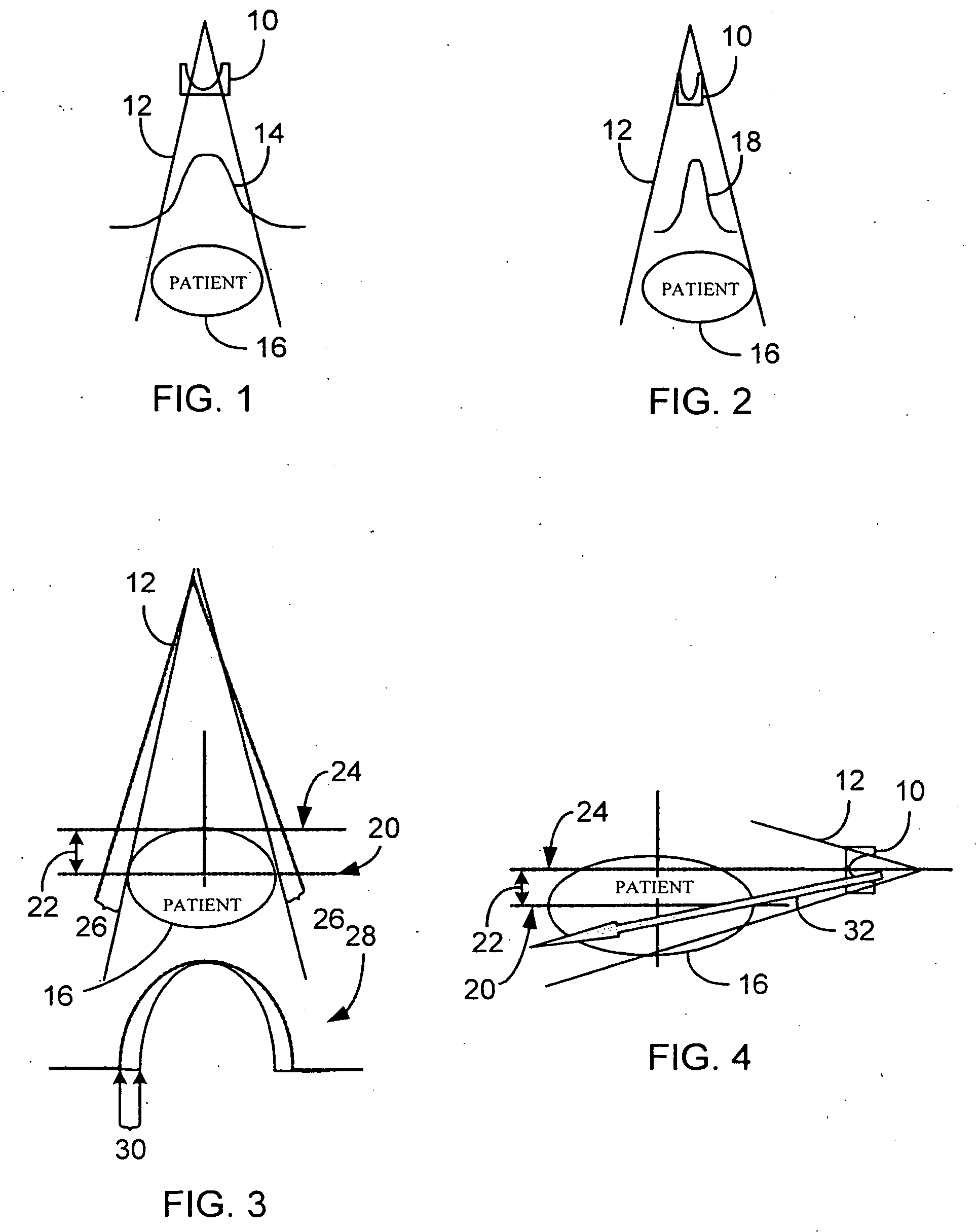
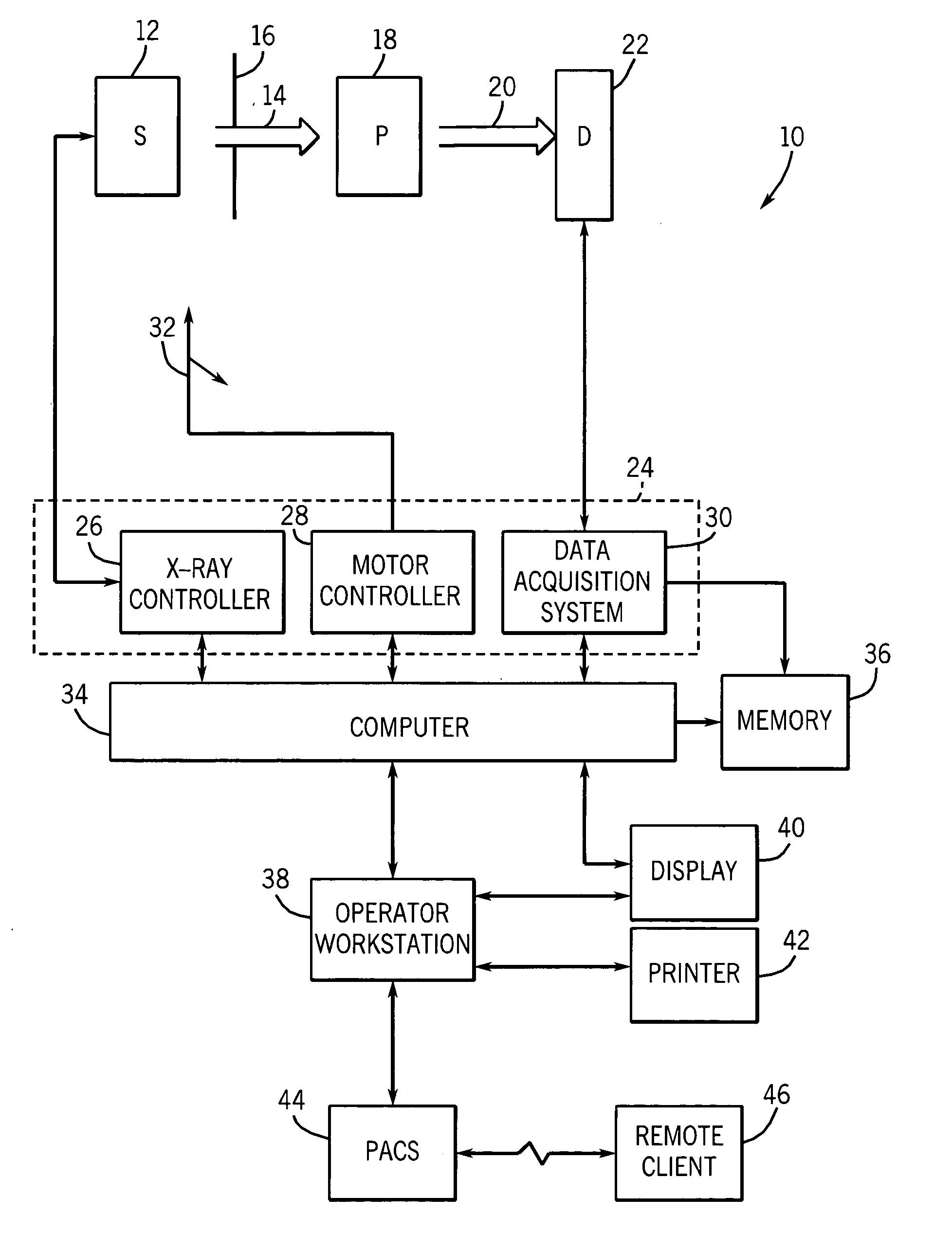
The present invention relates to an apparatus for aiding operation of an interventional x-ray imager during image acquisition, to a method of aiding operation of an x-ray imager, to an interventional x-ray imager, to a computer program element and to a computer readable medium. The X-ray imager is capable of varying X-ray dosages depending on differences in X-ray attenuation levels across an object of interest to be imaged and is capable of assuming any one of a plurality of imaging geometry positions when acquiring an image. An indication, visual, acoustic or haptic, to the operator of an X-ray imager is provided on the incurred change in X-ray dosage when changing from a current projection view to an updated projection view, provided that a given constant image quality is to be maintained throughout the different views.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
System and method of x-ray flux management control
ActiveUS7068750B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingUltrasound attenuationX-ray
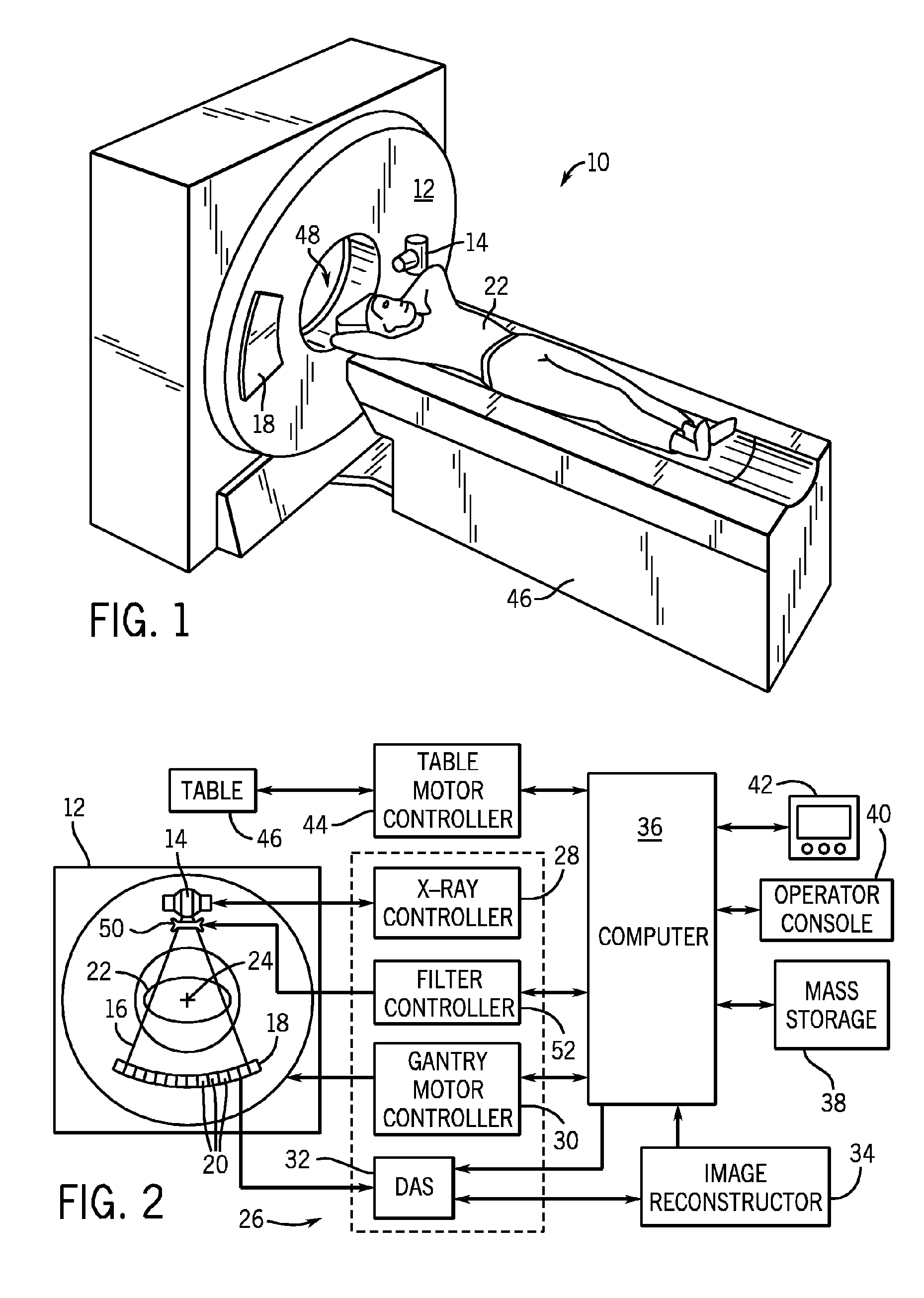
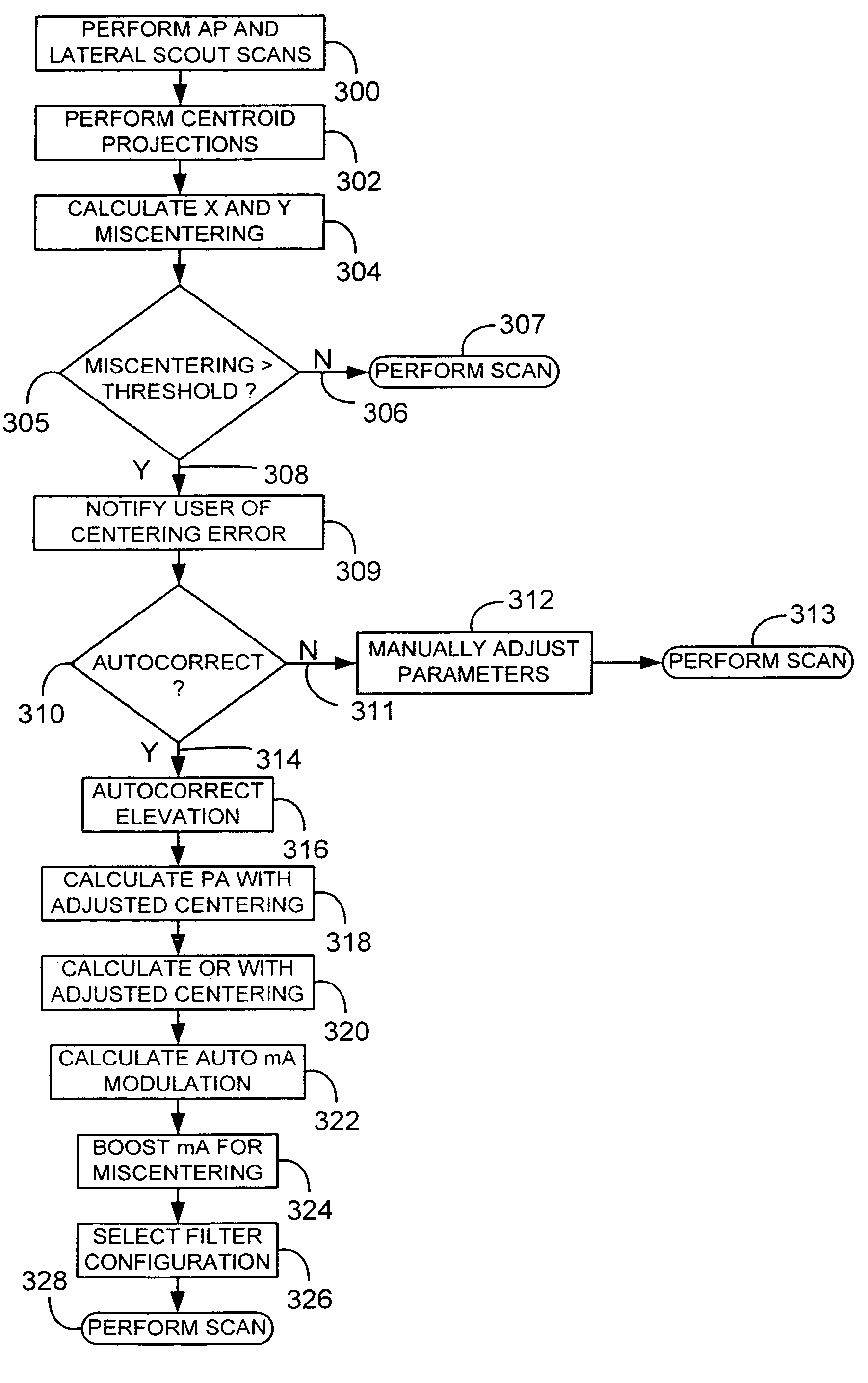
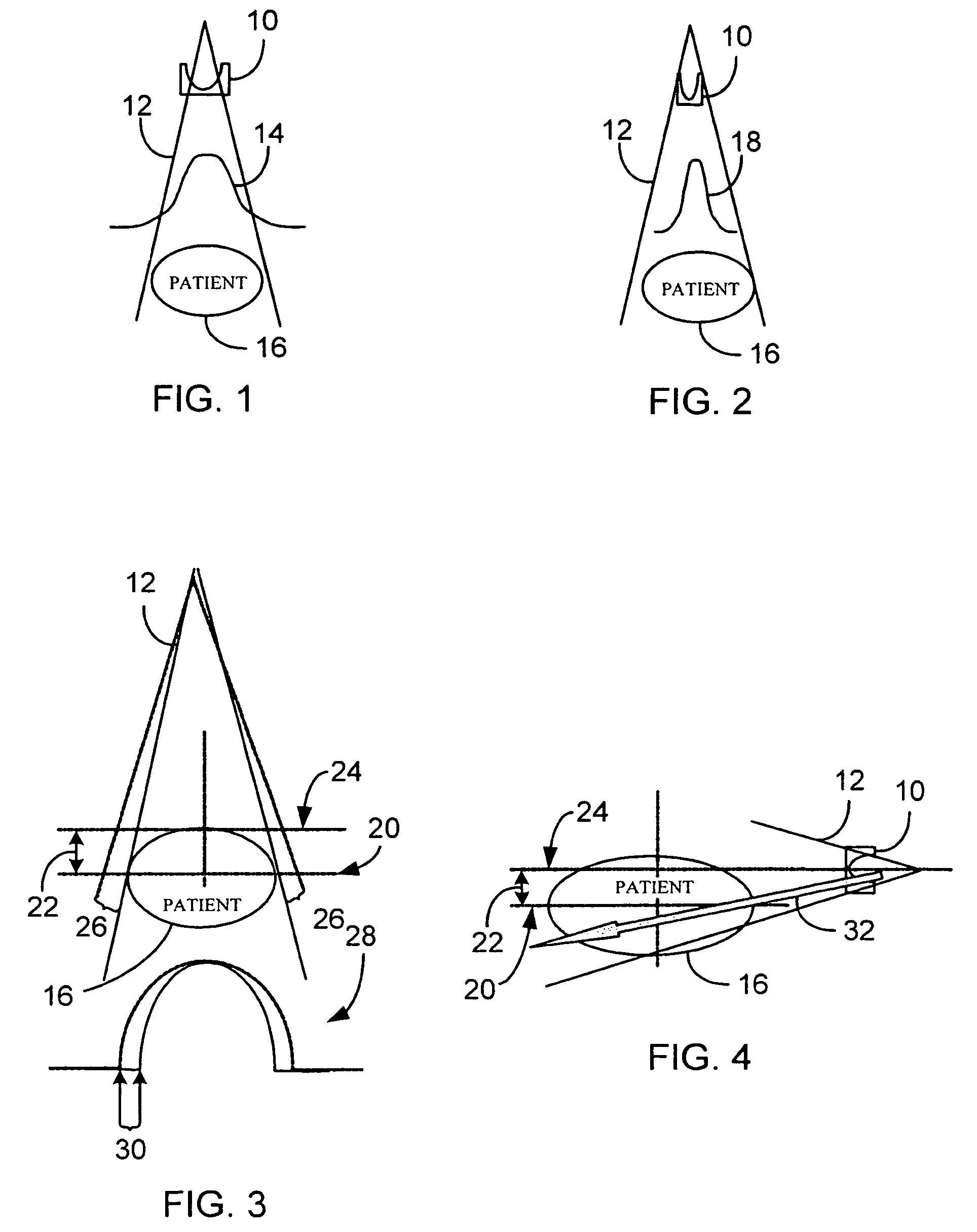
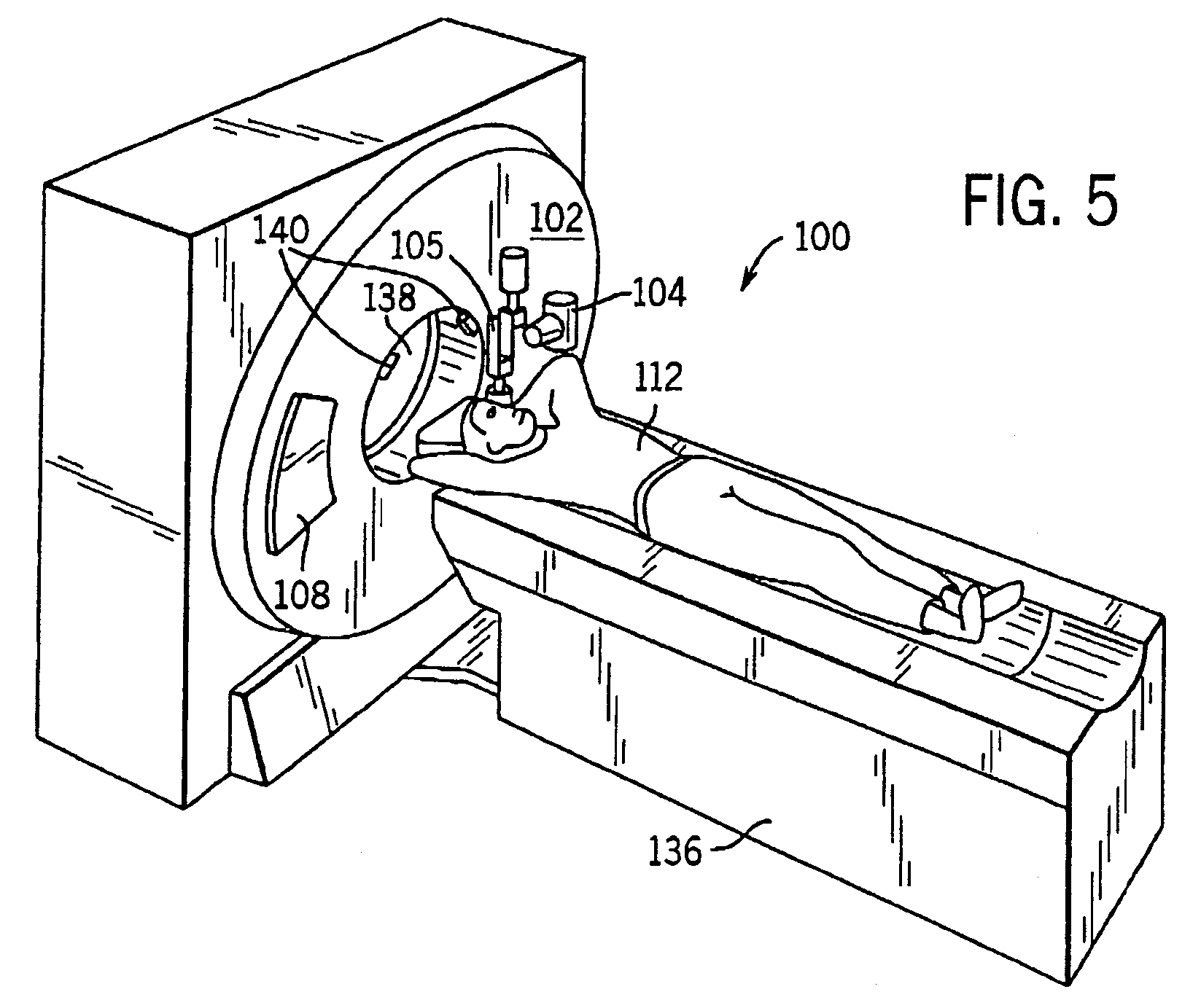
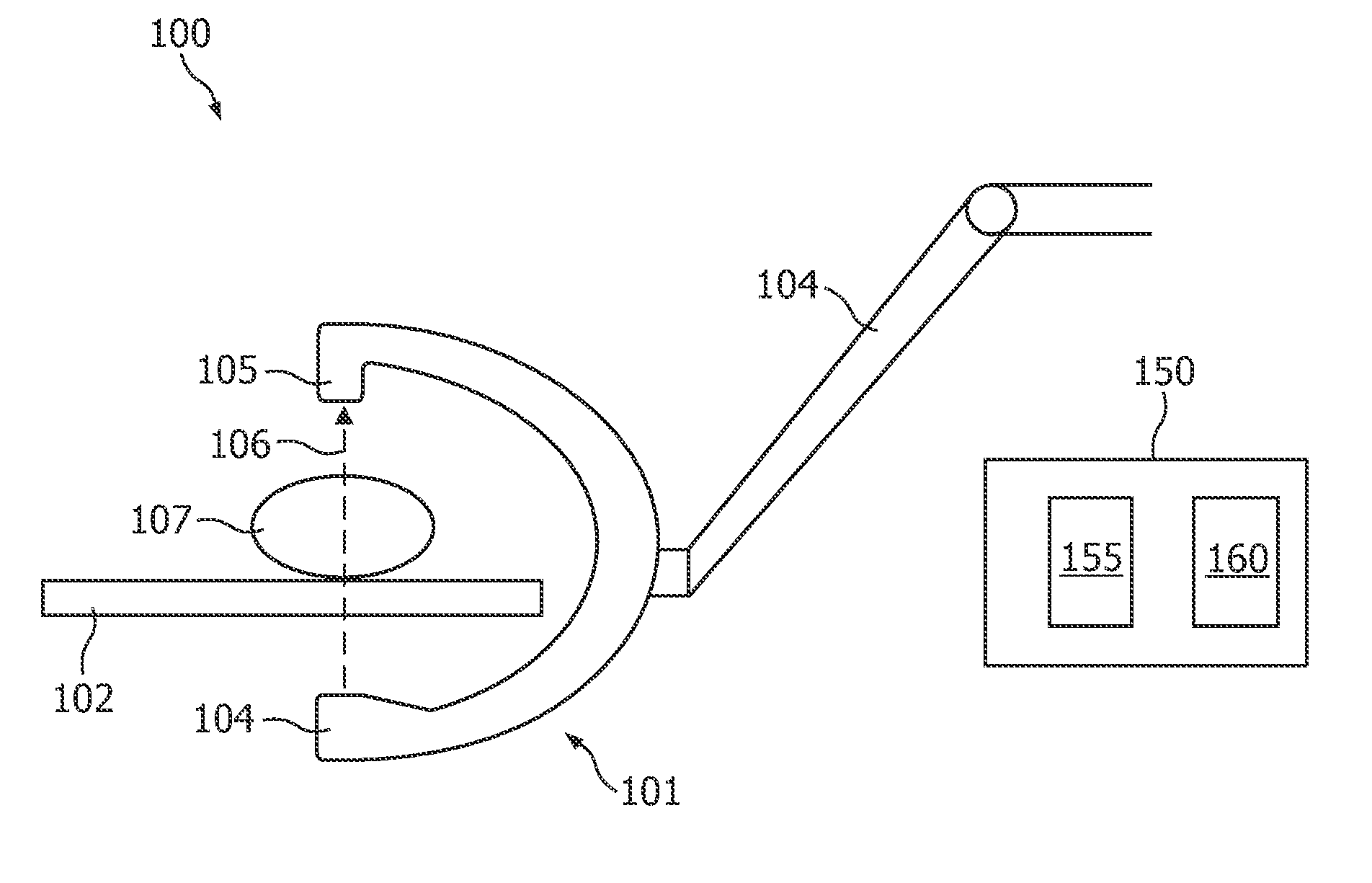
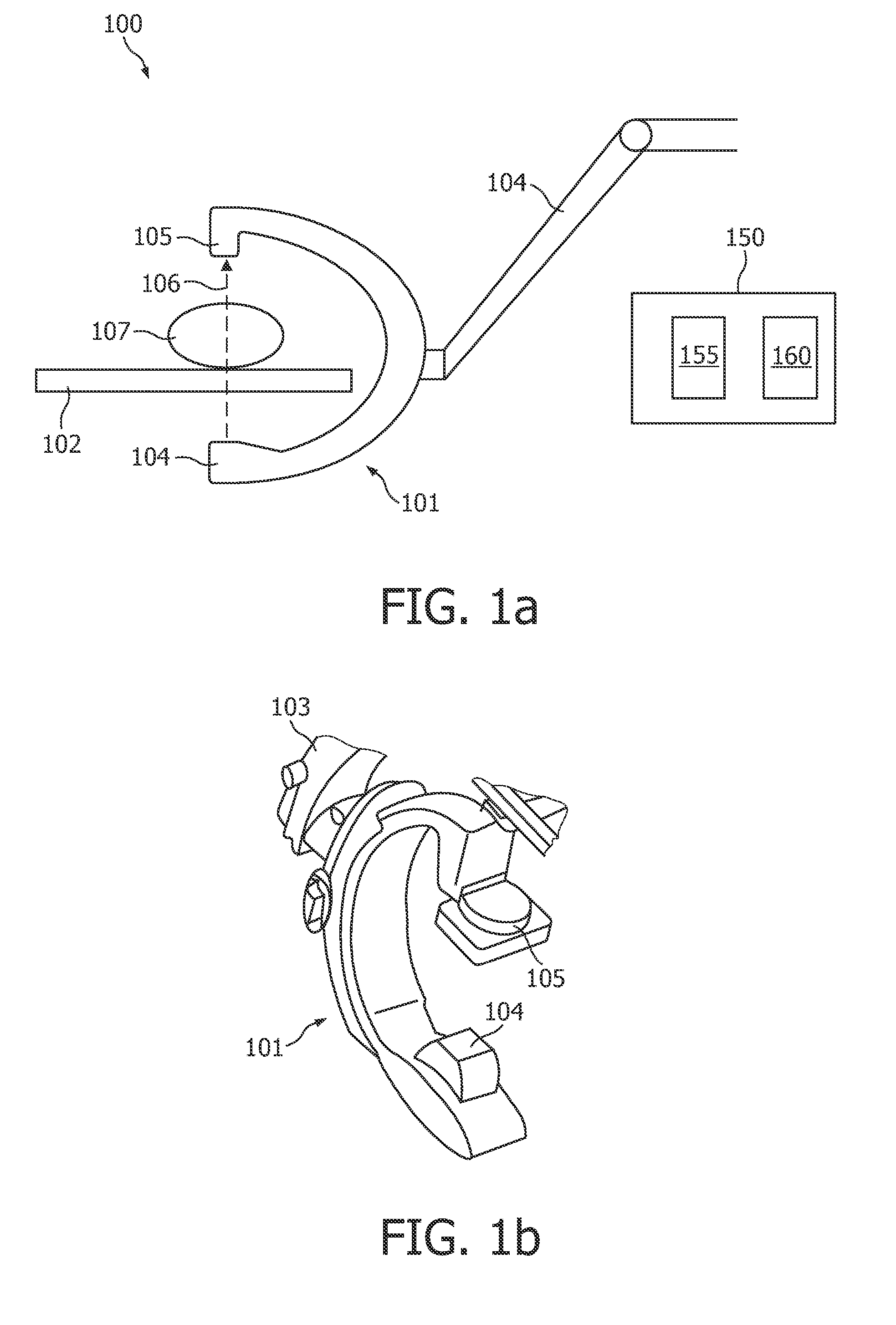
A system and method of diagnostic imaging is provided that includes determining a position of a subject in a scanning bay and tailoring x-ray attenuation such that the specific position of the subject is taken into consideration. The present invention automatically selects a proper attenuation filter configuration, corrects patient centering, and corrects noise prediction errors, thereby increasing dose efficiency and tube output.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
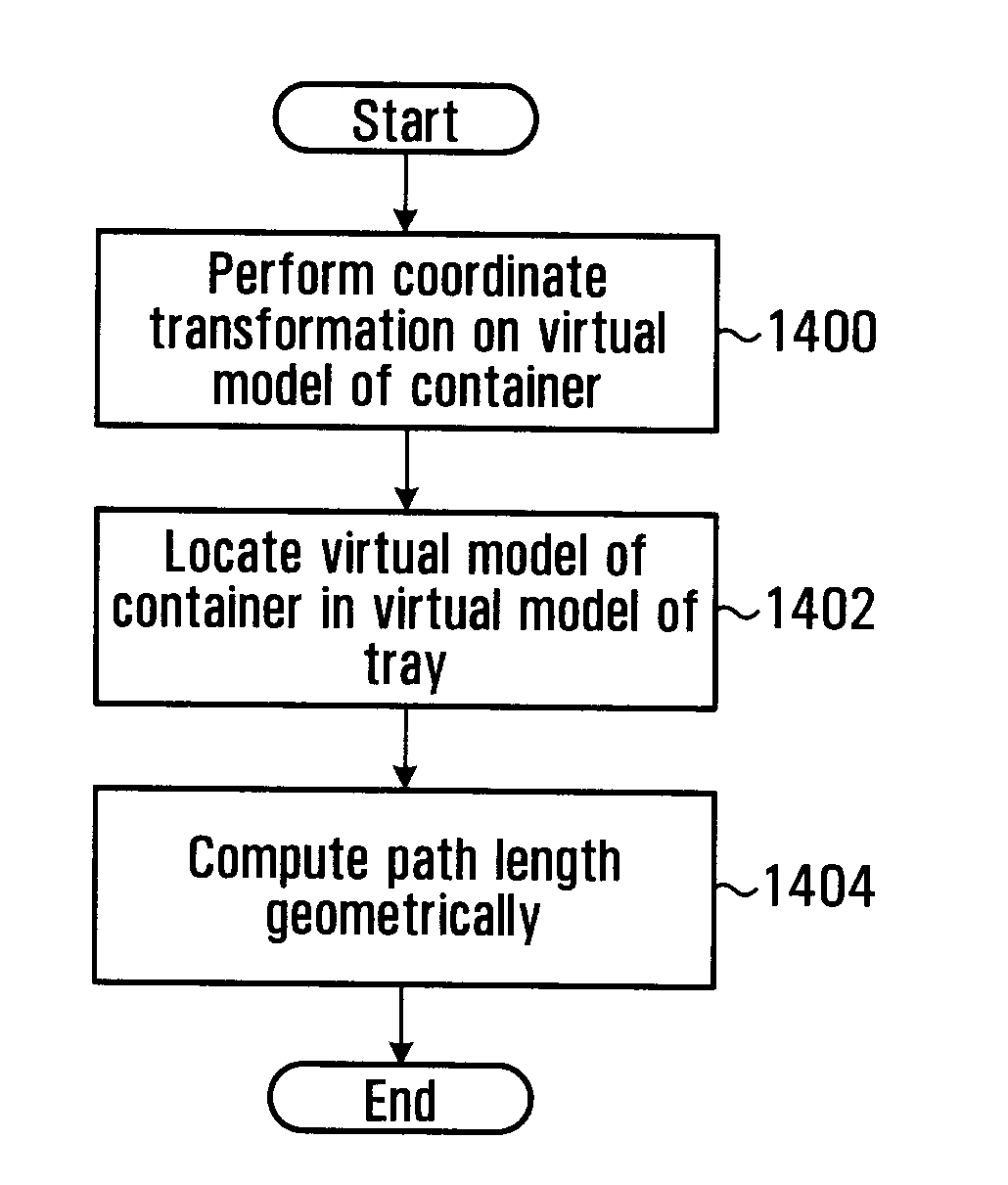
Spatial characterization of a structure located within an object by identifying 2d representations of the structure within section planes
InactiveUS20100099979A1Clear visualizationPrecise quantitative comparisonImage enhancementImage analysisSection planeSonification
It is described a virtual pullback as a visualization and quantification tool that allows an interventional cardiologist to easily assess stent expansion. The virtual pullback visualizes the stent and / or the vessel lumen similar to an Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) pullback. The virtual pullback is performed in volumetric data along a reference line. The volumetric data can be a reconstruction of rotational 2D X-ray attenuation data. Planes perpendicular to the reference line are visualized as the position along the reference line changes. This view is for interventional cardiologists a very familiar view as they resemble IVUS data and may show a section plane through a vessel lumen or a stent. In these perpendicular section planes automatic measurements, such as minimum and maximum diameter, and cross sectional area of the stent can be calculated and displayed. Combining these 2D measurements allows also volumetric measurements to be calculated and displayed.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method of x-ray flux management control
