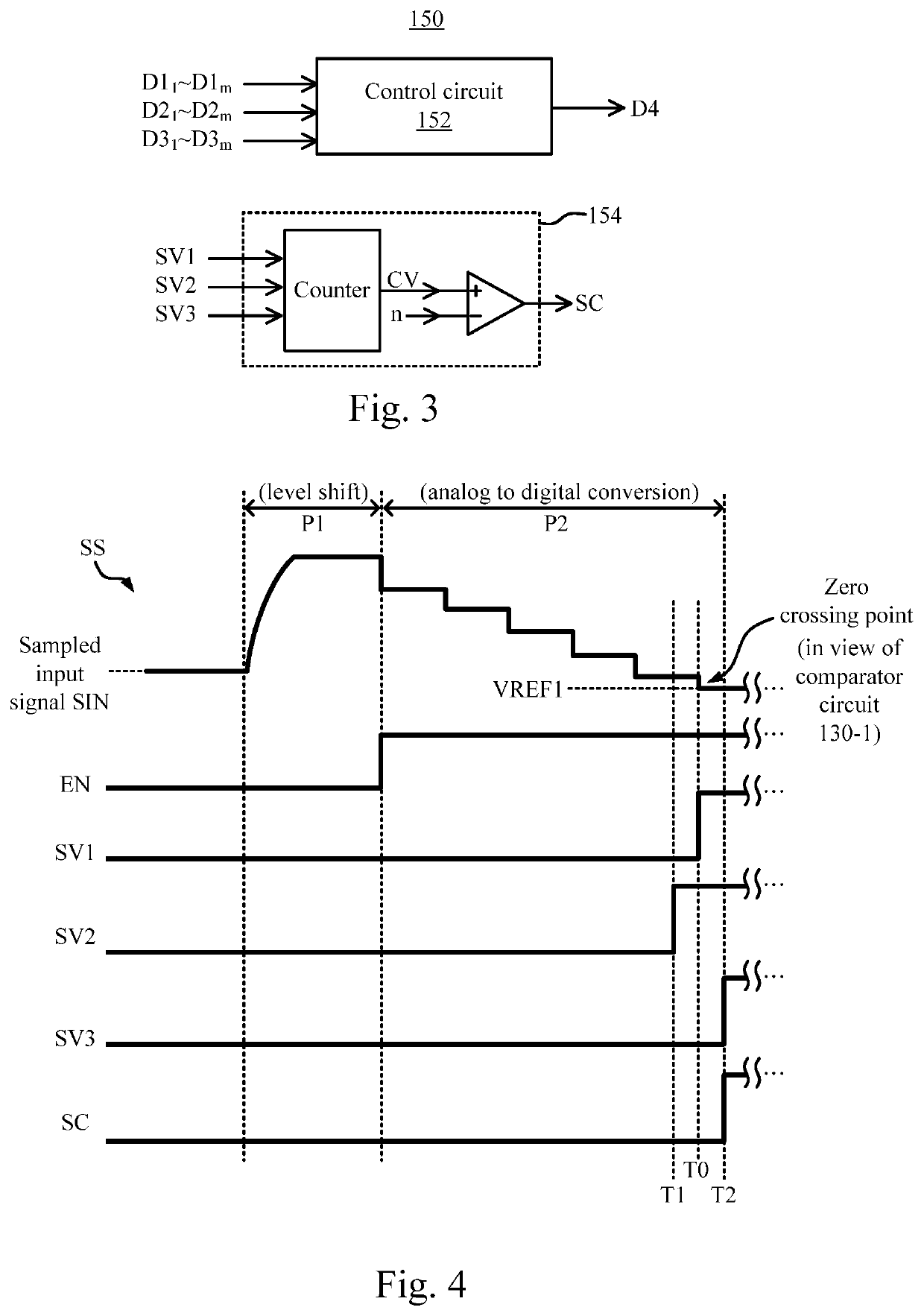
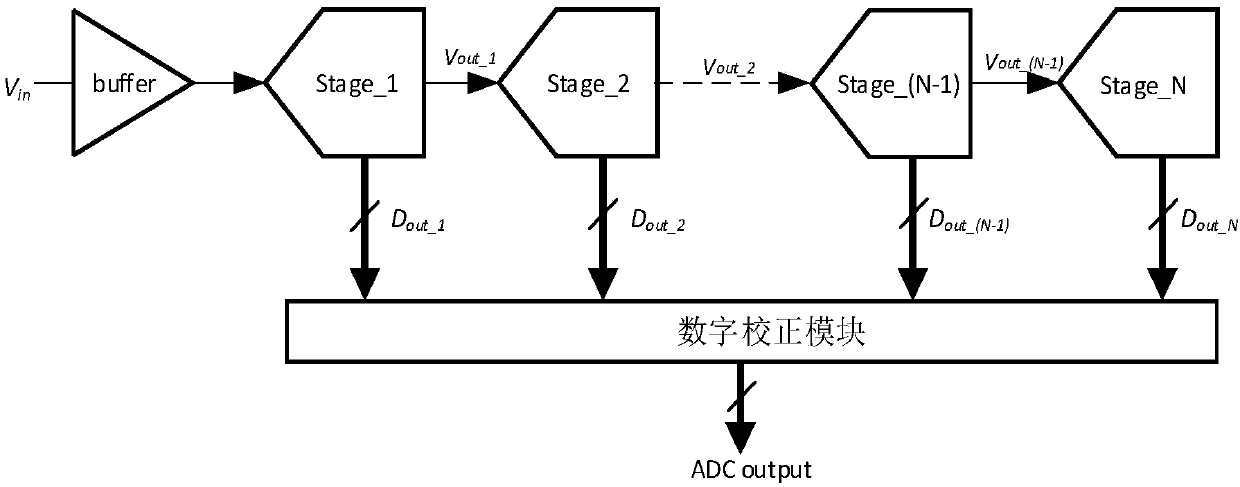
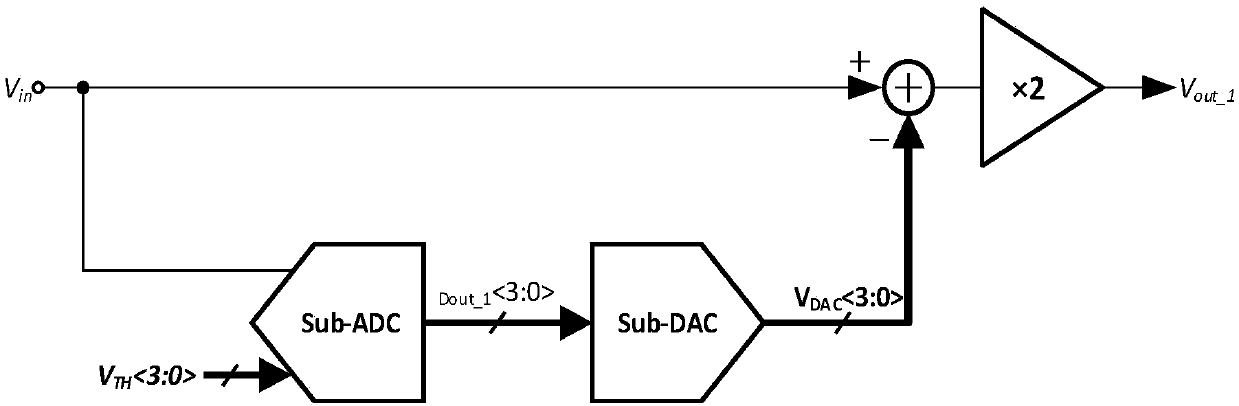
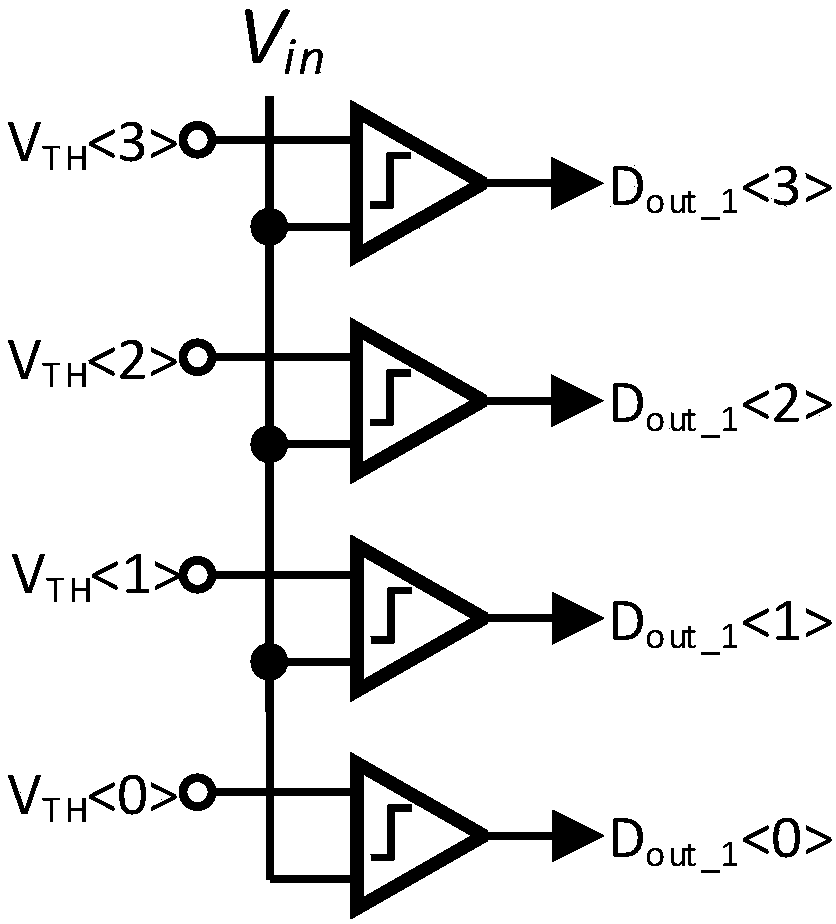
Patents
Literature
32results about "Conversion using stochastic techniques" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
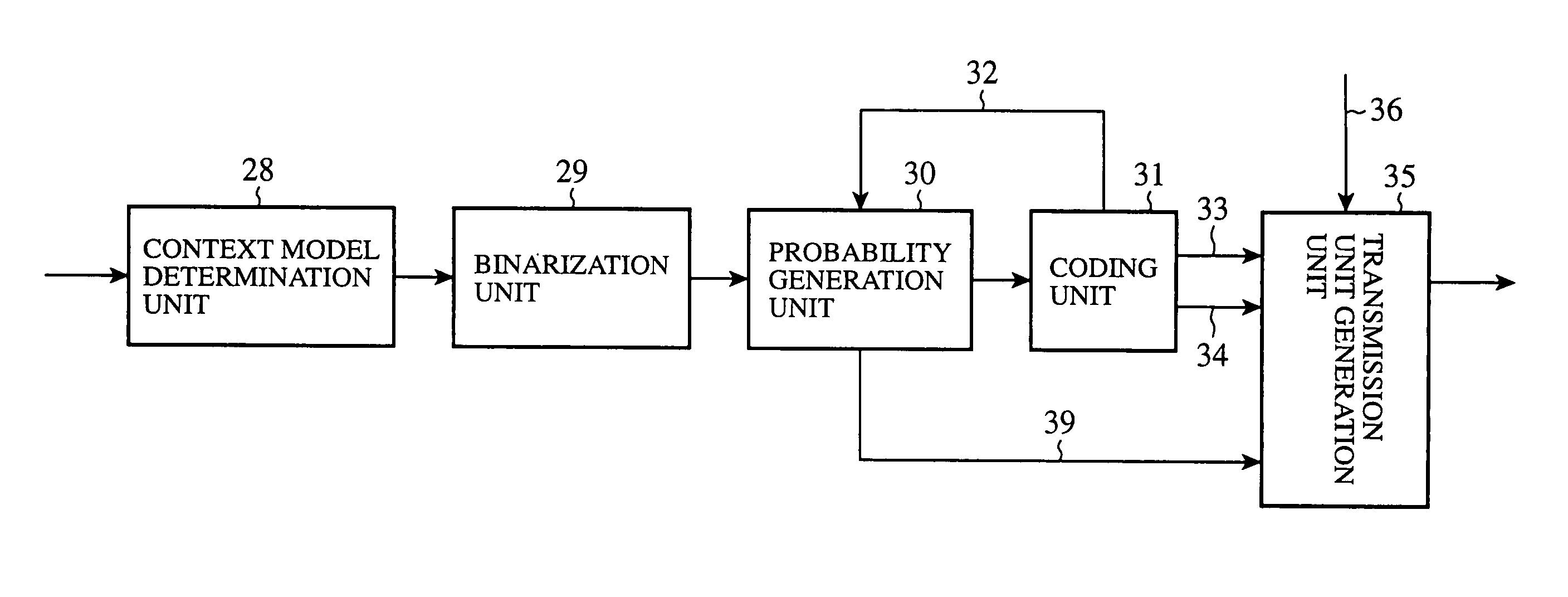
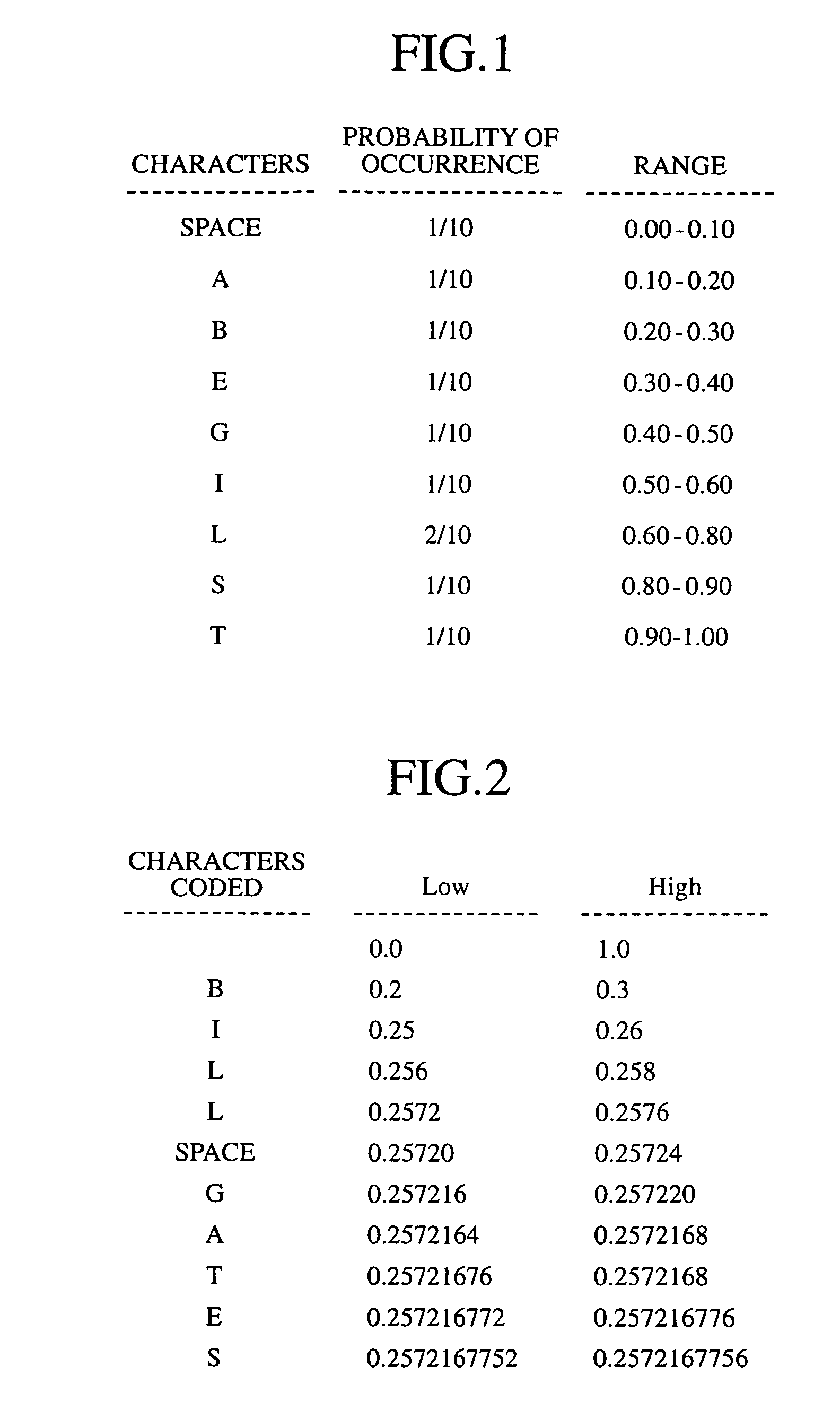
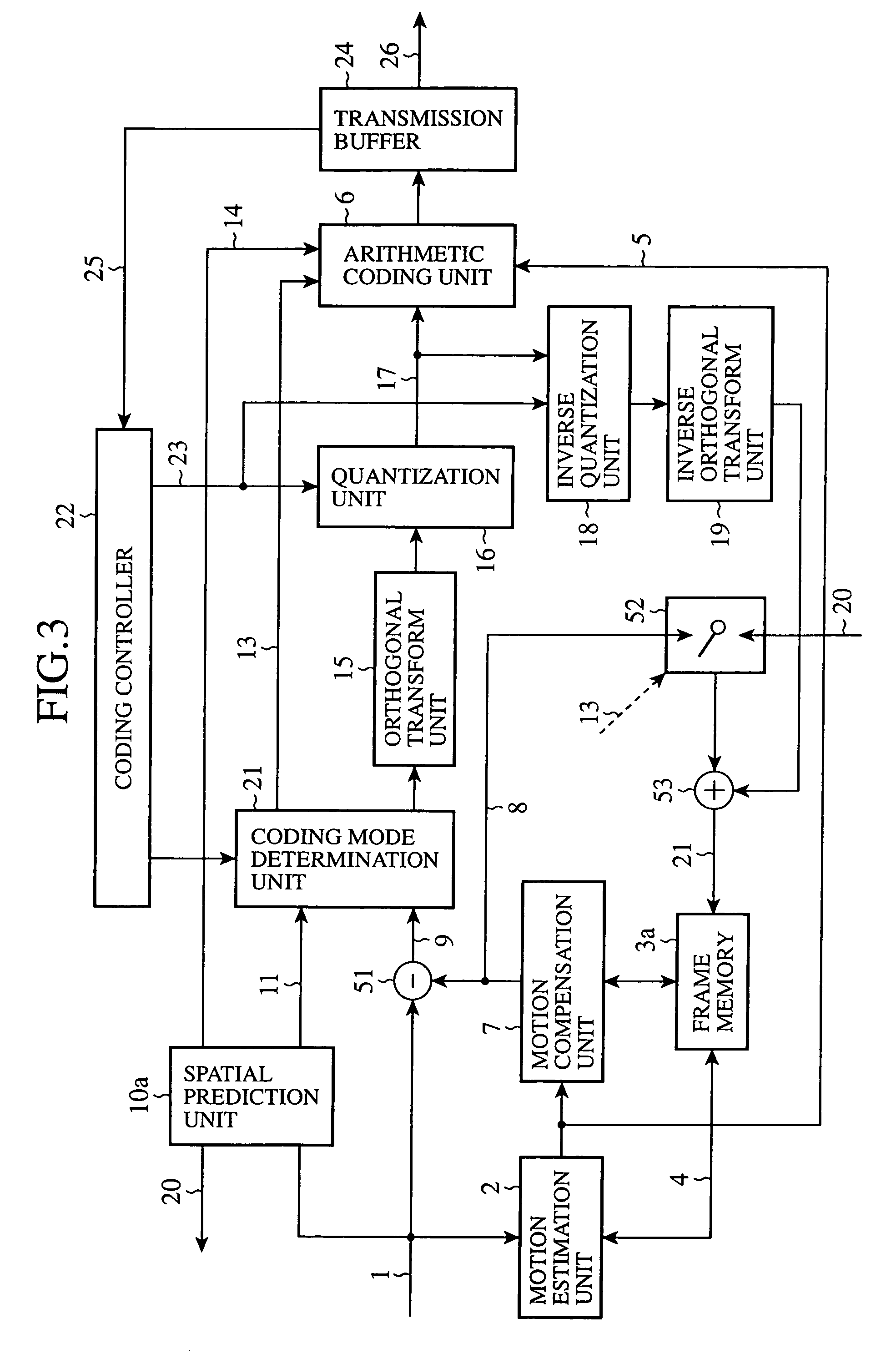
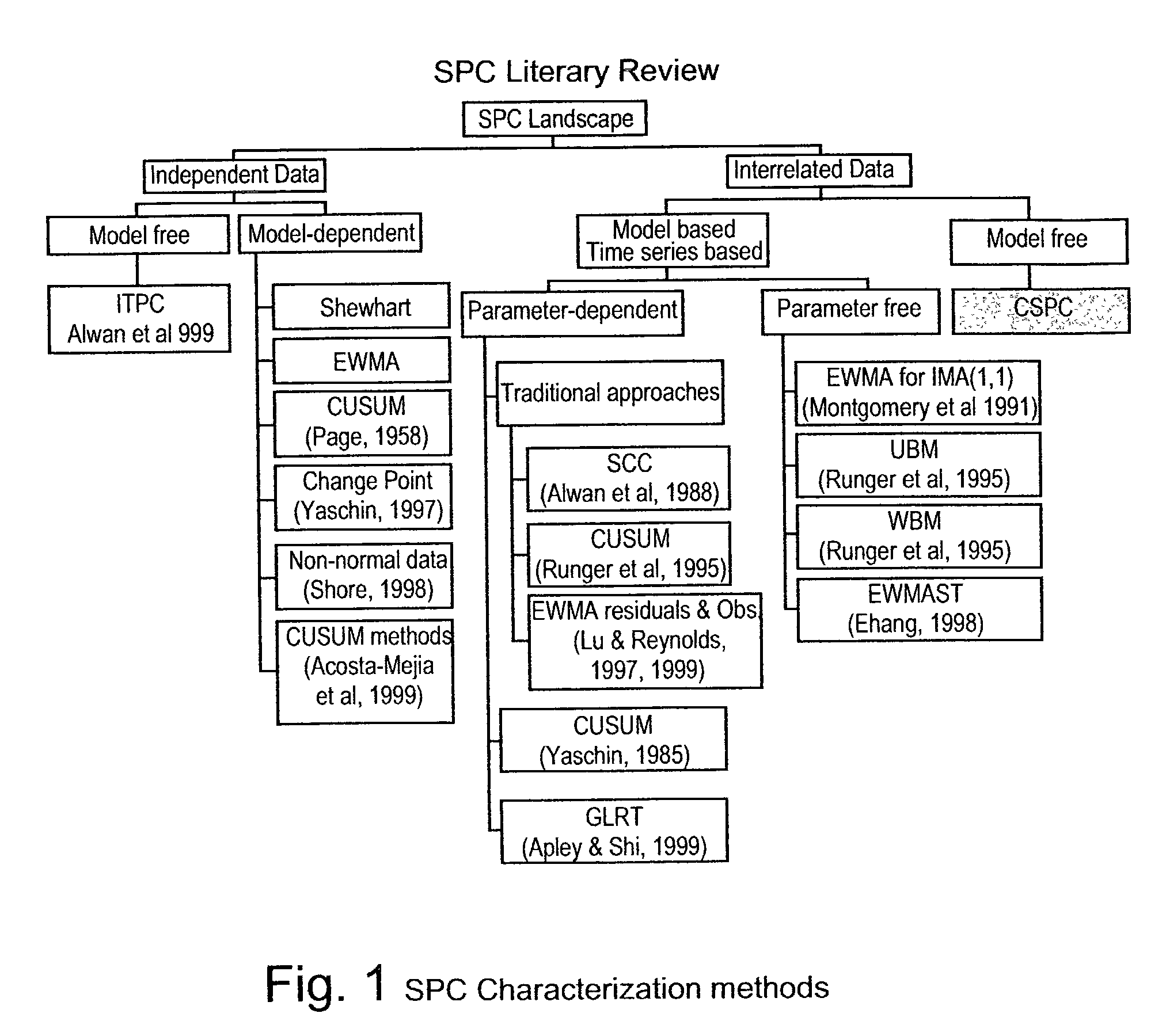
Digital signal encoding device, digital signal decoding device, digital signal arithmetic encoding method and digital signal arithmetic decoding method
InactiveUS7095344B2Improve coding efficiencyHigh degreeElectric signal transmission systemsPulse modulation television signal transmissionProcessor registerArithmetic coding
Owner:XYLENE HLDG SA
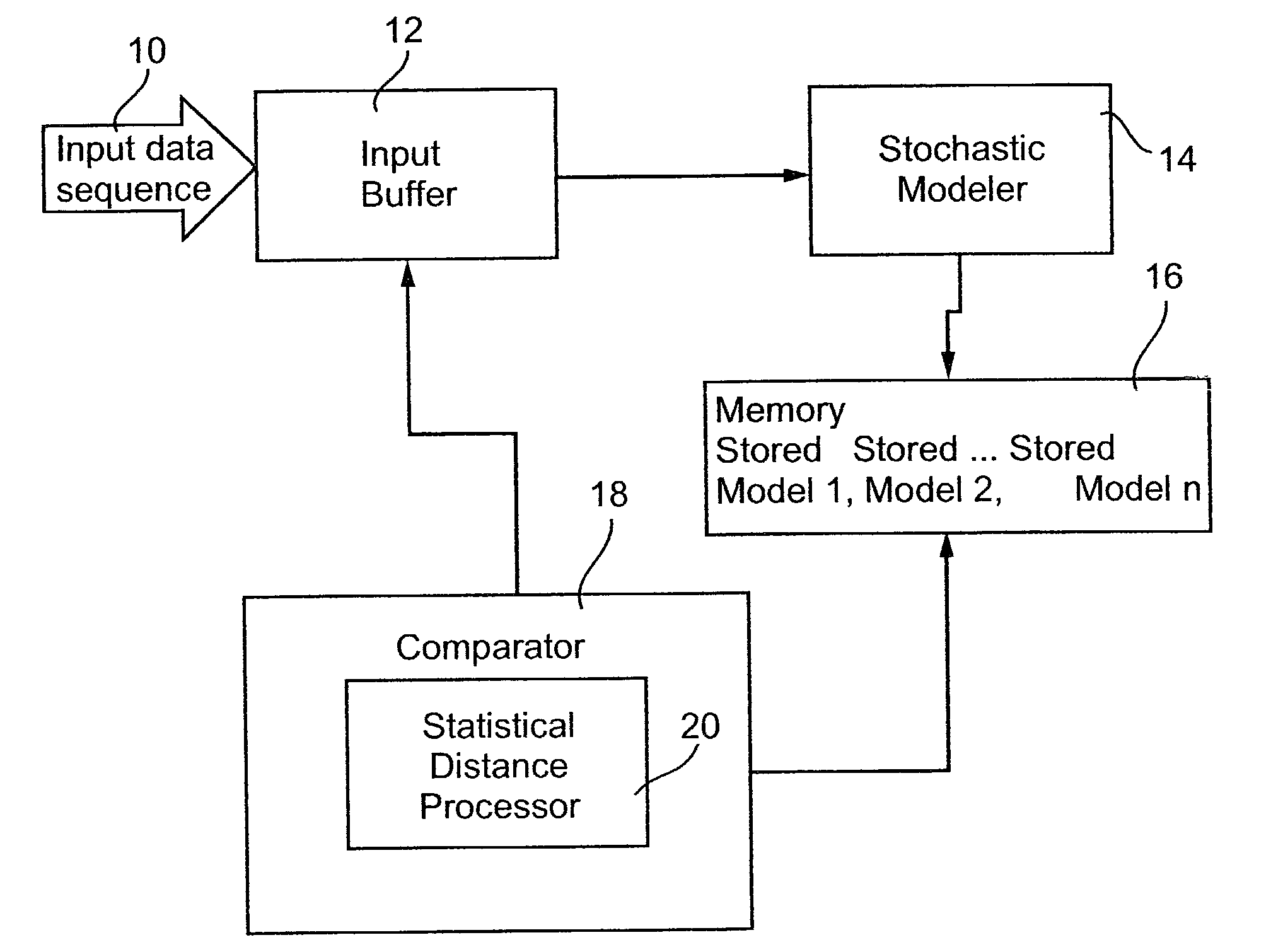
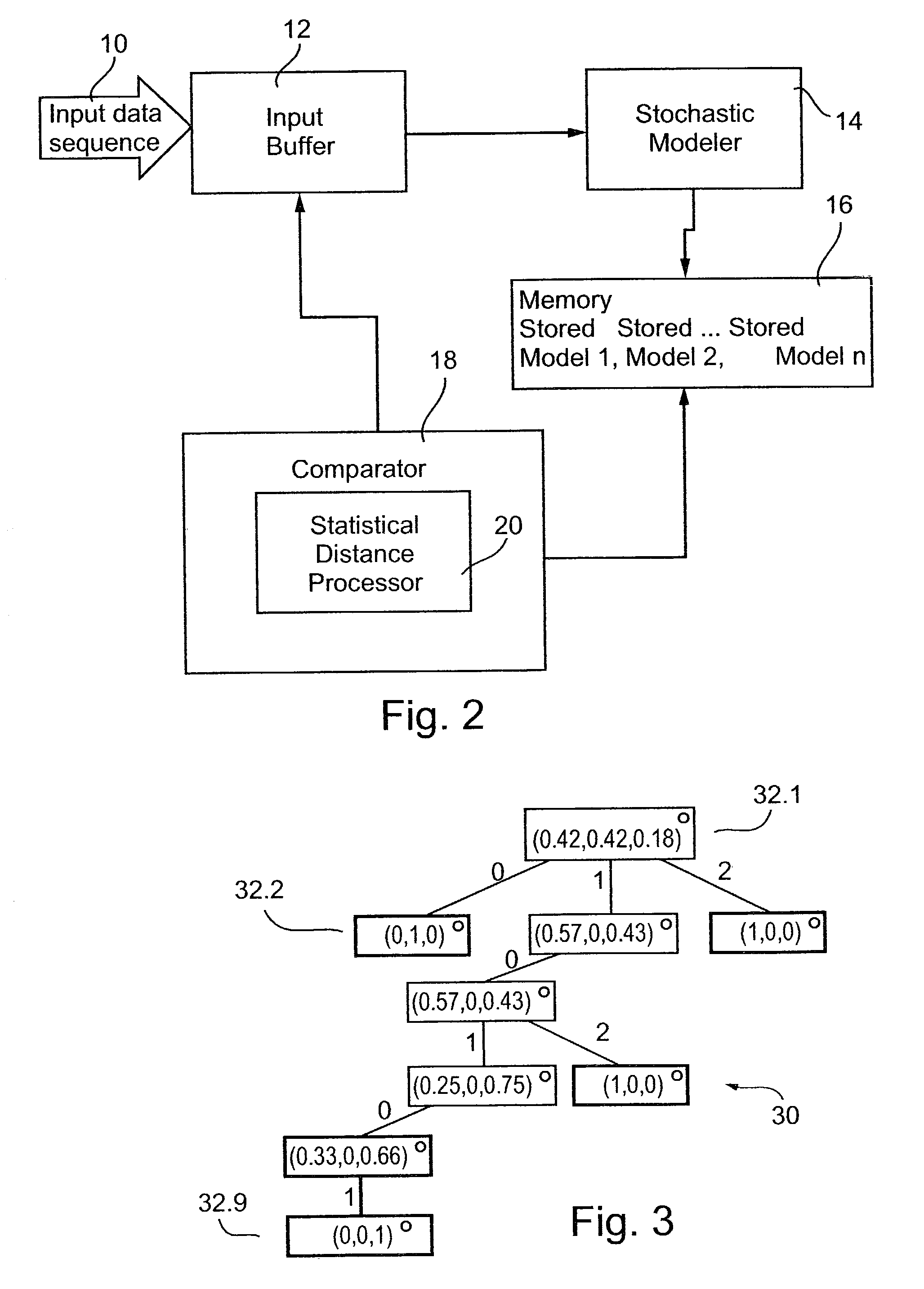
Stochastic modeling of time distributed sequences
Apparatus for building a stochastic model of a time sequential data sequence, the data sequence comprising symbols selected from a finite symbol set, the apparatus comprising: an input for receiving said data sequence, a tree builder for expressing said symbols as a series of counters within nodes, each node having a counter for each symbol, each node having a position within said tree, said position expressing a symbol sequence and each counter indicating a number of its corresponding symbol which follows a symbol sequence of its respective node, and a tree reducer for reducing said tree to an irreducible set of conditional probabilities of relationships between symbols in said input data sequence. The tree may then be used to carry out a comparison with a new data sequence to determine a statistical distance between the old and the new data sequence.
