Patents
Literature
45 results about "Martian packet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
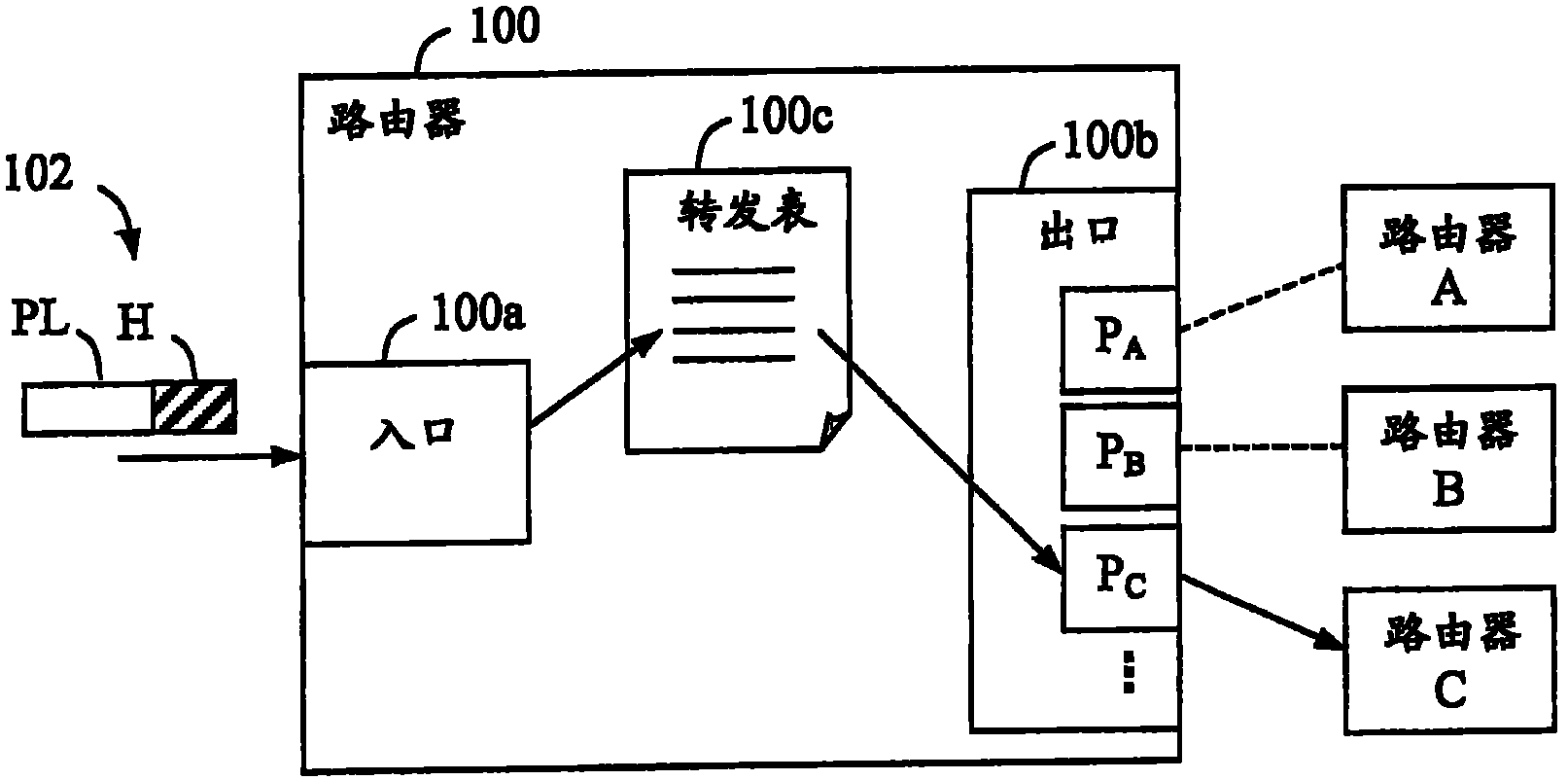
A Martian packet is an IP packet seen on the public Internet that contains a source or destination address that is reserved for special-use by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). On the public Internet, such a packet either has a spoofed source address, and it cannot actually originate as claimed, or the packet cannot be delivered. The requirement to do this is found in RFC 1812, Section 5.2.3 (Local Delivery Decision).
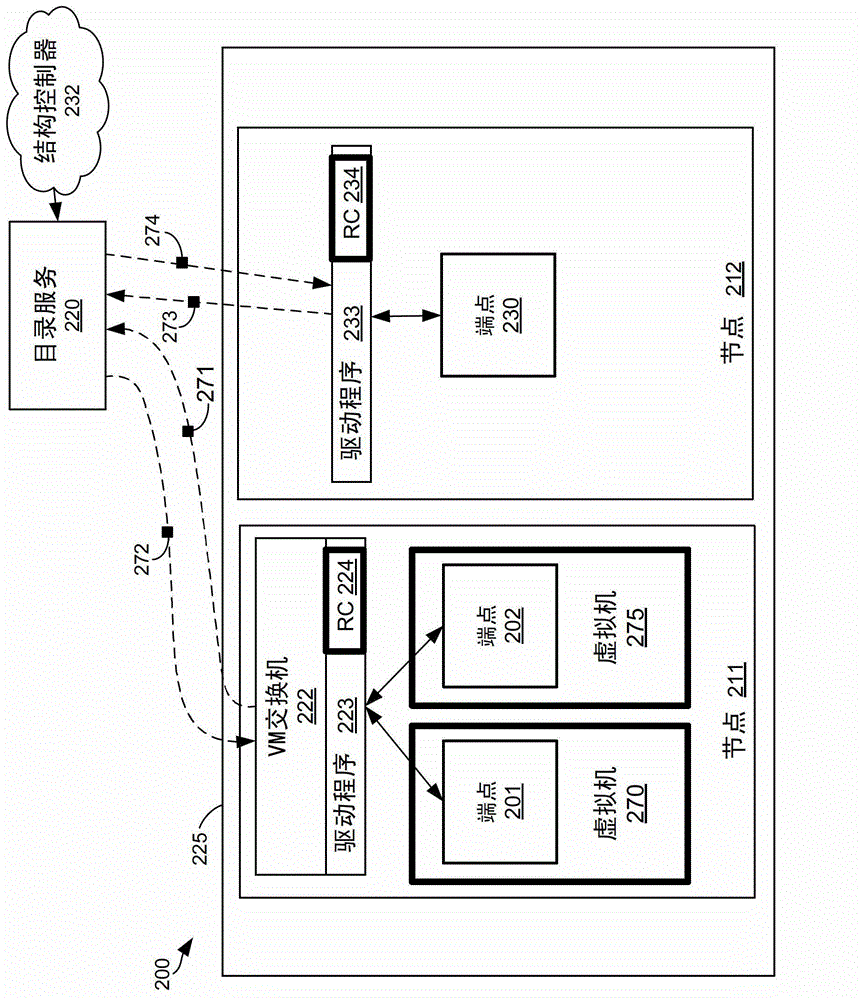
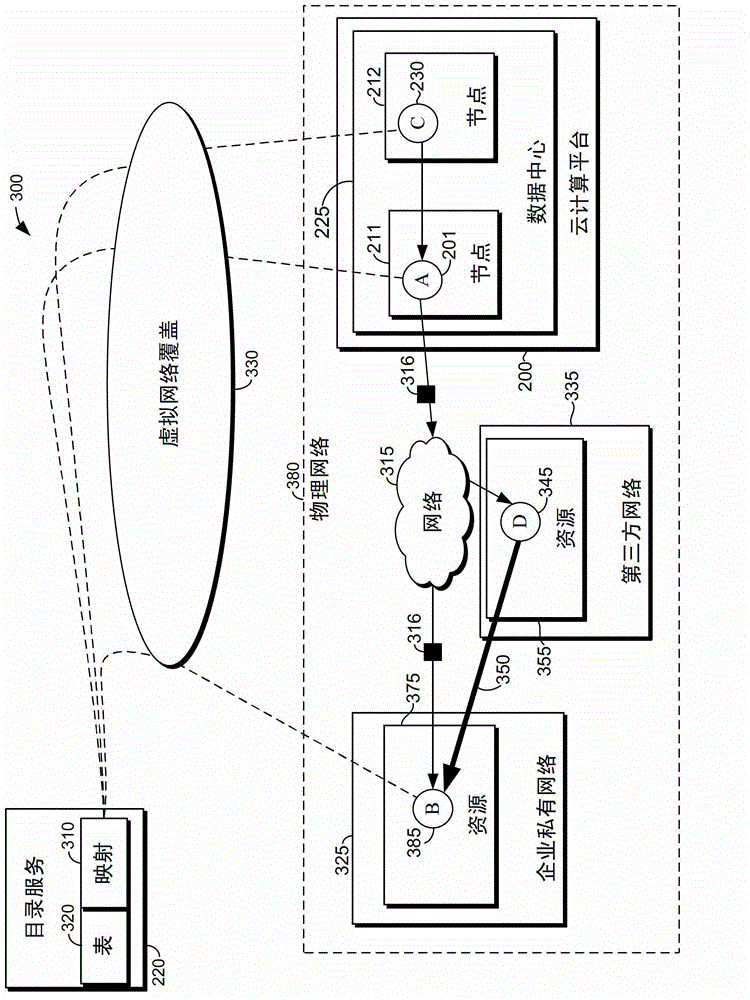
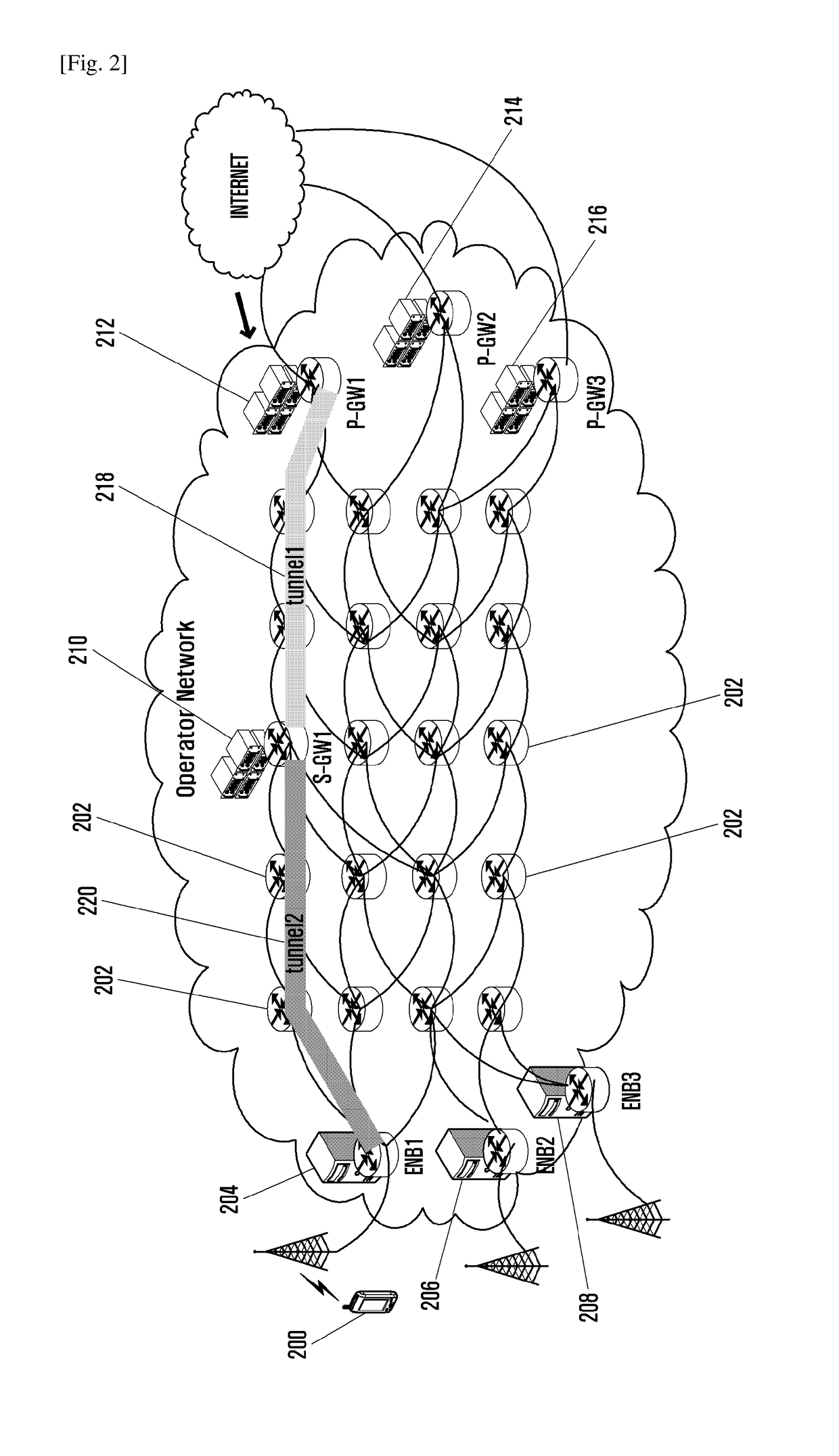
Distributed virtual network gateways
Computerized methods, systems, and computer-readable media are provided for distributing virtualized gateway functionality to multiple nodes within a physical network. Initially, drivers that carry out the gateway functionality are provisioned to cooperate with endpoints instantiated on the network nodes, while a directory service is implemented to maintain a mapping between virtual internet protocol (IP) addresses and location-dependent addresses, as well as a table enumerating transformation actions according to known pathways connecting the endpoints within a network. In operation, the directory service replies to requests from the driver (carrying source and destination IP addresses of data packets) with the appropriate location-dependent addresses (utilizing the mapping) and the appropriate transformation action(s) (utilizing the table). The transformation action(s) include rewriting headers of the data packets to include the location-dependent addresses, encapsulating the data packets as inner data packets within respective outer data packets, or configuring the data packets with a tunneling protocol.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and arrangement in a telecommunication system with signalling of assigned data packets in a bundling window
ActiveCN102017504AError prevention/detection by using return channelWireless communicationComputer terminalTelenet
An object of the present invention is to provide a mechanism for improving the detection of missed DL assignment. A method in a base station (110) for sending a data packet to a mobile terminal (120) is provided. The base station (110) uses a current bundling window for transmitting data packets in subframes of a radio channel. The bundling window comprises a number of data packets, already transmitted or to be transmitted to the mobile terminal (120). The data packets are to be confirmed by the mobile terminal (120). In a first subframe, the base station signals to the mobile terminal (120), a first downlink assignment of a first data packet of the bundling window. The downlink assignment comprises knowledge about a minimum total number of data packets within the bundling window that are scheduled to be transmitted to the mobile terminal (120).
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
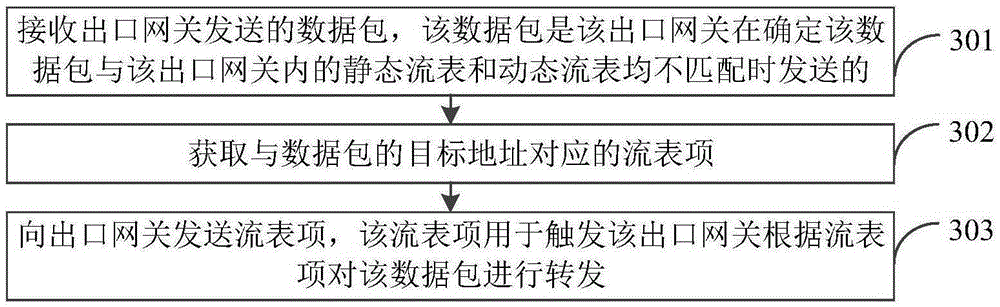
Saturation attack defending method, device and system of buffer queue in outlet gateway
InactiveCN105357146APrevent overflowResolve overflowData switching networksNetwork packetComputer terminal
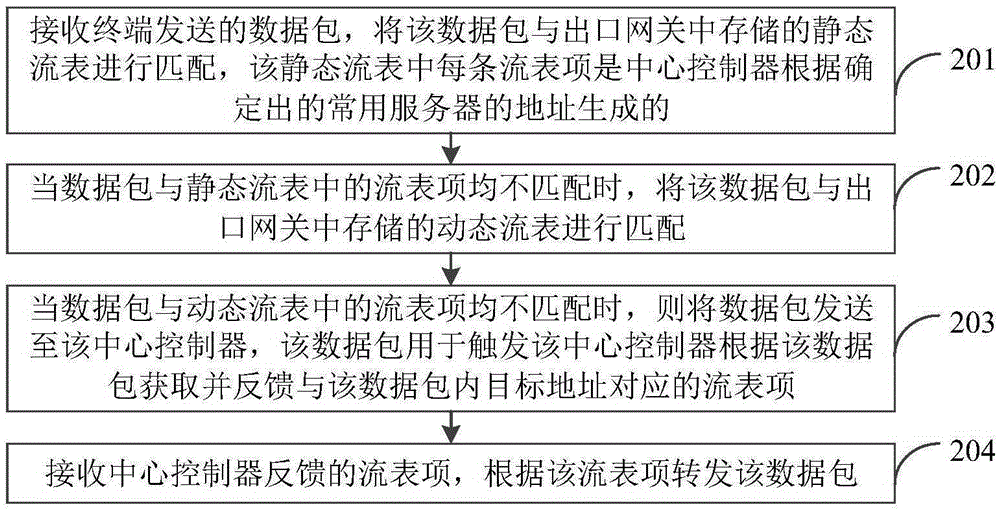
The invention discloses a saturation attack defending method, device and system of a buffer queue in an outlet gateway, and belongs to the field of network safety. The method comprises the steps of receiving a data packet transmitted by a terminal; when flow table items in a data packet static flow table and a dynamic flow table are unmatched, transmitting the data packet to a central controller; and forwarding the data packet based on a flow table item fed back by the central controller. According to the saturation attack defending method, device and system of the buffer queue in the outlet gateway, the problem that buffer queue overflow is resulted easily to enable the whole SDN (Software Defined Network) to be supersaturated when a malicious user transmits a large number of data packets having different destinations and carrying with relatively great loads is solved, and the effect of avoiding buffer queue overflow due to that the outlet gateway suddenly receives a large number of data packets having different destinations when a mobile network suffers from network attack of an illegal terminal is realized as frequently-used data packets are directly matched in the outlet gateway rather than being added into the buffer queue to be transmitted to the central controller.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
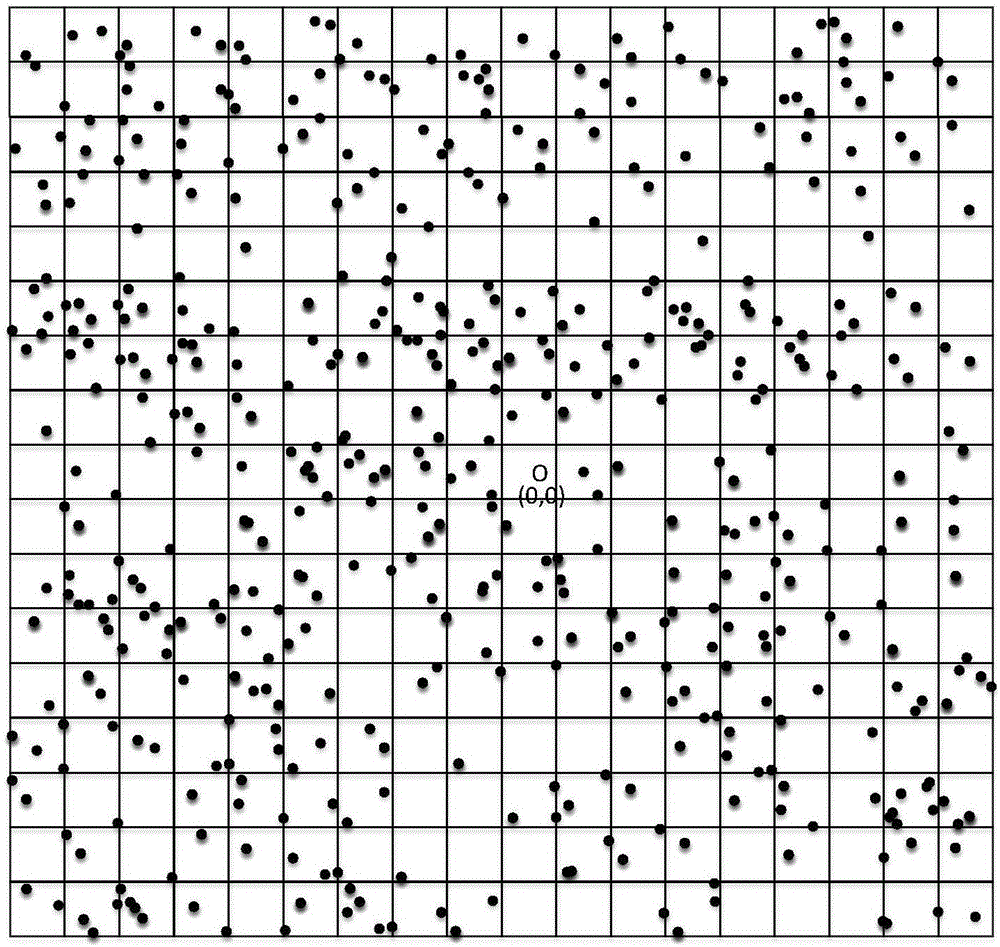
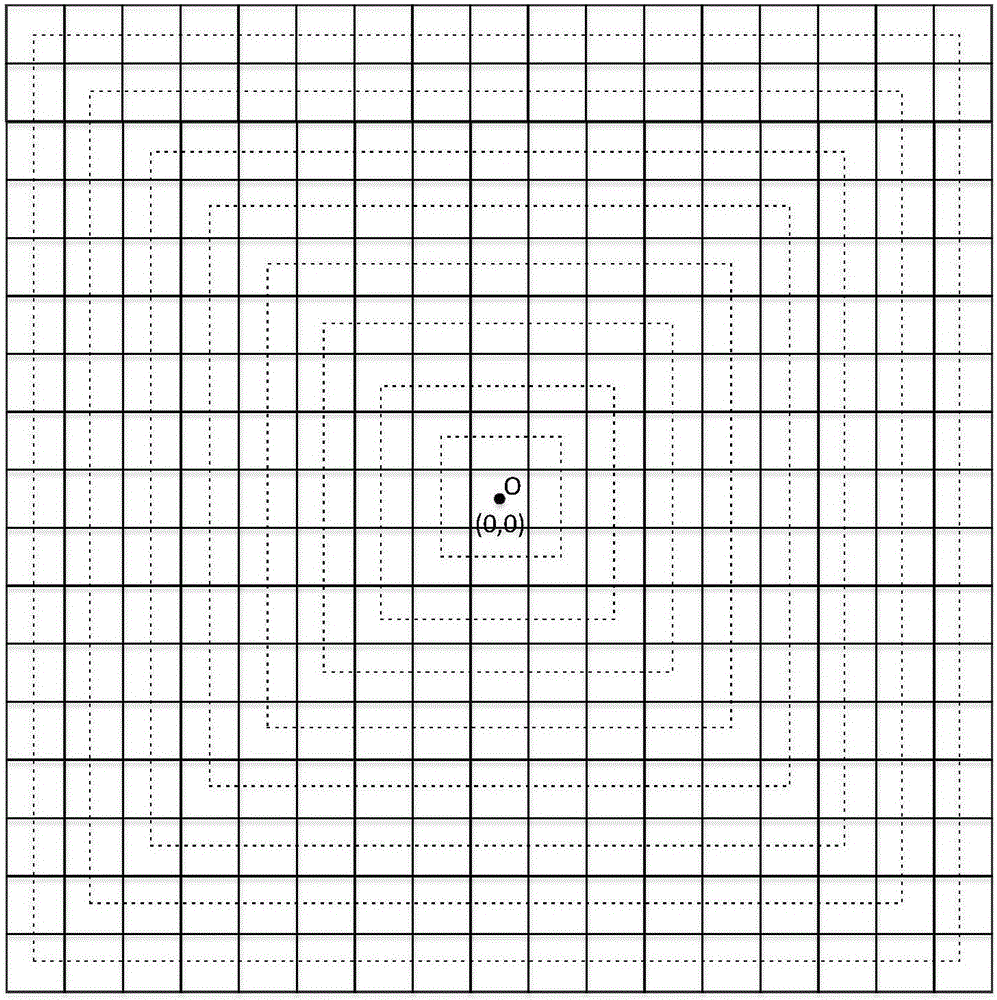
Node privacy protection method based on directional random routing in wireless sensor network
ActiveCN105979508AReduce energy consumptionIncrease diversityNetwork topologiesSecurity arrangementMartian packetPrivacy protection
The invention relates to a node privacy protection method based on directional random routing in a wireless sensor network. The method comprises the following six steps: establishment of grids, establishment of rings, determination of the grid, where a node locates, in the network, determination of the ring, where the node locates, in the network, routing of a real data packet and routing of confusion data packets. The confusion data packets are introduced to each direction of the network to prevent direction attack of an attacker, and network traffic is equalized; ring-based routing is introduced at the start position of a data packet to prolong the safety period of the network; through a time-domain confusion mechanism, the attacker cannot continue tracing after tracing back to the last node; and the directional routing policy of the real data packet increases diversity of the routing, and improves attack difficulty of the attacker. The node privacy protection method based on the directional random routing in the wireless sensor network can protect a source node and a base station node simultaneously through the design of grid and ring based routing, is suitable for the case of mobile source nodes and multisource nodes, and has good expansibility.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
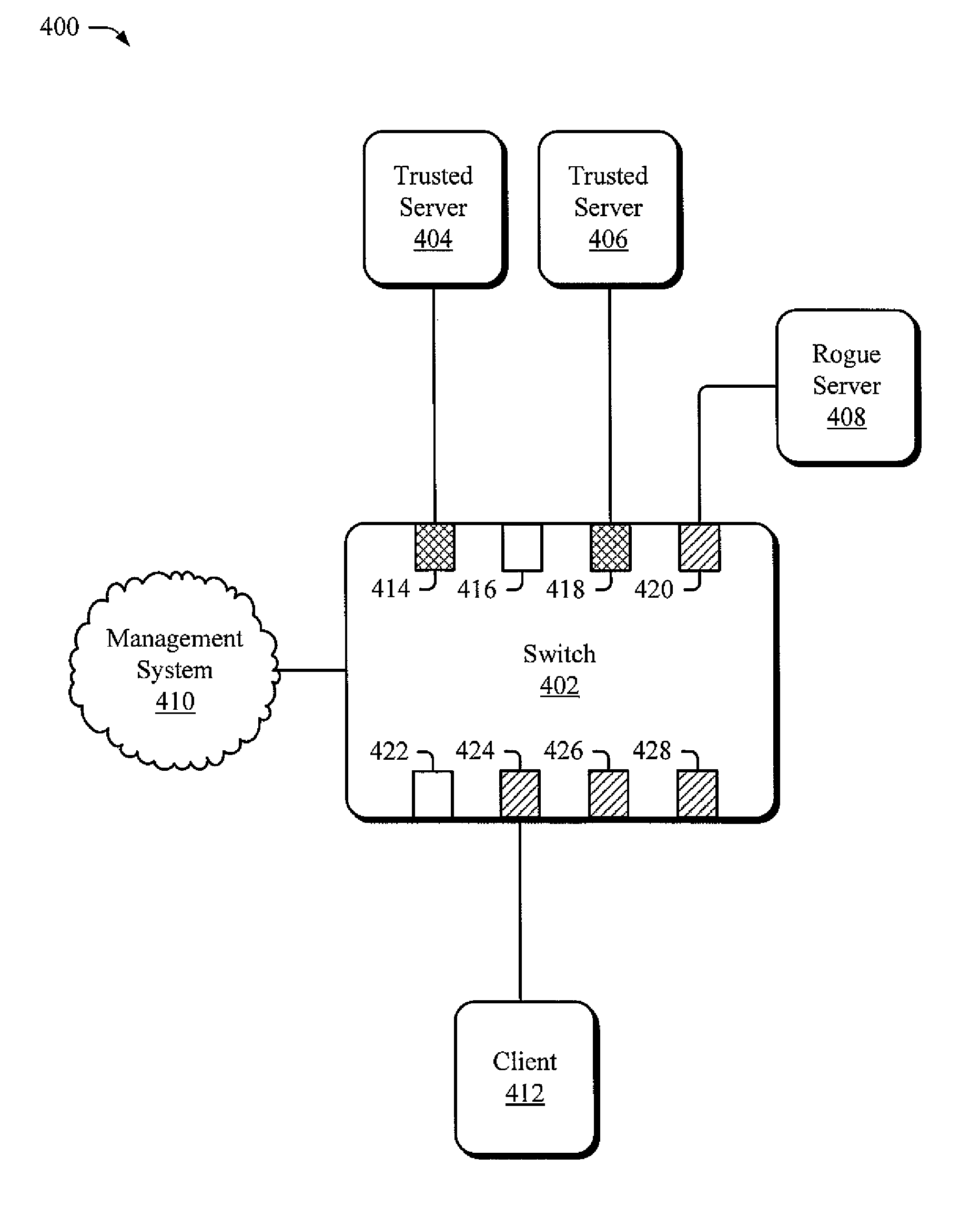
Limiting data packet forwarding to trusted ports
ActiveUS7869394B1Well formedData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsA domainDocumentation
This document describes tools that forward data packets to trusted ports and prevent data packets from egressing non-trusted ports. To do so, the tools receive a data packet having a destination address specifying that the data packet be forwarded to a set of ports associated with a domain. The tools identify a subset of the set of ports as trusted ports and forward the data packet to the subset. The tools prevent the data packet from egressing non-trusted ports of the set. In one embodiment, the tools may classify a port as trusted. To do so, the tools receive a configuration communication identifying trusted devices. The tools broadcast a request to the trusted devices and receive a reply from a reply device on a reply port. The tools determine that the reply device is one of the trusted devices and mark the reply port as a trusted port.
