Patents
Literature
65 results about "Stress engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
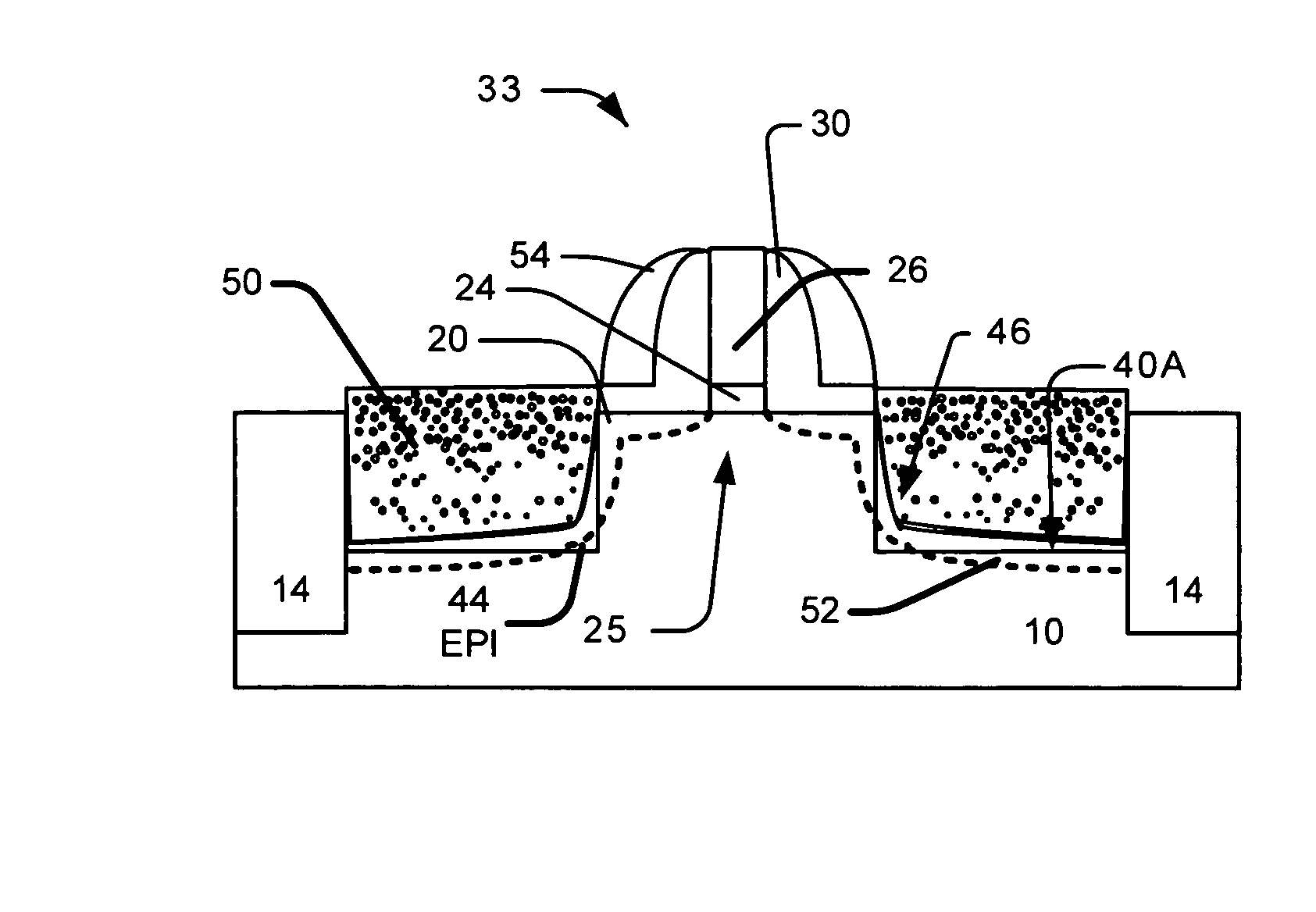
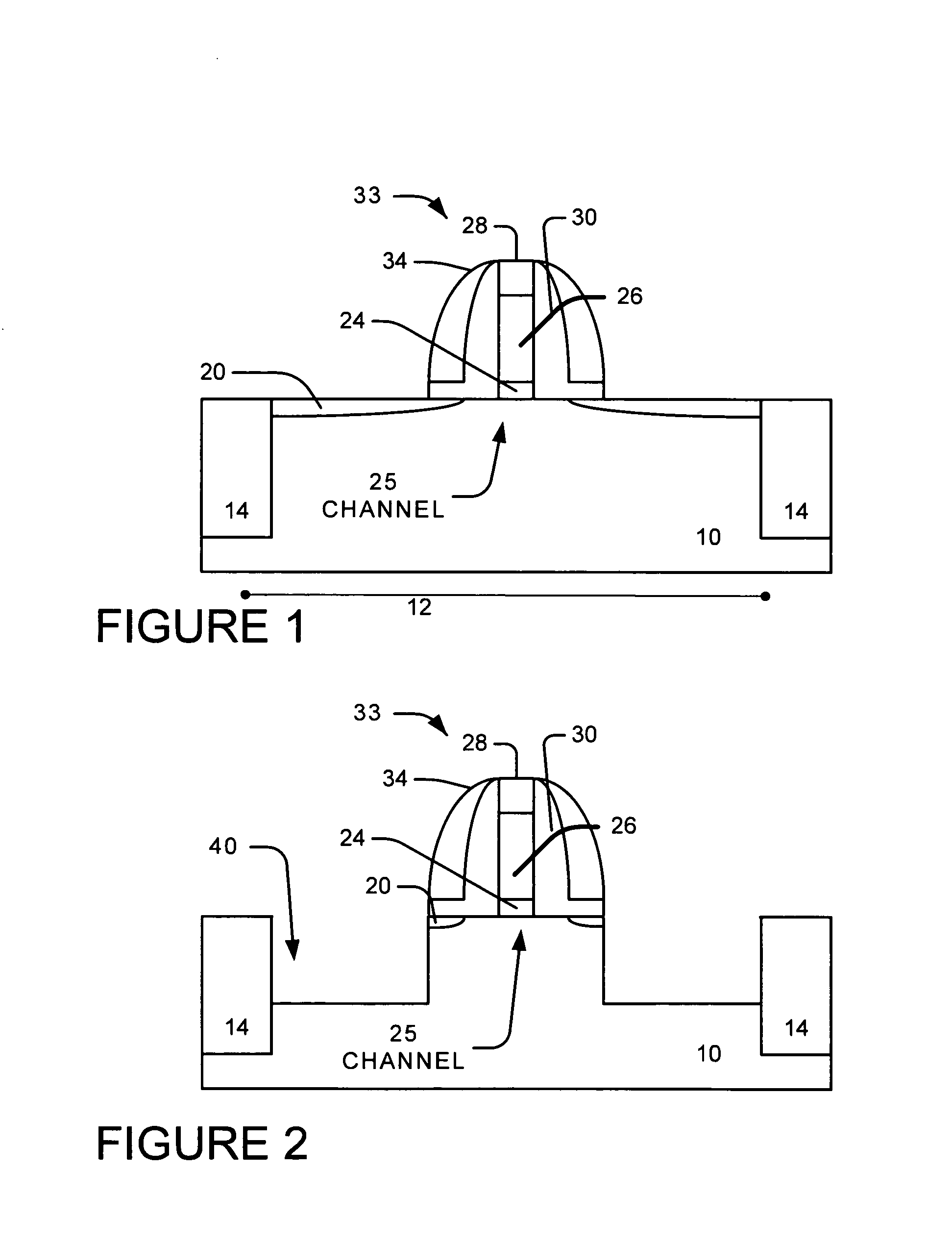
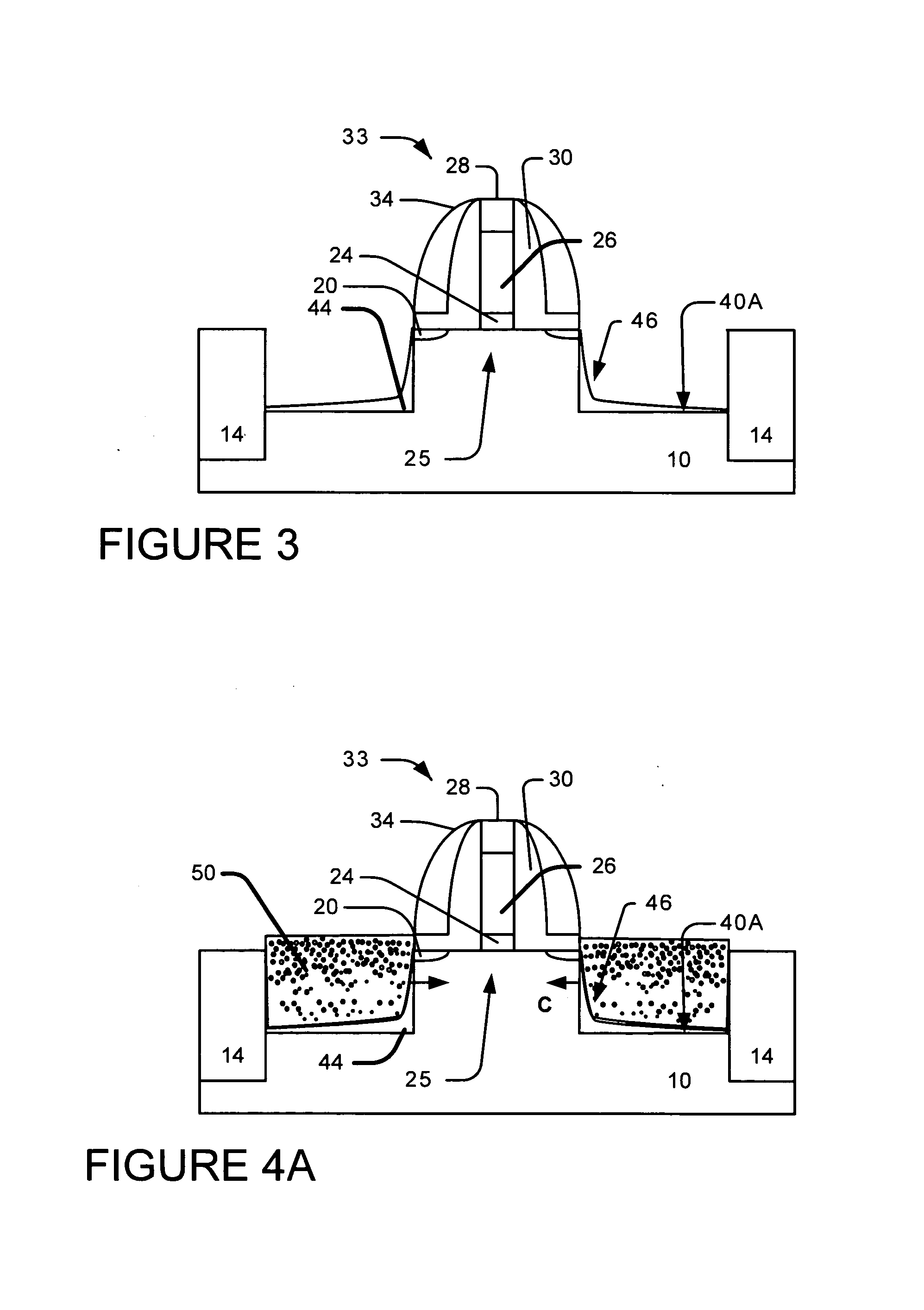
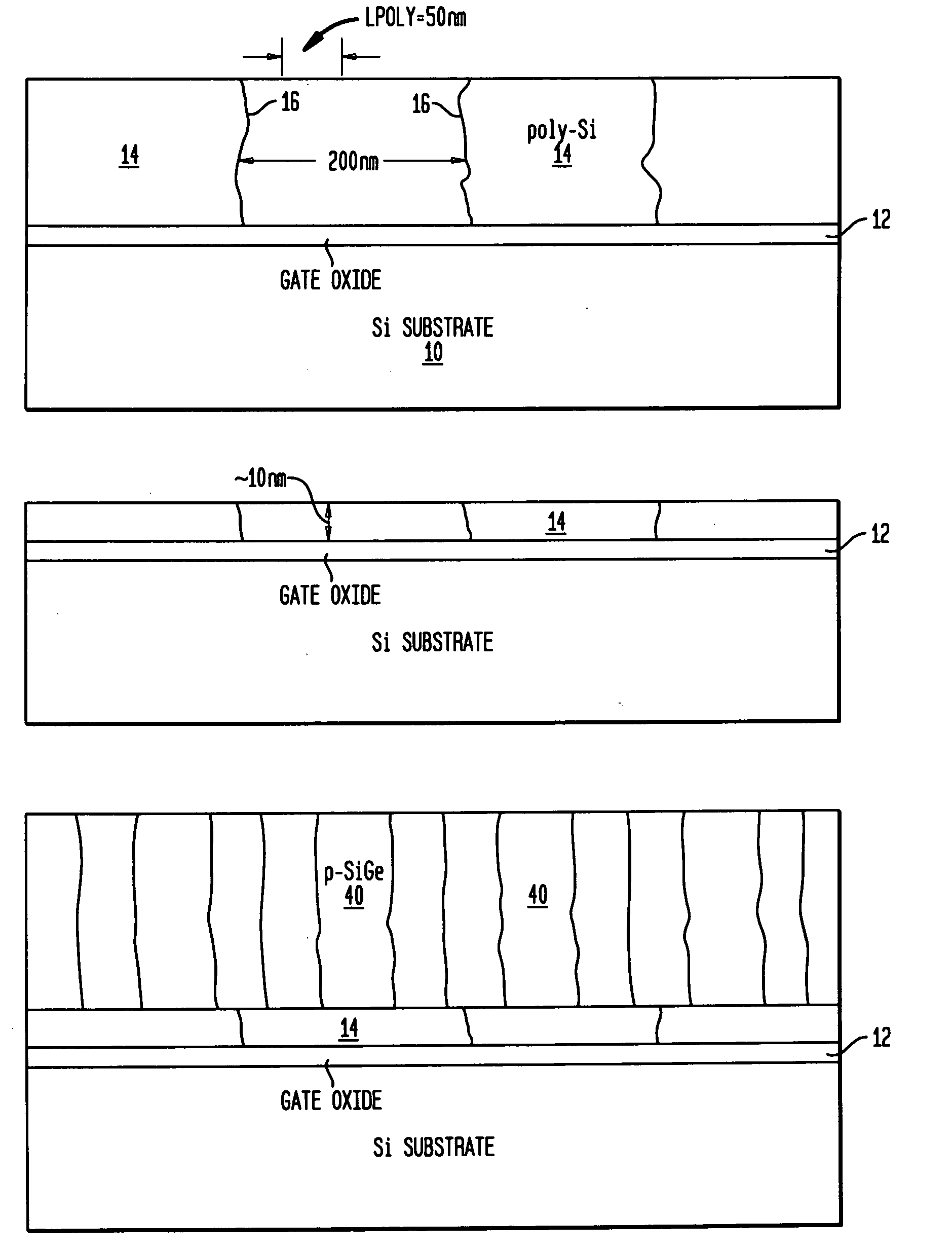
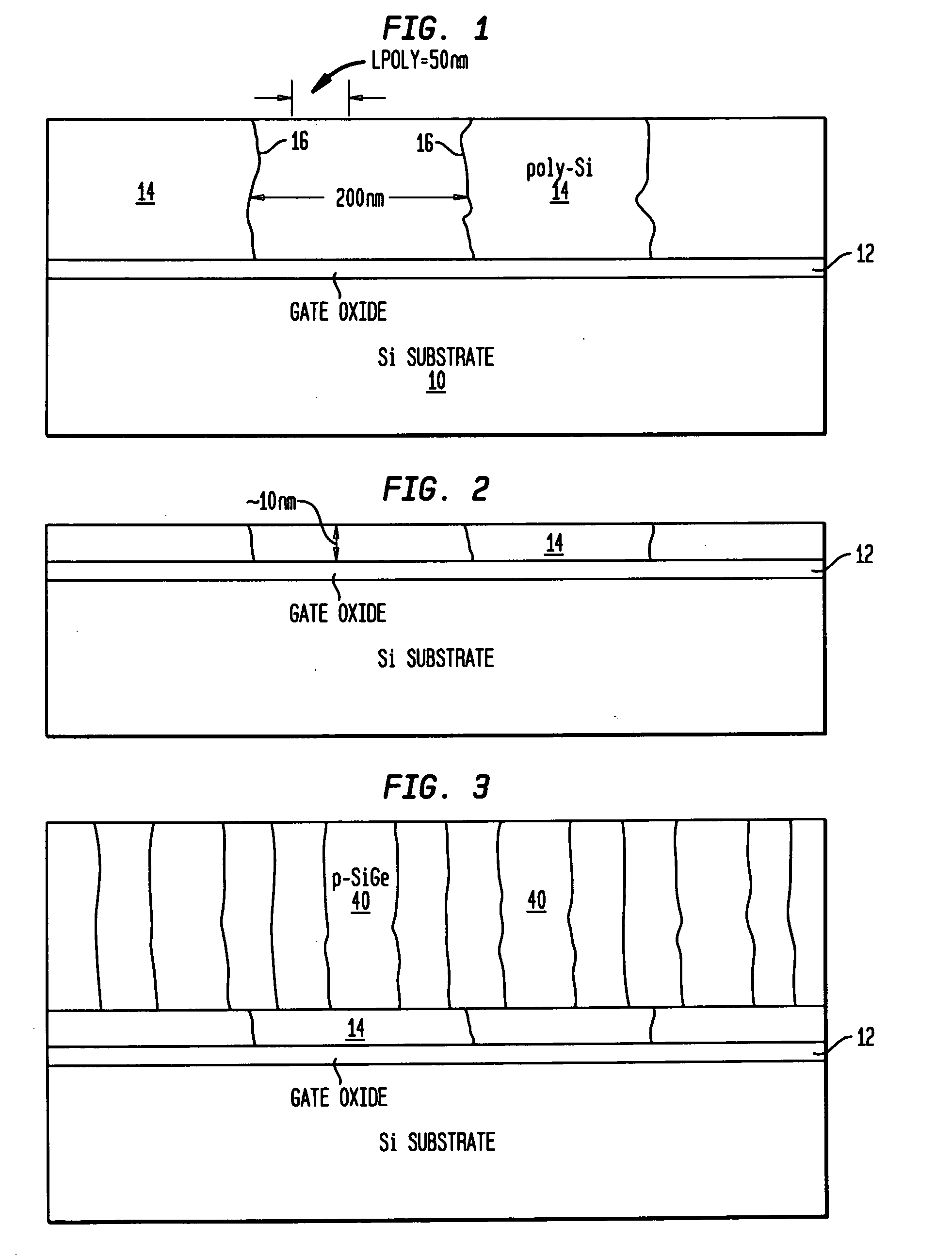
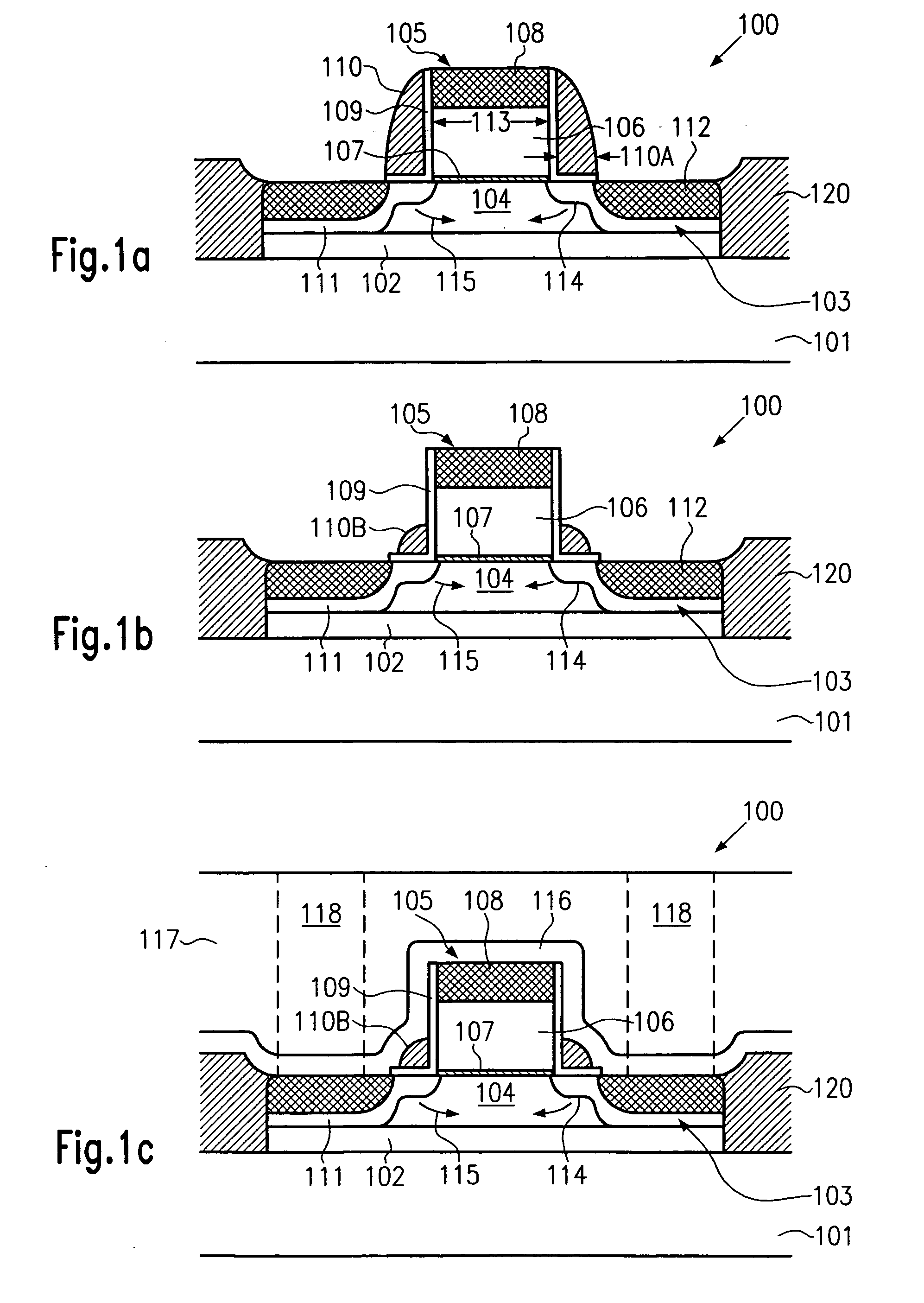
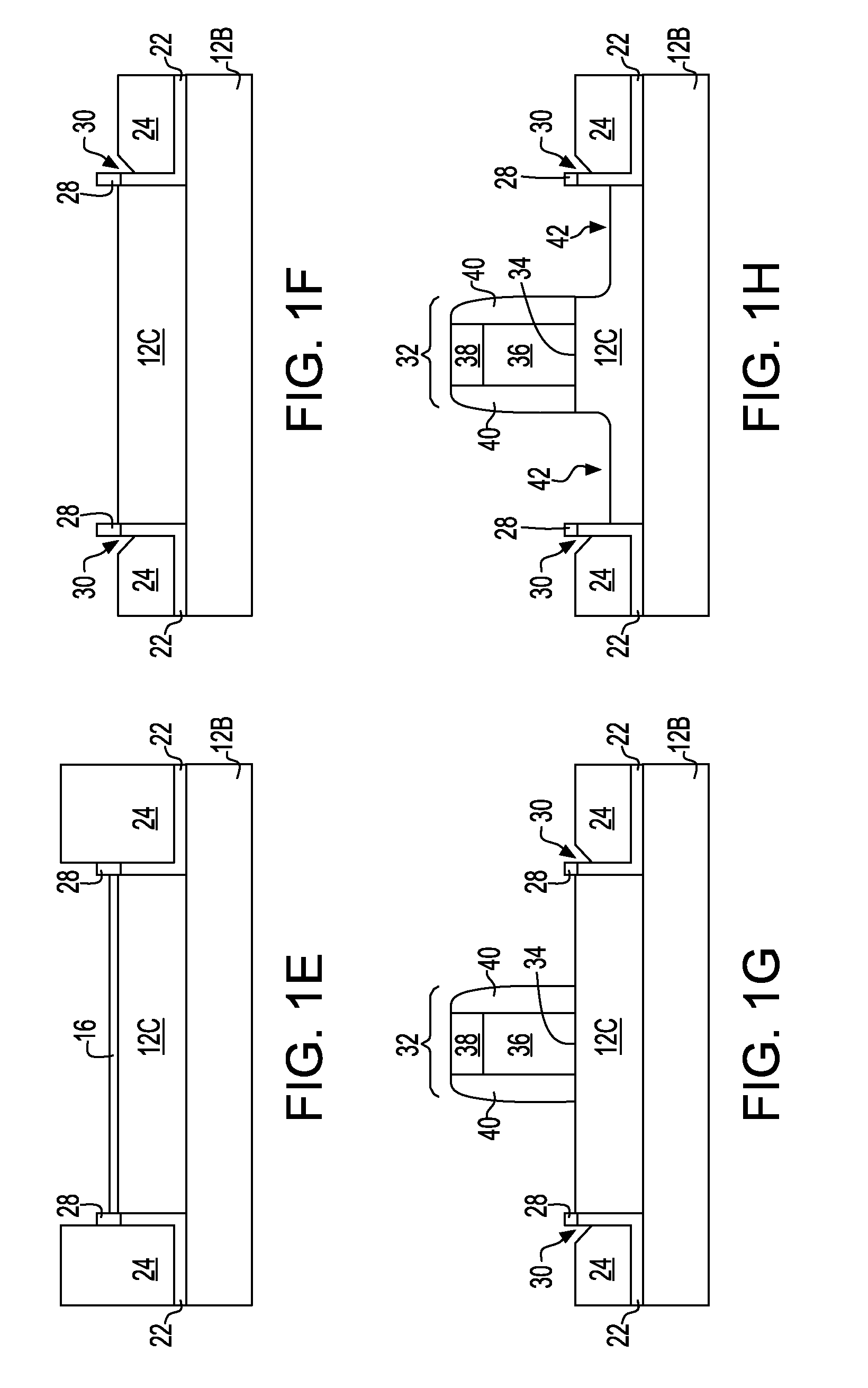
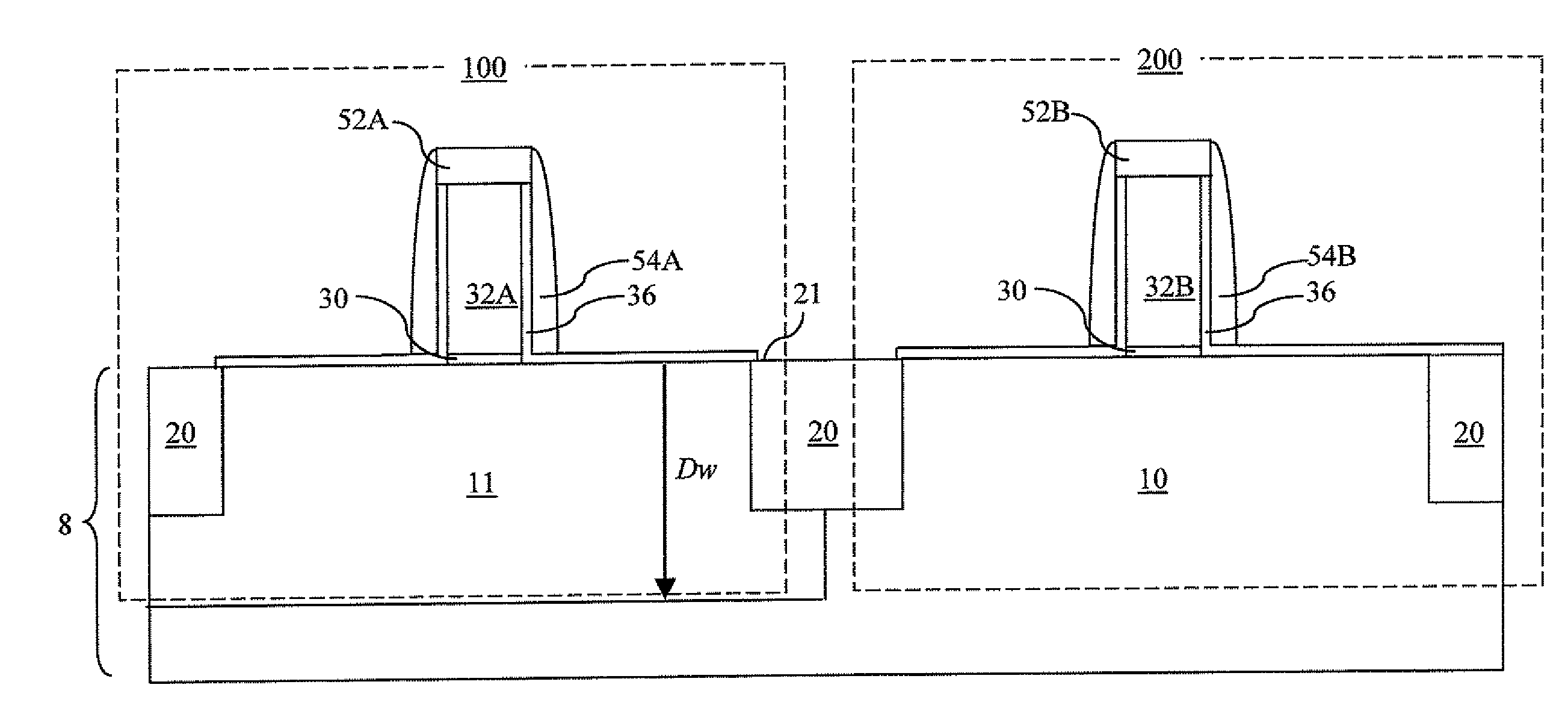
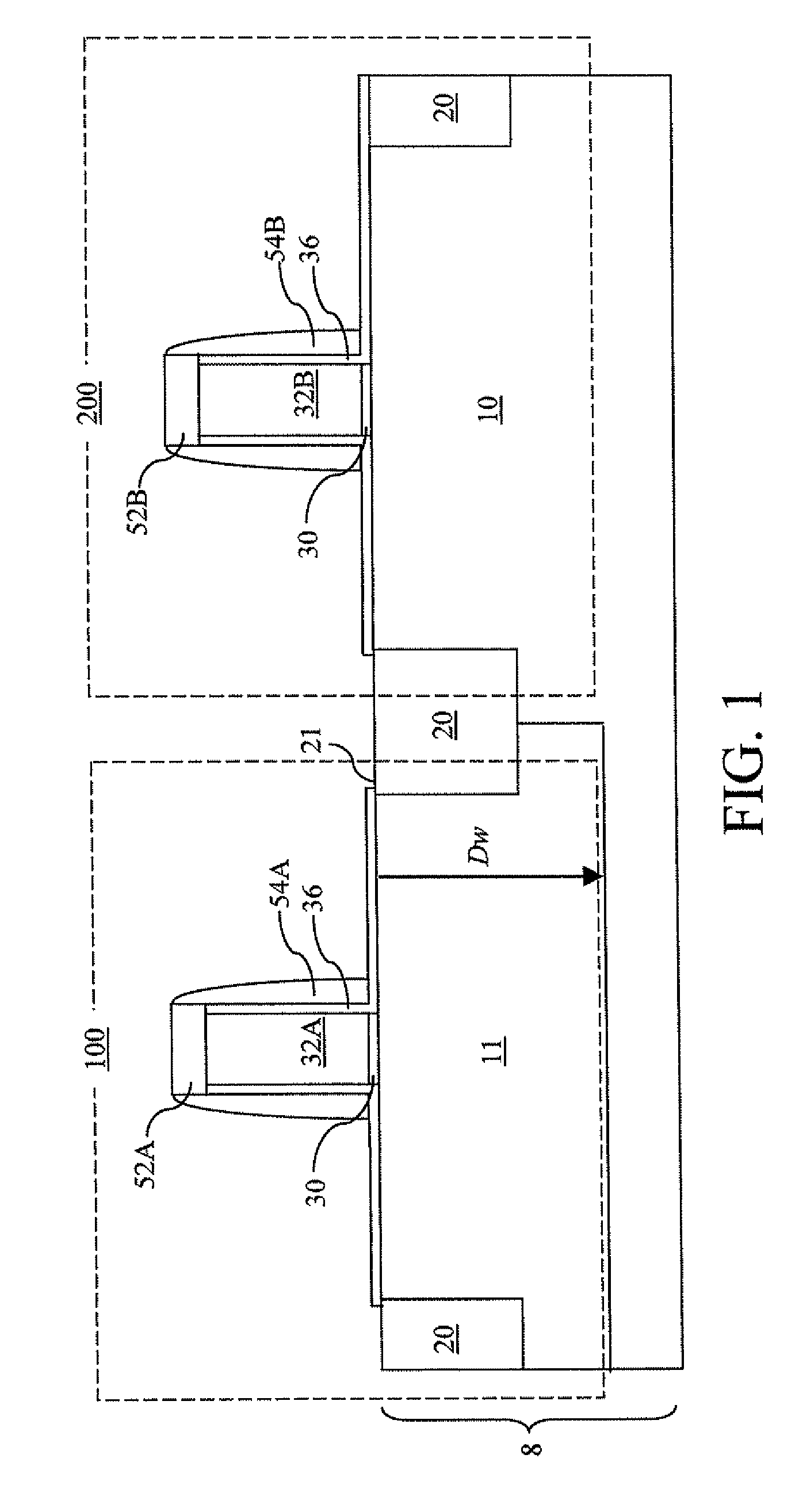
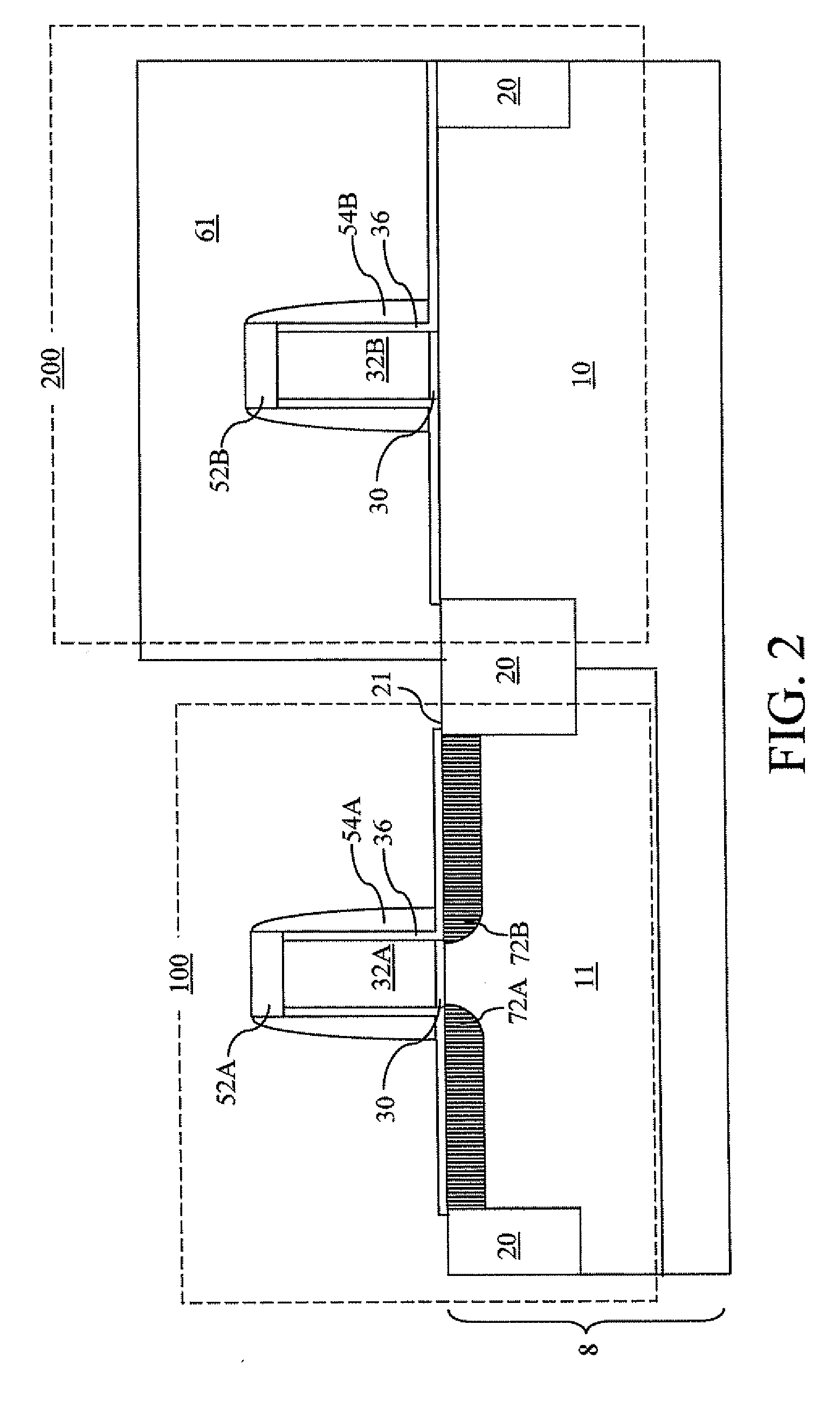
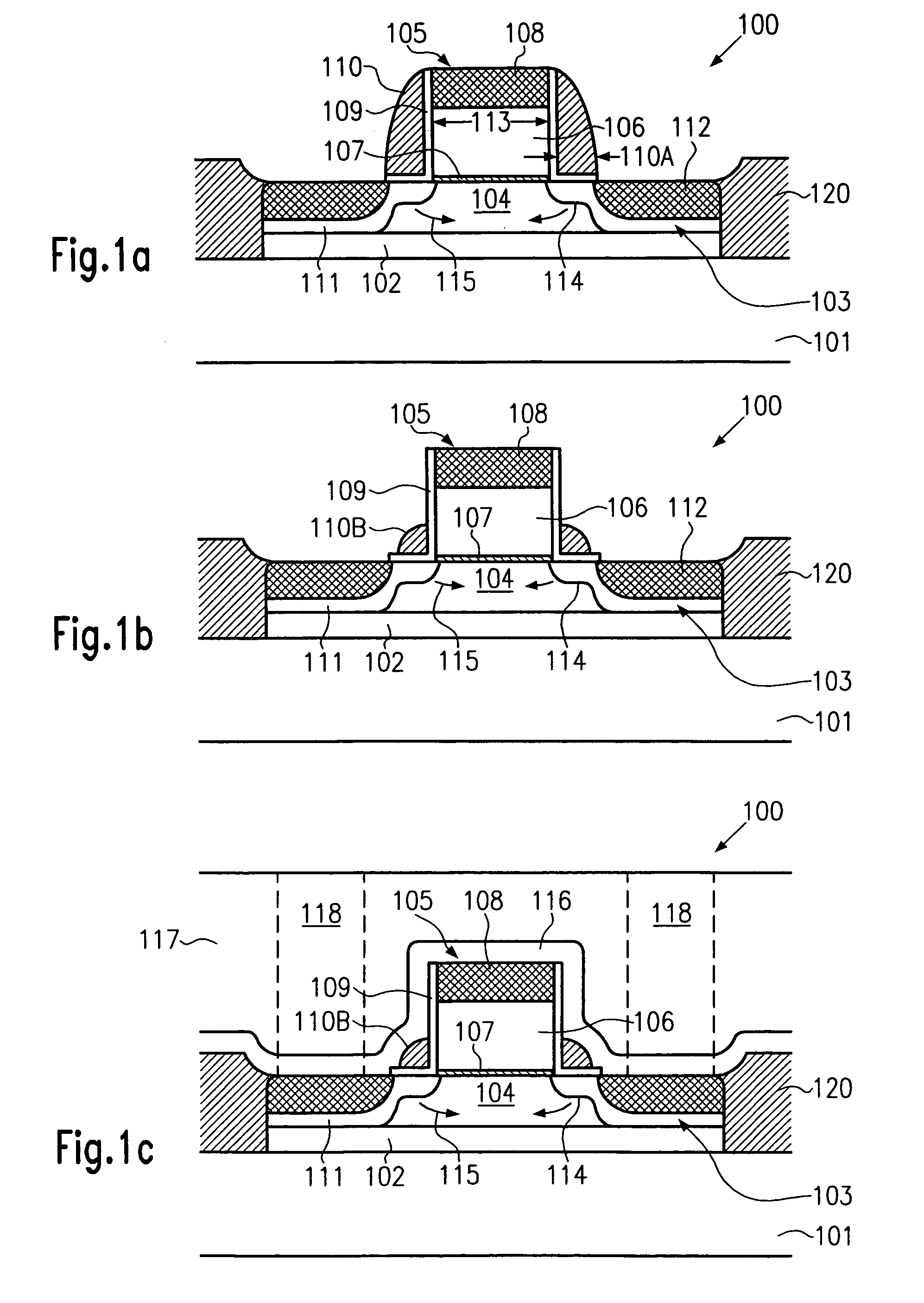
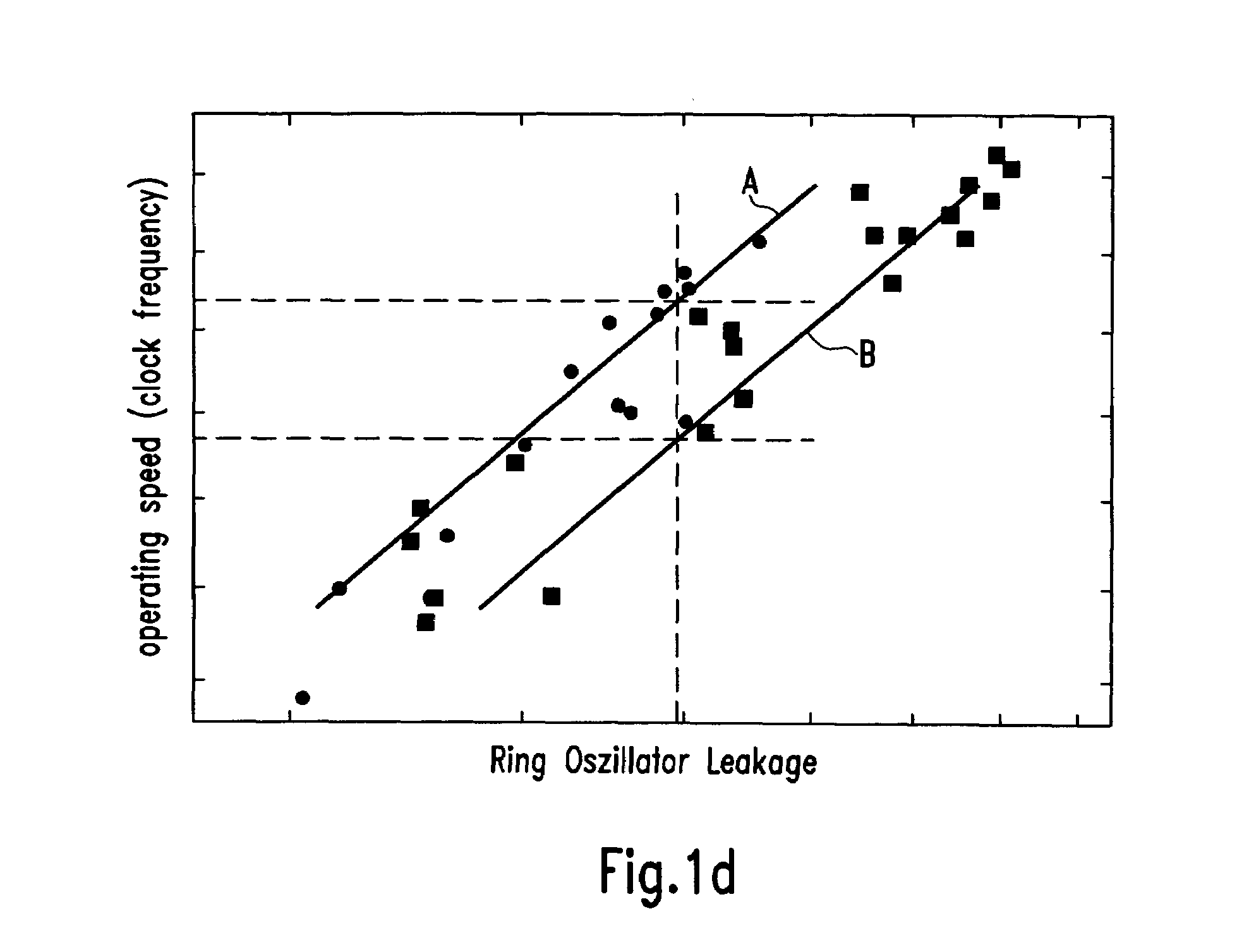
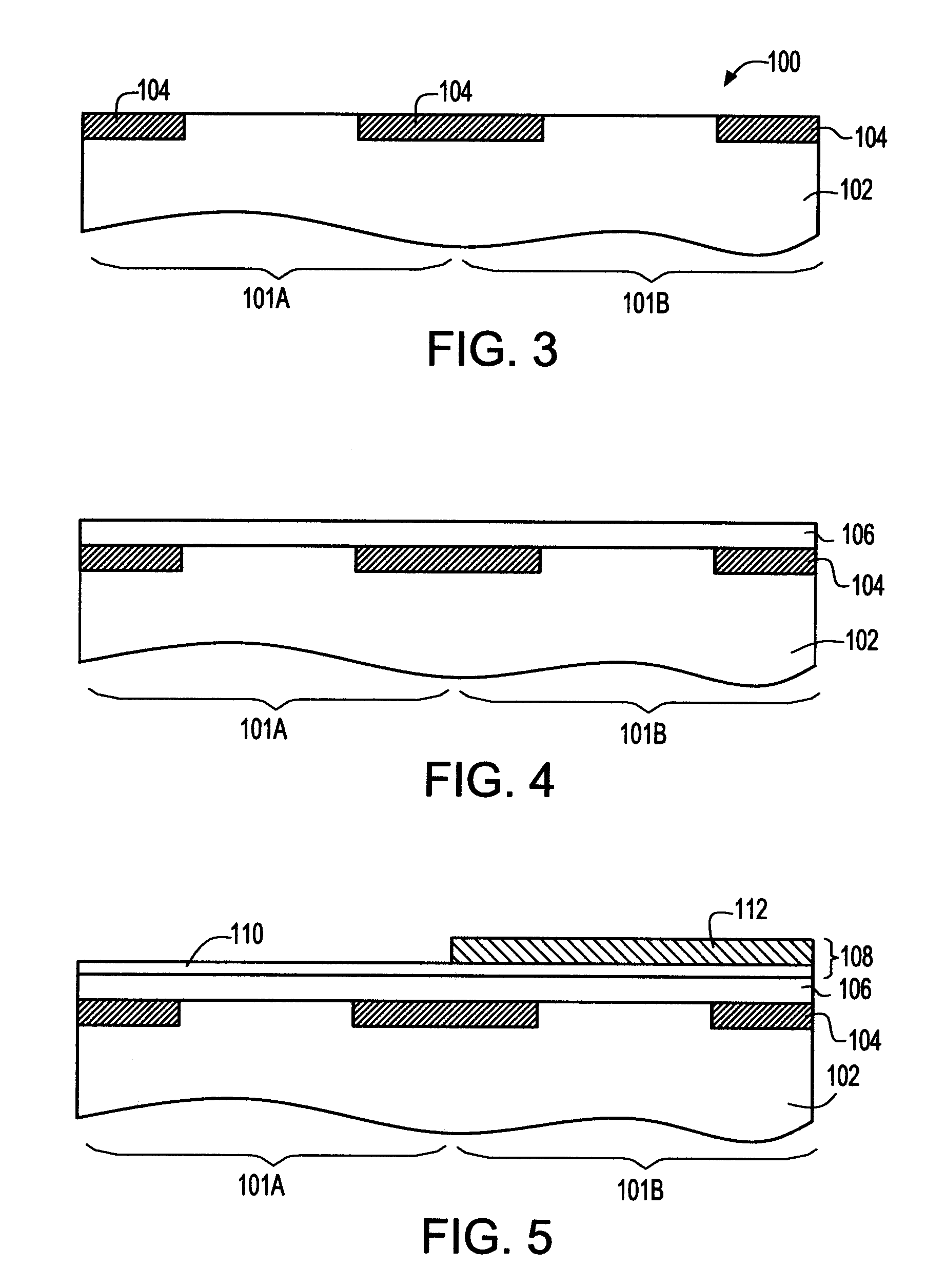
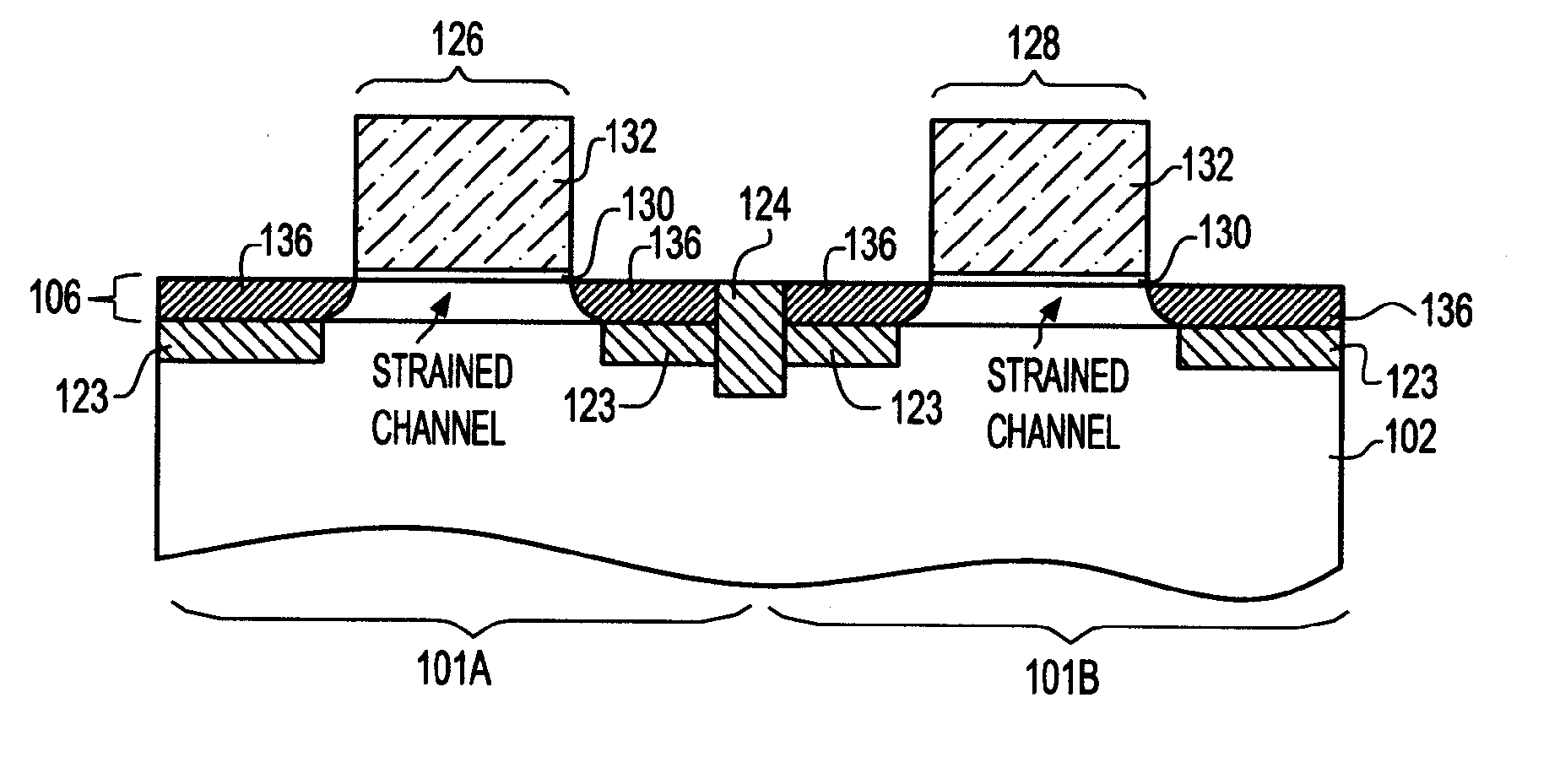
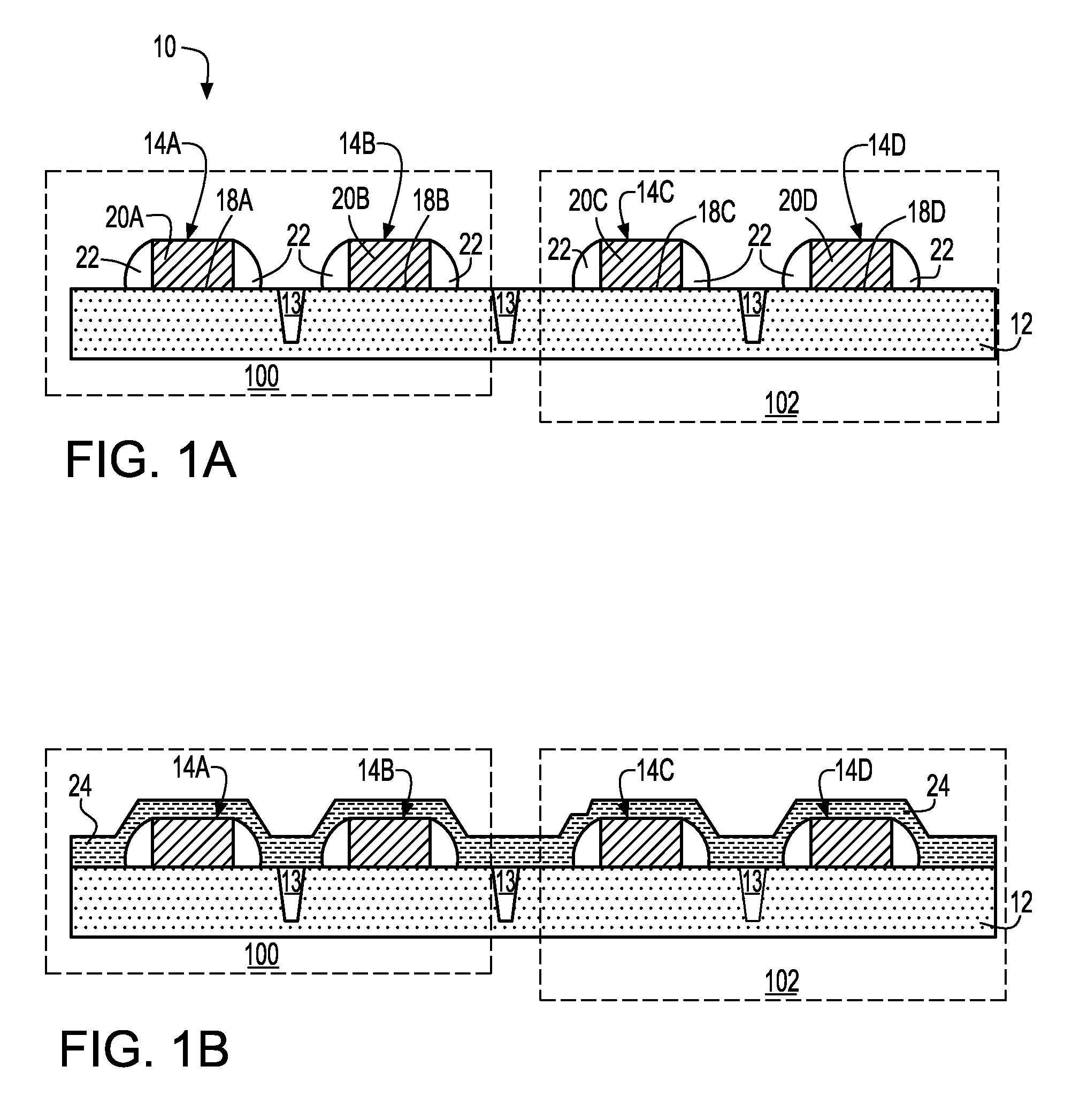
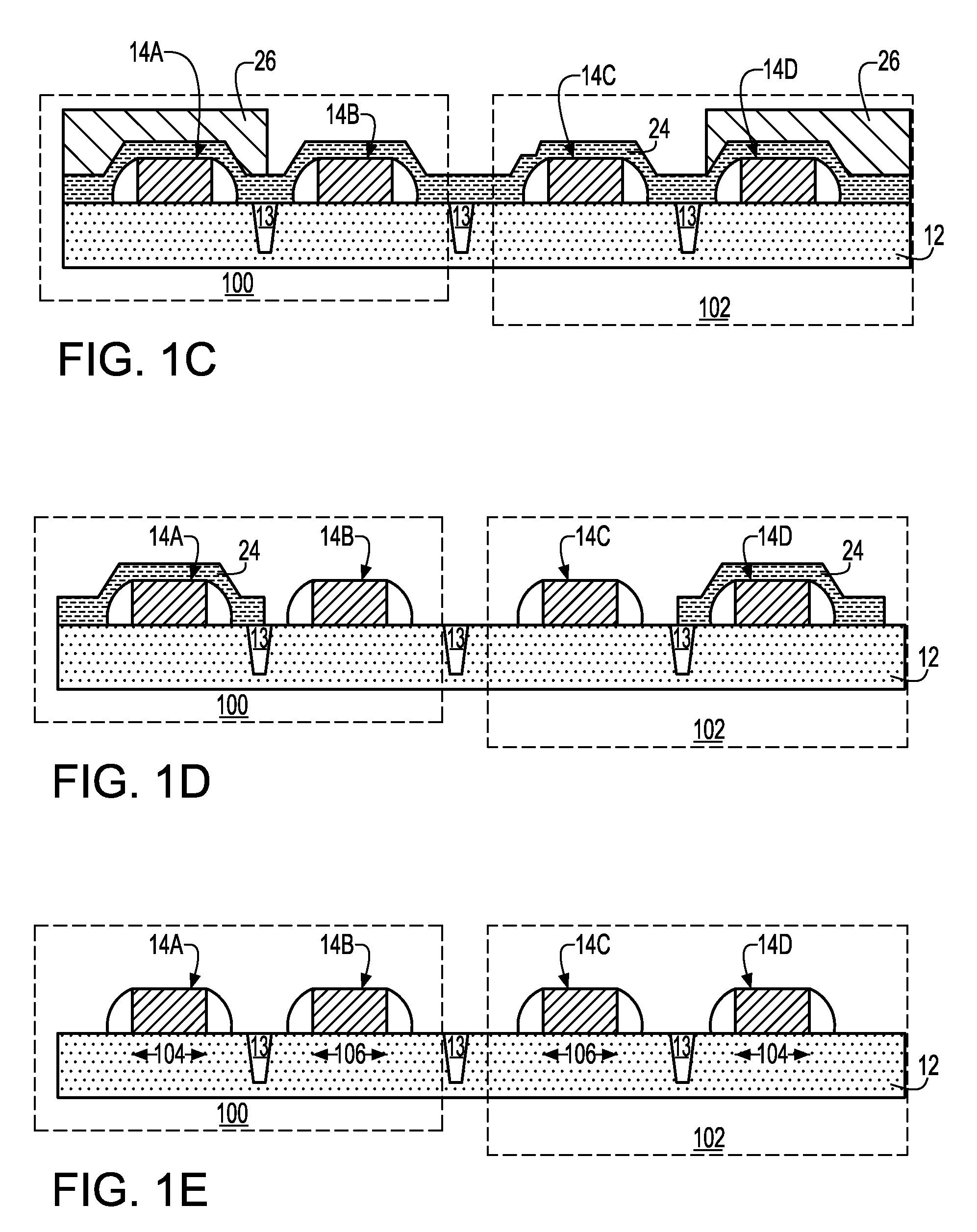
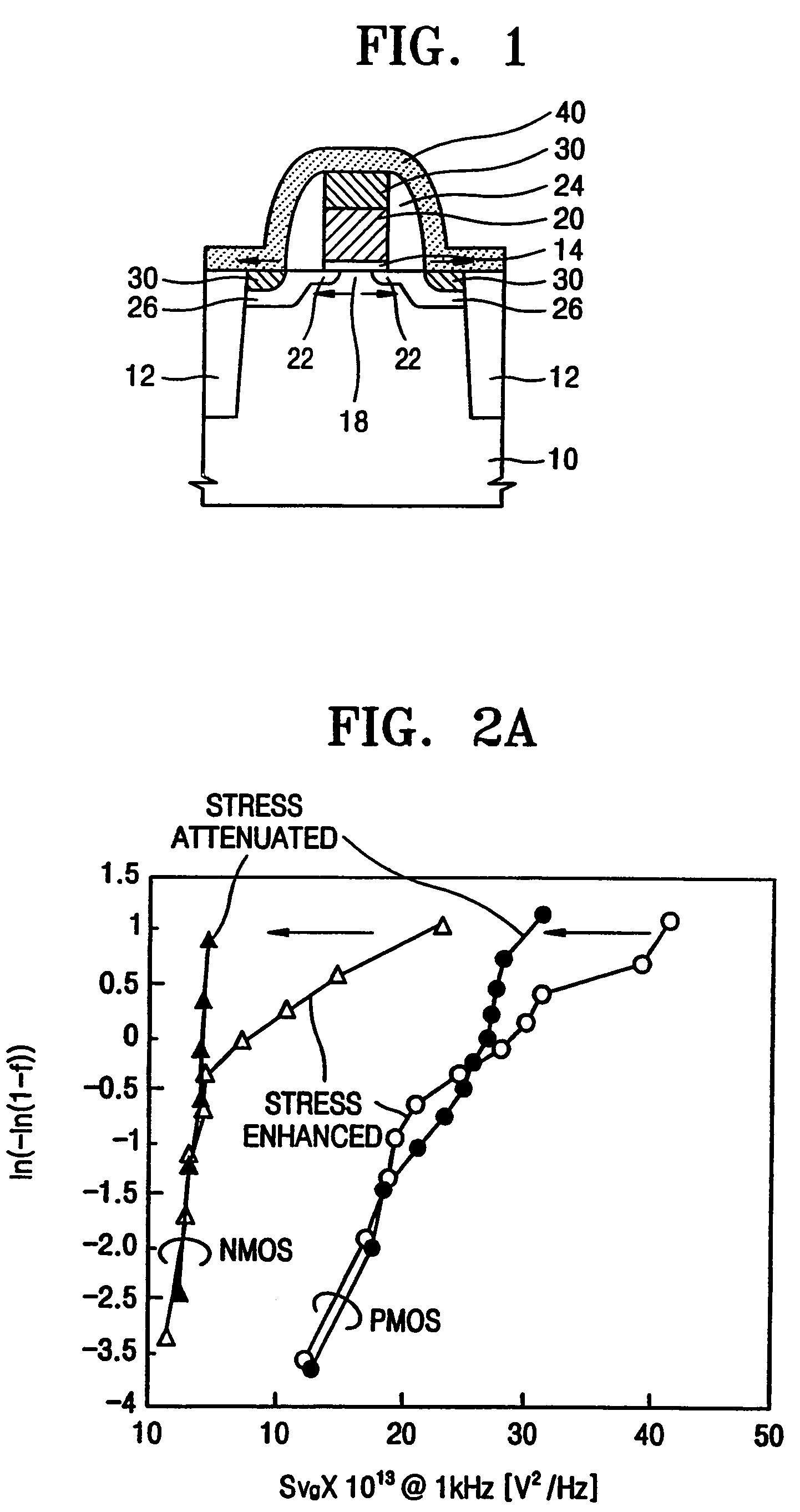
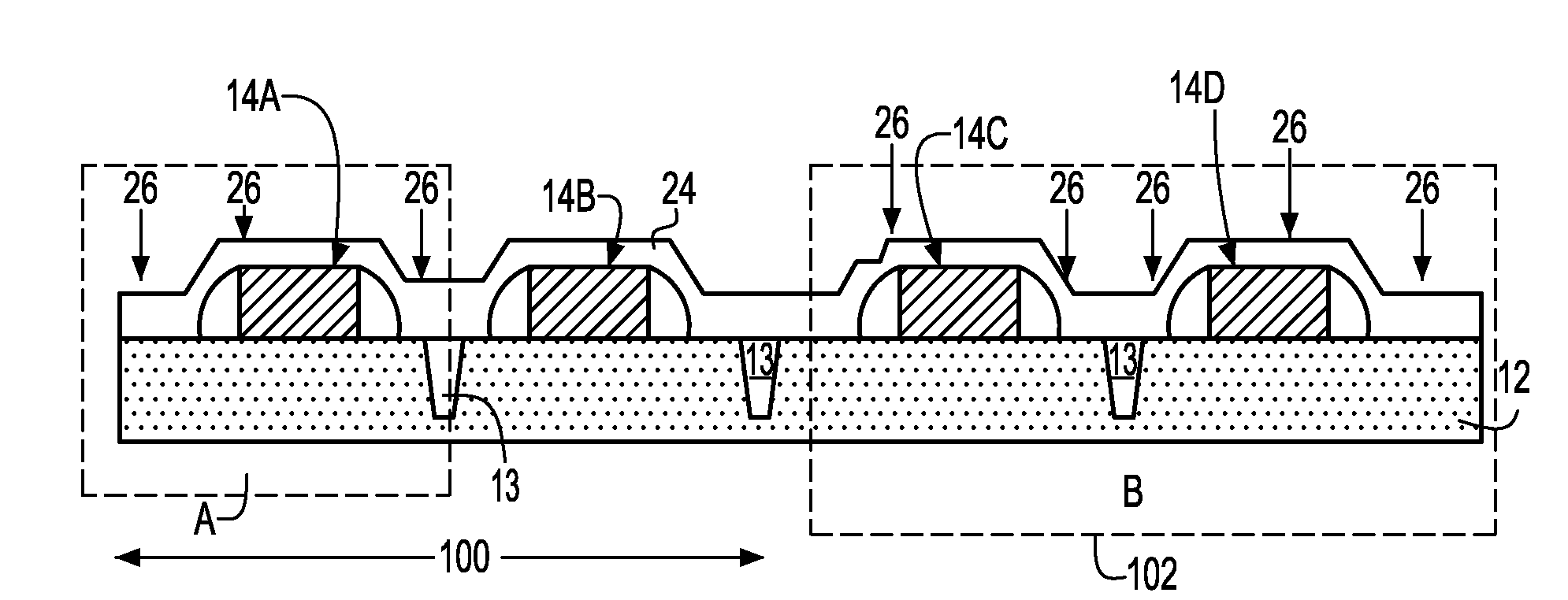
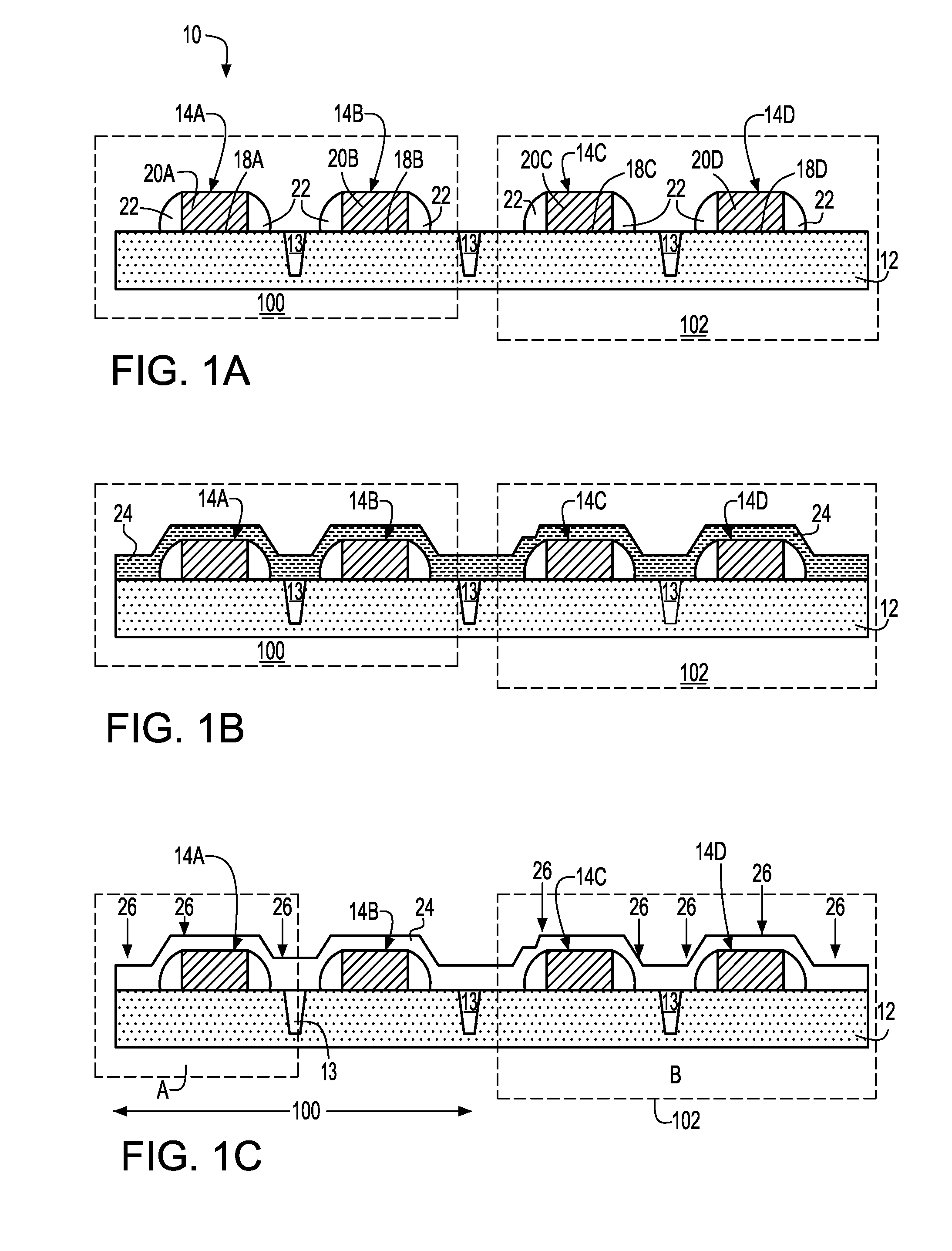
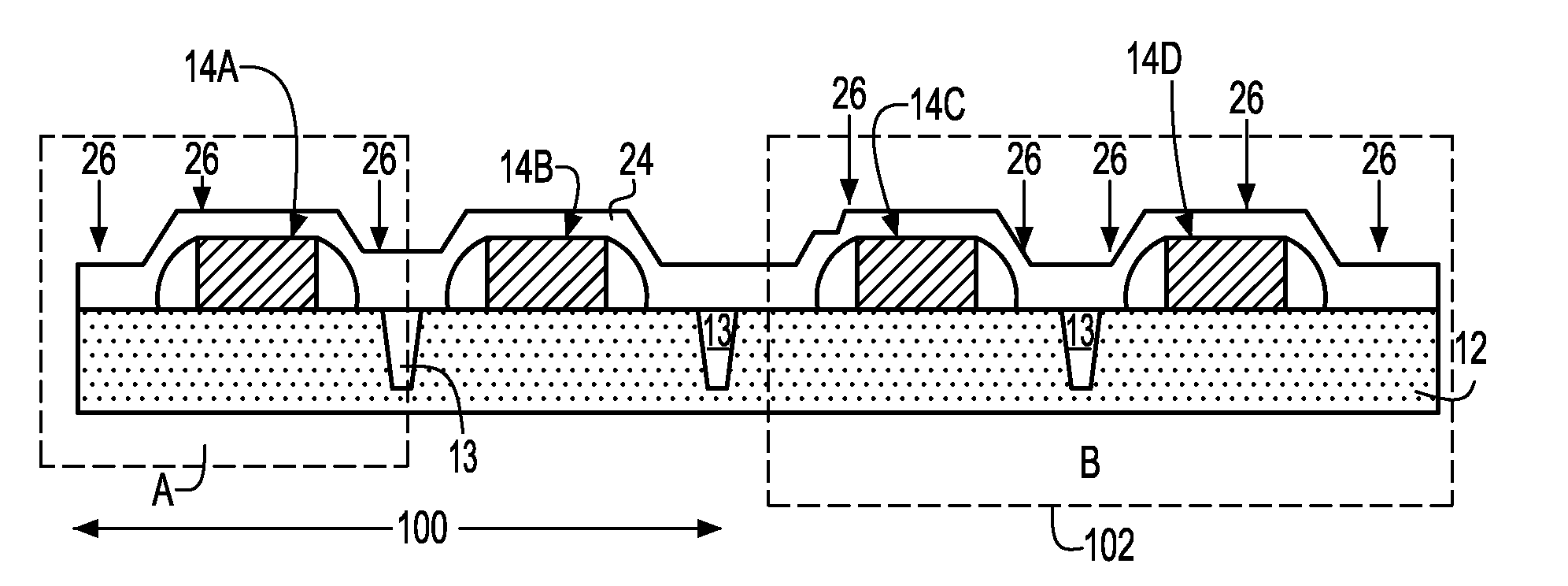
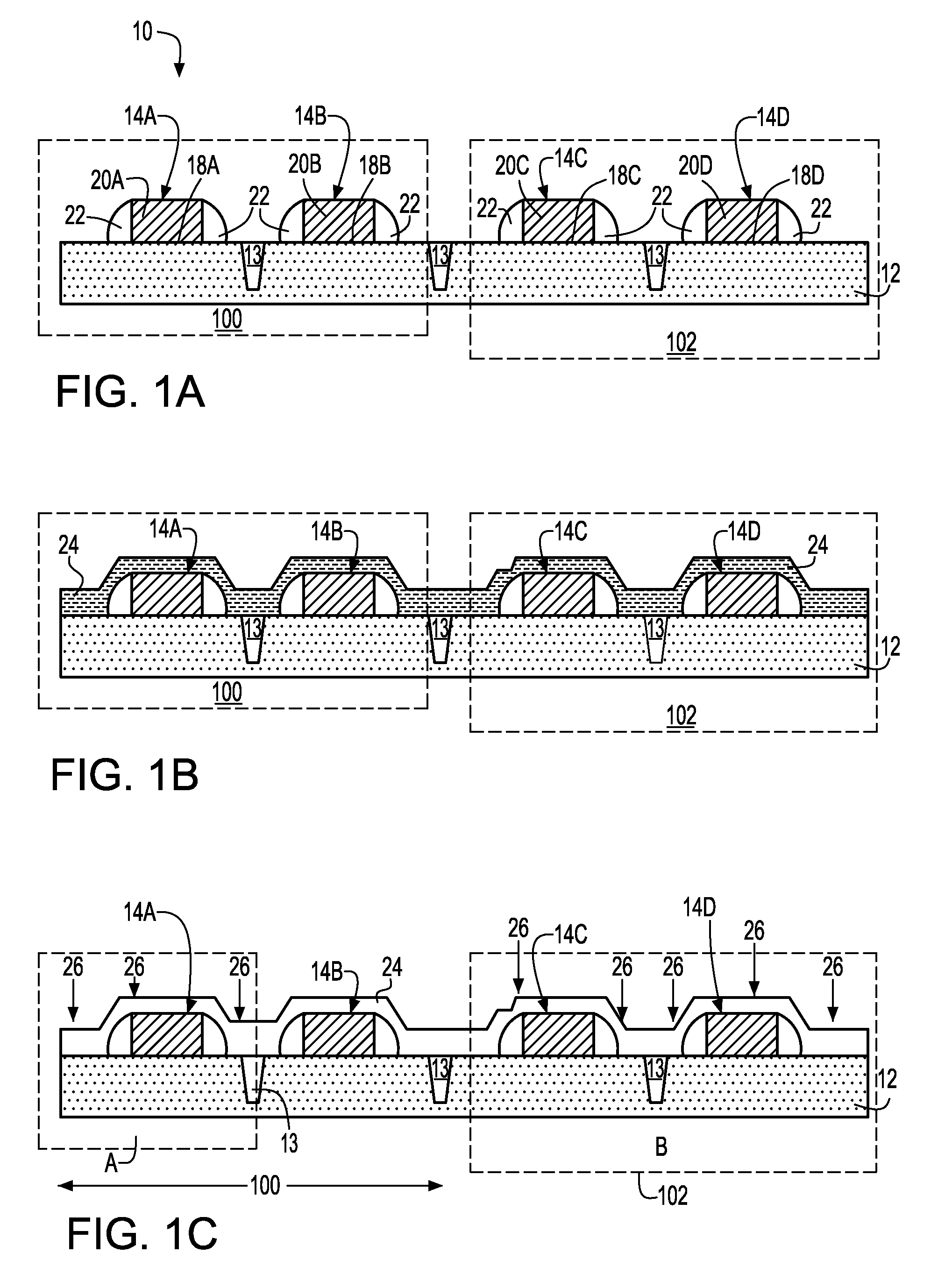
Method to control source/drain stressor profiles for stress engineering
ActiveUS20070235802A1Reduce duplicationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStress inducedGate dielectric