Owner:CONTEXT BASED 4 CASTING C B4
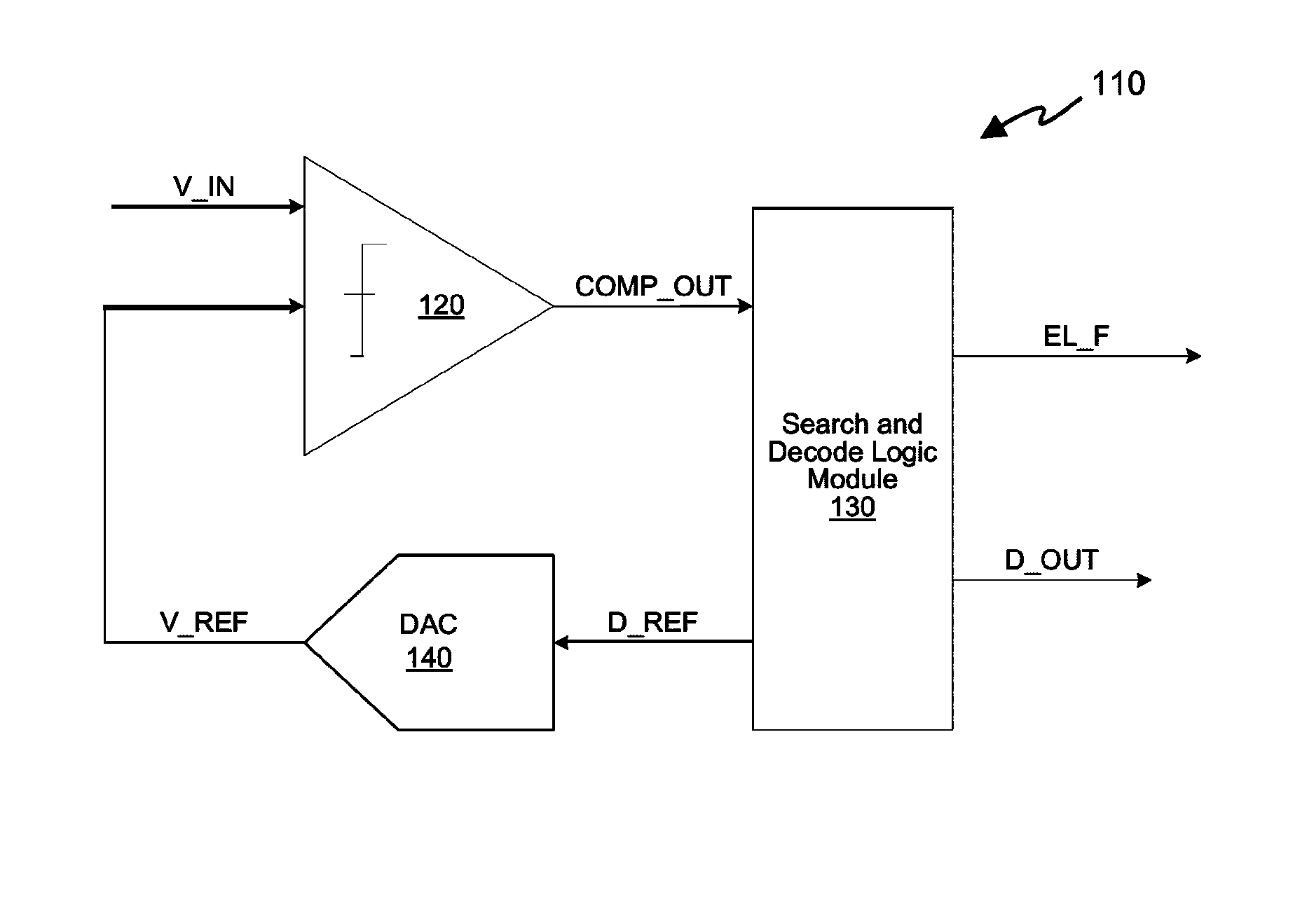
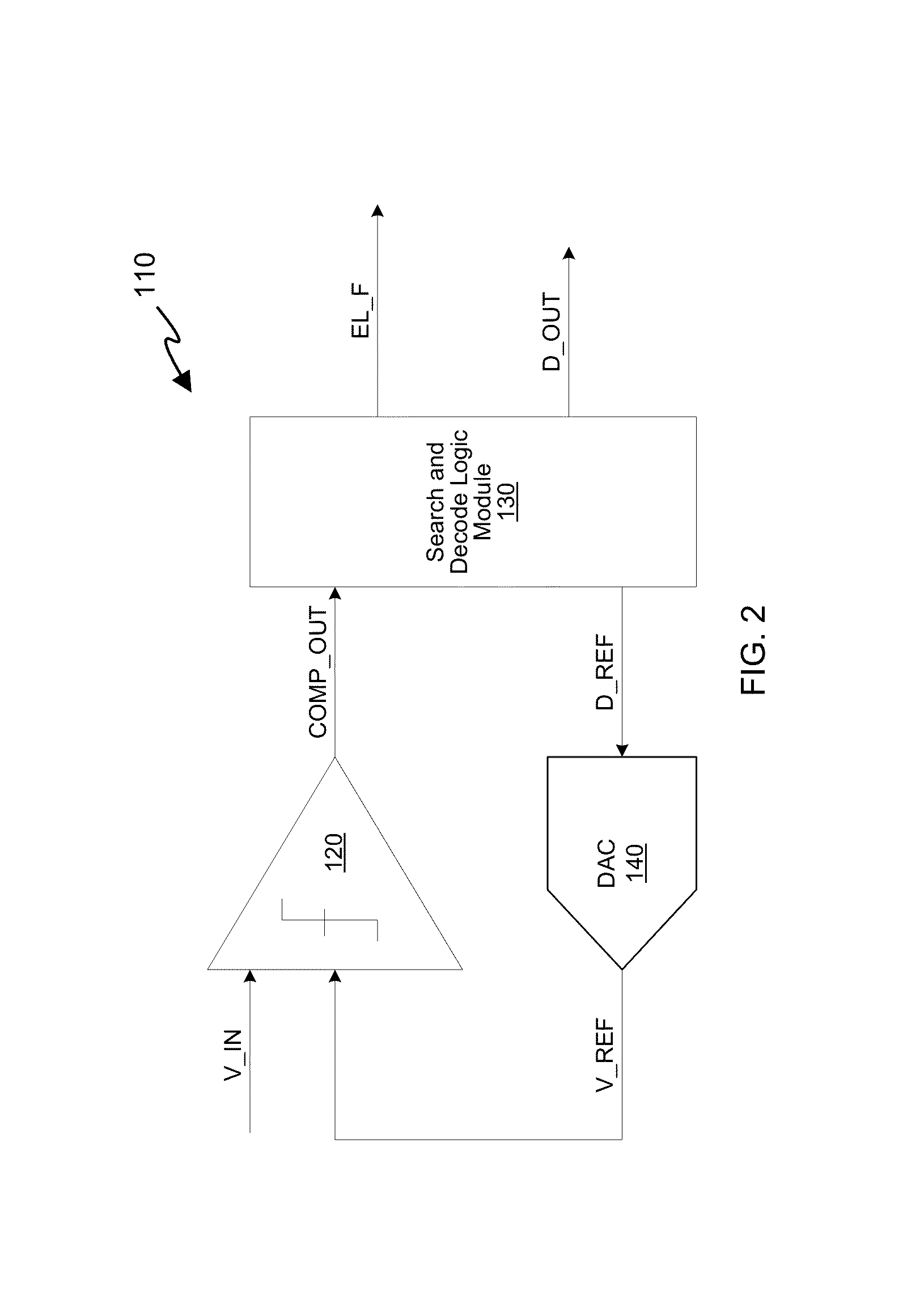
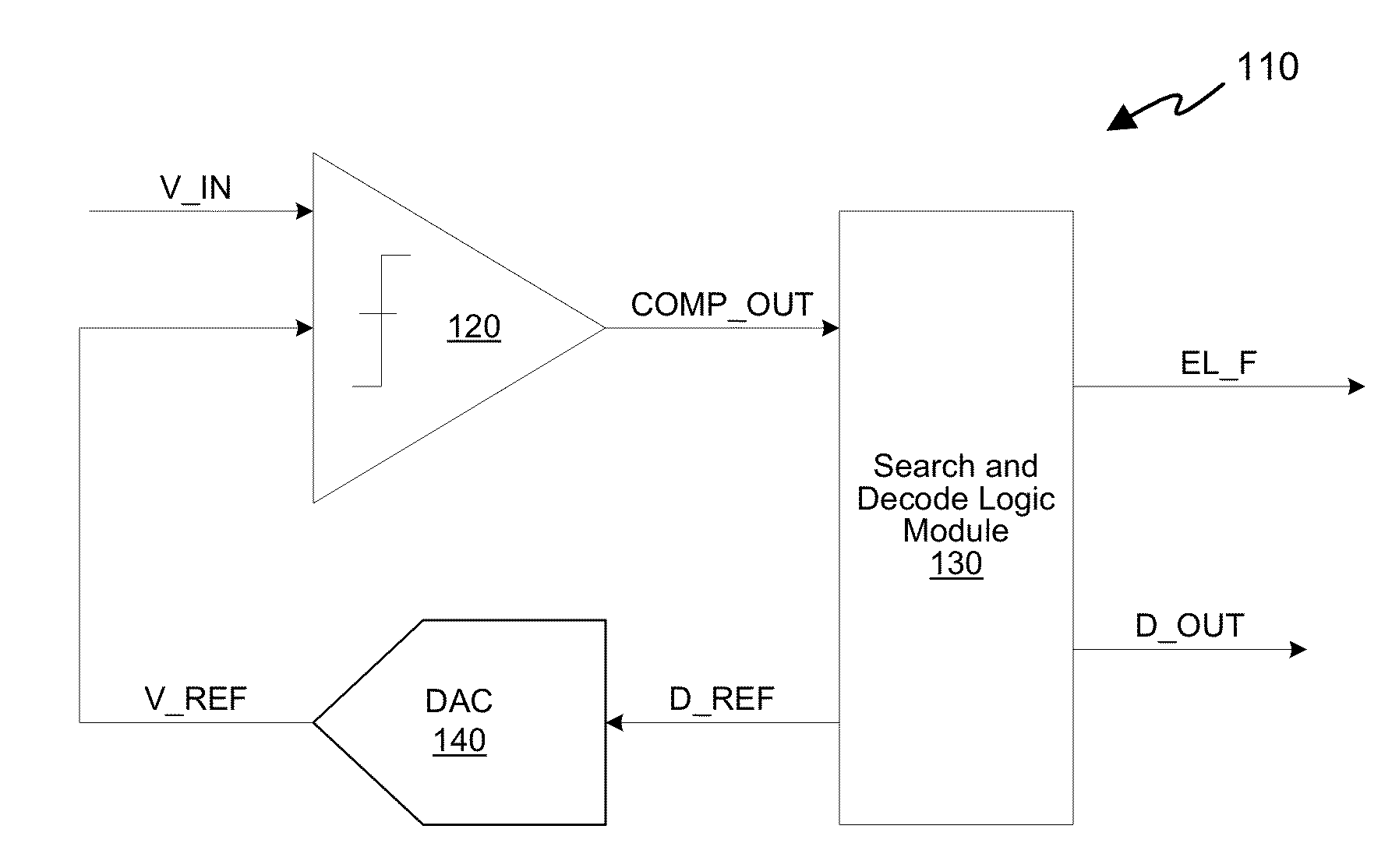
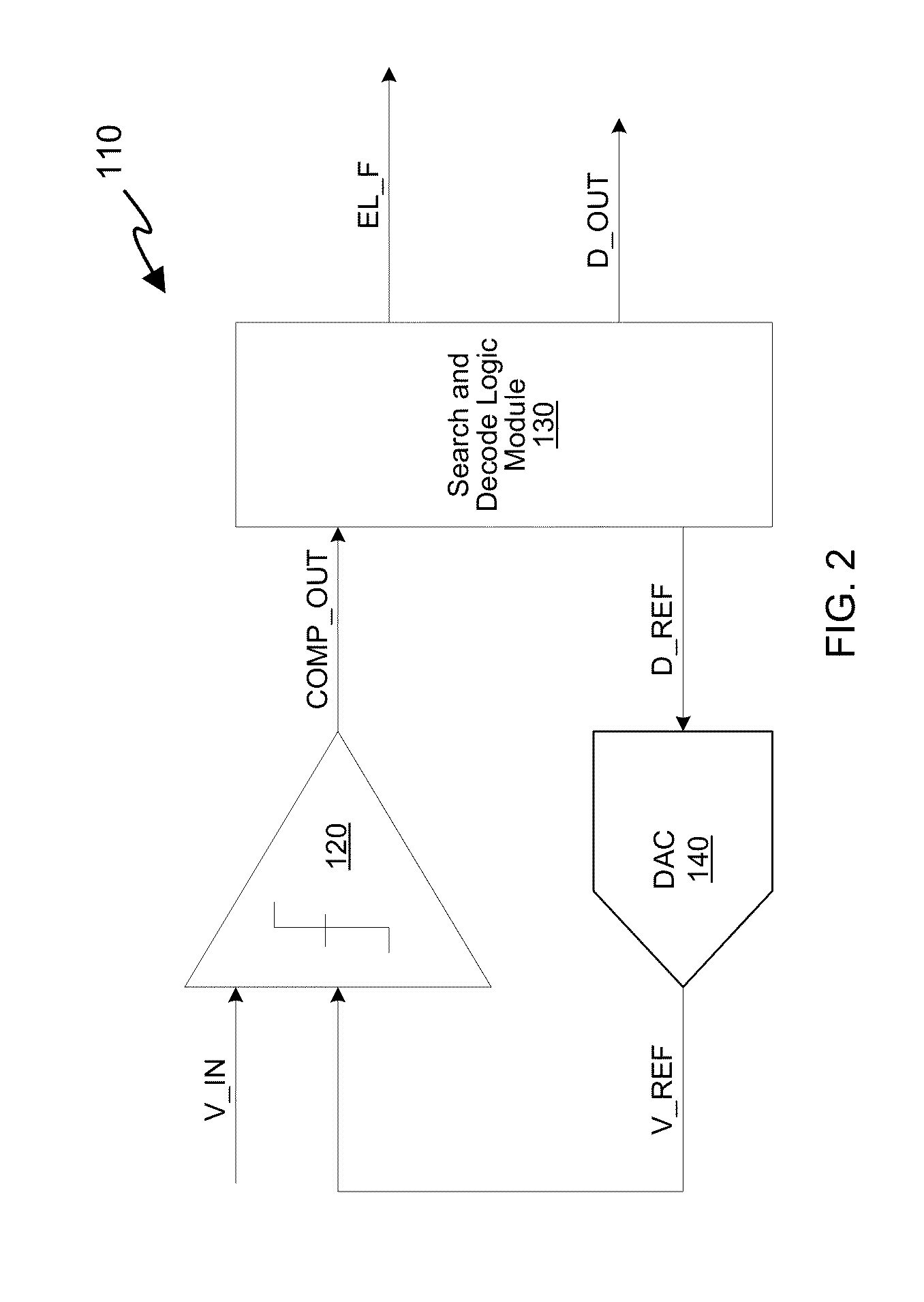
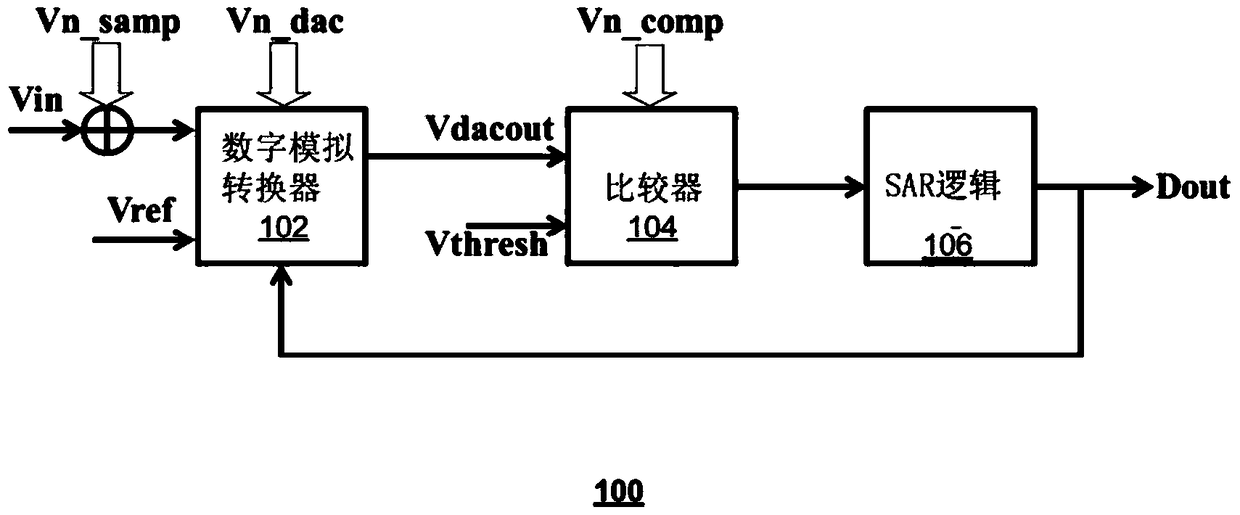
Successive approximation analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with dynamic search algorithm
ActiveUS8928506B2Power saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsDigital down converterDigital analog converter
Aspects of a method and system for a successive approximation analog-to-digital converter with dynamic search algorithms are provided. In some embodiments, a successive approximation analog-to-digital converter includes a digital-to-analog converter, a comparator, and a search and decode logic modules which cooperate to generate a digital output code representative of the analog input voltage based on a dynamic search algorithm. The dynamic search algorithms may alter a sequence of reference voltages used to successively approximate the analog input voltage based on one or more characteristics of the analog input voltage.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
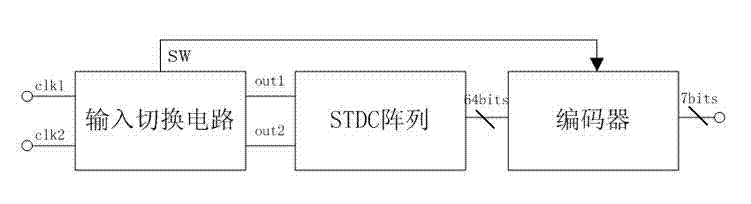
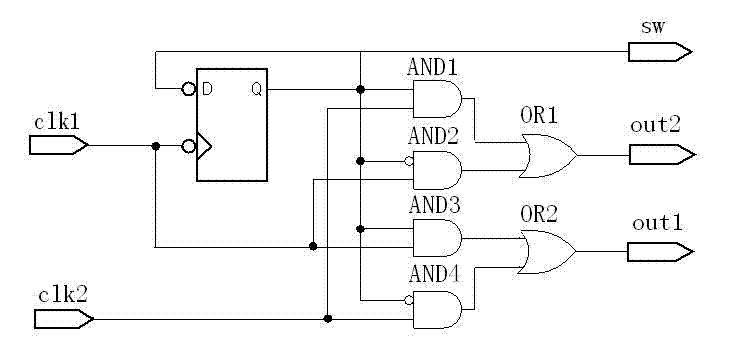
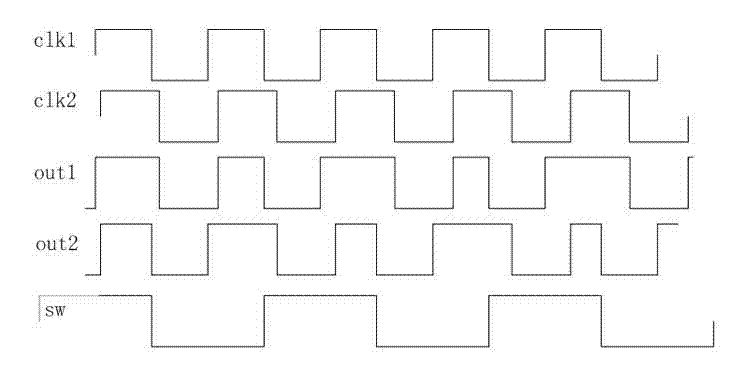
A random time-to-digital converter
InactiveCN102291138AEliminate the effects ofHalve consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsTime-to-digital convertersControl signalPhase difference
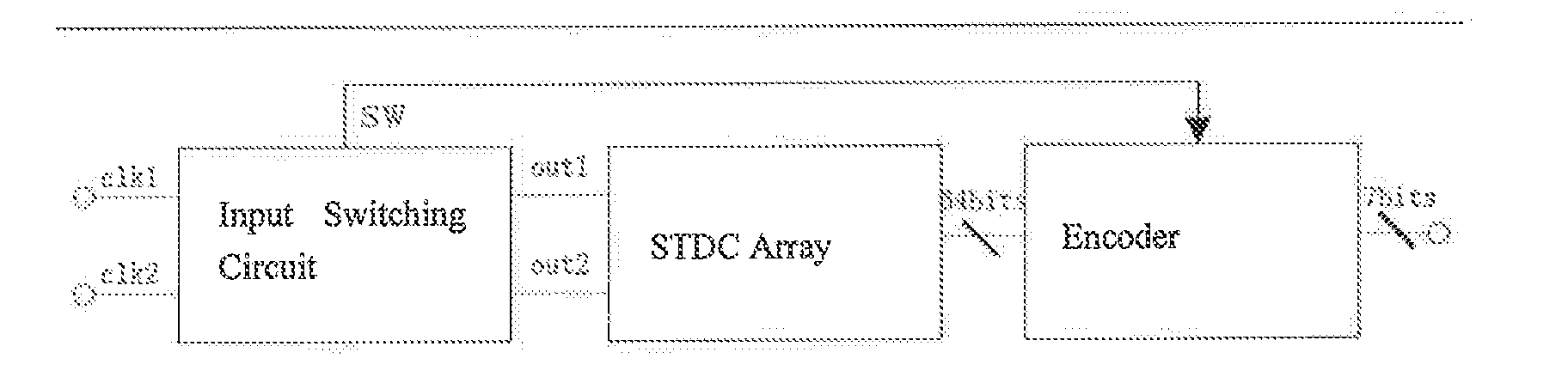
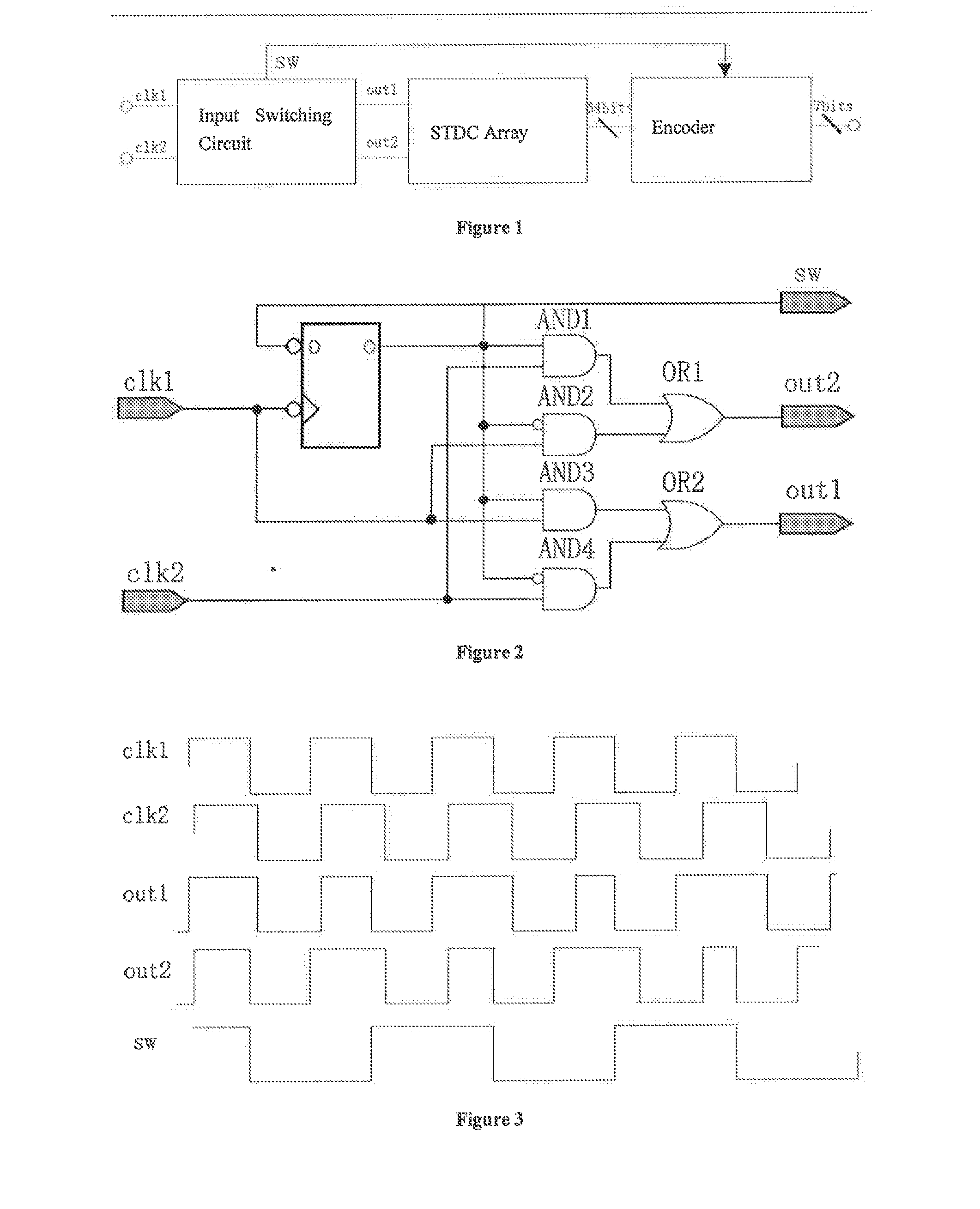
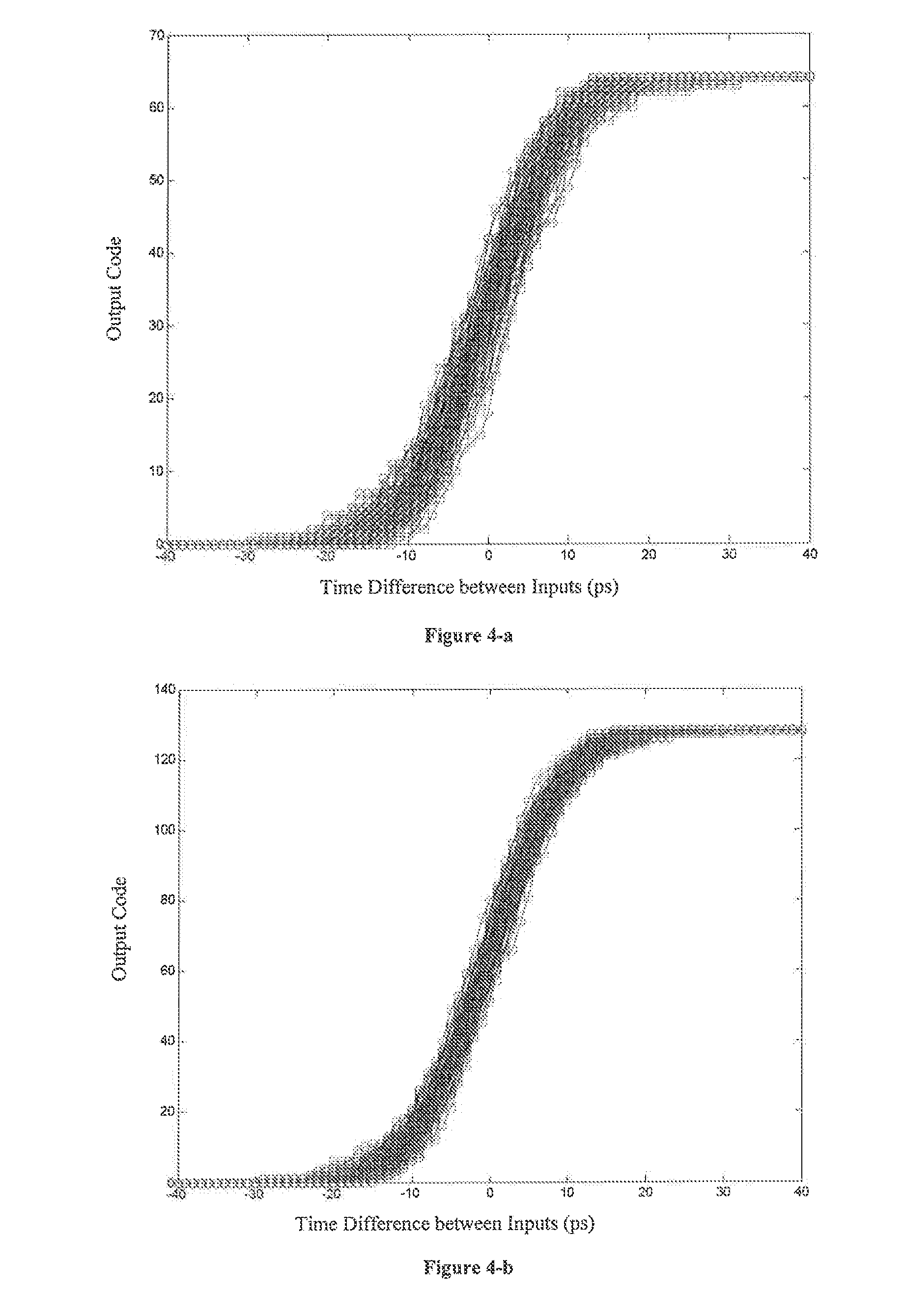
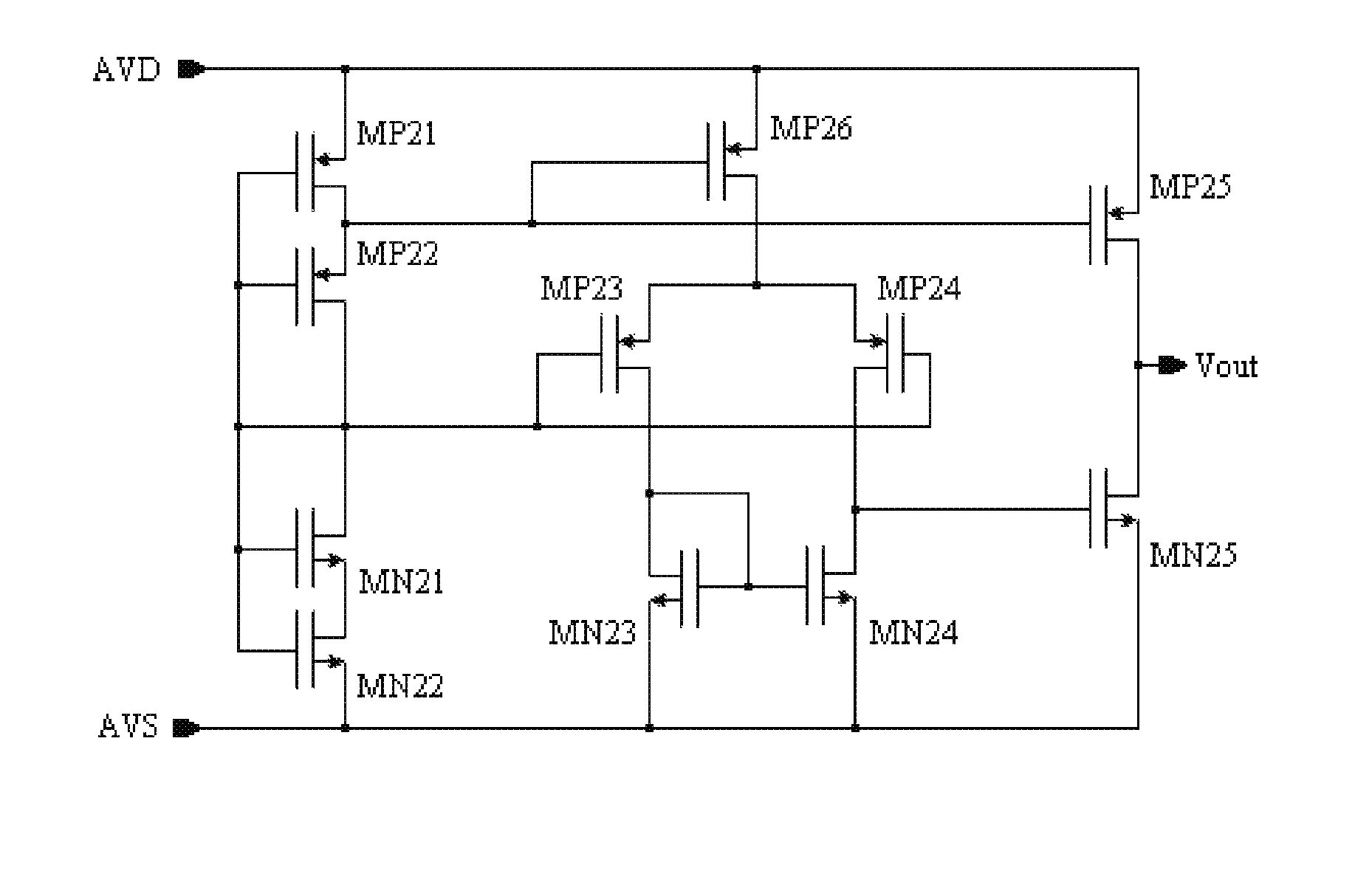
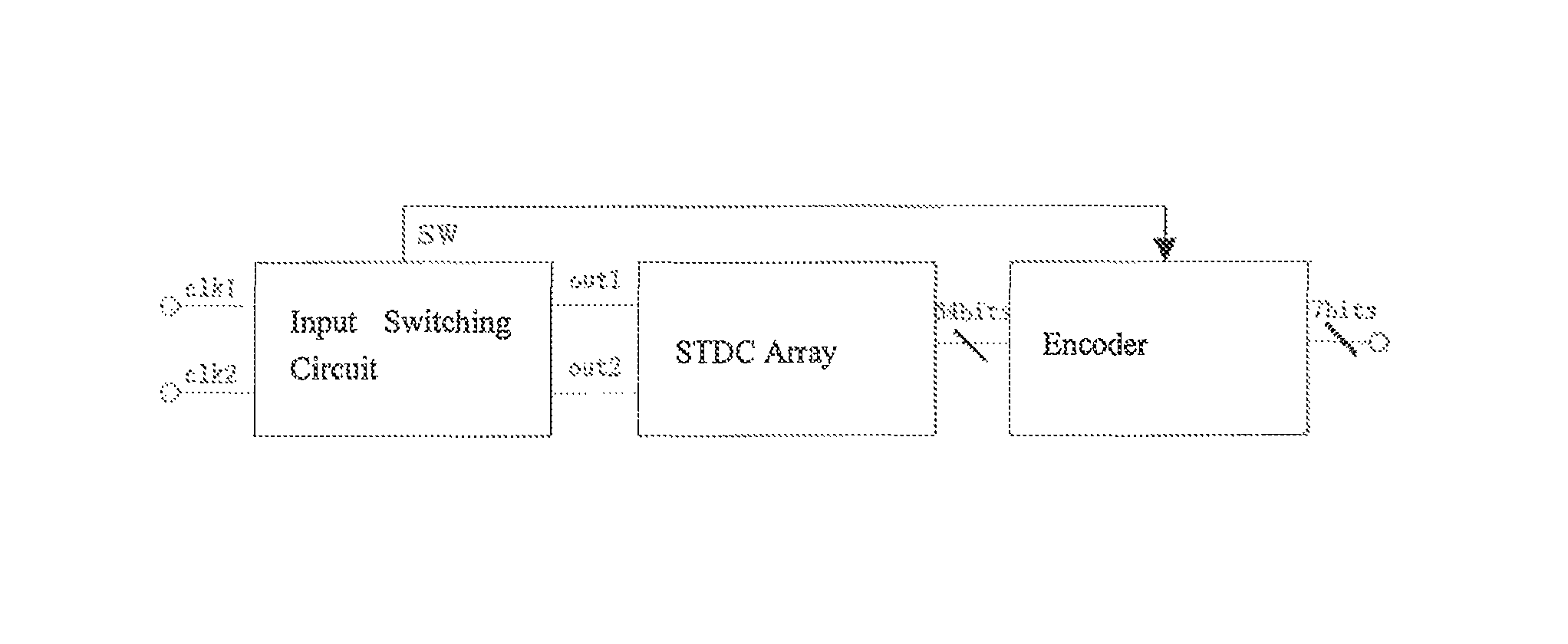
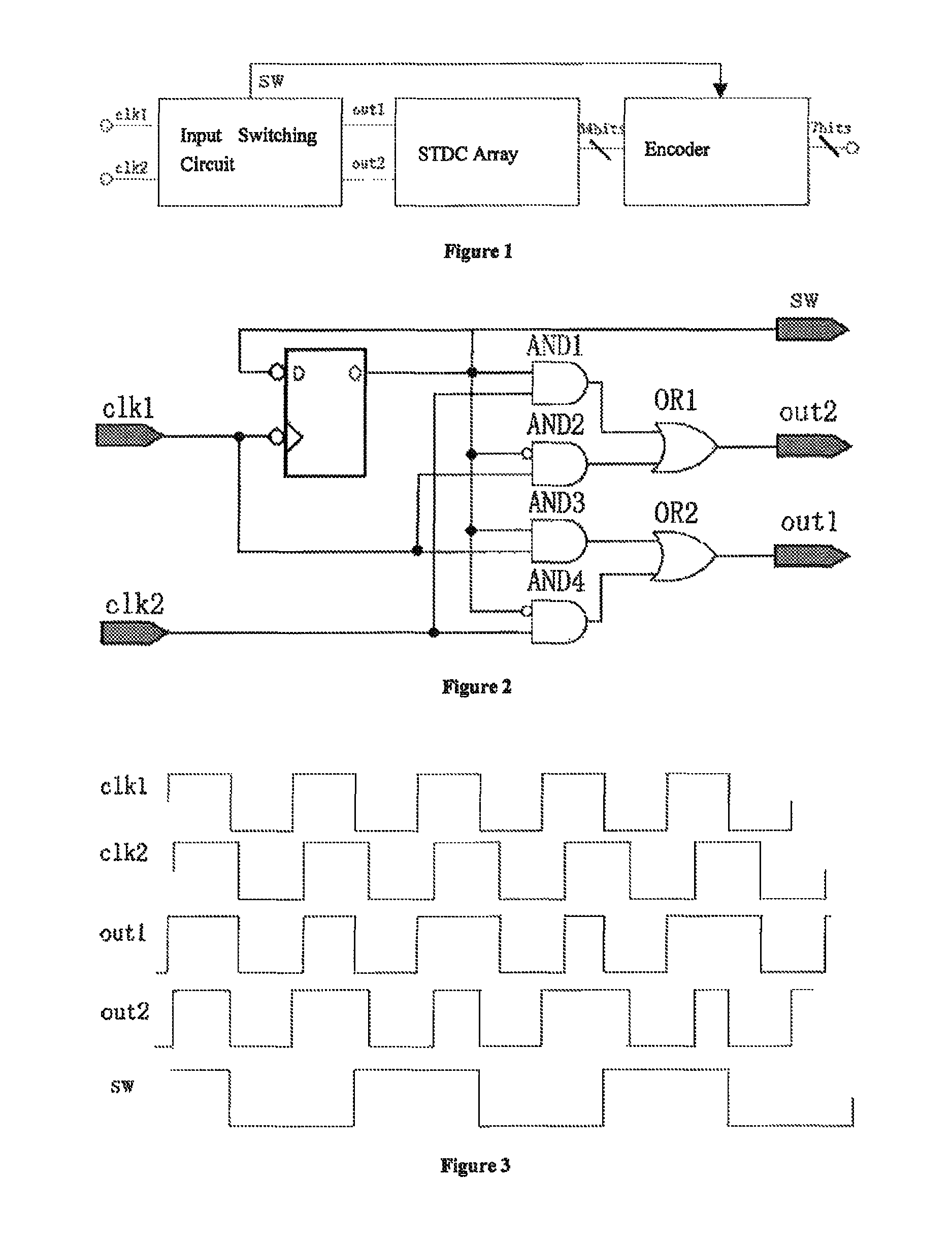
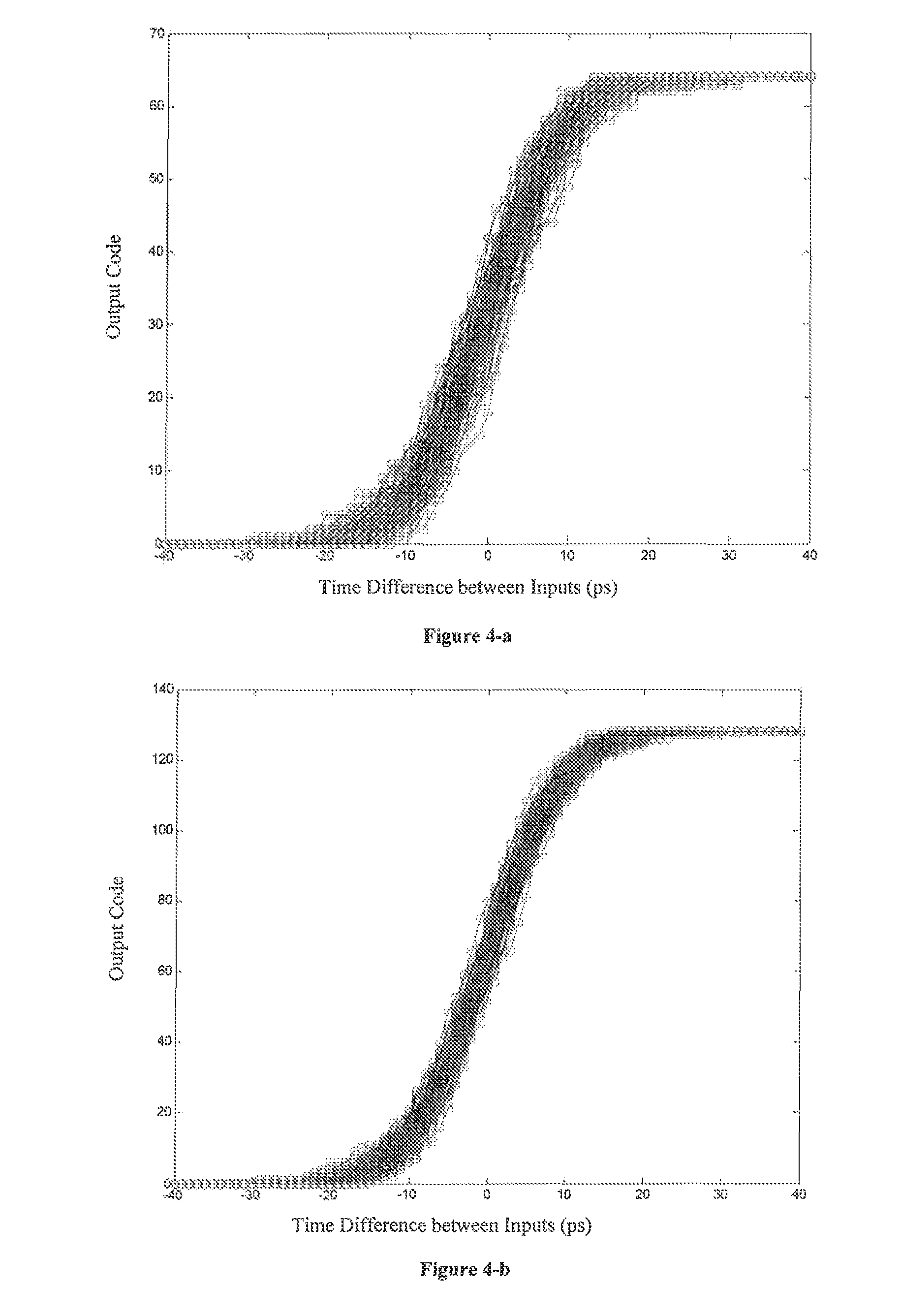
The invention discloses a stochastic time-digital converter, which comprises an input switching circuit, a stochastic time-digital converter (STDC) array and an encoder. A clock circuit inputs two clock signals into the two input ends of the input switching circuit respectively. The input switching circuit transmits the two clock signals input by the clock signal to the two input ends of the STDC array in form of alternate transposition, and simultaneously outputs a triggering control signal to the encoder. Each comparator in the STDC array independently judges the speed of each clock signal, and transmits a judgment result to the encoder for summarization. The encoder outputs the magnitude and plug-minus of a phase difference between the two clock signals. The number of equivalent comparators in the STDC array is multiplied by utilizing the stochastic characteristics of the STDC to maximally eliminate device mismatching and the influence of a process, power voltage and temperature on the circuit; and compared with the conventional STDC circuit, the STDC has the characteristics of hardware saving, low power consumption and small area.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV WUXI CAMPUS
Successive approximation analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with dynamic search algorithm
ActiveUS20140300499A1Power saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsA d converterVoltage reference