Owner:WORLD WIDE PACKETS INC
Transmission layer control method oriented to data packet deadline
InactiveCN108809859AImprove experienceError prevention/detection by using return channelChannel coding adaptationLoss ratePacket arrival
The invention discloses a transmission layer control method oriented to data packet deadline. The active packet loss and admission control are performed at a sending end transmission layer, and the data capable of arriving overtime is not sent; the transmission layer places the data packets with different priorities and issued by an application layer in different sending queues, and a forward error correction redundancy packet is generated according to the network packet loss rate and packet arrival time requirement, and the data packet which cannot arrive before the deadline is abandoned, andthen a scheduler computes the number of the data packet capable of arriving before the deadline according to the bandwidth, the delay and the packet arrival time requirement, and the corresponding number of data packet is selected to send. The admission control is performed at the transmission layer of the sending end, thereby guaranteeing that the data packet transmitted to the receiving end canarrive before the deadline, the retransmission caused by the random packet loss of the network is avoided, the delay is enlarged, and the retransmission cannot be avoided without using the redundancyencoding.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
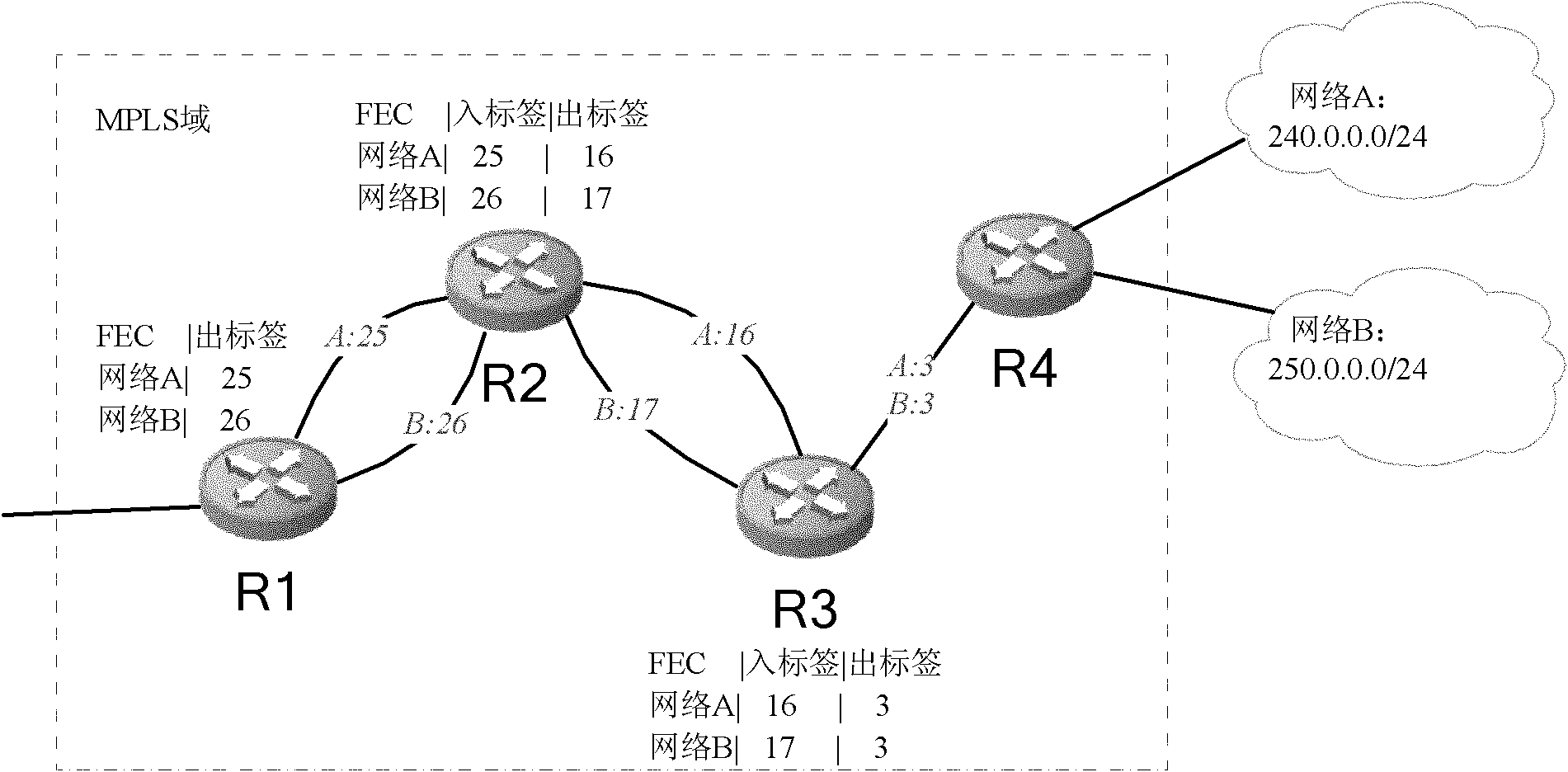
Label distribution method and system for data packets in MPLS network
ActiveCN102025632AReduce in quantityImprove forwarding efficiencyData switching networksDistribution controlDistribution method
The invention provides a label distribution method and a label distribution system for data packets in a multiple protocol label switching (MPLS) network in order to reduce the number of label switching paths (LSP) in an MPLS domain and consumption of system resources. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a distributed label according to elements of the data packets in an ordered label distribution control mode; distributing the same label for the data packets if the elements of the data packets are the same; and distributing different labels for the data packets if the elements of the data packets are different, wherein the data packets are a group of data packets which are processed in an equivalent mode during forwarding. Through the method and the system, the number of the LSP and label information to be stored are reduced, the system resources are saved, an MPLS forwarding table entry to be installed is reduced, a label distribution flow is simplified and the data forwarding efficiency is increased.
Owner:MAIPU COMM TECH CO LTD
Wireless sensor network security data discovery and dissemination method based on Hash tree
ActiveCN103368731AGuaranteed efficiencyEnsure safetyPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationMartian packetWireless sensor network
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for forwarding data packet, system, and device
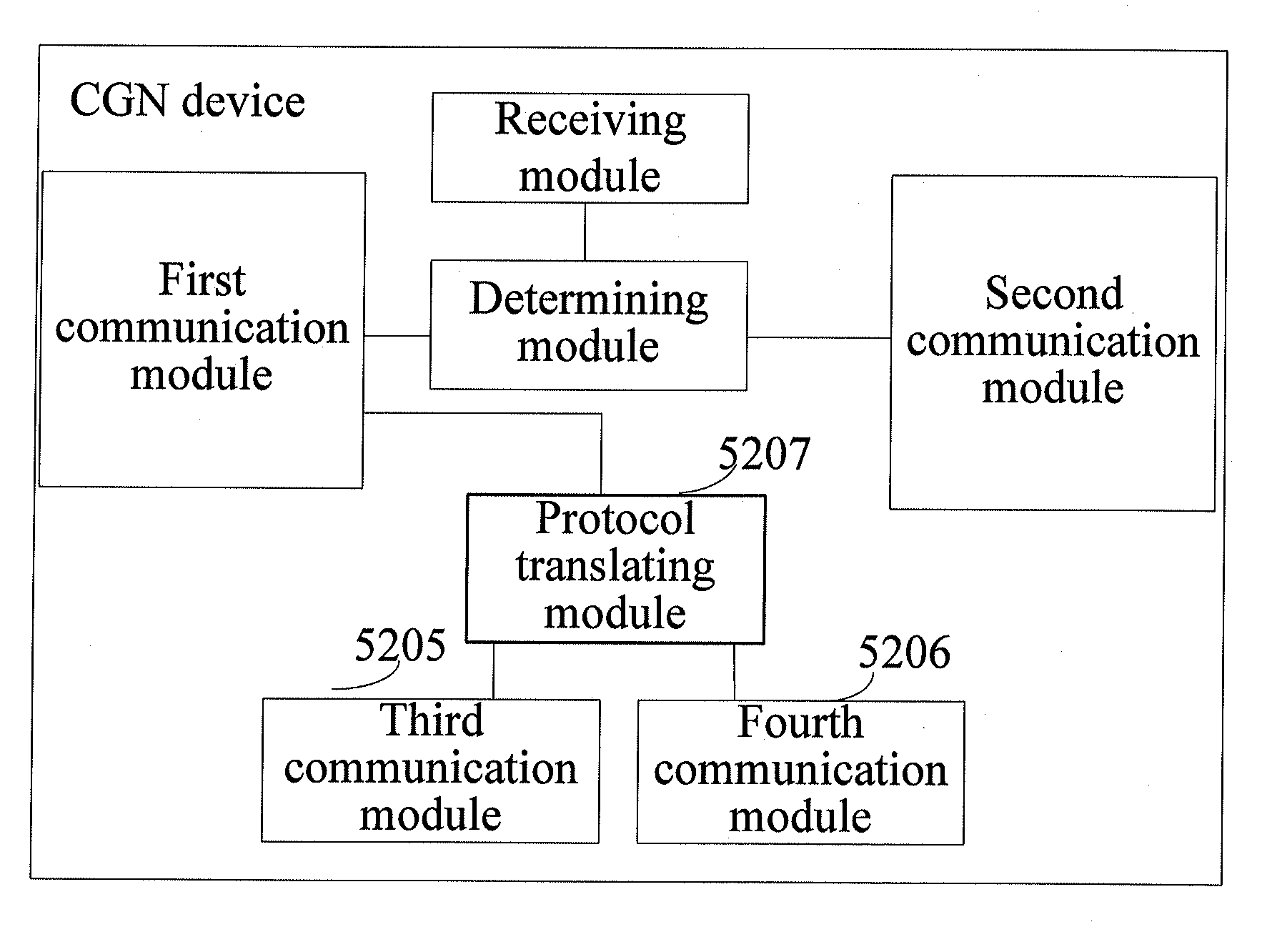
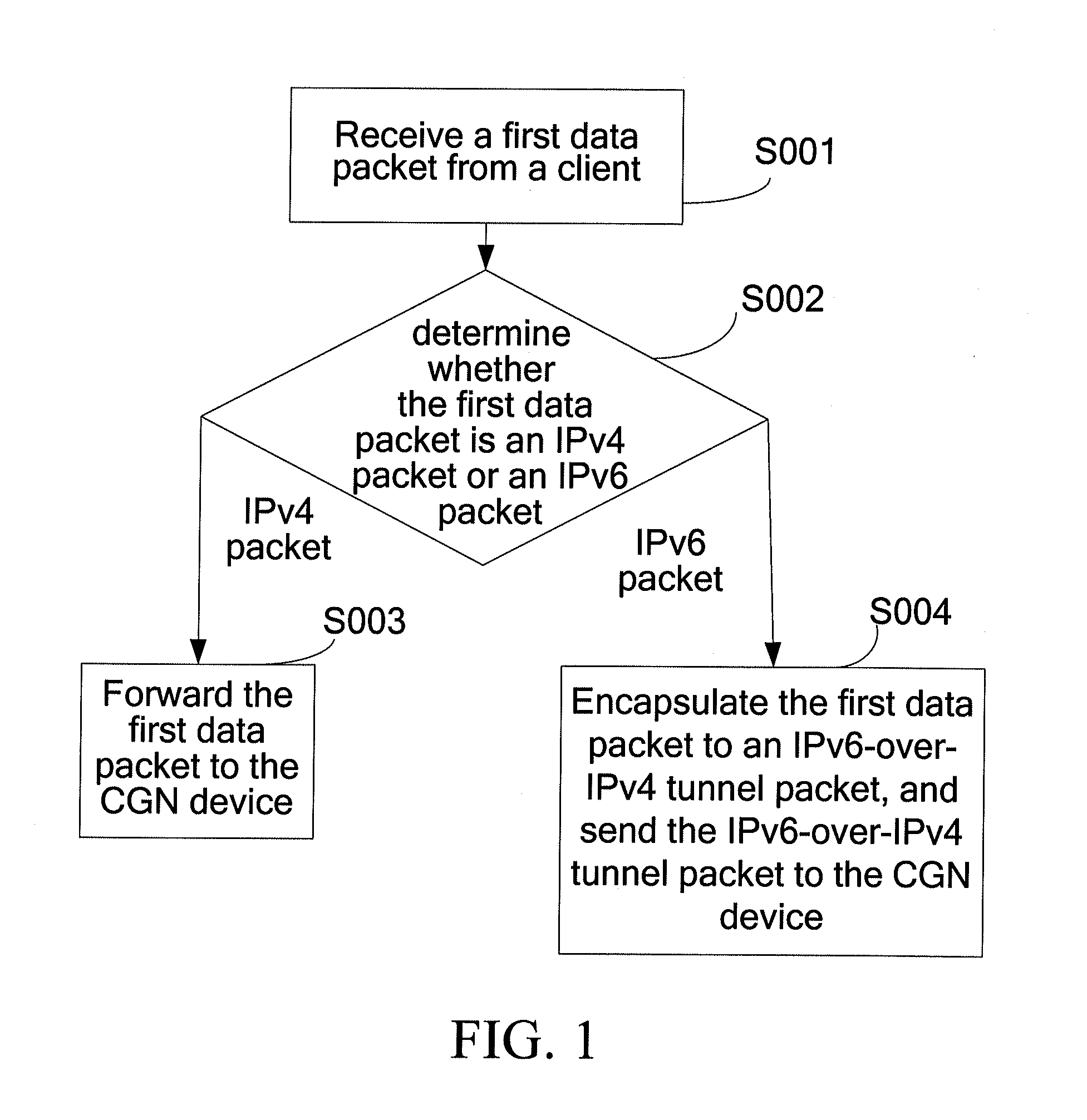
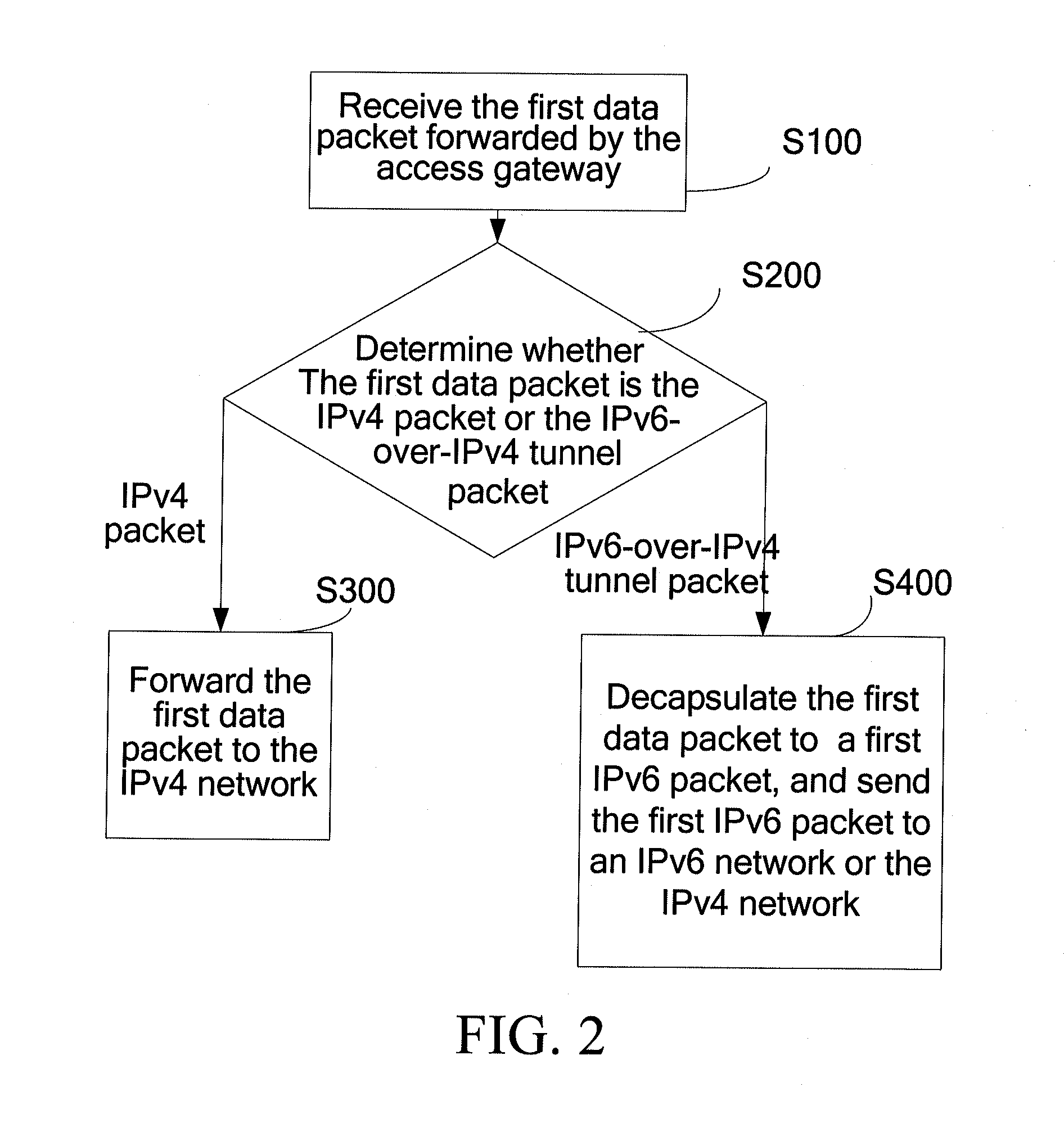
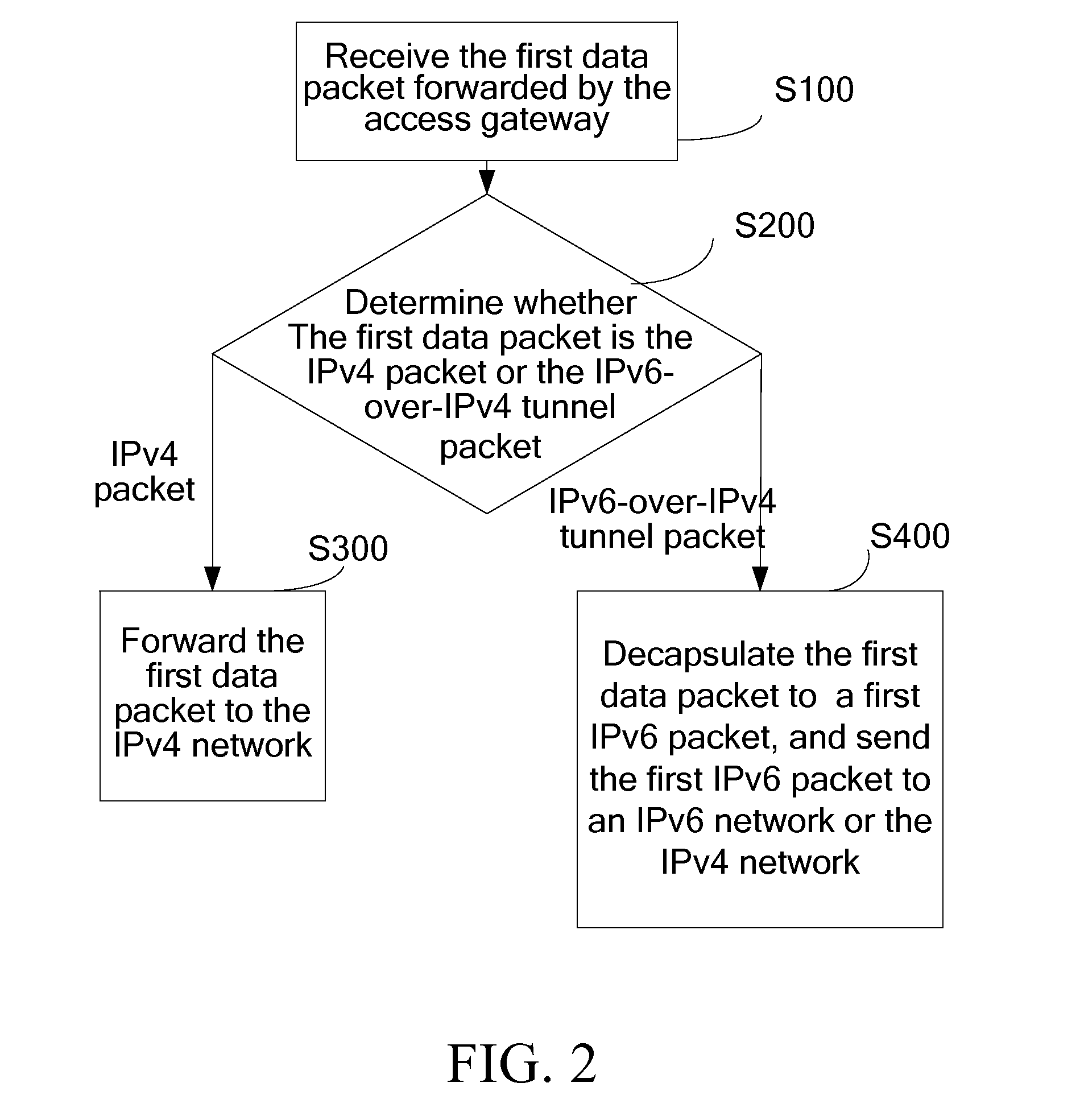
ActiveUS20110222543A1Facilitate smooth transitionOptimize networkError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemCarrier grade
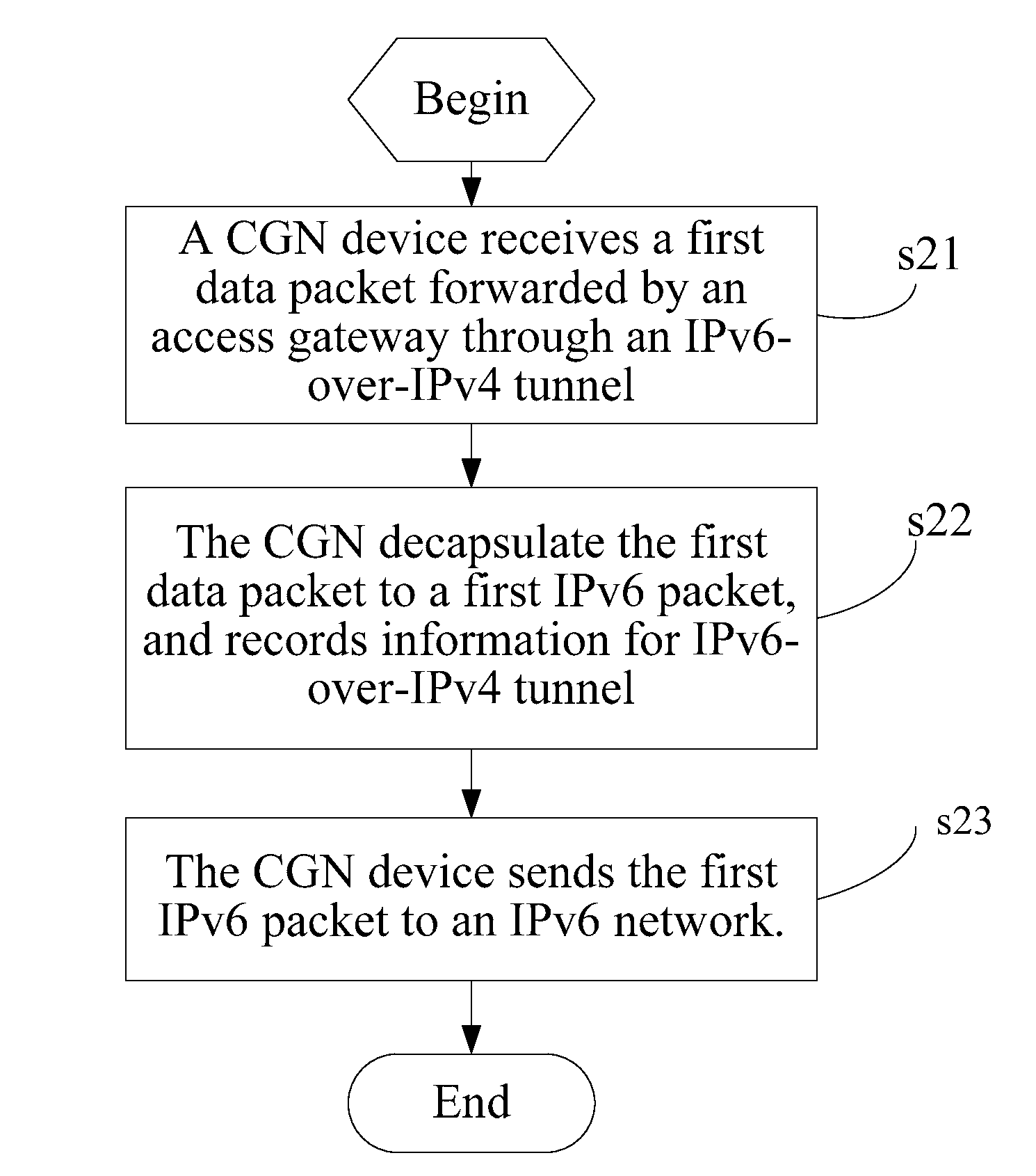
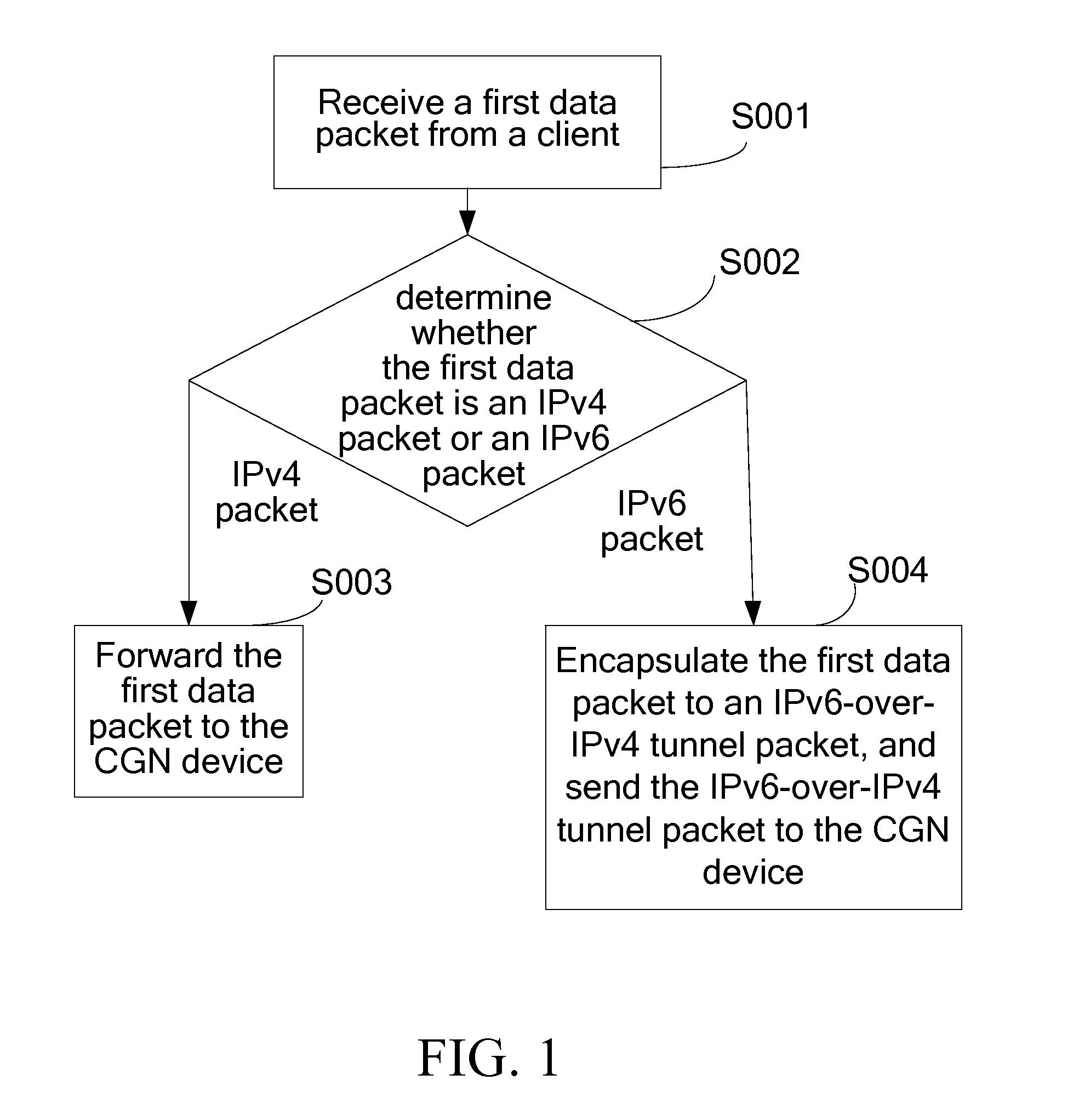
