Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Reduced clearance rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions and methods for intraocular delivery of fibronectin scaffold domain proteins
InactiveUS20080220049A1Easy to optimizeImprove bioavailabilitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineFibronectin
The present disclosure relates to novel sustained-release intraocular drug delivery systems and improvements in the treatment of retinopathies. In particular, fibronectin scaffold domain proteins that selectively inhibit VEGFR-2 are contemplated.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
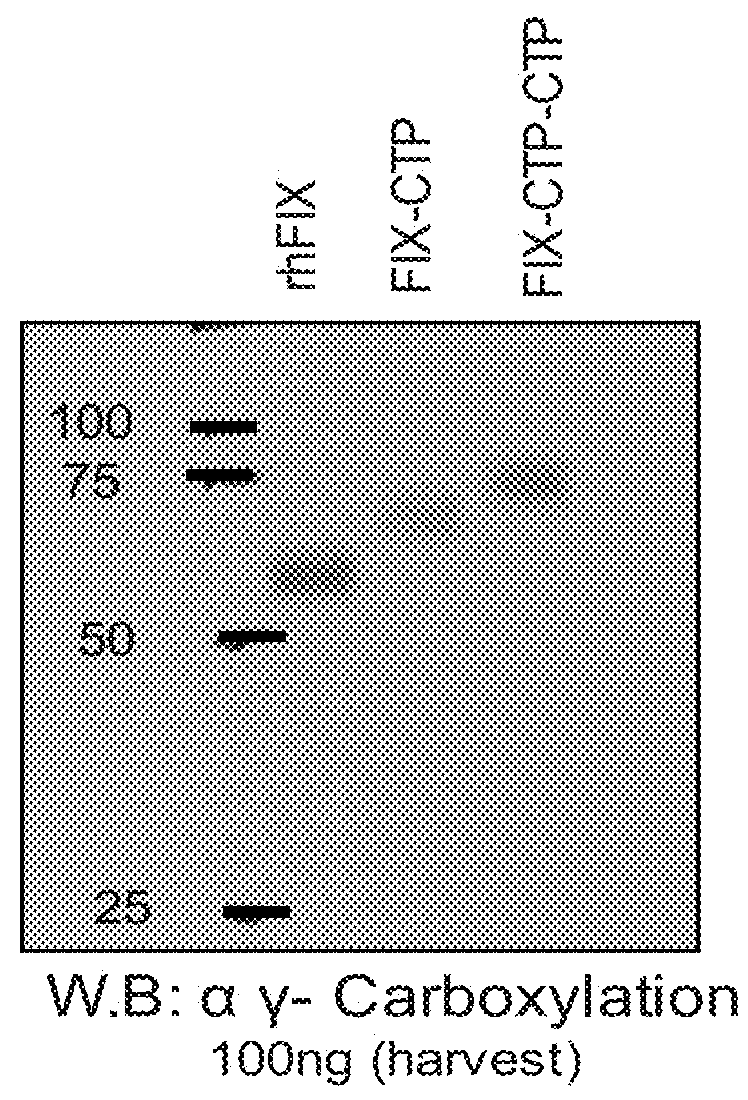
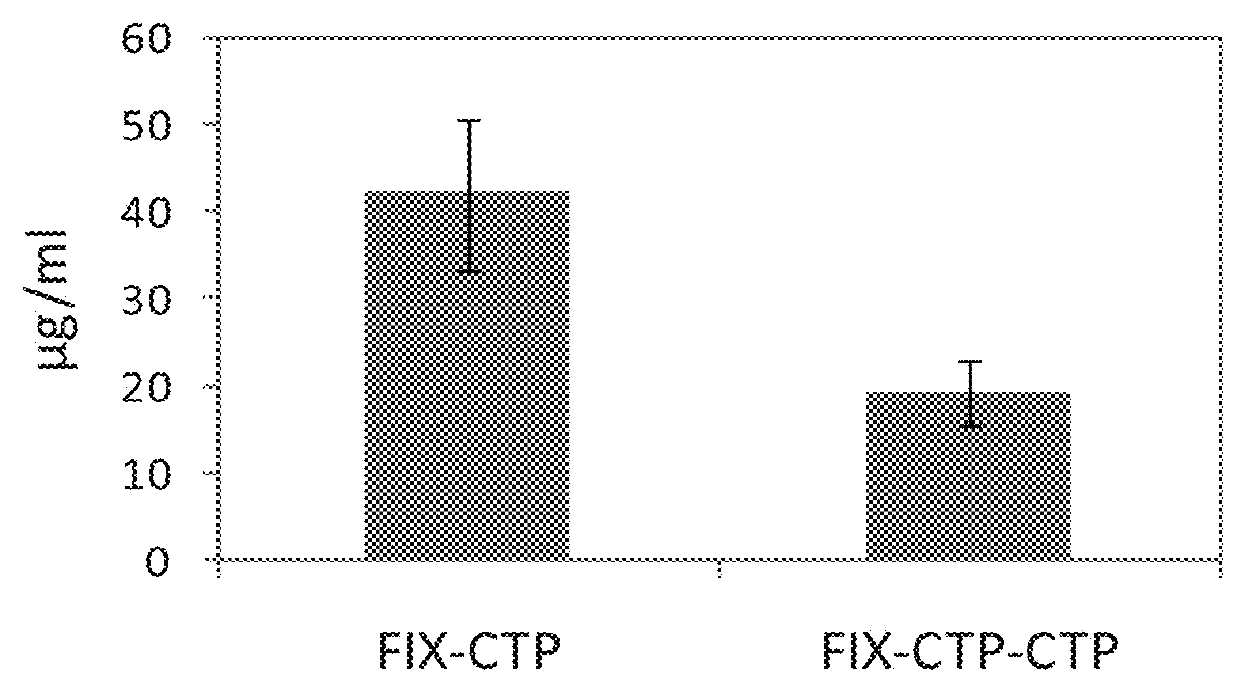
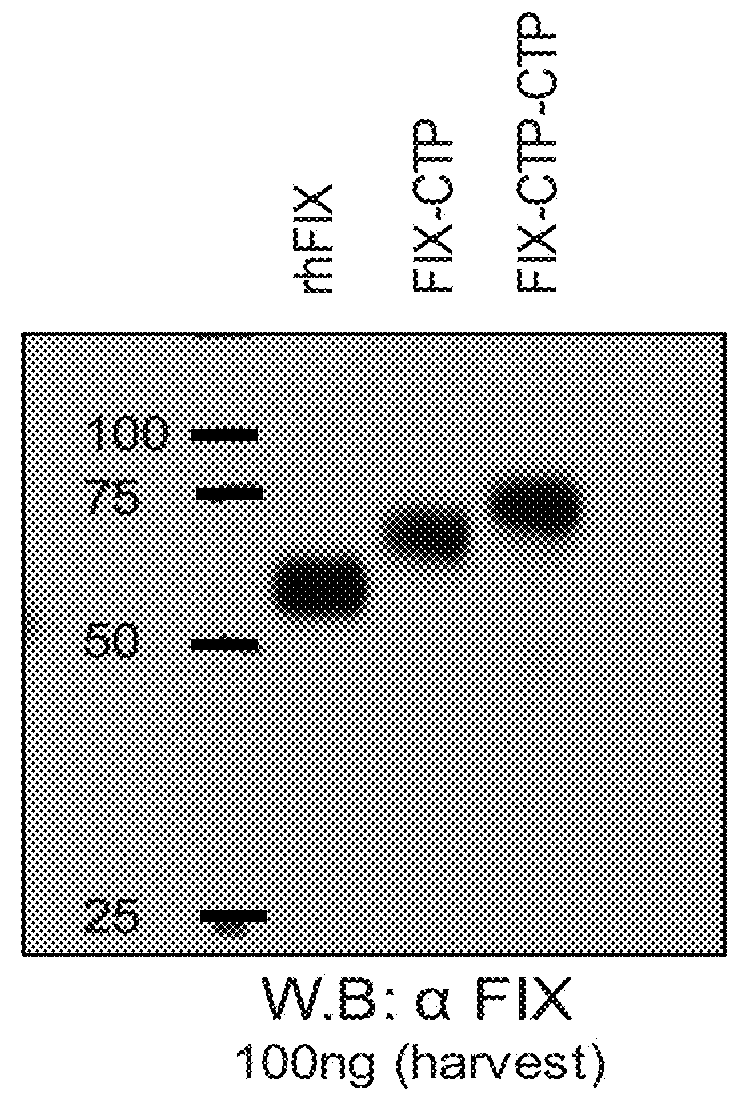
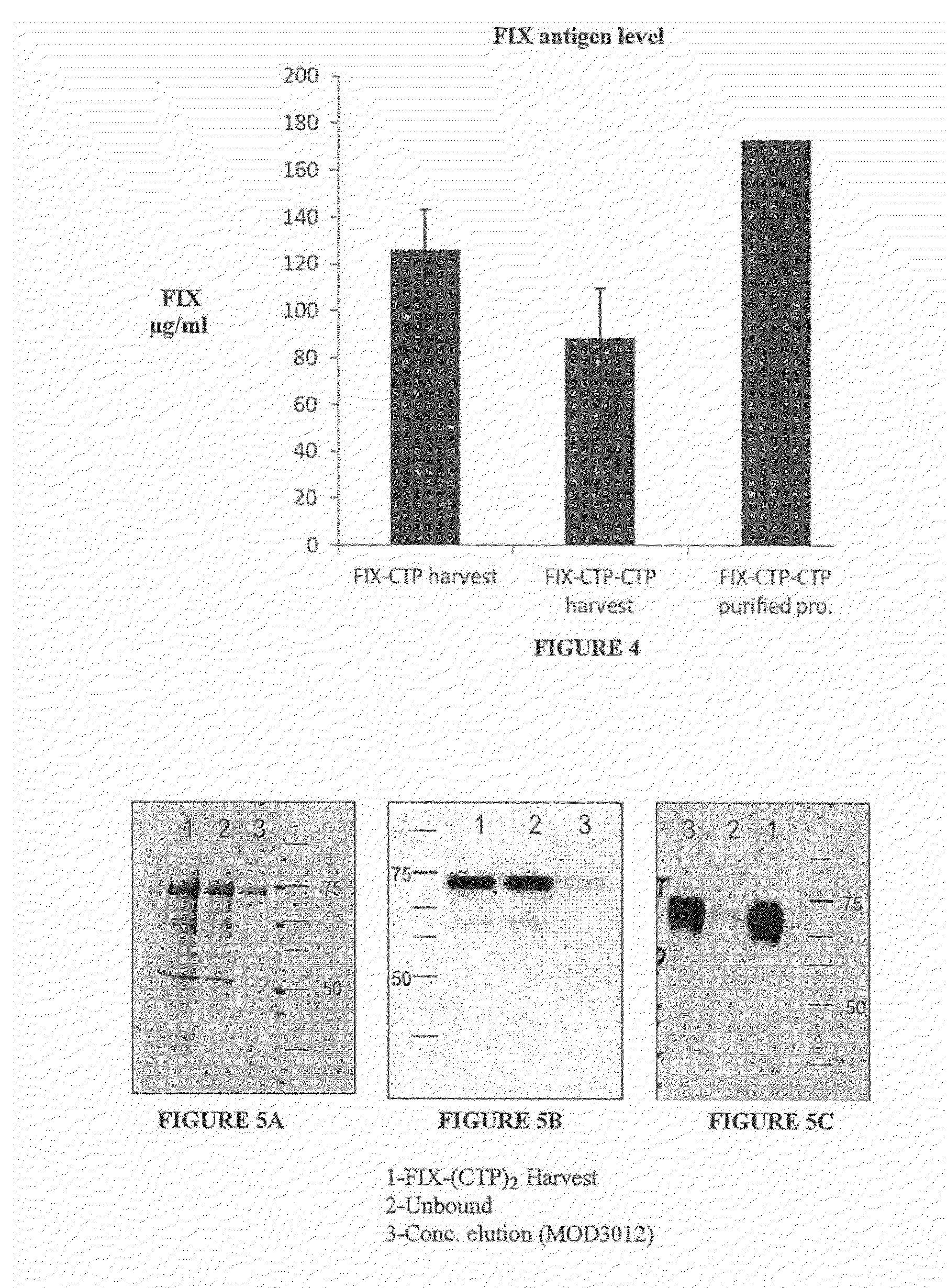
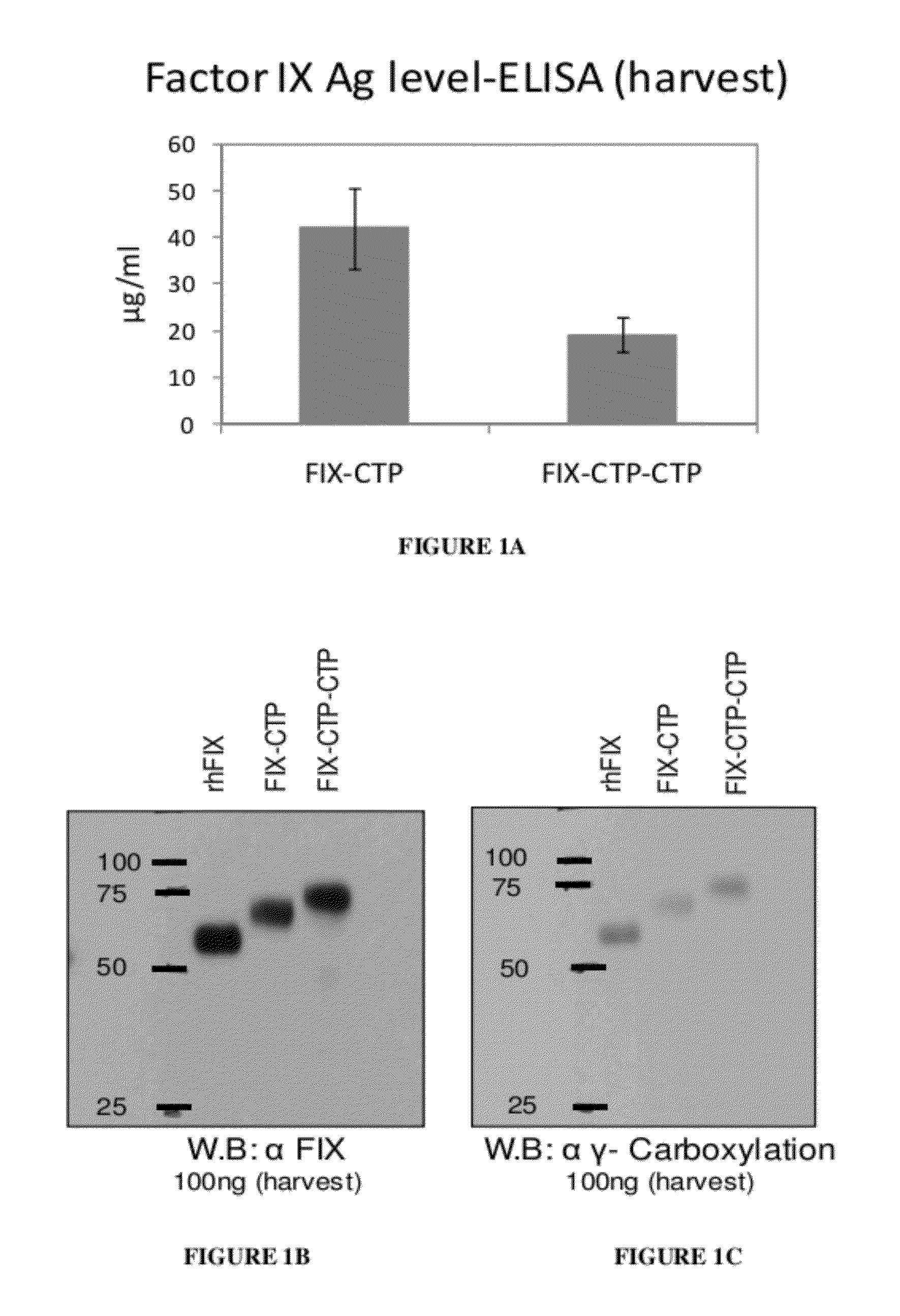
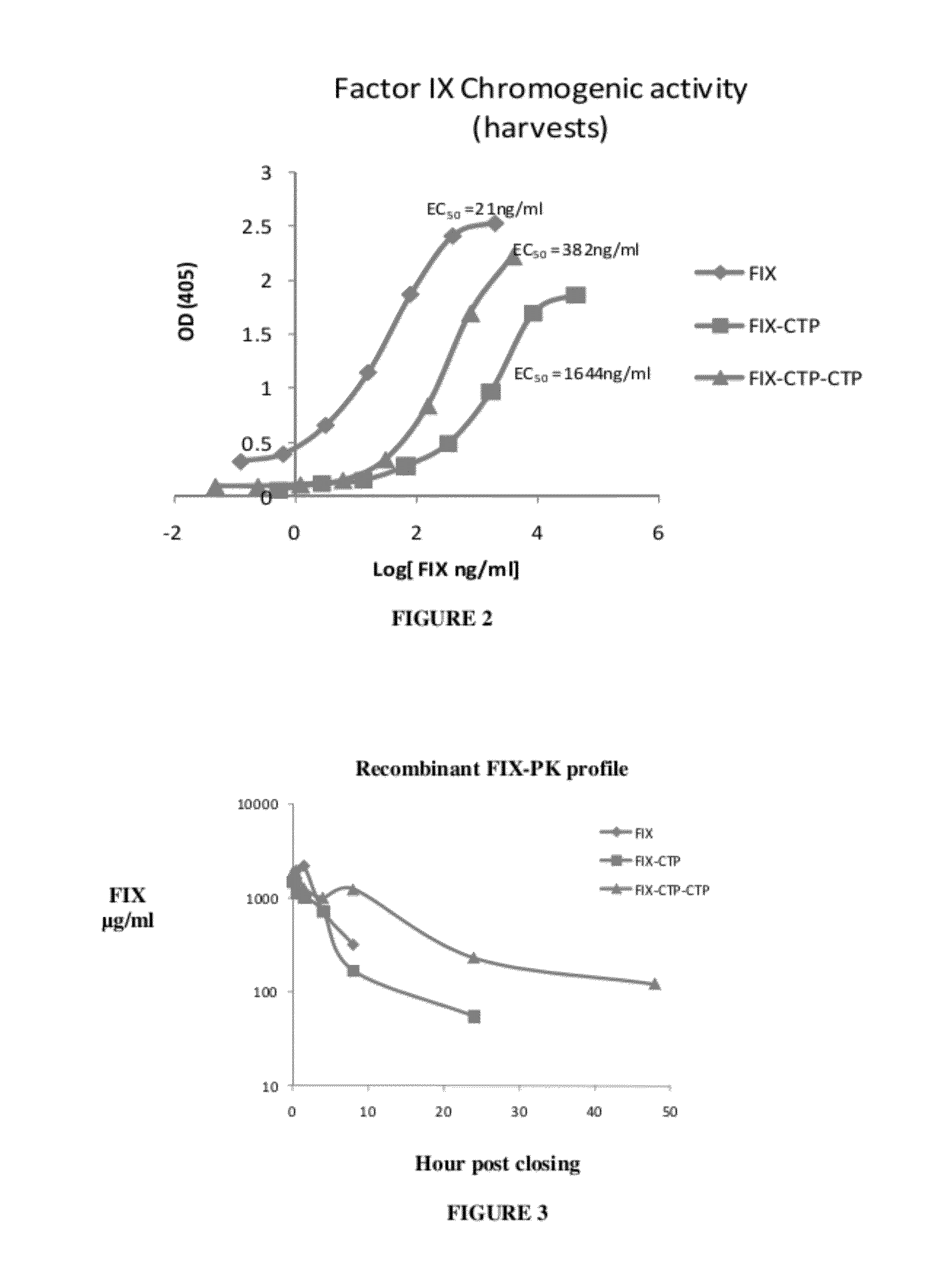
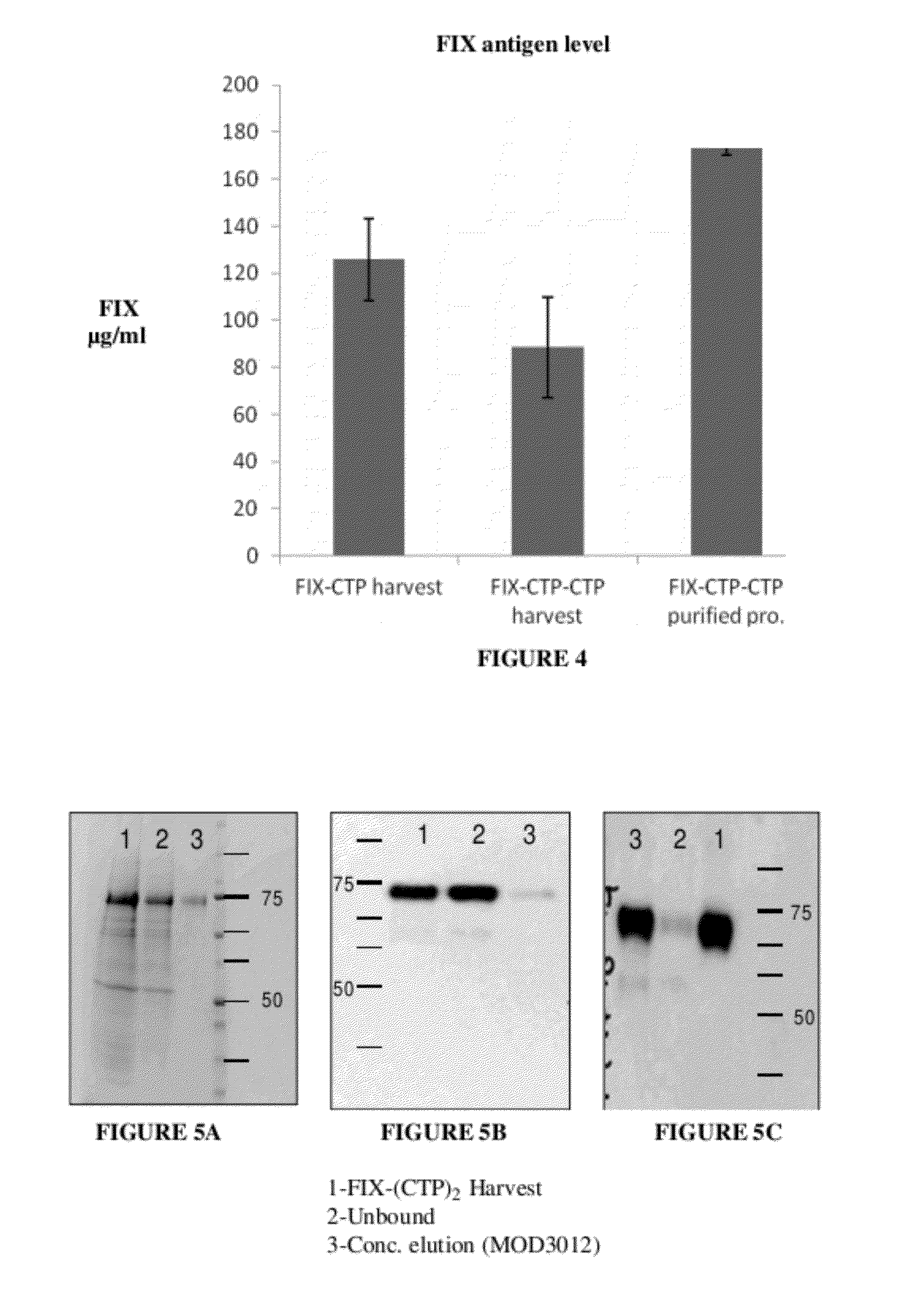
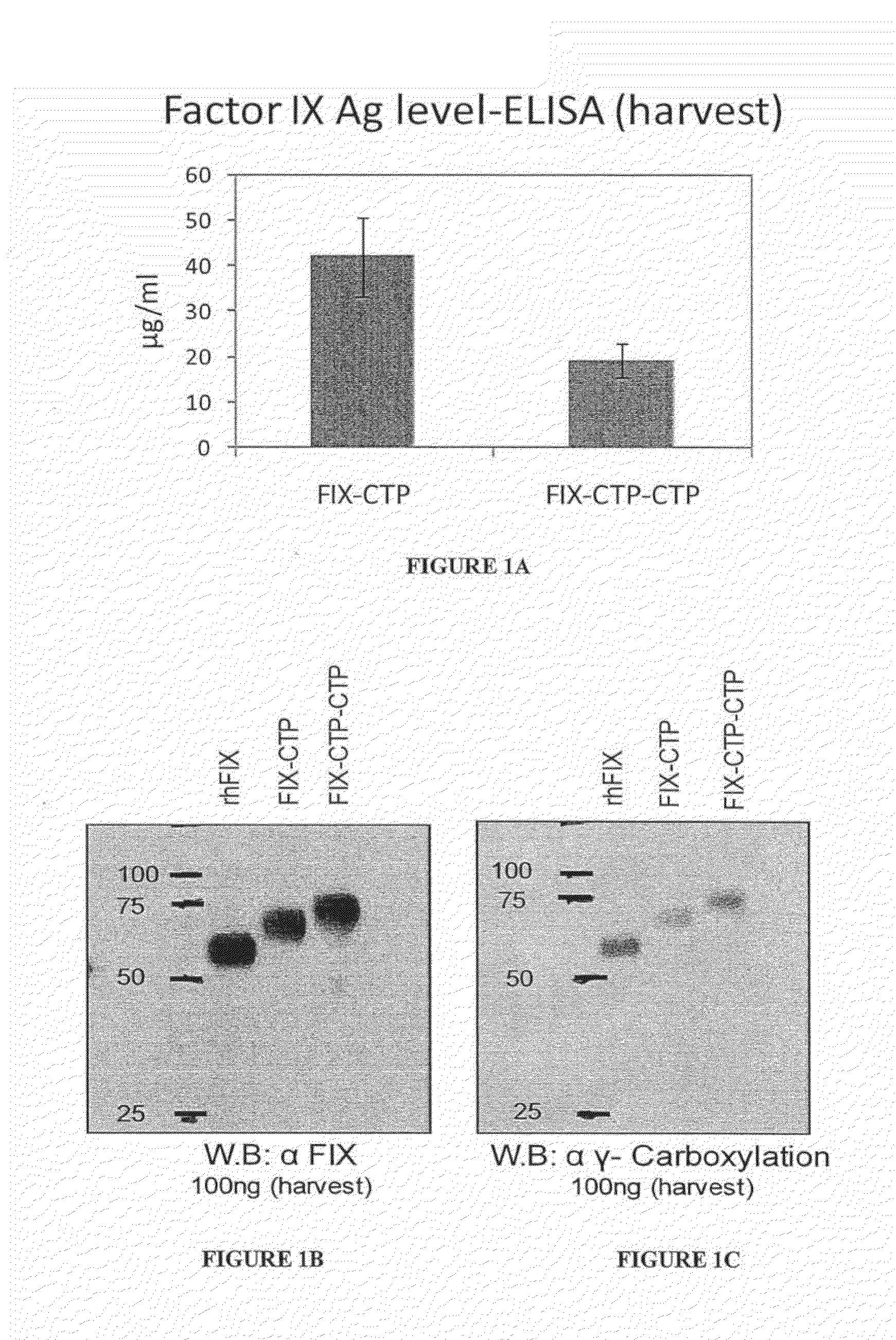
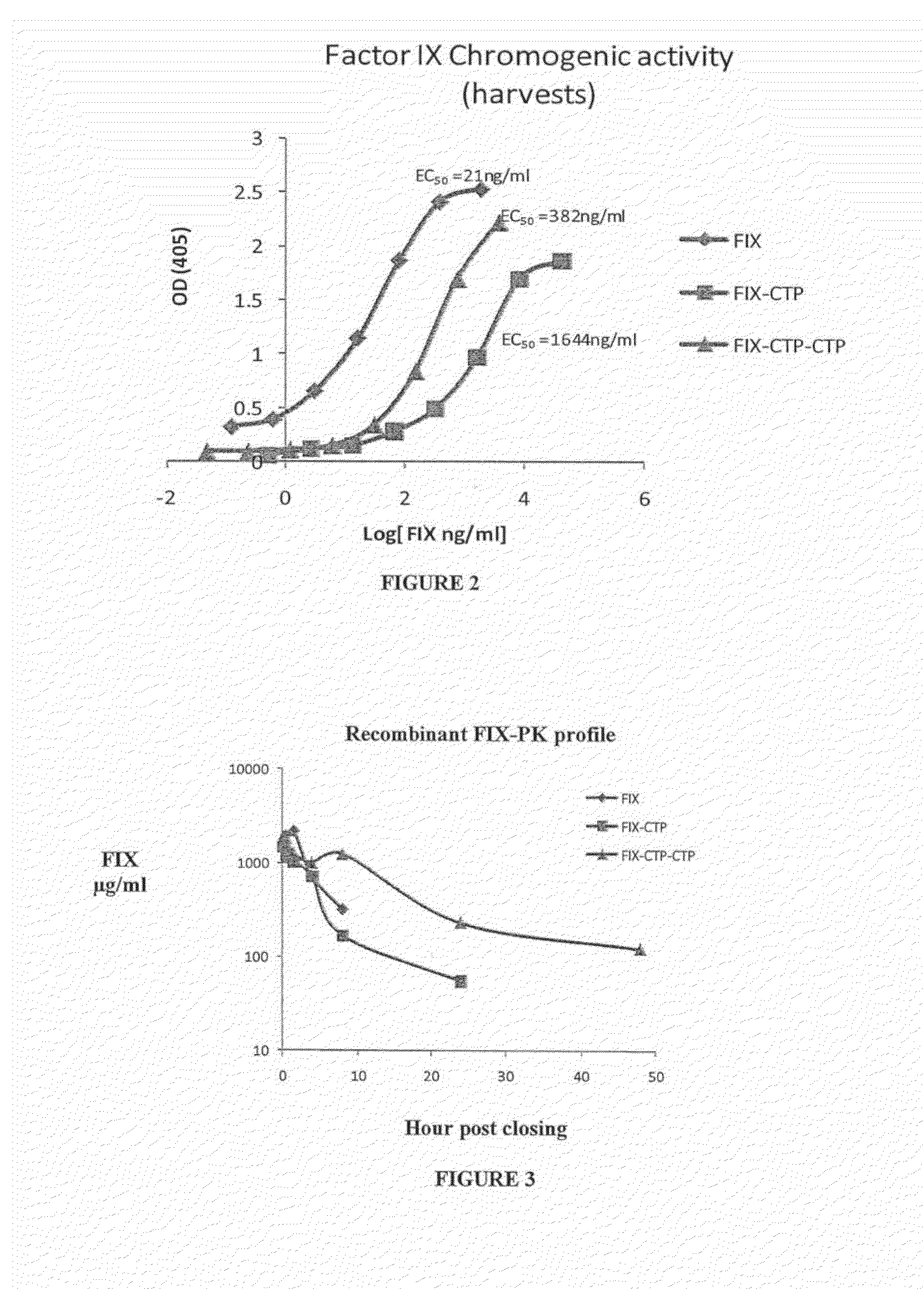
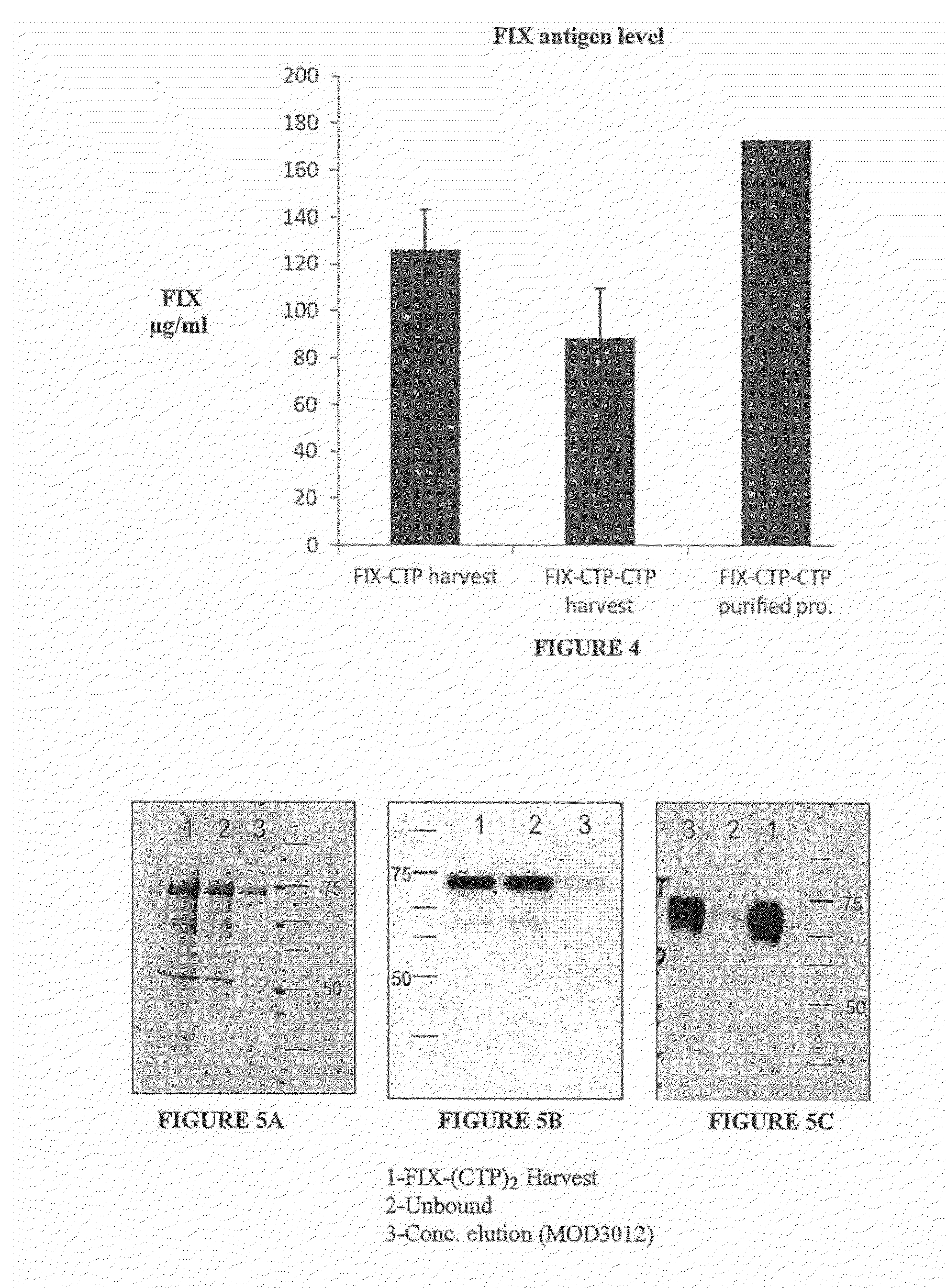
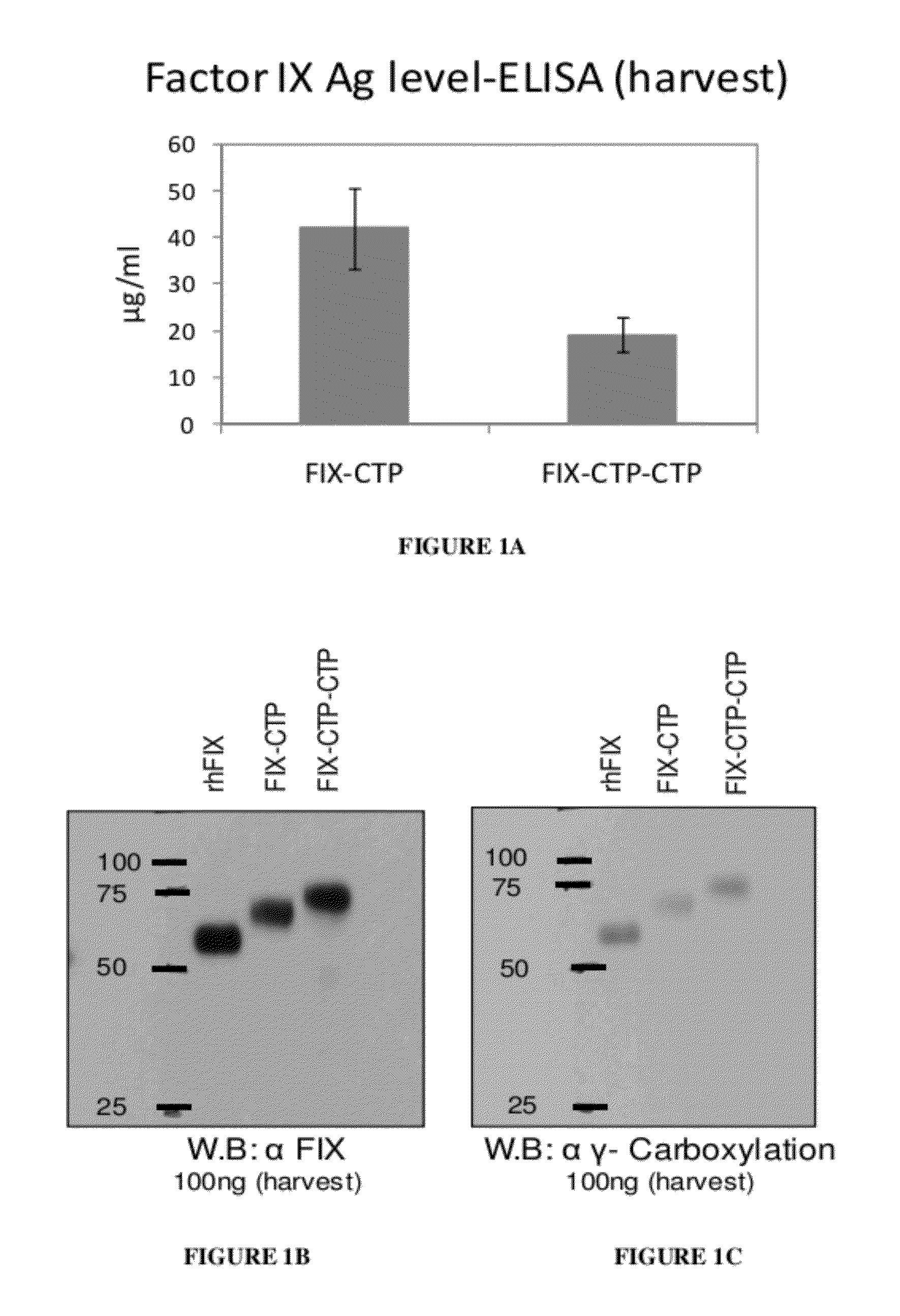
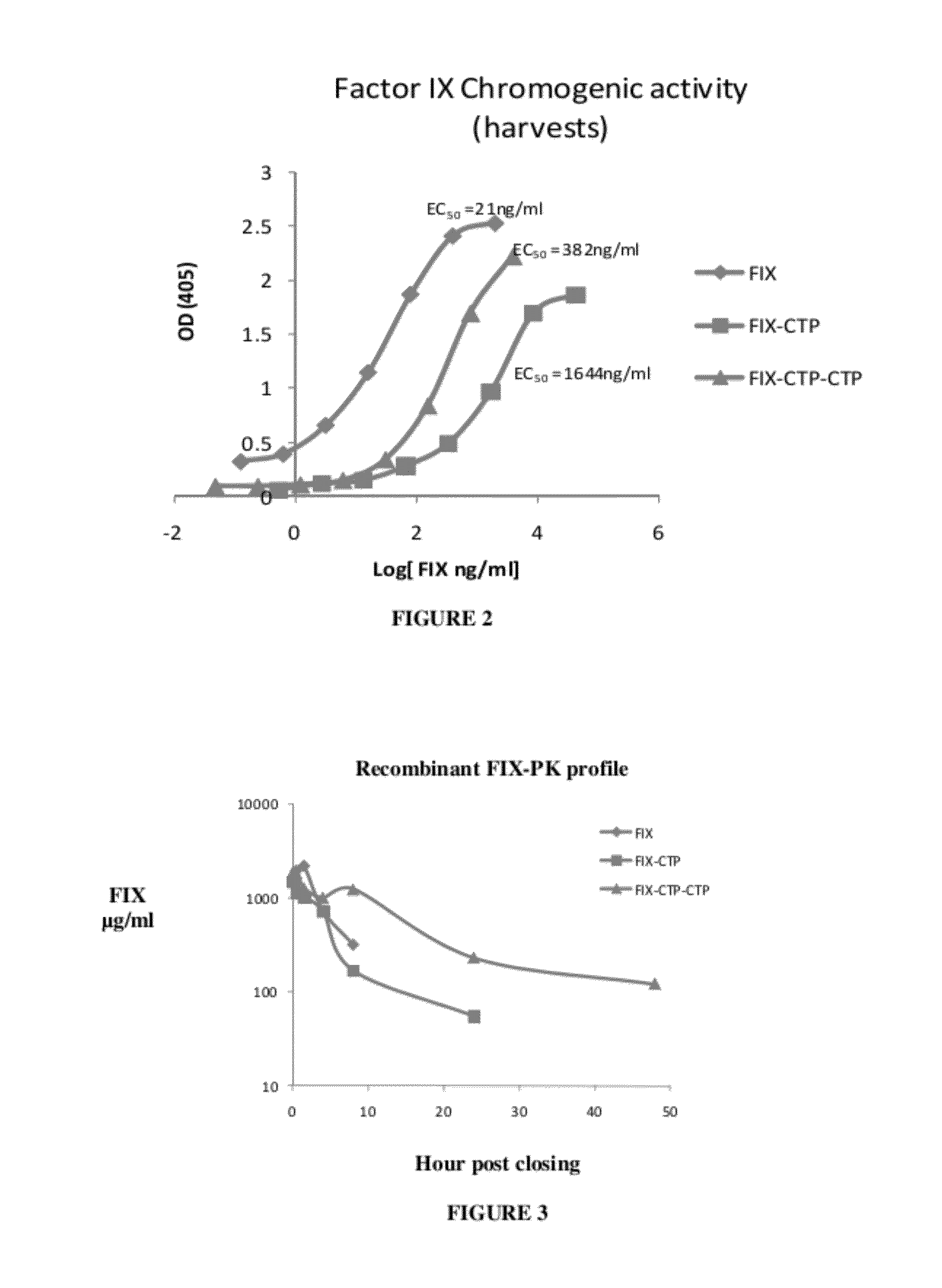
Long-acting coagulation factors and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20130243747A1Prevent coagulationPreventing hemophiliaBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotidePolynucleotide
Polypeptides comprising at least one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to the carboxy terminus but not to the amino terminus of a coagulation factor and polynucleotides encoding the same are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using and producing same are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
Biological entities and the pharmaceutical and diagnostic use thereof
InactiveUS20050175581A1Extended half-lifeEnhanced interactionAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseasePharmaceutical drug
The present invention provides method for the treatment of a disease by applying a medicament comprising a protease with a defined specificity is capable to hydrolyze specific peptide bonds within a target substrate related to such disease. The proteases with such a defined specificity can further be used for related therapeutic or diagnostic purposes.
