Patents
Literature
64results about How to "Ease of execution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
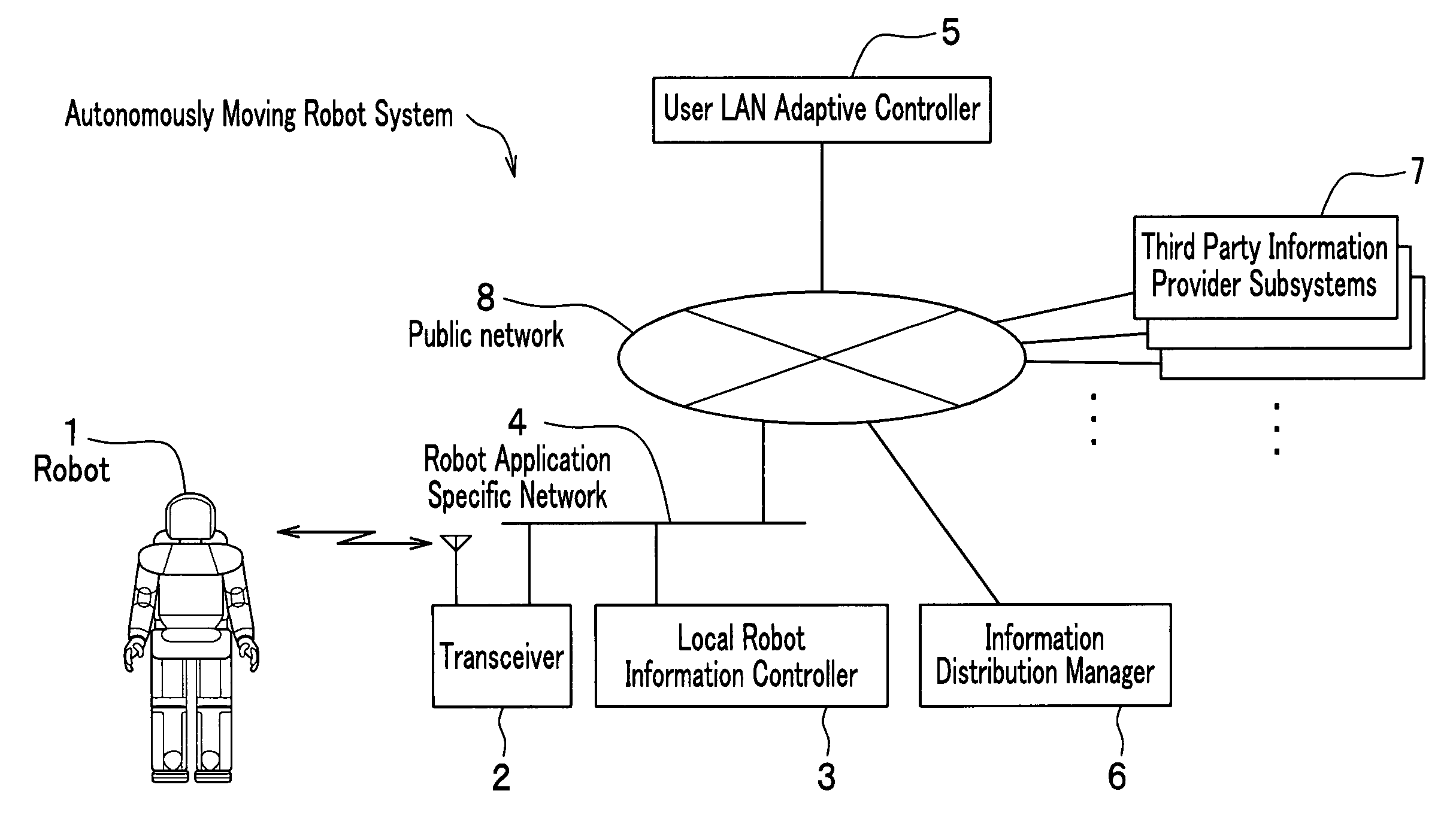
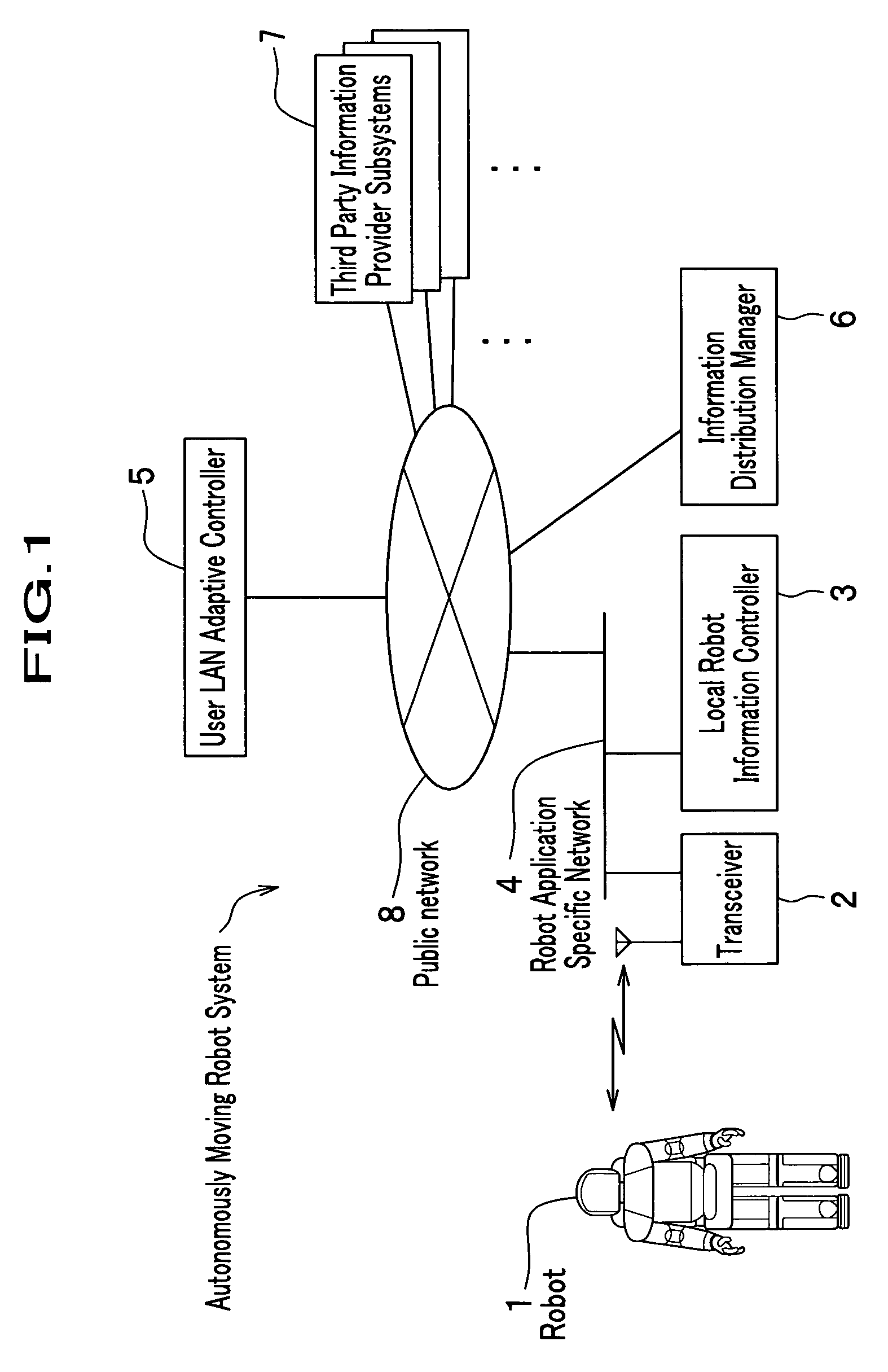
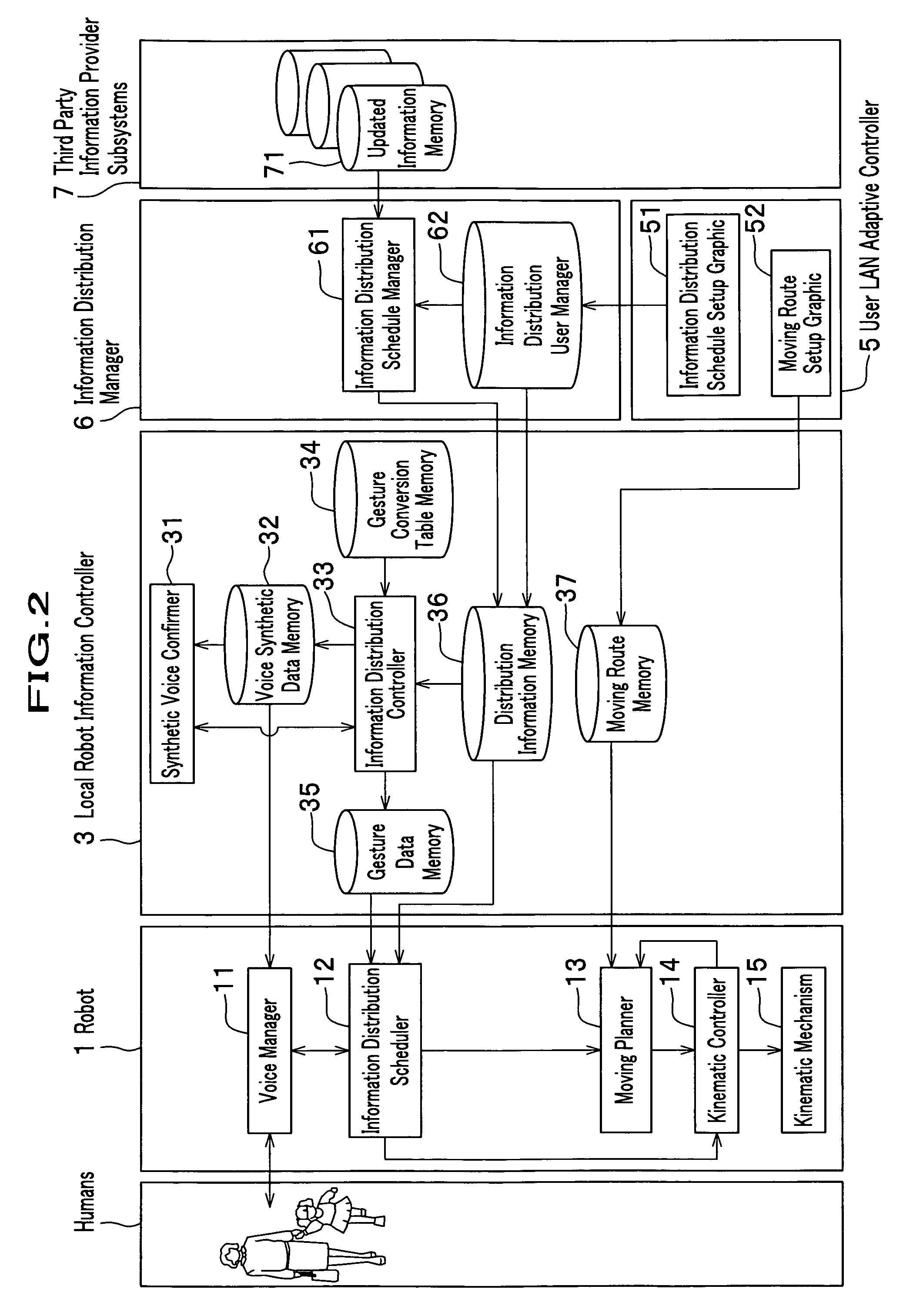
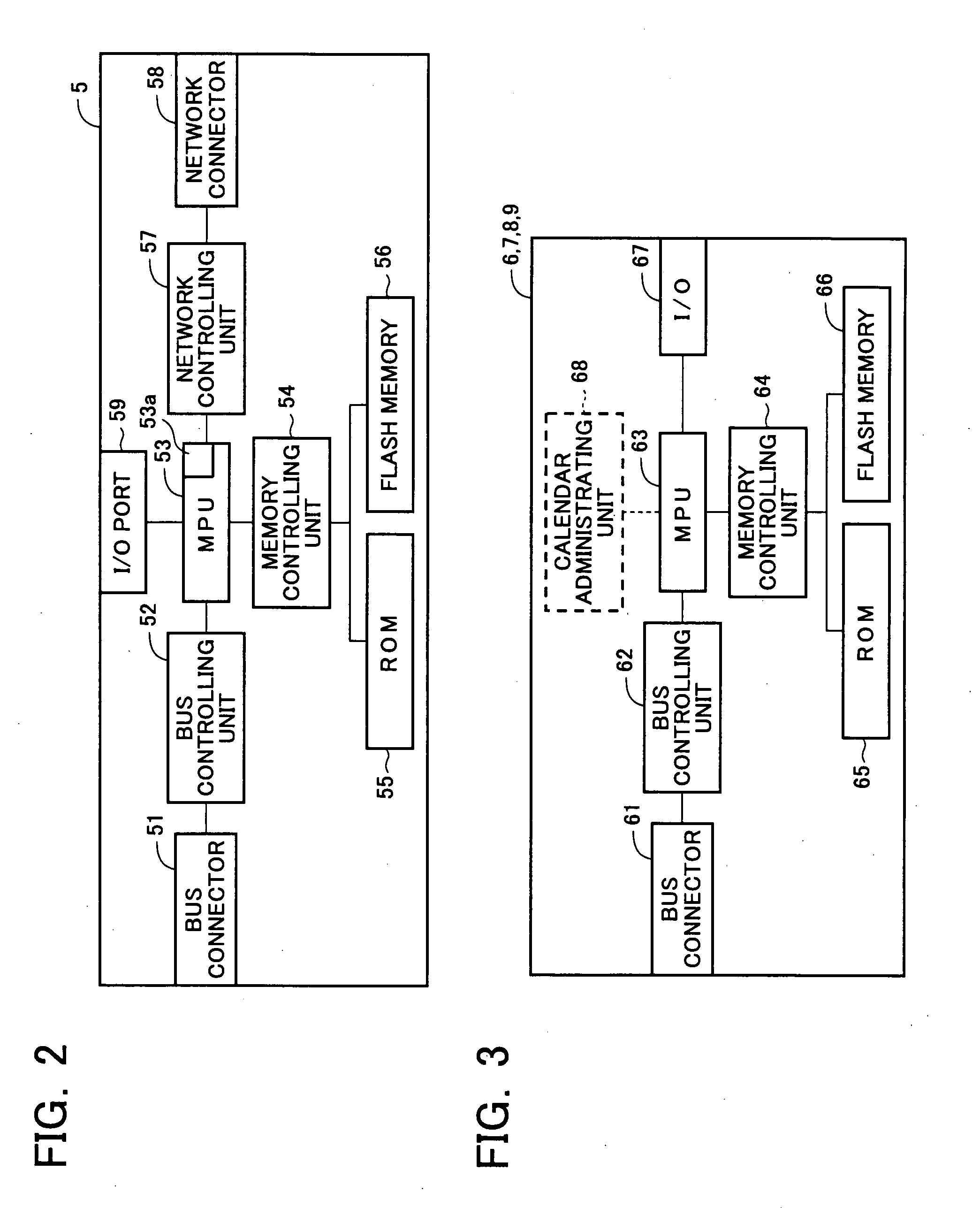
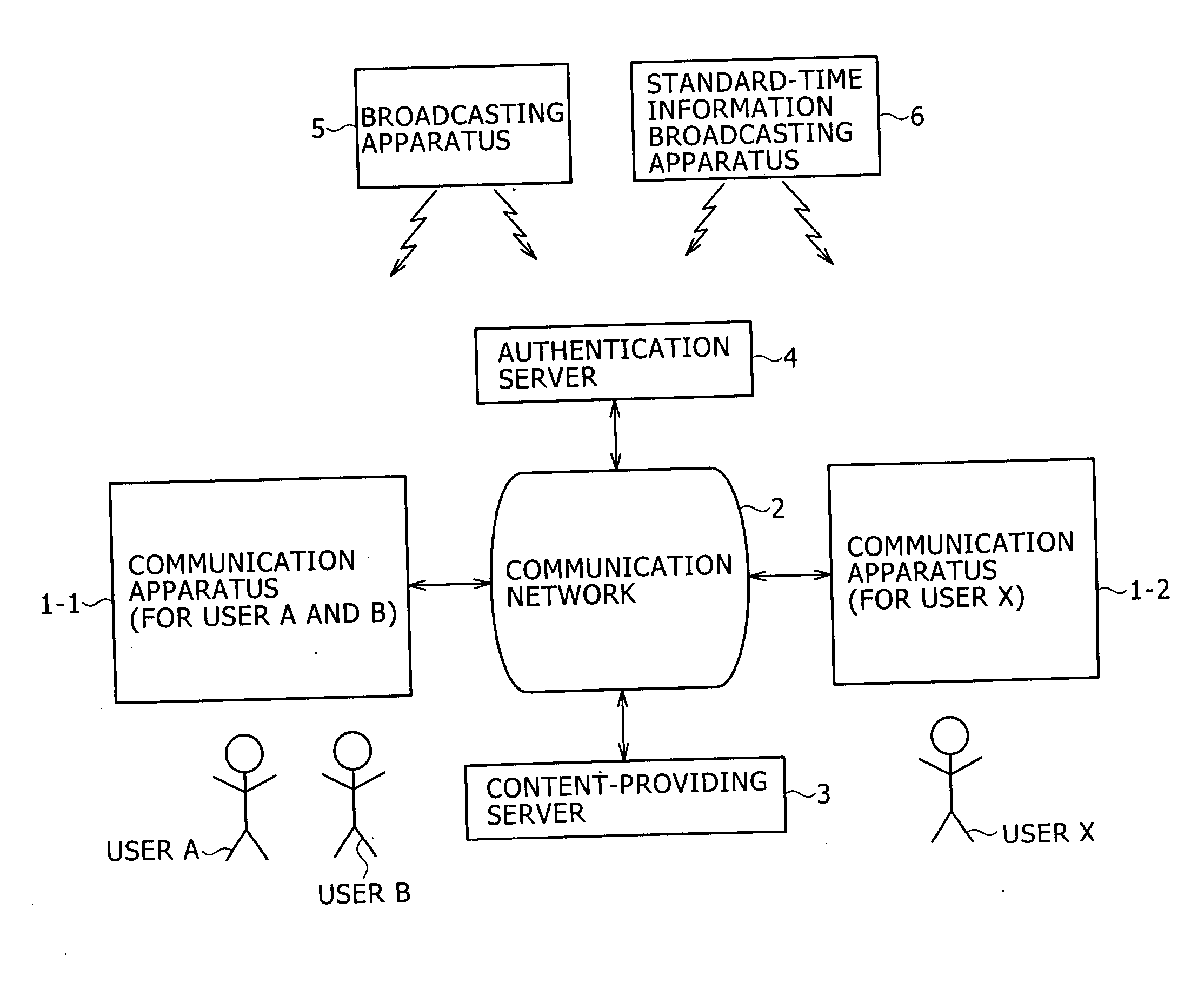
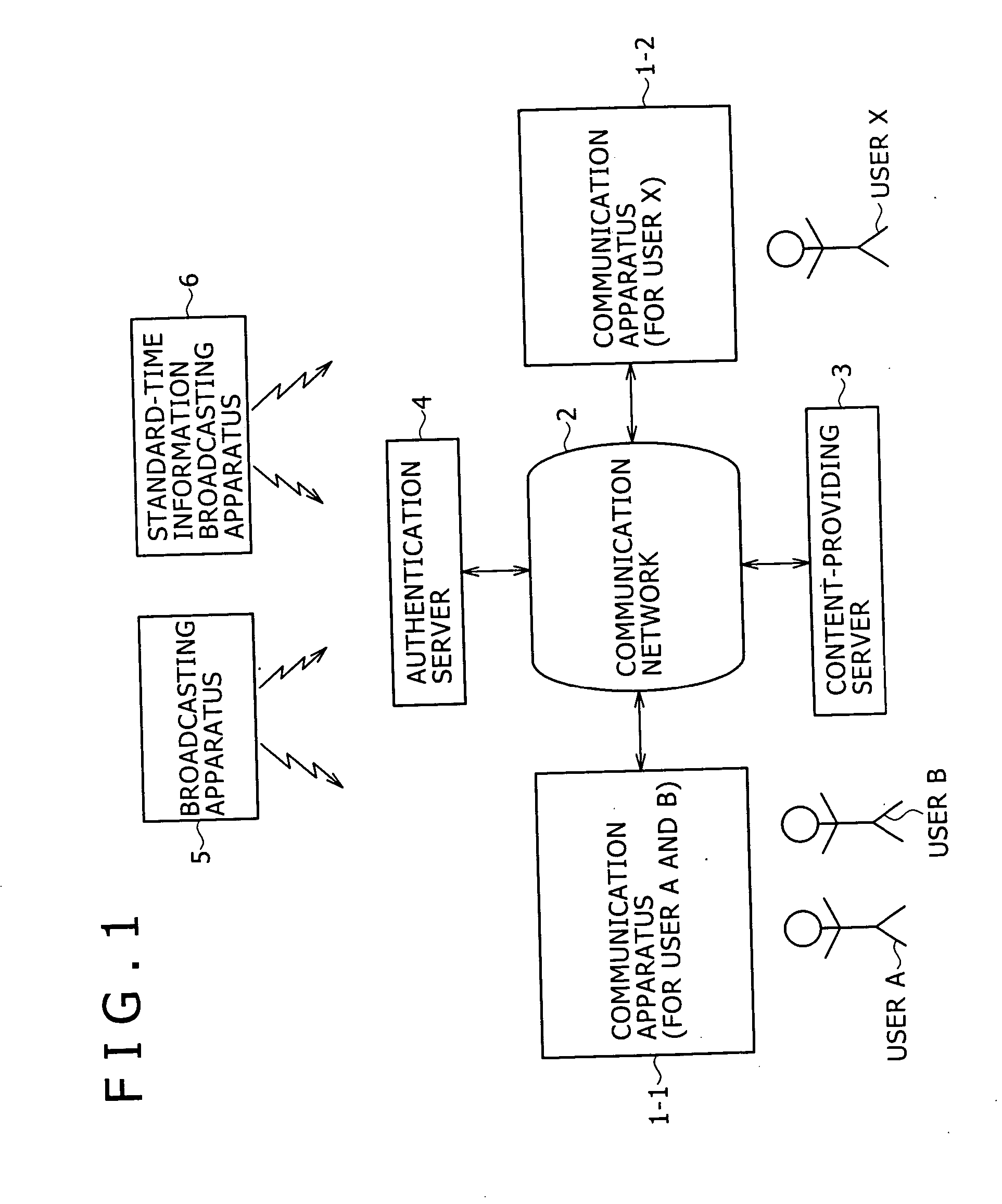
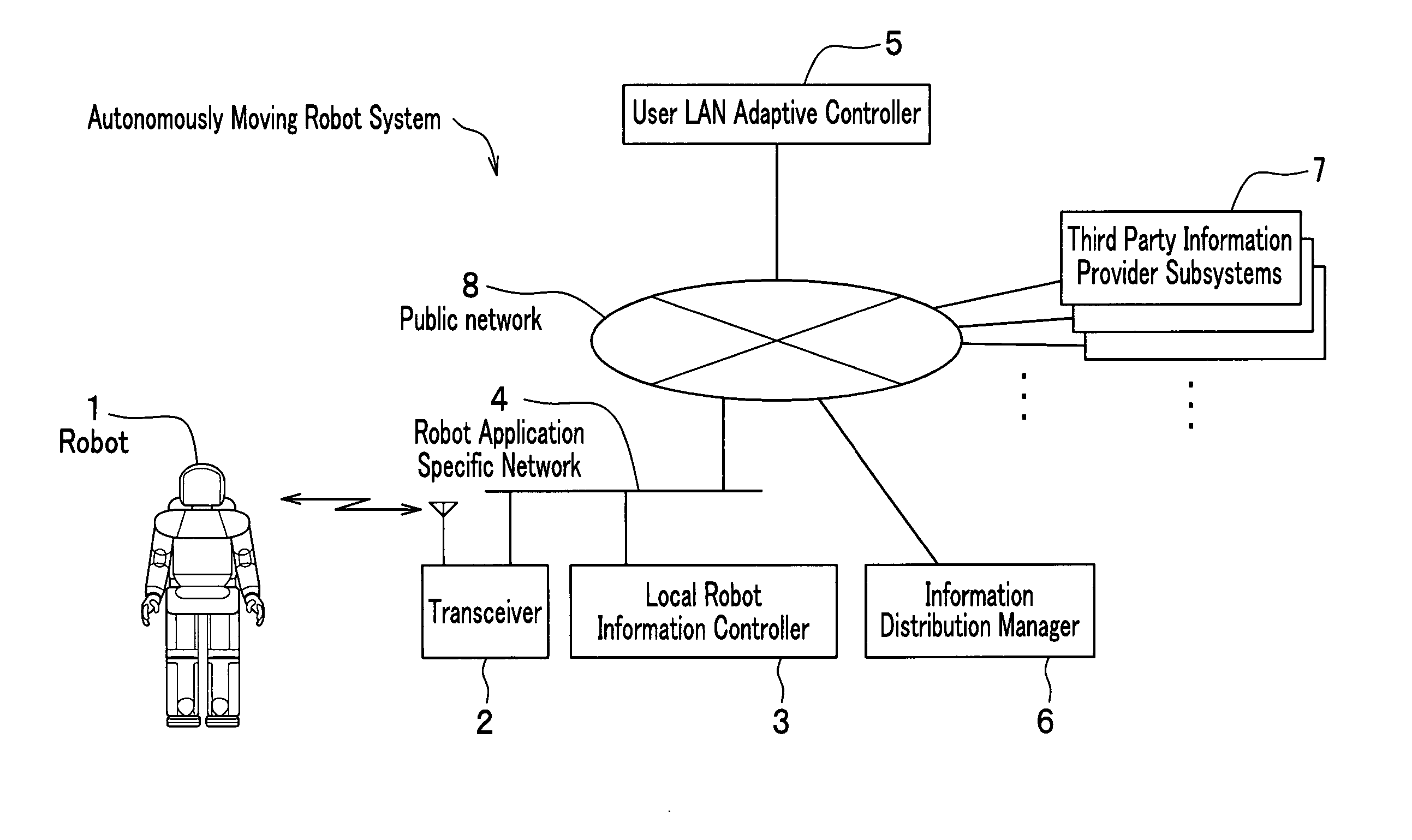
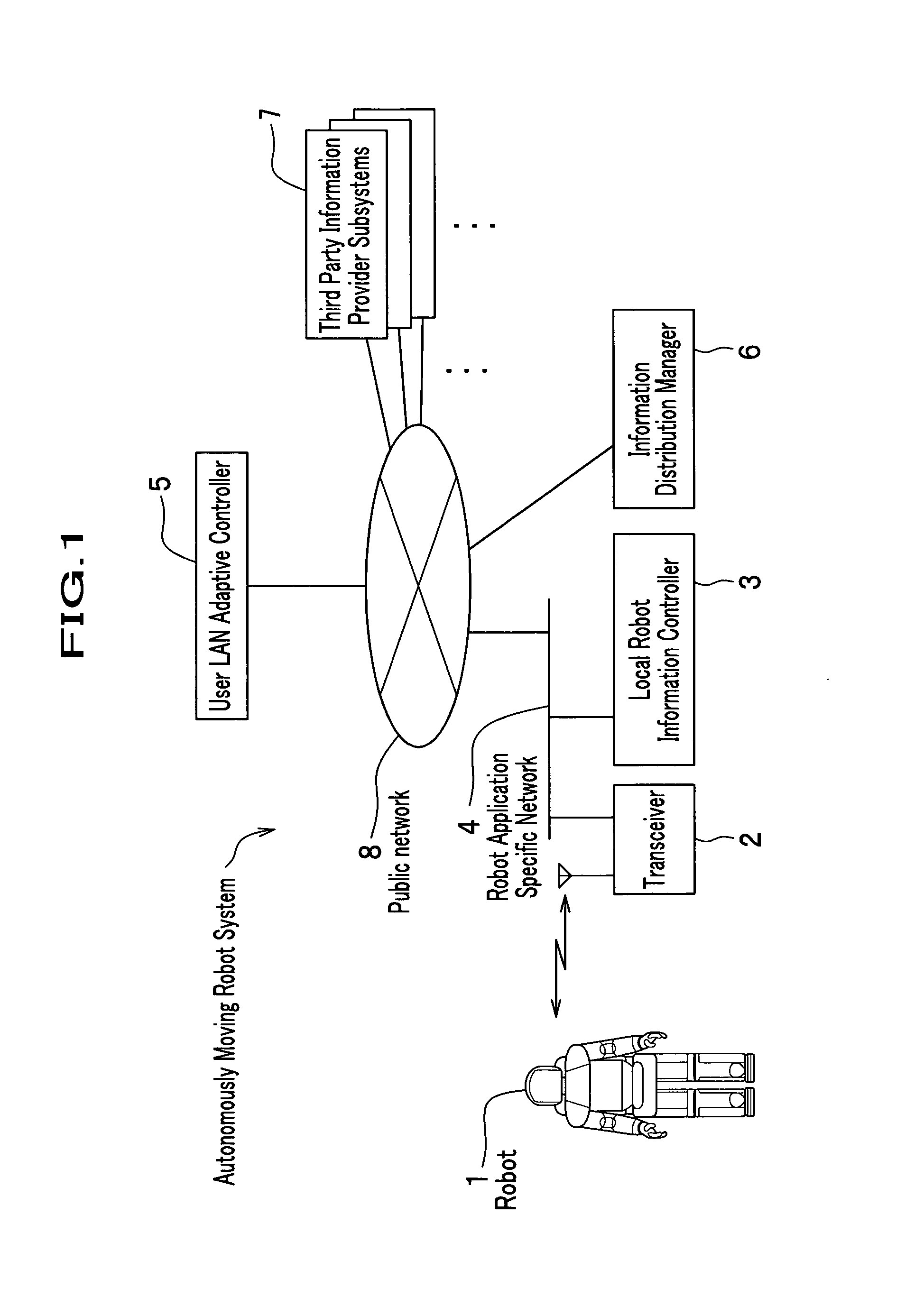
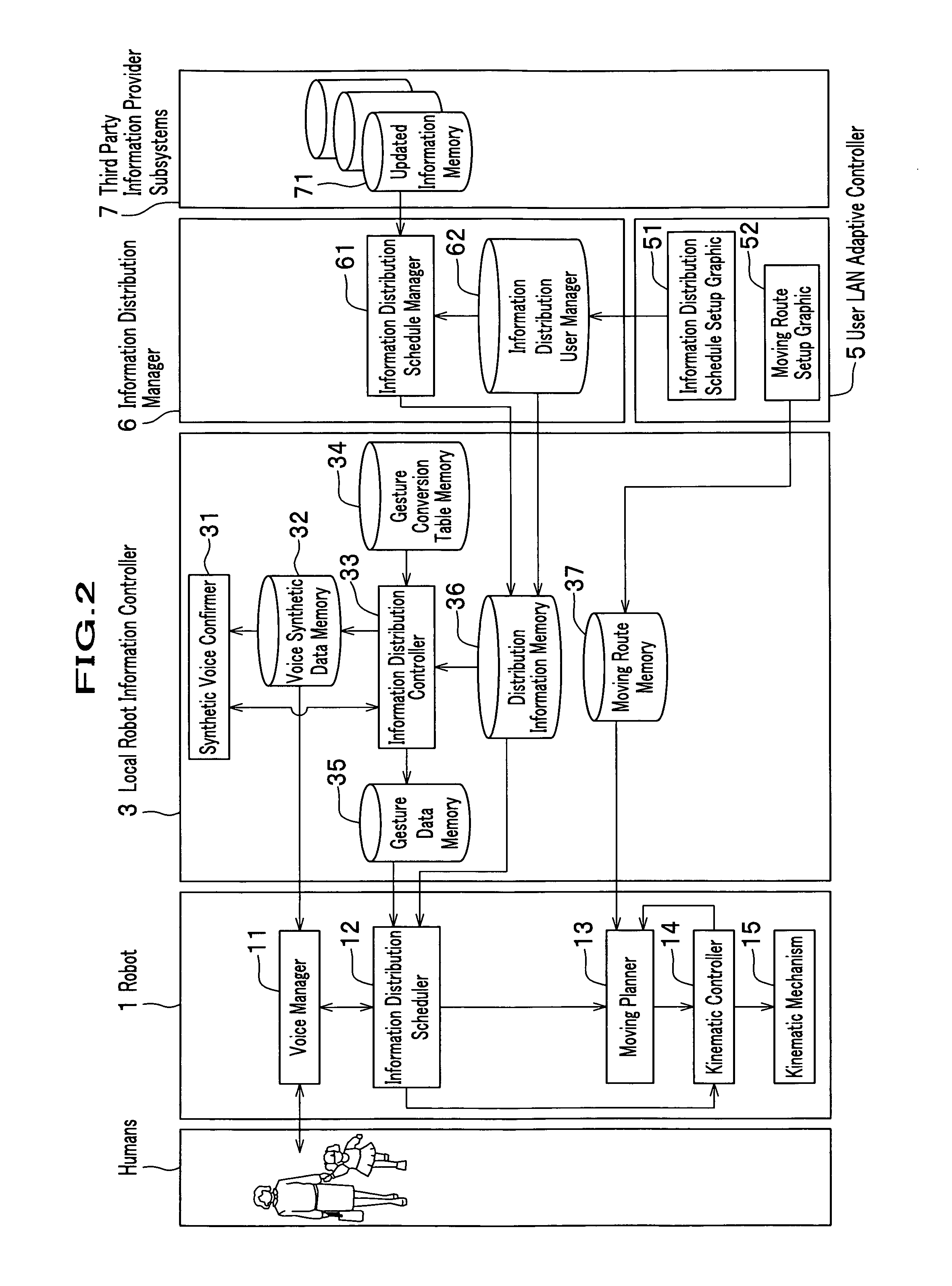
Autonomously moving robot management system
InactiveUS7467026B2Ease of executionFlexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlThird partyTransceiver
An autonomous robot is controlled by the local robot information controller which is connected to a robot application network to which the transceiver to communicate with the autonomous robot is attached. The robot application network, a user LAN adaptive controller an information distribution manager and the third party information provider subsystem are linked with a public network. The information distribution manager acquires the information from the third party information provider subsystem on the schedule which is set by the user LAN adaptive controller. The local robot information controller receives the information distribution manager and convert it into the data that generates robot gestures. The robot performs actions in accordance to the gesture data received from the local robot information controller.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
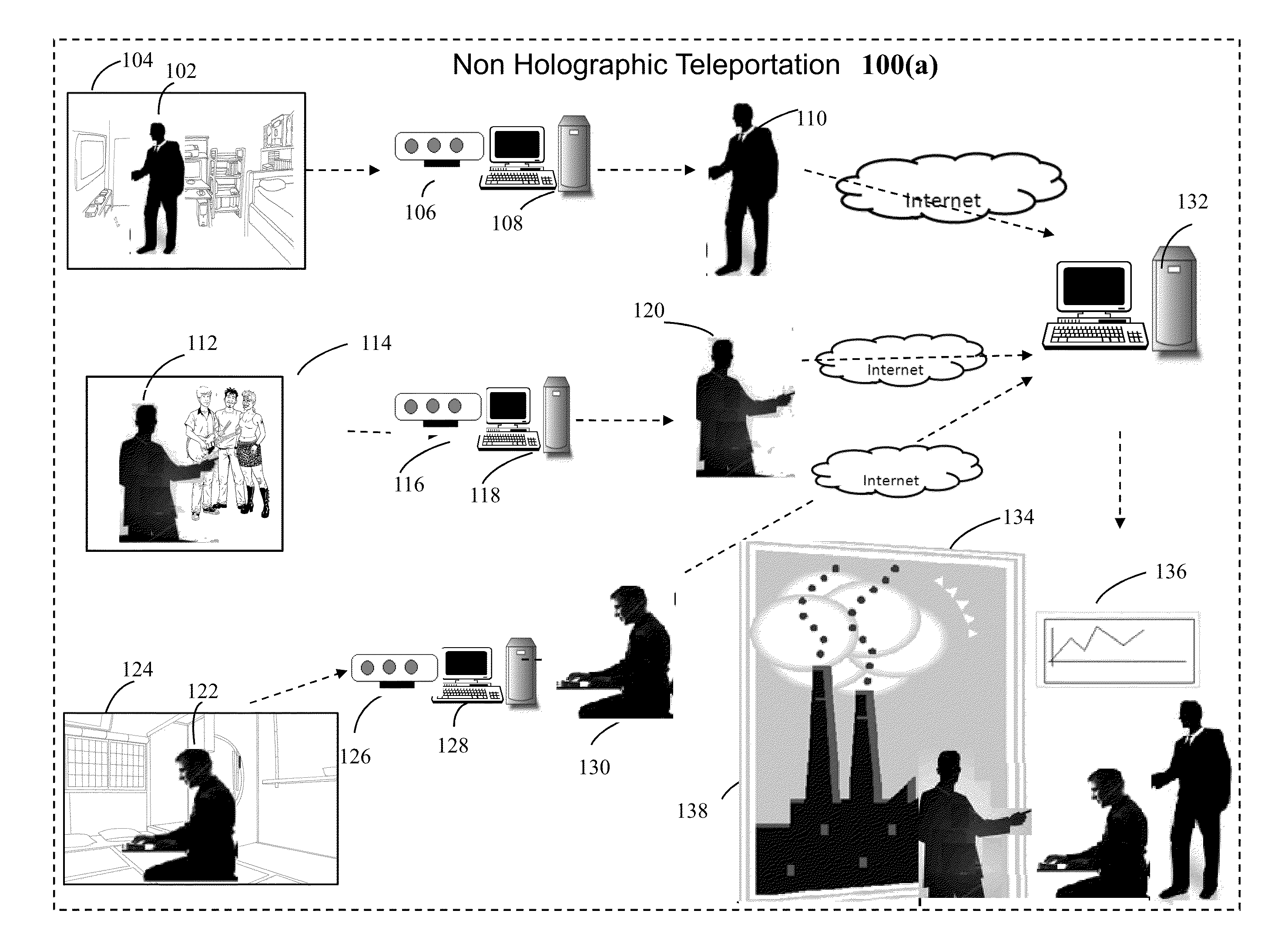
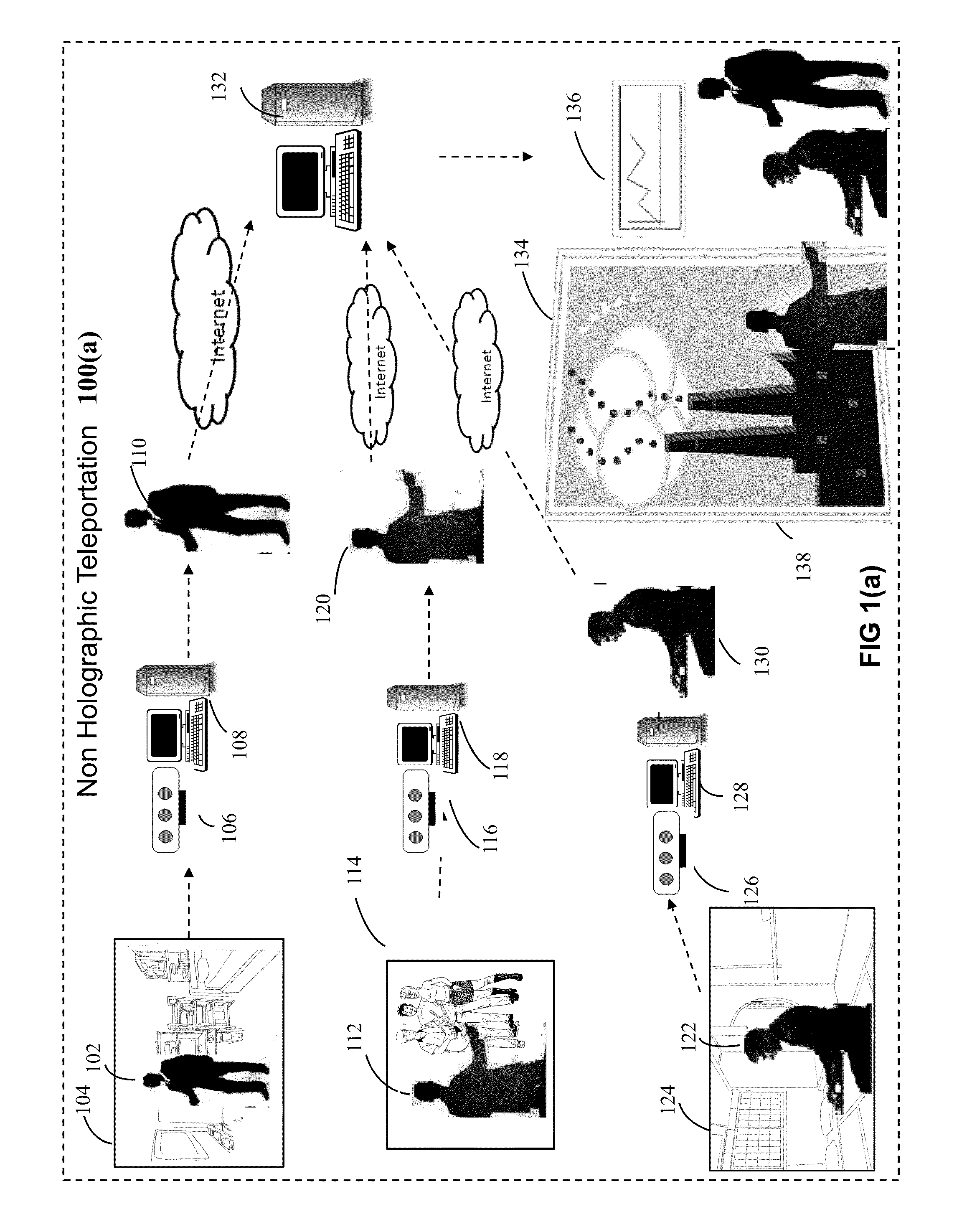
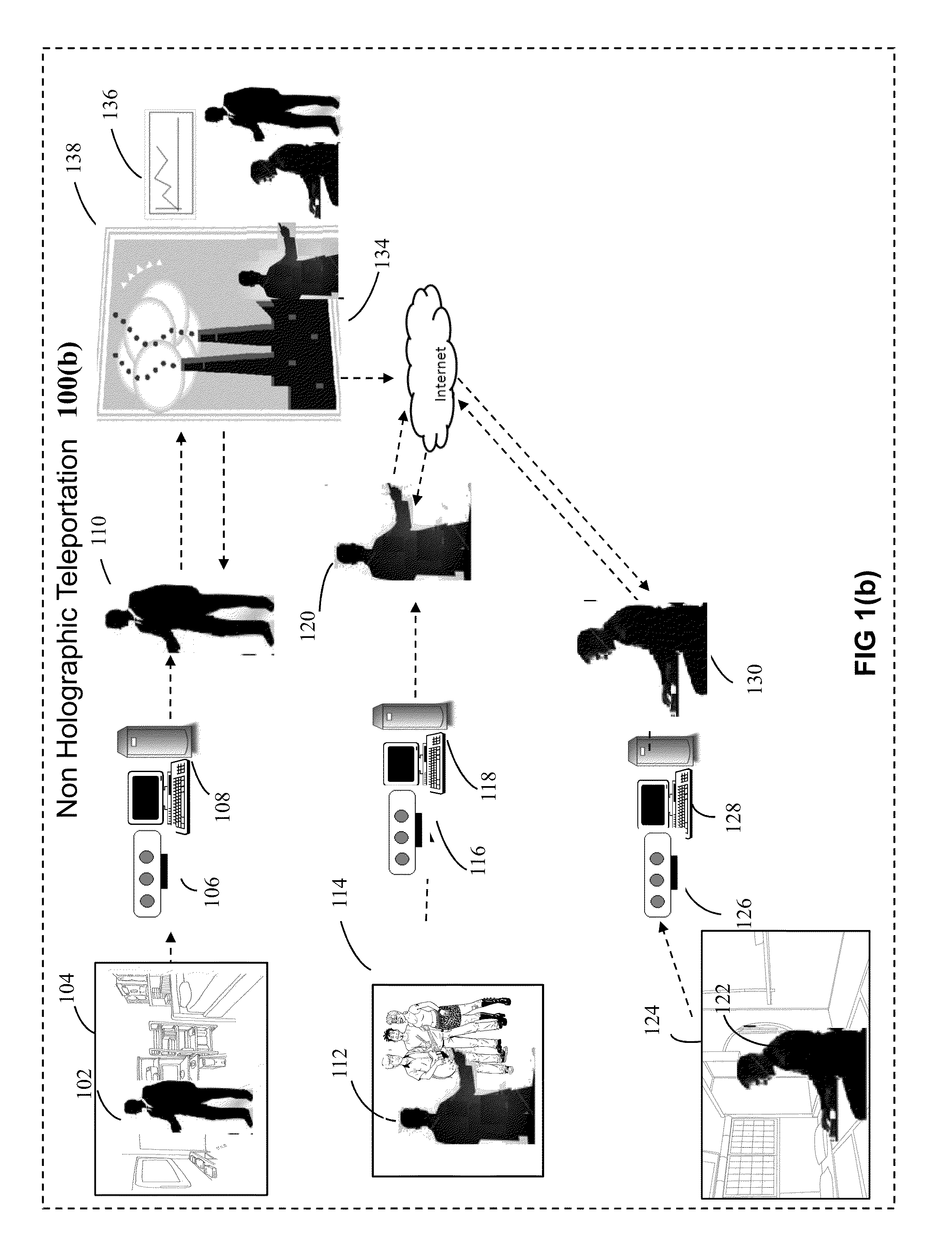
System and method for non-holographic teleportation
InactiveUS20150091891A1Easy to installEffective and accessible for massAmusementsTelevision systemsVirtual trainingRgb image
The present invention discloses a system and method for non-holographic virtual teleportation of one or more remote objects to a designated three-dimensional space around a user in realtime. This is achieved by using a plurality of participating teleportation terminals, located at geographically diverse locations, that capture the RGB and depth data of their respective environments, extract RGB images of target objects from their corresponding environment, and transmit the alpha channeled object images via Internet for integration into a single composite scene in which layers of computer graphics are added in the foreground and in the background. The invention thus creates a virtual 3D space around a user in which almost anything imaginable can be virtually teleported for user interaction. This invention has application in intuitive computing, perceptual computing, entertainment, gaming, virtual meetings, conferencing, gesture based interfaces, advertising, ecommerce, social networking, virtual training, education, so on and so forth.
