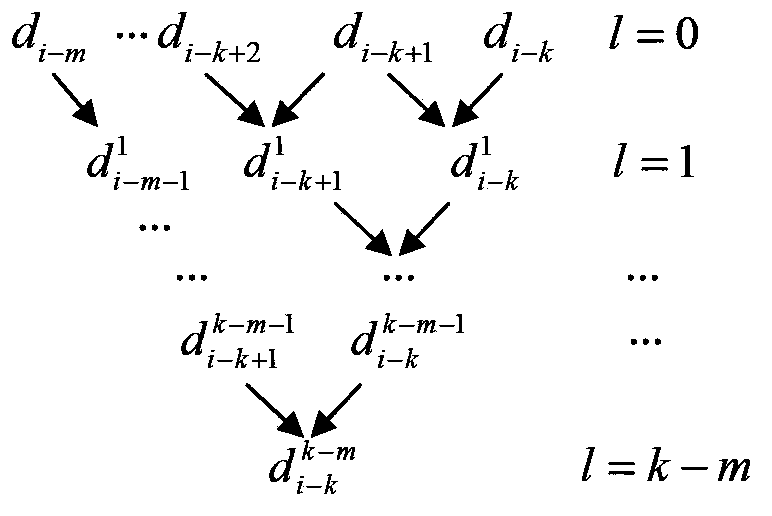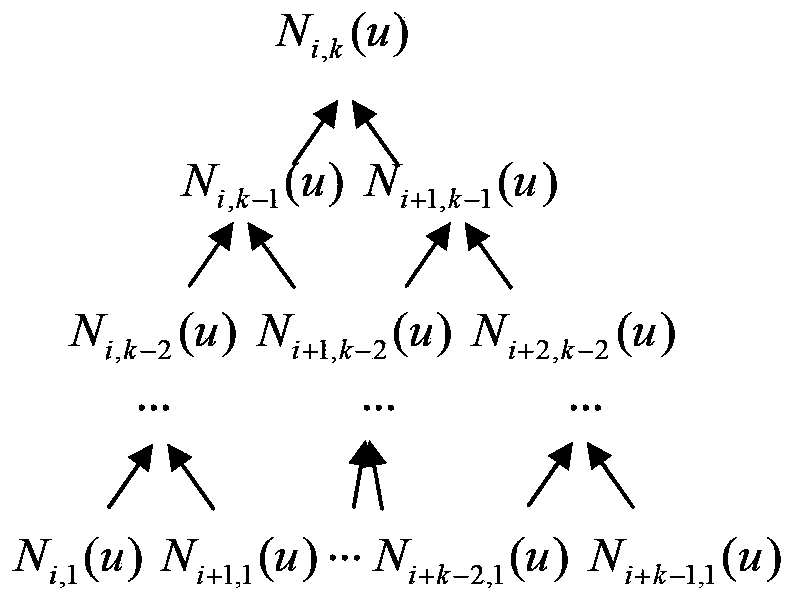Patents
Literature
69 results about "Computational complexity theory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
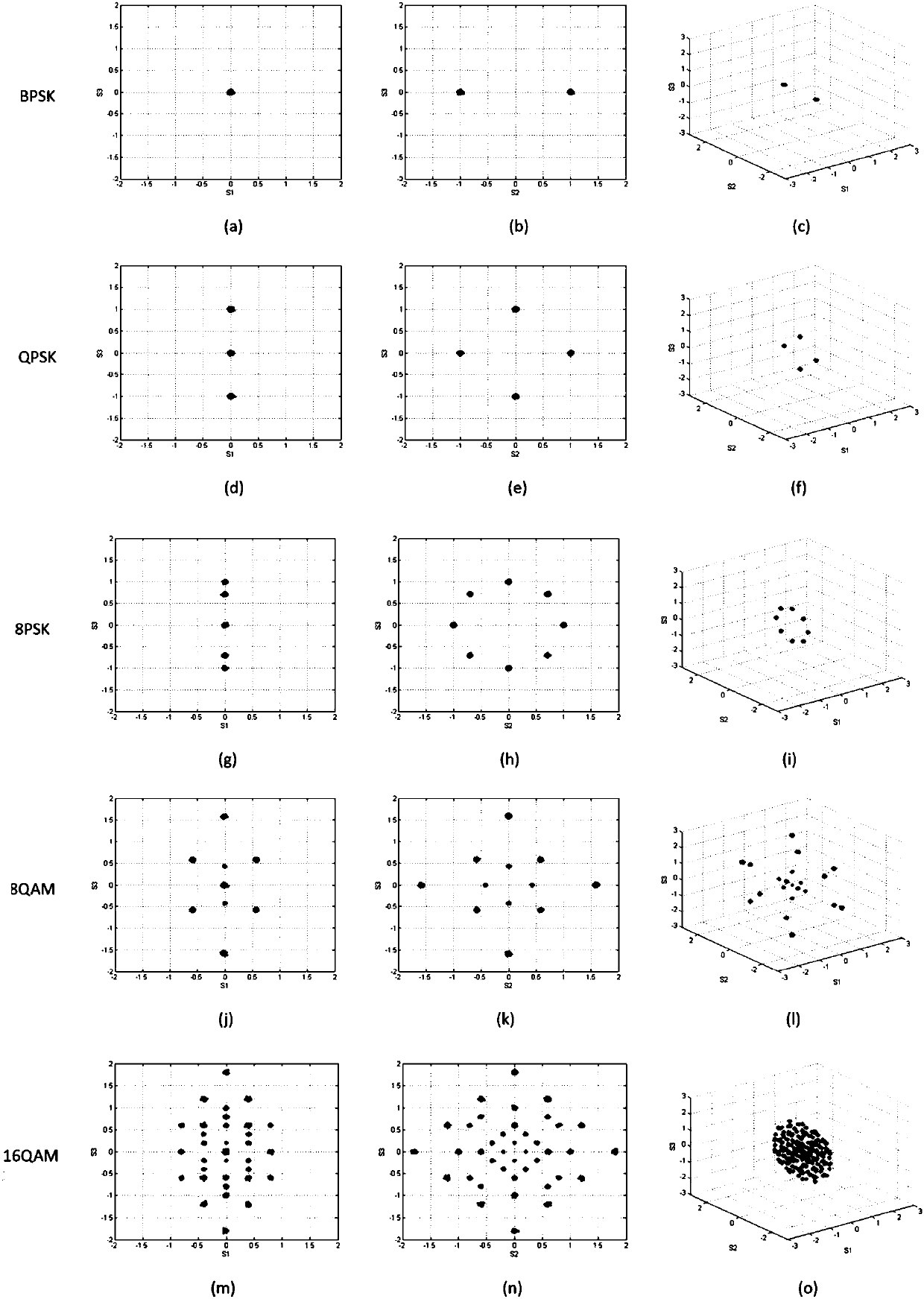
Computational complexity theory focuses on classifying computational problems according to their inherent difficulty, and relating these classes to each other. A computational problem is a task solved by a computer. A computation problem is solvable by mechanical application of mathematical steps, such as an algorithm.
Visual ranging-based simultaneous localization and map construction method
ActiveCN105469405AReduce computational complexityEliminate accumulationImage enhancementImage analysisSimultaneous localization and mappingComputation complexity
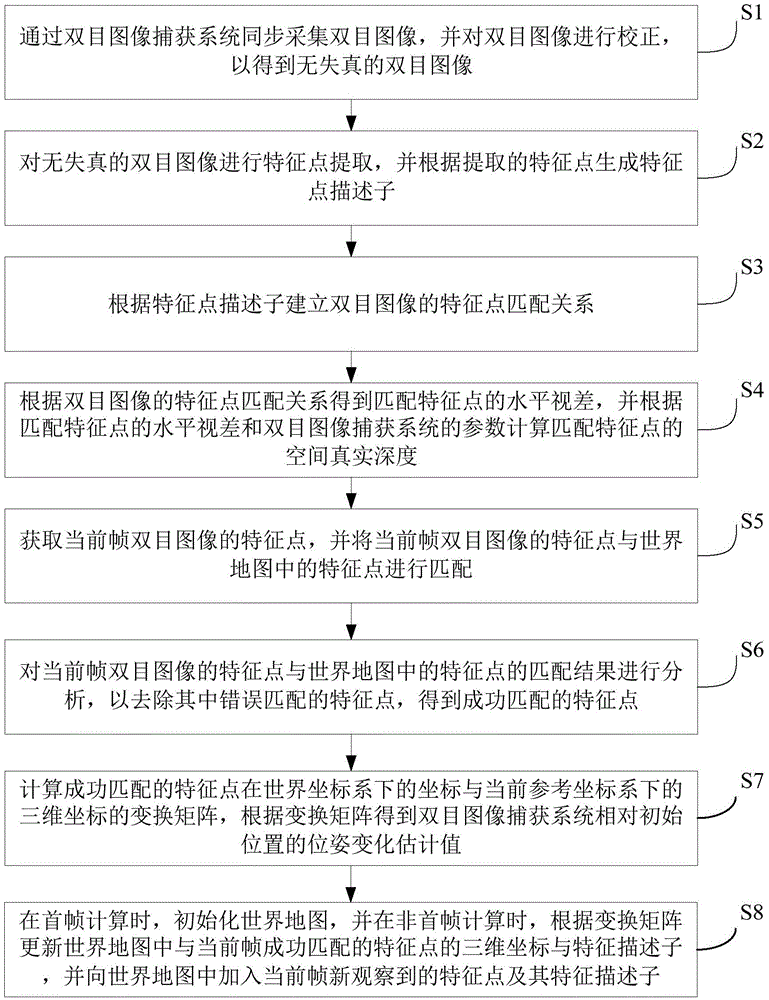
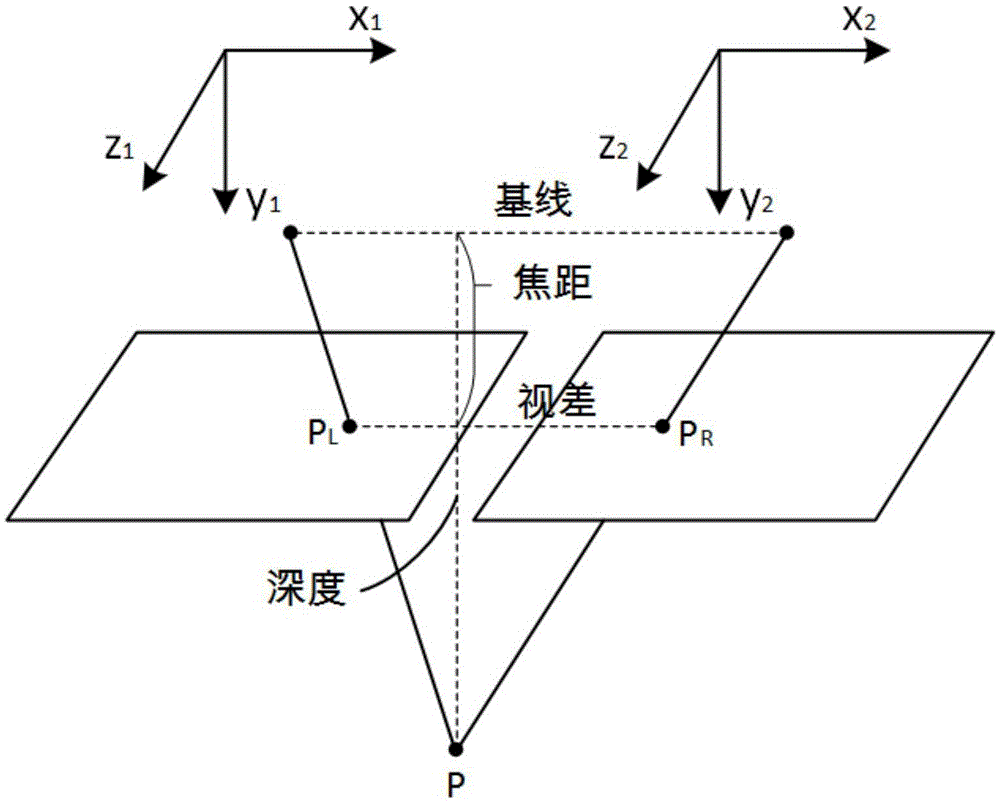
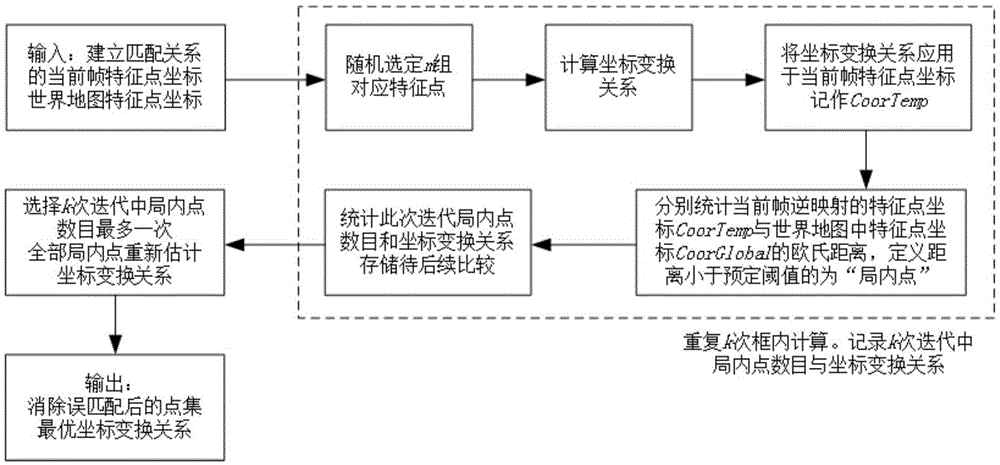
The invention provides a visual ranging-based simultaneous localization and map construction method. The method includes the following steps that: a binocular image is acquired and corrected, so that a distortion-free binocular image can be obtained; feature extraction is performed on the distortion-free binocular image, so that feature point descriptors can be generated; feature point matching relations of the binocular image are established; the horizontal parallax of matching feature points is obtained according to the matching relations, and based on the parameters of a binocular image capture system, real space depth is calculated; the matching results of the feature points of a current frame and feature points in a world map are calculated; feature points which are wrongly matched with each other are removed, so that feature points which are successfully matched with each other can be obtained; a transform matrix of the coordinates of the feature points which are successfully matched with each other under a world coordinate system and the three-dimension coordinates of the feature points which are successfully matched with each other under a current reference coordinate system is calculated, and a pose change estimated value of the binocular image capture system relative to an initial position is obtained according to the transform matrix; and the world map is established and updated. The visual ranging-based simultaneous localization and map construction method of the invention has low computational complexity, centimeter-level positioning accuracy and unbiased characteristics of position estimation.
Owner:北京超星未来科技有限公司
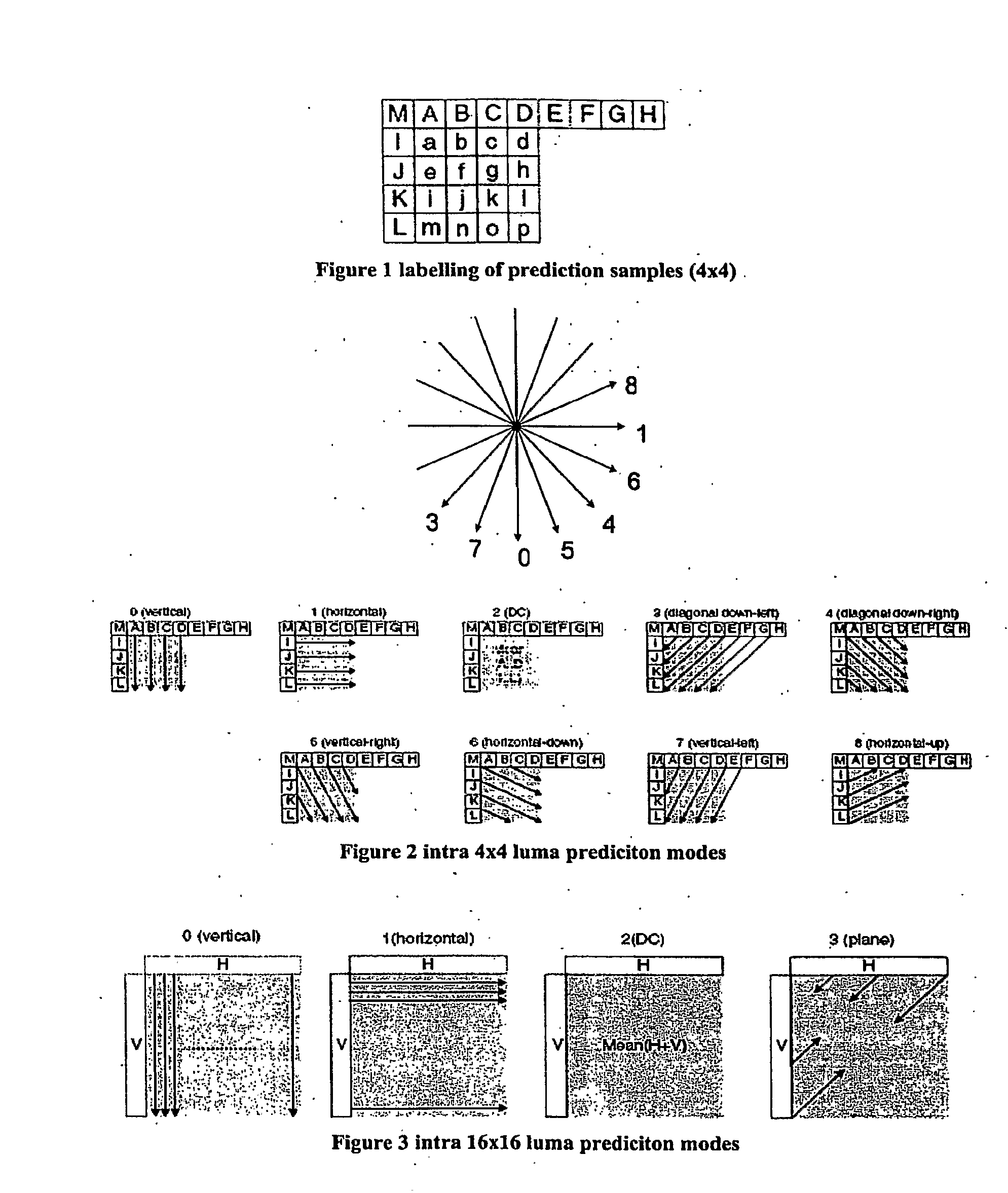
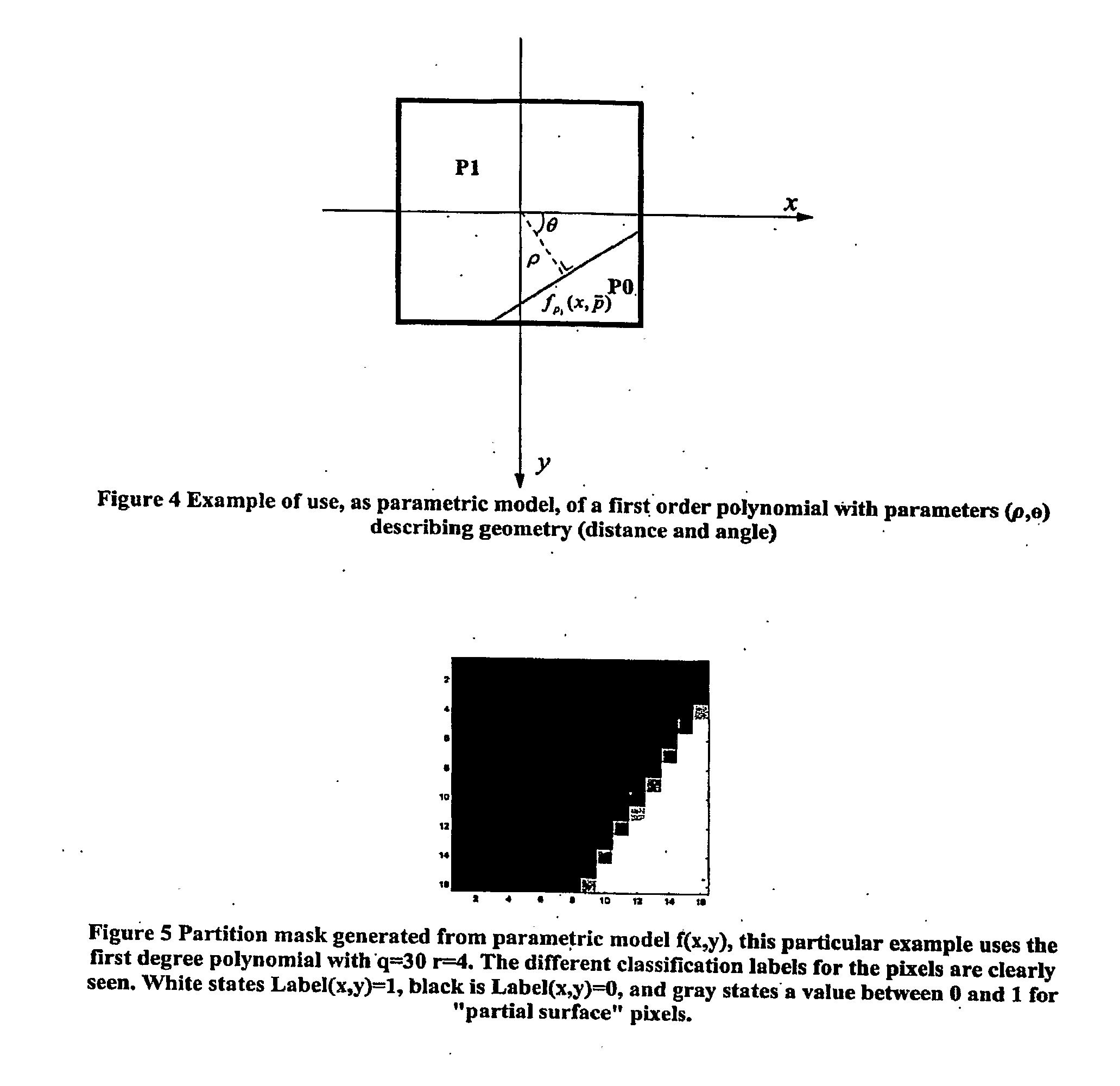
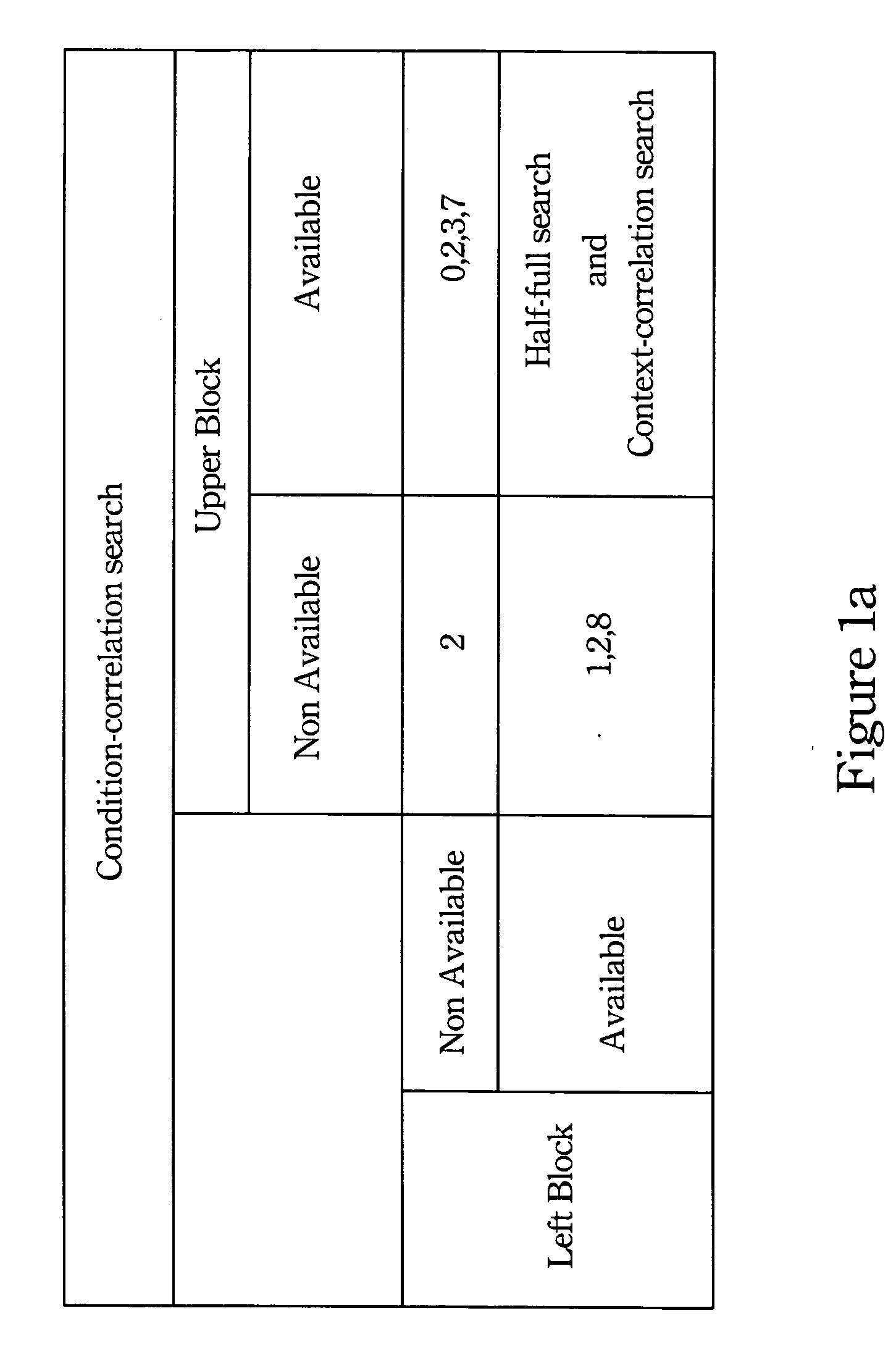
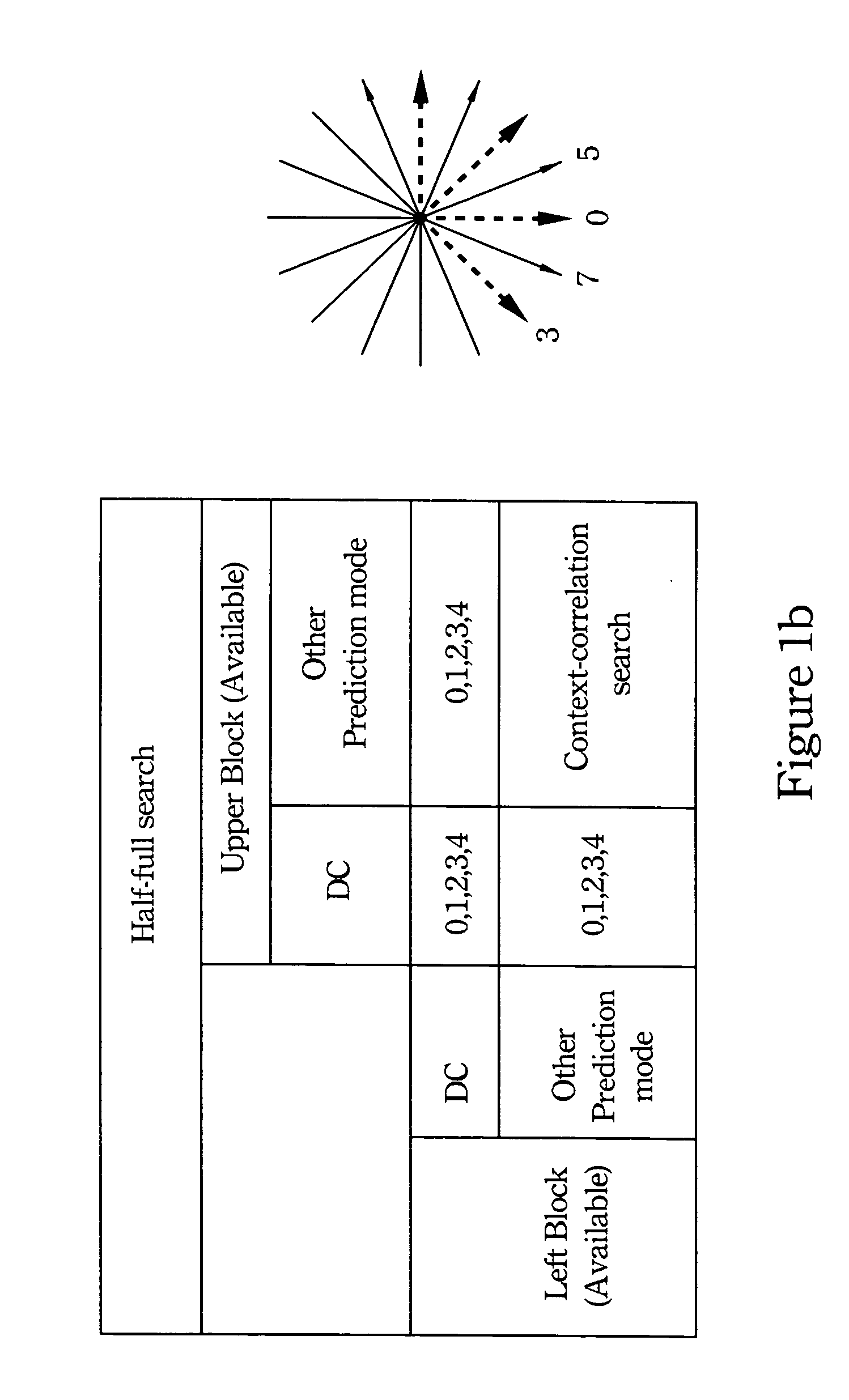
Geometric intra prediction
