Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Reduce construction length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
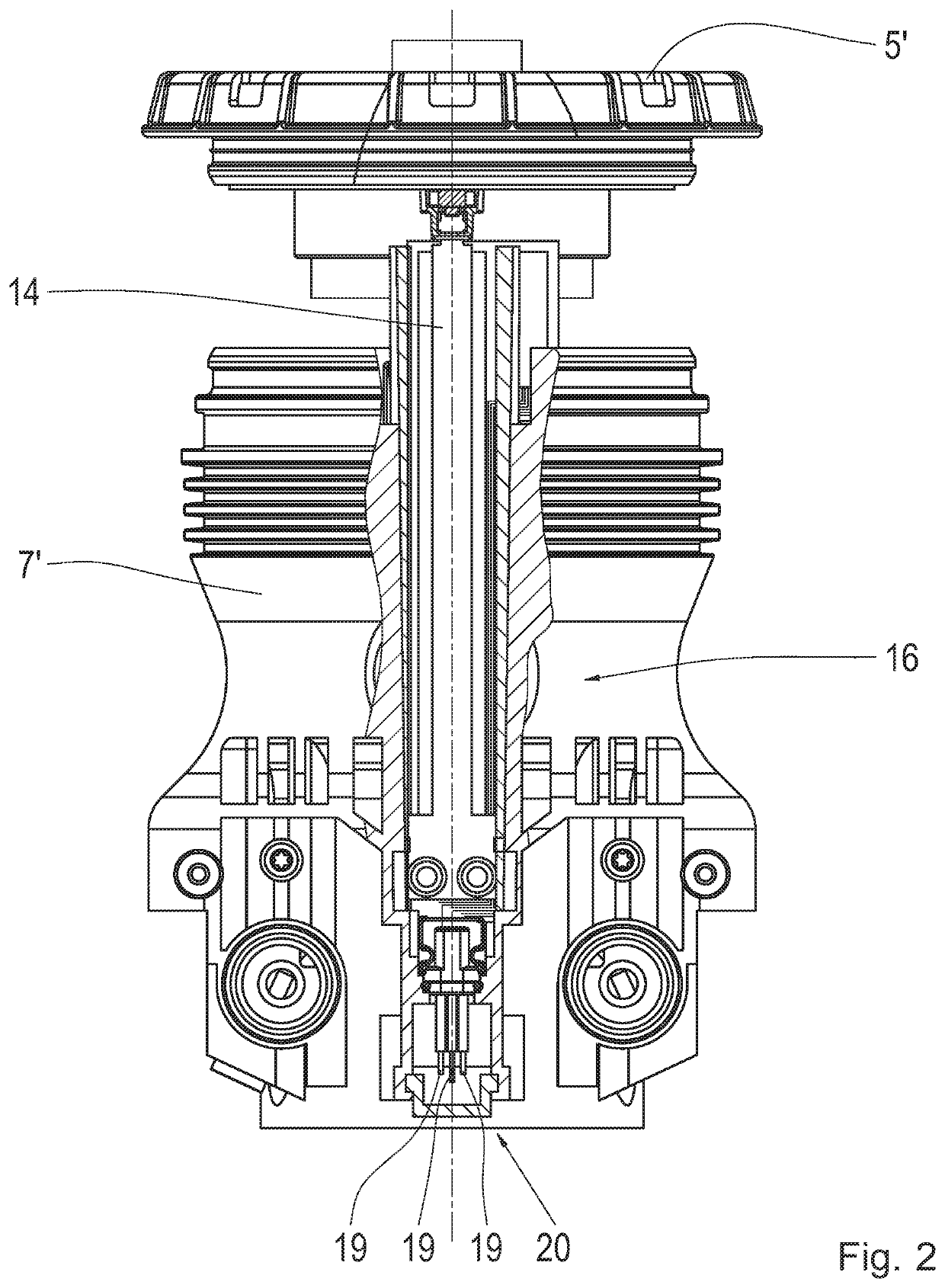
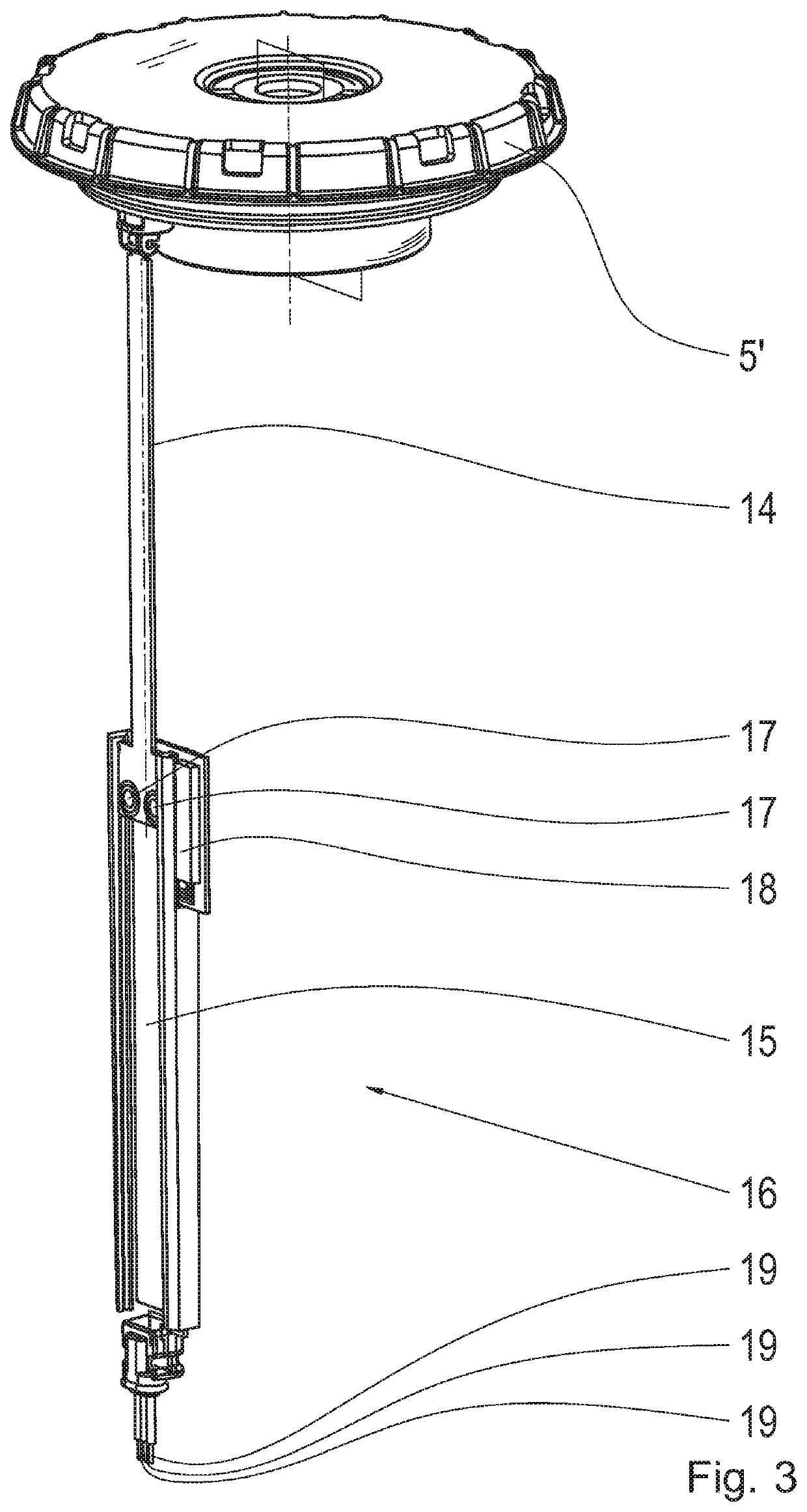
Antenna system for a level measurement apparatus
InactiveUS20030151560A1Longitudinal extension of the antenna system can be reducedMore compactMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsMeasurement deviceLevel measurement
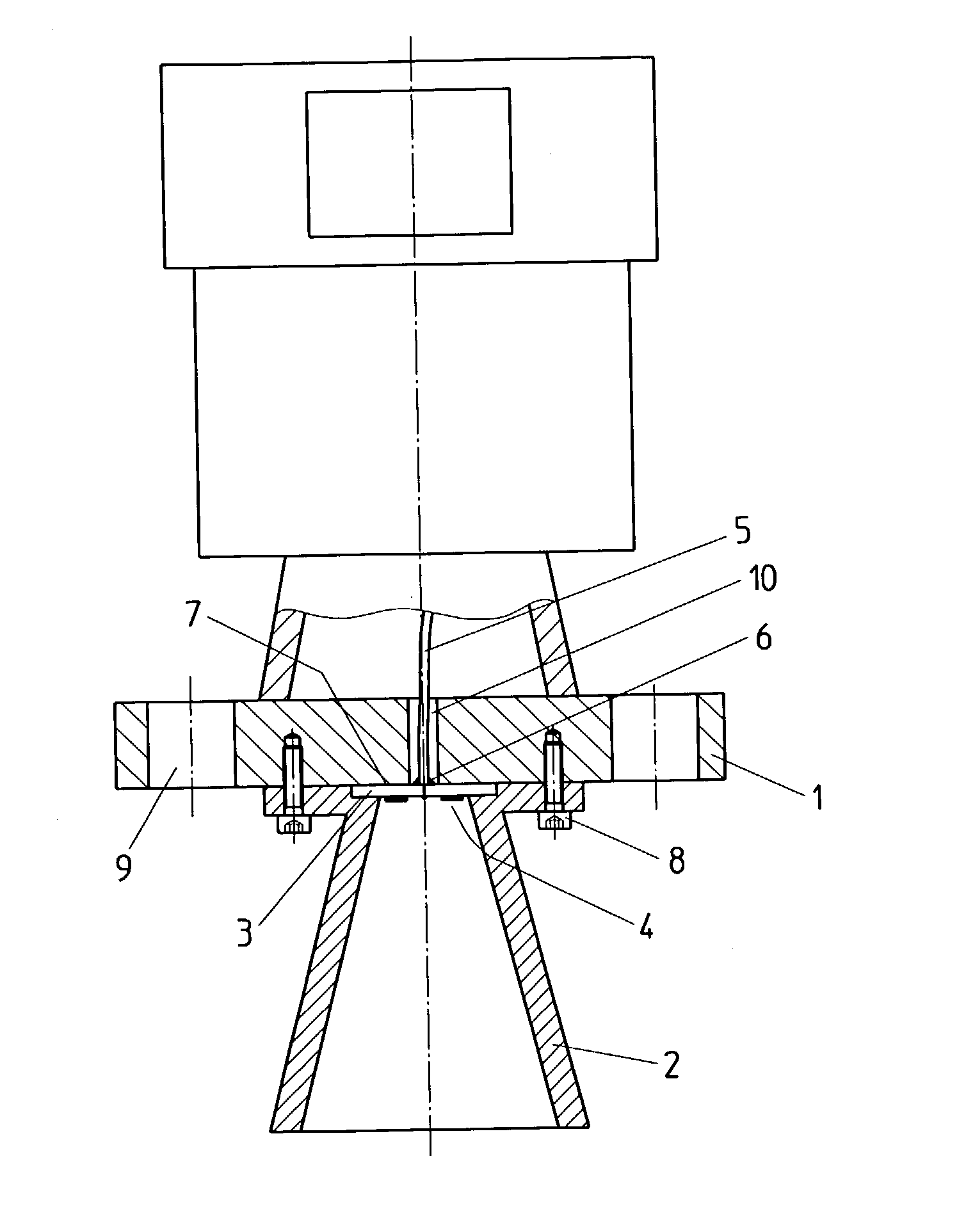
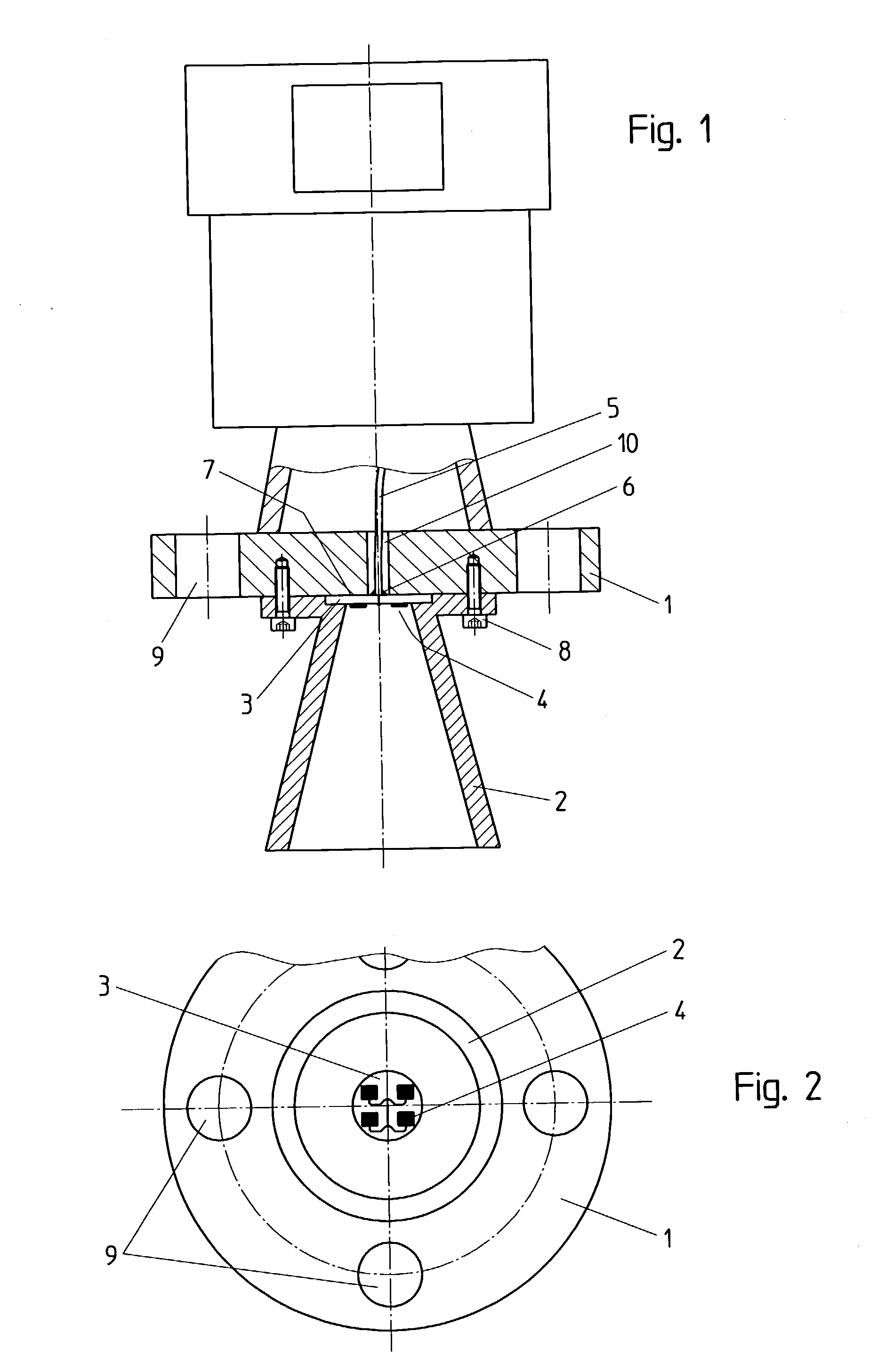
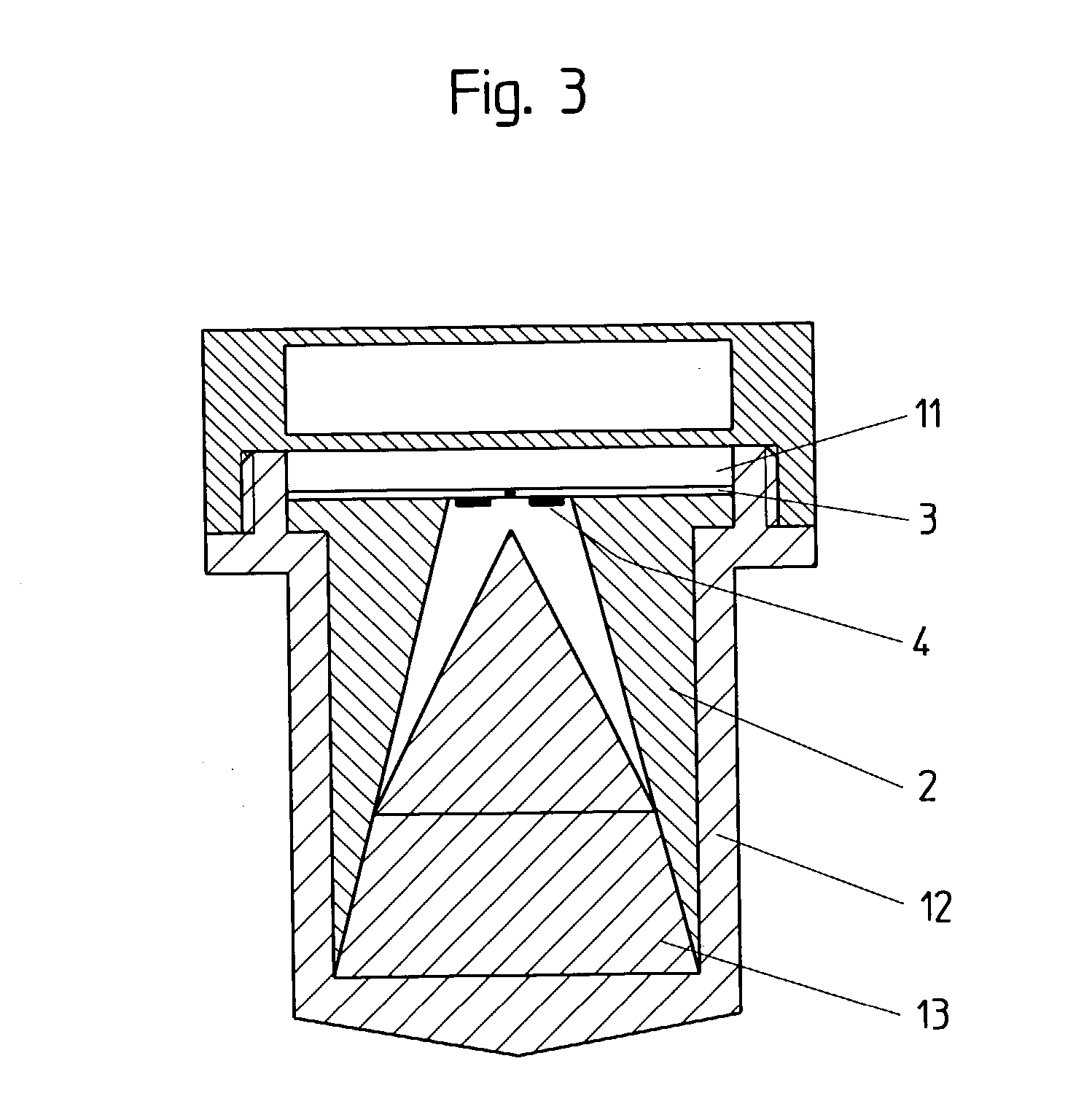
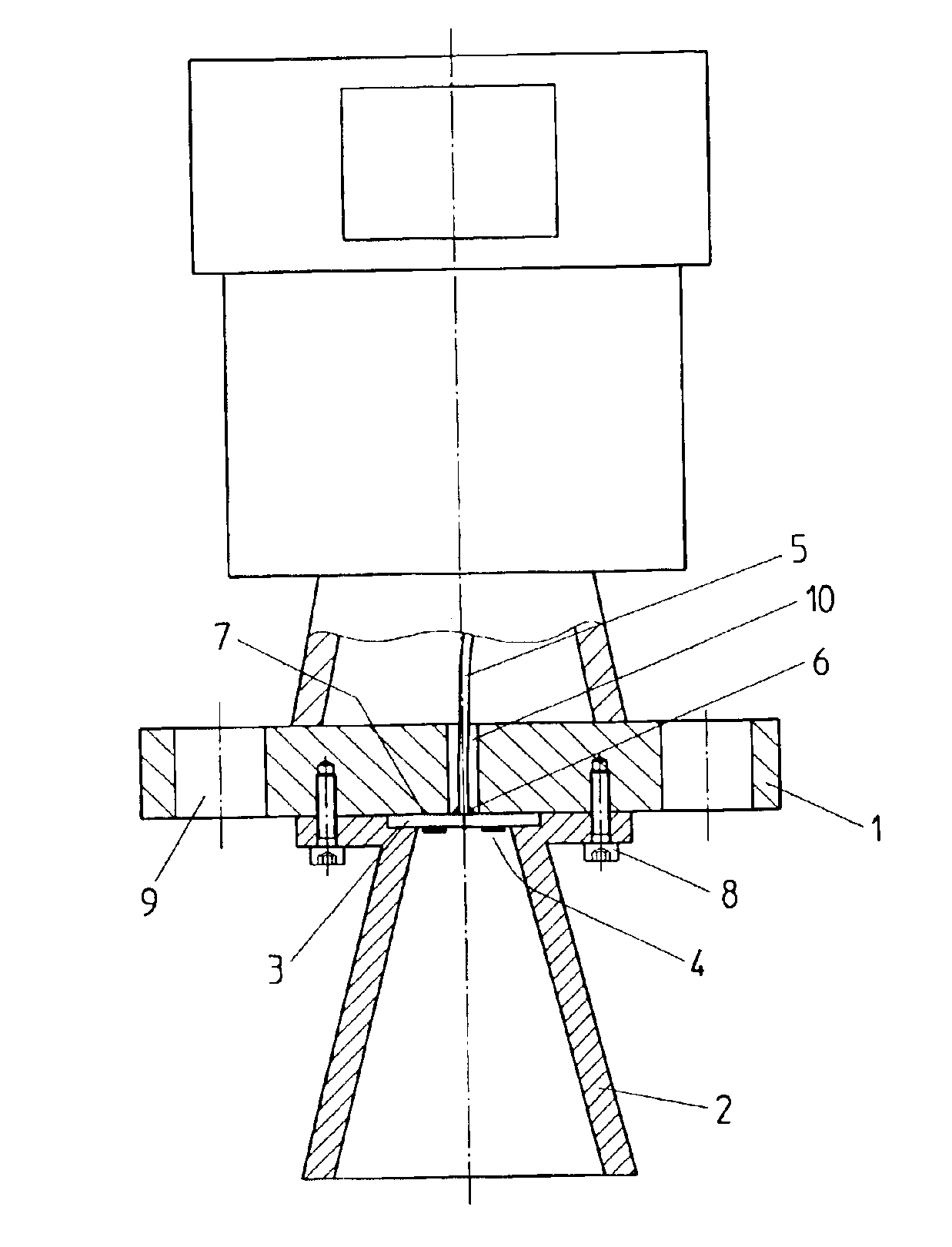
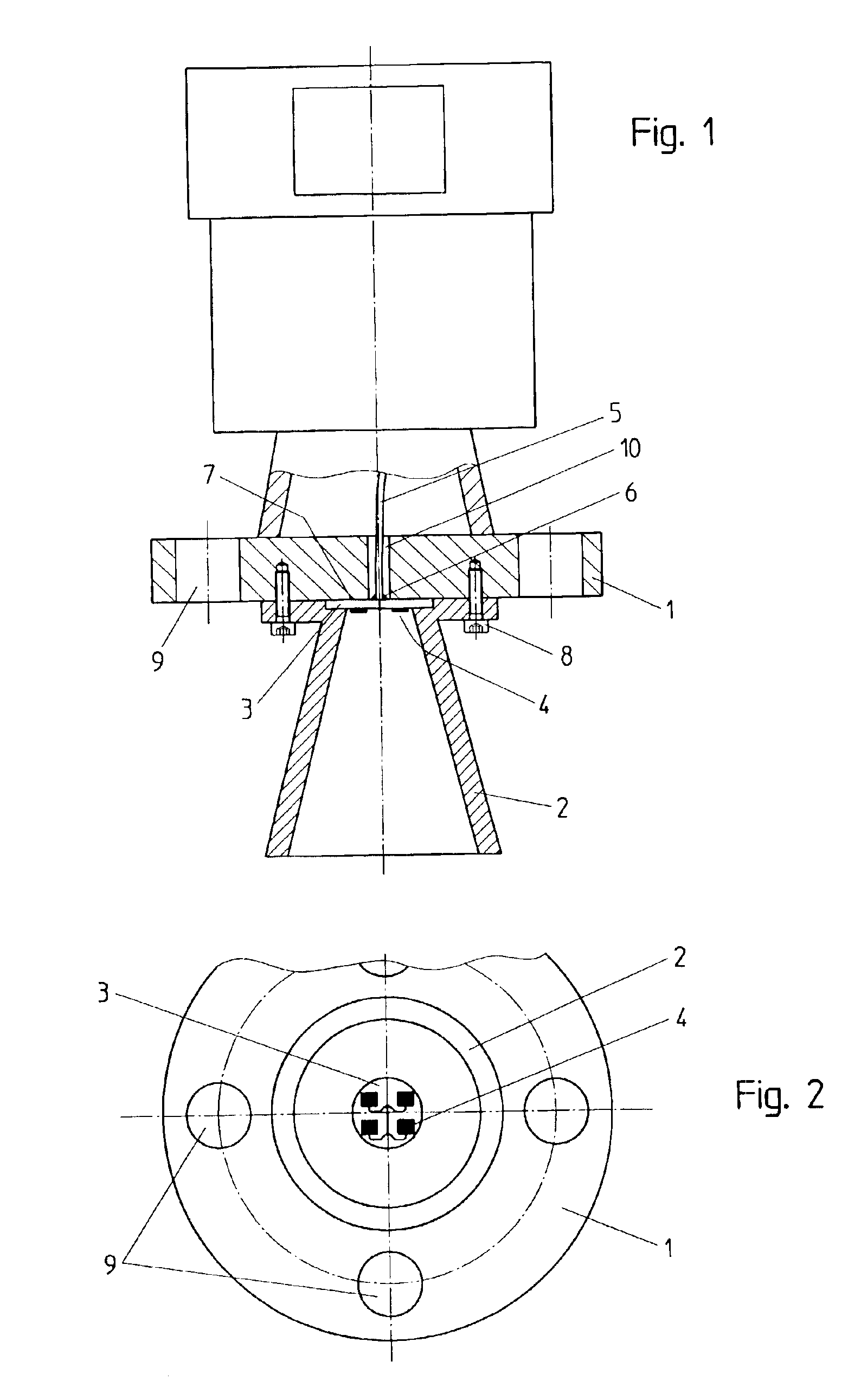
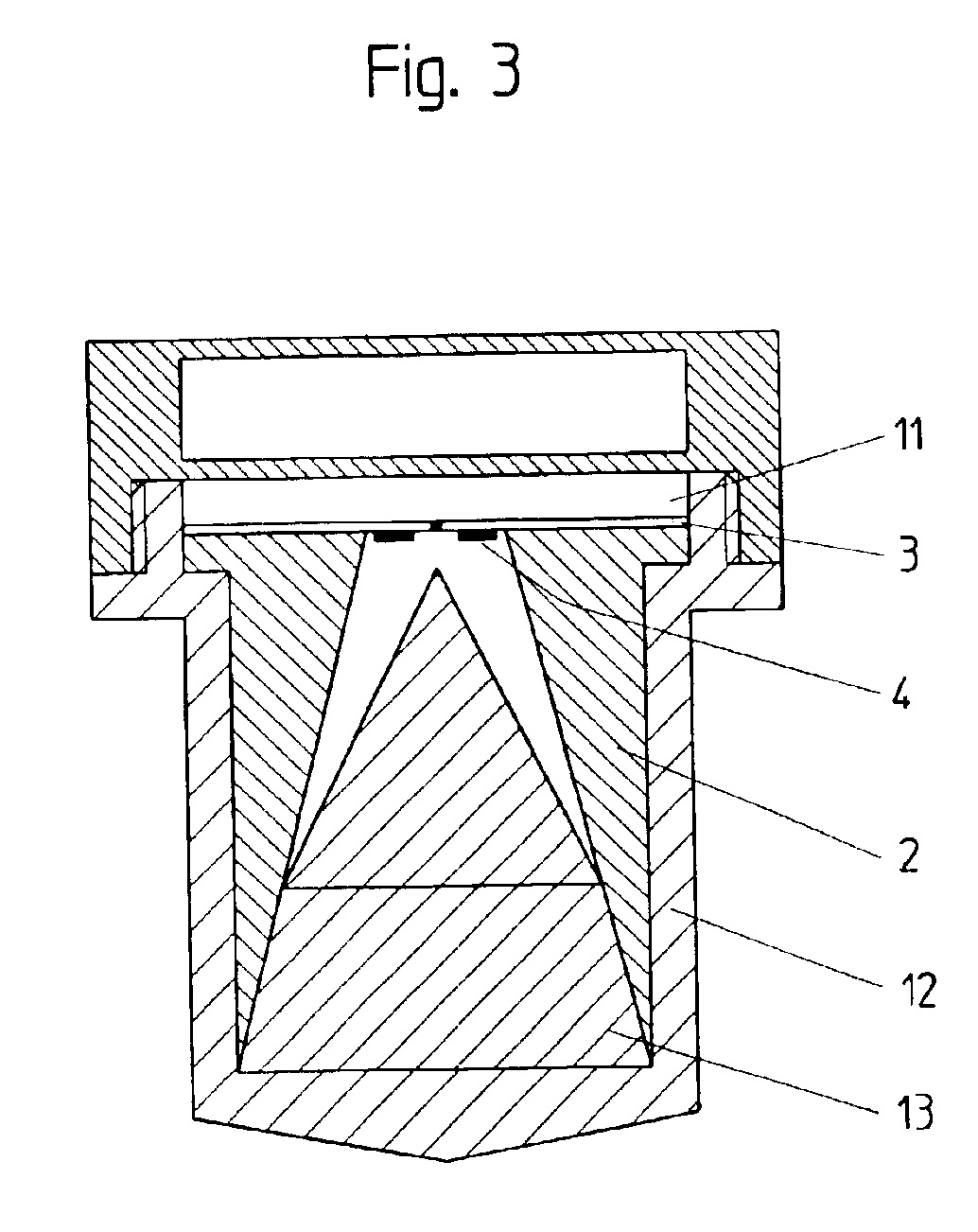
The present invention relates to an antenna system for a level measuring device for emitting microwaves by means of an antenna horn (2), at the front side of the smaller funnel aperture thereof, HF energy in the form of microwave signals is directly axially coupled by means of planar structures having one patch or several patches (4).