Aspects of a method and system for a successive approximation analog-to-digital converter with dynamic search algorithms are provided. In some embodiments, a successive approximation analog-to-digital converter includes a digital-to-analog converter, a comparator, and a search and decode logice modules which cooperate to generate a digital output code representative of the analog input voltage based on a dynamic search algorithm. The dynamic search algorithms may alter a sequence of reference voltages used to successively approximate the analog input voltage based on one or more characteristics of the analog input voltage.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
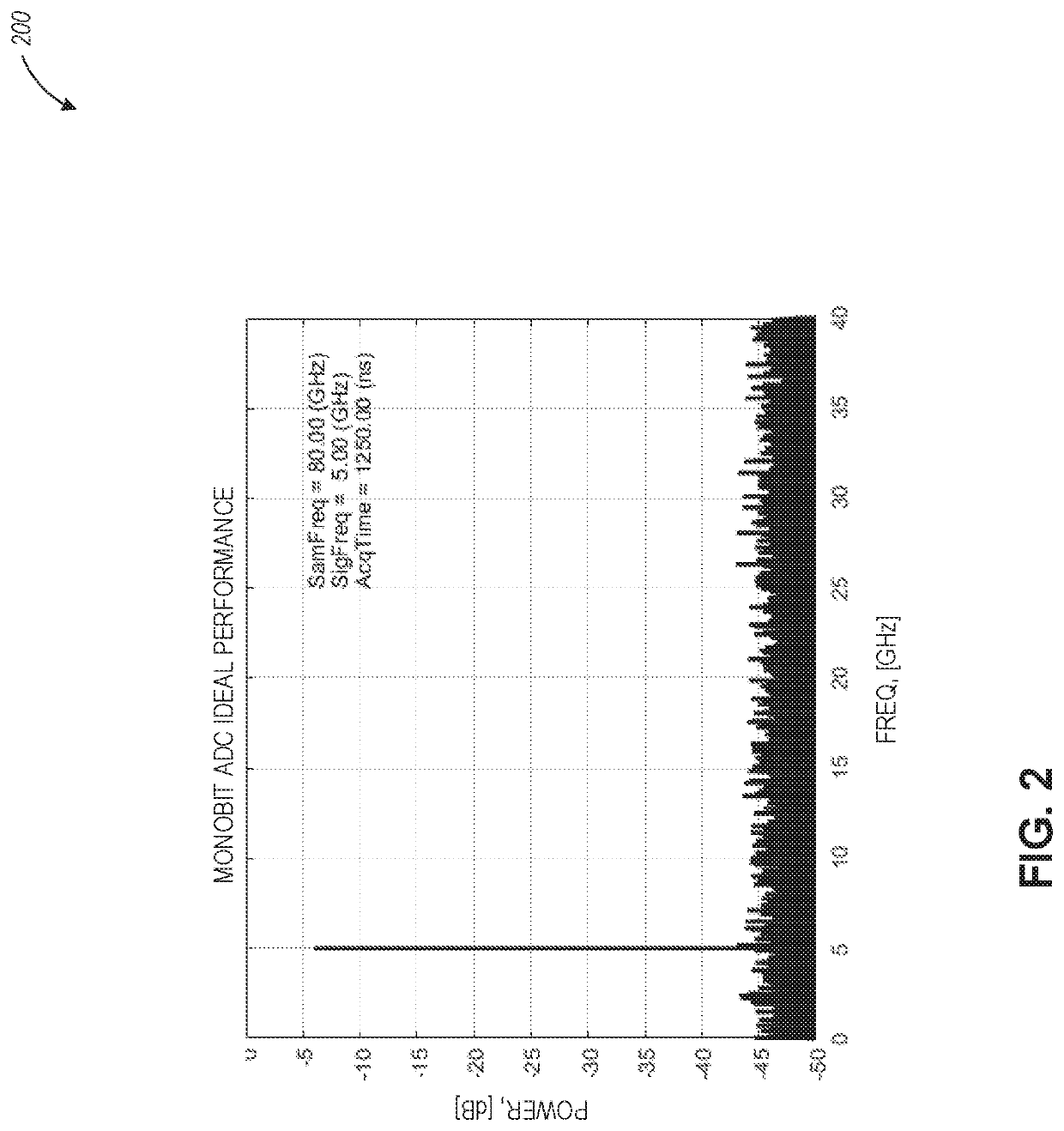
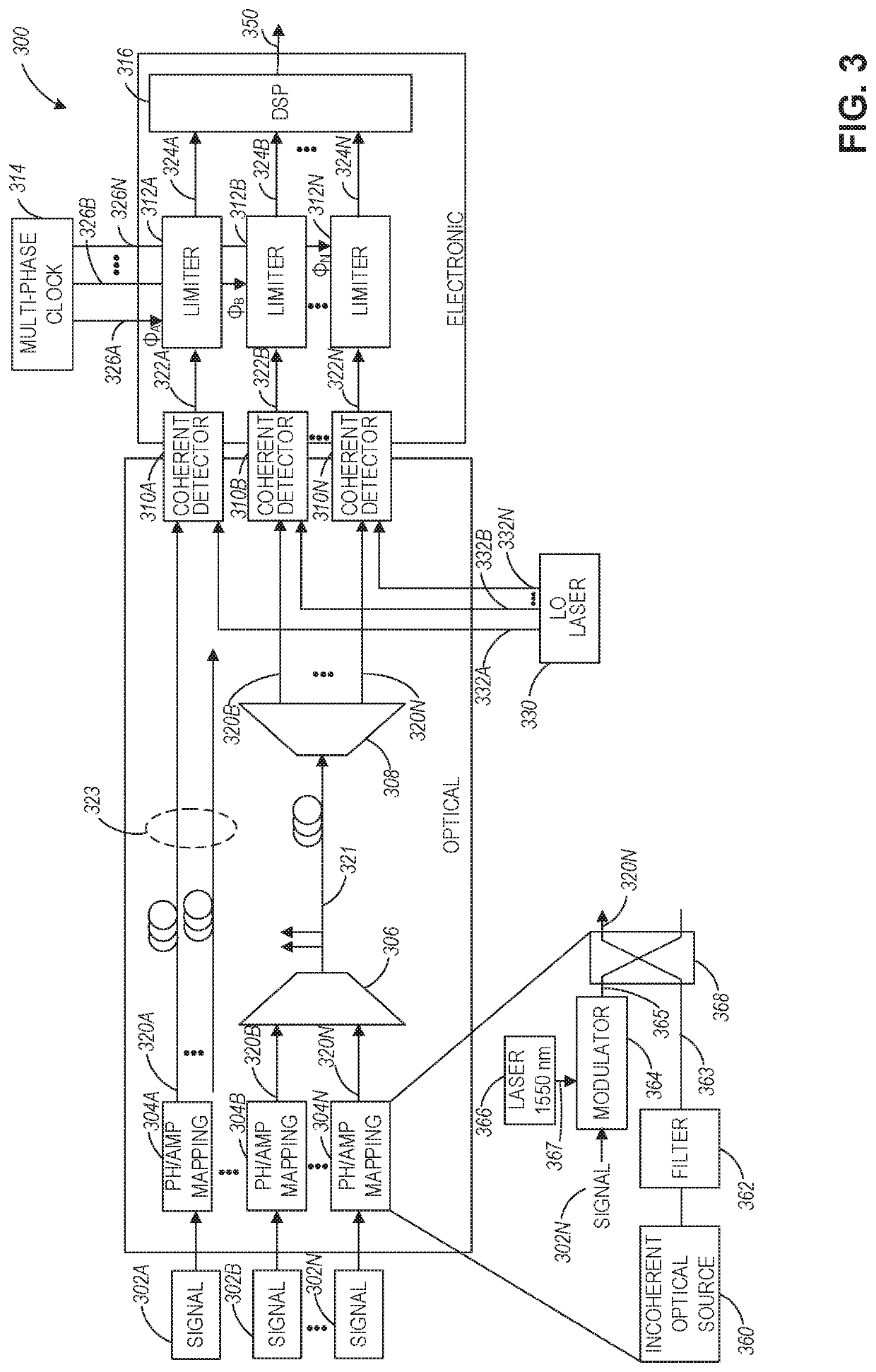
Distributive photonic monobit analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS10700700B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital/analogue conversionPhotodetectorPhase difference
A distributive photonic monobit analog-to-digital converter includes a plurality of signal processing chains configured to receive a corresponding plurality of analog input electrical signals. Each processing chain includes an incoherent optical source configured to generate an optical noise signal, an optical modulator configured to modulate an analog input electrical signal of the plurality of analog input electrical signals onto an input optical signal to generate an optical modulated signal, a coupler configured to couple the optical modulated signal with the optical noise signal to generate a coupled signal, a photodetector configured to generate a phase difference between the optical modulated signal and the optical noise signal using the coupled signal, and a limiter configured to output a decision signal based on the phase difference and using a clock signal. A multi-phase clock generator is configured to generate the clock signal for each of the plurality of signal processing chains.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
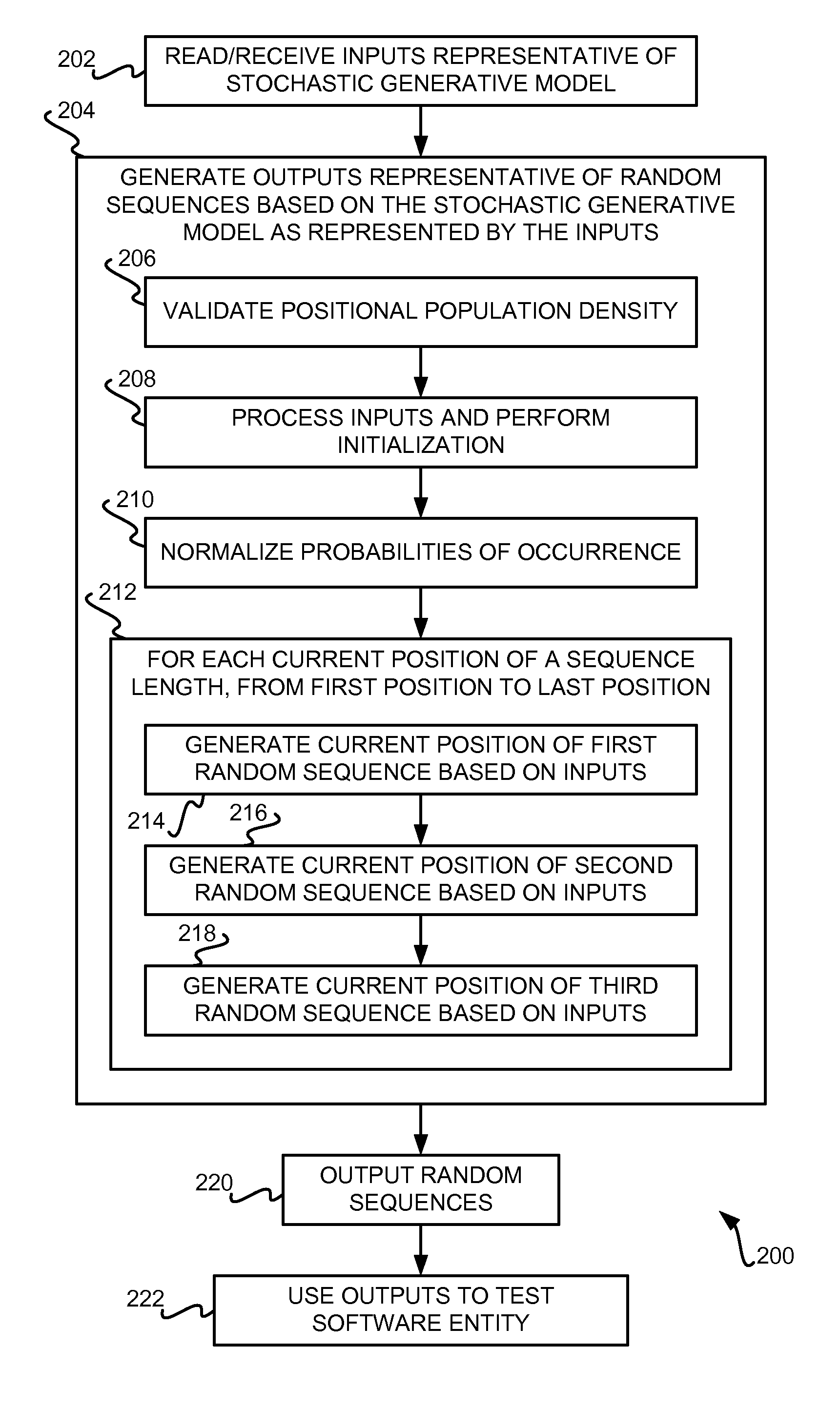
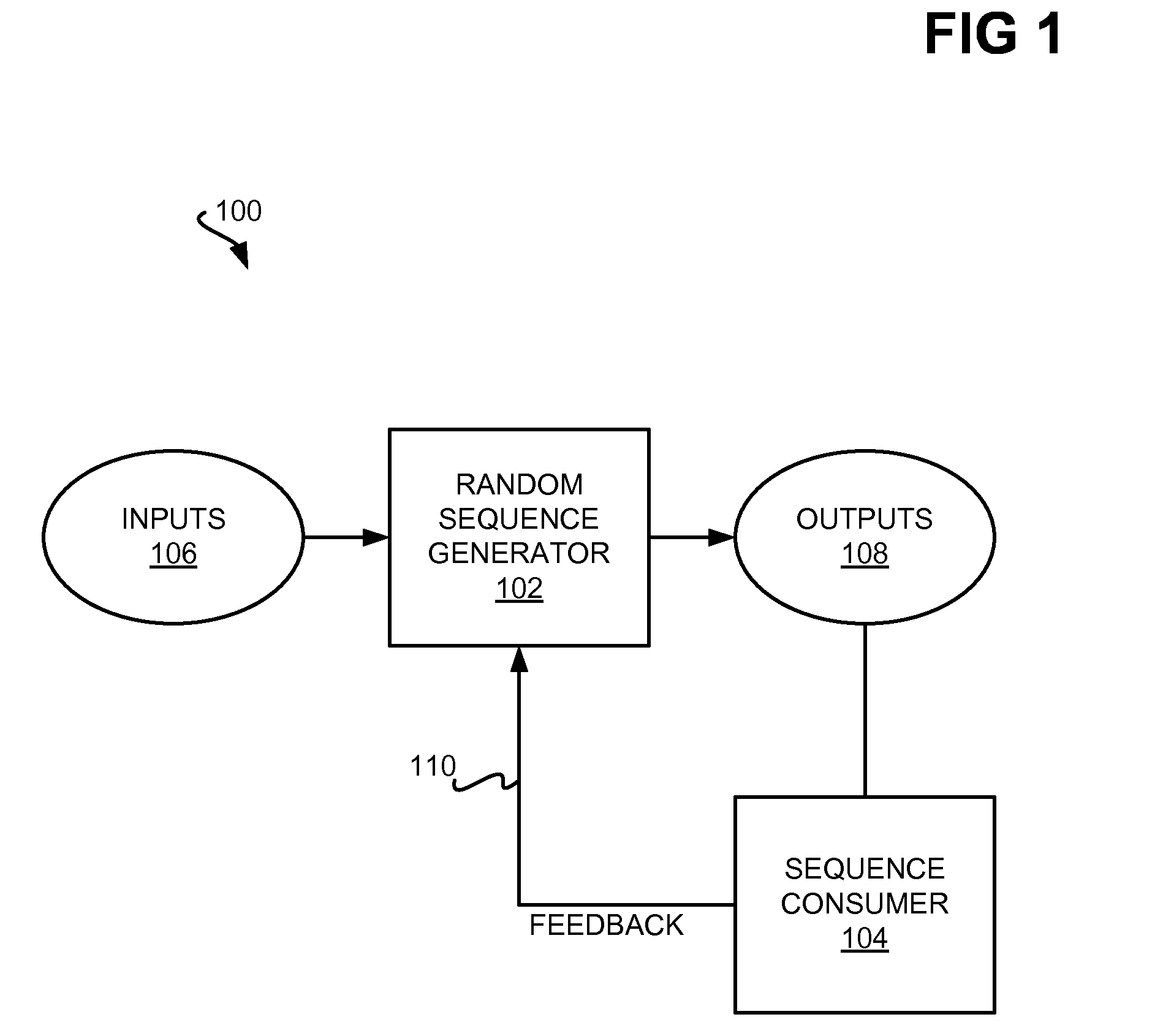
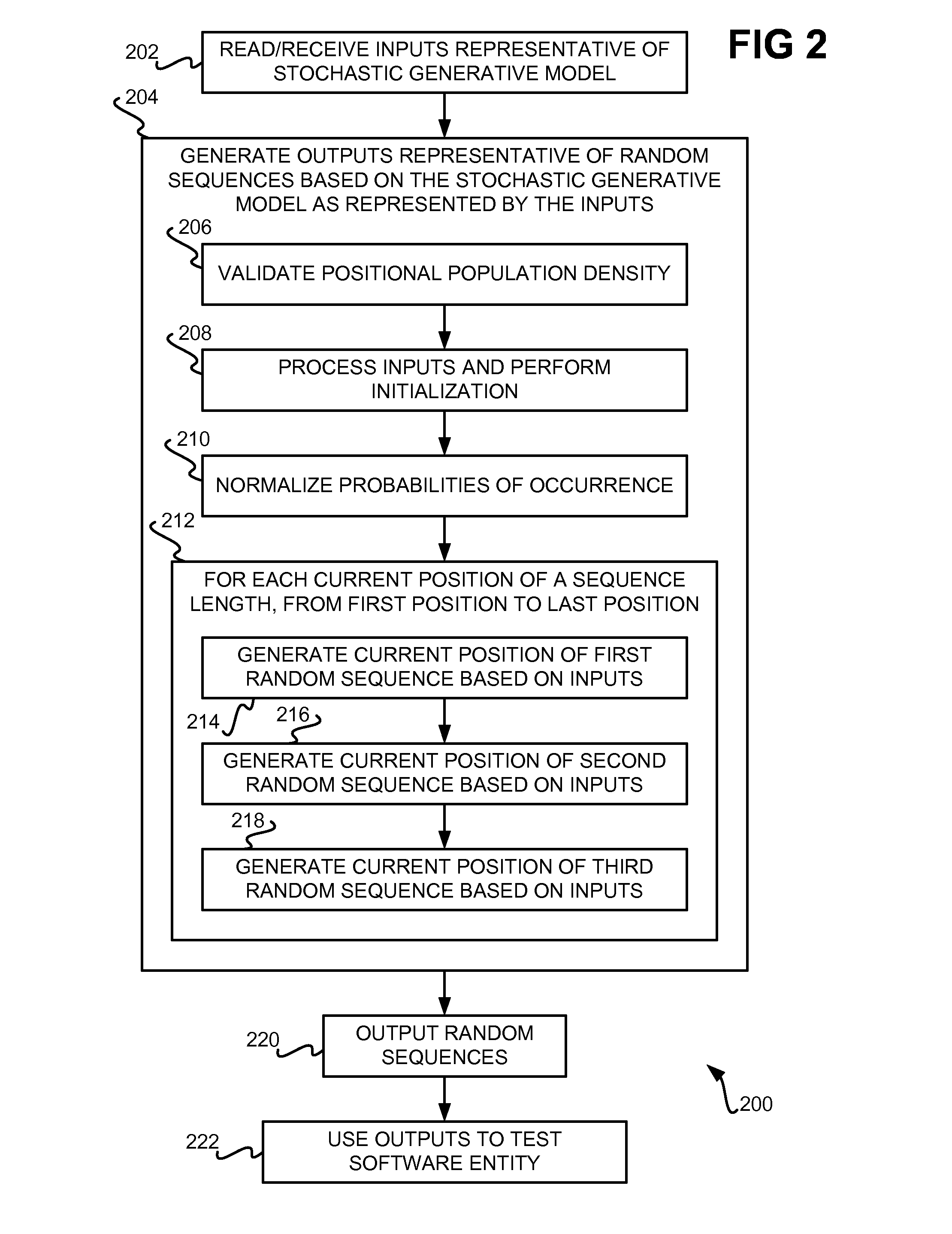
Generating random sequences based on stochastic generative model having multiple random variates
InactiveUS8161329B2Electric signal transmission systemsError detection/correctionRandom choiceComputer science
Random sequences are generated based on a stochastic generative model having multiple random variates. Inputs representative of the stochastic generative model are received. The inputs include a first random variate having a finite set of alphabets, a second random variate having a set of alphabets, and a third random variate having a finite set of alphabets. Outputs representative of the random sequences are generated based on the stochastic generative model. The outputs include a first random sequence that is a finite-length random sequence of alphabets randomly selected from the first random variate, a second random sequence having a set of alphabets selected from the second random variate, and a third random sequence having a set of alphabets randomly selected from the third random variate.