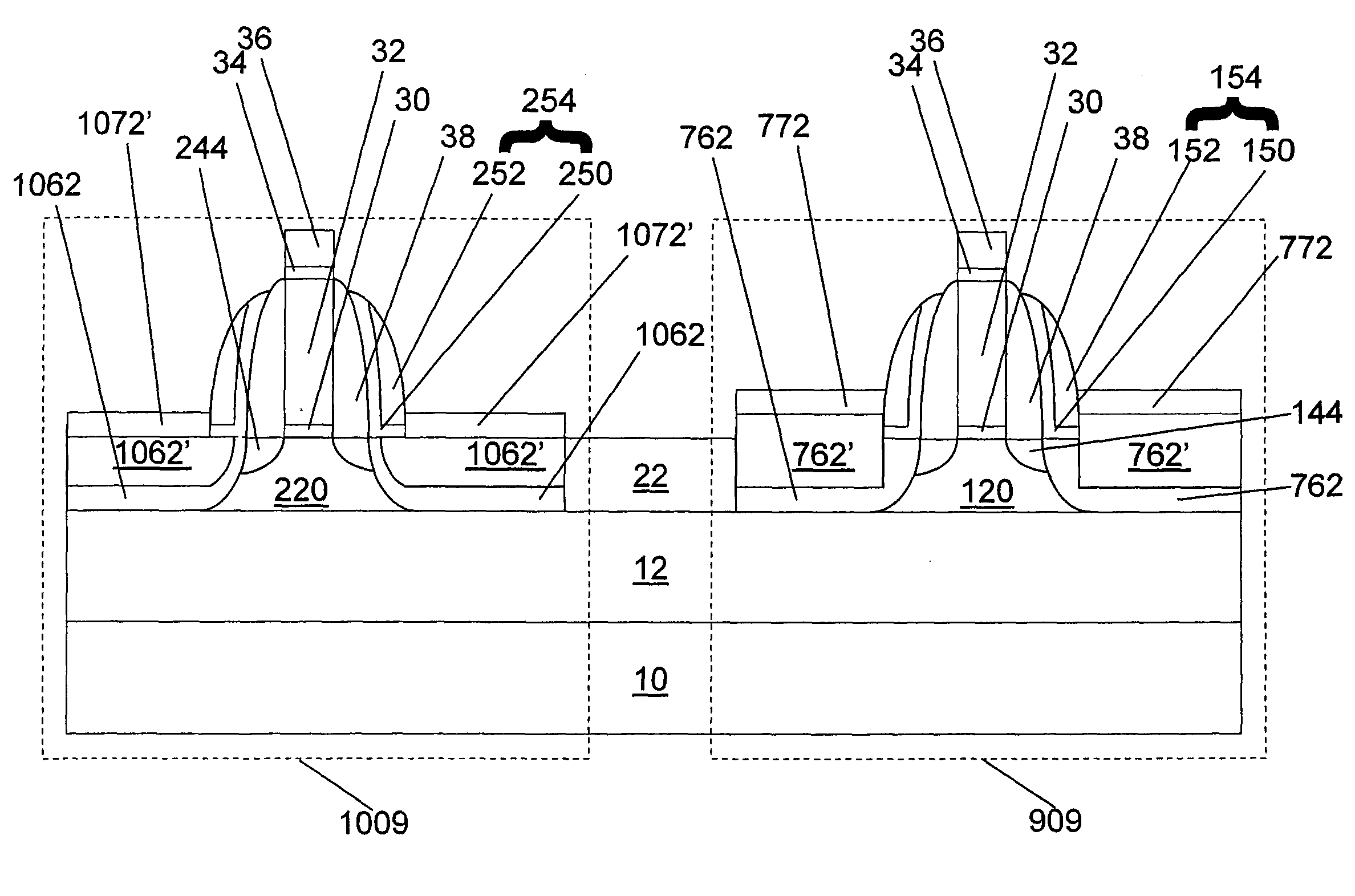
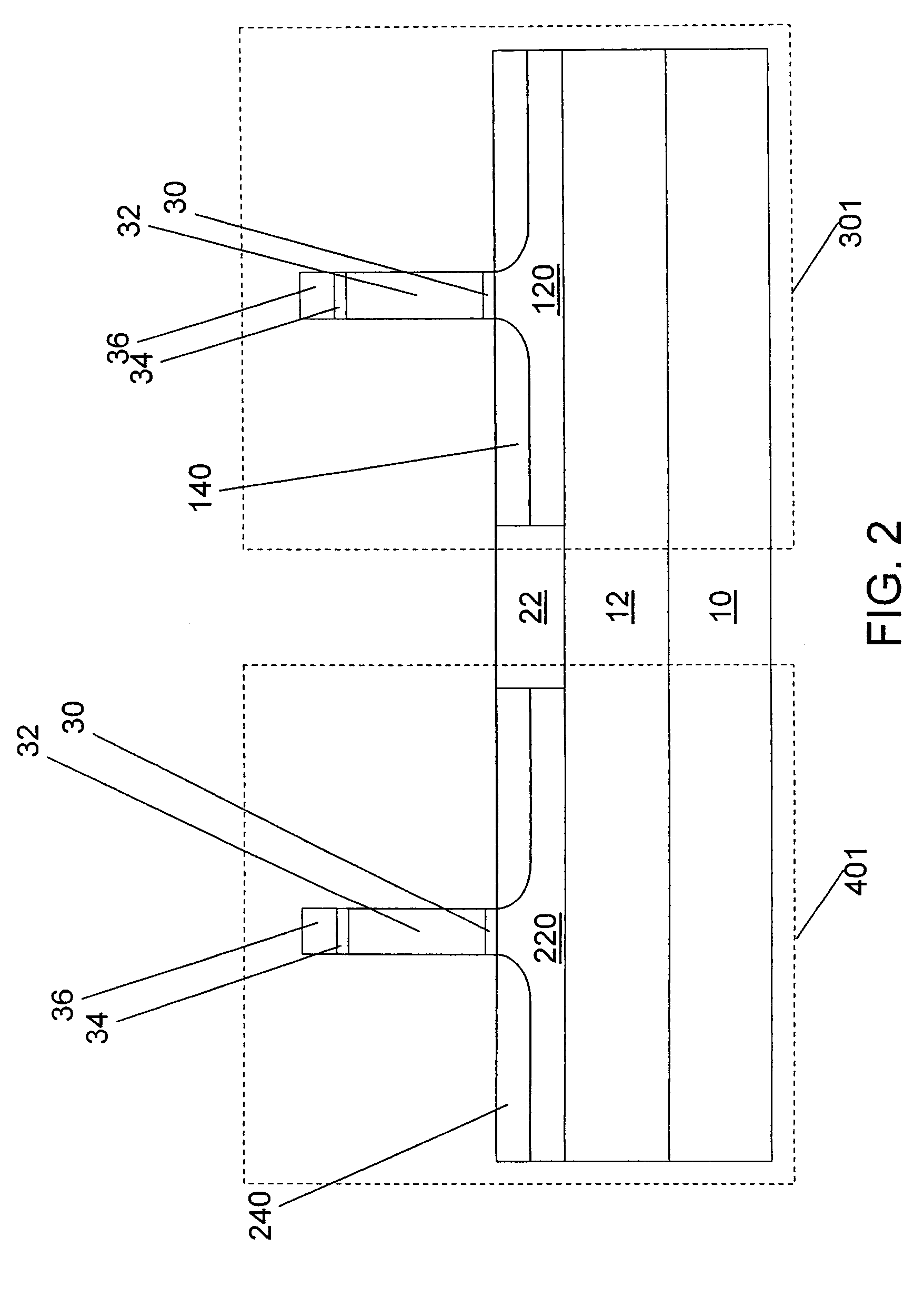
An example embodiment of a strained channel transistor structure comprises the following: a strained channel region comprising a first semiconductor material with a first natural lattice constant; a gate dielectric layer overlying the strained channel region; a gate electrode overlying the gate dielectric layer; and a source region and drain region oppositely adjacent to the strained channel region, one or both of the source region and drain region are comprised of a stressor region comprised of a second semiconductor material with a second natural lattice constant different from the first natural lattice constant; the stressor region has a graded concentration of a dopant impurity and / or of a stress inducing molecule. Another example embodiment is a process to form the graded impurity or stress inducing molecule stressor embedded S / D region, whereby the location / profile of the S / D stressor is not defined by the recess depth / profile.