Owner:DIREVO BIOTECH
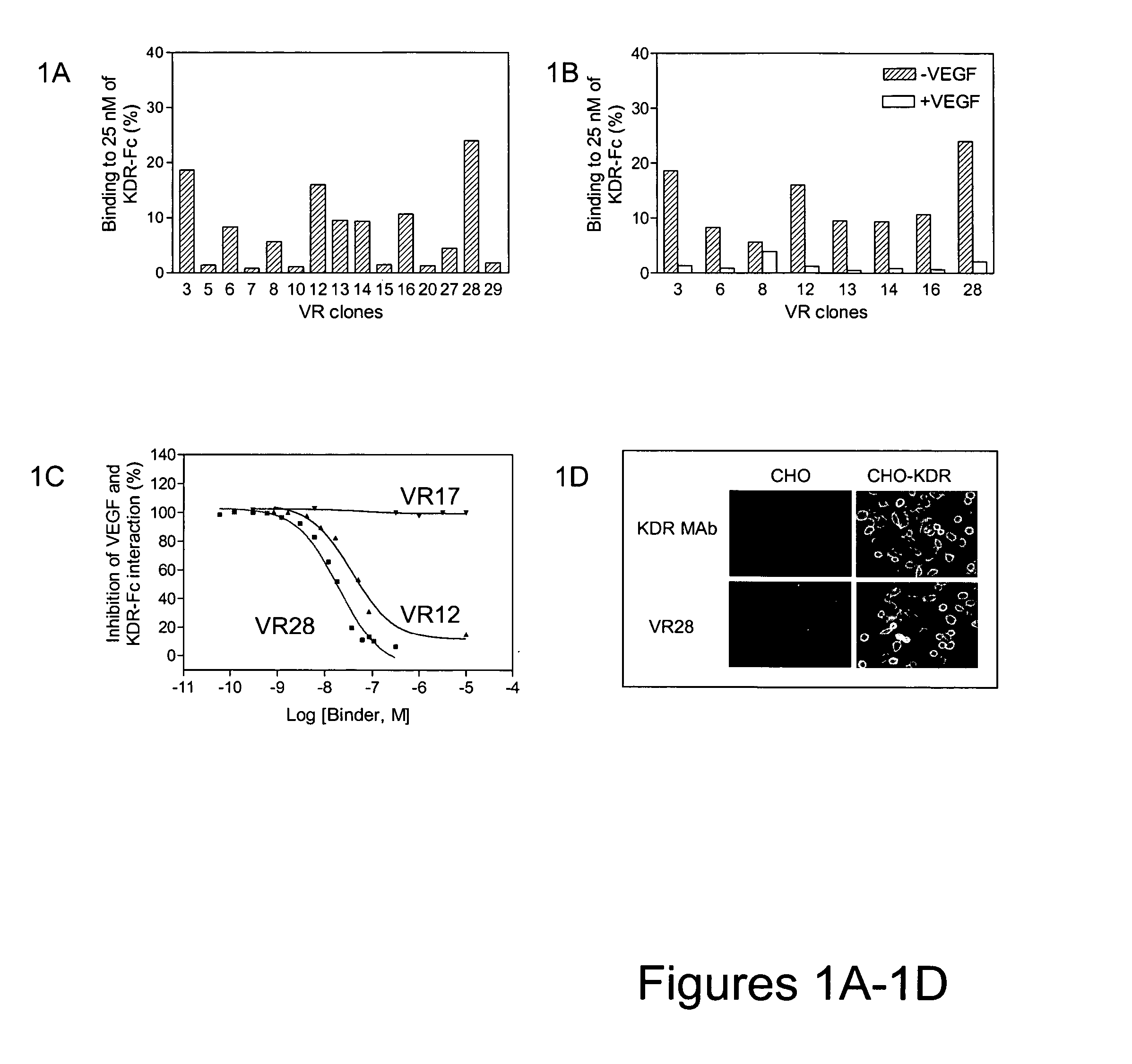
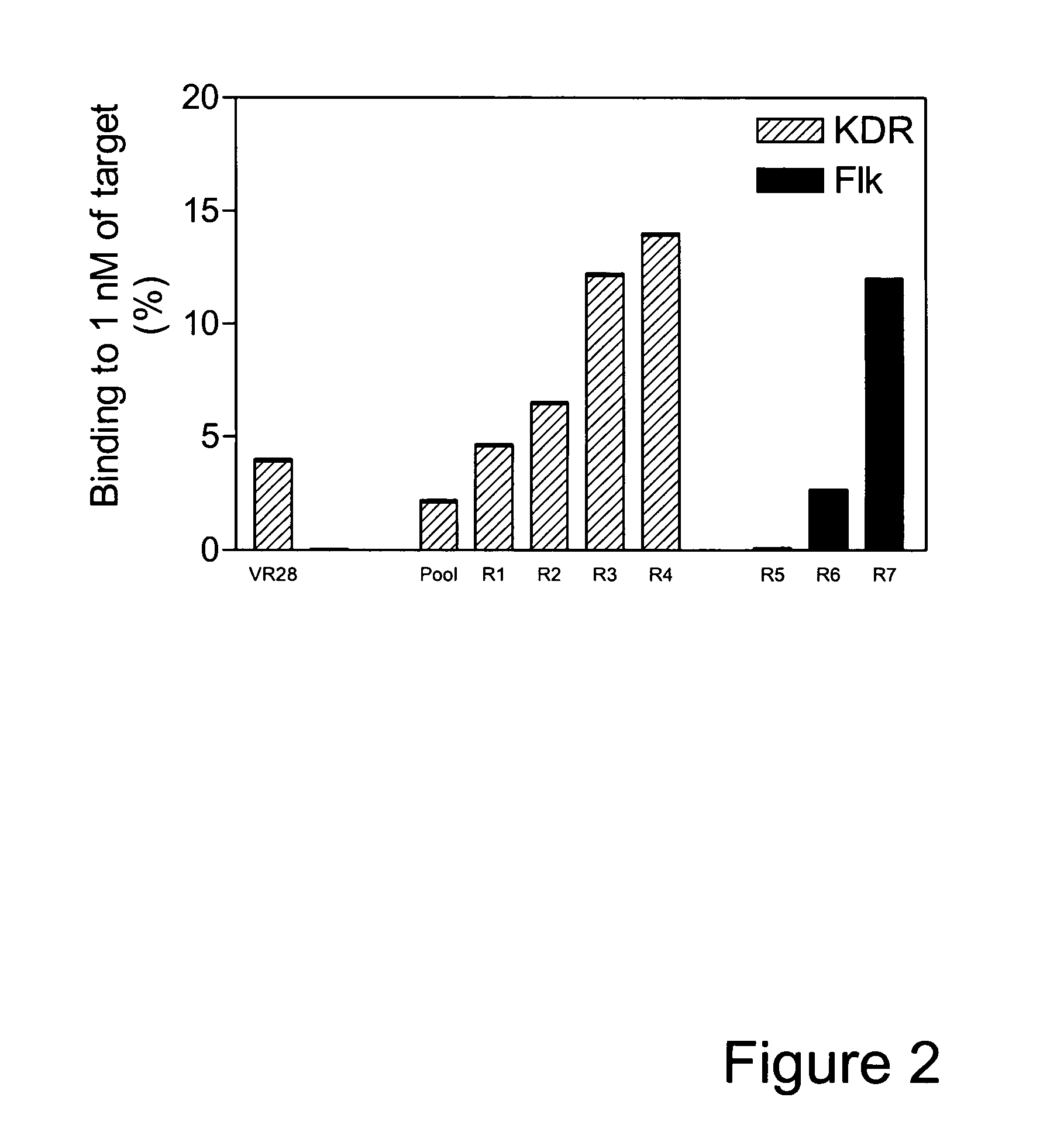
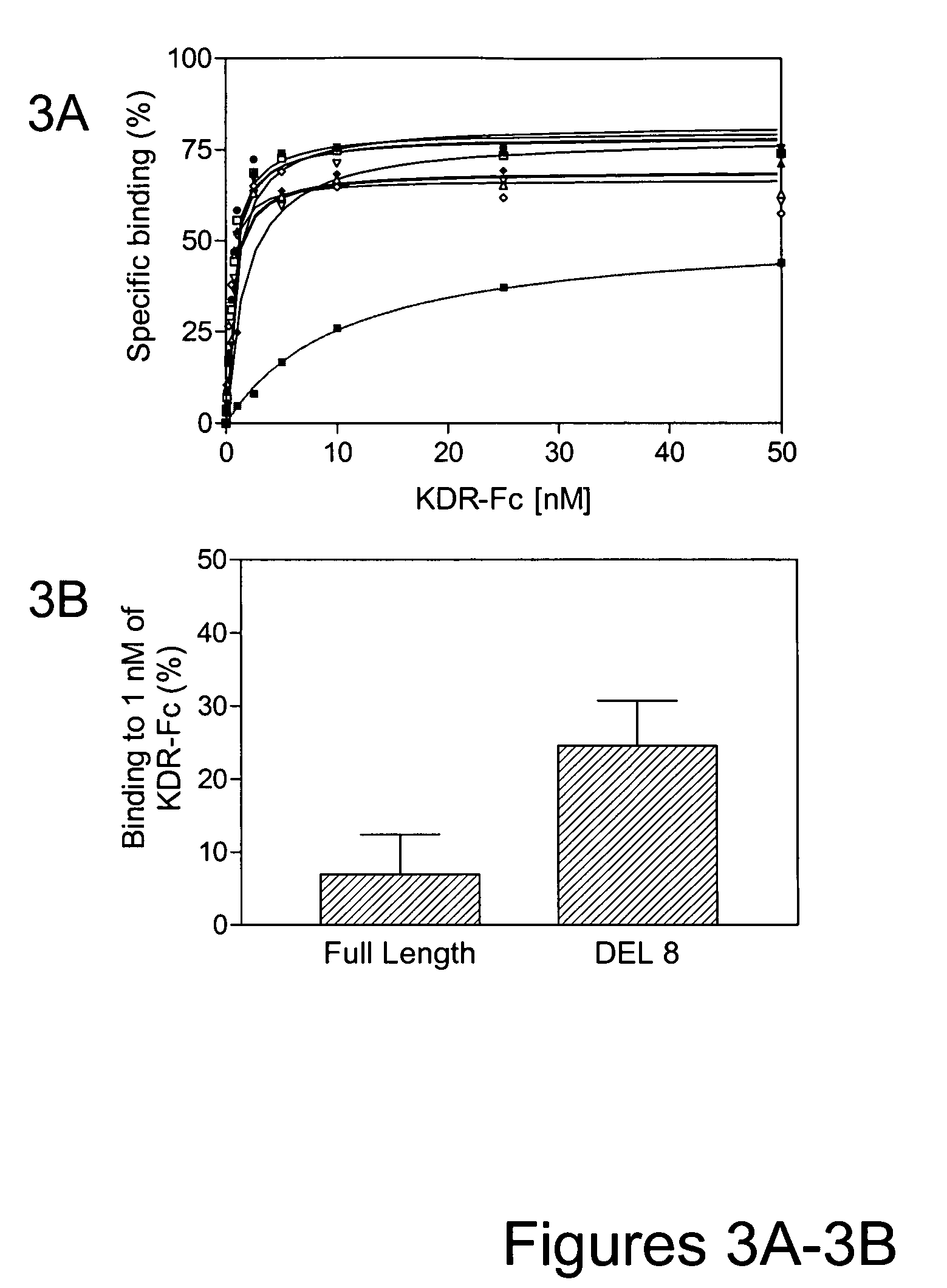
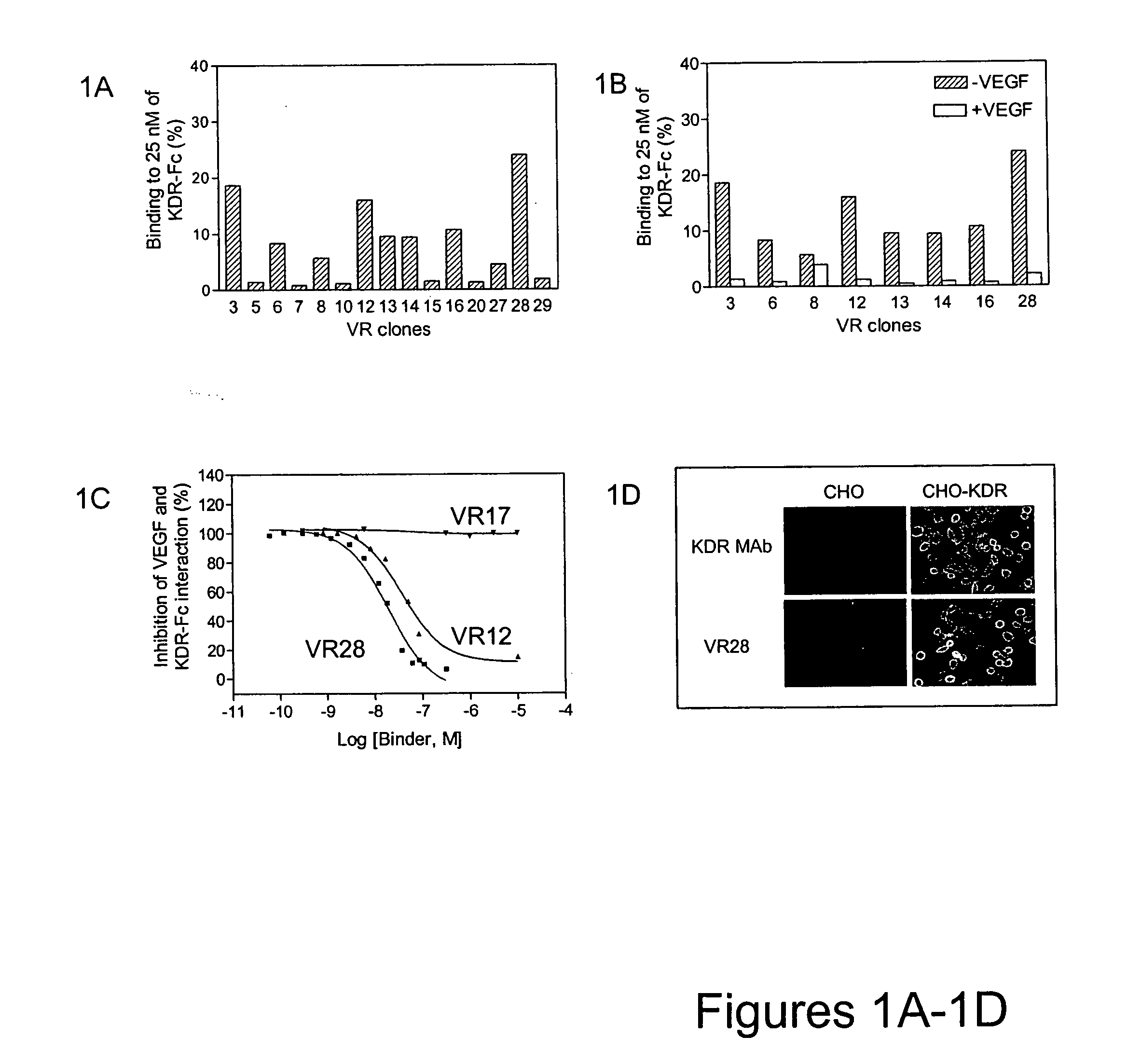
Inhibitors of type 2 vascular endothelial growth factor receptors
ActiveUS20070148126A1Improve pharmacokineticsIncrease target binding affinityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderVascular Endothelial Growth Factor ReceptorDrug biological activity
The present disclosure relates to novel vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-binding polypeptides and methods for using these polypeptides to inhibit biological activities mediated by vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs). The present disclosure also provides various improvements relating to single domain binding polypeptides.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Long-acting coagulation factors and methods of producing same
Polypeptides comprising at least one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to the carboxy terminus but not to the amino terminus of a coagulation factor and polynucleotides encoding the same are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using and producing same are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
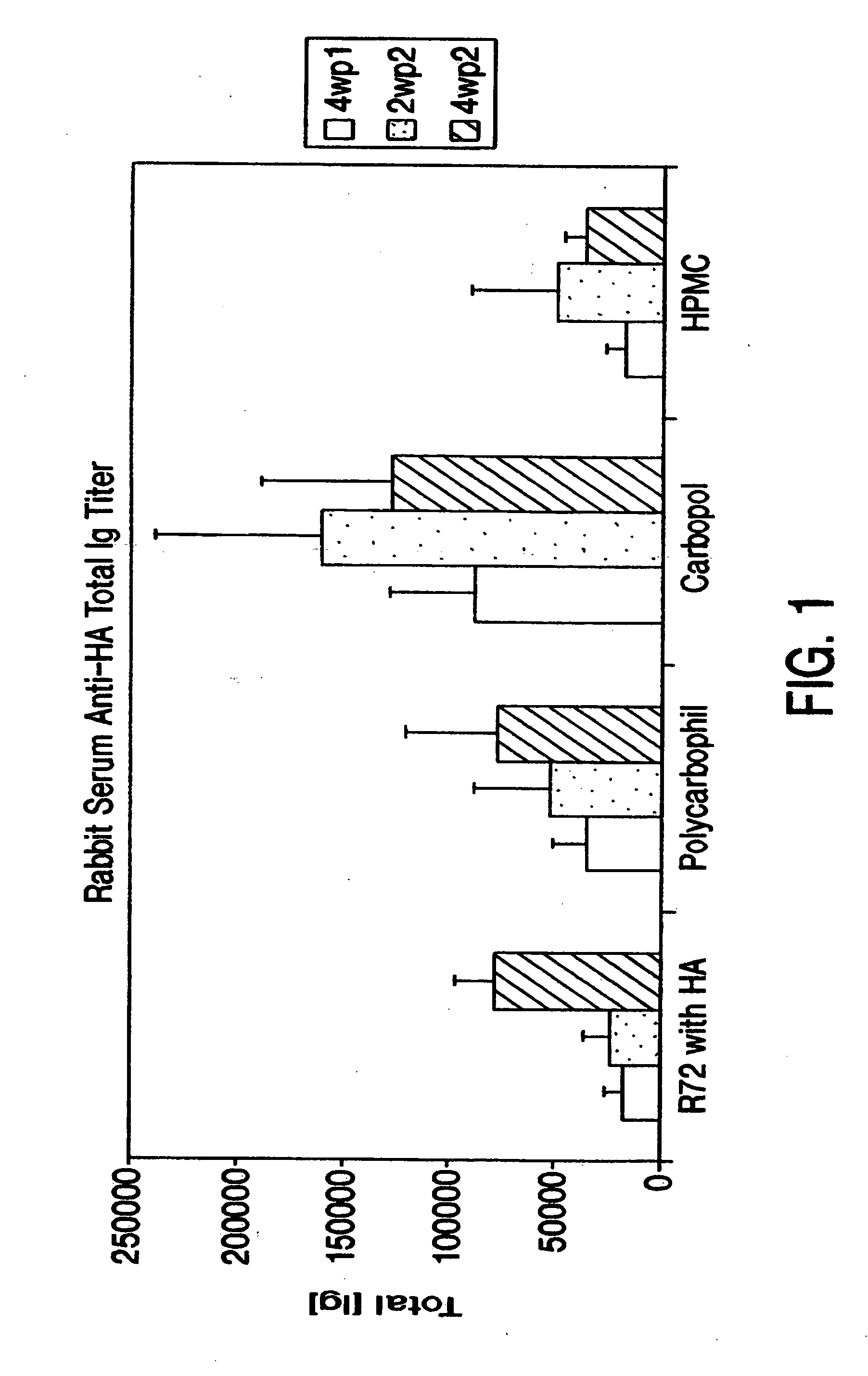
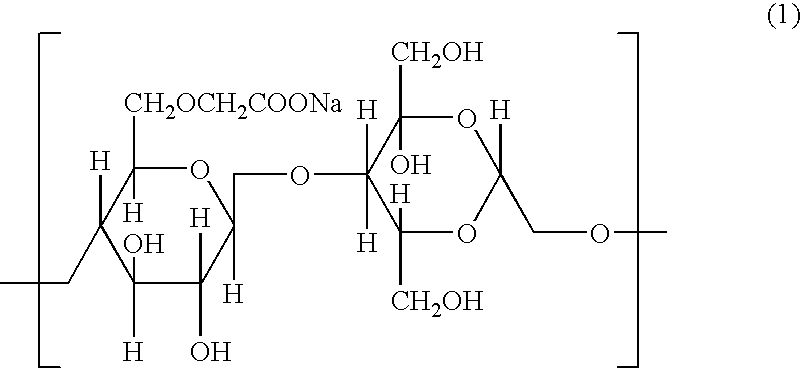
Use of bioadhesives and adjuvants for the mucosal delivery of antigens
InactiveUS20050281843A1Efficient methodImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Pharmacokinetic modulation and compositions for modified Fn3 polypeptides
ActiveUS20070160533A1Improve continuityReduce the differenceSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor ReceptorDrug biological activity
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Monovalent antibody fragments useful as therapeutics
InactiveUS20080063641A1Superior pharmacokinetic attributeExtended half-lifeSugar derivativesBacteriaAntibody fragmentsChemistry
The invention provides methods and compositions comprising a novel stabilized monovalent antibody fragment.