InactiveUS20090268810A1Efficient captureColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionComputation complexity
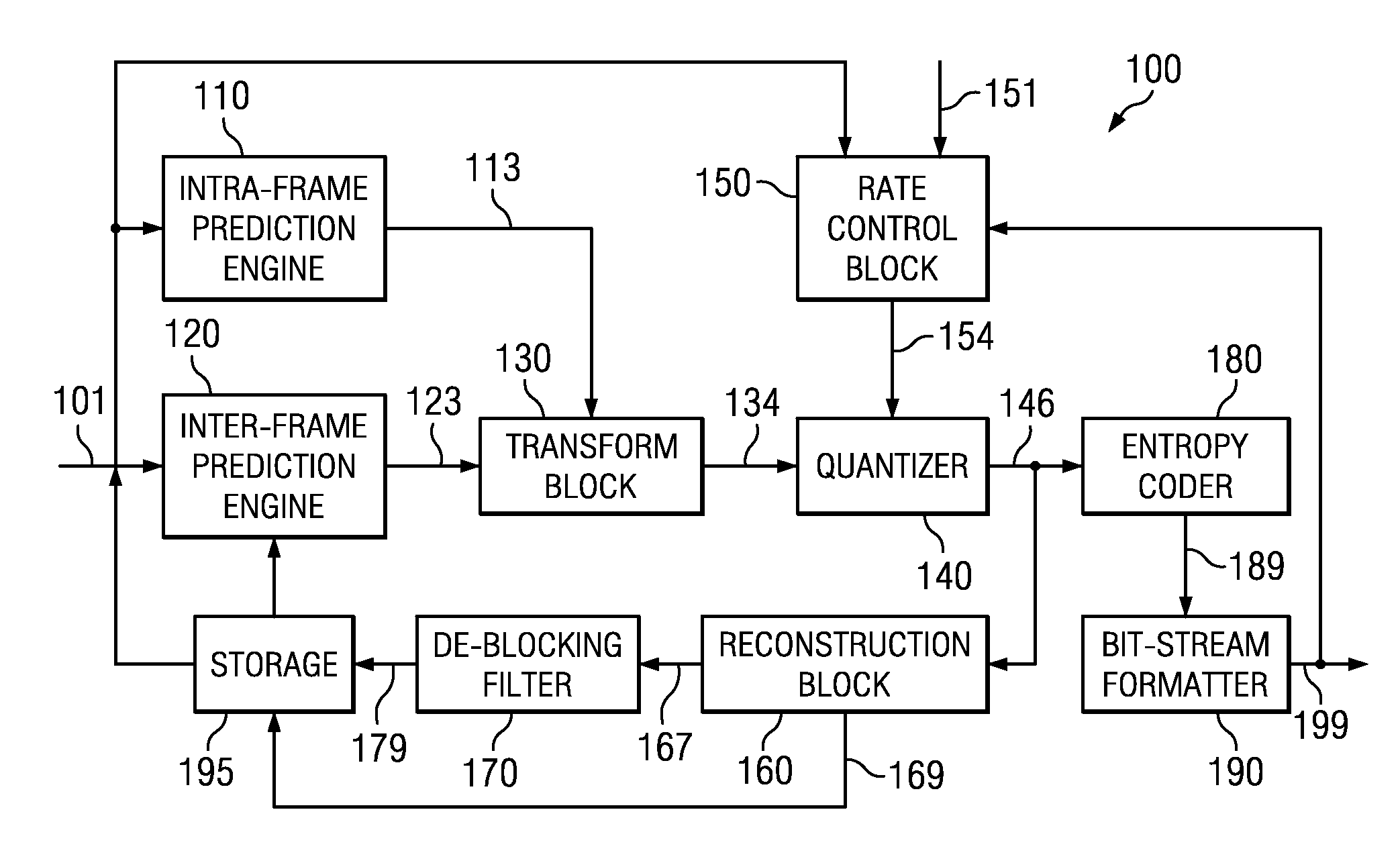
The use of parametric models to capture and represent local signal geometry allows a new geometric intra prediction scheme to better encode video images. The encoding scheme gives the video encoder the flexibility and scalability to match the video frame content with the desired computational complexity. It also allows the encoder to encode the images more efficiently using intra prediction because it reduces the artificial edges that occur during standard intra encoding.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Robust and efficient compression/decompression providing for adjustable division of computational complexity between encoding/compression and decoding/decompression
InactiveUS20070253479A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputation complexityHand held
Various embodiments of the present invention include compression / decompression methods, systems, and devices that adjust a division of a total computational complexity of compression and decompression between encoding and decoding. These embodiments include an encoder that encodes a received signal at a selectable level of computational complexity and a decoder that decodes a received, encoded signal at a selectable level computational complexity. Video-codec embodiments of the present invention may be incorporated into relatively inexpensive video-recording devices, including hand-held, video-recording consumer devices such as video recorders and cell phones.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
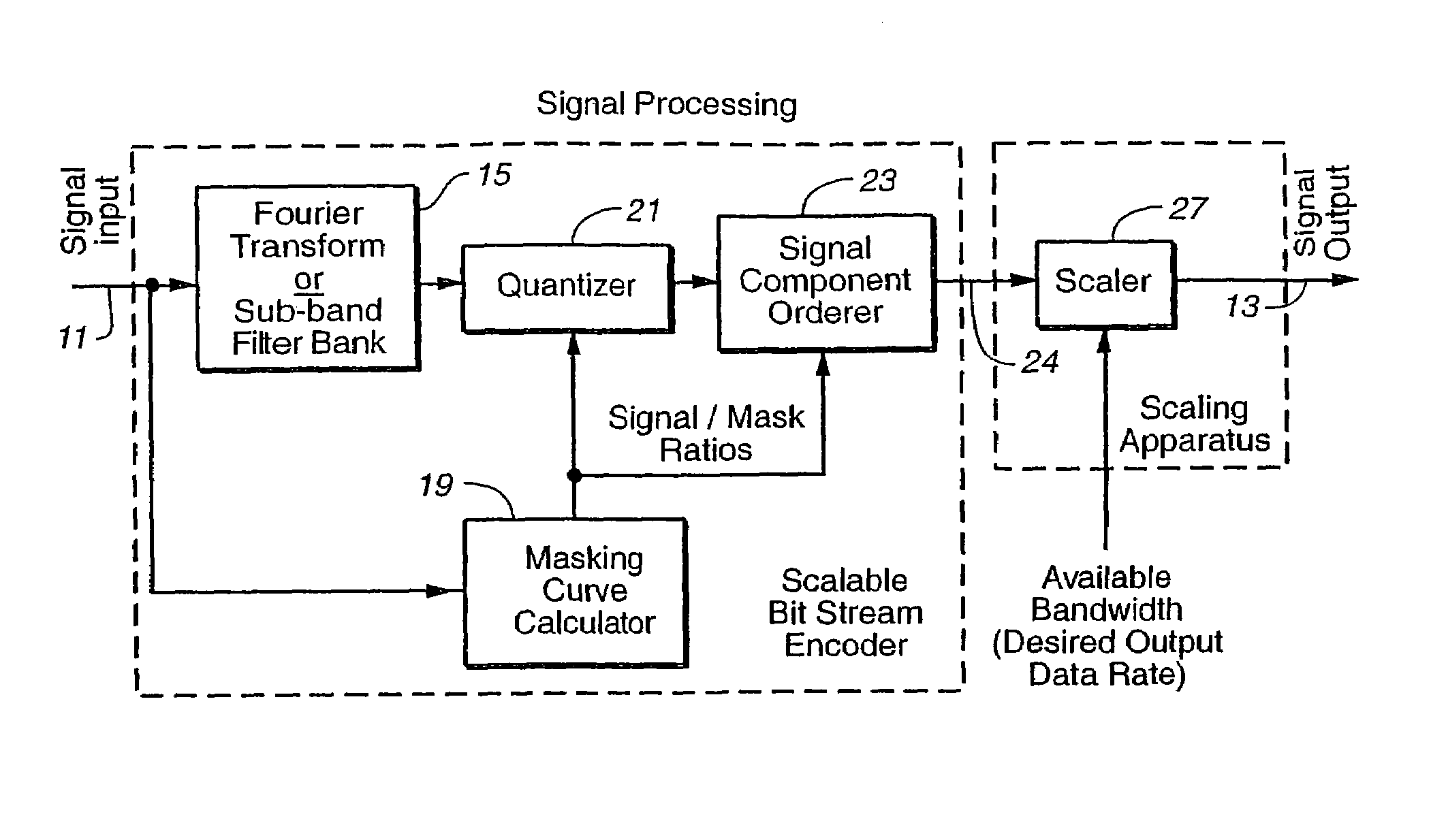
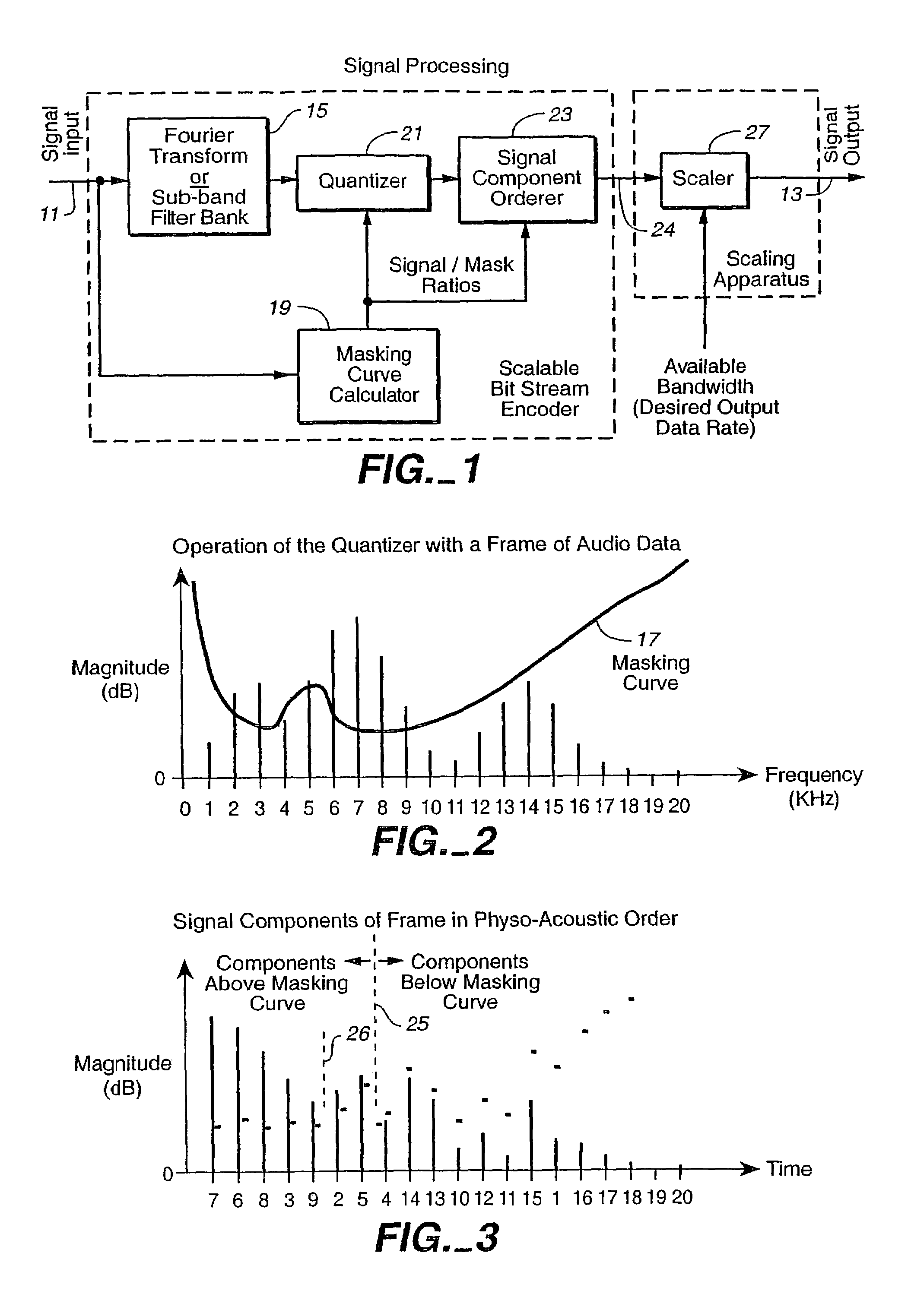
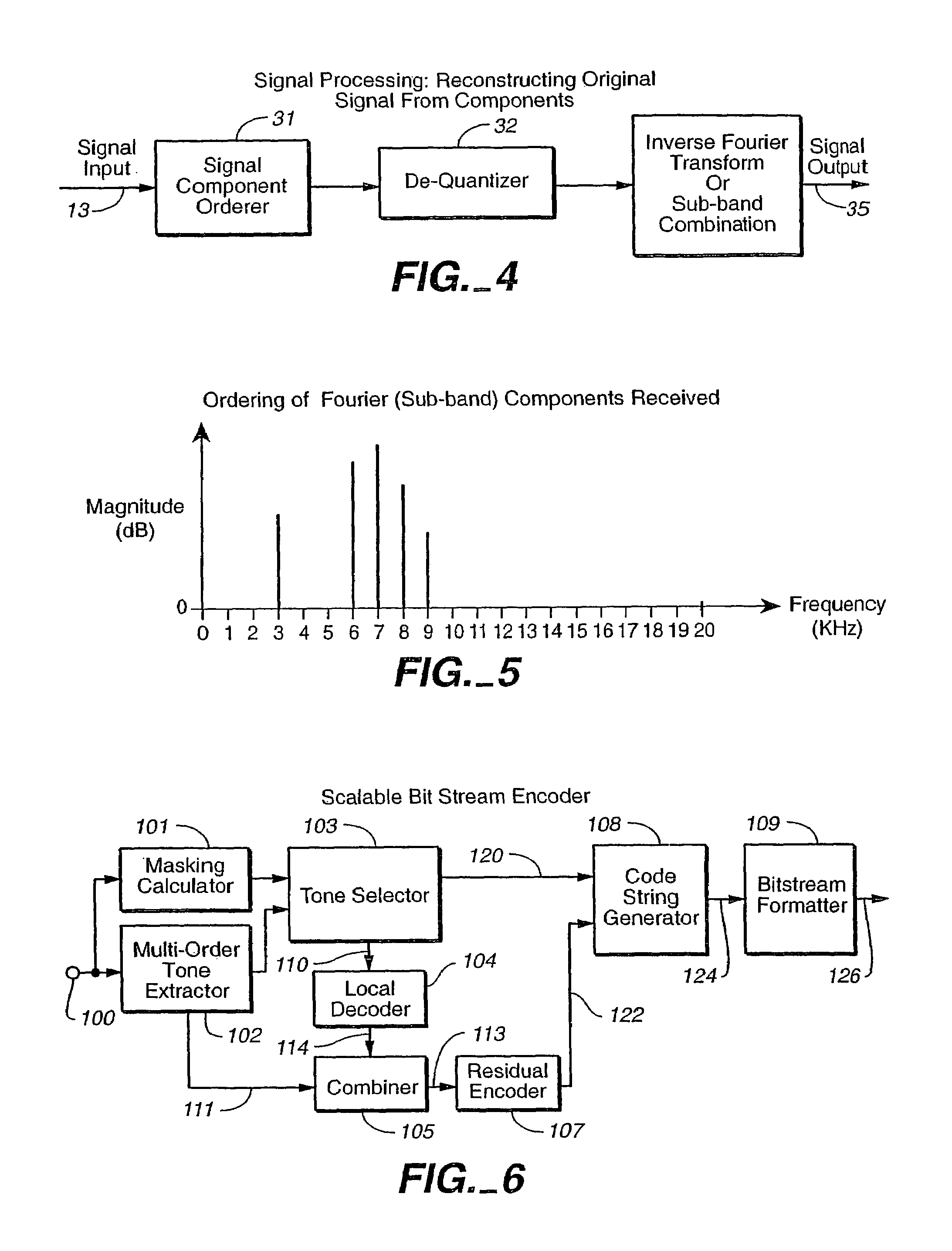
Modular scalable compressed audio data stream
InactiveUS7333929B1Reduce bitrateSmooth and fine resolution reduction of bit stream bit rateSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsComputation complexityData stream
Methods and apparatus are provided for the creation and utilization of unique compressed data stream compositions, structures and formats which allow for the alteration of the data stream's data rate without first decoding the data stream back to its uncompressed form and then re-encoding the resulting uncompressed data at a different data rate. Such methods and apparatus perform this data rate alteration, known as scaling, such that optimal quality is maintained at each scaled data rate, while performing said scaling with low computational complexity. In addition, the present invention provides for data rate alteration in small increments. A unique application for the disclosed bit rate scaling method and apparatus is also described.