Owner:VEGA GRIESHABER GMBH & CO
Antenna system for a level measurement apparatus
InactiveUS6891513B2Longitudinal extension of the antenna system can be reducedMore compactSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMeasurement deviceLevel measurement
The present invention relates to an antenna system for a level measuring device for emitting microwaves by means of an antenna horn, at the front side of the small funnel aperture thereof. HF energy in the form of microwave signals is directly axially coupled by means of planar structures having one patch or several patches.
Owner:VEGA GRIESHABER GMBH & CO
Chuck
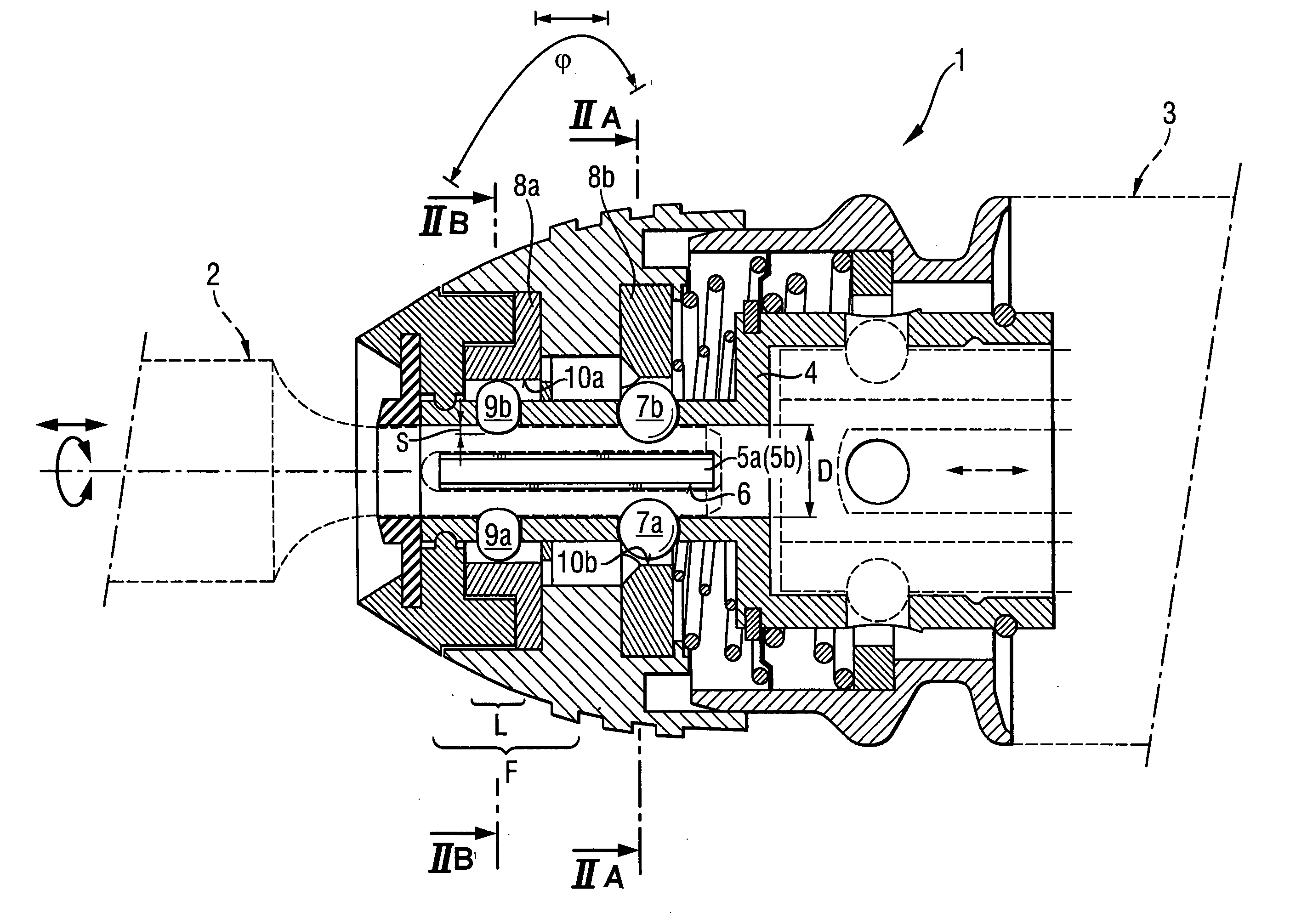
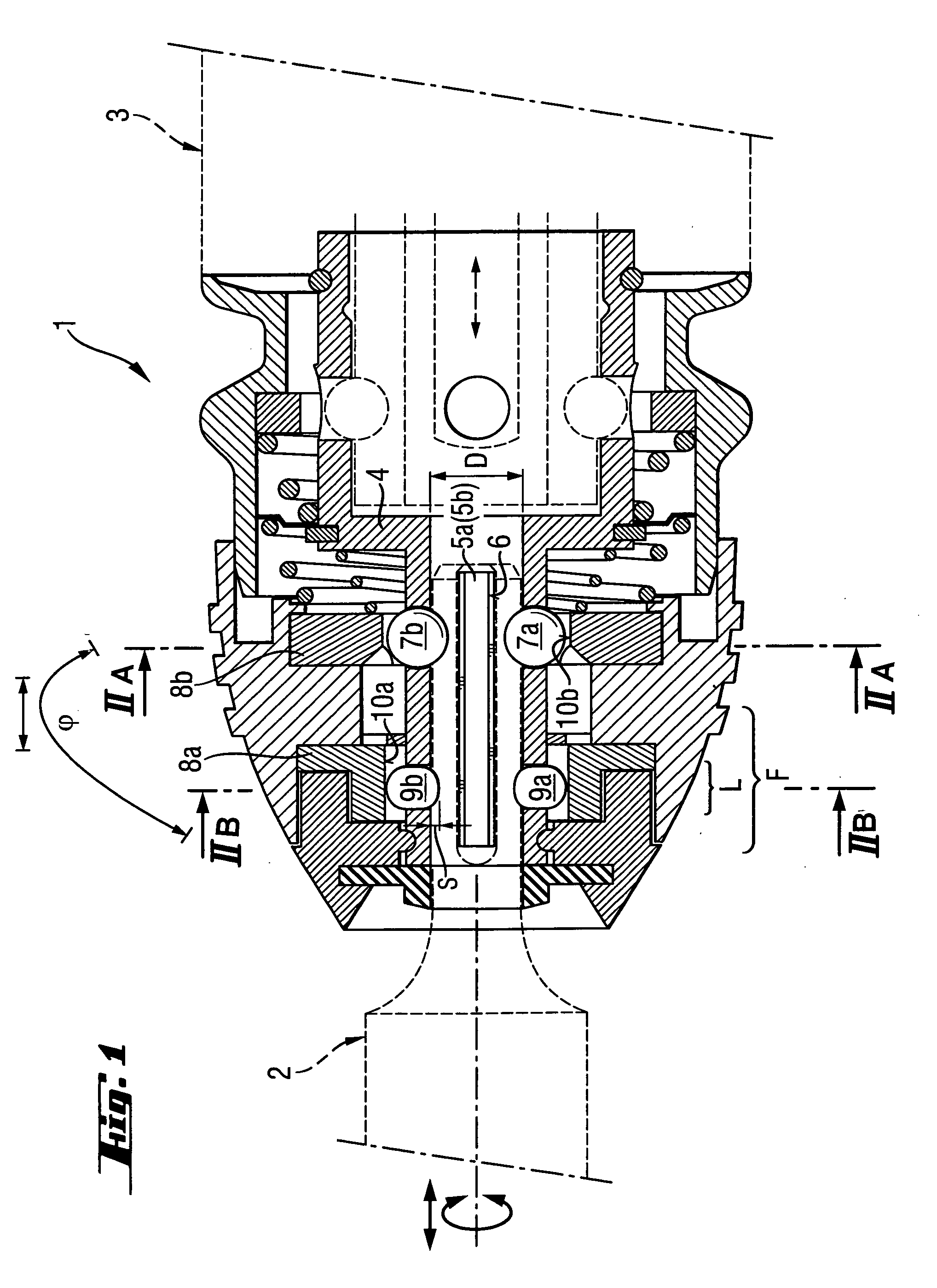
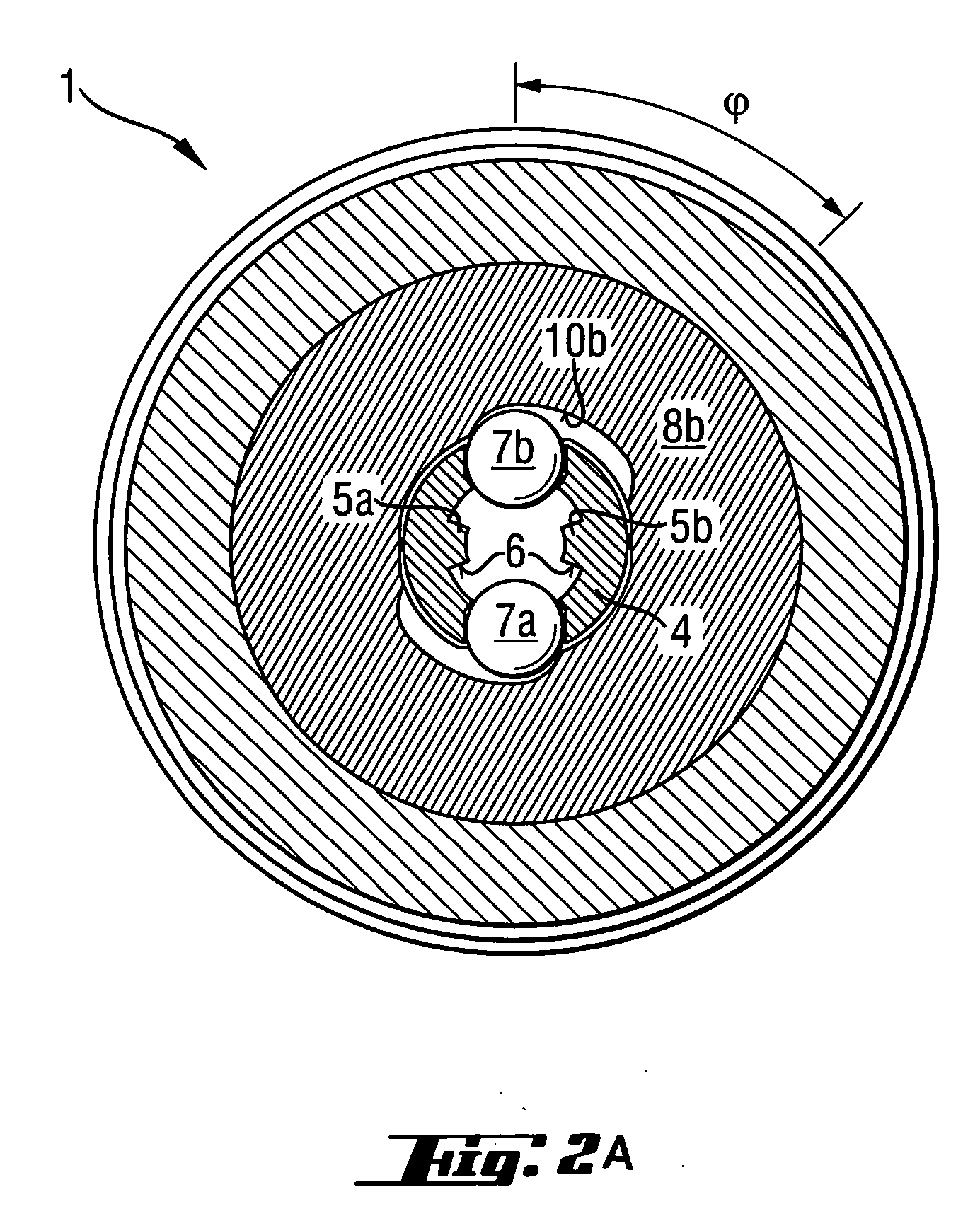
InactiveUS20060192350A1Shorten the lengthReduce construction lengthSleeve/socket jointsPortable percussive toolsEngineeringPower tool
A chuck for receiving a working tool driven by a power tool includes a hollow cylindrical sleeve (4) for receiving the working tool (2), strip-shaped, rotation-transmitting webs (5a, 5b) projecting radially inward from the receiving sleeve (4), at least one radially displaceable locking member (7a); at least two guide members (9a, 9b) provided in a working tool-side guide region (F) of the guide diameter (D) of the receiving sleeve and spaced from the rotation-transmitting webs (5a, 5b), and a manually rotatable clamping sleeve (8a) for displacing the guide members (9a, 9b) radially inwardly.
Owner:HILTI AG
In-place heat regeneration integrated machine for bituminous pavements and control method
ActiveCN104727208AExtend heating timeExtend the mixing timeRoads maintainenceStopped workControl system
The invention provides an in-place heat regeneration integrated machine for bituminous pavements and a control method, wherein the in-place heat regeneration integrated machine for bituminous pavements integrates the functions of pavement milling-planing, bituminous mixture heating, remixing and the like. The regeneration integrated machine comprises a chassis, a milling-planing device, a conveyor, a conveyor heating device, an agitating pan, agitating pan heating devices, and a control system, wherein the conveyor is located behind the milling-planing device, the conveyor heating device is located above the conveyor, the agitating pan heating device is arranged at the top of the agitating pan, and the control system is used for controlling the travelling speed of the chassis, the heating temperature, the mixture metering and the agitating time of the agitating pan. The control method comprises the following steps: starting to accumulate travelling pulses, and if a required travelling distance reaches, switching a material distribution board to the other side; if the material distribution board is overturned, opening an agitating cylinder on the other side, discharging for a period of time, and waiting for the next switching of the material distribution board; and repeating the steps until the machine stops working.
Owner:SHANDONG LUQIAO GROUP
Locking device with a key-activated cylinder core
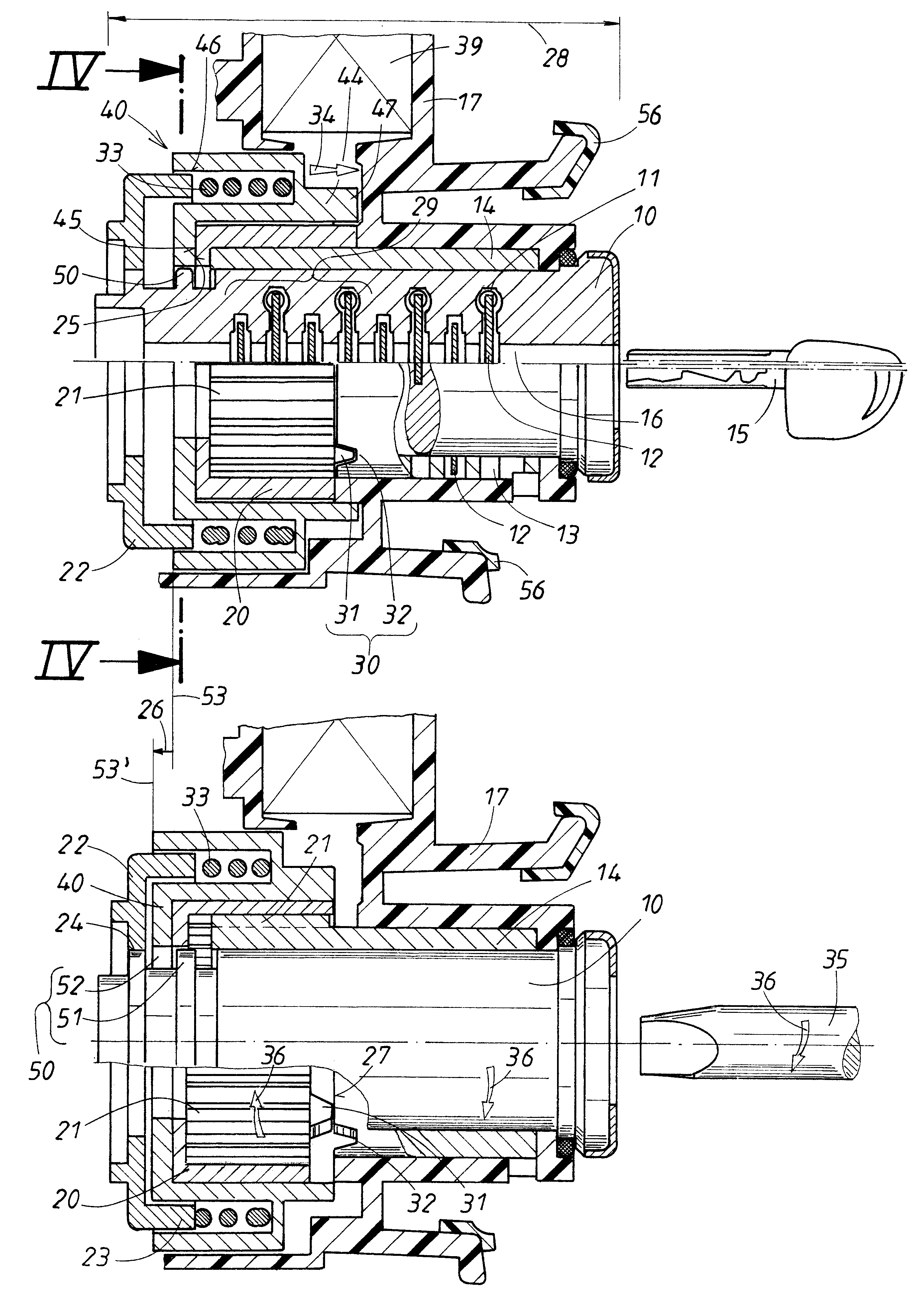
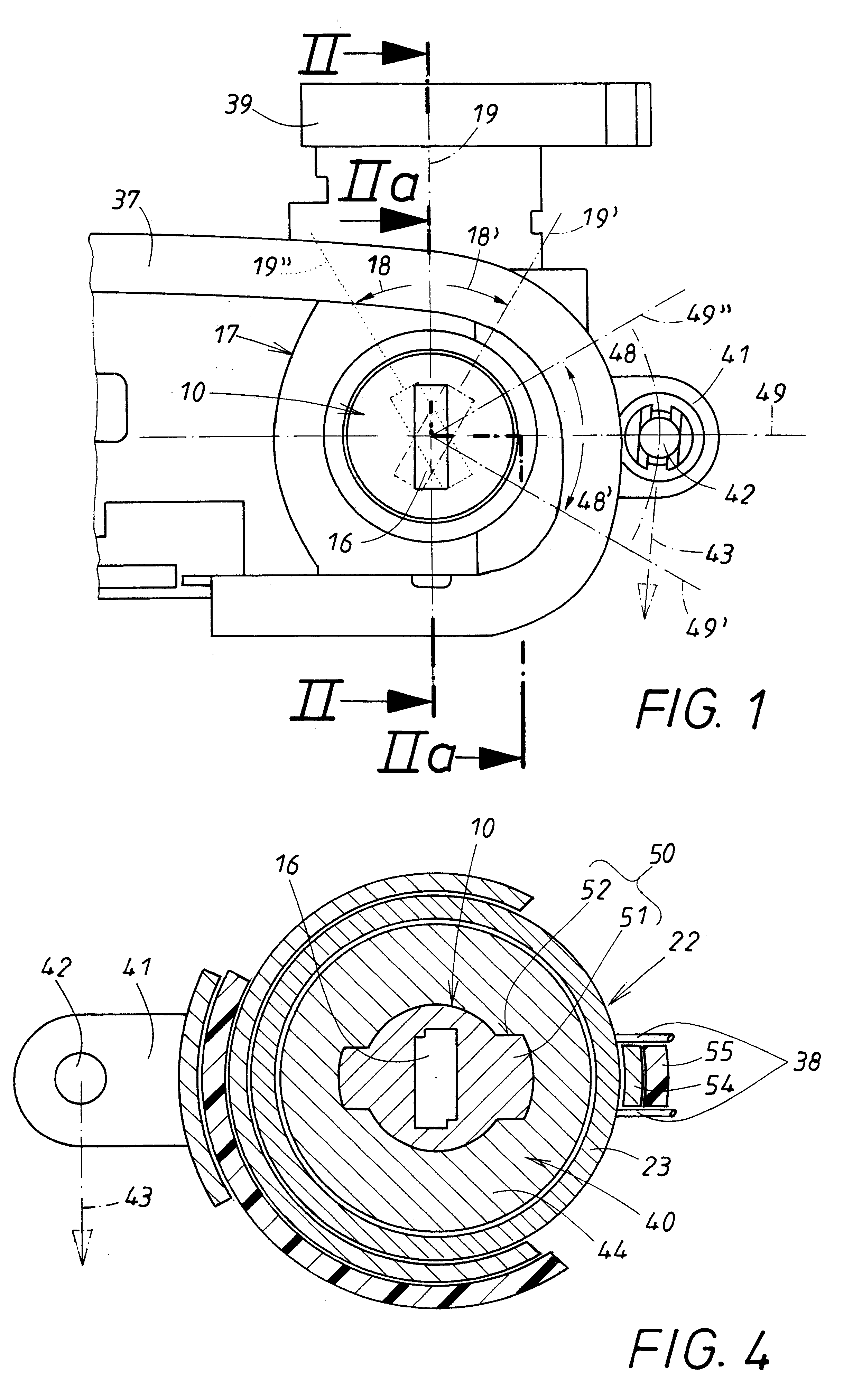
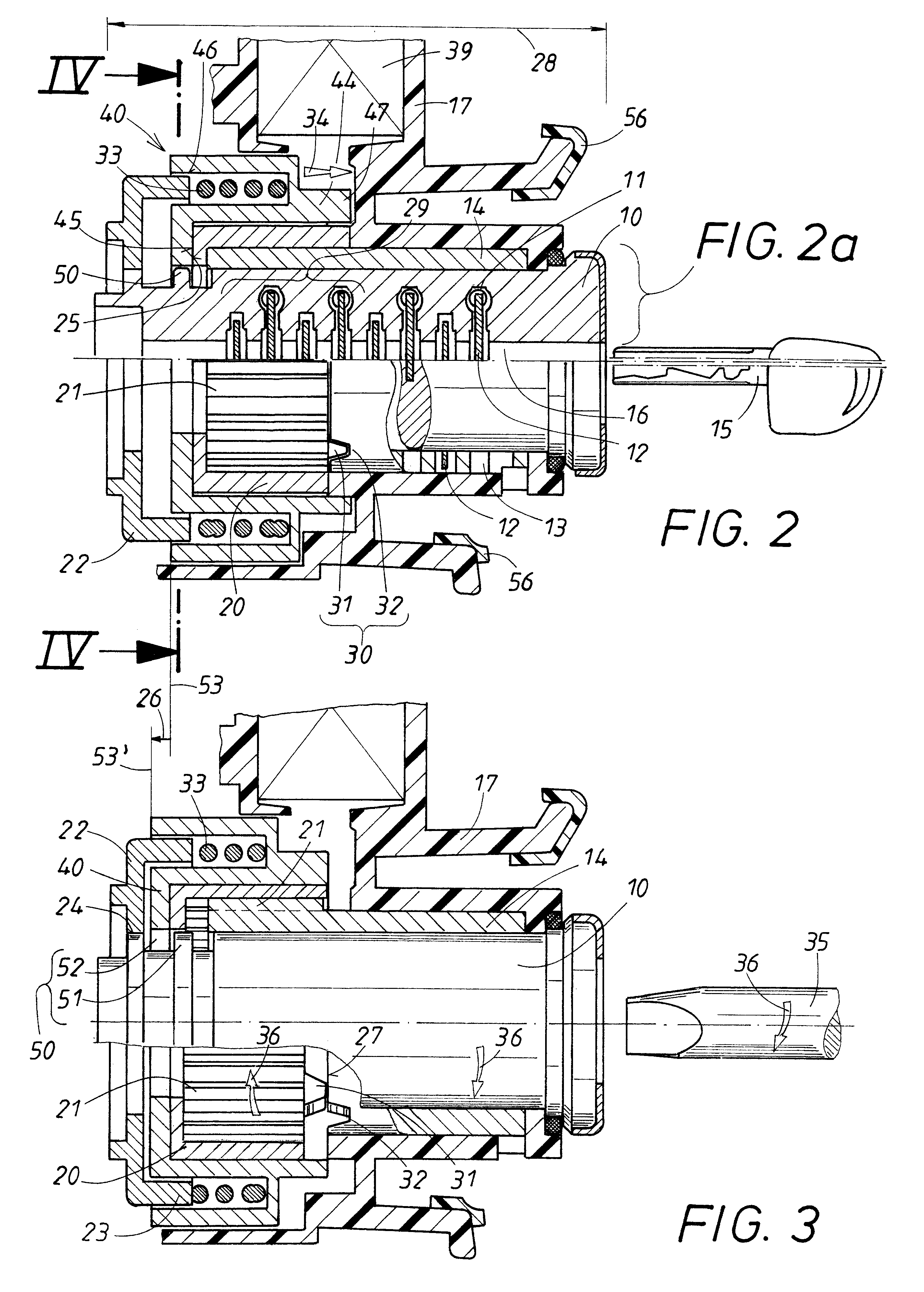
InactiveUS6425275B1Convenient ArrangementReduce construction lengthCylinder locksCouplingEngineering
A locking device with a key-actuated cylinder core has a cylinder guide rotationally supporting the cylinder core and stopping points for tumblers. One area of the cylinder guide is received axially fixed but rotatably in a housing, while the other area is surrounded by a sliding member non-rotatably but axially slidably supported on the cylinder guide. A turning member surrounds the sliding member and is rotatable relative to and synchronously axially movable with the sliding member. A spring acts axially on the turning member. An overload protection device has a control element arranged on the housing and a counter control element, arranged on the sliding member and spring-loaded against the control element, for axially moving the sliding and turning members in an overload situation to release an axial coupling having one coupling member fixedly connected to the cylinder core and another coupling member arranged on the turning member.
