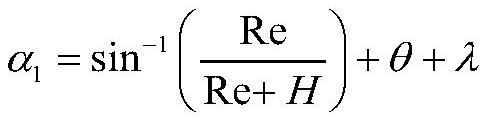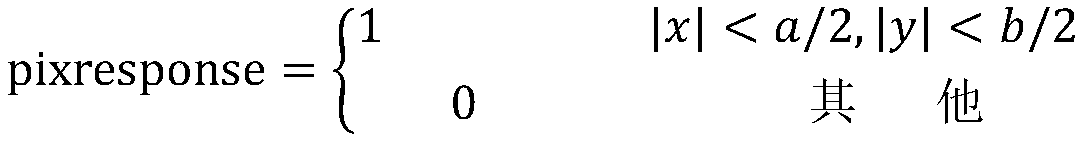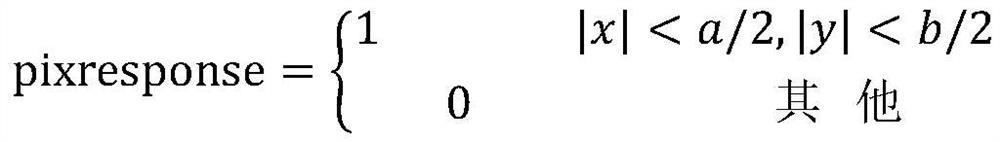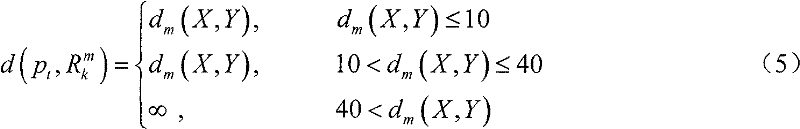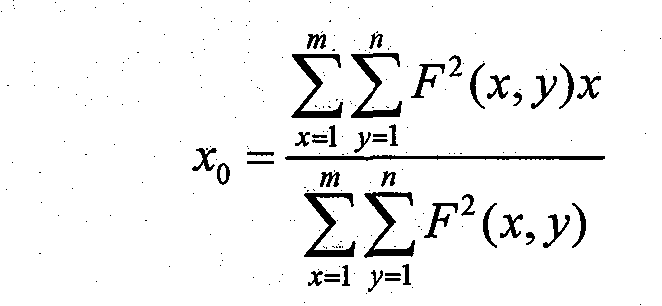Patents
Literature
35 results about "Star position" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
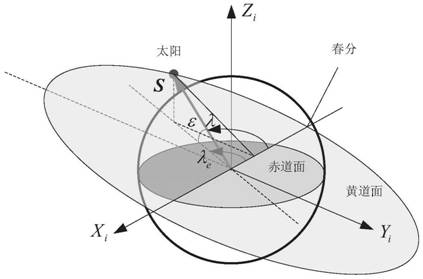
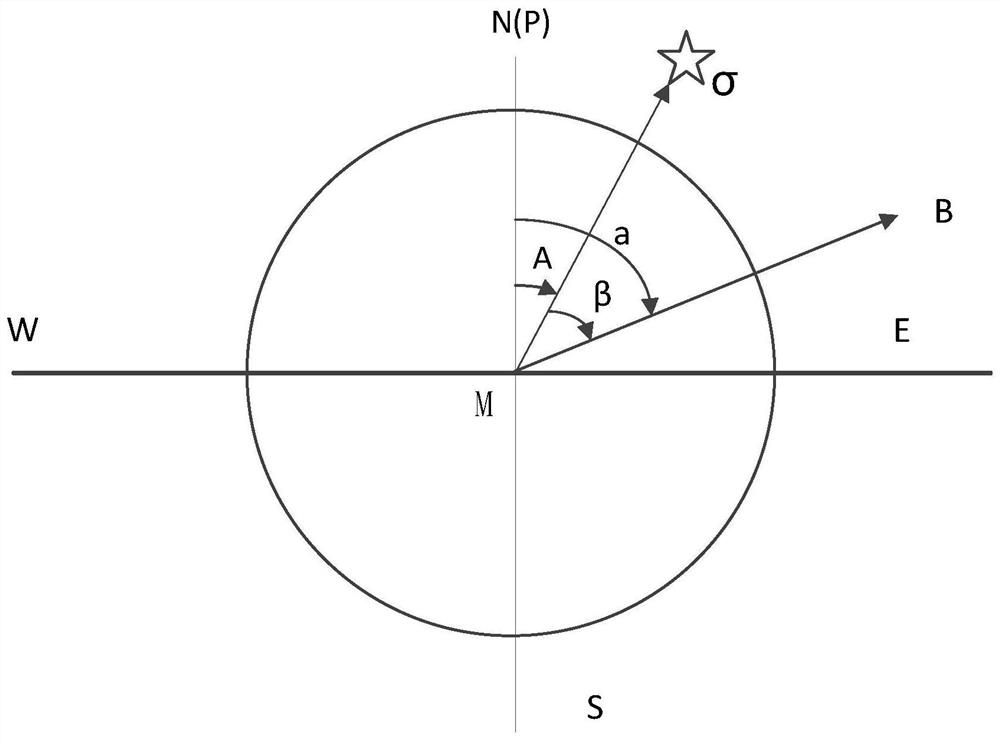
Star position is the apparent location of any given star in the sky, which seems fixed onto an arbitrary sphere centered on Earth. The location is defined by a pair of angular coordinates relative to the celestial equator: right ascension (α) and declination (δ). This pair based the equatorial coordinate system.
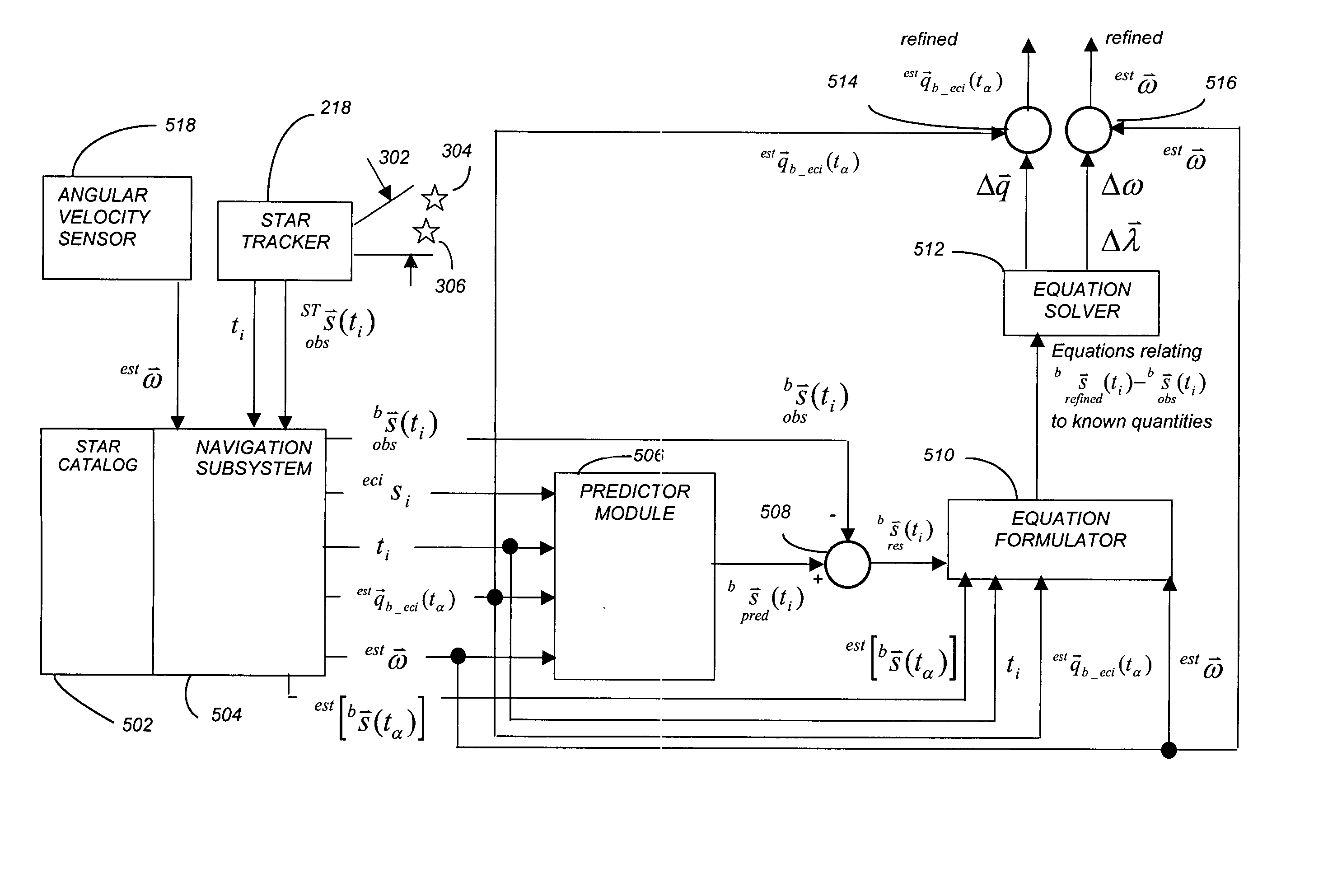
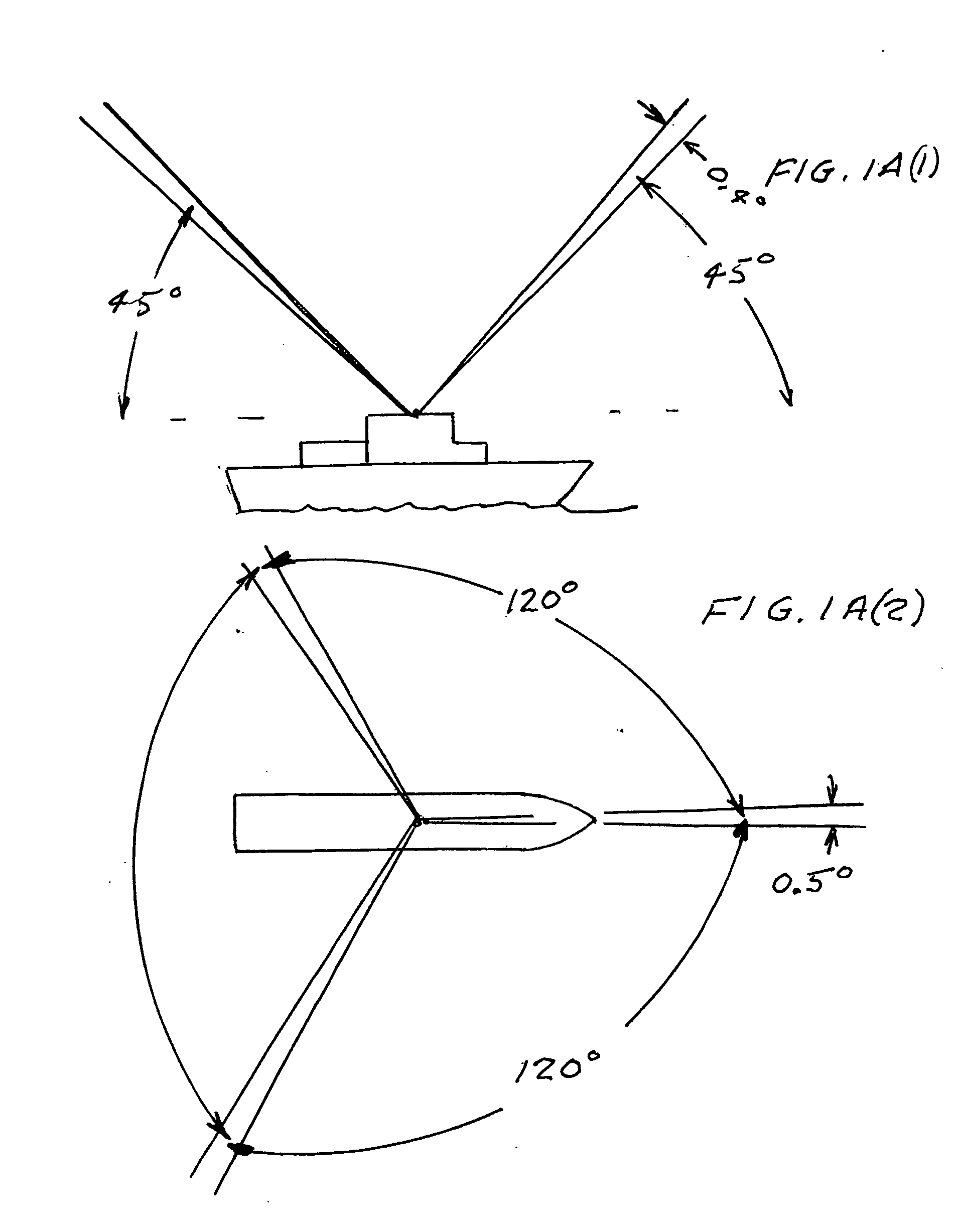
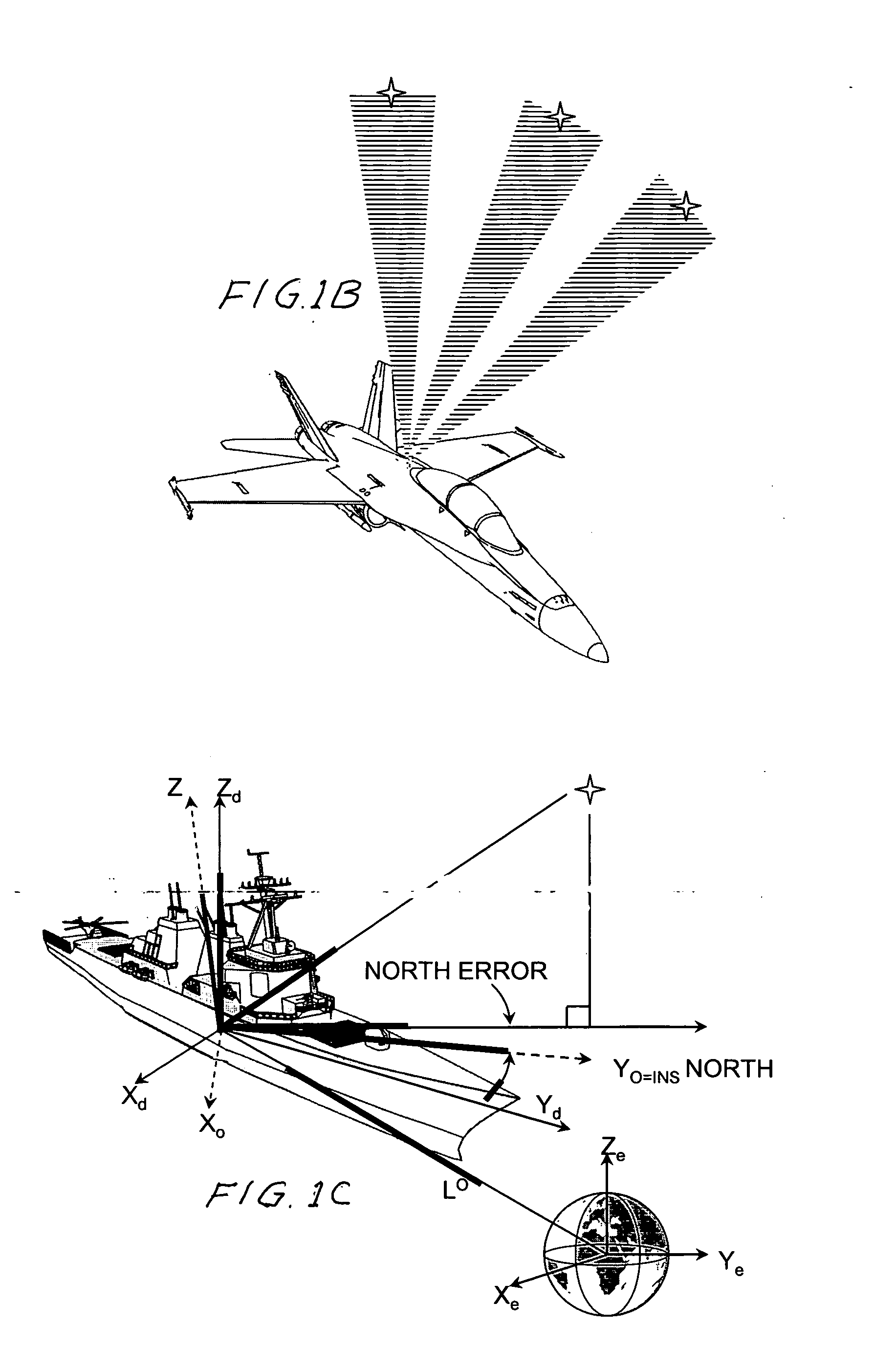
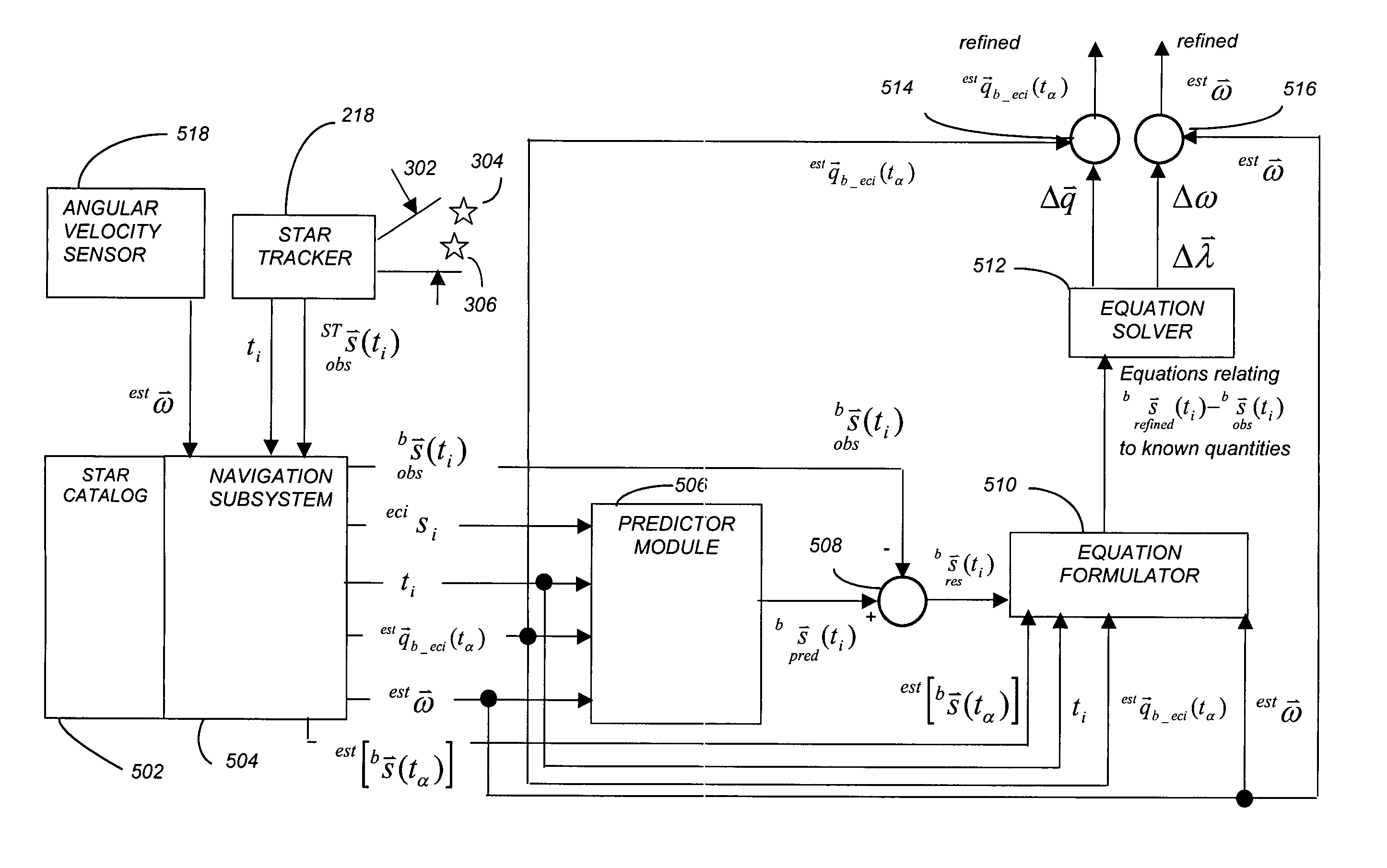
Refinement of spacecraft angular velocity and attitude estimates using star data
ActiveUS20050071055A1Cosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsAngular velocityStar position
A method and apparatus for refining a spacecraft state estimate, such as an attitude estimate or an angular velocity estimate, is disclosed. The method computes a plurality equations using residuals describing the difference between observed star positions and predicted positions based on inertial measurements, and solves those equations to generate refined estimates of the spacecraft state estimates.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS20060085129A1Turbulence effectIncrease probabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansDisplay deviceLongitude
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. A preferred embodiment uses three telescopes with each of the three telescopes rigidly mounted with respect to each other and rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Telescope optics focuses, onto the pixel array of a sensor, H-band or K-band light from stars in the field of view of each telescope. The system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to cataloged infrared star charts. The processor is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the cataloged star charts information to determine positions of the platform. At least two telescopes pointed far enough from the sun detect stars. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude, longitude and absolute azimuth, all of which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor. In a preferred embodiment each of the three telescopes are fixed on a moving ship and views a 0.5×0.4 degree region of the sky for H-band starlight from stars with brightness greater than 6.4 H-band magnitude. Located stars are then compared with star positions from the star catalog within a selected 5×5 degree region of the sky. A correlation of the data from the three telescopic measurements determines the position of the ship to a precision of 30 meters.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
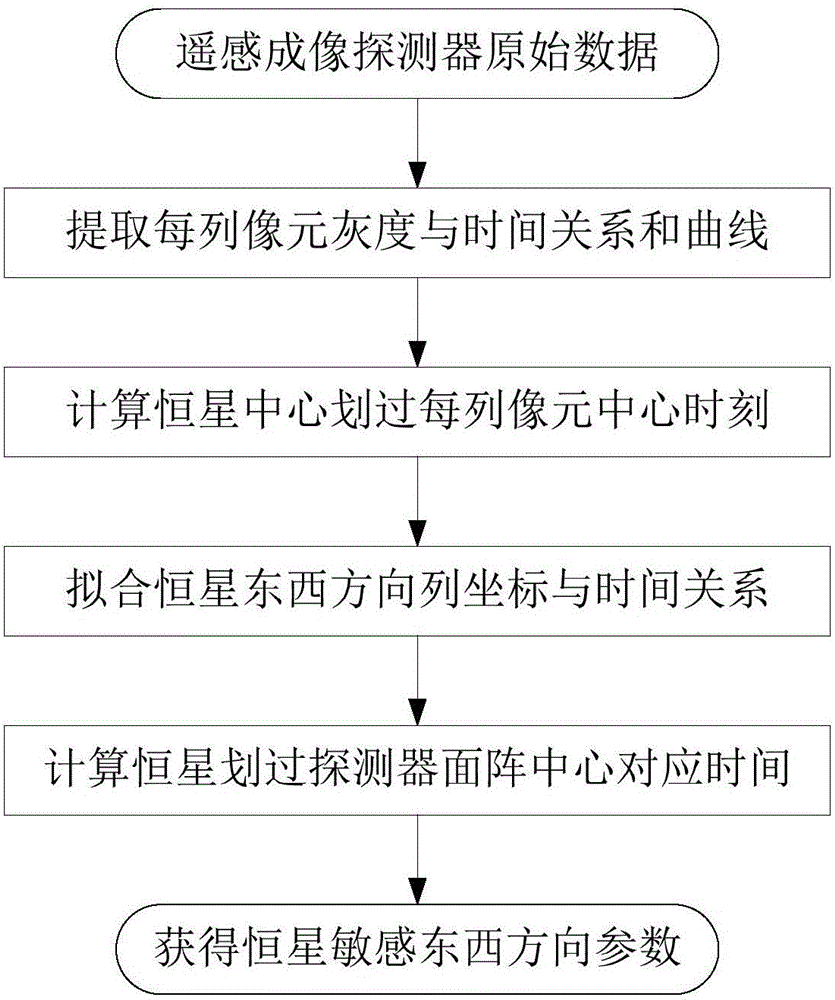
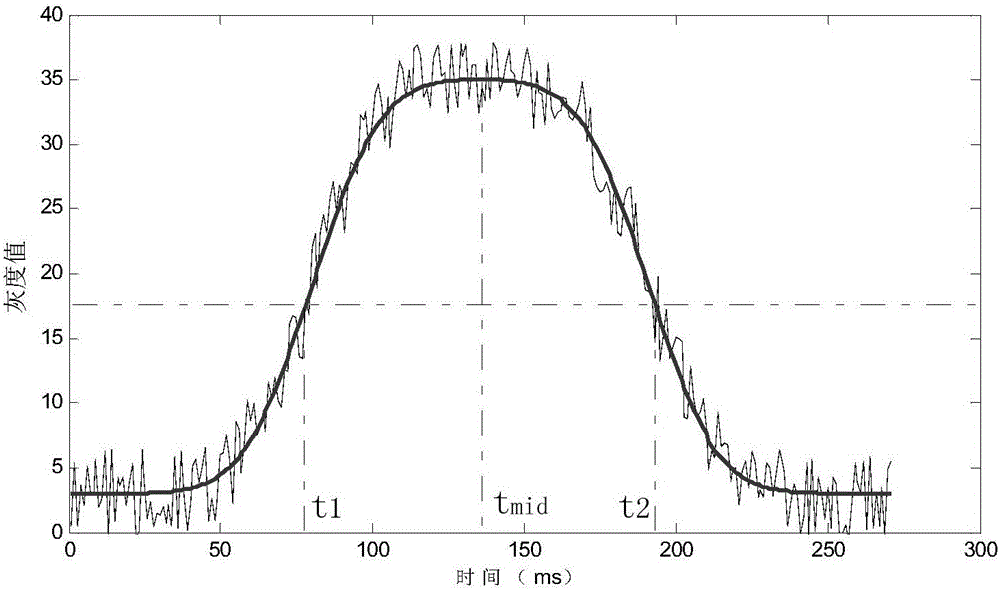
