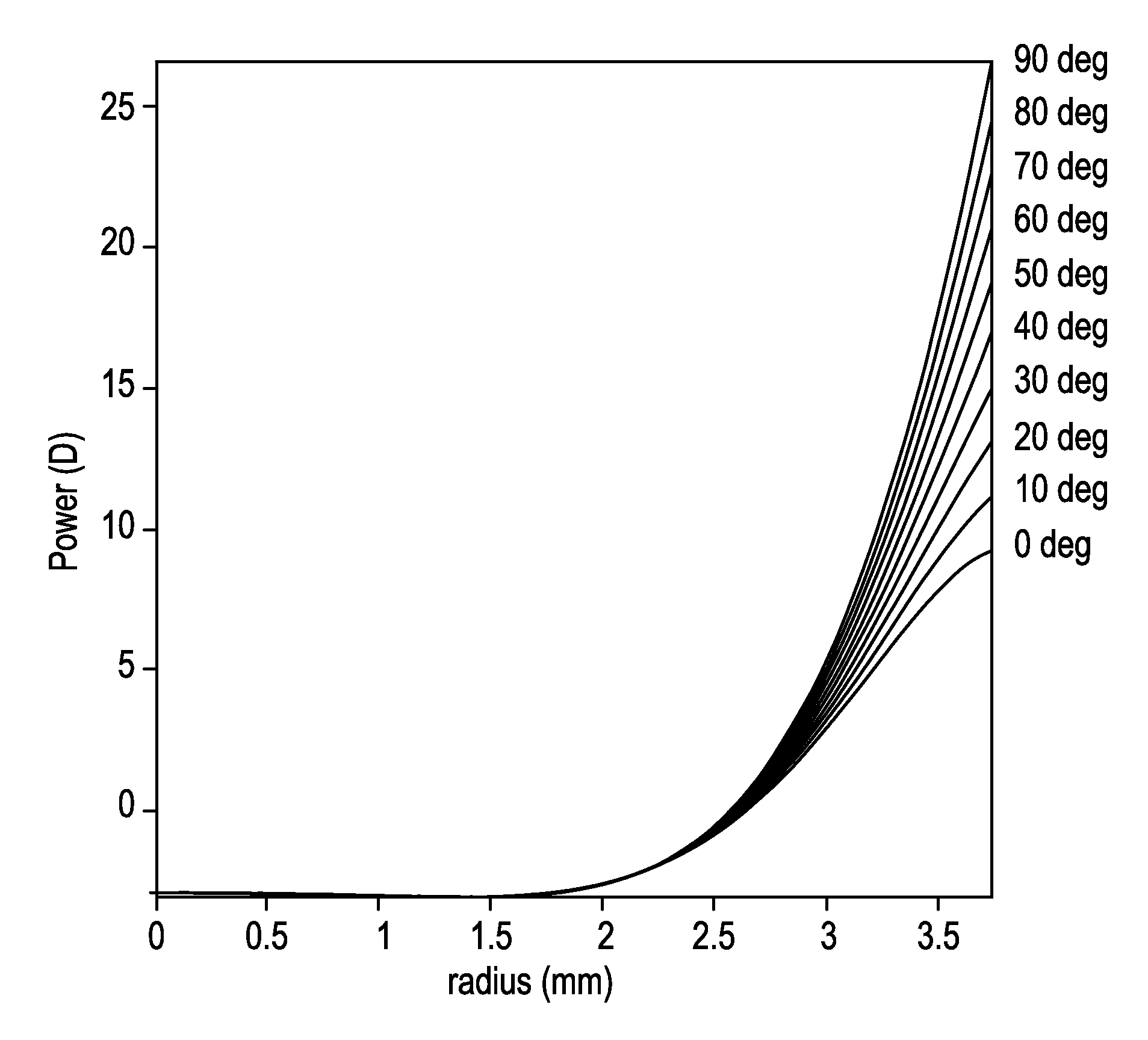
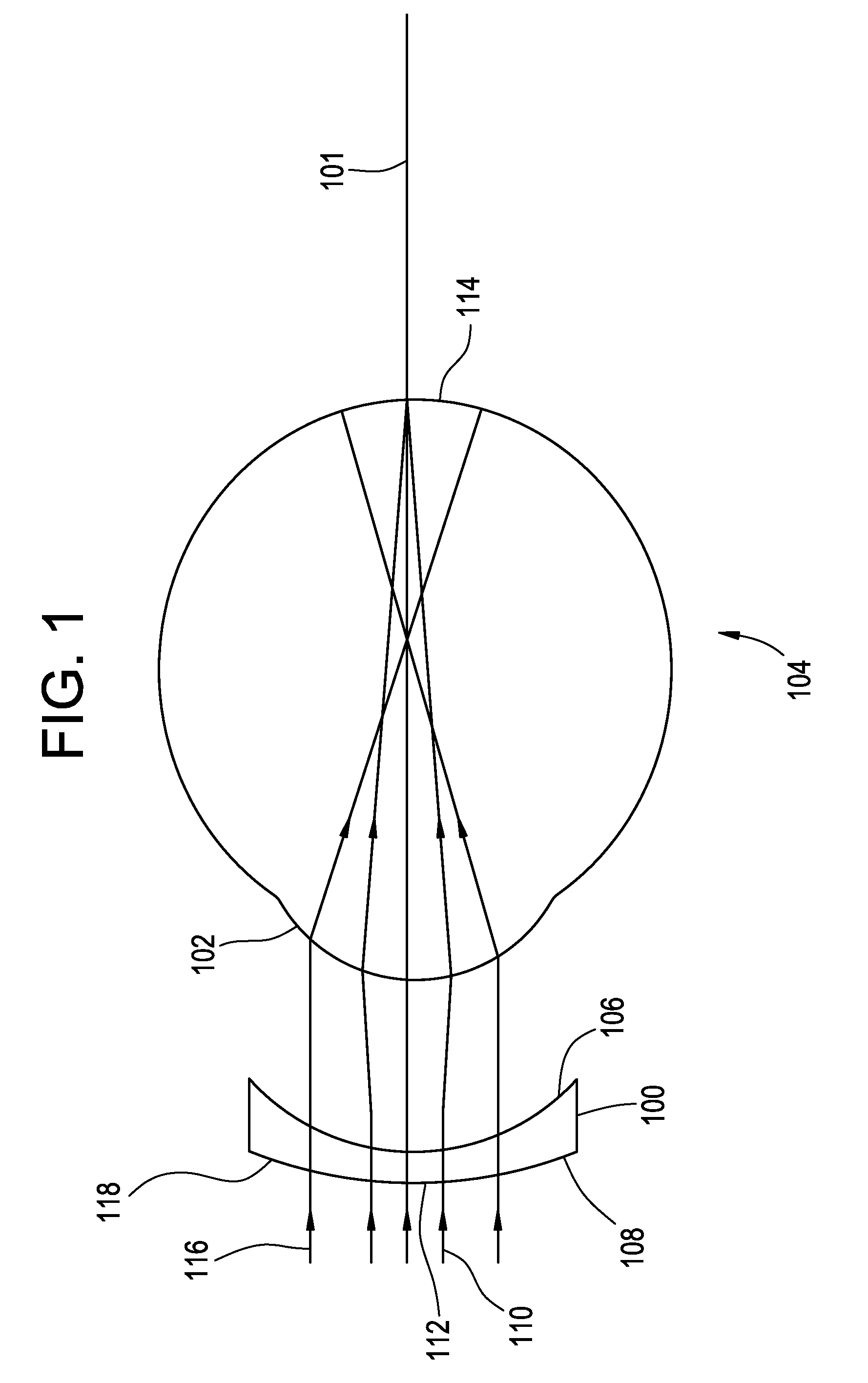
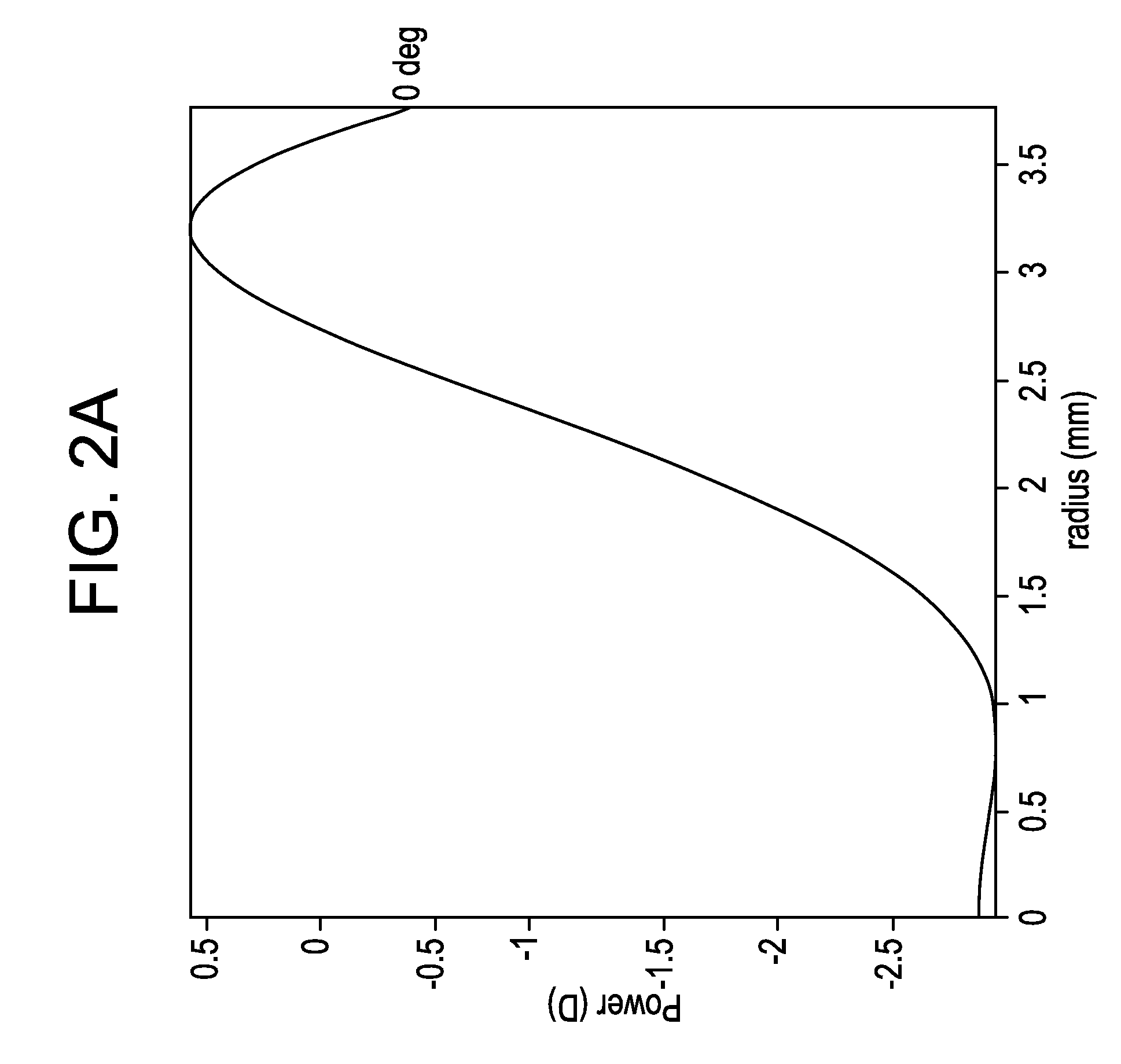
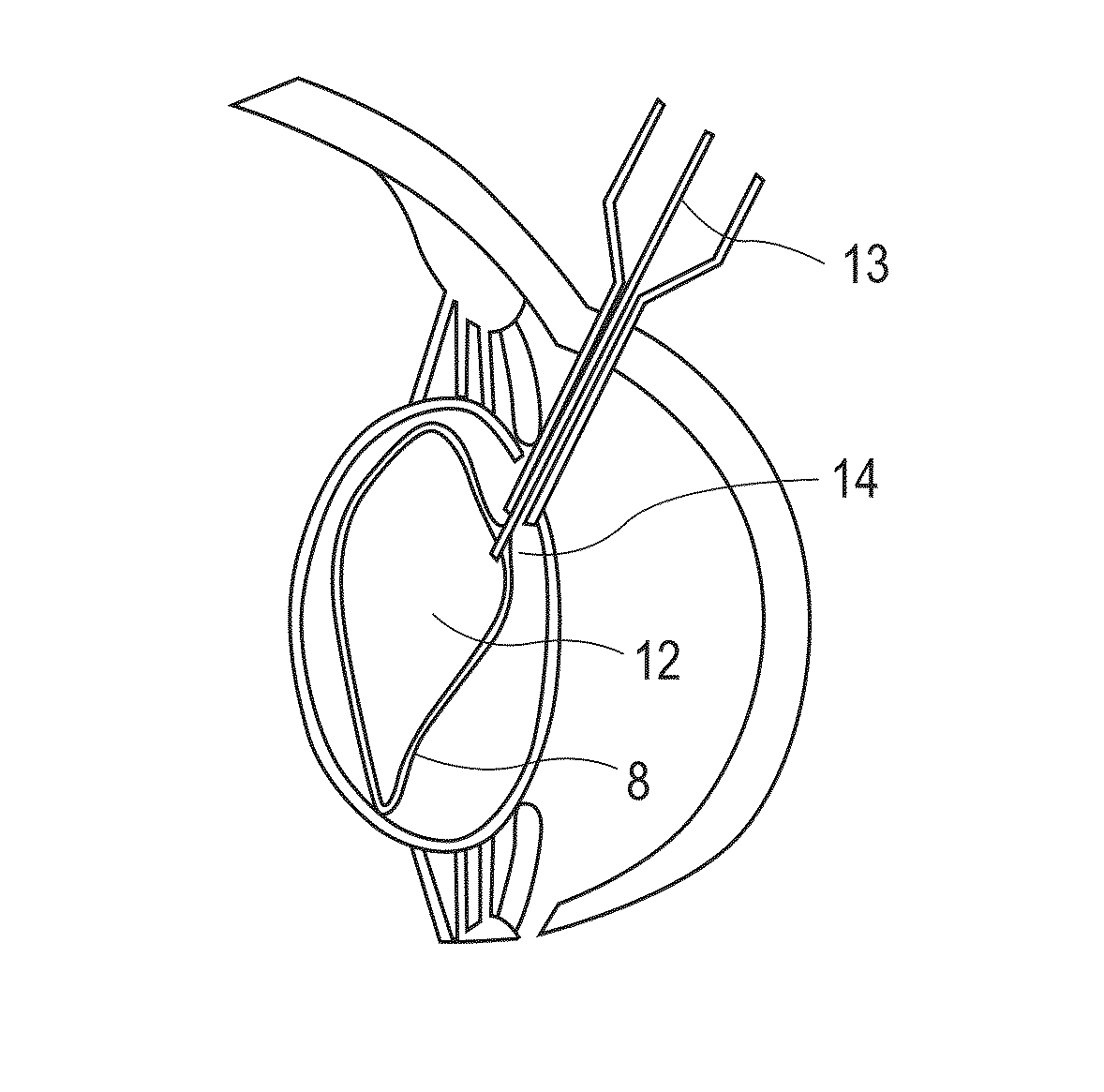
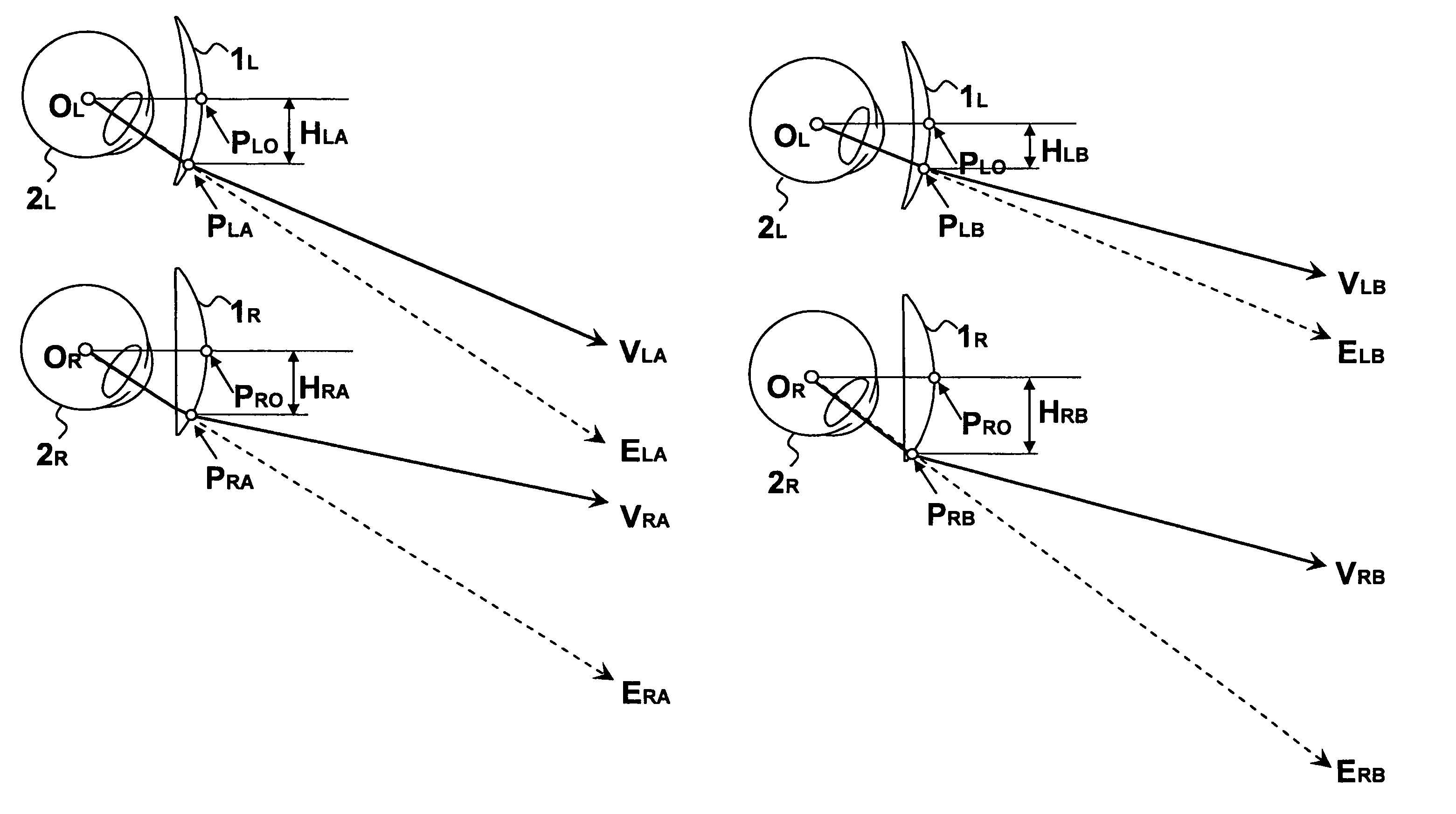
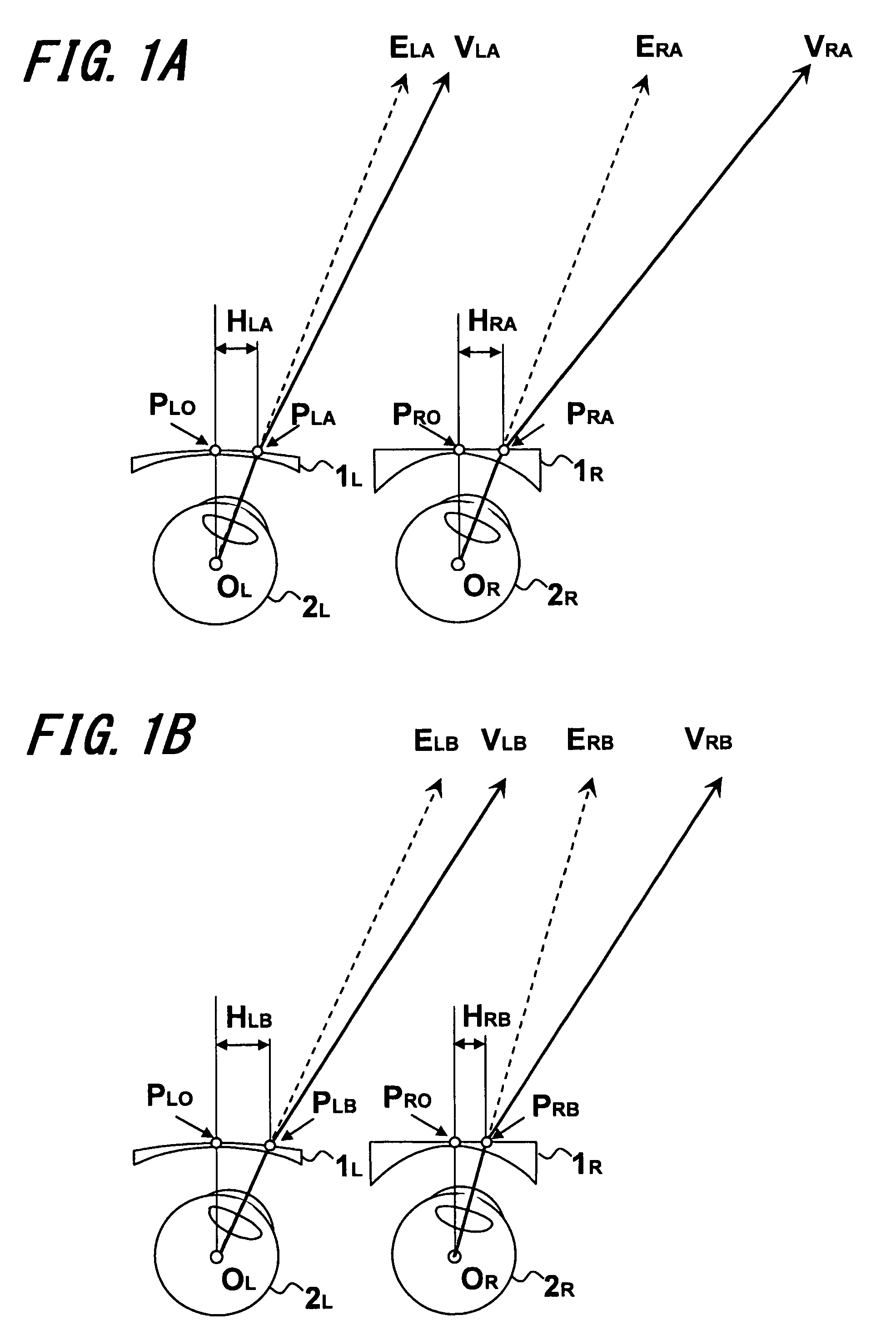
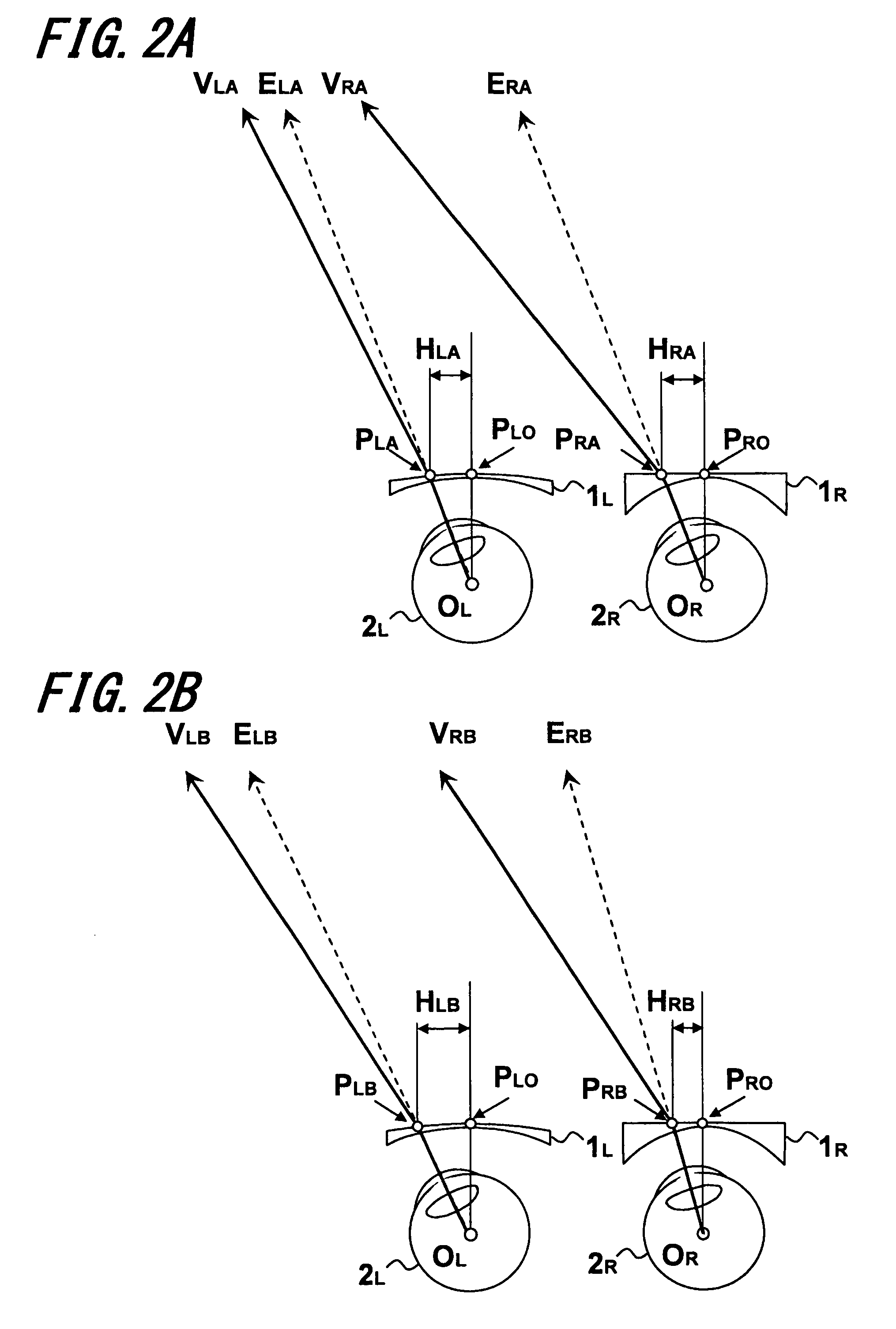
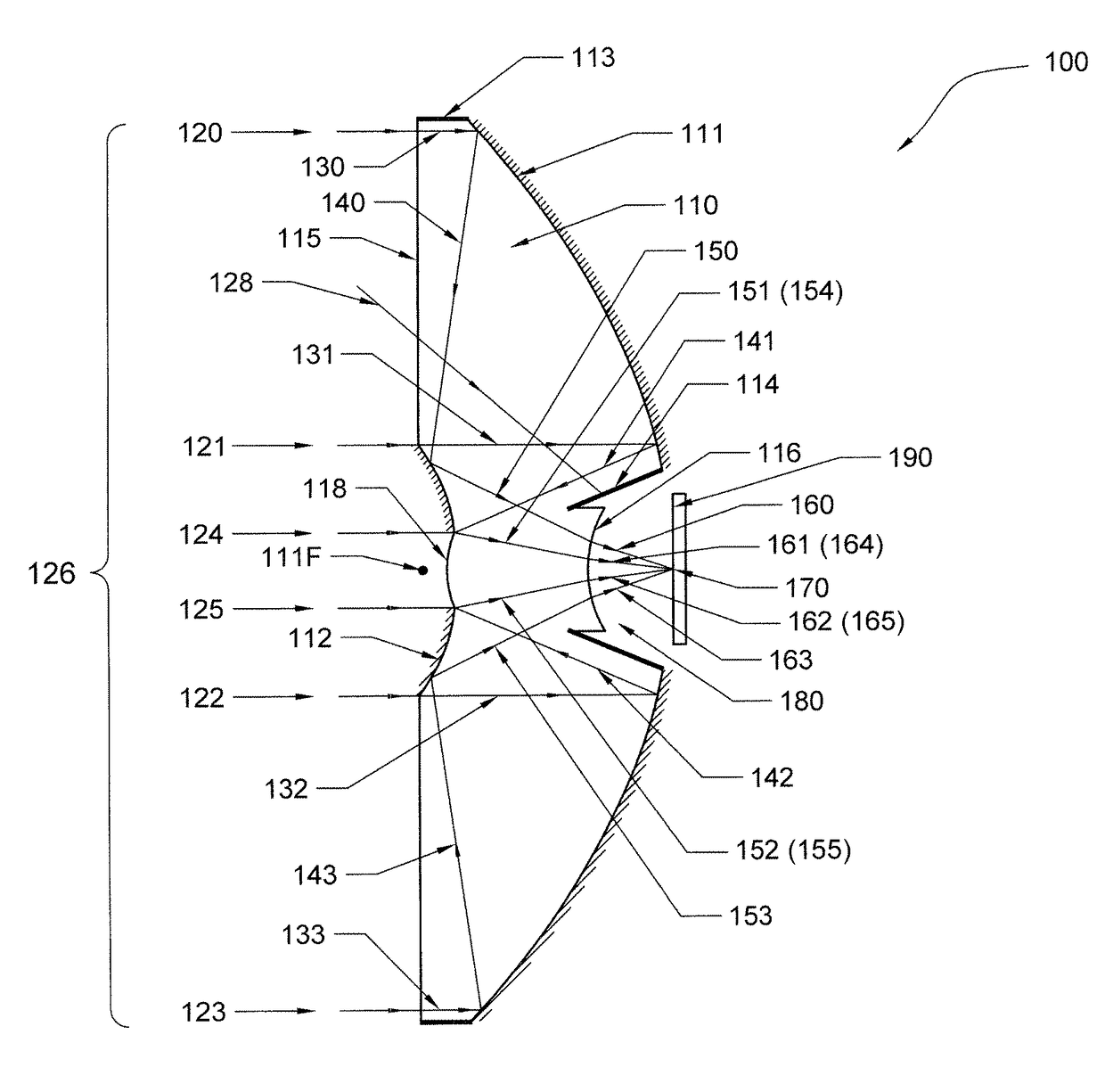
Patents
Literature
54 results about "Dioptrics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
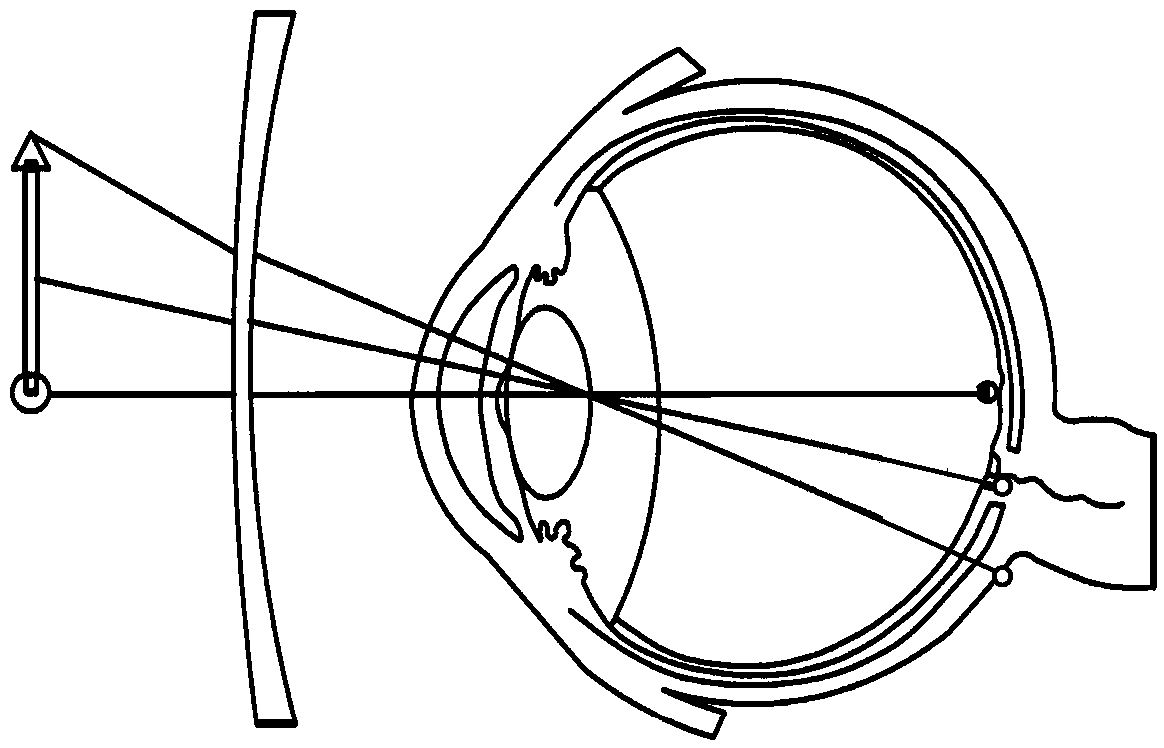
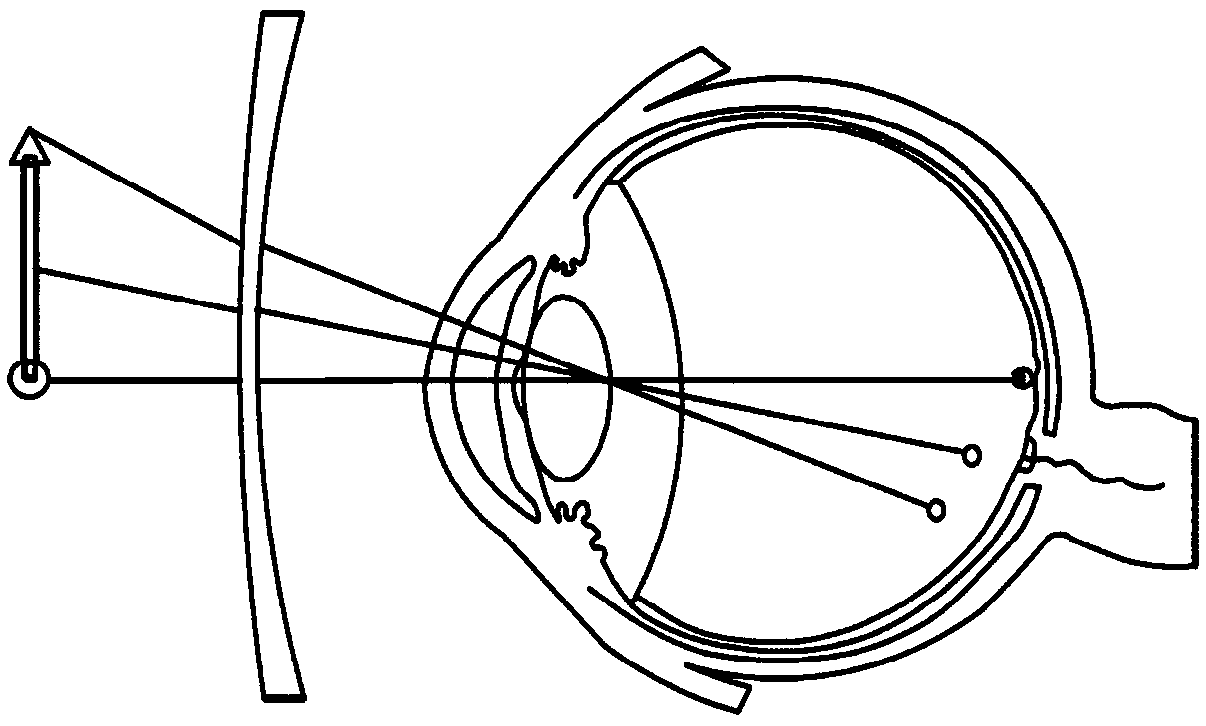
Dioptrics is the study of the refraction of light, especially by lenses. Telescopes that create their image with an objective that is a convex lens (refractors) are said to be "dioptric" telescopes. An early study of dioptrics was conducted by Ptolemy in relationship to the human eye as well as refraction in media such as water. The understanding of the principles of dioptrics was further expanded by Alhazen, considered the father of modern optics.
