Patents
Literature
41results about How to "None provide any indication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Social network-based internet search engine
InactiveUS20060235873A1Promote resultsGreat likelihoodDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsInternet contentInternet search engines
Filtering Internet content includes receiving a search query message comprising a search query to an Internet search engine. Data is received from the Internet search engine, responsive to the search query message. Filtering of the data produces a data subset. The filter selects data for inclusion in the data subset based upon occurrence of the data in a database. The database includes content selected for inclusion by designated users. The data subset is displayed in a browser.
Owner:JOOKSTER NETWORKS
Social network-based internet search engine
InactiveUS20050091202A1Great likelihoodFunction increaseDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsInternet contentInternet search engines
Filtering Internet content includes receiving a search query message comprising a search query to an Internet search engine. Data is received from the Internet search engine, responsive to the search query message. Filtering of the data produces a data subset. The filter selects data for inclusion in the data subset based upon occurrence of the data in a database. The database includes content selected for inclusion by designated users. The data subset is displayed in a browser.
Owner:THOMAS KAPENDA J
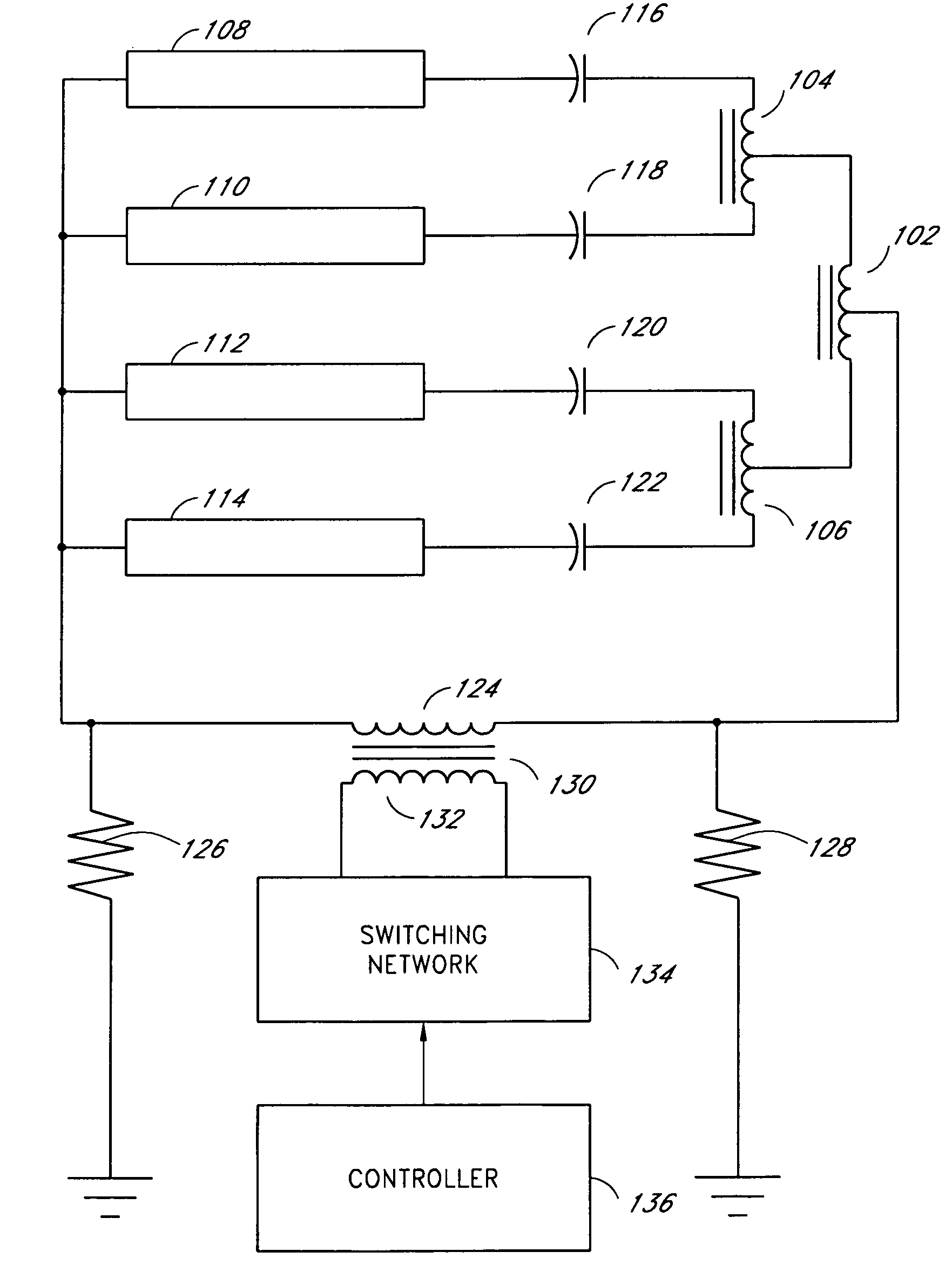
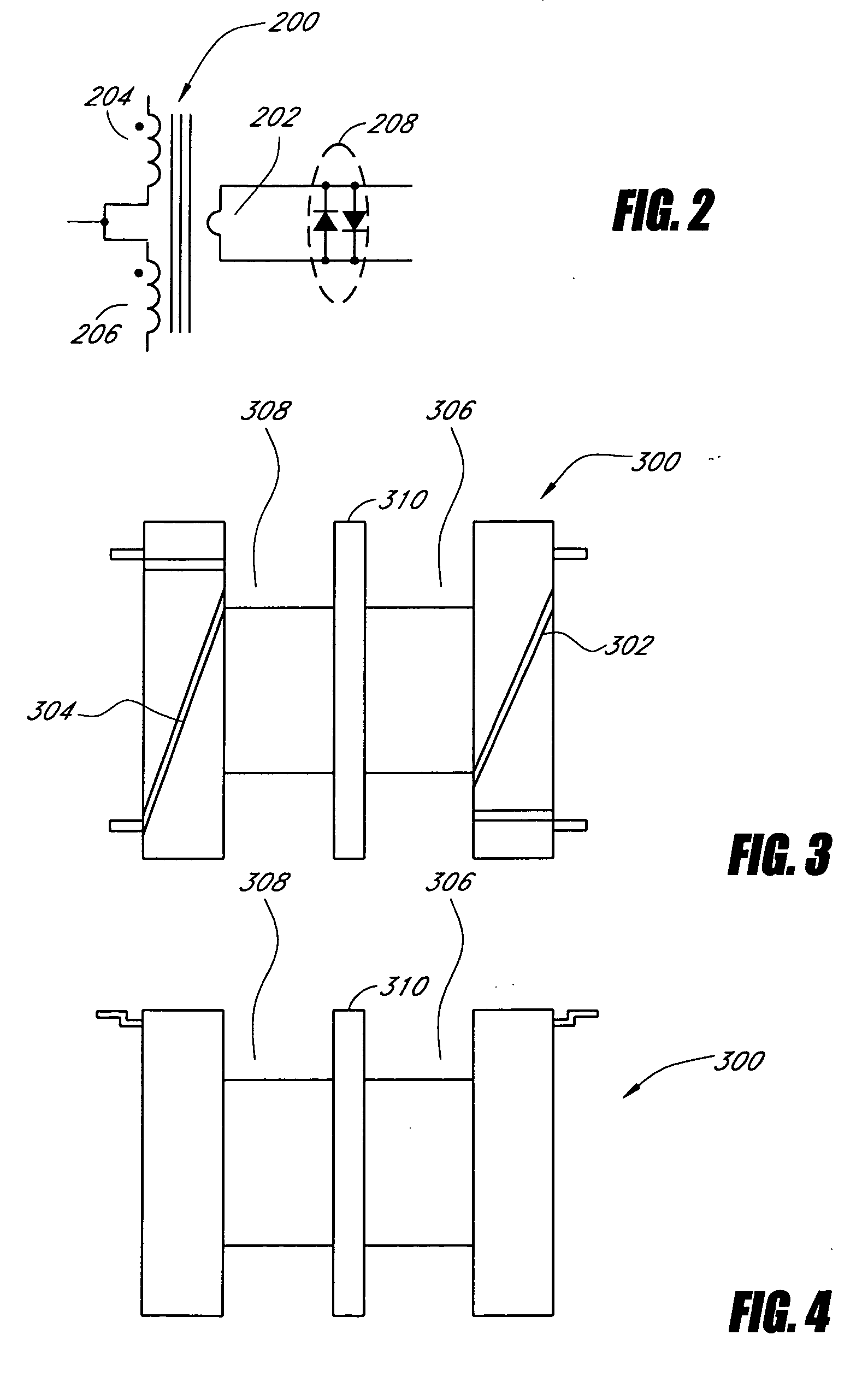
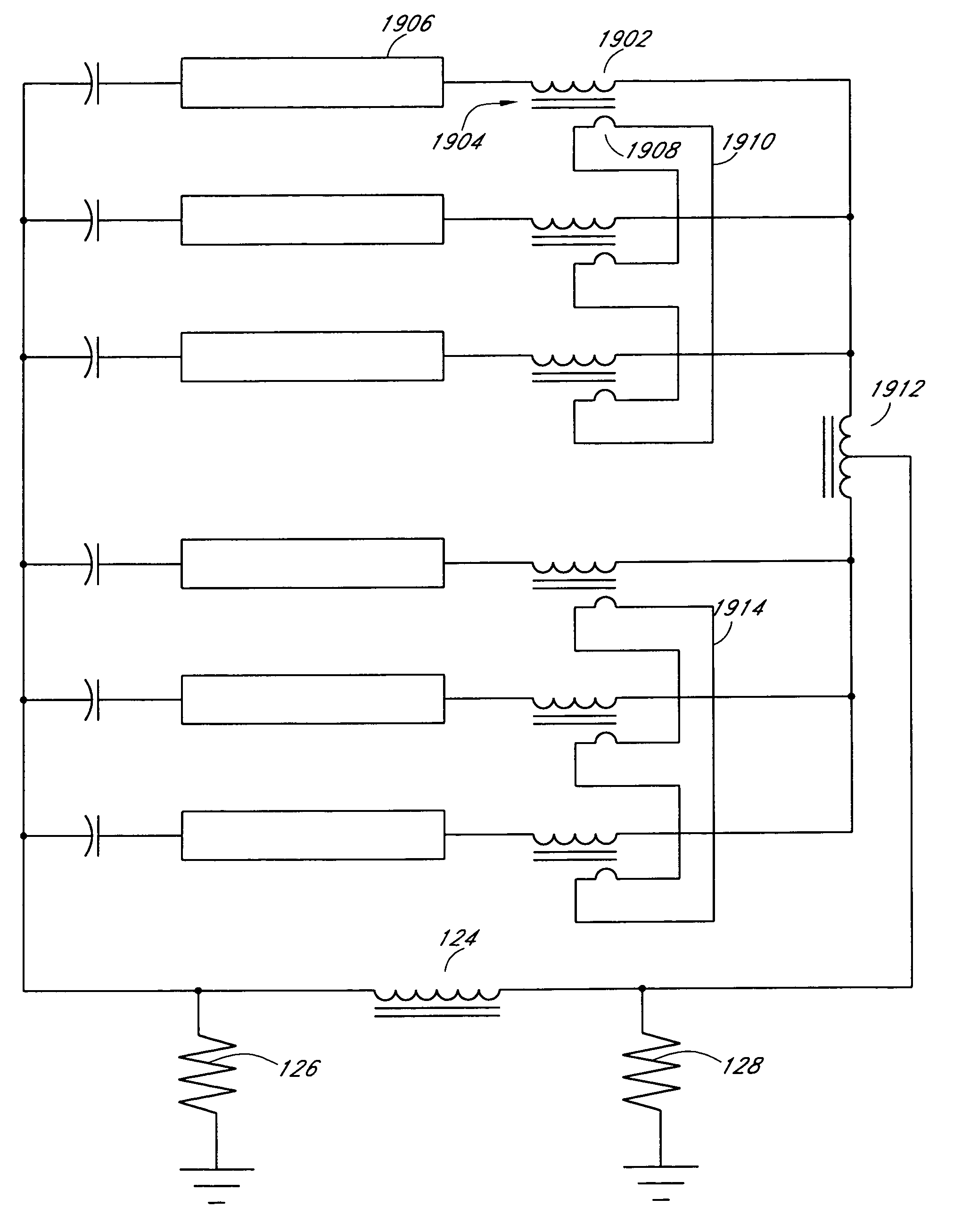
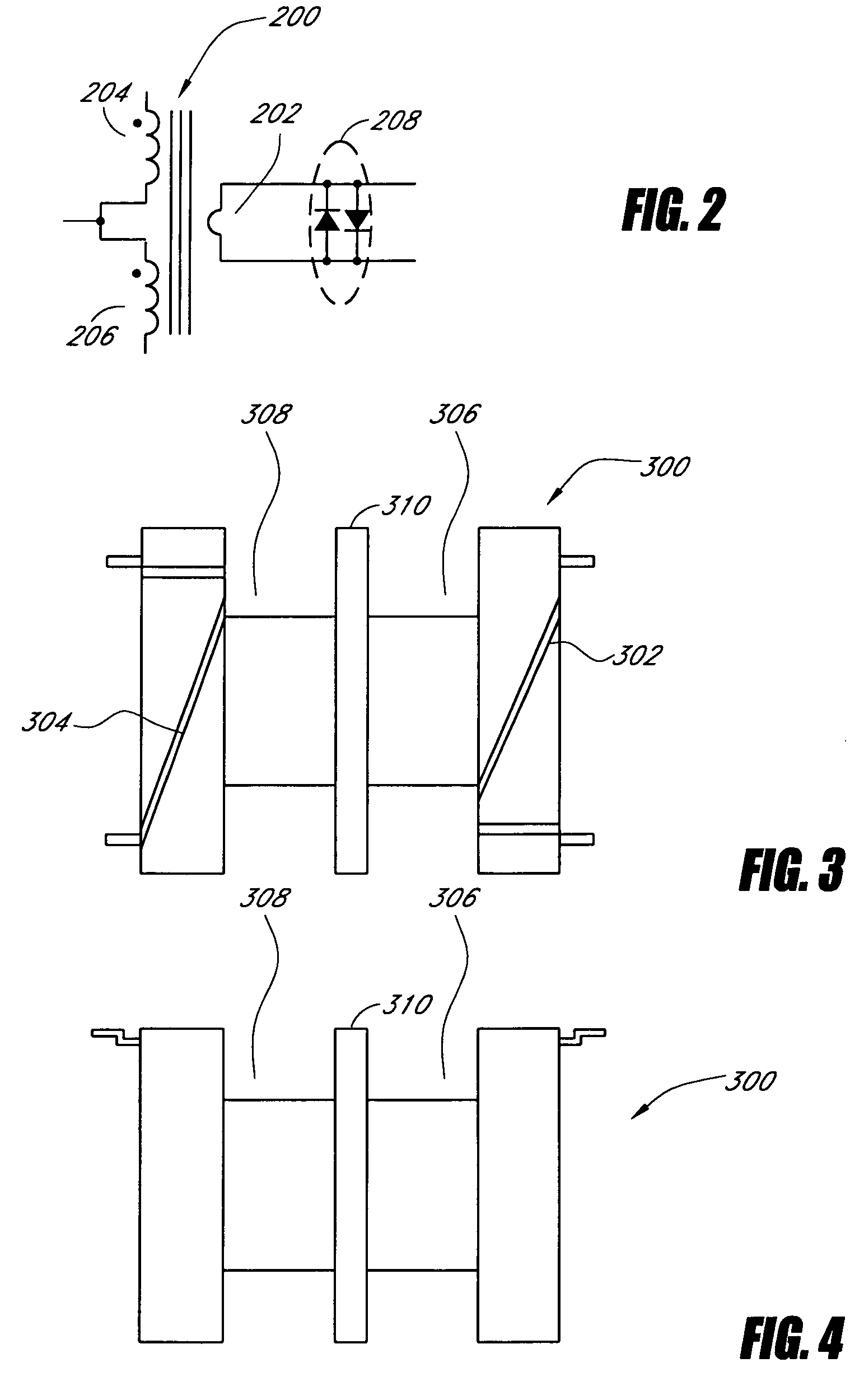
Systems and methods for a transformer configuration with a tree topology for current balancing in gas discharge lamps
InactiveUS20050093482A1None provide any indicationImprove balanceEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectric light circuit arrangementPower inverterGas-discharge lamp
An apparatus and methods for balancing current in multiple negative impedance gas discharge lamp loads. Embodiments advantageously include balancing transformer configurations that are relatively cost-effective, reliable, efficient, and good performing. Embodiments include configurations that are applicable to any number of gas discharge tubes, such as cold cathode fluorescent lamps. The balancing transformer configuration techniques permit a relatively small number of power inverters, such as one power inverter, to power multiple lamps in parallel. One embodiment of a balancing transformer includes a safety winding which can be used to protect the balancing transformer in the event of a lamp failure and can be used to provide an indication of a failed lamp.
Owner:MICROSEMI CORP
Secure video camera device
ActiveUS20130222609A1Efficient and secure switchingExtend activation timeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensComputer hardware
A secure video camera device for reducing the risk of visual and audio eavesdropping has a video camera and an electromechanical shutter behind a transparent cover in a secured enclosure. The shutter optically obscures the camera lens when the device is in secure state. A visual indicator indicates when the device is in operational state. A switch controllable by the user, select the state of the device by concurrently disabling the camera turning off the visual indicator in a secure state; and setting said device in an operational state by concurrently enabling the camera and turning on said lighted indicator. The device has a built in, or auxiliary microphone, and audio outputs which are disabled in secure state of the device. The device is tempered proof by an anti-tempering circuitry.
Owner:HIGH SEC LABS LTD
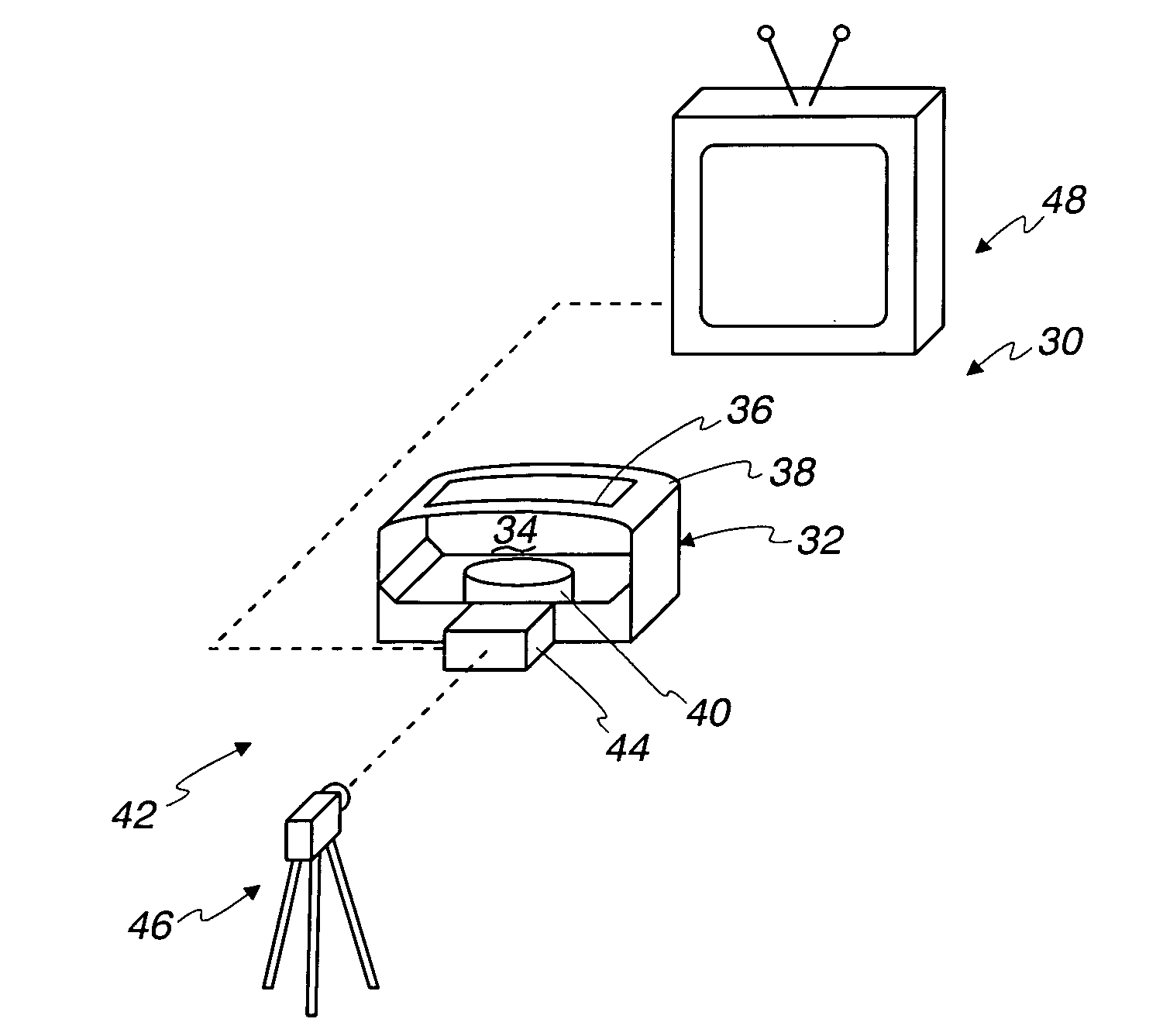
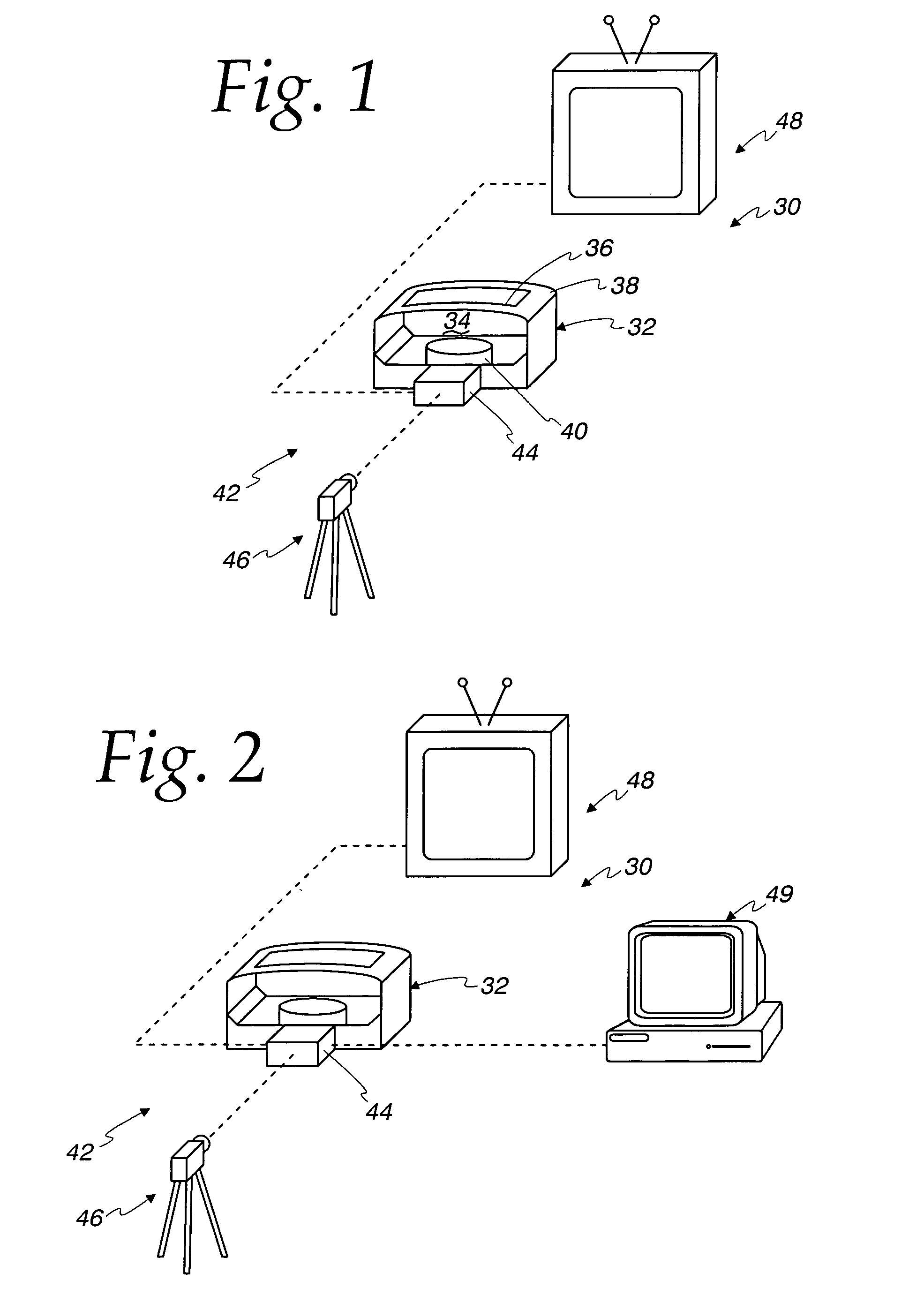
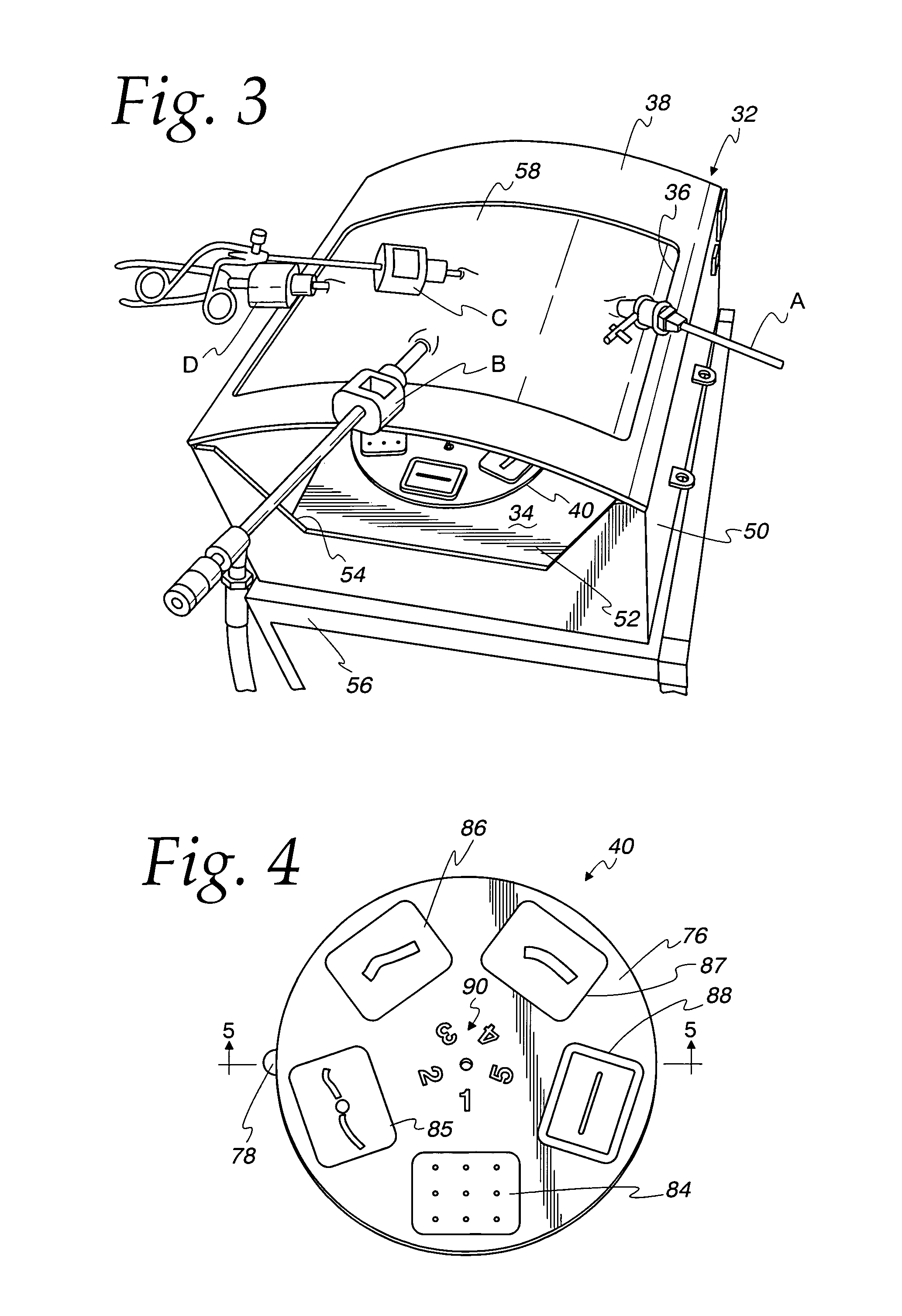
Medical training apparatus
InactiveUS7997903B2None provide any indicationEducational modelsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationControl cell
A medical training apparatus comprises a frame defining a work space simulating a body cavity and having an access opening to allow introduction of a medical instrument to the working space from externally of the working space. A sensor platform is rotationally mounted in the working space for rotating the platform to select angular positions for performing a series of simulated medical procedures. A plurality of modules are mounted around a perimeter of the platform. Each module comprises a different model upon which an associated medical procedure can be performed with a medical instrument. A plurality of sensors are each operatively associated with one of the modules for sensing progress of the associated medical procedure. A control unit is coupled to the sensors for monitoring progress of the medical procedures and providing an indication of status of the medical procedures.