Extracting method for fixed star sensitive east and west parameters of stationary satellite imaging navigation and registration
ActiveCN105758400AHigh precisionImproving Imaging NavigationNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsNatural satellite
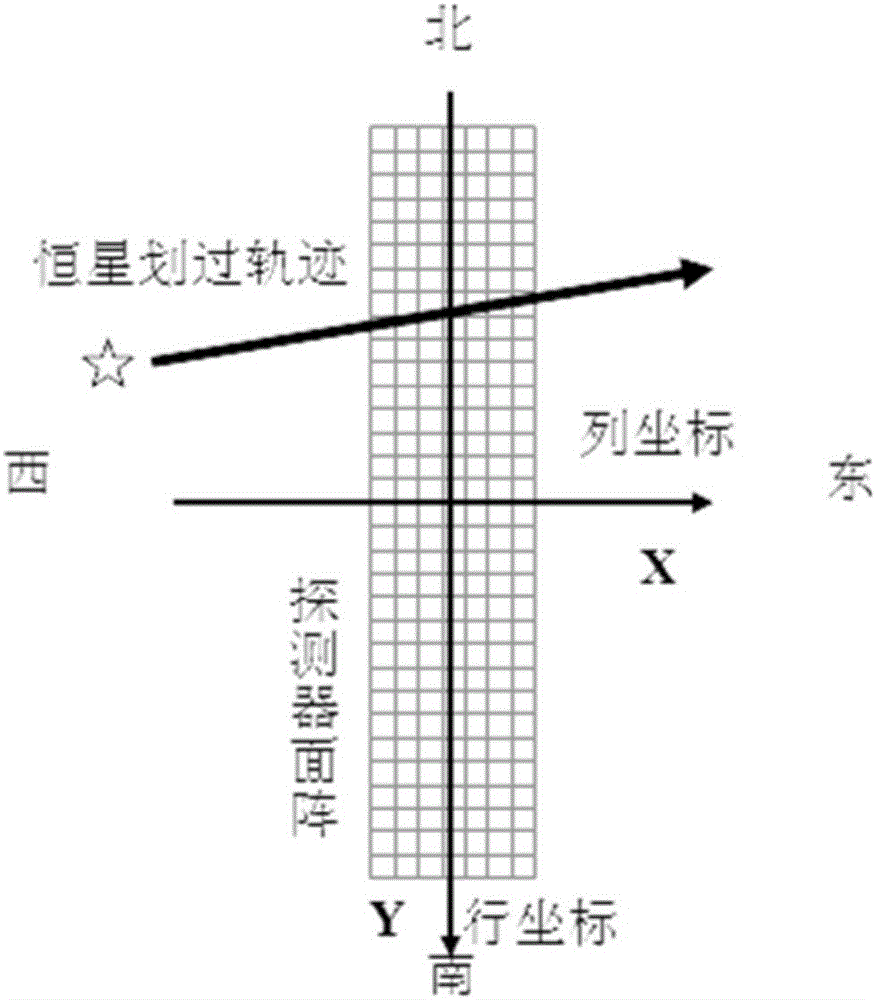
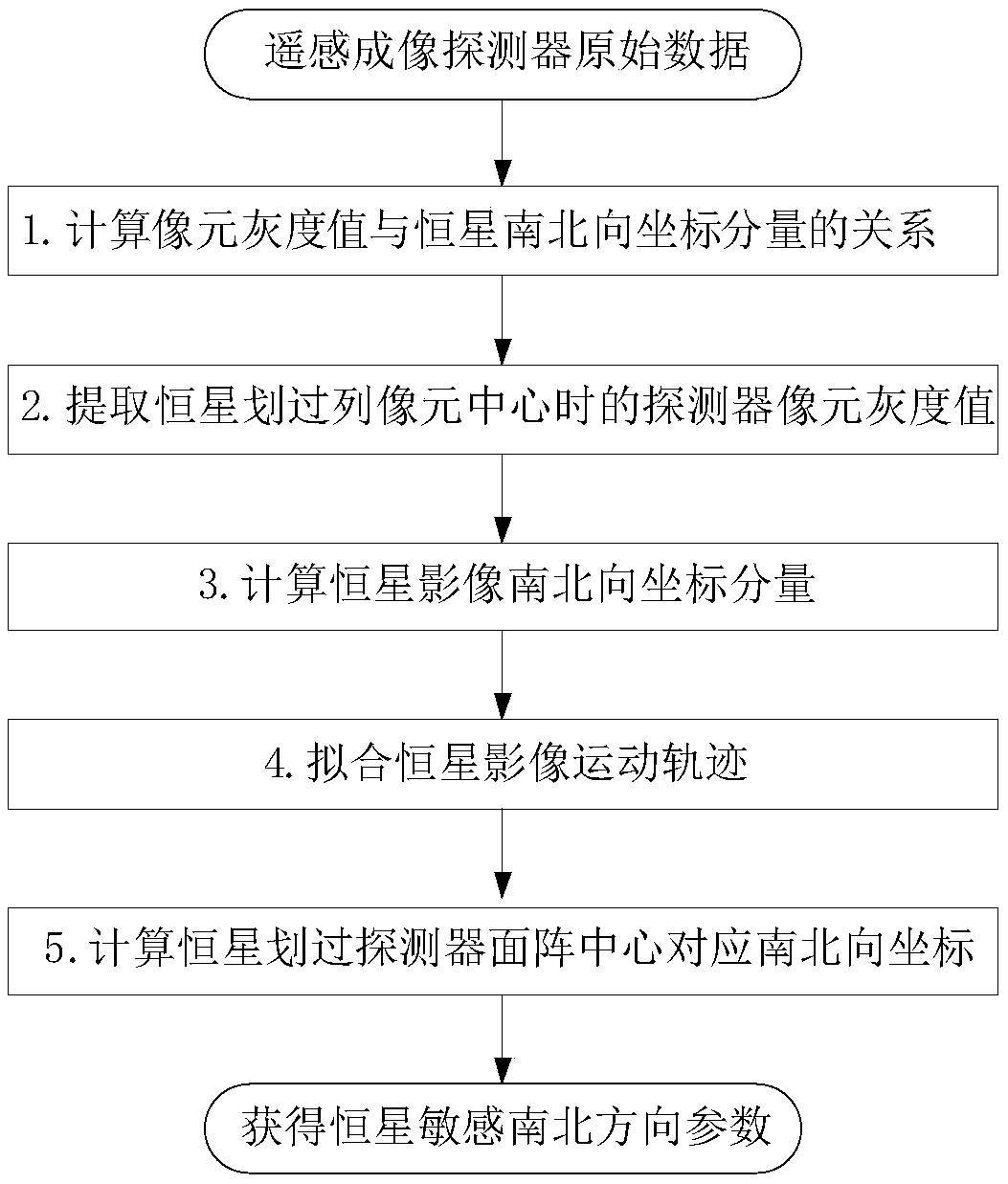
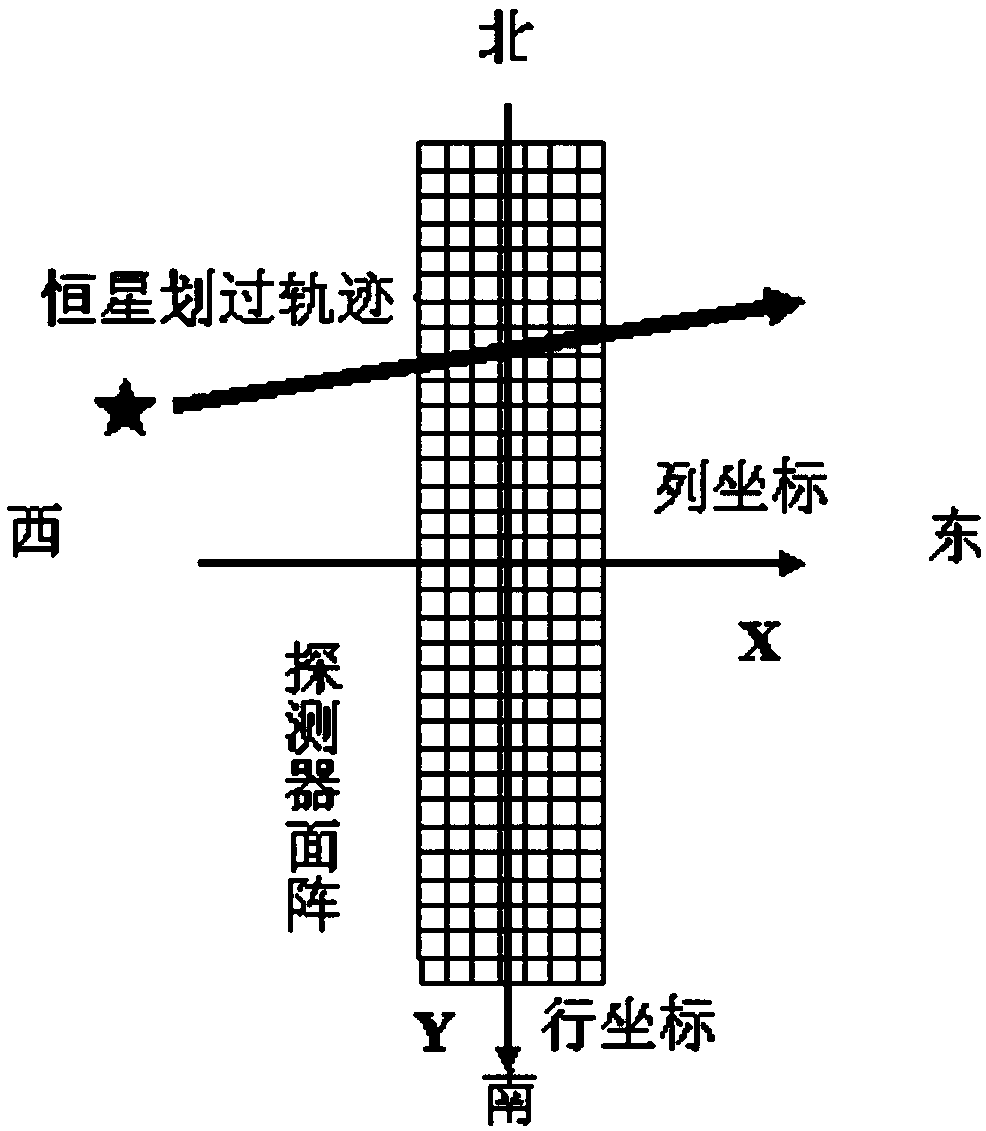
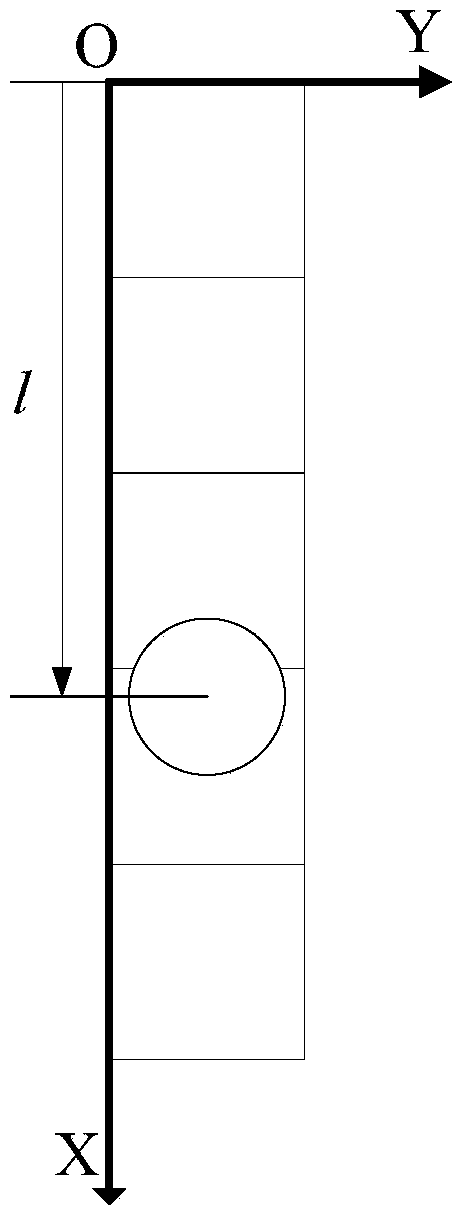
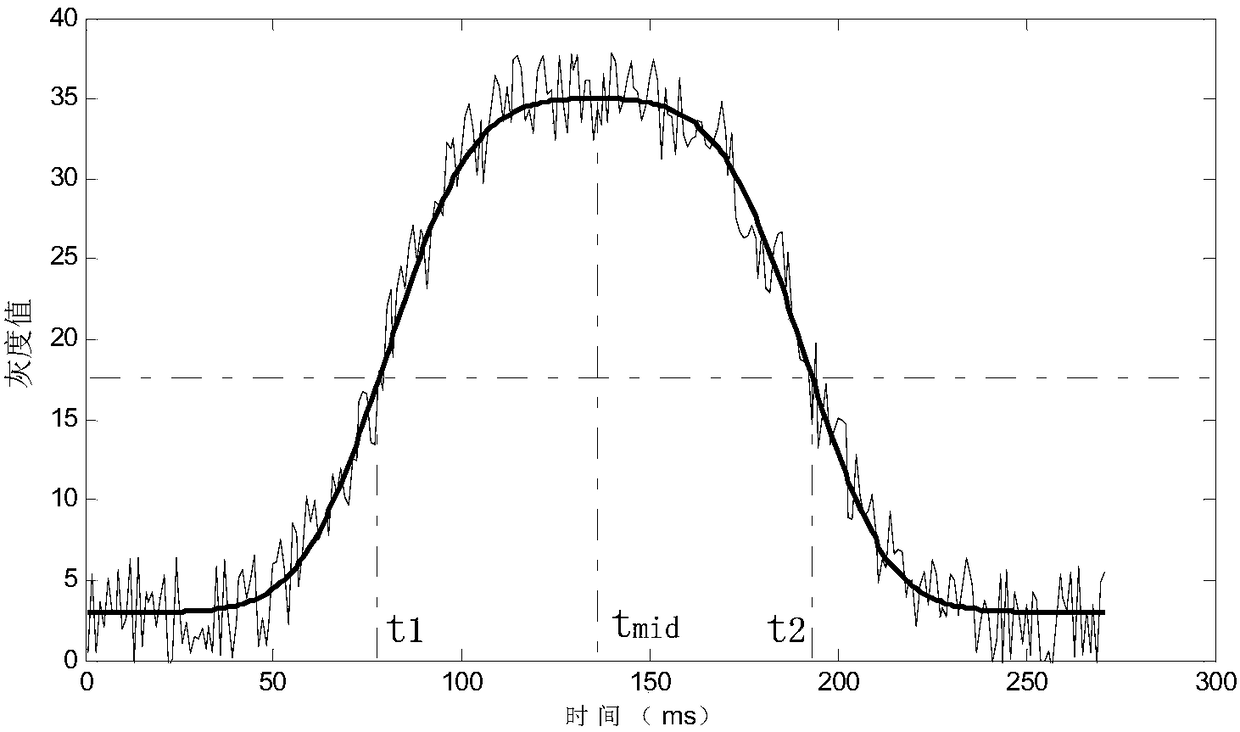
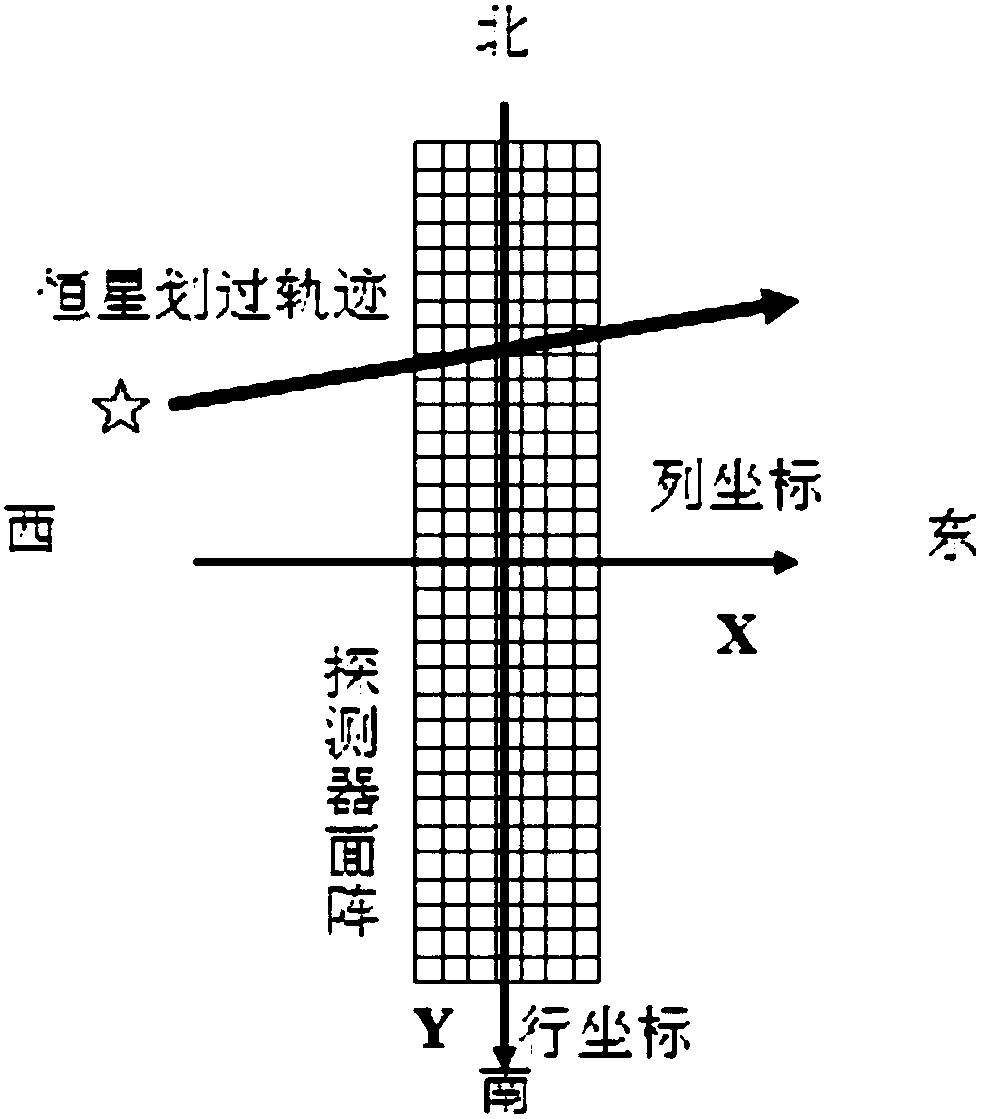
The invention provides an extracting method for fixed star sensitive east and west parameters of stationary satellite imaging navigation and registration. The extracting method comprises the following steps of obtaining a changing curve of a total gray value of pixels of each line along with time; obtaining a moment that a fixed star image center crosses a center line of the pixels of the line; fitting a motion law of the fixed star image center in east and west line coordinates of a satellite remote sensing detector array; obtaining a moment that the fixed star image center crosses a center line of the east-west direction of the satellite remote sensing detector array. According to the extracting method provided by the invention, high-frequency error of star positions caused by factors such as optical imaging of the detector, circuit noises, high-frequency wobble of a satellite and the like can be eliminated by multiframe data information fusion processing and curve fitting, thereby improving the identification accuracy of fixed star position parameters. The extracting method can be used for stationary satellite imaging navigation and registration, and has important significance for improving on-orbit thermal deformation precision of a remote sensing imaging system and the imaging navigation and registration processing property by acquiring parameters such accurate time and the like that the fixed star crosses the center of the detector array.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Quick matching and recognition method for star tracking apparatus
InactiveCN1880917ASmall amount of calculationHigh speedInstruments for comonautical navigationArtificial satellitesVisual field lossComputer science
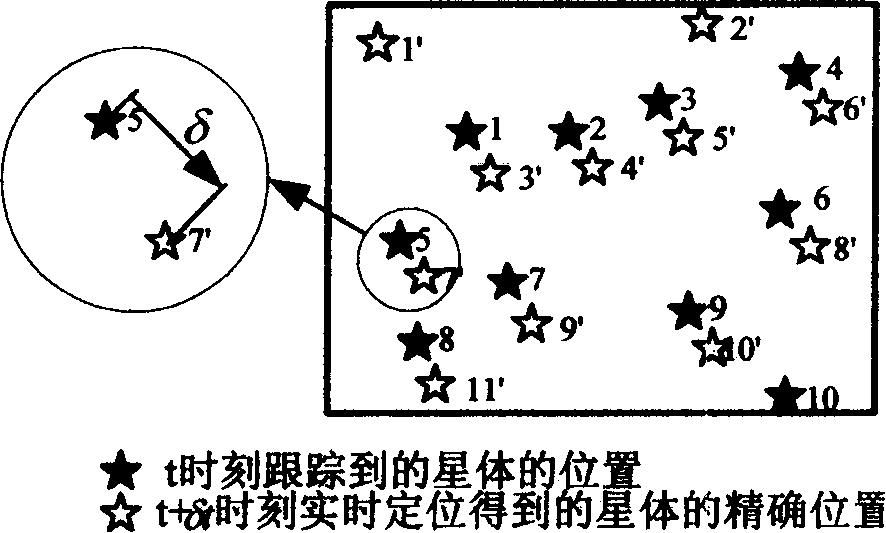
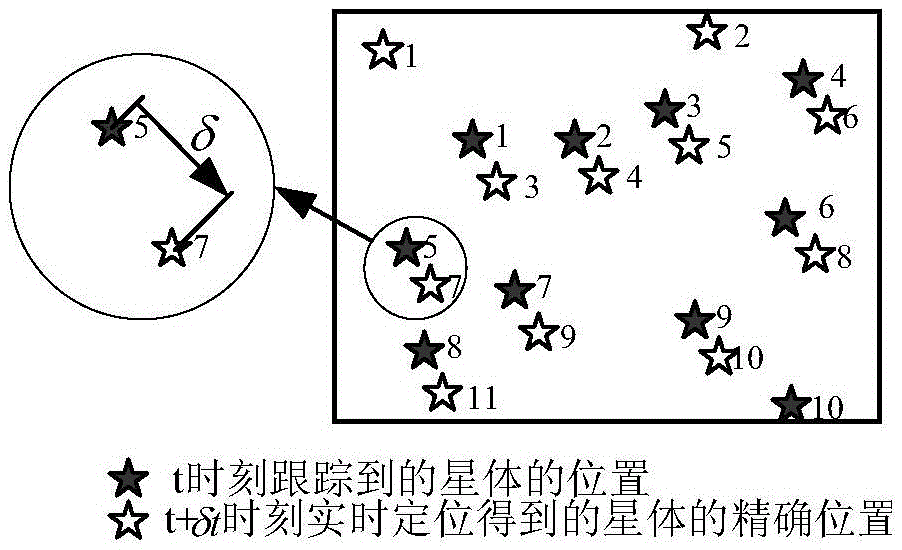
The invention discloses a modified mating method of star tracer in the astronomical navigational technological domain, which comprises the following steps: collating stars of present time and spot according to X coordinate position to generate sequence A; estimating the traced star of last time and spot in the position of present visual field; collating the traced star position to generate sequence B; proceeding mating identification for sequence A and B.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Refinement of spacecraft angular velocity and attitude estimates using star data
ActiveUS7062363B2Minimize the differenceCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsAngular velocityStar position