A method for forwarding data packet, a communication system, a Carrier Grade Network Address Translation (CGN) device, and an access gateway are provided. The CGN device communicates with the access gateway through an Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) network and is used for receiving a first data packet forwarded by the access gateway and determining whether the first data packet is an IPv4 packet or an IPv6-over-IPv4 tunnel packet; forwarding the first data packet to the IPv4 network if the first data packet is the IPv4 packet; and decapsulating the first data packet if the first data packet is the IPv6-over-IPv4 tunnel packet to a first IPv6 packet, and sending the first IPv6 packet to an IPv6 network or the IPv4 network. Therefore, technical problems of fully utilizing the IPv4 network and, gradually increasing deployment of the IPv6 network, and realizing communication are solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
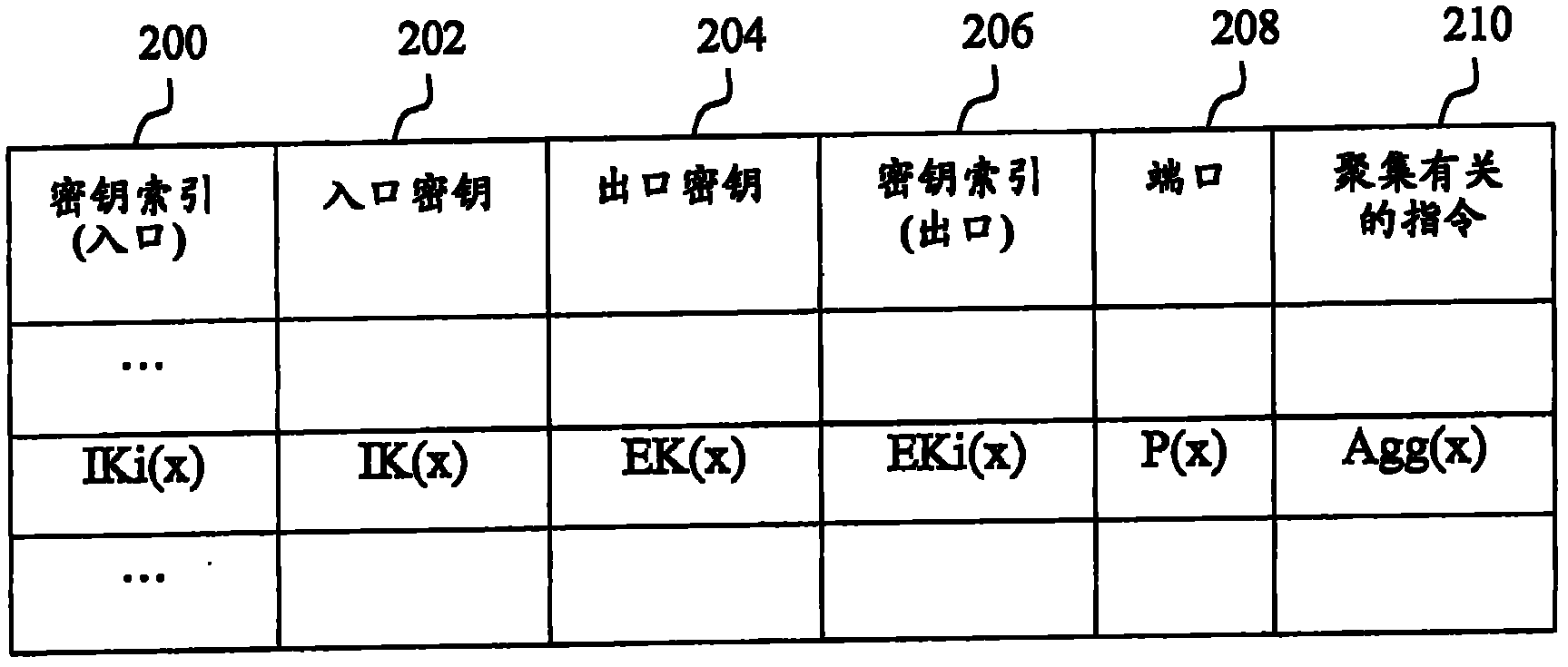
Method and apparatus for forwarding data packets using aggregating router keys
InactiveCN102210126AAvoid packet switchingAvoid teleportationData switching networksComputer networkKey management
Method and apparatus for supporting the forwarding of received data packets in a router (402,702) of a packet- switched network. A forwarding table (706a) is configured in the router based on aggregating router keys and associated aggregation related instructions received from a key manager (400,700). Each aggregating router key represents a set of destinations. When a data packet (P) is received comprising an ingress tag derived from a sender key or router key, the ingress tag is matched with entries in the forwarding table. An outgoing port is selected for the packet according to a found matching table entry that further comprises an associated aggregation related instruction. An egress tag is then created according to the aggregation related instruction, and the packet with the created egress tag attached is sent from the selected outgoing port to a next hop router.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
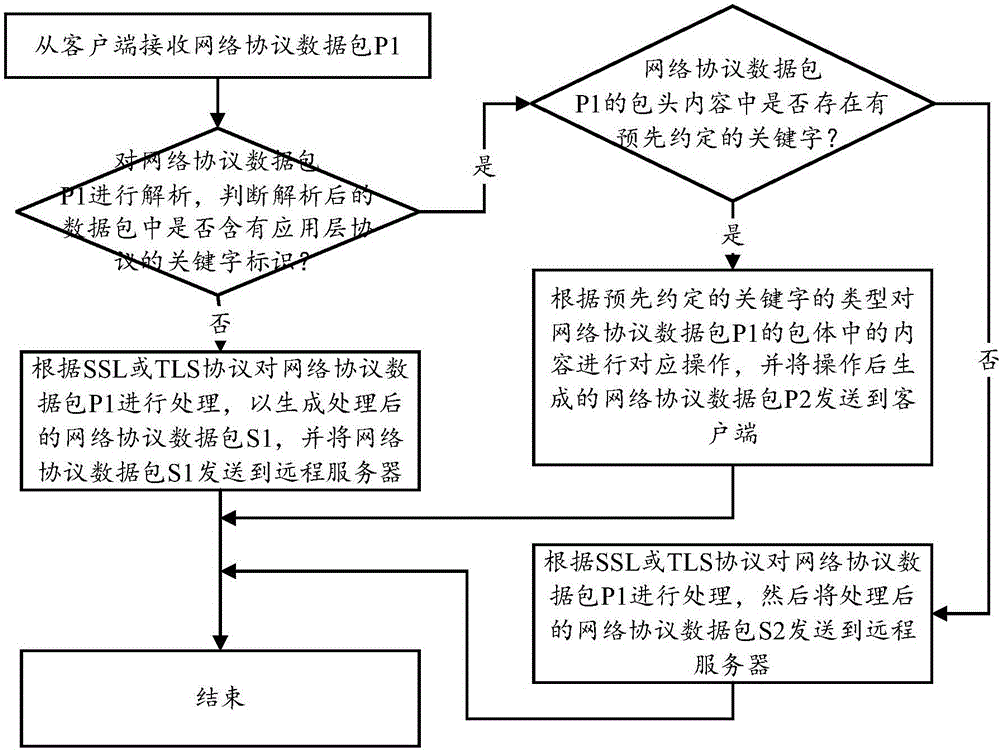
Safe processing method of network protocol data packet and system thereof
ActiveCN106254355AImprove securityOvercoming technical issues that are prone to leaksTransmissionNetworking protocolMessage integrity
The invention discloses a safe processing method of a network protocol data packet. The method comprises the following steps of receiving a network protocol data packet P1 from a client; analyzing the network protocol data packet P1; determining whether the analyzed data packet contains a keyword identification of an application layer protocol; if the keyword identification is found, determining whether a packet header content of the network protocol data packet P1 contains a predetermined keyword; and if the predetermined keyword exists, according to a type of the predetermined keyword, carrying out corresponding operation on a content in a packet body of the network protocol data packet P1 and sending a generated network protocol data packet P2 after the operation to a client. In the invention, through safely transmitting the data packet to a remote server, network attacks of different layers can be withstood so that safety of data packet transmission is increased; in addition, different types of the data packets can be distinguished, signature message integrity is verified, and an identity of a sender is confirmed so that a repudiation condition in a transaction is prevented.