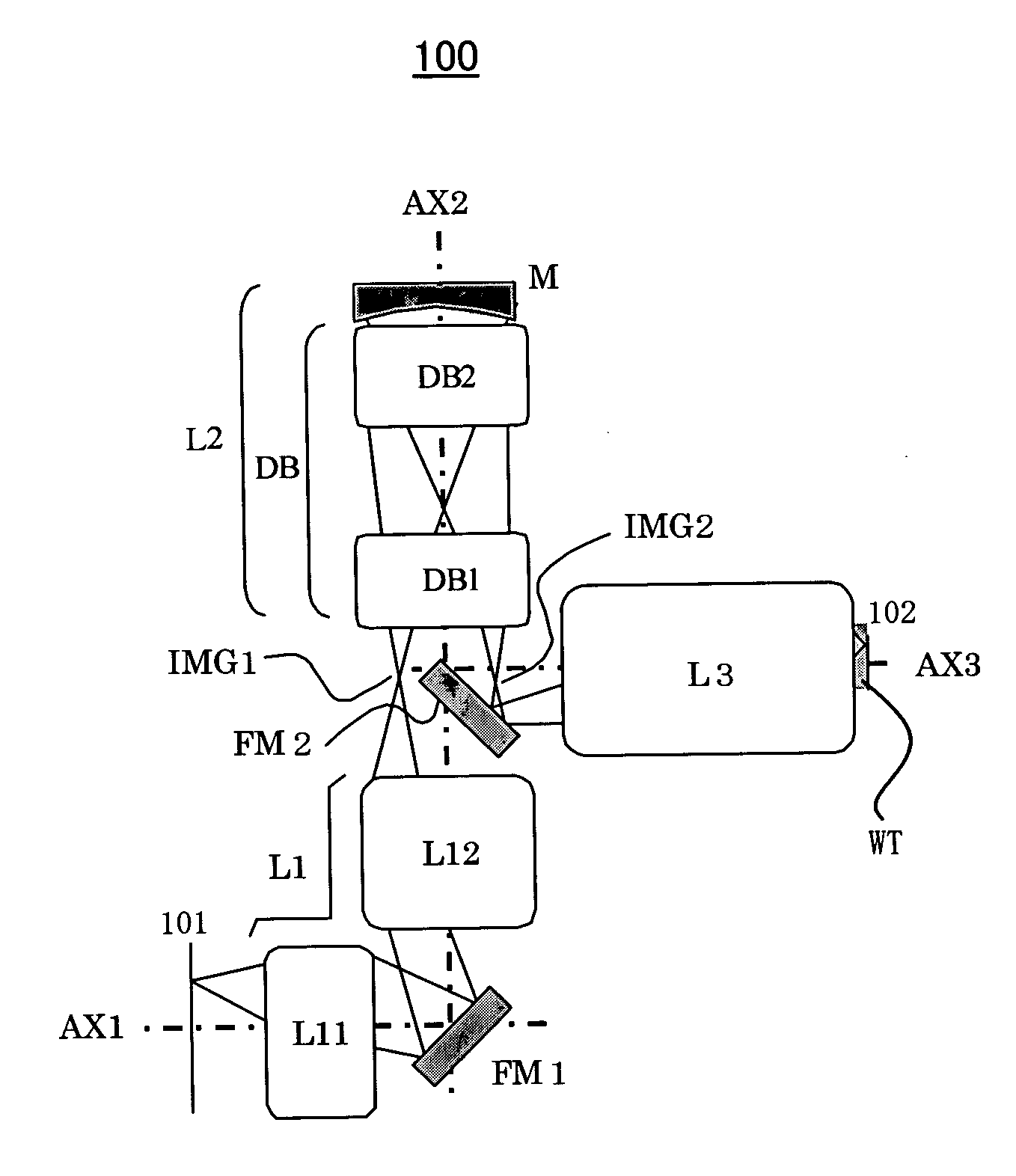
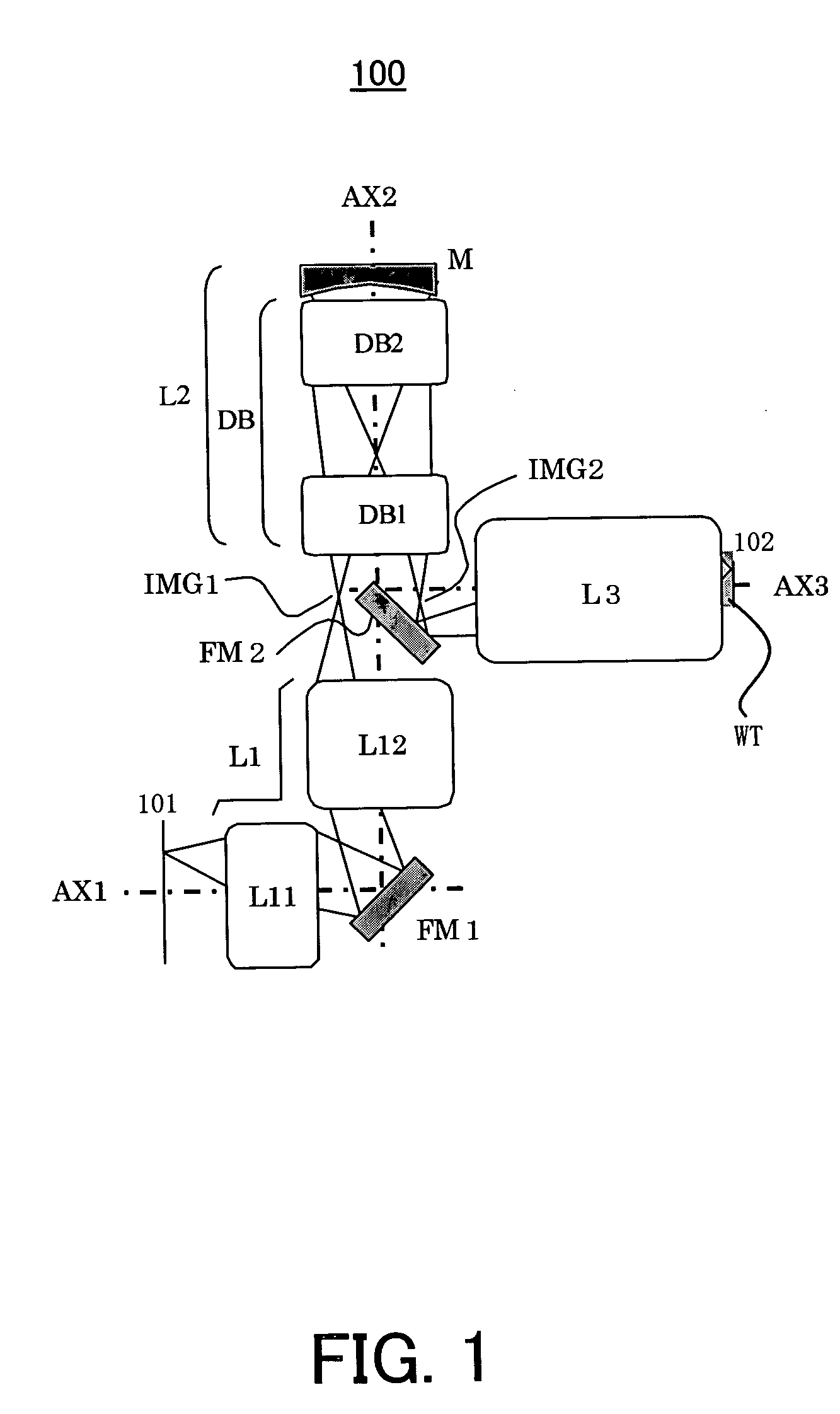
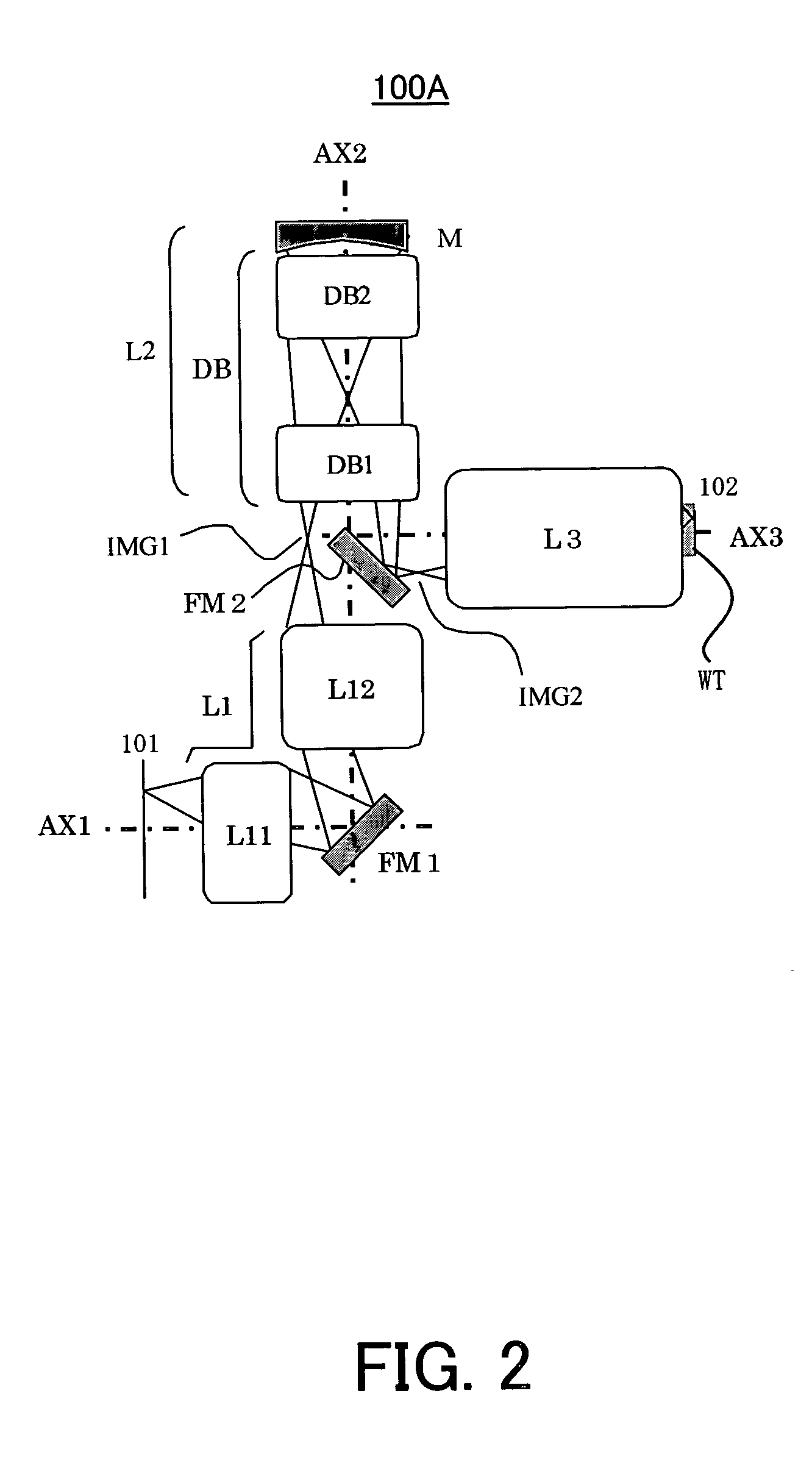
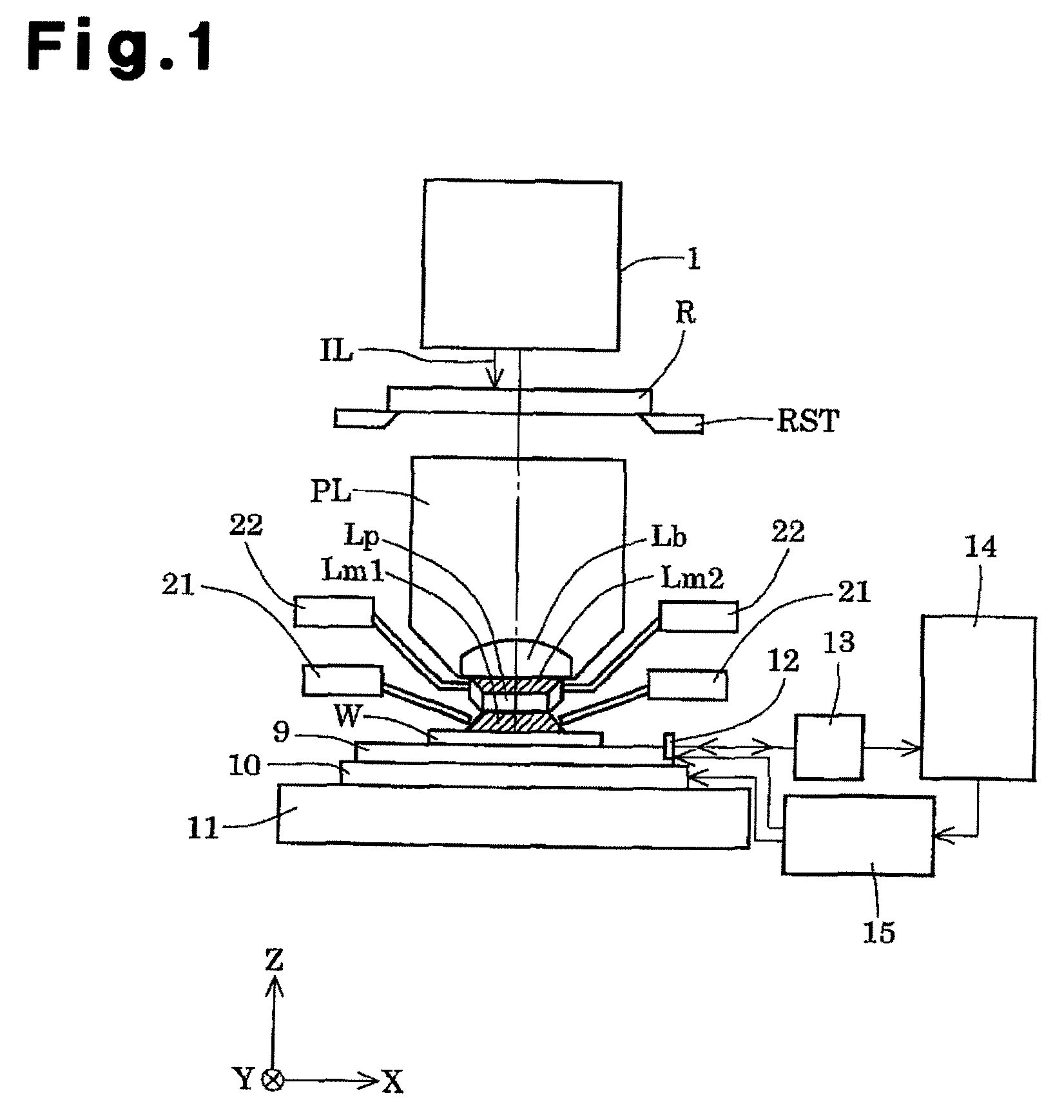
Projection optical system, magnification projection optical system, magnification projection apparatus, and image projection apparatus
ActiveUS7048388B2Increase in sizeReduce spacingProjectorsNon-linear opticsProjection opticsIntermediate image
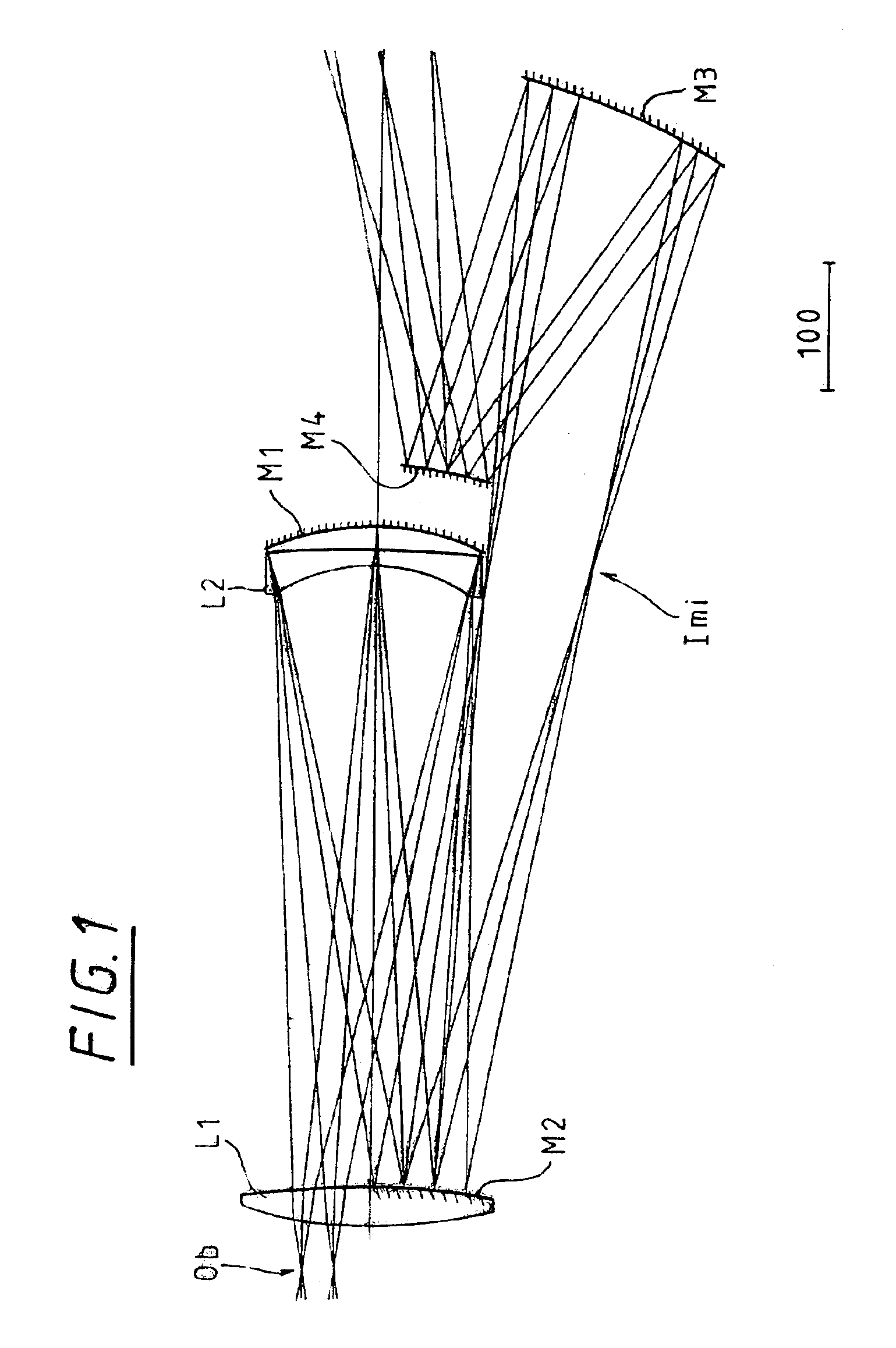
A projection optical system guiding and projecting a light beam from a projected object surface onto a projection surface in an upstream-downstream direction through a transmission dioptric system and a reflection dioptric system. An intermediate image surface of the projected object surface is positioned closer to the reflection dioptric system than to the transmission dioptric system, and an intermediate image on the intermediate image surface is formed as the final image on the projection surface via the reflecting mirrors, which include at least one anamorphic polynomial free-formed surface having different vertical and lateral powers. A light beam from the reflection dioptric system to the projection surface is guided at an angle to a normal of the projection surface and the transmission dioptric system is decentered with respect to a normal of the projected object surface, the transmission refractive elements prevented from being decentered with respect to each other.
Owner:RICOH KK
Microlithographic reduction projection catadioptric objective
InactiveUS6873476B2Reduce complexityIncrease the number ofProjectorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntermediate imageVirtual image
The invention concerns a microlithographic reduction projection catadioptric objective having an even number greater than two of curved mirrors, being devoid of planar folding mirrors and featuring an unobscured aperture. The objective has a plurality of optical elements, and no more than two optical elements deviate substantially from disk form. The objective has an object side and an image side, and has in sequence from the object side to the image side a catadioptric group providing a real intermediate image, a catoptric or catadioptric group providing a virtual image, and a dioptric group providing a real image.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
Asymmetric lens design and method for preventing and/or slowing myopia progression
ActiveUS20140211147A1Slowing and retarding and preventing myopia progressionPrevent and retard progressionSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsNon symmetricEngineering
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Projection optical system, magnification projection optical system, magnification projection apparatus, and image projection apparatus
ActiveUS20060126032A1Increase in sizeReduce spacingProjectorsNon-linear opticsProjection opticsIntermediate image
A projection optical system guiding and projecting a light beam from a projected object surface onto a projection surface in an upstream-downstream direction through a transmission dioptric system and a reflection dioptric system of one or two reflecting mirrors. An intermediate image surface of the projected object surface is positioned closer to the reflection dioptric system than to the transmission dioptric system, and an intermediate image on the intermediate image surface is formed as the final image on the projection surface via the reflecting mirrors, which include at least one anamorphic polynomial free-formed surface having different vertical and lateral powers. A light beam from the reflection dioptric system to the projection surface is guided at an angle to a normal of the projection surface and the transmission dioptric system is decentered with respect to a normal of the projected object surface, the transmission refractive elements prevented from being decentered with respect to each other.
Owner:RICOH KK
Catadioptric projection optical system, exposure apparatus having the same, device fabrication method
InactiveUS20060028715A1Reduce distanceImprove imaging effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesProjection opticsIntermediate image
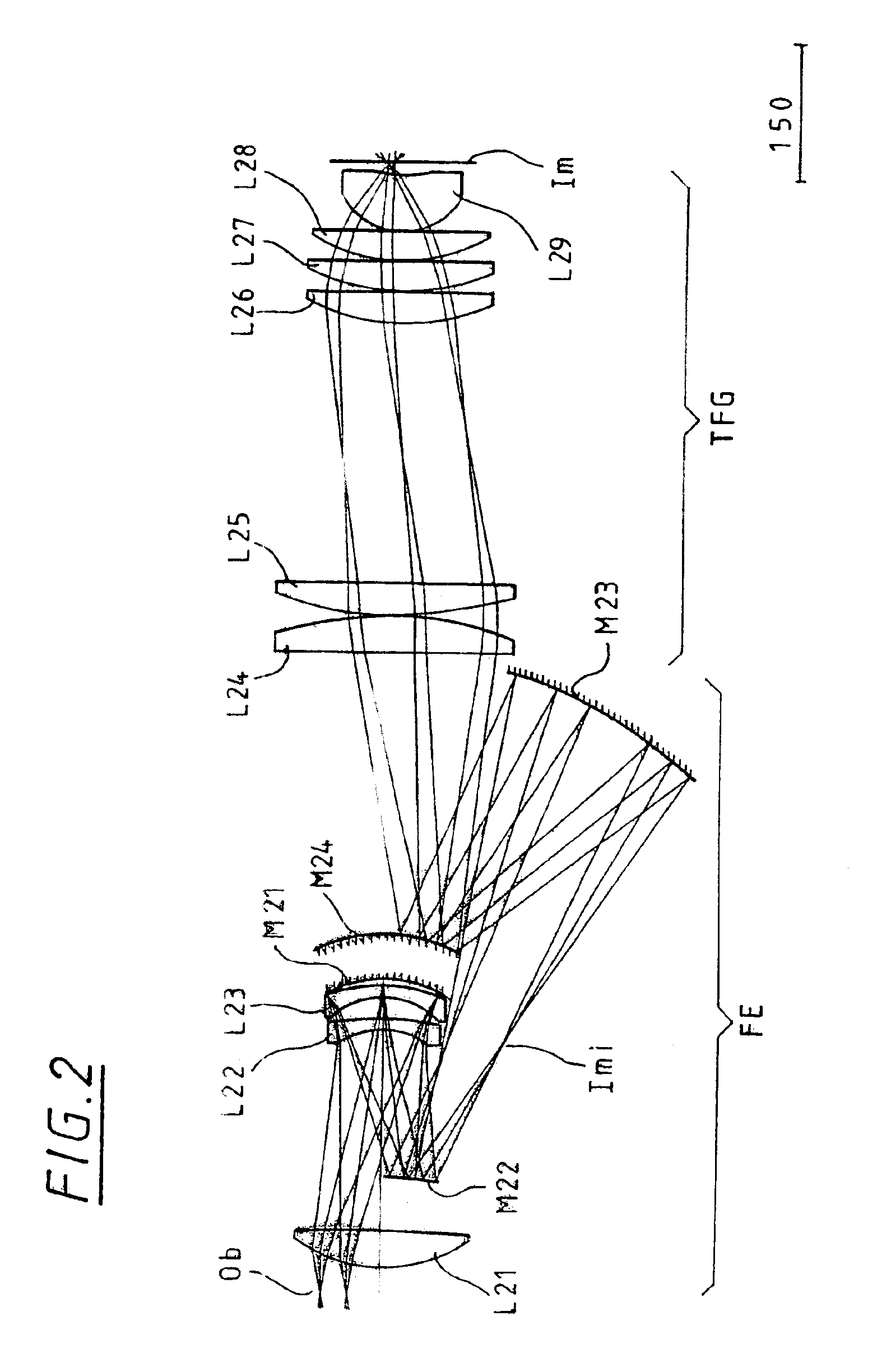
A catadioptric projection optical system for forming an intermediate image of a first object twice and for forming an image of the intermediate image onto a second object, said catadioptric projection optical system comprising, in order from the first object side and along an optical axis of said catadioptric projection optical system, a first dioptric group that does not form a reciprocating optical system (double-pass optical system) that an incidence light and reflected light pass, said first dioptric group including a first lens group that has a positive refractive power and a second lens group that has a positive refractive power, a catadioptric group that forms the reciprocating optical system (double-pass optical system), said catadioptric group including a third lens group that forms the reciprocating optical system (double-pass optical system), a second dioptric group that does not form the reciprocating optical system (double-pass optical system), a first deflective reflector that arranges between the first lens group and the second lens group, and a second deflective reflector that arranges between the second lens group and the third lens group or between the second dioptric group and the third lens group.