Owner:REALSIM SYST
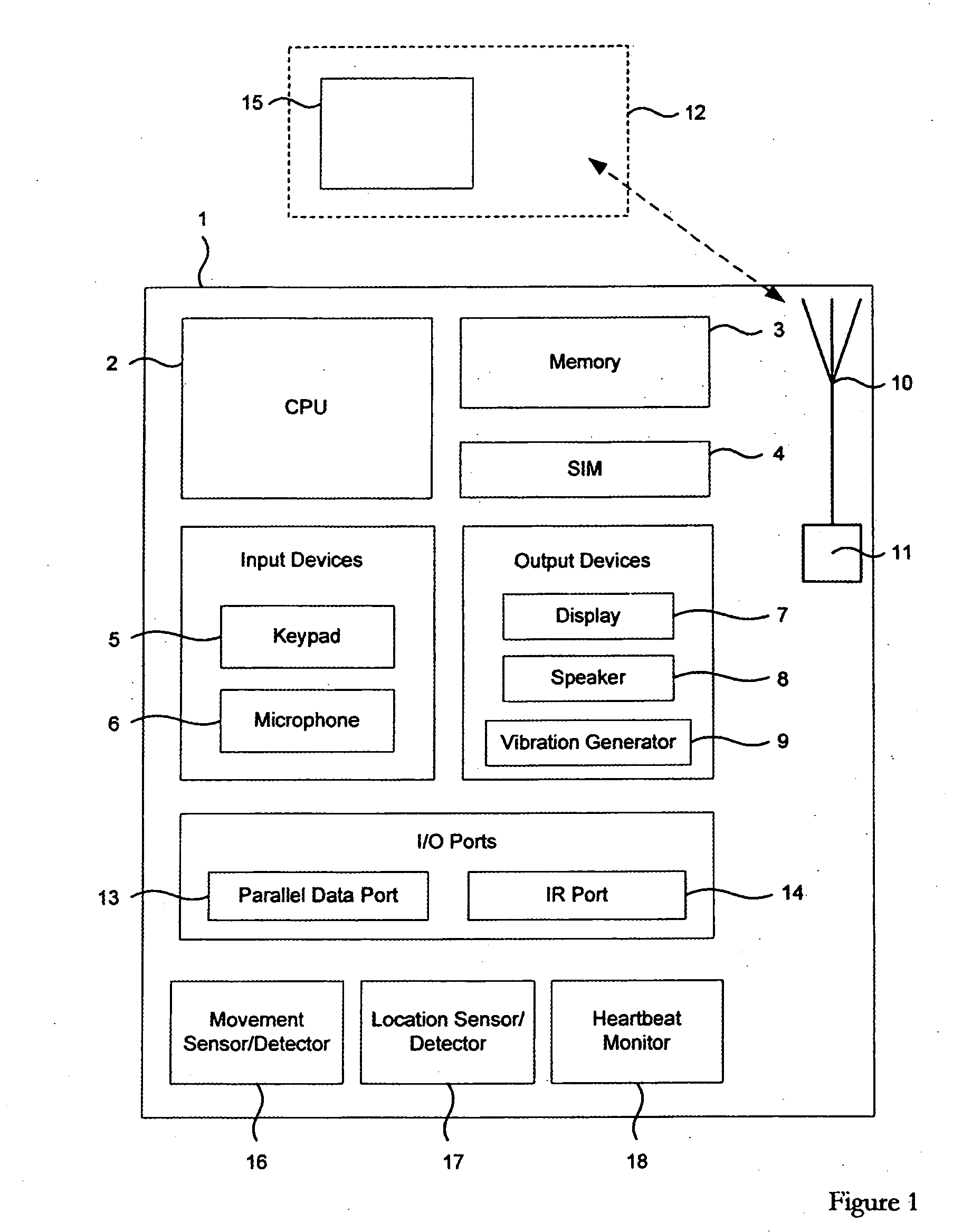
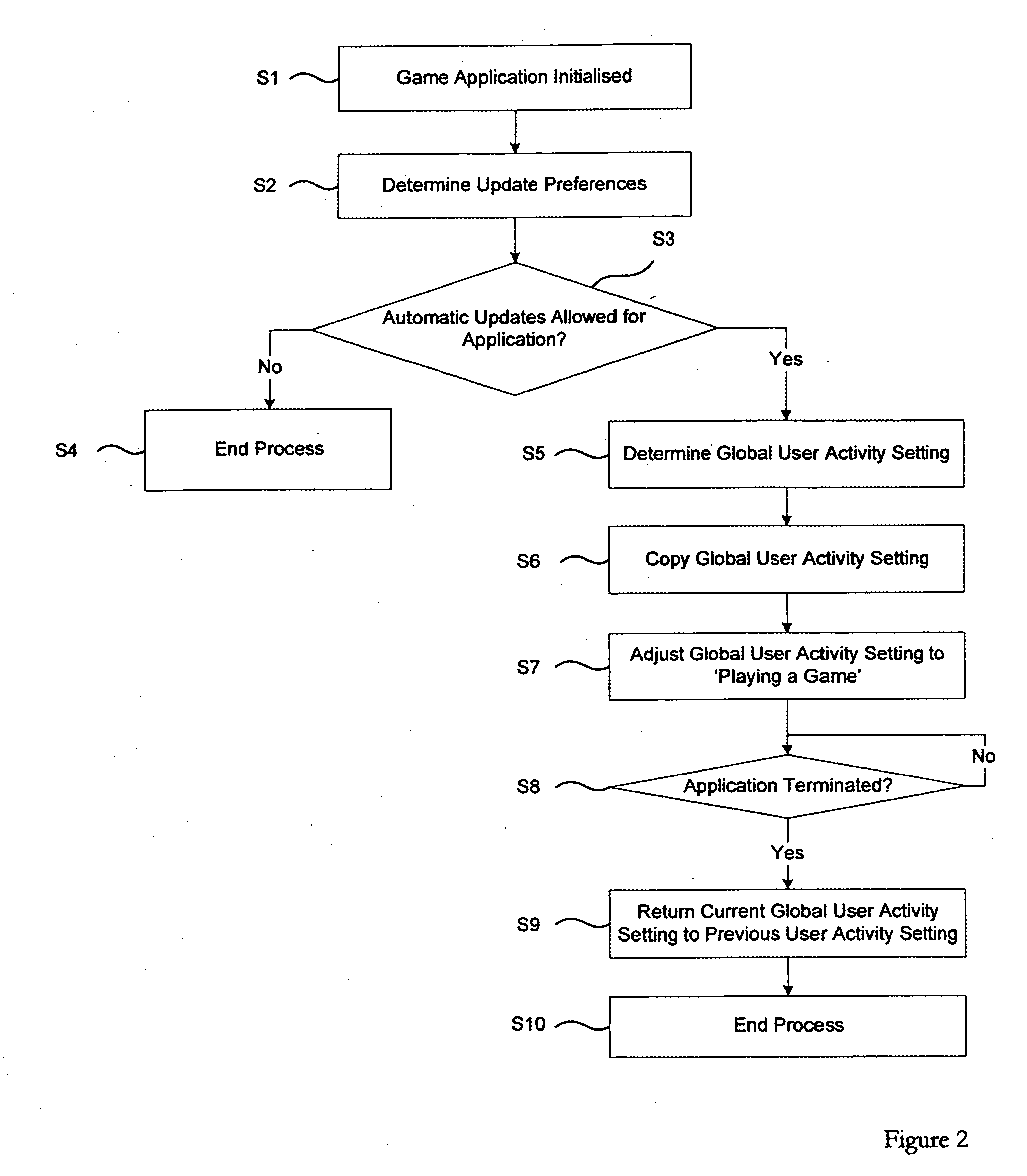
Mobile device, a network element and a method of adjusting a setting associated with a mobile device
InactiveUS20060205394A1Reduce riskIncrease the importanceUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsMobile deviceInstant messaging
User activity settings and other settings such as sound and vibration settings of applications that run on mobile devices are automatically adjusted. In one example, the mobile device includes a processor configured to adjust a user activity setting automatically according to an activity being carried out by a user. The activity of the user is determined by detected changes such as changes in the location or movement of the mobile device. The user activity setting can be associated with an application such as an instant messaging (IM) application stored in the memory of the mobile device.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
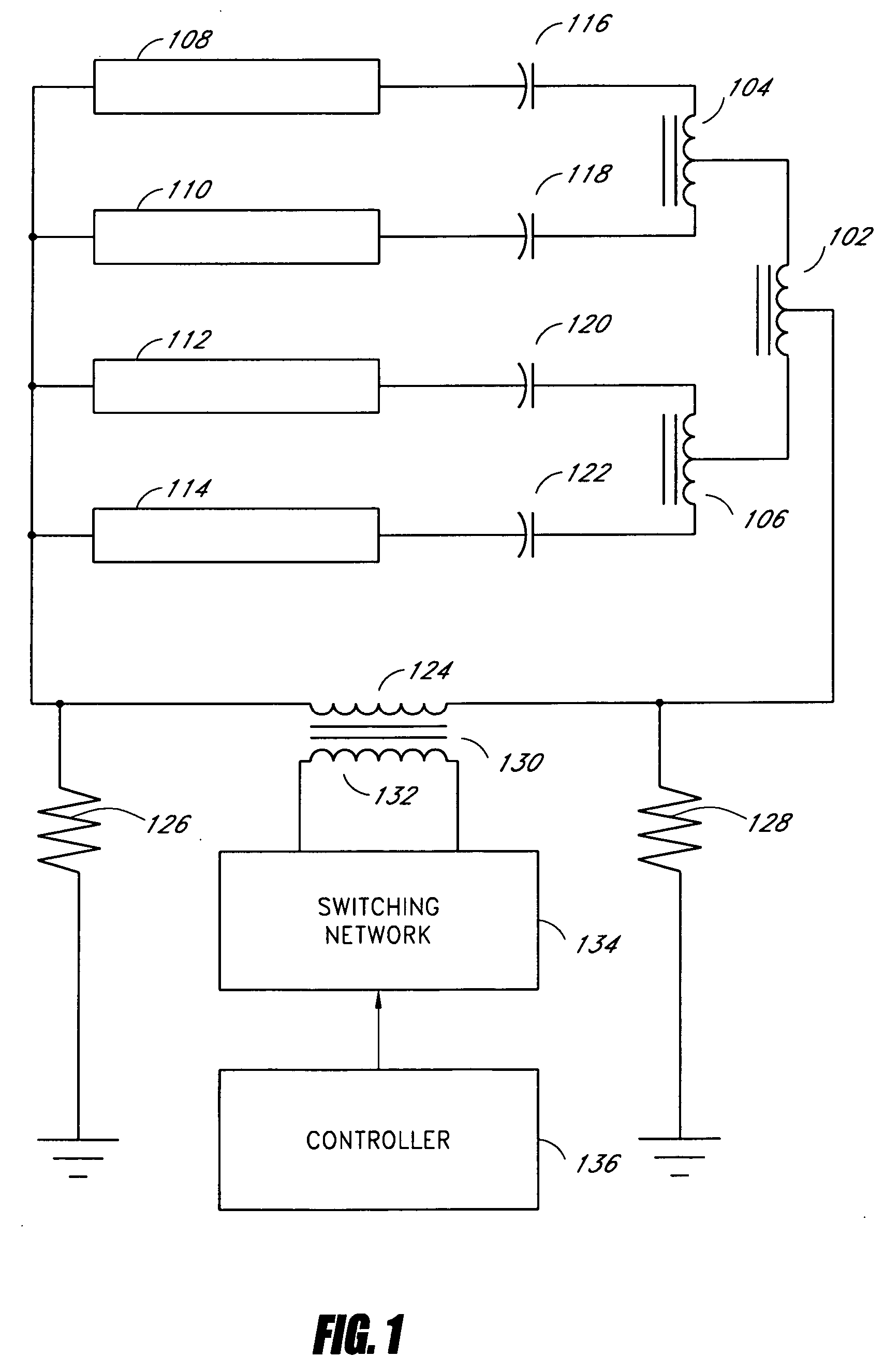
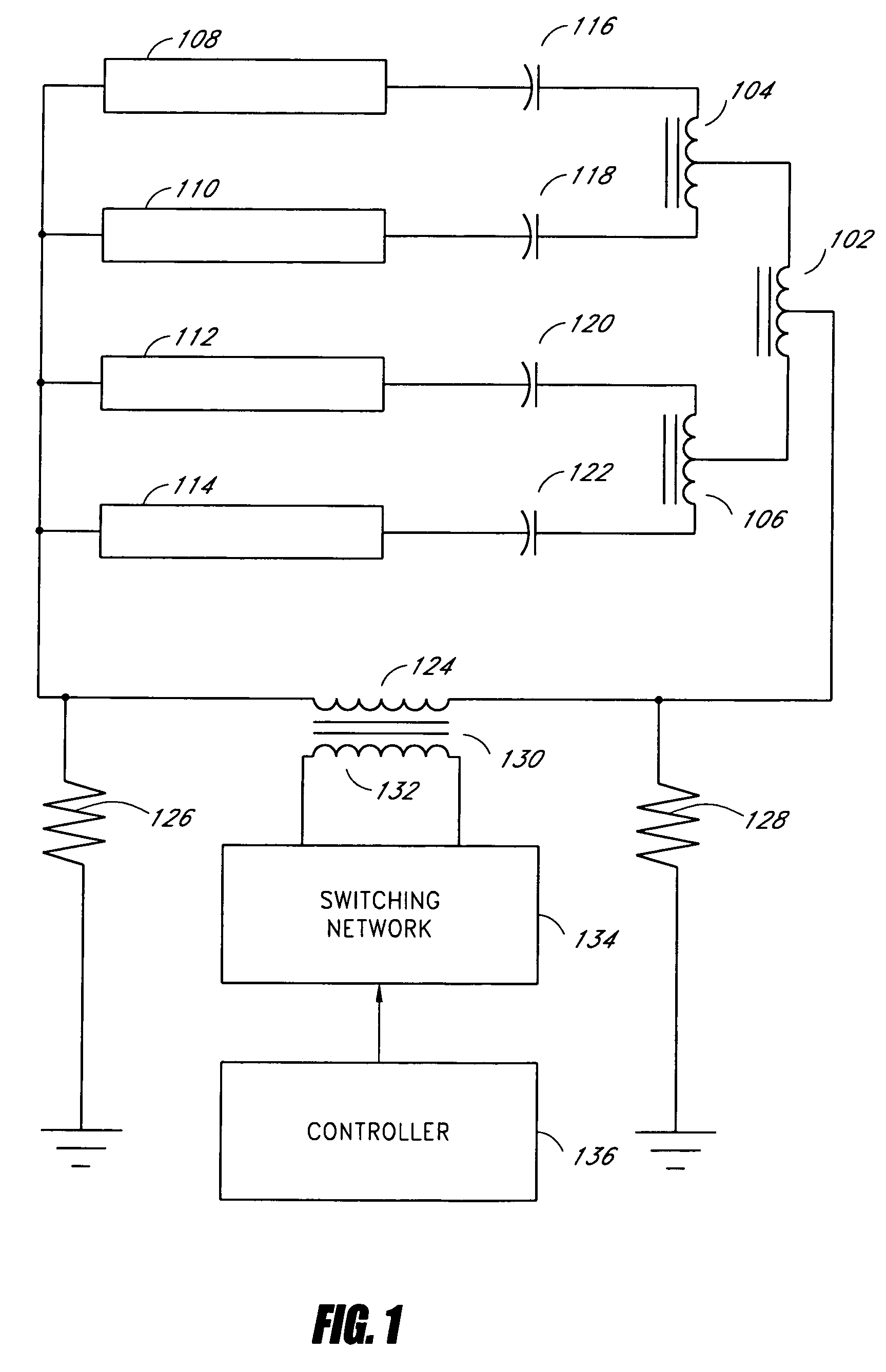
Systems and methods for a transformer configuration for driving multiple gas discharge tubes in parallel
InactiveUS7141933B2None provide any indicationImprove balanceElectric light circuit arrangementSolid cathode detailsGas-discharge lampPower inverter
Owner:MICROSEMI CORP
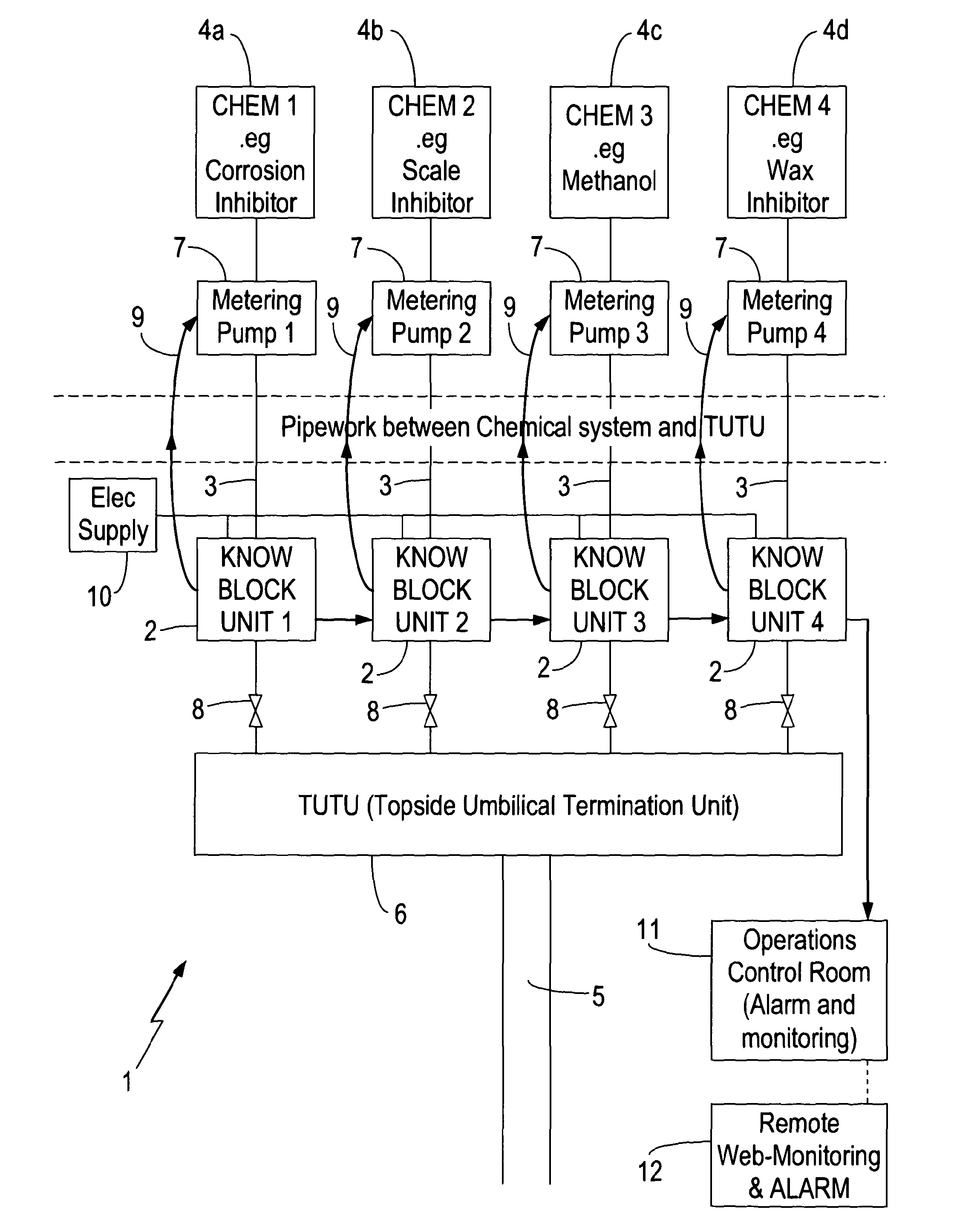
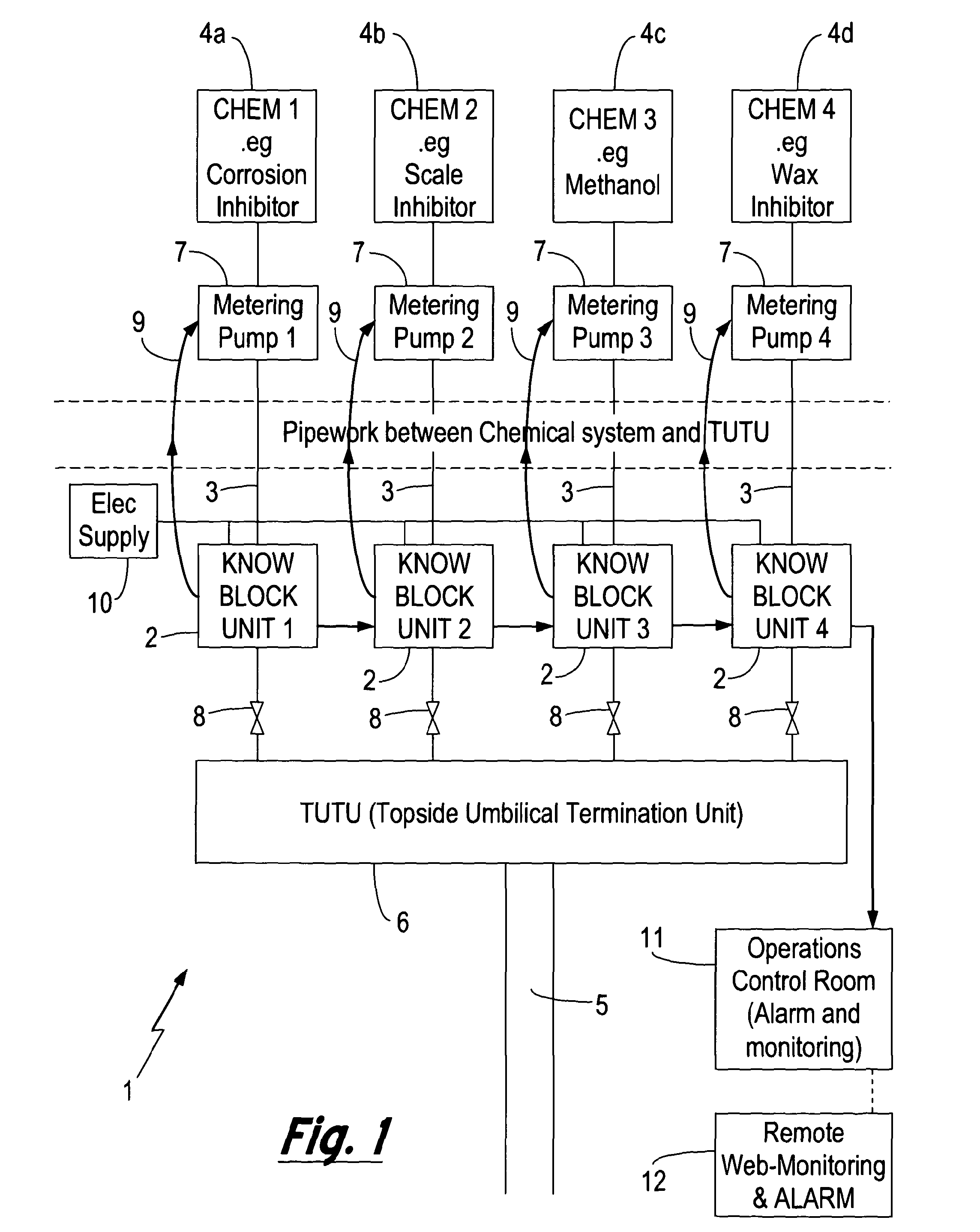
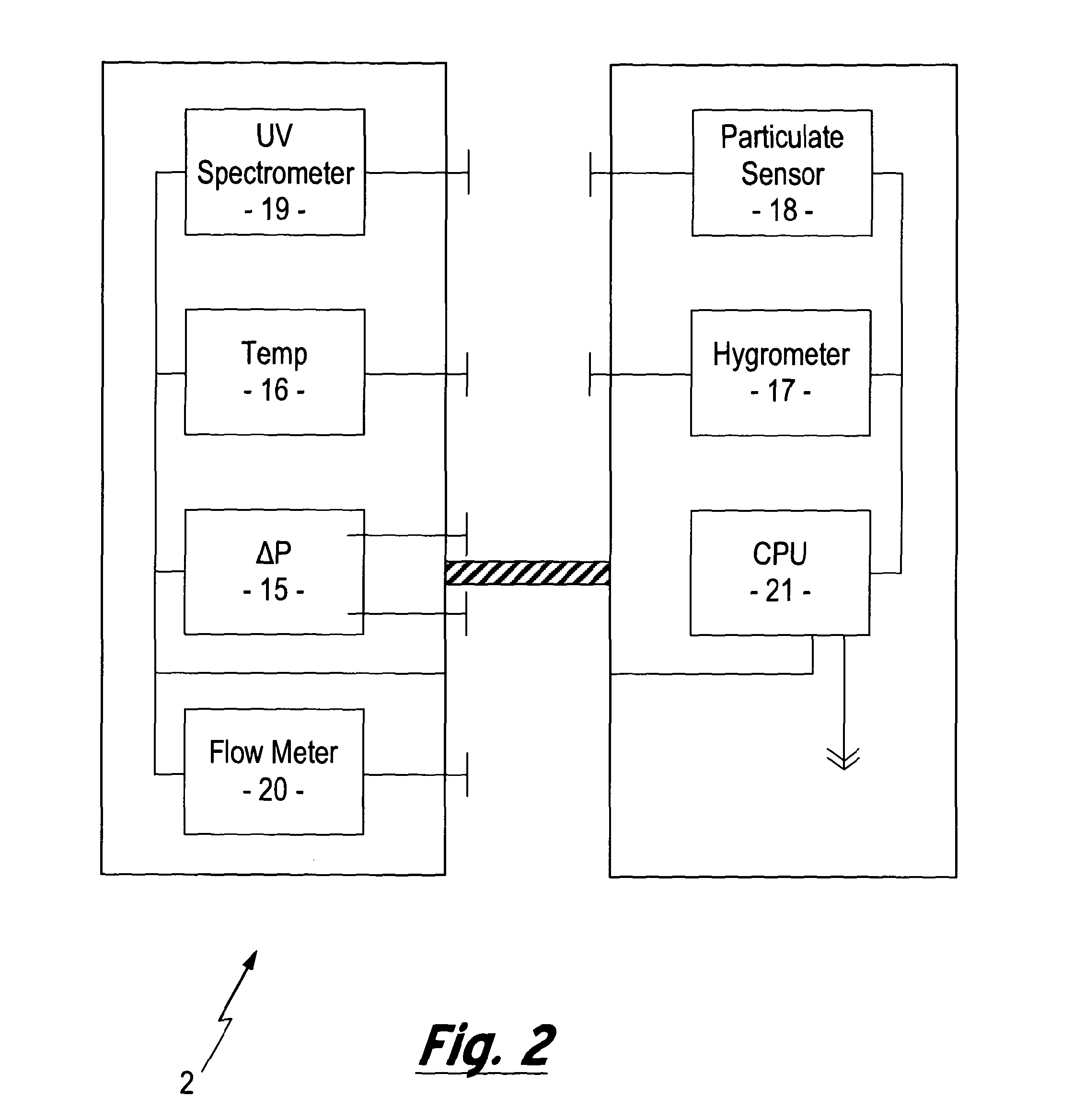
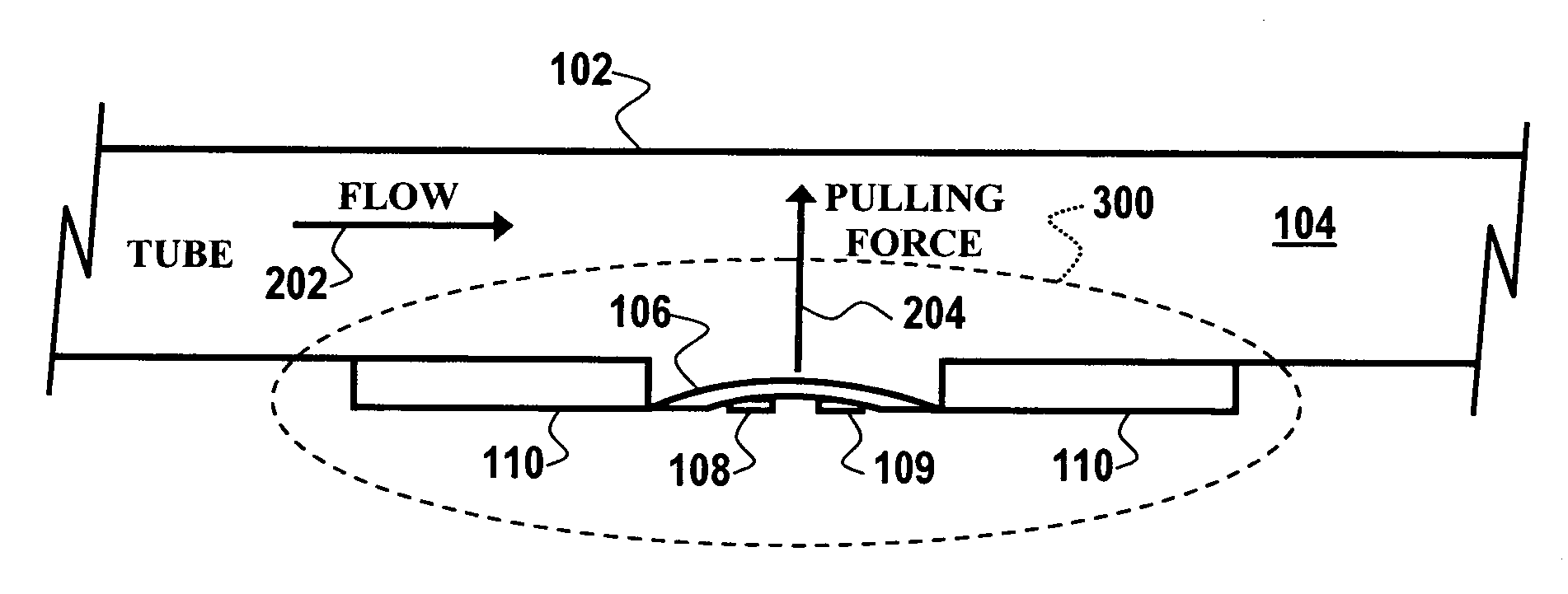
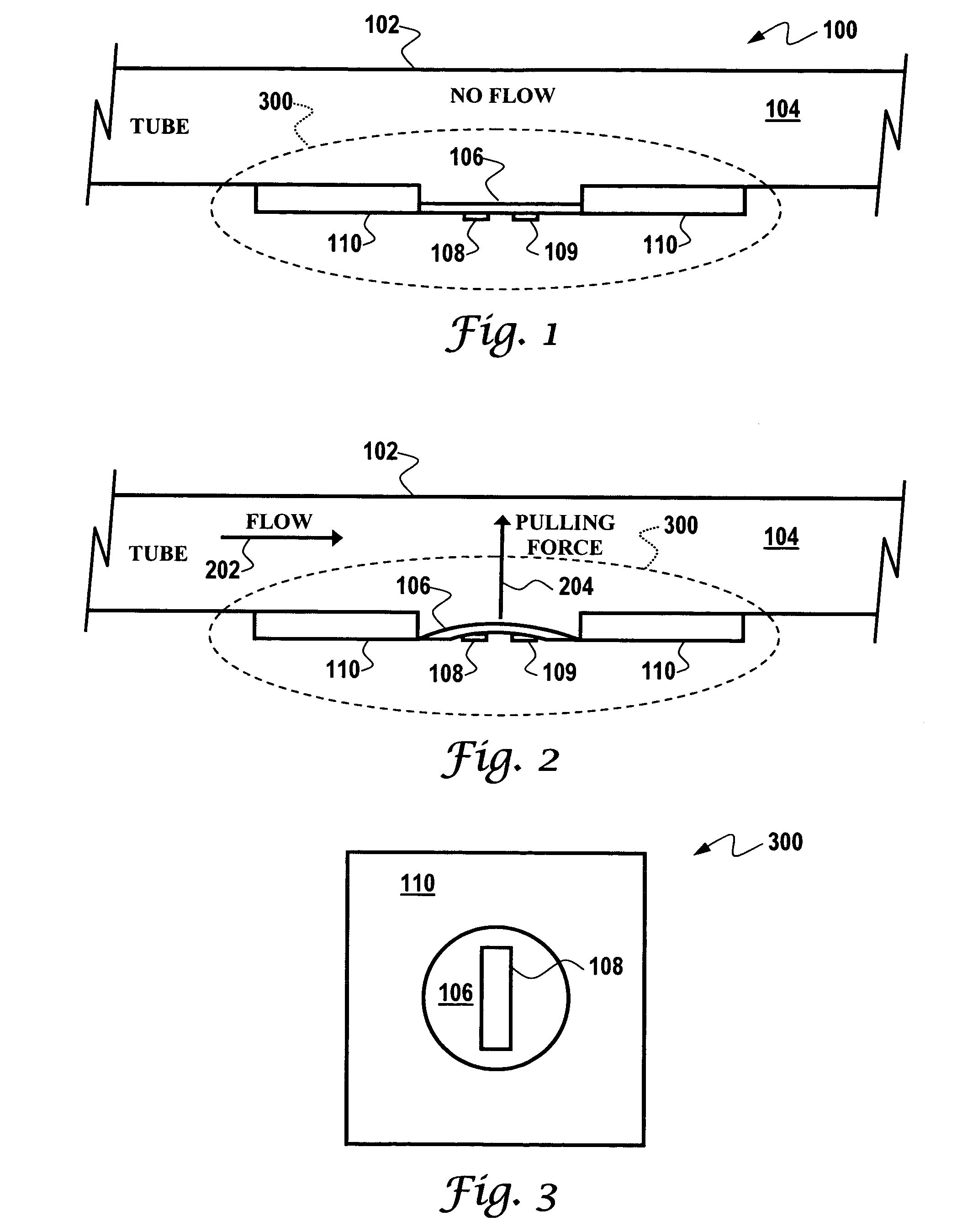
Method and apparatus for monitoring fluids
InactiveUS20120160329A1Reduce riskReduce flow rateOptical radiation measurementFunctional valve typesHydrocarbon explorationCorrosion
A method and apparatus for monitoring a fluid that is to be transported through a fluid conduit within a hydrocarbon exploration and production installation is described. A monitoring zone is established upstream of the fluid conduit configured such the fluid supply to the fluid conduit is introduced via the monitoring zone. The fluid supply within the monitoring zone is monitored for the occurrence of events detrimental to the flow of the fluid supply through the fluid conduit. Monitoring the fluid supply prior to entering the fluid conduit allows for the early detection of an event detrimental to the flow of the fluid supply e.g. a chemical reaction indicative of corrosion of the fluid conduit or the formation of a potential blockage within the fluid conduit. In this way the risk of costly blockages or structural failure occurring within the fluid conduit is reduced.