Owner:DUMEDIA
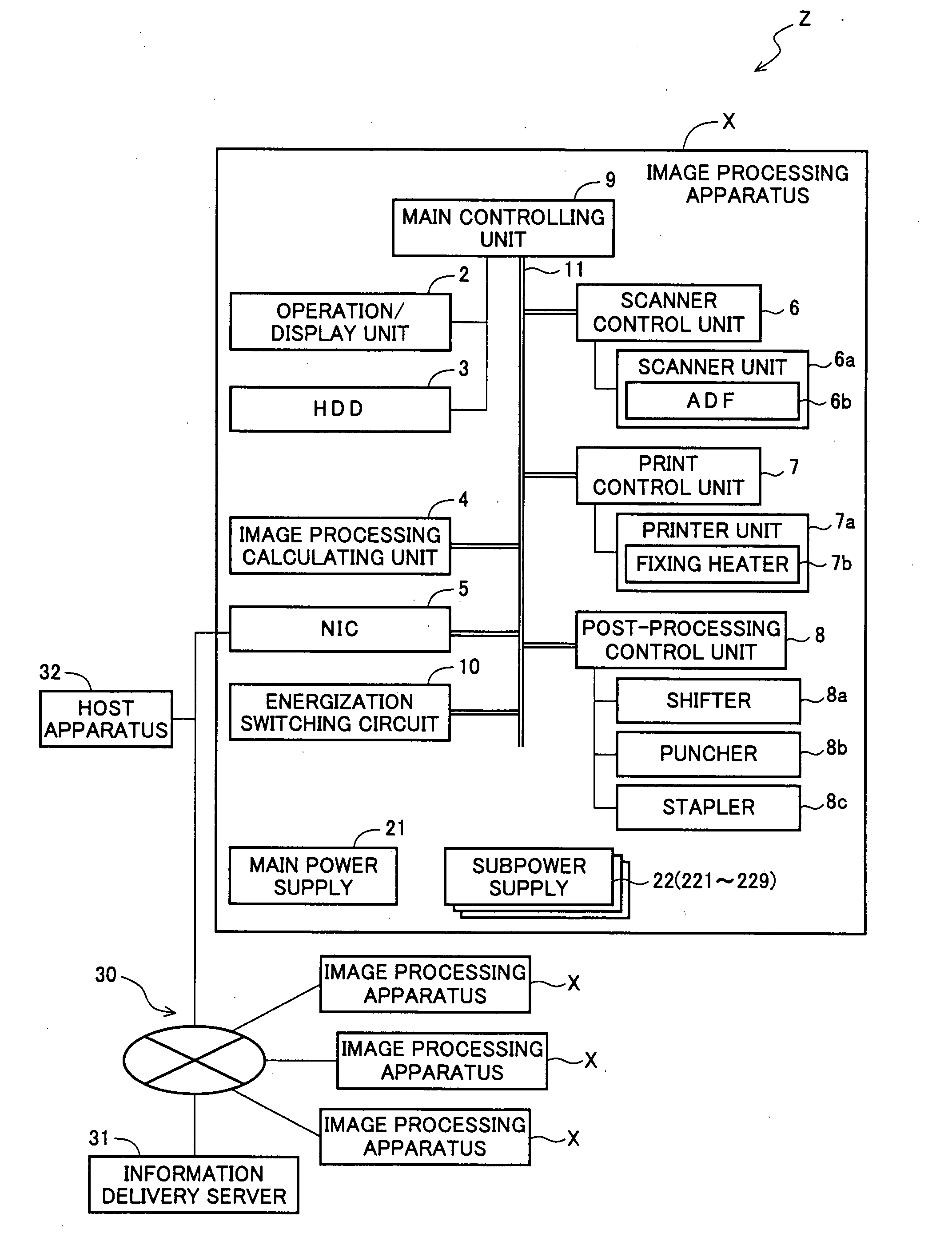
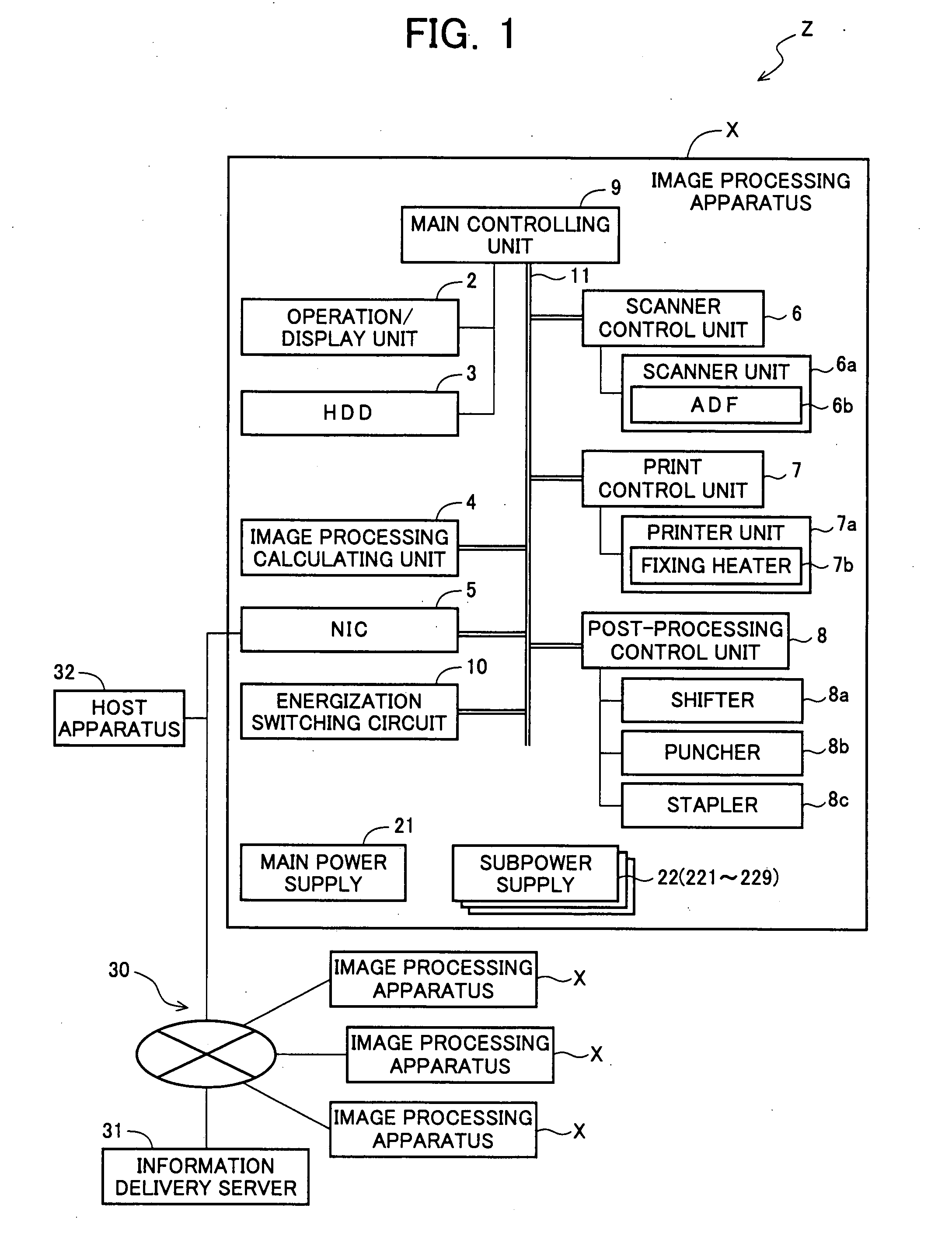
Image processing apparatus
ActiveUS20070236734A1Suppress power consumptionEase of executionEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringImaging processingStart up
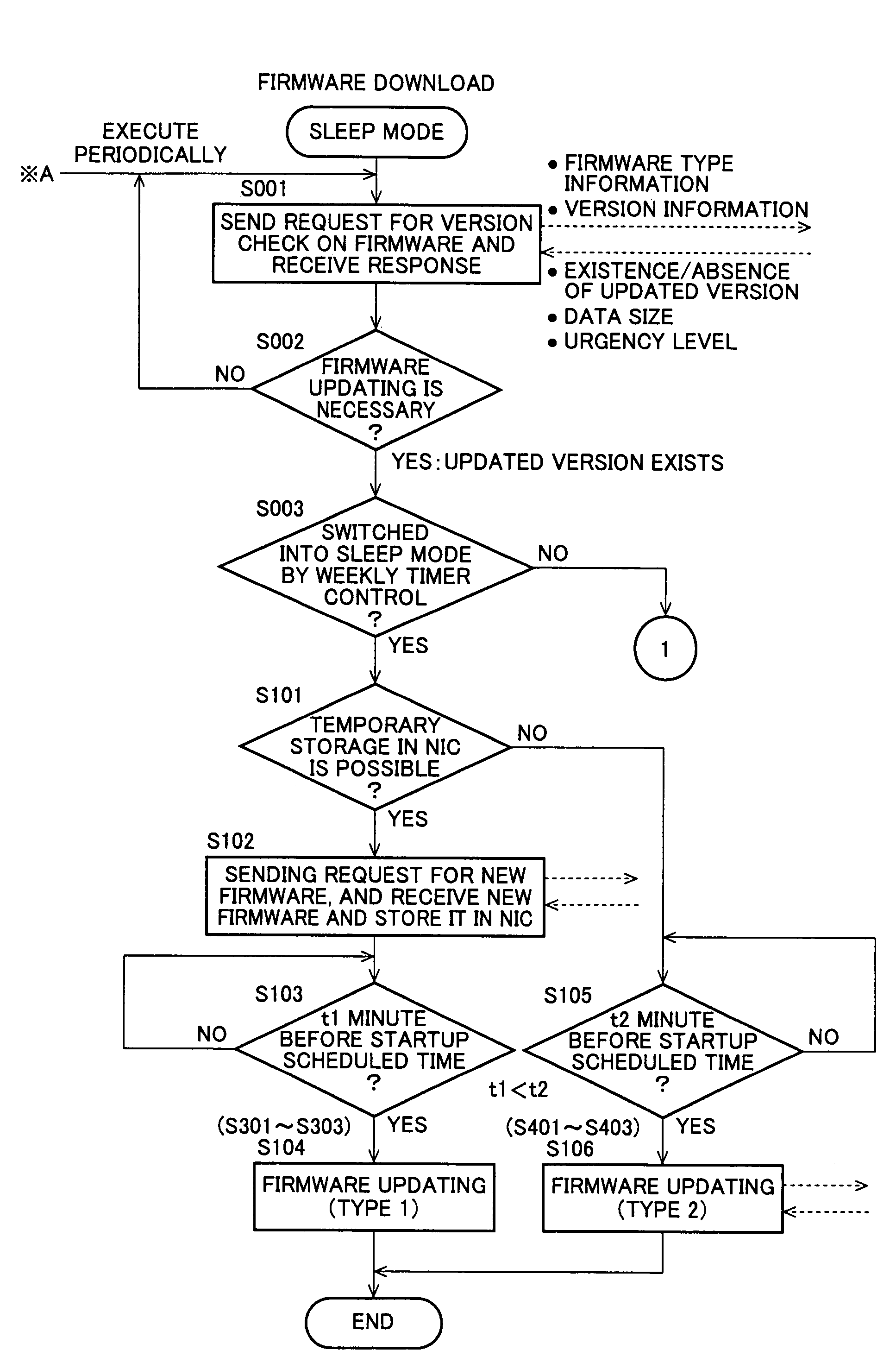
An image processing apparatus executes the processing of updating control information kept in the controlling units included in it without suspending an on-going processing and delaying the execution of a new processing request with less power consumption. When the controlling units are in a sleep mode or in non-energized state, NIC determines whether or not updating of firmware kept in each controlling unit is necessary by communicating with the information delivery server. The NIC controls an energization switching circuit to start up exclusively the controlling unit keeping the firmware determined necessary to be updated and replaces the firmware kept in the started controlling unit with the latest version of firmware obtained from the information delivery server.
Owner:SHARP KK
Information-processing apparatus, information-processing methods, recording mediums, and programs
InactiveUS20060031682A1Ease of executionSmooth communicationComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsInformation processingComputer network
The present invention provides an information-processing apparatus including disclosure-information sender means for transmitting user-disclosure information to an other apparatus, disclosure-information receiver means for receiving other user-disclosure information from the other apparatus, display control means for controlling a process to display information received by the disclosure-information receiver means, connection request means for making a request for a connection to an other apparatus in accordance with a user operation, connection-permission determination means for producing a determination result as to whether or not a connection requested by the connection request means as a connection to an other apparatus has been permitted by the other apparatus on the basis of a response received from the other apparatus, and communication means for transmitting an image and voice of the user to an other apparatus and receiving an image and voice of an other user from the other apparatus in case a determination result produced by the connection-permission determination means indicates that a connection with the other apparatus has been permitted by the other apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
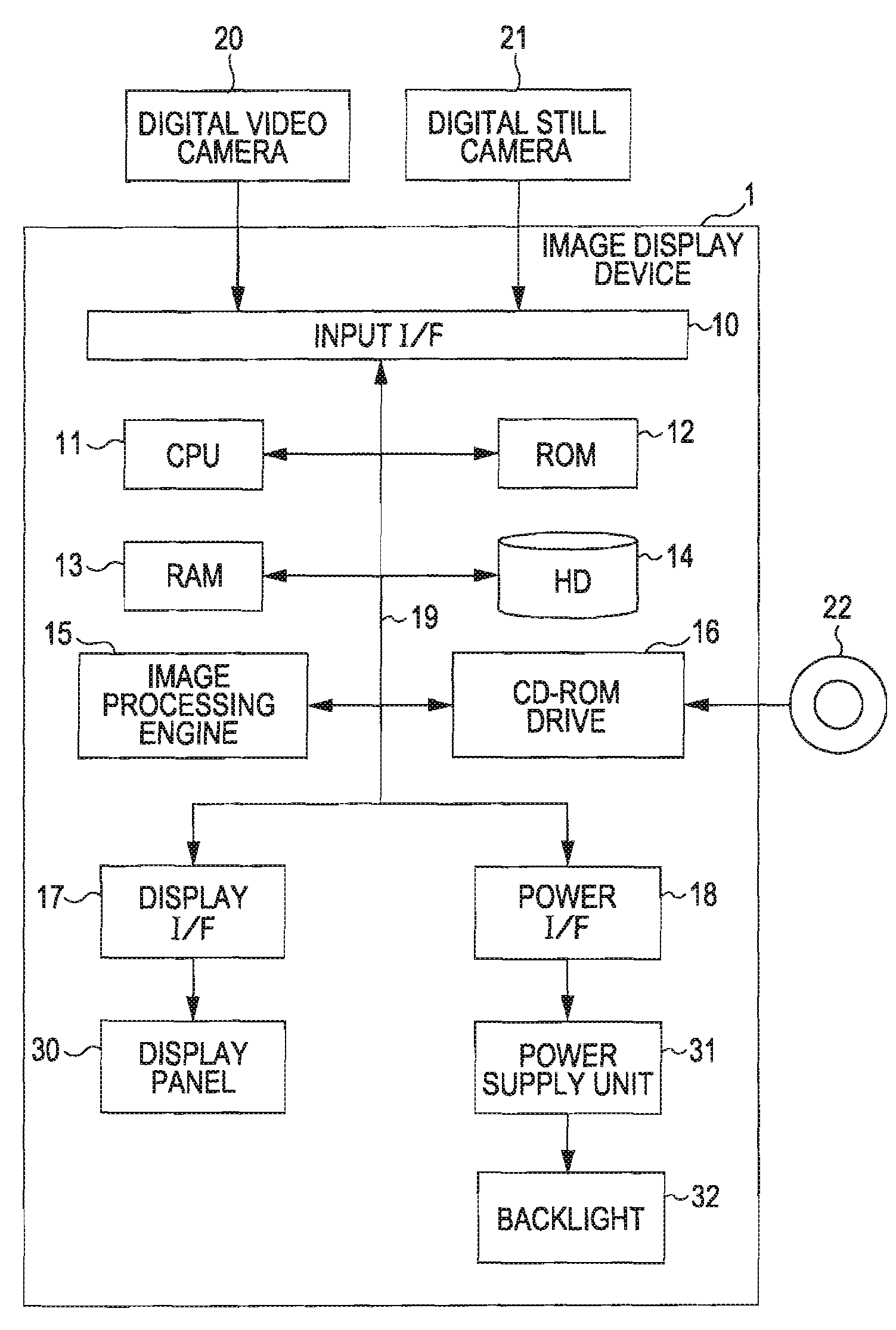
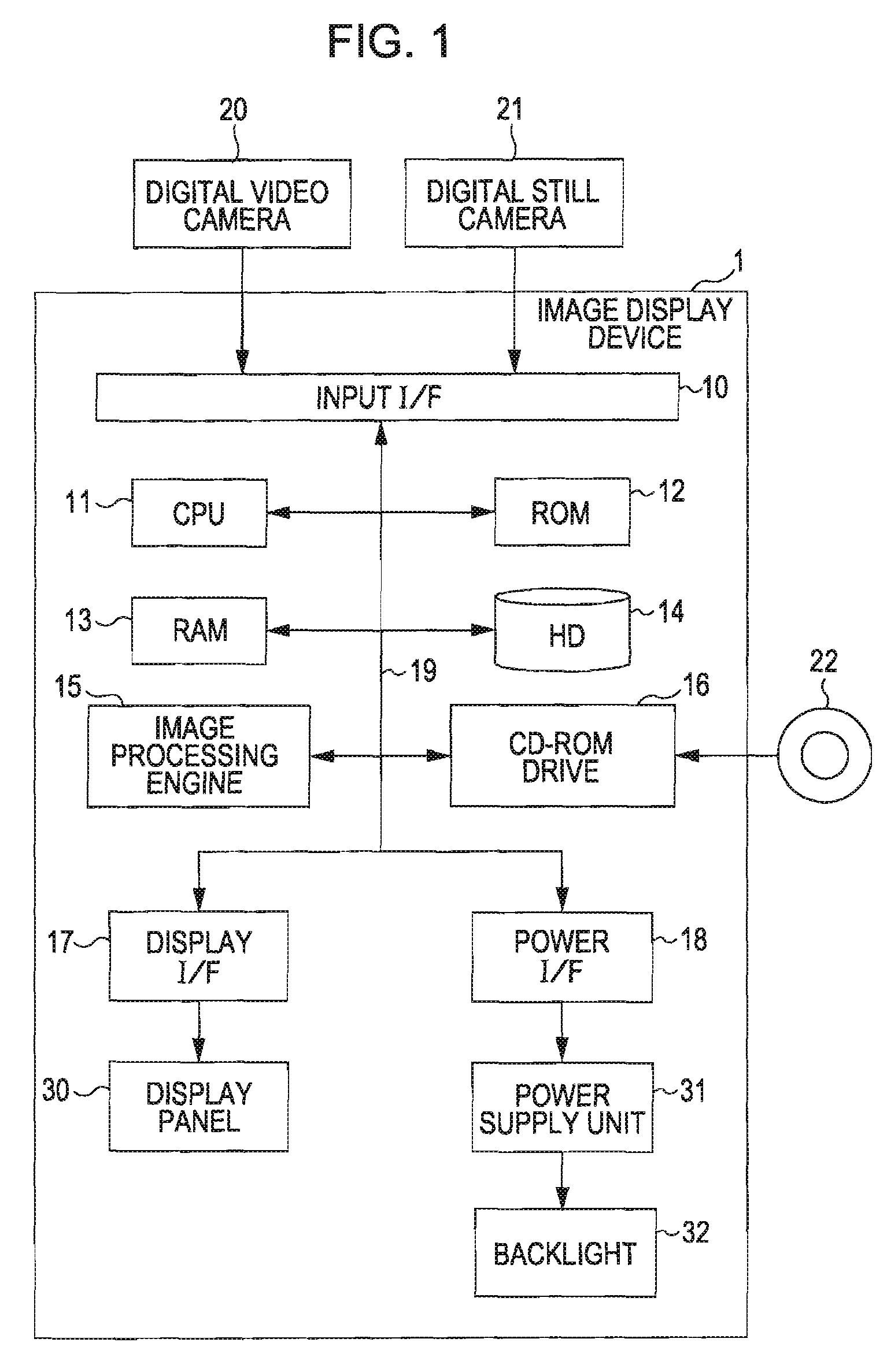
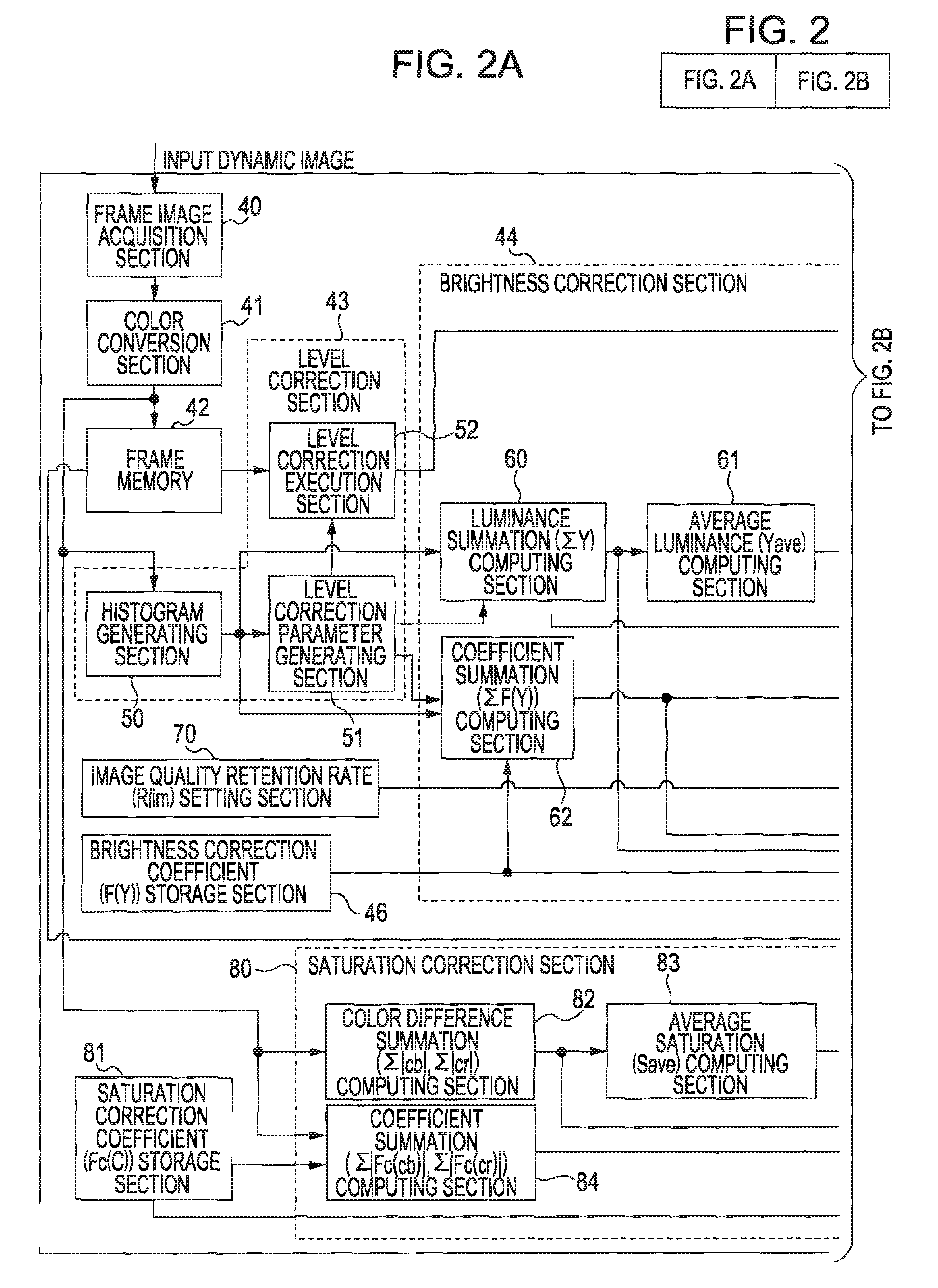
Image Display Device, Image Display Method, Image Display Program, Recording Medium Containing Image Display Program, and Electronic Apparatus
InactiveUS20080100554A1Slow changeReduce saturationColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Display device
An image display device corrects image data, which are used for displaying an image, using a gray scale value assigned to each pixel and also controls the amount of source light emitted from a light source. The image display device includes a source light amount control device and an image correction device. The source light amount control device determines the amount of source light and then controls the amount of source light. The image correction device corrects a signal used for changing saturations of the image data so as to reduce a change in the saturations due to a change in the amount of source light, the change in the amount of source light being performed by the light source amount control device.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
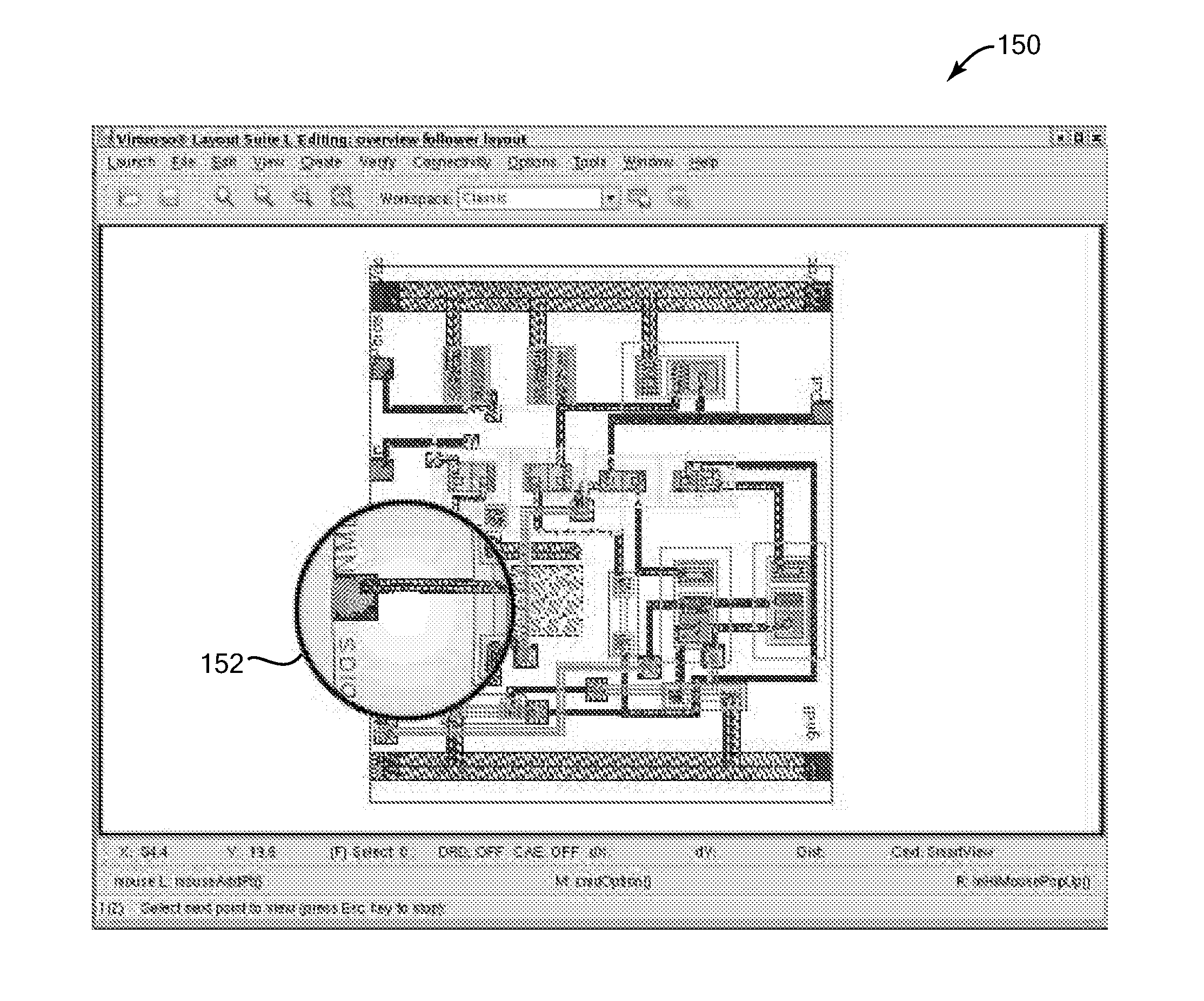
Method and system for viewing and editing an image in a magnified view
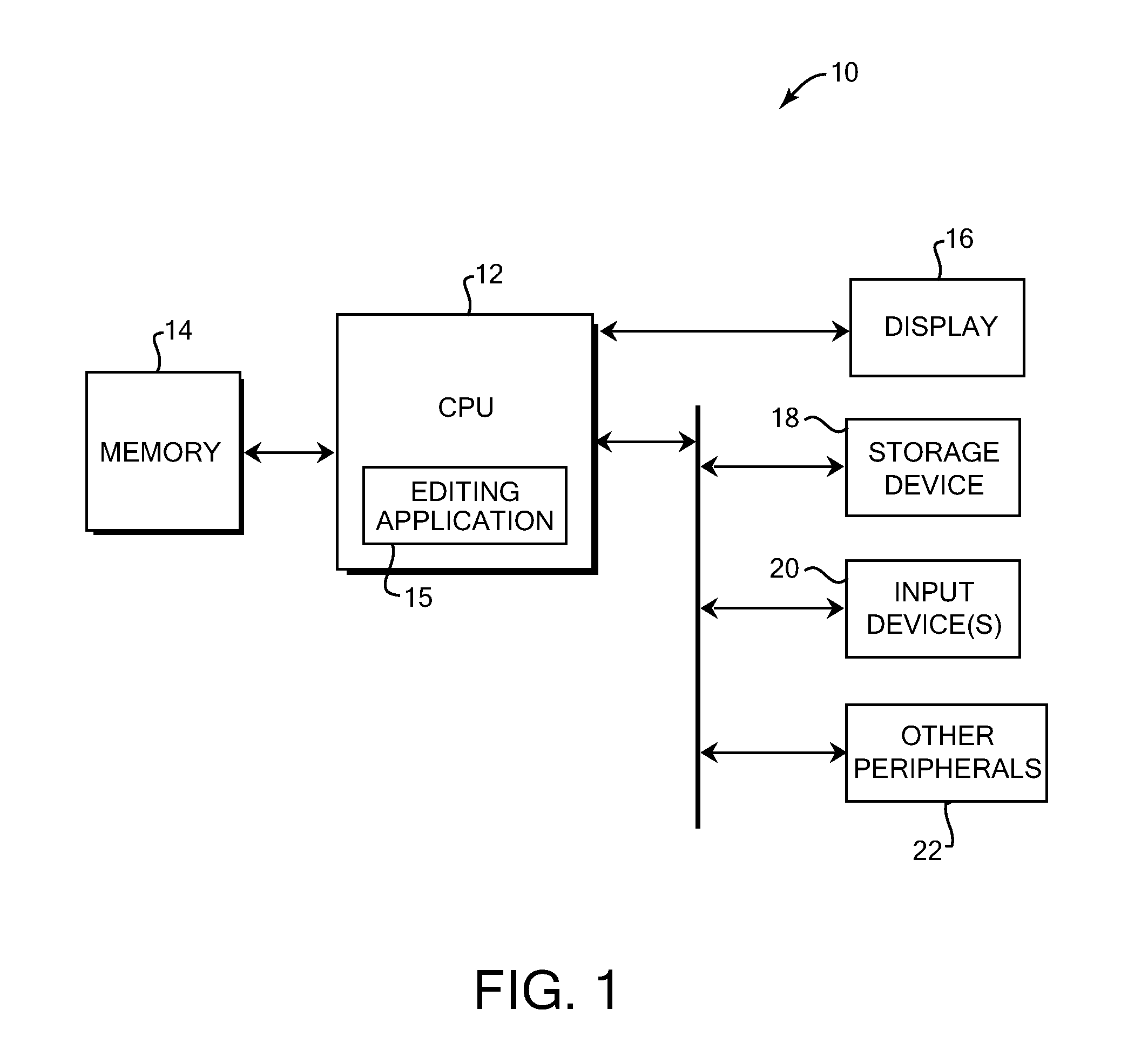