A method and apparatus for refining a spacecraft state estimate, such as an attitude estimate or an angular velocity estimate, is disclosed. The method computes a plurality equations using residuals describing the difference between observed star positions and predicted positions based on inertial measurements, and solves those equations to generate refined estimates of the spacecraft state estimates.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
High-dynamic rapid star tracking method
ActiveCN104964684AFast predictionImprove accuracyNavigation by astronomical meansWide fieldPrediction rate
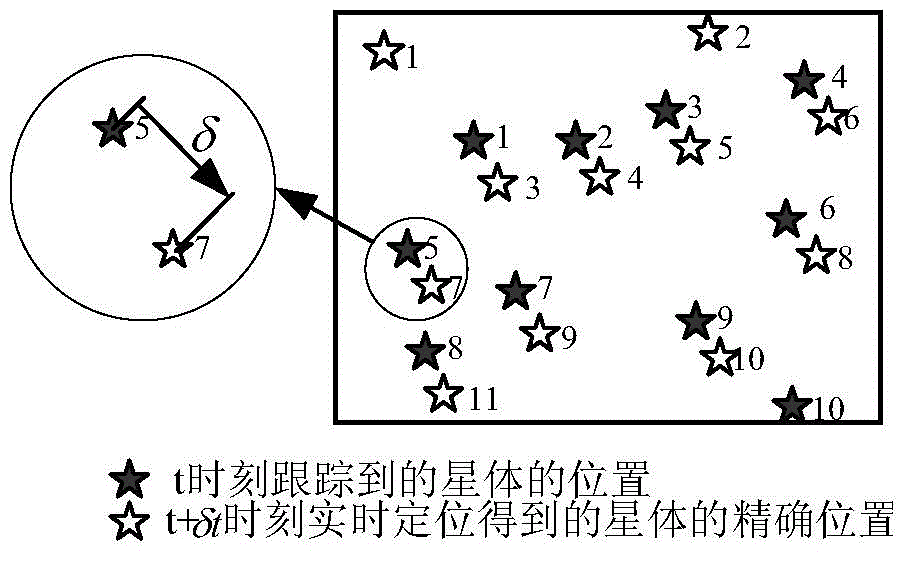
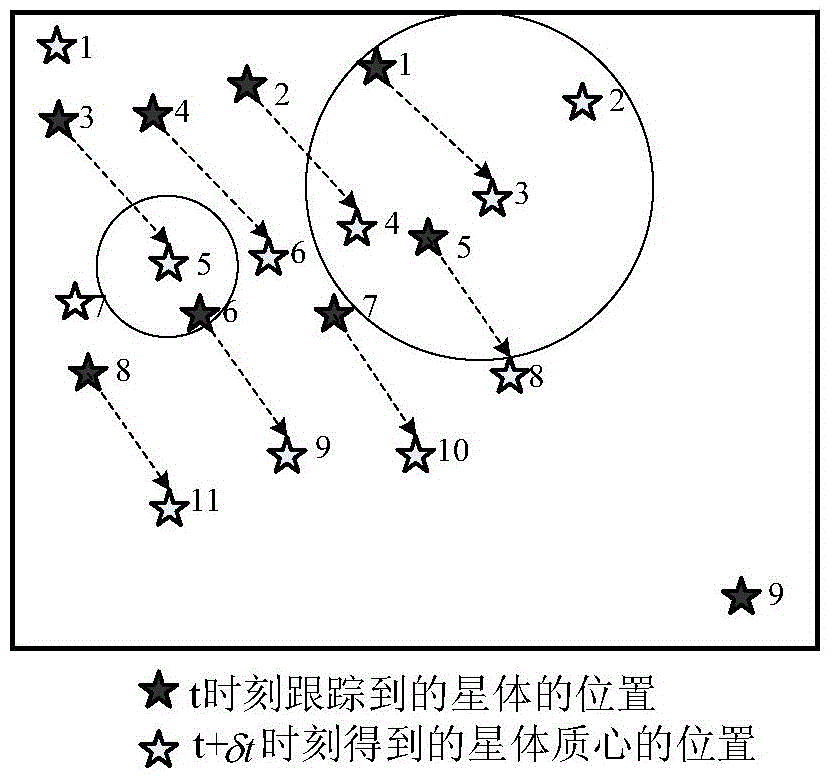
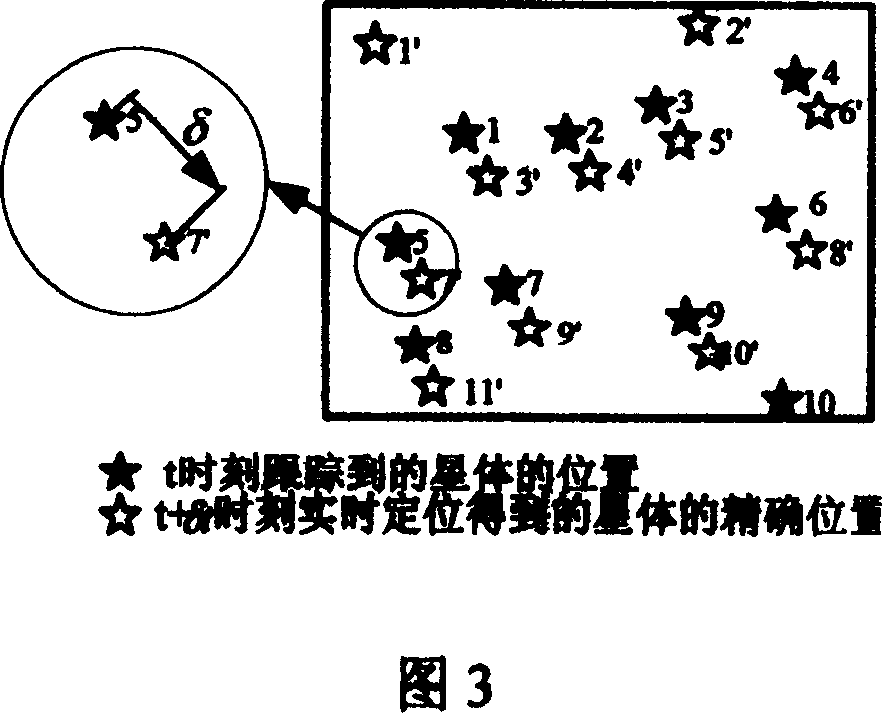
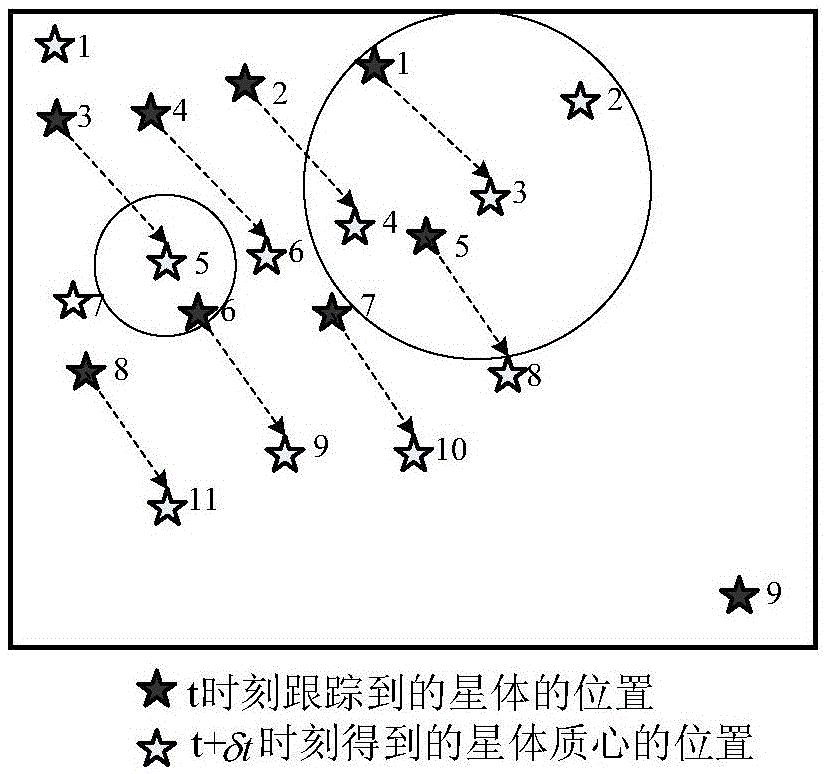
The invention discloses a high-dynamic rapid star tracking method. The method comprises 1, designing a weighted value according to multiframe attitude information output by a star sensor at the T1-Tn moment and a proximity relationship of the multiframe attitude information, forecasting attitude of the star sensor at the next T<n+1> moment, searching a star point corresponding to the attitude from a star database by the forecasted attitude, and producing a virtual forecasted large view field star image for matching by mapping, and 2, carrying out matching identification on a star position A and a star mass center position B at t+delta t moment to realize star tracking. The high-dynamic rapid star tracking method utilizes multi-frame attitude information prediction, has a fast prediction rate, improves prediction accuracy, realizes tracking and matching based on a forecasted virtual wide field star image without novel star identification and improves a star tracking algorithmic speed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Compact celestial navigation device
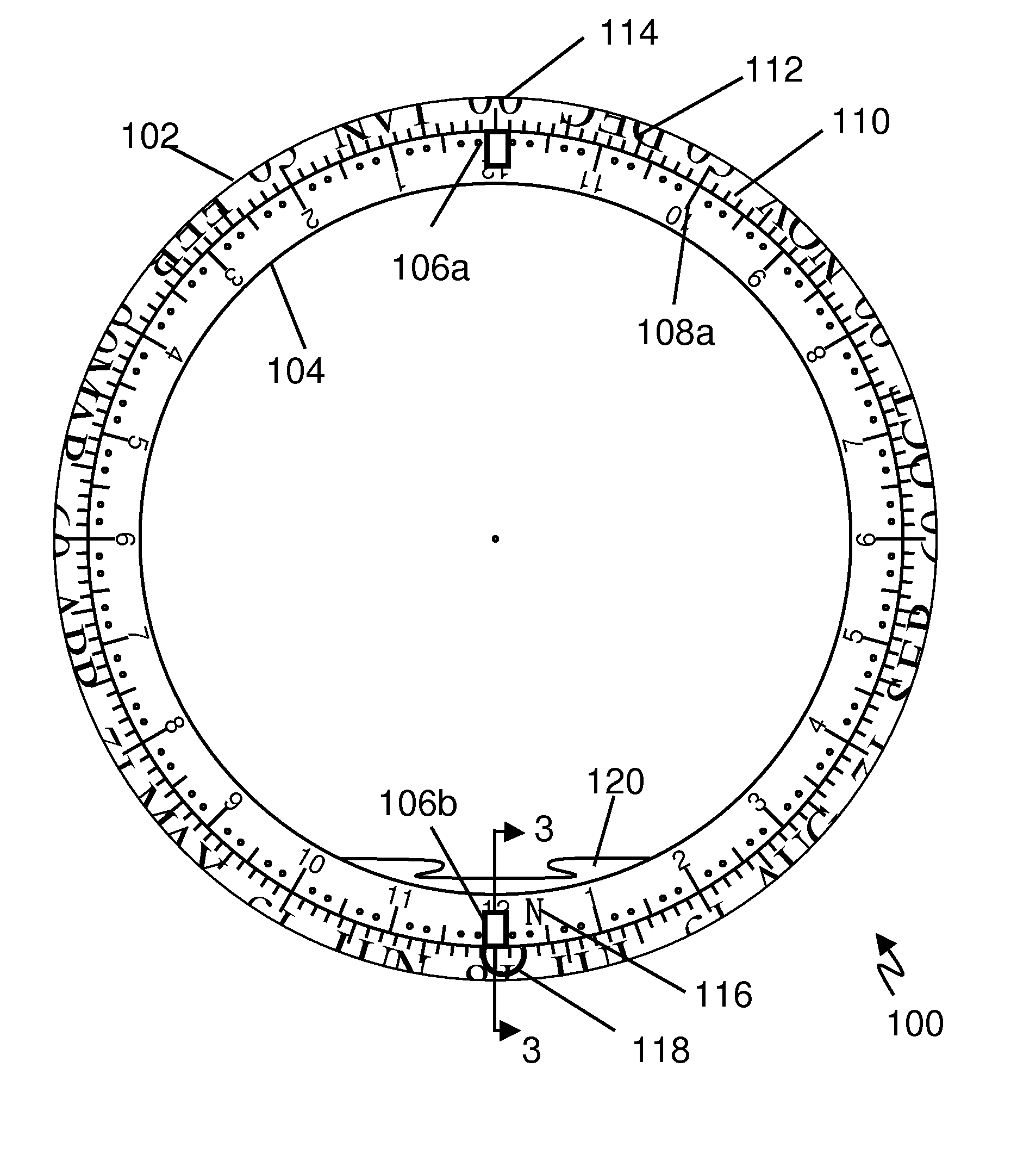
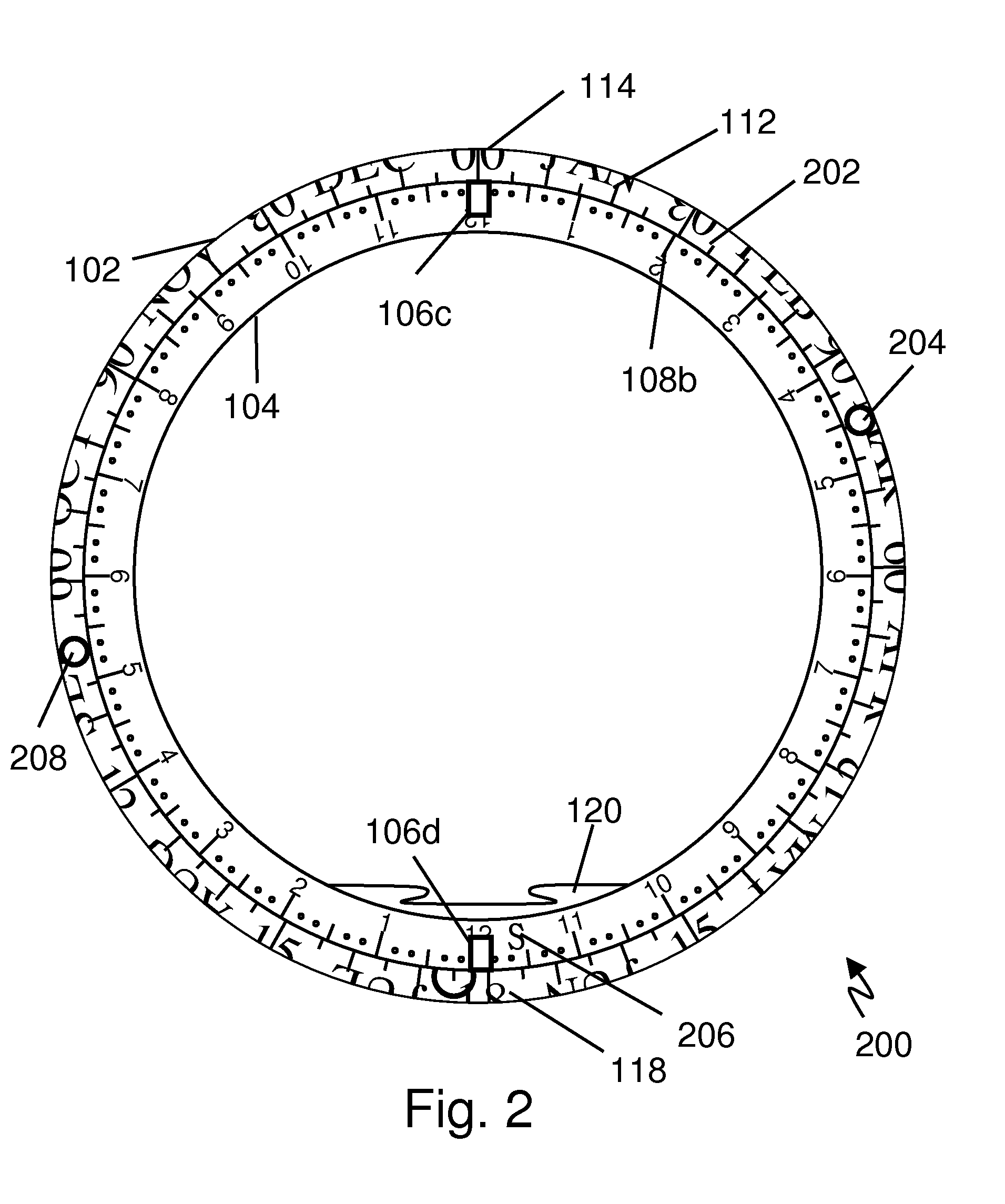
A celestial navigation device. A full-featured embodiment is useful as a sundial and planisphere and for measuring, among other things, latitude, longitude, and for time to angle conversions. The device may have one or more rings and is based on a transparent circular tube having a gravity indicator, typically a ball or bubble, in the circular tube, which locates the lowest or highest point in the tube to indicate time or angle measurements against a corresponding scale. The device may have a 24-hour time scale, a calendar scale, and / or an angle scale. One embodiment includes a split analemma with separate north and south portions. Each analemma portion is used with a corresponding gnomon of a pair of gnomons, each on opposite sides of the tubular ring. A two-ring embodiment has an inner ring and outer ring rotatably slidable relative to one another. Two additional gnomons and star position marks may be provided for star sighting observations. The device has a hollow center and may be worn as a bracelet and may be constructed with precious metals and / or gems to enhance the value of the bracelet aspect.