Owner:PARADIGM FLOW SERVICES
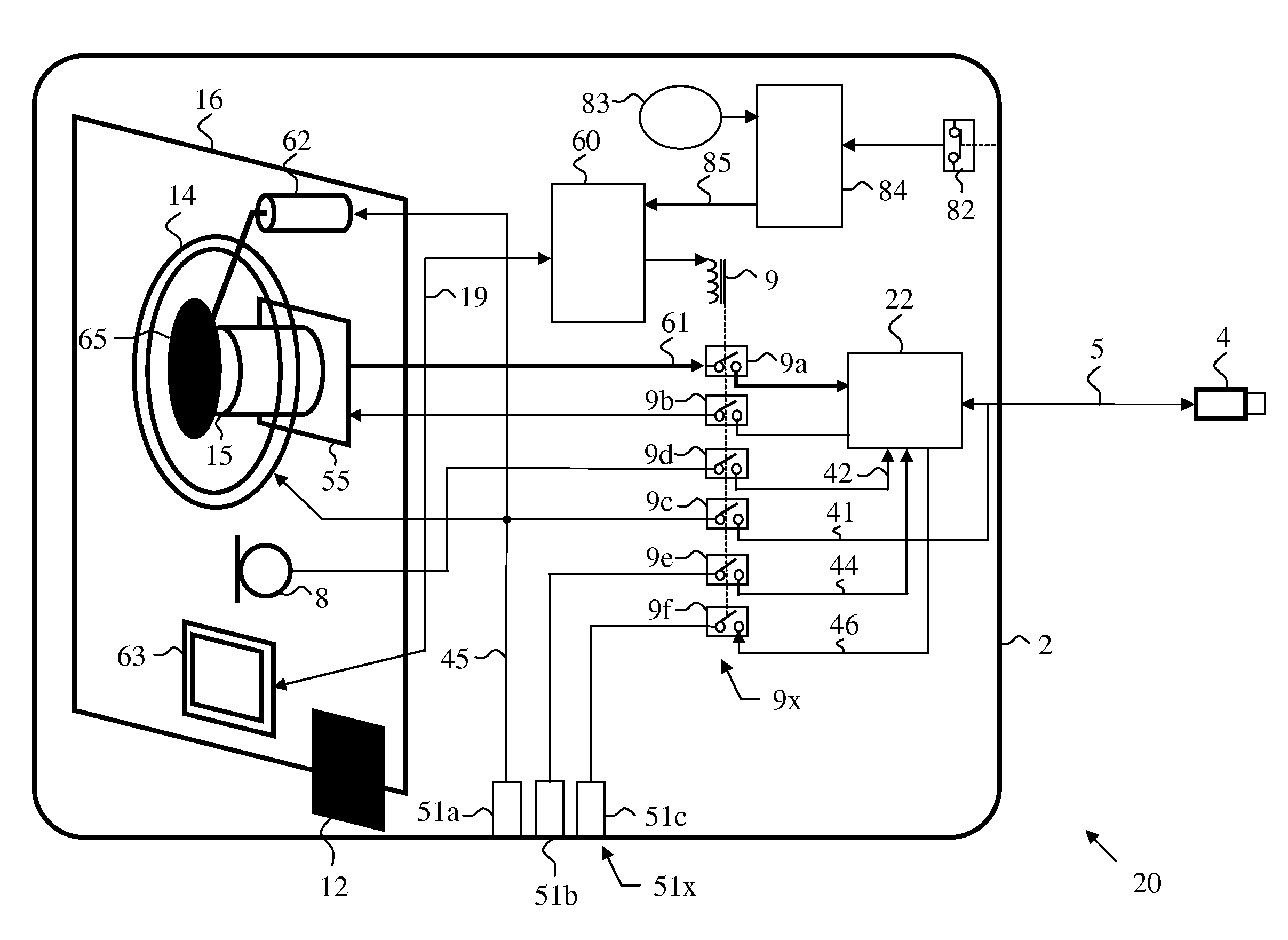
Biological parameter monitoring system and method therefor
InactiveUS20080219319A1Measure directlyNone provide any indicationThermometer detailsPhysical therapies and activitiesMonitoring systemEngineering
A system and method for monitoring biological parameters that allows a user to wirelessly monitor one or more biological parameters of one or more individuals, either continuously or periodically is disclosed. The system may send an alert when the biological parameter exceeds a predetermined threshold, and also provides information to the user about selected individuals or about components of the system.
Owner:HOTHEAD TECH
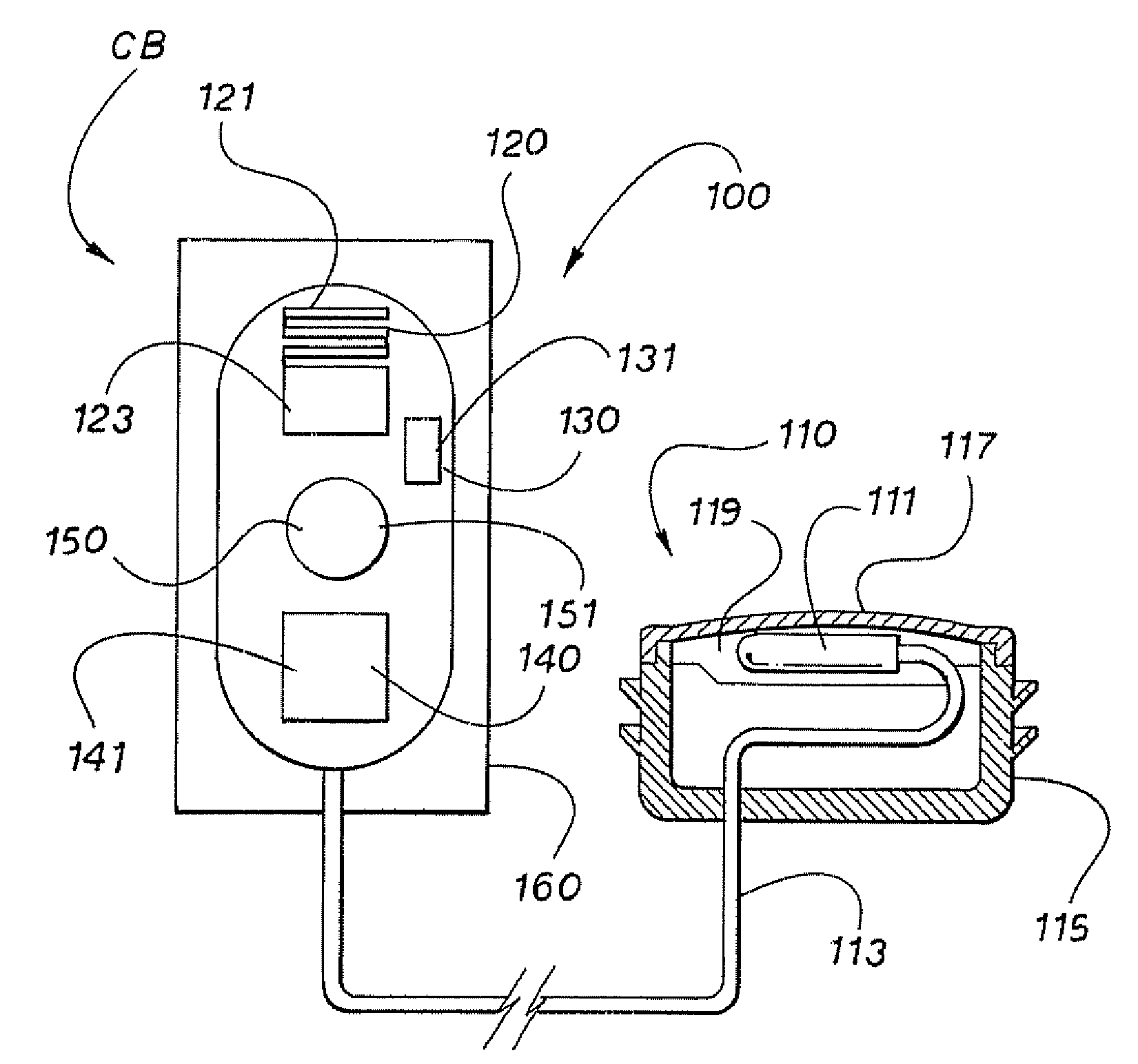
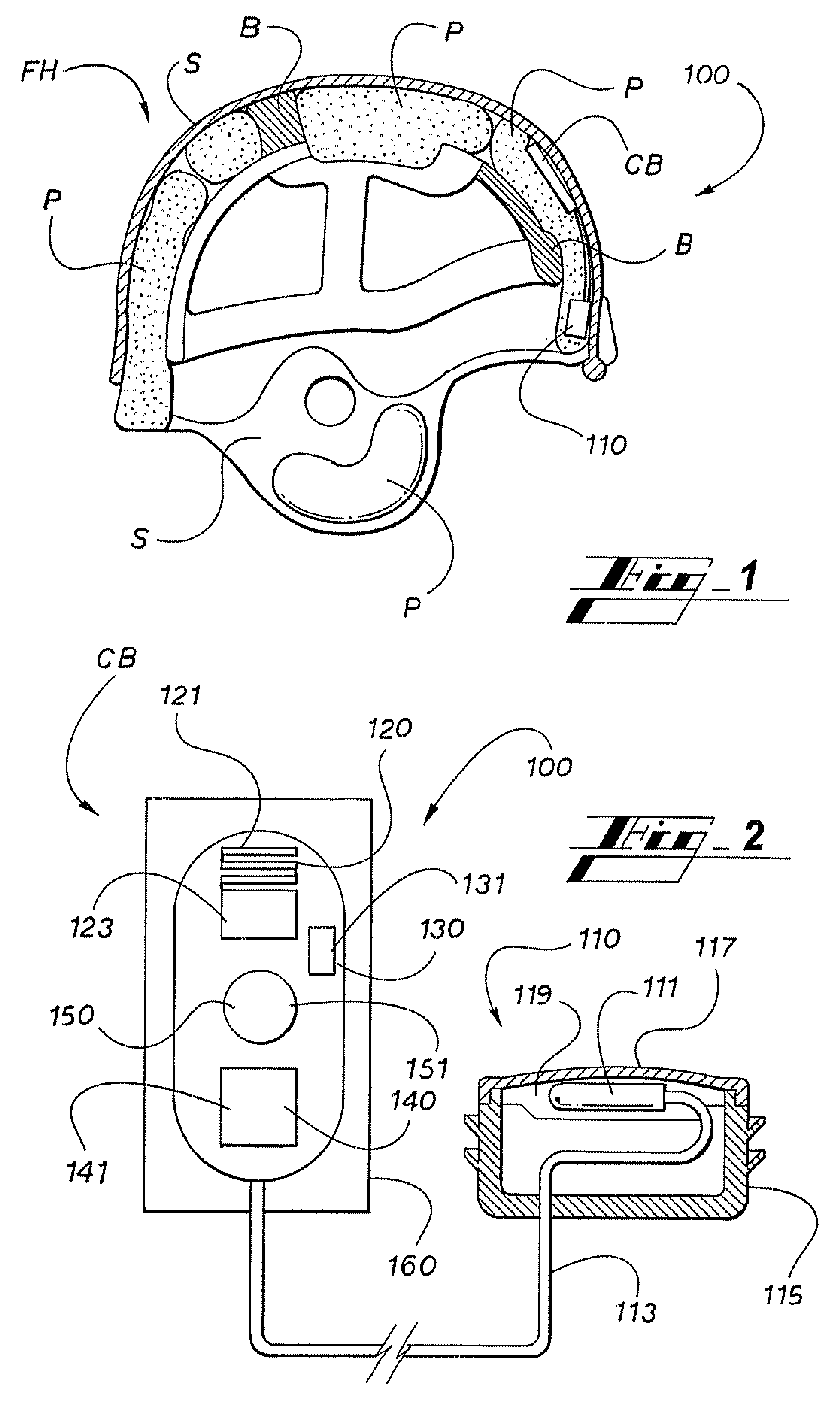
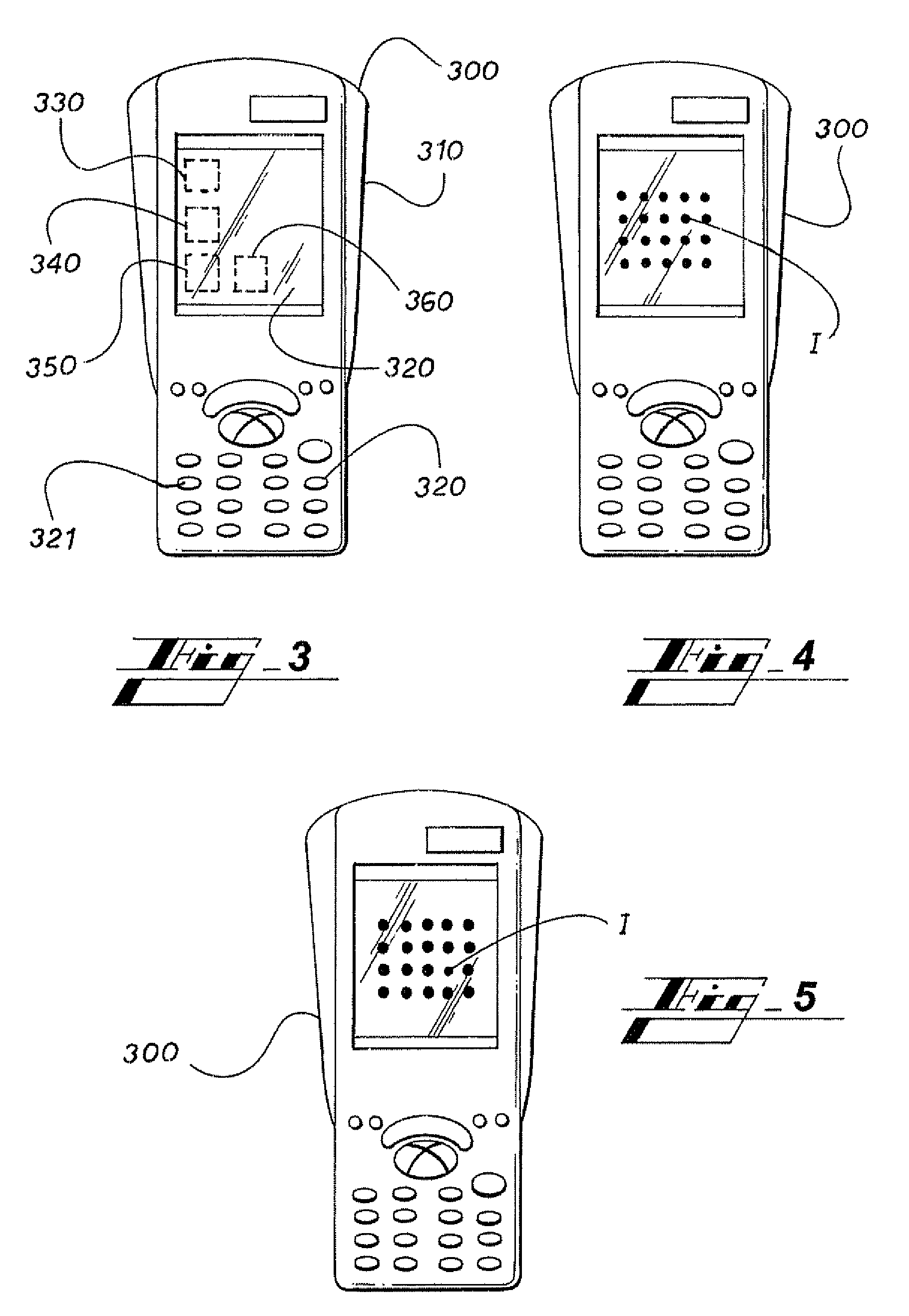
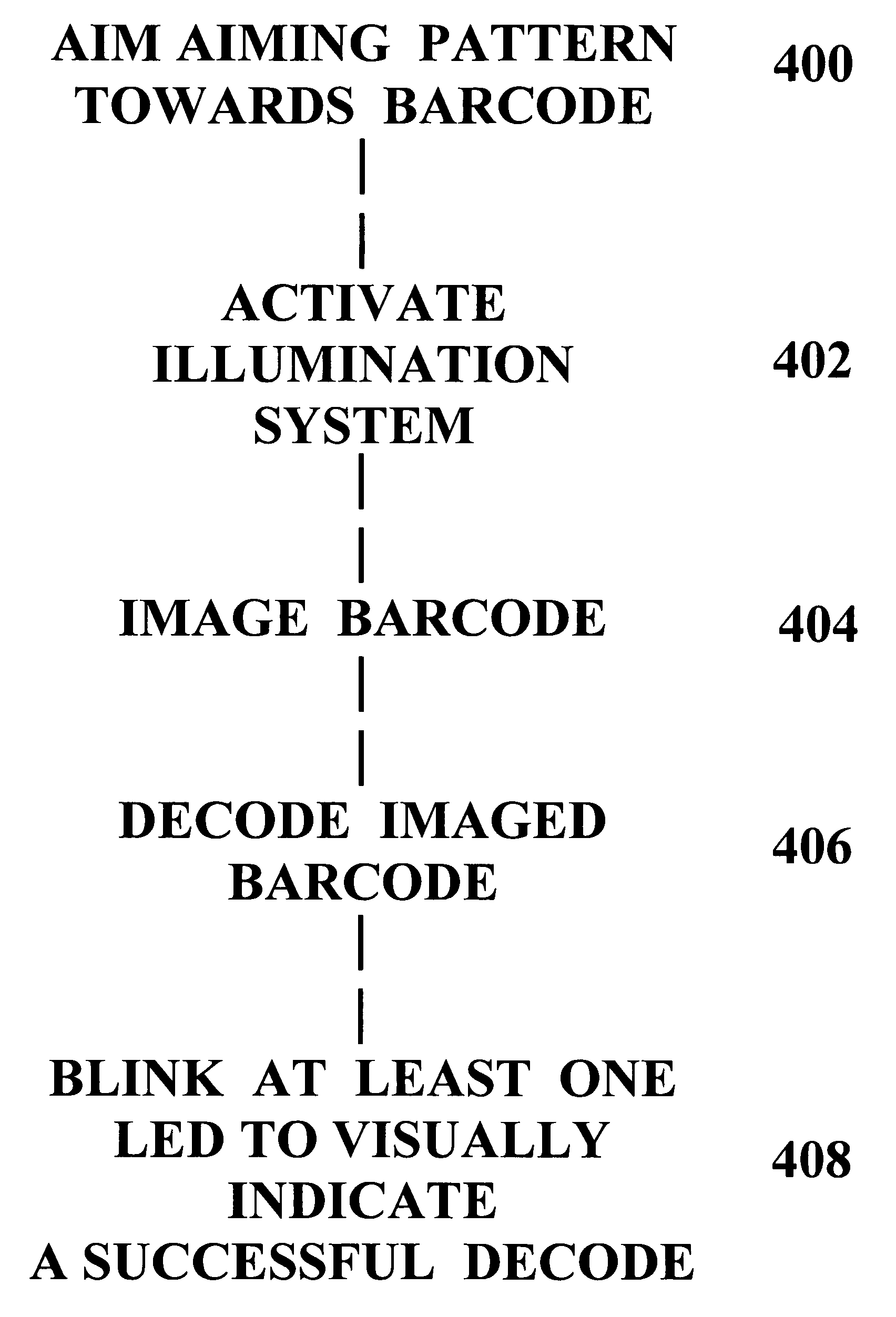
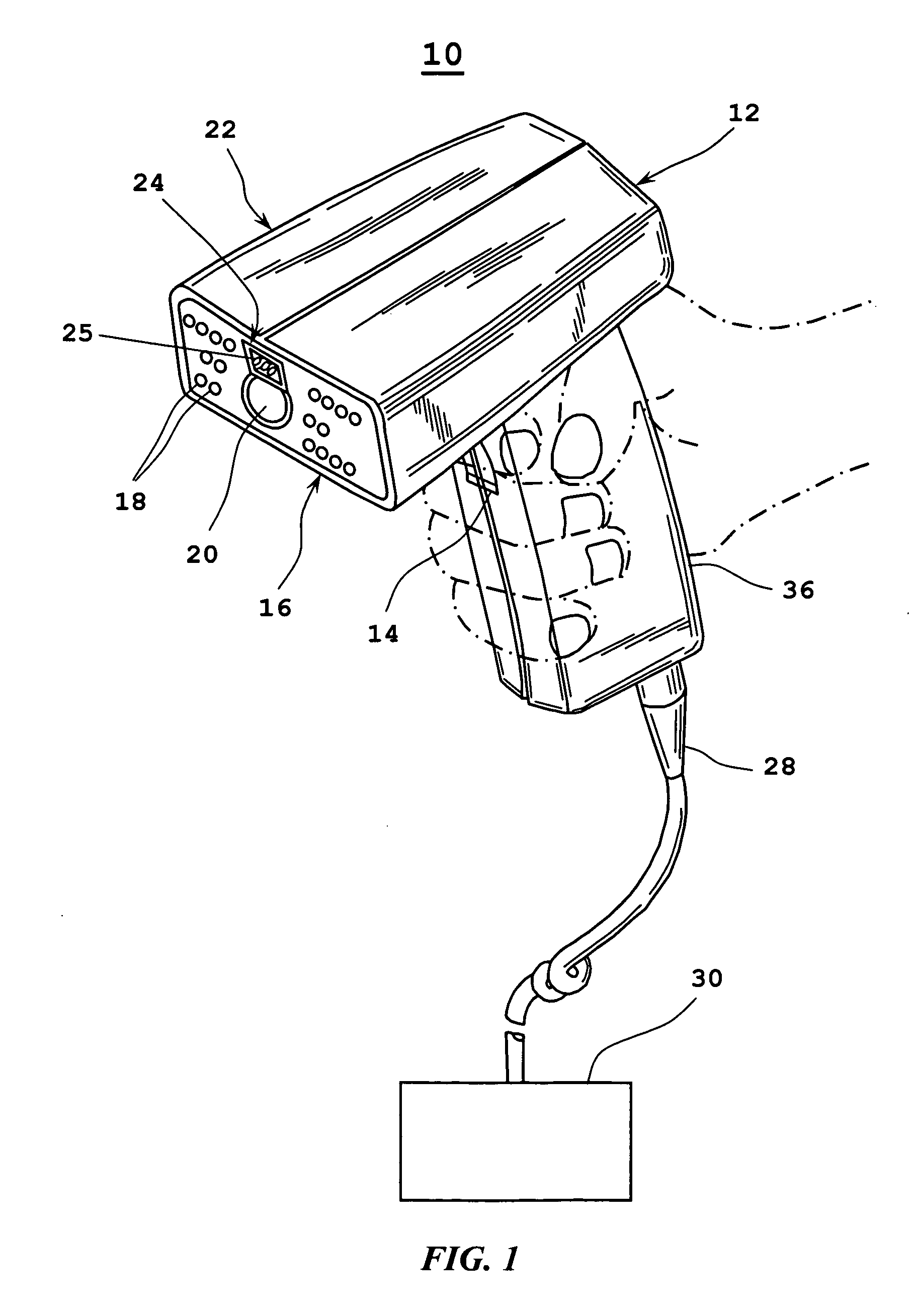
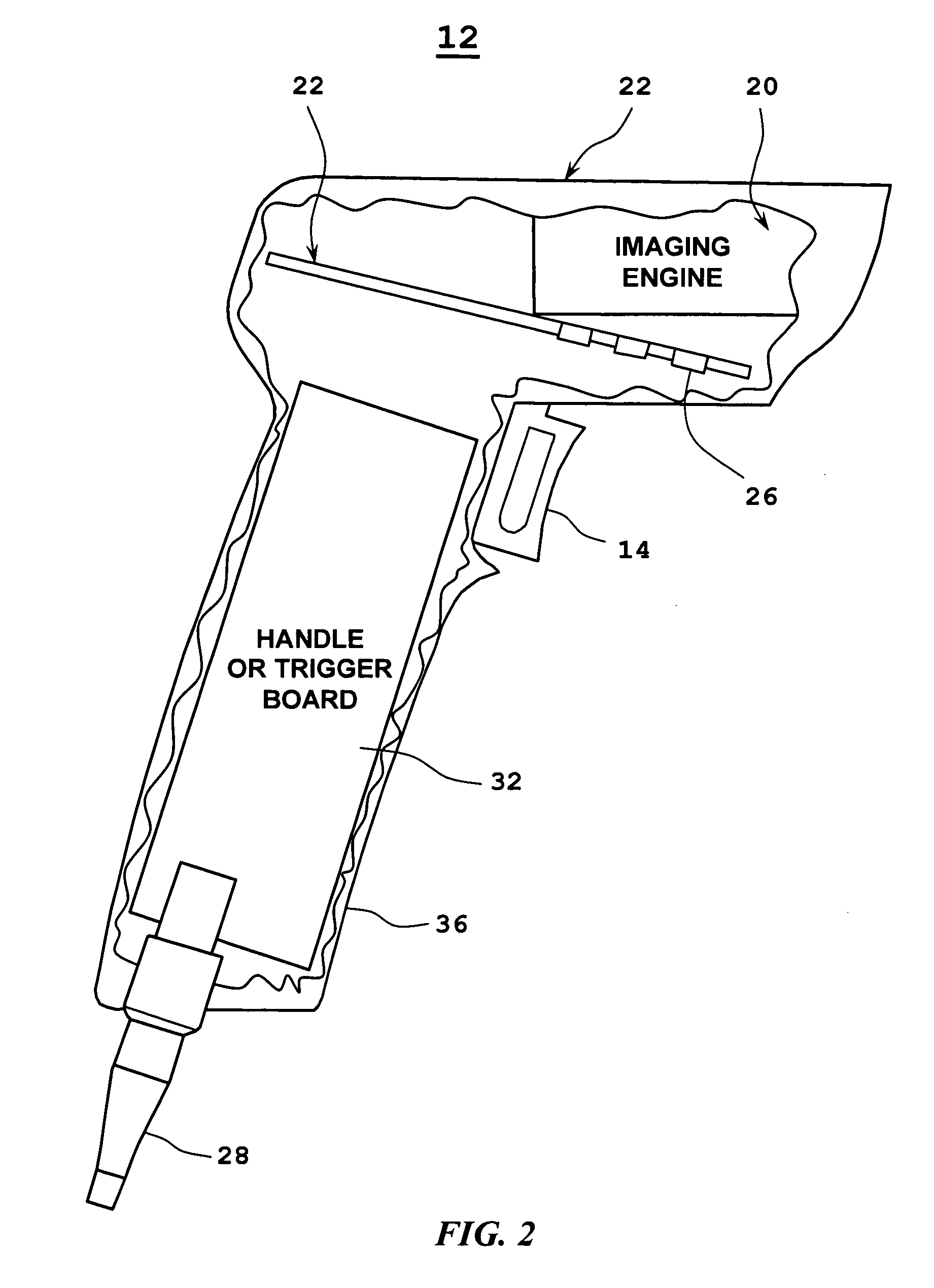
Barcode imaging and laser scanning systems having improved visual decoding indication
ActiveUS20060113389A1None provide any indicationCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationBarcodeLaser scanning
Barcode imaging and laser scanning systems are disclosed having at least one processor storing barcode decoding algorithms each corresponding to a respective symbology. The at least one processor causes at least one LED and / or a projected laser beam of the barcode imaging system to blink by rapidly turning it off and on one time or several times whenever a successful decode occurs. In the laser scanning system, the at least one processor causes a projected laser beam to be blinked by turning a laser beam system off and on one time or several times whenever a successful decode occurs. The act of blinking the at least one LED and / or the projected laser beam in the barcode imaging system or the act of blinking the projected laser beam in the laser scanning system provides a visual indication to a user of a successful decode. The act of blinking can also be used to visually indicate other information to a user. The act of blinking can be replaced by the act of changing the brightness of the at least one LED and / or projected laser beam in the barcode scanning systems.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
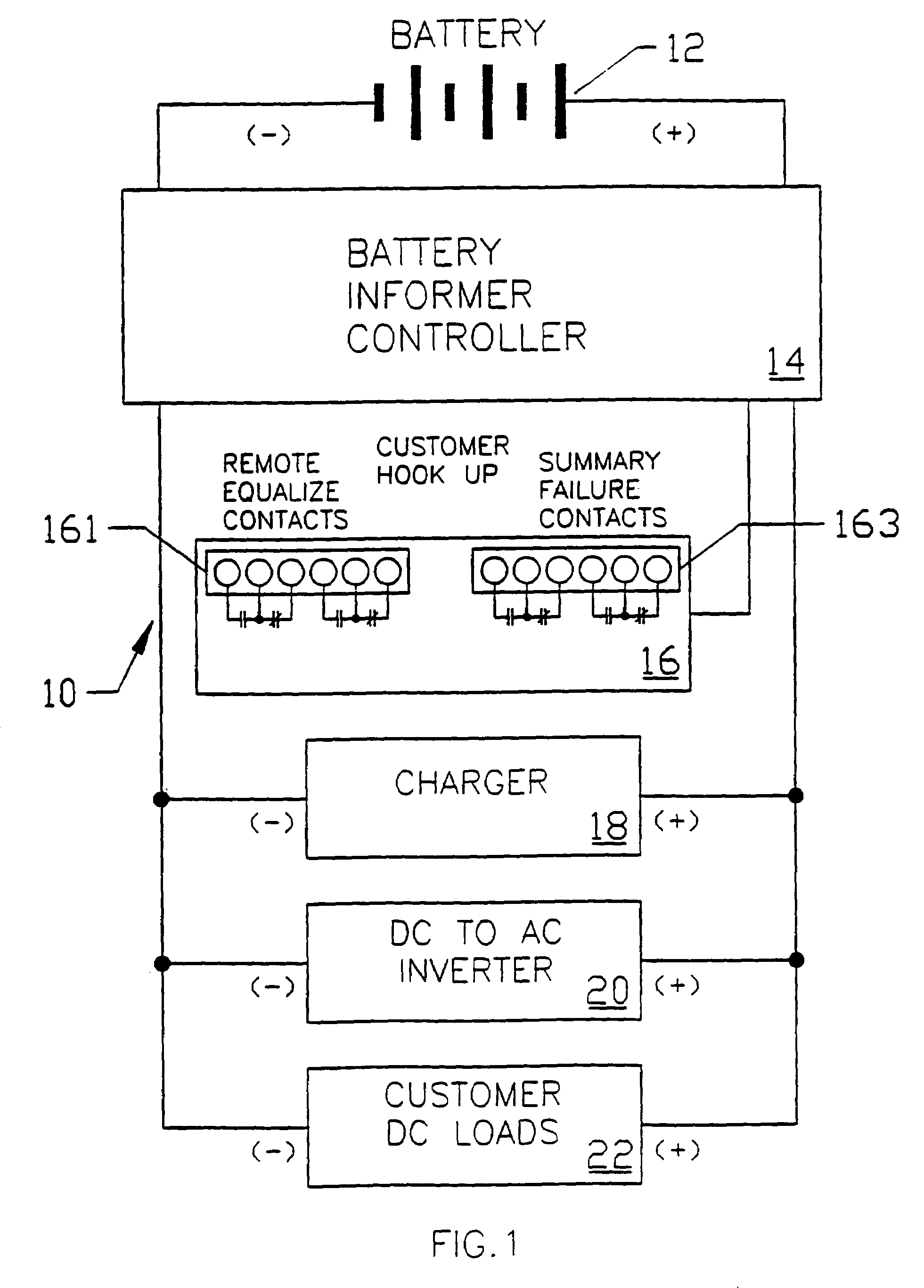
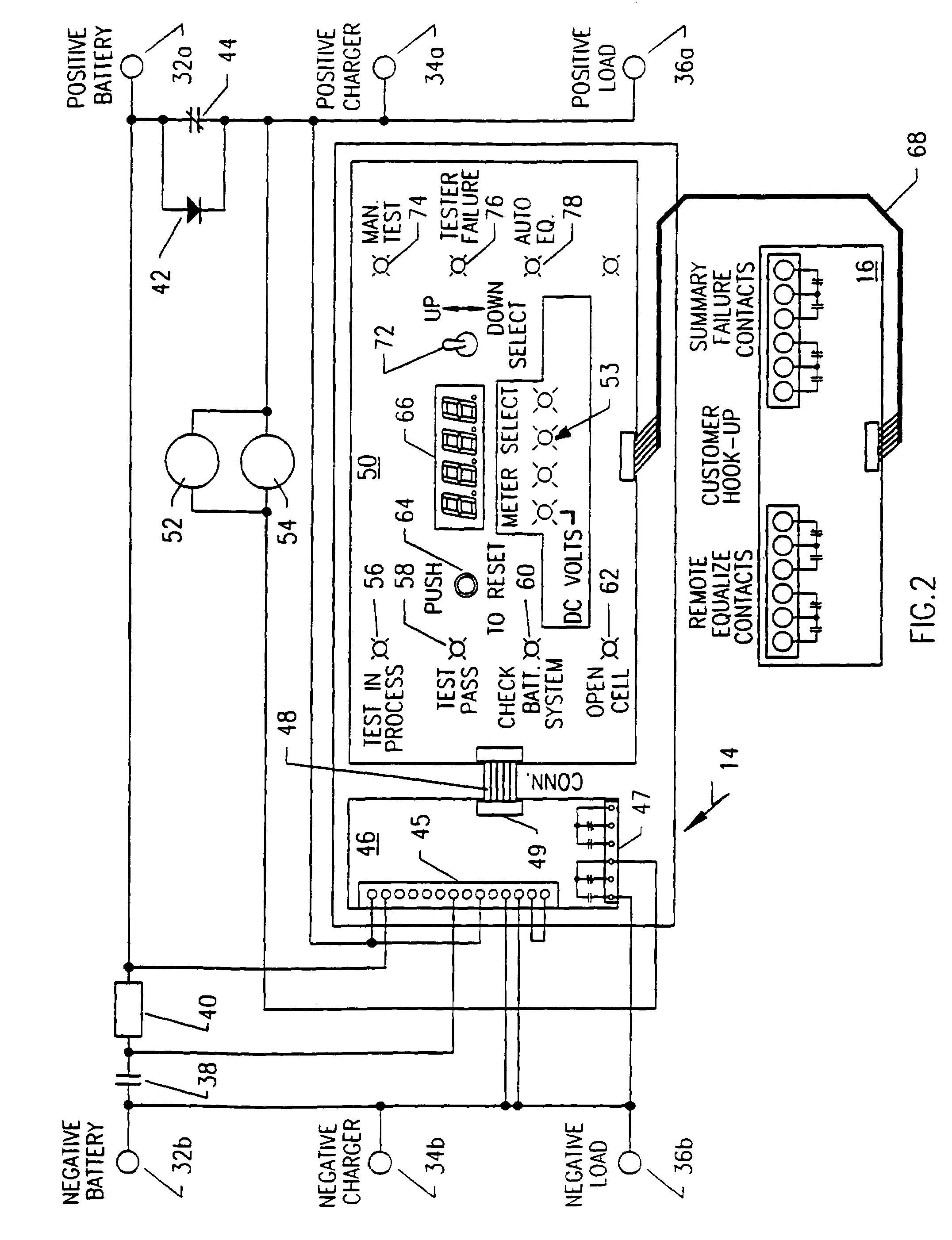
Arrangement for testing battery while under load and charging
InactiveUS6992487B1None provide any indicationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingTest batteryElectrical battery