Owner:DTS
Geometric intra prediction
InactiveCN101523917AEfficient captureAddressing Adaptive IssuesPulse modulation television signal transmissionImage codingPattern recognitionComputation complexity
The use of parametric models to capture and represent local signal geometry allows a new geometric intra prediction scheme to better encode video images. The encoding scheme gives the video encoder the flexibility and scalability to match the video frame content with the desired computational complexity. It also allows the encoder to encode the images more efficiently using intra prediction because it reduces the artificial edges that occur during standard intra encoding.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
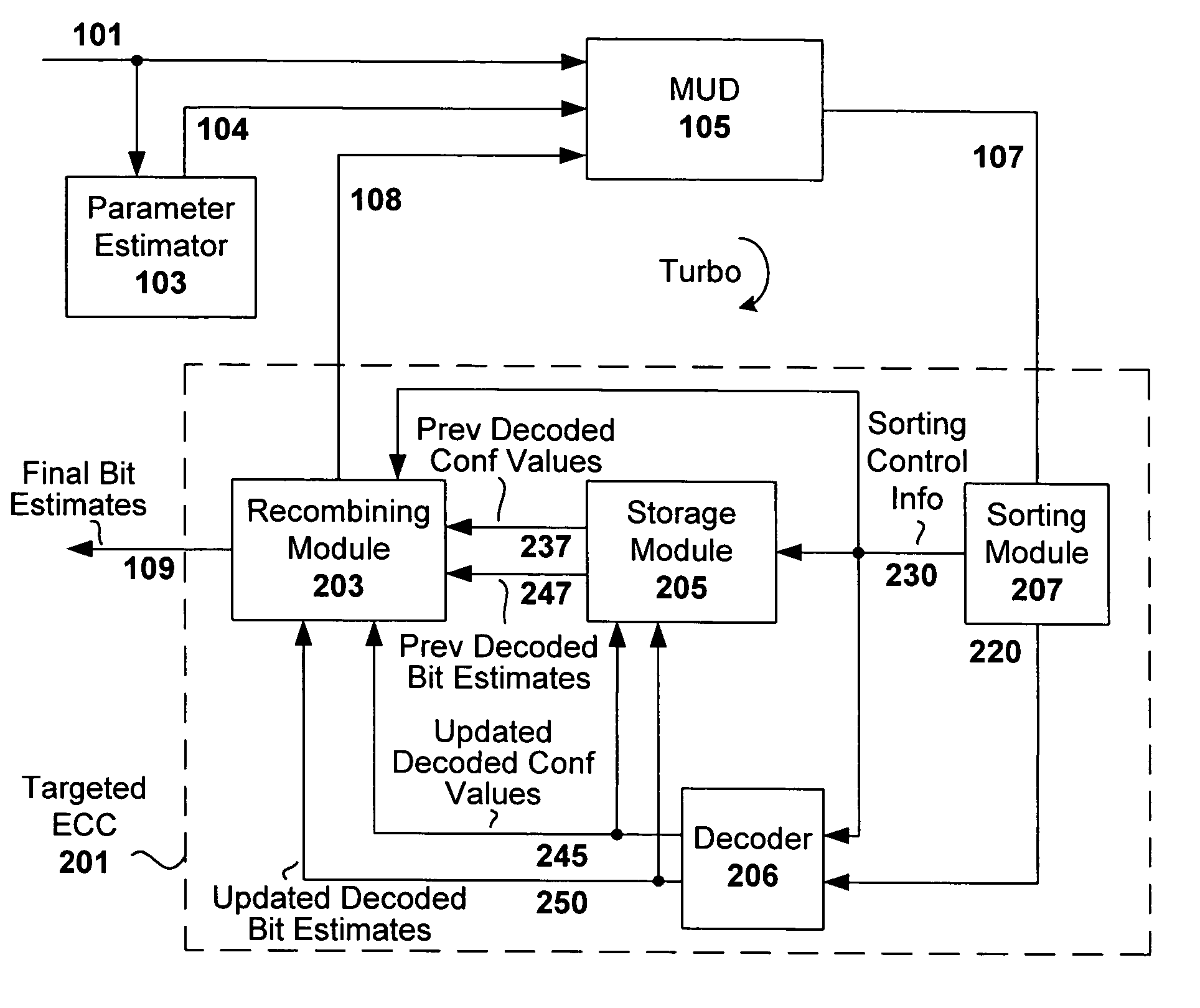
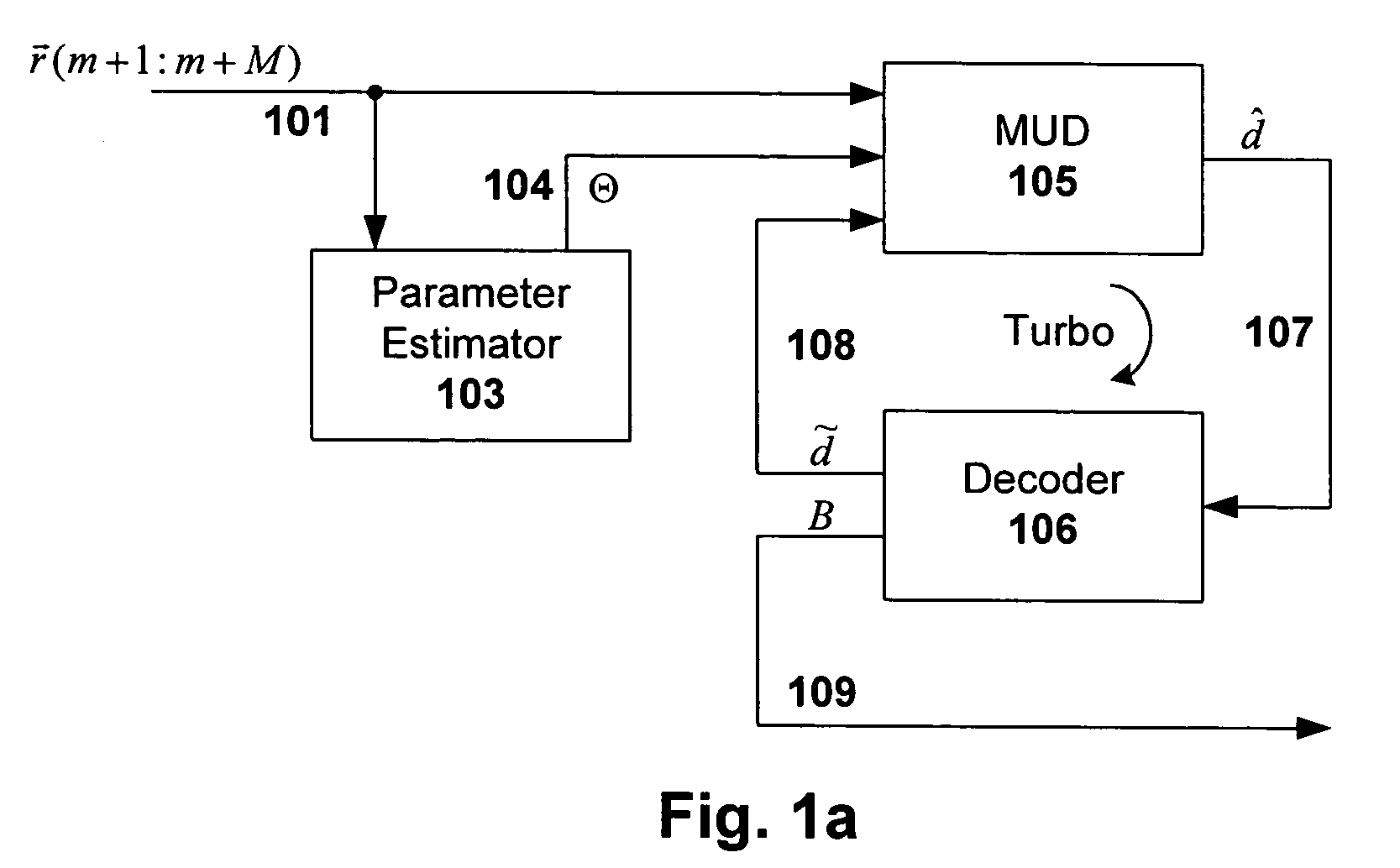
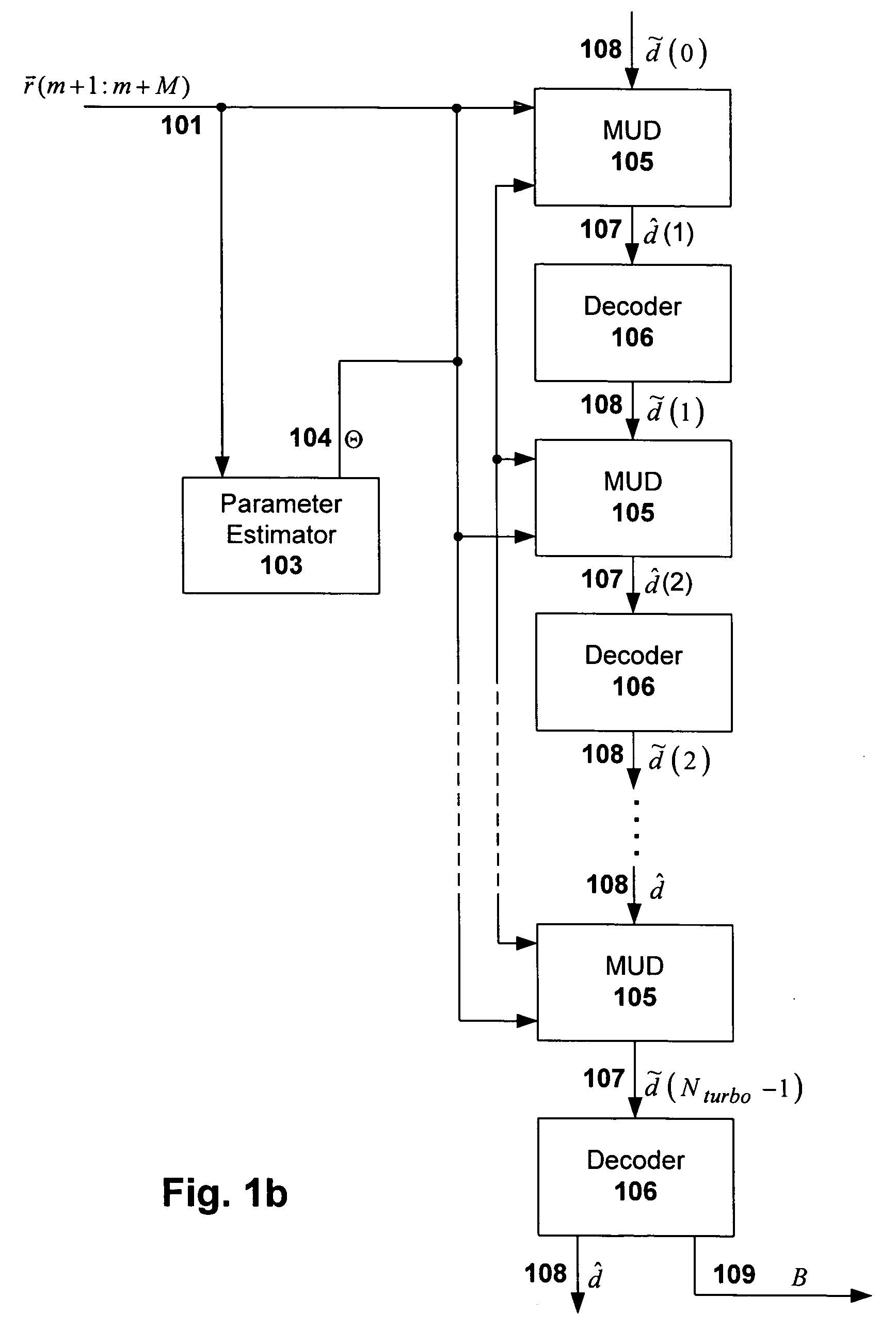
Multiuser detection with targeted error correction coding
InactiveUS7092464B2Reducing error correction complexityReducing error correction coding complexityJoint error correctionOther decoding techniquesMultiuser detectionQuality of service
An error correction decoding (ECC) processing scheme is disclosed that reduces computational complexity normally associated with multiuser detection (e.g., TurboMUD) solutions, without causing degradation in quality of service or decreasing the total throughput. Error correction decoding algorithms are applied only to portions of the estimates that were affected by the immediately previous MUD update process. Even though the MUD and / or ECC updating is targeted so as to reduce complexity of each iteration, all of the estimates are maintained and remain candidates for future updates. As such, there is no negative impact real-time or future performance. This targeting approach can be used in conjunction with many variations of MUD, including full-complexity or reduced complexity, and may include MUD with confidence ordering or voting, and other techniques for facilitating efficient and effective MUD processing.
Owner:COLLISION COMM INC
Audio bandwidth expansion
ActiveUS7676043B1Broadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisFundamental frequencyEqualization
Bandwidth expansion for audio signals by frequency band translations plus adaptive gains to create higher frequencies; use of a common channel for both stereo channels limits computational complexity. Adaptive cut-off frequency determination by power spectrum curve analysis, and bass expansion by both fundamental frequency illusion and equalization.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
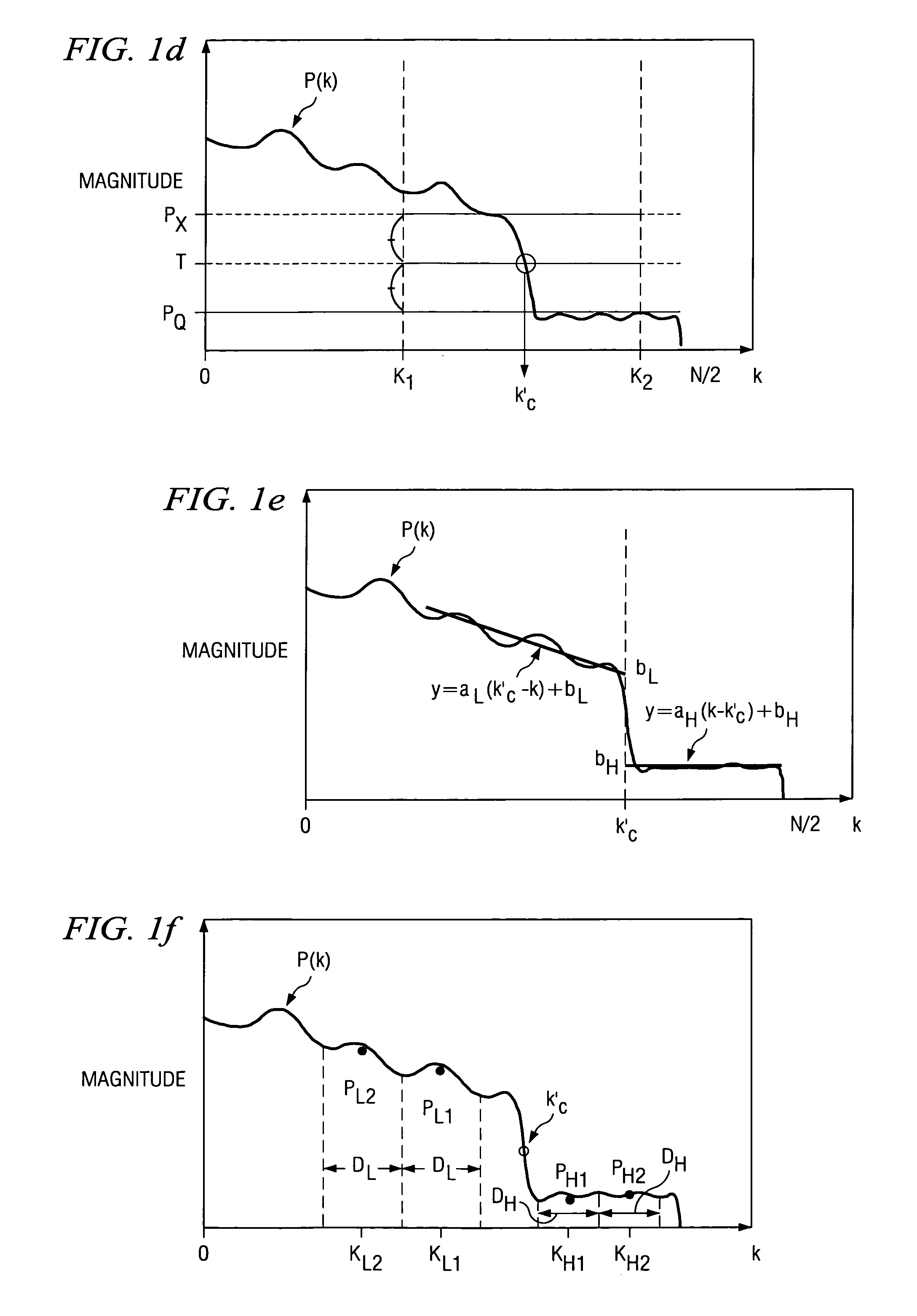
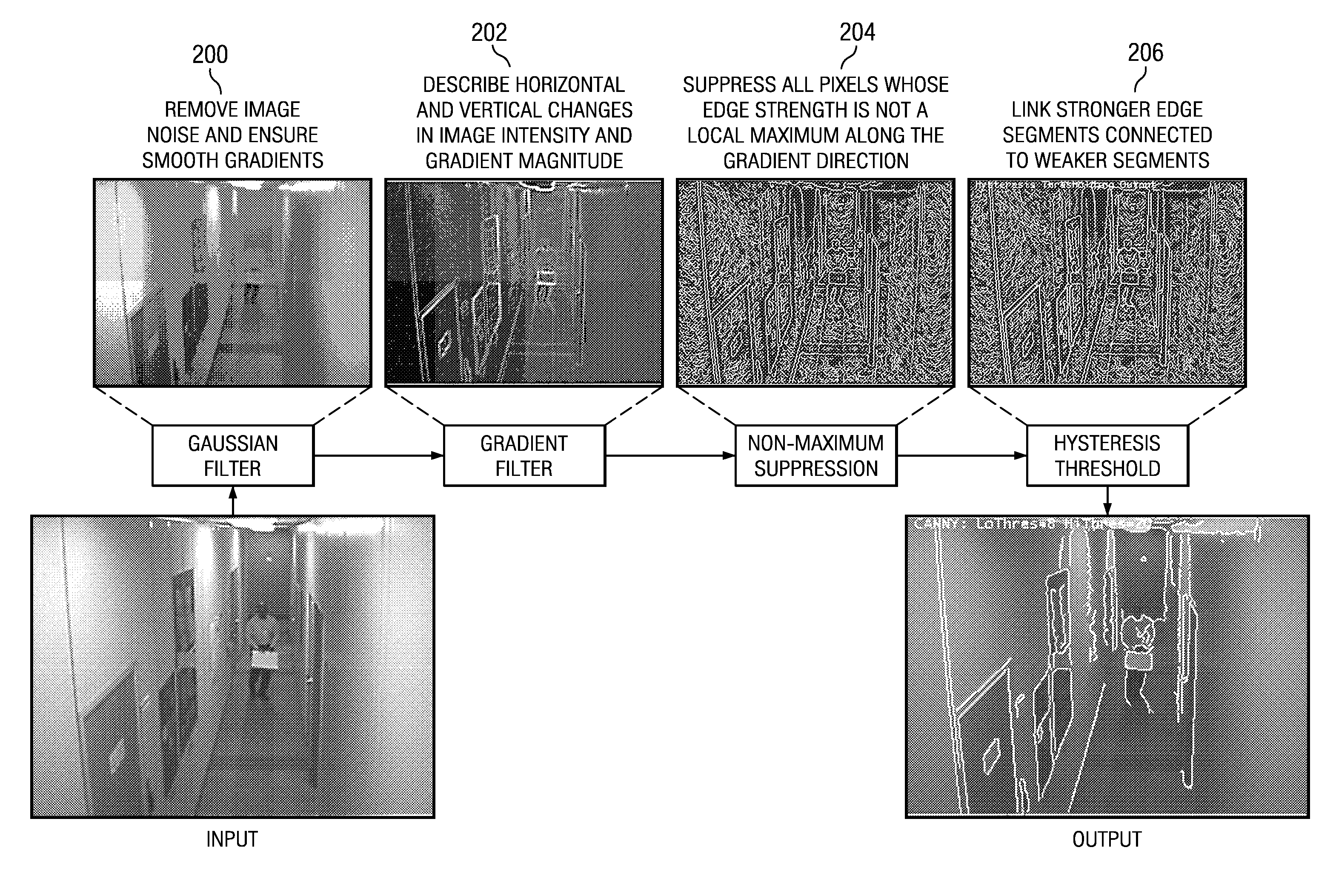
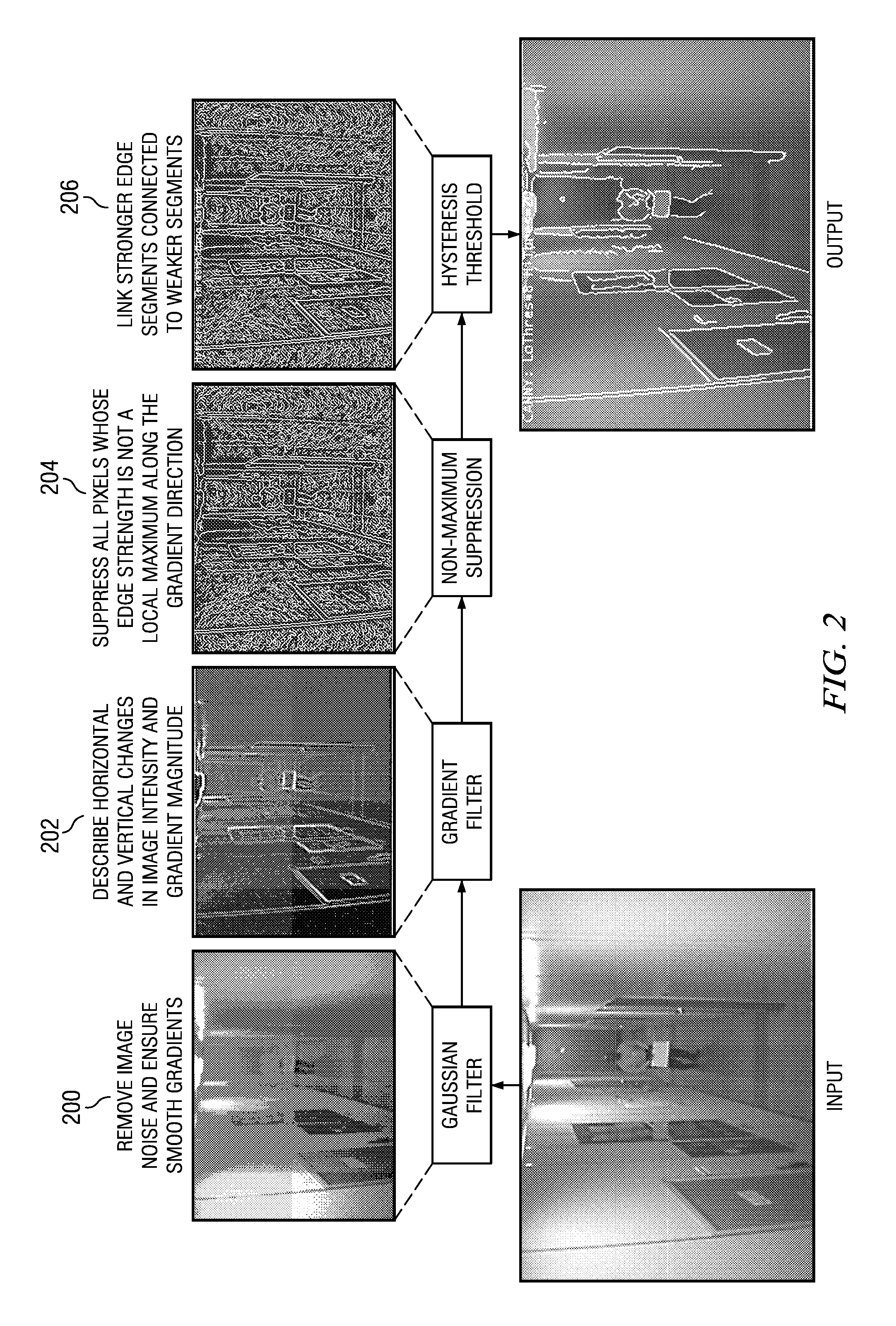
Fast Hysteresis Thresholding in Canny Edge Detection
A method of image processing is provided which includes non-recursive hysteresis thresholding in Canny edge detection. The non-recursive hysteresis thresholding reduces computational complexity and eliminates the potential for call stack overflow. More specifically, hysteresis thresholding is performed in a raster-scan order pass over the image data to connect edge segments to form continuous edges.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
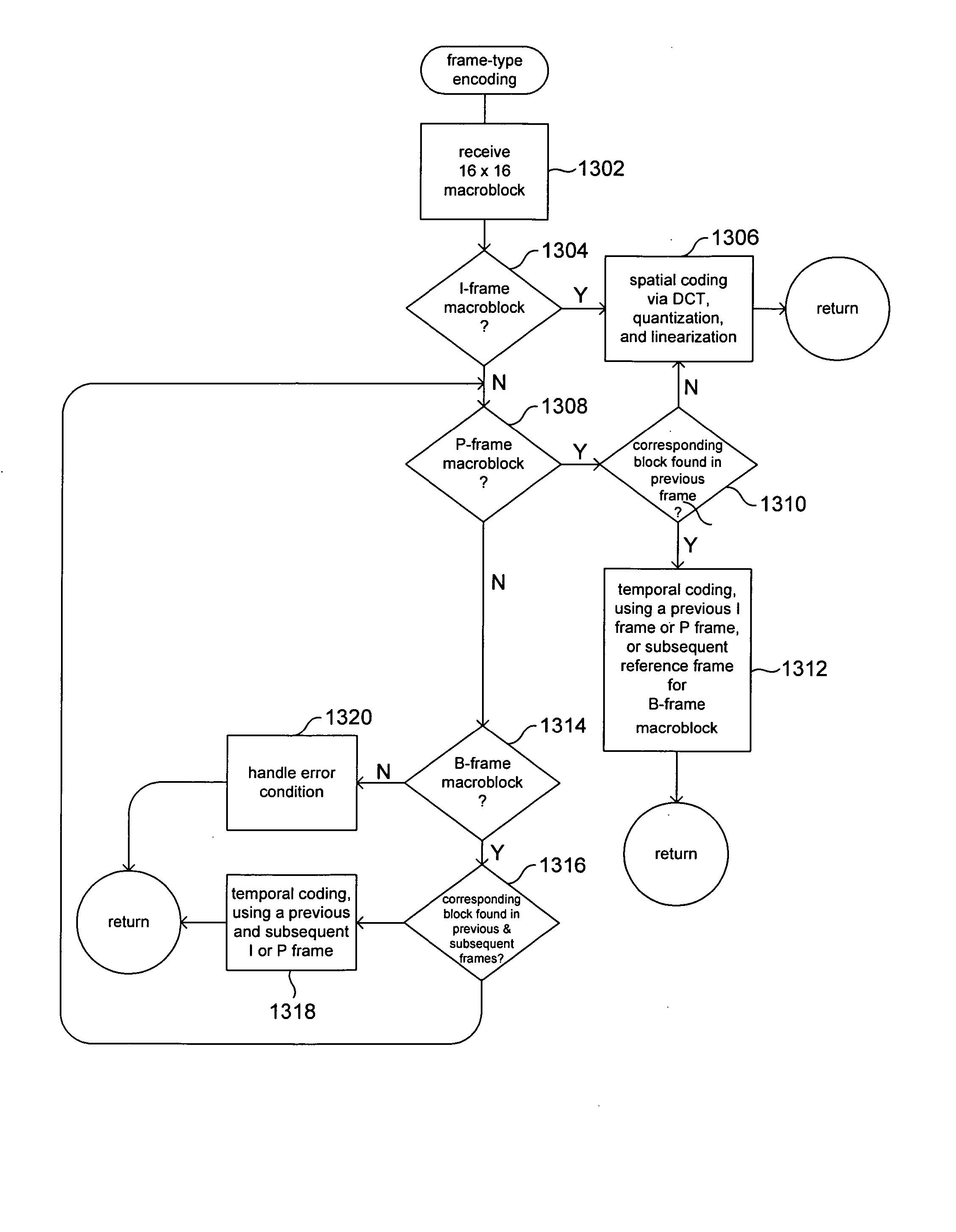
Reducing computational complexity when video encoding uses bi-predictively encoded frames
ActiveUS20100284464A1High computational complexityReduce computational complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputation complexityVideo encoding
Several techniques aimed at reducing computational complexity when encoding uses bi-predictively encoded frames (B-frames) are implemented in a video encoder. In an embodiment, B-frames are not used as reference frames for encoding P-frames and other B-frames. Non-use of B-frames allows a de-blocking filter used in the video encoder to be switched off when reconstructing encoded B-frames, and use of a lower complexity filter for fractional-resolution motion search for B-frames. In another embodiment, cost functions used in motion estimation for B-frames are simplified to reduce computational complexity. In one more embodiment, fractional pixel refinement in motion search for B-frames is simplified. In yet another embodiment, predictors used in motion estimation for a macro-block in a P-frame are selected from a B-frame that uses a same reference frame as the P-frame.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