Owner:IBM CORP +2
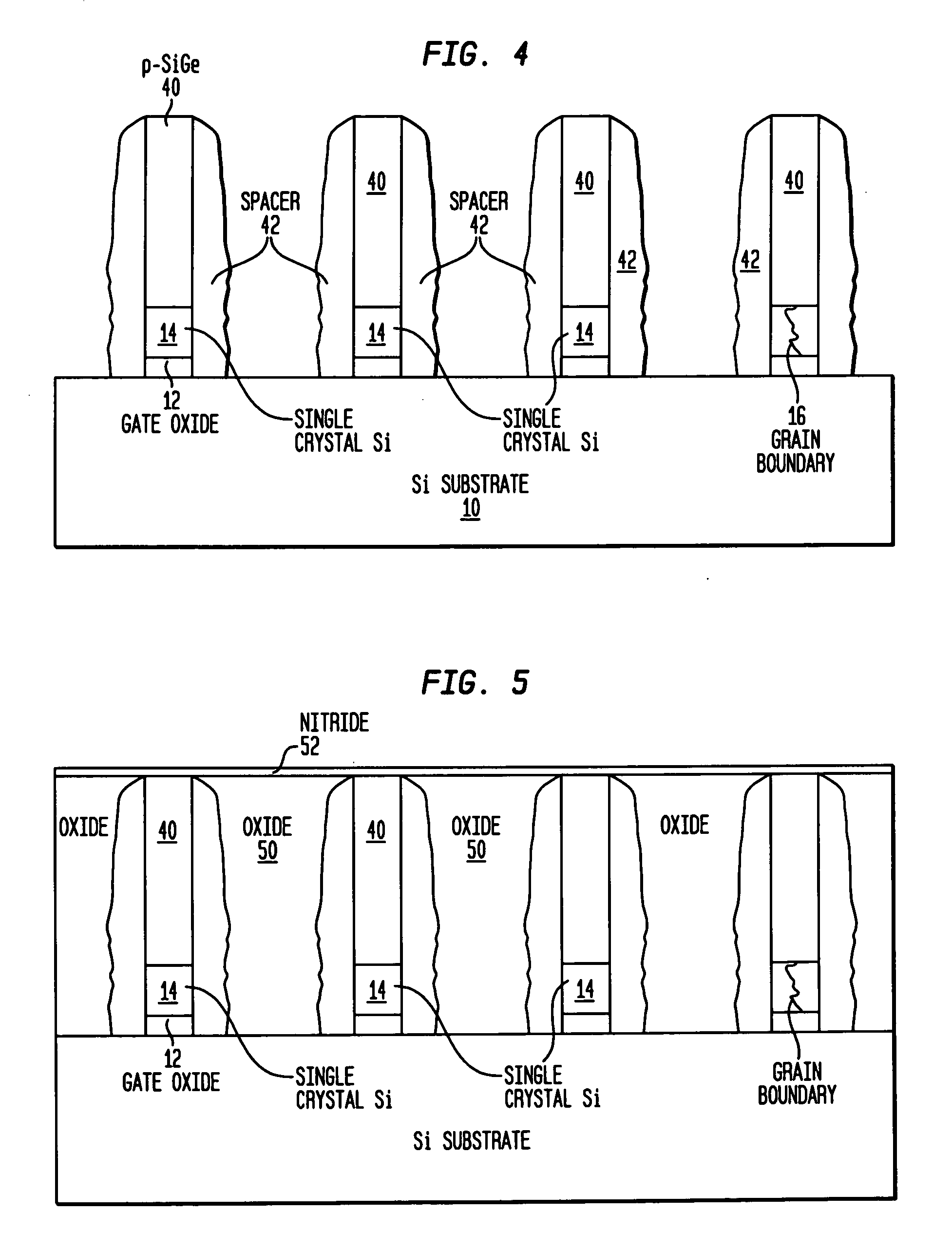
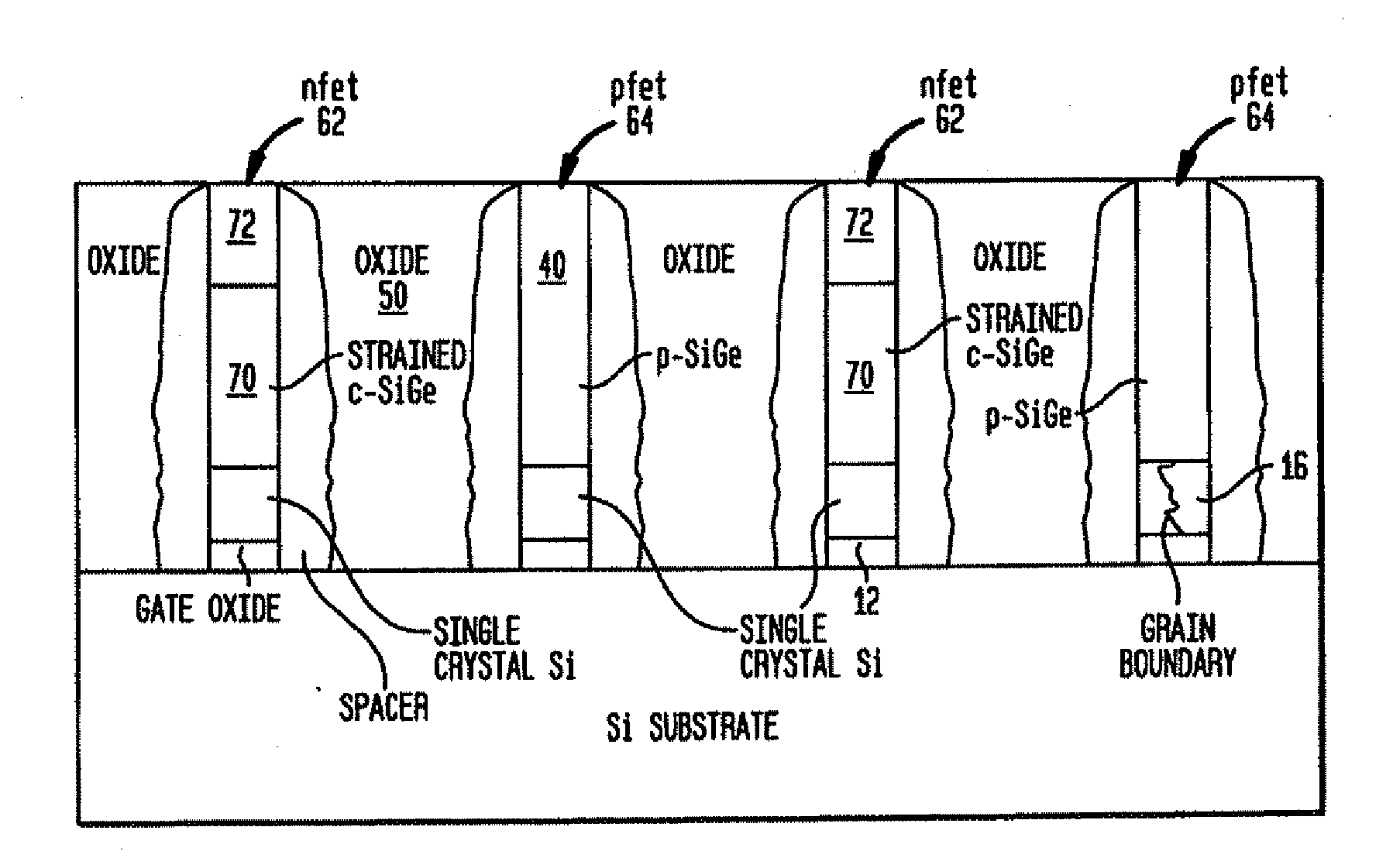
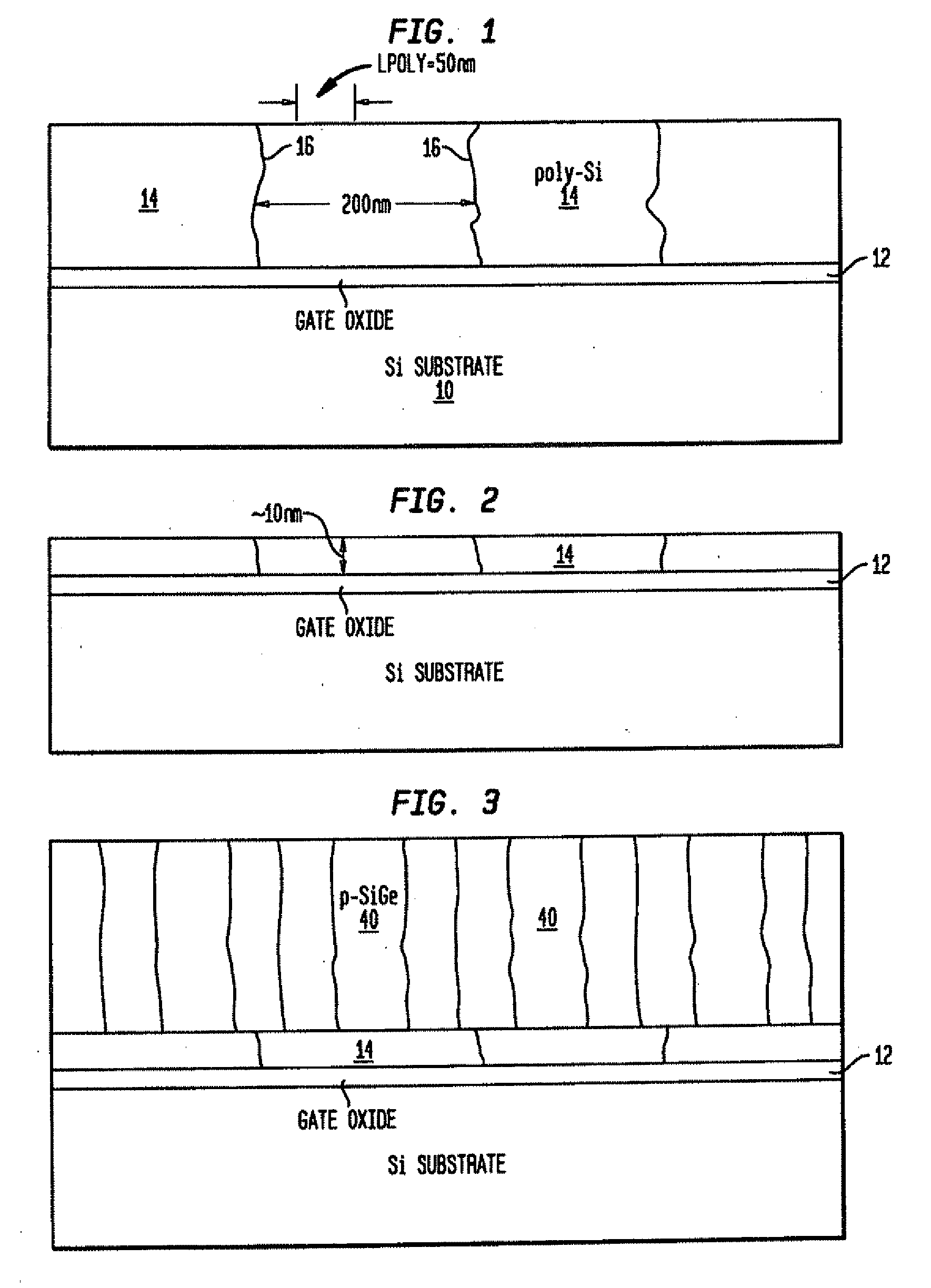
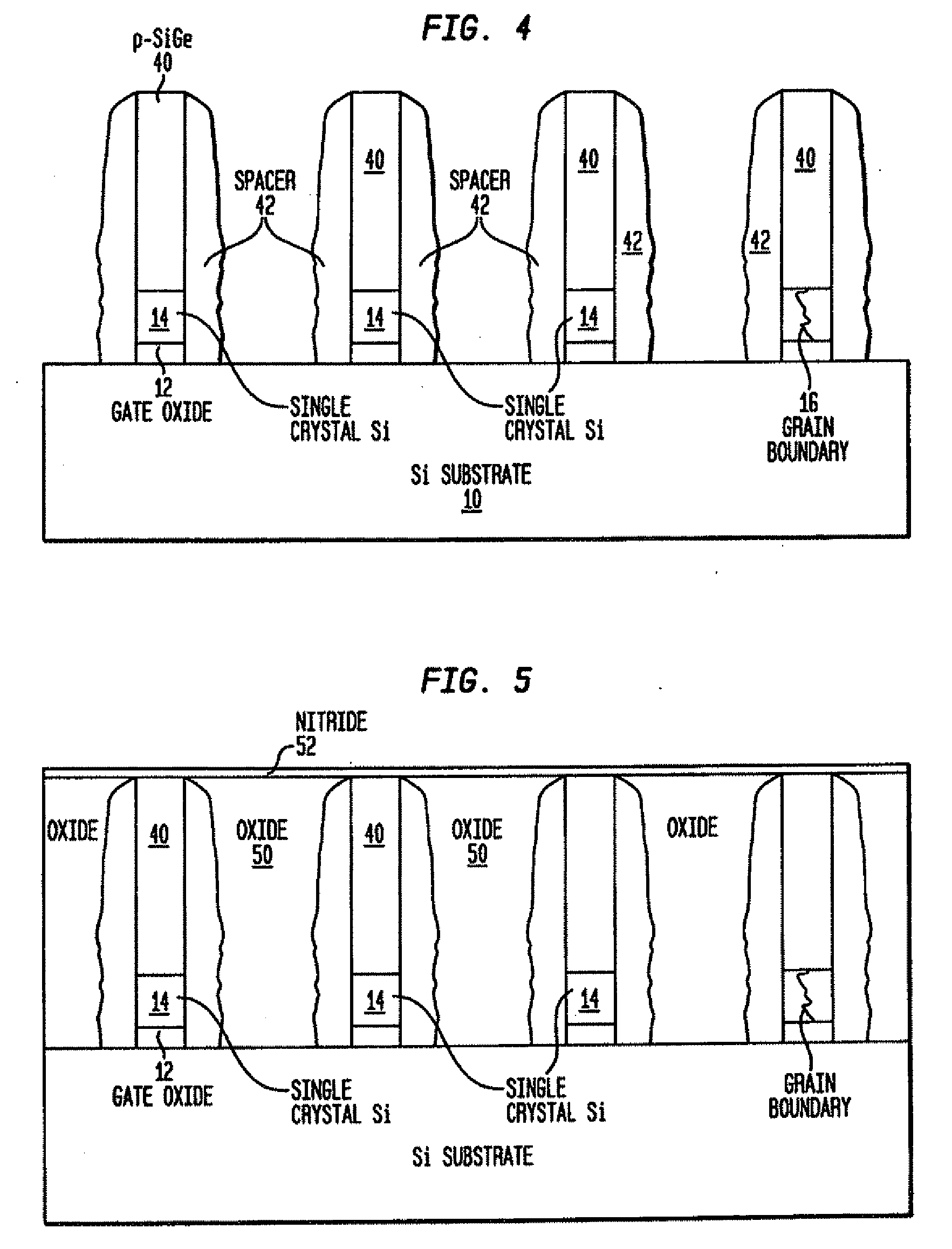
STRUCTURES AND METHODS FOR MANUFACTURING OF DISLOCATION FREE STRESSED CHANNELS IN BULK SILICON AND SOI CMOS DEVICES BY GATE STRESS ENGINEERING WITH SiGe AND/OR Si:C
ActiveUS20050236668A1Avoid misalignmentReduce generationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSoi cmosCMOS
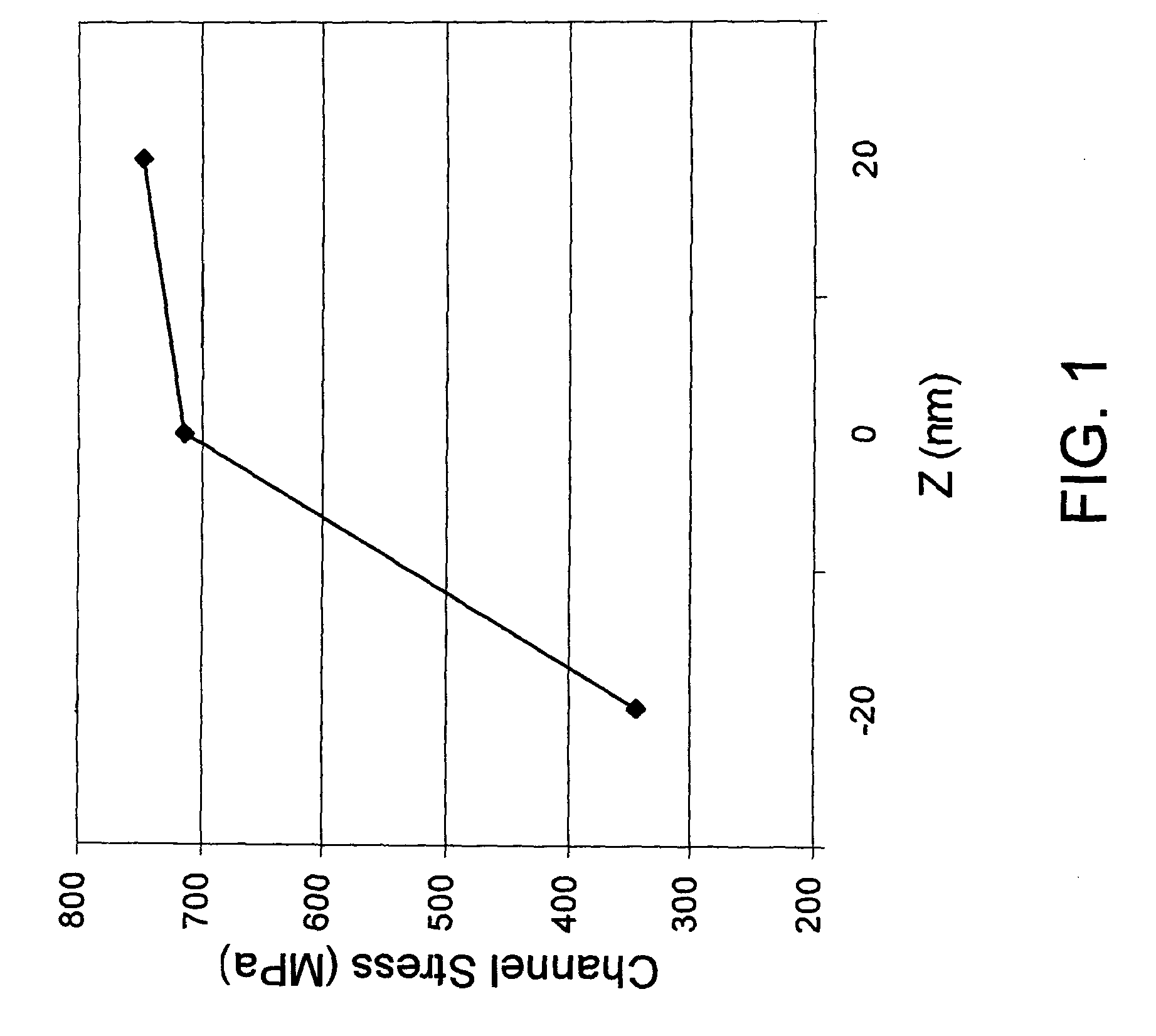
Structures and methods of manufacturing are disclosed of dislocation free stressed channels in bulk silicon and SOI (silicon on insulator) CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) devices by gate stress engineering with SiGe and / or Si:C. A CMOS device comprises a substrate of either bulk Si or SOI, a gate dielectric layer over the substrate, and a stacked gate structure of SiGe and / or Si:C having stresses produced at the interfaces of SSi(strained Si) / SiGe or SSi / Si:C in the stacked gate structure. The stacked gate structure has a first stressed film layer of large grain size Si or SiGe over the gate dielectric layer, a second stressed film layer of strained SiGe or strained Si:C over the first stressed film layer, and a semiconductor or conductor such as p(poly)-Si over the second stressed film layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
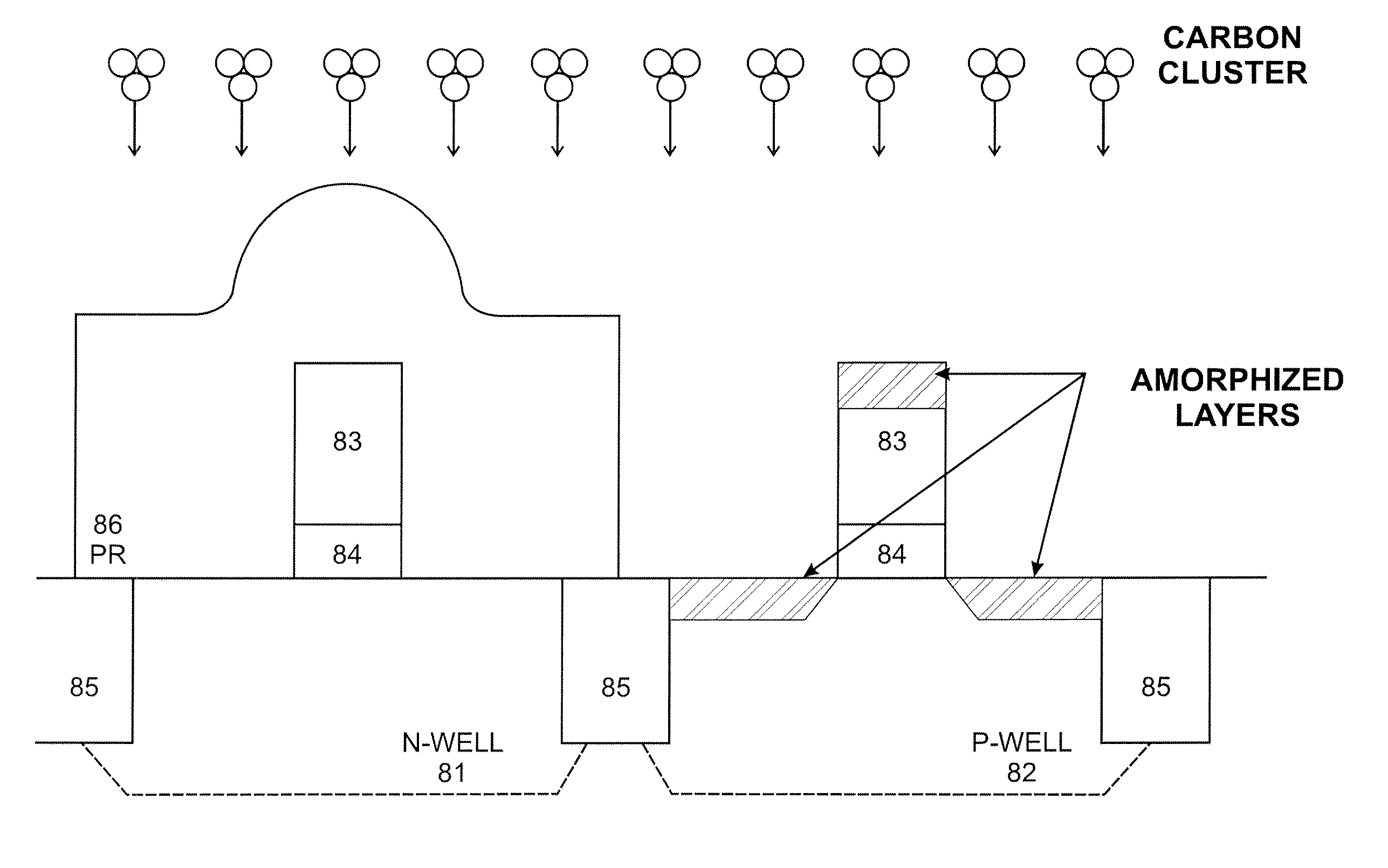
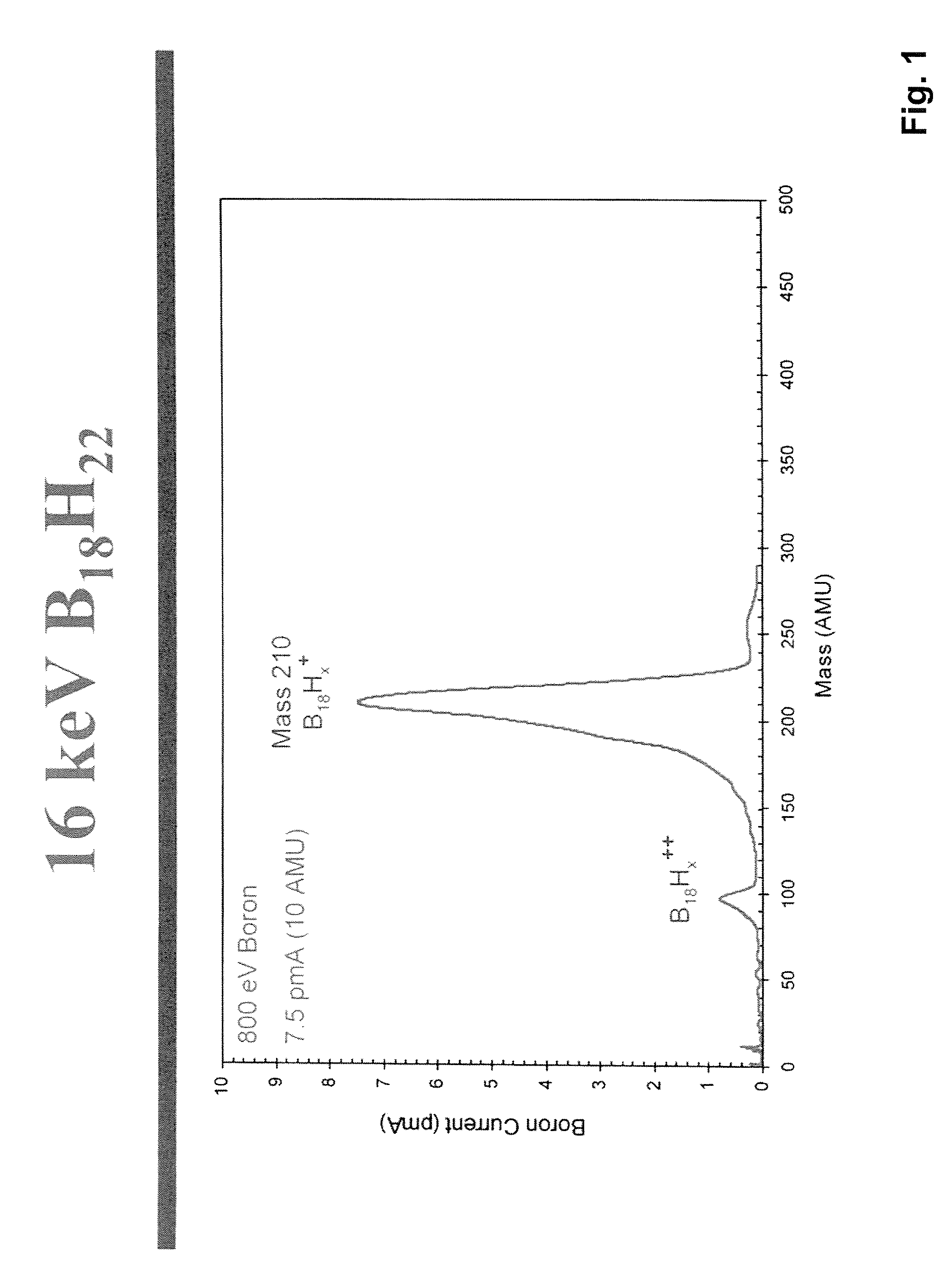
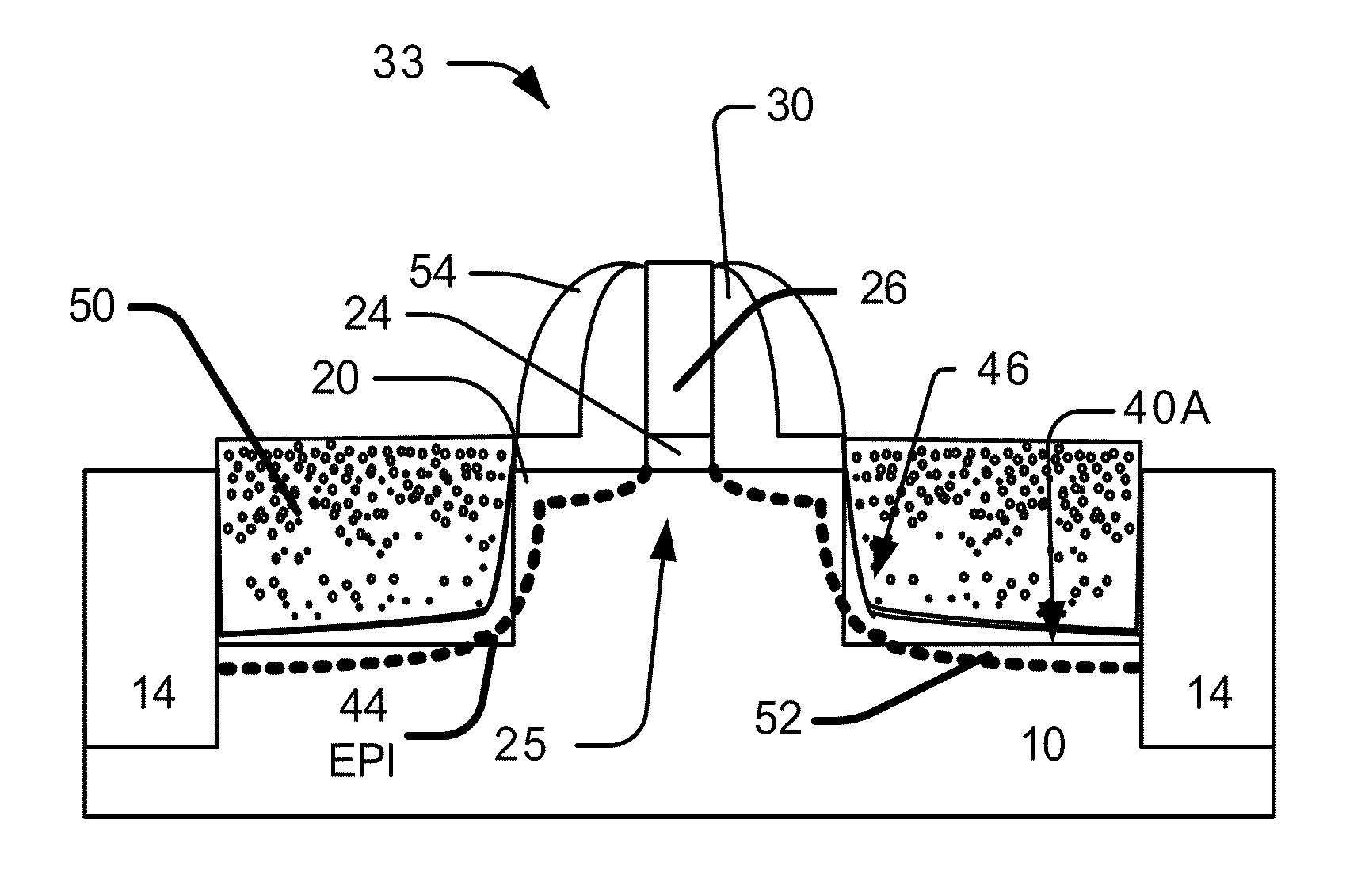
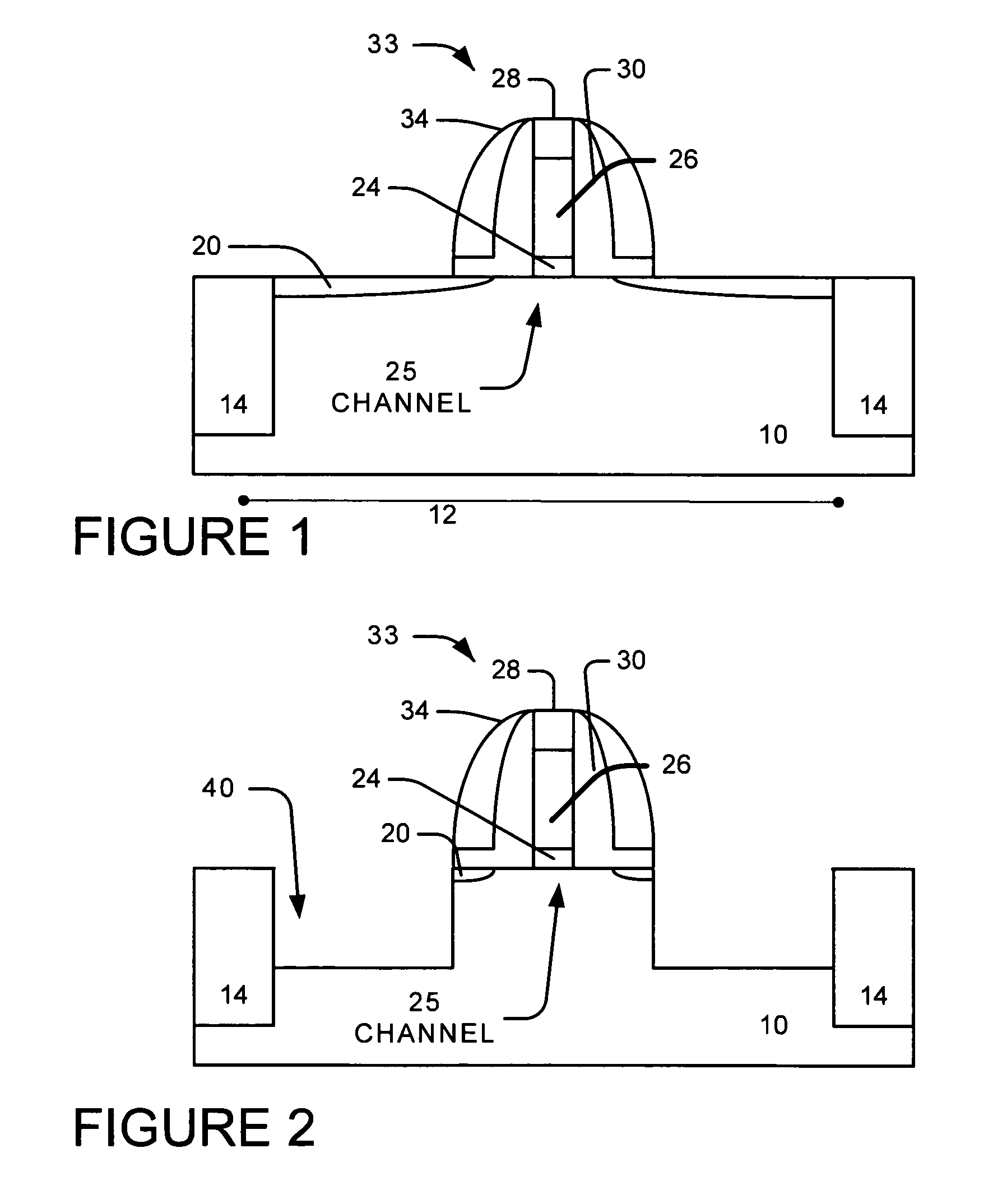
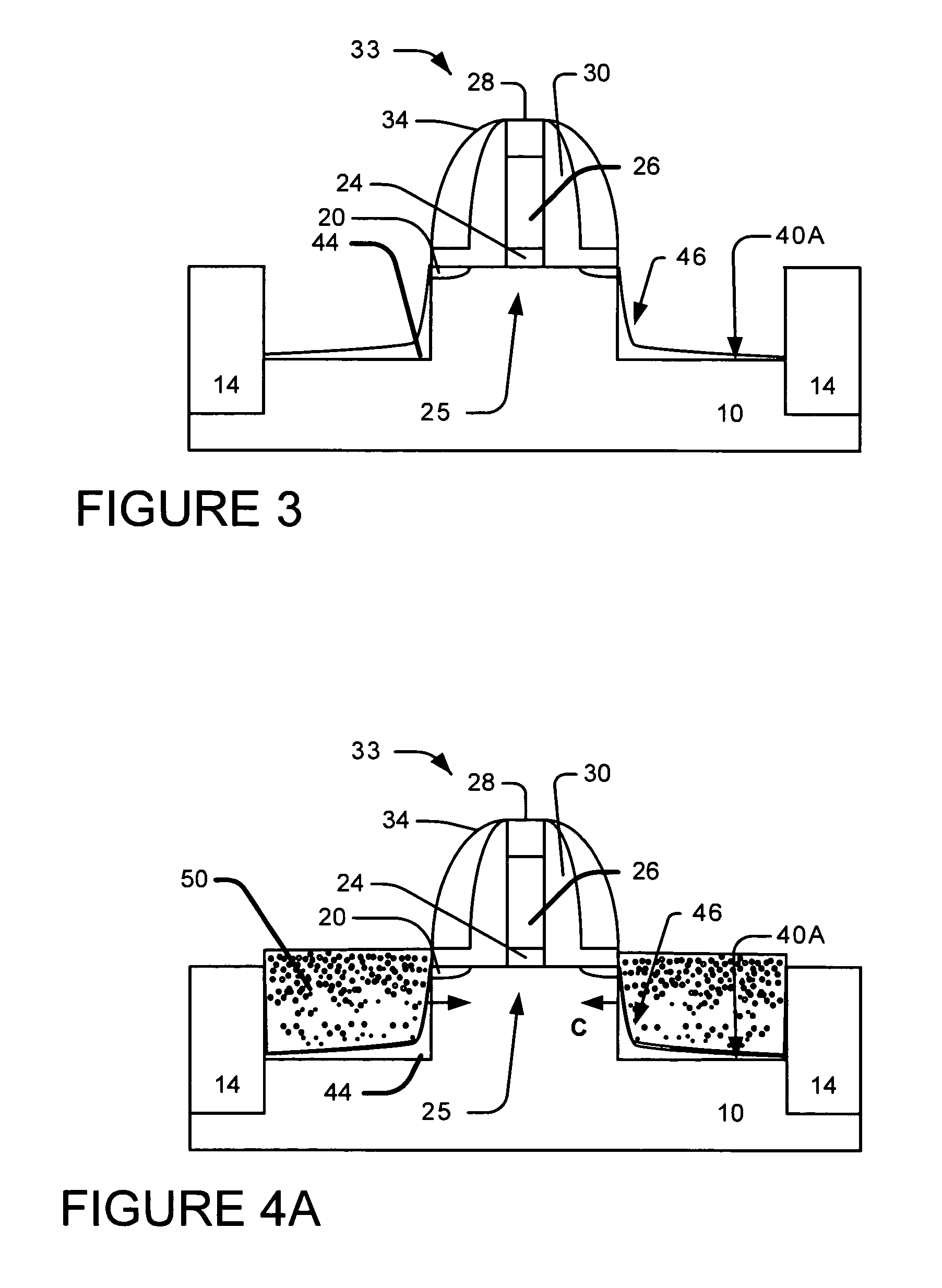
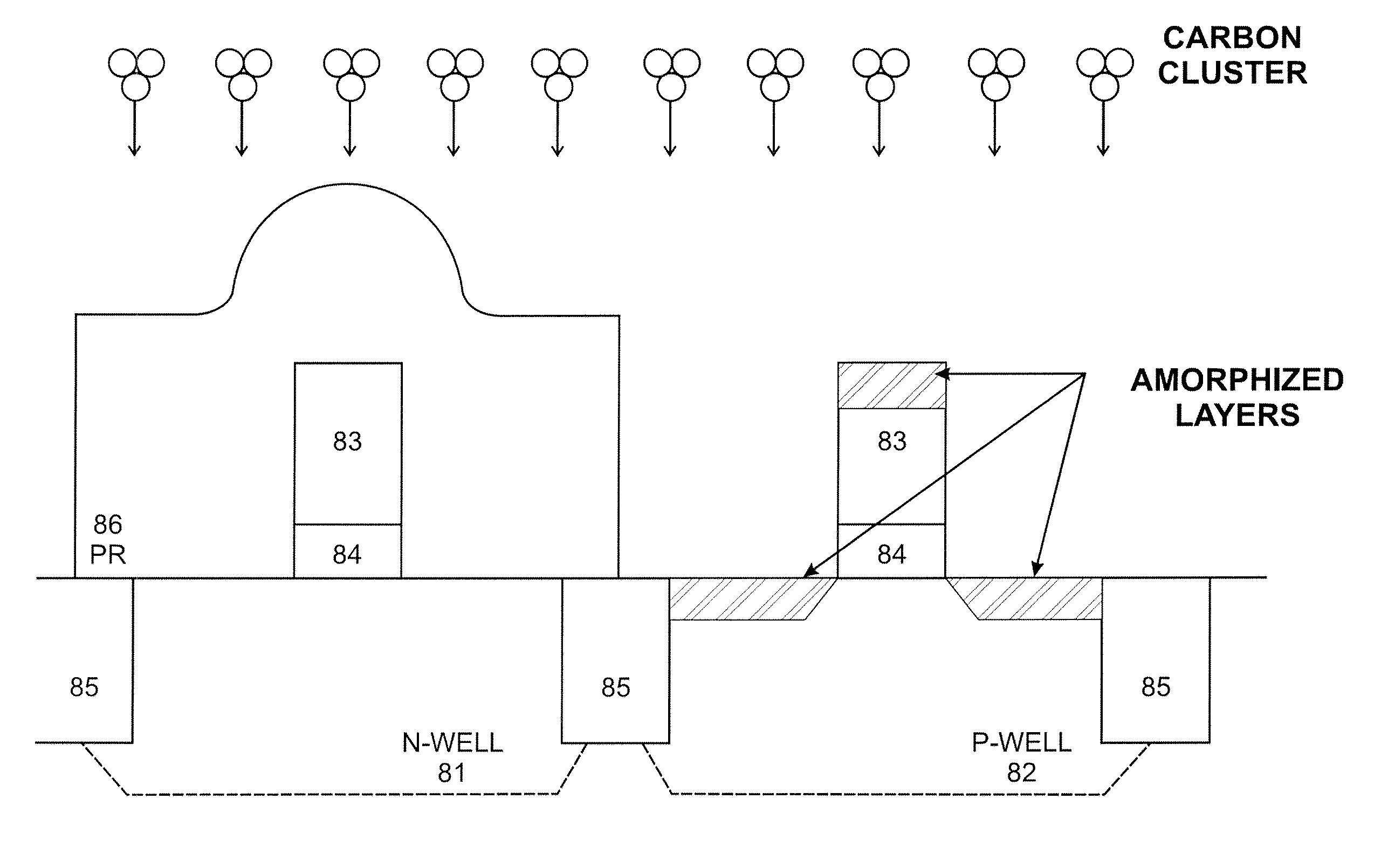
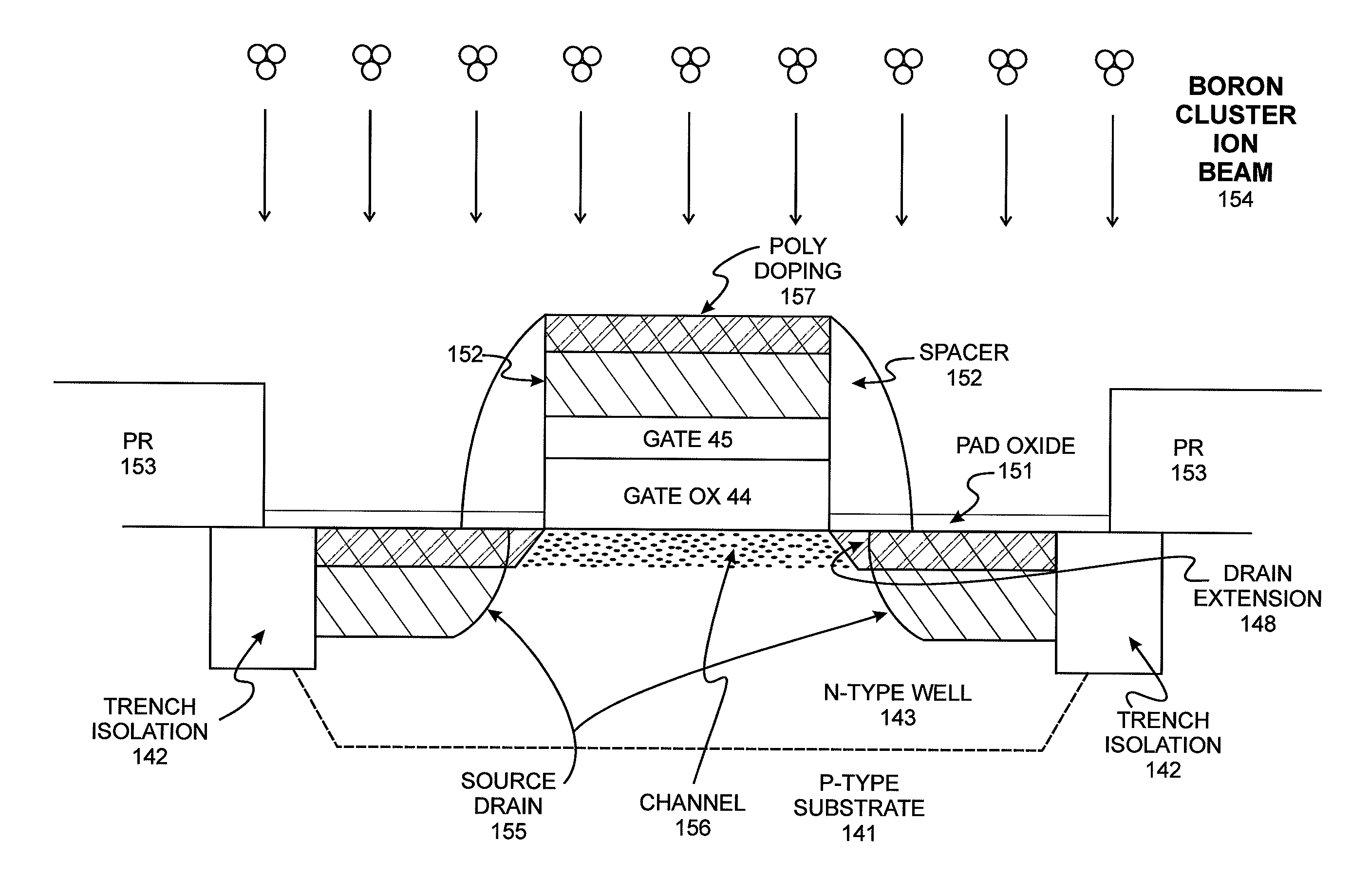
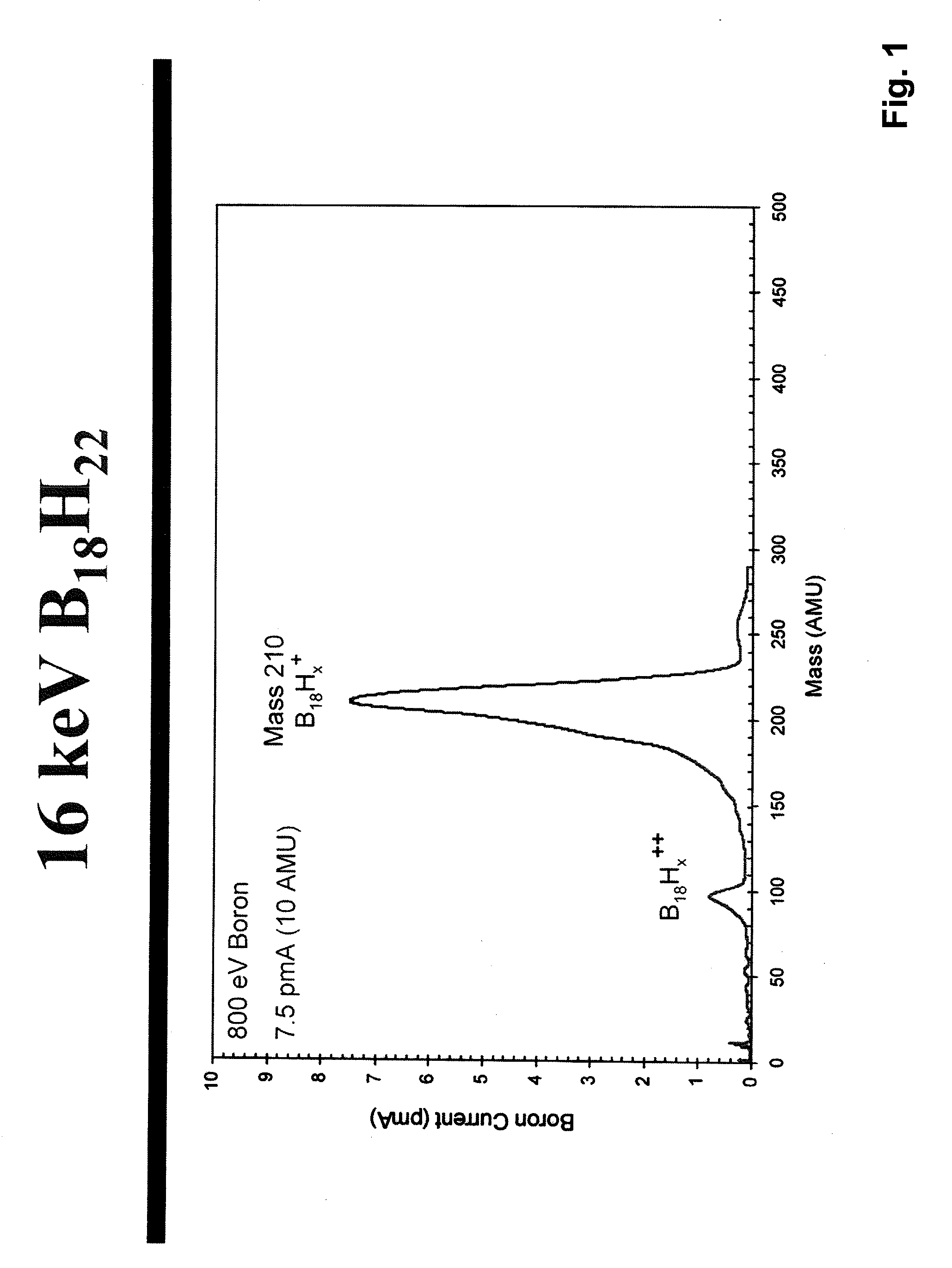
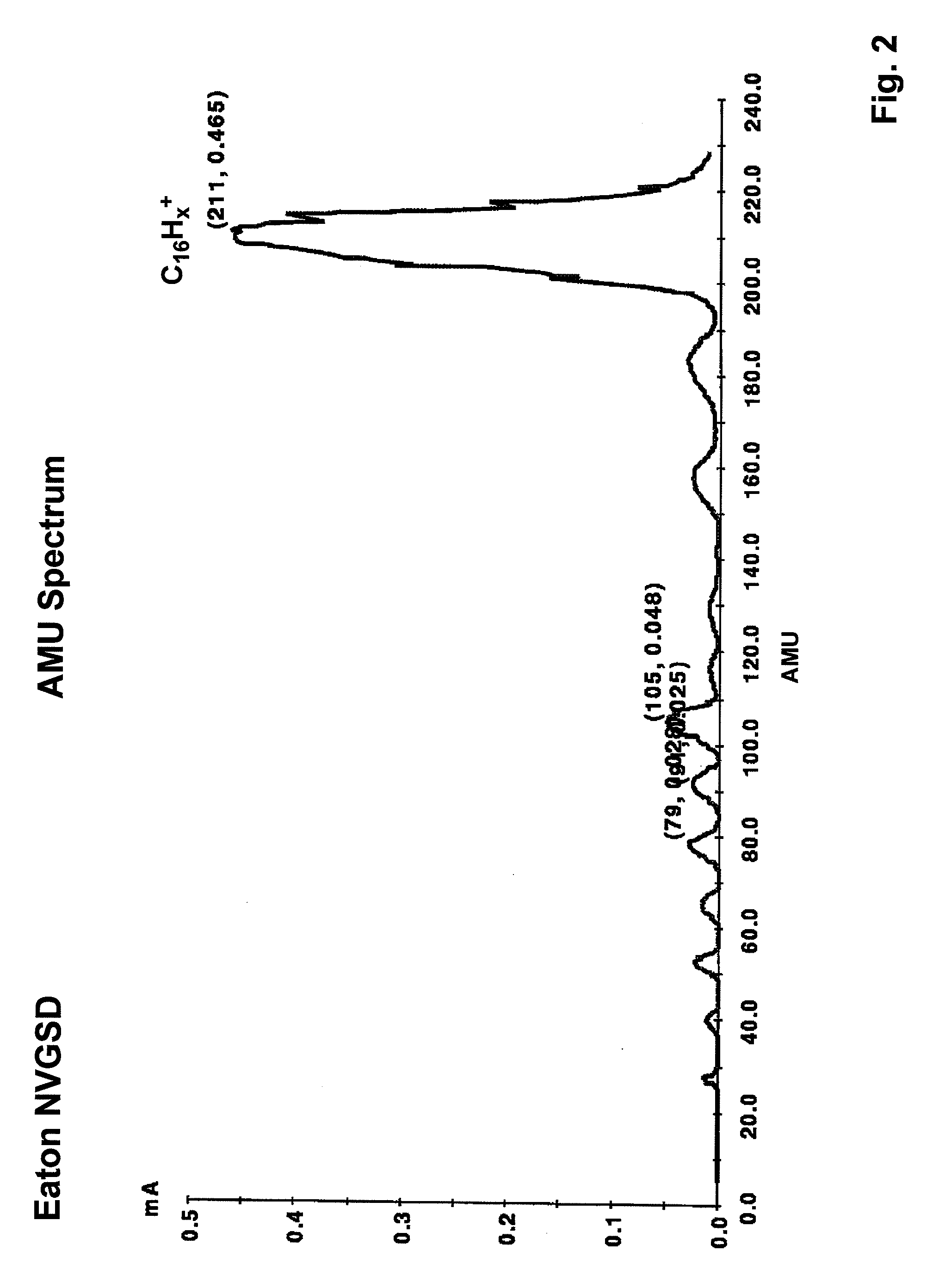
System and method for the manufacture of semiconductor devices by the implantation of carbon clusters
InactiveUS20070148888A1Improve productivityMinimize doseTransistorElectric discharge tubesDevice materialEngineering
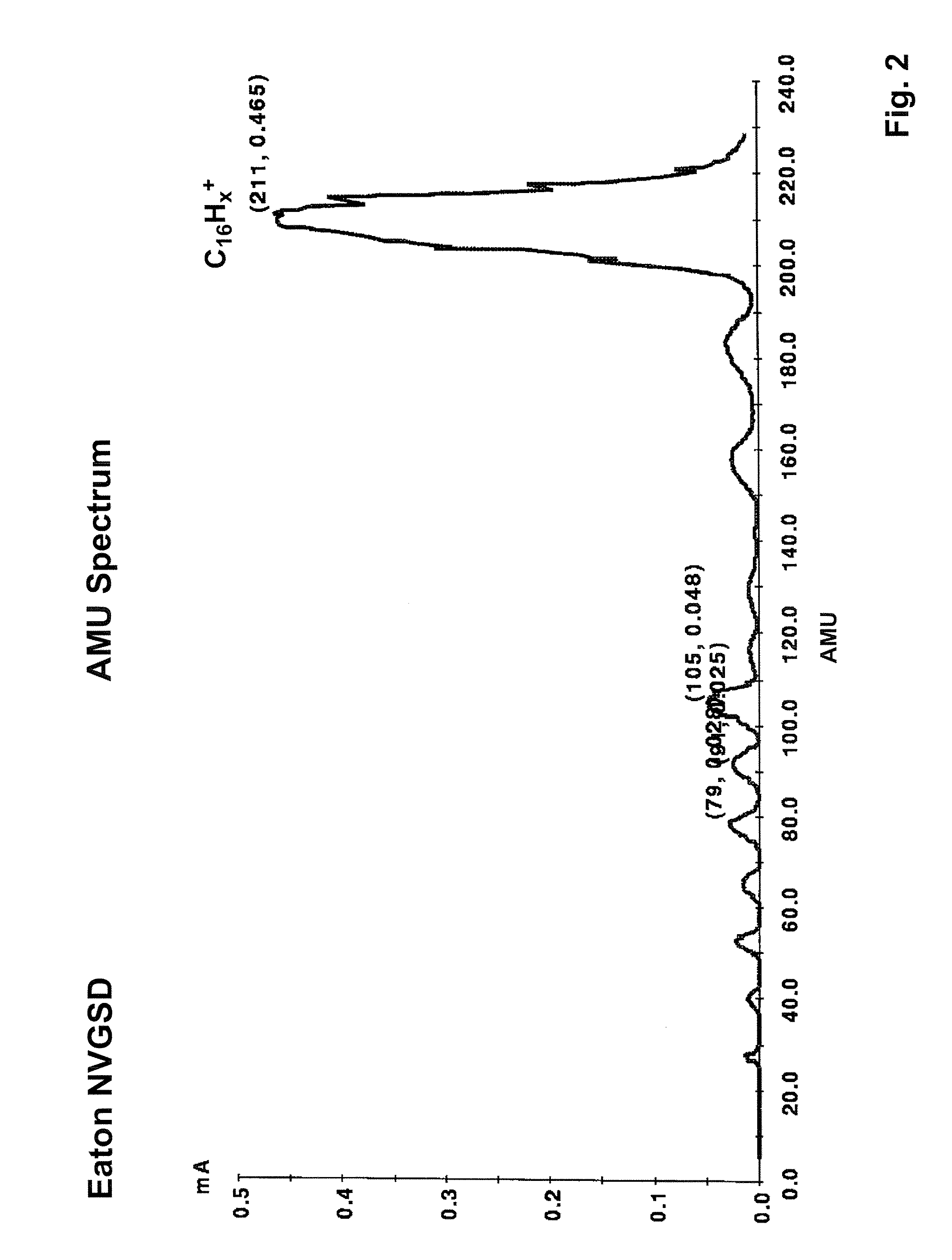
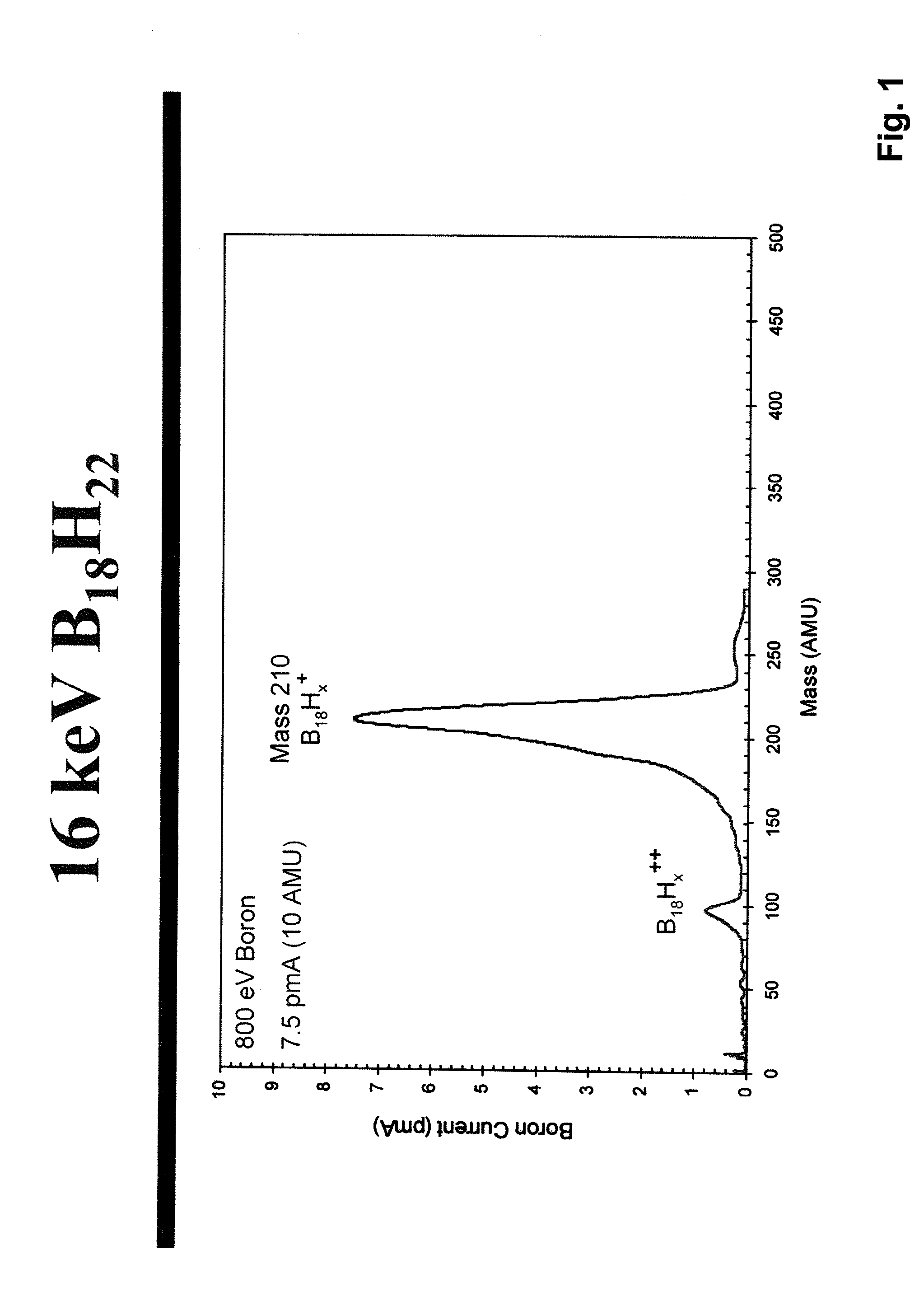
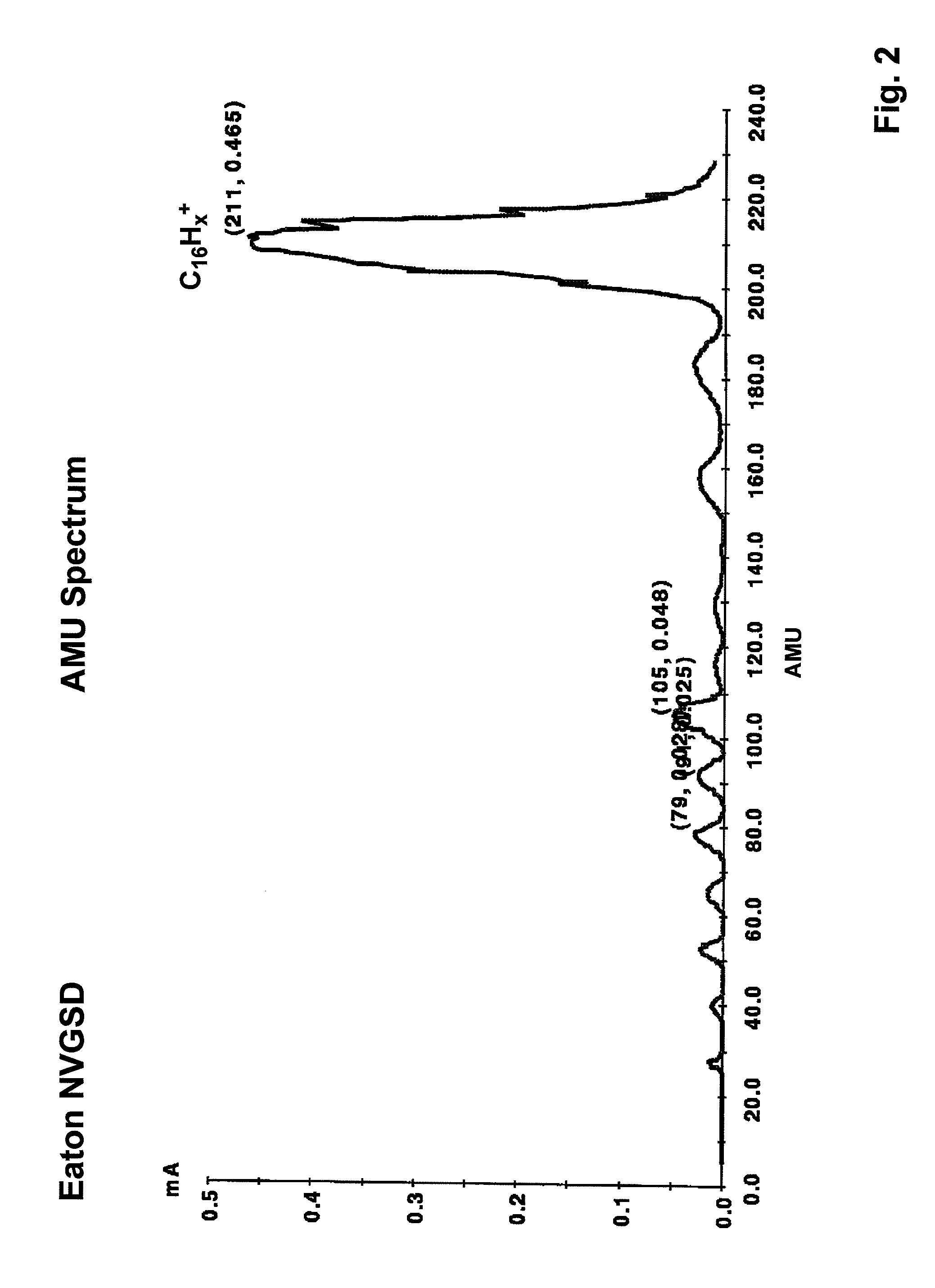
A process is disclosed which incorporates implantation of a carbon cluster into a substrate to improve the characteristics of transistor junctions when the substrates are doped with Boron and Phosphorous in the manufacturing of PMOS transistor structures in integrated circuits. There are two processes which result from this novel approach: (1) diffusion control for USJ formation; and (2) high dose carbon implantation for stress engineering. Diffusion control for USJ formation is demonstrated in conjunction with a boron or shallow boron cluster implant of the source / drain structures in PMOS. More particularly, first, a cluster carbon ion, such as C16Hx+, is implanted into the source / drain region at approximately the same dose as the subsequent boron implant; followed by a shallow boron, boron cluster, phosphorous or phosphorous cluster ion implant to form the source / drain extensions, preferably using a borohydride cluster, such as B18Hx+ or B10Hx+. Upon subsequent annealing and activation, the boron diffusion is reduced, due to the gettering of interstitial defects by the carbon atoms.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Structure and method for mobility enhanced MOSFETs with unalloyed silicide
ActiveUS8217423B2Stable and low contact resistanceReduce contact resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETSalicide
While embedded silicon germanium alloy and silicon carbon alloy provide many useful applications, especially for enhancing the mobility of MOSFETs through stress engineering, formation of alloyed silicide on these surfaces degrades device performance. The present invention provides structures and methods for providing unalloyed silicide on such silicon alloy surfaces placed on semiconductor substrates. This enables the formation of low resistance contacts for both mobility enhanced PFETs with embedded SiGe and mobility enhanced NFETs with embedded Si:C on the same semiconductor substrate. Furthermore, this invention provides methods for thick epitaxial silicon alloy, especially thick epitaxial Si:C alloy, above the level of the gate dielectric to increase the stress on the channel on the transistor devices.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
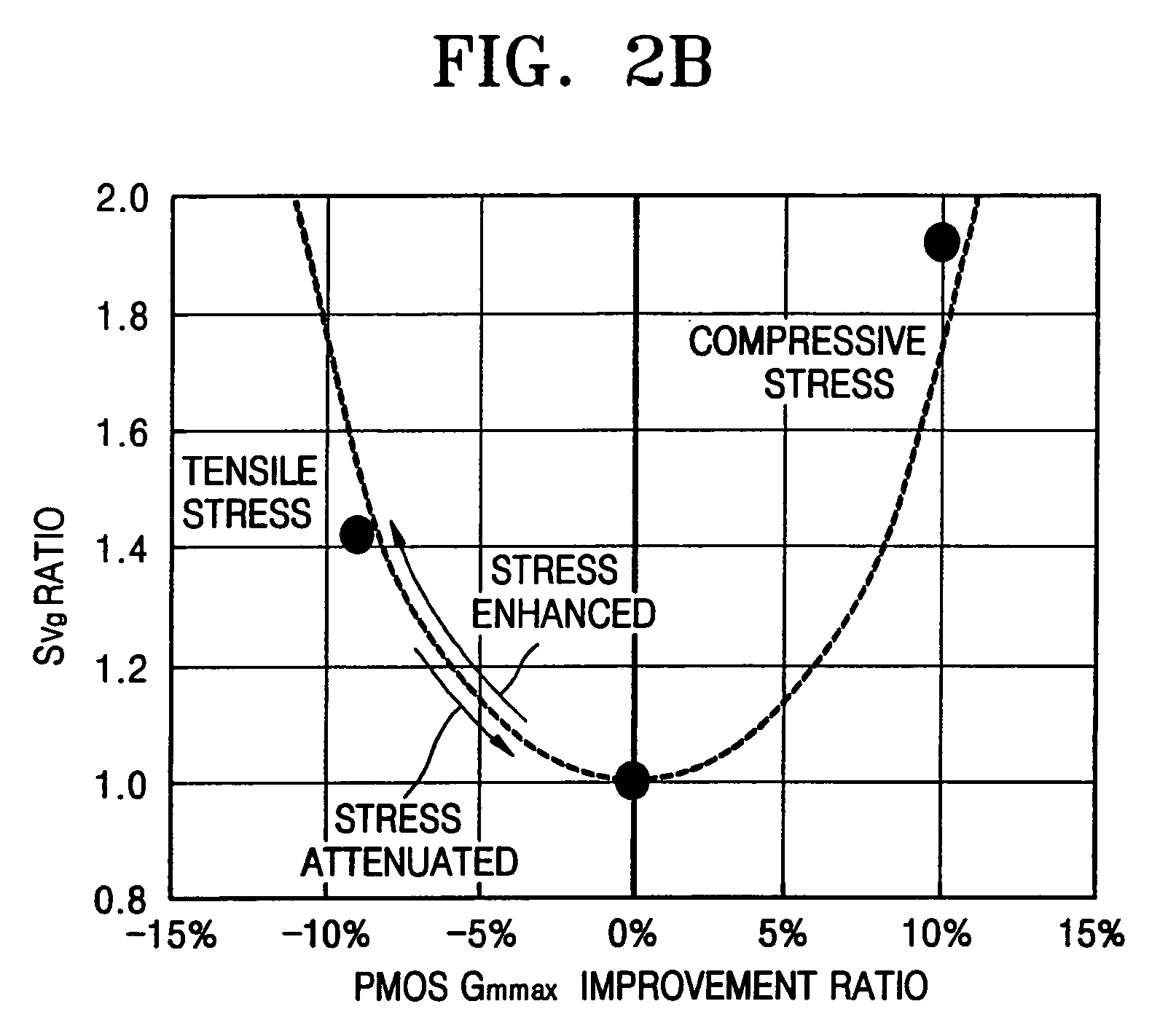
Low noise and high performance LSI device, layout and manufacturing method
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
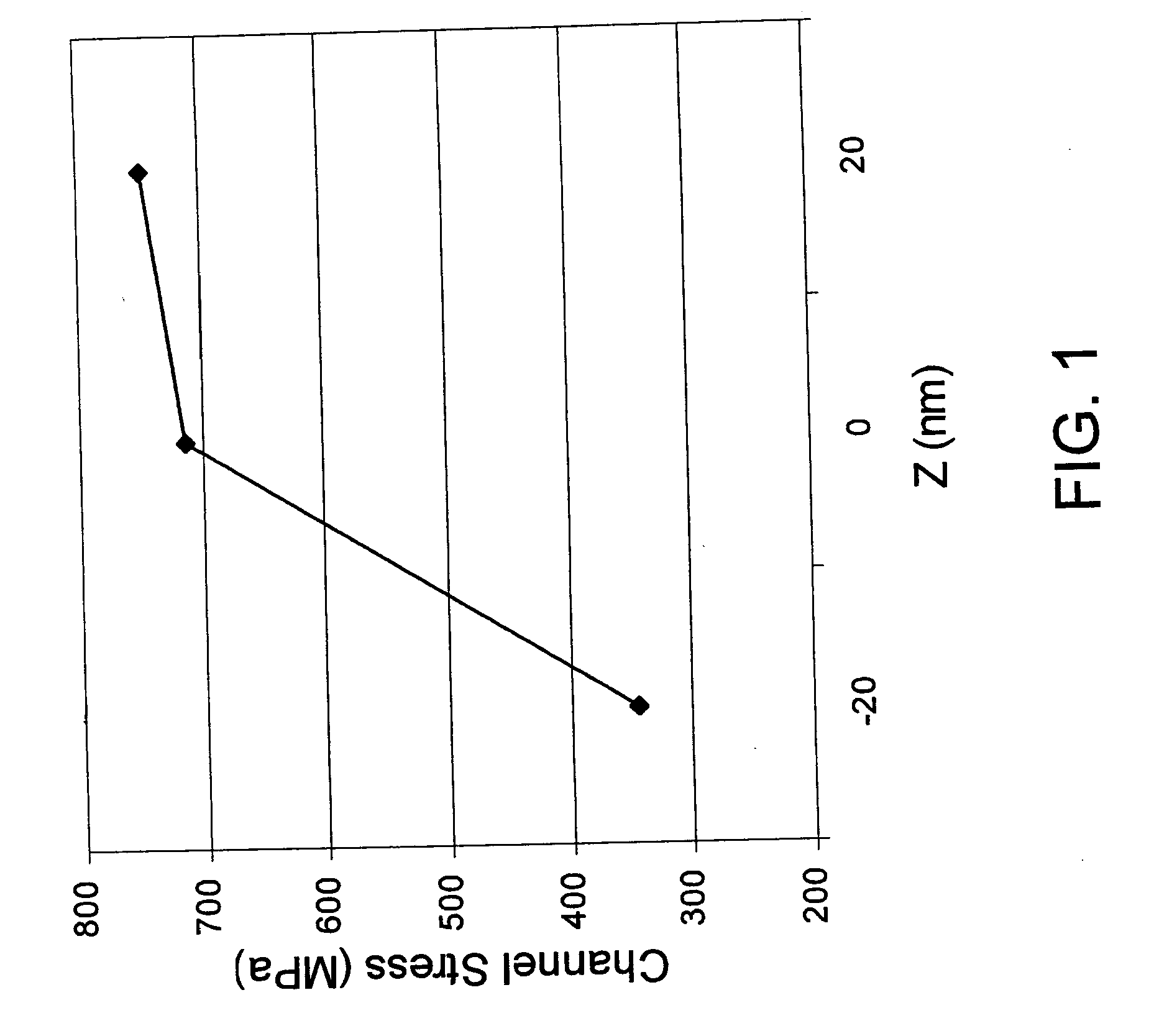
Techique for controlling mechanical stress in a channel region by spacer removal
ActiveUS20050266639A1Increase flexibilitySignificant stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCouplingEngineering
During the formation of a transistor element, sidewalls spacers are removed or at least partially etched back after ion implantation and silicidation, thereby rendering the mechanical coupling of a contact etch stop layer to the underlying drain and source regions more effective. Hence, the mechanical stress may be substantially induced by the contact etch step layer rather than by a combination of the spacer elements and the etch stop layer, thereby significantly facilitating the stress engineering in the channel region. By additionally performing a plasma treatment, different amounts of stress may be created in different transistor devices without unduly contributing to process complexity.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
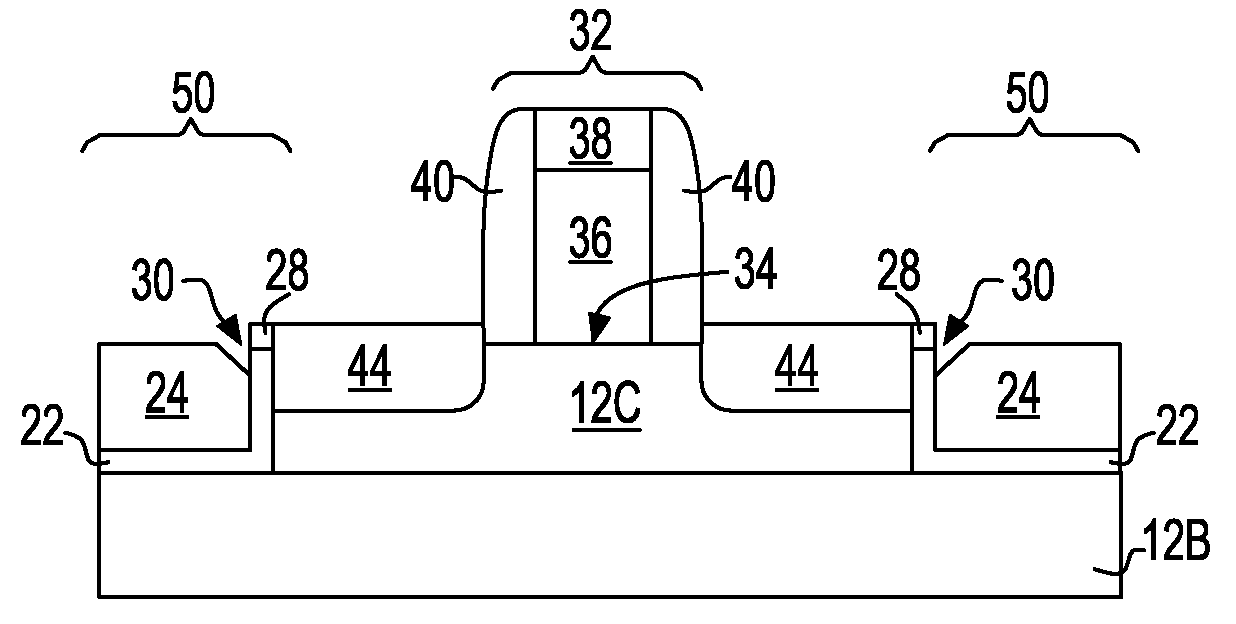
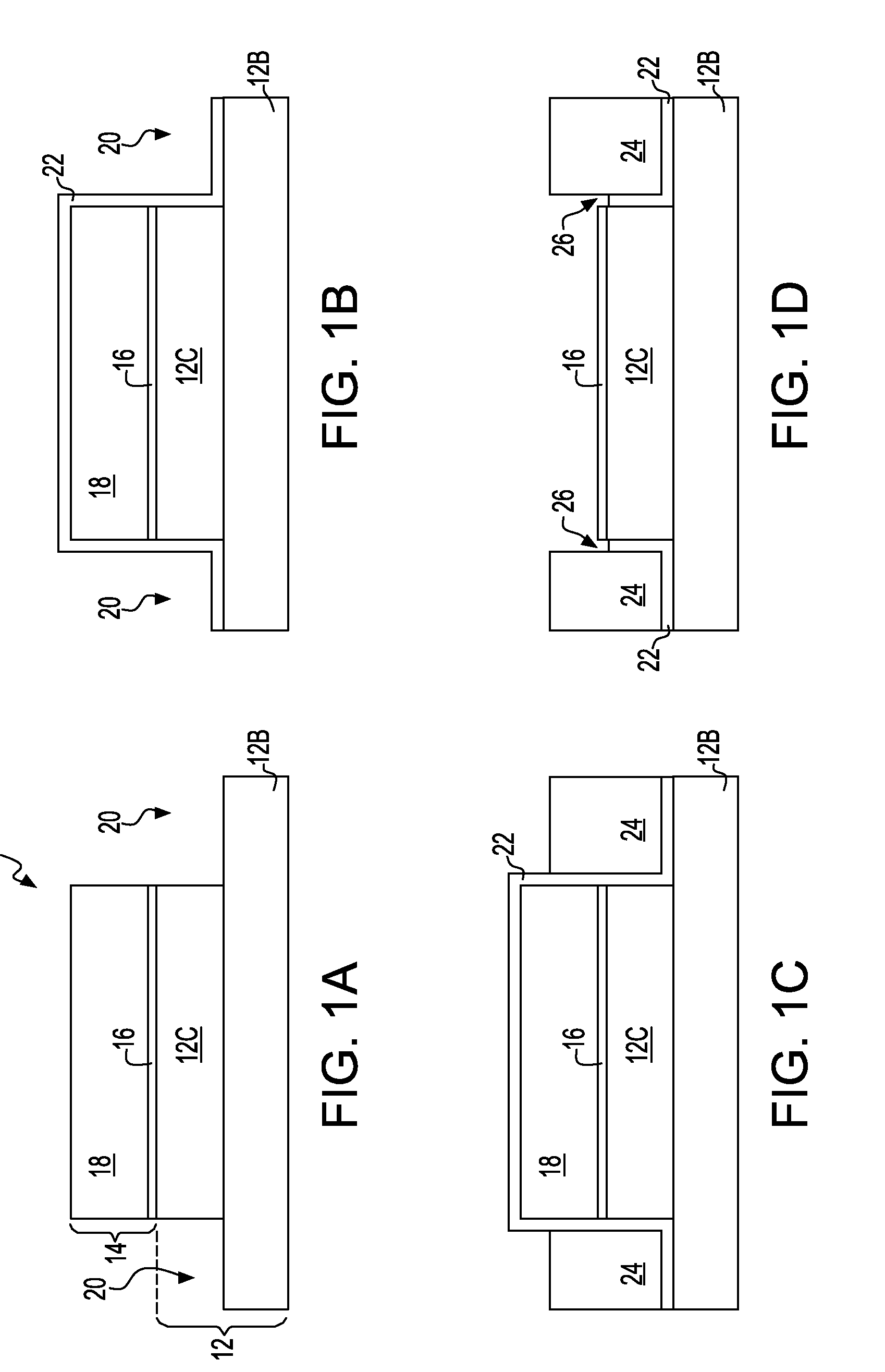
Stress liner surrounded facetless embedded stressor mosfet
The present invention provides an STI bounded transistor structure having enhanced performance which is not diminished due to embedded stressor facets that can be present at the edge of the source / drain regions that contacts an embedded stressor material. Considering that the facet in the prior art is due to an STI divot formed during several necessary wet etching processes, the MOSFET source / drain edge of the inventive structure is surrounded by a liner to prevent facet growth during the epitaxial growth of the stressor material. As such, a part of the semiconductor substrate edge is preserved. The liner employed in the present invention is a stress engineering material such as, for example, silicon nitride.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Structure and method for mobility enhanced mosfets with unalloyed silicide
ActiveUS20080164491A1Increase heightStable and low contact resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETElectrical resistance and conductance
While embedded silicon germanium alloy and silicon carbon alloy provide many useful applications, especially for enhancing the mobility of MOSFETs through stress engineering, formation of alloyed silicide on these surfaces degrades device performance. The present invention provides structures and methods for providing unalloyed silicide on such silicon alloy surfaces placed on semiconductor substrates. This enables the formation of low resistance contacts for both mobility enhanced PFETs with embedded SiGe and mobility enhanced NFETs with embedded Si:C on the same semiconductor substrate. Furthermore, this invention provides methods for thick epitaxial silicon alloy, especially thick epitaxial Si:C alloy, above the level of the gate dielectric to increase the stress on the channel on the transistor devices.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
Local stress engineering for CMOS devices