Owner:HUANG ARTHUR JYH YEN +2
Monovalent antibody fragments useful as therapeutics
InactiveUS20050227324A1Superior pharmacokinetic attributeExtended half-lifeBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody fragmentsChemistry
The invention provides methods and compositions comprising a novel stabilized monovalent antibody fragment.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
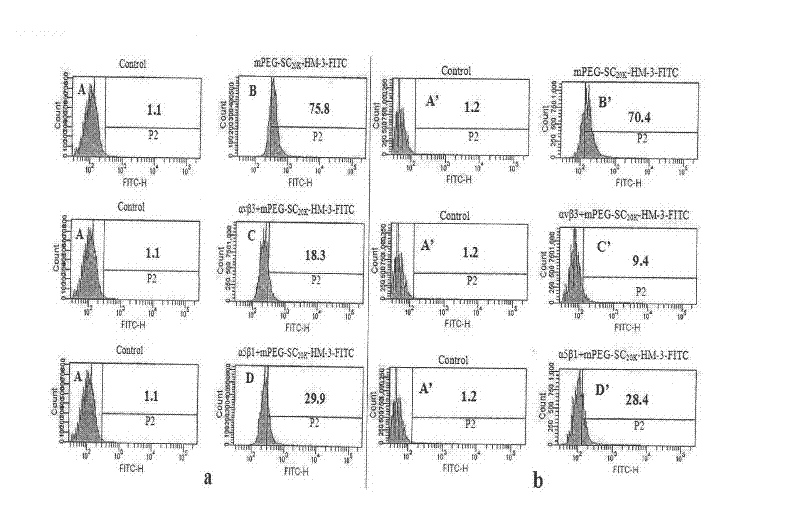
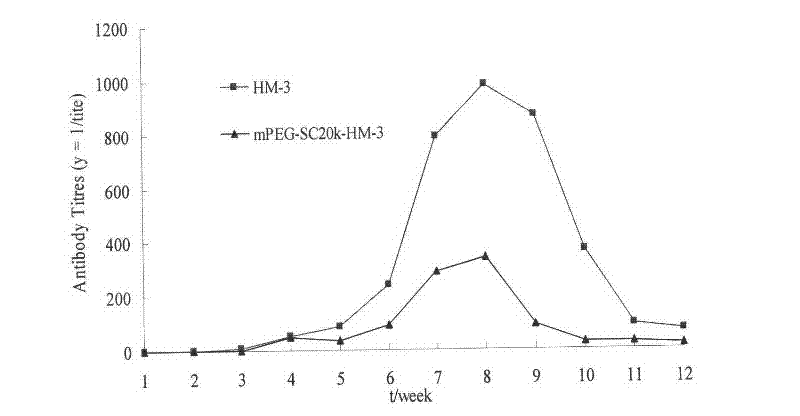
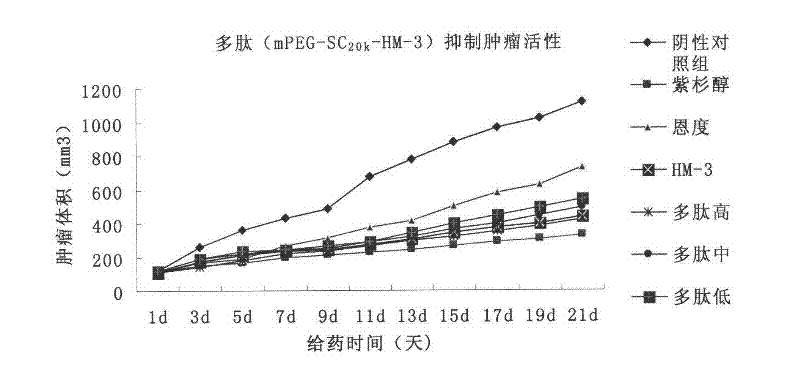
Polyethylene glycol-modified integrin blocking agent HM-3 and application thereof
InactiveCN102417540AExtended half-lifeDoes not affect the activity in vivo and in vitroConnective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor angiogenesisPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to the field of medicaments, in particular to an integrin blocking agent HM-3 which has the function of inhibiting tumor angiogenesis, integrin affinity and a bonding capacity and application thereof. The blocking agent is a polypeptide modified with polyethylene glycol, and the modified integrin blocking agent polypeptide can be applied to treatment of solid tumors. During application of the integrin blocking agent to preparation of a tumor treatment medicament, the sequence and structure of the integrin blocking agent is mPEG-SC20k-Ile-Val-Arg-Arg-Ala-Asp-Arg-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp. The integrin blocking agent polypeptide designed in the invention is scientific, reasonable, practical and effective, can be used for preparing a treatment medicament for treating human solid tumors, and has remarkable social value and market value; and the treatment spectrum of the integrin blocking agent is expanded greatly, and novel thought and prospect are provided for future development of medicaments.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
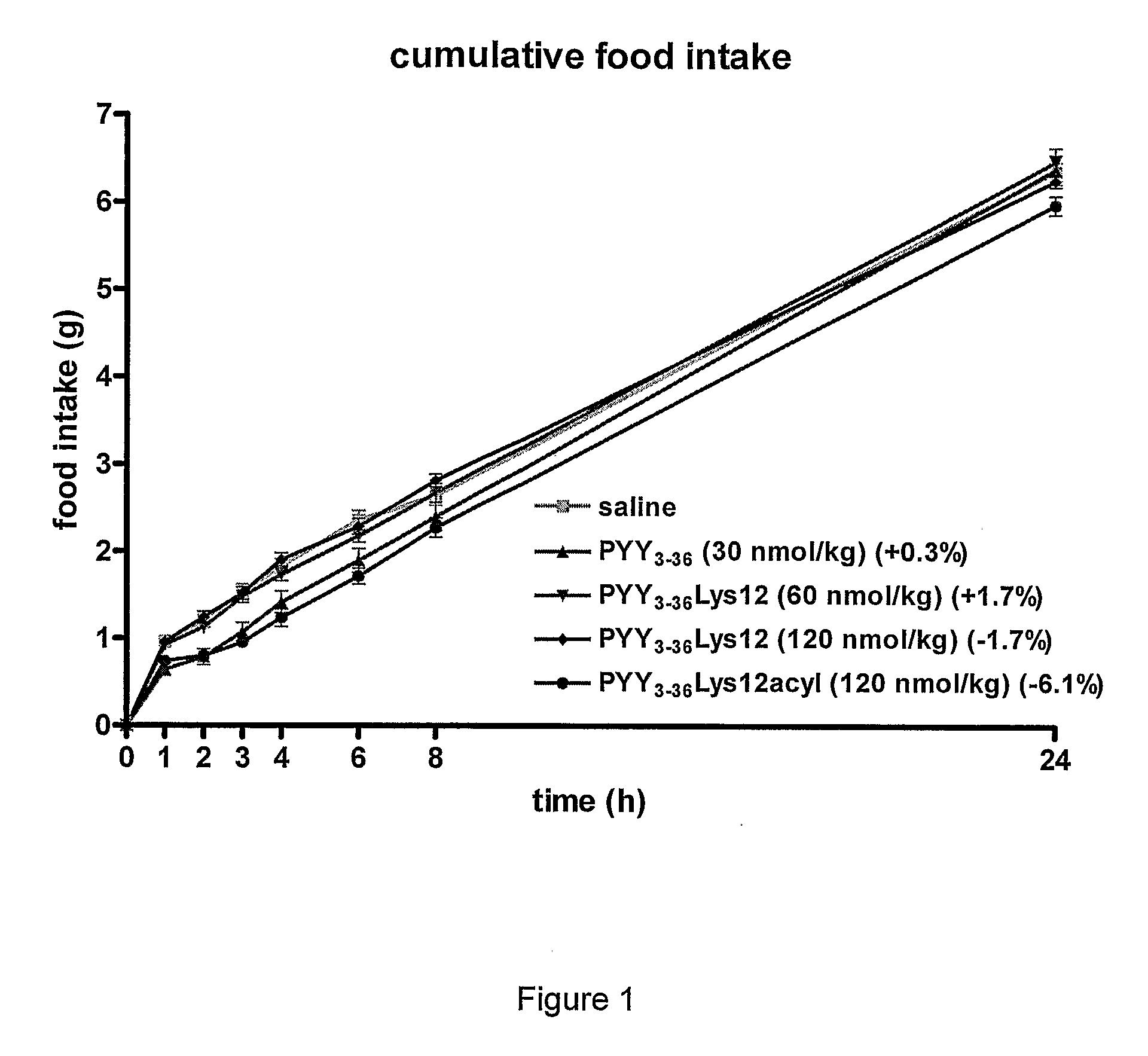
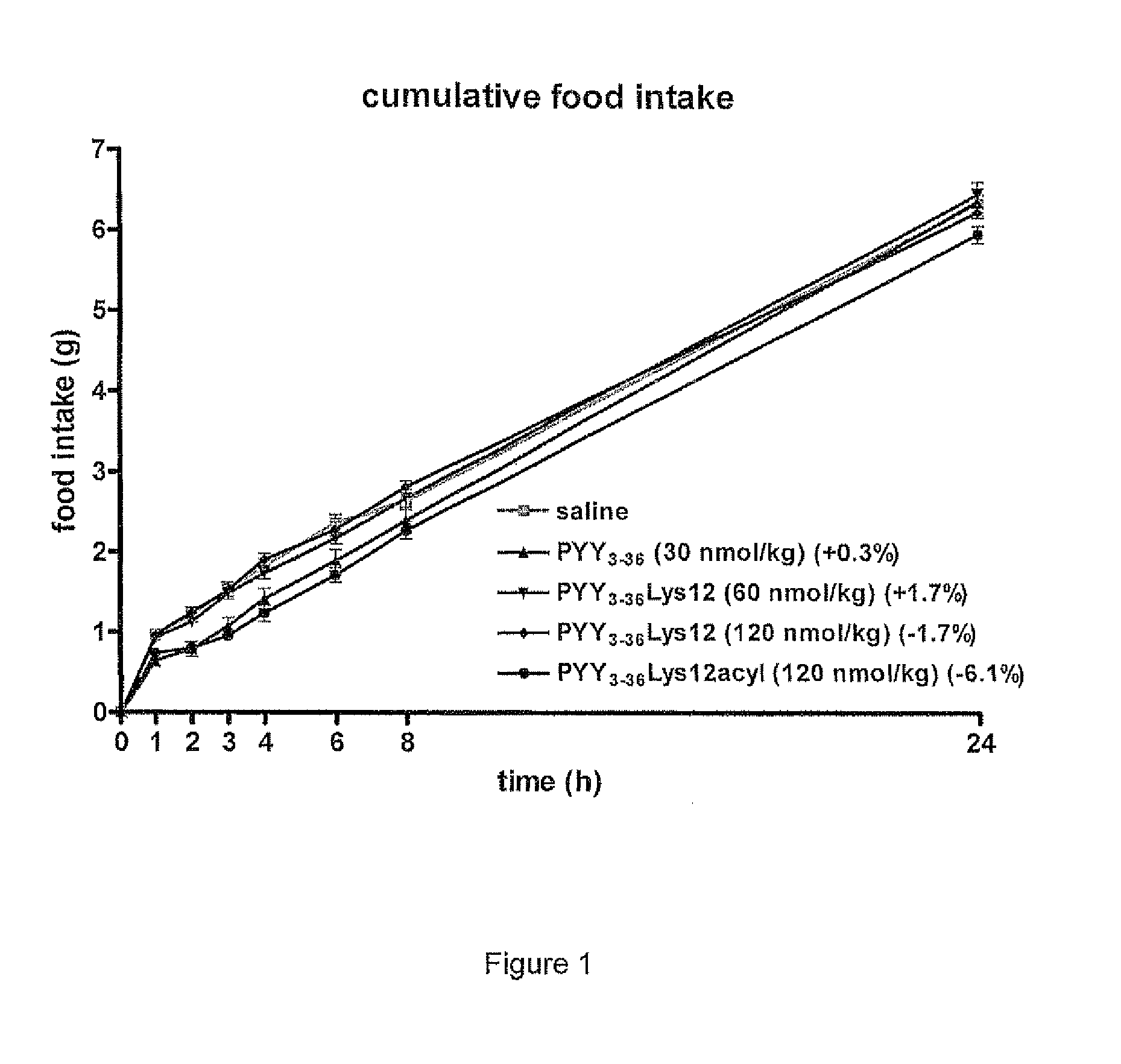
Compounds and their effects on feeding behaviour
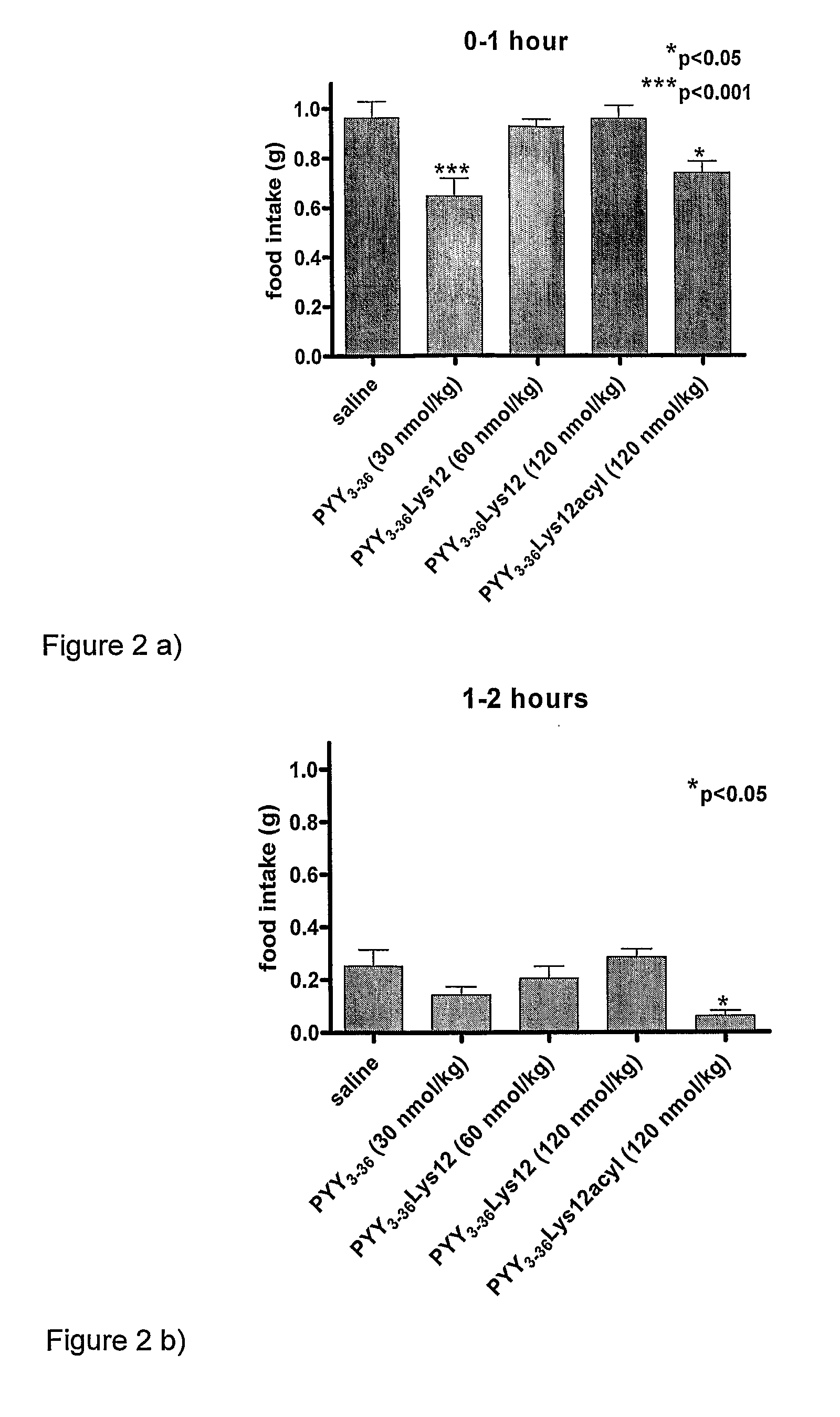
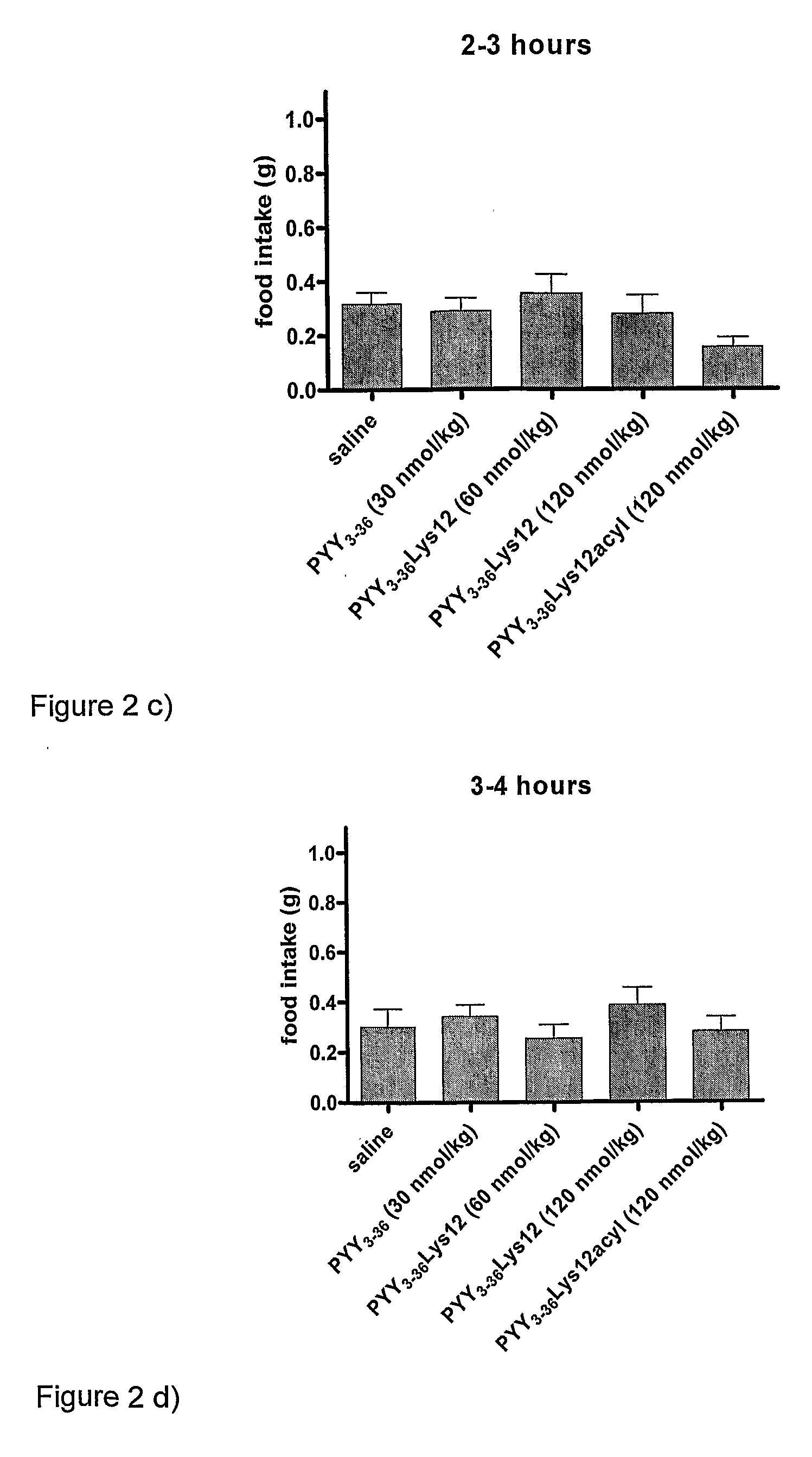
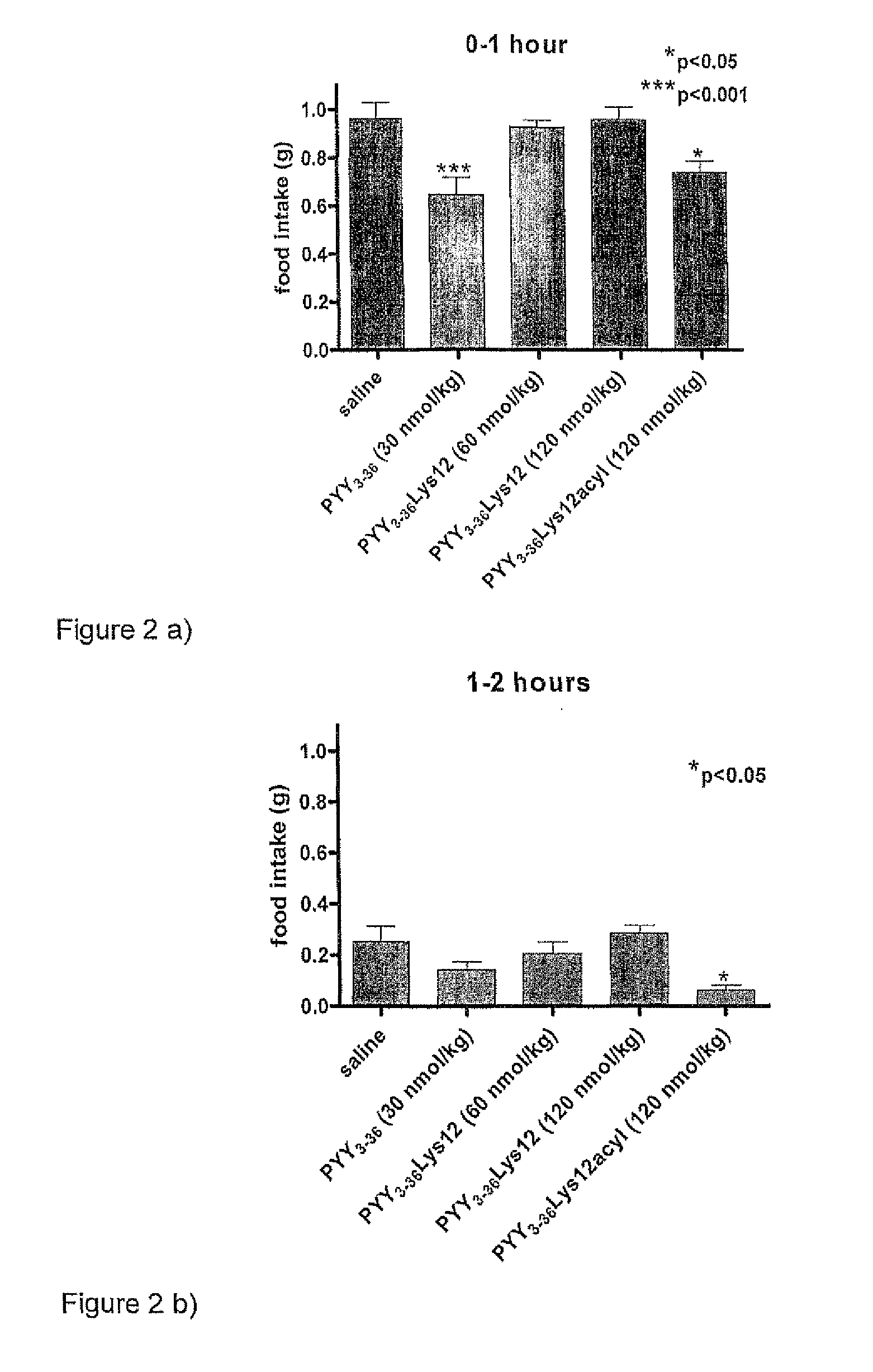
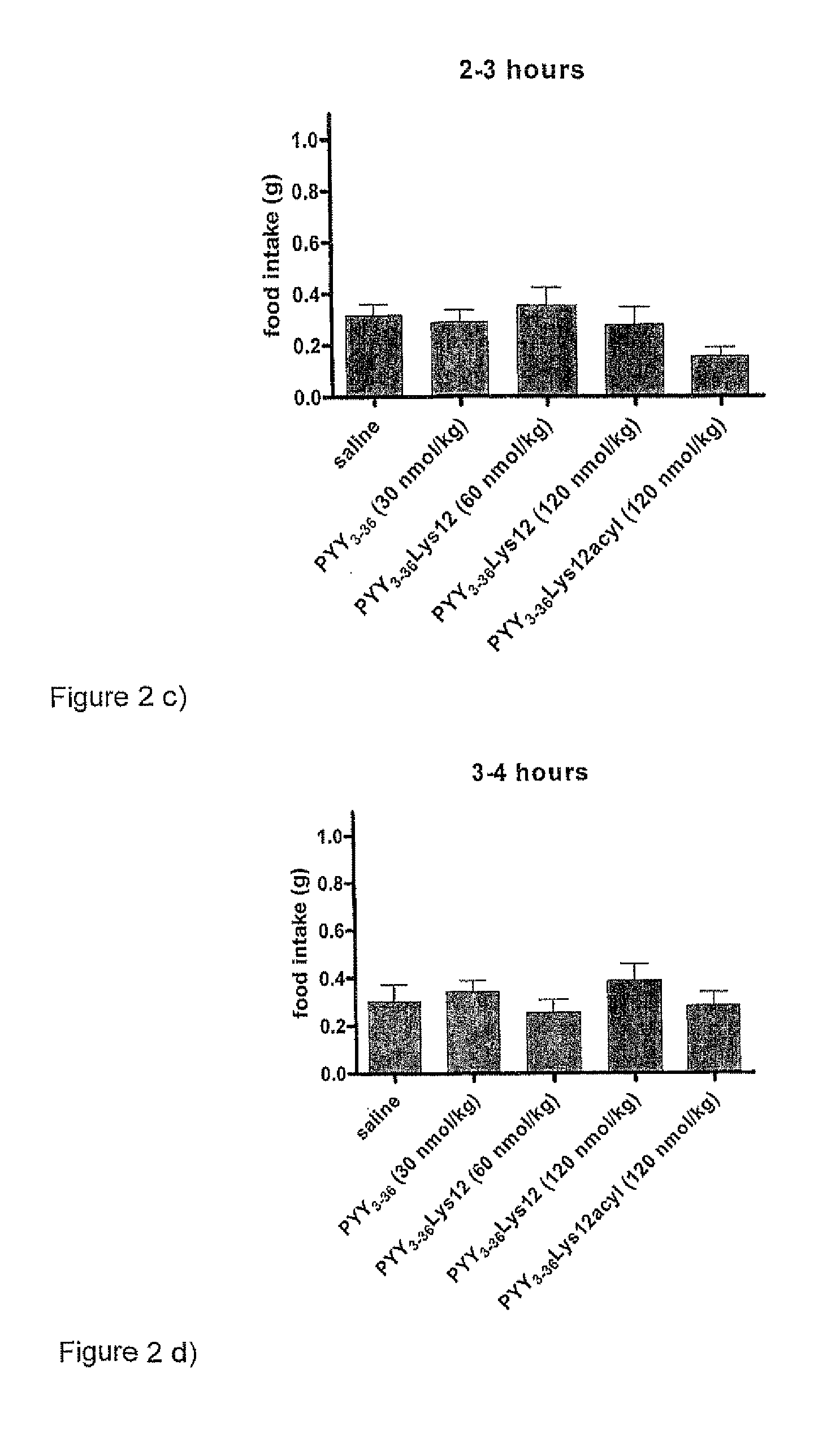
InactiveUS8263736B2Reduced clearance rateExtended durationHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsArylDisease
The invention provides a compound of formula (I): X-PYY* (3-36) (I) wherein X is selected from H, PYY1-2 (ie Tyr Pro) and D-Allo-Ue; PYY*(3-36) representing PYY (3-36) in which one or more residues is replaced by an acylated lysine group, the acyl group being selected from: CO—C1-20 alkyl, CO—C2-20 alkenyl, CO—C5-10 aryl and CO—C5-10 ar-C1-20 alkyl; a variant or derivative thereof; or a salt or solvate thereof. The compounds are effective in inducing satiety and suppressing appetite and they are thus useful in treating various diseases, including obesity.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Conjugated biological molecules and their preparation
ActiveUS7939630B2Favourably alter pharmacokineticsExtended circulation timePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsHydrogen atomMedicinal chemistry
Novel biologically active compounds of the general formula (I) in which one of X and X′ represents a polymer, and the other represents a hydrogen atom; each Q independently represents a linking group; W represents an electron-withdrawing moiety or a moiety preparable by reduction of an electron-withdrawing moiety; or, if X′ represents a polymer, X-Q-W— together may represent an electron withdrawing group; and in addition, if X represents a polymer, X′ and electron withdrawing group W together with the interjacent atoms may form a ring; each of Z1 and Z2 independently represents a group derived from a biological molecule, each of which is linked to A and B via a nucleophilic moiety; or Z1 and Z2 together represent a single group derived from a biological molecule which is linked to A and B via two nucleophilic moieties; A is a C1-5 alkylene or alkenylene chain; and B is a bond or a C1-4 alkylene or alkenylene chain; are formed by conjugating a suitable polymer to a suitable biologically active molecule via nucleophilic groups in said molecule, preferably via a disulphide bridge.
Owner:ABZENA UK LTD
