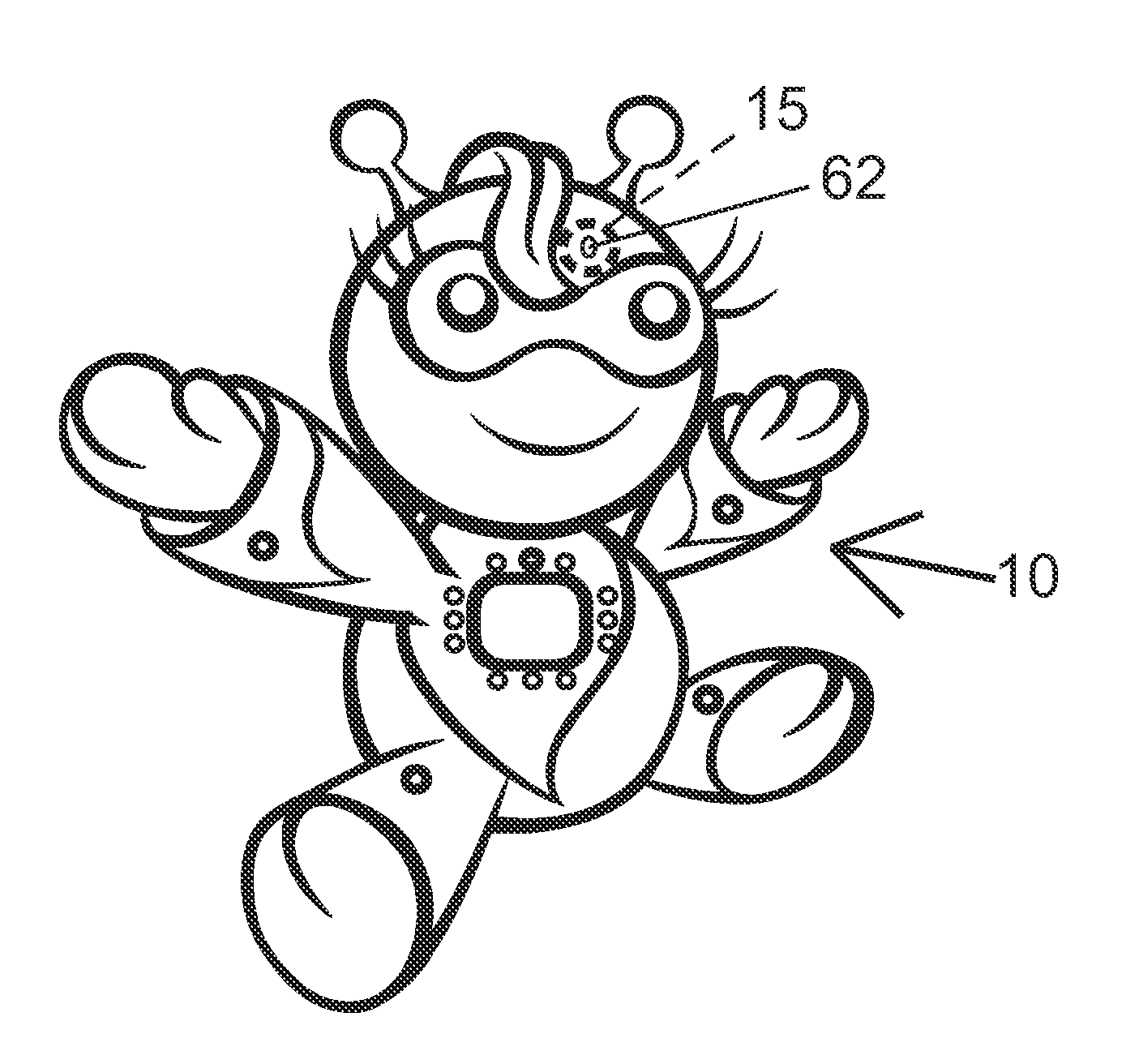Patents
Literature
445 results about "Direct execution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
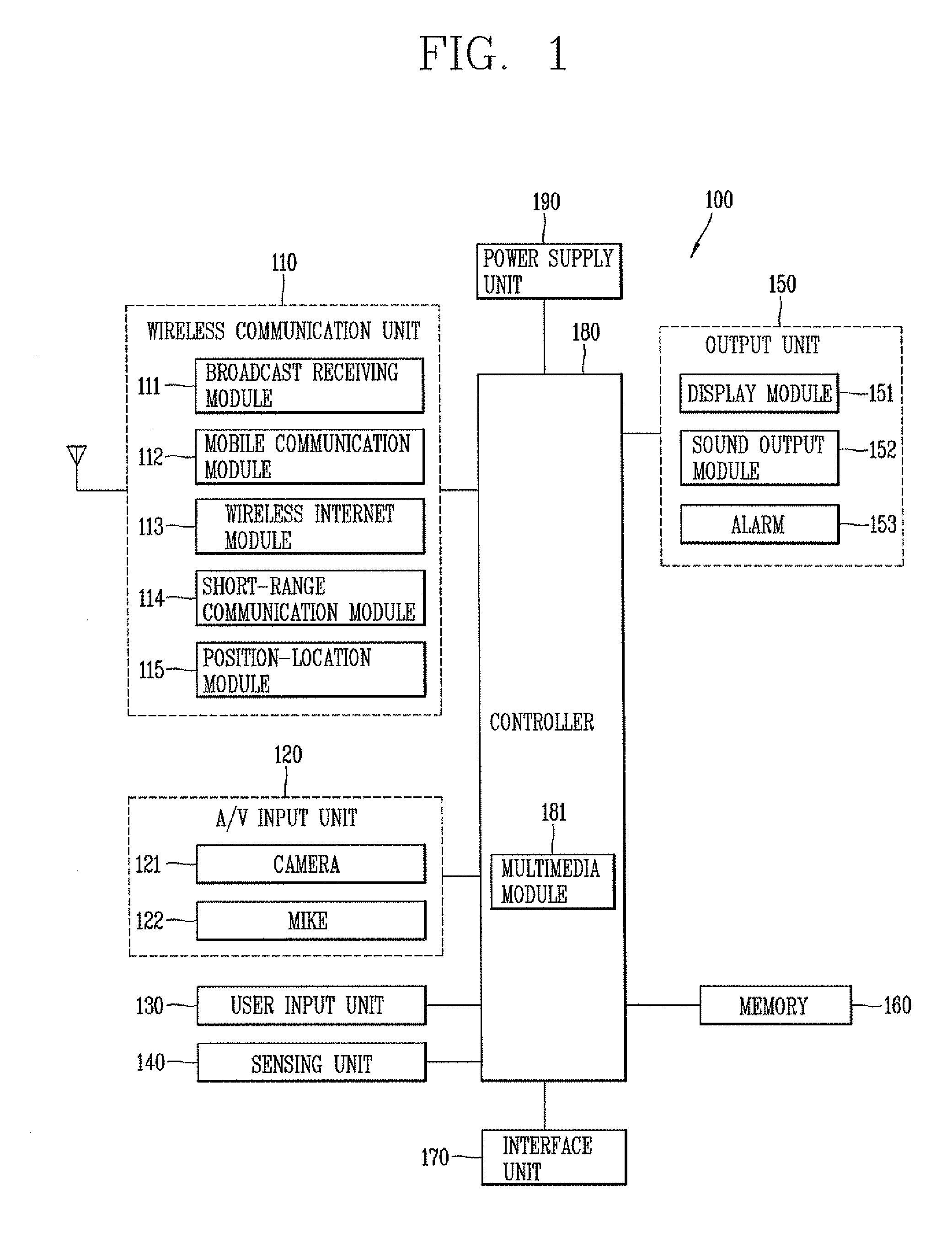
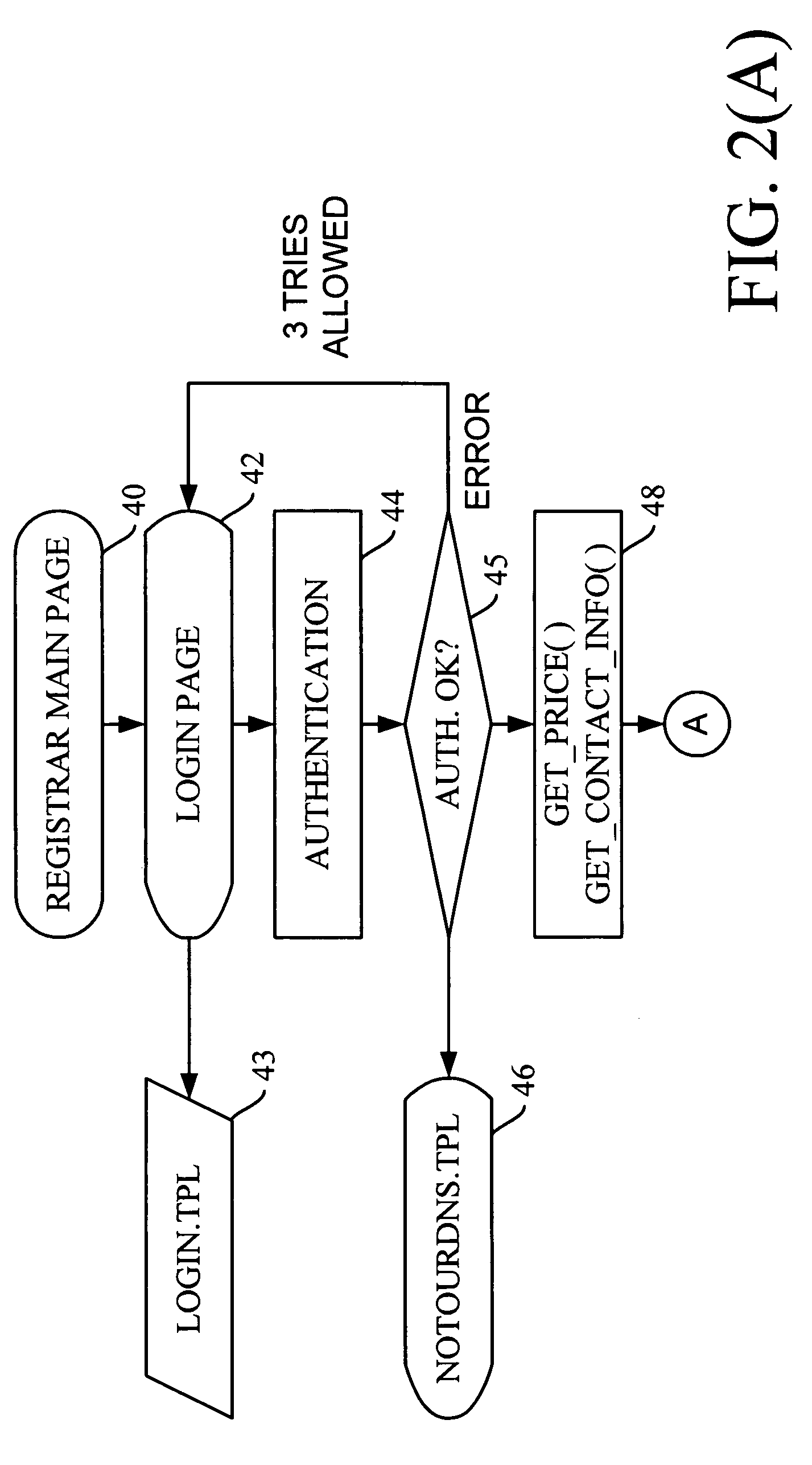
Computer security and management system
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Computer security and management system
ActiveUS20020129264A1Memory loss protectionData taking preventionComputer security modelDirect execution
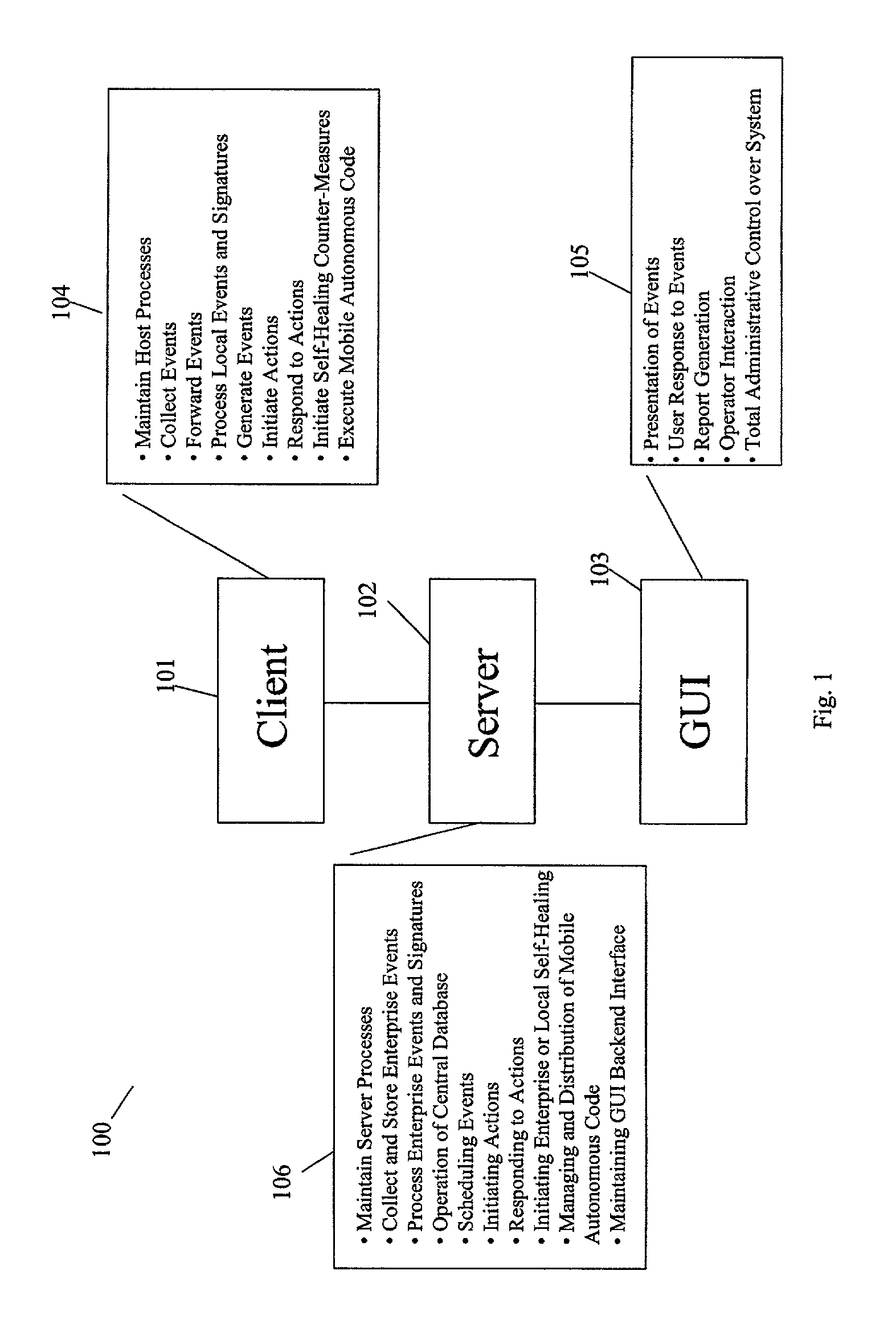
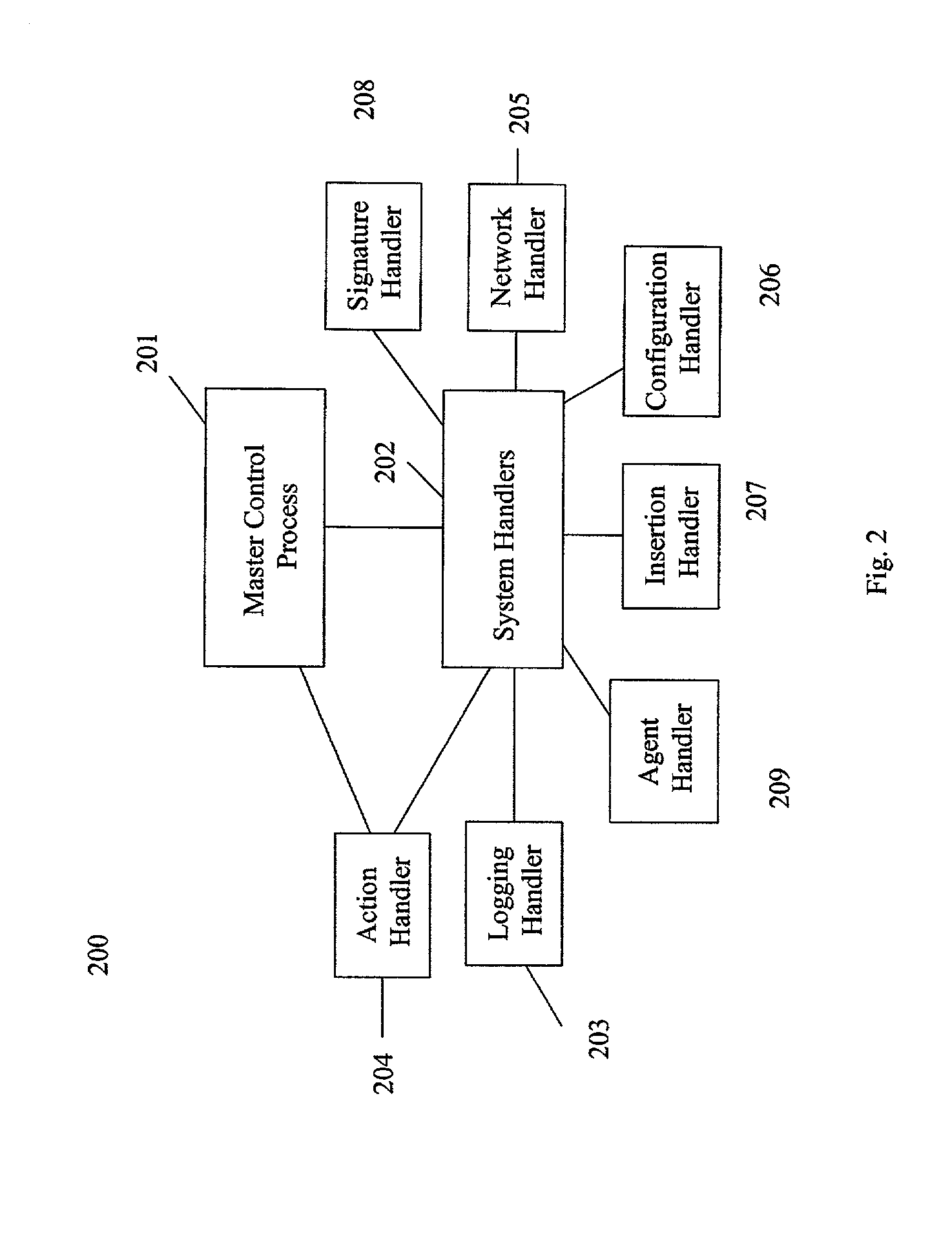
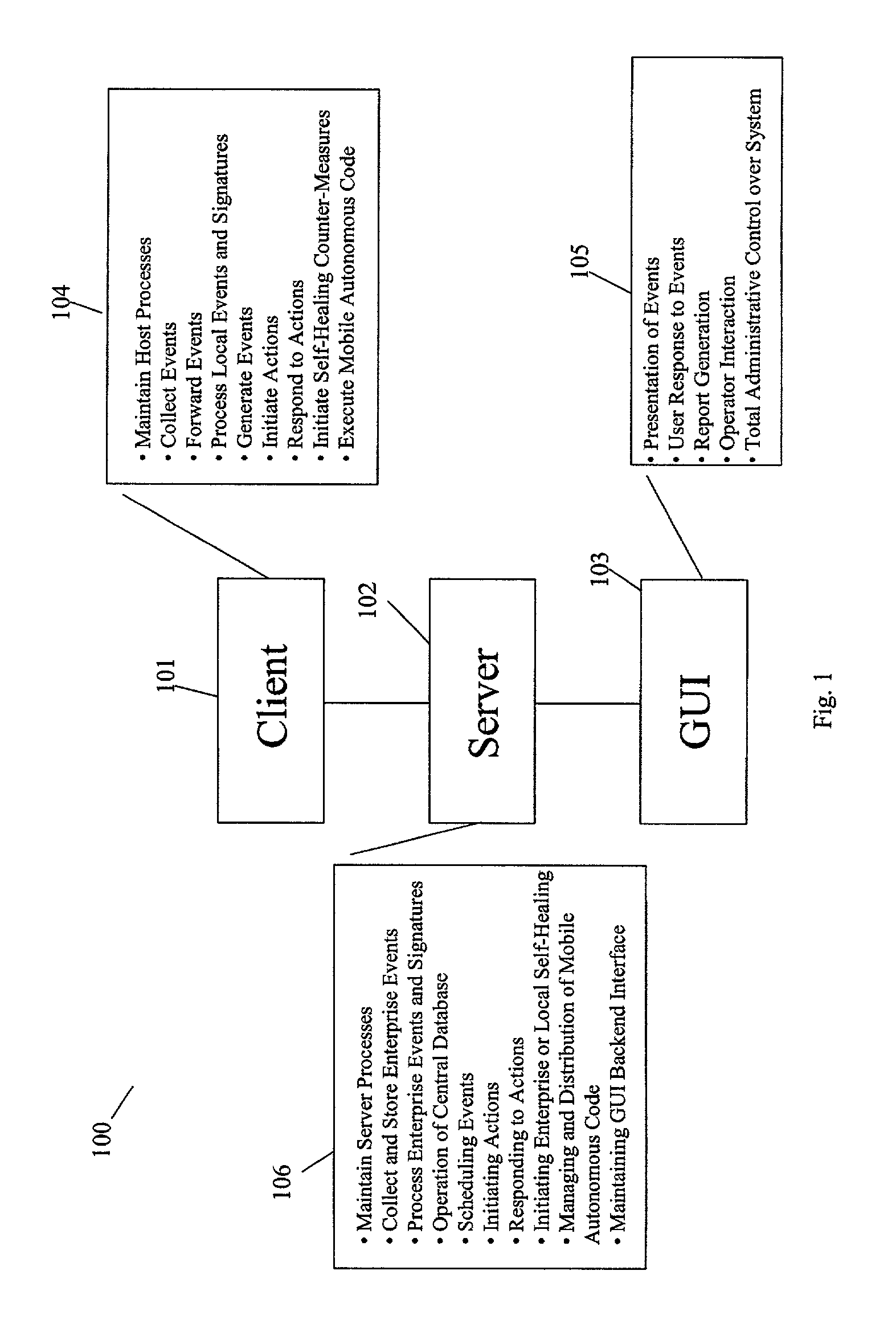
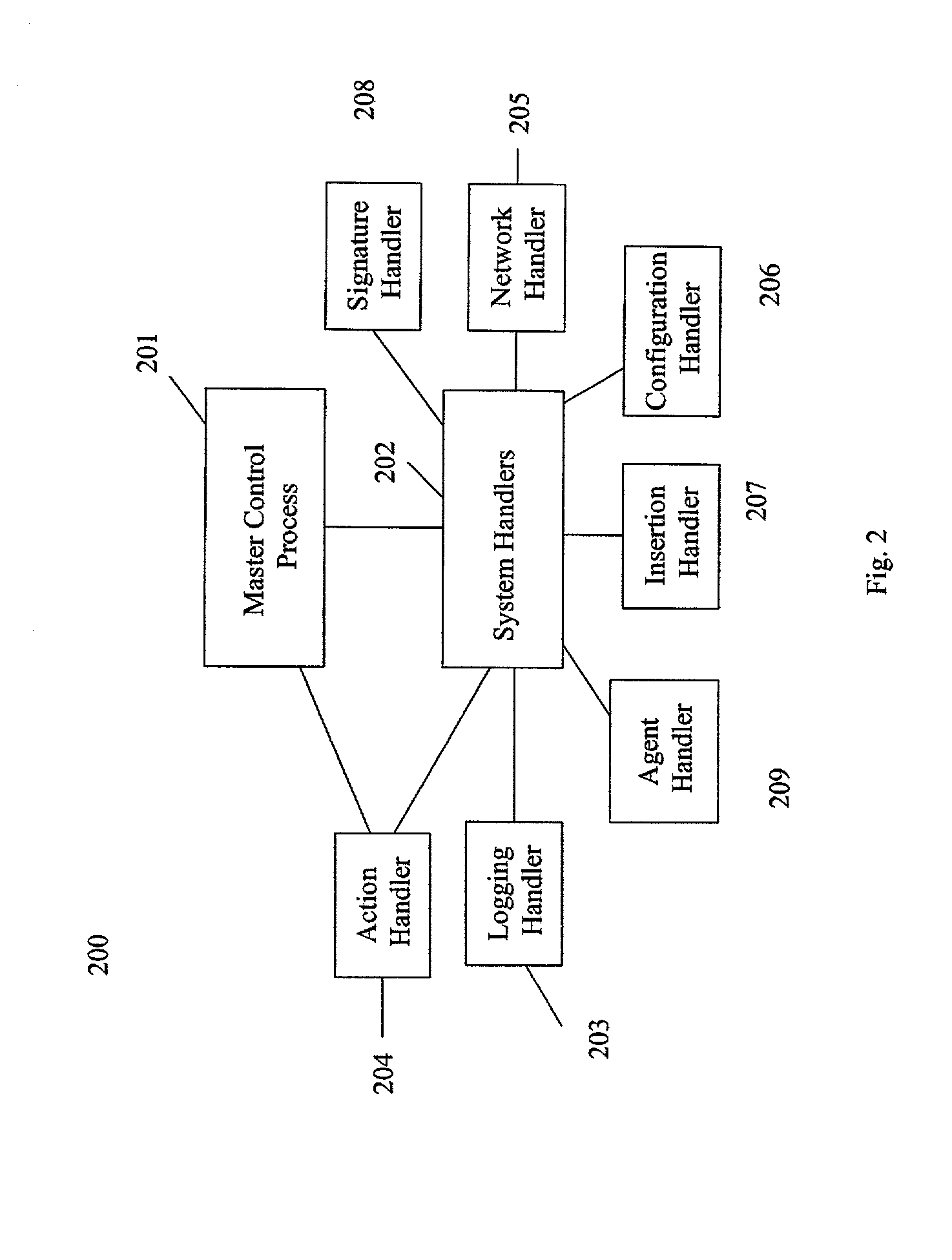
The present invention provides a generic distributed command, control, and communication framework that allows computer systems, devices, and operational personnel to interact with the network as a unified entity. The present invention provides these services by building upon a core communication architecture that permits local or remote execution of mobile program code, static execution of program code, flexible communication formats, self-healing network techniques, and expansion by the addition of new system modules, software handlers, or mobile autonomous agents.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Hardware virtual machine instruction processor
InactiveUS6021469AProhibitive expenseLow costMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTThe InternetCellular telephone
