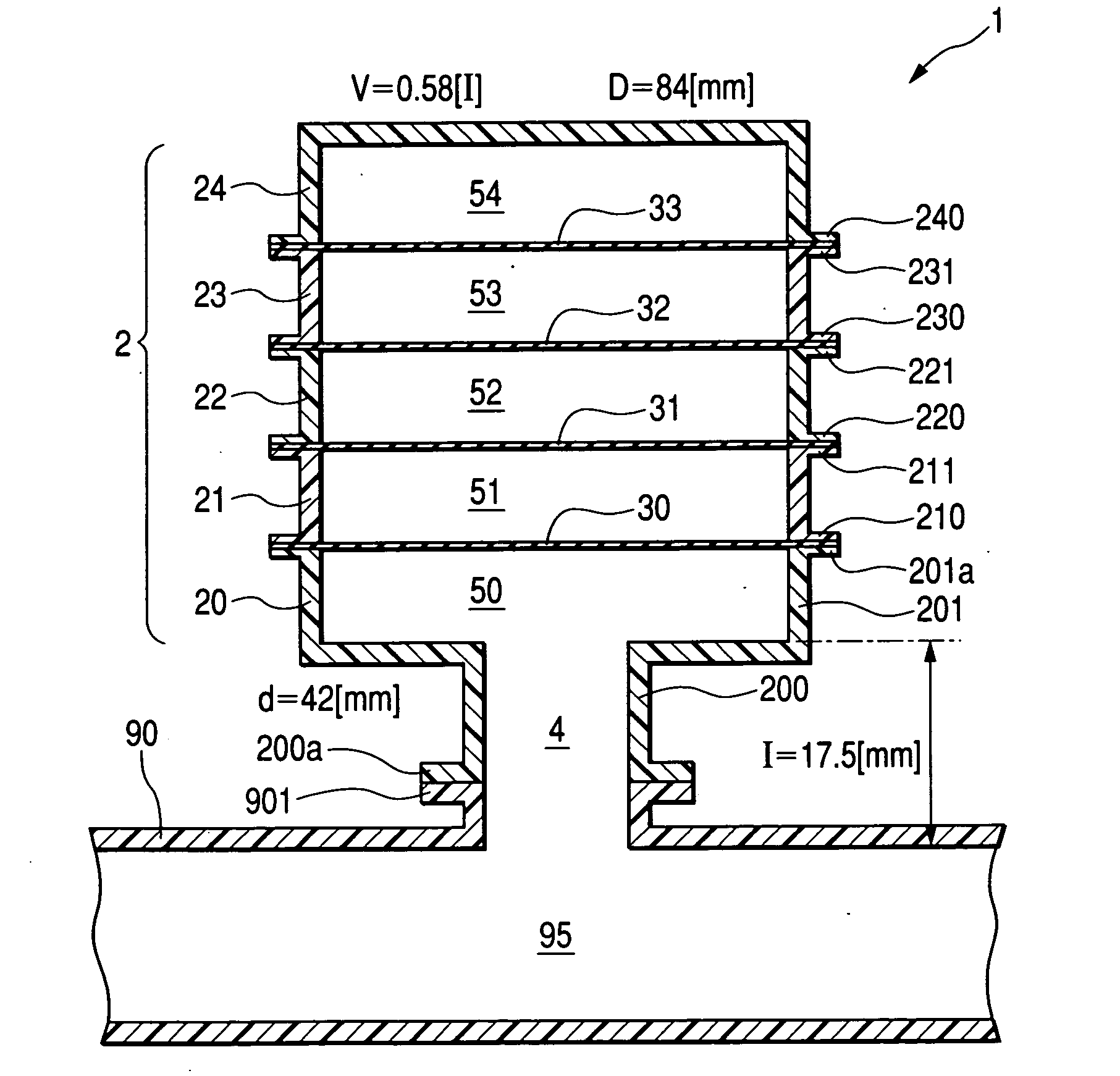
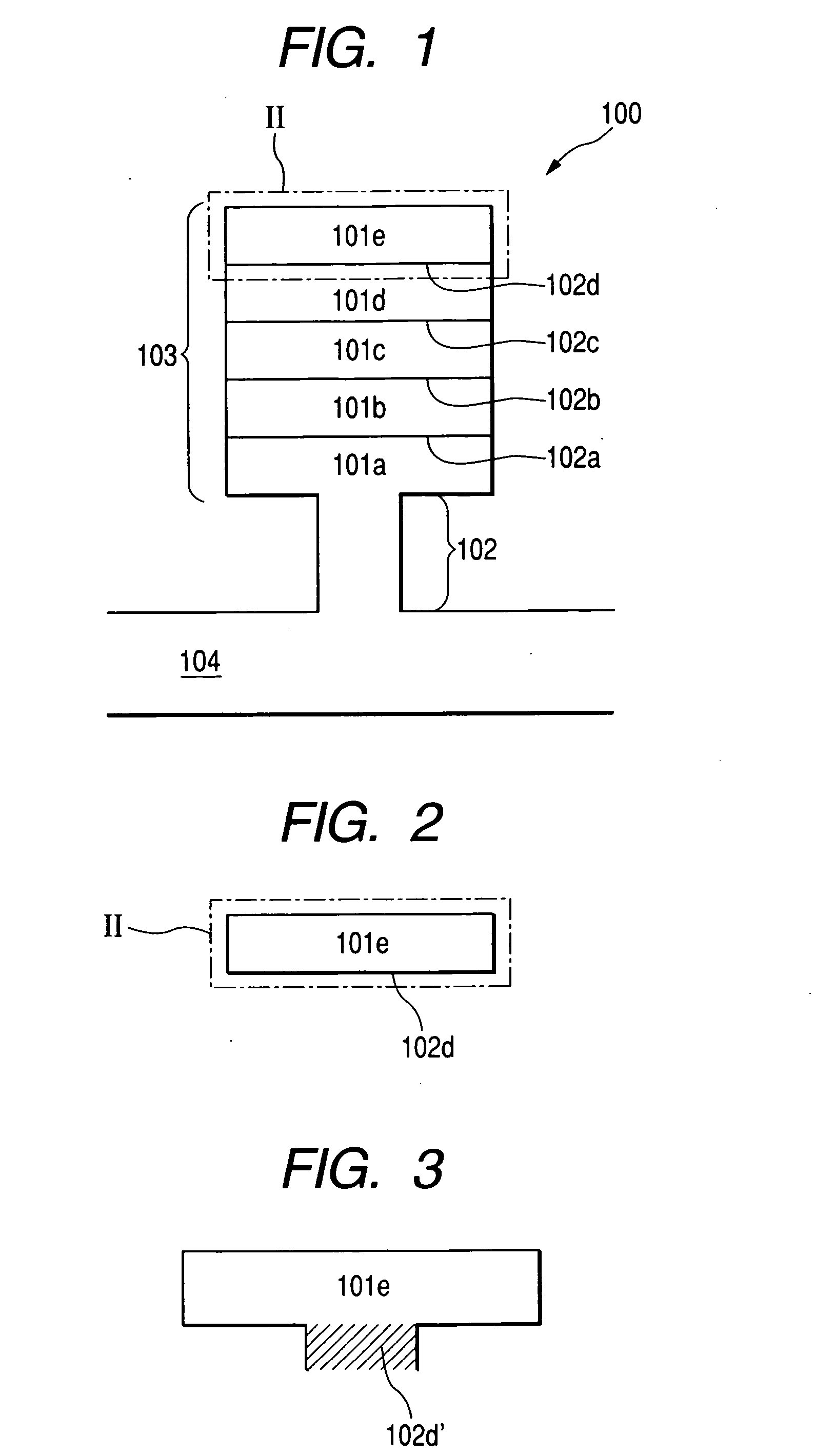
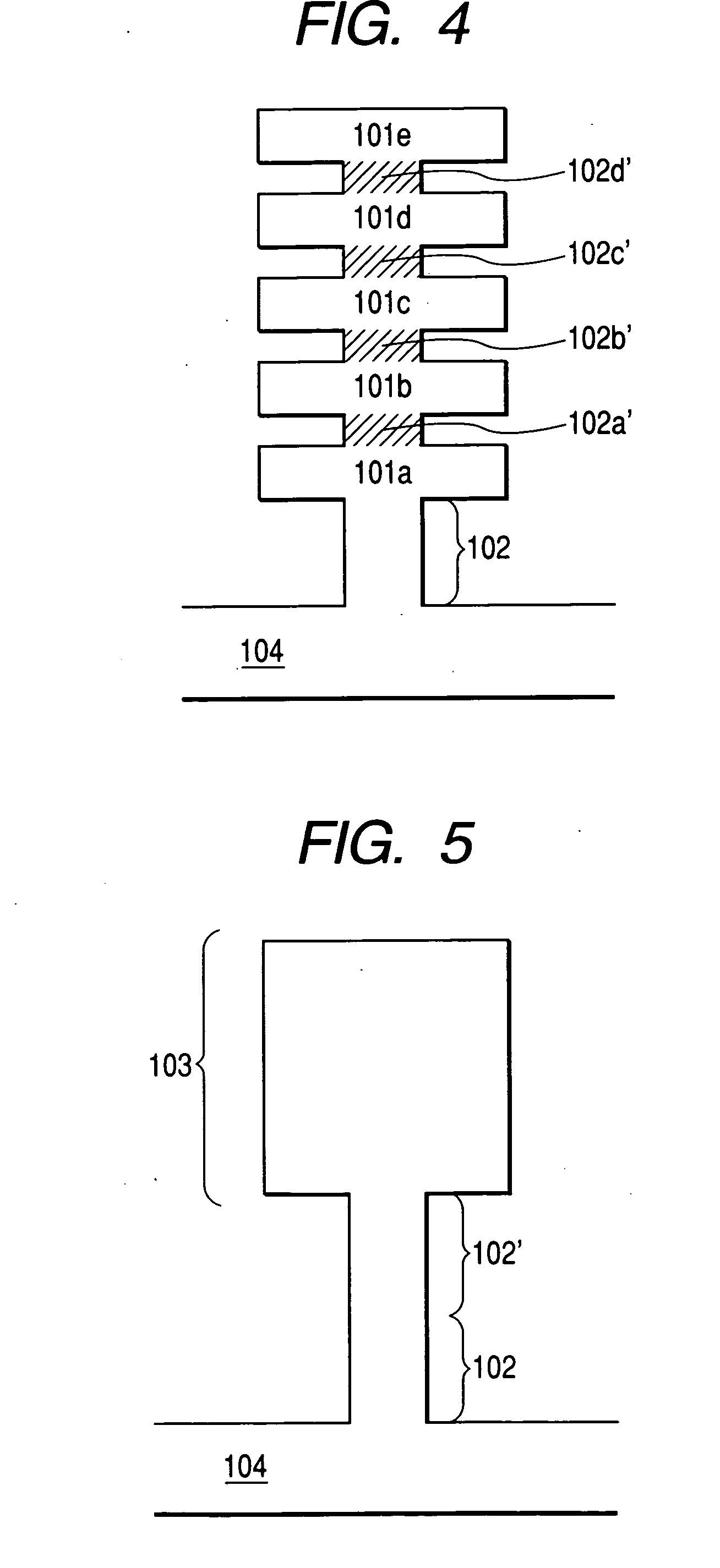
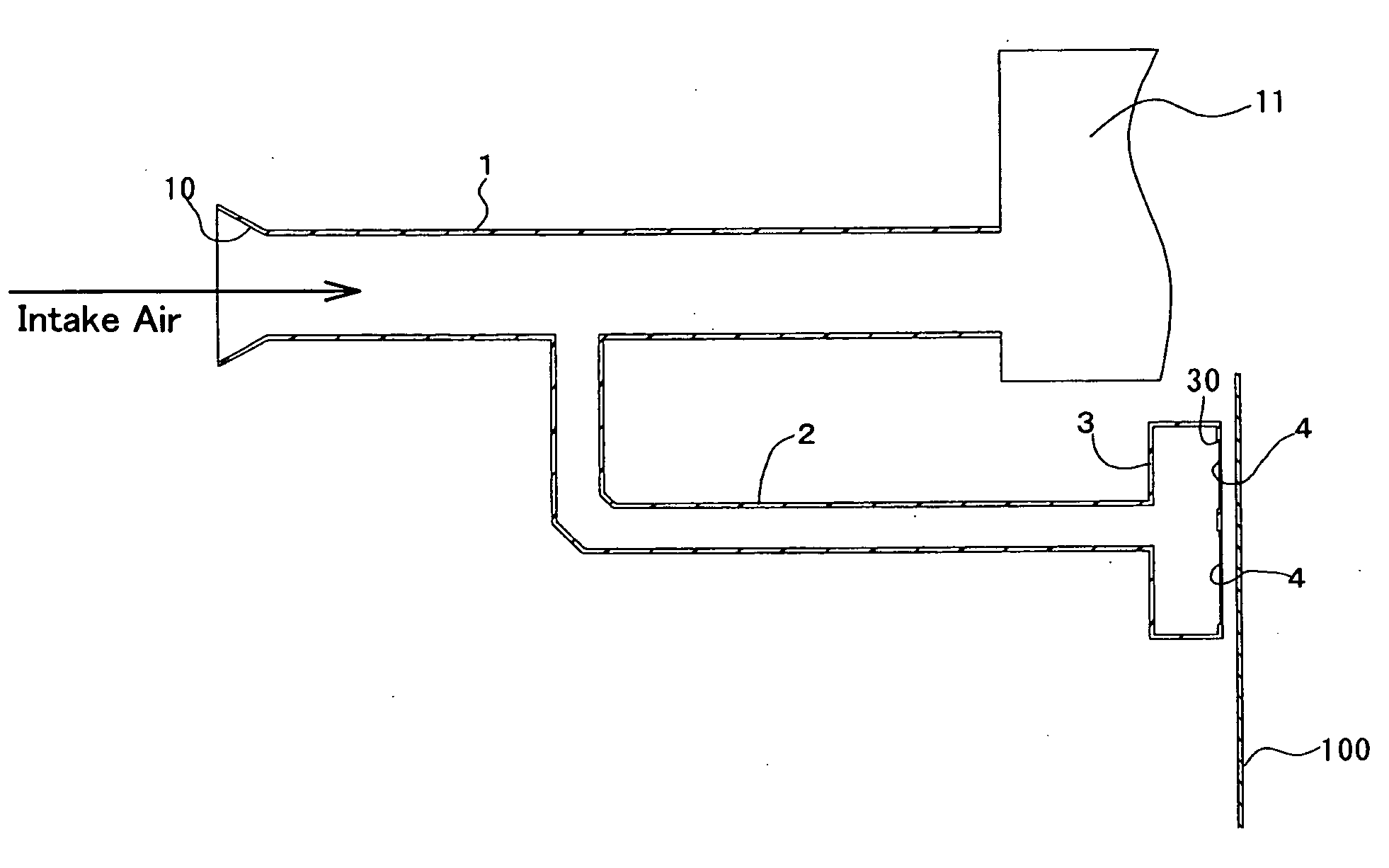
Patents
Literature
4245results about "Air intakes for fuel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
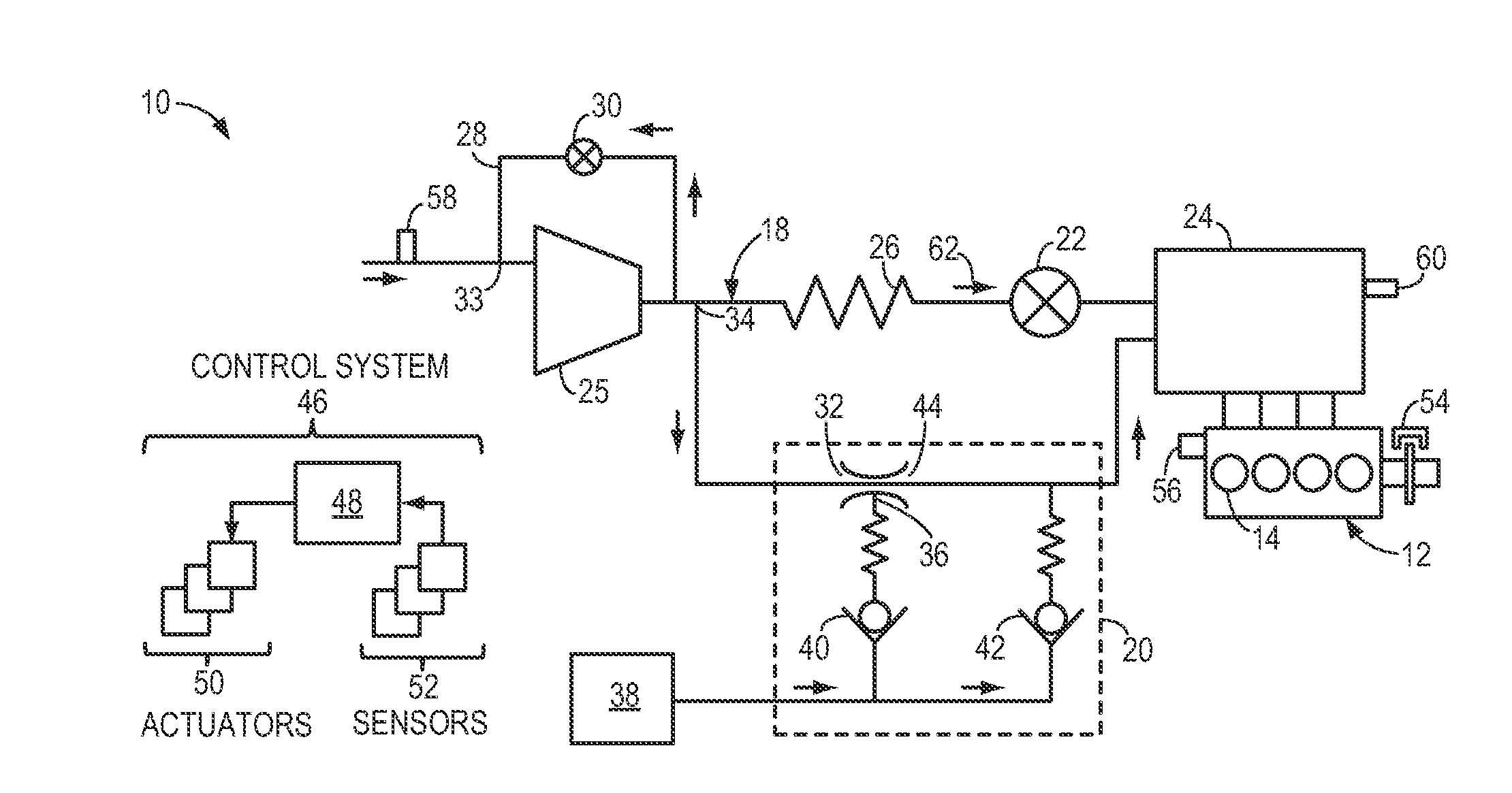
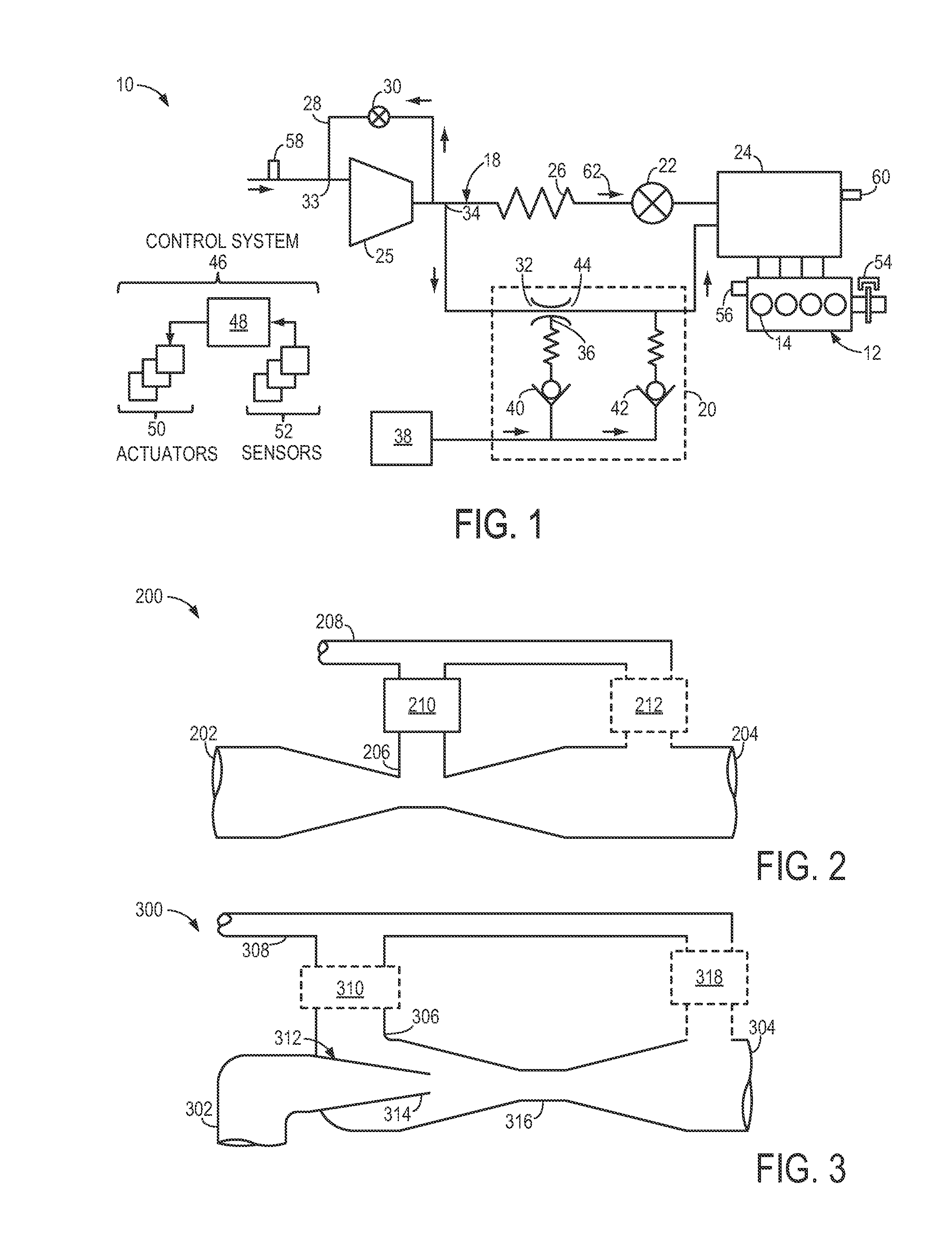
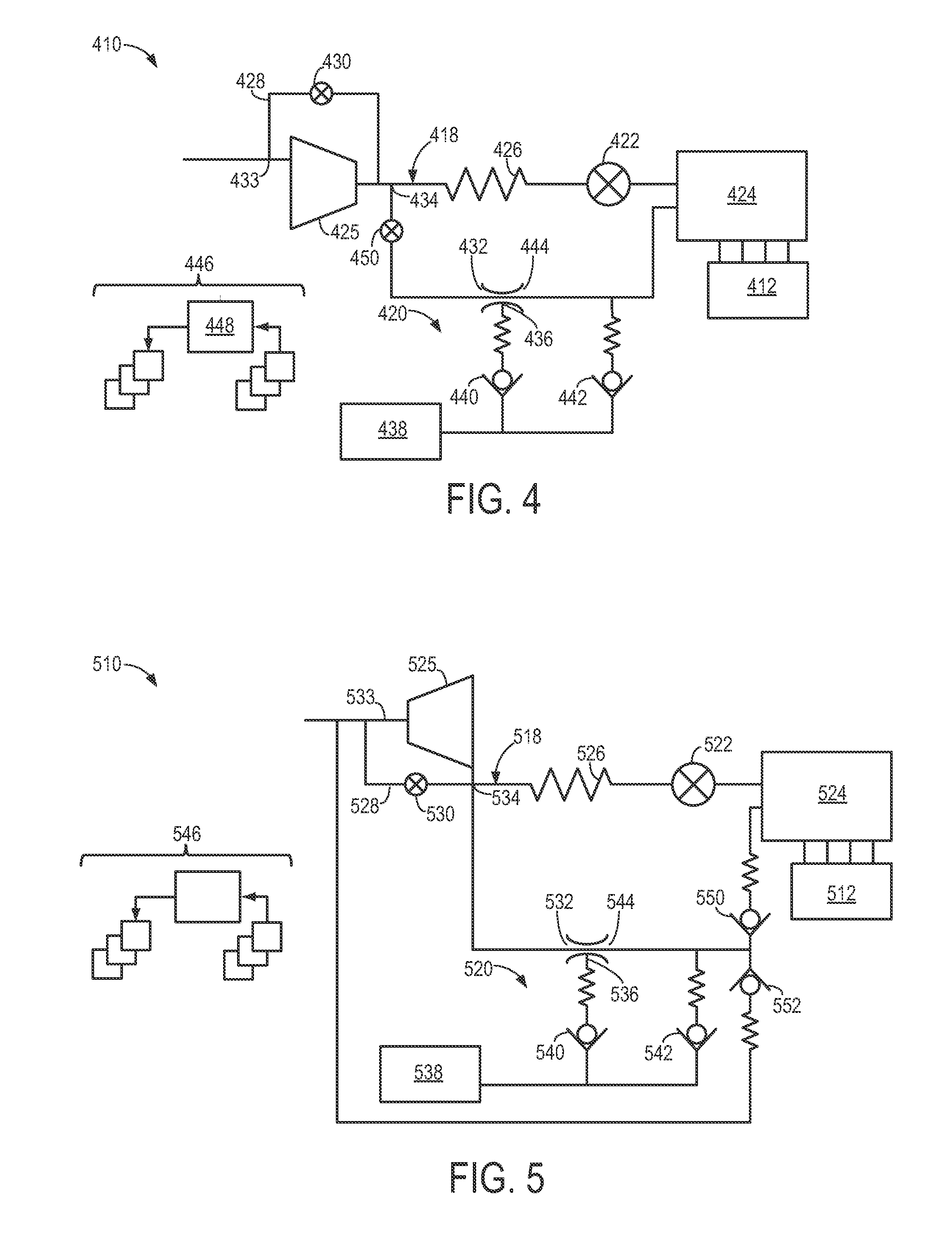
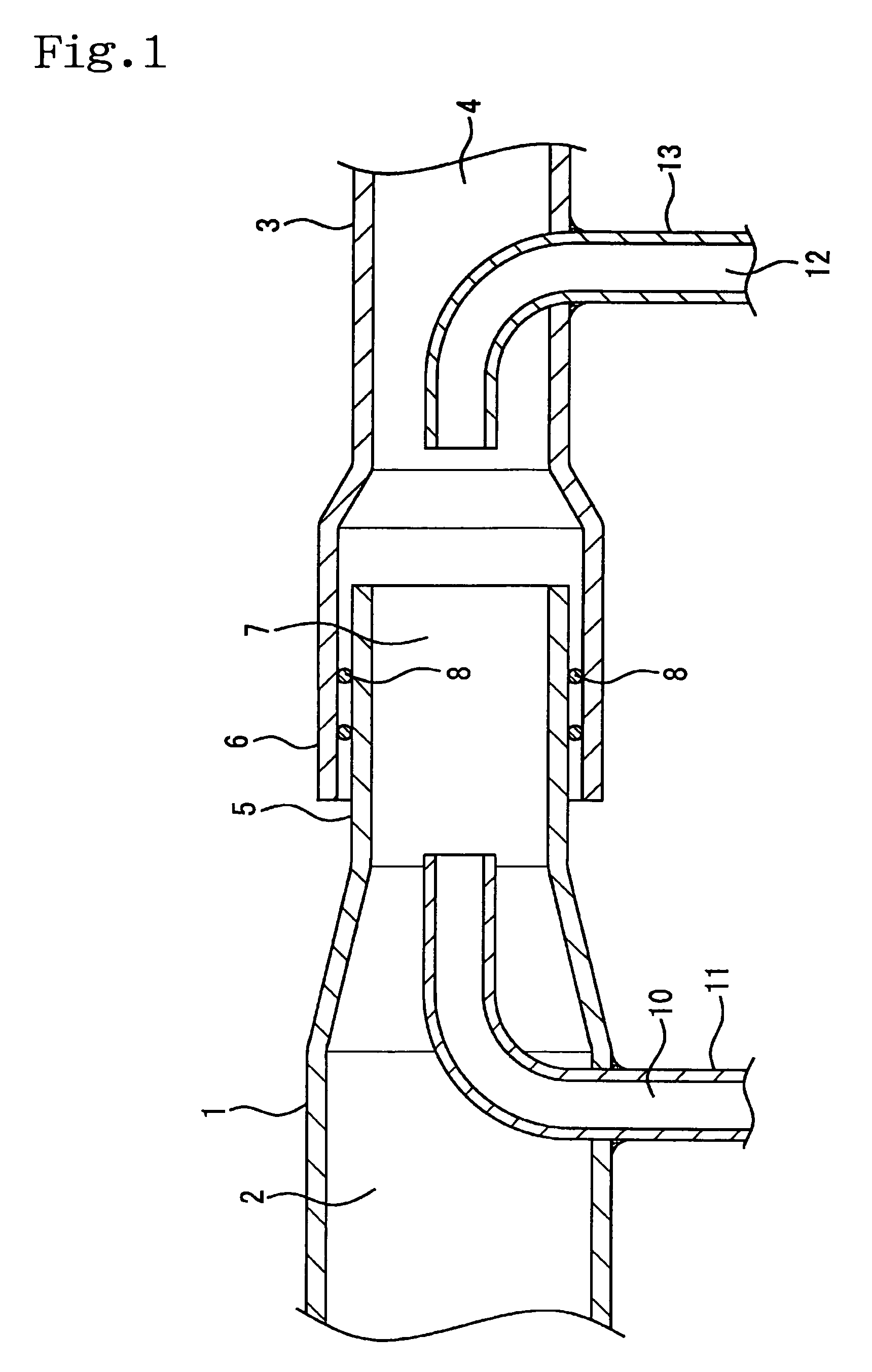
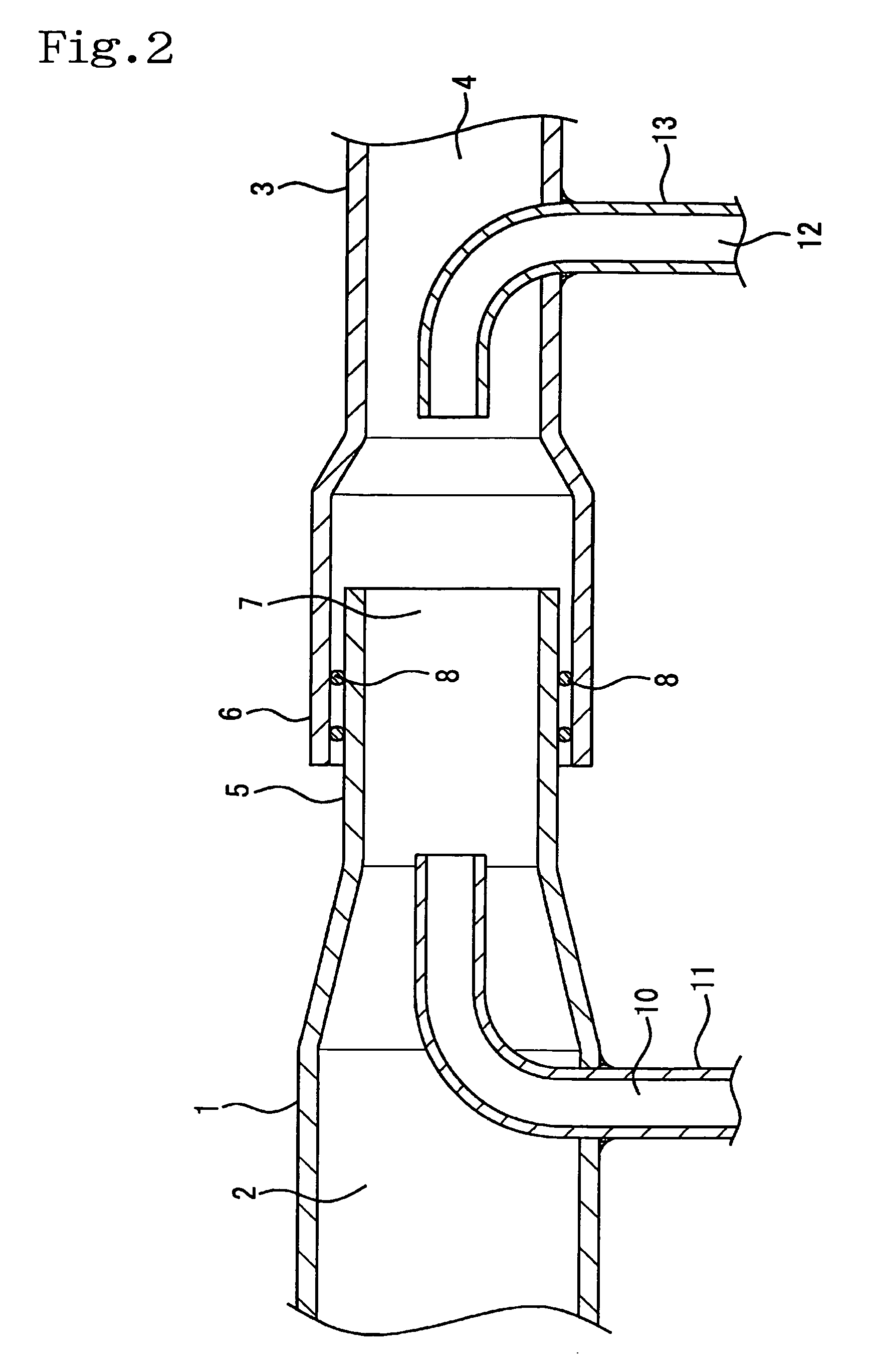
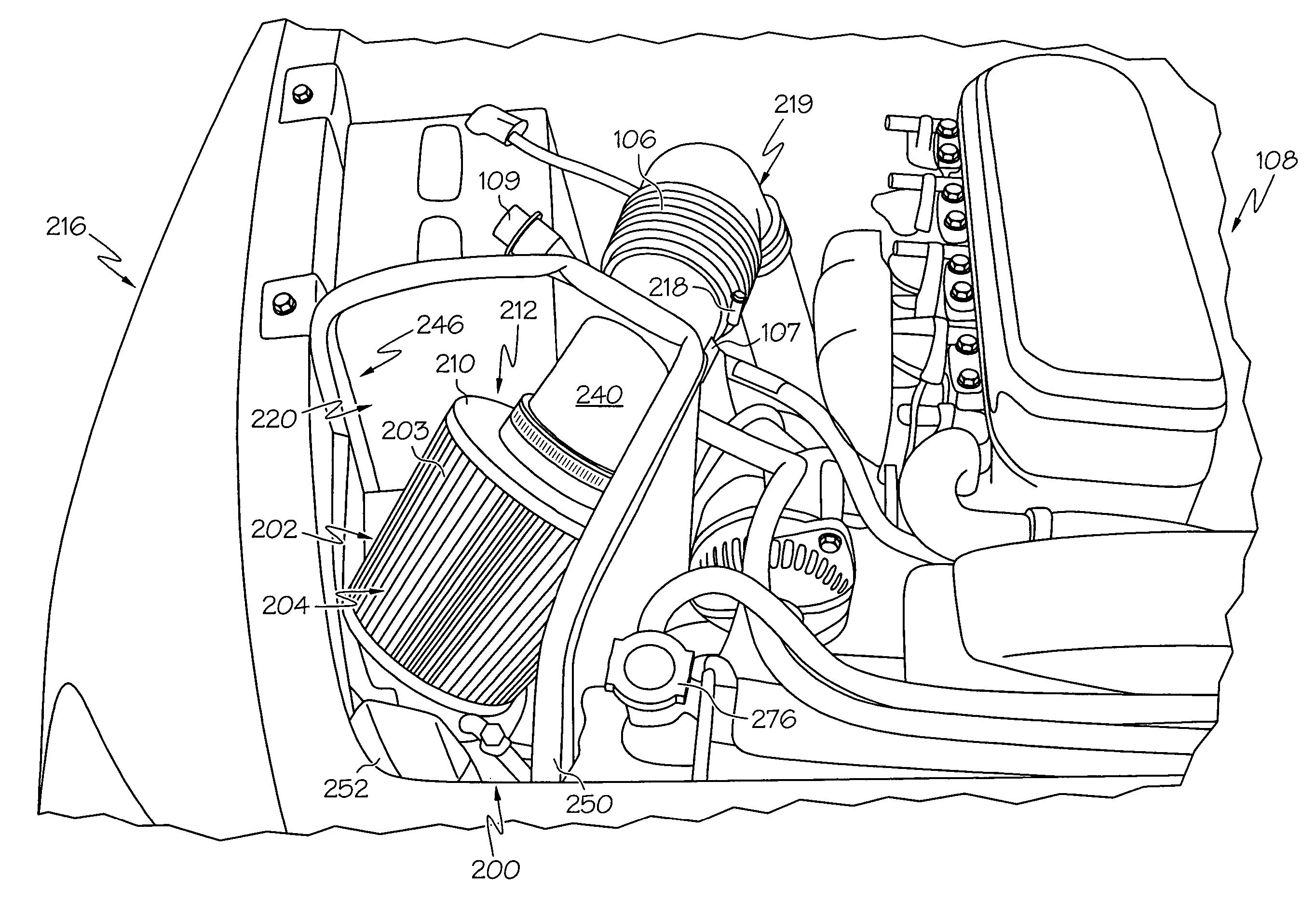
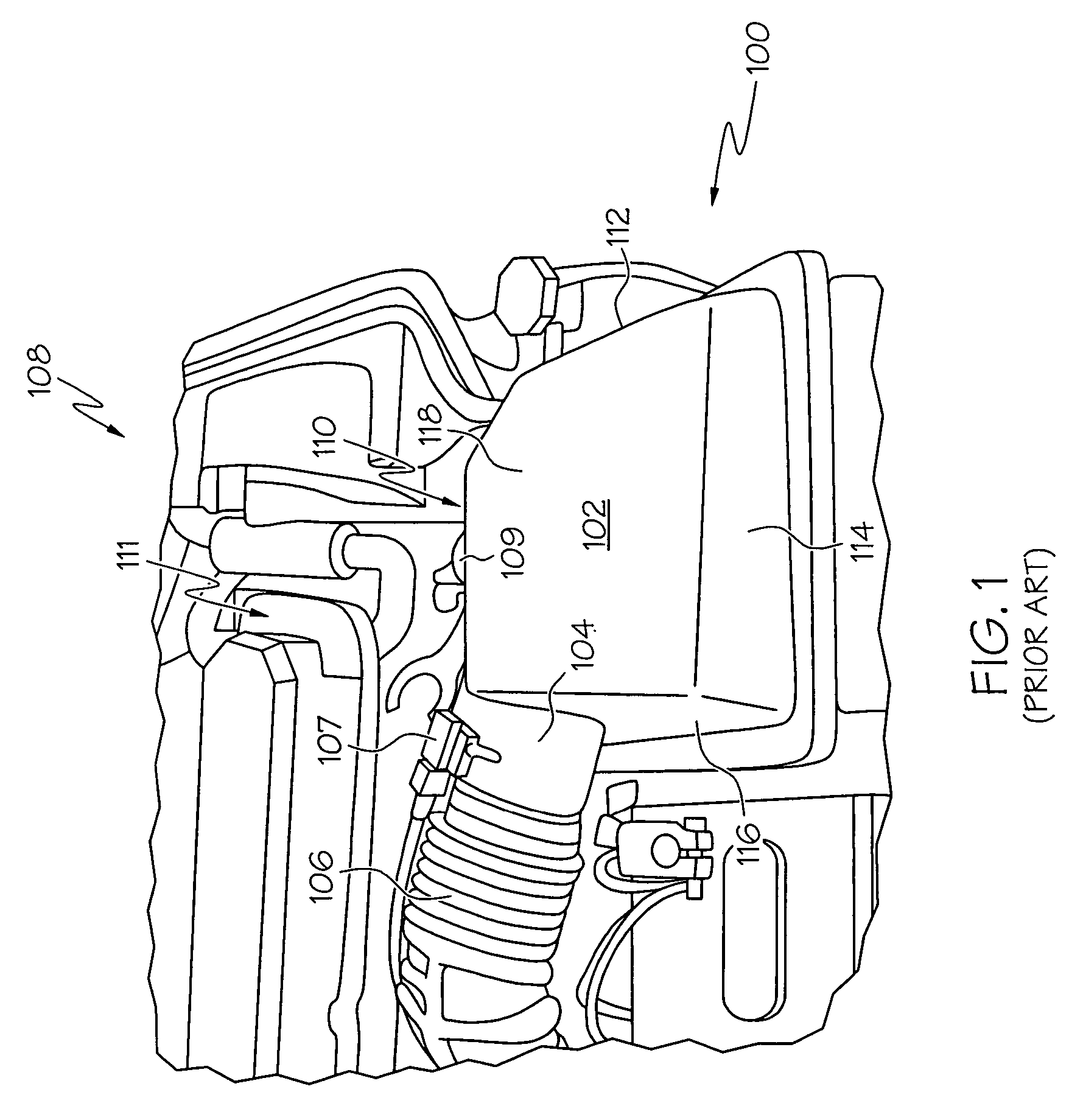
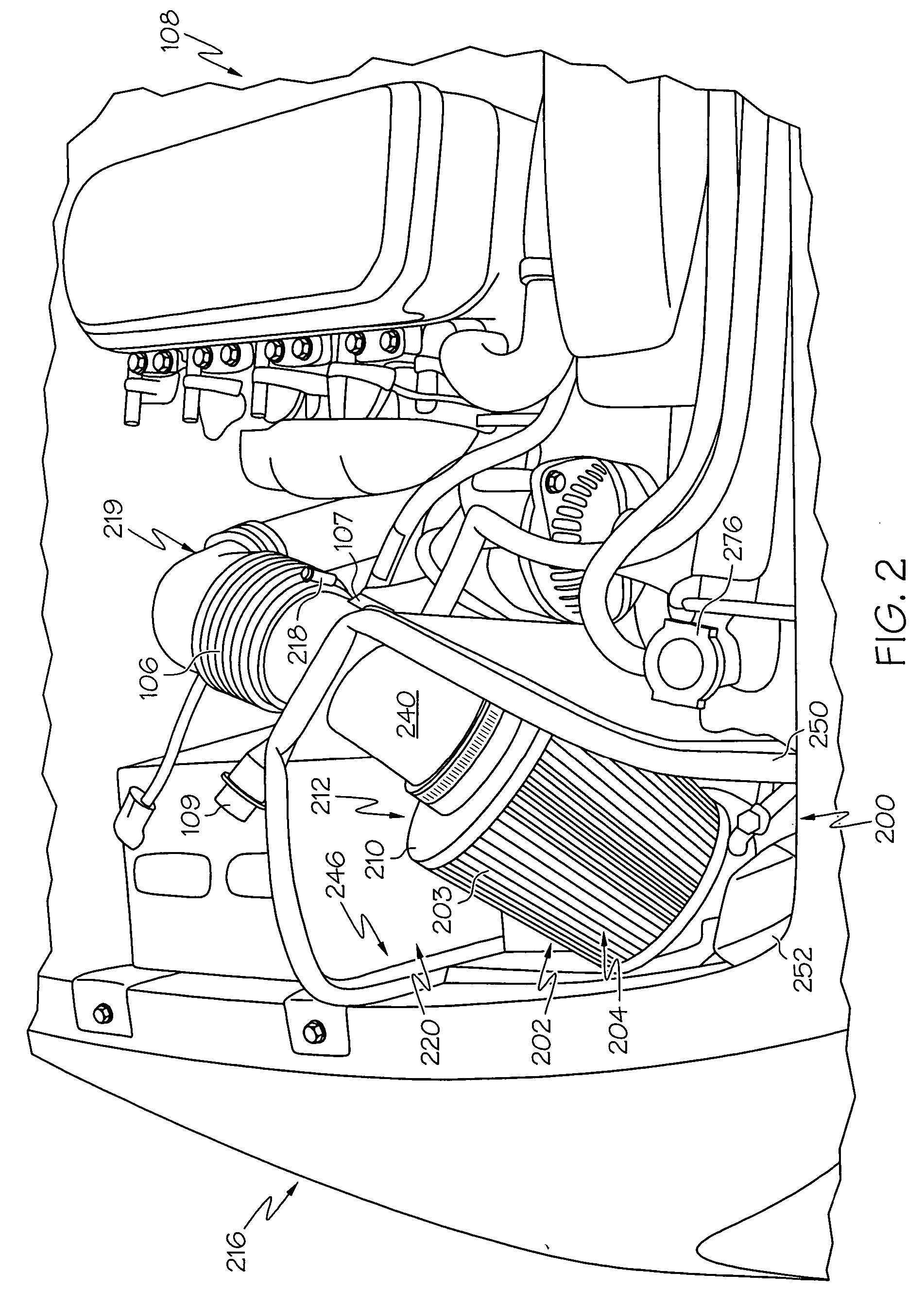
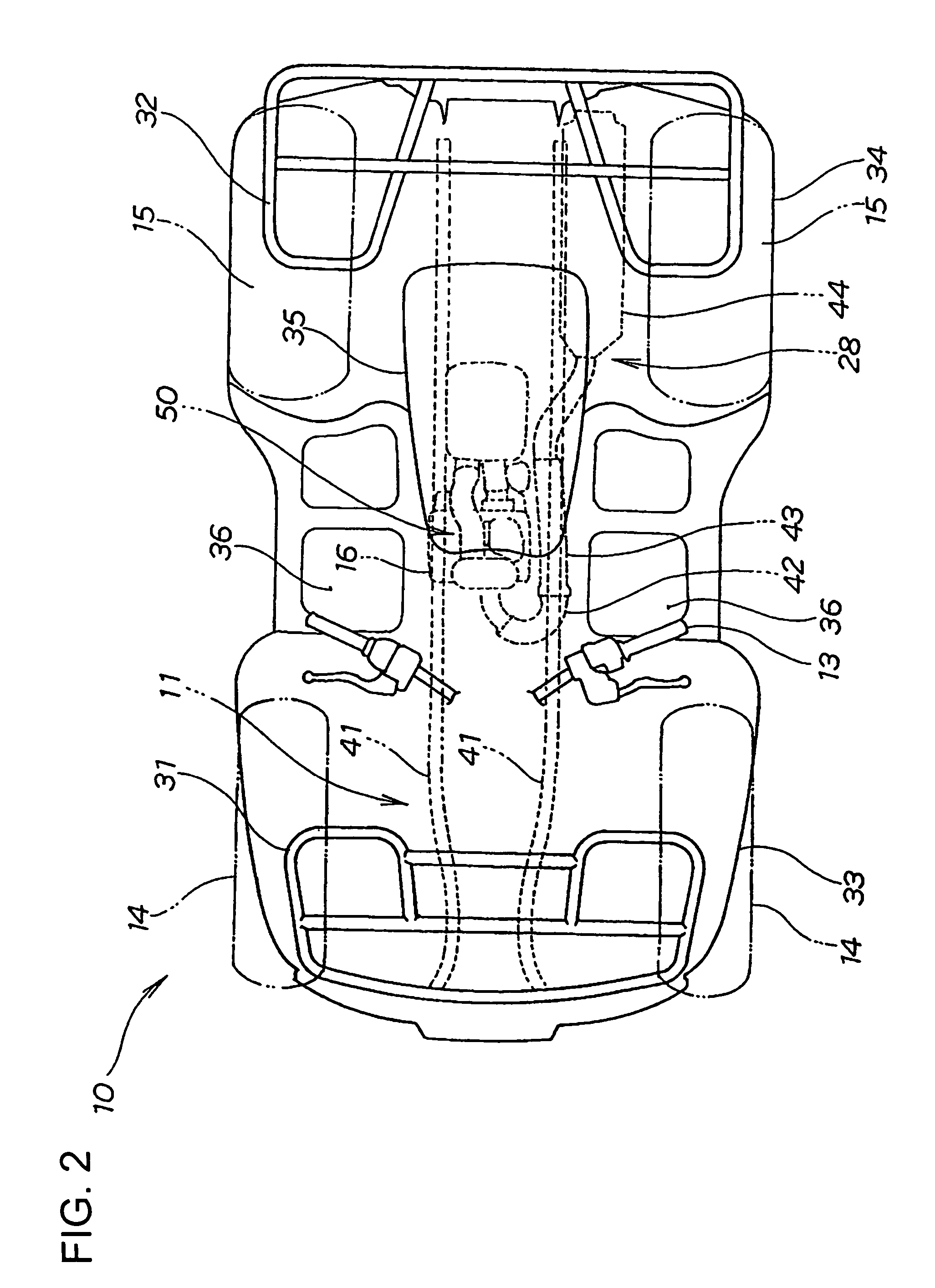
Intake system including vacuum aspirator
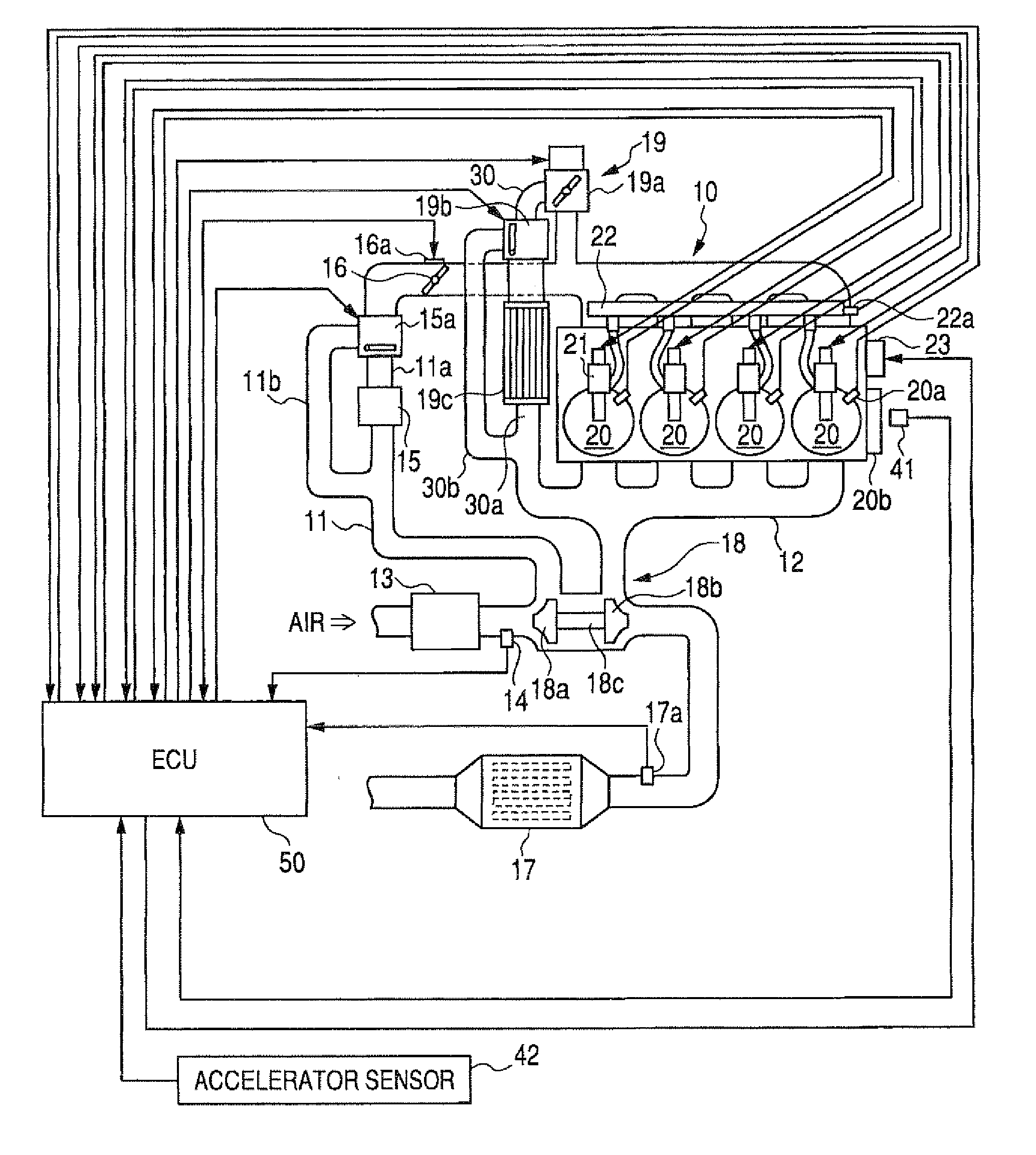
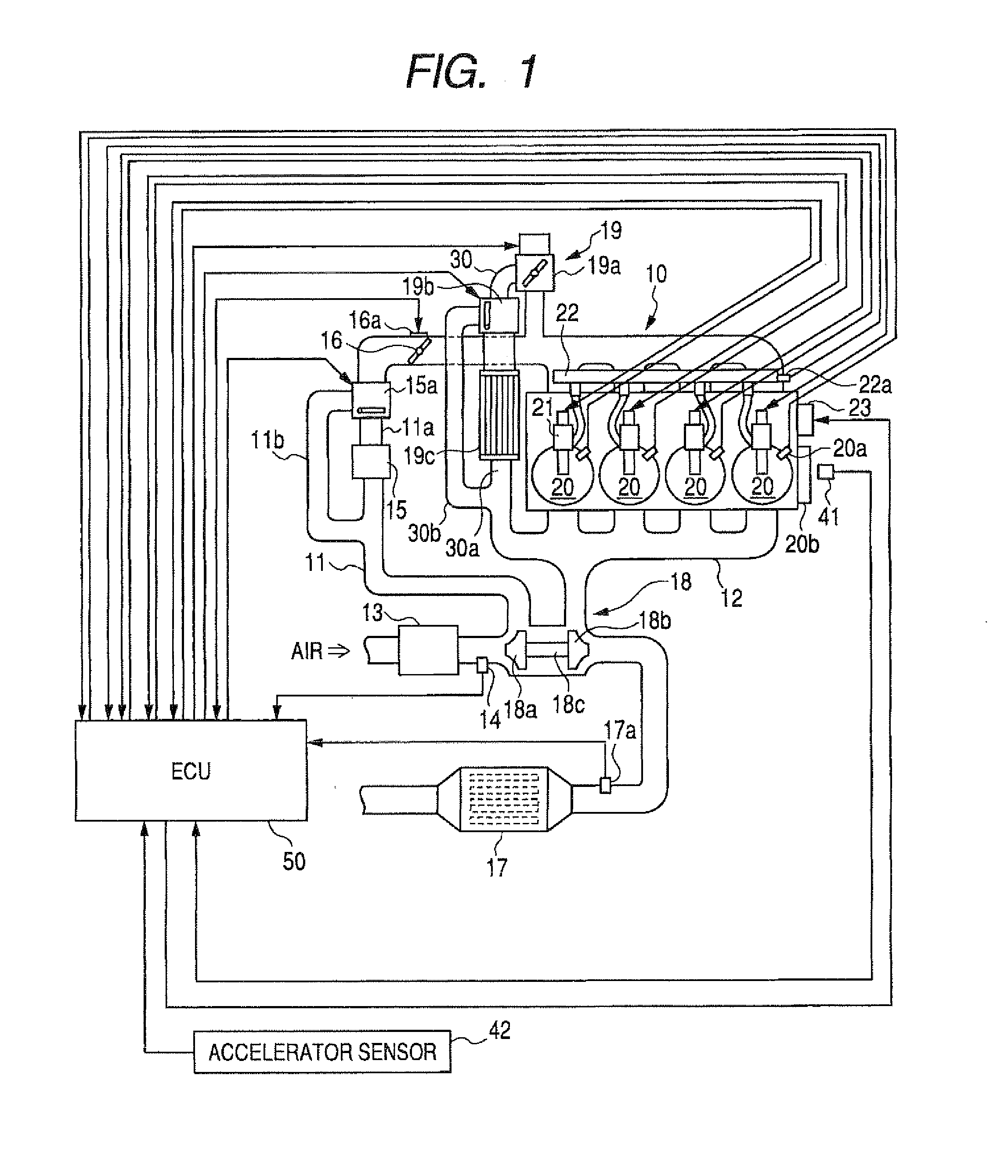
InactiveUS20110132311A1Reduce capacityImprove efficiencyCombustion enginesSpeed sensing governorsEngineeringVacuum aspirator
In some examples, reduced engine displacement reduces an engine's ability to provide brake booster vacuum. The present application relates to intake systems including a vacuum aspirator to generate vacuum.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Vapor-adsorbent filter for reducing evaporative fuel emissions, and method of using same