A first dielectric layer is formed over a PFET gate and an NFET gate, and lithographically patterned to expose a PFET area, while covering an NFET area. Exposed PFET active area is etched and refilled with a SiGe alloy, which applies a uniaxial compressive stress to a PFET channel. A second dielectric layer is formed over the PFET gate and the NFET gate, and lithographically patterned to expose the NFET area, while covering the PFET area. Exposed NFET active area is etched and refilled with a silicon-carbon alloy, which applies a uniaxial tensile stress to an NFET channel. Dopants may be introduced into the SiGe and silicon-carbon regions by in-situ doping or by ion implantation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Technique for controlling mechanical stress in a channel region by spacer removal
ActiveUS7314793B2Significant stressLittle elasticitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCouplingEngineering
During the formation of a transistor element, sidewalls spacers are removed or at least partially etched back after ion implantation and silicidation, thereby rendering the mechanical coupling of a contact etch stop layer to the underlying drain and source regions more effective. Hence, the mechanical stress may be substantially induced by the contact etch step layer rather than by a combination of the spacer elements and the etch stop layer, thereby significantly facilitating the stress engineering in the channel region. By additionally performing a plasma treatment, different amounts of stress may be created in different transistor devices without unduly contributing to process complexity.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
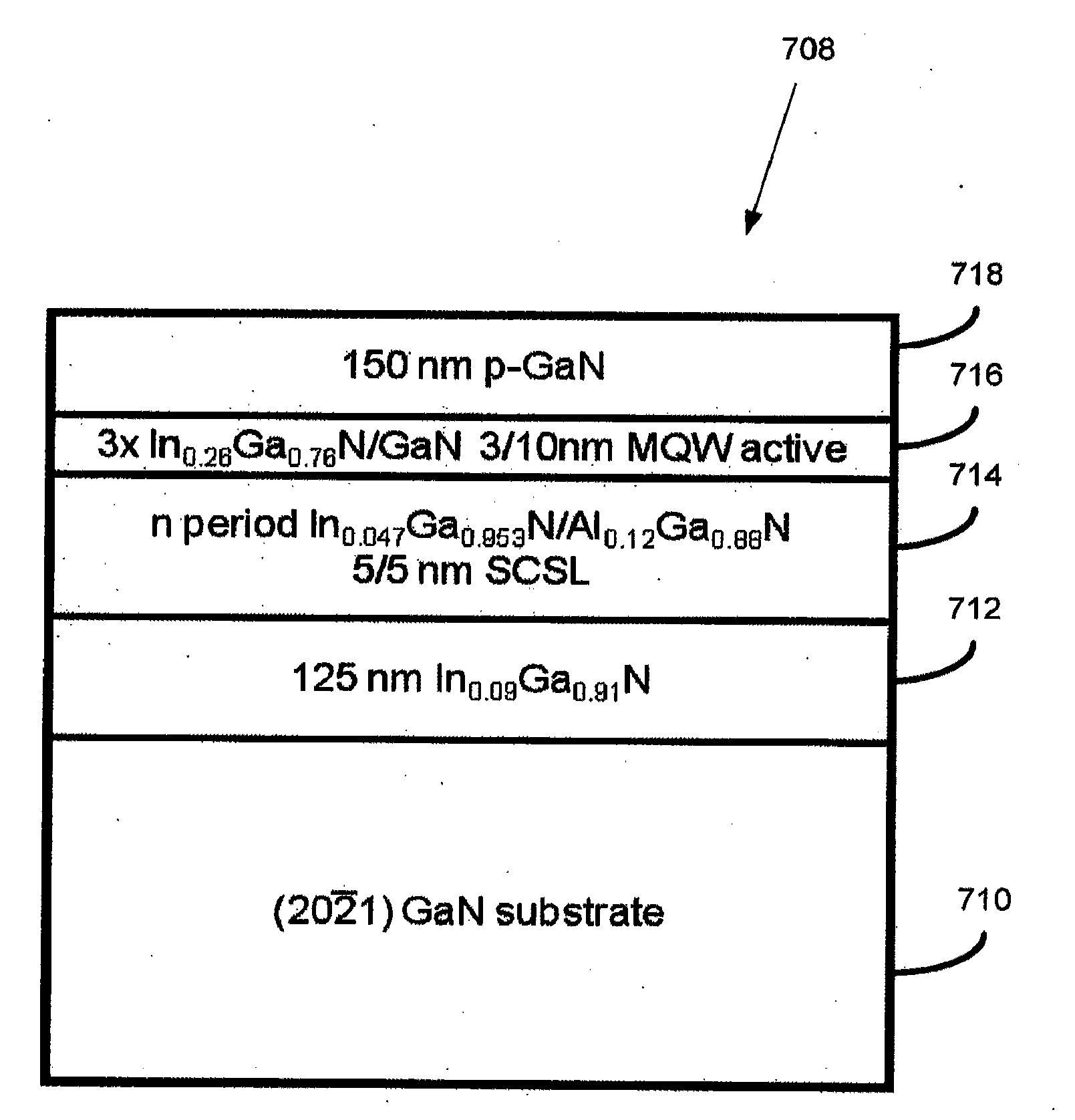
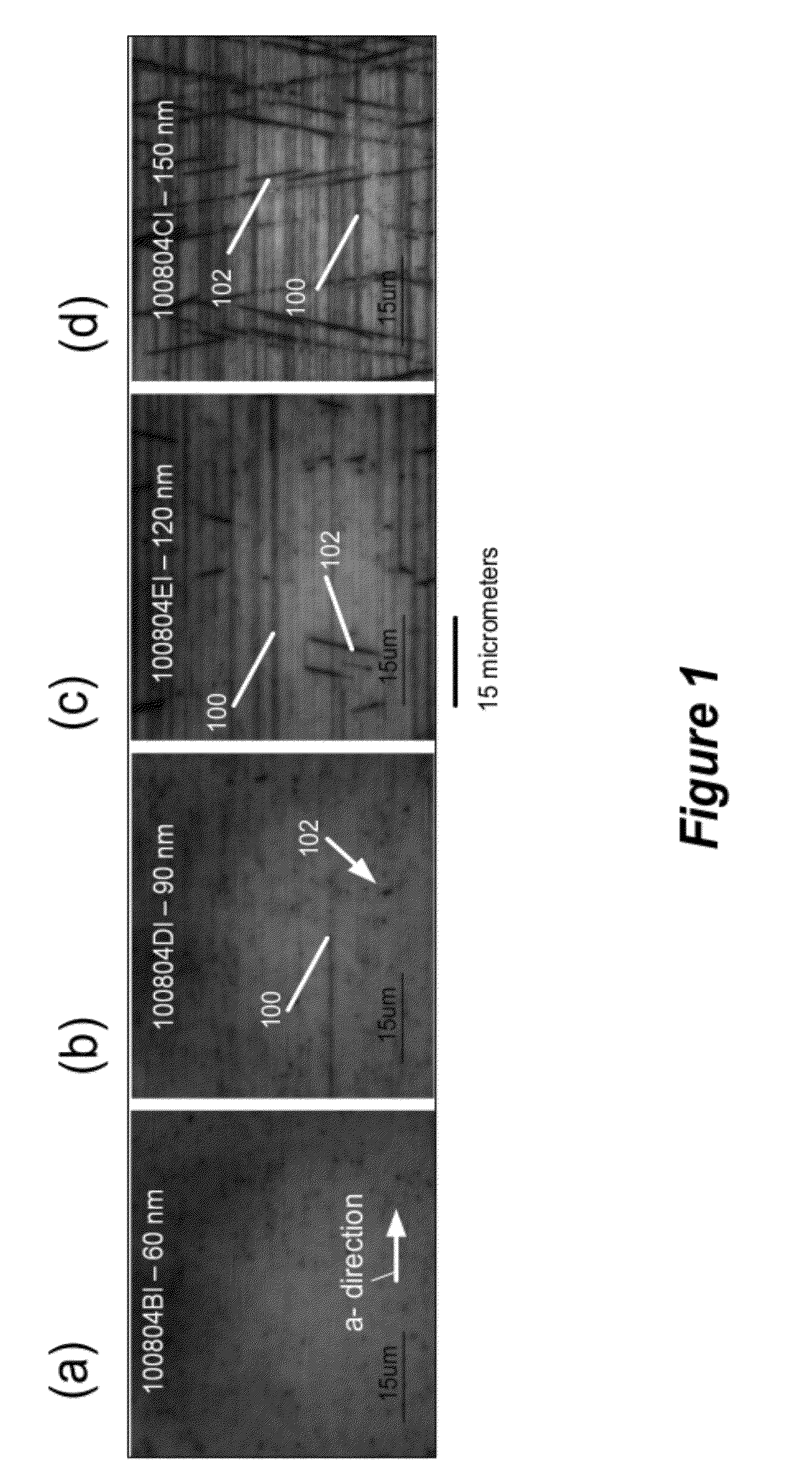
Strain compensated short-period superlattices on semipolar or nonpolar GAN for defect reduction and stress engineering
InactiveUS20120104360A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsComputational physicsLattice constant
An (AlInGaN) based semiconductor device, comprising a first layer that is a semipolar or nonpolar nitride (AlInGaN) layer having a lattice constant that is partially or fully relaxed, deposited on a substrate or a template, wherein there are one or more dislocations at a heterointerface between the first layer and the substrate or the template; one or more strain compensated layers on the first layer, for defect reduction and stress engineering in the device, that is lattice matched to a larger lattice constant of the first layer; and one or more nonpolar or semipolar (AlInGaN) device layers on the strain compensated layers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
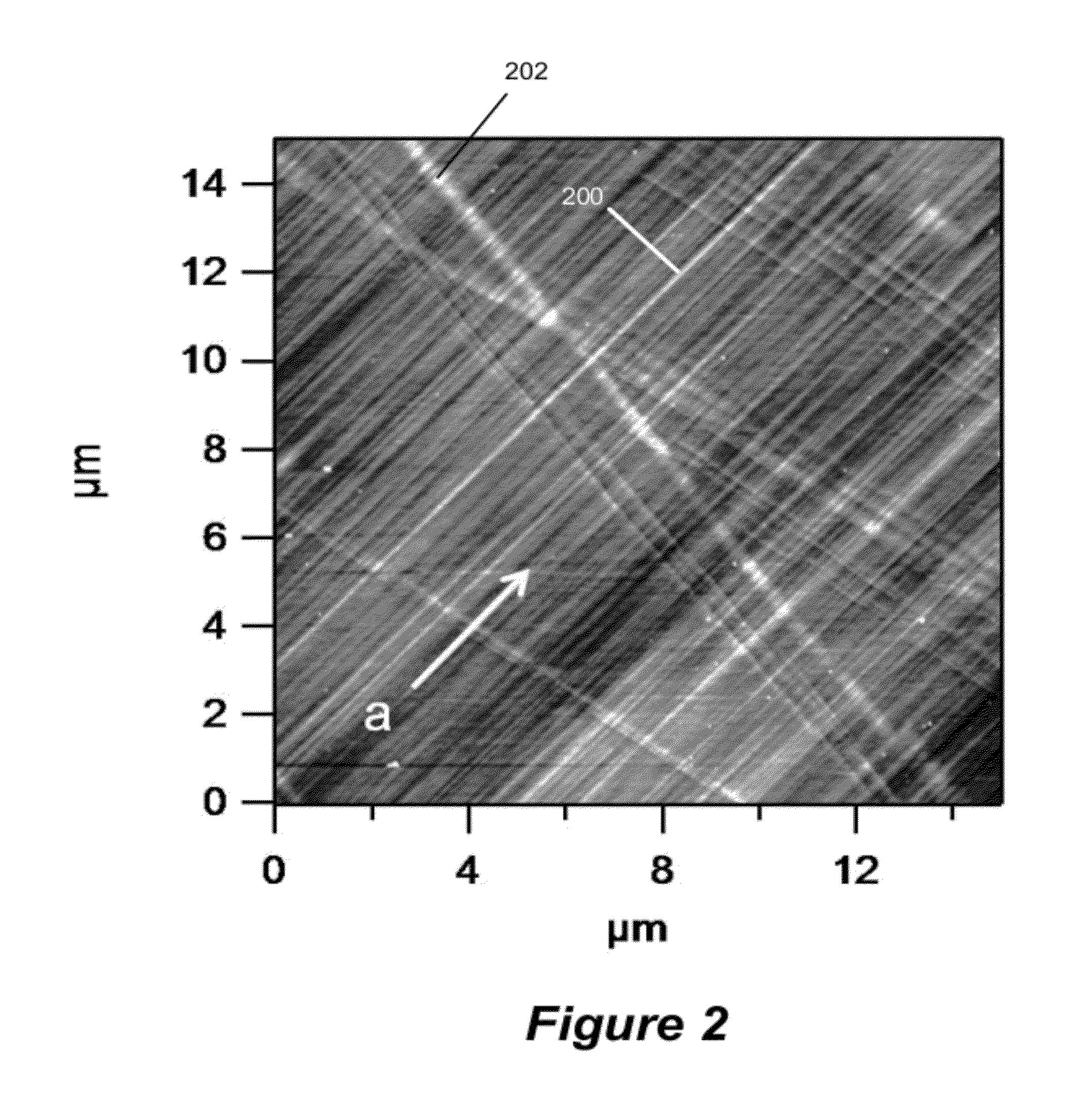
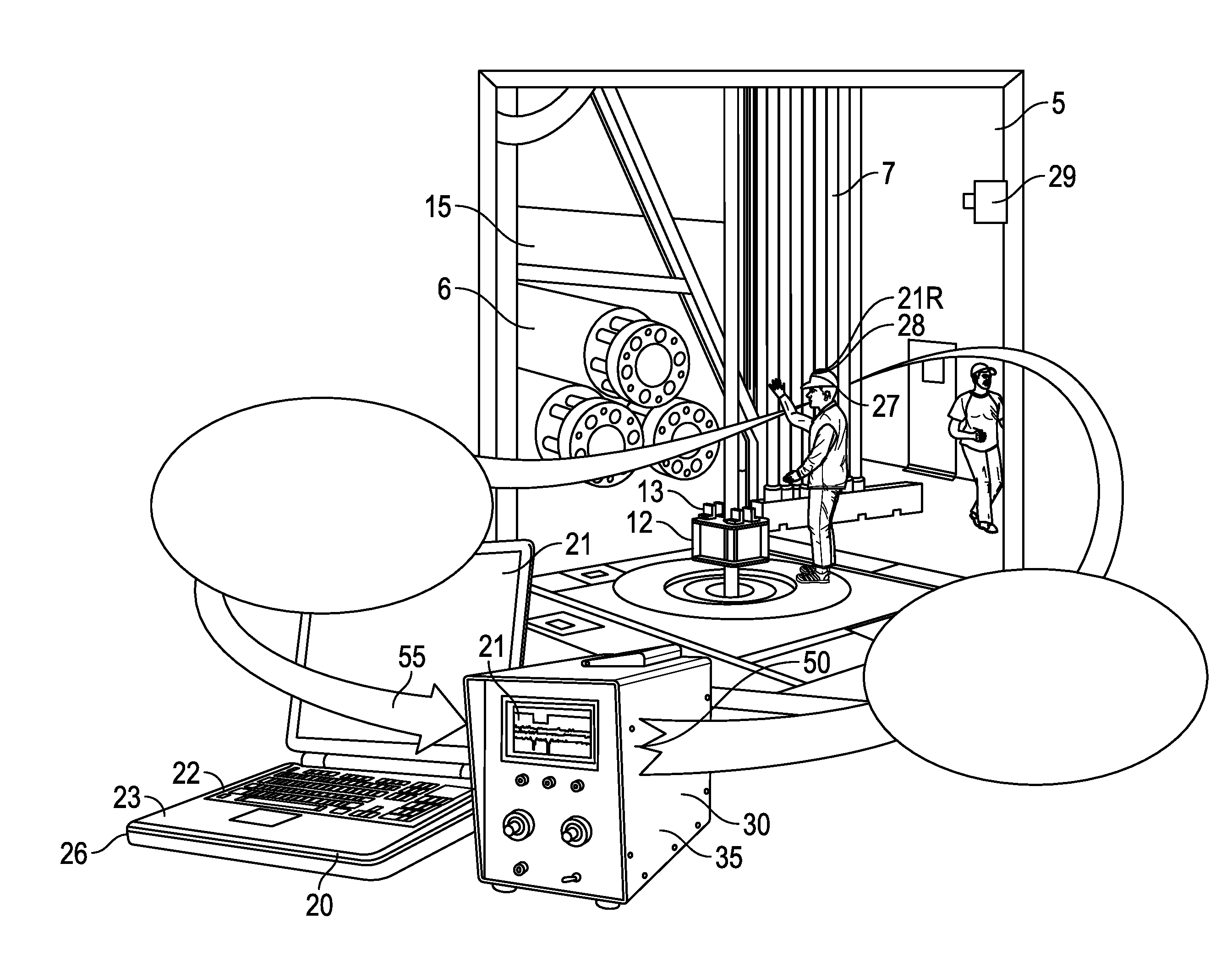
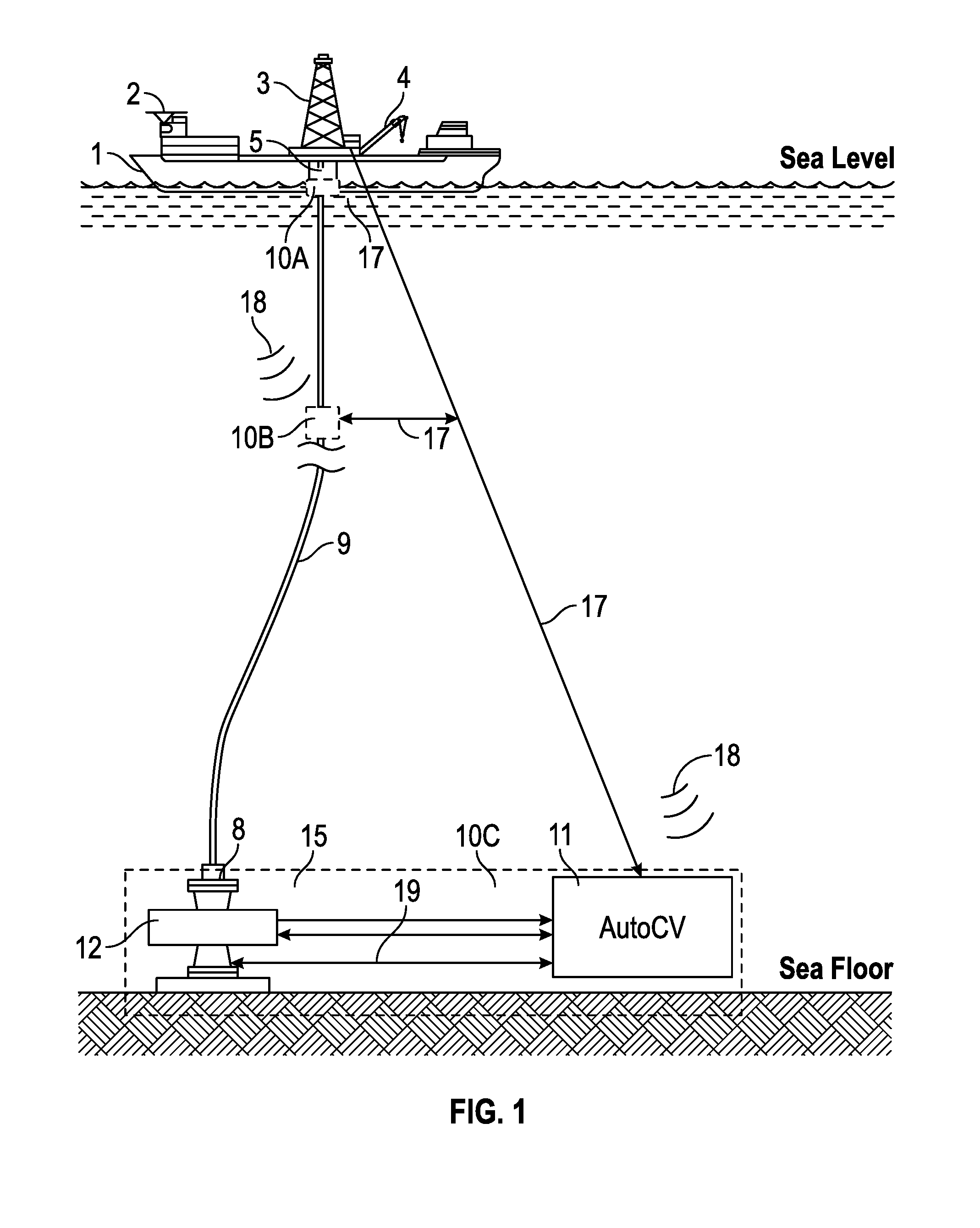
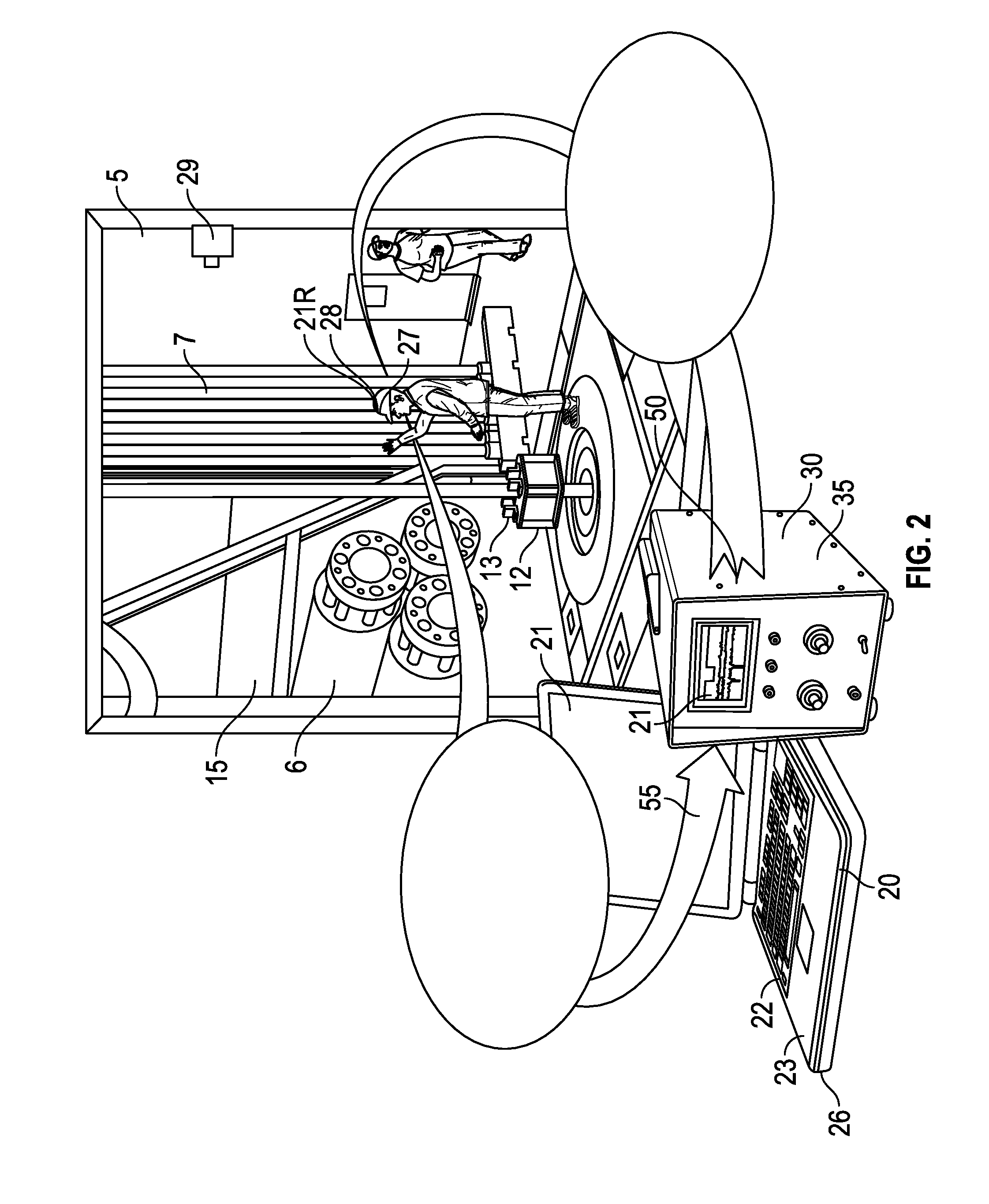
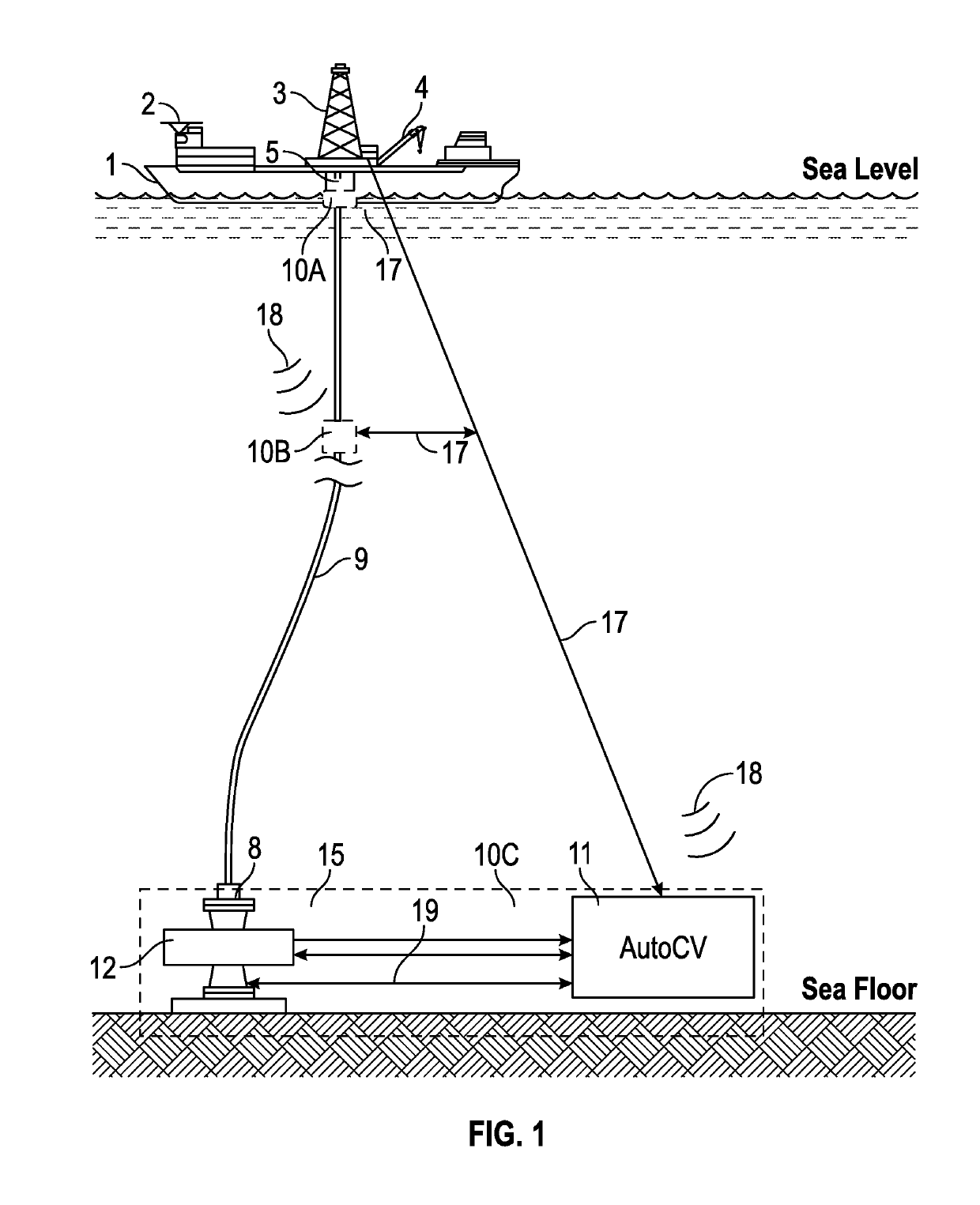
Stress engineering assessment of risers and riser strings
InactiveUS20160237804A1Limit any harmful consequenceIncrease the gapSurveyDrilling rodsData acquisitionFailure risk
Riser stress-engineering-assessment equipment to verify the integrity and the in-deployment-integrity of a riser string by knowing the status, details and location of each riser joint and by monitoring the deployment parameters. When the failure risk exceeds an acceptable level, the equipment activates a local and / or a remote alarm using voice, sound and lights. The system comprises a computer with communication means, a material properties and geometry detection system, a data acquisition system acquiring deployment and other parameters, a database comprising of riser historical data and captured expert knowledge, a failure-criteria calculation to calculate maximum-stresses under different loads and the combined effects of the different loads to determine if the riser string is still fit-for-deployment.
