Patents
Literature
57 results about "Bus contention" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
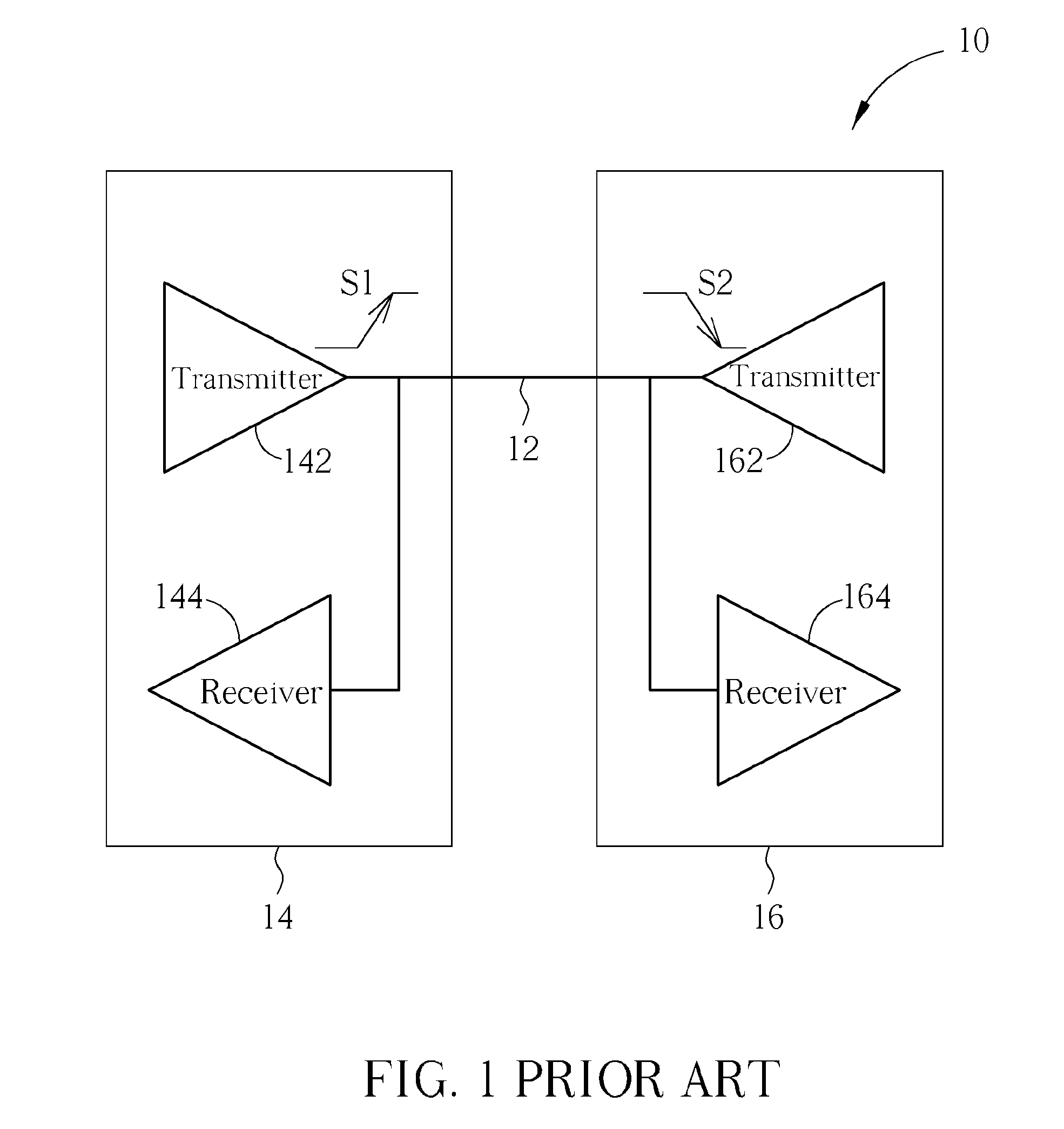
Bus contention, in computer design, is an undesirable state of the bus in which more than one device on the bus attempts to place values on the bus at the same time. Most bus architectures require their devices to follow an arbitration protocol carefully designed to make the likelihood of contention negligible. However, when devices on the bus have logic errors, manufacturing defects, or are driven beyond their design speeds, arbitration may break down and contention may result. Contention may also arise on systems which have a programmable memory mapping when illegal values are written to the registers controlling the mapping.
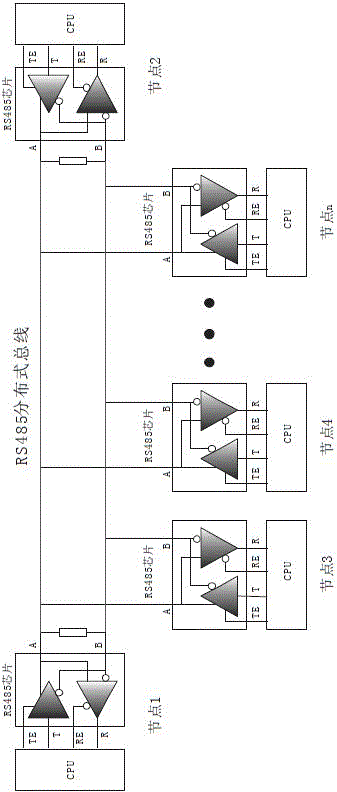
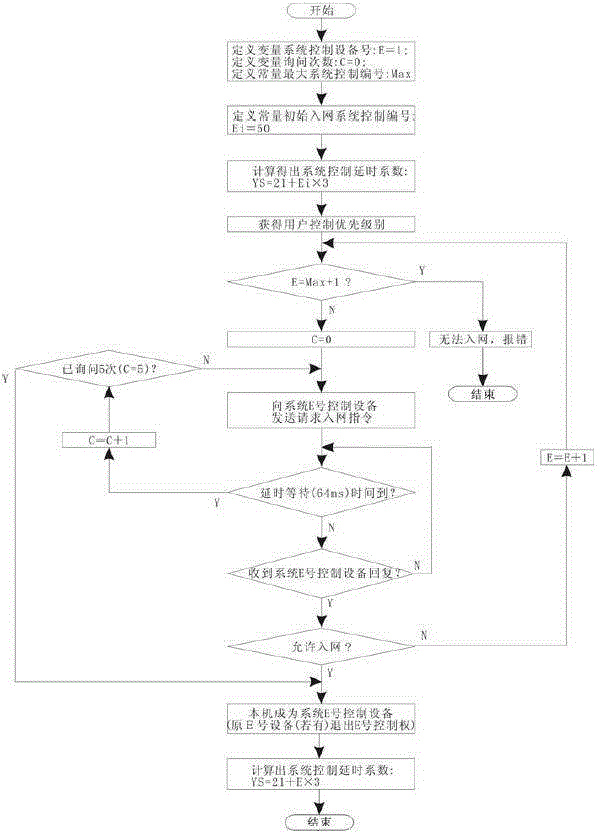
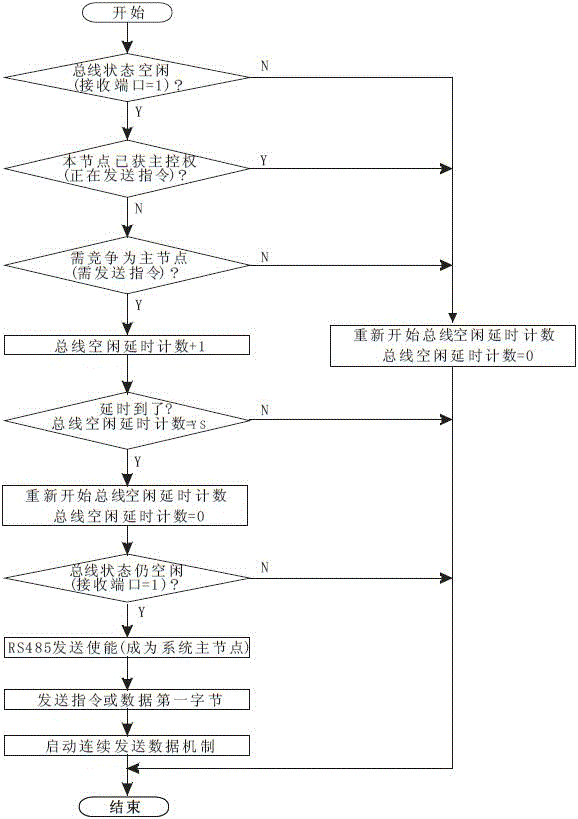
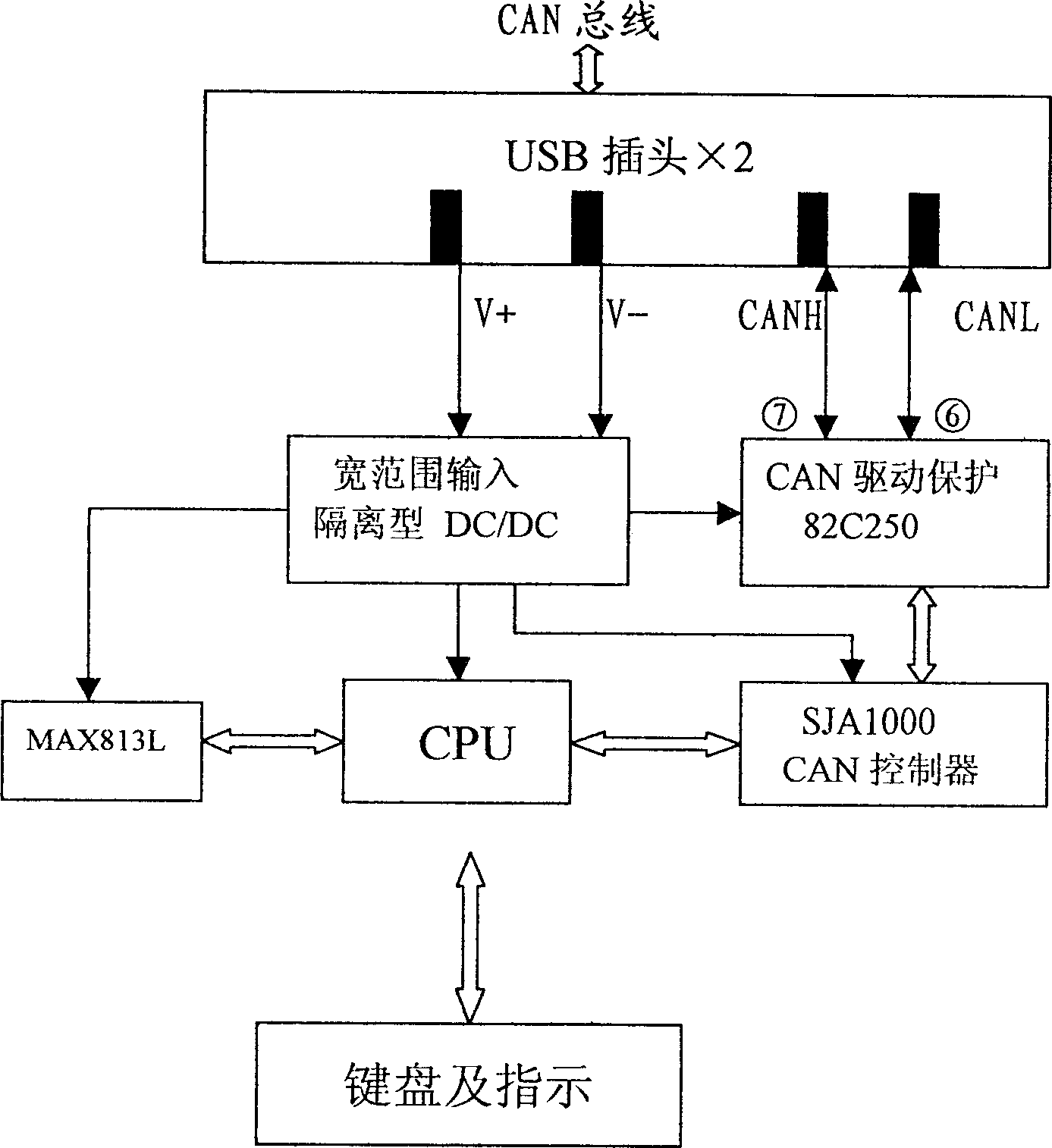
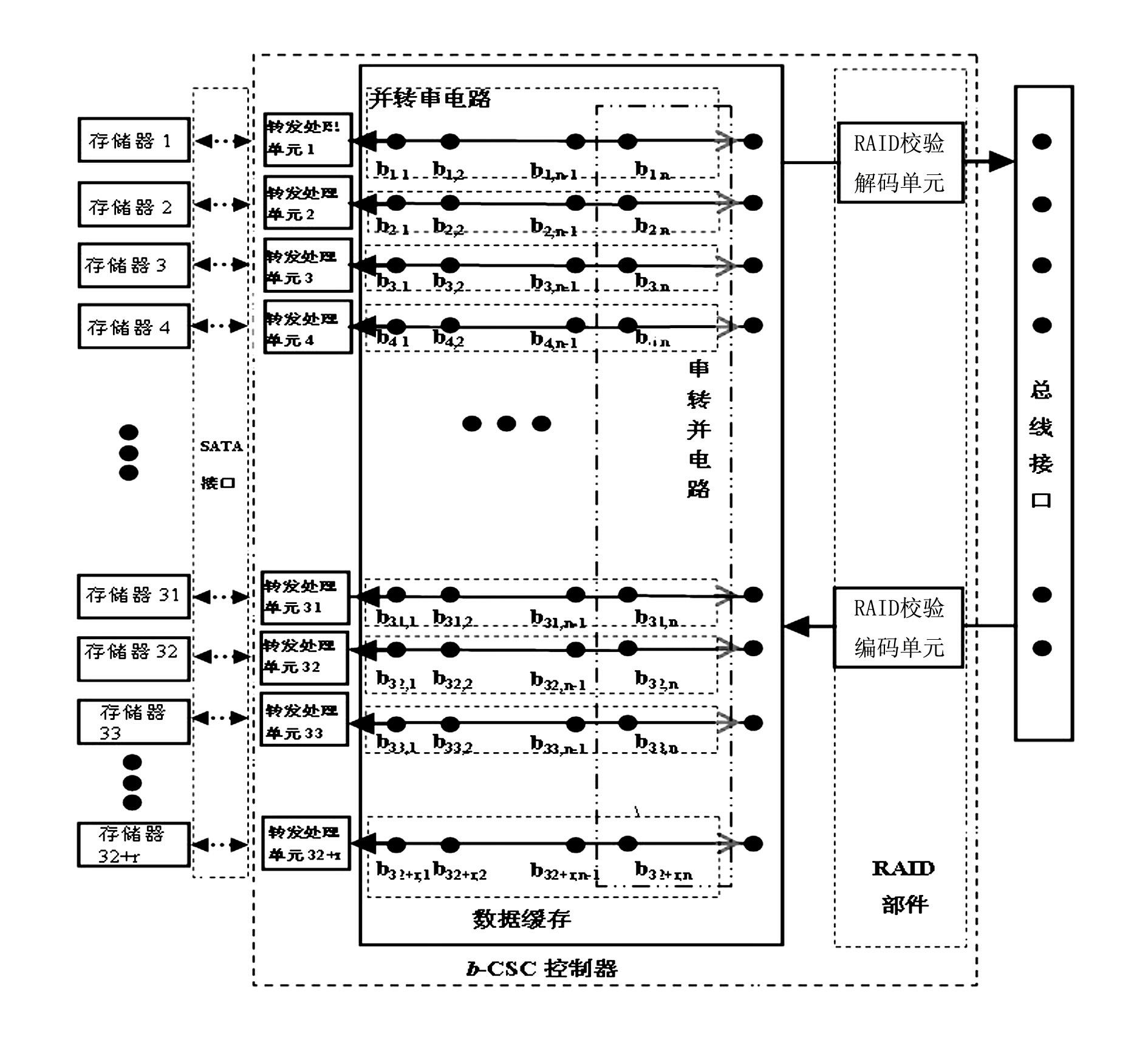
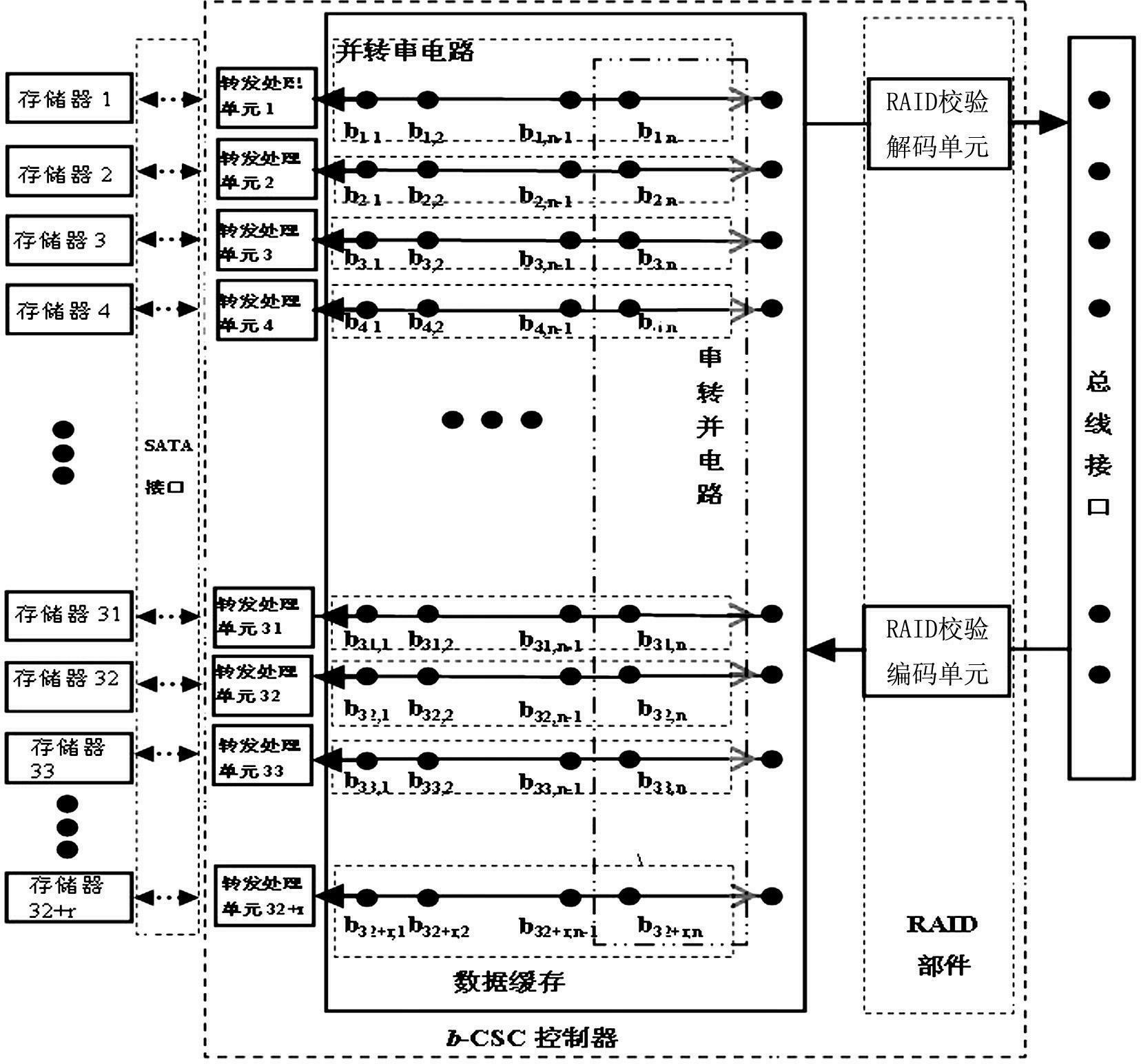
RS485 distributed bus system based control method
InactiveCN105354159ALow microcontroller requirementsEasy to implementElectric digital data processingEngineeringBus mastering
The invention discloses an RS485 distributed bus system based control method. Each node in an RS485 distributed bus is only in a receiving state at the beginning, and a state of the RS485 distributed bus is monitored; when the node needs to transmit an instruction or data, a bus control right competition obtaining mechanism is started; the state of the RS485 distributed bus is closely detected; if the state of the bus is always in an idle state within a certain time (bus competition delay detection time), it is determined that the RS485 distributed bus is in the idle state, a transmission enable pin ''TE'' of an RS485 chip of the node can be set, the bus is occupied, and the data are transmitted in time; and until the data of the node is completely transmitted, the transmission enable pin ''TE'' of the RS485 chip of the node is eliminated and resources of the RS485 distributed bus are released. The control method adopts the technical scheme that a bus control right is obtained through competition by monitoring the idle state of the bus.
Owner:上海海视电子有限公司
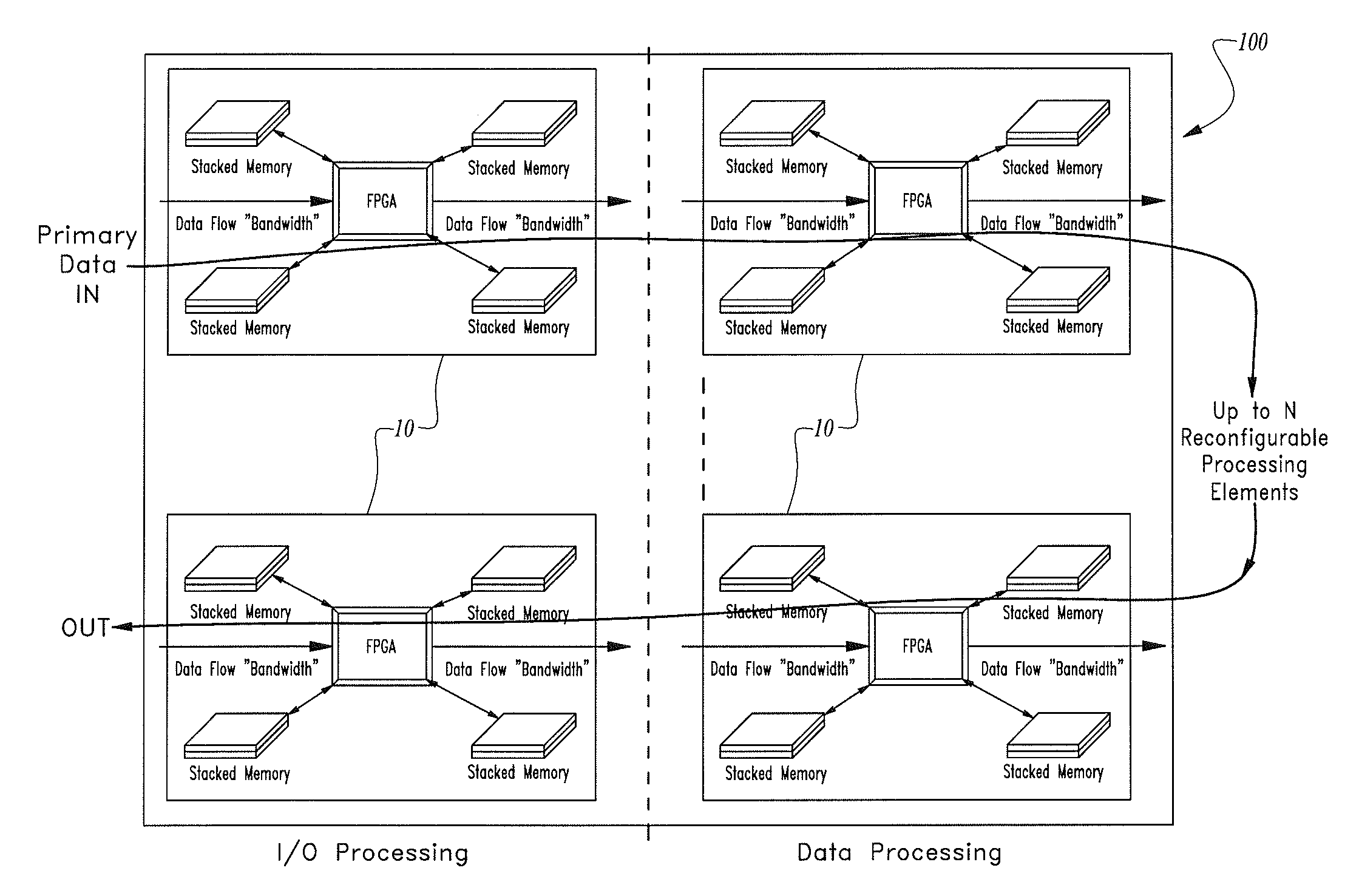
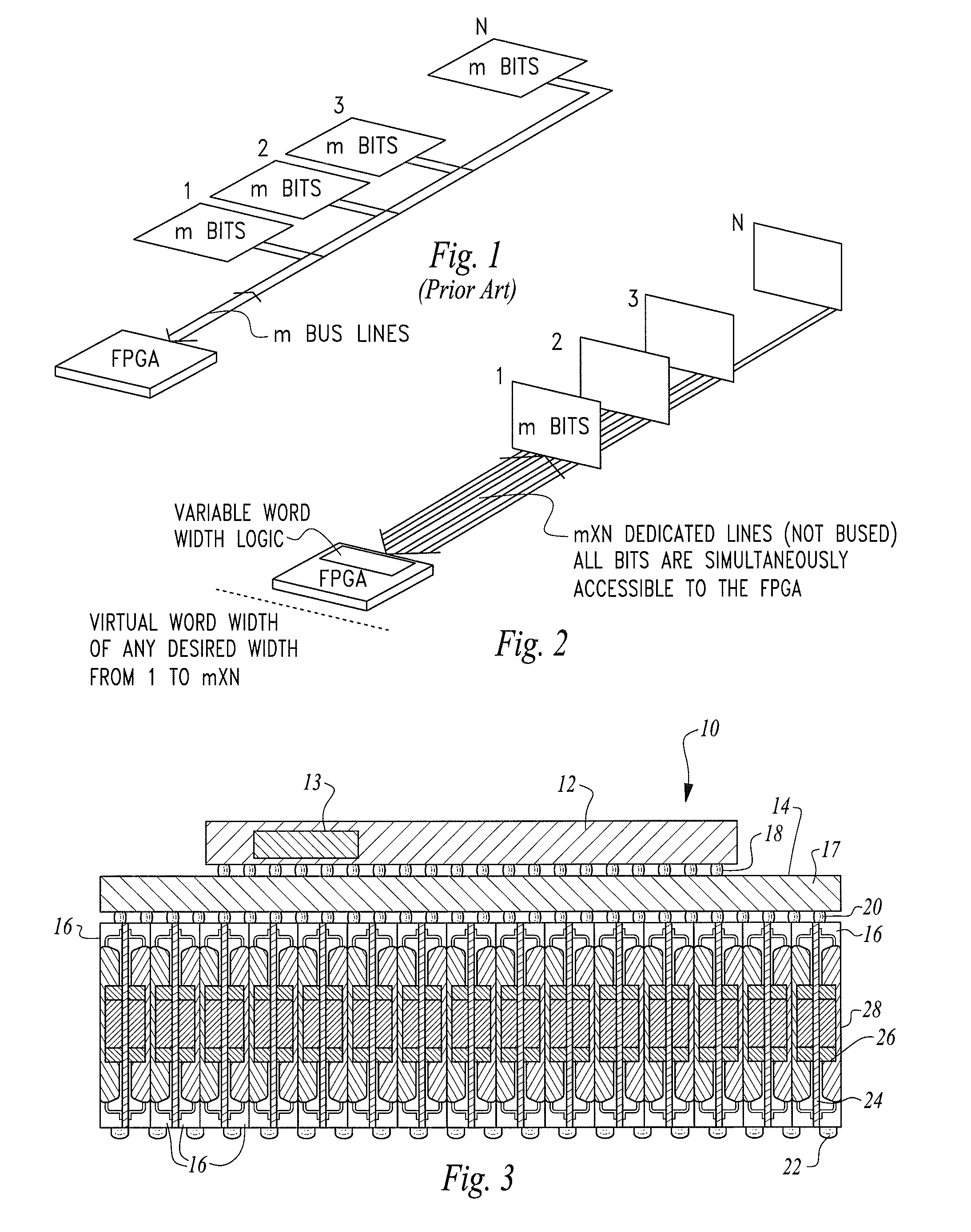
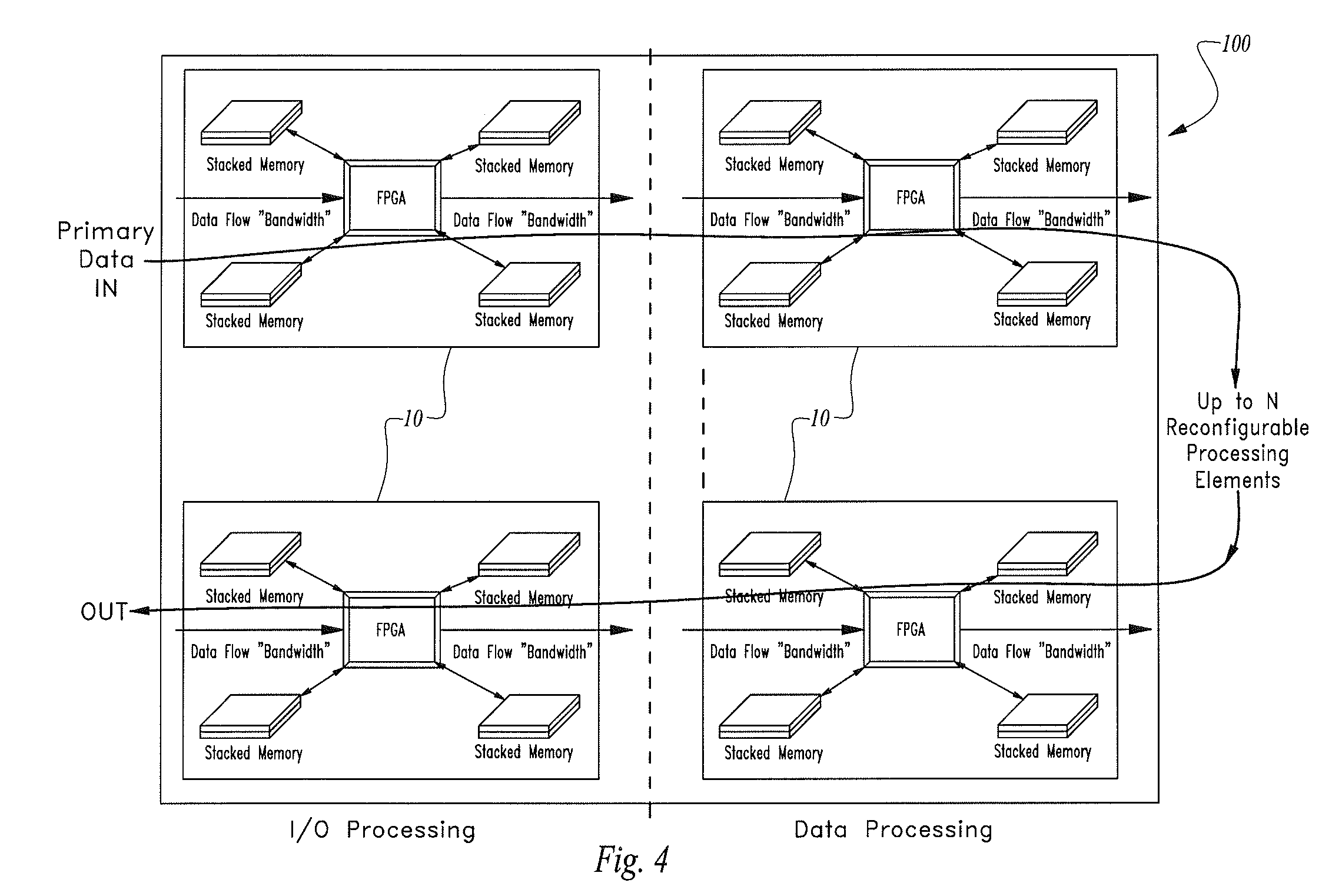
High-speed processor core comprising direct processor-to-memory connectivity
ActiveUS8519739B1Digital computer detailsLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsInterconnectivityProcessor element
A high-speed processor core having a plurality of individual FPGA-based processing elements configured in a synchronous or asynchronous pipeline architecture with direct processor-to-memory interconnectivity that avoids the latency and bus contention delays of FPGAs using conventional bused memory.The high-speed processor core has one or more memory structures such as SDRAM or QDR electronic memory and is electrically coupled directly to one or more FPGAs using an access lead network to provide a pipelined set of FPGA-based processor elements for processing one or more predetermined operations such as one or more detection algorithms at line rates.