A live circuit battery tester allows for determining the condition of batteries under load without disconnecting the batteries and a battery charger from the load or in any way disrupting system operation during the test. Battery testing is prevented when the batteries are being used in an emergency or if they are recharging from a recent discharge. The battery tester is under microcomputer control and incorporates automatic-self diagnostics and provides a visual indication if the batteries are good or if a specific problem is detected such as if the batteries are missing, have open cells, are sulfated or are in imminent danger of failure. The battery tester determines if the charger is operating properly and tests for an open cell, bad battery connection, sulfated battery, and a weak battery and provides a visual indication of any of these problems as well as an indication of a properly operating battery.
Owner:LA MARCHE MFG
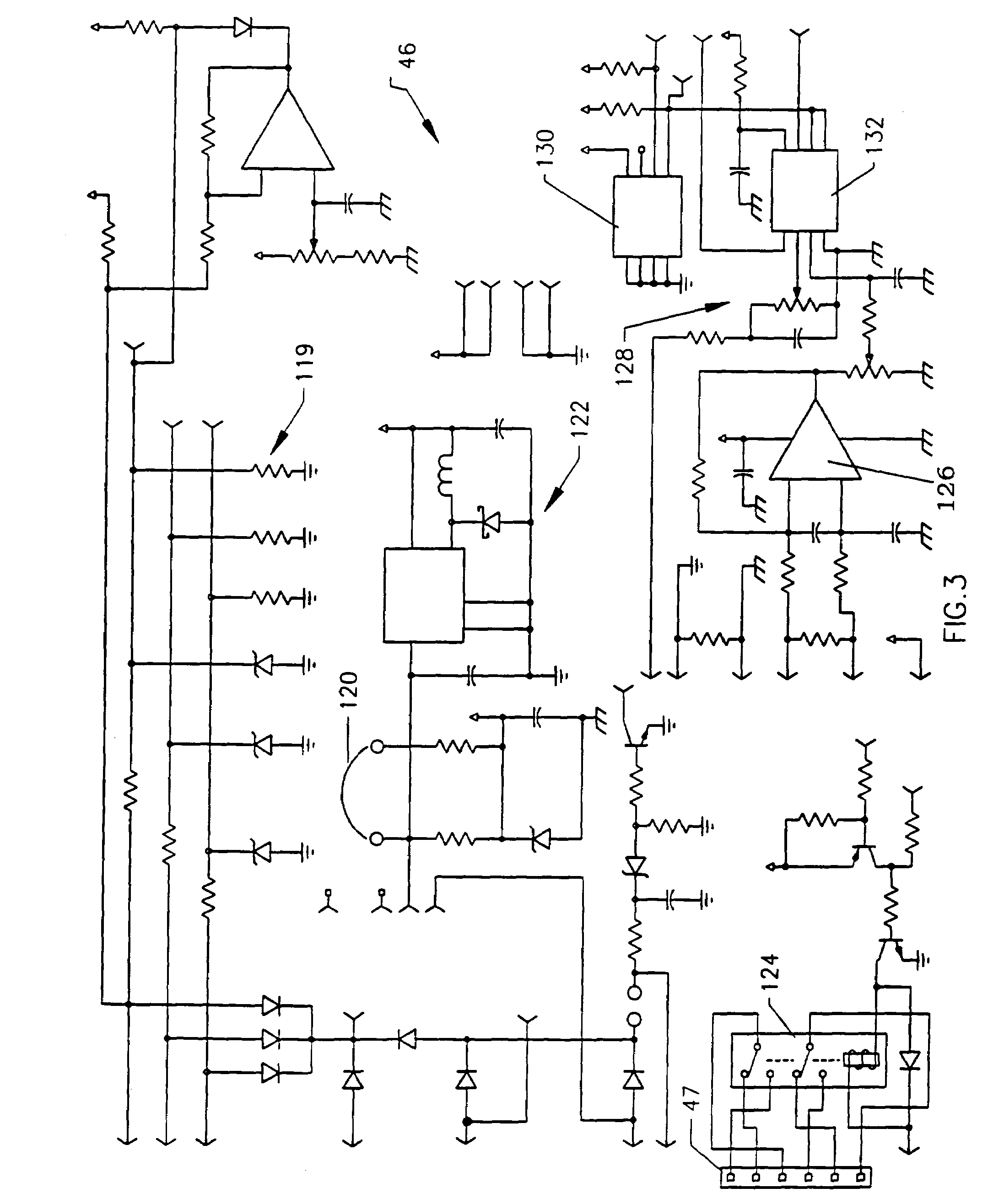
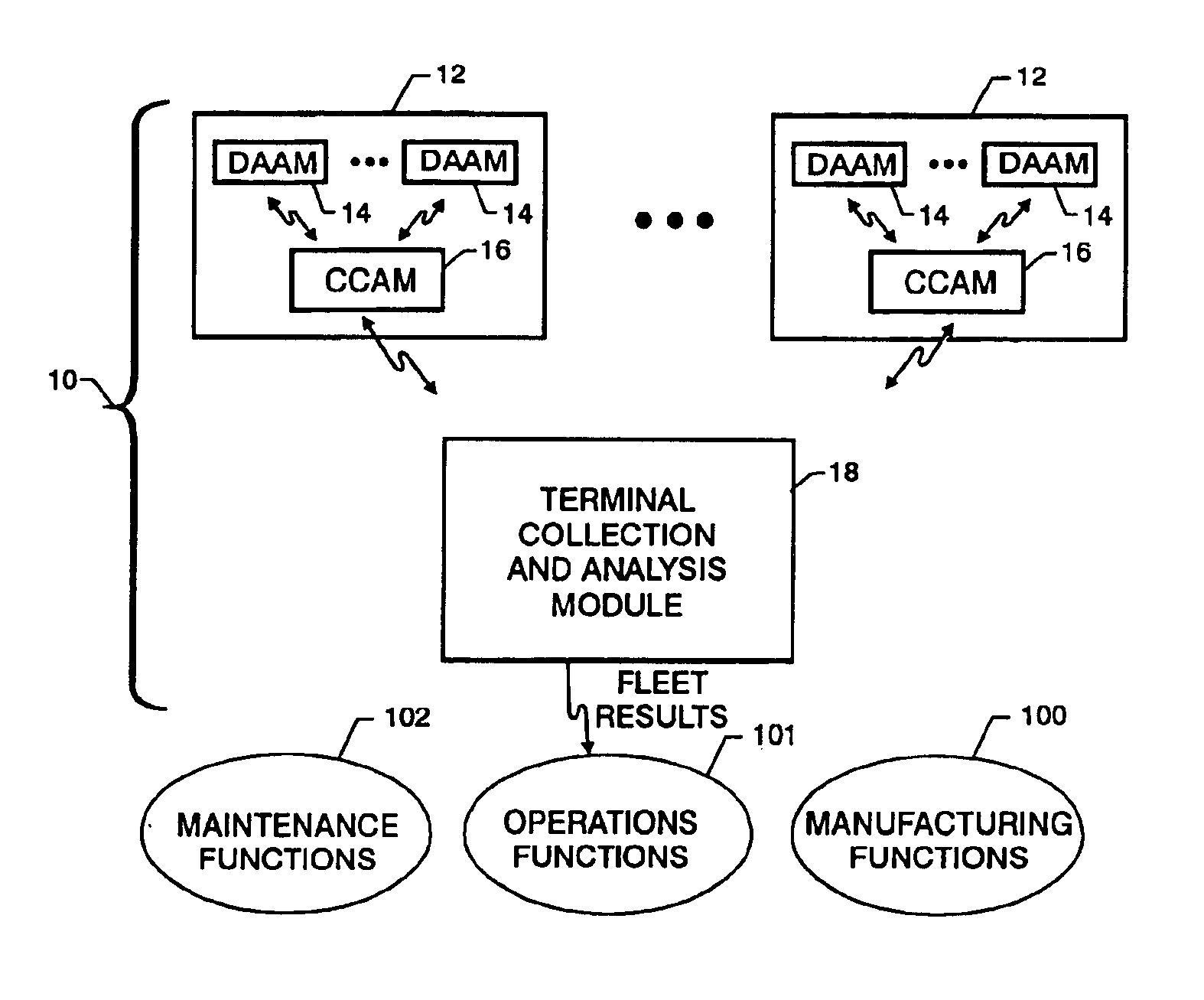
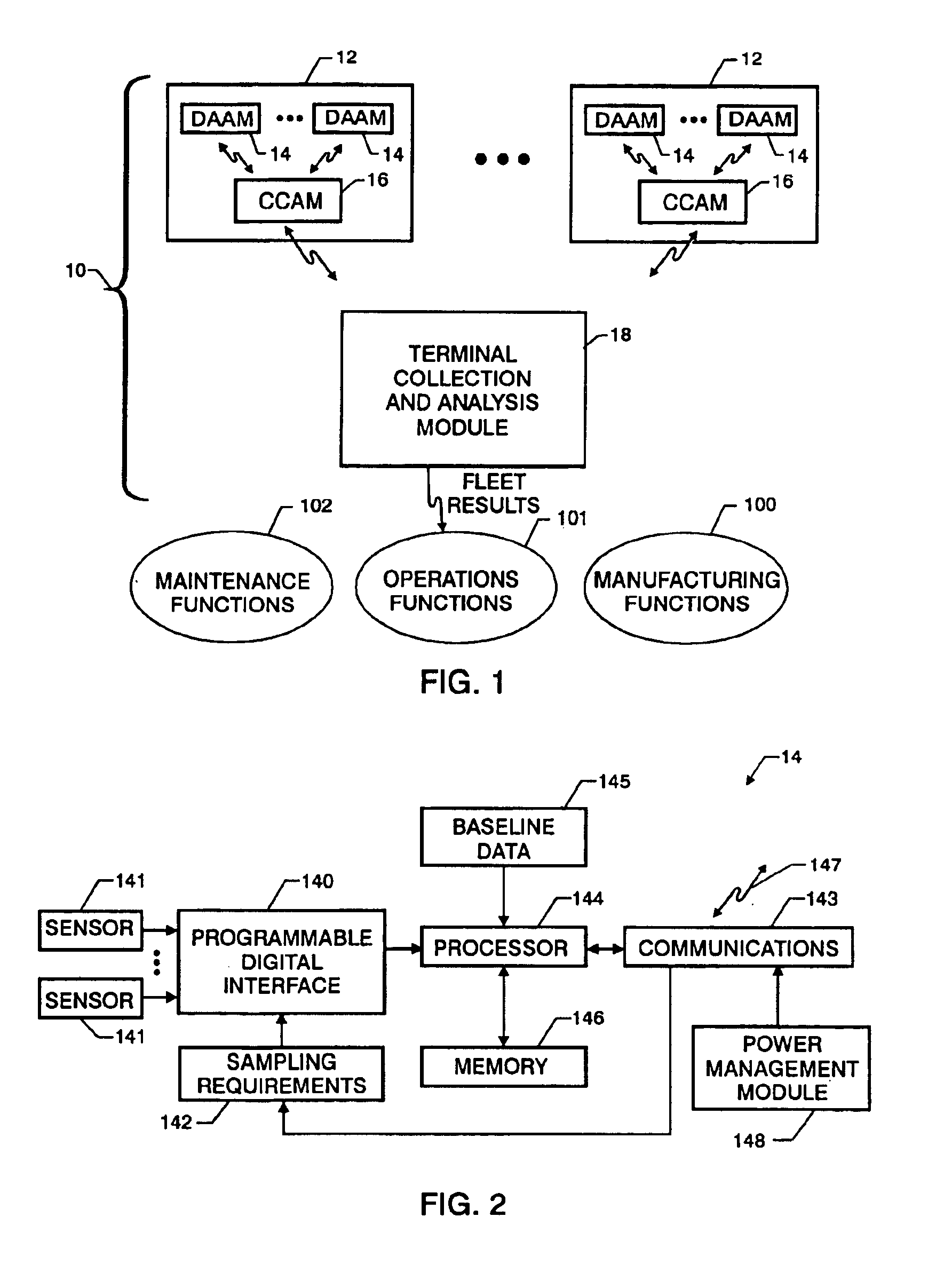
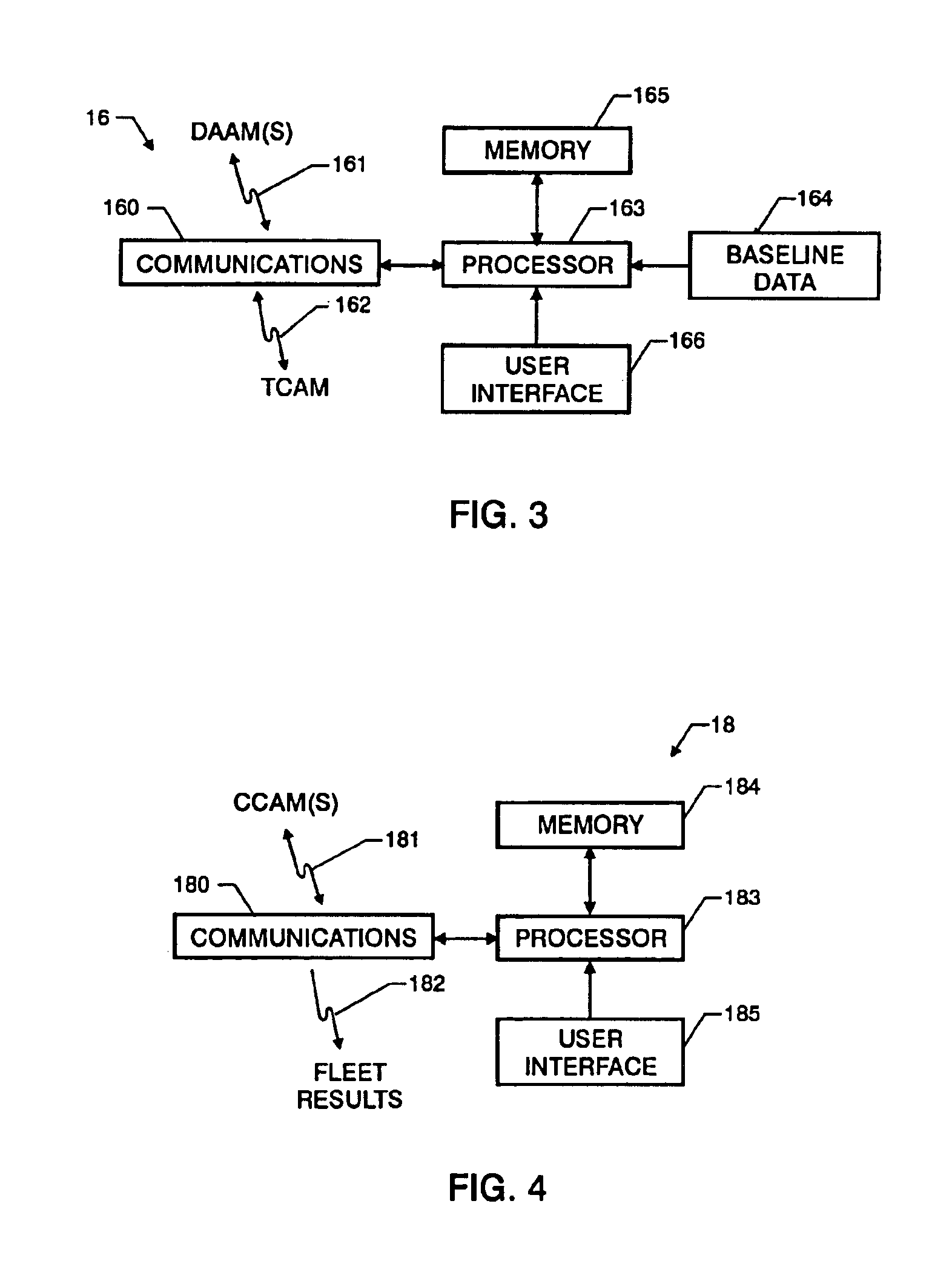
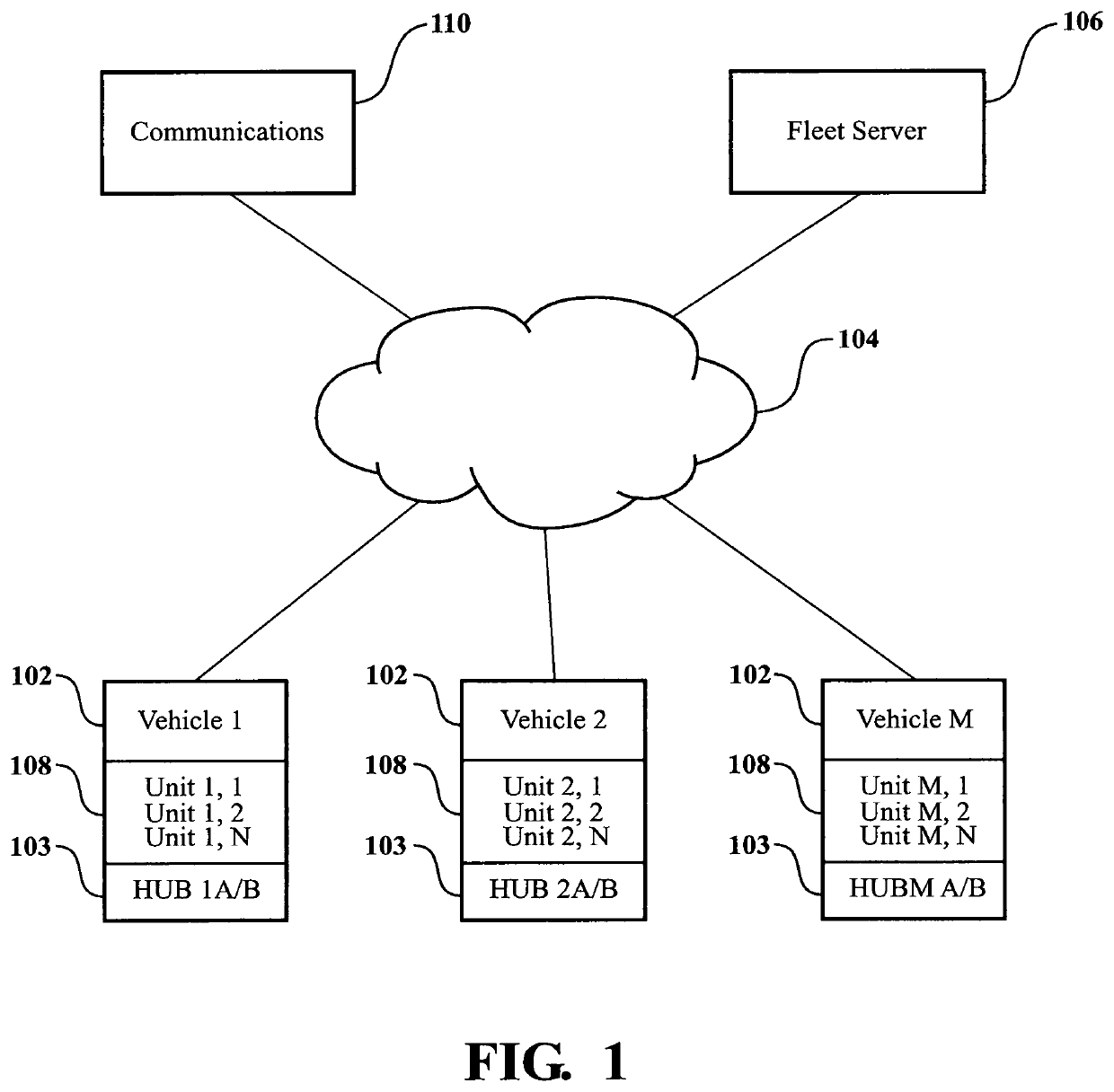
Tributary analysis monitoring system
InactiveUS6879893B2None provide any indicationVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesData acquisitionMonitoring system
A monitoring system for a fleet of vehicles includes at least one data acquisition and analysis module (DAAM) mounted on each vehicle in the fleet, a control module on each vehicle in communication with each DAAM, and terminal module located remotely with respect to the vehicles in the fleet. Each DAAM collects / analyzes sensor data to generate analysis results that identify the state of a plurality of systems of the vehicle. Each vehicle's control module collects / analyzes the analysis results from each onboard DAAM to generate vehicle status results that identify potential sources of vehicle anomalies. The terminal module collects / analyzes the analysis results and vehicle status results transmitted from each control module from the fleet of vehicles to identify multiple occurrences of vehicle anomalies and multiple occurrences of those vehicle systems operating at a performance level that is unacceptable. Results of the terminal module's analysis are provided to organizations responsible for the operation, maintenance and manufacturing of the vehicles in the fleet as well as the plurality of systems used in the fleet.