Owner:SPIRE JR GAROLD DEAN
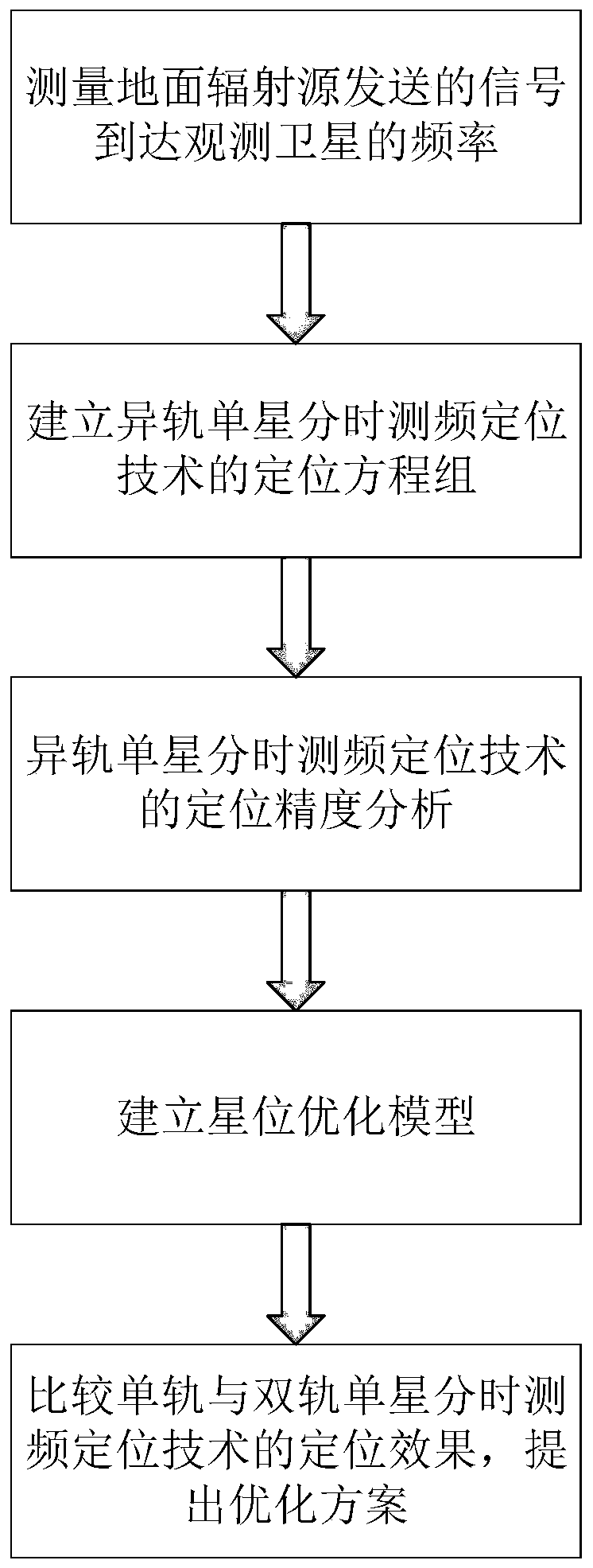
Different-orbit single-satellite time-sharing frequency measurement positioning method based on star position optimization
PendingCN110988851APrecise positioningHigh precisionUsing reradiationSingle starSatellite observation
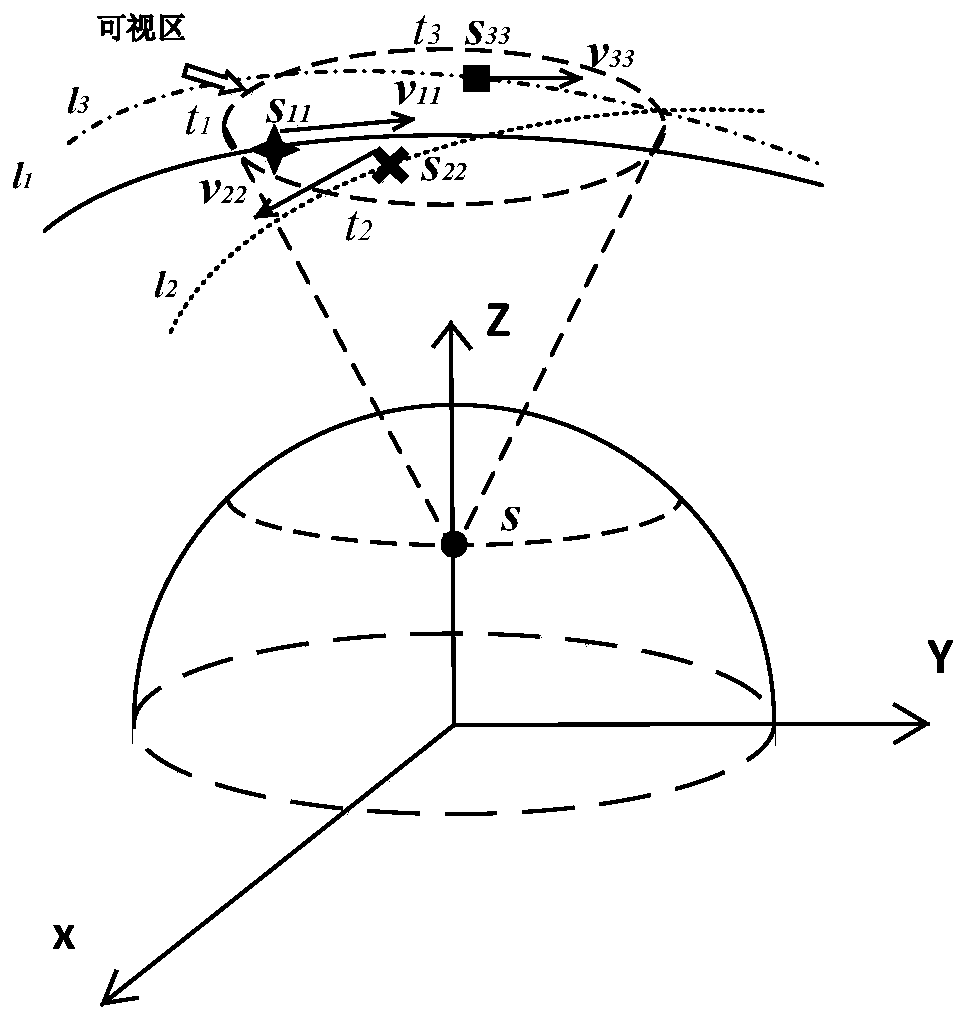
The invention discloses a different-orbit single-satellite time-sharing frequency measurement positioning method based on star position optimization. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the frequency of a signal sent by a ground radiation source reaching an observation satellite; establishing a different-orbit single-satellite time-sharing frequency measurement positioning model, selecting a plurality of satellites with different orbits to respectively carry out frequency measurement at different moments, and establishing a positioning equation set according to a plurality of measured different signal frequencies; deriving geometric dilution precision factors, and analyzing the influence of various factors on the positioning precision; and establishing a star position optimization model, and optimizing the selection of orbit and satellite observation moments to improve the positioning precision. According to the invention, within a limited range of visibility, single satellites flying through different orbits of a positioning visual area at different moments are used for repeatedly and independently observing the same interference source; due to the difference in the aspects of flight direction, observation position distribution and the like, compared with a single-orbit single-satellite time-sharing frequency measurement positioning scheme, the positioning effect is stable, the precision is higher, the space between satellites is larger, and the selection of measurement positions can be more flexible.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Software implementation method for three-dimensional go
InactiveCN105854290AEasy to observeEasy to operateVideo gamesThree-dimensional spaceComputer science
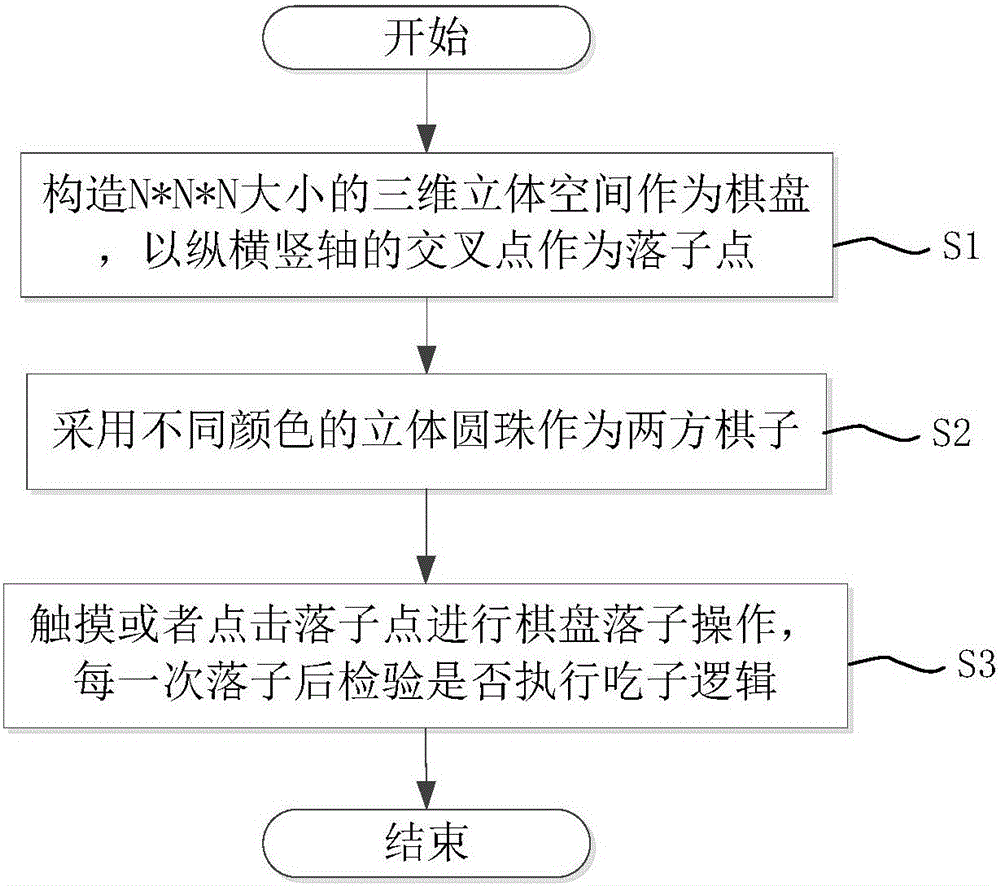
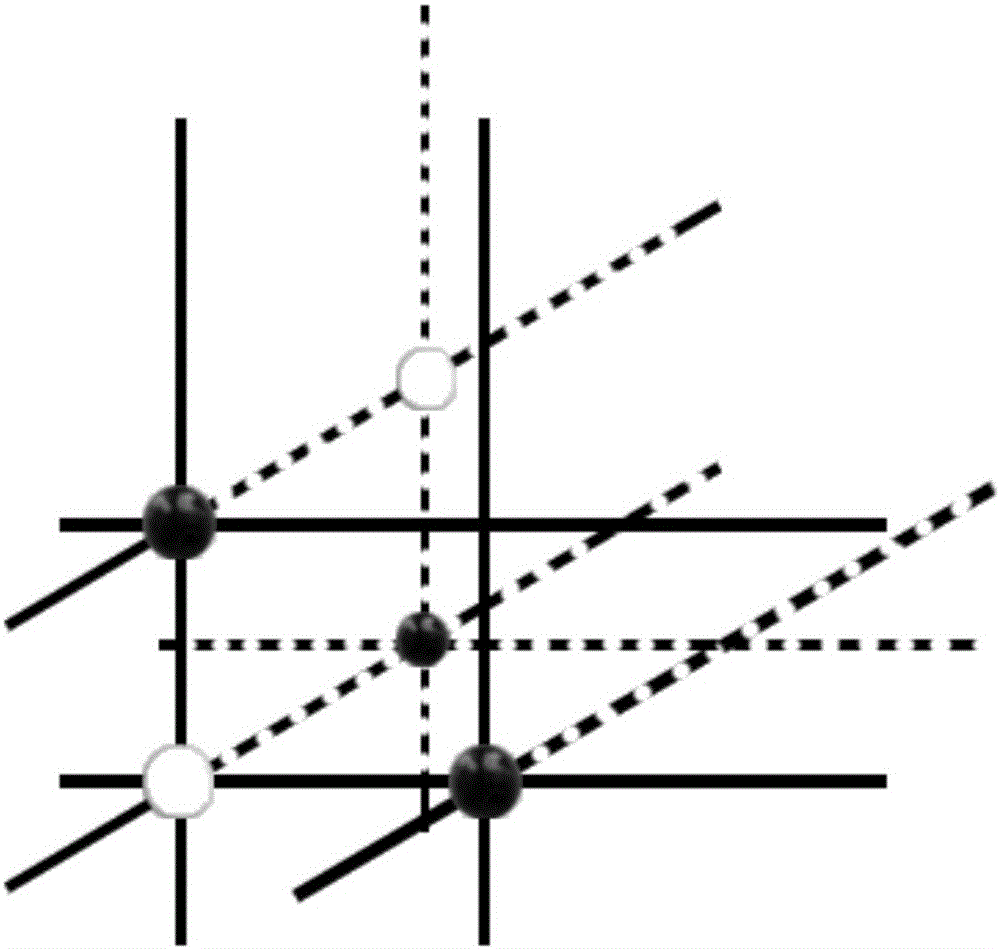
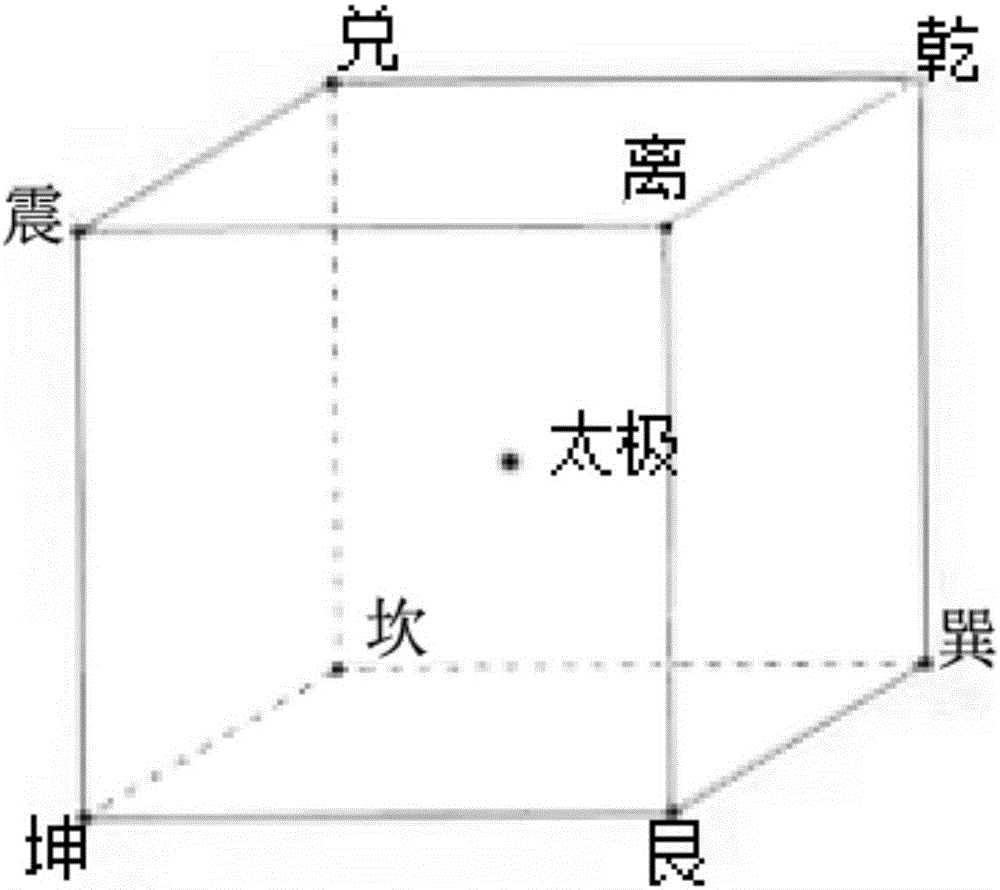
The invention discloses a software implementation method for a three-dimensional go. The method comprises the following steps that a, a three-dimensional space with the size of N*N*N is built as a go board, and crossed points of longitudinal shafts and transverse shafts are used as go piece placement points, wherein N is a natural number; b, three-dimensional balls of different colors are adopted as go pieces of two parties; c, the go piece placement points are touched or clicked to place go pieces on the go board, and whether a capturing logic is executed or not is checked each time go piece placement is carried out. The step a further comprises substeps of setting poles and star positions of the go board and displaying connection lines between the go piece placement points and the poles and connection lines between the go piece placement points and the star positions; the go piece placement points are filled with materials with certain transparency; when a mouse is suspended on one certain go piece placement point, the color of the go piece placement point is changed, the mouse is moved out, and the original go piece placement point style is recovered. According to the software implementation method for the three-dimensional go, operation is easy, mastering is easy, and players can conveniently observe the go board layout comprehensively in multiple view angles.
Owner:HUNAN KUAIWAN NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Photoelectric theodolite directional calibration method based on common star
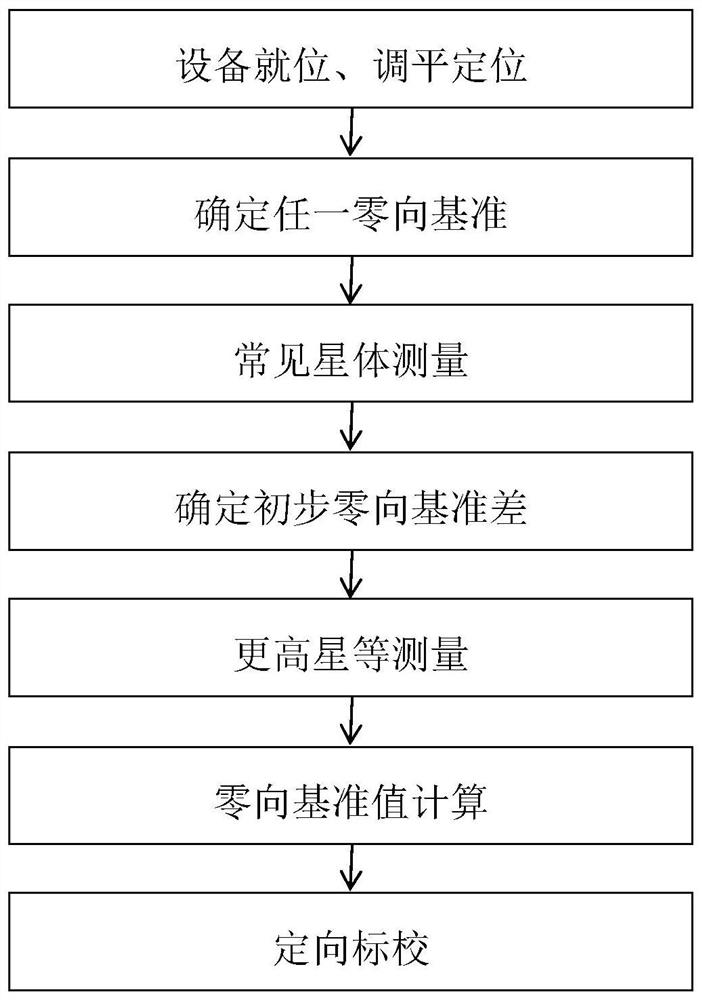
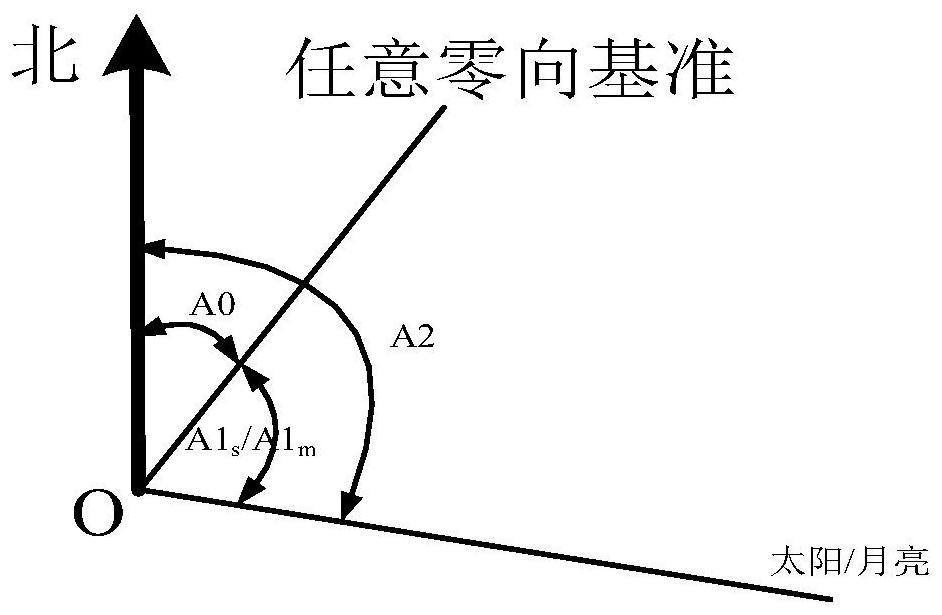
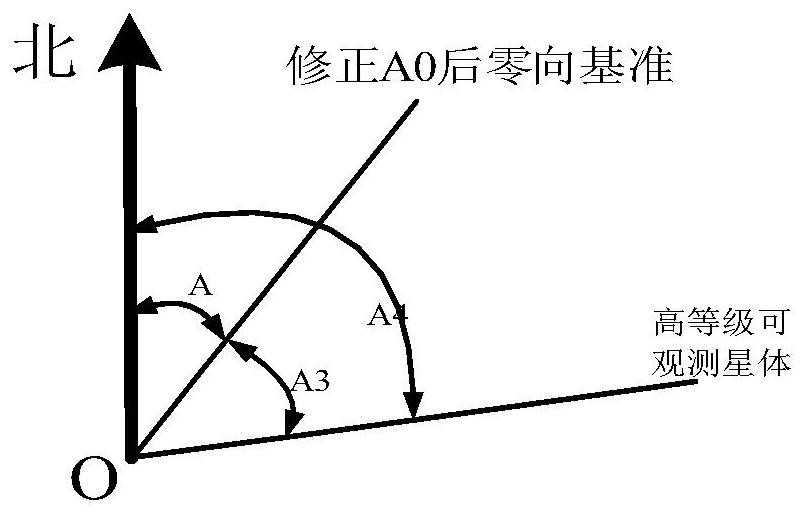
PendingCN111811538ASolving Orientation Calibration ChallengesEasy accessMeasurement devicesTheodoliteStar position
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectric measurement and discloses a photoelectric theodolite orientation calibration method based on a common star. Any first zero-direction reference is determined after leveling and positioning of a photoelectric theodolite, then common star position measurement is carried out to calculate a preliminary reference value, on this basis, zero-direction reference value calculation is carried out through higher star position measurement to obtain a second zero-direction reference value, and equipment orientation calibration is completed. The method is advantaged in that the zero-direction reference of the photoelectric theodolite is rapidly obtained based on the position of the common star, a problem of orientation calibration in the calibration process of the photoelectric theodolite is solved, the equipment calibration time is shortened, and calibration efficiency is improved.