Owner:HUF HULSBECK & FURST GMBH & CO KG
Electrical switching system
ActiveUS20070267388A1Low overall lengthMore compact constructionSwitchgear arrangementsHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesElectrical connectionVacuum switch
An electrical switching system, preferably a medium-voltage switching system, has a power switch or load switch, a disconnecting switch, and a grounding switch configured as a vacuum switching chamber. Low separation distance lengths and a more compact construction of a switching system is achieved by means of a housing in which the disconnecting switch, configured as a vacuum switching chamber, the grounding switch, and the power switch or load switch are disposed, and in which a central switch is disposed, with which the vacuum switching chambers of disconnecting switch and grounding switch can be mechanically activated. Electrical connections between connector contacts of power switch or load switch, disconnecting switch, and grounding switch can be produced.
Owner:RAIL POWER SYST GMBH
Dual clutch transmission
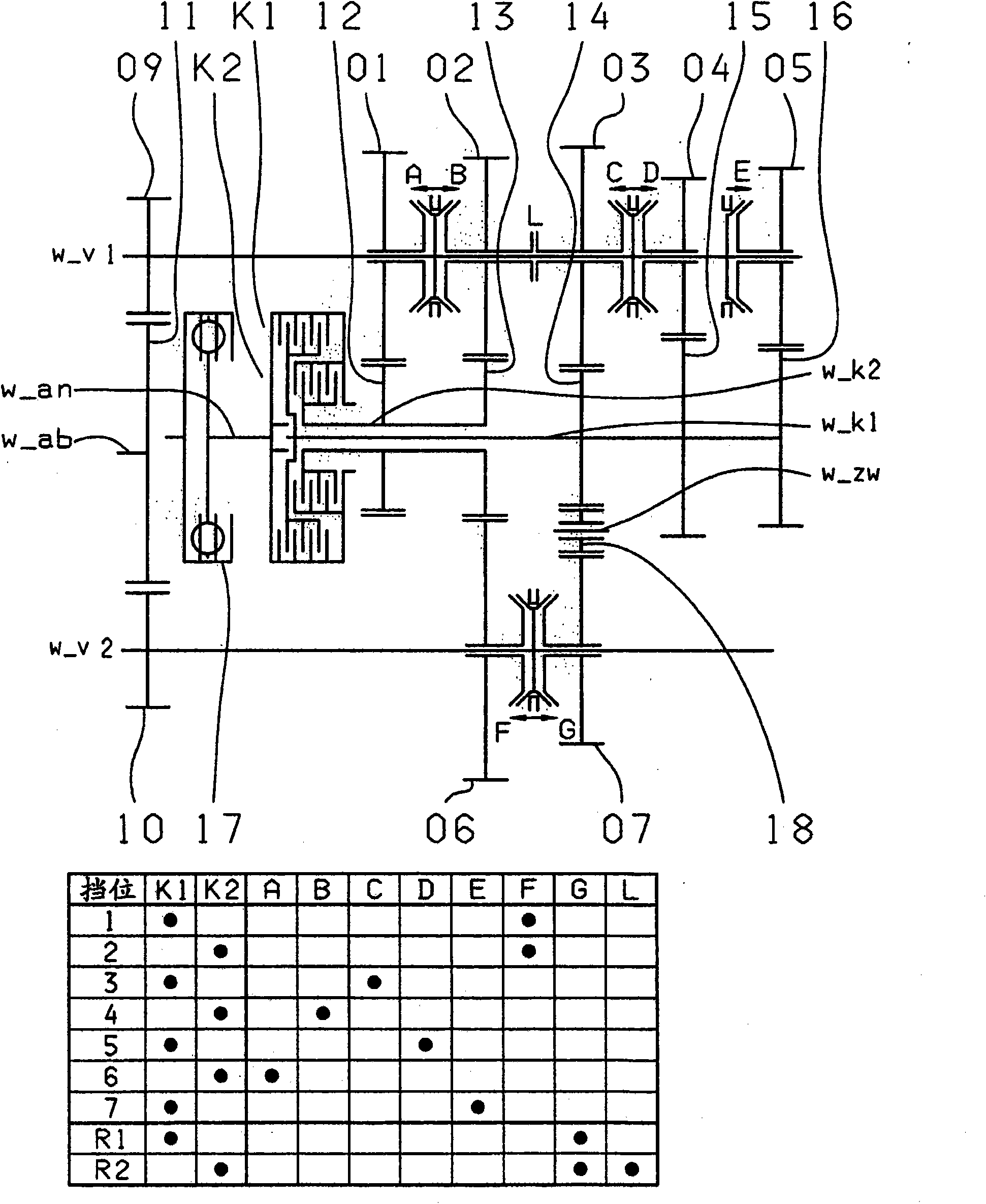
InactiveCN101802448AReduce construction lengthFree choice of transmission ratioToothed gearingsTransmission elementsCouplingPower take-off
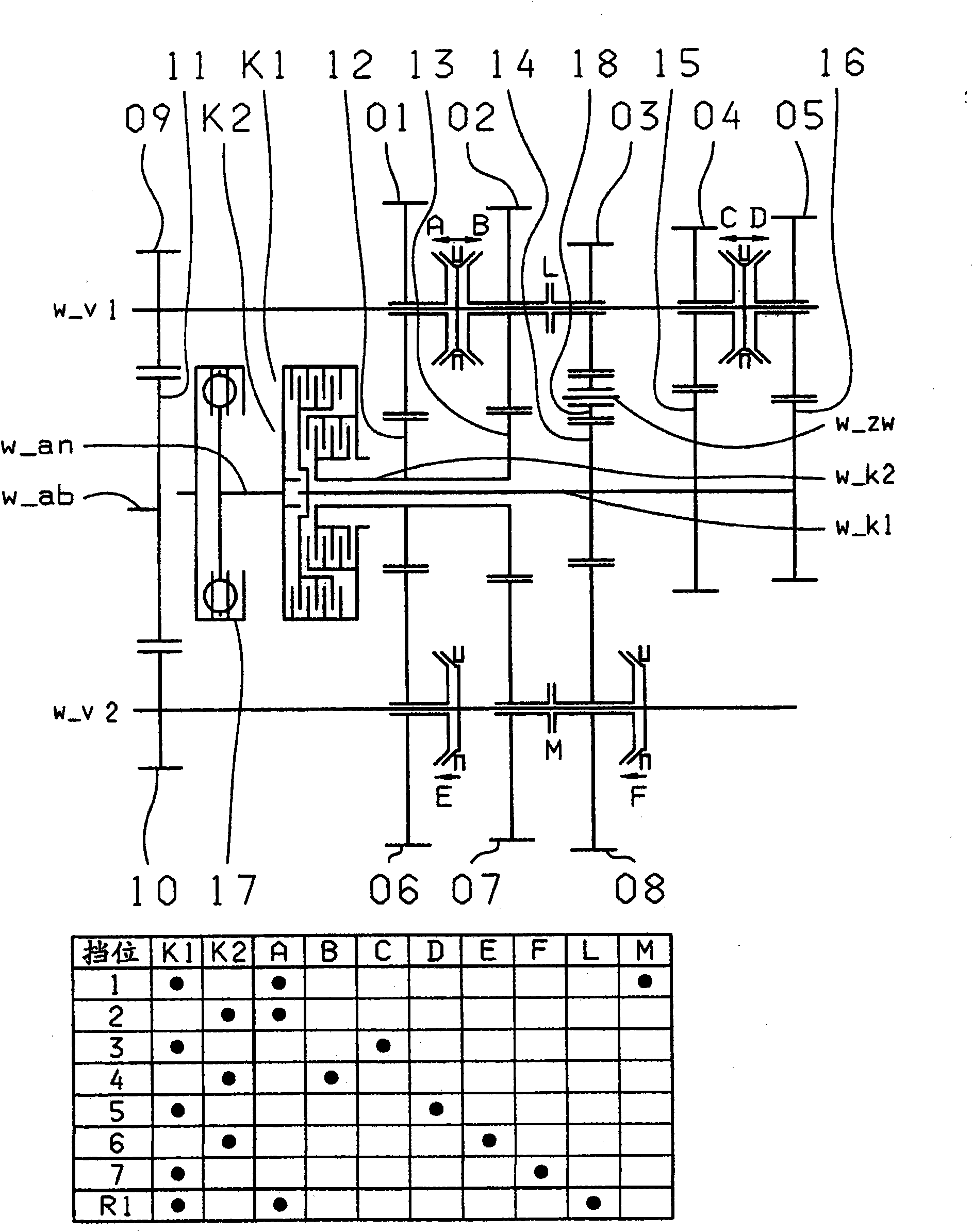
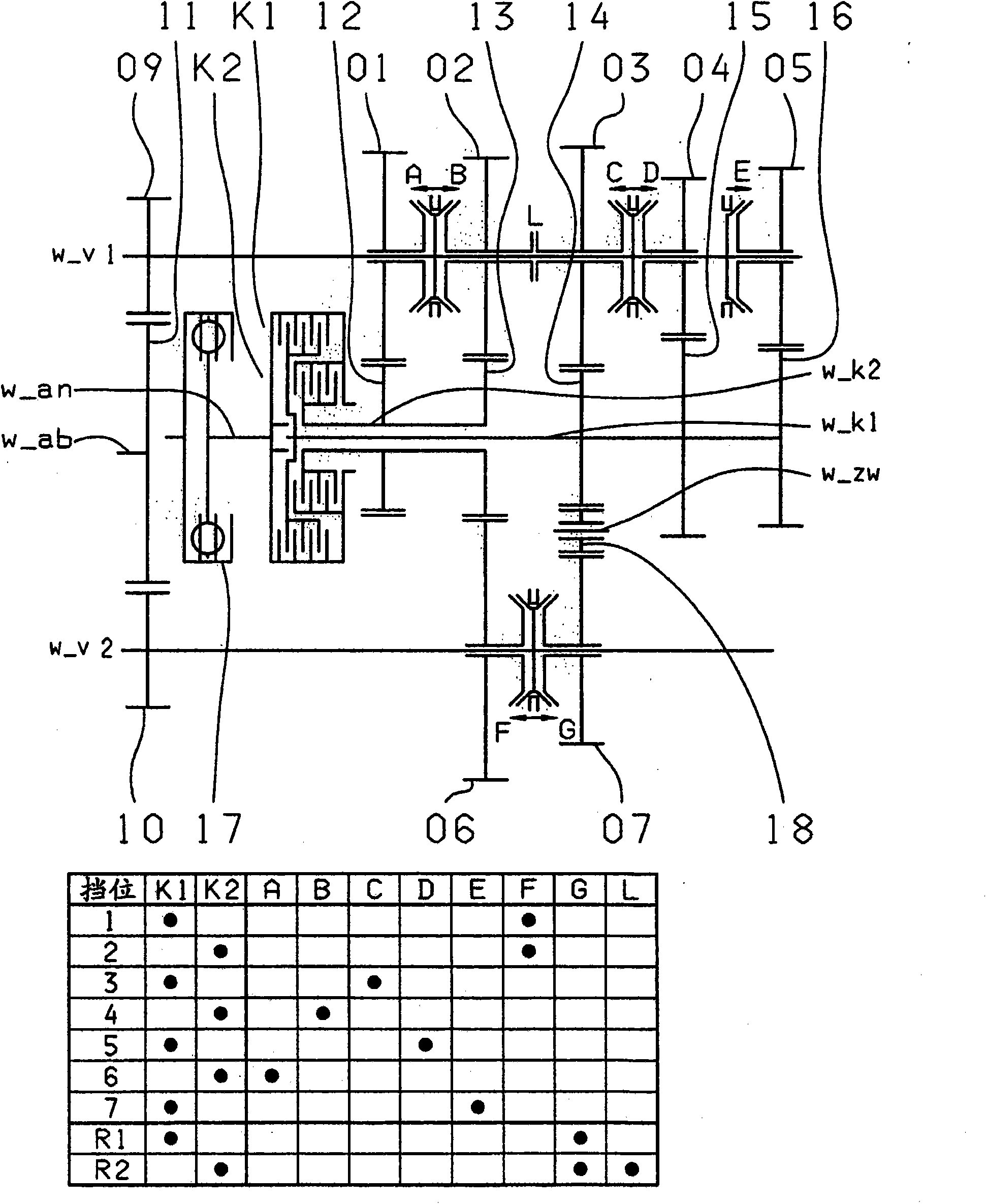
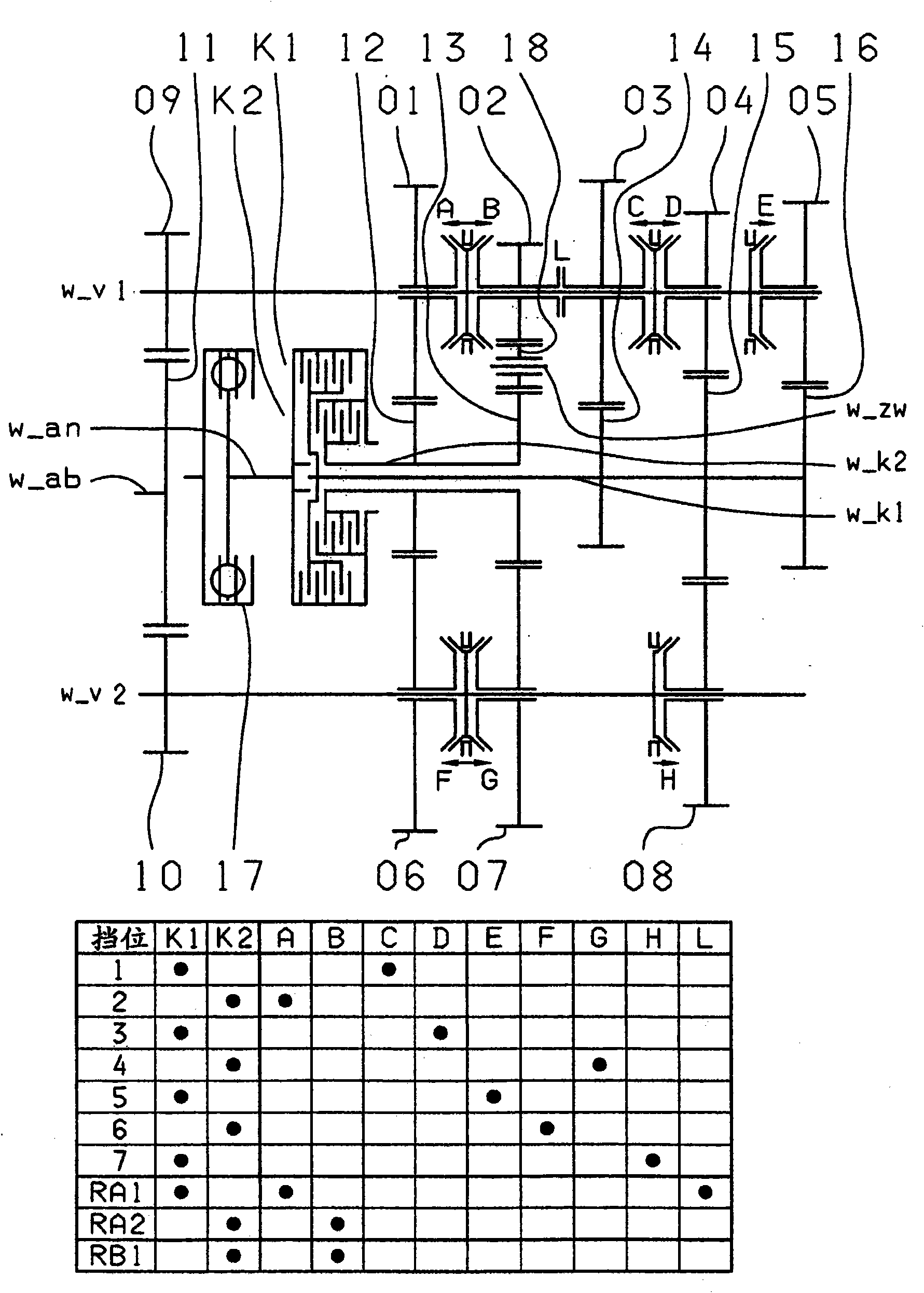
The invention relates to a dual clutch transmission comprising two clutches (K1, K2) the input sides of which are connected to an input shaft (w_an) and the output sides of which are connected to one of two transmission input shafts (w_K1, w_K2) that are arranged coaxially relative each other; at least two countershafts (w_countershaft1, w_countershaft2) on which toothed gearwheels, configured asidler gears (01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 08), are rotatably received; toothed gearwheels that are non-rotatably arranged on the two transmission input shafts (w_K1, w_K2), that are configured as fixed gears (12, 13, 14, 15, 16) and that engage at least partially with the idler gears (01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 08); a plurality of coupling devices (A-B, C-D, F-G, E, H, F) for the non-rotatable connection of an idler gear (01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07) to a countershaft (w_countershaft1, w_countershaft2) and respective pairs of power take-off gears (09, 10) mounted on the two countershafts (w_countershaft1, w_countershaft2), said pairs of power take-off gears being coupled to a toothed section of a power take-off shaft (w_ab); and at least one shift element (L) for coupling the two transmission input shafts (w_K1, w_K2), at least seven power-shifted forward gears (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) and at least one reverse gear (RA1, R1) being shiftable. The dual clutch transmission is characterized in that five gear planes (01-12, 01-06; 02-06, 02-07; 03-07, 03-14, 03-08; 04-15, 04-08; 05-16) are arranged in such a manner that at least one power-shifted winding path gear can be shifted via at least one shift element (L, M).
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Railway vehicle and train
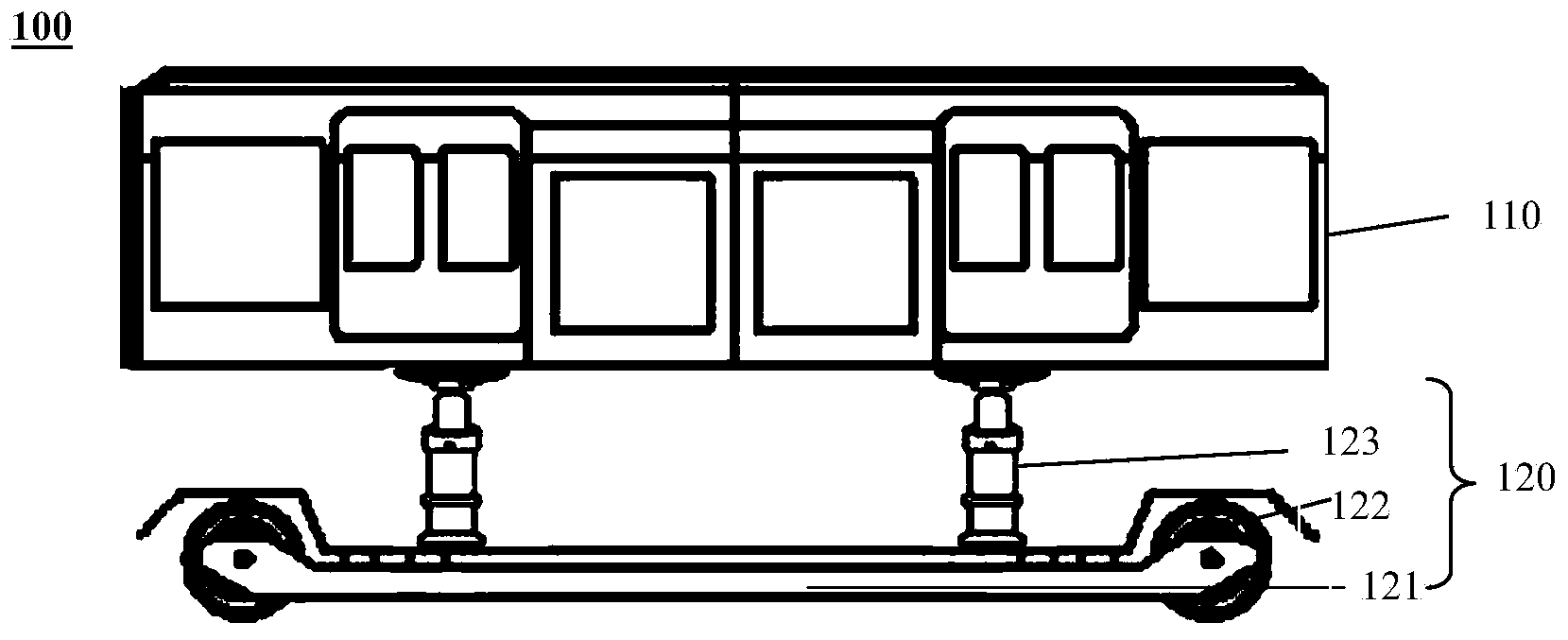
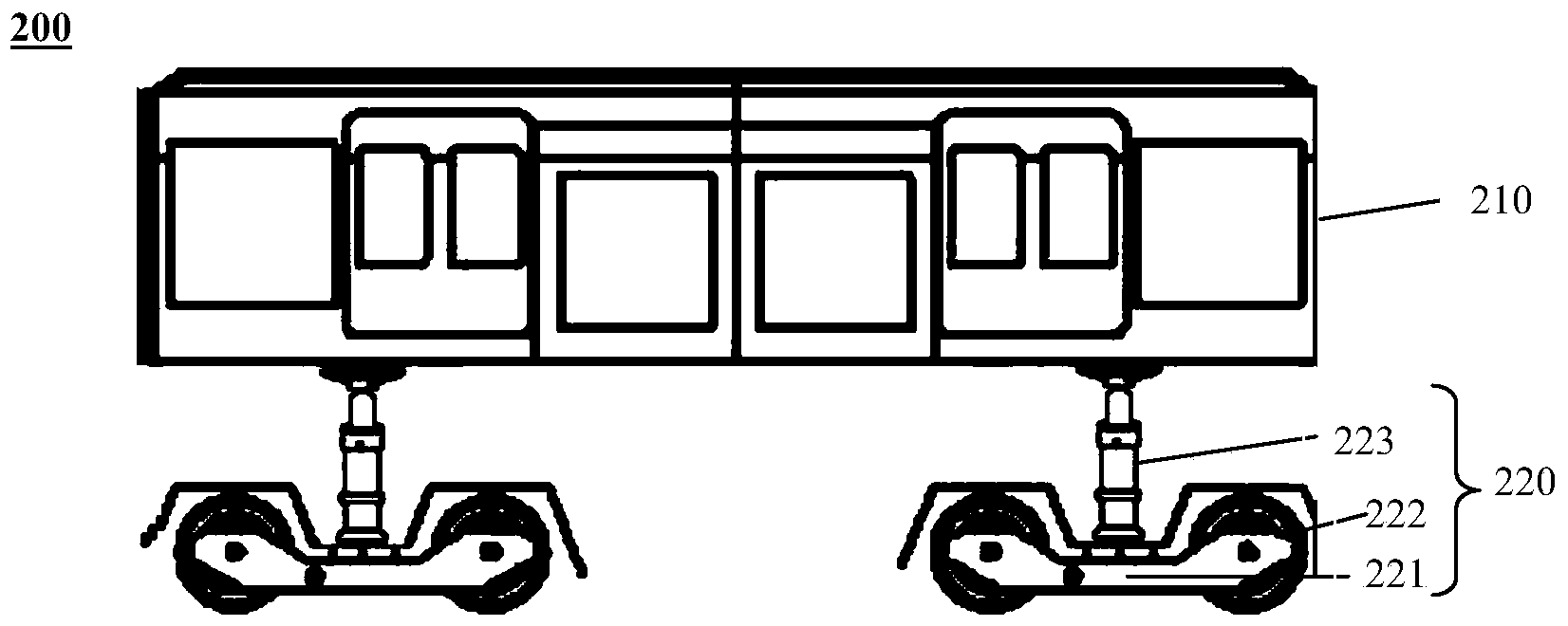
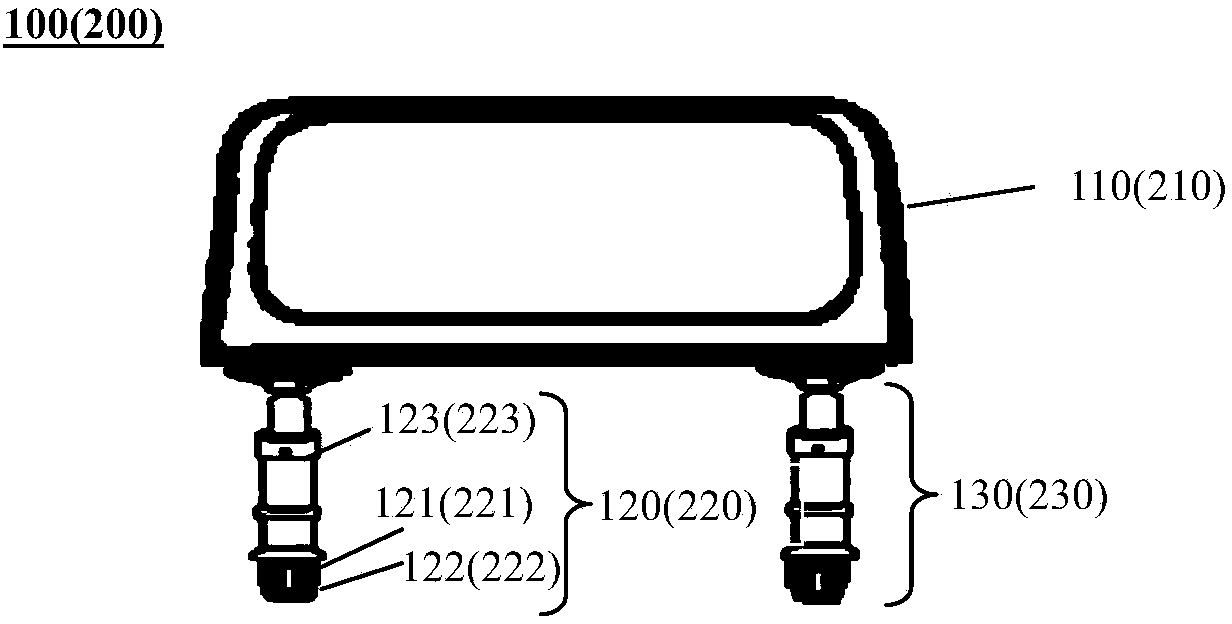
InactiveCN103832441ALower the altitudeReduce construction lengthPassenger carriagesWagons/vansEngineeringInverted u
The invention provides a railway vehicle and a train. The railway vehicle comprises a brake system, and further comprises a carriage, a left-side support, a right-side support, at least one left-side walking portion and at least one right-side walking portion, wherein the carriage comprises a left carriage wall and a right carriage wall and is used for containing people or goods; the left-side support is located on the left side of the left carriage wall and connected with the left carriage wall through at least one left-side lifting mechanism to enable the carriage to lift along the left-side support; the right-side support is located on the right side of the right carriage wall and connected with the right carriage wall through at least one right-side lifting mechanism to enable the carriage to lift along the right-side support; the left-side walking portion is provided with the left-side support; the right-side walking portion is provided with the right-side support; the brake system is used for braking the left-side walking portion and the right-side walking portion; each walking portion comprises a walking frame and at least two metal wheels installed on the walking frame to enable the railway vehicle to be suitable for running on a railway; the railway vehicle is in an inverted U shape in the running direction so as to allow other vehicles to pass through from the position below the carriage.