Owner:PFG IP +1
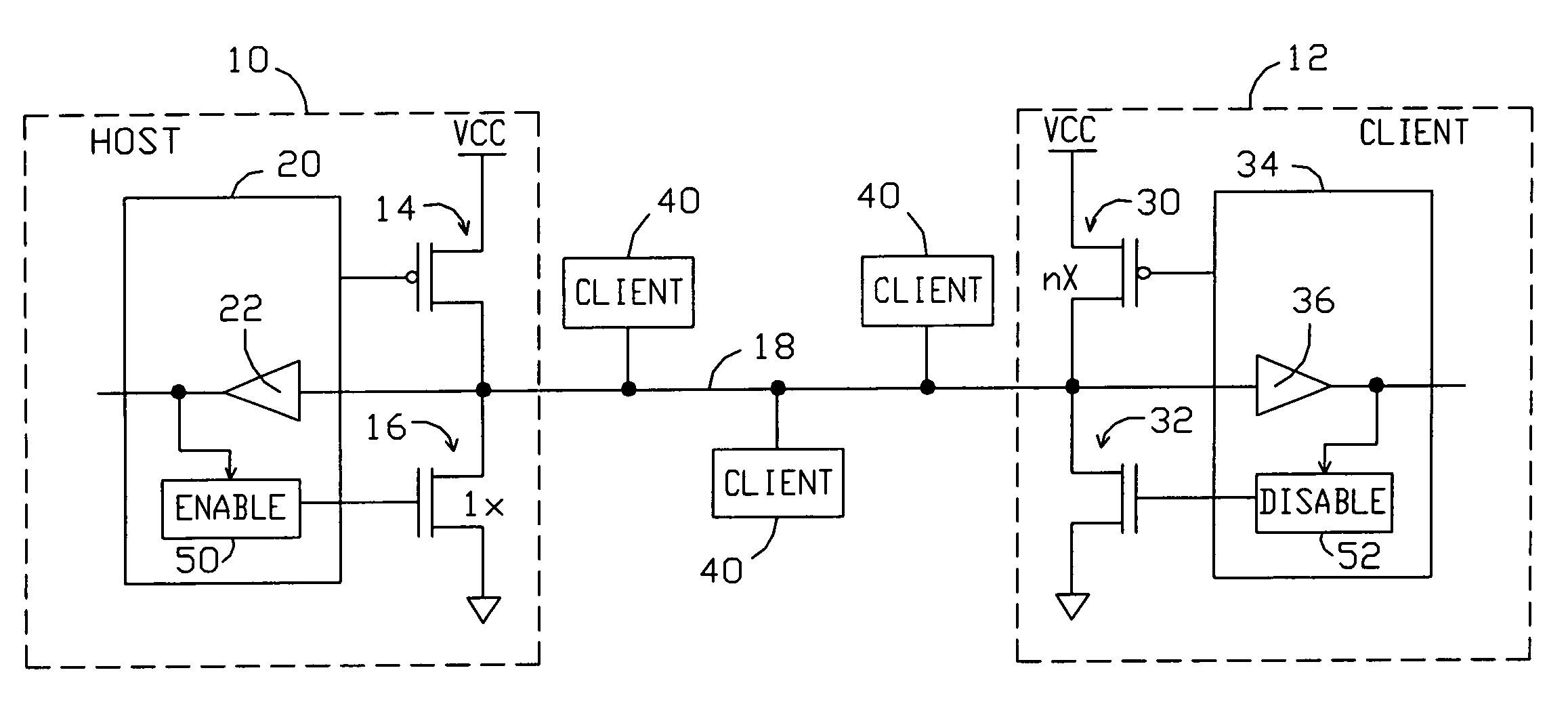
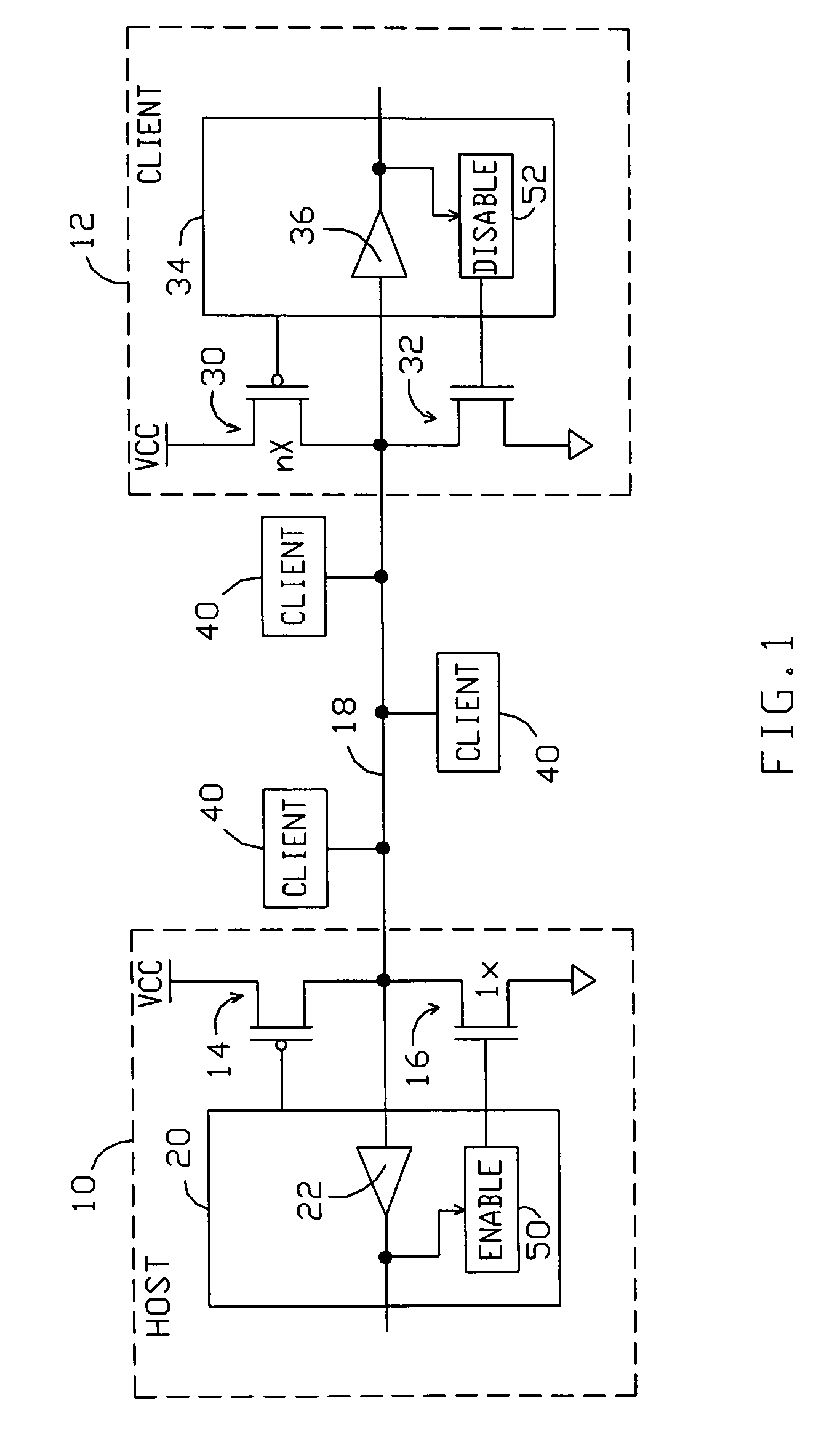
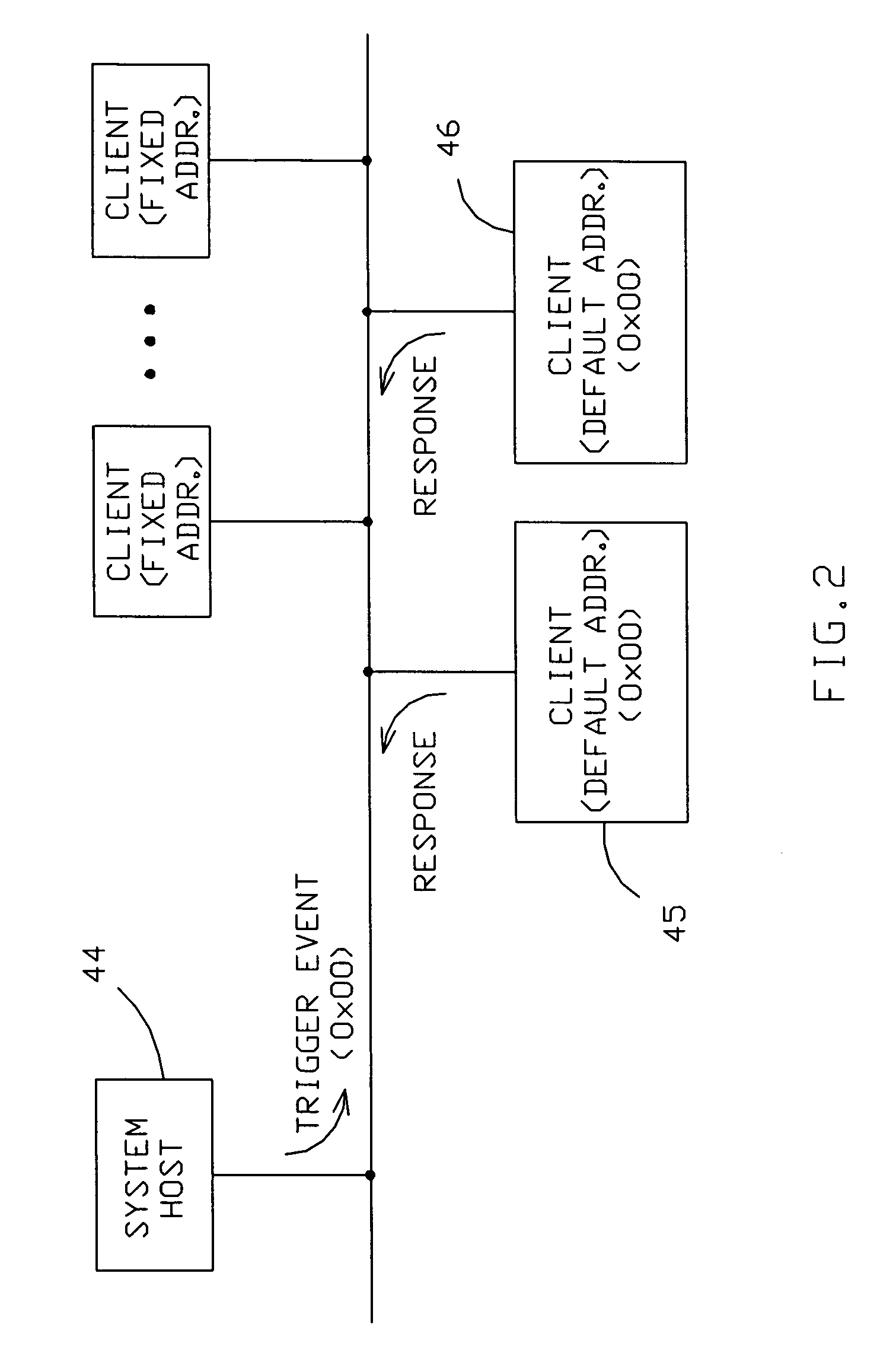
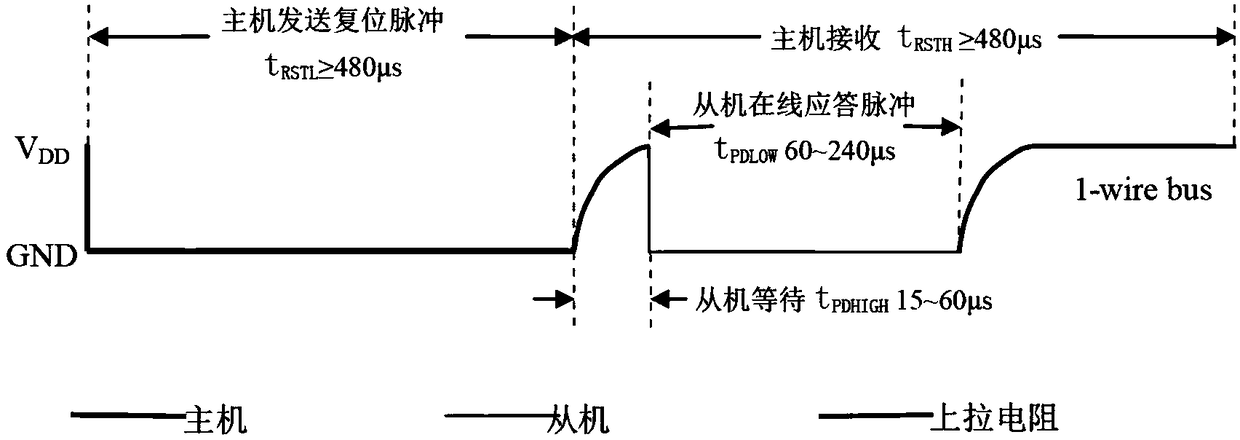
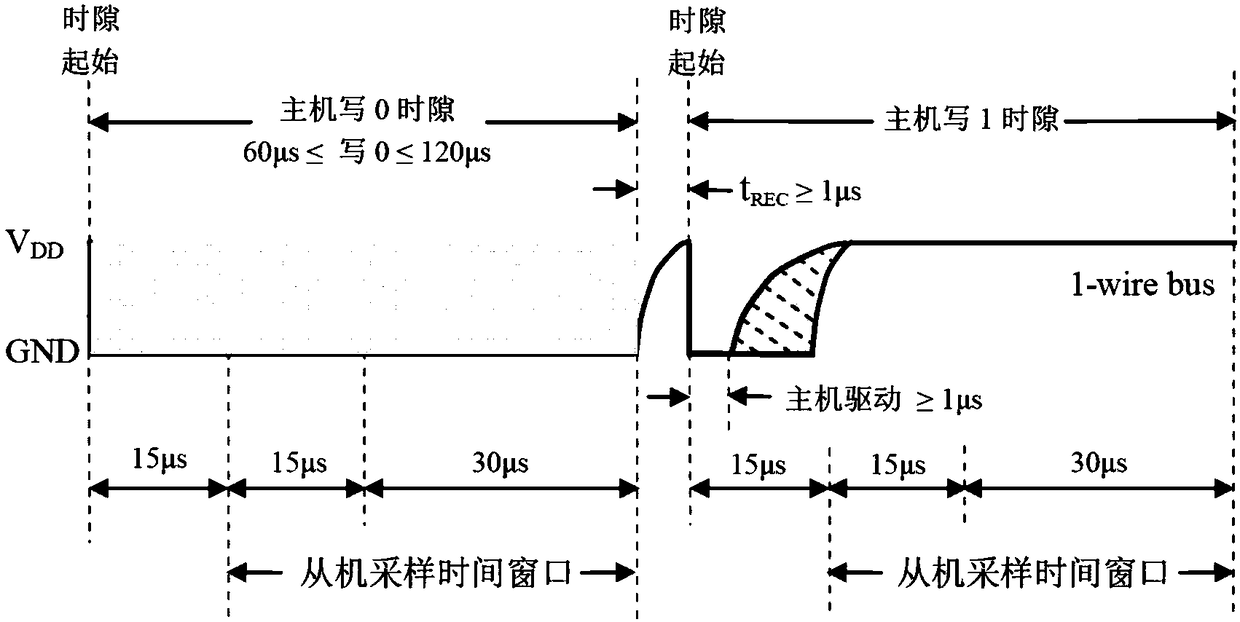
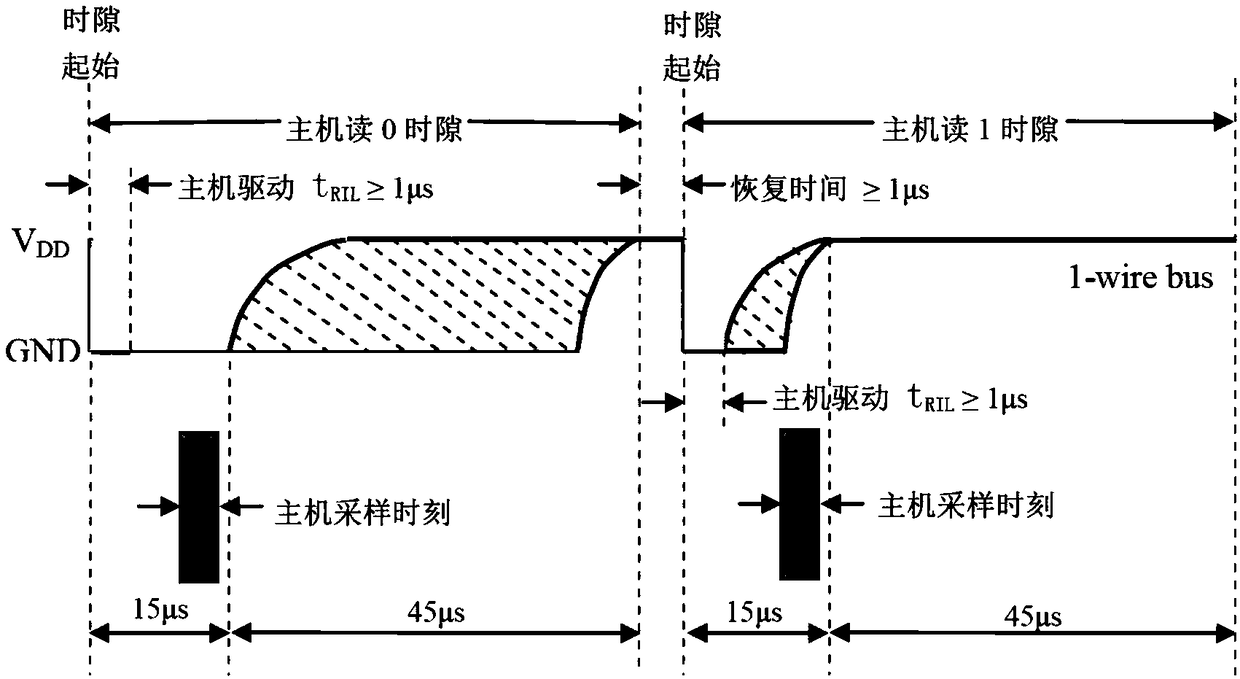
Single wire bus communication system with method for handling simultaneous responses from multiple clients
ActiveUS7095250B1Reliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingCommunications systemTransistor
A single wire bus communication system comprises a bus wire, a host device, and at least one client device, with each host and client device having pull-up and pull-down transistors to pull the bus wire “high” or “low”, respectively. The system is arranged such that, in response to a “trigger event” that requires responses from multiple client devices simultaneously, the host device enables its pull-down transistor, and each client device disables its pull-down transistor when conveying a “low” logic level onto the bus. To avoid bus contention, each client's pull-up transistor is arranged to conduct more current when enabled than the host's pull-down transistor. Then, one or more of the client devices' strong pull-ups will overcome the single weak pull-down on the bus, thereby enabling numerous client devices to respond to a command that requires a response from multiple clients.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
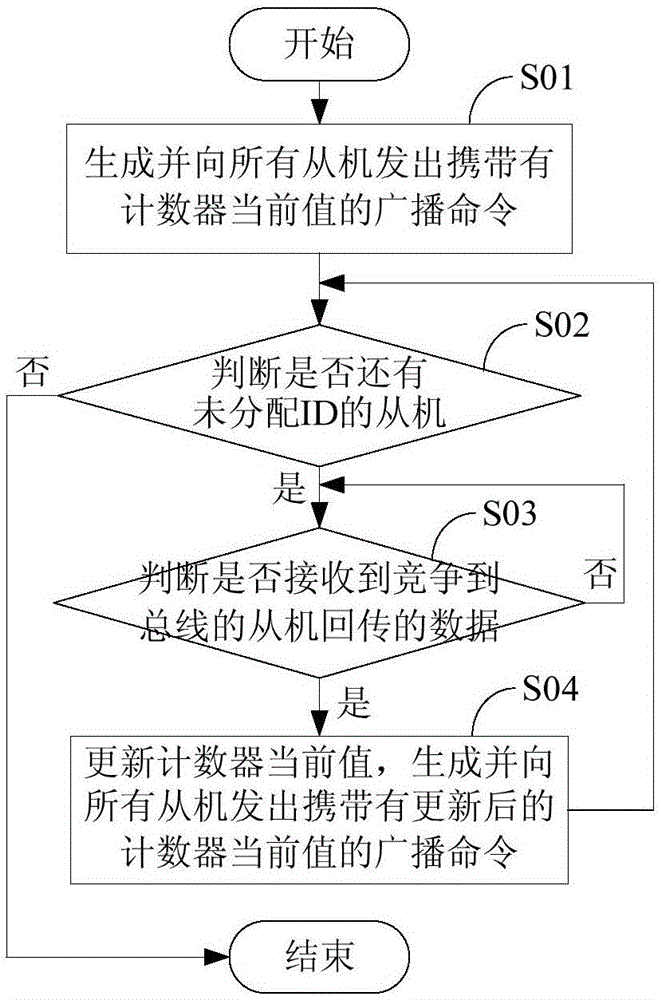
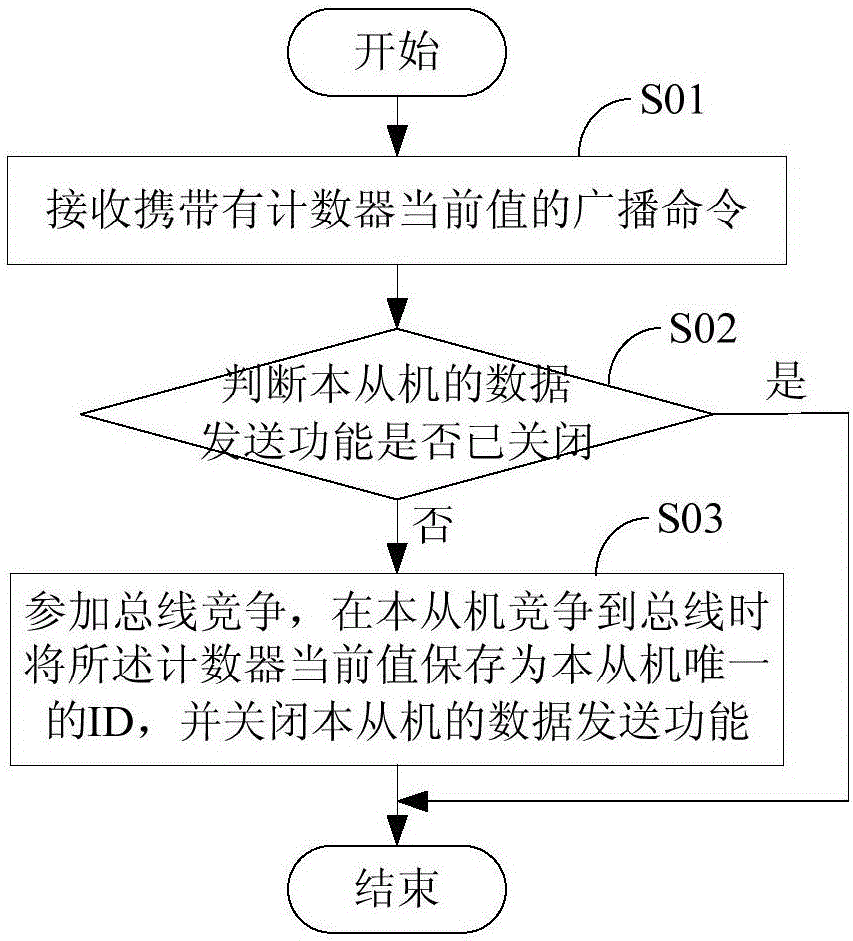
Master-slave multi-computer communication system, master computer, slave computers and slave computer ID (identification) assigning method
InactiveCN106330644ALow costElectric digital data processingBus networksCommunications systemComputer-mediated communication
The invention discloses a master-slave multi-computer communication system, a master computer, slave computers and a slave computer ID (identification) assigning method for assigning slave computer ID without increasing hardware cost. The method includes the steps: generating a broadcast command carrying a current value of a counter and transmitting the broadcast command to all the slave computers; judging whether ID unassigned slave computers are present in the system or not; updating the current value of the counter and generating and transmitting the broadcast command carrying the updated current value of the counter to all the slave computers