InactiveUS20100287493A1Reduce in quantityEase of executionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Display device
Viewing and editing of a displayed image in a magnified view. In one aspect, a method for displaying a magnified image using a computer system includes causing a display on a display device of a first image, and causing a display on the display device of a second image that is a portion of the first image. The second image has a zoomed-in view that is a closer view of the portion than in the first image. At least one edit is caused to the second image in response to at least one input received at the second image.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
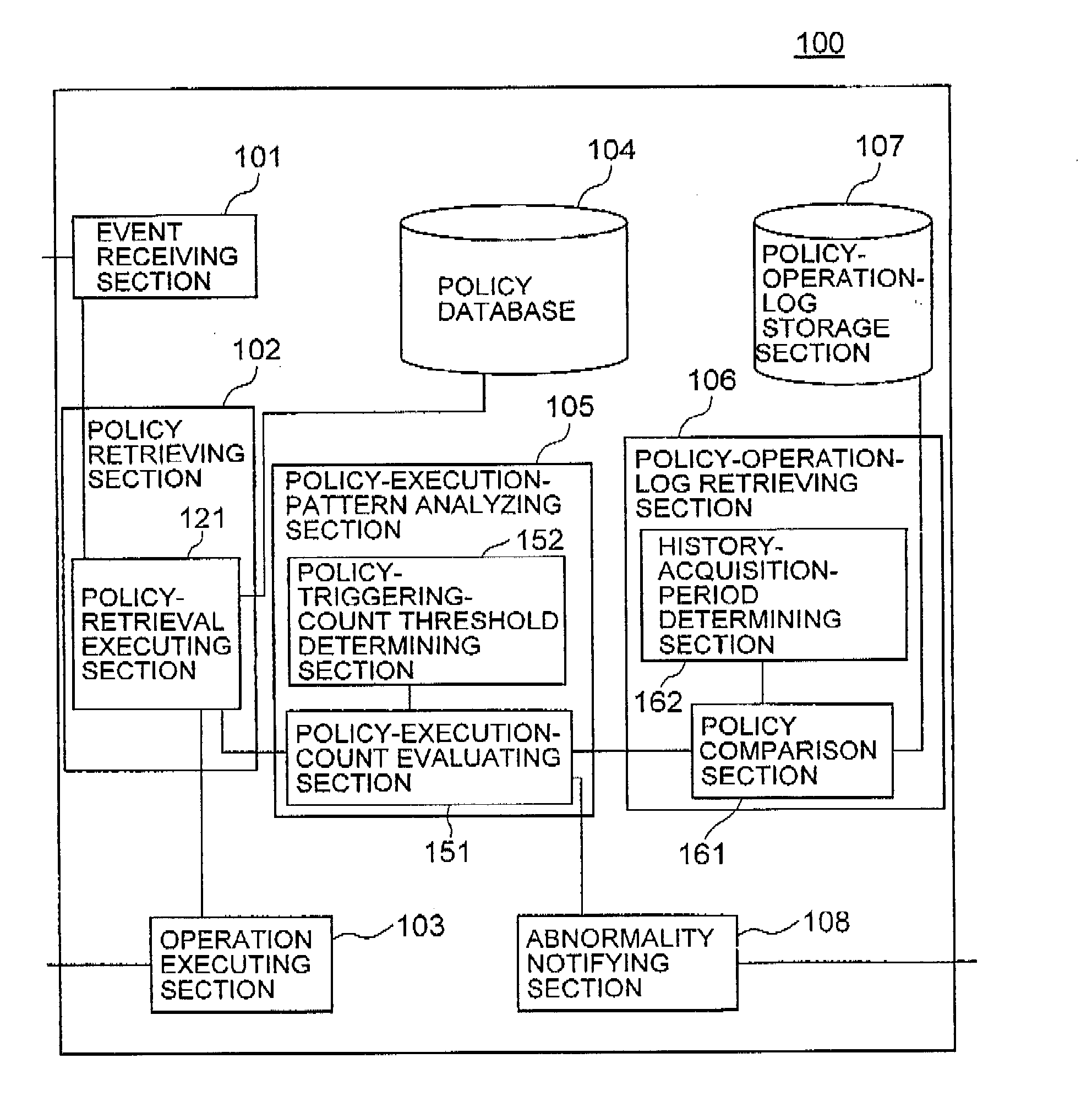
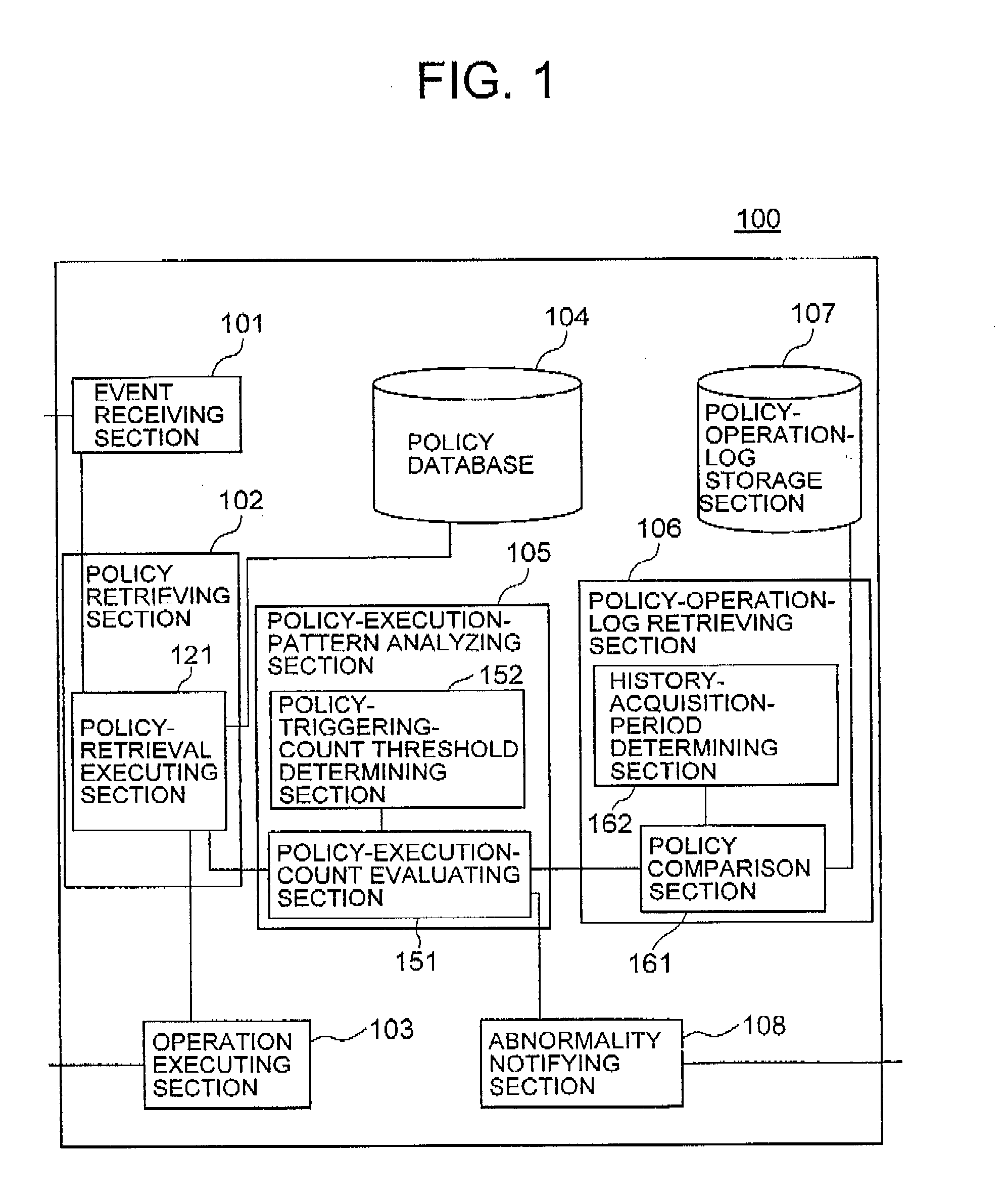
Policy processing system, method, and program
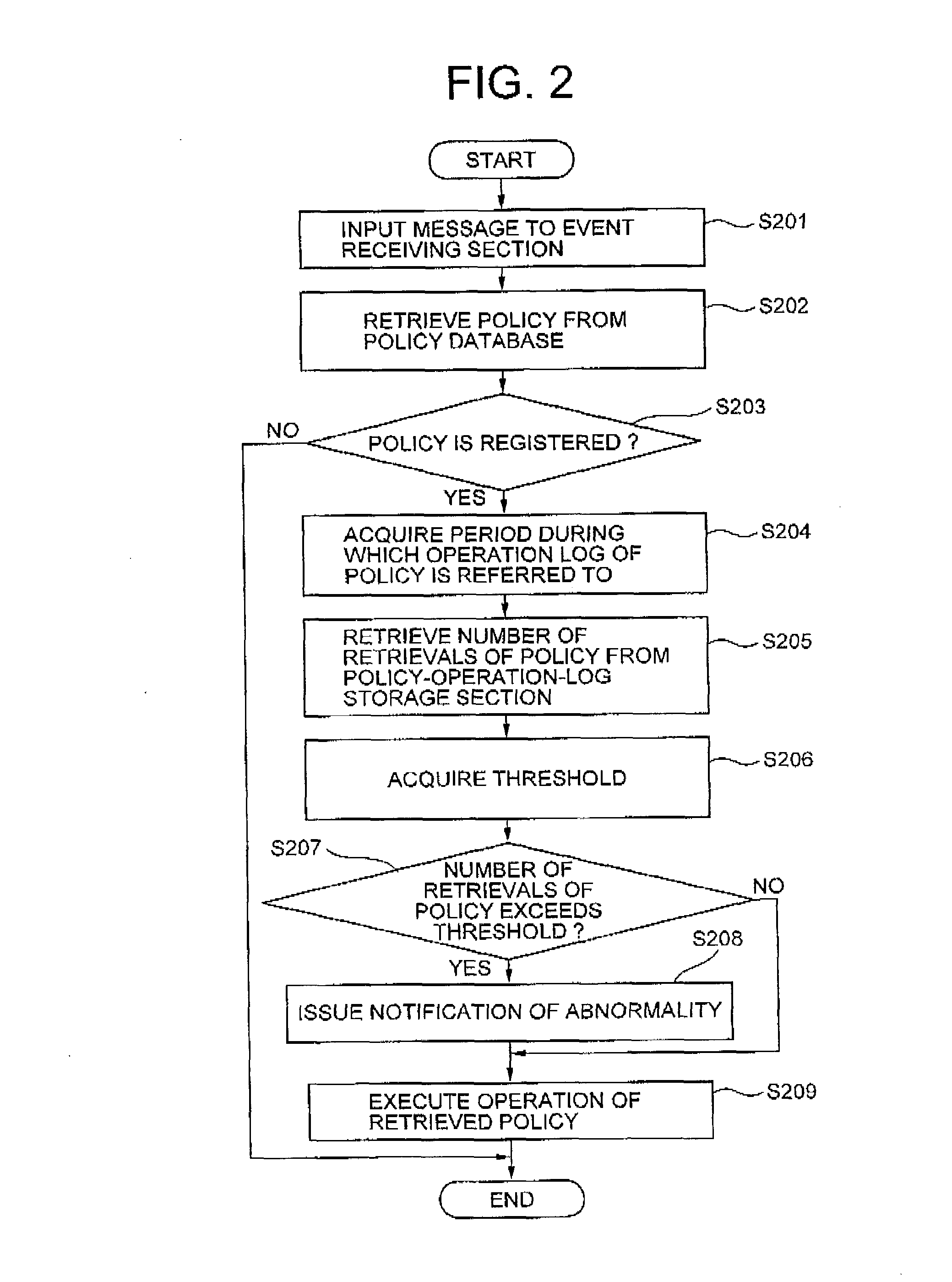
ActiveUS20090260051A1Detecting errorMinimizing adverse affectUser identity/authority verificationNon-redundant fault processingHandling systemLibrary science
In a policy handling system performing automatic execution, management, and control of a system, a policy retrieving section (102) retrieves a policy associated with a triggering condition, and notifies a policy-execution-pattern analyzing section (105) of the retrieved policy. A policy-operation-log retrieving section (106) refers to a policy-operation-log storage section (107) to acquire the number of triggering times of the retrieved policy in a predetermined history acquisition period. The policy-execution-pattern analyzing section (105) compares the number of triggering times of the retrieved policy against a predetermined threshold and causes an abnormality notifying section (108) to issue abnormality information when the number of triggering times exceeds the threshold.
Owner:NEC CORP
Program execution control device, program execution control method, control program, and recording medium
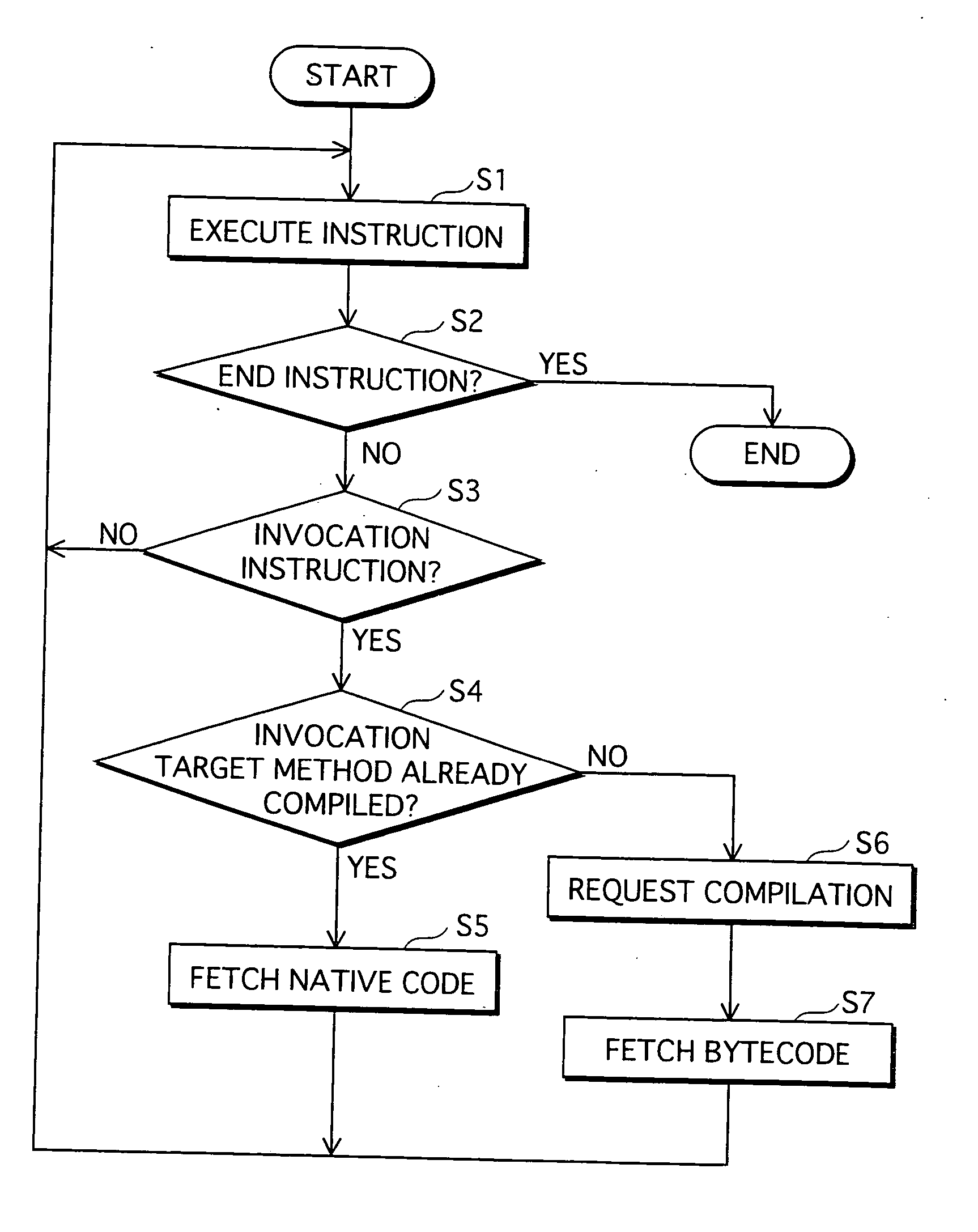
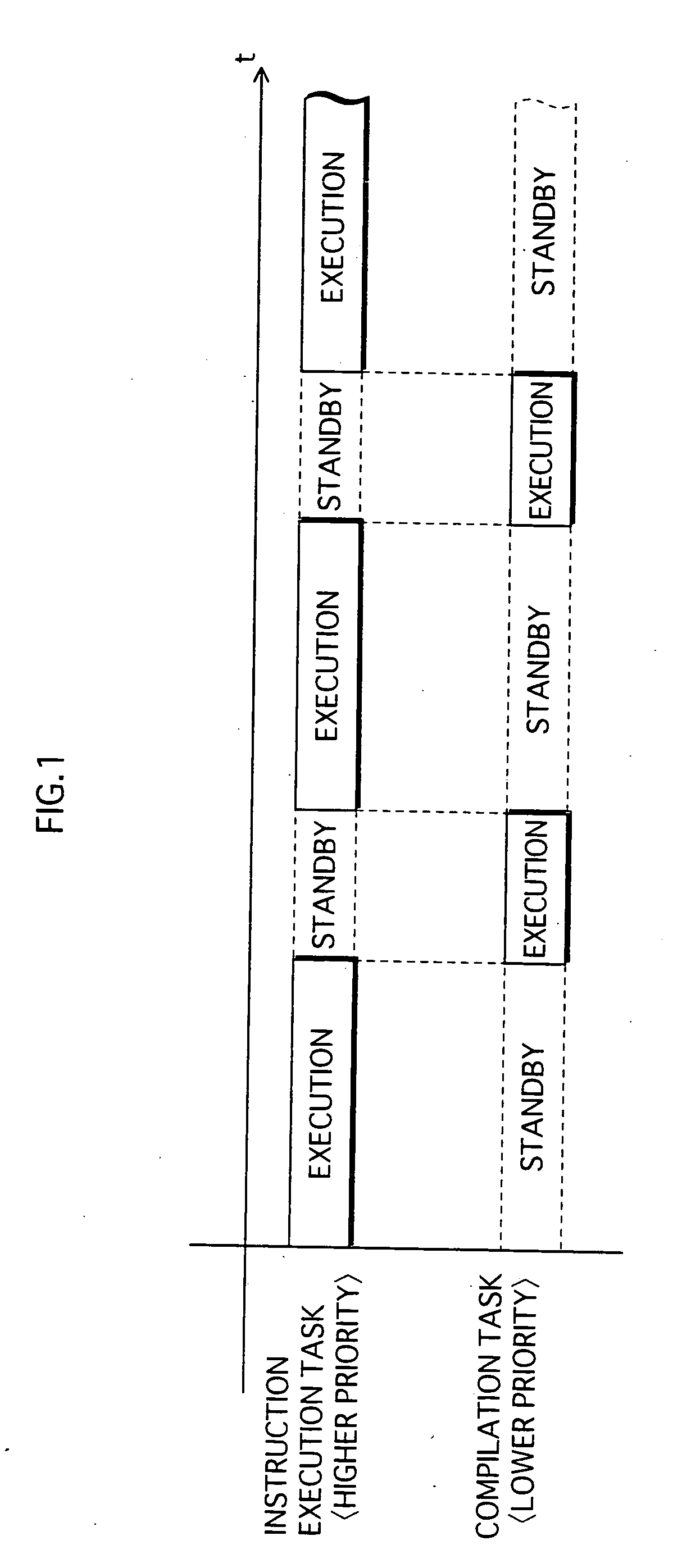
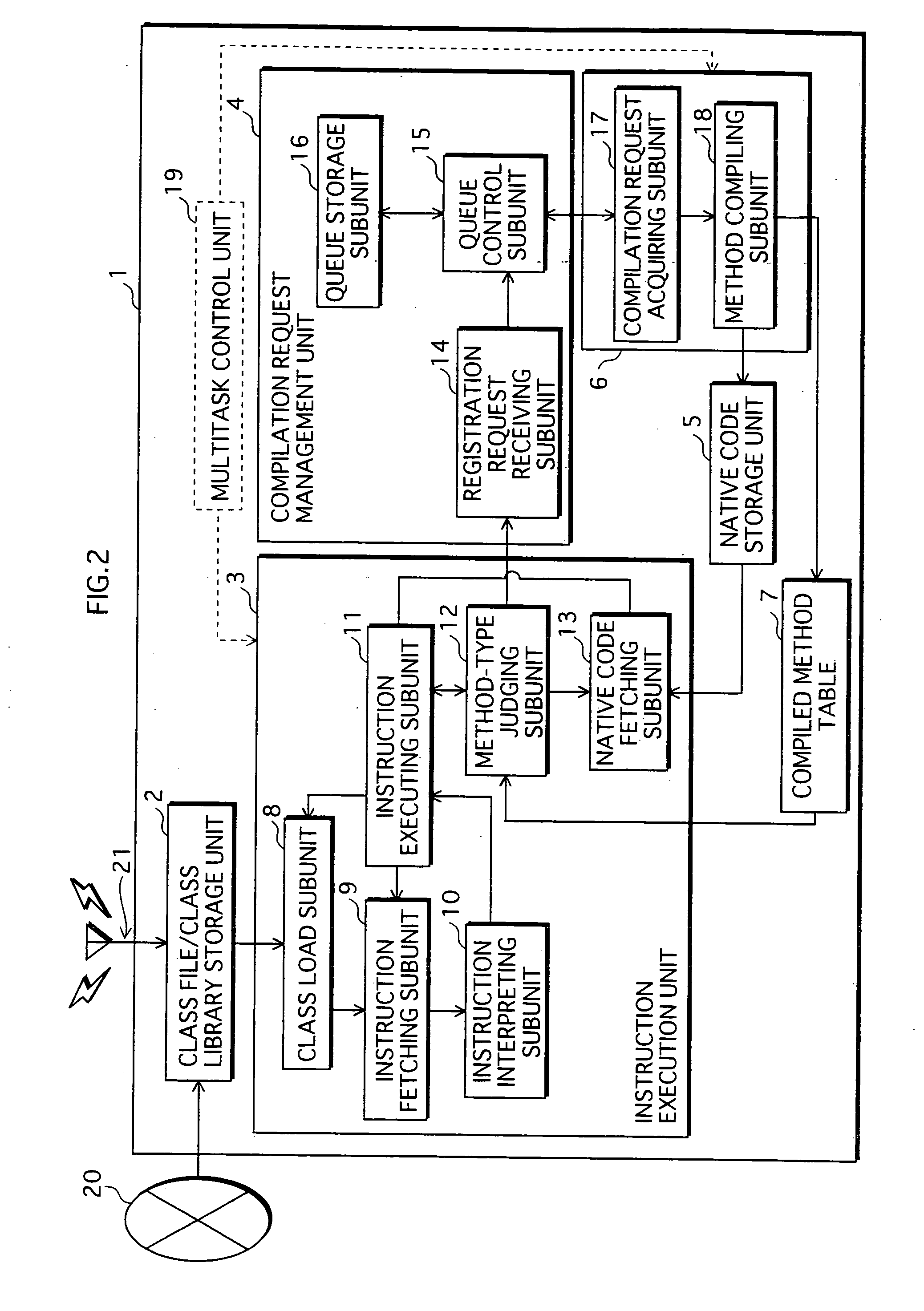
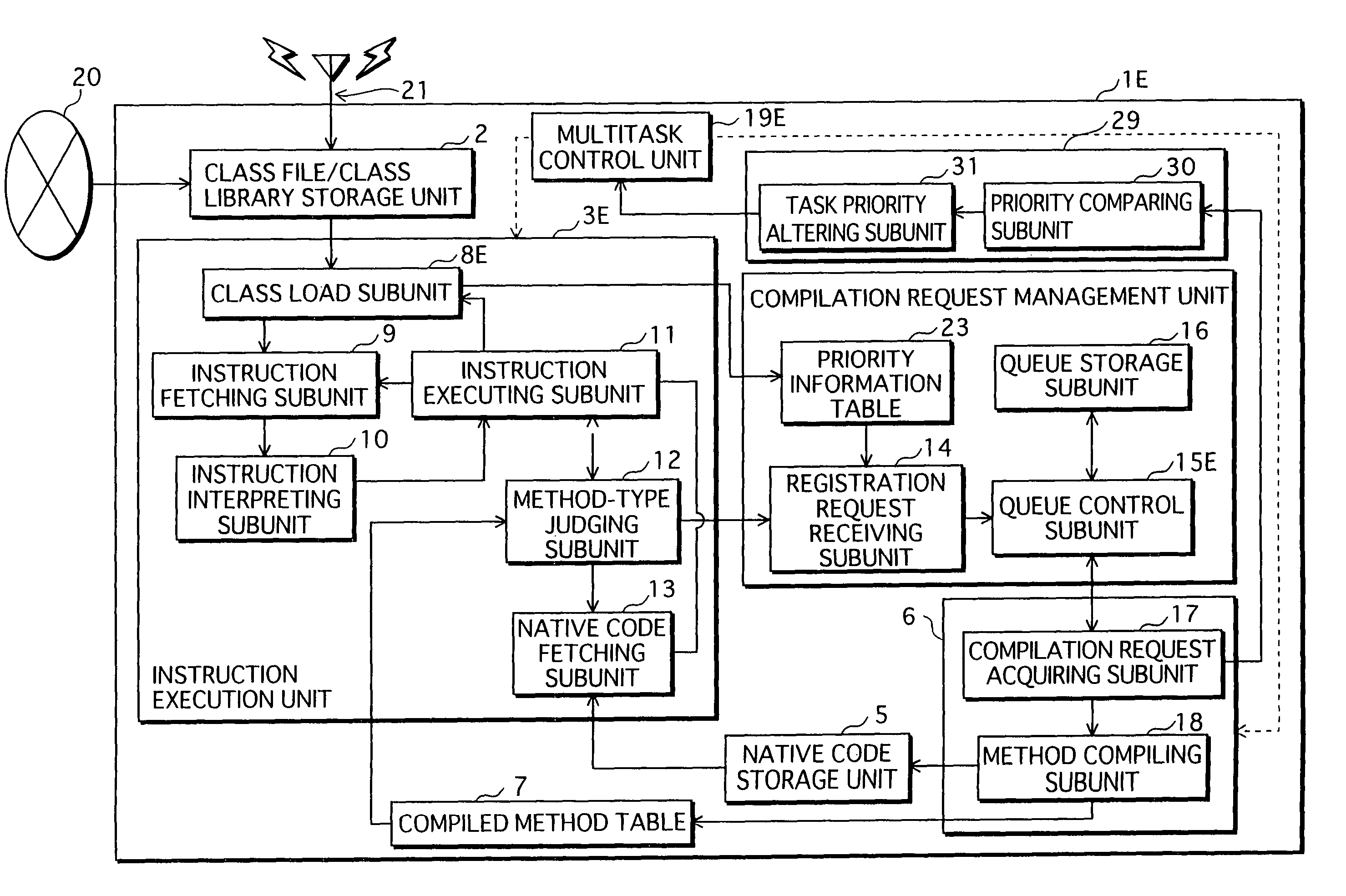
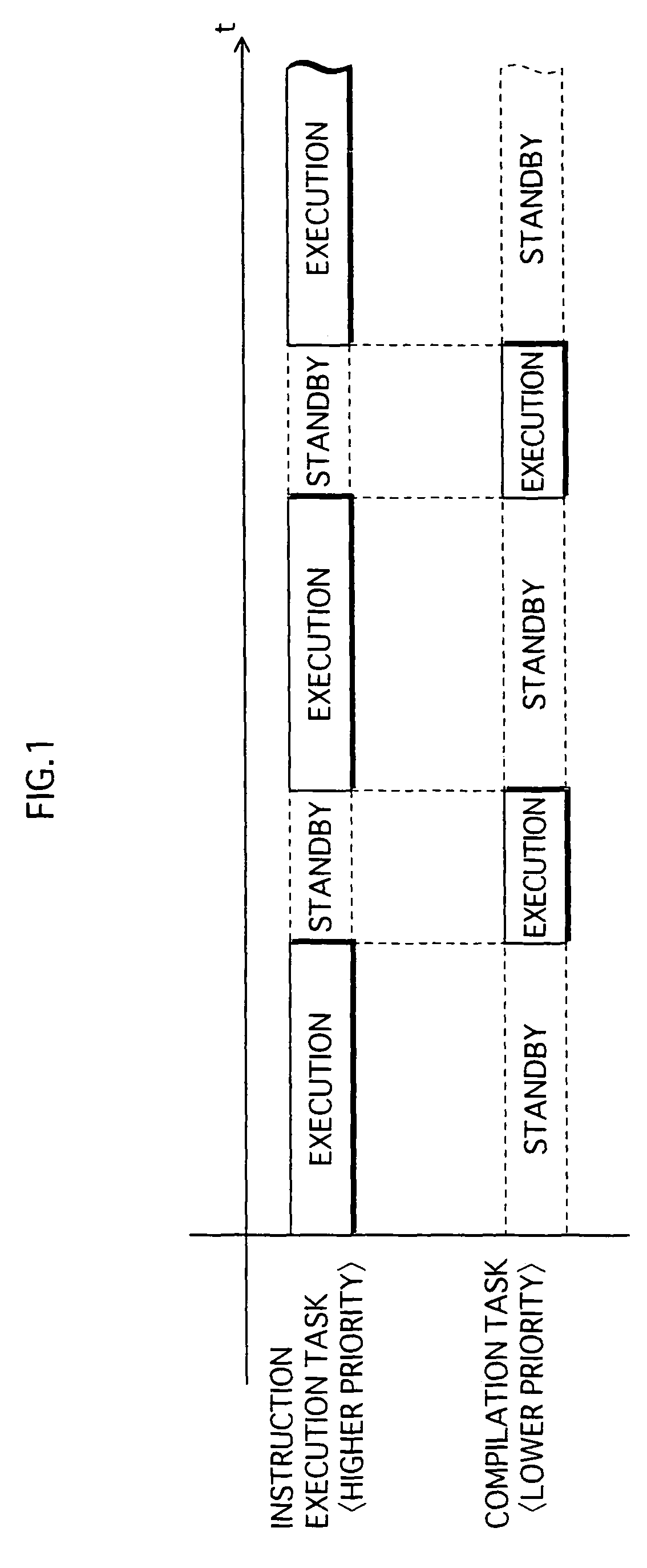
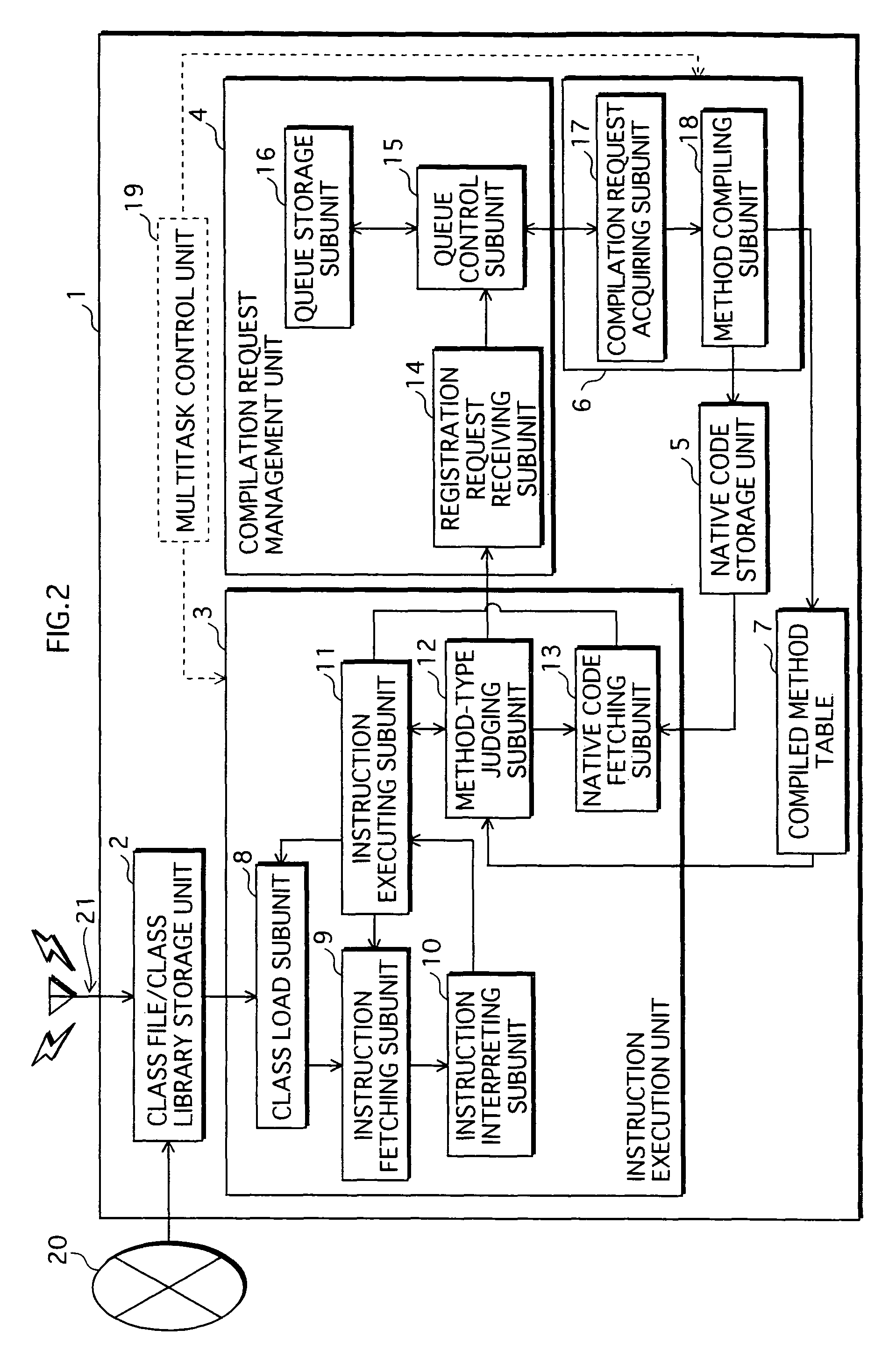
ActiveUS20070226714A1Suppressing reduction of execution speedSuppress execution speedTransformation of program codeSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationParallel computingExecution control
When a home appliance equipped with a processor implementing a conventional JVM with a JIT compiler executes uncompiled methods, the execution speed is slower because the methods are compiled at runtime. To suppress the execution speed reduction, a program execution control device judges, on invocation of a method during program execution, whether a method invoked has previously been compiled. If the method is uncompiled, the device executes the method by interpreting associated bytecodes, and also issues a compilation request for the method. If the method is compiled, the device executes native code having been generated by compiling the method. Compilation of a method requested is executed as a separate task from tasks of instruction execution such as interpreter execution or native code execution.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
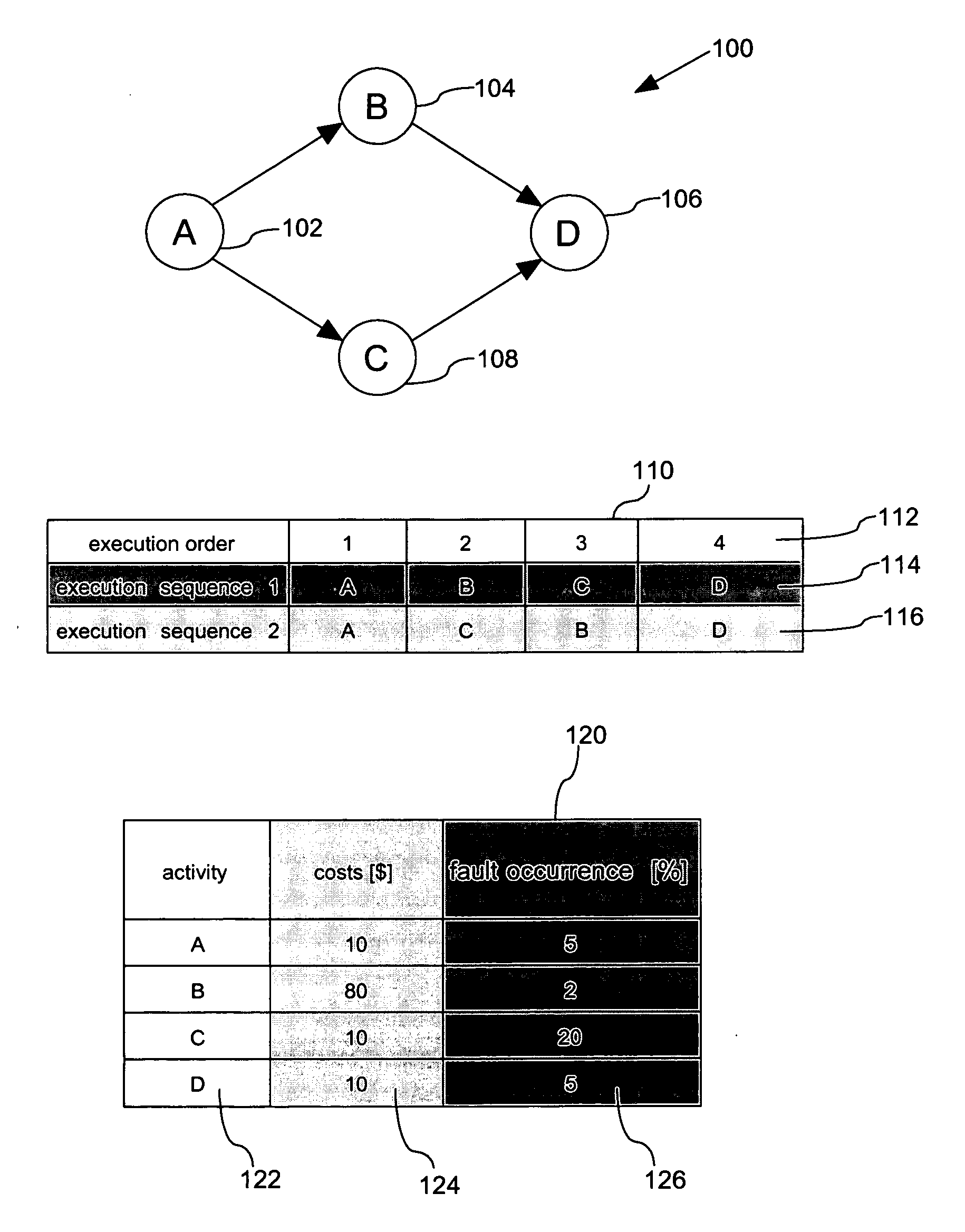
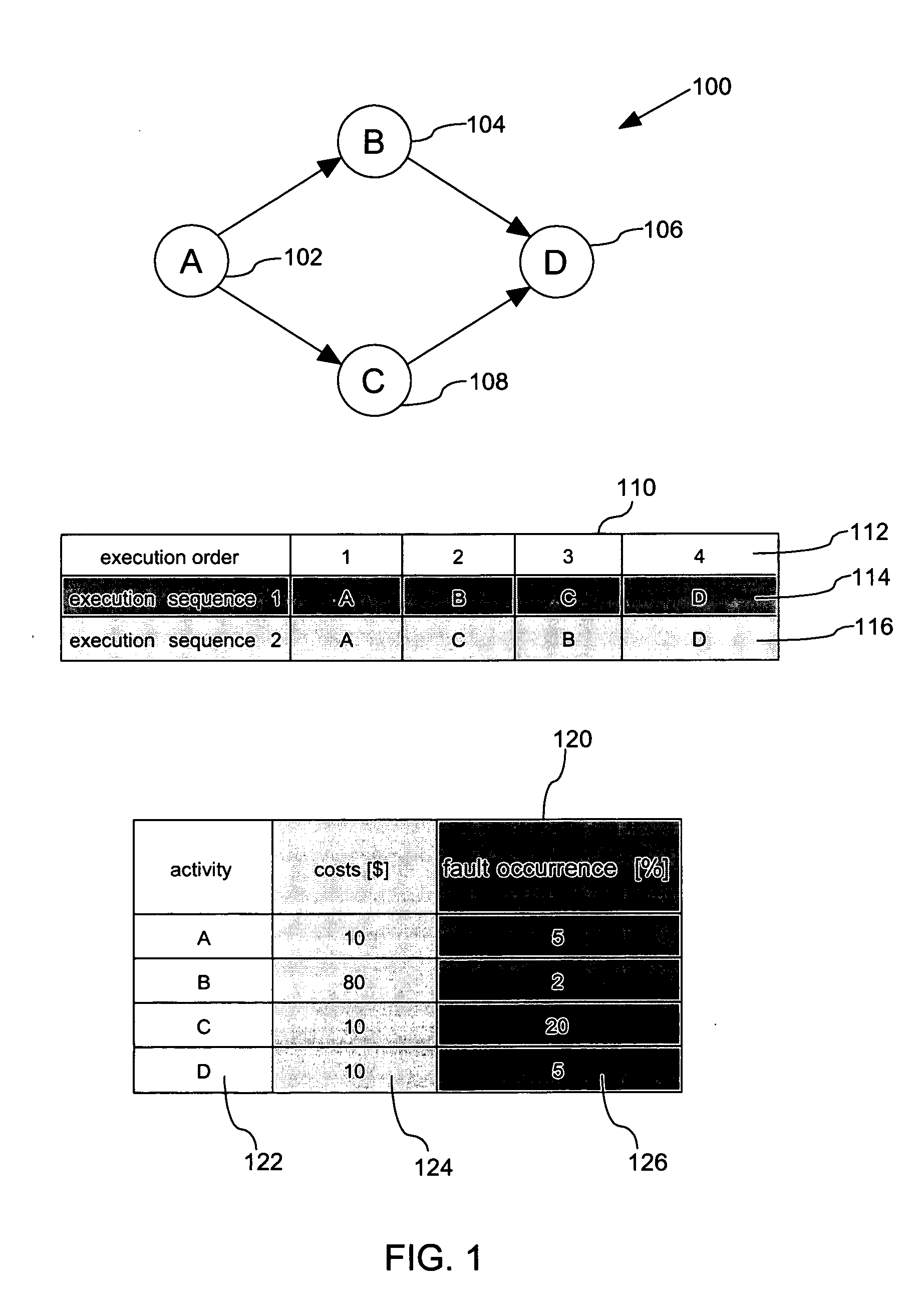
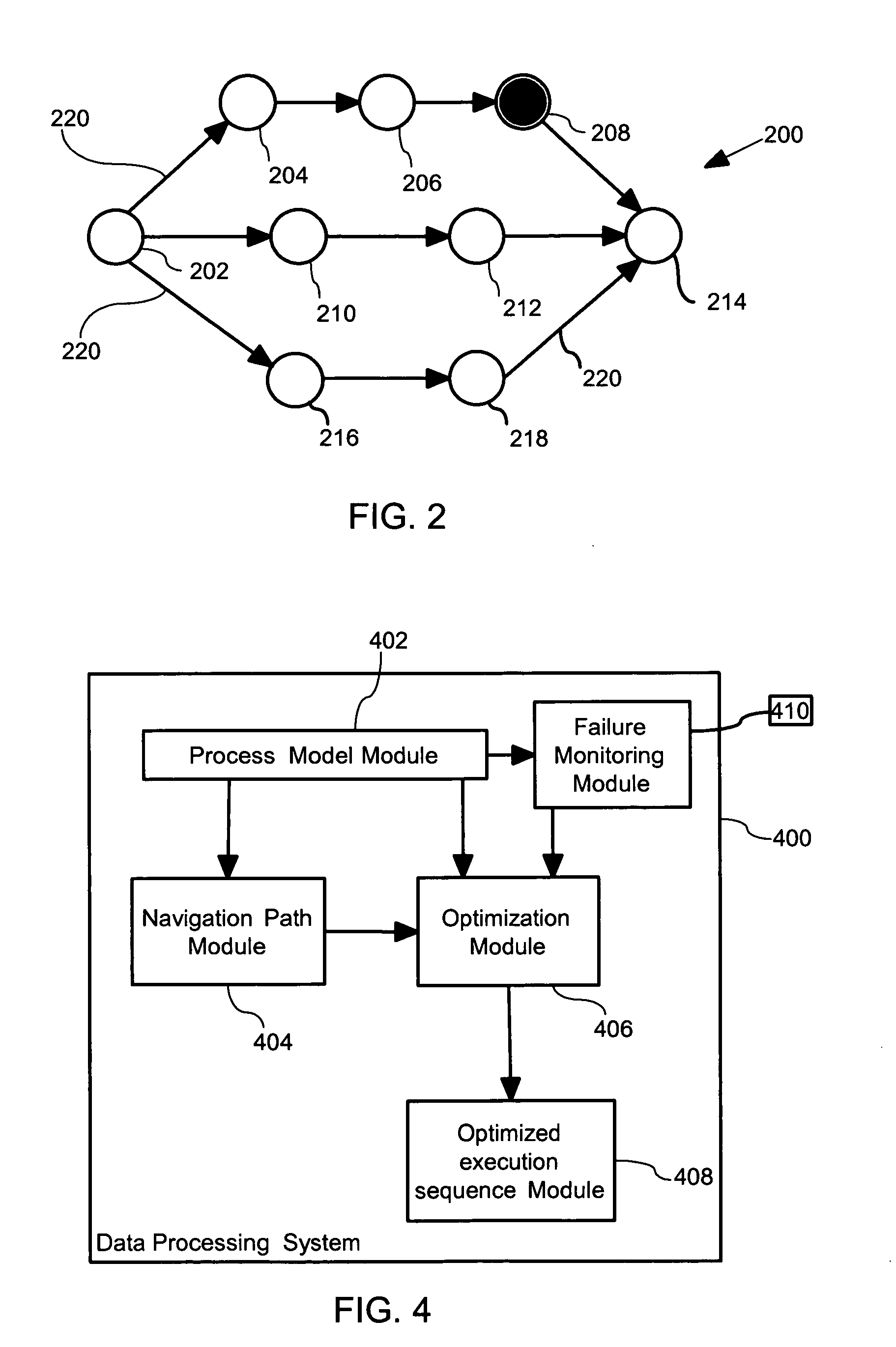
Optimization of process properties for workflows with failing activities
InactiveUS20050209841A1Ease of executionNavigation costReliability/availability analysisProgram controlData processing systemData treatment