Owner:STYLWAN IP HLDG LLC
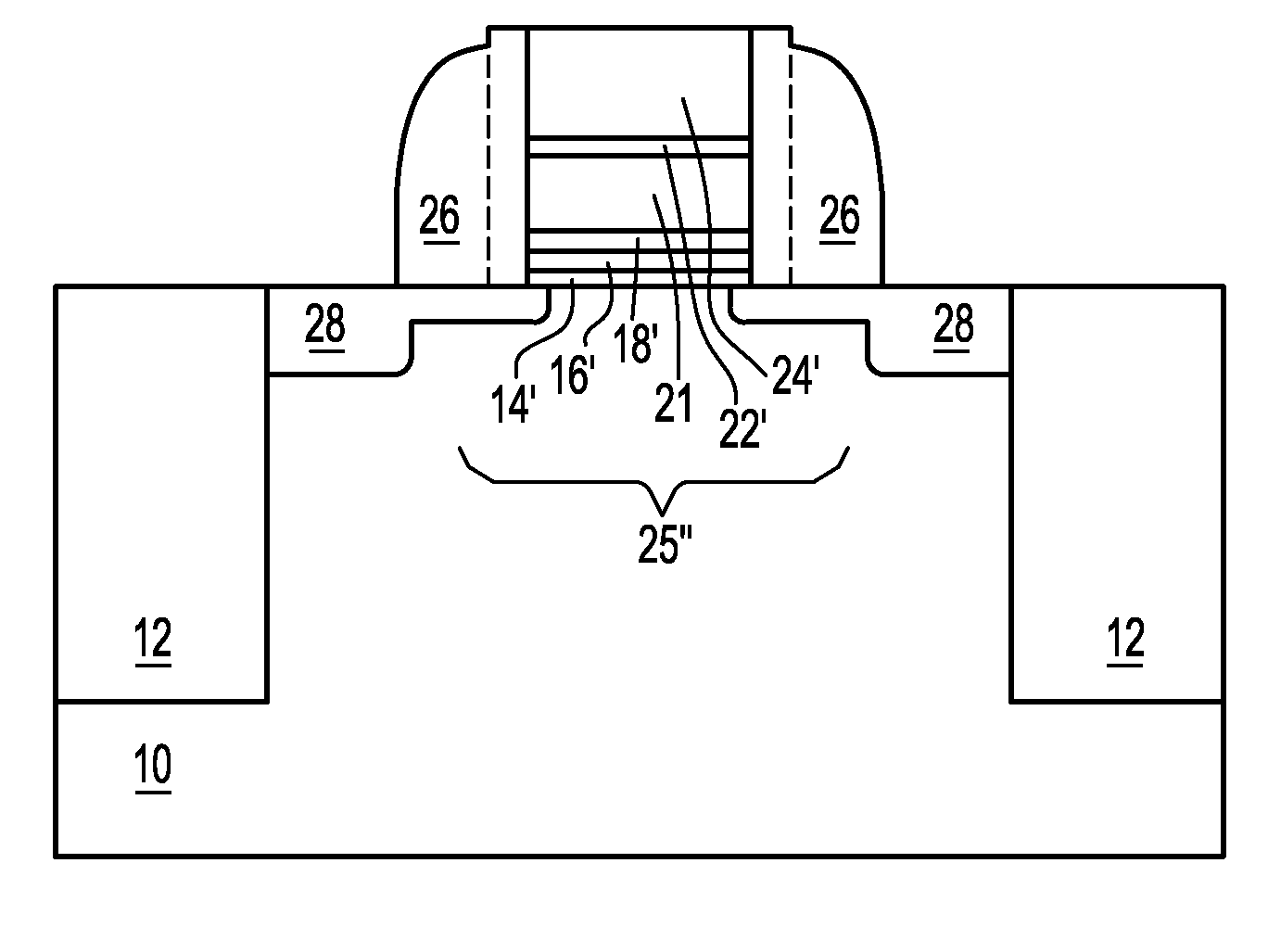
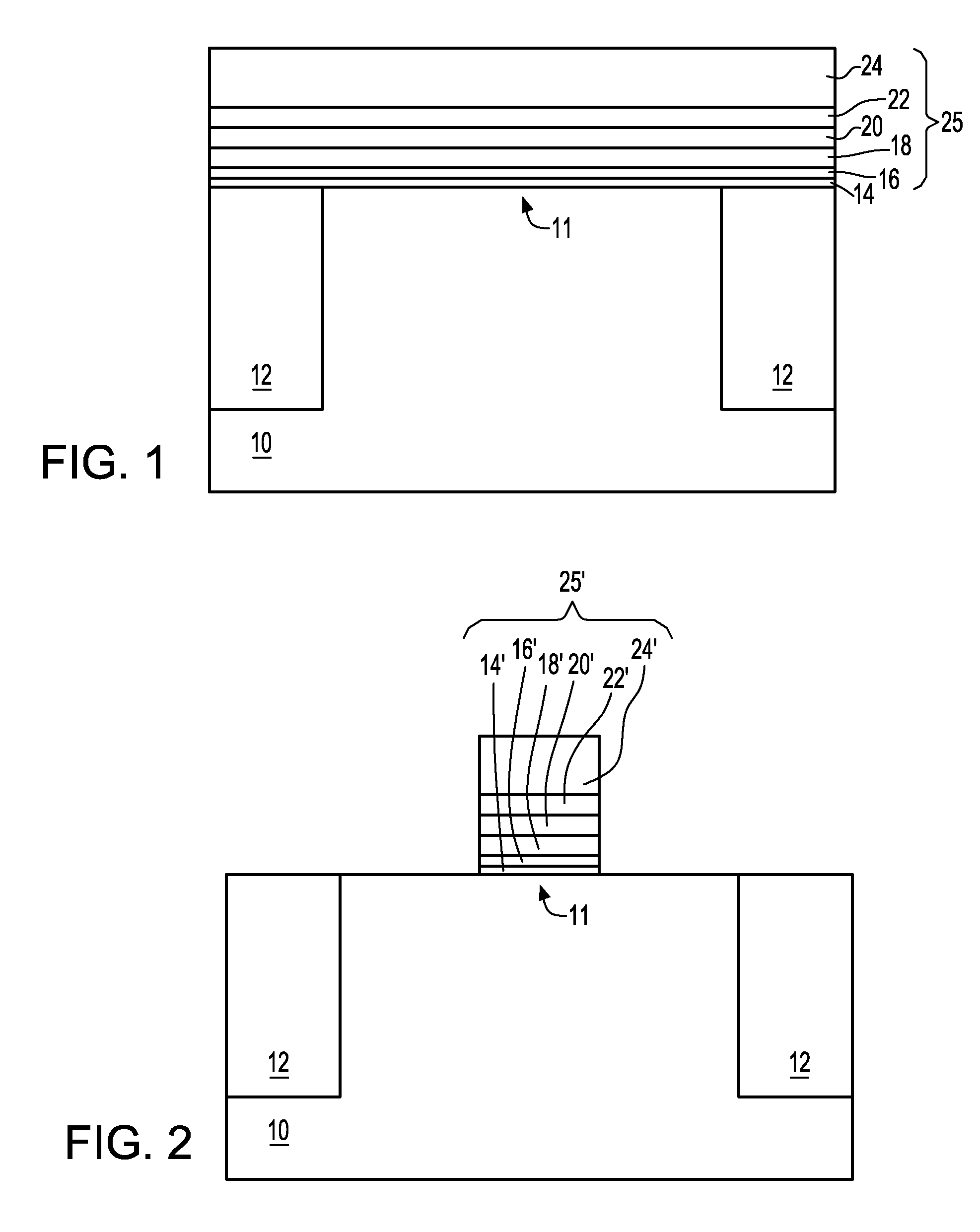
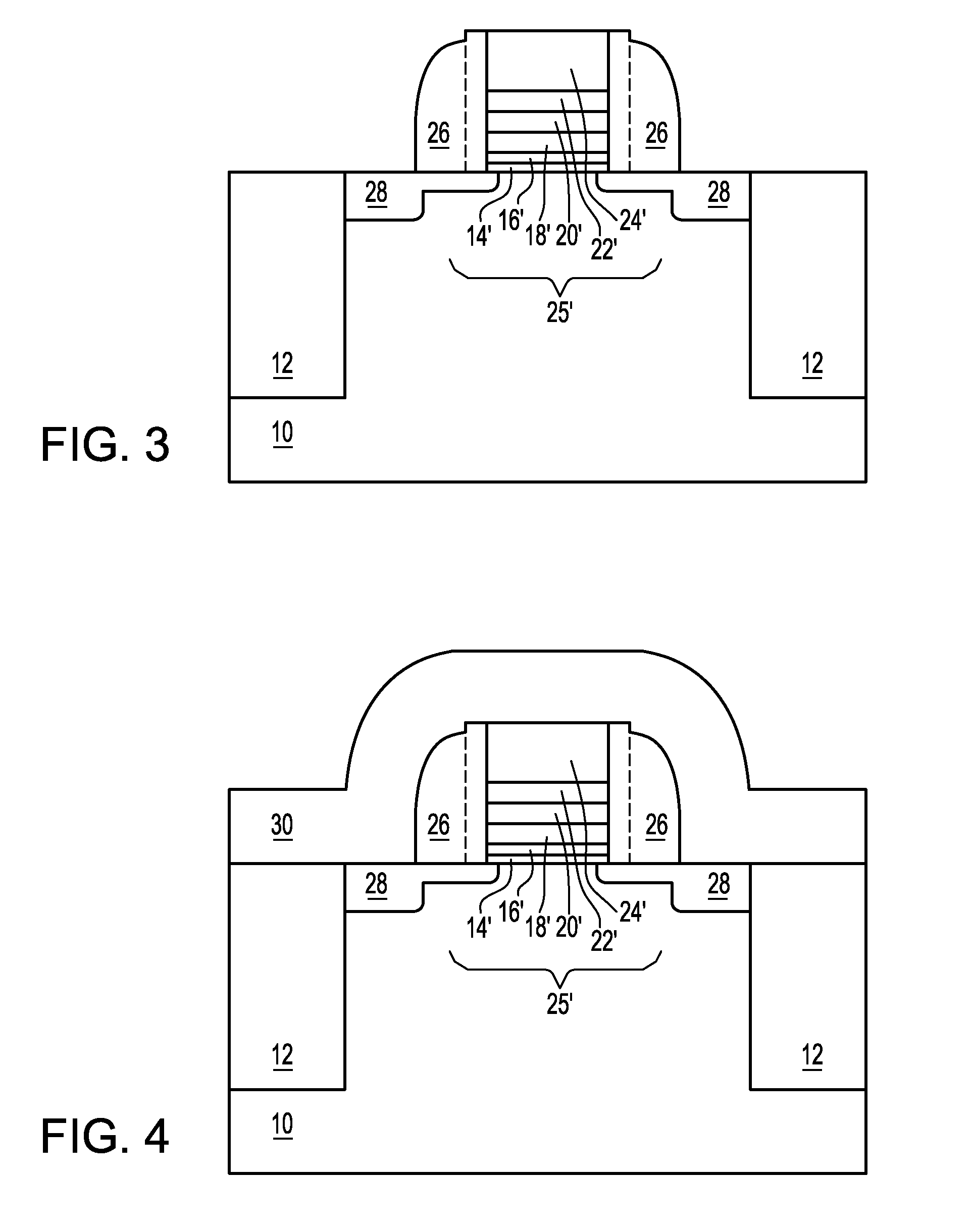
Method to control source/drain stressor profiles for stress engineering
ActiveUS8017487B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStress inducedGate dielectric
A strained channel transistor structure and methods of forming a semiconductor device are presented. The transistor structure includes a strained channel region having a first semiconductor material with a first natural lattice constant. A gate dielectric layer overlying the strained channel region, a gate electrode overlying the gate dielectric layer and a source region and drain region oppositely adjacent to the strained channel region are provided. One or both of the source region and drain region include a stressor region having a second semiconductor material with a second natural lattice constant different from the first natural lattice constant. The stressor region has graded concentration of a dopant impurity and / or of a stress inducing molecule.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +2
System and method for the manufacture of semiconductor devices by the implantation of carbon clusters
InactiveUS7666771B2Increase junction depthReduce leakage currentTransistorElectric discharge tubesDevice materialEngineering
A process is disclosed which incorporates implantation of a carbon cluster into a substrate to improve the characteristics of transistor junctions when the substrates are doped with Boron and Phosphorous in the manufacturing of PMOS transistor structures in integrated circuits. There are two processes which result from this novel approach: (1) diffusion control for USJ formation; and (2) high dose carbon implantation for stress engineering. Diffusion control for USJ formation is demonstrated in conjunction with a boron or shallow boron cluster implant of the source / drain structures in PMOS. More particularly, first, a cluster carbon ion, such as C16Hx+, is implanted into the source / drain region at approximately the same dose as the subsequent boron implant; followed by a shallow boron, boron cluster, phosphorous or phosphorous cluster ion implant to form the source / drain extensions, preferably using a borohydride cluster, such as B18Hx+ or B10Hx+. Upon subsequent annealing and activation, the boron diffusion is reduced, due to the gettering of interstitial defects by the carbon atoms.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
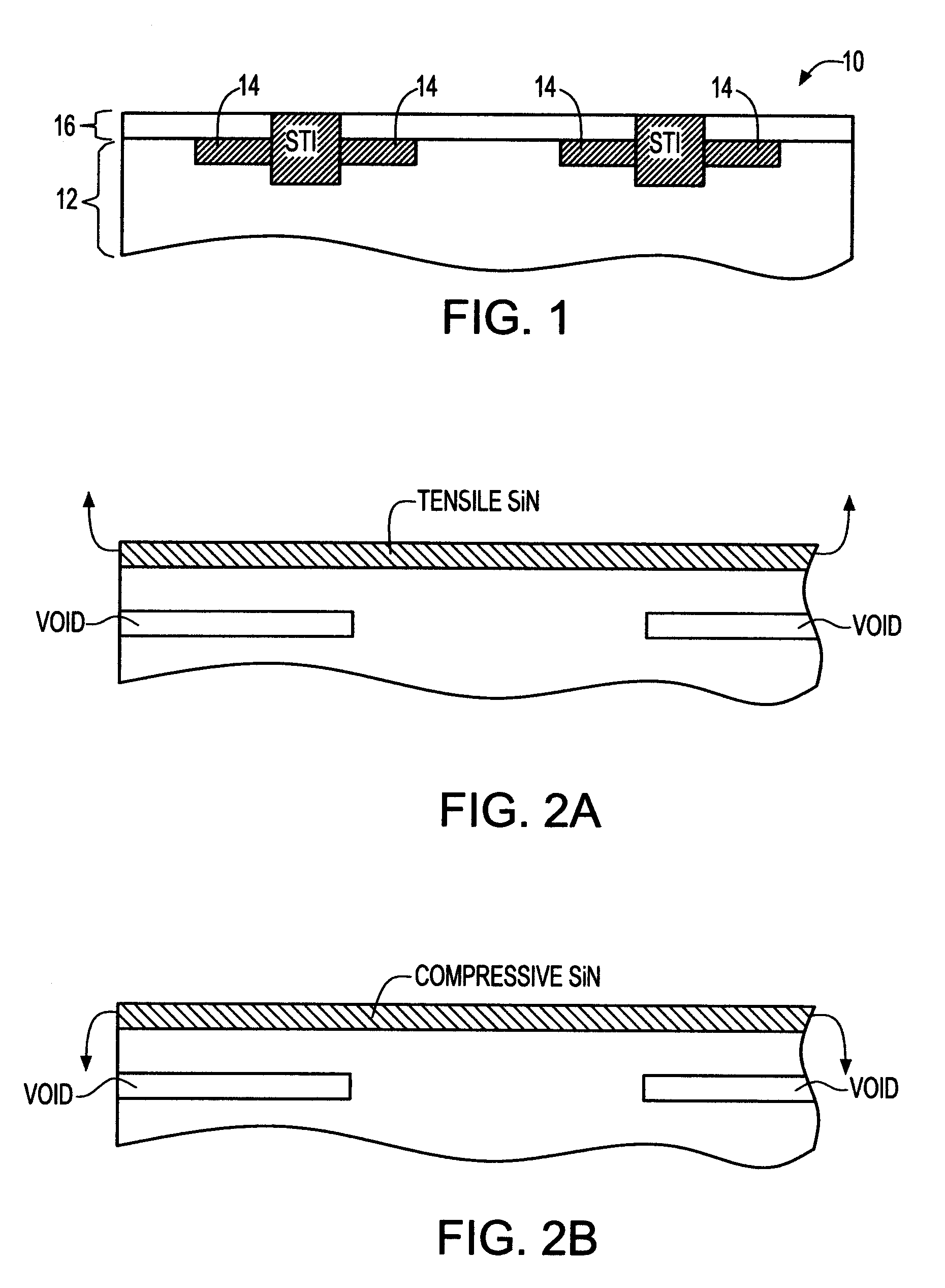
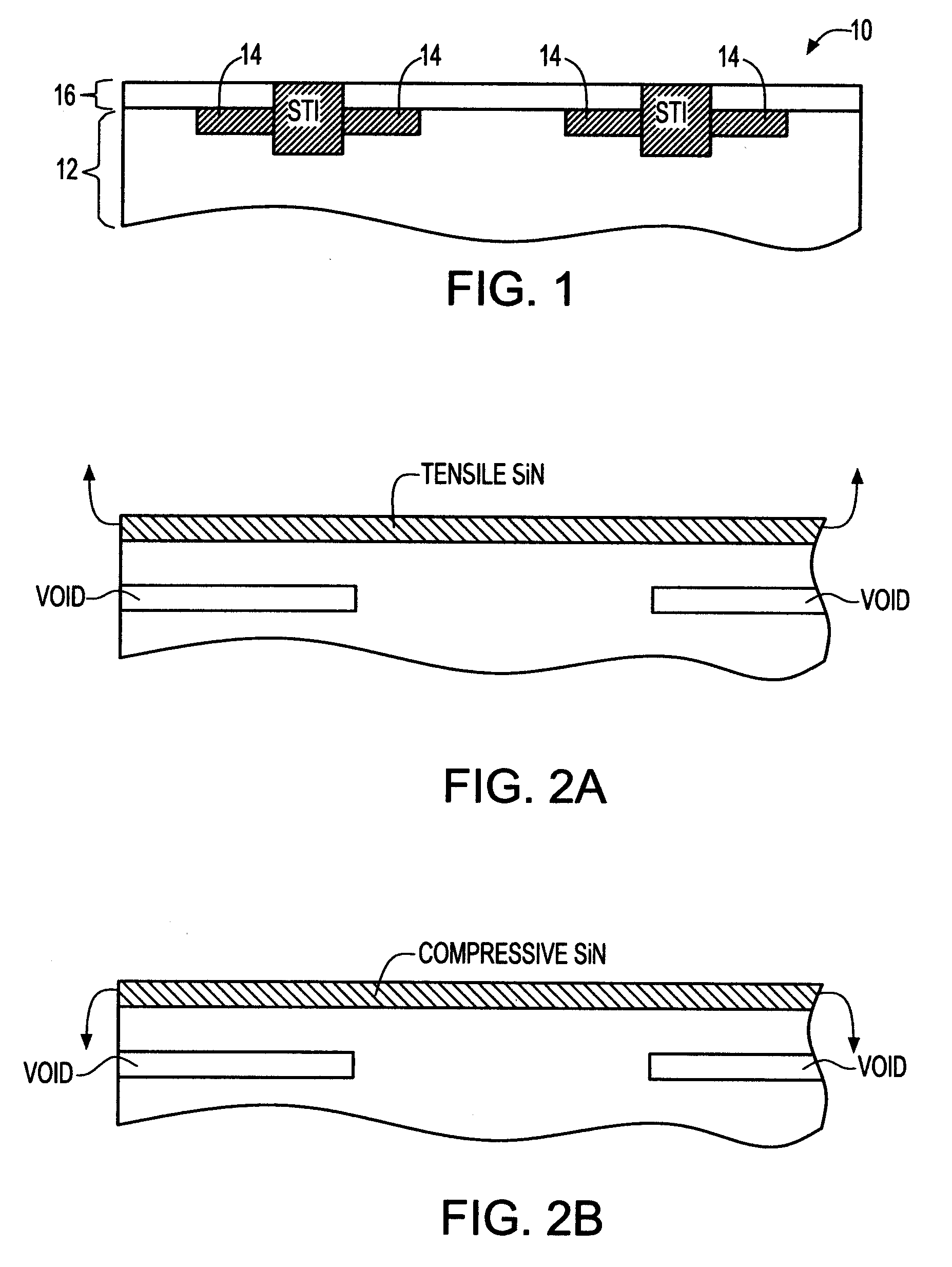
Stress engineering using dual pad nitride with selective SOI device architecture
ActiveUS7202513B1Increase valueSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorMaterials science
A method for engineering stress in the channels of MOS transistors of different conductivity using highly stressed nitride films in combination with selective semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) device architecture is described. A method of using compressive and tensile nitride films in the shallow trench isolation (STI) process is described. High values of stress are achieved when the method is applied to a selective SOI architecture.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
System and method for the manufacture of semiconductor devices by the implantation of carbon clusters
InactiveUS20090286367A1Increase junction depthReduce leakage currentTransistorElectric discharge tubesCarbon ionHigh doses
A process is disclosed which incorporates implantation of a carbon cluster into a substrate to improve the characteristics of transistor junctions when the substrates are doped with Boron and Phosphorous in the manufacturing of PMOS transistor structures in integrated circuits. There are two processes which result from this novel approach: (1) diffusion control for USJ formation; and (2) high dose carbon implantation for stress engineering. Diffusion control for USJ formation is demonstrated in conjunction with a boron or shallow boron cluster implant of the source / drain structures in PMOS. More particularly, first, a cluster carbon ion, such as C16Hx+, is implanted into the source / drain region at approximately the same dose as the subsequent boron implant; followed by a shallow boron, boron cluster, phosphorous or phosphorous cluster ion implant to form the source / drain extensions, preferably using a borohydride cluster, such as B18Hx+ or B10Hx+. Upon subsequent annealing and activation, the boron diffusion is reduced, due to the gettering of interstitial defects by the carbon atoms.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Stress engineering assessment of risers and riser strings
ActiveUS20190228777A1Limit any harmful consequenceDesign optimisation/simulationSpeech recognitionData acquisitionEngineering
Riser stress-engineering-assessment equipment to verify the integrity and the in-deployment-integrity of a riser string by knowing the status, details and location of each riser joint and by monitoring the deployment parameters. When the failure risk exceeds an acceptable level, the equipment activates a local and / or a remote alarm using voice, sound and lights. The system comprises a computer with communication means, a material properties and geometry detection system, a data acquisition system acquiring deployment and other parameters, a database comprising of riser historical data and captured expert knowledge, a failure-criteria calculation to calculate maximum-stresses under different loads and the combined effects of the different loads to determine if the riser string is still fit-for-deployment.