Owner:CANON KK
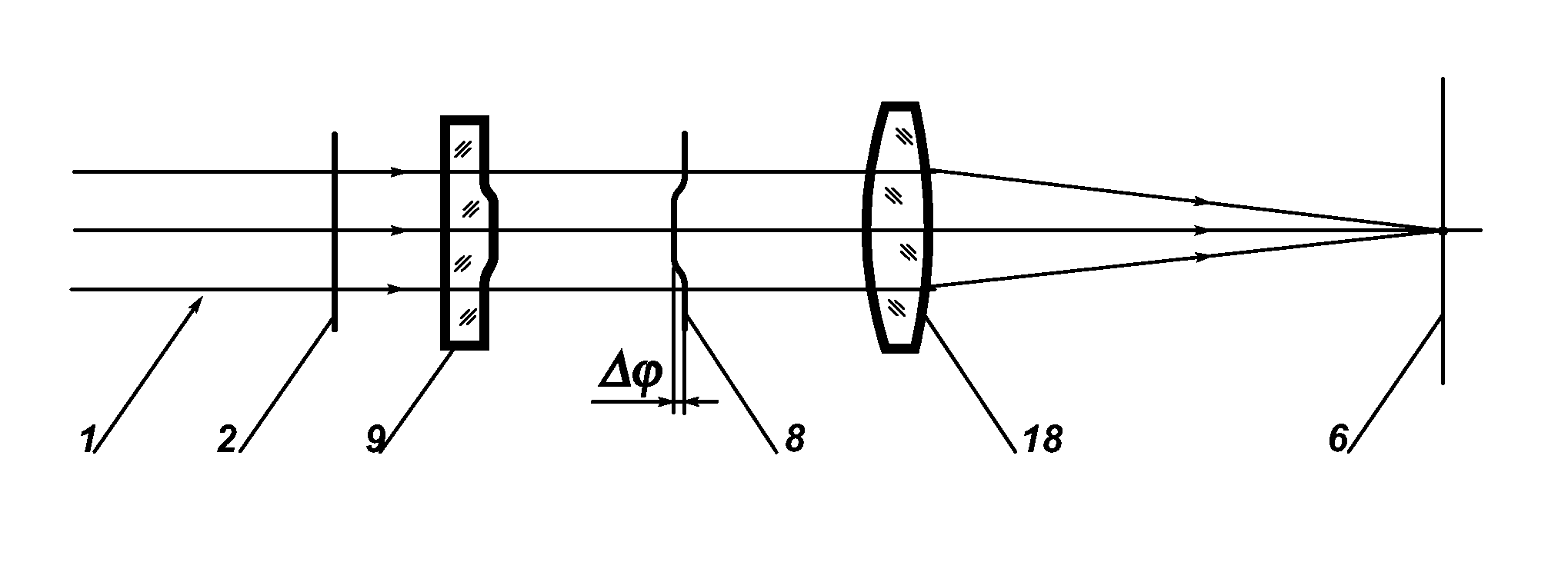
Method and apparatus for shaping focused laser beams
ActiveUS9285593B1Suppressed loss of laser energyUniform intensity distributionOptical elementsTelescopeLaser beams
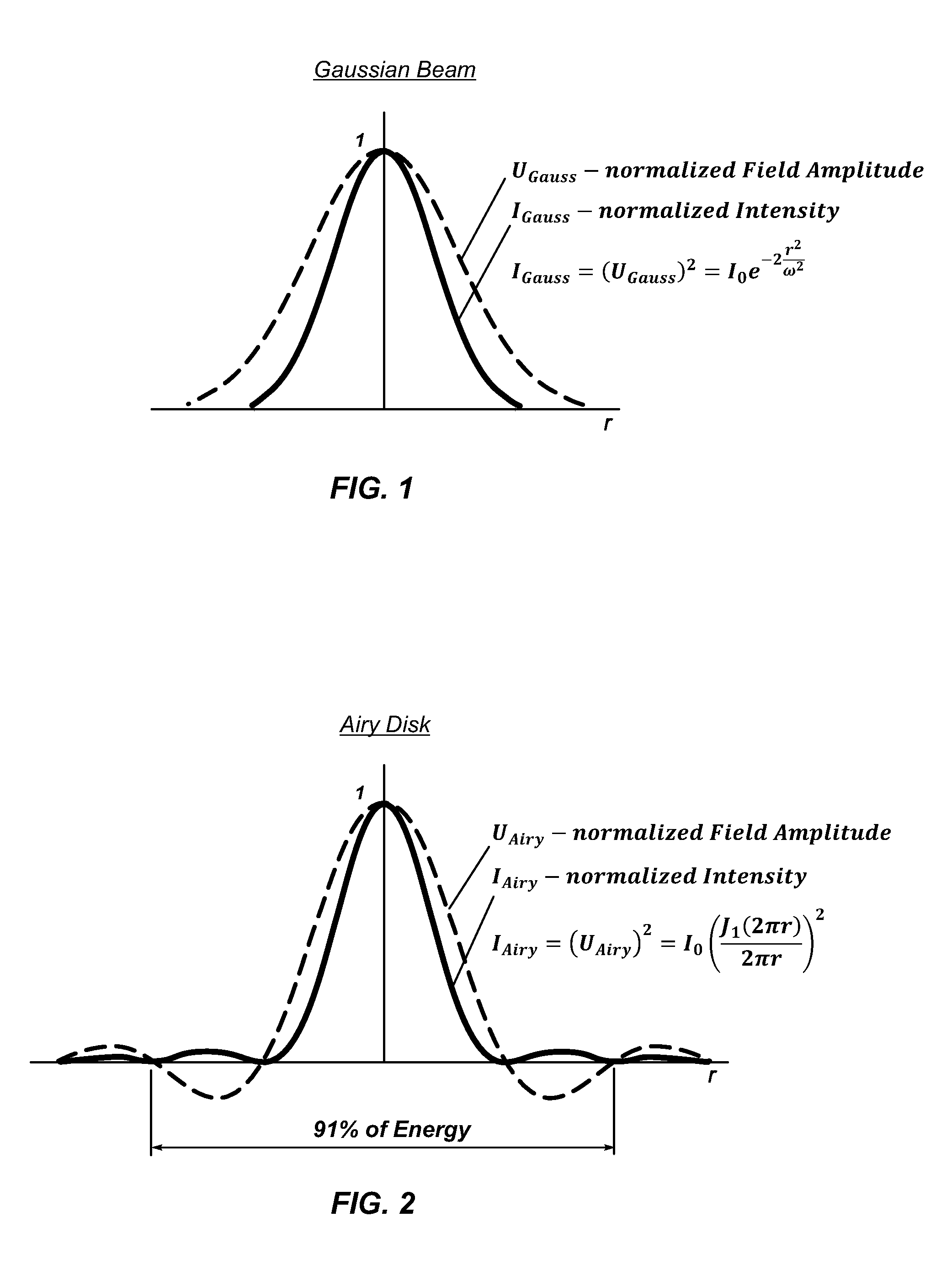
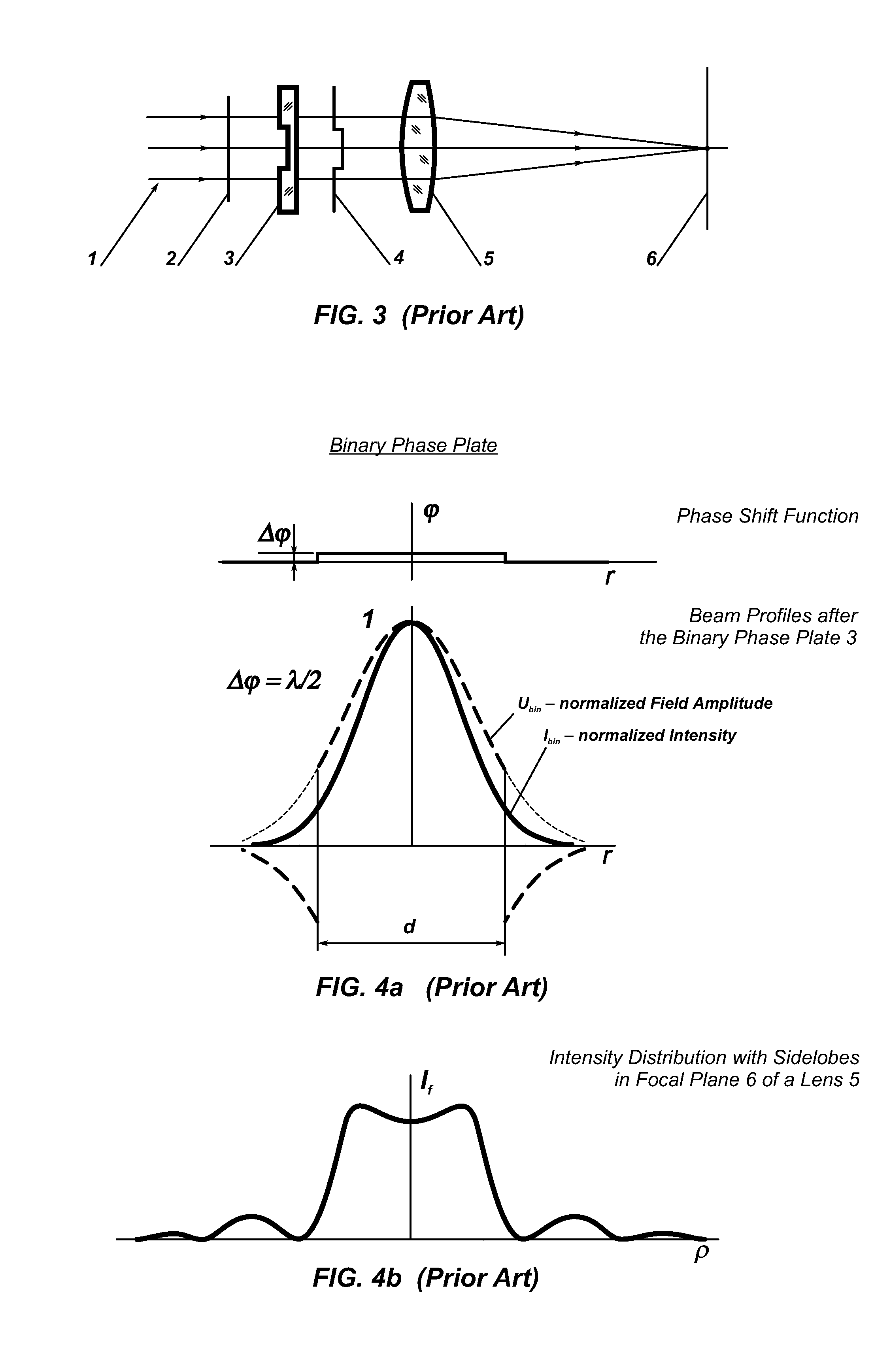
Beam shaping methods, systems, devices and apparatus to provide transformation of a TEM00 beam which intensity distribution is described by the Gaussian or similar functions to a focused spot of round or square shape with uniform intensity distribution achieved through introducing in the TEM00 beam a phase shift function with smooth phase transition and further focusing of the transformed beam; the resulting intensity distributions are created around the focal plane of a focusing optical system. The phase shift function is introduced by a phase transforming optical system implemented in apparatuses of the invention in form of a plate, or a telescope, or a collimator, or integrated to the focusing optical system: the phase transforming optical system including an aspheric optical surface providing the phase shift function with smooth phase transition. As a focusing optical system any diffraction limited optics with positive dioptric power can be applied.
Owner:ADLOPTICA OPTICAL SYST
Apparatus and method for topographical parameter measurements
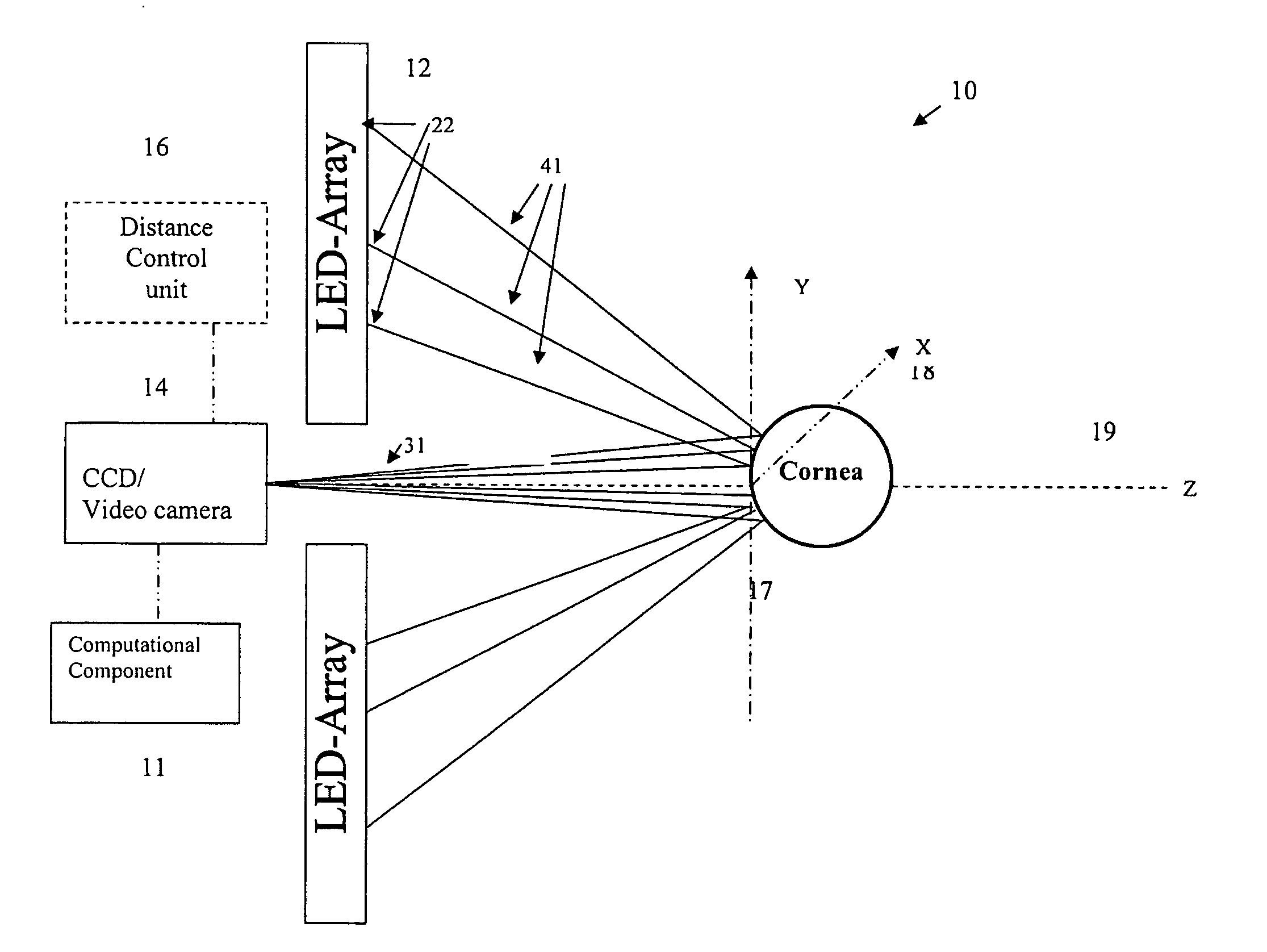
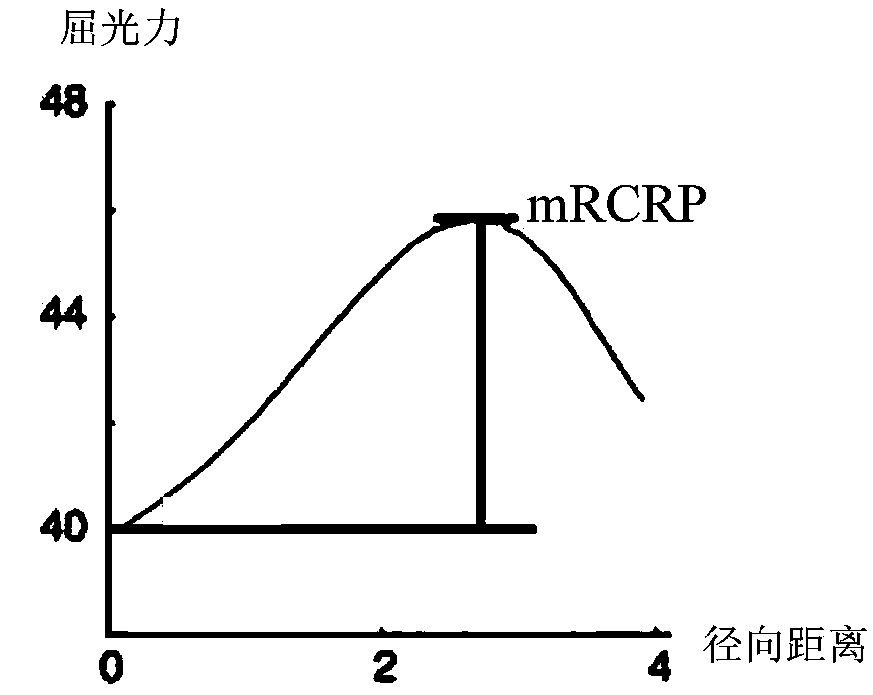
A topographical parameter measuring device and method utilizes a technique based on wave front reconstruction according to, e.g., Hartmann-Shack principles. The device includes a planar illuminator comprising a known array of illumination sources for projecting a light spot pattern onto a target surface. A CCD camera detects the positions of the reflected image spots in a manner similar to that in a Hartmann-Shack wave front sensor. The displacements of the light spots from reference coordinates are indicative of the slope of the surface at the plurality of sample points. A computational component is used to fit the slope data of a reference surface and the target surface to a polynomial, for example, a Zernike polynomial. The polynomial, properly weighted with the calculated coefficients, provides a continuous mapping of the elevation of the target surface. Based on the elevation data, all other topographical parameters including axial curvature, dioptric power, sphere, cylinder and others can be computed and displayed.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Pair of progressive power lens and method for designing same
ActiveUS20100271590A1Reduce and eliminate inconvenienceAvoid visionOptical partsUses eyeglassesMultifocal lenses