The present invention provides a method, a data processing system as well as a computer program product for optimizing process properties for workflows with failing activities. The invention makes use of monitoring occurrence of failure of each activity of a process model of a workflow and further monitoring properties that are associated to compensating activities that are required in order to repair the failure of an activity. The method makes explicit use of determining alternative execution sequences and selecting one of the plurality of alternative execution sequences of the process model, that optimizes the process property in case of failure of an activity of the process model. The process model itself remains unaffected and need not to be remodeled.
Owner:IBM CORP
Autonomously moving robot management system
InactiveUS20050065652A1FlexibilityEase of executionProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlSelf adaptiveTransceiver
An autonomous robot is controlled by the local robot information controller which is connected to a robot application network to which the transceiver to communicate with the autonomous robot is attached. The robot application network, a user LAN adaptive controller an information distribution manager and the third party information provider subsystem are linked with a public network. The information distribution manager acquires the information from the third party information provider subsystem on the schedule which is set by the user LAN adaptive controller. The local robot information controller receives the information distribution manager and covert it into the data that generates robot gestures. The robot performs actions in accordance to the gesture data received from the local robot information controller.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
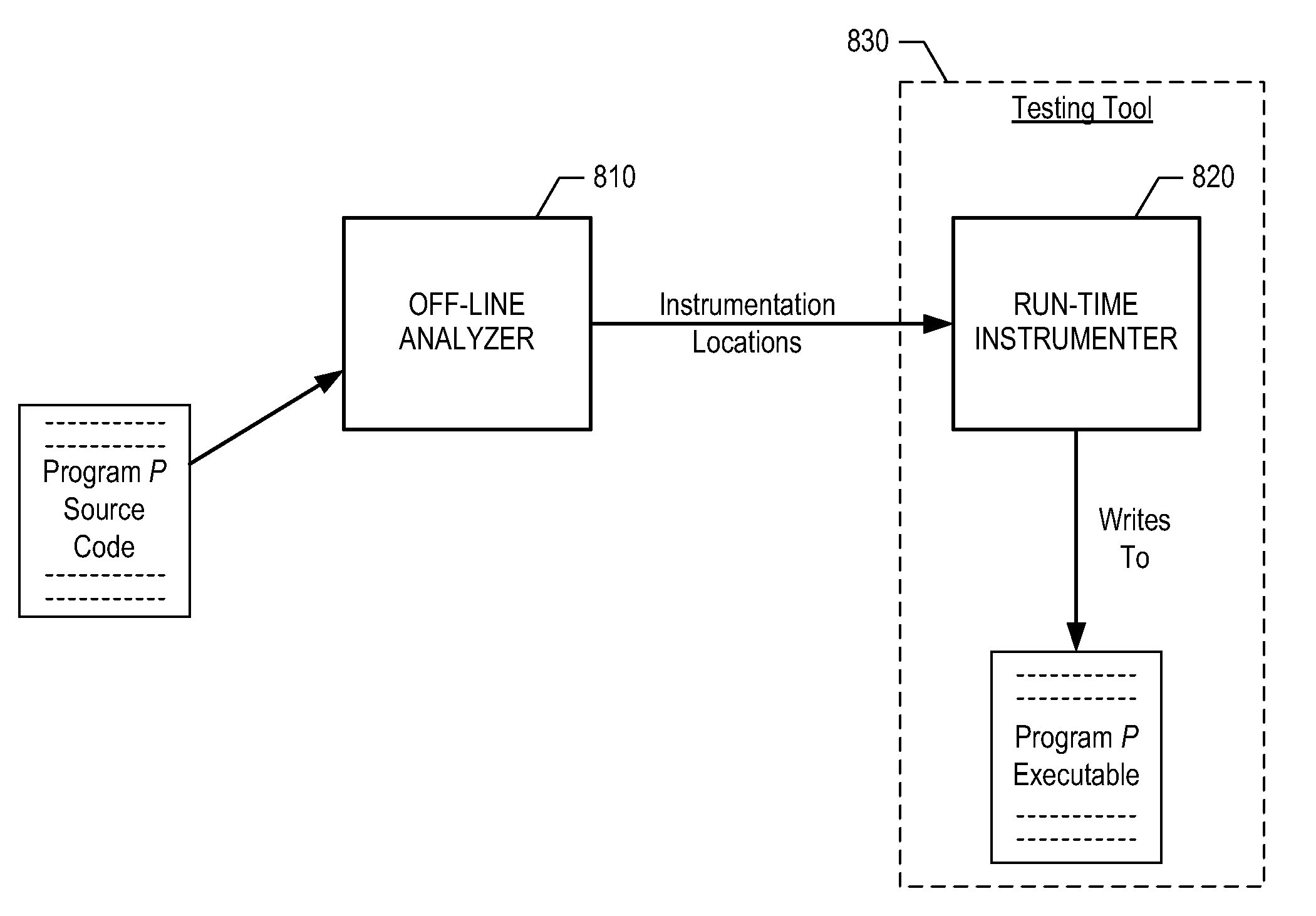
Efficient Program Instrumentation
InactiveUS20090249309A1Minimizes instrumentation overheadSlow down program executionError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsTheoretical computer scienceProcedure device
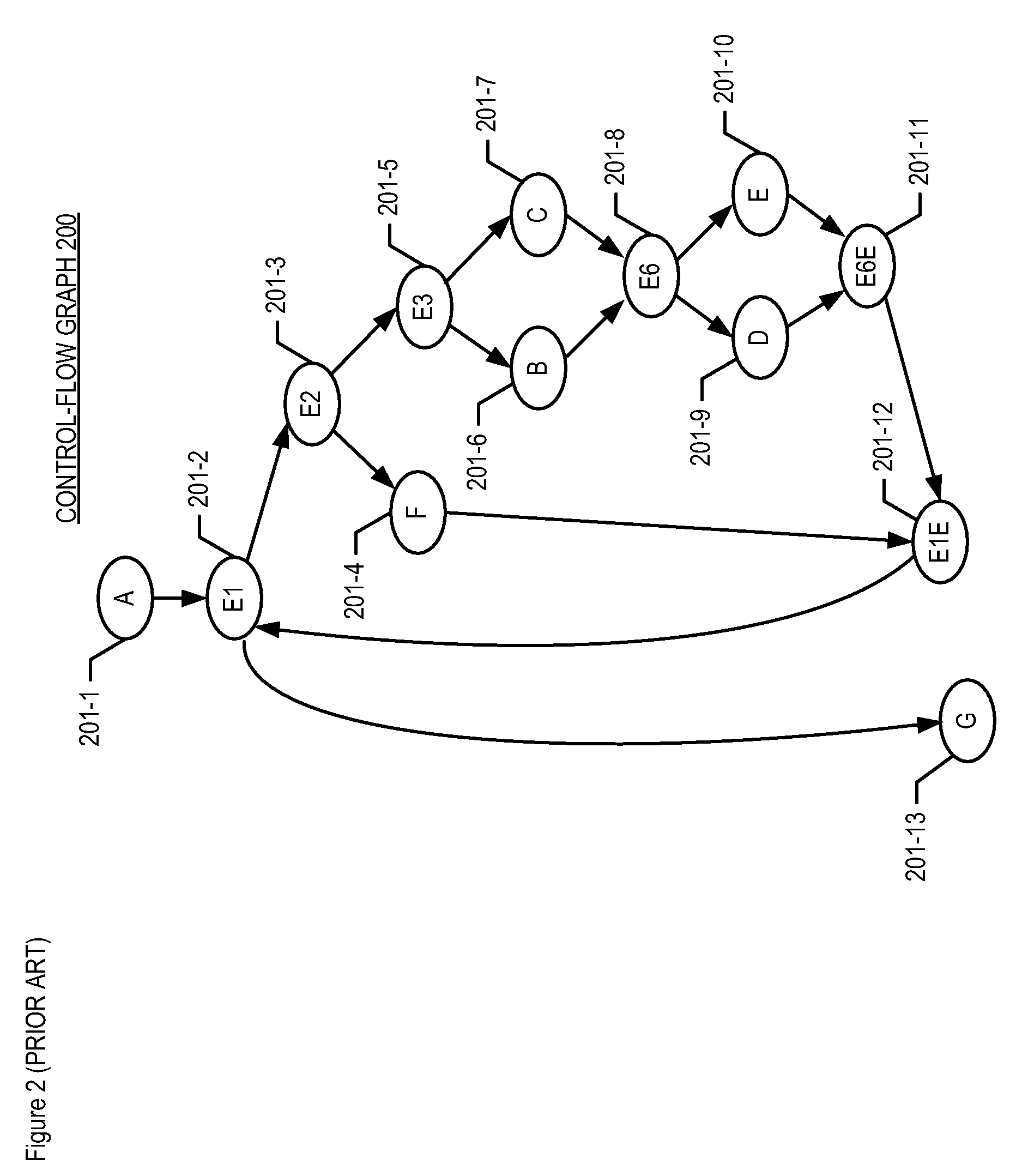
A method for determining the number and location of instrumentation probes to be inserted into a program is disclosed. The method advantageously inserts the minimum number of probes that are required to obtain execution coverage for every node in the program's control-flow graph. In addition, the method requires only type of node marking and one bit to store each probe, and does not require the assignment of weights to arcs or nodes of the control-flow graph. In the illustrative embodiment, the nodes of a control-flow graph are partitioned into non-empty sets, where each non-empty set corresponds to a super nested block of the program.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Image processing apparatus having an energization switching unit and control information updating unit
ActiveUS7872774B2Suppress power consumptionEase of executionEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringImaging processingStart up
An image processing apparatus executes the processing of updating control information kept in the controlling units included in it without suspending an on-going processing and delaying the execution of a new processing request with less power consumption. When the controlling units are in a sleep mode or in non-energized state, NIC determines whether or not updating of firmware kept in each controlling unit is necessary by communicating with the information delivery server. The NIC controls an energization switching circuit to start up exclusively the controlling unit keeping the firmware determined necessary to be updated and replaces the firmware kept in the started controlling unit with the latest version of firmware obtained from the information delivery server.
Owner:SHARP KK
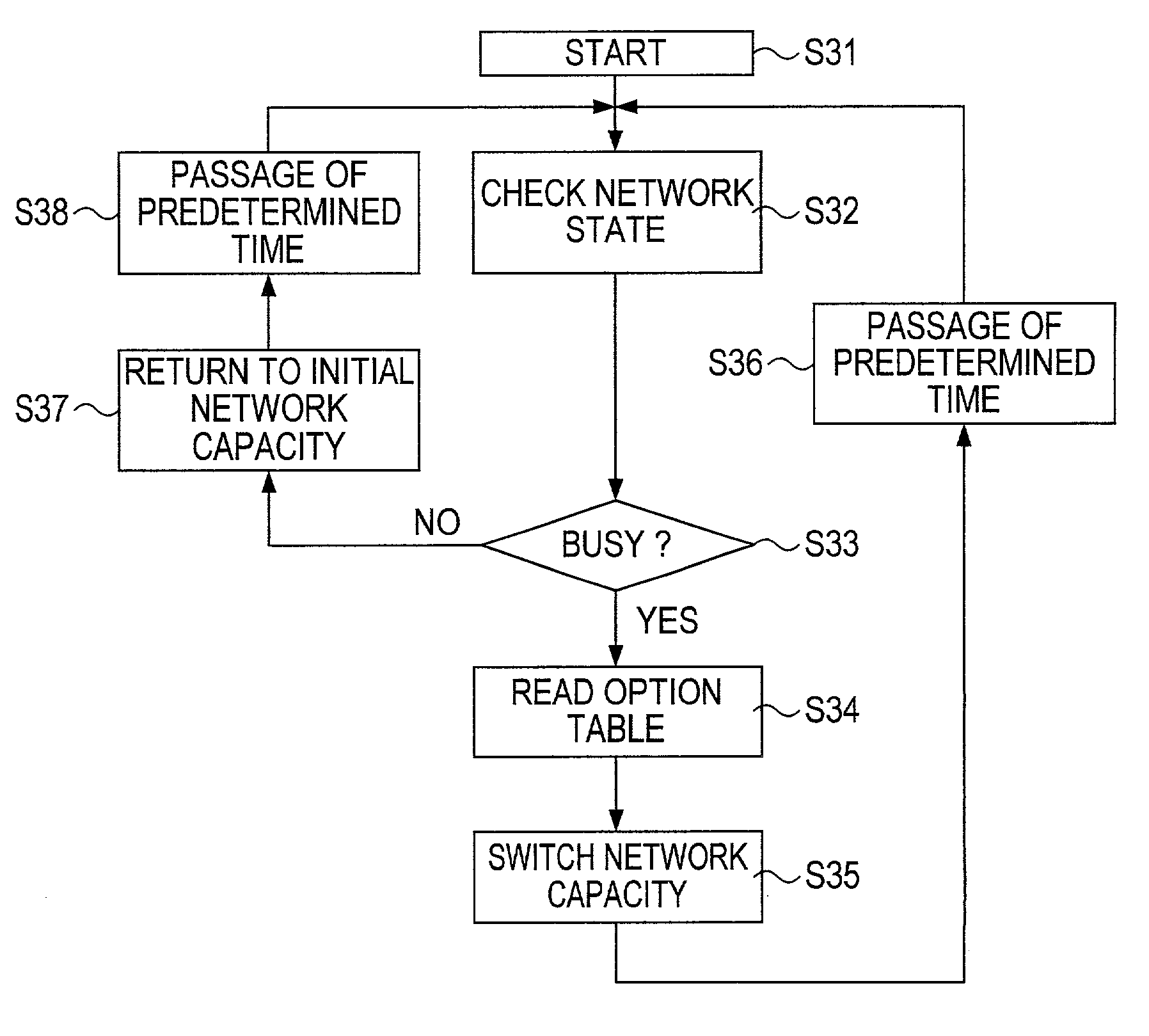
Method for charging fee for use of network resources and method and system for allotting network resources
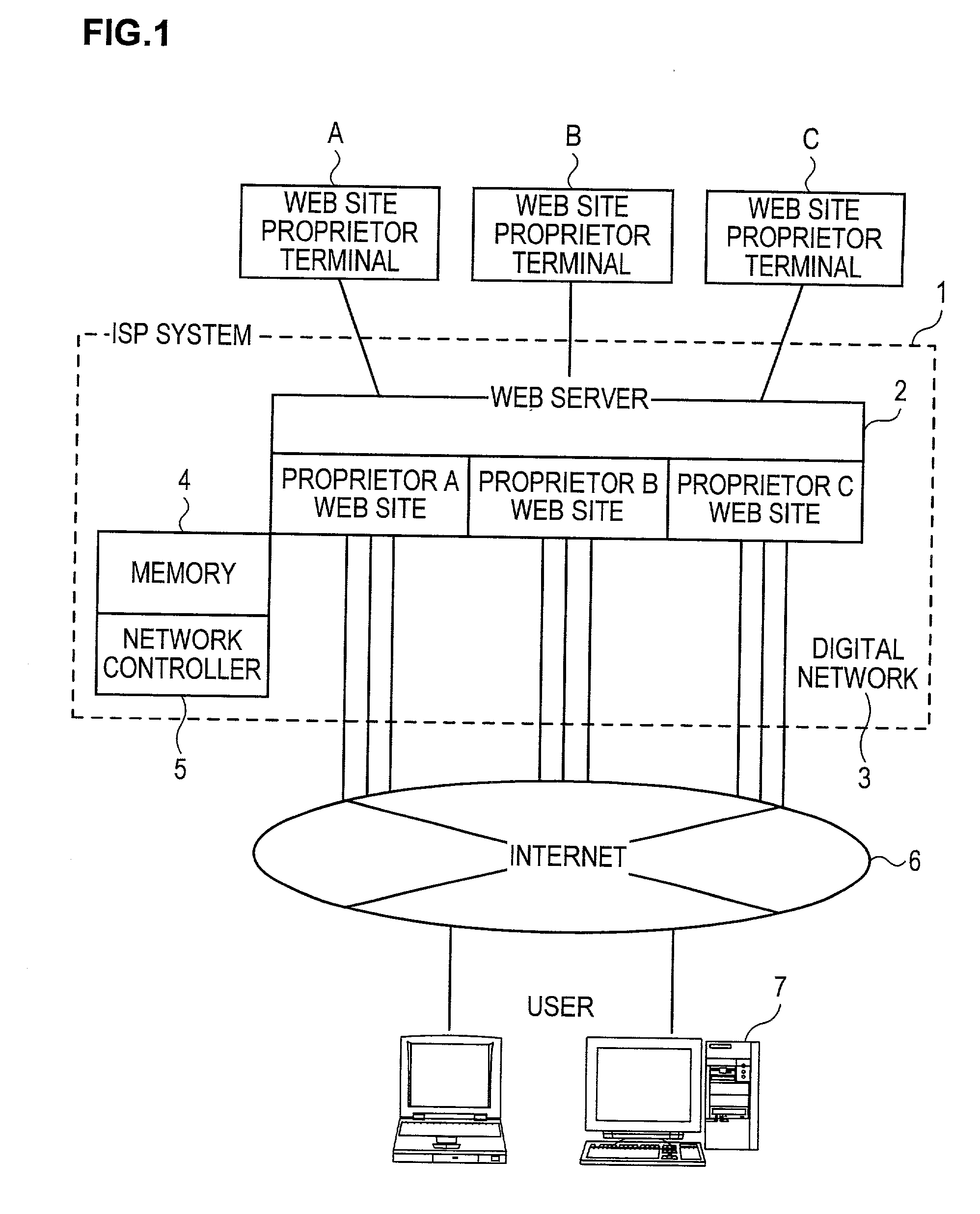
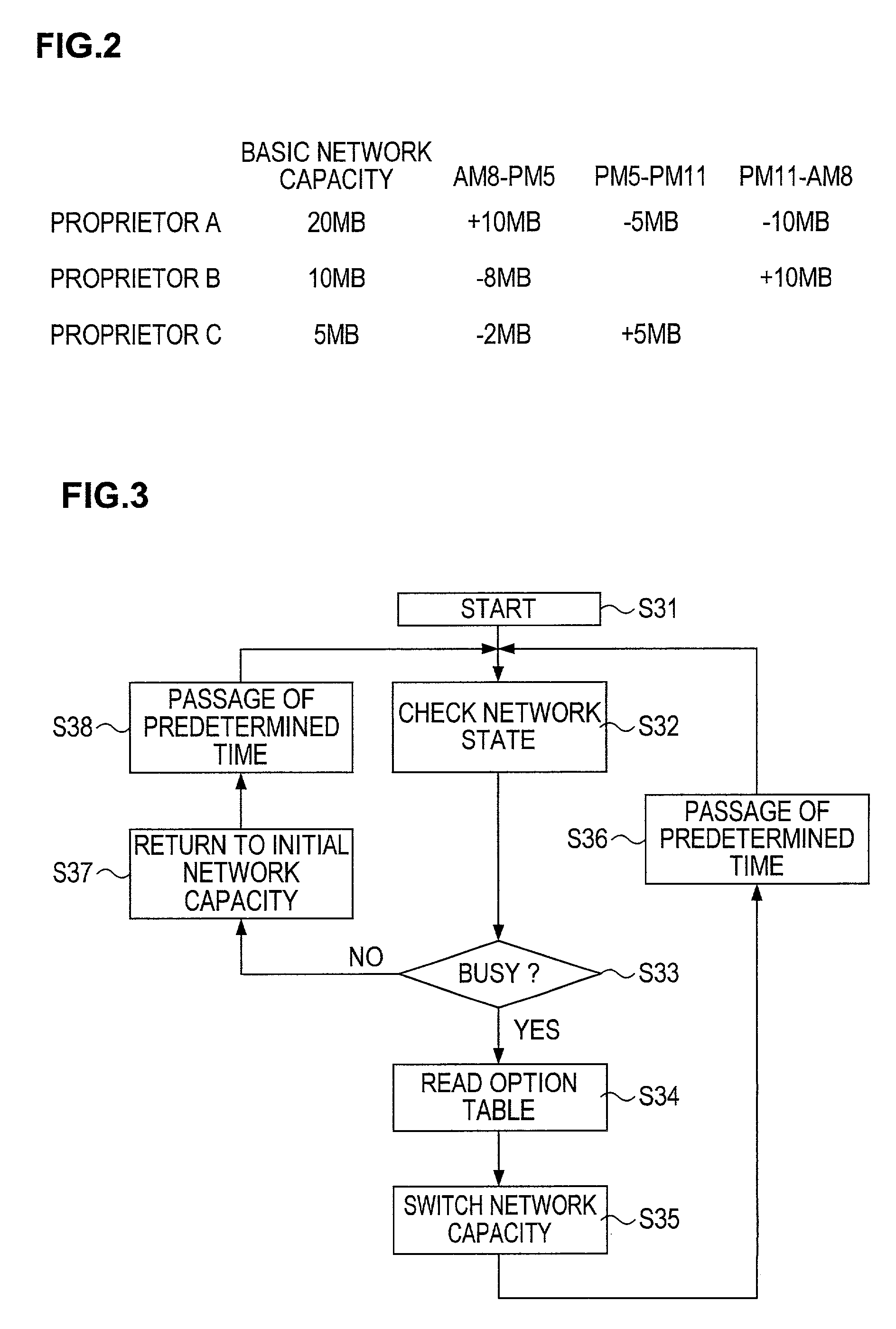