Owner:张迪
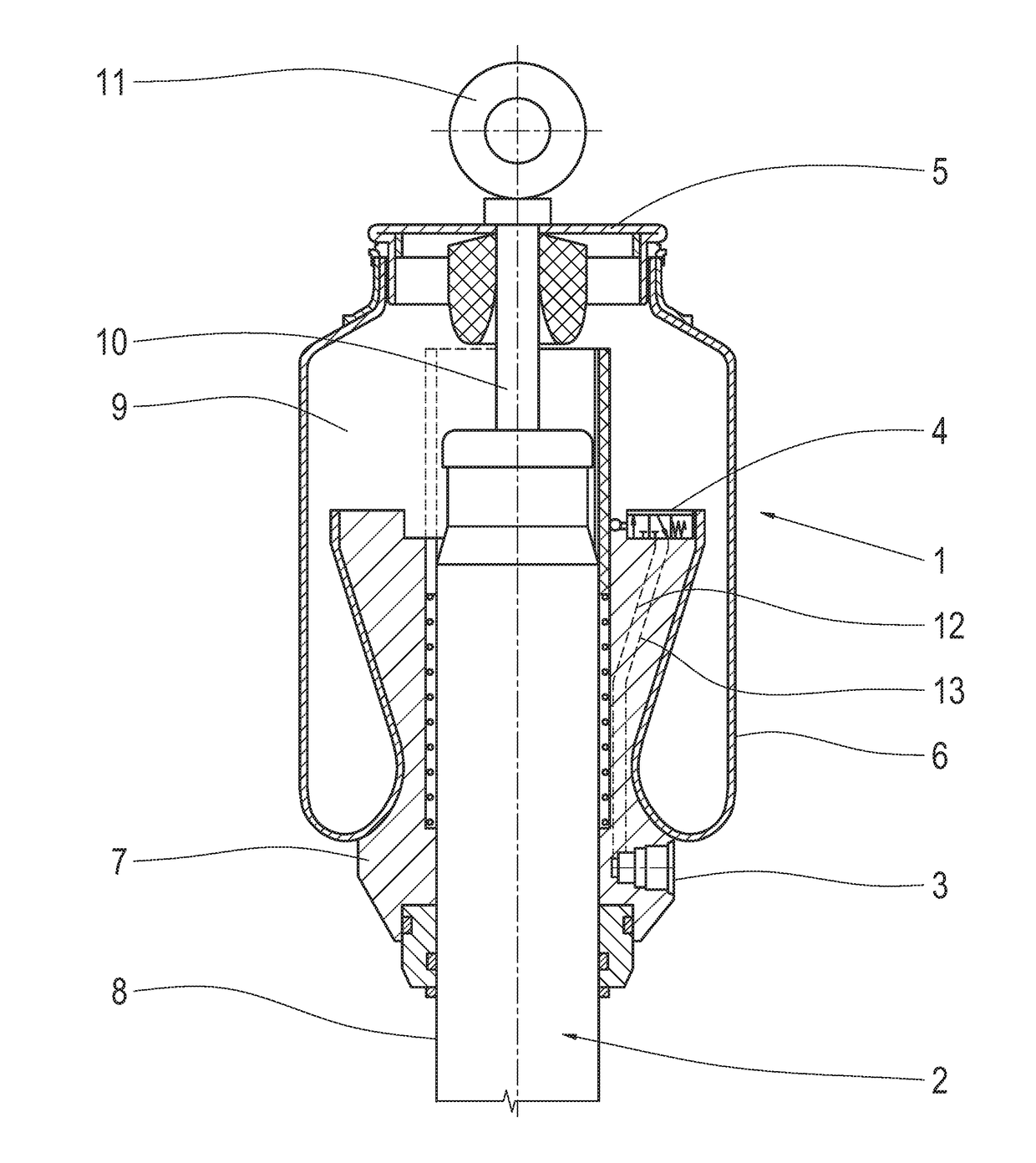
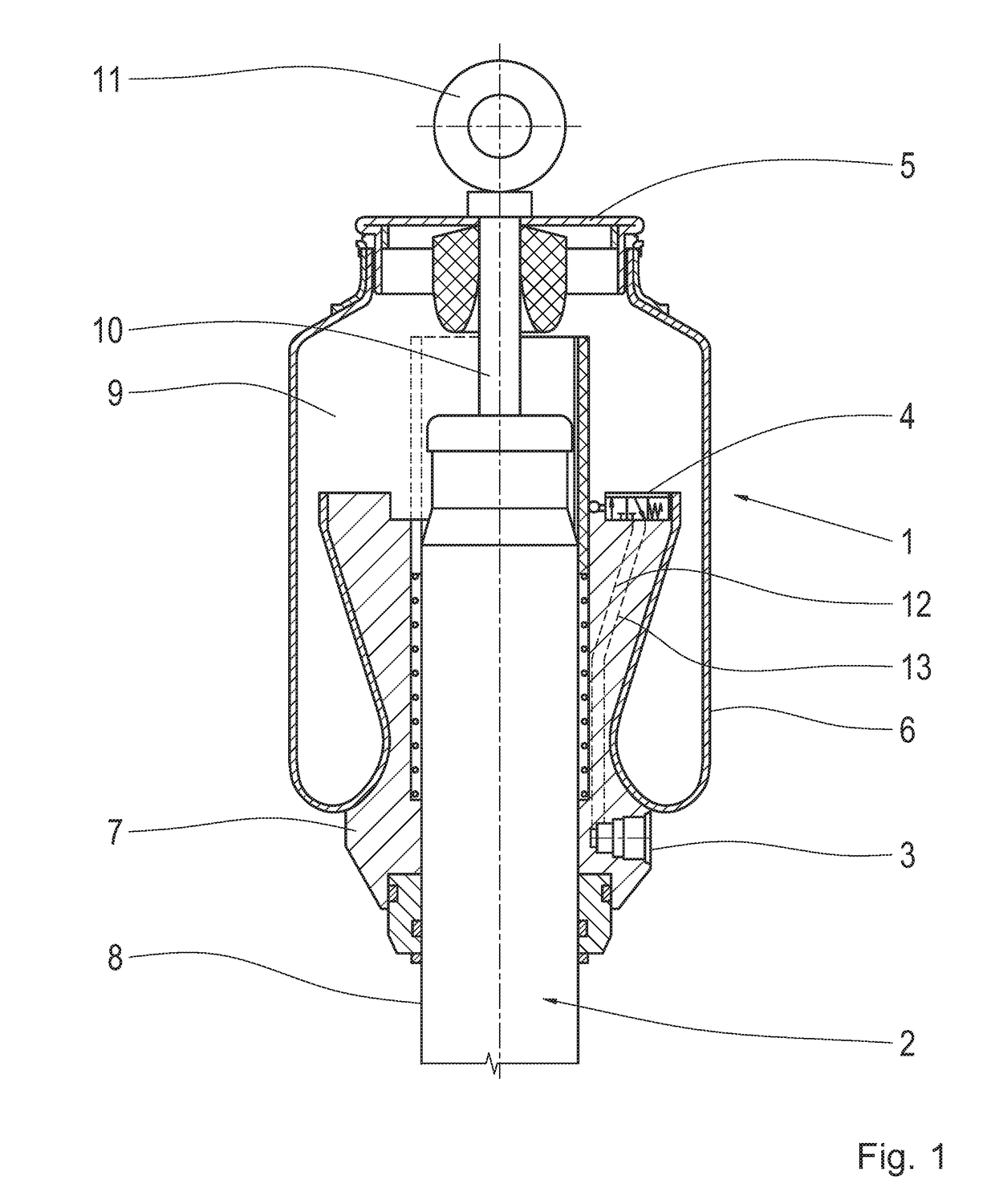
Cold Gas Generator
InactiveUS20030137135A1Guaranteed precise adjustabilityHigh filling pressurePedestrian/occupant safety arrangementProduct gasEngineering
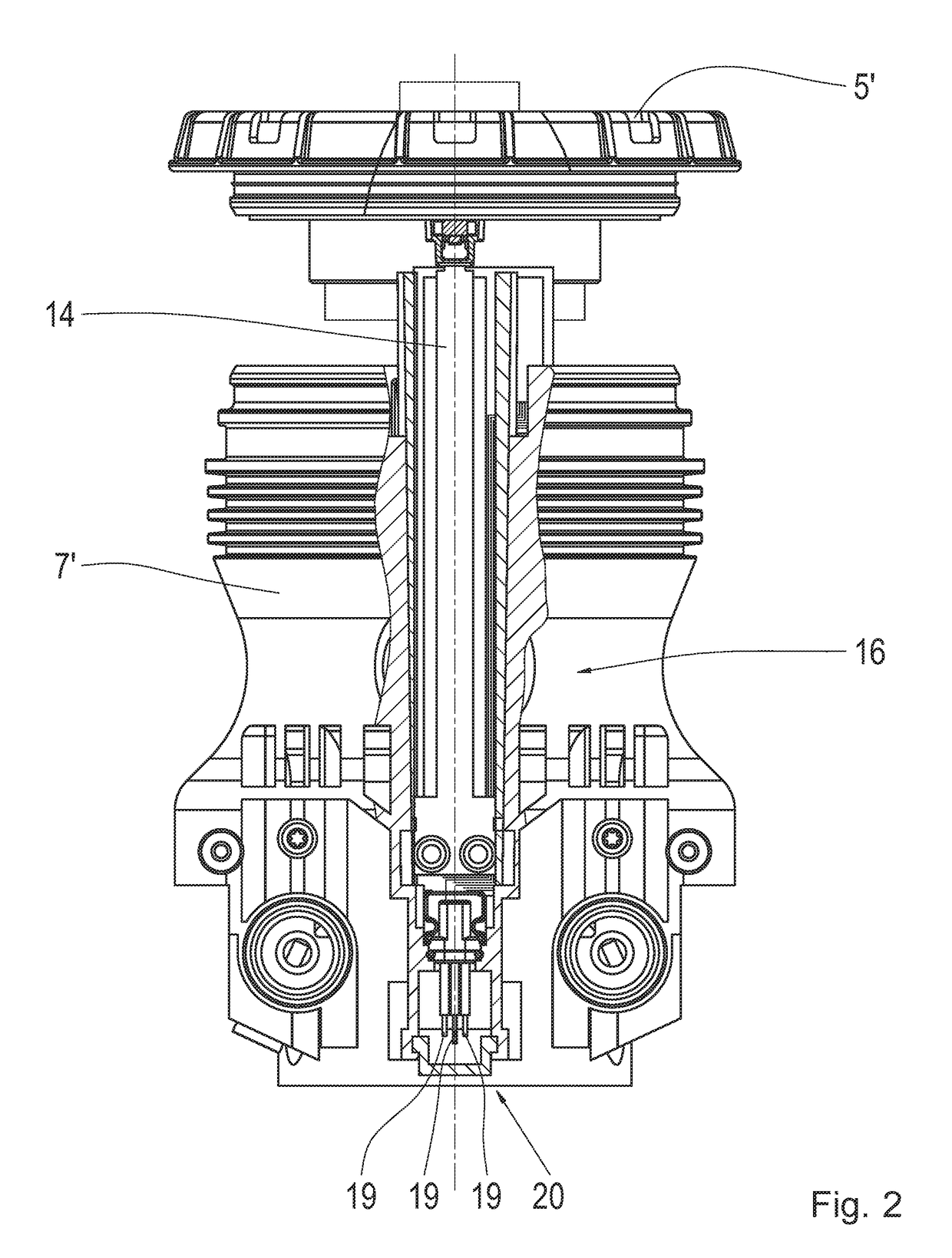
Abstract of Disclosure A cold gas generator for an airbag system has a storage device filled with a gas under pressure. The storage device has a first end and a second end. A triggering device is provided at the first end for introducing the gas when needed into an airbag. The second end has a convexly curved bottom with a receiving opening arranged approximately centrally in the bottom. A safety valve is inserted into the receiving opening as a closure and attached by welding to the receiving opening.
Owner:WELZ INDPROD
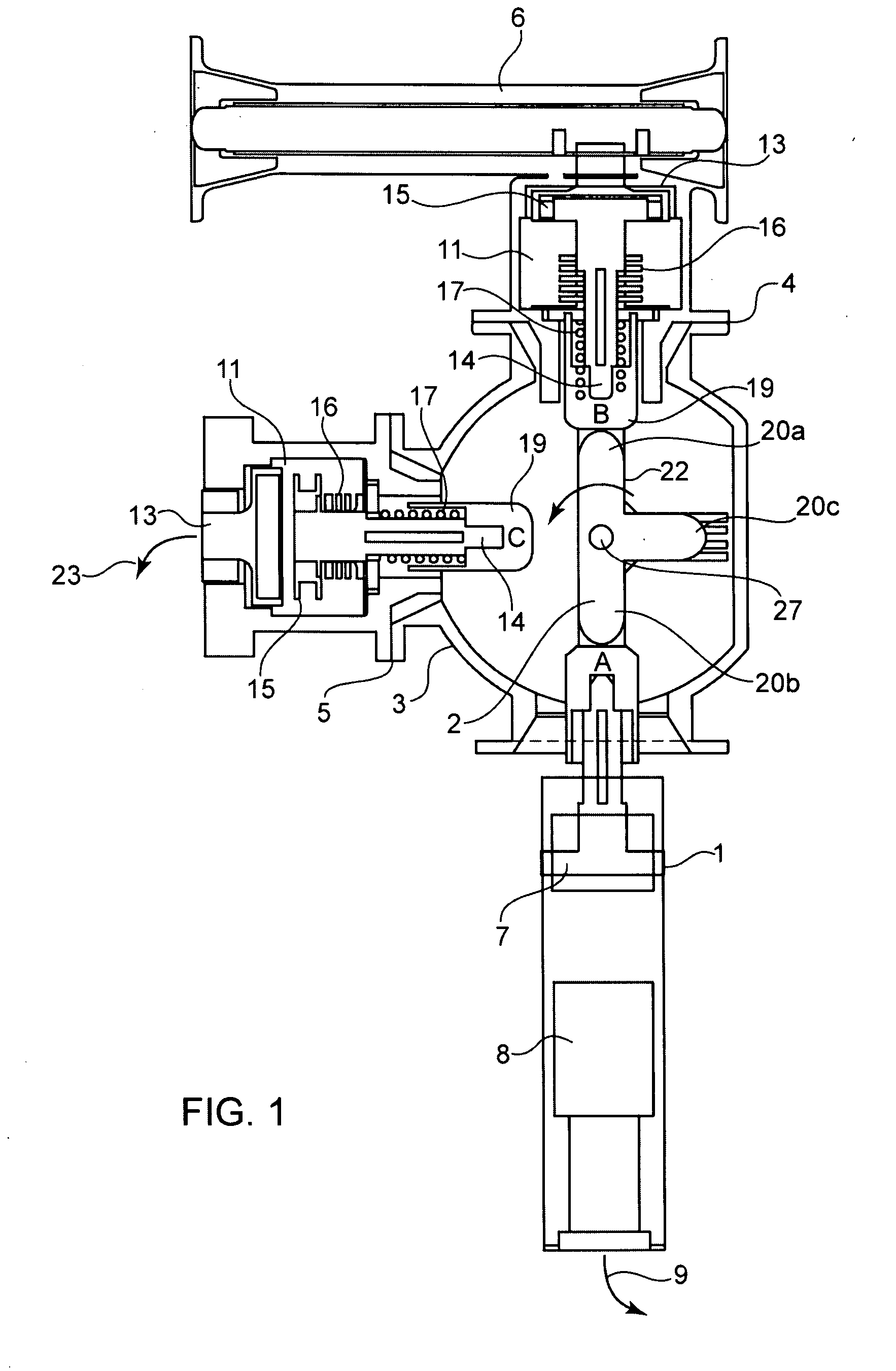
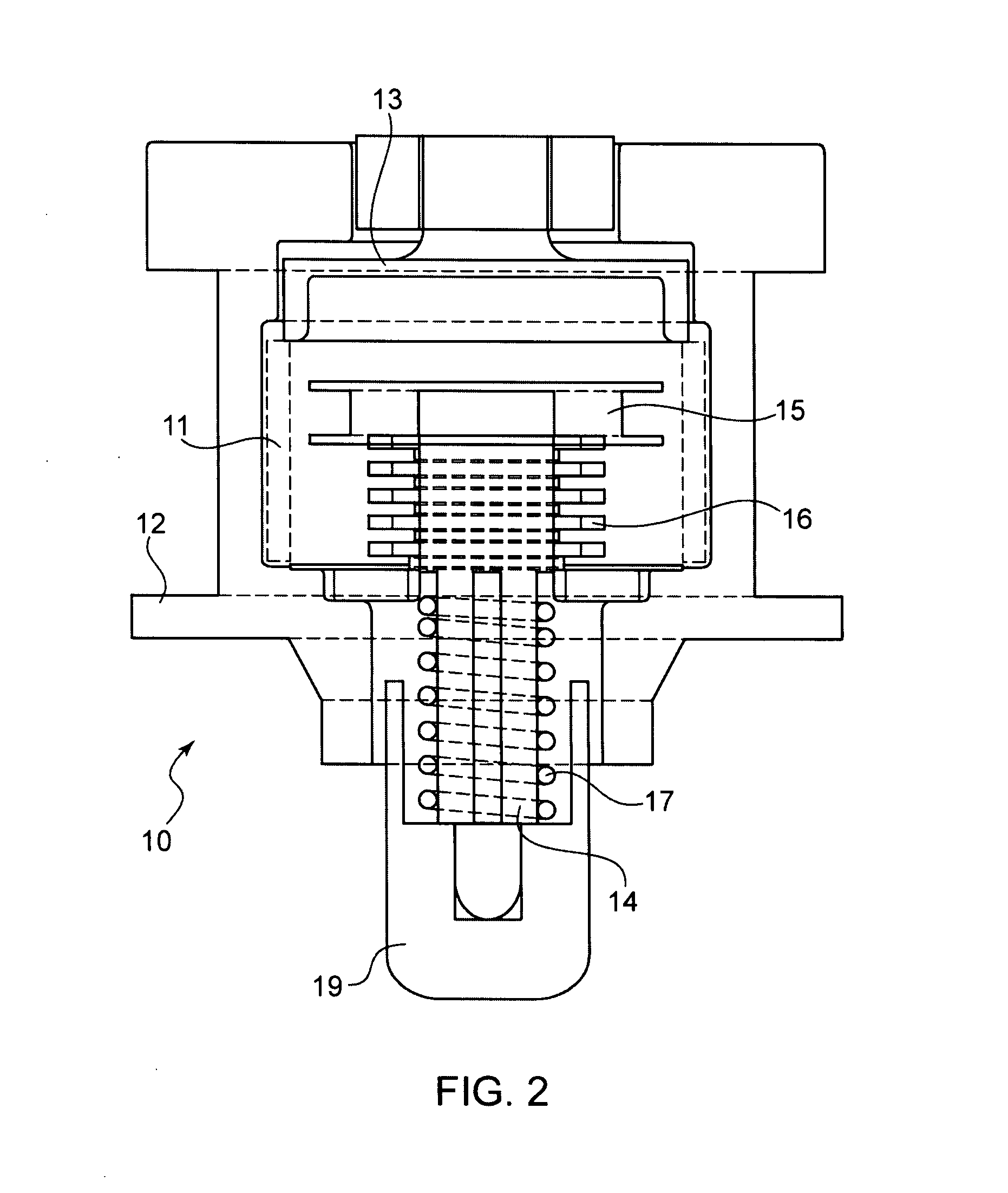
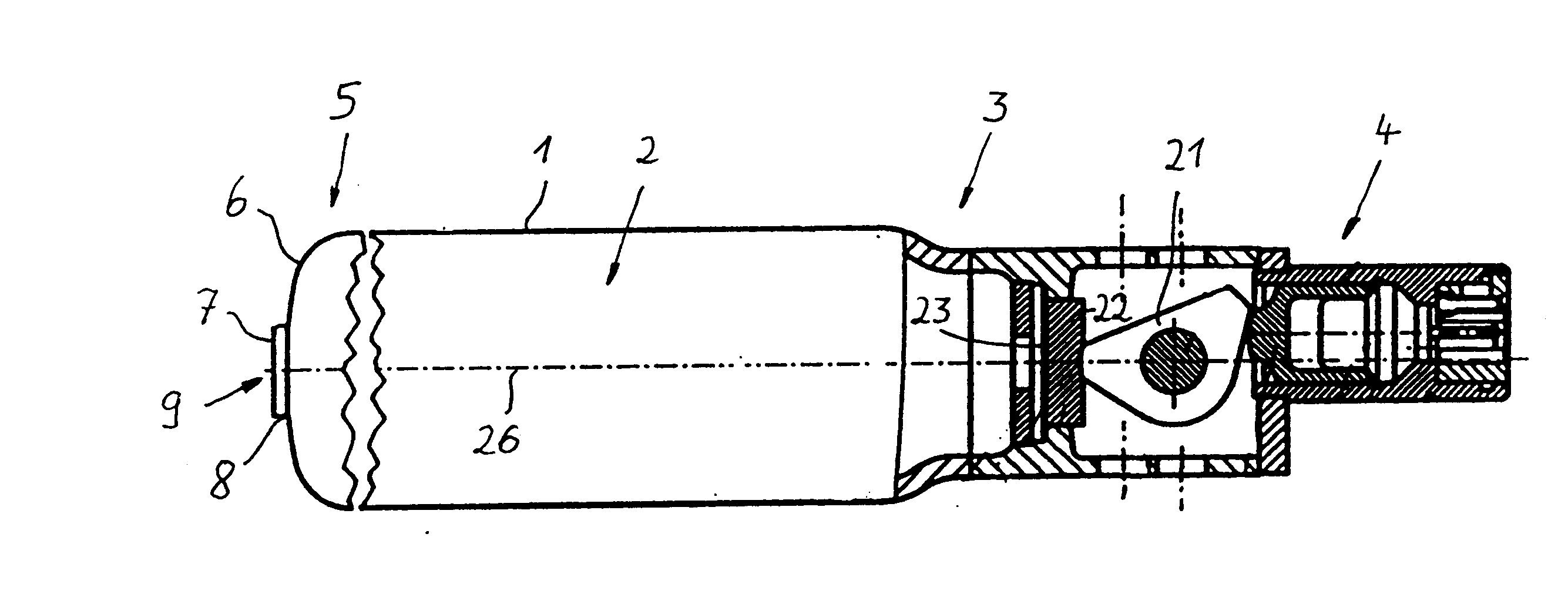
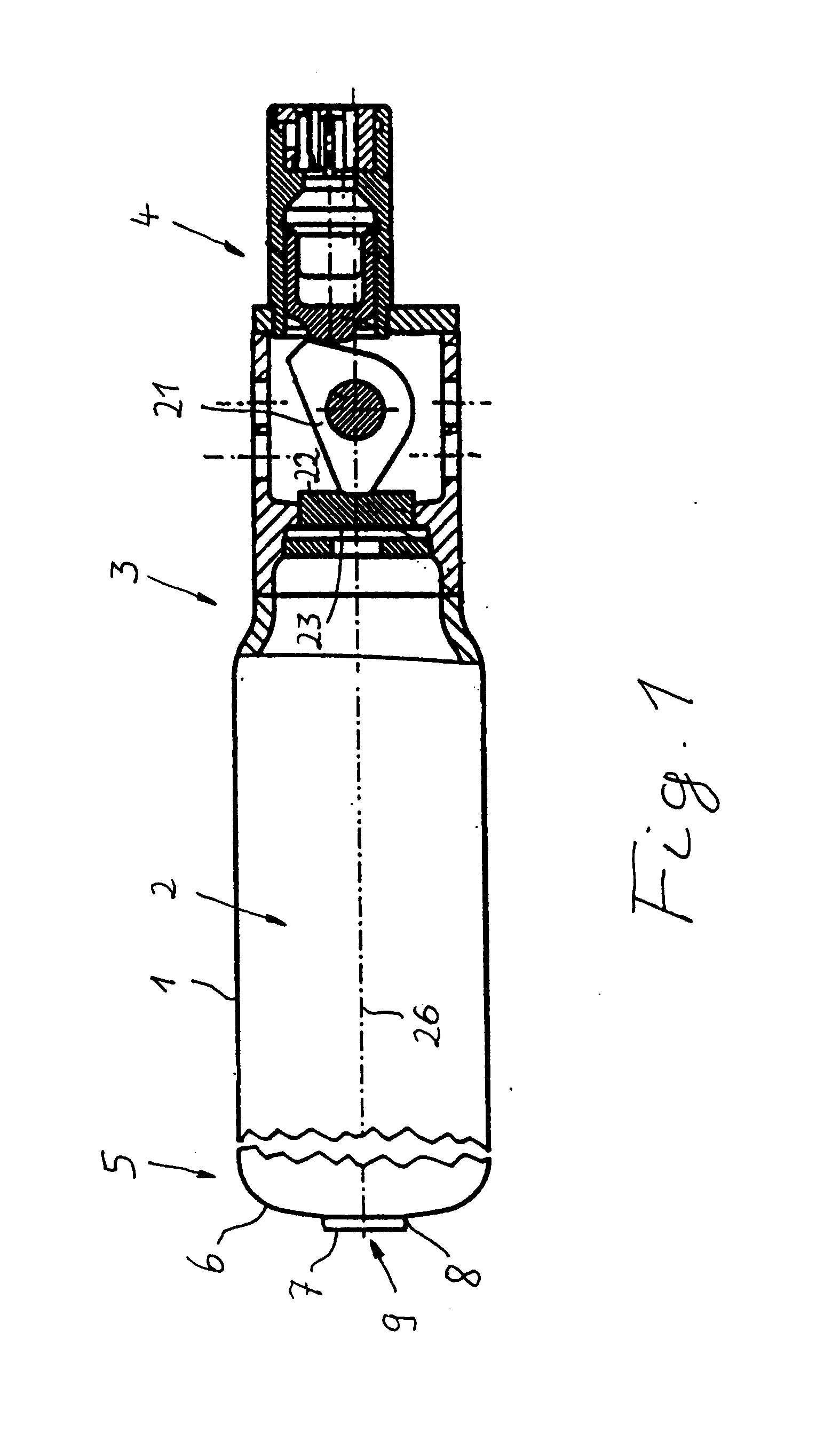
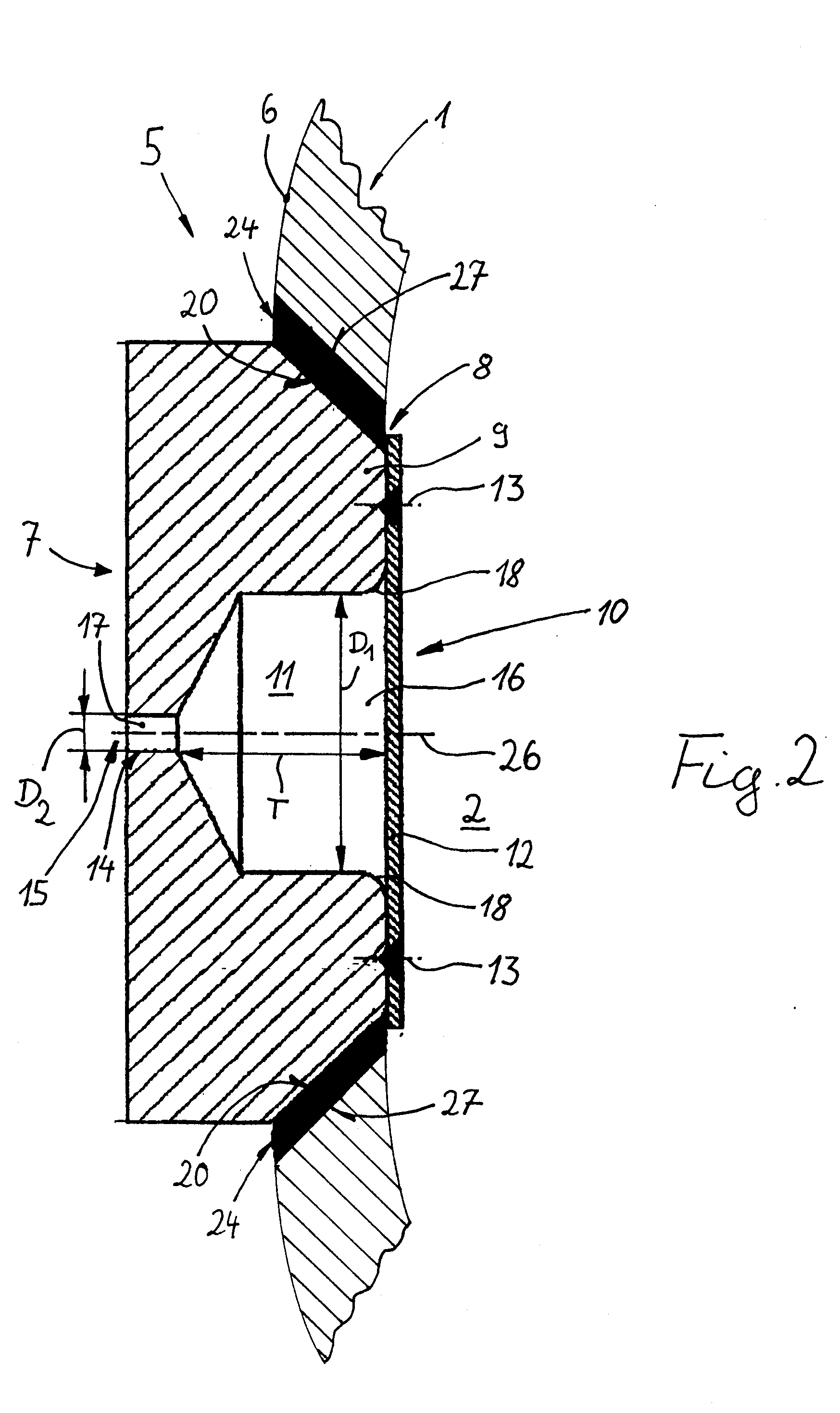
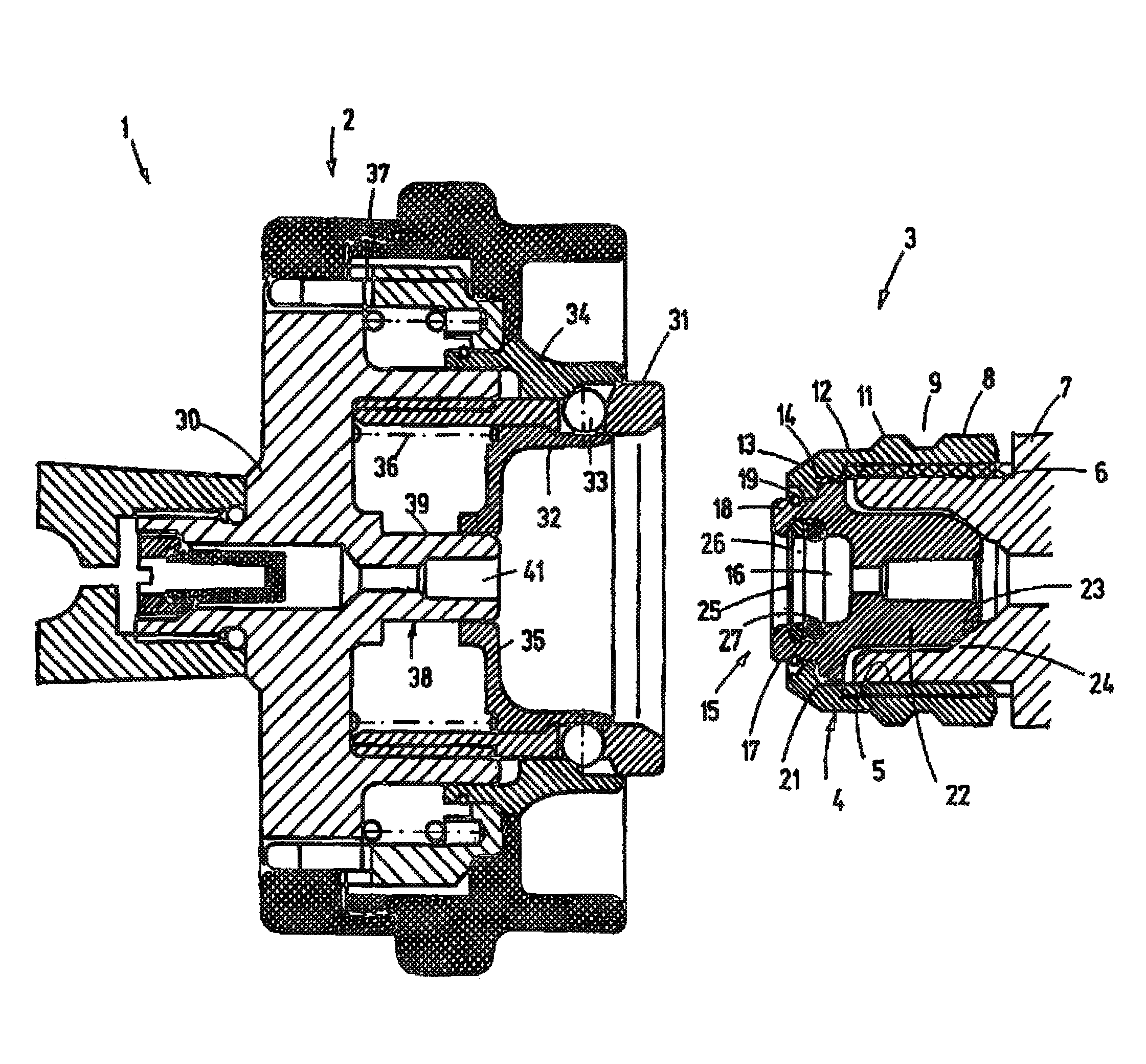
Short-body plug for fluid couplings
ActiveUS8596689B2Reduce construction lengthFirmly connectedAdjustable jointsCouplingsFluid couplingEngineering
Owner:RECTUS
Electrical switching system
ActiveUS7679019B2Compact structureLow overall lengthSwitchgear arrangementsHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesElectrical connectionEngineering
An electrical switching system, preferably a medium-voltage switching system, has a power switch or load switch, a disconnecting switch, and a grounding switch configured as a vacuum switching chamber. Low separation distance lengths and a more compact construction of a switching system is achieved by means of a housing in which the disconnecting switch, configured as a vacuum switching chamber, the grounding switch, and the power switch or load switch are disposed, and in which a central switch is disposed, with which the vacuum switching chambers of disconnecting switch and grounding switch can be mechanically activated. Electrical connections between connector contacts of power switch or load switch, disconnecting switch, and grounding switch can be produced.
Owner:RAIL POWER SYST GMBH
Diversion drainage structure for tunnel inside in water conservancy and hydropower project and construction method of diversion drainage structure
ActiveCN104912043AReduce construction lengthShort construction periodWater-power plantsHydro energy generationHydropower engineeringEngineering
