Patents
Literature
50results about How to "High antenna gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
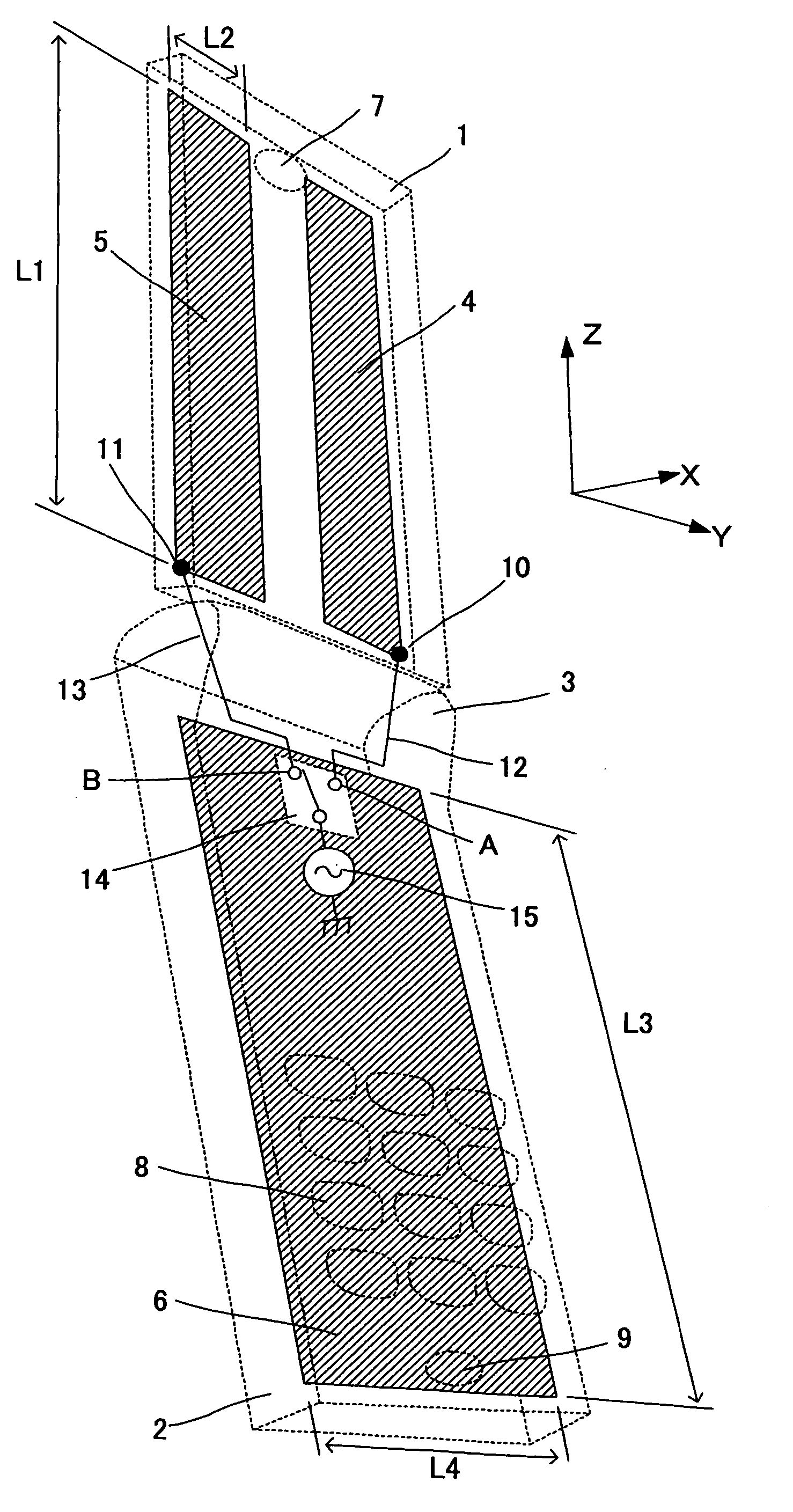
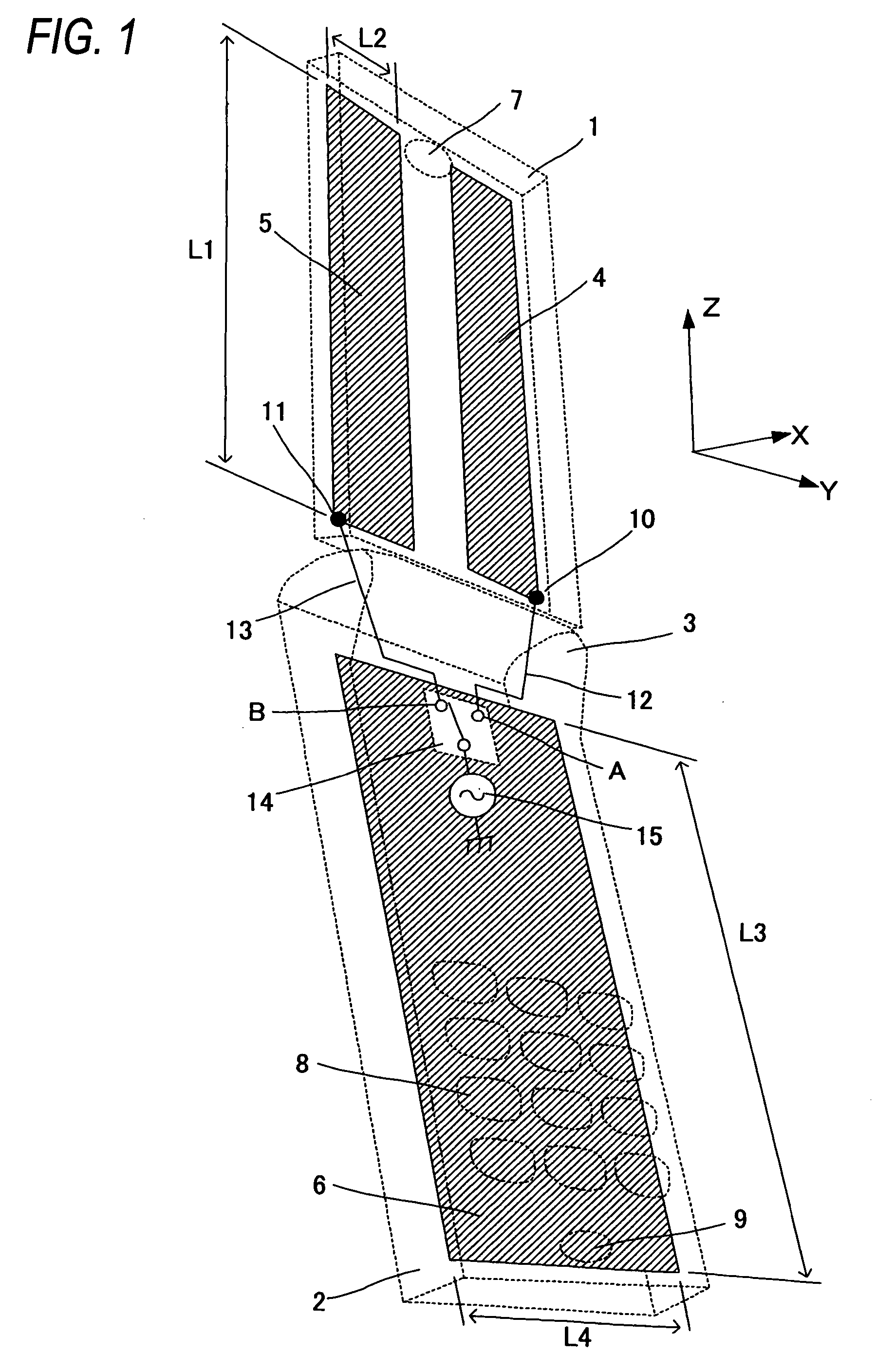
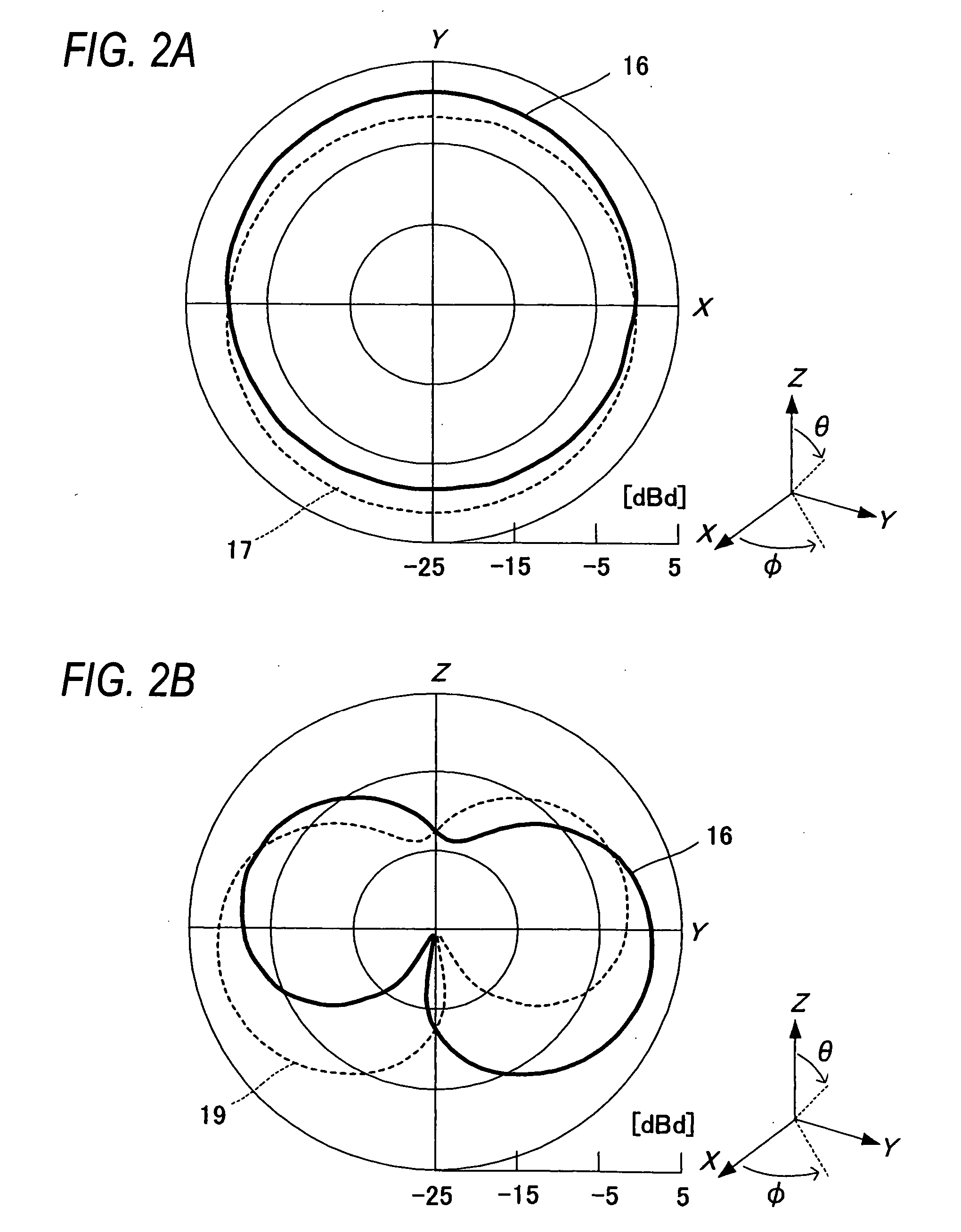
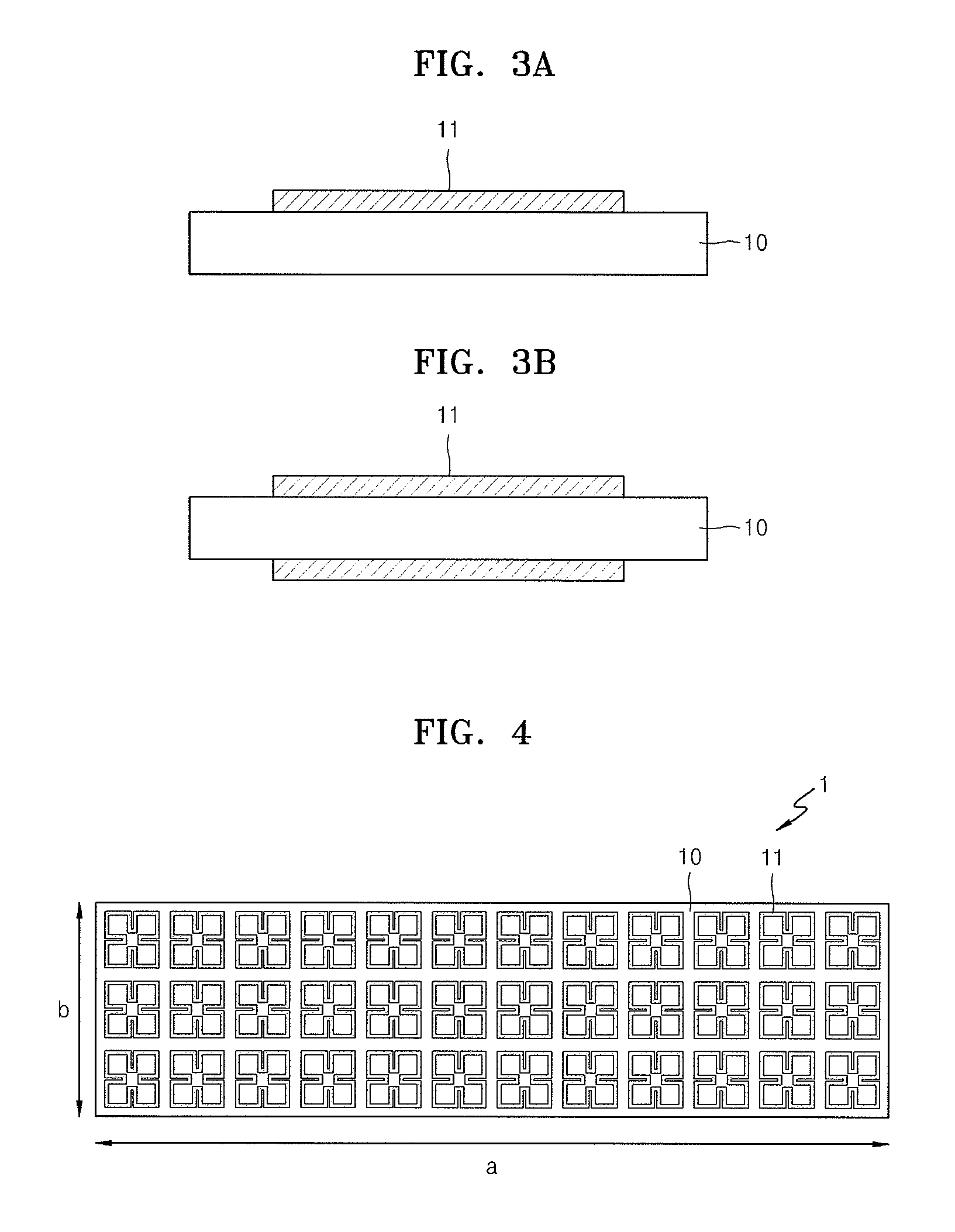
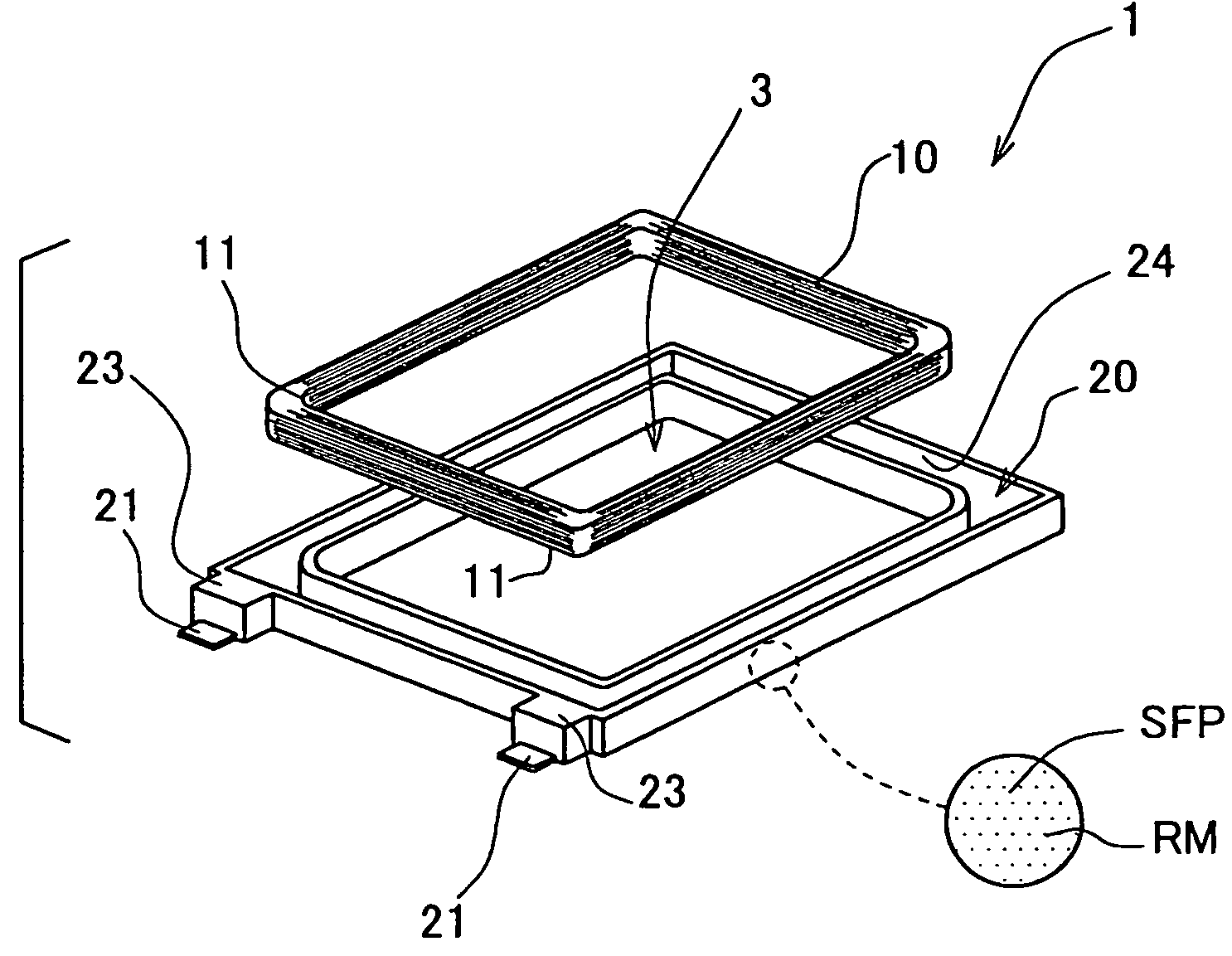
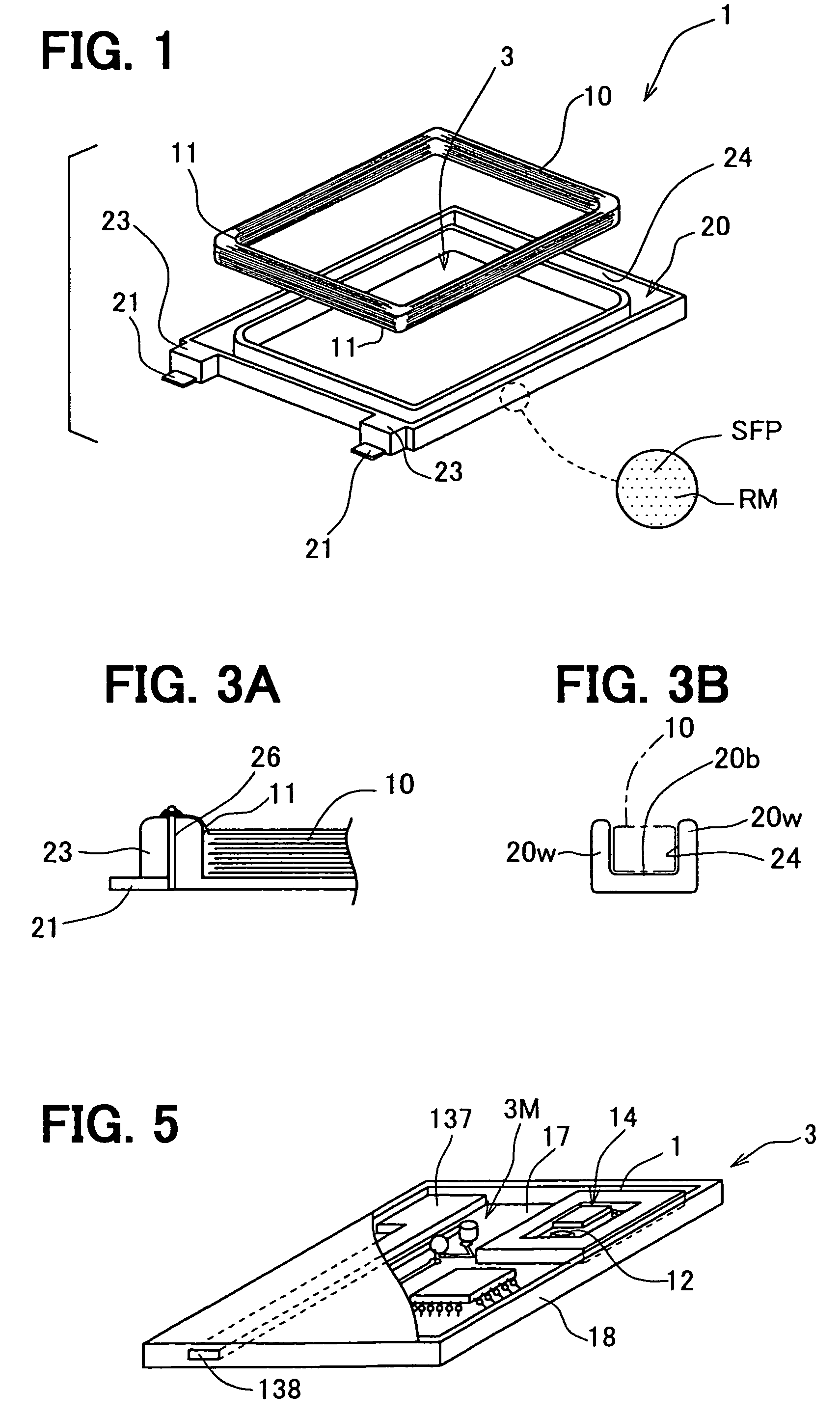
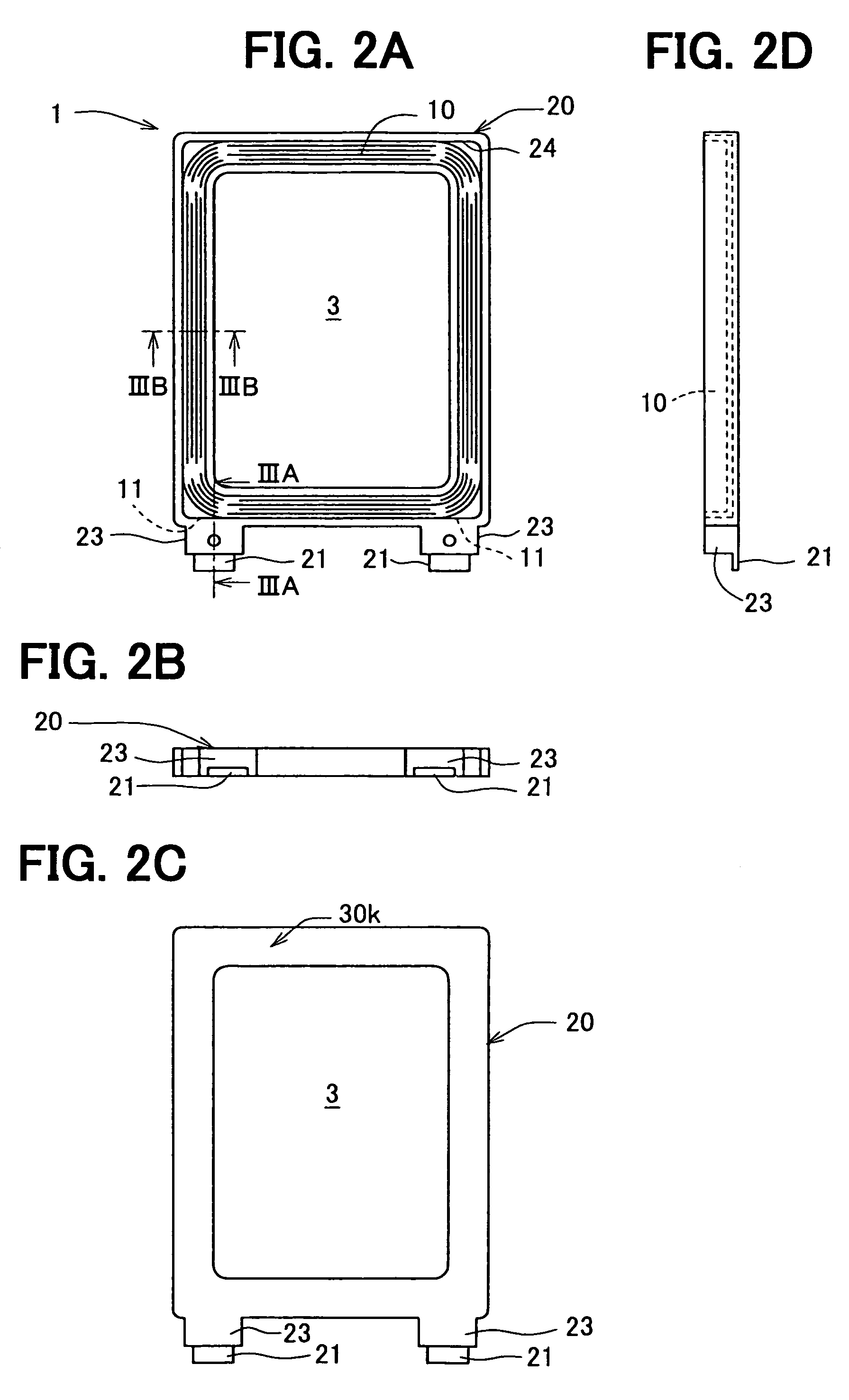
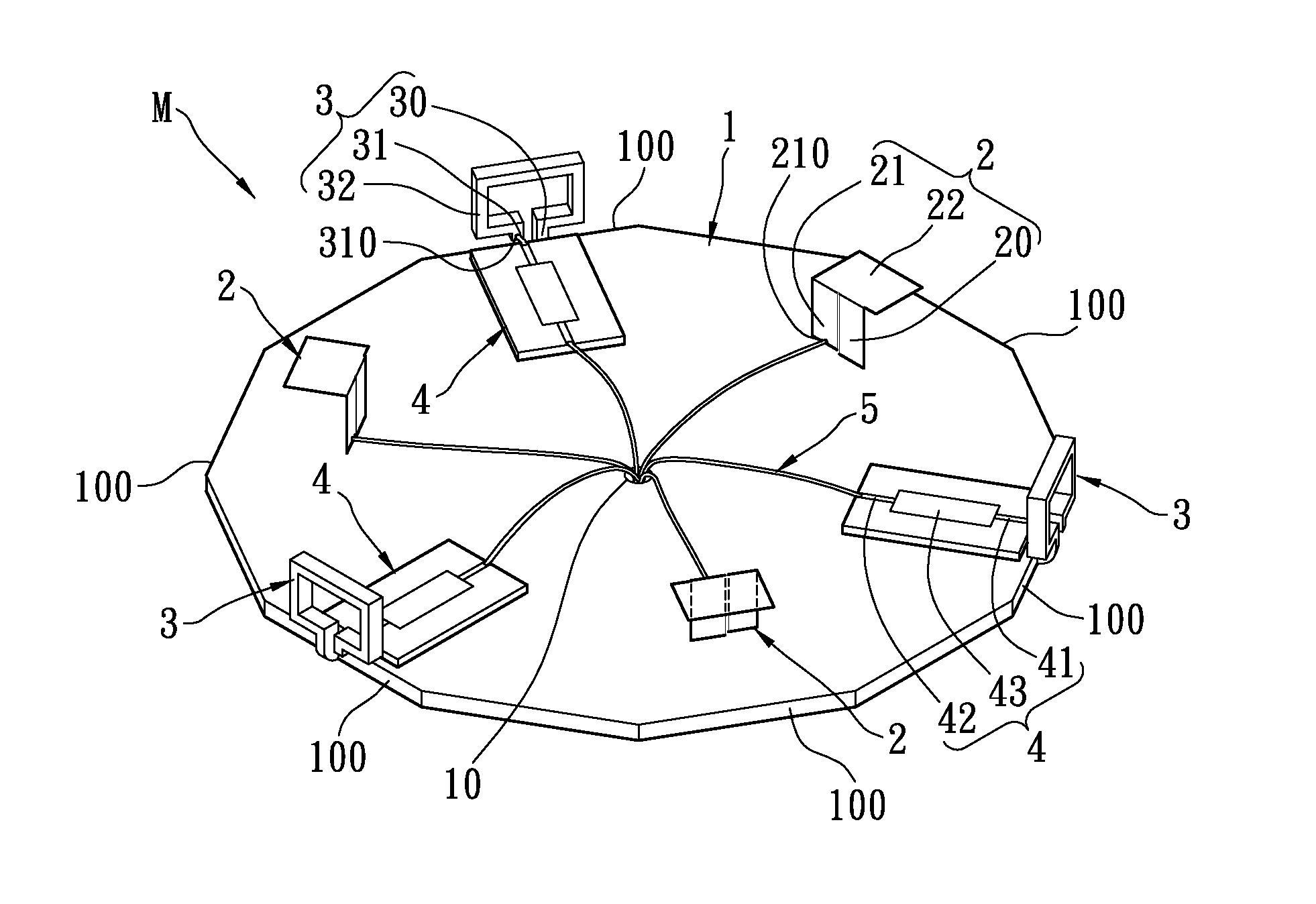
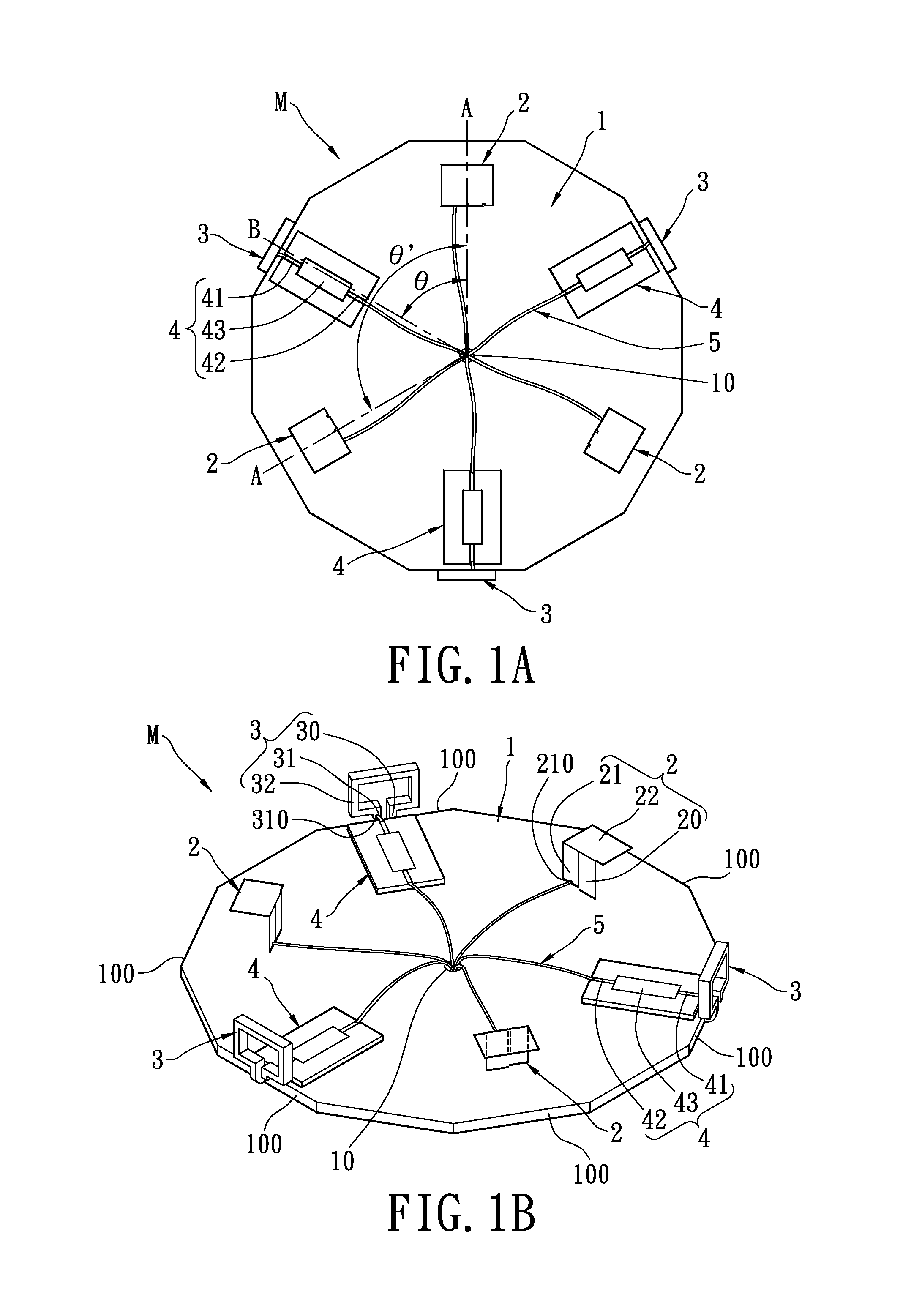
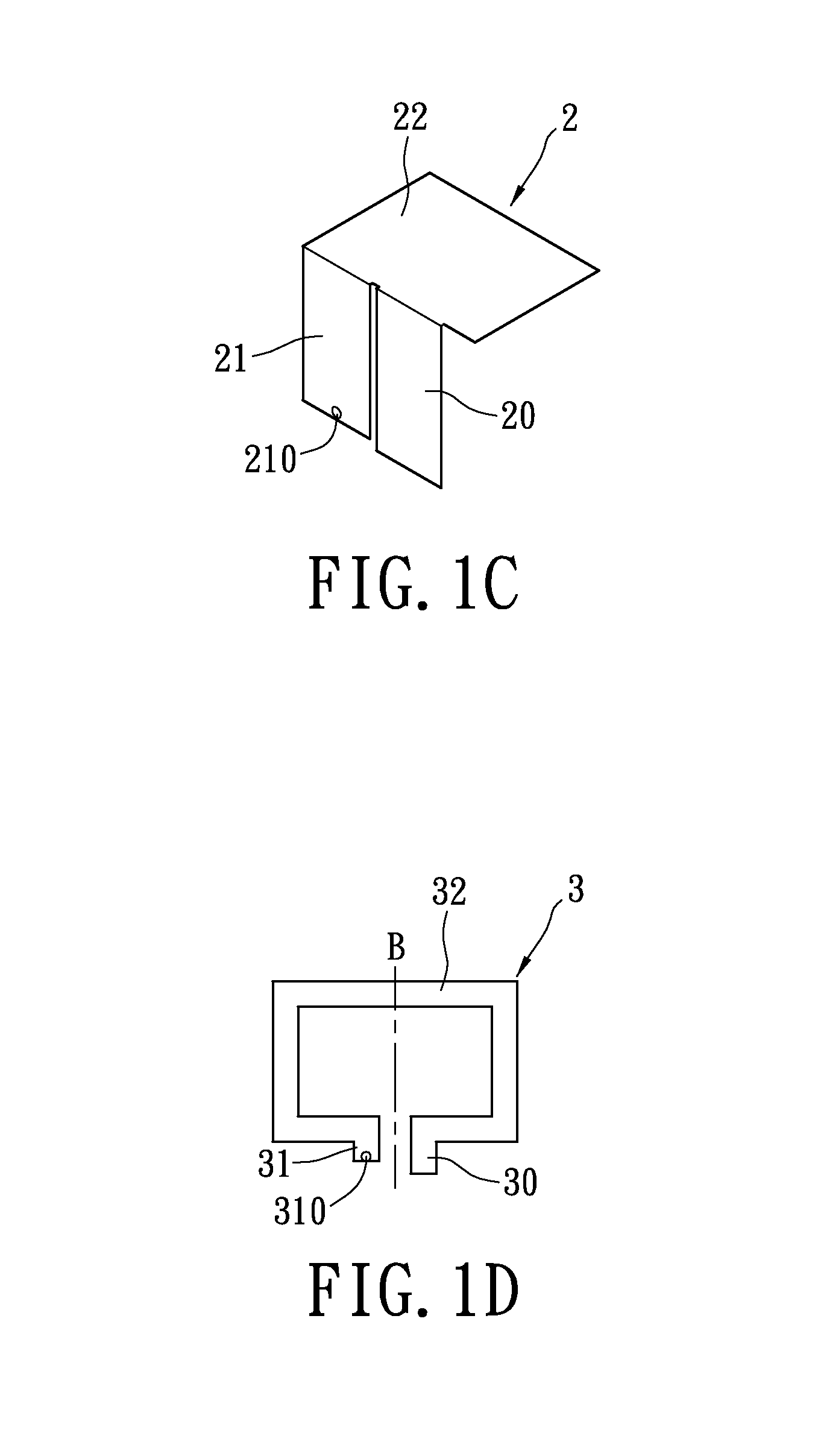
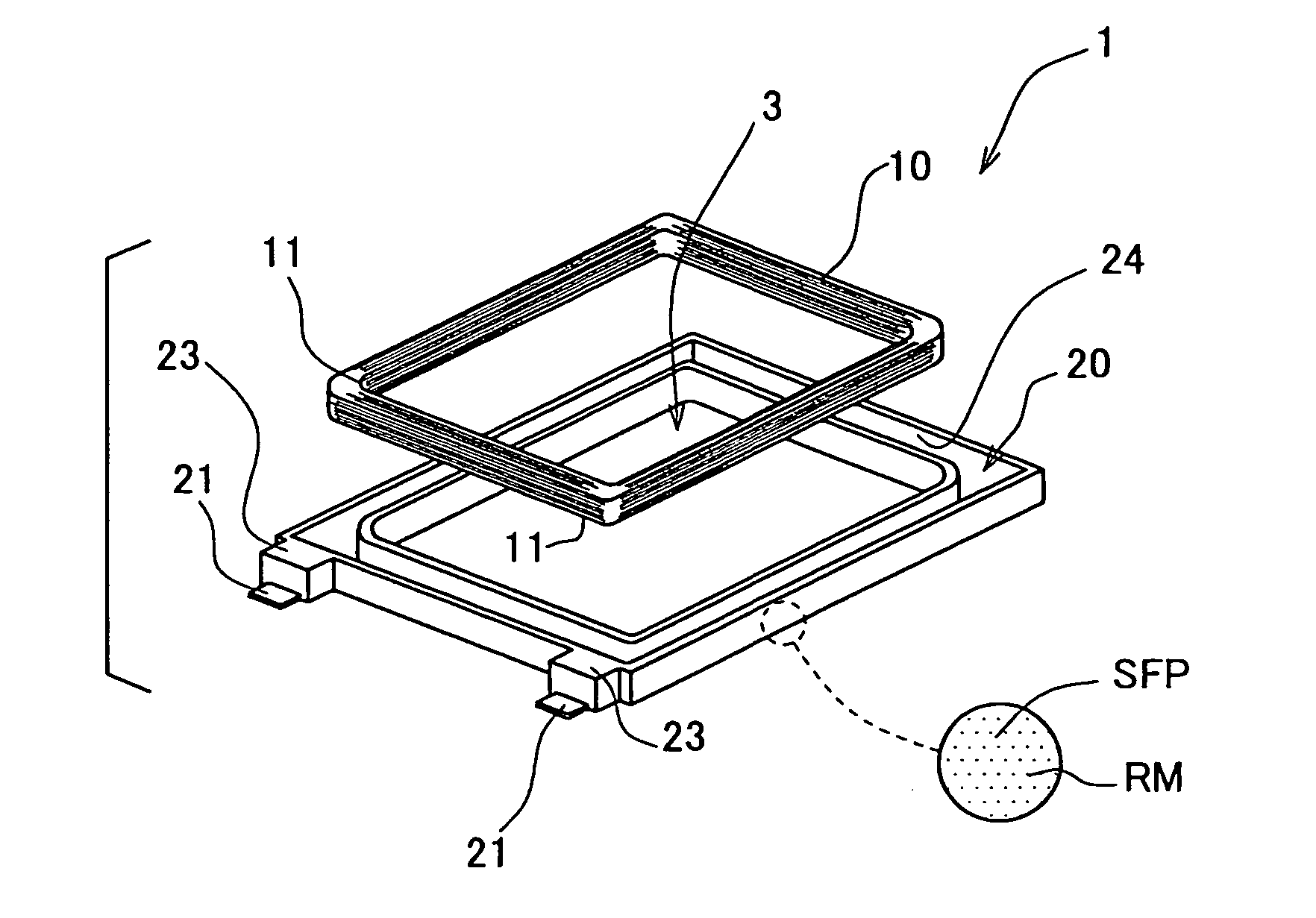
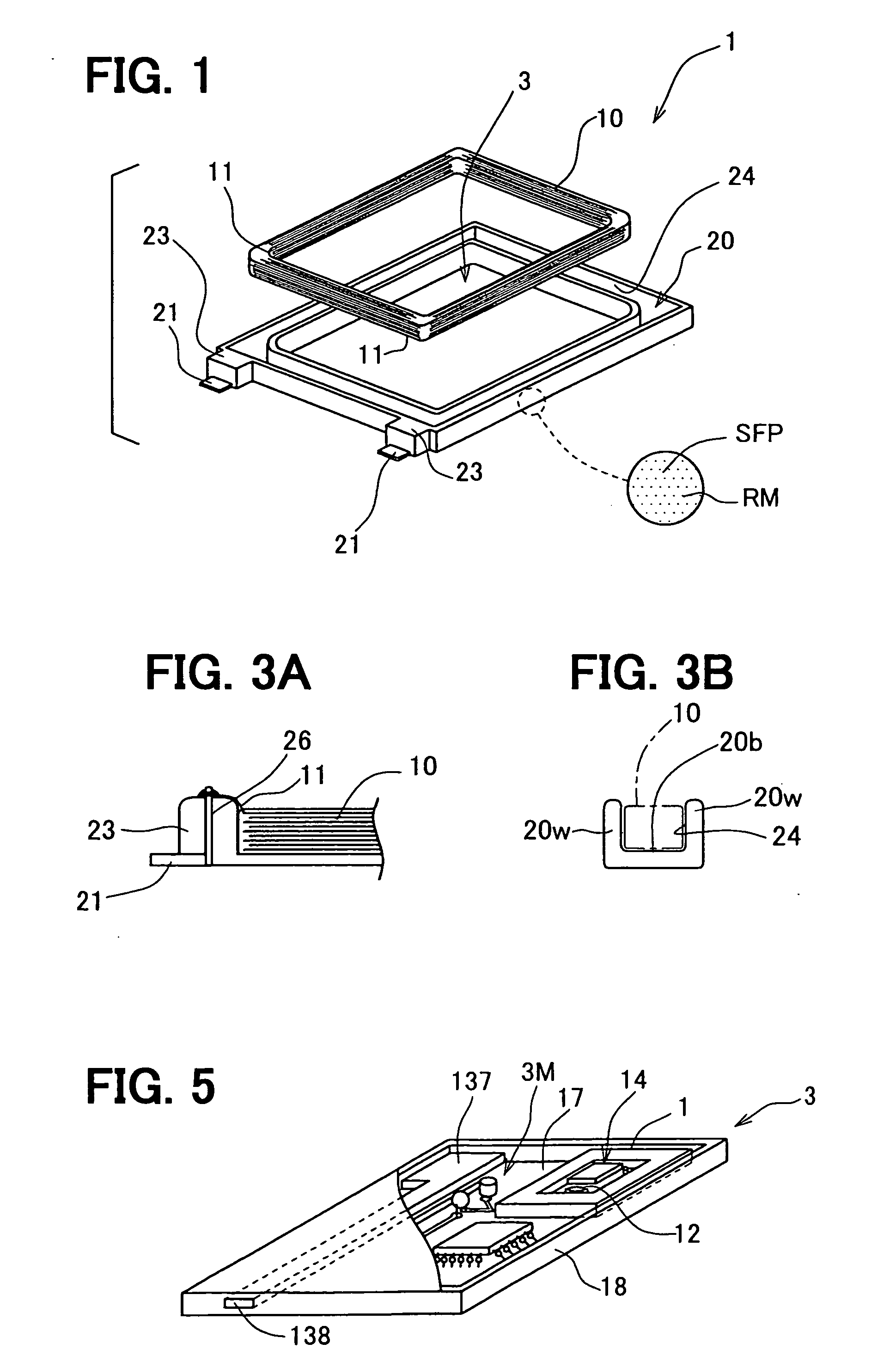
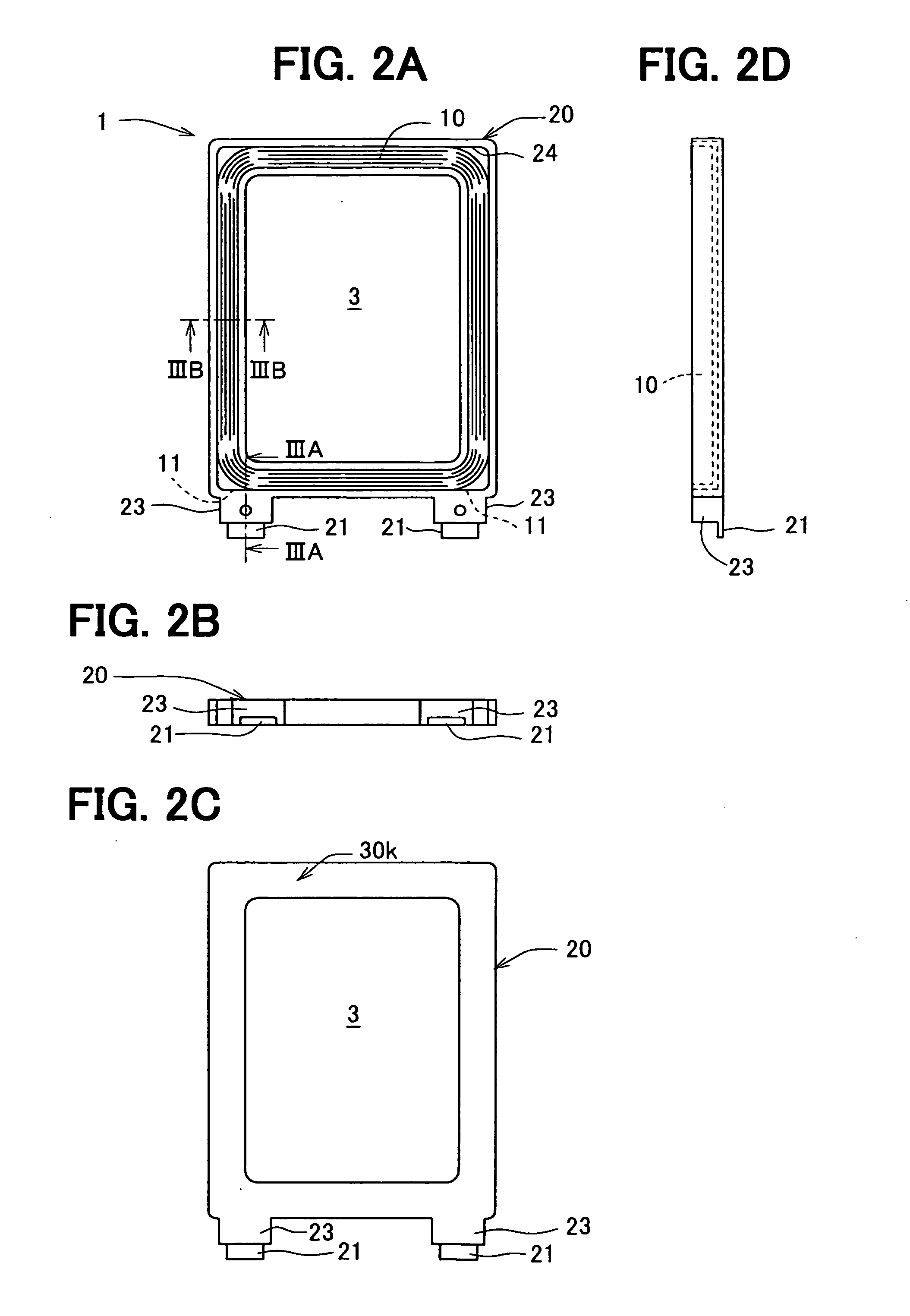
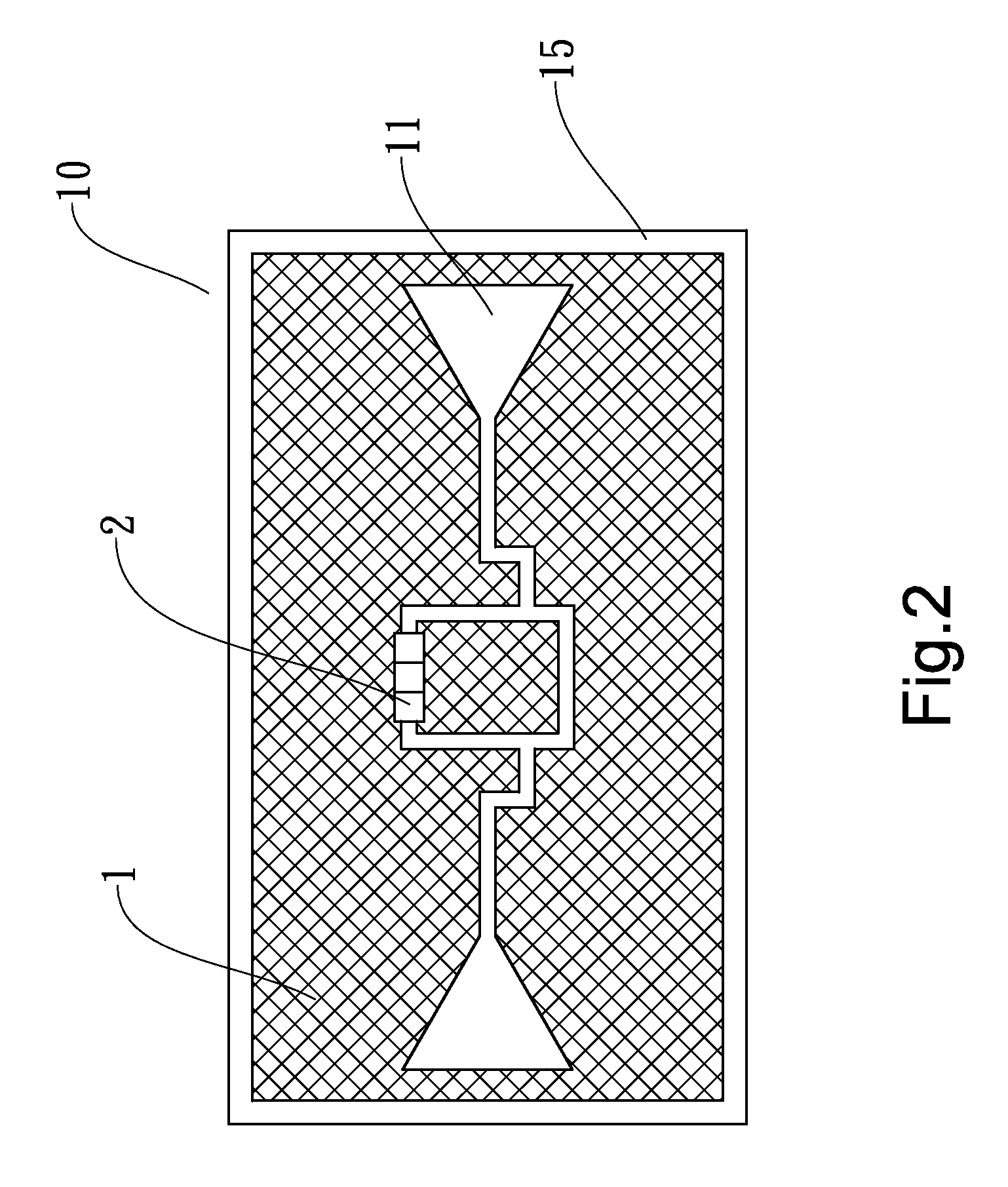
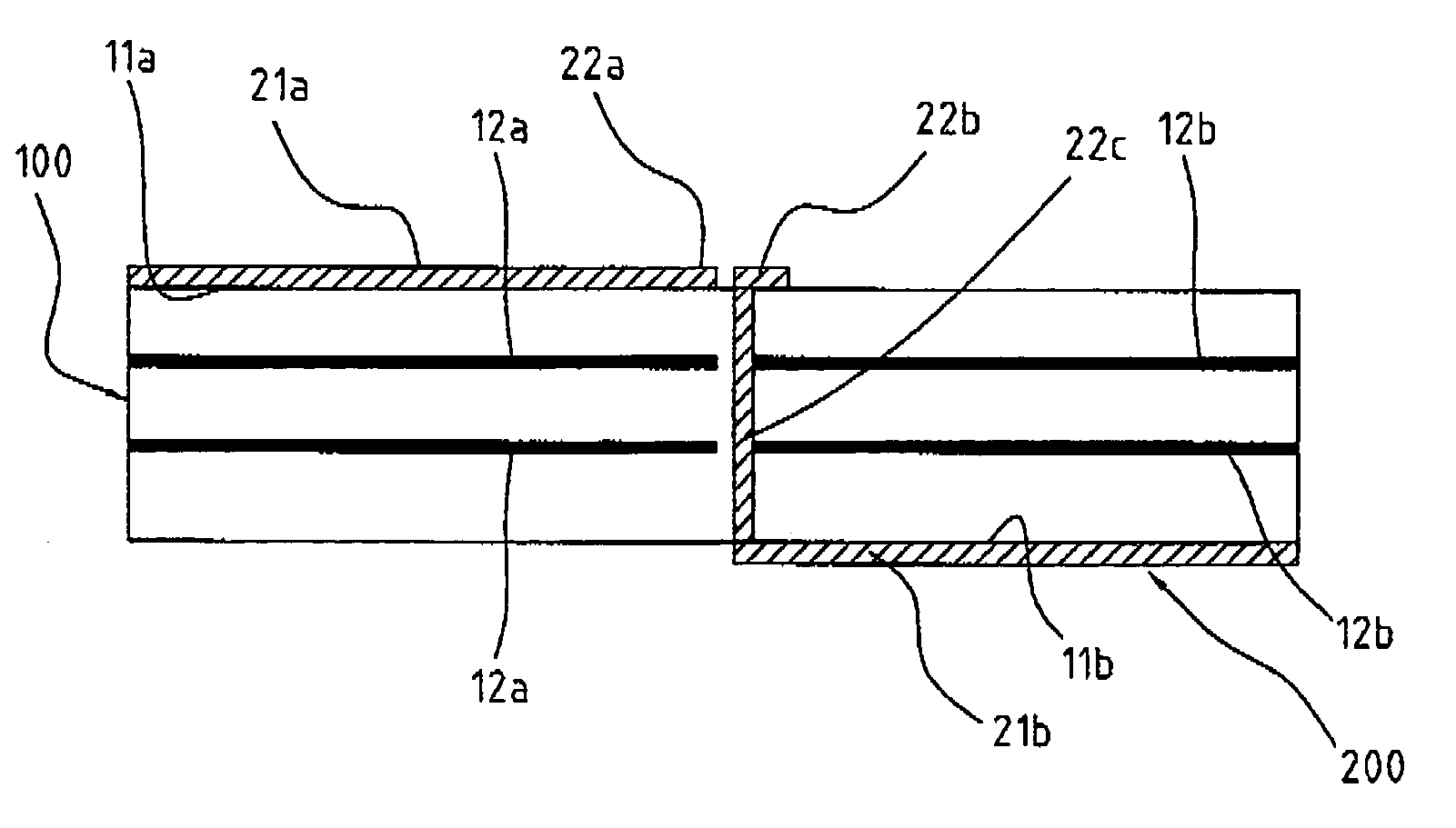
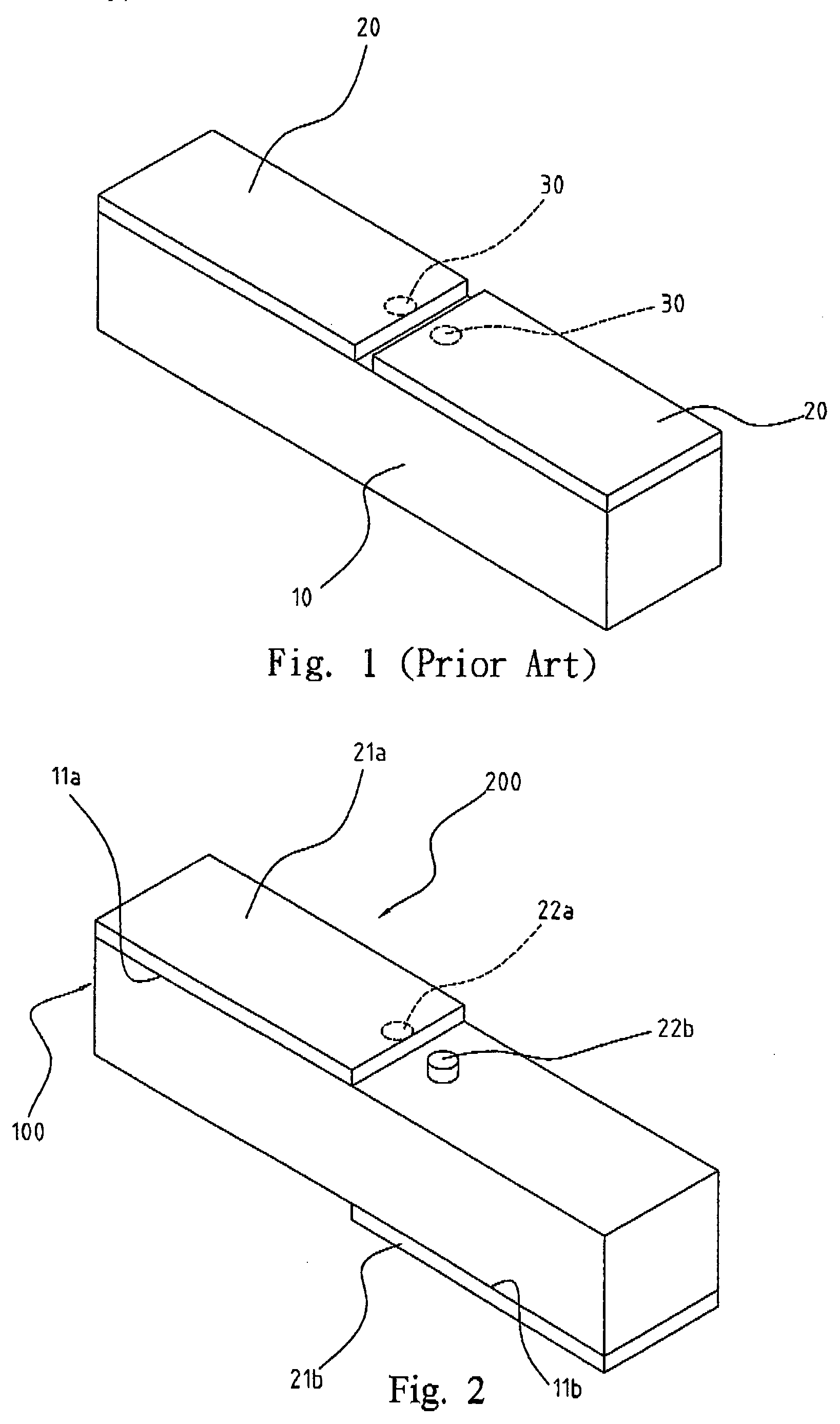
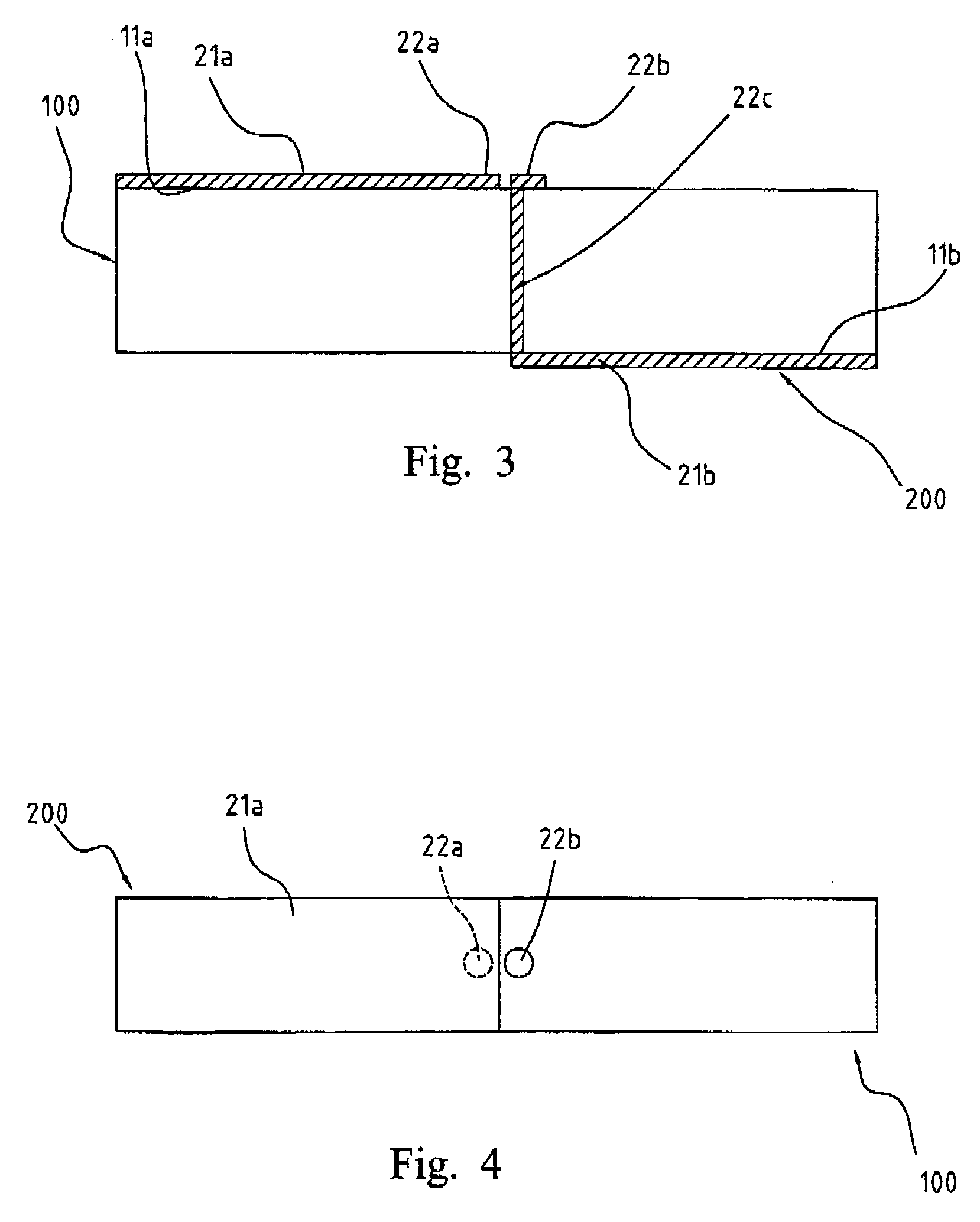
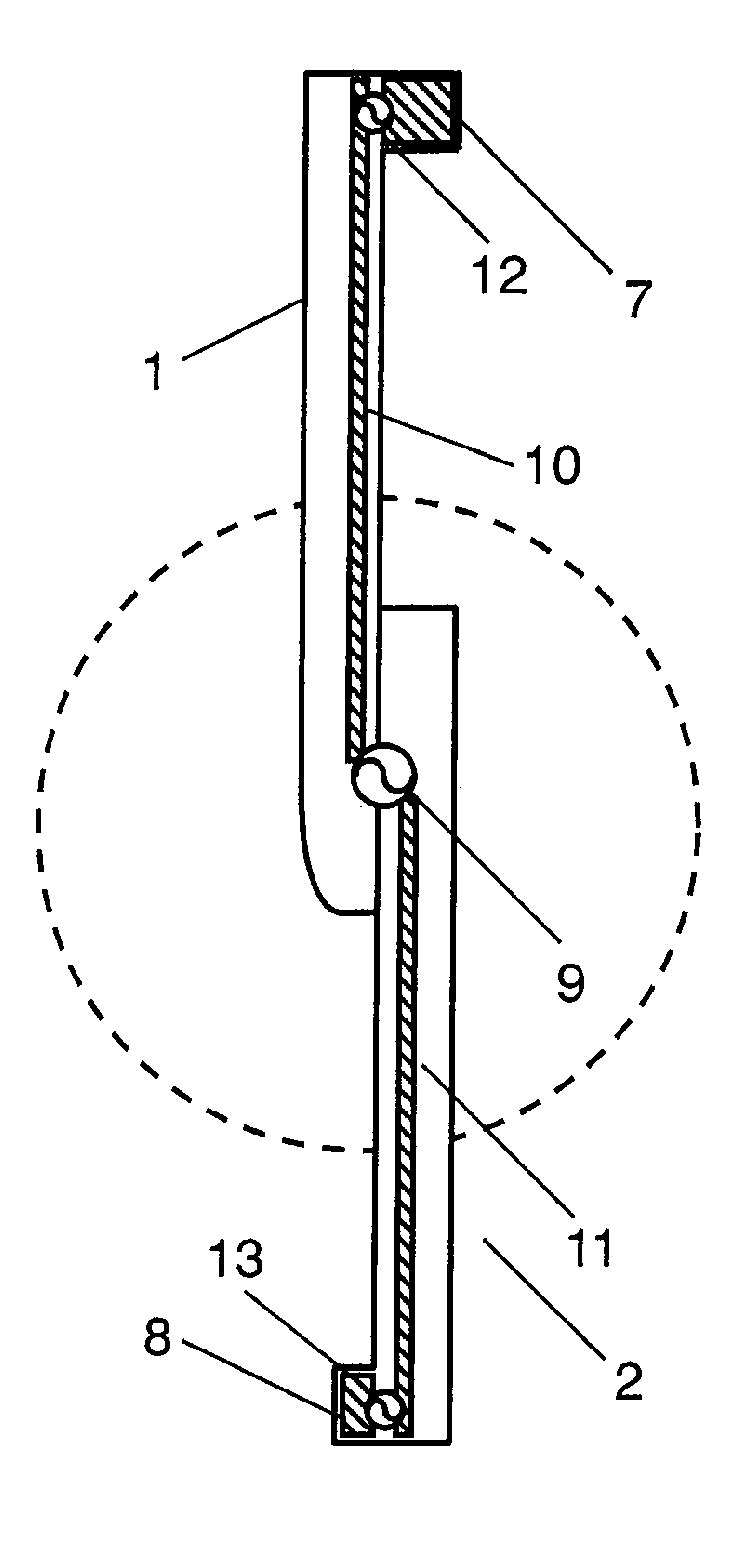
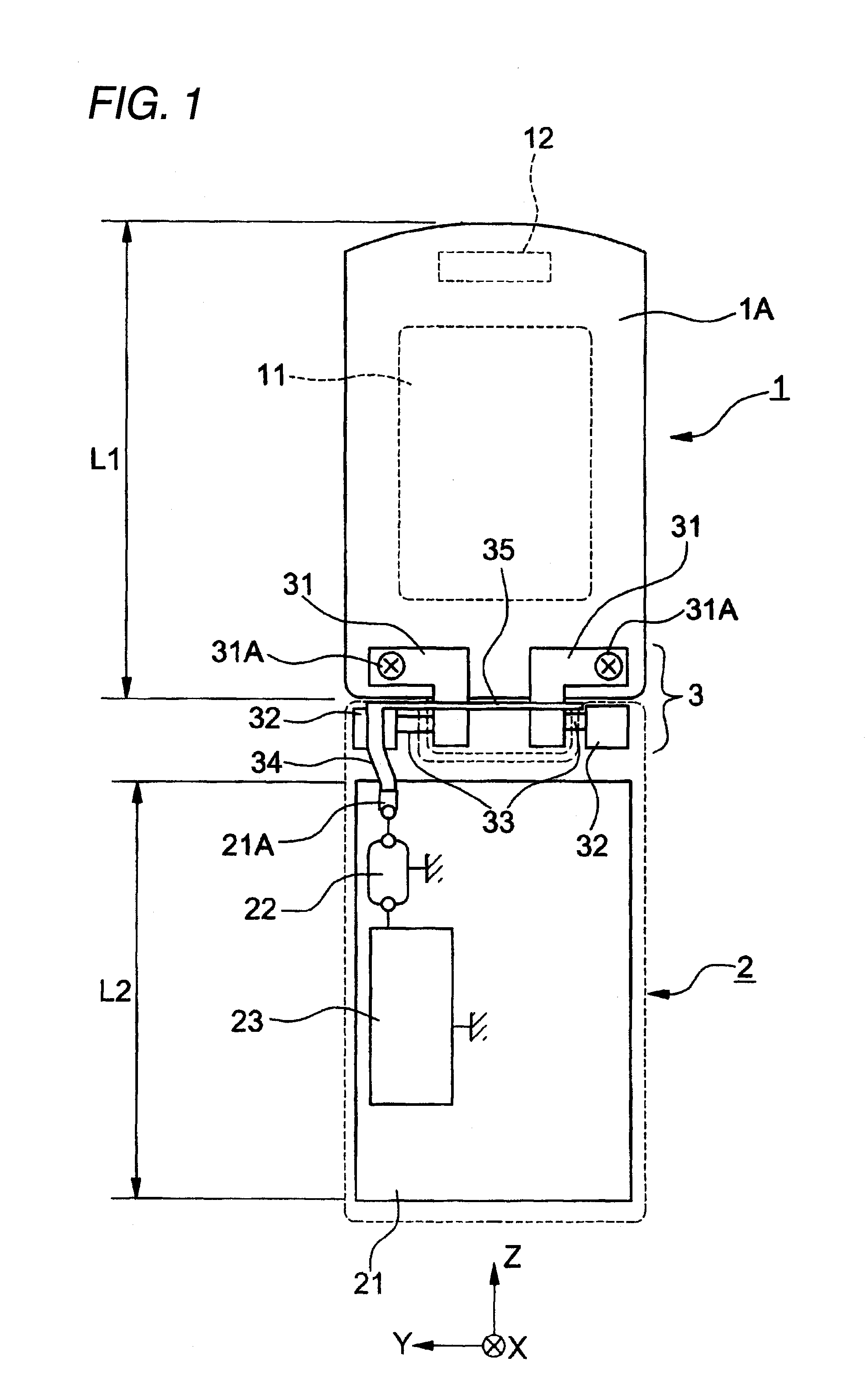
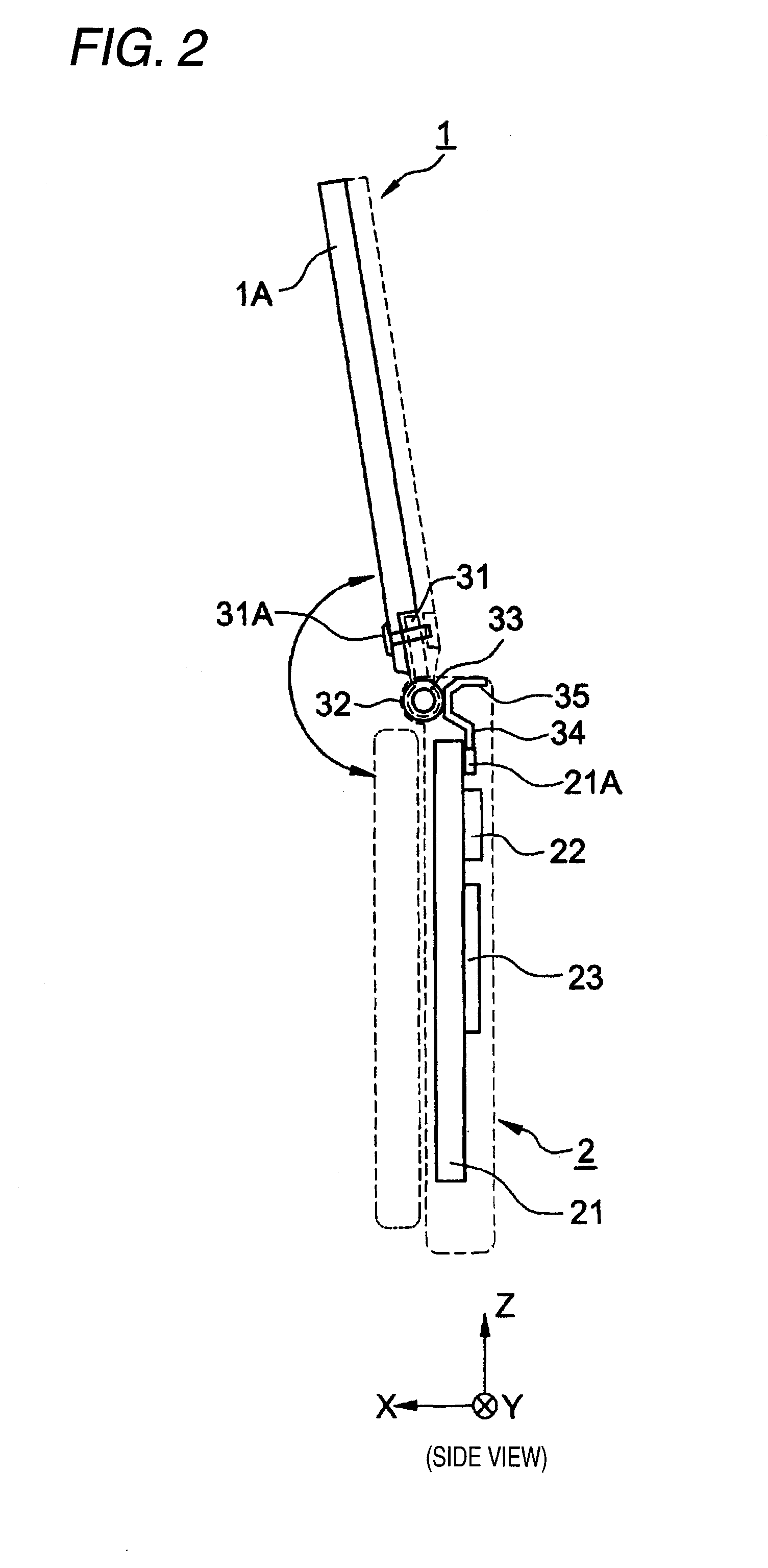
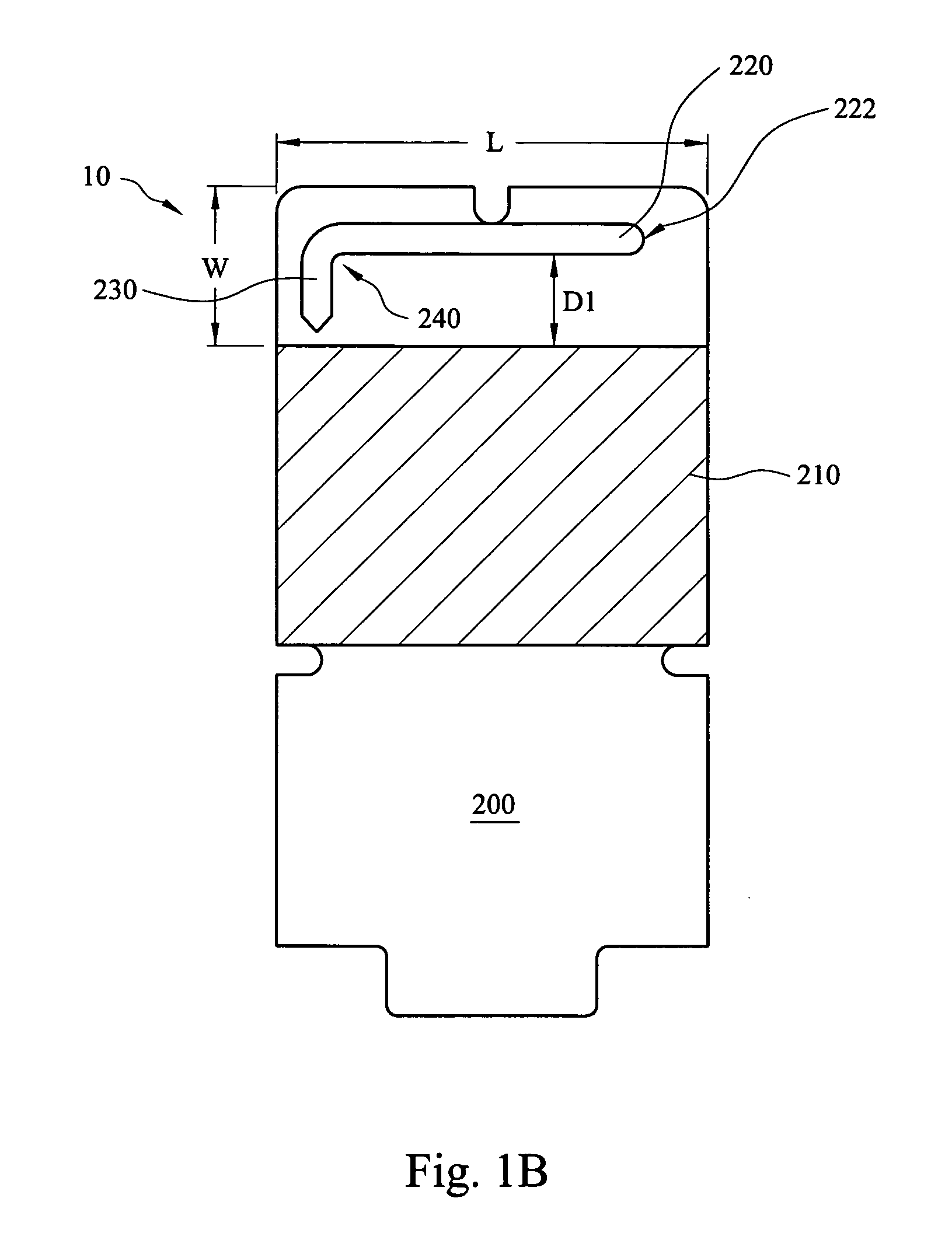
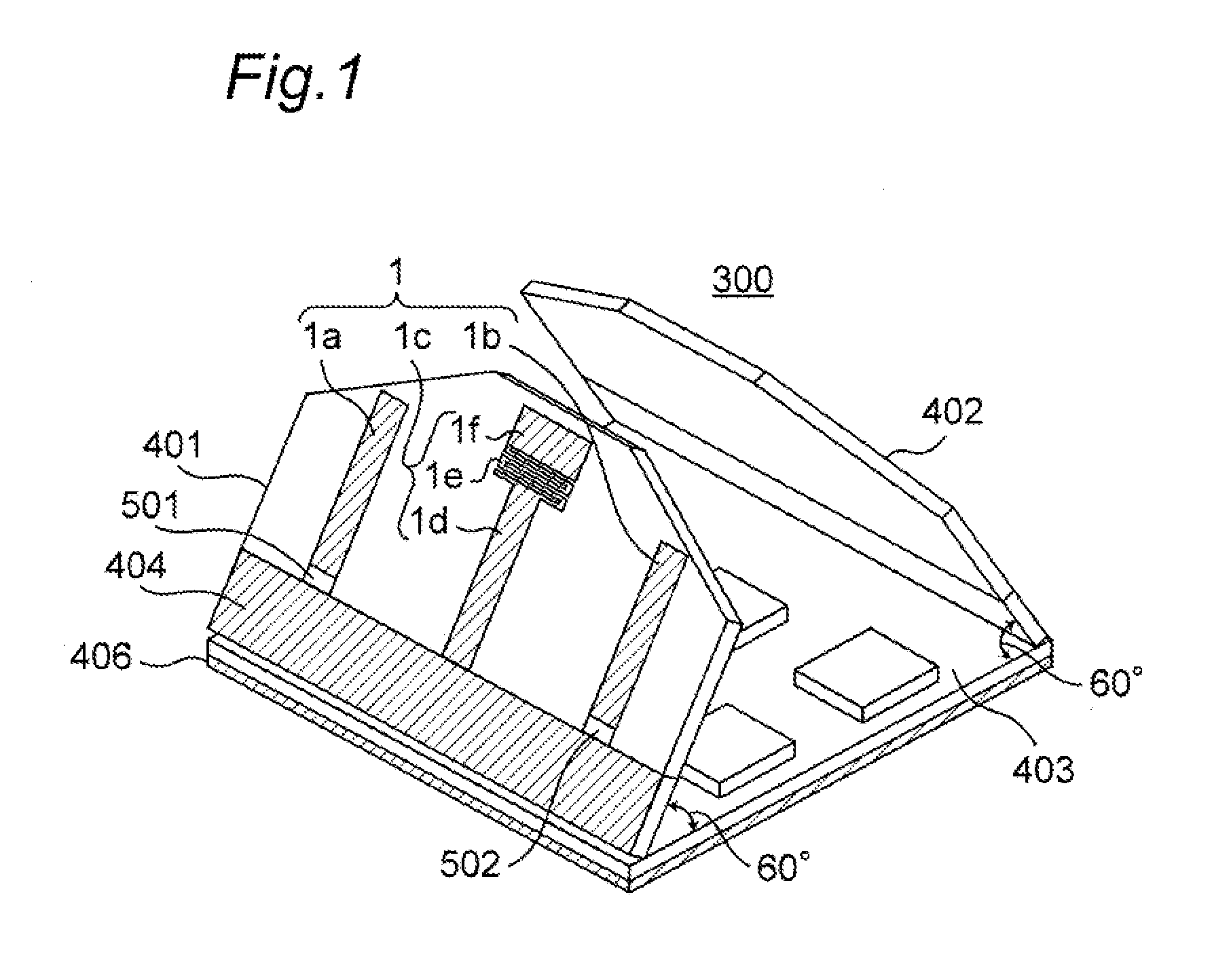
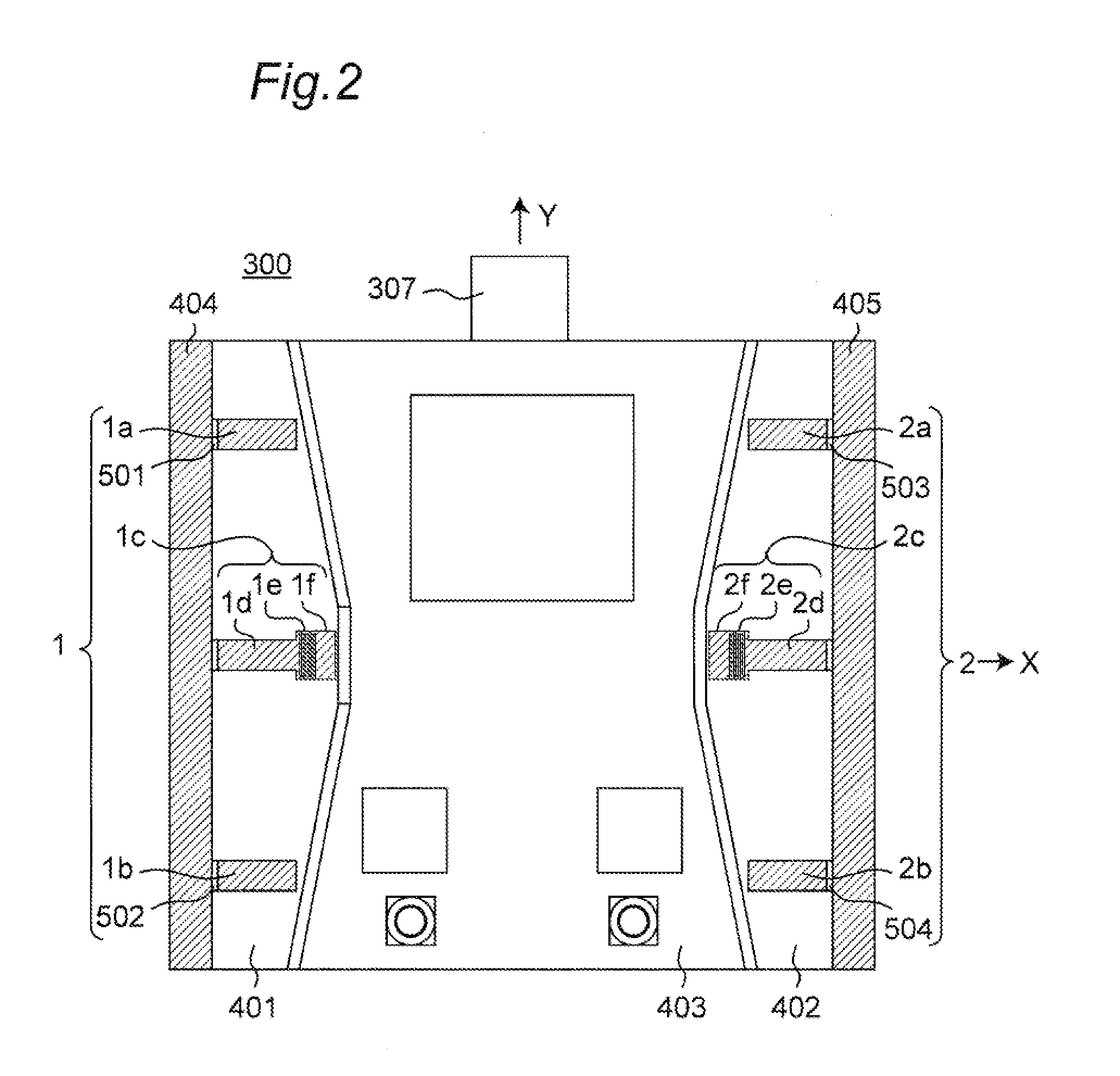
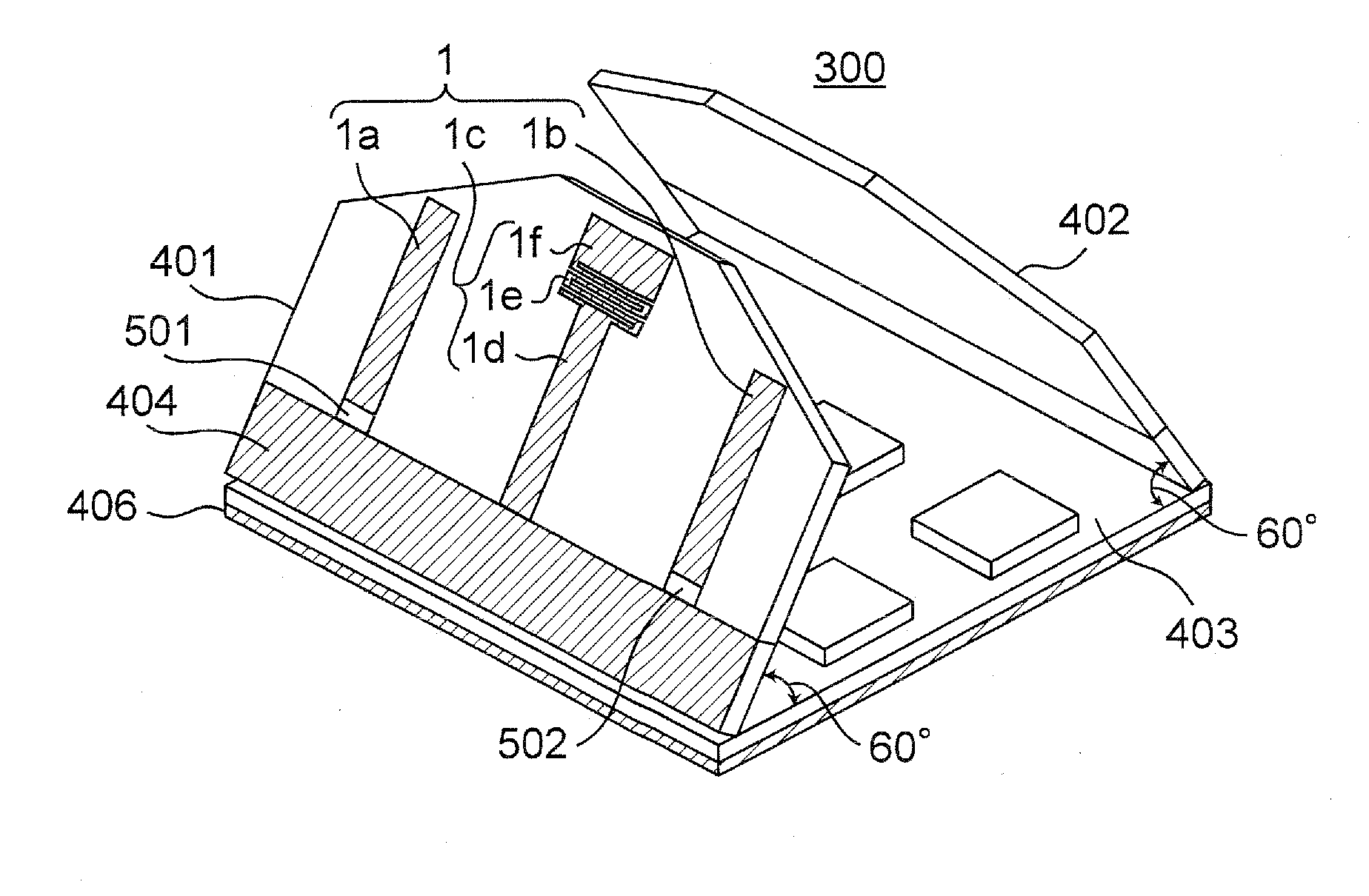
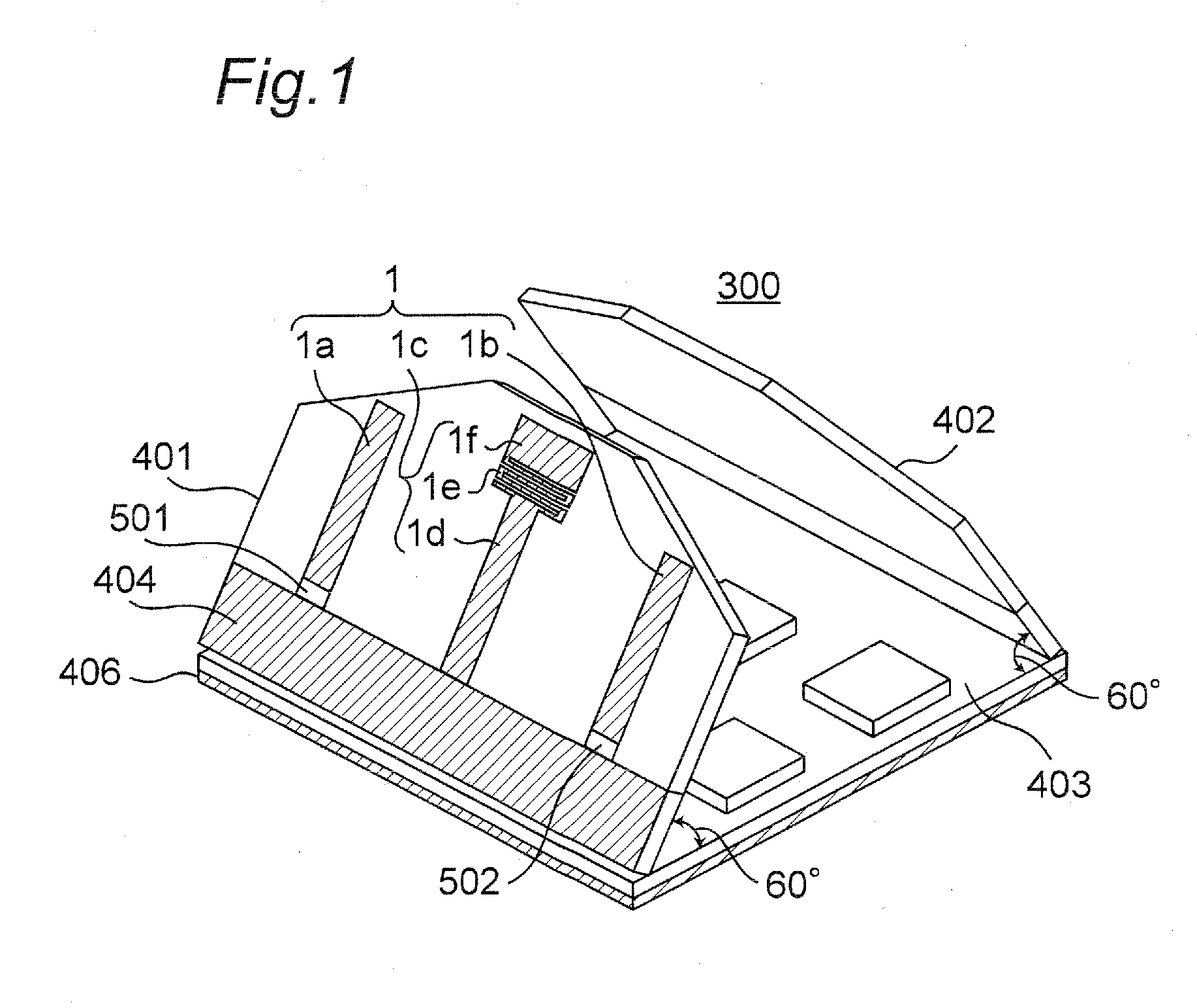
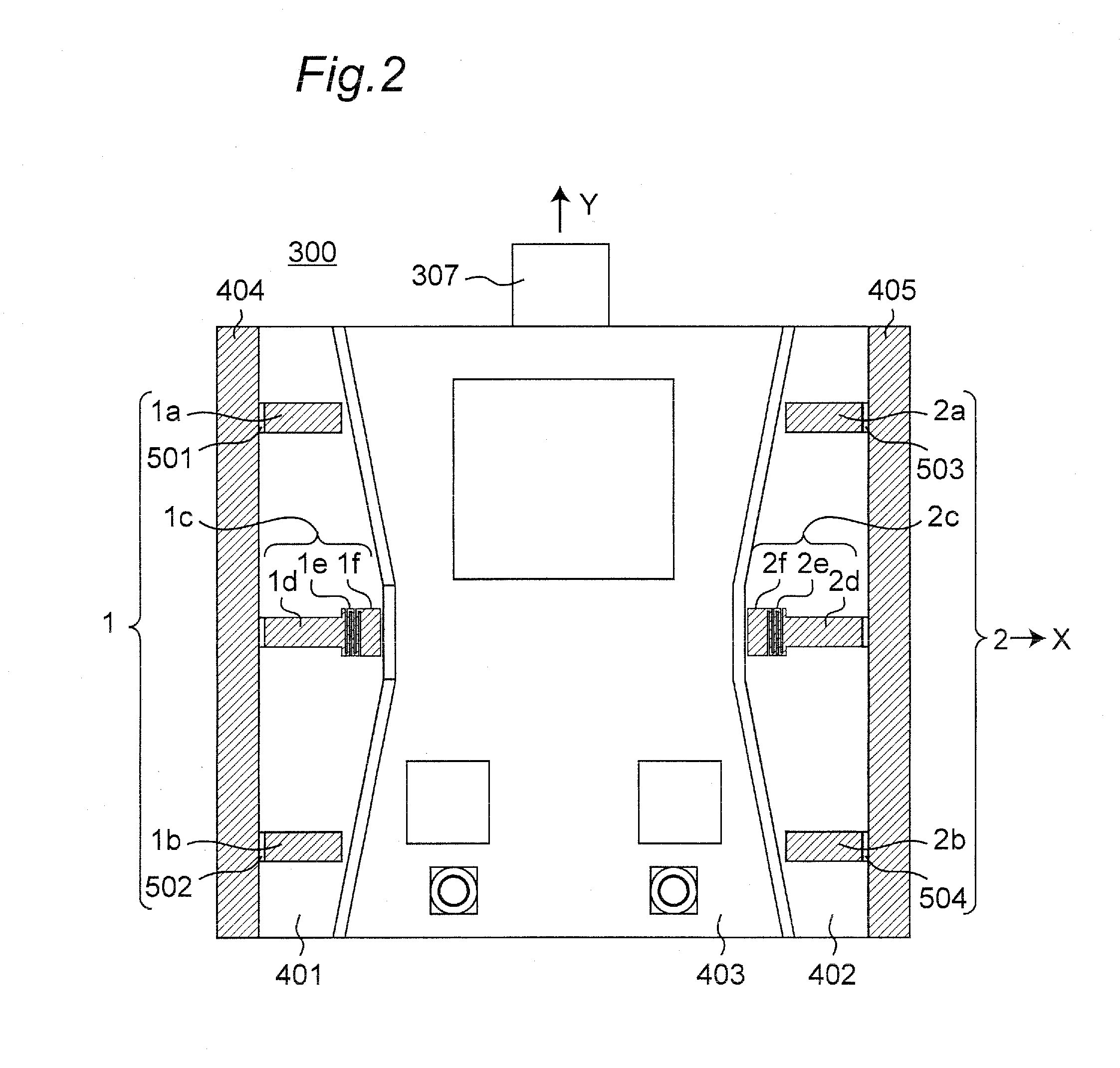
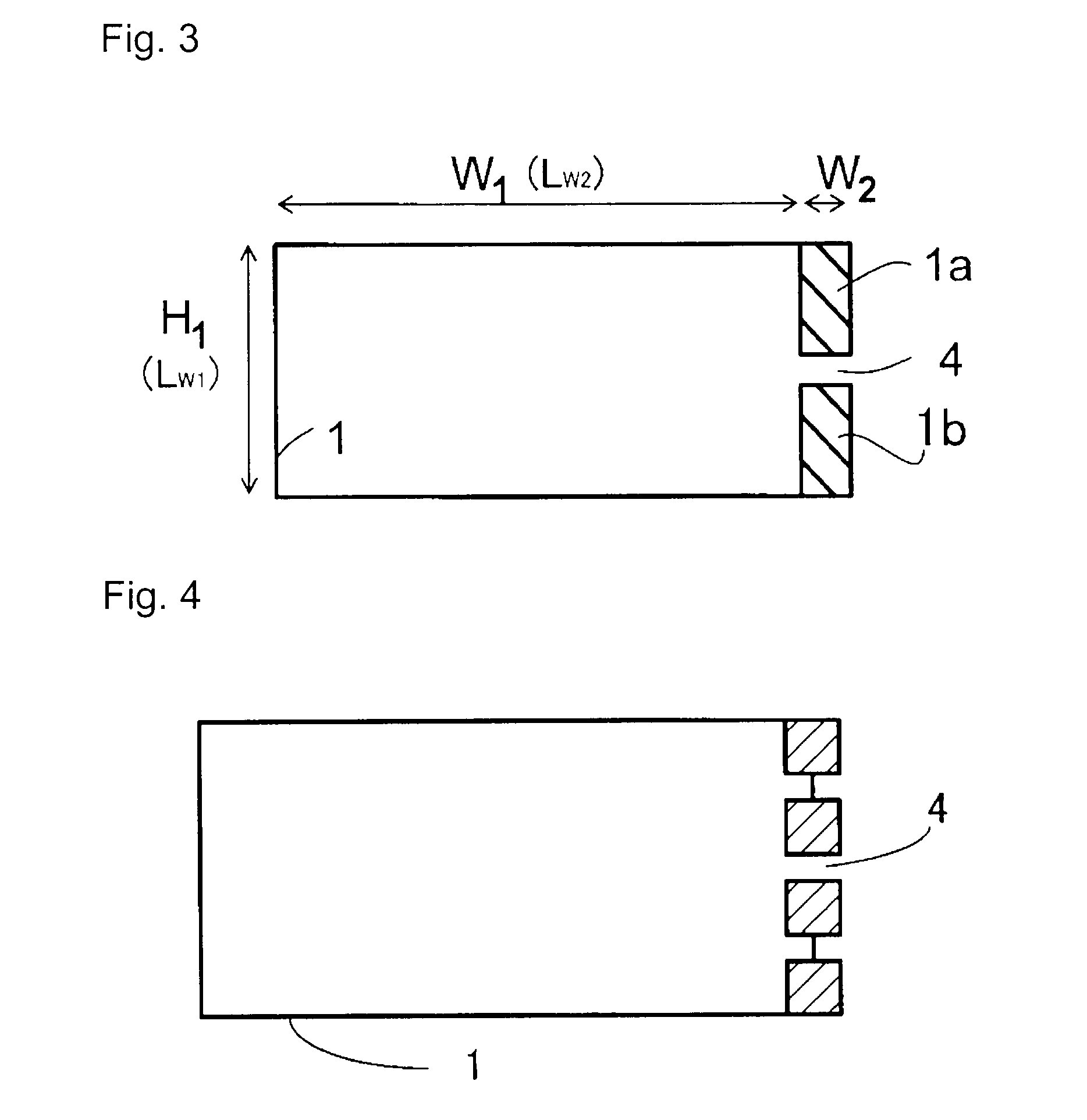
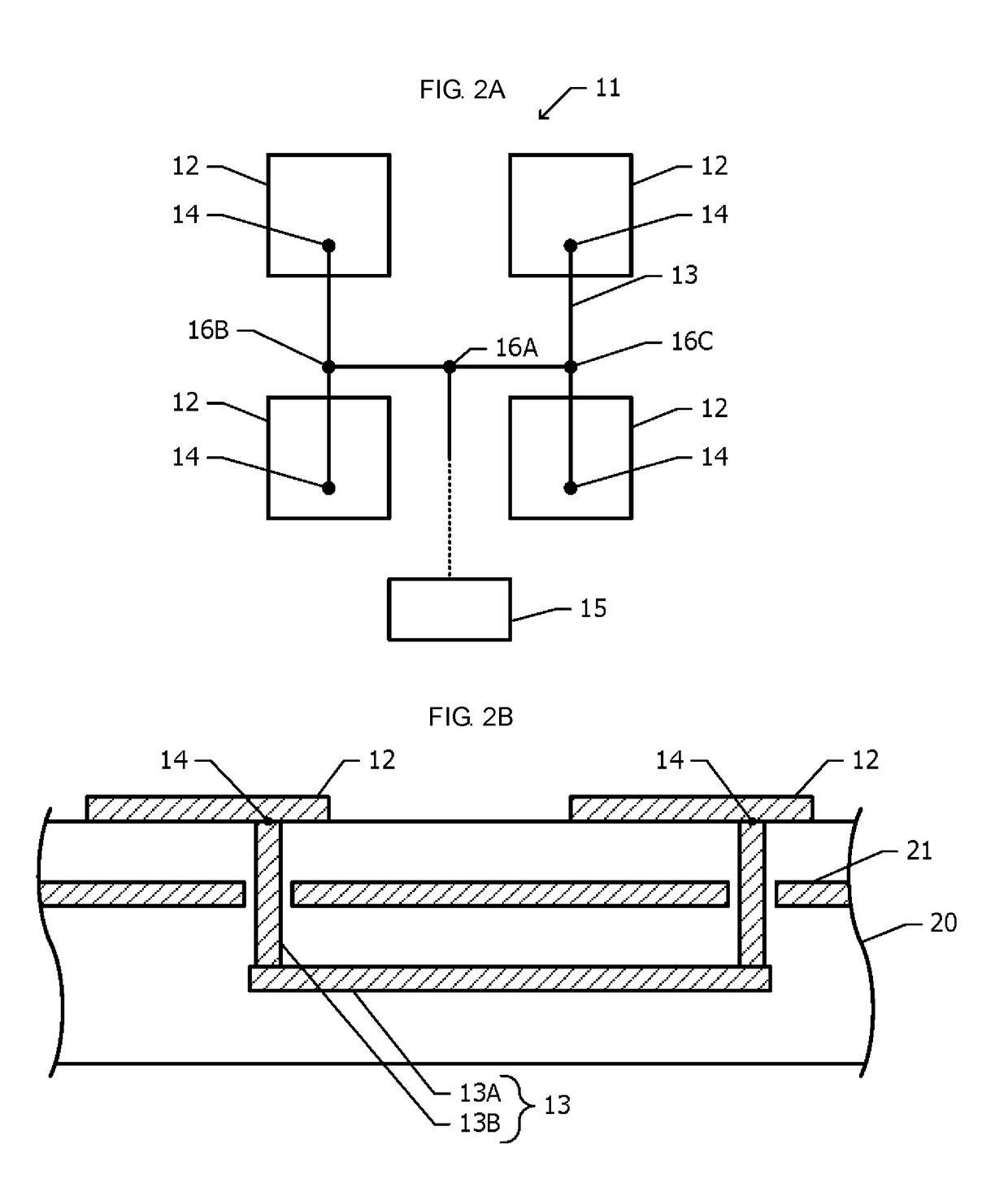
Portable wireless machine
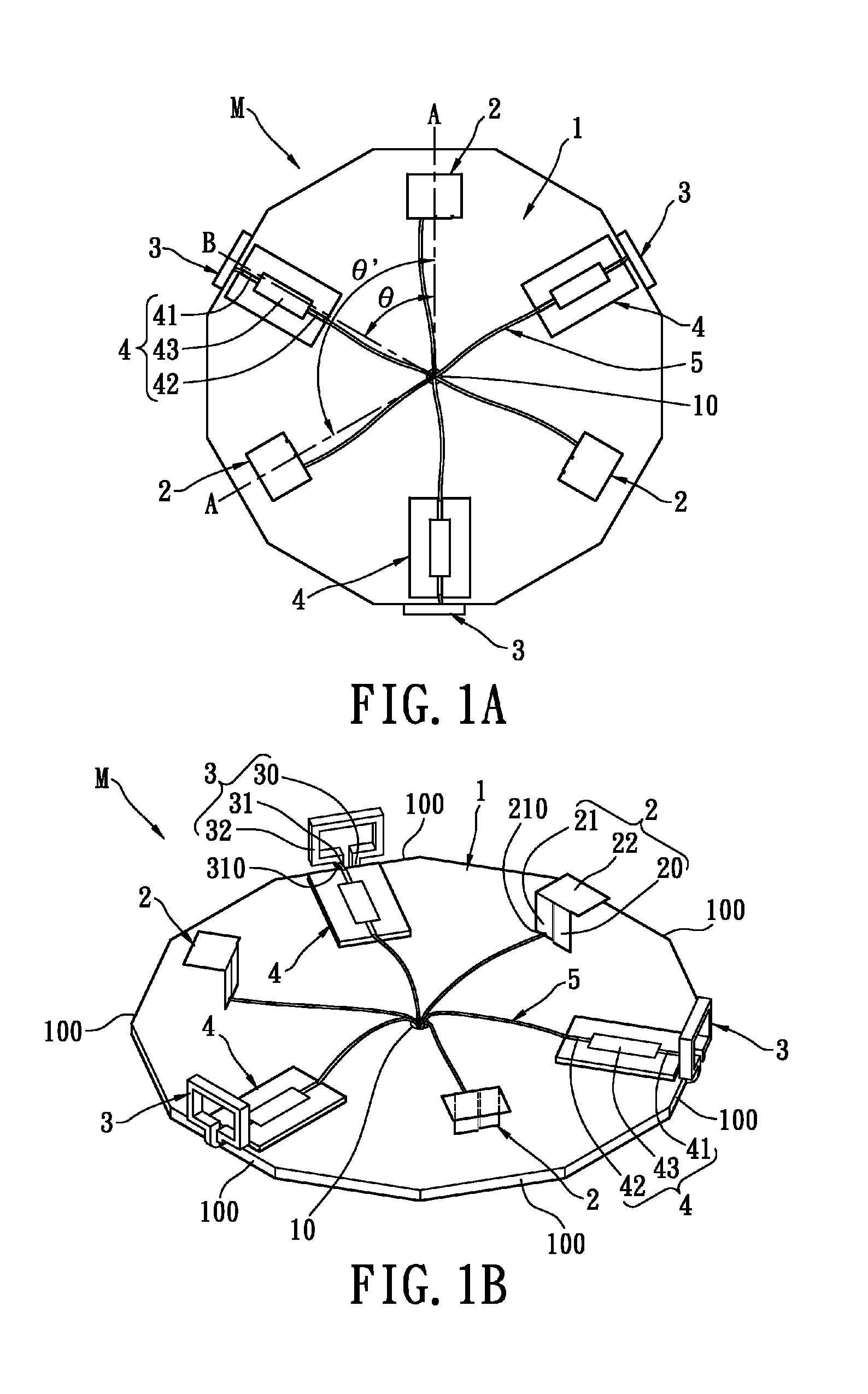
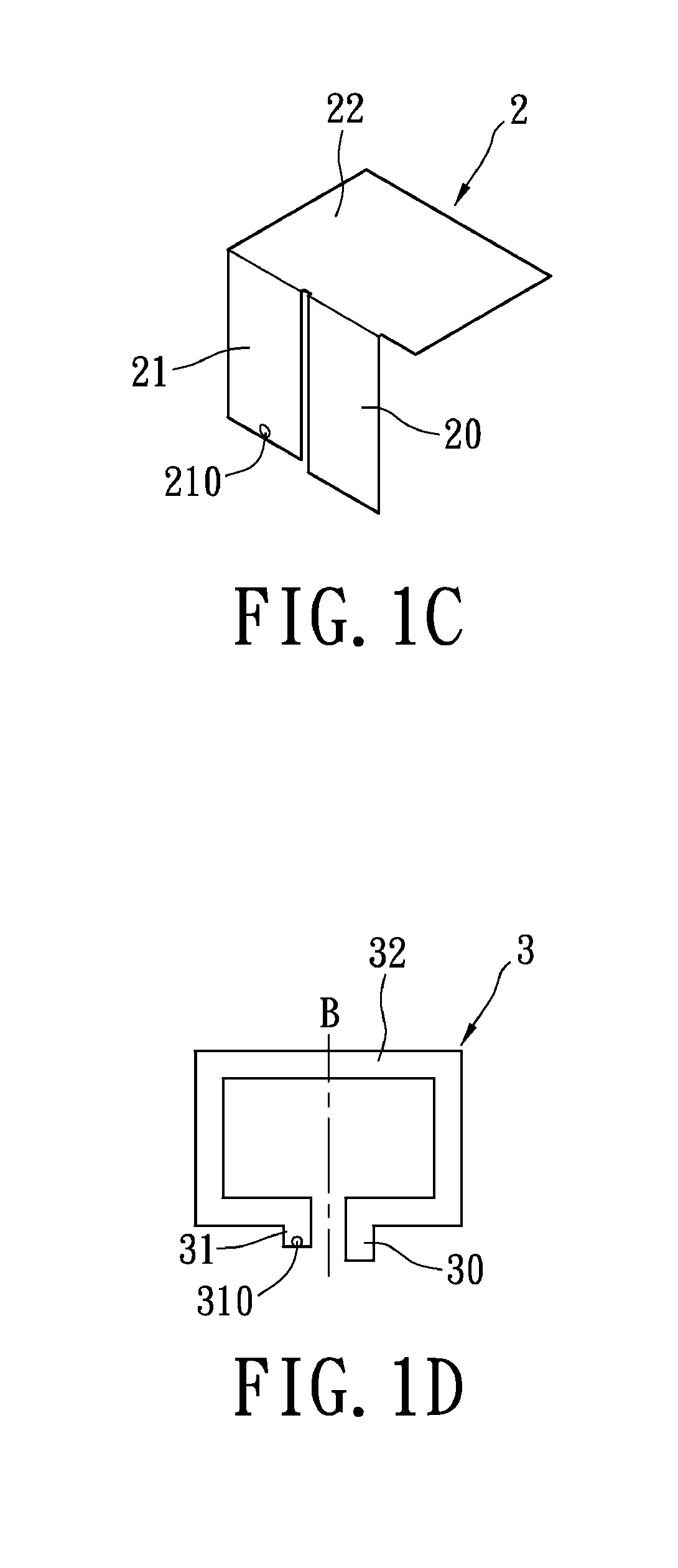
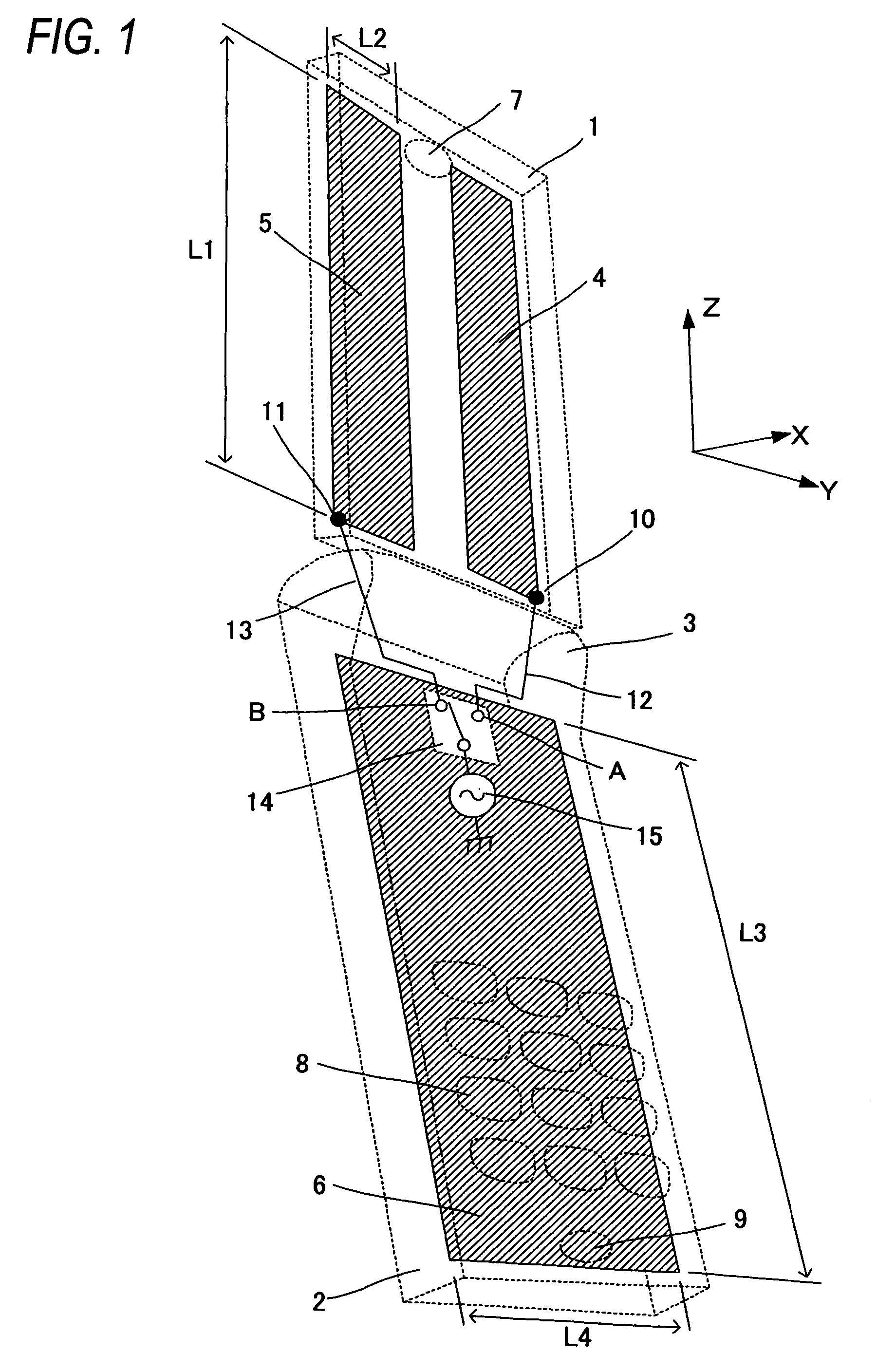
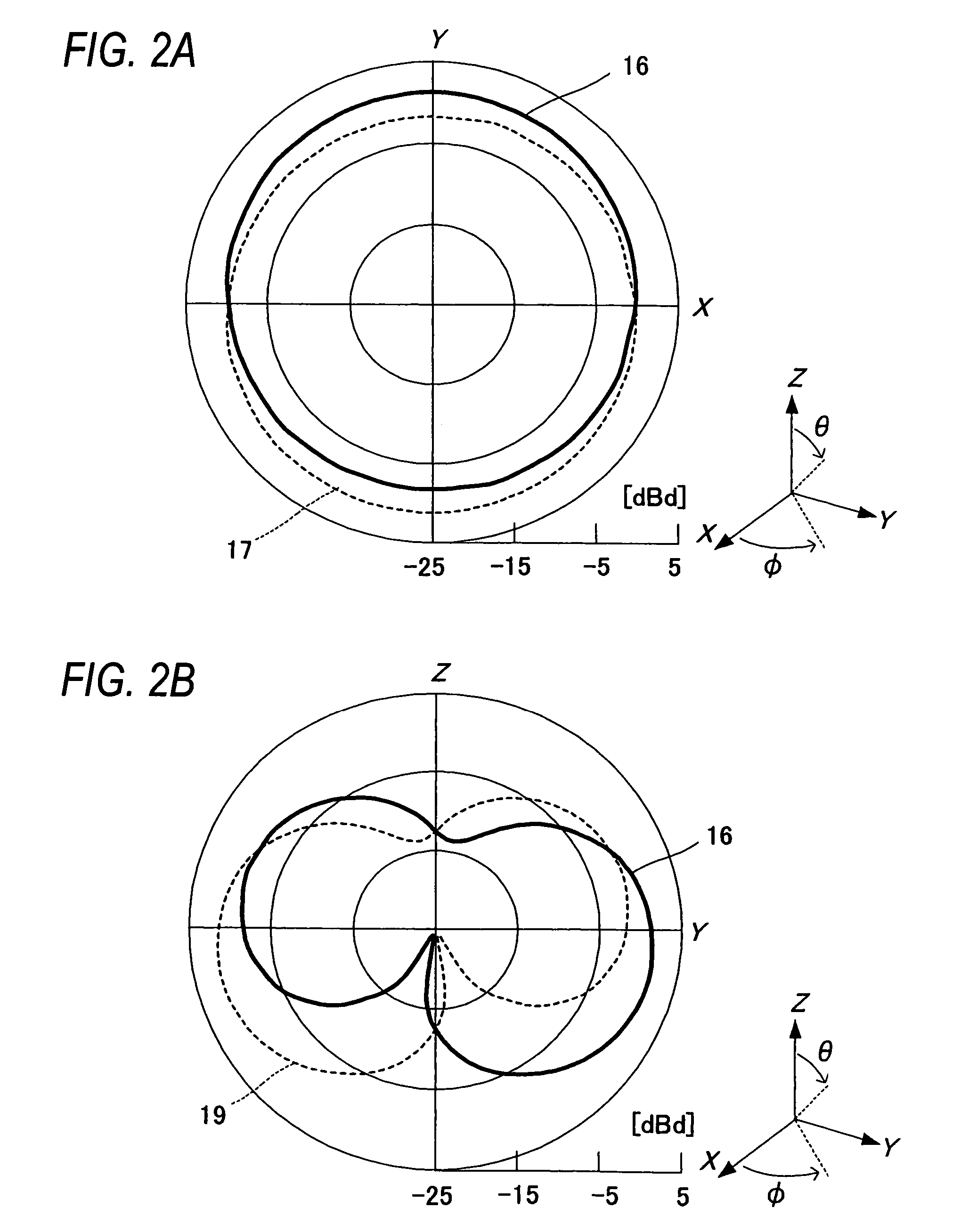
InactiveUS20050239519A1Reduce thicknessHigh antenna gainAntenna supports/mountingsElongated active element feedElectrical conductorEngineering