An object is to reduce the inconvenience given to the binocular vision function when wearing and using spectacles making use of a pair of progressive power lenses having different distance dioptric power for right and left. For this reason, the present invention associates, in a pair of progressive power lenses corresponding to the right and left eyes, an average dioptric power distribution and an astigmatism distribution determined from prescribed dioptric power and a wear state of one of the progressive power lenses with an average dioptric power distribution and an astigmatism distribution determined from prescribed dioptric power and a wear state of the other progressive power lens, and thereby average dioptric power distributions and astigmatism distributions of the respective progressive power lenses are changed.6
Owner:HOYA CORP
Asymmetric lens design and method for preventing and/or slowing myopia progression
ActiveUS8998408B2Higher effective add powerImprove visual effectsSpectales/gogglesOptical partsNon symmetricEngineering
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Accommodating intraocular lens
InactiveUS20140227437A1Bright colorEasy to findOptical articlesTissue regenerationElastomerIntraocular lens
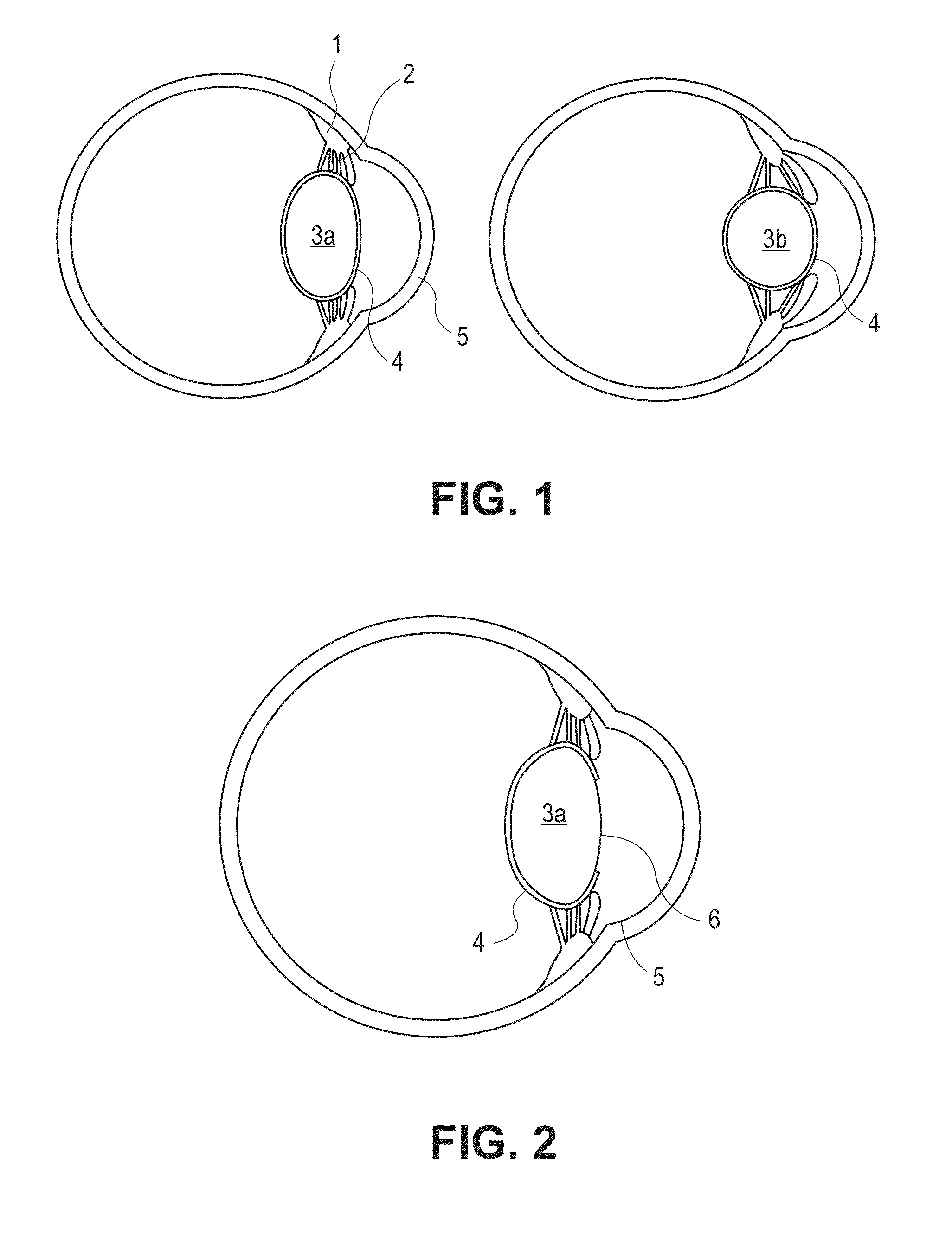
Systems, devices, and methods are presented for a prosthetic injectable intraocular lens. The lenses can be made from silicone, fluorosilicone, and phenyl substituted silicone and be semipermeable to air. One or more silicone elastomeric patches located outside the optical path on the anterior side but away from the equator can be accessed by surgical needles in order to fill or adjust optically clear fluid within the lens. The fluid can be adjusted in order to set a base dioptric power of the lens and otherwise adjust a lens after its initial insertion. The elastomeric patches are sized so that they self-seal after a needle is withdrawn. A straight or stepped slit in the patch can allow a blunt needle to more easily access the interior of the lens.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Projection optical system and image projector
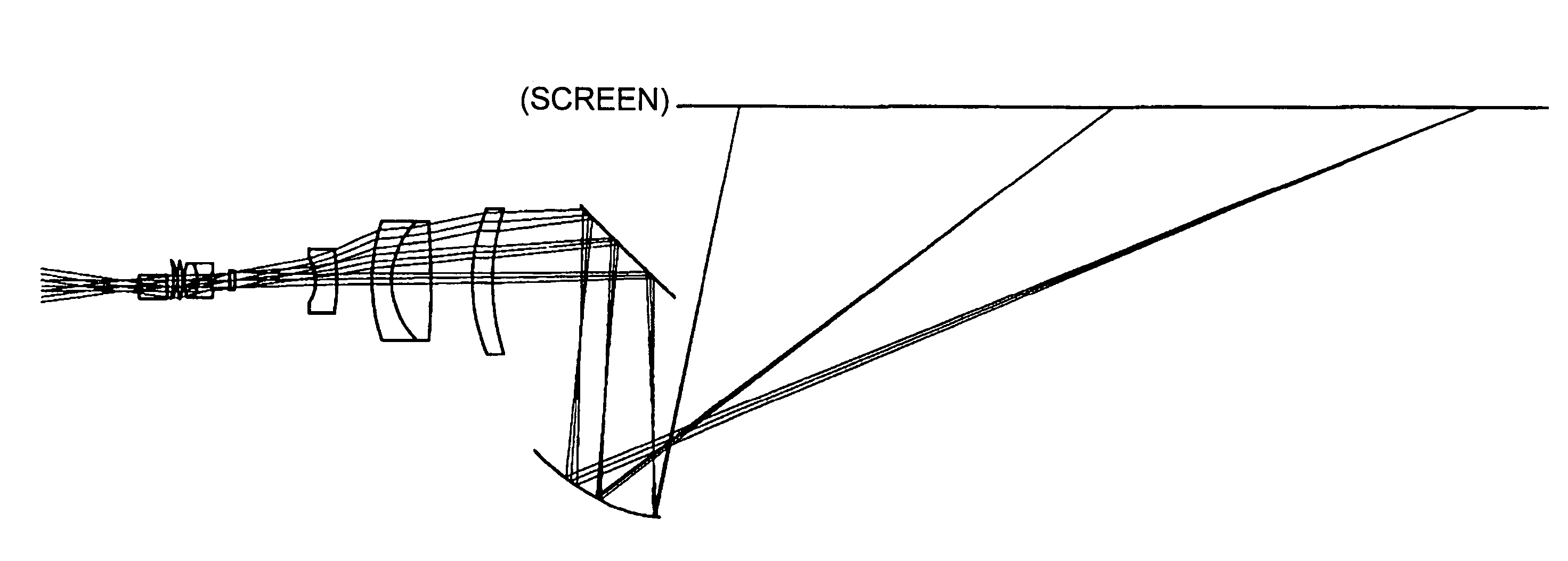
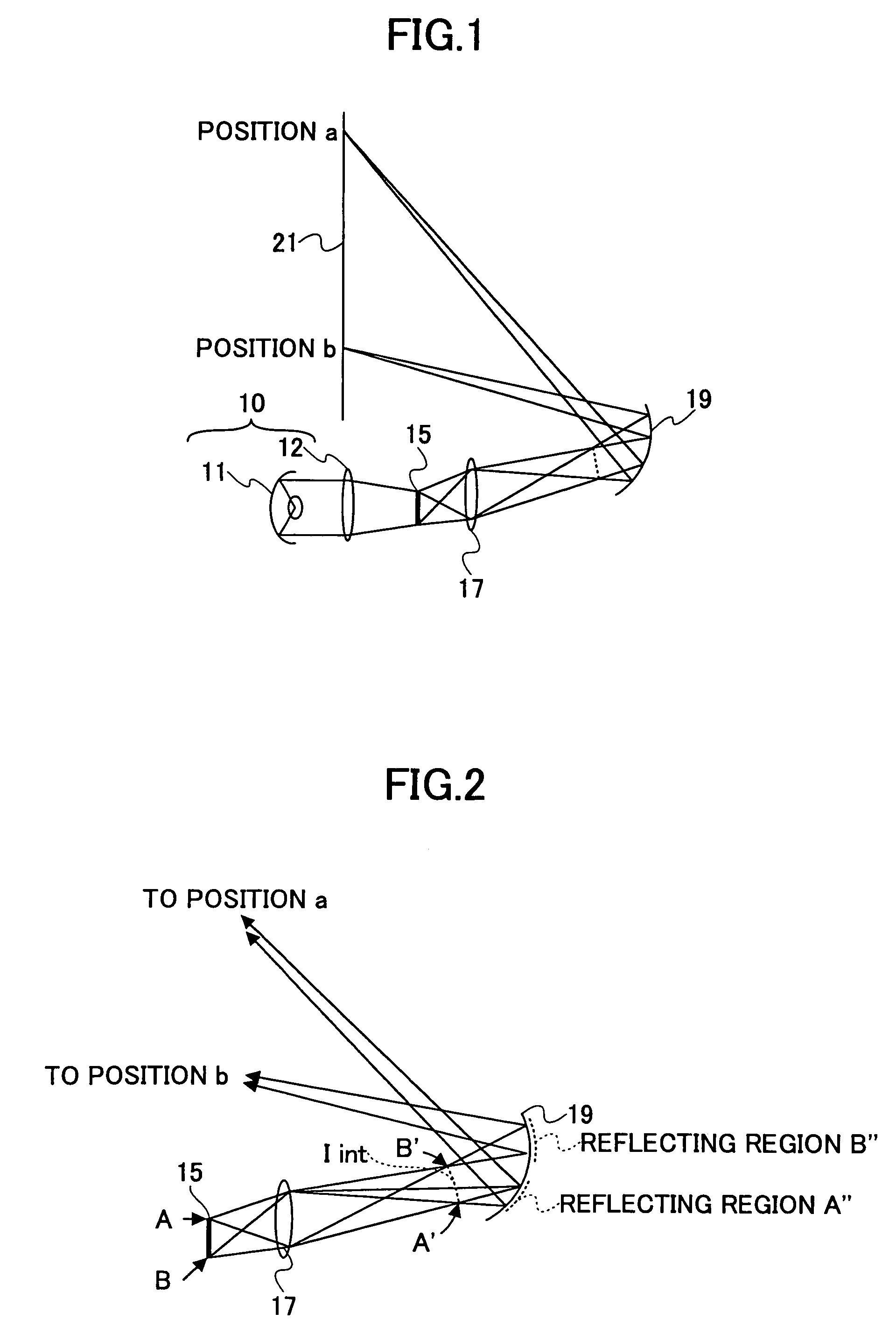
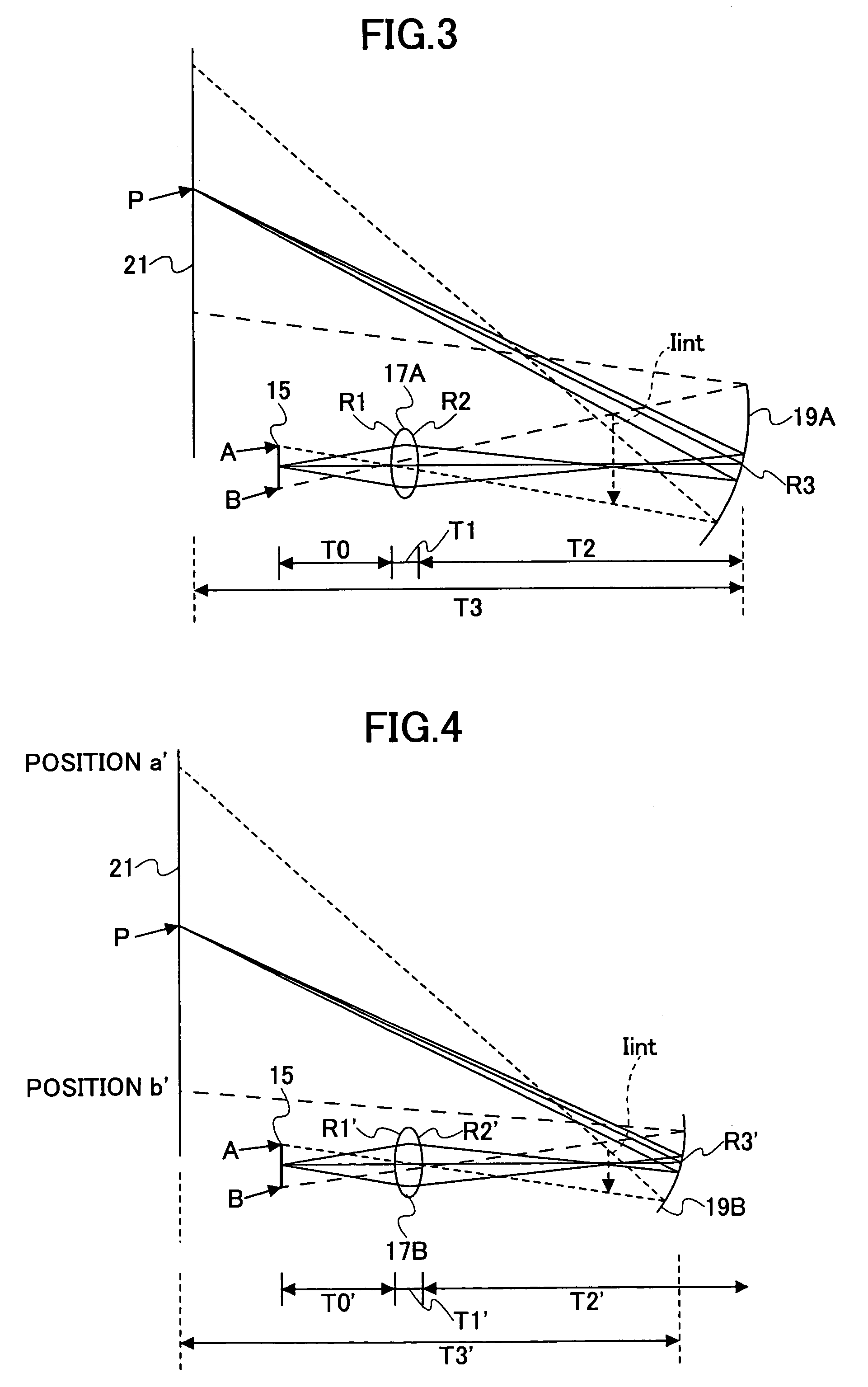
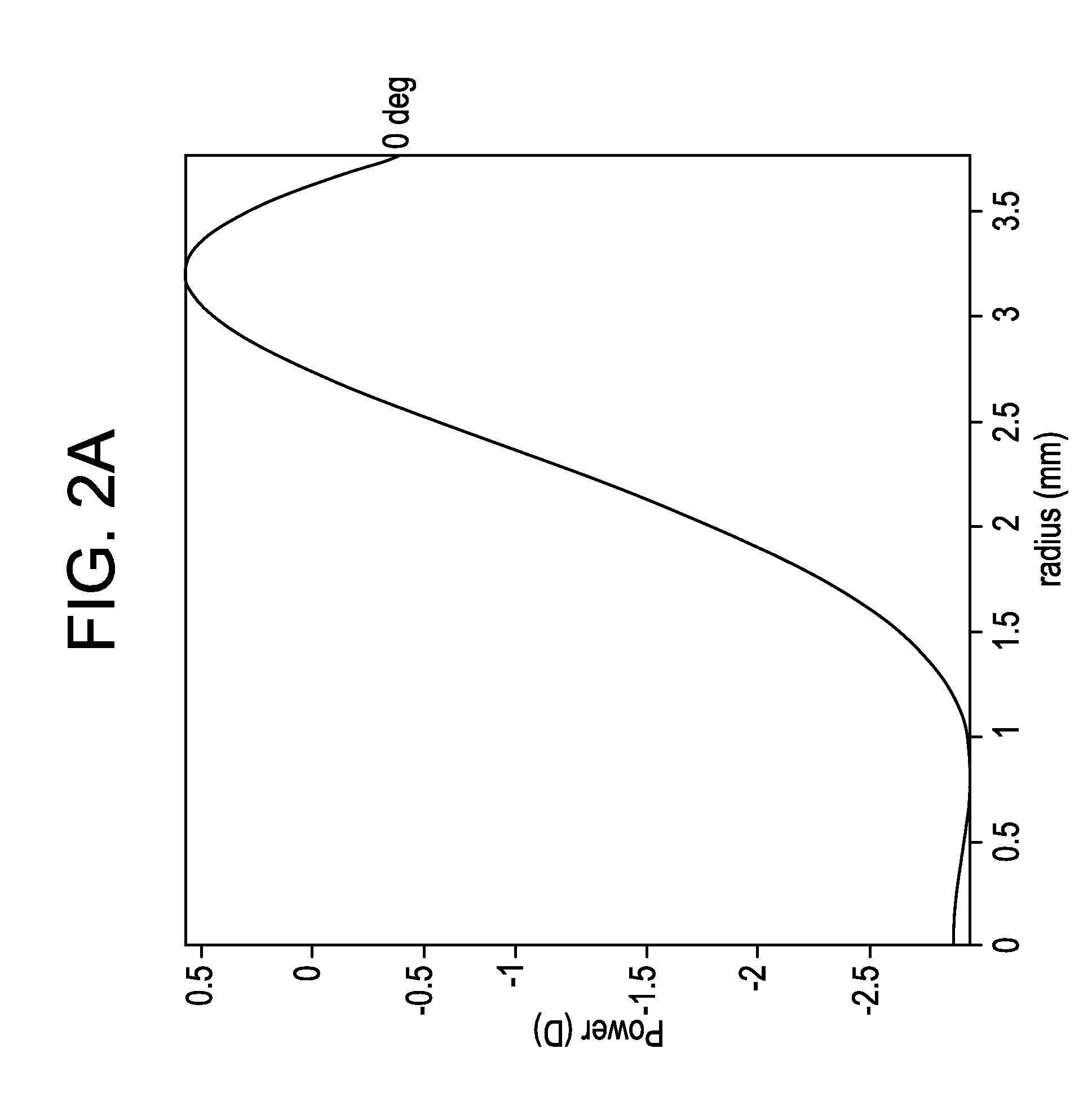
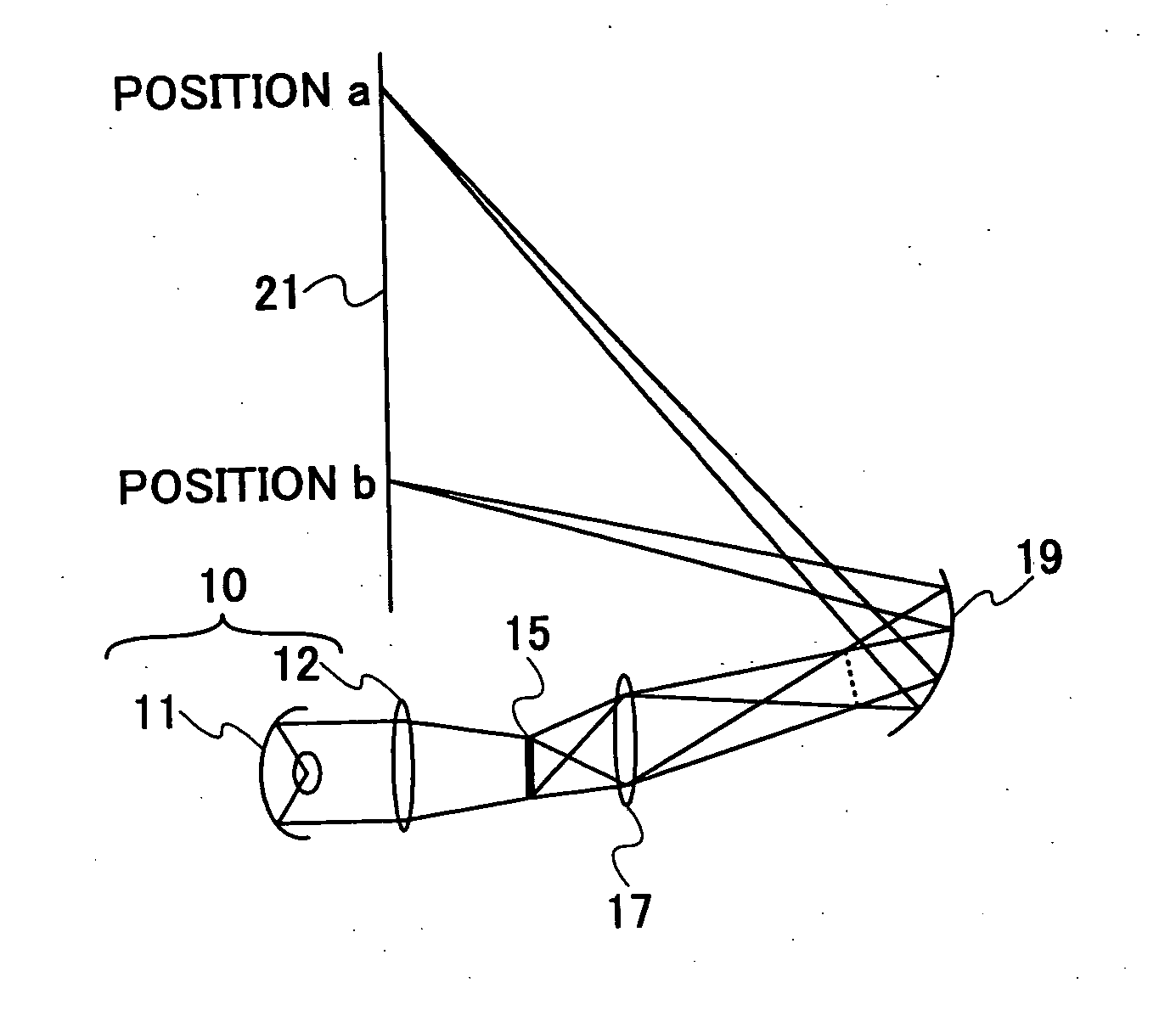
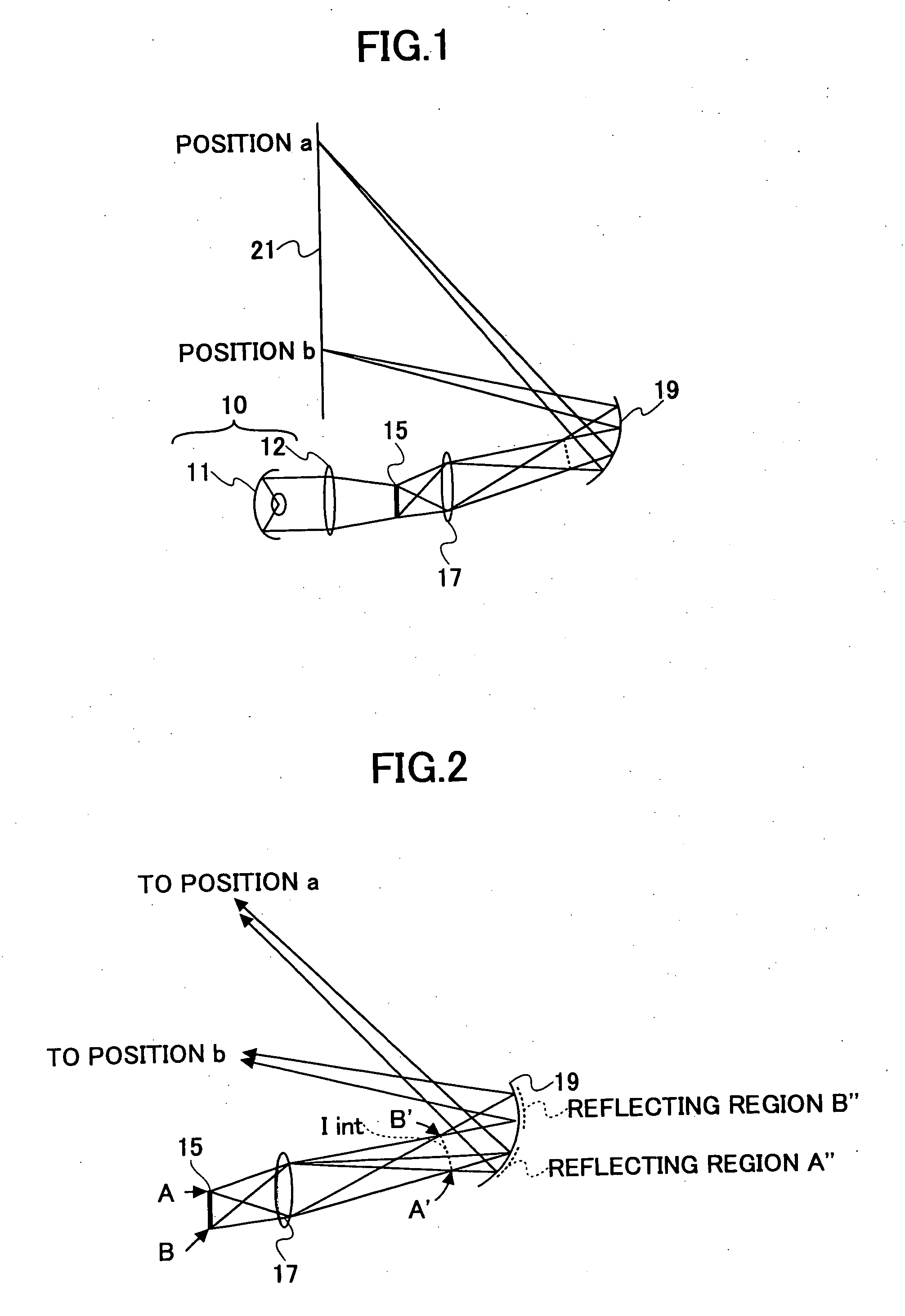
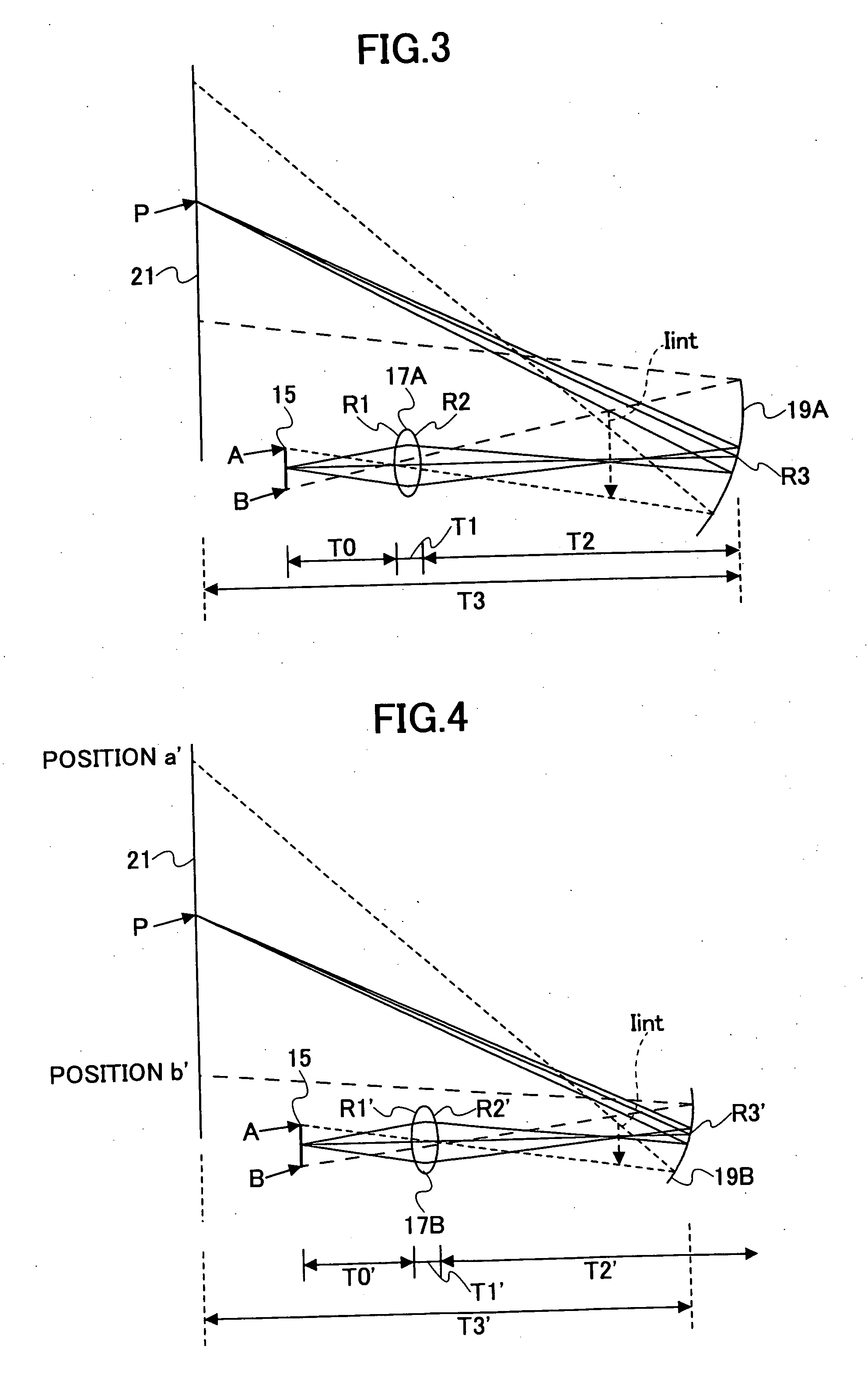
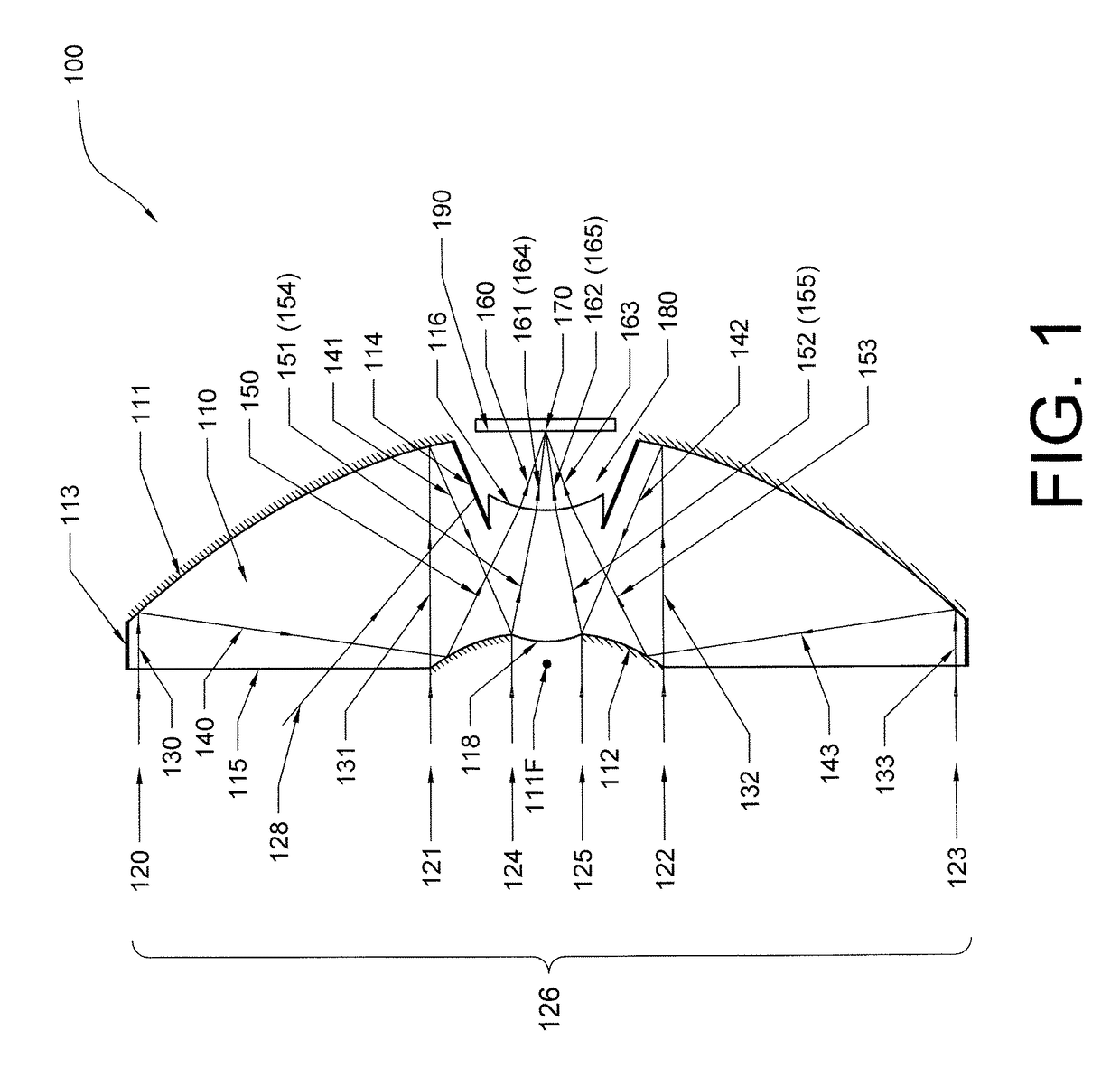
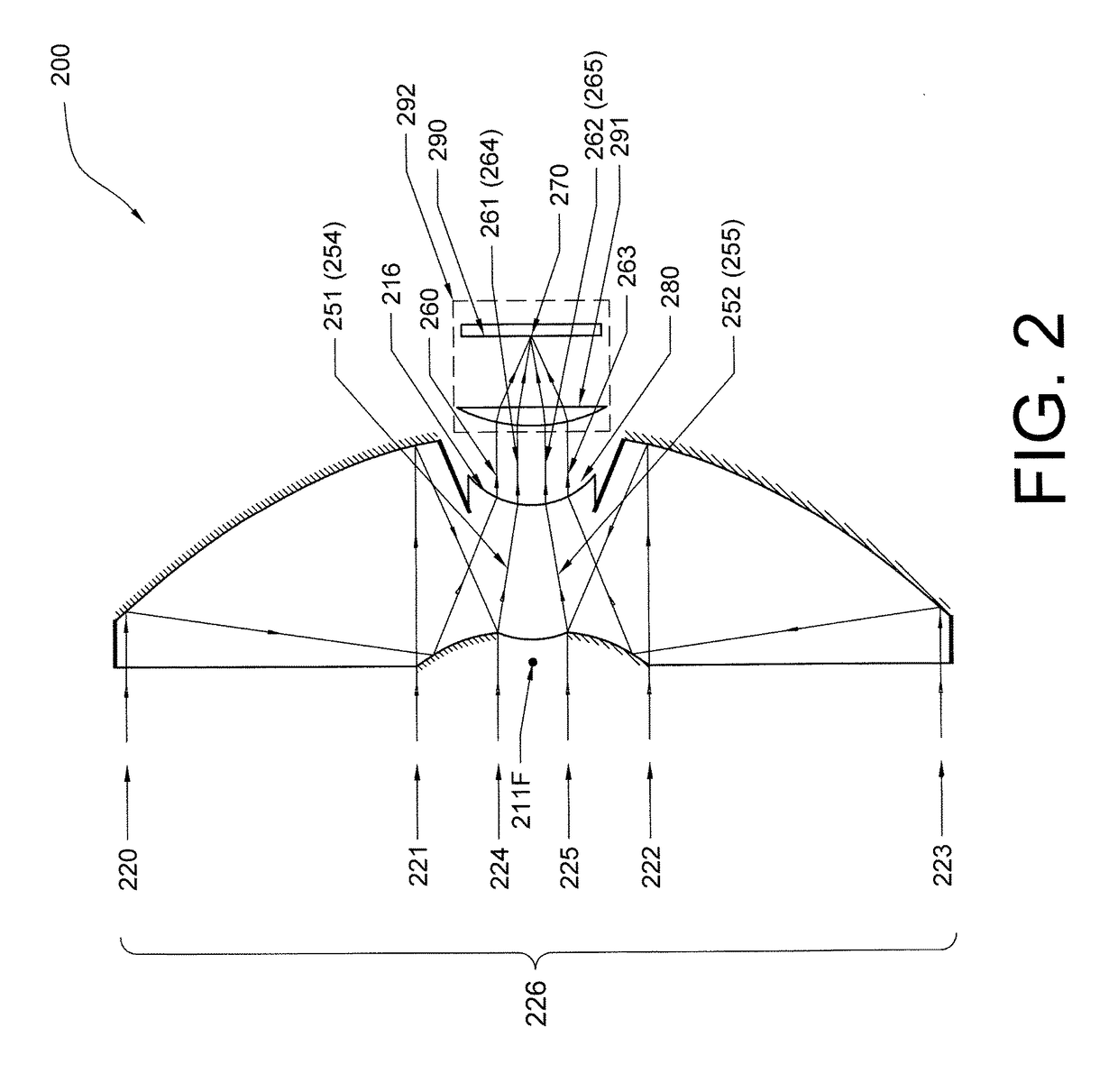
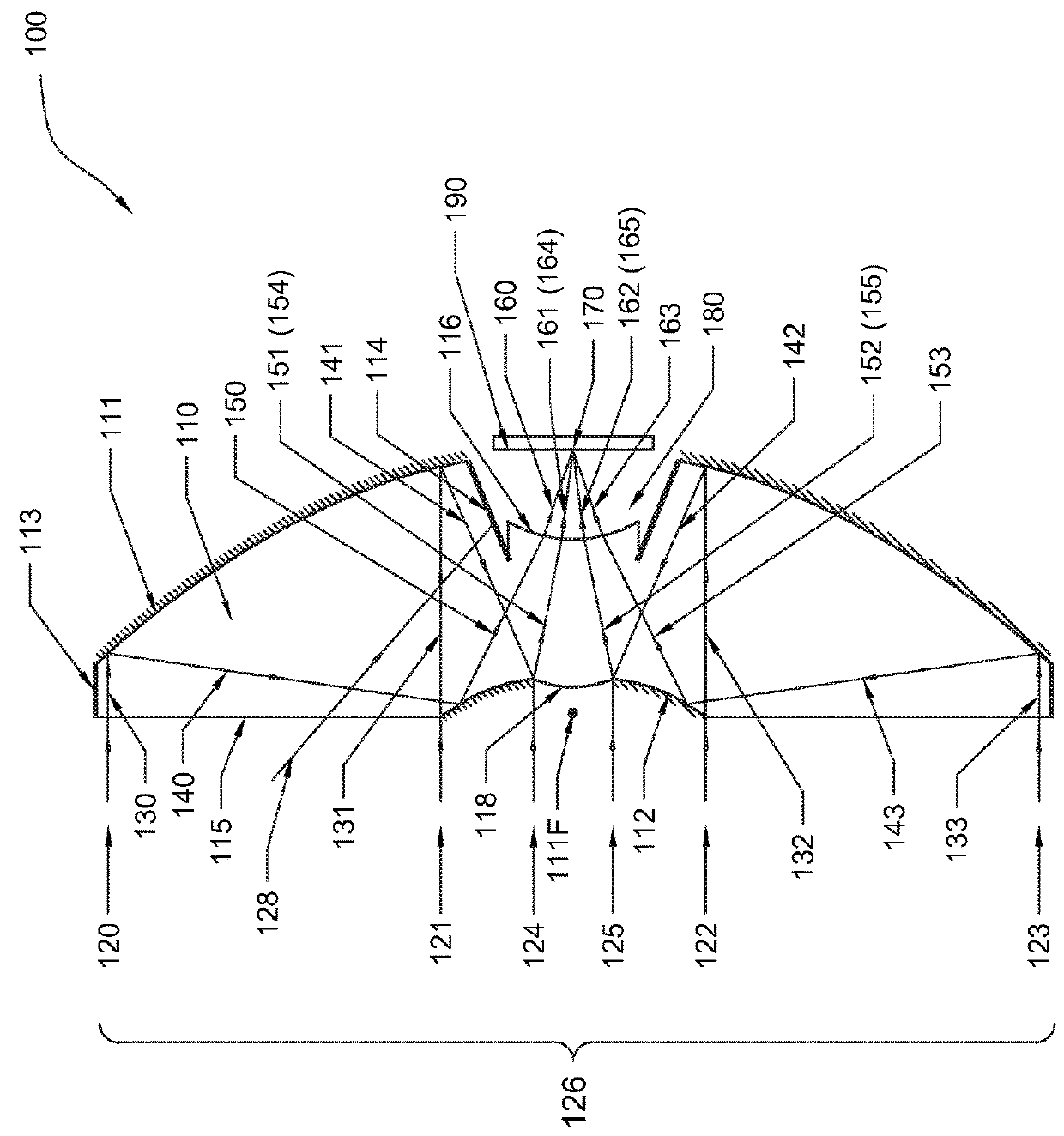
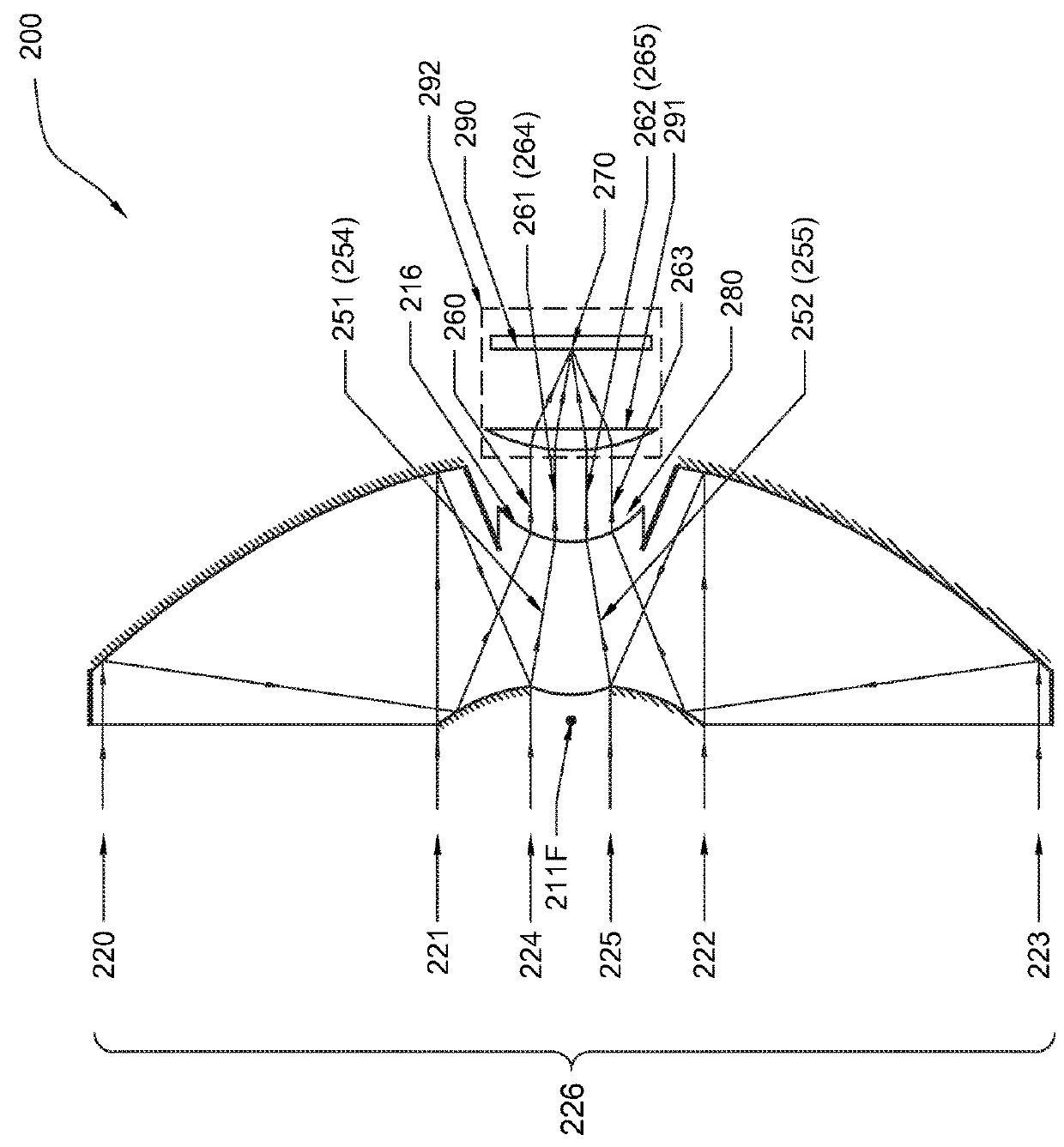
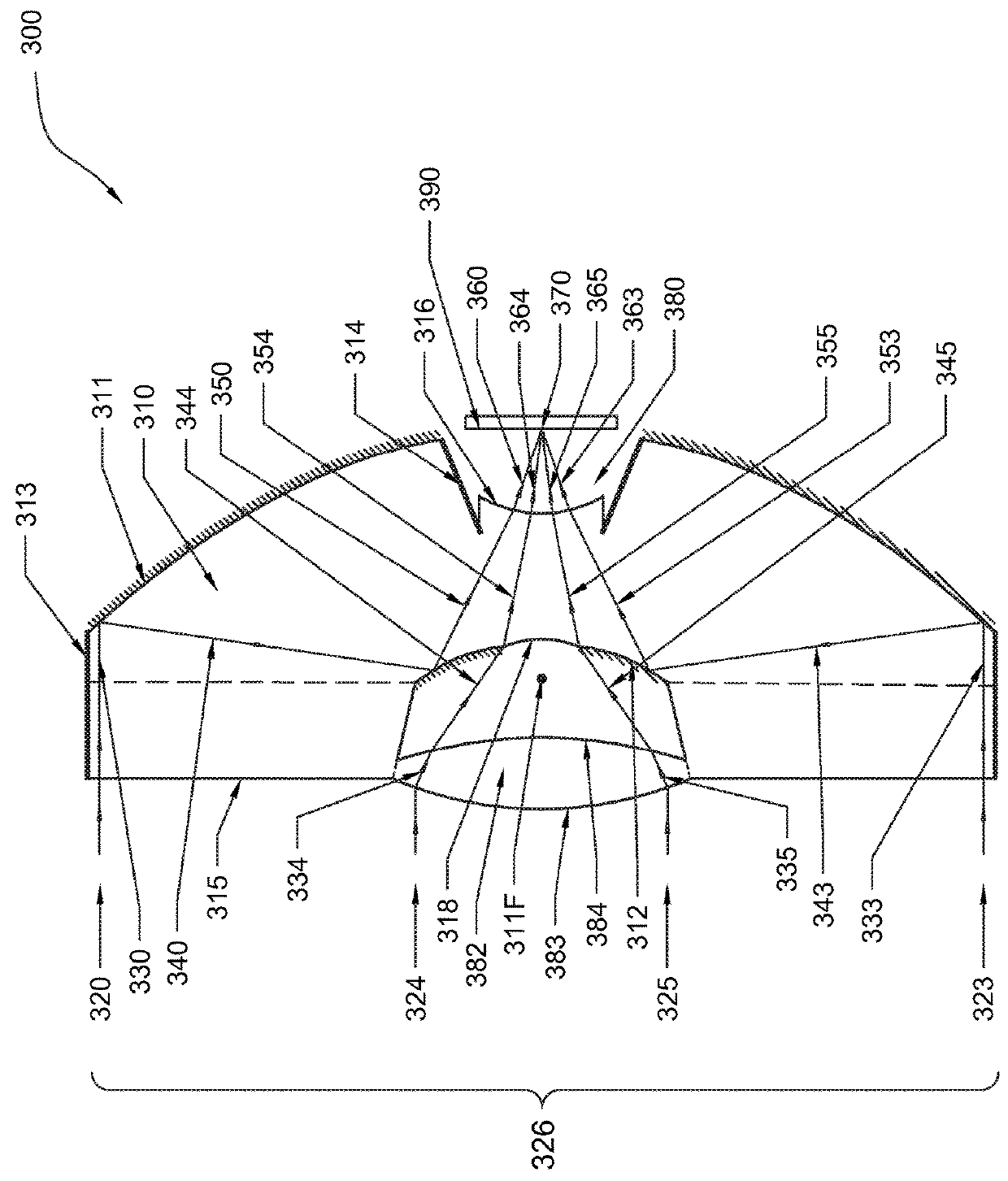
A projection optical system configured to project an image onto a projection surface includes a first optical system including at least one dioptric system and having positive power as a whole; a second optical system including a reflection region and a transmission region; and a third optical system including at least one reflecting surface having power, and having positive power as a whole, wherein light entering the projection optical system passes through the first optical system to have a path thereof bent by the reflection region of the second optical system to be incident on the third optical system, and the light incident on the third optical system has the path thereof bent by the third optical system to pass through the transmission region of the second optical system to be incident on the projection surface.