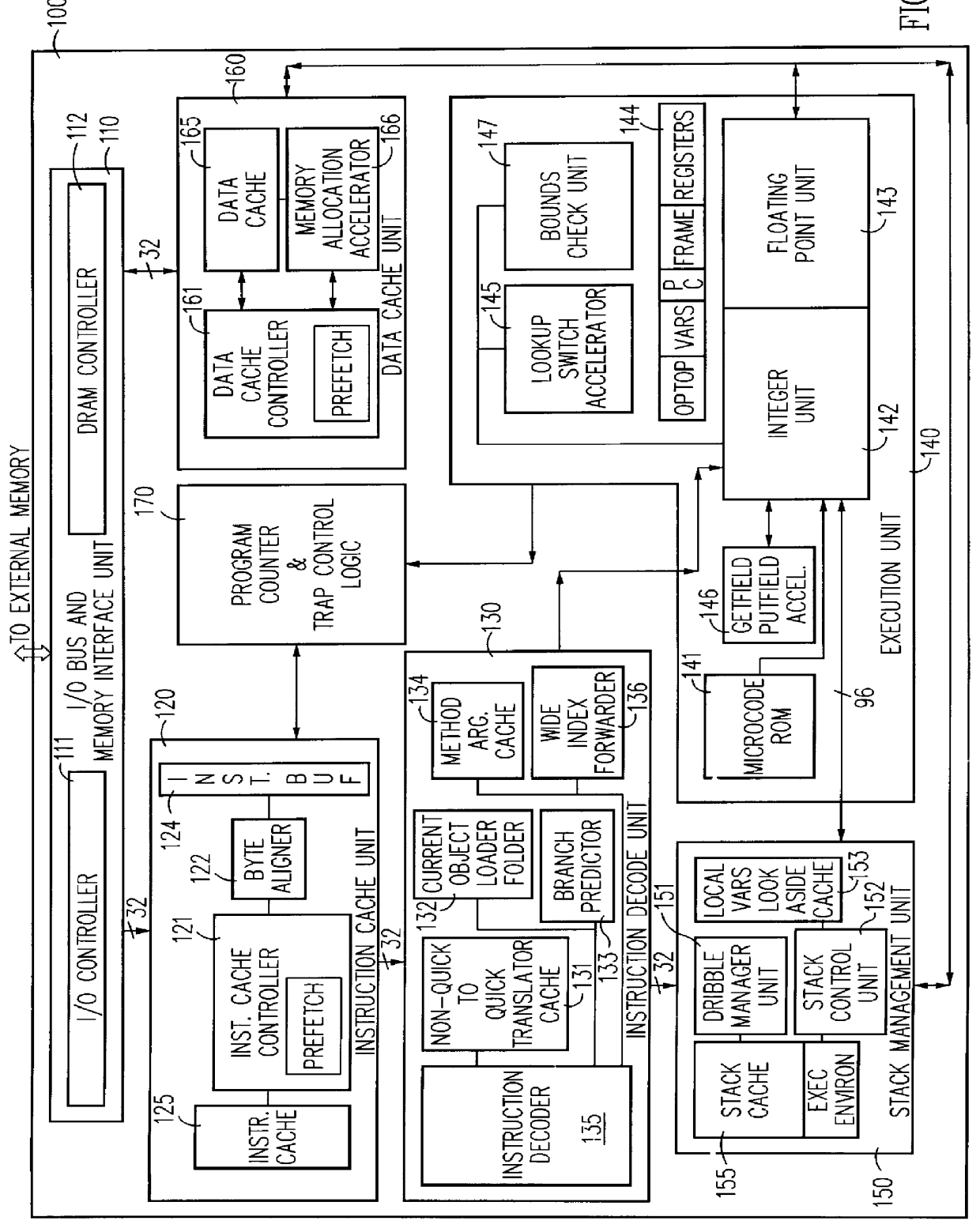
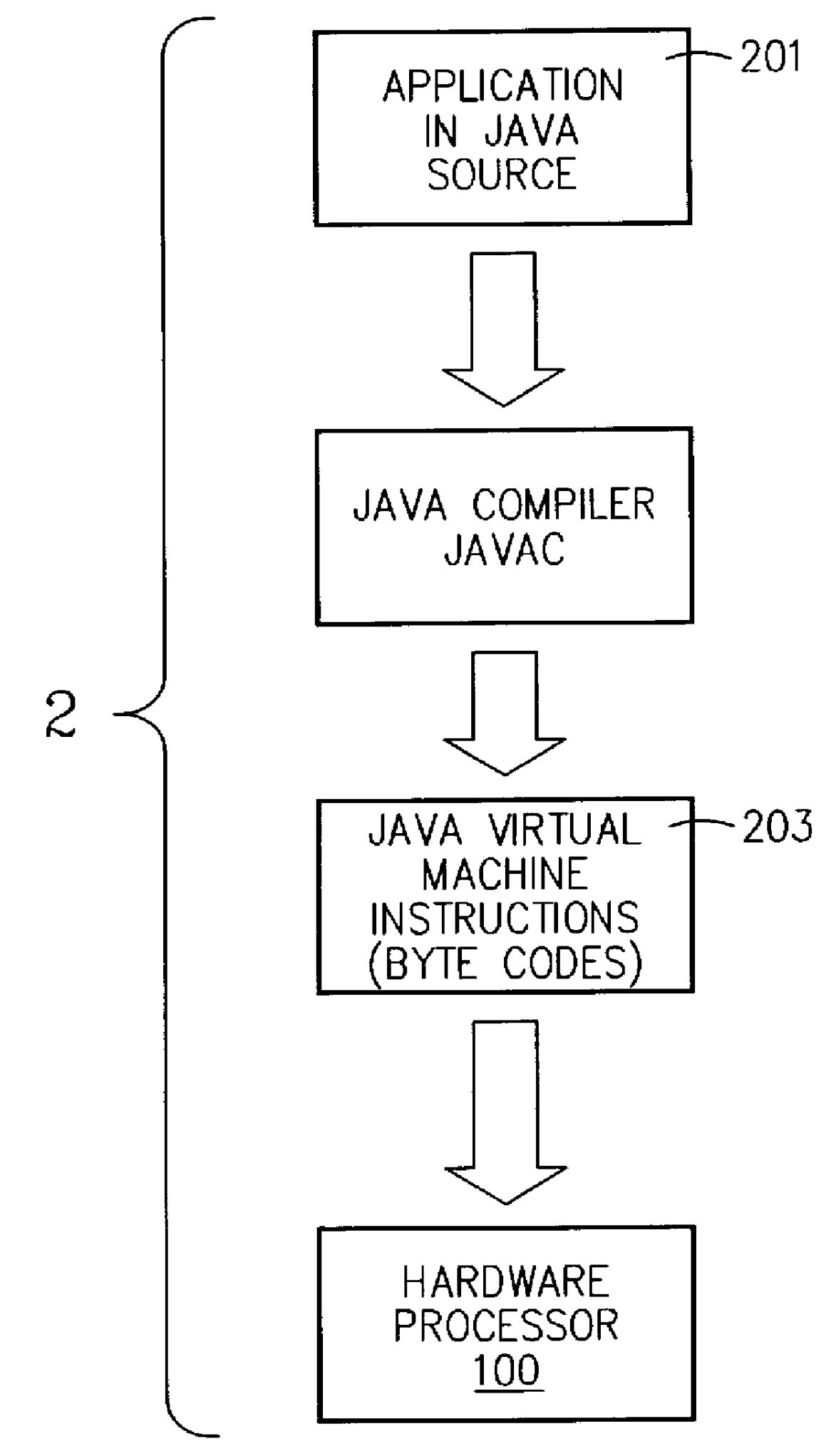
A hardware virtual machine instruction processor directly executes virtual machine instructions that are processor architecture independent. The hardware processor has high performance; is low cost; and exhibits low power consumption. The hardware processor is well suited for portable applications. These applications include, for example, an Internet chip for network appliances, a cellular telephone processor, other telecommunications integrated circuits, or other low-power, low-cost applications such as embedded processors, and portable devices.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Methods and systems for direct execution of XML documents
InactiveUS20020111965A1Reduce program complexityDigital computer detailsSemi-structured data retrievalDocumentation procedureDocument type definition
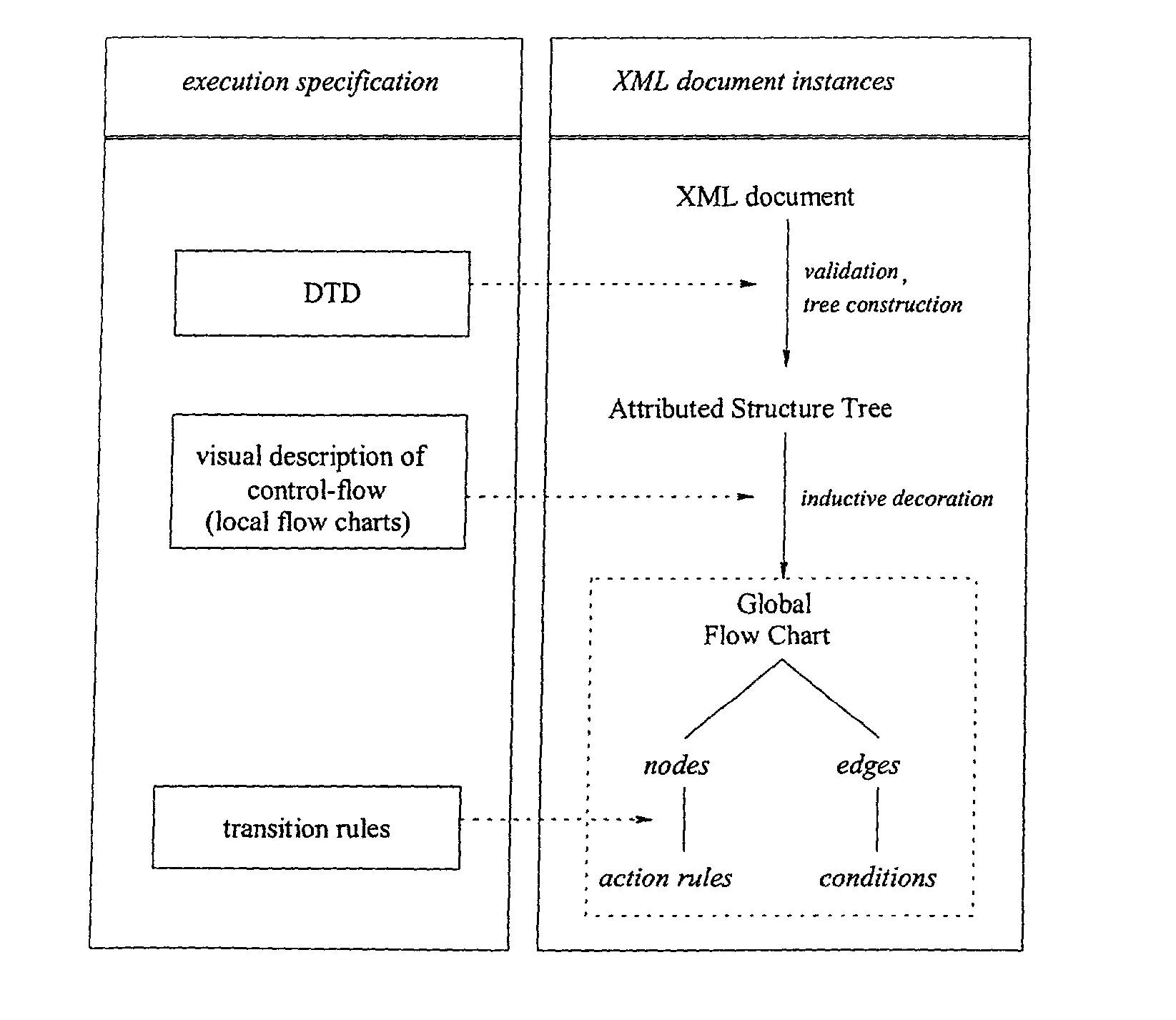
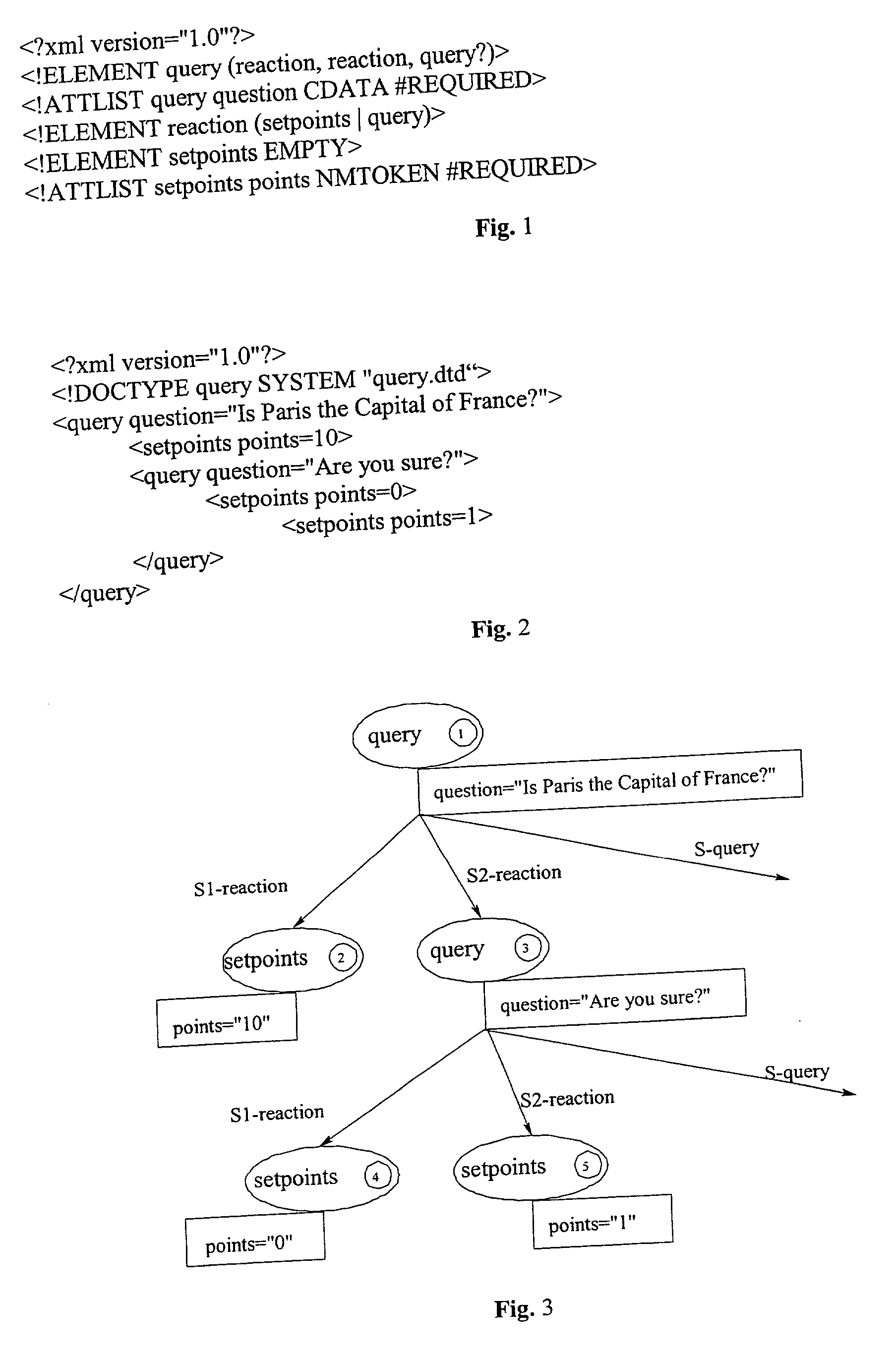
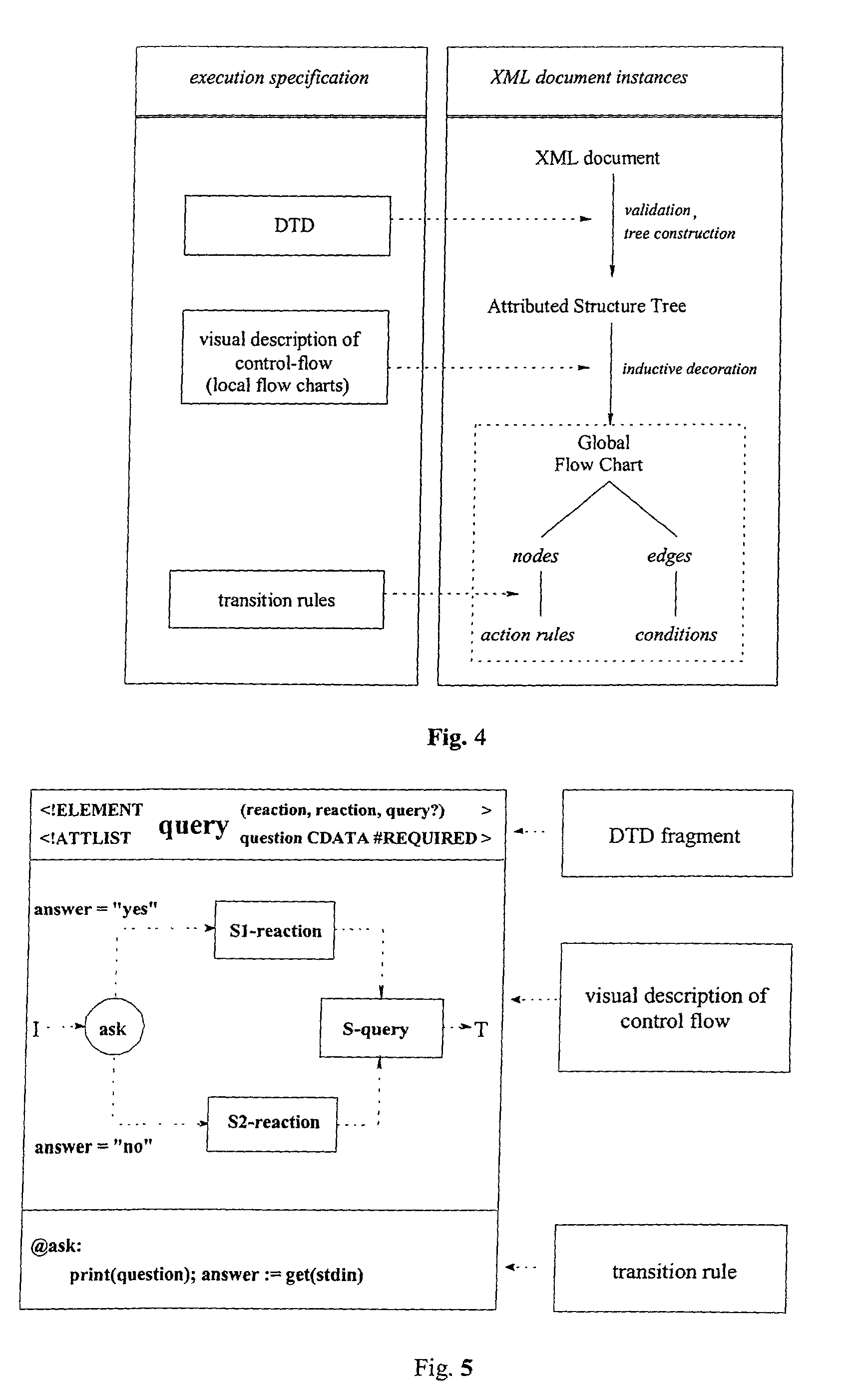
The invention relates to a method, system and apparatus for the direct execution of XML-documents by means of decoration of a XML-document, a document type definition (DTD) or their representation as structure tree, respectively, with textual or graphical flow charts. The structure of the XML-document' is reused for, and integrated with, the code processing the XML document.