ActiveUS20050089135A1Optimize radiation exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingUltrasound attenuationX-ray
A system and method of diagnostic imaging is provided that includes determining a position of a subject in a scanning bay and tailoring x-ray attenuation such that the specific position of the subject is taken into consideration. The present invention automatically selects a proper attenuation filter configuration, corrects patient centering, and corrects noise prediction errors, thereby increasing dose efficiency and tube output.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Time resolved computed tomography angiography
InactiveUS6983182B2Reducing invasivenessLess discomfortCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsData setImage resolution
A contrast enhanced dynamic study of a subject is performed with a CT system. A series of undersampled image data sets are acquired during the study with successive data sets acquired at interleaved projection angles. More fully sampled image data sets are formed by transforming the x-ray attenuation projection data to k-space and then sharing peripheral k-space data between undersampled k-space data sets. Artifacts due to undersampling are thus reduced without significantly affecting the time resolution of a series of reconstructed images.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
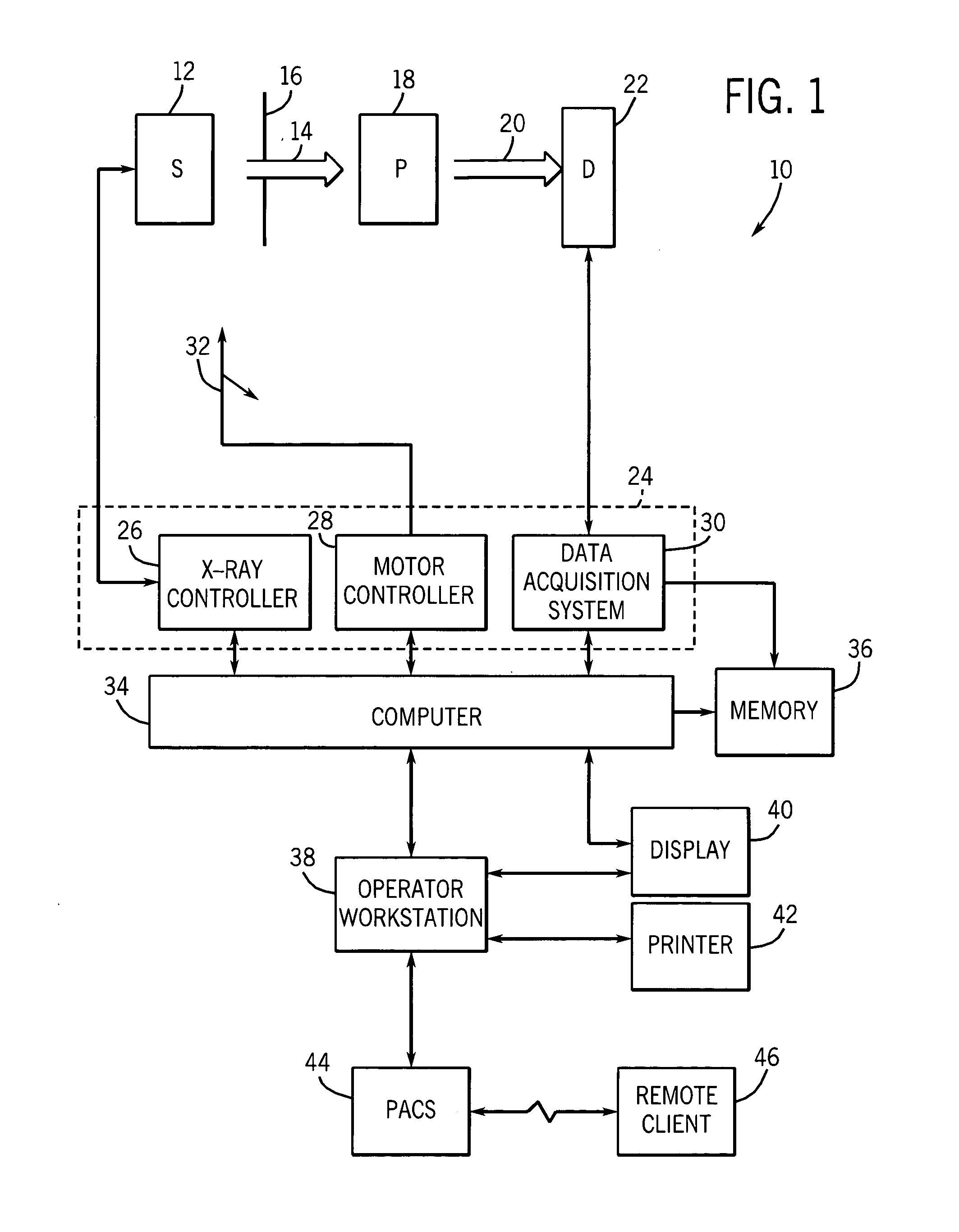
Method and arrangement for medical X-ray imaging and reconstruction from sparse data
InactiveUS7269241B2Utilize priori informationEfficient use ofReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltrasound attenuationSoft x ray
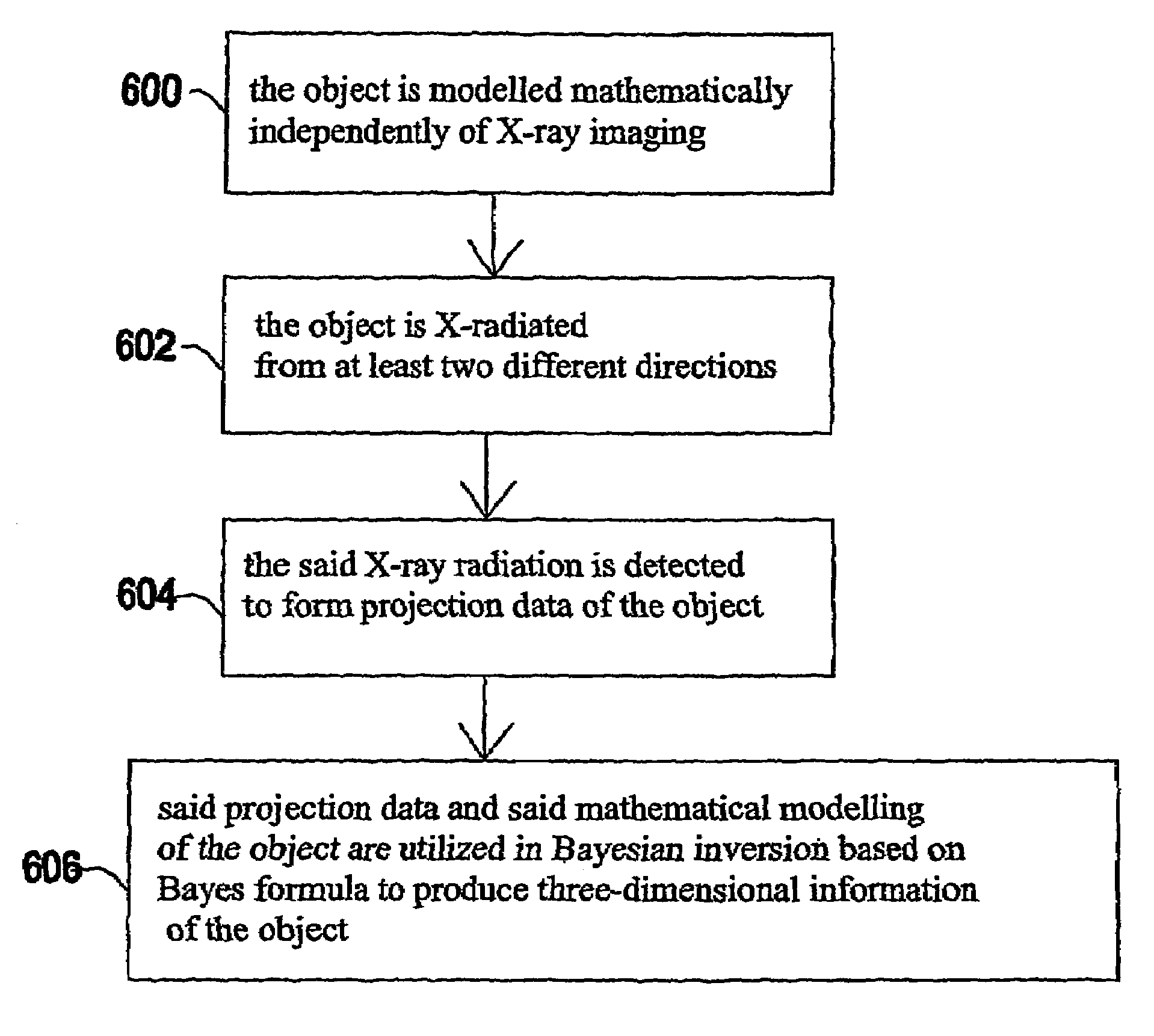
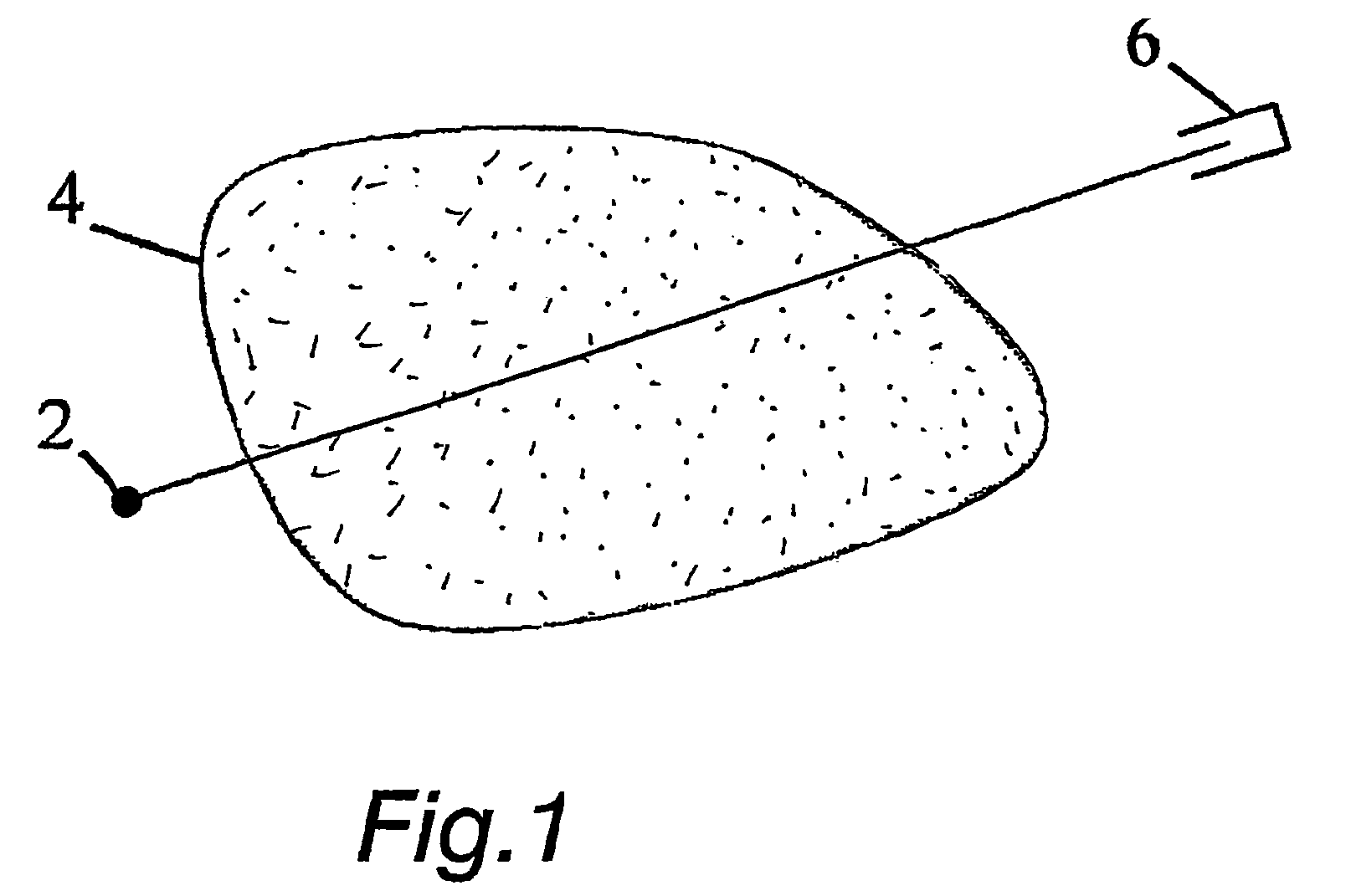
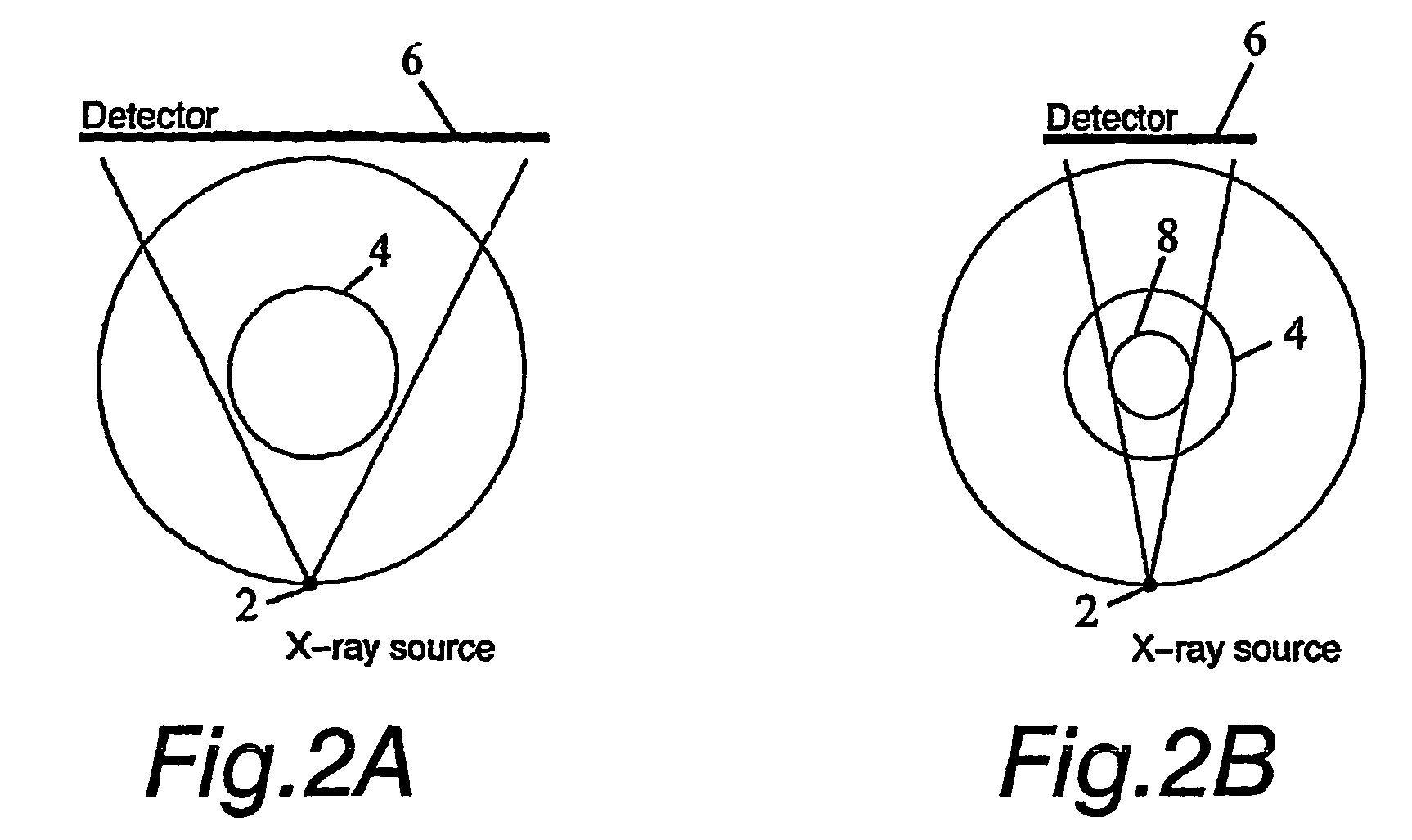
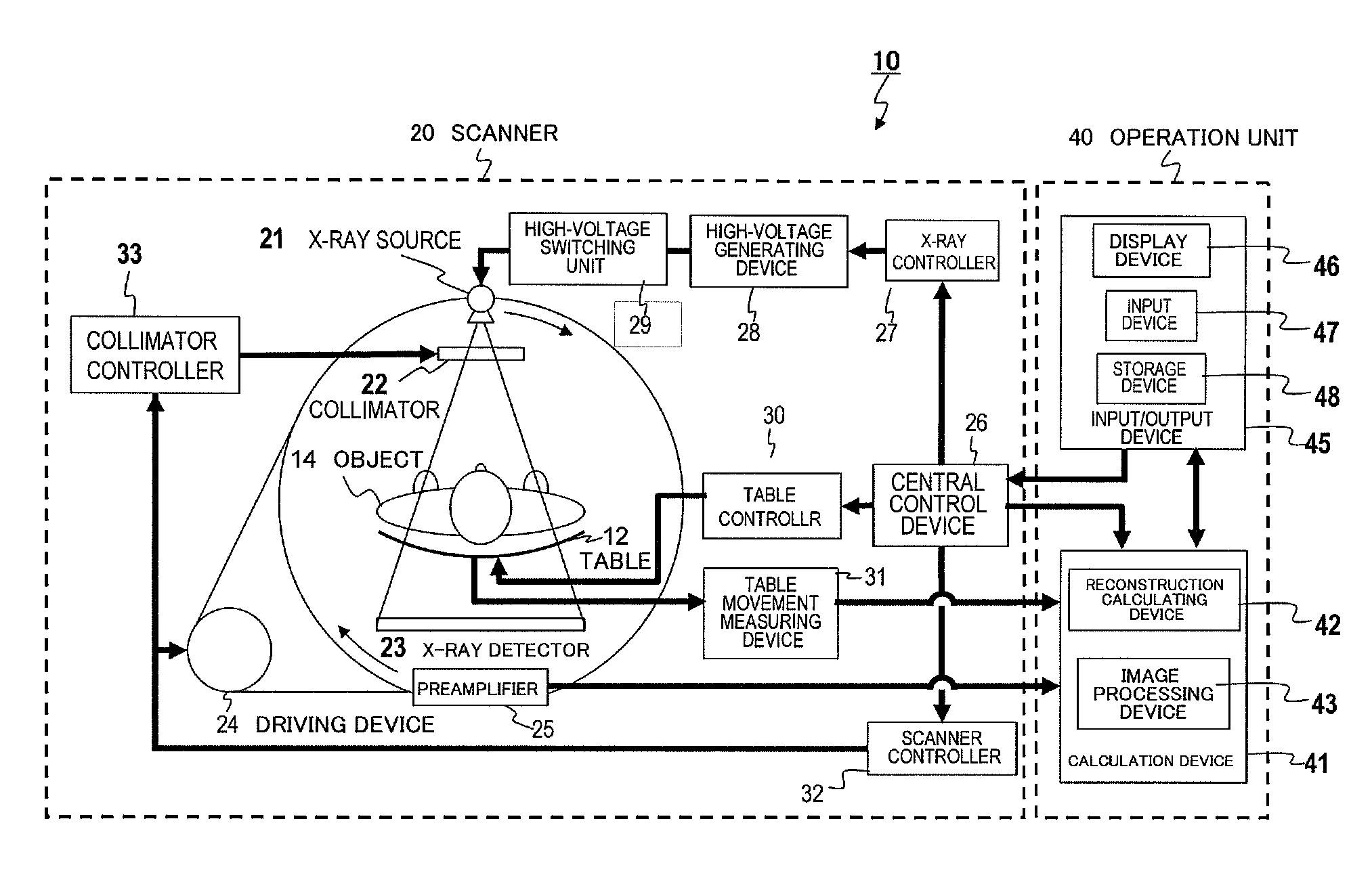
The invention relates to a medical X-ray device 5 arrangement for producing three-dimensional information of an object 4 in a medical X-ray imaging medical X-ray device arrangement comprising an X-ray source 2 for X-radiating the object from different directions and a detector 6 for detecting the X-radiation to form projection data of the object 4. The medical X-ray device 5 arrangement comprises:means 15 for modelling the object 4 mathematically independently of X-ray imagingand means 15 for utilizing said projection data and said mathematical modelling of the object in Bayesian inversion based on Bayes' formulap(xm)=ppr(x)p(mx)p(m)to produce three-dimensional information of the object, the prior distribution ppr(x) representing mathematical modelling of the object, the object image vector x, which comprise values of the X-ray attenuation coefficient inside the object, m representing projection data, the likelihood distribution p(m|x) representing the X-radiation attenuation model between the object image vector x and projection data m, p(m) being a normalization constant and the posteriori distribution p(x|m) representing the three-dimensional information of the object 4.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE FINLAND