InactiveUS6432179B1Minimized pressure dropCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationFiberOrganic solvent
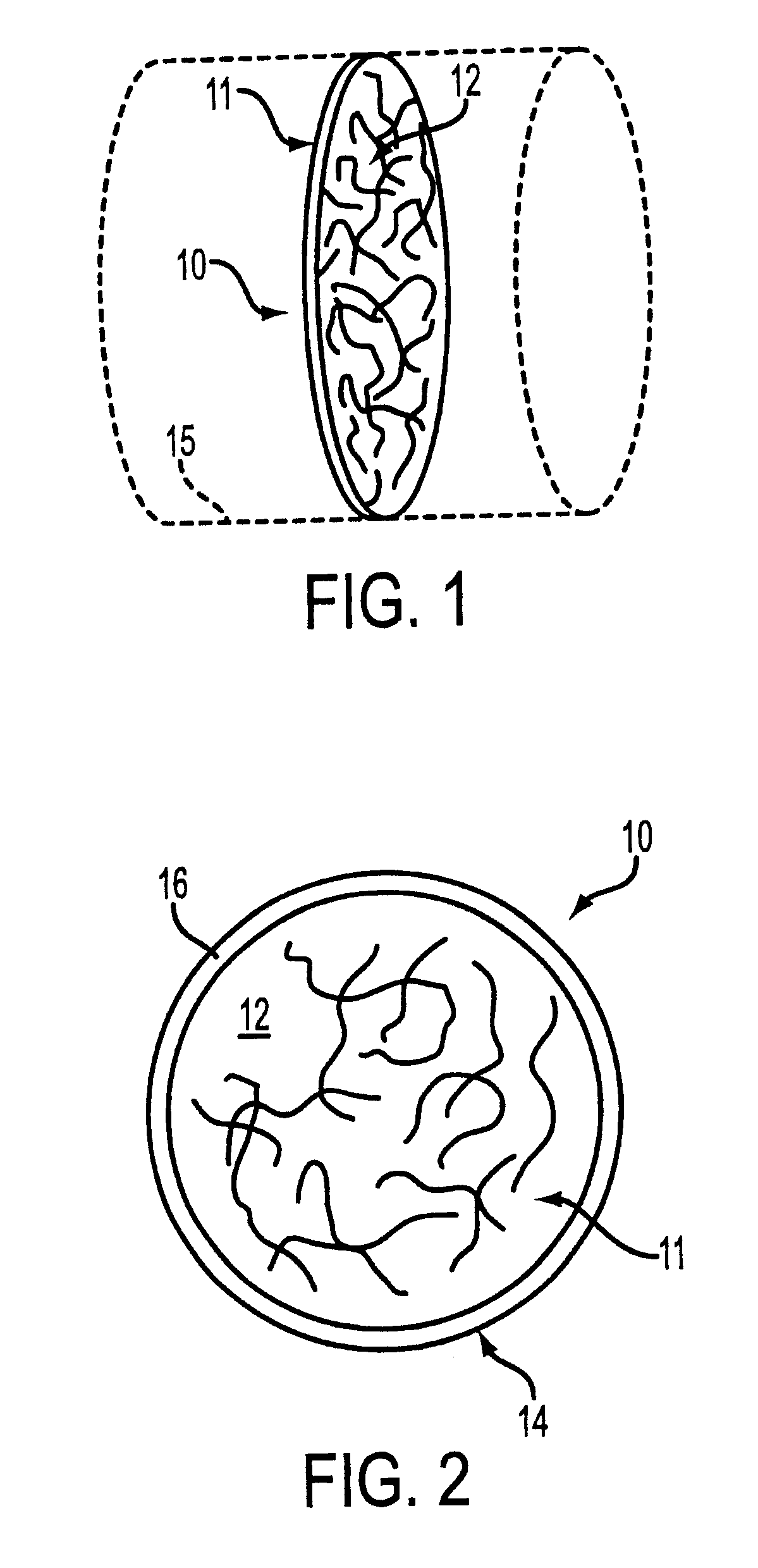
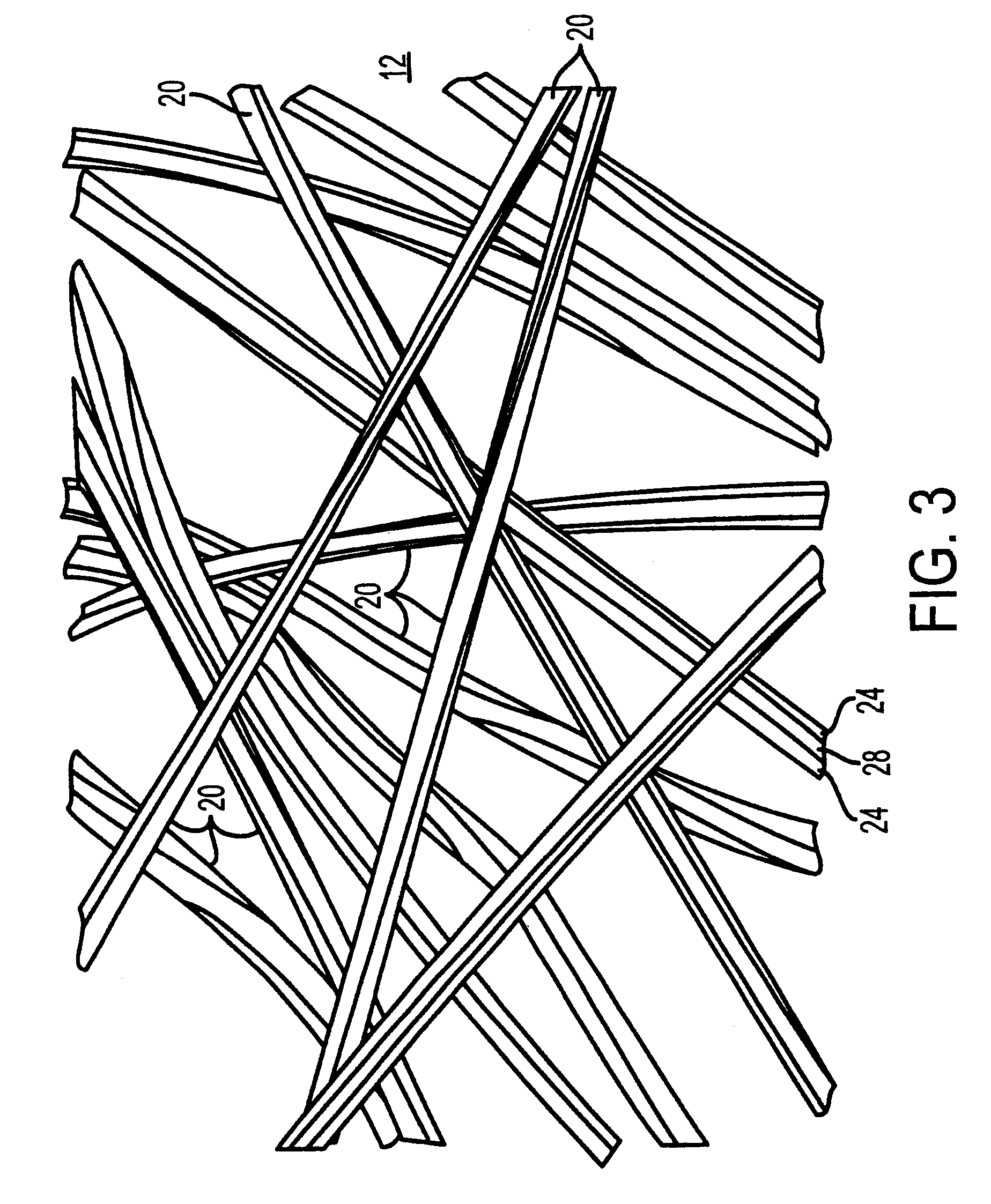
A filter, for use in removing residual fuel vapors from within an engine's intake system, includes a filter element having a plurality of fibers, for placement in communication with an intake air flow passage. Each of the fibers has an internal cavity formed therein, and a longitudinally extending slot formed therein extending from the internal cavity to the outer fiber surface. The filter also includes a hydrocarbon-absorbing material disposed within the internal cavities of the fibers. The hydrocarbon-absorbing material may be a solid material such as, e.g., carbon, or may be a liquid such as a relatively non-volatile organic solvent. Alternatively, the material may be a combined solid and liquid. In one embodiment, each of the elongated fibers includes a central stem and a plurality of lobes extending outwardly from the central stem, with a longitudinally extending slot defined between adjacent lobes. Specific useful filter configurations are detailed.