The invention discloses a diversion drainage structure for a tunnel inside in a water conservancy and hydropower project and a construction method for building the diversion drainage structure, and belongs to the technical field of design and construction of buildings in the water conservancy and hydropower project. The invention provides the diversion drainage structure for the tunnel inside in the water conservancy and hydropower project and the construction of the building construction method. The diversion drainage structure for the tunnel inside in the water conservancy and hydropower project is short in construction period, low in construction investment cost and capable of meeting the requirement of upward moving of an opening of a diversion drainage tunnel. The construction method includes that a section of a drainage tunnel is constructed on the upstream side of a drainage tunnel body in a river flow direction, a construction maintenance diversion tunnel which communicates the drainage tunnel and the drainage tunnel body is constructed before the drainage tunnel and the drainage tunnel body are communicated, the requirement for temporary diversion drainage of an upstream river channel is met, then the connection position of the drainage tunnel and the drainage tunnel body is completely broken through, a waste upper section of the drainage tunnel body is blocked, finally, simultaneous drainage of the drainage tunnel and the downstream section of the drainage tunnel body as well as the drainage tunnel, the construction maintenance diversion tunnel and the downstream section of the drainage tunnel body is realized.
Owner:POWERCHINA CHENGDU ENG
Weir structure and construction method thereof
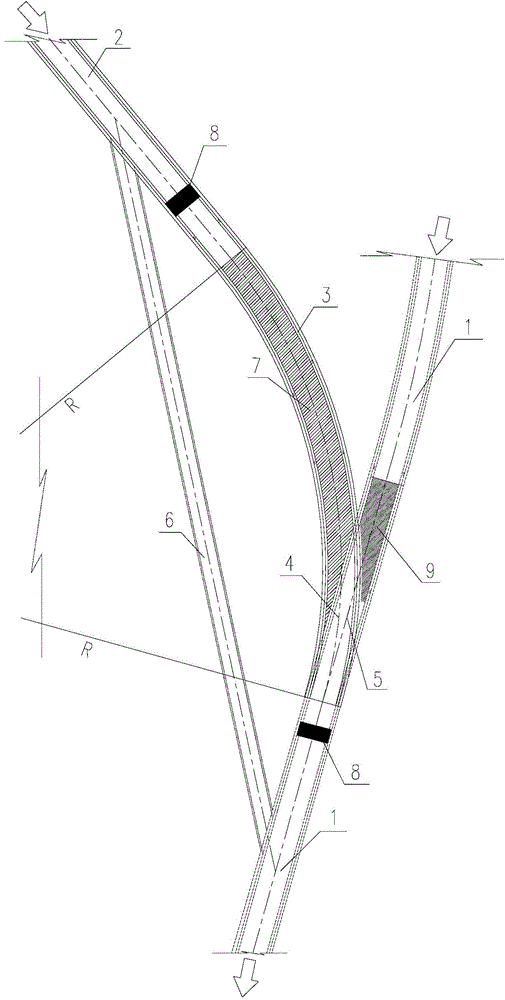
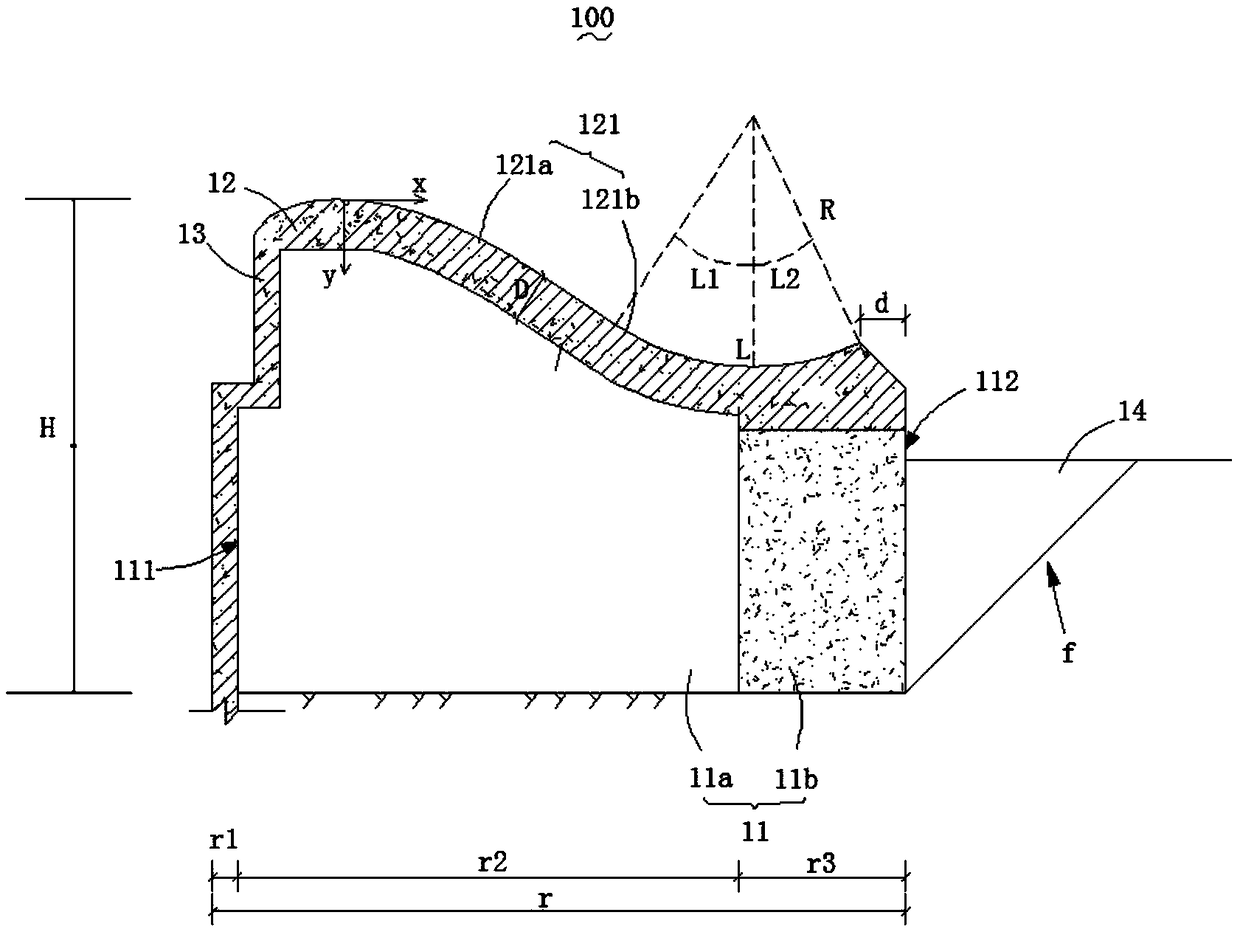
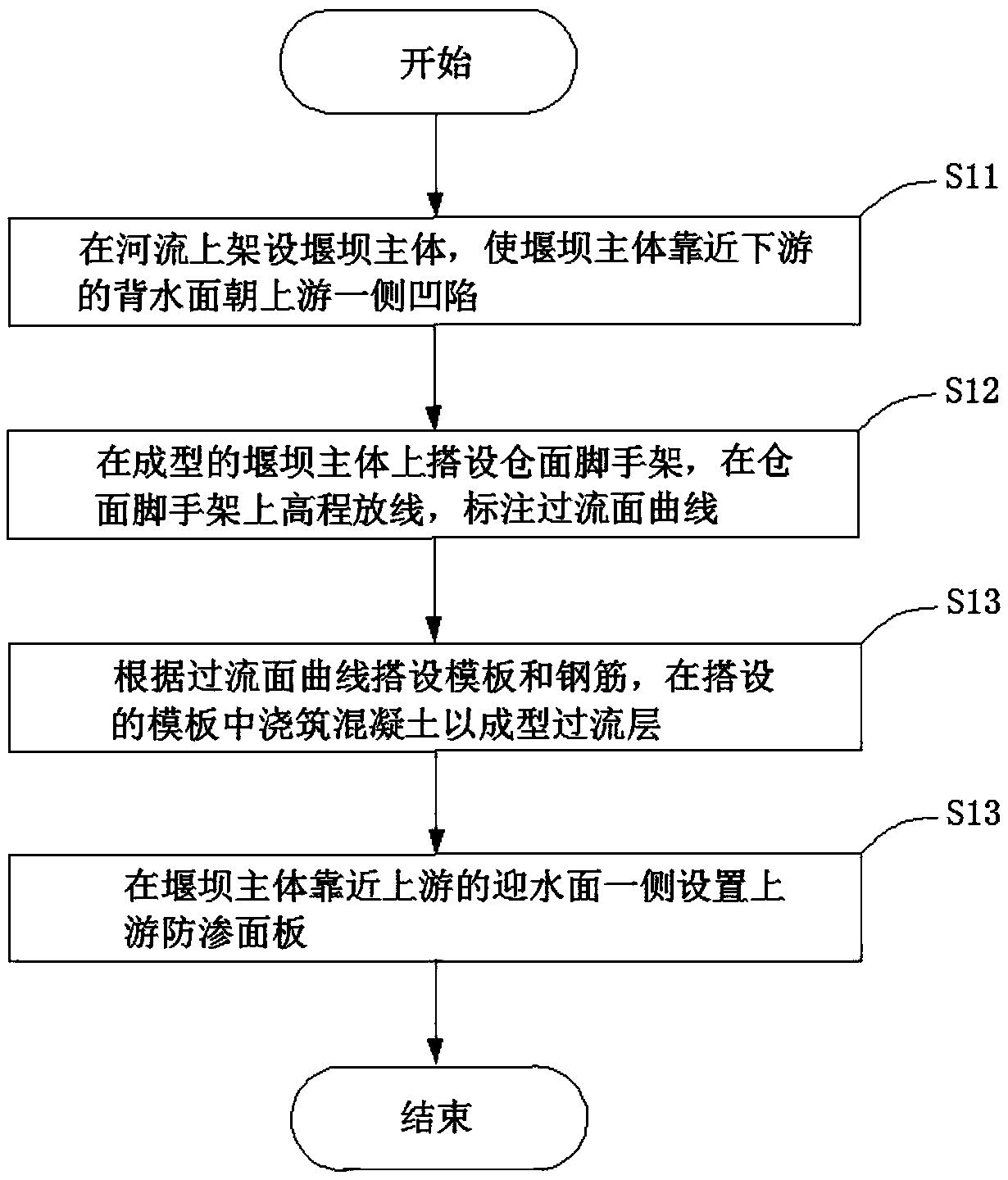
InactiveCN108625345AIncrease the lengthWiden the width of the flood dischargeBarrages/weirsEngineeringWater resources
The invention relates to the technical field of water resource facilities, and discloses a weir structure and a construction method thereof. The weir structure comprises a weir main body, an overflowing layer and an upstream anti-seepage panel; the weir main body is erected on a riverbed, and comprises an upstream face facing the upstream side and a downstream face facing the downstream side; thedownstream face is sunken towards the upstream side; the overflowing layer is arranged on the upper side of the weir main body along a top outline of the weir main body and used for overflowing riverwater; and the upstream anti-seepage panel is arranged on one side of the upstream face of the weir main body. According to the weir structure and the construction method of the weir structure, the flood discharge width can be increased, burdens of downstream energy dissipation measures can be reduced, and the cost of the downstream energy dissipation measures is lowered.