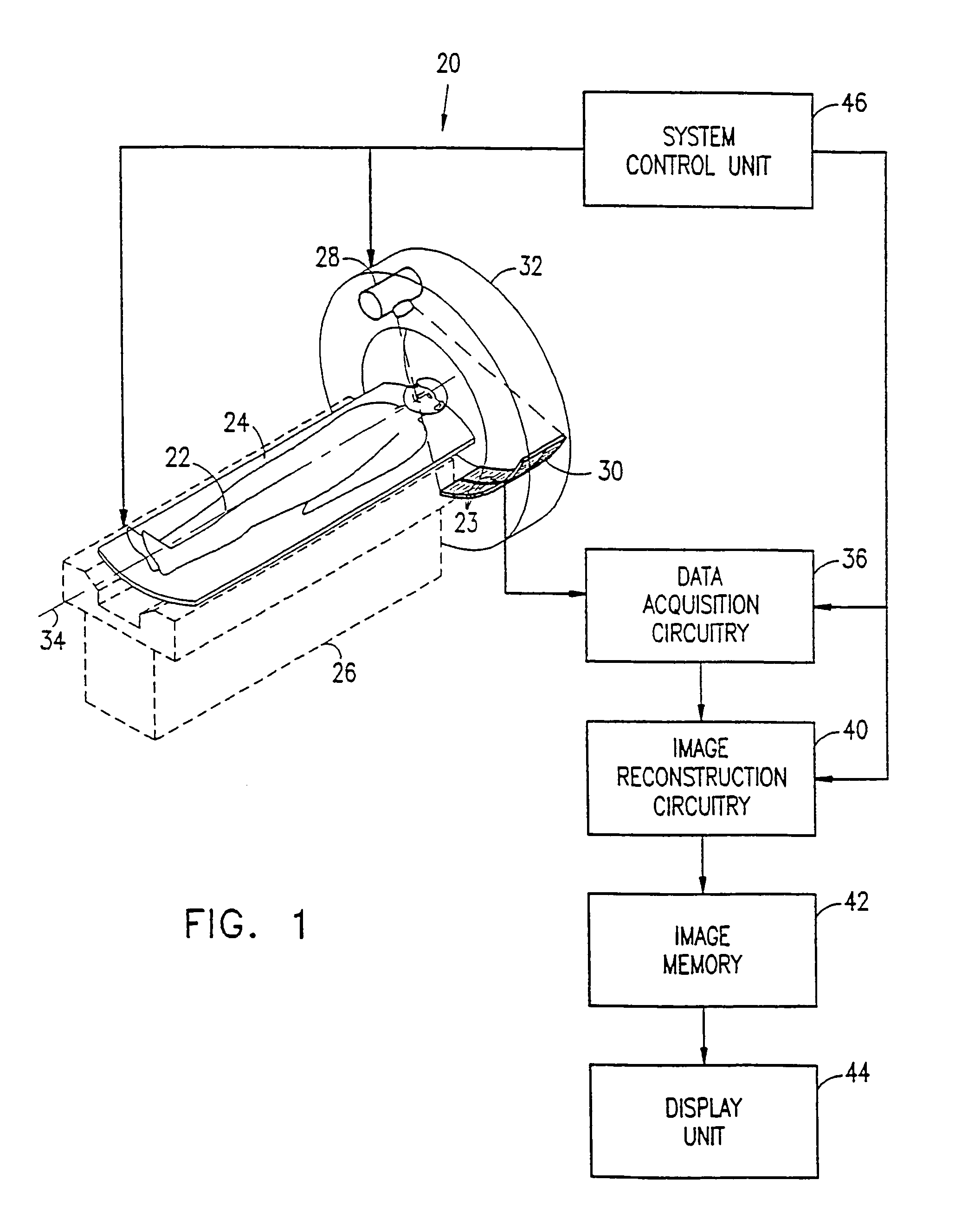
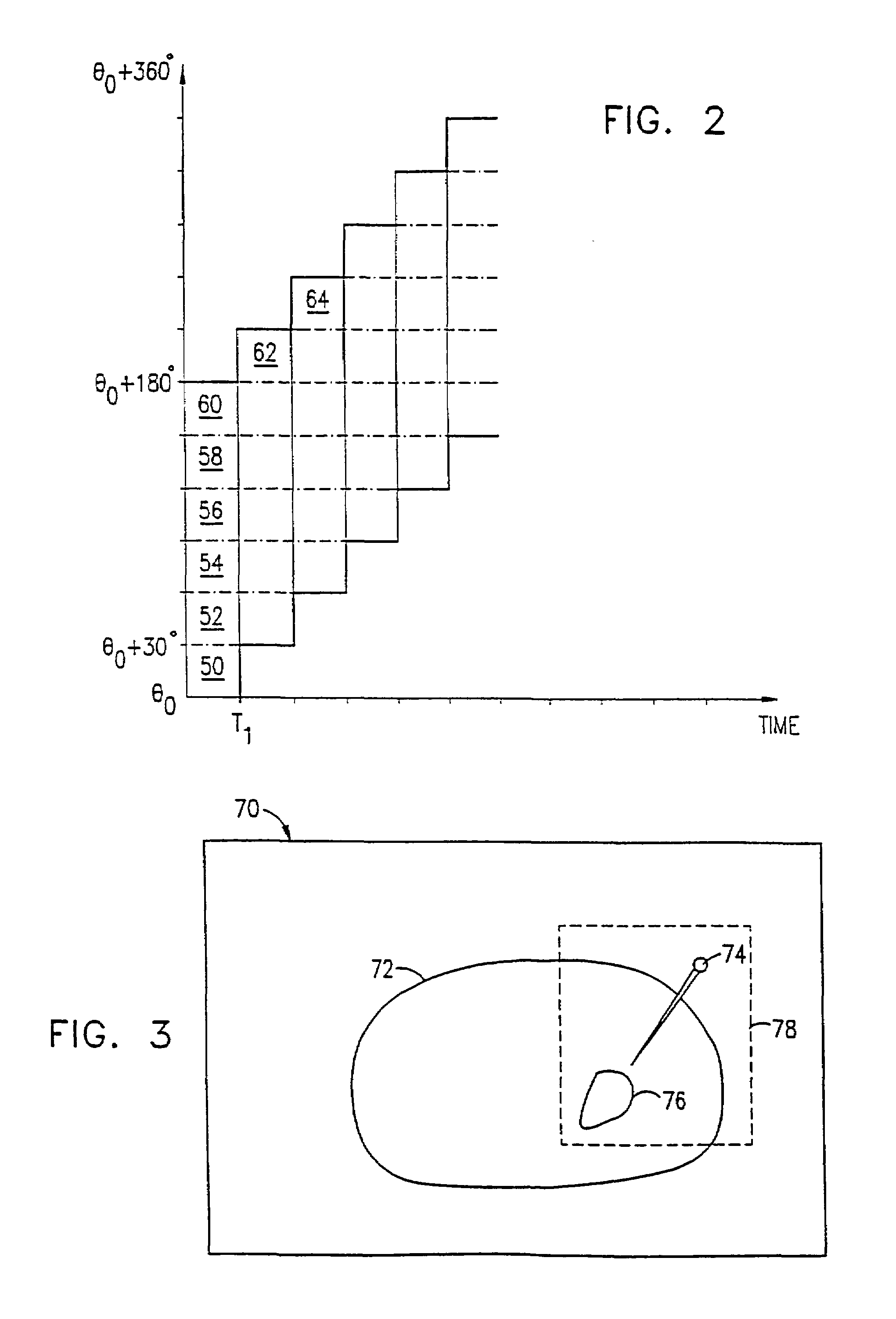
Real-time dynamic image reconstruction
InactiveUS6970585B1Rapid image reconstructionImprove update rateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasound attenuationCt scanners
A method for modifying a planar image slice in a CT scanner having a predetermined reconstruction angle, comprising: reconstructing an image of the slice using initial X-ray attenuation data acquired along an initial scan path sector; acquiring additional X-ray attenuation data along an additional scan path sector in a vicinity of the axial position of the slice, the sector having an angular extent substantially less than the reconstruction angle; and modifying the image, to provide a modified image of the slice, responsible to the additional attenuation data.
Owner:MARCONI MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
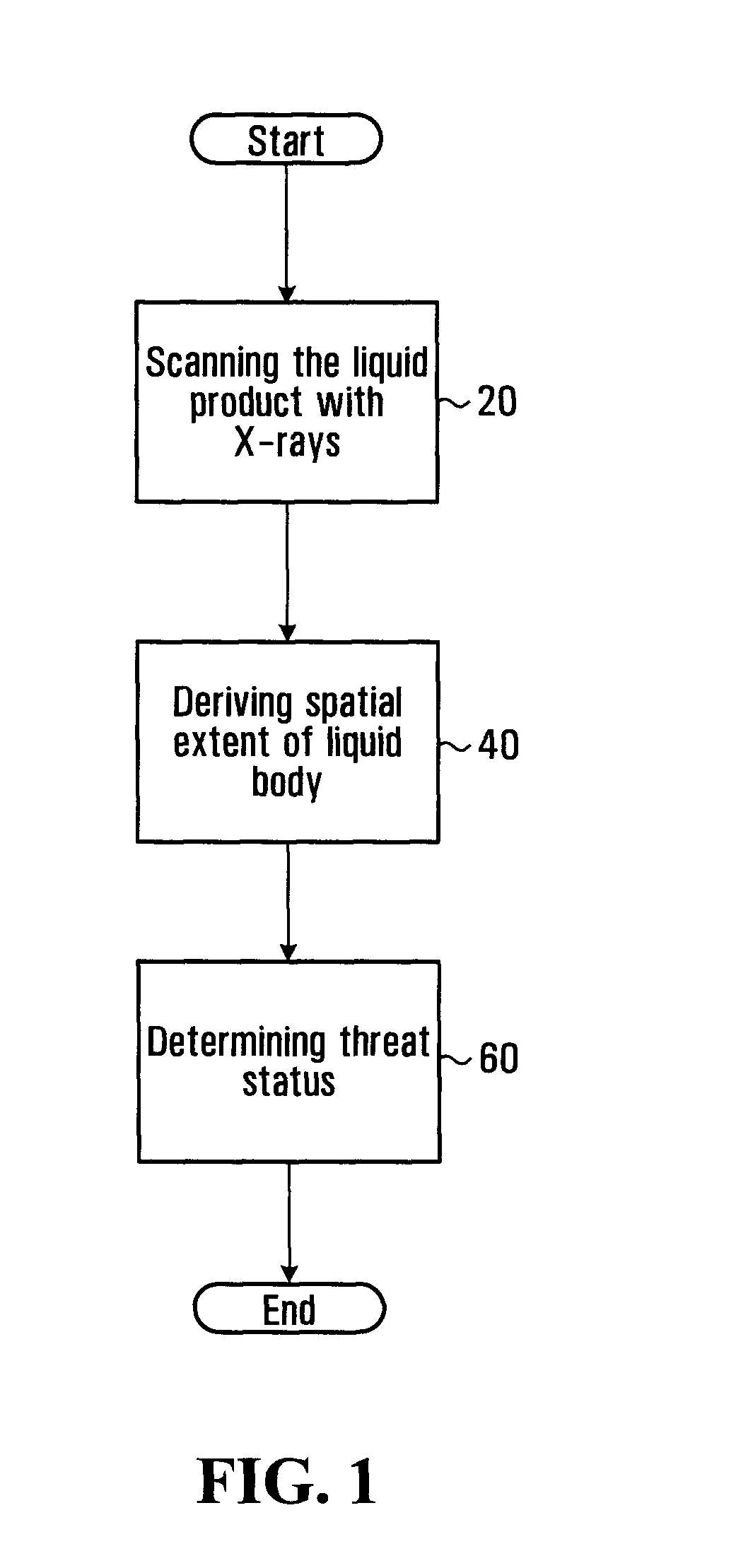
Method and apparatus for asssessing properties of liquids by using x-rays
InactiveUS20110172972A1Computation using non-denominational number representationUsing optical meansX-rays resultsLiquid product
A method and a system are provided for determining if a liquid product comprising a container which holds a body of liquid is a security threat. Attenuation data conveying information about attenuation of X-rays resulting from interaction of X-rays with the body of liquid is derived by scanning the liquid product with X-rays. Container characterization data is then processed to derive path length data indicative of an approximate length of a path followed by X-rays through the body of liquid and that interact with the body of liquid. The security threat of a liquid product is determined by processing the path length data and the attenuation data.
Owner:OPTOSECURITY
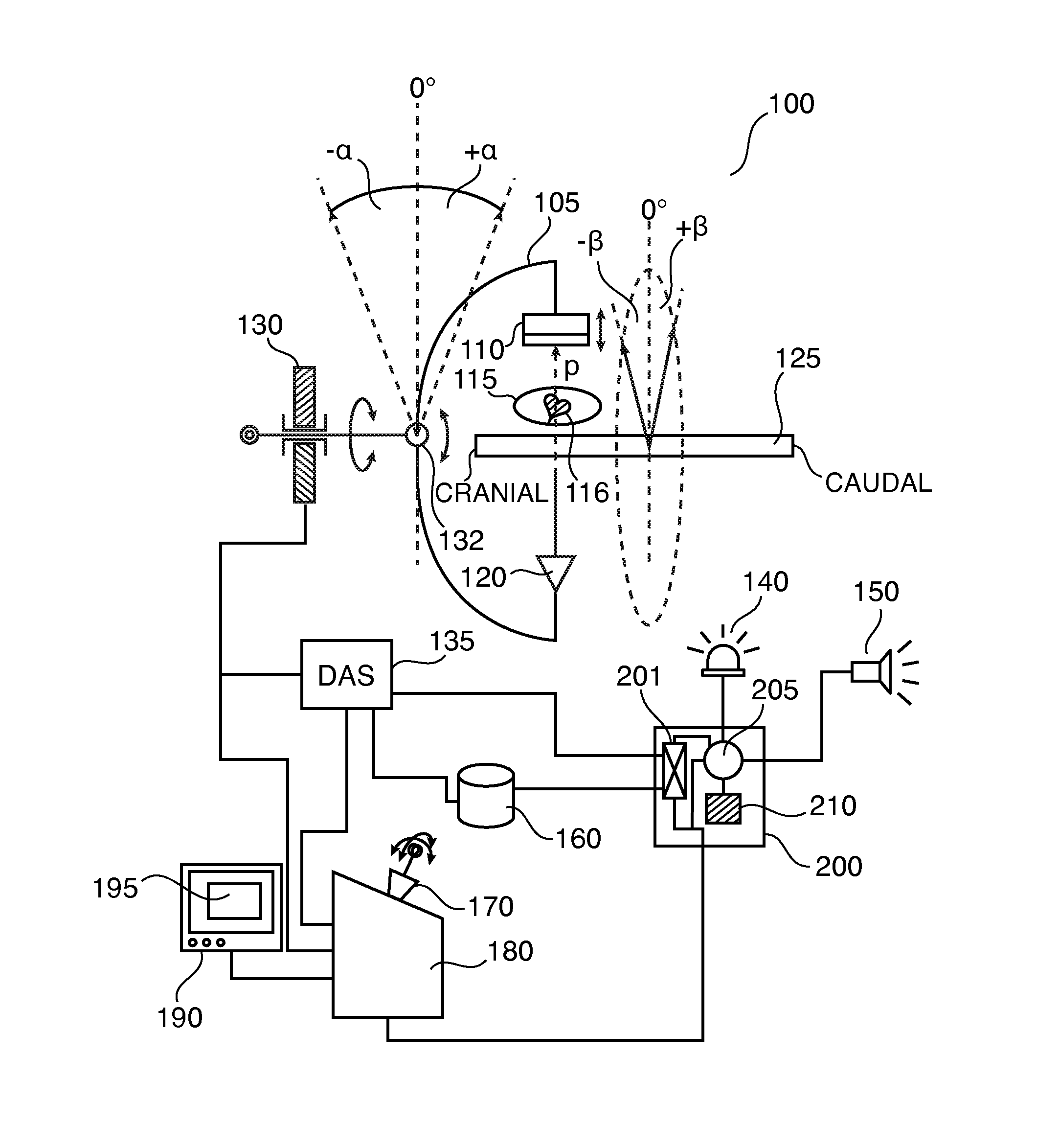
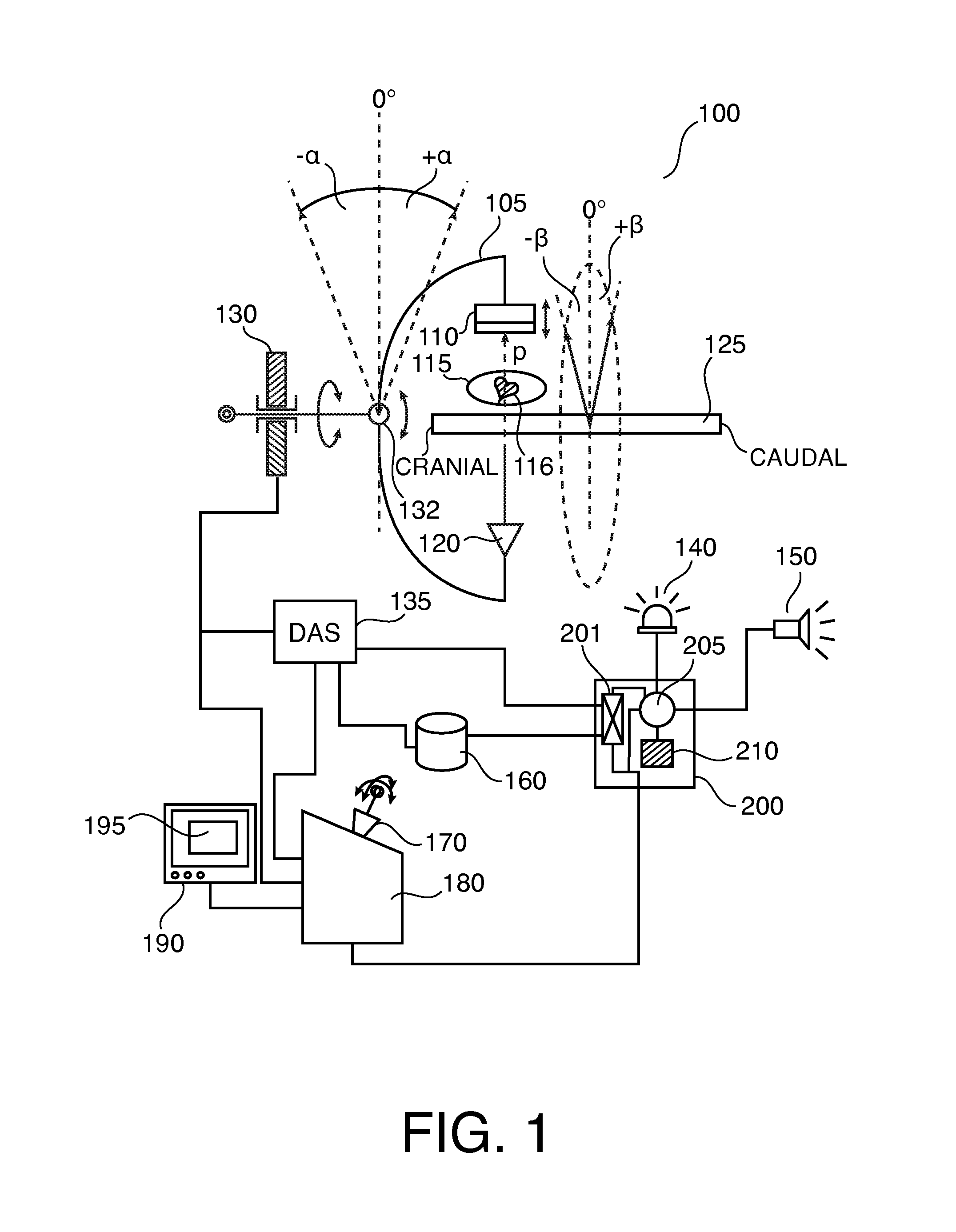
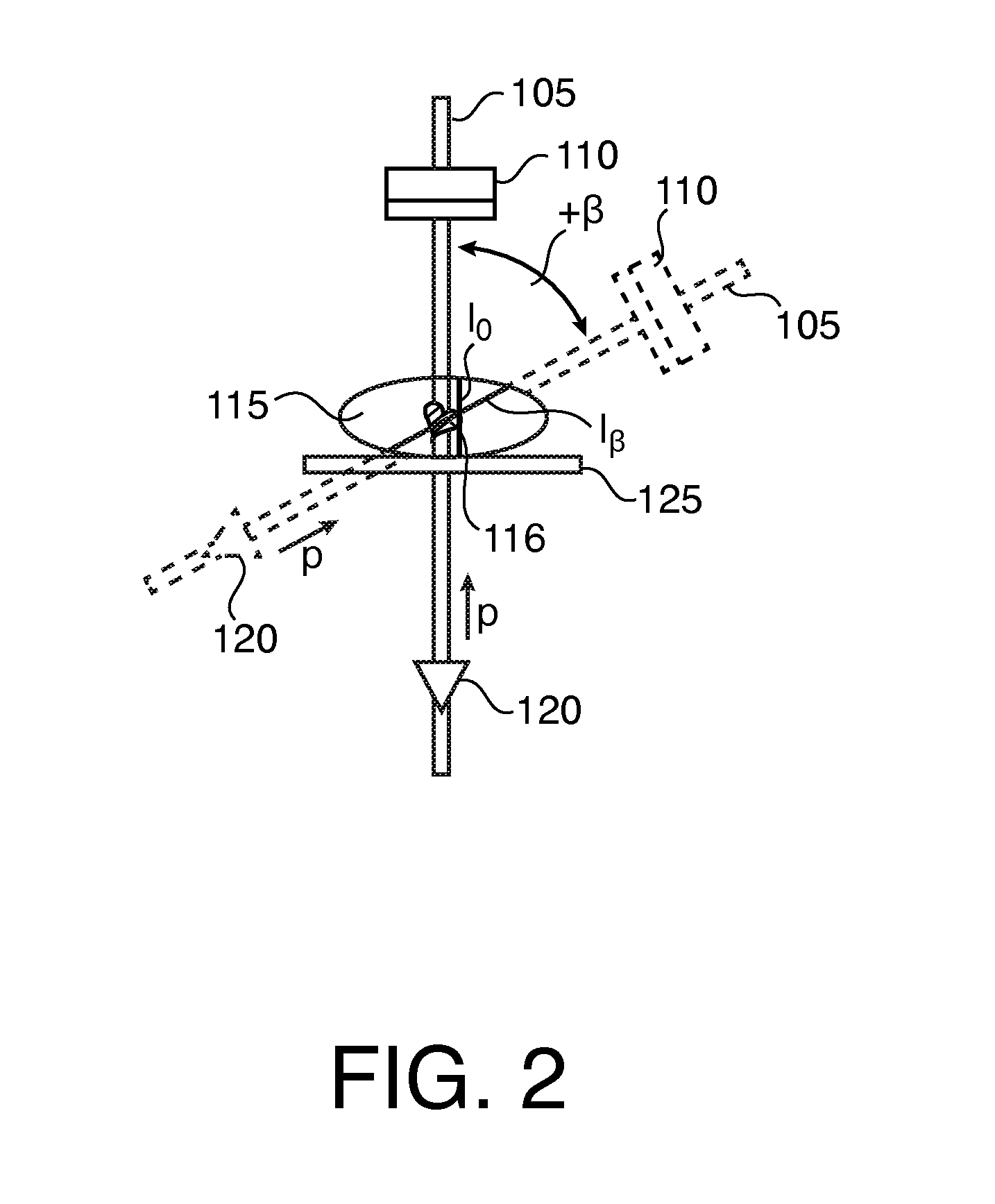
System and method for performing bi-plane tomographic acquisitions
ActiveUS20150238159A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingInterventional imagingData set
A method includes, in a bi-plane interventional imaging system, moving a first C-arm supporting a first X-ray source and a first X-ray detector about first and second axes while obtaining a plurality of first X-ray attenuation data sets relating to a subject of interest; moving a second C-arm, positioned crosswise with respect to the first C-arm and supporting a second X-ray source and a second X-ray detector, about the first axis while obtaining a plurality of second X-ray attenuation data sets relating to the subject of interest; and synchronizing the movement of the first and second C-arms to avoid collision therebetween.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
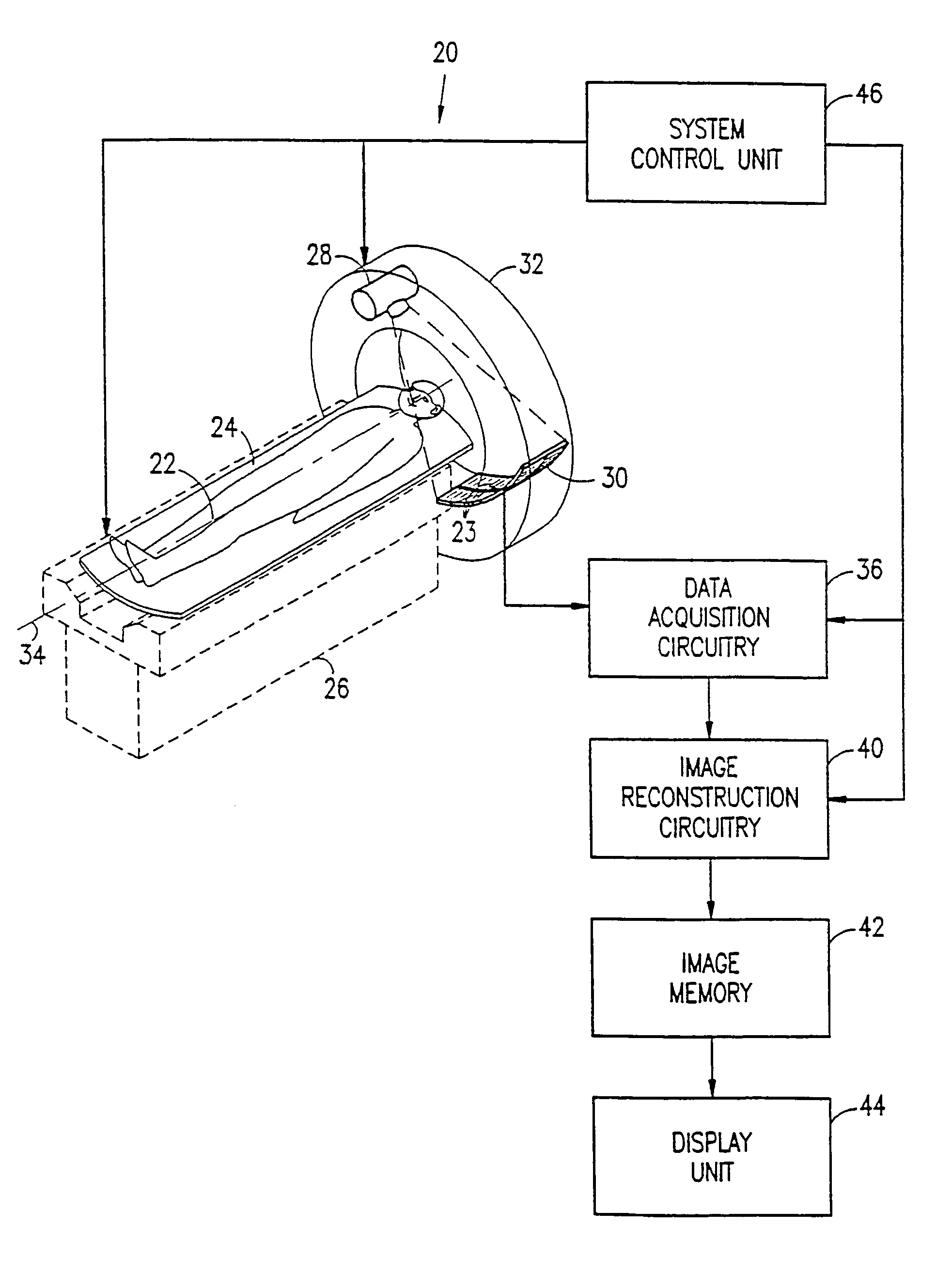
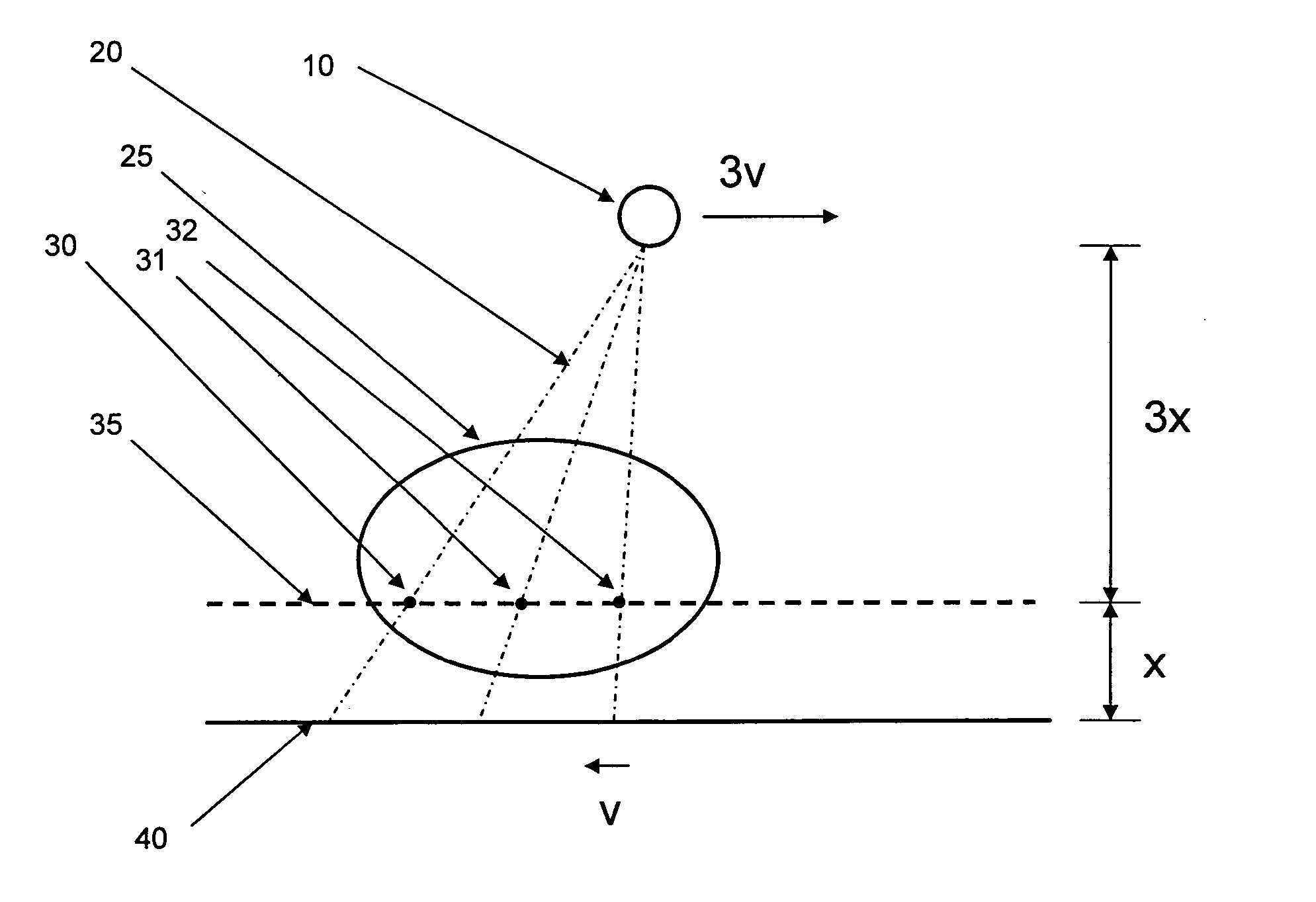
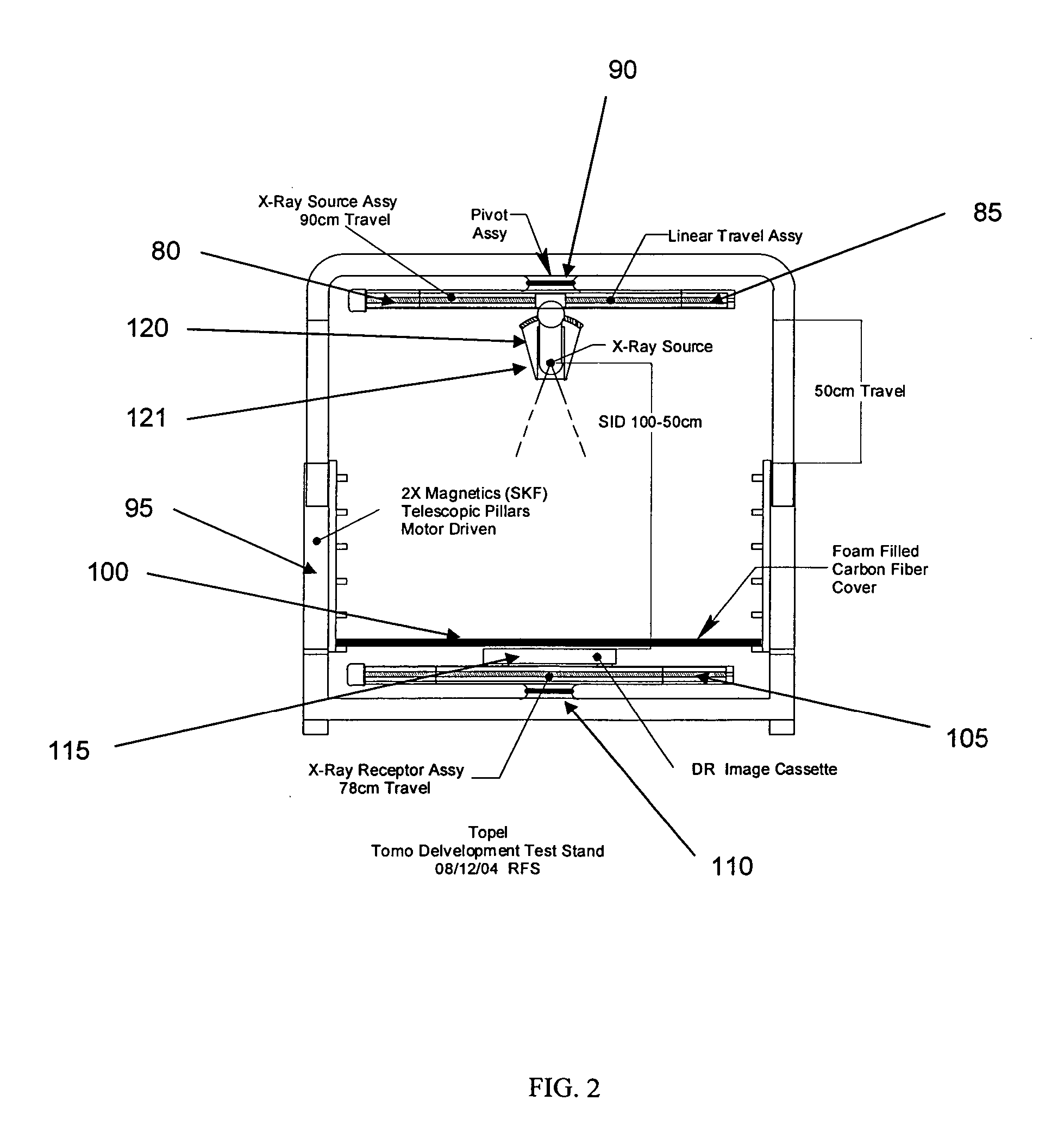