Owner:NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR
Secure video camera device
ActiveUS8988532B2Efficient and secure switchingExtend activation timeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensComputer hardware
A secure video camera device for reducing the risk of visual and audio eavesdropping has a video camera and an electromechanical shutter behind a transparent cover in a secured enclosure. The shutter optically obscures the camera lens when the device is in secure state. A visual indicator indicates when the device is in operational state. A switch controllable by the user, select the state of the device by concurrently disabling the camera turning off the visual indicator in a secure state; and setting said device in an operational state by concurrently enabling the camera and turning on said lighted indicator. The device has a built in, or auxiliary microphone, and audio outputs which are disabled in secure state of the device. The device is tempered proof by an anti-tempering circuitry.
Owner:HIGH SEC LABS LTD
Combination and method including a visual marker for determining compliance with a medication regimen
InactiveUS7062312B2None provide any indicationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCompounds screening/testingOral medicationPharyngeal cavity
A method and combination including a visual marker for monitoring a patient to determine compliance with a medication regimen. An orally administrable medication composition is provided in combination with a visual marker. When the combination is orally ingested, the marker causes a coloration or discoloration of the oral and / or pharyngeal cavity of a subject. By visually observing the oral and / or pharyngeal cavity of the subject, one can determine whether medication has been ingested based upon the presence or absence of the coloration / discoloration.
Owner:UNION SPRINGS PHARMA
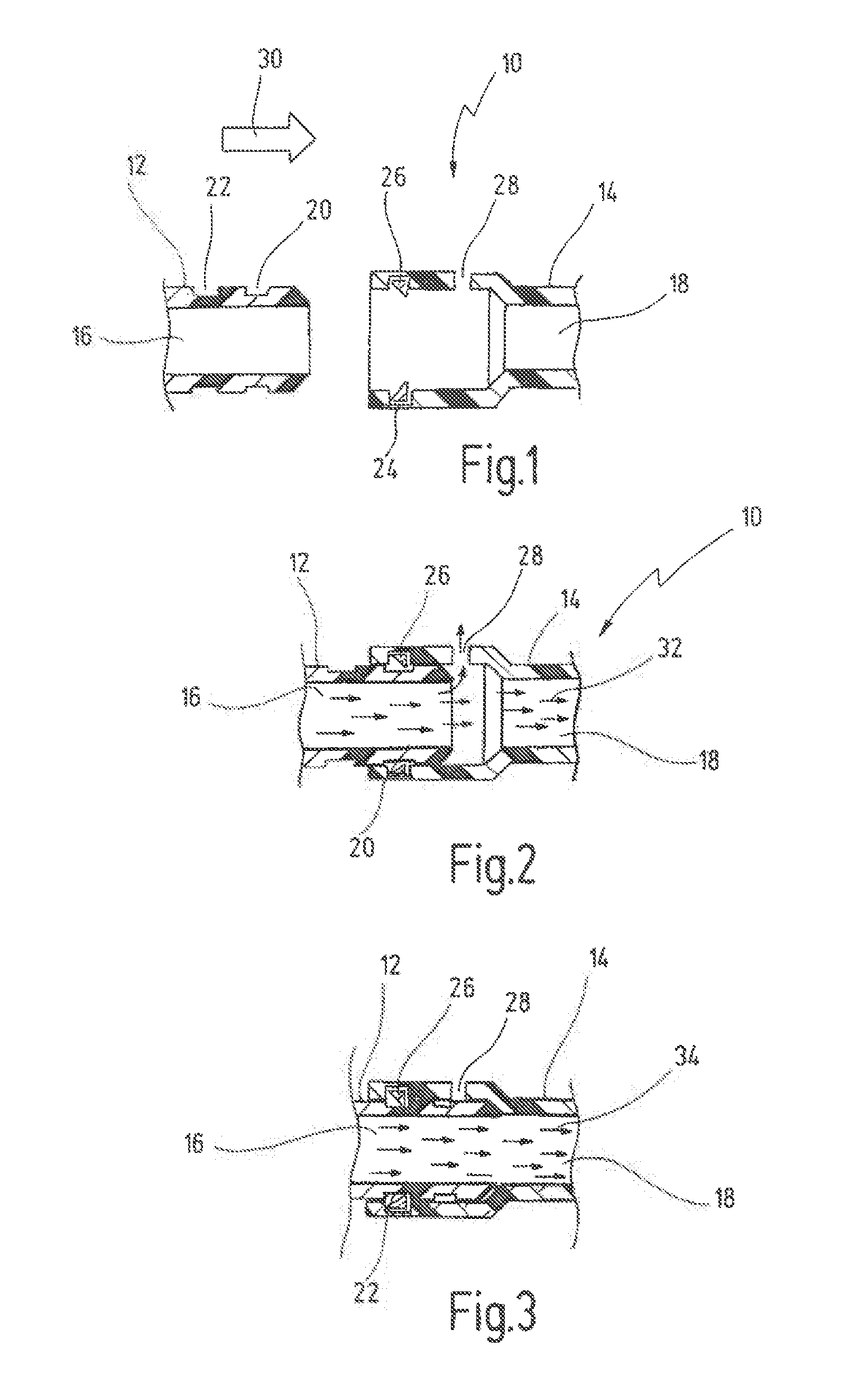
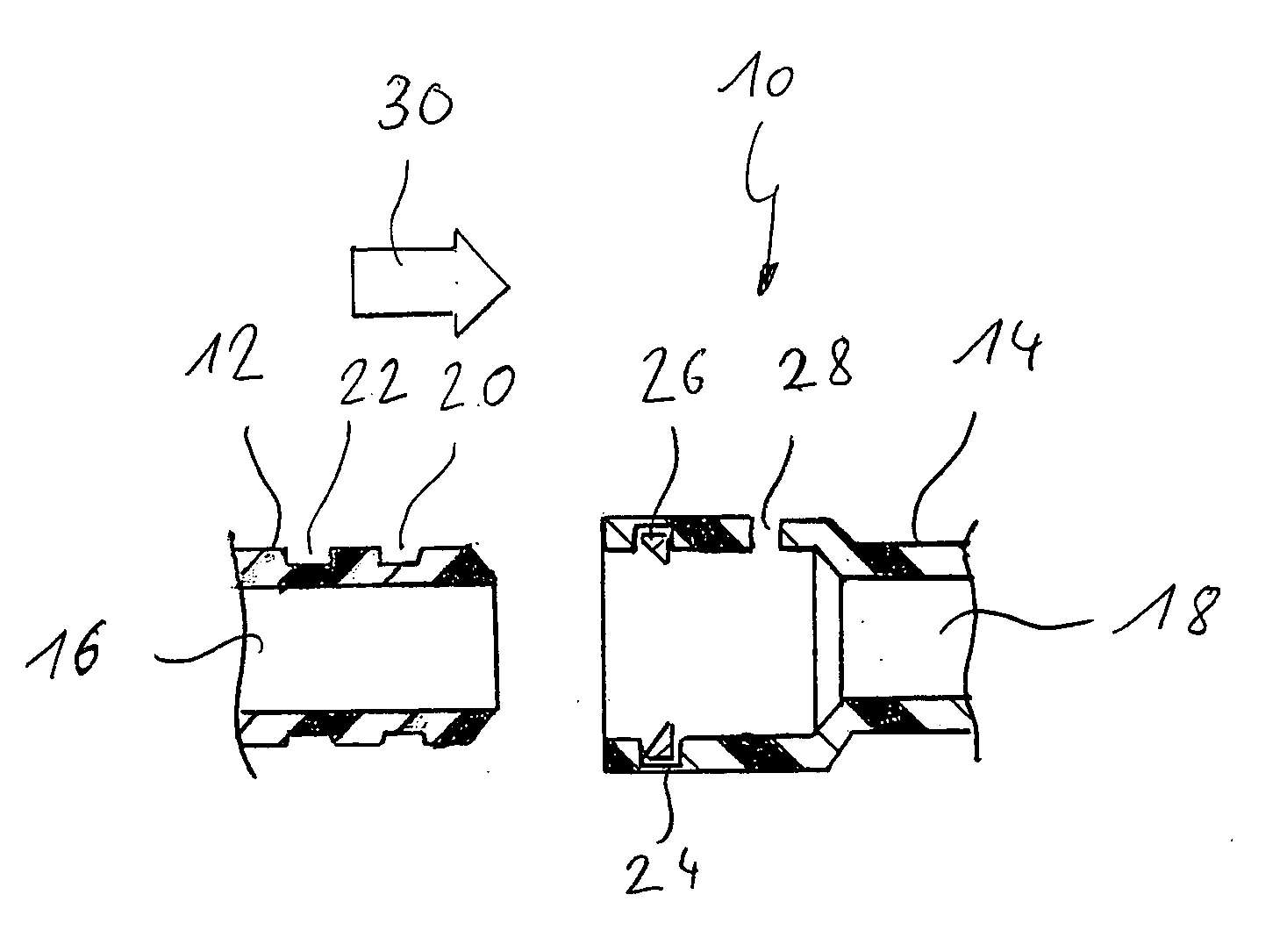
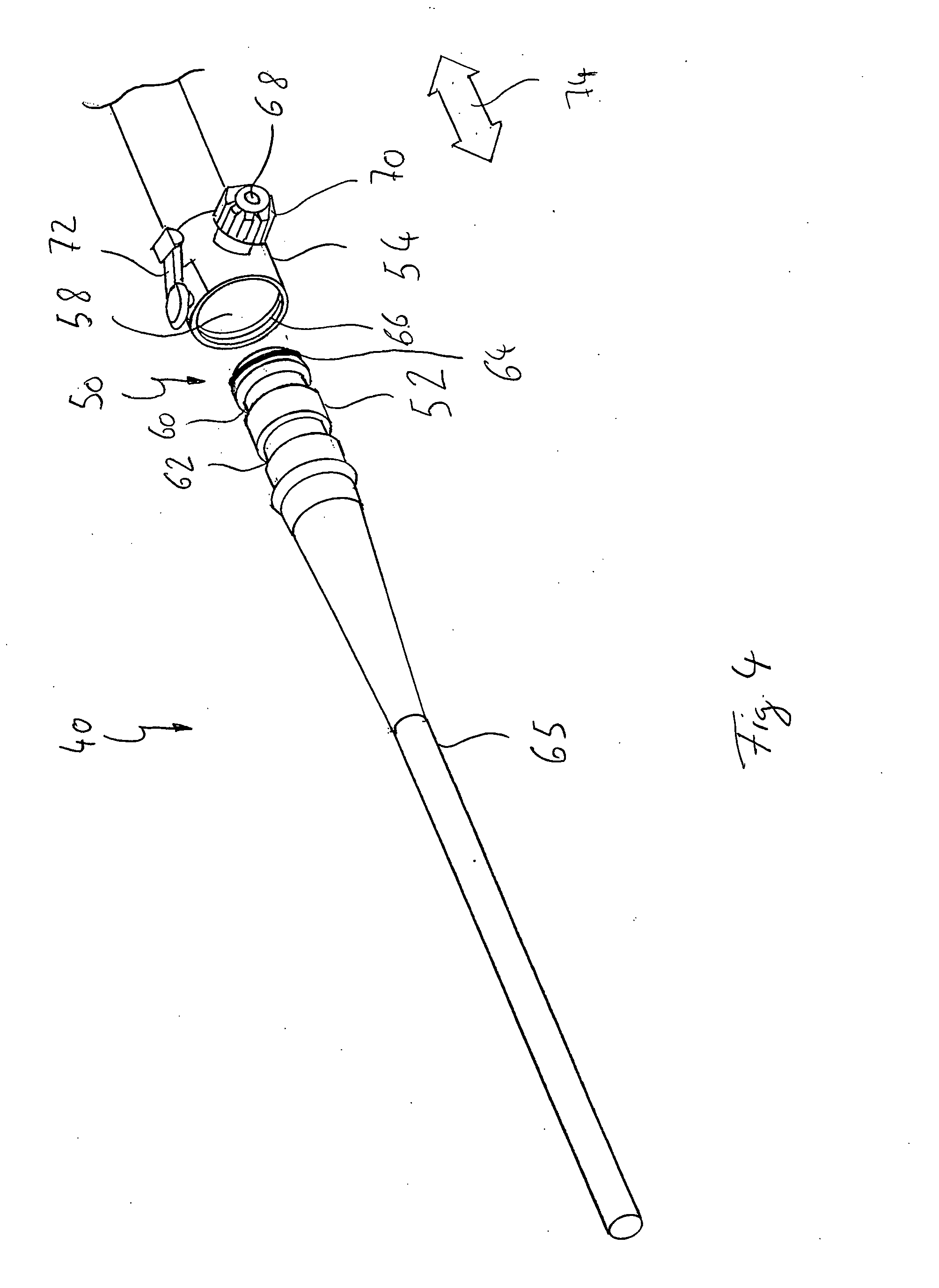
Coupling for tubular elements
The invention relates to a coupling for tubular elements, with at least one plug and one socket, which plug can be inserted into the socket and can be locked therein, and both the plug and the socket have, extending approximately along their longitudinal axis, a channel for a fluid, said channel being arranged in such a way that the fluid can flow through the coupling in a locked state thereof. The plug can be locked in the socket in at least two locking positions, and the socket and / or the plug has at least one opening such that, in a first locking position, the opening connects the channel for a fluid to the environment, and, in a second locking position, the channel for a fluid is isolated from the environment. The invention relates further to a cannula that comprises such a coupling.
Owner:NOVALUNG
Coupling for tubular elements
InactiveUS20070249197A1Easy accessEasy to openEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsSurgeryCouplingEngineering
The invention relates to a coupling for tubular elements, with at least one plug and one socket, which plug can be inserted into the socket and can be locked therein, and both the plug and the socket have, extending approximately along their longitudinal axis, a channel for a fluid, said channel being arranged in such a way that the fluid can flow through the coupling in a locked state thereof. The plug can be locked in the socket in at least two locking positions, and the socket and / or the plug has at least one opening such that, in a first locking position, the opening connects the channel for a fluid to the environment, and, in a second locking position, the channel for a fluid is isolated from the environment. The invention relates further to a cannula that comprises such a coupling.
Owner:NOVALUNG
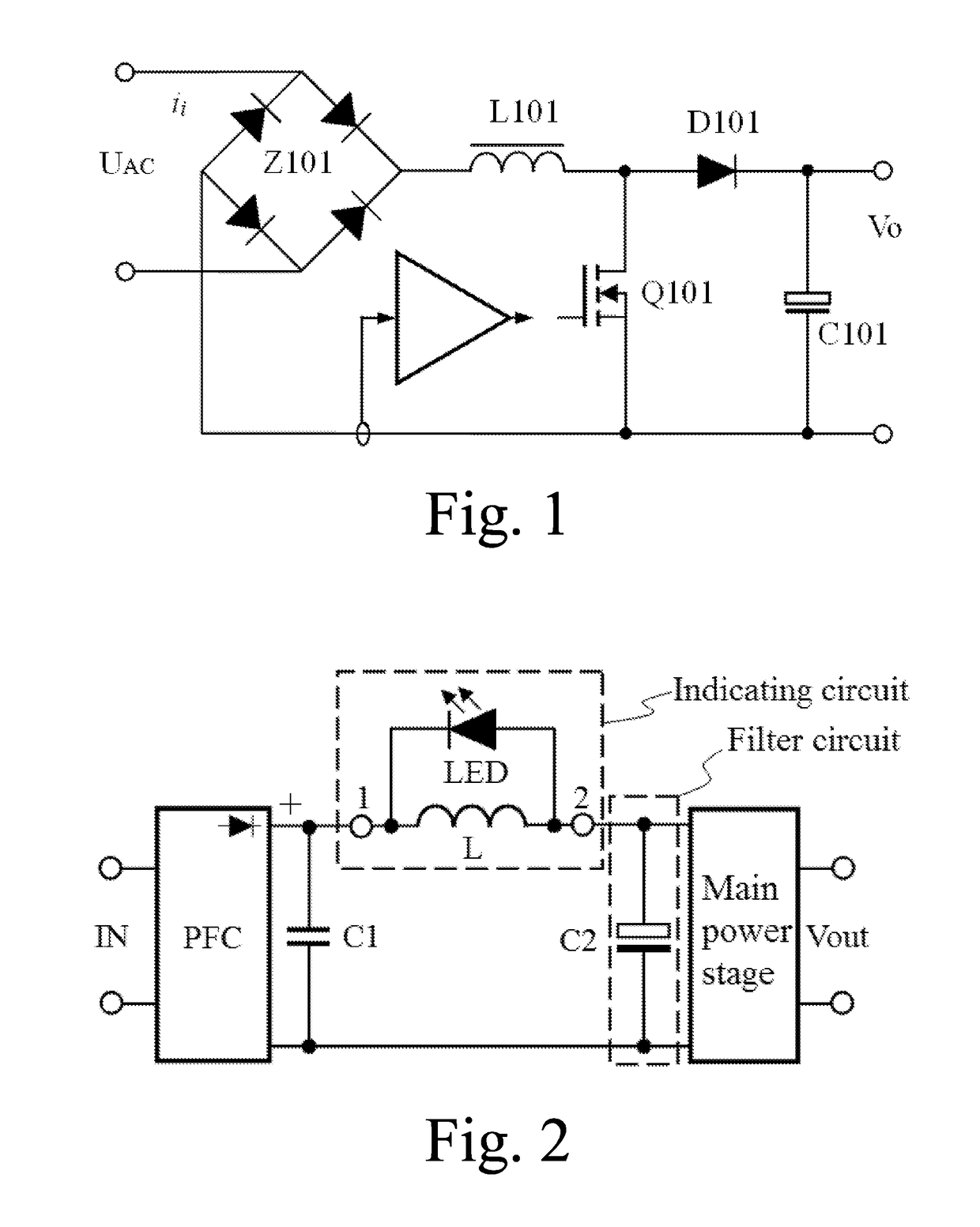
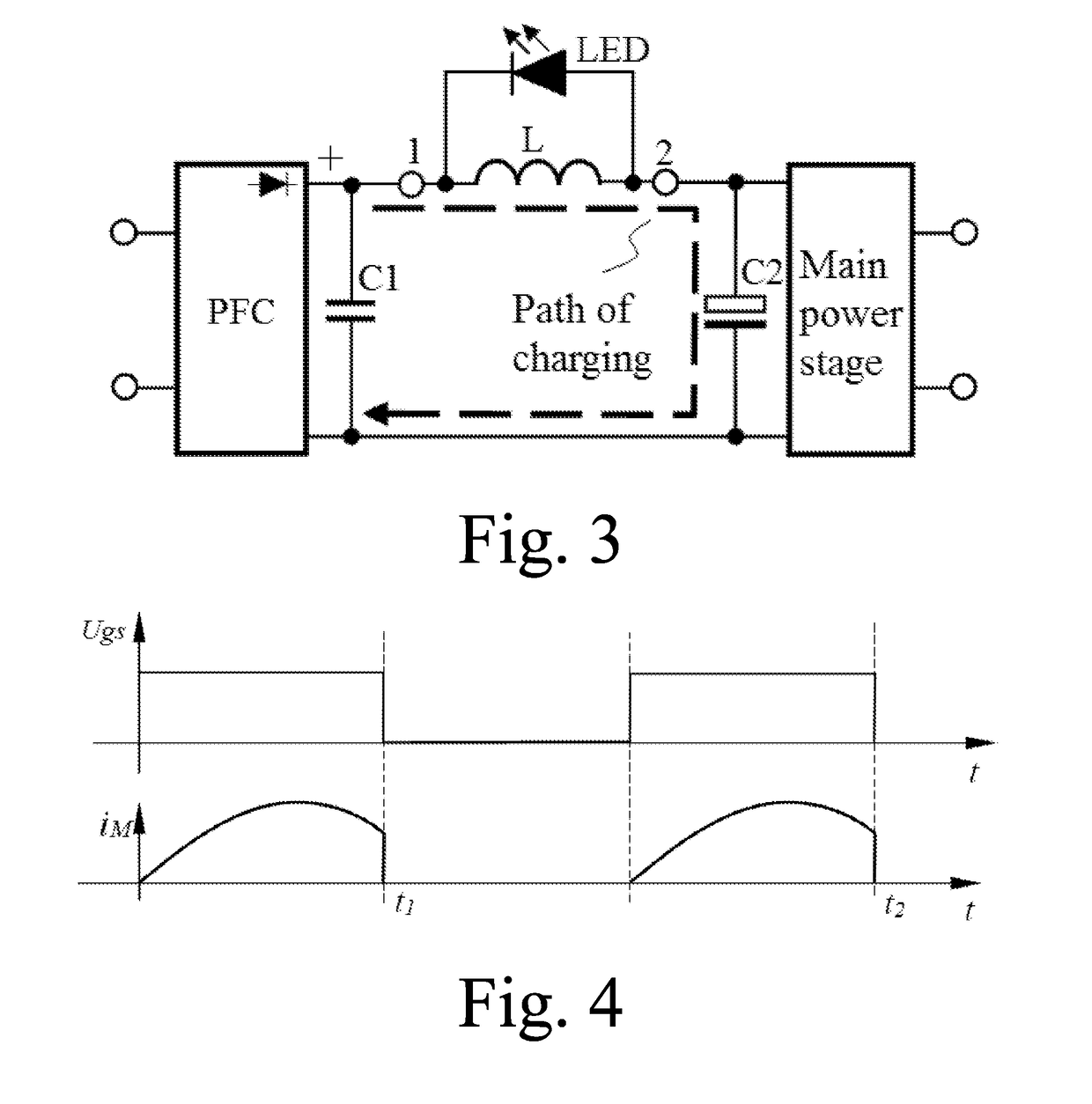
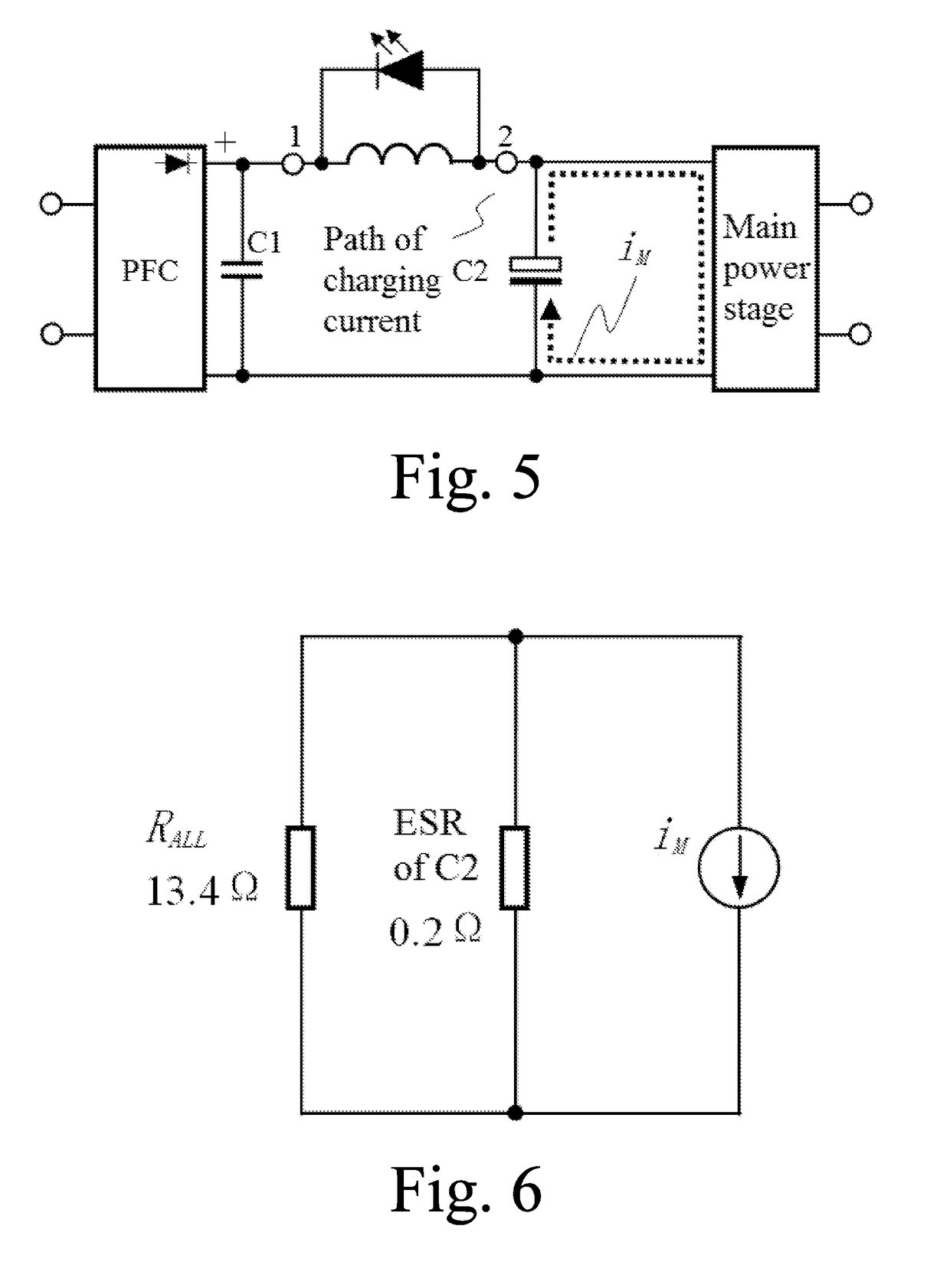
Switching power supply having active power factor correction
ActiveUS20190029086A1Easy wiringSmall volumeEfficient power electronics conversionVolume/mass flow measurementActive power factor correctionEngineering
A switch power supply having active power factor correction is provided, including a power factor correction (PFC) circuit, a filter circuit, a main power stage, a first capacitor (C1) and an indicating circuit. An alternating-current input (IN) is connected to the first capacitor through the PFC circuit and is connected to the filter circuit through the indicating circuit. The indicating circuit consists of a light emitting diode (LED) having unidirectional conductivity and an inductor (L); and the current direction of power supplied from the PFC circuit to the main power stage through the inductor is opposite to the conduction direction of the LED. The LED may also be a light emitter of a photocoupler. The filter circuit at least comprises an electrolytic capacitor (C2). When the electrolytic capacitor is normal, an exciting current of the main power stage basically does not appear in the inductor and the LED does not emit light. When the equivalent series resistance (ESR) of the electrolytic capacitor sharply rises, the exciting current appears in the inductor. When a power transistor in the main power stage is switched off, the exciting current in the inductor cannot be abruptly changed; instead, the exciting current passes through the LED for freewheeling and enables the LED to emit light, thereby notifying a user or a circuit that the electrolytic capacitor may have the risk of failure. The switch power supply has low additional cost and unchanged efficiency and is easy to implement.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
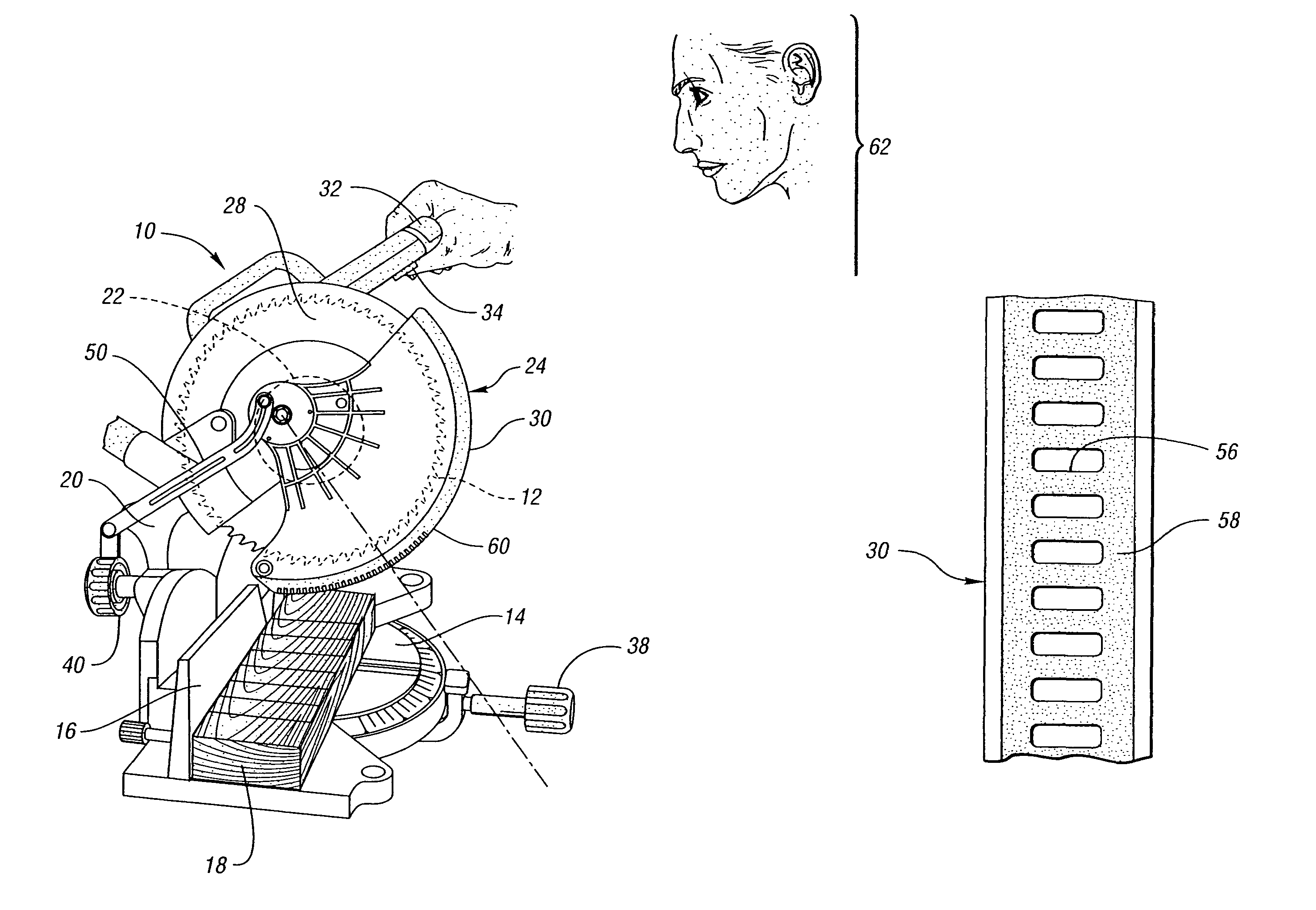
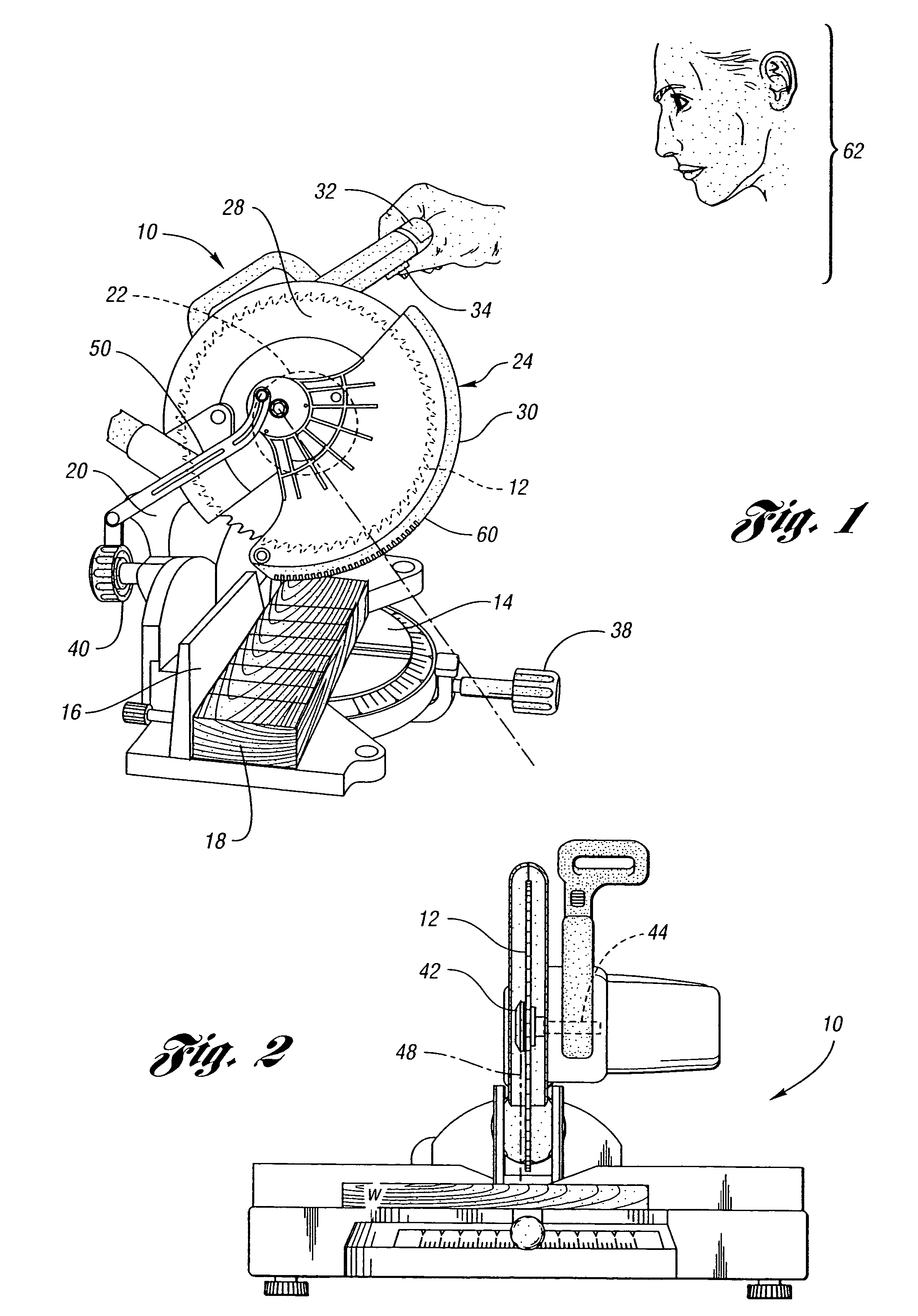
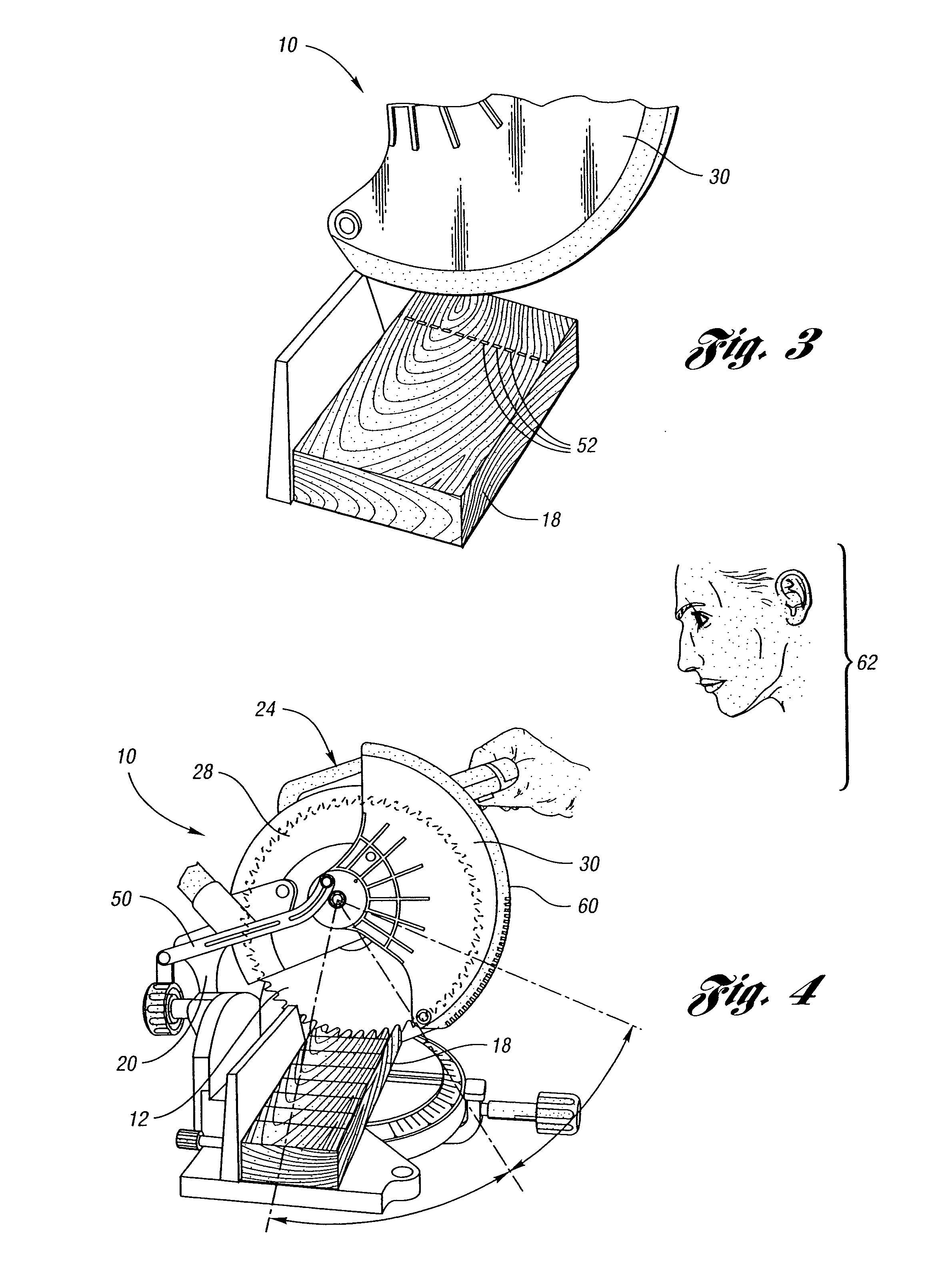
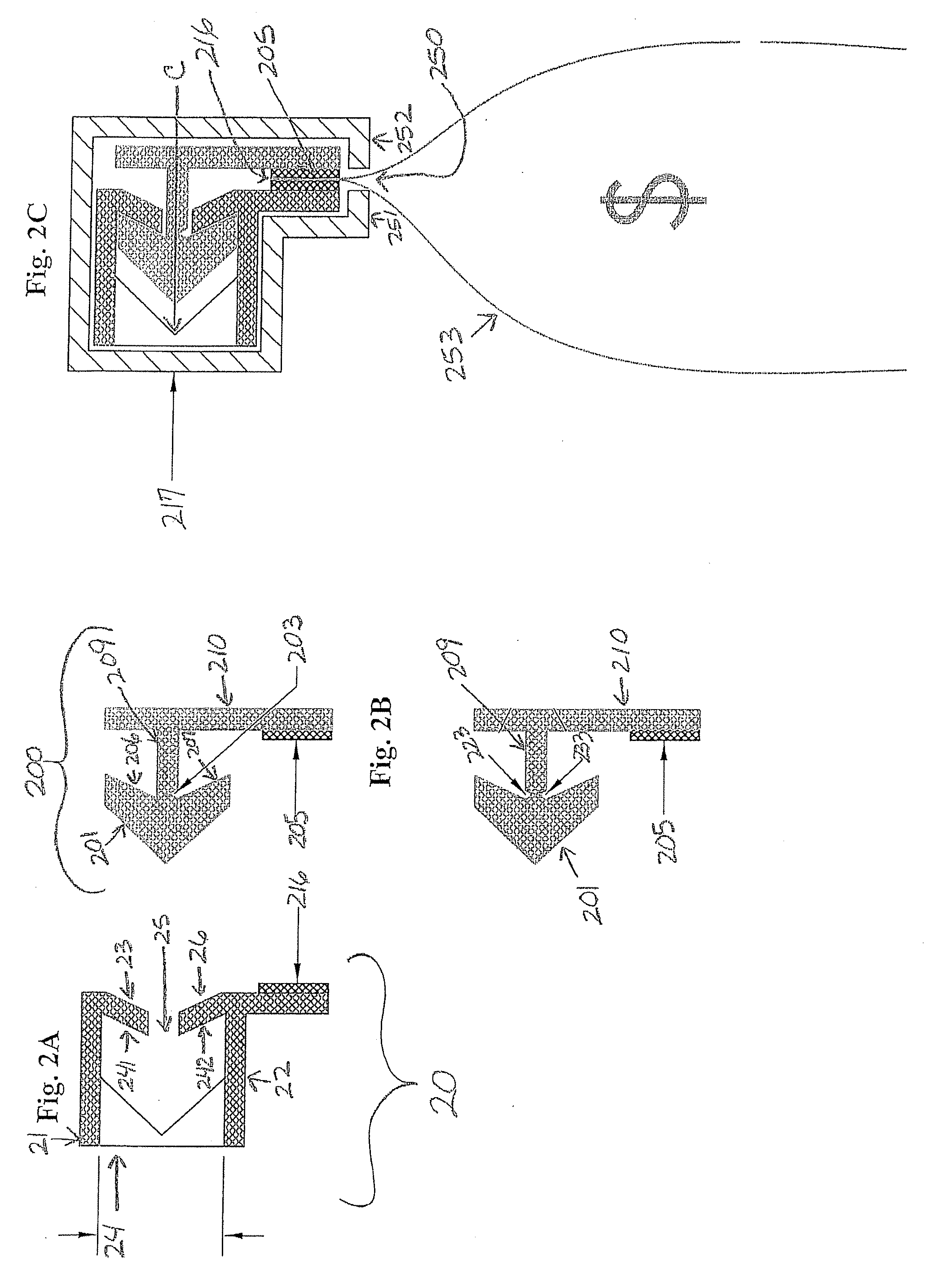
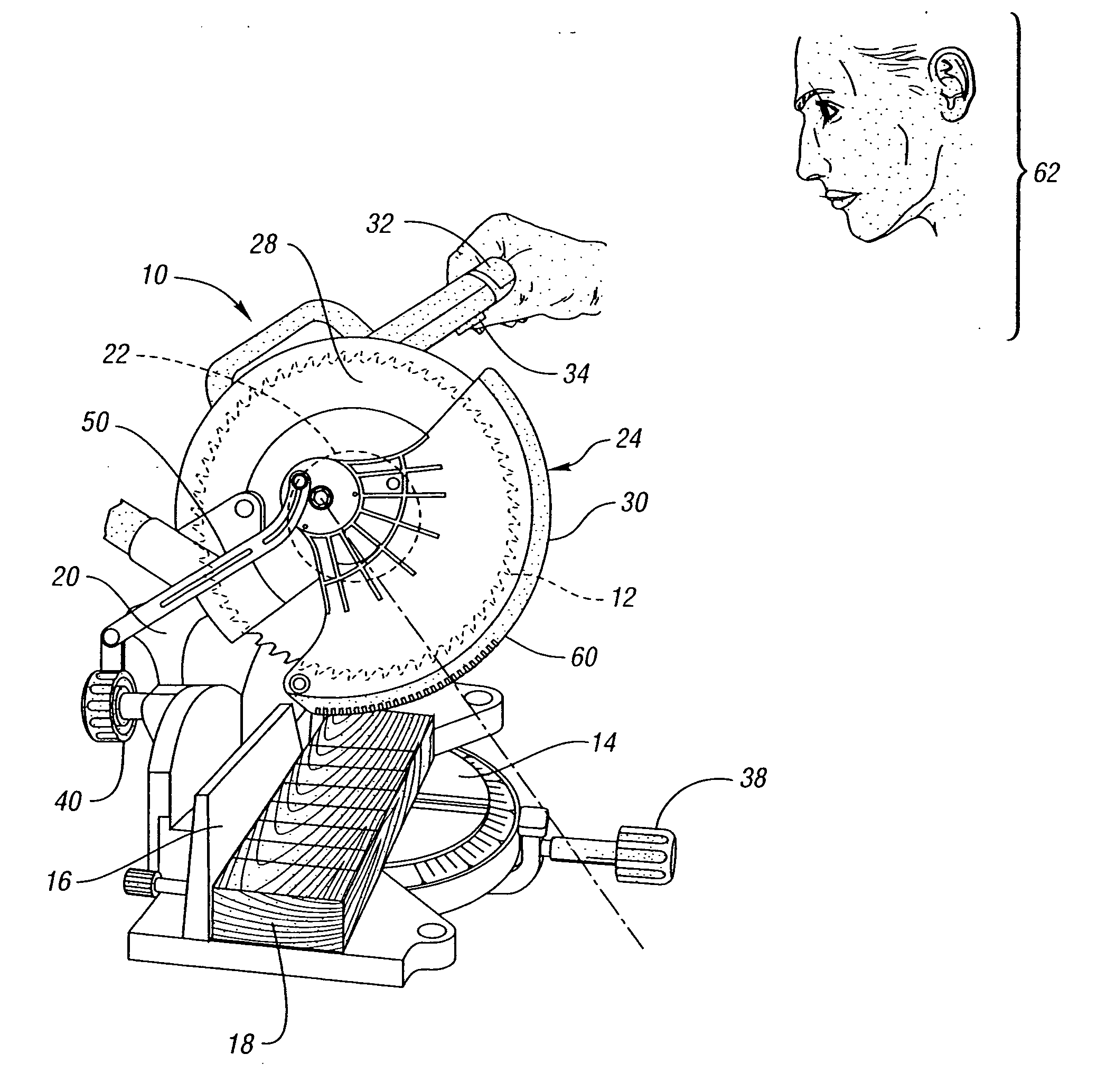
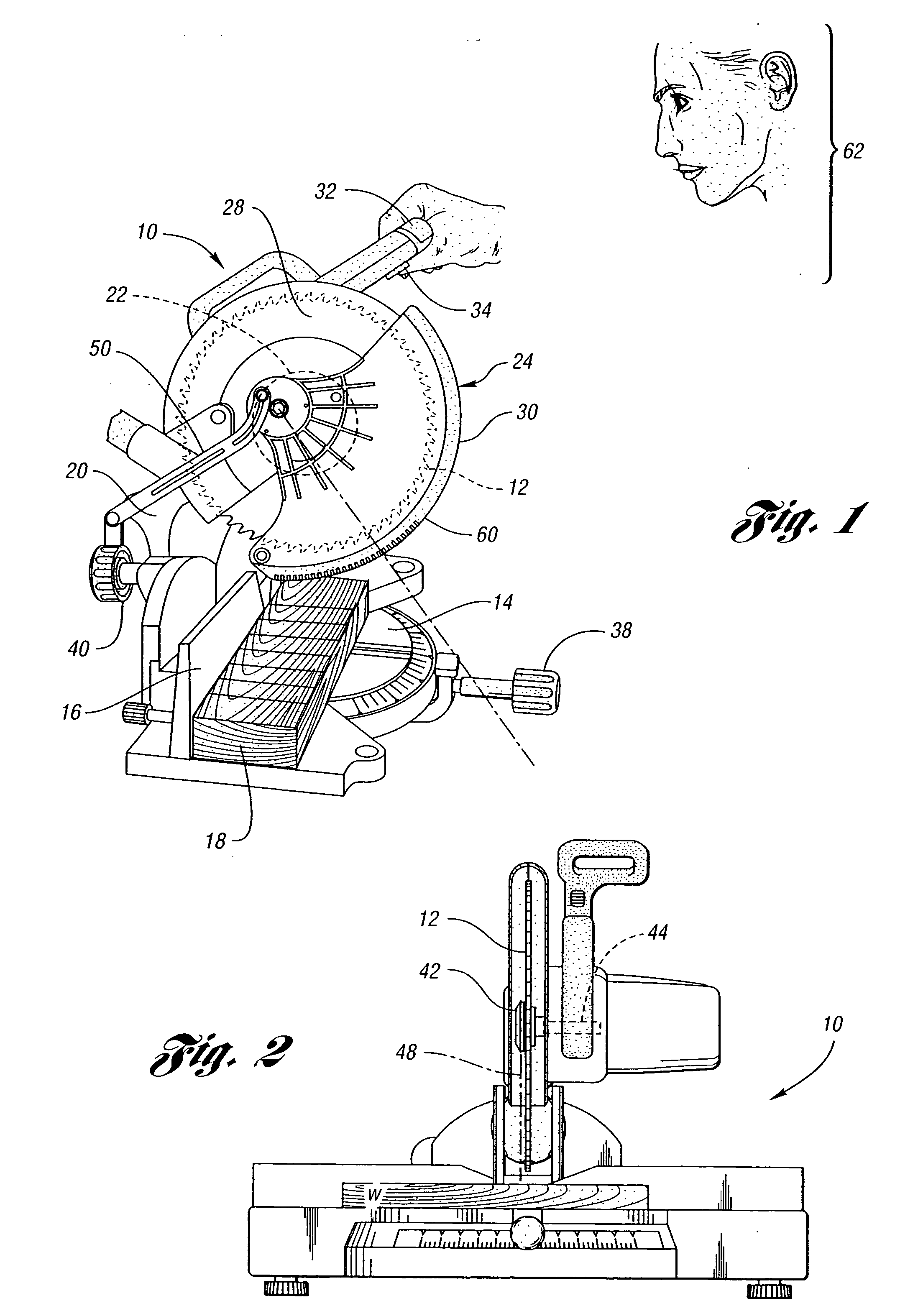
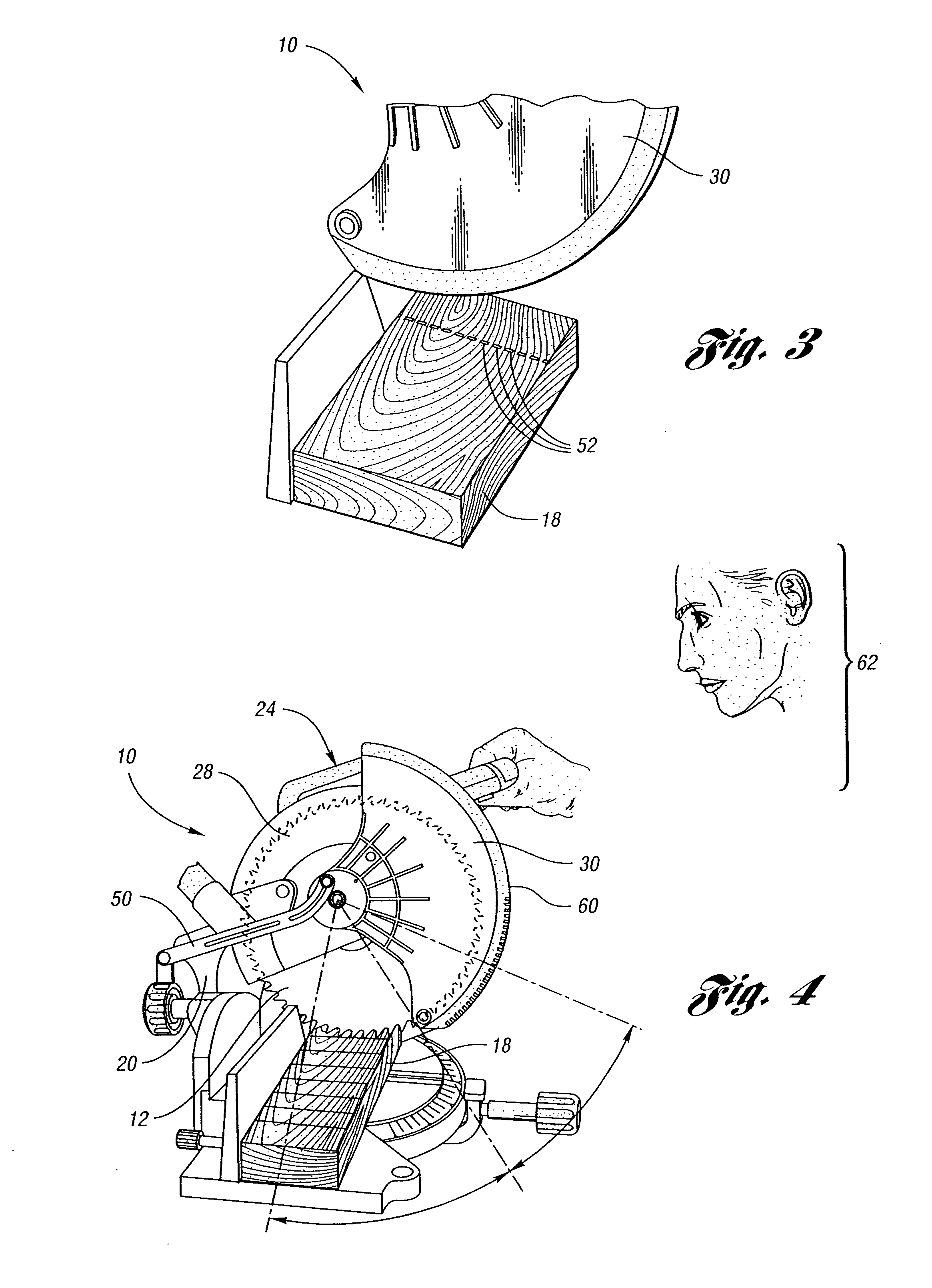
Miter saw having a light beam alignment system
InactiveUS7398719B2Easy alignmentPrecise alignmentMetal sawing devicesMetal sawing accessoriesLight beamOptoelectronics
A table saw such as a chop saw, a miter saw, compound miter saw or a sliding compound miter saw that is provided with a laser arbor alignment system. An opaque shield or transparent shield having an opaque mask blocks the laser beam from being projected into a range of normal operator eye positions. One or more openings in the shield or opaque mask provide a sight line on a workpiece initially. As the saw is moved into engagement with the workpiece, the shield is pivoted away from the workpiece and a solid laser line is projected on the workpiece.