Owner:SHENZHEN SPRINGWOODS HLDG CO LTD
Belt buckle with release lock
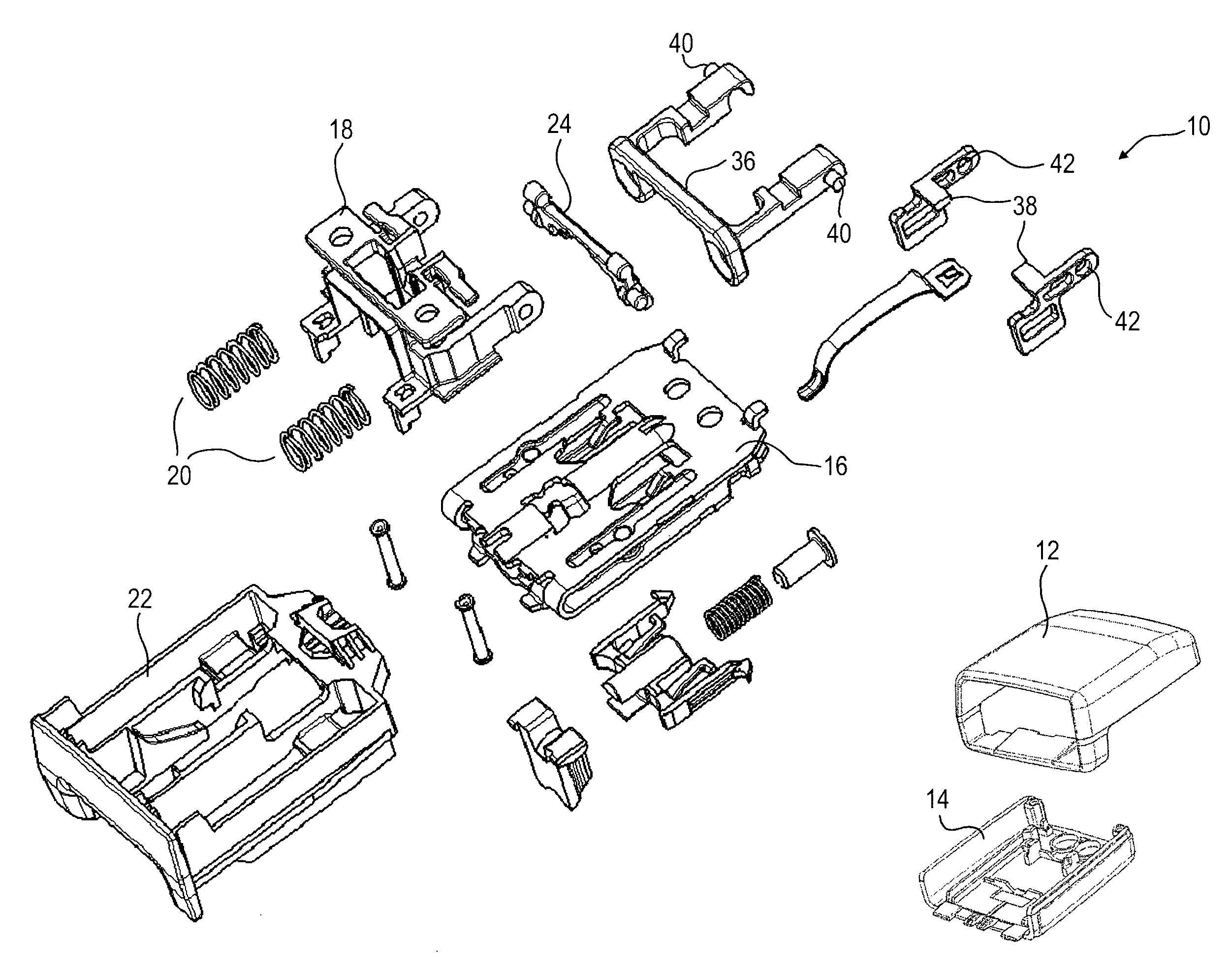
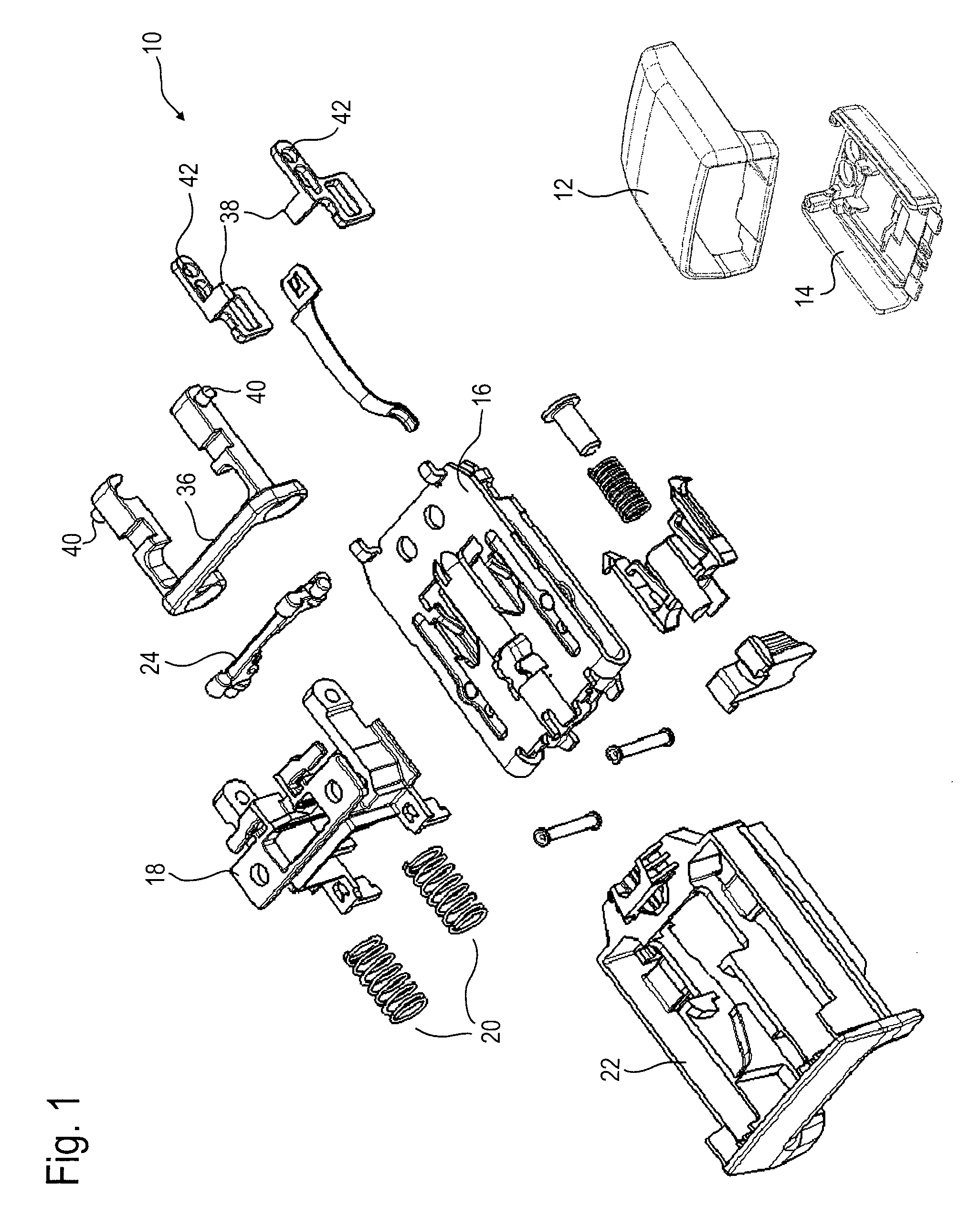
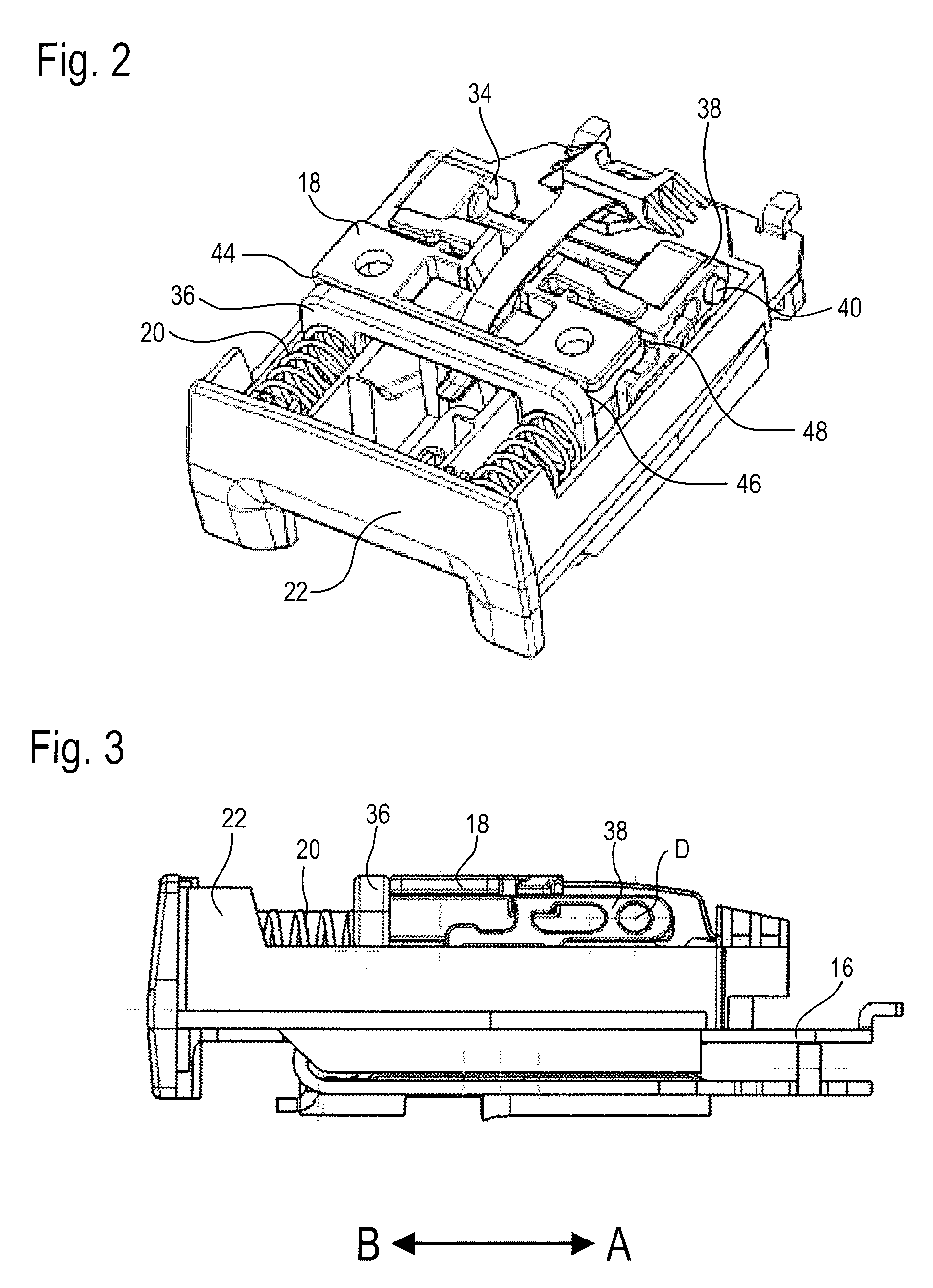
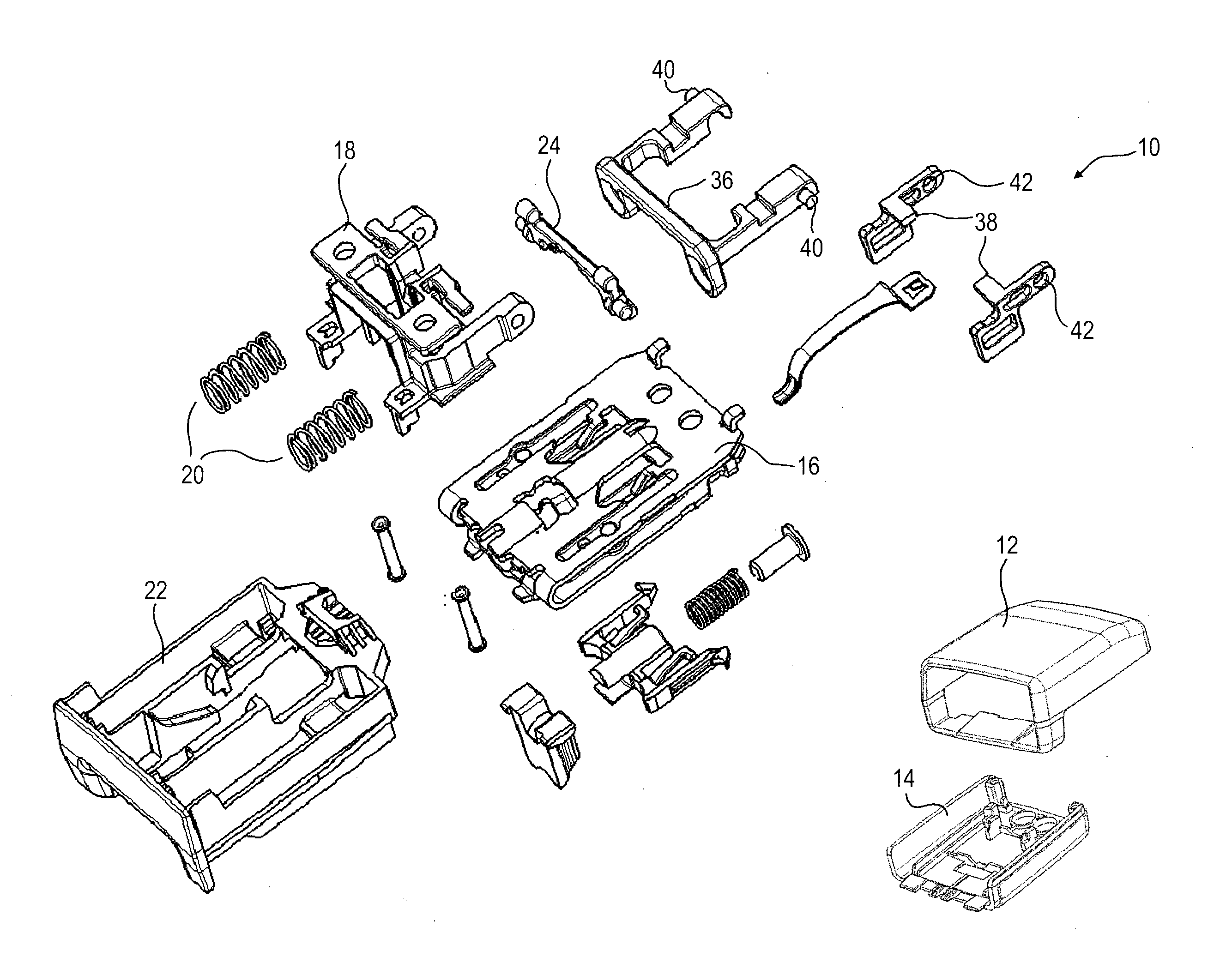
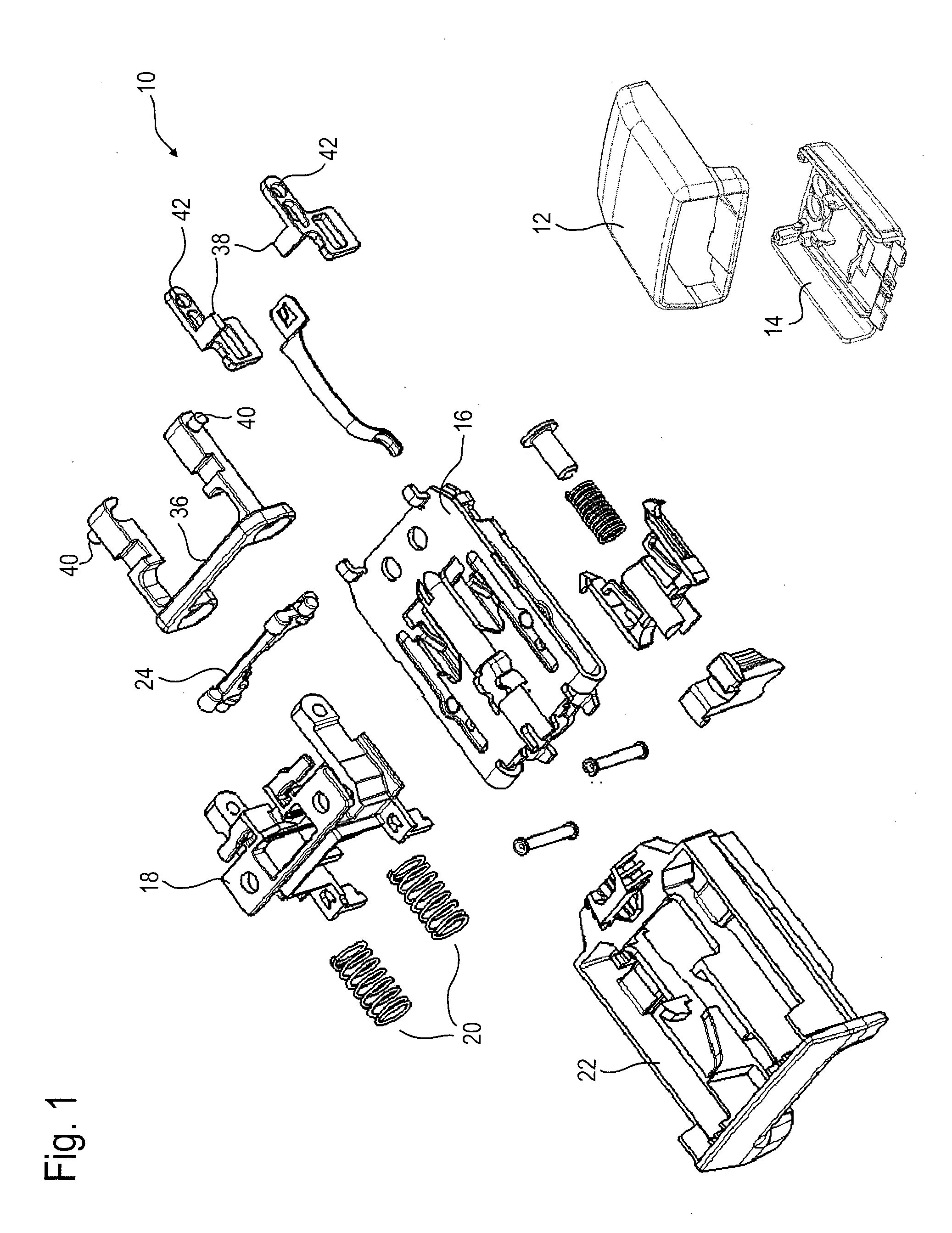
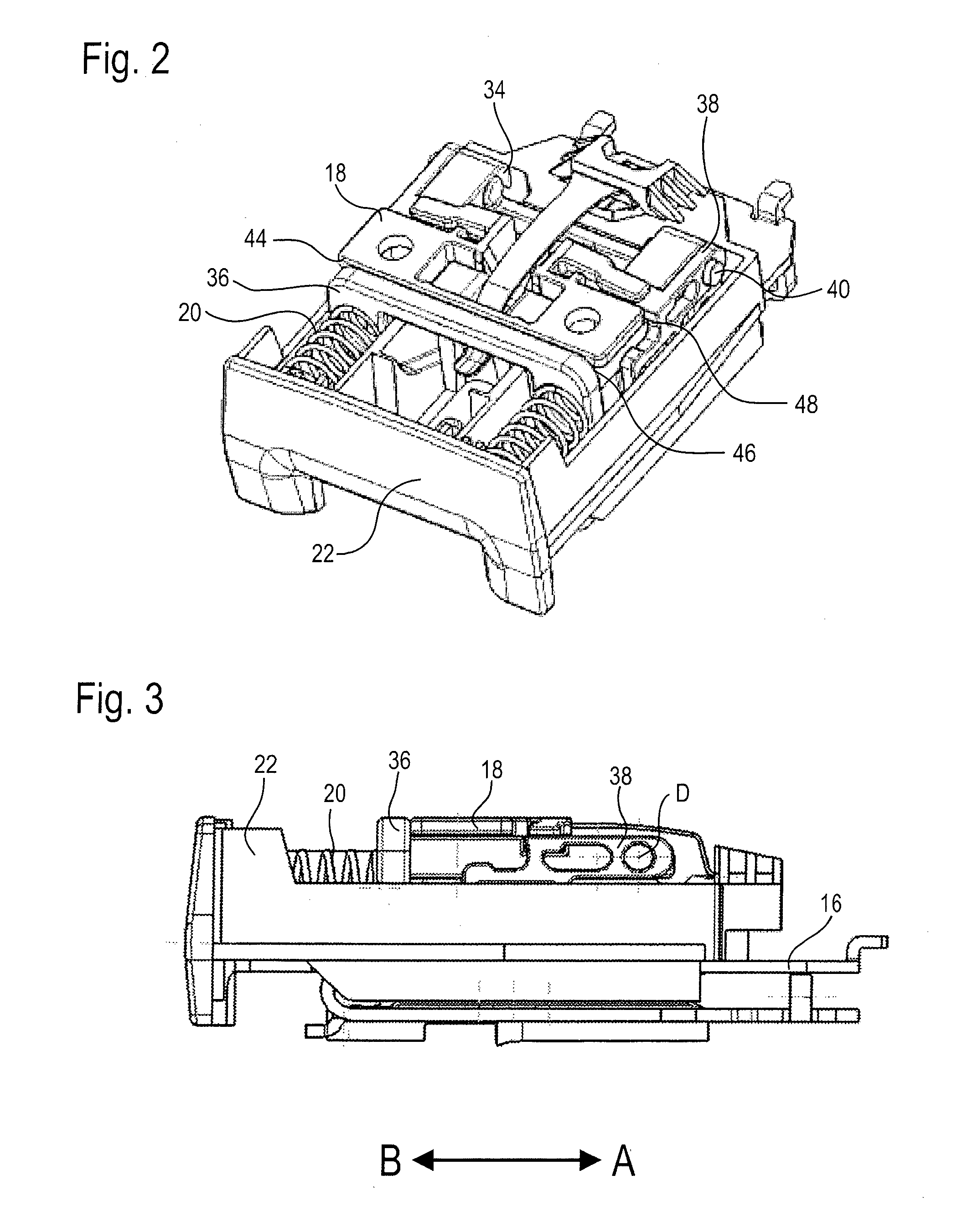
ActiveUS9402446B2Easy to integrateReduce manufacturing costVehicle componentsBucklesLocking mechanismCoupling
A belt buckle (10) for a seat belt includes a buckle housing (16), a locking mechanism for locking a plug-in tongue inserted in the buckle housing (16), a release button (22) which is movable in a first direction relative to the buckle housing (16) for unlocking the plug-in tongue, and a safety mechanism for preventing automatic displacement of the release button (22) in the first direction. The safety mechanism includes a mass body (36) movable in the first direction relative to the buckle housing (16) and a movably supported coupling lever (24) including an axis of rotation which is stationary relative to the buckle housing (16). The coupling lever (24) is coupled to the mass body (36) and to the release button (22) so that, upon acceleration of the belt buckle (10) in a second direction opposed to the first direction, it transmits an inertia force acting on the mass body (36) in the first direction to the release button (22) in the opposite second direction.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Railway vehicle and train
InactiveCN103832442AReduce construction lengthReduce construction costsPassenger carriagesWagons/vansInverted uBraking system
The invention provides a railway vehicle and a train. The railway vehicle comprises a brake system, and further comprises a carriage, at least one left-side walking portion located on the left side below the carriage, and at least one right-side walking portion located on the right side below the carriage, wherein the carriage is used for containing people or goods; the brake system brakes the left-side walking portions and the right-side walking portions. Each walking portion comprises a walking frame, at least two metal wheels and at least one lifting mechanism, wherein the metal wheels are installed on the walking frame and used for enabling the railway vehicle to be suitable for running on a railway, and the lifting mechanism is connected to the position between the walking frame and the carriage to adjust the distance between the carriage and the walking frame. The railway vehicle is in an inverted U shape in the running direction so as to allow other vehicles to pass through from the position below the carriage.
Owner:张迪 +6
Hydraulic rotary motor
InactiveUS20080031759A1Little effectReduce thicknessEngine of arcuate-engagement typeOscillating piston enginesHydraulic motorExcavator
A hydraulic rotary motor, in particular to a stewing gear for elevating plant such as excavator grabs, etc., comprising a housing in which a rotor is rotatably received as well as a ring piston having an inner toothed arrangement and an outer toothed arrangement which is seated between the rotor and the housing so that displacement chambers are formed between the ring piston and an outer toothed arrangement of the rotor and / or an inner toothed arrangement of the housing, with a first motor connector being rotatably fixedly connected to the housing and a second motor connector being rotatably fixedly connected to the rotor. The hydraulic rotary motor is characterized in that the rotor is axially and radially supported at the housing via plain bearings and the second motor connector connected to the rotor is solely supported via the plain bearings at the housing.