when receiving data returned by a bus competition slave computer if the ID unassigned slave computers are present in the system; judging whether ID unassigned slave computers are present in the master-slave multi-computer communication system or not again until judging that ID is assigned for all the slave computers. The broadcast command is used for controlling the ID unassigned slave computers to participate in bus competition, and the bus competition slave computer is used for storing the current value of the counter carried by the broadcast command as a sole ID and stopping the data transmission function of the slave computer.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
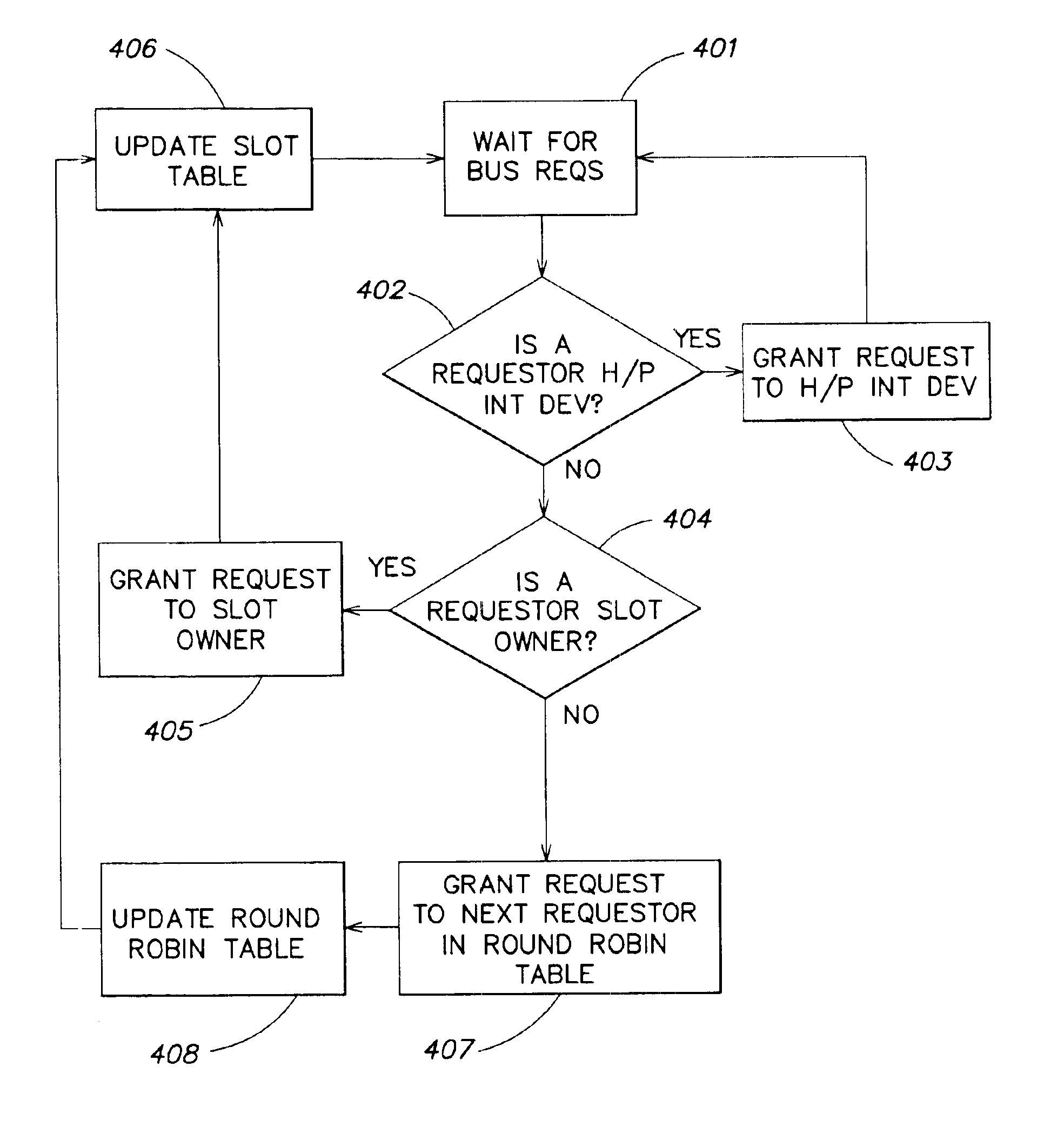
Bus arbitration method employing a table of slots suitably distributed amongst bus masters
InactiveUS6895459B2Network traffic/resource managementComputer controlRotation methodComputer science
A multiple bus architecture includes multiple processors, and one or more shared peripherals such as memory. The architecture includes plural bus masters, each connected to its own bus. There are also plural bus slaves, each connected to its own bus. A bus arbitration module selectively interconnects the buses, so that when the plural bus masters each access a different bus slave, no blocking occurs, and when the plural bus masers each access a same bus slave, bandwidth starvation is avoided. The architecture is supported by a bus arbitration method including hierarchical application of an interrupt-based method, an assigned slot rotation method and a round-robin method, which avoids both bandwidth starvation and lockout during extended periods of bus contention.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
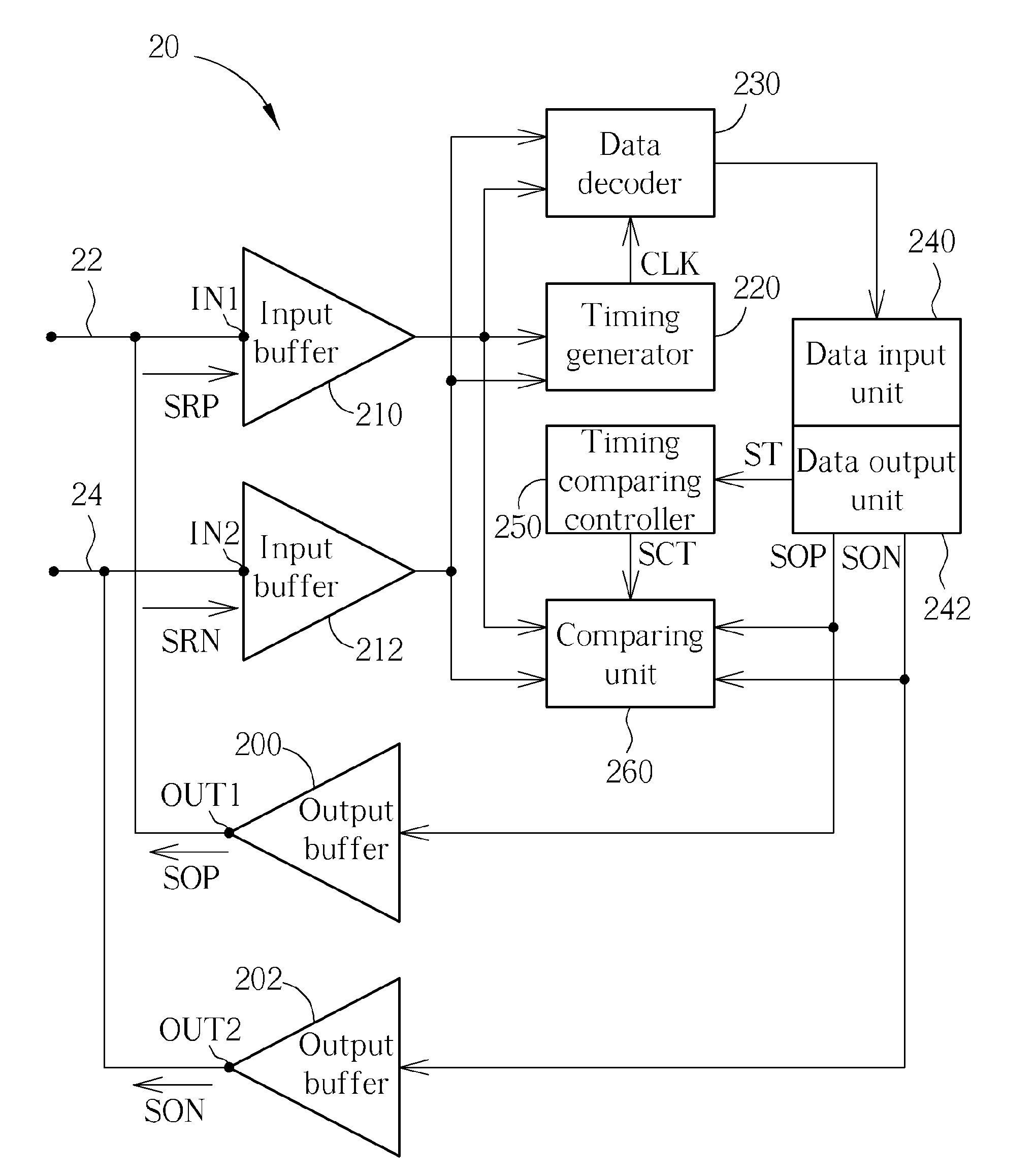
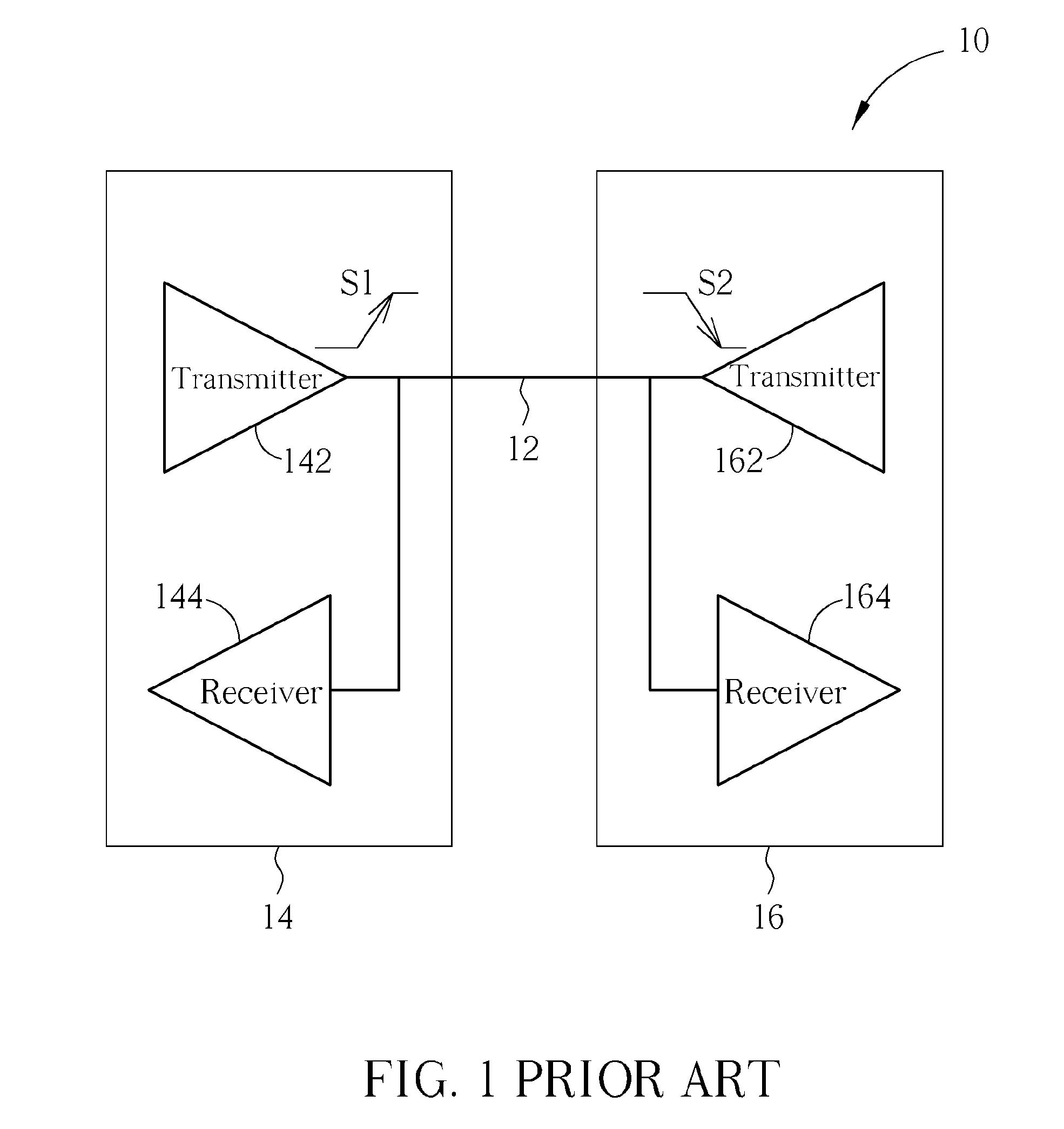
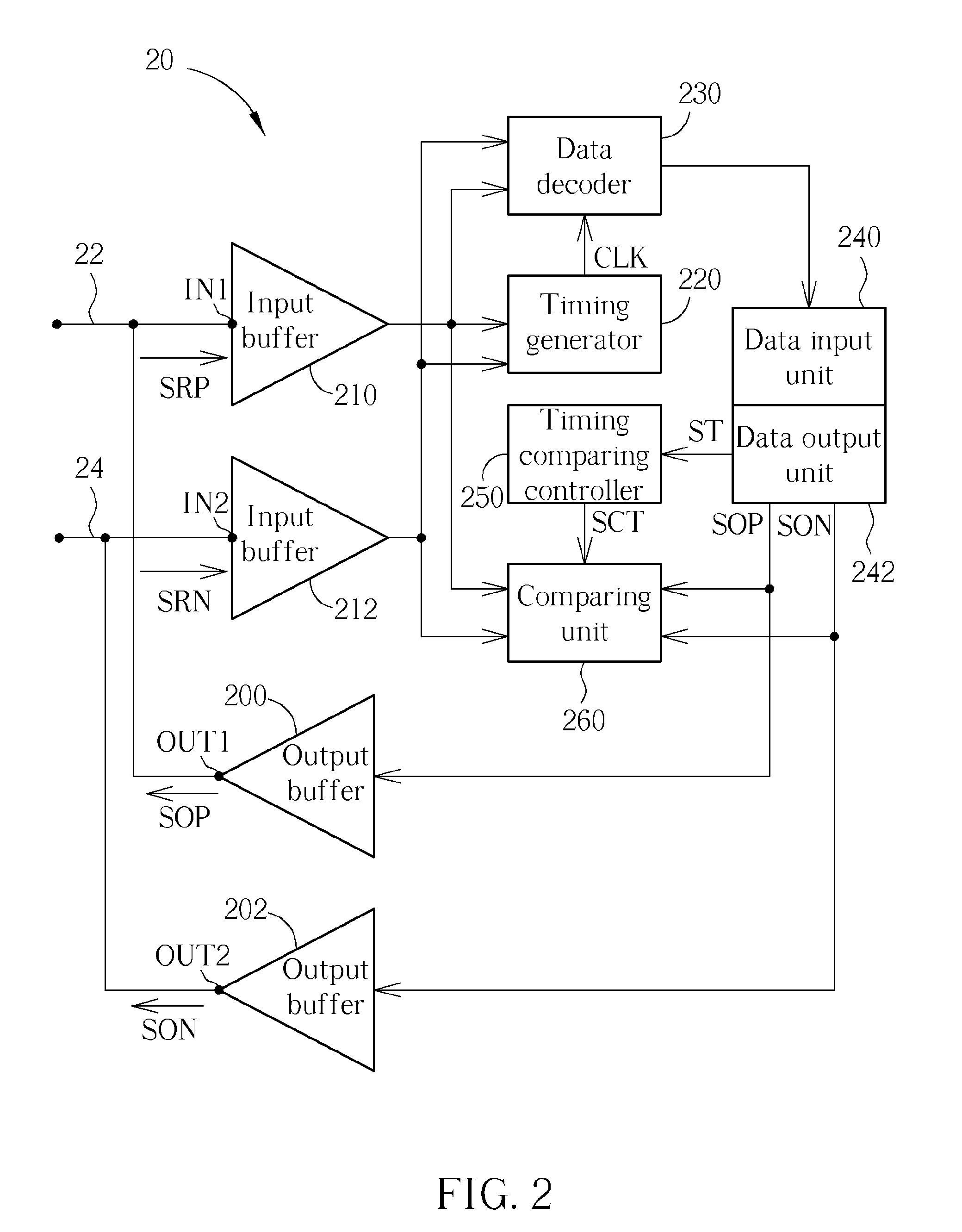
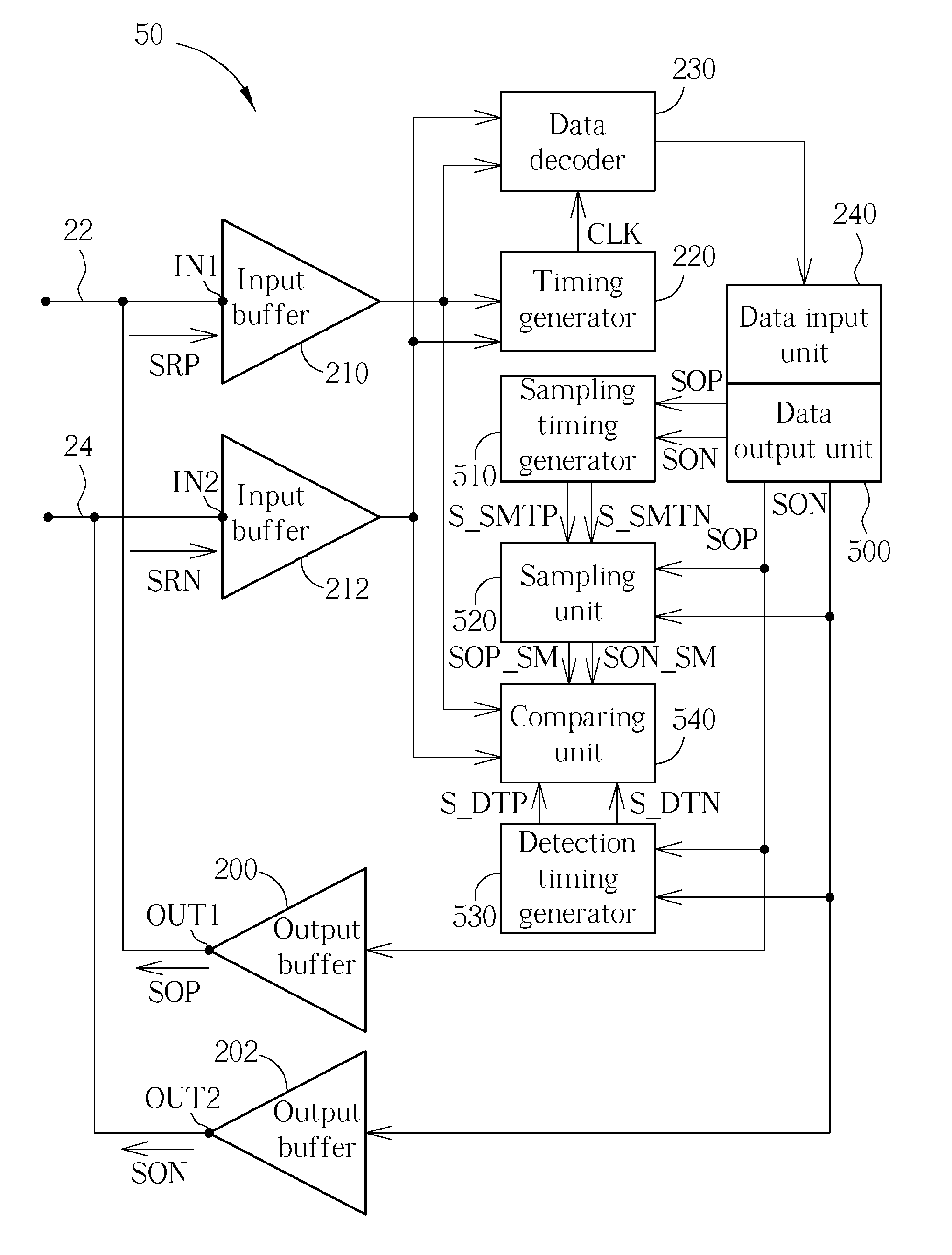
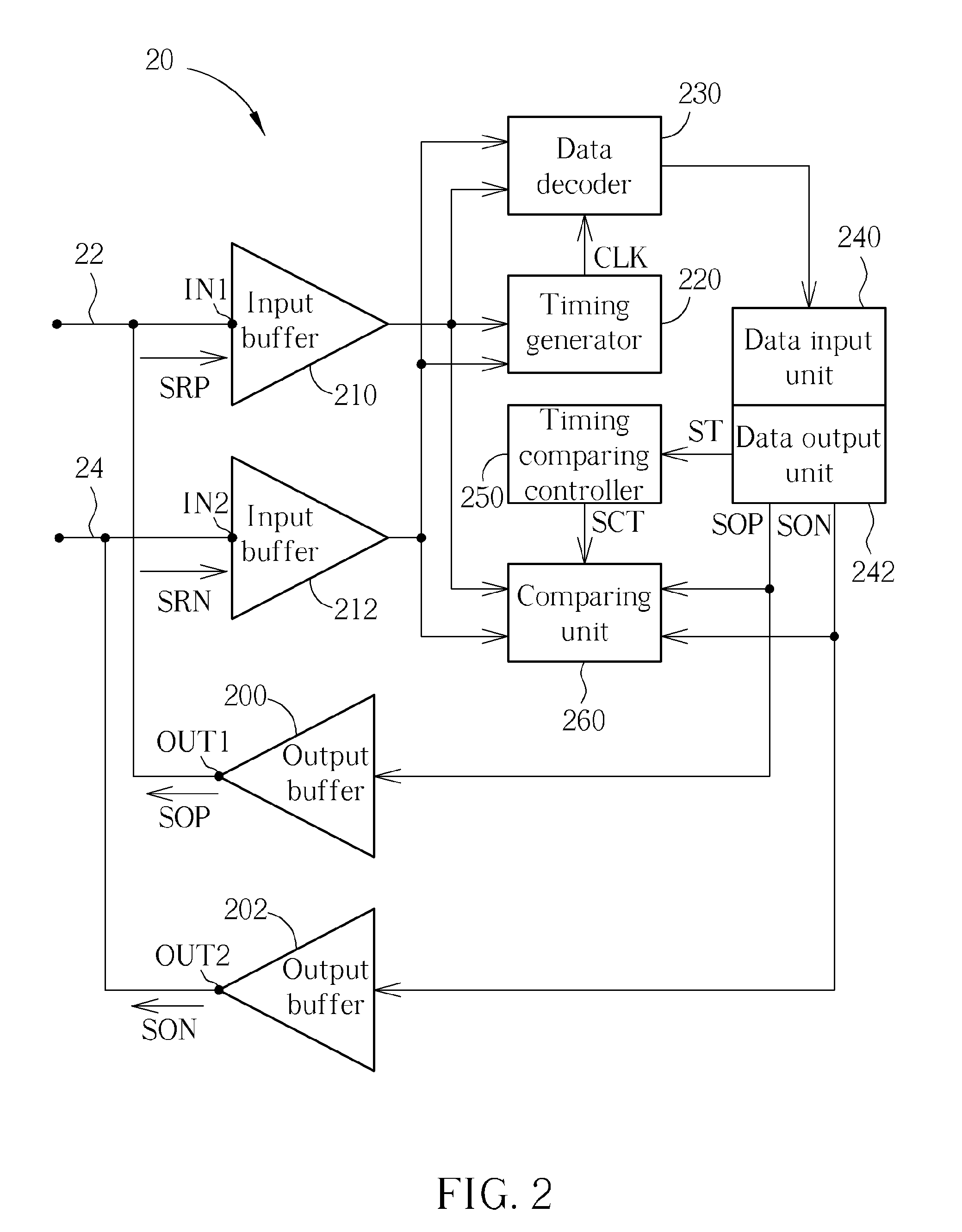
Electronic device for contention detection of bidirectional bus and related method
ActiveUS20090254687A1Avoid failureTime-division multiplexLoop networksElectronic equipmentBus contention