Owner:FRAM GROUP IP +1
Combustion engine
InactiveUS6460337B1Improve performanceReduce the temperatureValve arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveCombustion
A turbo-fed internal combustion engine has a first and a second exhaust-gas valve per cylinder, these exhaust-gas valves each being connected to their respective exhaust manifold. One exhaust manifold conducts exhaust gases to an exhaust-gas turbine and the other exhaust manifold conducts subsequent exhaust gases past this exhaust-gas turbine which drives a compressor for charge air. The intake valve of the cylinder is arranged so as, as the engine speed increases, to close either earlier, before the piston reaches its bottom dead center, or later, after the piston has passed its bottom dead center. In this way, the temperature increase resulting from compression in the cylinder is reduced. Cooled air from the compressor can be taken in so as to obtain an adequate degree of filling in the cylinder, with a lower final temperature.
Owner:SAAB AUTOMOBILE AB
EGR control apparatus for engine
InactiveUS6945236B2Increased durabilityReliable heatingElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberEngineering
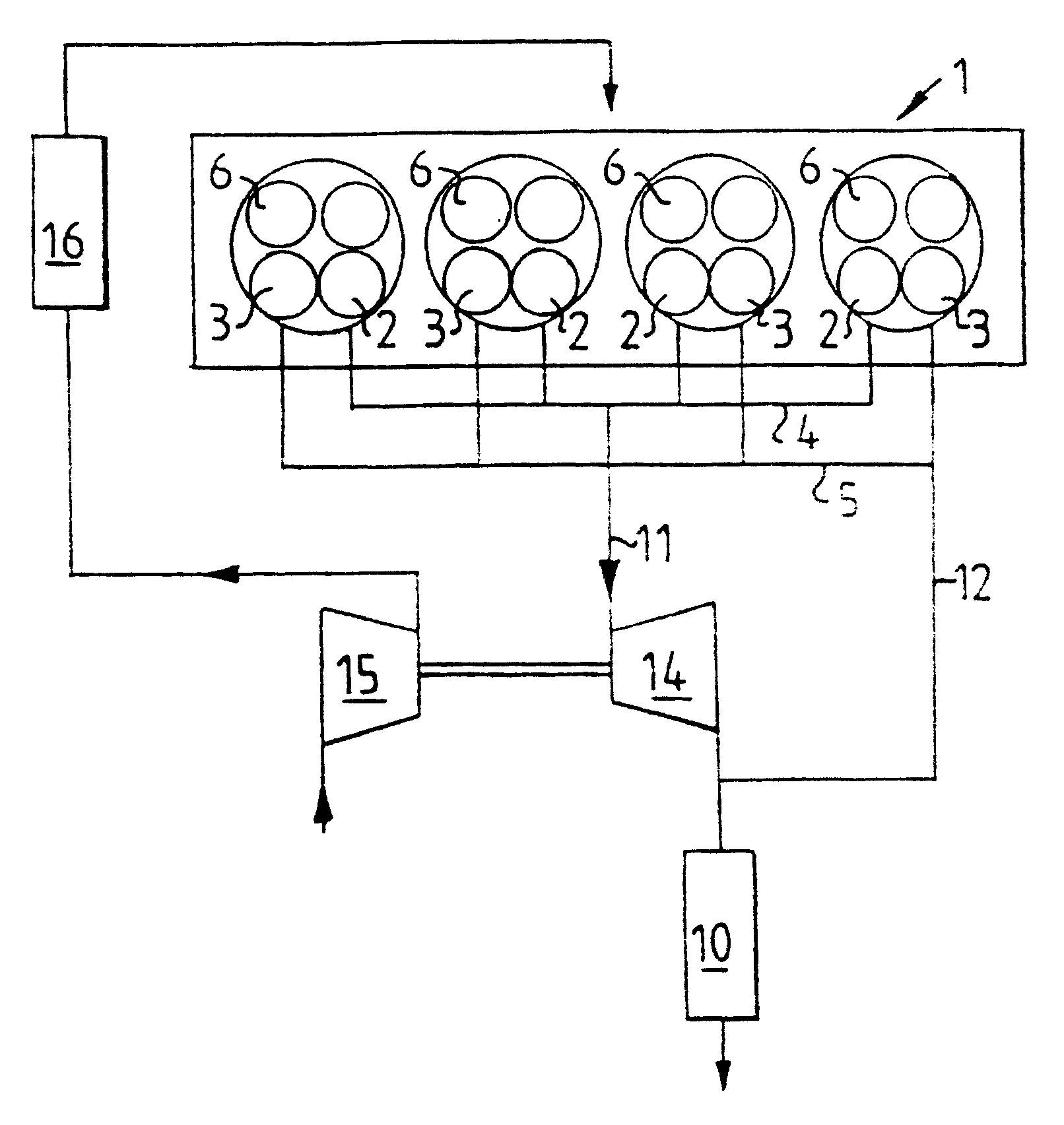
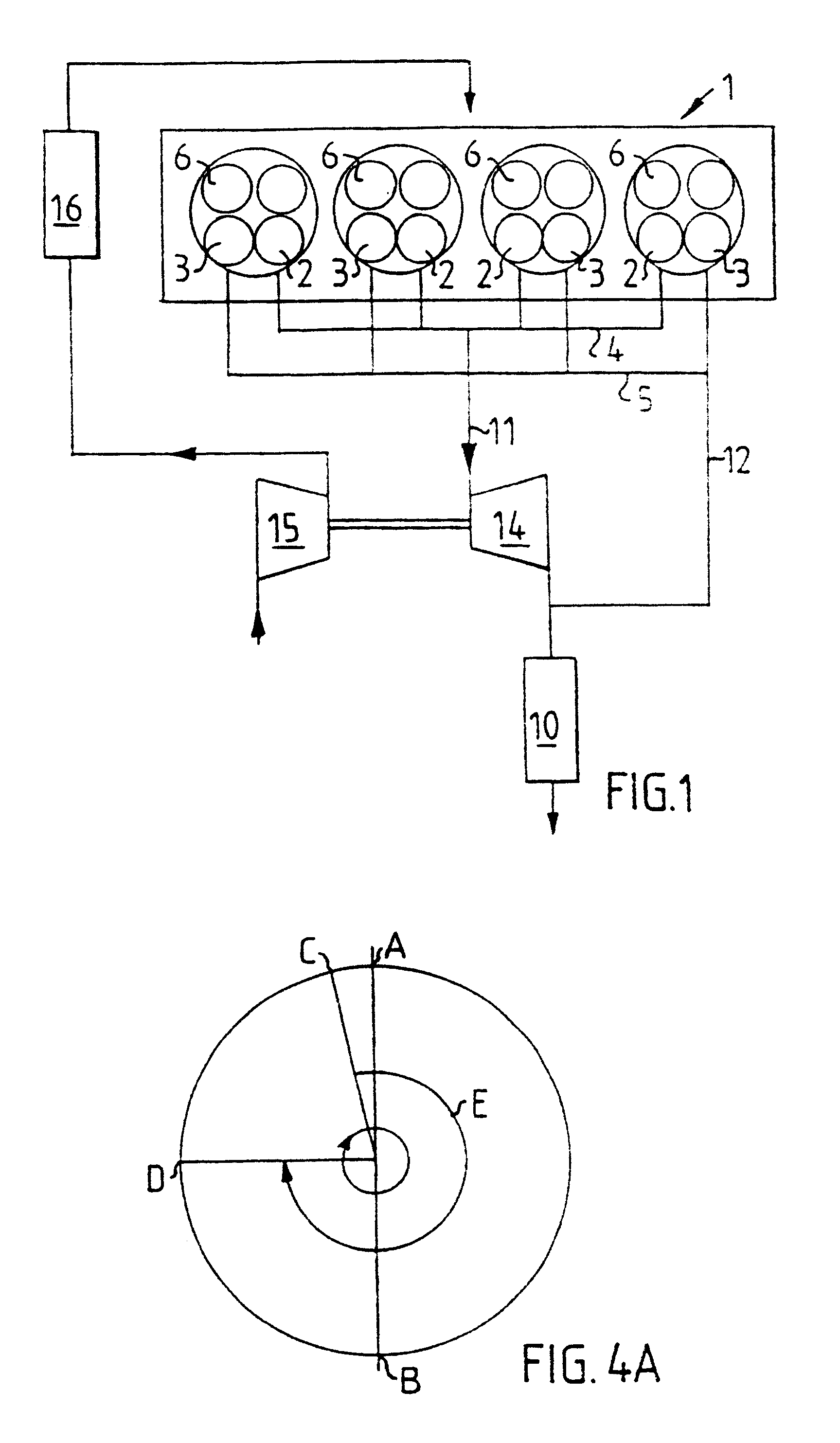
According to the invention, an EGR control apparatus of an engine includes intake ports to which an intake passage is connected, the intake ports opening into each combustion chamber of the engine, an EGR port to which an EGR passage branching out from an exhaust passage is connected, the EGR port opening into each combustion chamber of the engine, an electrically-operated compressor disposed in the EGR passage for regulating pressure at which EGR gas is introduced into each combustion chamber, and an EGR control valve disposed in the EGR passage at a point downstream of the electrically-operated compressor for controlling the amount of EGR gas introduced into each combustion chamber. The EGR passage branches out from the exhaust passage at a point downstream of an emission control device disposed in the exhaust passage.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
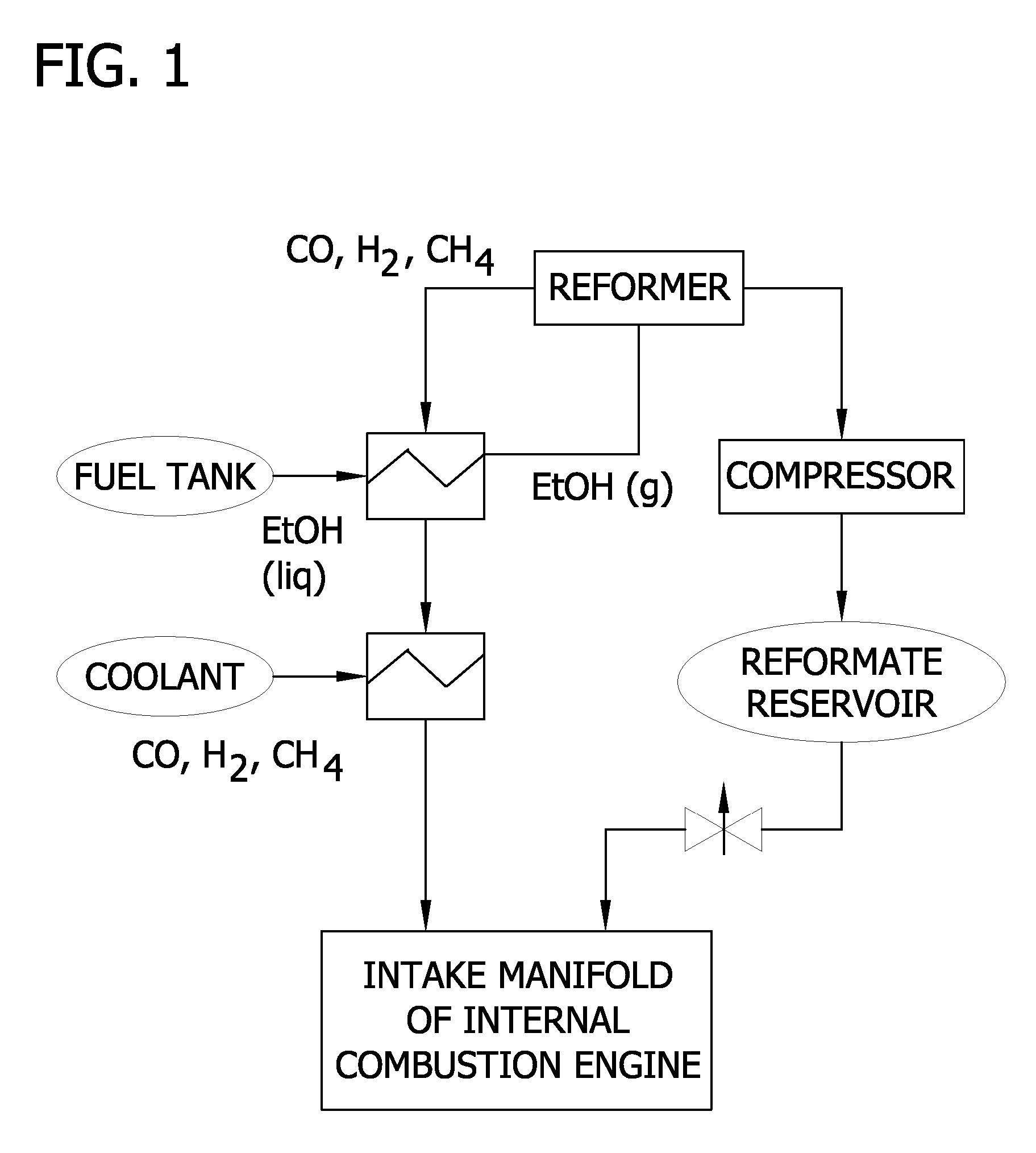
Reformed alcohol power systems
Improved alcohol reforming processes and reformed alcohol power systems utilizing those processes are disclosed. In preferred embodiments, the alcohol reforming processes utilize a thermally conductive reforming catalyst that allows efficient, low-temperature reforming of an alcohol fuel to produce a reformate gas mixture comprising hydrogen. The present invention makes possible the efficient utilization of alcohol fuels in an internal combustion engine to generate electrical or mechanical power such as in vehicular applications.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
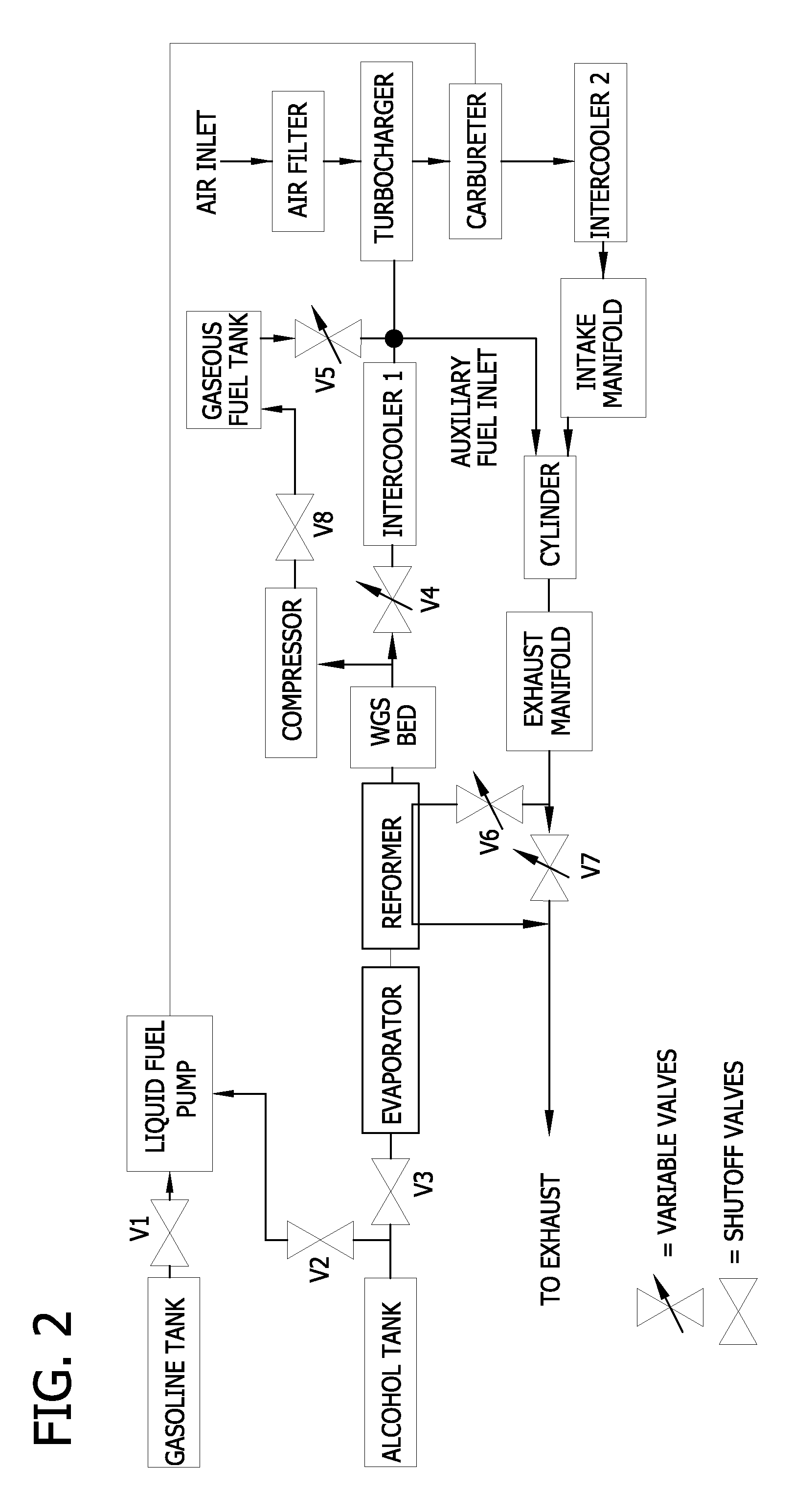
Supercharging system for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7281530B2Simple structureSmall sizeNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesInternal pressureExhaust fumes
A supercharging system for an internal combustion engine includes an exhaust introduction passage for introducing exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine; an exhaust discharge passage for introducing the exhaust gas from the exhaust introduction passage and exhausting the exhaust gas to an exterior; a mixture part arranged between the exhaust introduction passage and the exhaust discharge passage, for changing internal pressure into negative pressure upon accelerating flowing velocity of the exhaust gas with a narrowed flowing passage set to have a smaller diameter than the exhaust introduction pipe; an absorption passage for mixing outside air and the exhaust gas inside the mixture part upon introducing the outside air with use of negative pressure into an inside of the mixture part; and an intake passage for taking out and returning a part of mixed gas mixed inside the mixture part to a side of the internal combustion engine.
Owner:USUI KOKUSAI SANGYO KAISHA LTD
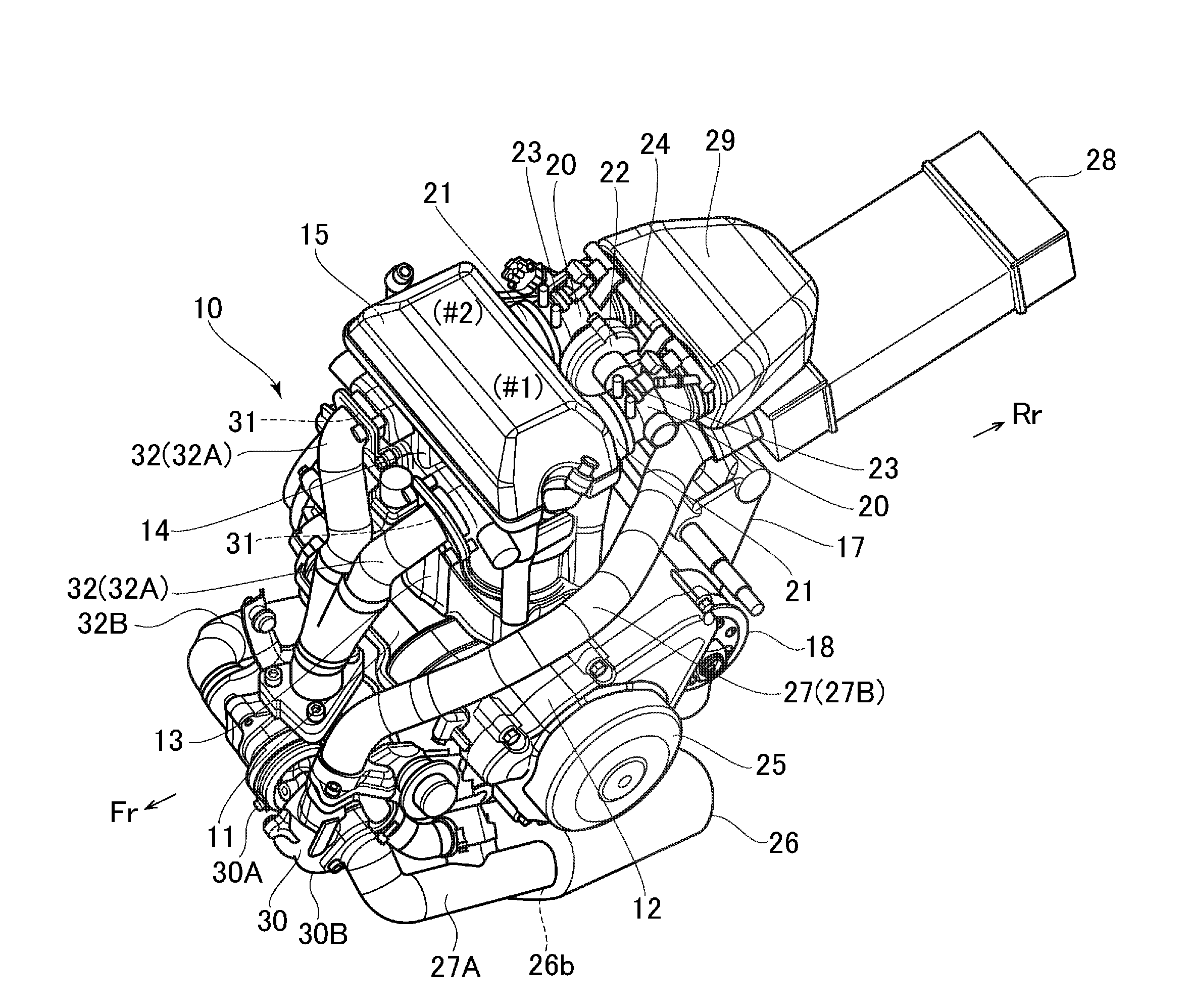
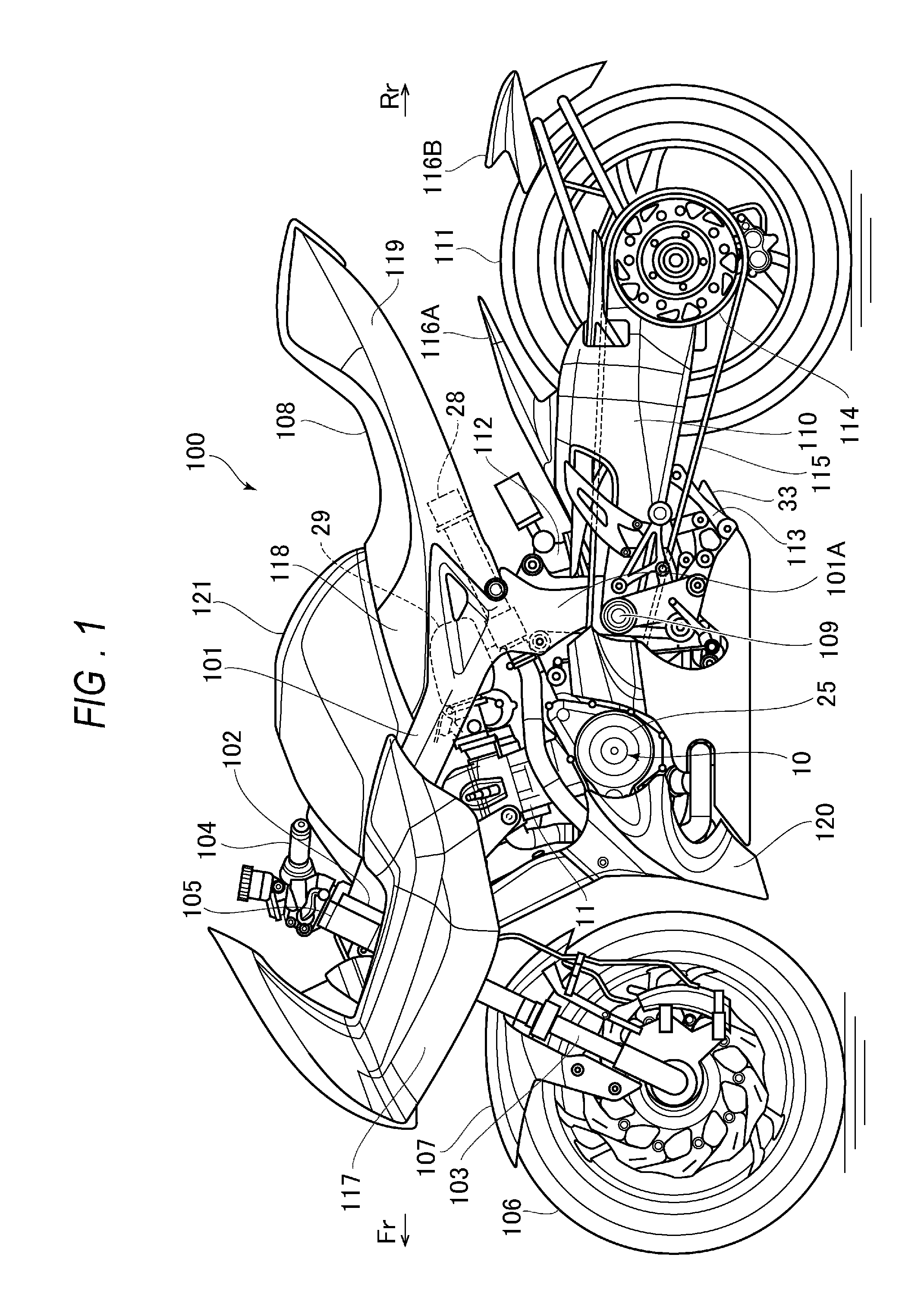
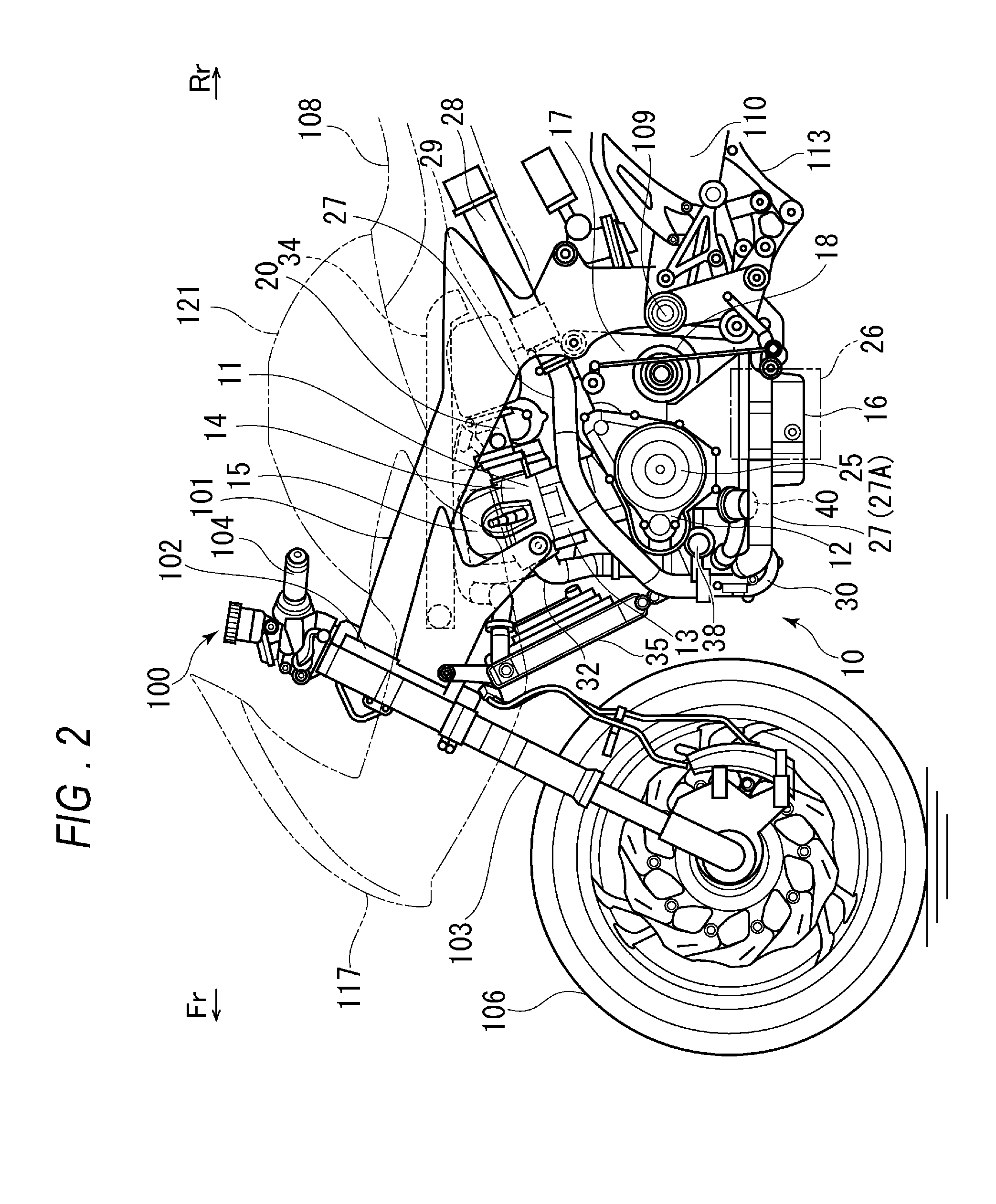
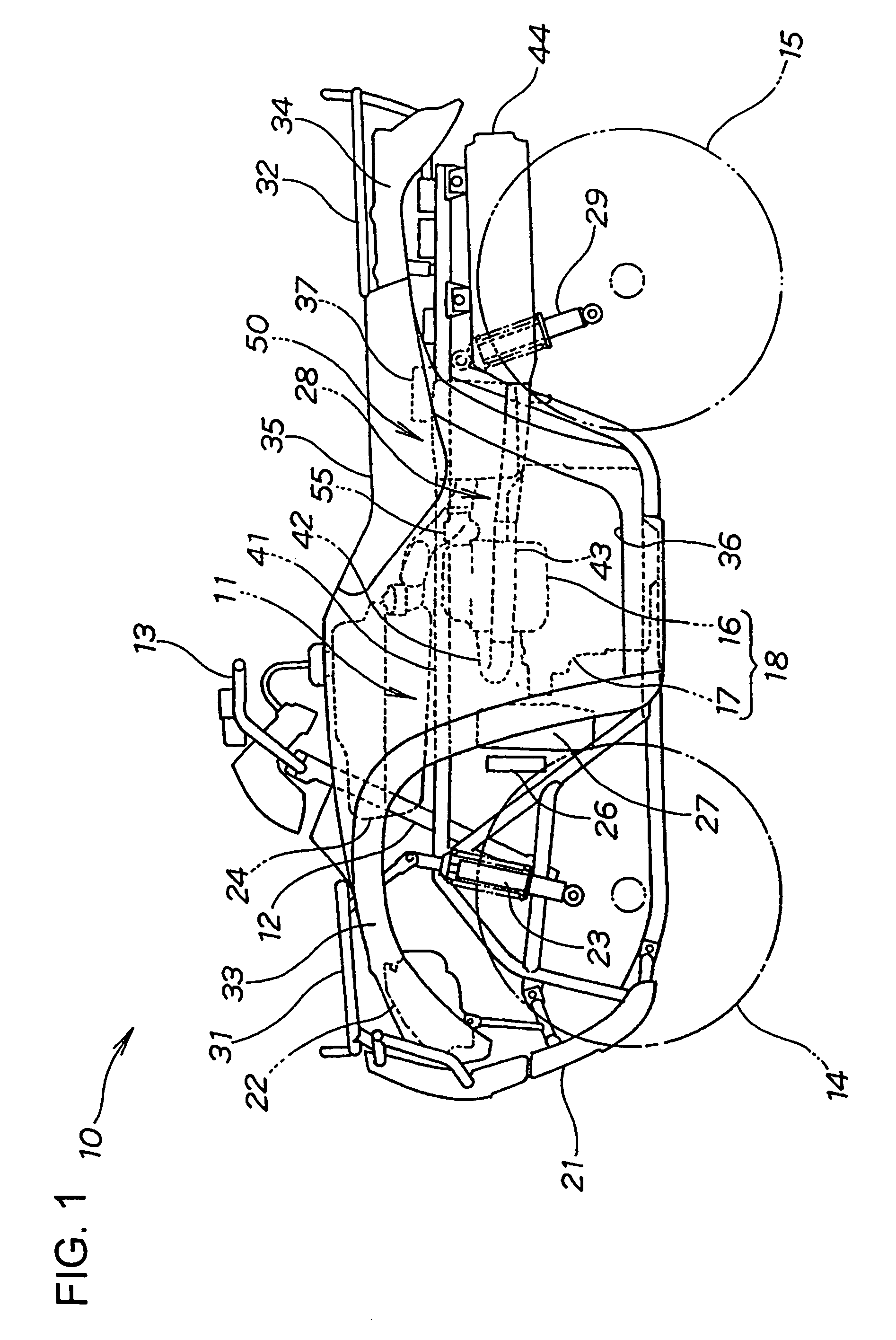
Motorcycle with turbocharger
ActiveUS20150101875A1Simple and optimum pipe dispositionLower center of gravityInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersTurbochargerEngineering
An engine; an air cleaner which filtrates fuel air; a turbocharger which compresses intake fuel air; an intake pipe which connects the air cleaner and the turbocharger; and an intake passage which induces the fuel air taken from an intake port at an end part to the air cleaner, are included. The turbocharger is located at a front side lower part of the engine, and the air cleaner is located under a crankcase. The intake passage extends rearward from a rear part of the air cleaner, and thereafter, bends upward.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