Owner:IBM CORP
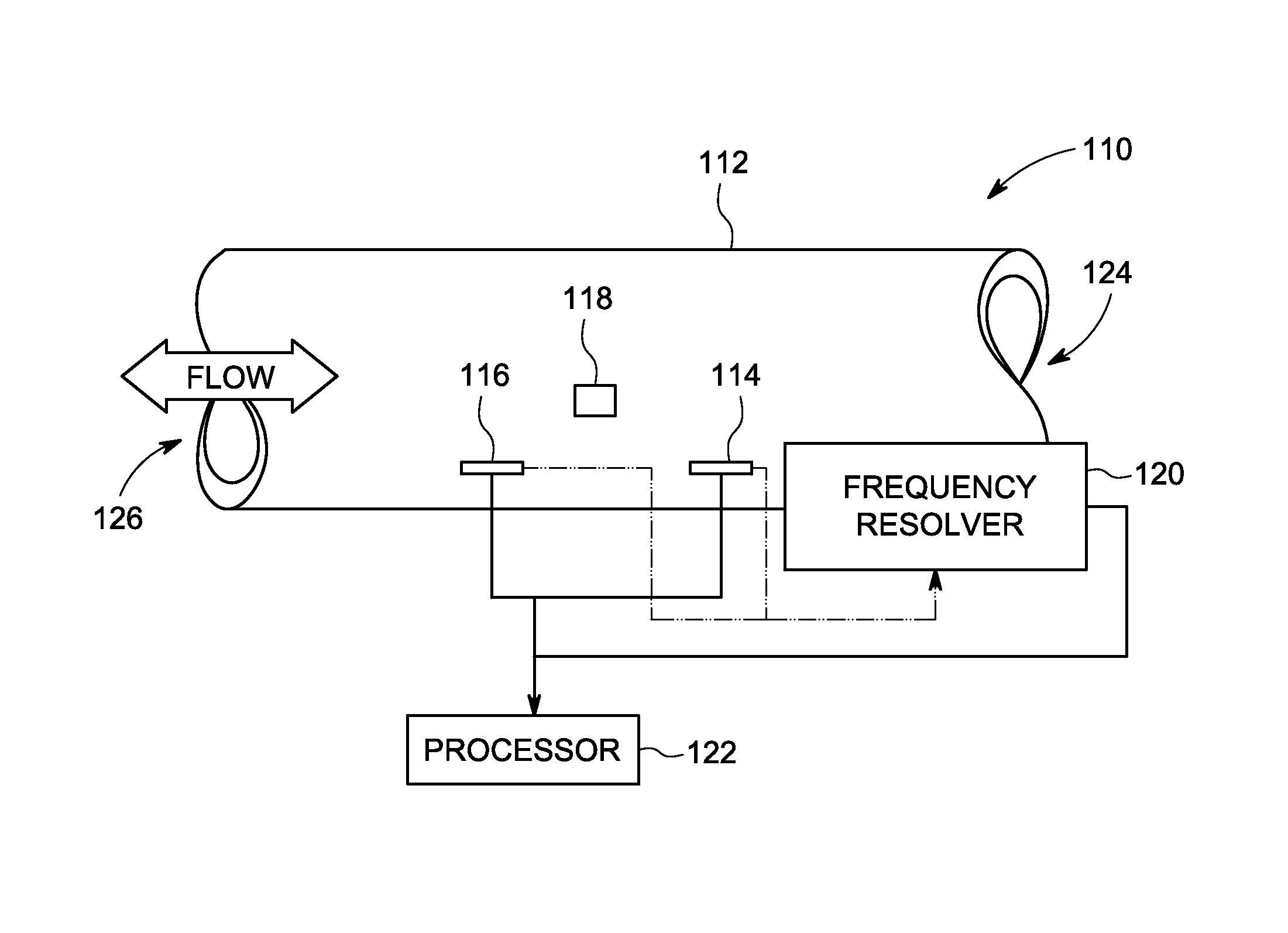
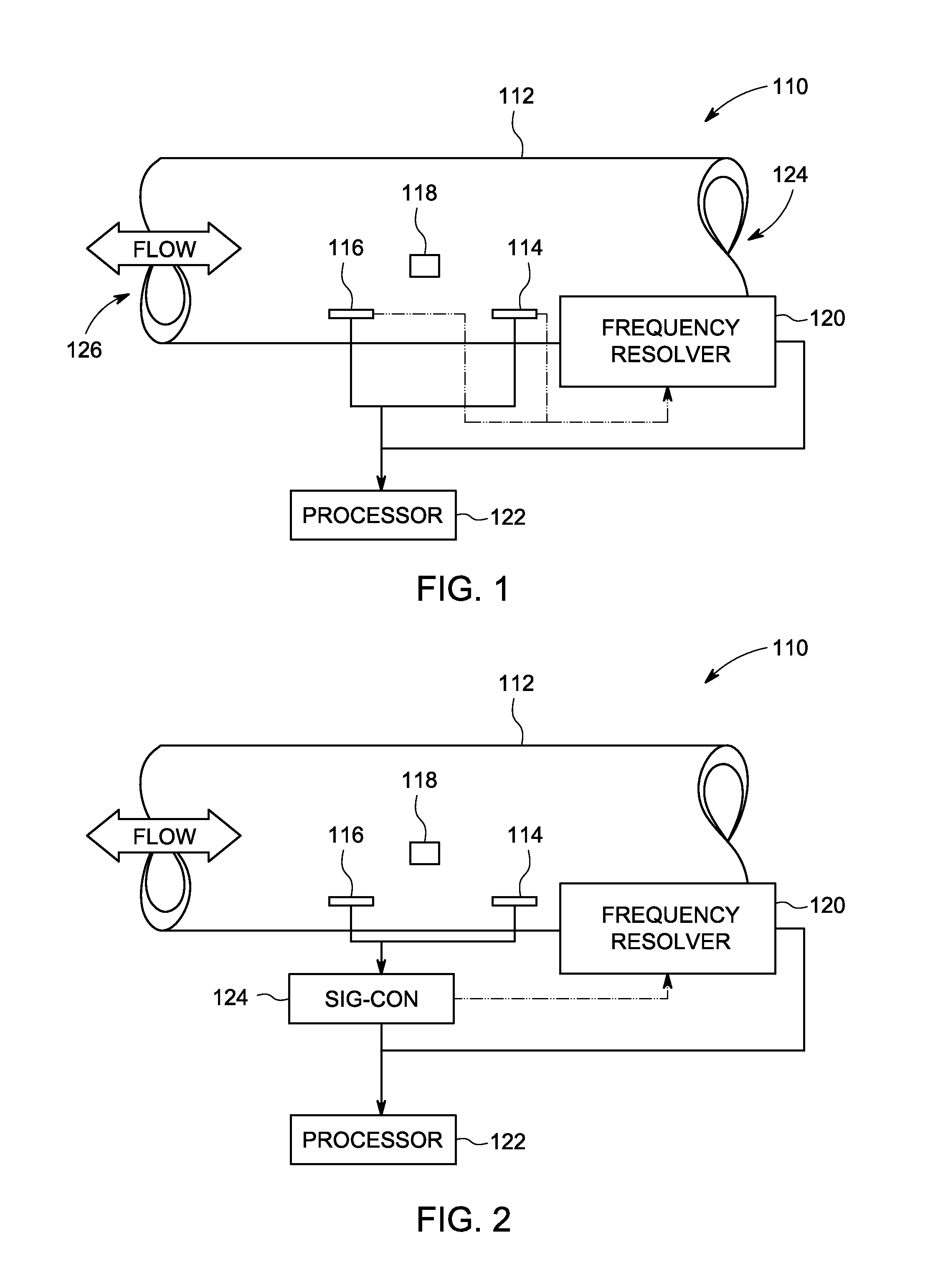
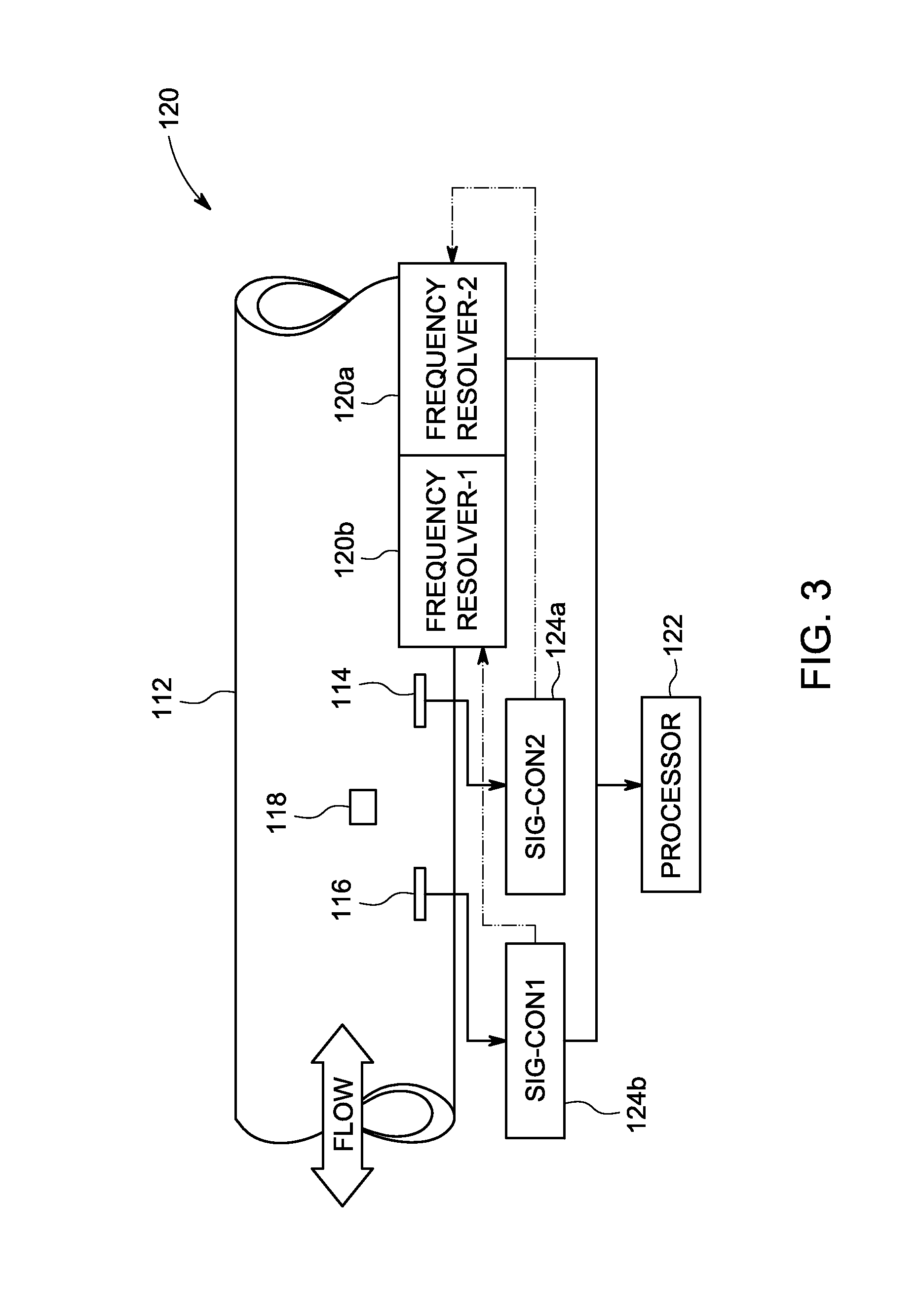
Systems and methods for flow sensing in a conduit
Systems and methods for flow sensing in a conduit are provided. One system includes a flow disturber disposed in a flow conduit and configured to impart a flow disturbance to the fluid flow. The system further includes a plurality of flow sensors disposed in the flow conduit and responsive to flow characteristics in the flow conduit. The system also includes a frequency resolver configured to determine frequency information related to the fluid flow based on the flow characteristics. The frequency resolver uses one or more time sample windows to select data samples for use in determining the frequency information, wherein a length of one or more of the time sample windows is based at least in part on the flow characteristics. The system additionally includes a processor configured to determine a flow rate of the fluid flow in the flow conduit using the frequency information.
Owner:AMPHENOL THERMOMETRICS
Stochastic time-digital converter
InactiveUS20130307711A1Take advantage ofDoubling numberElectric signal transmission systemsTime-to-digital convertersDigital down converterPhase difference
A stochastic time-digital converter (STDC) including an input switching circuit, an STDC array, and an encoder. A clock circuit inputs two clock signals into two input terminals of the input switching circuit; the input switching circuit transmits the two clock signals in a cyclic cross-transposition form to two input terminals of the STDC array, and simultaneously outputs a trigger control signal to the encoder; each comparator in the STDC array independently judges the speeds of the two clock signals and sends the judgement results to the encoder for collection and processing; and the encoder outputs the size and positivity or negativity of the phase difference of the two clock signals. The technical solution utilizes the stochastic characteristic of the STDC to double the number of the equivalent comparators in the STDC array, eliminating the effects on the circuitry of device mismatching and processes, power supply voltage, and temperature.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Circuit and method for generating the stochastic signal
ActiveUS8384569B2Ensuring uniquenessLow costMultiple-port networksDigital data processing detailsSignal processing circuitsEngineering
Owner:IPGOAL MICROELECTRONICS (SICHUAN) CO LTD
Digital slope analog to digital converter device and signal conversion method
ActiveUS11159171B1Electric signal transmission systemsConversion using stochastic techniquesConvertersSoftware engineering
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Analog-digital converter circuit
ActiveCN107809243ADefects that slow downHigh sampling rateConversion using stochastic techniquesConvertersA d converter
The invention discloses an analog-digital converter circuit. The analog-digital converter circuit comprises a sub-ADC circuit and a sub-DAC circuit which are electrically connected, wherein the sub-ADC circuit comprises a plurality of comparators; the sub-DAC circuit comprises a plurality of DAC units; each comparator is corresponding to the corresponding DAC unit; the number of the comparators isthe same as the number of the DAC units; the analog-digital converter circuit further comprises a threshold voltage generating circuit; the threshold voltage generating circuit is used for generatingthreshold voltages of the plurality of comparators; the threshold voltage generating circuit comprises a dynamic element matching circuit; and the dynamic element matching circuit is used for connecting the outputs of the comparators and the inputs of the DAC units in a random sequence in a one-to-one mode. According to the analog-digital converter circuit provided by the invention, the data delay of the sub-ADC to the sub-DAC is greatly reduced, and the complexity of the circuit is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI BEILING