Owner:KINSHOFER
Short-body plug for fluid couplings
ActiveUS20100066078A1Reduce construction lengthFirmly connectedAdjustable jointsCouplingsFluid couplingScrew thread
Owner:RECTUS
Multi-stage centrifugal pump (axial face seal)
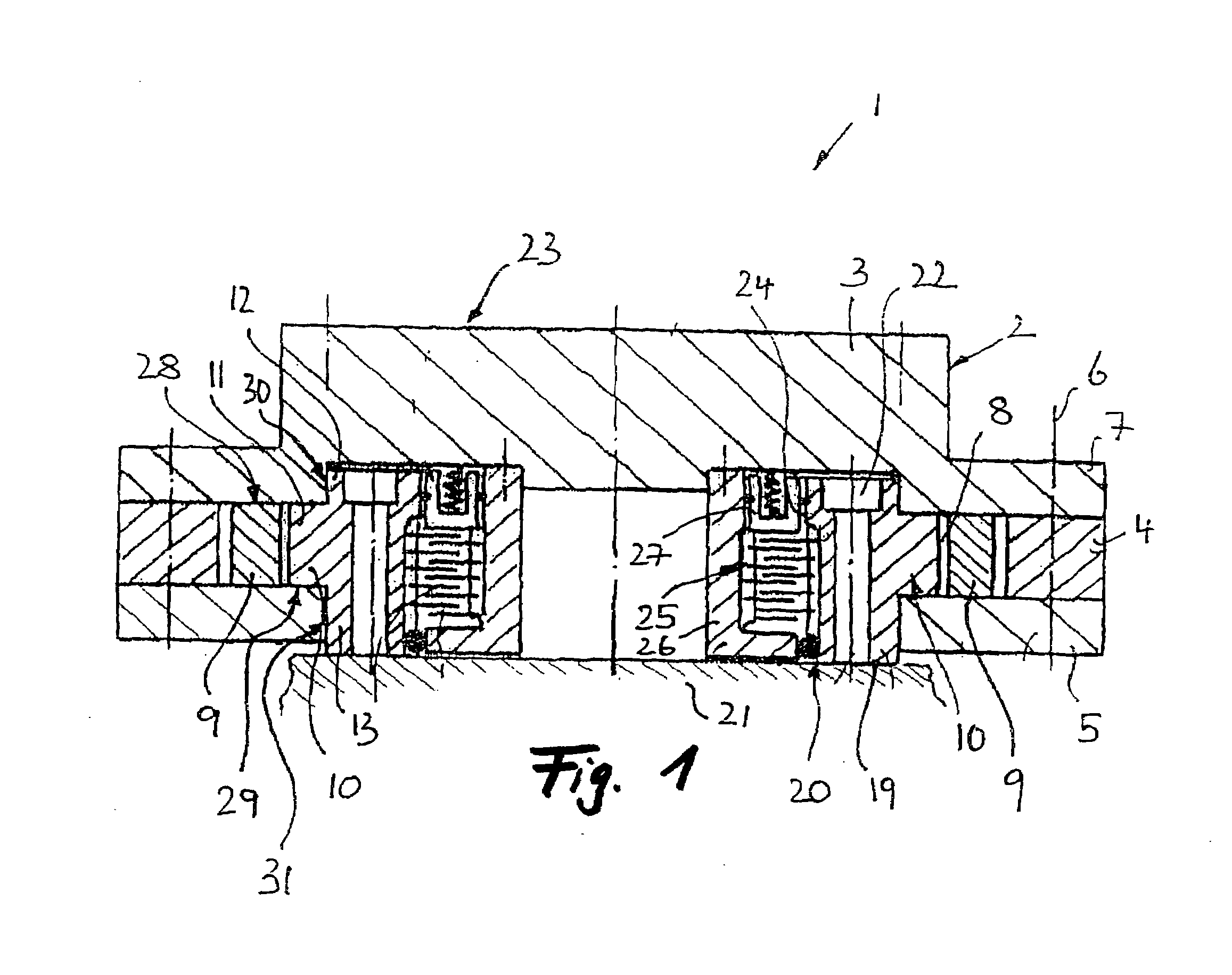
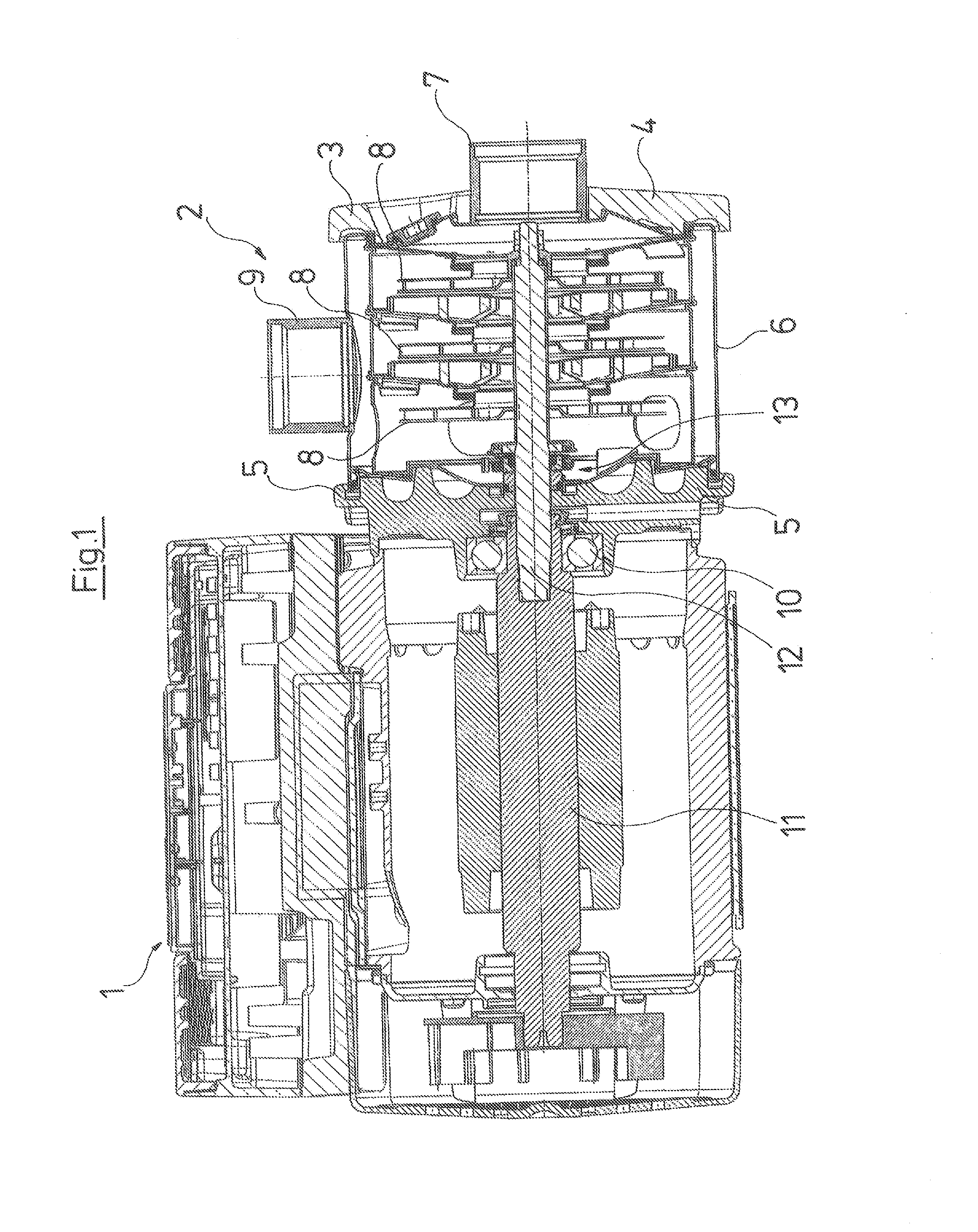
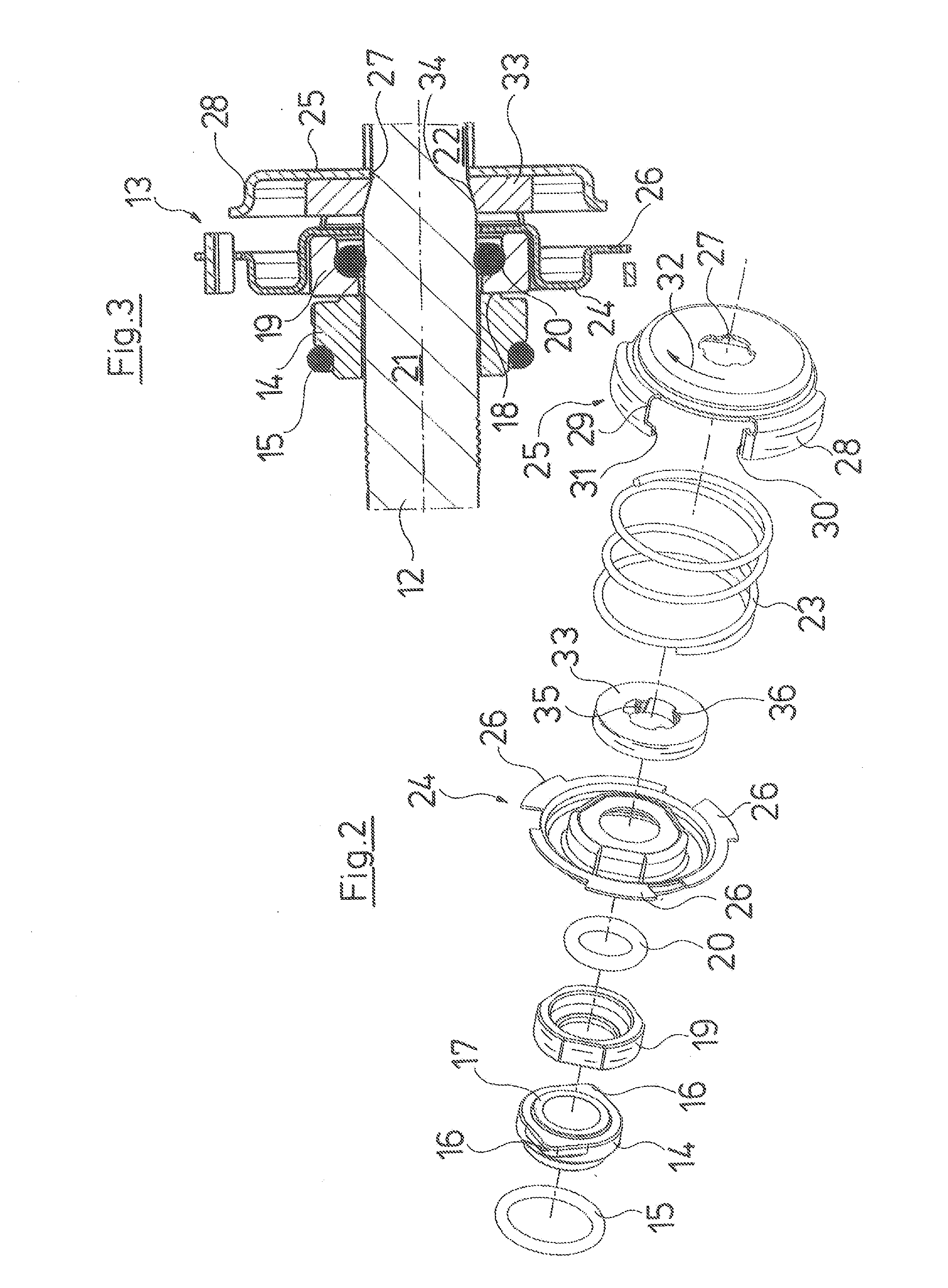
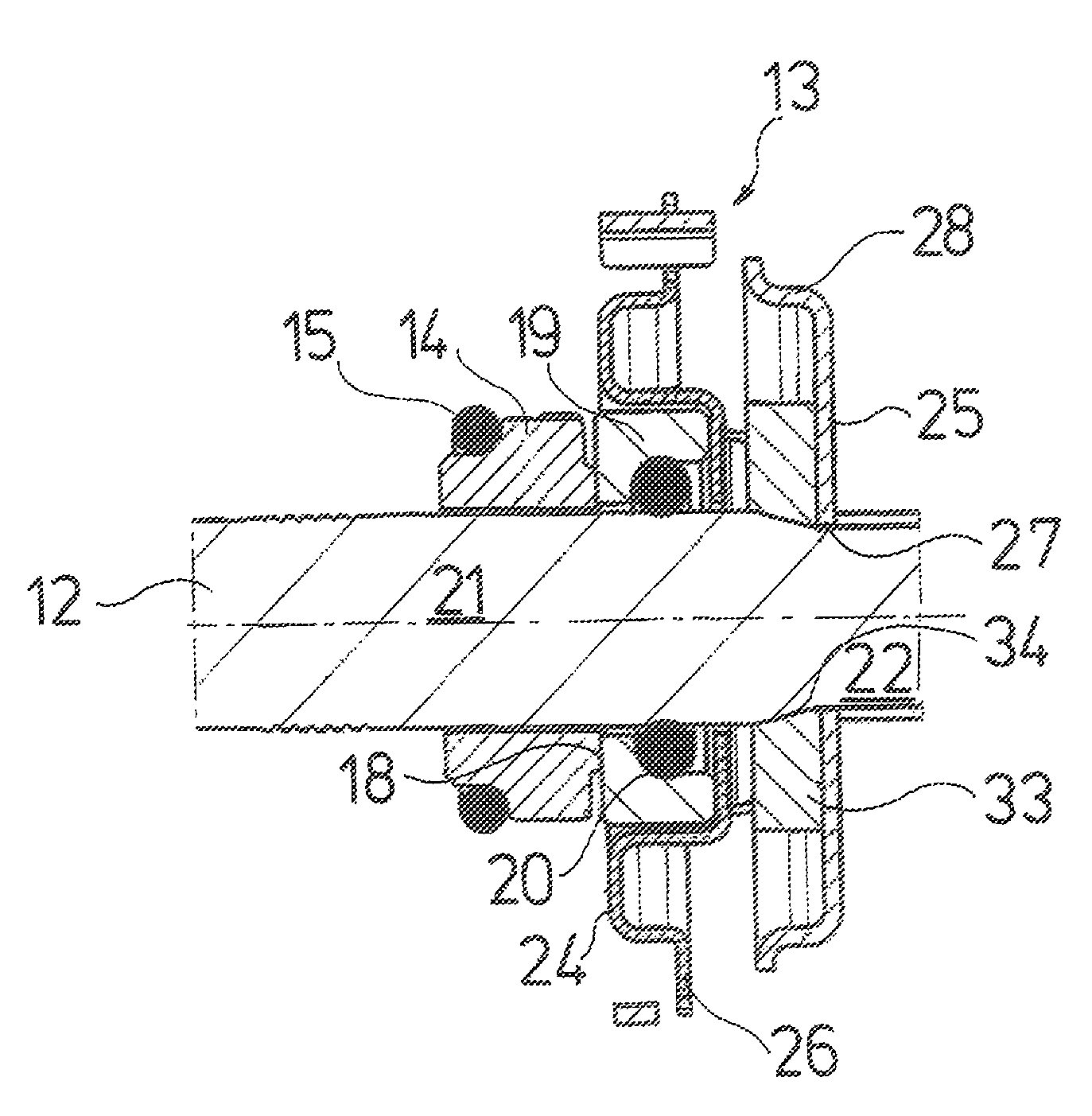
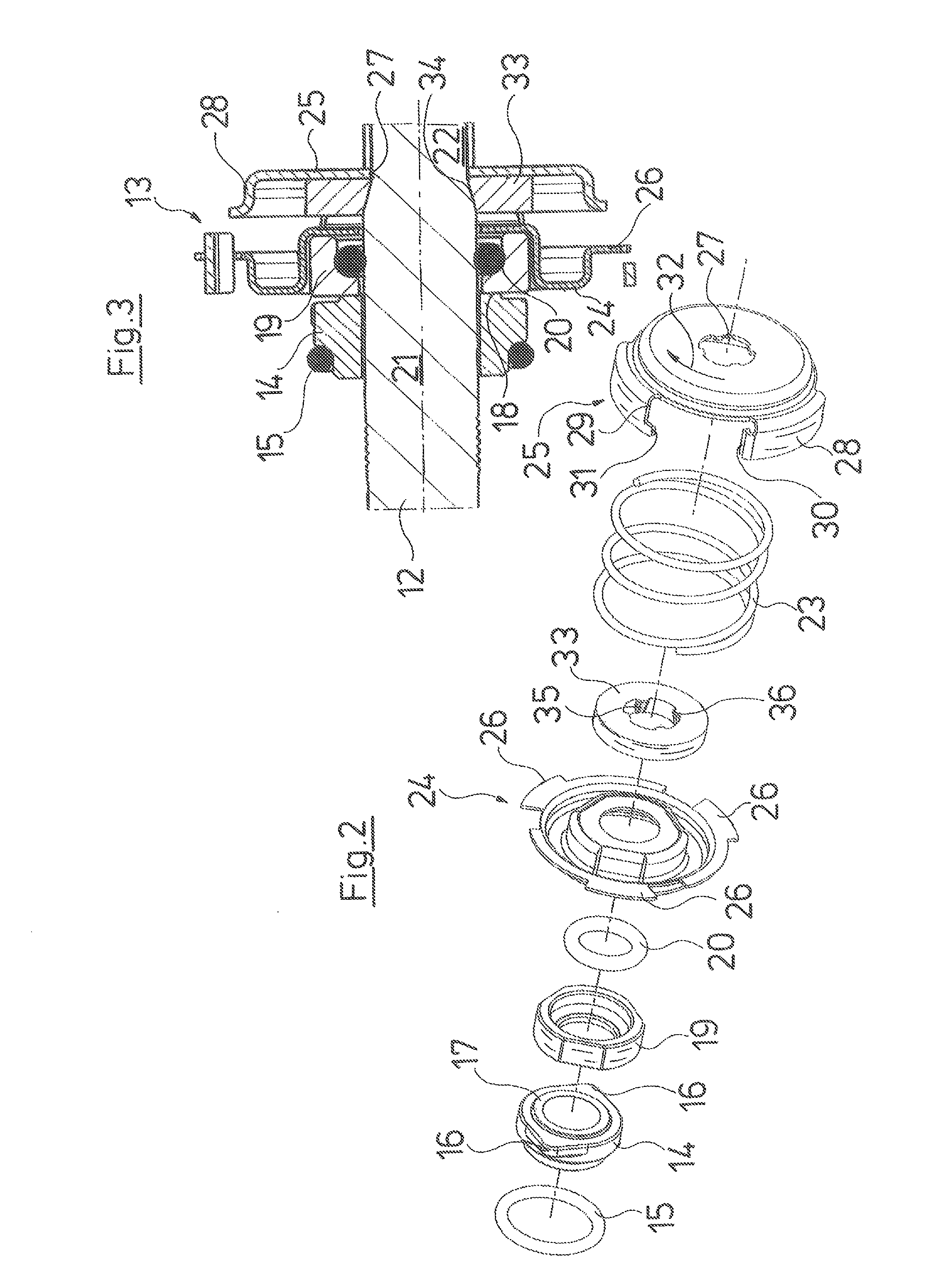
ActiveUS20100232949A1Reduce construction lengthSuitable designPump componentsStatorsCentrifugal pumpTorsion spring
An axial face seal (13), which seals a pump housing in the region of the pump shaft (12), is constructed in an axially compact manner. Spring holders (24, 25), which transmit the required pressing force of a compression spring (23), are connected to one another with a positive fit in a rotation direction, and hold a rotating axial face seal ring (19) in a rotationally fixed manner to the pump shaft (12). The spring holders (24, 25) are compact and enclose an abutment ring (33) for pump impellers as well as the compression spring (23). A motor-side spring (24) engages over the rotating axial face seal ring (19), by which an axially extremely short constructional length is achieved.
Owner:GRUNDFOS MANAGEMENT AS
Dynamically variable potential energy type laminar flow cooling device
PendingCN107282661APrevent turbulenceReduce construction lengthWork cooling devicesMetal rolling arrangementsInstabilityStrip steel
The invention discloses a dynamic potential energy type laminar flow cooling device, which is applied in the technical field of hot continuous rolling; it mainly includes a slideway, a pulley, a water tank, a water inlet pipe, cooling water, a telescopic outlet pipe, an upper branch pipe, and a lower branch pipe , rotating pipe, upper header, roller table, lower header, and fixed outlet pipe; mainly through the connection of the water tank that can be dynamically raised and lowered with the fixed outlet pipe and the telescopic outlet pipe, the upper header and the lower header are supplied with cooling at different stable pressures The water cools the steel strips with different thickness specifications; after the application of the invention, the problems of limited cooling capacity for thicker steel strips, long cooling distance and unstable cooling water pressure can be better avoided.
Owner:XINJIANG BAYI IRON & STEEL
Circular stockyard
PendingCN107298275AReduce investment and construction costsReduce production and operation costsStorage devicesClassical mechanicsEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of storage and conveying facilities of bulk materials and relates to a circular stockyard. The circular stockyard comprises a sealed storage shed, a material feeding and piling system, a material taking and discharging system, storage cells, radial retaining walls and an annular retaining wall, wherein the inner side of the annular retaining wall forms the storage bin in an enclosed manner, and the outer side of the annular retaining wall and the radial retaining walls form the storage cells in an enclosed manner; a first annular rail is arranged on the annular retaining wall, a second annular rail is arranged at the outer edges of the radial retaining walls, a storage cell material taking frame is arranged on a gantry type frame between the first annular rail and the second annular rail, and the radial retaining walls and the annular retaining wall support each other. The circular stockyard has the advantages that the annular retaining wall structure has good space force transmission performance, a load bearing structure high in bearing capacity and large in rigidity can be formed by a small structural thickness, the stockyard structure can evidently reduce the length and thickness of the retaining walls, civil engineering cost is low, and the circular stockyard has extremely high engineering application value.
Owner:CISDI RES & DEV CO LTD
Coffee mill and automatic coffee machine having a coffee mill
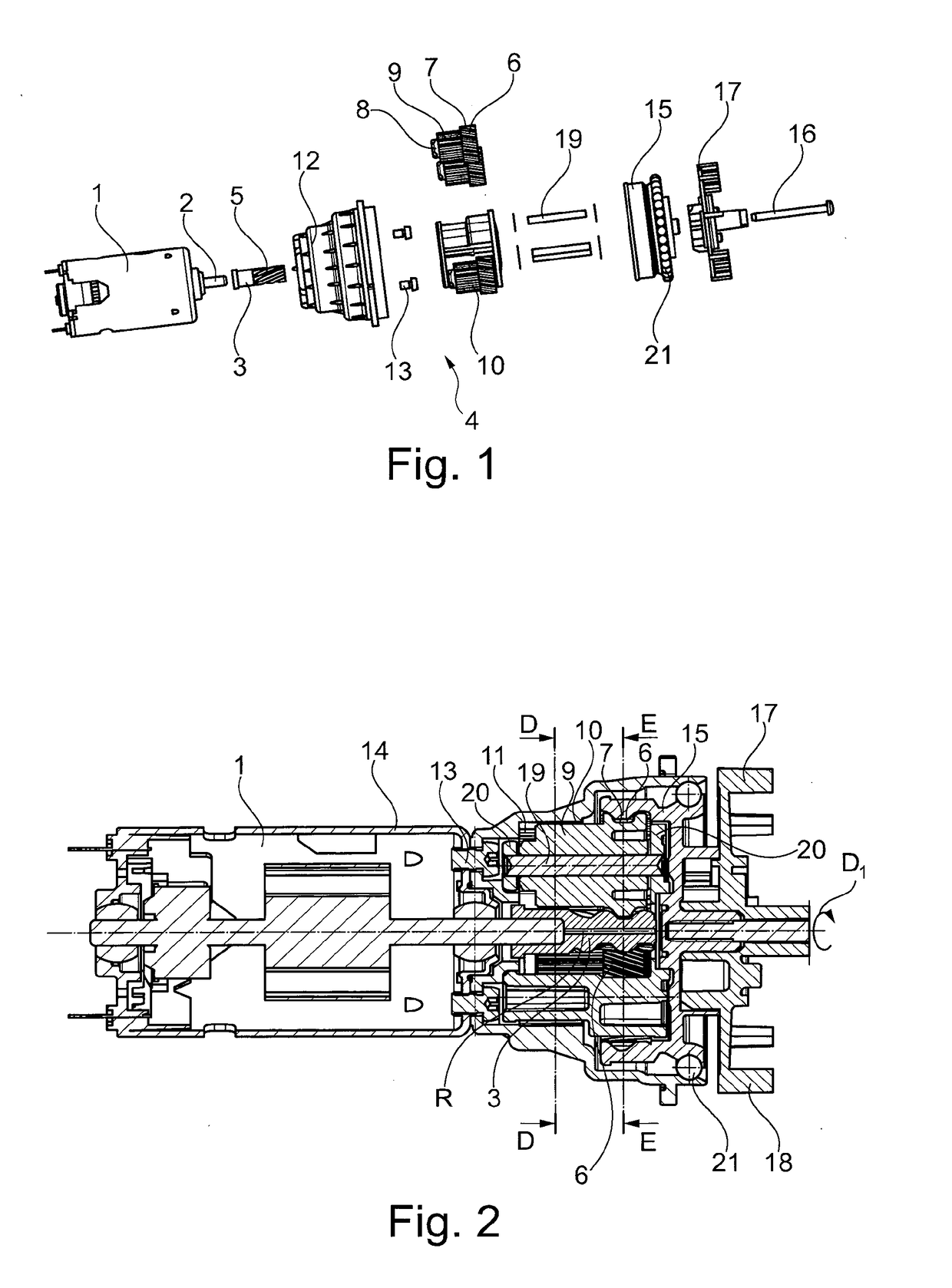
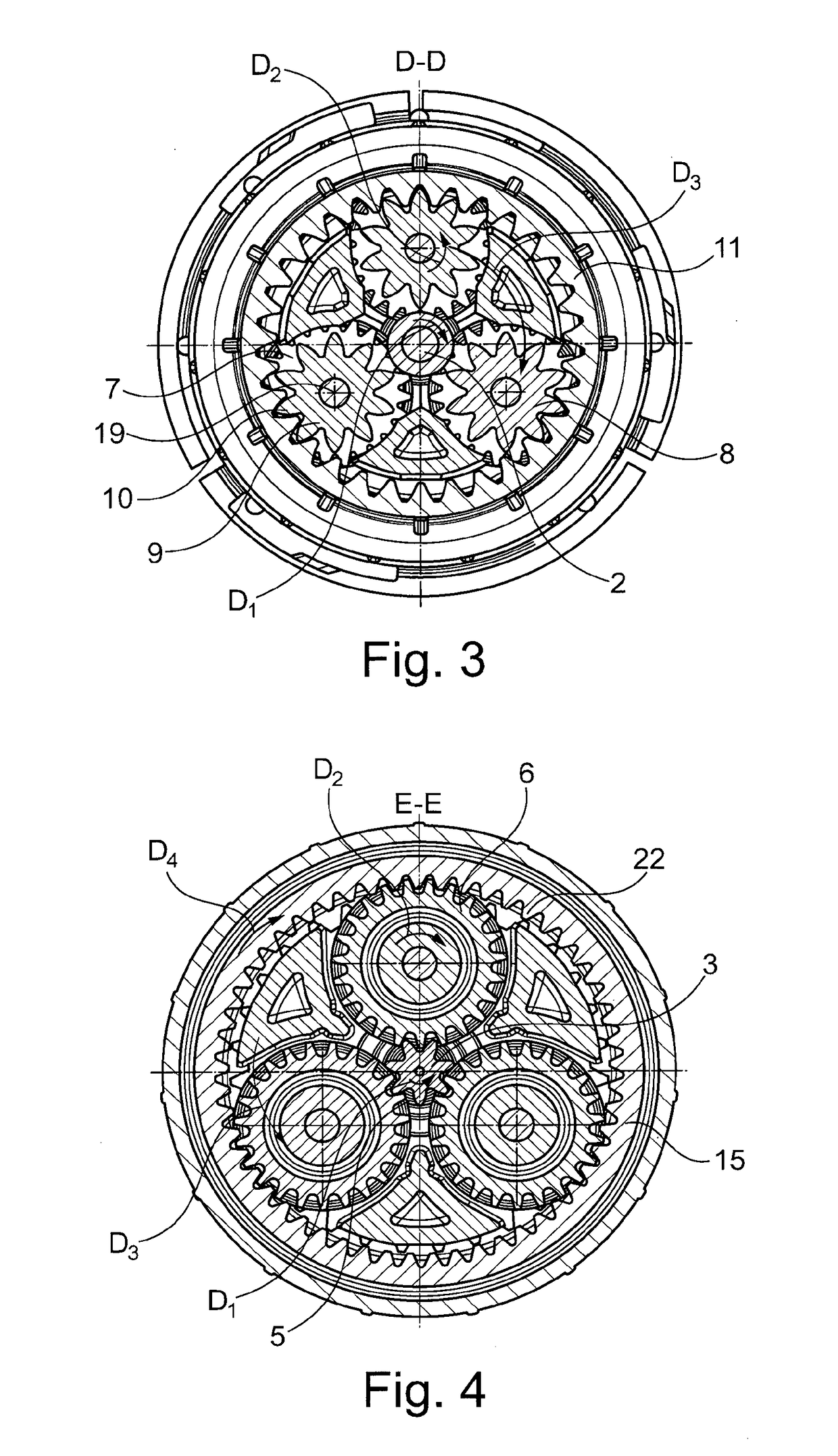
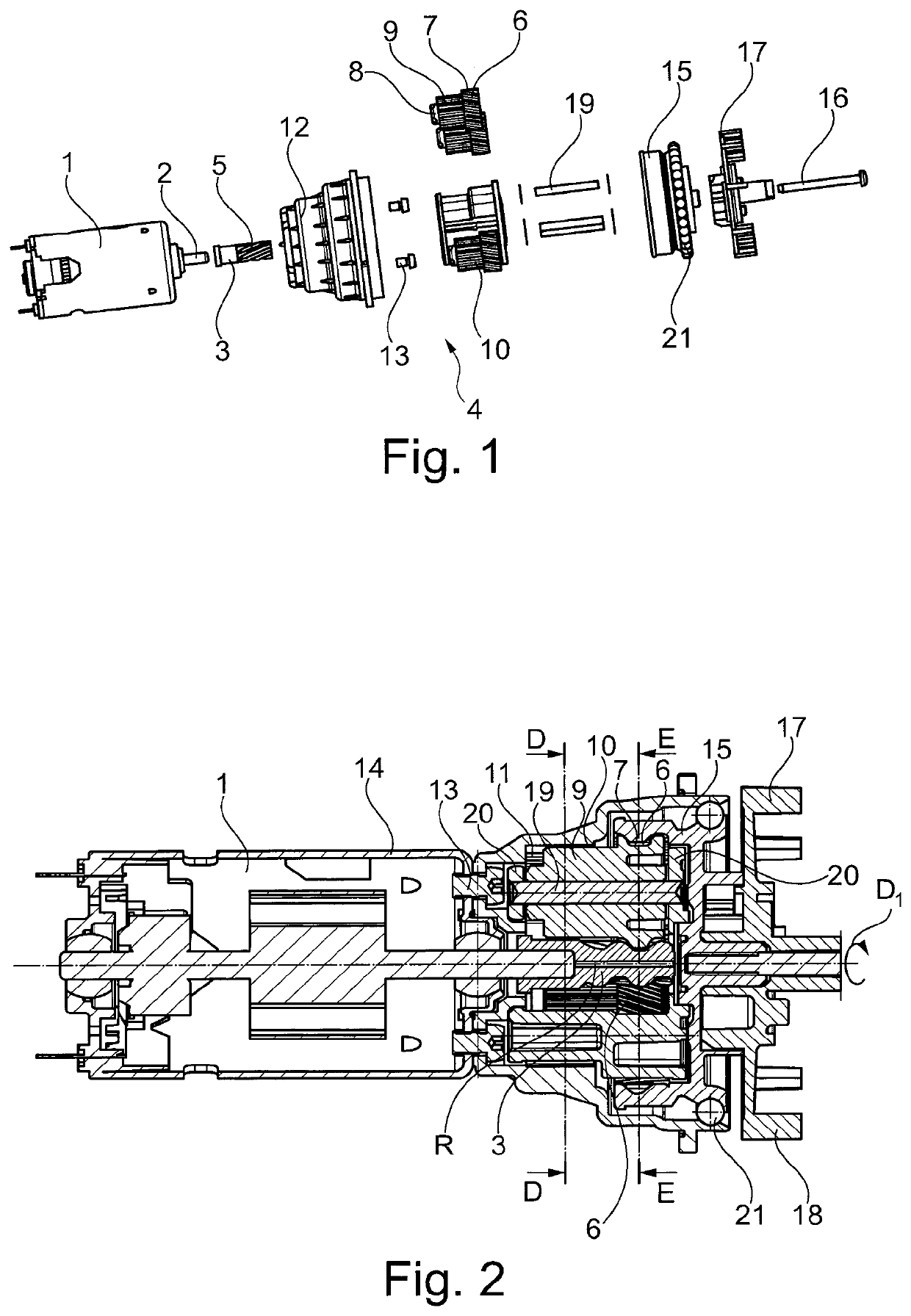
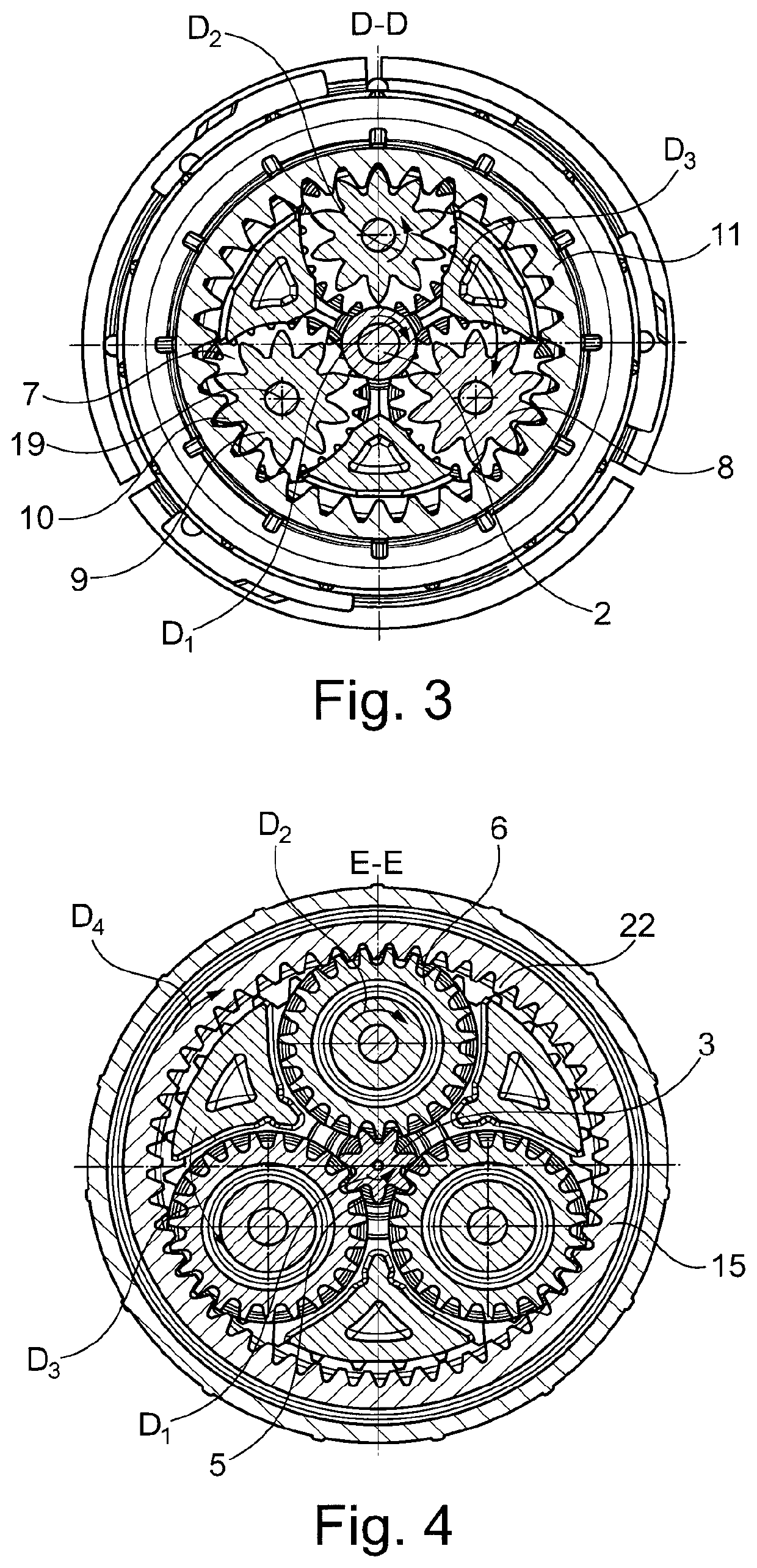
ActiveUS20190000271A1Reduce in quantitySmall axial construction lengthCoffee millsSpice millsElectric driveDrive motor
A coffee grinder, in particular for the installation in a fully-automatic coffee machine, including an electric drive motor (1) for driving a grinding unit, wherein a reduction gear (4) formed as a planetary gear is arranged between drive motor (1) and grinding unit, with the sun gear (3) of this planetary gear being drivable by the drive motor (1). The planetary gear includes multiple planetary rods (8) arranged in the circumferential direction around the sun gear (3), these rods including a first axial portion (7) meshing with the sun gear (3) as well as an axially neighboring, second axial portion (9) with a second diameter different from, preferably smaller than, a first diameter of the first axial portion (7), with this second axial portion meshing with a stationary ring gear (11). The toothed racks are arranged to drive an output element (15) with their first axial portions (7).