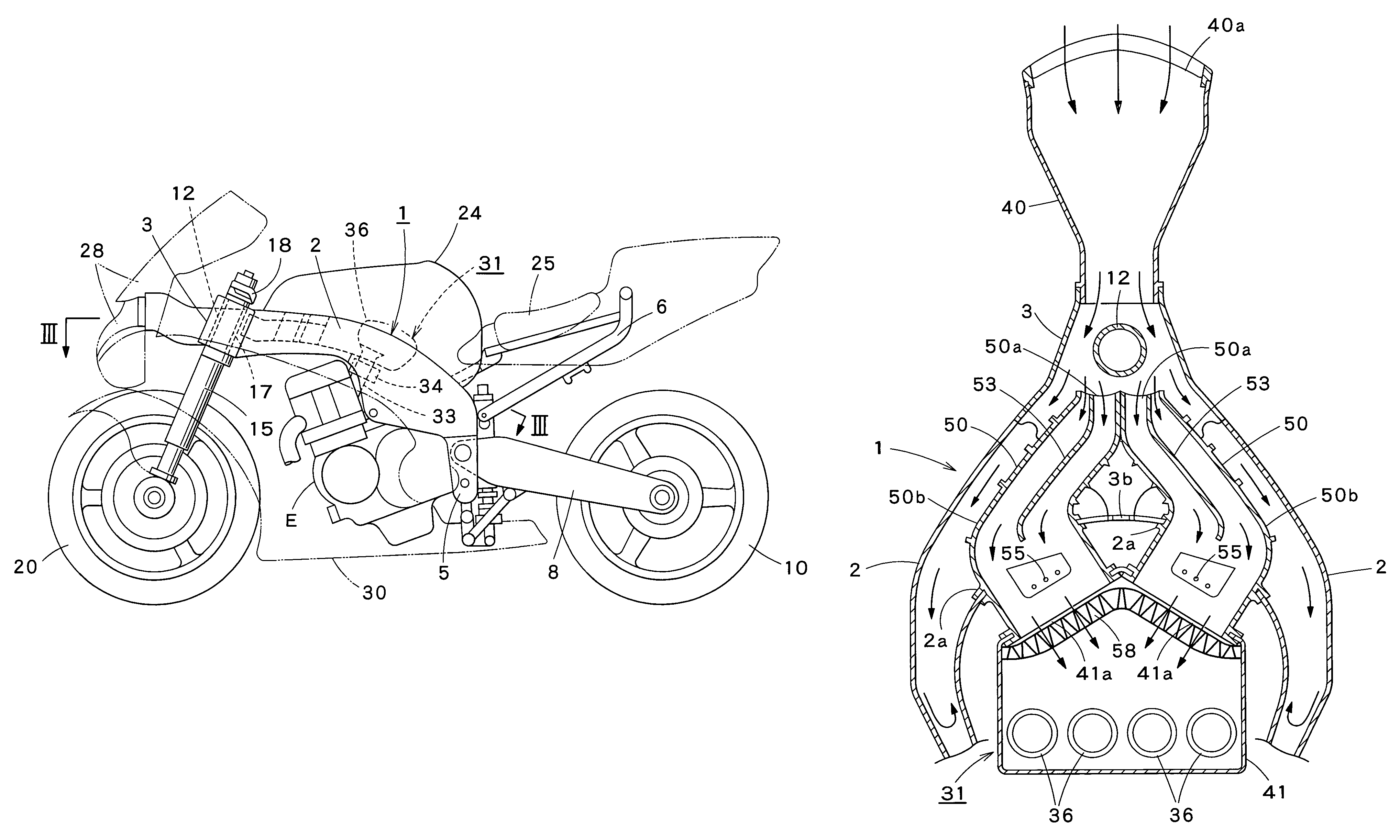
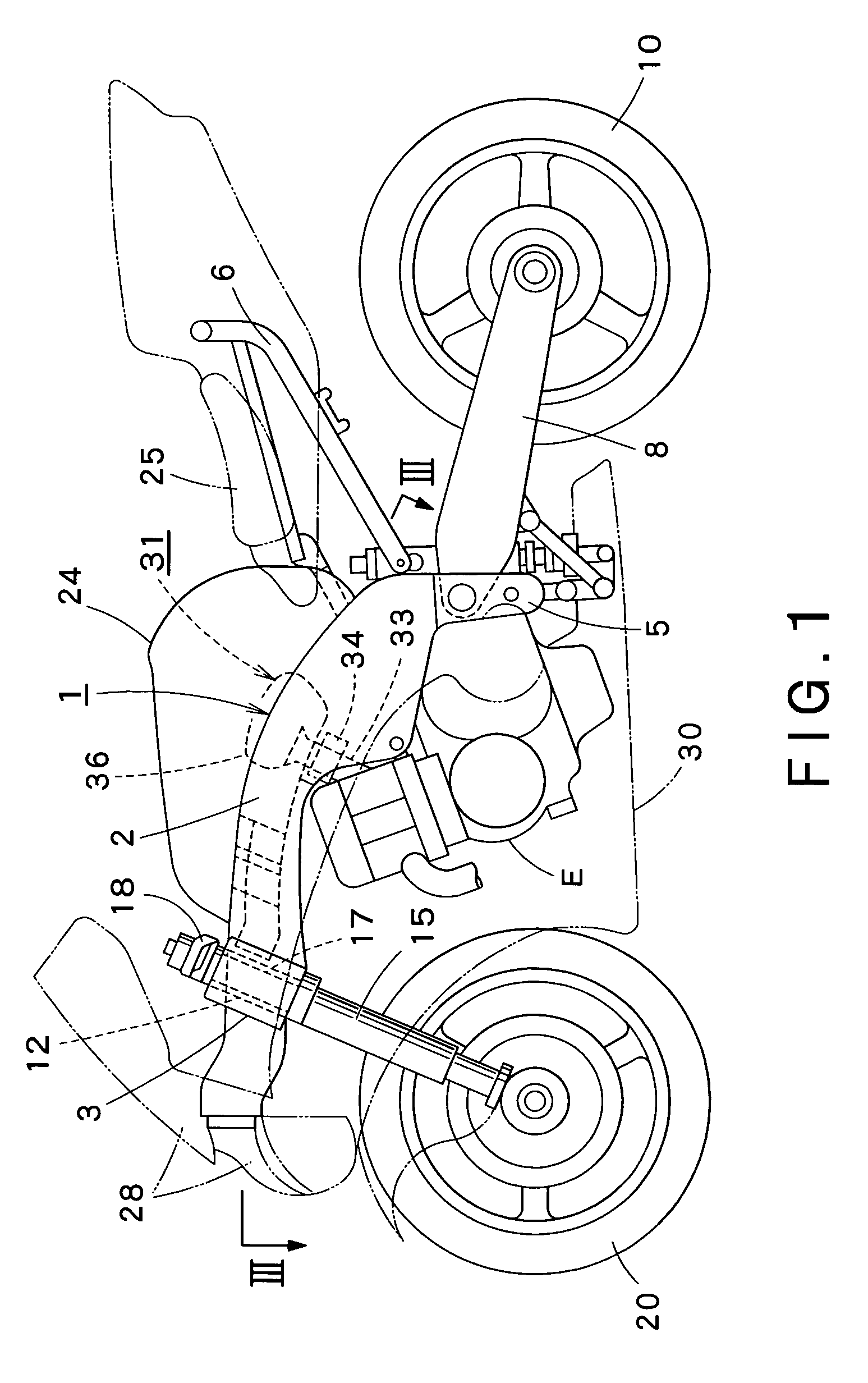
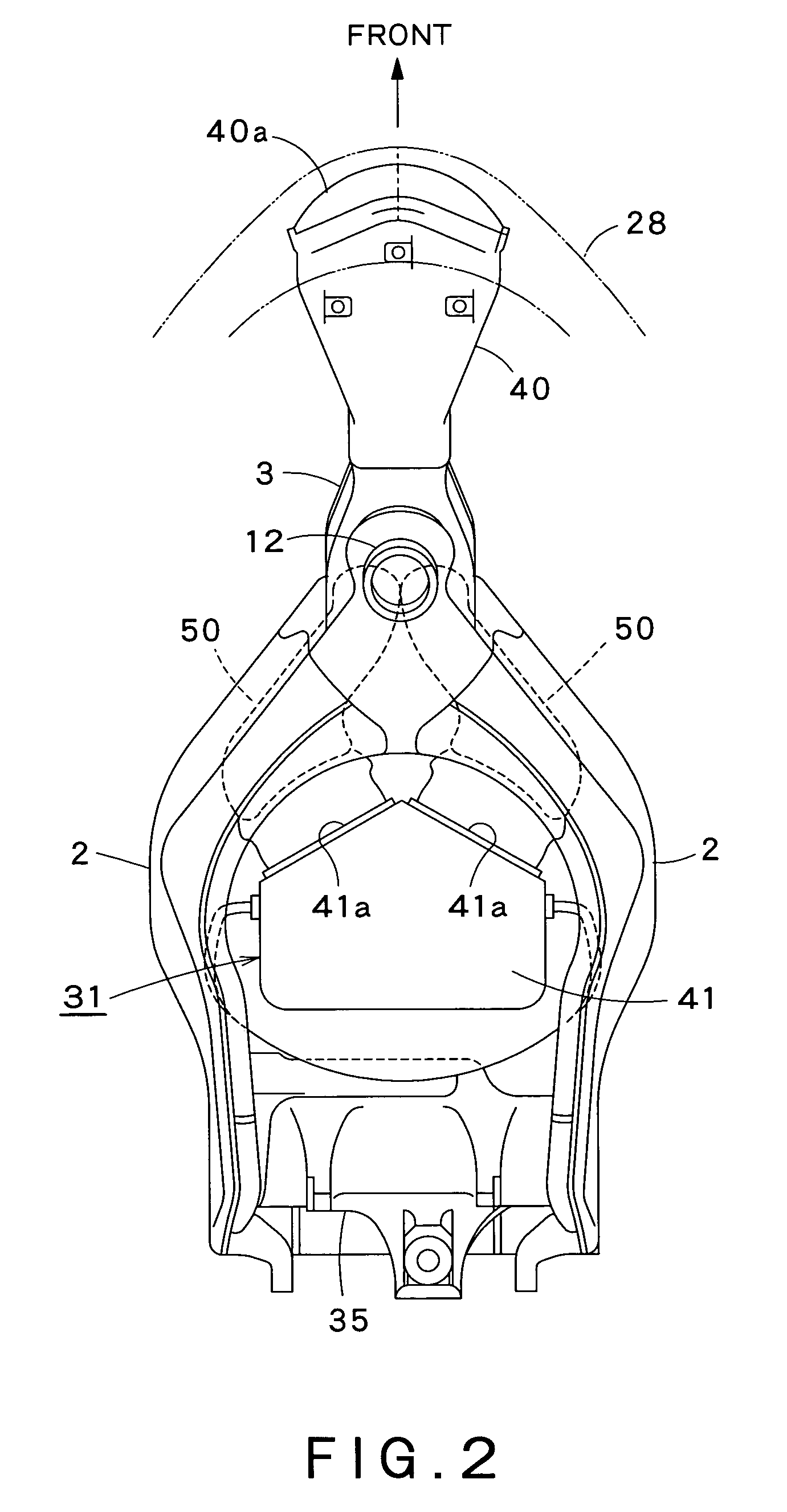
Air intake structure for motorcycle
InactiveUS7380624B2Effectively preventSuppress noiseCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringAir cleaners
An air intake structure in a motorcycle having a body frame including a hollow head member in its front wall with an air inlet opening and supporting a steering shaft and paired hollow main frame members extending rearward from the head member on right and left sides of the motorcycle. The structure includes an air cleaner disposed behind the head member, an inlet duct having an open front end and an open rear end, an intake duct in the hollow main frame member, respectively having a front part extended toward the head member in the hollow main frame member and having an open front end, and a rear part connected to the air cleaner. An air passage defined by the intake duct has a sectional area increased downstream with respect to the direction of air flow. The intake ducts are internally provided with straightening plate, respectively.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
Heat shielded air intake system
InactiveUS20050217625A1Non-fuel substance addition to fuelMachines/enginesThermal isolationAir filtration
An air filter system includes a housing having, for example, a rear panel and a side panel, each having a top edge formed to interface to the hood of a vehicle so that the housing incorporates the vehicle hood to provide thermal isolation of intake air from engine compartment heat. The air filter system connects to a stock air intake tract through an air intake tube. The housing has a diagonal panel that the air intake tube is attached to and passes through. The diagonal panel is disposed at an angle that provides positioning of the air intake tube so that an effluent end of the air intake tube matches the stock location of the stock air intake tract. A washable, reusable air filter supported by the air intake tube filters the intake air and passes it through the air intake tube into the stock air intake tract.
Owner:ADVANCED FLOW ENG
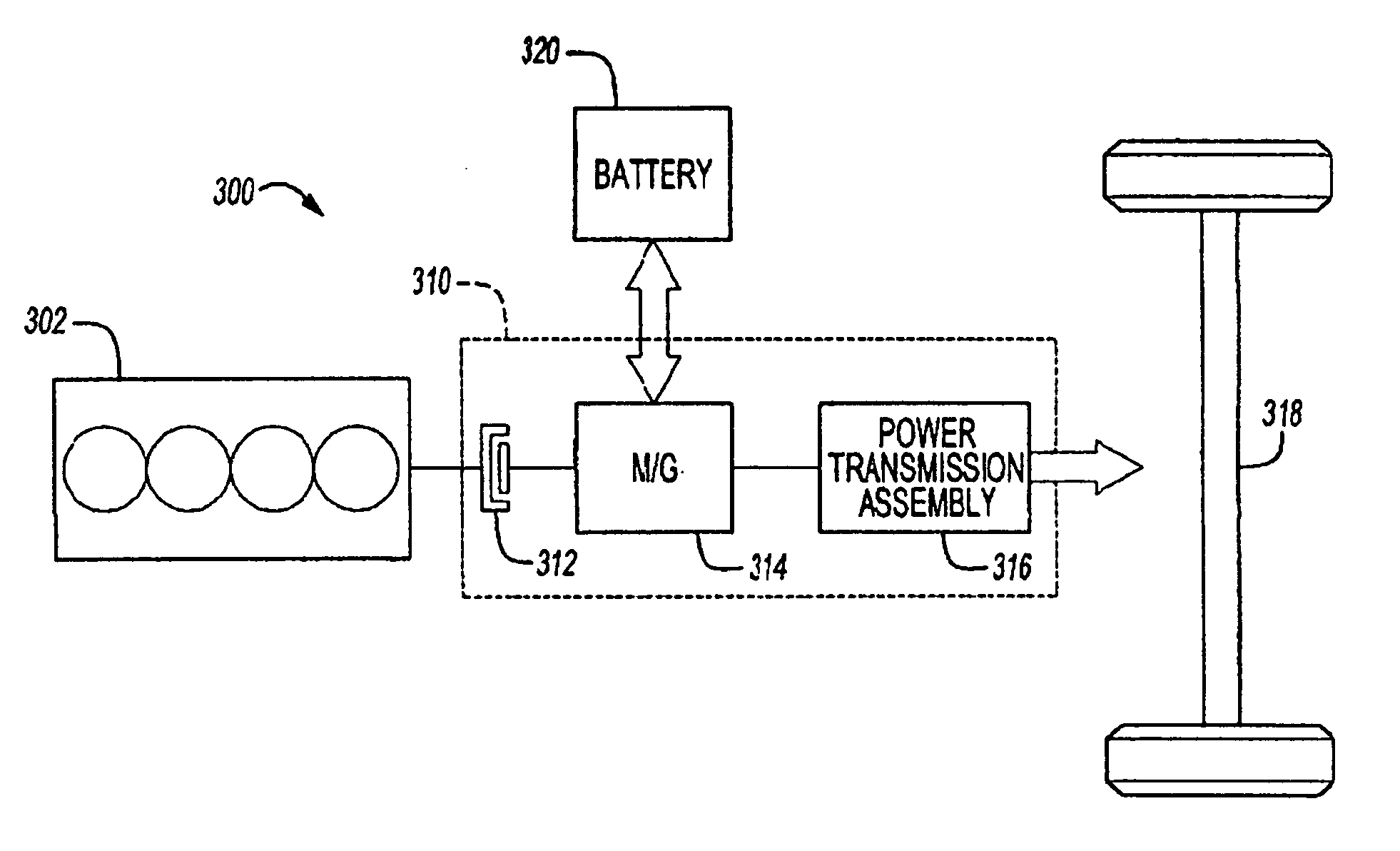
Hydrogen fuelled hybrid powertrain and vehicle
InactiveUS20060174624A1Increase output torqueImprove performanceReciprocating combination enginesElectrical controlDrivetrainEngineering
A hydrogen-powered hybrid powertrain system includes a hydrogen-fuelled internal combustion engine operating at a lean air / fuel mixture, and a supercharger for boosting a primary drive torque produced by the engine primarily over a high operating speed range. An electric motor / generator generates a secondary drive torque for the vehicle, such that the secondary drive torque complements the boosted primary drive torque over at least a low operating speed range of the powertrain. A disconnect clutch disposed between the engine and the motor / generator engages and disengages the engine from the motor / generator, and serves to transfer the boosted primary driver torque through the motor / generator and to a power transmission system. The input at the power transmission is thus a combination of the boosted primary drive torque and the secondary drive torque having an enhanced torque characteristic over at least the low operating speed range.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
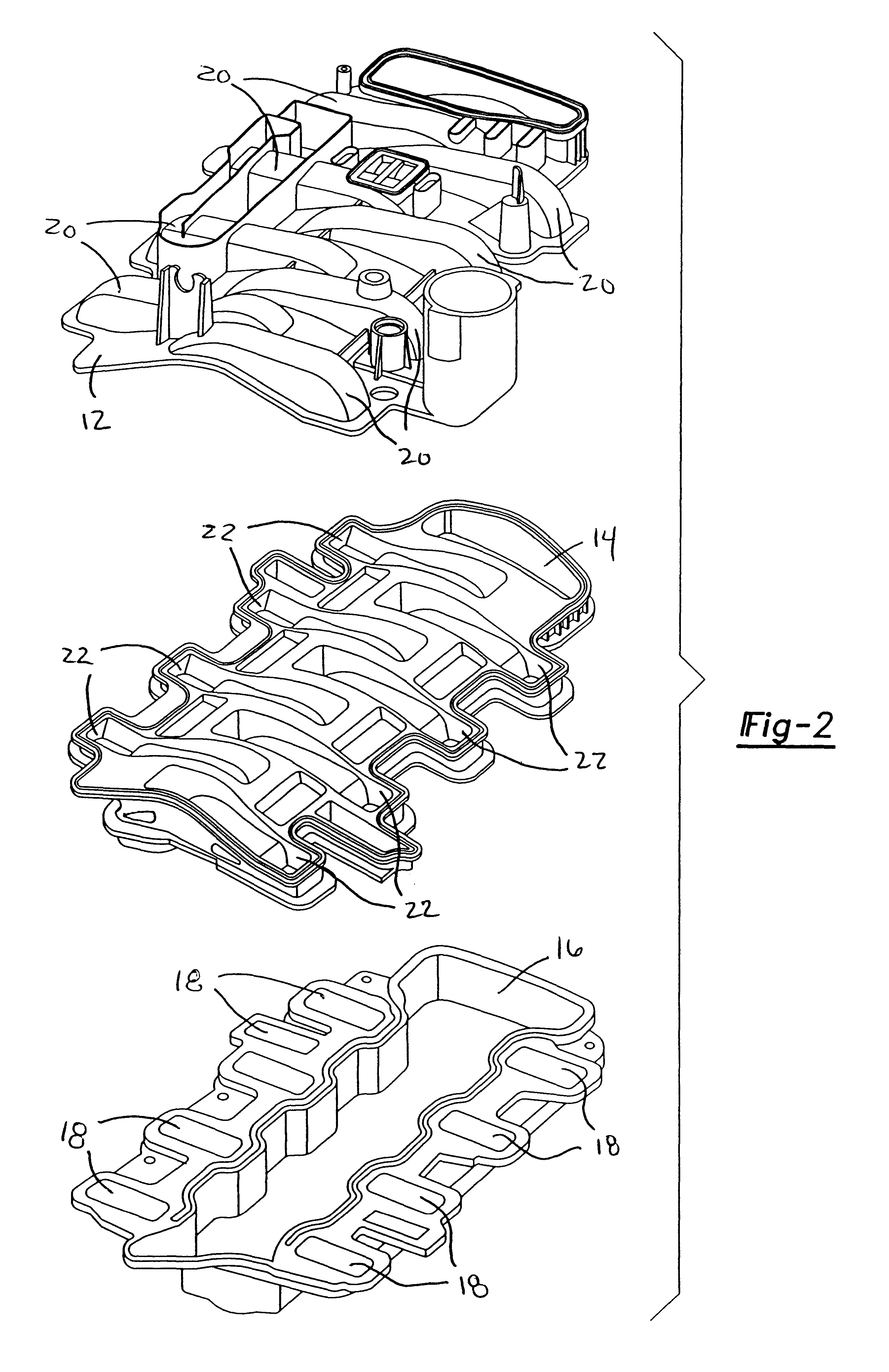
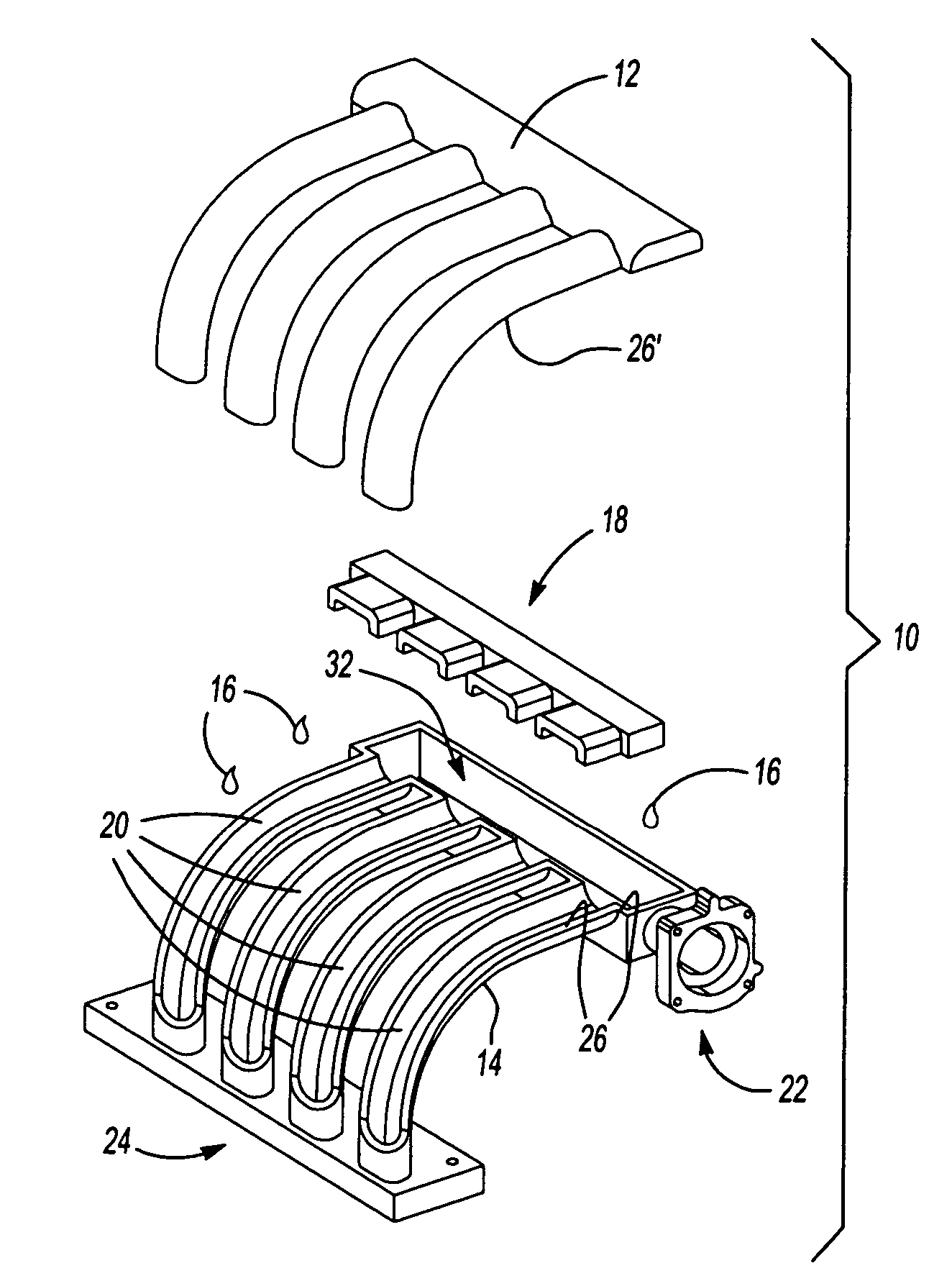
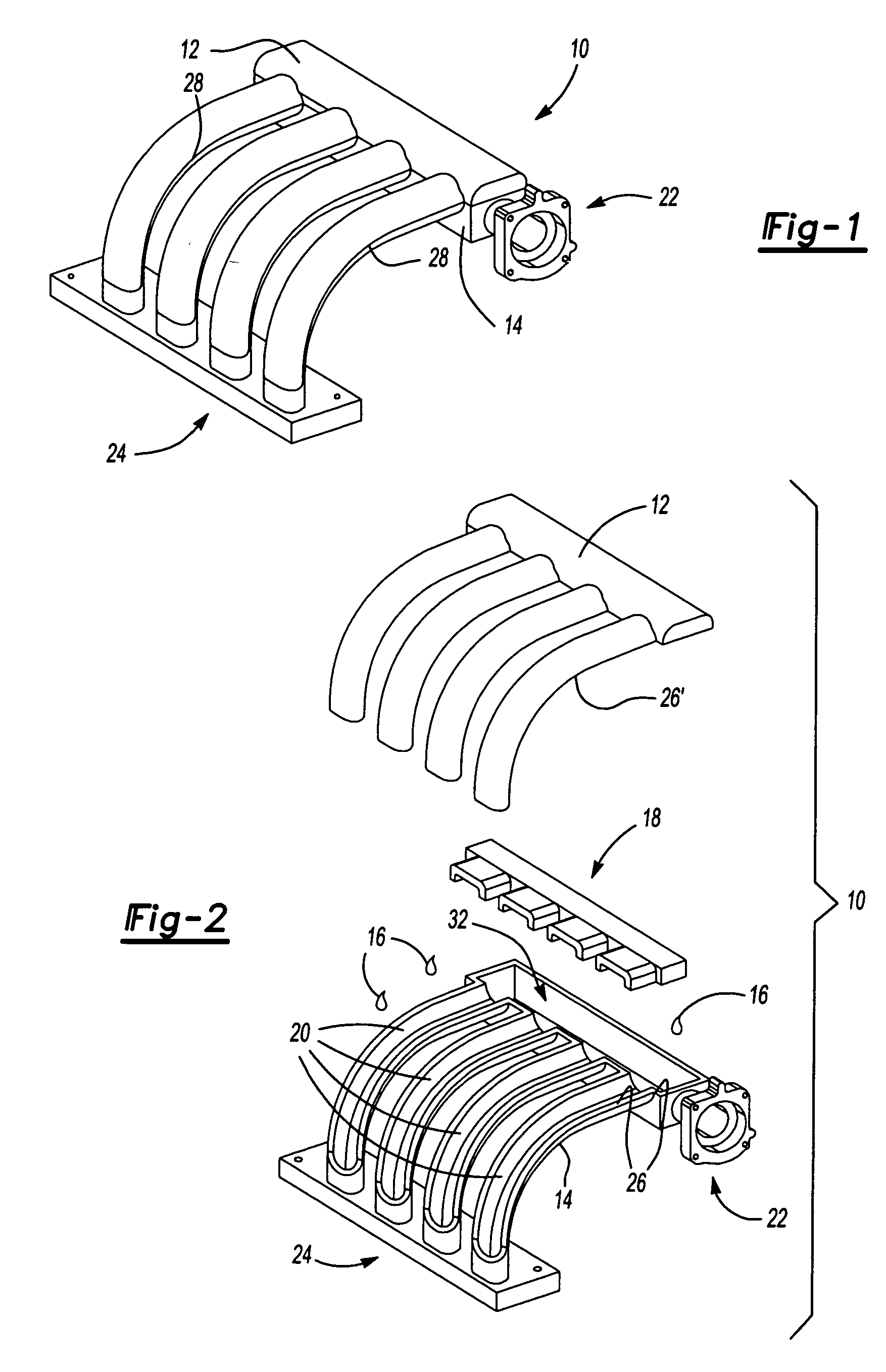
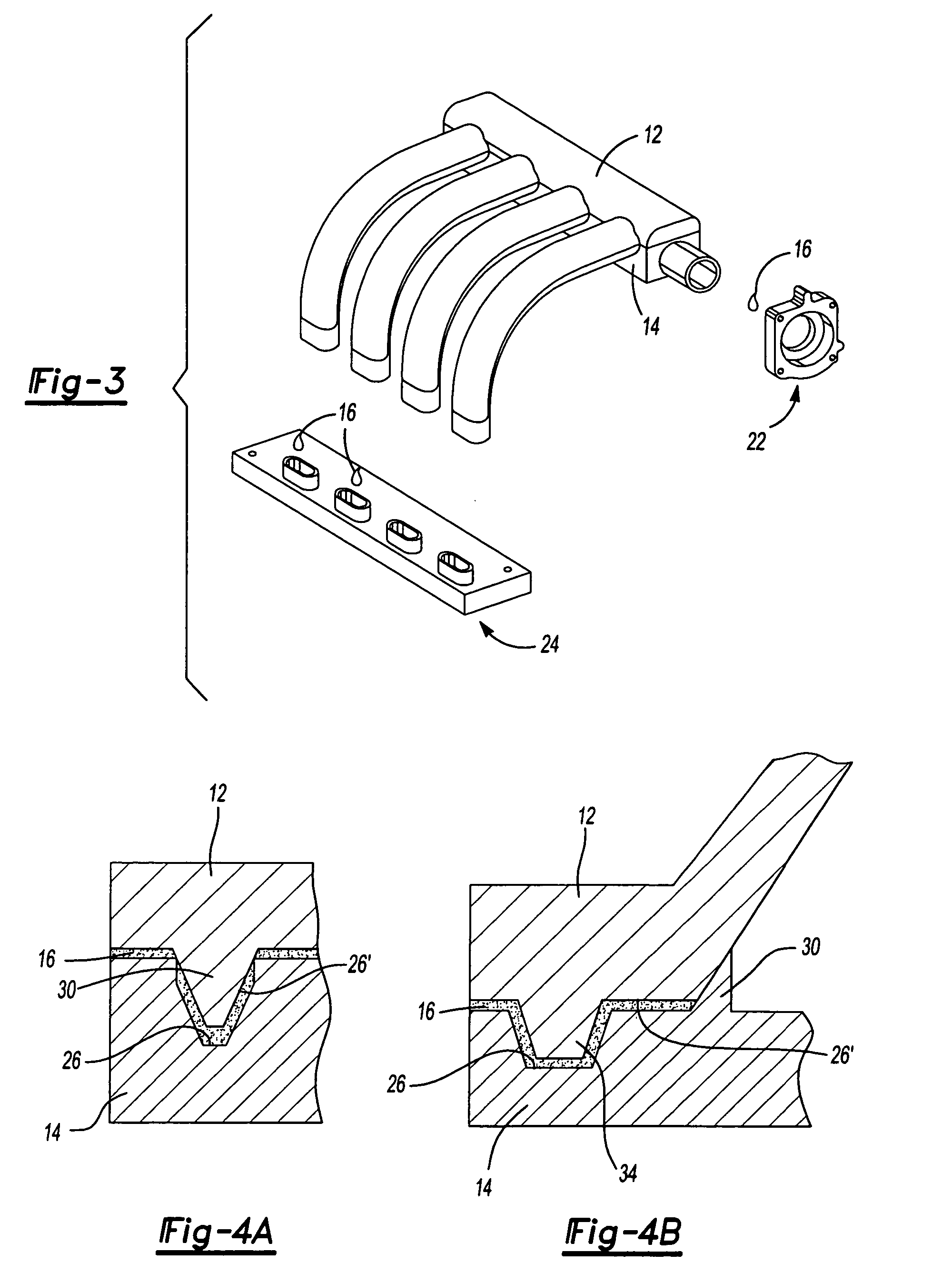
Intake manifold with internal fuel rail and injectors
InactiveUS6308686B1Internal combustion piston enginesLow pressure fuel injectionElectricityCylinder head
An intake manifold includes an upper shell, a lower shell, and a middle shell that interconnects the upper and lower shells. The lower shell has a plurality of longitudinally spaced shell ports. Each shell port is adapted for installation over a corresponding intake port for an engine cylinder head. The upper shell has a plurality of runners that are used to guide air to the shell ports. The middle shell has a plurality of channels that interconnect the runners and the shell ports such that air can flow through the runner to the cylinder intake port. Fuel injector pockets are formed within the upper, middle, and lower shells with each of the pockets having an injector opening in communication with the corresponding shell port. An internal fuel rail, formed between the upper and middle shells, supplies fuel to each of the injector pockets. A fuel injector is installed into each injector pocket such that the injectors are substantially enclosed within the manifold. An internal wire harness rail, formed between the upper and middle shells, supports a wire harness that electrically connects each of the injectors to a power supply.