Owner:KUTTER PHILIPP W
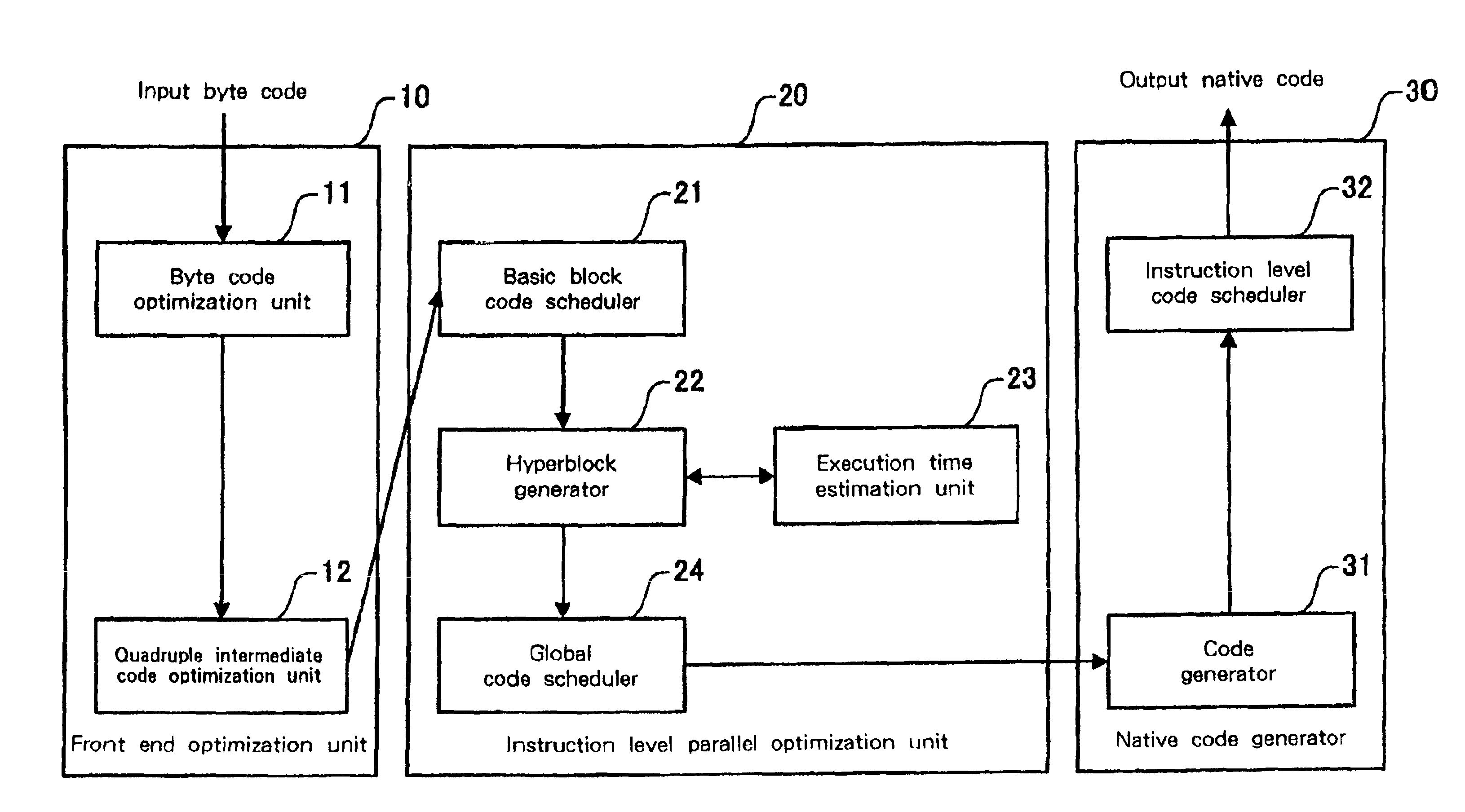
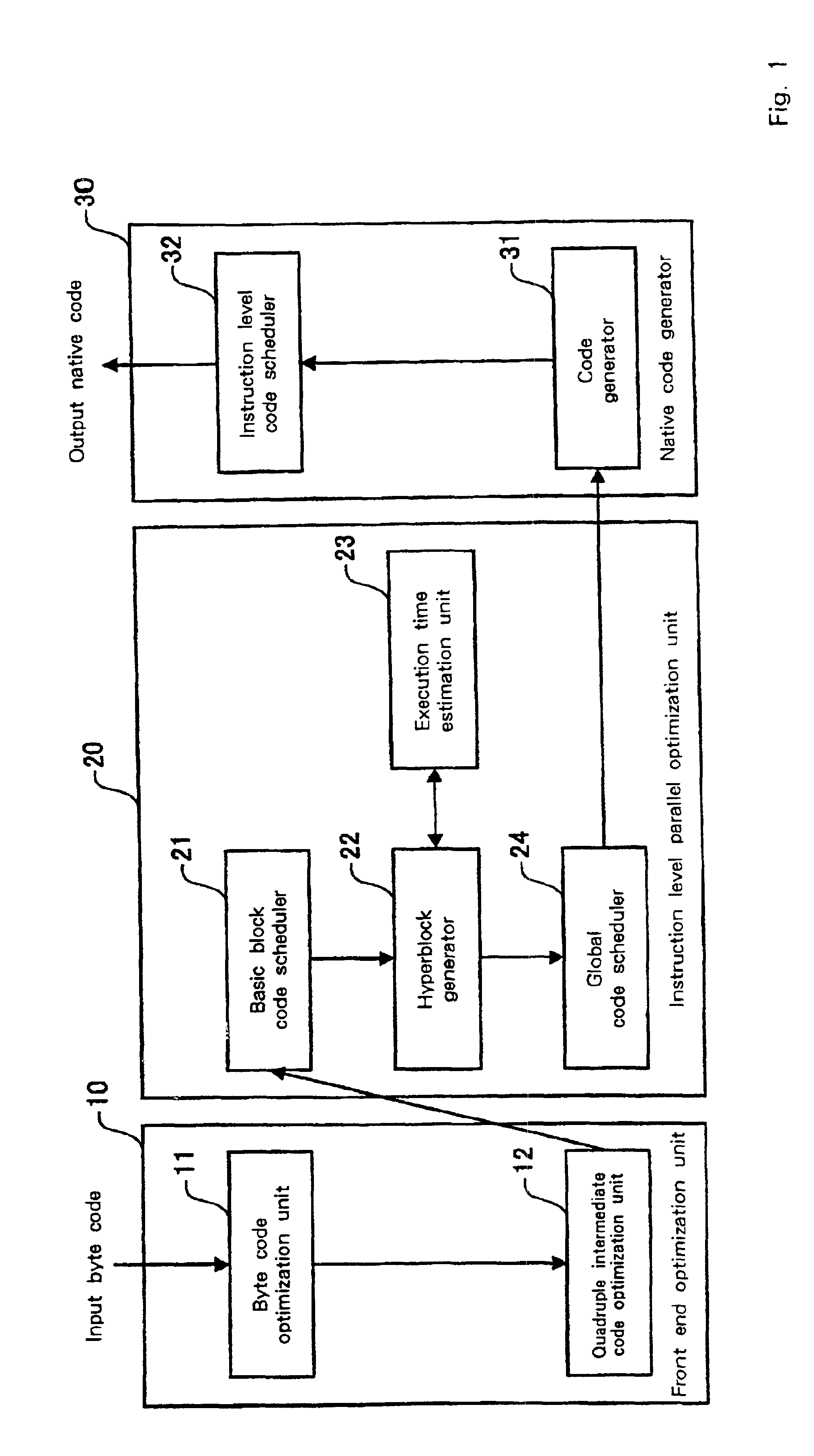
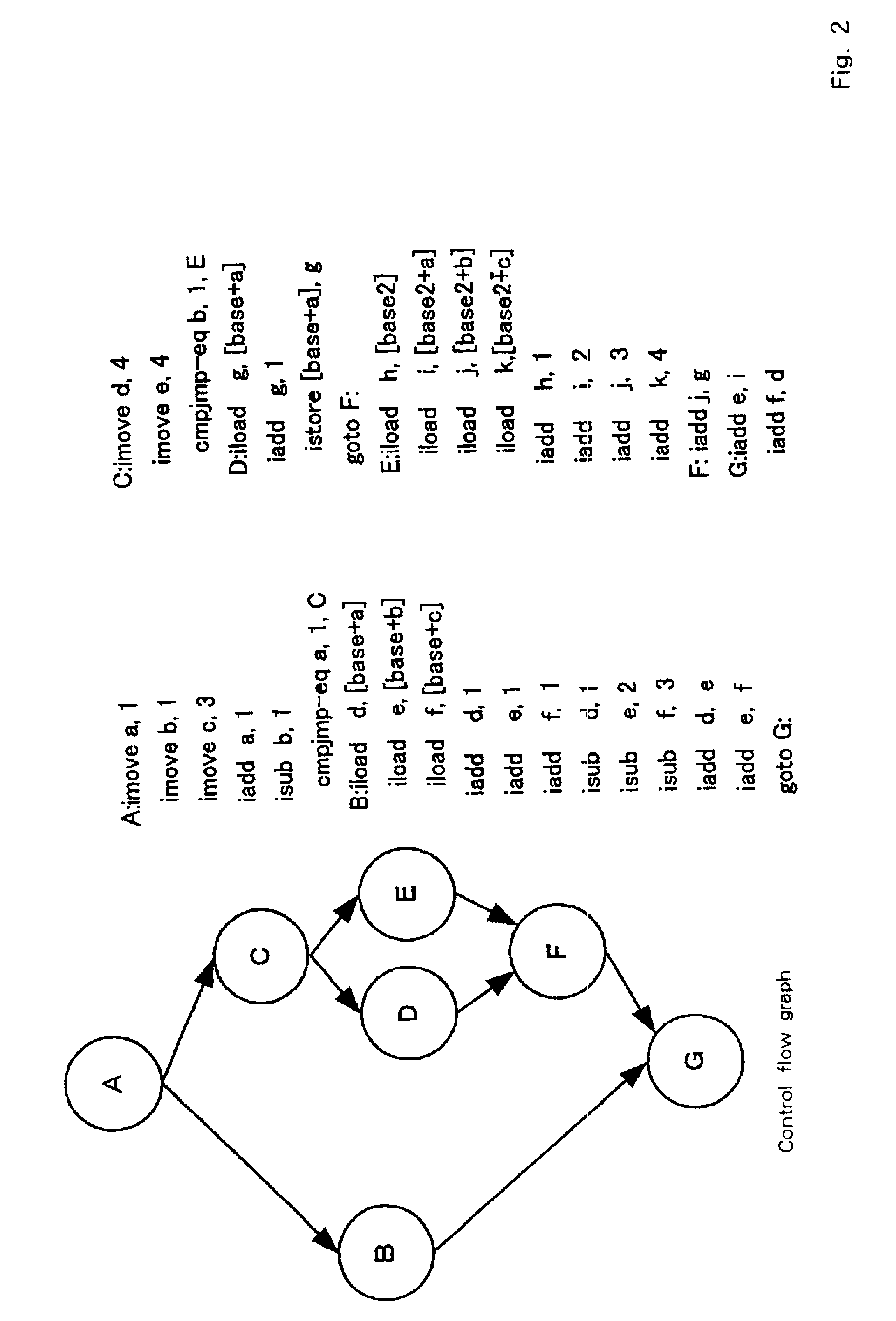
Program optimization method, and compiler using the same
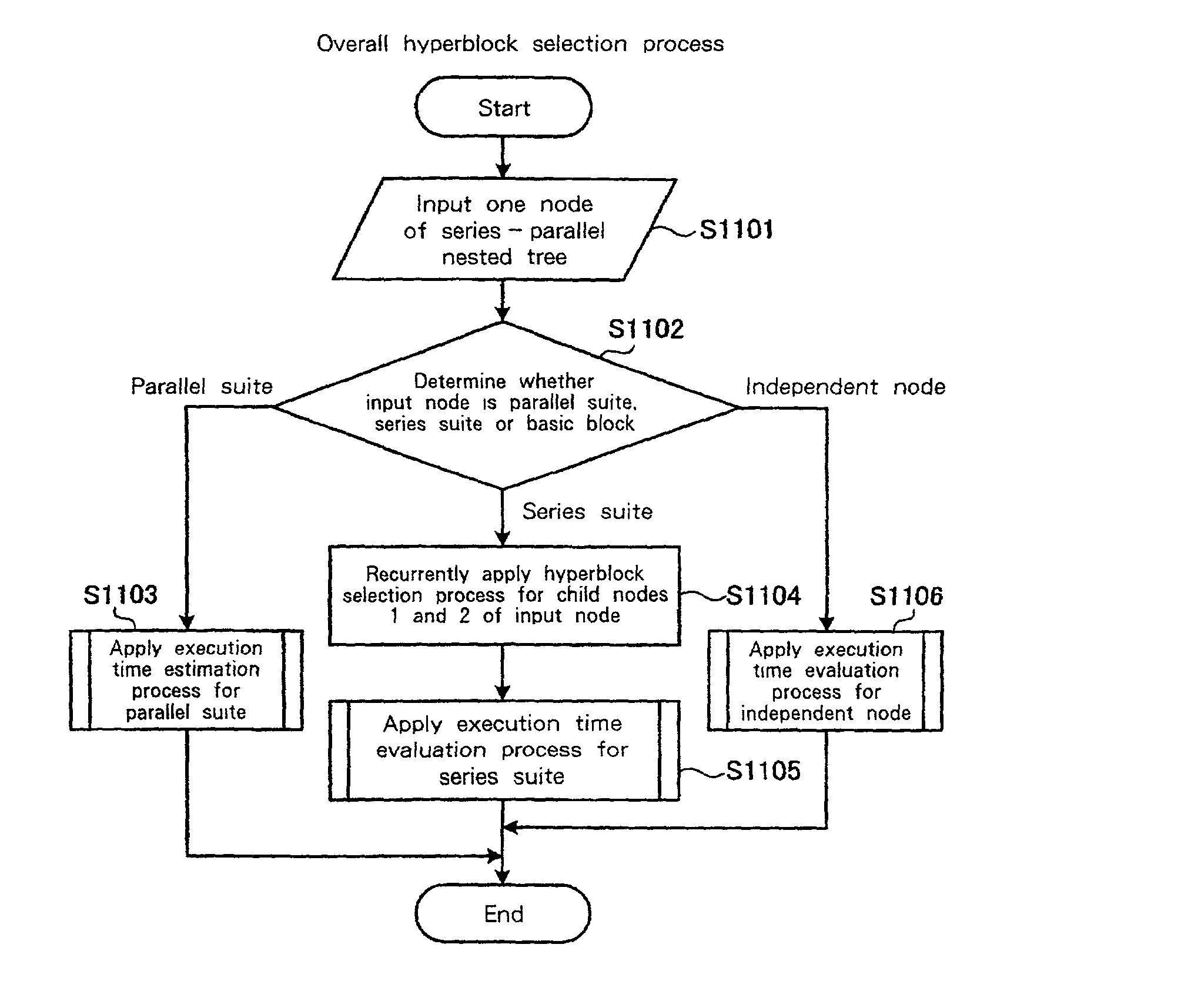
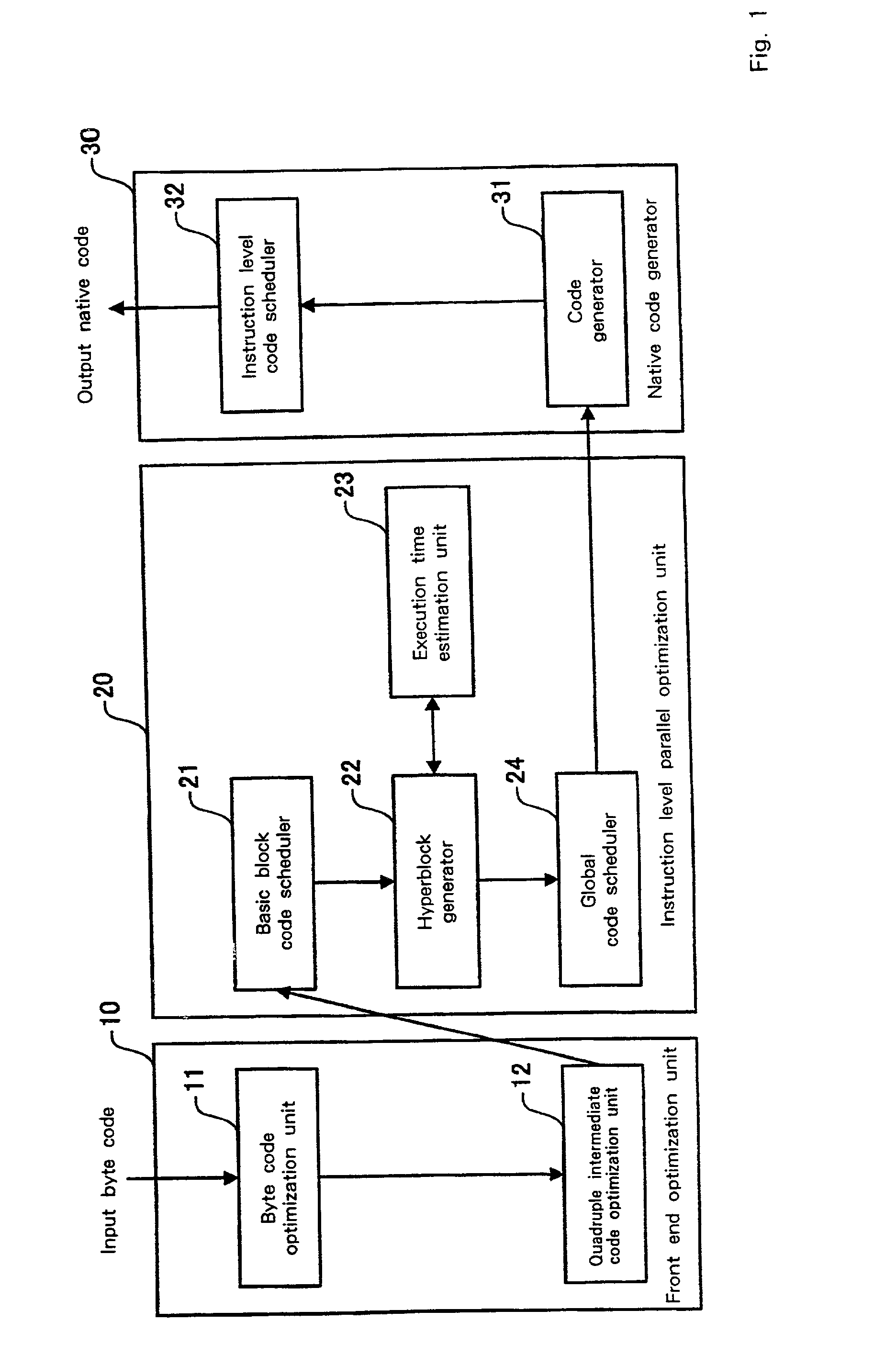
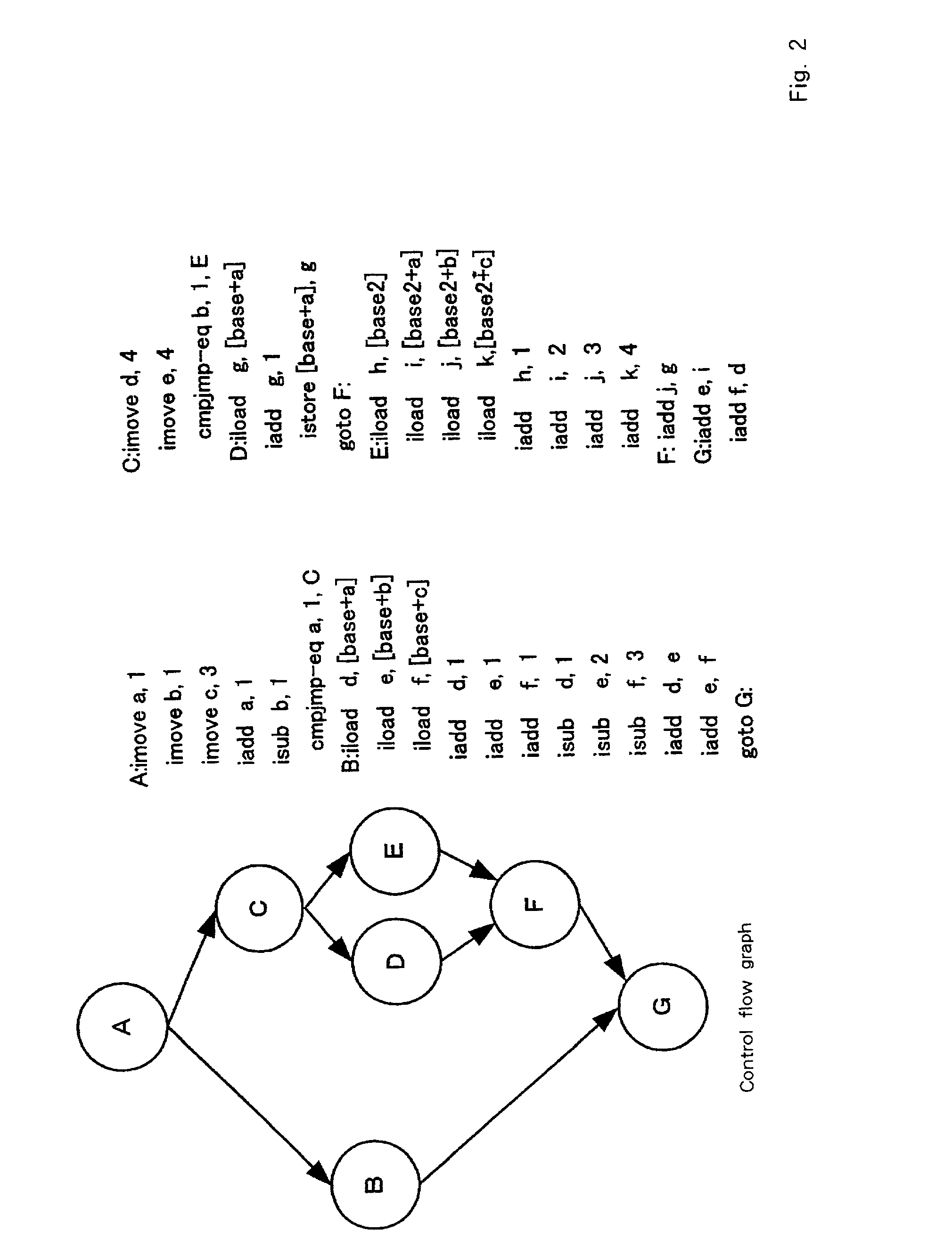
InactiveUS20020095666A1Short processing timeEfficient executionSoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsSource codeBasic block
An optimization method and apparatus for converting source code for a program written in a programming language into machine language and for optimizing the program includes employing a basic block as a unit to estimate an execution time for the program to be processed, generating a nested tree that represents the connections of the basic blocks using a nesting structure, when a conditional branch is accompanied by a node in the nested tree, employing the execution time estimated by using the basic blocks as units to obtain an execution time at the node of the program when a conditional branching portion of a program is directly executed and when the conditional branching portion is executed in parallel, and defining the node as a parallel execution area group when the execution time required for the parallel execution is shorter or dividing multiple child nodes of the nodes into multiple parallel execution areas when the execution time for the conditional branching portion is shorter.
Owner:IBM CORP
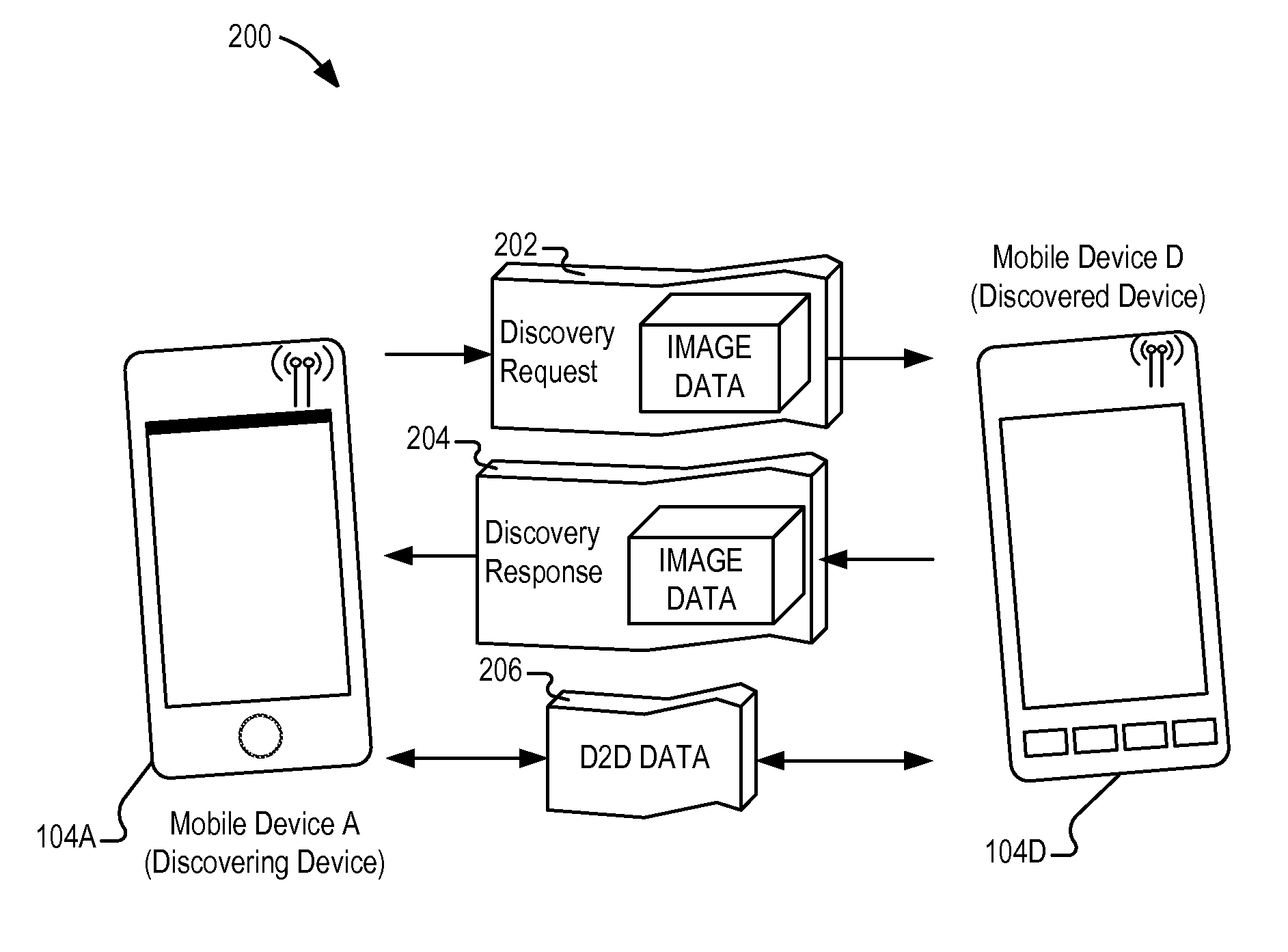
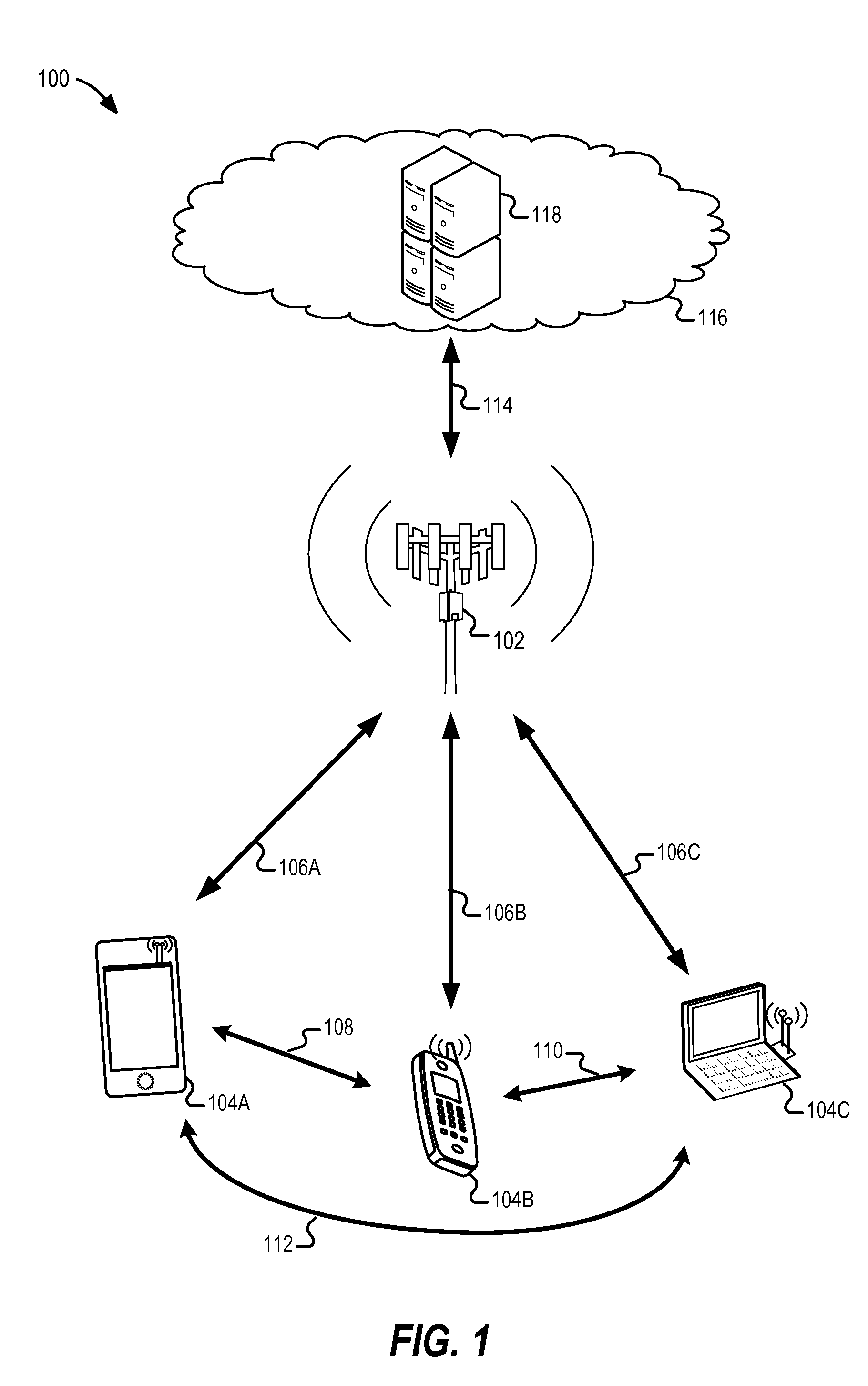
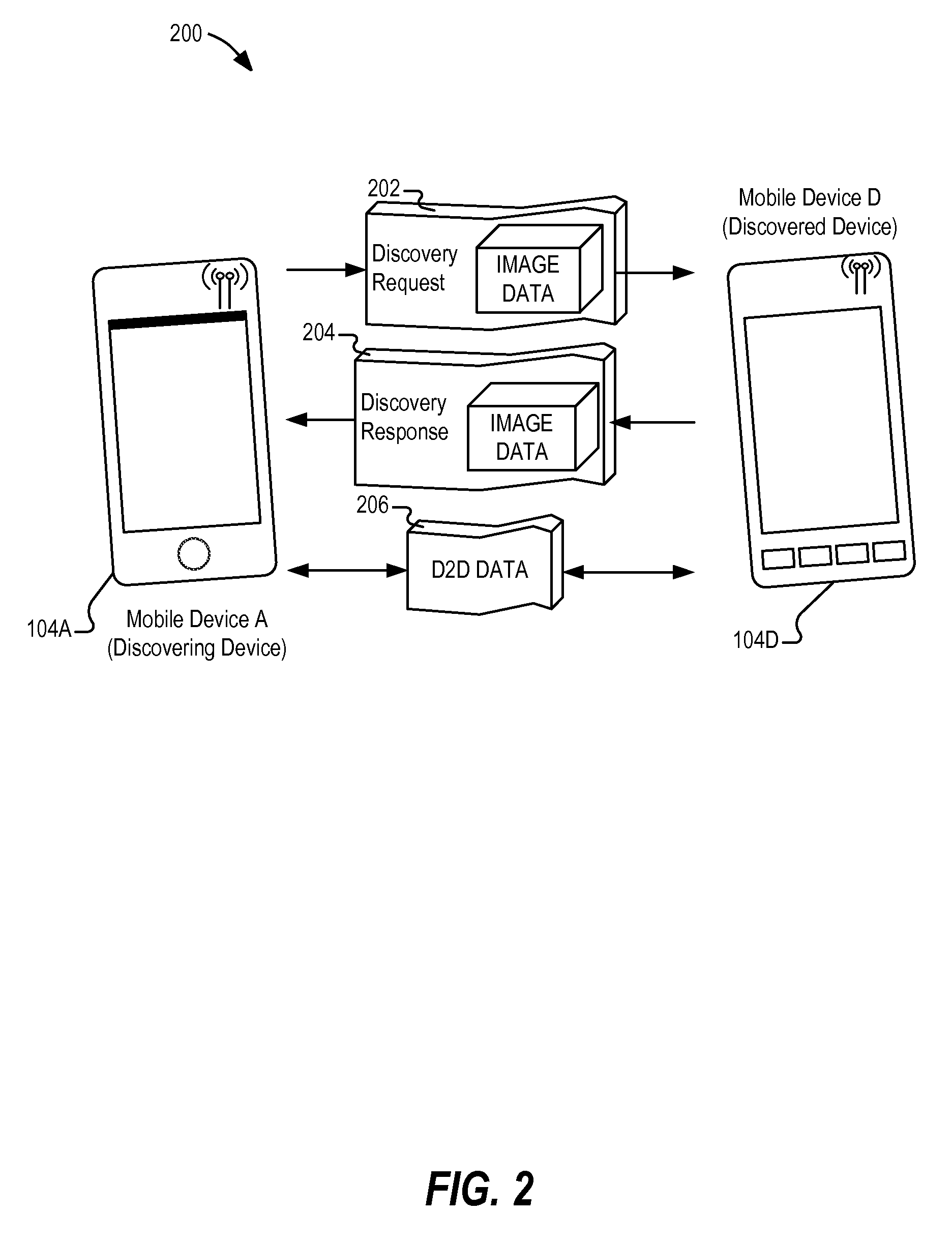
Device to-device (D2D) discovery without authenticating through cloud
InactiveUS8594632B1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsImaging processingImaging data
Embodiments of device-to-device (D2D) discovery, authentication, and connection techniques are generally described herein. In an example, a device-to-device connection establishment technique may be performed directly between peer-to-peer wireless communication devices without obtaining authentication information from a cloud network or an external service. The device-to-device connection establishment technique may include a transmission of a discovery request to available devices, a transmission of a response from available devices including authentication data, and a verification of the authentication data. The authentication data may include previously stored image data associated with a device or human user associated with a device. In further examples, image processing and image recognition techniques may be used to verify a particular device or human user associated with a device.