Long-acting coagulation factors and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20130295072A1Prevent coagulationPreventing hemophiliaBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPolynucleotideBiology
Polypeptides comprising at least one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to the carboxy terminus but not to the amino terminus of a coagulation factor and polynucleotides encoding the same are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using and producing same are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
Long-acting coagulation factors and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20150368630A9Reduce dosing frequencyIncrease the areaBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotidePolynucleotide
Polypeptides comprising at least one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to the carboxy terminus but not to the amino terminus of a coagulation factor and polynucleotides encoding the same are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using and producing same are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
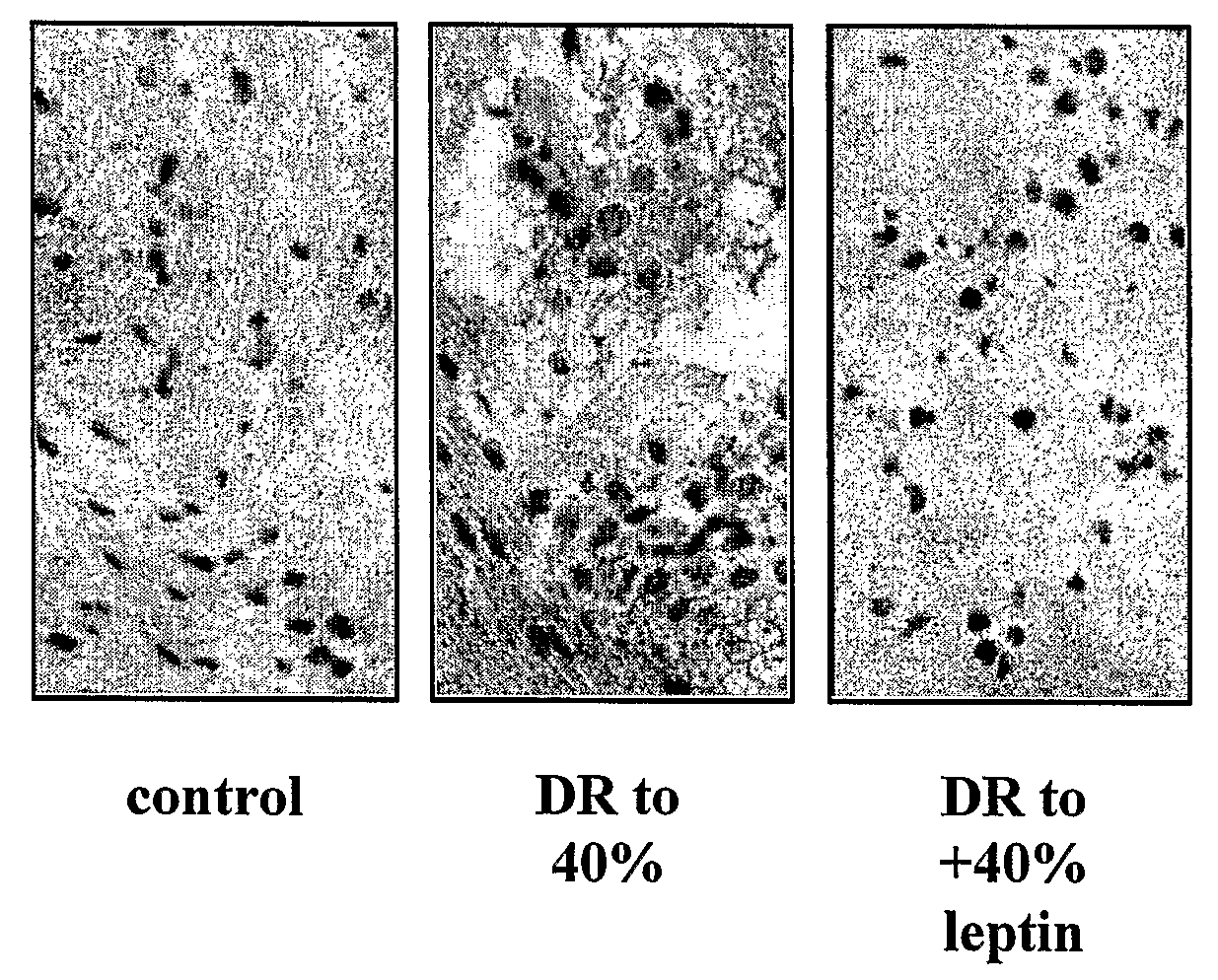
Compounds for Improving Nutritional Status, Cognition and Survival
InactiveUS20090175841A1Reverse deleterious effectModulates cognitive abilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideDrugLeptin
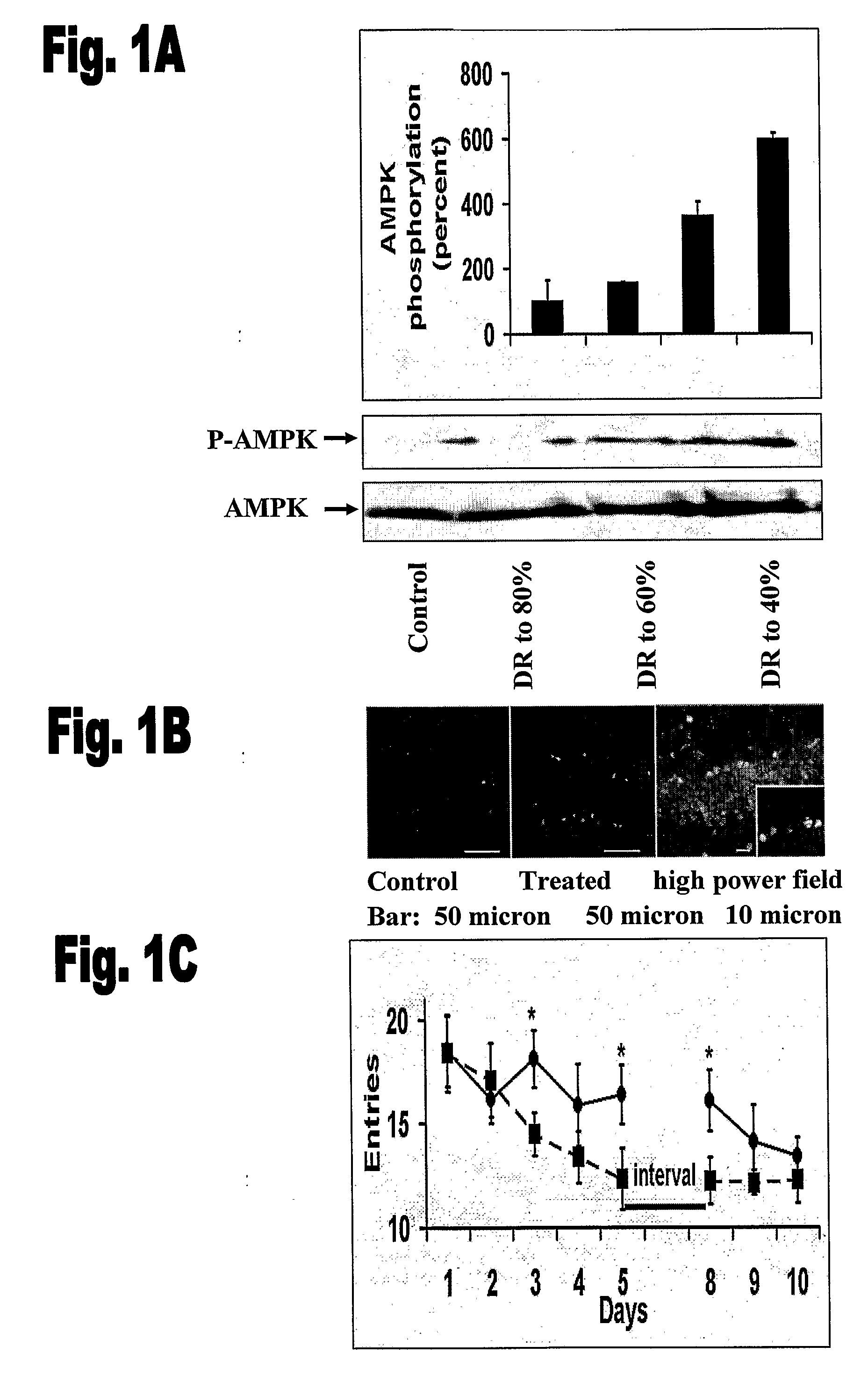
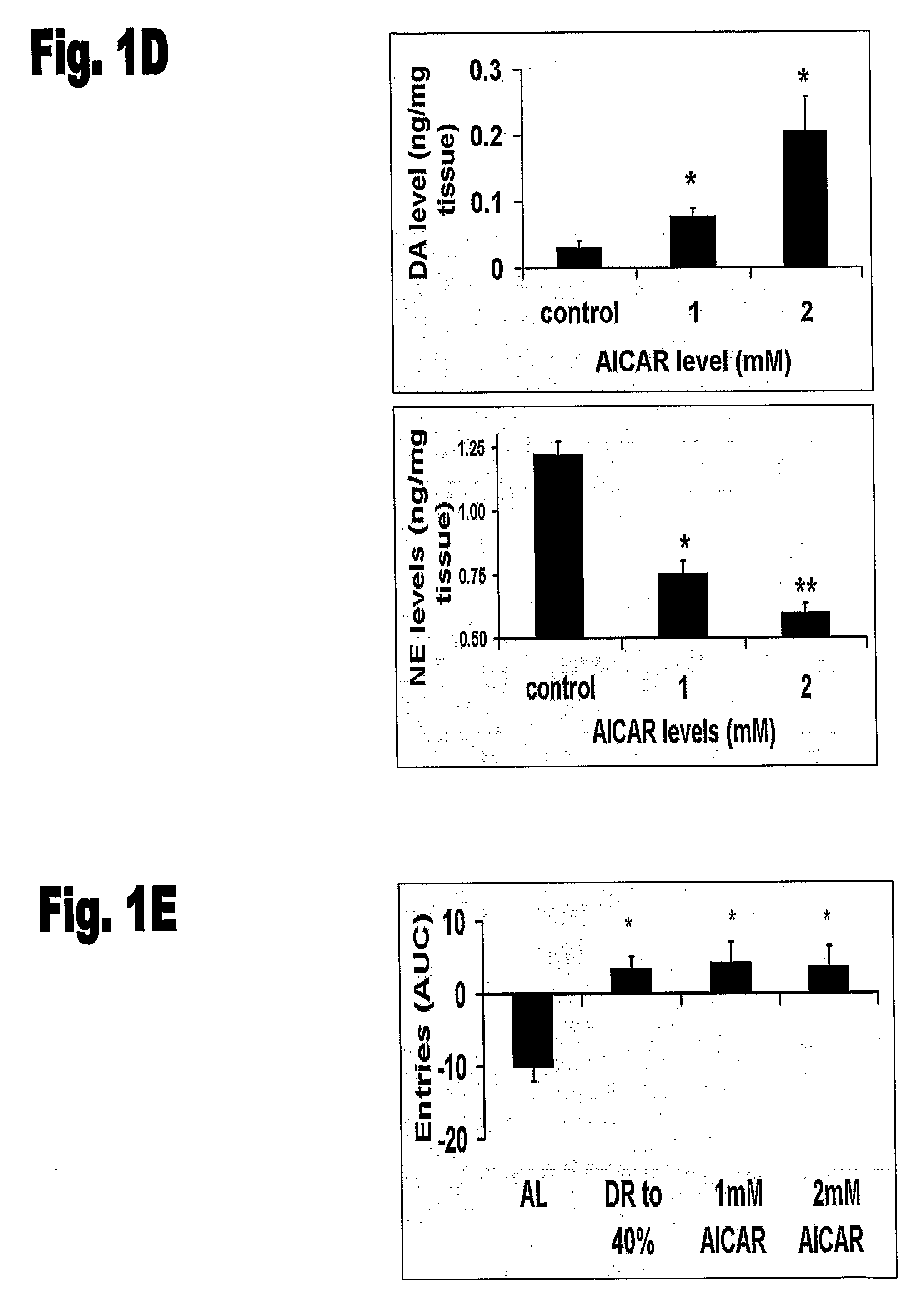
The present invention concerns using a leptin protein, a variant fragment or mimic of a leptin protein, or an activator of the AMPK signal transduction pathway for preparing a medicament that can either be used to improve cognitive function or to treat treatment of undesirable manifestations of a nutritional stress condition and to prolong survival.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREW UNIV OF JERUSALEM LTD
Traditional Chinese medicine for treating insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes
InactiveCN102335362AImprove the immunityMedicinal and calmMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsSide effectBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
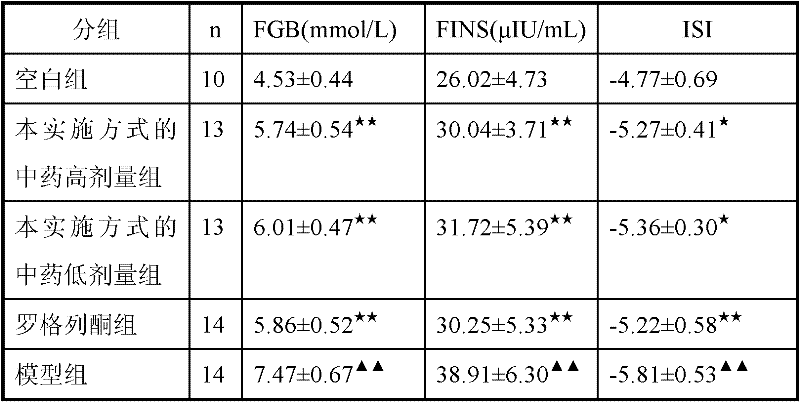
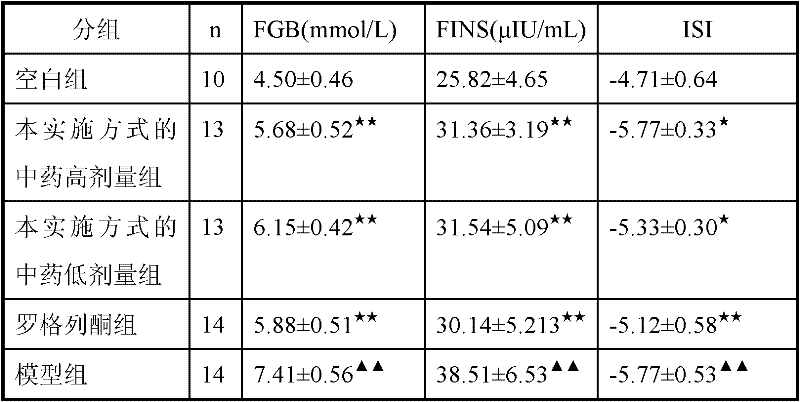
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine for treating insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes, and is used for solving the problem that the safe and efficient drugs for treating insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes are not available at present. The traditional Chinese medicine for treating insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 10-20 parts of American ginseng, 20-40 parts of coix seed and 10-20 parts of alisma. The traditional Chinese medicine has mild drug property and low toxic and side effect, and is used for treating insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes with the main characteristics, such as deficiency of spleen qi and interior accumulation of dampness and turbid. Compared with the similar traditional Chinese medicines, the traditional Chinese medicine has clear main active ingredients and definite disease treatment effect, and can obviously improve insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Aqueous solution of recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101954067AReduced clearance rateProlong biological half-lifeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsArginineInterferon alpha
The invention relates to stable aqueous solution of a recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein and belongs to the technical field of biological preparations. The aqueous solution of the recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein is prepared by dissolving the recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein and pharmaceutically acceptable stable auxiliary material in pharmaceutically acceptable buffer solution, and is characterized in that the pharmaceutically acceptable stable auxiliary material is arginine at a concentration of 5 to 30 g / L. The aqueous solution of therecombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein can prevent the aggregation, degradation, oxidation, denaturation and the like of the recombinant fusion protein effectively so as to retain bioactivity and is suitable to be used in clinic.