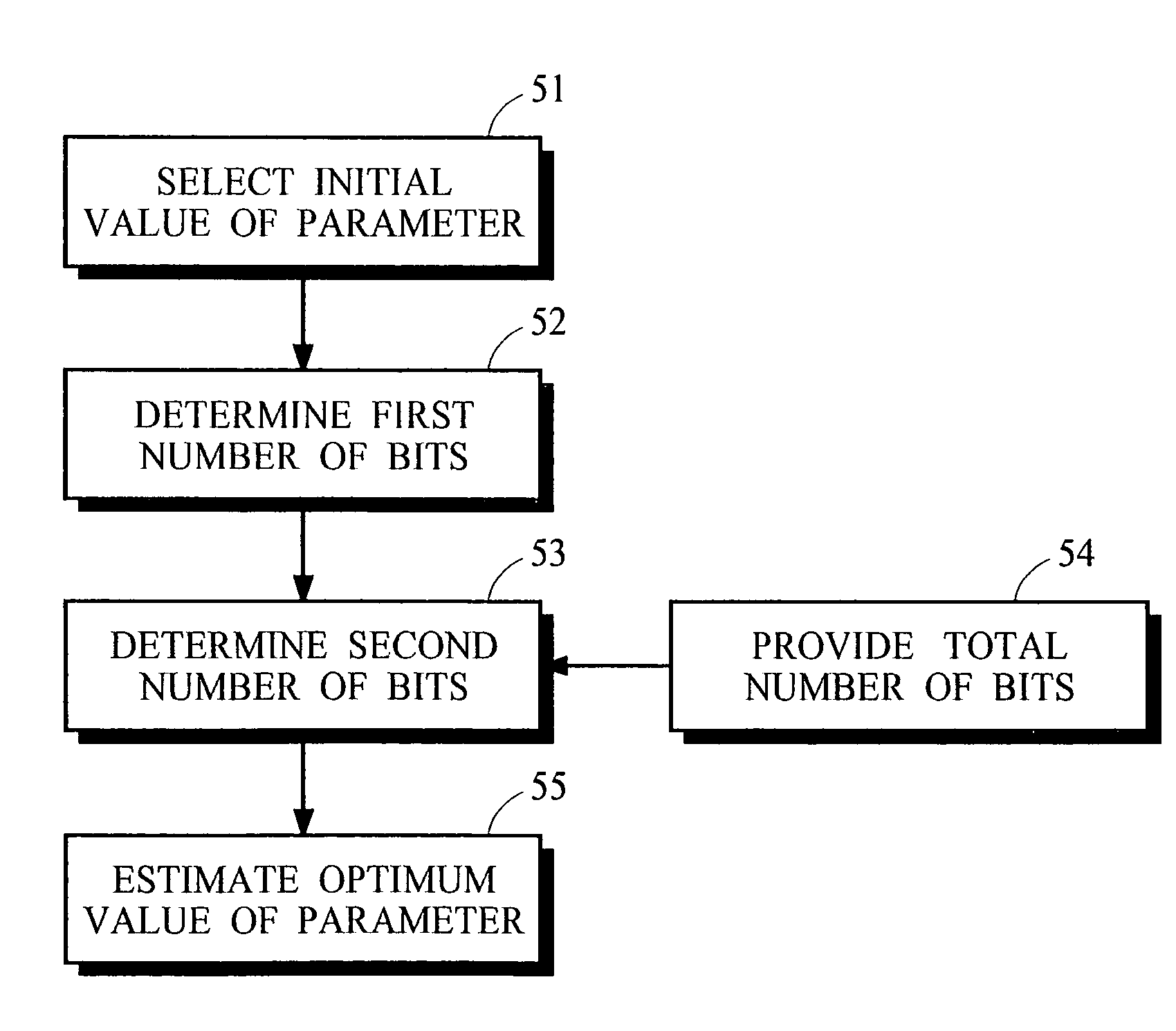
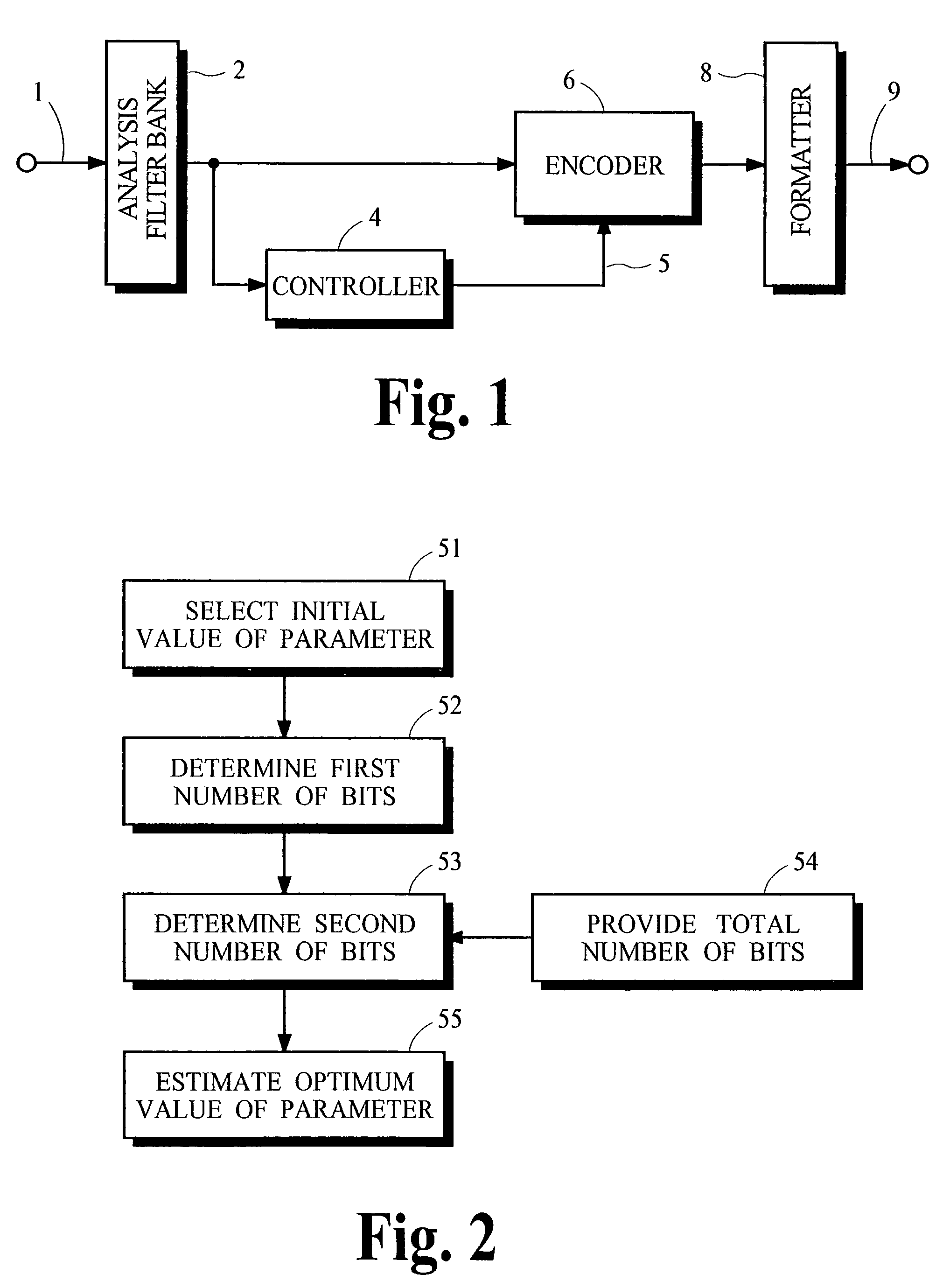
Method for reducing computational complexity of video compression standard
InactiveUS20080056355A1Reduce luminance computationDecrease in luminanceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputation complexityComputational complexity theory
A method for reducing computational complexity of video compression standard is provided, and it includes an intra 4×4 macroblock (I4MB) search algorithm, an intra 16×16 macroblock (I16MB) search algorithm and a chroma search algorithm. The I4MB search algorithm and I16MB search algorithm accelerate the prediction process of the luma macroblock, and the chroma search algorithm accelerates the prediction process of chroma macroblock. The above algorithms can greatly reduce the computation of prediction mode of video compression standard.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
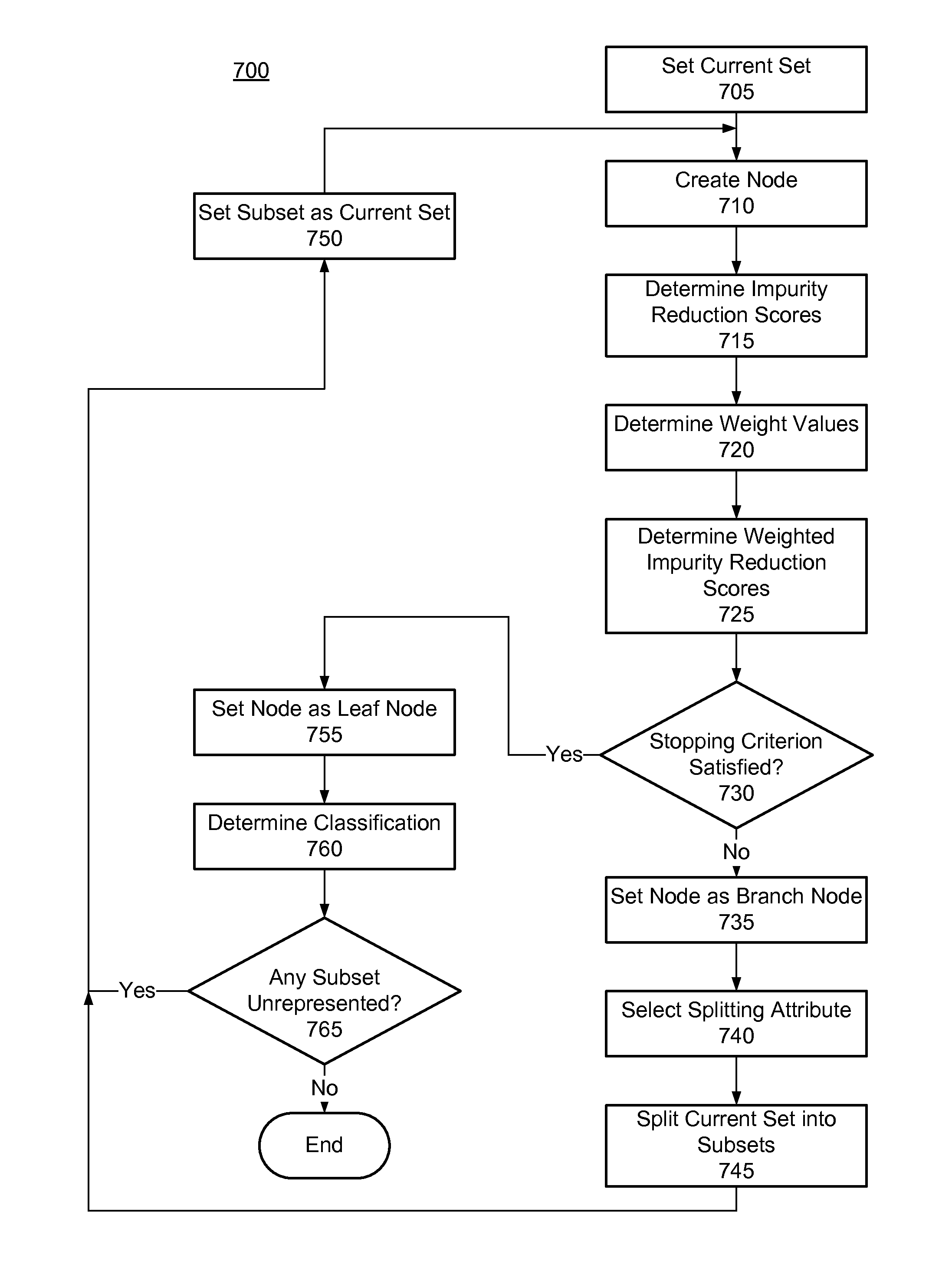
Decision tree induction that is sensitive to attribute computational complexity
ActiveUS8190647B1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsNODALComputation complexity
A decision tree for classifying computer files is constructed. Computational complexities of a set of candidate attributes are determined. A set of attribute vectors are created for a set of training files with known classification. A node is created to represent the set. A weighted impurity reduction score is calculated for each candidate attribute based on the computational complexity of the attribute. If a stopping criterion is satisfied then the node is set as a leaf node. Otherwise the node is set as a branch node and the attribute with the highest weighted impurity reduction score is selected as the splitting attribute for the branch node. The set of attribute vectors are split into subsets based on their attribute values of the splitting attribute. The above process is repeated for each subset. The tree is then pruned based on the computational complexities of the splitting attributes.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Video data CODEC system with low computational complexity
InactiveUS20020191698A1Reduce complexityReduce computing power consumptionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputation complexityComputational complexity theory
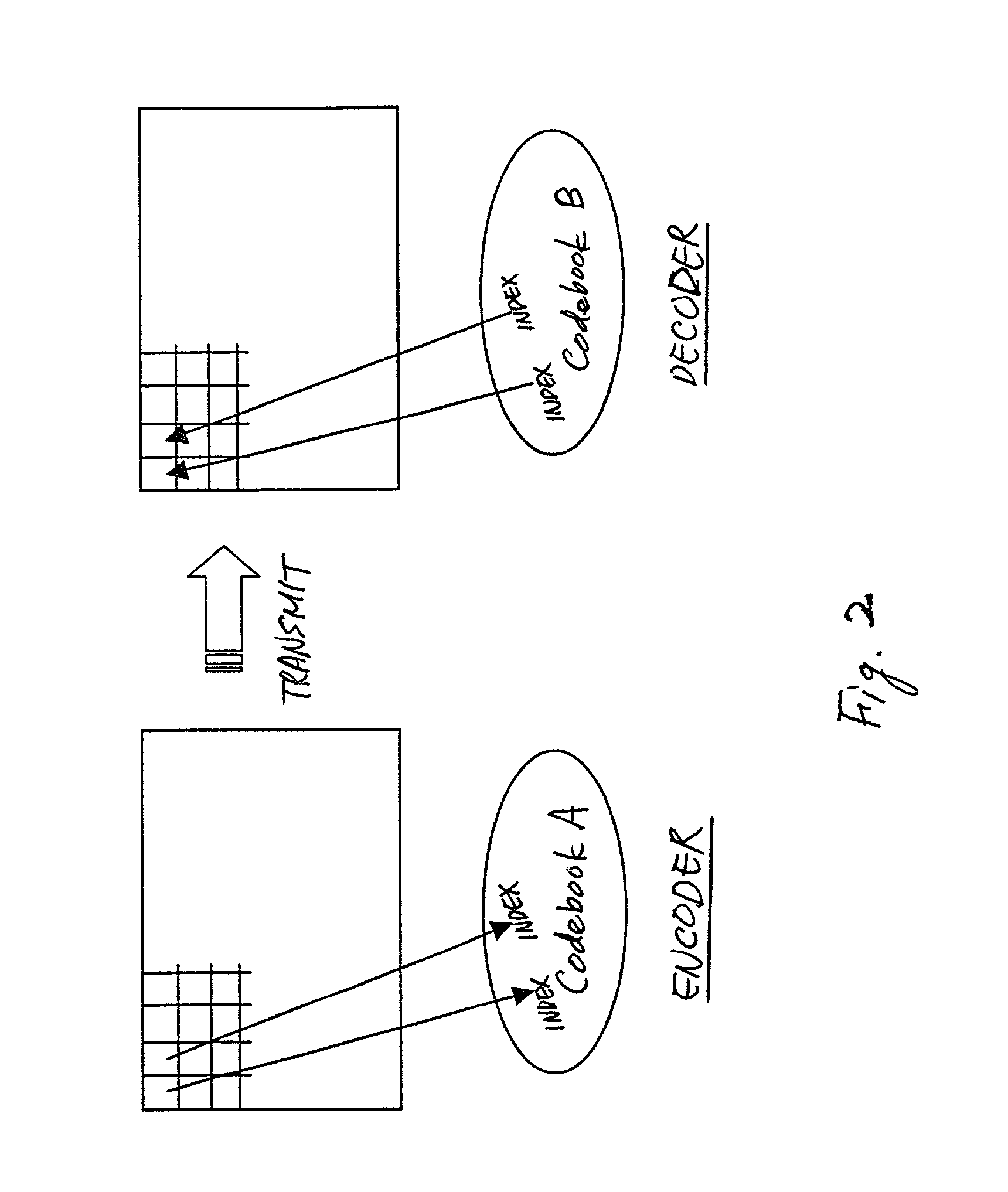
A method for encoding video data includes the steps of providing video data having a plurality of frames each of which has a plurality of blocks each of which has a predetermined number of pixels, providing a codebook having indices each representing a different pattern, performing an intra-coding process with respect to a first set of frames of the plurality of frames to select from the codebook best match indices for respective blocks of the first set of frames, performing a predictive coding process with respect to a second set of frames of the plurality of frames to obtain codes for respective blocks of the second set of frames, wherein each of the codes has an index-body determined using the best match indices for the blocks of the first set of frames and best match indices selected from the codebook for the blocks of the second set of frames, and performing a bi-directional predictive coding process with respect to a third set of frames of the plurality of frames to obtain codes for respective blocks of the third set of frames, wherein each of the codes has an index-body determined using the best match indices for the blocks of the first and second sets of the frames and best match indices selected from the codebook for the blocks of the third set of frames.