An upper case (1) is connected to a lower case (2) in a hinge portion (3) so as to freely rotate. A plate shaped conductor (4) and a plate shaped conductor (5) are disposed along the surface of the case in the upper case (1). A ground plate (6) is formed in a ground pattern of a circuit board disposed in the lower case (2). The plate shaped conductor (4) and the plate shaped conductor (5) are selected by a high frequency switch (14) and connected to one end of a feeding portion (15). The other end of the feeding portion (15) is connected to the ground plate (6) to form a dipole antenna.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Compact smart antenna for mobile wireless communications
InactiveUS20120299765A1Suppress interferenceJam suppressionRadio transmissionIndividually energised antenna arraysLow noiseBand-pass filter
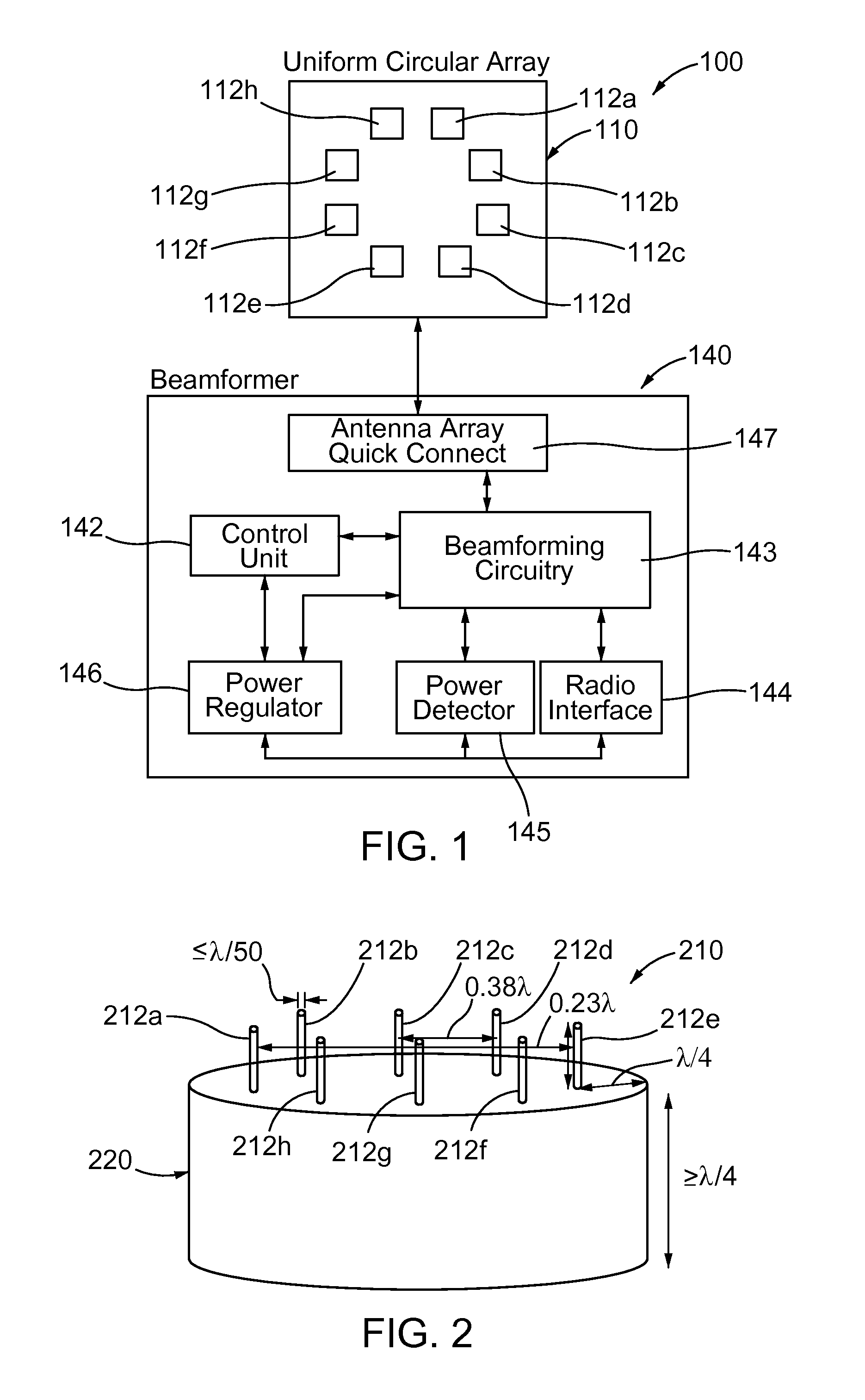
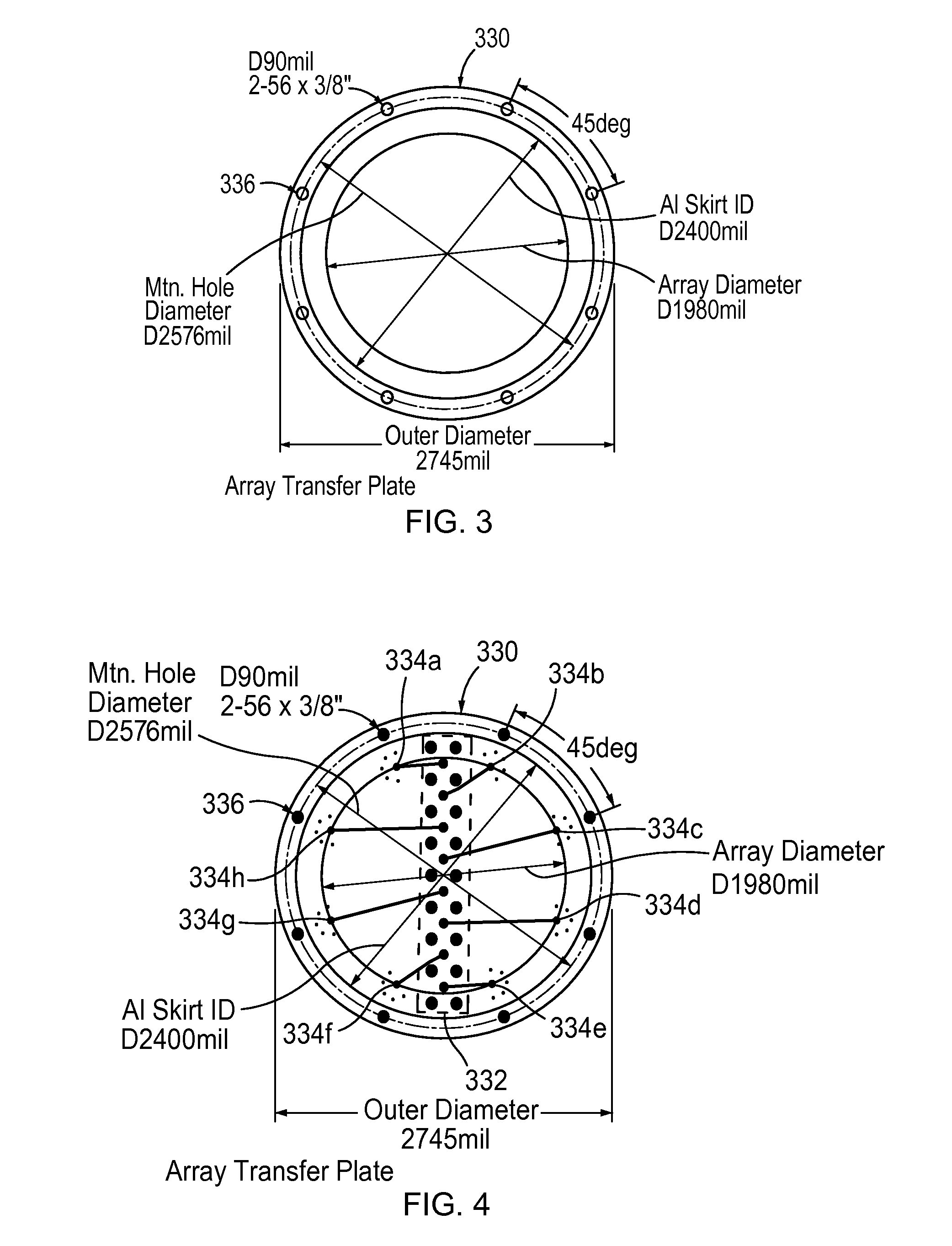
A compact, high gain 8-element circular smart antenna is able to scan a beam azimuthally through 360°. The 8-element array is placed on a ground skirt and connected to an 8-channel beamforning board via a transfer plate. Each channel has two T / R switches, one band pass filer, one power amplifier, two low noise amplifiers, one phase shifter, and one attenuator. The 8-channel-signal is combined through power splitters / combiners and then sent to a connected radio. An FPGA chip controls the digital phase shifters, attenuators and switches for signal searching, beamforming