Owner:INTEL CORP
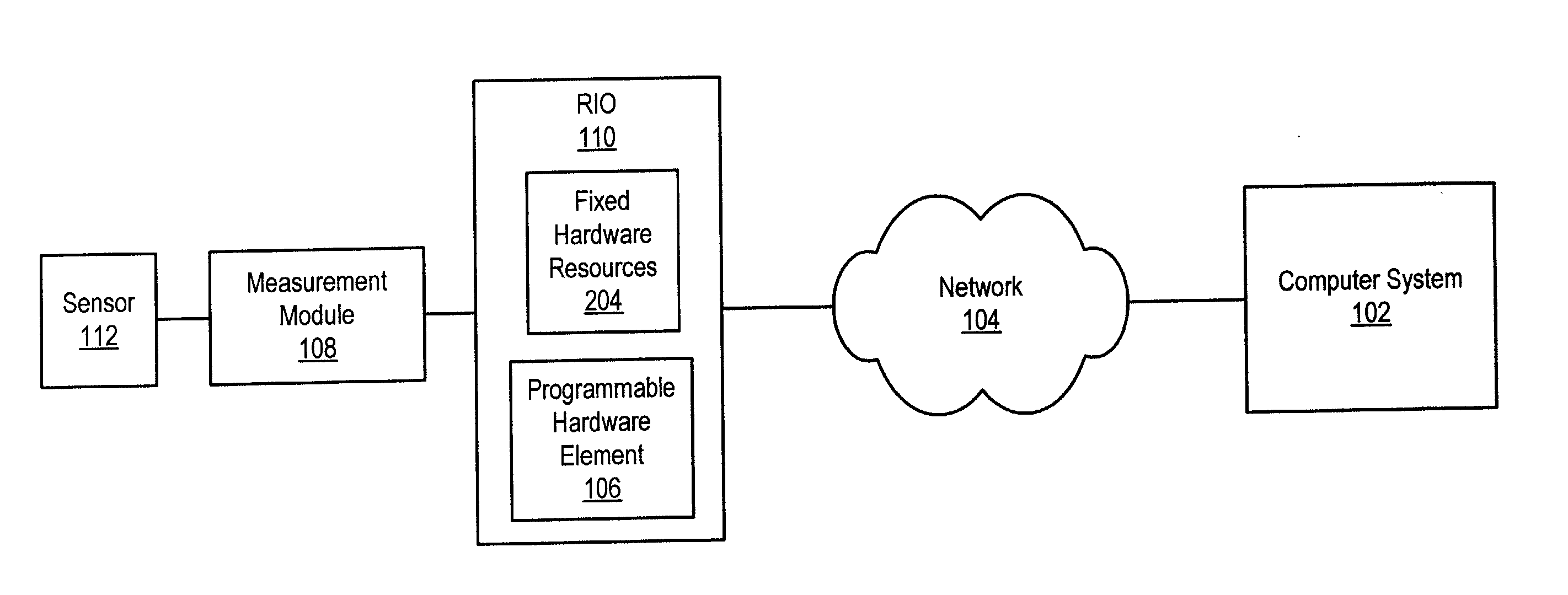
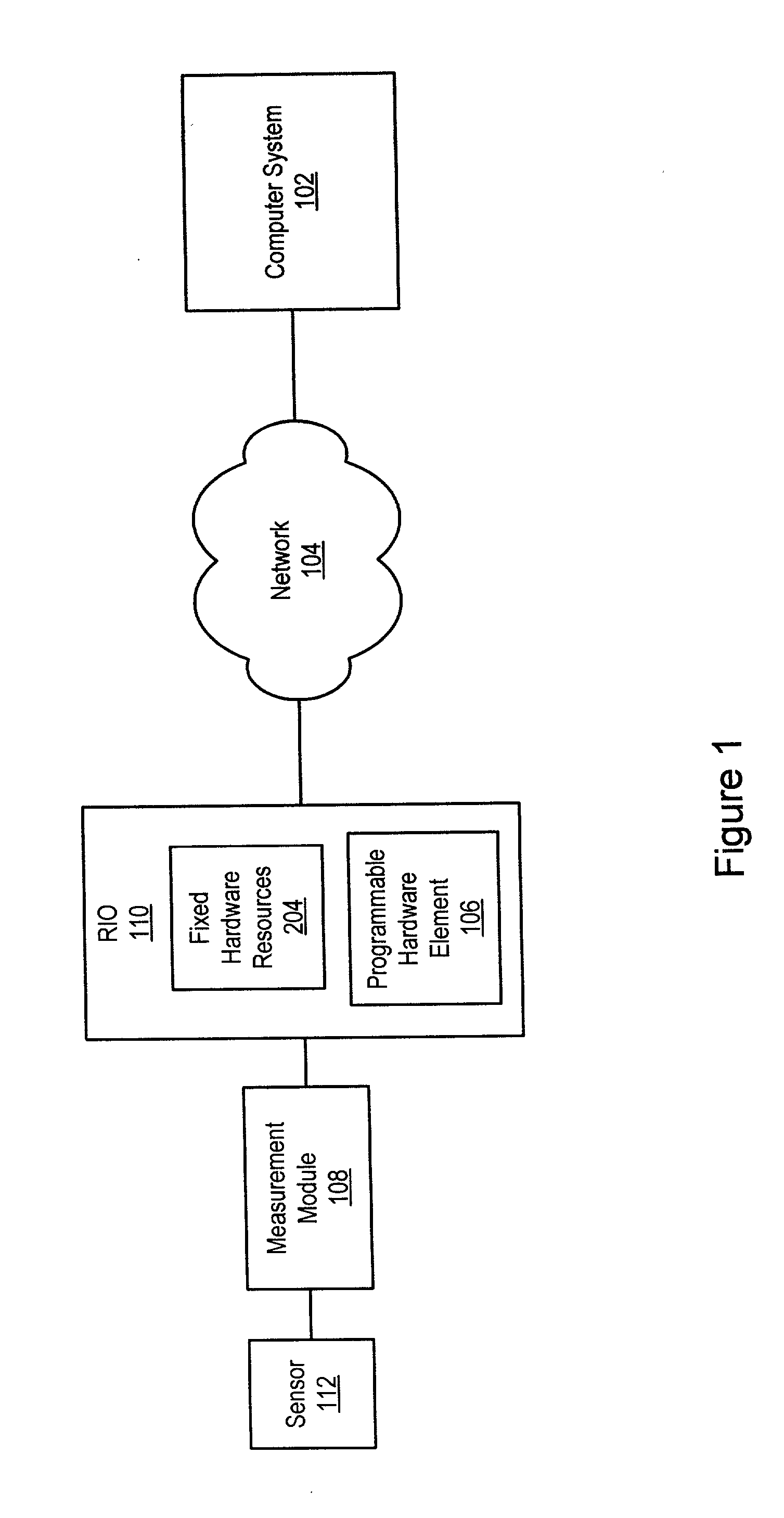
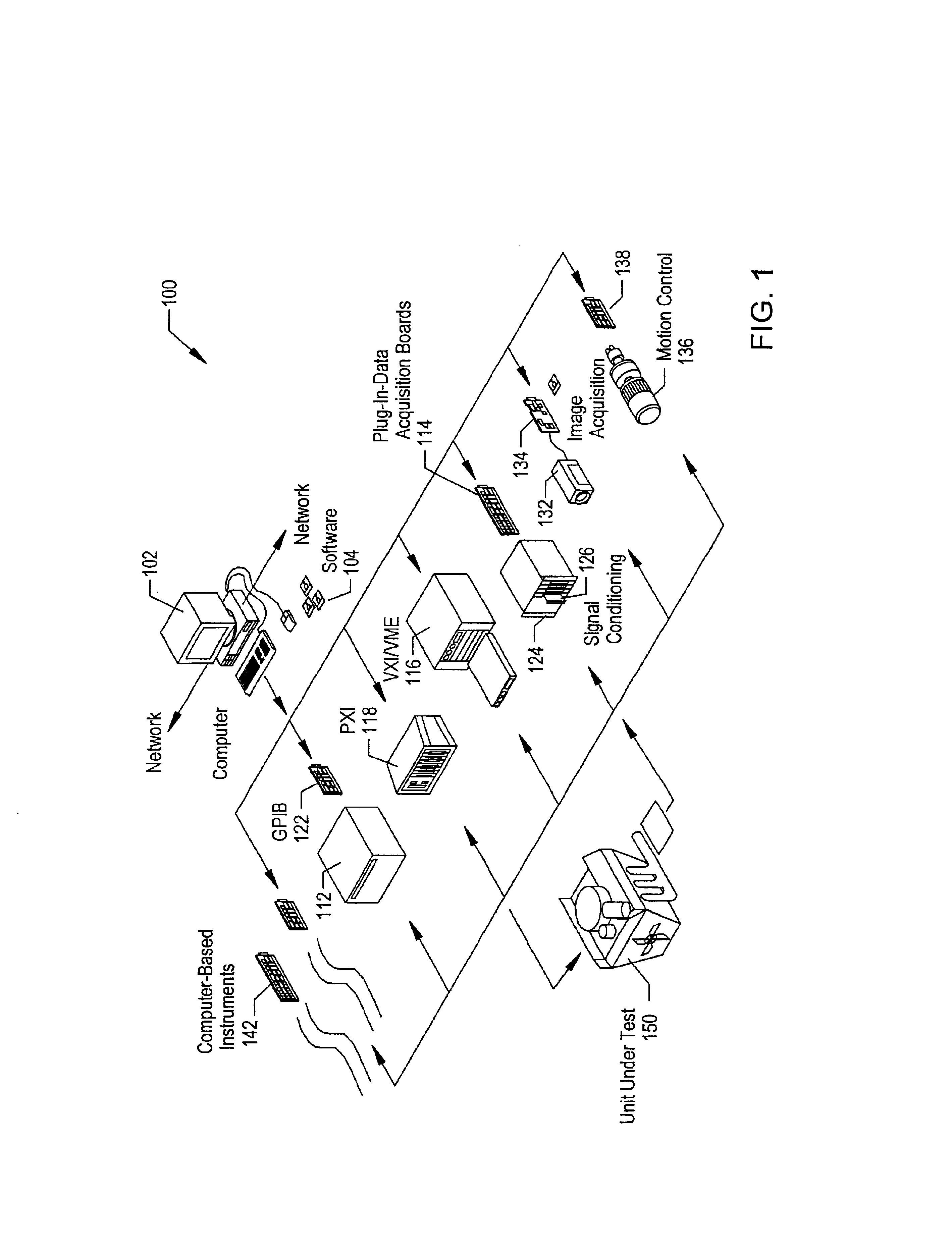
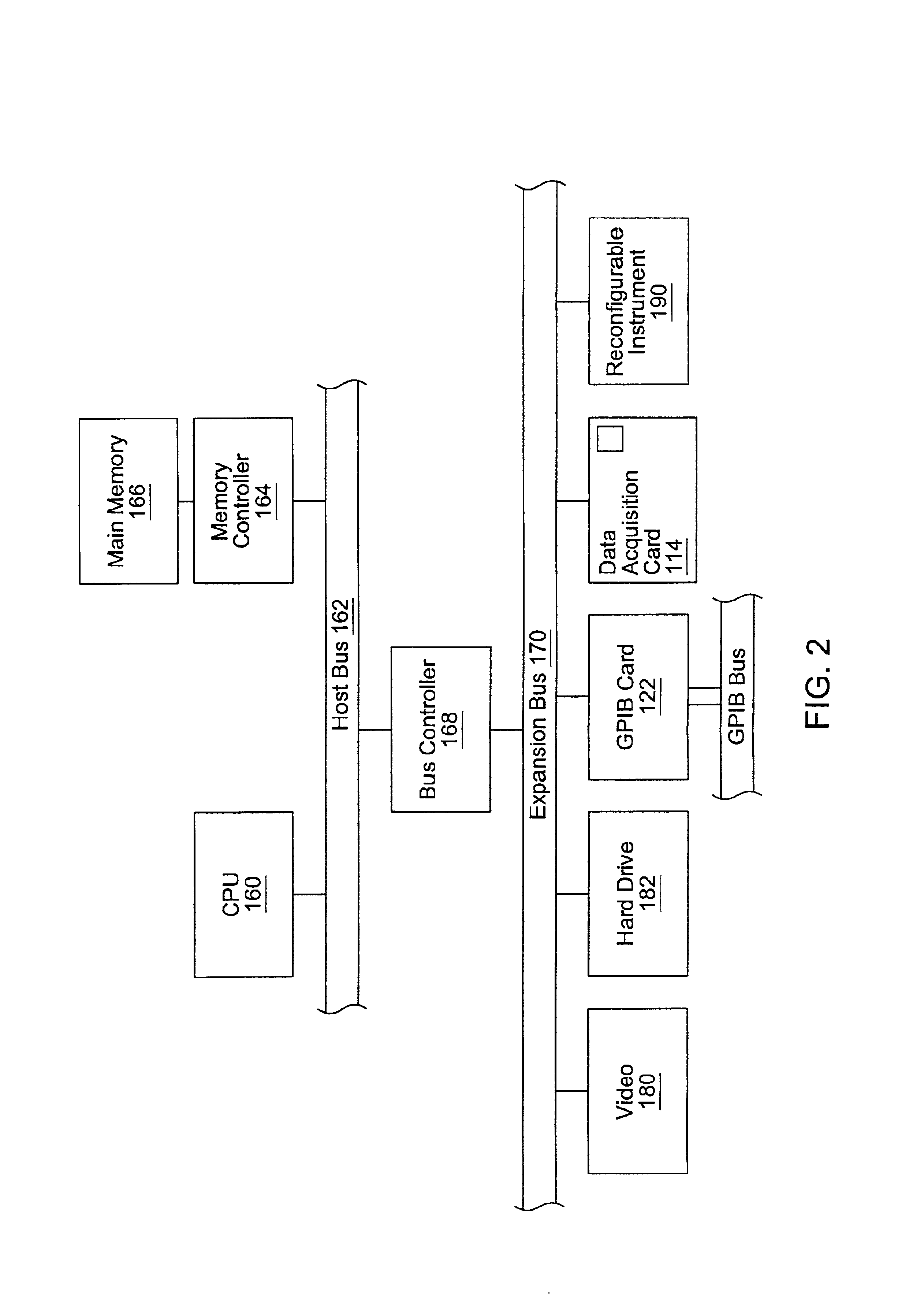
Reconfigurable measurement system utilizing a programmable hardware element and fixed hardware resources
InactiveUS20050143968A9Accurate and efficient matchingEfficient and flexibleError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareSignal conditioning
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Autonomous Context Scheduler For Graphics Processing Units
InactiveUS20090160867A1Processor architectures/configuration3D-image renderingMultiple contextGraphics
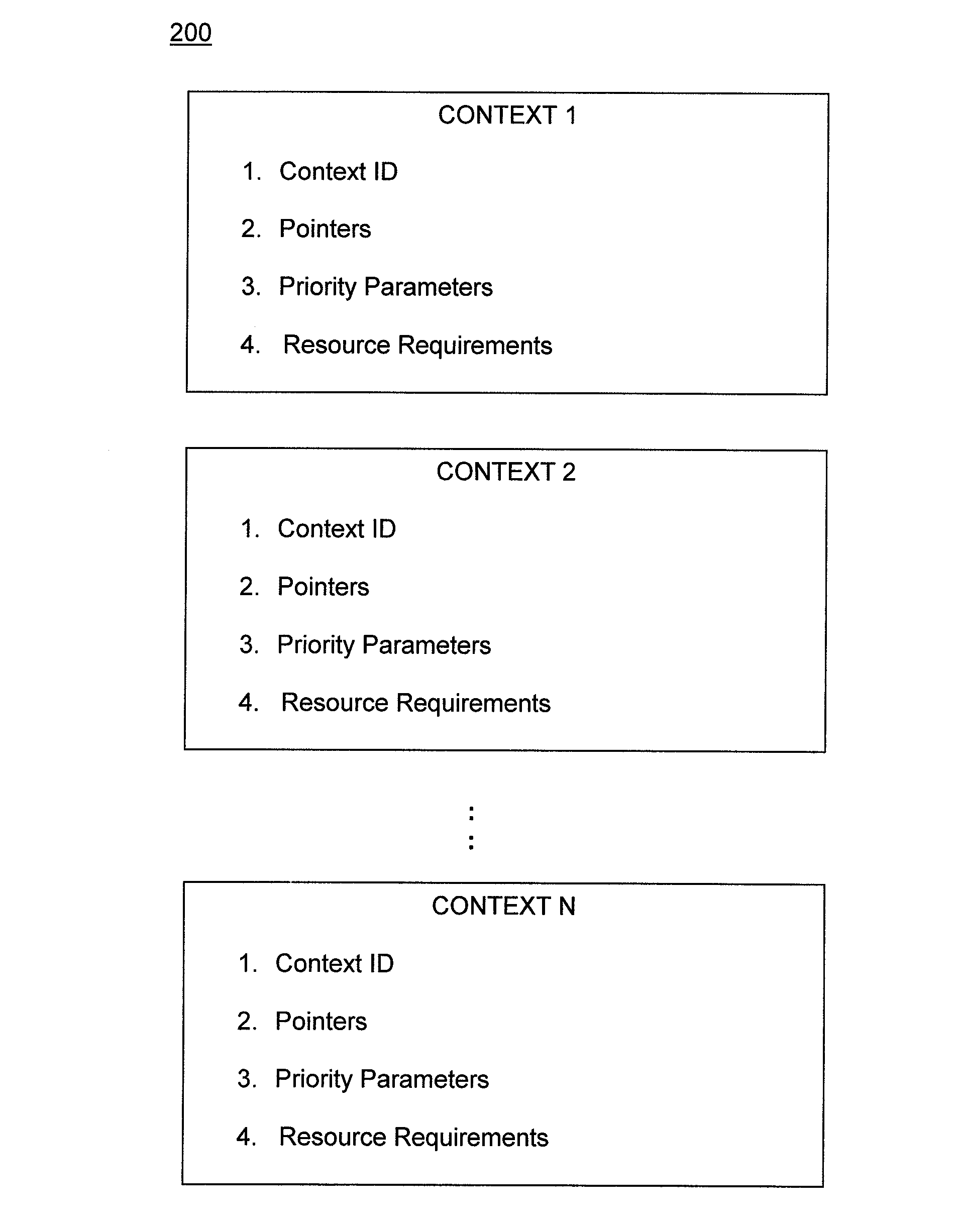
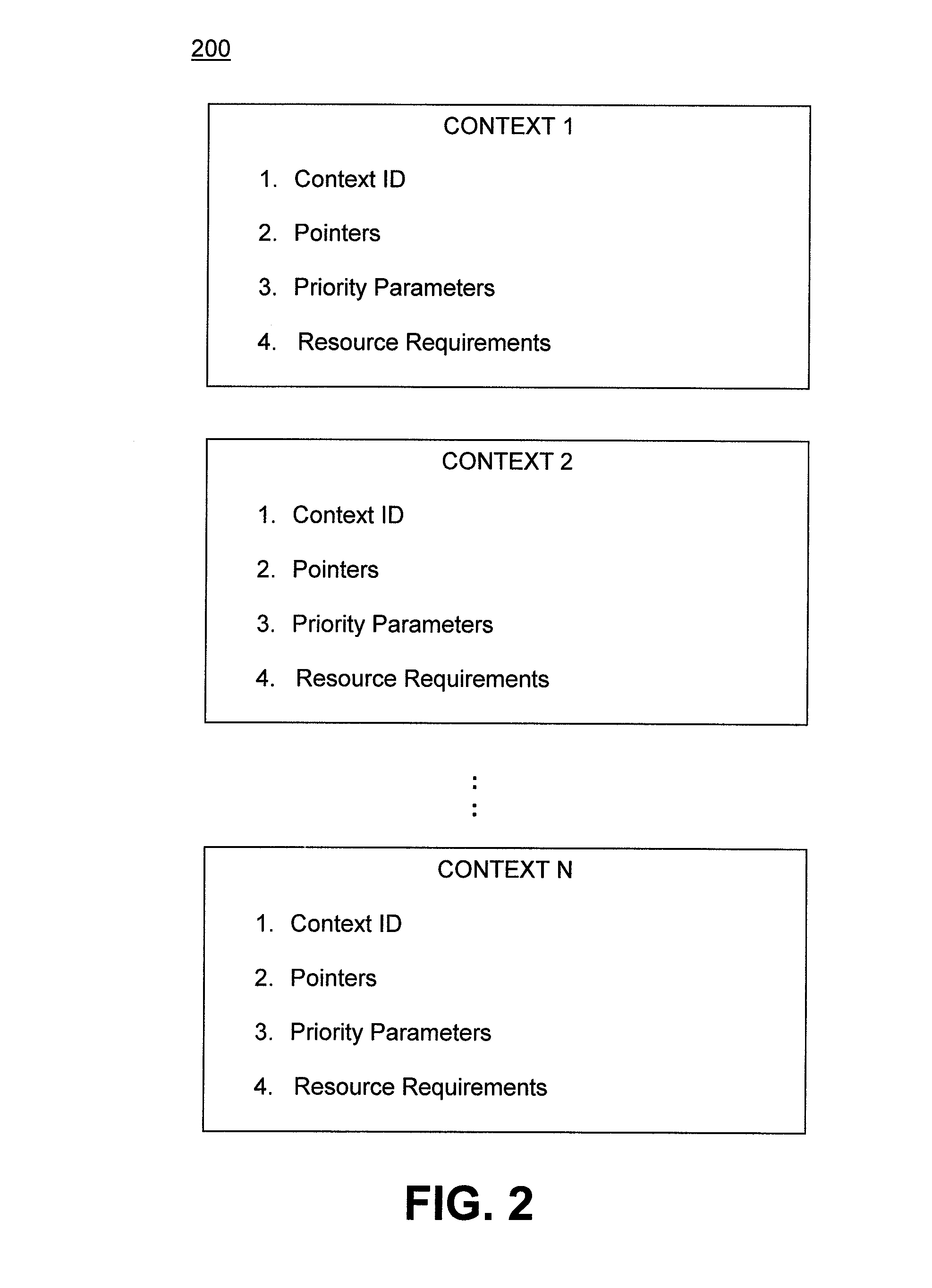
Embodiments directed to an autonomous graphics processing unit (GPU) scheduler for a graphics processing system are described. Embodiments include an execution structure for a host CPU and GPU in a computing system that allows the GPU to execute command threads in multiple contexts in a dynamic rather than fixed order based on decisions made by the GPU. This eliminates a significant amount of CPU processing overhead required to schedule GPU command execution order, and allows the GPU to execute commands in an order that is optimized for particular operating conditions. The context list includes parameters that specify task priority and resource requirements for each context. The GPU includes a scheduler component that determines the availability of system resources and directs execution of commands to the appropriate system resources, and in accordance with the priority defined by the context list.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
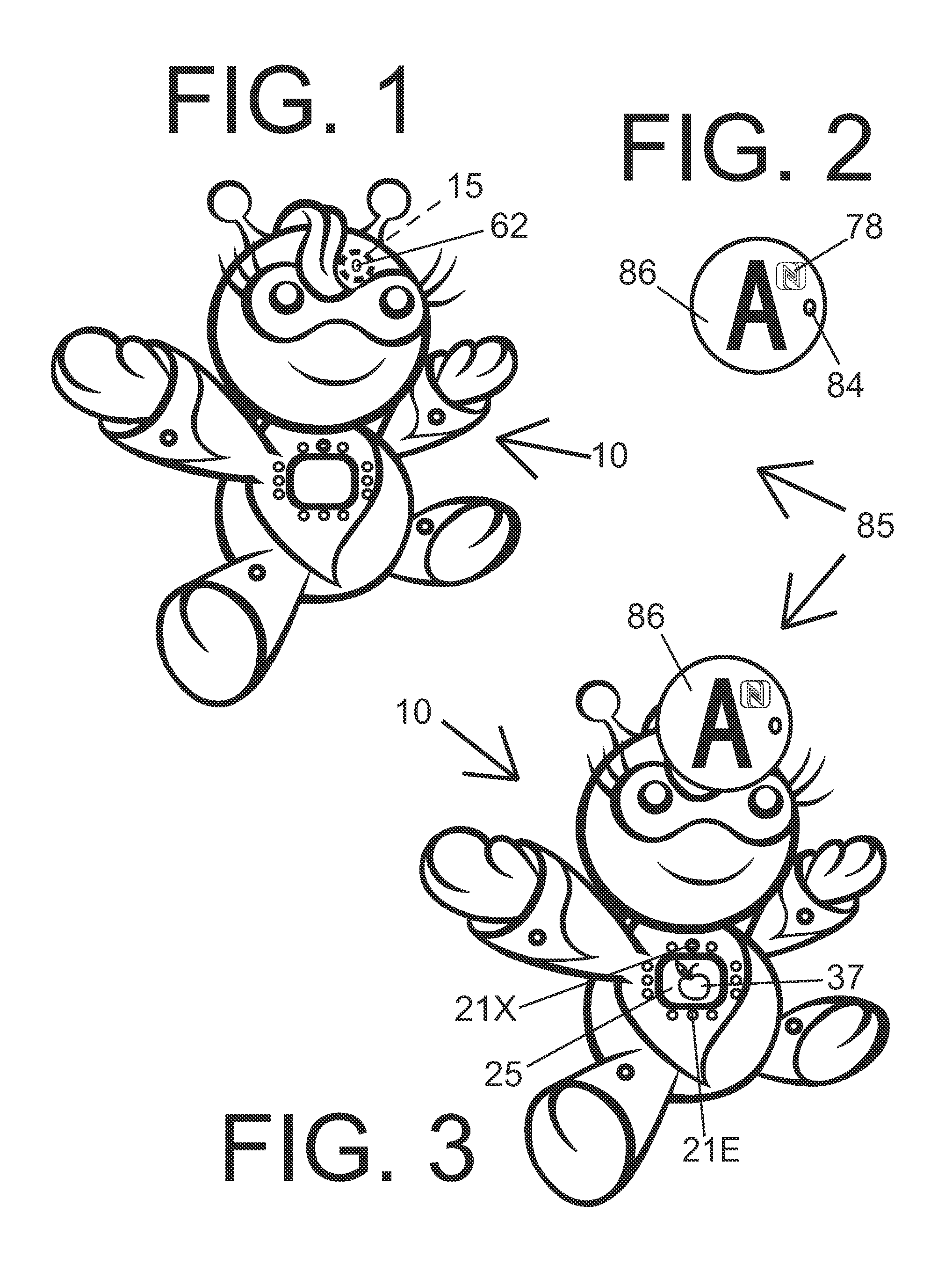
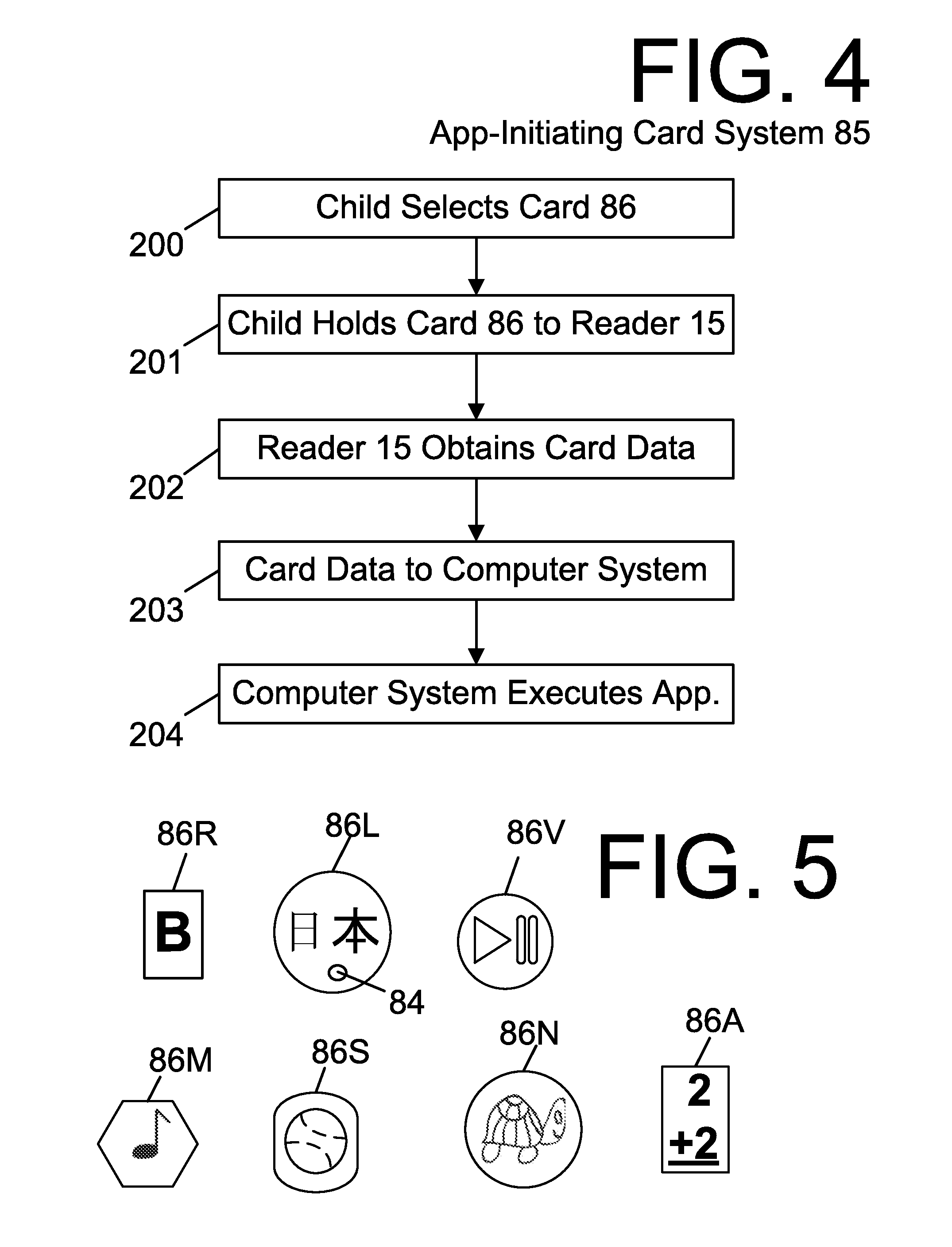
Doll Companion Integrating Child Self-Directed Execution of Applications with Cell Phone Communication, Education, Entertainment, Alert and Monitoring Systems
ActiveUS20120295510A1Easily expandableEasily modifiableNear-field transmissionDollsSmall Island Developing StatesApp store
The presented cell phone-enabled doll companion allows a child novel ways to self-select and self-execute applications while requiring no intervention or supervision from the parent. Further, it provides learning, entertainment and safety by integrating cell phone communication, education, entertainment, alert and monitoring systems. While providing a convenient means of communication between the child and parent, the system allows surveillance of a child's real-time environment, GPS monitoring and SIDS / health monitoring. The functionality and the physical elements of the system are programmable through installation of applications downloadable from an application store. Various options for parental access to a configuration interface to modify settings and download applications are provided, including via a cell phone, a website, customer service call center and / or the doll companion touch screen.