Owner:SOLIDSTREAMING
Dynamic reuse partitioning and subchannel allocation scheme in multicell OFDMA downlink systems
InactiveUS20070077934A1Less amount of communication overheadLess computing powerRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork planningRadio networksComputation complexity
The reuse partitioning problem for a cellular orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) system with dynamic subcarrier allocation is considered. One objective is to allocate the network resources in an efficient way in order to maximize the system's total throughput under individual user's quality-of-service (QoS) constraint. A suboptimal two-step approach is used where the radio network controller (RNC) solves the network planning problem and each base station (BS) solves the cell throughput maximization problem. Compared with the optimal resource allocation scheme, the approach described herein has much lower computational complexity in the RNC. Moreover, the communication overhead between each BS and the RNC is reduced substantially which renders our approach more practical for delay sensitive applications. Throughput increase is demonstrated
Owner:SIEMENS CORP RES INC
Reducing Computational Complexity in Determining an Illuminant of a Scene
In an embodiment, computational complexity of estimating the actual illuminant of a scene is reduced by examining only a subset of the pixel values generated for a received image frame. In another embodiment, number of rotations of color values is minimized by selecting an area which contains the color cue values of a color in an original / unrotated coordinate space and has boundaries which parallel the axis of the original coordinate space, and rotating a color value only if the color value is within the selected area. In another embodiment, such an area is used in conjunction with a histogram-based approach to determine the actual illuminant.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
System evaluation and detection method by Bayesian model
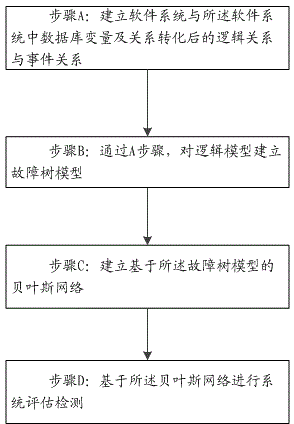
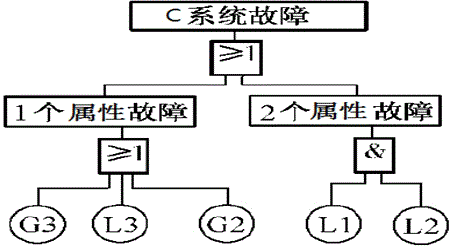
InactiveCN104573386ASmall amount of calculationReduce computational difficultySpecial data processing applicationsSoftware systemComputational complexity theory
The invention discloses a system evaluation and detection method by a Bayesian model. The method includes: step A, establishing a logic relationship and an event relationship between a software system and a database therein after variable and relationship conversion; step B, establishing a fault tree model for a logic model according to the step A; step C, establishing a Bayesian network based on the fault tree model; step D, conducting system evaluation and detection based on the Bayesian network. The system evaluation and detection method by the Bayesian model has the advantages of low computational complexity, low computational difficulty, simplicity and practicality when used for system evaluation and detection by the Bayesian model.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
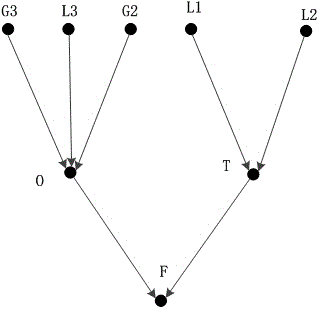
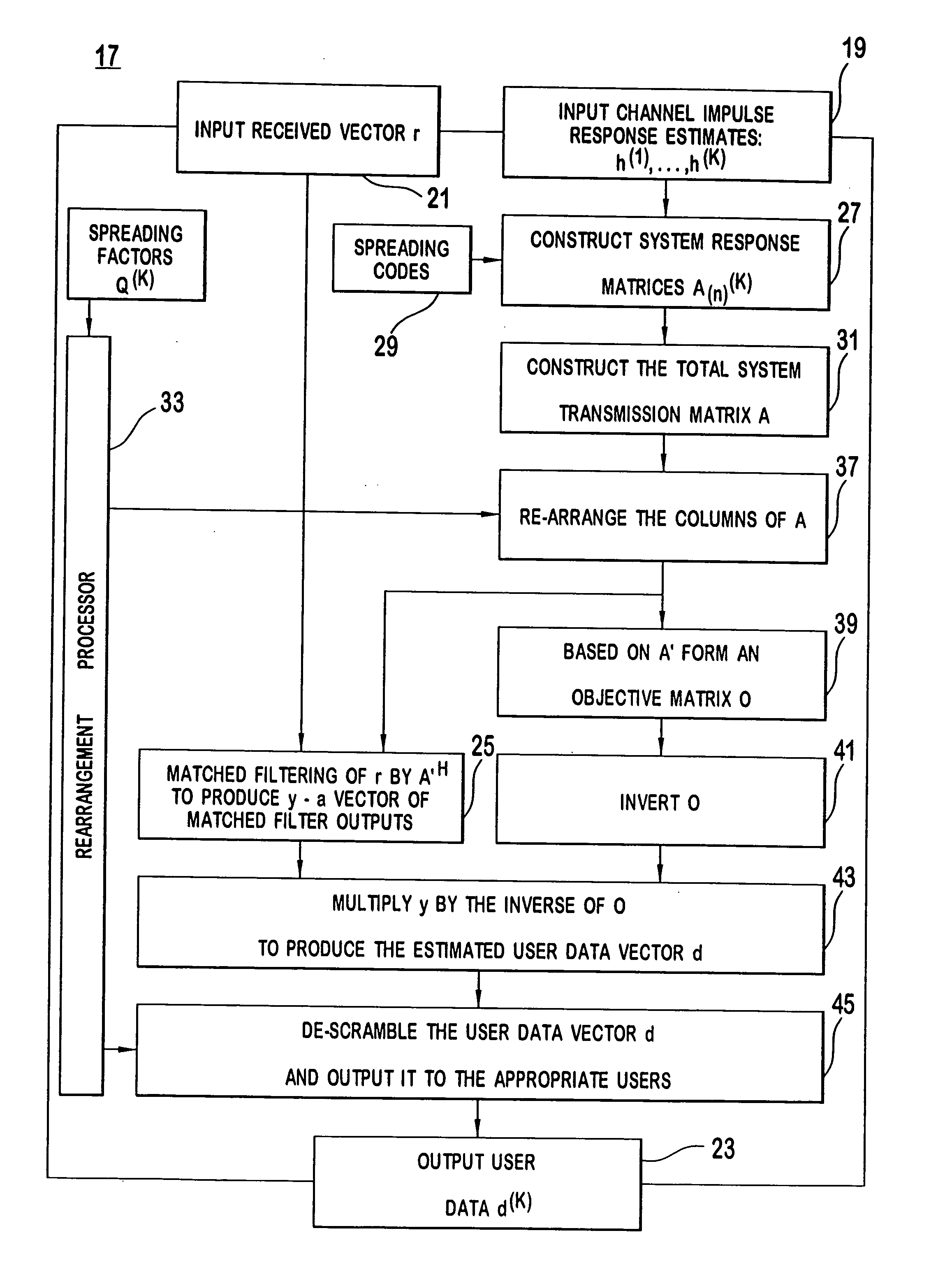
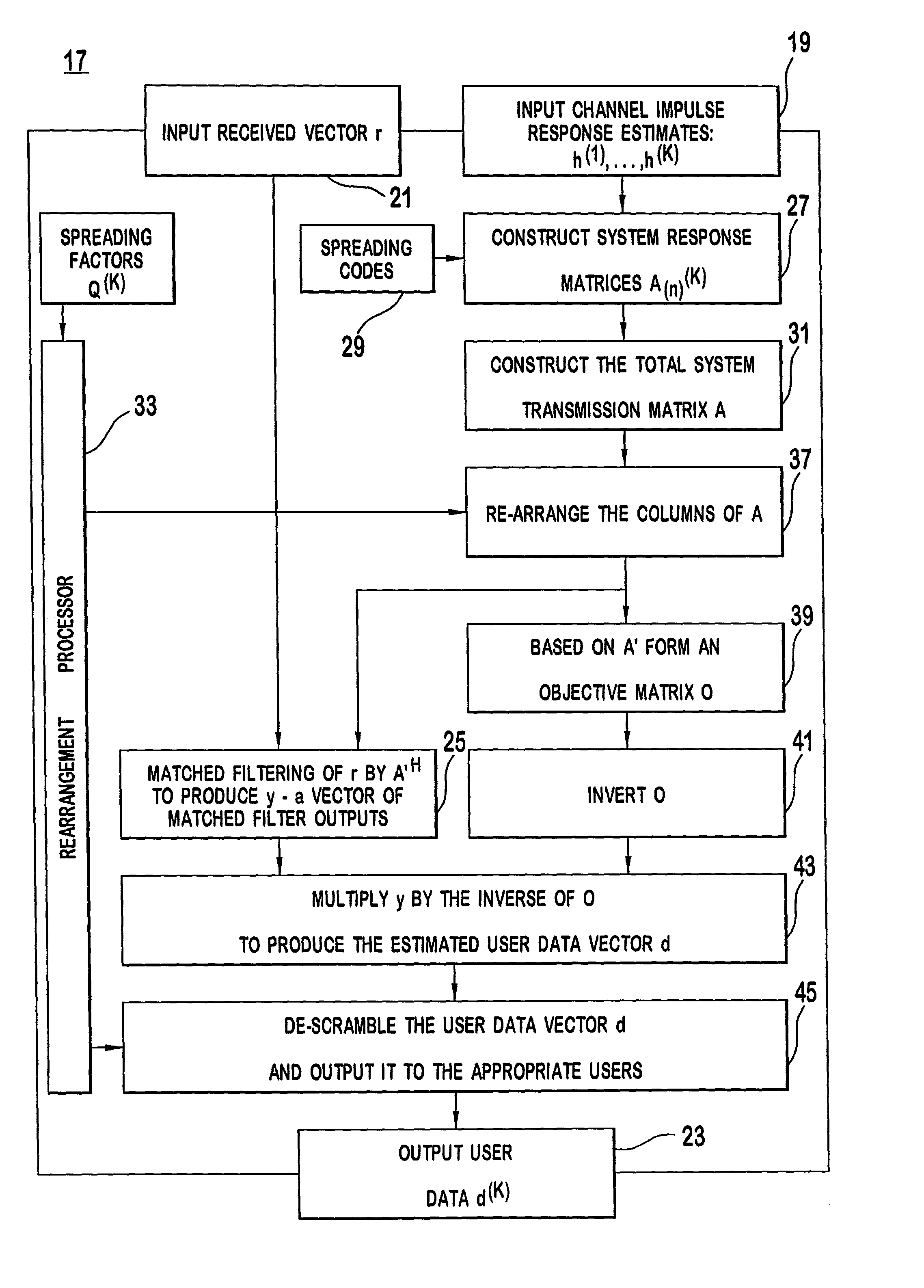
Multiuser detector for variable spreading factors
InactiveUS20080198828A1Reduce complexityMiniaturizationCode division multiplexRadio transmissionComputation complexityMatched filter
A multiuser detector method and receiver that detects and decodes synchronous or asynchronous CDMA subchannels having different spreading factors with reduced computational complexity. The multiuser receiver is compatible with ZF-BLE, MMSE, decorrelating detectors and the like using Cholesky decomposition to minimize numeric operations. The receiver and method arranges the columns of system transmission response matrices representing the response characteristics of individual users into a total system transmission response matrix which represents a plurality of matched-filter responses for a given block of received data. The invention when used in conjunction with Cholesky decomposition reduces the number of required mathematic operations prior to parallel matched filtering.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
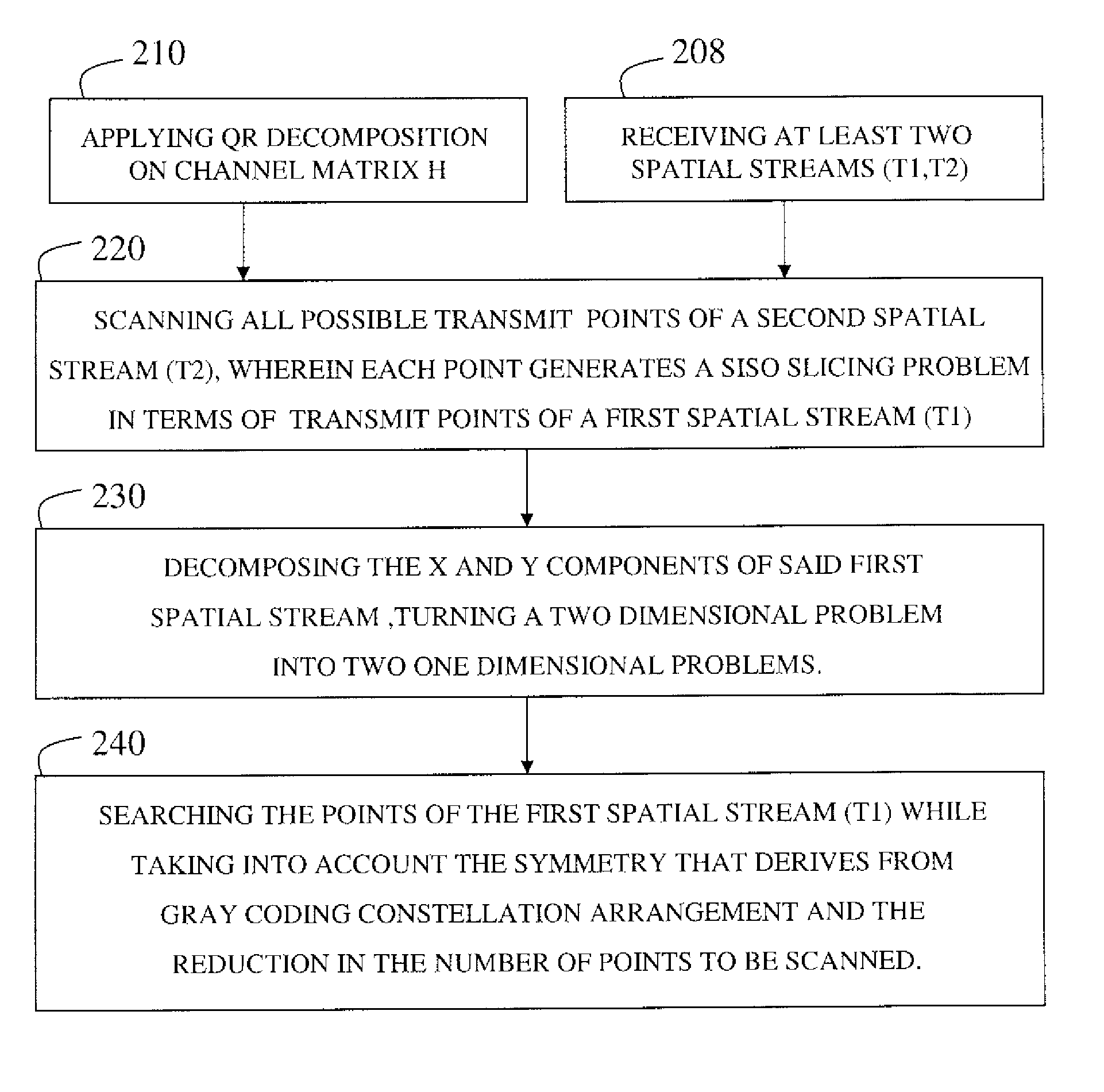
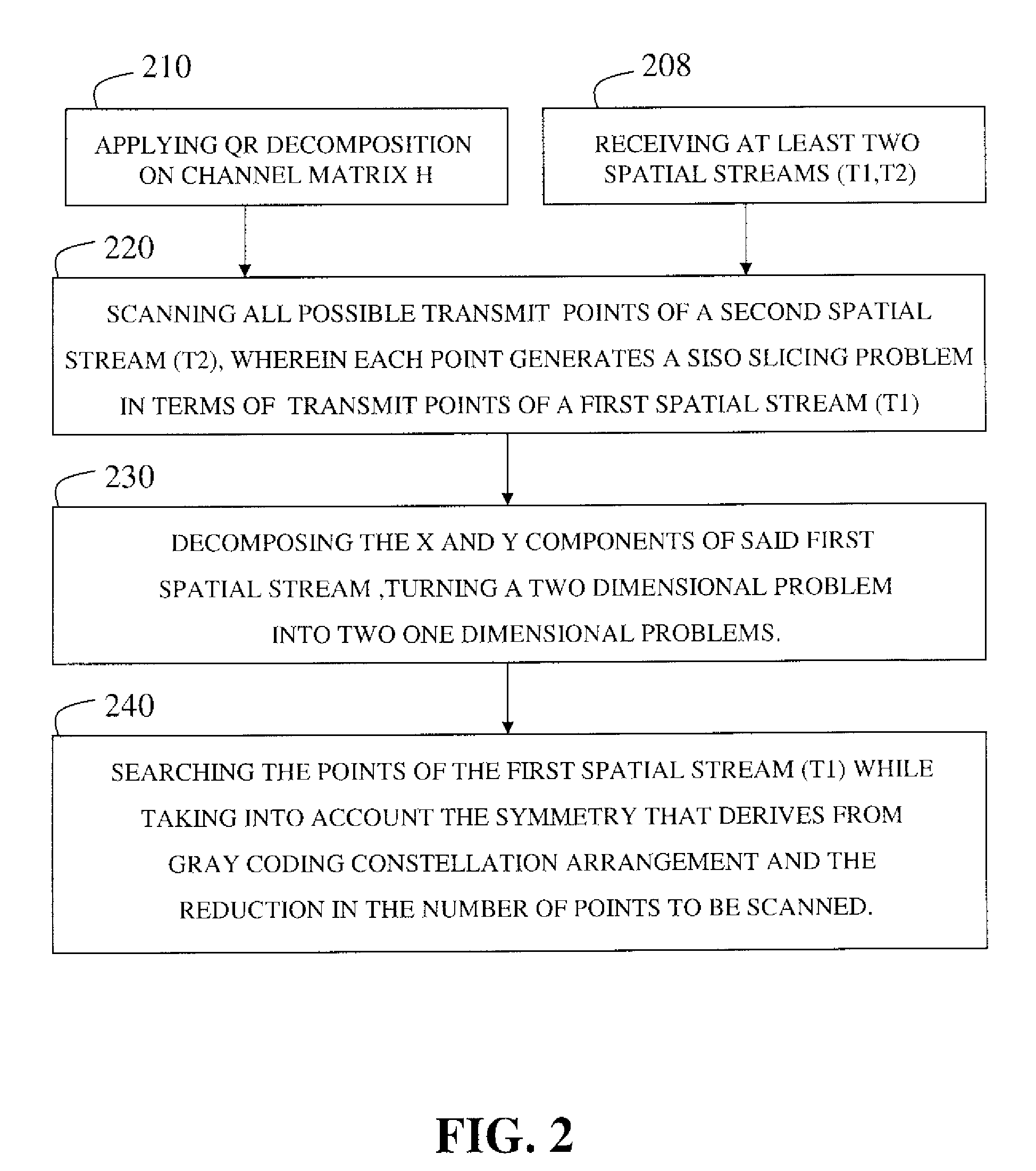
Reducing computational complexity in maximum likelihood MIMO OFDM decoder
ActiveUS7912140B2Reduce complexityImprove performanceData representation error detection/correctionPolarisation/directional diversityComputation complexityDecomposition
A method and a system for reducing computational complexity in a maximum-likelihood MIMO decoder, while maintaining its high performance. A factorization operation is applied on the channel Matrix H. The decomposition creates two matrixes: an upper triangular with only real-numbers on the diagonal and a unitary matrix. The decomposition simplifies the representation of the distance calculation needed for constellation points search. An exhaustive search for all the points in the constellation for two spatial streams t(1), t(2) is performed, searching all possible transmit points of (t2), wherein each point generates a SISO slicing problem in terms of transmit points of (t1); Then, decomposing x,y components of t(1), thus turning a two-dimensional problem into two one-dimensional problems. Finally searching the remaining points of t(1) and using Gray coding in the constellation points arrangement and the symmetry deriving from it to further reduce the number of constellation points that have to be searched.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