and tracking. The smart antenna can be operated as a compact switched beam system or with an additional processor as an adaptive array system. The smart antenna is capable of tracking mobile targets, directionally communicating with desired users, suppressing interference and jamming, and enabling long range communications with high throughput and reliable connection because of its high antenna gain.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Antenna having metamaterial superstrate and providing gain improvement and beamforming together
InactiveUS20100277374A1Lower ratioImproving gain and beamformingSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsResonatorBeamforming
Provided is antenna having metamaterial and providing gain improvement and beamforming together. The antenna includes a resonator and a superstrate. A feed antenna is disposed in the resonator. The superstrate includes a conductive pattern on the resonator for improving gain and beamforming of the feed antenna.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Card type wireless device, antenna coil, and method for manufacturing communication module
InactiveUS7545336B2Improve permeabilityHigh sensitivityLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreRadiating elements structural formsAir coreProjection plane
An antenna coil includes: an air-core type flat coil body; and a coil support member disposed between the coil body and a substrate so that the coil body is supported on a surface of the substrate. The thickness of the coil body is smaller than a radius of a circle, an area of which is equal to an area of a region surrounded with an outline of a projected coil body, the projected coil body provided by projecting the coil body on a projection plane perpendicular to the axial direction of the coil body. The coil support member is made of resin hardened soft magnetic material.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Hybrid multiple-input multiple-output antenna module and system of using the same
ActiveUS20110241953A1Small sizeLow profileResonant long antennasAntenna earthingsDual frequencyElectricity
The hybrid multiple-input multiple-output antenna module includes a grounding unit, a plurality of radiating units, loop units and filter units. The radiating units and the loop units are arranged around a geometric center of the grounding unit and are alternately and symmetrically arranged on the grounding unit. The loop units are arranged along the outer peripheral side of the grounding unit. The filter units are respectively electrically connected to the loop units. The present invention not only has some advantages such as small size, low profile, good isolation, high antenna gain and good radiation properties, but also can replace the external dual-band access-point antenna of the prior art for 2.4 / 5 GHz operation with no need of an extra diplexer. In addition, the hybrid multiple-input multiple-output antenna module can be hidden in the wireless communication device in order to enhance the appearance of the product.