Owner:LEARNING SQUARED INC
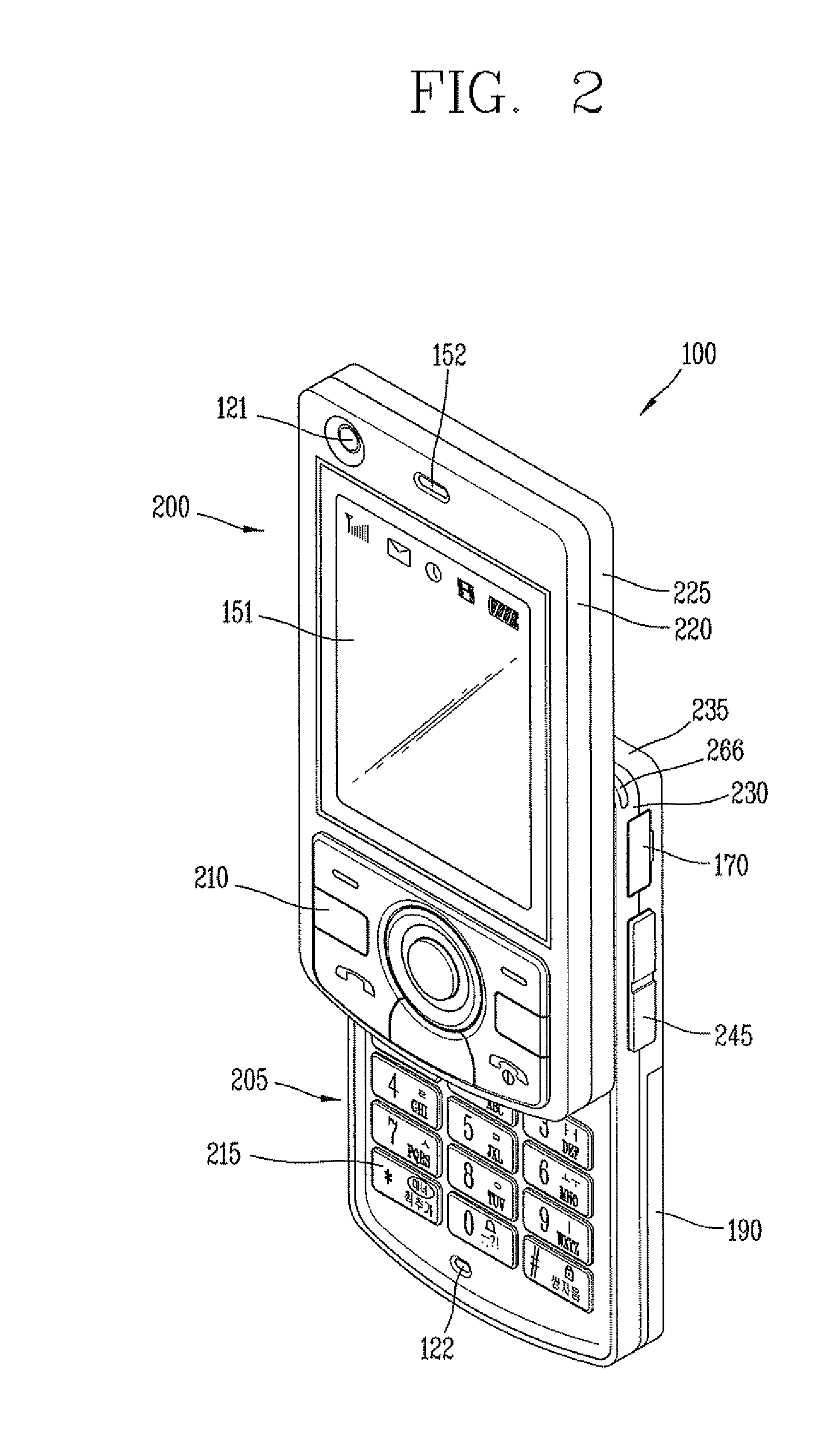
Mobile terminal and method for displaying menu thereof
ActiveUS20100009719A1Television system detailsDevices with voice recognitionComputer hardwareSpecific function
Disclosed is a method for automatically displaying a menu relating to a specific function by recognizing a user's voice command in a call mode, and for directly executing the menu, and a mobile terminal having the same. A mobile terminal may include a microphone configured to receive a user's voice in a video call mode, a display for displaying information, and a controller configured to recognize the voice, detect a voice command included in the voice, and automatically display a menu corresponding to the detected voice command on the display.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Computer implemented machine learning method and system including specifically defined introns
InactiveUS6493686B1Loss in flexibilityImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital computer detailsArray data structureAlgorithm
In a computer implemented learning and / or process control system, a computer model is constituted by the most currently fit entity in a population of computer program entities. The computer model defines fitness as a function of inputs and outputs. A computing unit accesses the model with a set of inputs, and determines a set of outputs for which the fitness is highest. This associates a sensory-motor (input-output) state with a fitness in a manner that might be termed "feeling".The learning and / or control system preferably utilizes a Compiling Genetic Programming System (CGPS) in which one or more machine code entities such as functions are created which represent solutions to a problem and are directly executable by a computer. The programs are created and altered by a program in a higher level language such as "C" which is not directly executable, but requires translation into executable machine code through compilation, interpretation, translation, etc. The entities are initially created as an integer array that can be altered by the program as data, and are executed by the program by recasting a pointer to the array as a function type. The entities are evaluated by executing them with training data as inputs, and calculating fitnesses based on a predetermined criterion. The entities are then altered based on their fitnesses using a genetic machine learning algorithm by recasting the pointer to the array as a data (e.g. integer) type. This process is iteratively repeated until an end criterion is reached.
Owner:FRANCONE FR D +2
Program optimization method, and compiler using the same
InactiveUS6817013B2Short processing timeEfficient executionSoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsBasic blockSource code
An optimization method and apparatus for converting source code for a program written in a programming language into machine language. The program includes a basic block as a unit to estimate an execution time for the program to be processed, generating a nested tree that represents the connections of the basic blocks using a nesting structure, when a conditional branch is accompanied by a node in the nested tree, employing the execution time estimated by using the basic blocks as units to obtain an execution time at the node of the program when a conditional branching portion of a program is directly executed and when the conditional branching portion is executed in parallel, and defining the node as a parallel execution area group when the execution time required for the parallel execution is shorter or dividing multiple child nodes of the nodes into multiple parallel execution areas.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
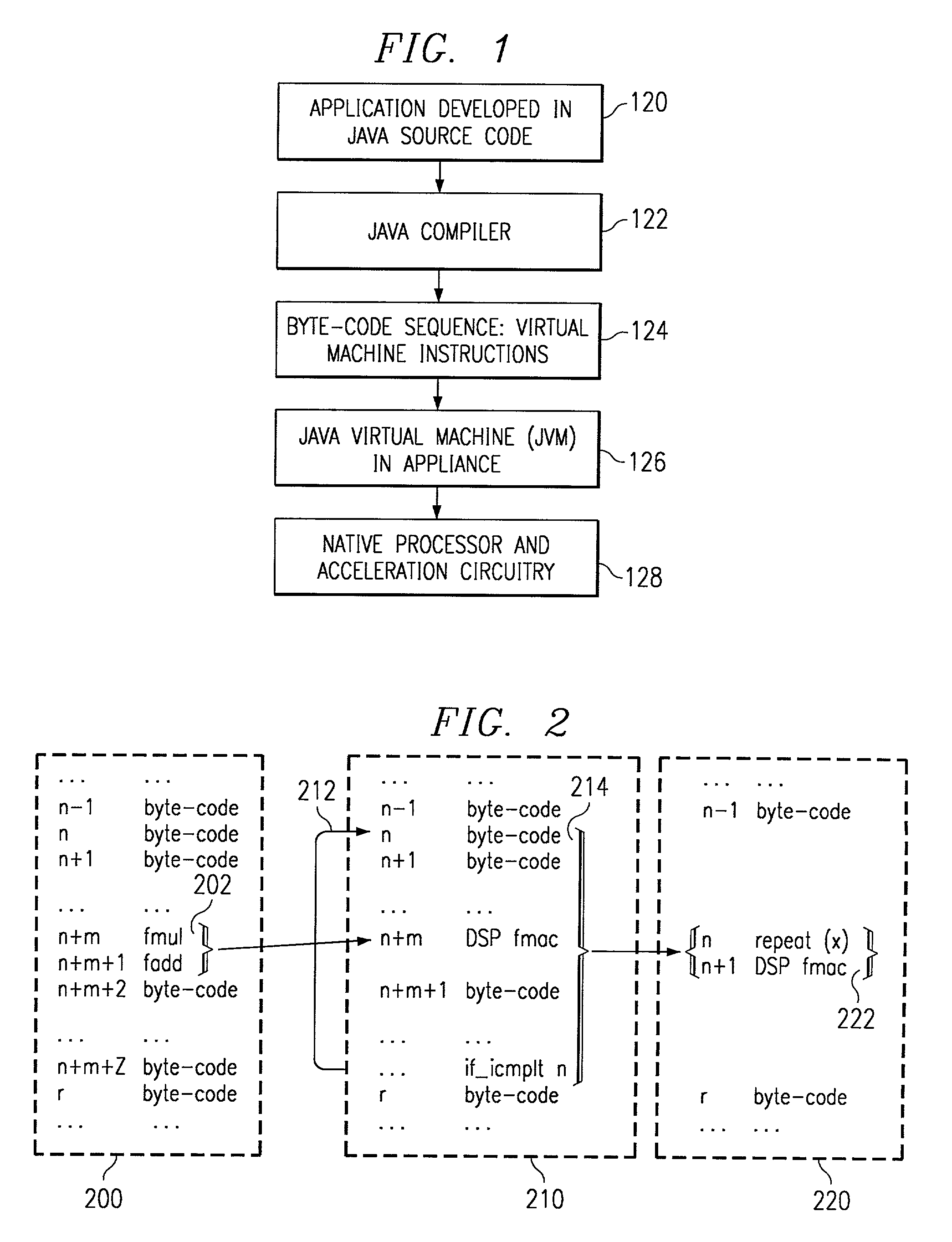
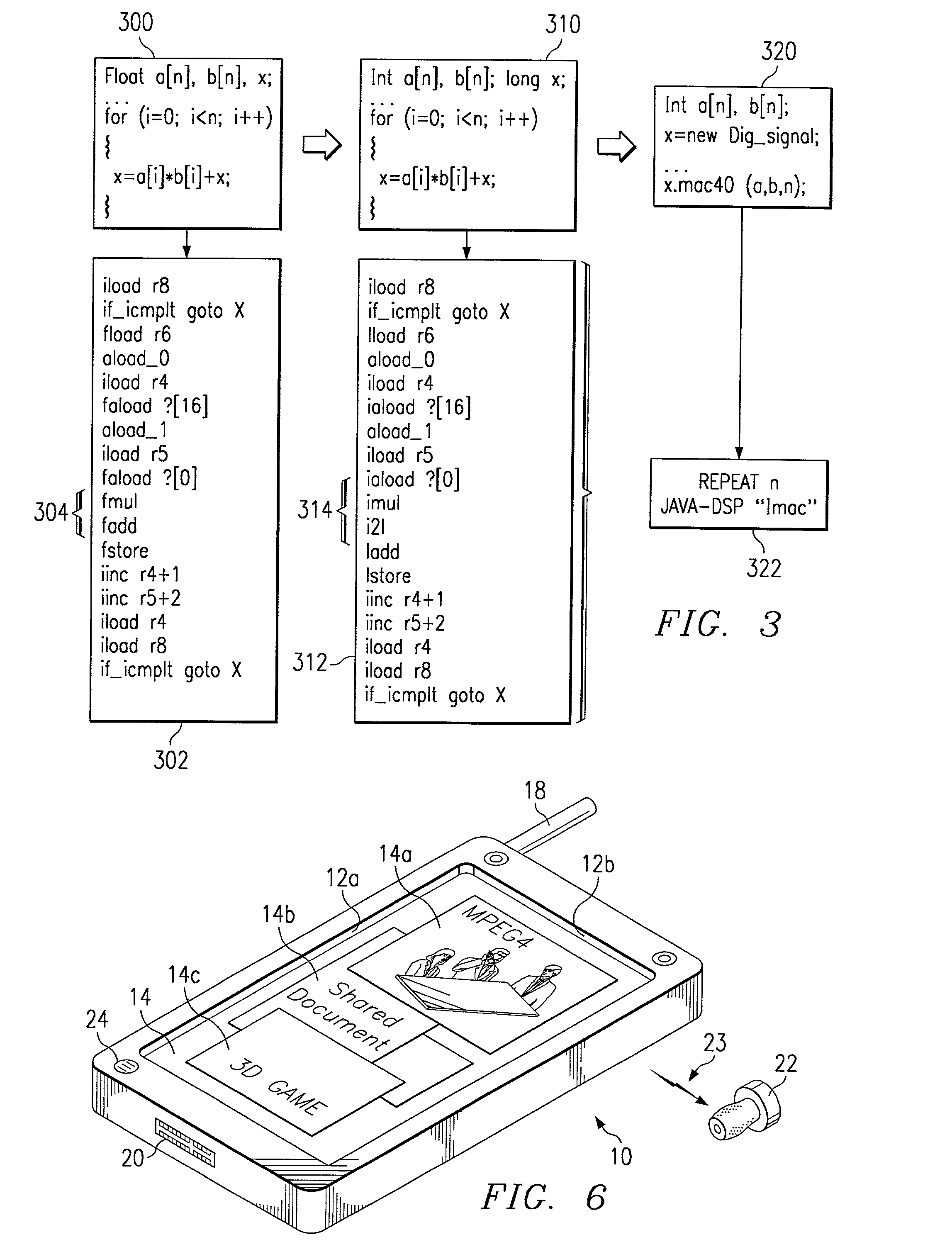
JAVA DSP acceleration by byte-code optimization
ActiveUS7146613B2Significant performanceSignificant energySoftware engineeringComputer security arrangementsParallel computingDirect execution
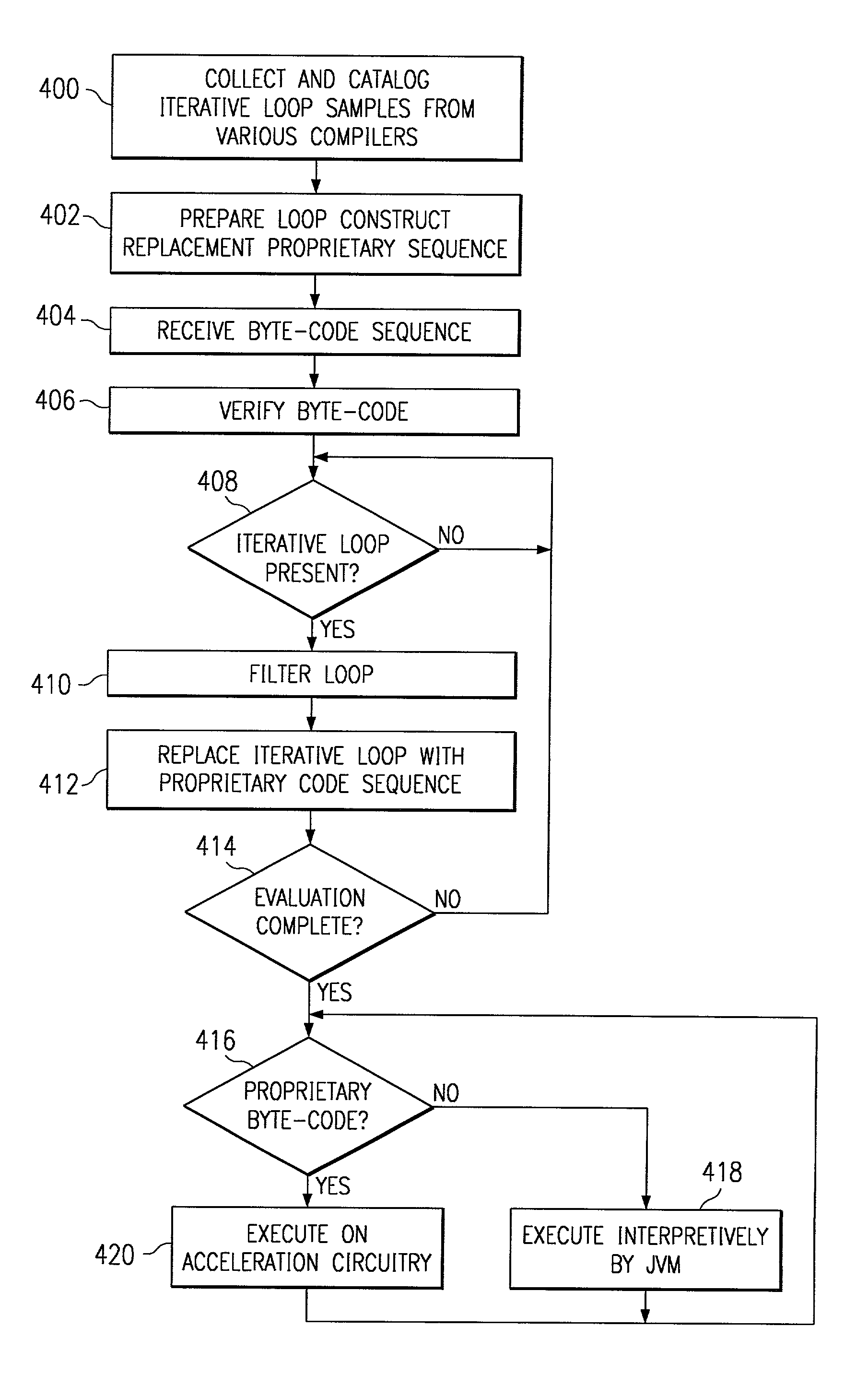
A digital system and method of operation is which the digital system has a processor with a virtual machine environment for interpretively executing instructions. First, a sequence of instructions is received (404) for execution by the virtual machine. The sequence of instructions is examined (408–414) to determine if a certain type of iterative sequence is present. If the certain type of iterative sequence is present, the iterative sequence is replaced (412) with a proprietary code sequence. After the modifications are complete, the modified sequence is executed in a manner that a portion of the sequence of instructions is executed in an interpretive manner (418); and the proprietary code sequences are executed directly by acceleration circuitry (420).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method enabling hierarchical execution of a test executive subsequence
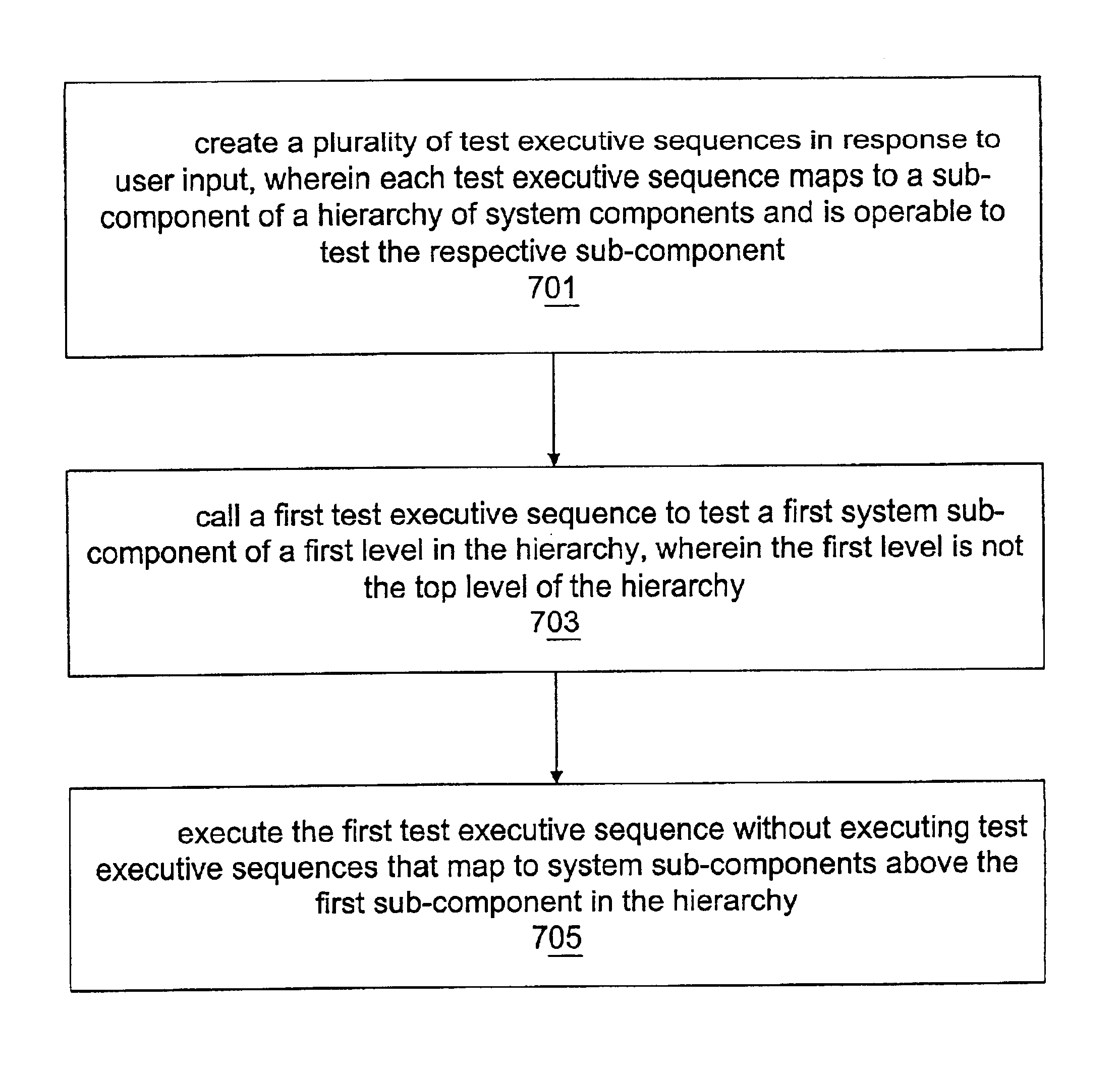
InactiveUS6868508B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic circuit testingLocal variableDirect test
Individual test executive sequences may correspond to individual sub-components of a hierarchical system. To test a system sub-component directly without testing “upper” sub-components in the hierarchy, a first test executive sequence corresponding to that system sub-component may be executed directly, without requiring execution of test executive sequences above the first test executive sequence in the hierarchy, or requiring only partial execution of test executive sequences above the first test executive sequence in the hierarchy. Another embodiment of the invention comprises a system and method for enabling propagation or inheritance of test executive sequence local variables.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Computer implemented machine learning method and system
One or more machine code entities such as functions are created which represent solutions to a problem and are directly executable by a computer. The programs are created and altered by a program in a higher level language such as "C" which is not directly executable, but requires translation into executable machine code through compilation, interpretation, translation, etc. The entities are initially created as an integer array that can be altered by the program as data, and are executed by the program by recasting a pointer to the array as a function type. The entities are evaluated by executing them with training data as inputs, and calculating fitnesses based on a predetermined criterion. The entities are then altered based on their fitnesses using a machine learning algorithm by recasting the pointer to the array as a data (e.g. integer) type. This process is iteratively repeated until an end criterion is reached. The entities evolve in such a manner as to improve their fitness, and one entity is ultimately produced which represents an optimal solution to the problem. Each entity includes a plurality of directly executable machine code instructions, a header, a footer, and a return instruction. The instructions include branch instructions which enable subroutines, leaf functions, external function calls, recursion, and loops. The system can be implemented on an integrated circuit chip, with the entities stored in high speed memory in a central processing unit.