Owner:RICOH KK
Accommodating intraocular lens
ActiveUS20120303118A1Bright colorEasy to findEye surgeryTissue regenerationIntraocular lensProsthesis
Systems, devices, and methods are presented for a prosthetic injectable intraocular lens. One or more silicone elastomeric patches located outside the optical path on the anterior side but away from the equator can be accessed by surgical needles in order to fill or adjust optically clear fluid within the lens. The fluid can be adjusted in order to set a base dioptric power of the lens and otherwise adjust a lens after its initial insertion. The elastomeric patches are sized so that they self-seal after a needle is withdrawn. A straight or stepped slit in the patch can allow a blunt needle to more easily access the interior of the lens.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Pair of progressive power lens and method for designing same
ActiveUS8162478B2Reduce and eliminate inconvenienceAvoid visionOptical partsUses eyeglassesMultifocal lenses
An object is to reduce the inconvenience given to the binocular vision function when wearing and using spectacles making use of a pair of progressive power lenses having different distance dioptric power for right and left. For this reason, the present invention associates, in a pair of progressive power lenses corresponding to the right and left eyes, an average dioptric power distribution and an astigmatism distribution determined from prescribed dioptric power and a wear state of one of the progressive power lenses with an average dioptric power distribution and an astigmatism distribution determined from prescribed dioptric power and a wear state of the other progressive power lens, and thereby average dioptric power distributions and astigmatism distributions of the respective progressive power lenses are changed.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Compact catadioptric lenses and lens systems with improved image quality and methods of using same
InactiveUS9933604B1Guaranteed high quality outputLittle and no blurringMirrorsLensTelephoto lensCatoptrics
A catadioptric telephoto lens system which: receives incident light rays in a parallel path of both catoptrics and dioptrics, where some of the incident light rays go through a reflective path involving mirrors / reflective surfaces and others of the incident light rays go through a refractive path involving lenses; or receives incident light rays in a serial path of catoptrics and dioptrics, where all the incident light rays initially go through a reflective path involving mirrors / reflective surfaces and then go through a refractive path involving lenses. The system eliminates the black pupil / iris blur disadvantages associated with conventional telescopic lens systems and may be provided in a very compact form.
Owner:LU WEIMIN
A solar device with parallel refraction lens
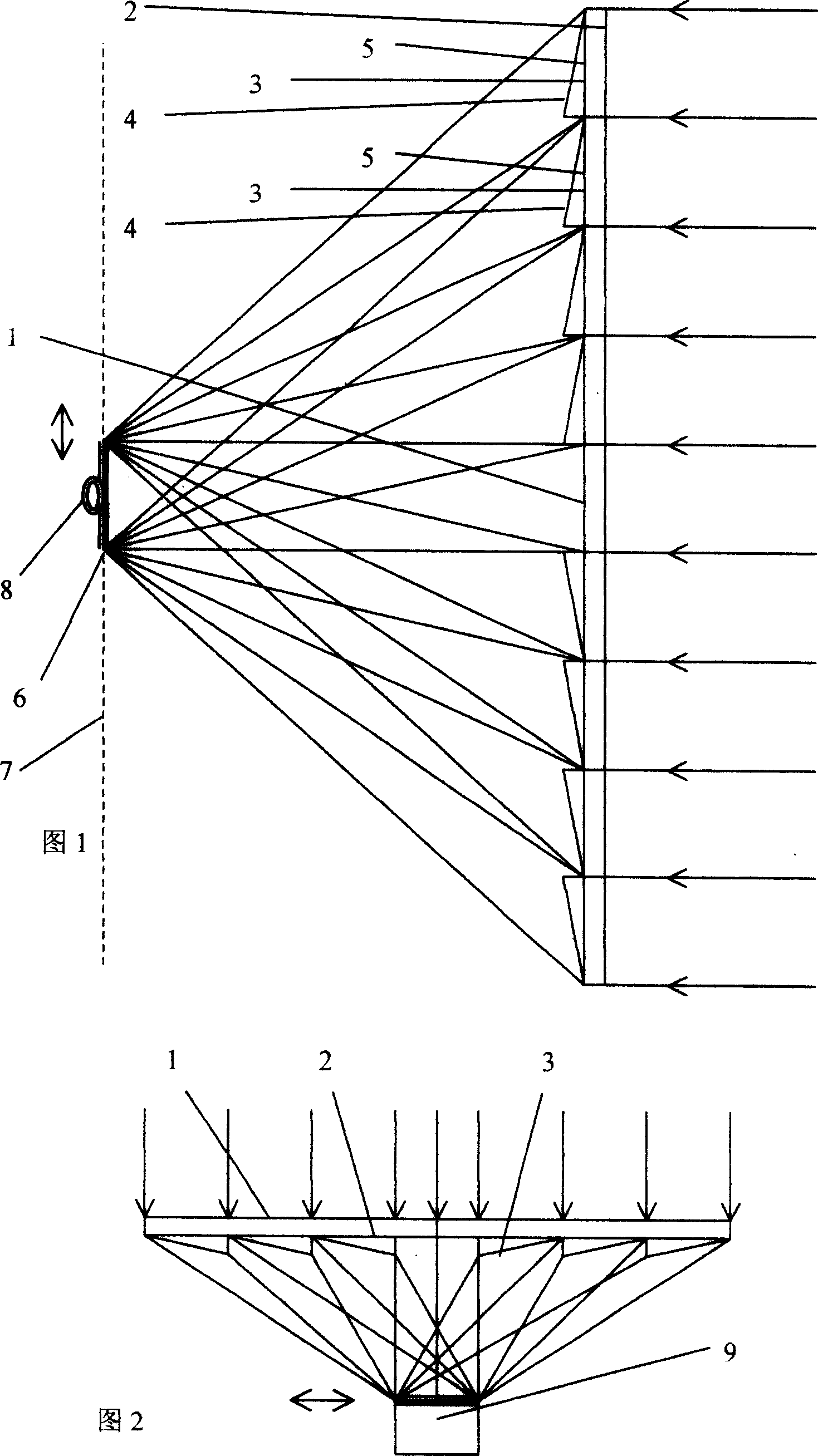
InactiveCN101170291AImprove working conditionsImprove power generation efficiencyPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationThermal energyElectricity
A solar energy device with parallel dioptric lens: parallel rays are emitted through a dioptric lens before overlapping and projecting in an area on a focusing plane, but no focus is formed. Compared with convex lenses, the maximum temperature of the invented focusing and photoelectric cell while working can be lowered by nearly one hundred centigrades in the same ratio; therefore, the power generation efficiency is rather high. Besides, two actual examples are also provided including a solar energy device with a one-dimensional parallel dioptric lens. The dioptric lens 1 comprises a plurality of saw-tooth shaped dioptric lenses 3 on a glass plate 2. The dioptric lenses 3 are composed of an inclined plane of refraction 4 and an horizontal plane of refraction 5. The rays emitted through the dioptric lens include refraction, but no focus, and the projection formed on the photoelectric cell 6 is a beam. Sun-light is focused through the one-dimensional dioptric lens 1 on the photoelectric cell 6 before being converted into electric energy and thermal energy. The electric energy is output through cables; the thermal energy is exchanged through a heat exchanger 8 for transmission. When the incident angle of sun-light is changed, the photoelectric cell 6 can also move vertically while tracing the light in a focusing plane 7.
Owner:施国庆
Imaging lens
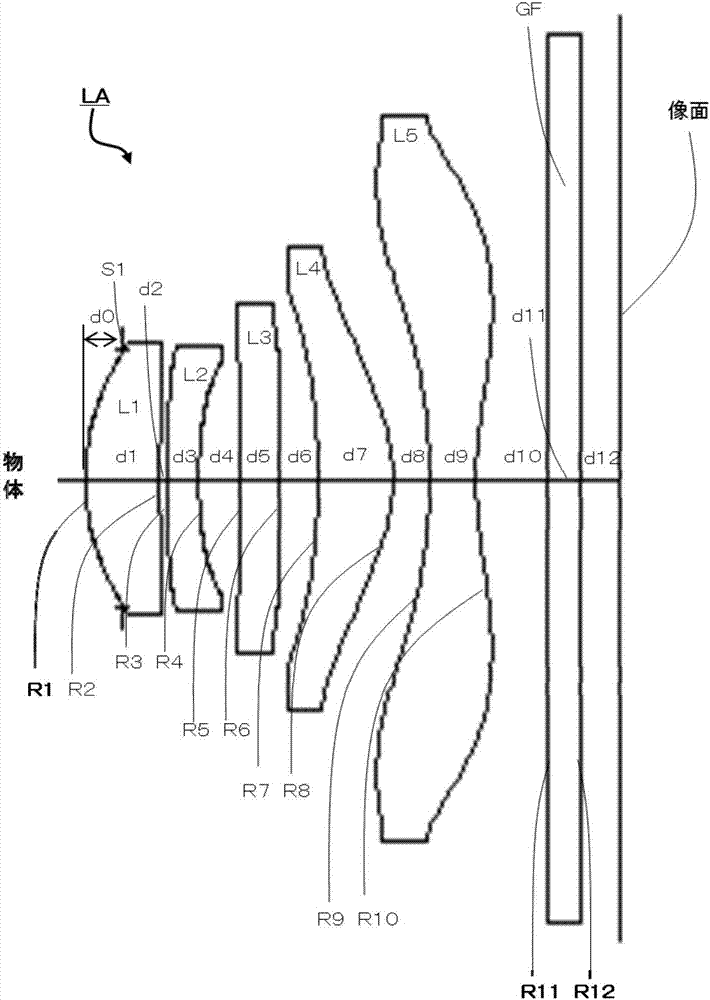
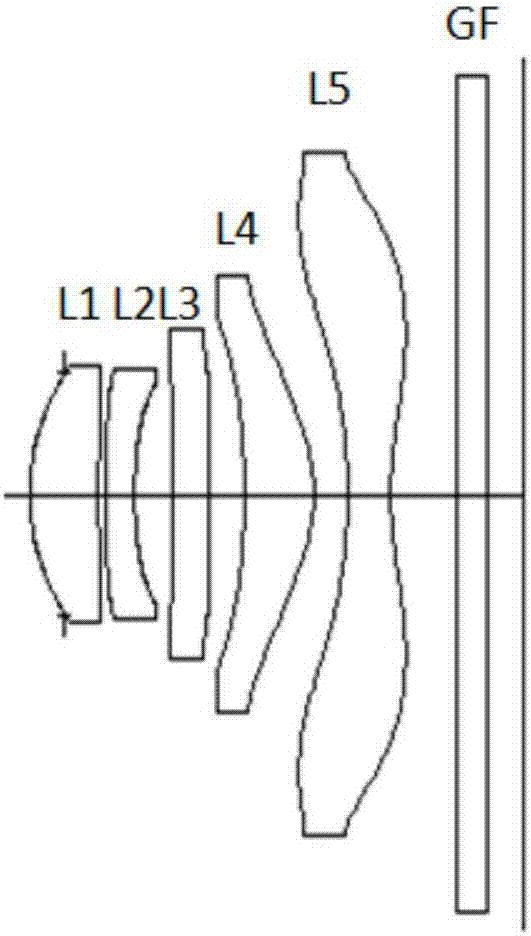
ActiveCN106959503AExcellent optical propertiesExcellent ultra-thinOptical elementsCamera lensImaging lens
The present invention provides an imaging lens composed of 5 lenses having excellent optical characteristics, ultra-thin, wide angle and high pass light; a first lens having positive dioptric power, a second lens having negative diopters, a third lens having positive dioptric power, a fourth lens having a positive diopter, and a fifth lens having a positive diopter are arranged in order from the object side, and the regulated conditions are specified.
Owner:AAC OPTICS SOLUTIONS PTE LTD
Accommodating intraocular lens
ActiveUS20130150960A1Bright colorEasy to findEye treatmentTissue regenerationElastomerIntraocular lens
Systems, devices, and methods are presented for a prosthetic injectable intraocular lens. The lenses can be made from silicone, fluorosilicone, and phenyl substituted silicone and be semipermeable to air. One or more silicone elastomeric patches located outside the optical path on the anterior side but away from the equator can be accessed by surgical needles in order to fill or adjust optically clear fluid within the lens. The fluid can be adjusted in order to set a base dioptric power of the lens and otherwise adjust a lens after its initial insertion. The elastomeric patches are sized so that they self-seal after a needle is withdrawn. A straight or stepped slit in the patch can allow a blunt needle to more easily access the interior of the lens.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Method of designing both-plane aspherical progressive refractive power lens group and both-plane aspherical progressive refractive power lens group
ActiveCN101203796AWide field of visionIncreased efficiency in batch manufacturingSpectales/gogglesOptical partsFar-sightednessVisual Disorders
A double aspheric progressive refractive index lens group capable of reducing processing costs. In the double aspheric progressive index lens, the relationship: DHf+DHn<DVf+DVn and DHn<DVn or further the relationship: DVn−DVf>ADD / 2 and DHn−DHf<ADD / 2 is satisfied. DHf and DVf are respectively designated as the surface refractive index in the horizontal direction and the surface refractive index in the vertical direction at the farsighted power measurement position F1 on the first refraction surface as the object-side surface; DHn and DVn are respectively designated as The surface refractive index in the horizontal direction and the surface refractive index in the vertical direction at the myopia power measurement position N1 on the first refraction surface. The surface glare components at F1 and N1 of the first refractive surface are eliminated by the second refractive surface, the first and second refractive surfaces being combined to provide far vision power (Df) and add power (ADD) based on prescribed values. Therein, the same first refractive surface is used for at least two or more different addition degrees.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Human eye Hartmann contrast sensitivity measuring instrument
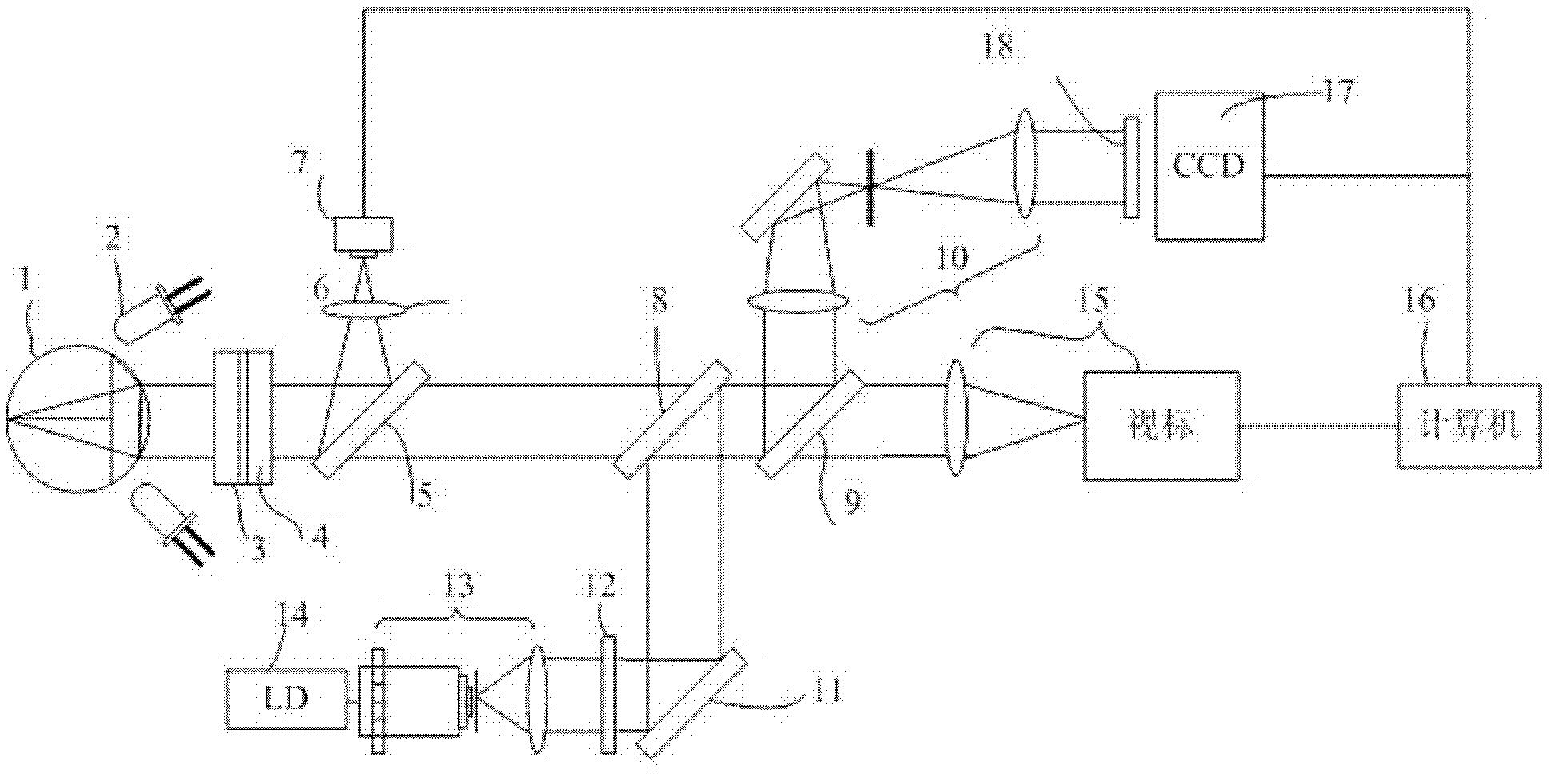
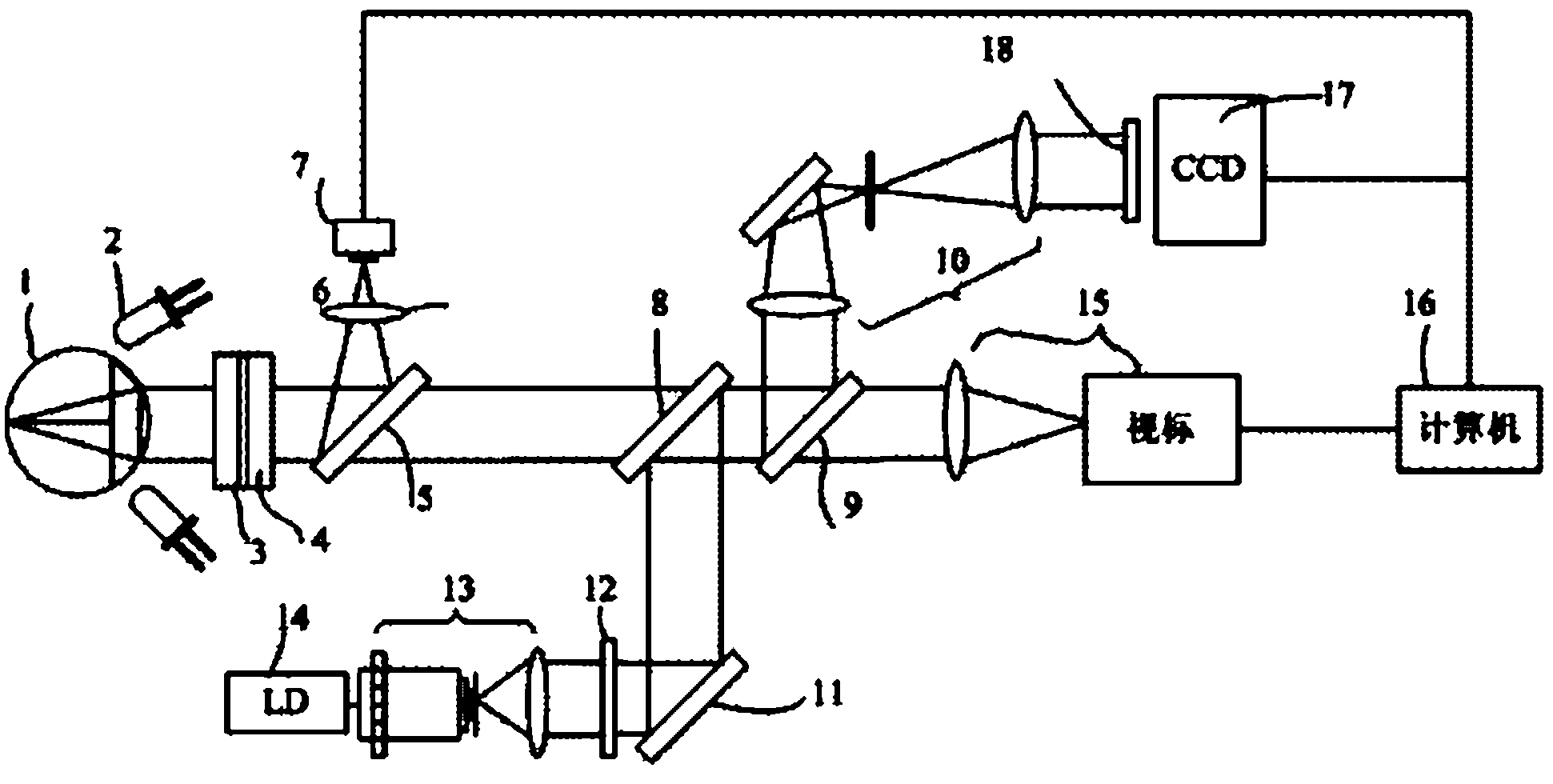
The invention provides a human eye Hartmann contrast sensitivity measuring instrument, which consists of a light source, a pre-compensation mechanism, a light beam matching system, a pore diameter cutting element, a photoelectric detector, a grating display system, a computer system and a human eye bracket, wherein the pore diameter cutting element and the photoelectric detector constitute a Hartmann wave-front sensor; the pre-compensation mechanism can be used for correcting the lower order aberration of eyes; and the computer system is used for testing the contrast sensitivity and recording and analyzing a test result. When human eyes are subjected to contrast sensitivity test through an observation test object generating system, the Hartmann sensor can be used for measuring the aberration of the human eyes simultaneously, and a human eye optical system contrast sensitivity curve is obtained, so that contrast sensitivity curves of a human eye dioptric system and a nerve system are obtained simultaneously, a visual system is evaluated segmentally, quantitative preoperative prediction is performed on the visual function after ophthalmologic operation, and bases are provided for early discovery and in-time treatment of various ophthalmologic diseases.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
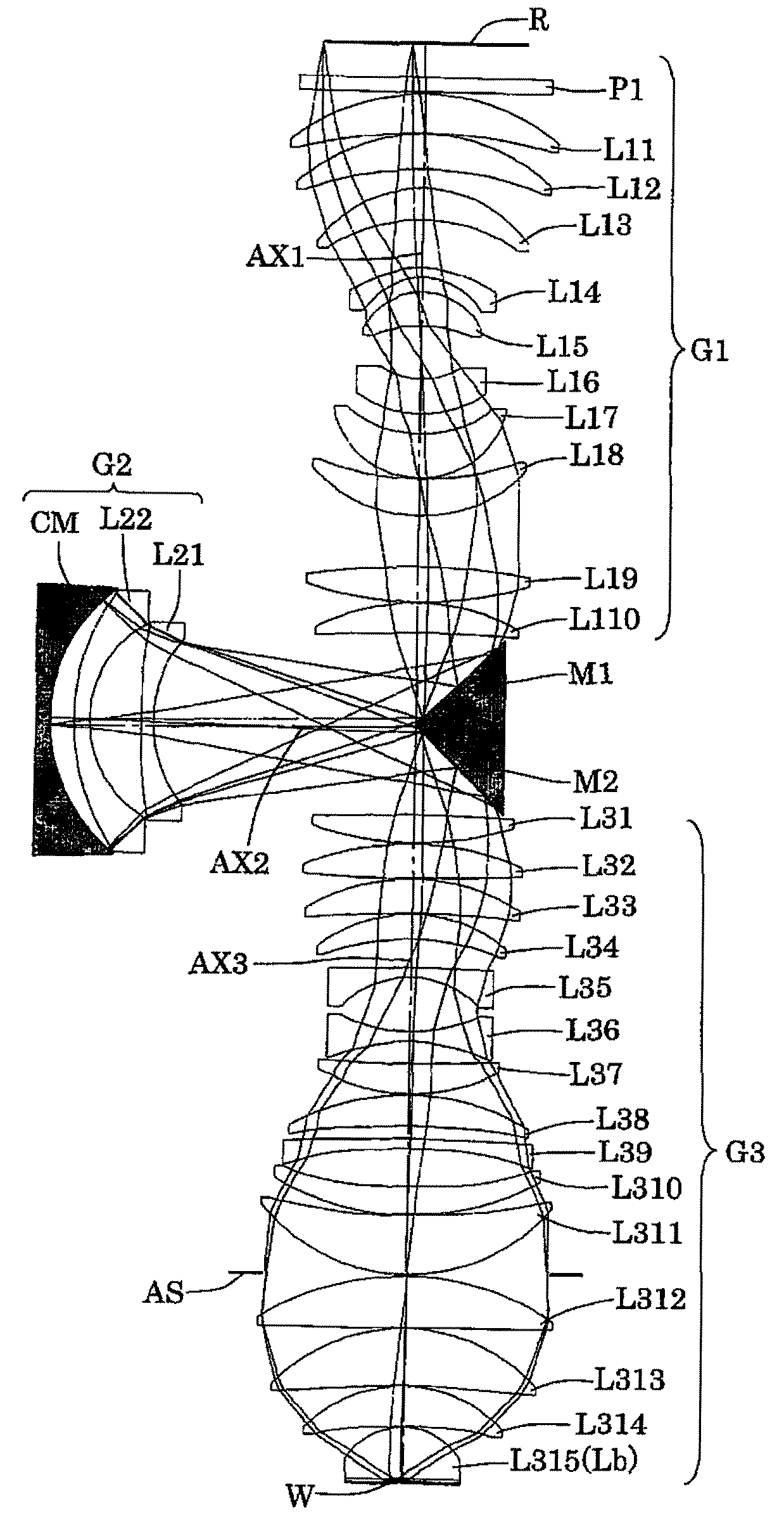
Catadioptric imaging system, exposure device, and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20080304036A1Large numerical apertureImprove accuracyPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingIntermediate imageHigh numerical aperture
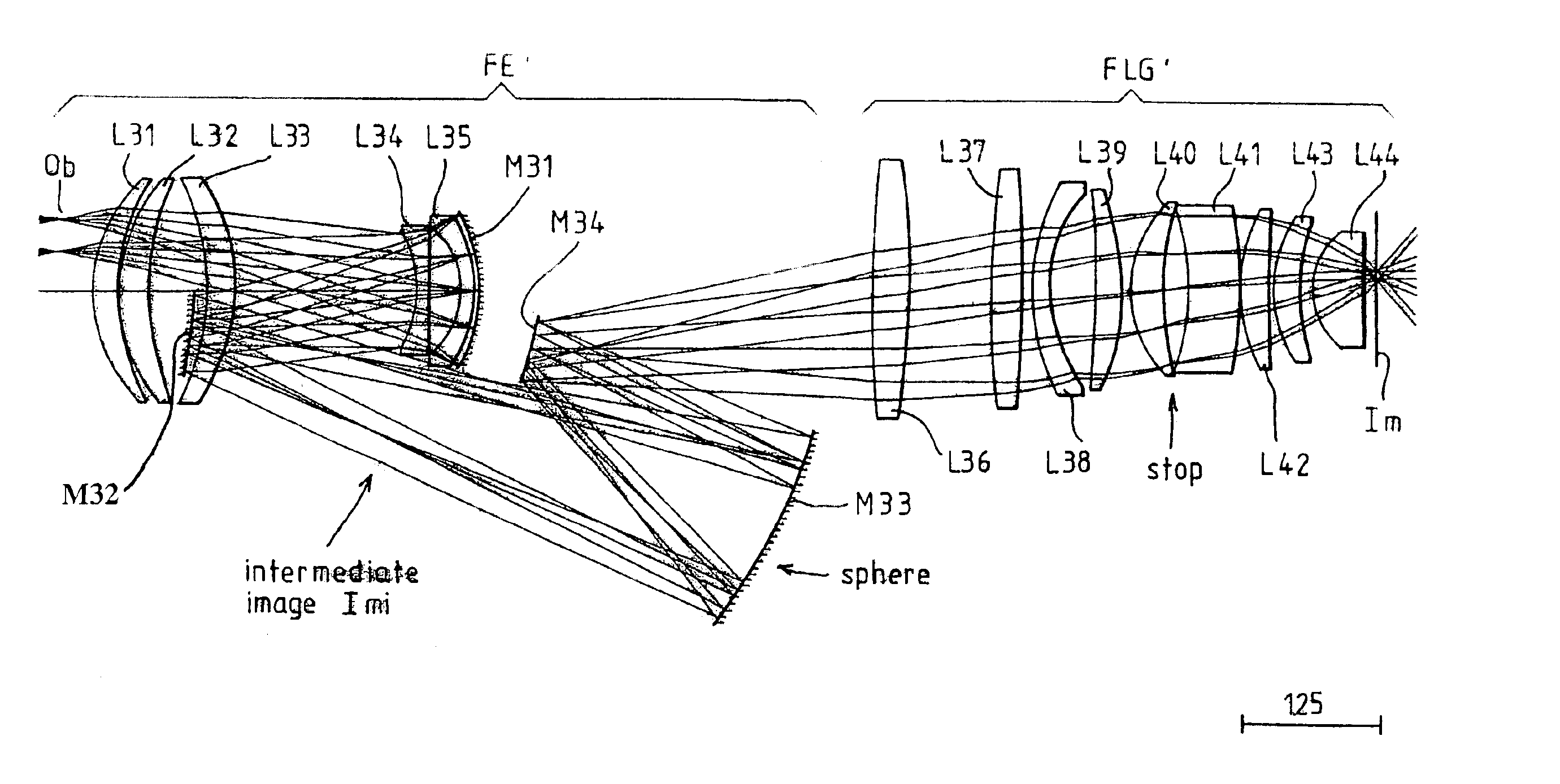
A catadioptric imaging optical system with a high numerical aperture and including an effective imaging region shaped optimally for use in a batch type exposure apparatus and having an imaging magnification with a small absolute value. The catadioptric imaging optical system includes a dioptric first imaging system, which forms a first intermediate image based on light from the first plane, a second imaging system, which forms a second intermediate image based on light from the first intermediate image, a third dioptric imaging system, which forms a reduced image on the second plane based on light from the second intermediate image, and a deflecting mirror arranged in an optical path extending from the first imaging system to the second imaging system and an optical path extending from the second imaging system to the third imaging system. The first imaging system and the second imaging system provide a composite imaging magnification having an absolute value β12 of less than 0.55, and the third imaging system has an imaging magnification with an absolute value β3 of less than 0.35.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Progressive power lens
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Lenses, glasses and methods for obtaining defocusing amount parameters, ophthalmic dispensing and evaluating effect
The invention discloses lenses, glasses and methods for obtaining defocusing amount parameters, ophthalmic dispensing and evaluating an effect. The peripheral defocusing lens comprises a central optical zone, the central optical zone is externally provided with an annular defocusing zone, and the defocusing amount of the defocusing zone varies in the circumferential direction. At least one of a base curve zone and a reverse curve zone of the orthokeratology lens has a structural change in the circumferential direction. The method for obtaining the defocusing amount parameters comprises the steps that the defocusing amount of a plurality of sample points on a dioptric system composed of a myopic patient cornea and the lens or on a user cornea is collected, and the sample points are distributed on a plurality of direction angles in a coordinate system with the cornea center as the origin; and the defocusing amount parameters are obtained according to the defocusing amount of the multiplesample points on the cornea. The method for determining the myopia control effect of the orthokeratology on a myopia patient according to the defocusing amount parameters is further provided.