Owner:中国人民解放军63660部队
Quick matching and recognition method for star tracking apparatus
InactiveCN100344937CSmall amount of calculationHigh speedInstruments for comonautical navigationArtificial satellitesVisual field lossComputer science
The invention discloses a modified mating method of star tracer in the astronomical navigational technological domain, which comprises the following steps: collating stars of present time and spot according to X coordinate position to generate sequence A; estimating the traced star of last time and spot in the position of present visual field; collating the traced star position to generate sequence B; proceeding mating identification for sequence A and B.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Forecasting method and system for evaluating satellite stability and pointing precision in-orbit performance
ActiveCN113063436AAccurate locationAccurate magnitude informationMeasurement devicesFixed starsSatellite observation
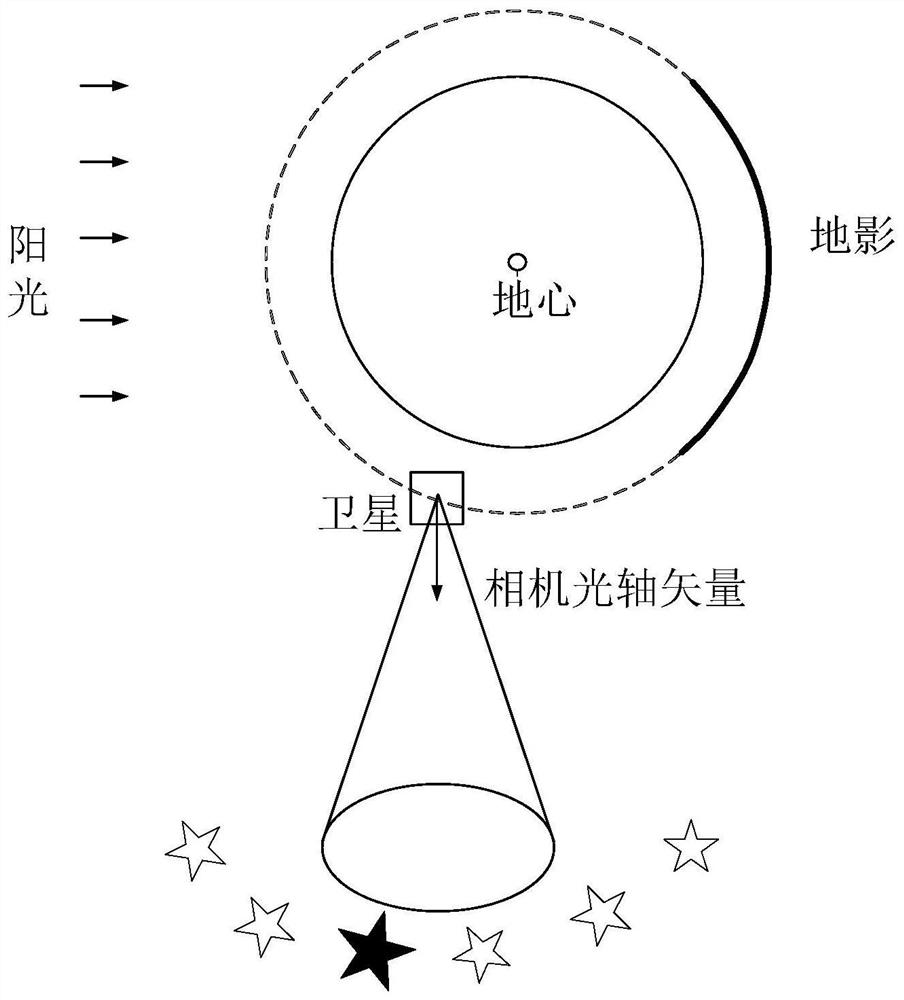
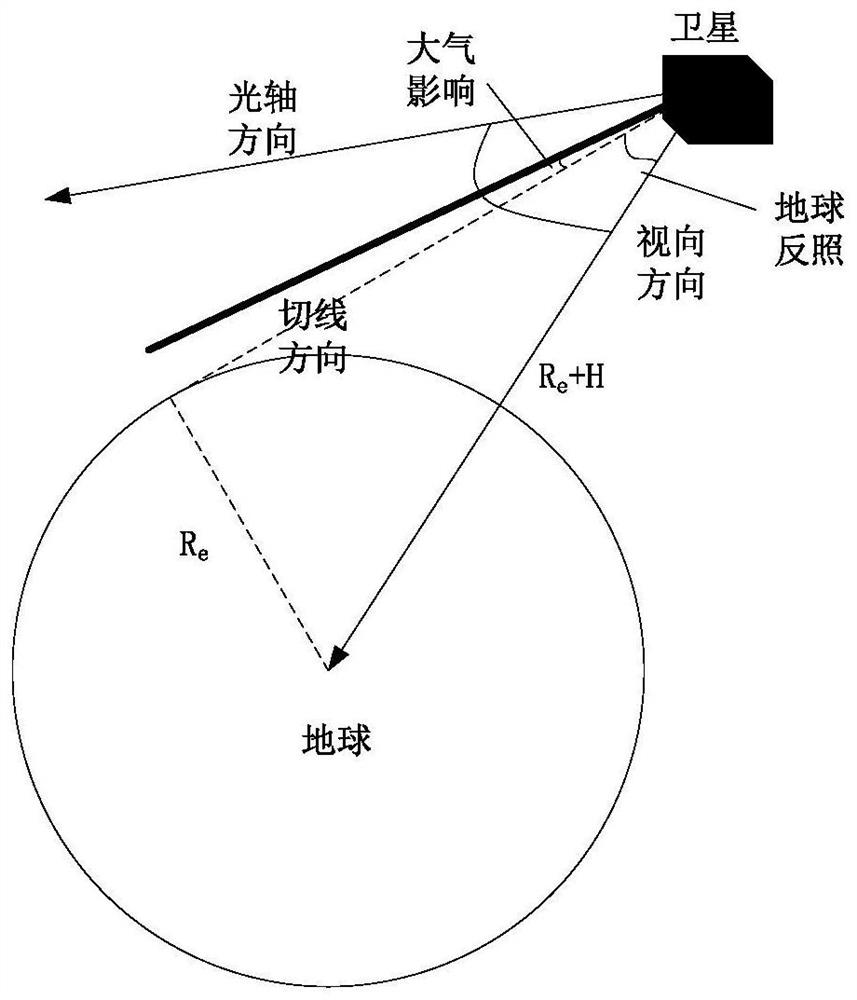
The invention provides a forecasting method and system for evaluating satellite stability and pointing precision in-orbit performance. The forecasting method comprises the following steps of S1, calculating a highlight protection angle of a star sensor, S2, calculating a strong light protection angle of the optical camera, S3, calculating an effective arc section of fixed star observation, and obtaining fixed star observation opportunity information, S4, calculating the projection of the optical axis vector of the optical camera in the inertial space, and S5, selecting a fixed star of which the maneuvering angle and the brightness both meet the requirements near the optical axis direction of the camera, obtaining the position and magnitude information of the target fixed star, and obtaining forecasting result information for evaluating the satellite stability and the pointing precision in-orbit performance. The method searches the fixed star suitable for satellite observation, predicts the fixed star observation opportunity, provides accurate fixed star position and star magnitude information, and provides support for evaluation of high-precision satellite stability and pointing precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
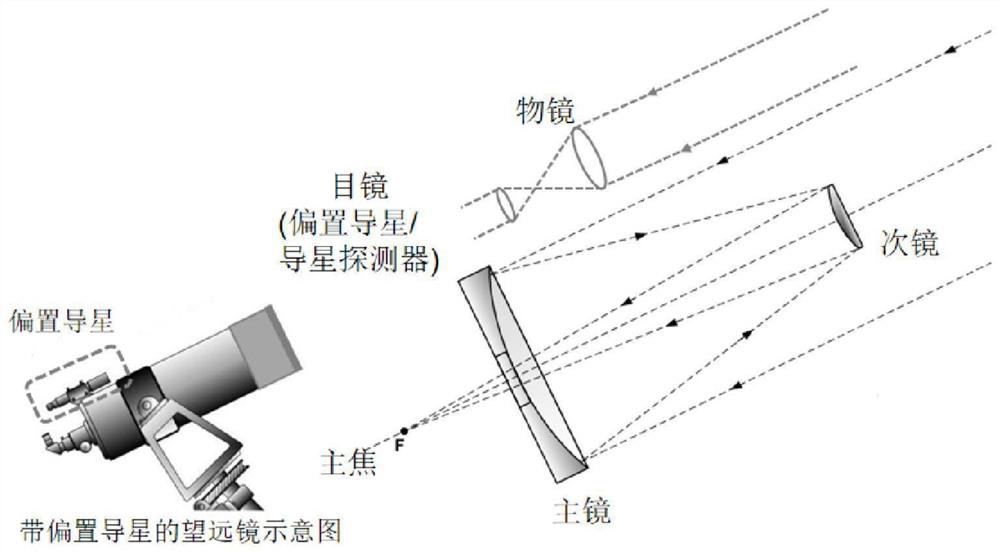
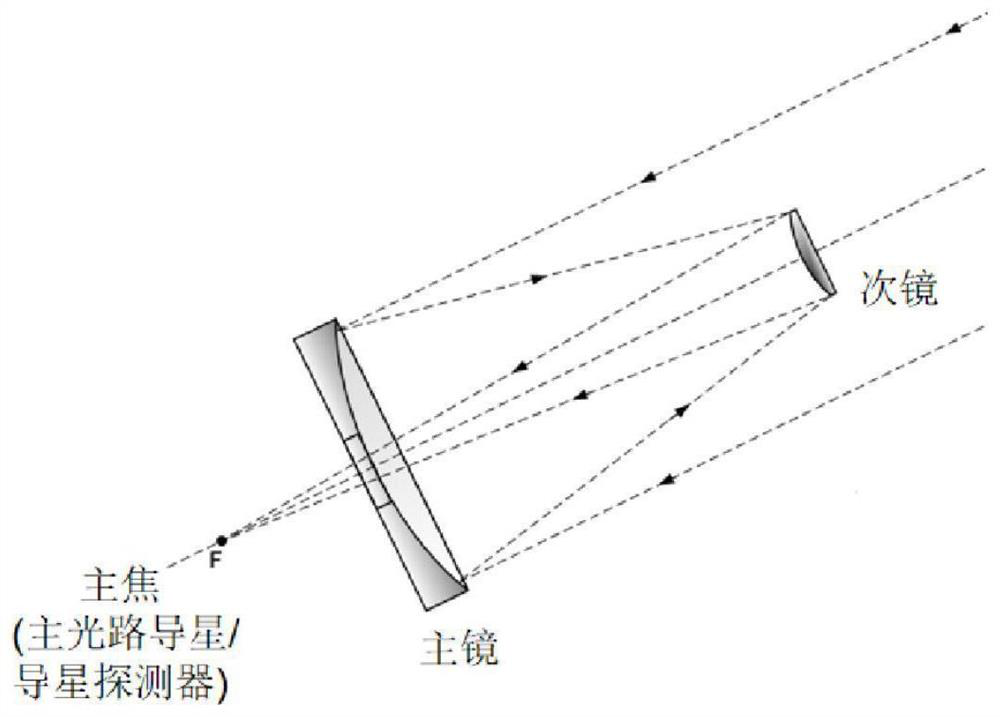
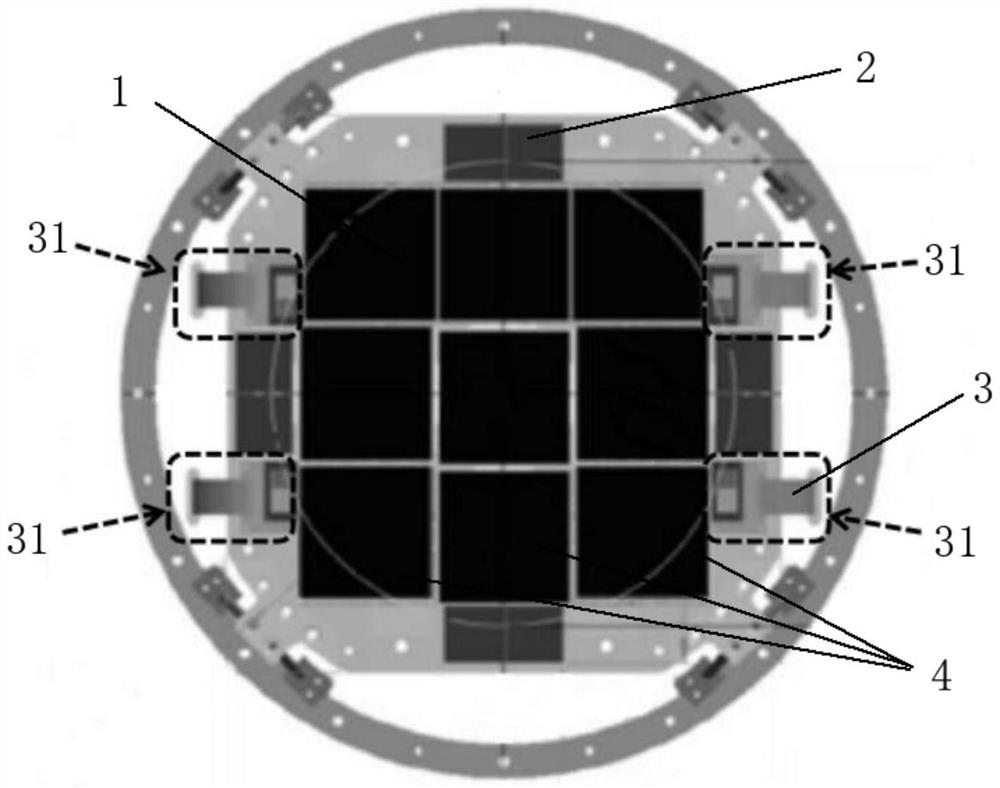
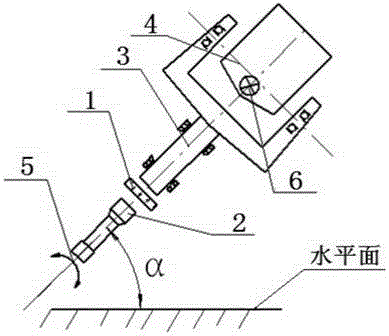
Telescope main light path guide star device and guide star offset calculation method
PendingCN114860196ARaise guide starImprove tracking accuracyImage analysisDigital data processing detailsImaging processingExposure
The invention relates to a telescope main light path star guiding device which comprises a telescope main focus detector and a star guiding detector, the telescope main focus detector is located on a telescope focal plane, the star guiding detector is installed near the telescope main focus detector, the star guiding detector and the main focus detector are located on the same focal plane, and the star guiding detector and the telescope main focus detector share the same light path. According to the invention, main light path star guiding is realized, so that position and angle errors of the star guiding detector and the main detector are eliminated, and star guiding and tracking precision of the telescope is improved. The invention further discloses a guide star offset algorithm, the guide star camera sends a formed image to a program for processing within a certain exposure time, the program finds a star in image data by using a method in the field of image processing, and XY (row and column in the image) offset is obtained according to historical records of star positions, so that the guide star offset is obtained. And the offset is returned to the movement mechanism of the telescope to make the movement mechanism perform correction movement, so that the purpose of compensation is achieved, and a more reliable closed-loop control system is formed.
Owner:ZIJINSHAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical detection method for polar axis type telescope polar axis shaking errors
ActiveCN103913301AHigh measurement accuracyThe principle is simpleOptical apparatus testingFixed starsPlane mirror
The invention relates to the field of telescope axis detection, in particular to an optical detection method for polar axis type telescope polar axis shaking errors. The problems that when a star calibration method is used for detecting the polar axis shaking errors of a polar axis type telescope, the calculating process is complex, the position of a fixed star needs to be known in advance, and the method is limited by weather and places are solved. The method comprises the steps that a plane mirror is arranged on an axis head of a polar axis, meanwhile, an obliquely-arranged 0.2'' parallel collimator is adopted to be aligned to the plane mirror, and the optical axis of the 0.2'' parallel collimator is parallel to the axis of the polar axis; the polar axis is rotated once every a certain angle, meanwhile, component data in the pitching direction and the orientation direction are respectively read on the 0.2'' parallel collimator, the polar axis is continuously rotated by 360 degrees, and the process is repeated four times; data processing is carried out through a Fourier hamonic function, and the root-mean-square value of the axis of the polar axis on pitching and orientation shaking components is calculated based on the Bessel formula. According to the method, the position of the fixed star does not need to be known, the method is not limited by the weather and the places, no complex mathematical calculation process exists, implementation is easy, convenience and reliability are achieved, and measuring precision is high.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
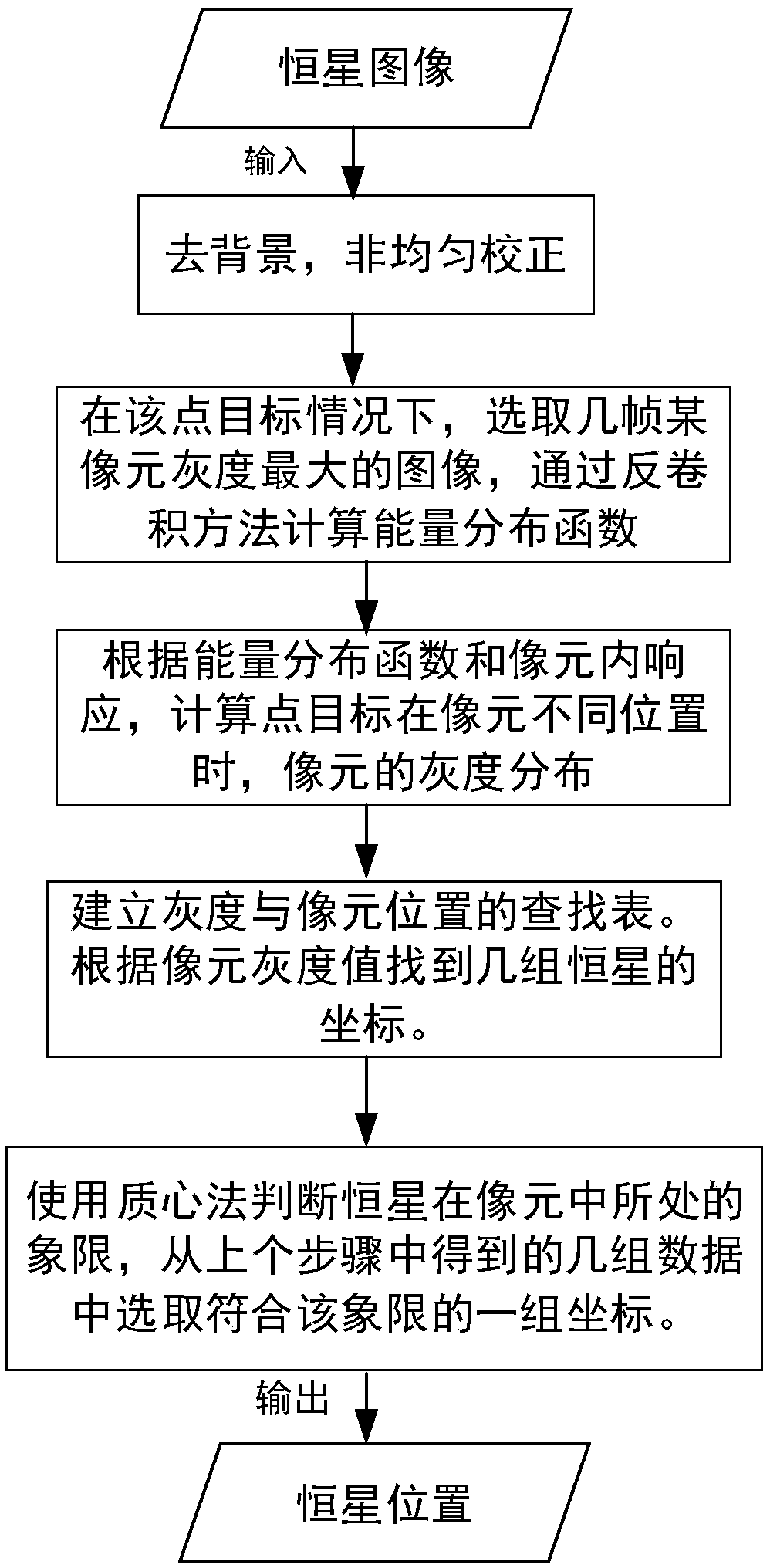
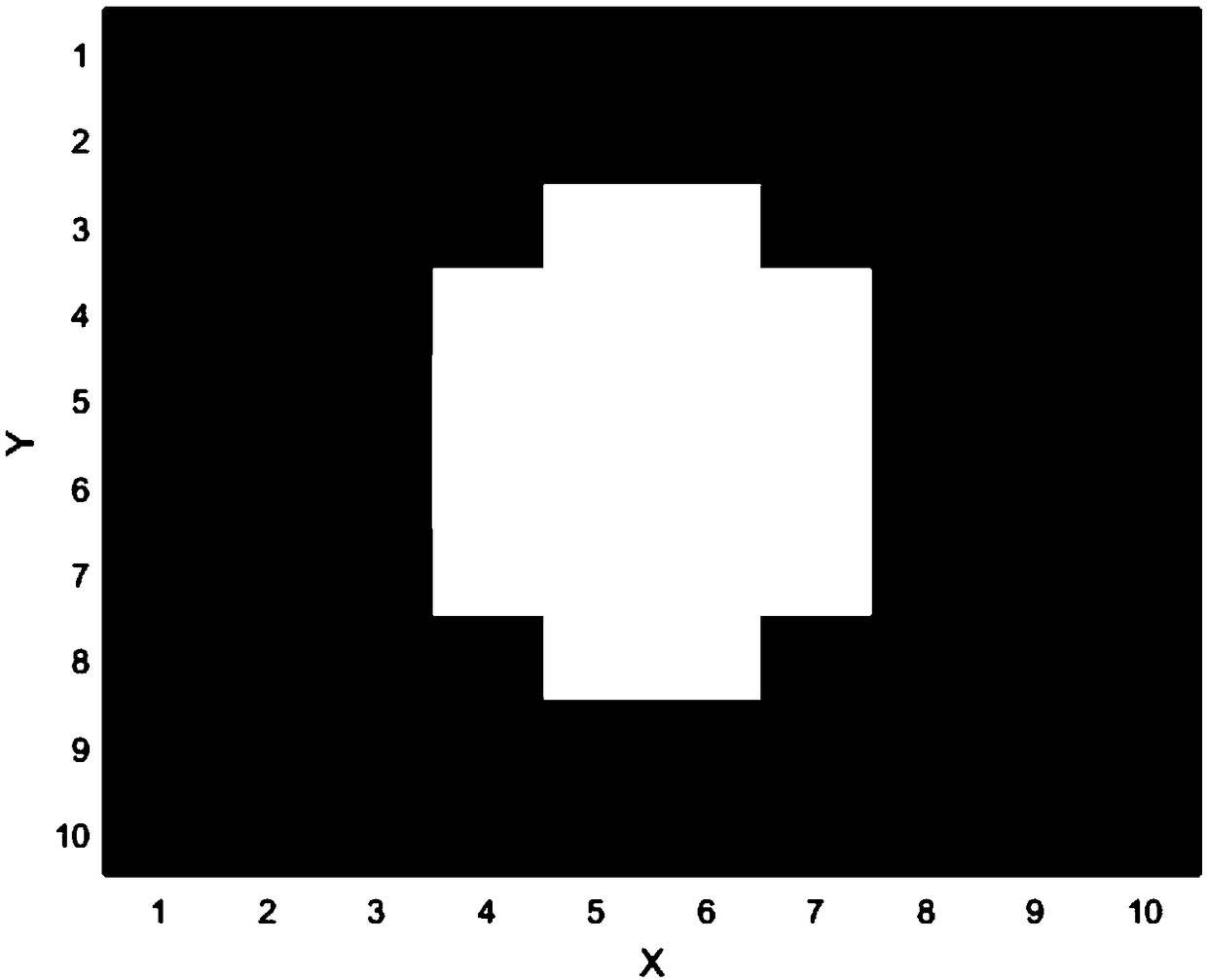
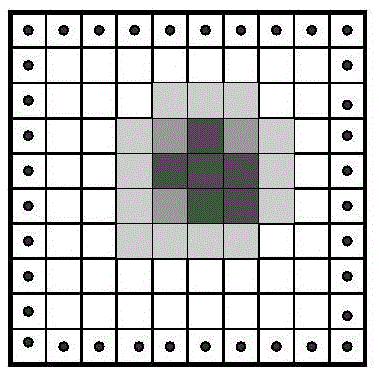
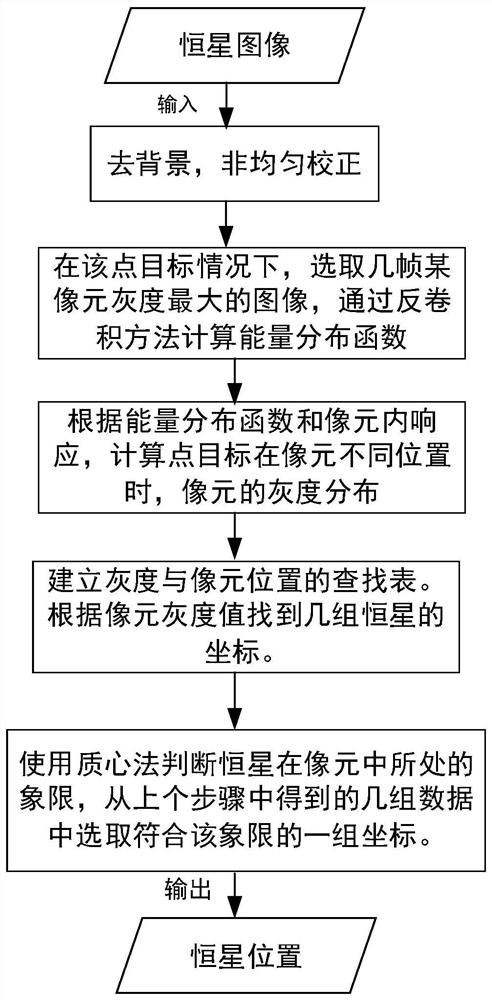
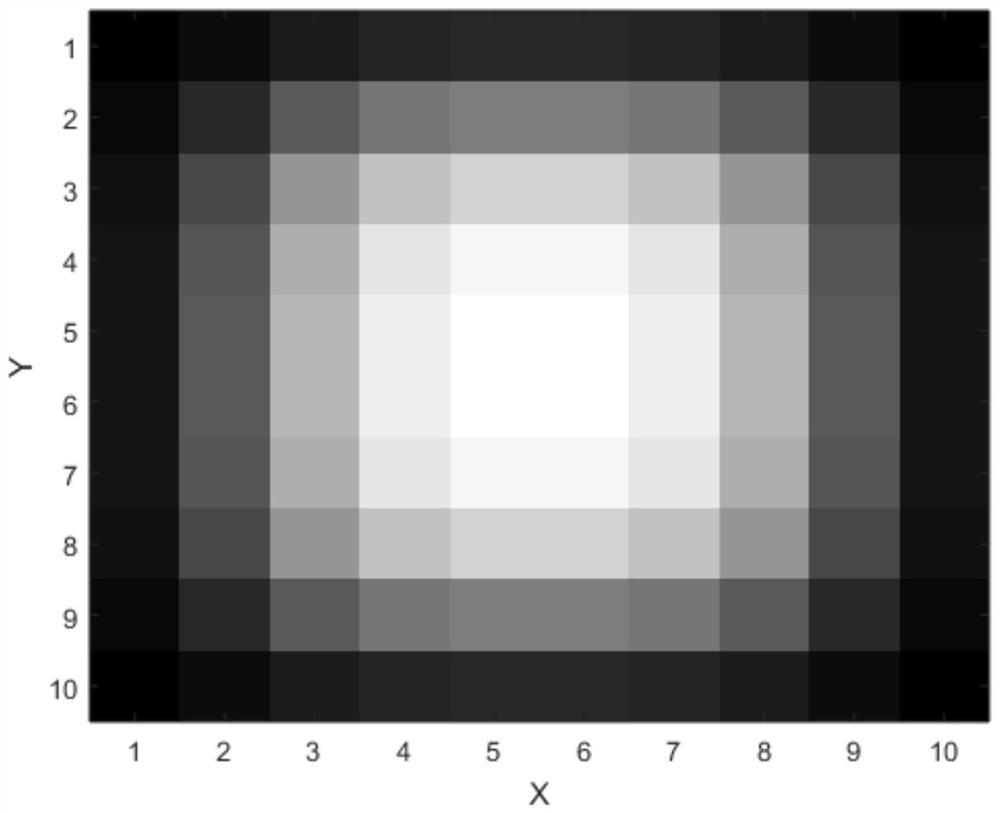
Star high-precision position extraction method based on pixel internal response
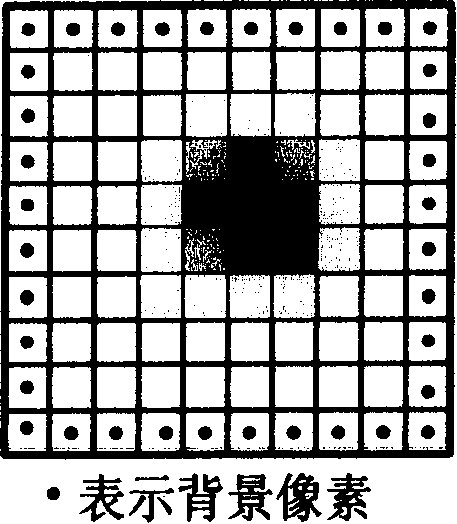