InactiveUS20020016842A1Easy to useIncrease and decrease network resourceMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsDigital computer detailsWeb siteTelecommunications
When an internet service provider (ISP) 1 charges web site (web site) proprietors A, B and C a fee for using their desired basic network capacity from the network resources thereof, the ISP 1 give one web site proprietor (e.g. A) a preferential option enabling one web site proprietor terminal to temporarily use a part of the basic network resources or its entirety thereof allotted to the other web site proprietor terminals (e.g. B and C) as well as a non-preferential option enabling the other web site proprietor terminals to temporarily use a part of the basic network resources or its entirety thereof allotted to the one web site proprietor terminal, and the ISP 1 charges web site proprietors the fee for their use of the basic network capacity at a premium rate / discount rate in correspondence with their purchased preferential option / non-preferential option. Accordingly, with the purchase of preferential option / non-preferential option, the basic network capacity may be substantially increased or decreased, so that the effective use of the digital network is facilitated and also, the fee for the use of the basic network capacity is made reasonable with adoption of the premium rate / discount rate in correspondence with the preferential option / non-preferential option.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
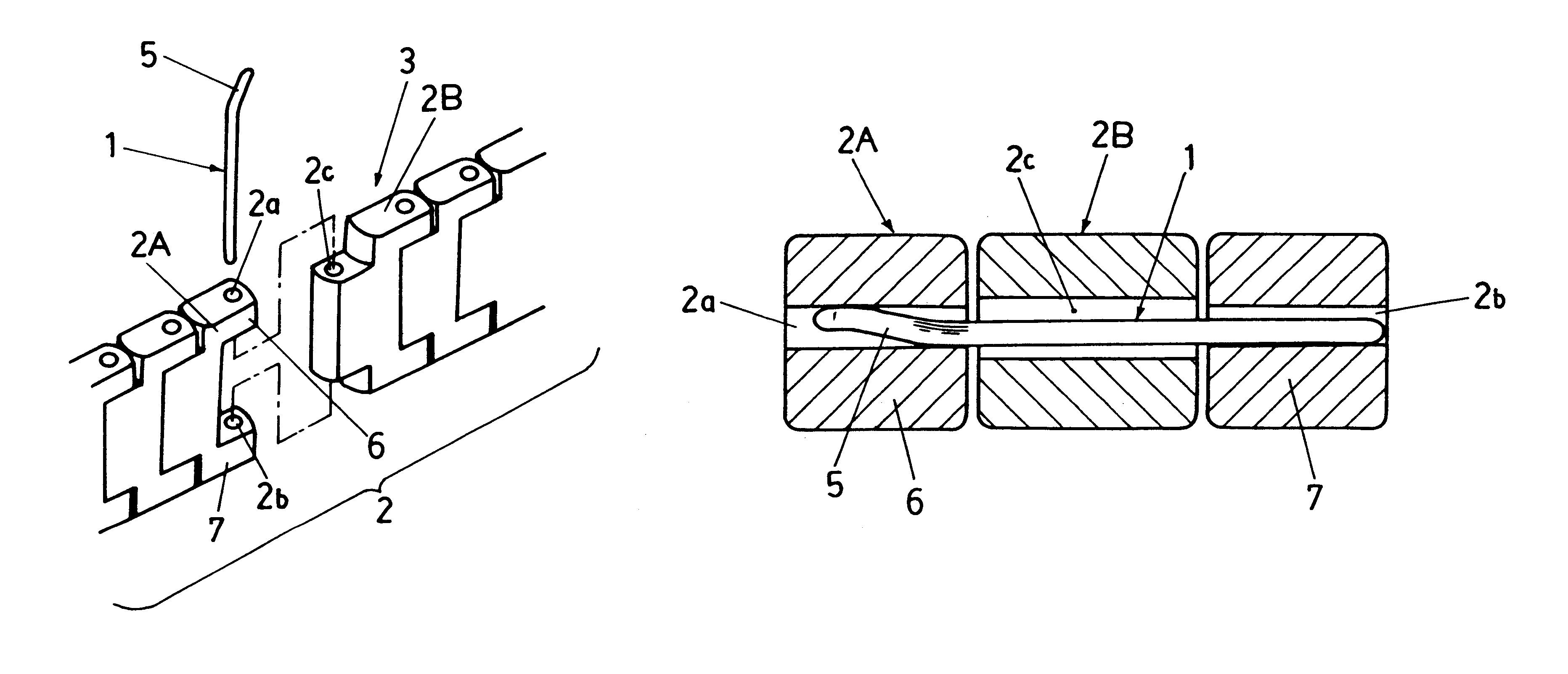
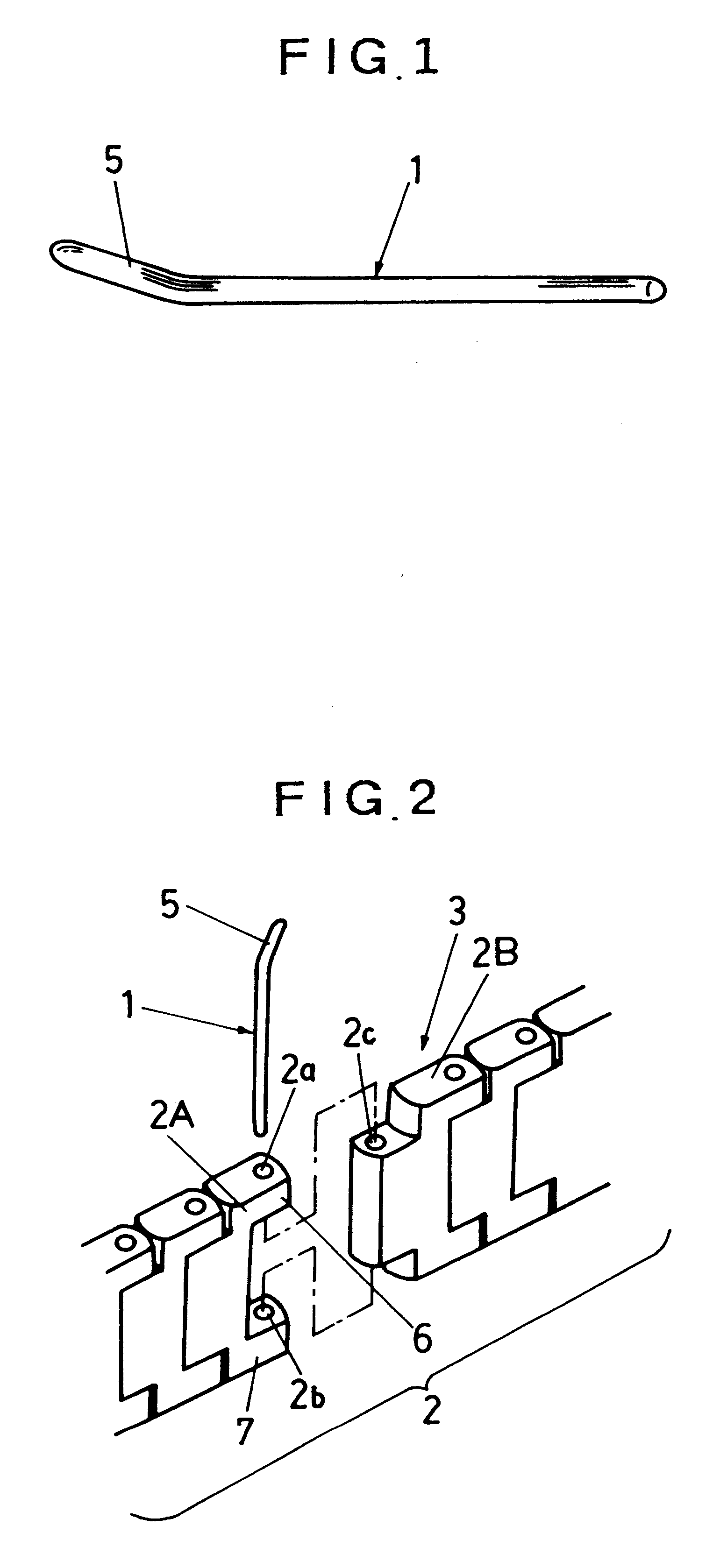
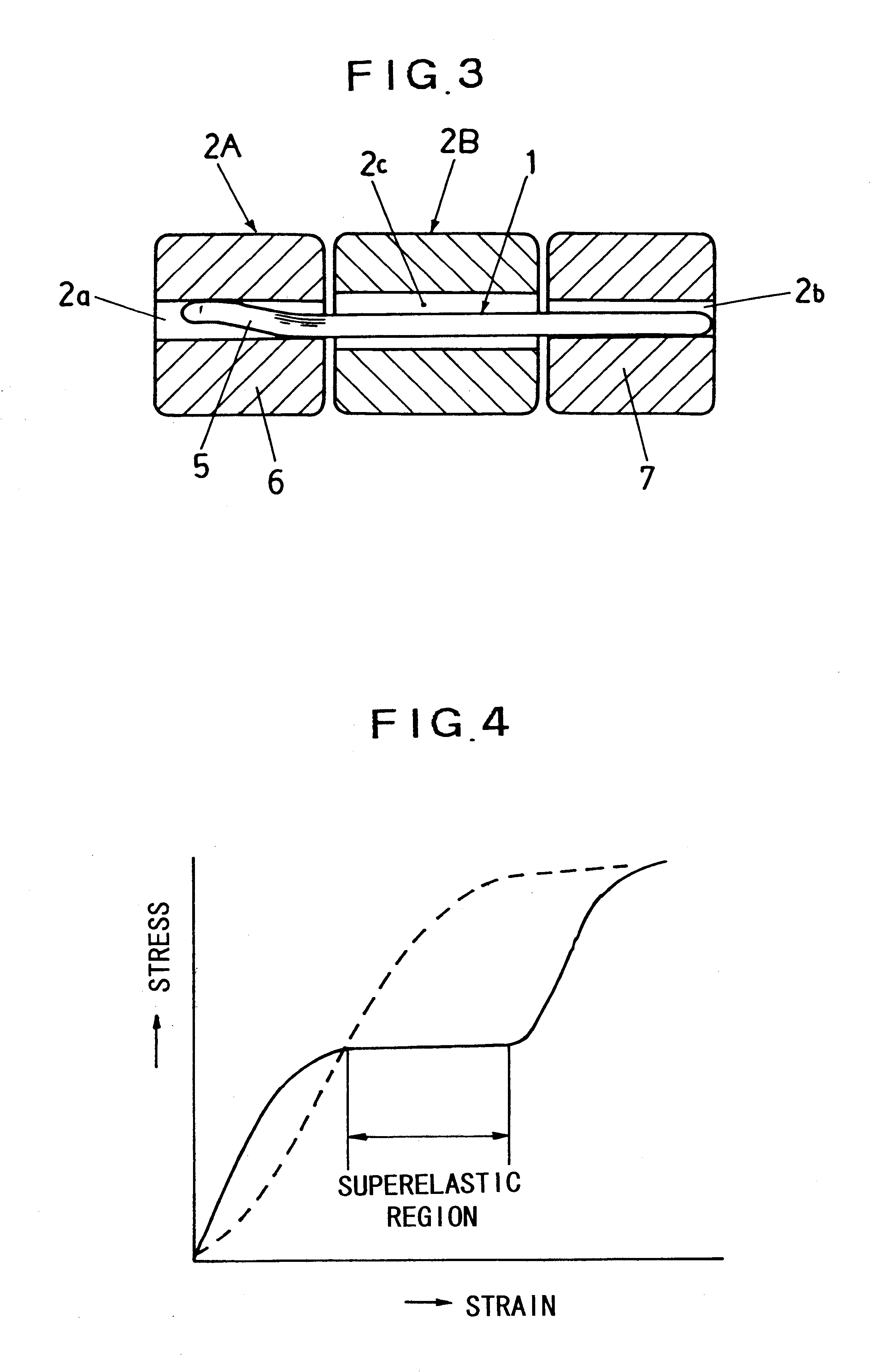
Wrist watch band adjust pin, method of manufacturing the pin, and wrist watch band connection structure
InactiveUS6406177B1Insertion and extraction thereofEase of executionScarvesClockwork casesSpring forceWrist
An adjust pin (1) for connecting a plurality of blocks (2) to each other to make up a wrist watch band (3) is formed of a metal with a property having a superelastic region where a stress remains constant against variation in strain. The adjust pin (1) is provided with a bent part (5) for causing a bending stress in the superelastic region to act on the inner wall face of a connecting through-hole (2a) of a block (2) in a state wherein the block (2) is joined with an adjoining block (2). When the adjust pin (1) is inserted in the blocks (2), and the bent part (5) is positioned in the connecting through-hole (2a), the bent part (5) provides a force acting on the inner wall of the connecting through-hole (2a) by the agency of the bending stress in the superelastic region, thereby securely holding the adjust pin (1) by a spring force thereof.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
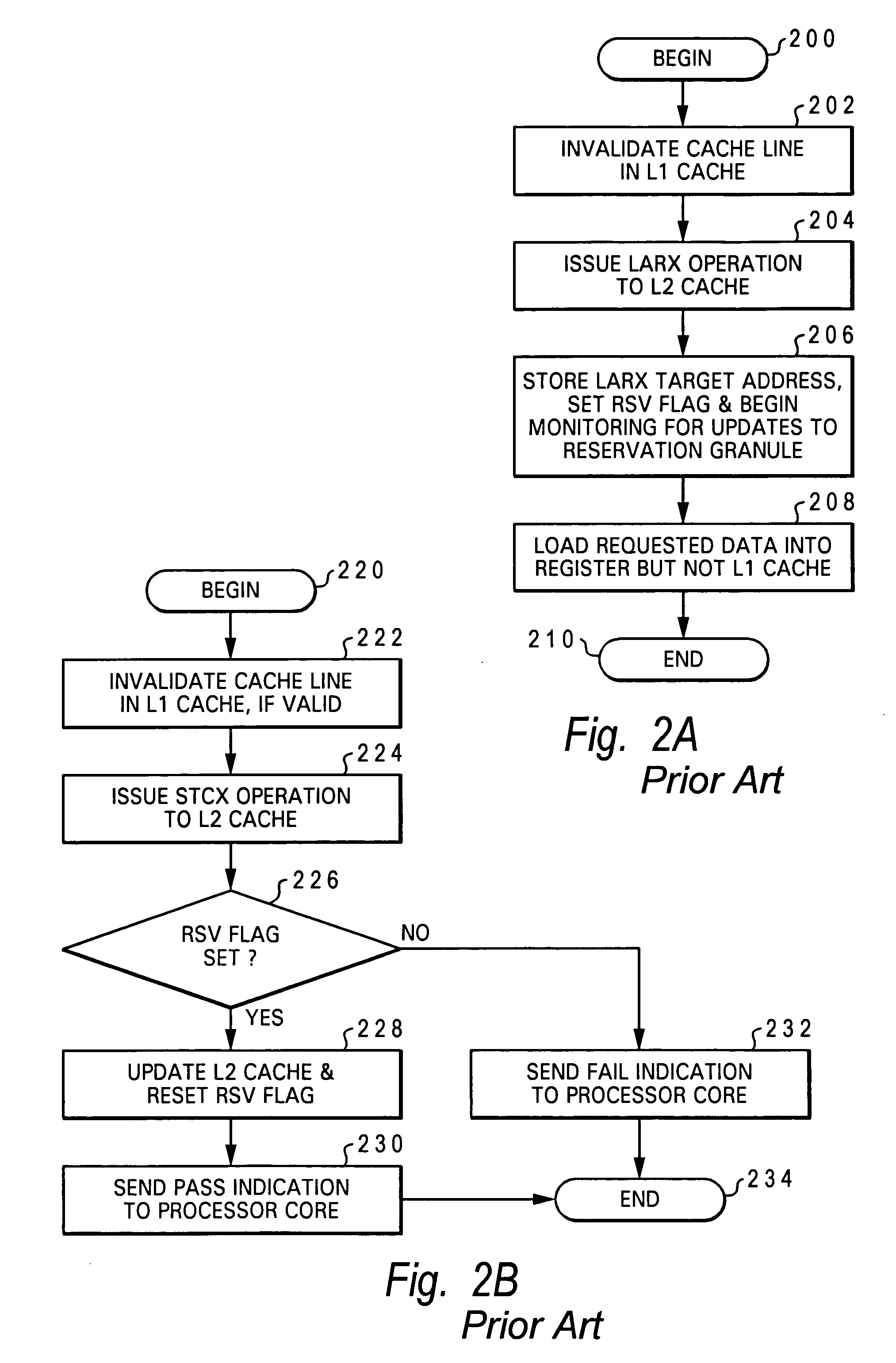
Processor, data processing system and method for synchronizing access to data in shared memory
InactiveUS20060085604A1Ease of executionDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsData processing systemMulti processor
A processing unit for a multiprocessor data processing system includes a processor core including a store-through upper level cache, an instruction sequencing unit that fetches instructions for execution, a data register, and at least one instruction execution unit coupled to the instruction sequencing unit that concurrently executes multiple threads of instructions. The processor core, responsive to the at least one instruction execution unit executing a load-reserve instruction in a first thread that binds to a load target address in the store-through upper level cache during a reservation hazard window associated with a conflicting store-conditional operation of a second thread, causes a subsequent store-conditional operation of the first thread to a store target address matching the load target address to fail if the store-conditional operation of the second thread succeeds.
Owner:IBM CORP