Owner:LITE ON TECH CORP +1
Card type wireless device, antenna coil, and method for manufacturing communication module
InactiveUS20060267853A1Improve permeabilityHigh sensitivityLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreRadiating elements structural formsAir coreProjection plane
An antenna coil includes: an air-core type flat coil body; and a coil support member disposed between the coil body and a substrate so that the coil body is supported on a surface of the substrate. The thickness of the coil body is smaller than a radius of a circle, an area of which is equal to an area of a region surrounded with an outline of a projected coil body, the projected coil body provided by projecting the coil body on a projection plane perpendicular to the axial direction of the coil body. The coil support member is made of resin hardened soft magnetic material.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Structure for radio frequency identification and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20100320275A1Reduce power consumptionNo pollution in the processRecord carriers used with machinesAntenna detailsAntenna gainConductive materials
A improved structure RFID includes: a substrate with an entire side of a metal conductive material; a slot antenna disposed on the metal side of the substrate; and an identification chip disposed on the substrate and electrically connected to the slot antenna. The RFID is manufactured using a simpler and cheaper method, so manufacturing costs are significantly reduced while providing low energy consumption, pollution-free, recyclability, and the RFID has high antenna gain, strong reflectivity, and high conductivity. Shield effects provided by the whole metal side of the substrate can also reduce effects to the electrical properties of the RFID caused by the target object and the environment, so the RFID is more suitable for metal objects and conductors with moisture.
Owner:ELKA INT
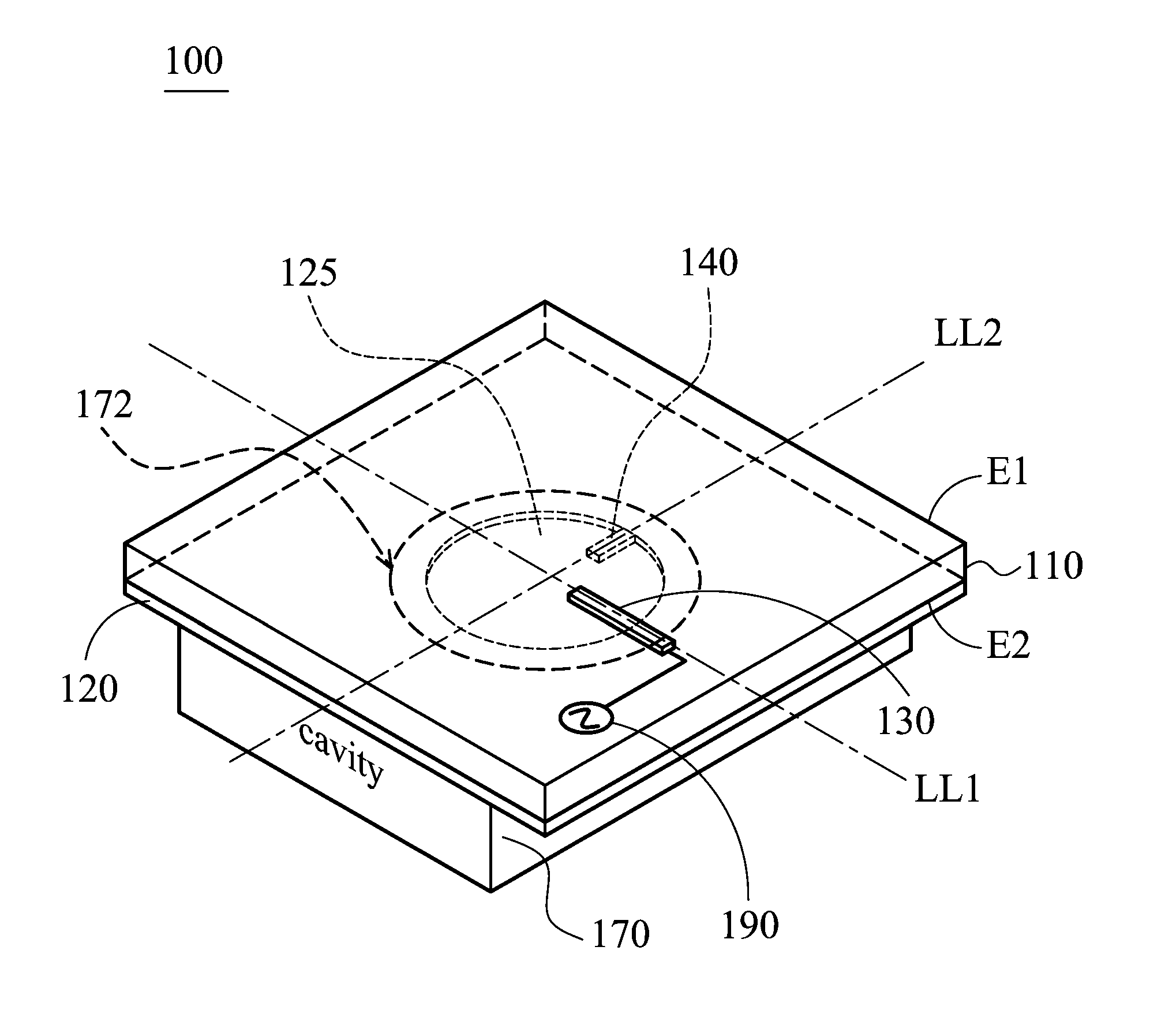
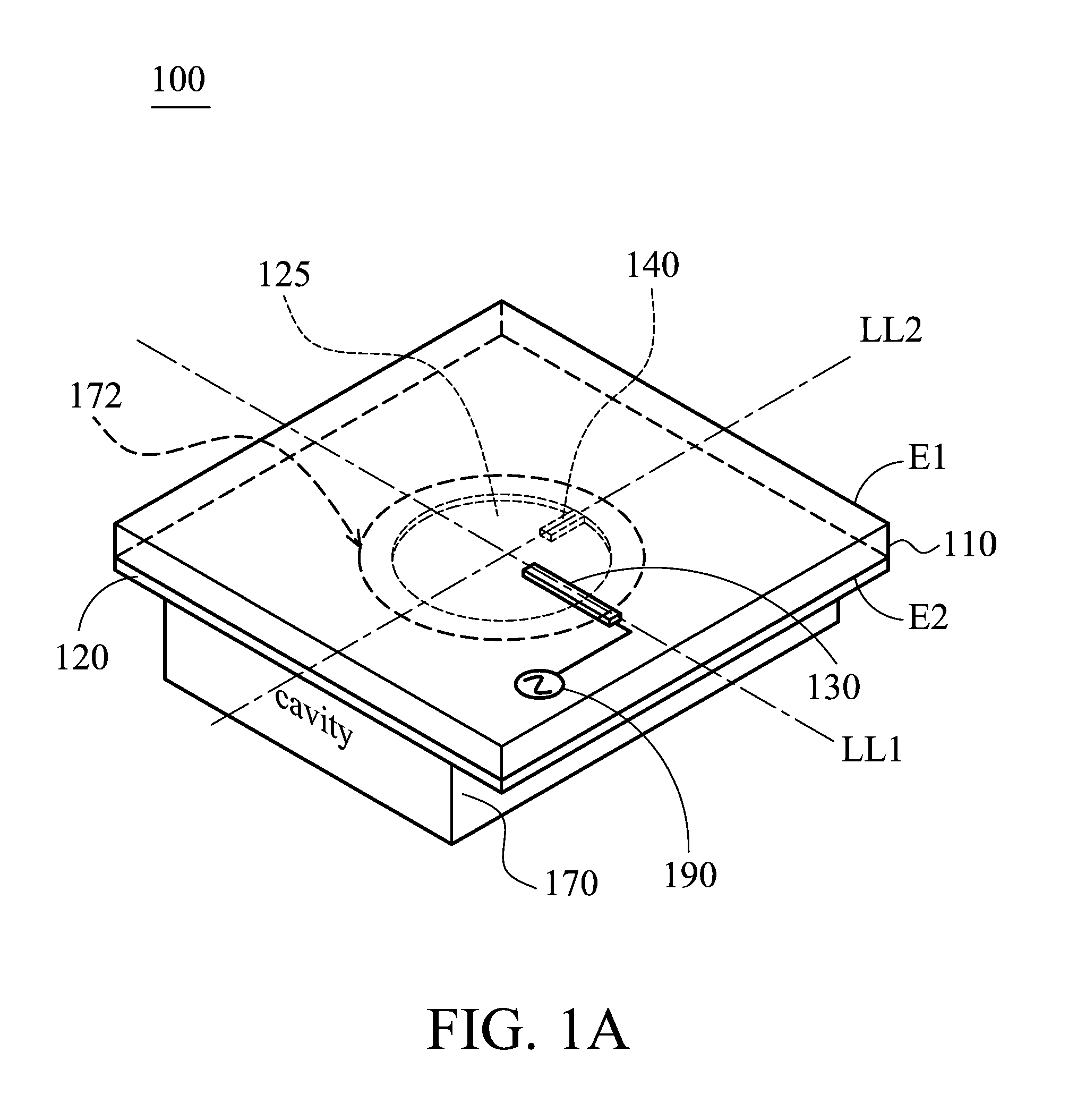
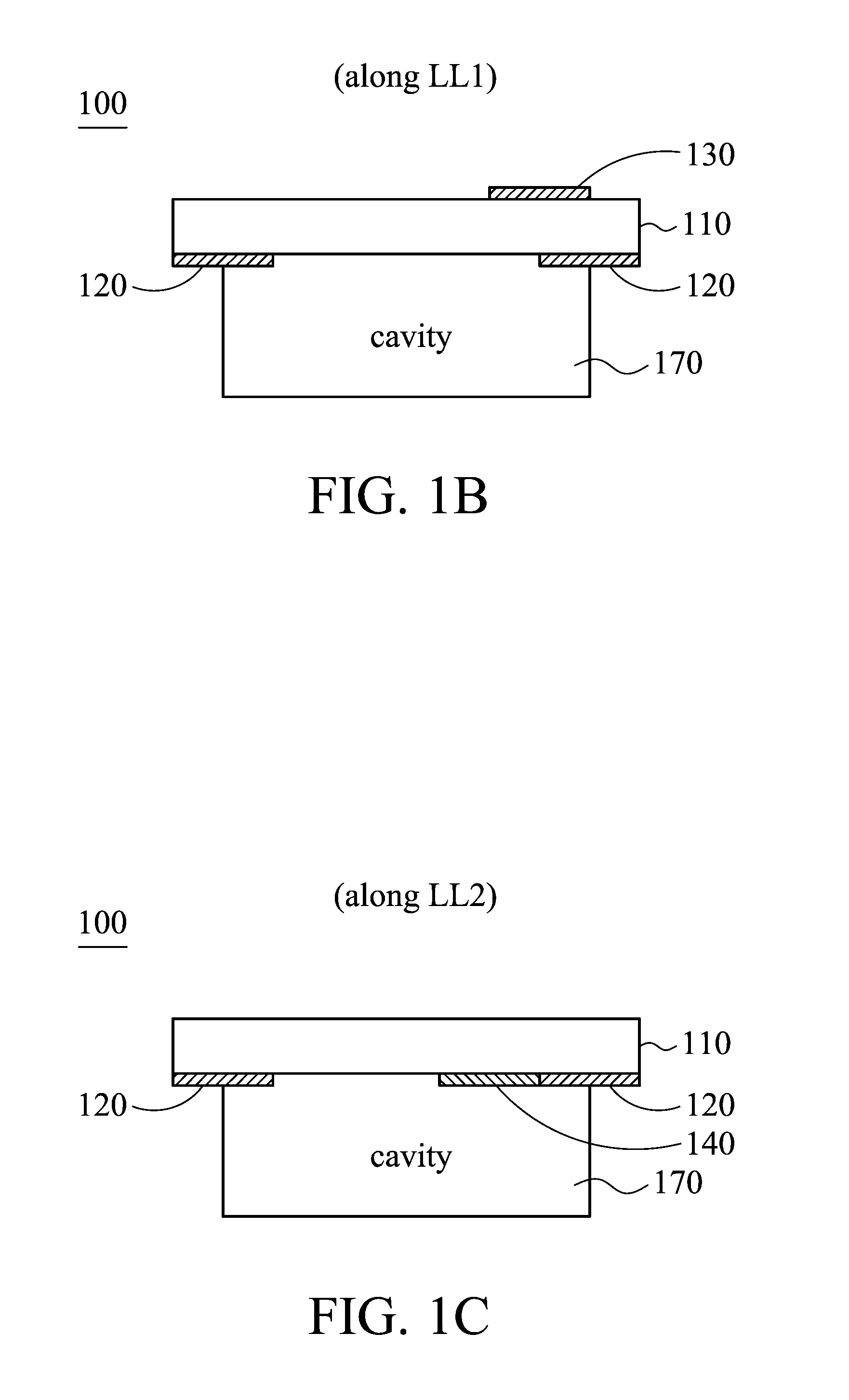
Circular polarization antenna
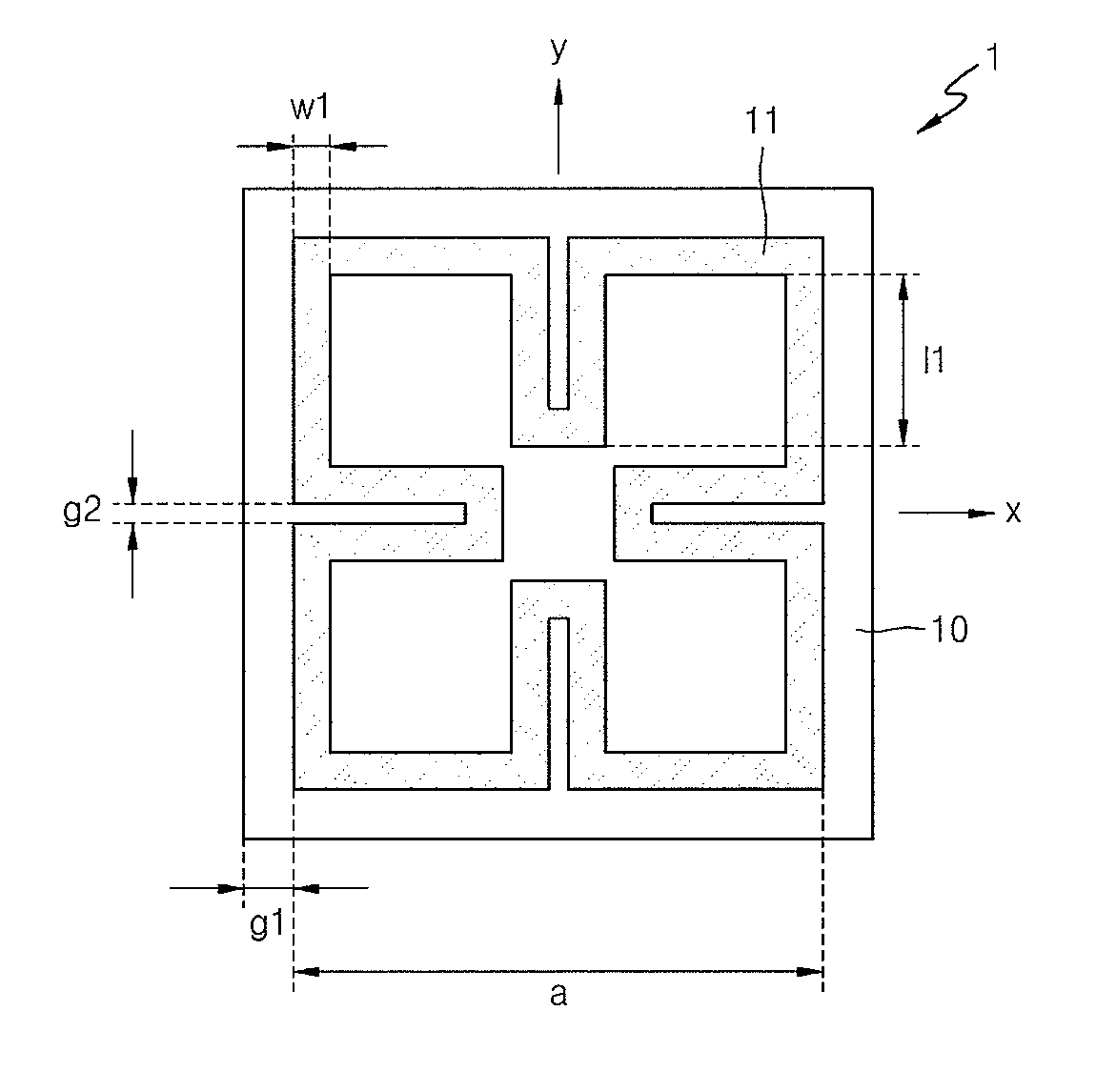
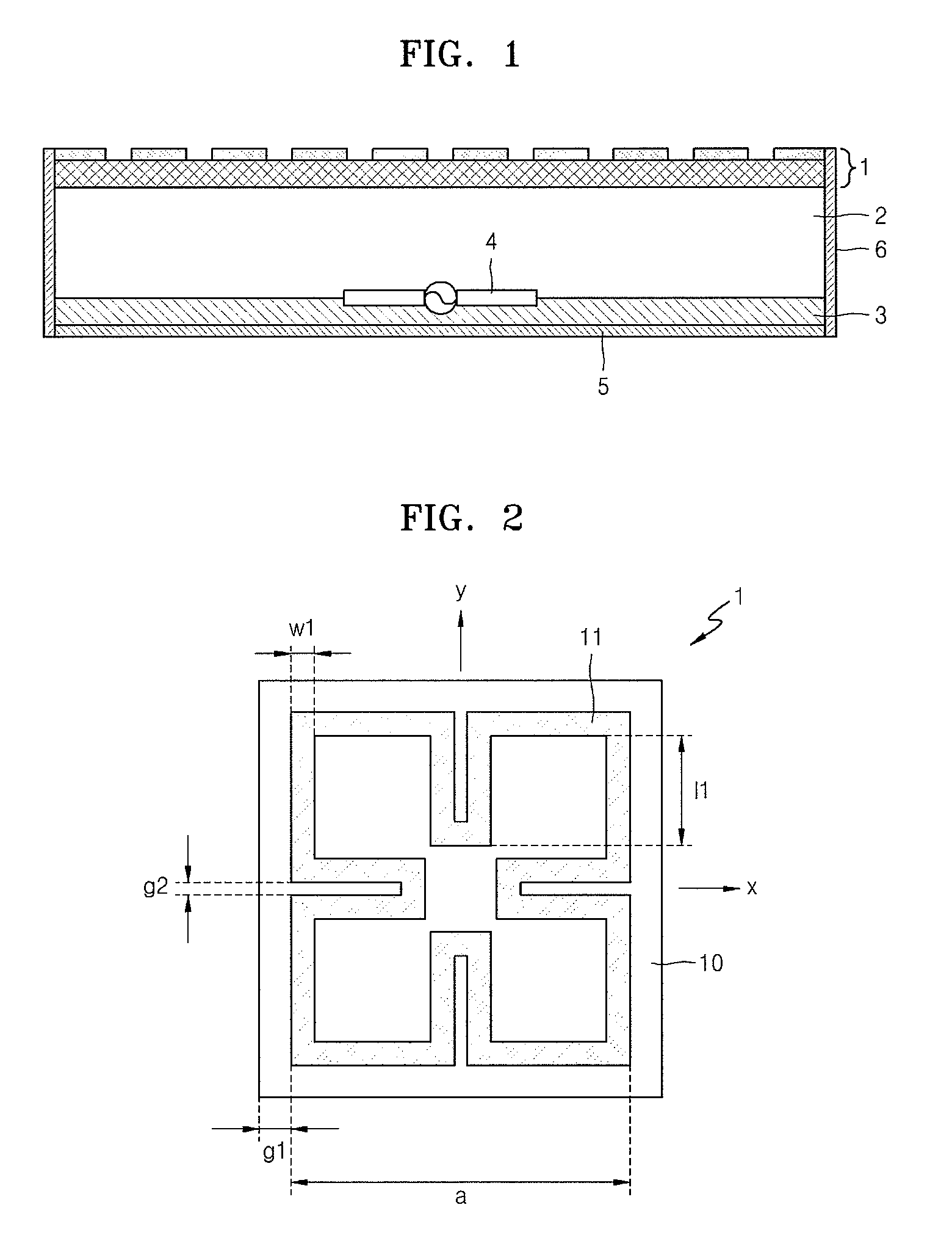
ActiveUS20130169494A1High antenna gainElectrically long antennasPolarised antenna unit combinationsCircularly polarized antennaGround plane
A circular polarization antenna includes a substrate, a ground plane, a tuning stub, a feeding element, and a cavity structure. The substrate has a first surface and a second surface. The feeding element is disposed on the first surface of the substrate. The ground plane is disposed on the second surface of the substrate and has a hole. The tuning stub is disposed on the second surface of the substrate and connected to the edge of the hole. The cavity structure is connected to the ground plane and configured to reflect an electromagnetic wave.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Dipole antenna
InactiveUS6956536B2High antenna gainWide bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsAntenna gainImpedance matching
A dipole antenna is disclosed, and two electrodes thereof are respectively disposed on two surfaces of a substrate, wherein those two surfaces are parallel to each other. Metallic layers allocated in the substrate are used to control impedance match, and to promote the antenna gain and operation bandwidth of the dipole antenna.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Hybrid multiple-input multiple-output antenna module and system of using the same
ActiveUS8482471B2Good lookingSmall sizeResonant long antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsComputer moduleAntenna gain
The hybrid multiple-input multiple-output antenna module includes a grounding unit, a plurality of radiating units, loop units and filter units. The radiating units and the loop units are arranged around a geometric center of the grounding unit and are alternately and symmetrically arranged on the grounding unit. The loop units are arranged along the outer peripheral side of the grounding unit. The filter units are respectively electrically connected to the loop units. The present invention not only has some advantages such as small size, low profile, good isolation, high antenna gain and good radiation properties, but also can replace the external dual-band access-point antenna of the prior art for 2.4 / 5 GHz operation with no need of an extra diplexer. In addition, the hybrid multiple-input multiple-output antenna module can be hidden in the wireless communication device in order to enhance the appearance of the product.
Owner:LITE ON TECH CORP +1
Portable wireless machine
InactiveUS8060167B2High antenna gainReduce thicknessAntenna supports/mountingsElongated active element feedElectrical conductorDipole antenna
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
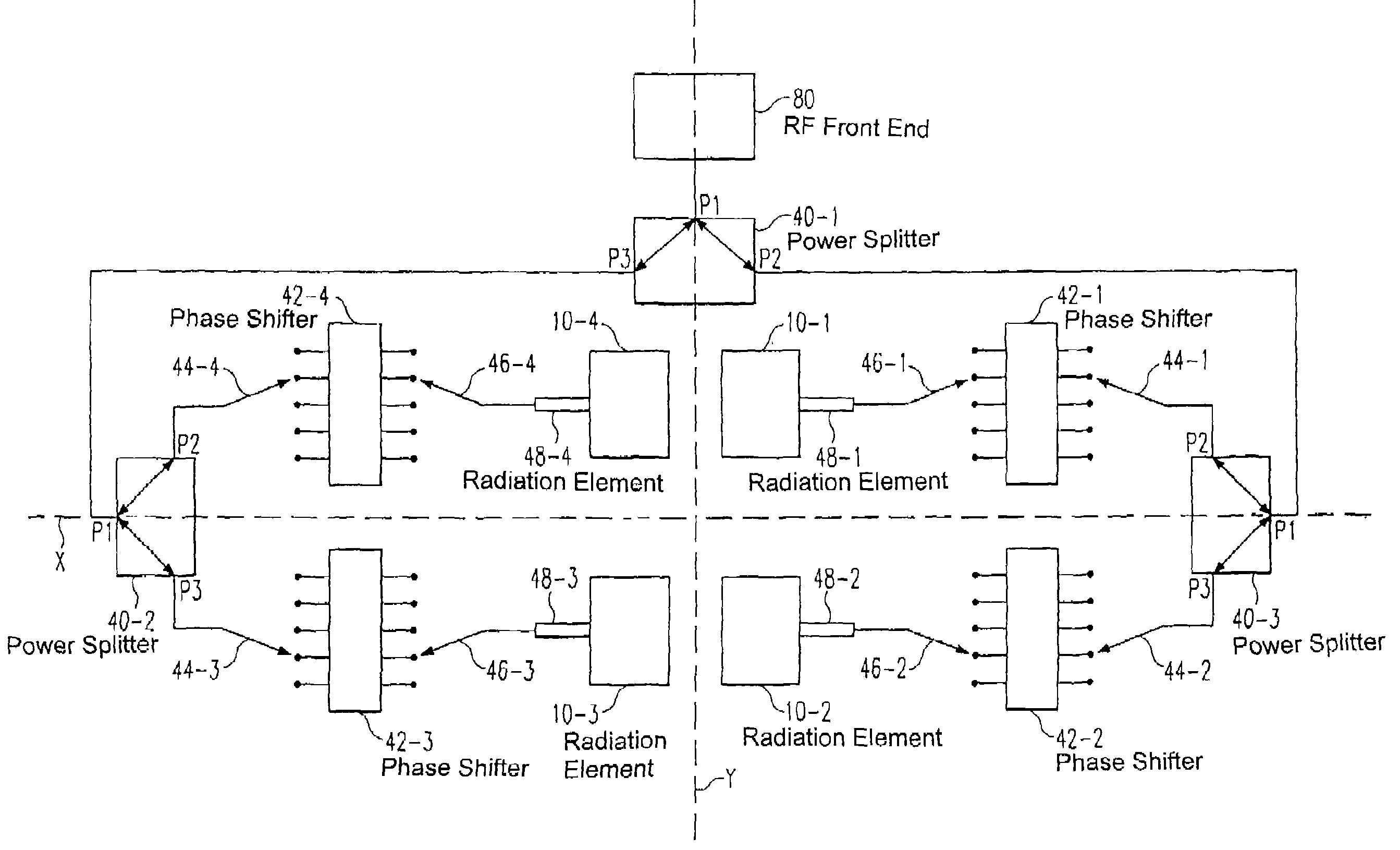
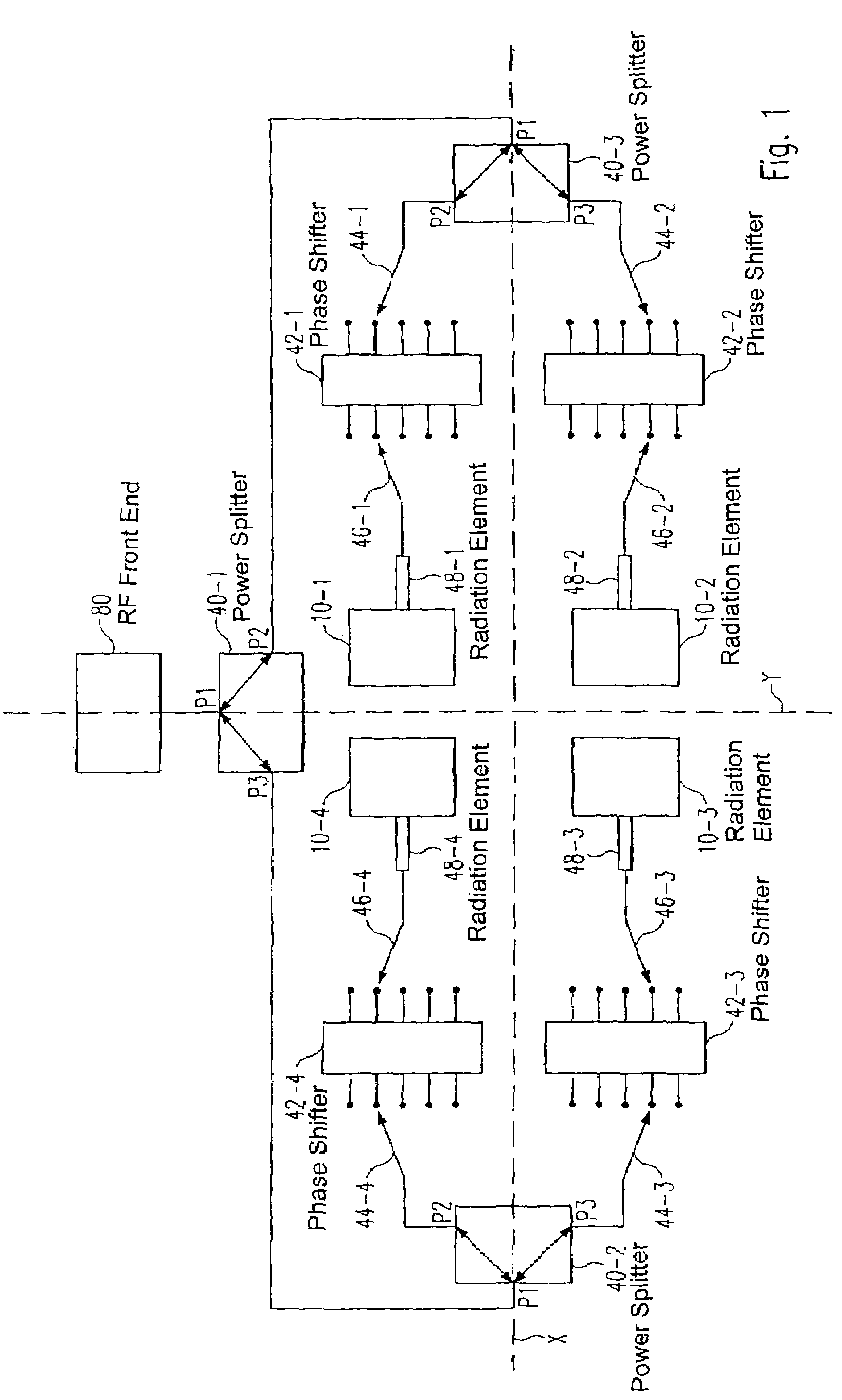
Broadband beam steering antenna
ActiveUS20080238774A1High antenna gainReduce total powerAntenna arraysElectrically short antennasTransceiverRelative phase
The present invention relates to an antenna apparatus with steerable beam pattern, an RF transceiver comprising the antenna apparatus and a mobile device comprising the antenna apparatus. The antenna apparatus according to the present invention is attachable to the front-end of a transceiver circuitry and comprises at least two balanced radiation elements forming a planar structure, for transmitting and / or receiving a corresponding number of partial signals, a signal splitter and / or combiner for splitting a signal received from an attached transceiver circuitry into said partial signals and / or combining said partial signals into a signal to be transmitted to an attached transceiver circuitry, a phase shifter device operable to apply relative phase shifts between at least two of said partial signals, whereby said relative phase shifts are selectable from a group of at least two relative phase shift values provided by said phase shifter device.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
Portable wireless unit
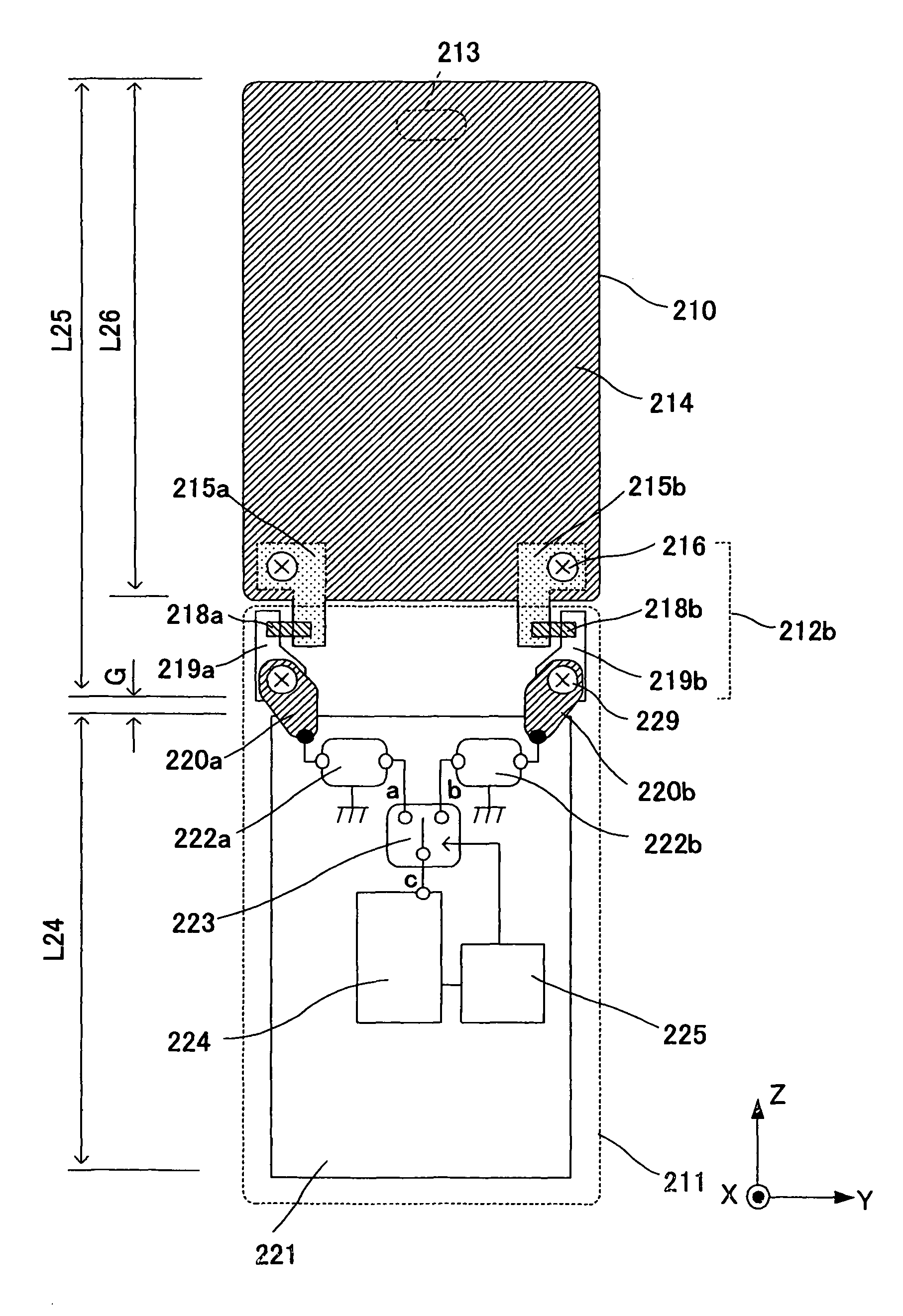
InactiveUS20090066585A1High antenna gainImprove communication qualityAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentCouplingDipole antenna
A portable wireless unit having high antenna performance, which comprises: a first case having a first antenna element, a second antenna element and a second feeding section; a second case having a third antenna element, a third feeding section and a circuit board provided with a ground pattern; and a coupling section consisting of first and second electrically connected conductive coupling elements and coupling the first case and the second case to be extended and housed freely. The second coupling element is provided in the first case while being connected electrically with the first antenna element, the first coupling element is provided in the second case while being connected electrically with the first feeding section, and the first antenna element, the coupling section, and the ground pattern are operated as a dipole antenna.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Collapsible Mobile Radio Device
InactiveUS20080020812A1Reduce local mean sarHigh antenna gainSubstation equipmentElongated active element feedHinge angleEngineering
A conductive metal frame and a first hinge portion fitted onto an upper case are connected electrically, first and second hinge portions are joined to turn on a rotating shaft, and the first and second hinge portions and the rotating shaft are formed of a conductive metal and conducted electrically via respective contact points. The second hinge portion as the feeding portion is connected to a matching circuit on a circuit board, and one end of a conductive metal element having a predetermined length is connected to the second hinge portion to have an electrical conduction thereto and the other end of the conductive metal element is opened. The conductive metal element is arranged in parallel with a direction orthogonal with a longitudinal direction of a lower case, and is arranged near a surface on the opposite side to the surface on which the operation keys are arranged.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Monopole antenna
InactiveUS20070052591A1Low costSmall sizeSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorAntenna gain
A monopole antenna is disclosed. The monopole antenna comprises a base board, a first substantially L-shaped conductor, a first ground plane, a second substantially L-shaped conductor, a second ground plane and a feeding strip, and the monopole antenna further has a plurality of evenly-distributed through holes penetrating the base board from the first substantially L-shaped conductor to the second substantially L-shaped conductor. When the monopole antenna is operated at about 2.4-2.5 GHz, good radiation patterns and antenna gain are obtained for being applicable to IEEE802.11b / g specifications.