An electronic device of detecting contention of a bidirectional bus for avoiding failing to drive a bidirectional bus due to bus contention includes: an output terminal, an input terminal and a data output unit, a timing comparing controller and a comparing unit. The output terminal is coupled to the bidirectional bus and used for outputting a data output signal to the bidirectional bus. The input terminal is coupled to the output terminal and the bidirectional bus and used for receiving a data reception signal from the bidirectional bus. The data output unit is used for providing the data output signal. The timing comparing controller is used for generating a timing comparison signal according to the data output signal. The comparing unit is used for comparing the data reception signal with the data output signal according to the timing comparison signal to determine a contention state of the bidirectional bus.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
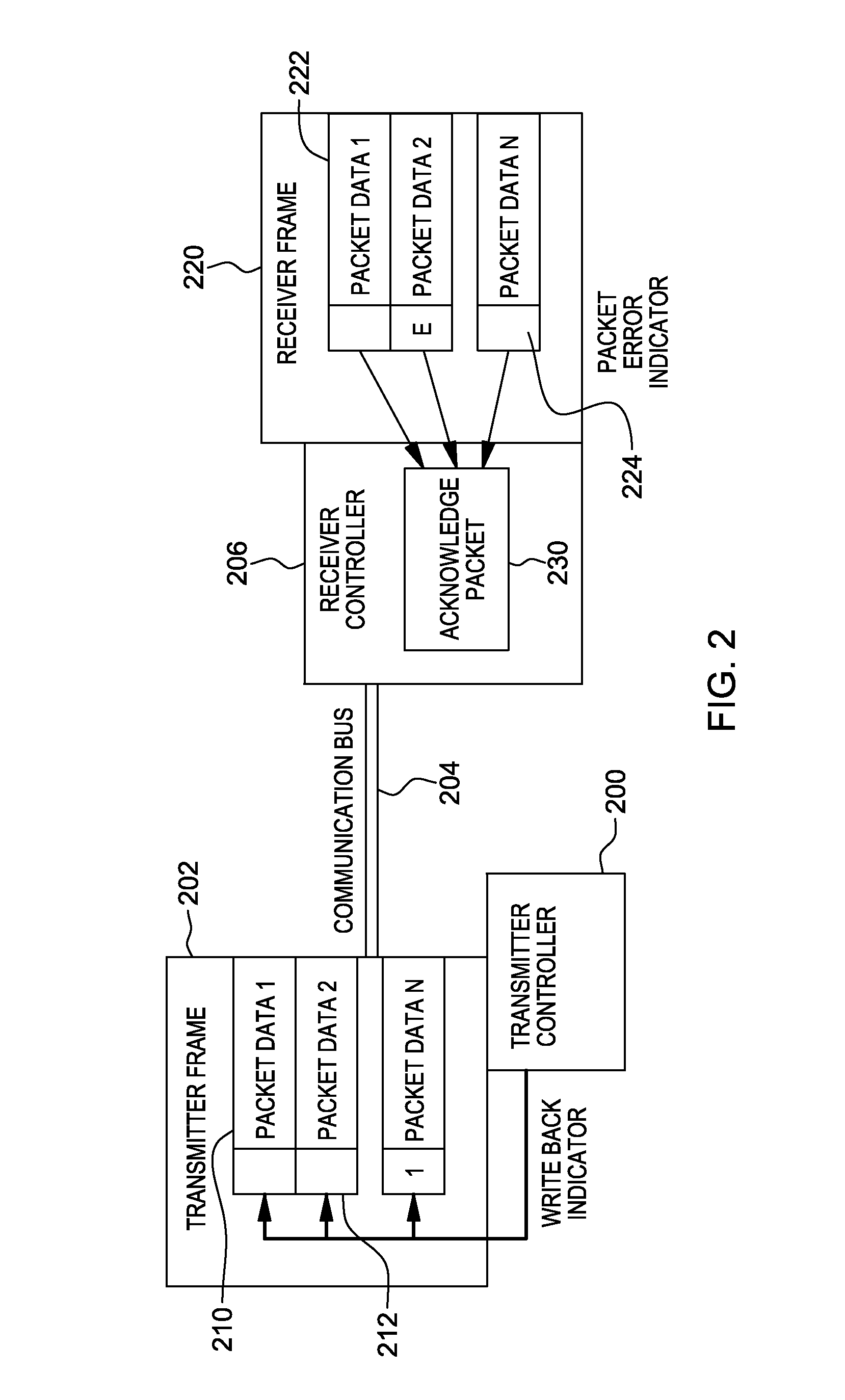
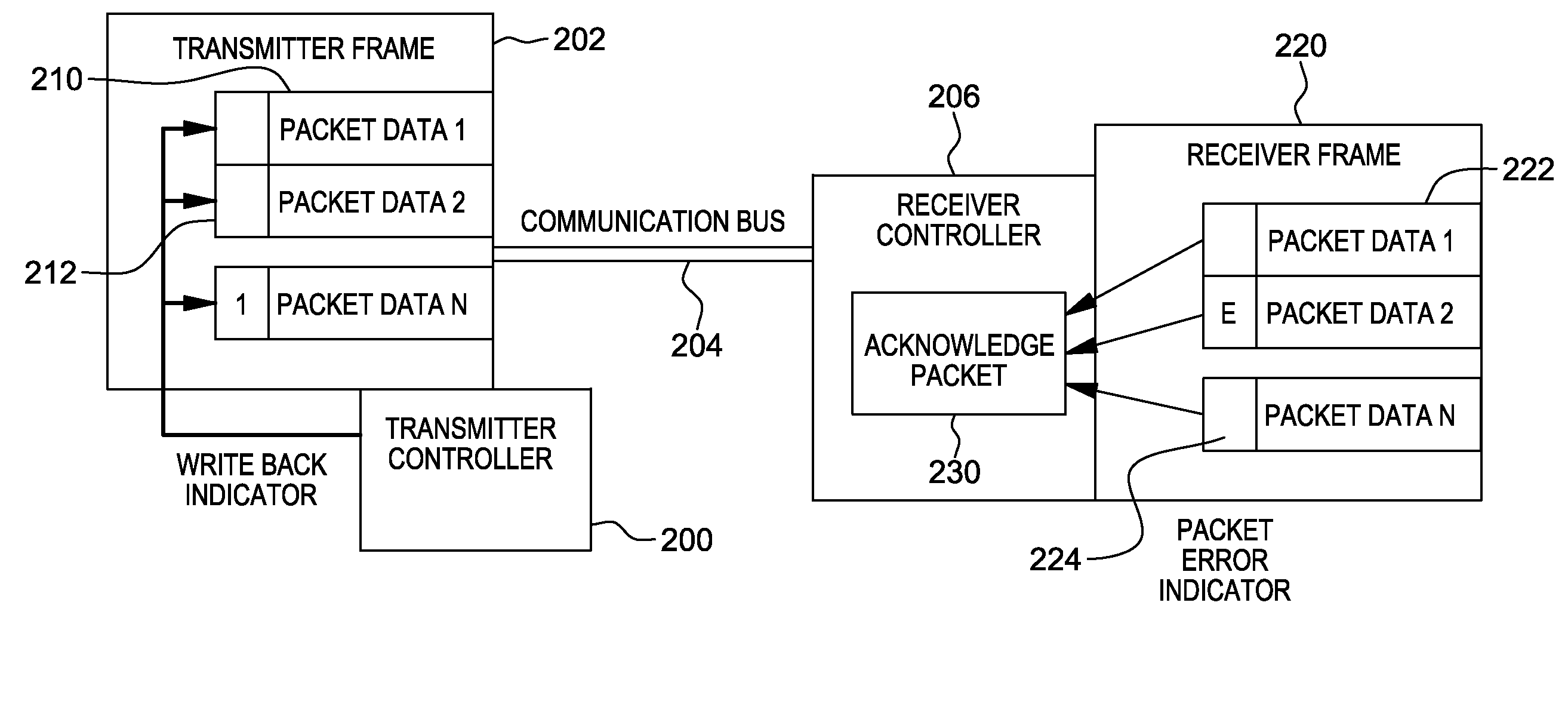
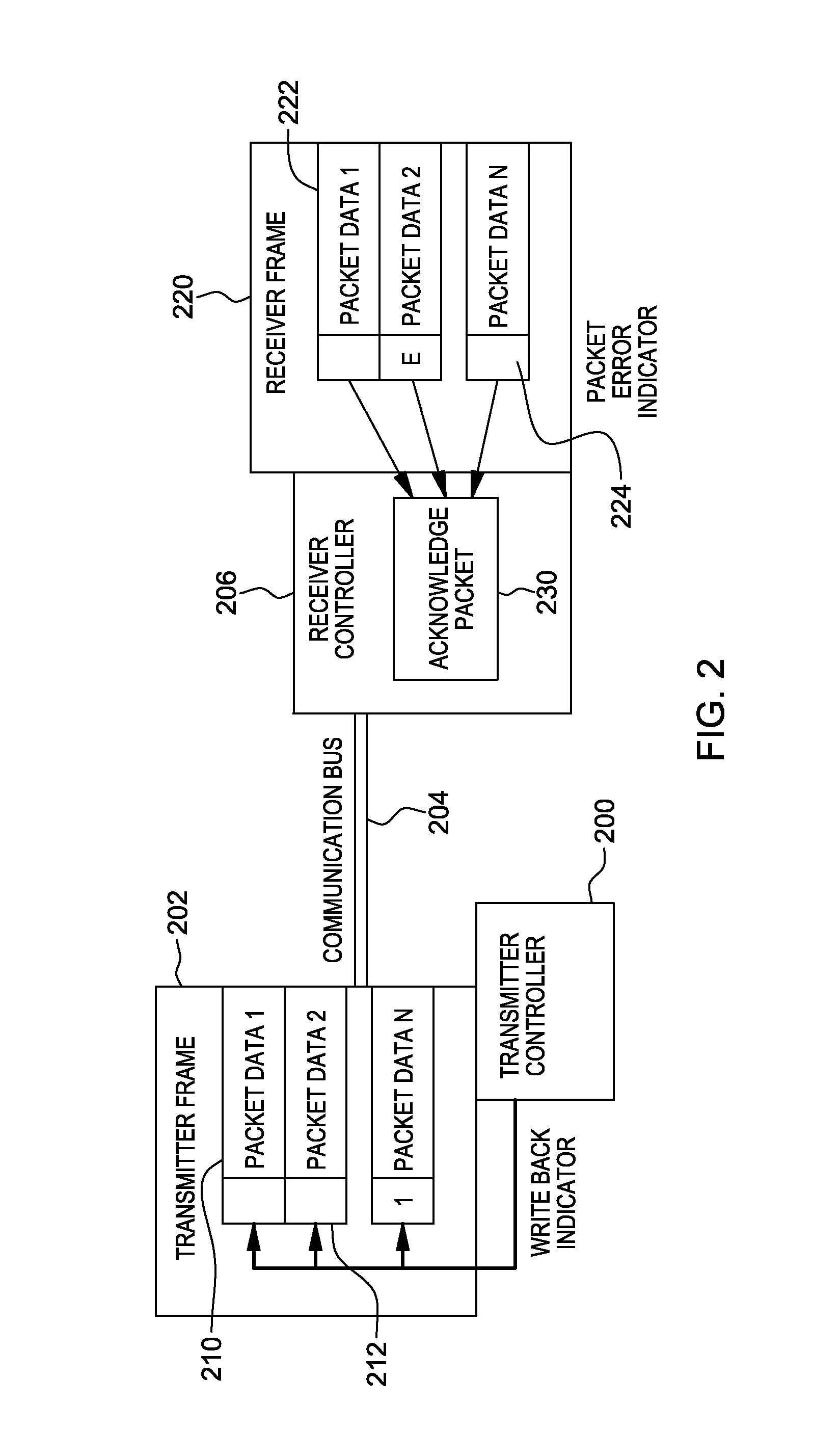
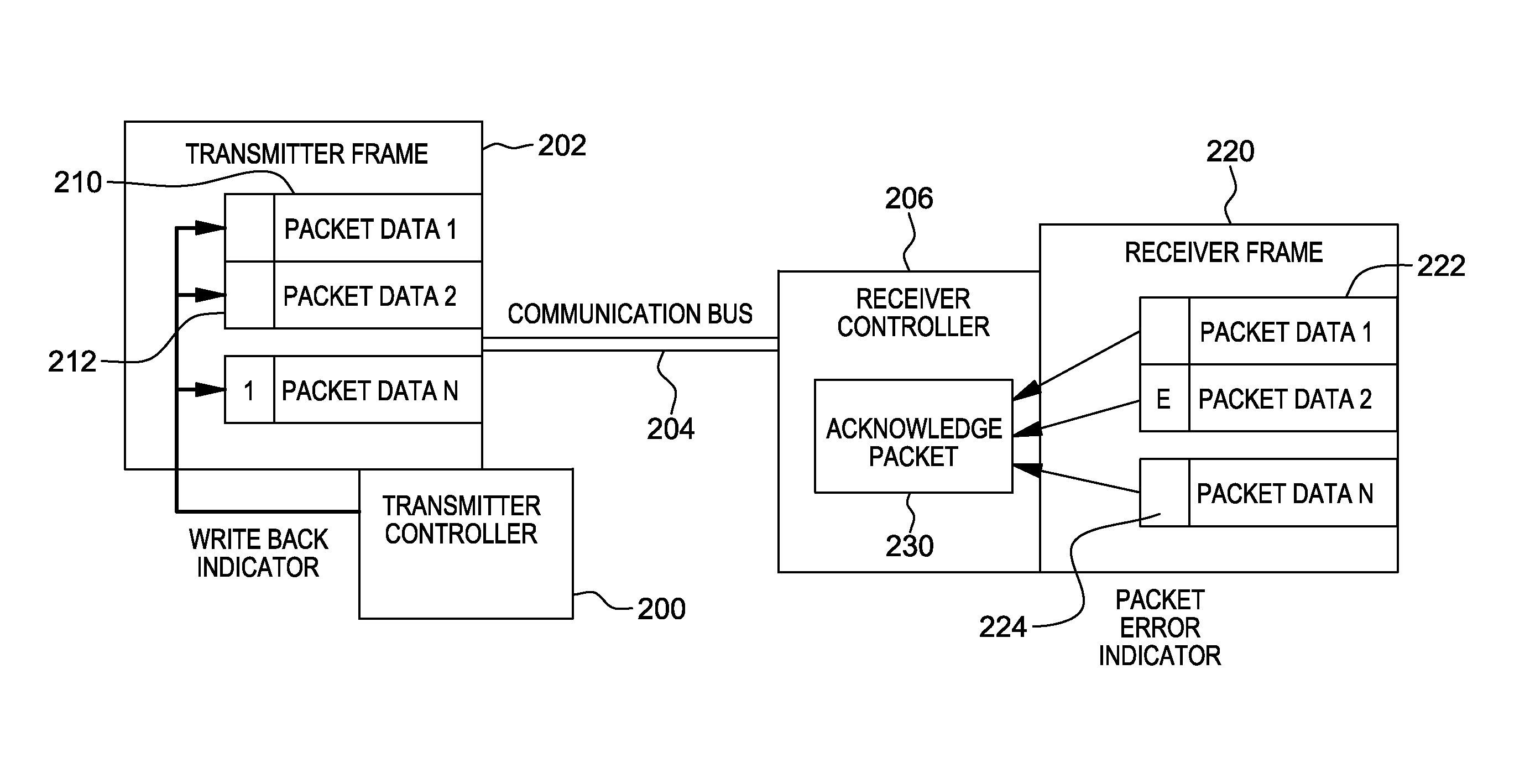
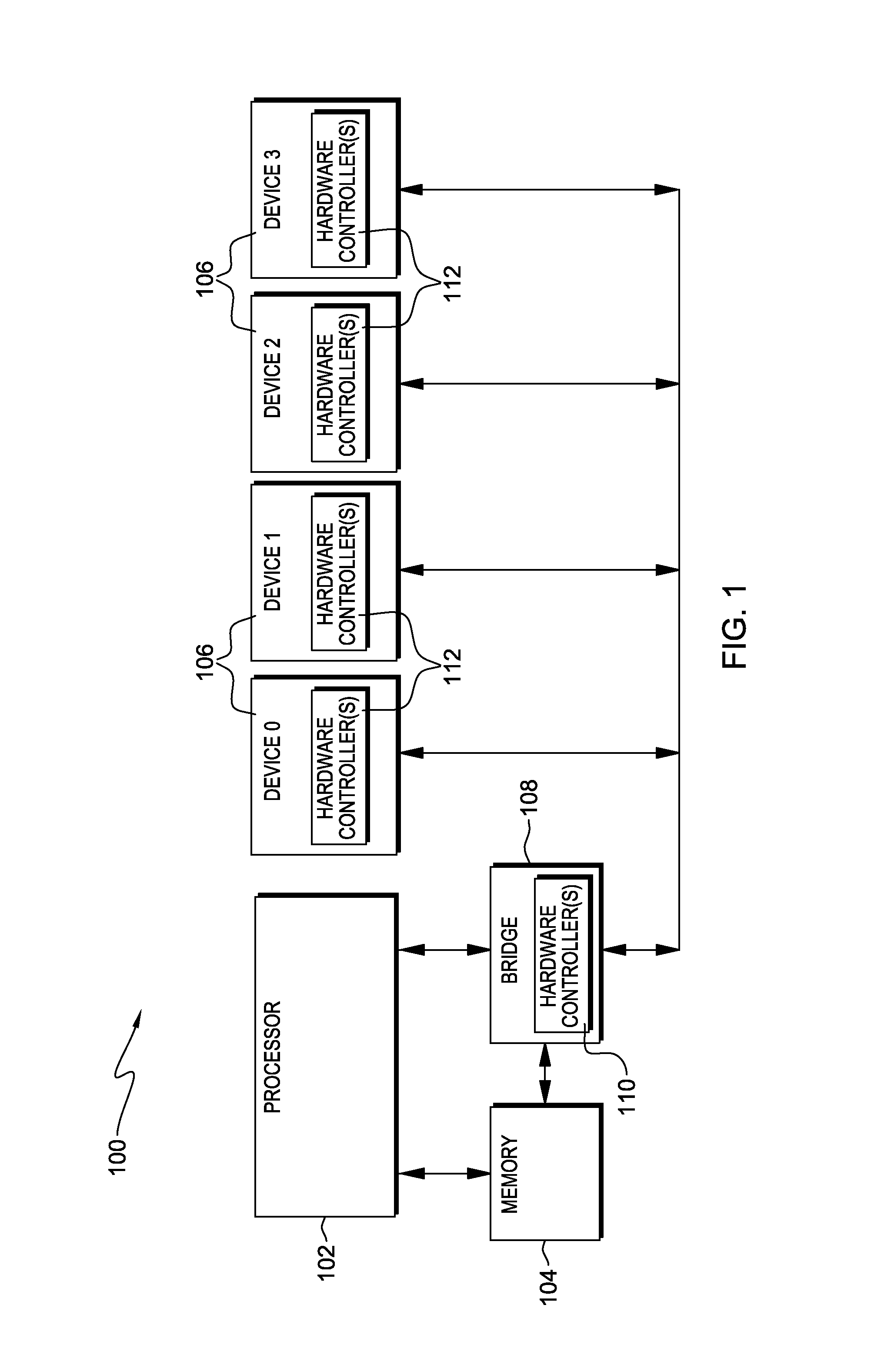
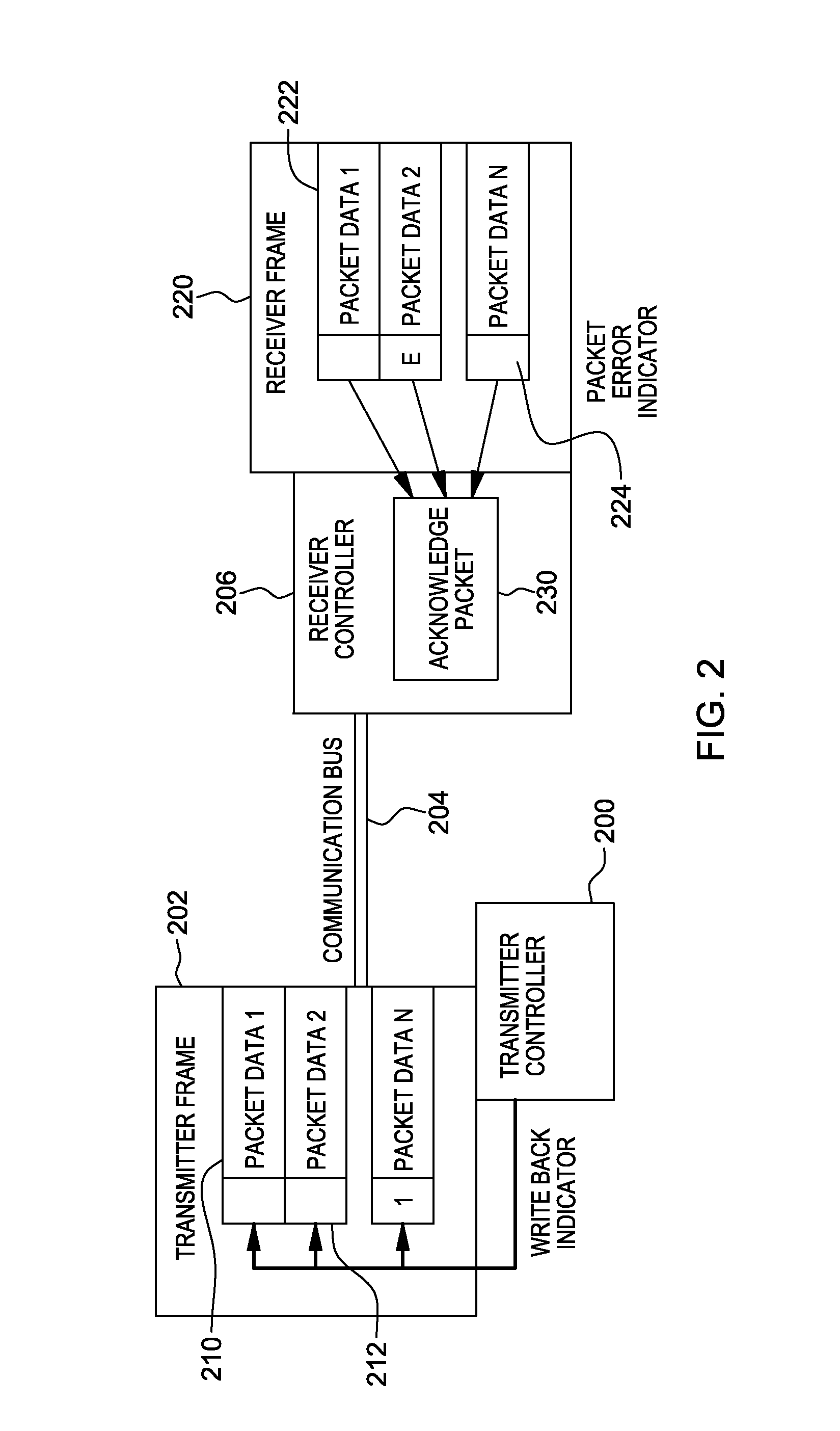
Variable acknowledge rate to reduce bus contention in presence of communication errors
ActiveUS20130290803A1Facilitate communicationError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsData transmissionBus contention
A variable write back indicator control is provided to control the amount of data to be re-transmitted when a packet error occurs. A hardware controller obtains an indication that an acknowledge rate or an amount of set write back indicators of a data frame is to be adjusted. The indication is based on an error rate of data transmission over a communication bus. Based on obtaining the indication that the amount of set write back indicators is to be adjusted, one or more write back indicators are adjusted.
Owner:IBM CORP
Variable acknowledge rate to reduce bus contention in presence of communication errors
ActiveUS20130290802A1Facilitate communicationError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsData transmissionBus contention
A variable write back indicator control is provided to control the amount of data to be re-transmitted when a packet error occurs. A hardware controller obtains an indication that an acknowledge rate or an amount of set write back indicators of a data frame is to be adjusted. The indication is based on an error rate of data transmission over a communication bus. Based on obtaining the indication that the amount of set write back indicators is to be adjusted, one or more write back indicators are adjusted.