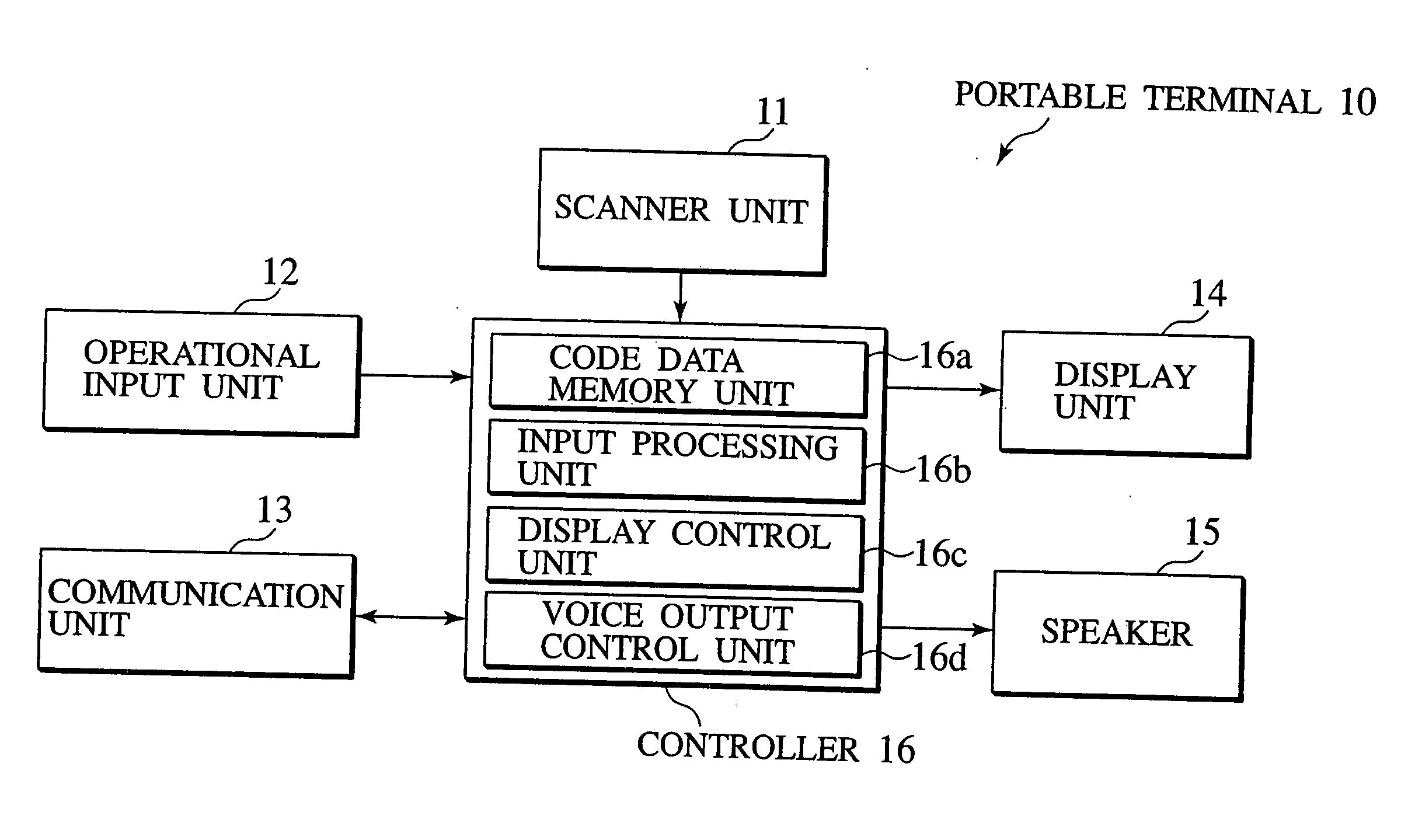
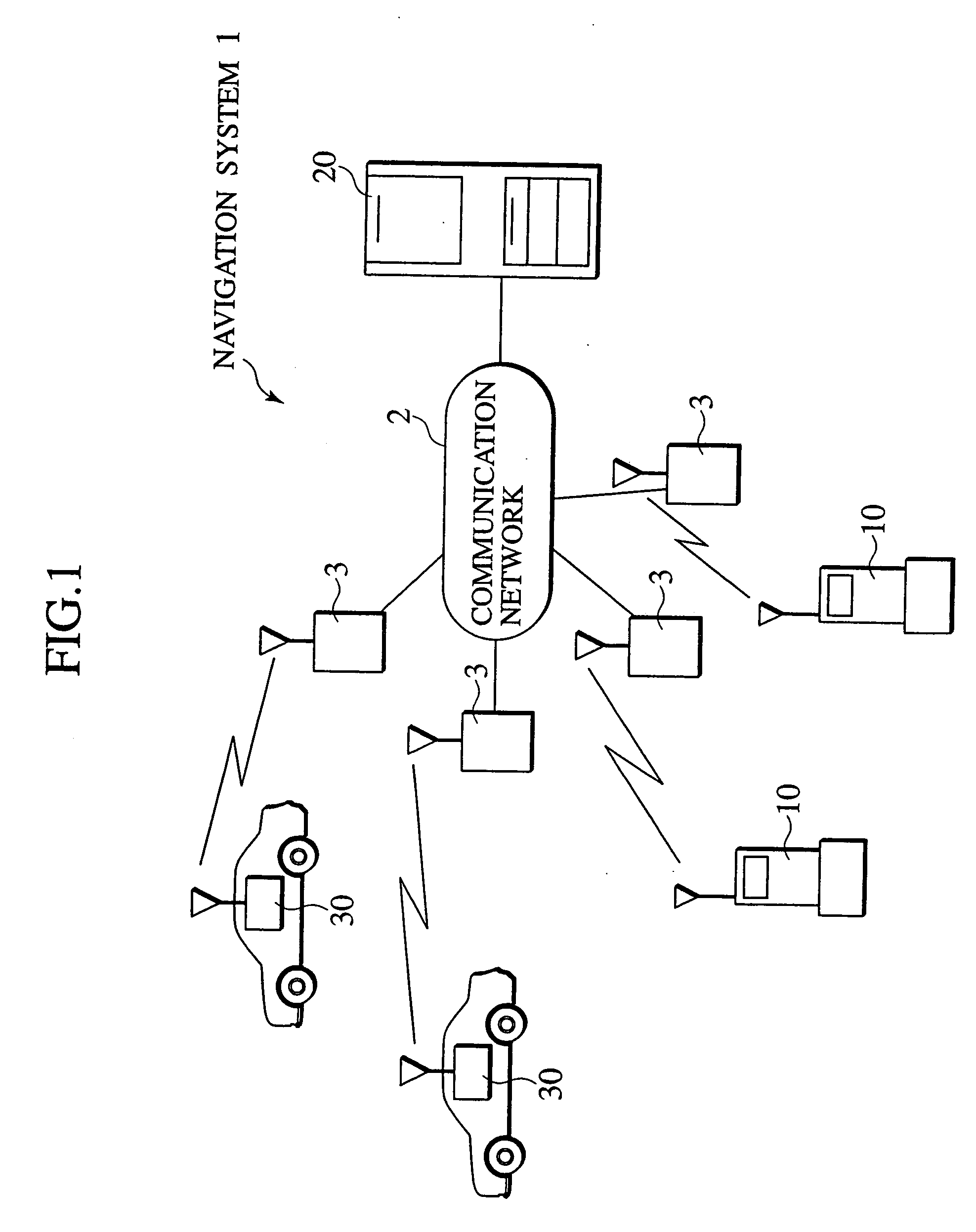
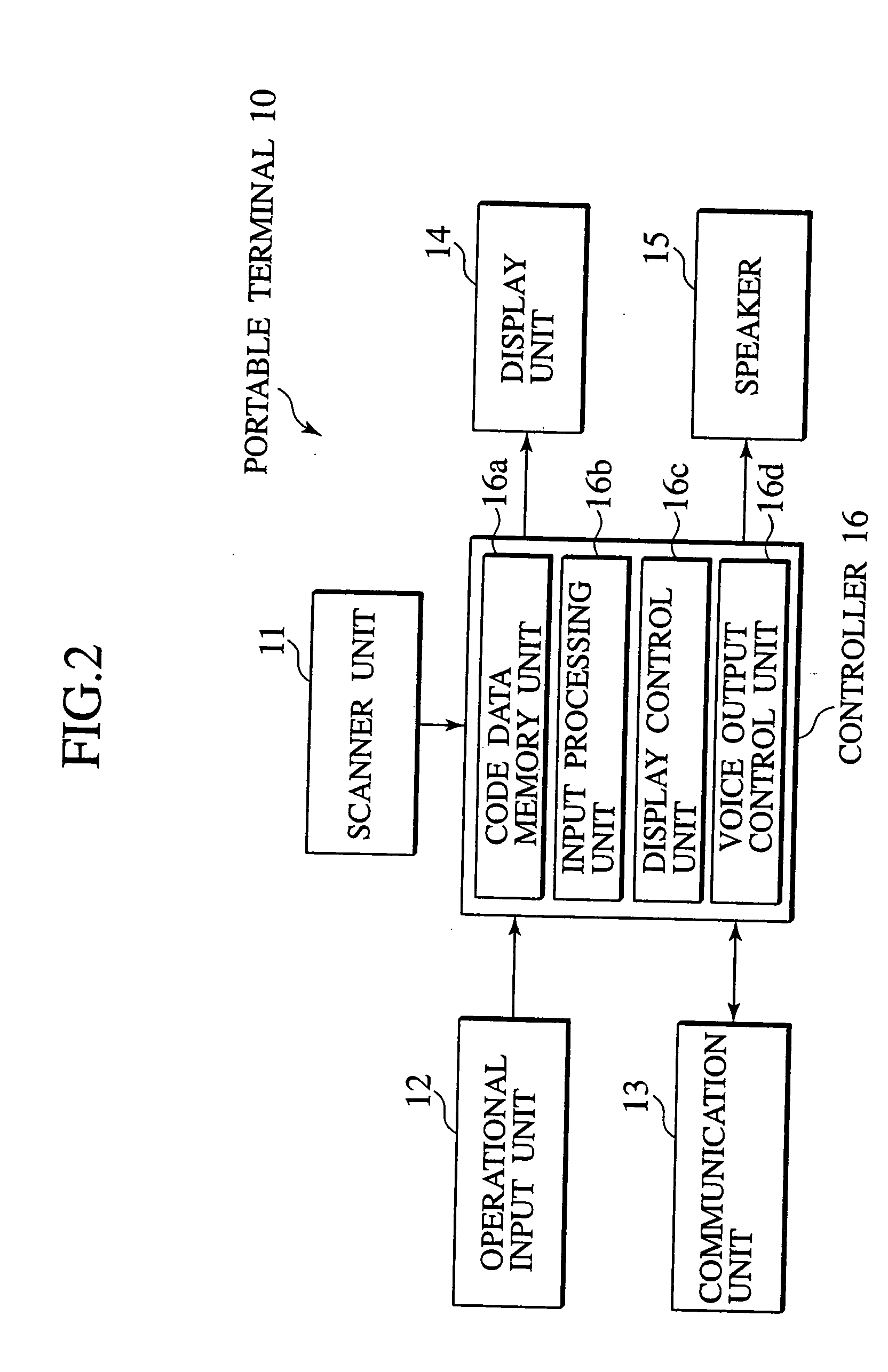
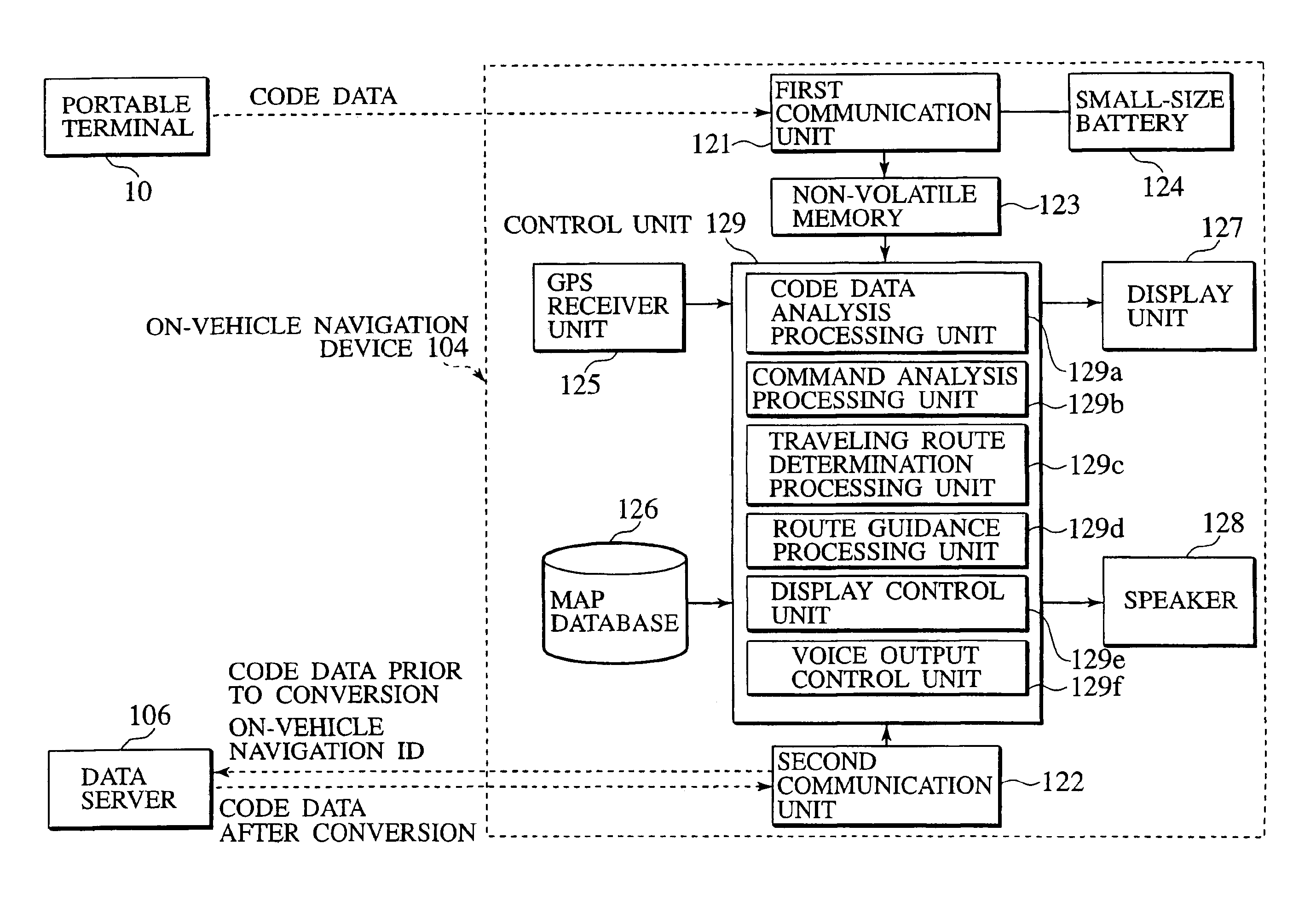
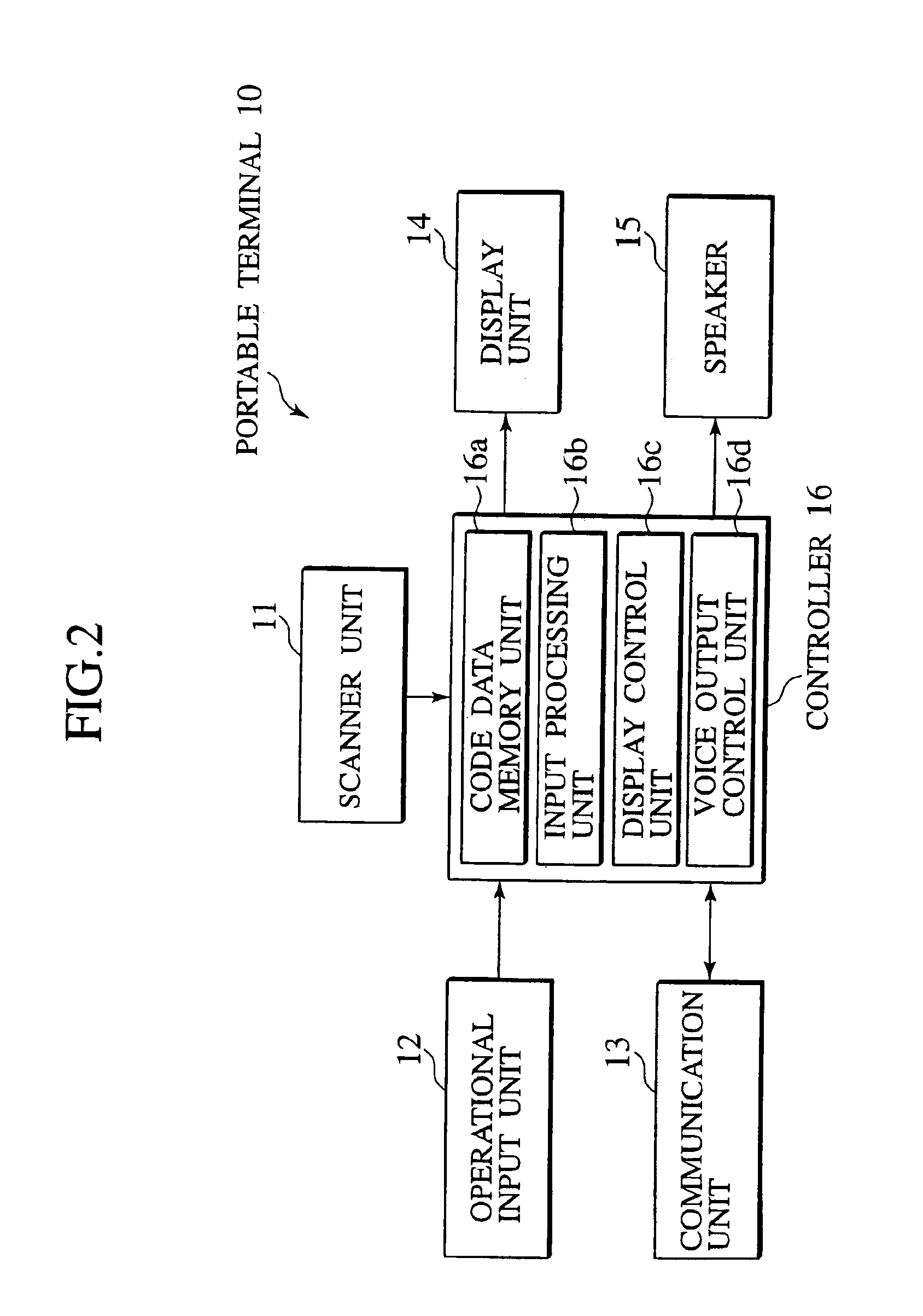
Navigation system, data server, traveling route establishing method and information providing method
InactiveUS20060009907A1Easy to useEase of executionInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlInformation processingNavigation system
A navigation system, portable information processing device and its control program, data server, information processing server, navigation method, traveling route establishing method, information providing method, and area information providing method are disclosed having a portable terminal (10,54,210) to read out code data, indicative of area information of a destination and routed spots, from a print product (112,114). The code data are converted into area information and stored in a storage unit (23,66,72, 123,223,232,323), from which particular area information is retrieved and transmitted to an on-vehicle navigation device (30,58,104,230) by which a traveling route of the vehicle is established on the basis of area information to guide the vehicle to the destination.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
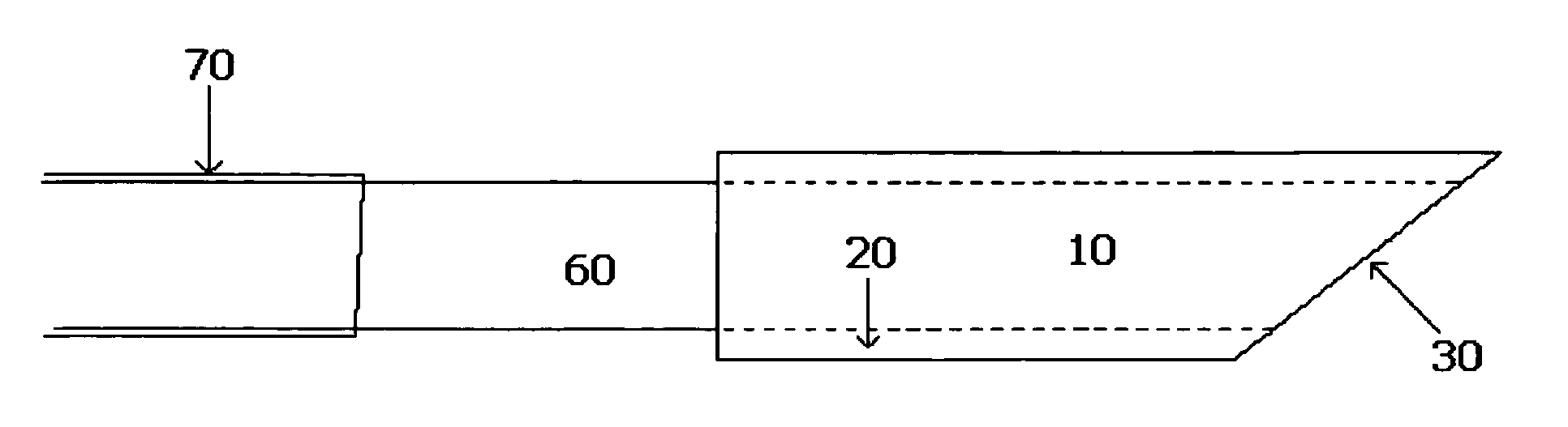
Sleeved optical fiber for reduced lateral loss and method for making the same
ActiveUS7447409B2Low costEase of executionCladded optical fibreSurgical instrument detailsFiberOptical fiber cable
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC +1
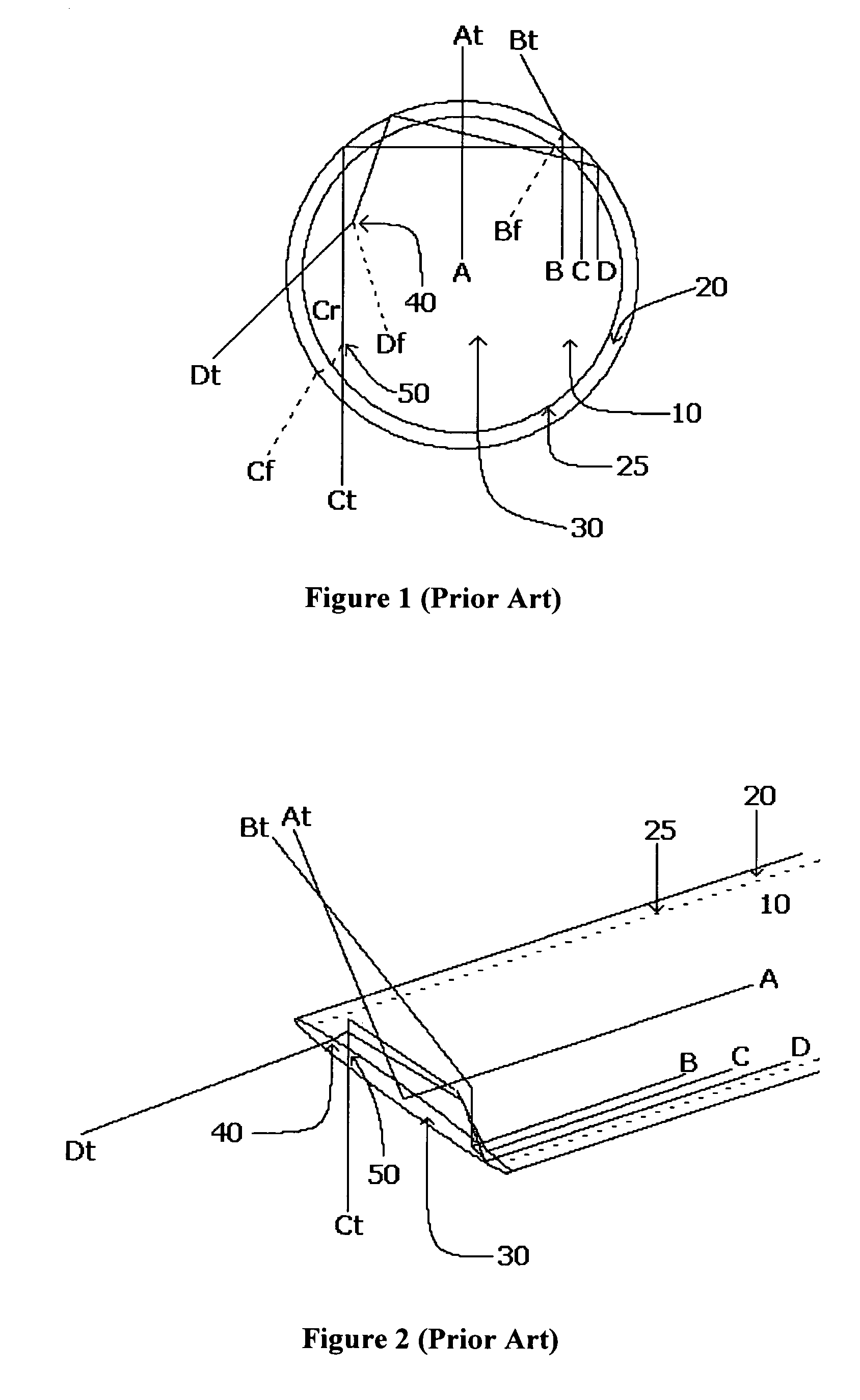
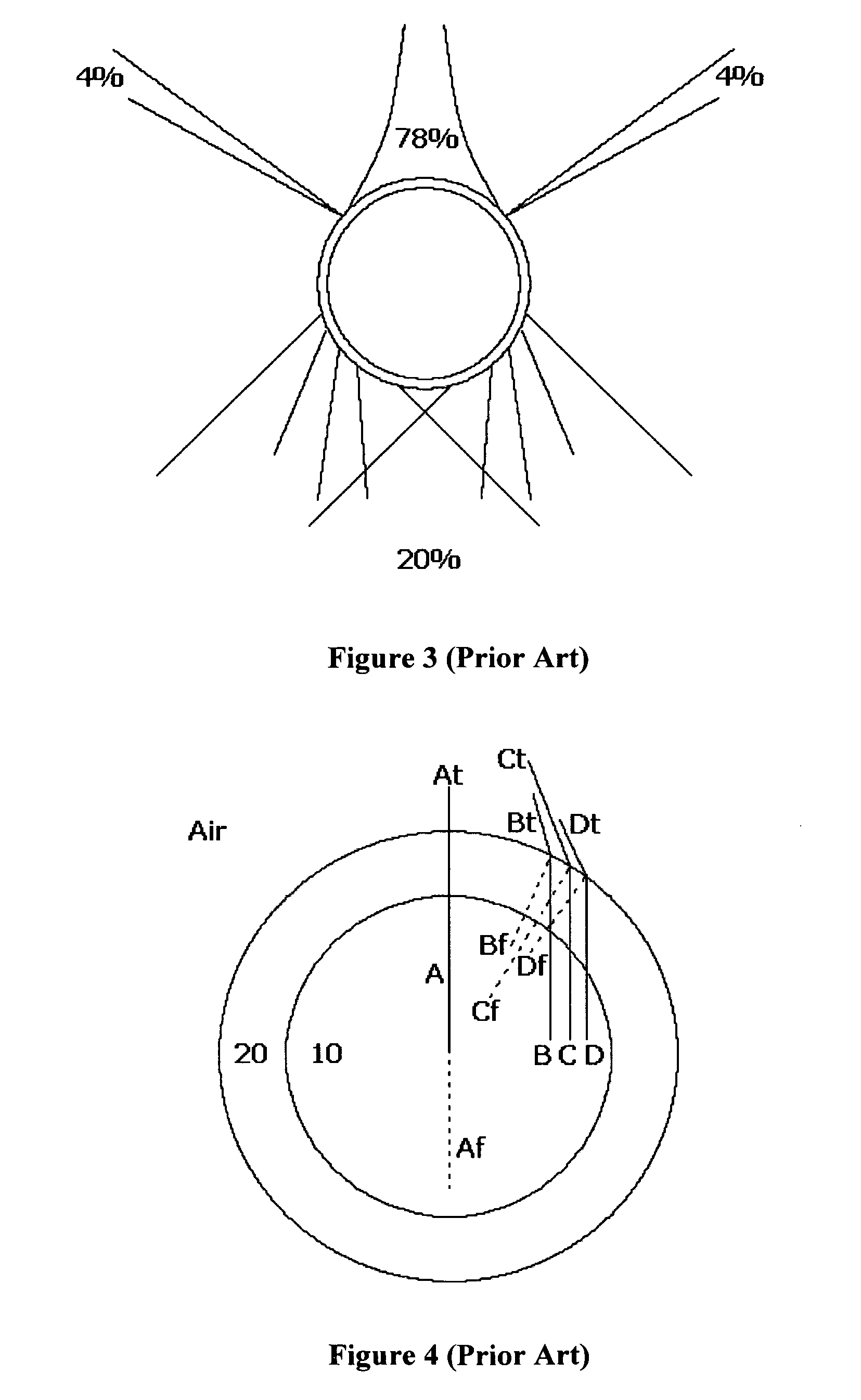
Specified object detection apparatus
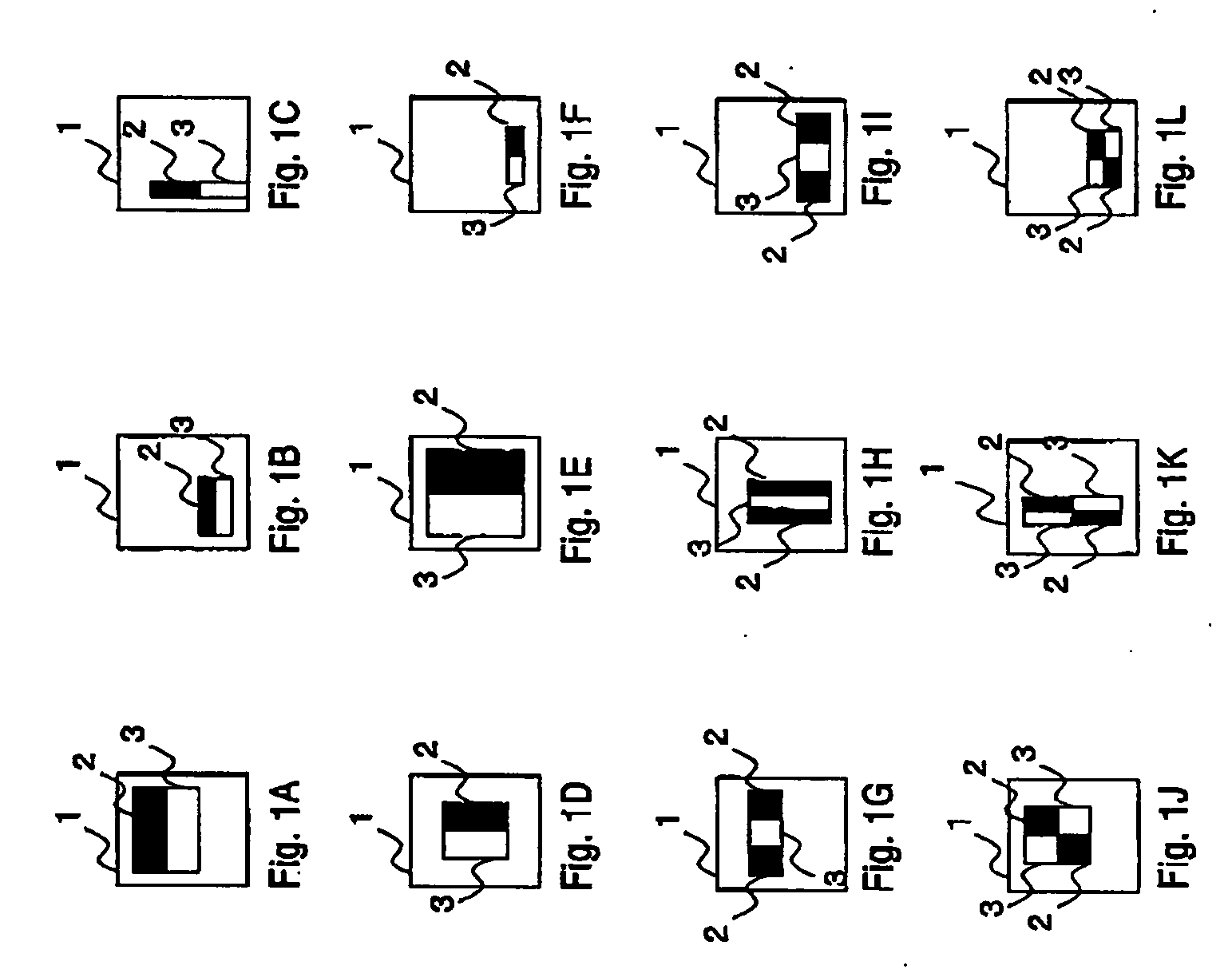
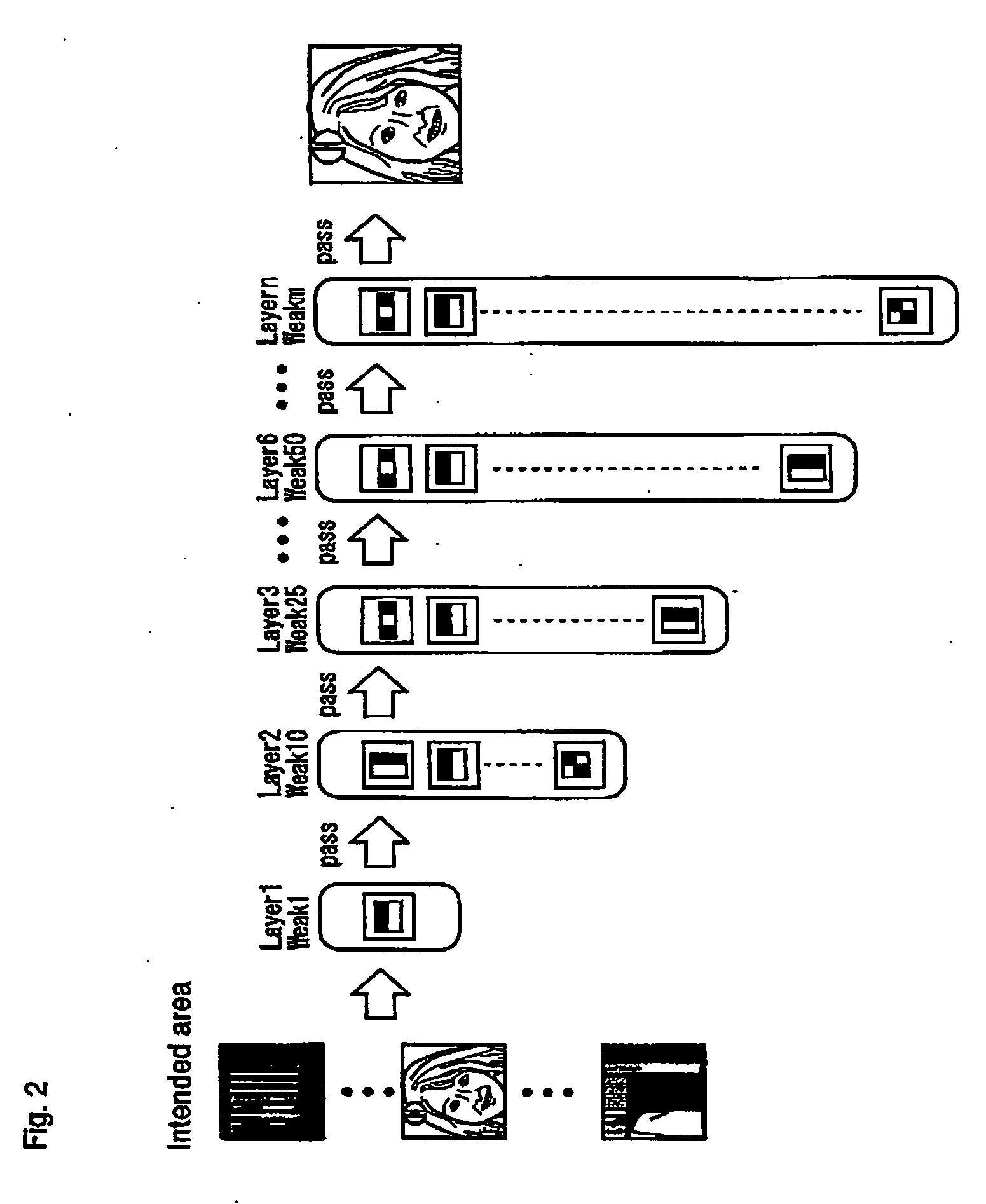
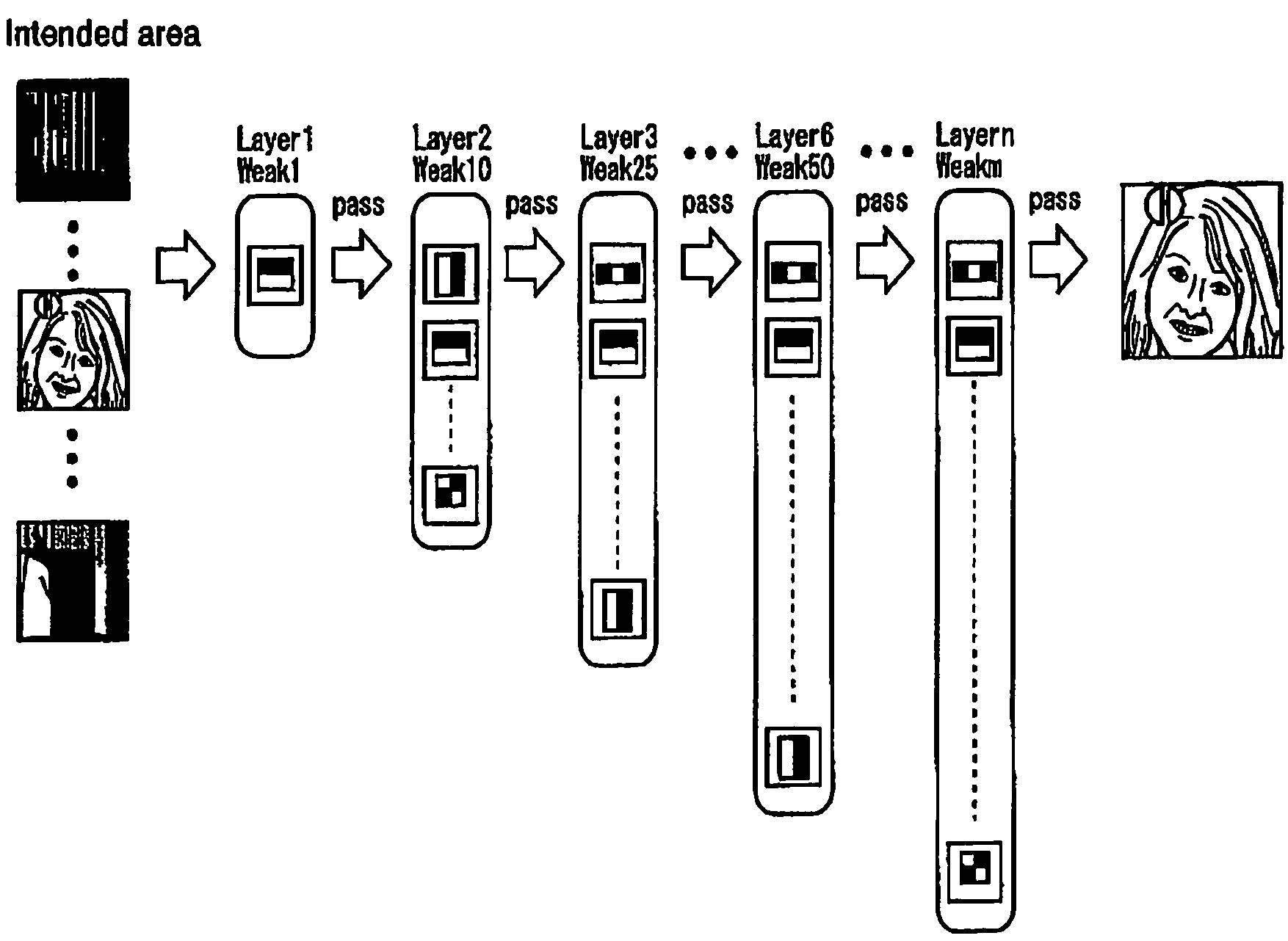
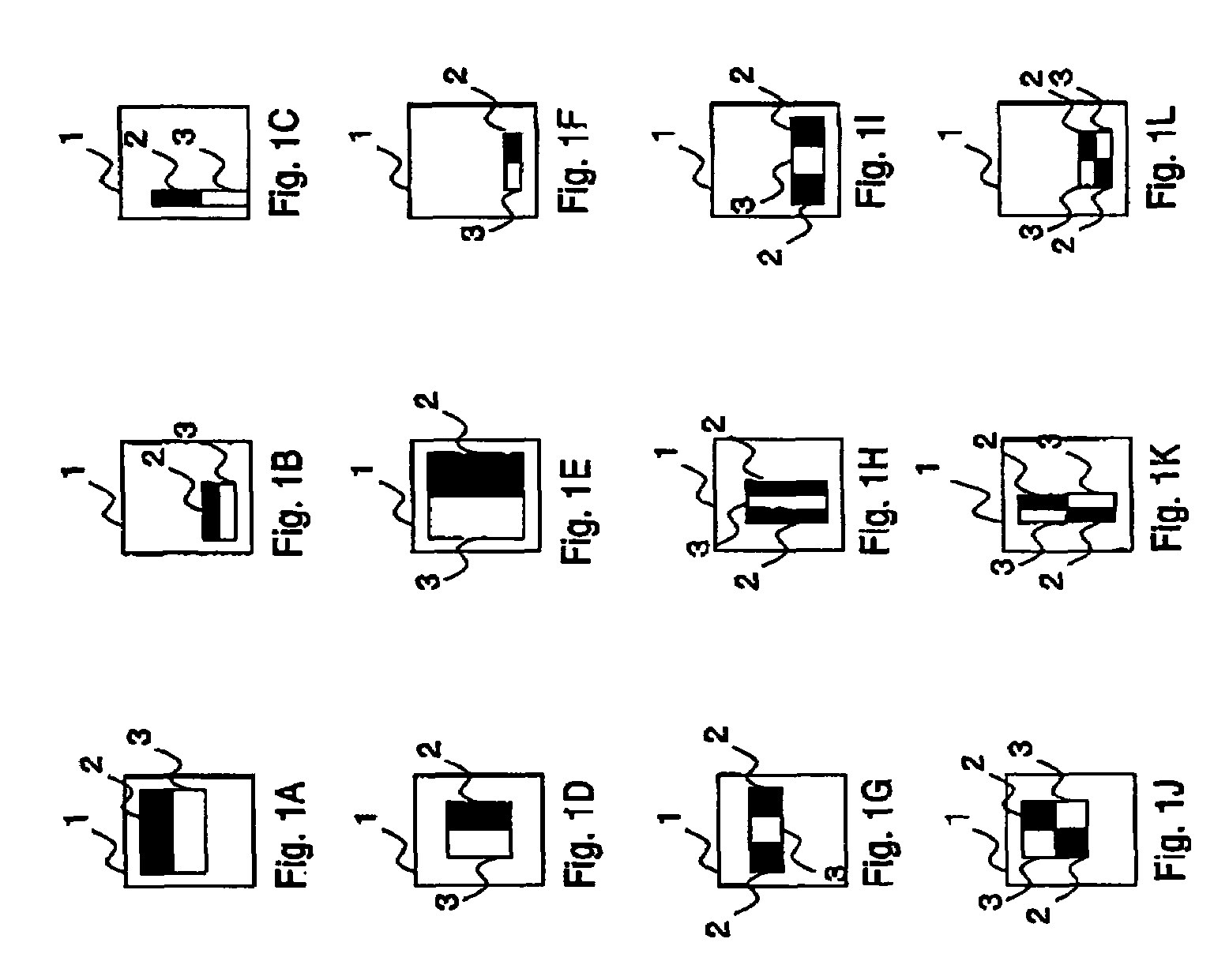
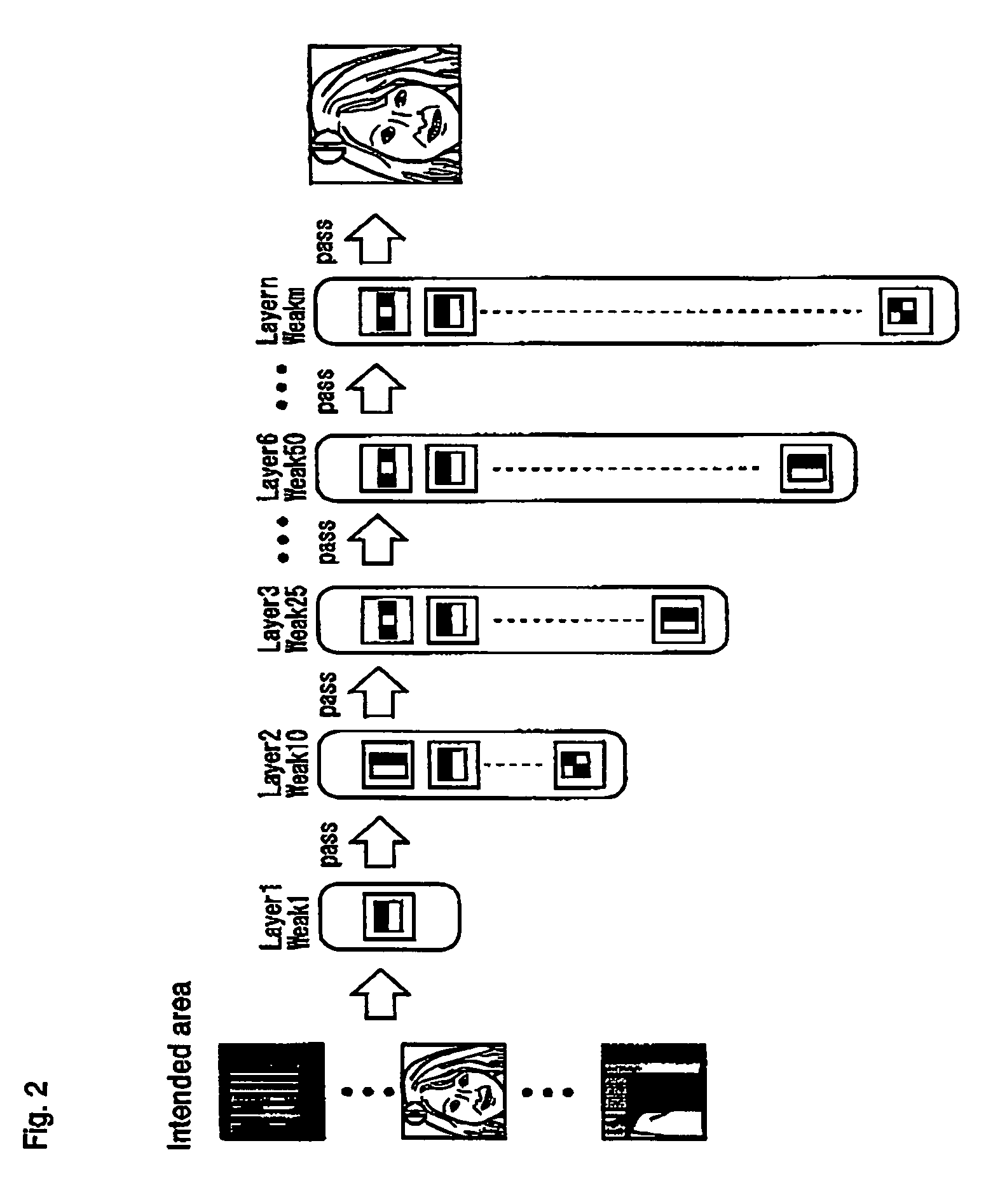
ActiveUS20050271245A1Accurate correspondenceAccurate judgmentTelevision system detailsImage analysisObject detectionProcessing accuracy
Unlike in the prior art in which the correspondence between a feature and a judgment value in an intended area is obtained by a single threshold value, the correspondence of the judgment value is obtained independently for each feature by use of a look-up table or the like. This makes it possible to achieve an accurate correspondence between the judgment value and the feature and thus to improve the high processing accuracy. Also, in the prior art, the judgment is repeated several times to secure the accuracy of the judgment and based on the total result thereof, the final judgment is made. Since the accuracy of each process is improved, however, the number of times the judgment is repeated is reduced for a higher processing speed.
Owner:ORMON CORP +1
System and method for improving backup performance of media and dynamic ready to transfer control mechanism
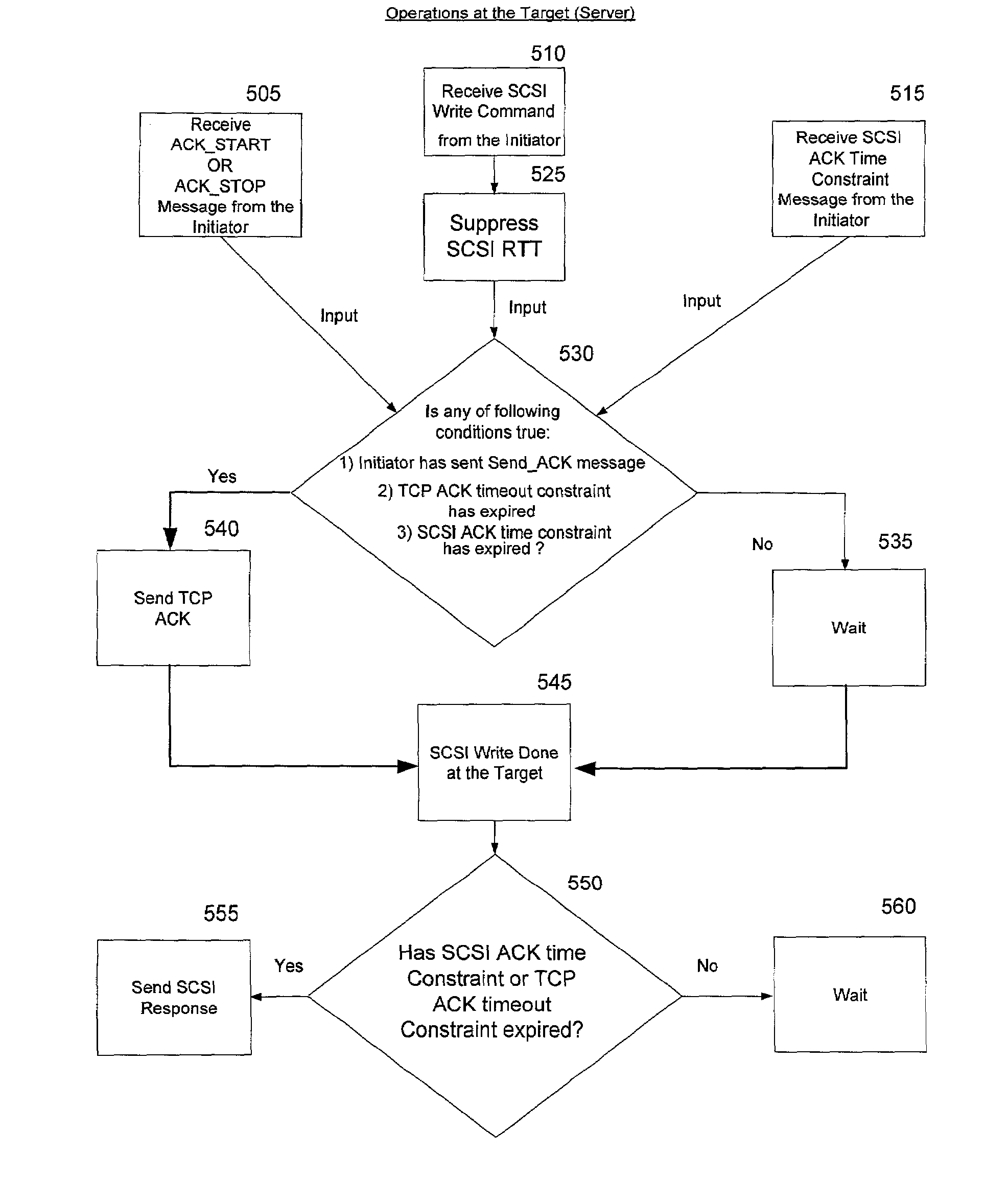
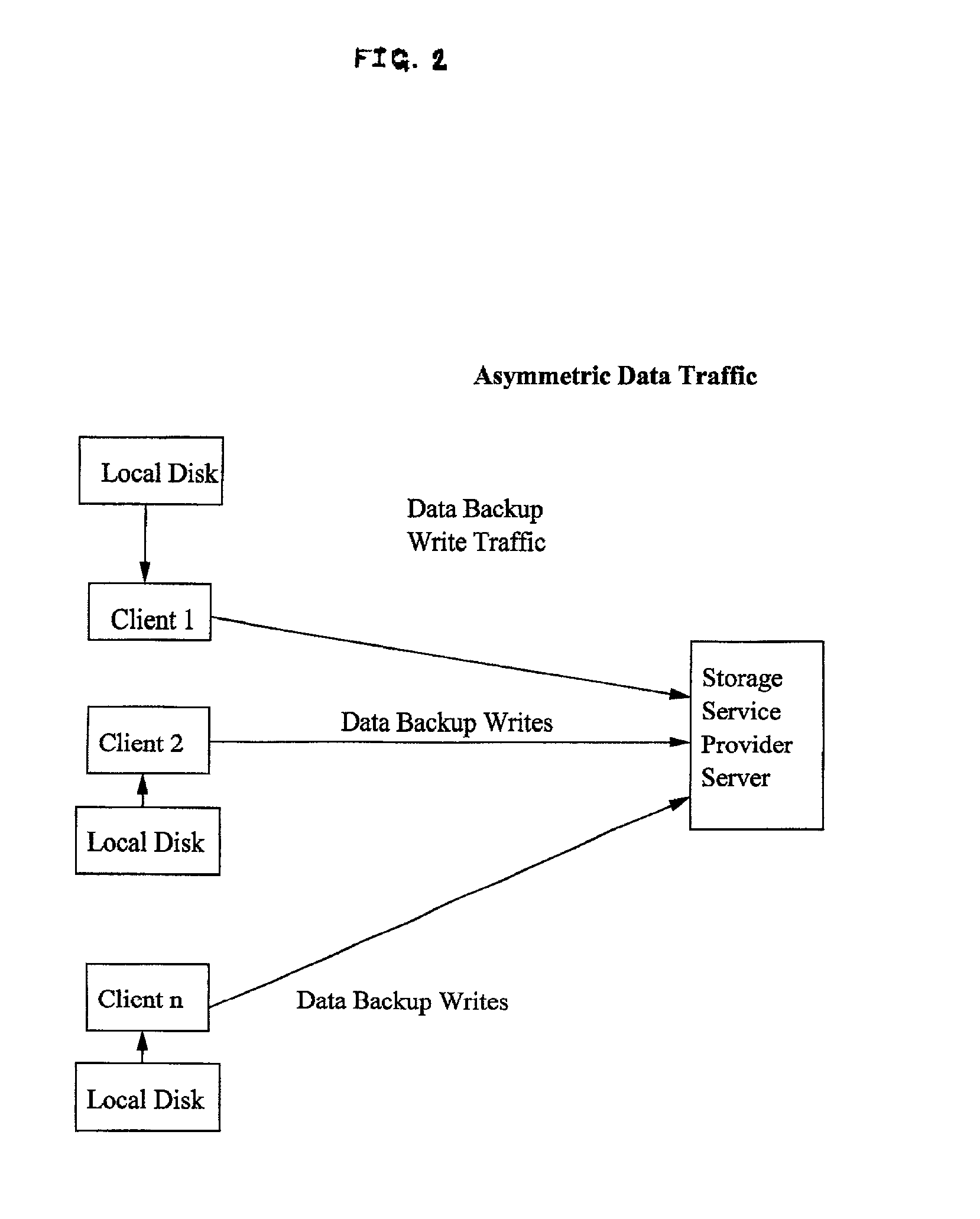
InactiveUS7197571B2Improve performancePrevent the target bufferError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacitySCSI
A system and method improve the performance of block storage over a network with asymmetric traffic by reducing the exchange of control messages between clients and servers. Before the source and the target begin exchanging data, they need to exchange control messages first to ensure the integrity of the data transfer operations. The acknowledgment messages affect the performance of backup operations when using a storage protocol such as SCSI over a reliable wide-area network protocol such as TCP / IP. SCSI protocol level and TCP / IP protocol level acknowledgment messages are combined to reduce CPU utilization at both the source and the target systems, which improves the overall system throughput and performance, and also reduces the bottleneck at the network level.