Owner:WUHAN ARGUSEC TECH
Communication method avoiding p2p traffic identification
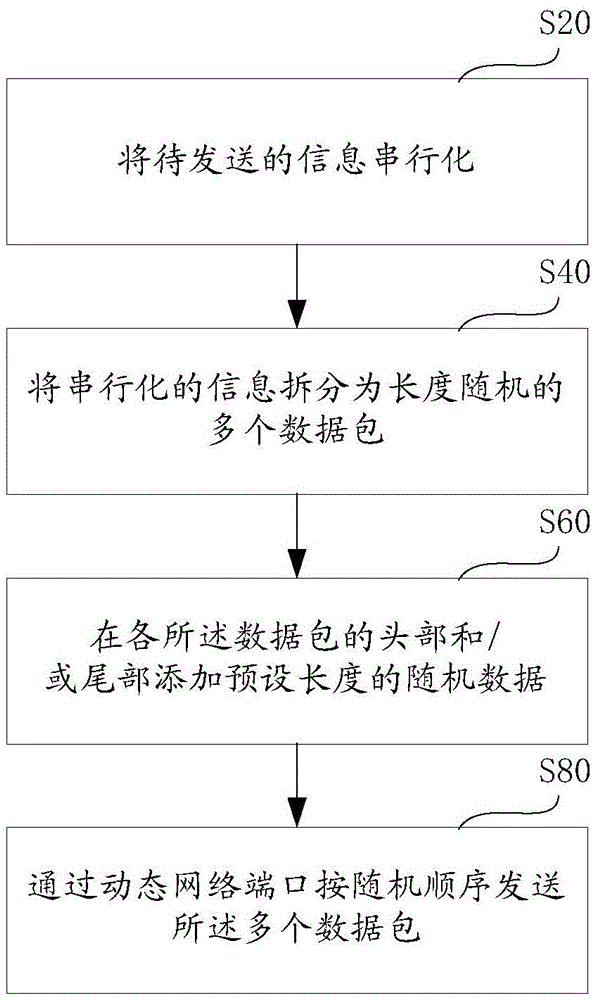
InactiveCN105516021AAvoid identificationAvoid interceptionData switching networksComputer hardwareTraffic capacity
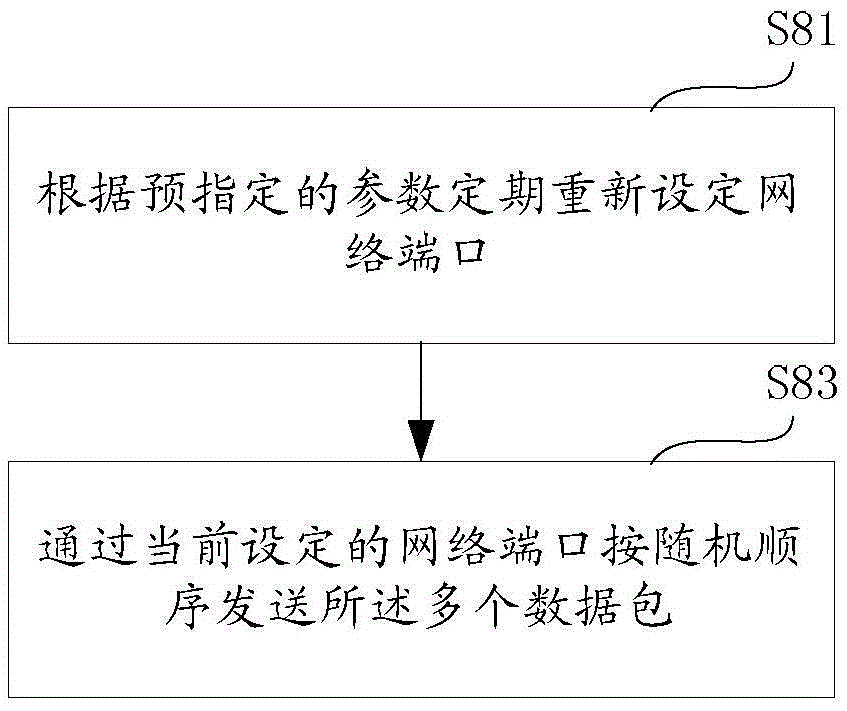
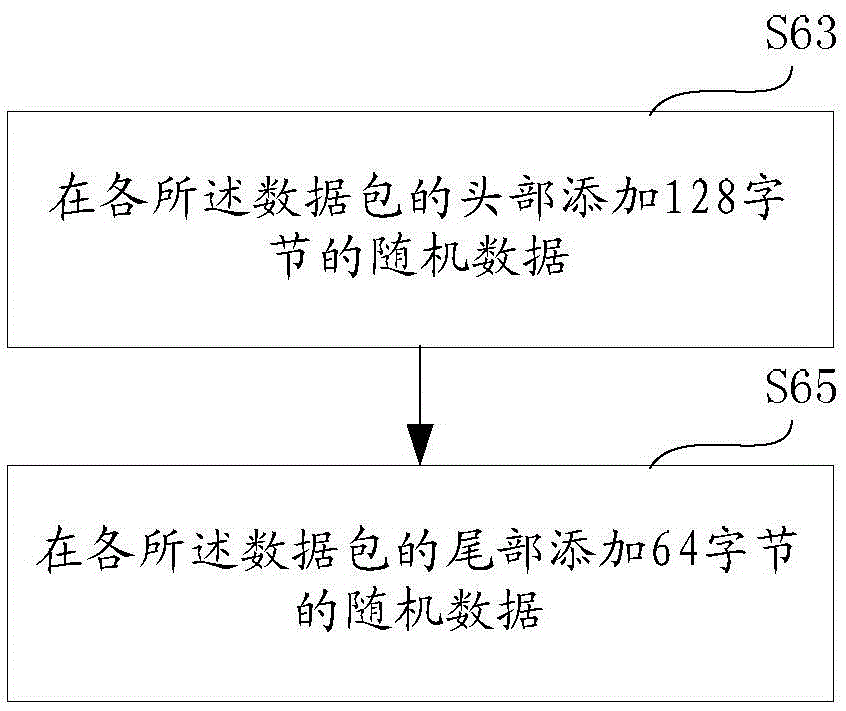
The invention discloses a communication method avoiding p2p traffic identification. The method comprises the following steps: S20: serializing information to be sent; S40: splitting the serialized information into a plurality of data packets with random lengths; S60: adding random data with preset lengths at the heads and / or tails of the data packets; and S80: sending the plurality of data packets in a random sequence through a dynamic network port. According to the communication method disclosed by the invention, the means of serializing the information to binary, splitting the data, randomly setting the lengths of the data packets, filling random data in important identification areas, sending the data packets in the random sequence and sending the data packets through the dynamic port and the like are integrated to effectively avoid the identification of the existing p2p traffic identification means and realize speed limitation or interception, and no single module needs to be set to establish an additional communication channel; such means as encrypting the data packets and adding random disturbing data packets and the like are further integrated to reduce the identification rate; and the instruction and the data are divided into double-channel communication to further reduce the identification rate.
Owner:北京广密华安科技有限公司
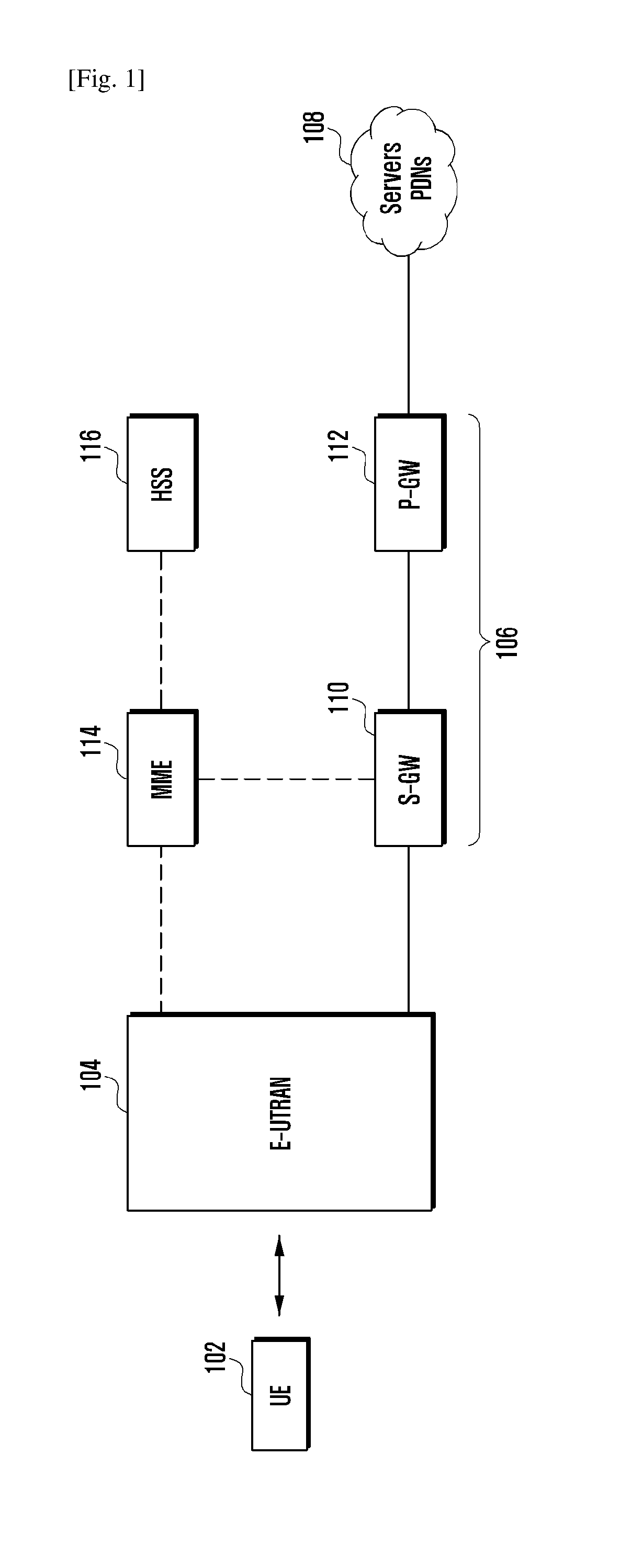
Internet protocol address preservation in mobile operator networks
ActiveUS20180152877A1Optimising content provisioning/user plane delayData switching networksWireless communicationTTEthernetIp address
A method of operating a mobile communications network arranged to communicate data packets between a mobile terminal and a packet data network via one or more routers, wherein the one or more routers include routing information for routing data packets, the method comprising establishing a data packet pathway for communicating data packets between a first Internet Protocol, IP, address associated with the mobile terminal and a second IP address associated with the packet data network, the data packet pathway including a first local gateway, wherein a local gateway is a first point within the mobile communications network through which all data packets communicated over the data packet pathway from the second IP address to the first IP address must pass; communicating one or more data packets between the first and second IP addresses via the data packet pathway; selecting a second local gateway; updating the routing information of at least one of the routers such that the second local gateway replaces the first local gateway in the data packet pathway; and communicating one or more data packets between the first and second IP addresses via the data packet pathway.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
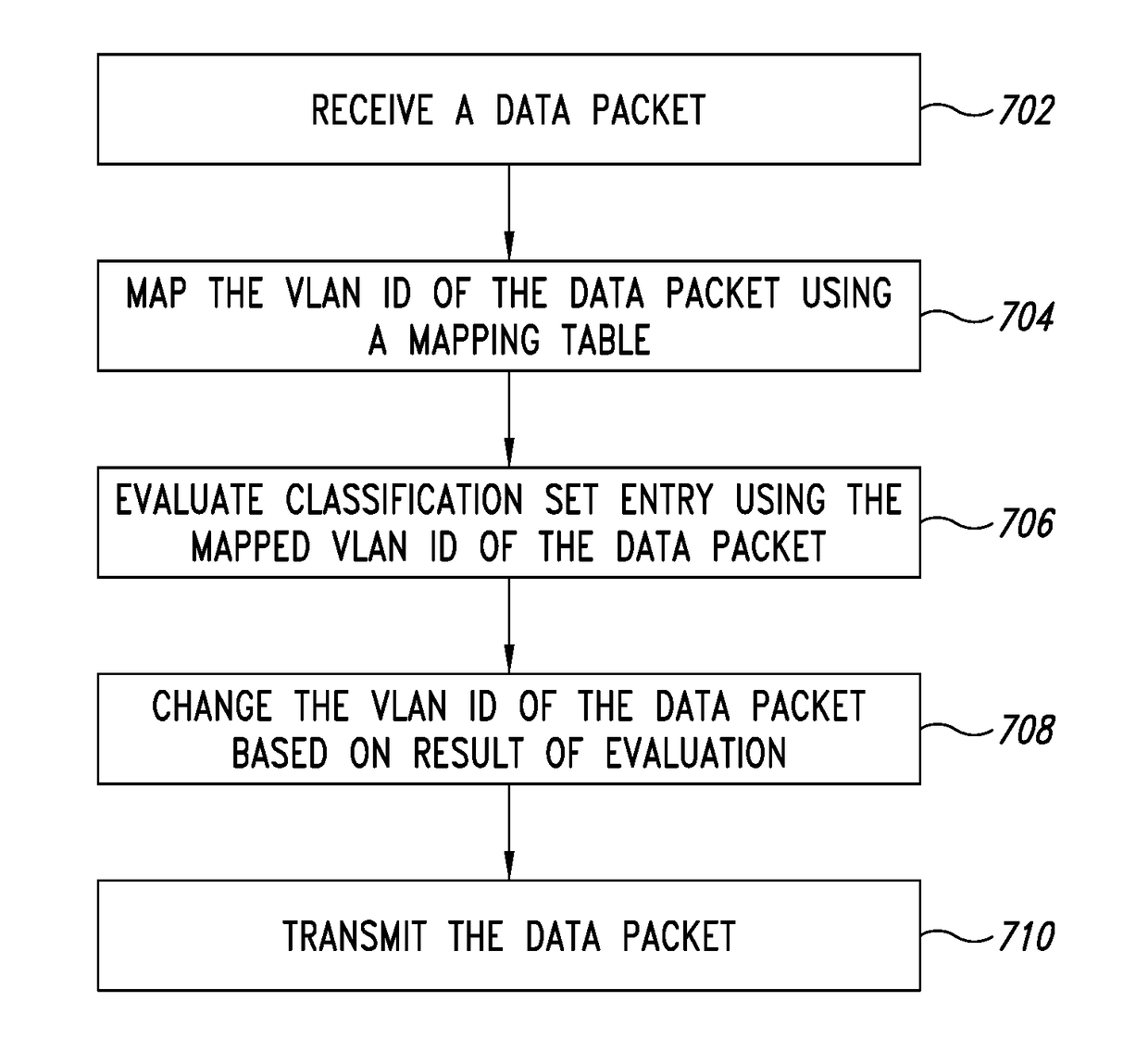
Multipath switching using per-hop virtual local area network classification
A method and apparatus for multipath switching using per-hop virtual local area network (VLAN) remapping is disclosed. In the method and apparatus, a data packet is forwarded for transmission over one of a first port and a second port. The device identifies a VLAN ID of the data packet as a second VLAN ID and changes the second VLAN ID to a first VLAN ID. Then one or more criteria of a classification set entry for forwarding the data packet over the second port are evaluated. The data packet is forwarded over the second port if the criteria are met and the data packet is associated with the second VLAN ID. Alternatively, the data packet is forwarded over the first port and is associated with the first VLAN ID if a dynamic entry specifies the data packet is to be forwarded over the first port.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Dynamically provisioning middleboxes
ActiveUS8923294B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityNetwork service