Owner:STYLWAN IP HLDG LLC
Stress engineering using dual pad nitride with selective SOI device architecture
ActiveUS20070069294A1Increase valueSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorMaterials science
A method for engineering stress in the channels of MOS transistors of different conductivity using highly stressed nitride films in combination with selective semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) device architecture is described. A method of using compressive and tensile nitride films in the shallow trench isolation (STI) process is described. High values of stress are achieved when the method is applied to a selective SOI architecture.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
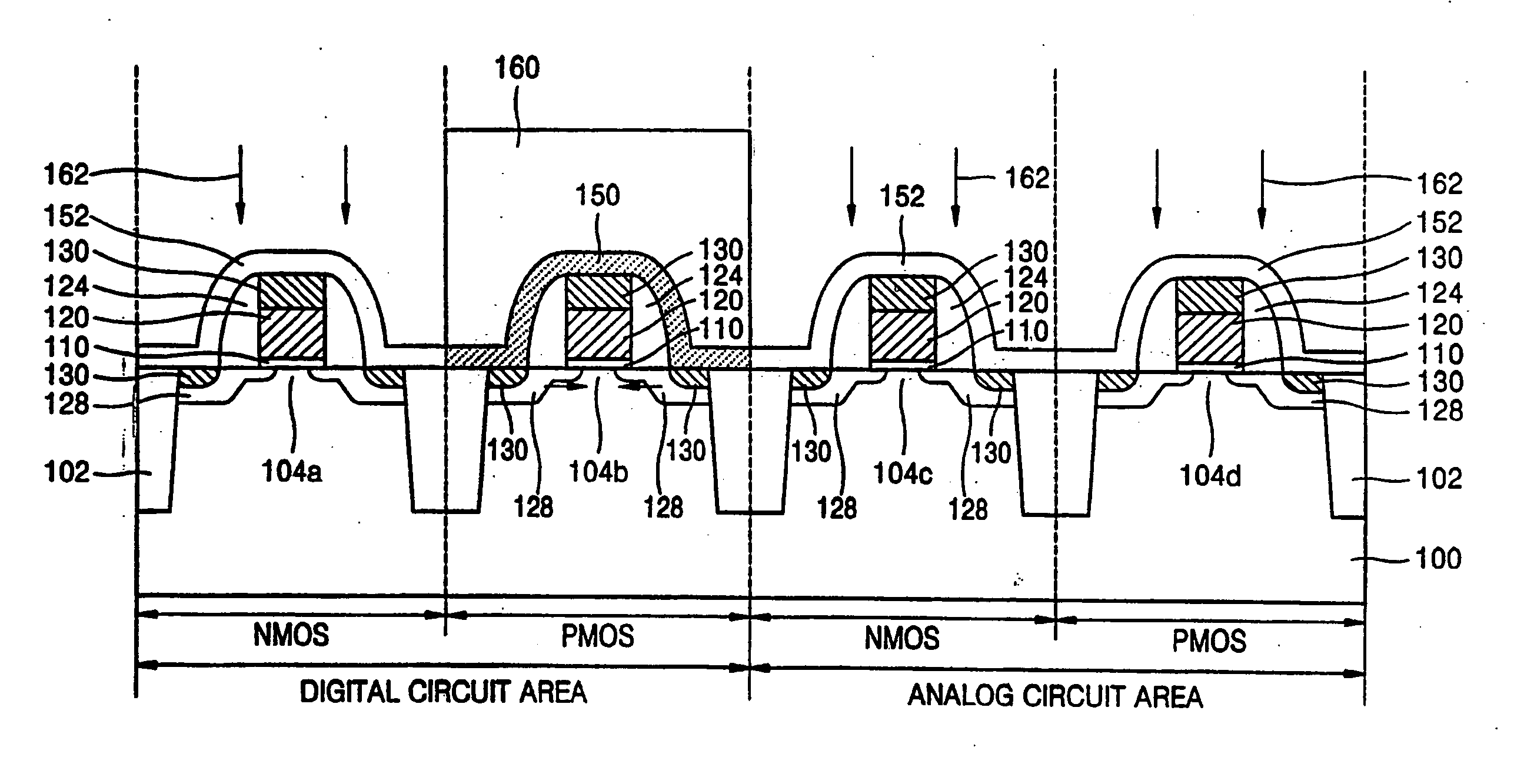
Low noise and high performance LSI device, layout and manufacturing method
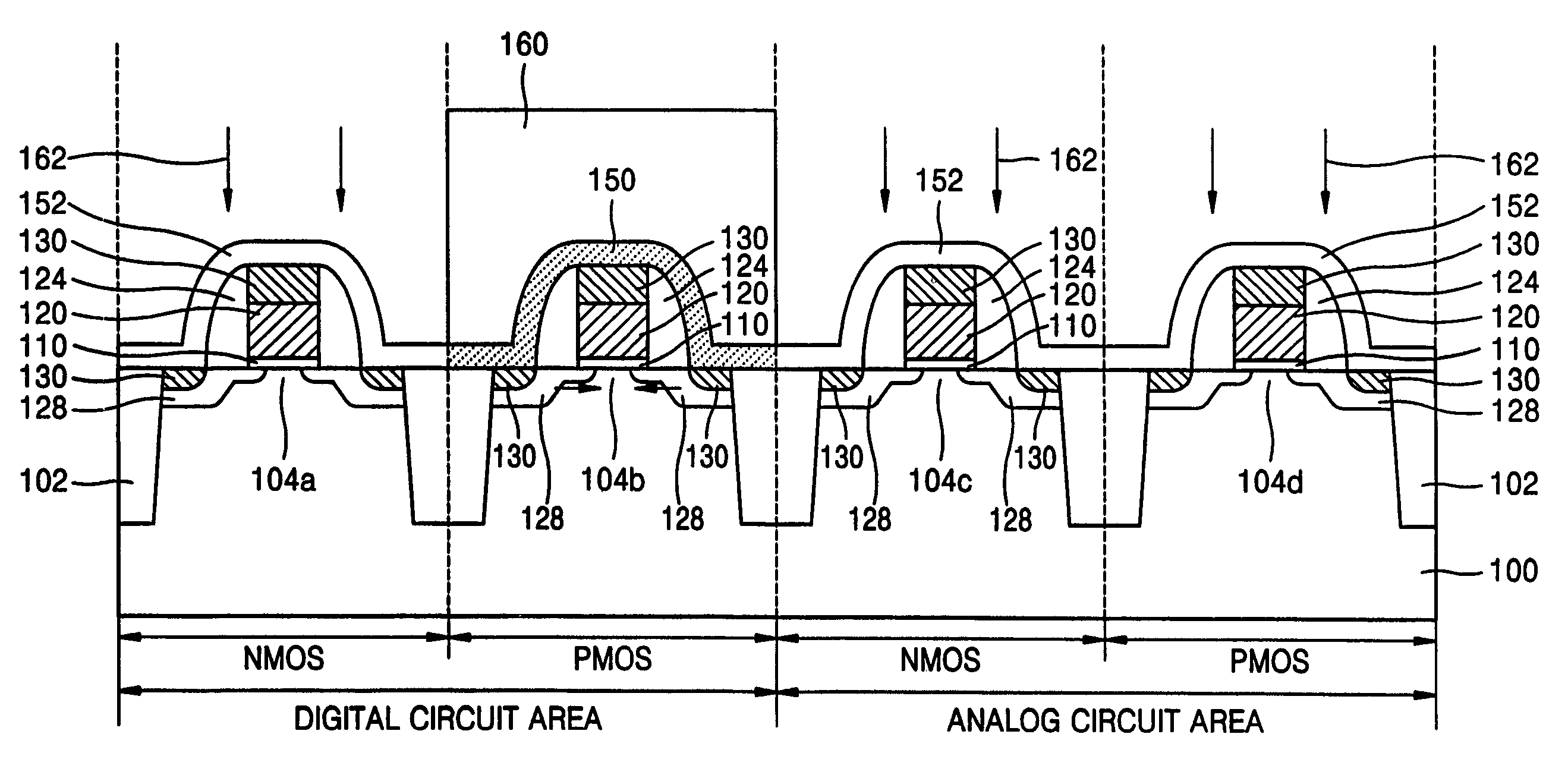
ActiveUS20080099786A1Improve device performanceReduce impactTransistorSolid-state devicesLow noiseLow speed
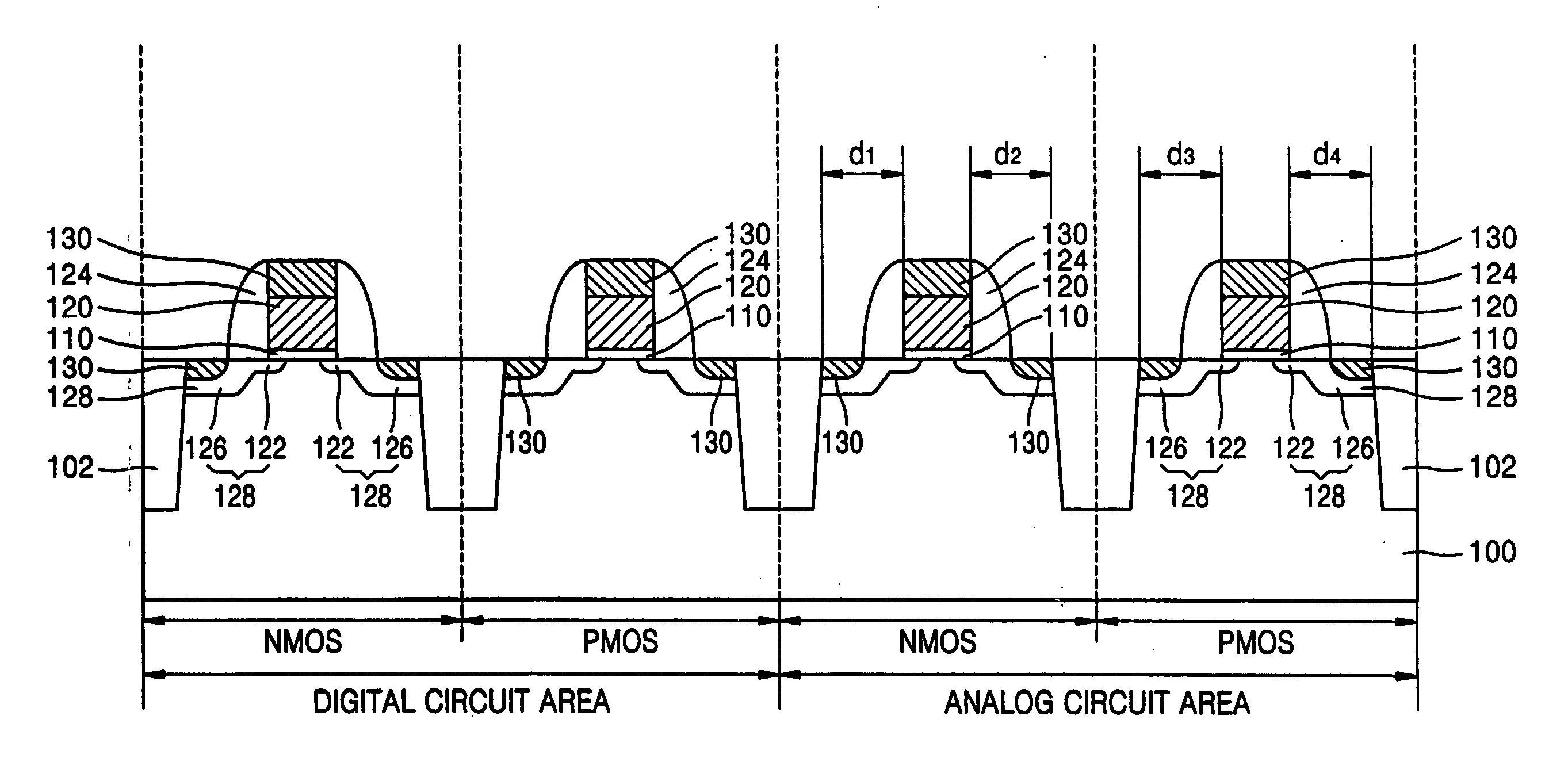
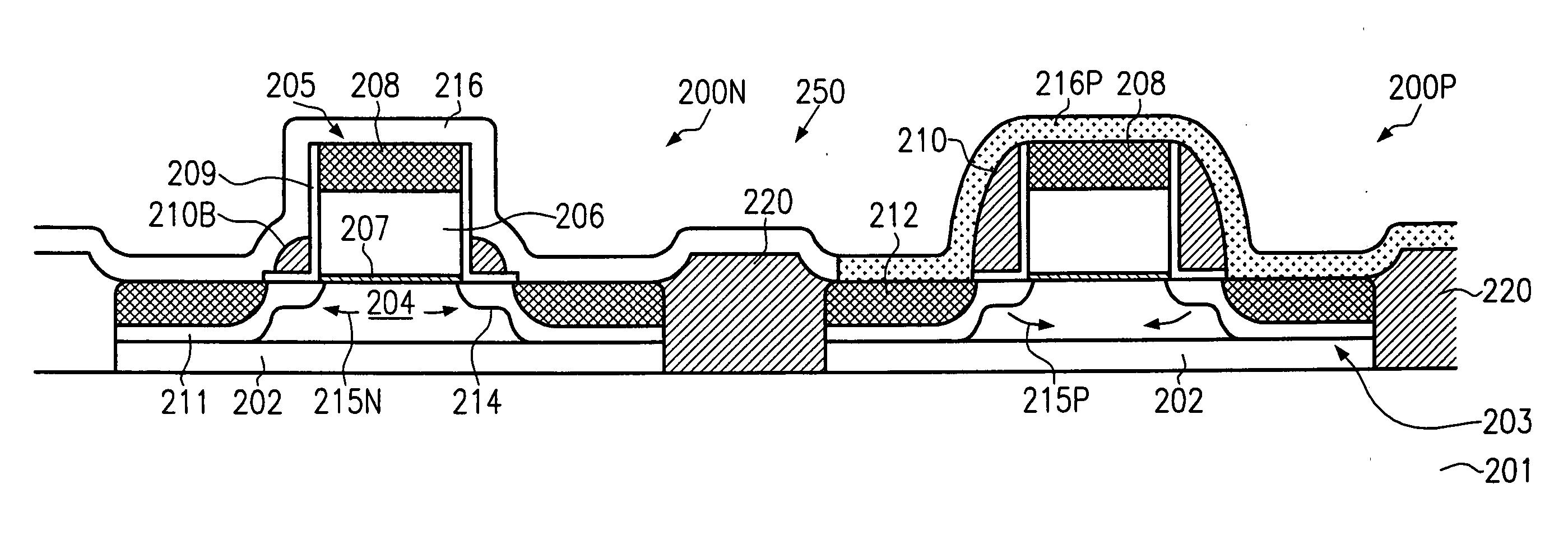
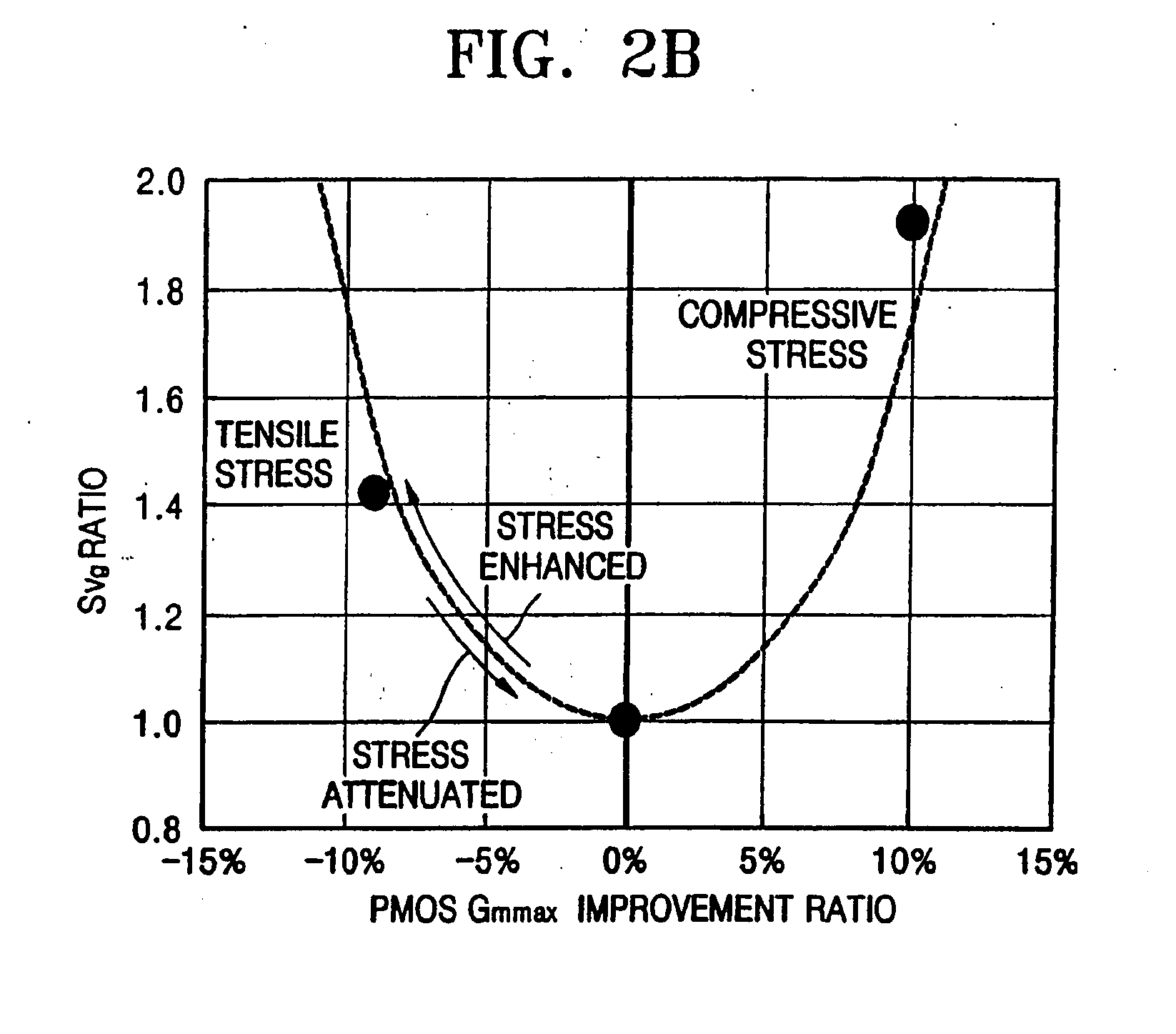
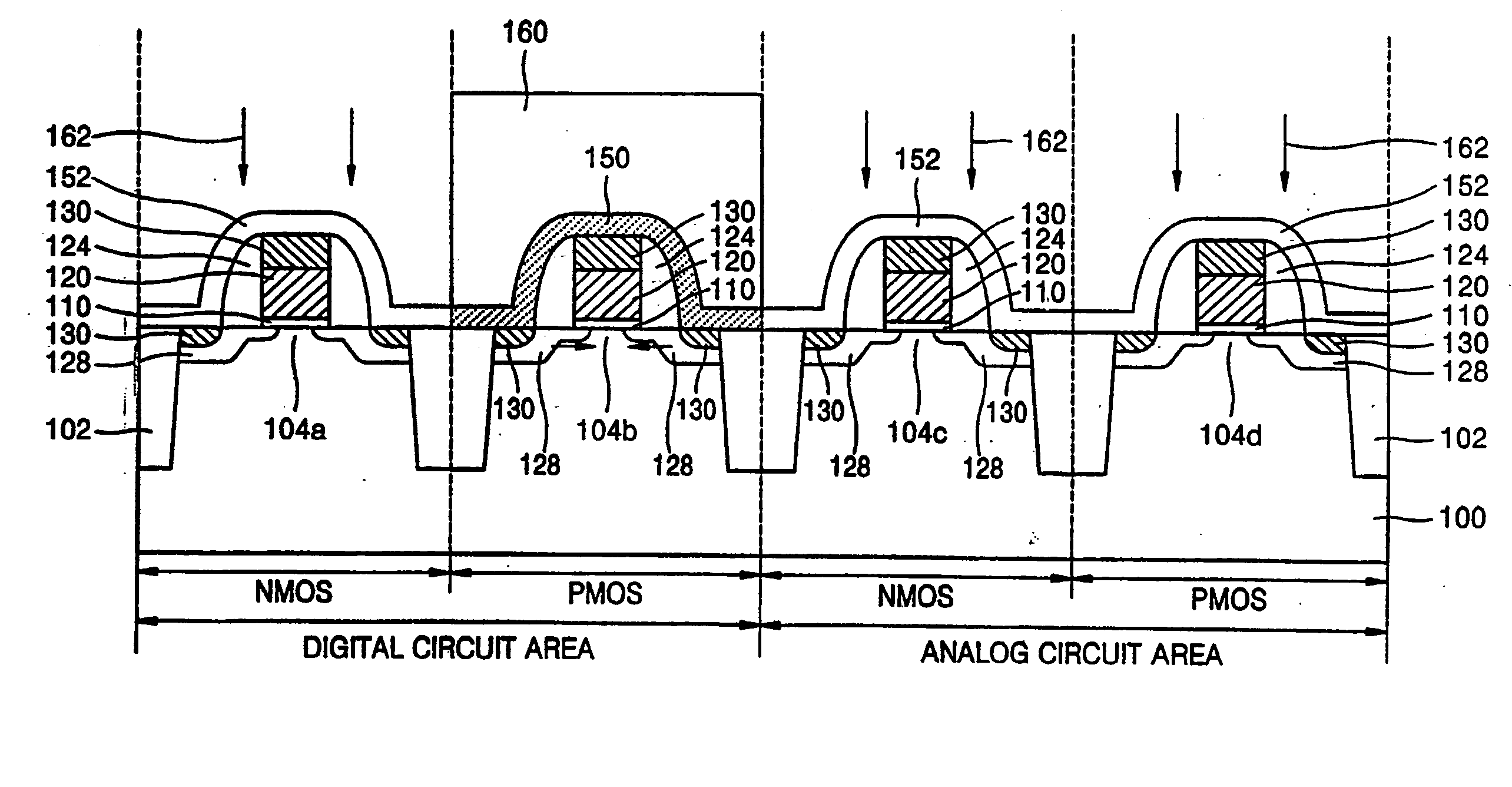
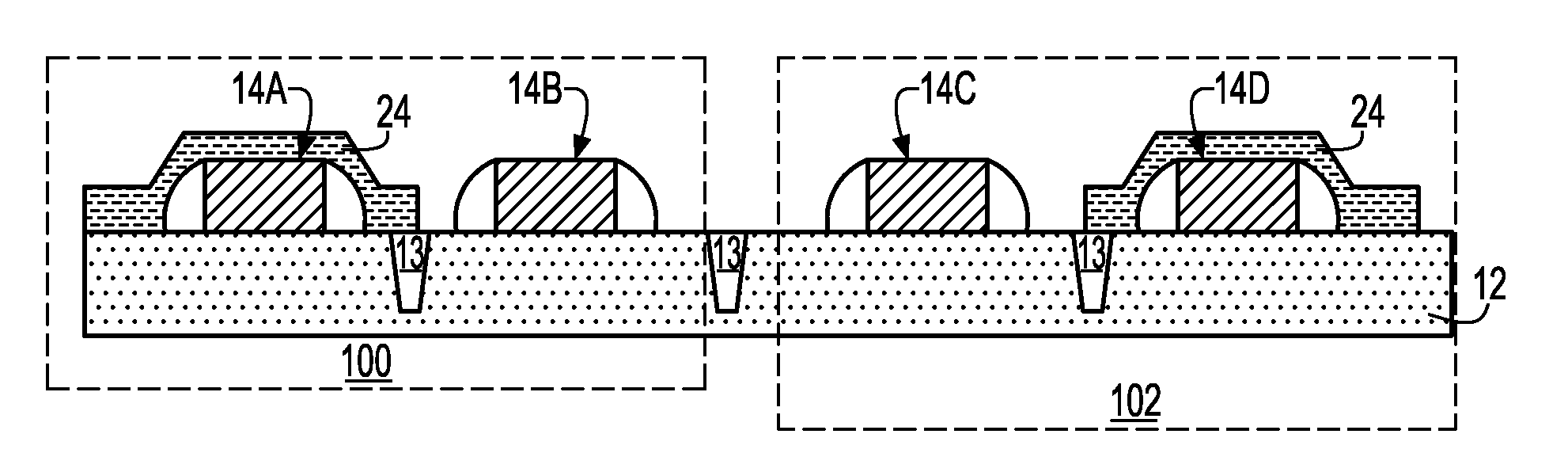
In semiconductor devices in which both NMOS devices and PMOS devices are used to perform in different modes such as analog and digital modes, stress engineering is selectively applied to particular devices depending on their required operational modes. That is, the appropriate mechanical stress, i.e., tensile or compressive, can be applied to and / or removed from devices, i.e., NMOS and / or PMOS devices, based not only on their conductivity type, i.e., n-type or p-type, but also on their intended operational application, for example, analog / digital, low-voltage / high-voltage, high-speed / low-speed, noise-sensitive / noise-insensitive, etc. The result is that performance of individual devices is optimized based on the mode in which they operate. For example, mechanical stress can be applied to devices that operate in high-speed digital settings, while devices that operate in analog or RF signal settings, in which electrical noise such as flicker noise that may be introduced by applied stress may degrade performance, have no stress applied.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
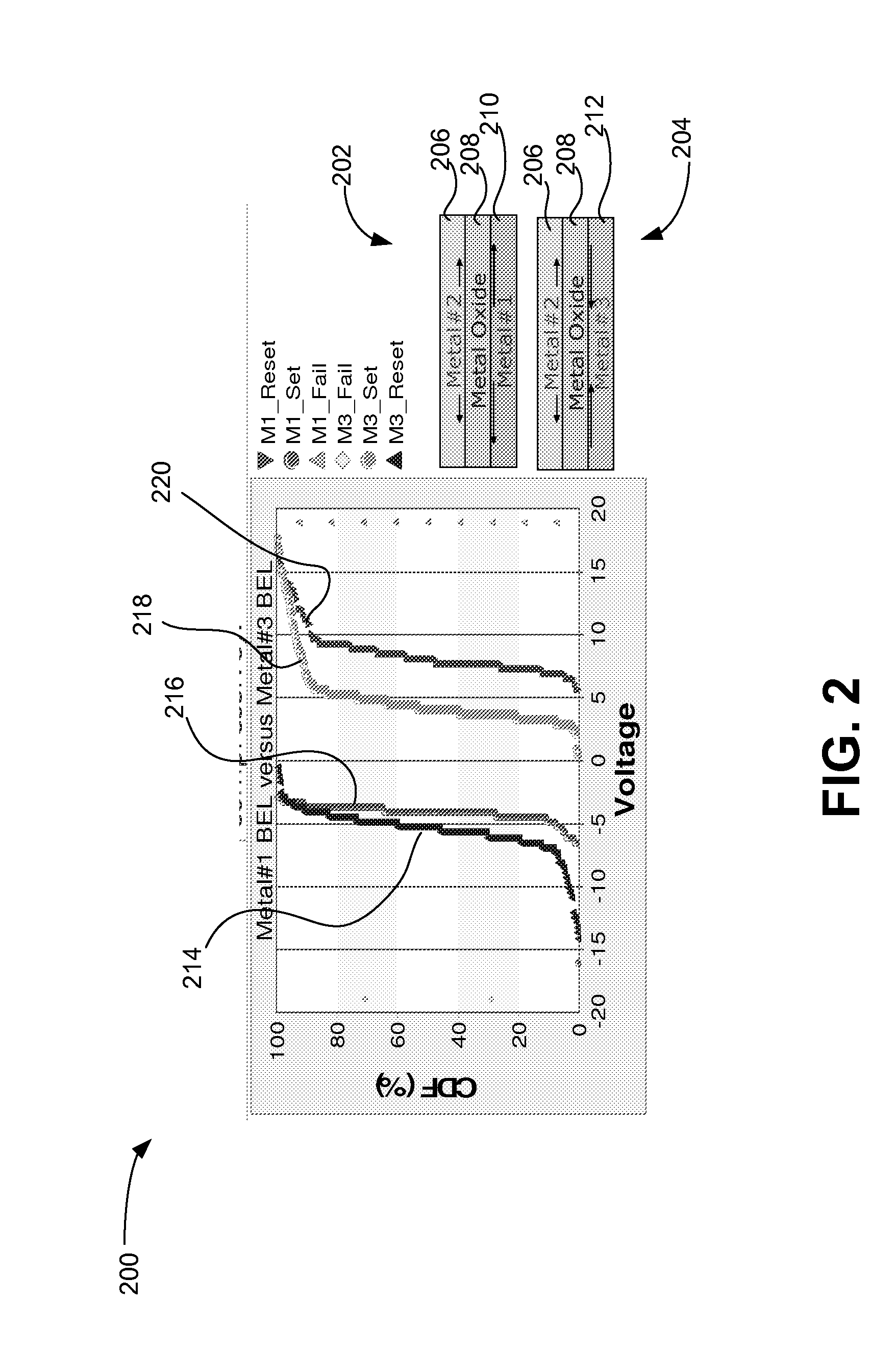
Stress-engineered resistance-change memory device
ActiveUS8049305B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceComputational physics
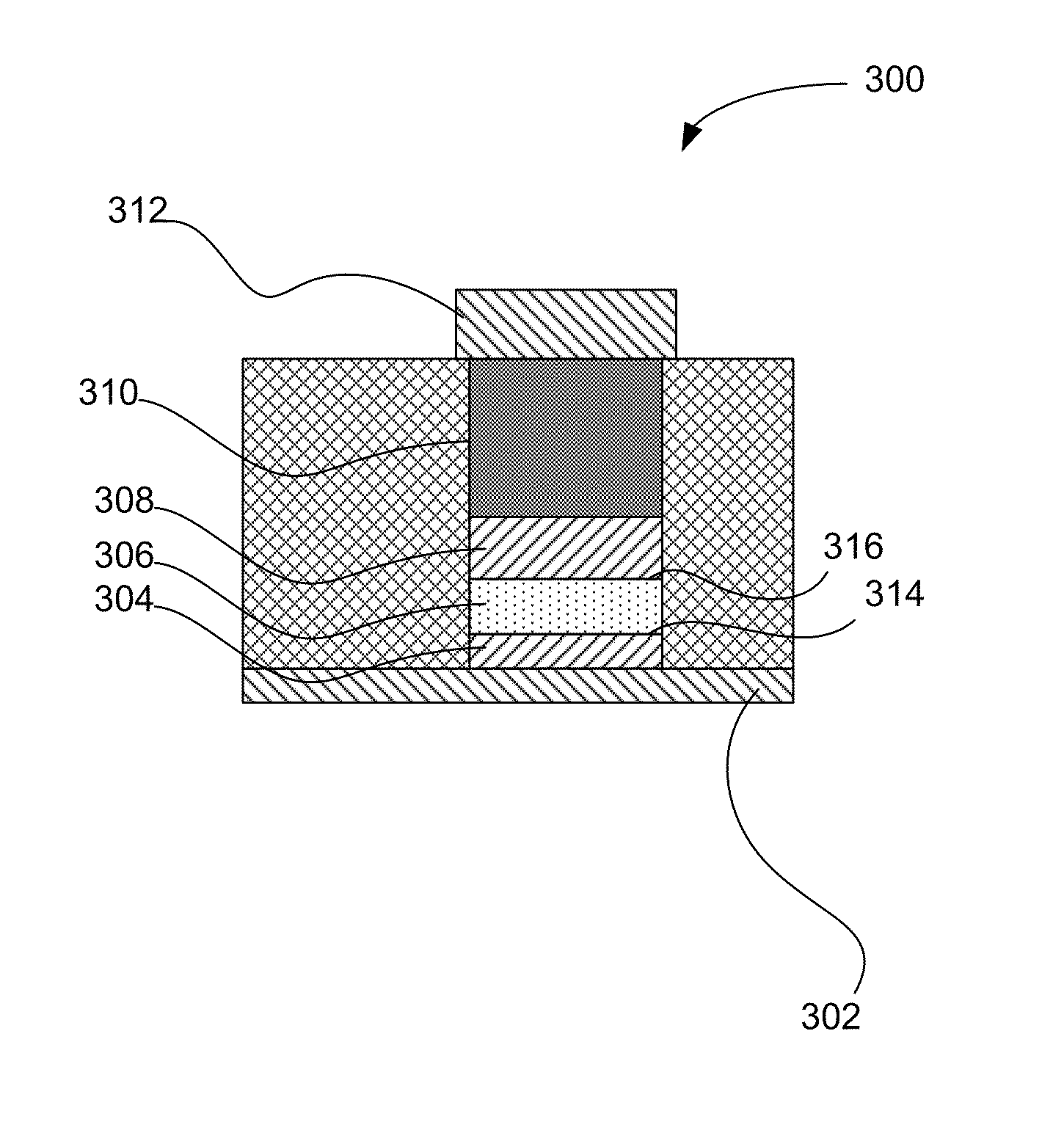
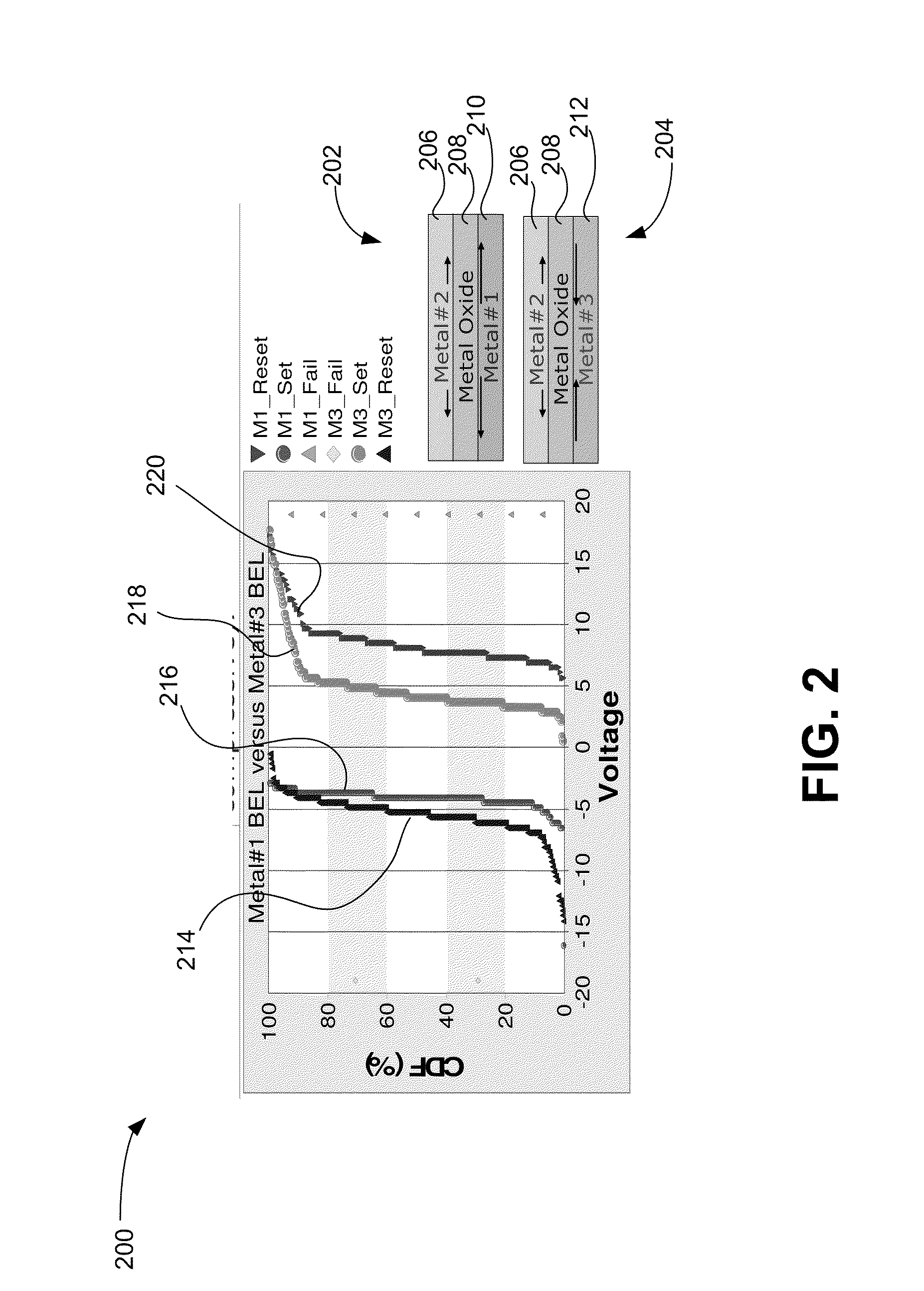
A resistance-change memory device using stress engineering is described, including a first layer including a first conductive electrode, a second layer above the first layer including a resistive-switching element, a third layer above the second layer including a second conductive electrode, where a first stress is created in the switching element at a first interface between the first layer and the second layer upon heating the memory element, and where a second stress is created in the switching element at a second interface between the second layer and the third layer upon the heating. A stress gradient equal to a difference between the first stress and the second stress has an absolute value greater than 50 MPa, and a reset voltage of the memory element has a polarity relative to a common electrical potential that has a sign opposite the stress gradient when applied to the first conductive electrode.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Low noise and high performance LSI device, layout and manufacturing method
ActiveUS20080064157A1Improve device performanceReduce impactTransistorSolid-state devicesLow noiseLow speed
In semiconductor devices in which both NMOS devices and PMOS devices are used to perform in different modes such as analog and digital modes, stress engineering is selectively applied to particular devices depending on their required operational modes. That is, the appropriate mechanical stress, i.e., tensile or compressive, can be applied to and / or removed from devices, i.e., NMOS and / or PMOS devices, based not only on their conductivity type, i.e., n-type or p-type, but also on their intended operational application, for example, analog / digital, low-voltage / high-voltage, high-speed / low-speed, noise-sensitive / noise-insensitive, etc. The result is that performance of individual devices is optimized based on the mode in which they operate. For example, mechanical stress can be applied to devices that operate in high-speed digital settings, while devices that operate in analog or RF signal settings, in which electrical noise such as flicker noise that may be introduced by applied stress may degrade performance, have no stress applied.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
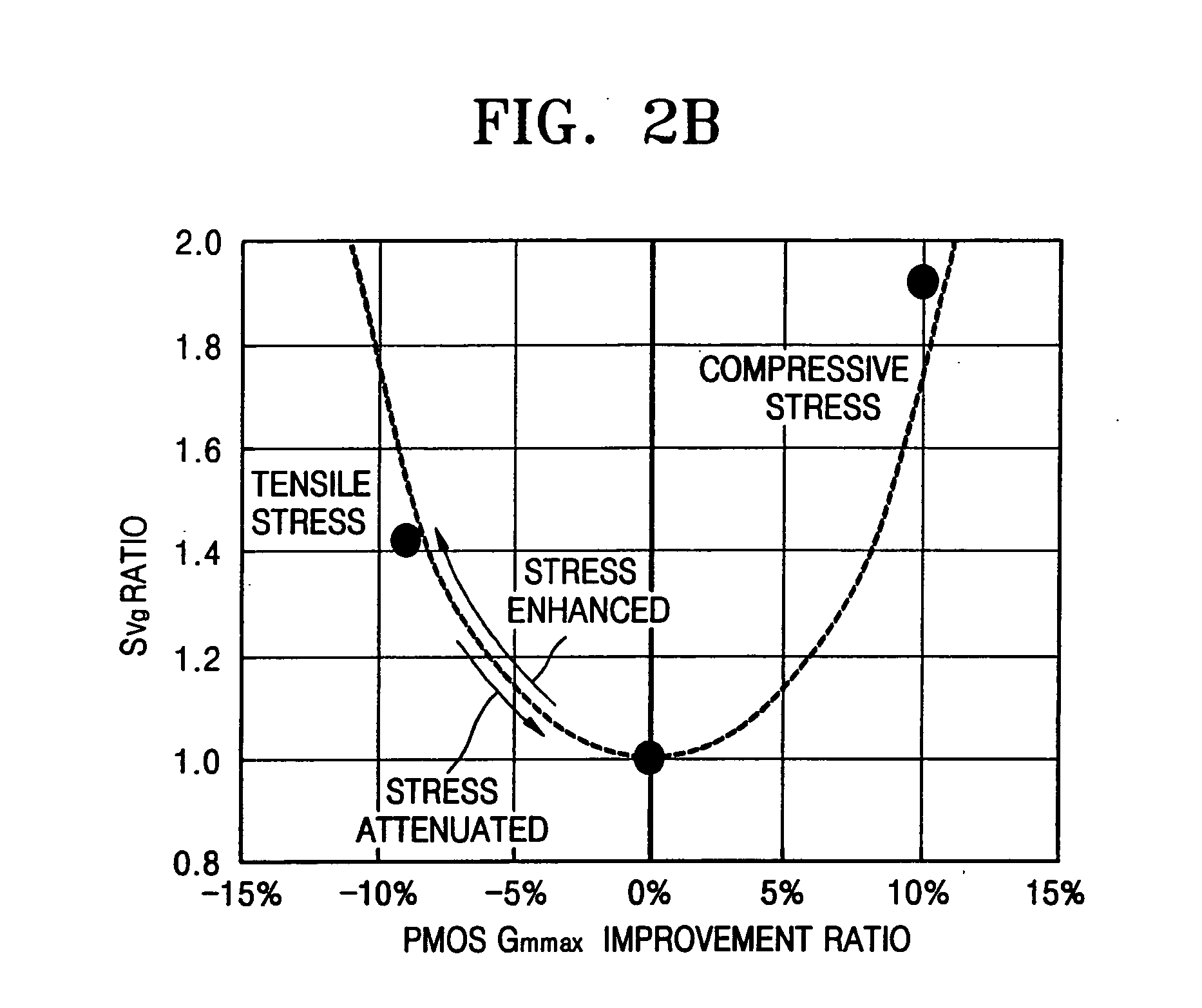
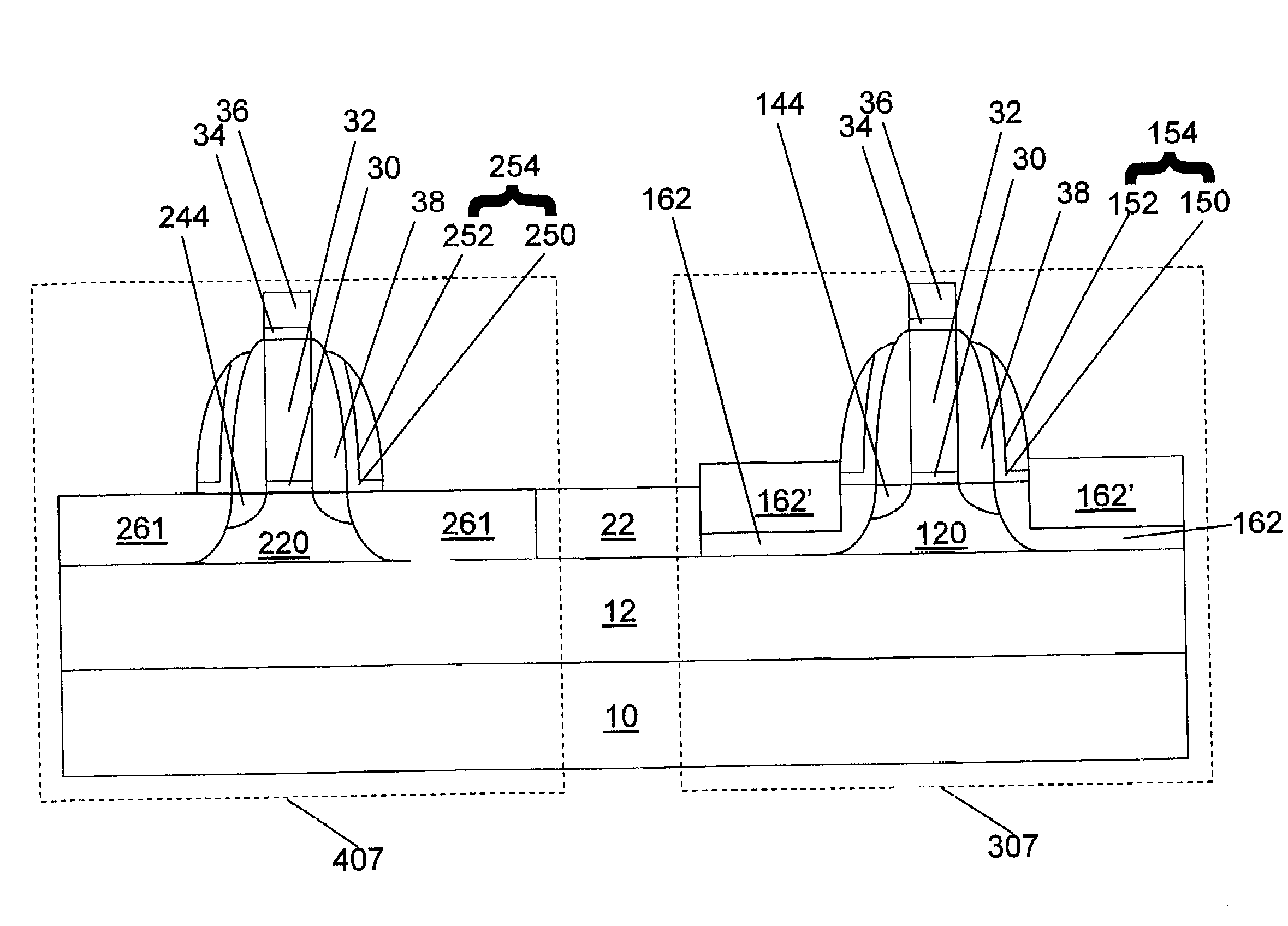
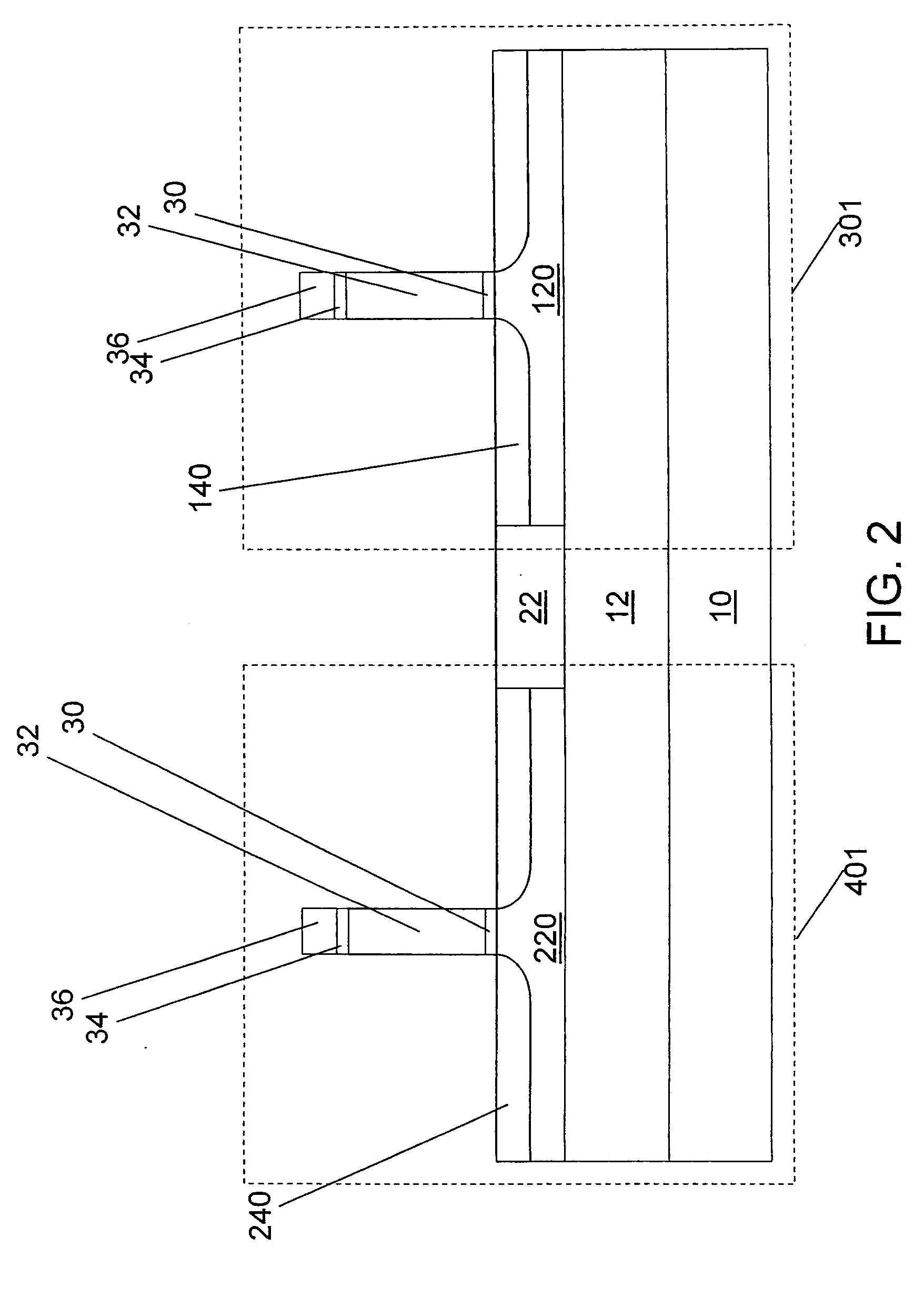
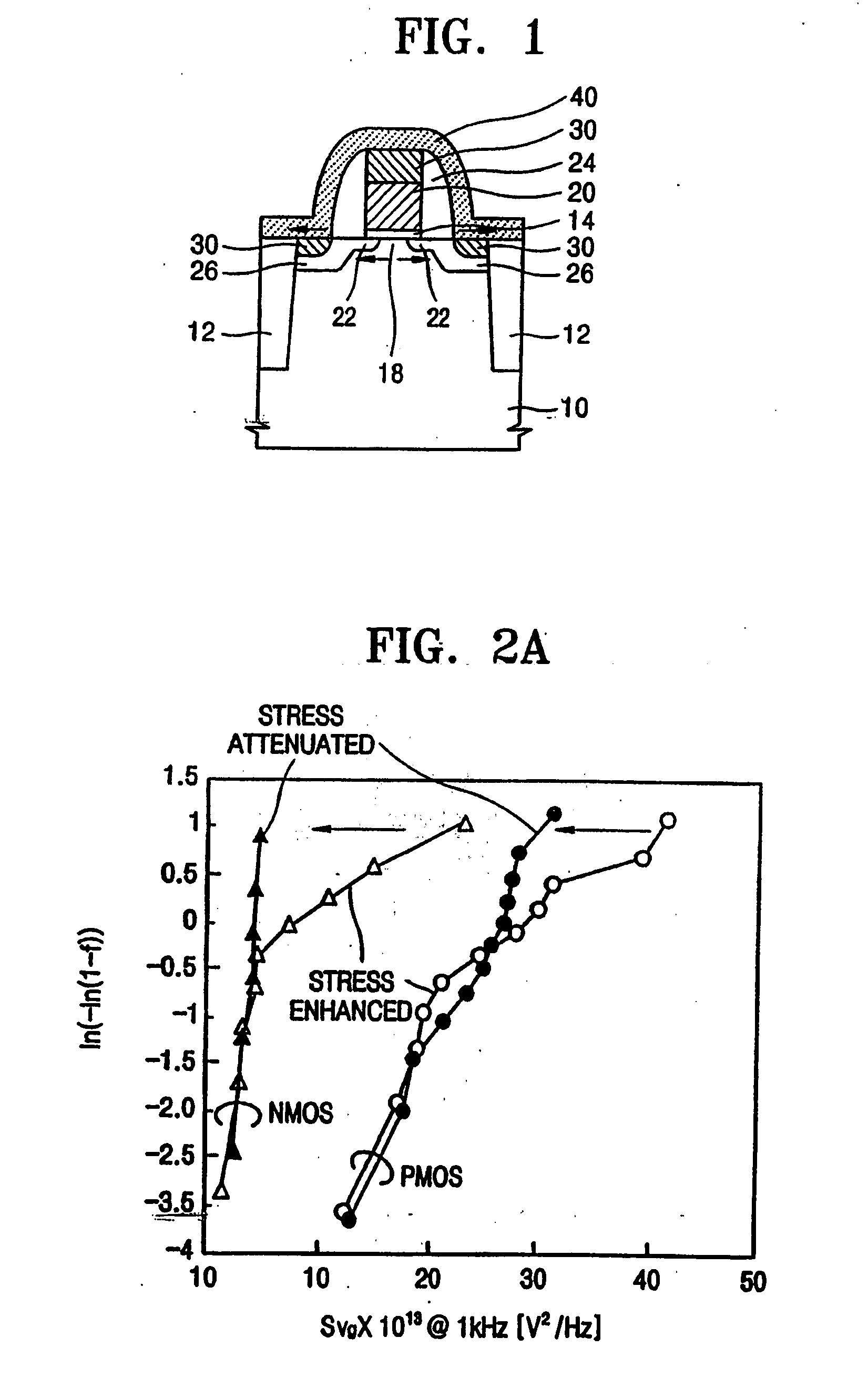
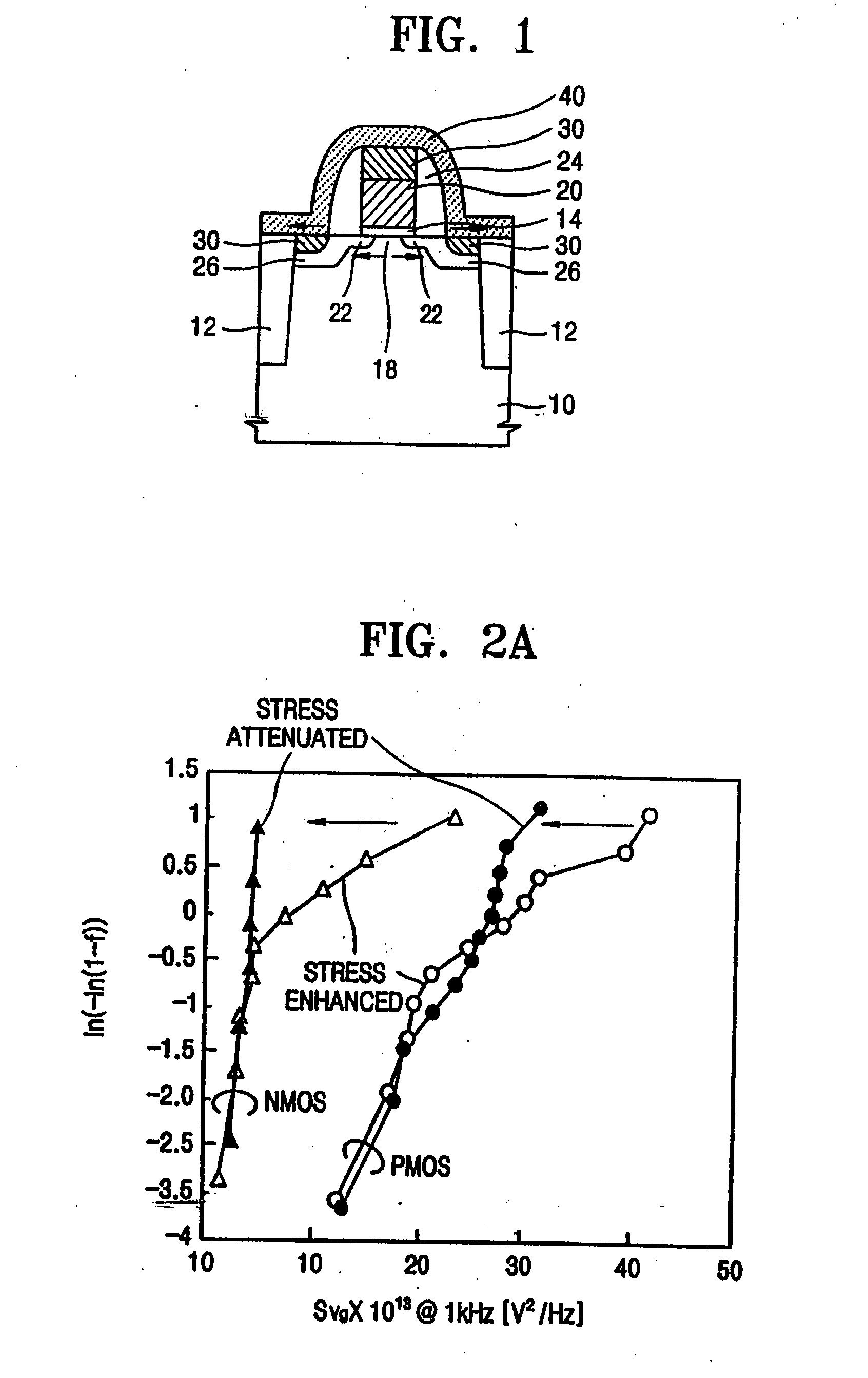
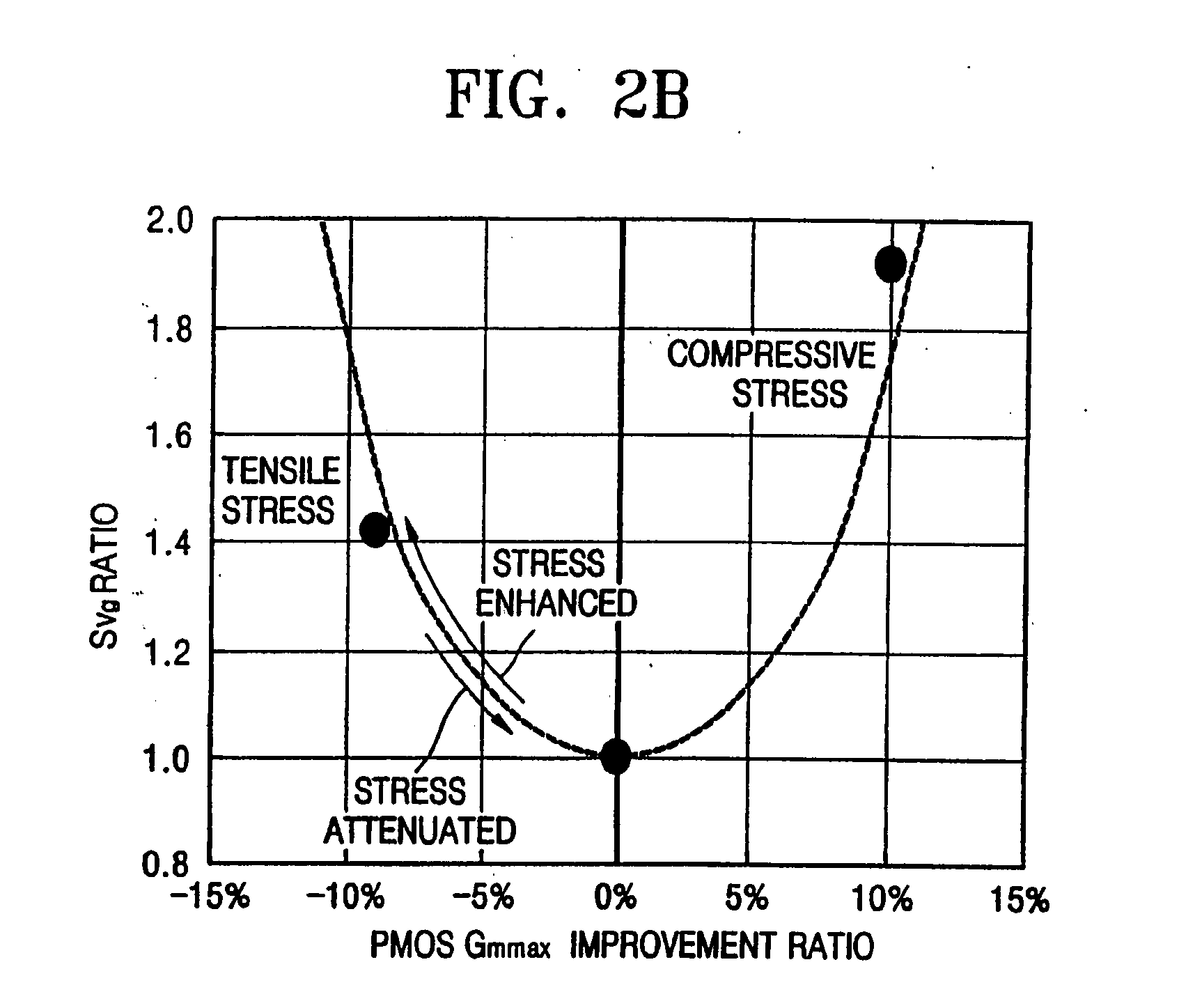
Selective stress engineering for SRAM stability improvement
InactiveUS7388267B1Improve stabilityImprove performanceTransducer detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSGreek letter beta
An integrated circuit (IC) structure including a SRAM cell is provided in which the performance of the pass-gate transistors is degraded in order to increase the beta ratio of the transistors within the SRAM cell. In particular, the increased beta ratio is obtained in the present invention by intentionally improving only the performance of the pull-down transistors, while degrading the performance of the pass-gate transistors. This result is achieved in the present invention by implementing stress memorization technique on logic complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) nFETs and SRAM pull-down transistors to improve the nFET performance. The stress memorization technique is not performed at the pFET region to avoid performance degradation as well as at the SRAM pass-gate transistors to avoid the improvement. With performance improvement at the pull-down transistors and no performance improvement at the pass-gate transistors, the beta ratio of the SRAM transistors is improved.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
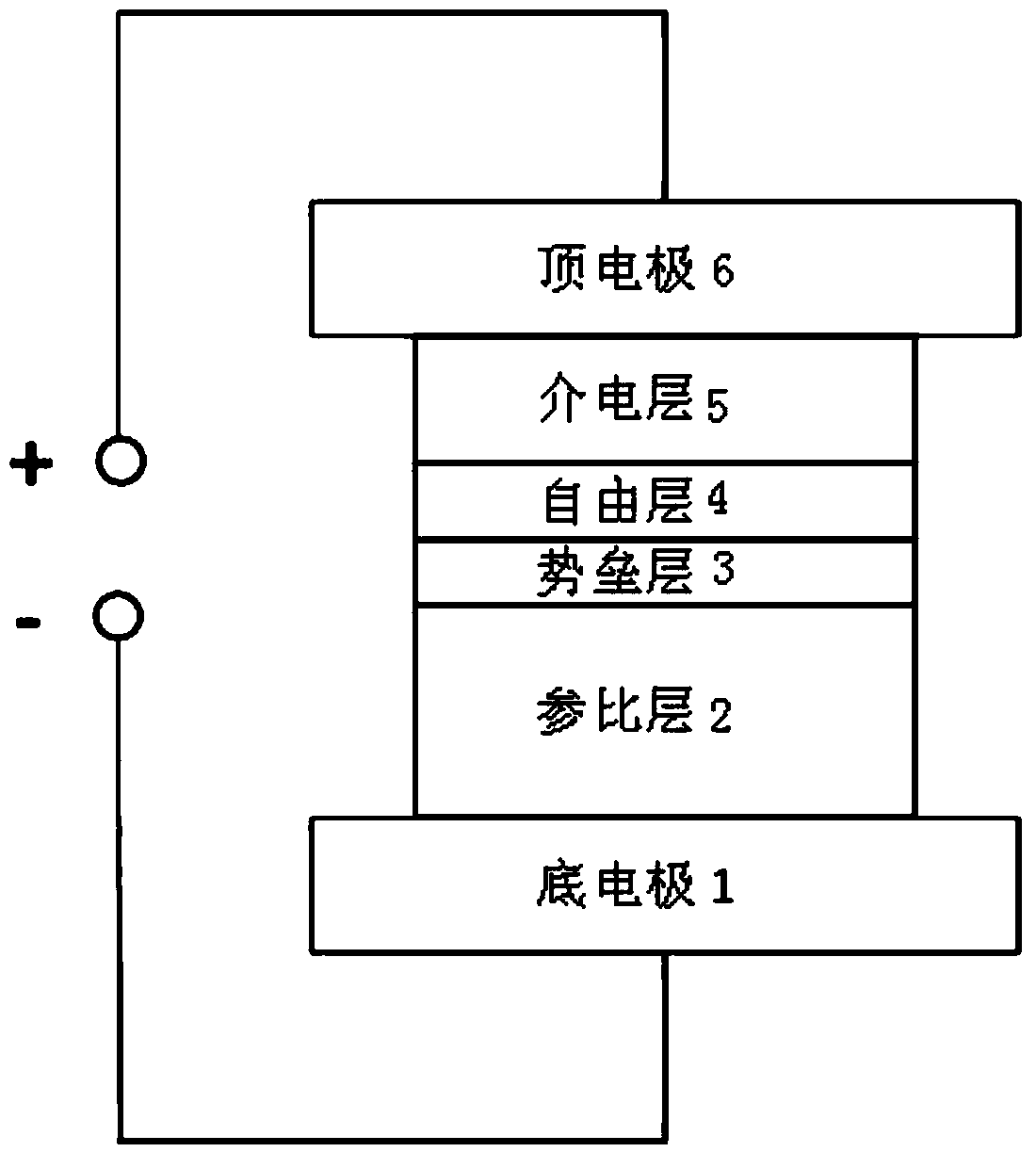
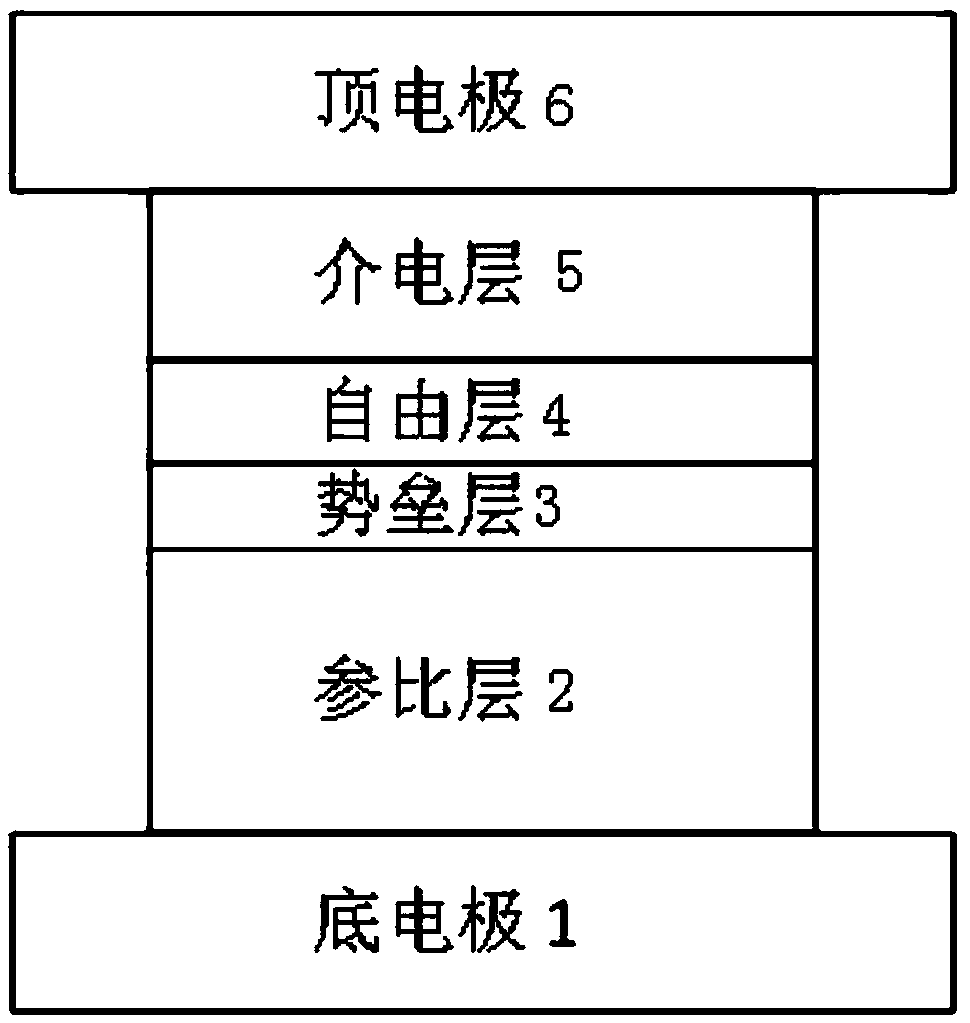
Stress-assisted spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory, preparation method thereof, and usage method thereof
ActiveCN105374934ASmall working currentReduced perpendicular magnetic anisotropyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic device detailsPerpendicular anisotropySpin-transfer torque