Owner:QILU PHARMA
Long-acting coagulation factors and methods of producing same
ActiveUS8759292B2Extended half-lifeIncreased AUCBacteriaSaccharide peptide ingredientsPolynucleotideBiology
Polypeptides comprising at least one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to the carboxy terminus but not to the amino terminus of a coagulation factor and polynucleotides encoding the same are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using and producing same are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
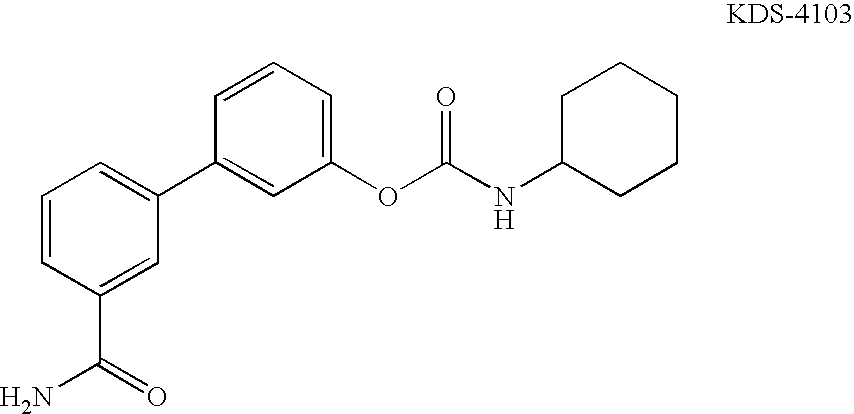
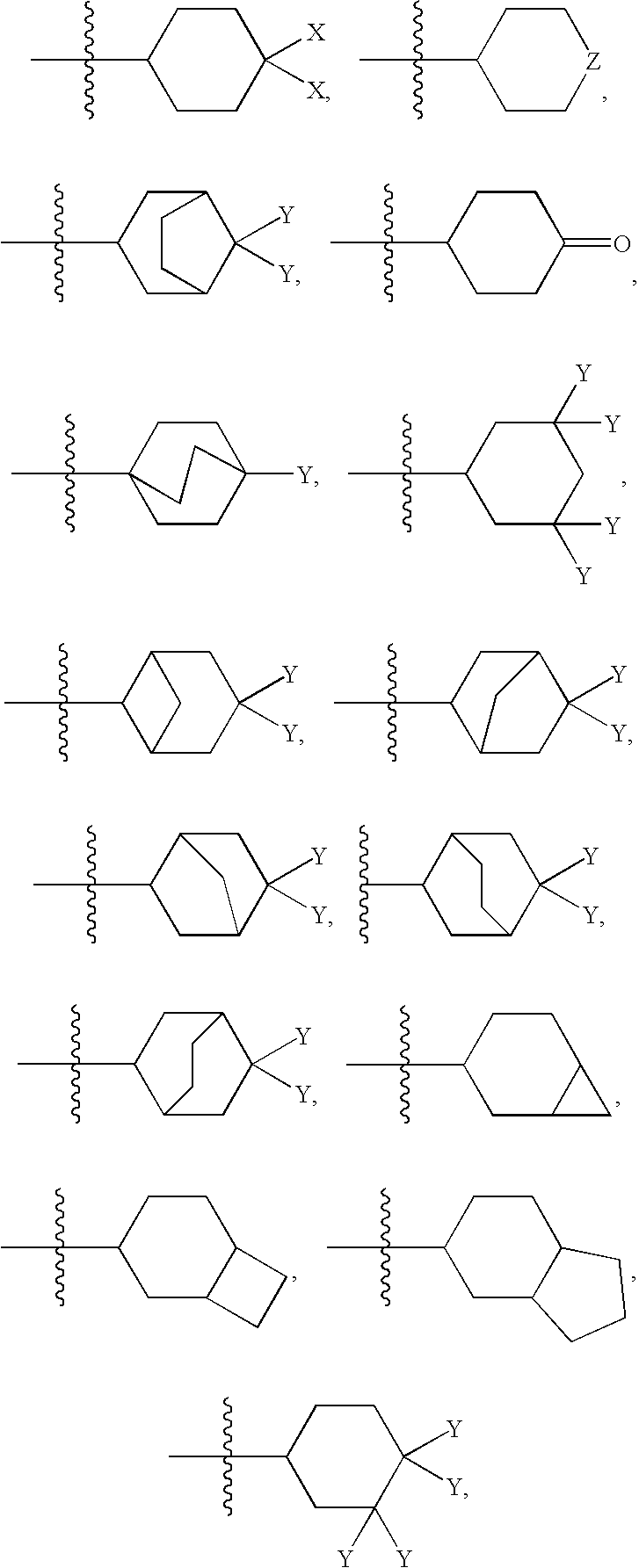
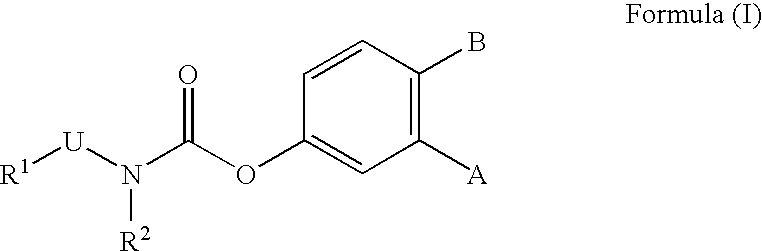
Novel benzo[d][1,3]-dioxol derivatives
Owner:CONCERT PHARMA INC
Metabolically-stabilized inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase
InactiveUS20080119549A1Improve the level ofElevates endogenous levelBiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationMedicinal chemistryEnzyme
Pharmacological inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity leads to increased levels of fatty acid amides. Esters of alkylcarbamic acids are disclosed that are inhibitors of FAAH activity. Compounds disclosed herein inhibit FAAH activity. Described herein are processes for the preparation of esters of alkylcarbamic acid compounds, compositions that include them, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:NV ORGANON
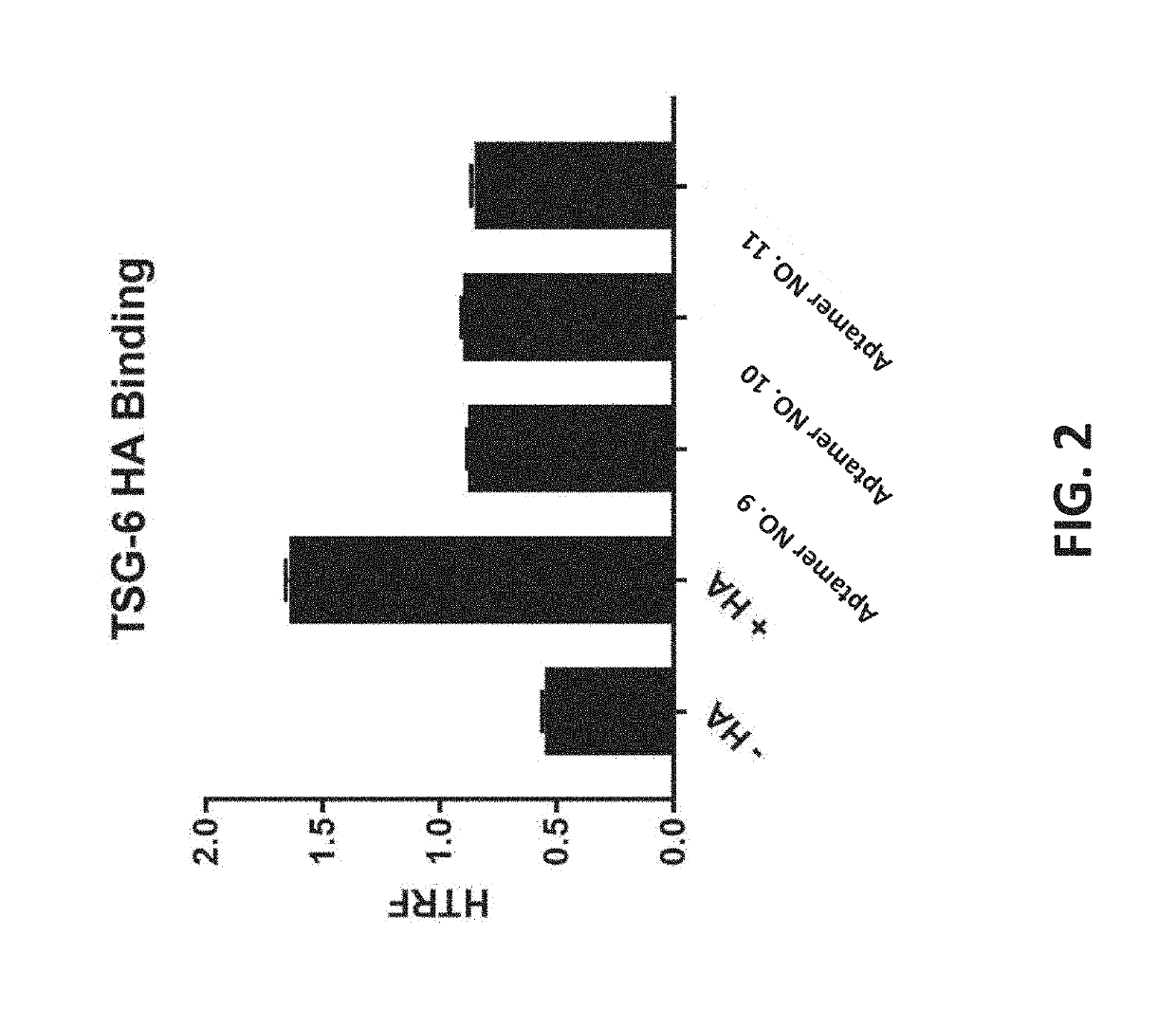
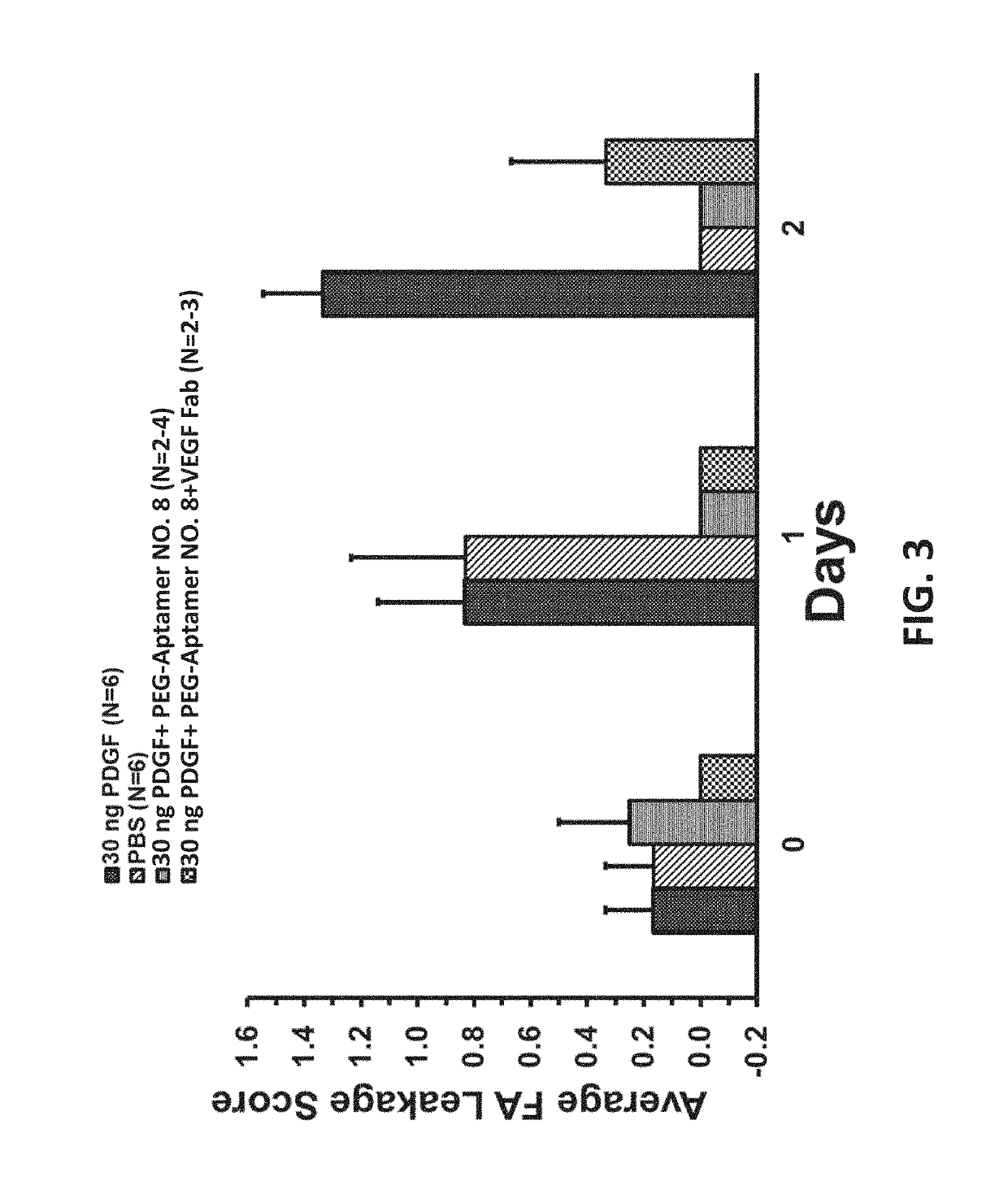
Compositions with improved intravitreal half-life and uses thereof
InactiveUS10308943B2Reduced clearance rateImprove retentionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseVitreous Humors
Provided herein are compositions and methods for the treatment of retinal diseases. The compositions and methods include a therapeutic agent conjugated to a vitreous component binding moiety. The vitreous component binding moiety may be an aptamer or a small molecule that binds to a structural component of the vitreous humor (e.g., hyaluronic acid, collagen or vitronectin).