Stochastic Time-Digital Converter
InactiveUS8810440B2Influences of minimizedTemperature minimizedElectric signal transmission systemsModulated-carrier systemsPhase differenceControl signal
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
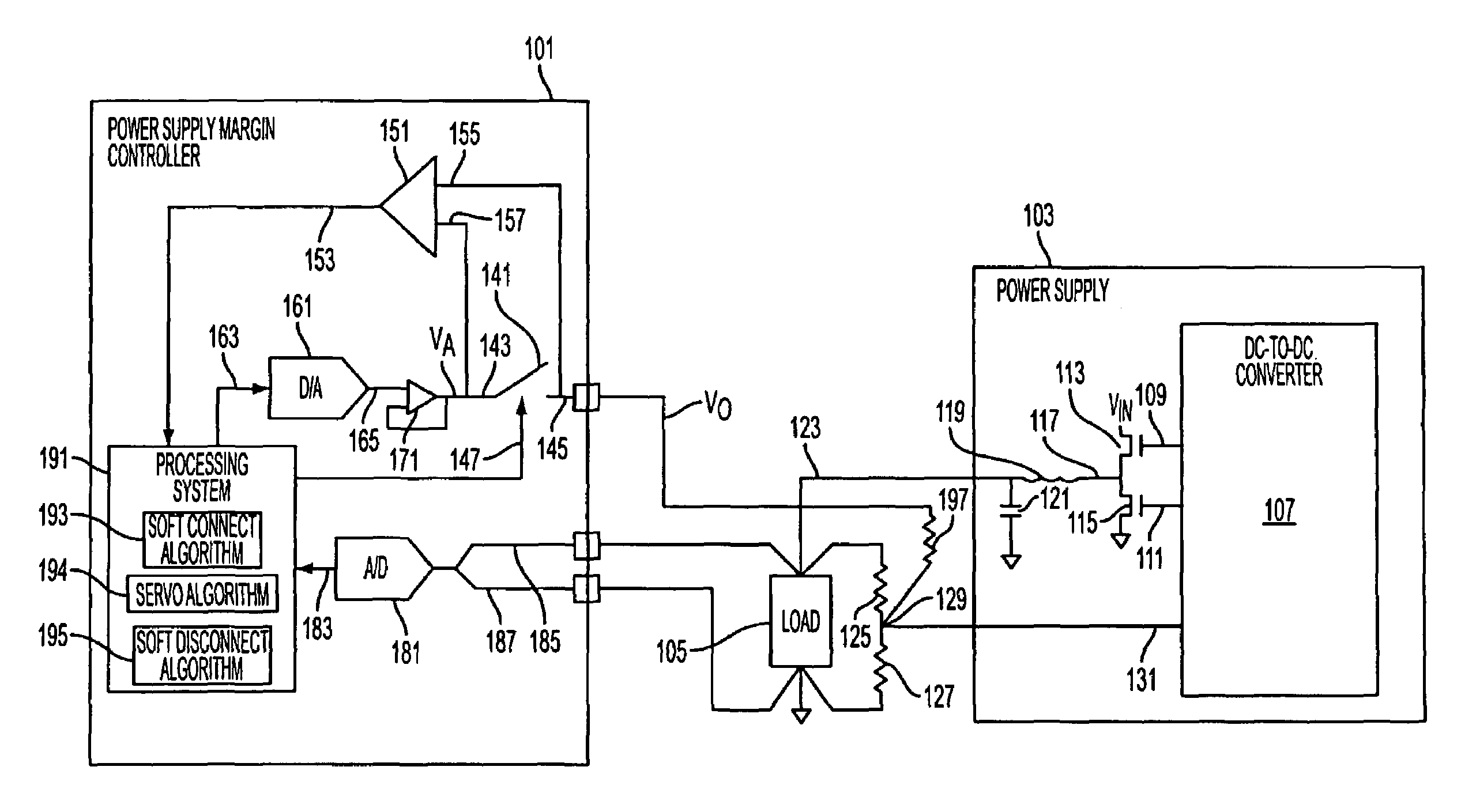
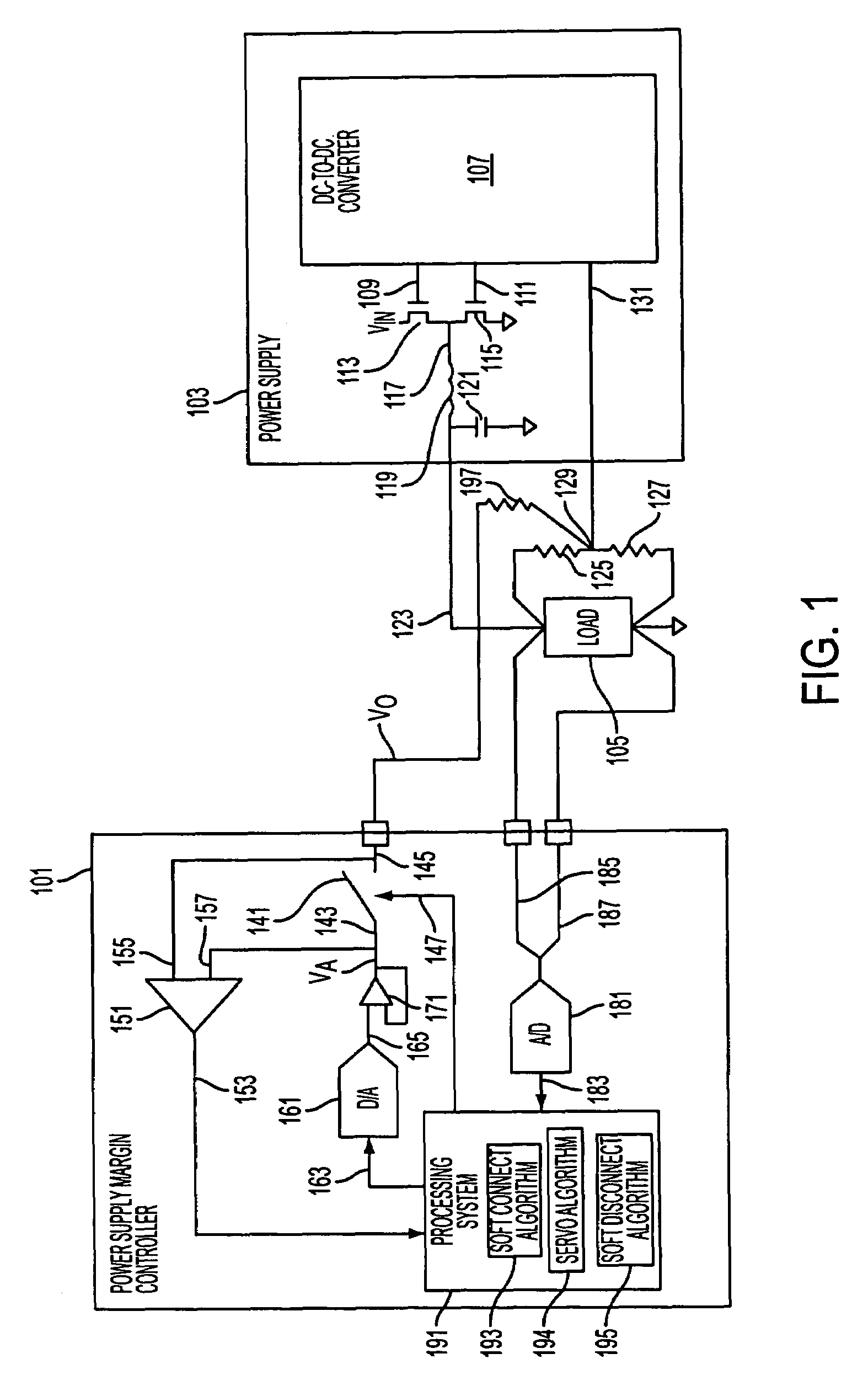
Non-perturbing power supply margin controller
ActiveUS7382303B1Electric signal transmission systemsDc-dc conversionDigital analog converterControl signal
A power supply margin controller may alter the voltage of a control signal used to control the output voltage of a power supply. The controller may include a digital-to-analog converter having an input and an output, and a comparator having a first input coupled to receive the control signal, a second input coupled to the output of the digital-to-analog converter, and an output. The controller may include a processing system configured to deliver data to the input of the digital-to-analog converter based on the output from the comparator that causes signals at the inputs to the comparator to be substantially equal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
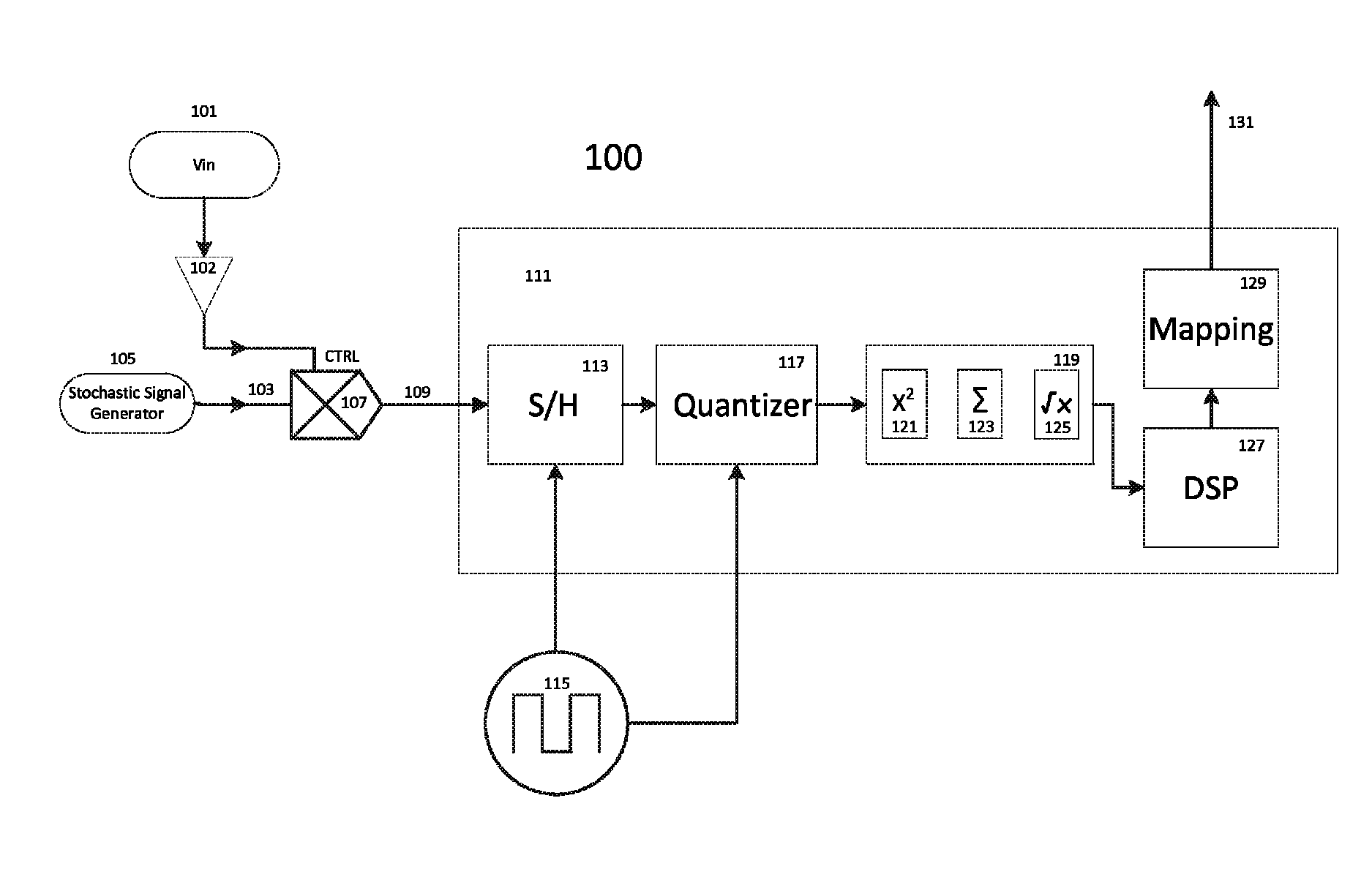
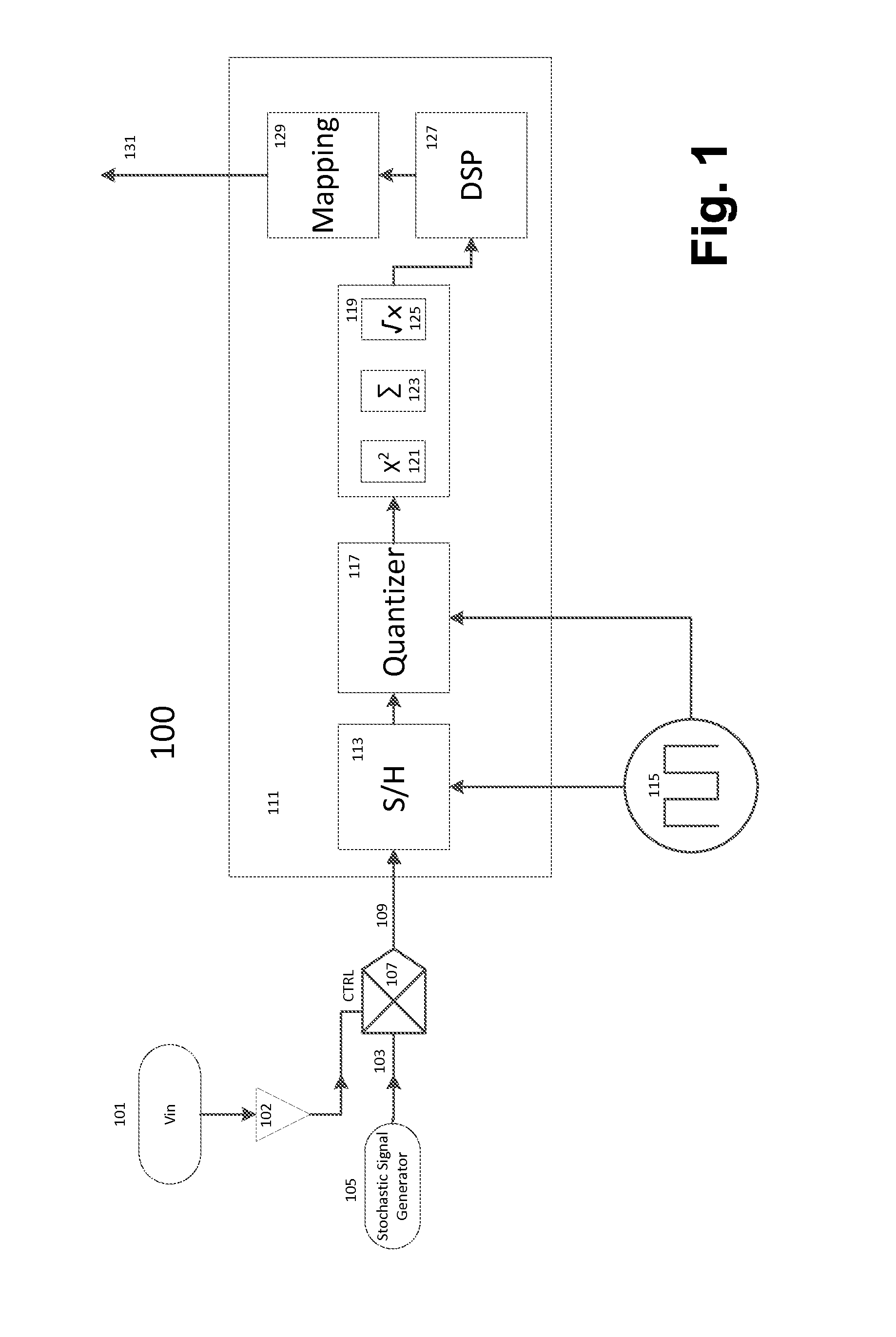
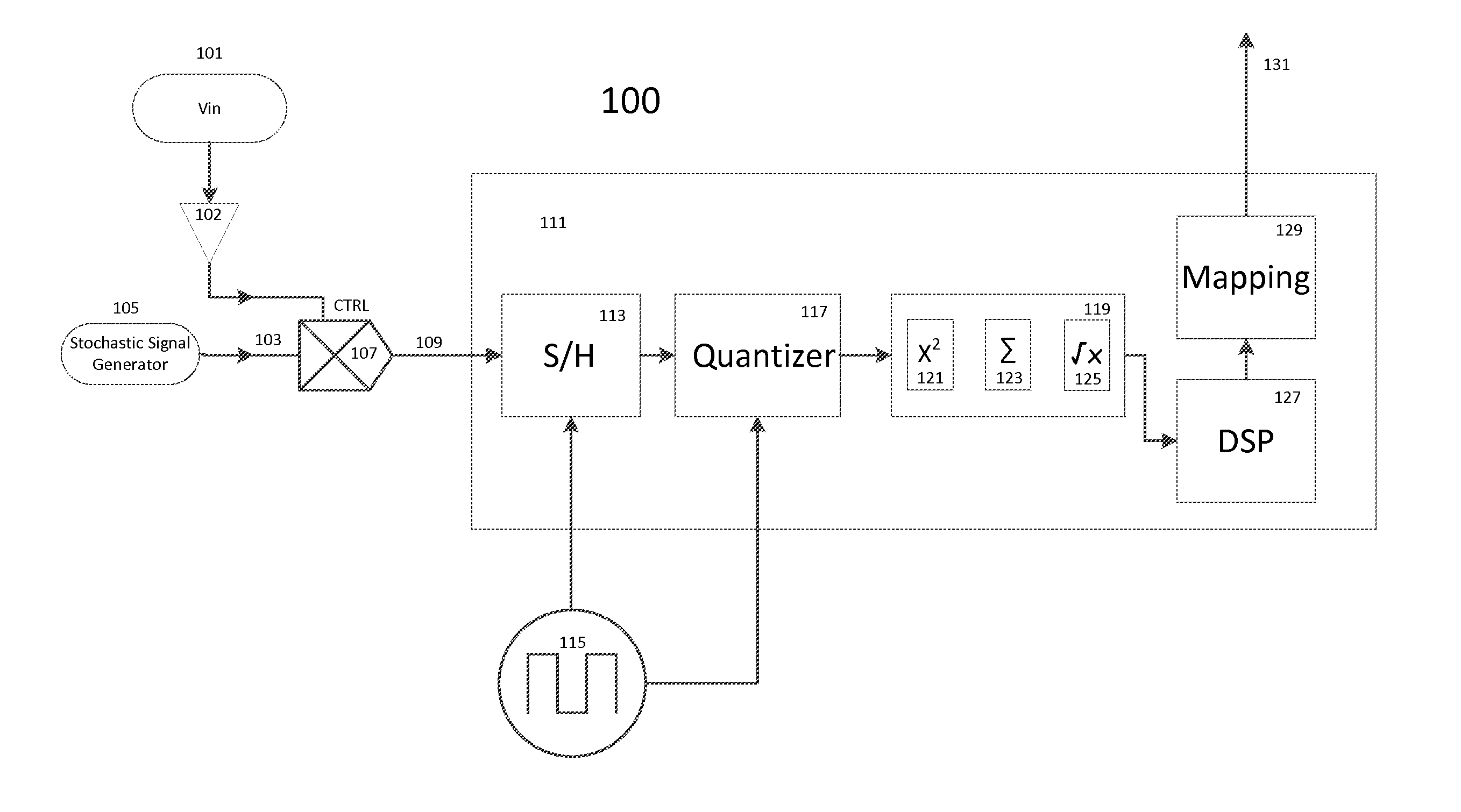
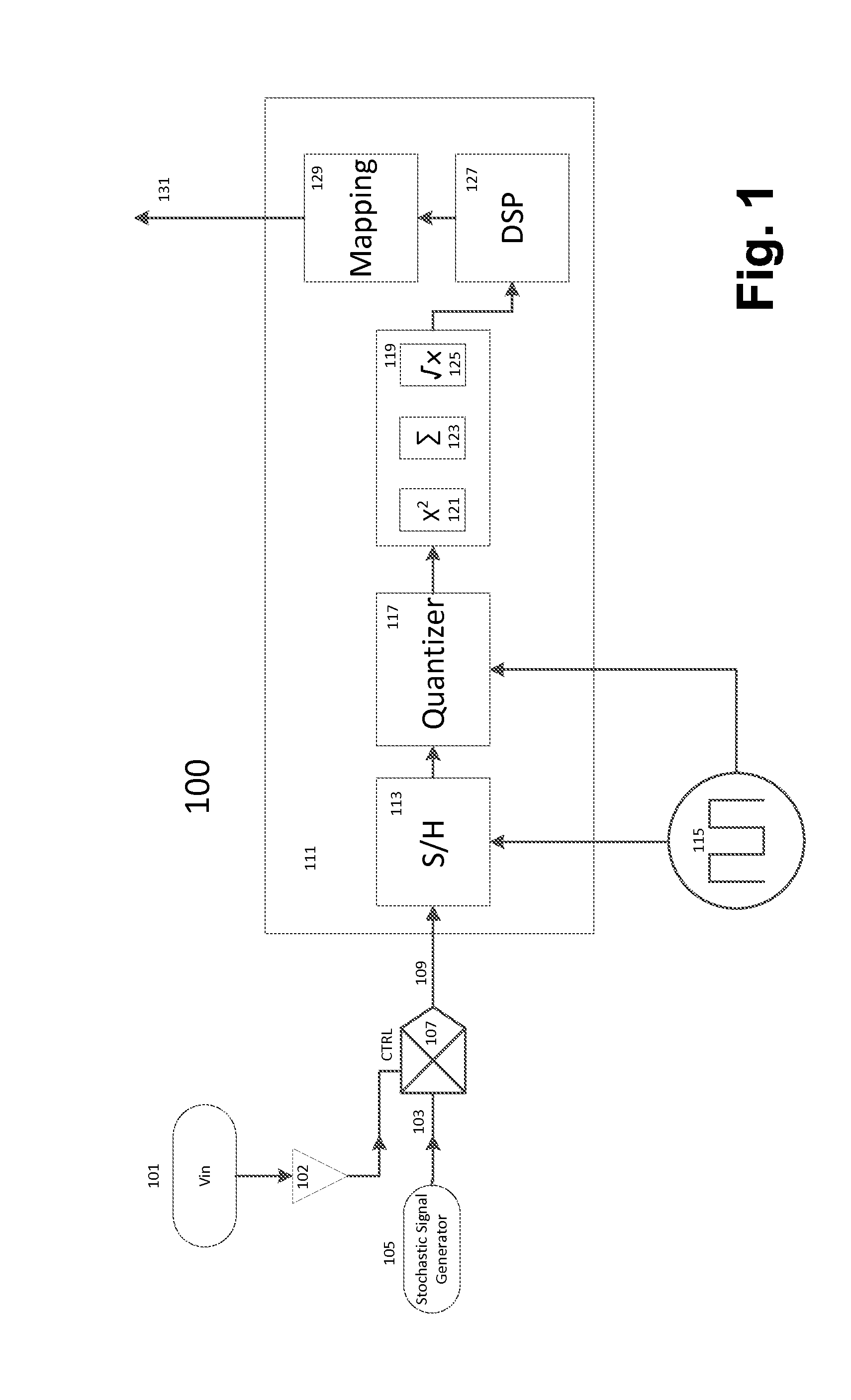
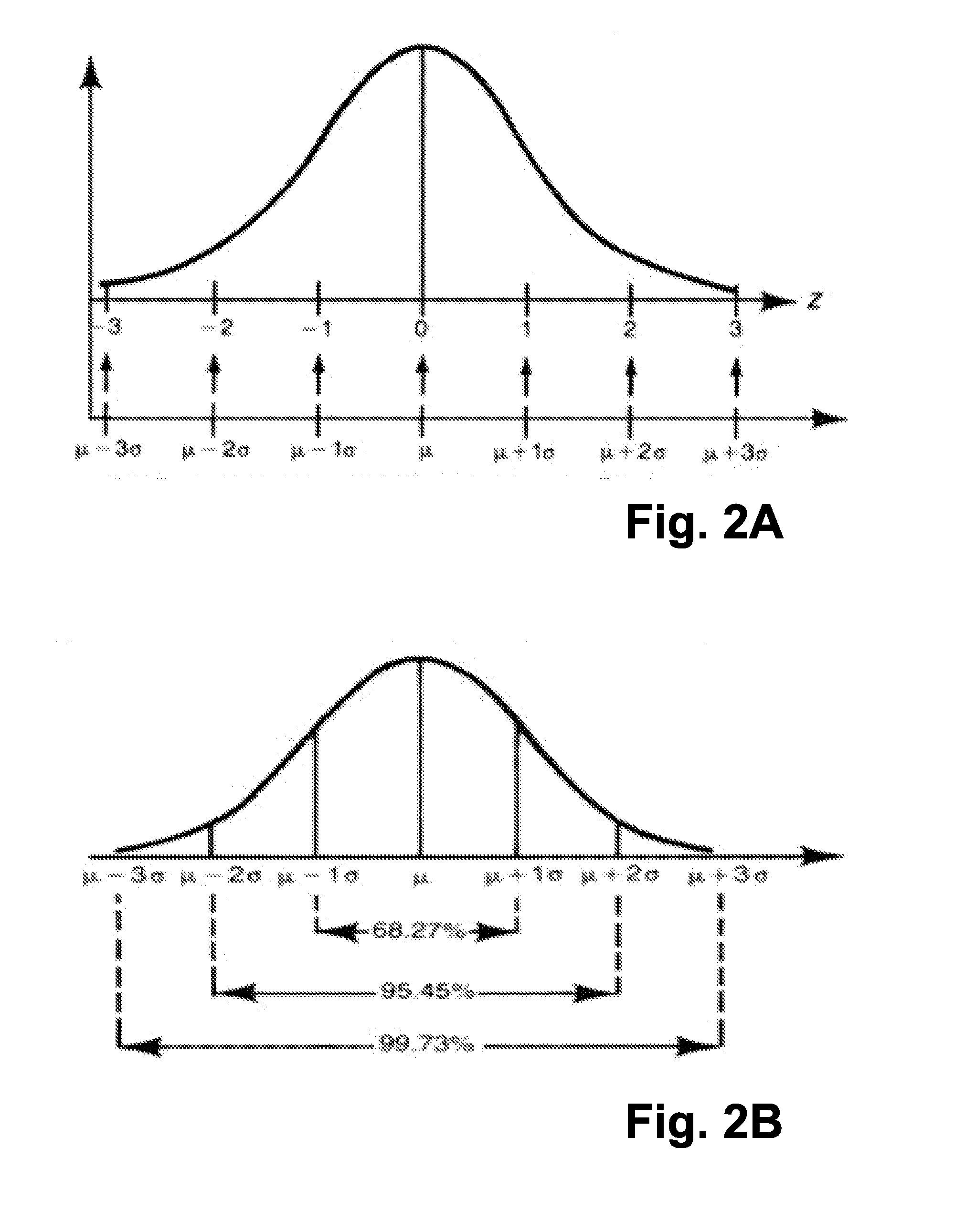
Stochastic encoding in analog to digital conversion
ActiveUS9077363B2Analogue-digital convertersDigital-analogue convertorsAnalog signalAnalog-to-digital converter
A method and system for encoding an analog signal on a stochastic signal, the encoded signal then converted to a digital signal by an analog to digital converter, the analog to digital converter thereafter decoding from the encoded signal a digital signal, which corresponds to the analog signal. The stochastic signal may be a noise signal shaped to a Gaussian normal curve. An encoding process is performed by a multiplication circuit, which multiplies the stochastic signal by the analog signal, producing a product signal for an analog to digital conversion. During analog to digital conversion, the product signal is decoded. The decoding is performed using an arithmetic operation, which may be a Root Sum Square function or a Root Means Square function. The decoded signal is then mapped to account for offset error, gain error, and endpoint adjustment. The result is a decoded digital signal corresponding to the analog signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
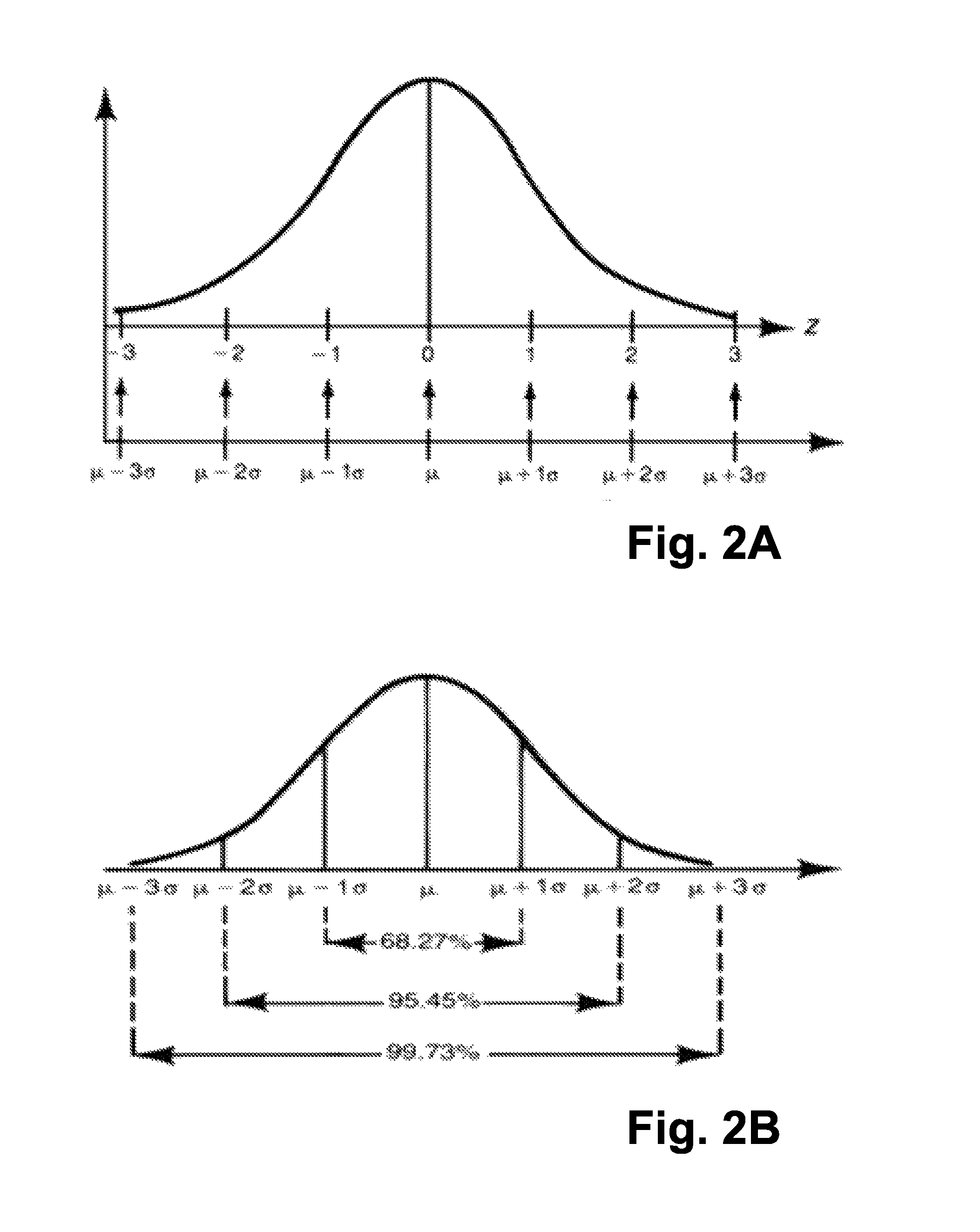
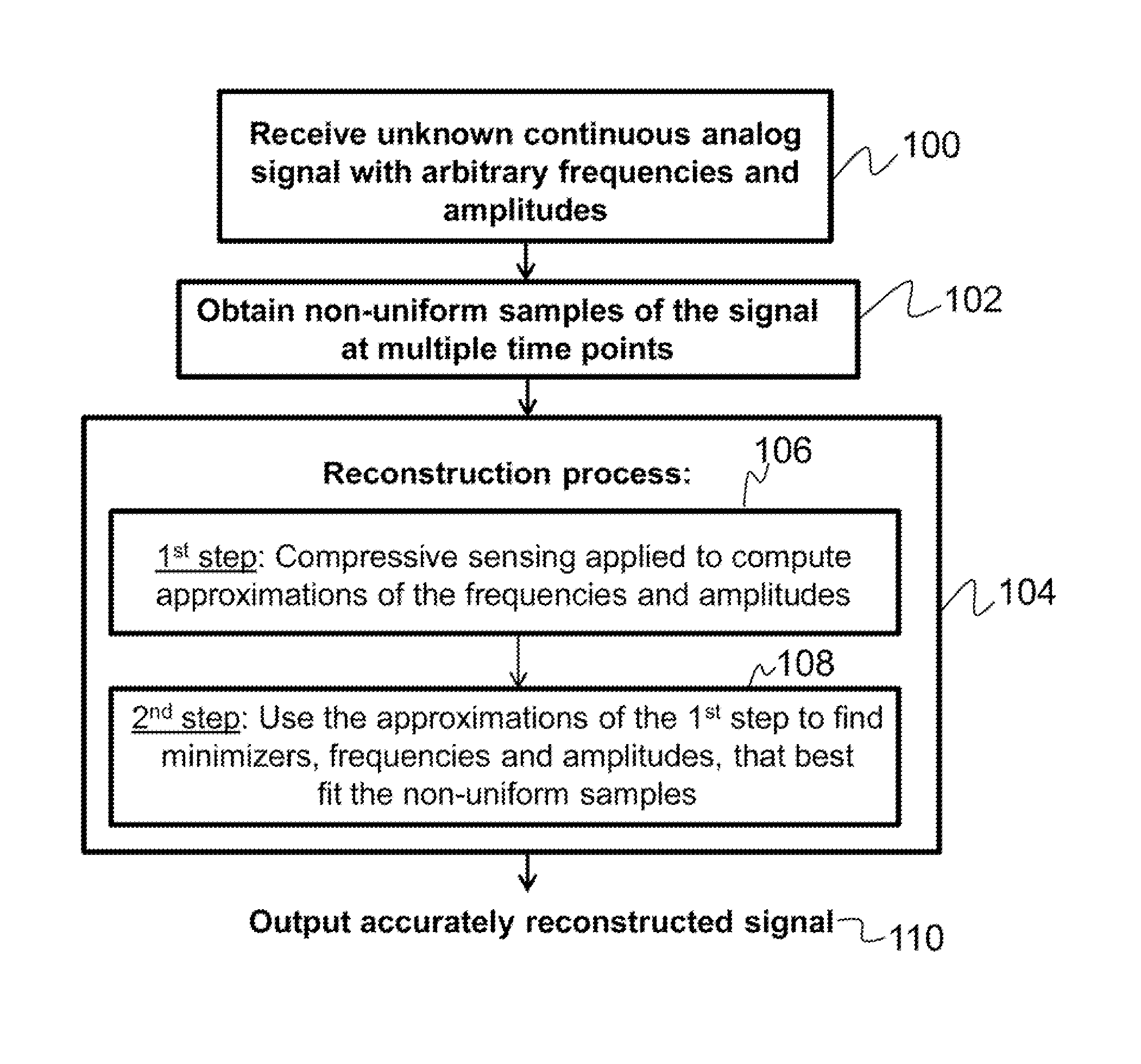
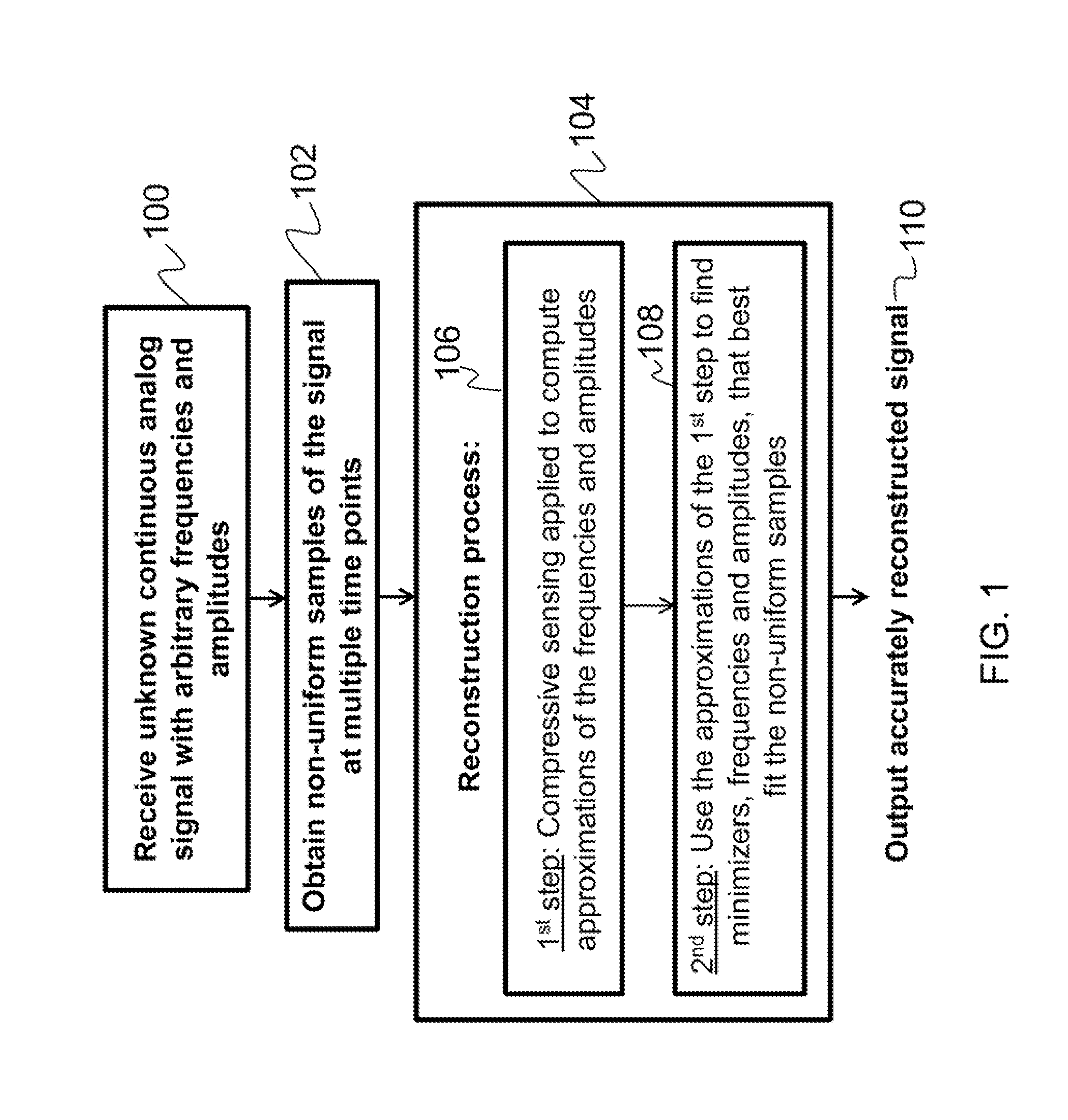
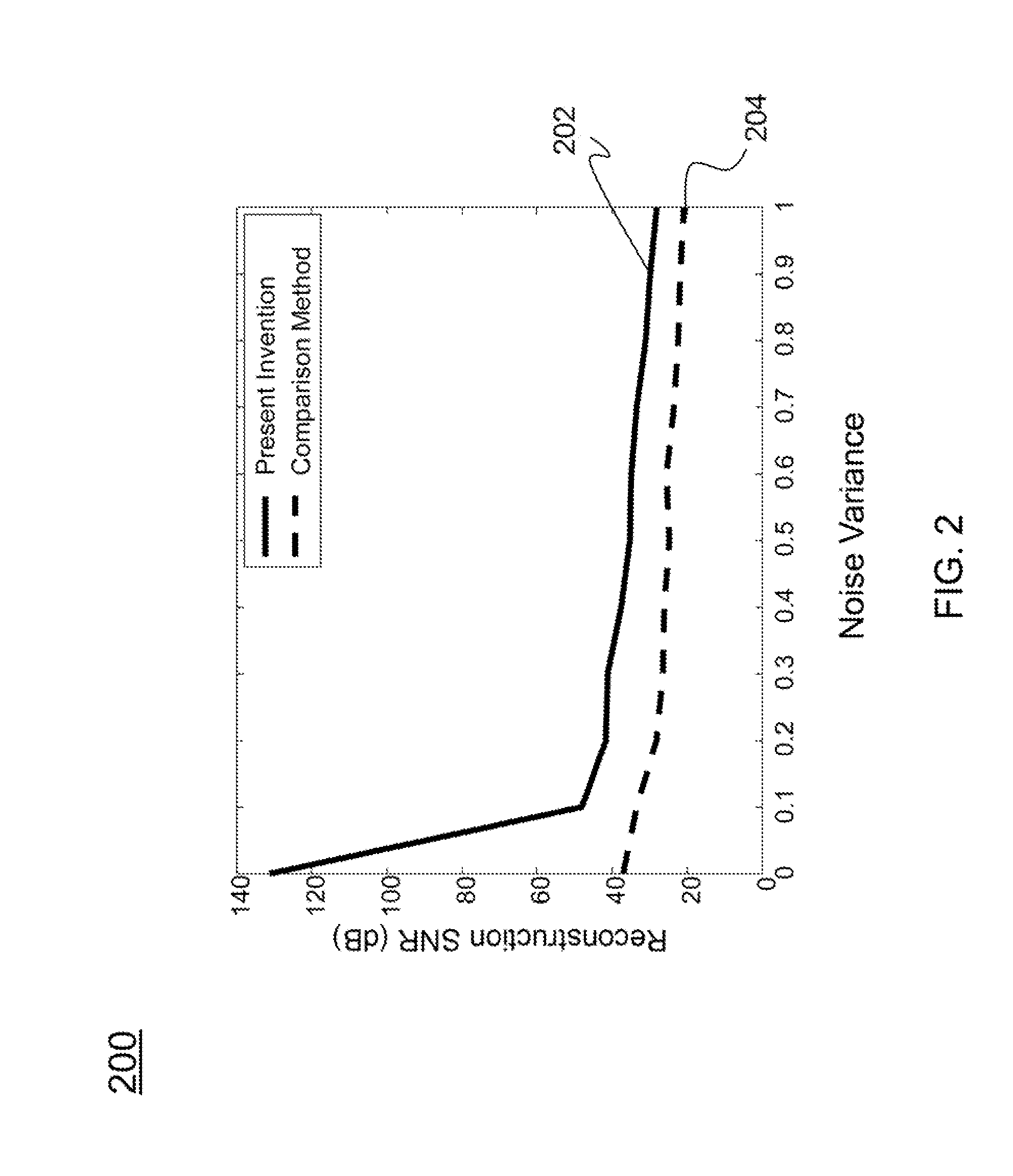
Accurate reconstruction of frequency-sparse signals with arbitrary frequencies from non-uniform samples
InactiveUS9064136B1Accurate reconstructionComputing operations for optimisationComputing operations for multiplication/divisionAnalog signalCompressed sensing
Described is a method for accurately reconstructing analog signals. The present invention considers a general parameter estimation problem, extends the utility of compressive sensing to real scenarios, and is able to accurately estimate center frequencies and amplitudes. Specifically, an unknown continuous analog signal comprising a set of arbitrary frequencies and amplitudes is received. A set of non-uniform samples of the unknown continuous analog signal is then obtained at multiple times. Finally, an iterative reconstruction process is utilized to determine a set of frequencies and a set of amplitudes that best fit the set of non-uniform samples in a global minimum problem in order to accurately reconstruct the continuous analog signal.