Owner:SIEMENS CANADA LTD +1
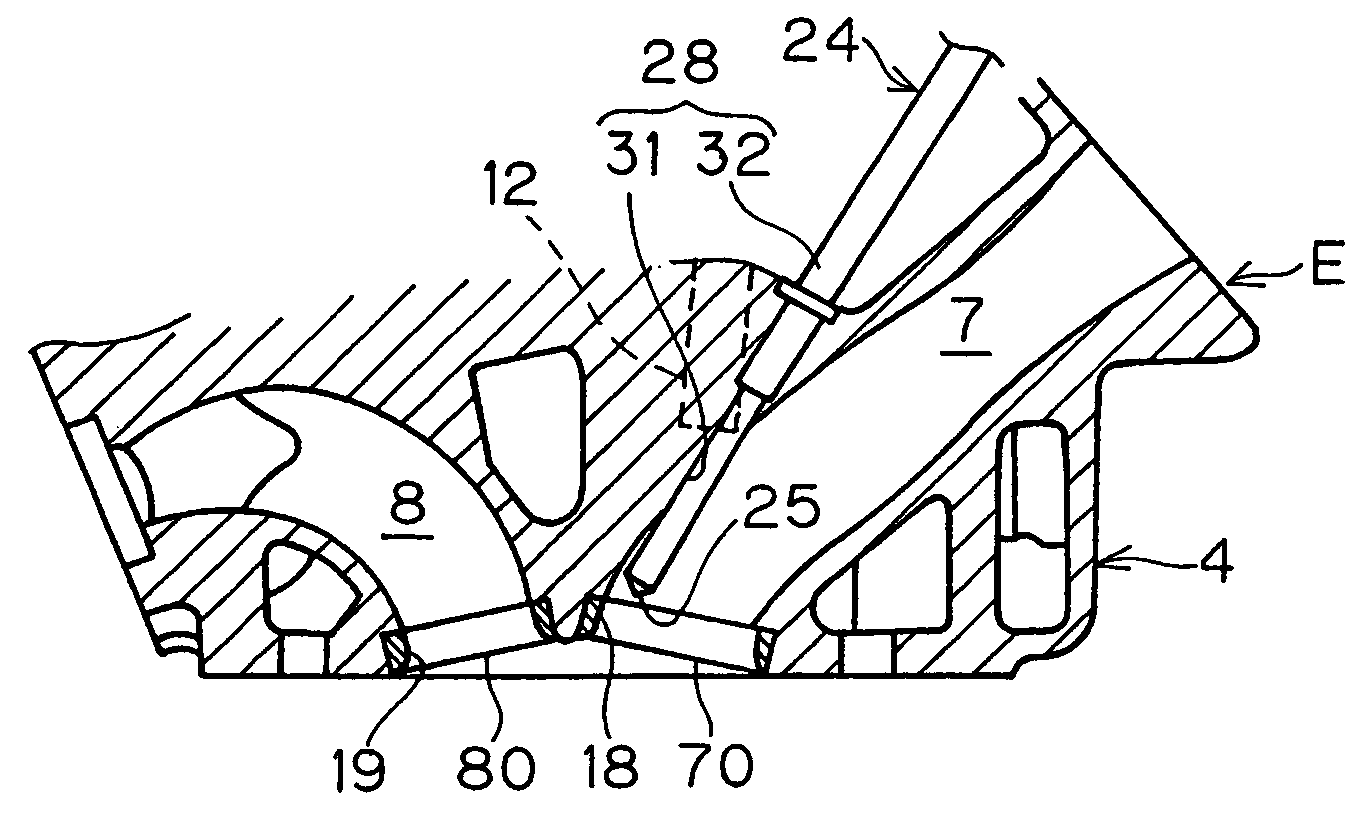
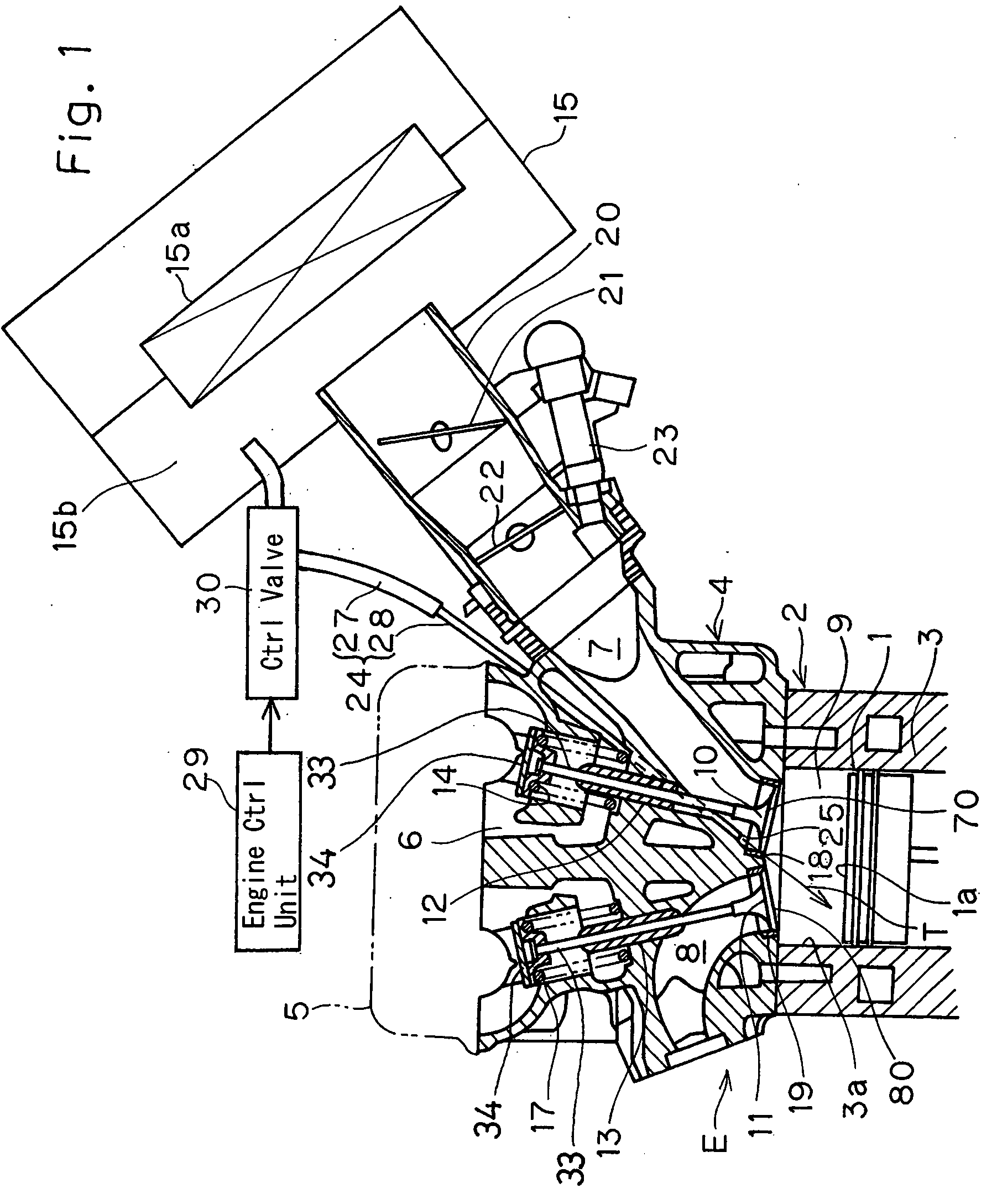
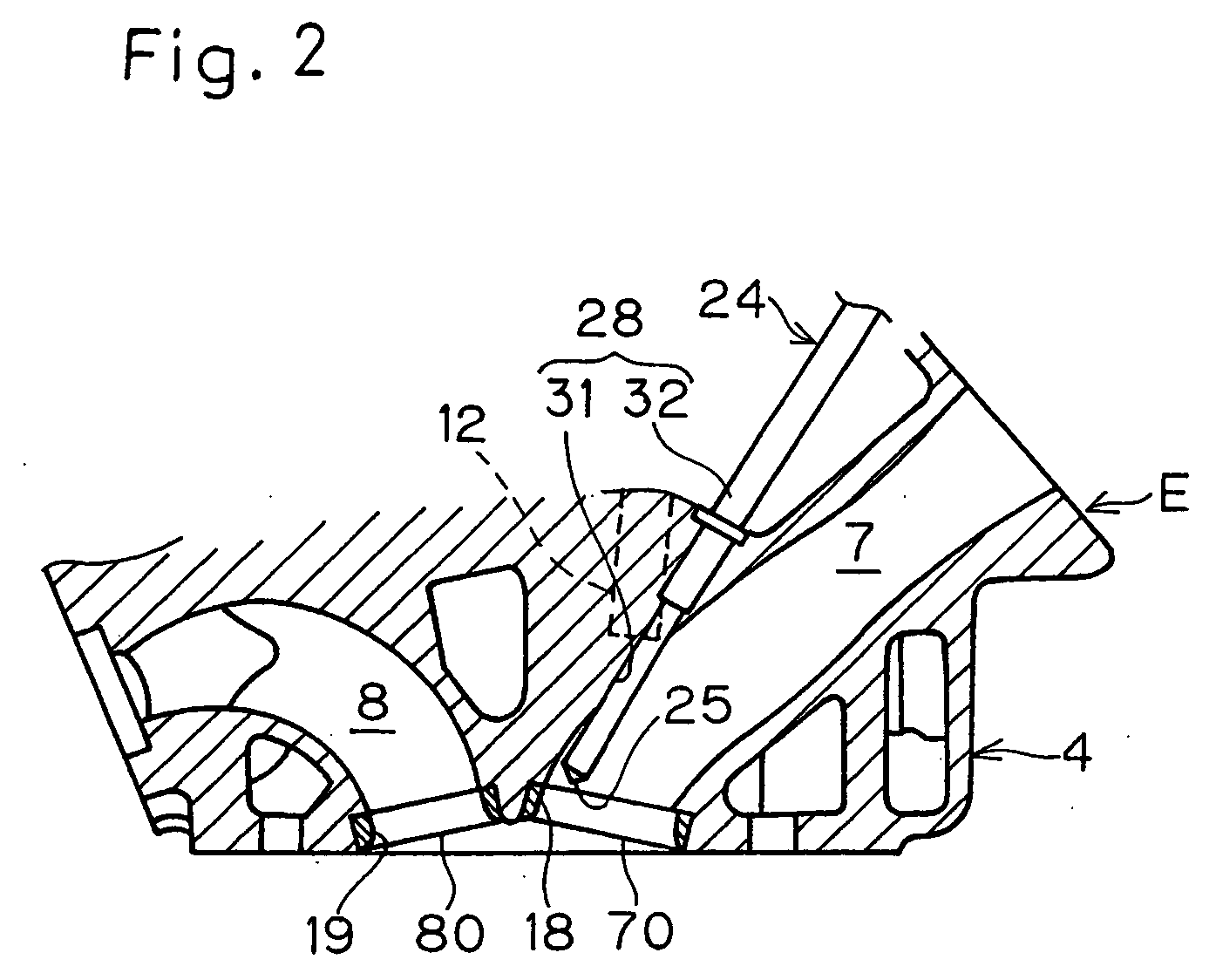
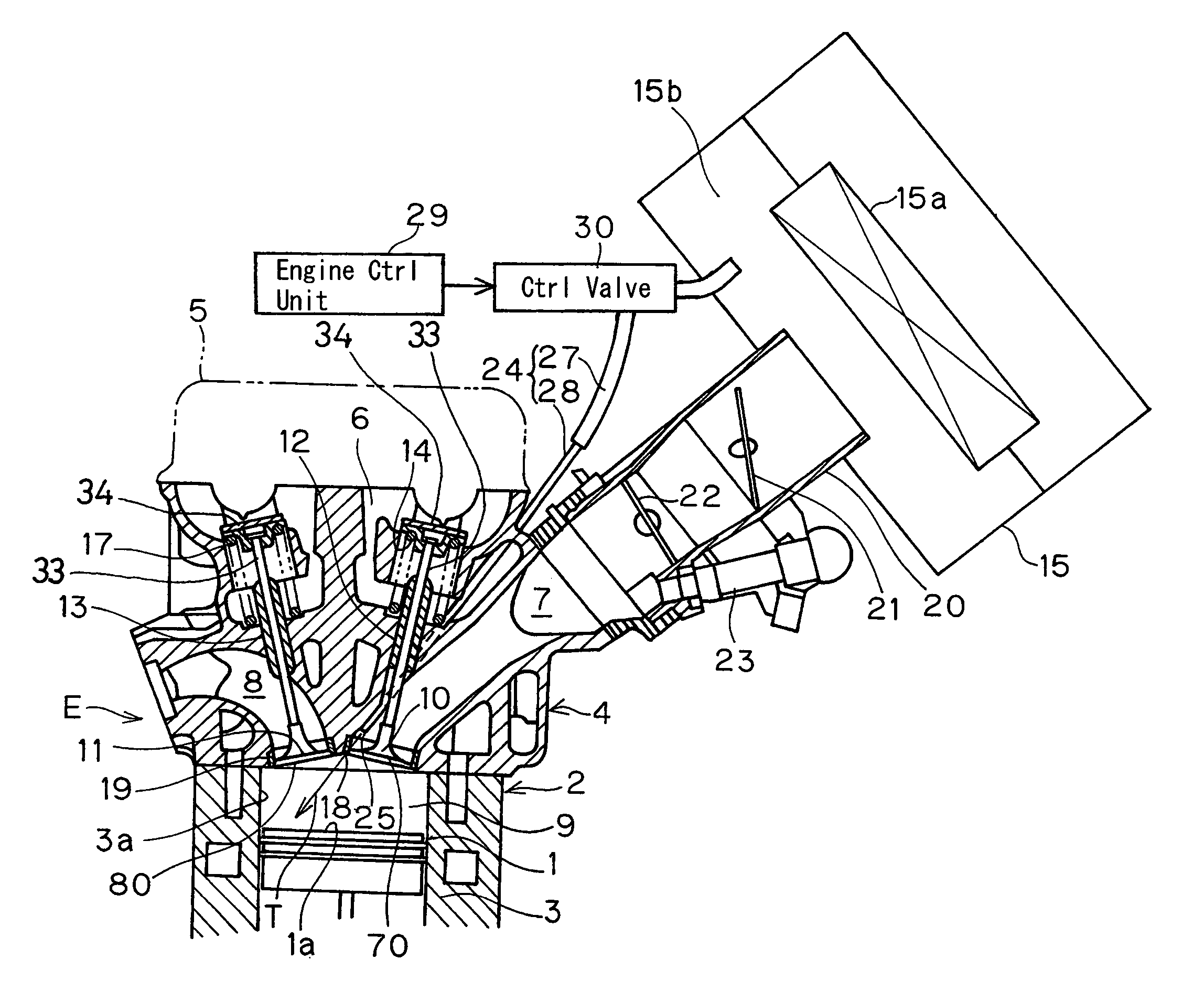
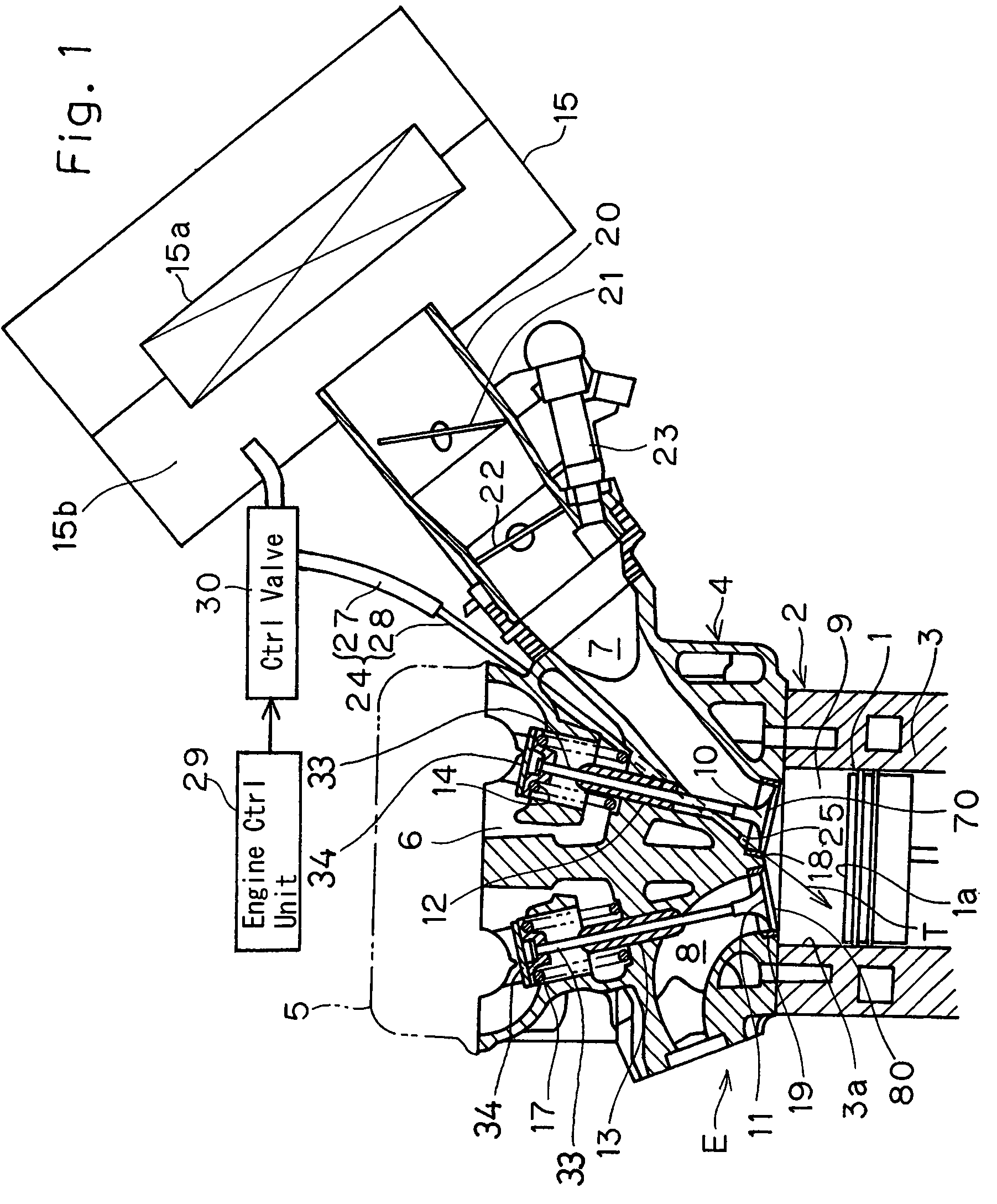
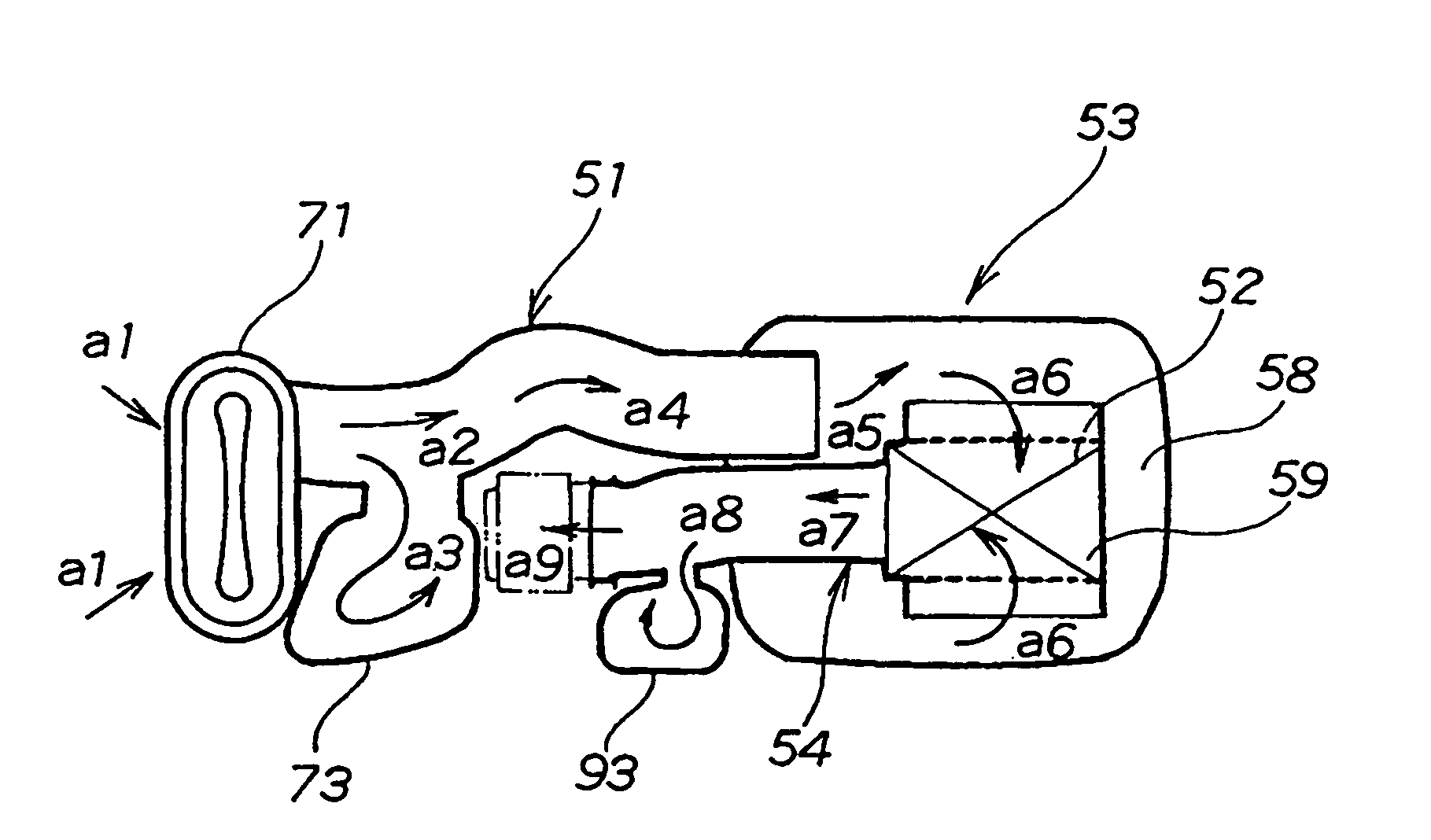
Swirl forming device in combustion engine
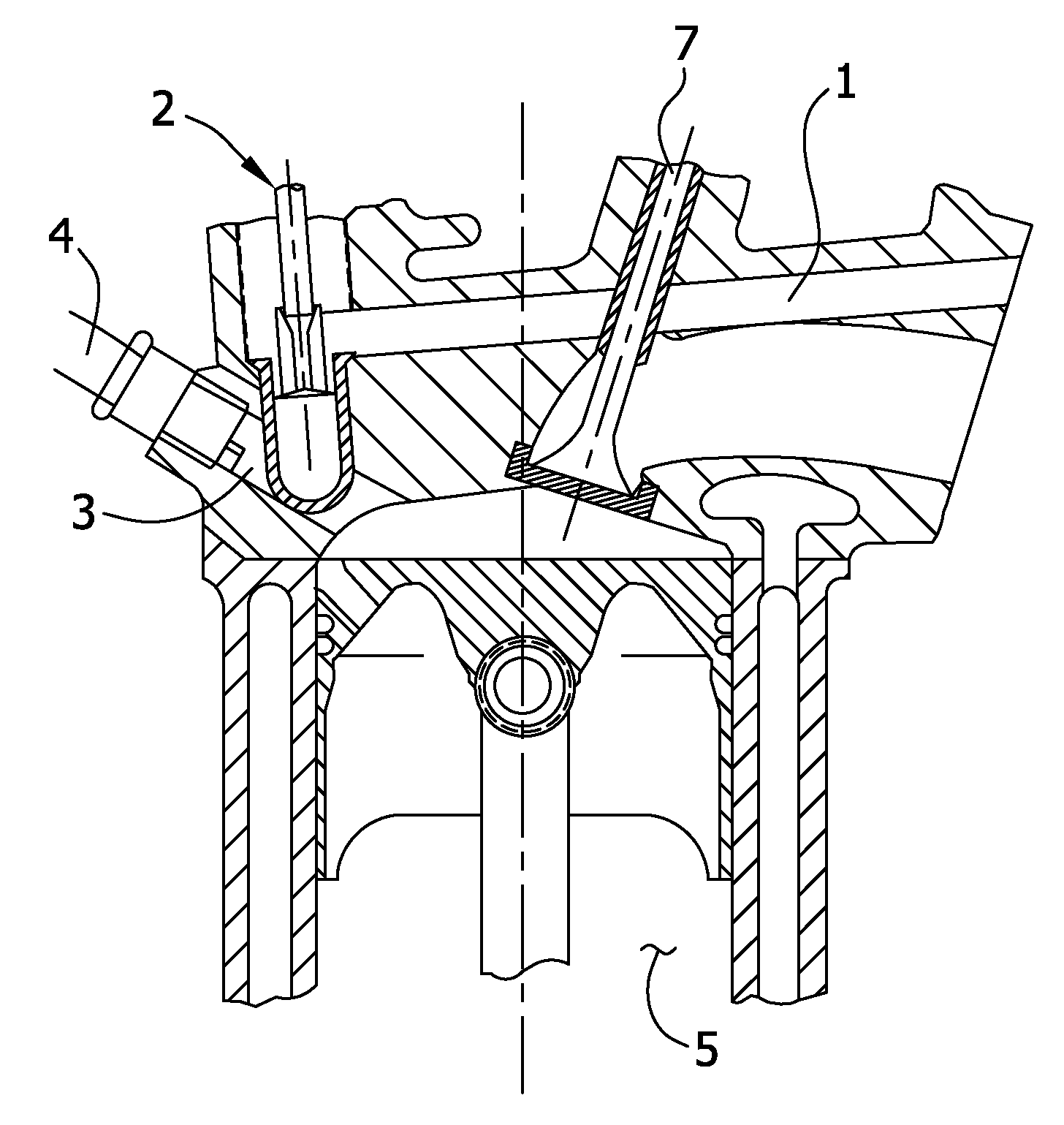
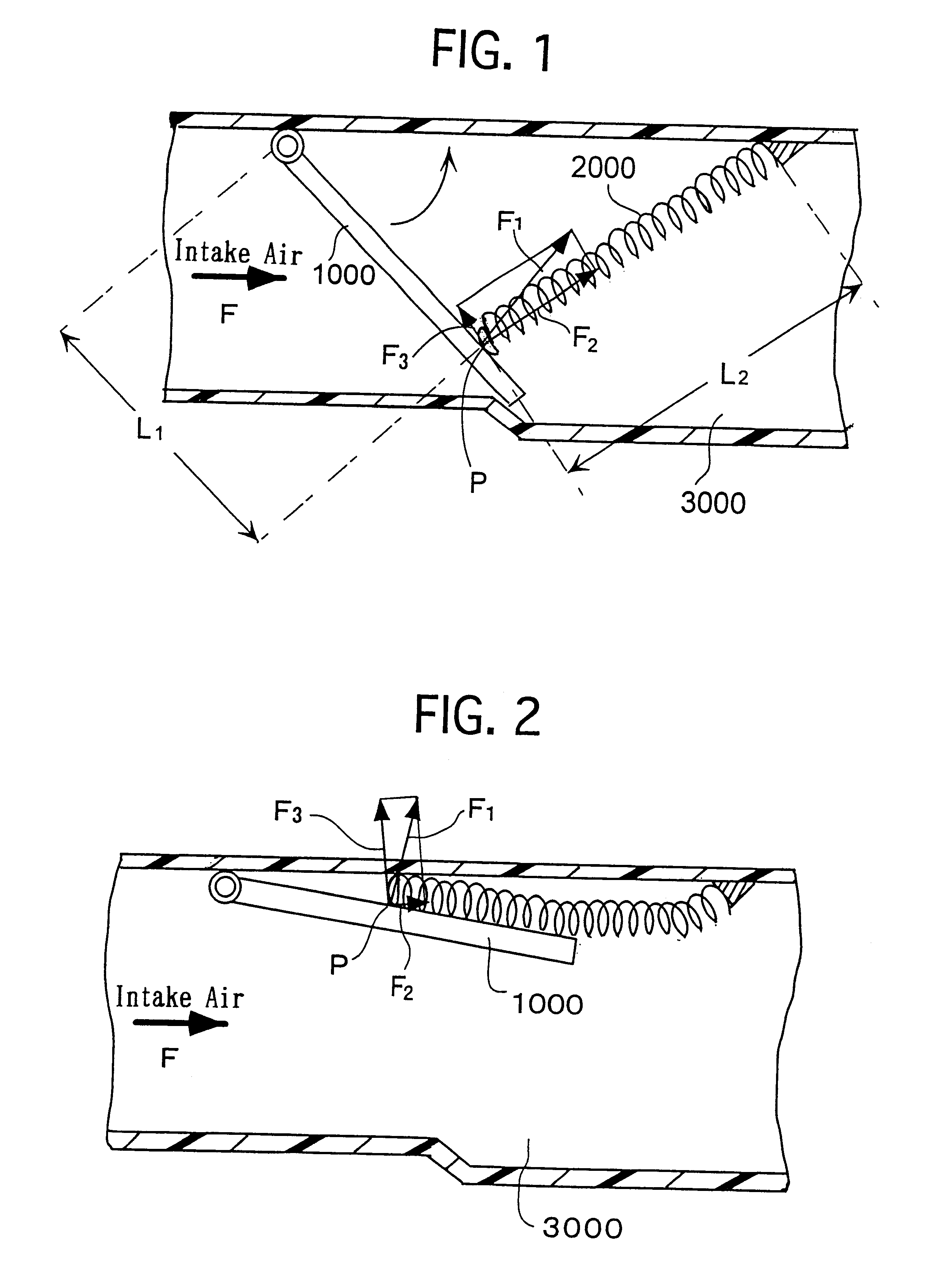
InactiveUS20050193976A1Promote effectiveInternal combustion piston enginesAir intakes for fuelCombustion chamberEngineering
To provide an improved swirl forming device in a combustion engine, which is effective to promote a vigorous and massive swirling motion of the charge mixture within the combustion chamber, the swirl forming device includes an auxiliary passage (24) for introducing an auxiliary gas, which may be either air or a charge mixture, into the combustion chamber (9) from a location immediately upstream of the intake port (70) that is selectively opened and closed by the intake valve (10). This auxiliary passage (24) has an open end (25) positioned adjacent the exhaust port (80), such that when viewed from top in a direction conforming to the longitudinal axis (CC) of the cylinder bore (3), the auxiliary gas is introduced in a direction different from the direction (N) normal to the inner peripheral surface (3a) of the cylinder bore (3) to thereby form a swirl (S) along the inner peripheral surface (3a) of the cylinder bore (3).