Owner:IBM CORP
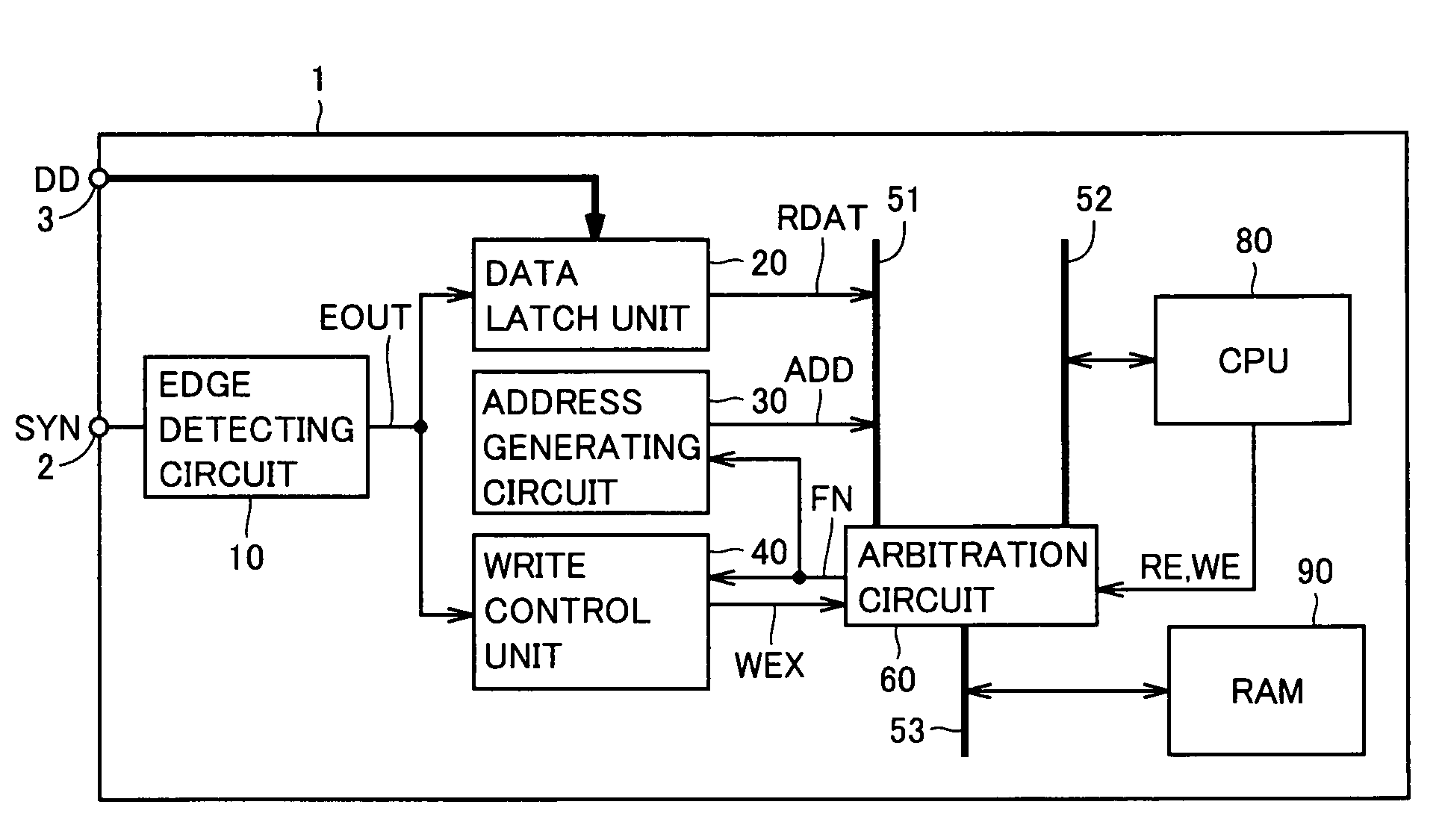
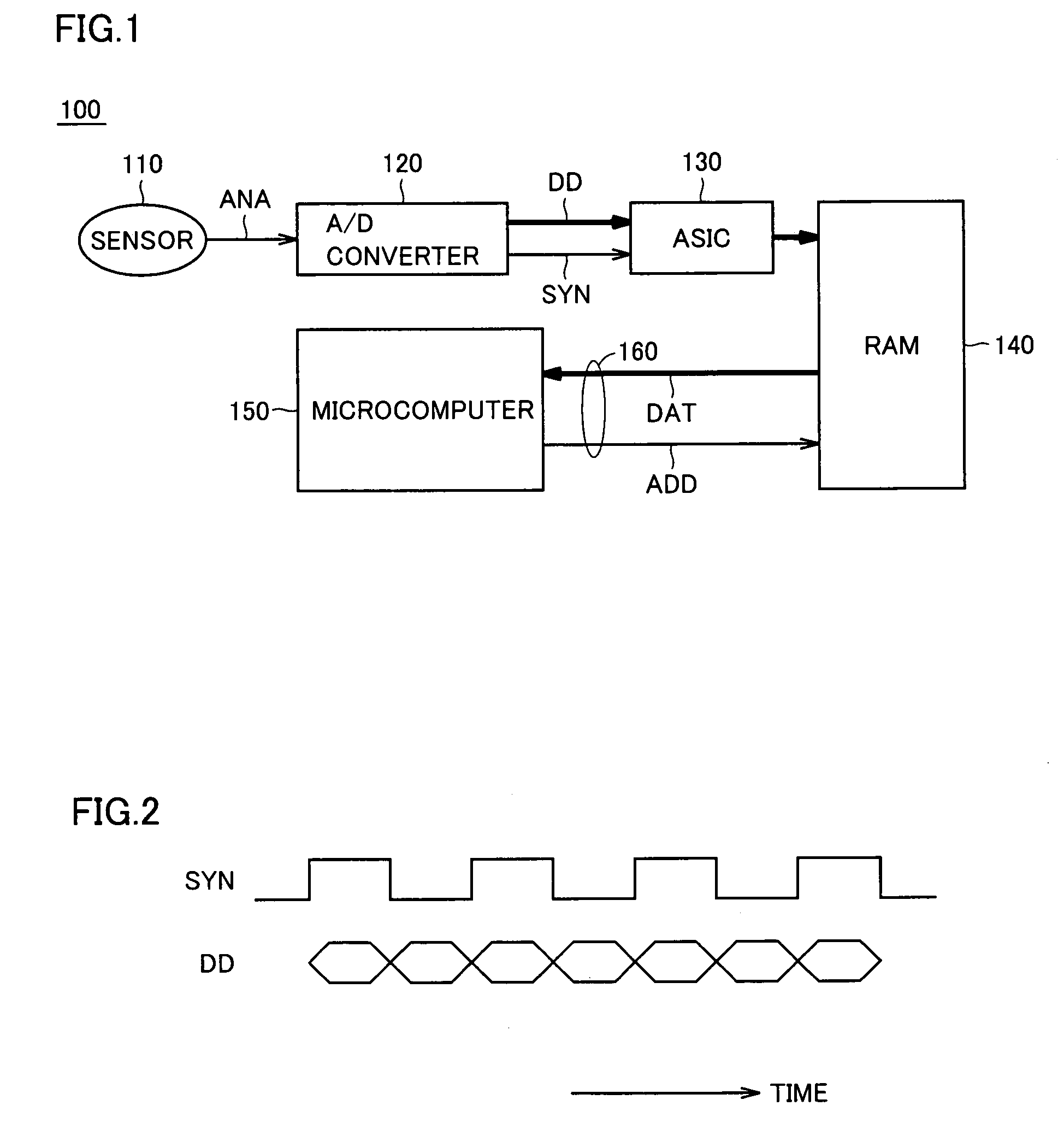
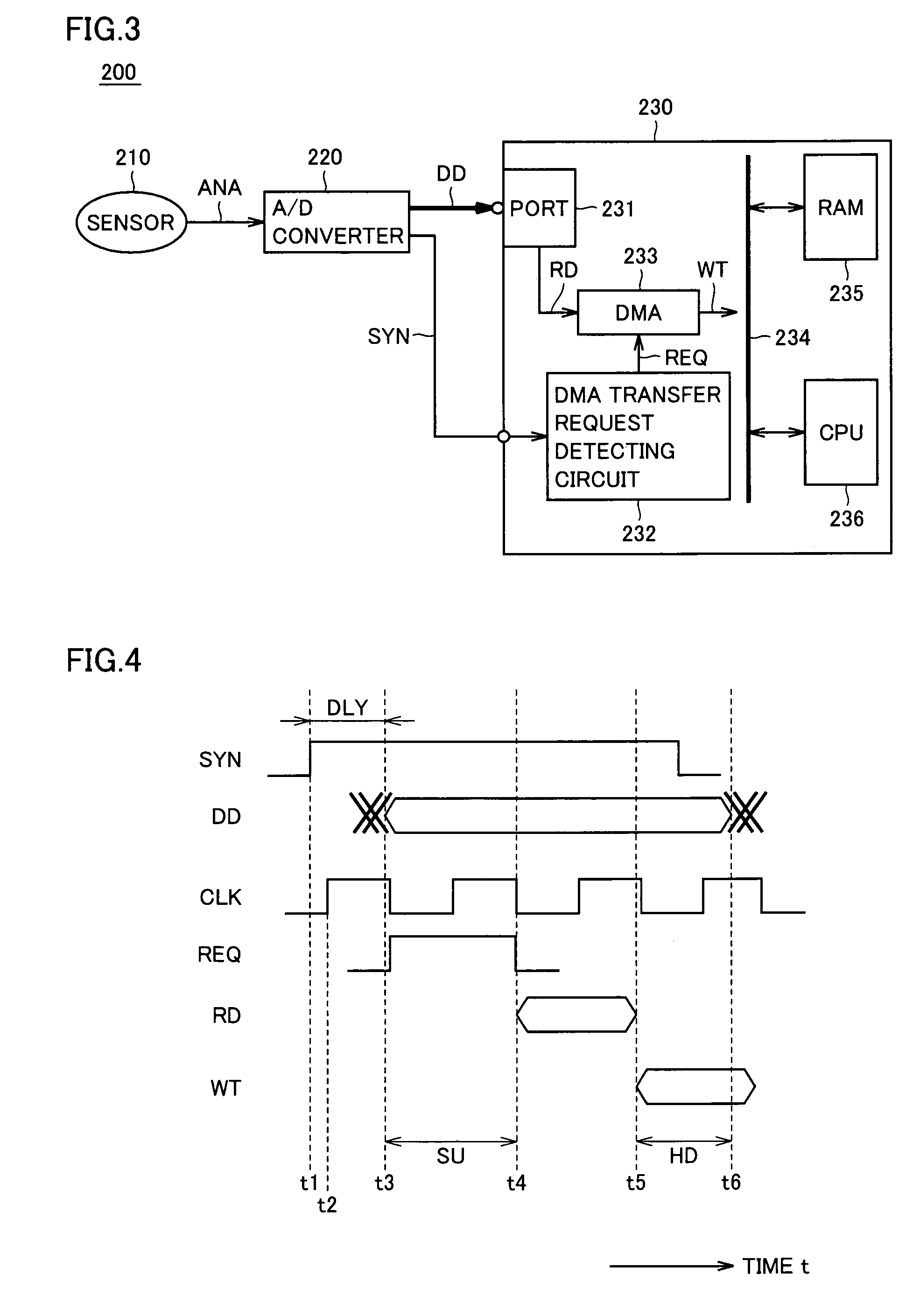
Microcomputer minimizing influence of bus contention
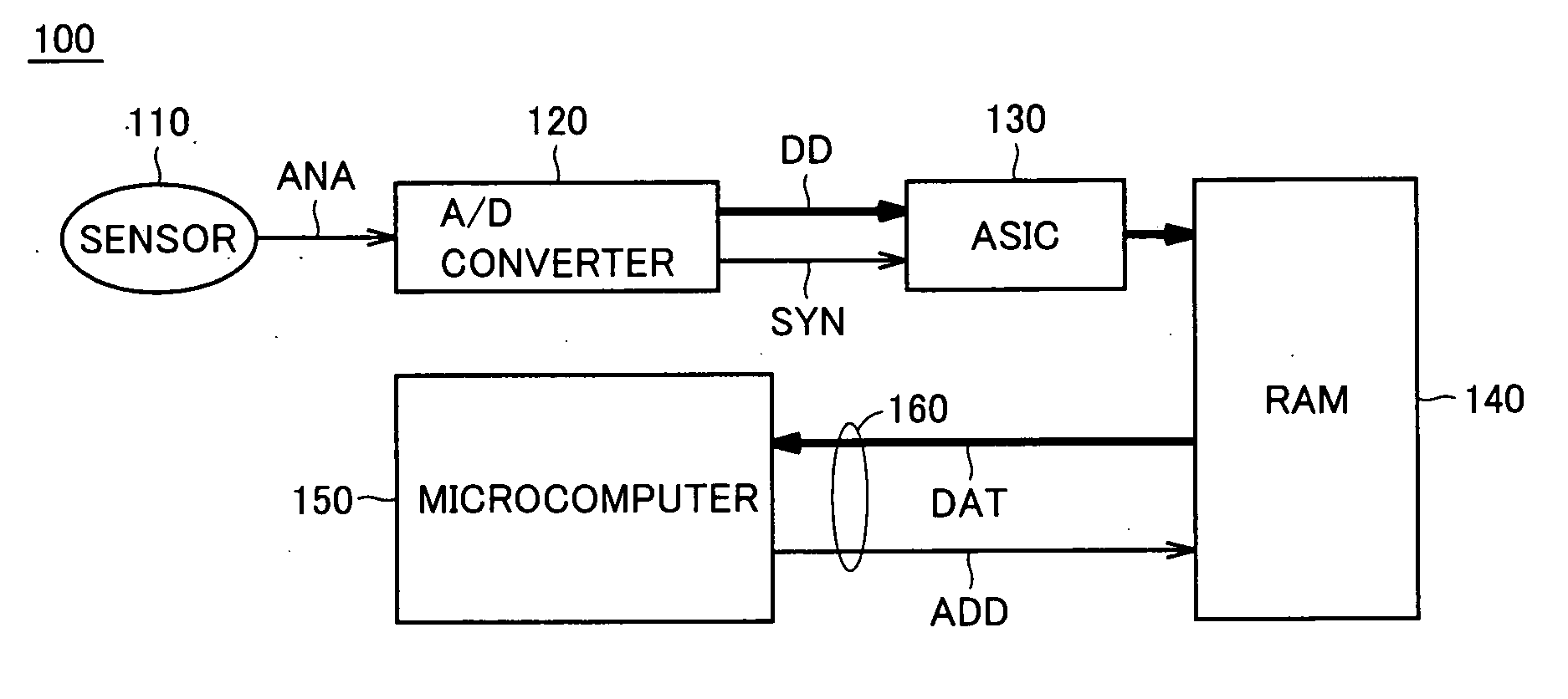
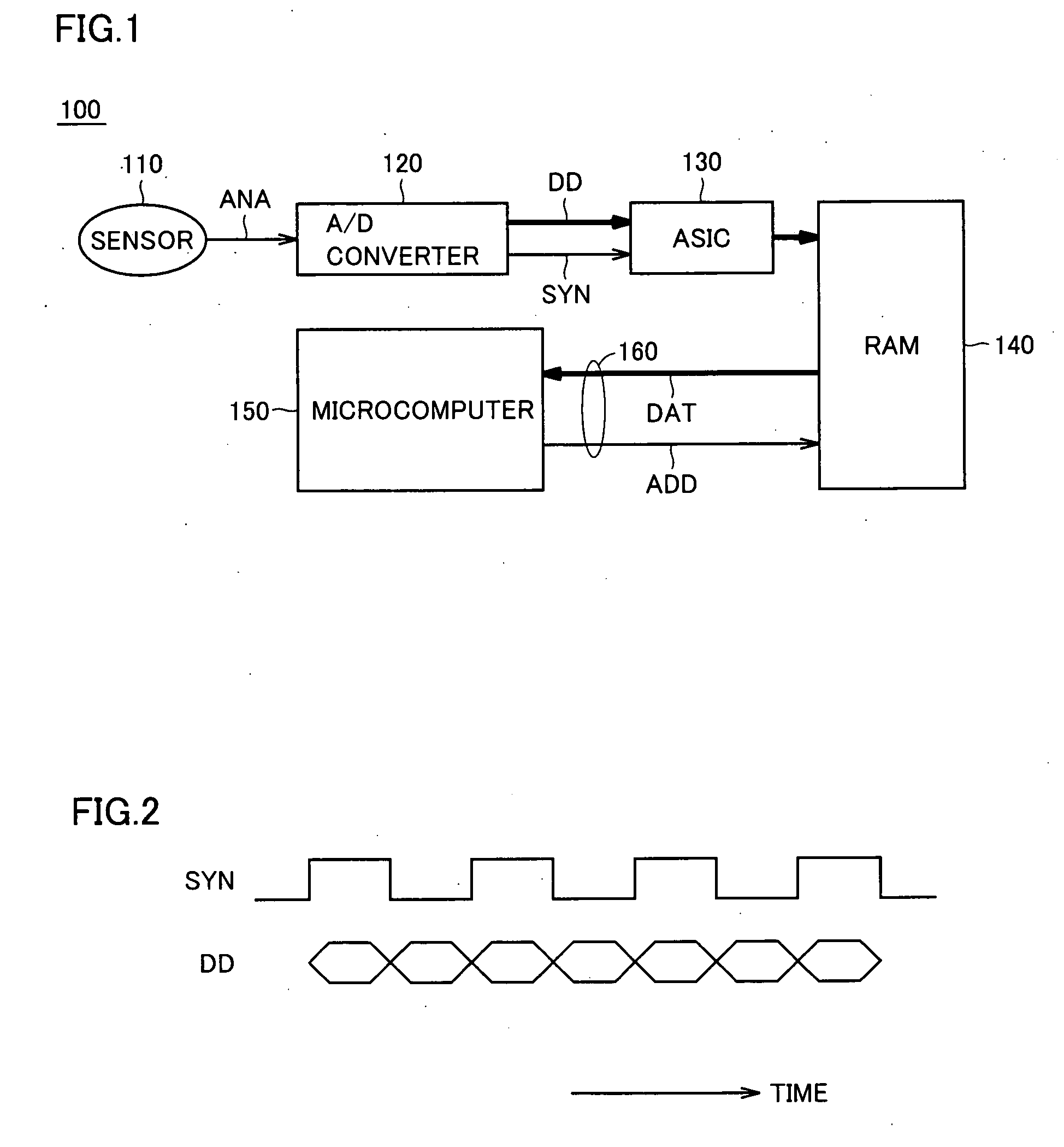
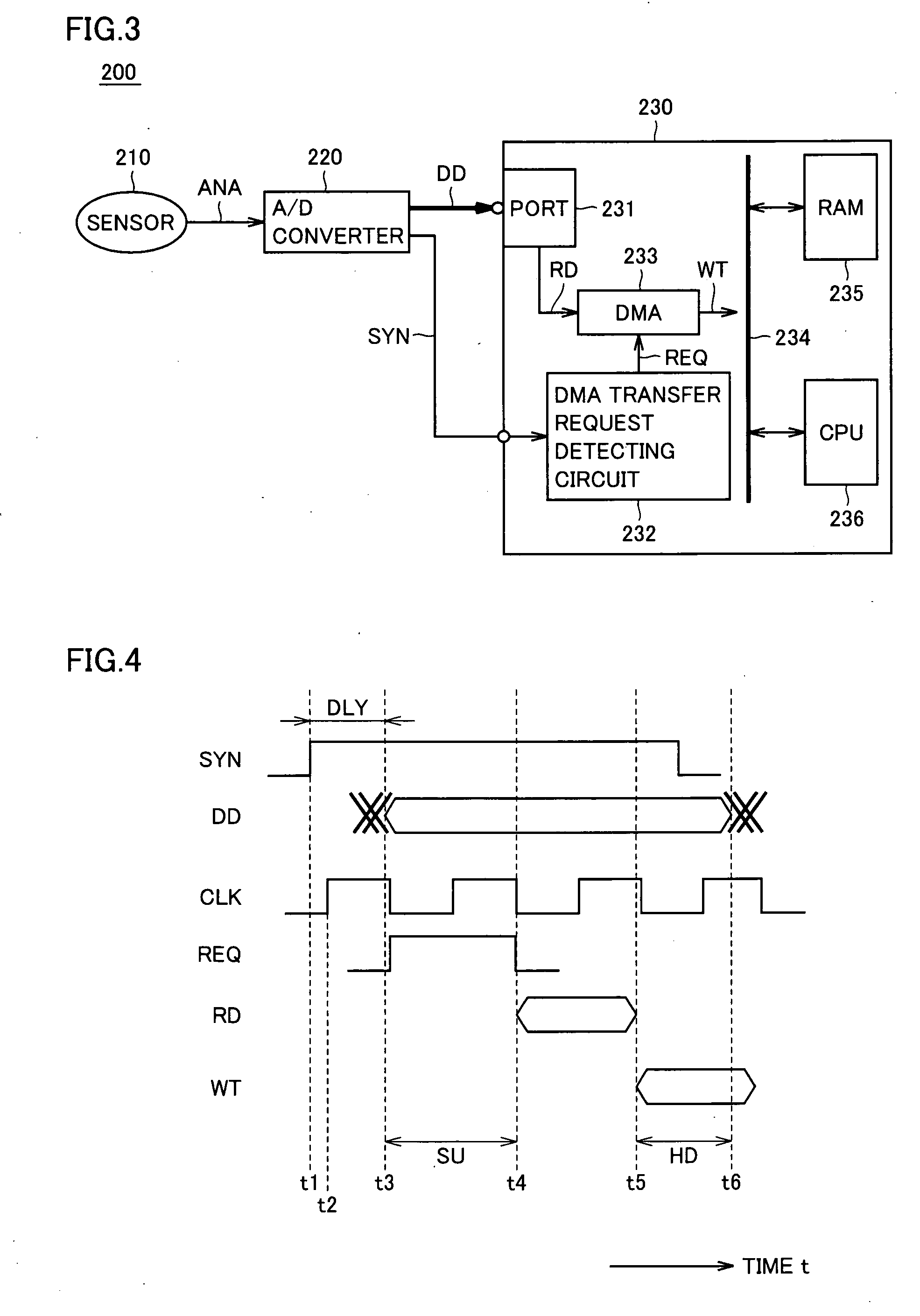
InactiveUS20050198420A1Minimize impactFlexible changeArchitecture with single central processing unitMemory systemsMicrocomputerDigital data
An edge detecting circuit detects an input level change (edge) of a synchronous signal provided from a synchronous signal input terminal. A data latch unit latches digital data provided from an external data input terminal. An address generating circuit provides an address signal. A write control unit activates / deactivates a write enable signal for writing to a RAM. An arbitration circuit monitors a write control enable signal, a read enable signal and a write enable signal, and detects a cycle, in which a CPU does not access the RAM.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Variable acknowledge rate to reduce bus contention in presence of communication errors
ActiveUS8904246B2Facilitate communicationError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsData transmissionBus contention
A variable write back indicator control is provided to control the amount of data to be re-transmitted when a packet error occurs. A hardware controller obtains an indication that an acknowledge rate or an amount of set write back indicators of a data frame is to be adjusted. The indication is based on an error rate of data transmission over a communication bus. Based on obtaining the indication that the amount of set write back indicators is to be adjusted, one or more write back indicators are adjusted.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multi-master lossless bus competition technology
InactiveCN103546355AArbitration is fastEasy to implementBus networksAsynchronous communicationTelecommunications engineering
The invention discloses a multi-master lossless bus competition technology, belongs to the technical field of communication engineering and control engineering, and relates to a field bus use right arbitration technology. When a plurality of devices are connected to run through a bus, each device can serve as a device for actively sending information through the multi-master lossless bus competition technology, and the situation that the devices obtain the right to use the bus in a request-response master-slave mode is not needed; when the devices send the information at the same time, information sending conflict is formed by the devices, the devices compete for the right to use the bus, the device which wins the competition obtains the right to use the bus, and continues to send data, the data sent in the process of the competition are still valid, namely, loss of data sent by the device which wins the competition for the bus is not caused, and the speed of data sending is increased; the devices which fail in the competition for the bus stop sending data, and wait for participation in the next competition for the right to use the bus. The multi-master lossless bus competition technology can be used for field buses for synchronous communication, and can also be used for field buses for asynchronous communication.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Variable data rate control protocol
There is disclosed a protocol which can use the existing network bandwidth limitations for transmission during at least the bus contention period after which the remaining portion of the data should be collision-free but allow for a choice of signalling rate within the frame after that bus contention period for the payload data to be transmitted, thus allowing the use of a different data rate in parts of a frame. Additionally there is disclosed advantages to be gained by making best use of available but otherwise not used network bandwidth capability at different parts of the transmission of a frame, such that the protocol enhancement should be compatible with existing installed devices and associated controllable arrangements, so that a system existing in a network can be upgraded, by adding one or more of the devices and associated controllable arrangements which can transmit and receive both the original standard (typically lower) data rate as well as the newer (typically higher) data rate transmissions, at the convenience of the owner of the network without a cost burden associated with replacement or the upgrading of all existing devices or associated controllable arrangements.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC (AUSTRALIA) PTY LTD