Owner:HRL LAB
Stochastic encoding in analog to digital conversion
ActiveUS20150155878A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAnalog signalAnalog-to-digital converter
A method and system for encoding an analog signal on a stochastic signal, the encoded signal then converted to a digital signal by an analog to digital converter, the analog to digital converter thereafter decoding from the encoded signal a digital signal, which corresponds to the analog signal. The stochastic signal may be a noise signal shaped to a Gaussian normal curve. An encoding process is performed by a multiplication circuit, which multiplies the stochastic signal by the analog signal, producing a product signal for an analog to digital conversion. During analog to digital conversion, the product signal is decoded. The decoding is performed using an arithmetic operation, which may be a Root Sum Square function or a Root Means Square function. The decoded signal is then mapped to account for offset error, gain error, and endpoint adjustment. The result is a decoded digital signal corresponding to the analog signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
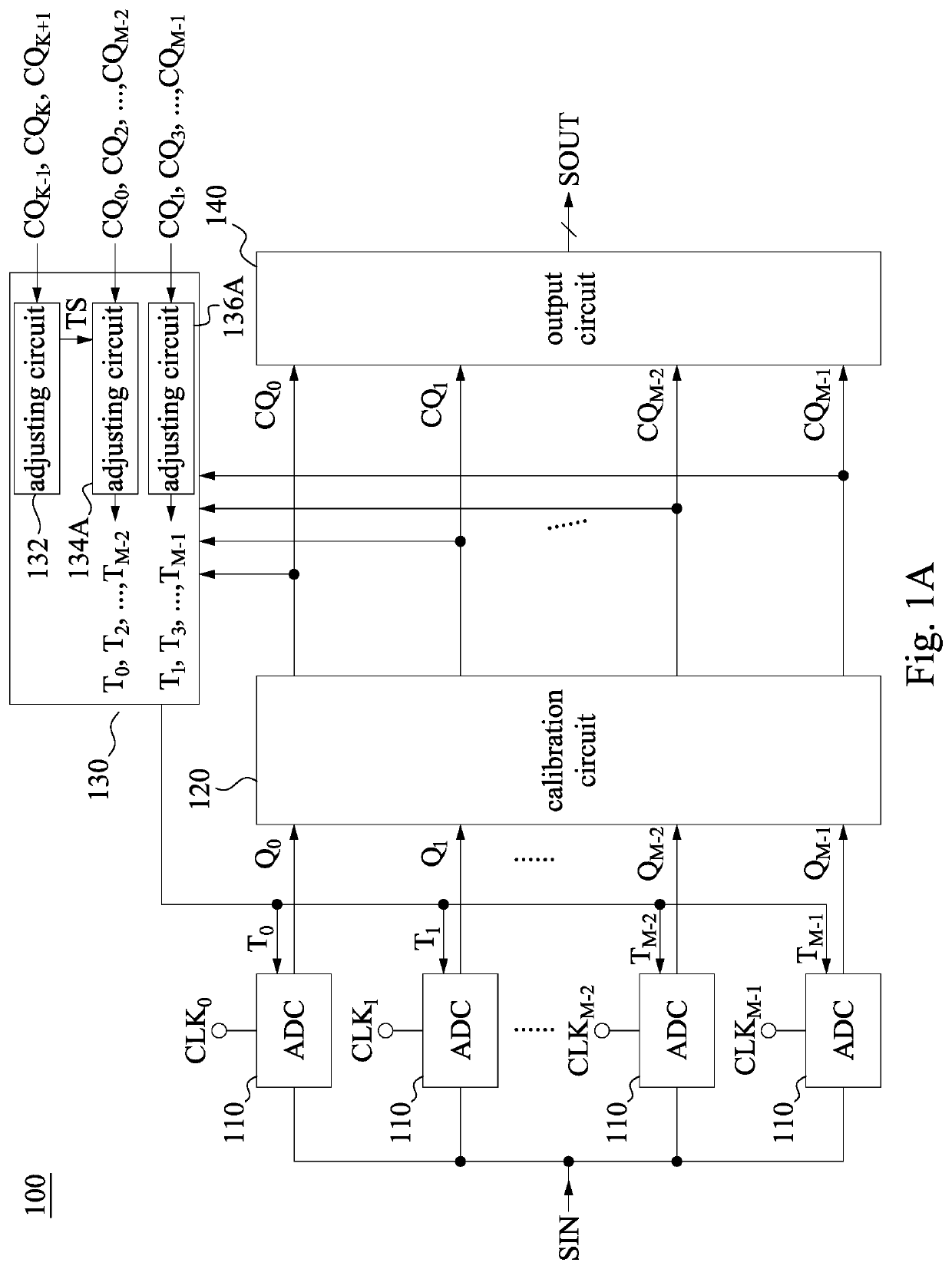
Analog to digital converter device and method for calibrating clock skew
ActiveUS11075640B1Calibration period be reducedReduce power consumptionAnalogue-digital convertersPhysical parameters compensation/preventionA d converterHemt circuits
An analog to digital converter (ADC) device includes ADC circuits, a calibration circuit, and a skew adjusting circuit. The ADC circuits are configured to convert an input signal according to interleaved clock signals to generate first quantized outputs. The calibration circuit is configured to perform at least one calibration operation according to the first quantized outputs to generate second quantized outputs. The skew adjusting circuit further includes a first adjusting circuit. The first adjusting circuit is configured to analyze adjacent clock signals according to part of the second quantized outputs to generate adjusting information. The skew adjusting circuit is configured to analyze time difference information within even-numbered sampling periods of the clock signals according to the second quantized outputs and the adjusting information to generate adjustment signals. The adjustment signals are configured to reduce clock skews of the ADC circuits.
Owner:GLOBAL UNICHIP CORPORATION +1
Digital slope analog to digital converter device and signal conversion method
ActiveUS20210328596A1Electric signal transmission systemsConversion using stochastic techniquesCapacitanceSoftware engineering
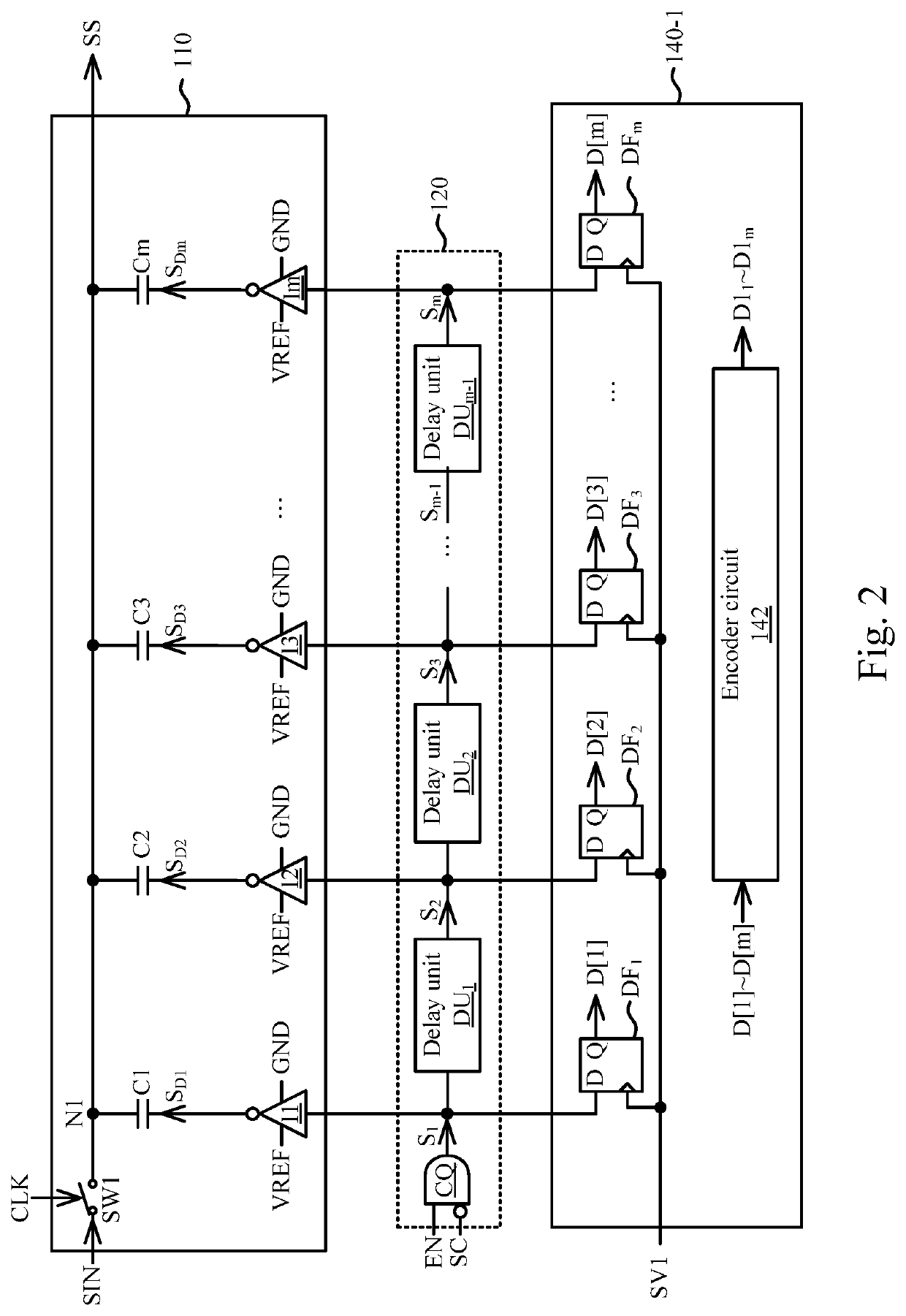
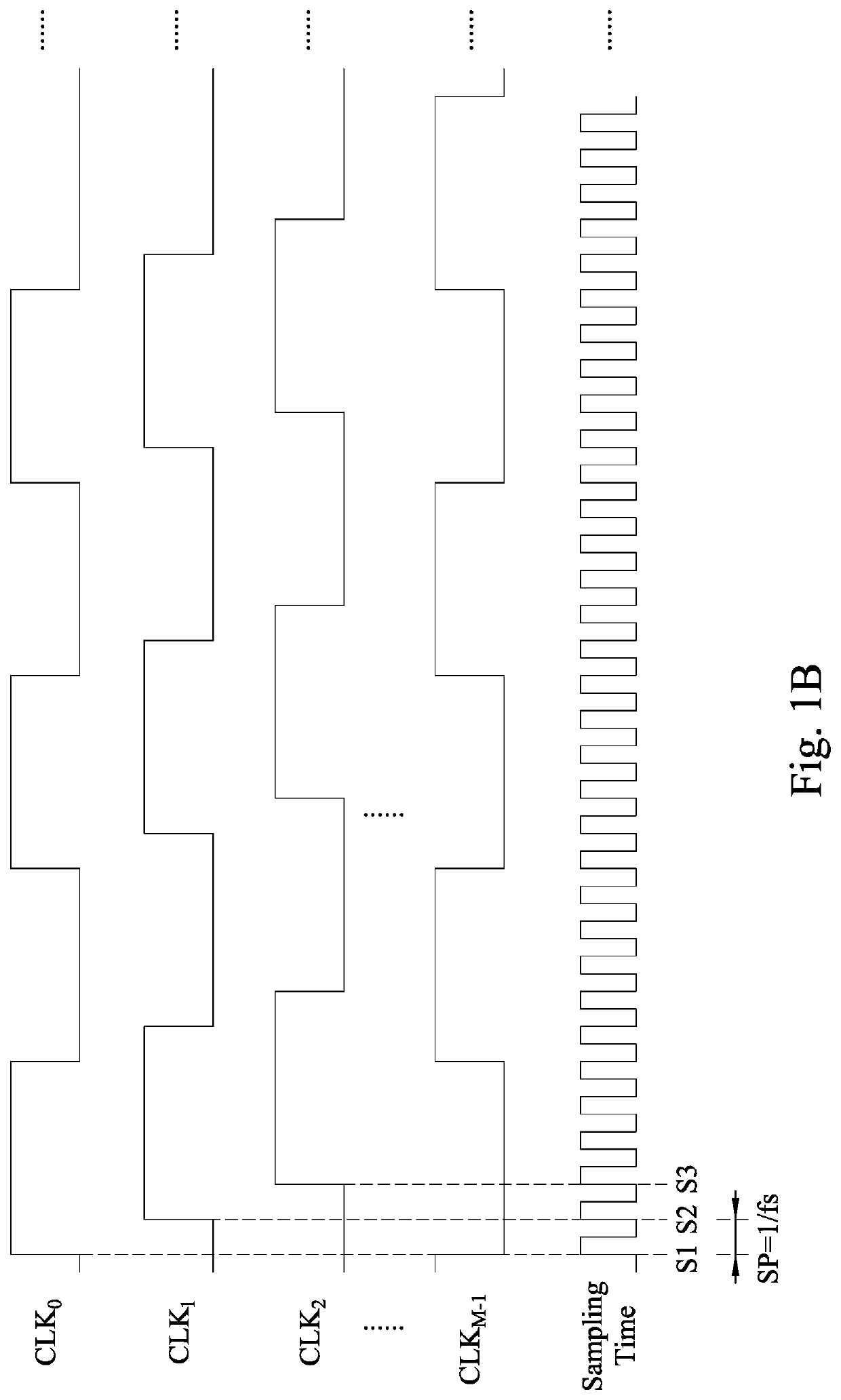
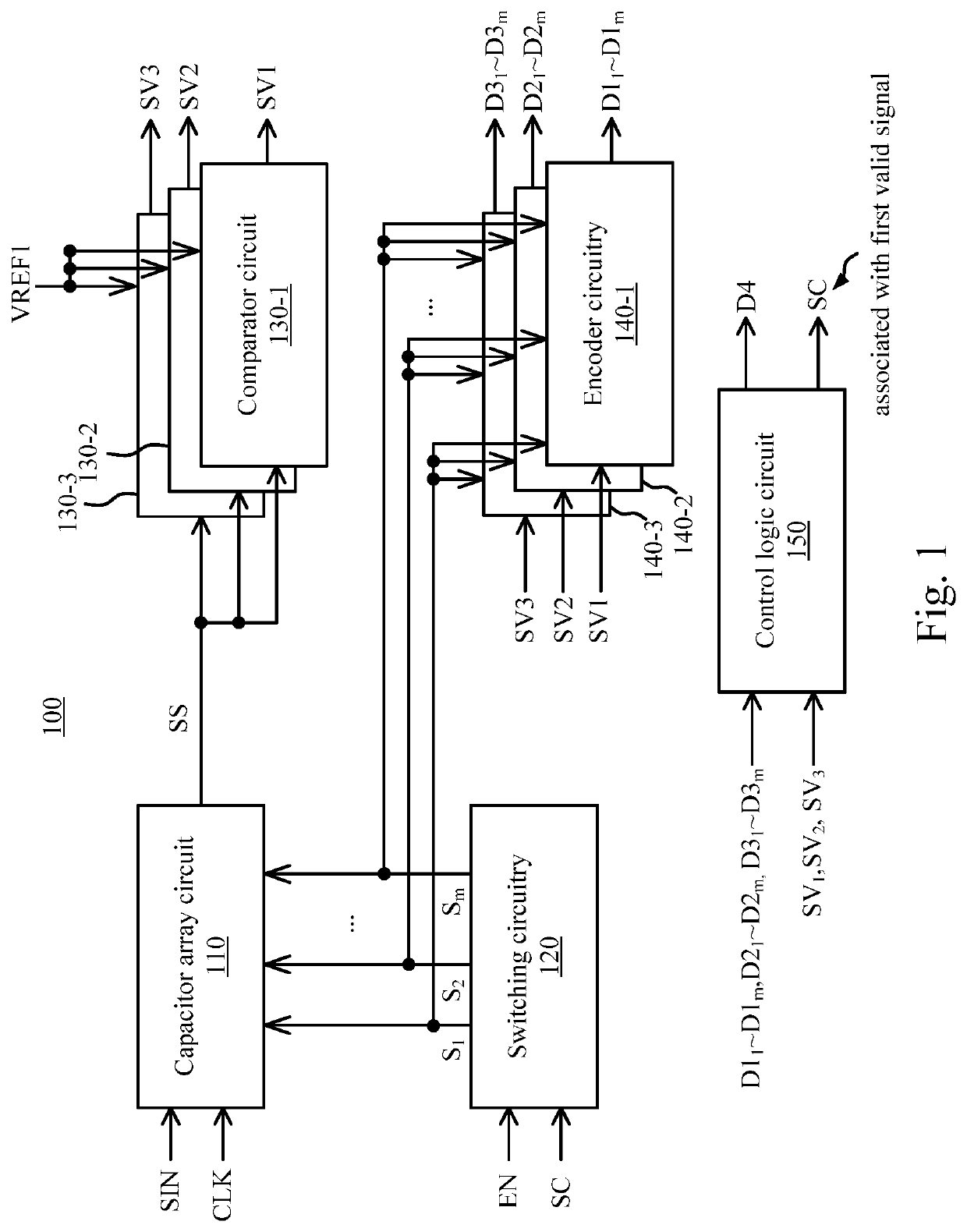
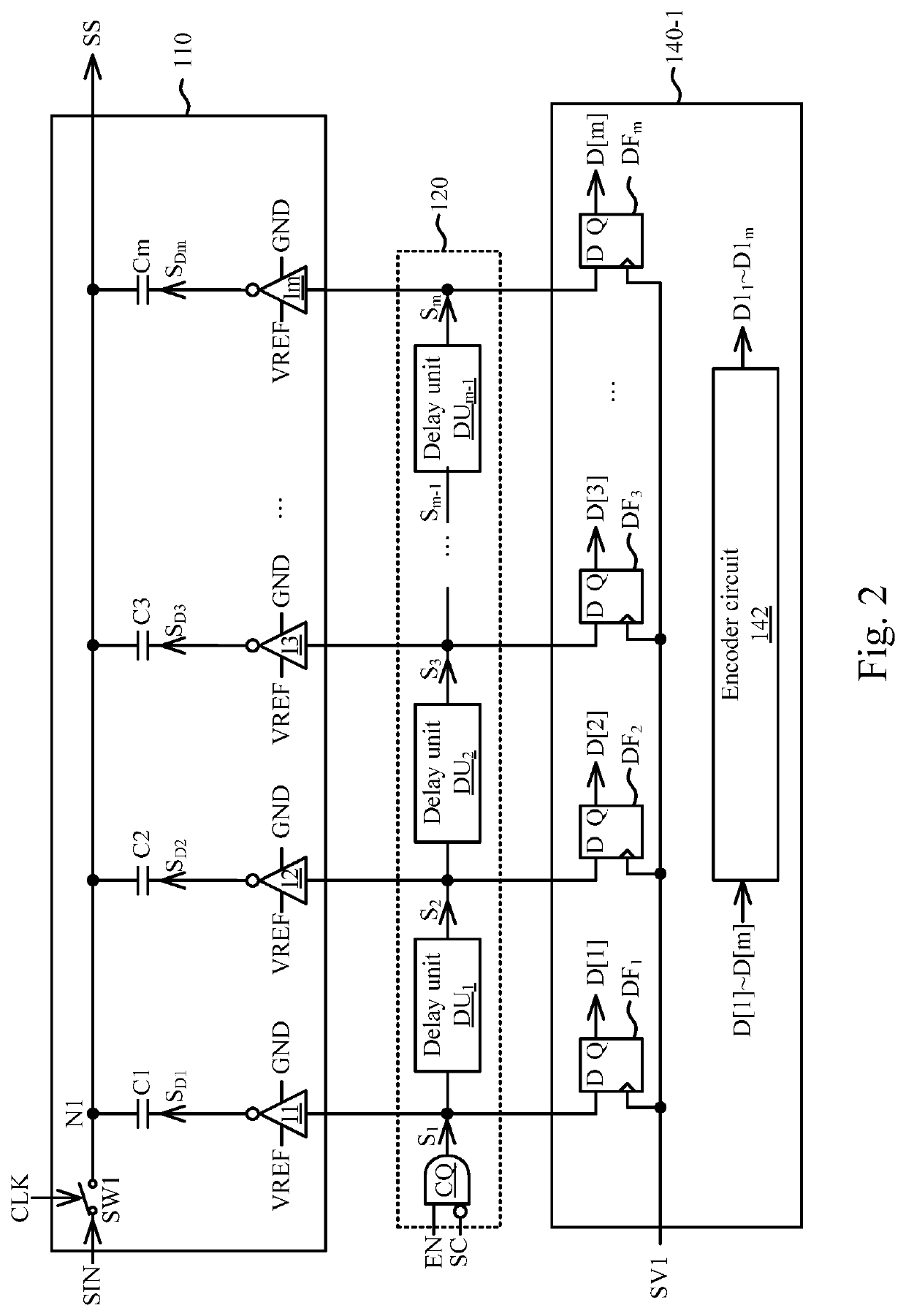
A digital slope analog to digital converter device includes a capacitor array circuit, a switching circuitry, comparator circuits, encoder circuitries, and a control logic circuit. The capacitor array circuit generates a first signal according to an input signal and switching signals. The switching circuitry generates the switching signals according to an enable signal and a first valid signal in the valid signals. Each of the comparator circuits compares the first signal with a predetermined voltage, in order to generate a corresponding one of the valid signals. Each of the encoder circuitries receives the switching signals according to a corresponding one of the valid signals, in order to generate a corresponding one of sets of first digital codes. The control logic circuit performs a statistics calculation according to the sets of first digital codes, in order to generate a second digital code.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Analog-to-digital converter circuit
PendingCN113508531ADelta modulationPhysical parameters compensation/preventionConvertersSoftware engineering
An ADC circuit (50) is disclosed. The ADC circuit (50) comprises a global input configured to receive an input voltage (Vin) and a plurality of converter circuits (105l-105N). Each converter circuit (105j) comprises a comparator circuit (70j) having a first input connected to the global input, a second input, and an output configured to output a one-bit output signal of the comparator circuit (70j). Furthermore, each converter circuit (105j) comprises a one-bit current-output DAC (110j) having an input directly controlled from the output of the comparator circuit (70j) and an output connected to the second input of the comparator circuit (70j). The second inputs of all comparator circuits are interconnected. The ADC circuit (50) further comprises a digital output circuit (130) configured to generate an output signal z[n] of the ADC circuit (50) in response to the one-bit output signals of the comparator circuits (70j).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Systems and methods for designing adcs based on memory-based probabilistic switching
InactiveCN103814525BElectric signal transmission systemsConversion using stochastic techniquesSoftware engineeringA d converter
Certain aspects of the present disclosure provide a probabilistic analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The probabilistic ADC can be configured to convert an analog input into a variable length or variable amplitude pulse, apply the pulse as a switching pulse to a plurality of memory elements, and store a value based on the memory element after the switching pulse is applied. The number of elements to determine the digital value.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Circuit and method for generating the stochastic signal
ActiveUS20110260897A1Ensuring uniquenessLow costMultiple-port networksDigital data processing detailsSignal processing circuitsInformation security
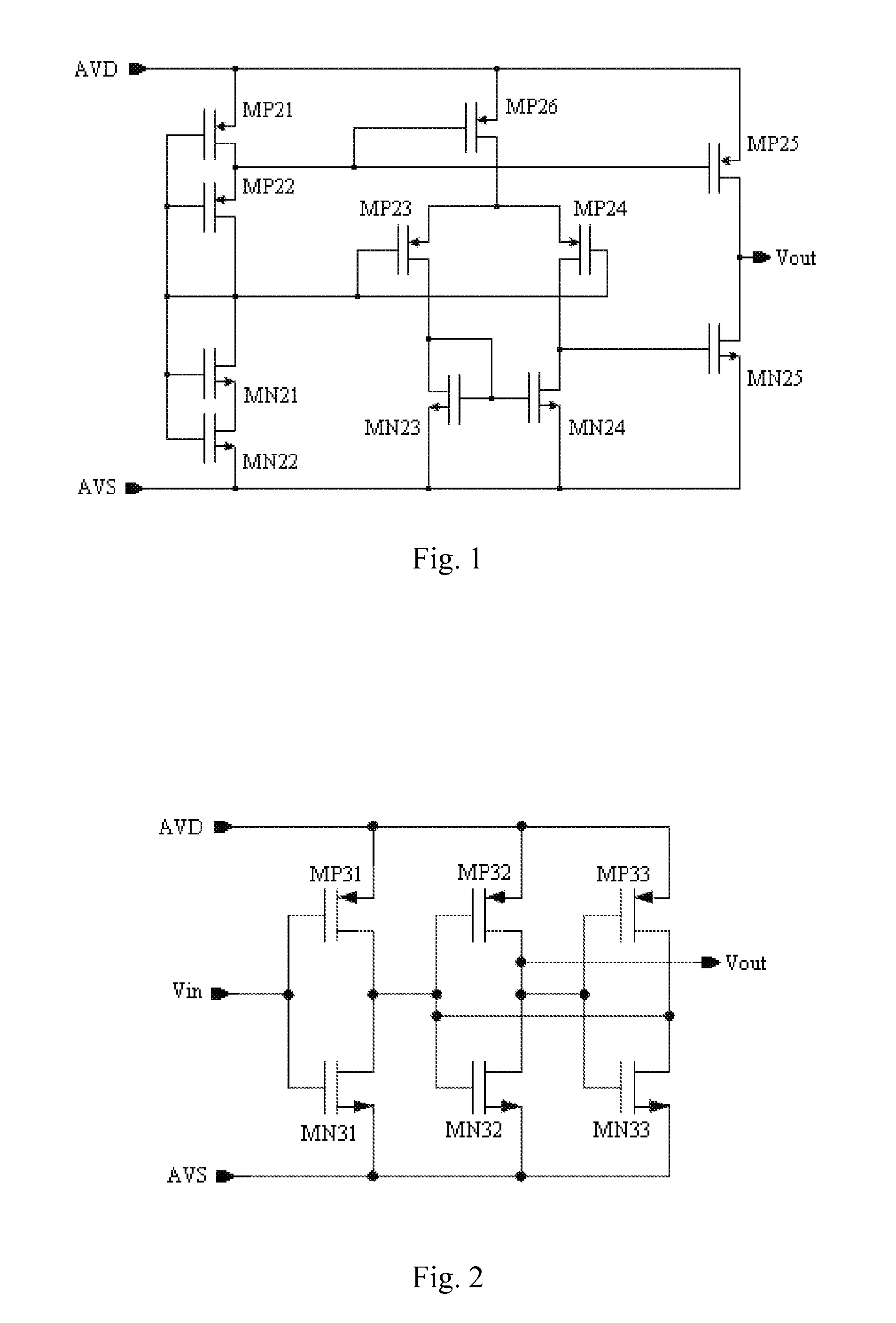
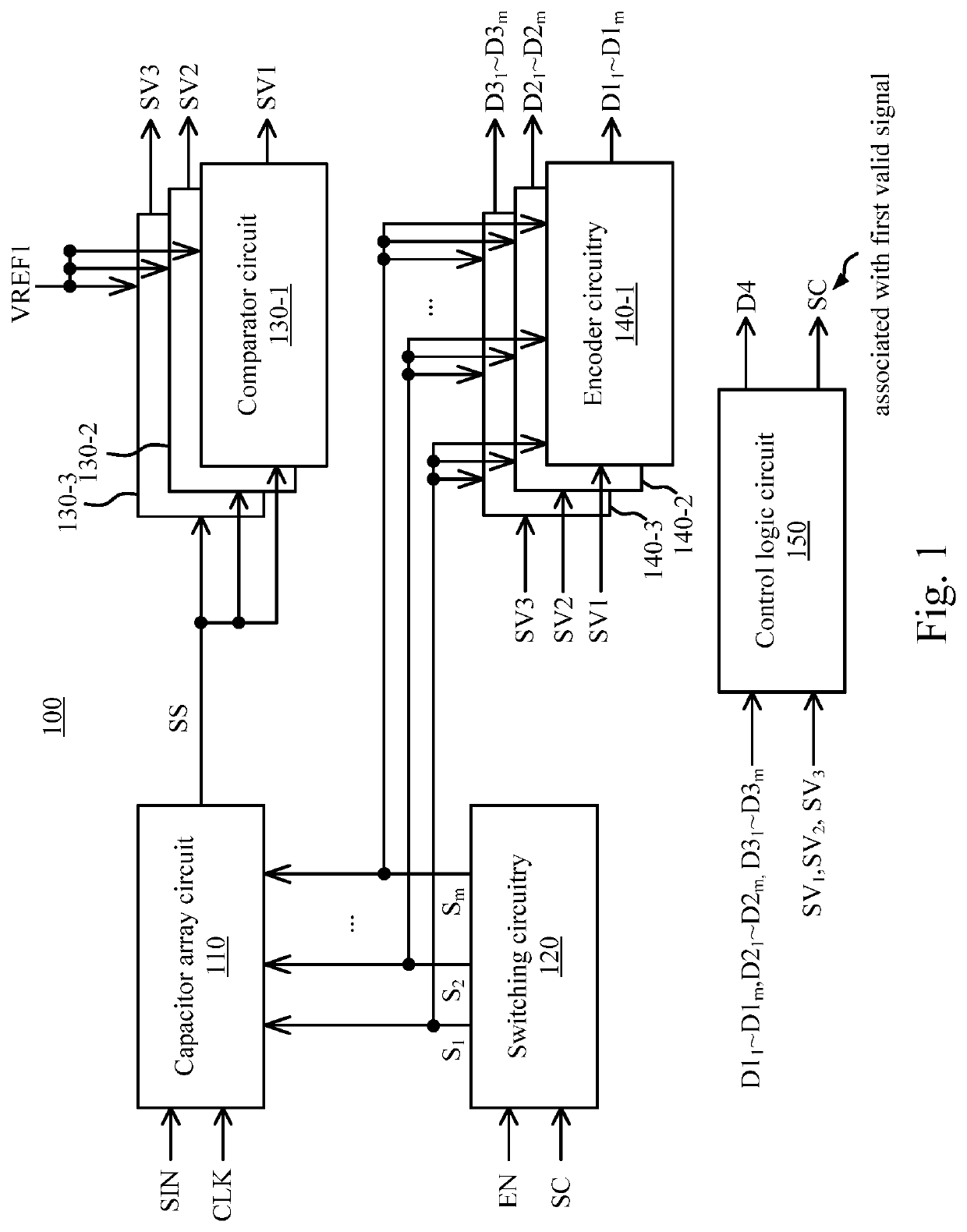
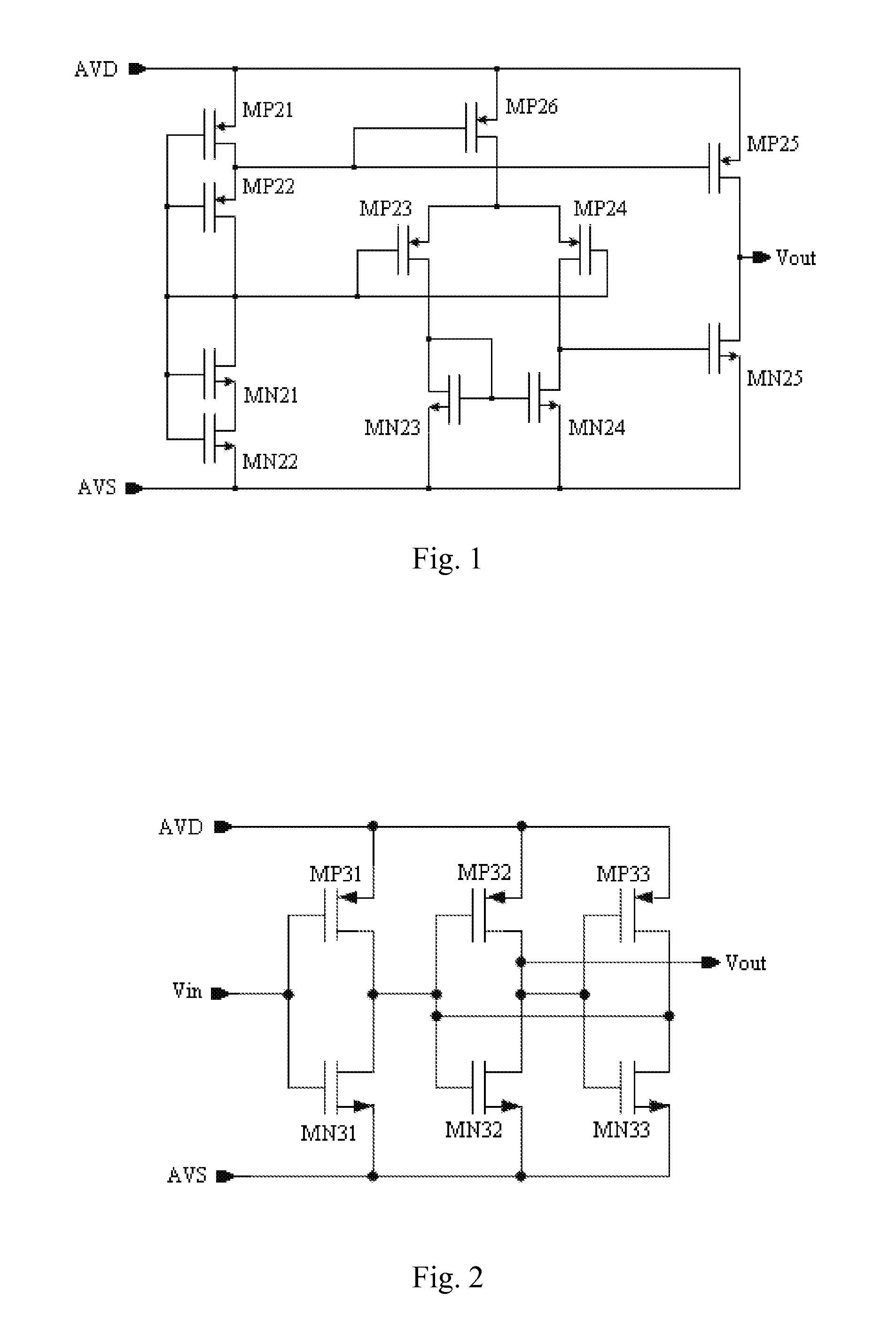
A stochastic signal generation circuit includes a signal output circuit and a signal processing circuit connected with the signal output circuit. The signal output circuit includes two matching semiconductor components, wherein the signal output circuit detects a slight mismatch between the two matching semiconductor components, converts the detected slight mismatch into a corresponding electric signal, amplifies the electric signal, and outputs an analog voltage signal. The signal processing circuit converts the analog voltage signal into a stochastic digital signal. Also, a method for generating a stochastic signal is provided. The present invention decreases the cost of the integrated circuit, and better ensures the information security of the electronic products.