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
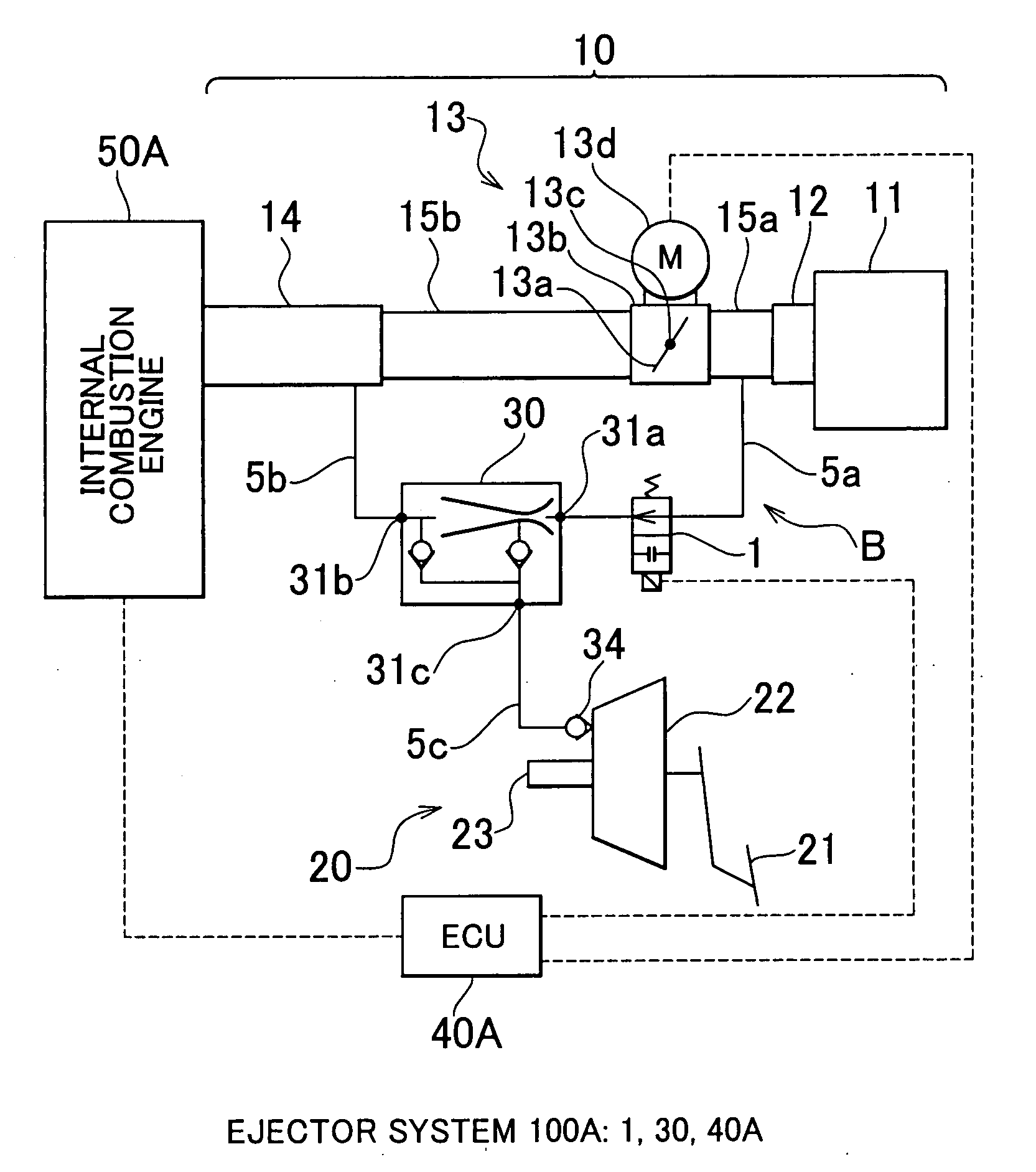
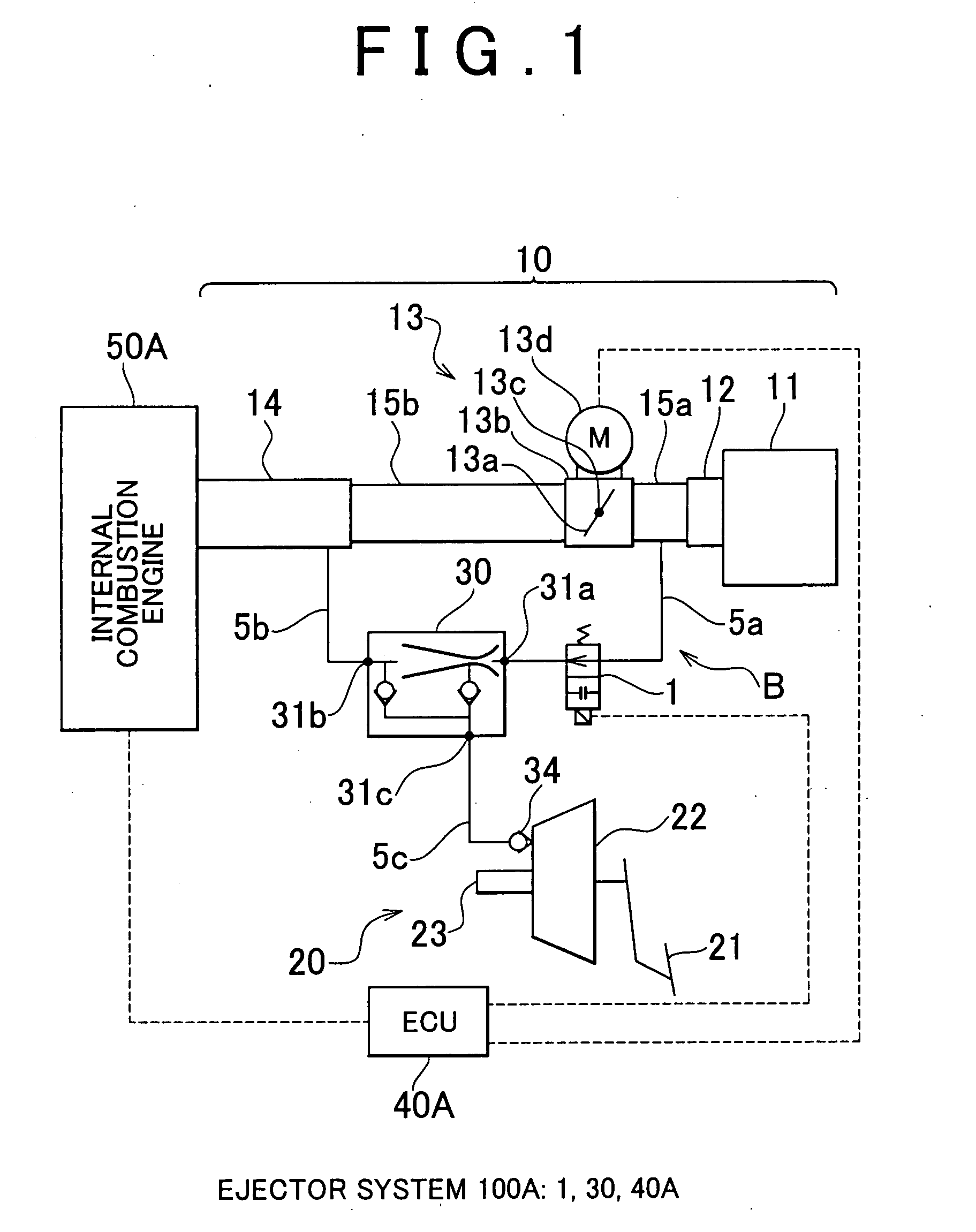
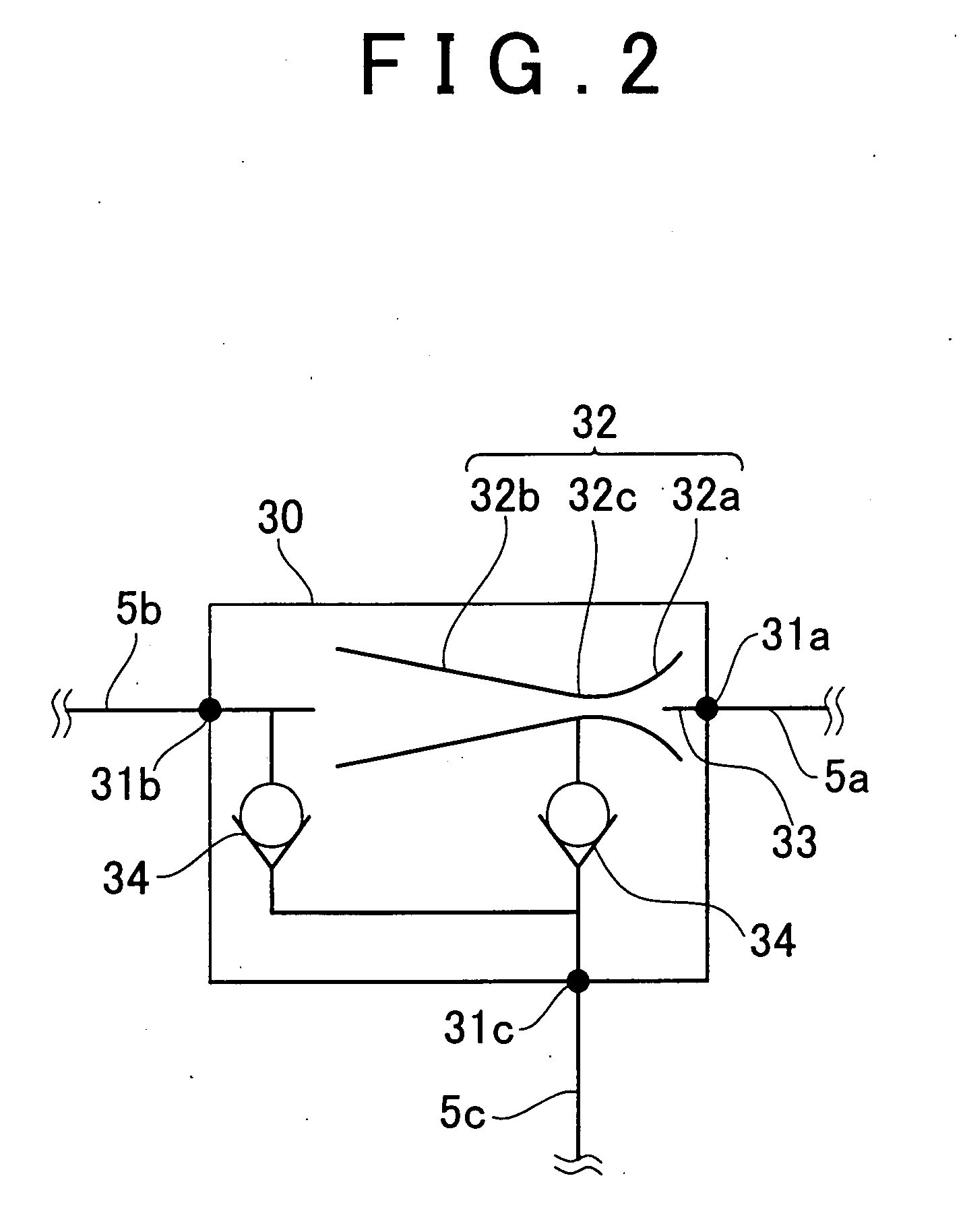
Vehicular ejector system and control method thereof
InactiveUS20070295303A1Reduce vehicle costReduce adverse effectsElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsInlet manifoldThrottle
A vehicular ejector system having an ejector that generates a negative pressure that is greater than the intake manifold negative pressure that is to be extracted from an intake manifold, a VSV that causes the ejector to function or stop functioning, and an ECU that controls the VSV. The ECU includes a control device that controls the VSV so as to cause the ejector to function if an ISC request amount for controlling, during idling, a throttle valve that adjusts the intake air flow amount supplied to the internal combustion engine is greater than a predetermined amount.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Intake air duct
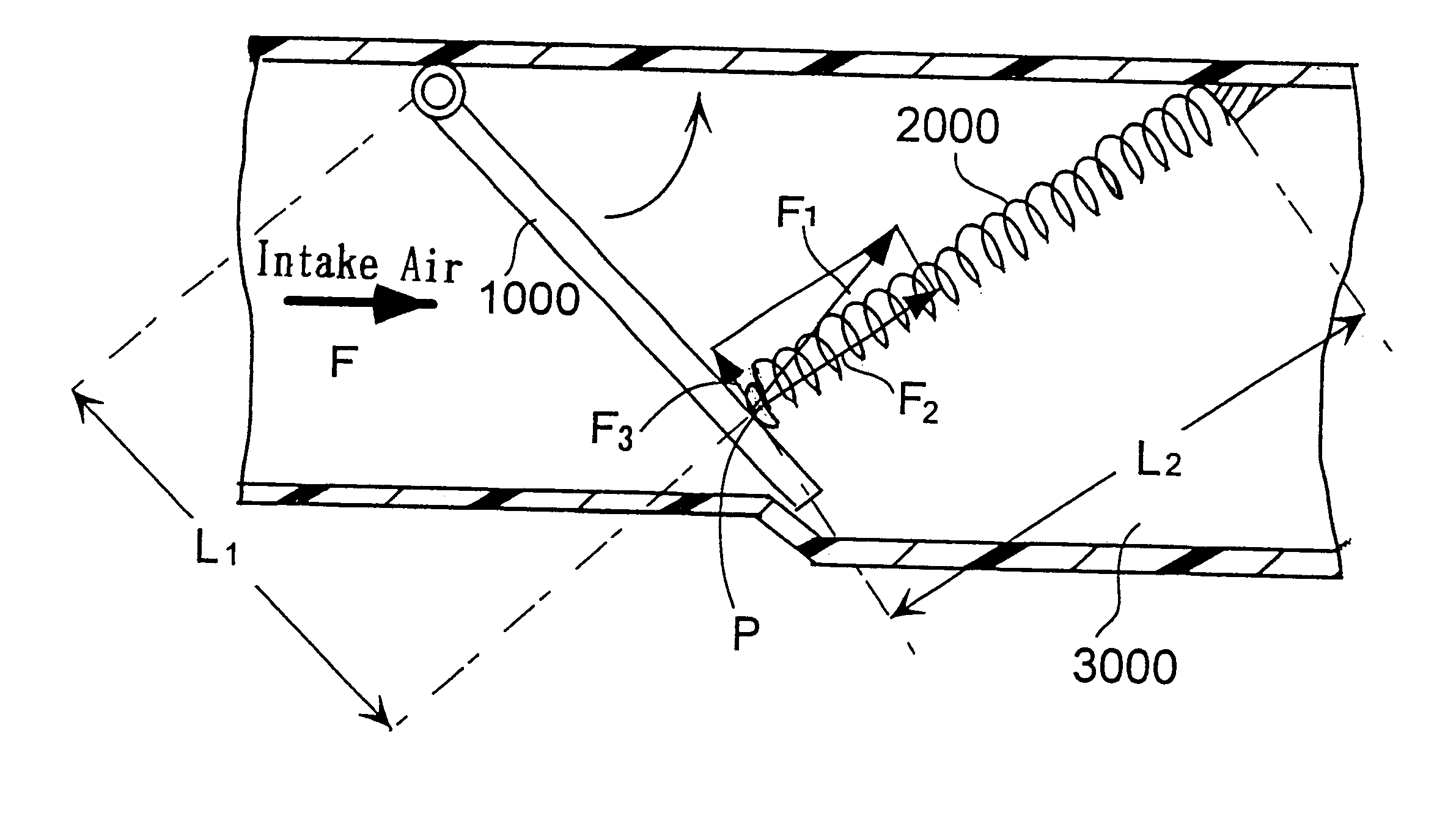
InactiveUS6332442B1Reduce intake noiseLow costInternal combustion piston enginesSilencing apparatusCoil springEngineering
An intake air duct serves as a passage for supplying air to an engine, and includes a first intake air passage, a second intake air passage, an opening-and-closing valve, an interlocking member and a coiled spring. The opening-and-closing valve is disposed swingably in the second intake air passage so as to open and close the second intake air passage. The interlocking member is disposed outside the first intake air passage or the second intake air passage, and swings by interlocking with the swinging of the opening-and-closing valve. The coiled spring is disposed swingably outside the first intake air passage or the second intake air passage, and has a swinging end, which is brought into contact with a surface of the interlocking member. The swinging end slides on a surface of the interlocking member as the swinging of the interlocking member. The second intake air passage is opened by the opening-and-closing valve when a first urging force, which acts onto the coiled spring while the interlocking member swings so as to interlock with the opening-and-closing valve being swung in an opening direction by a negative pressure exerted in the second intake air passage, is larger than a second urging force, which is exerted by a spring elasticity of the coiled spring. The second intake air passage is closed when the first urging force is smaller than the second urging force.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Engine control apparatus
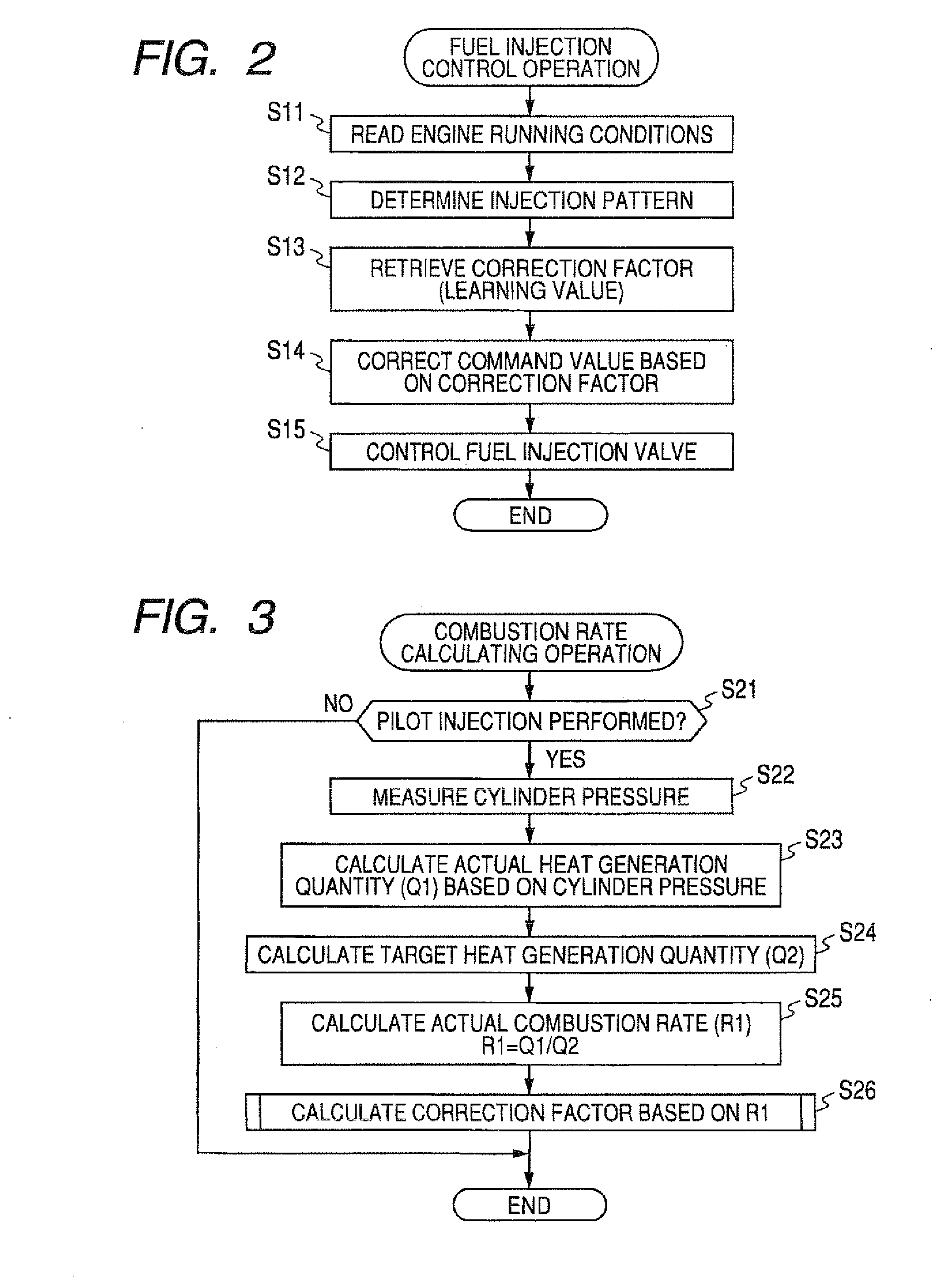
ActiveUS20080167786A1Accelerate emissionsImprove fuel economyAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlEngineeringControl variable
An engine control apparatus comprised of an engine control ECU has a program preloaded therein for determining a combustion rate (actual combustion rate) corresponding to the ratio of an ideal heat generation quantity (target heat generation quantity) estimated to be generated from a fuel supply quantity, and an actual heat generation quantity actually generated by the fuel supply quantity. The engine control apparatus controls pilot injection timing with a controlled variable corresponding to the thus determined combustion rate so as to increase the combustion rate.
Owner:DENSO CORP
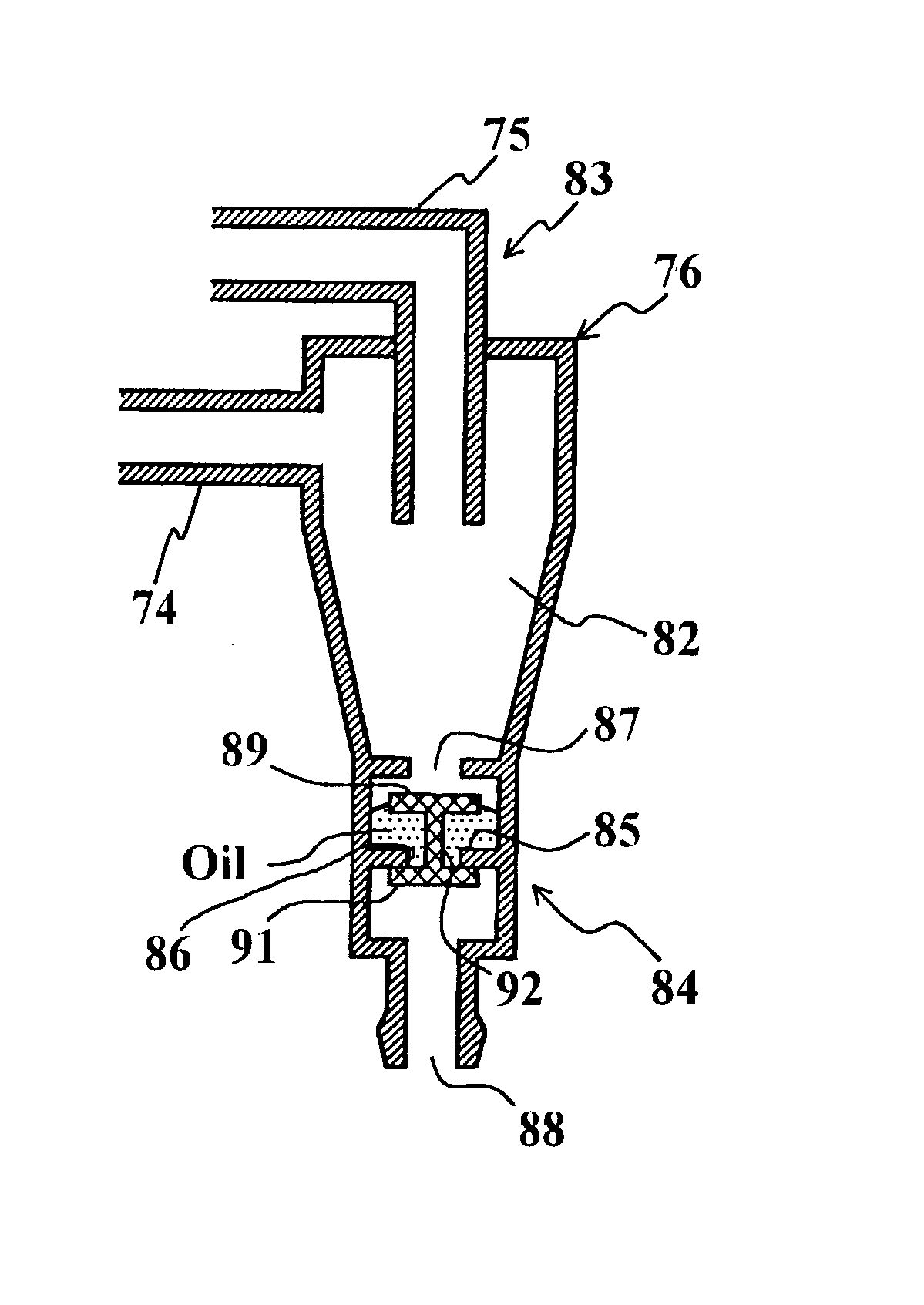
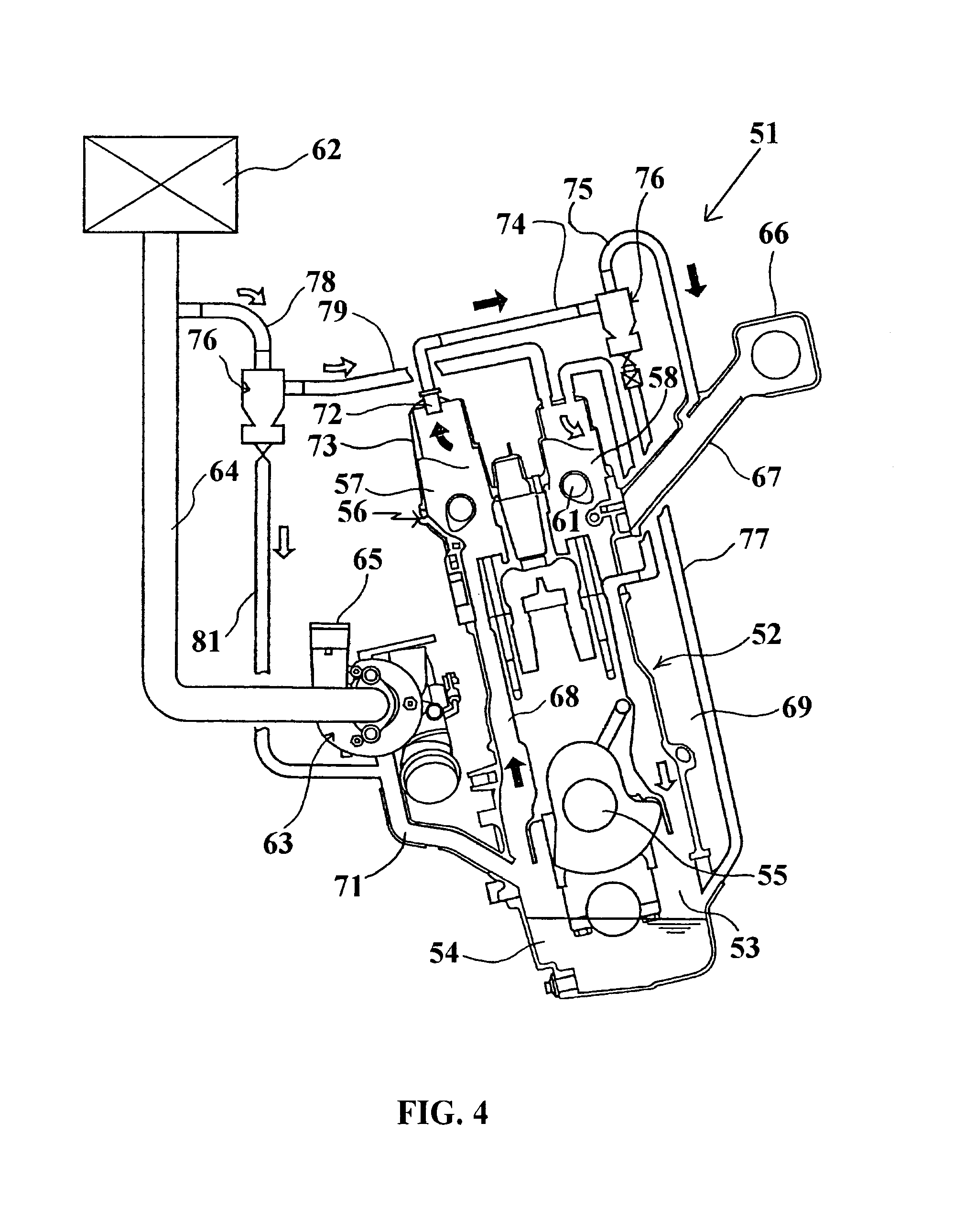
Evaporative emissions control system including a charcoal canister for small internal combustion engines
InactiveUS20050178368A1Easy to collectEasy to trapNon-fuel substance addition to fuelLarge containersAtmospheric airControl system
Owner:TECUMSEH PROD CO +1
EGR control apparatus for engine
InactiveUS20050000497A1Increased durabilityHeat resistance reliabilityElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberEngineering
According to the invention, an EGR control apparatus of an engine includes intake ports to which an intake passage is connected, the intake ports opening into each combustion chamber of the engine, an EGR port to which an EGR passage branching out from an exhaust passage is connected, the EGR port opening into each combustion chamber of the engine, an electrically-operated compressor disposed in the EGR passage for regulating pressure at which EGR gas is introduced into each combustion chamber, and an EGR control valve disposed in the EGR passage at a point downstream of the electrically-operated compressor for controlling the amount of EGR gas introduced into each combustion chamber. The EGR passage branches out from the exhaust passage at a point downstream of an emission control device disposed in the exhaust passage.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
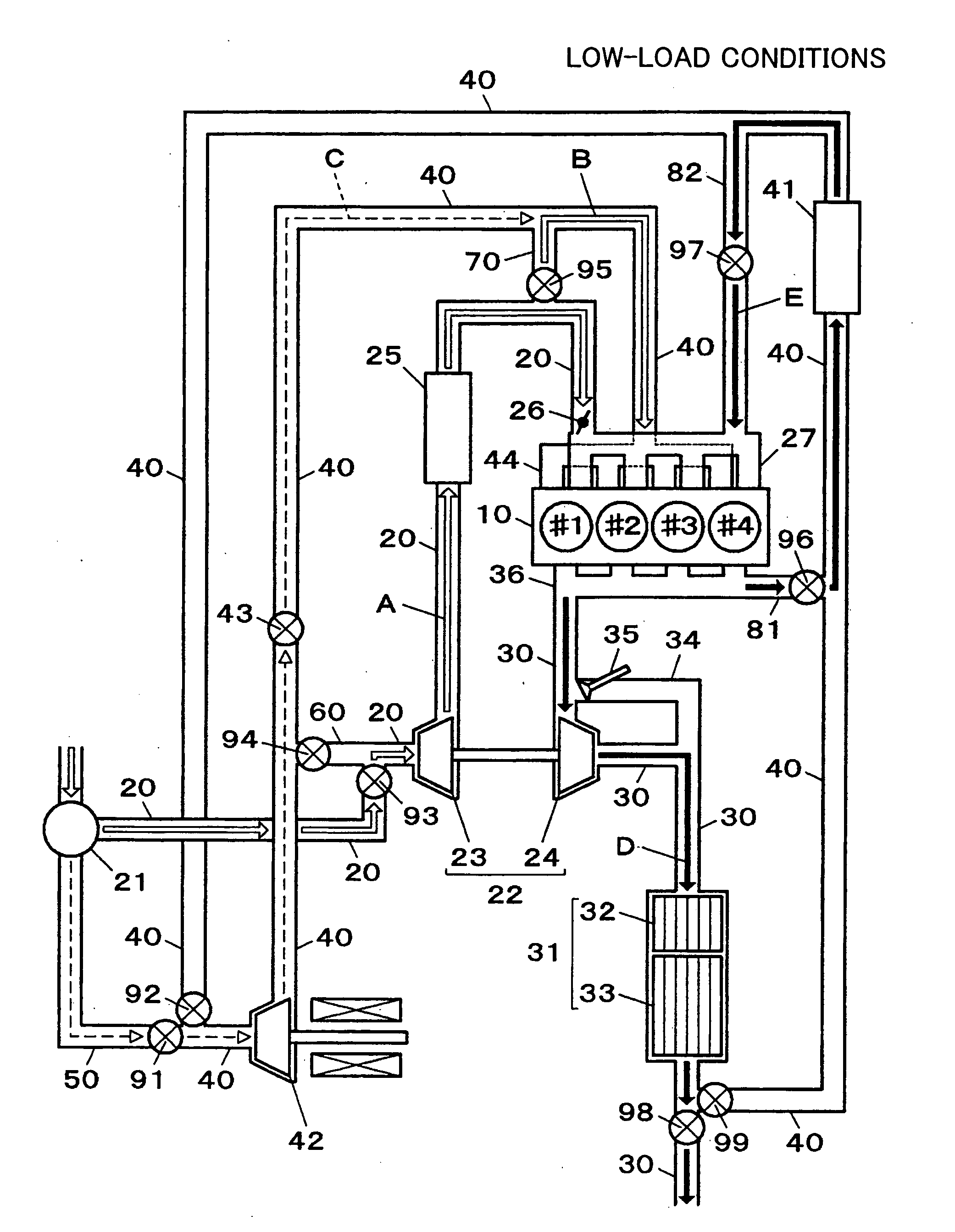
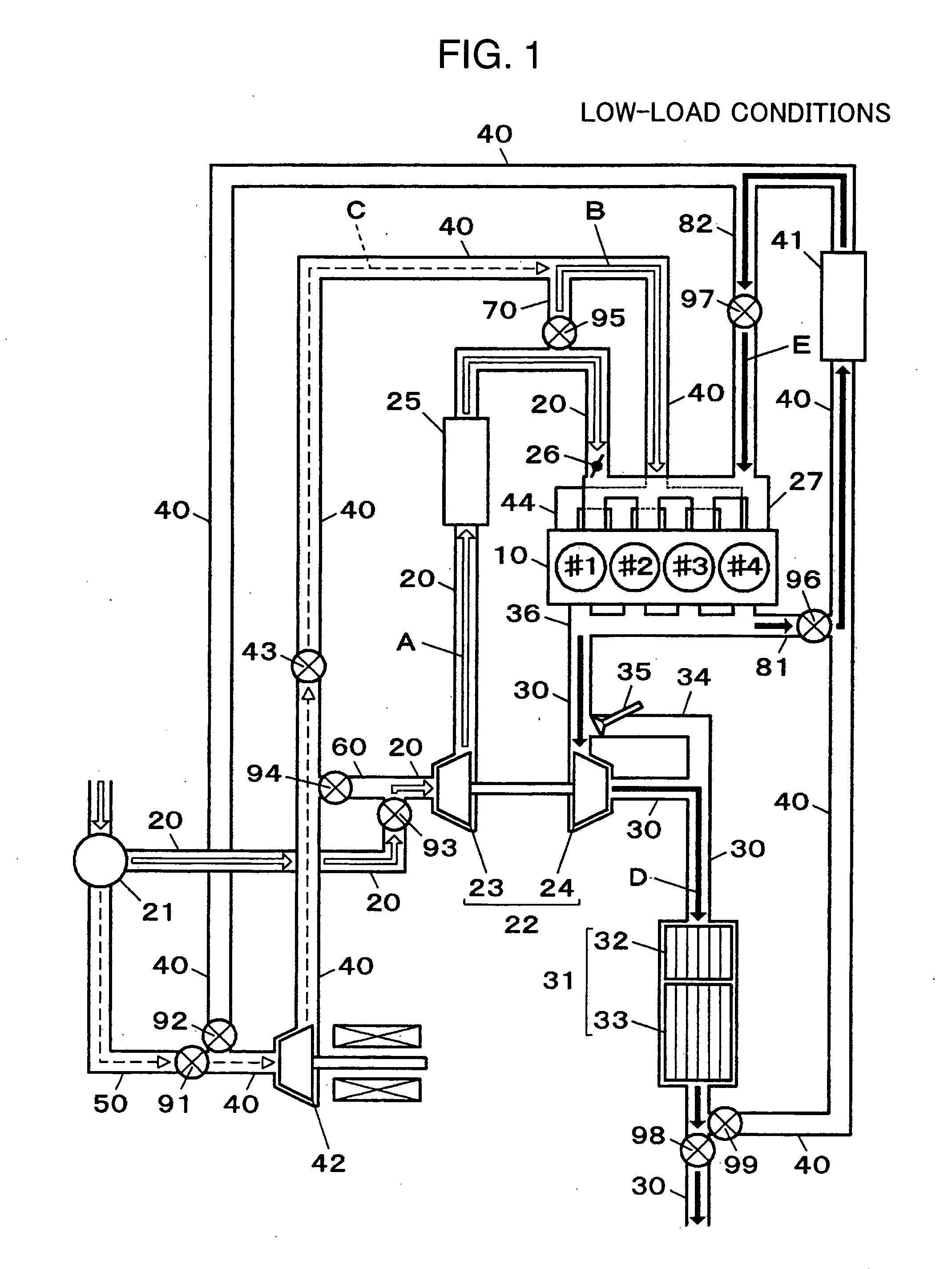
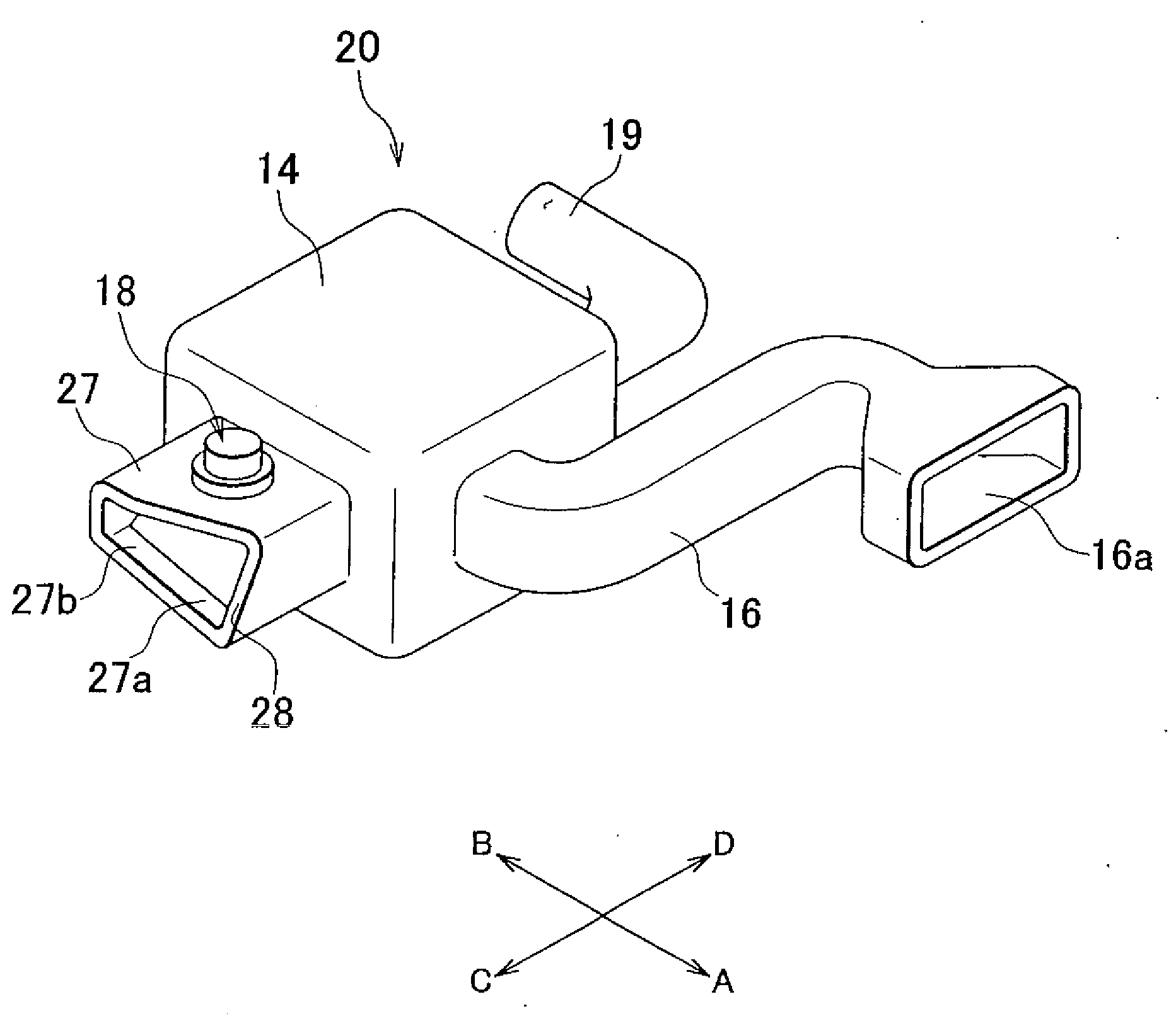
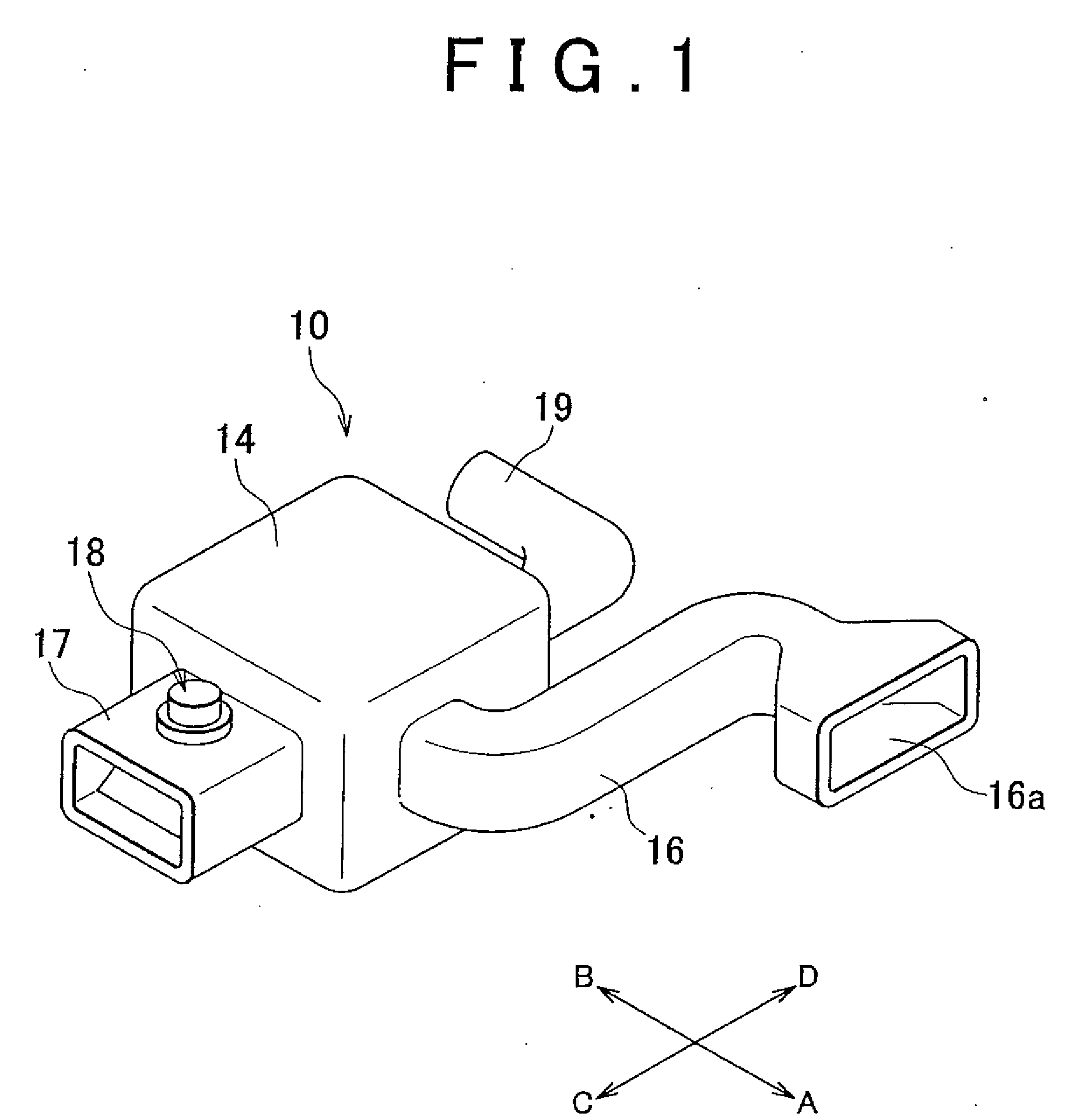
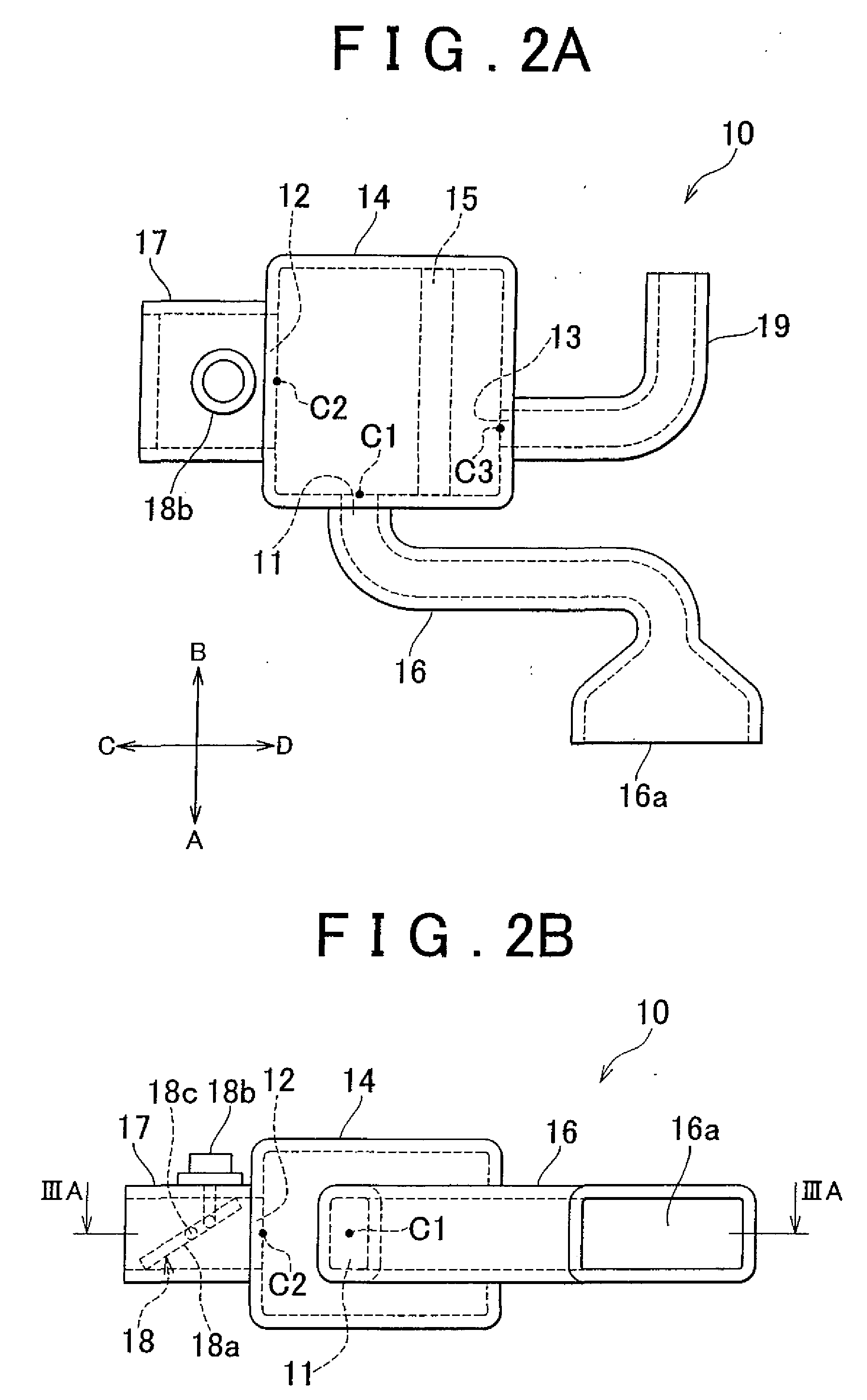
Intake system for vehicle internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20100083928A1Improve engine performanceImprove performanceCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentInternal combustion engineAir cleaners
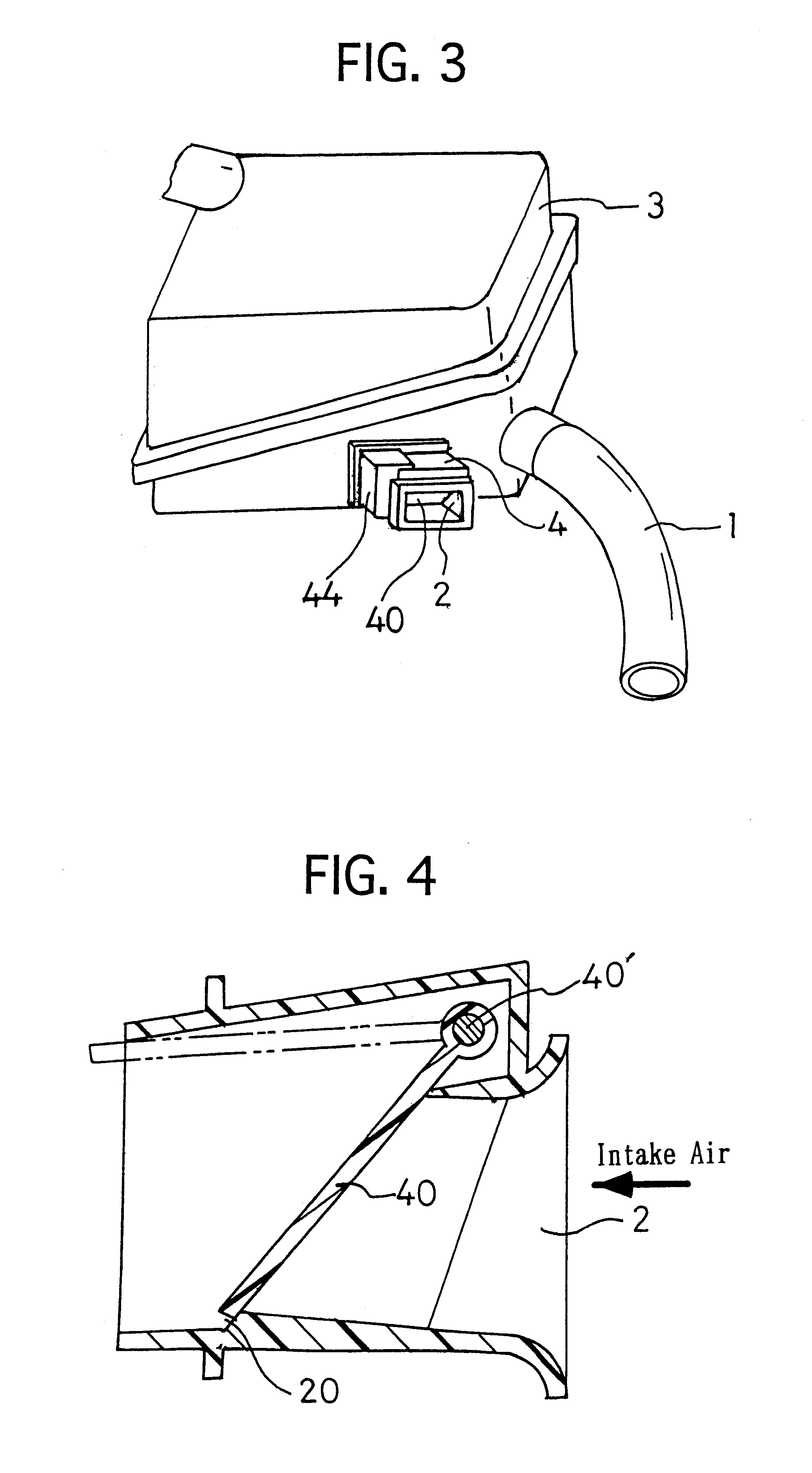
An intake system (10, 20) for a vehicle internal combustion engine is provided in which a first air intake duct (16), having an air intake inlet (16a) to inhale external air, is connected to an air cleaner box (14). A second air intake duct (17, 27) is also connected to the air cleaner box. The air intake inlet is closer to the air cleaner box than the second air intake duct is. The cross section area of a second air intake duct is greater than the cross section area of the first air intake duct. The center axis of the second air intake duct at an end on the side of a second air intake opening (12, 22) intersects with the center axis of the first air intake duct at an end on the side of a first air intake opening (11).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Swirl forming device in combustion engine