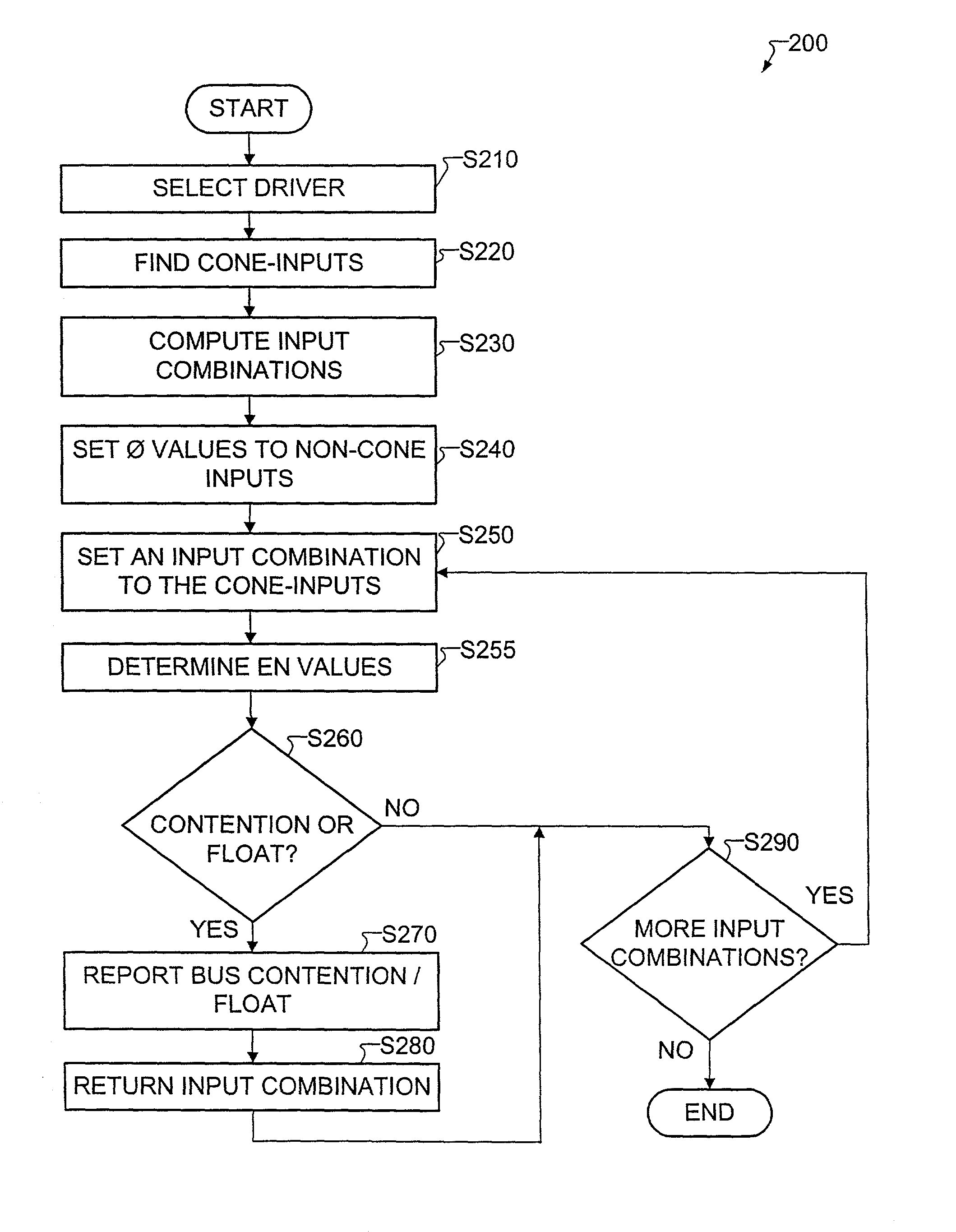
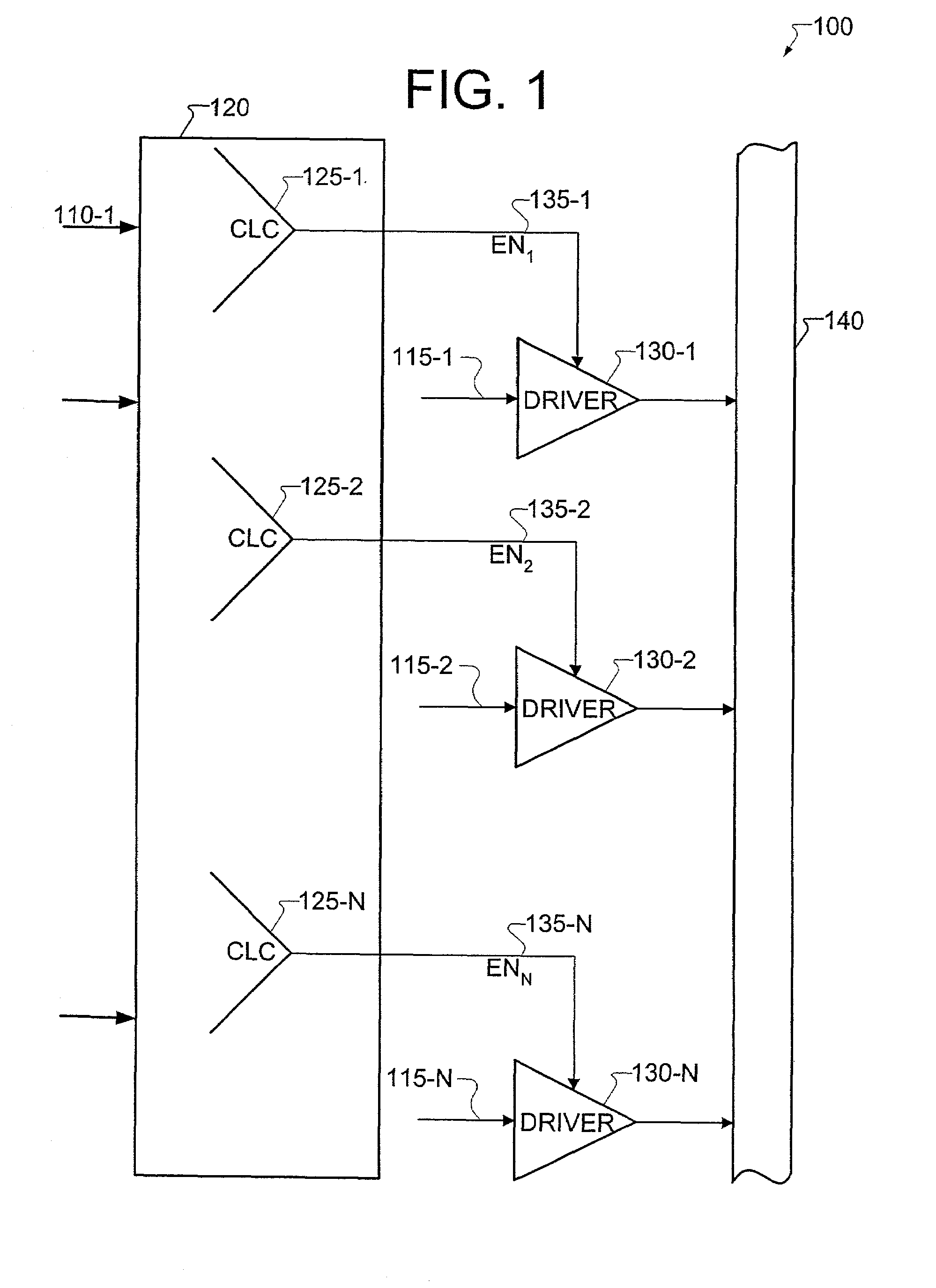
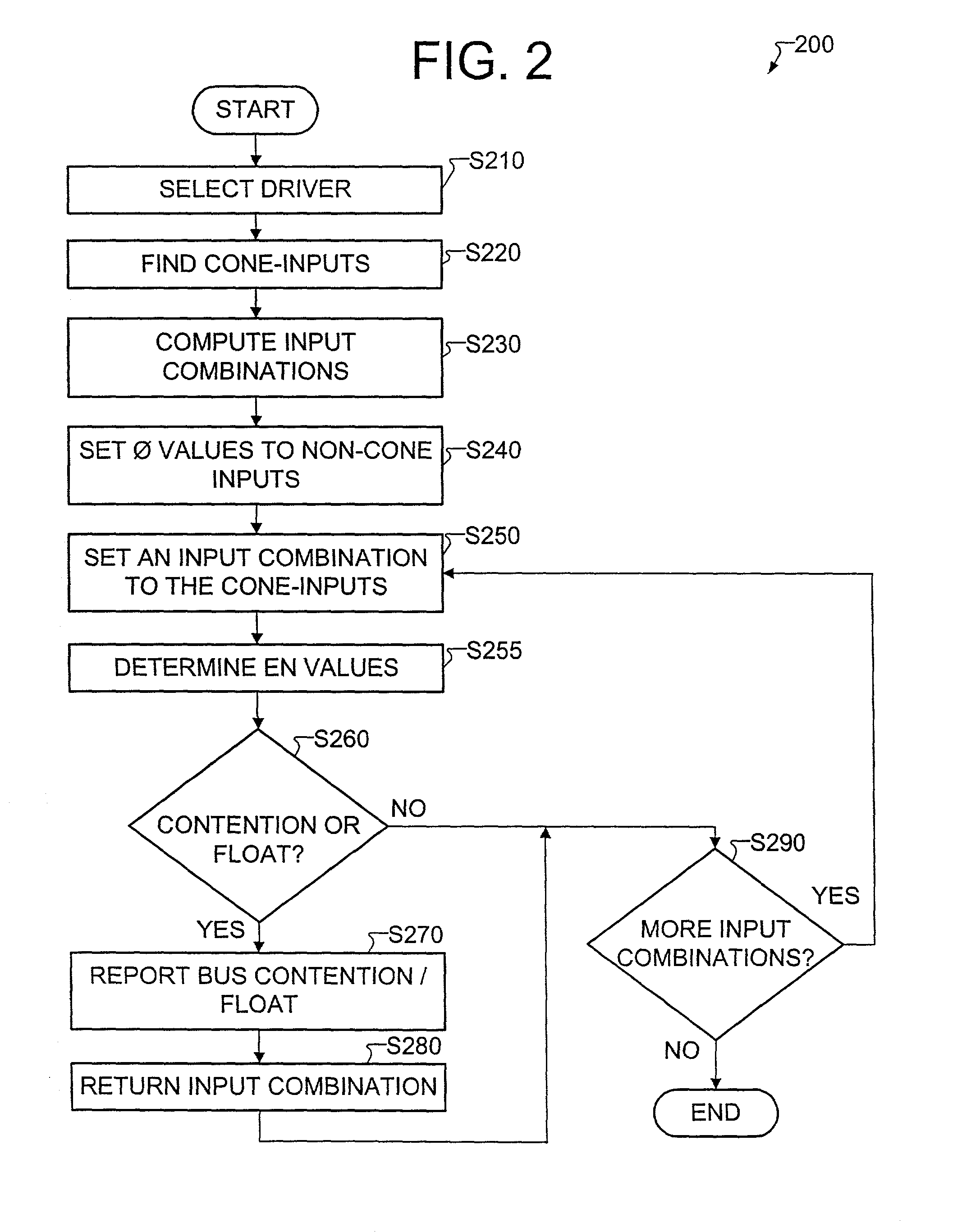
Method for detecting bus contention from RTL description
A method for efficiently detecting bus contention from a register transfer level (RTL) description is provided. A bus contention occurs if more than two components try to propagate data onto a bus at the same time. The provided method simulates possible input combinations and detects whether there is a possibility for a bus contention. In addition, the provided method is designed for testability, therefore using the method, the designer may identify contention that may exist in test mode at the RTL level of the design even when such conditions may not occur in system mode. The method provides the designer with the input combination as well as the RTL statement that caused the contention. The method detects the bus contention by simulating a small number of input combinations.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Bus sharing method
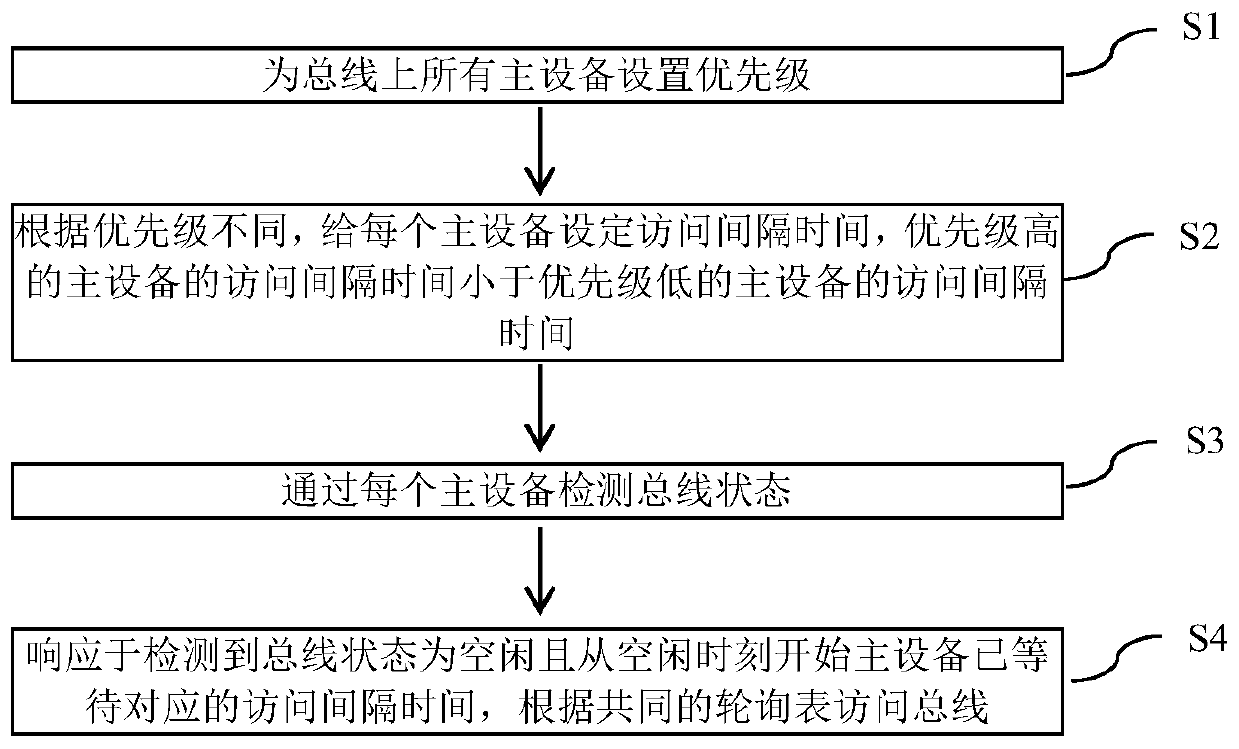
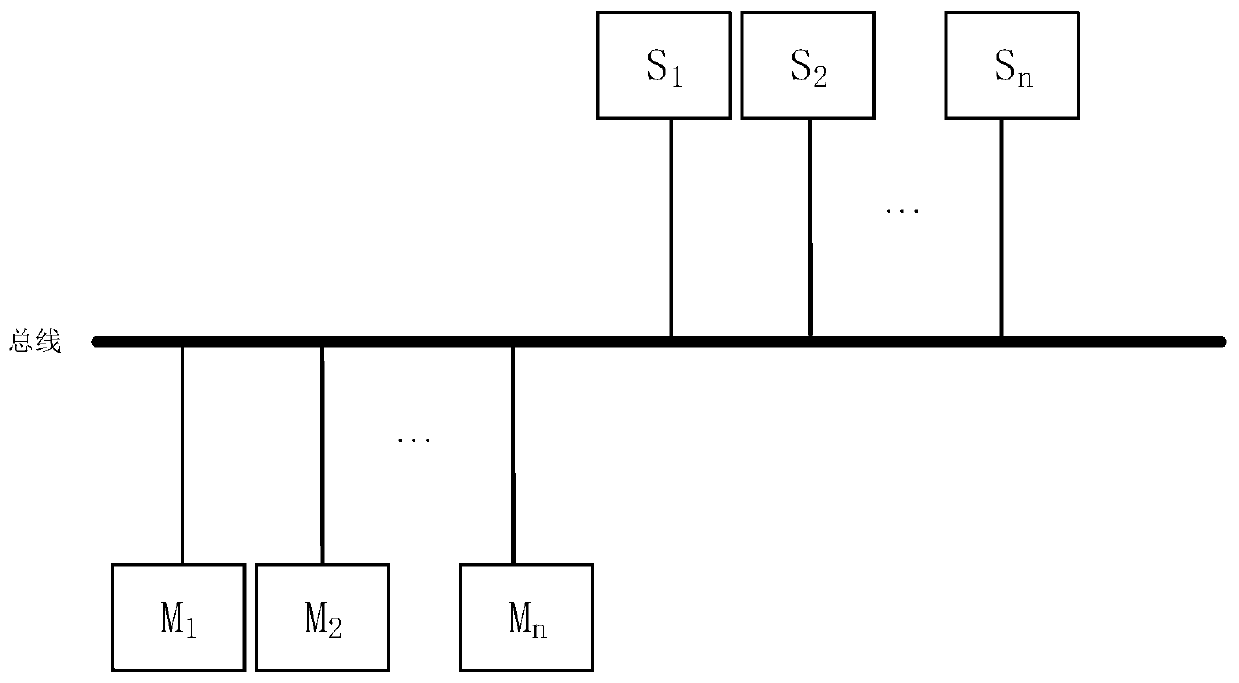
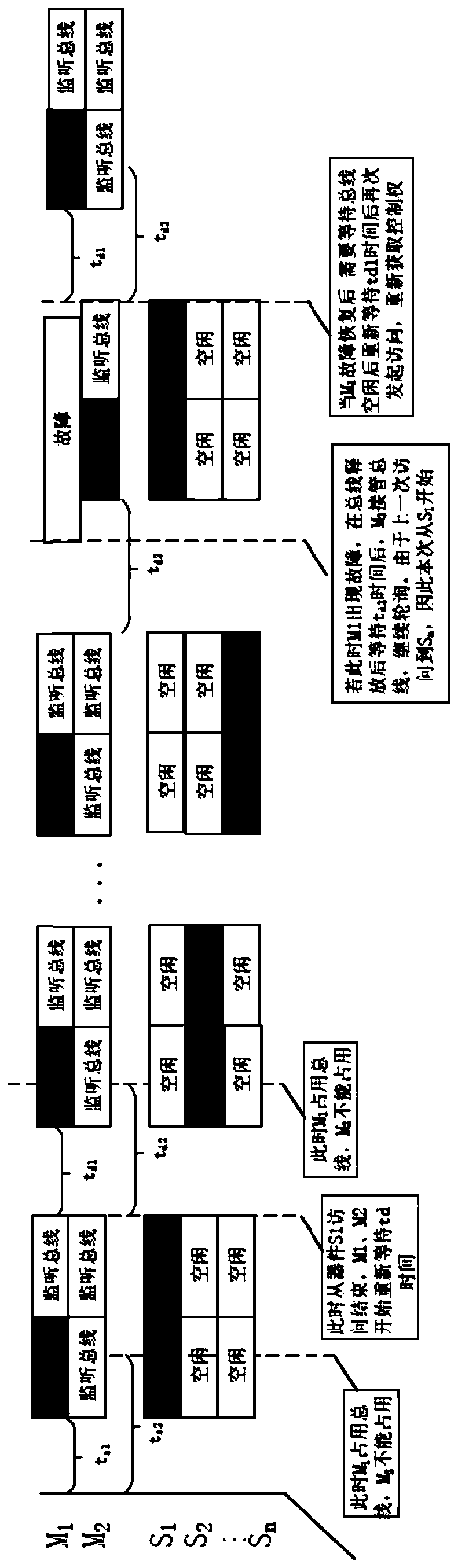
ActiveCN111090600AAchieve sharingRealize the arbitration functionElectric digital data processingAccess timeEngineering
The invention provides a bus sharing method. The method comprises the following steps: setting priorities for all main devices on a bus; according to different priorities, setting access interval timefor each master device, and the access time intervals of the master devices with the higher priorities are smaller than that of the master device with the lower priority; detecting a bus state through each master device; and in response to detecting that the bus state is idle and each master device has waited for the corresponding access interval time from the idle moment, accessing the bus according to a common polling table. According to the invention, under the design of double management modules or multiple management modules, bus sharing can be realized without adding extra devices, a bus arbitration function is realized, bus competition conflicts are avoided, the reliability of devices can be improved, information synchronization among the multiple management modules is realized, and the utilization rate of buses is greatly improved.
Owner:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
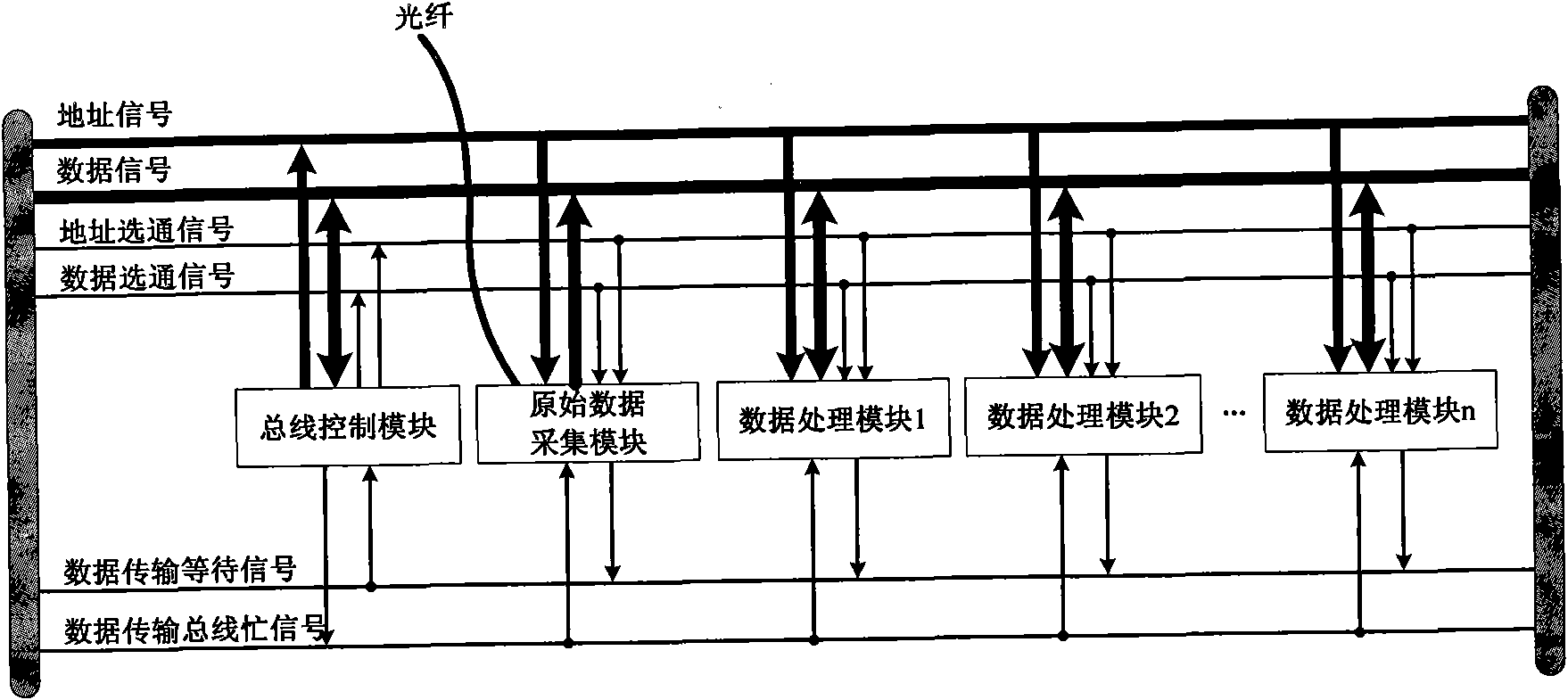
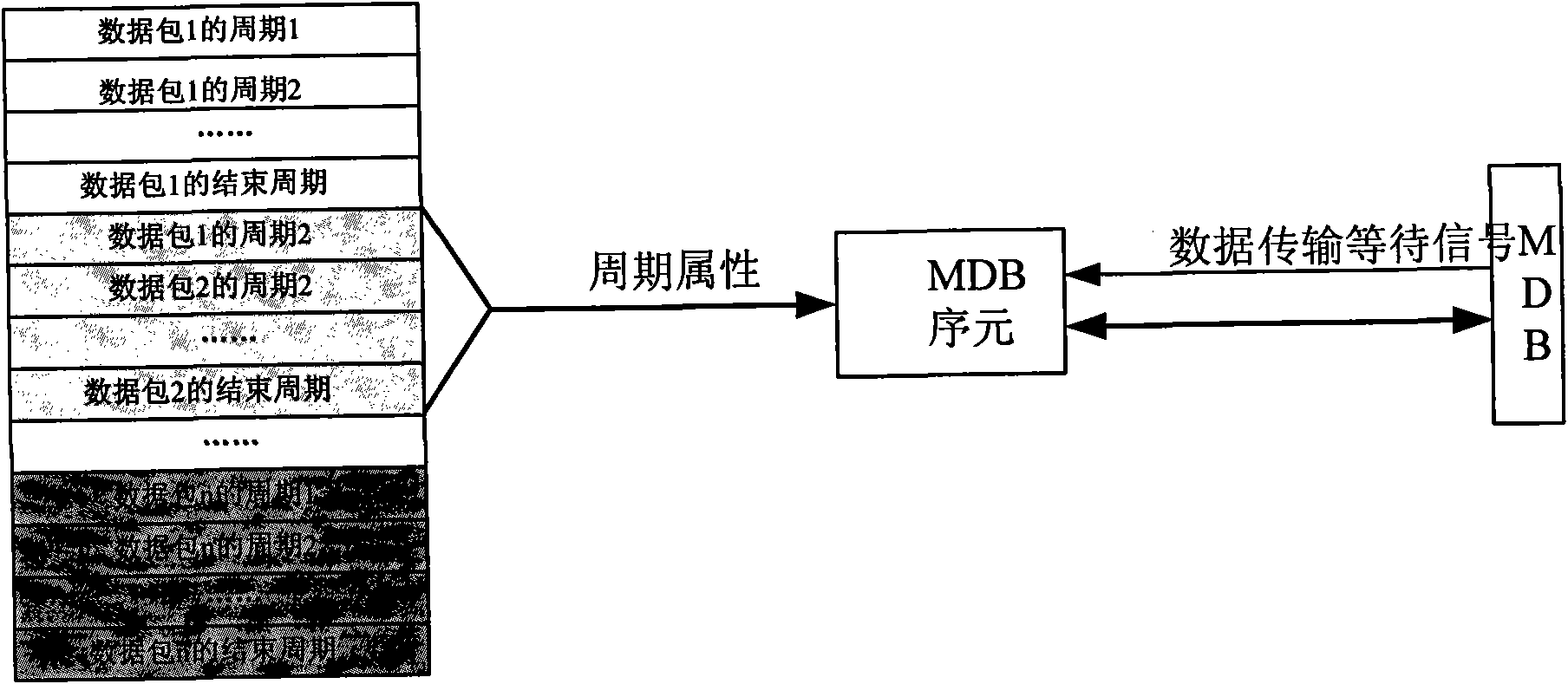
Data transmission bus system
ActiveCN102075395ANo bus contentionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOriginal dataControl data
The invention discloses a data transmission bus system, which comprises a data transmission bus, a bus control module, a raw data acquisition module and a plurality of data processing modules, wherein the bus control module specifies a data transmission source in the raw data acquisition module or the data processing modules, receives a data transmission waiting signal from the data transmission source, controls the data transmission source to output data according to a current transmission state, controls the data processing modules to receive the data, and simultaneously outputs a data transmission bus busying signal. The data transmission bus system provided by the invention controls data transmission by the bus control module, and can ensure that only one data processing module initiates the data transmission at a certain time, and avoid bus contention when the plurality of data processing modules simultaneously initiate the data transmission.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
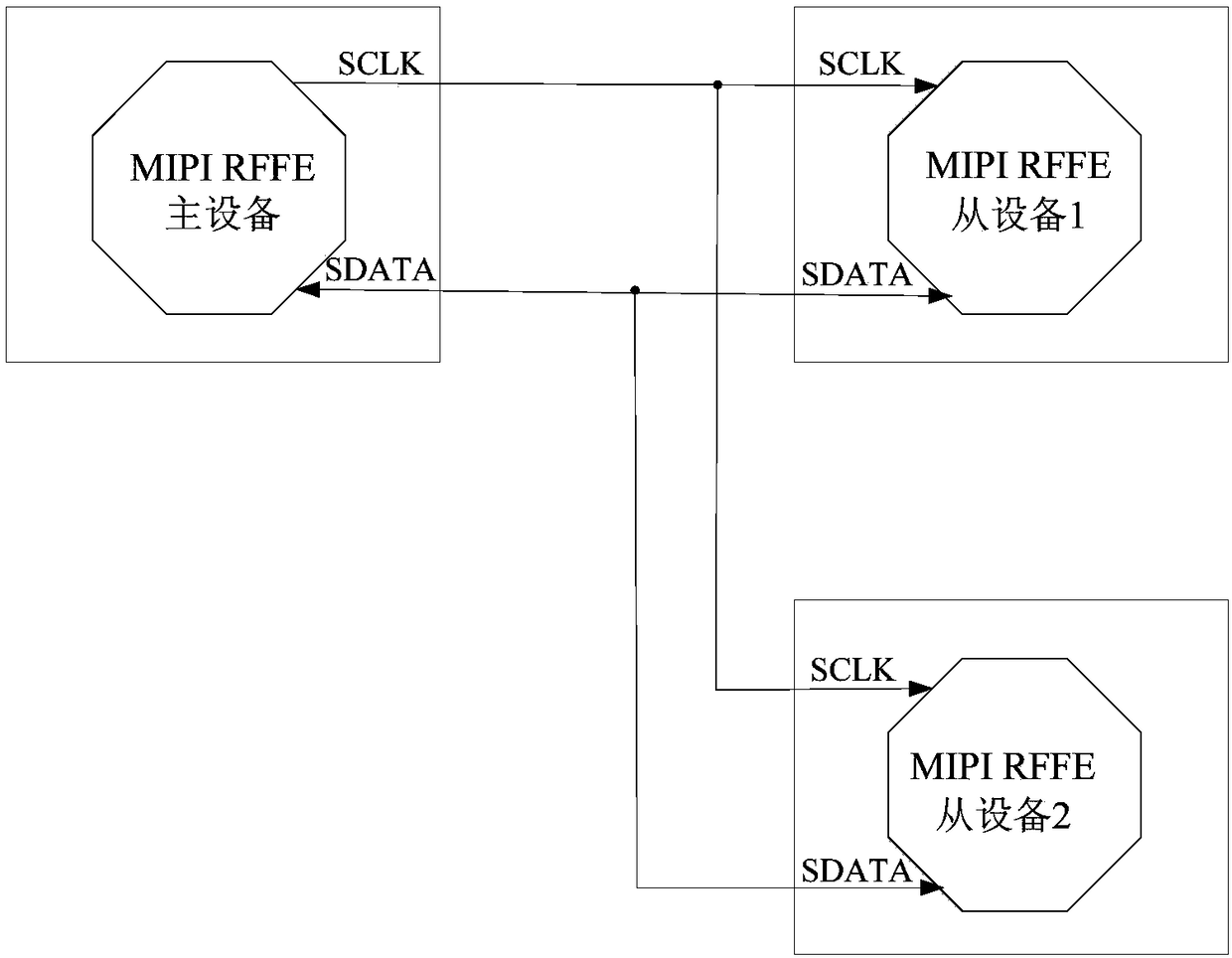
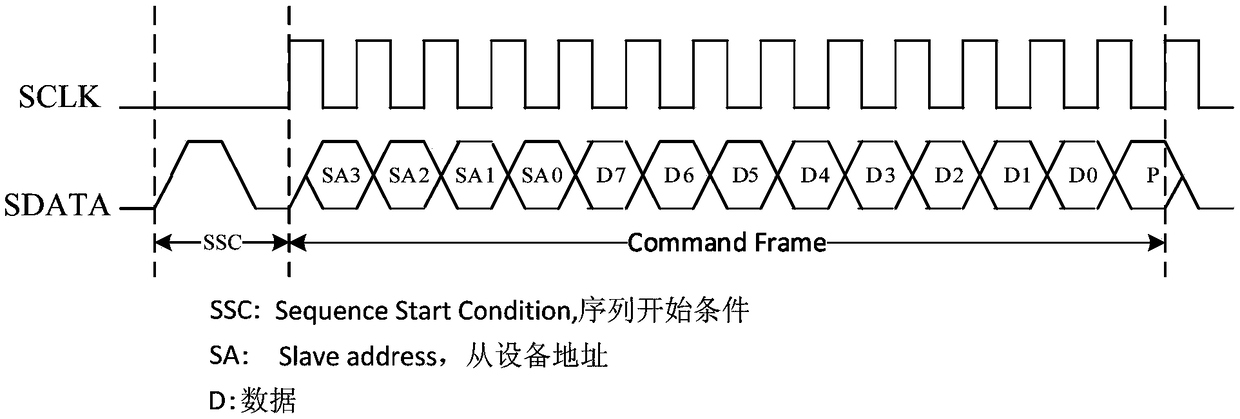
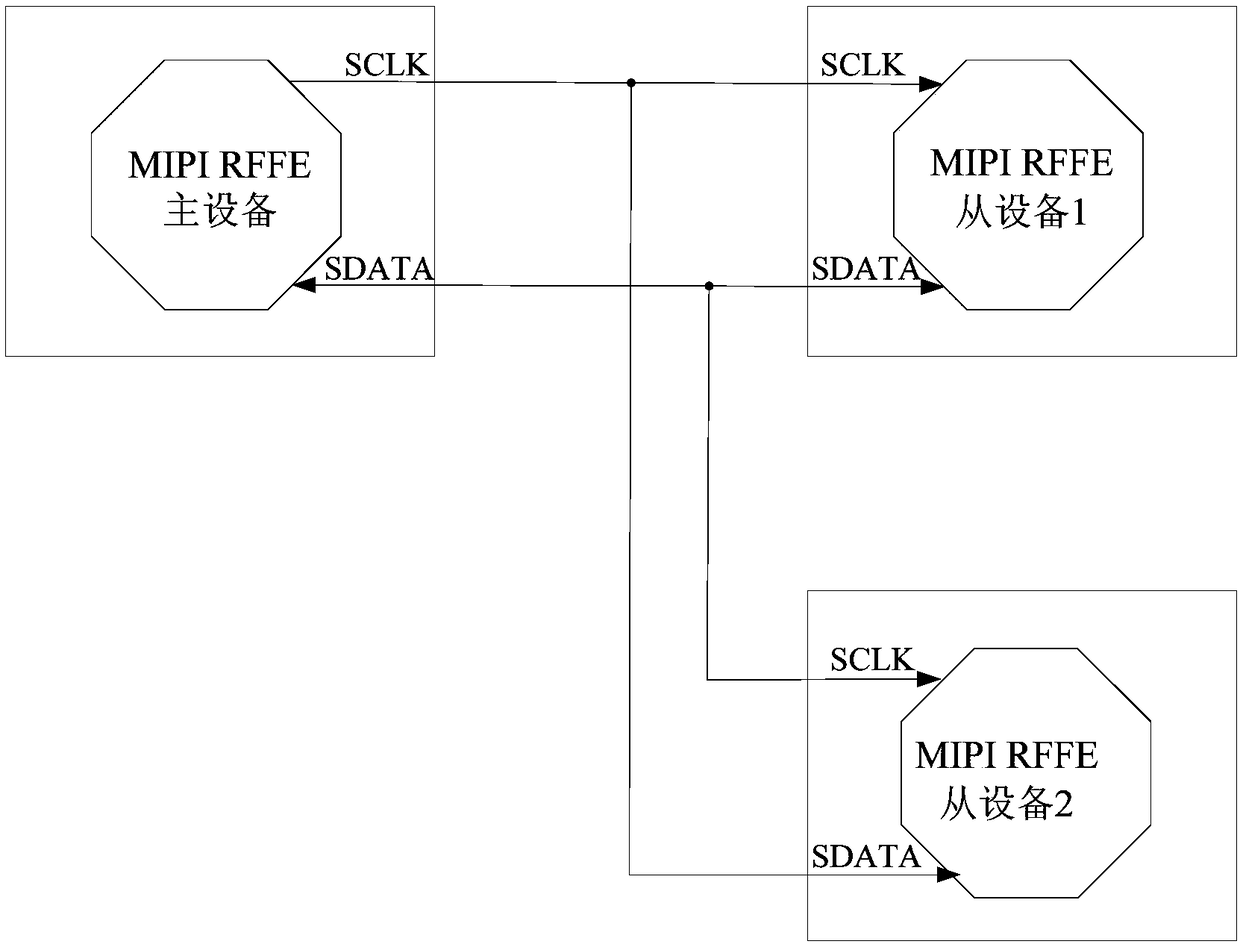
Data signal detecting device, MIPI RFFE equipment and system.