Digital x-ray tomosynthesis system
InactiveUS20050226369A1Minimizing x-ray doseReduce artifactsRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisTomosynthesisDigital data
Method and device for digital x-ray tomosynthesis. Tomographic and / or three-dimensional images of an object are obtained with an x-ray source and a digital x-ray image sensor. The source, object and sensor are positioned relative to each other and attenuation data is obtained for a large number of rays of x-radiation through the object. A special algorithm is provided to convert the data into images. To calculate the images the algorithm uses iterative processes with a least squares type technique but with generalized (as opposed to specific) functions. The algorithm solves for the functions which are the images. Preferred embodiments include a system having an x-ray point source with a cone of diverging x-rays, a two-dimensional digital x-ray image sensor, two linear translation stages to independently move both the x-ray source and the digital x-ray image sensor, two rotation mechanisms to rotate the two linear translation stages, a microprocessor to control the data acquisition, and a computer programmed with a special algorithm to calculate the tomographic images. A plurality of sets of digital data (representing x-ray algorithm images of an object) are acquired by the digital x-ray image sensor, with the x-ray source and the digital x-ray image sensor located at different positions and angles relative to the object. The digital data representing the x-ray attenuation images is stored in the computer. Special mathematical algorithms then compute multiple images of the object using the acquired digital data. These images could include multiple tomographic images, a three-dimensional image, or a multiple three-dimensional images.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
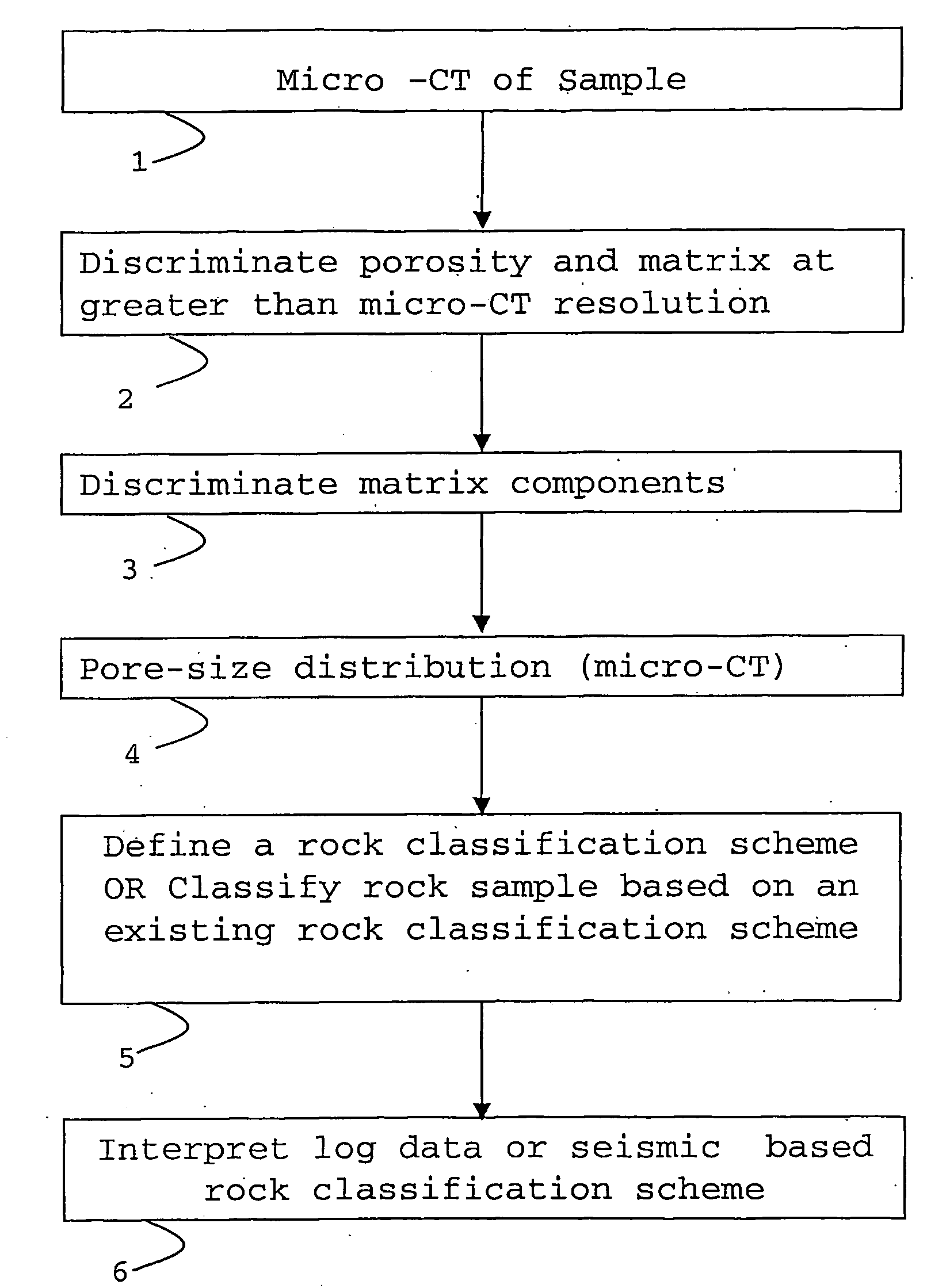
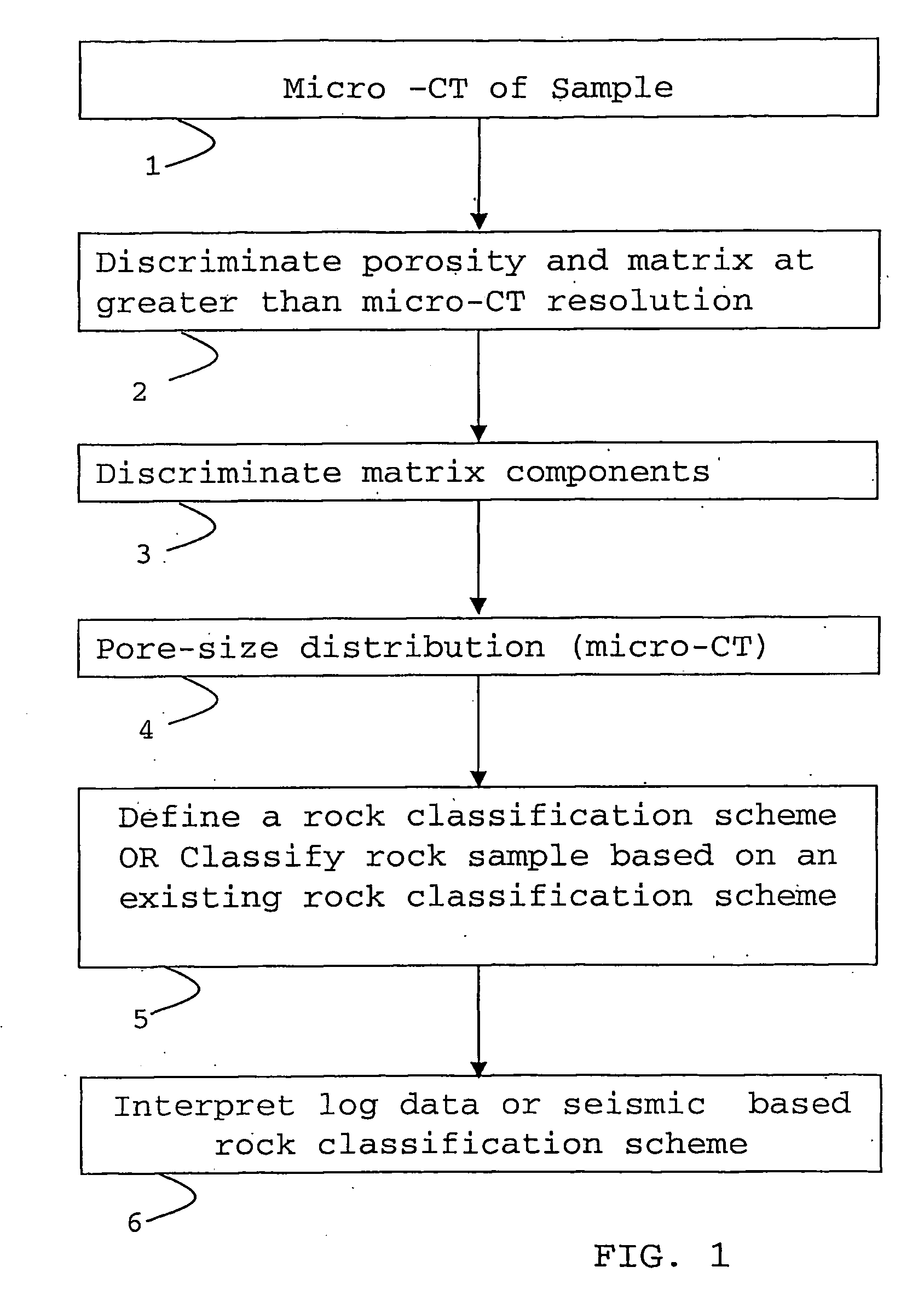
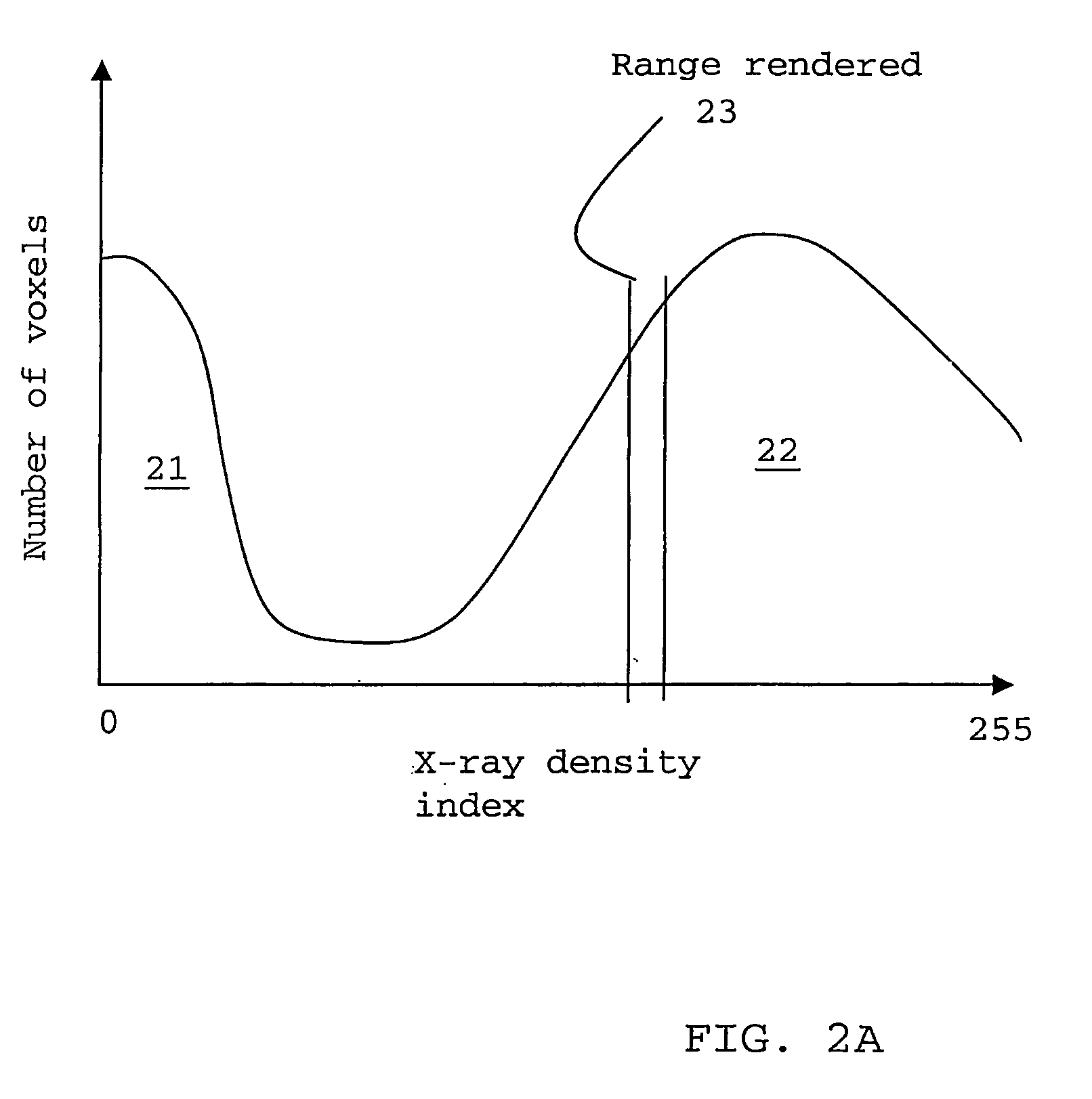
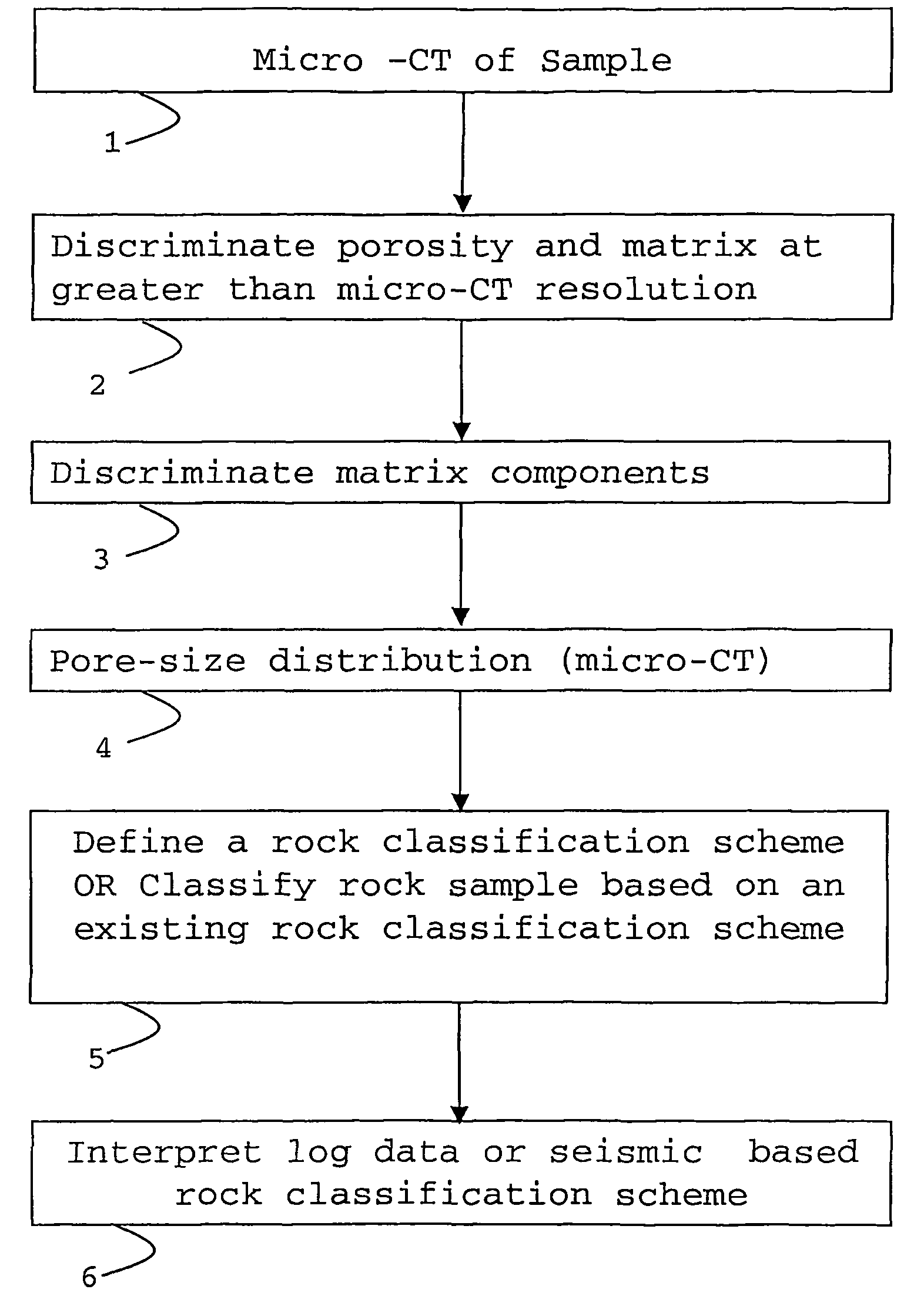
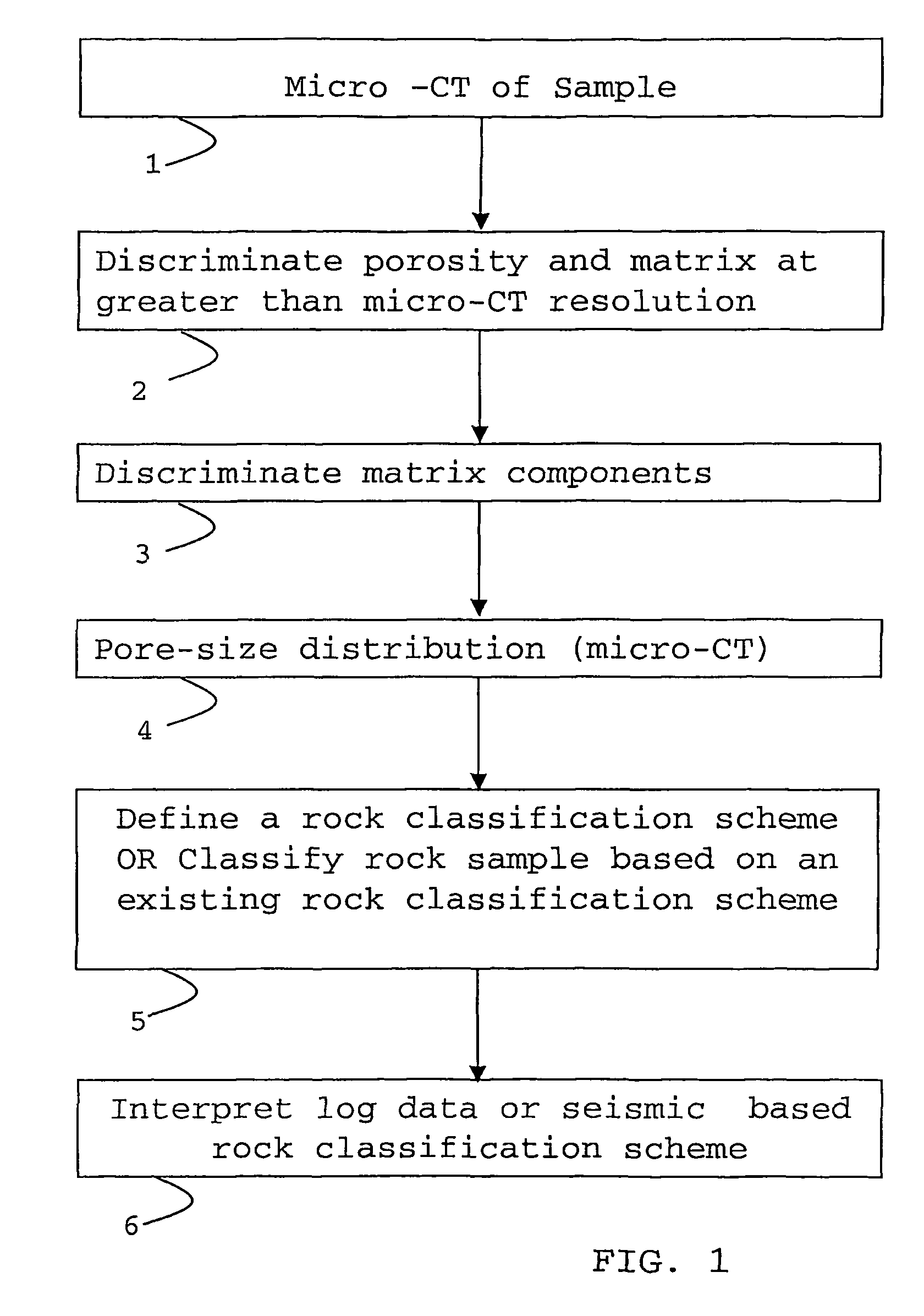
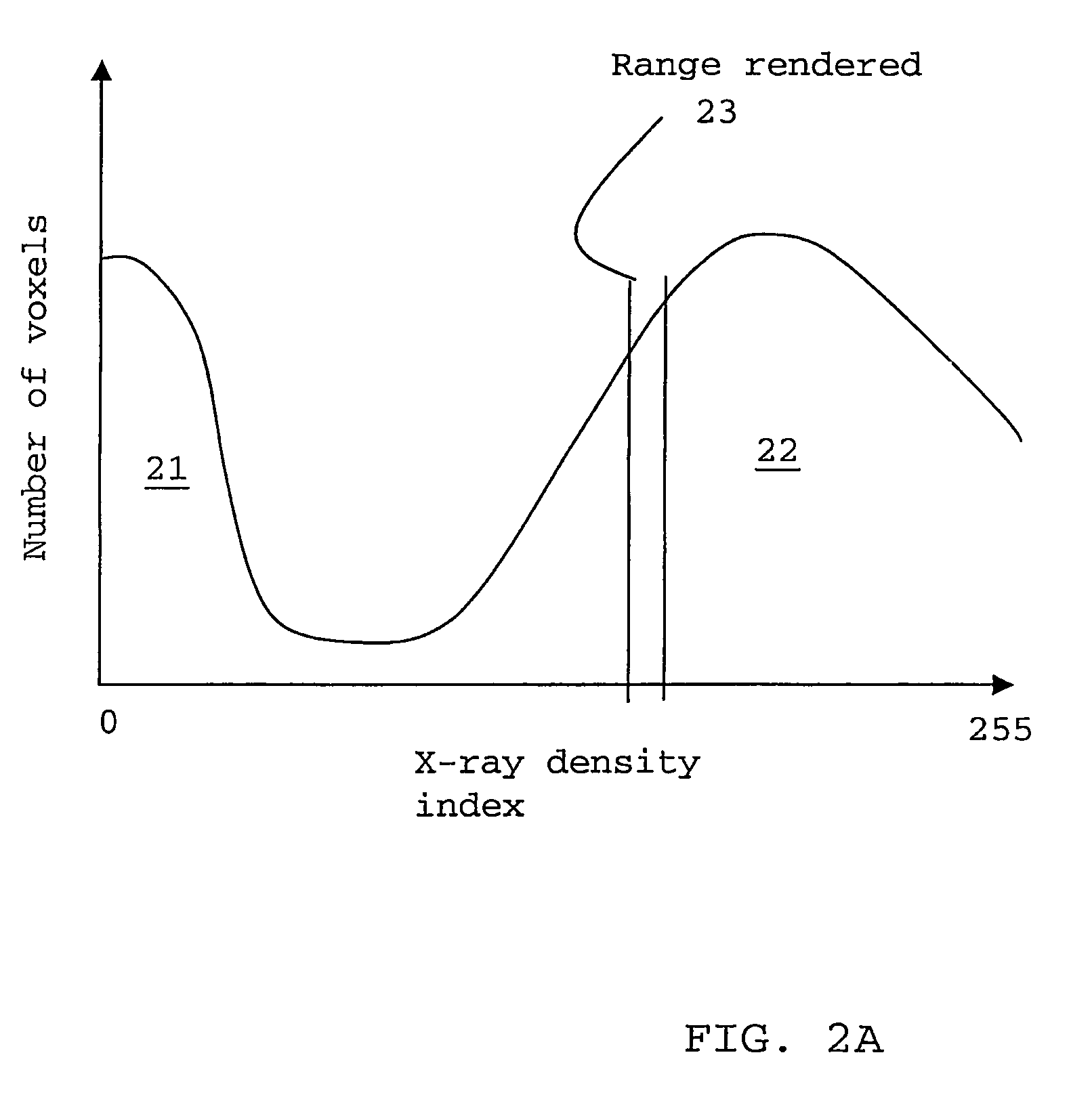
Classification method for sedimentary rocks
ActiveUS20090103677A1Improve accuracyX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationClassification methodsMaceral
A method of determining a parameter of interest of reservoir rock formation is described using the steps of measuring an x-ray attenuation or absorption distribution of a sample of said rock formation, identifying the mineral phase part of said distribution, and subdividing the mineral phase part of said distribution to derive classification or rock type information of said sample.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
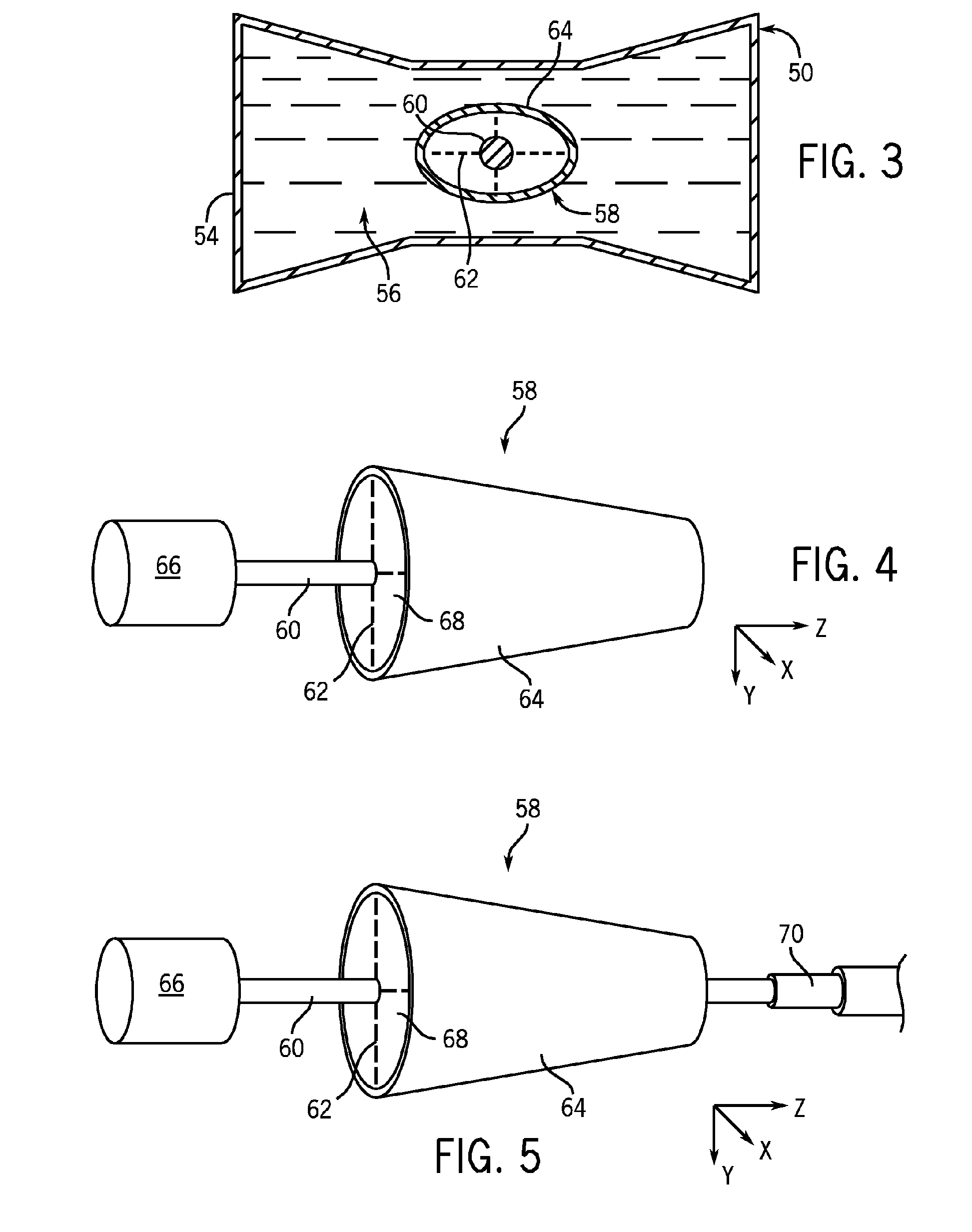
X-ray filter having dynamically displaceable x-ray attenuating fluid
InactiveUS20070092066A1High rateLower levelMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingShape changeX-ray filter