Owner:EASTWAY FAIR
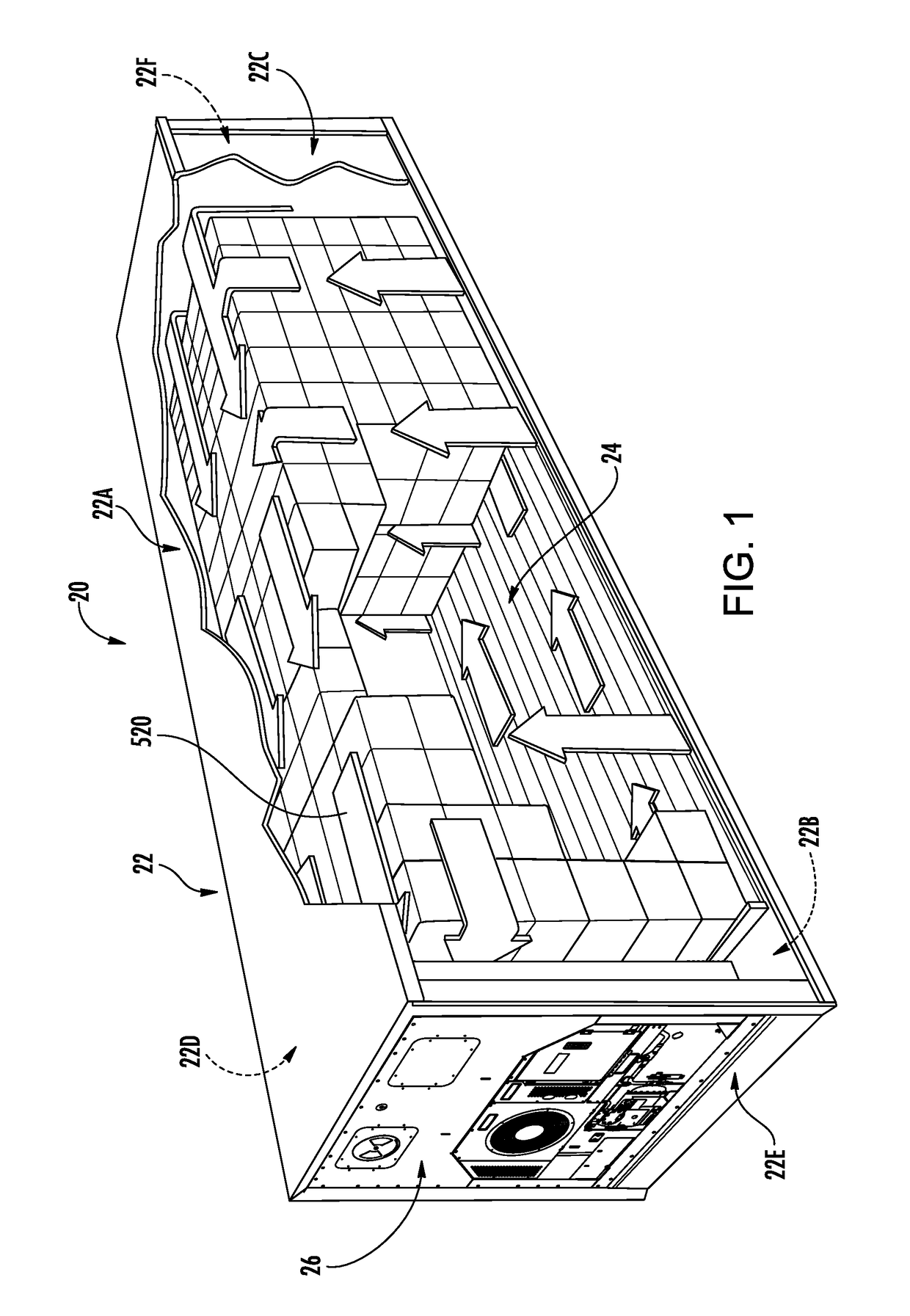
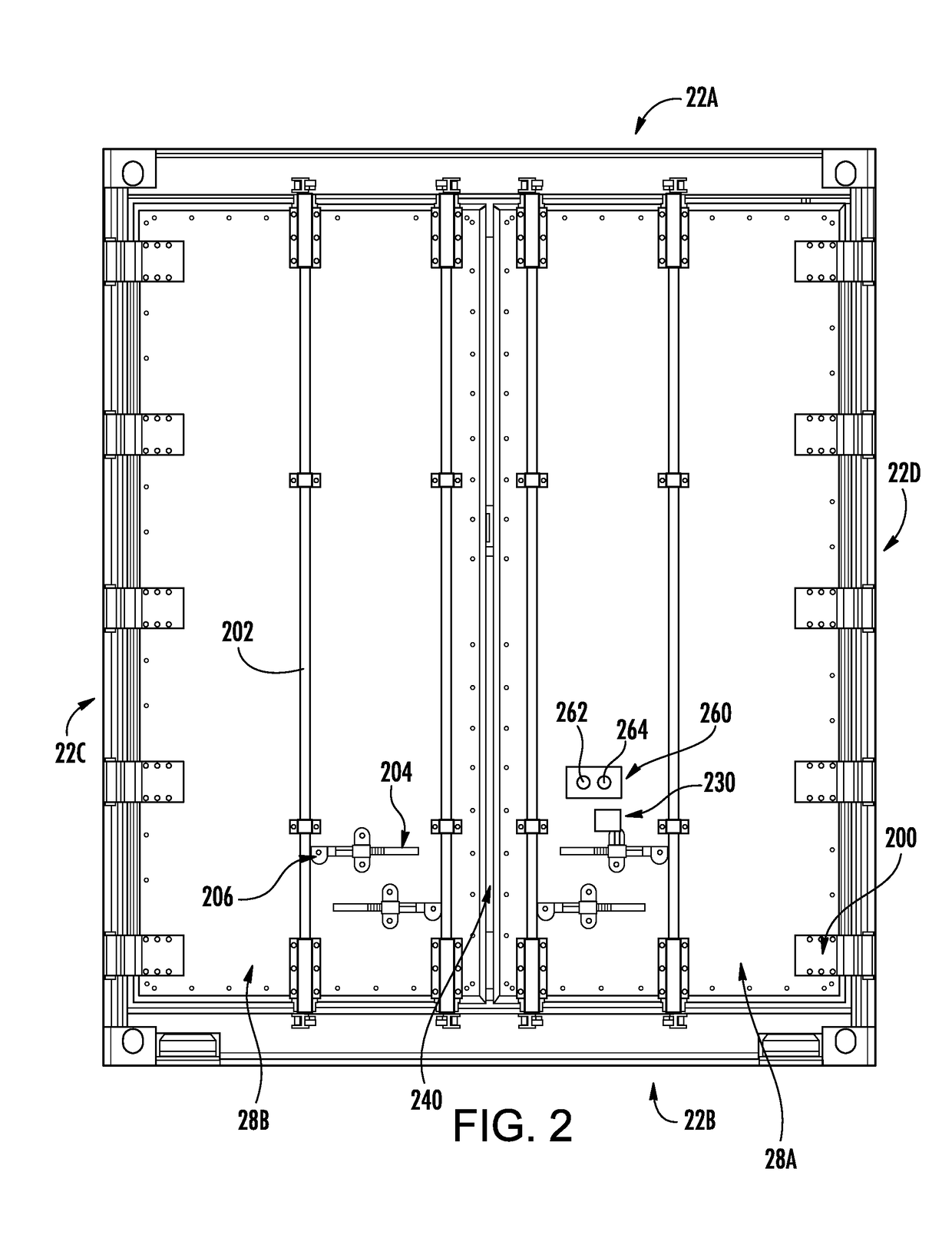
Refrigerated Transport System with Refrigerant Dilution
InactiveUS20180327179A1None provide any indicationRefrigerated goods vehicleDomestic refrigeratorsTransport systemEngineering
A refrigerated transport system (20) comprises: a body (22) enclosing a refrigerated compartment. A refrigeration system (30) comprises: a charge of refrigerant; a compressor (36) for driving the refrigerant along a refrigerant flowpath (34); a first heat exchanger (38) along the refrigerant flowpath and positioned to reject heat to an external environment in a cooling mode; and a second heat exchanger (42) along the refrigerant flowpath and positioned to absorb heat from the refrigerated compartment in the cooling mode. The refrigerated transport system has a detector (232) for detecting leakage of the refrigerant.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Bag with tamper evidencing closure
InactiveUS20060269169A1None provide any indicationSlide fastenersBagsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A closure has at least one channel portion adapted to receive an interlocking profile portion. The channel has at least one window permitting visual inspection of a profile interlocked therein. At least one profile is disposed for interlocking with the channel and includes a stem joined to the closure and one or more latching projections formed by a frangible connection to the stem, wherein one or more projections are adapted to cooperatively interlock with the channel portion of the closure, thereby sealing the closure. In one closure, a tamper evident structure is included in the form of a slider having a shaver to engage in shaving contact with interlocking closure members when passed along the closure in a direction opposite to the closing direction. The various closure members can include different colors. The closures can be used on bag structures.
Owner:REYNOLDS CONSUMER PROD INC
Miter saw having a light beam alignment system
InactiveUS20050217445A1Easy alignmentPrecise alignmentMetal sawing devicesMetal sawing accessoriesLight beamOptoelectronics
A table saw such as a chop saw, a miter saw, compound miter saw or a sliding compound miter saw that is provided with a laser arbor alignment system. An opaque shield or transparent shield having an opaque mask blocks the laser beam from being projected into a range of normal operator eye positions. One or more openings in the shield or opaque mask provide a sight line on a workpiece initially. As the saw is moved into engagement with the workpiece, the shield is pivoted away from the workpiece and a solid laser line is projected on the workpiece.
Owner:EASTWAY FAIR
Waterproof indicator and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20150283335A1None provide any indicationInfusion syringesMedical devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A medical device having an indicator to indicate whether the medical device has a waterproof seal enclosing an interior volume. The medical device includes a housing having an indicator formed on the exterior surface of the housing. The indicator is capable of moving from a first position to a second position, where the first position indicates that the medical device housing has a waterproof seal to prevent ingress of water into the interior volume of the medical device and the second position indicates that there is a leak in the housing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Apparatus and method for vehicular monitoring, analysis, and control of wheel end systems
InactiveUS20200134942A1Improve vehicle performanceExtend tire lifeBearing assemblyRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCommunication interfaceControl engineering
A vehicular monitoring system includes a plurality of wheel-end units, each of which is attachable to the wheel-end of a wheeled vehicle. The system monitors sensor readings and may analyze the readings to diagnose conditions related to vehicle components, including tires, axles, bearings or components of the monitoring system. The system may analyze readings to predict, or prognosticate, conditions related to vehicle components or to components of the monitoring system. Each wheel-end unit includes a communications interface for communications among wheel-end units associated with a vehicle monitored by the system.
Owner:APPL MECHATRONIC PROD LLC
Training device
InactiveUS20150306484A1Reduce physical stressIncrease speedGymnastic exercisingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMedicine
The disclosed technology is a training device particularly well suited for training fighters as well as people simply interested in personal fitness. The device comprises a body portion defining an elongated flexible shape configure to be associated with a cover portion such as a modified focus mitt. The focus mitt defines a planar region further defining a target zone to be hit by the trainee. The body portion provides a flex region configured to absorb at least part of the inertia associated with a strike on the target zone to reduce the load on the trainer and trainee.
Owner:NUSSBAUM MATTHEW T
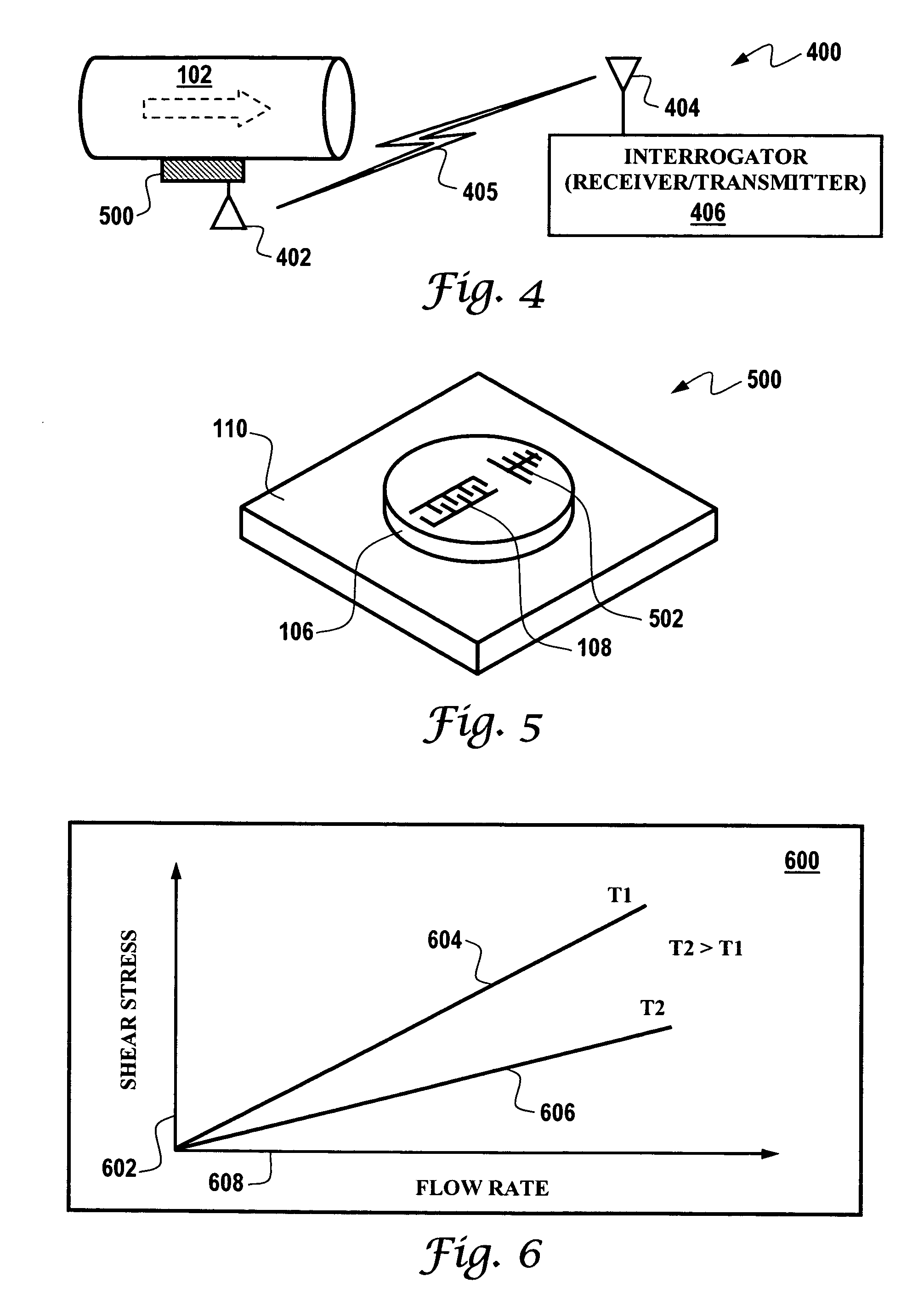
Acoustic wave flow sensor
InactiveUS7140261B2None provide any indicationVolume/mass flow measurementPhase changeInterdigital transducer
An acoustic wave flow sensor is disclosed, which includes a sensor substrate and an acoustic wave diaphragm etched upon the sensor substrate, wherein mechanical stress or strain is concentrated in the acoustic wave diaphragm. One or more interdigital transducers can be configured upon the acoustic wave diaphragm, wherein the sensor substrate, the acoustic wave diaphragm and the interdigital transducer(s) form an acoustic wave flow sensor, such that when the interdigital transducer and the acoustic wave diaphragm are exposed to a fluid in flow, the fluid in flow causes the acoustic wave diaphragm to experience a change in the mechanical stress or strain resulting in a detectable frequency and / or phase change in order to provide an indication of fluid flow.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
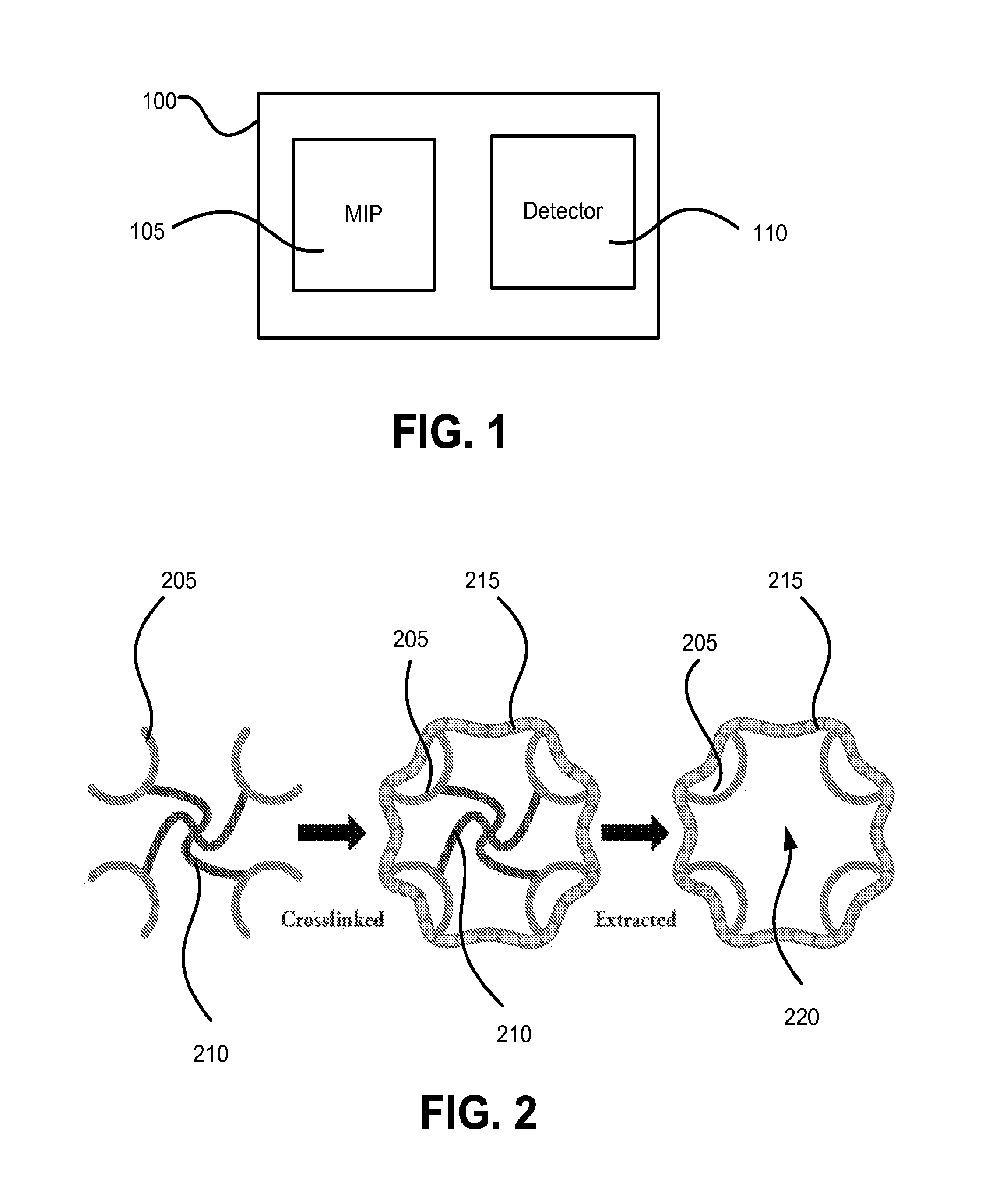
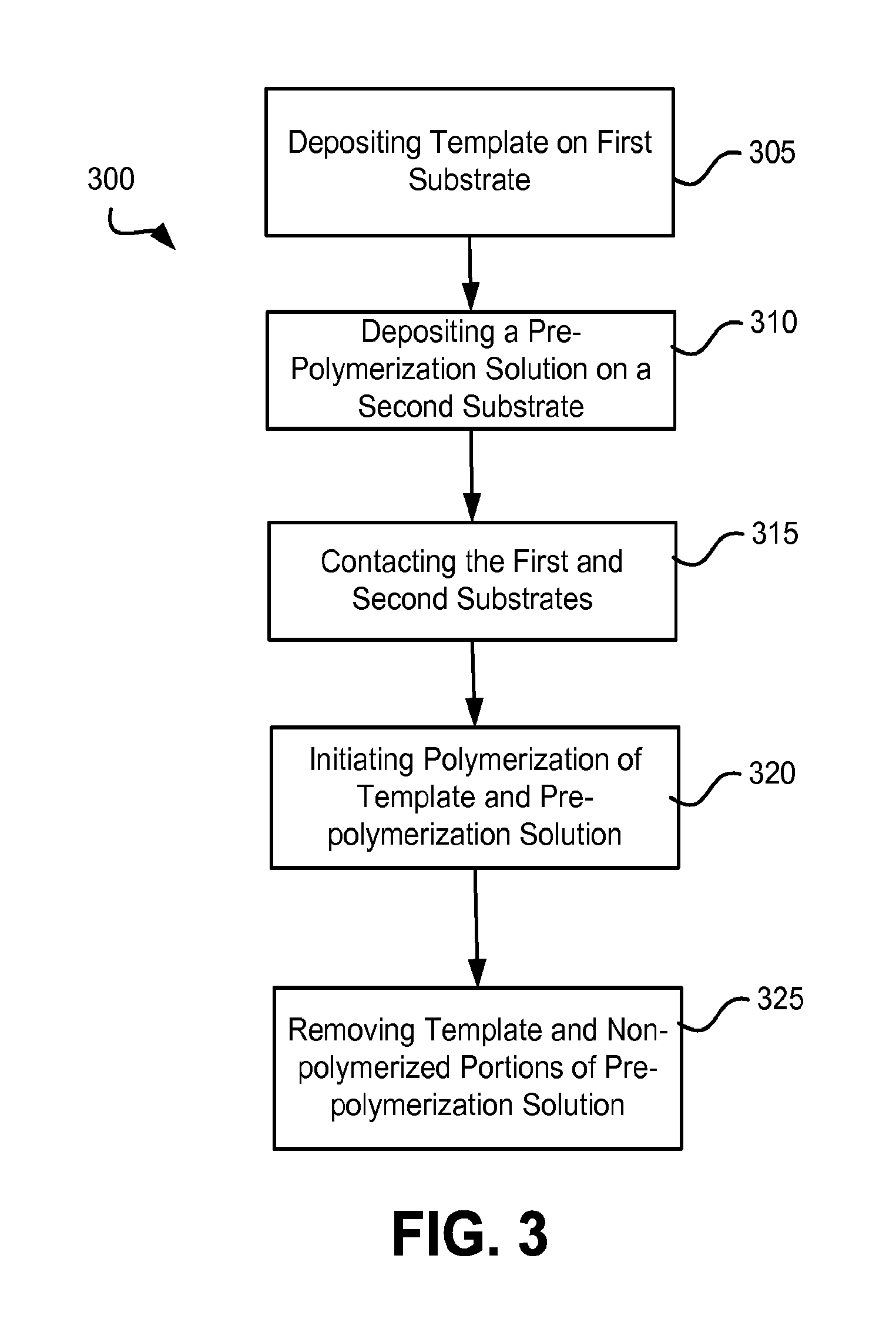
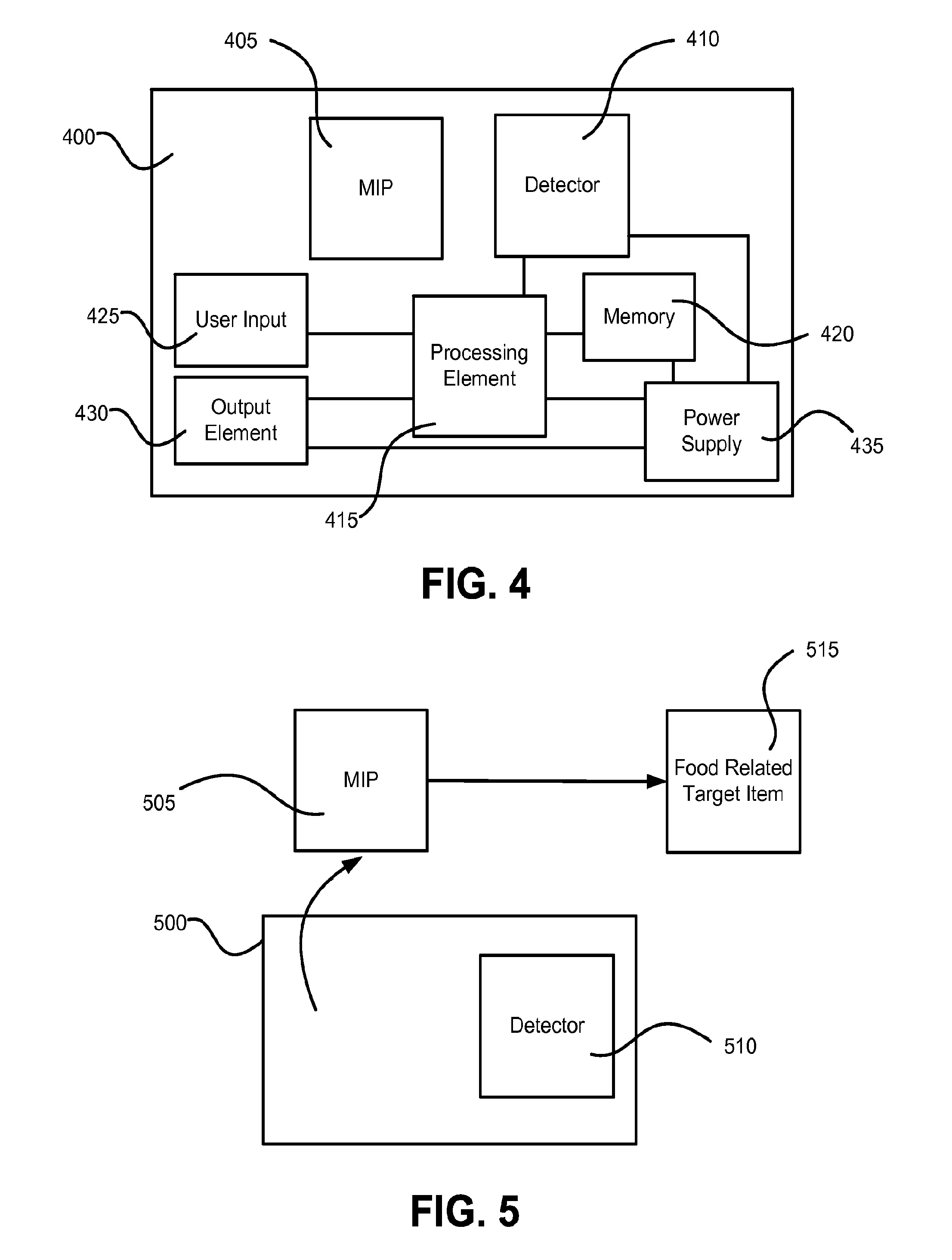
Food Allergen Detection Methods and Systems Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
InactiveUS20160209420A1None provide any indicationMaterial analysis using immobilised reagentsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAllergens foodMolecularly imprinted polymer
Methods and devices for the detection of food allergens using molecularly imprinted polymers that are imprinted for a target food allergen. A molecularly imprinted polymer may be imprinted using surface imprinting or other procedures. Detection of food allergens, such as peanut allergens, may be accomplished using all or a portion of a protein food allergen as a template to produce a molecularly imprinted polymer for food allergen detection. A portion utilized can be one that creates receptor sites in the molecularly imprinted polymer that are unique or more unique to the target food allergen than receptor sites that would be created if an entire food allergen molecule were utilized.