Owner:天津医科大学眼科医院
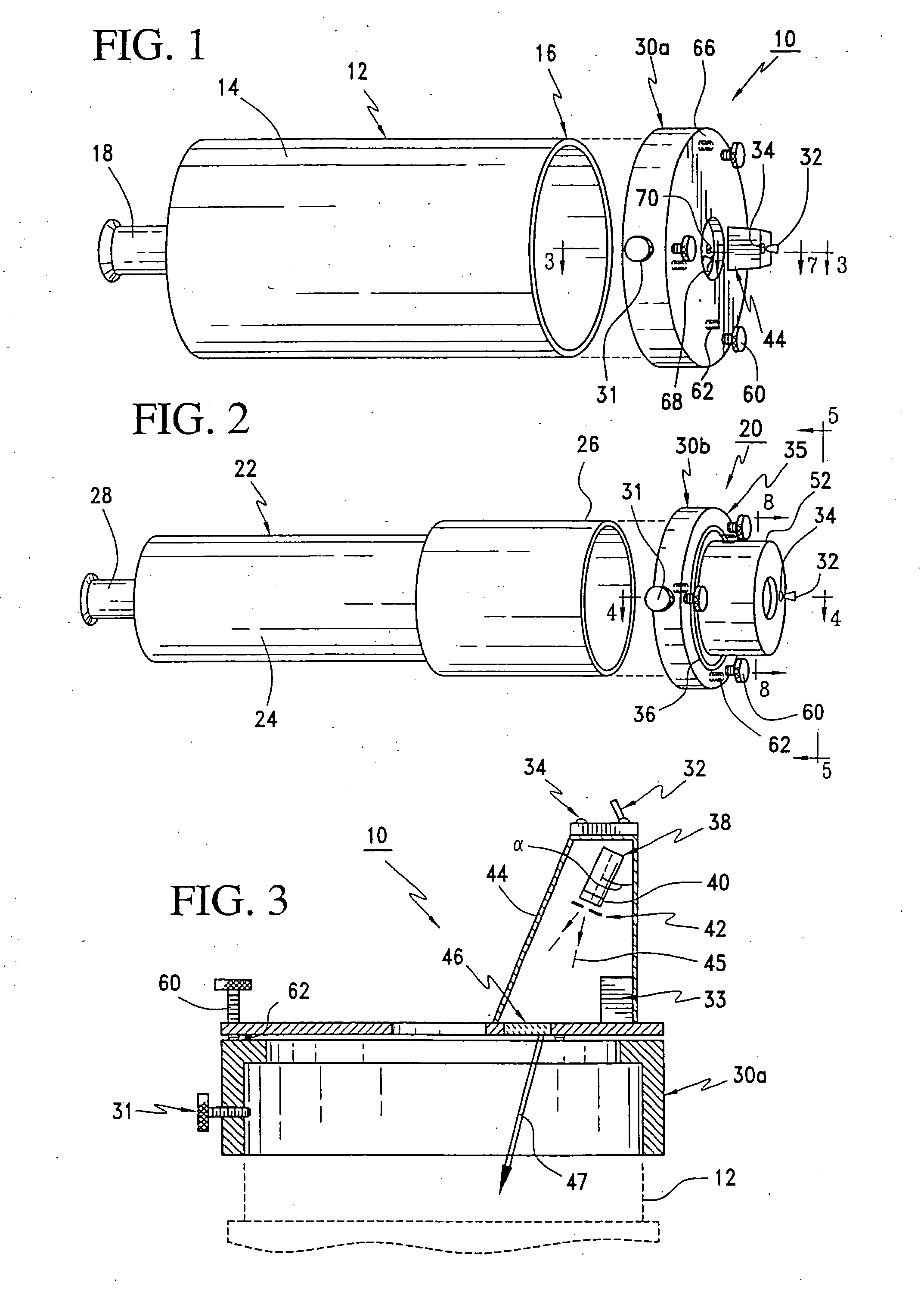
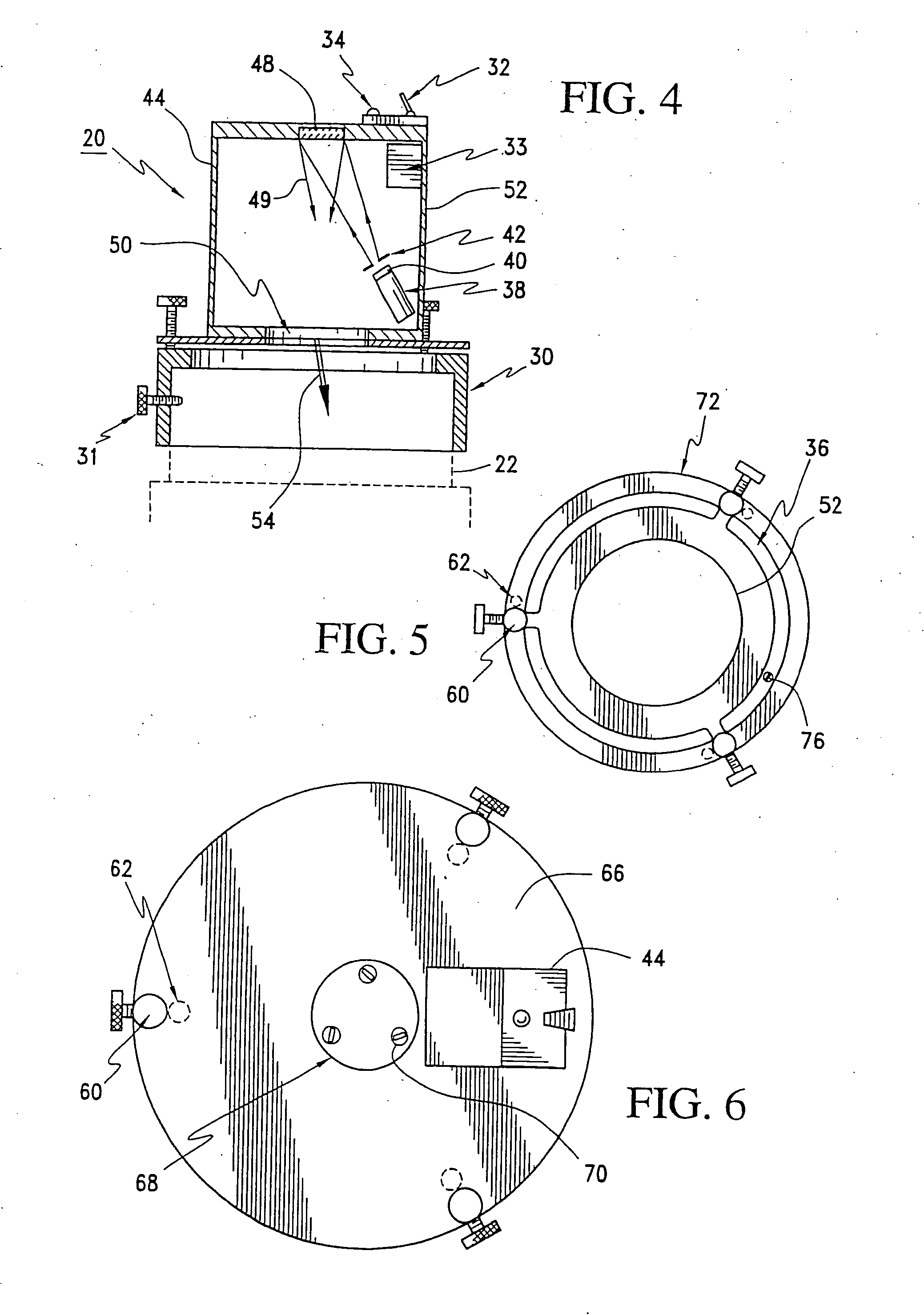
Artificial star generation apparatus and method for telescope systems
InactiveUS20050195456A1Eliminate the effects ofHigh precision collimation for focusing the telescopeTelescopesCatoptricsCatadioptric system
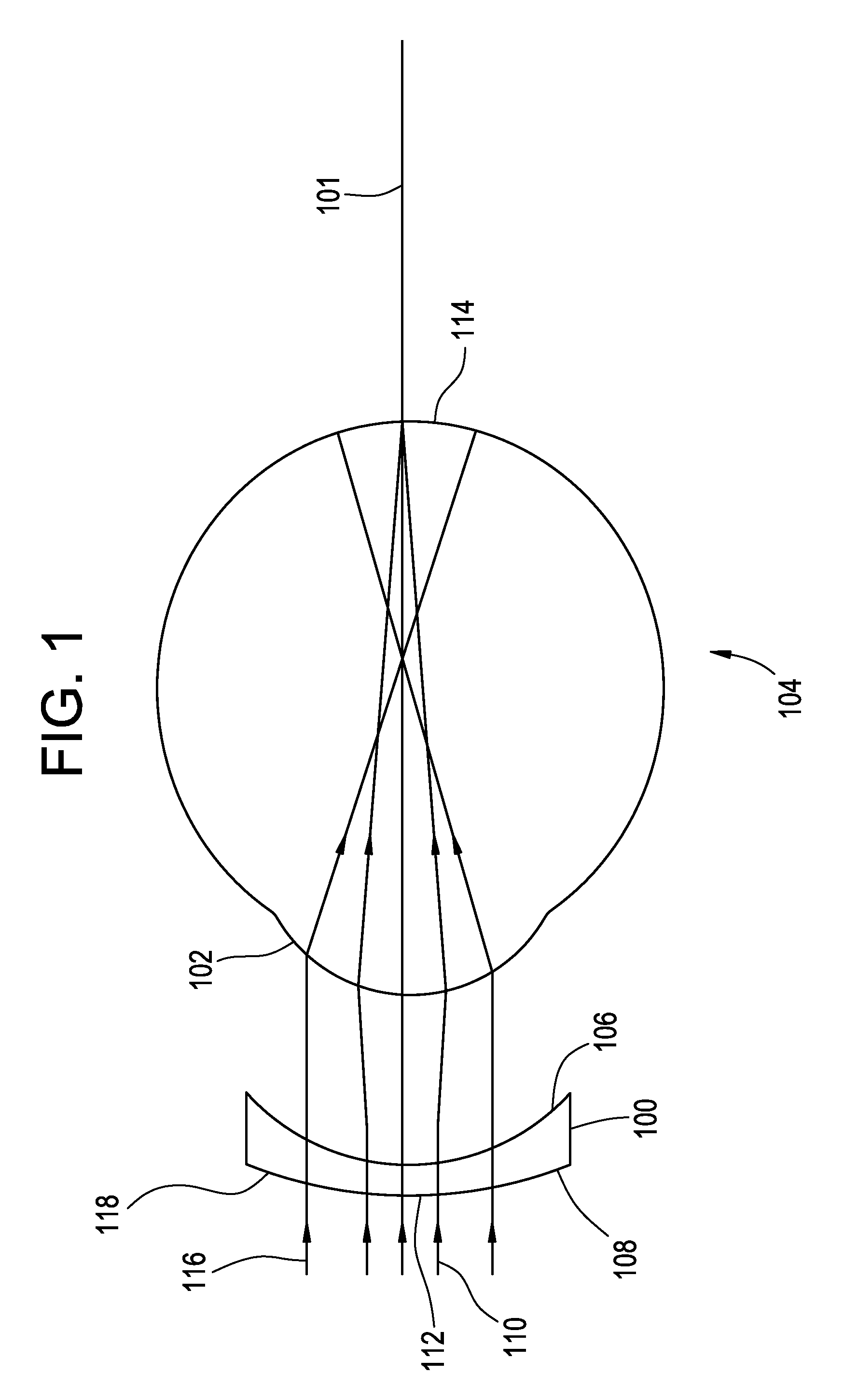
This invention describes an apparatus and method for generating artificial stars for the simple collimation of catoptric, dioptric, and catadioptric telescopes using a light source along with an appropriate hologram and housing to generate collimated laser beams that enter the front aperture of the telescope. The apparatus of this invention can be fastened to the outside of the telescope aperture. In addition, this invention allows the apparatus position to be adjusted at its tip and tilt axis to center an artificial star under the view of the ocular. The light source illuminates the hologram from some off axis position. Once the hologram is illuminated, the collimated beam emanates from the hologram with a slightly different angle. When these beams are then viewed with the telescope they appear as artificial stars.
Owner:LASERMAX
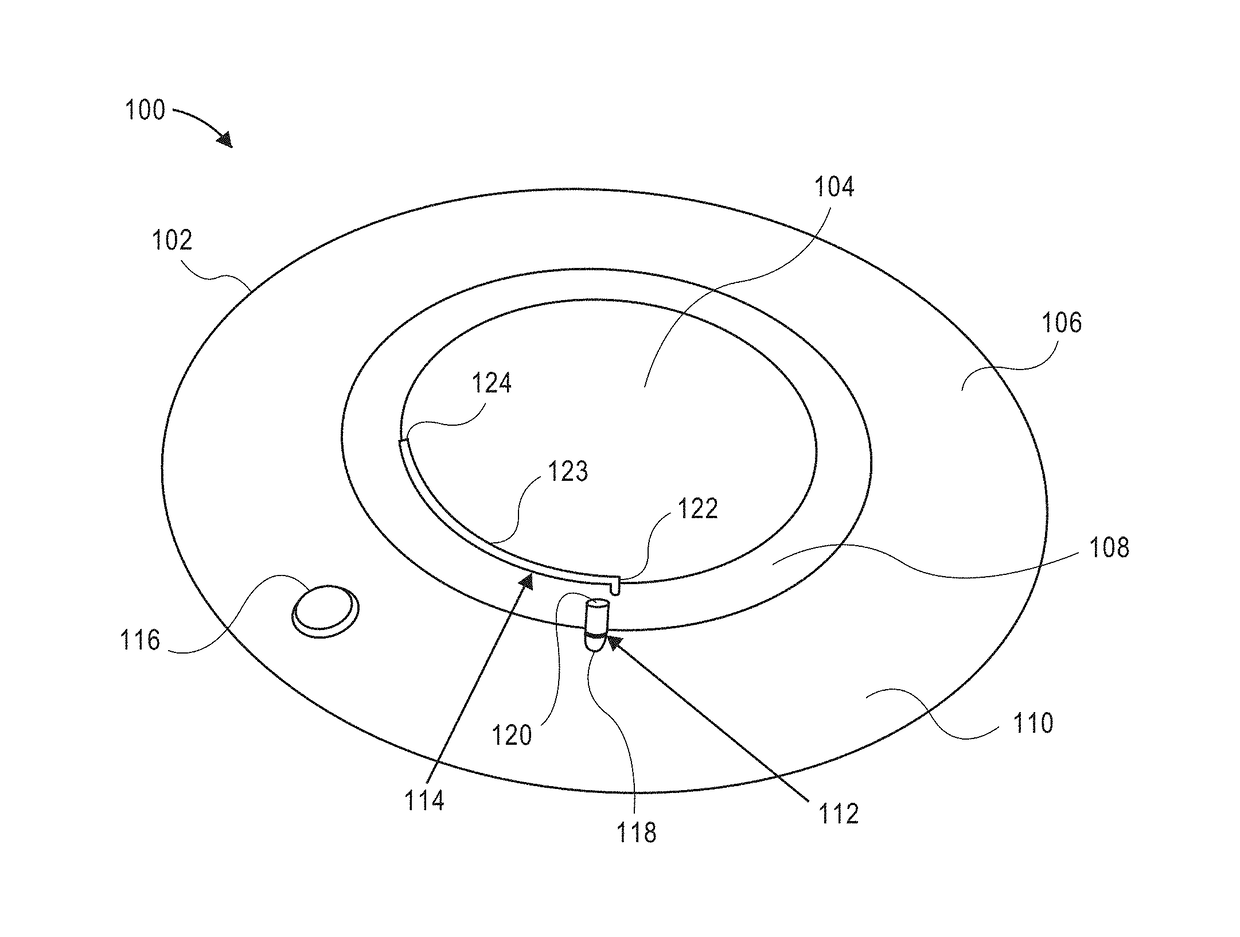
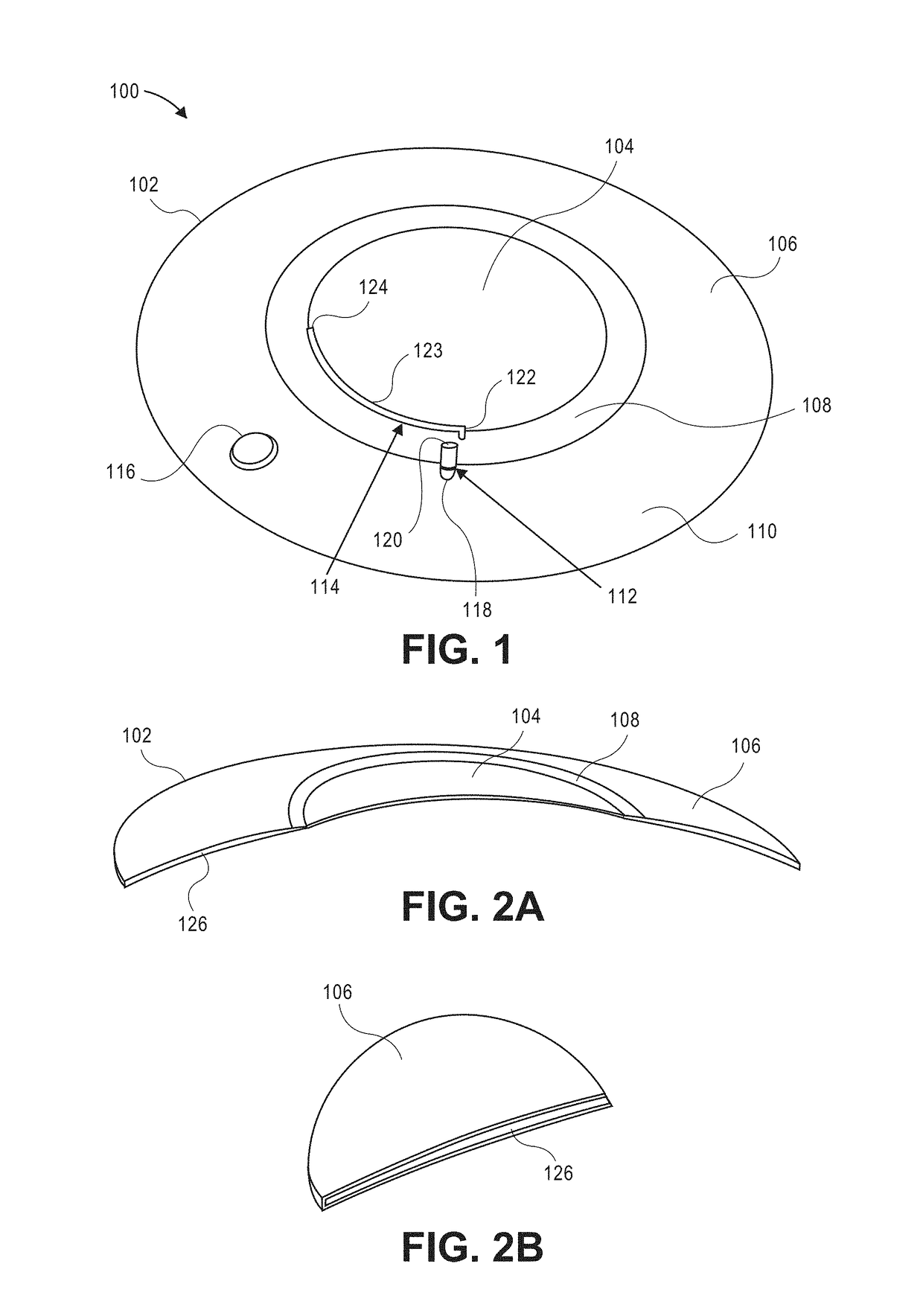
Contact lens with metered liquid system
A contact lens fluid delivery device having a liquid reservoir connected to a channel with a flow regulator is described. Other eye hydration and variable dioptric power contact lenses are described herein. Also described are implantable liquid delivery apparatuses having a liquid storage reservoir connected to a channel with a flow regulator. These devices and apparatuses are useful for specific, targeted delivery of therapeutic liquids within a subject. In some embodiments, the devices incorporate actuation chambers which provide a driving force releasing the fluid into the targeted area e.g., the eye. The actuation chambers described herein can contain phase change materials or osmotic chambers or a combination thereof to drive the release of fluid.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
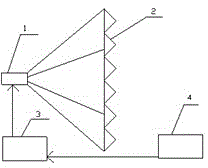
Display device for telescope system
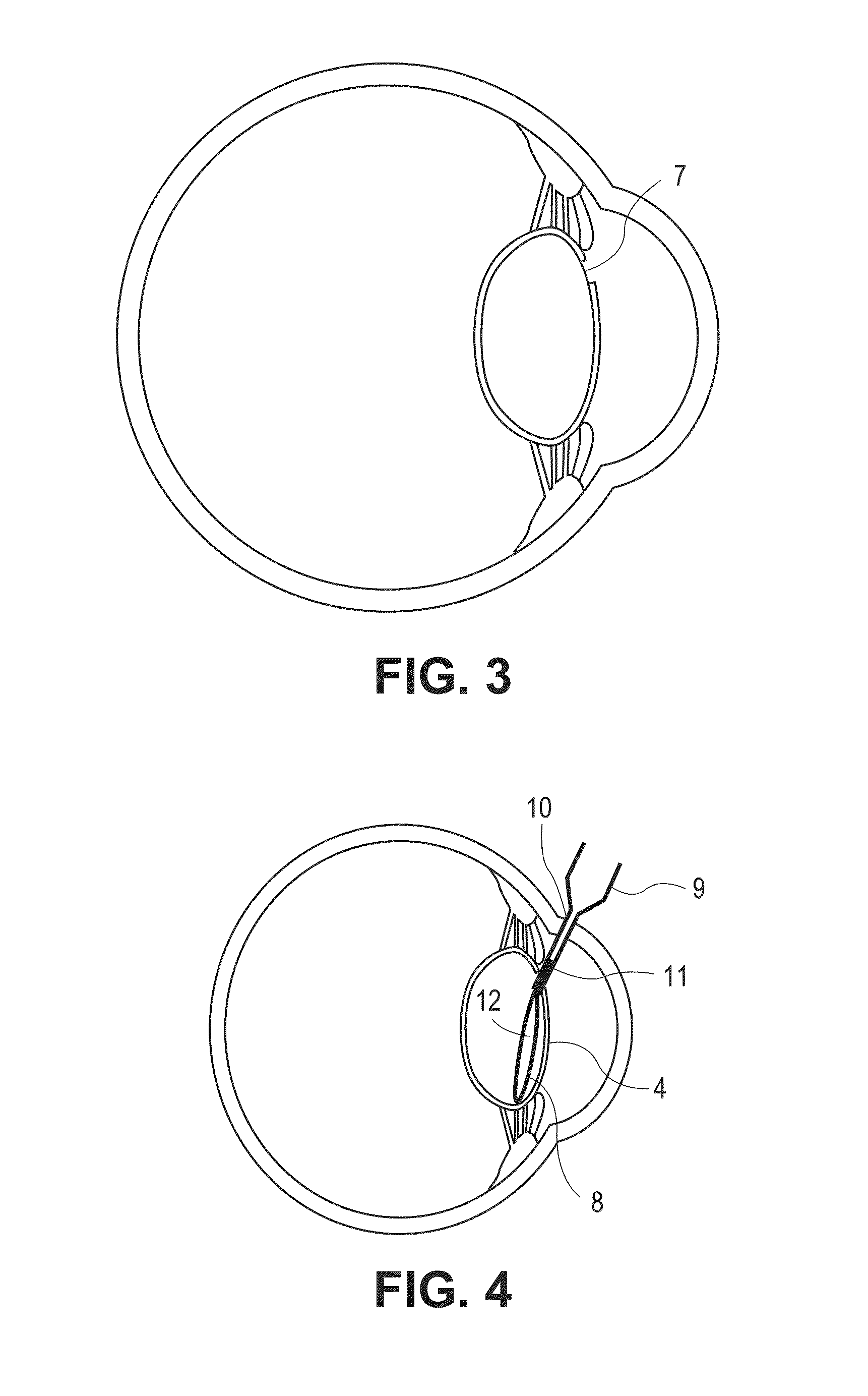
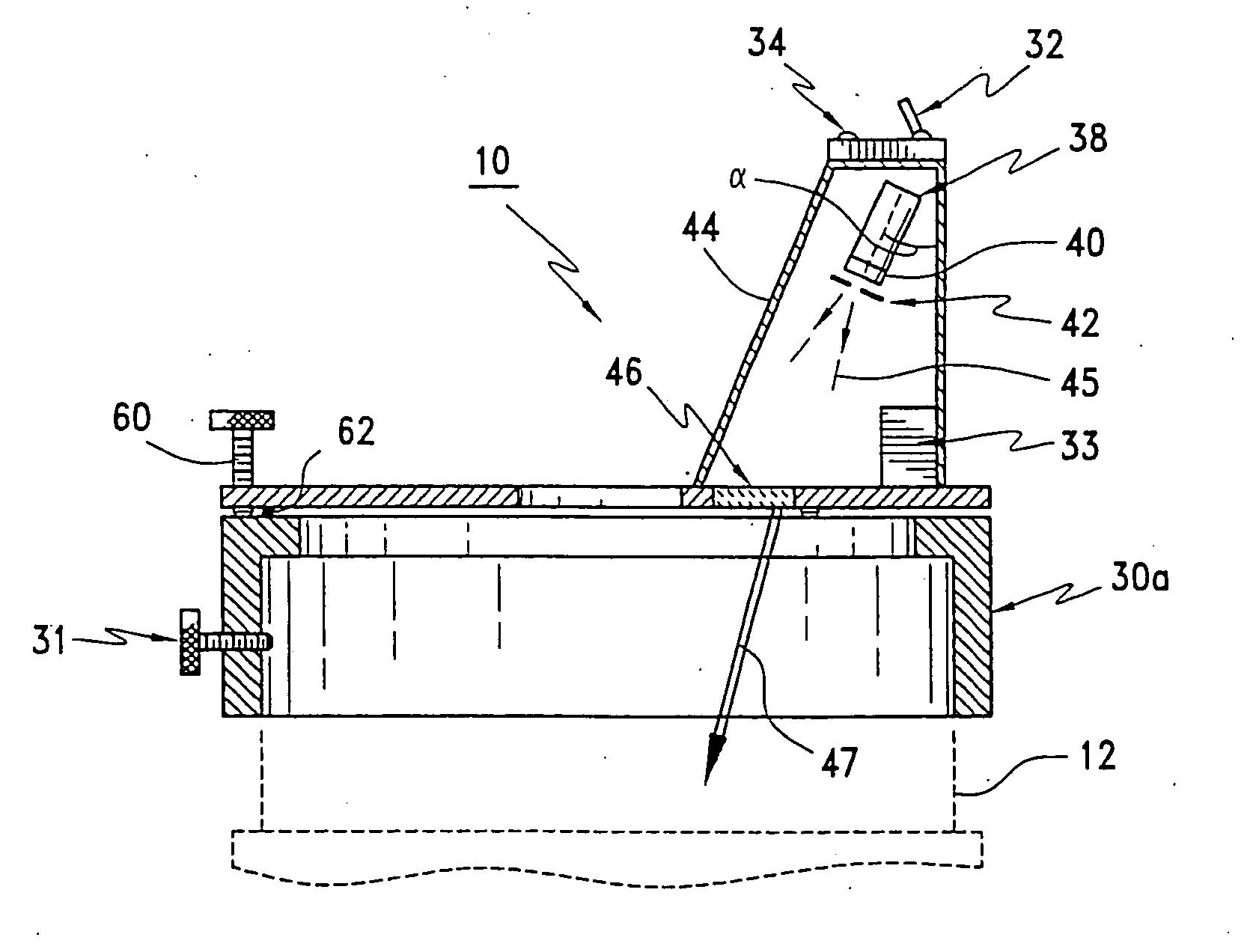
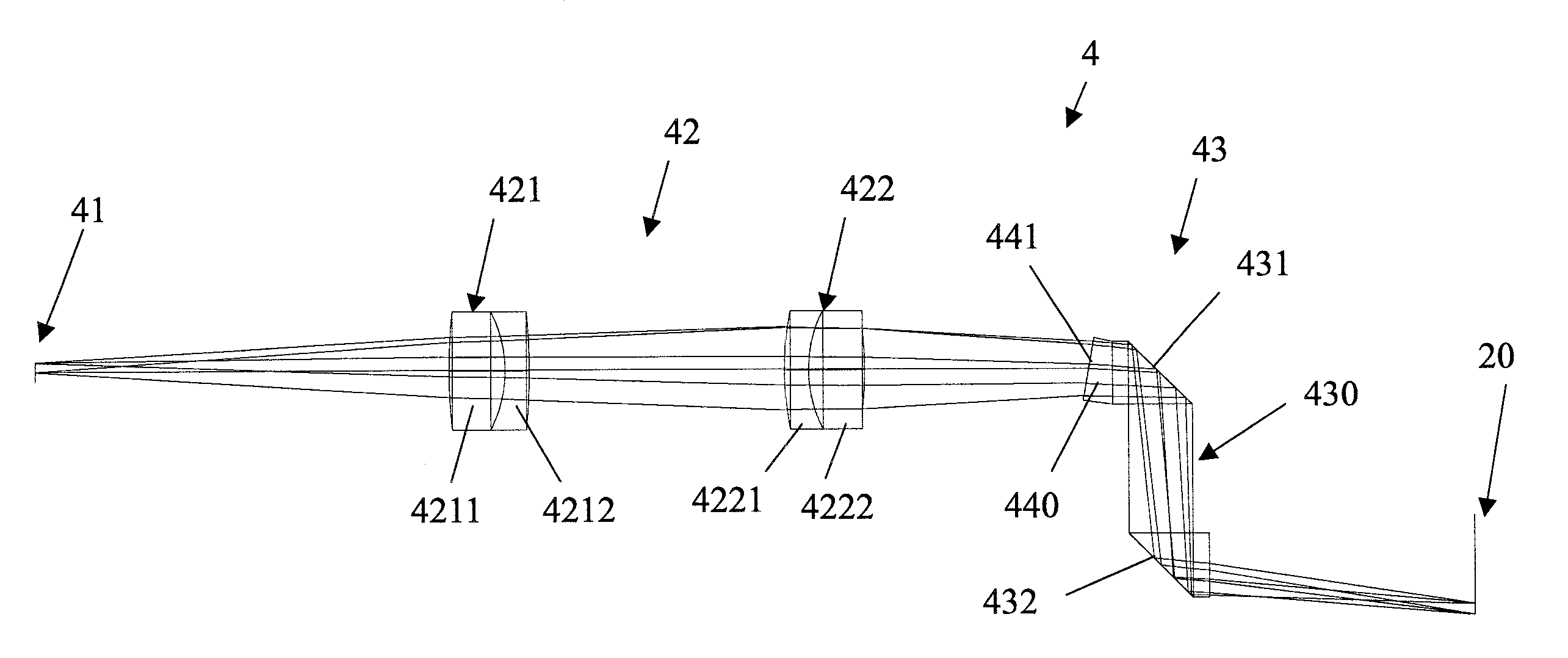
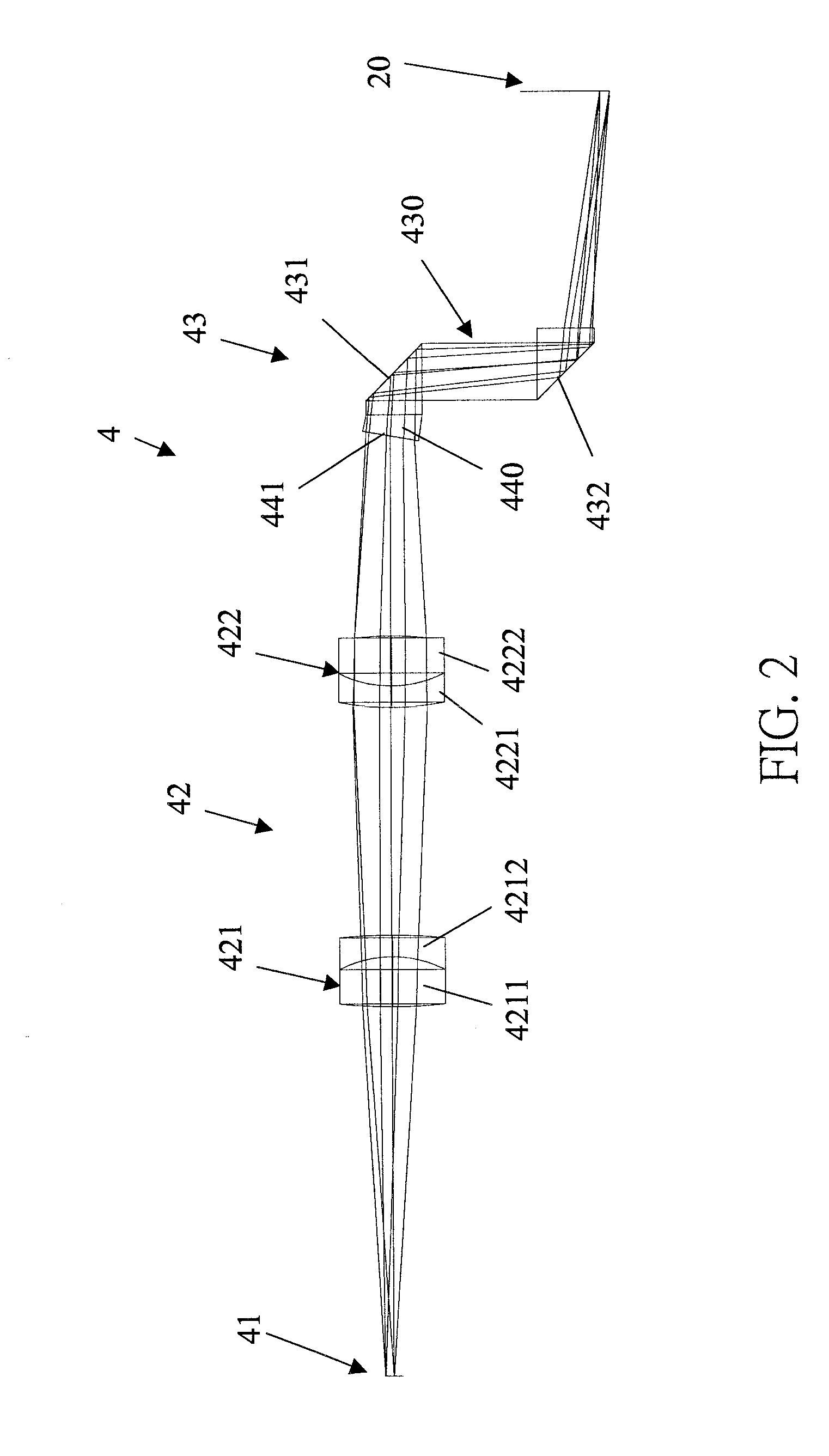
A display device (4) for a telescope system is disposed between a first image plane (10) and a second image plane (20) of the telescope system. The display device includes a signal emitter (41), a converging lens group (42) positioned adjacent to the signal emitter, and a dioptric imaging lens group (43) positioned adjacent to the converging lens group. The optical signal emitted by the signal emitter is first transmitted through the converging lens group, then incident onto the dioptric imaging lens group, and finally imaged onto the second image after reflection of the dioptric imaging lens group. Therefore, both the image size and brightness of the displayed signal viewed by the observer can maintain unchanged in spite of the magnification variation of the telescope system.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL INT LTD