Owner:NORDIN PETER +1
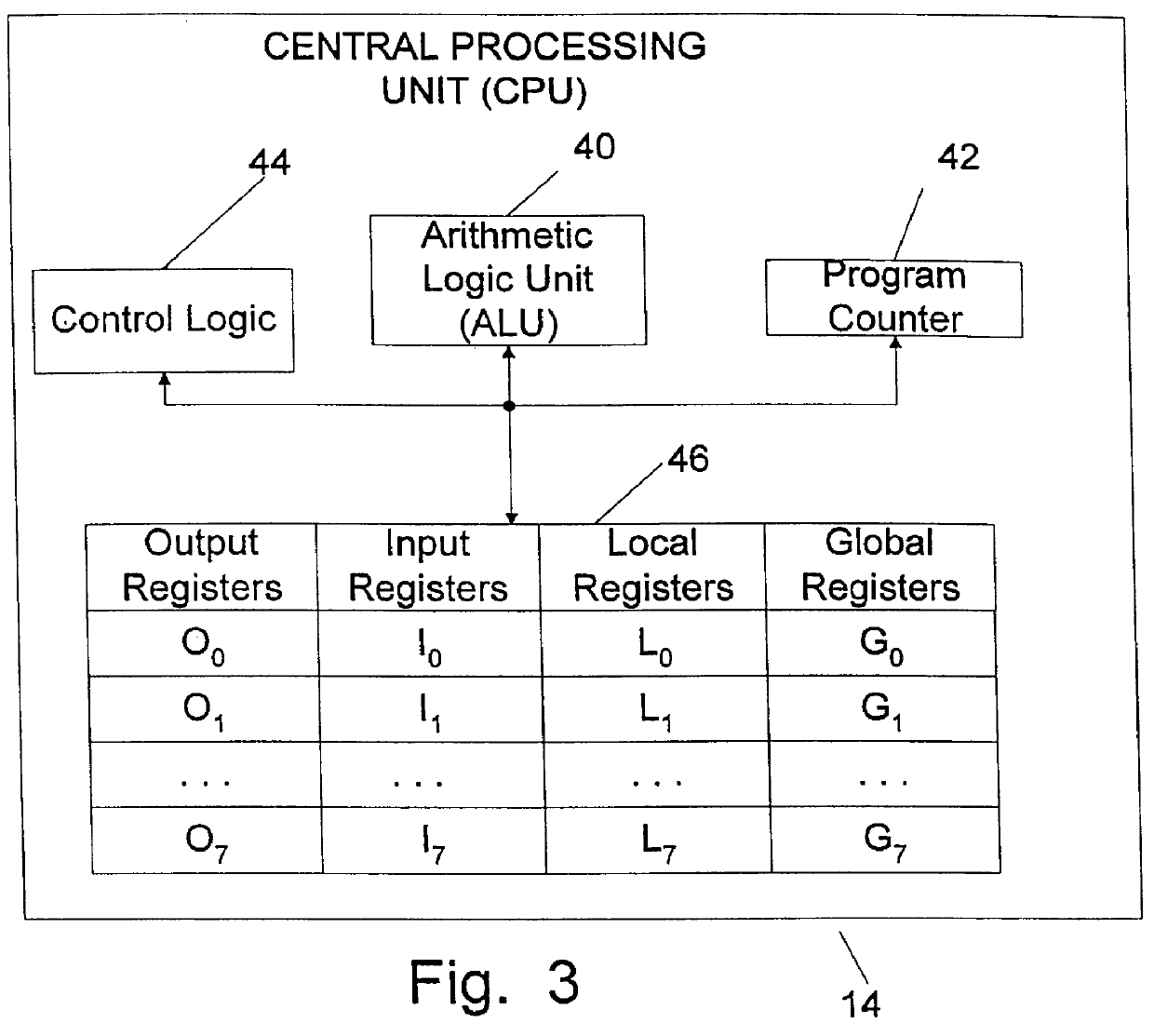
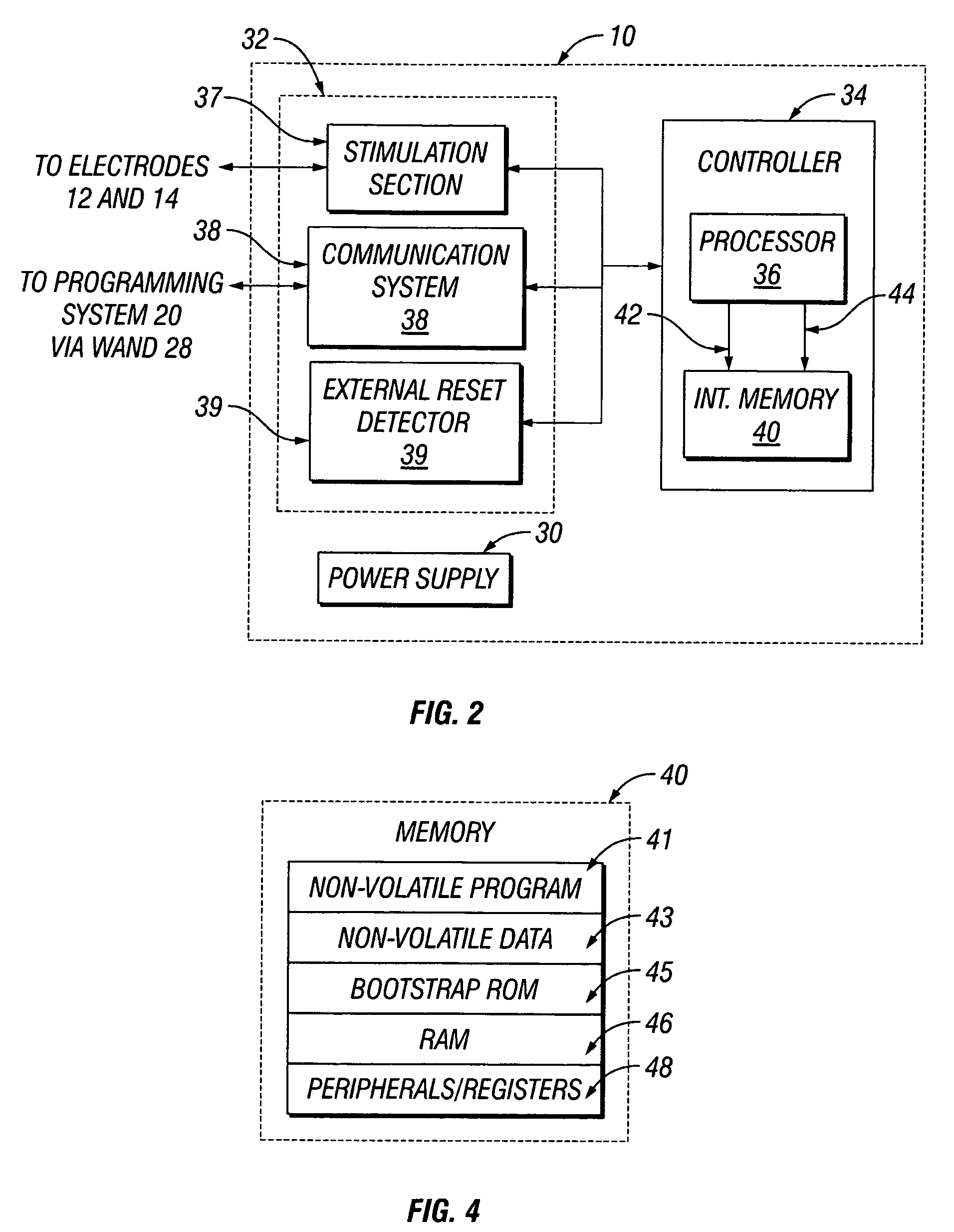
Implantable medical device with reconfigurable non-volatile program
A device comprises a stimulus generator comprising an instruction processor. The stimulus generator is configured to deliver stimuli to a biological tissue. The device also comprises a non-volatile memory for storing instructions directly executable by the instruction processor, the instructions controlling, at least in part, the operation of the device. The instruction processor generates an erase control signal to erase at least a segment of the non-volatile memory and a write control signal to write one or more new instructions to at least a segment of the non-volatile memory, thereby modifying the operation of the device.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
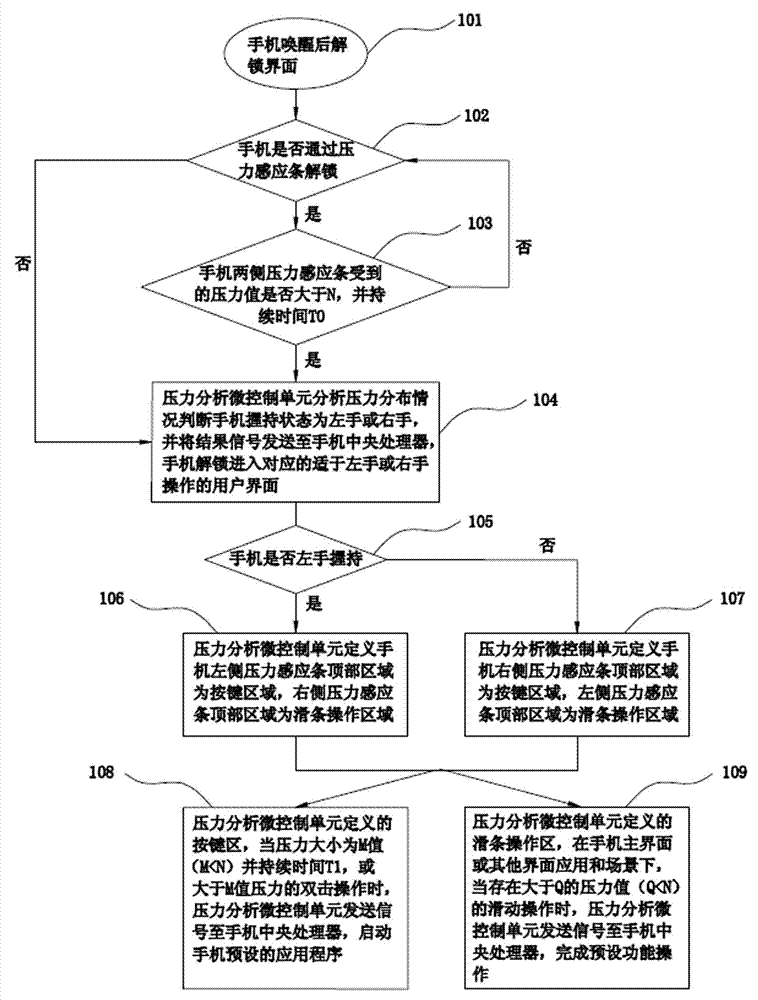
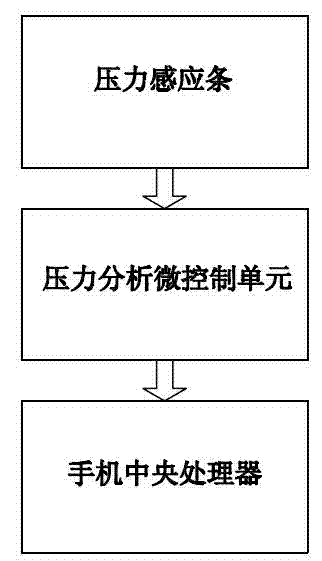
Method of realizing single hand operation of mobile phone based on pressure sensing
ActiveCN103118166ARealize one-handed controlReliable interactionSubstation equipmentAssociated functionPressure sense
The invention discloses a method of realizing single hand operation of a mobile phone based on pressure sensing. The mobile phone comprises pressure sensing bars which are arranged on two sides of the mobile phone, a pressure analysis micro-control unit and a mobile phone central processing unit. The method of realizing single hand operation of the mobile phone based on the pressure sensing comprises the following steps: a, entering an pressure-to-unlock interface after waking up the mobile phone; b, judging whether the mobile phone is in a screen-locked state or not, if the mobile phone is in a screen-locked state, carrying out pressure unlocking, if the mobile phone is not in a screen-locked state, directly carrying out the next step; c, the pressure analysis micro-control unit analyzes the holding state of the mobile phone and enables the mobile phone to enter into a corresponding operation interface; d, the pressure sensing bars judge according to a hand signal and starts corresponding pre-set application programs or performs relative functional operations. Due to the fact that the pressure sensing bars are arranged on the two sides of the mobile phone, different holding pressure of a left hand and a right hand is identified, a user can enter a user interface of left hand operation or right hand operation, and more perfect usage experience is brought to the user.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
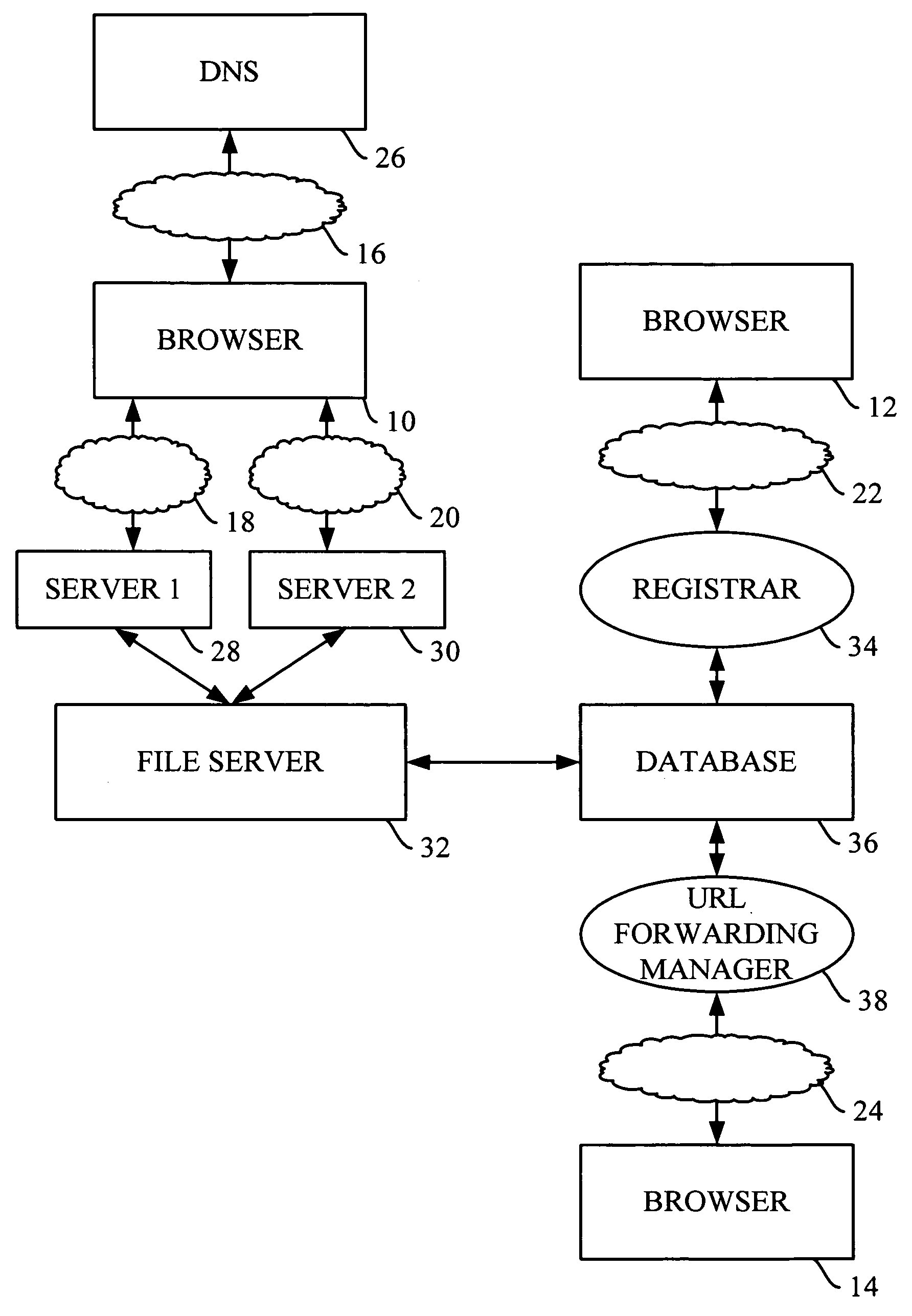
Method and apparatus for URL forwarding
A domain name is associated with the IP address of a first, URL forwarding web server within the domain name system (DNS) so that a request for a website or other resource associated with the domain name is presented to the URL forwarding web server. The URL forwarding web server accesses a file stored on a file server and determining from the contents of the file the IP address to which the domain name should resolve. The file associated with that domain name may contain information that initiates display of static or dynamic content from the URL forwarding web server. Alternately, the file may contain instructions to associate the requested domain name with the IP address of a second, destination web server that has the requested content or resource. Most preferably, the URL forwarding web server performs this access to the file server directly, without executing a script or other interface program supplementary to the URL forwarding web server. For example, the URL forwarding web server may include a module that receives a domain name, accesses the file from the file server and evaluates the contents of the file. When the file includes an IP address to which the domain name should resolve, preferred implementations of the module recognize the presence of the IP address within the file and return the IP address of the destination web server to the browser through which the user made the request.
Owner:WEB COM GRP
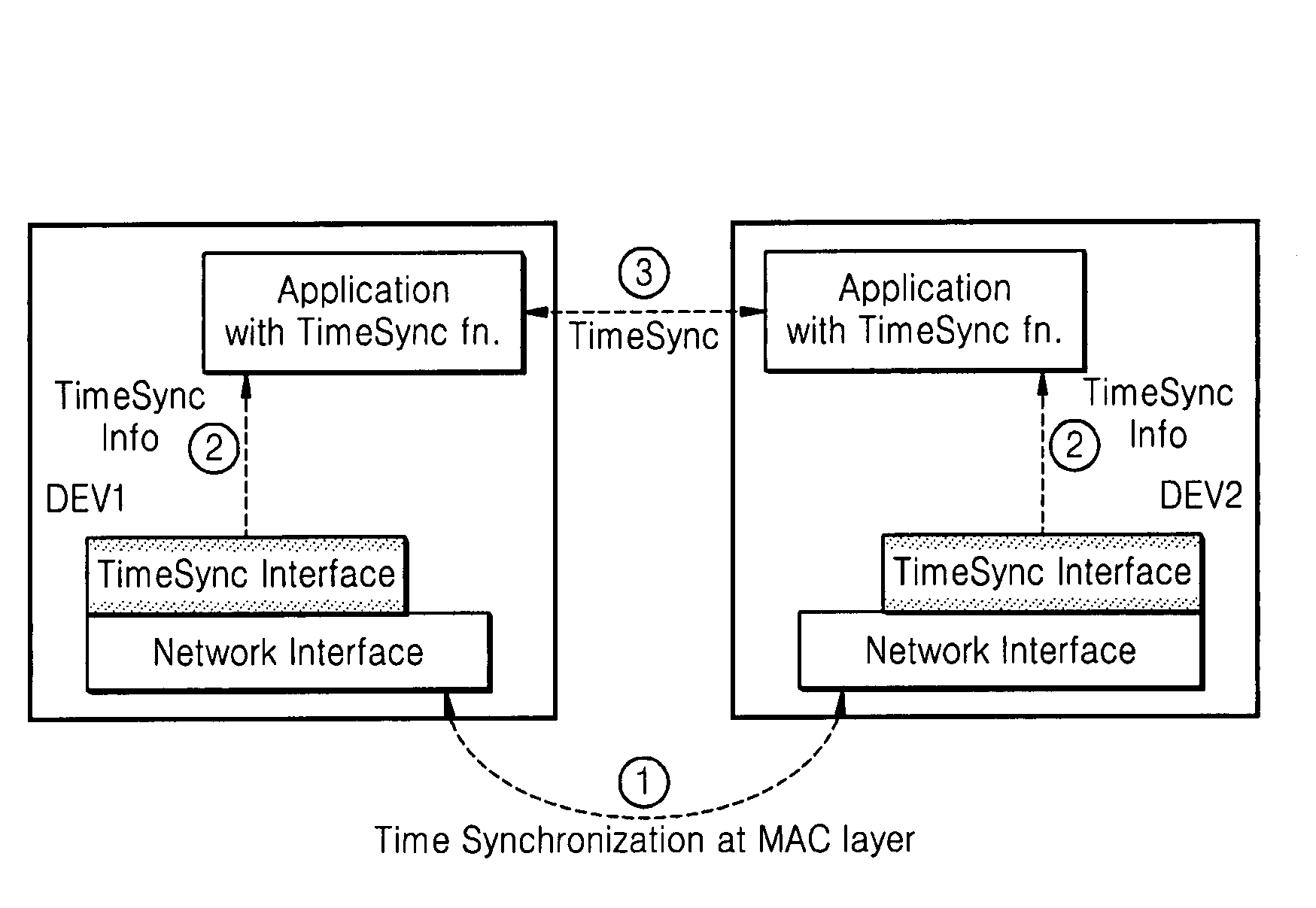
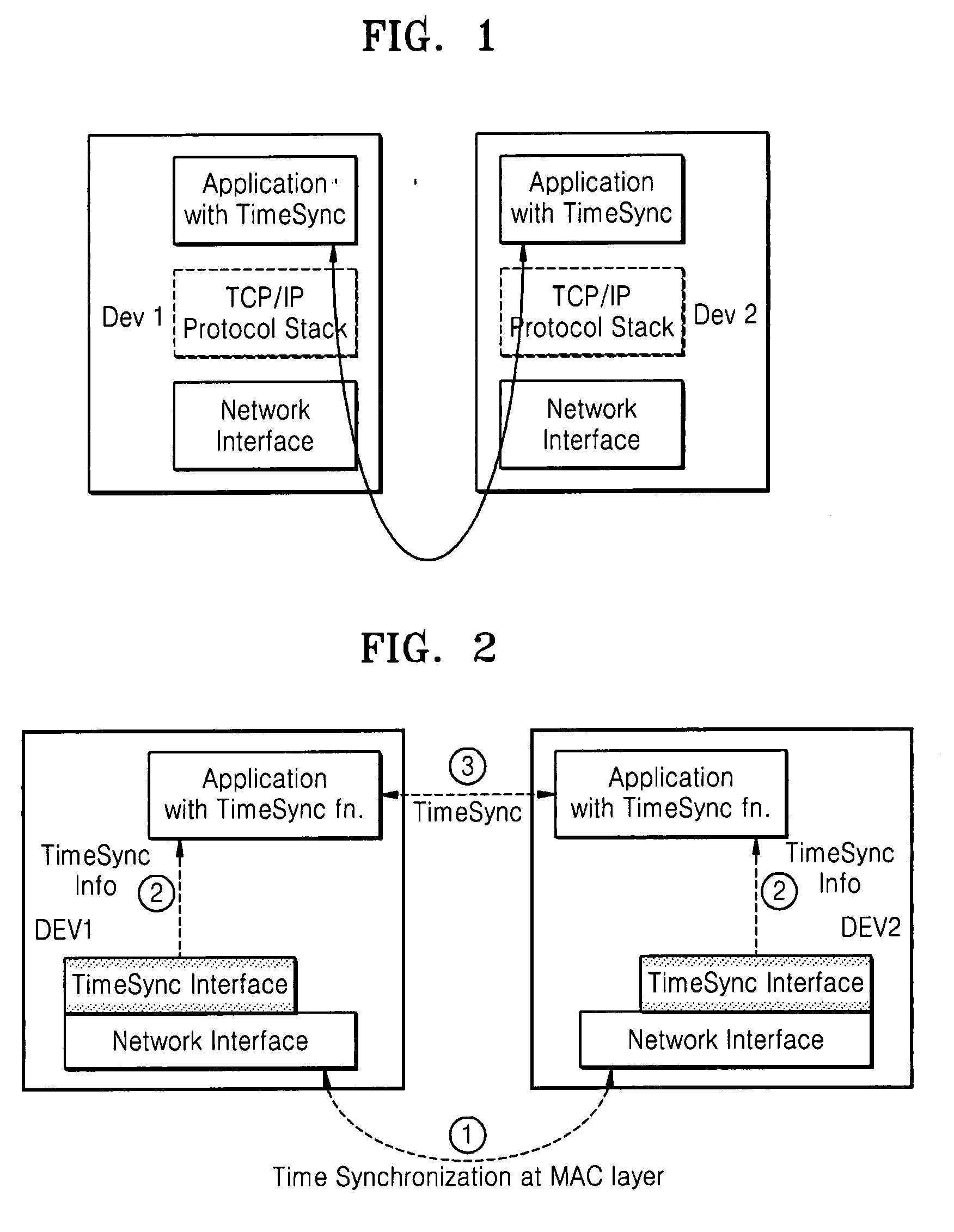
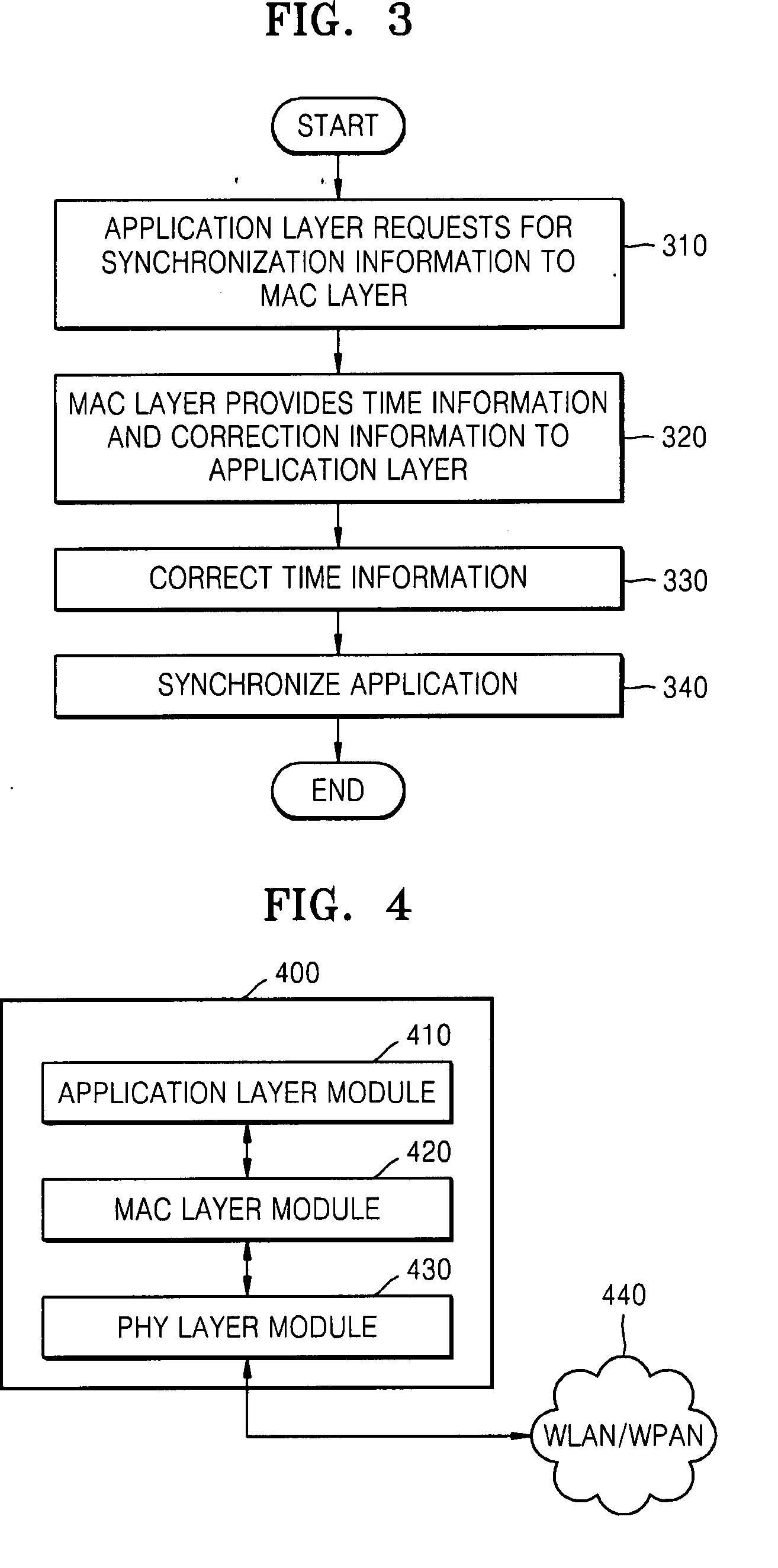
Method and apparatus for synchronizing applications of terminals in communication network
ActiveUS20080075126A1Time-division multiplexWireless network protocolsTime informationSynchronization networks