PendingCN108718192ASolving Bus Conflict ProblemsSynchronisation information channelsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionData signalComputer science
The embodiment of the invention discloses a data signal detecting device, MIPI RFFE equipment and system. The data signal detecting device comprises two acquisition circuits and a selection and outputcircuit; a first input end of a first acquisition circuit is connected with a second input end of a second acquisition circuit, and a second input end of the first acquisition circuit is connected with a first input end of the second acquisition circuit; output ends of the two acquisition circuits are connected with an input end of the selection and output circuit; the acquisition circuits use signals received by the first input ends to collect signals received by the second input ends, and it is verified whether or not the collected signals meet characteristics of data signals; the selectionand output circuit selects and outputs the collected signals from the received collected signals and invalid signals. An MIPI RFFE slave device constructed by the data signal detecting device fully considers various abnormal conditions, so that the bus contention problem of two identical MIPI RFFE slave devices in the MIPI RFFE system can be effectively solved.
Owner:MAXSCEND MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Single bus communication protocol with multi node equipment interconnection
Said invention is unibus communication protocol for multi - node interconnected equipment,It contains adopting unique signal characteristic communication node address format and communication frame structure mode to make each communication node to be same position and capable of constituting derelict interlinkage network of communication, due to bus rate is opened so different application area can adopt different rate, Interlinkage in Integrated circuit chip can use highs speed, connection in Commission system board can use intermediate rate, slow speed can be adopted in larger distribution range field such as detecting, data acquisition, scene safety protection system etc, The highest rate reached by a specific communication bus is determined by bus load and bus driving ability.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
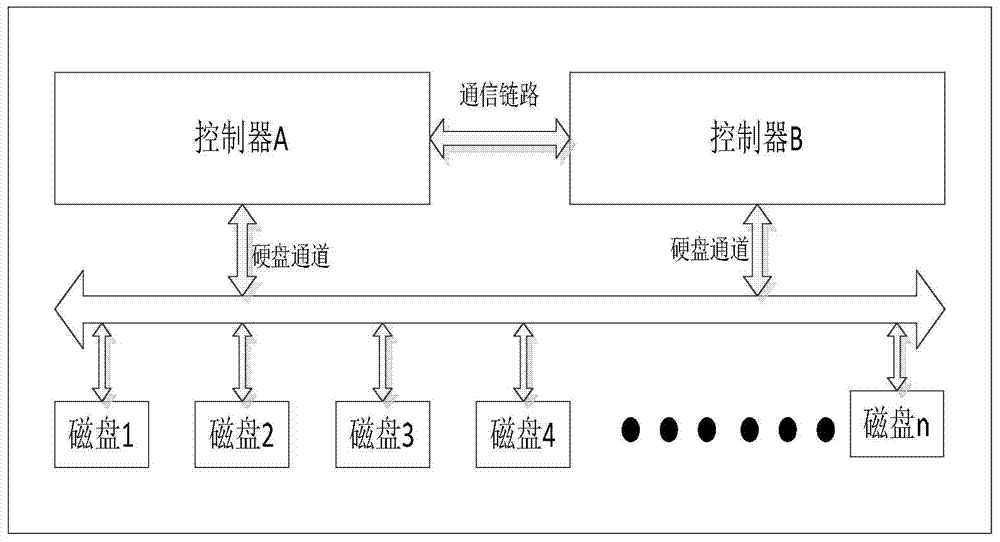
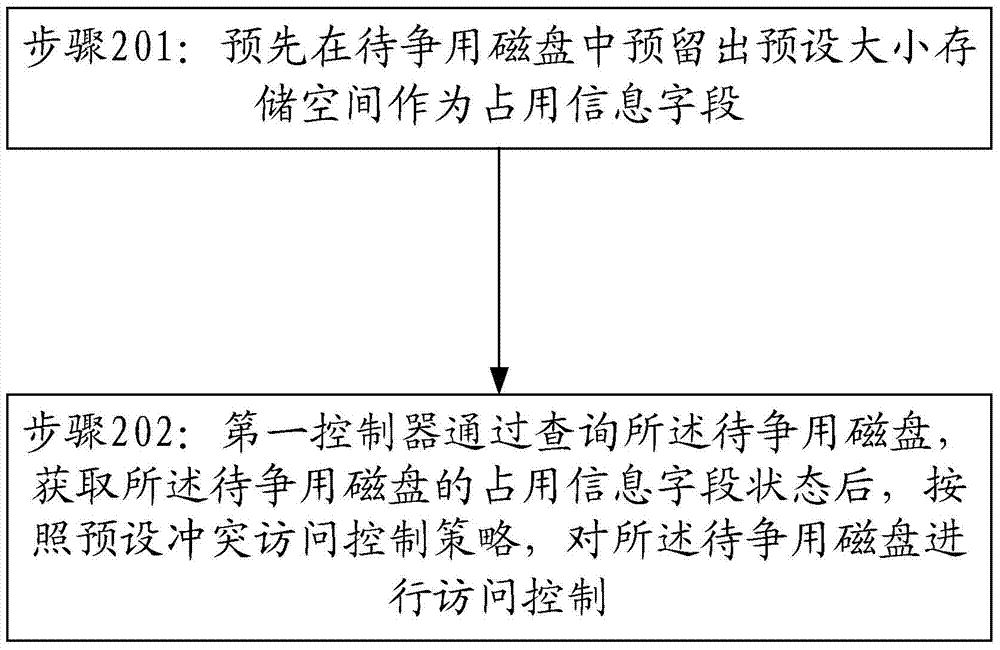
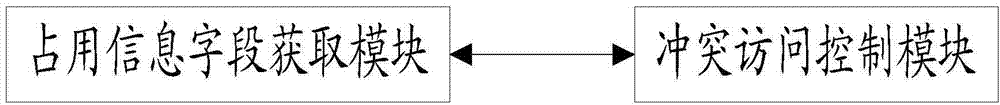
Contention arbitrating method and system for shared disk of double-control storage array
ActiveCN104503709AAvoid using conflictsAvoid split brainInput/output to record carriersTelecommunications linkCommunication link
The invention provides a contention arbitrating method and system for a shared disk of double-control storage array. The method comprises the following steps: reserving the storage space with preset size as the occupation information field in the to-be-contended disk; through inquiring the to-be-contended disk, after obtaining the occupation information field status of the to-be-contended disk, according to the preset conflict access control policy, and performing the access control to the to-be-contended disk by a first controller. The disk is used as the arbitrating medium for disk contention in the double-control storage array system, so the method is capable of effectively avoiding the brain-split caused by the communication link failure of the double-control storage array system, and preventing the use conflict of two controllers about the shared disk.
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
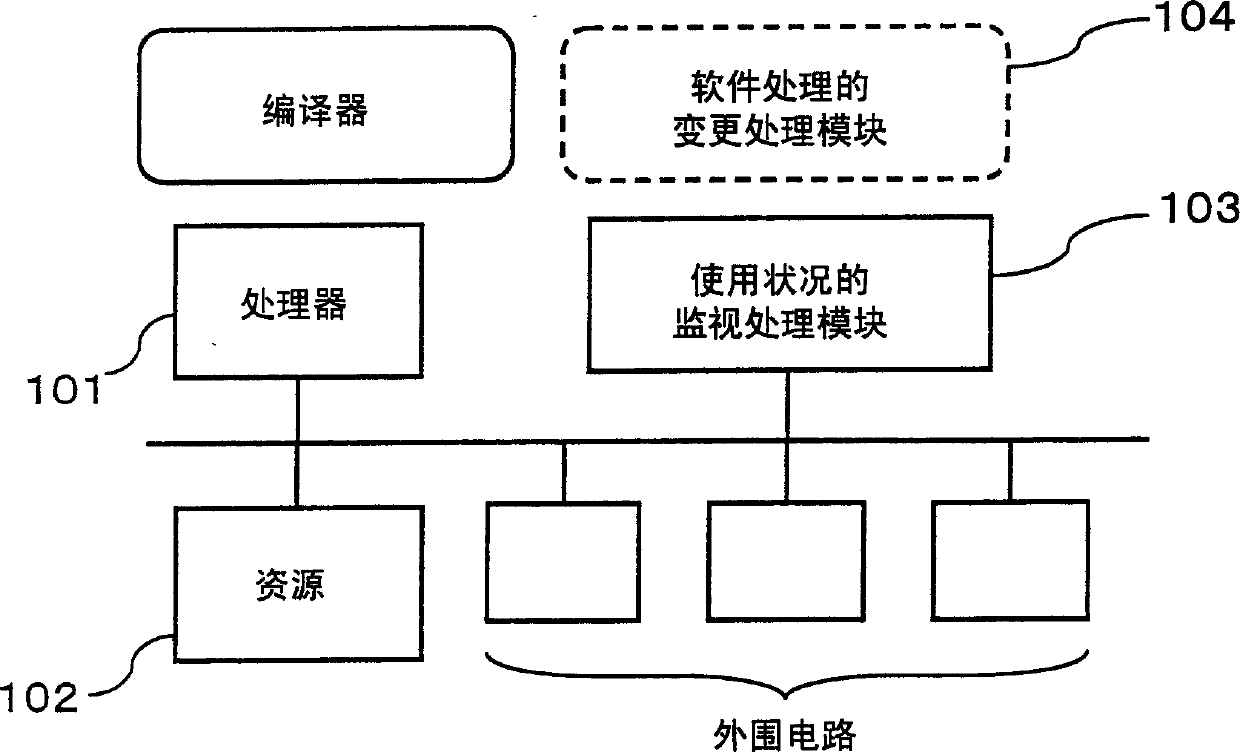
Software processing method and software processing system
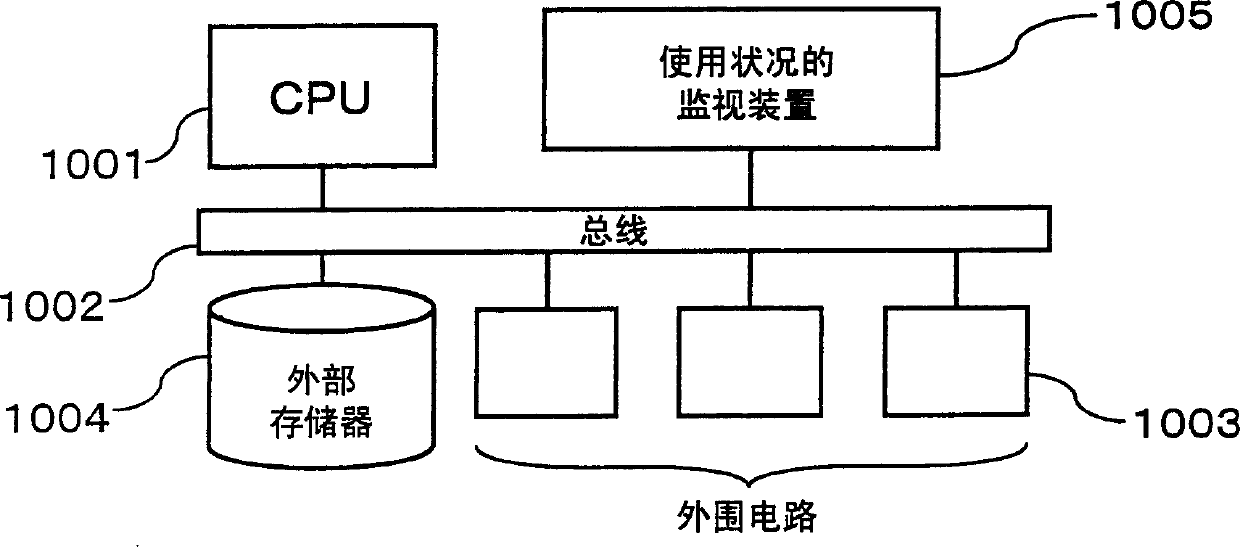
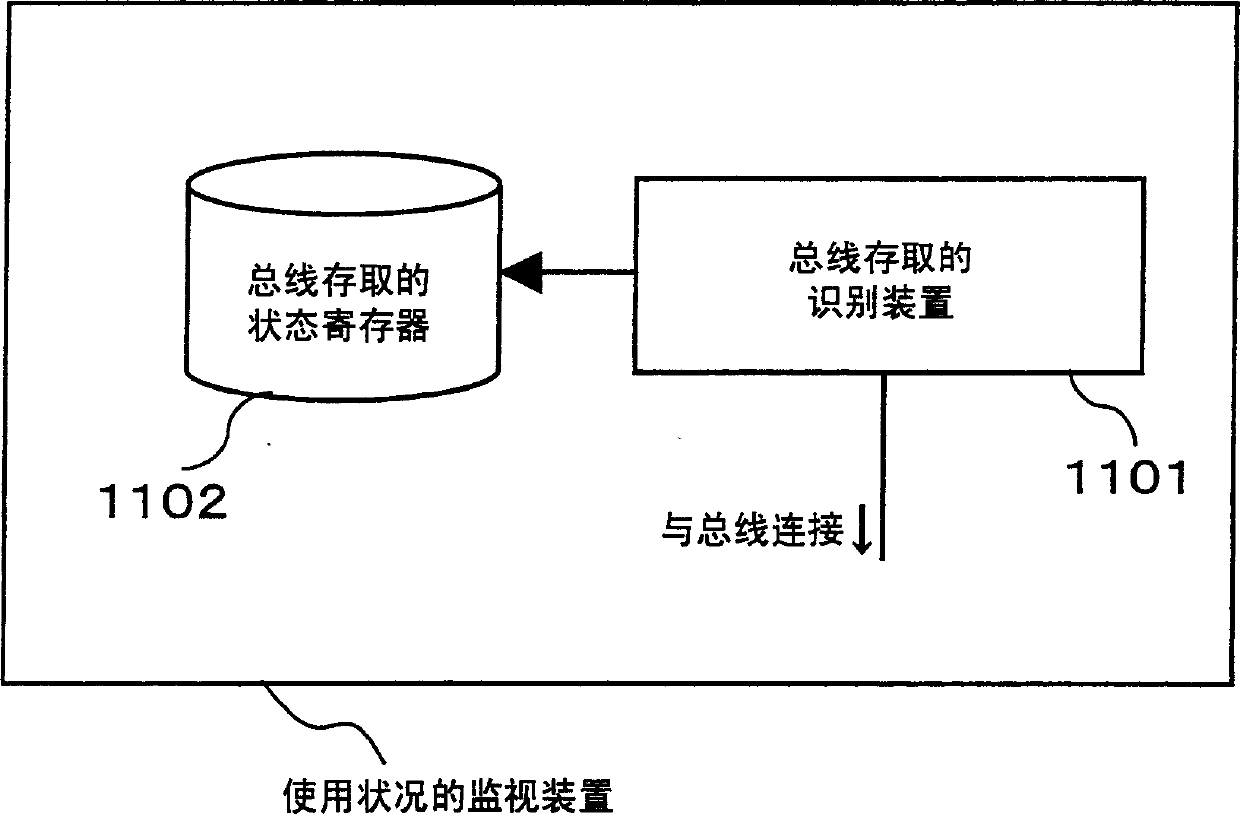
ActiveCN1506827ASuppress processing speed dropAvoid stopProgram synchronisationDigital computer detailsExternal storageMulti processor
In a multi-processor system constituted by a processor such as a CPU and a DSP, in which the processor and the DSP have an external memory and a bus as shared resources and the DSP carries out a process in response to a processing request from the processor, a monitoring step for status of use includes a step of monitoring the status of use of the DSP, and when contention information obtained in the monitoring step for the status of use indicates frequent uses, an altering step for software process appropriately alters a software processing method to be executed, and switches the corresponding process to an equivalent process so that it becomes possible to avoid bus contention, and consequently to prevent a reduction in the processing speed.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
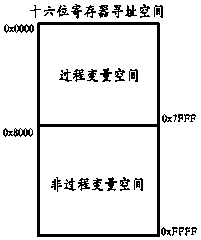
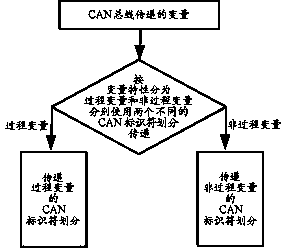
Application layer allocation method through utilization of two CAN (Controller Area Network) identifier divisions
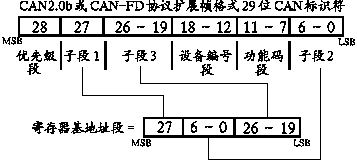
ActiveCN108810102AIncrease the lengthTotal factory controlBus networksArea networkProcessor register
The invention discloses an application layer allocation method through utilization of two CAN (Controller Area Network) identifier divisions. According to an application layer, two different CAN identifier divisions are used for transferring process variables and non-process variables. Different bus competition ways are provided for the variables. According to the CAN identifier division for transferring the process variables, in a mode of extracting a plurality of bit segments in CAN identifiers and rearranging, splicing and combining the bit segments, a register base address segment for transferring the process variables in the application layer is formed, so the contradiction between variable segmented management and bus competition allocation imbalance is solved well. According to theapplication layer, division allocation and meaning allocation of the CAN identifiers have clear application protocol instruction meanings. A designed application layer protocol has good direct readingperformance and openness, is easy to analyze and is convenient for a user to establish application layer sub-protocols applicable to employing environments in a framework, and seamless compatibilitycan be carried out on a CAN-FD (CAN with Flexible Data rate) protocol.
Owner:邓晓燕
Method, device and system for automatically releasing dead lock of a hot-plug I2C bus
InactiveCN103856381AGuaranteed Competitive ArbitrationAddress competitionBus networksControl flowBus interface
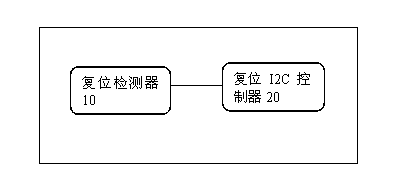
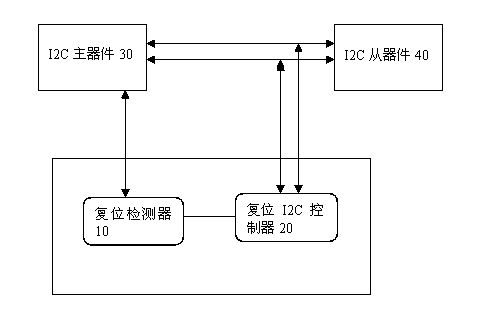
This invention discloses a method, a device and a system for automatically releasing dead lock of a hot-plug I2C bus. The device comprises a reset detector and a reset I2C controller. The reset detector is connected to an I2C master device for detecting the busy state of the I2C bus, and the reset I2C controller is effectively connected to the I2C bus for resetting the I2C bus. The bus contention arbitration is guaranteed through using a hardware I2C bus interface to connect the I2C master device and an I2C slave device on hardware, and the bus contention is solved. A flow of resetting the I2C bus is added in the software control flow, and once the dead lock of the I2C bus is detected, the I2C controller is reset, the I2C bus is activated, SDA and SCL signals are restored and the I2C bus can exit the dead lock state. This invention can effectively solve the problem of the dead lock of the I2C local bus under the hot-plug mechanism.