Owner:IPGOAL MICROELECTRONICS (SICHUAN) CO LTD
Pipeline level arithmetic device and pipeline analog-to-digital converter
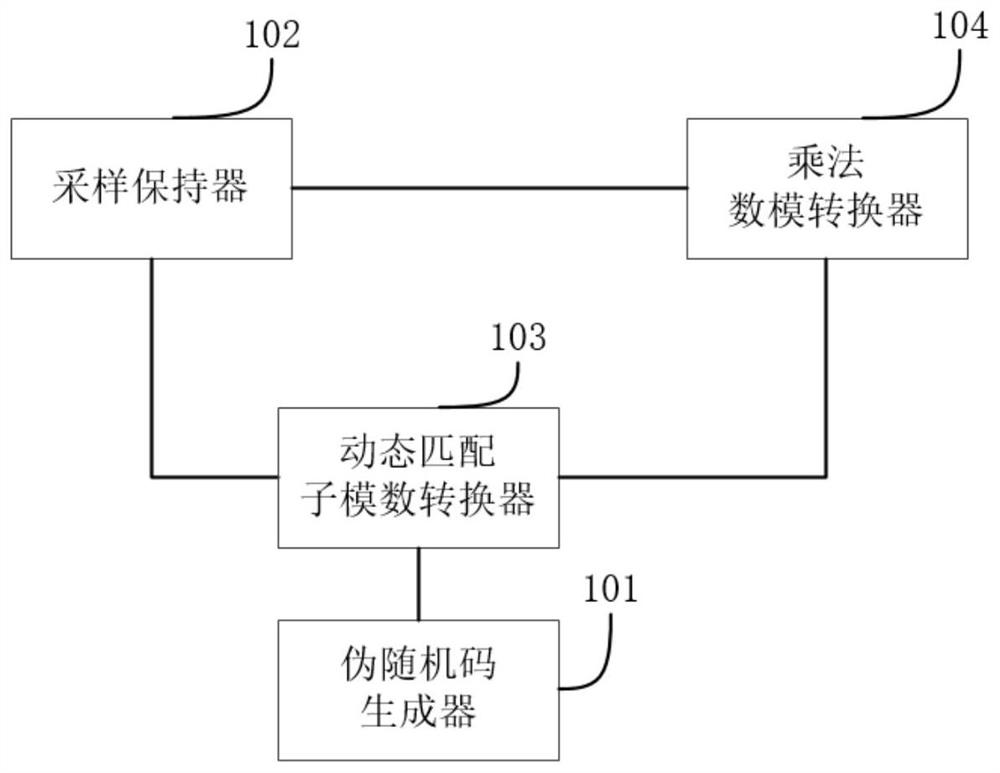
PendingCN114070309AImprove linearityRealize dynamic matchingPhysical parameters compensation/preventionConversion using stochastic techniquesConvertersCapacitance
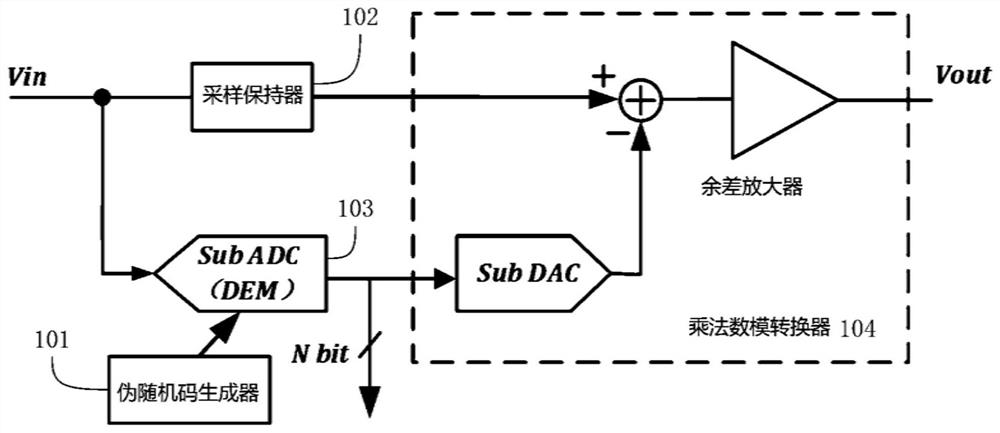
The invention discloses a pipeline level operation device and a pipeline analog-to-digital converter. The pipeline level operation device comprises a dynamic matching sub-analog-to-digital converter, a sampling holder, a pseudo-random code generator and a multiplication digital-to-analog converter, wherein the multiplication digital-to-analog converter is respectively connected with the dynamic matching sub-analog-to-digital converter and the sampling holder, and the dynamic matching sub-analog-to-digital converter is connected with the pseudo-random code generator. Based on the dynamic matching sub-analog-to-digital converter, the threshold voltages of comparators can be changed by using pseudo-random codes, and the dynamic matching of the comparators is realized, so the dynamic matching of a capacitor array in the sub-analog-to-digital converter in the multiplication digital-to-analog converter is realized, and capacitor mismatching caused by process errors, manufacturing processes and the like is scattered. As the threshold voltages of the comparators only need to be prepared before comparison of the comparators, the dynamic matching technology of the threshold voltages can be applied to the retention period of the whole analog-to-digital conversion, and on the basis of not occupying the analog-to-digital conversion time, harmonic distortion is reduced and the linearity of the analog-to-digital converter is improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Real-time Processing Method of Dynamic Signal of Inertial Sensor
ActiveCN107257242BReal-time processingHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention discloses a real-time processing method for dynamic signals of inertial sensors. Firstly, the random sampling technology is used to fully reduce the sampling data of the signal; The algorithm completes the accurate reconstruction of the original signal to improve the output accuracy of the dynamic signal of the inertial sensor. Compared with the traditional method, the invention can effectively improve the precision of the output signal while greatly reducing the sampling data of the signal, so as to realize the real-time processing of the dynamic signal of the inertial sensor.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Random multiphase clock generation circuit
ActiveCN111181556AImprove dynamic performanceAnalogue-digital convertersPhysical parameters compensation/preventionComputer architectureEngineering
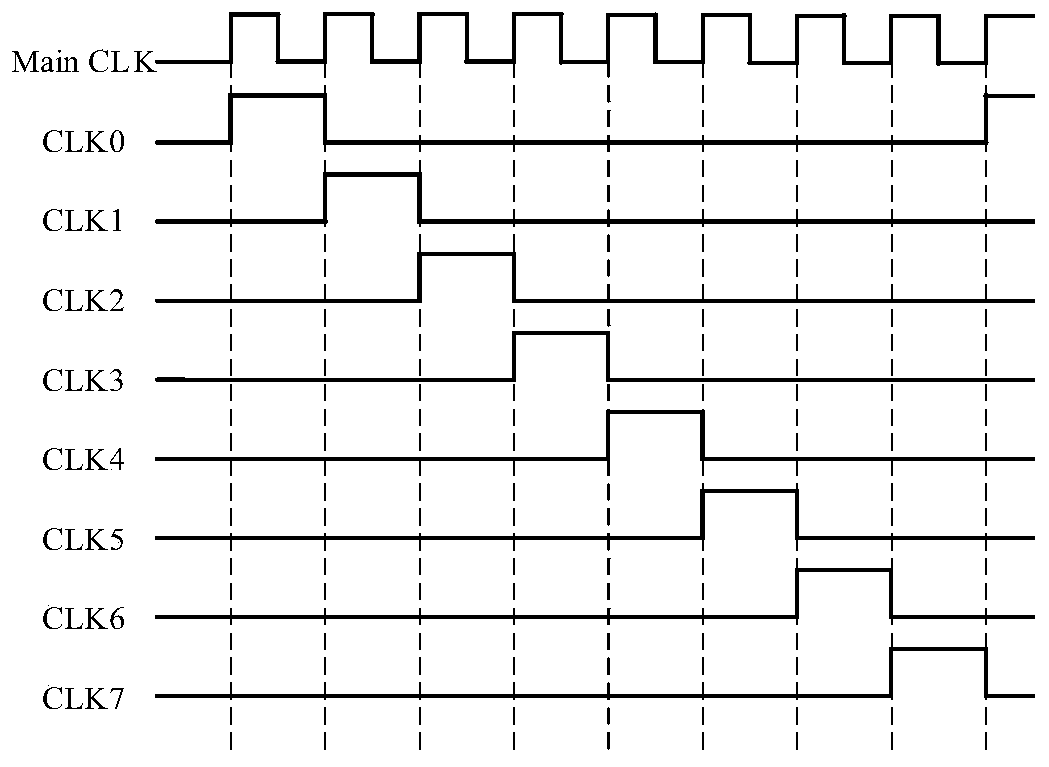
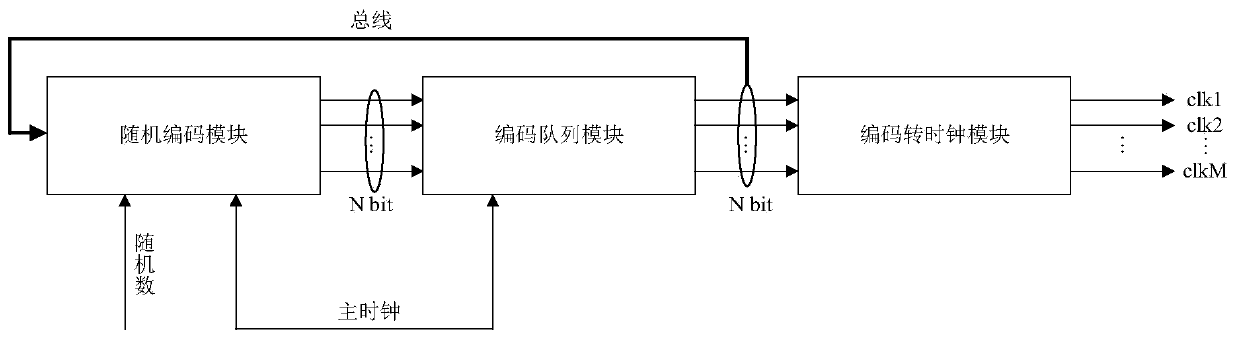
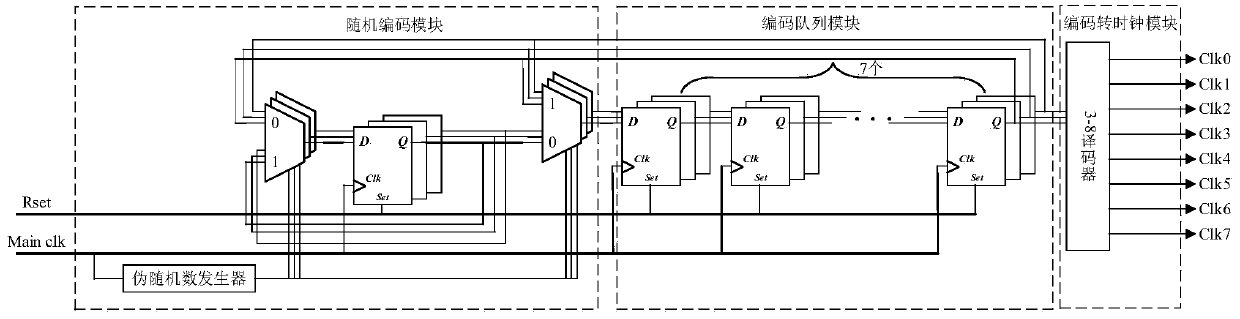
The invention discloses a random multiphase clock generation circuit, which comprises a random encoding module, an encoding queue module and a code-to-clock module, wherein the random encoding modulecomprises a first register, the encoding queue module comprises M-1 cascaded second registers, M sub-clock signals are correspondingly numbered, and the M numbers are encoded and serve as initial storage values of the first register and the M-1 second registers respectively; the encoding queue module is used for outputting the code stored in the last cascaded second register to the random encodingmodule and the code-to-clock module in each clock period of the main clock signal; the random encoding module is used for randomly selecting one code from the code stored in the first register and the code output by the encoding queue module and outputting the selected code to a cascaded first second register in the encoding queue module in each clock period of the main clock signal; and the code-to-clock module is used for outputting a sub-clock signal corresponding to the code output by the encoding queue module.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
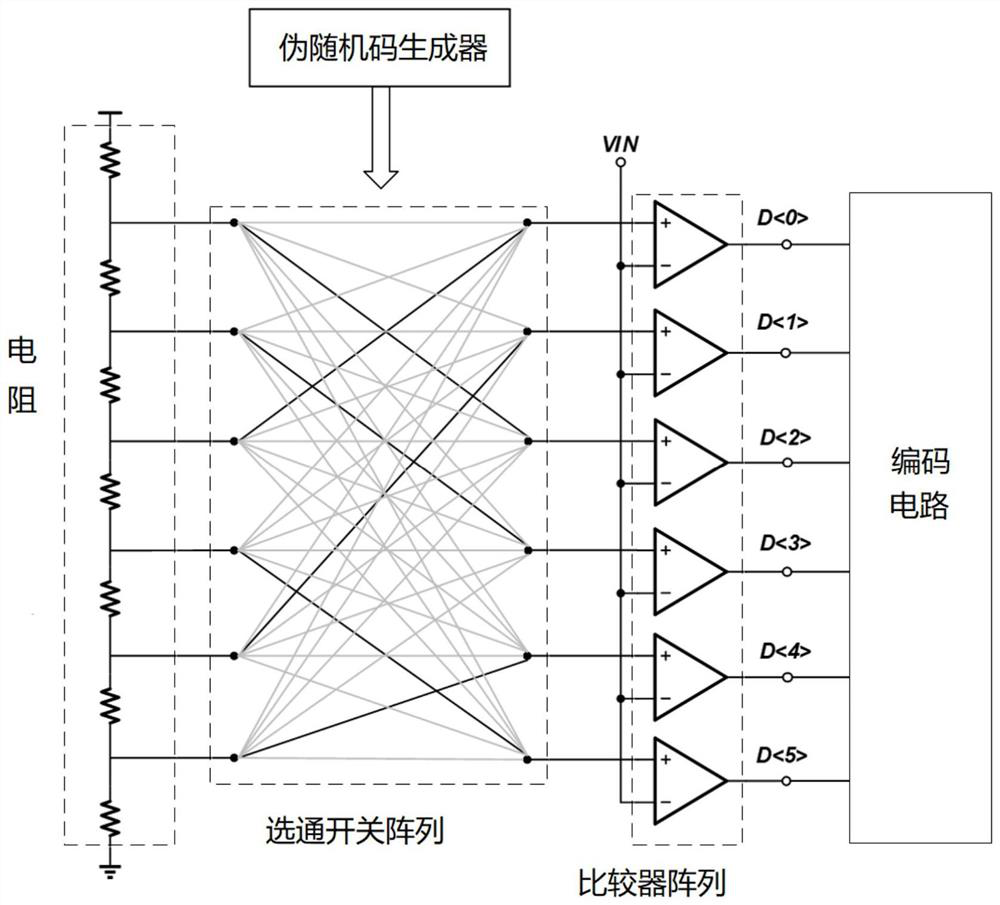
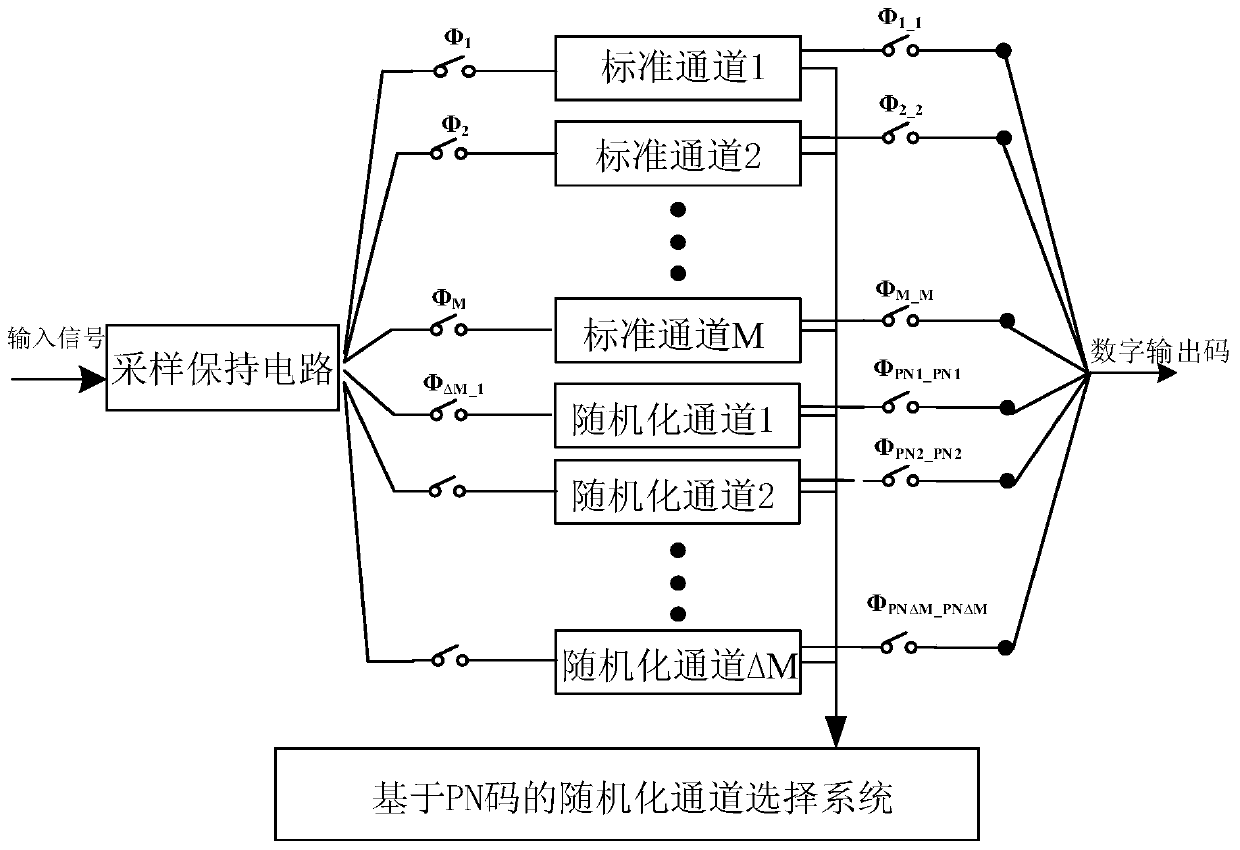
Randomized channel calibration method and system based on pseudo-random codes
PendingCN111049522AAchieve randomizationReduce mistakesAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingConversion using stochastic techniquesTime domainFrequency spectrum
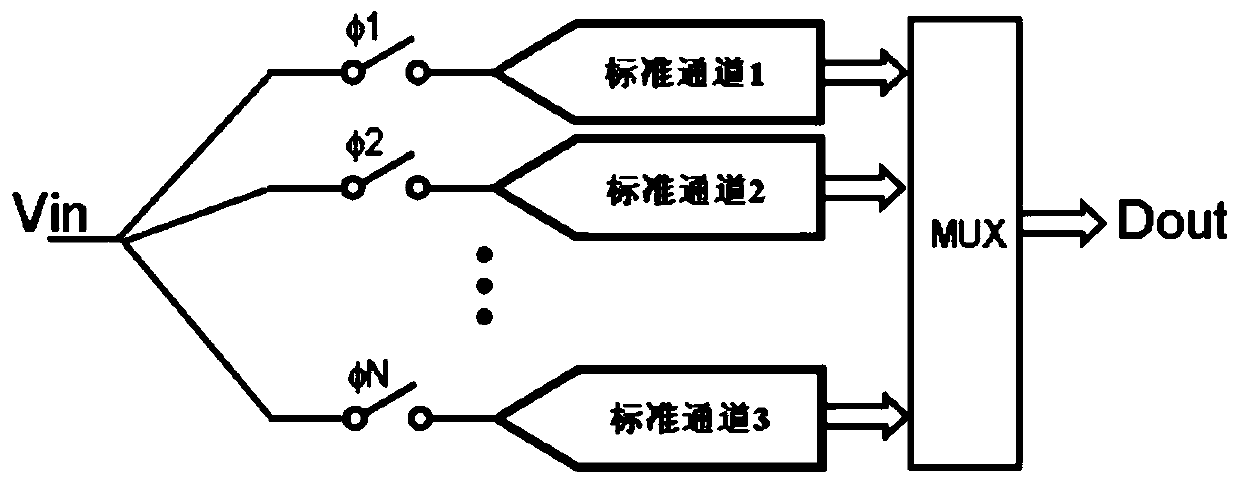
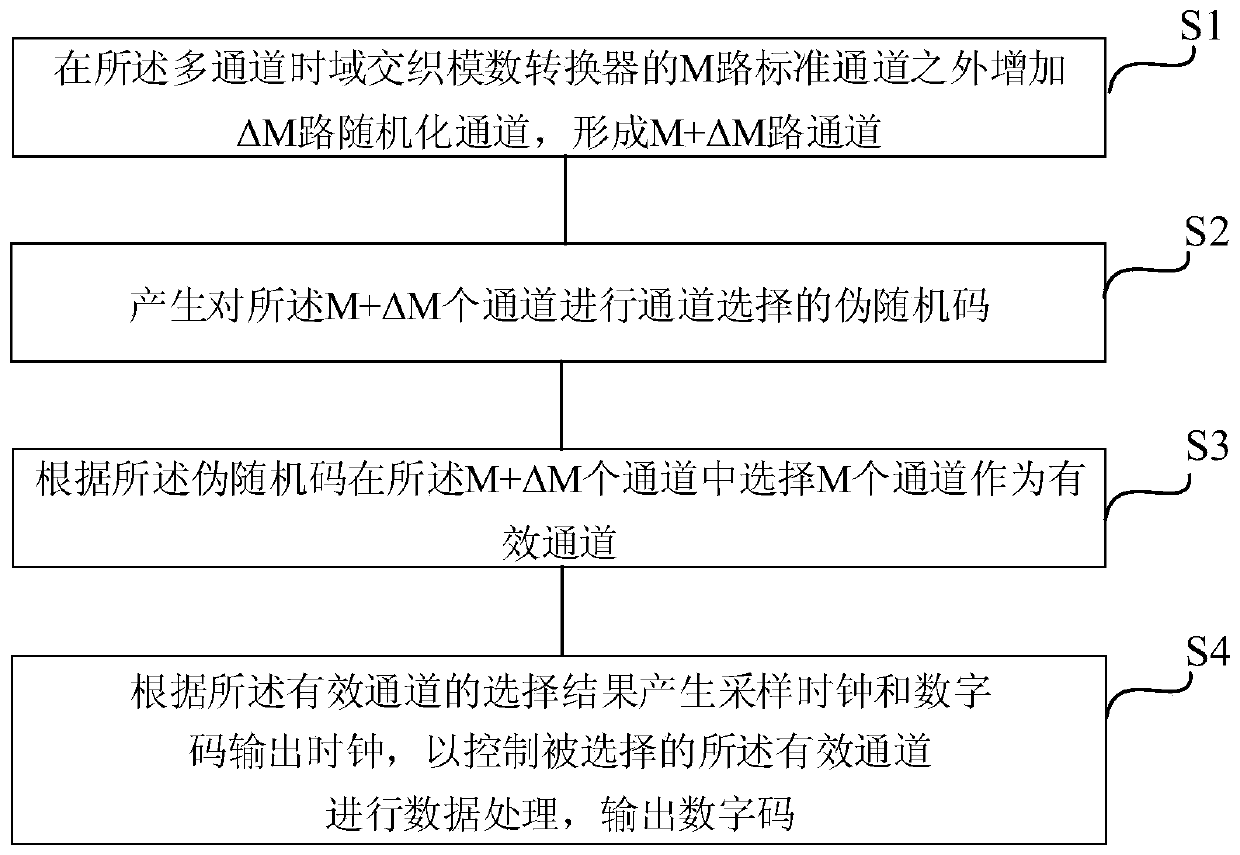