Owner:IBM CORP
Priority adjustment of dynamic random access memory (DRAM) transactions prior to issuing a per-bank refresh for reducing dram unavailability
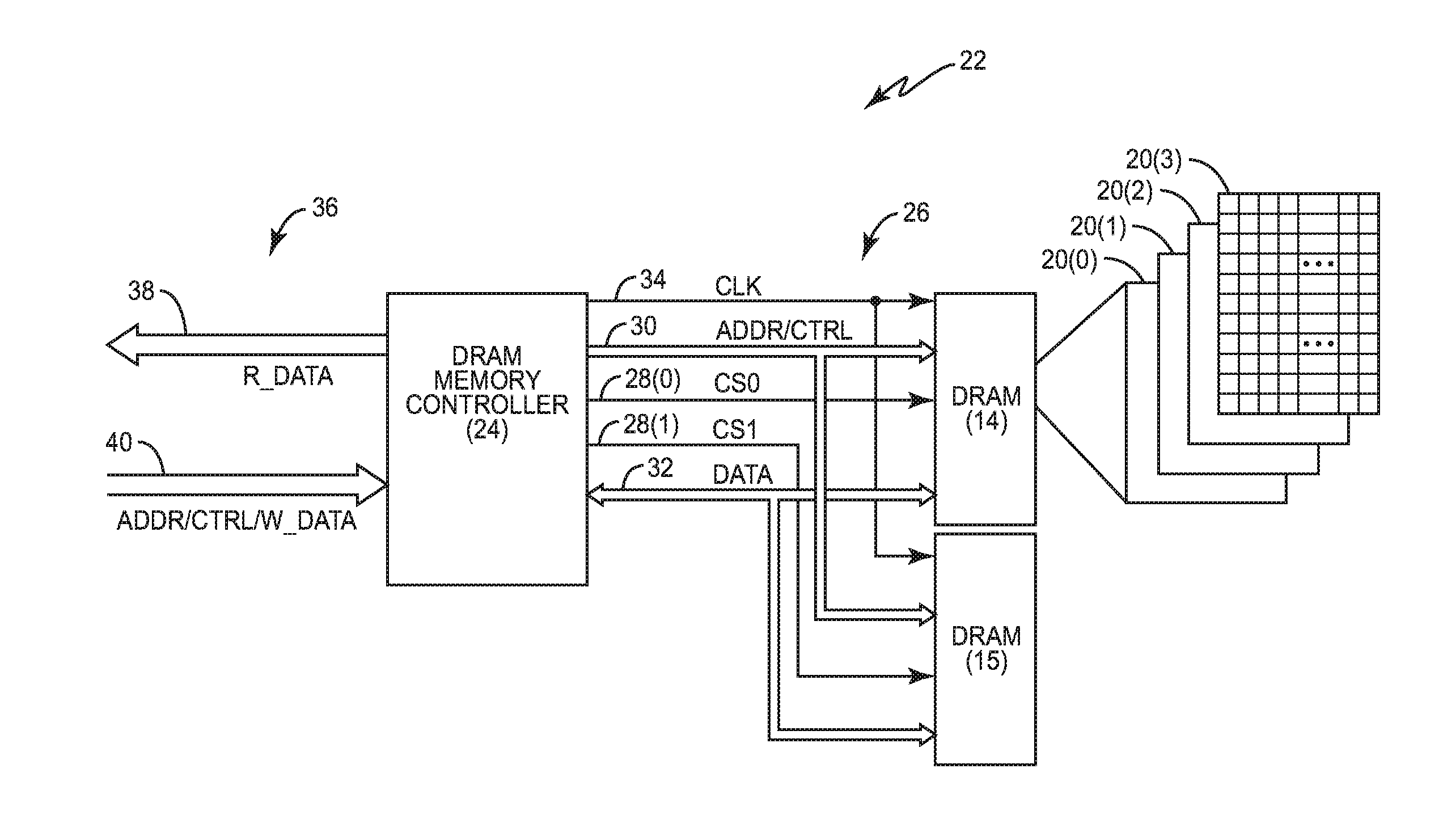
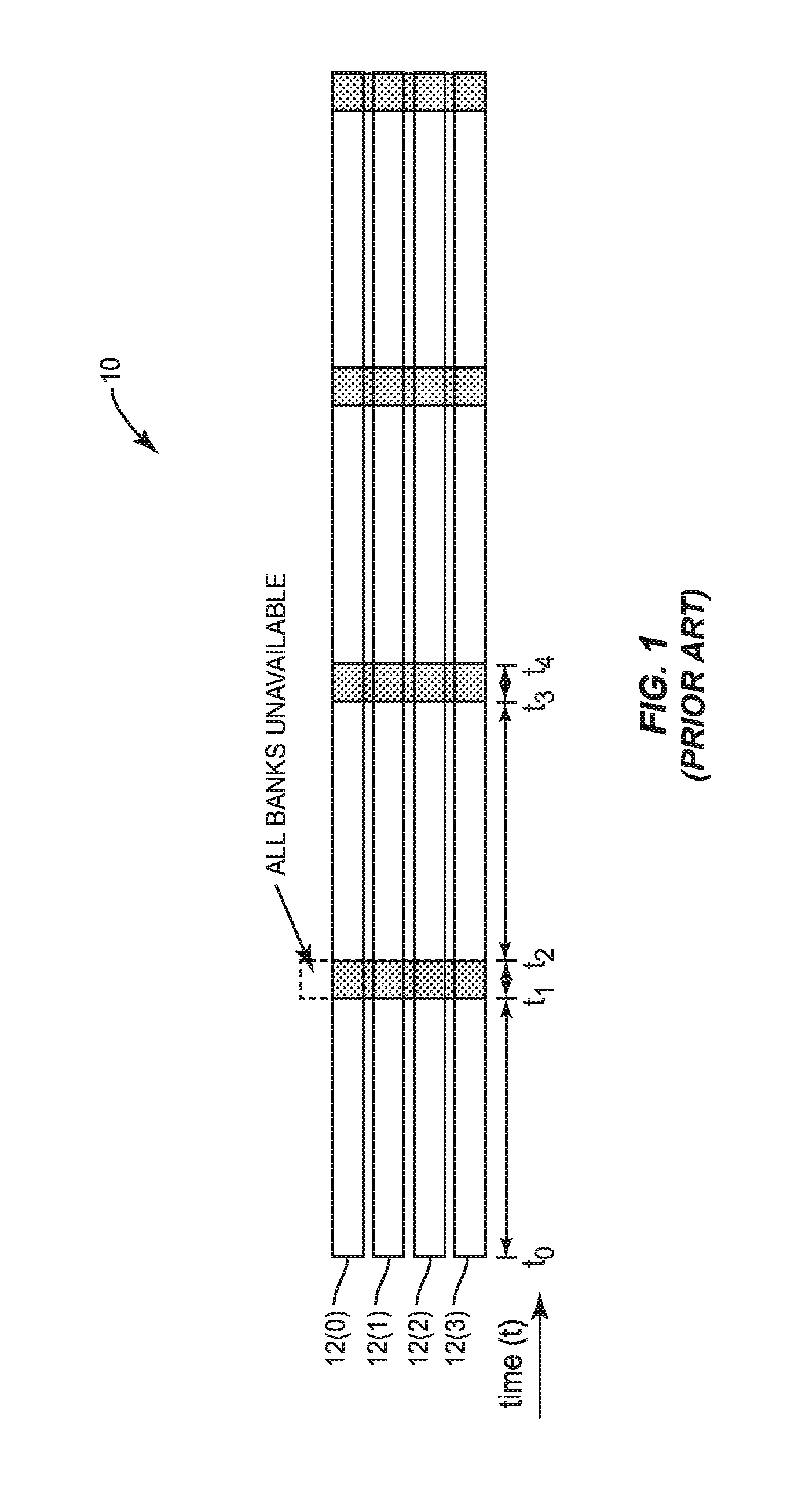
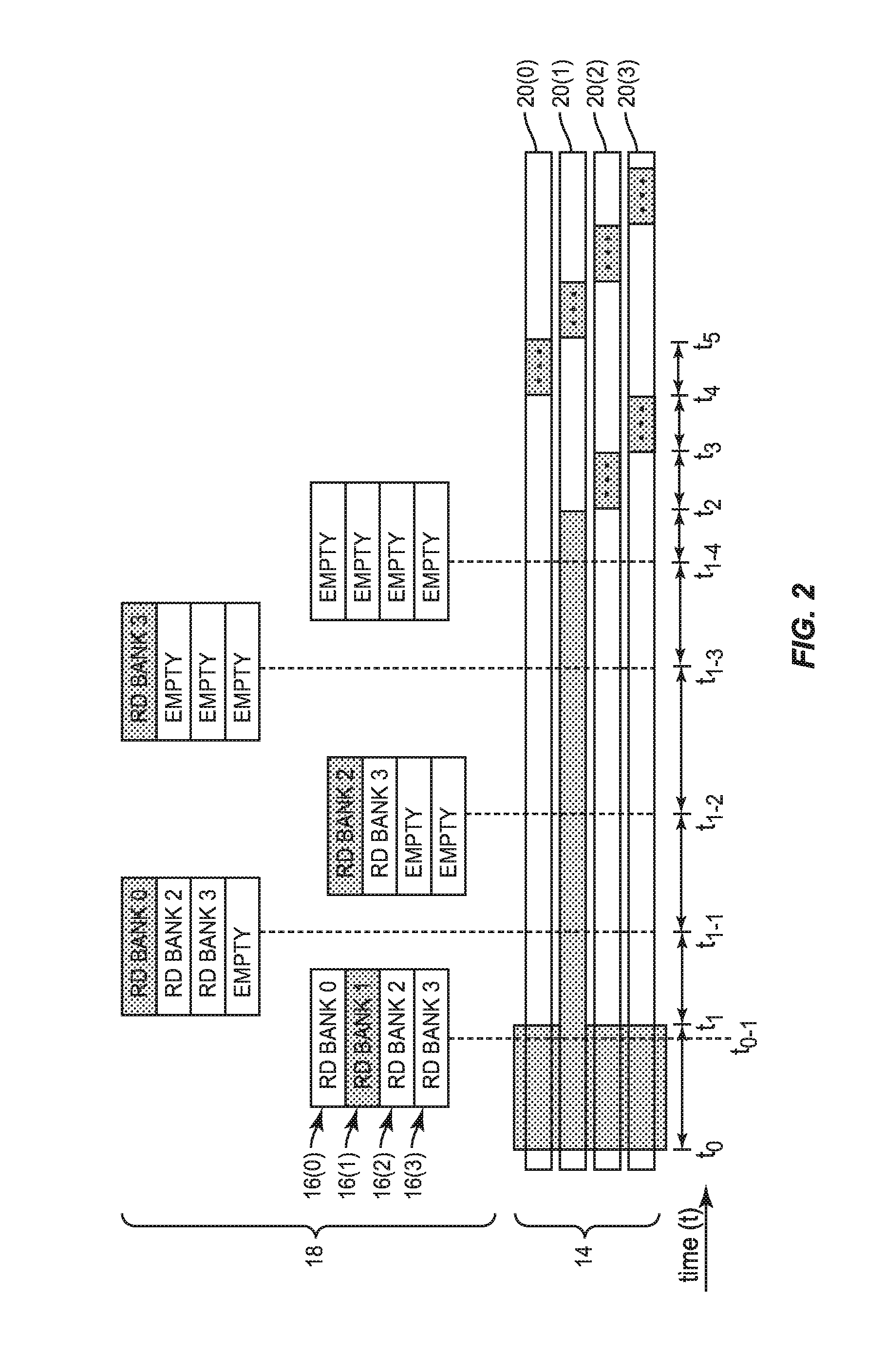
InactiveUS20150318035A1Reduce unavailabilityLow priorityDigital storageElectric digital data processingStatic random-access memoryMemory bank
Priority adjustment of dynamic random access memory (DRAM) transactions prior to issuing a per-bank refresh for reducing DRAM unavailability is disclosed. In one aspect, DRAM is refreshed on a per-bank basis. If a queued memory transaction corresponds to a memory bank that will soon be refreshed, the transaction may be delayed if a refresh of the corresponding memory bank begins prior to execution of the transaction. To avoid delaying execution of the transaction while waiting for the corresponding memory bank to be refreshed, a priority of the memory transactions may be adjusted based on a memory bank refresh schedule. The priority of the transaction corresponding to the memory bank to be refreshed may be increased, and the priority of other memory transactions may be decreased, if such an adjustment would avoid or reduce delaying execution due to unavailability of the corresponding memory bank.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Navigation system, data server, traveling route establishing method and information providing method
InactiveUS6937934B2Easy to operateImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlInformation processingNavigation system
A navigation system, portable information processing device and its control program, data server, information processing server, navigation method, traveling route establishing method, information providing method, and area information providing method are disclosed having a portable terminal (10,54,210) to read out code data, indicative of area information of a destination and routed spots, from a print product (112,114). The code data are converted into area information and stored in a storage unit (23,66,72,123,223,232,323), from which particular area information is retrieved and transmitted to an on-vehicle navigation device (30,58,104,230) by which a traveling route of the vehicle is established on the basis of area information to guide the vehicle to the destination.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
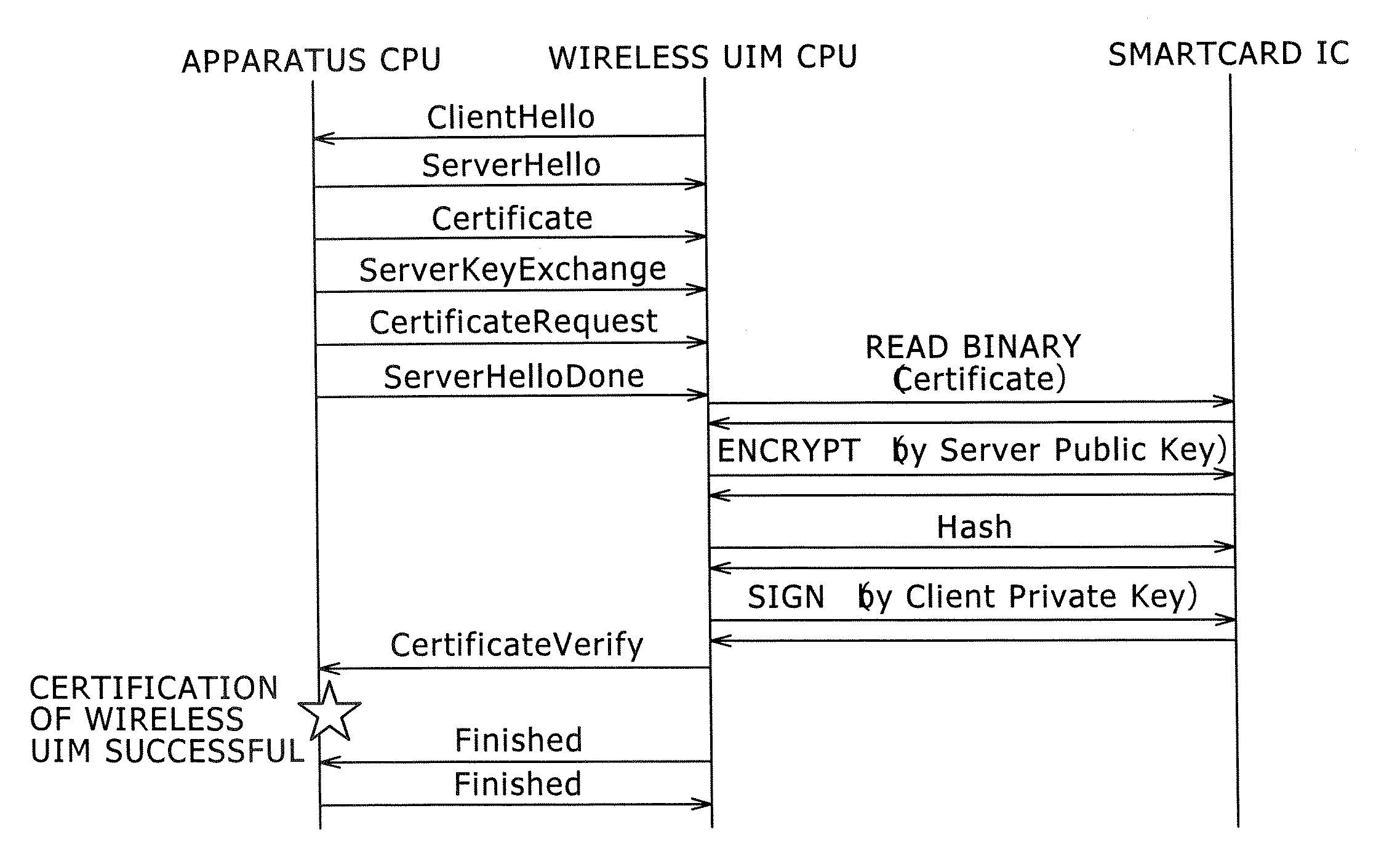
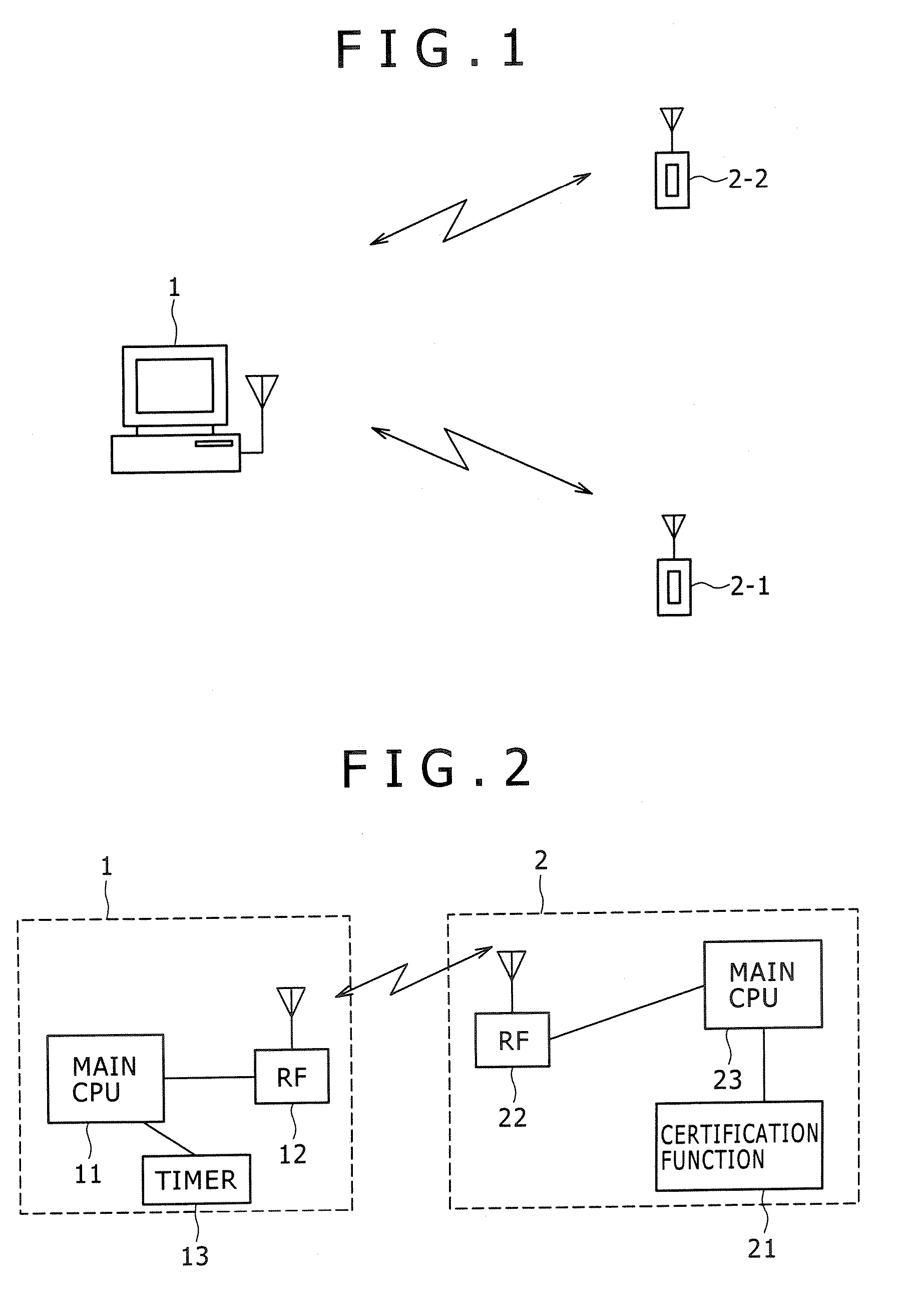
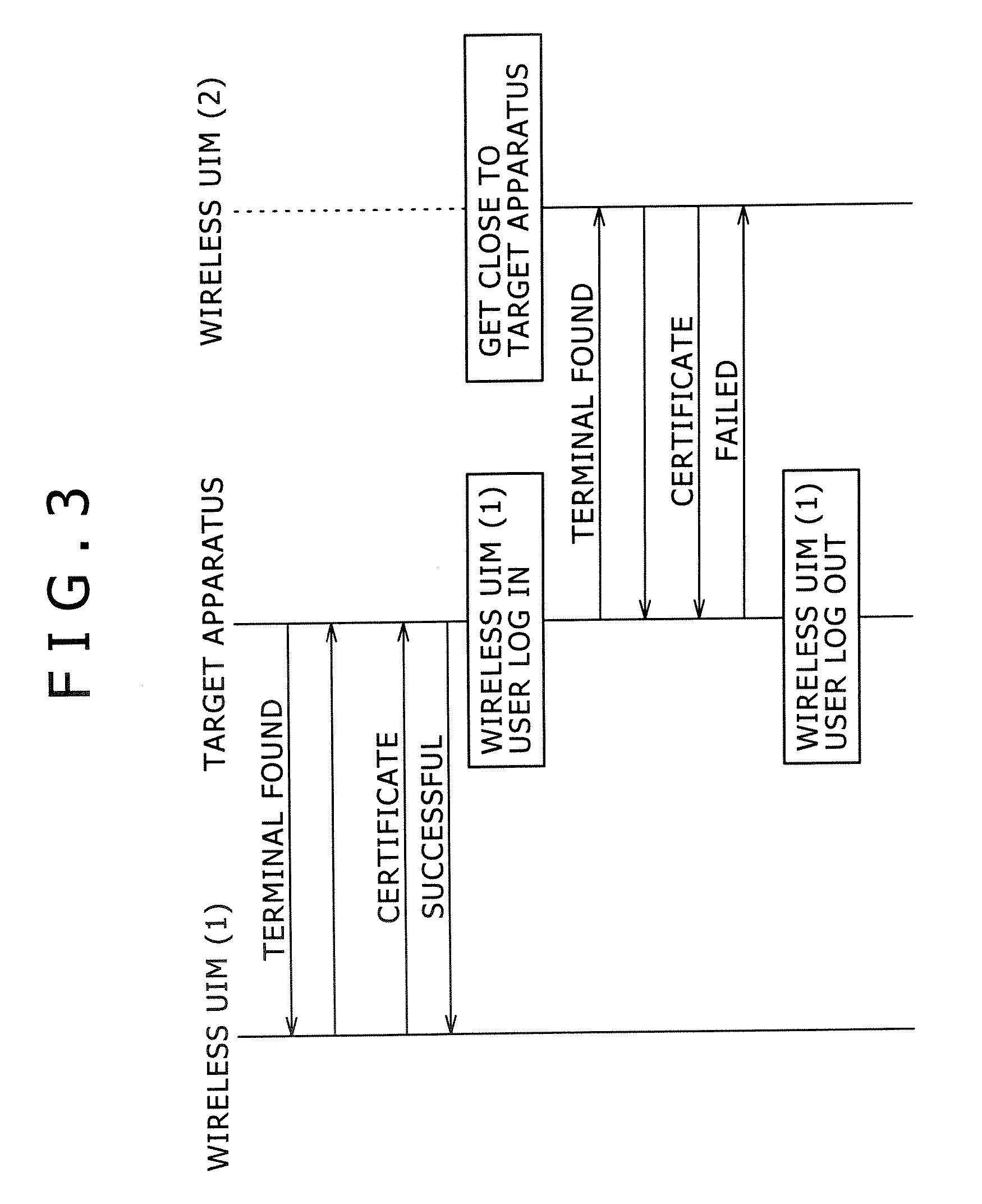
Target apparatus, certification device, and certification method
InactiveUS20070043950A1Improve user friendlinessReduce necessityUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationEngineering
Owner:SONY CORP
Intubation laryngoscope with two-sided blade
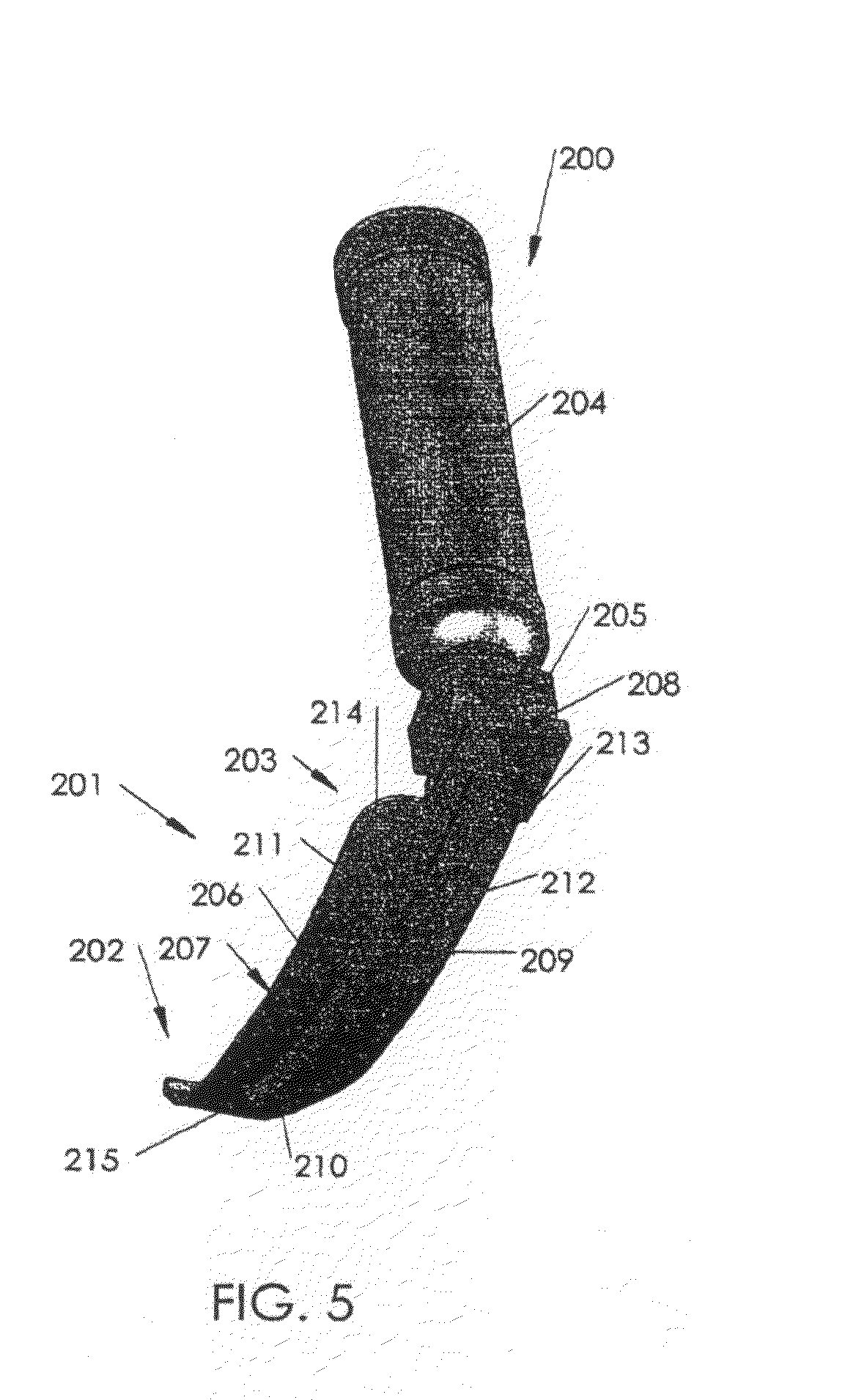
InactiveUS20100004514A1Improve abilitiesEase of executionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesTracheal tubeCatheter
Intubation laryngoscope comprises blade (201) including upper elongated part (206) and lower longitudinal part (211) disposed below upper elongated part (206) between its left (207) and right (209) edges. Lower longitudinal part (211) along with a right portion of upper elongated part (206) form right passageway (213), and lower longitudinal part (211) along with a left portion of upper elongated part (206) form left passageway (214). This allows both the right-handed operation using right-passageway (213) for the advancement of endotracheal tube, while left passageway (214) can be used for arrangement of an oxygenation tube, suction tube or endoscope probe, and the left-handed operation using left passageway (214) for the advancement of endotracheal tube, while right passageway (213) can be used for the arrangement of mentioned auxiliary means.
Owner:M S VISION
Specified object detection apparatus
ActiveUS7457432B2Improve accuracyJudge more accuratelyTelevision system detailsImage analysisAlgorithmData mining
Unlike in the prior art in which the correspondence between a feature and a judgment value in an intended area is obtained by a single threshold value, the correspondence of the judgment value is obtained independently for each feature by use of a look-up table or the like. This makes it possible to achieve an accurate correspondence between the judgment value and the feature and thus to improve the high processing accuracy. Also, in the prior art, the judgment is repeated several times to secure the accuracy of the judgment and based on the total result thereof, the final judgment is made. Since the accuracy of each process is improved, however, the number of times the judgment is repeated is reduced for a higher processing speed.
Owner:ORMON CORP +1
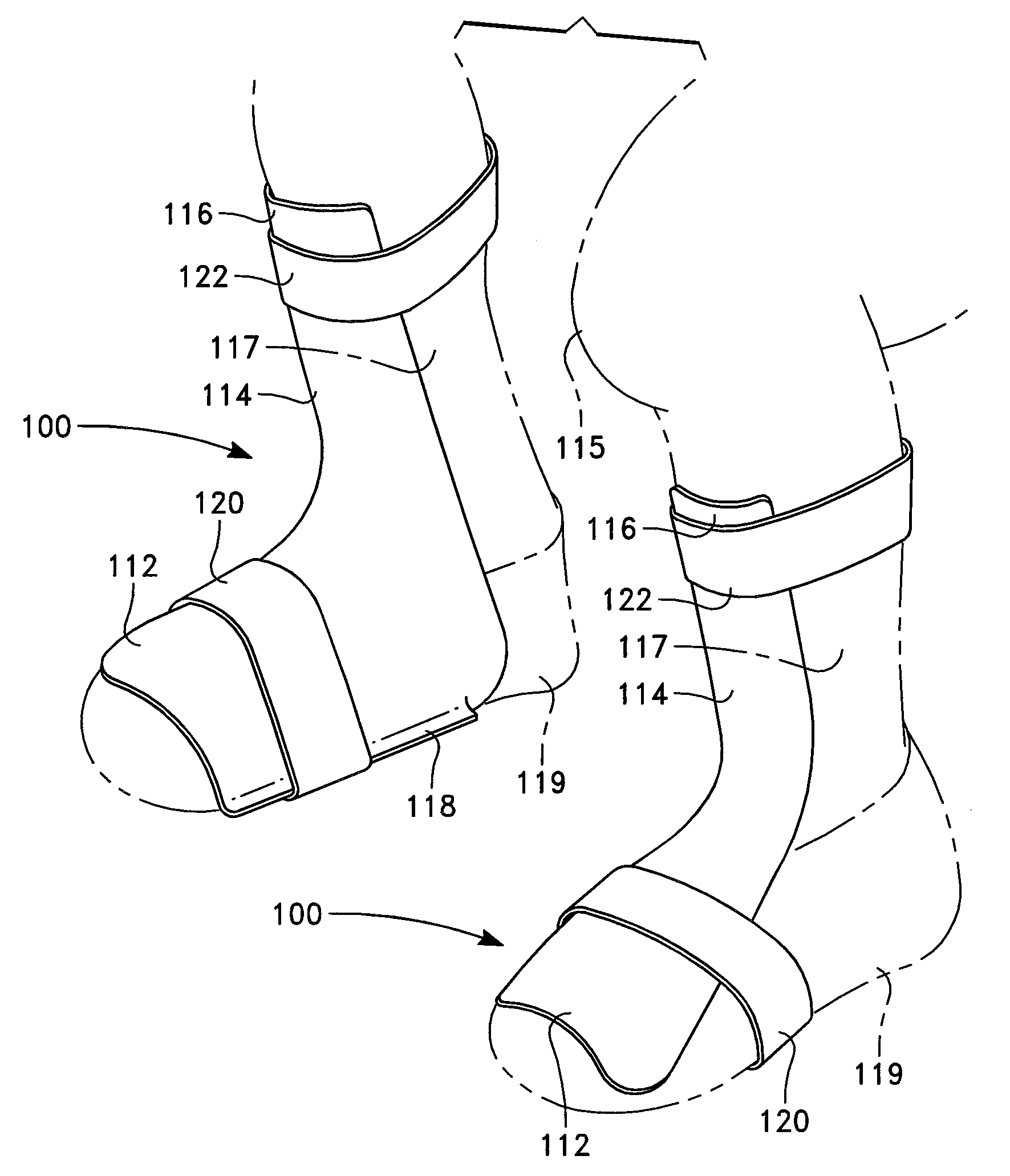
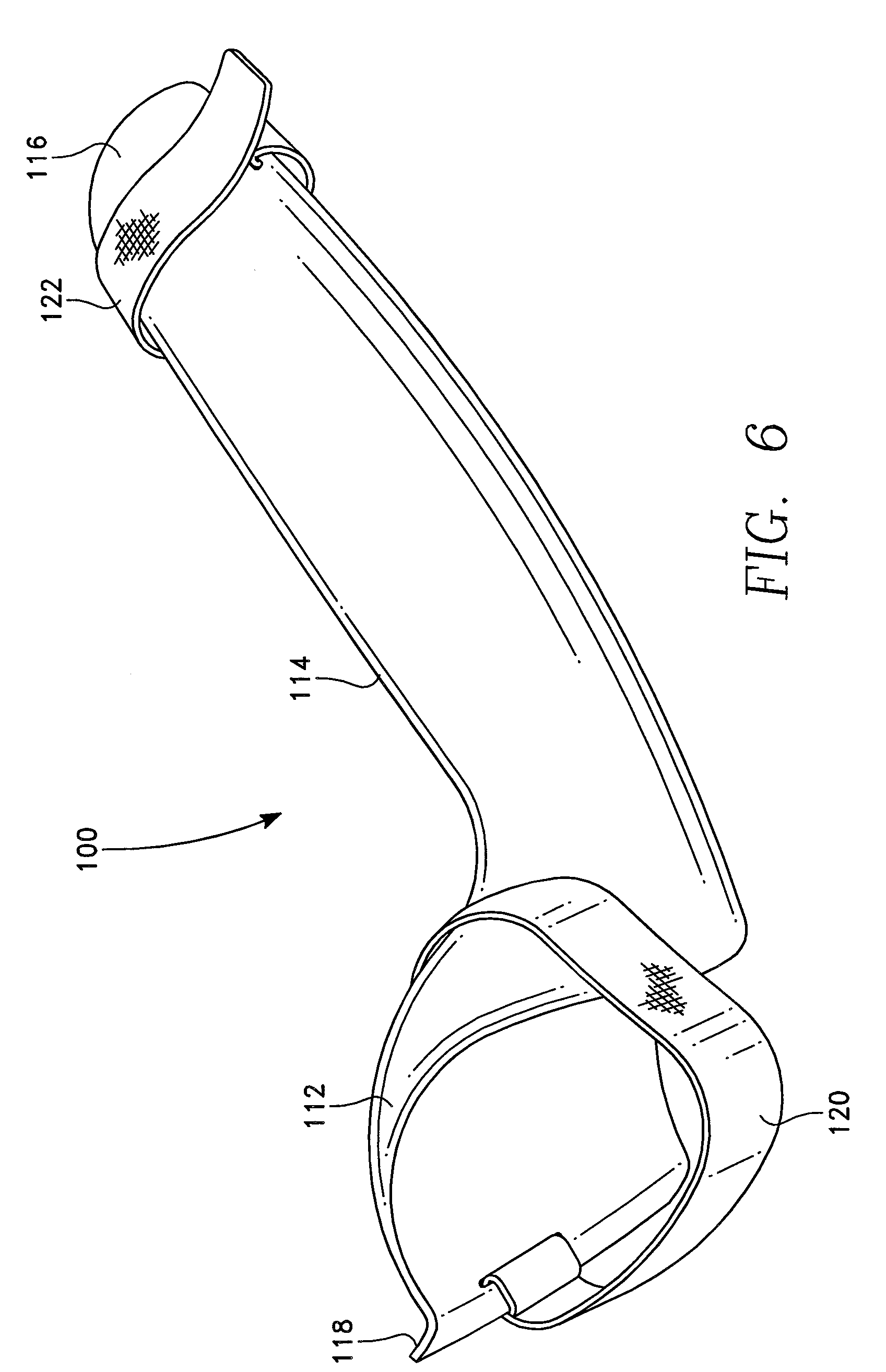
Squat and Lunge Training Device
InactiveUS20100274166A1Improve securityEasily employedGymnastic exercisingNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A device which restricts movement of the knee during lunge and squatting exercises prevents weight imbalance which may result in undue strain and knee injury. The device has a foot engagement member which is either stepped upon by the user and held in place by the user's weight, or the foot engagement member conforms to the side of the user's foot and is held in place by a strap or other means. Attached to the foot engagement is a vertical member which extends upwardly from the foot engagement member. A shin engagement member attached to the vertical member. The shin engagement member is generally positioned in a position along the lower leg of the user, below the knee and laterally adjacent to the user's tibia. As the user does a lunge, squat, or similar exercise, the shin engagement member prevents the user's knees from forward movement which extends forward of the user's feet. The device also has structure which prevents inward collapse of the knees during the exercise.
Owner:TERRIO TIMOTHY
Drug delivery implant implanted into bone
Disclosed is a drug delivery implant implanted into a bone. The drug delivery implant includes an implant fixture provided with an inlet formed at the upper end thereof and a drug supply cartridge coupled to the fixture, the drug supply cartridge includes a cap to close the inlet of the fixture and a cartridge main body provided under the cap, coupled with the cap and accommodated in the fixture to release a drug, and a cartridge hole to accommodate the cartridge main body and drug channels to guide the drug released from the inside of the cartridge main body to the outside of the fixture are formed in the fixture. The drug delivery implant may continuously administer the drug into bone tissues and mount the drug cartridge together with the cap in the fixture, thus facilitating mount of the drug cartridge in the fixture and replacement of the drug cartridge.