Owner:VITRISA THERAPEUTICS INC
Fusion protein of human epidermal growth factor and metallothionein and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a fusion protein of a human epidermal growth factor and metallothionein, which comprises a first part and a second part, wherein the first part is the human epidermal growth factor, the second part is the human metallothionein, and the human metallothionein is positioned at the C terminal of the human epidermal growth factor. The invention further provides an application of the fusion protein in the preparation of drugs for treating burns or scalds or wounds or ulcers and the application of the fusion protein in the preparation of skin nursing drugs. Compared with the original human epidermal growth factor and the metallothionein, the fusion protein can increase the stability, reduce the clearance rate, reduce the degradation, bring benefits and convenience to the use of the EGF-MT fusion protein and further reduce the using dosage and the medication frequency. Simultaneously, the formed fusion protein is a bifunctional molecule which has double effects of EGF and MT.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIRUIBAO BIOTECH
Novel compounds and their effects on feeding behaviour
InactiveUS20090318347A1Reduced clearance rateExtended durationHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAryl
The invention provides a compound of formula (I): X-PYY*(3-36) (I) wherein X is selected from H, PYY1-2 (ie Tyr Pro) and D-Allo-Ue; PYY*(3-36) representing PYY (3-36) in which one or more residues is replaced by an acylated lysine group, the acyl group being selected from: CO—C1-20 alkyl, CO—C2-20 alkenyl, CO—C5-10 aryl and CO—C5-10 ar-C1-20 alkyl; a variant or derivative thereof; or a salt or solvate thereof. The compounds are effective in inducing satiety and suppressing appetite and they are thus useful in treating various diseases, including obesity.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Long-acting coagulation factors and methods of producing same
ActiveUS9249407B2Reduce dosing frequencyIncrease the areaBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideChorionic gonadotrophin
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
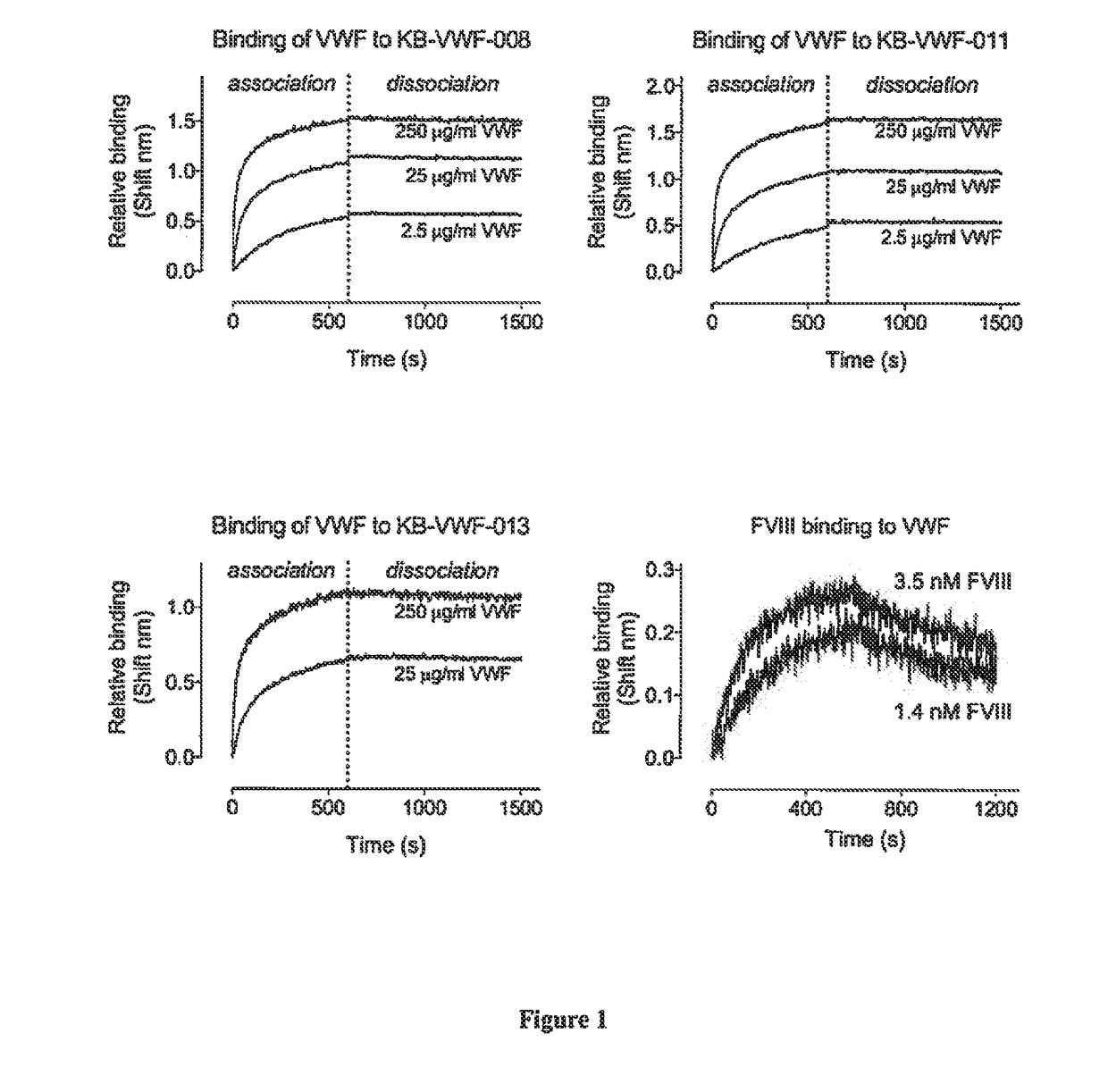
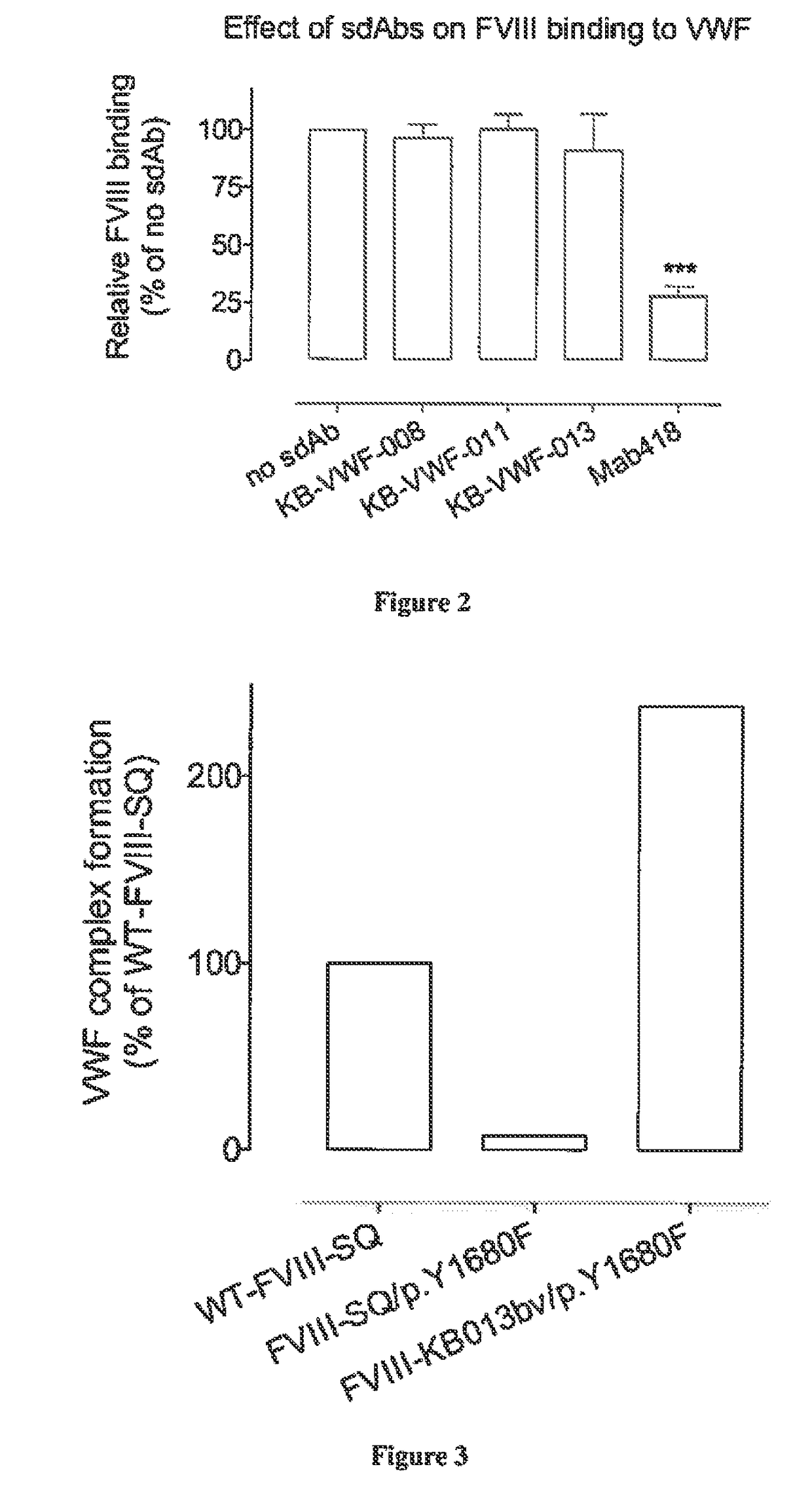
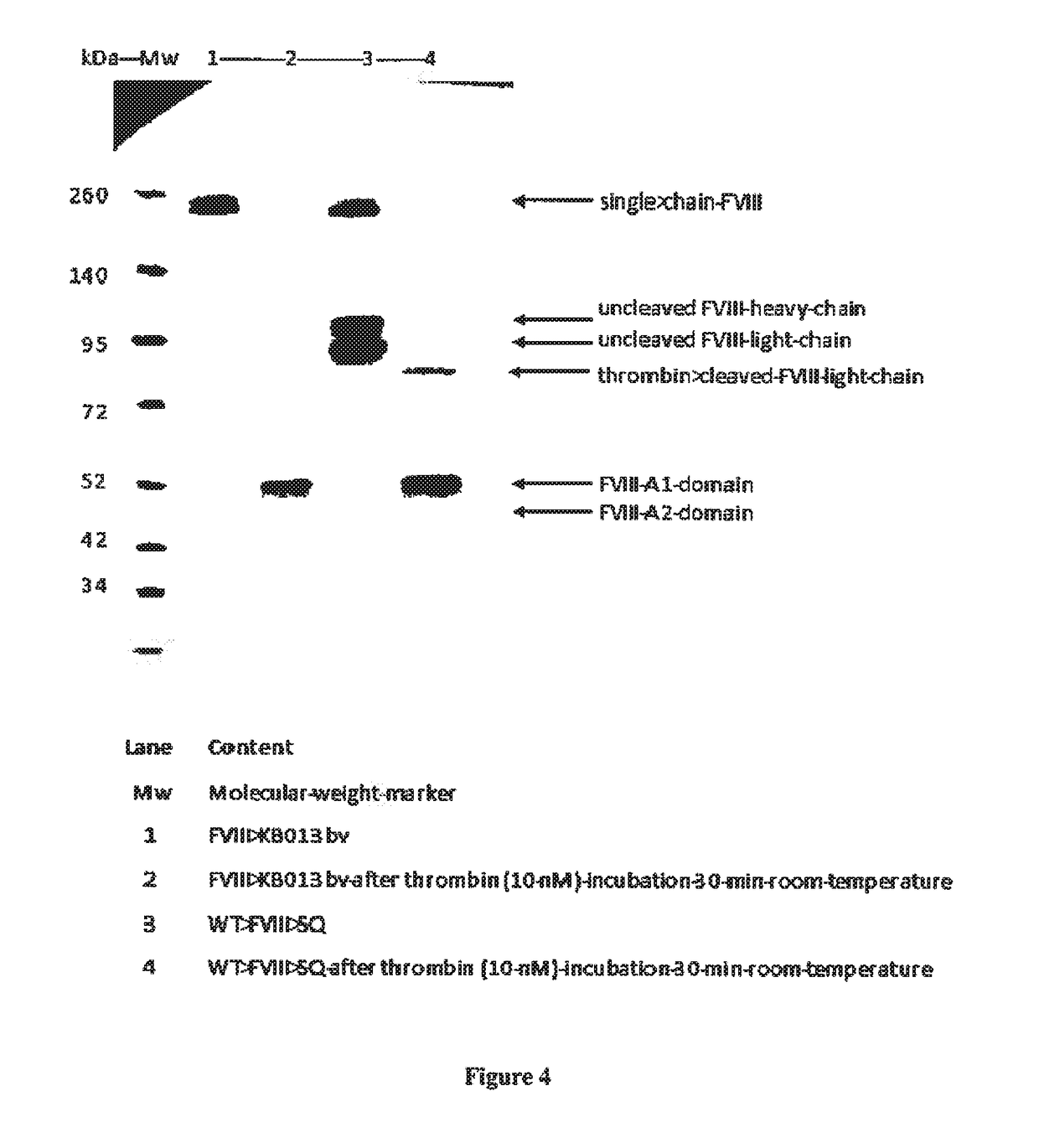
Anti-vwf d'd3 single-domain antibodies and polypeptides comprising thereof
ActiveUS20190085096A1Reduced clearance rateExtended half-lifeImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIHemostatic DisordersFactor VIII vWF
The invention relates to isolated single-domain antibodies (sdAb) directed against von Willebrand Factor (VWF) D′D3 domain and chimeric polypeptides comprising thereof such as blood clotting factors and their uses in therapy such as in the prevention and treatment of hemostatic disorders. The invention also rotates to a method of extending or increasing half-life of a therapeutic polypeptide comprising a step of adding to the polypeptide sequence of said therapeutic polypeptide at least one sdAb directed against VWF D′D3 domain.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Multimeric oligonucleotides having decreased kidney clearance
ActiveUS20180223284A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeReduced clearance rateOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryKidneyOligonucleotide
The present invention relates to methods of administering to a subject multimeric oligonucleotides having monomeric subunits joined by linkers. The multimeric oligonucleotides have a molecular weight of at least about 45 kD and other characteristics, such that their clearance due to glomerular filtration is reduced. The present invention also relates to such multimeric oligonucleotides and methods of synthesizing such multimeric oligonucleotides.
Owner:MPEG LA
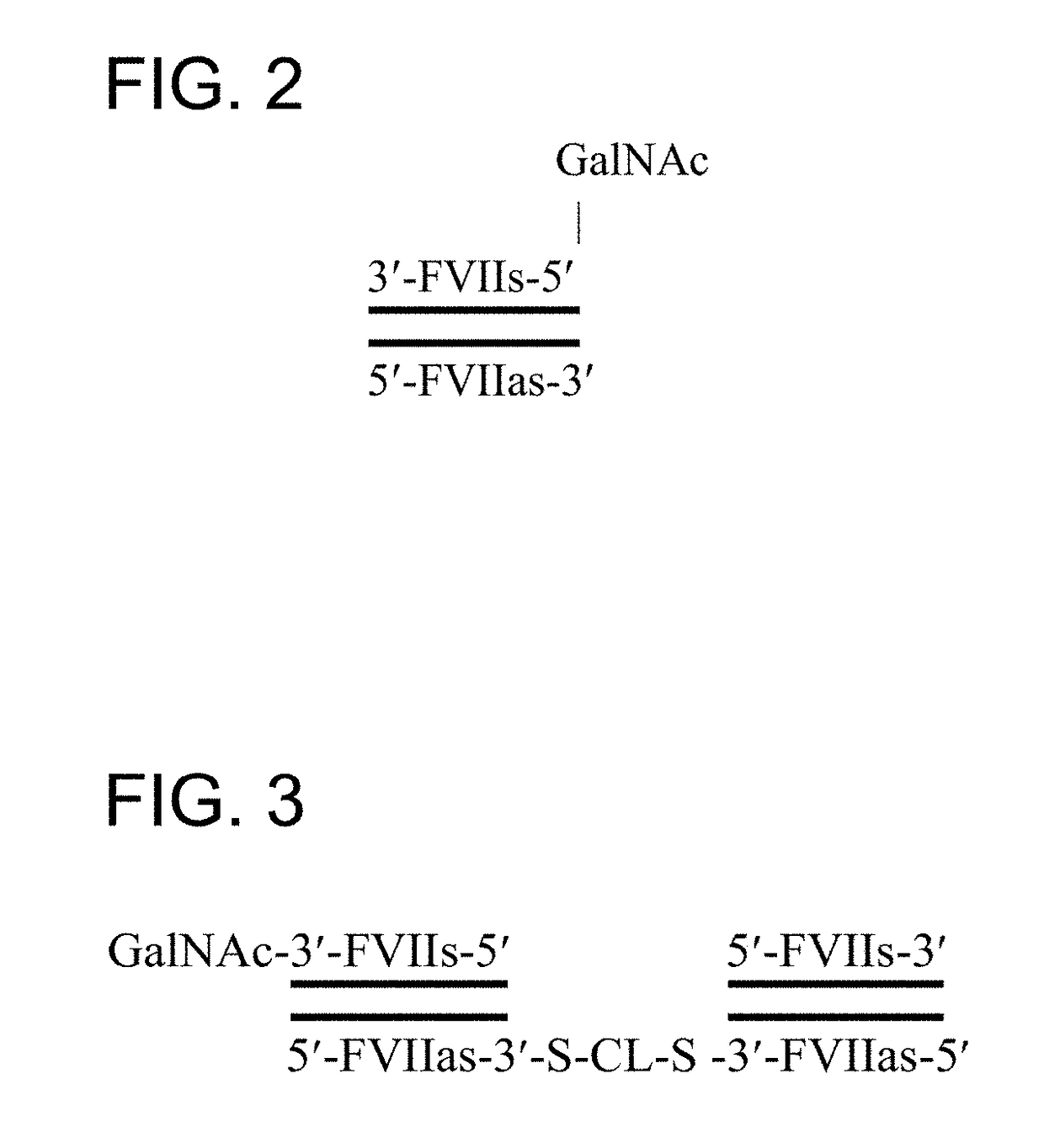
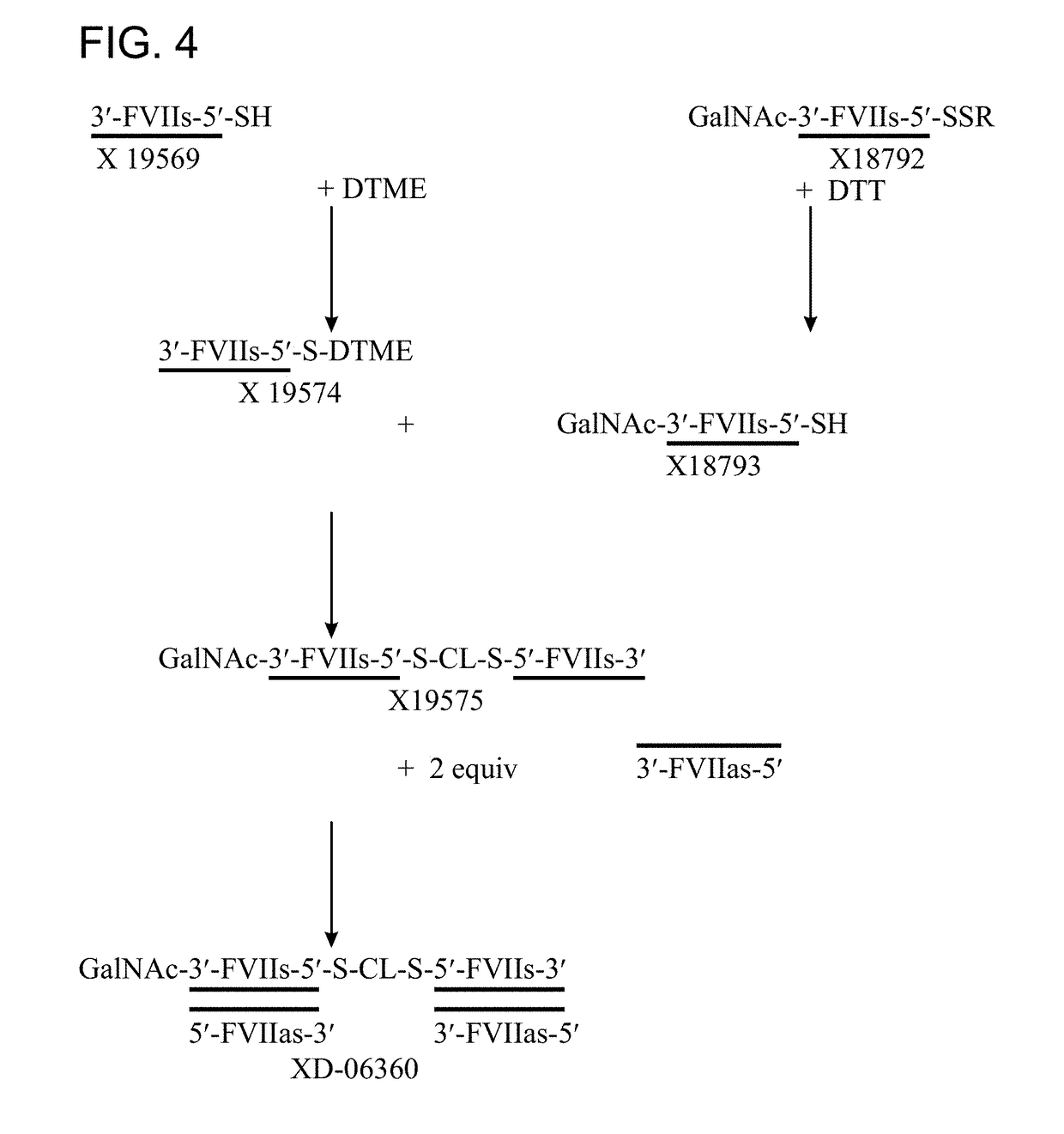