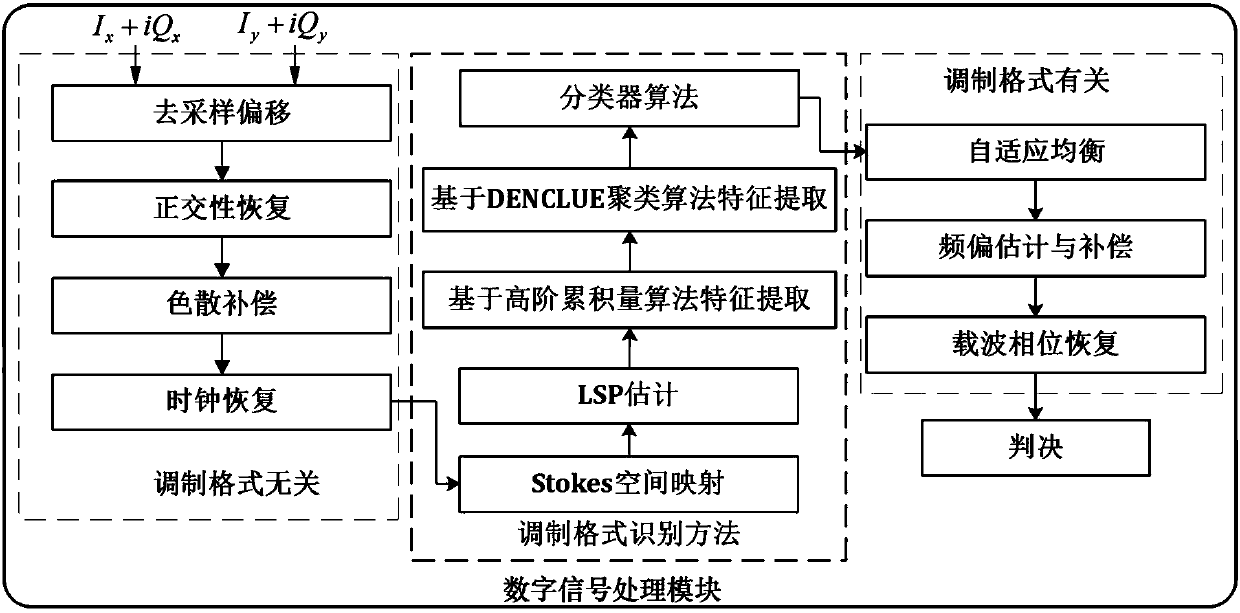
Stokes space coherent light modulation format recognition method based on DENCLUE clustering
ActiveCN108173599AAccurate judgmentImprove accuracyElectromagnetic receiversComputation complexitySignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention provides a modulation format recognition method, which adopts high-order cumulant of signals in a Stokes space and clustering center points clustered based on a DENCLUE algorithm as characteristic parameters for recognizing modulation format signals; a simple decision tree classifier is adopted; the method has low computational complexity and is insensitive to optical fiber channel damage such as polarization rotation, carrier frequency deviation, carrier phase noise and the like; recognition with relatively high accuracy can be realized under the condition of low signal-to-noiseratio; the modulation format recognition method is high in fusion degree with an existing commercial optical fiber communication system and is easy to upgrade from an existing system.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
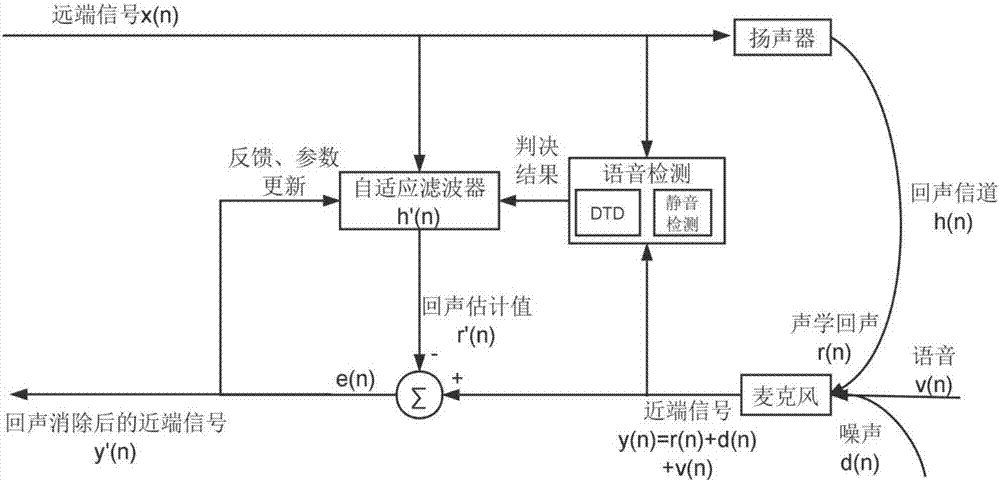
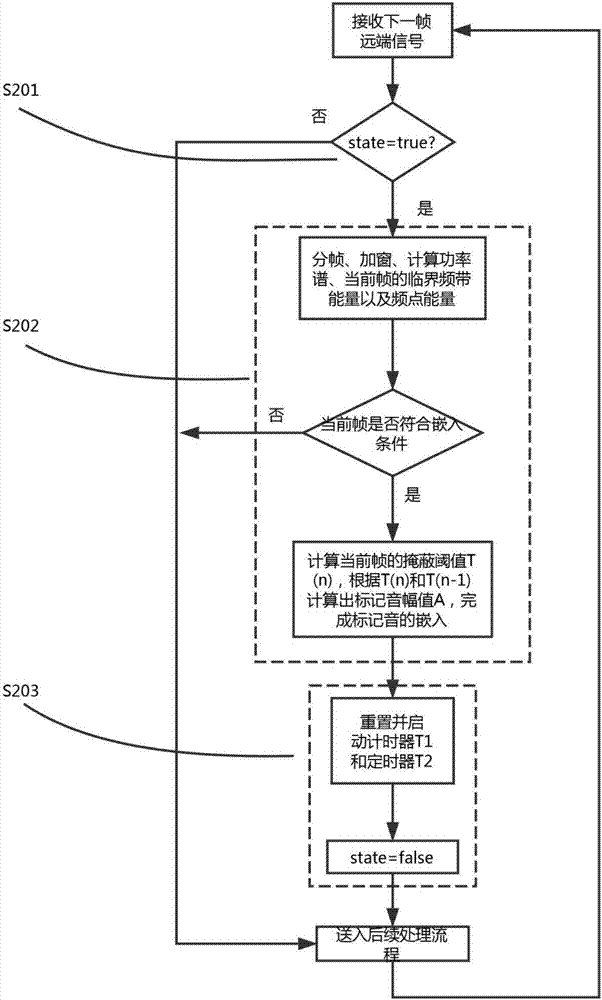
Echo delay estimating and tracking method
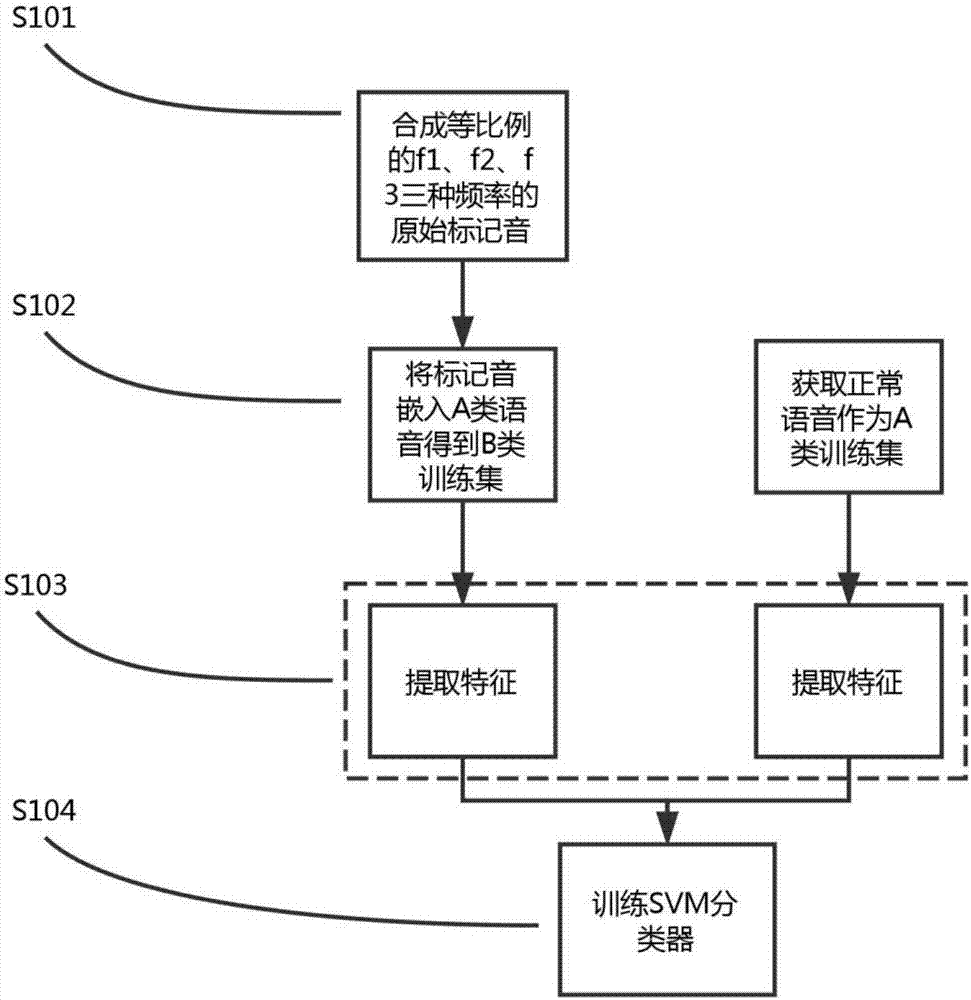
ActiveCN107333018AImprove real-time performanceImprove reliabilityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisRobustificationPattern recognition
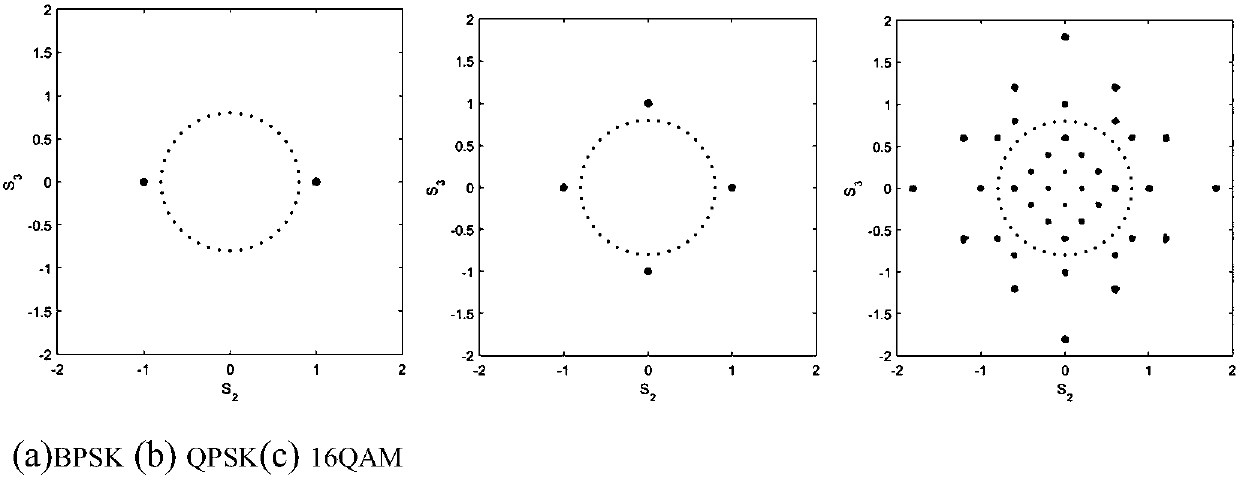
The invention discloses an echo delay estimating and tracking method. According to the method, the echo delay is estimated based on embedding / detection of marking tone in an SVM classifier, thereby simplifying the audio feature extraction process, meanwhile the position and the amplitude of the embedded marking tone are controlled by using a psychoacoustic model based on human ear auditory masking effect so as to avoid auditory distortion after embedding and maximally guarantee the integrity and accuracy of original remote signals, in addition, the embedding program and the detection program of the marking tone are alternately executed, for each embedded and detected marking tone, range verification is executed, and the echo delay is updated according to the detection result, thereby realizing dynamic tracking of the echo delay, compared with the traditional cross-correlation algorithm, the echo delay estimating and tracking method has the advantages of high real-time performance, strong robustness and low computational complexity, and the method does not depend on the background noise or the independence assumption of the remote signal, and has higher reliability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
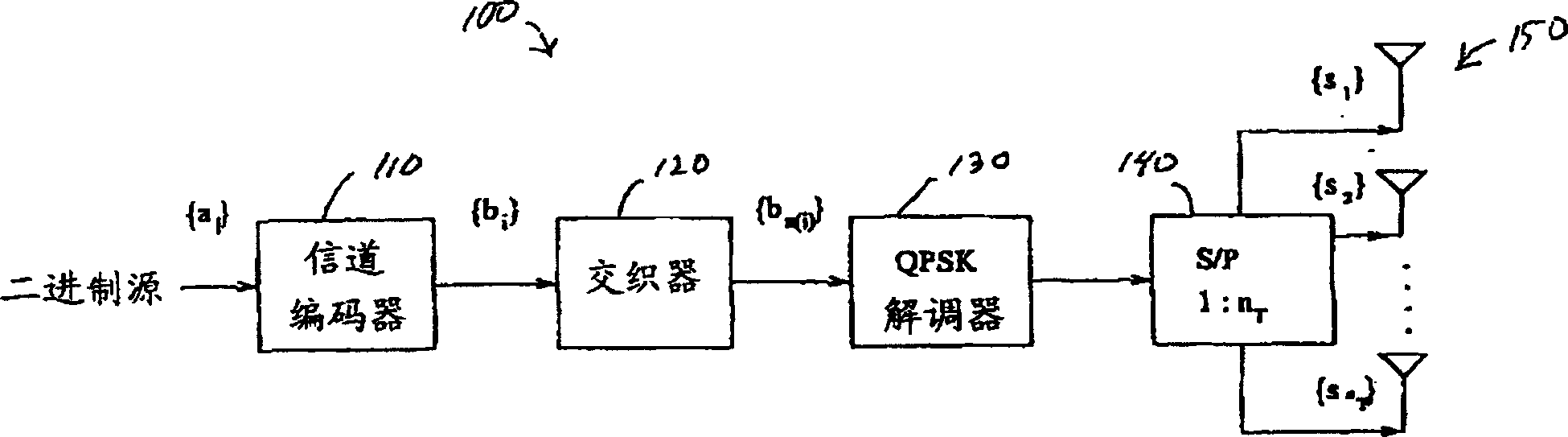
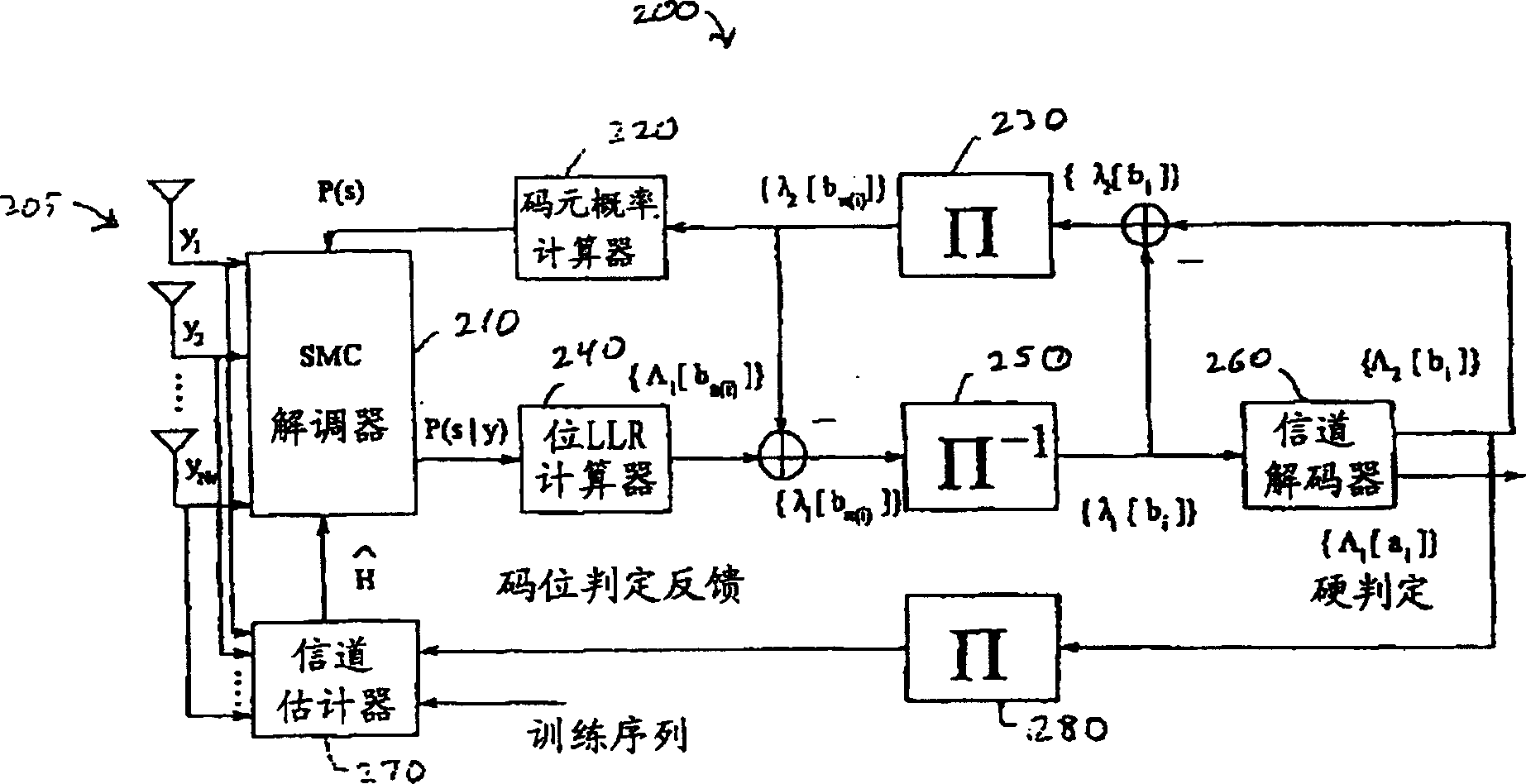
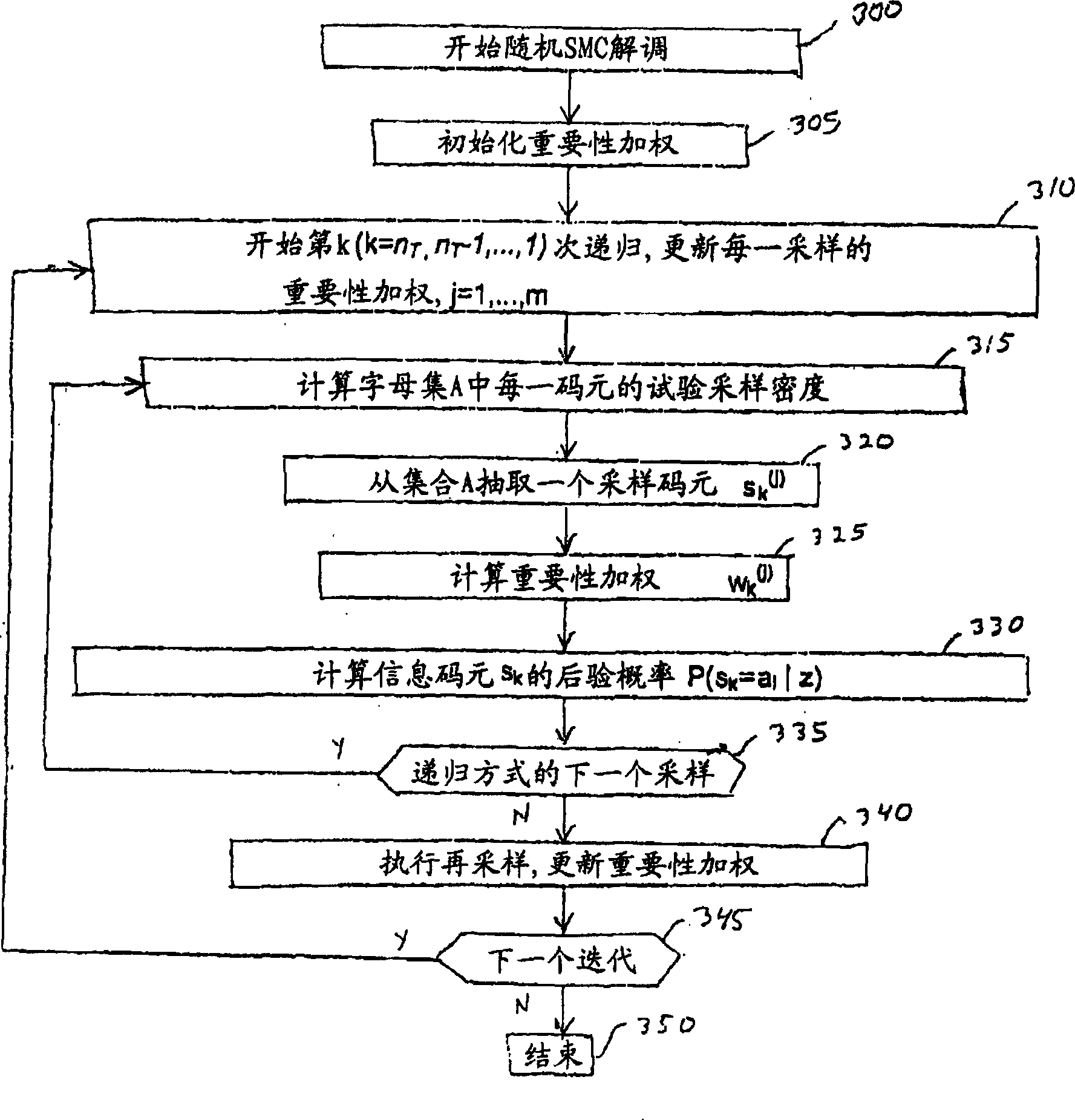
Near-optimal multi-input multi-ouput channel detection via sequential monte carlo
A class of soft-input soft-output demodulation schemes for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) channels, based on to sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) framework under both stochastic and deterministic settings. The stochastic SMC sampler generates MIMO symbol samples based on importance sampling and resampling techniques, while the deterministic SMC approach recursively performs exploration and selection steps in a greedy manner. By exploiting the artificial sequential structure of the existing simple Bell Labs Layered Space Time (BLAST) detection method based on nulling and cancellation, the proposed algorithms achieve an error probability performance that is orders of magnitude better than the traditional BLAST detection schemes while maintaining a low computational complexity. Performance is comparable with that of the sphere decoding algorithm, with a much lower complexity. Both the stochastic and deterministic SMC detectors can be employed as the first-stage demodulator in an iterative or turbo receiver in coded MIMO systems.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multicarrier Communication System for Doubly Selective Channels Using Virtual Trajectories Receiver
ActiveUS20180309598A1Reduce complexityImprove performanceModulated-carrier systemsPilot signal allocationComputation complexityCommunications system
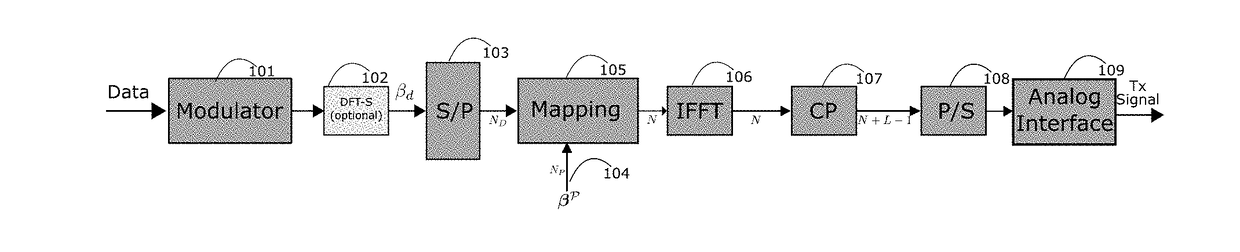
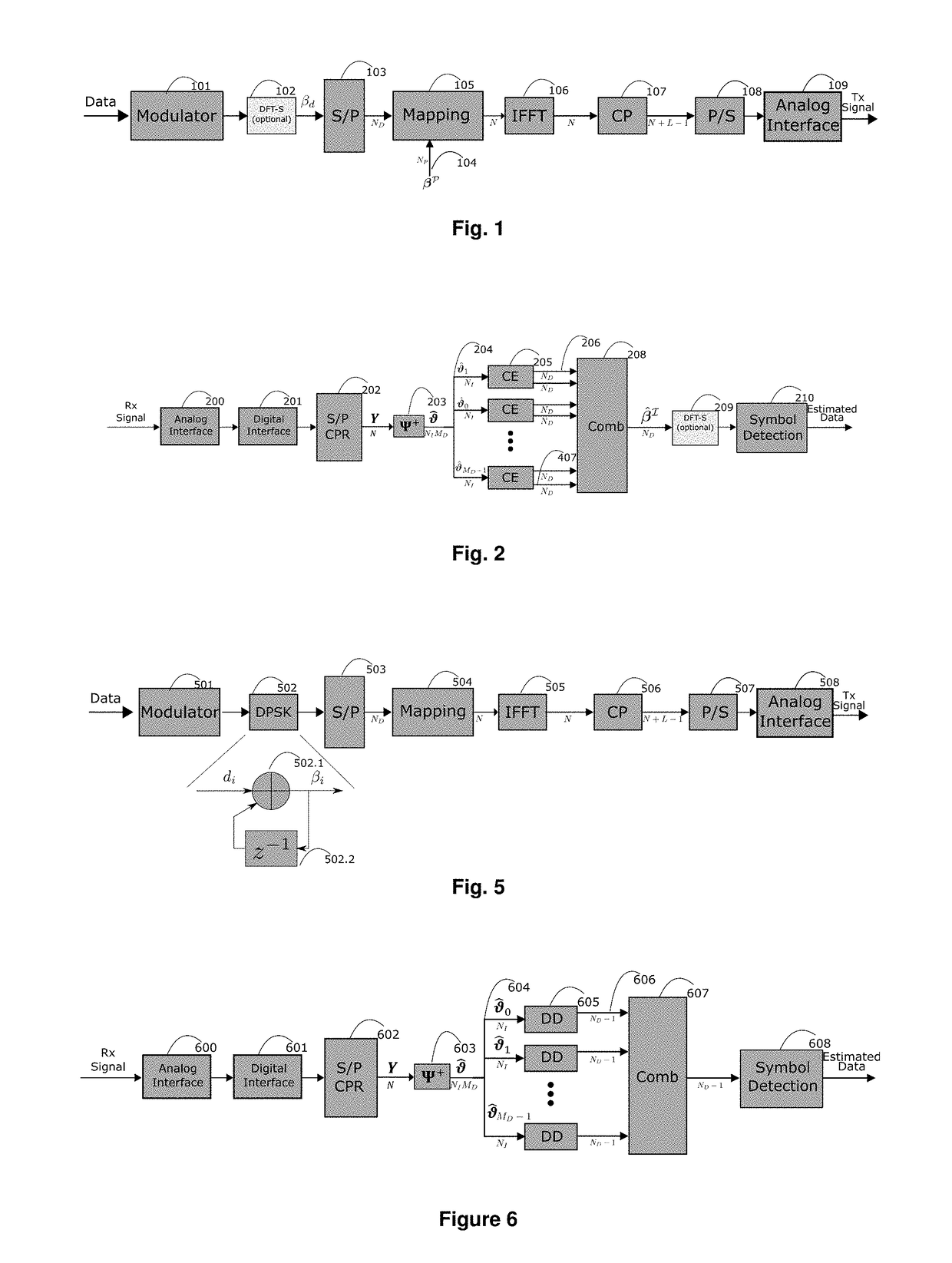
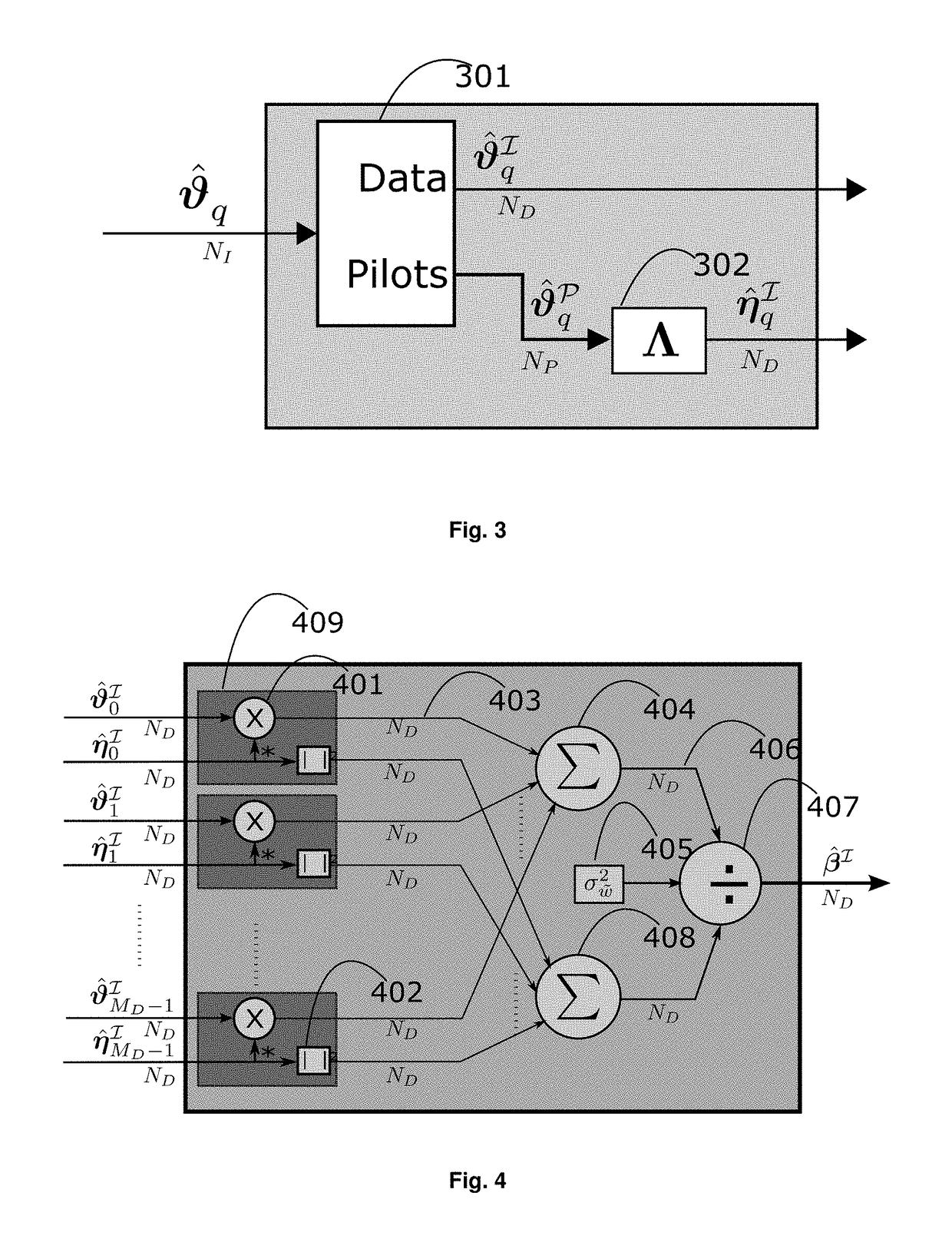
A modified orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) communication system based on virtual decomposition of the channel is proposed. The system is fully compatible with standard OFDM transmitters and maintains several blocks of standard OFDM receivers. The proposed approach achieves also incoherent reception of multicarrier signals even with a simple autocovariance DPSK detector. This novel system substantially surpasses the performance of current approaches while requiring low computational complexity. Two preferred embodiments are described; one with coherent reception using pilot signals, and the second with incoherent receiver of differentially encoded signals.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACION & DE ESTUDIOS AVANZADOS DEL INST POLITECNICO NACIONAL