Owner:SUZHOU IND PRAK NEW HONGBO COMM TECH
Integrated circuit having programmable address in integrated circuit environment
InactiveCN1461440AEliminate contentionElectric digital data processingDesign phaseIntegrated circuit
An apparatus, system and method provides for the modification or programmability of an address of an I<2>C device. The modification or programming may be accompmlished via an input signal received by an I / O terminal of the device. In another form, the present invention also provides for substantially simultaneous modification of first and second addresses of respective first and second I<2>C devices. The modification or programming may be accomplished via an input signal received by an I / O terminal coupled to both the first and second I<2>C devices. The present invention obviates bus contention problems in an I2C bus / protocol system due to IC address conflict through the ability to modify (change) or program the I<2>C address. Modification or programming can be accommplished during the design phase or thereafter via software.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Portable site bus-type voting system
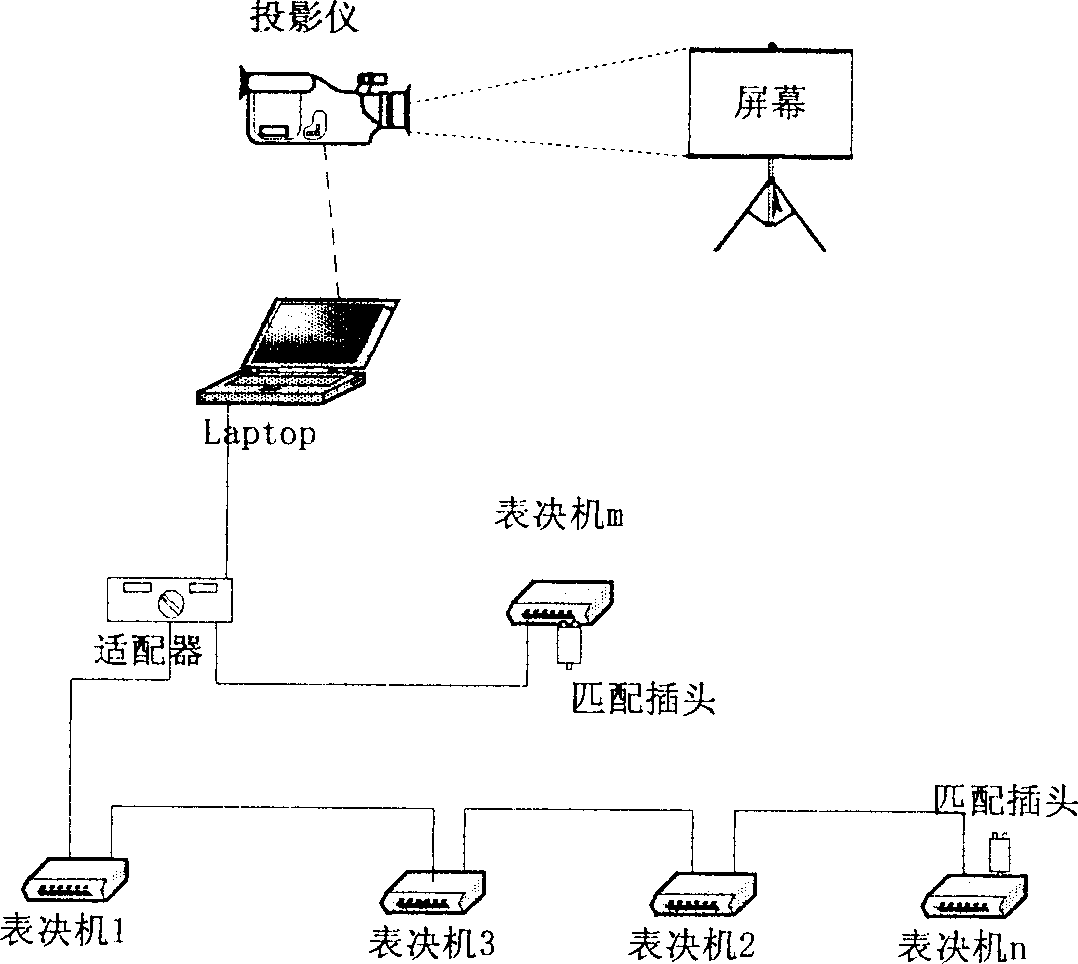
InactiveCN1403931AMaintain authorityConvenient mobile reviewElectric digital data processingAnti jammingUSB
The portable field bus-type voting system consists of special software and hardware. The hardware includes computer, projector, communication adaptor and several voting machines, the computer transfers the display information to the projector and performs bi-directional communication with the voting matchines via the adaptor. The present invention features the bi-directional communication between the adaptor and the voting machines via CAN field bus; and the cascade of the voting machine via two USB interfaces and the USB interface of the communication adaptor. The portable structure is favorable to mobile use; and the industrial CAN field bus structure makes the system fast, reliable anti-jamming, and has many other advantages.
Owner:武汉市工程科学技术研究院自动化研究所
Bus arbitration system and method based on single bus communication protocol
ActiveCN108287800AElectric digital data processingBus networksTime segmentNetwork Communication Protocols
The invention provides a bus arbitration system and method based on a single bus communication protocol. The system is used in a single bus network and comprises multiple hosts which are used for conducting transmission control on the bus of the single bus network; arbitration is conducted among the hosts according to a time-segment bit arbitration mechanism, distributed arbitration is conducted on an arbitration domain of a transaction sequence by analyzing the transaction sequence of the bus and adopting bus idle determination, and limited competition is conducted by using bus competition instructions. According to the method, a slave machine can directly access into the single bus system constructed according to the method without needing to perform any revision, the control of the constructed bus is only determined by an initialized sequence and command words, ROM codes and data transmitted and received by main equipment, and no central host exists, so that the bus does not have any predetermined priority. Under special situations, if an iButton needs to be supported, a designated host can be designated when the bus system is constructed.
Owner:BEIJING 7Q TECH
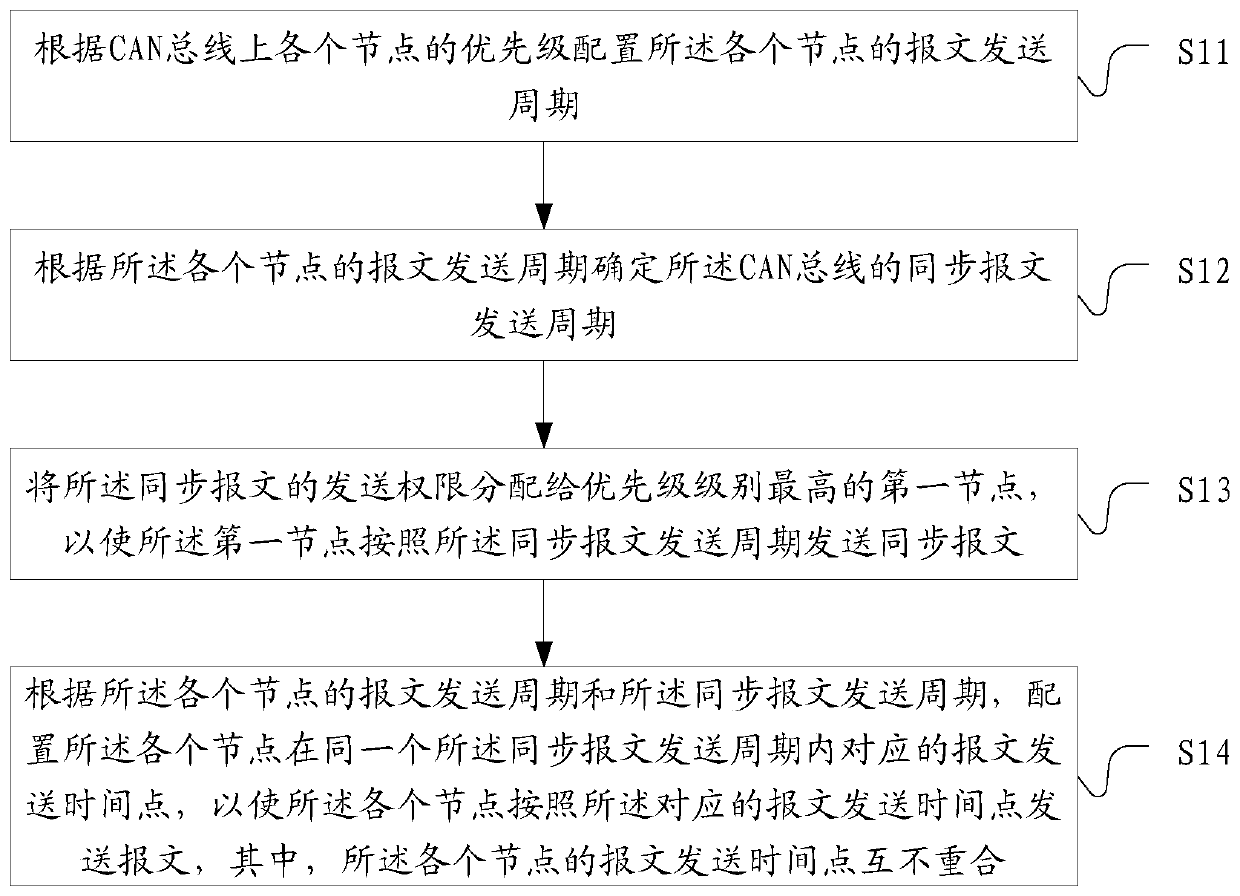
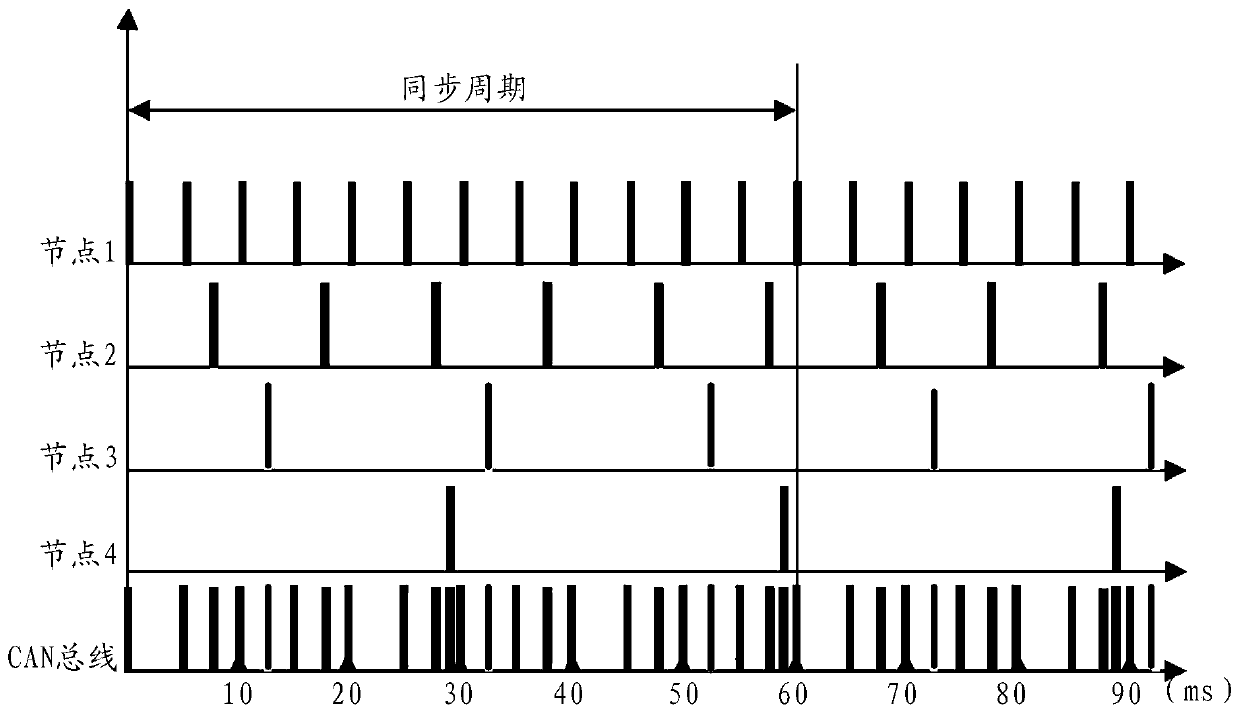
CAN message sending method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment
PendingCN111106987AImprove data transfer efficiencyResolve delayTime-division multiplexBus networksTelecommunicationsBus
The invention provides a CAN message sending method and device, a storage medium and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: configuring a message sending period of each node according to the priority of each node on a CAN bus; determining a synchronous message sending period of the CAN bus according to the message sending period of each node; allocating a sending permission of the synchronization message to a first node with the highest priority level, so that the first node sends the synchronization message according to the synchronization message sending period; andaccording to the message sending period of each node and the synchronous message sending period, sending the synchronization message, and configuring a corresponding message sending time point of eachnode in the same synchronization message sending period, so that each node sends a message according to the corresponding message sending time point, and the message sending time points of the nodesdo not coincide with each other. According to the invention, CAN network bus competition can be avoided, the problem of CAN message delay is solved, and the CAN bus transmission efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI GUANGTONG AUTOMOBILE +1
Communication method based on intelligent switch
InactiveCN104065544AAchieve mutual communicationImprove communication efficiencyBus networksStructure of Management InformationComputer module
The invention provides a communication method based on an intelligent switch. The communication method is realized based on a network provided with a plurality of switch panels. The communication method is characterized in that the switch panels are provided with at least one group of buttons, each group of buttons is used to independently control different states of a same material object, each switch panel can be provided with any number of scene buttons, each scene button is used to customize a scene mode, the switch panels are controlled mutually through the communication method; and the communication method comprises a physical network topological structure module, a bus contention processing module and a node data processing module. According to the invention, the mutual communication between intelligent switch nodes can be realized, and at the same time, reverse recording is adopted by the method of the invention, the nodes are processed in a distributed manner and received, stored and controlled independently, so the communication efficiency, performance and flexibility of the intelligent switch can be greatly improved.
Owner:FUJIANG GAKATO INTERNET OF THINGS TECH
Method for determining wireless sending state, device and wireless access point
ActiveCN102523079AReduce processingReduced throughput performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelTime delaysControllability
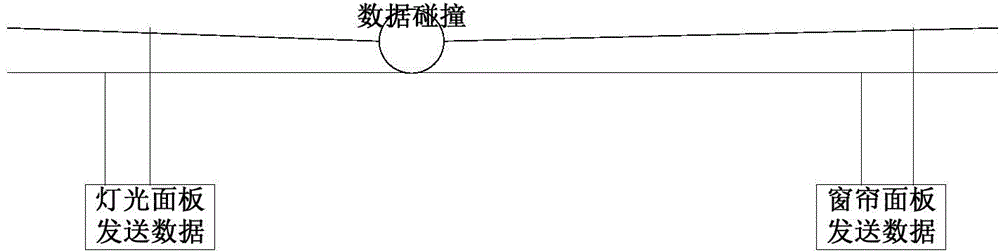
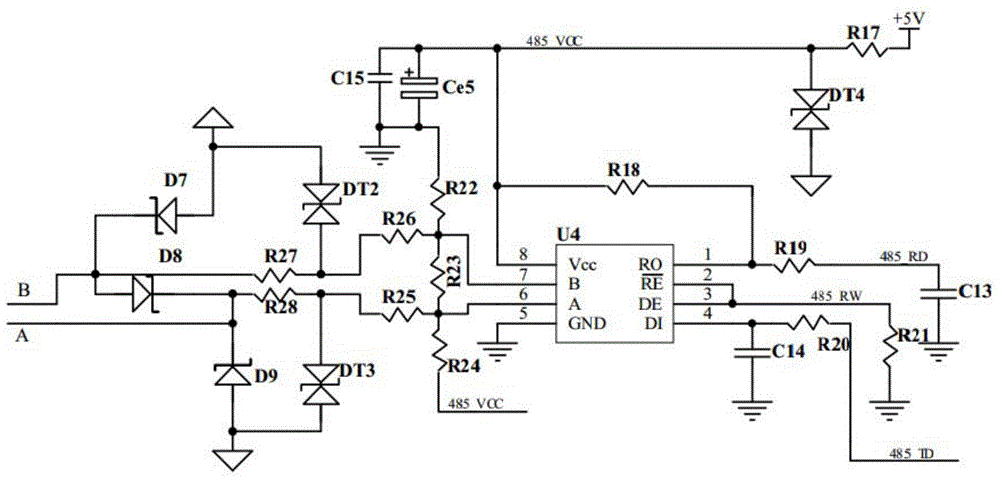
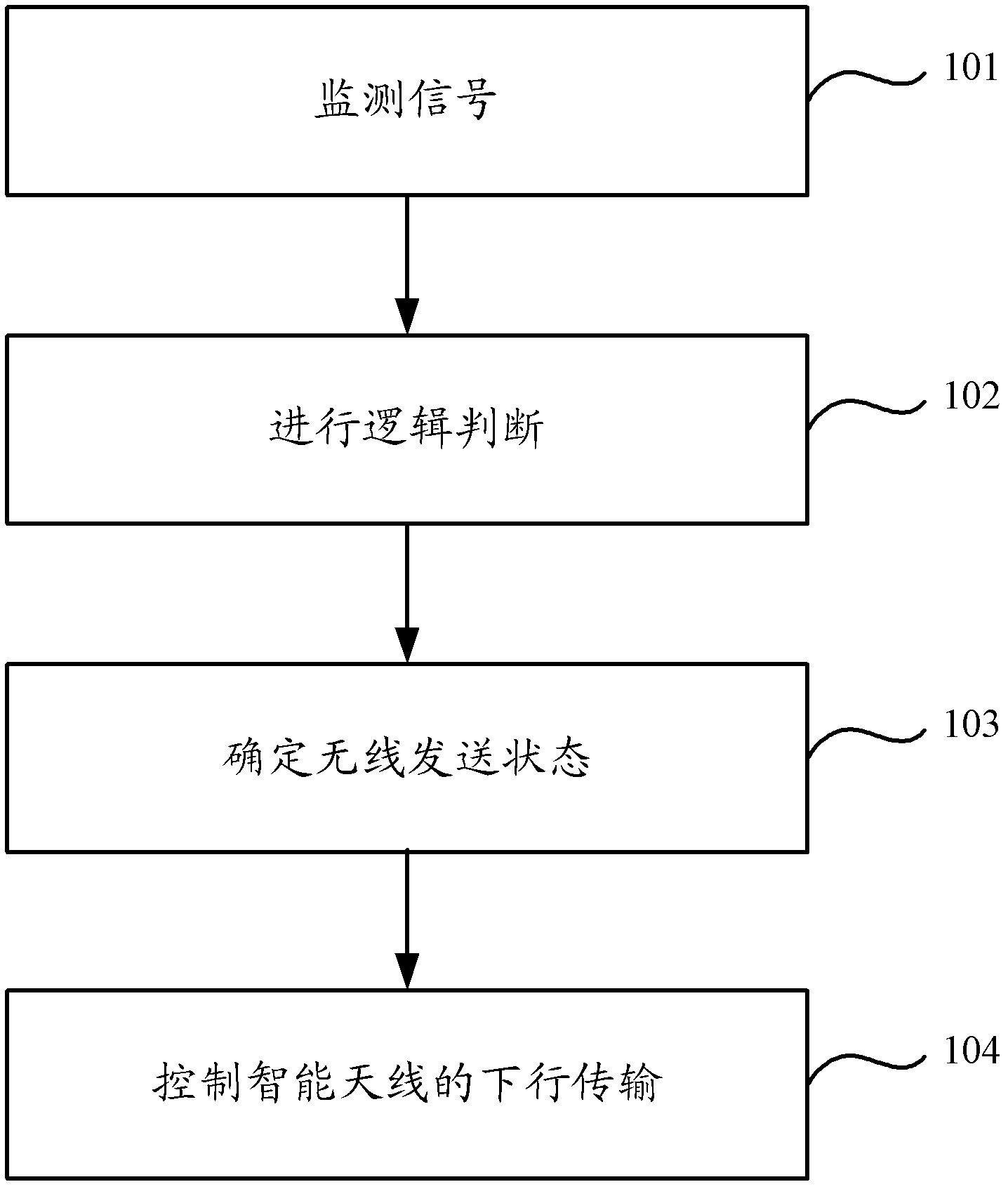
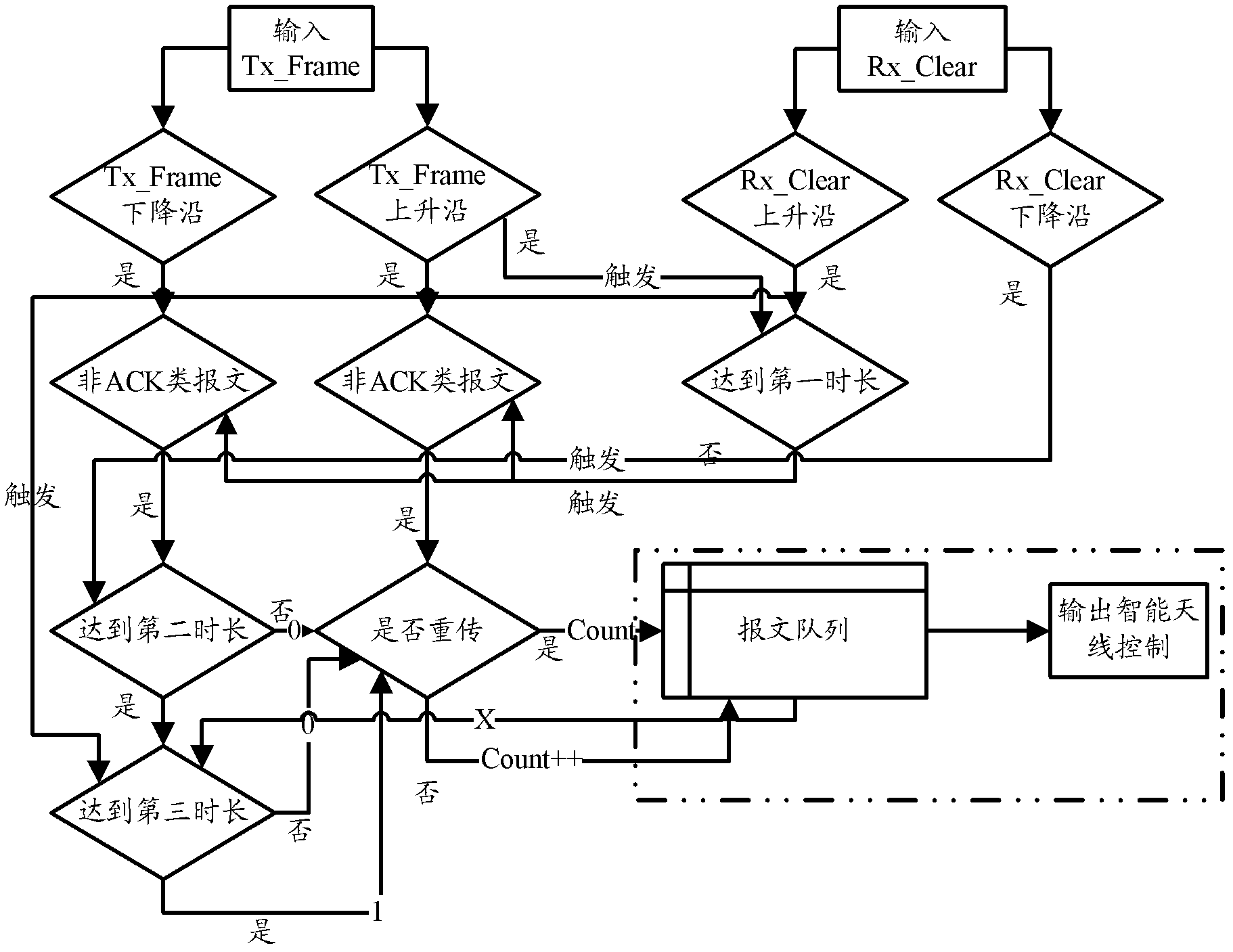
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for determining a wireless sending state, a device and a wireless access point; the method comprises the following steps that: logic judgment is carried out according to an Rx_clear signal and a Tx_frame signal provided by a wireless chip, so that the wireless sending state of the wireless chip is determined according to a logic judgment result, complicated chip research and development or signal sampling, reduction and encoding do not need to be carried out; consequently, high-difficulty data processing is prevented, calculation time delay is reduced, and compared with a method for forwarding a message to the wireless chip by rewriting a central processing unit (CPU), the throughput performance of a wireless network is prevented from being reduced, bus competition is prevented, and the controllability in determining the wireless sending state is ensured.
Owner:RUIJIE NETWORKS CO LTD
Bit-based serial transmission cloud storage method and device
InactiveCN102693096AEliminate bus contentionRemove loadInput/output to record carriersSerial transferData stream
The invention relates to the information storage technology, and specifically relates to a bit-based serial transmission cloud storage method and a device. The invention helps to solve problems of a conventional data storage medium array mode that bus competition of a plurality of memories cannot be fundamentally eliminated and that load imbalance is easily caused. The bit-based serial transmission cloud storage method is realized by the following steps: 1) parallel writing of data: with bit as a segmentation unit, transforming a received parallel data flow of K bits into K serial data flows of one bit; and 2) serial reading of data: assembling the K serial data flows of one bit that are read out into a parallel data flow of K bits. The device can be applied to data storage of a variety of storage medium arrays having ports that support serial access, and is especially applicable for mass data storage.
Owner:SHANXI DAXINHE TECH
Electronic device for contention detection of bidirectional bus and related method
An electronic device of detecting contention of a bidirectional bus for avoiding failing to drive a bidirectional bus due to bus contention includes: an output terminal, an input terminal and a data output unit, a timing comparing controller and a comparing unit. The output terminal is coupled to the bidirectional bus and used for outputting a data output signal to the bidirectional bus. The input terminal is coupled to the output terminal and the bidirectional bus and used for receiving a data reception signal from the bidirectional bus. The data output unit is used for providing the data output signal. The timing comparing controller is used for generating a timing comparison signal according to the data output signal. The comparing unit is used for comparing the data reception signal with the data output signal according to the timing comparison signal to determine a contention state of the bidirectional bus.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Microcomputer minimizing influence of bus contention
InactiveUS7177966B2Minimize impactFlexible changeArchitecture with single central processing unitMemory systemsMicrocomputerDigital data
An edge detecting circuit detects an input level change (edge) of a synchronous signal provided from a synchronous signal input terminal. A data latch unit latches digital data provided from an external data input terminal. An address generating circuit provides an address signal. A write control unit activates / deactivates a write enable signal for writing to a RAM. An arbitration circuit monitors a write control enable signal, a read enable signal and a write enable signal, and detects a cycle, in which a CPU does not access the RAM.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com