Owner:EUGSTER FRISMAG
Coffee mill and automatic coffee machine having a coffee mill
ActiveUS10702102B2Reduce in quantitySmall axial construction lengthCoffee millsSpice millsGear wheelElectric machinery
A coffee grinder, in particular for the installation in a fully-automatic coffee machine, including an electric drive motor (1) for driving a grinding unit, wherein a reduction gear (4) formed as a planetary gear is arranged between drive motor (1) and grinding unit, with the sun gear (3) of this planetary gear being drivable by the drive motor (1). The planetary gear includes multiple planetary rods (8) arranged in the circumferential direction around the sun gear (3), these rods including a first axial portion (7) meshing with the sun gear (3) as well as an axially neighboring, second axial portion (9) with a second diameter different from, preferably smaller than, a first diameter of the first axial portion (7), with this second axial portion meshing with a stationary ring gear (11). The toothed racks are arranged to drive an output element (15) with their first axial portions (7).
Owner:EUGSTER FRISMAG
Drive-assisted vertical slot fishway structure and fish collection method
ActiveCN104404929BImprove adaptabilityImprove fish passing efficiencyBarrages/weirsClimate change adaptationAutomatic controlControl system
Owner:嘉善永升五金厂
Multi-stage centrifugal pump (axial face seal)
ActiveUS8366388B2Reduce construction lengthSuitable designPump componentsStatorsEngineeringTorsion spring
Owner:GRUNDFOS MANAGEMENT AS
Construction device and construction method of self-adaptive post-tensioning prefabricated box girder
ActiveCN110900820BReduce construction lengthEasy to operateCeramic shaping apparatusStress concentrationArchitectural engineering
The invention discloses a construction device and a construction method for a prefabricated box girder by an adaptive post-tensioning method. The construction device comprises a fixed pedestal and two adjustable pedestals respectively arranged at both ends of the fixed pedestal. The adjustable pedestal comprises a pedestal foundation and an upper hinged pedestal. , the lower hinged pedestal, the pedestal translation track and the pedestal translation track, the pedestal translation track is set on the base of the pedestal, the lower hinged pedestal is movably set on the pedestal translation track, the upper hinged pedestal and the lower hinged pedestal are hinged through a hinge shaft, and the upper A locking component is also arranged between the hinged base and the lower hinged base to limit the relative rotation of the two, the base of the base is abutted against the fixed base, and the top surface of the upper hinged base is flat. Construction methods include pedestal installation, upper hinged pedestal positioning, formwork installation, concrete pouring, formwork removal and tensioning. The invention can ensure that the bottom of the beam is always in the state of surface contact and load before and after tensioning, and effectively solves the problems of stress concentration and cracking of the beam end concrete during the tensioning process.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY 12TH BUREAU GRP +1
Air spring for a motor vehicle
ActiveUS10508704B2Simple and economical structureLow defect sensitivitySpringsSprings/dampers design characteristicsAir springEngineering
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Air Spring For A Motor Vehicle
ActiveUS20180216689A1Simple and economical structureLow defect sensitivitySpringsSprings/dampers design characteristicsMobile vehicleAir spring
An air spring for a motor vehicle having a rolling bellows filled with gas under pressure, one end of the rolling bellows is connected to a load receiver and the other end is fastened to a roll-off piston’. The load receiver and the roll-off piston are moveable relative to one another depending on a force impinging on the load receiver toward the roll-off piston. A sensor device is arranged inside the rolling bellows by which a distance between the load receiver and the roll-off piston is detected. A pressure piece extending in direction of the roll-off piston is arranged at the load receiver and a sensor body is movably drivable along a sensor track of the sensor device by an end region of the pressure piece facing the roll-off piston. The sensor device generates an electric signal corresponding to the position of the sensor body on the sensor track.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Dual clutch transmission
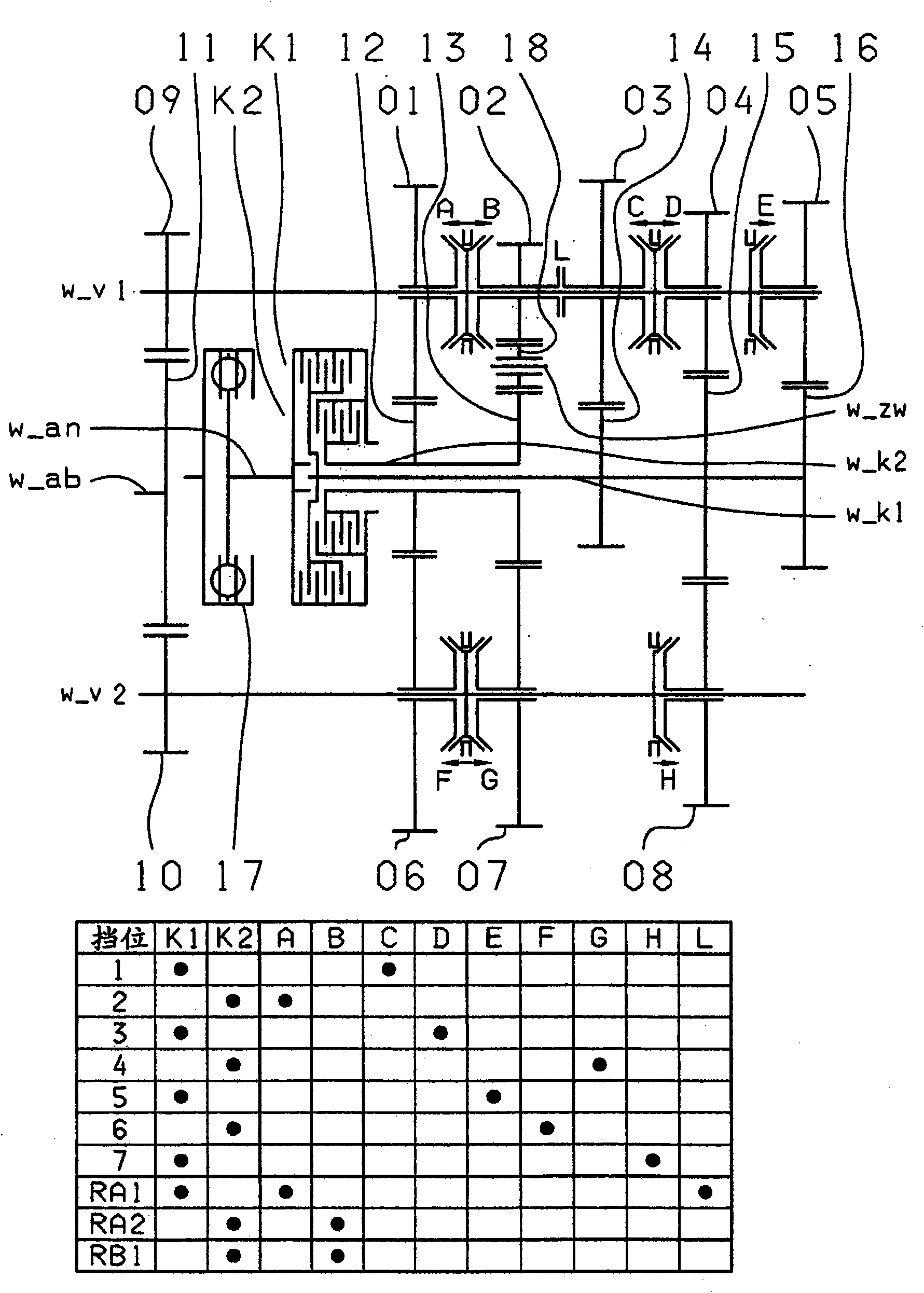
InactiveCN101802448BReduce construction lengthFree choice of transmission ratioToothed gearingsTransmission elementsDrive shaftCoupling
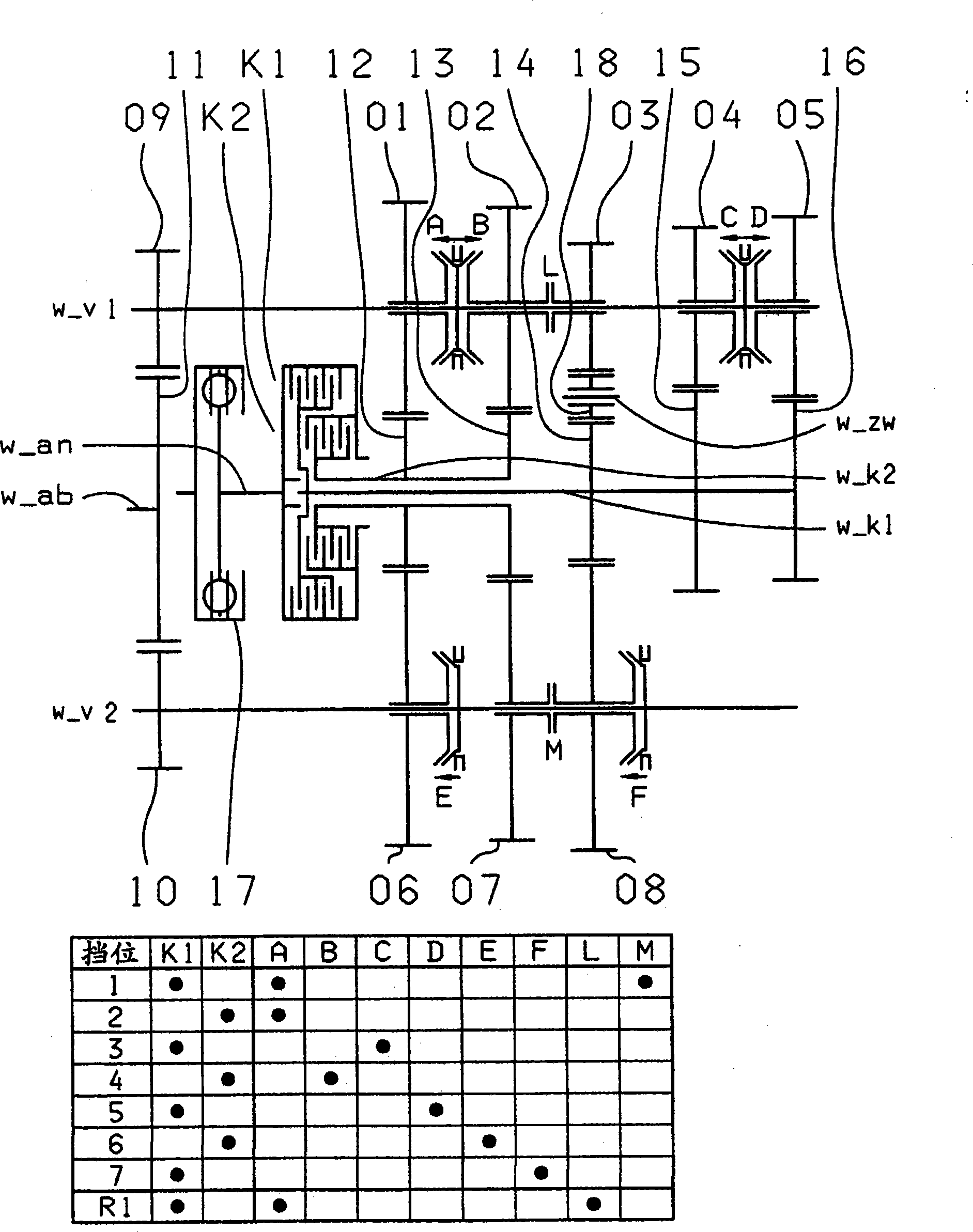
A double clutch transmission with two clutches connected to a drive shaft and to one of two transmission input shafts. Fixed gears are coupled to the input shafts and engage idler gears. Several coupling devices connect the idler gears to a countershaft which have an output gear that couple gears of an output shaft such that at least seven power shift forward gears and at least one reverse gear can be shifted, and four gear wheel planes are arranged in such a way that at least one power shift winding-path gear can be shifted via the shifting device, such that at least seven power shift forward gears and at least one reverse gear can be shifted, and five gear planes are positioned in such a way that at least one power shift winding-path gear can be shifted via a shifting device.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Belt buckle with release lock
ActiveUS20160007691A1Easy to integrateReduce manufacturing costSnap fastenersClothes buttonsLocking mechanismCoupling
A belt buckle (10) for a seat belt includes a buckle housing (16), a locking mechanism for locking a plug-in tongue inserted in the buckle housing (16), a release button (22) which is movable in a first direction relative to the buckle housing (16) for unlocking the plug-in tongue, and a safety mechanism for preventing automatic displacement of the release button (22) in the first direction. The safety mechanism includes a mass body (36) movable in the first direction relative to the buckle housing (16) and a movably supported coupling lever (24) including an axis of rotation which is stationary relative to the buckle housing (16). The coupling lever (24) is coupled to the mass body (36) and to the release button (22) so that, upon acceleration of the belt buckle (10) in a second direction opposed to the first direction, it transmits an inertia force acting on the mass body (36) in the first direction to the release button (22) in the opposite second direction.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Compressor arrangement
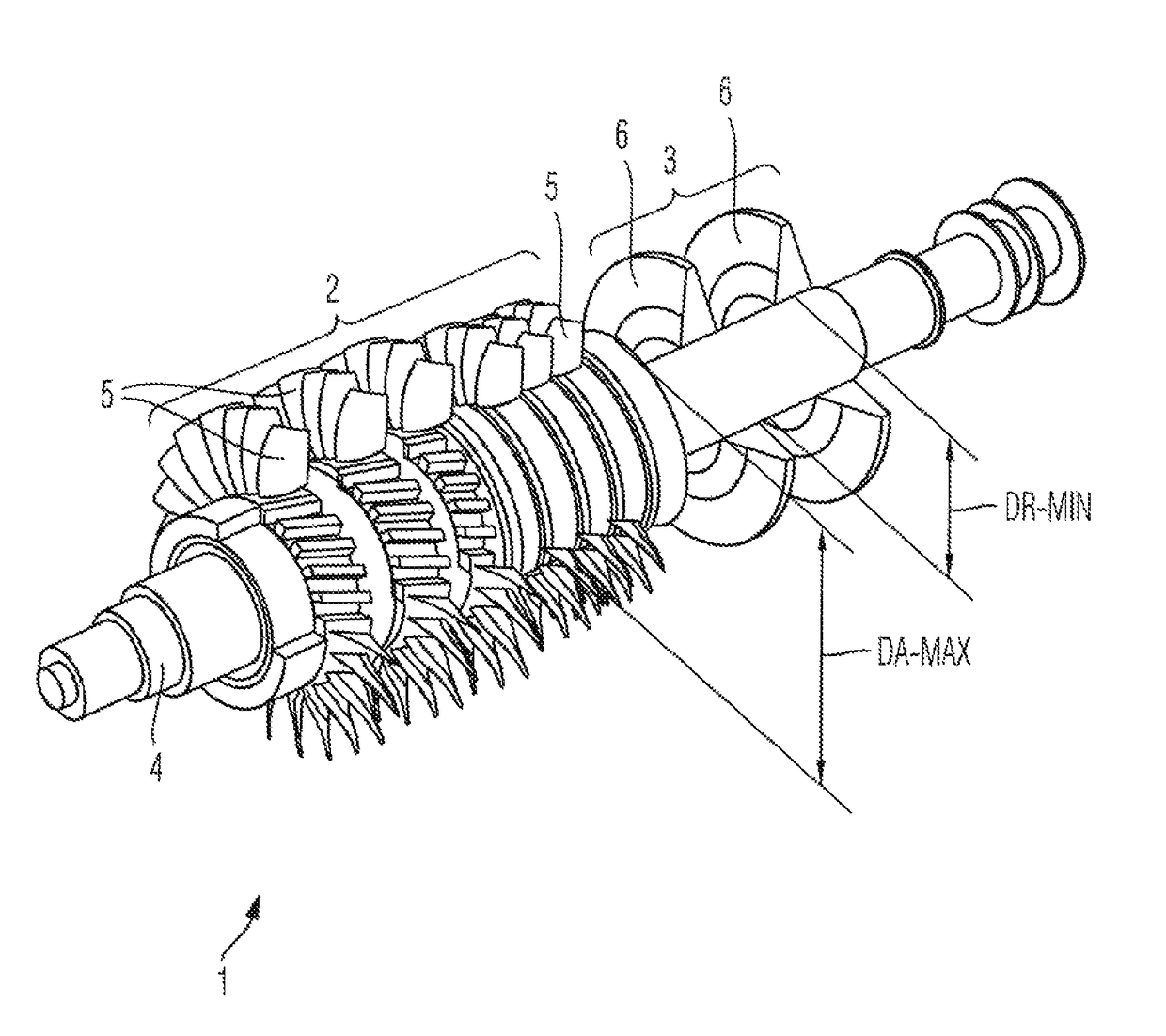
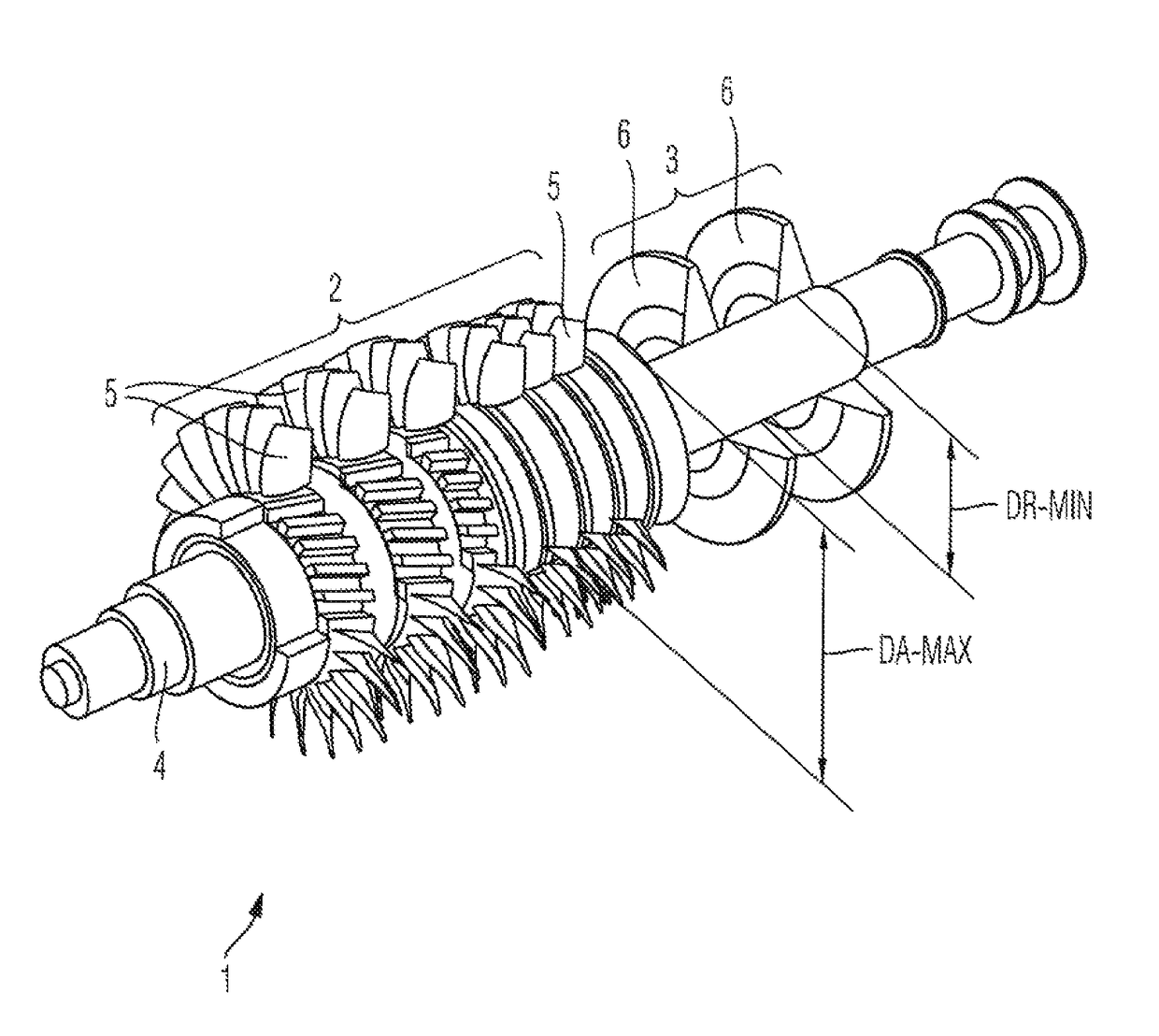
ActiveUS9752584B2Increase pressureReduce construction lengthPump componentsBlade accessoriesAxial compressorImpeller
A compressor arrangement has a common shaft, an axial compressor having at least a single-stage, and a radial compressor having at least single-stage. Assemblies of the, or each, axial compressor stage on the rotor side and assemblies of the, or each, radial compressor stage on the rotor side are attached to a common shaft (4). A ratio between a maximum diameter of the shaft (4) in the region of the axial compressor (2) and a minimum radial impeller seat diameter of the shaft (4) in the region of the radial compressor (3) is between 1.5 and 3.0.
Owner:MAN ENERGY SOLUTIONS SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com