Hybrid security architecture (HSA) provides a platform for middlebox traversal in the network. The HSA decouples the middlebox control from network forwarding. More specifically, such embodiments may receive a data packet having a packet header including an Ethernet header identifying source and destination addresses in the network. A traffic type of the data packet is determined. Then, layer-2 forwarding information, which encodes a set of non-forwarding network service provider middleboxes in the network to be traversed by the data packet, is determined based on the traffic type. The layer-2 forwarding information is inserted into the Ethernet header and the data packet is forwarded into the network. The data packet will then traverse, according to the layer-2 forwarding information, a sequence of the middleboxes in the network, wherein at least one non-forwarding network service will be provided by each of the middleboxes to the data packet in a sequence.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
IPSec VPN safety forwarding method and system for handling power protocols
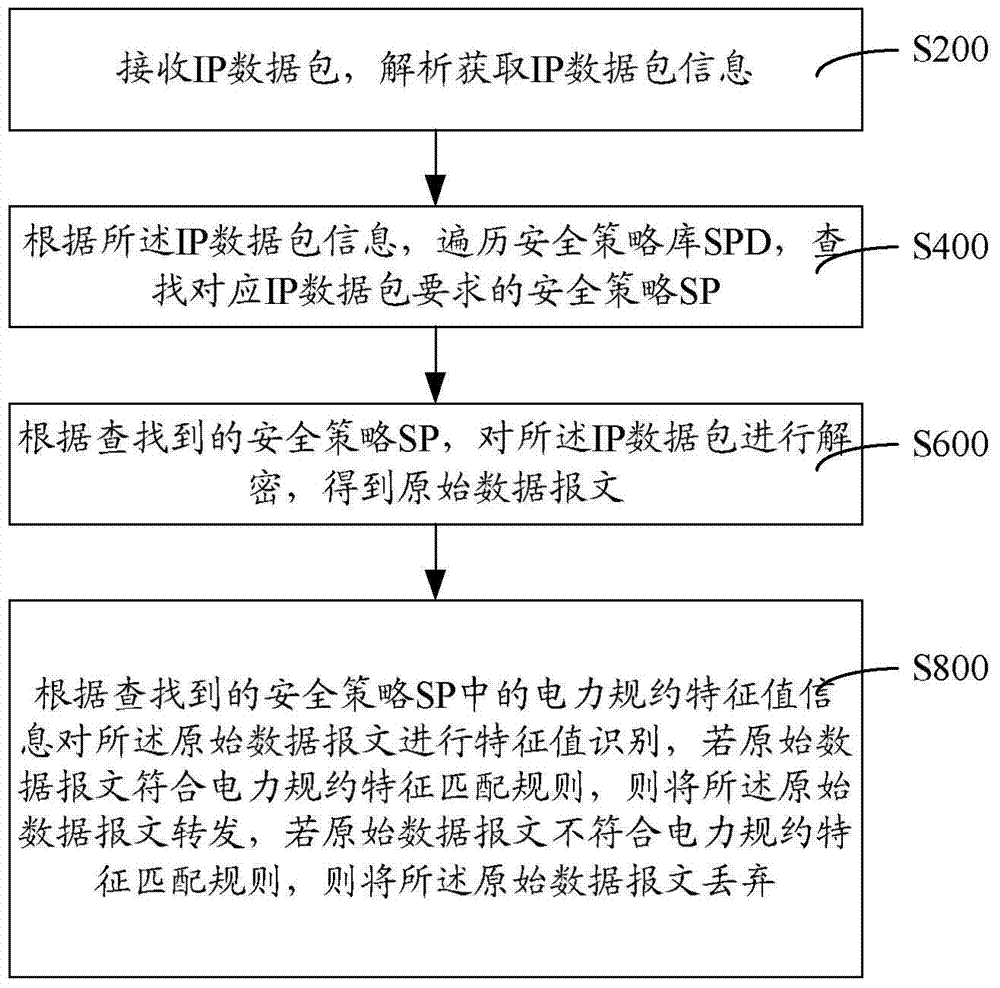
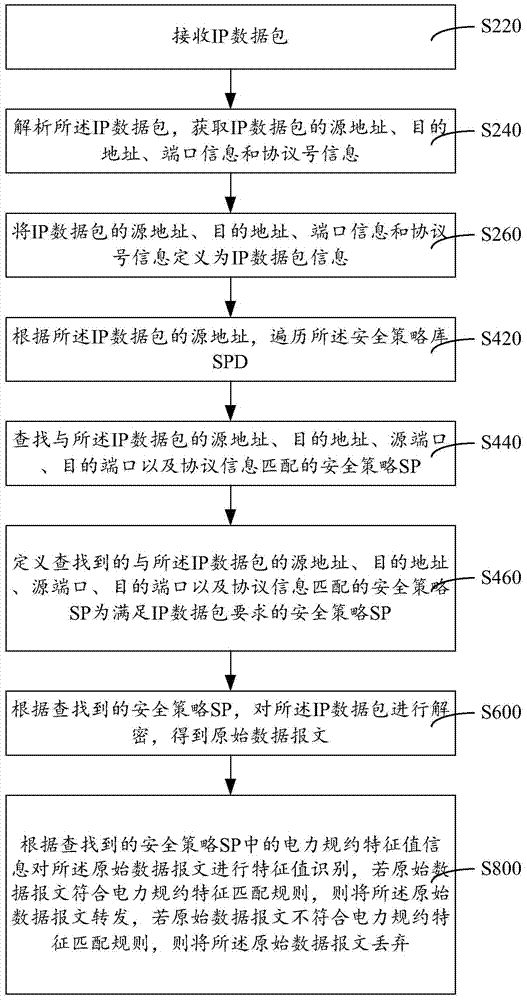
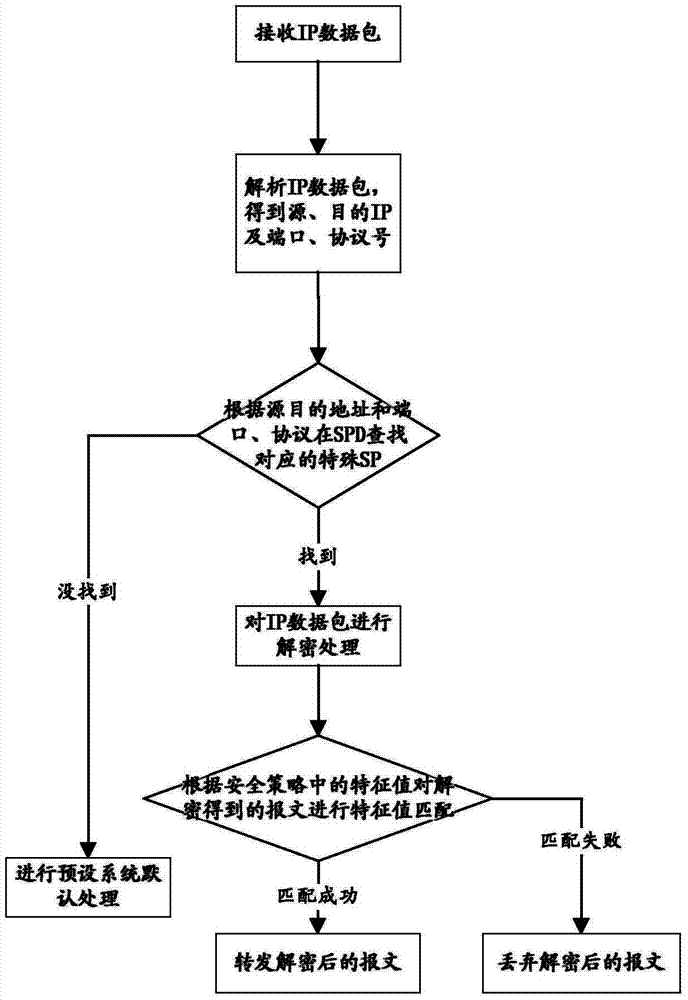
ActiveCN103929423ASimplify policy configurationImprove usabilityNetworks interconnectionNetwork packetOriginal data
The invention provides an IPSec VPN safety forwarding method and system for handling power protocols. When an IP data packet enters an IPSec VPN device, a safety policy according with the IP data packet is sought for in a safety policy database according to IP message grouping information, data decryption is performed on the IP message grouping information according to the SP, and an original data message is obtained; then, power protocol characteristic value information identification is performed on the original data message according to characteristic value information in the SP to judge whether the current IP data packet message needs to be forwarded or not. Through the SP subjected to power protocol characteristic identification, fine grit inspecting and matching can be performed on the IP data packet bearing power service, in-tunnel attack to the data packet can be prevented, and thus the problems that because a large number of firewall policies are added into the IPSec VPN device and the data packet enters a protocol stack twice, performance is lowered, and operation maintenance difficulty is increased can be avoided, and the forwarding performance and the forwarding safety of the IPSec VPN data packet are promoted.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Network session traffic alignment method based on address translation
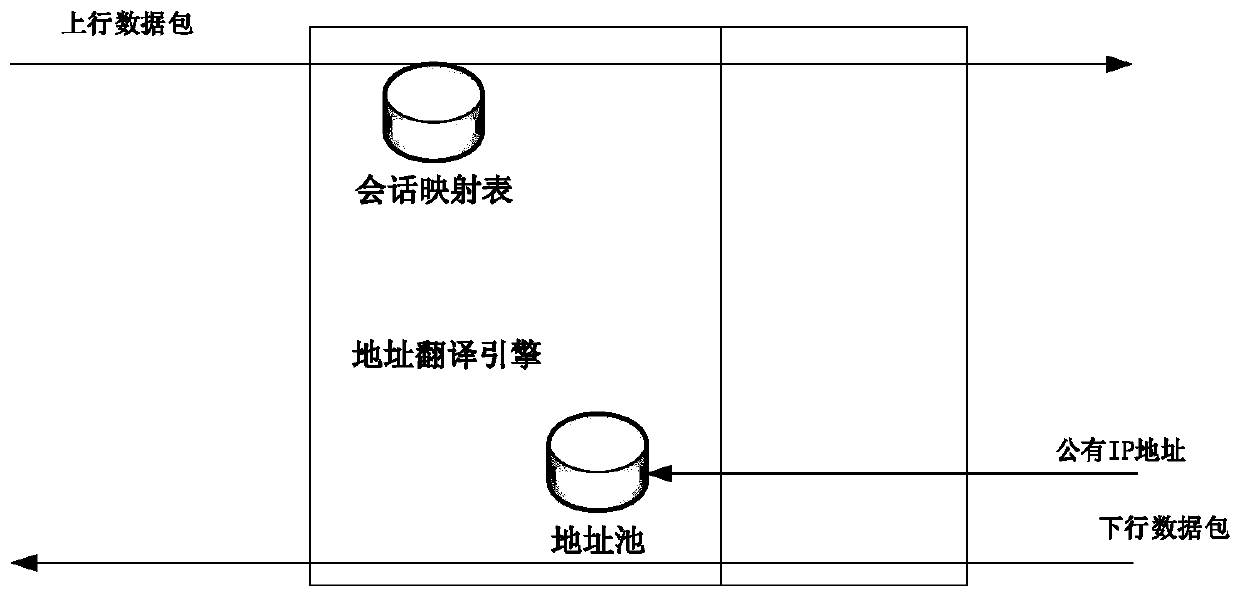
InactiveCN110365807AAvoid alignment problemsThe method is efficient and fastTransmissionTraffic capacityServer allocation
The invention provides a network session traffic alignment method based on address translation. The network session traffic alignment method comprises the specific steps: distributing a correspondingavailable address pool for each flow processing server, wherein the address pool comprises a group of available IP addresses; when the traffic server acquires an uplink data packet, selecting an IP address from a corresponding address pool to replace a source IP address in the data packet, then extracting a quintuple of the uplink data packet, and storing the quintuple into a session mapping table; when the target receives the uplink data packet, generating a downlink data packet, and when the downlink data packet passes through another traffic server, sending the downlink data packet to a traffic processing server corresponding to the uplink; and obtaining the quintuple of the data packet after the traffic server receives the downlink data packet, completing alignment when determining that the data packet is the same session data packet after comparing the quintuple with the stored session mapping table, and otherwise, re-injecting the data packet into the network. According to the invention, the function that a specific point only uses a specific IP address is realized, and the scene that bidirectional flow needs to be processed in related applications such as network auditing and network security is satisfied, and the network session traffic alignment method is fast and efficient.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for forwarding data packet, system, and device
ActiveUS20120020359A1Facilitate smooth transitionOptimize networkError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemCarrier grade