A method and apparatus for synchronizing applications of network terminals are provided. Time information, which is synchronized and managed with other terminals for controlling use of media in the network in a media access control (MAC) layer, is transmitted to an application layer so as to directly execute the application using a synchronization interface. Accordingly, it is possible to synchronize applications without exchanging packets for obtaining synchronization information of terminals using a TCP / IP protocol.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
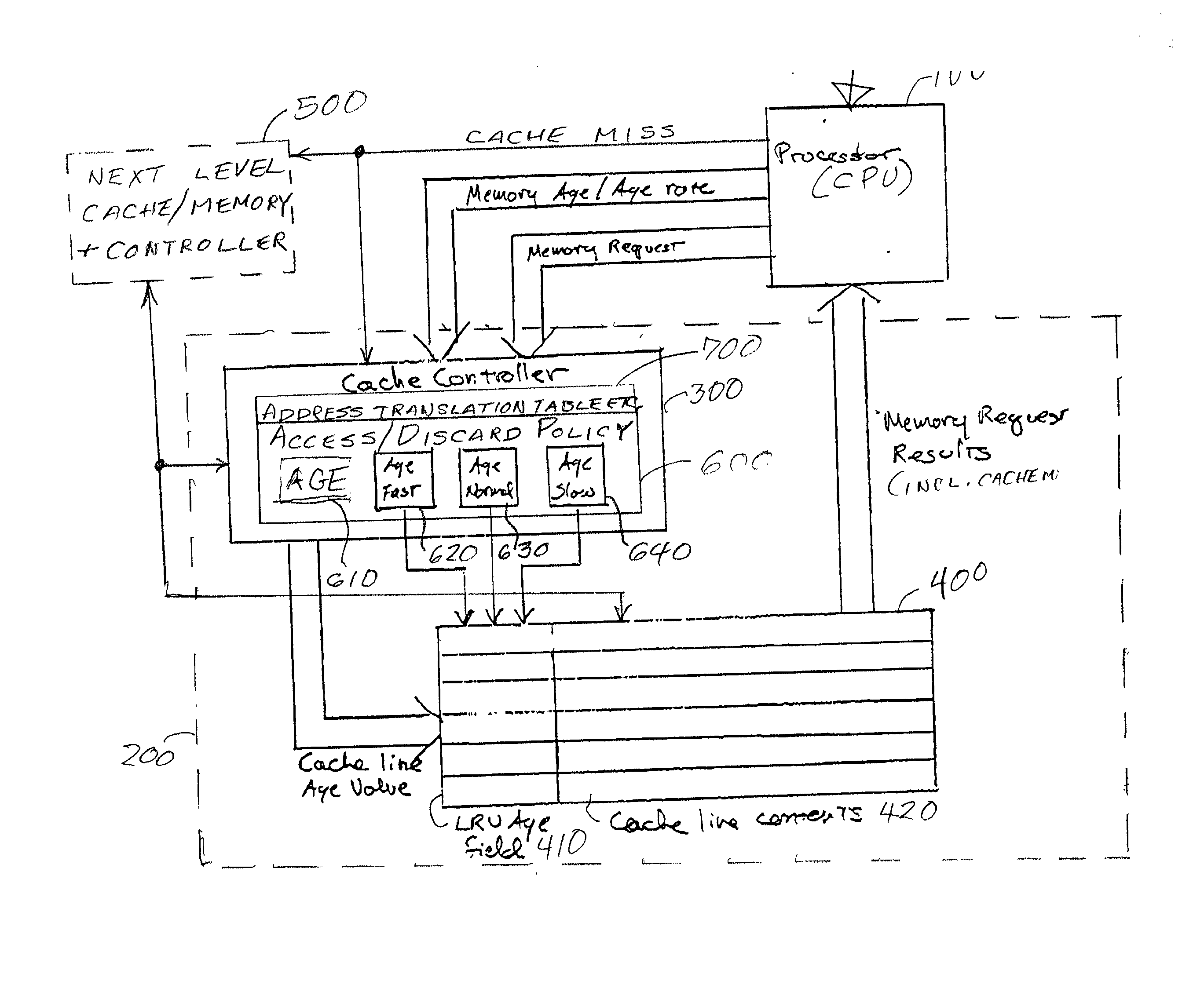
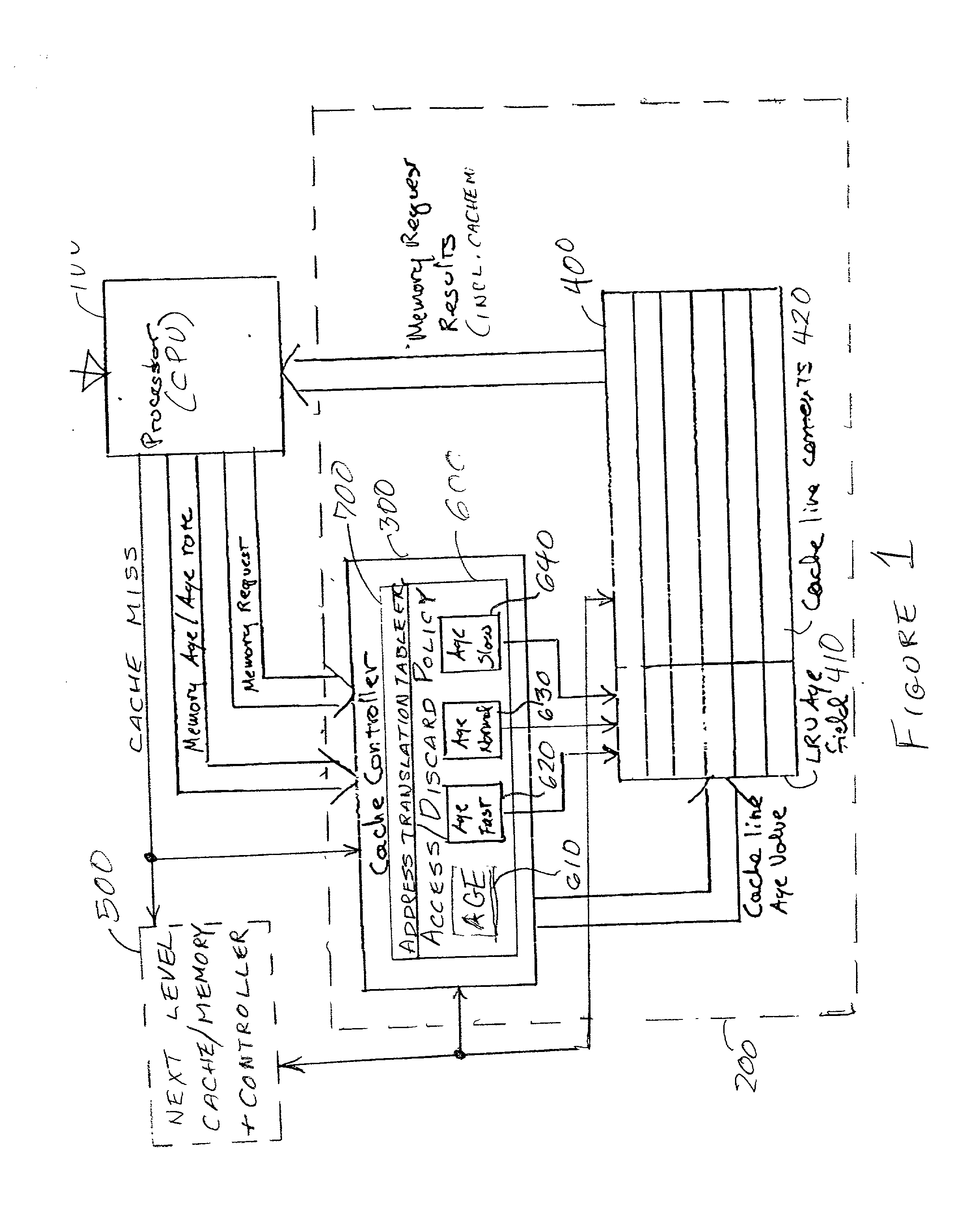
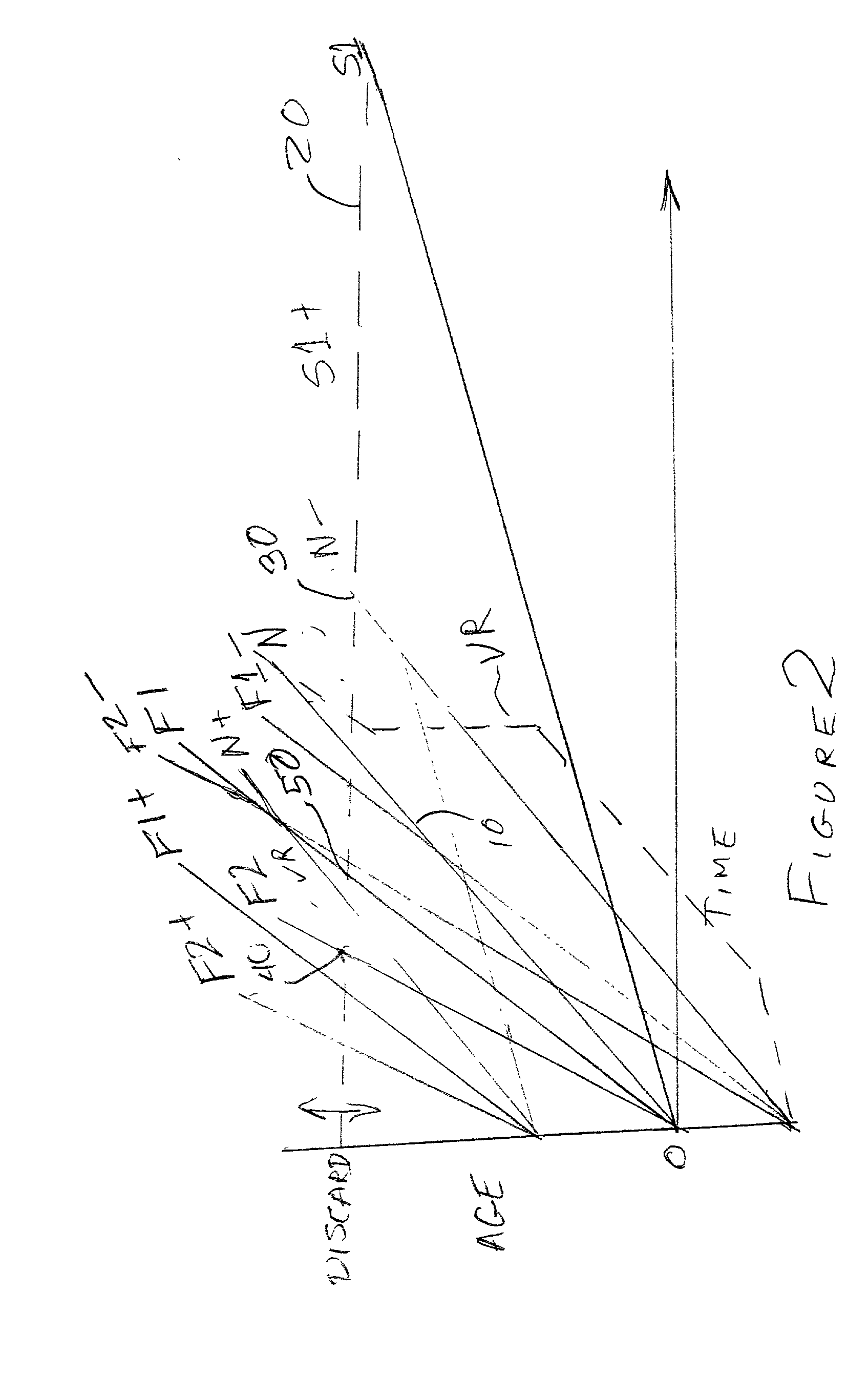
Directed least recently used cache replacement method
InactiveUS20020152361A1Performance maximizationImprove cache hit ratioEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingLeast recently frequently used
Fine grained control of cache maintenance resulting in improved cache hit rate and processor performance by storing age values and aging rates for respective code lines stored in the cache to direct performance of a least recently used (LRU) strategy for casting out lines of code from the cache which become less likely, over time, of being needed by a processor, thus supporting improved performance of a processor accessing the cache. The invention is implemented by the provision for entry of an arbitrary age value when a corresponding code line is initially stored in or accessed from the cache and control of the frequency or rate at which the age of each code is incremented in response to a limited set of command instructions which may be placed in a program manually or automatically using an optimizing compiler.
Owner:IBM CORP
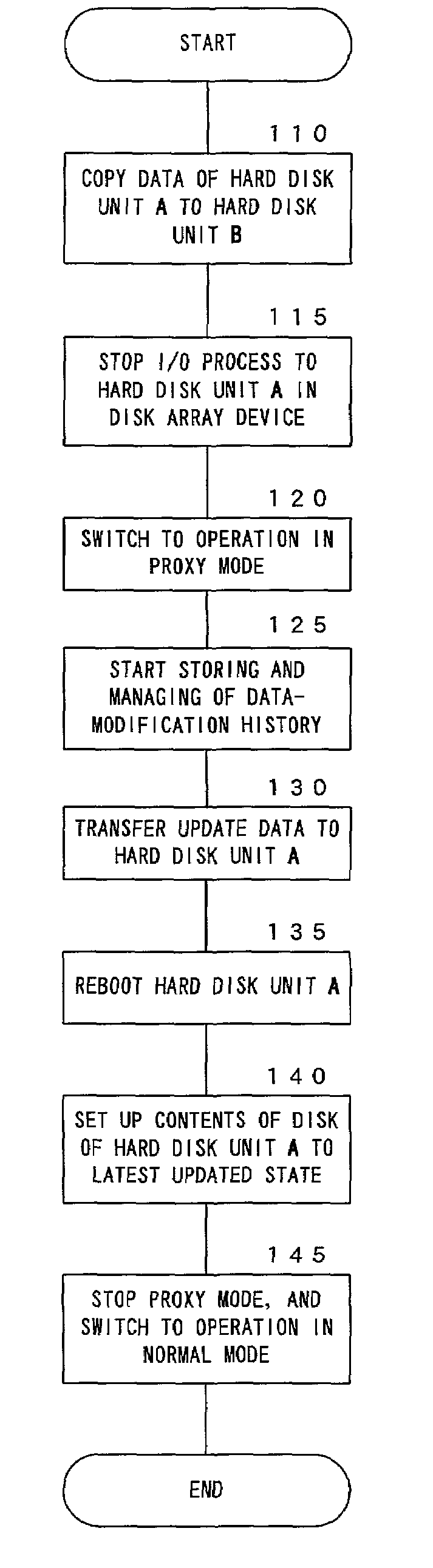
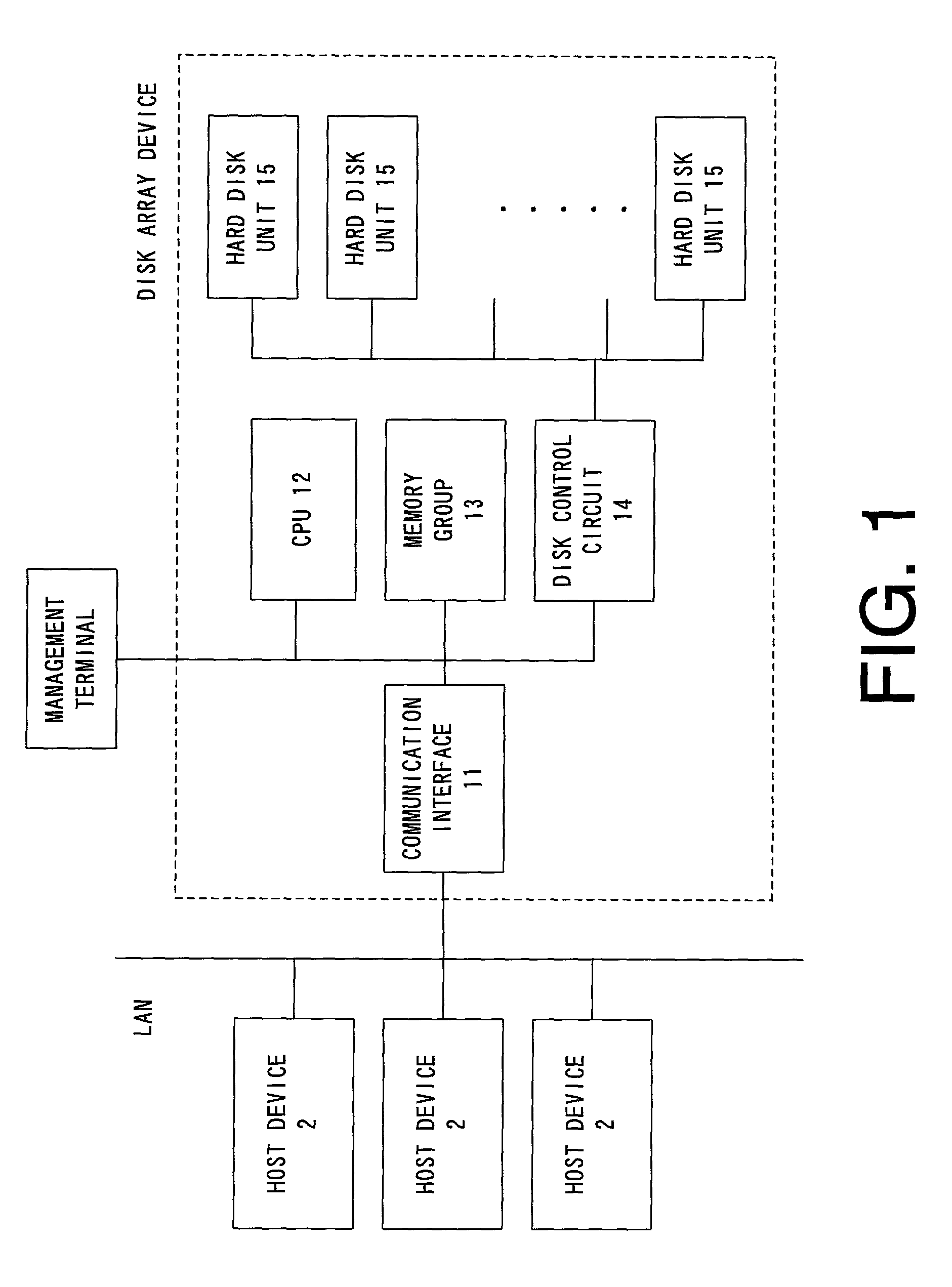
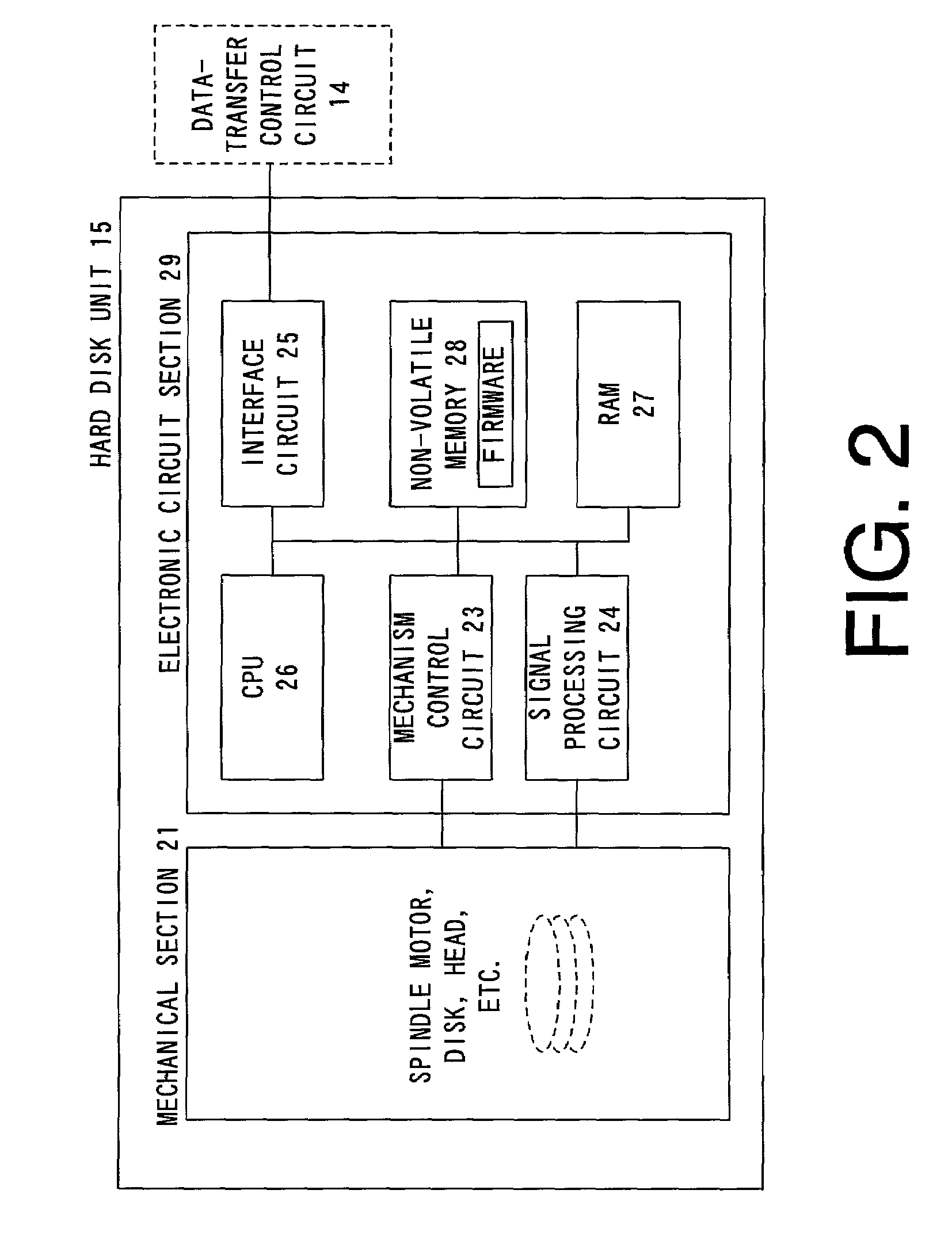
Updating method of firmware of hard disk unit mounted on disk array device and disk array device with function for performing updating method
InactiveUS7032218B2Small processing loadReduce processing timeInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionNormal modeDisk array
Data recorded in a disk of a hard disk unit is copied to another hard disk unit. A proxy mode, for making the other hard disk unit which has been copied with the data to perform an I / O process to the hard disk unit in place thereof, is performed. Meanwhile, the firmware of the original hard disk unit is updated, and contents of the disk is set up to a latest updated state. Then, the operation in the proxy mode is stopped, and the operation is switched to an operation in a normal mode where the I / O process is directly performed to the original hard disk unit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
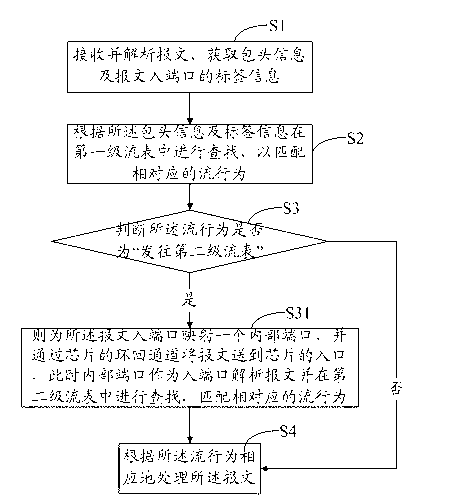
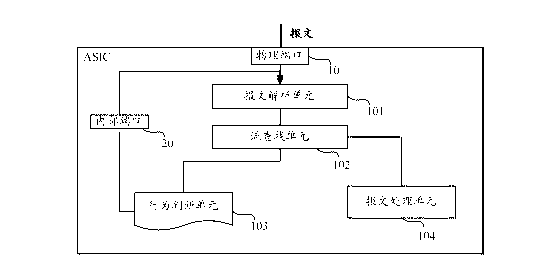
Method achieving Open flow two-stage flow table through chip loopback and system thereof
ActiveCN103095583AAchieve orientationIncrease the number ofData switching networksSoftware engineeringLoopback
The invention provides a method achieving an Open flow two-stage flow table through a chip loopback and a system of the method achieving the Open Flow two-stage flow table through the chip loopback. The method includes: S1, receiving and parsing a message, and obtaining header information and tag information of a message inlet interface; S2, searching in a first stage flow table to match corresponding flow behavior according to the header information and the tag information; S3, judging whether the flow behavior is 'sending to a second stage flow table', if the flow behavior is 'sending to a second stage flow table', the message inlet interface maps an internal interface, and sends the message to the outlet of the chip through a loopback of the chip, at the moment the internal interface is the inlet interface, the message inlet interface parses the message and searches in the second stage flow table, matches corresponding flow behavior, and conducts step S4; if the flow behavior is not 'sending to a second stage flow table', conducting step S4 directly; S4, processing the message correspondingly according to the flow behavior. On the basis of keeping chip cost, the method achieving the Open flow two-stage flow table through the chip loopback and the system of the method achieving the Open flow two-stage flow table through the chip loopback increase numbers of flow entries and support more flow behaviors through building the two-stage flow table of Open flow, and directional logic of the two grade flow tables is simple.