Owner:ARCADYAN
Antenna having metamaterial superstrate and providing gain improvement and beamforming together
InactiveUS8350759B2Lower ratioImproving gain and beamformingSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsResonatorBeamforming
Provided is antenna having metamaterial and providing gain improvement and beamforming together. The antenna includes a resonator and a superstrate. A feed antenna is disposed in the resonator. The superstrate includes a conductive pattern on the resonator for improving gain and beamforming of the feed antenna.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
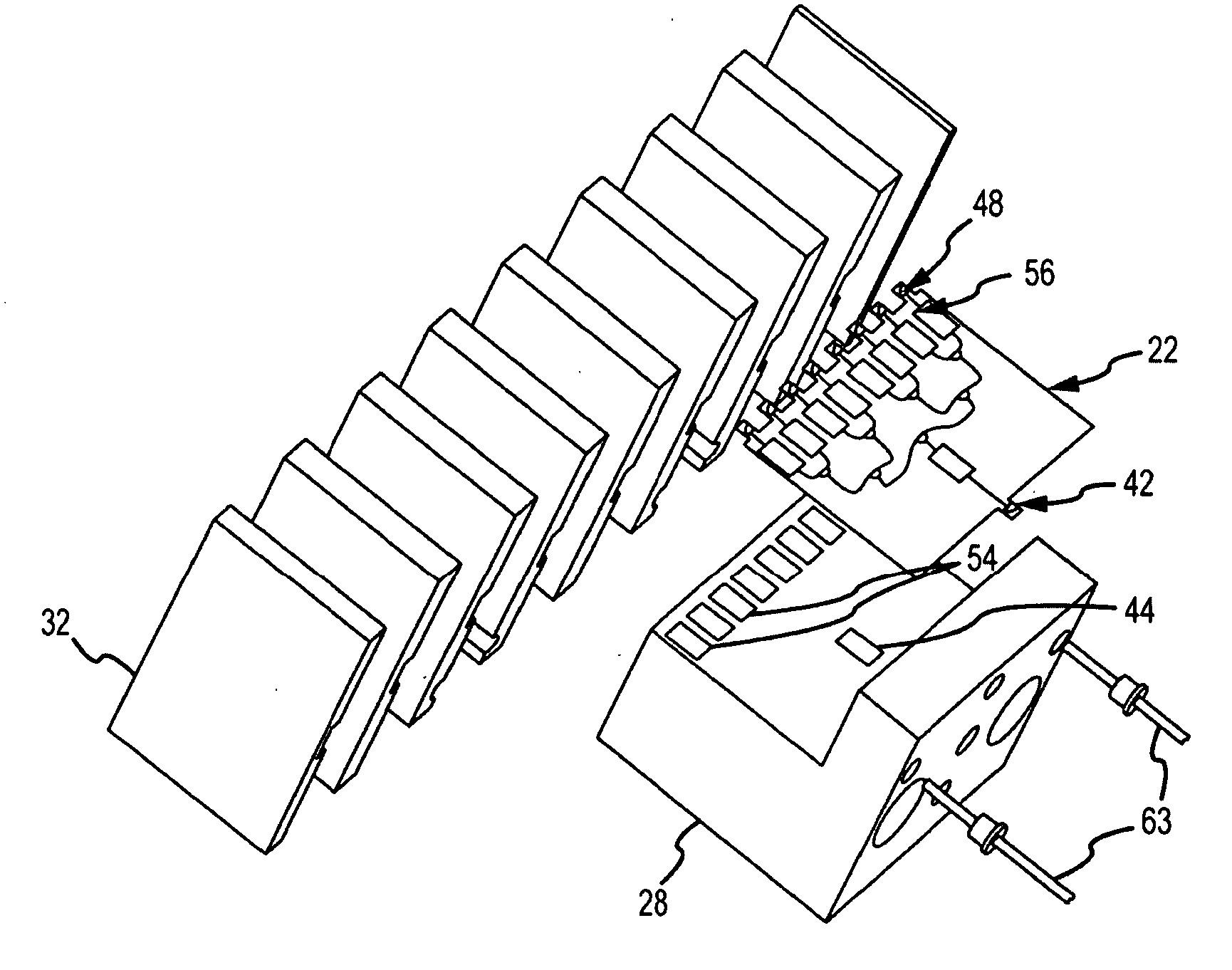
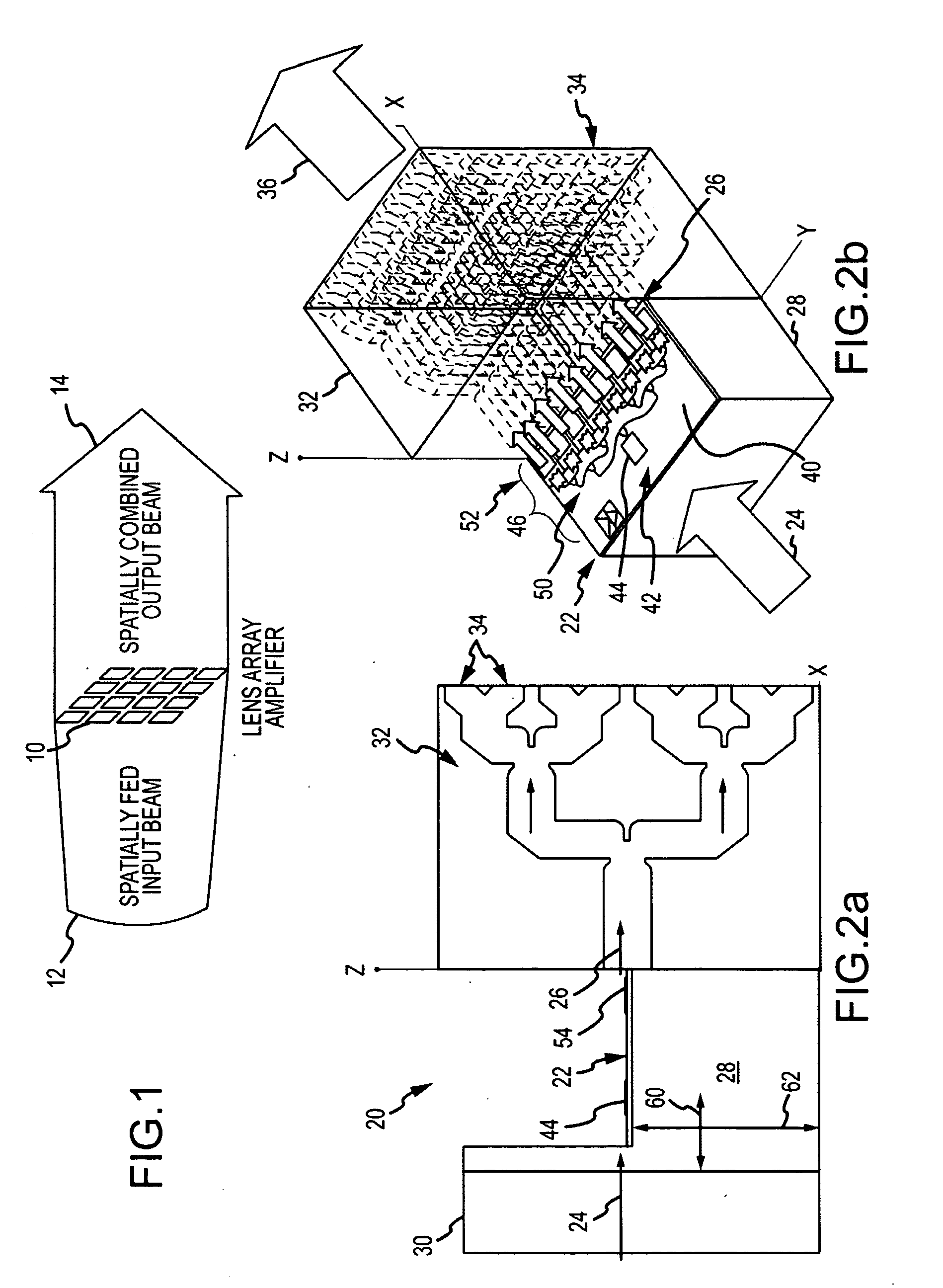
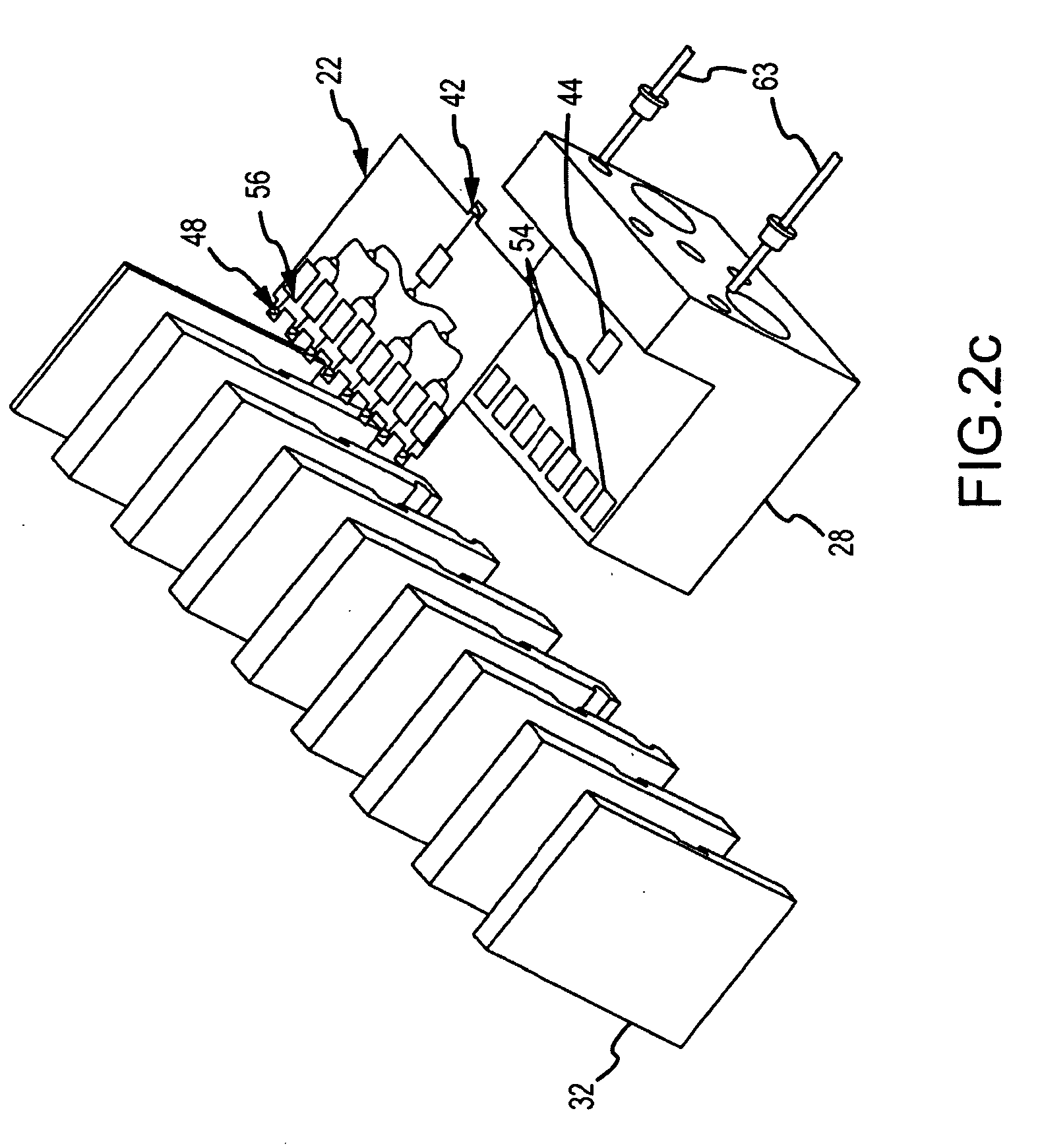
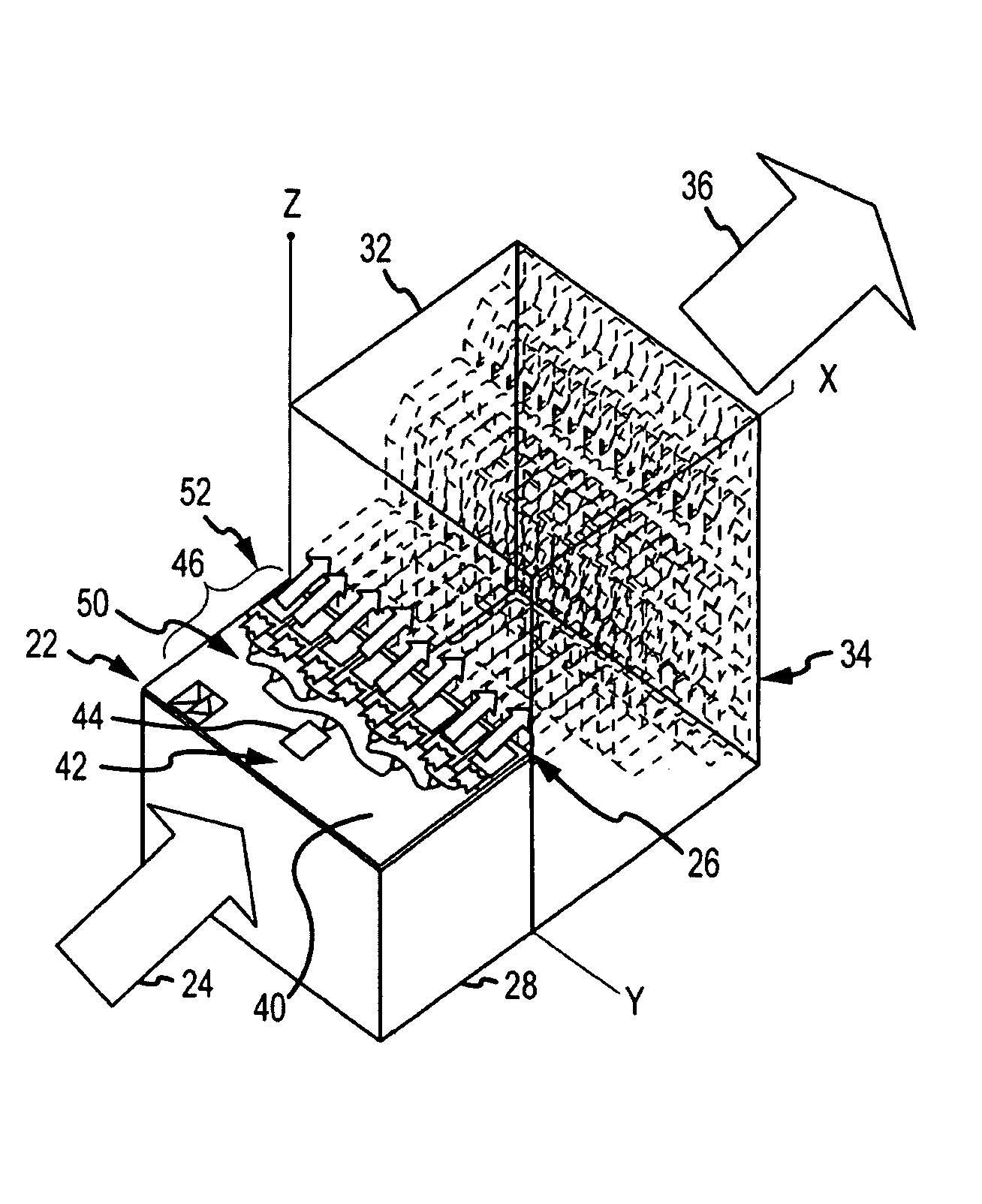
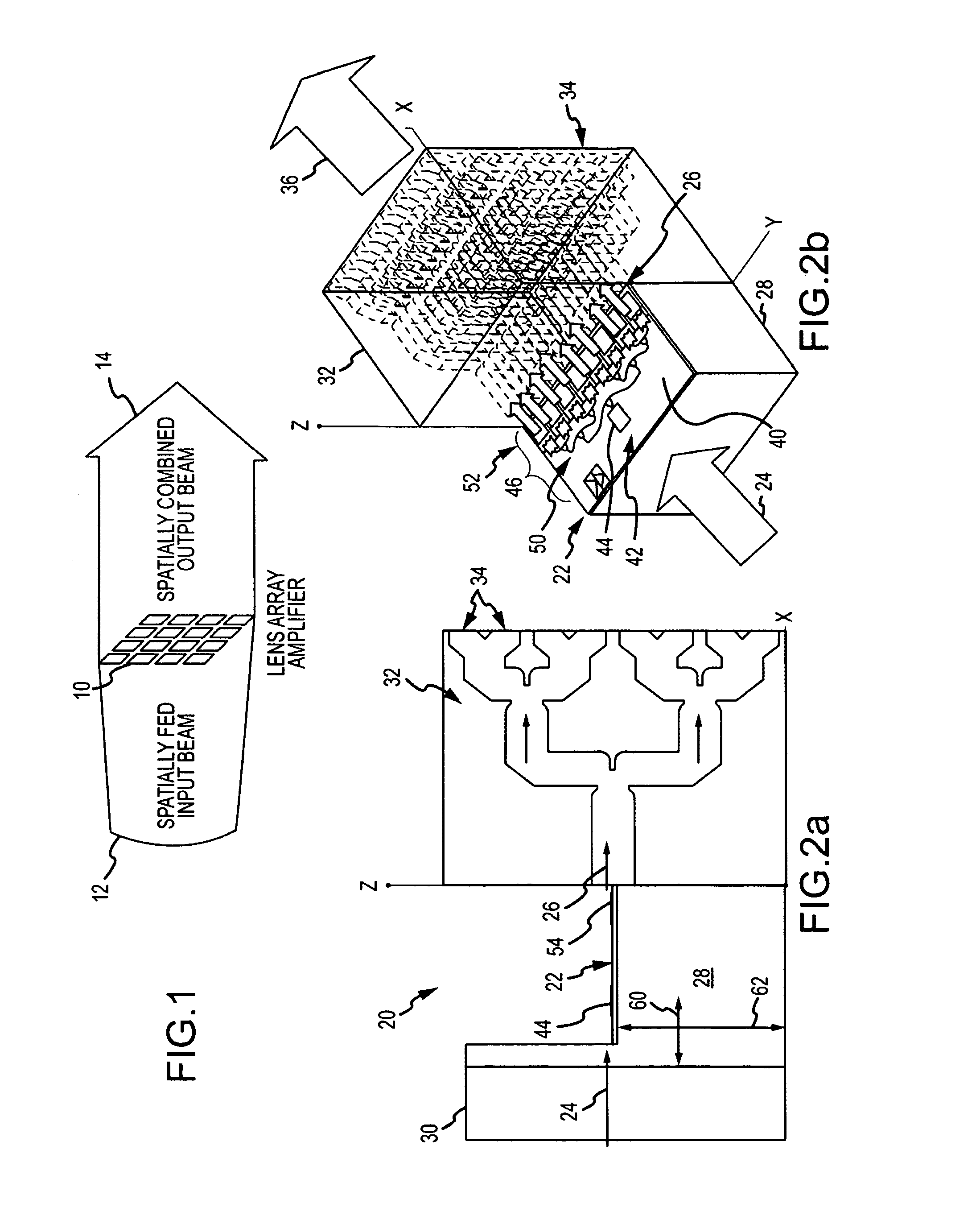
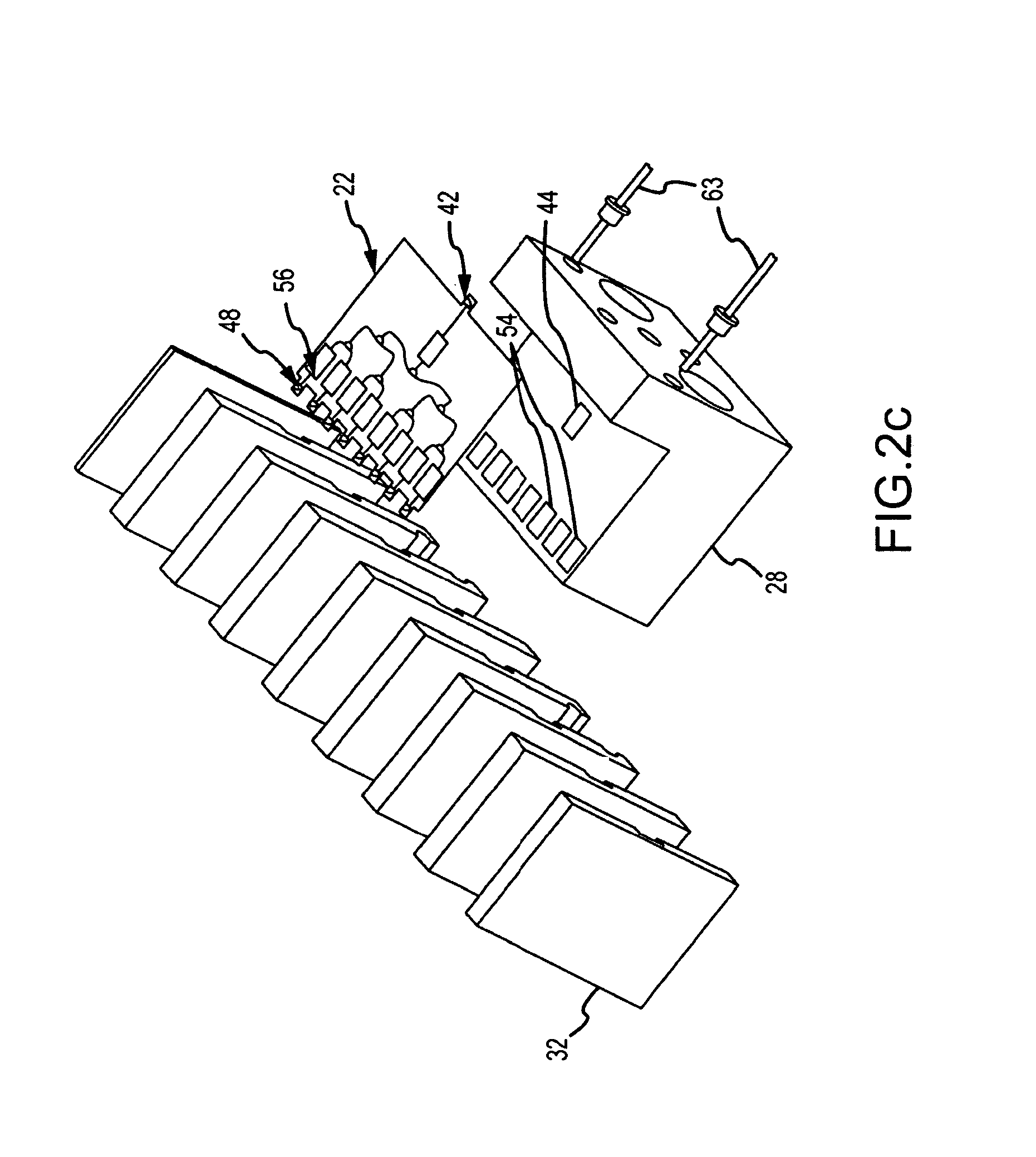
Modular solid-state millimeter wave (MMW) RF power source
ActiveUS20100210225A1Easy and less-expensive to manufactureEnhanced couplingAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesModular arraysAudio power amplifierAntenna gain
A modular solid-state MMW power source based on a topology of the lens array amplifier provides both the flexibility to scale output power and effective thermal management. The modular power source includes a single submodule that uses one or more power dividers and one or more solid-state amplification stages to divide and amplify an RF input signal into R amplified RF signals. The submodule is mounted (suitably in the X-Y plane) on the surface of a heat sink, suitably coupled to a cold backplane, to remove heat. R 1:N low loss power dividers route the amplified RF signals to R*N radiating elements. Each of the 1:N power dividers suitably reside in the X-Z plane and are stacked in the Y direction to provide a planar output of the R*N radiating elements in the Y-Z plane. Placement of the amplifier chips on the single submodule decouples the number of amplifier chips, hence output power, from the number of radiating elements. Placement of the amplifier chips away from the radiating face provides a short path with large thermal cross-section through the heat sink to the backplane to remove heat. The topology can produce high output power combined with a high antenna gain to produce large power-aperture products previously only achievable with a Gyrotron. As amplifier chips become more powerful, the topology can be adapted to use fewer chips.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
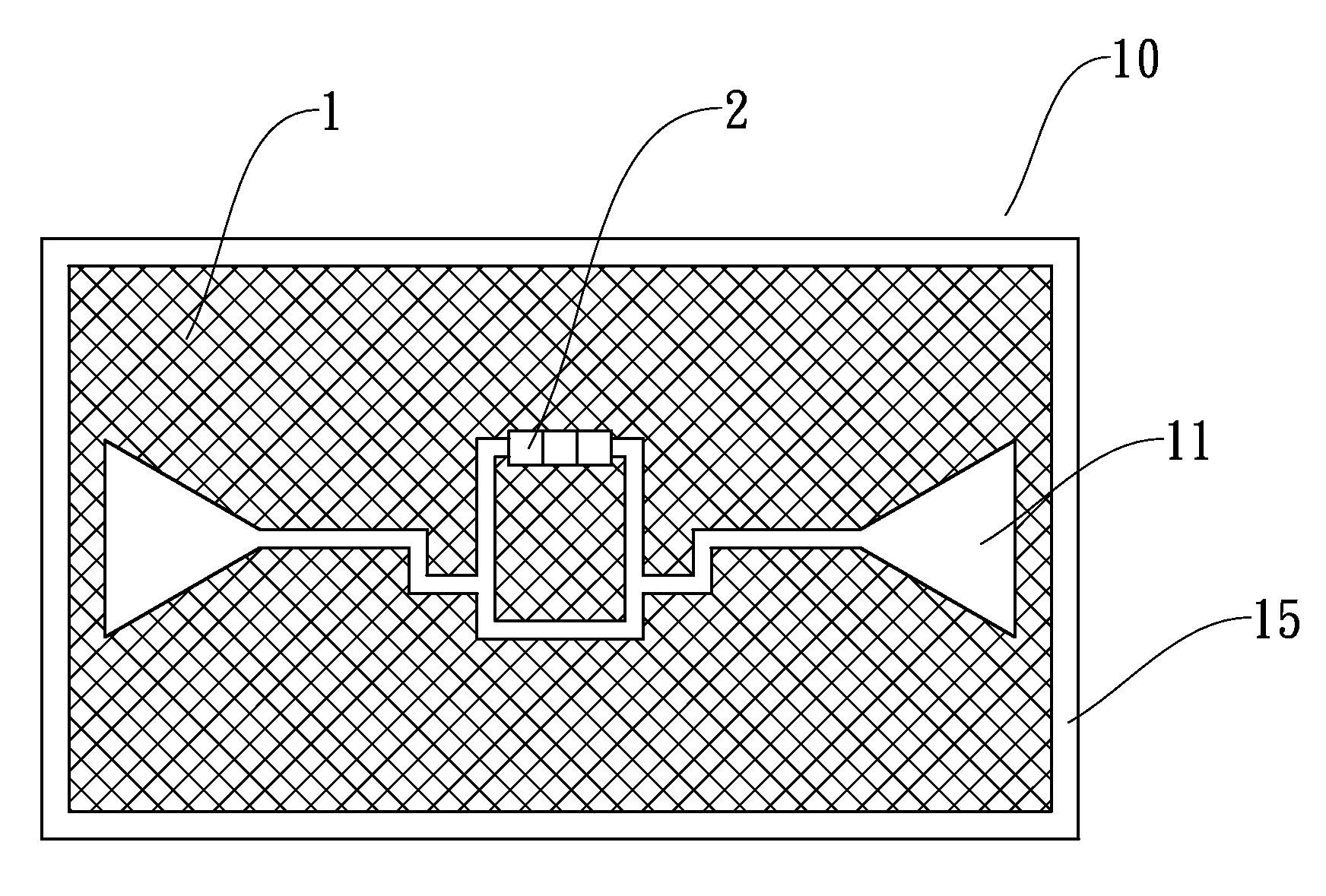
Variable directional antenna device
InactiveUS20120075156A1High antenna gainLarge FB ratioSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna detailsDual frequencyDirectional antenna
A feed element is configured to include a first antenna element having a first width, a dual-band forming inductor, and a second antenna element having a second width wider than the first width, where the first antenna element, the dual-band forming inductor, and a second antenna element are connected in series. The inductor is formed in a meander shape which has a trapezoidal envelope external shape to have a width formed to widen from the first width of a portion connected to the first antenna element toward a portion connected to the second antenna element.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Broadband beam steering antenna
ActiveUS7595753B2Reduces power and energyEasy to receiveAntenna arraysElectrically short antennasTransceiverRelative phase
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
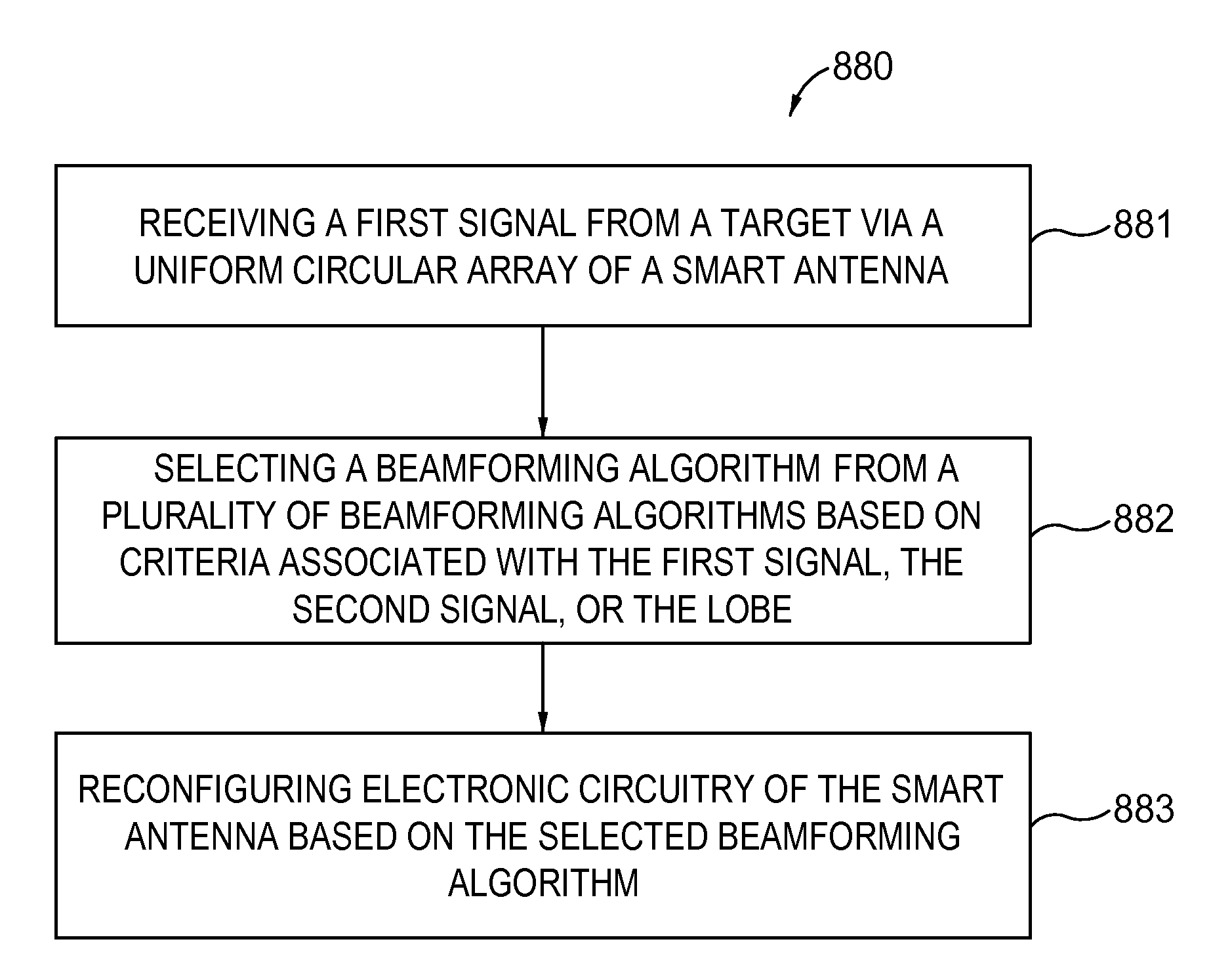
Communication devices and methods with beamforming training
ActiveUS20190319693A1High antenna gainReduce the probability of collisionSpatial transmit diversityAssess restrictionTraining phaseCommunication device
A communication device, e.g. an access point, for RF-based communication with another communication device, e.g. a station, comprises antenna circuitry configured to transmit and receive RF signals and beamforming circuitry configured to perform beamforming. The beamforming circuitry controls the antenna circuitry to transmit data, in a beacon transmission phase prior to the beamforming training phase, using a set of third directive transmit beams in subsequent time slots and to listen, in the beamforming training phase, using a set of first directive receive beams in subsequent time slots that is different from the set of third directive transmit beams.