The invention discloses a randomized channel calibration method and system based on pseudo-random codes , which are used for a multi-channel time domain interleaved analog-to-digital converter, and the method comprises the following steps of: adding delta M randomized channels outside M standard channels of the multi-channel time domain interleaved analog-to-digital converter to form M + delta M channels; generating a pseudo-random code for performing channel selection on the M + delta M channels; selecting M channels from the M + delta M channels as effective channels according to the pseudo-random code; and generating a sampling clock and a digital code output clock according to the selection result of the effective channel so as to control the selected effective channel to perform dataprocessing and output a digital code. The method and system are based on a pseudo-random code generation circuit, complete randomization of channels can be achieved under the condition that time is long enough, frequency spectrum stray of output signals can be effectively reduced, random gain errors and offset errors between the channels are effectively reduced, and the performance of the whole analog-digital converter is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
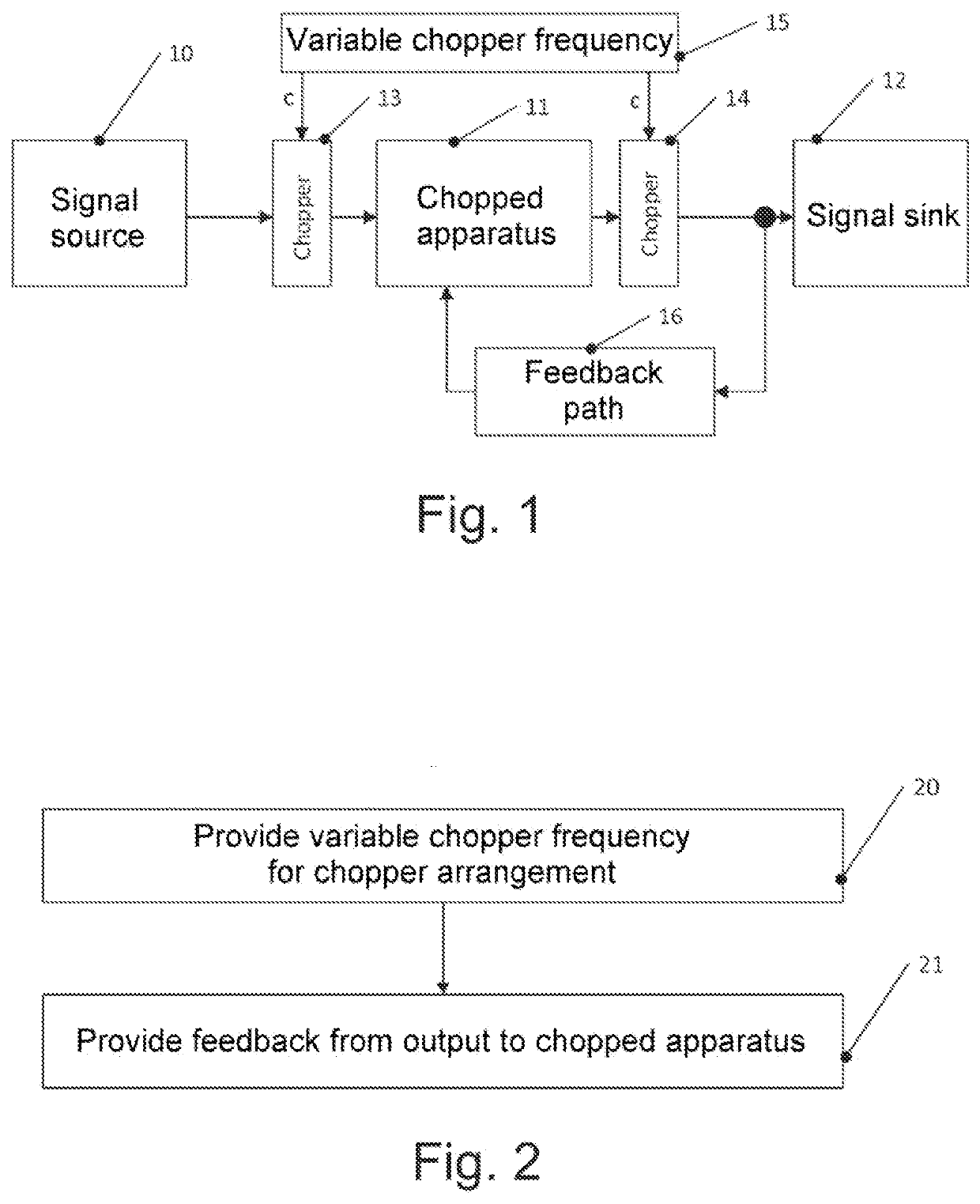
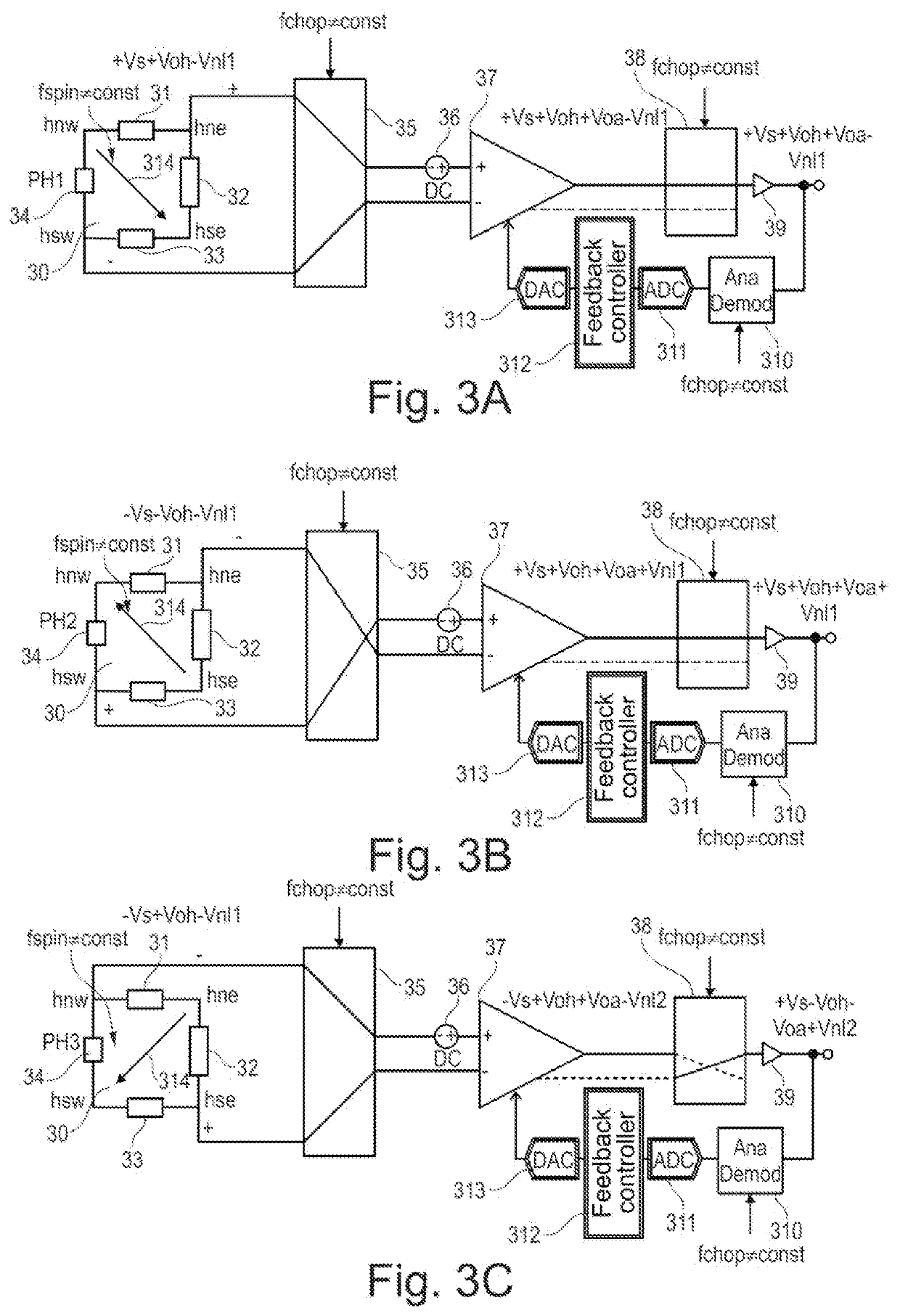
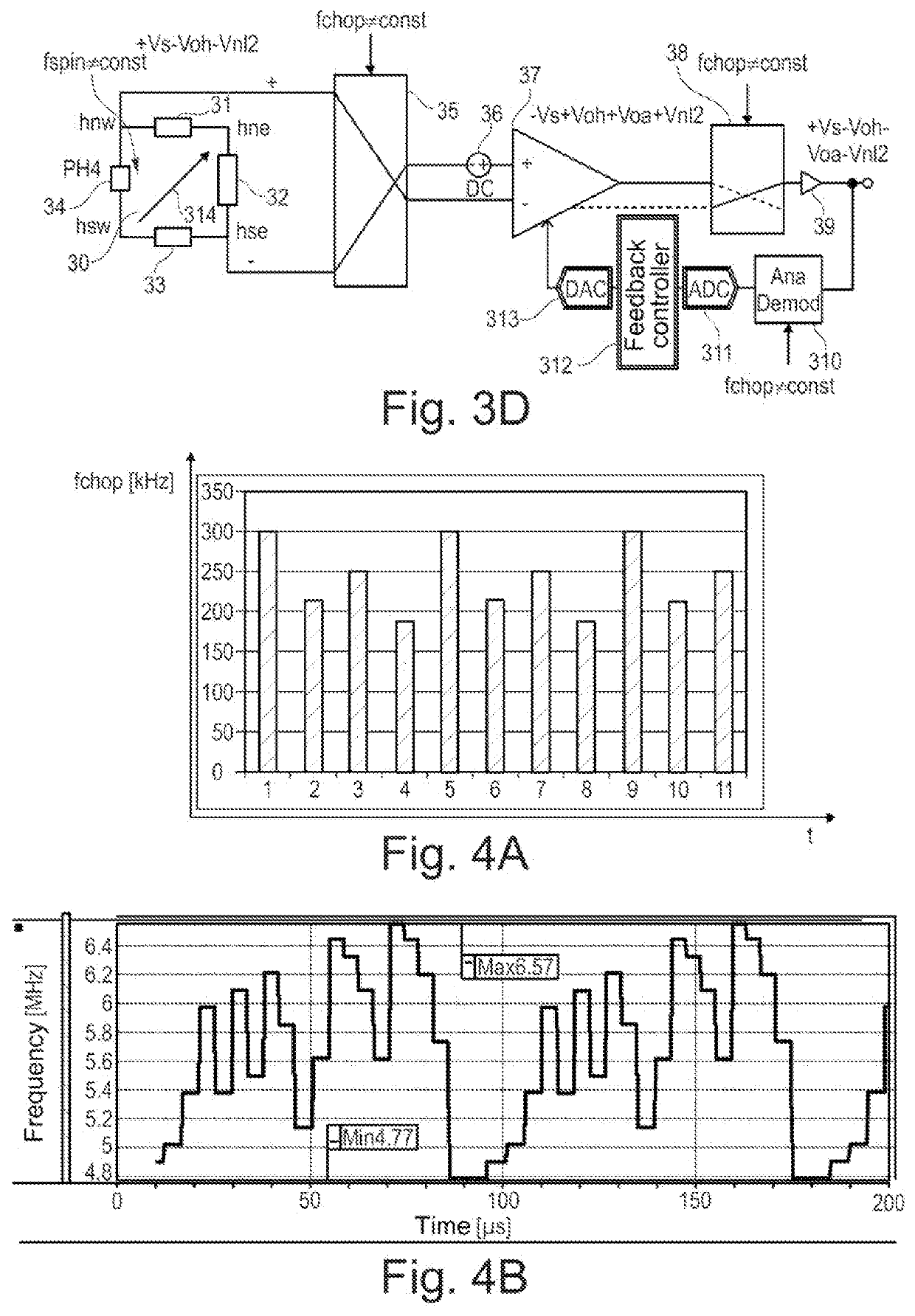
Chopper system and method
PendingUS20210344315A1Reduce offsetReduce rippleMagnetic measurementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSoftware engineeringChopper
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Resonator Device, Electronic Apparatus, And Vehicle
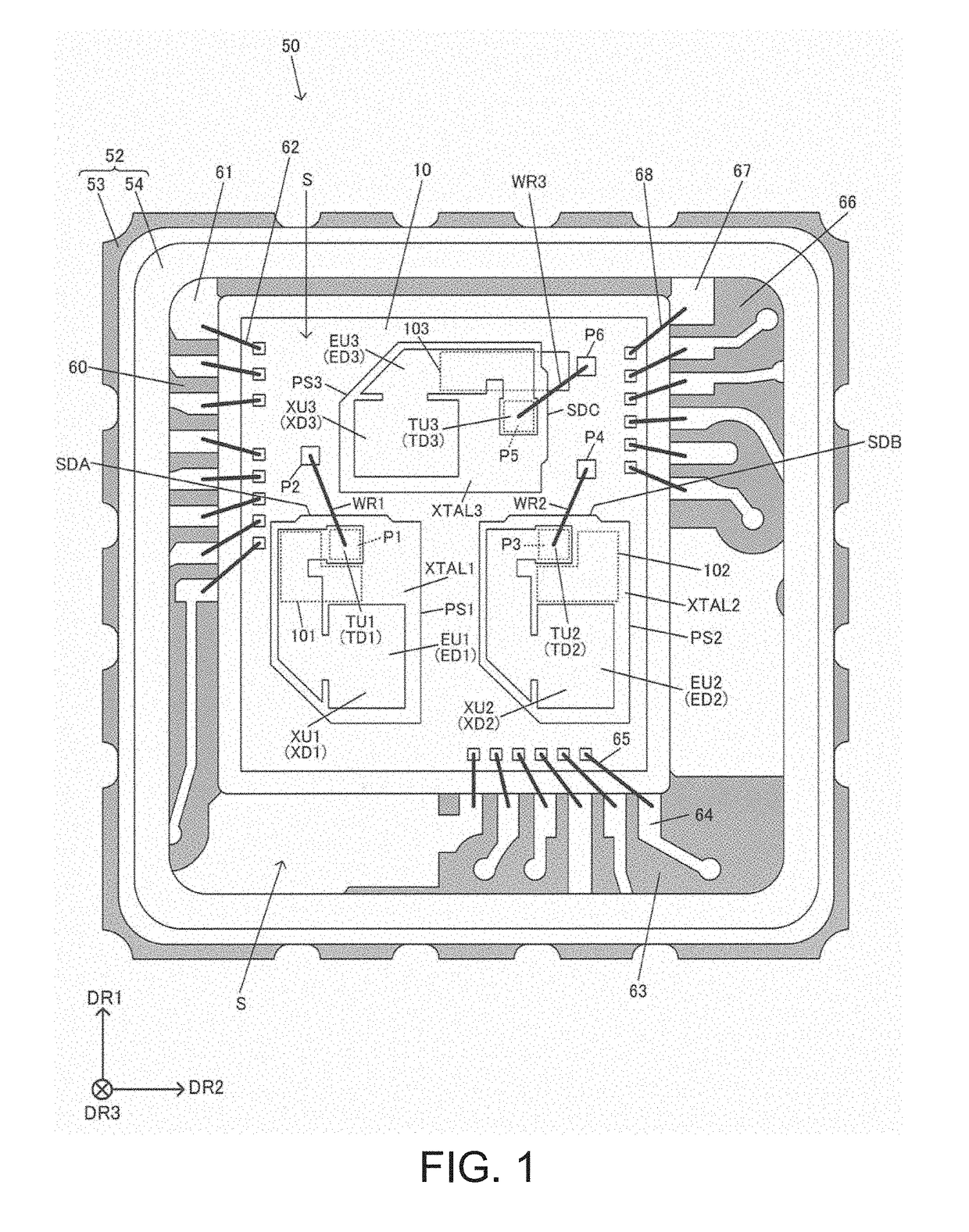
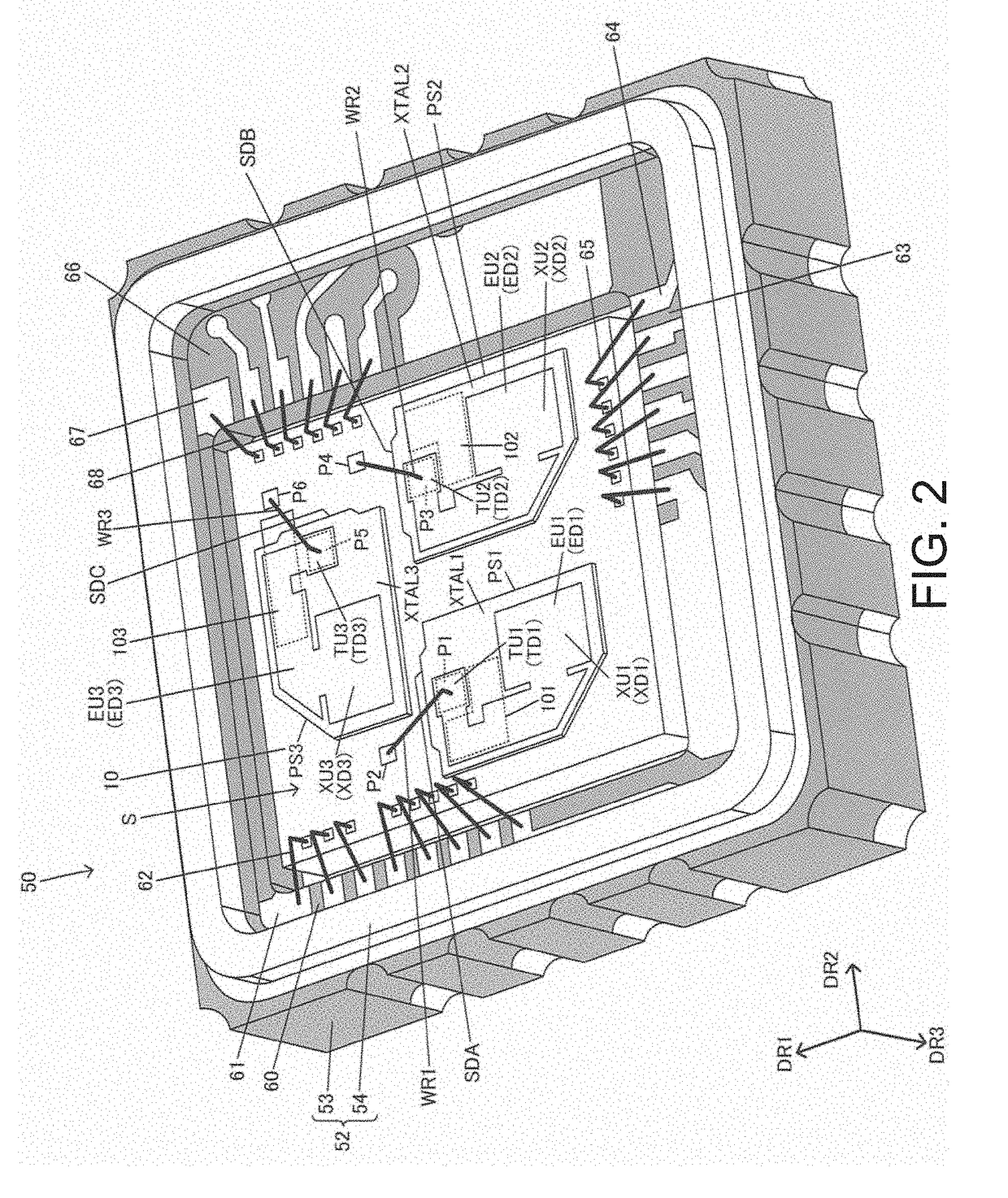
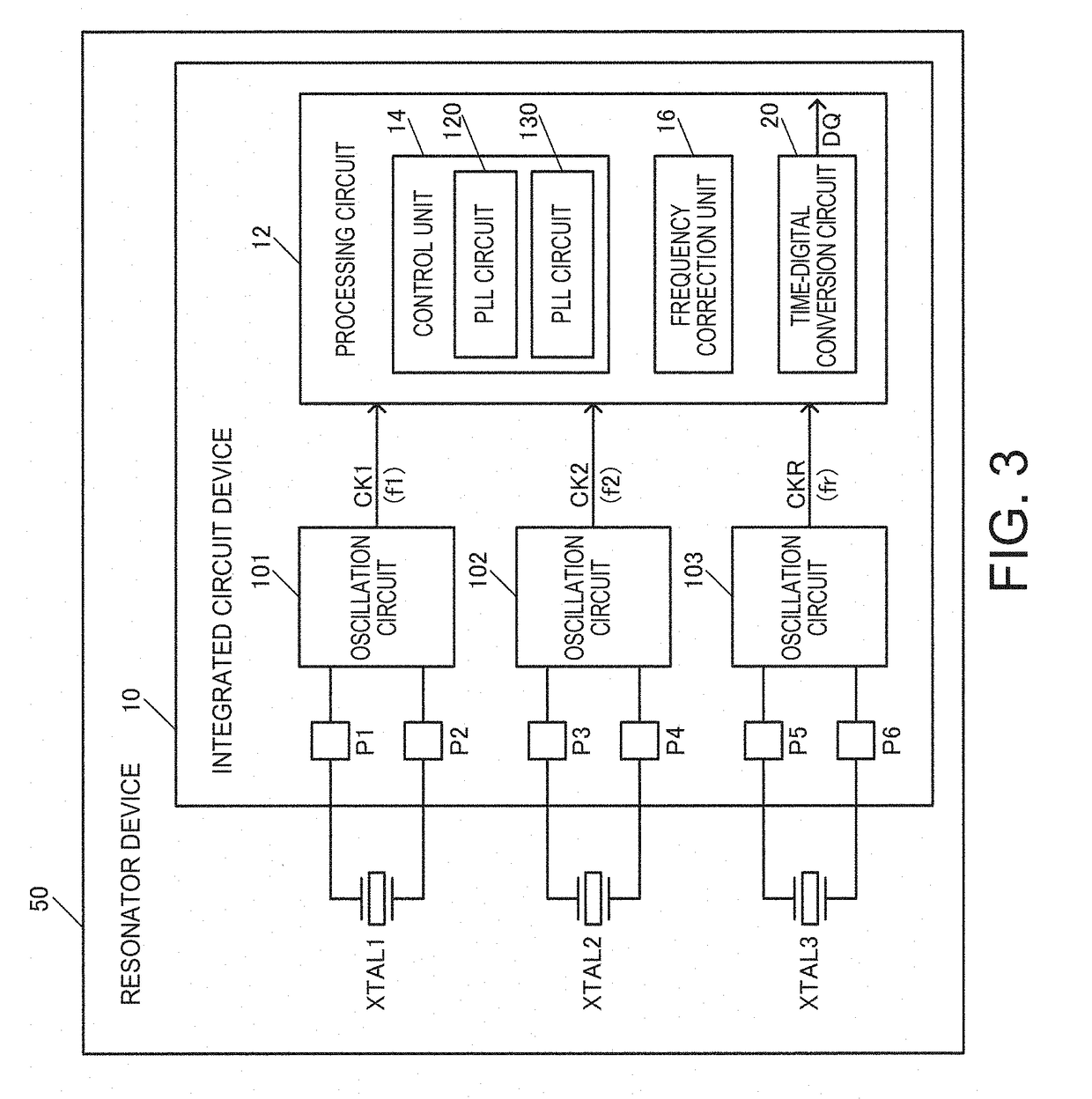
ActiveUS20190006989A1Easy to processSuppress fluctuationsImpedence networksOscillations generatorsResonatorIntegrated circuit
A resonator device includes first and second resonators and an integrated circuit device. The integrated circuit device includes a first oscillation circuit configured to oscillate the first resonator, a second oscillation circuit configured to oscillate the second resonator, and a processing circuit configured to perform processing by using frequency difference information or frequency comparison information between a first clock signal generated by oscillating the first resonator and a second clock signal generated by oscillating the second resonator. The first resonator is supported on the integrated circuit device by a first support portion. The second resonator is supported on the integrated circuit device by a second support portion.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Circuit and method performed by the circuit
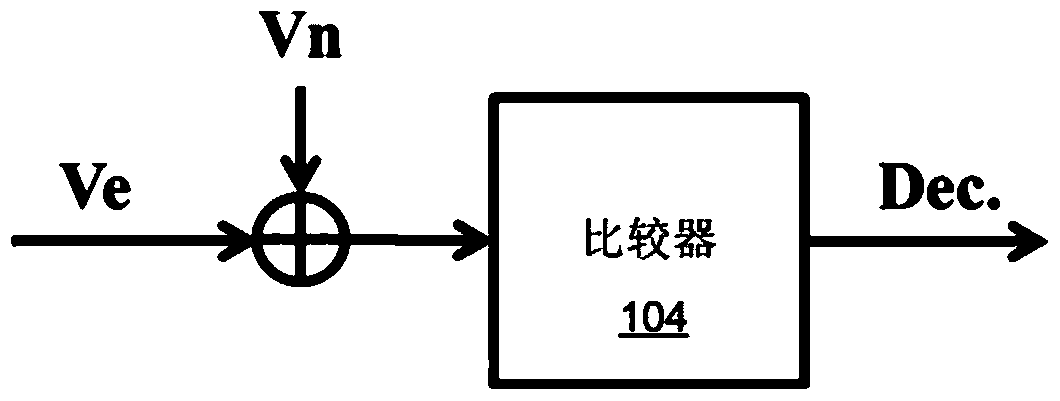
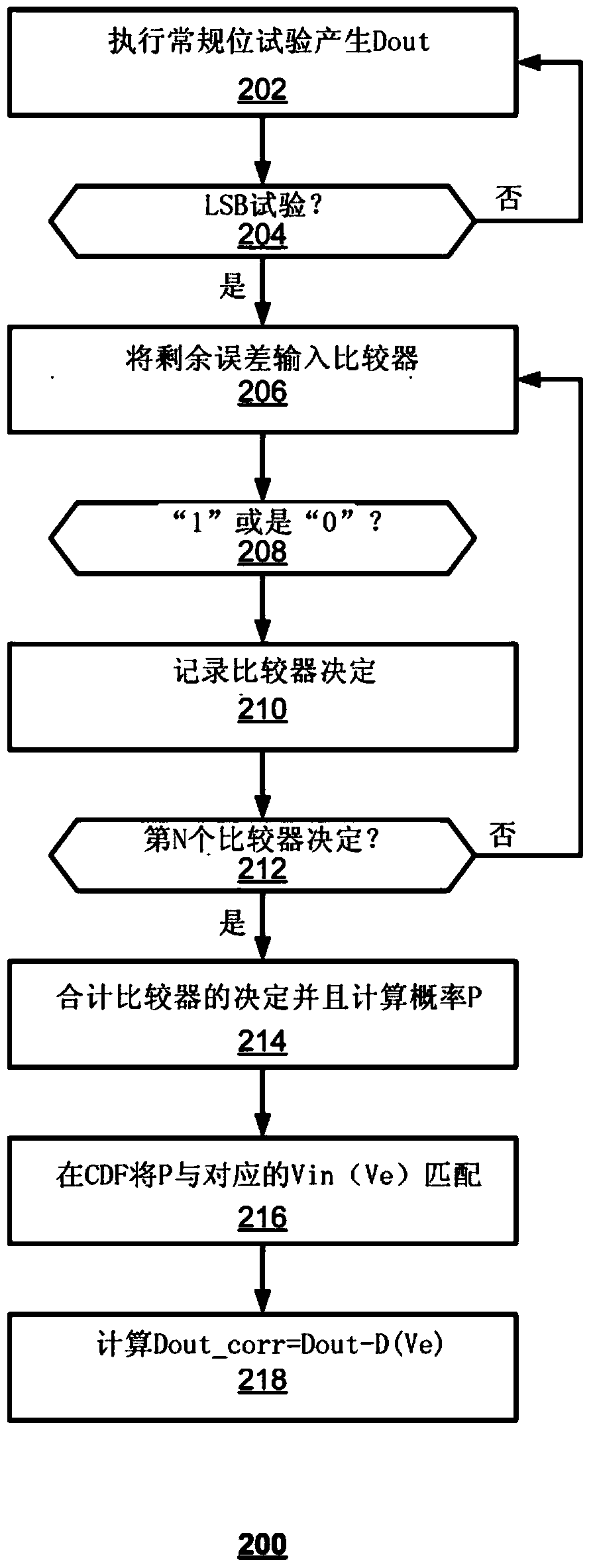
ActiveCN104518796BAnalogue-digital convertersAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingErrors and residualsSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
Example embodiments of the present invention provide accuracy enhancement techniques to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of an ADC. For example, a normal bit test and an additional bit test of a digital word from the most significant bit (MSB) to a predetermined least significant bit can be performed. The results of the normal bit and additional bit trials are combined to generate a digital output signal. The residual error is measured and then the digital output signal is adjusted based on said measured residual error.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Gun for laser stimulation shooting training
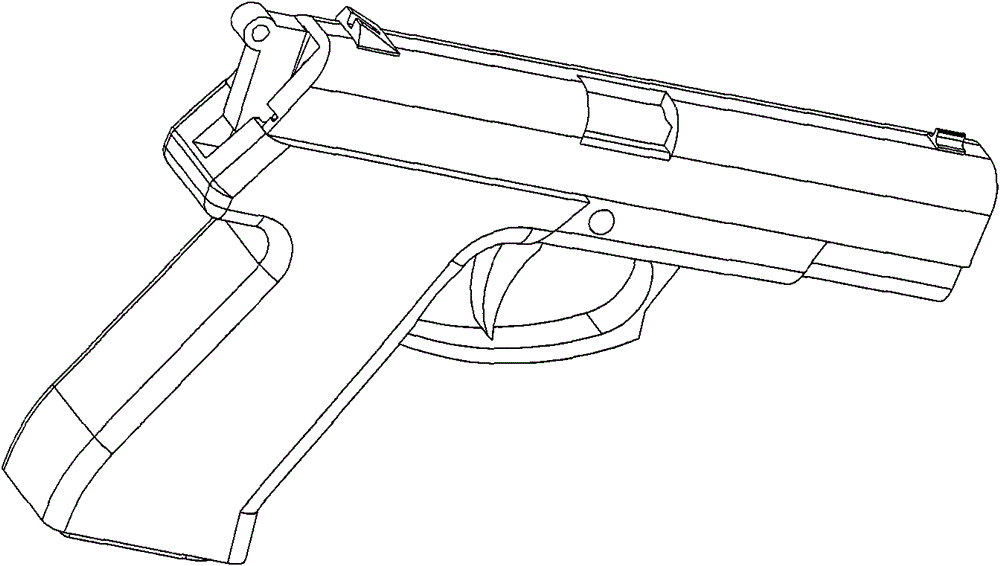
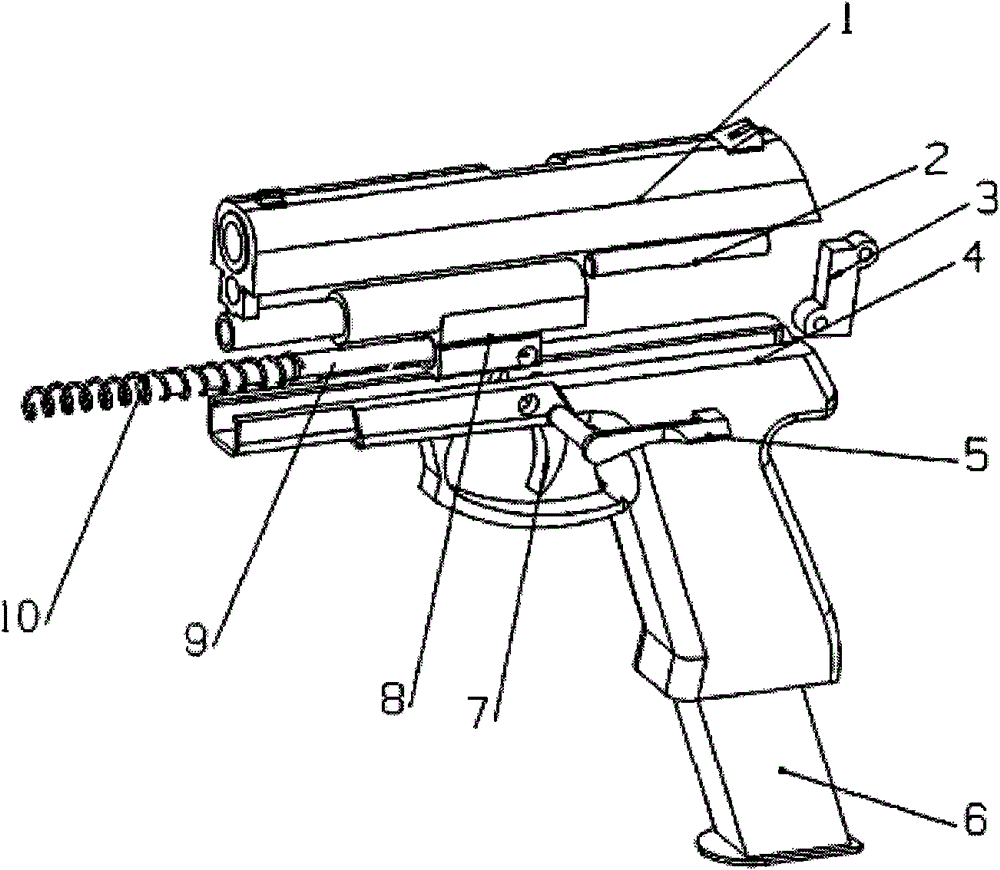
InactiveCN101660887BImprove securityLow site requirementsConversion using stochastic techniquesLaser transmitterEngineering
The invention discloses a gun for laser stimulation shooting training, comprising a lower gun body and an upper gun body, wherein the lower gun body is installed with a laser transmitter integration;a reversing lever and a reversing spring are installed in front of the laser transmitter; the hole at the lower part of the upper gun body is sleeved on the reversing lever and can slide along the upper plane backward; a trigger is installed below the lower gun body and a hammer is arranged at the rear part of the lower gun body; a striker is arranged between the hammer and the laser transmitter;a gun disassembly switch knob is installed at the upper edge of the lower gun body, and a clip is arranged in the handle of the lower gun body; and the laser transmitter integration comprises a limited block, a limited rod, a return spring, an insulating bush, a contact switch, a rack, a laser transmitter and a laser transmission port. The gun for laser stimulation shooting training of the invention has high stimulation, can be disassembled like real guns, has the processes of bullets filling and hammer percussion, and has the use feeling extremely similar to real guns; and bullet falling points are stimulated by laser, therefore, the security is extremely high, the cost of combination training is low, and the training effect is good.
Owner:宁波市北仑勤业机械制造有限公司
Popular searches
Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubes Picture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanning Picture reproducers using projection devices Image coding Picture reproducers using solid-state color display Television signal transmission by single/parallel channels Digital video signal modification Color motion picture films scanning Selective content distribution Signal generator with optical-mechanical scanning
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com