Compact Catadioptric Lenses And Lens Systems With Improved Image Quality And Methods Of Using Same
InactiveUS20180180862A1Guaranteed high quality outputLittle and no blurringOptical elementsCamera lensTelephoto lens
A catadioptric telephoto lens system which receives incident light rays in a parallel path of both catoptrics and dioptrics, where some of the incident light rays go through a reflective path involving mirrors / reflective surfaces and others of the incident light rays go through a refractive path involving lenses; or receives incident light rays in a serial path of catoptrics and dioptrics, where all the incident light rays initially go through a reflective path involving mirrors / reflective surfaces and then go through a refractive path involving lenses. The system eliminates the black pupil / iris blur disadvantages associated with conventional telescopic lens systems and may be provided in a very compact form.
Owner:LU WEIMIN
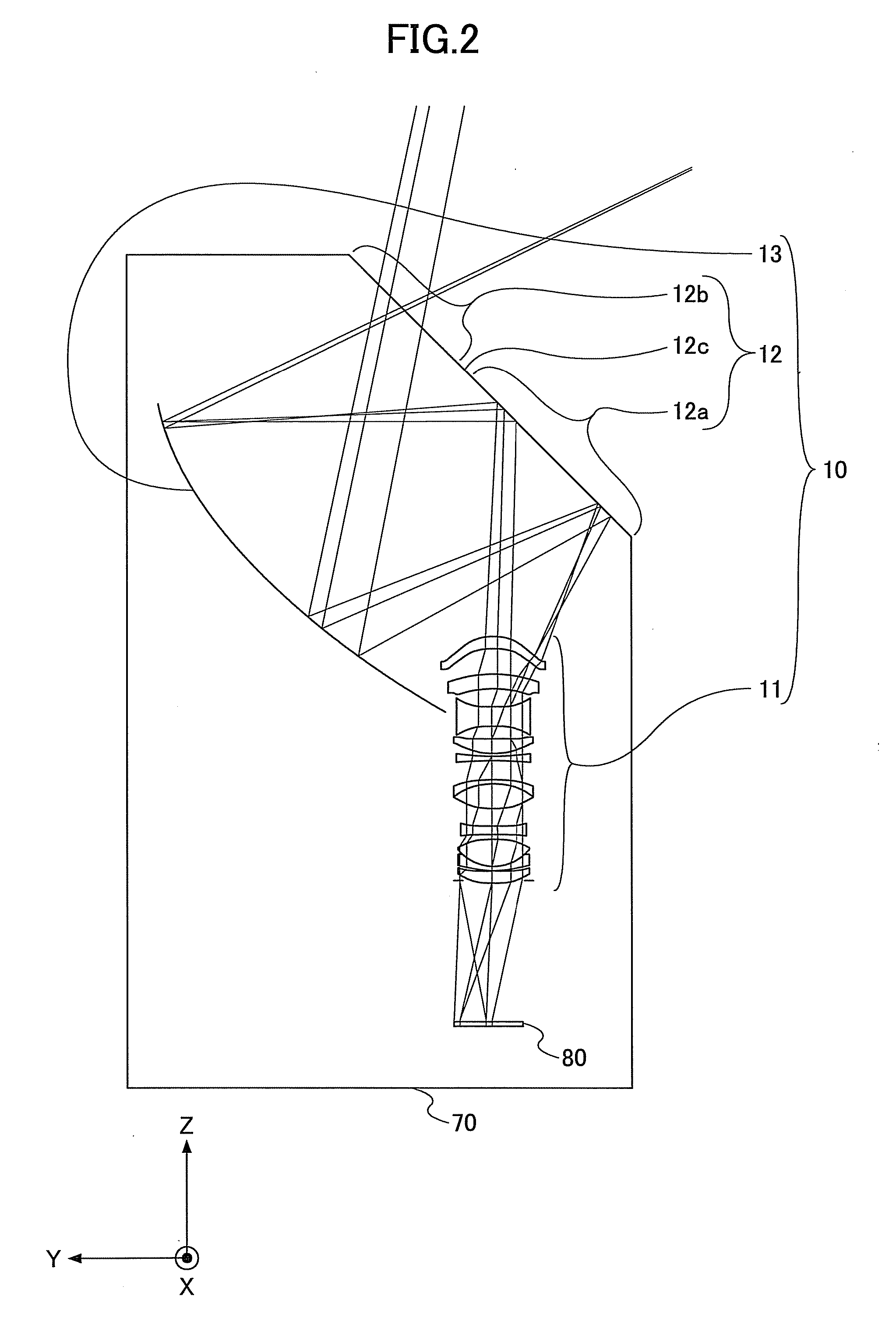
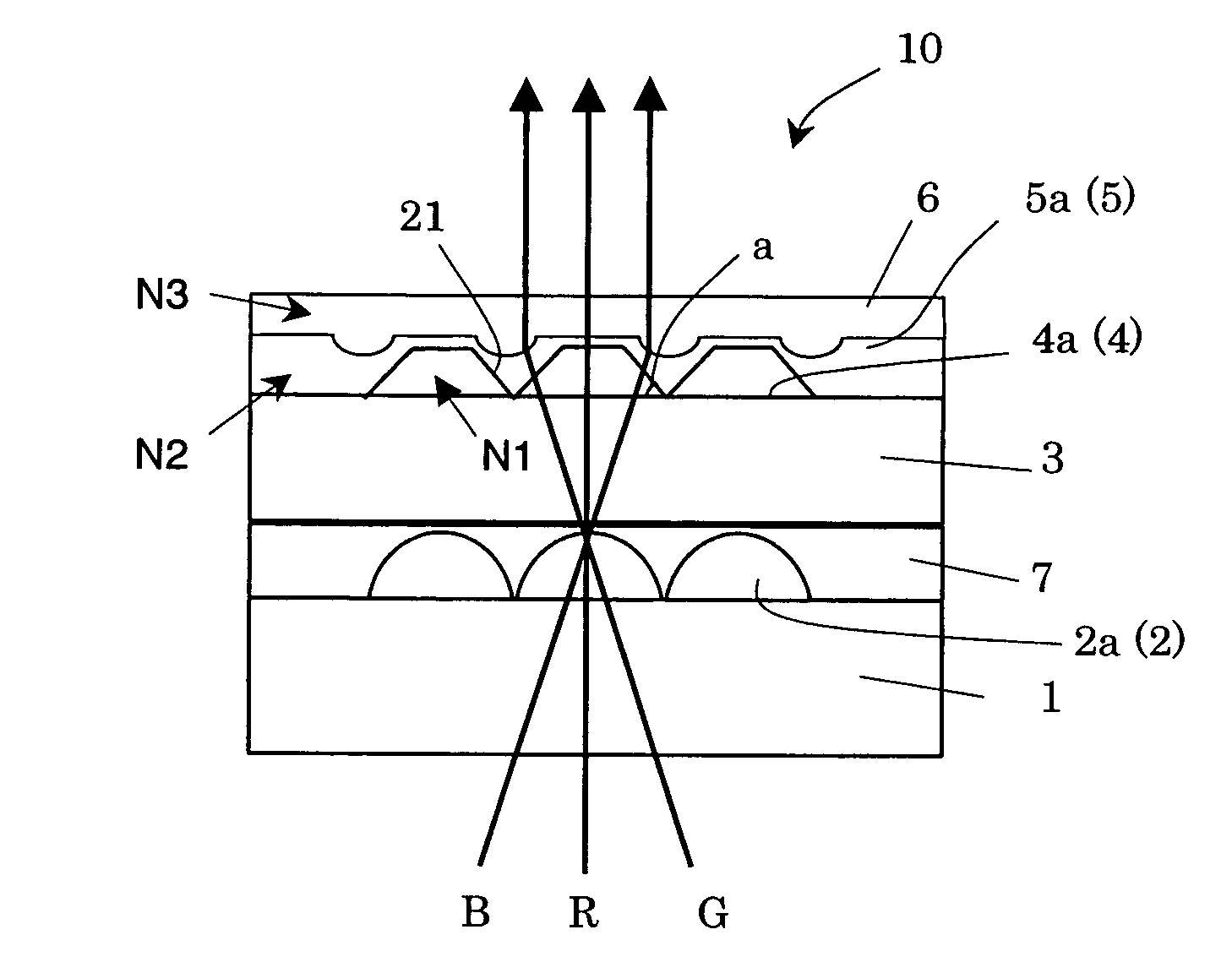
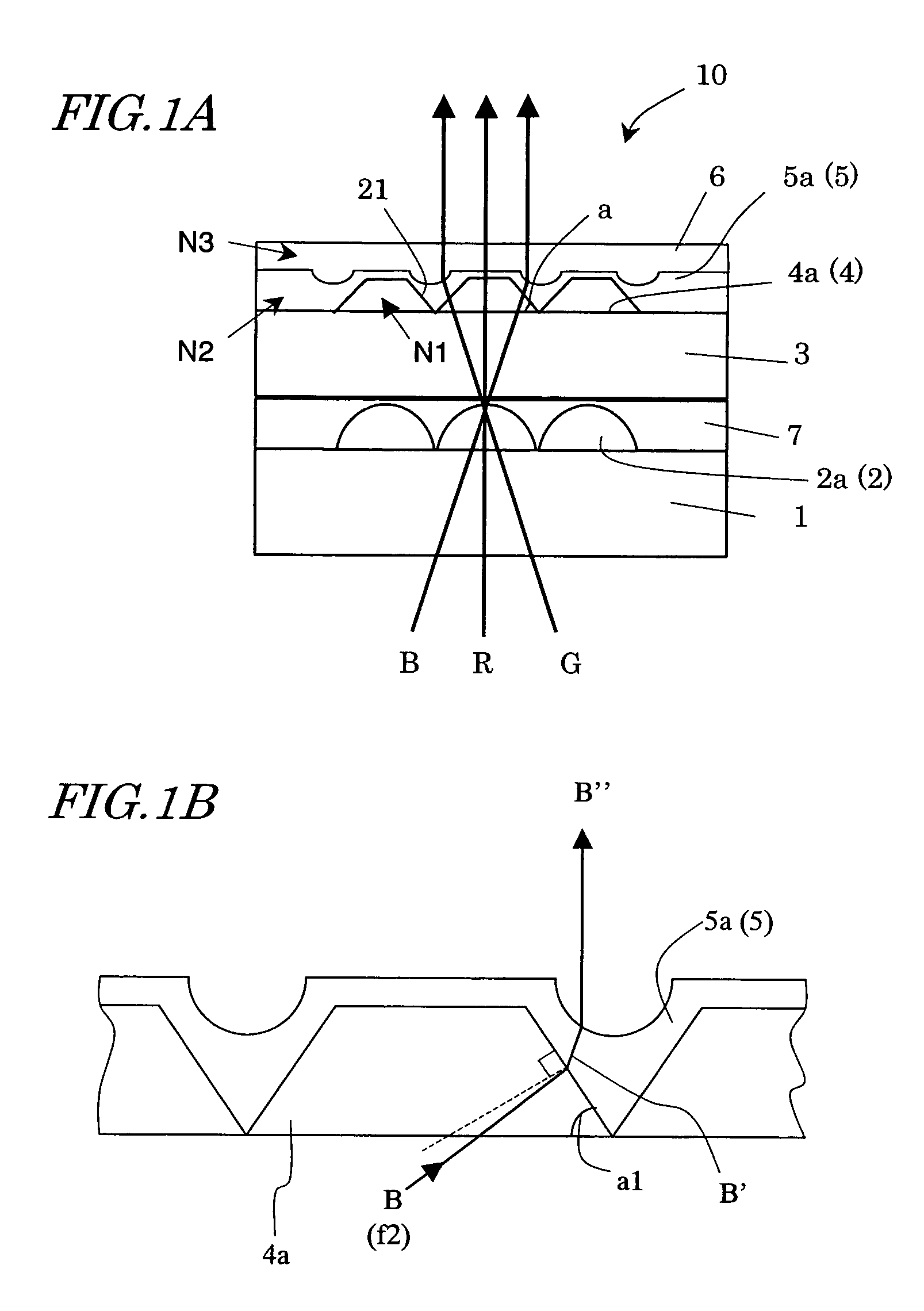
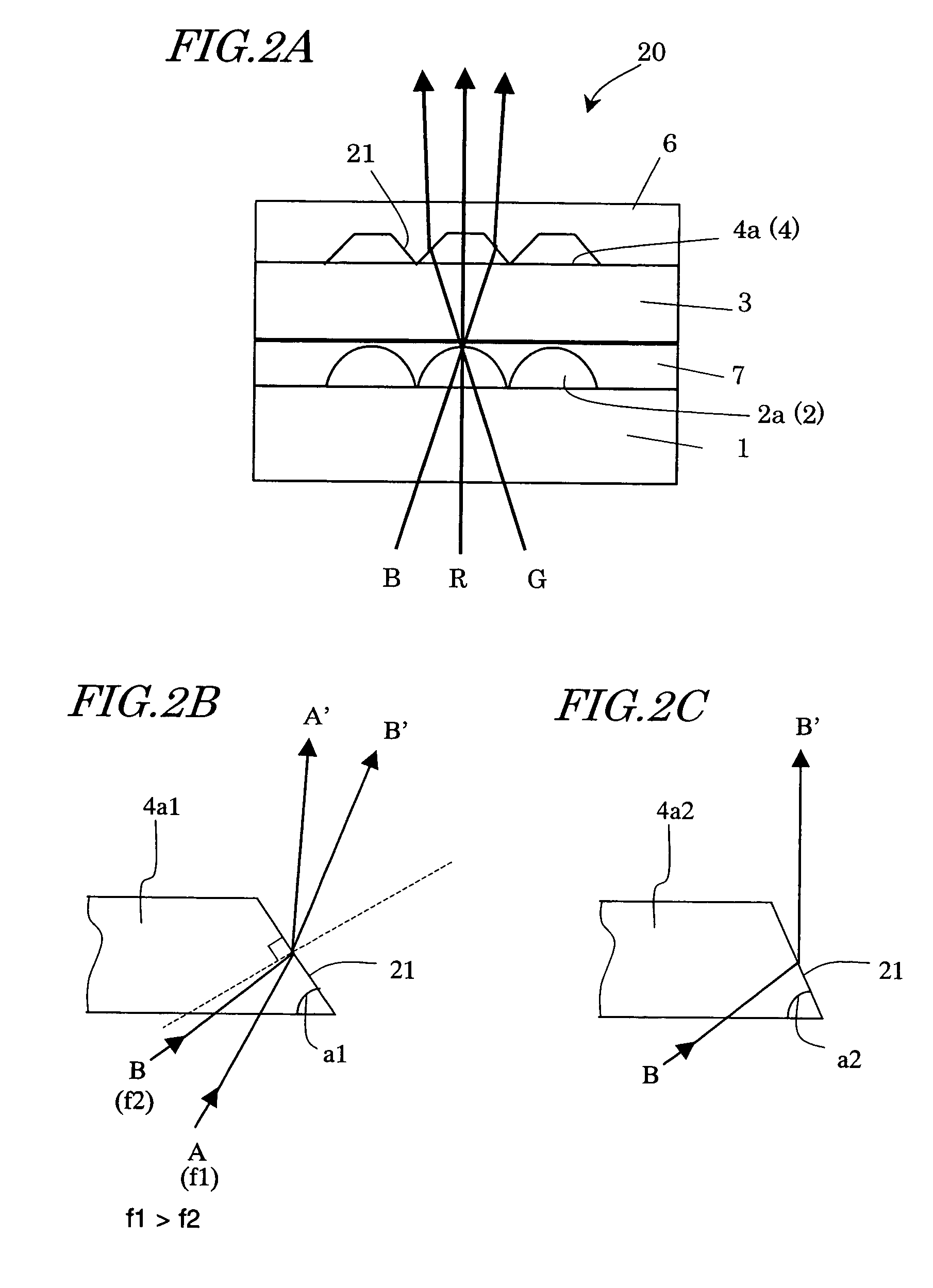
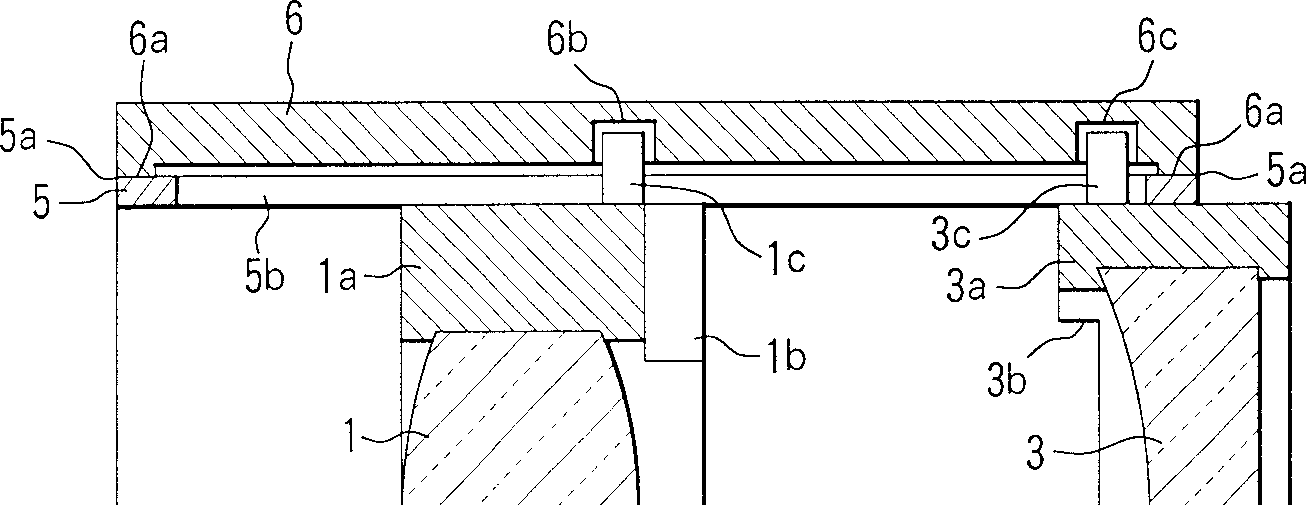
Dioptric element array substrate, image display device and image display apparatus
ActiveUS7542101B2Improve light utilization efficiencyImprove display qualityNon-linear opticsLensRefractive indexDisplay device
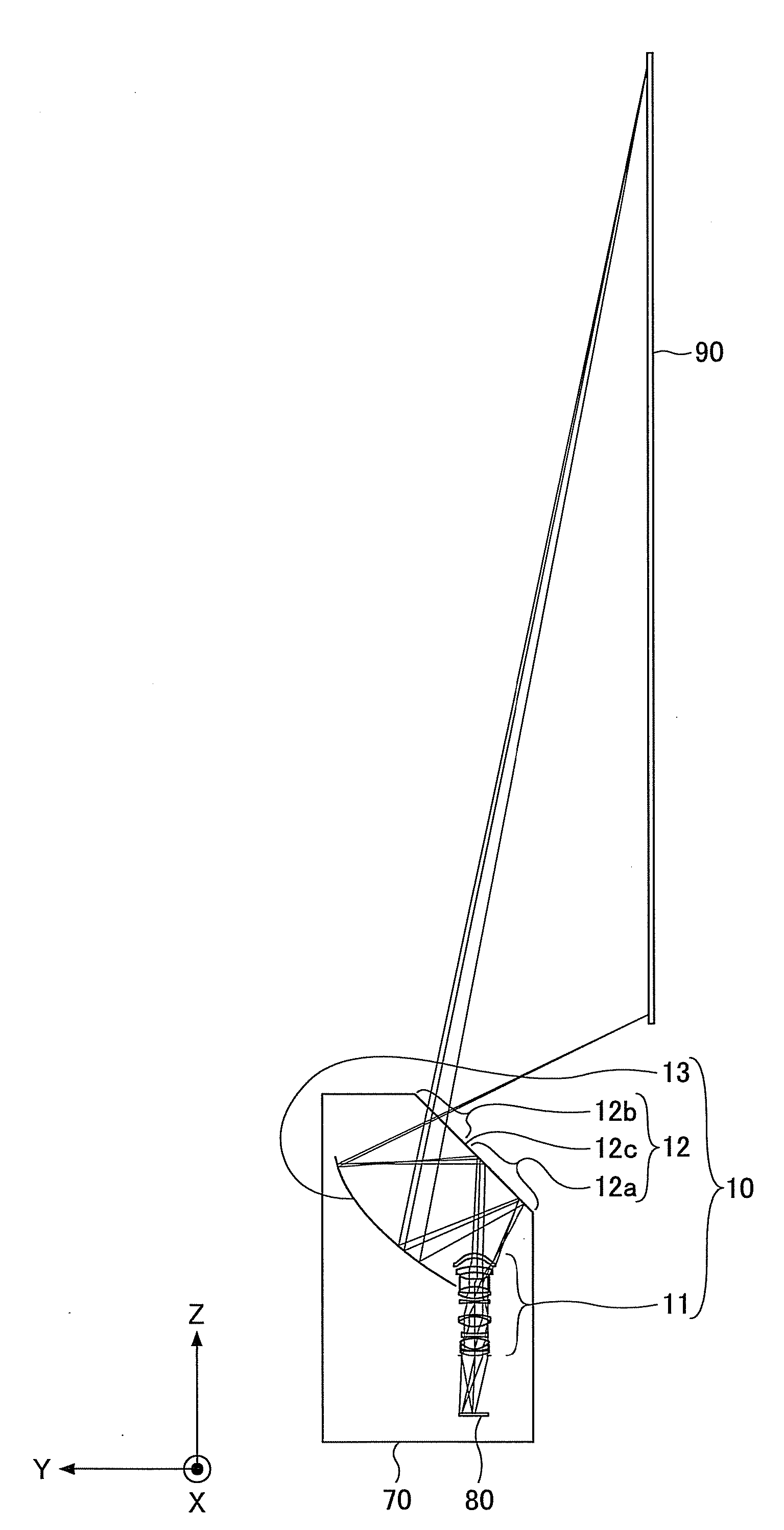
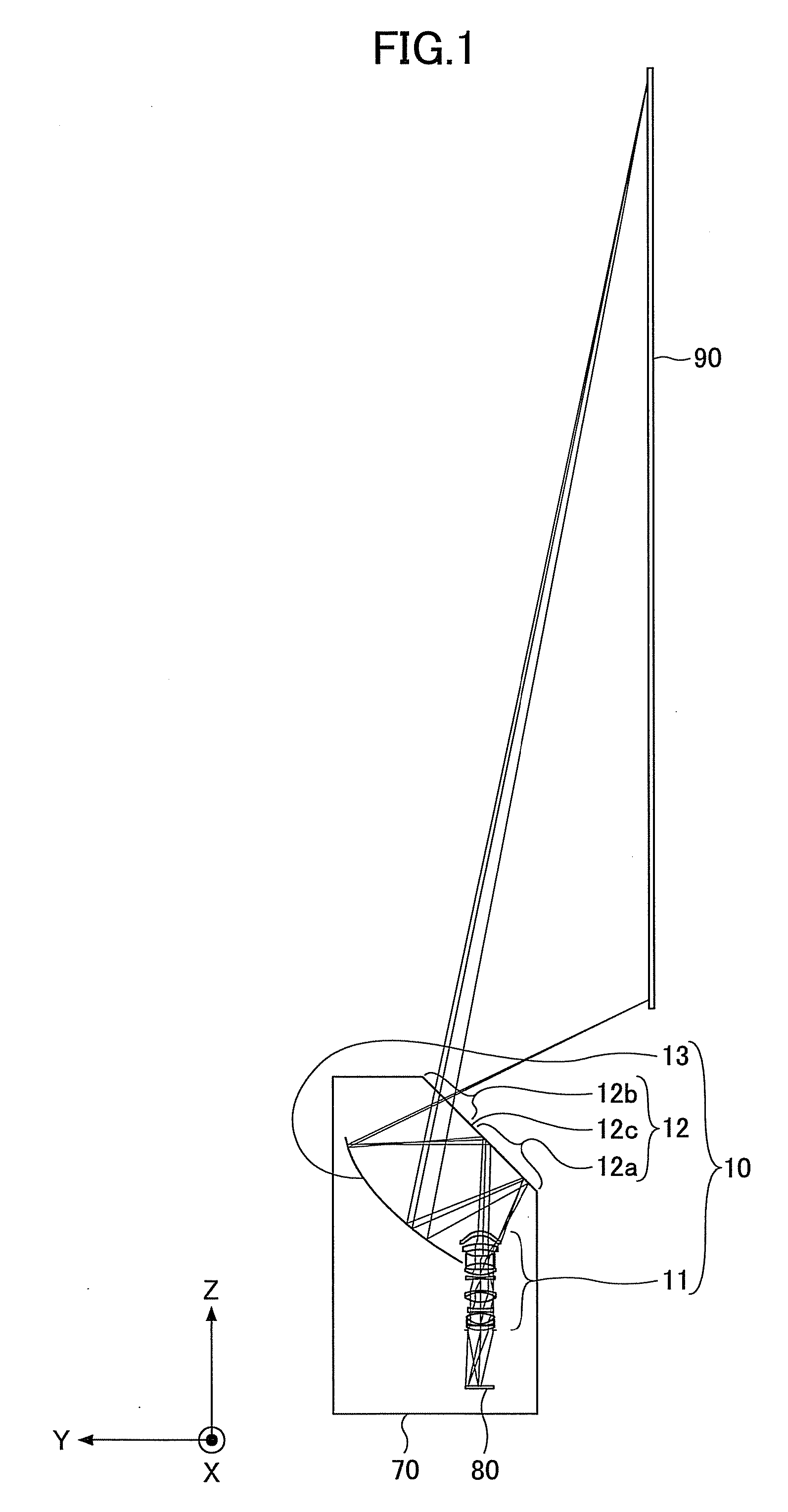
A dioptric element array substrate 10 includes: a first dioptric element array 2 having a plurality of first dioptric elements 2a arranged two-dimensionally; a second dioptric element array 4 having a plurality of second dioptric elements 4a having a first refractive index arranged two-dimensionally in one-to-one correspondence with the first dioptric elements; and a third dioptric element array 5 having a second refractive index different from the first refractive index. Principal rays of beams incident on the first dioptric element array at different angles and converged with the first dioptric element array are collimated with the second and third dioptric element arrays.
Owner:SHARP KK
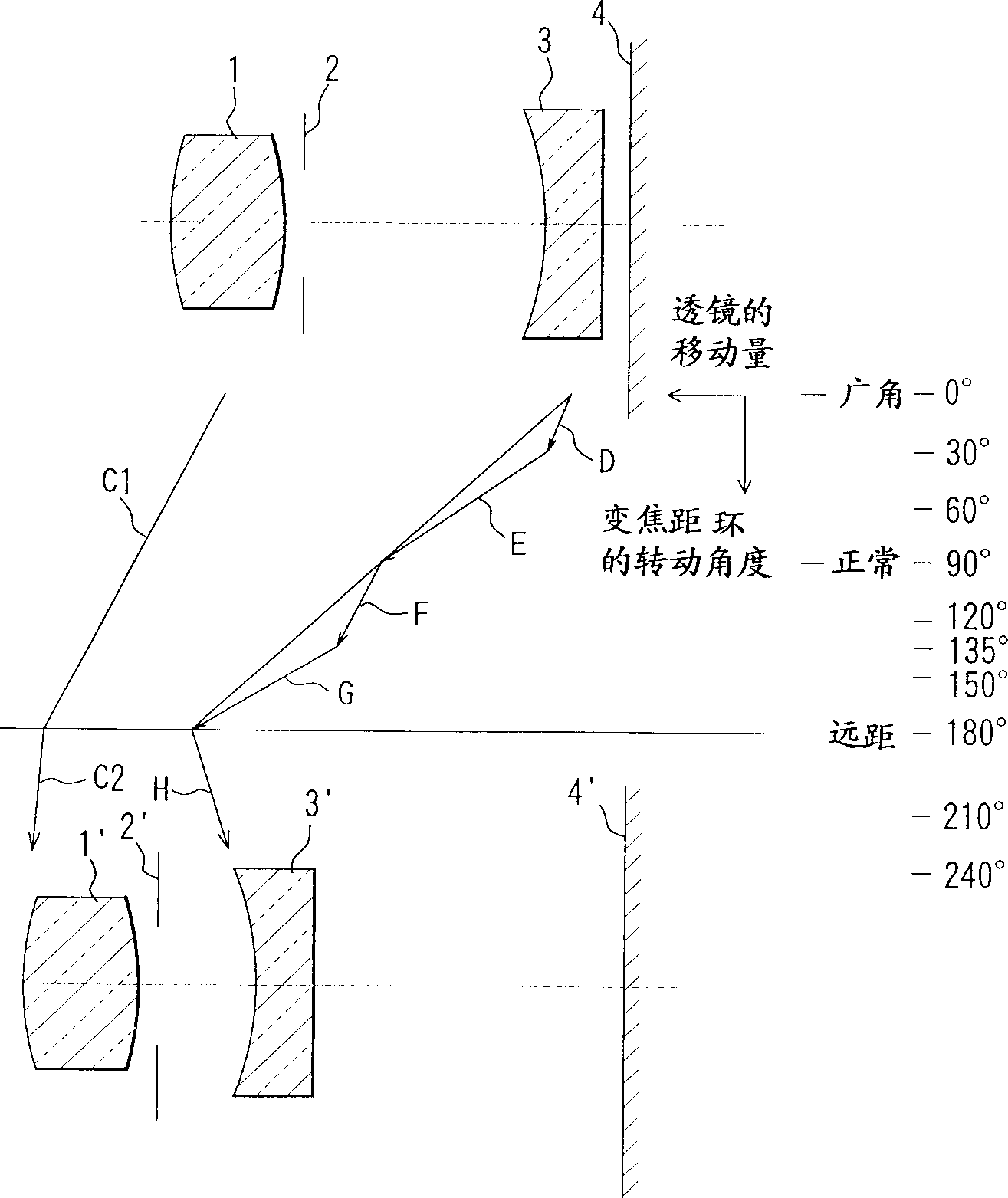
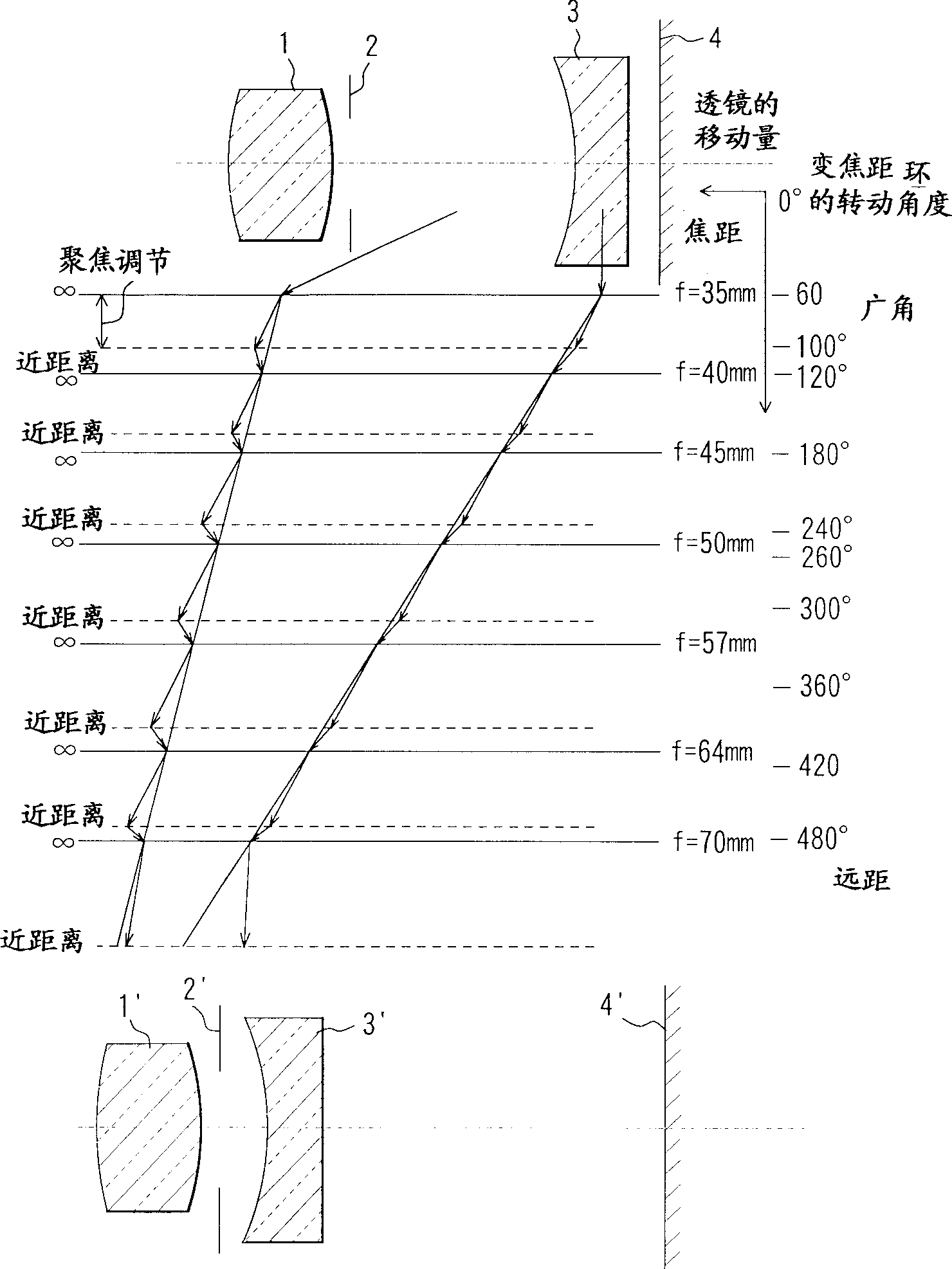
Lens barrel with variable dioptric strength and camera
The invention discloses a variable-focus lens barrel and camera, the lens barrel has a first lens unit located on the side closest to the object, and a cam barrel with first cams, and the first cams alternately and continuously have a a set of variable-focus cam sections that drive the first lens unit to change its power in the direction of the optical axis, and a set of focus cam sections that drive the first lens unit driven by the corresponding variable-focus cam sections , so as to focus in the direction of the optical axis, and the focus cam portion of the first cam that drives the first lens unit is raised less in the direction of the optical axis at the telephoto end than the focus cam that drives the first cam of the first lens unit The amount of lift of the part in the direction of the optical axis at other variable focus positions.