Efficient rate allocation for multi-resolution coding of data
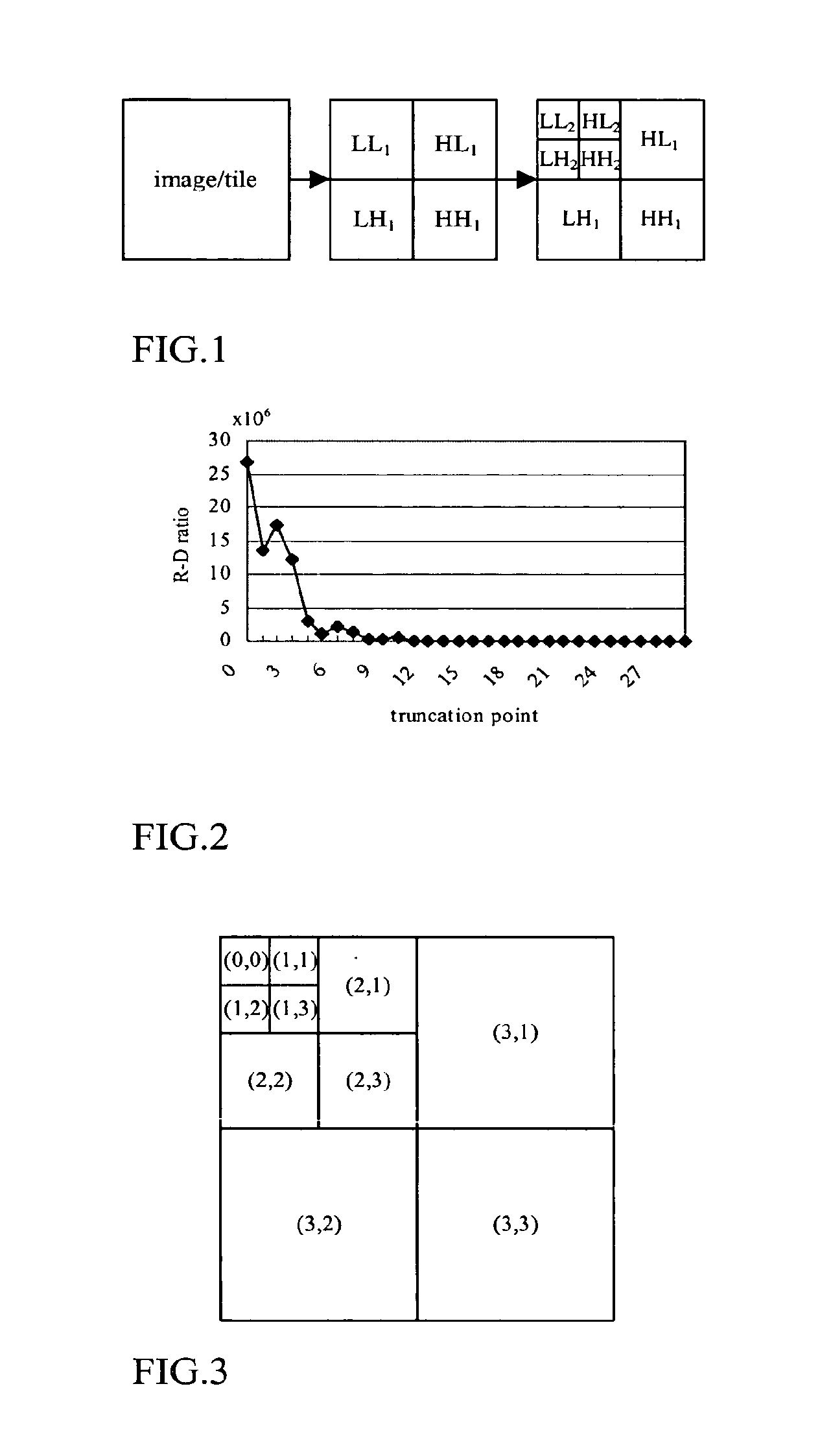
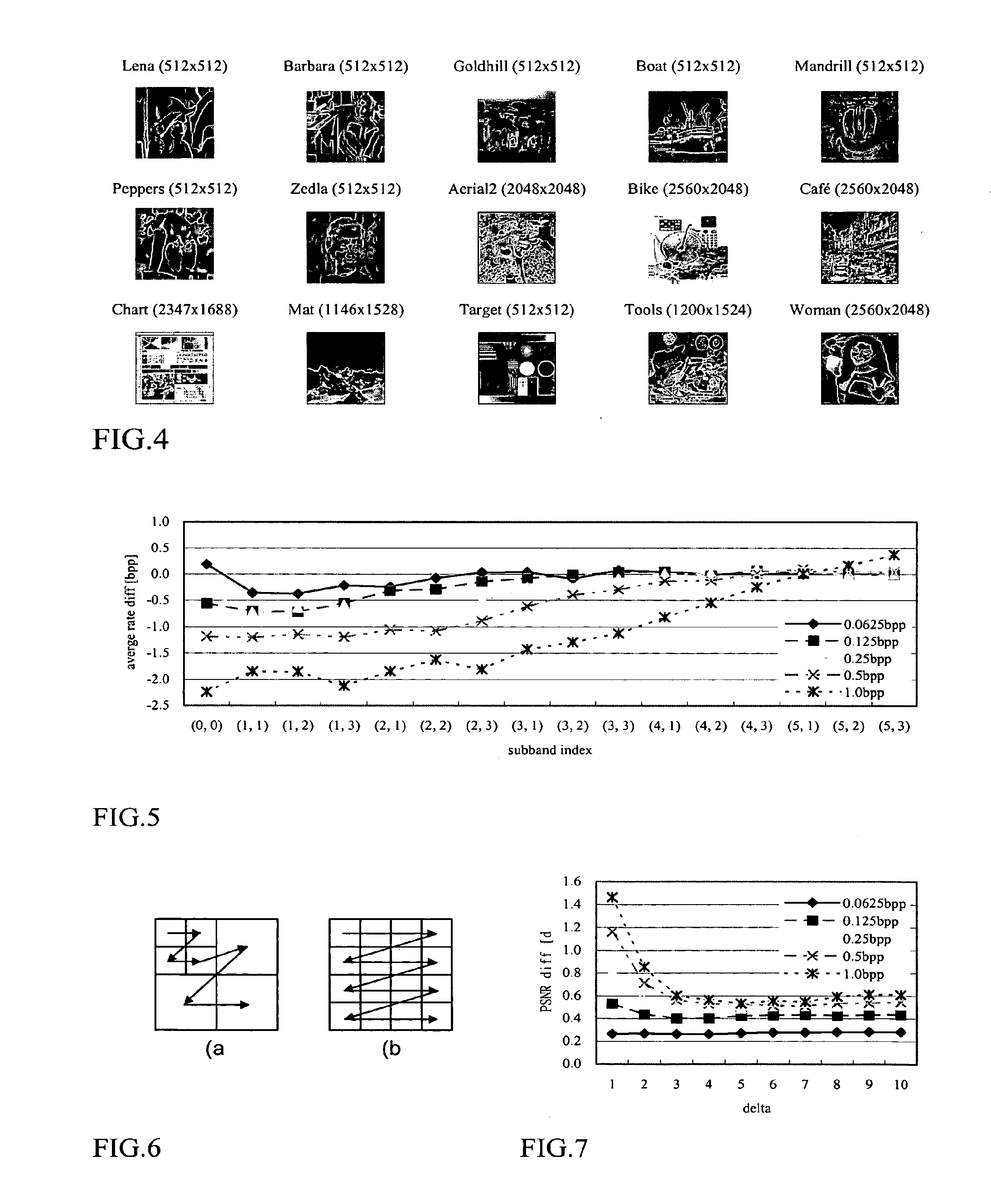
InactiveUS20100150463A1Faster rateReduce and remove computationCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsComputation complexityTransmission latency
There are disclosed three fast rate control methods that can efficiently reduce or remove the computation and memory usage redundancy over conventional PCRD methods. The first method, called successive bit-plane rate allocation (SBRA), assigns the maximum allowable bit-rate for each bit-plane of each code-block by using the currently available rate-distortion information only. The second method is called priority scanning rate allocation (PSRA). This first predicts the order of magnitude of each truncation point's rate-distortion slope and then encodes the truncation points based on the order (priority) information. The third method uses PSRA to obtain a significantly smaller amount of data than PCRD for optimal truncation and is called priority scanning with optimal truncation (PSOT). SBRA provides the highest computational complexity and memory usage reduction, and the lowest coding / transmission delay. The computational complexity reduction can be up to about 90% of the entropy coding process. However this method gives the lowest PSNR performance of the three. PSRA provides higher PSNR performance than SBRA with the penalty of lower memory usage reduction and higher delay. PSOT provides the best (optimal) quality while it is the least efficient method in term of computational complexity, memory usage and the coding / transmission delay. The three methods provide different degree of computation complexity and memory reduction, coding / transmission delay and PSNR performance. The most suitable rate control method can be chosen based on application requirements.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Decision tree induction that is sensitive to attribute computational complexity
ActiveUS8495096B1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionComputation complexityRound complexity
Owner:CA TECH INC
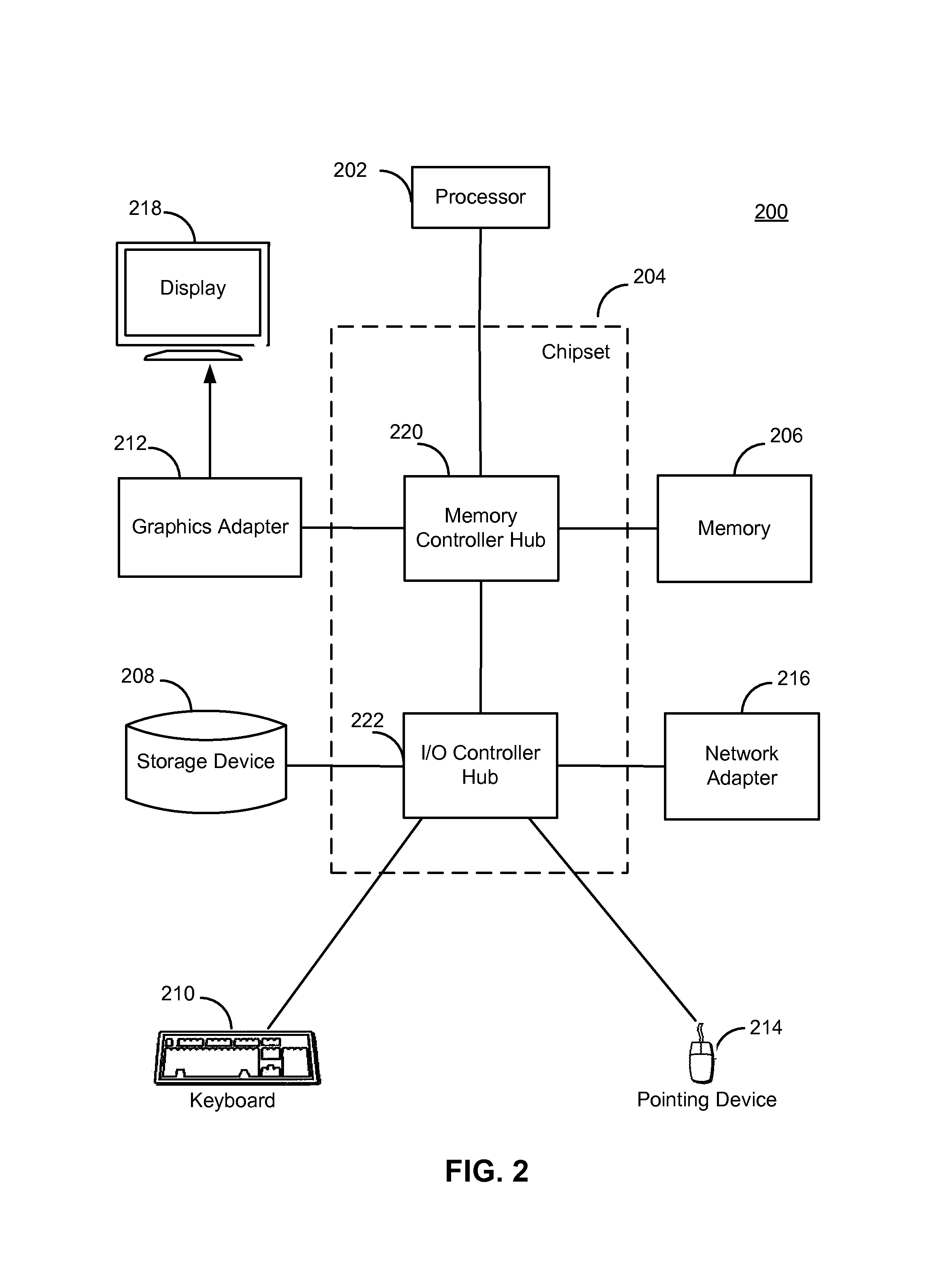
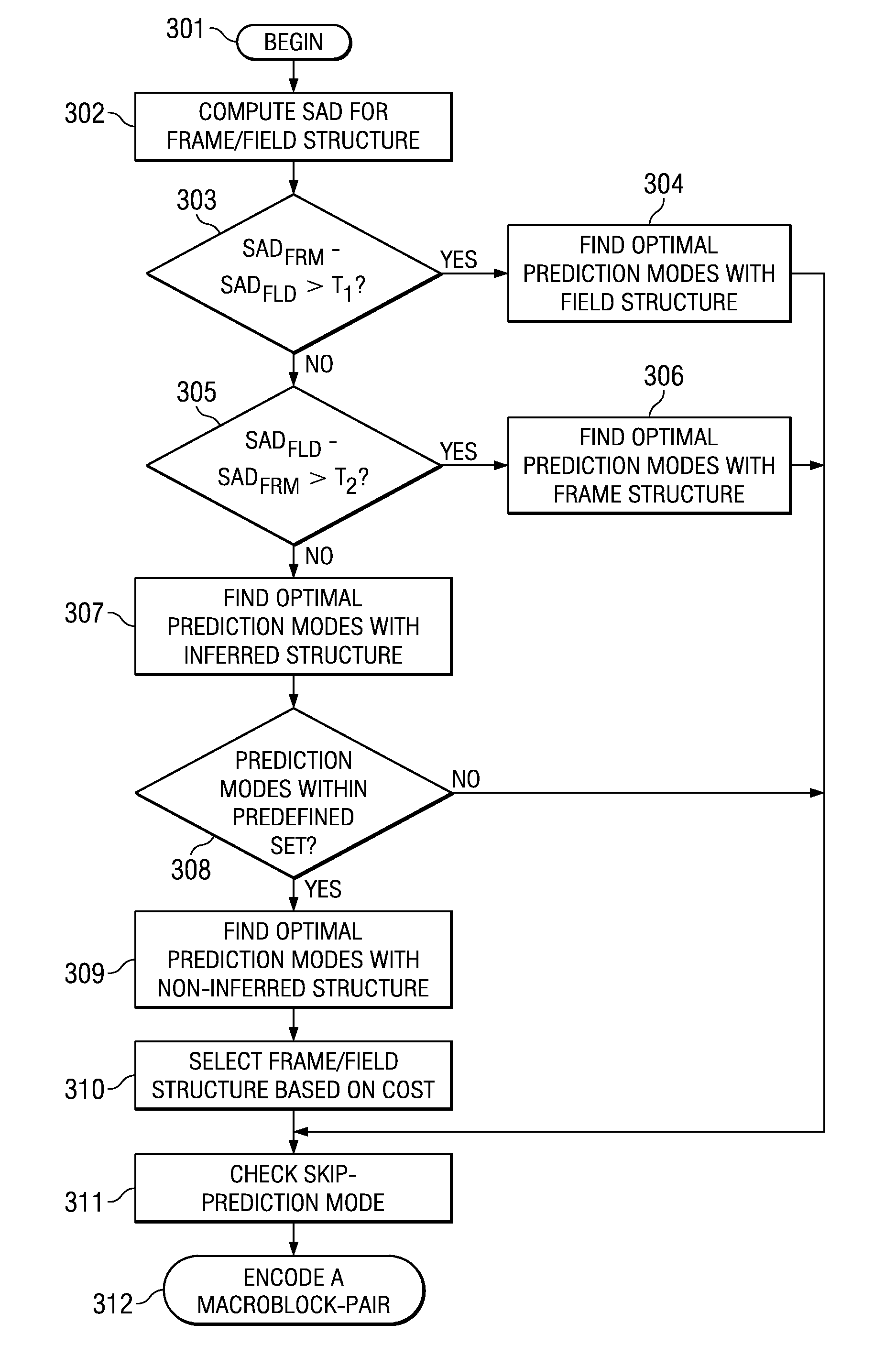
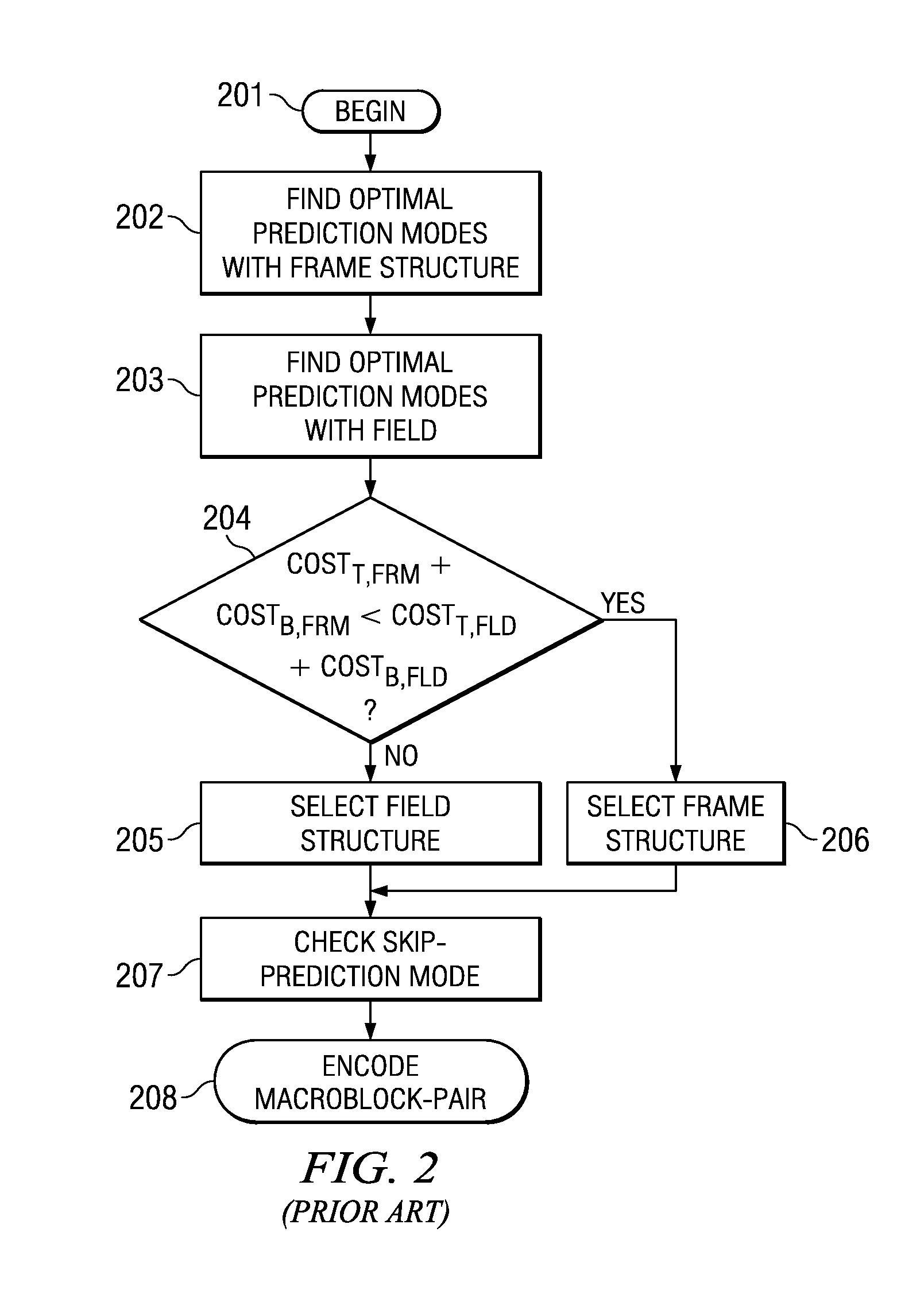
Fast Macroblock Structure Decision Using SAD Discrepancy and its Prediction Mode
ActiveUS20100074339A1Facilitate decision-makingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputation complexityComputational complexity theory
The present invention is a method to accelerate the frame / field decision by estimating more suitable structure using SAD (sum of absolute difference) between picture samples and their mean. Next the uses the correlation observed between the optimal macroblock prediction modes found with the inferred structure and the probability of the non-inferred structure being better than the inferred one. The invention can lead to the significant reduction of the computational complexity at the cost of slight degradation of coding efficiency.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Reduced computational complexity of bit allocation for perceptual coding
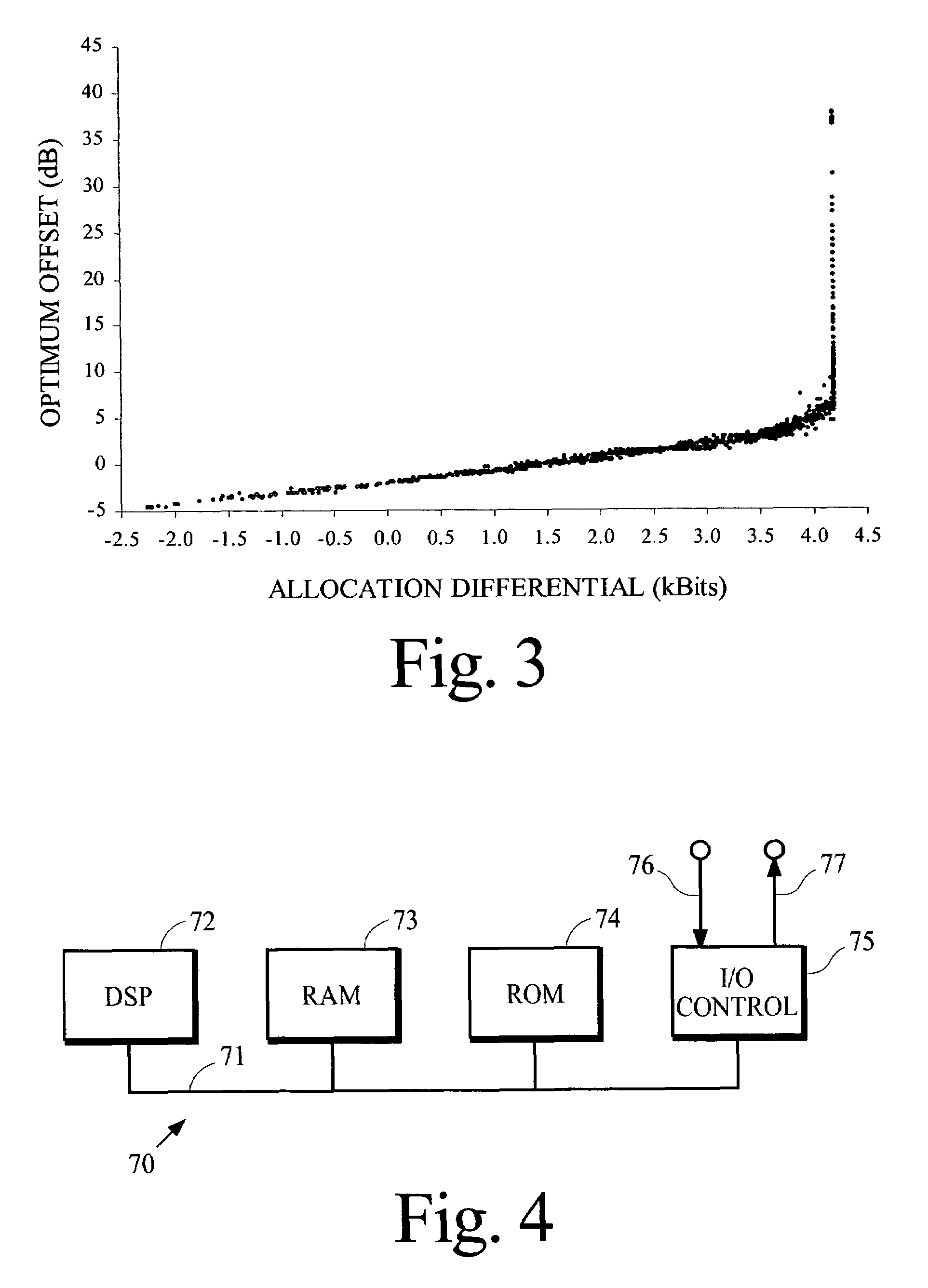
InactiveUS7406412B2Increase valueEfficient implementationSpeech analysisComputation complexityFrequency spectrum
A process that allocates bits for quantizing spectral components in a perceptual coding system is performed more efficiently by obtaining an accurate estimate of the optimal value for one or more coding parameters that are used in the bit allocation process. In one implementation for a perceptual audio coding system, an accurate estimate of an offset from a calculated psychoacoustic masking curve is derived by selecting an initial value for the offset, calculating the number of bits that would be allocated if the initial offset were used for coding, and estimating the optimum value of the offset from a difference between this calculated number and the number of bits that are actually available for allocation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Reducing computational complexity in determining an illuminant of a scene
ActiveUS20100103289A1Color signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexityColor cues
In an embodiment, computational complexity of estimating the actual illuminant of a scene is reduced by examining only a subset of the pixel values generated for a received image frame. In another embodiment, number of rotations of color values is minimized by selecting an area which contains the color cue values of a color in an original / unrotated coordinate space and has boundaries which parallel the axis of the original coordinate space, and rotating a color value only if the color value is within the selected area. In another embodiment, such an area is used in conjunction with a histogram-based approach to determine the actual illuminant.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method and apparatus to encode a moving image with fixed computational complexity