A bowtie filter is constructed to have a fluidic envelope filled with attenuating fluid and a displacement insert that can present various x-ray attenuation profiles during a scan. The insert is designed to displace the attenuating fluid to achieve a denied attenuating or filtering profile. The insert can be rotated, twisted, moved, and otherwise contorted within the fluidic envelope as needed during the course of a scan. As the angle, position and shape of the zombie is changed, the x-ray profile of the filter changes. The insert may have a default shape when at rest, but can have its shape changed when external forces are placed thereon. As x-ray filtering needs change during the course of the scan, the insert can be compressed, stretched, and / or contorted to achieve additional filtering profiles.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and device for determining the type of fluid in a fluid mass in an object
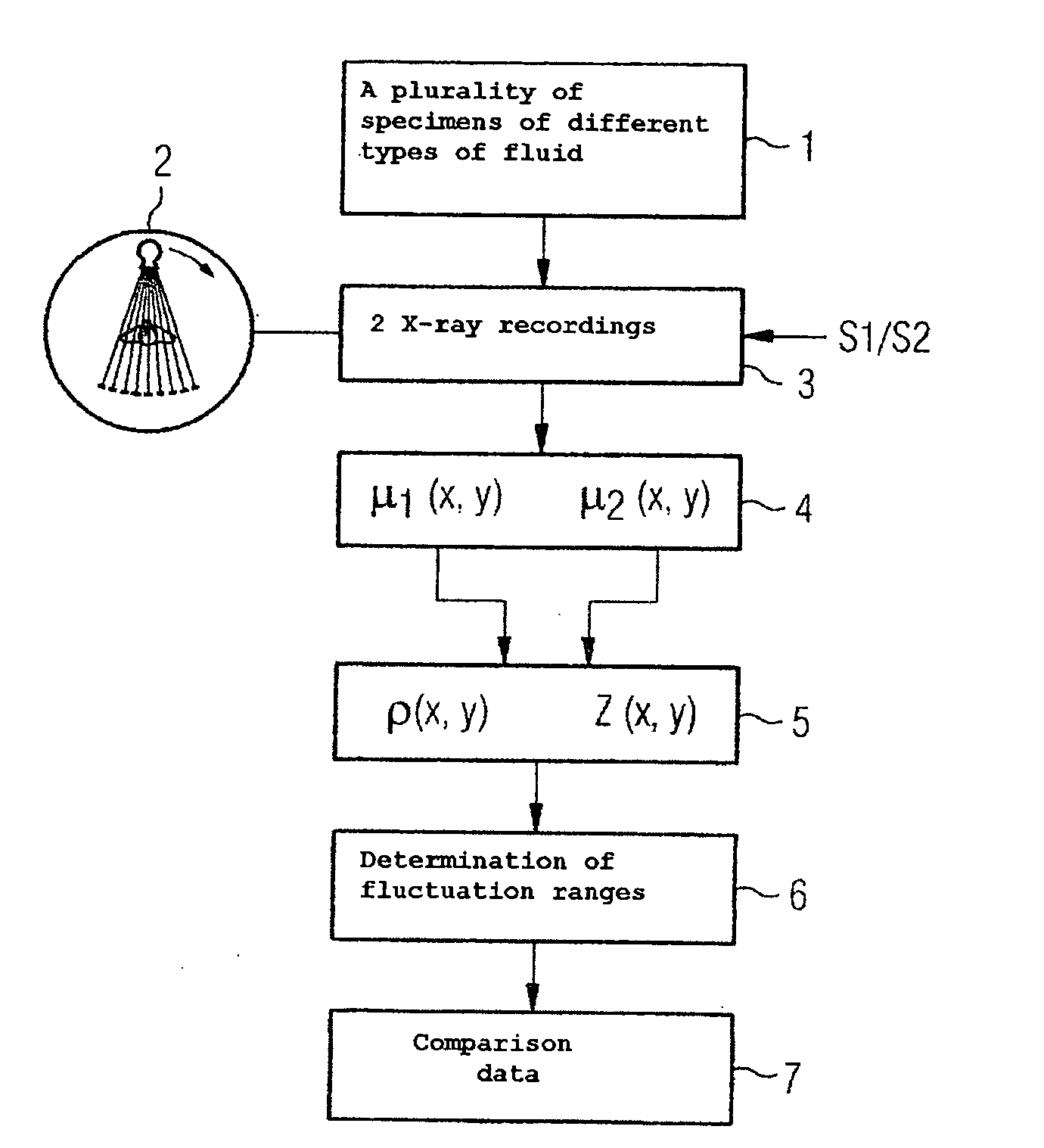
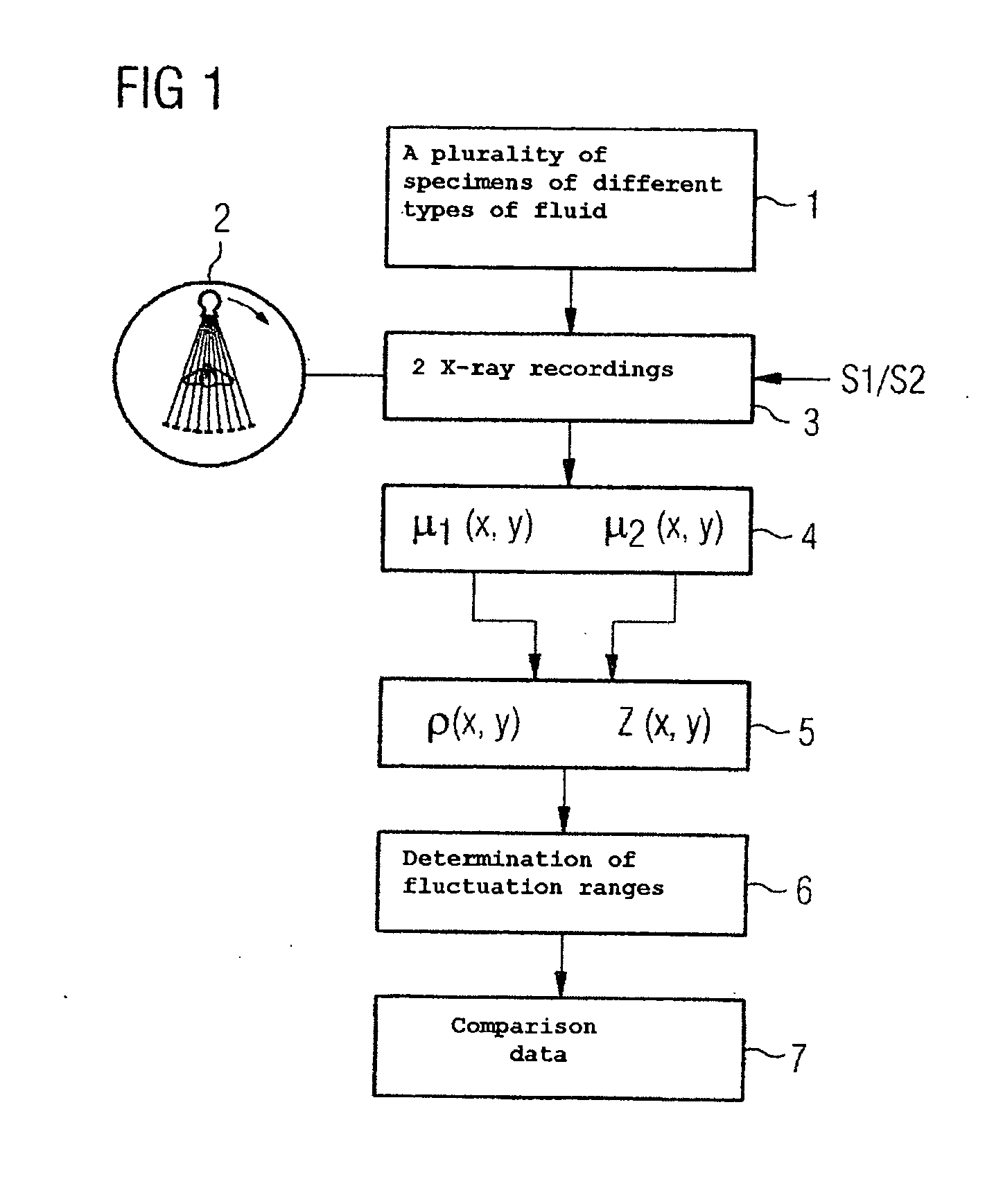
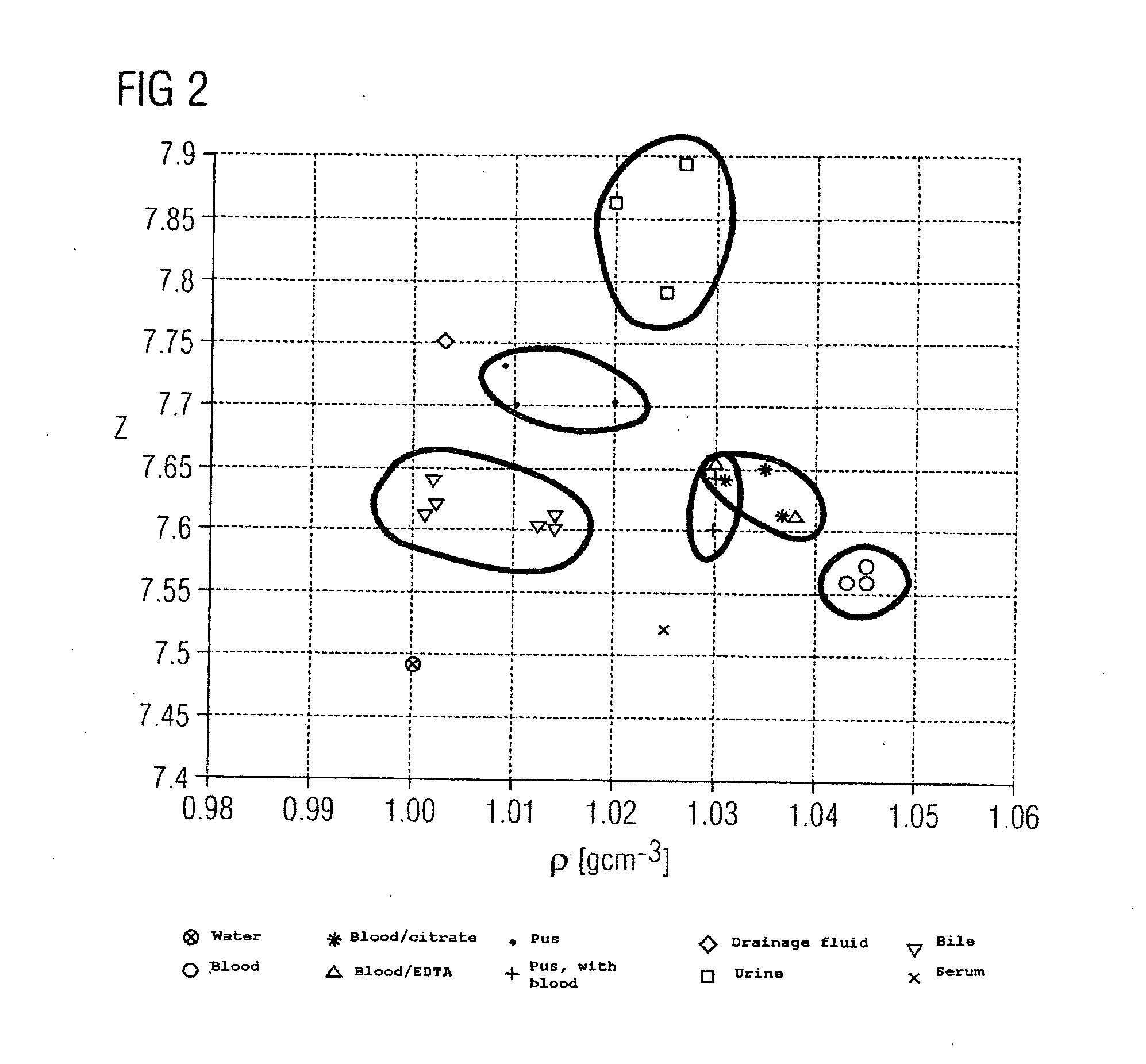
InactiveUS20050084063A1High resolutionQuick changeRadiation/particle handlingRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsX ray spectraVolumetric Mass Density
A method and a device are proposed for determining the type of fluid in a fluid mass in an object. X-ray attenuation data is supplied from one or a plurality of X-ray recordings of an object area including the fluid mass in the object, which were acquired with at least two different X-ray spectra or detector weightings. The X-ray attenuation data is used to determine values for effective atomic number and density for the fluid mass and average these to obtain a mean value for effective atomic number and density for the fluid mass. Comparison data is also supplied, which indicates fluctuation ranges for combinations of effective atomic number and density for different types of fluid. The mean values for effective atomic number and density of the fluid mass are compared with the comparison data to determine the fluctuation range and thereby the type of fluid, into which the two mean values fall. The method and associated device can be used to determine the type of fluid in a fluid mass in an object in a reliable and unambiguous manner.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Cone-beam filtered backprojection image reconstruction method for short trajectories
ActiveUS7203272B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationReconstruction methodX-ray
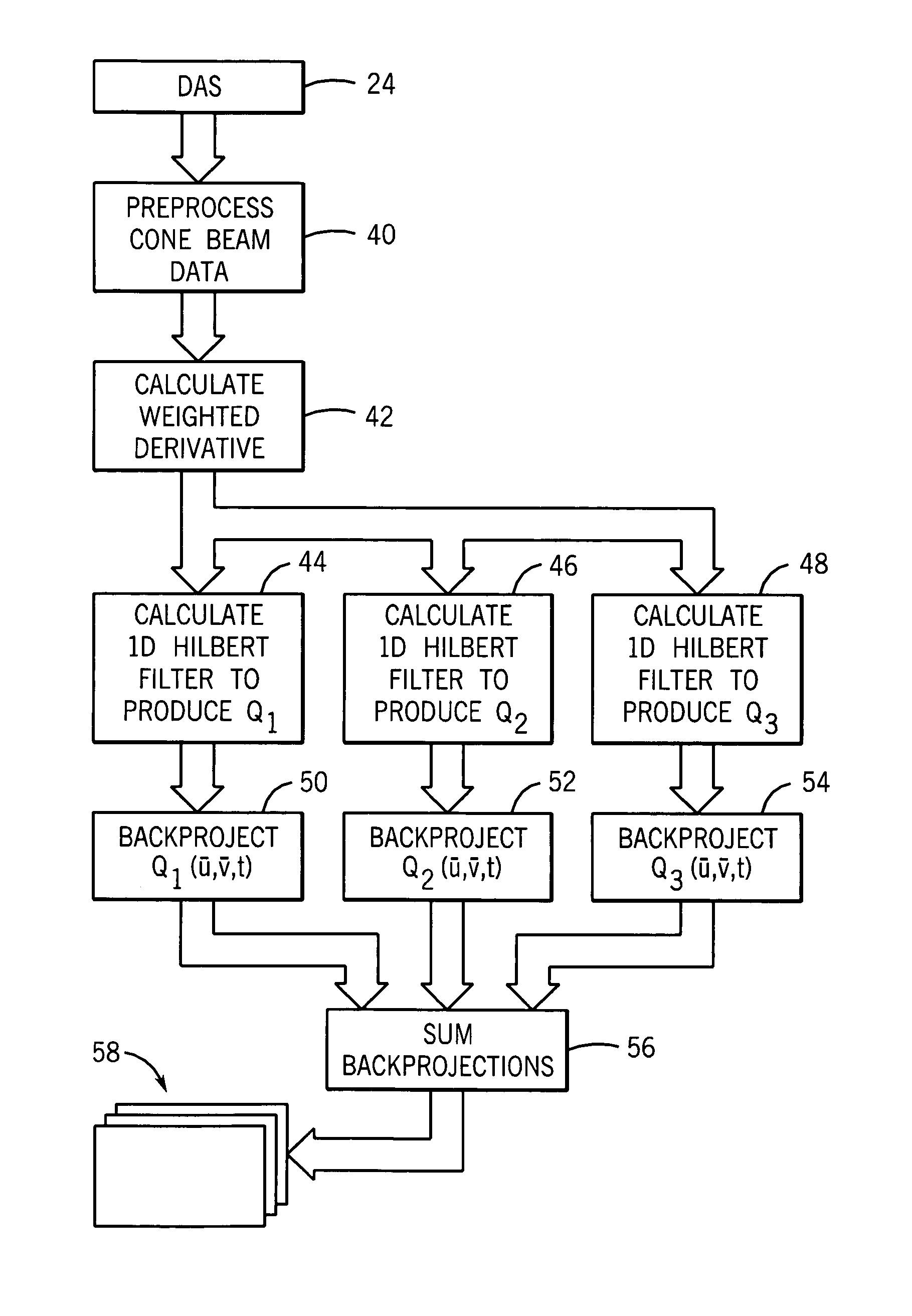
An image reconstruction method for cone beam x-ray attenuation data acquired over a super-short-scan, short-scan or full-scan includes backproejcting over three adjacent segments of the arc traversed by the x-ray source. Each backprojection consists of a weighted combination of 1D Hilbert filtering of the modified cone-beam data along both horizontal and non-horizontal directions.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Non-uniform view weighting tomosynthesis method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050111616A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesisBack projection