Owner:SONY CORP
Variable directivity antenna apparatus including parasitic elements having cut portion of rectangular shape
ActiveUS20120127053A1High antenna gainBig ratioSimultaneous aerial operationsIndividually energised antenna arraysEngineeringInductor
A feed element is configured to include a first antenna element having a first width, a dual-band forming inductor, and a second antenna element having a second width wider than the first width, where the first antenna element, the dual-band forming inductor, and a second antenna element are connected in series. The inductor is formed in a meander shape which has a trapezoidal envelope external shape to have a width formed to widen from the first width of a portion connected to the first antenna element toward a portion connected to the second antenna element. Cut portions each having a rectangular shape are further formed at corner portions of another ends of the parasitic elements, respectively.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
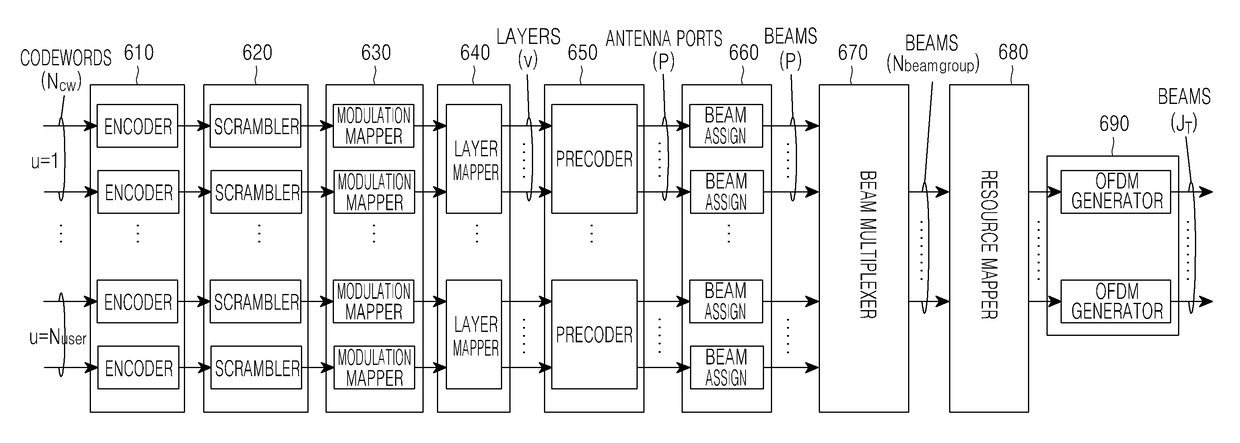
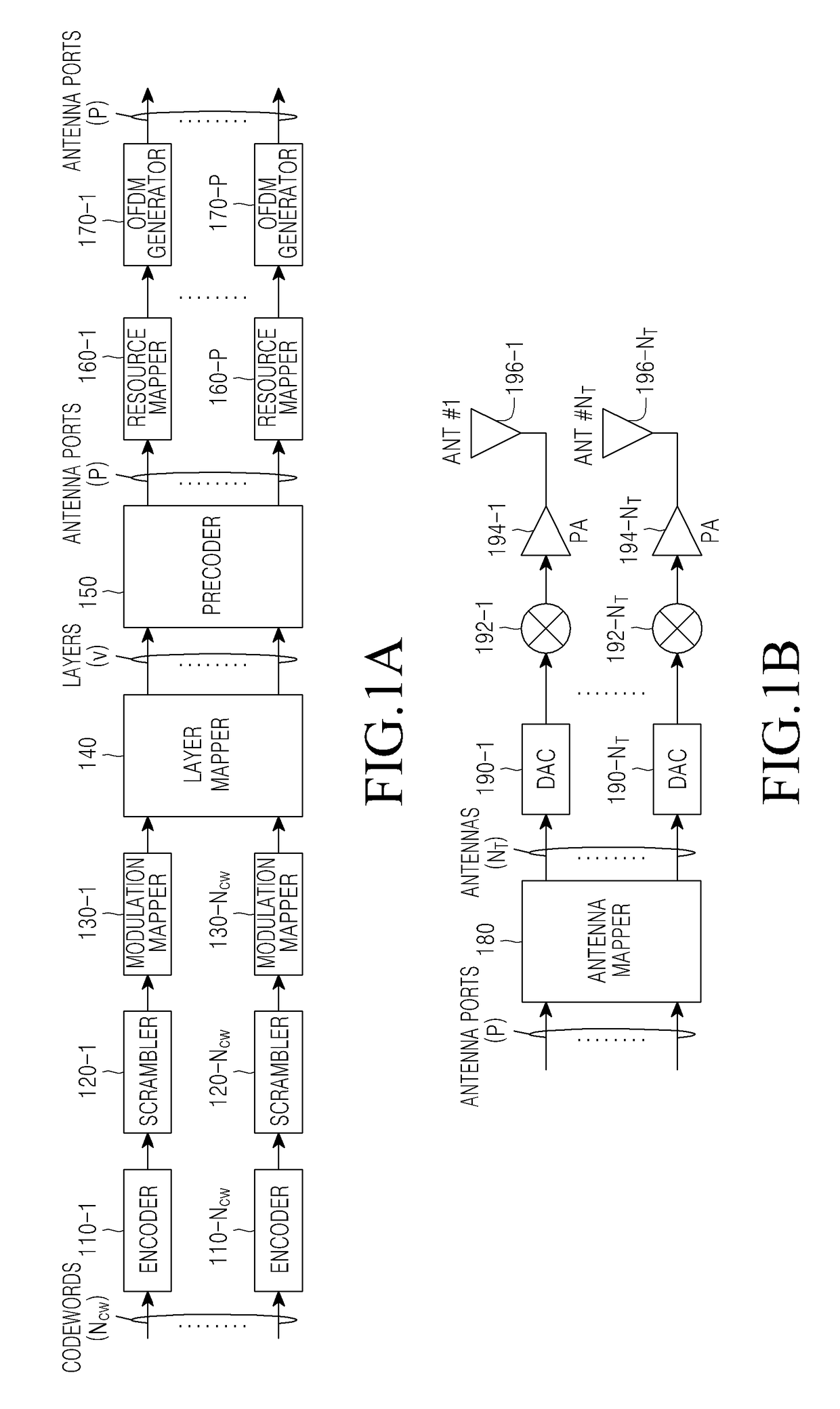
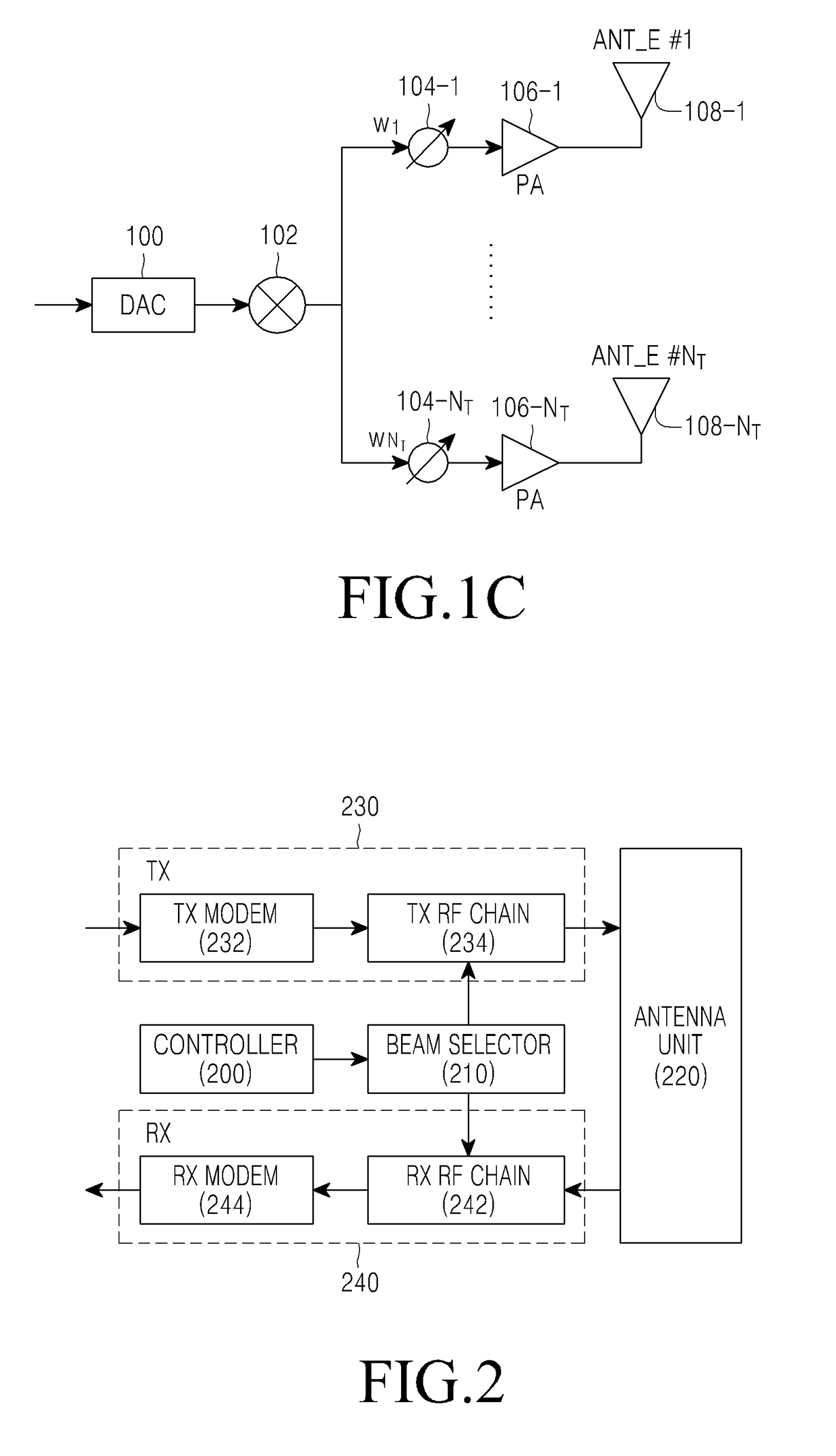
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving signals in multi-antenna communication system
ActiveUS9614594B2Effective supportFlexible responseSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsMultiplexingCommunications system
A method for transmitting a signal in a multi-antenna system is provided. The method includes designating an analog beam to a plurality of generated modulation symbol sequences corresponding to a plurality of antenna ports, for each antenna port of the plurality, multiplexing signals, to which a beam is designated by the beam assignment, to a plurality of beam groups each having the same antenna beam combination, mapping beam group signals generated by the beam multiplexing, to at least one Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbol and time and frequency resources, generating OFDM symbol signals corresponding to one or more antenna beams by OFDM-converting the beam group signals according to the resource mapping, converting the OFDM symbol signals into analog Radio Frequency (RF) signals, and transmitting the analog RF signals via a plurality of antenna elements by carrying the analog RF signals on associated antenna beams by analog beamforming.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High frequency wave glass antenna for an automobile and window glass sheet for an automobile with the same
InactiveUS20080246673A1High antenna gainSimple structureAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesLoop antennasLoop shapingEngineering
A high frequency wave glass antenna for an automobile includes an antenna conductor adapted to be disposed in or on an automobile window glass sheet, the antenna conductor being formed in such a loop shape that a portion of the loop shape is cut out by a length to dispose a discontinuity, both ends of the discontinuity or portions of the antenna conductor close to the discontinuity serving as feeding points, and a portion of the antenna conductor with the discontinuity disposed therein or a portion of the antenna conductor close to the discontinuity having a conductor width of 8.0 to 40 mm.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
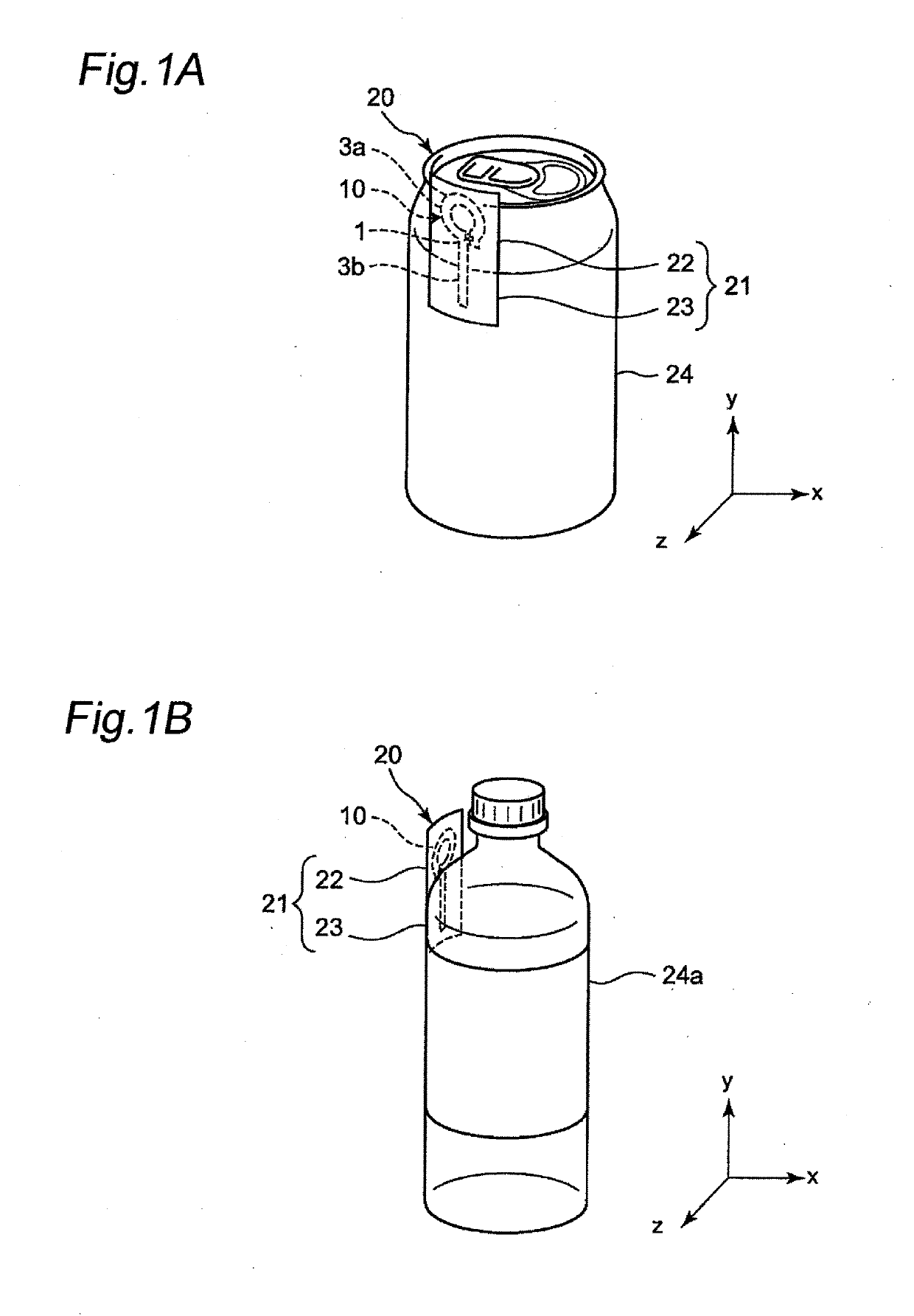
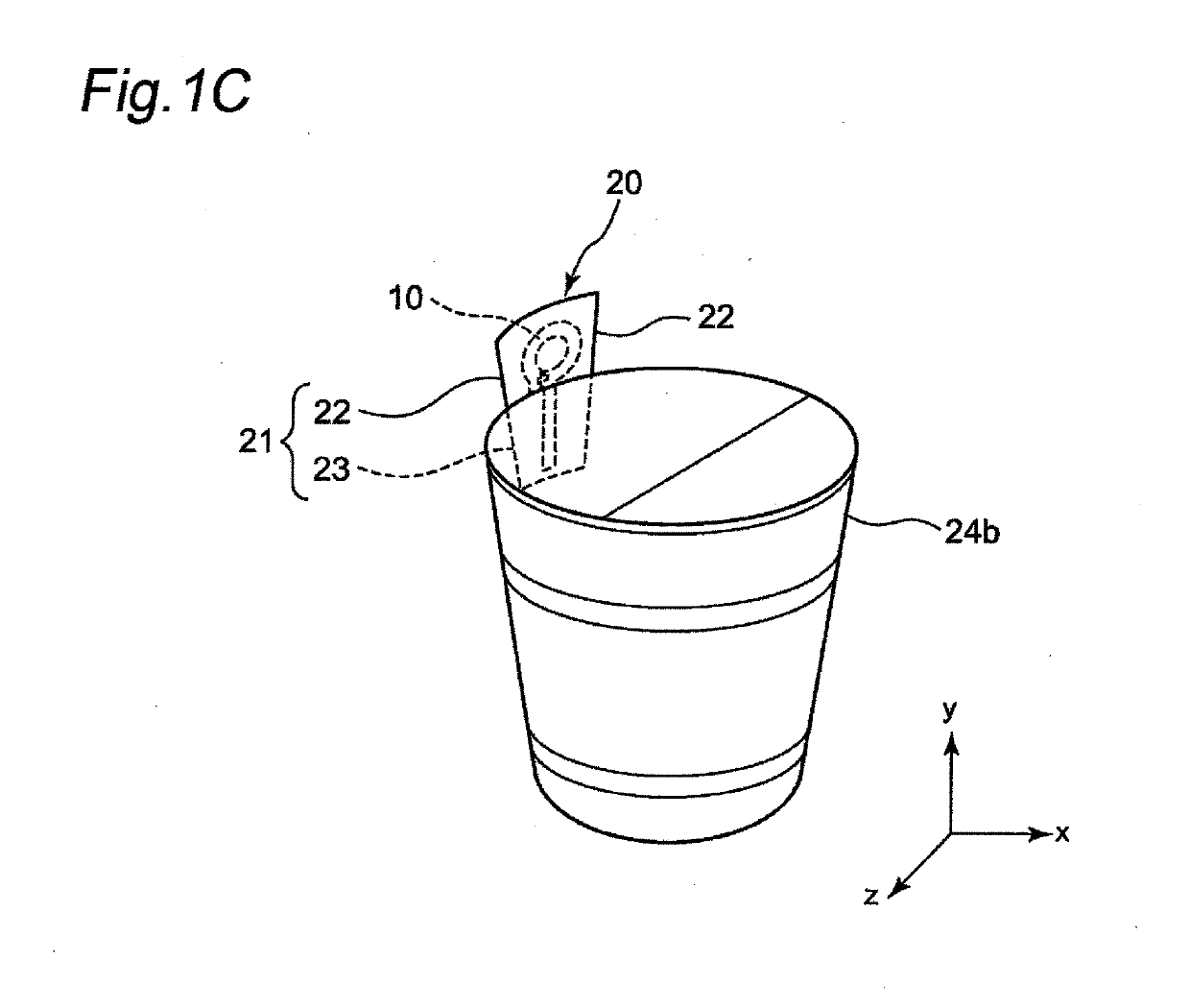
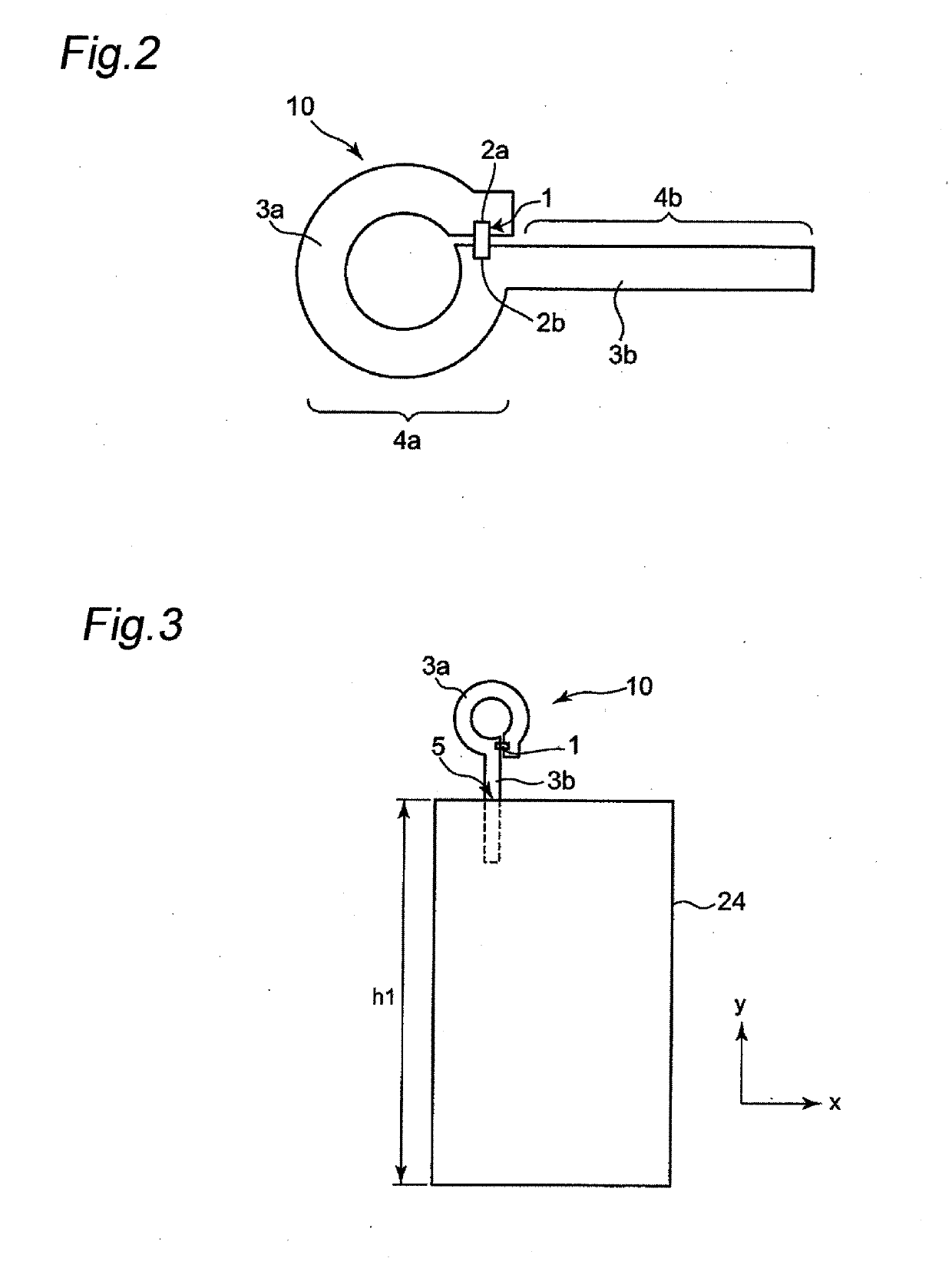
Attention tag for retail article and retail article having same attached thereto
ActiveUS20190130239A1High antenna gainStampsParticular environment based servicesElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
An attention tag for a retail article that includes a label having an adhesive region bonded to a retail article and a protruding region that protrudes from the retail article when the label is attached thereto. Moreover, an RFID tag is disposed on the label and includes an RFIC element and an antenna pattern including first and second antenna portions that are respectively connected to first and second ends of the RFIC element. Moreover, the first antenna portion is disposed in the protruding region of the label while the second antenna portion of the RFID tag is disposed in the adhesive region of the label at a position facing a portion of the retail article.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Radar apparatus and antenna apparatus
InactiveUS20130187808A1Prevent beam pattern distortionHigh antenna gainRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarBeam pattern
The present invention relates to radar and antenna technologies. More particularly, the present invention relates to an antenna apparatus and radar apparatus that have an antenna structure that enables a high antenna gain and a balanced beam pattern by preventing a distortion of a beam pattern caused by a coupling phenomenon between antenna arrays.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Radar device
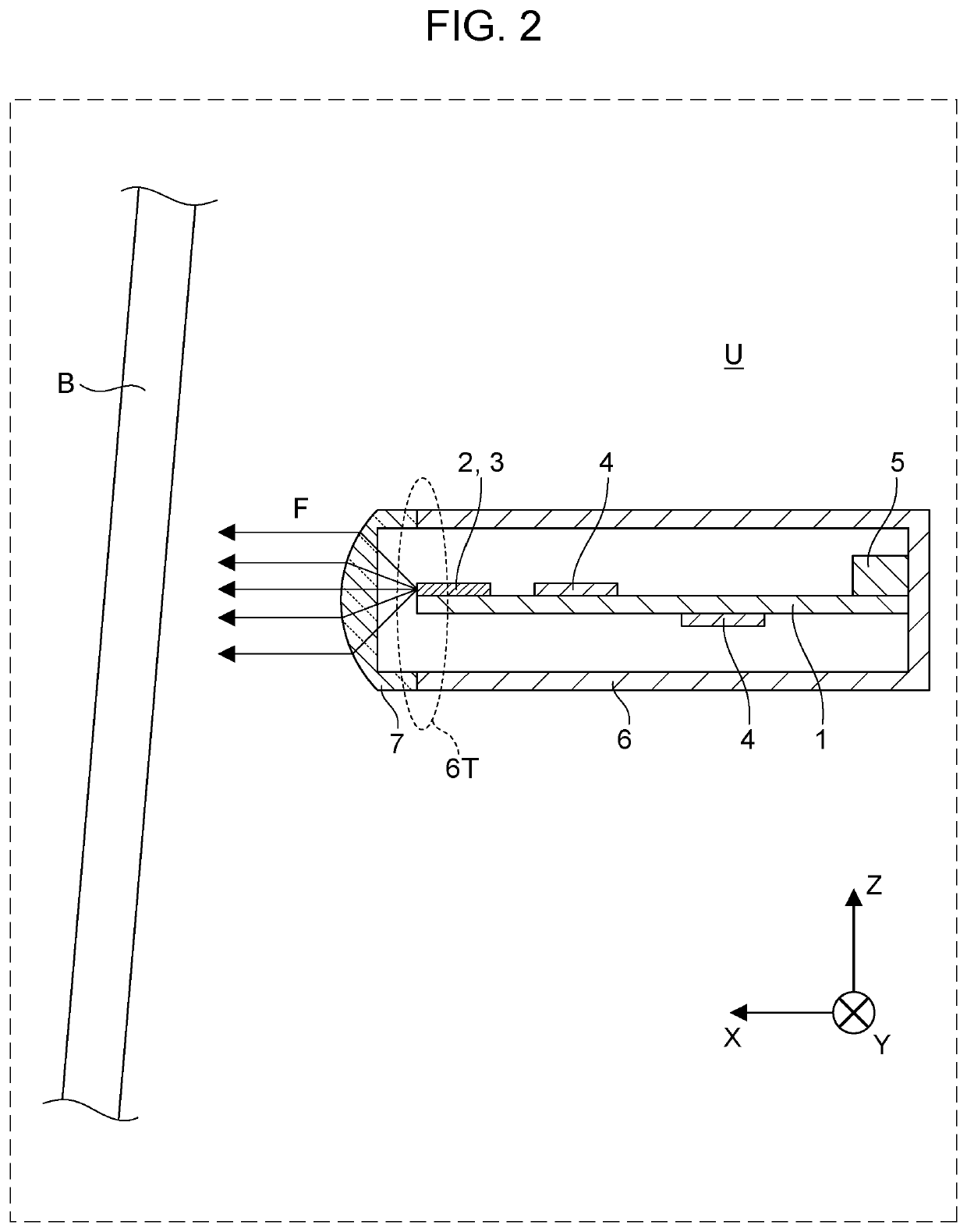
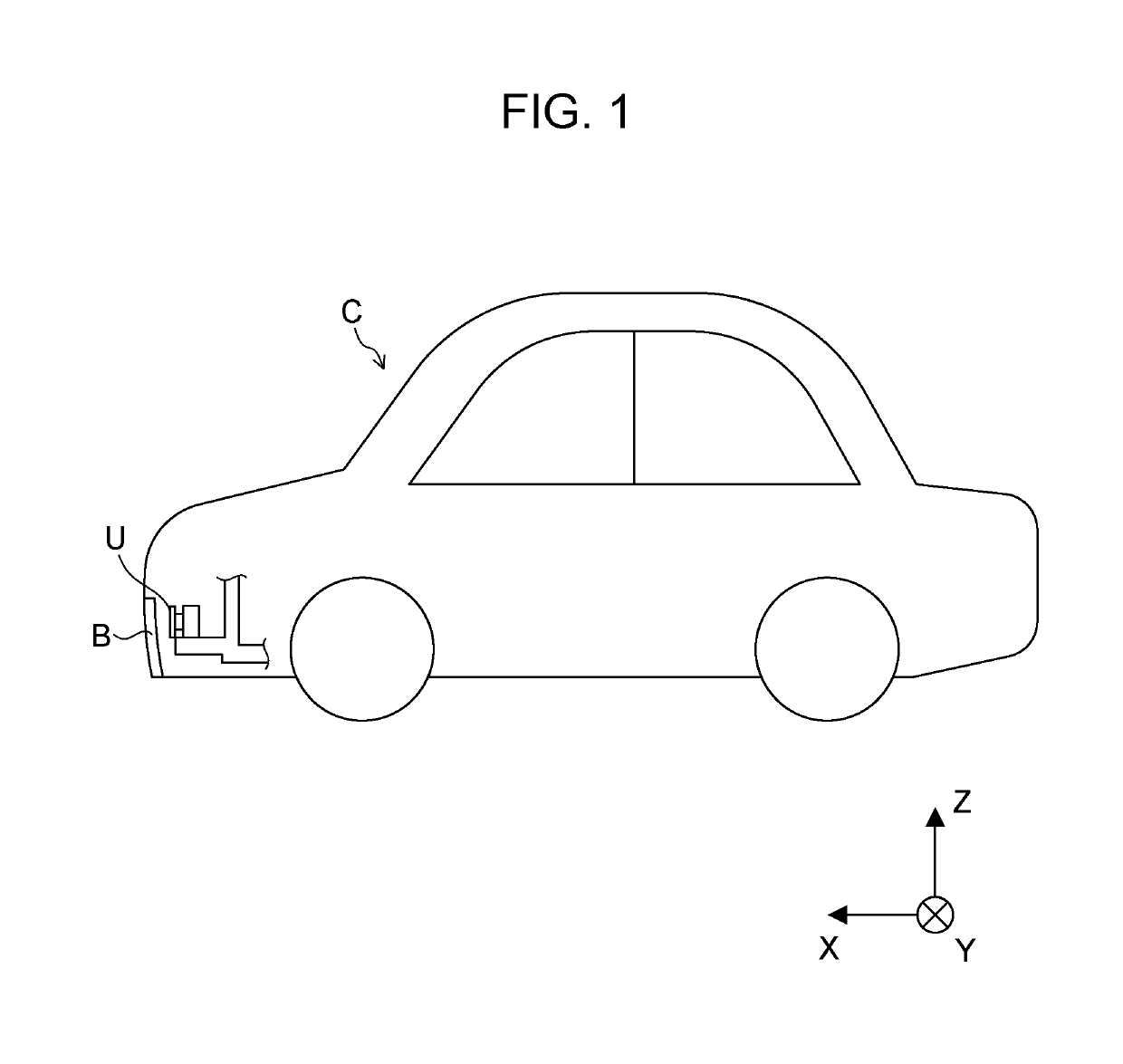
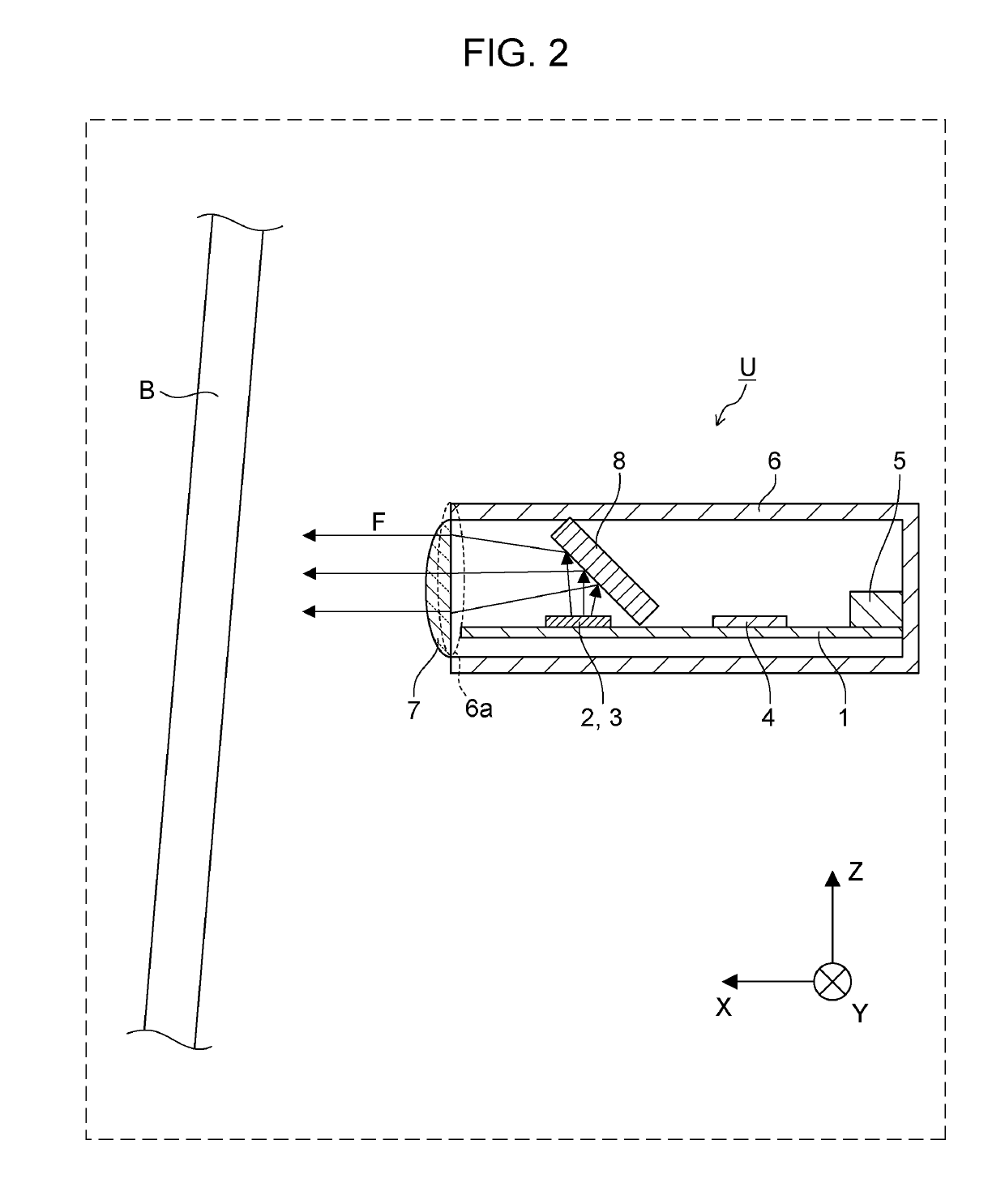
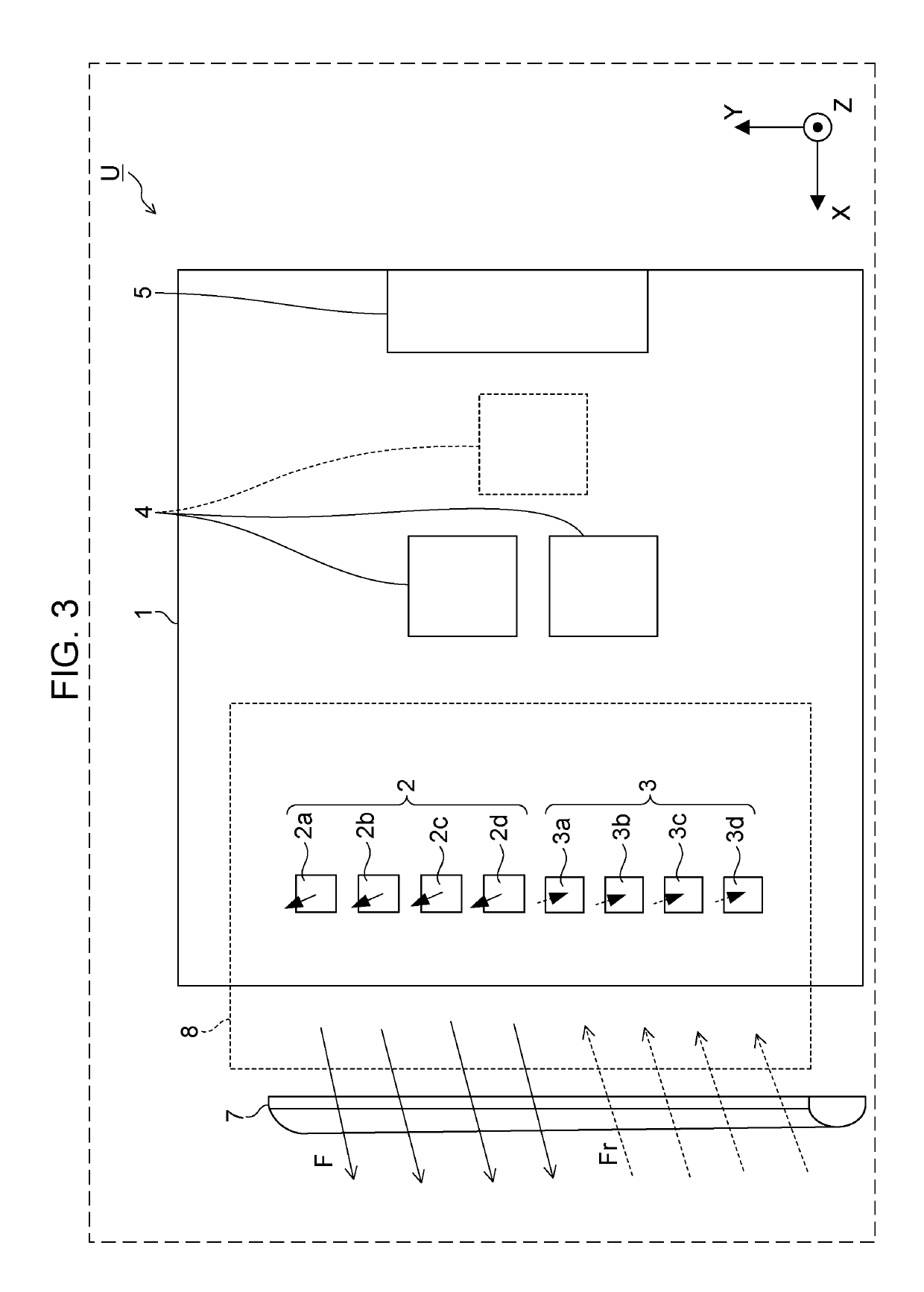