The invention discloses a star high-precision position extraction method based on pixel internal response. According to the response distribution in the pixel, the relationship between the point target position and the pixel gray level is established, and the high-precision position extraction of the star is realized. The steps of position extraction are as follows: 1, removing background and non-uniform correction of the obtained image; 2, according to the pixel filling factor, the energy distribution function of the star after passing through the optical system is obtained by selecting ten frames of images with the largest pixel gray value. 3. According to the energy distribution function and pixel filling factor, the pixel gray values of a series of star objects at different positions are obtained, and the look-up table of star positions and pixel gray values is established by interpolation. 4. Find the corresponding pixel position according to the gray value of pixel. Because of the symmetry of energy distribution and pixel response, we can get several groups of pixel positions. 5. using the centroid method, star positions are selected from the set of pixel positions obtained in step 4.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Double-layer heterogeneous network power control method
ActiveCN113747557ASmall and simpleNo energy consumptionPower managementHigh level techniquesAlgorithmTournament selection
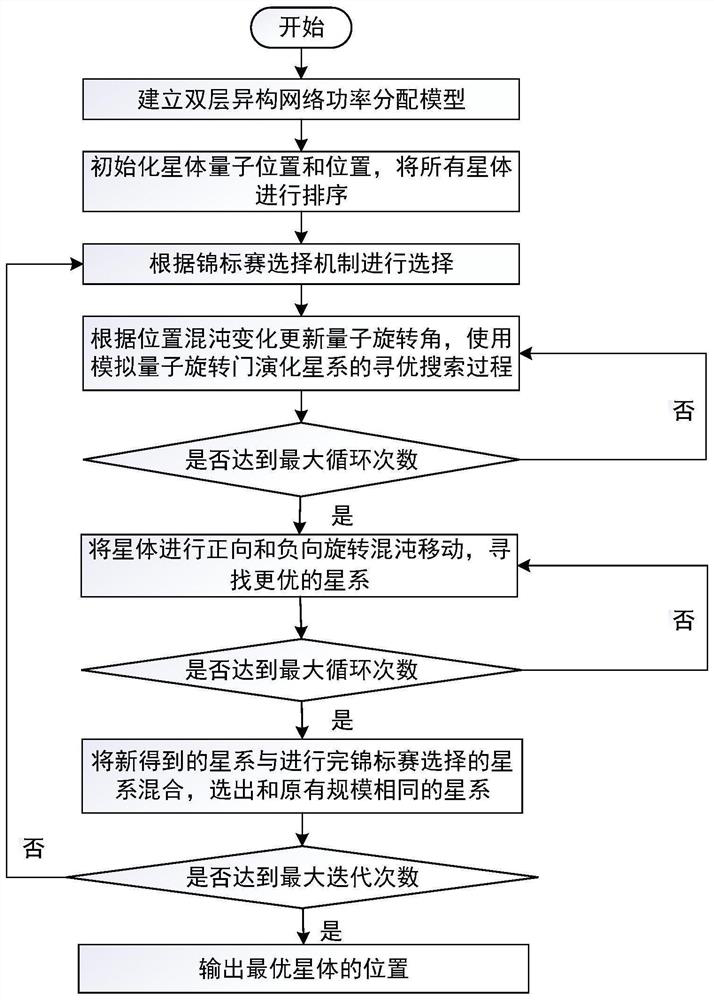
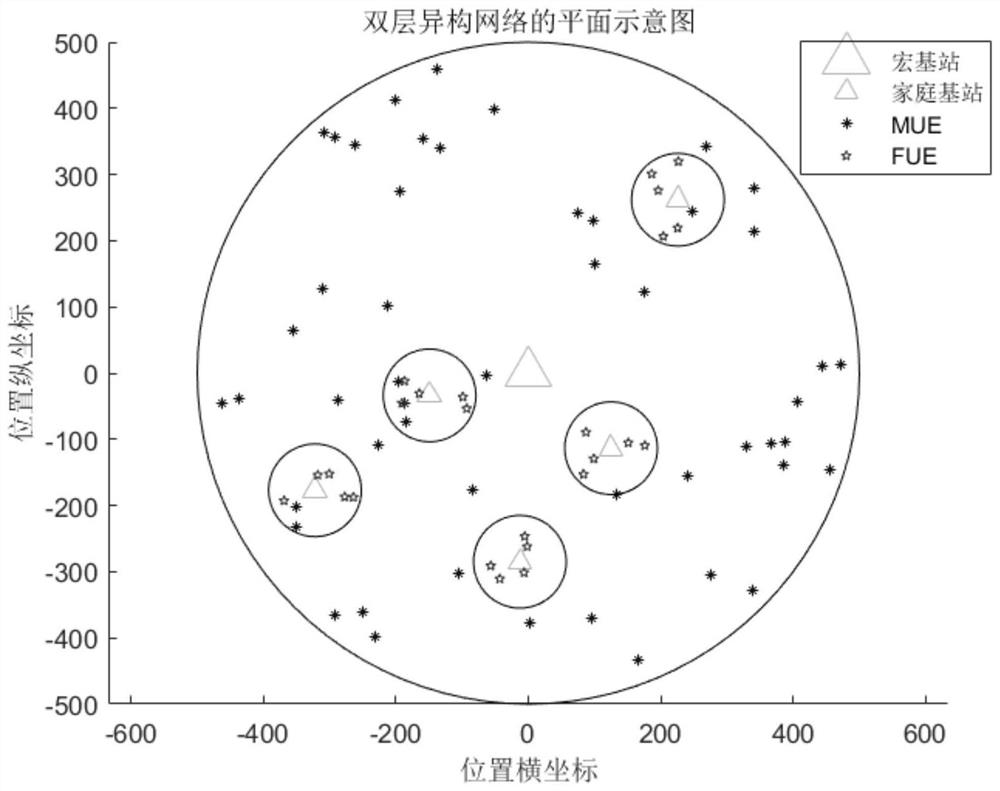
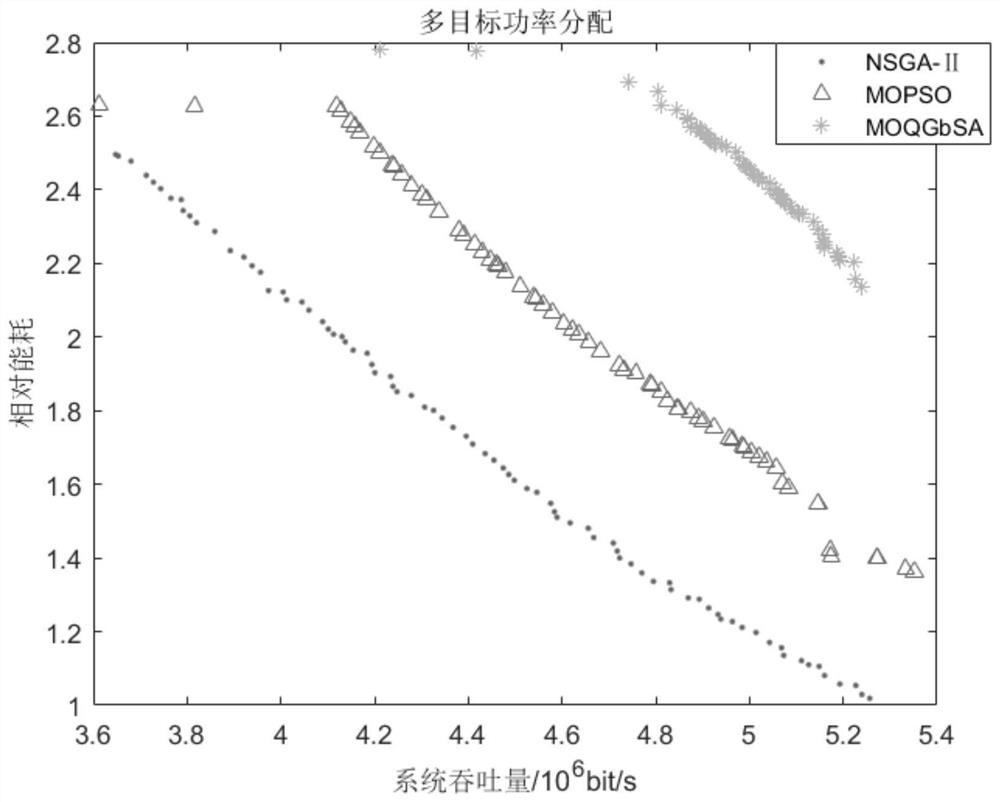
The invention discloses a double-layer heterogeneous network power control method. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a double-layer heterogeneous network power control model; initializing star positions and quantum positions and sorting the star positions and the quantum positions; selecting a new galaxy according to a tournament selection mechanism; updating a quantum rotation angle according to the chaos change of the position, and using a simulated quantum rotation door to evolve an optimization searching process of a galaxy; if the maximum cycle index is not reached, returning to the previous step until the maximum cycle index is reached, otherwise, terminating the cycle, performing positive and negative rotation chaotic movement on the star, and searching a better galaxis; if judging that the maximum number of cycles is not reached, returning to the previous step; otherwise, stopping the circulation, mixing the newly obtained galaxy with the initial galaxy, and selecting a galaxy with the same scale as the initial galaxy; if judging that the maximum number of iterations is not reached, returning to select a new galaxis according to the tournament selection mechanism; otherwise, stopping iteration to acquire an optimal power distribution scheme. The system throughput and the system energy consumption which conflict with each other can be optimized at the same time.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
A Fast Star Tracking Method under High Dynamics
ActiveCN104964684BFast predictionImprove accuracyNavigation by astronomical meansWide fieldPrediction rate
The invention discloses a high-dynamic rapid star tracking method. The method comprises 1, designing a weighted value according to multiframe attitude information output by a star sensor at the T1-Tn moment and a proximity relationship of the multiframe attitude information, forecasting attitude of the star sensor at the next T<n+1> moment, searching a star point corresponding to the attitude from a star database by the forecasted attitude, and producing a virtual forecasted large view field star image for matching by mapping, and 2, carrying out matching identification on a star position A and a star mass center position B at t+delta t moment to realize star tracking. The high-dynamic rapid star tracking method utilizes multi-frame attitude information prediction, has a fast prediction rate, improves prediction accuracy, realizes tracking and matching based on a forecasted virtual wide field star image without novel star identification and improves a star tracking algorithmic speed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multi-parameter high-precision star map detection device for star simulator
The invention discloses a multi-parameter and high-precision star map detection device for a star simulator. The multi-parameter and high-precision star map detection device is composed of a height adjusting mechanism, an azimuth angle adjusting mechanism, a pitch angle adjusting mechanism, a theodolite host engine base, a theodolite axis system, a theodolite optical system, a theodolite eyepiece system, a transfer lens and an area array CCD (Charge Coupled Device). Under the condition that a theodolite structure is not damaged, compressive high-precision detection of an angular distance between stars, a single-star position, a single-star field angle, single stars and the like of the star simulator can be realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Satellite Rolling Attitude Planning Method Based on Line-of-Sight Pointing Considering Thermal Control, Measurement and Control Constraints
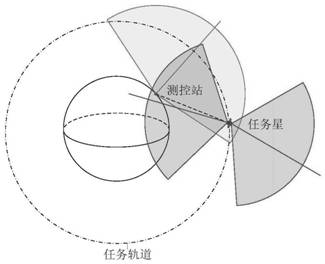
The present invention provides a satellite rolling attitude planning method based on line-of-sight pointing and considering thermal control measurement and control constraints, including: (1) injecting the mission star position information and the target star position and attitude measurement information into the ground measurement and control station; (2) solving the task Sunlight unit vector in the star orbit coordinate system; (3) Solve the position vector of the measurement and control station under the J2000 geocentric inertial system; (4) Determine the thermal control and measurement and control constraints; (5) Determine the orbiting axis and the maximum orbiting (6) Obtain the value set of the flying angle; (7) Obtain the feasible region of the roll angle satisfying the thermal control constraint, the feasible region of the rolling angle satisfying the measurement and control constraint, and the rolling angle satisfying the thermal control measurement and control constraint for the flying angle (8) Obtain the feasible region of roll angle satisfying the thermal control constraint, the feasible region of roll angle satisfying the measurement and control constraint and the feasible region of roll angle satisfying the measurement and control constraint of thermal control during the whole flight process; (9) generate the mission star Scroll the angular expectation sequence, and put a star on it.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
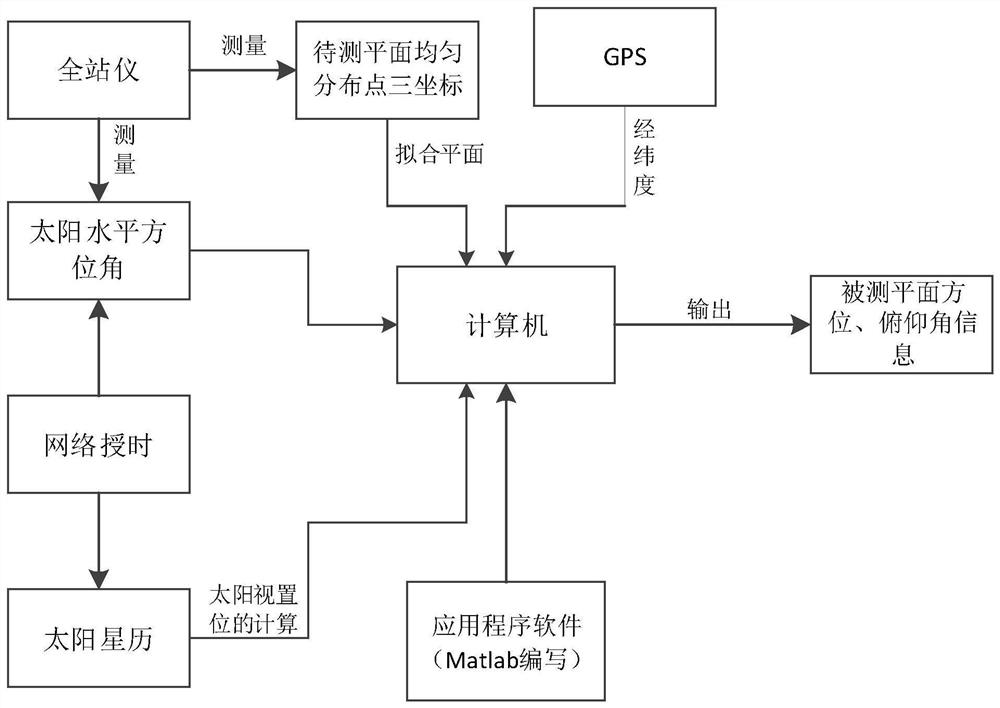