A method for forwarding data packet, a communication system, a Carrier Grade Network Address Translation (CGN) device, and an access gateway are provided. The CGN device communicates with the access gateway through an Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) network and is used for receiving a first data packet forwarded by the access gateway and determining whether the first data packet is an IPv4 packet or an IPv6-over-IPv4 tunnel packet; forwarding the first data packet to the IPv4 network if the first data packet is the IPv4 packet; and decapsulating the first data packet if the first data packet is the IPv6-over-IPv4 tunnel packet to a first IPv6 packet, and sending the first IPv6 packet to an IPv6 network or the IPv4 network. Therefore, technical problems of fully utilizing the IPv4 network and, gradually increasing deployment of the IPv6 network, and realizing communication are solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Access node device for forwarding data packets
ActiveCN105960782AReduce startup timeLess signalingNetwork connectionsWireless communicationComputer networkState pattern
The present invention relates to access node device (1) arranged for receiving and forwarding data packets in a communication network (2), the device comprising at least one processor (20) arranged to: receive data packets from an user node (3); and forward the data packets in a stateless mode over a first path to a destination gateway node (4), the first path being a default path, or forward the data packets in a stateful mode over a second path to a destination node, the second path being determined by user and / or session specific information for said user node (3). Furthermore, the invention also relates to a corresponding gateway node device, a method in an access node, a method in a gateway node, a computer program, and a computer program product thereof.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
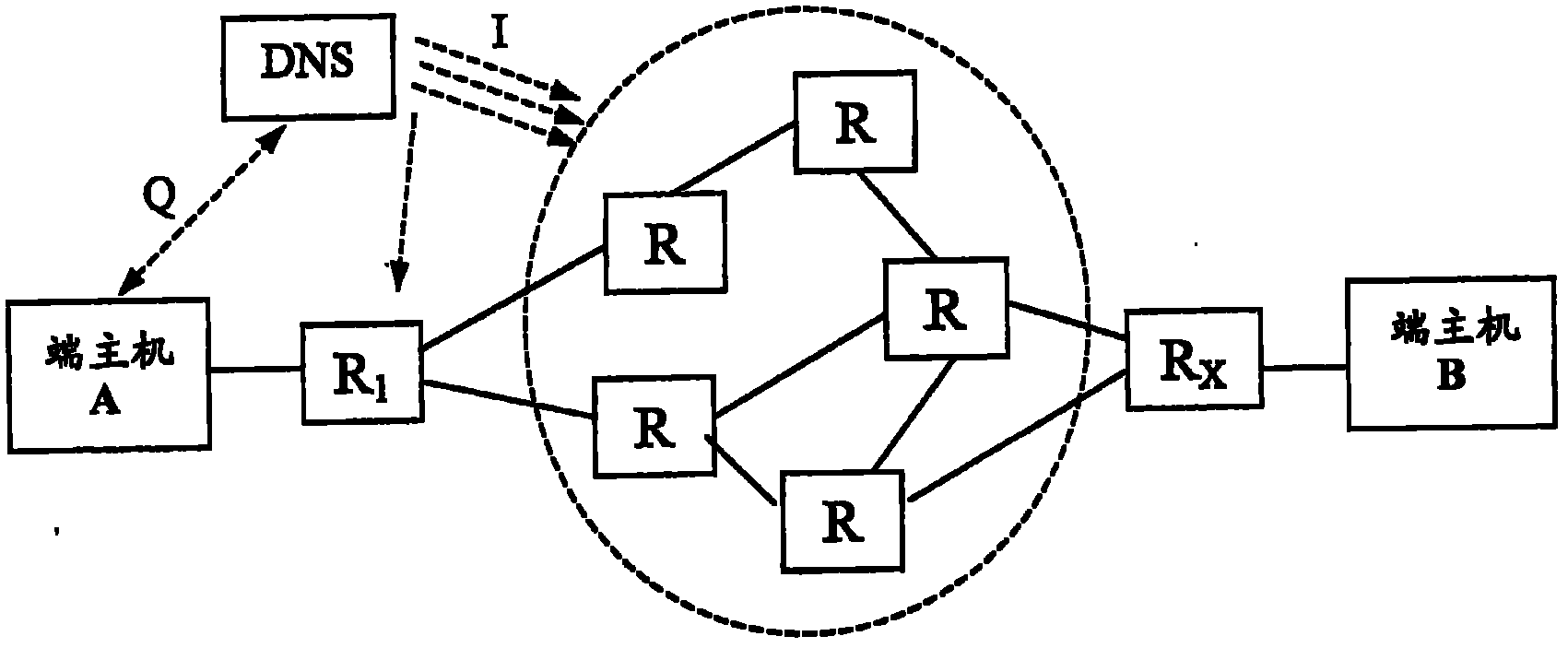
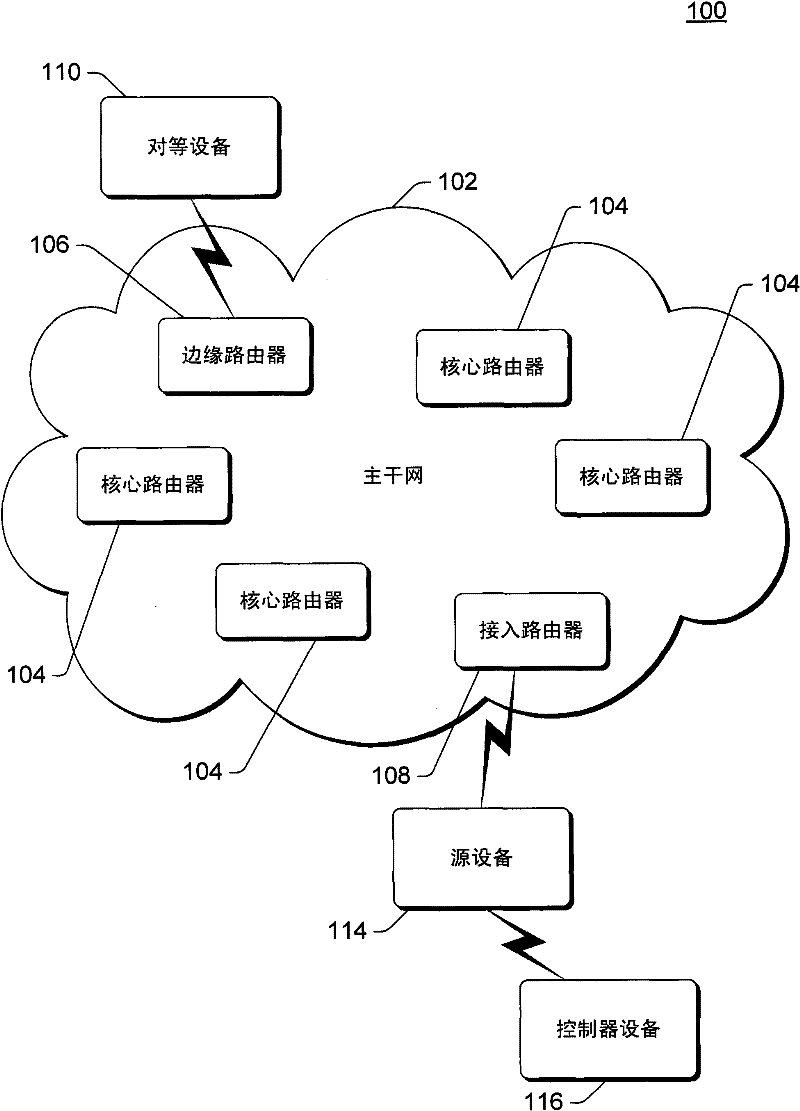
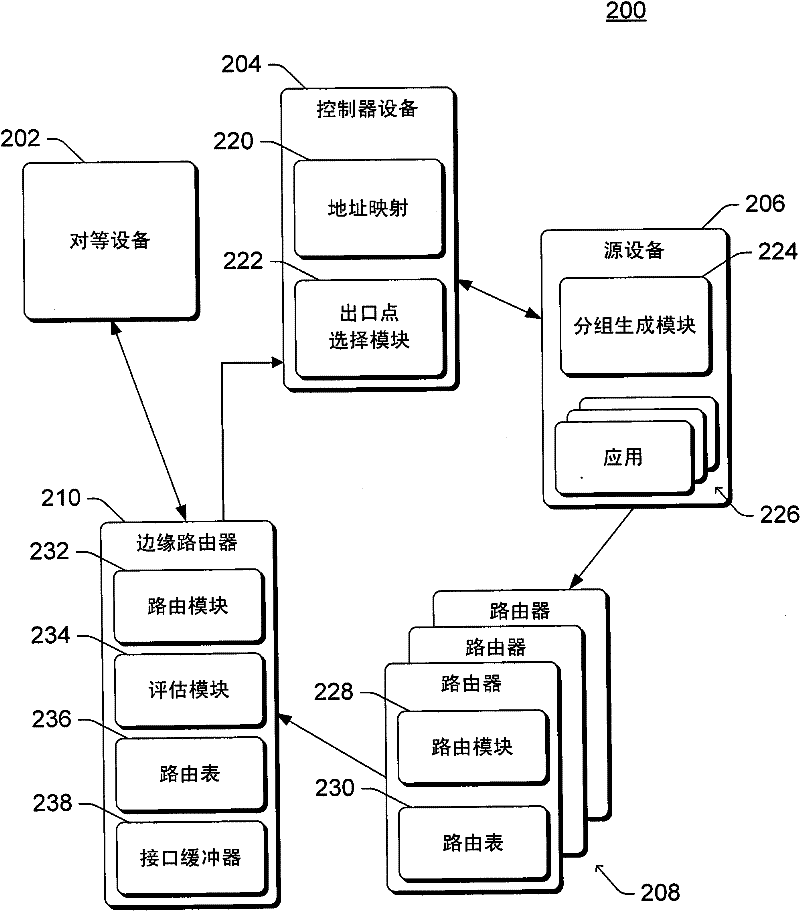
Backbone network with policy driven routing
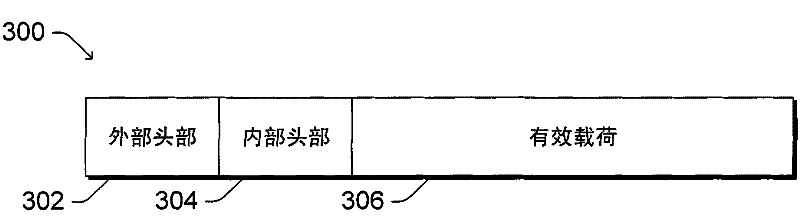
The invention relates to a backbone network with policy driven routing. A source device obtains a data packet that includes both a destination address and a payload. The source device selects an exit point address of multiple exit point addresses corresponding to the destination address based on one or more policies. The source device encapsulates the data packet with a header that includes the selected exit point address, and the encapsulated data packet is provided to the backbone network. The encapsulated data packet is routed through the backbone network based on the exit point address, and an edge router of the backbone network identifies an interface of the edge router that corresponds to the exit point address. The header is removed from the encapsulated data packet, and the data packet is added to a buffer of the interface for routing to one or more other devices outside of the backbone network.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
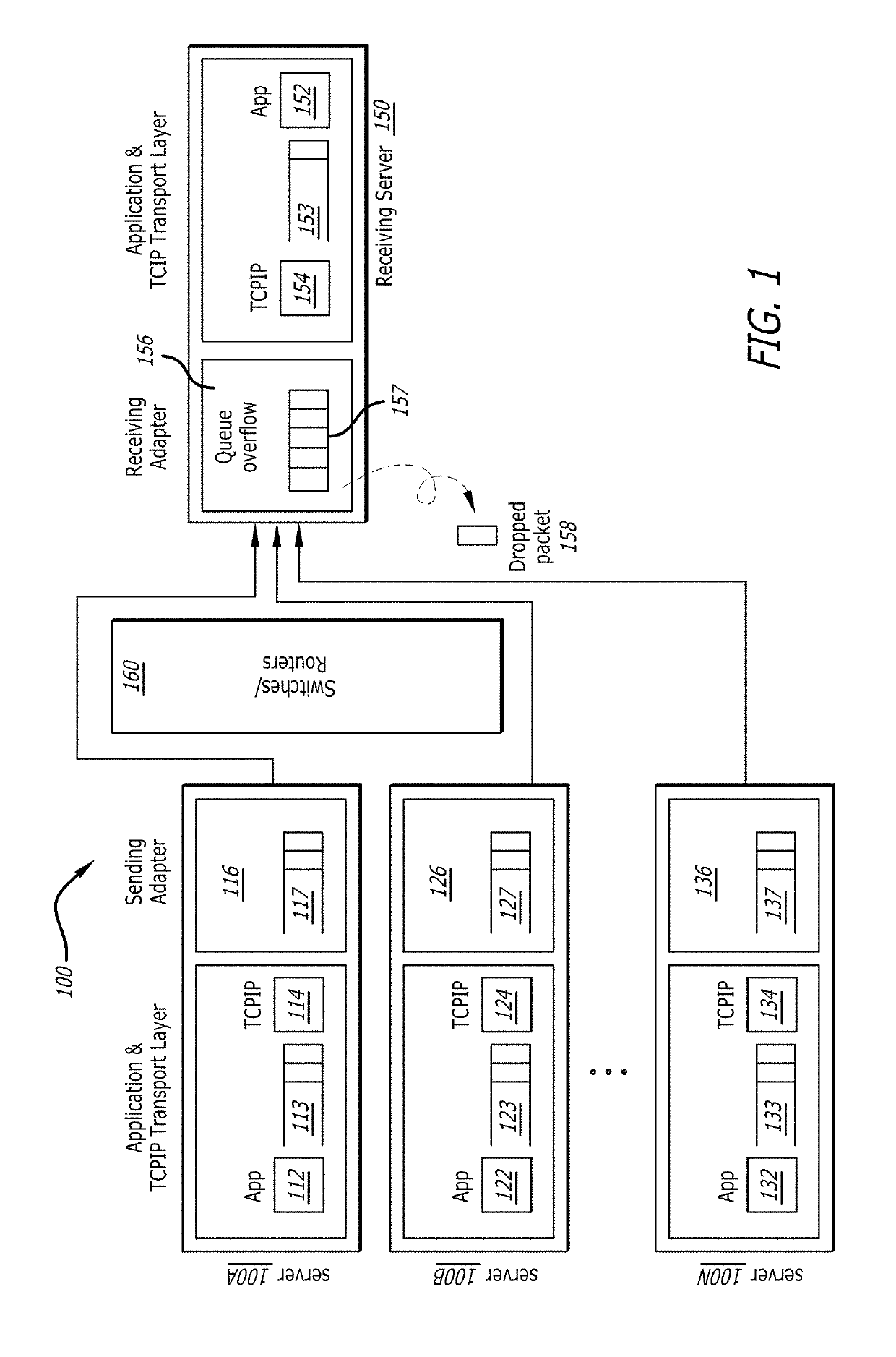
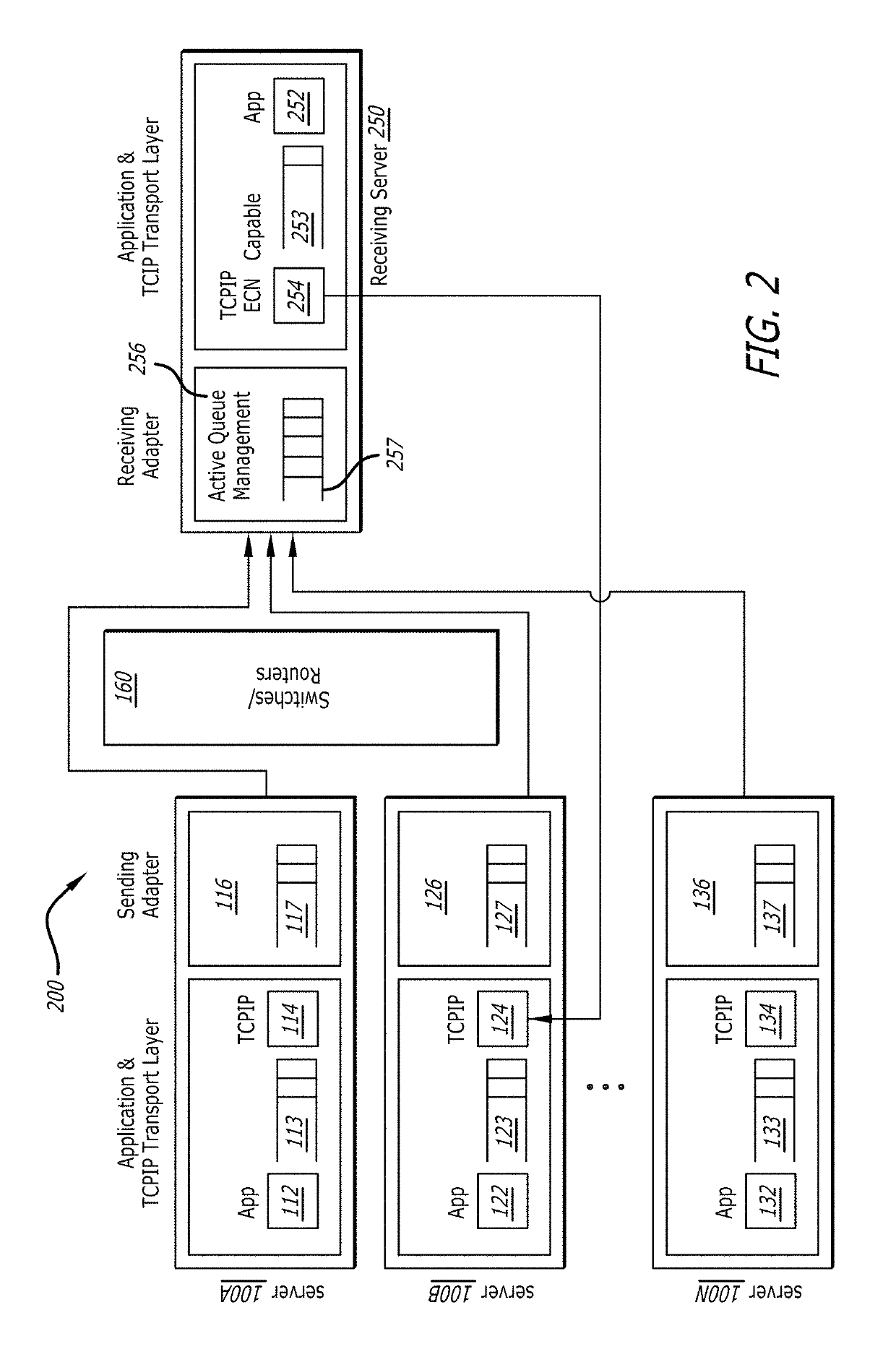
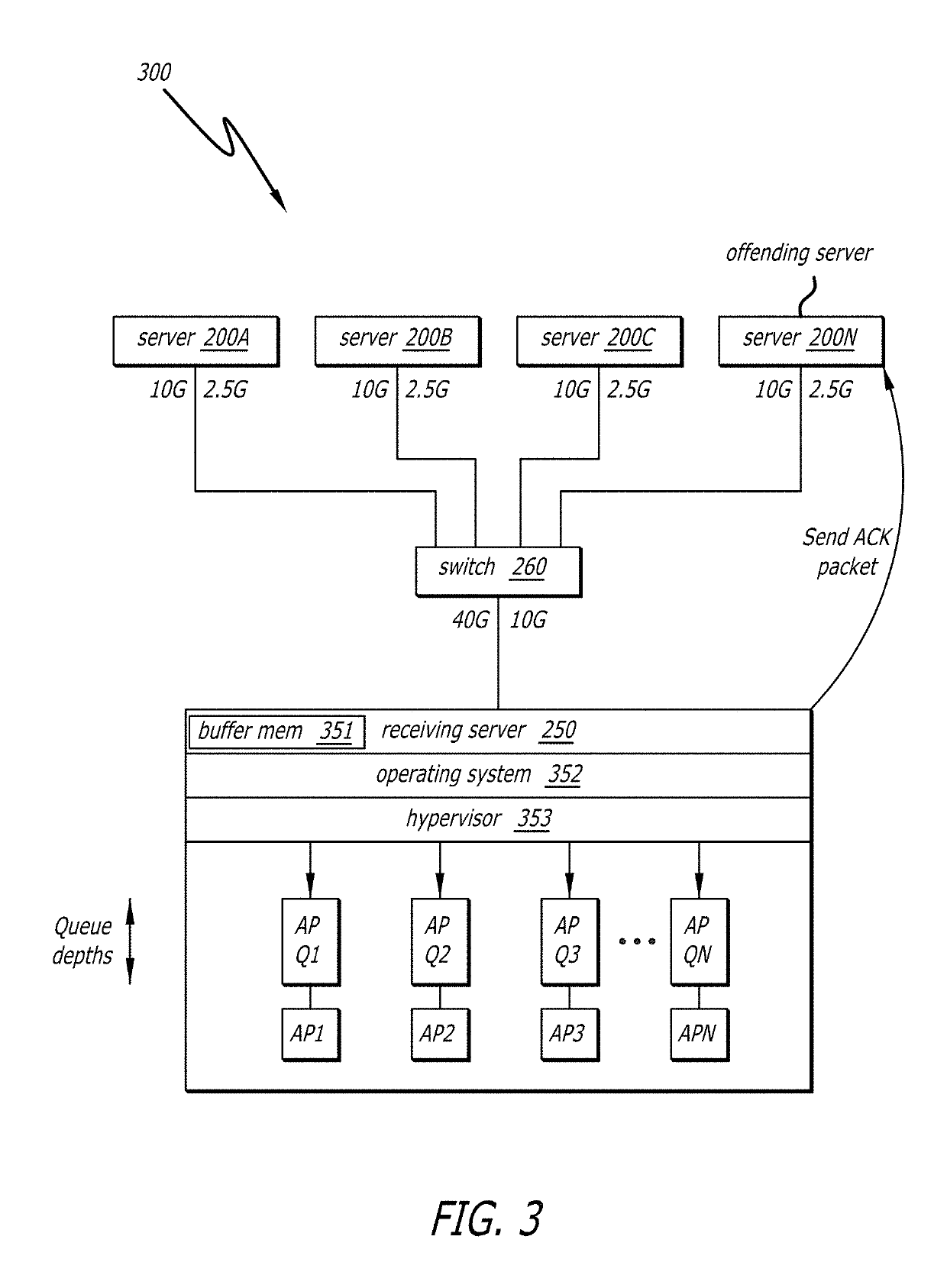
Avoiding dropped data packets on a network transmission
ActiveUS10425344B2Add depthIncrease resourcesError prevention/detection by using return channelSignal allocationFiberNetwork packet
A method, system, and apparatus are provided to avoid dropping data packets between computers coupled on a network. In one example, the system receives a plurality of data packets from one or more sending servers into a receive queue of a first network interface device (e.g., Fiber Channel host bus adapter) in a receiving server. The receive queue includes addresses to data buffers to store a predetermined number of data packets. The system monitors the number of data packets stored in the data buffers waiting for read out by a software application. The system detects a potential overflow of the receive queue in response to a number of unused data buffers of the receive queue. In response to detecting the potential overflow, the system performs preemptive actions to avoid dropping at least one of the plurality of data packets.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
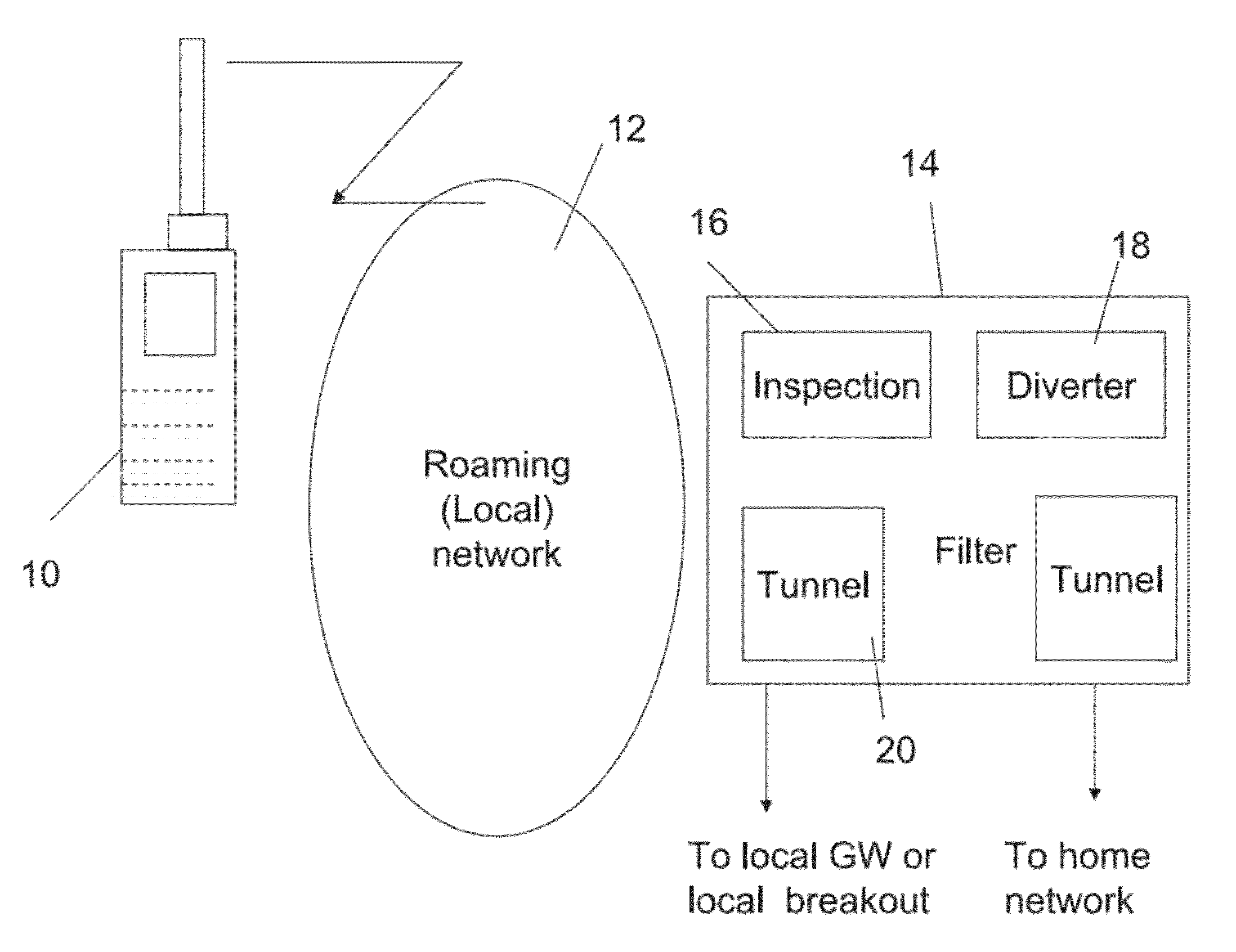
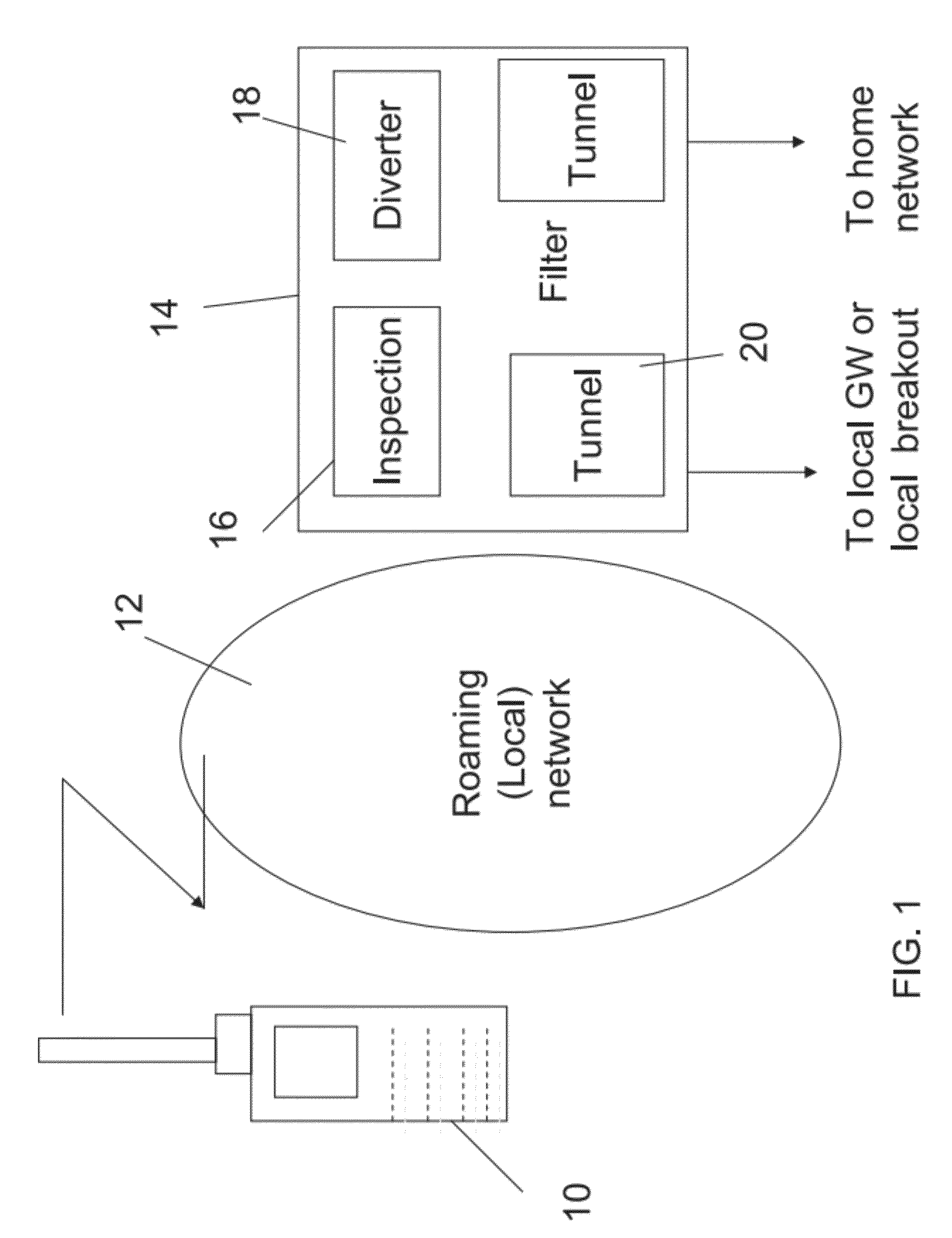
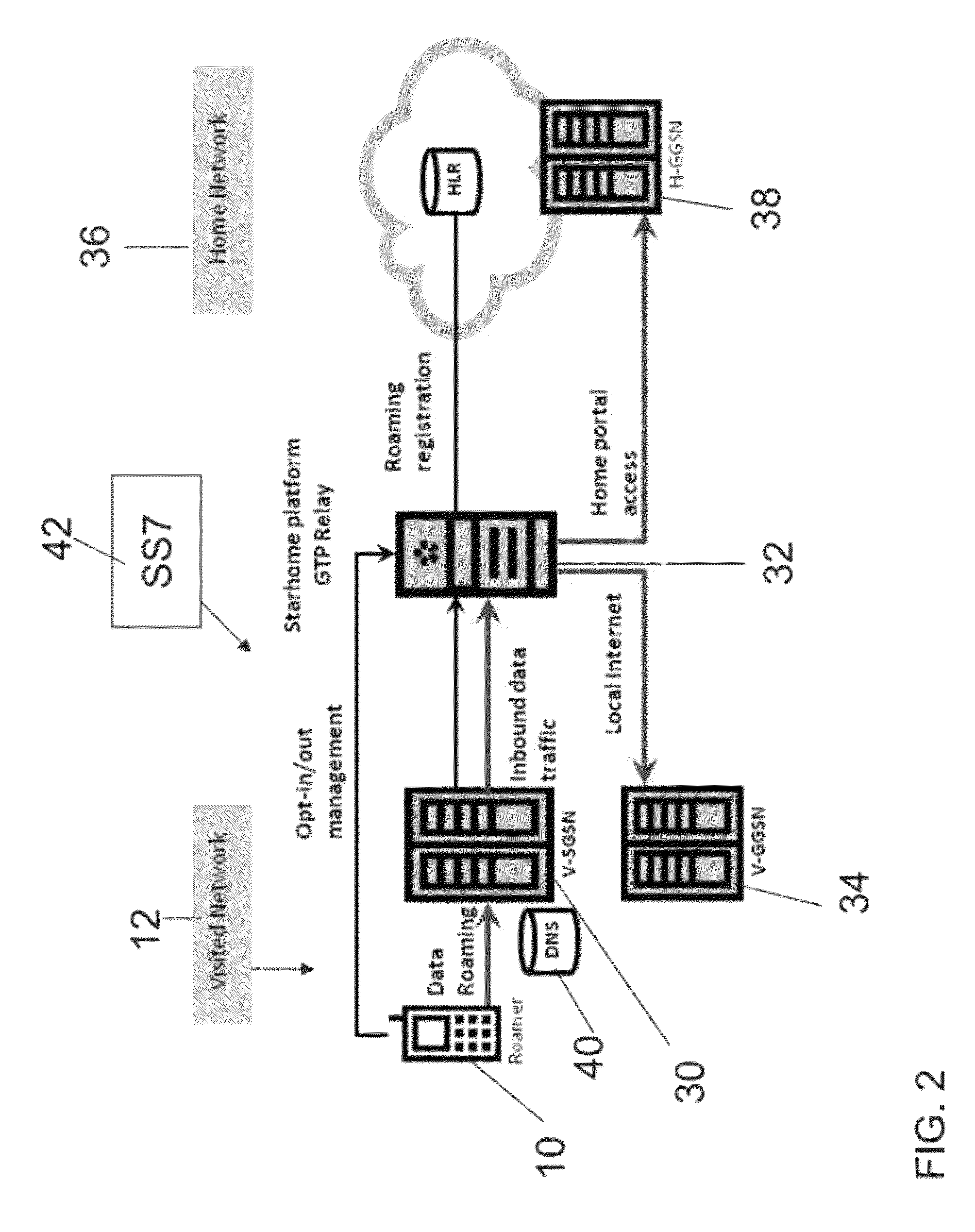
Local access to data while roaming with a mobile telephony device
ActiveUS8711757B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceThe Internet