InactiveUS7140347B2Promote effectiveInternal combustion piston enginesAir intakes for fuelCombustion chamberInlet valve
To provide an improved swirl forming device in a combustion engine, which is effective to promote a vigorous and massive swirling motion of the charge mixture within the combustion chamber, the swirl forming device includes an auxiliary passage (24) for introducing an auxiliary gas, which may be either air or a charge mixture, into the combustion chamber (9) from a location immediately upstream of the intake port (70) that is selectively opened and closed by the intake valve (10). This auxiliary passage (24) has an open end (25) positioned adjacent the exhaust port (80), such that when viewed from top in a direction conforming to the longitudinal axis (CC) of the cylinder bore (3), the auxiliary gas is introduced in a direction different from the direction (N) normal to the inner peripheral surface (3a) of the cylinder bore (3) to thereby form a swirl (S) along the inner peripheral surface (3a) of the cylinder bore (3).
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
Power booster fuel saver
InactiveUS6837213B1Improve vehicle performanceInternal combustion piston enginesFuel re-atomisation/homogenisationDiagonalExhaust pipe
The power booster fuel saver is made of a cut and formed piece of stainless steel in the shape of a cylinder. The strip is provided in a length sufficient to correspond to the inner diameter of the inlet pipe to a vehicle engine or from its turbo fan outlet, or into the inlet pipe leading to the turbo fan or in the exhaust pipe from the engine. A series of square-shaped tabs are cut along one side of the strip and then bent diagonally to form a series of dog-ears. Finally, the strip is rolled into the shape of a cylinder in which the edges meet and the resulting device is inserted into the intake of a vehicle.
Owner:BURNETT DAVID T
Blow-by gas separator
InactiveUS7007682B2Internal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCrankcase ventilation systemInduction system
An improved crankcase ventilation system including an improved blow-by gas separator wherein it will be insured that oil cannot accumulate in the separator chamber under any running conditions so that the oil is totally precluded from being able to pass into the induction system.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Engine intake manifold assembly
An engine intake manifold assembly including a first portion configured with a first material and a second portion configured with a second material, wherein the first and second portions are adhesively bonded together. Preferably, the intake manifold assembly is additionally configured with a cylinder head flange, for mounting the same to an automotive engine component, and a throttle body attachment for attachment of a throttle body component. The cylinder head flange and throttle body attachment may be an integral component of the first or second portions or attached to the same during or after assembly of the first and second portions. Optionally, an insert is located between the assembled first and second portion to create one or more plenums thereby creating one or more air flow paths through the intake manifold assembly.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
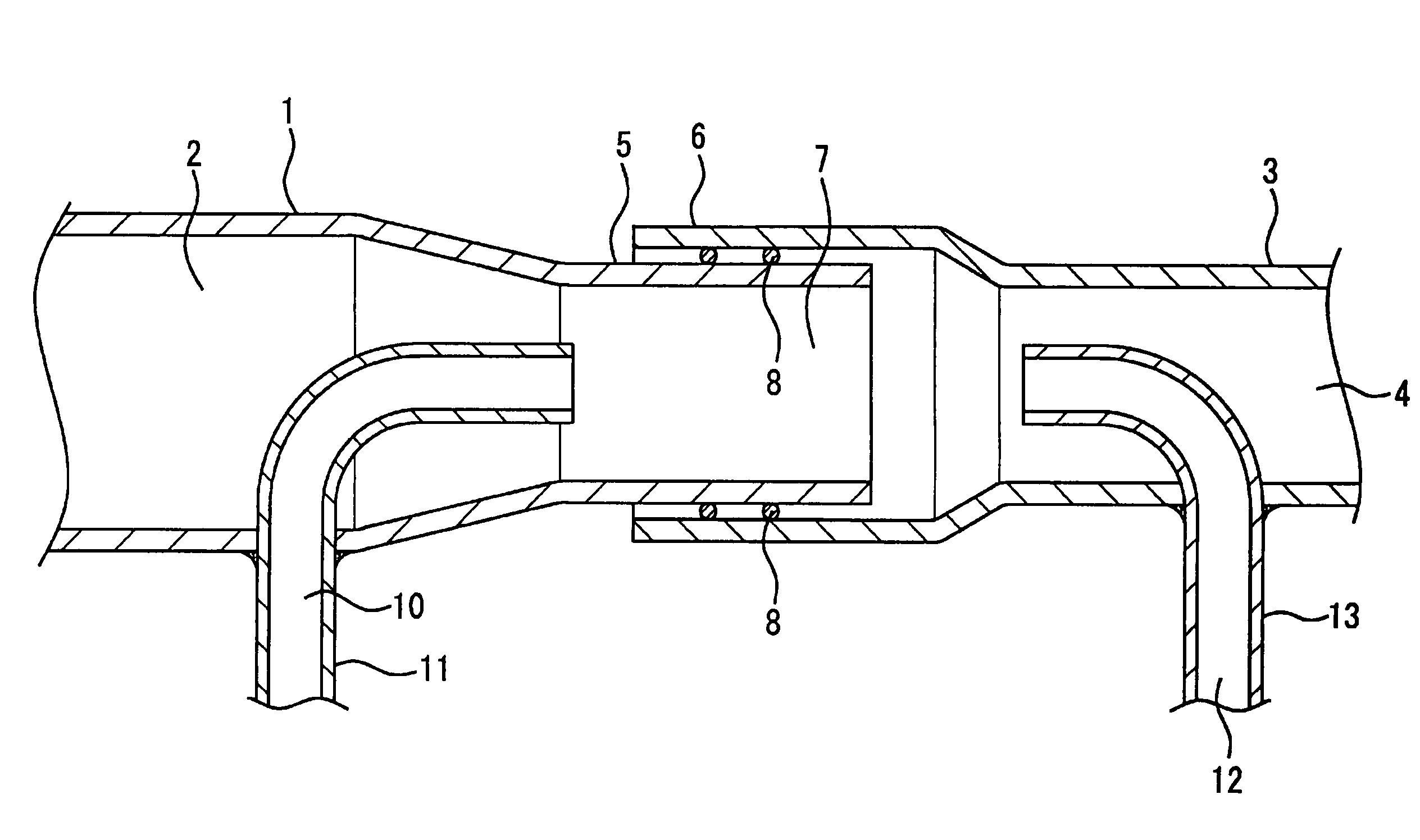
Duct and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20070278034A1Simple structureOccurrence of noiseSilencing apparatusIsotope separationNonwoven fabricBiomedical engineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a duct having a simple structure and capable of suppressing occurrences of an intake noise and a dropping-out of an adsorbent, and to a process for producing the same capable of producing easily. The present duct (1) is one comprising a duct body (2) in tubular, and the duct body (2) is comprised of a nonwoven fabric in which an adsorbent (3) in at least one type among granular, powdery and fibrous is disposed as an intermediate layer. The duct body (2) is preferably composed of a first fiber layer (7) located on an inner circumferential side, a second fiber layer (8) located on an outer circumferential side, and the adsorbent (10) is disposed between the first fiber layer (7) and the second fiber layer (8).
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
Evaporative emissions control system including a charcoal canister for small internal combustion engines
InactiveUS7267112B2Facilitates collection and trappingNon-fuel substance addition to fuelLarge containersAtmospheric airControl system
An evaporative emissions control system for small internal combustion engines, including a charcoal canister which is in fluid communication with the air space above the liquid fuel within the carburetor of the engine and the air space above the liquid fuel within the fuel tank of the engine. The charcoal canister contains charcoal media, and when the engine is not running, fuel vapors from the carburetor and the fuel tank migrate to, and are trapped within, the charcoal media of the charcoal canister. The charcoal canister may comprise a separate component, or may be integrally formed with an engine component such as the air cleaner, the carburetor, or the body of the fuel tank, for example. During running of the engine, vacuum within the carburetor induces a flow of atmospheric air through the charcoal canister to purge the collected fuel vapors from the charcoal media, and the fuel vapors pass into the engine for consumption. In another embodiment, an evaporative emissions control system including a charcoal canister is provided for an engine which includes a fuel injection system.