Owner:UNIV IND COOP GRP OF KYUNG HEE UNIV
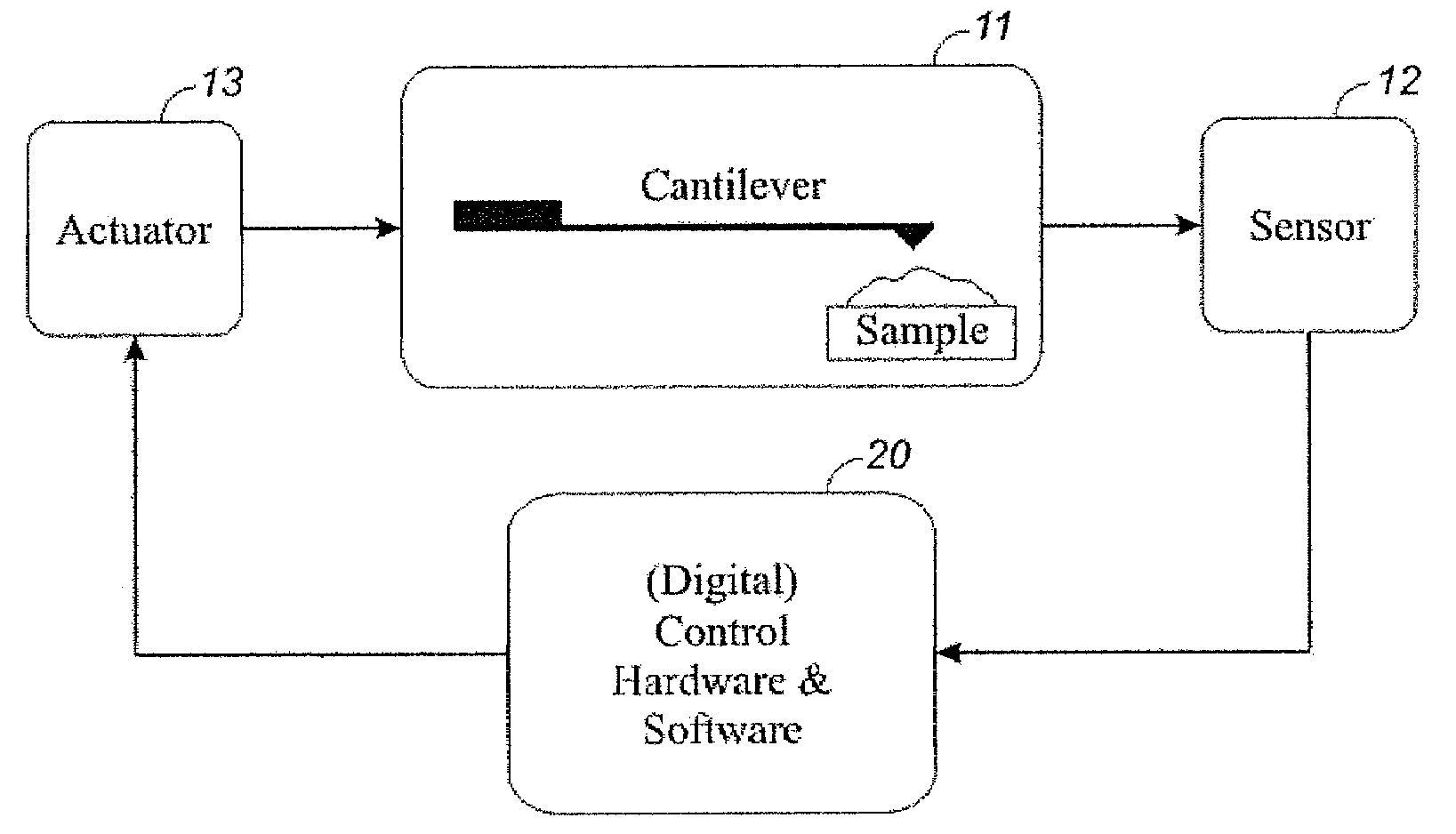
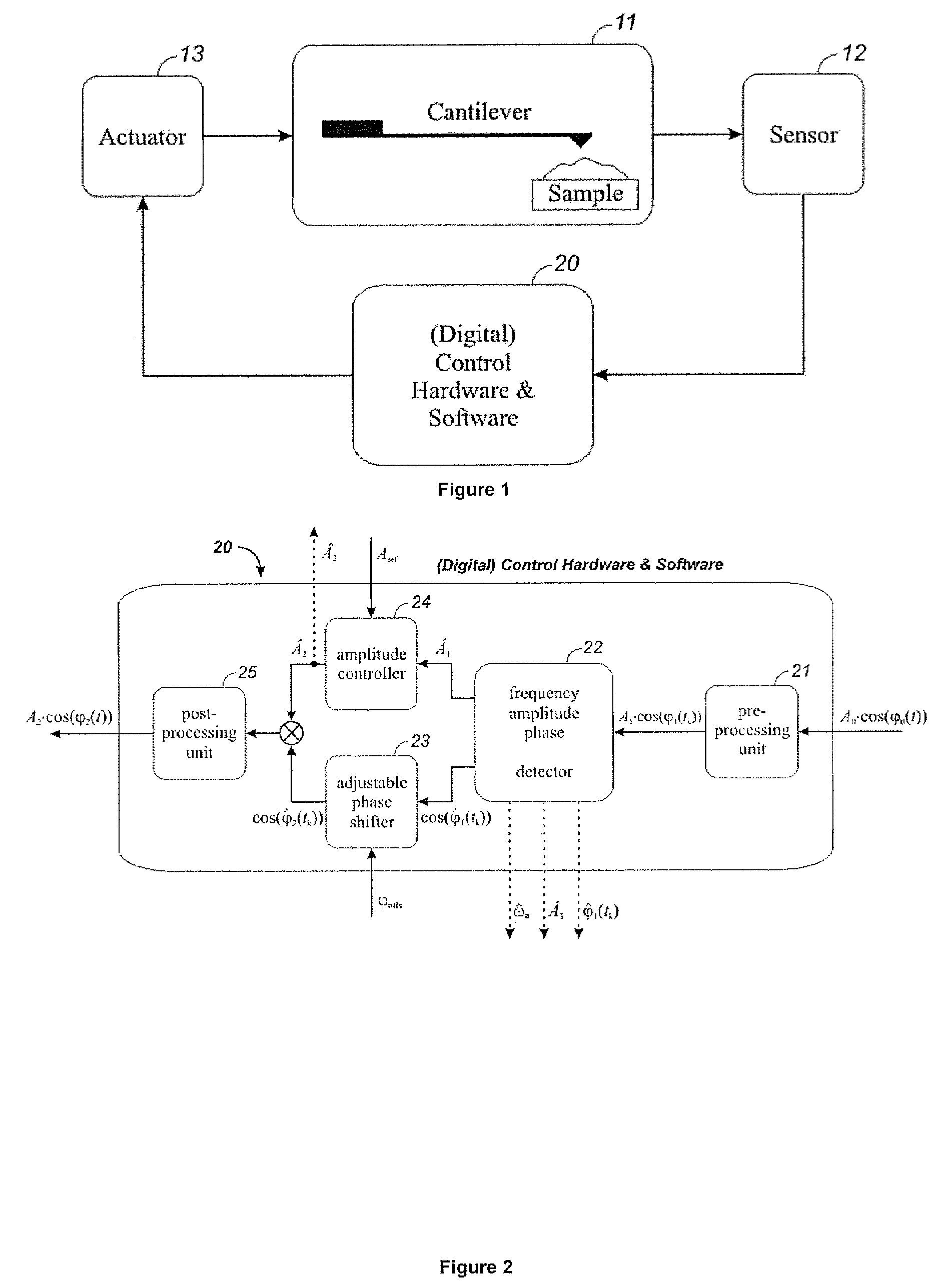
All-digital cantilever controller
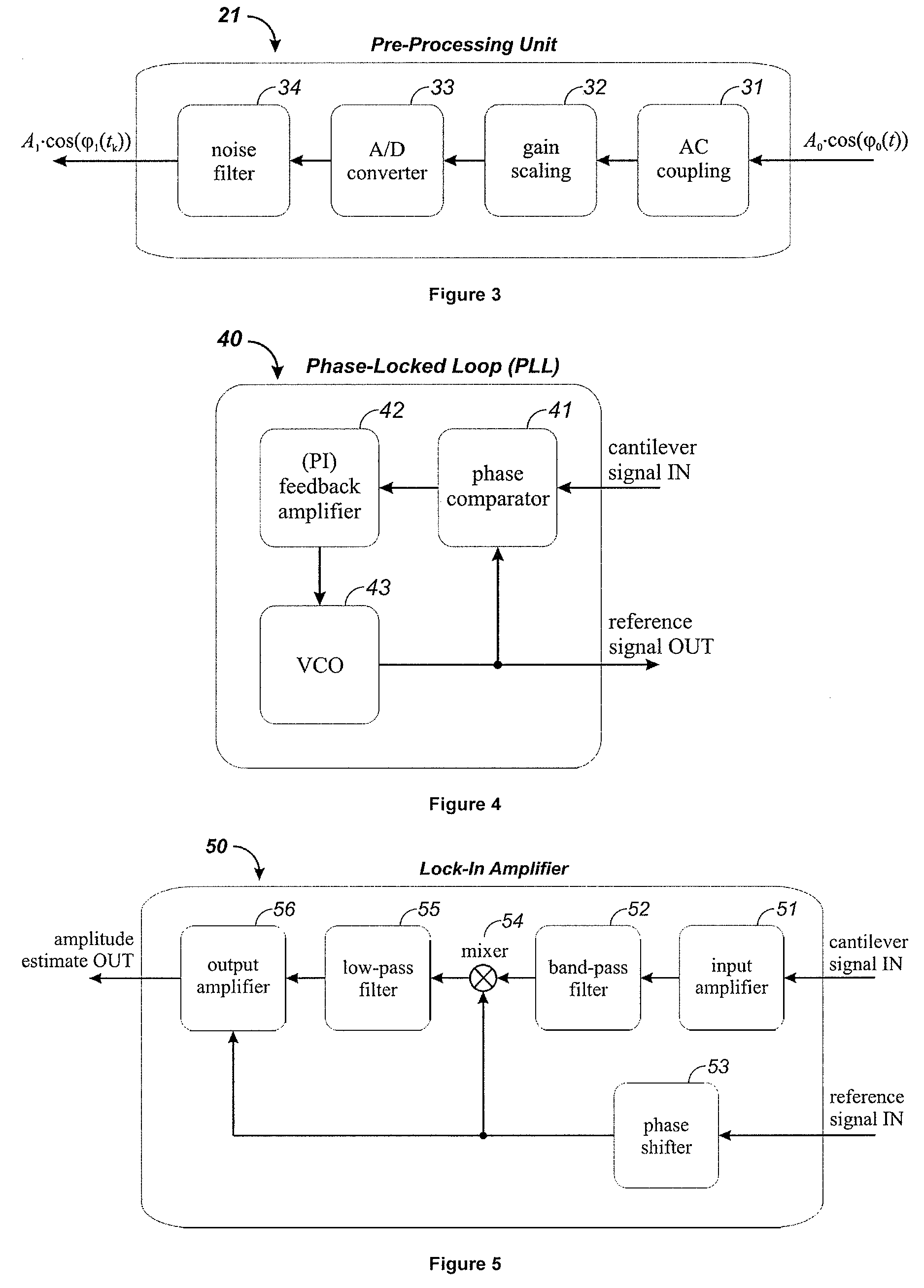
InactiveUS7574327B2Correction algorithmEase of executionFeeler-pin gaugesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansCantileverOrder of magnitude
An all-in-one digital cantilever controller applicable to all SFM systems is disclosed that can perform many relevant experiments for cantilever control in scanned force microscopy. A compact optimized digital implementation replaces analog components associated with cantilever signal processing and control. It has minimal thermal drift, at least an order of magnitude less than analog components. It has a number of meaningful tuning parameters available, as well as a user-friendly graphical interface (GUI) for adjusting those tuning parameters and performing different types of experiments.
Owner:SOLUTIONS
Semiconductor device
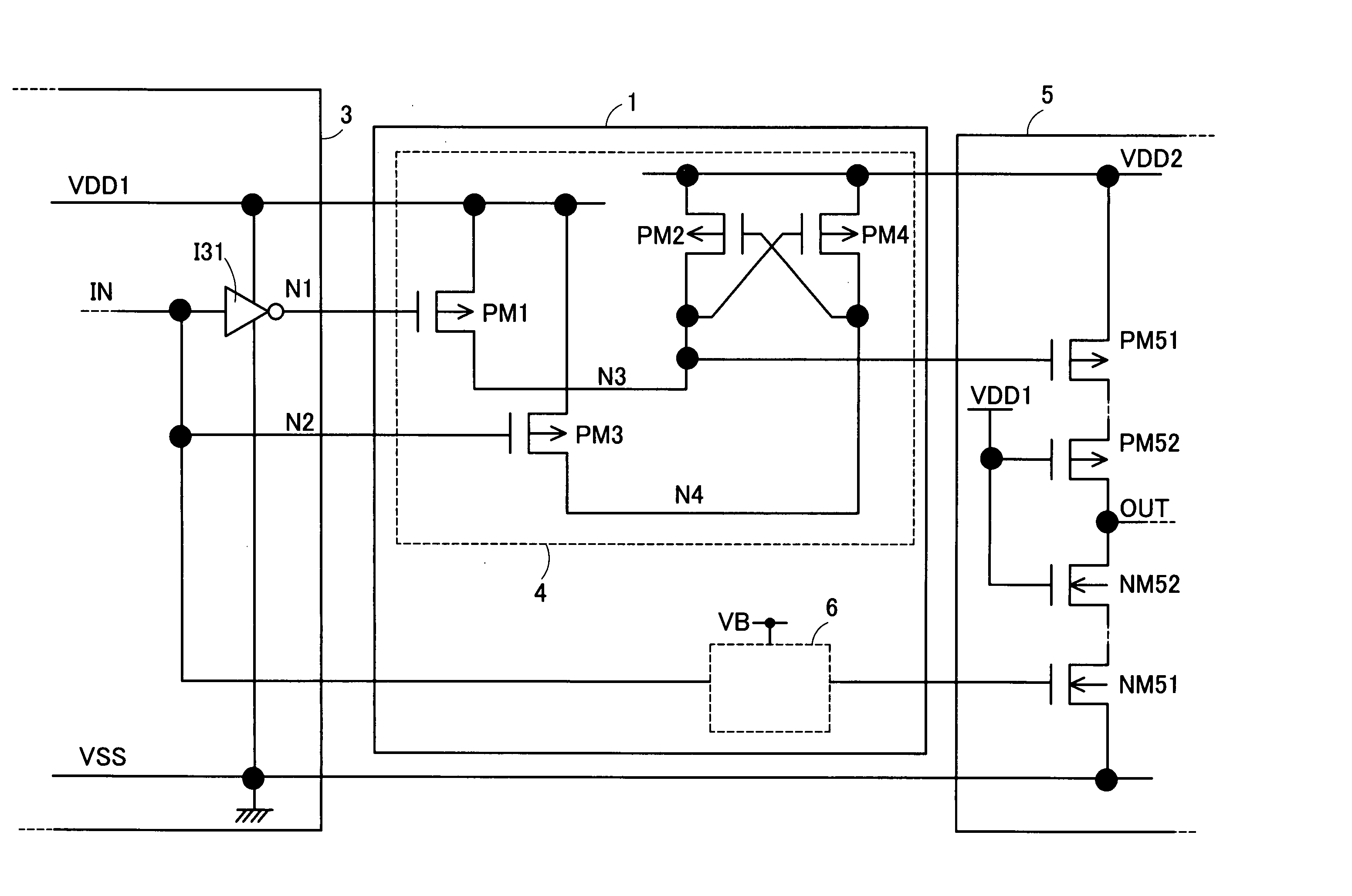
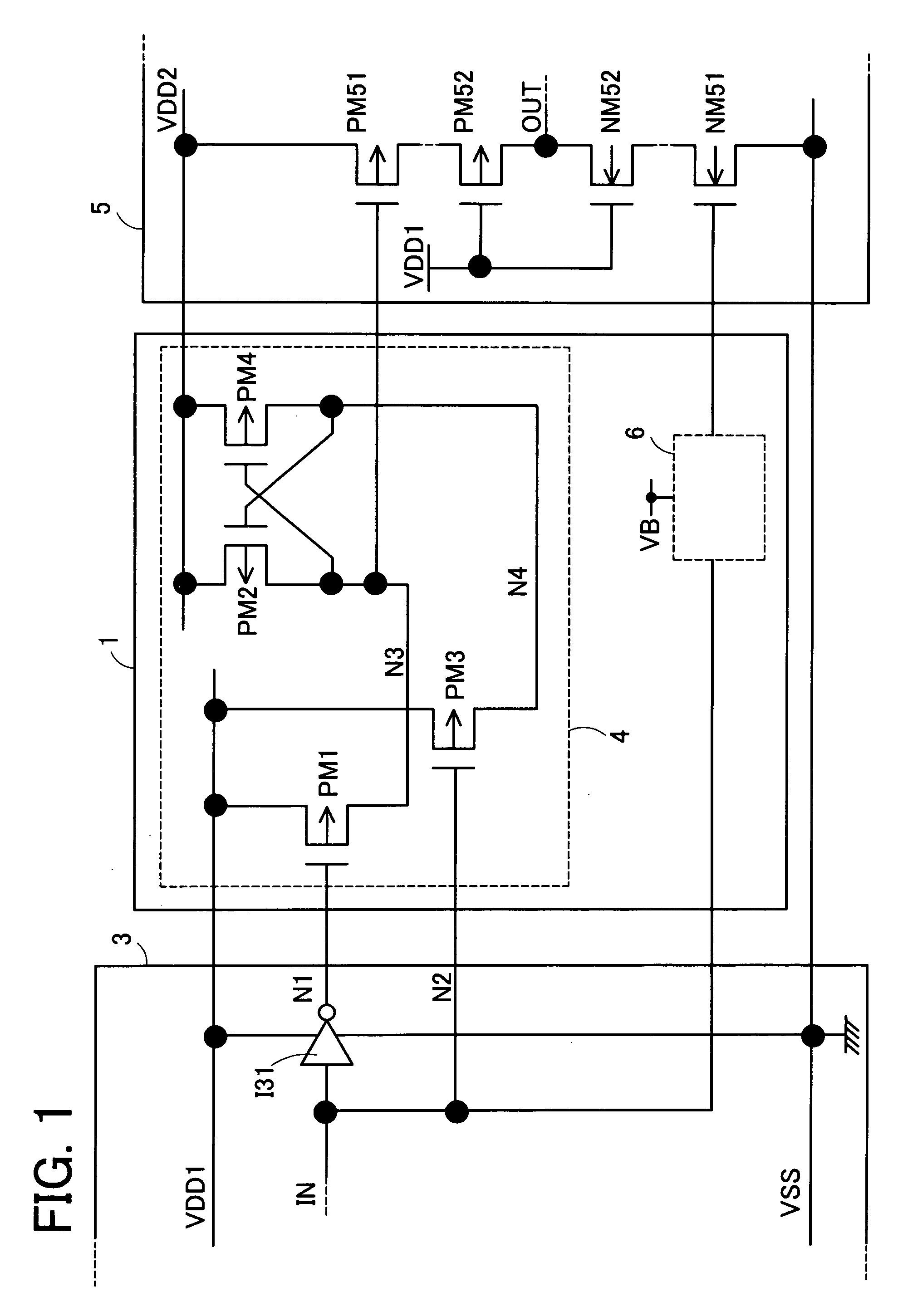
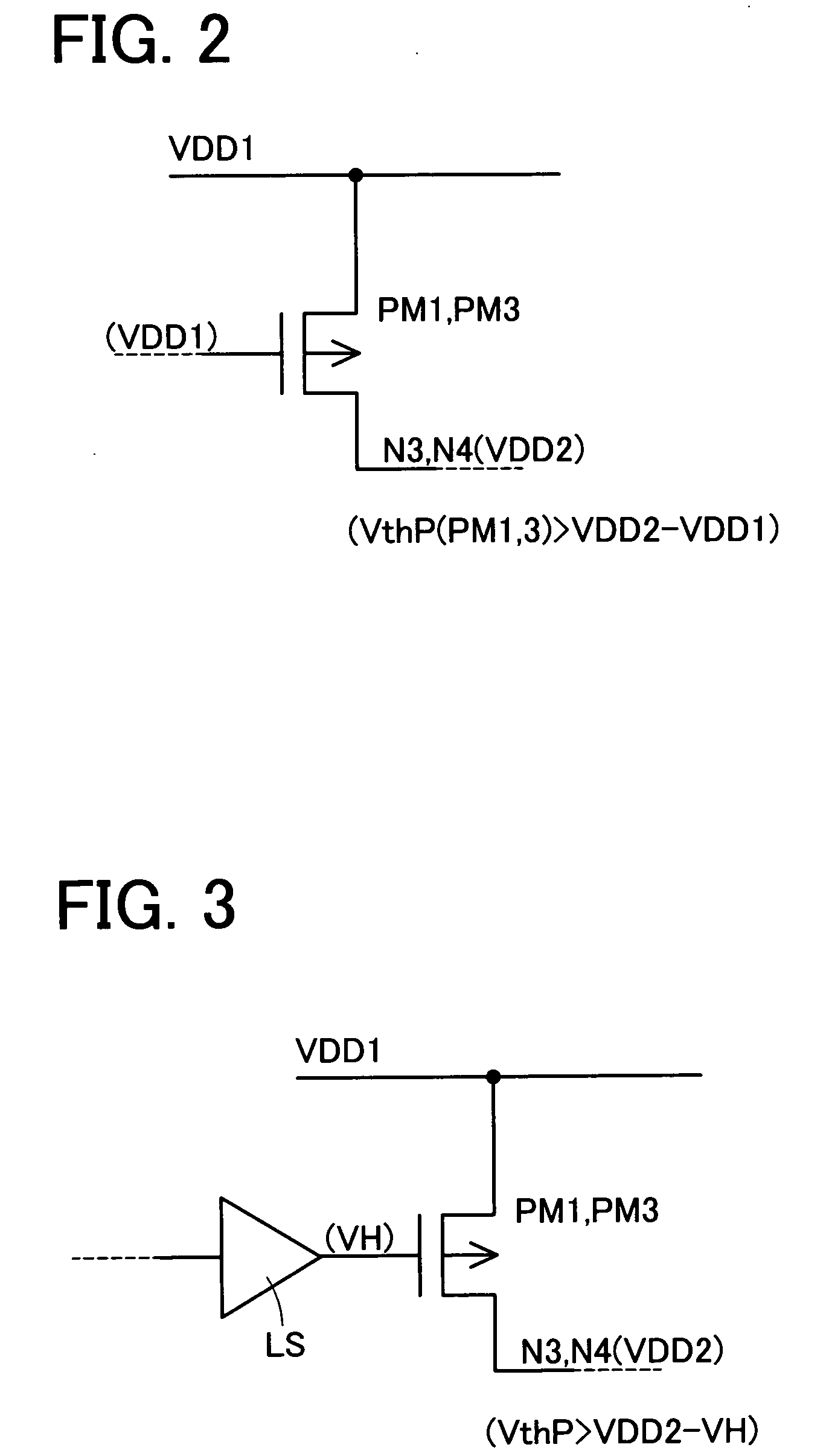
InactiveUS20050127977A1Ease of executionEasy to controlPulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsEngineeringSemiconductor
In an operation to supply an input signal IN having an amplitude equal to a first power-supply voltage VDD1 to the gate of a PMOS transistor PM51 operating at a second power-supply voltage VDD2 higher than the first power-supply voltage VDD1, the levels of signals are converted by using PMOS transistors PM1 to PM4. The sources of the PMOS transistors PM1 and PM3 are connected to a line of the first power-supply voltage VDD1 whereas the sources of the PMOS transistors PM2 and PM4 are connected to a line of the second power-supply voltage VDD2. The gate of the PMOS transistor PM4 is connected to the drains of the PMOS transistors PM1 and PM2. The gate of the PMOS transistor PM2 is connected to the drains of the PMOS transistors PM3 and PM4. An inverted signal of the input signal IN is supplied to the gate of the PMOS transistor PM1 and the input signal IN is supplied to the gate of the PMOS transistor PM2. The amplitude of the input signal IN is converted from a magnitude equal to a difference between a reference signal VSS and the first power-supply voltage VDD1 into a magnitude equal to a difference between the first power-supply voltage VDD1 and the second power-supply voltage VDD2. A signal obtained as a result of the conversion is output from the PMOS transistors PM1 and PM2, being used for controlling electrical conduction of a PMOS transistor PM51.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
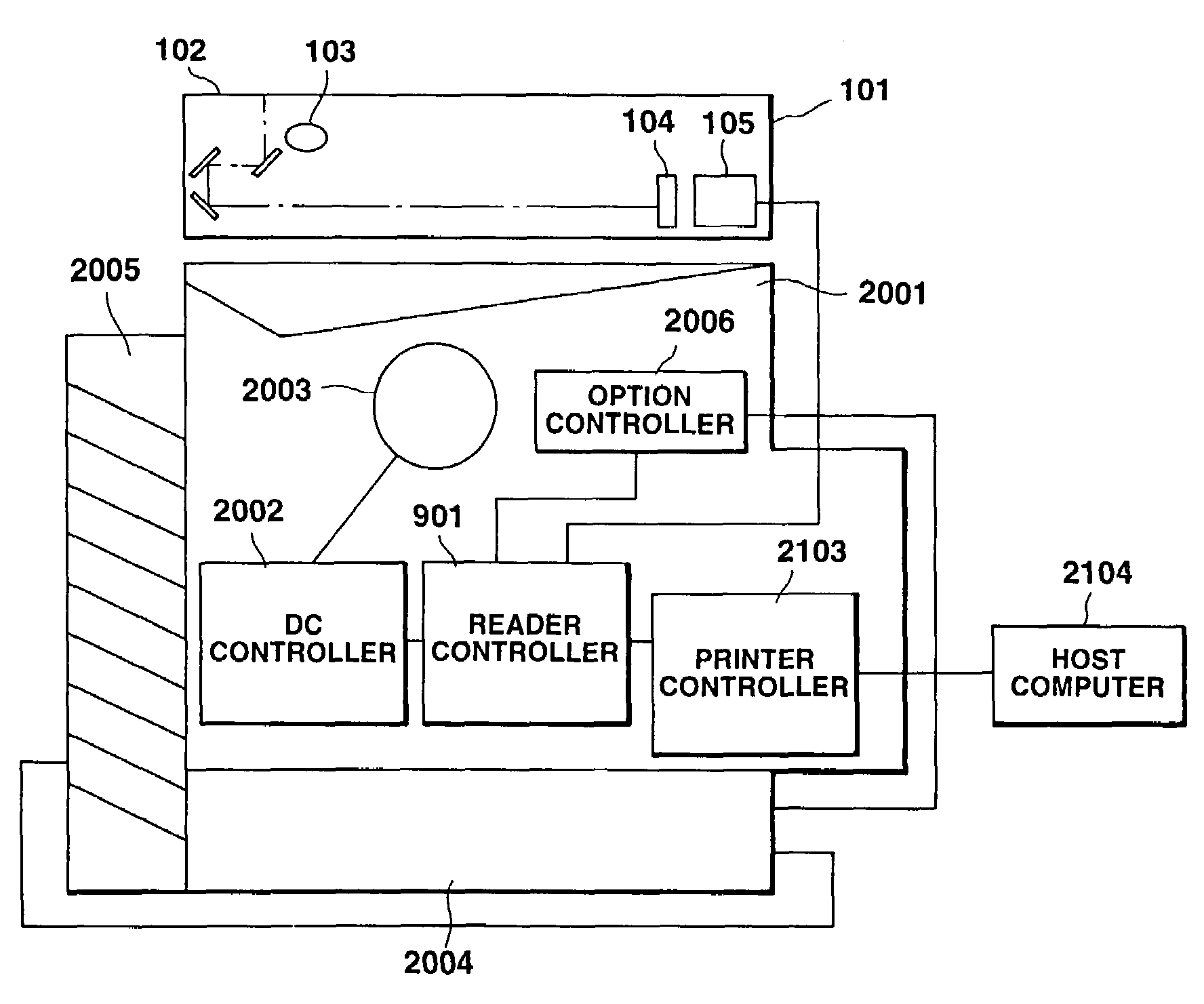
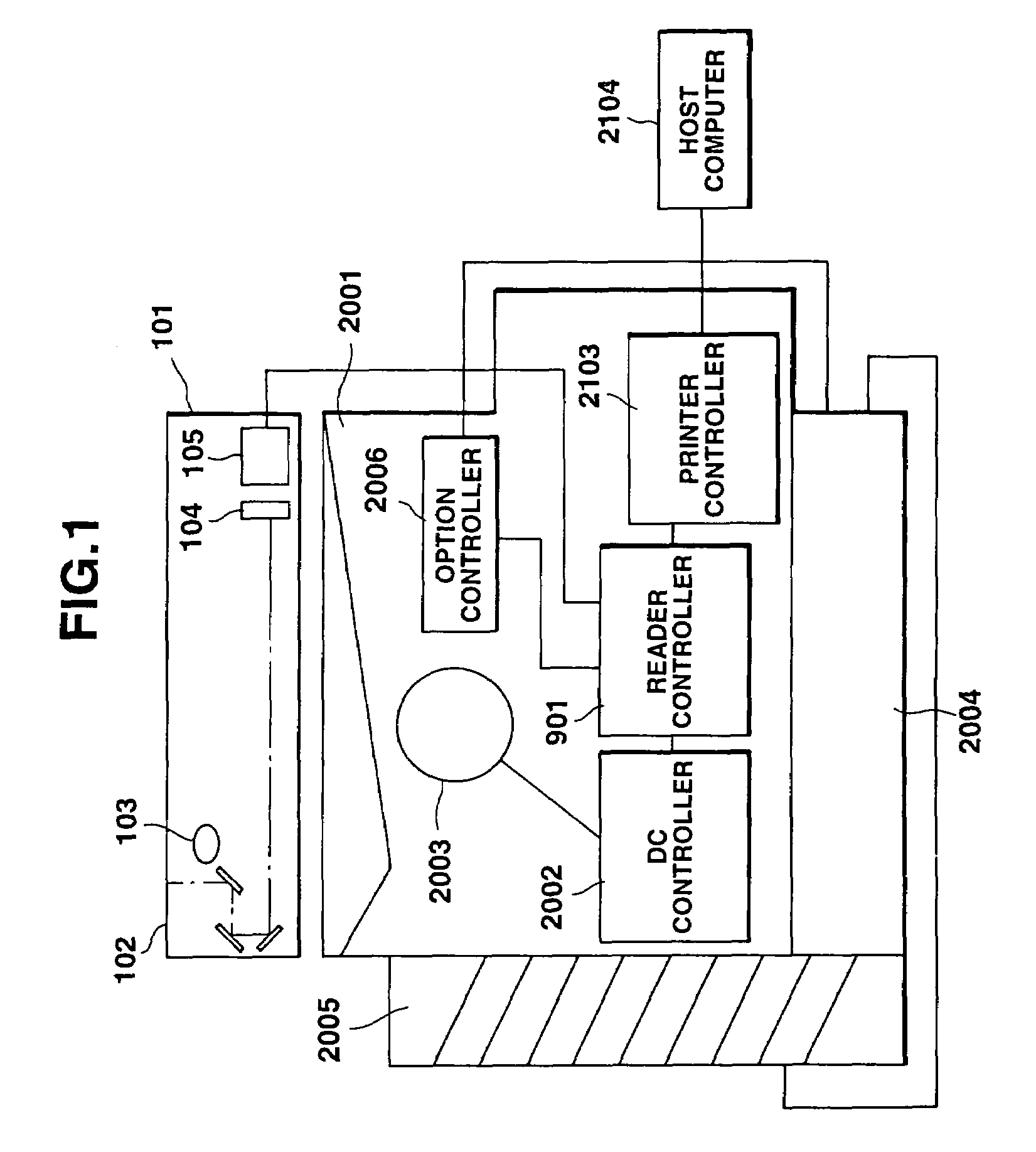
Image processing apparatus, a reader controller, and a method for controlling the reader controller
InactiveUS6992784B1Fast processingMaintain consistencyDigital computer detailsElectrographic process apparatusImaging processingComputer science
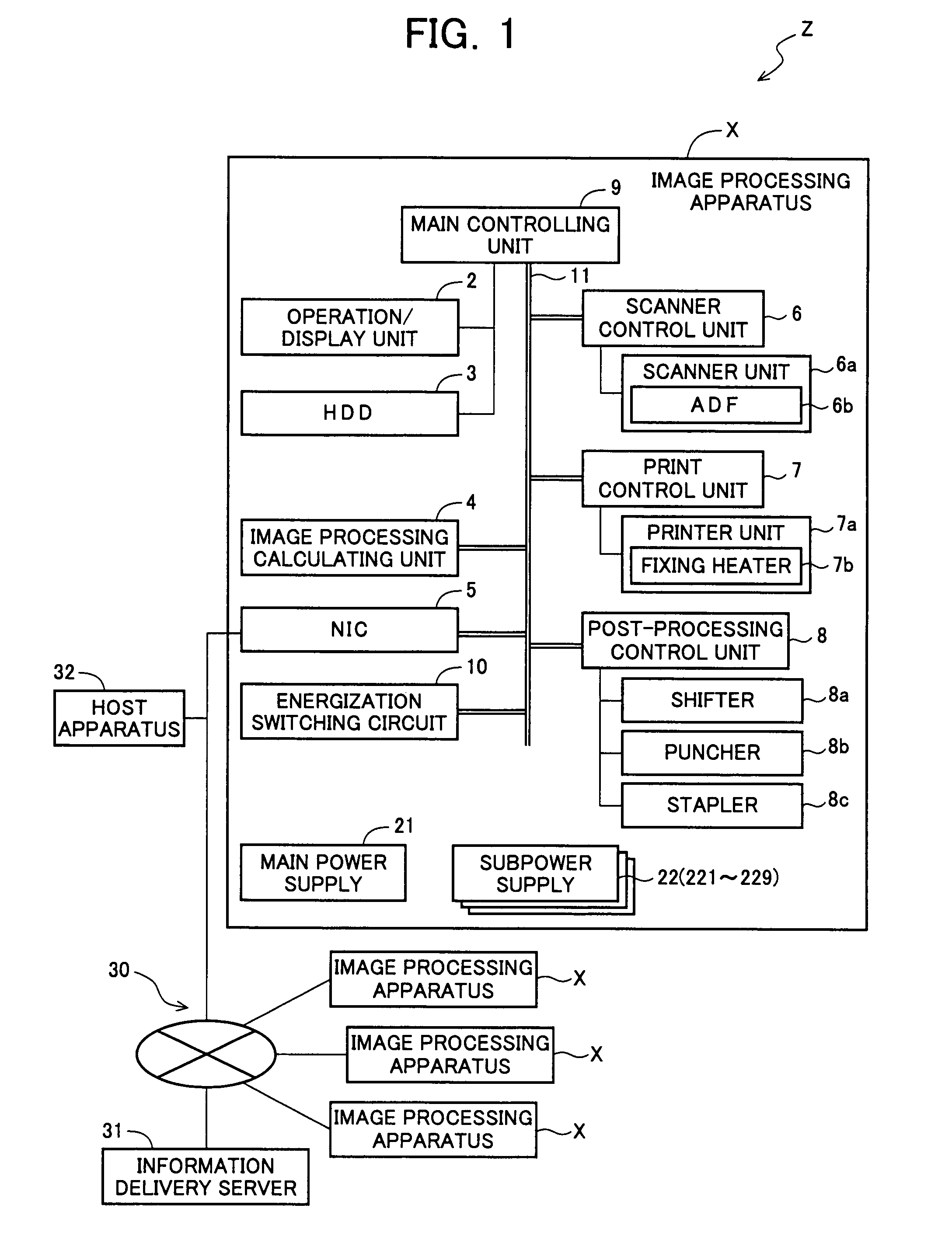
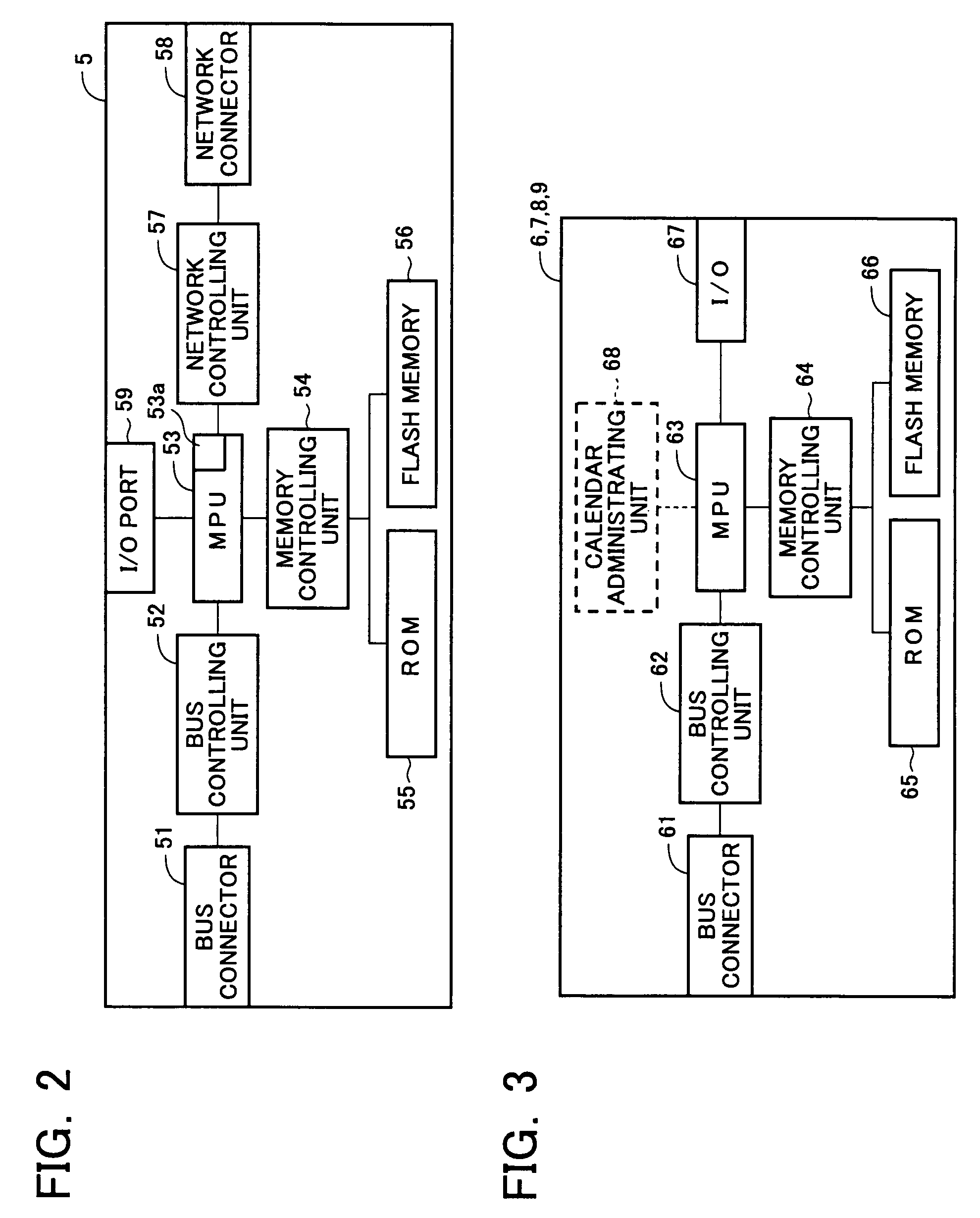
An image processing apparatus includes an engine controller for controlling an image forming mechanism for forming an image on a sheet based on image data, a printer controller for forming image data from printing data transferred from an external apparatus, for transmitting the image data to the engine controller, and for transmitting a command for setting an operation of the engine controller to the engine controller, and a reader controller for controlling an original-reading device for outputting image data by reading an image of an original, and for transmitting the image data output from the original-reading device to the engine controller. The reader controller is provided between the printer controller and the engine controller so as to be communicatable with each of the printer controller and the engine controller, and controls the acquisition of a right to use the engine controller with the printer controller.
Owner:CANON KK
Program execution control device, program execution control method, control program, and recording medium
InactiveUS7958499B2Suppress execution speedShorten speedTransformation of program codeSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationParallel computingExecution control
When a home appliance equipped with a processor implementing a conventional JVM with a JIT compiler executes uncompiled methods, the execution speed is slower because the methods are compiled at runtime. To suppress the execution speed reduction, a program execution control device judges, on invocation of a method during program execution, whether a method invoked has previously been compiled. If the method is uncompiled, the device executes the method by interpreting associated bytecodes, and also issues a compilation request for the method. If the method is compiled, the device executes native code having been generated by compiling the method. Compilation of a method requested is executed as a separate task from tasks of instruction execution such as interpreter execution or native code execution.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com