Apparatus for local access to data while roaming with a mobile telephony device at a roaming network. The apparatus is located at the roaming network and comprises a filter having a data packet or packet header inspection unit for inspecting packet information or headers to identify data packets addressed from the roaming telephony device for use via a home network data packet gateway, and a packet diverter for diverting at least some of the identified packets to a local data packet gateway; the filter setting up a diversion tunnel for additional packets of the same session for directly routing all packets of the identified session to the local data packet gateway. Mobile devices are today programmed to send data to their home network for browsing via the home network data packet gateway. The filter allows data to be redirected to the roaming network so that Internet browsing and like data uses can be carried out directly by the roaming user at less cost and greater efficiency and quality of service.
Owner:STARHOME GMBH
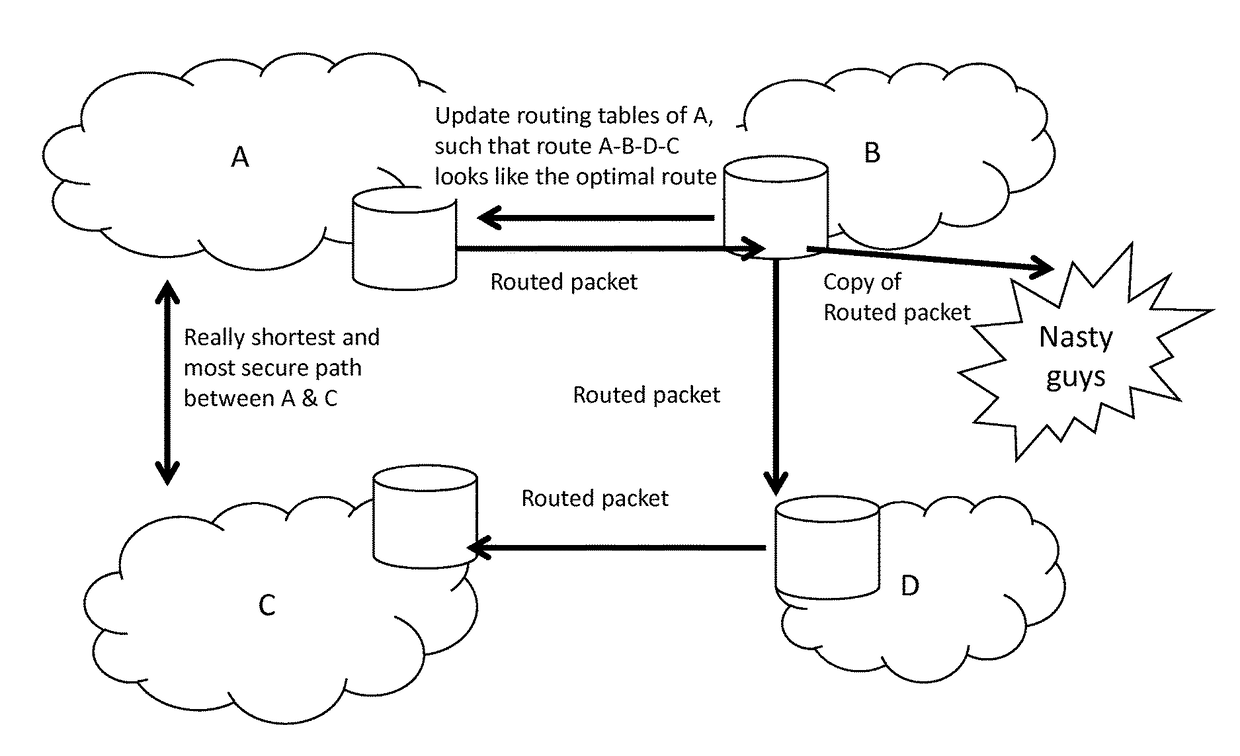
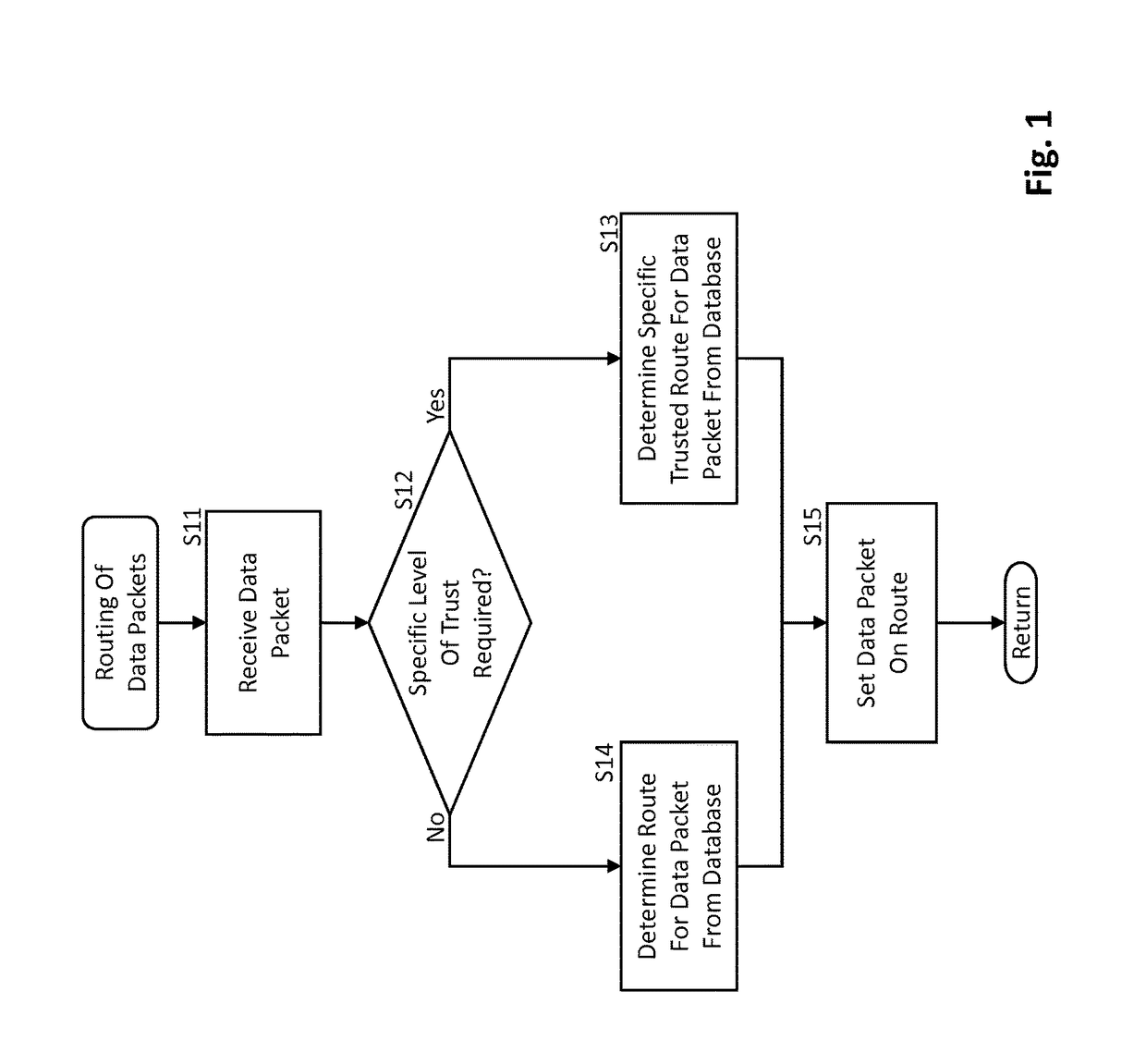
Trusted routing between communication network systems
An apparatus of a communication network system, which routes data packets and stores trusted routes between different communication network systems in a database, detects (S12) that a data packet requires a route with a specific level of trust, determines (S13), from the trusted routes stored in the database, a specific trusted route towards a destination as indicated in the data packet, and sets (S15) the data packet on the specific trusted route towards the destination.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
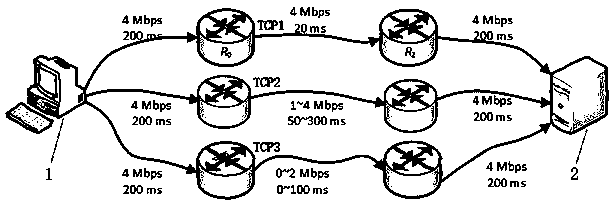
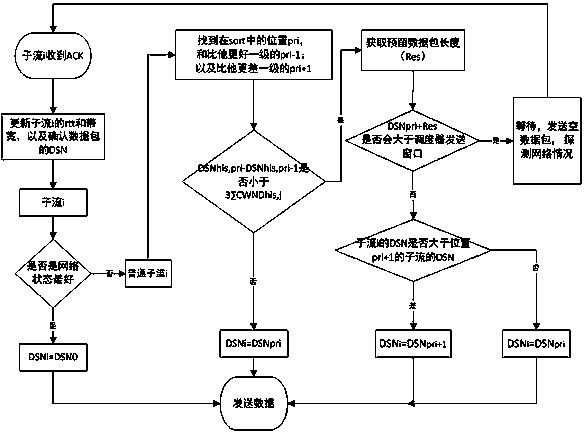
MPTCP scheduling method based on link state information in wireless network
ActiveCN110392394AImprove transmission efficiencyAlleviate the problem of frequent blockingNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission format adaptationWireless mesh networkData transmission
The invention discloses an MPTCP scheduling method based on link state information in a wireless network, and relates to the technical field of computer networks. The scheduling method comprises the following steps: after each TCP sub-stream receives an ACK data packet, updating the position of the TCP sub-stream in the sequence of the network states of all TCP sub-streams according to the networkstate of the TCP sub-stream, and selecting the sent data packet according to the position of the TCP sub-stream in the sequence. Each TCP sub-stream updates the network state of the TCP sub-stream aslong as receiving the ACK data packet, and then sends the next round of data packet without waiting for the next round of scheduling after all TCP sub-streams complete the data packet transmission task, so that the waiting time is greatly shortened, and the data transmission efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
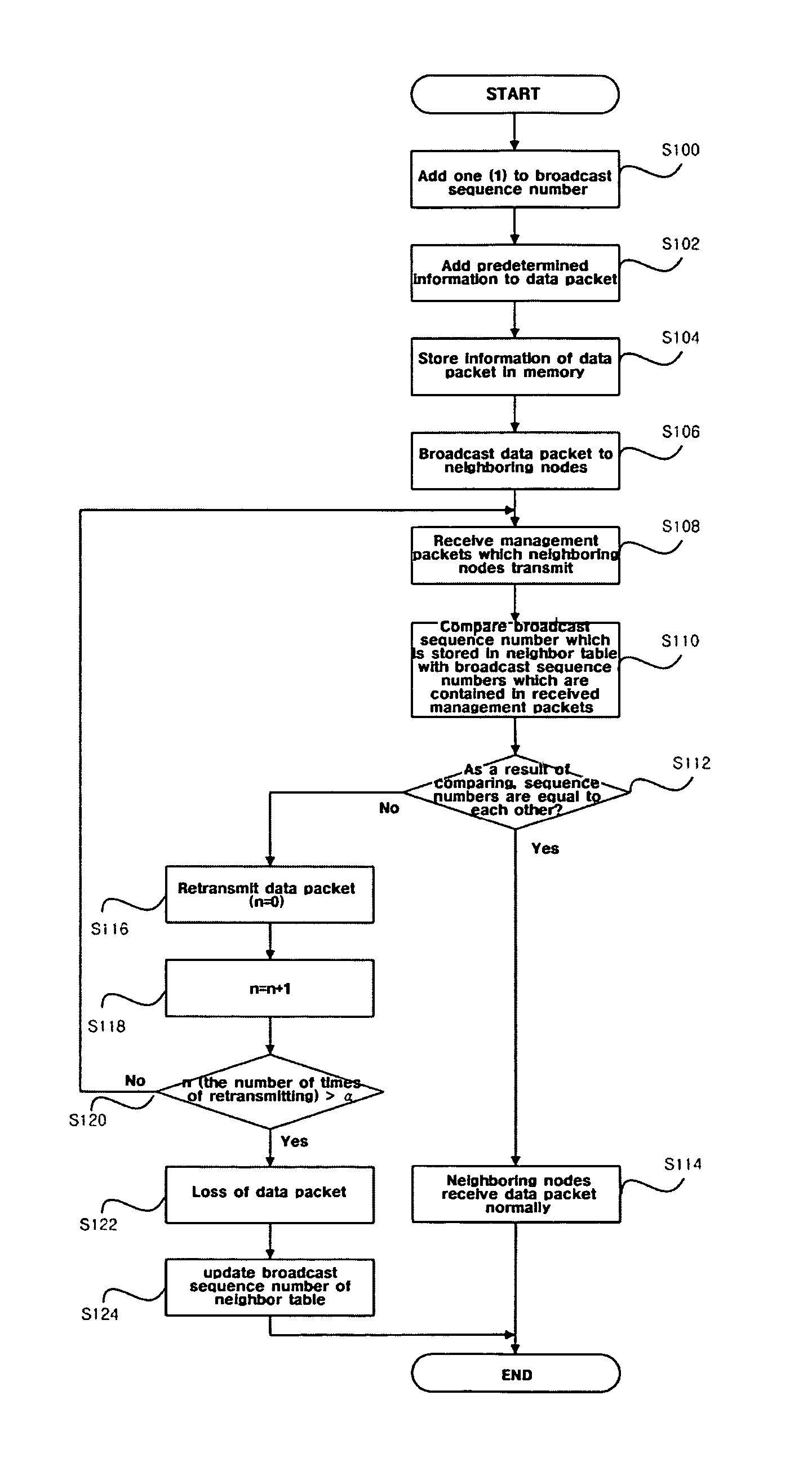
System and method of reliably broadcasting data packet under ad-hoc network environment
InactiveUS7894381B2Reliably broadcastReduce overloadSpecial service provision for substationError preventionBroadcast dataComputer science
A system for reliably broadcasting a data packet under an ad-hoc network environment including a determining unit for determining whether or not at least one node receiving the broadcast data packet is a relay node, a comparing unit for comparing a first relay node sequence number contained in a management packet which the node transmits with a second relay node sequence number stored in a neighbor table of the node, and a control unit for determining whether or not the data packet is retransmitted to the node according to a result of the comparison of the comparing unit. By comparing the second relay node sequence number stored in the neighbor table of the node which has broadcast the data packet with the first relay node sequence numbers transmitted through a Hello packet, it is possible to check whether or not the data packet is lost during broadcasting, and thus it is possible to reduce a loss factor of the data packet which is generated during broadcasting. Thereby, the data packet can be reliably broadcast.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Remote access method suitable for mobile router
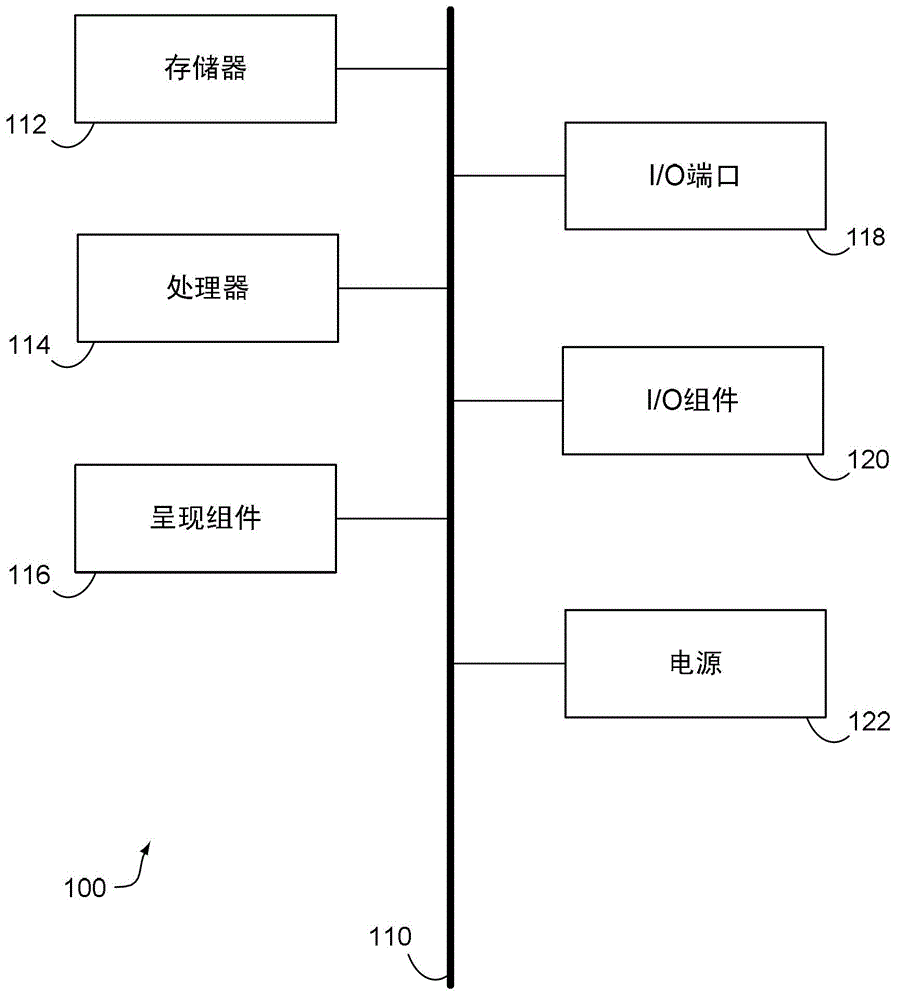
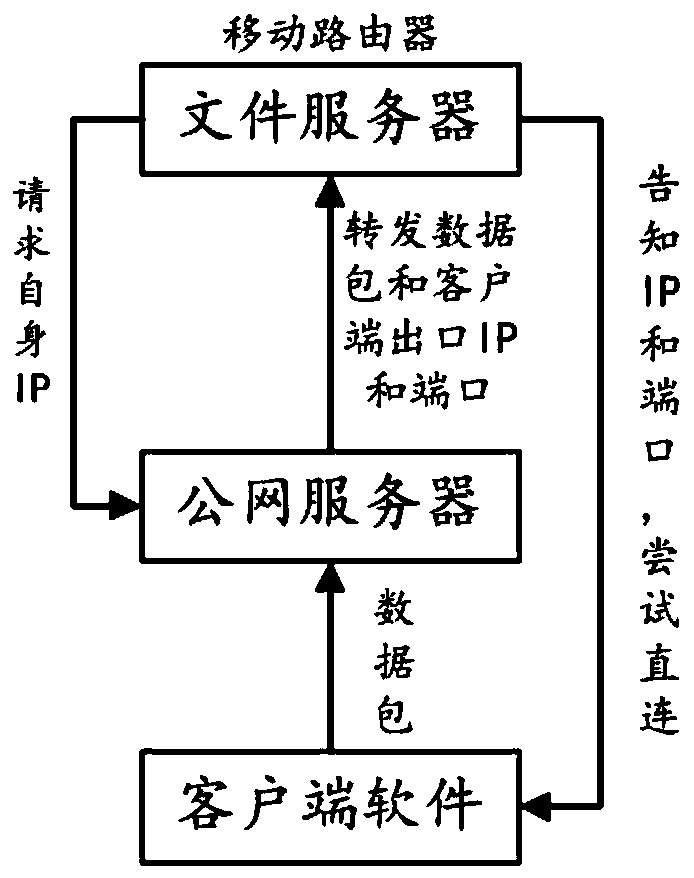
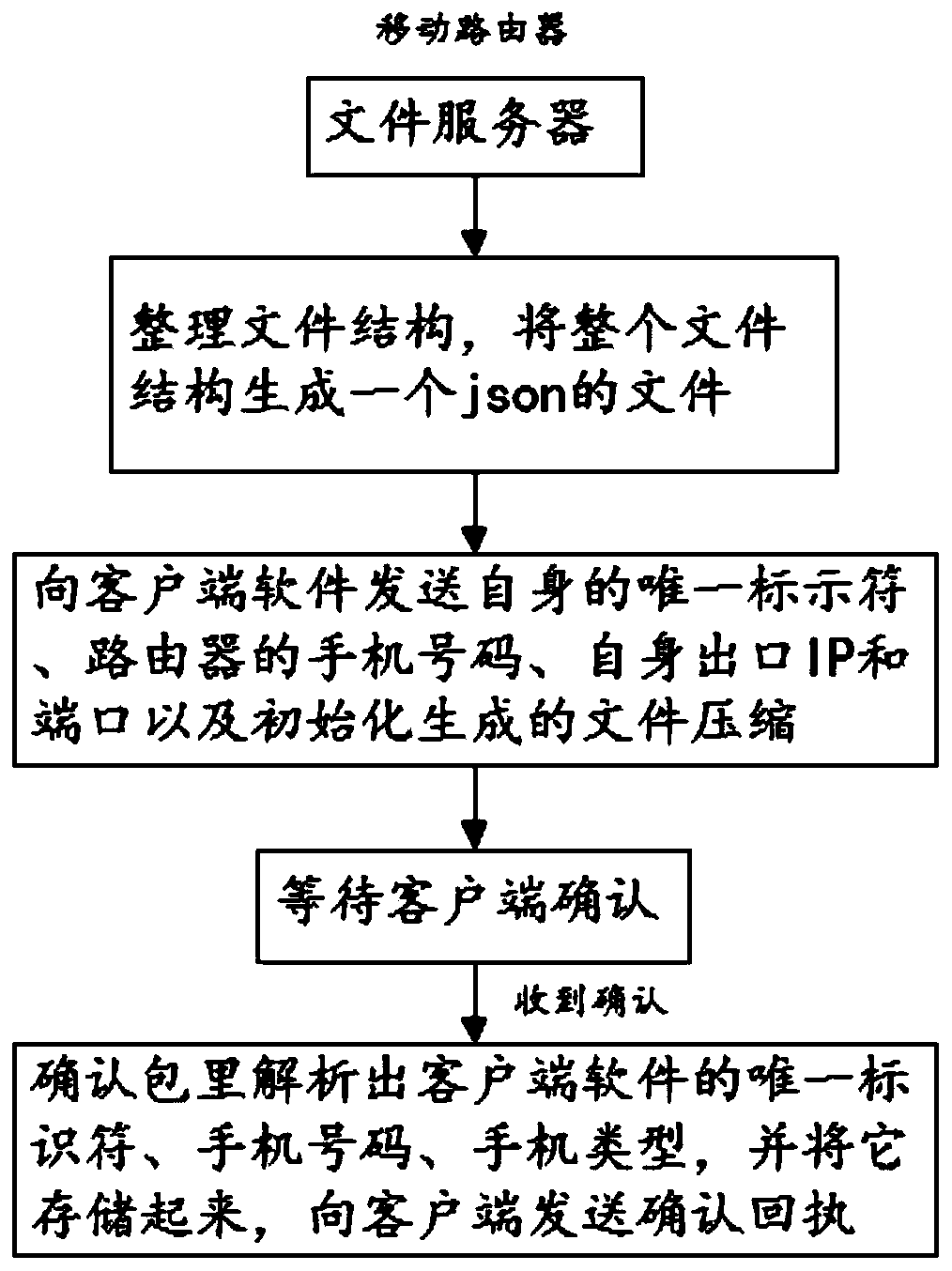
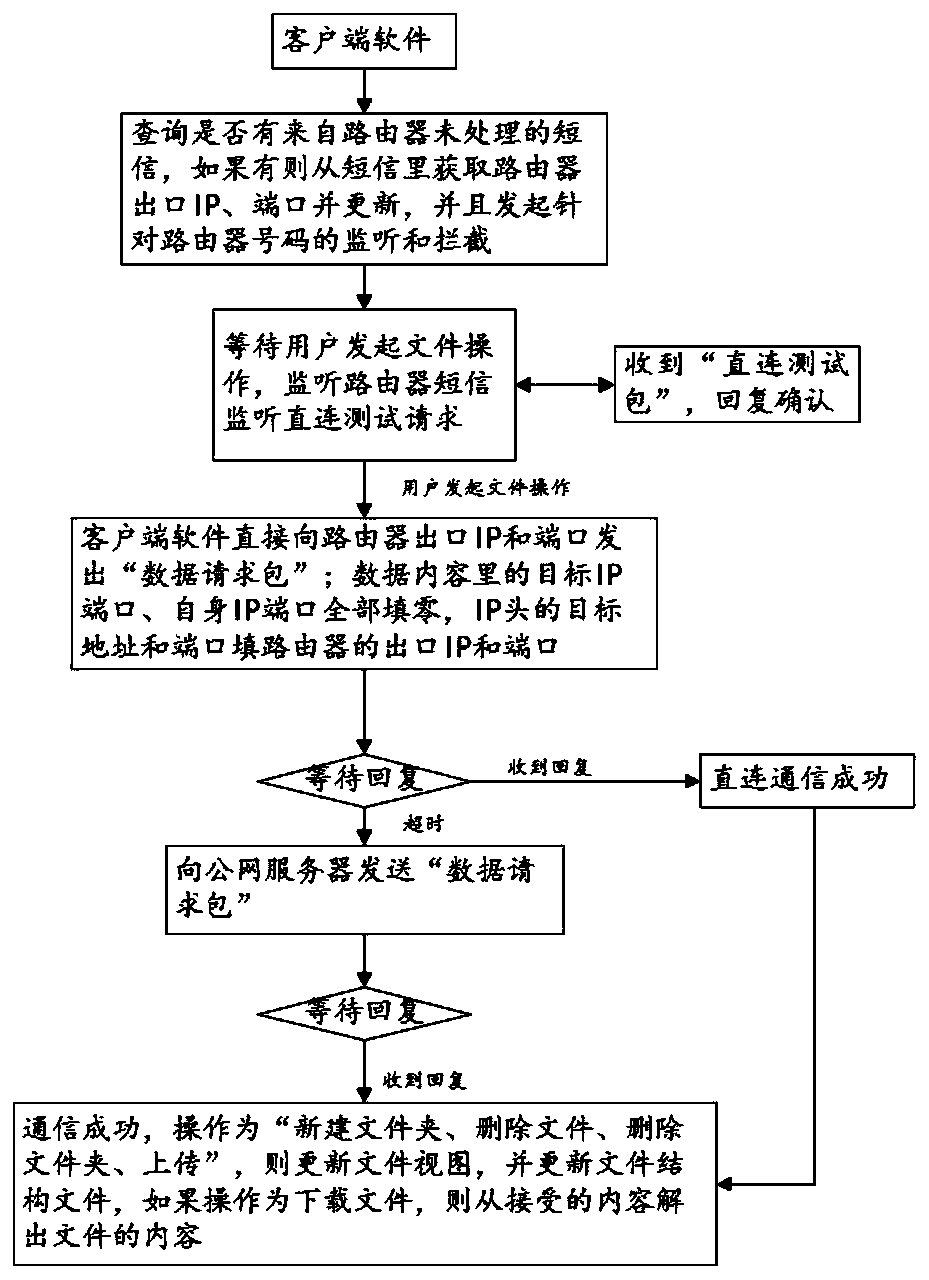
ActiveCN109995870ARelieve pressureSave resourcesMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsData switching networksAccess methodNetwork packet