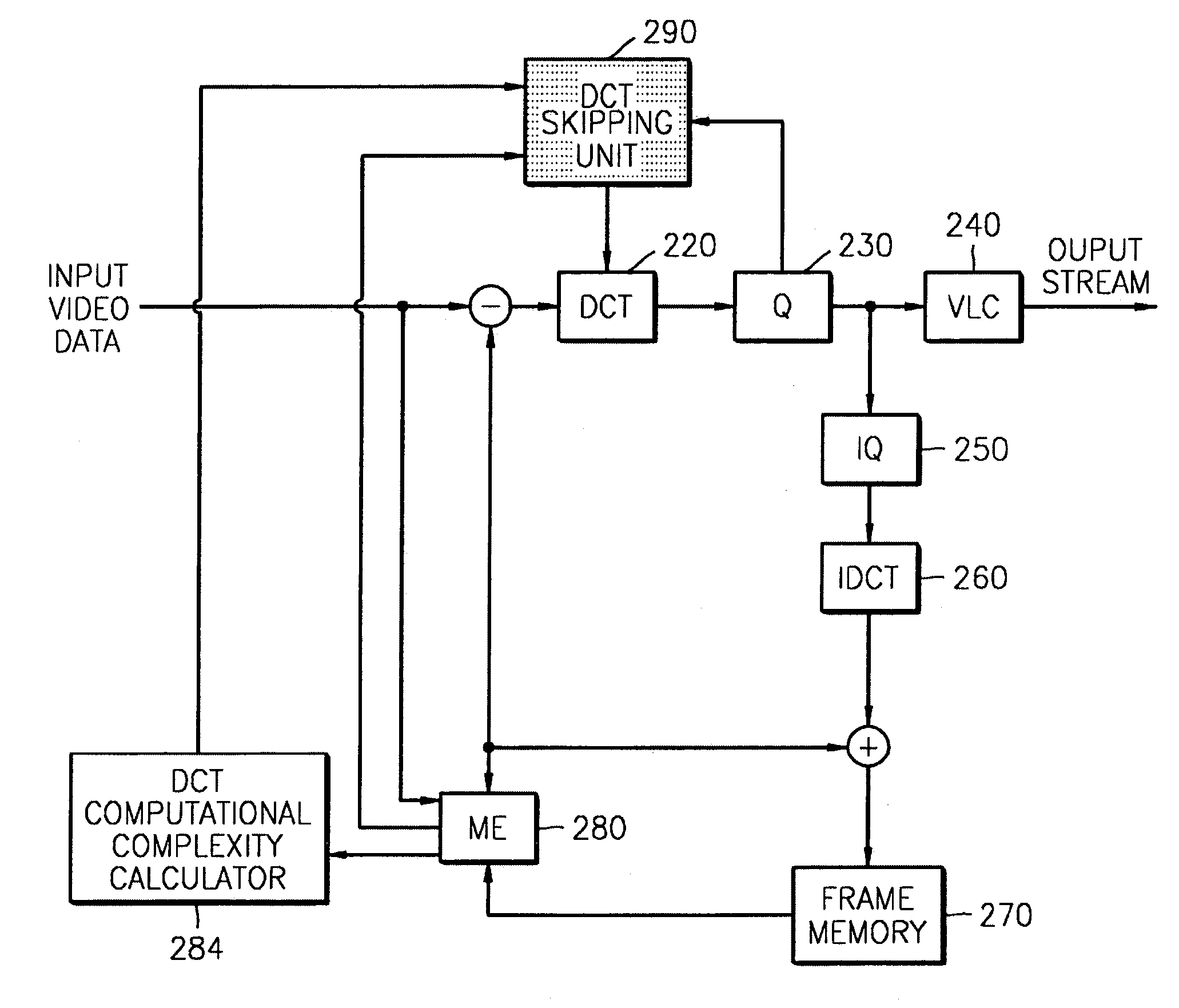
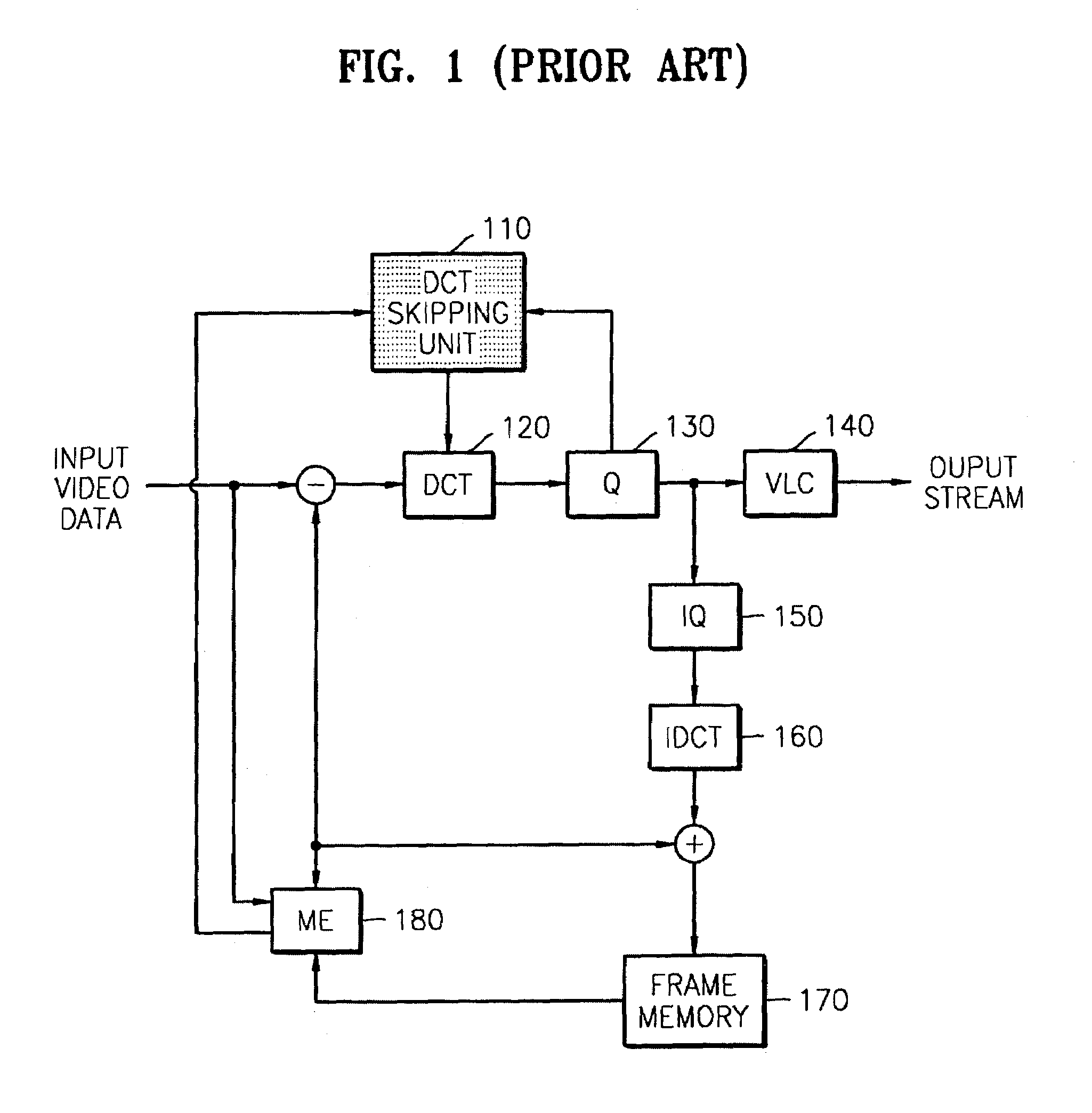
InactiveUS7123654B2Pulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputational scienceComputation complexity
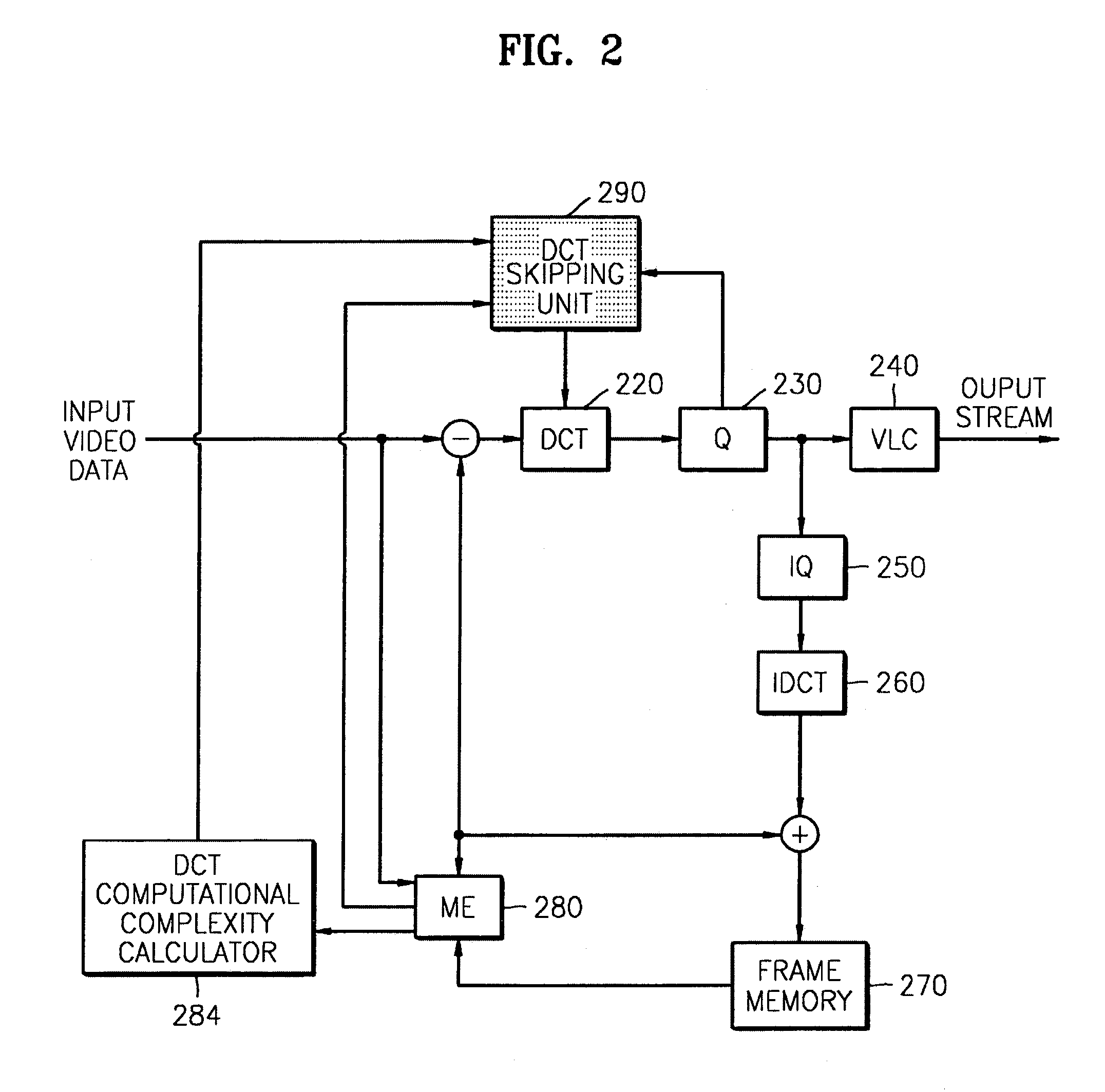
An apparatus and method thereof to encode a moving image include a discrete cosine transform (DCT) unit performing a DCT process on input video data, a quantizer, and a motion estimation (ME) unit calculating a motion vector and a SAD per macro block. A DCT computational complexity calculator calculates a computational complexity of the ME unit, estimates a difference between the ME computational complexity and a target ME computational complexity, and updates a target DCT computational complexity based on the estimated difference. A DCT skipping unit sets a threshold value to determine whether to skip performing the DCT process on the input video data, based on the target DCT computational complexity updated by the DCT computational complexity calculator, compares the SAD per macro block, and the quantization parameter with the threshold value, and determines whether to allow the DCT unit to perform the DCT process on the input video data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A binary classification method based on seepage analysis
ActiveCN109376790AHigh expressionExpressiveCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsComputational complexity theoryPhase change
The invention provides a binary classification method based on seepage analysis, which comprises the following steps: 1, constructing an index network based on a data vector; 2, seepage analysis of index network; 3, constructing a likelihood function and determining a key threshold; 4. evaluation and validation of the model. Through the above steps, the invention further provides technical supportand theoretical support for large-scale, high-dimensional and high-complexity system group classification and evaluation classification effect based on seepage analysis; in addition, the background knowledge is expressed by graph model and the network analysis is carried out by using the seepage theory based on phase change, which reduces the computational complexity, converges quickly and is suitable for large-scale computation and reduces the computational cost.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multiuser detector for variable spreading factors
InactiveUS7136369B2Reduce computational complexityMinimize numeric operationRadio transmissionAsynchronous cdmaComputation complexity
A multiuser detector that detects and decodes synchronous or asynchronous CDMA subchannels having different spreading factors with reduced computational complexity. The multiuser detector is compatible with ZF-BLE, MMSE, decorrelating detectors and the like using Cholesky decomposition to minimize numeric operations. The system and method arranges the columns of system transmission response matrices representing the response characteristics of individual users into a total system transmission response matrix which represents a plurality of matched-filter responses for a given block of received data. The invention in conjunction with Cholesky decomposition reduces the number of required mathematic operations prior to parallel matched filtering.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Computational complexity self-adaptation NURBS splined interpolation method
ActiveCN104238457AReduce computational complexityEfficient sharingProgramme controlComputer controlComputation complexityComputation process
The invention relates to the interpolation point computing technology of a numerical control system, in particular to a computational complexity self-adaptation NURBS splined interpolation method. By analyzing the computing structure generated when an interpolation point is computed with a de Boor-Cox method, a computational complexity formula for solving the interpolation point is built; the computing structure generated when the interpolation point is computed with a basis function method is simplified, the computational complexity is reduced by sharing an intermediate result, and a computational complexity formula used in the solving process of the basis function method is built; the performance judgment formulas generated when the interpolation point is computed with the de Boor-Cox method and the basis function method are built, and in the splined interpolation process, the method low in computational complexity is dynamically selected through the performance judgment formulas for interpolation. By the application of the method, the intermediate result in the computing process of a basis function algorithm can be effectively shared, the computational complexity of the algorithm is reduced, an efficient interpolation algorithm can be dynamically selected in a self-adaptation mode, and the NURBS splined interpolation efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENYANG GOLDING NC & INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com