Owner:AMULET
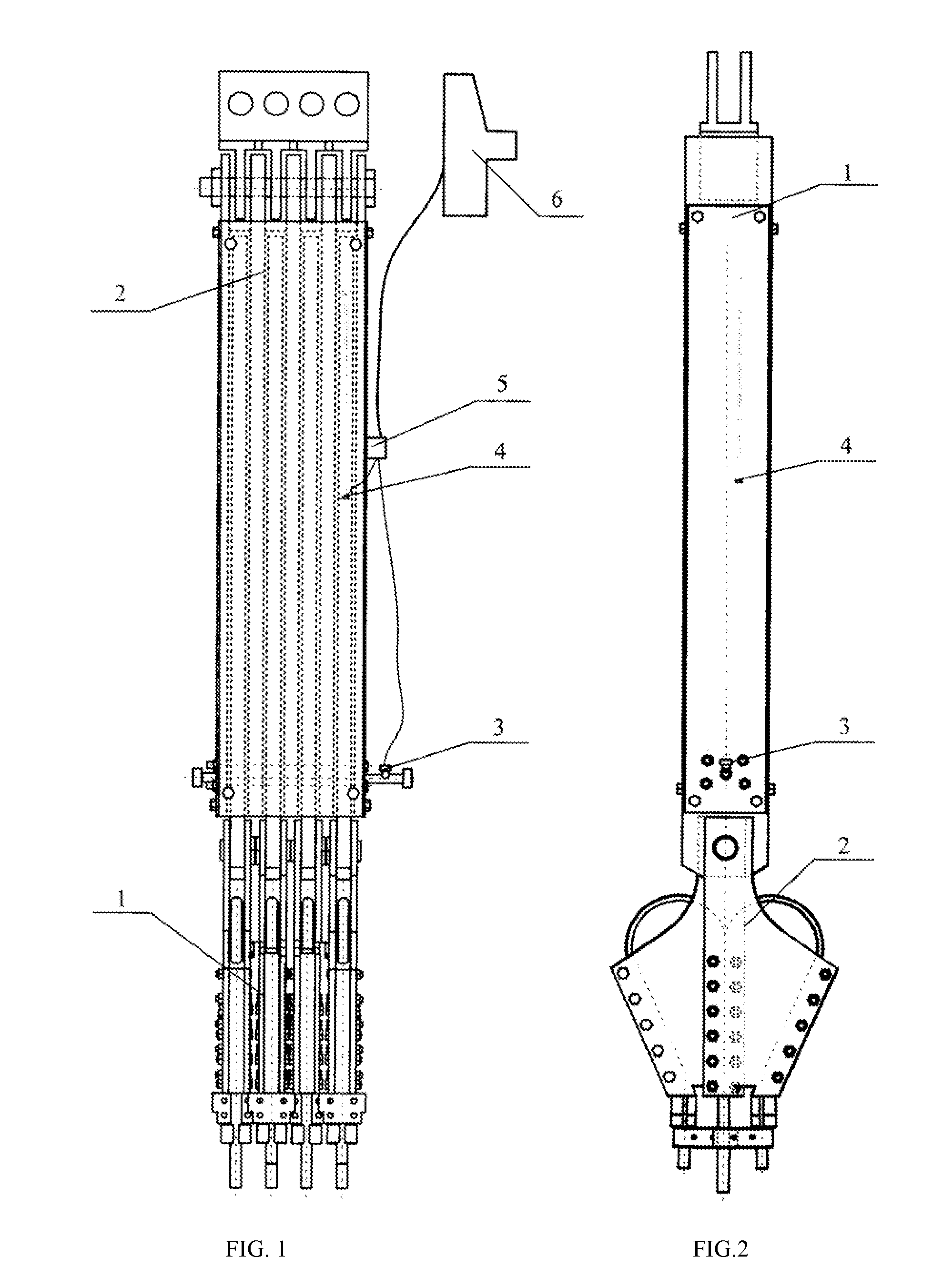
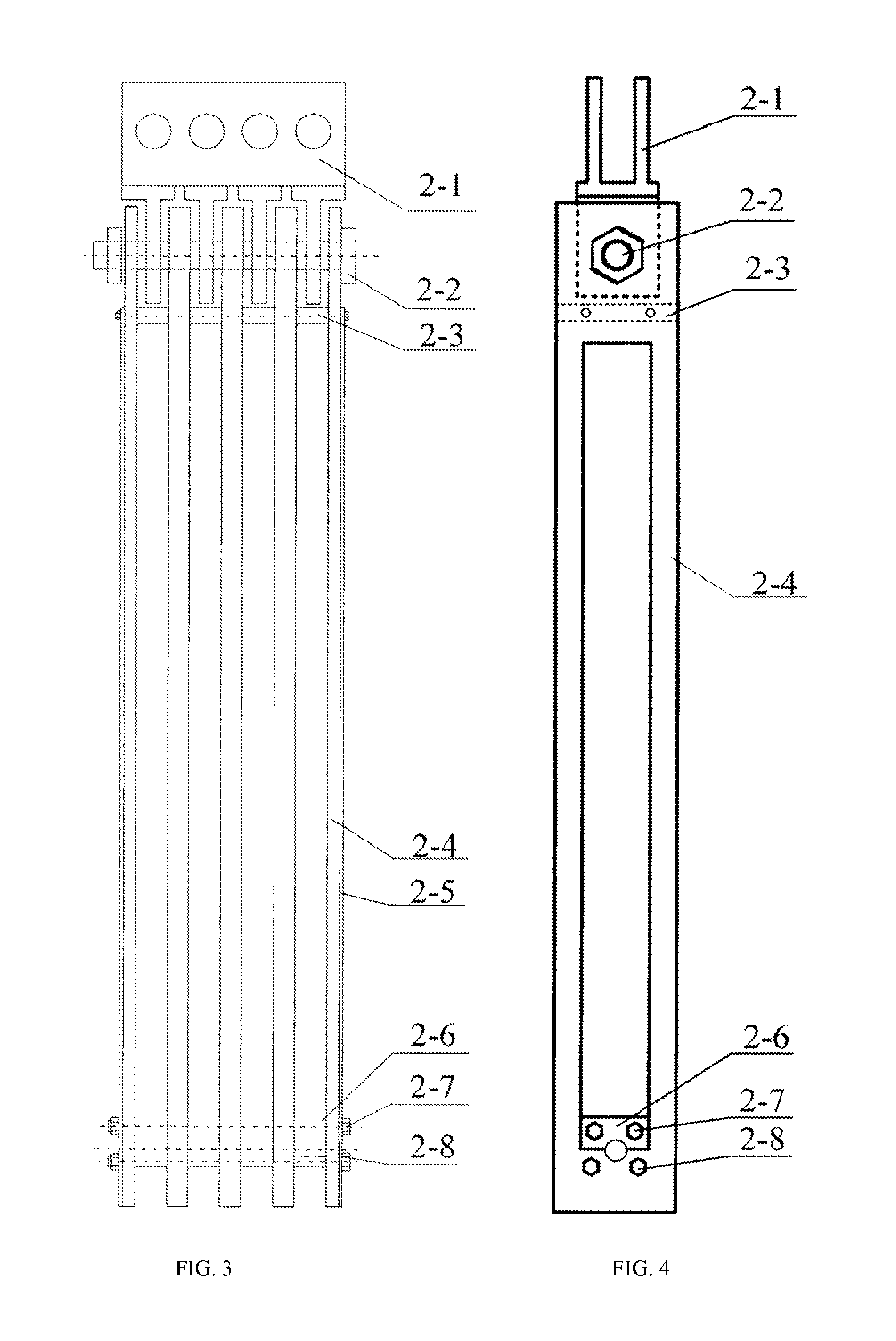
Mining elevator traction cable connecting apparatus and measuring method therefor
ActiveUS20130056313A1Simple structureGuaranteed uptimeAlarmsElevatorsHydraulic cylinderRelative displacement
A mining elevator traction cable connecting apparatus and a measuring method therefor, for use in a mining elevator serving a deep-mine. The apparatus includes an industrial personal computer (IPC), a signal collector connected to the IPC, multiple symmetrically arranged cable rings for use in connecting to one end of a traction cable, and a traction cable tension adjusting apparatus connected to the multiple of cable rings. Arranged within the traction cable tension adjusting apparatus are a plurality of hydraulic cylinders, and a plurality of draw wire displacement sensors for use in monitoring the relative displacement between each hydraulic cylinder plunger and a corresponding hydraulic cylinder body. The draw wire displacement sensors and an oil pressure sensor connected to a hydraulic pipeline are connected to the IPC via the signal collector, forming a traction cable tension and degree of adjustment measuring system.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
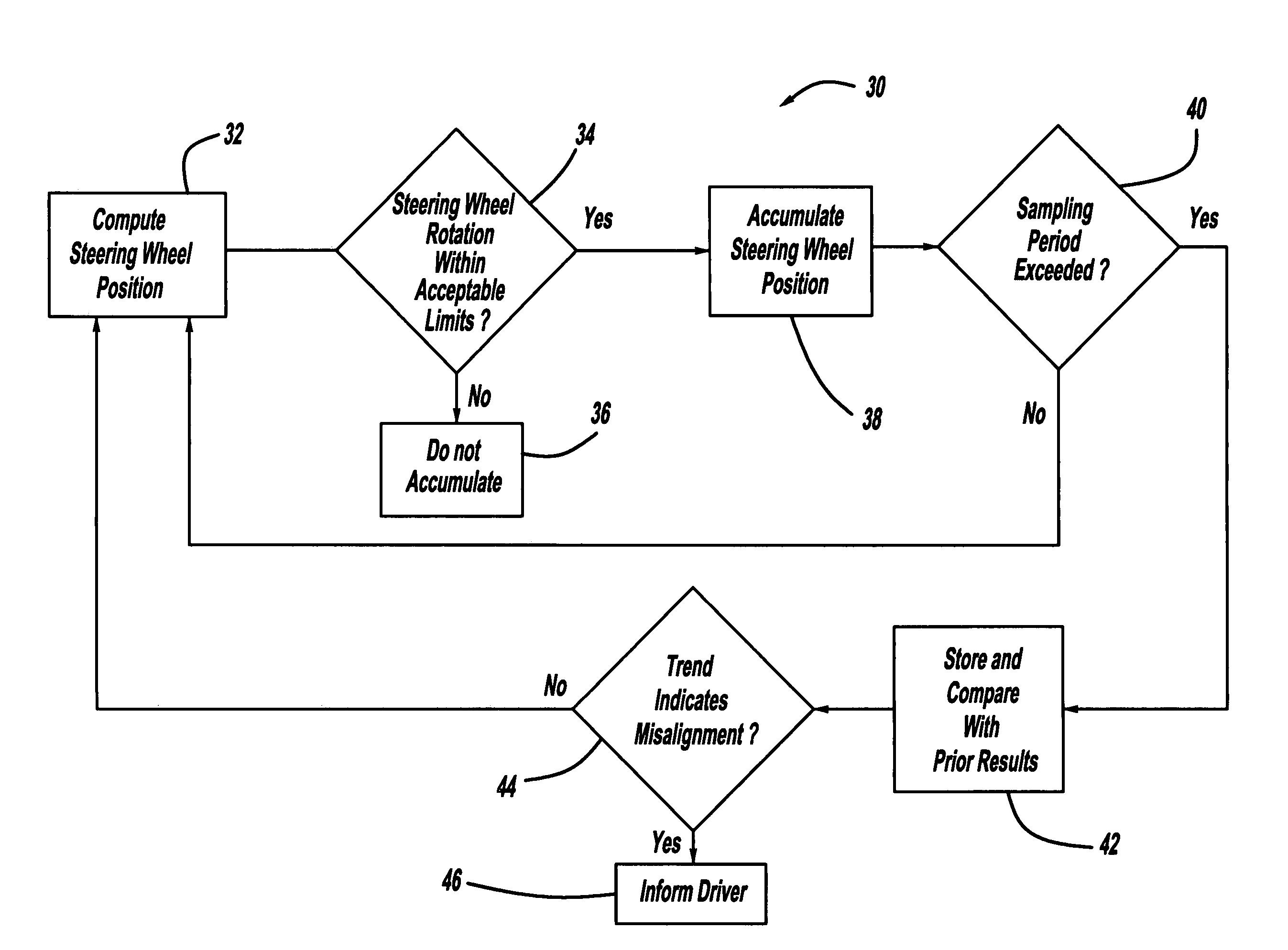
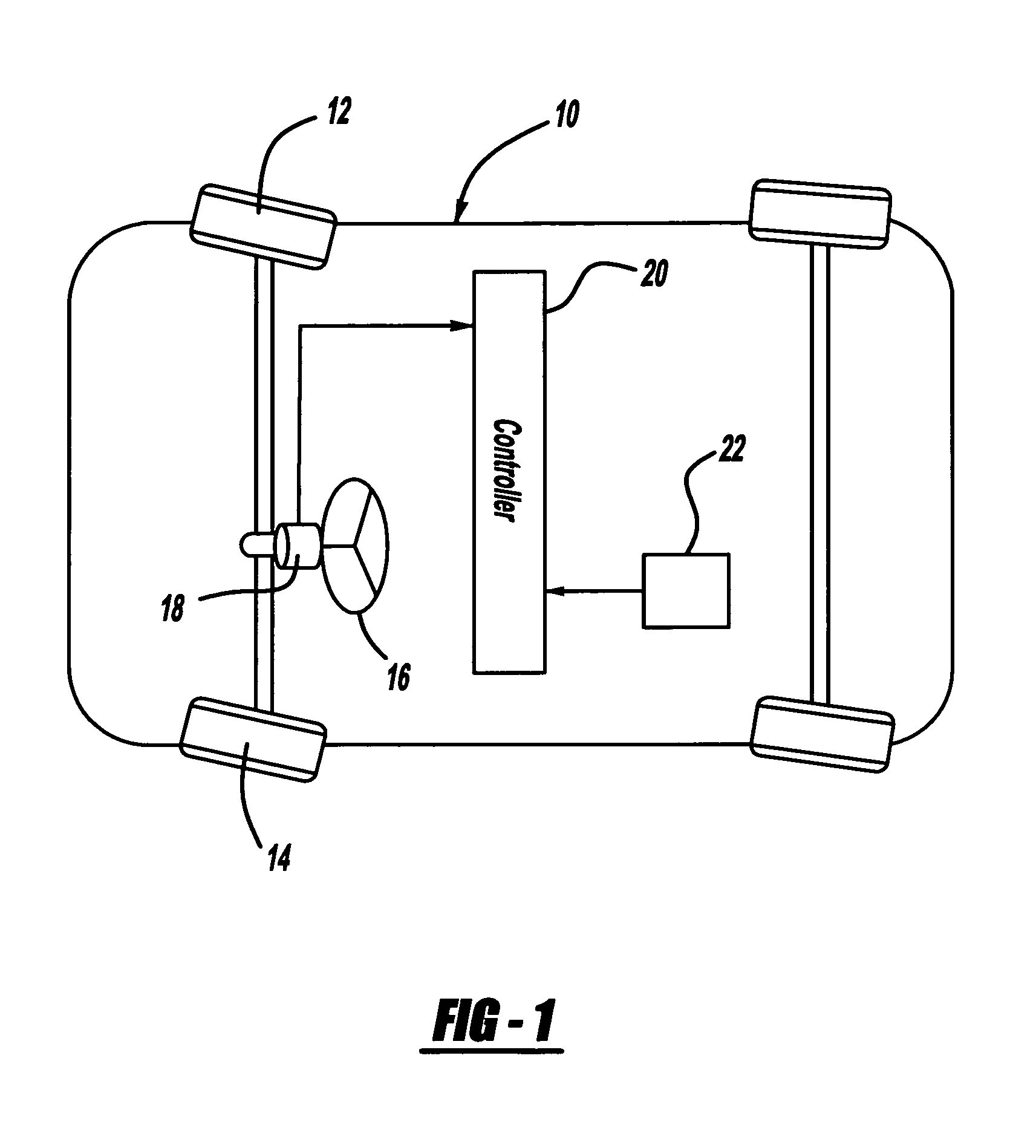
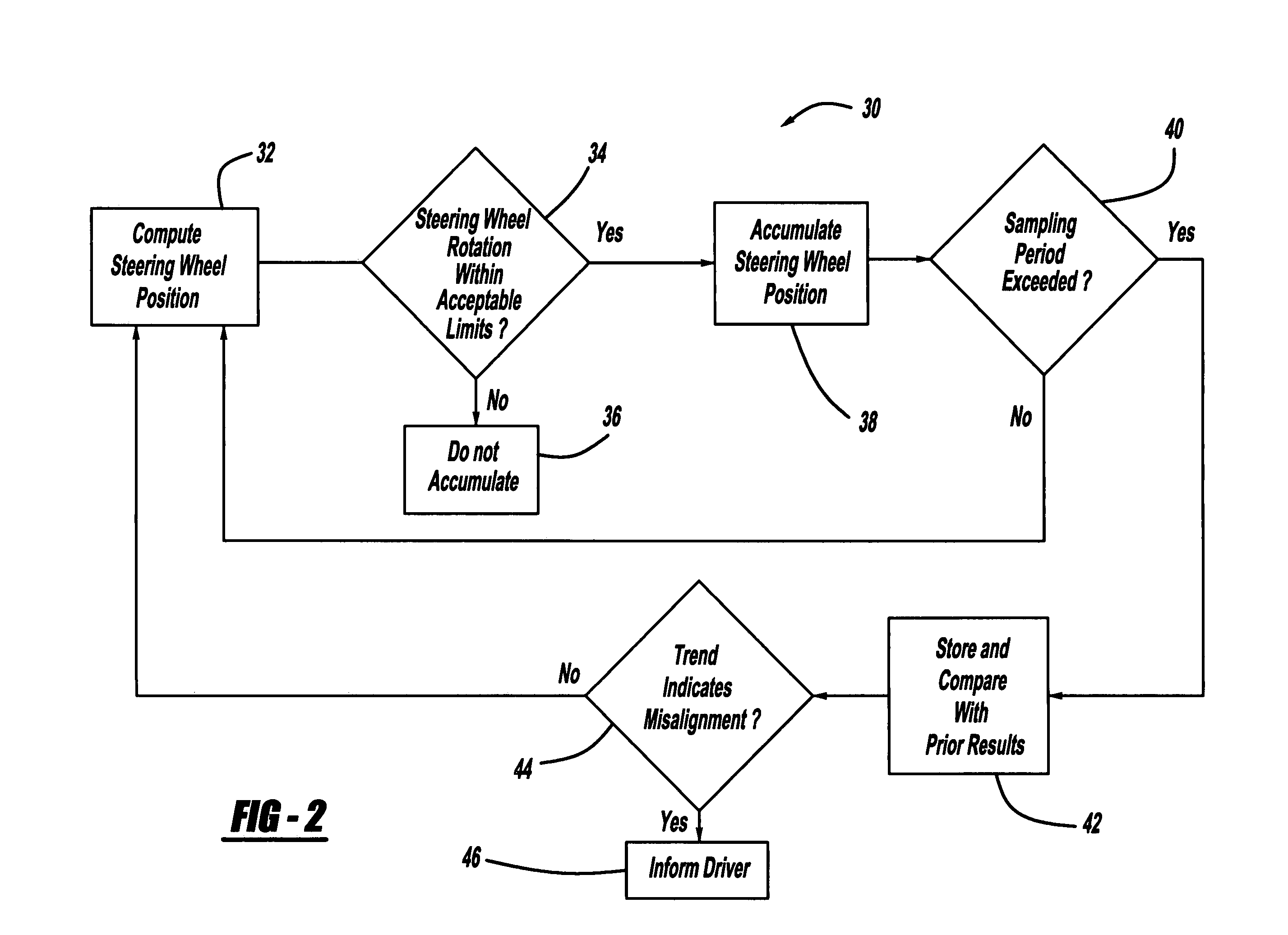
Algorithm for early detection of wheel misalignment using on-vehicle instrumentation
InactiveUS7698031B2Improve deviationConfidenceVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringInstrumentation
A system and method for determining vehicle wheel misalignment. The method includes accumulating the hand-wheel position using a hand-wheel sensor over a predetermined sampling period, and then comparing the accumulated hand-wheel position to previously accumulated hand-wheel positions to provide an indication of wheel misalignment. Because a vehicle will typically be driven so that the right turns will substantially equal the left turns over a sufficiently large sampling period, the accumulated hand-wheel position should average out to be about zero, unless there is a wheel misalignment which would cause the vehicle operator to continuously turn the hand-wheel in one direction when driving straight. Therefore, if the accumulated hand-wheel position exhibits a consistent algebraic deviation and shows a progressive increase over multiple sampling periods, the confidence of wheel misalignment will increase.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Combination and method including a visual marker for determining compliance with a medication regimen
InactiveUS20060235312A1None provide any indicationCompounds screening/testingPharmaceutical product form changeOral medicationPharyngeal cavity
A method and combination including a visual marker for monitoring a patient to determine compliance with a medication regimen. An orally administrable medication composition is provided in combination with a visual marker. When the combination is orally ingested, the marker causes a coloration or discoloration of the oral and / or pharyngeal cavity of a subject. By visually observing the oral and / or pharyngeal cavity of the subject, one can determine whether medication has been ingested based upon the presence or absence of the coloration / discoloration.
Owner:UNION SPRINGS PHARMA
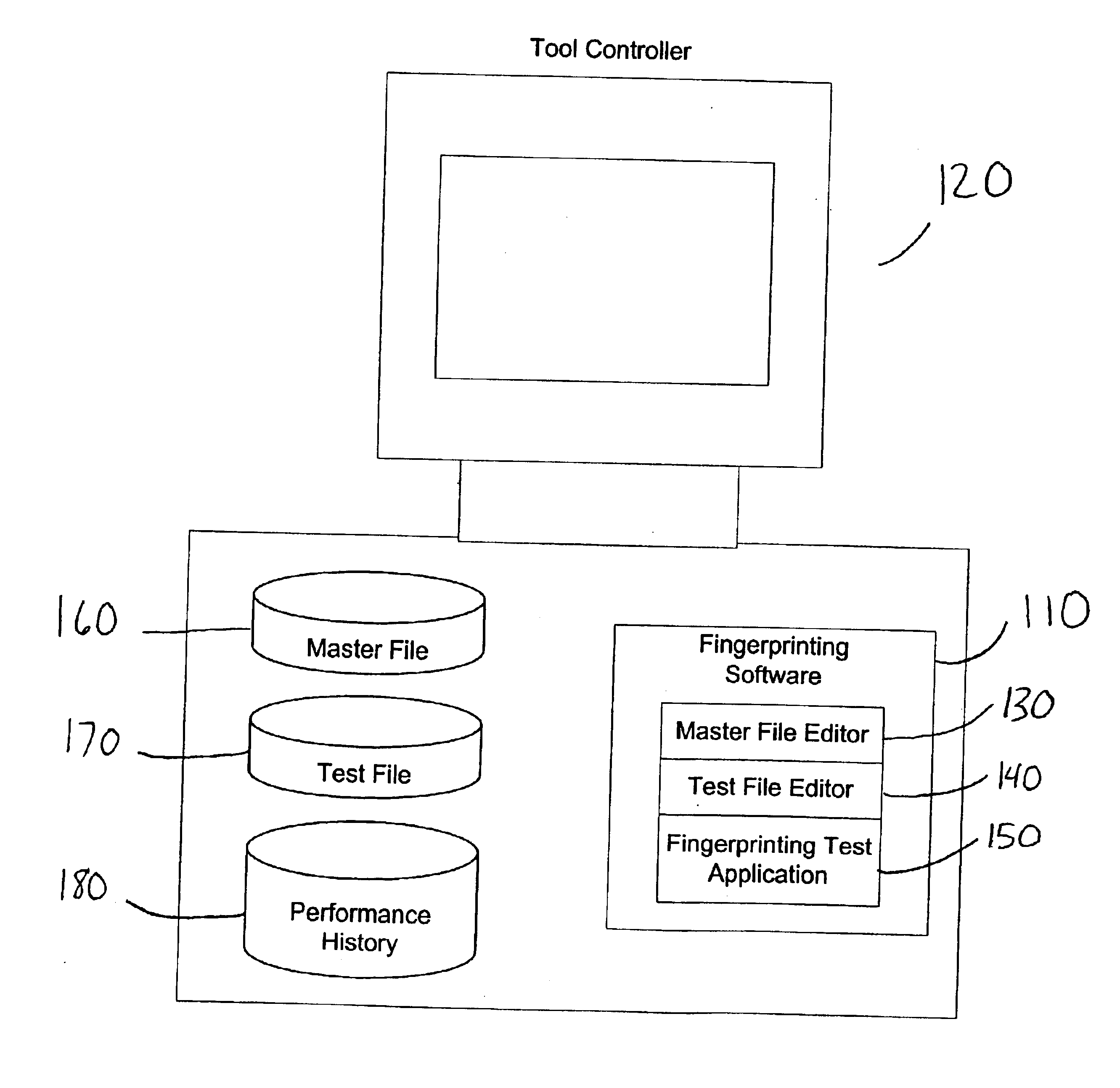
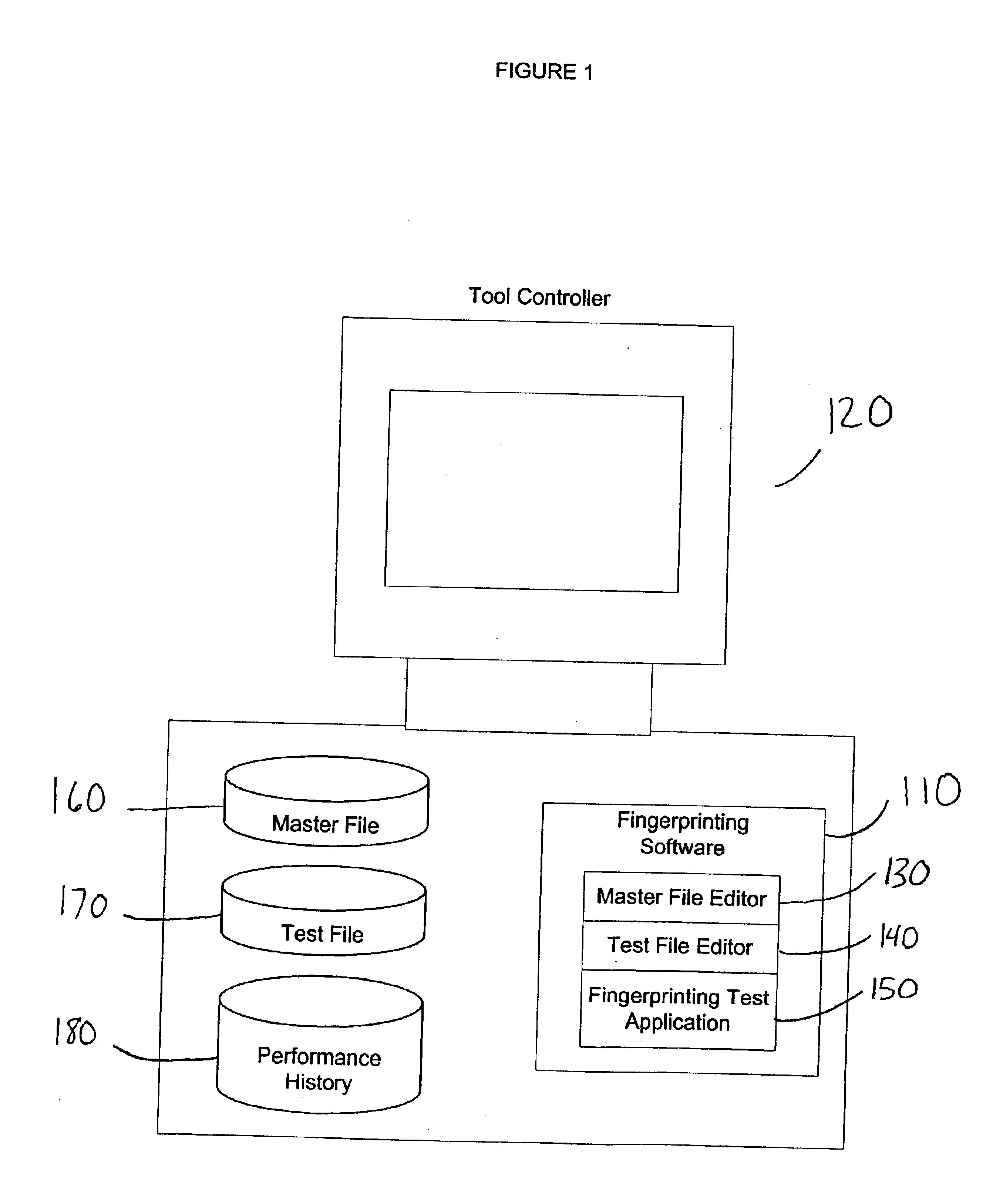
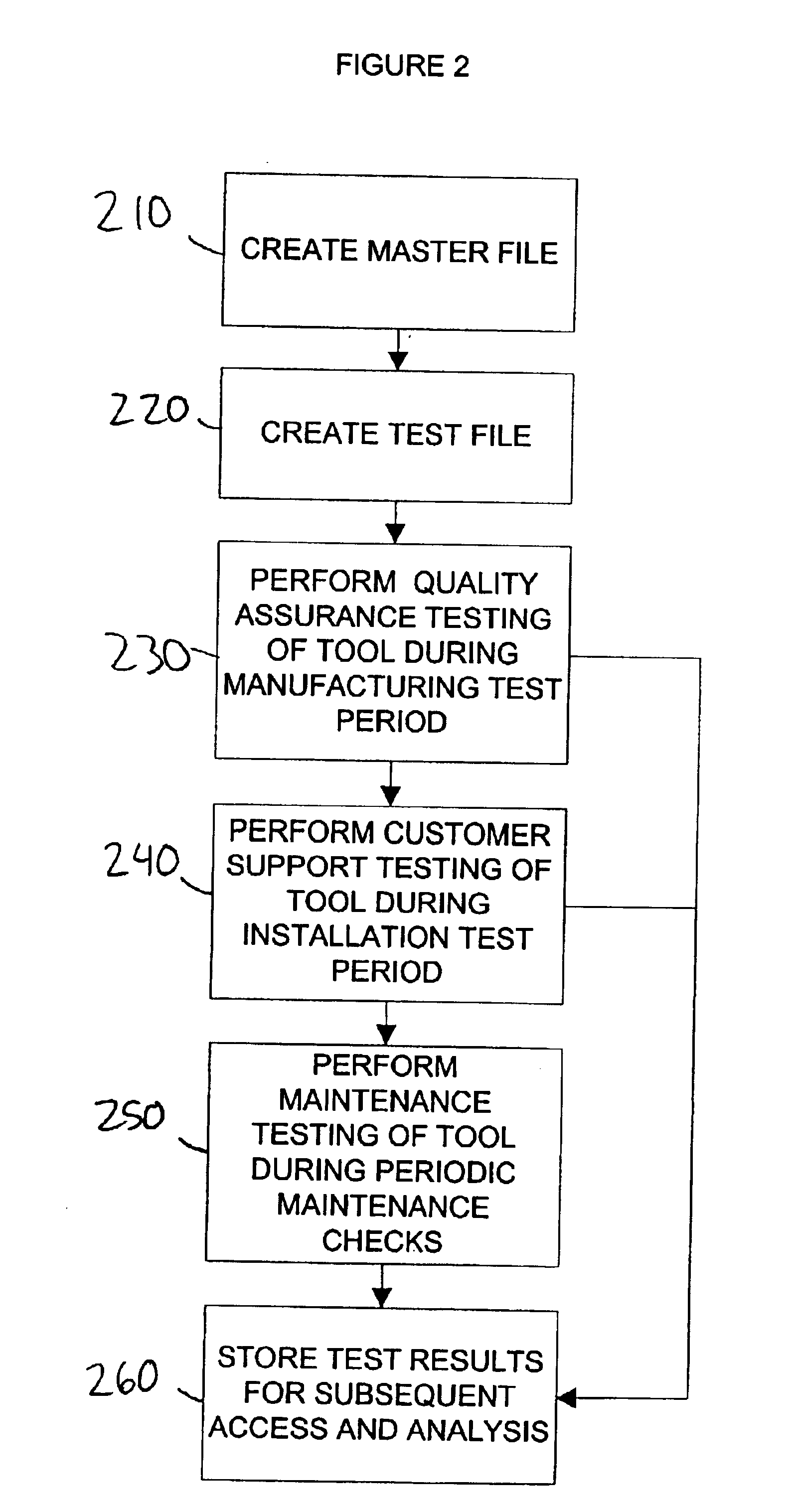
System and method for fingerprinting of semiconductor processing tools
ActiveUS6889149B2Easy to collectNone provide any indicationResistance/reactance/impedenceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFingerprintSoftware
A system and method is used for measuring the performance of semiconductor processing tools. A software component may be used to define a set of performance variables and associate performance limits. From the set of performance variables, a set of variables may be selected to create a customized test for a particular tool. The system may be used to store the results of the tests within the system for fast comparison with the associated performance limits, with previous test results, or both. The system may be used to display an overall status of groups of performance variables.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com