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile routers, in particular to a remote access method applicable to a mobile router, which comprises the following steps that: 1, a file server running in the mobile router requests a public network server for an IP (Internet Protocol) of the file server, and then returns an outlet IP and a port of the file server; 2, the file server informs clientsoftware of an outlet IP and a port of the mobile router in a short message mode, and the client software tries to be directly connected with the file server; 3, if the direct connection fails, the client software sends the data packet to a public network server, and the public network server adds an outlet IP and a port of the client software to the forwarded data packet and forwards the forwarded data packet to a file server; and 4, the file server makes a reply, attempts to directly connect, and sends the reply to the public network server if the direct connection fails. According to the invention, public network server resources can be better saved.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEWINS WIRELESS
System and method for transmitting data packets to a plurality of mobile terminations through a single IP connection
ActiveUS9232551B2Improve abilitiesConnection managementWireless commuication servicesTelecommunications networkRadio networks
The invention refers to a radio network entity for transmitting data packets from an IP gateway in a telecommunications network to a user terminal via a plurality of mobile terminations through a single IP connection. The radio network entity comprises:a module for establishing IP connections between the IP gateway and mobile terminations, for activating first and second IP connections and first and second radio connections in response to respective requests from first and second mobile terminations;a packet splitter that applies a splitting algorithm to determine which radio connection is to be used to transmit which data packets, the packet splitter being in communication with a packet combiner in the user terminal;wherein the packet splitter splits the data packets coming only from the first IP connection selected by the user terminal as the only IP connection through which the data packets are received, thereby transmitting data packets over said first and second radio connections for combining at the packet combiner.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
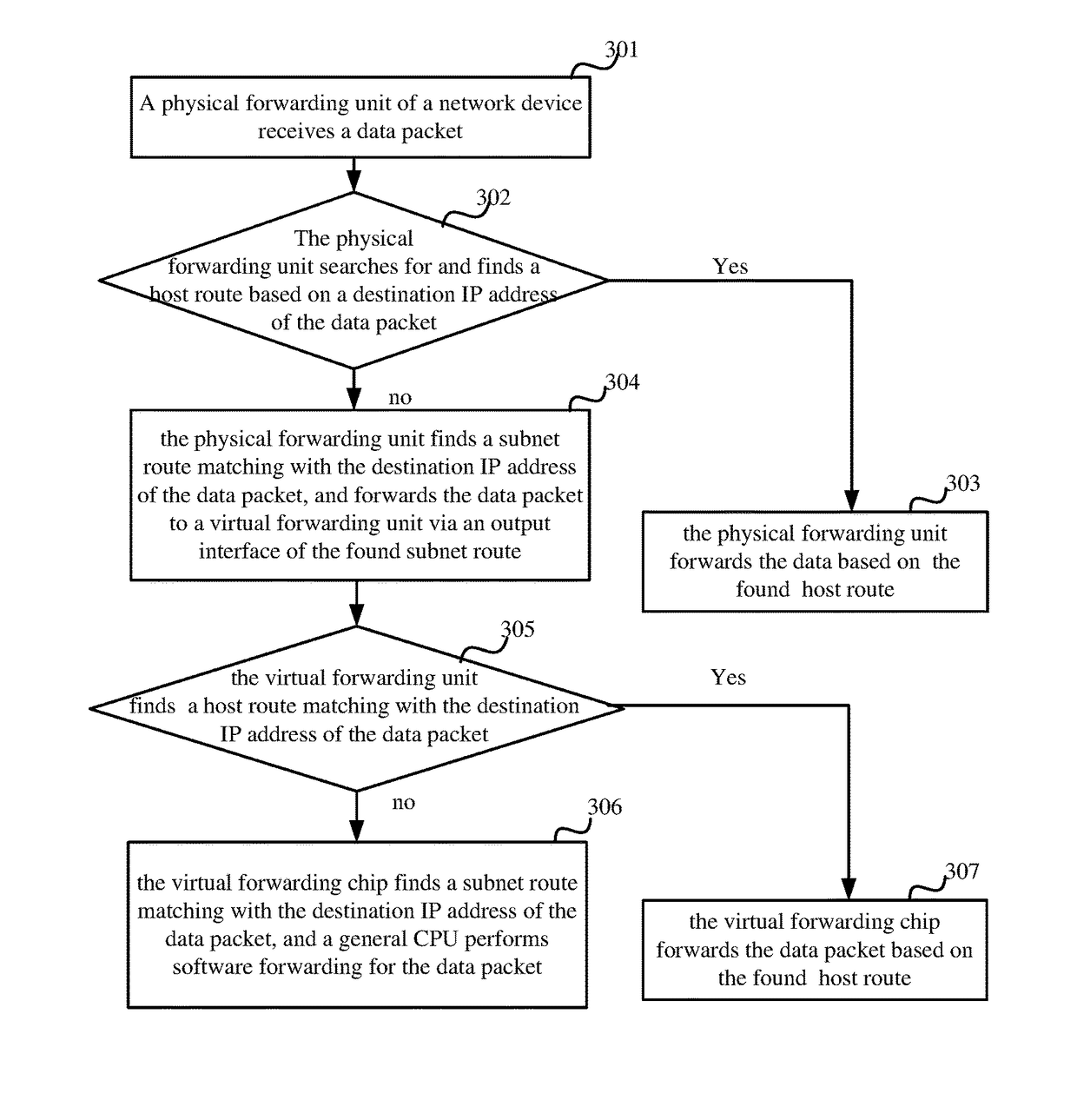
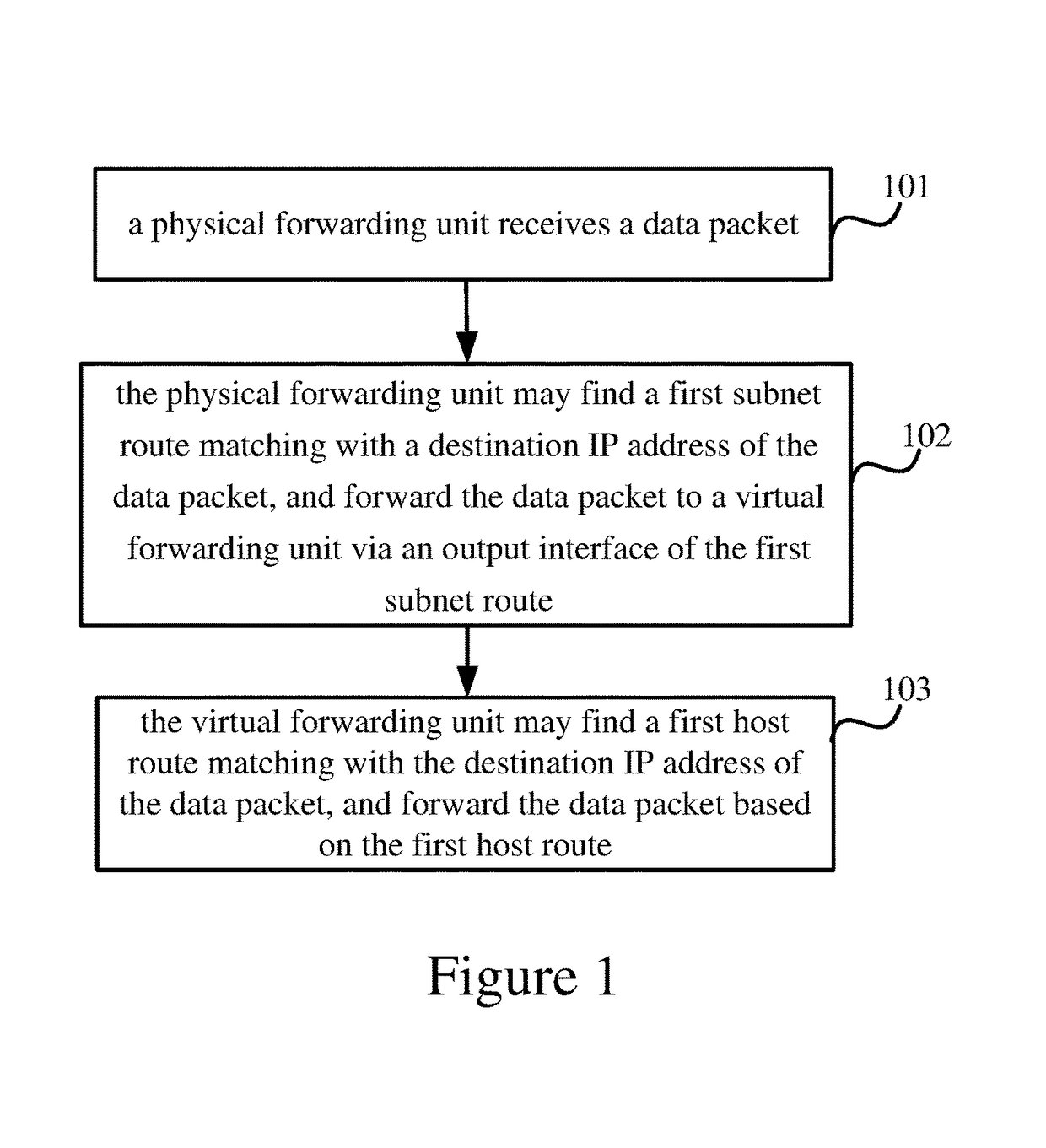
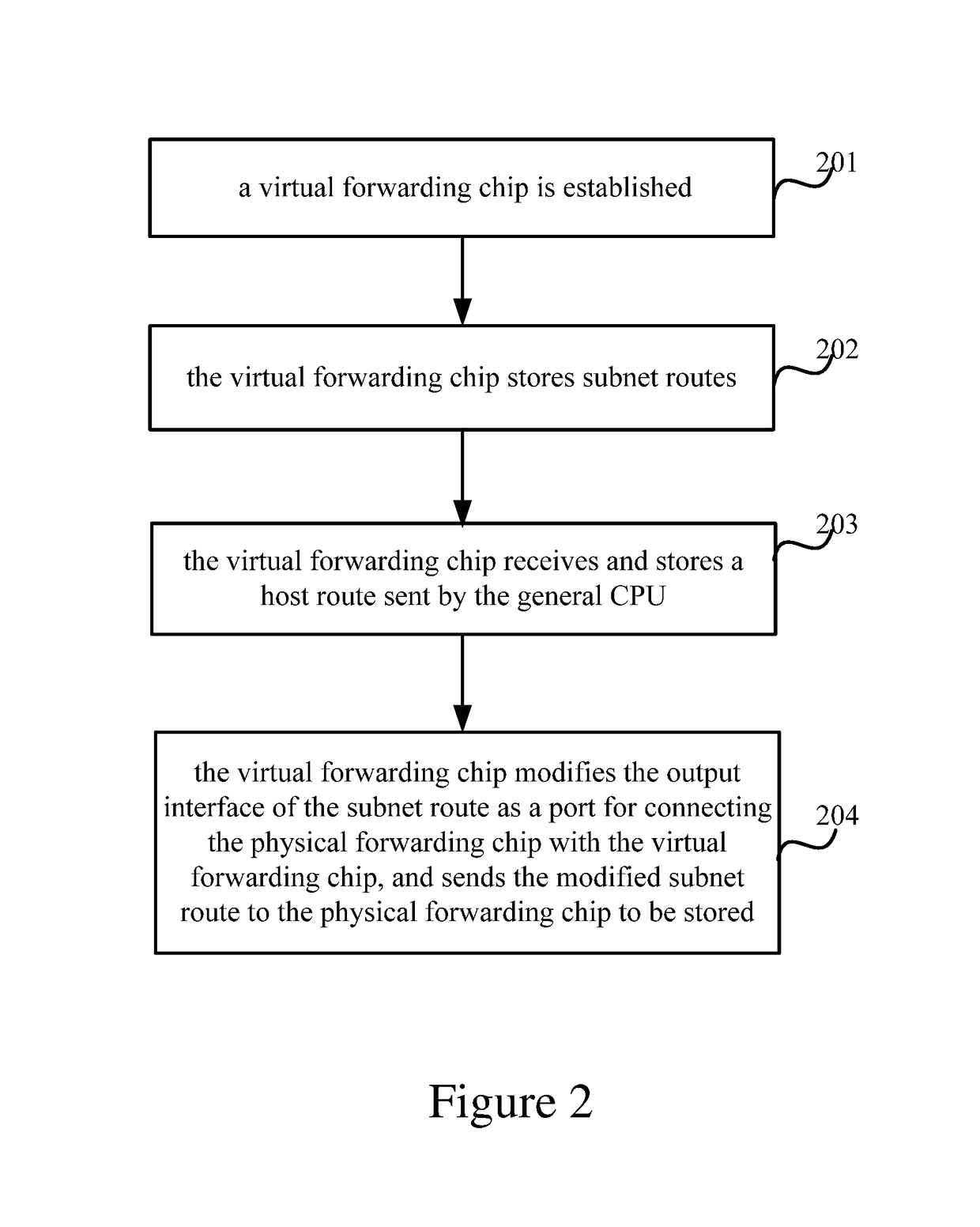
Packet forwarding using a physical unit and a virtual forwarding unit
In a method for forwarding a packet, a physical forwarding unit receives a data packet, may find a first subnet route based on a destination IP address of the data packet, and forwards the data packet to a virtual forwarding unit via an output interface of the first subnet route. The virtual forwarding unit receives the data packet may find a first host route based on the destination IP address of the data packet, and forwards the data packet based on the first host route.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
A method for securely transmitting data packets sent by sensors to base stations in the Internet of Things
InactiveCN106102048BIncrease randomnessImprove safety cycleSecurity arrangementNetwork packetThe Internet
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
A data transmission method for virtualized network, node controller and system
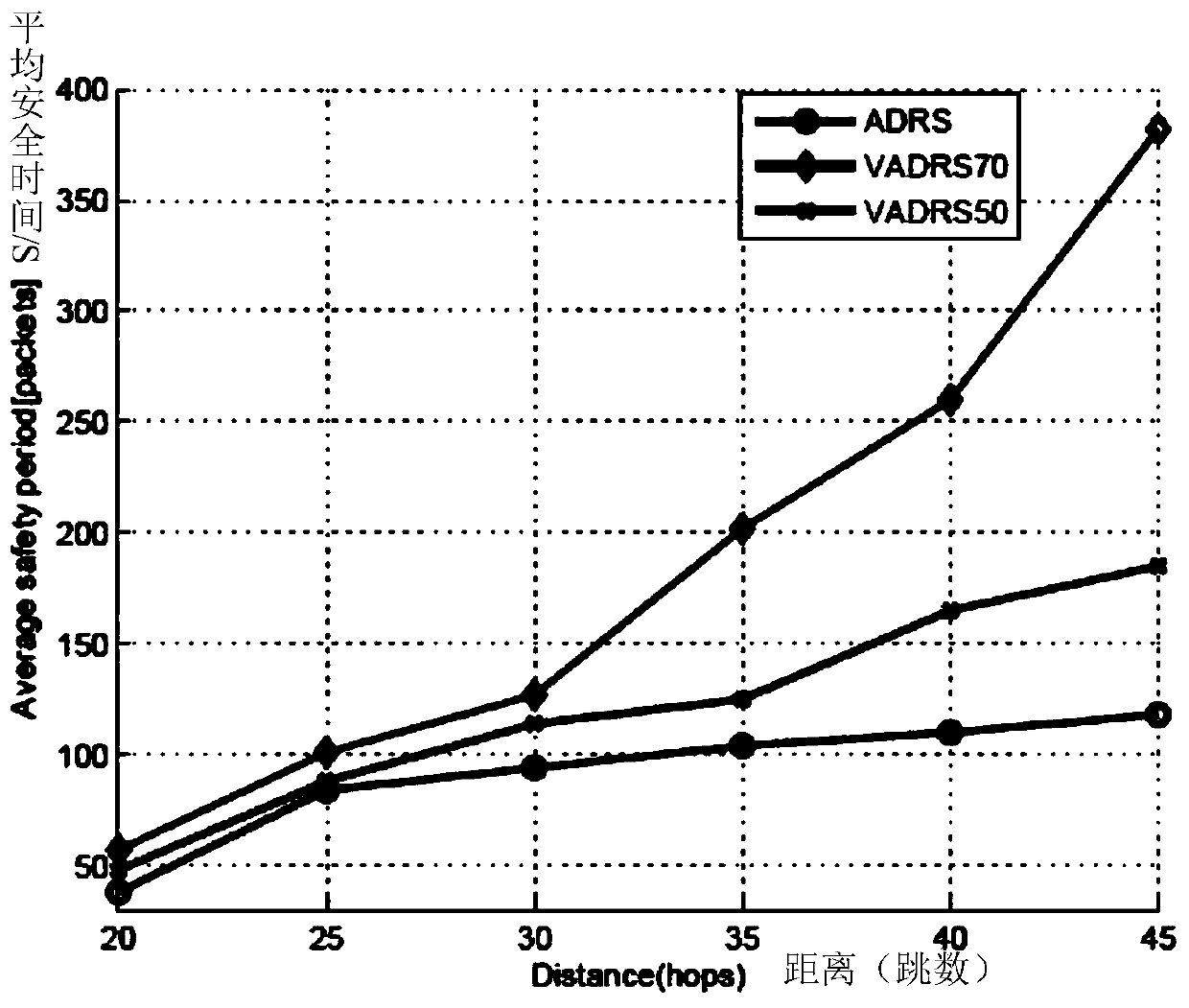
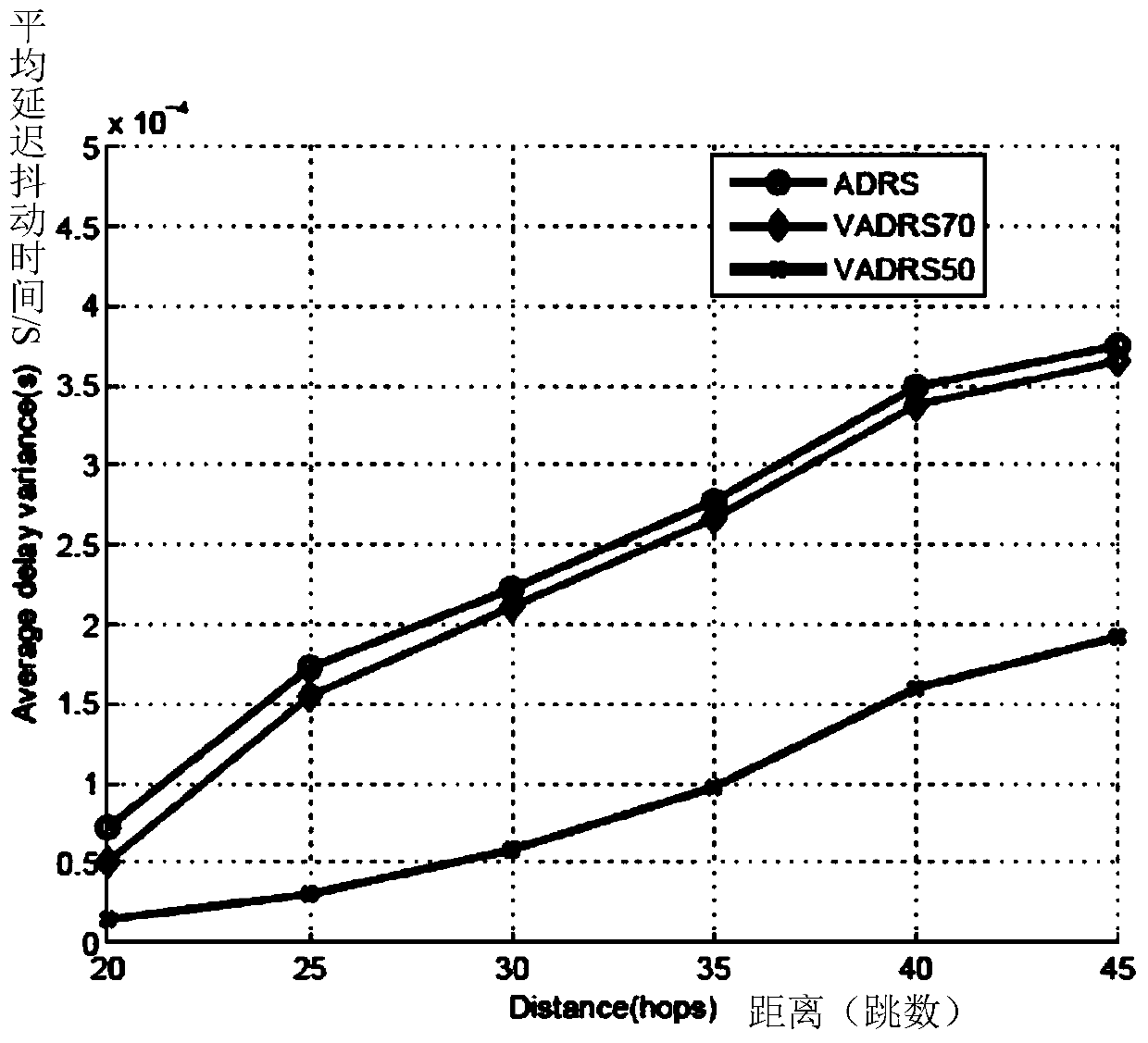
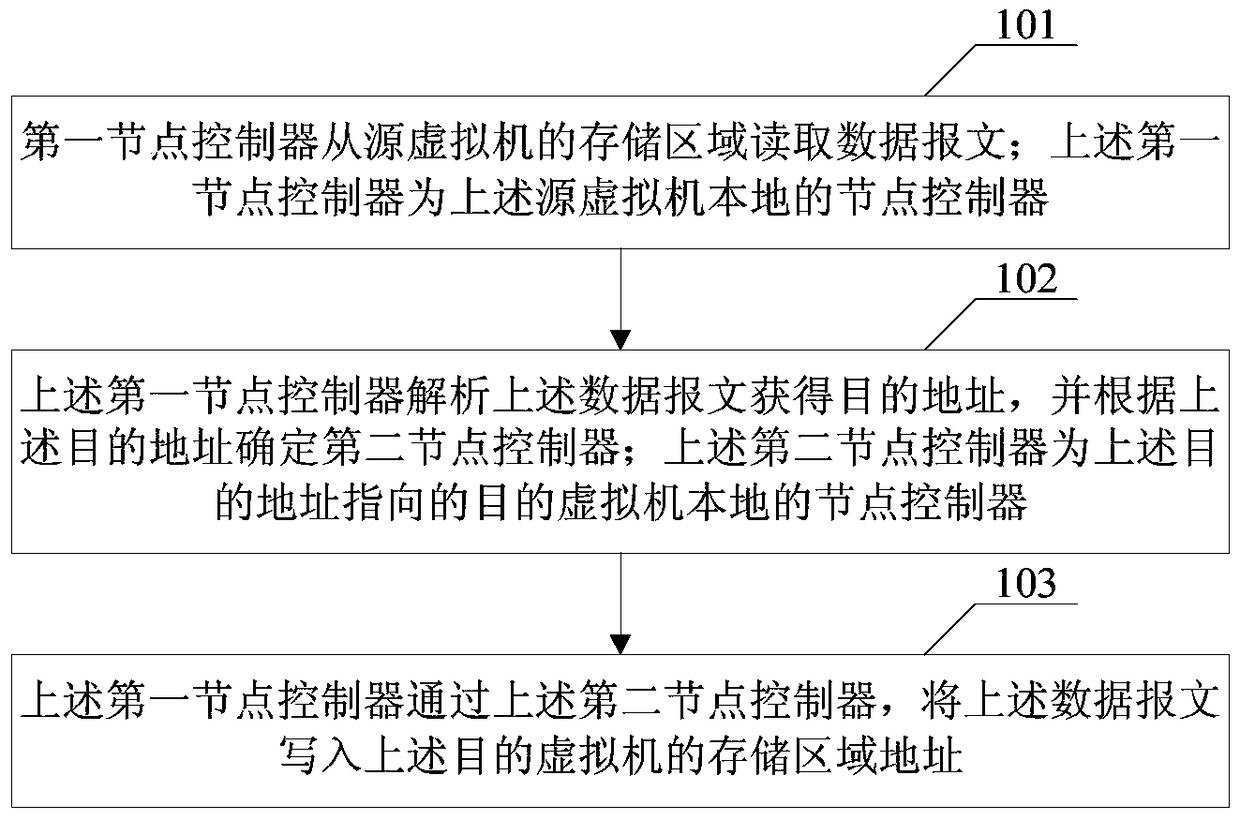
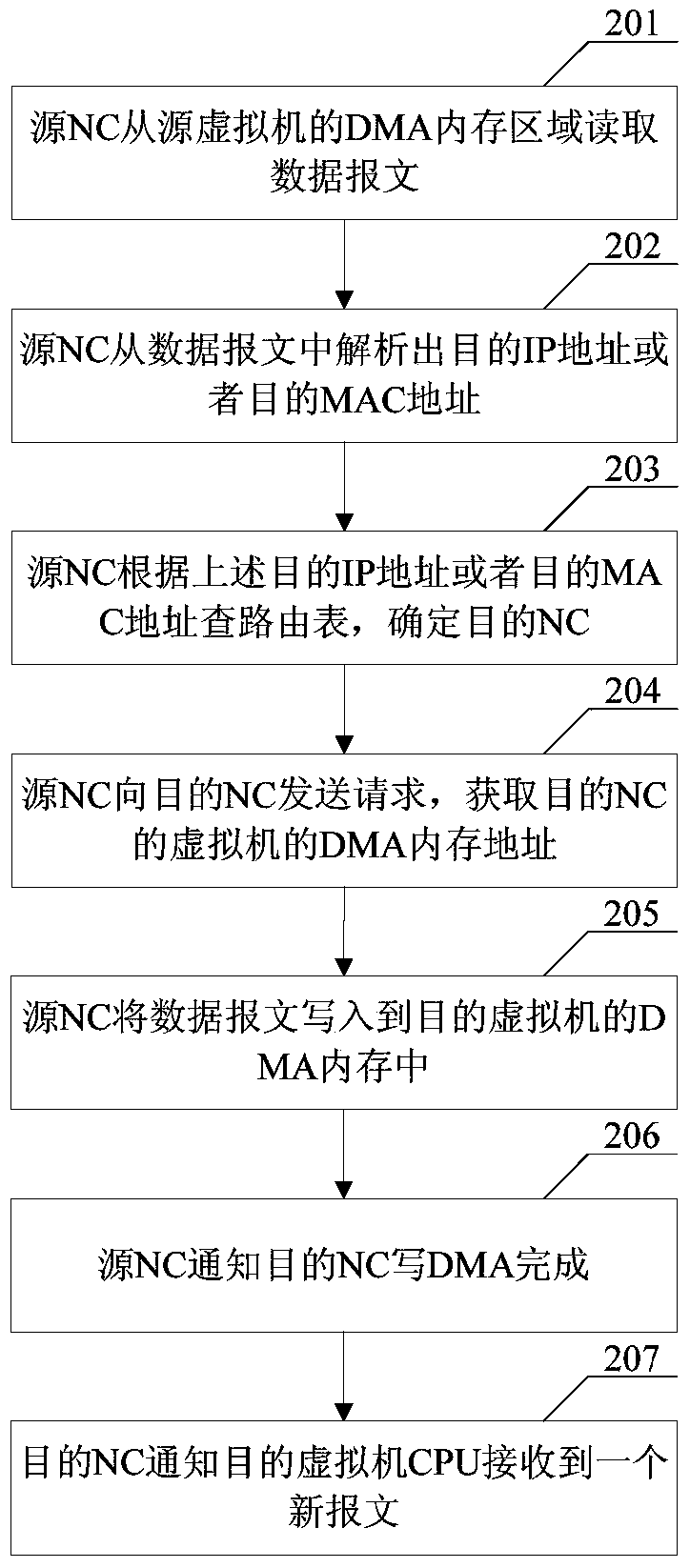
ActiveCN105704098BHigh speedAvoid performance bottlenecksTransmissionElectric digital data processingVirtualizationData transmission
Embodiments of the invention disclose a data transmission method for virtualized networks, a node controller and a data transmission system for virtualized networks. The method comprises the following steps: a first node controller reads a data packet from a storage area of a source virtual machine, wherein the first node controller is a local node controller of the source virtual machine; the data packet is parsed to get a destination address, and a second node controller is determined according to the destination address, wherein the second node controller is a local node controller of a destination virtual machine directed by the destination address; and the data packet is written into the storage area address of the destination virtual machine through the second node controller. A data packet transmitting operation is converted into a storage space shifting operation. The operation is quick, and there is no need to additionally occupy the protocol layer processing ability of NCs. Moreover, performance bottlenecks caused when network card equipment becomes an access hotspot are avoided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com