A technique is provided for non-uniform weighting in back-projection calculations in tomosythesis. The non-uniform weighting may include weighting based on a count map of the number of times pixels of individual slices are traversed by radiation in different projections. Weighting may also include non-uniform functions for contributions of features at different slice level to the sensed X-ray attenuation system response inconsistencies are accounted for by further weighting based upon projection maps which may be created in separate system calibration or configuration routines.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
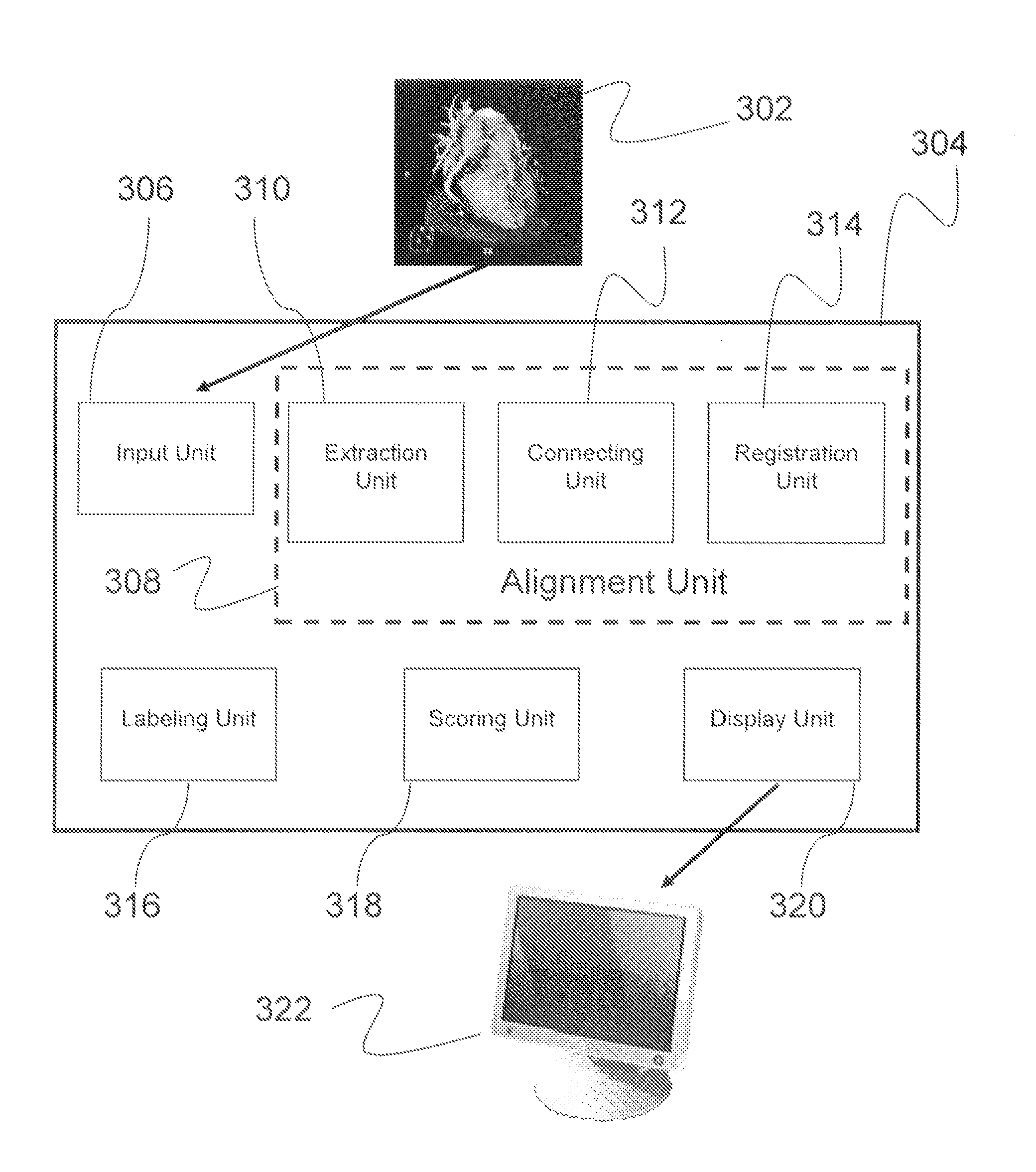
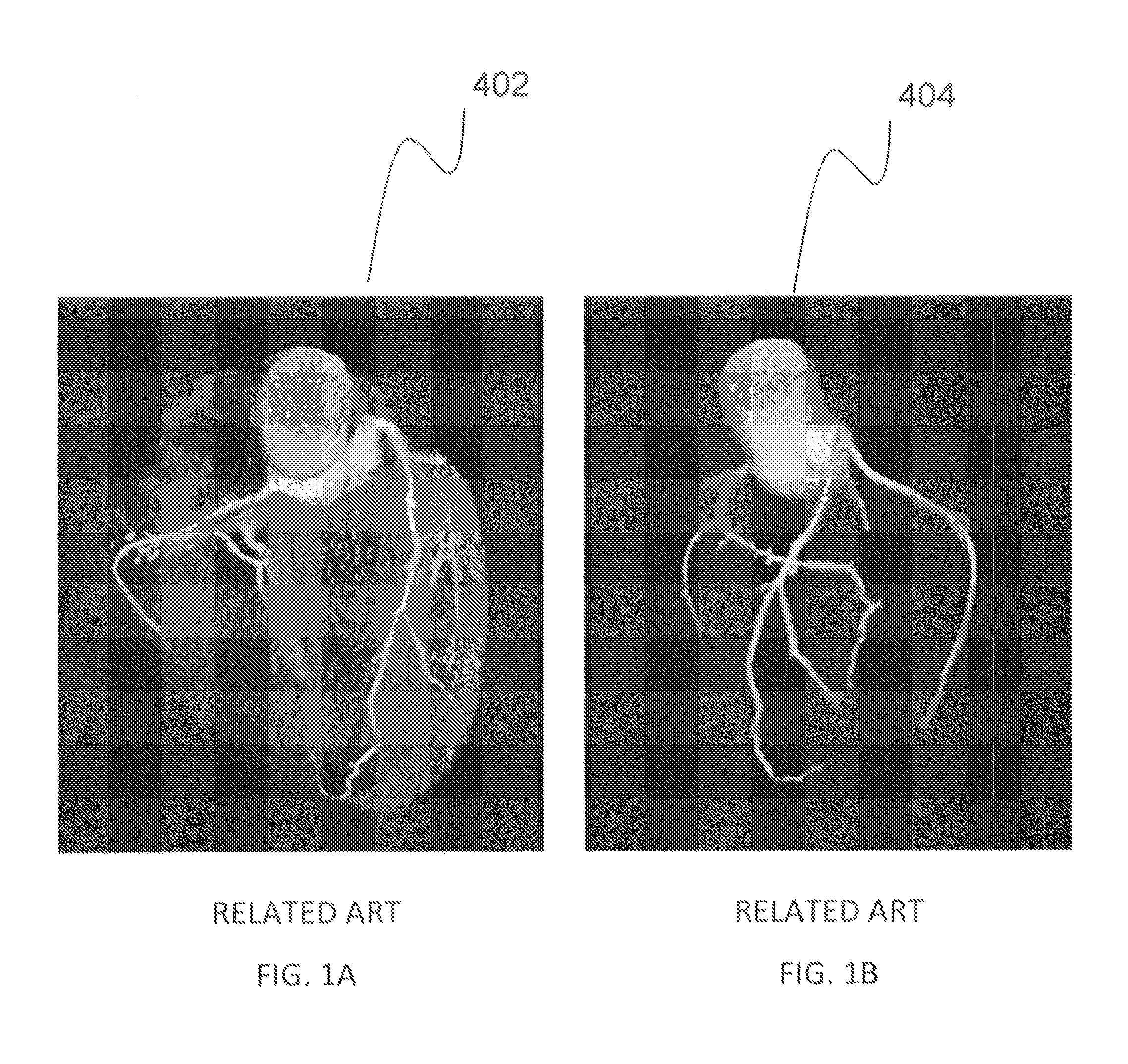
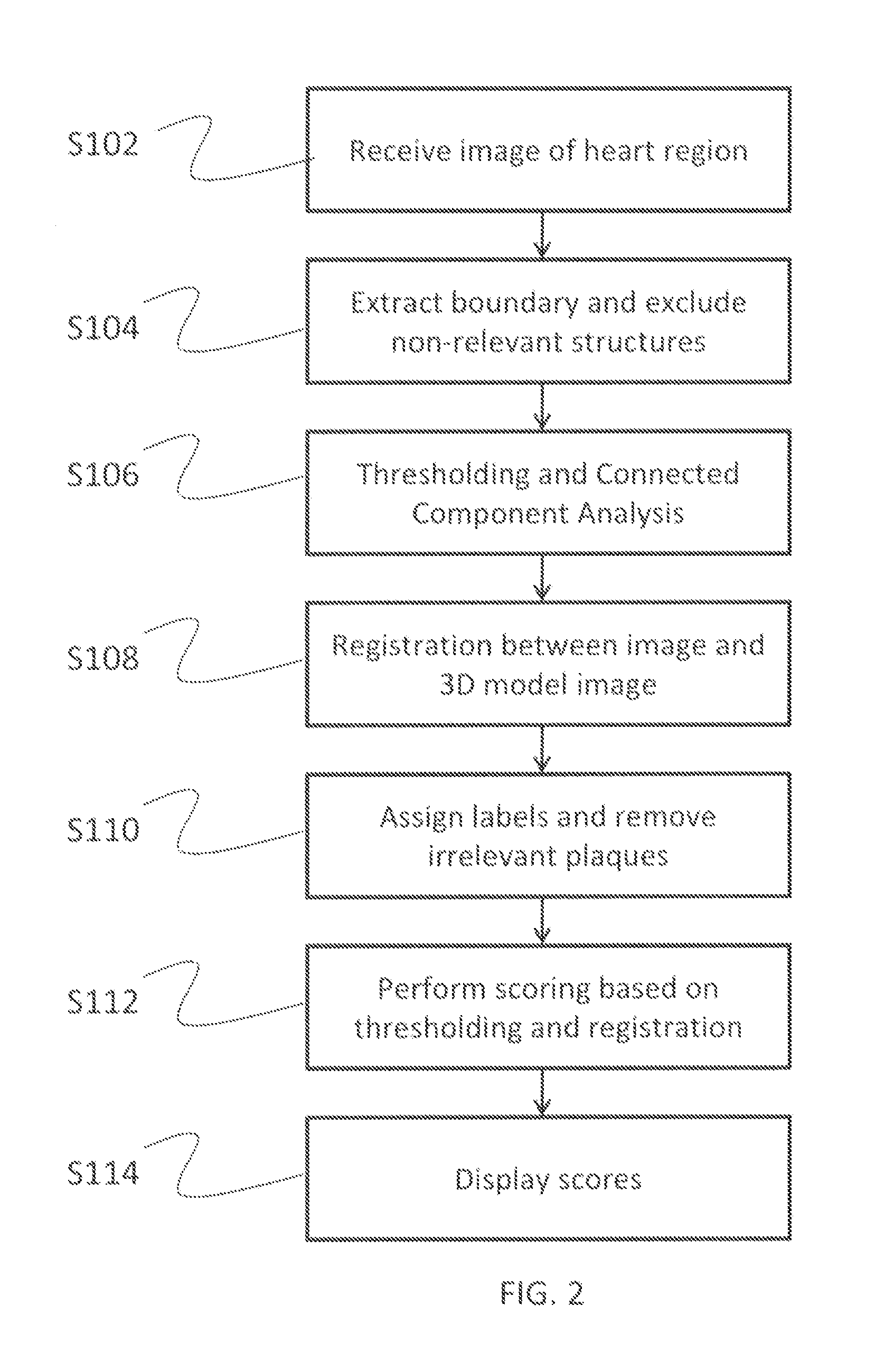
Model-based coronary artery calcium scoring
InactiveUS20130094749A1Improve assessment accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesDisease
A system and method are provided for model-based coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring. A model image of a heart region is aligned with an image of a patient's heart region in order to more easily identify the coronary arteries and other relevant anatomical features in the image. Once the images are aligned, relevant calcium plaques are identified by their presence within a coronary artery, and the relevant plaques are then labeled by the specific coronary artery in which they are located. The coronary arteries with the labeled plaques are scored individually based on their size and X-ray attenuation, and an overall score based on all of the relevant plaques is then computed, which is related to the patient's risk for coronary artery disease.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
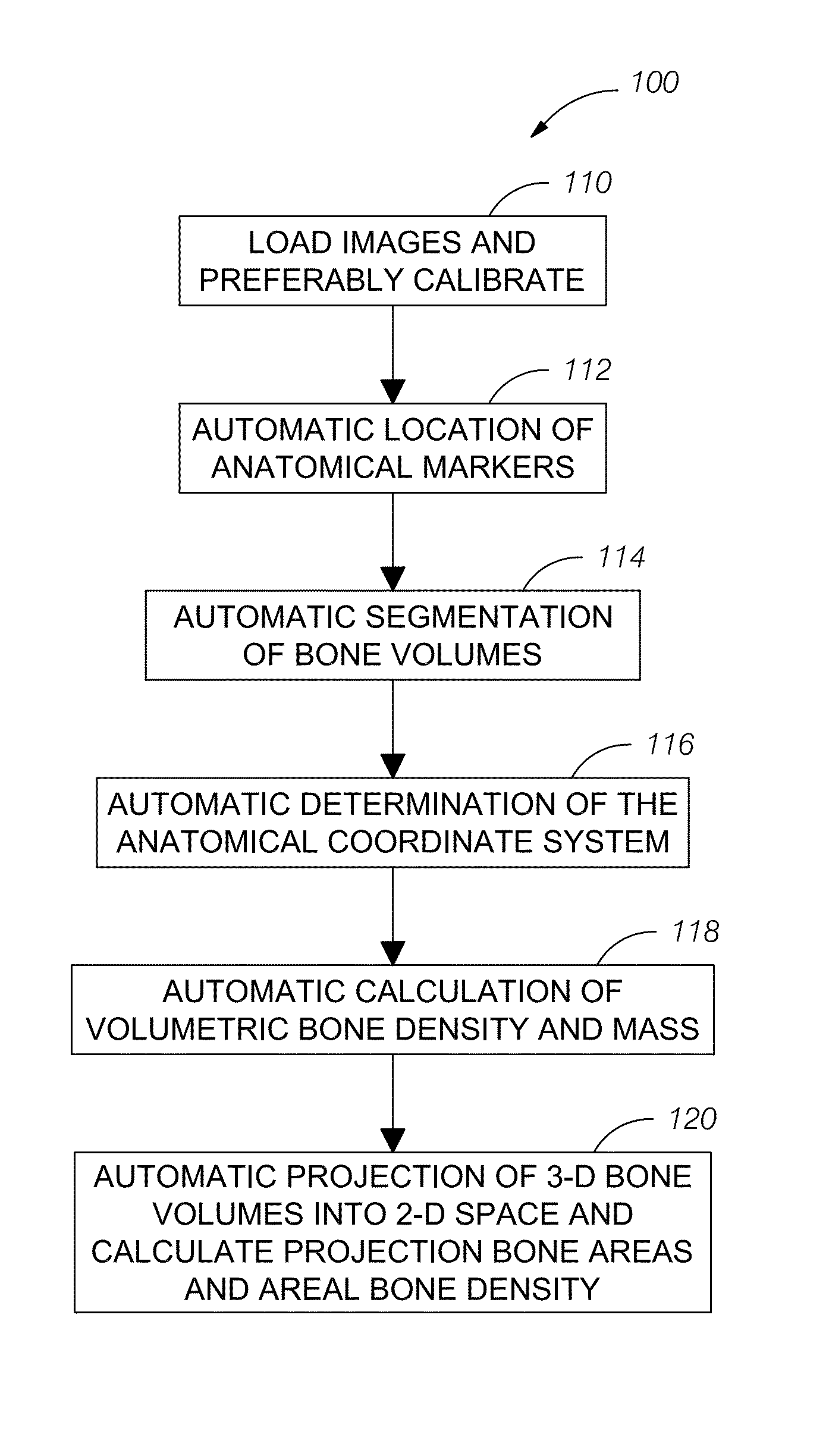
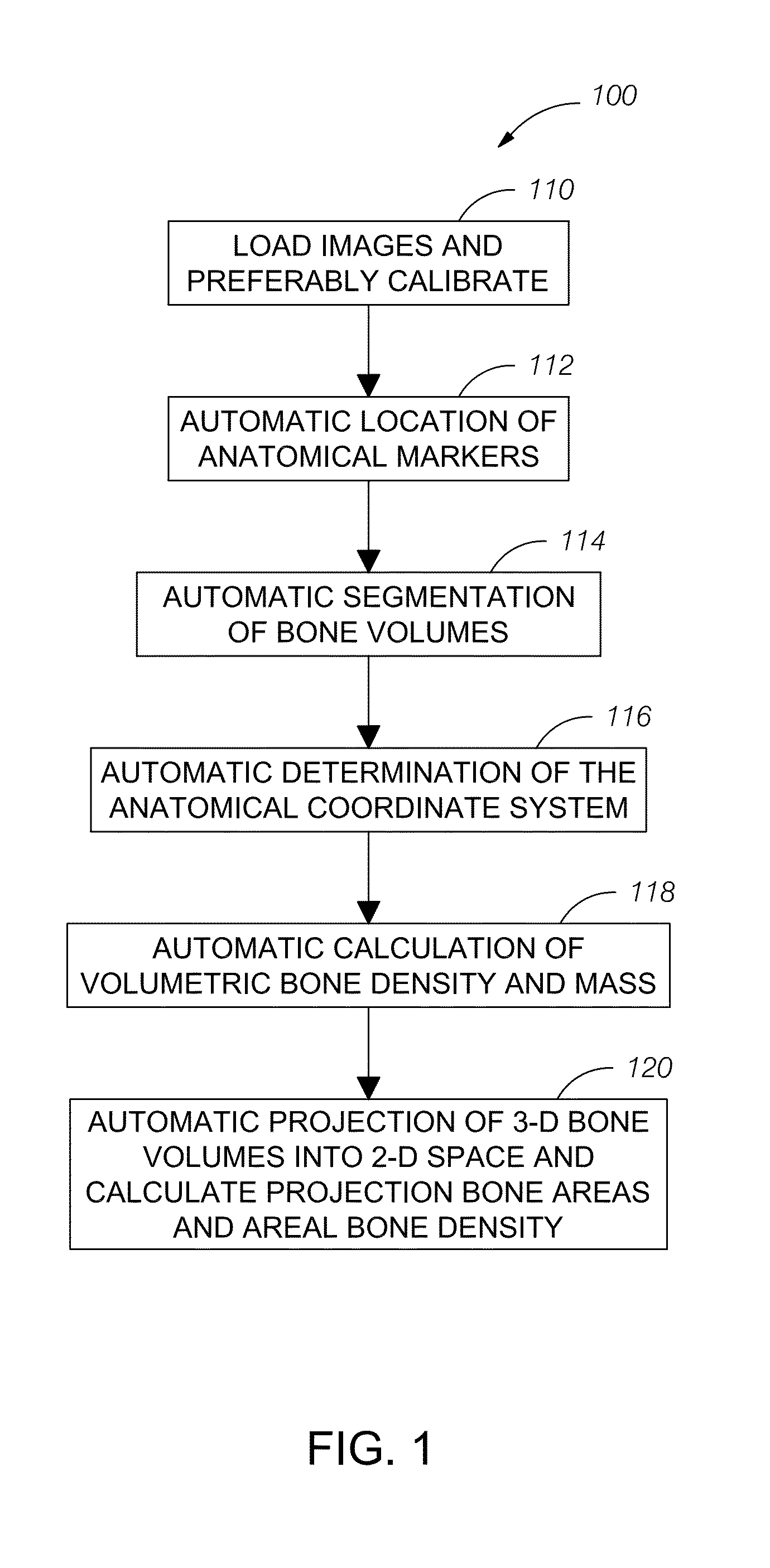
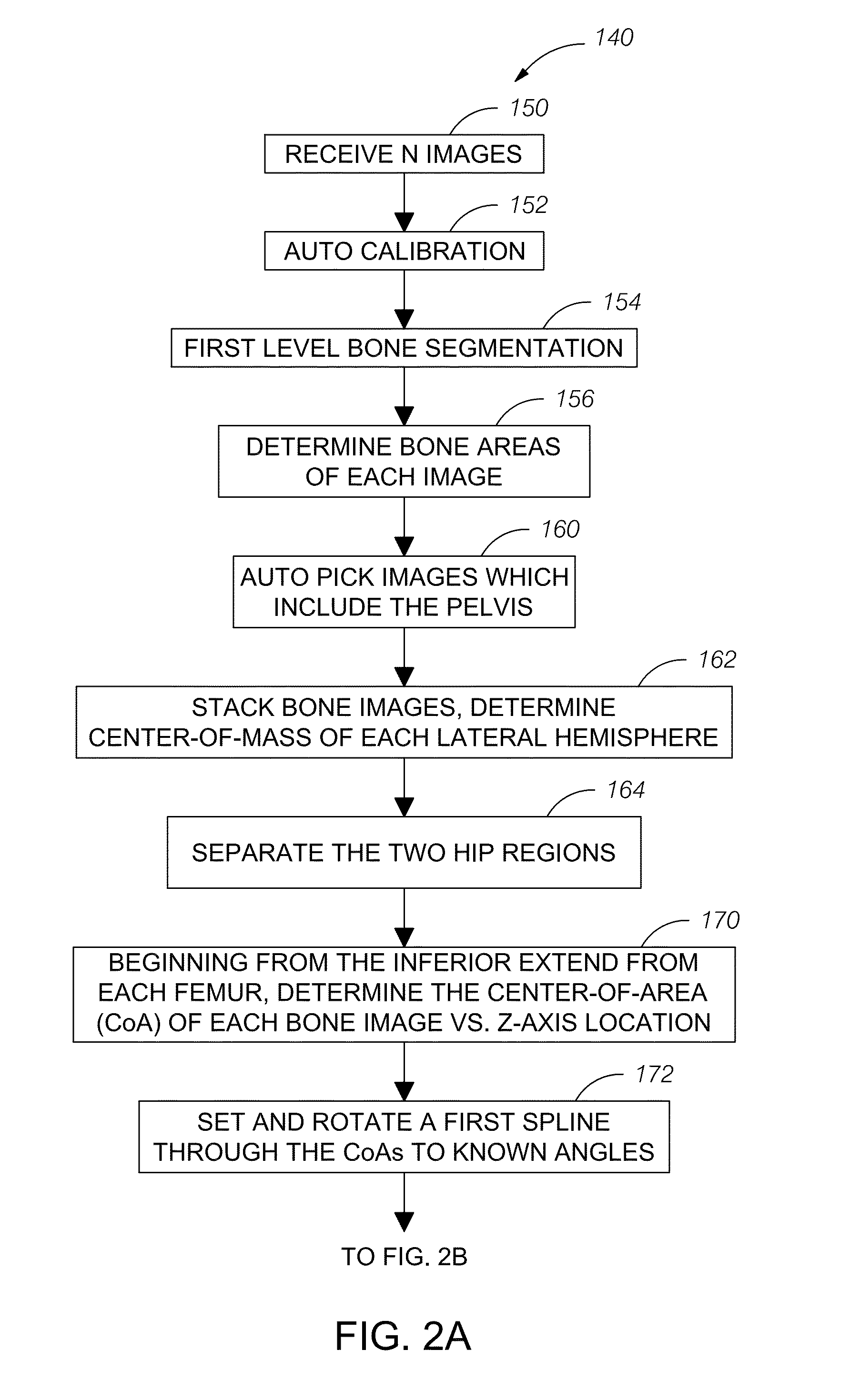
Automatic method and system for measurements of bone density and structure of the hip from 3-D X-ray imaging devices
ActiveUS8649577B1Reduce effortShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresVoxel
A method uses a computer and software to measure bone density and structure of the proximal femur of the hip from a volumetric set of images containing pixels representing x-ray attenuation of the subject which are acquired with three-dimensional X-ray imaging devices. The method automatically locates anatomical markers of the hip without operator interaction, automatically positions regions of interest (ROIs) for measurement, automatically determines bone density measures of the ROIs, and automatically reports the results for individual subjects. Bone density measurements of ROIs include the integral bone of the total hip and neck as well as trabecular bone. The method automatically identifies a three-dimensional region-of-interest (ROI) volume which includes the hip, determines a three-dimensional coordinate system referenced to the anatomy of the subject, analyzes the ROI volume to identify voxels in the volume which satisfy defined criteria, and determines a measure of bone structure.