Owner:CETHIK GRP
STRUCTURES AND METHODS FOR MANUFACTURING OF DISLOCATION FREE STRESSED CHANNELS IN BULK SILICON AND SOI MOS DEVICES BY GATE STRESS ENGINEERING WITH SiGe AND/OR Si:C
InactiveUS20080064197A1Avoid misalignmentReduce generationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSGate dielectric
Structures and methods of manufacturing are disclosed of dislocation free stressed channels in bulk silicon and SOI (silicon on insulator) CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) devices by gate stress engineering with SiGe and / or Si:C. A CMOS device comprises a substrate of either bulk Si or SOI, a gate dielectric layer over the substrate, and a stacked gate structure of SiGe and / or Si:C having stresses produced at the interfaces of SSi(strained Si) / SiGe or SSi / Si:C in the stacked gate structure. The stacked gate structure has a first stressed film layer of large grain size Si or SiGe over the gate dielectric layer, a second stressed film layer of strained SiGe or strained Si:C over the first stressed film layer, and a semiconductor or conductor such as p(poly)-Si over the second stressed film layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
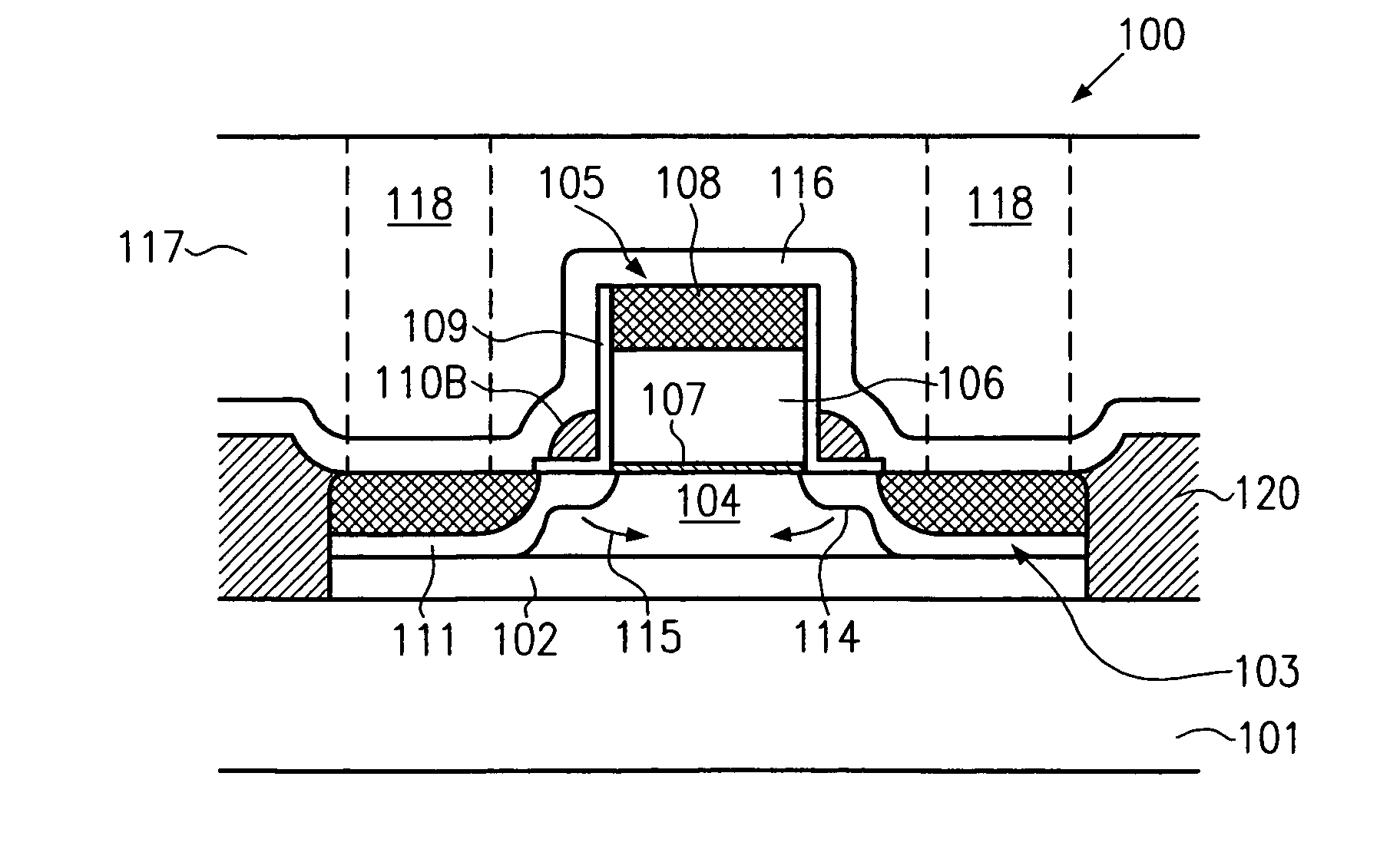
Channel stress engineering using localized ion implantation induced gate electrode volumetric change
InactiveUS20090090938A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesVolume variationSemiconductor structure
A method for fabricating a semiconductor structure uses a volumetric change ion implanted into a volumetric change portion of a gate electrode that is located over a channel region within a semiconductor substrate to form a volume changed portion of the gate electrode located over the channel region within the semiconductor substrate. The volume changed portion of the gate electrode is typically bidirectionally symmetrically graded in a vertical direction. The volume-changed portion of the gate electrode has a first stress that induces a second stress different than the first stress into the channel region of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Low noise and high performance LSI device, layout and manufacturing method
In semiconductor devices in which both NMOS devices and PMOS devices are used to perform in different modes such as analog and digital modes, stress engineering is selectively applied to particular devices depending on their required operational modes. That is, the appropriate mechanical stress, i.e., tensile or compressive, can be applied to and / or removed from devices, i.e., NMOS and / or PMOS devices, based not only on their conductivity type, i.e., n-type or p-type, but also on their intended operational application, for example, analog / digital, low-voltage / high-voltage, high-speed / low-speed, noise-sensitive / noise-insensitive, etc. The result is that performance of individual devices is optimized based on the mode in which they operate. For example, mechanical stress can be applied to devices that operate in high-speed digital settings, while devices that operate in analog or RF signal settings, in which electrical noise such as flicker noise that may be introduced by applied stress may degrade performance, have no stress applied.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Stress-engineered resistance-change memory device
InactiveUS20120001148A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesResistive switchingComputational physics
A resistance-change memory device using stress engineering is described, including a first layer including a first conductive electrode, a second layer above the first layer including a resistive-switching element, a third layer above the second layer including a second conductive electrode, where a first stress is created in the switching element at a first interface between the first layer and the second layer upon heating the memory element, and where a second stress is created in the switching element at a second interface between the second layer and the third layer upon the heating. A stress gradient equal to a difference between the first stress and the second stress has an absolute value greater than 50 MPa, and a reset voltage of the memory element has a polarity relative to a common electrical potential that has a sign opposite the stress gradient when applied to the first conductive electrode
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Stress engineering for SRAM stability
InactiveUS20080142895A1Improve stabilityGood writabilityTransistorTransducer detailsStatic random-access memoryEngineering
An IC is provided that includes at least one SRAM cell in which the performance of the SRAM cell is enhanced, yet maintaining good stability and writability. In particular, the present invention provides an IC including at least one SRAM cell wherein the gamma ratio is about 1 or greater. In the present invention, the gamma ratio is increased with degraded pFET device performance. Moreover, in the inventive IC there is no stress liner boundary present in the SRAM region and ion variation for all devices is reduced as compared to that of a conventional SRAM structure. The present invention, solves the above by providing an integrated circuit (IC) that comprises at least one static random access memory cell including at least one nFET and at least one pFET; and a continuous relaxed stressed liner located above and adjoining the at least one nFET and the at least one pFET.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Structure of static random access memory with stress engineering for stability
InactiveUS7471548B2Improve performanceStability and writabilityTransistorTransducer detailsStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +1
Reduced wafer warpage in semiconductors by stress engineering in the metallization system
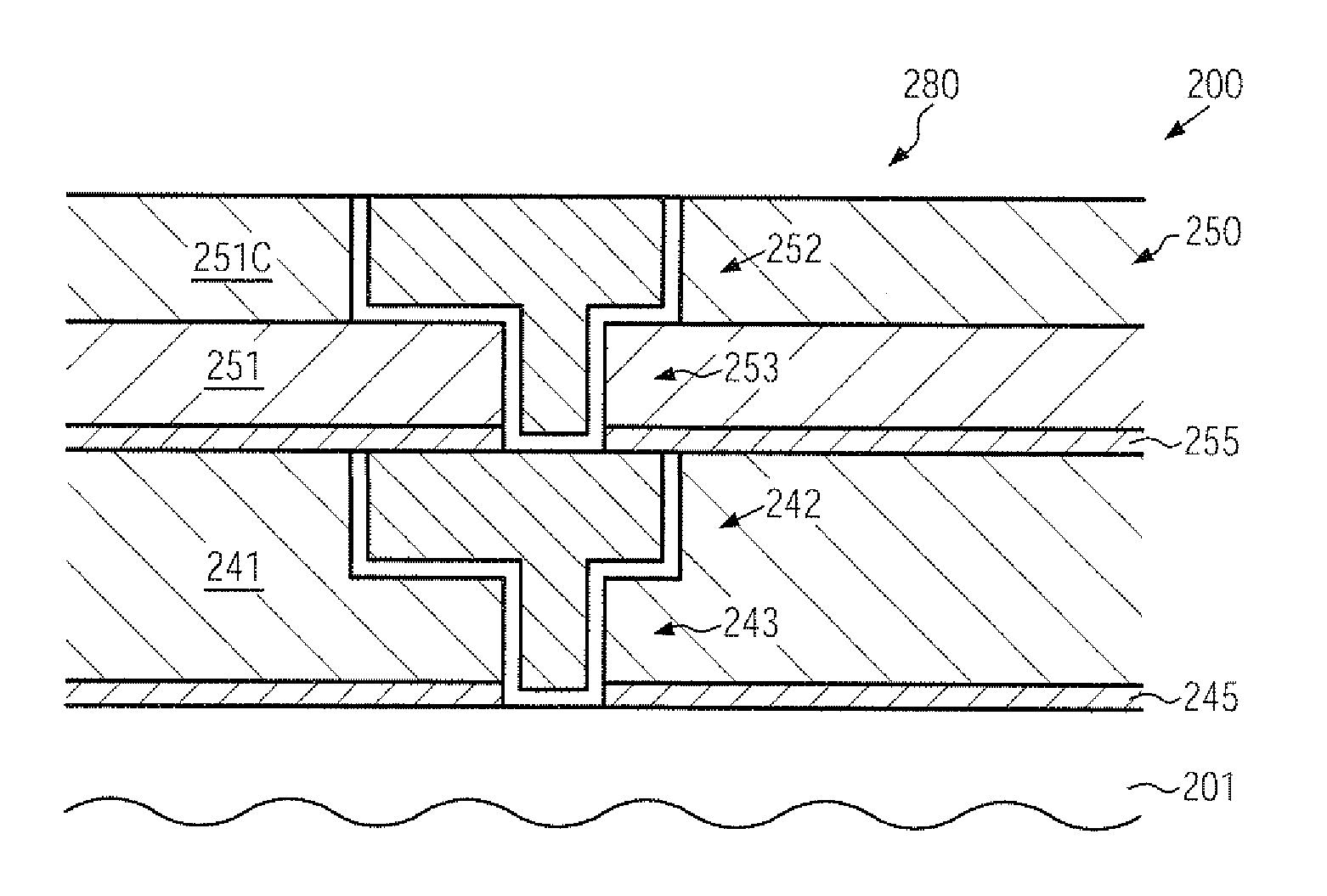
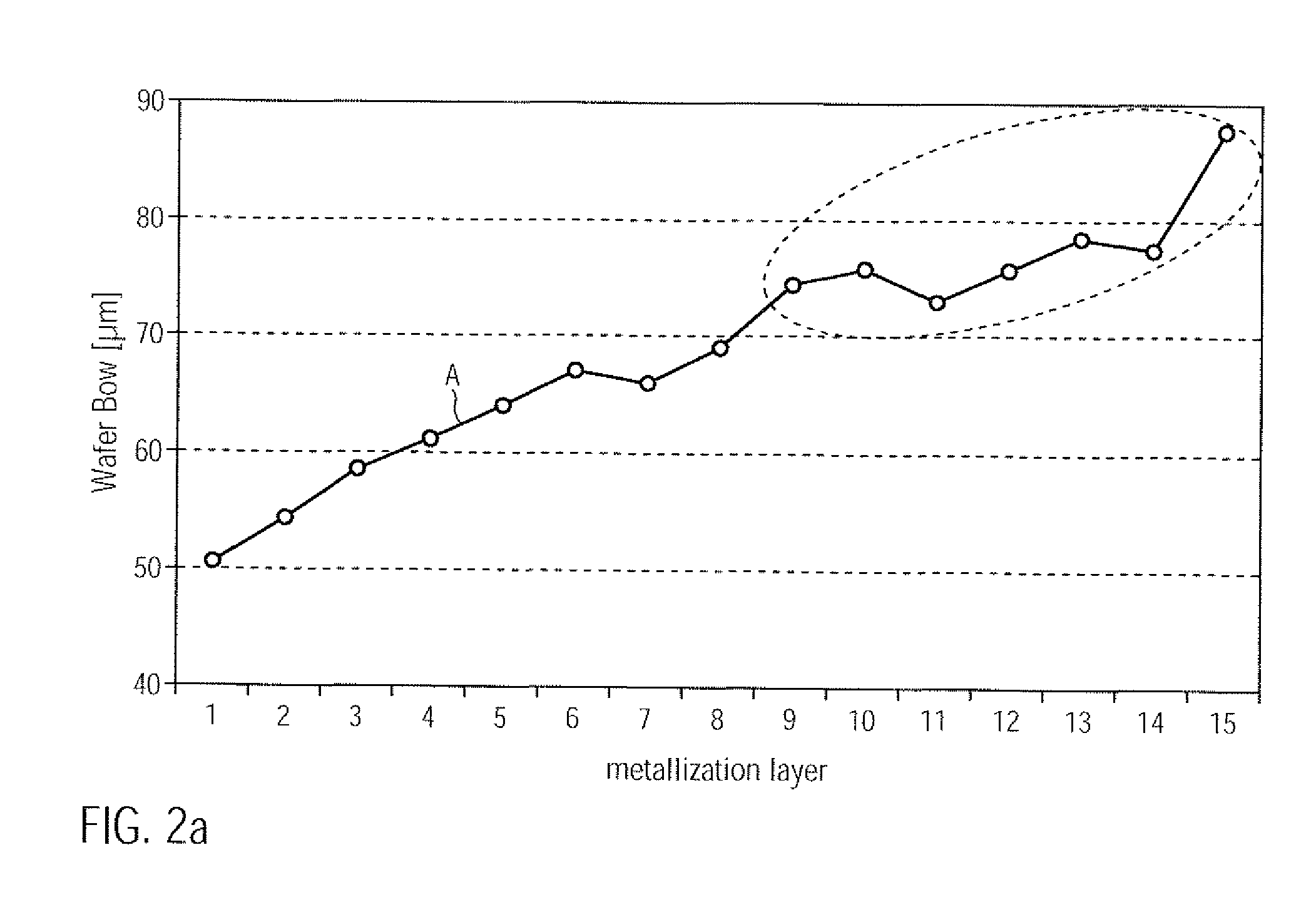
InactiveUS20100109131A1Improve compatibilityReduce probabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSubstrate deformation
In complex metallization systems of sophisticated semiconductor devices, appropriate stress compensation mechanisms may be implemented in order to reduce undue substrate deformation during the overall manufacturing process. For example, additional dielectric material and / or functional layers of one or more metallization layers may be provided with appropriate internal stress levels so as to maintain substrate warpage at a non-critical level, thereby substantially reducing yield losses in the manufacturing process caused by non-reliable attachment of substrates to substrate holders in process and transport tools.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com