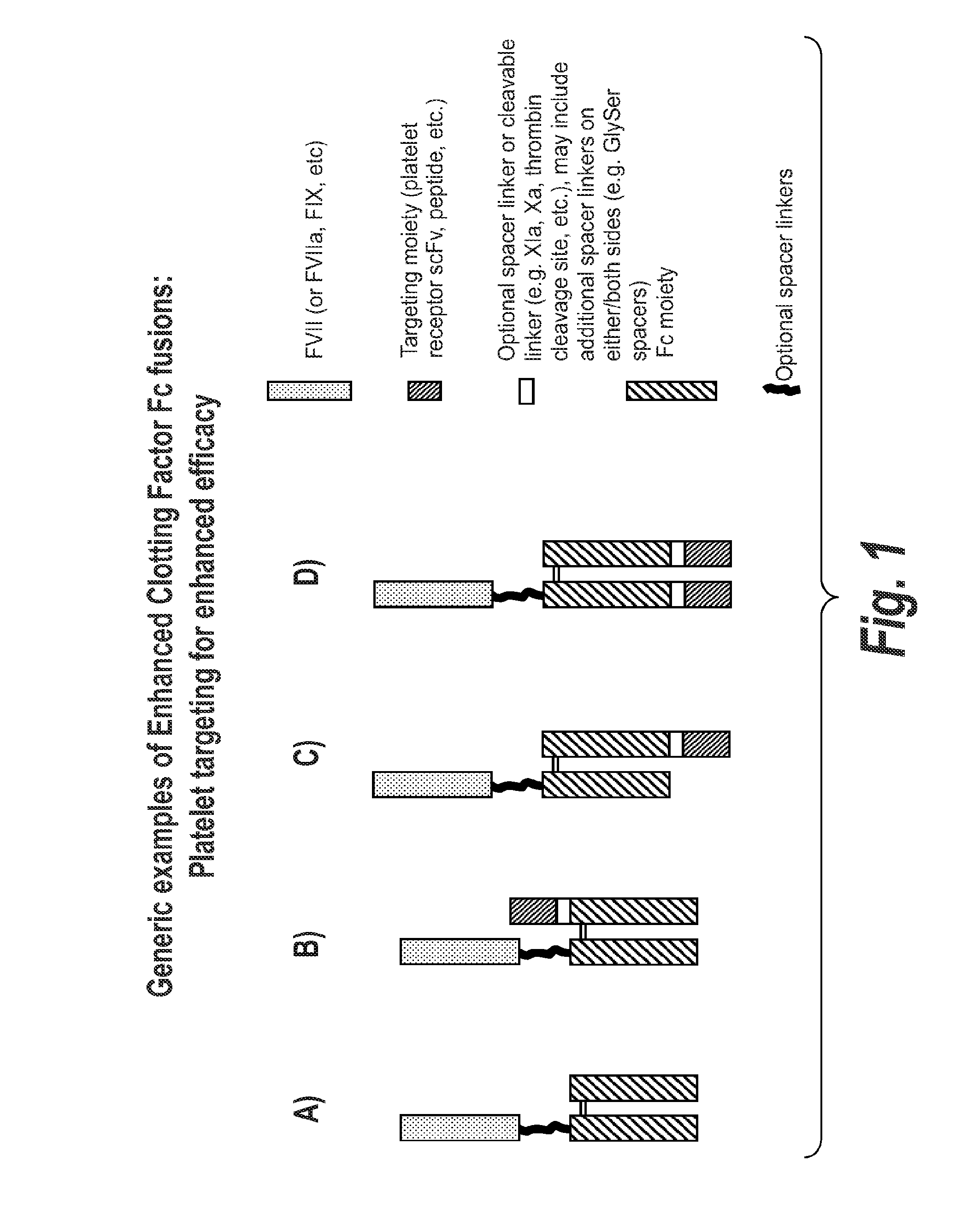
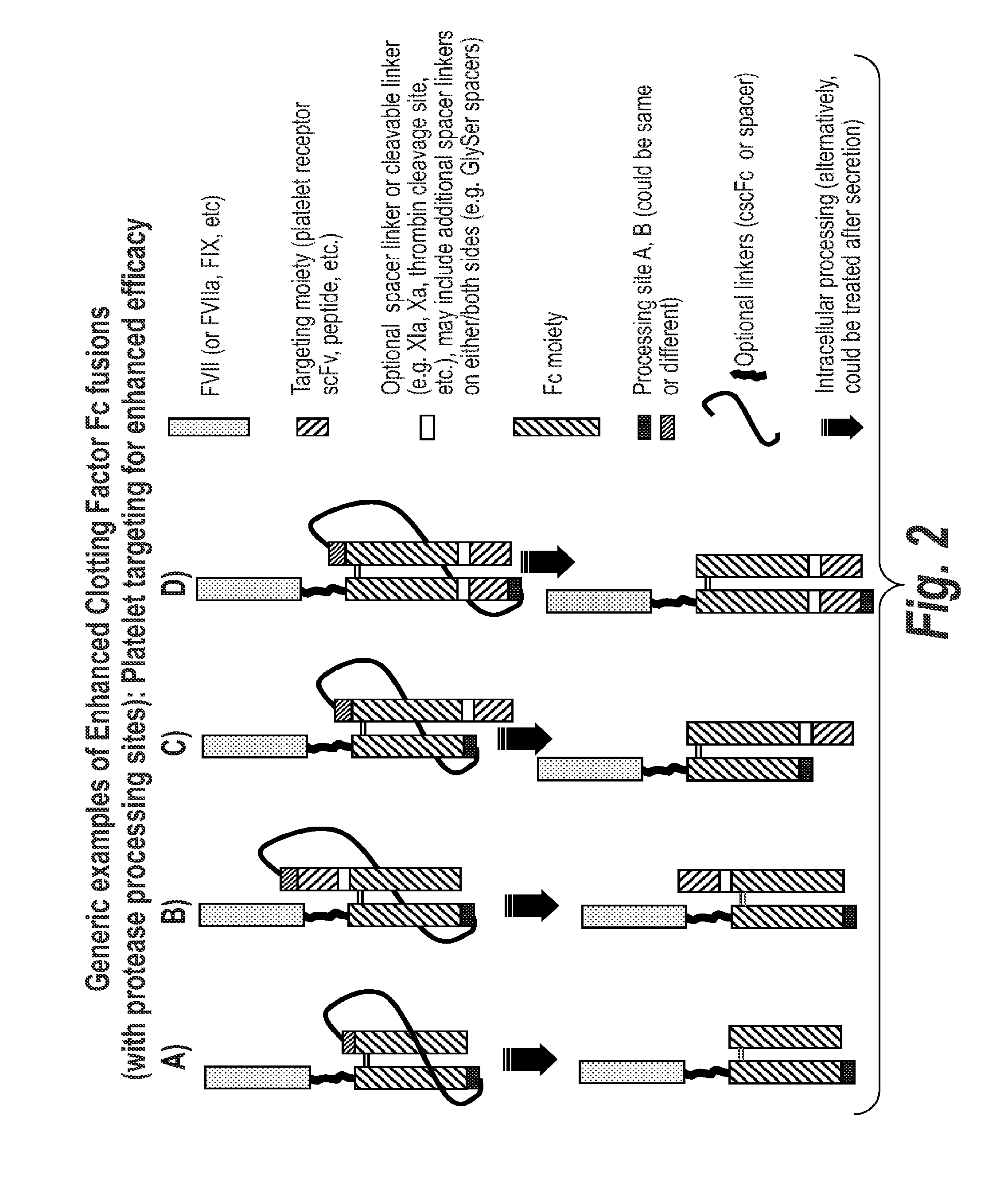
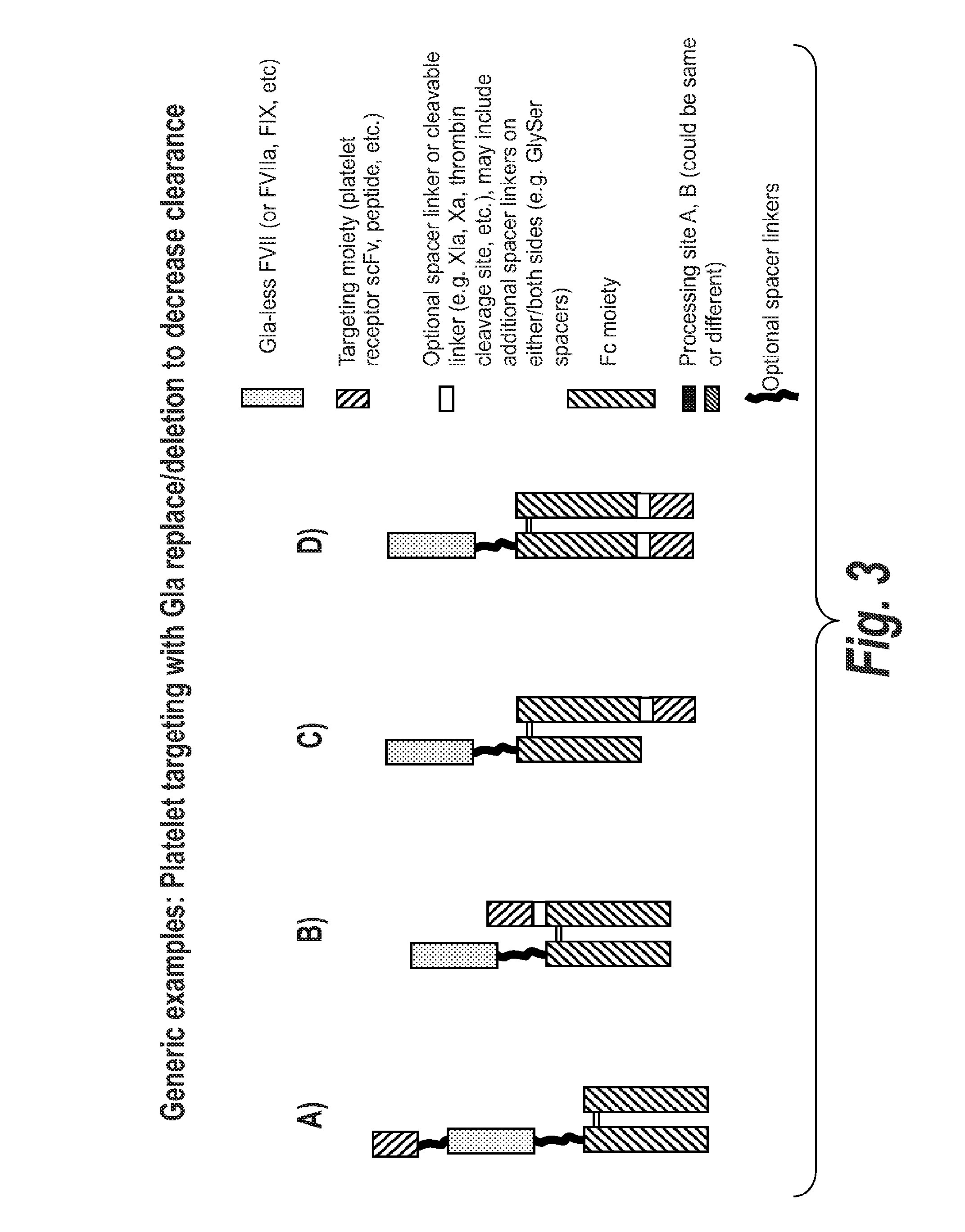
Chimeric Clotting Factors
ActiveUS20170044512A1High activityGood hemostasisFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineClearance rate
Chimeric clotting factors which localize the therapeutic to sites of coagulation (e.g., by being targeted to platelets or being activatable at sites of coagulation), have reduced clearance rates, have improved manufacturability, have reduced thrombogenicity, have enhanced activity, or have more than one of these characteristics are described as are methods for making chimeric clotting factors and methods for improving hemostasis using these clotting factors.
Owner:BIOVERATIV THERAPEUTICS INC
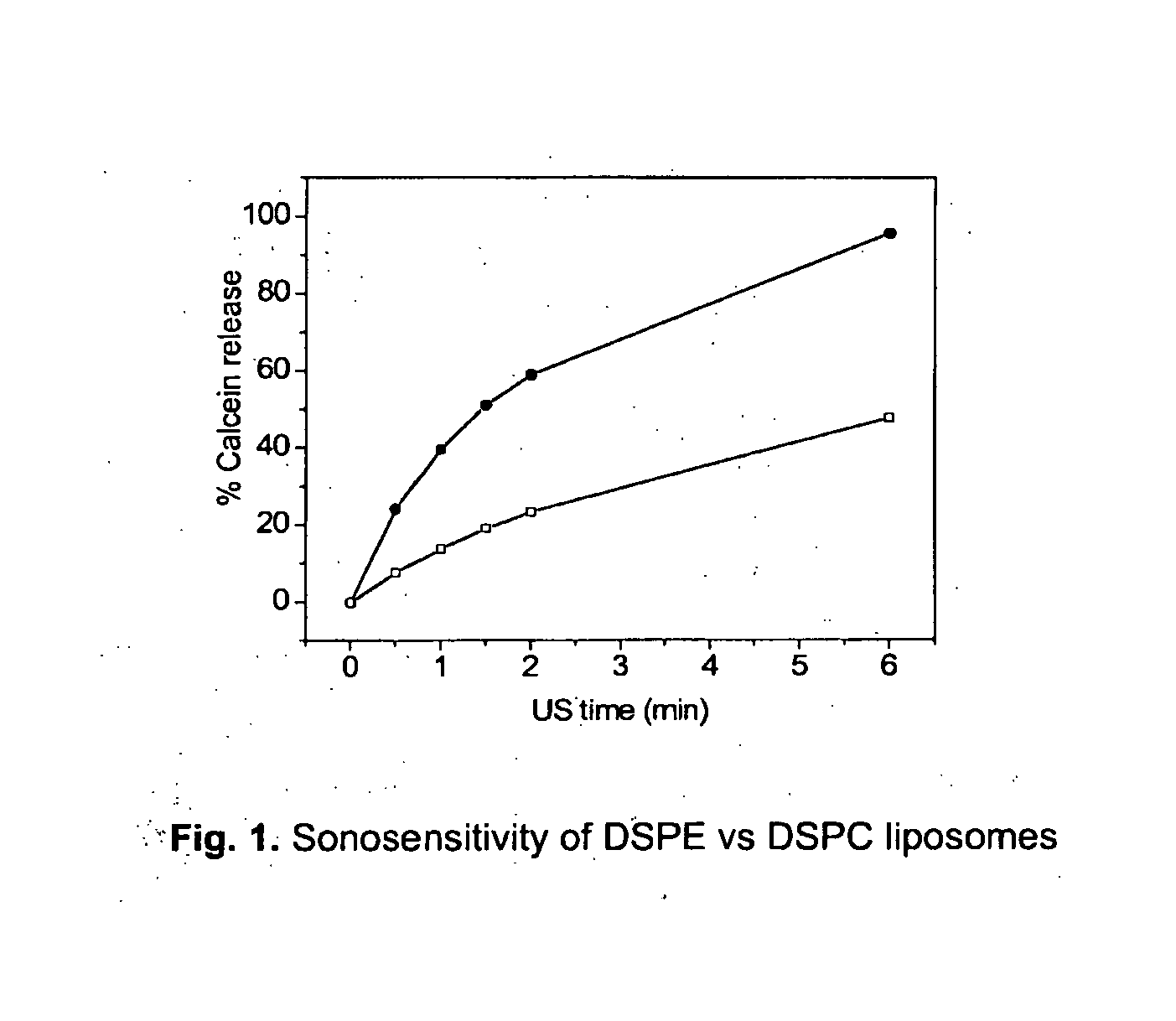
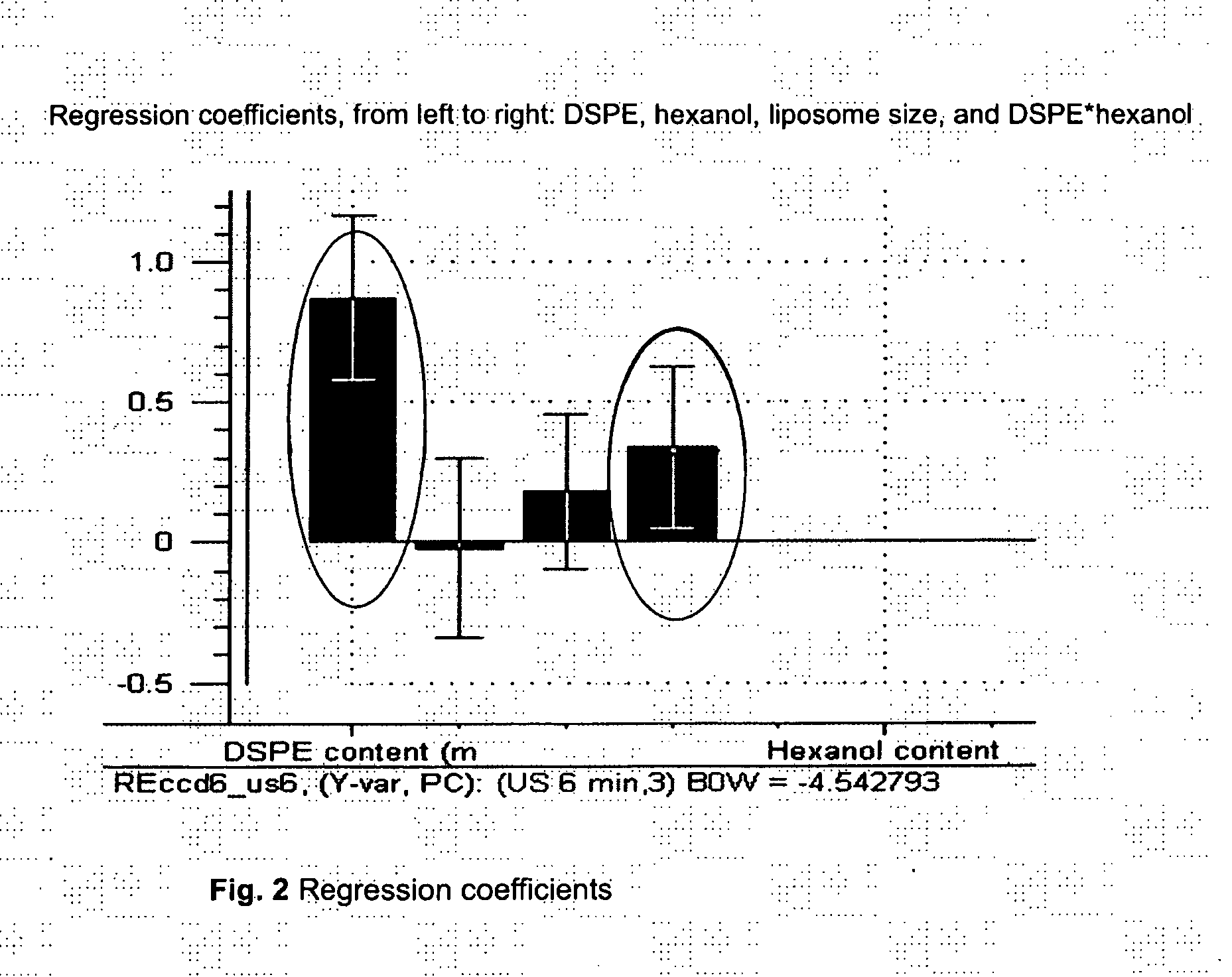
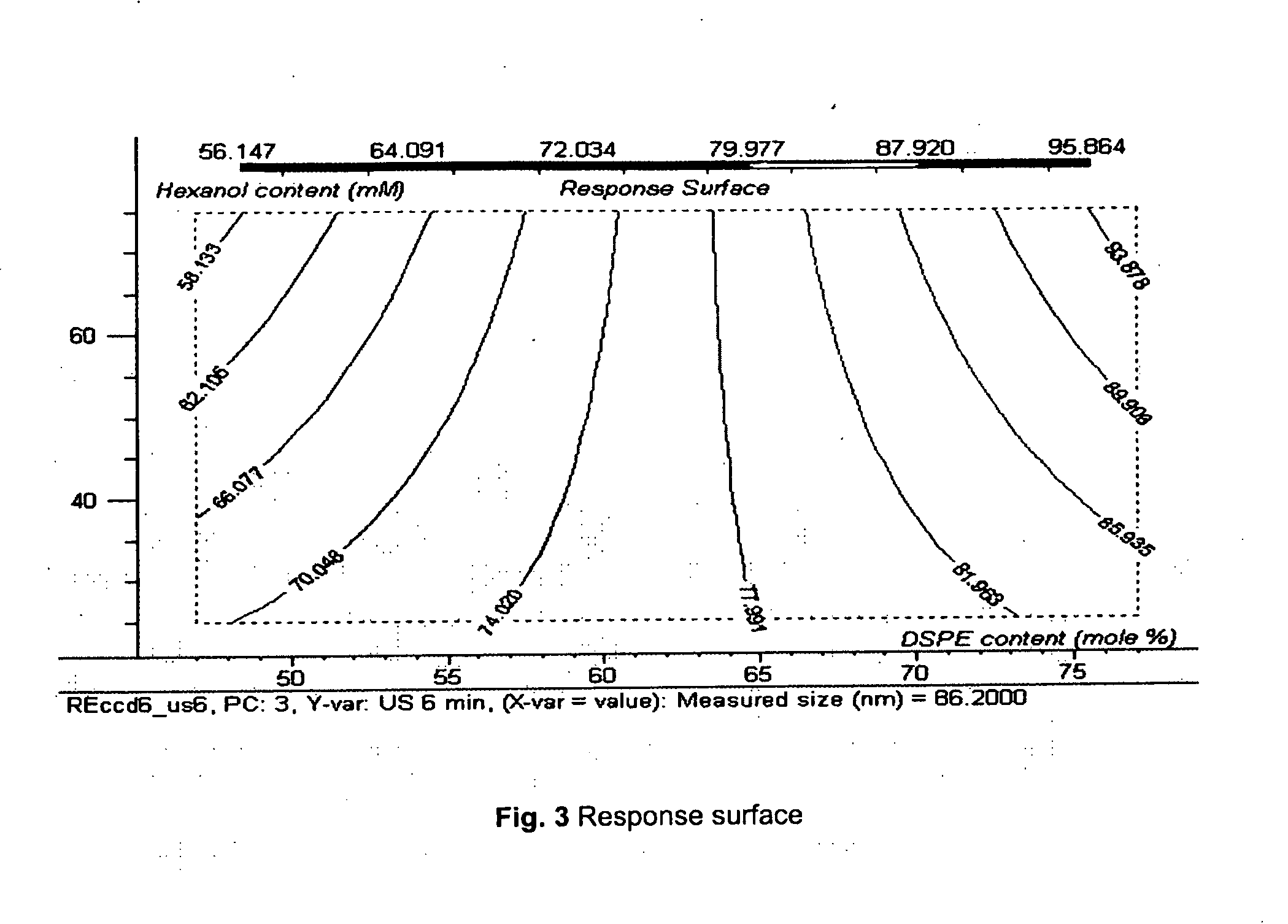
Acoustically sensitive drug delivery particles comprising low concentrations of phosphatidylethanolamine
InactiveUS20120288557A1Enhance sonosensitivityImprove clearanceBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDrugDrug delivery
Novel acoustically sensitive drug carrying particles comprising low concentrations of phosphatidylethanolamine are disclosed, as well as uses and methods thereof. The drug carrying particles accumulate in the diseased target tissue and efficiently release their payload upon exposure to acoustic energy.
Owner:EPITARGET
Vector comprising multiple homologous nucleotide sequences
ActiveUS20110236976A1High expressionEasy to purifySsRNA viruses negative-senseNucleic acid vectorNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to vectors comprising two or more homologous nucleotide sequences and methods for generating them. The invention concerns substituting bases in the homologous nucleotide sequences with different bases that do not alter the encoded amino acid sequence. The invention allows for the reduction of intramolecular recombination between homologous nucleotide sequences, in particular in mammalian cells. The invention further relates to nucleotide sequences containing substituted bases.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103432569AReduced clearance rateProlong biological half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemAdjuvantArginine
The invention relates to a stable recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution, belonging to the technical field of biological agents. The stable recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution is prepared by dissolving a recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein and a pharmaceutically acceptable stability adjuvant in a pharmaceutically acceptable buffer solution. The invention is characterized in that the pharmaceutically acceptable stability adjuvant is arginine, and the concentration is 5-30 g / L. The recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution provided by the invention can sufficiently prevent the recombinant fusion protein from aggregation, degradation, oxidation, denaturization or the like, thereby keeping the biological activity of the recombinant fusion protein; and the recombinant human serum albumin-interferon alpha fusion protein water solution is suitable for clinical application.
Owner:QILU PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![Novel benzo[d][1,3]-dioxol derivatives Novel benzo[d][1,3]-dioxol derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f1521681-86d5-4e63-9ce6-f24c65944863/US20080287495A1-20081120-C00001.png)
![Novel benzo[d][1,3]-dioxol derivatives Novel benzo[d][1,3]-dioxol derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f1521681-86d5-4e63-9ce6-f24c65944863/US20080287495A1-20081120-C00002.png)
![Novel benzo[d][1,3]-dioxol derivatives Novel benzo[d][1,3]-dioxol derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f1521681-86d5-4e63-9ce6-f24c65944863/US20080287495A1-20081120-C00003.png)