Owner:IMAGE ANALYSIS
Method and apparatus to reduce charge sharing in pixellated energy discriminating detectors
ActiveUS20080175347A1Reduce charge sharingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingElectricityX-ray
A CT detector includes a plurality of metallized anodes with each metallized anode separated from another metallized anode by a gap. A direct conversion material is electrically coupled to the plurality of metallized anodes and has a charge sharing region in which an electrical charge generated by an x-ray impinging the direct conversion material is shared between at least two of the plurality of metallized anodes. An x-ray attenuating material is positioned to attenuate x-rays directed toward the charge sharing region.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Non-destructive identification method for material of integral coil of distribution transformer
ActiveCN102749342ADoes not affect power supplyTimely claimMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNon destructiveUltrasound attenuation
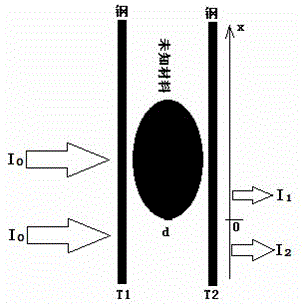
The invention discloses a non-destructive identification method for a material of an integral coil of a distribution transformer. The non-destructive identification method based on the difference of attenuation coefficients of copper, steel and aluminum to X rays includes photographing the distribution transformer in a integral state by the X rays; measuring blackness of photographed negative films of the rays by a black and white densitometer; inputting measured blackness values into a computer; and computing X-ray attenuation coefficient and transillumination thickness curves, which are stored in the computer, of the copper, the steel and the aluminum corresponding to different X-ray tubes and comparing the X-ray attenuation coefficient and transillumination thickness curves with a characteristic curve of the industrial ray films, and judging whether the winding coil of the distribution transformer is made of the aluminum or the copper.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST OF GUIZHOU POWER GRID CO LTD
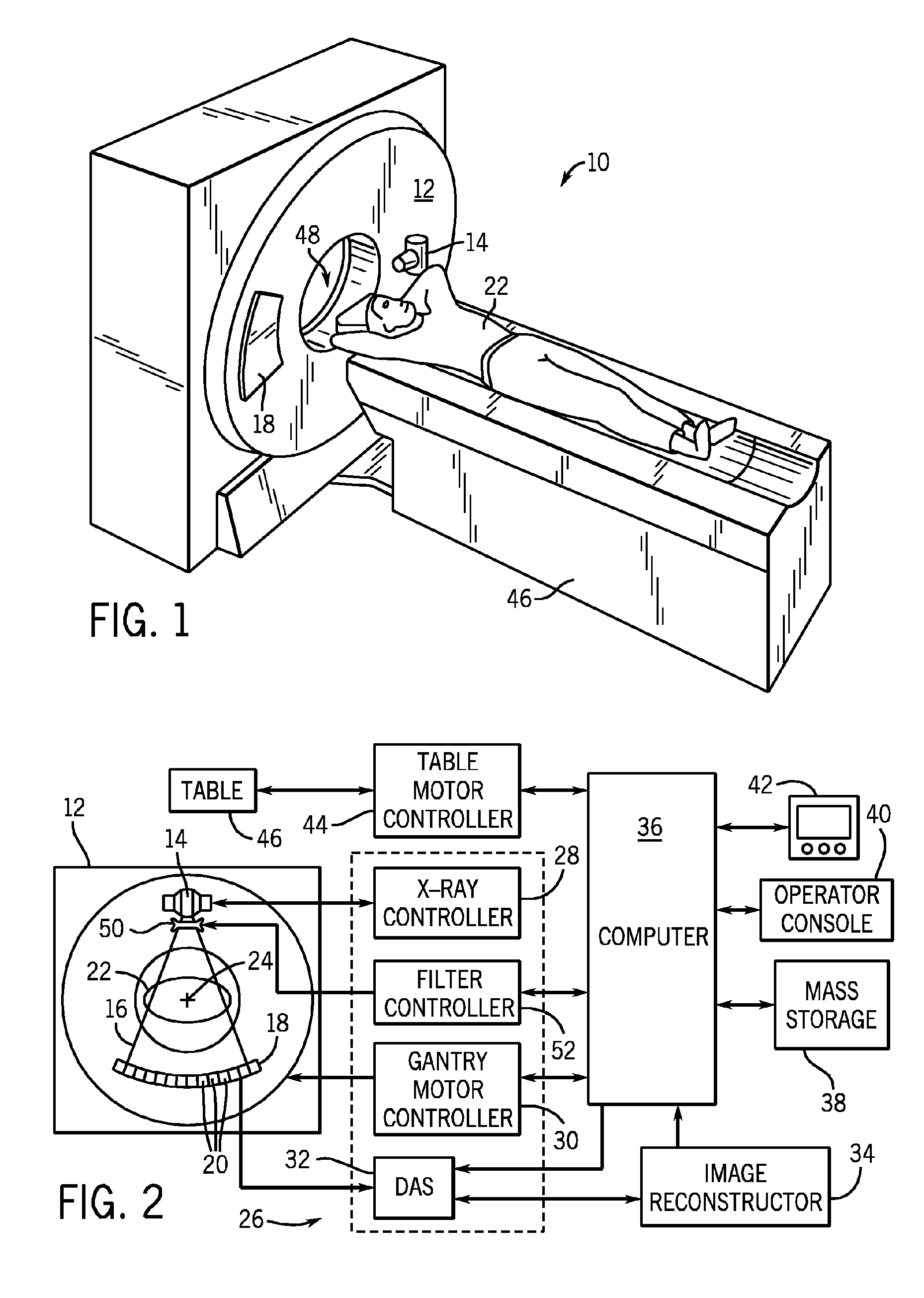
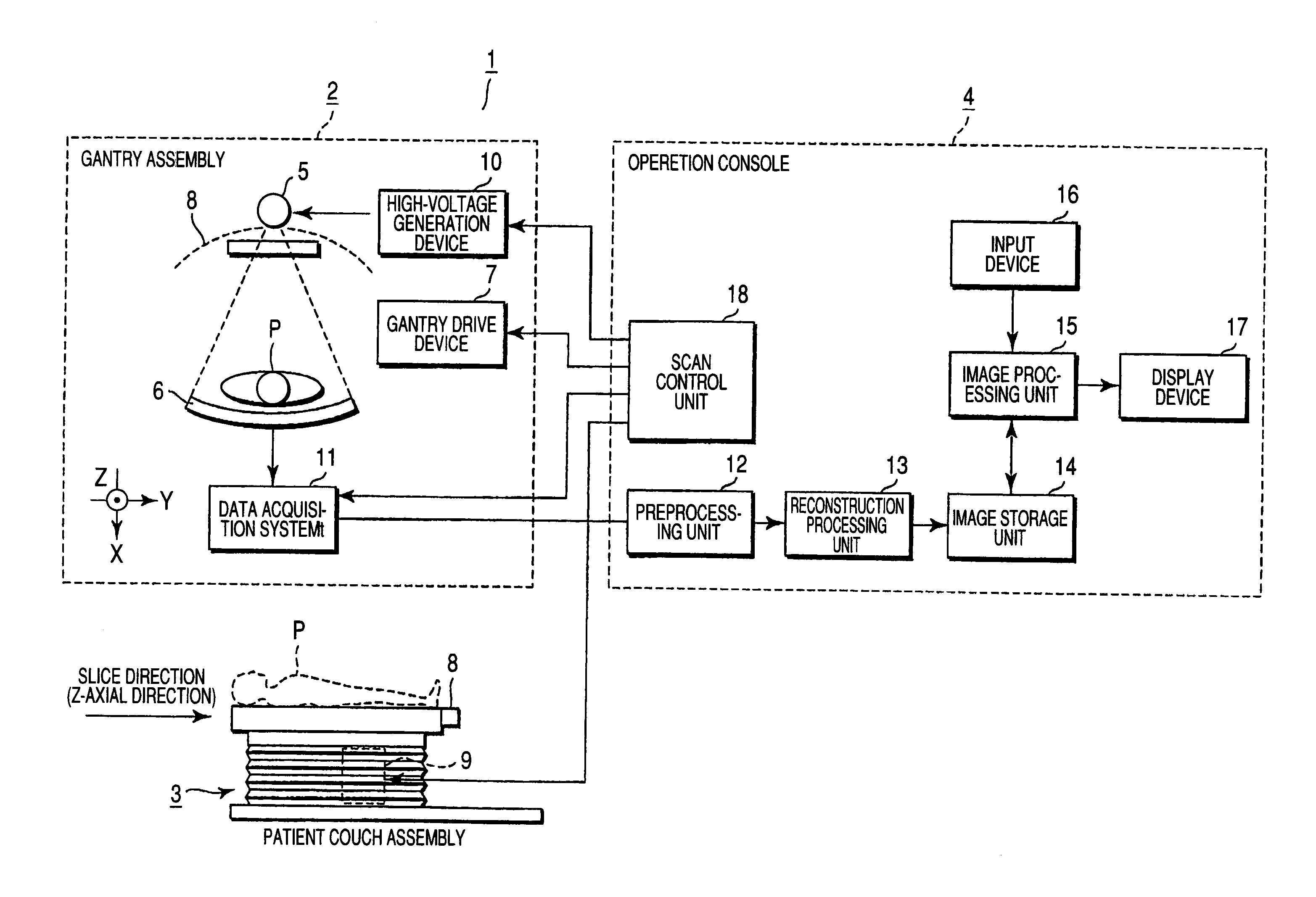
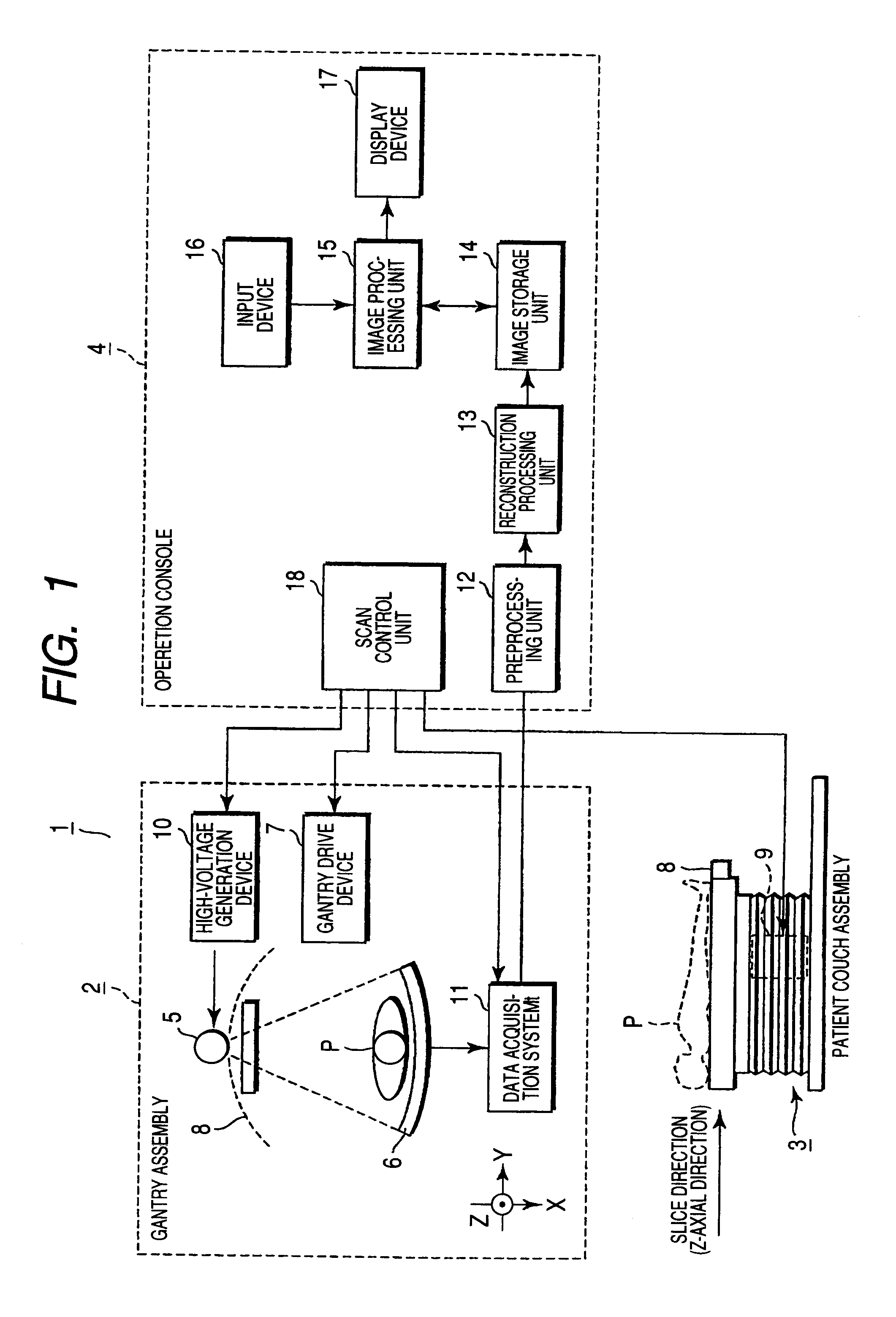
X-ray CT apparatus
ActiveUS7945013B2Suppress exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPower flowEllipse
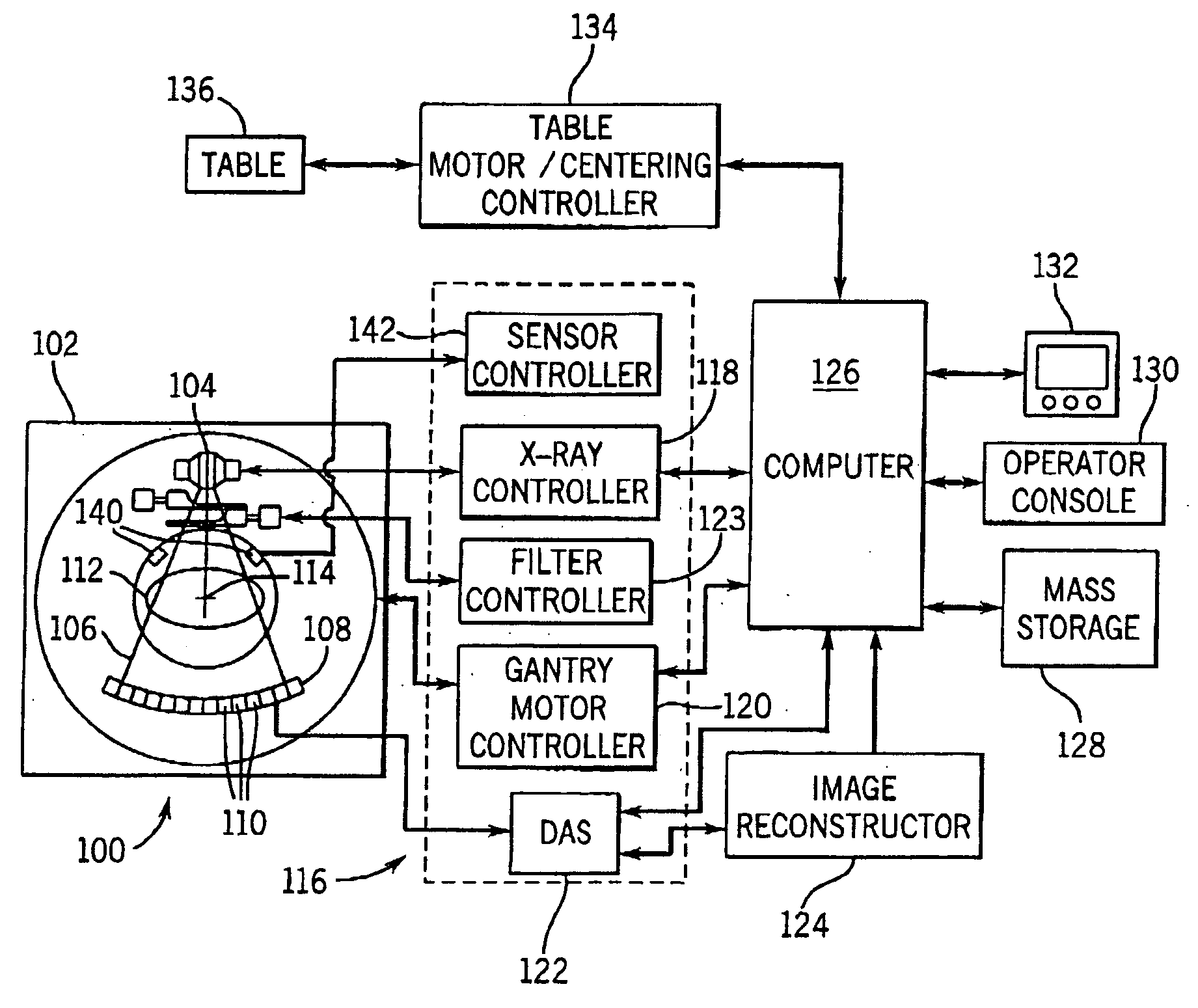
An X-ray CT apparatus acquires a scanogram of an object to be examined, generates an ellipse model having an X-ray attenuation coefficient equivalent to that of water and approximated to a tomographic image of the obtained imaged portion from the feature quantity of the projection value profile, determines whether or not the generated elliptic model is adequate as a model of the imaged portion from another feature quantity with respect to the projection value profile, generates a corrected elliptic model according to yet another feature quantity with respect to the projection value profile if the elliptic model is determined to be inadequate, and controls the modulation of the tube current in an X-ray source so that a predetermined target SD value is maintained in any scanning position when a tomographic image is reconstructed according to X-rays transmitted through the object by using the elliptic model or the corrected elliptic model.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
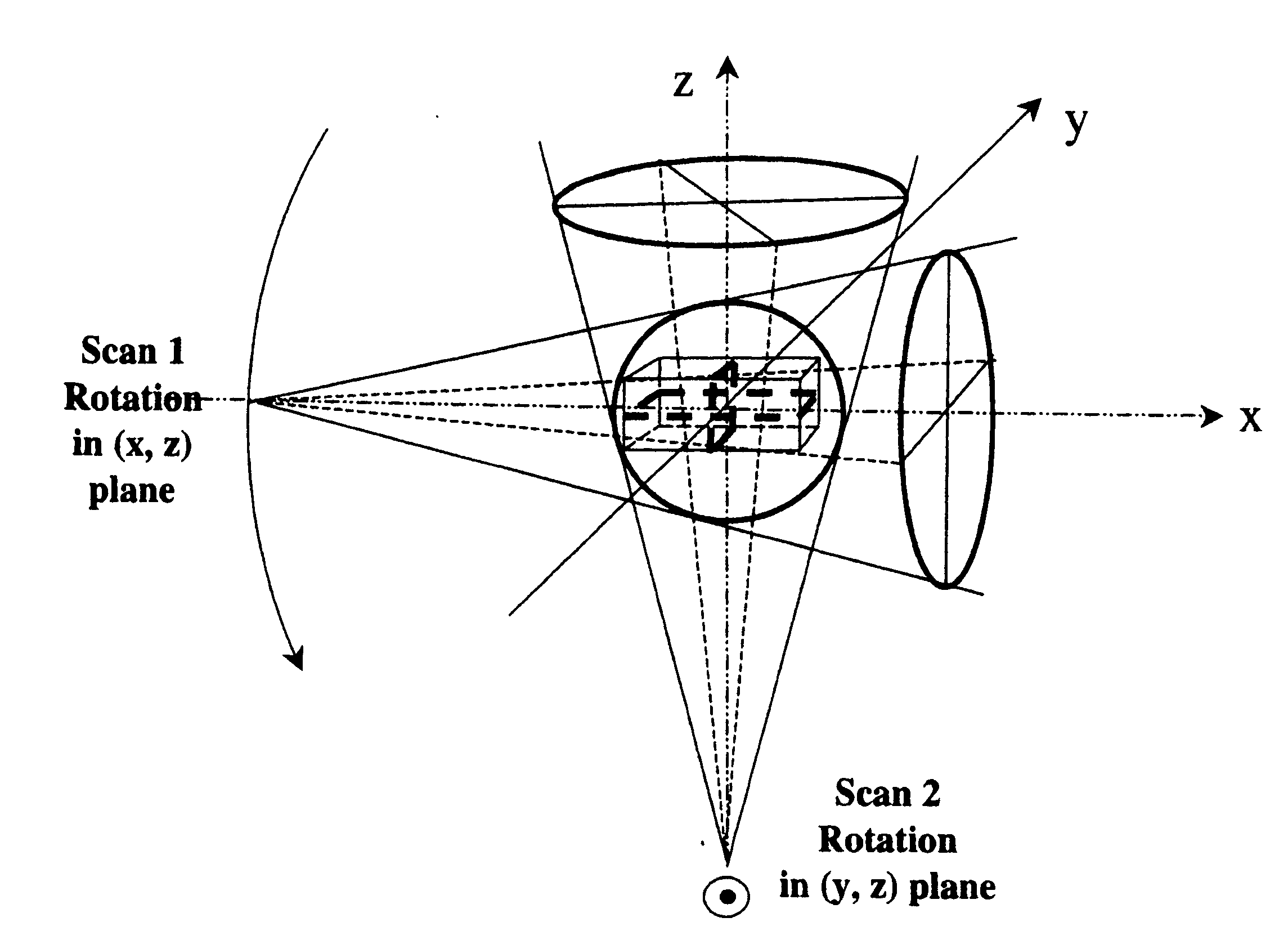
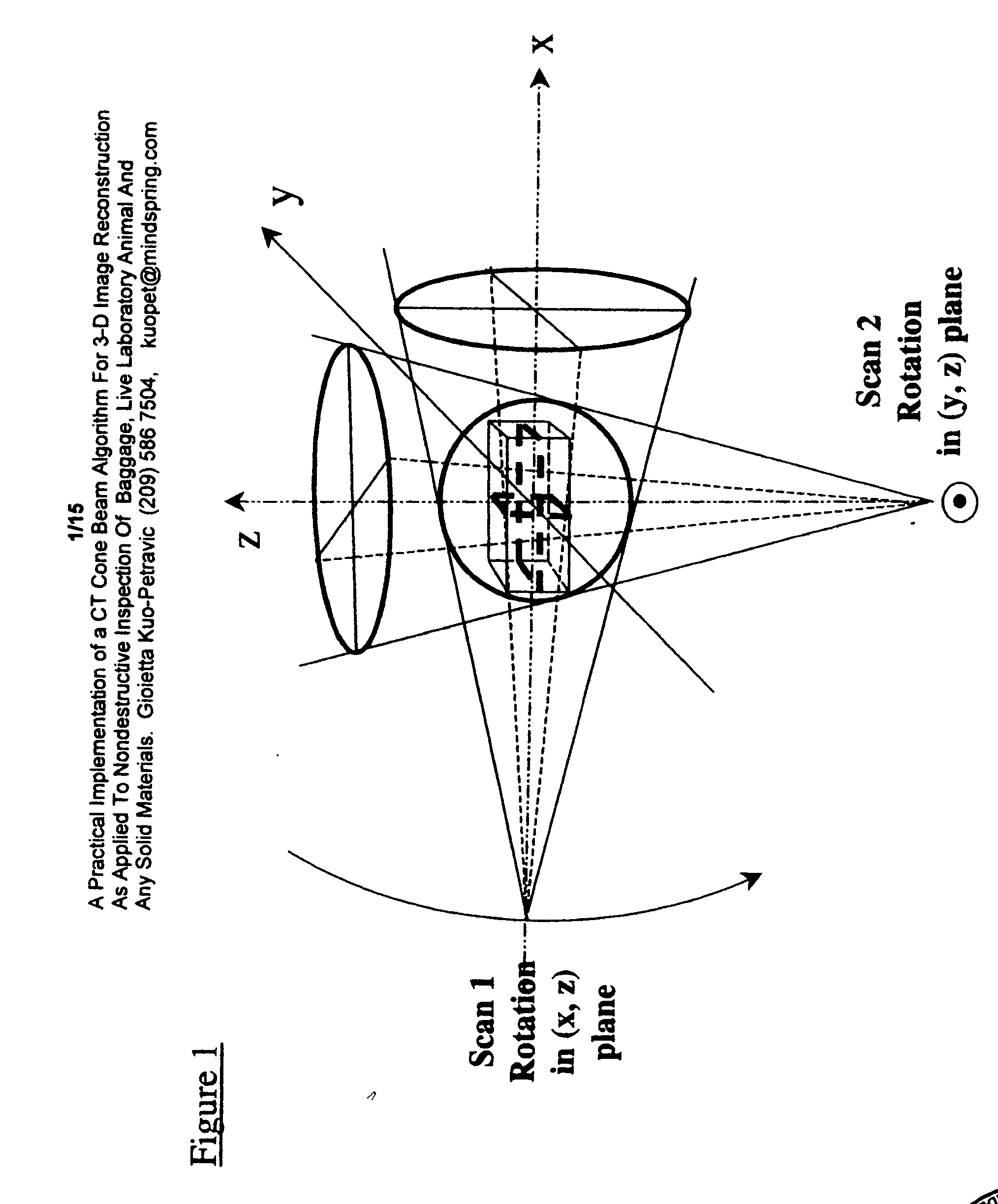
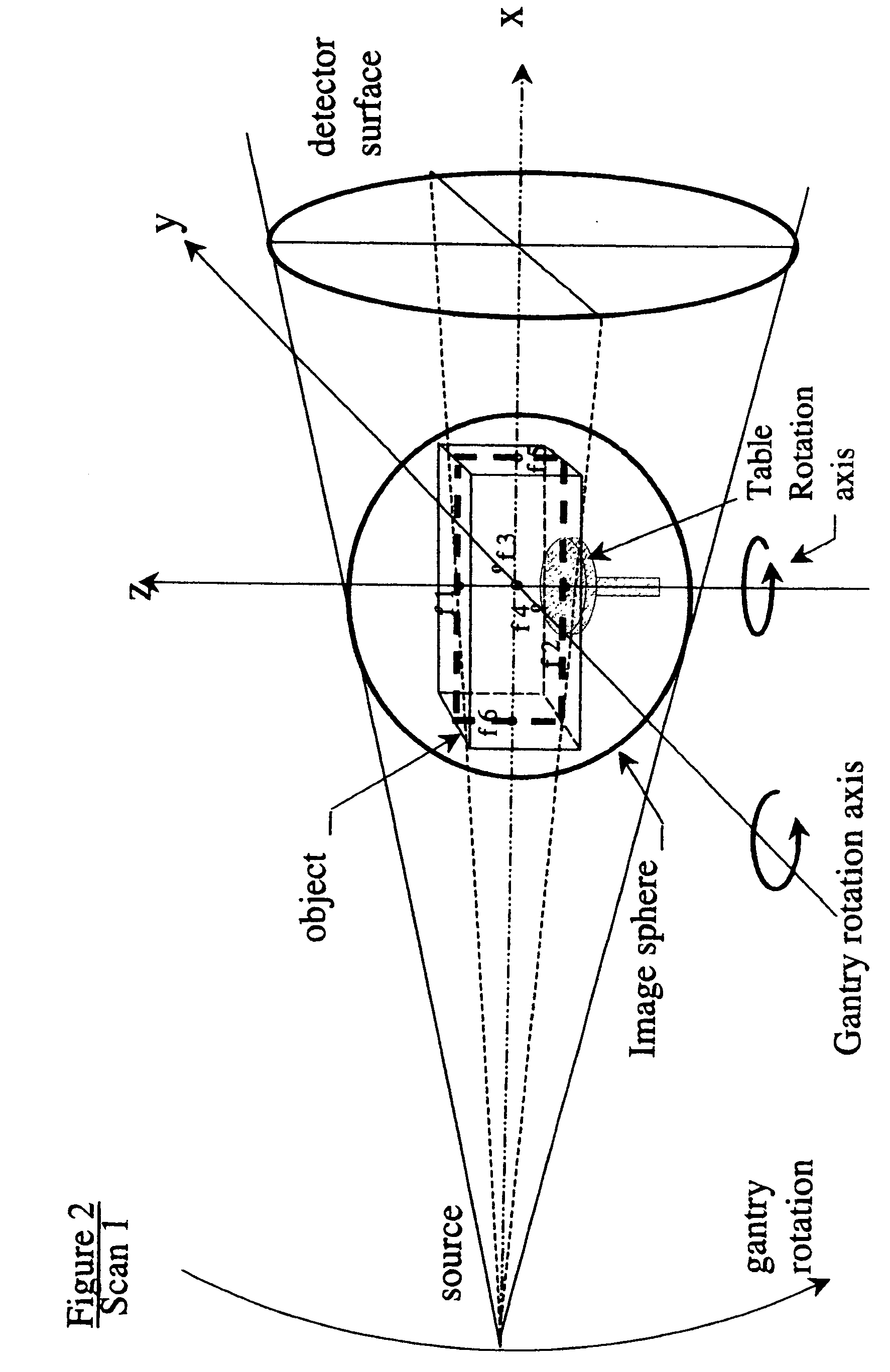
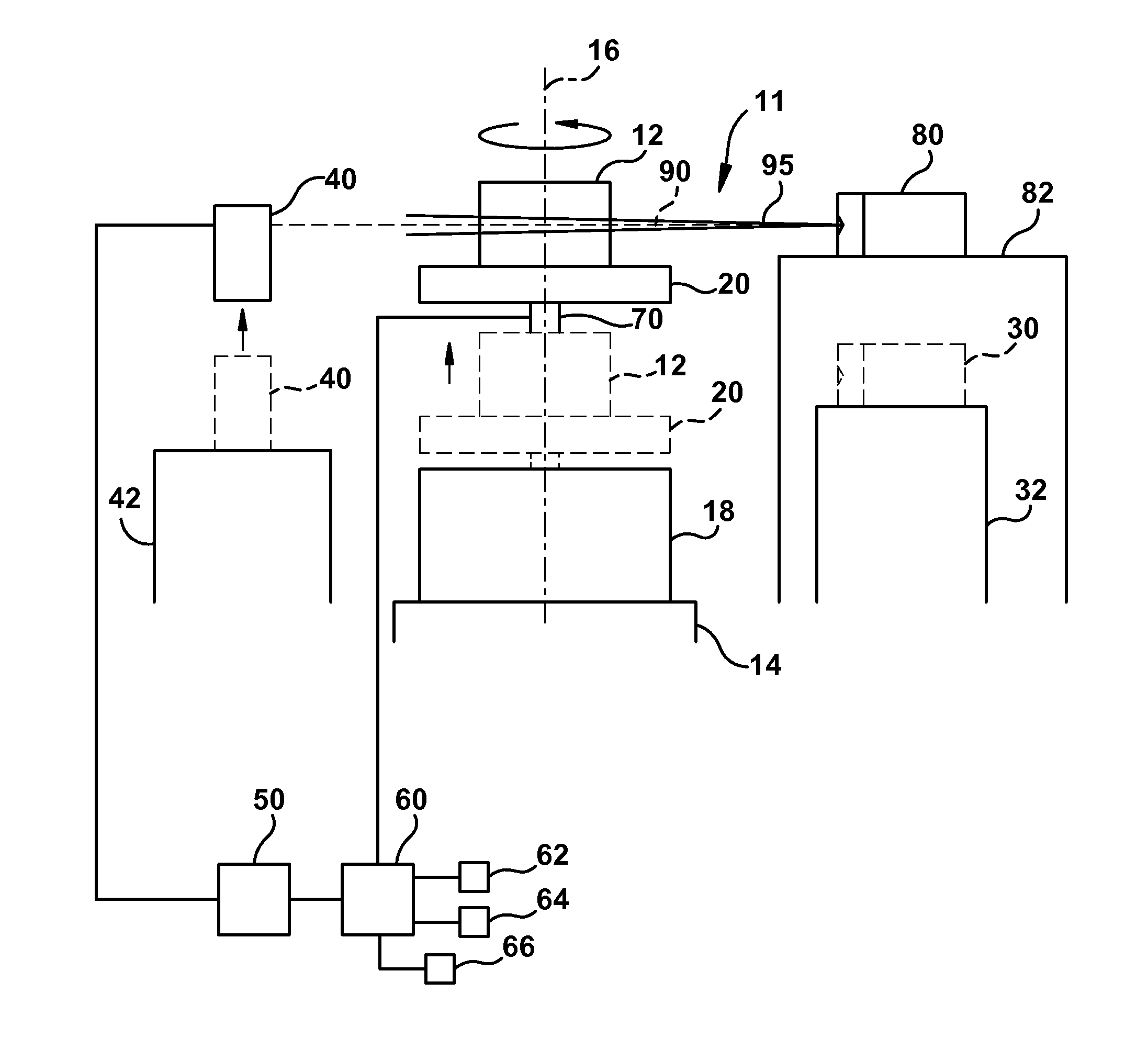
Practical implementation of a CT cone beam algorithm for 3-D image reconstruction as applied to nondestructive inspection of baggage, live laboratory animal and any solid materials
InactiveUS20050041771A1Enhance the imageReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingData setBeam source
This invention uses the CT (Computer Tomography) principle to obtain nondestructive image of different x-ray attenuation inside an object. In order to have fast data acquisition and high resolution, a cone beam source and a 2-D detector surface are necessary. However, for good cone beam image reconstruction datasets from 2 orthogonal planes about the object are required (U.S. Pat. No. 5,375,156,) December 1994 of Kuo-Petravic and Hupke), thus making its implementation difficult as well as raising the cost of the scanner. Here, we suggest a practical way of implementing the 2 orthogonal planes theory by replacing the 2 gantry rotations by 2 rotations of only one fixed gantry and one movement of the object position, making it simple and low cost. This method is applied to the nonintrusive inspection of baggage or imaging of mice for pharmaceutical purposes where the object has to remain in a horizontal plane throughout the procedure. This algorithm can also be applied to nondestructive testing of any solid materials, for example: imperfections in semi-conductors, fracture in turbo-engine blades, composition of uranium drums etc.