A method and system for plane normal astronomical orientation measurement based on total station
ActiveCN110146052BEasy to measureOrientation measurement process is simpleAngle measurementTheodoliteEngineering
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
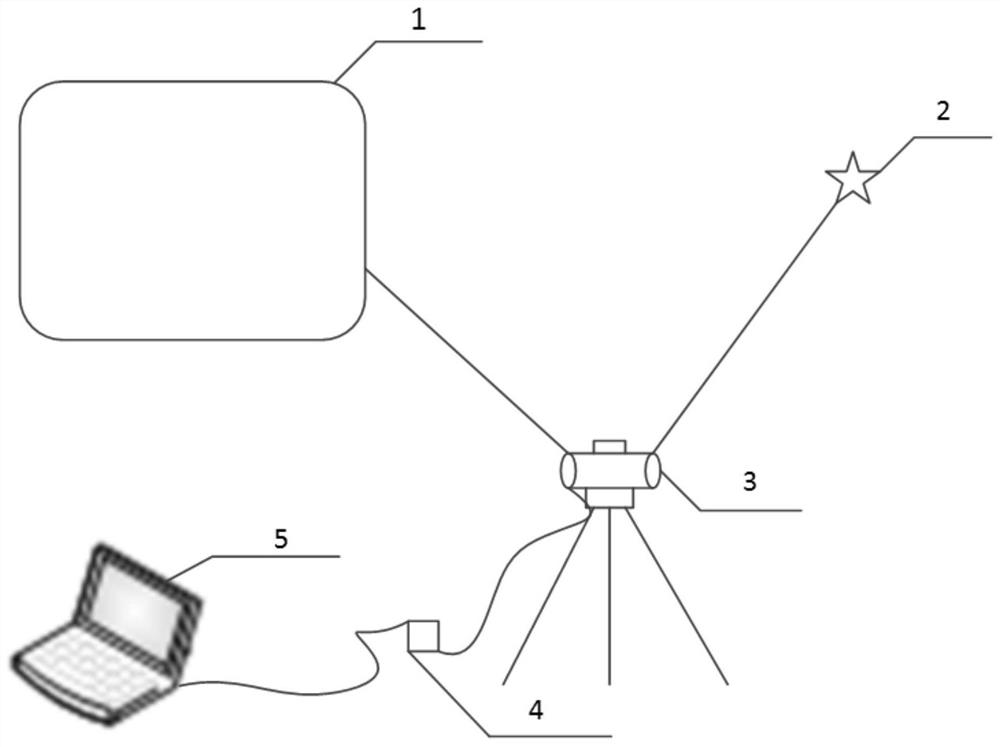
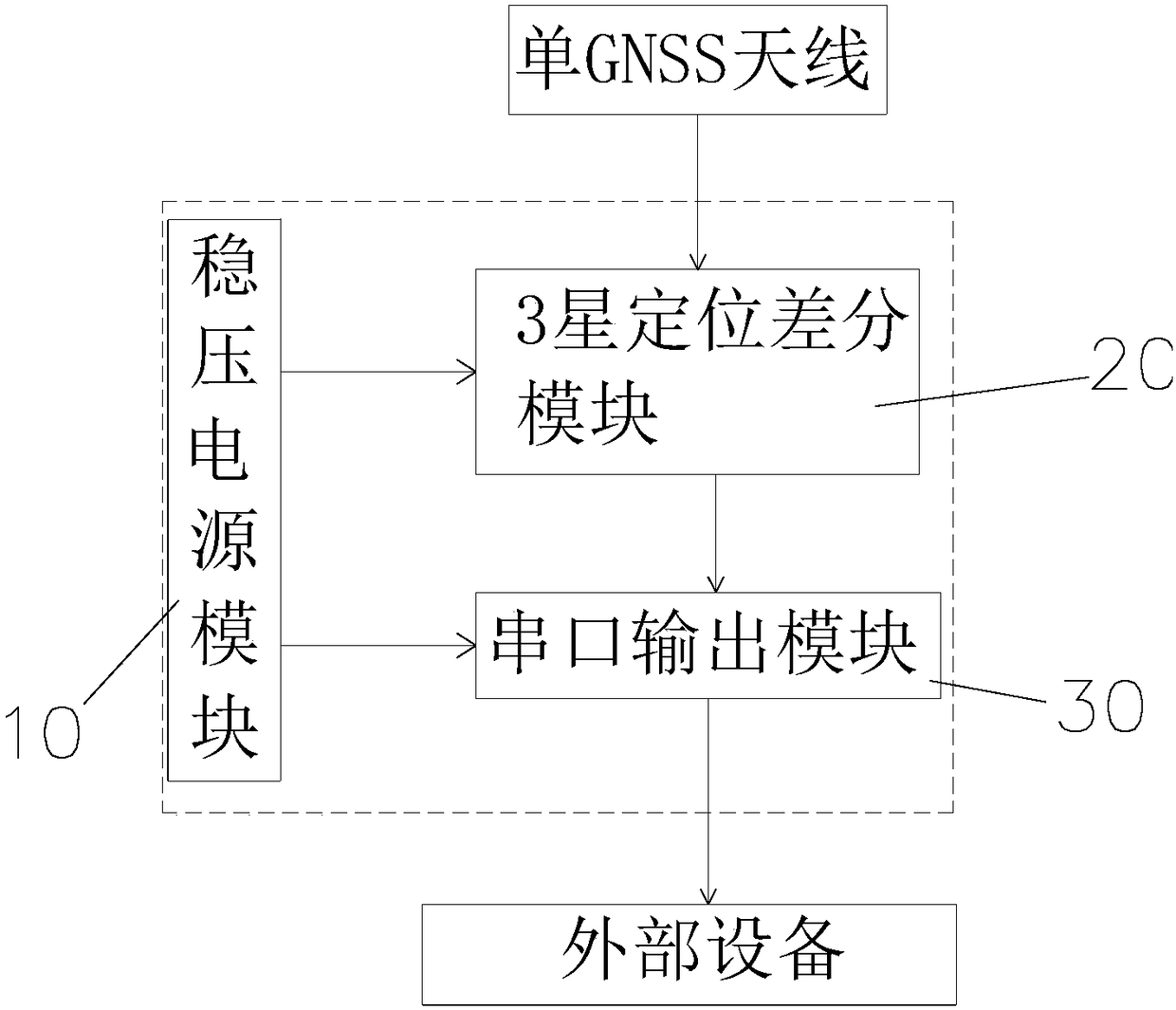
GPS positioning differential base station device
The invention relates to a GPS positioning differential base station device. The device comprises a shell, an integrated main board is arranged in the shell, a voltage-stabilized source module, a three-star positioning differential module and a serial port output module are arranged on the integrated main board, the voltage-stabilized source module is electrically connected with the three-star positioning differential module and the serial port output module, three-star multi-frequency chips are arranged on the three-star positioning differential module, the serial port output module is connected to a data output connecting tube on the front end surface of the shell, and wing plates are arranged on the two side faces of the shell. The device has high signal stability, only one base stationis needed, the installation is convenient, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:GUOHUA OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Geostationary Satellite Imaging Navigation and Registration Star North-South Parameter Extraction Method and System
ActiveCN106568437BReduce high frequency errorImprove recognition accuracyNavigation by astronomical meansNatural satelliteFixed stars
The invention provides a geostationary satellite imaging navigation and registration fixed star north and south parameter extraction method, and a system. The geostationary satellite imaging navigation and registration fixed star north and south parameter extraction method comprises following steps: 1, the relationship of the grey level of column image elements with fixed star image north and south direction coordinate components is established; 2, detector image element grey level when a fixed star passes through the column image element center is extracted; 3, the fixed star north and south direction coordinate components are calculated; 4, the north and south direction coordinate components when the center of a fixed star image passes through the center line of the east and west direction of the detector are calculated. According to the geostationary satellite imaging navigation and registration fixed star north and south parameter extraction method, in calculating of fixed star image coordinates, fixed star image shape and brightness distribution characters are taken into consideration fully, identification precision is increased greatly; and multiple column image elements calculation results are subjected to least square fit so as to reduce star position high-frequency error caused by factors such as detector optical imaging, circuit noise, and satellite high frequency jitter.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
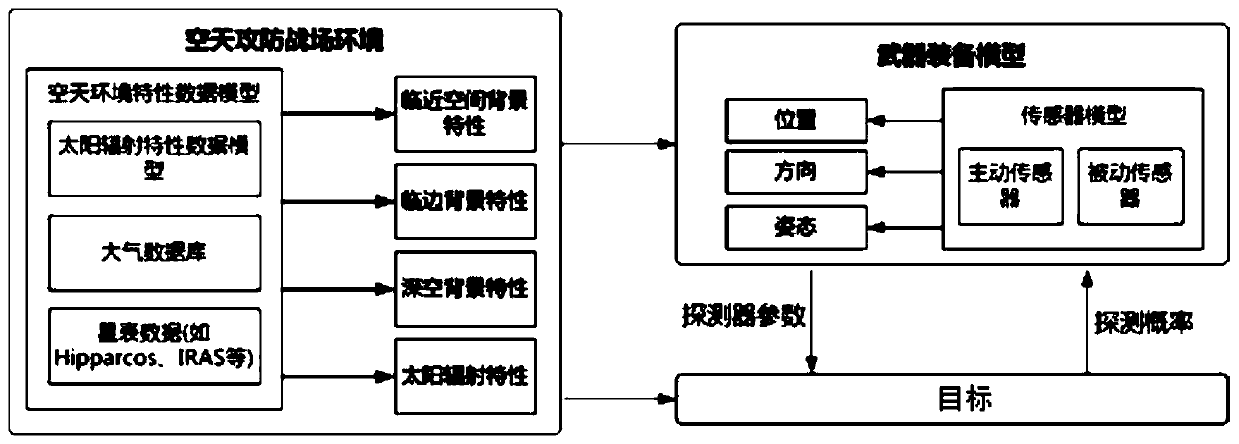
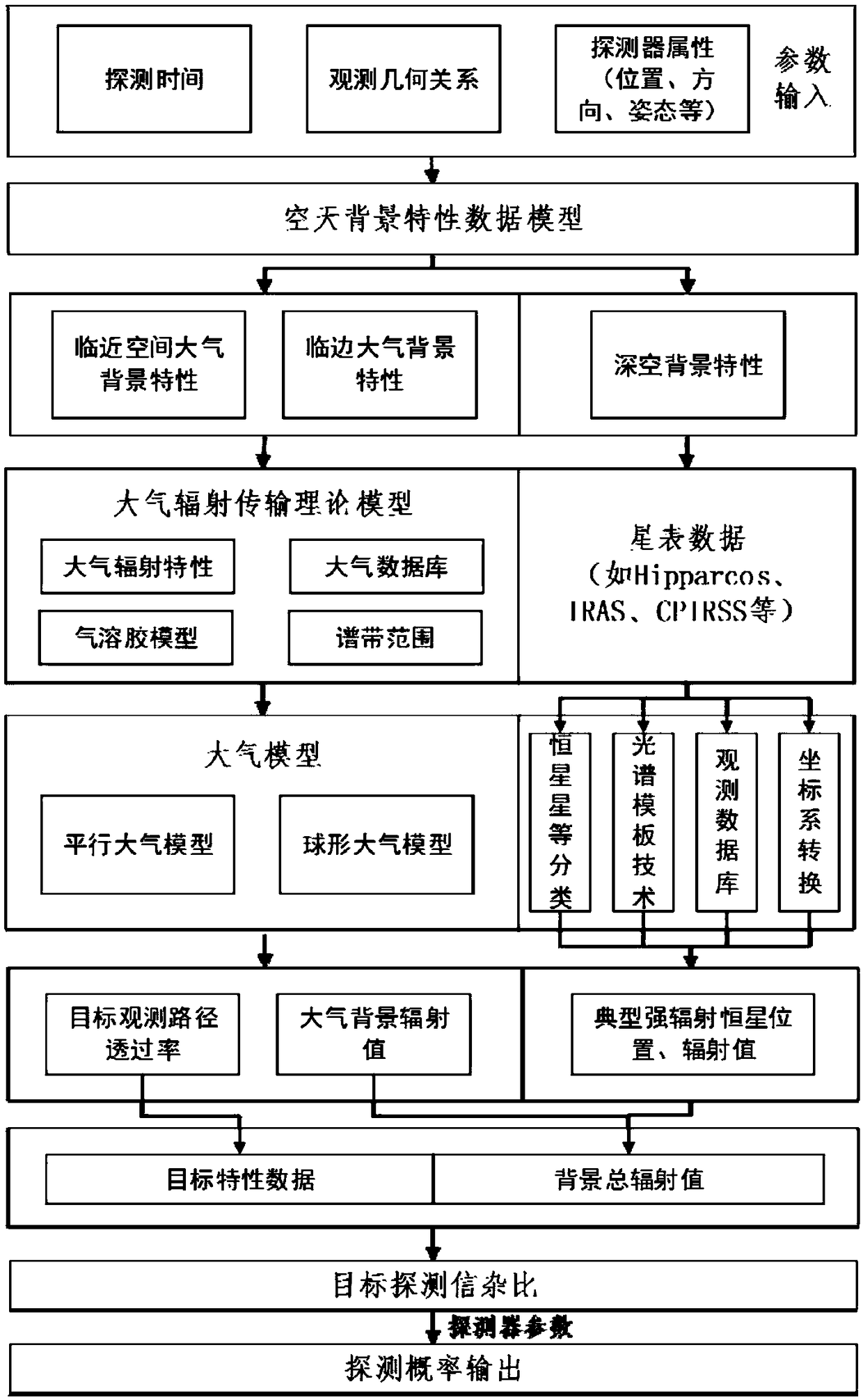
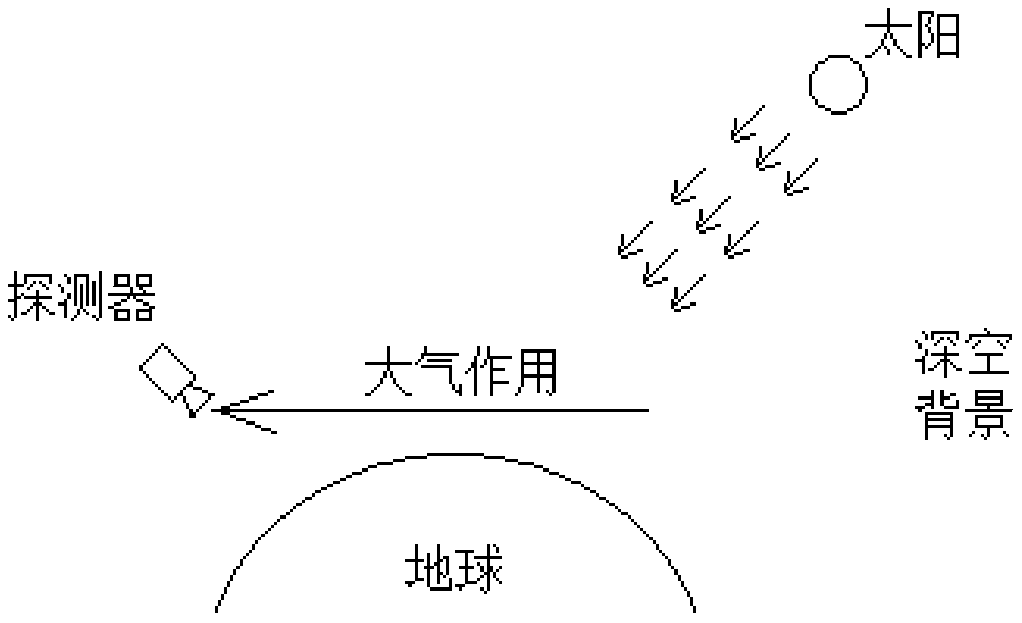
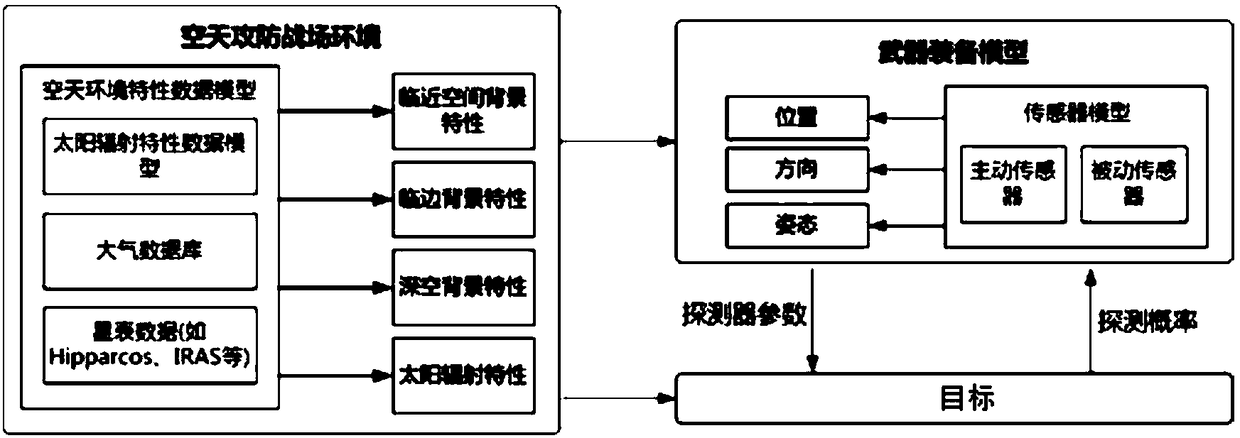
Modeling Method and System for Aerospace Environment Based on Data Model
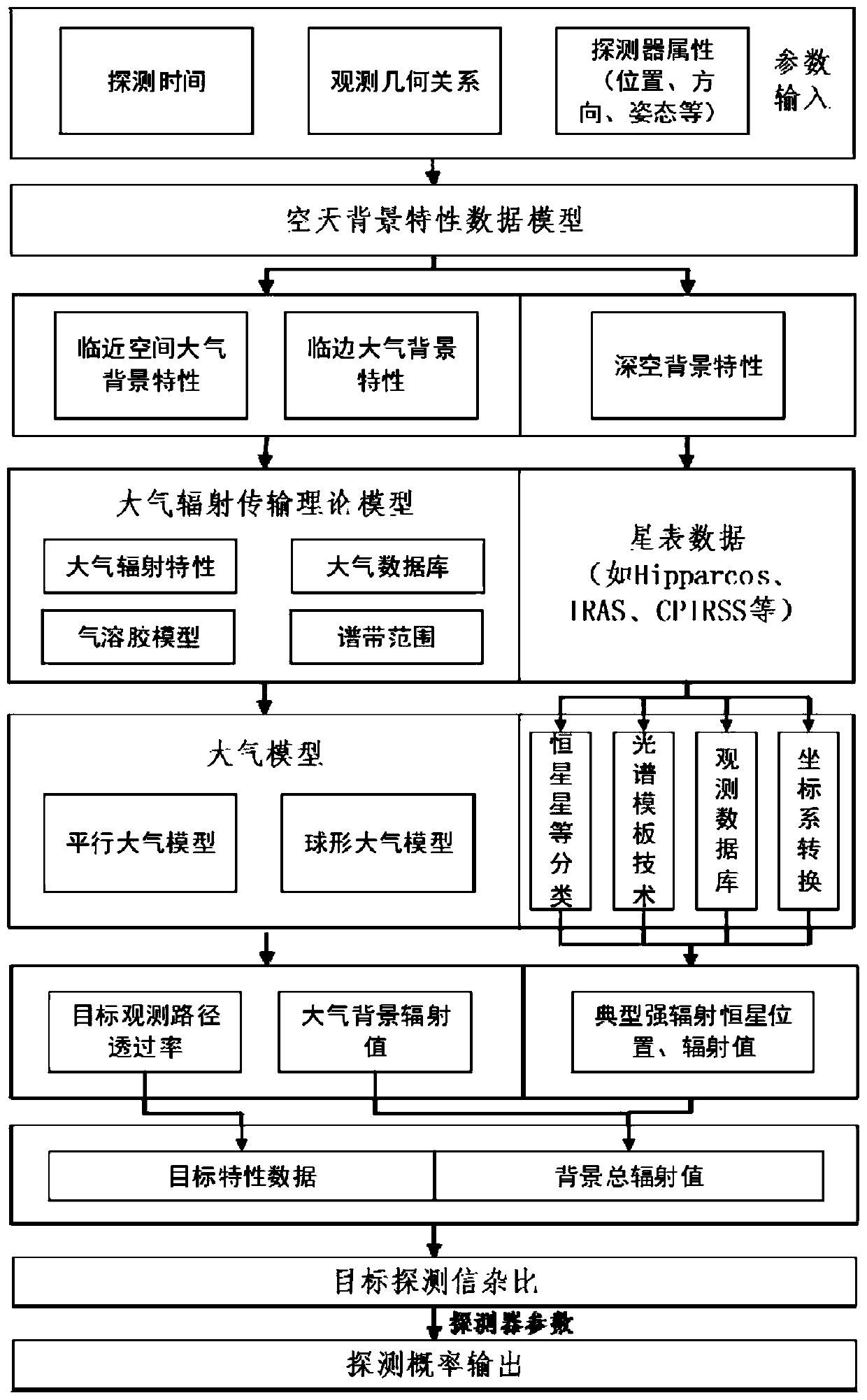
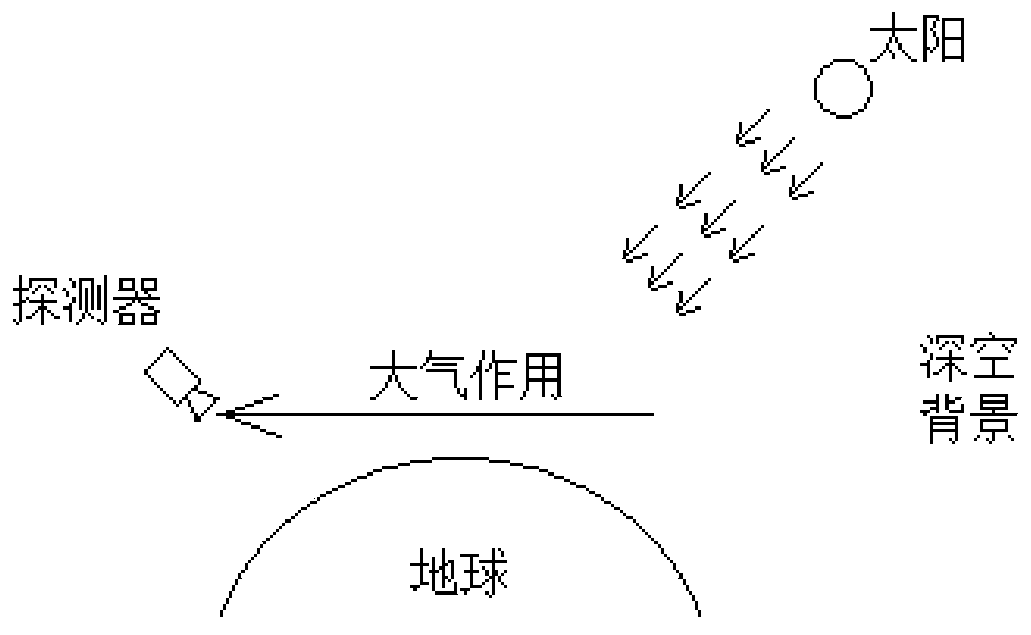
ActiveCN109255198BImprove accuracyGood modelingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTransmittanceComputer science
The invention provides an aerospace environment modeling method and a system based on a data model. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an observation geometry relationship between a detector and a target, a detection time of the detector and a property of the detector, and inputting an aerospace background characteristic data model; according to the transmittance of the target observation path, calculating the target characteristic data, according to the atmospheric background radiation value, the typical strong radiation star position, the typical strong radiation star radiation value, obtaining the background total radiation value, obtaining the target detection signal-to-clutter ratio according to the target characteristic data and the background total radiation value,calculating the detection probability according to the target detection signal-to-clutter ratio. The invention directly utilizes the existing data and the parameters of the detector to obtain the environmental characteristics, thereby obtaining the detection probability of the detection target, the data accuracy is high and the modeling is convenient.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ENG
A high-precision star position extraction method based on intra-pixel response
The invention discloses a high-precision star position extraction method based on the response within the pixel. According to the response distribution within the pixel, the relationship between the point target position and the gray level of the pixel is established to realize the high-precision position extraction of the star. The position extraction steps are: 1. Perform background removal and non-uniformity correction on the obtained image. 2. Select ten frames of images with the largest pixel gray value, and calculate the energy distribution function of the star target after passing through the optical system according to the filling factor of the pixel. 3. According to the energy distribution function and pixel filling factor, a series of pixel gray values of star targets at different positions are obtained, and a lookup table of star positions and pixel gray values is established by interpolation. 4. Find the corresponding pixel position according to the gray value of the pixel, and obtain several groups of pixel positions due to the symmetry of the energy distribution and the pixel response. 5. Use the centroid method to select star positions from several groups of pixel positions obtained in step 4.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method of using ccd detectors for astrometric telescopes to accurately measure the positions of stars
InactiveCN103900538BPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsMeasuring instrument
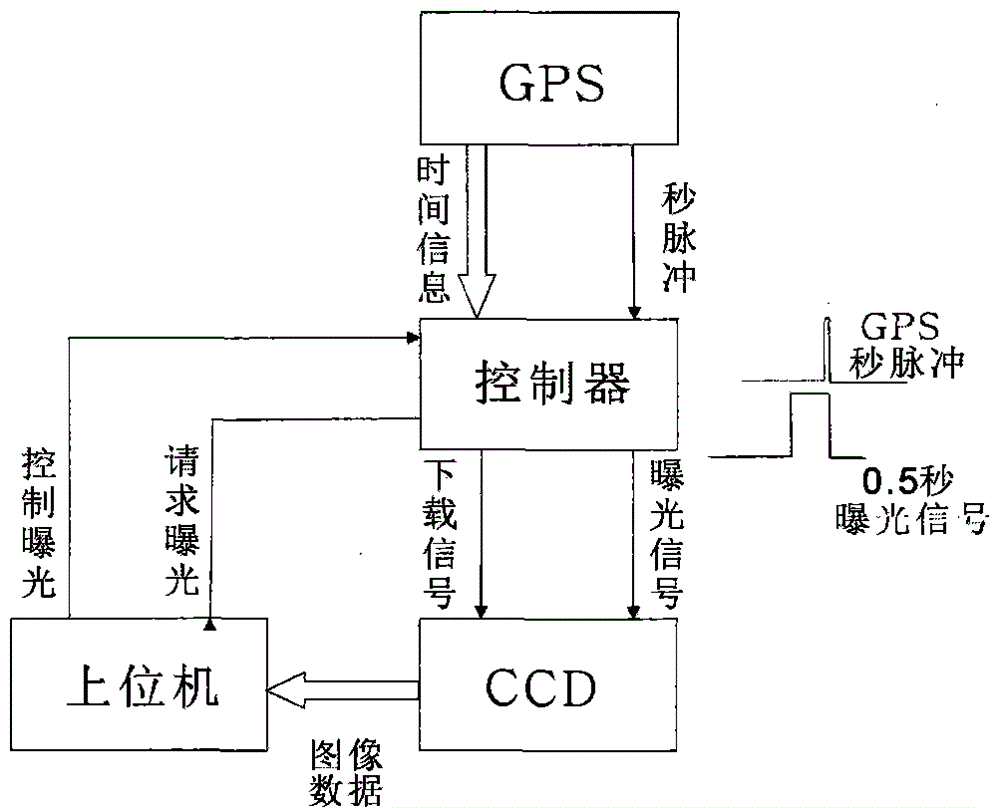
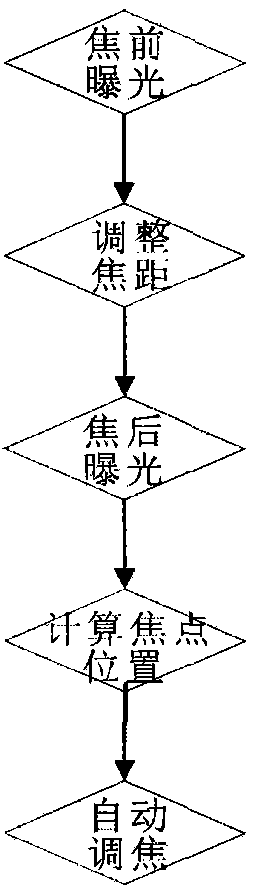