Owner:TECUMSEH PROD CO +1
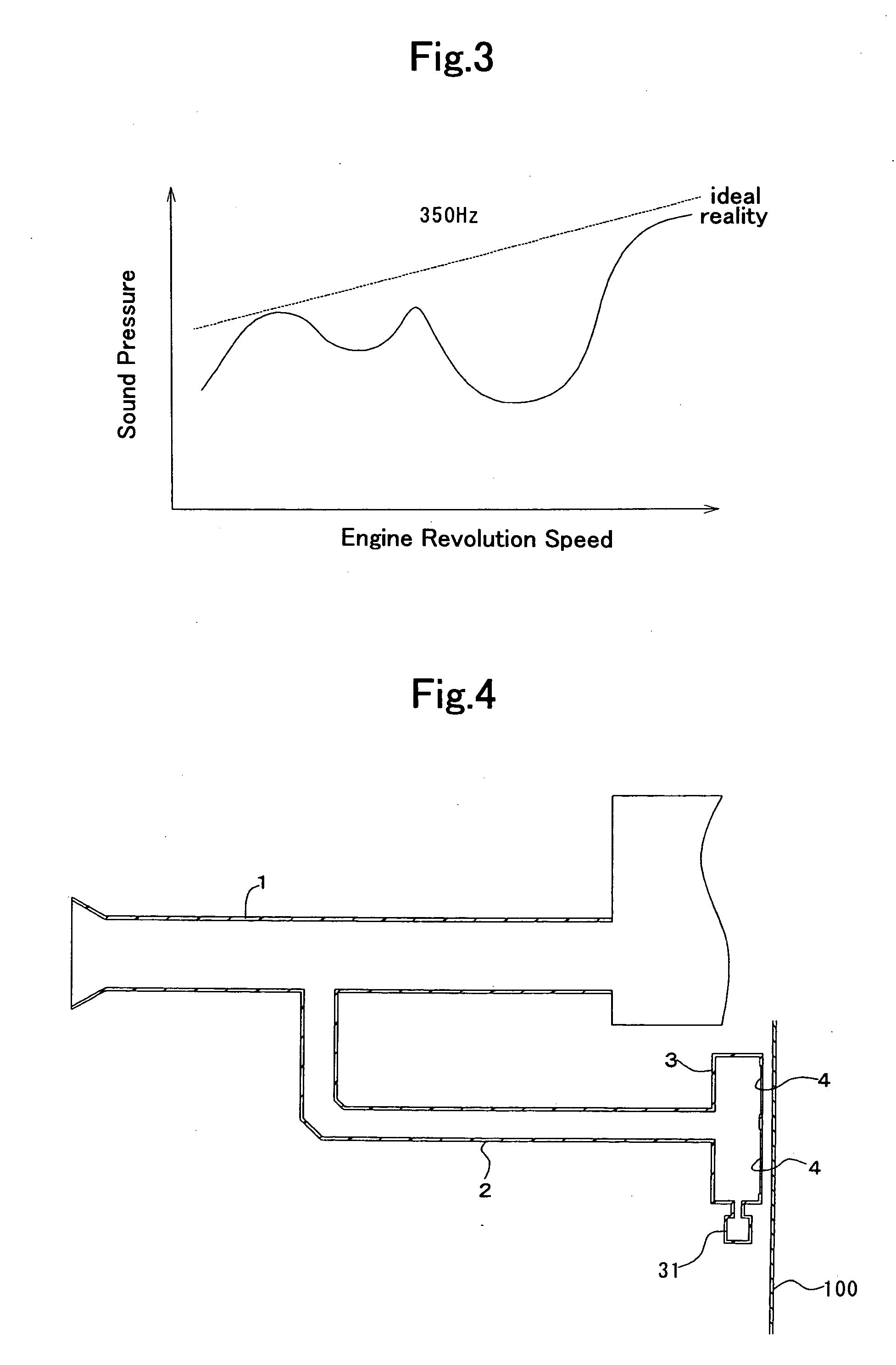
Resonator
InactiveUS20060065479A1Reduce tensionReduce frequencySilencing apparatusMachines/enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
A resonator is arranged in an intake system including a pipe section for partitioning an intake port from an intake passage that communicates the intake port with a combustion chamber of an engine, the resonator including: a branch pipe having one end branching to the pipe section and the other end closed so that a silencing chamber is defined therein; and at least one partition wall for partitioning the silencing chamber into at least one pneumatic spring chamber, the partition wall having a natural frequency lower than the frequency of silencing target sound of intake noise propagated from the intake passage.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
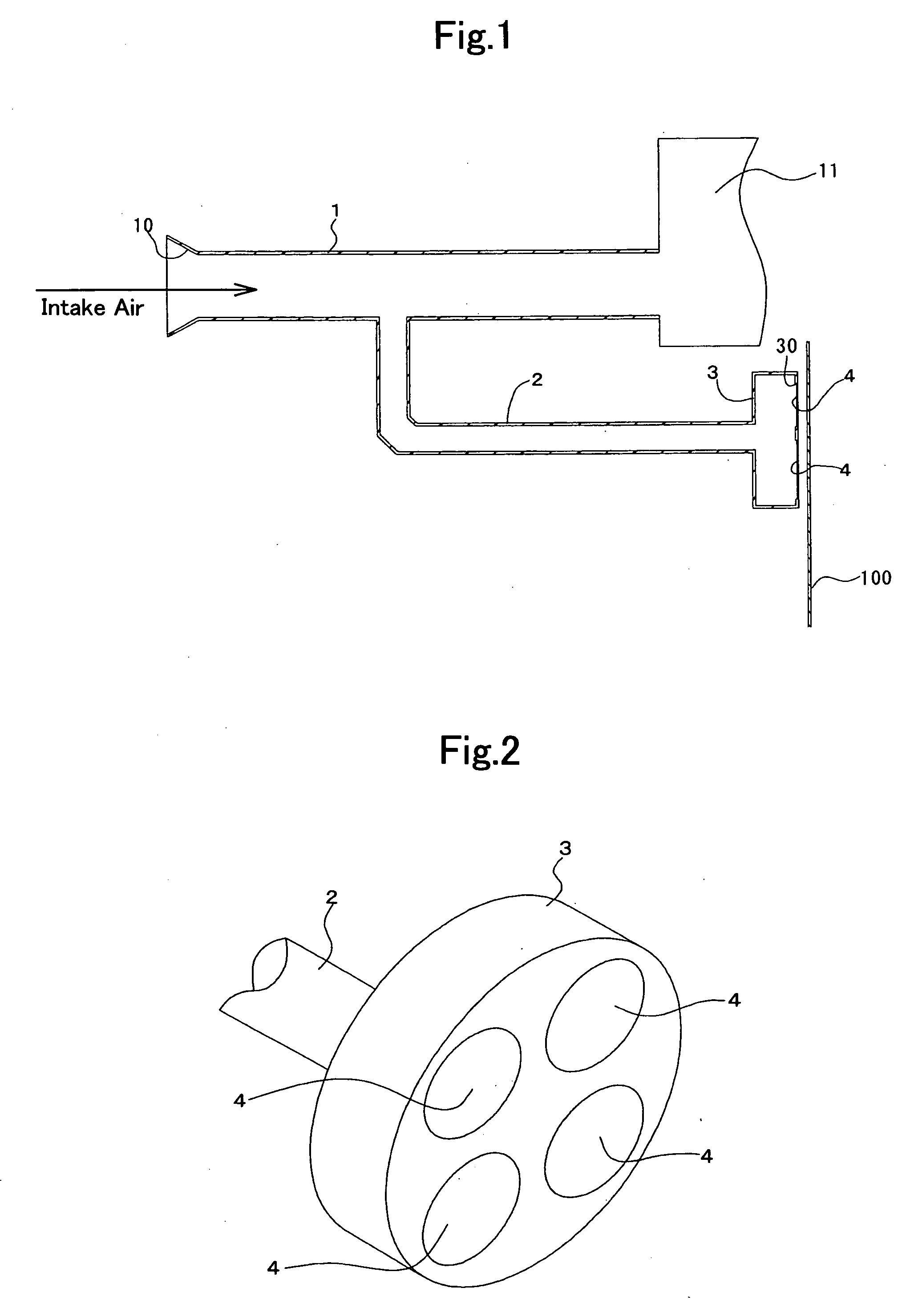
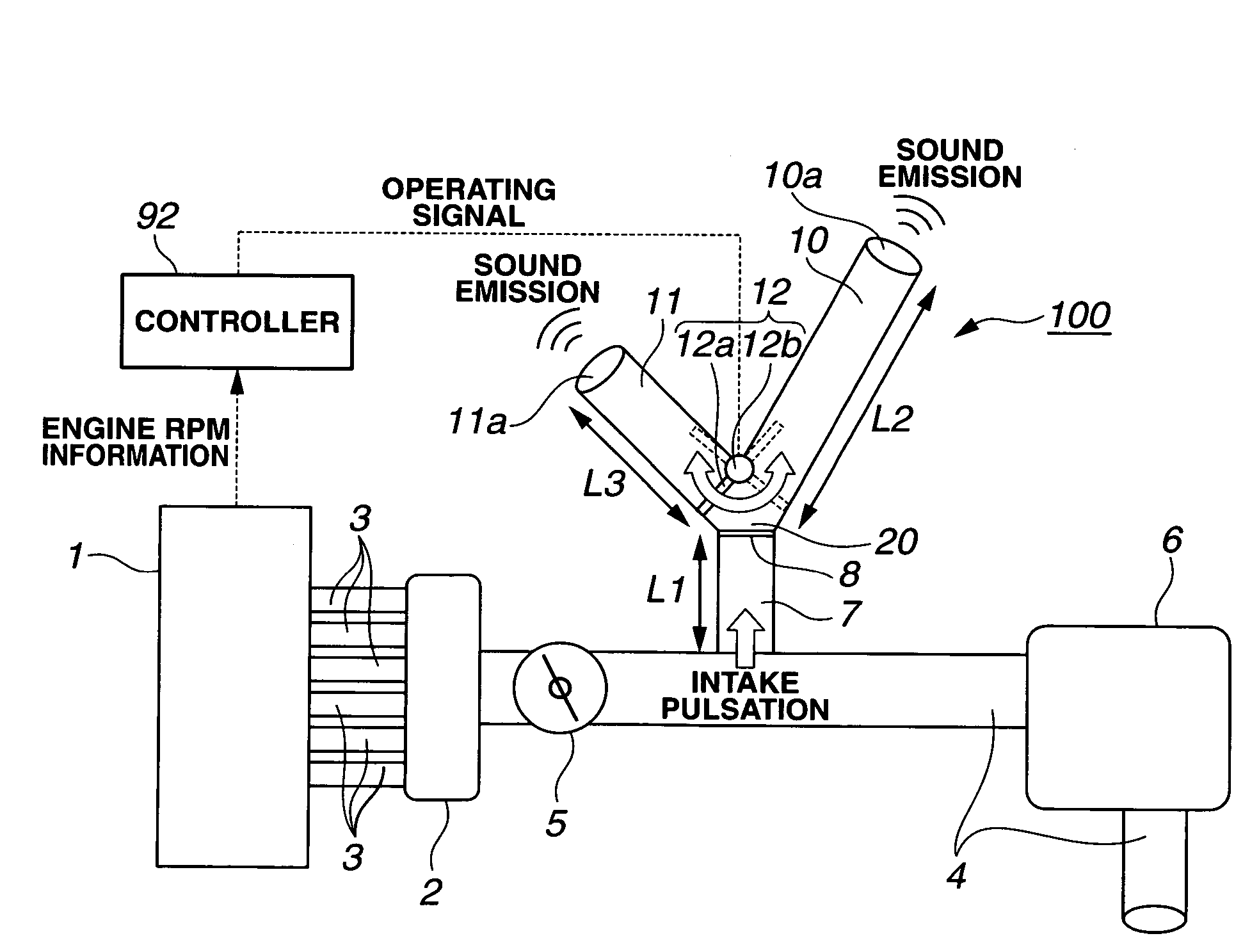
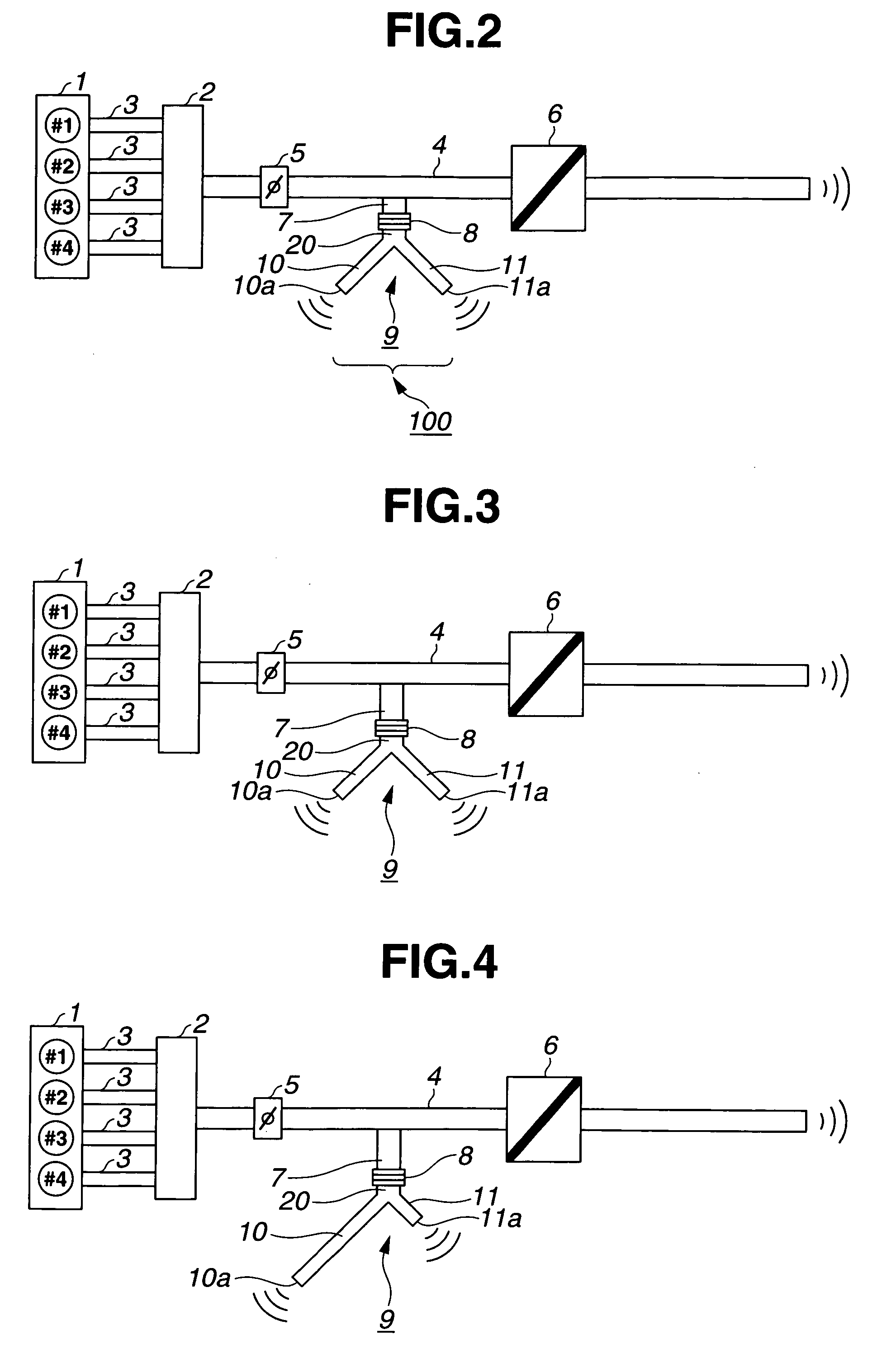
Air intake sound control structure
InactiveUS20070044747A1Low stiffnessIncrease sound pressureMachines/enginesSound producing devicesEngineering
An air intake sound control structure comprises a sound guiding pipe, a sound producing body, and a silencing means. The sound guiding pipe is branched off from a branch portion formed on a part of an air intake flow passage of an automobile, communicating with the air intake flow passage. The sound producing body is held by the sound guiding pipe at the position spaced apart from the branch portion, thereby sealing the sound guiding pipe, and producing a sound at a frequency which corresponds to its own natural vibration frequency by its vibration. The silencing means is disposed on the side of the branch portion of the sound guiding pipe and canceling a sound at a target frequency for suppression out of the air intake sound. The sound generated by the vibration of the sound producing body is transmitted into a vehicle interior.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Air intake device
ActiveUS7159557B2Reducing intake sound levelReduce sound levelMachines/enginesAir intakes for fuelCarburetorEngineering
The present invention relates to a vehicle's air intake device. In an embodiment, the intake device comprises an intake pipe, an air cleaner case in fluid communication with the intake pipe, a connection pipe in fluid communication with the air cleaner case, a carburetor attached to the connection pipe, and a plurality of resonators. In an embodiment, the intake device comprises an intake pipe, an air cleaner case in fluid communication with the intake pipe, a connection pipe in fluid communication with the air cleaner case, a carburetor attached to the connection pipe, and means for reducing intake sound levels.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Sound increase apparatus
InactiveUS7353791B2Nice voiceMachines/enginesAir intakes for fuelExternal combustion engineEngineering
A sound increase apparatus includes a first hollow body member that communicates with an intake flow path of an internal combustion engine, a second hollow body member that communicates with the first hollow body member, and a vibration member capable of vibrating in an out-of-plane direction, which is inserted in a connection between the first and second hollow body members and closes a cross section of the connection. The second hollow body member has a plurality of opening portions, each of which communicates with the air.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Fuel vapor adsorption device of internal combustion engine and method of desorbing fuel vapor from fuel vapor adsorbent
InactiveUS6698403B2Efficient desorptionImprove the desorption effectNon-fuel substance addition to fuelMachines/enginesDesorptionExternal combustion engine
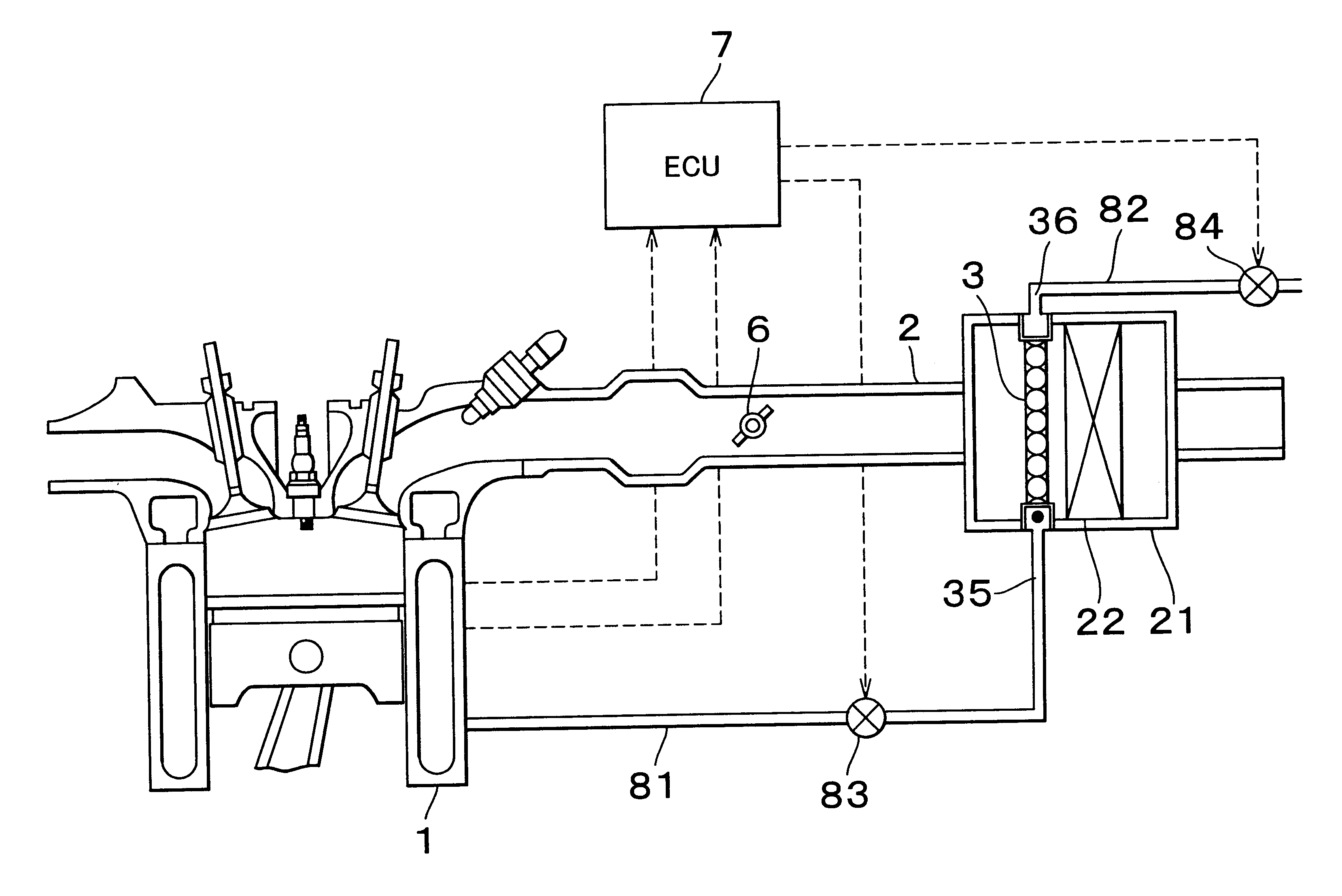
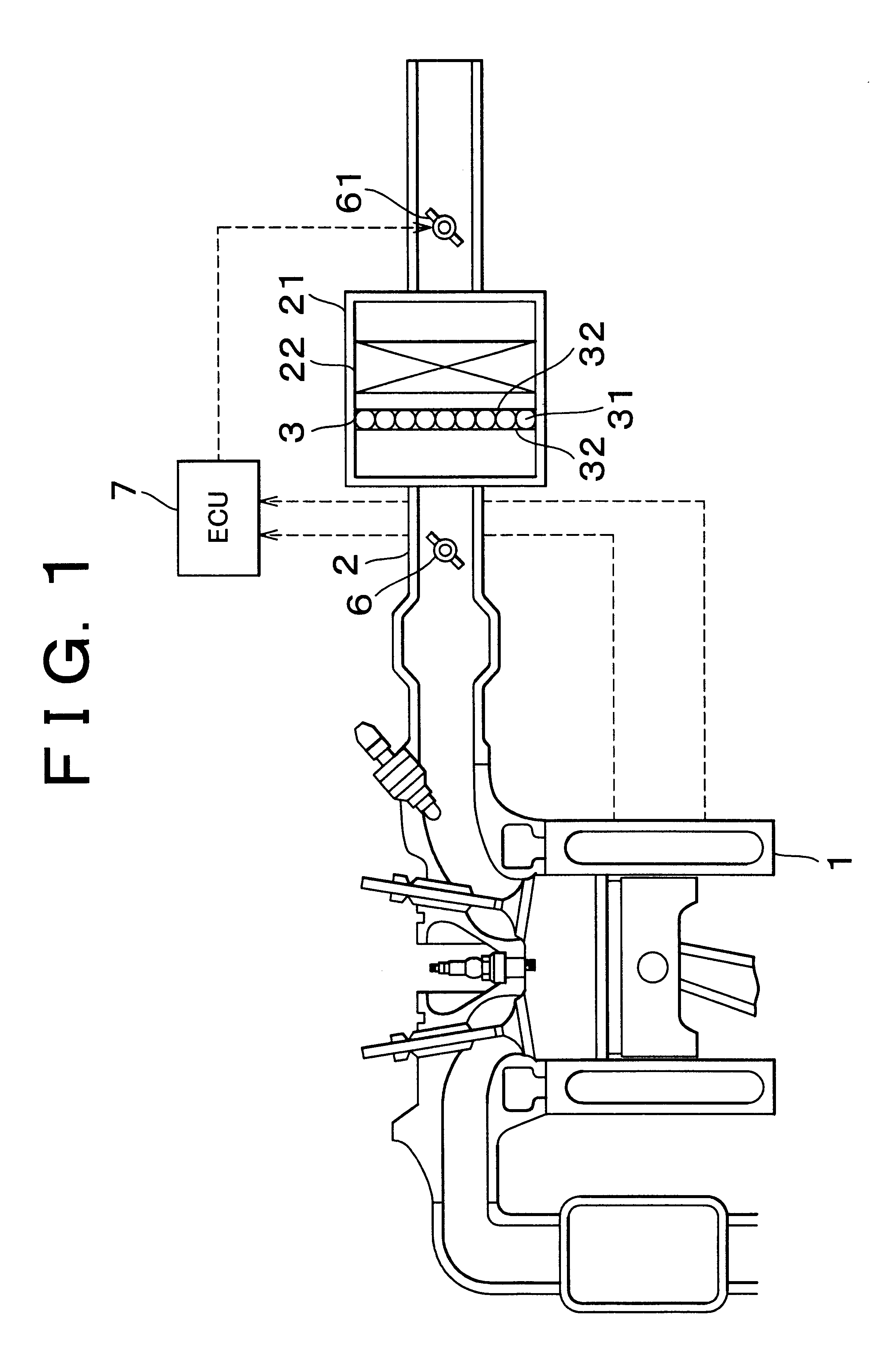
An absorbent, such as, for example, an active carbon, is provided in an intake air passage, for example, in an air cleaner, to efficiently adsorb fuel vapor. To ensure that fuel vapor adsorbed into the intake air passage can be efficiently desorbed even when there is only a small amount of the intake air, an intake throttle valve is provided upstream of the adsorbent and an opening of the intake throttle valve is throttled so as to decompress an area near the adsorbent. Desorption of fuel vapor also can be efficiently promoted by using a heater to directly heat the adsorbent in the intake air passage or by heating the intake air to indirectly heat the adsorbent.
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK +1
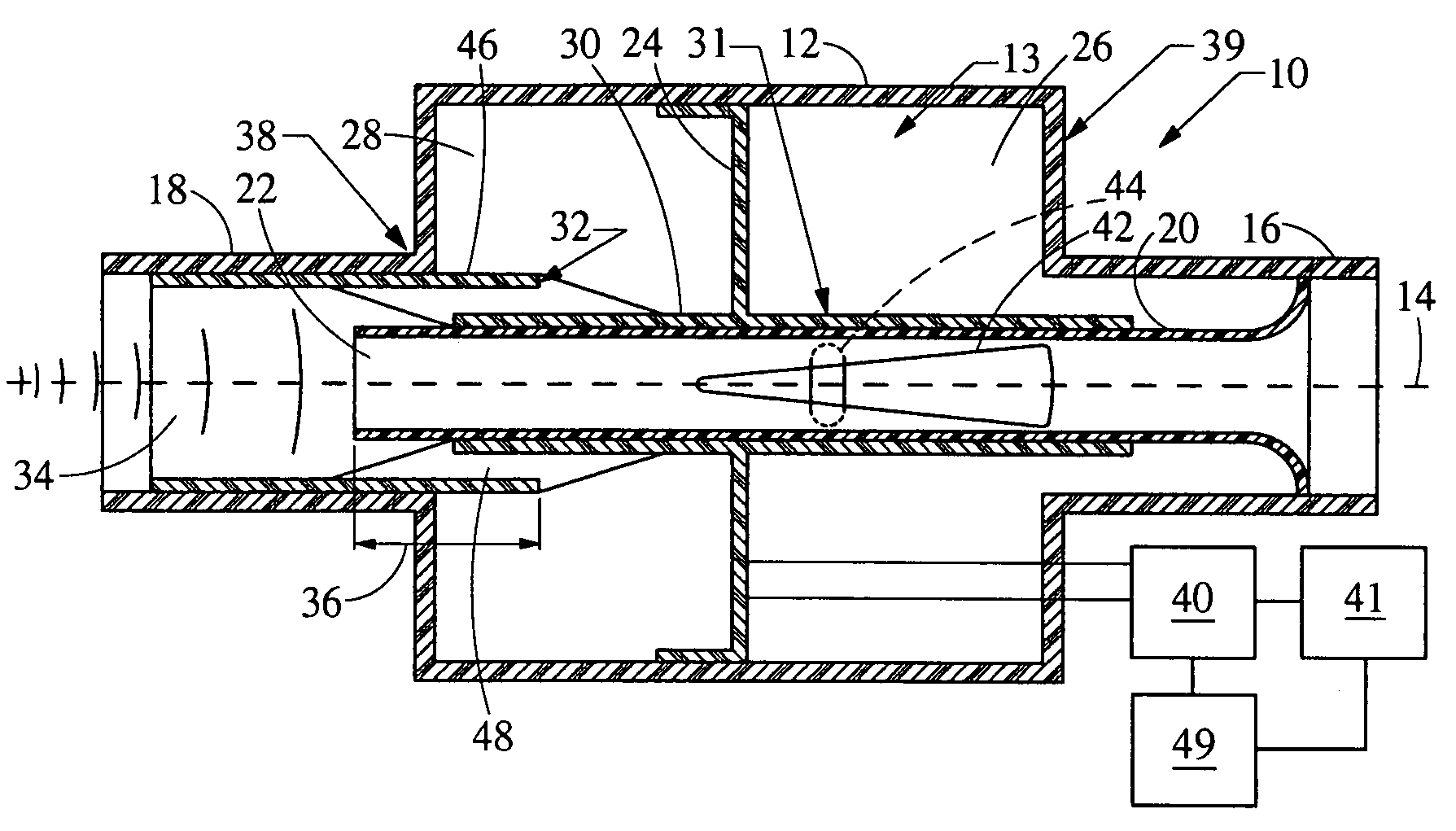
Electronically controlled dual chamber variable resonator
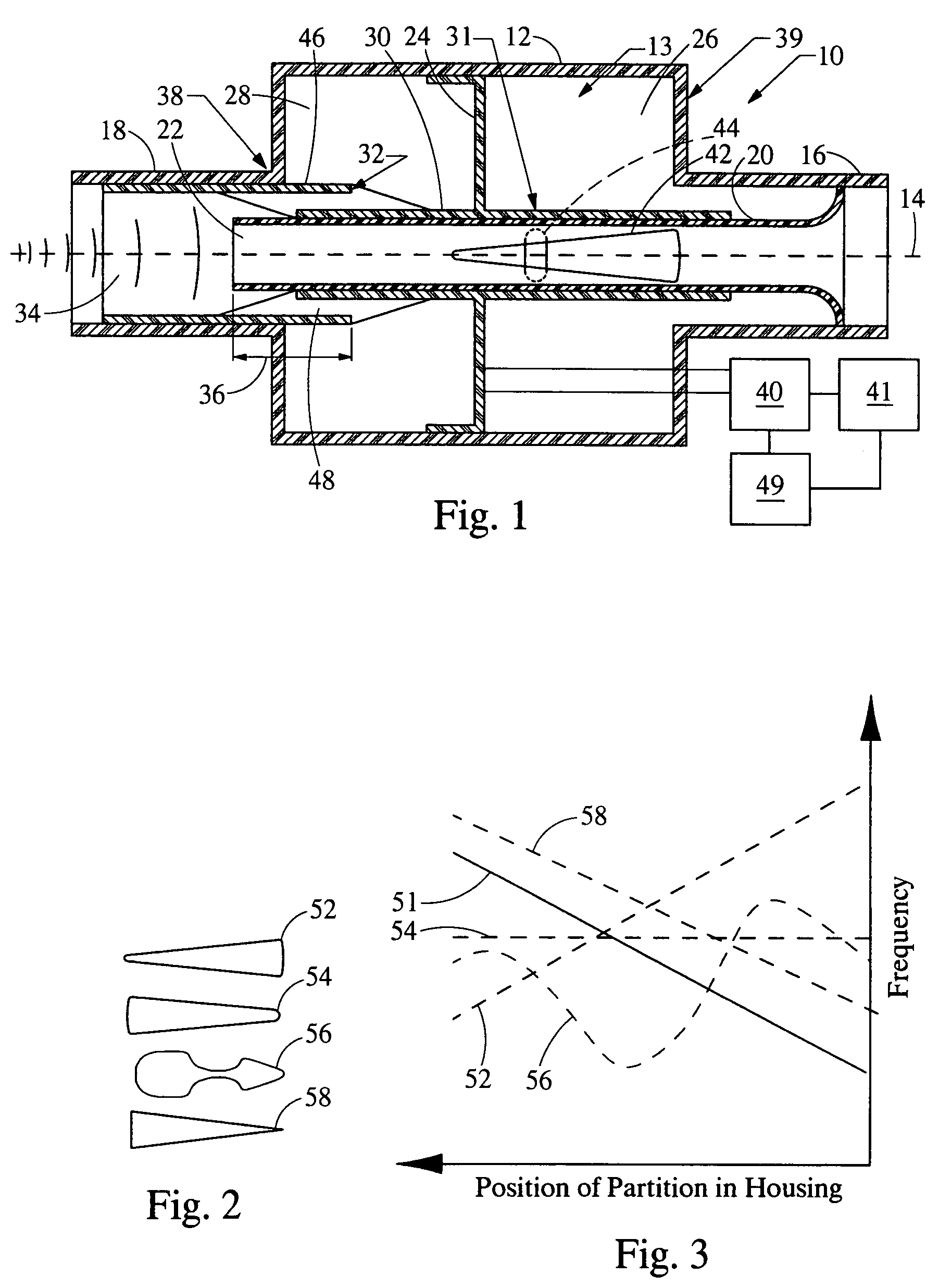
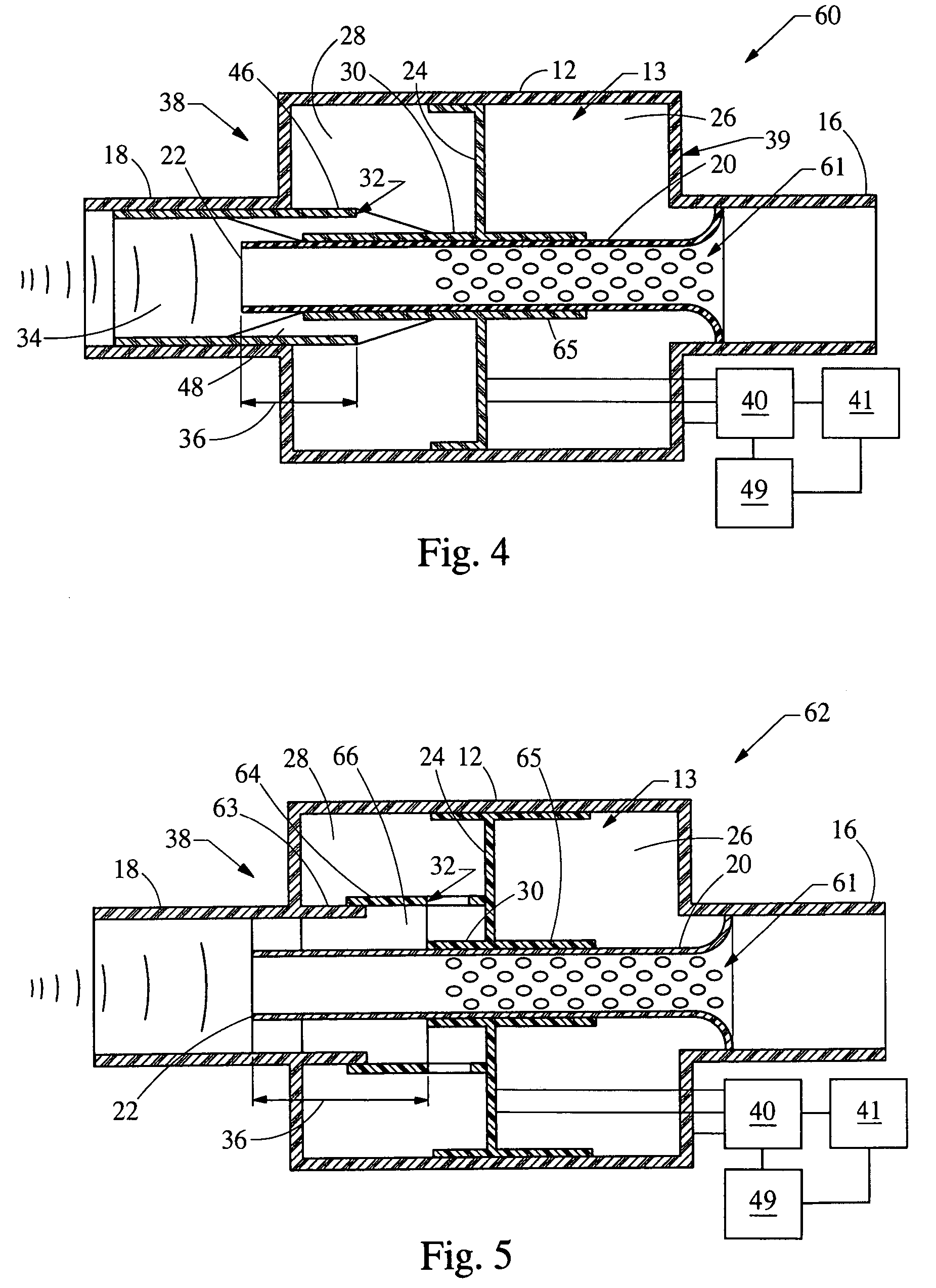
An in-line resonator for an air induction system of an internal combustion engine is provided. The system includes a resonator housing, an upstream duct, a downstream duct, a conduit, a partition, and a sleeve. The conduit extends through the resonator housing connecting the upstream duct and the downstream duct. The partition is moveable within the resonator housing and divides the housing into an upstream chamber and a downstream chamber. The downstream chamber, the conduit, and the downstream sleeve cooperate to form a first Helmholtz resonator that is in fluid communication with the downstream duct. The upstream chamber, the conduit, and the upstream sleeve cooperate to form a second Helmholtz resonator that is in fluid communication with the upstream duct. Further, a means is provided to axially move the partition to vary the volume of the chambers concurrently with the length and / or area of the passages.
Owner:HANON SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com