Owner:KUO PETRAVIC GIOIETTA +2
Classification method for sedimentary rocks
ActiveUS7869565B2Improve accuracyPermeability/surface area analysisMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationClassification methodsMaceral
A method of determining a parameter of interest of reservoir rock formation is described using the steps of measuring an x-ray attenuation or absorption distribution of a sample of said rock formation, identifying the mineral phase part of said distribution, and subdividing the mineral phase part of said distribution to derive classification or rock type information of said sample.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
XRD-based false alarm resolution in megavoltage computed tomography systems
InactiveUS7844027B2Increase rangeImprove signal-to-noise ratioImaging devicesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh densityMegavoltage ct
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Low temperature process for making radiopac materials utilizing industrial/agricultural waste as raw material
ActiveUS20060066013A1Saving on accountConsiderable heat energyCeramic shaping apparatusNon-woven fabricsPyrophyllitePhosphate binder
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
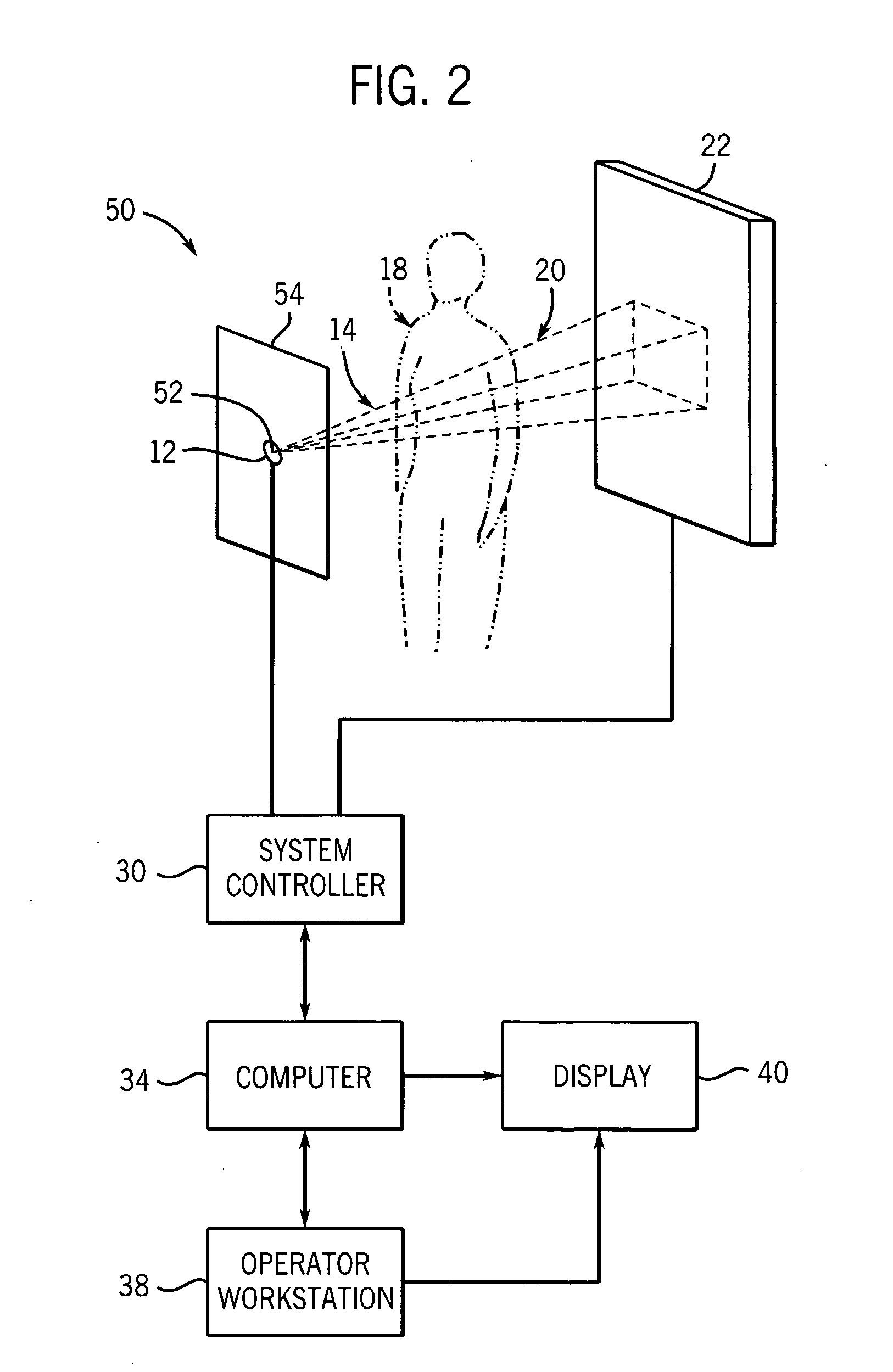
Optical alignment system and alignment method for radiographic X-ray imaging
InactiveUS7794144B2Eliminate differencesTomographyDiaphragms for radiation diagnosticsSoft x rayX-ray optics
An X-ray optical alignment system for X-ray imaging devices includes a visible-light point source and a multi-axis positioner therefor, fixedly mounted with respect to the X-ray focal spot. A mirror or beamsplitter is fixedly mounted with respect to the X-ray focal spot and disposed in the beam path of the X-ray source. The beamsplitter reflects light emitted from the light source and transmits X-rays emitted from the X-ray source. A first X-ray attenuating grid is fixedly but removably mountable with respect to the X-ray source, having a first X-ray attenuation pattern; and a second X-ray attenuating grid is adjustably mountable with respect to the first grid having a second X-ray attenuating pattern corresponding to the first X-ray attenuating pattern. When the grids are aligned, their attenuating patterns are also aligned and allow X-rays from the X-ray source and light reflected from the beamsplitter to pass therethrough.
Owner:REFLECTIVE X RAY OPTICS
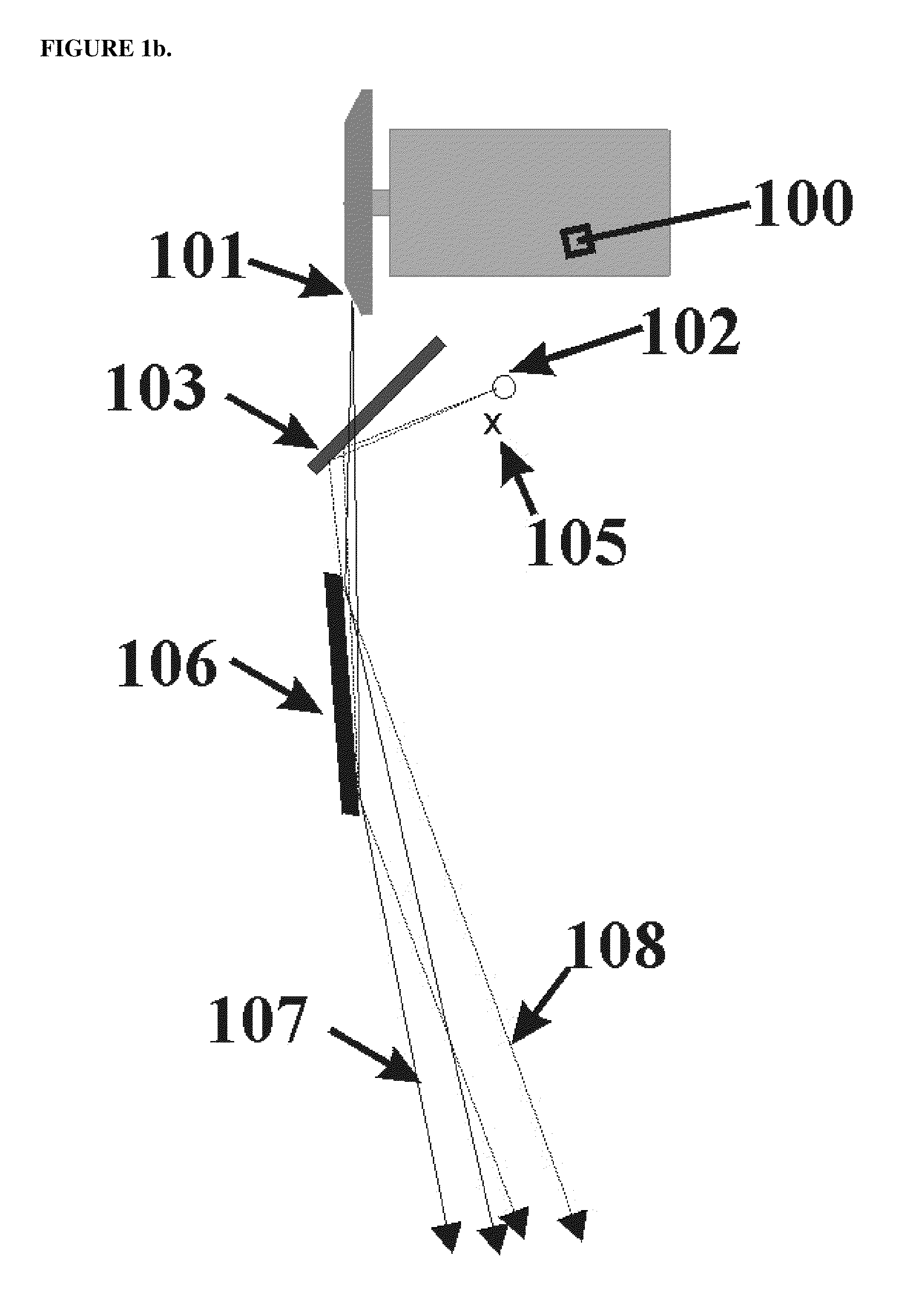
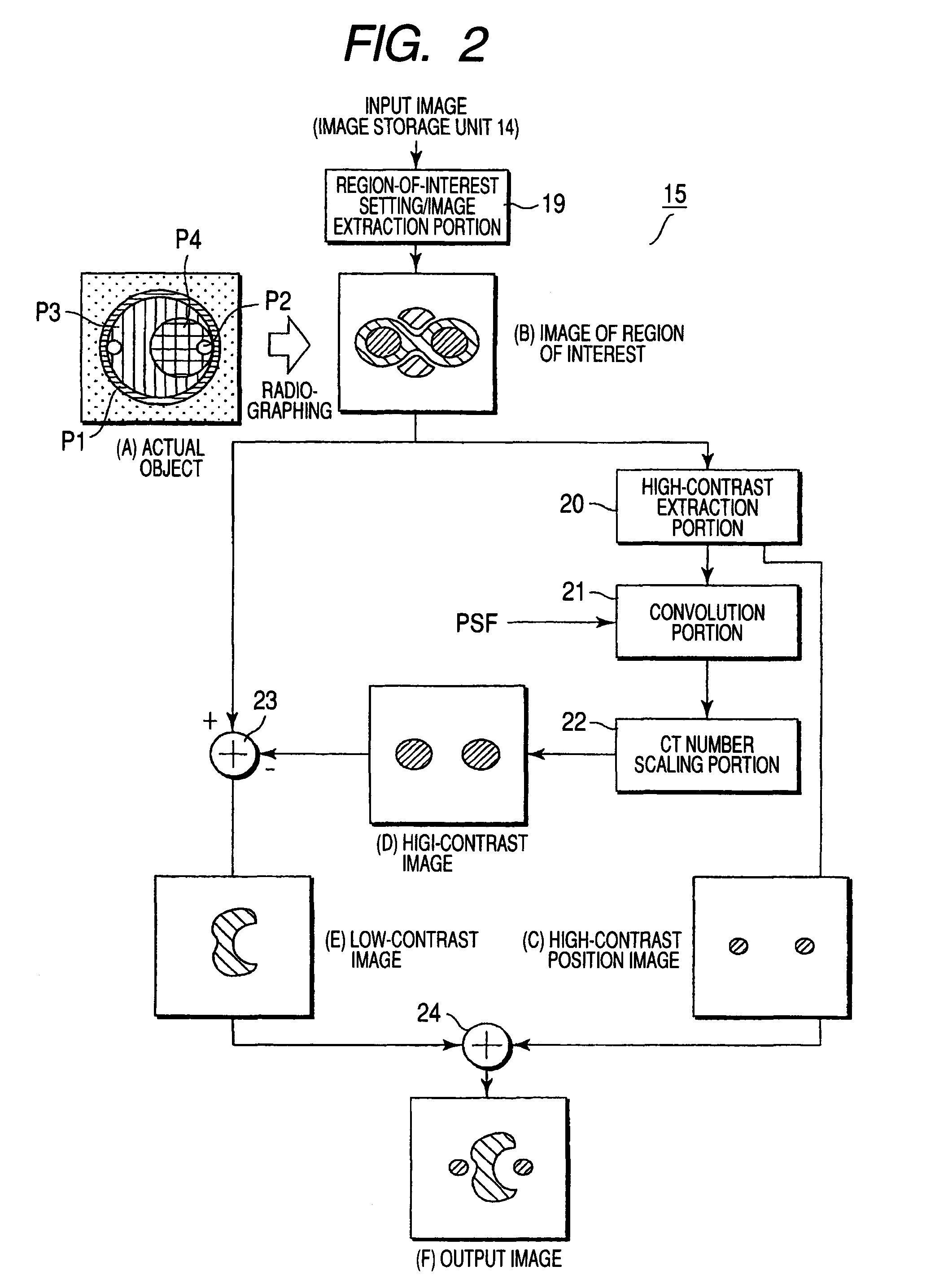
X-ray CT apparatus and image processing apparatus
InactiveUS7953263B2Reduce unclearReduction factorImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImaging processingPoint spread function
An X-ray CT apparatus includes a unit which extracts a high-contrast region of comparatively high X-ray attenuation coefficient from an image, units which generate an unsharp image concerning the high-contrast region, on the basis of the position of the extracted high-contrast region and a point spread function peculiar to the apparatus, and a unit which subtracts the unsharp image from the original image in order to generate a low-contrast image concerning a low-contrast region of comparatively low X-ray attenuation coefficient.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method and device for automatic distinguishing contrast agents in bone or calcium containing substance and soft tissue
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Non-uniform view weighting tomosynthesis method and apparatus
ActiveUS6980624B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesisBack projection
A technique is provided for non-uniform weighting in back-projection calculations in tomosythesis. The non-uniform weighting may include weighting based on a count map of the number of times pixels of individual slices are traversed by radiation in different projections. Weighting may also include non-uniform functions for contributions of features at different slice level to the sensed X-ray attenuation system response inconsistencies are accounted for by further weighting based upon projection maps which may be created in separate system calibration or configuration routines.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com