Owner:CANON KK
Projection module for applying to transparent glass and capable of multi-angle dioptric imaging
InactiveCN104155838ANovel structureBreak through the limitations of useProjectorsDioptricsLight beam
The invention discloses a projection module for applying to transparent glass and capable of multi-angle dioptric imaging. The projection module comprises a control terminal, a projector and imaging glass, wherein the control terminal is electrically connected with and controls the projector; the projector is placed on the back of the imaging glass and used for projecting light beams onto the imaging glass; the front surface of the imaging glass comprises a plurality of triangular transmission gratings; the triangular transmission gratings project the light beams projected on the gratings vertically in the original direction for imaging, and refract the light beams projected on the gratings slantly into two light beams differing in directions for imaging. Through the manner adopted in the projection module, the projection module for applying to transparent glass and capable of multi-angle dioptric imaging has the advantages of wide application, breakthrough of the application limitation of a projection screen, novel structure, multi-angle imaging, and the like, and has a wide market prospect on the popularization of the projection unit for applying to transparent glass and capable of multi-angle dioptric imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU T CREATE TECH
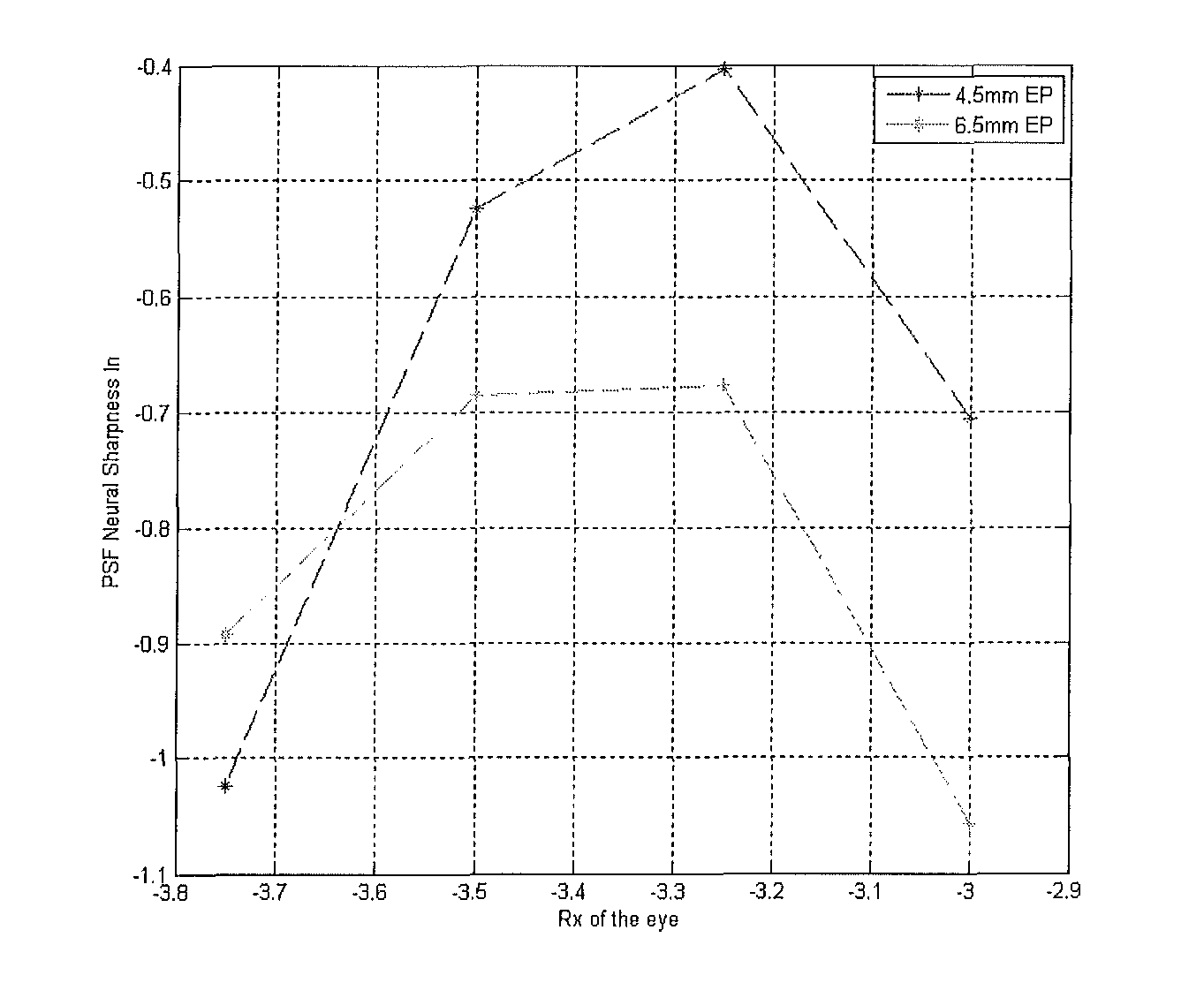
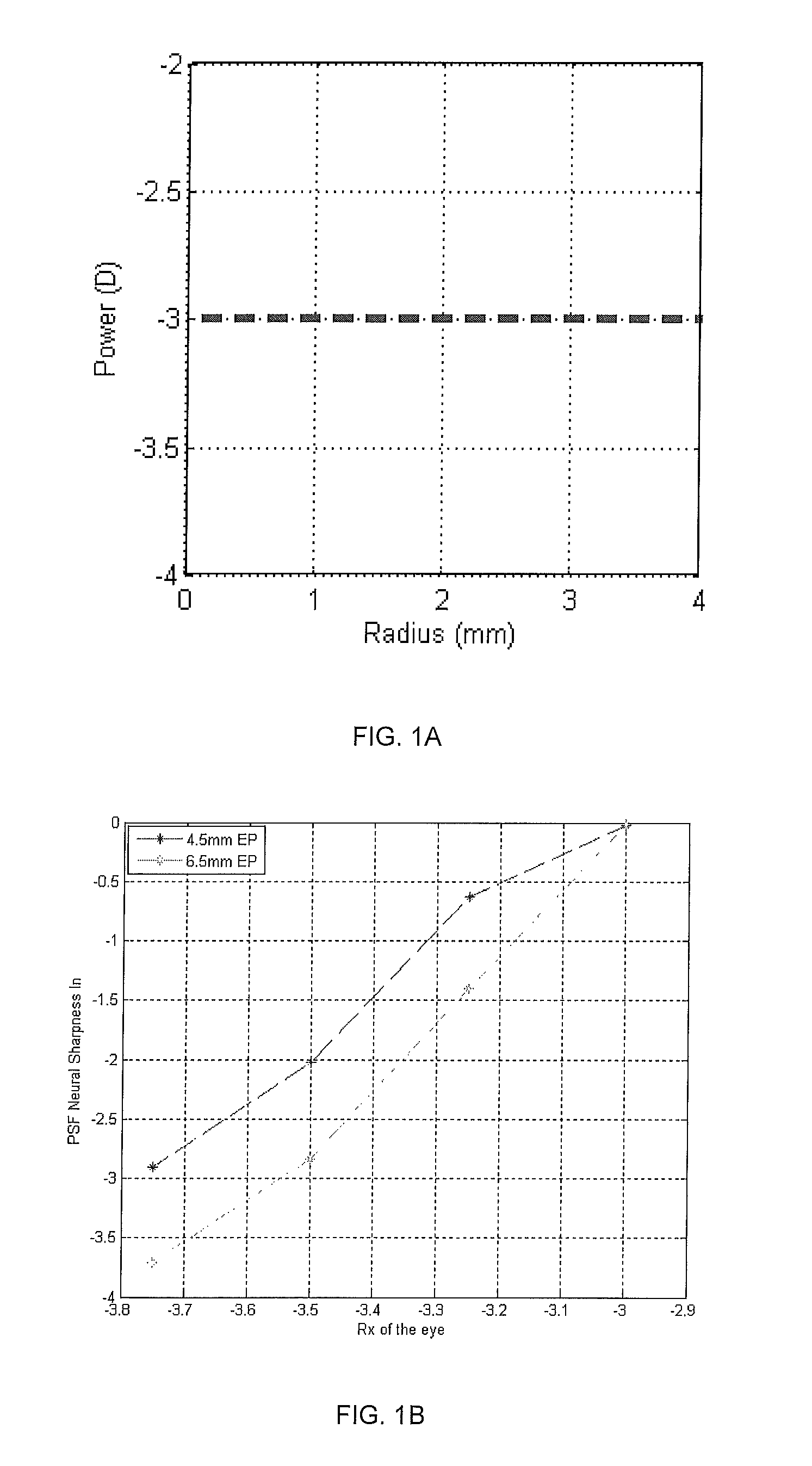
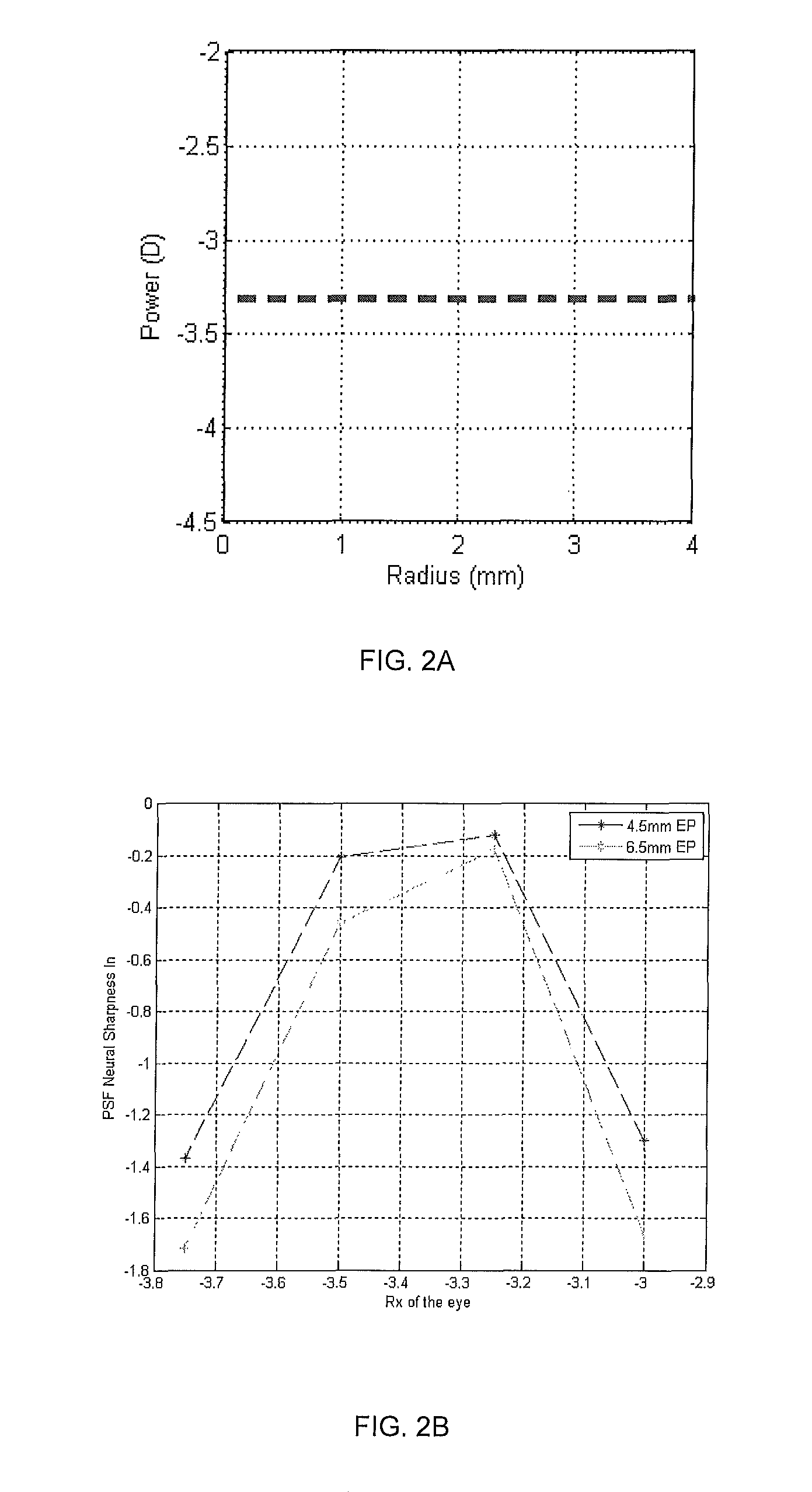
Lens design and method for minimizing visual acuity variation experienced by myopia progressors
ActiveUS9417463B2Minimizing visual acuity variationMinimize changesSpectales/gogglesEye treatmentImaging qualityEngineering
Contact lenses incorporate power profiles that minimize visual acuity variation for progressing myopes based upon minimization of the variation of neural sharpness image quality over a specific time period. The contact lens includes a center and at least one peripheral zone surrounding the center and having a different dioptric power than at the center. The lens has power profile selected from the group consisting of a power profile with spherical aberration, a multifocal power profile, a freeform power profile, and a segmented freeform power profile. The power profile is based on an initial paraxial power of a myopia progressor and a defined myopia progression rate over a specific time period, resulting in controlled change of the neural sharpness, thereby minimizing changes in changes in visual acuity at a beginning of the time period and at an end of the time period.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com