ActiveUS10985471B2Reduce spacingIncrease freedomPrinted circuit detailsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesTelecommunicationsElectromagnetic wave transmission
A radar device includes: a housing that includes an aperture in a front direction as a transmitting direction of an electromagnetic wave; a circuit board disposed in the housing such that a board surface extends along the front direction; an antenna unit that includes antenna elements being arrayed along a direction intersecting the front direction in a region on a side in the front direction of the circuit board, and that transmits the electromagnetic wave to the outside of the housing through the aperture and receives a reflected wave of the electromagnetic wave; and a dielectric lens that is disposed in the aperture of the housing to extend along a direction in which the antenna elements are arrayed and that has a semi-cylindrical shape or a parabolic-cylindrical shape projecting in the front direction.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Array antenna
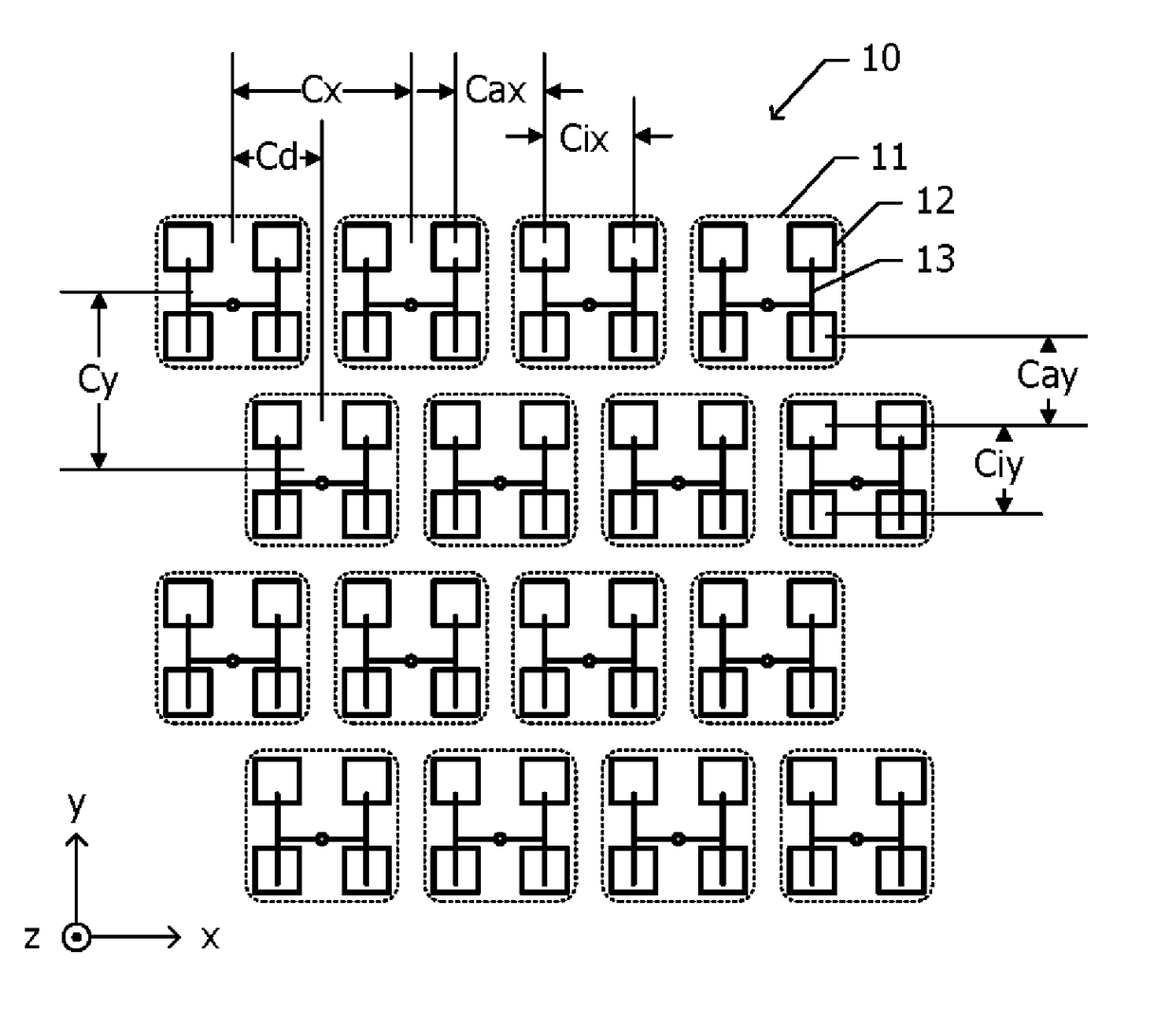
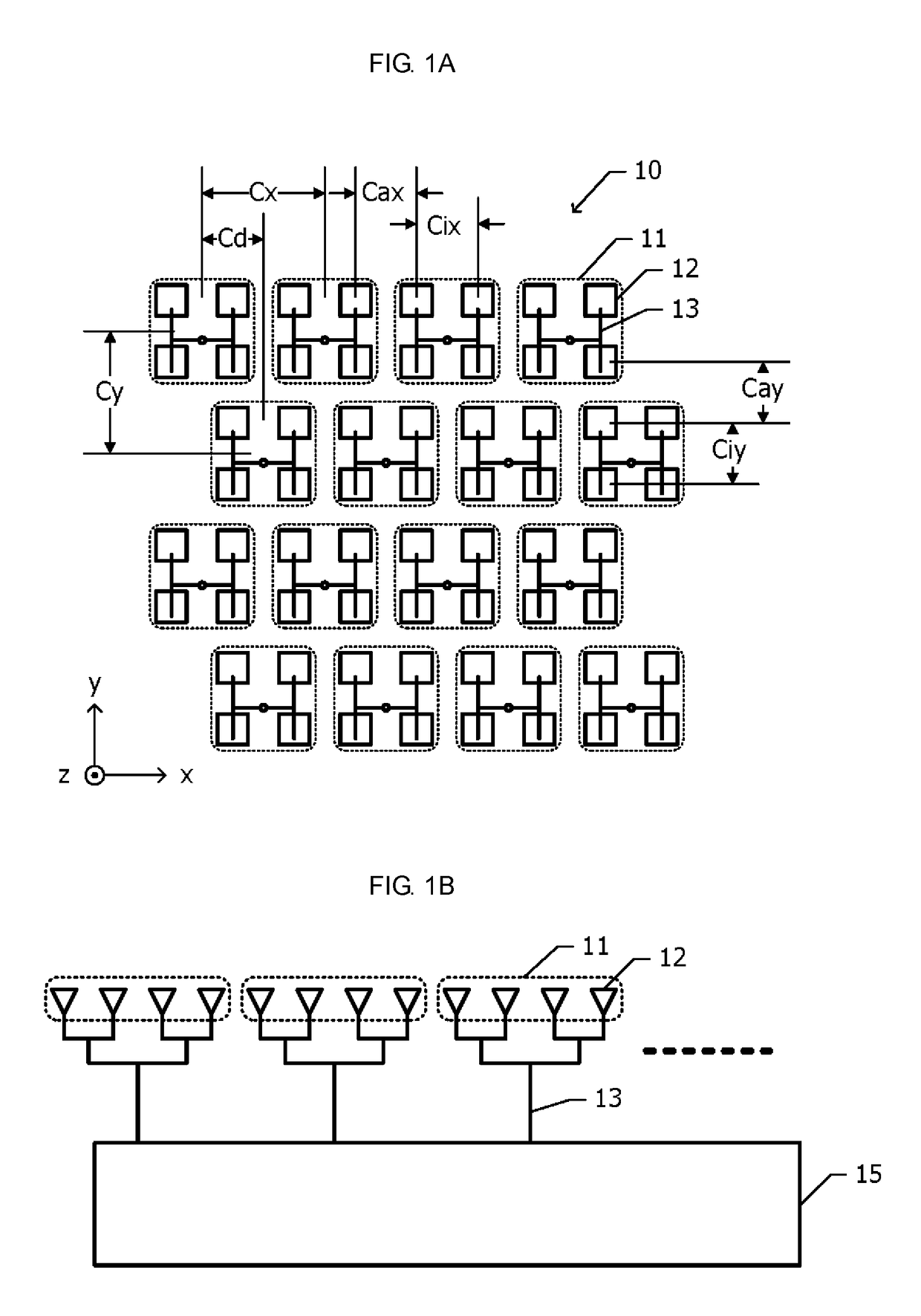
InactiveUS20180309210A1Reduce the numberHigh antenna gainParticular array feeding systemsIndividually energised antenna arraysRadiating elementElectric power
Provided is an array antenna in which a plurality of sub-arrays, which each include a plurality of radiating elements, are two-dimensionally arranged in a first direction and a second direction, which are perpendicular to each other. A plurality of power feeding lines individually feed power from a high-frequency input / output device to each of the plurality of sub-arrays. The plurality of sub-arrays are arranged along straight lines in the first direction, and are arranged in the second direction such that among two sub-arrays that are adjacent to each other in the second direction, one sub-array is shifted in the first direction with respect to the other sub-array.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Modular solid-state millimeter wave (MMW) RF power source
ActiveUS8107894B2Improved thermal managementIncrease output powerAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesModular arraysAudio power amplifierAntenna gain
A modular solid-state MMW power source based on a topology of the lens array amplifier provides both the flexibility to scale output power and effective thermal management. The modular power source includes a single submodule that uses one or more power dividers and one or more solid-state amplification stages to divide and amplify an RF input signal into R amplified RF signals. The submodule is mounted (suitably in the X-Y plane) on the surface of a heat sink, suitably coupled to a cold backplane, to remove heat. R 1:N low loss power dividers route the amplified RF signals to R*N radiating elements. Each of the 1:N power dividers suitably reside in the X-Z plane and are stacked in the Y direction to provide a planar output of the R*N radiating elements in the Y-Z plane. Placement of the amplifier chips on the single submodule decouples the number of amplifier chips, hence output power, from the number of radiating elements. Placement of the amplifier chips away from the radiating face provides a short path with large thermal cross-section through the heat sink to the backplane to remove heat. The topology can produce high output power combined with a high antenna gain to produce large power-aperture products previously only achievable with a Gyrotron. As amplifier chips become more powerful, the topology can be adapted to use fewer chips.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Radar device
InactiveUS20190165483A1Reduce spacingIncrease freedomPrinted circuit detailsPrinted circuit aspectsRadarElectromagnetic electron wave
A radar device includes: an antenna unit including antenna elements arrayed along a direction intersecting a front direction in a circuit board, transmitting an electromagnetic wave upward of a board surface of the circuit board, and receiving a reflected wave of the electromagnetic wave; a reflection unit supported above the board surface of the circuit board in a housing, reflecting the electromagnetic wave transmitted from the antenna unit to change a traveling direction of the electromagnetic wave to the front direction, and reflecting the reflected wave from the front direction to change a traveling direction of the reflected wave to a direction toward the antenna unit; and a dielectric lens disposed in an aperture of the housing to extend along a direction in which the antenna elements are arrayed, and having a semi-cylindrical shape or a parabolic-cylindrical shape projecting in the front direction.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
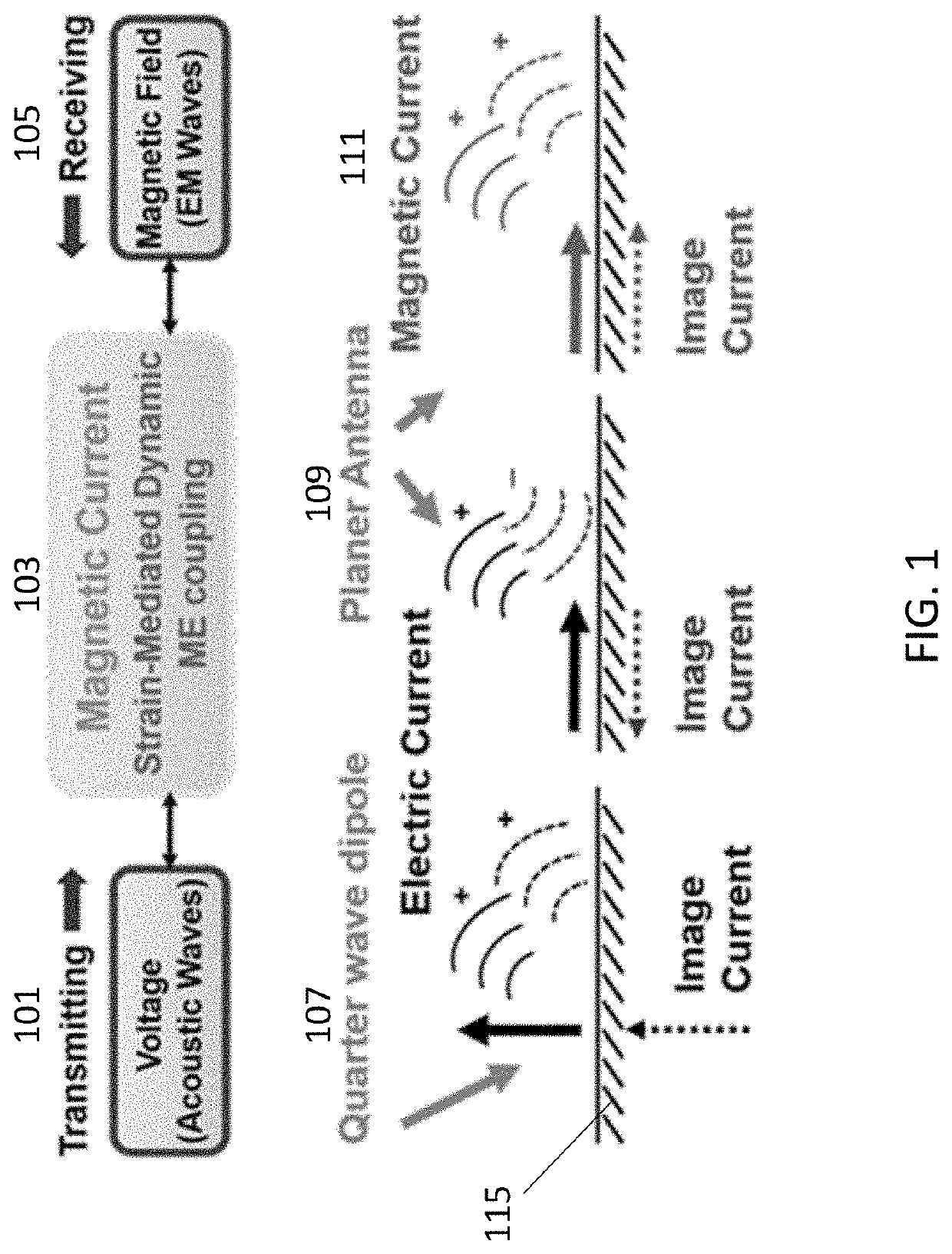
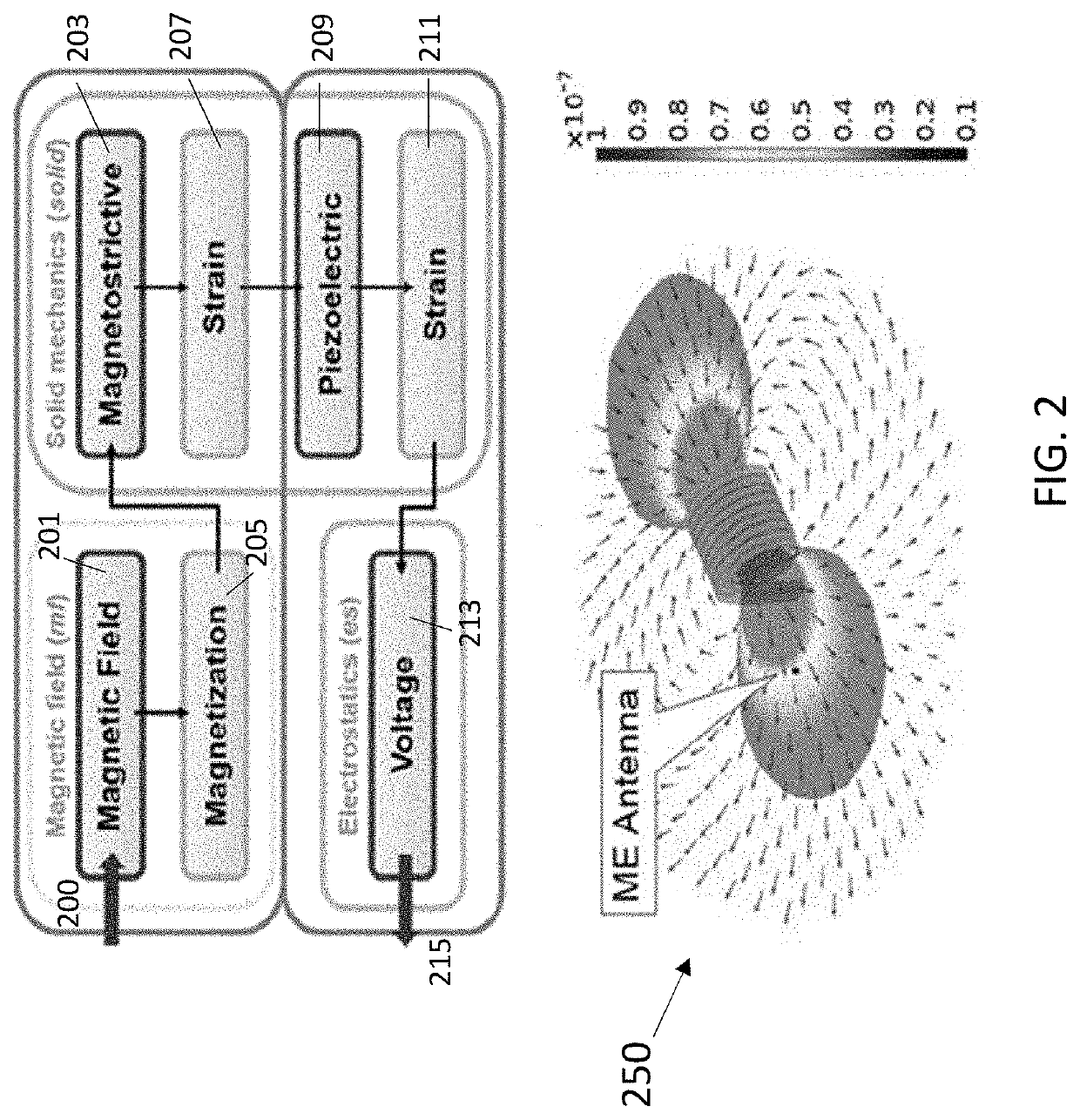
Magnetoelectric Antenna Arrays
PendingUS20220038074A1Relatively large bandwidthStrong ground plant immunityAntenna arraysImpedence networksElectrical conductorSoftware engineering
Two or more ME resonators are connected in series and in parallel generating a high sensitive, energy efficient and broadband miniature antenna and other conductor devices.
Owner:NIAN XIANG SUN +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com