The invention provides a method for accurately measuring the position of a fixed star by an astrometry telescope through a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) detector. The method specifically comprises the following steps: selecting the CCD detector used on a full-automatic astrometry instrument terminal, mounting and utilizing the CCD detector, utilizing an automatic focusing principle and an automatic focusing method of the CCD detector and accurately measuring the position of the fixed star by using a picture photographed by the CCD detector. According to the method provided by the invention, the measurement work of the position of the fixed star can be carried out on the astrometry telescope by using the CCD detector; the observation efficiency is improved, the structure is simple and the utilization is convenient; the method can be popularized and applied to the astrometry telescope.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
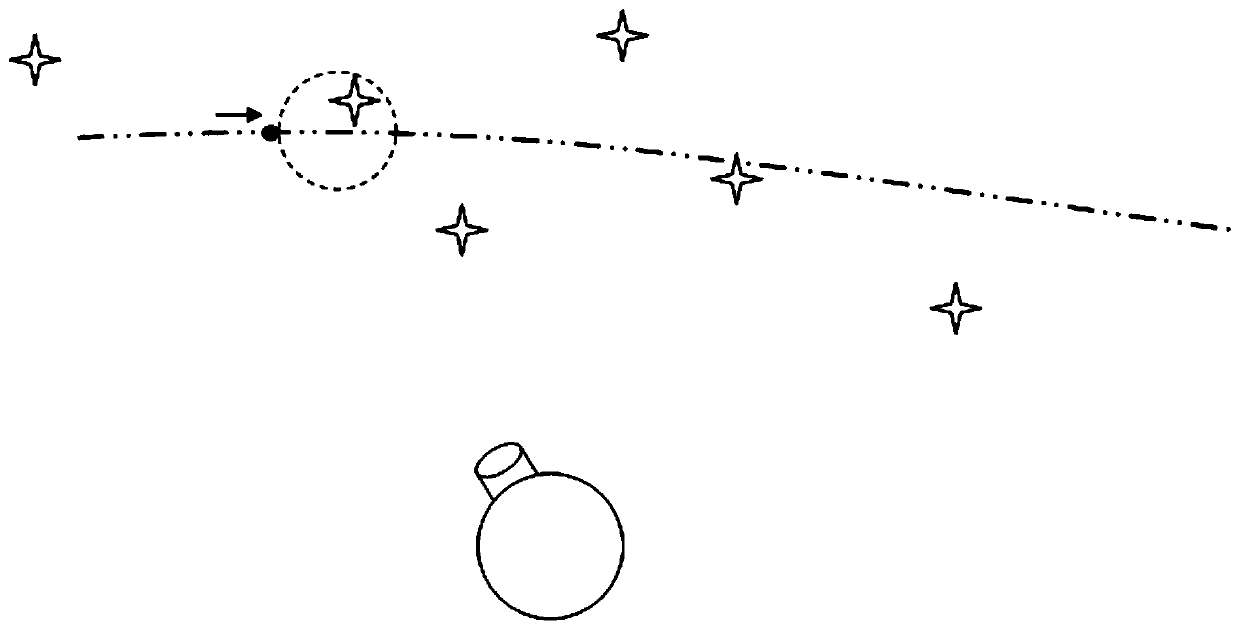
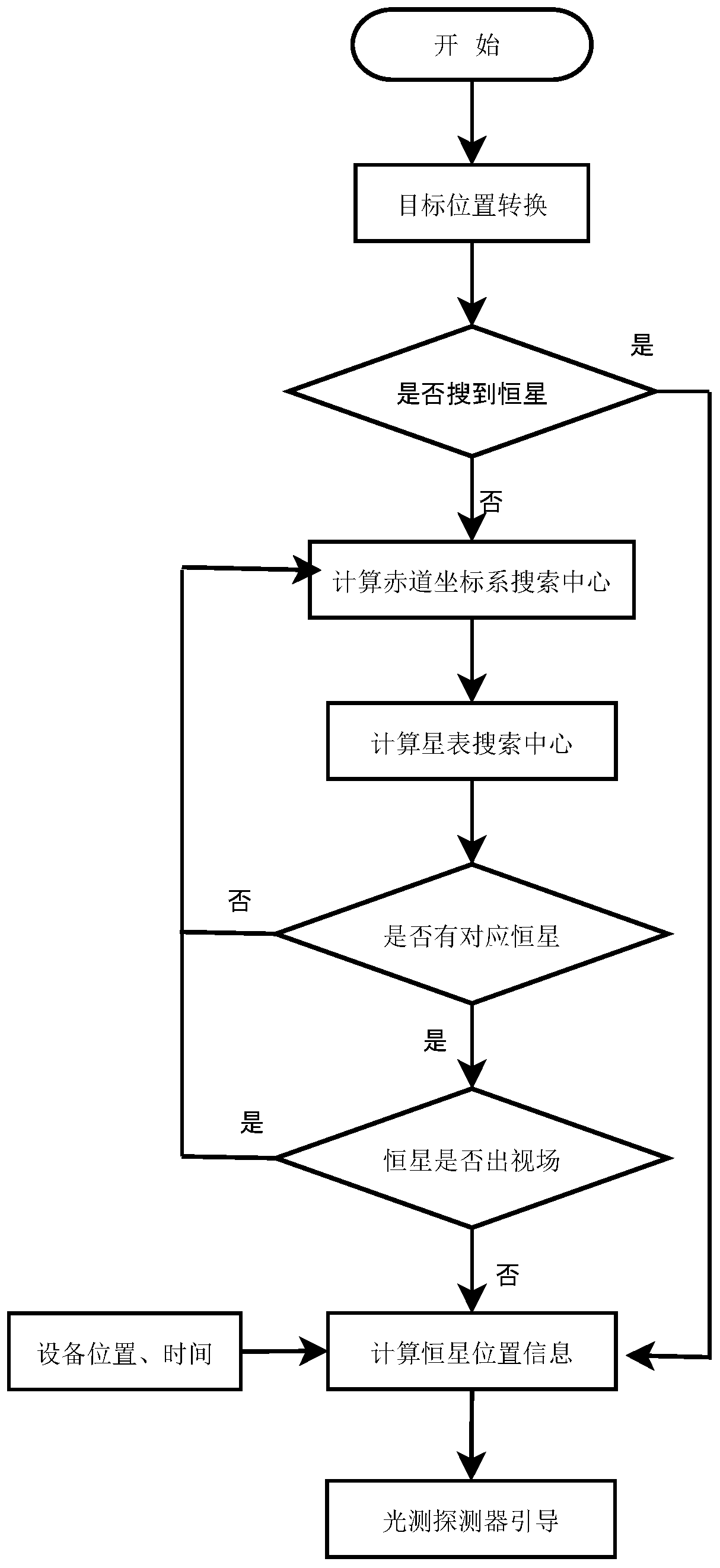
A real-time search method for stars near the pointing position of photoelectric tracking and measuring equipment
ActiveCN106896827BSimple relationshipReduce computationTarget-seeking controlFixed starsStar catalogue
The invention provides a real-time searching method for a fixed star around the directional position of a photoelectric tracking measurement device and mainly relates to the field of photoelectric tracking measurement and high-precision equipment guiding control. For the object tracking process, observation of fixed stars around the track is required. The invention designs a method to achieve the target tracking and to timely search fixed stars in a certain field angle range away from a target. The method uses the feature that the star position is basically constant in the second equatorial coordinate system, and avoids the problems that as the star and the target are moving in the level coordinate system, the calculation amount is large and the search complexity is big and so on. Through the virtual star, the relevant error is calculated to achieve the direct search in the star table, thereby reducing the search volume and improving the search efficiency and the hit rate of searching.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for extracting the parameters of sensitive objects for stationary satellite imaging navigation and registration
ActiveCN105758400BImprove extraction accuracyHigh precisionNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsData information
The invention provides an extracting method for fixed star sensitive east and west parameters of stationary satellite imaging navigation and registration. The extracting method comprises the following steps of obtaining a changing curve of a total gray value of pixels of each line along with time; obtaining a moment that a fixed star image center crosses a center line of the pixels of the line; fitting a motion law of the fixed star image center in east and west line coordinates of a satellite remote sensing detector array; obtaining a moment that the fixed star image center crosses a center line of the east-west direction of the satellite remote sensing detector array. According to the extracting method provided by the invention, high-frequency error of star positions caused by factors such as optical imaging of the detector, circuit noises, high-frequency wobble of a satellite and the like can be eliminated by multiframe data information fusion processing and curve fitting, thereby improving the identification accuracy of fixed star position parameters. The extracting method can be used for stationary satellite imaging navigation and registration, and has important significance for improving on-orbit thermal deformation precision of a remote sensing imaging system and the imaging navigation and registration processing property by acquiring parameters such accurate time and the like that the fixed star crosses the center of the detector array.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Detection method of small target of feature space
InactiveCN101546429BSmall amount of calculationEasy to detectImage analysisThree-dimensional spaceComputational physics
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
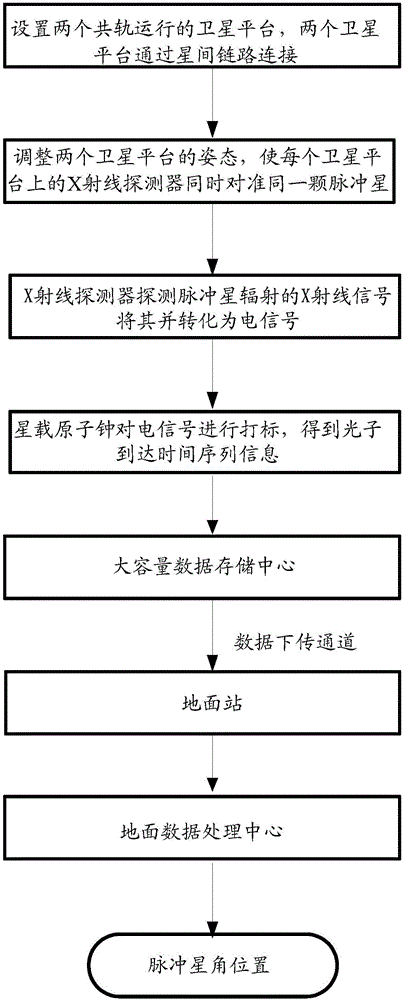
A system and method for measuring pulsar angular position based on a dual-satellite platform
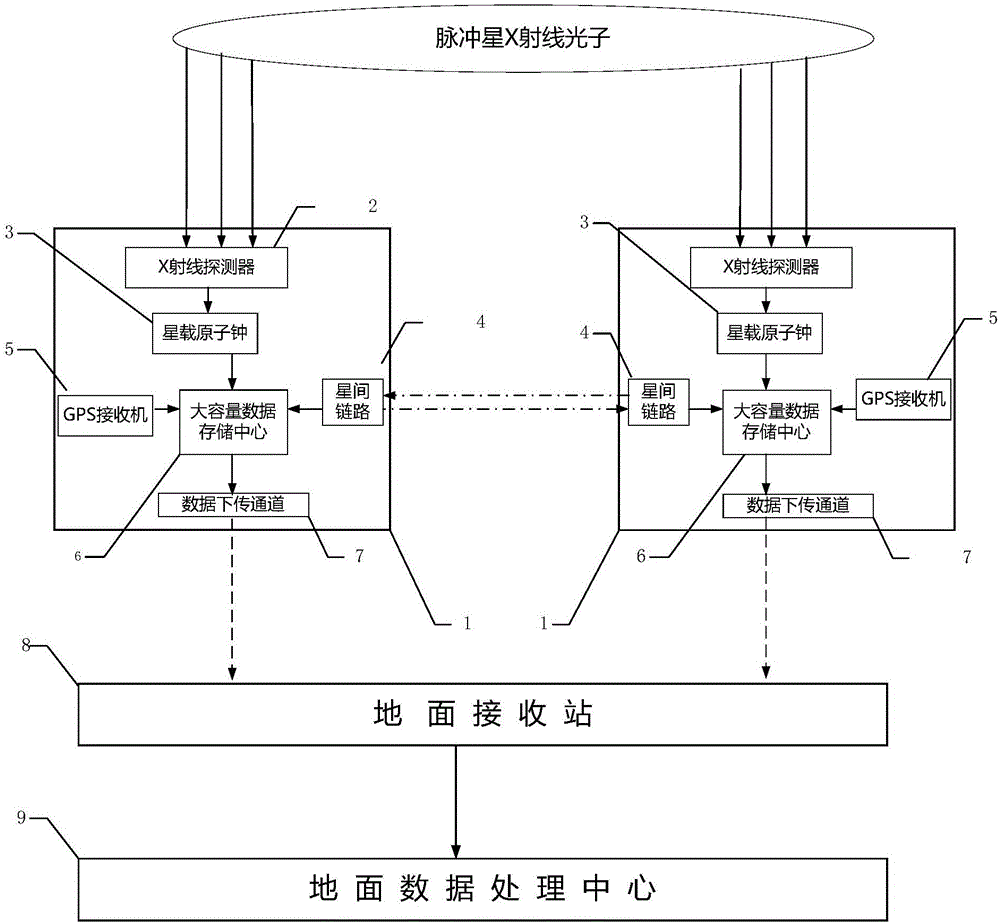
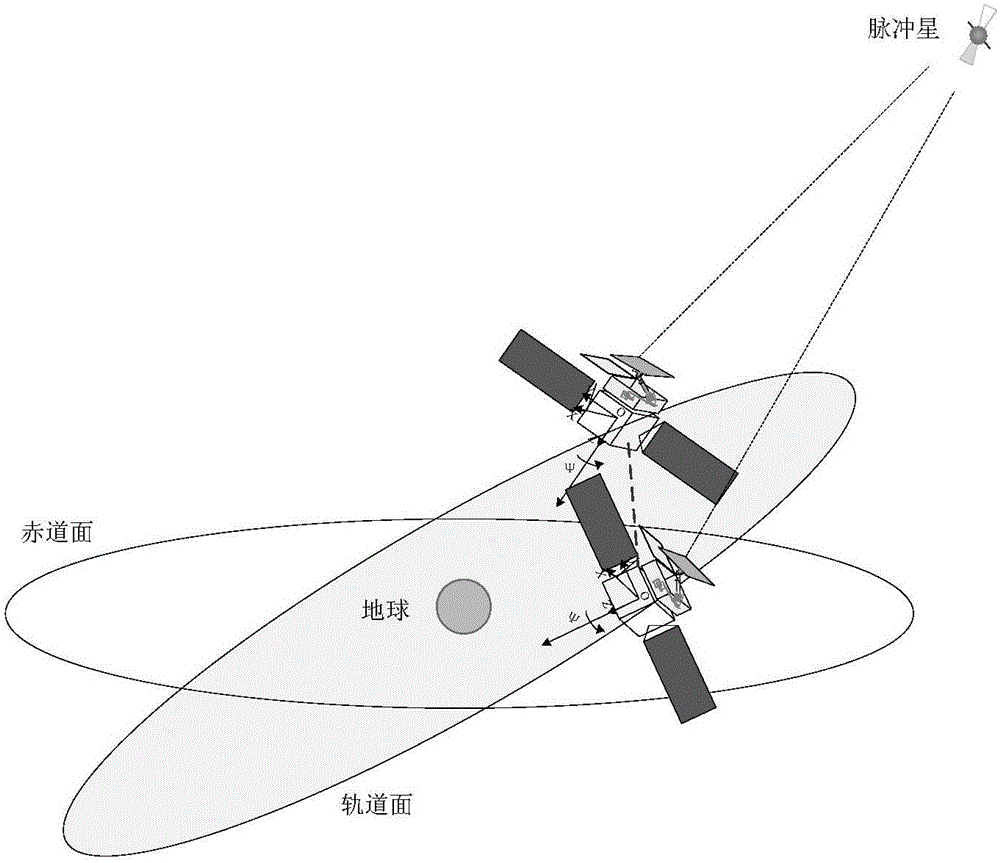
InactiveCN103644907BHigh measurement accuracyHigh precisionAngle measurementInstruments for comonautical navigationCommon railX-ray
The invention provides a pulsar angular position measurement system and a method based on double satellite platforms. In outer space, two satellites running on a common rail are utilized to observe a pulsar X-ray radiation signal simultaneously. A cross-correlation processing technology is employed to determine the angular position of the pulsar, and the measurement accuracy of the pulsar angular position is improved, thereby satisfying the application requirements of high-precision autonomous navigation based on X-ray pulsar.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Aerospace environment modeling method and system based on data model
ActiveCN109255198AImprove accuracyGood modelingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTransmittanceComputer science
The invention provides an aerospace environment modeling method and a system based on a data model. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an observation geometry relationship between a detector and a target, a detection time of the detector and a property of the detector, and inputting an aerospace background characteristic data model; according to the transmittance of the target observation path, calculating the target characteristic data, according to the atmospheric background radiation value, the typical strong radiation star position, the typical strong radiation star radiation value, obtaining the background total radiation value, obtaining the target detection signal-to-clutter ratio according to the target characteristic data and the background total radiation value,calculating the detection probability according to the target detection signal-to-clutter ratio. The invention directly utilizes the existing data and the parameters of the detector to obtain the environmental characteristics, thereby obtaining the detection probability of the detection target, the data accuracy is high and the modeling is convenient.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com