Owner:SUZHOU CENTEC COMM CO LTD
Restricting memory access to protect data when sharing a common address space
ActiveUS7281102B1Avoid accessMemory architecture accessing/allocationComputer security arrangementsVirtual computingDirect execution
A first software entity occupies a portion of a linear address space of a second software entity and prevents the second software entity from accessing the memory of the first software entity. For example, in one embodiment of the invention, the first software entity is a virtual machine monitor (VMM), which supports a virtual machine (VM), the second software entity. The VMM sometimes directly executes guest instructions from the VM and, at other times, the VMM executes binary translated instructions derived from guest instructions. When executing binary translated instructions, the VMM uses memory segmentation to protect its memory. When directly executing guest instructions, the VMM may use either memory segmentation or a memory paging mechanism to protect its memory. When the memory paging mechanism is active during direct execution, the protection from the memory segmentation mechanism may be selectively deactivated to improve the efficiency of the virtual computer system.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Methods, apparatuses and computer program products for simulating arbitrary unmodified code
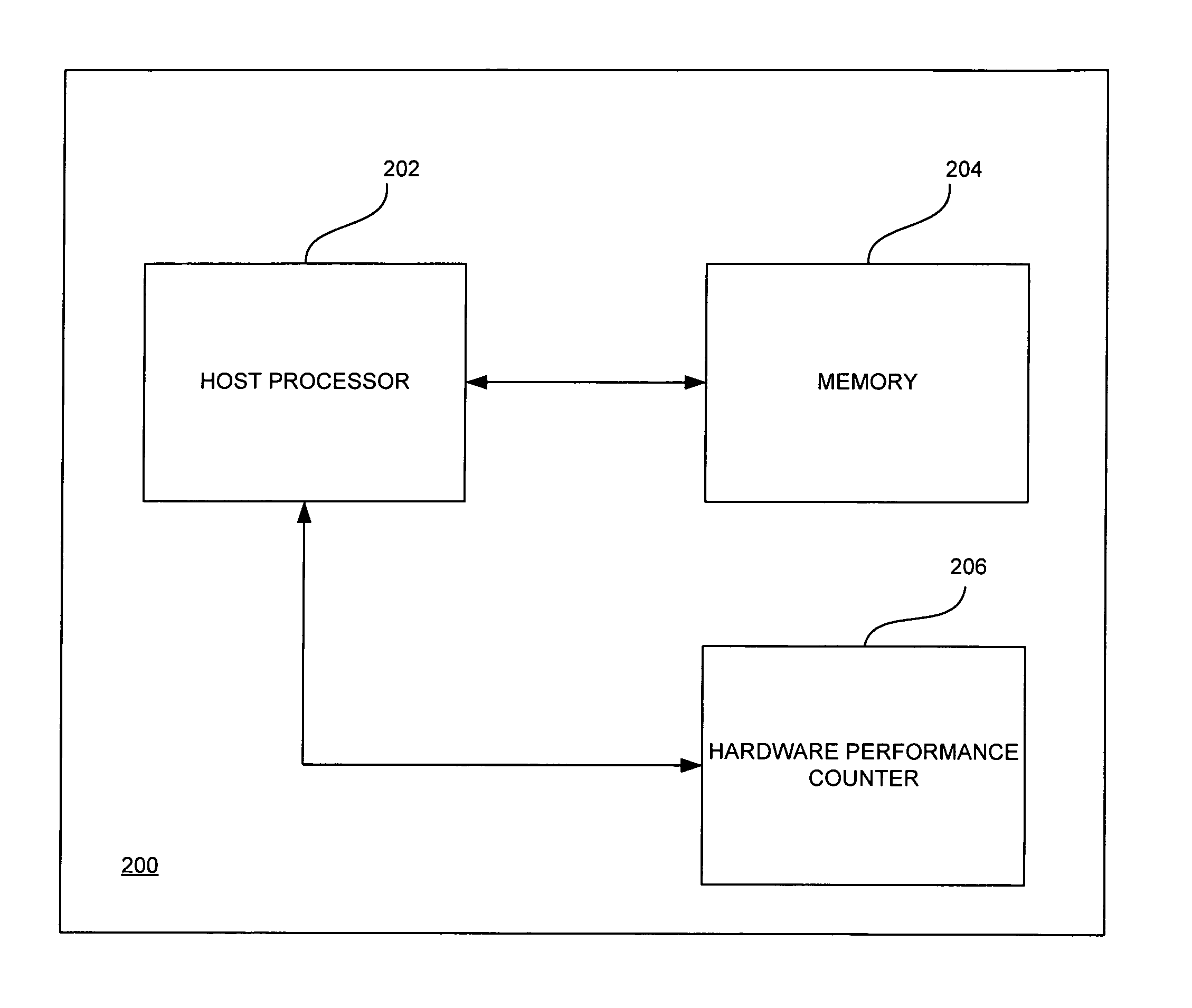
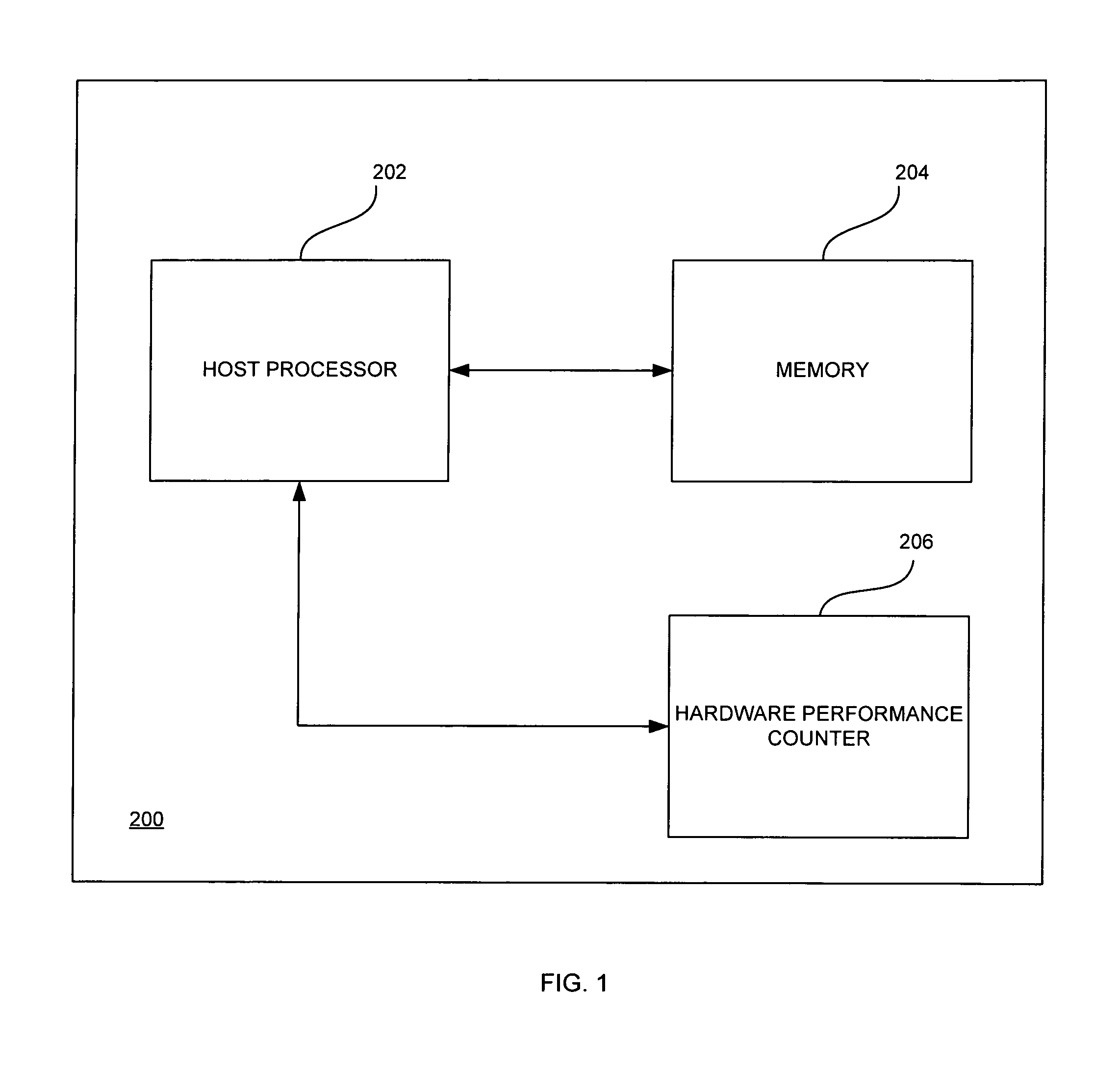
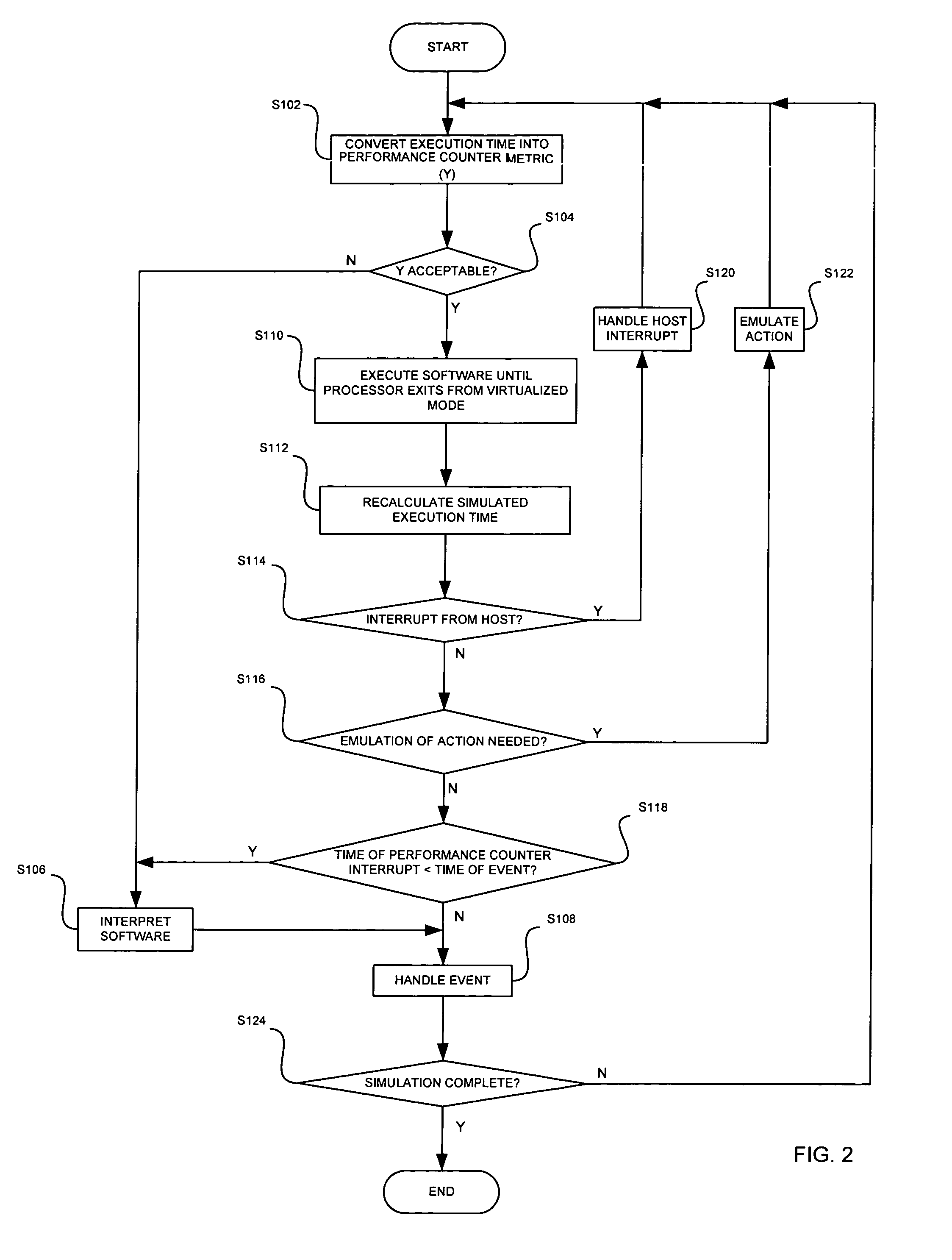
InactiveUS8170859B1Error detection/correctionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtualizationParallel computing
Arbitrary, unmodified code and / or software may be executed directly on a host processor operating in a virtualized mode using hardware virtualization support and performance counters. The arbitrary software may be run on the host processor until the host processor exits from the virtualized mode. An end execution time may be calculated in response to the host processor exiting from the virtualized mode. An event may then be handled based on an execution time at which the host processor exited from the virtualized mode and a time at which a scheduled event was to occur.
Owner:INTEL CORP
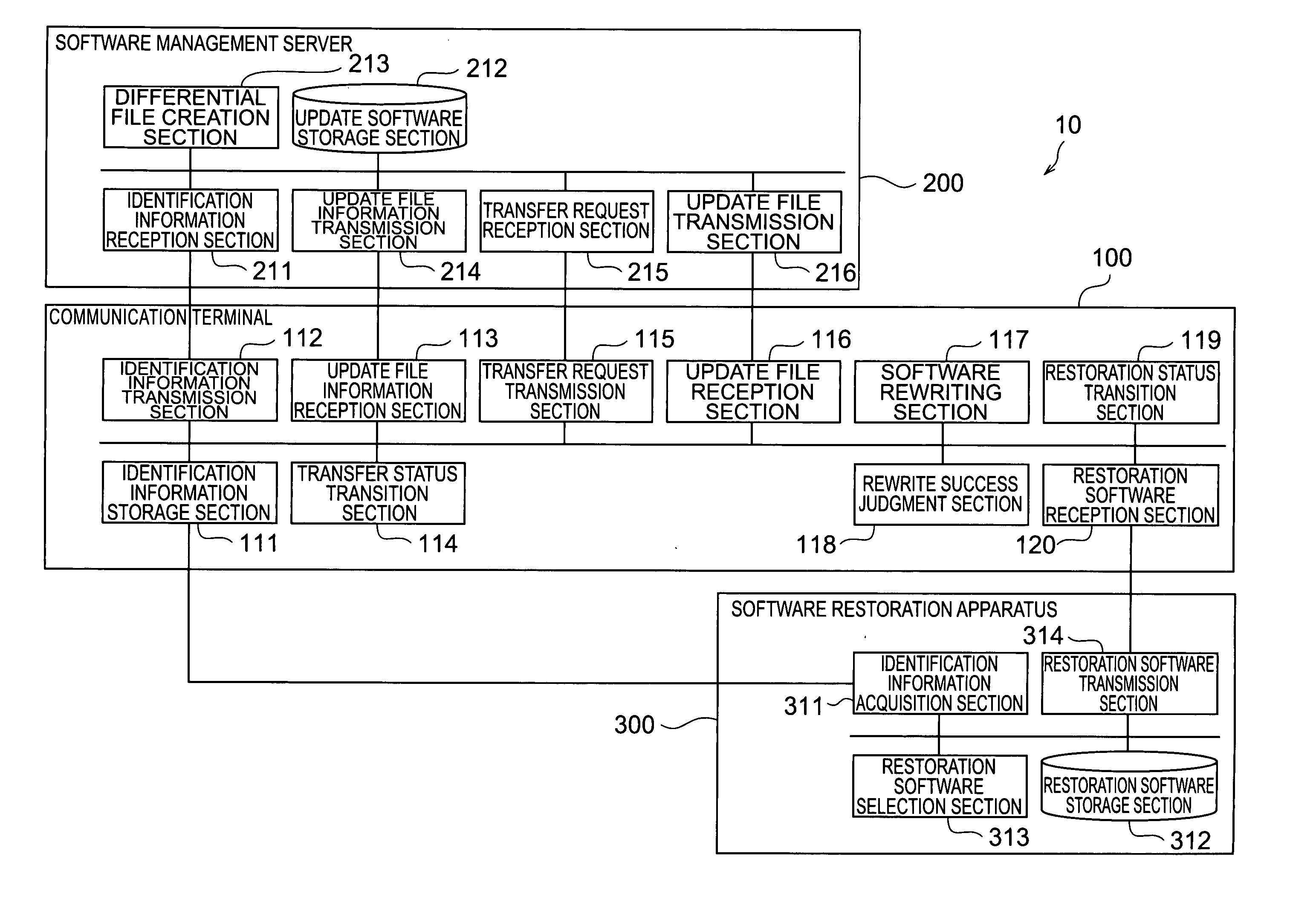
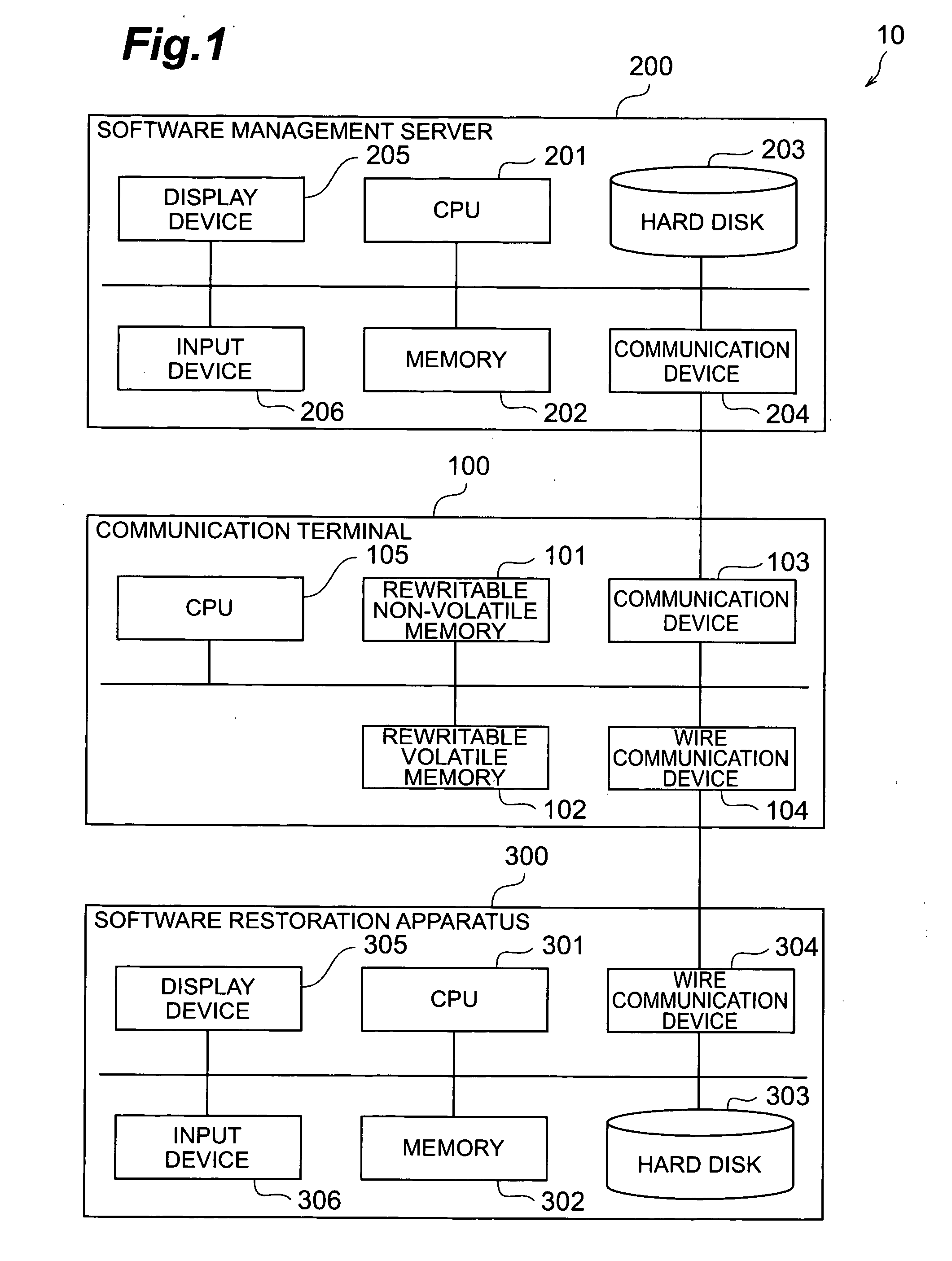
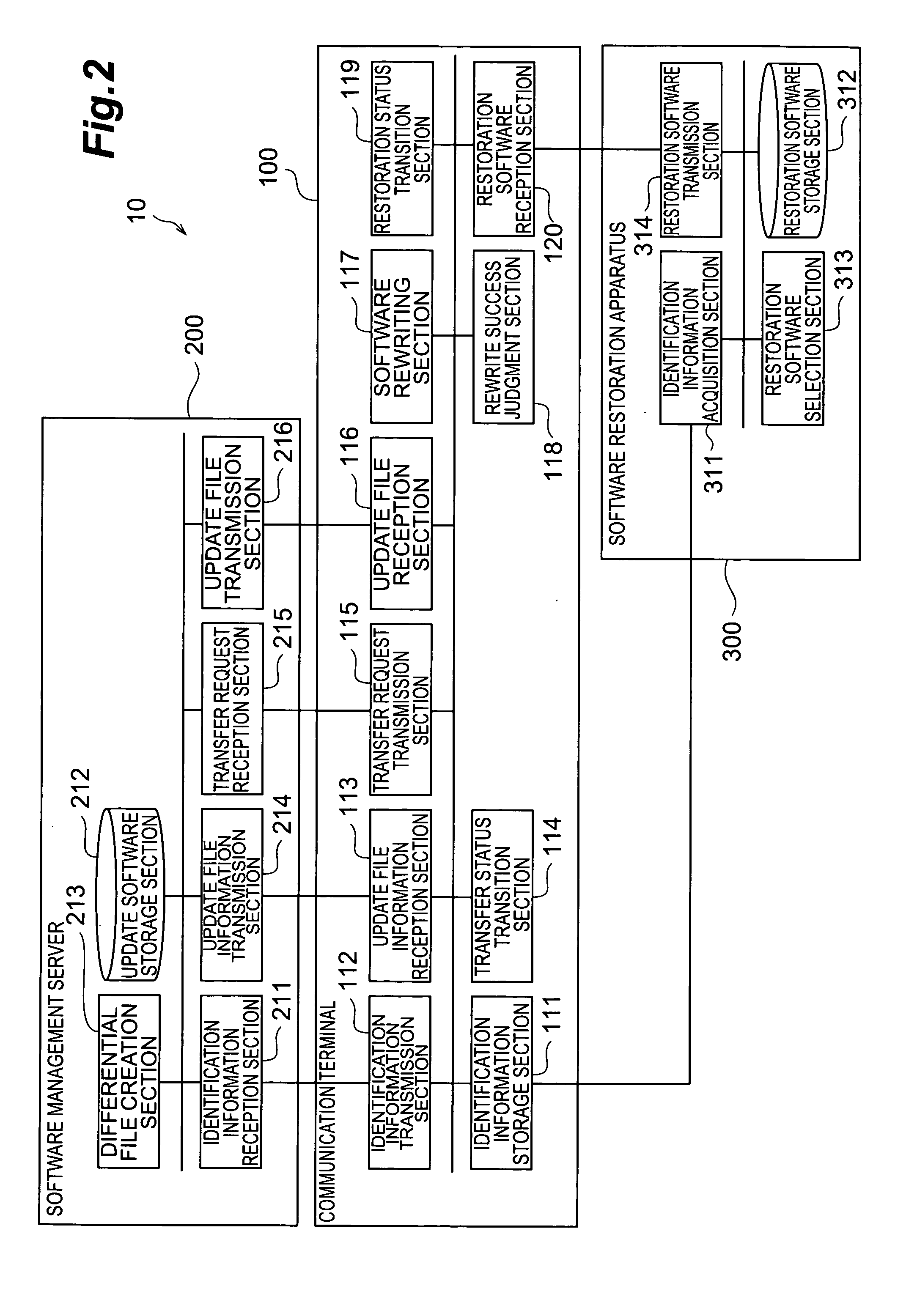
Communication terminal software updating method, communication terminal, and software updating method
InactiveUS20050210458A1Limit its operationProgram control using stored programsProgram loading/initiatingSoftware updateDirect execution
The method of the present invention is an update method of a software which is stored in a rewritable non-volatile memory of a communication terminal and is directly executed. The method comprises: an update file transfer step in which an update software is transferred to the communication terminal from a software management server for managing the update software which is to be stored in the rewritable non-volatile memory as an update file, and the update file is stored in a rewritable volatile memory of the communication terminal; and an update software rewriting step in which the software, which is stored in the rewritable non-volatile memory and is directly executed, is rewritten with the update software stored in the rewritable volatile memory as the update file after the update file transfer step.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
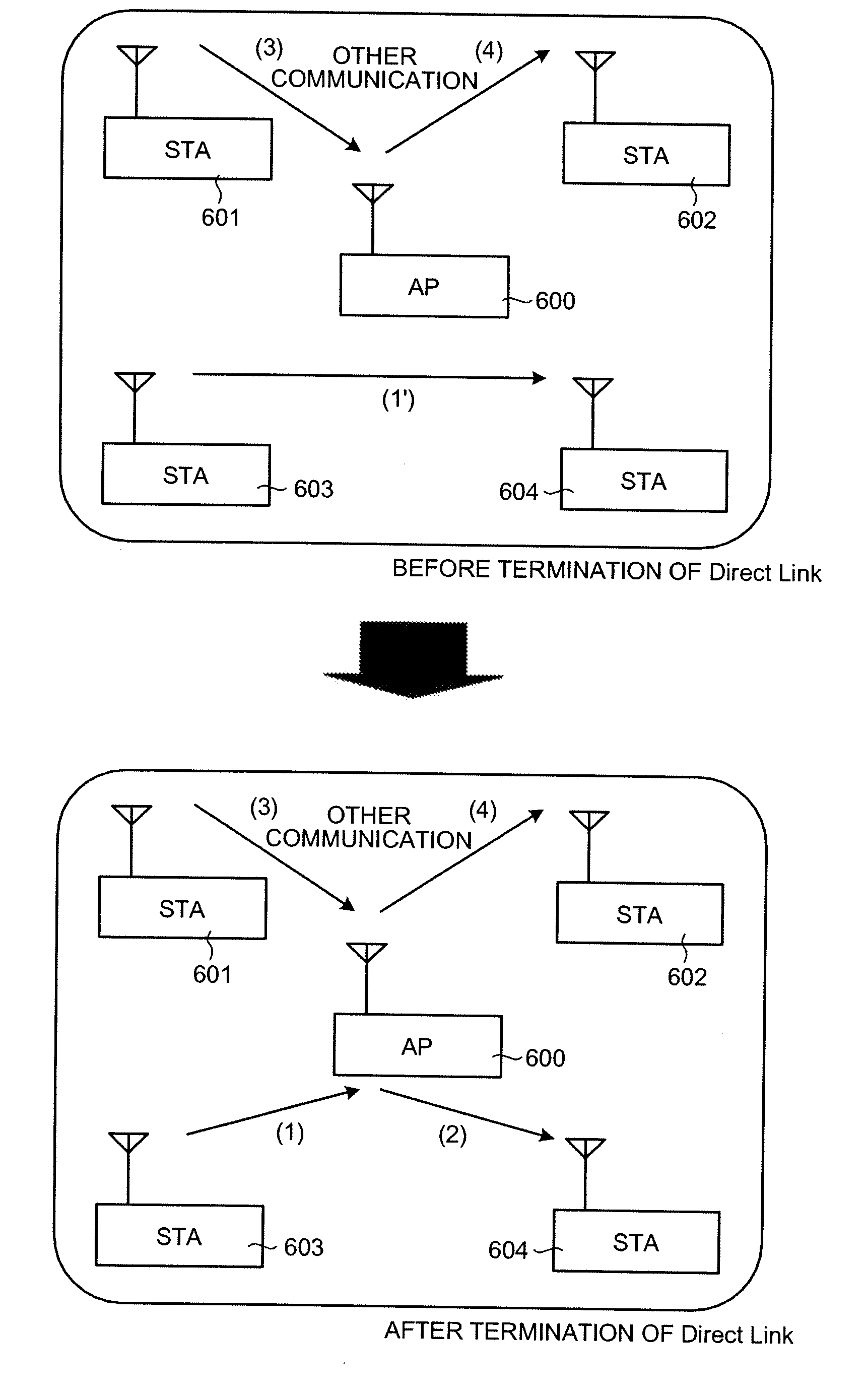
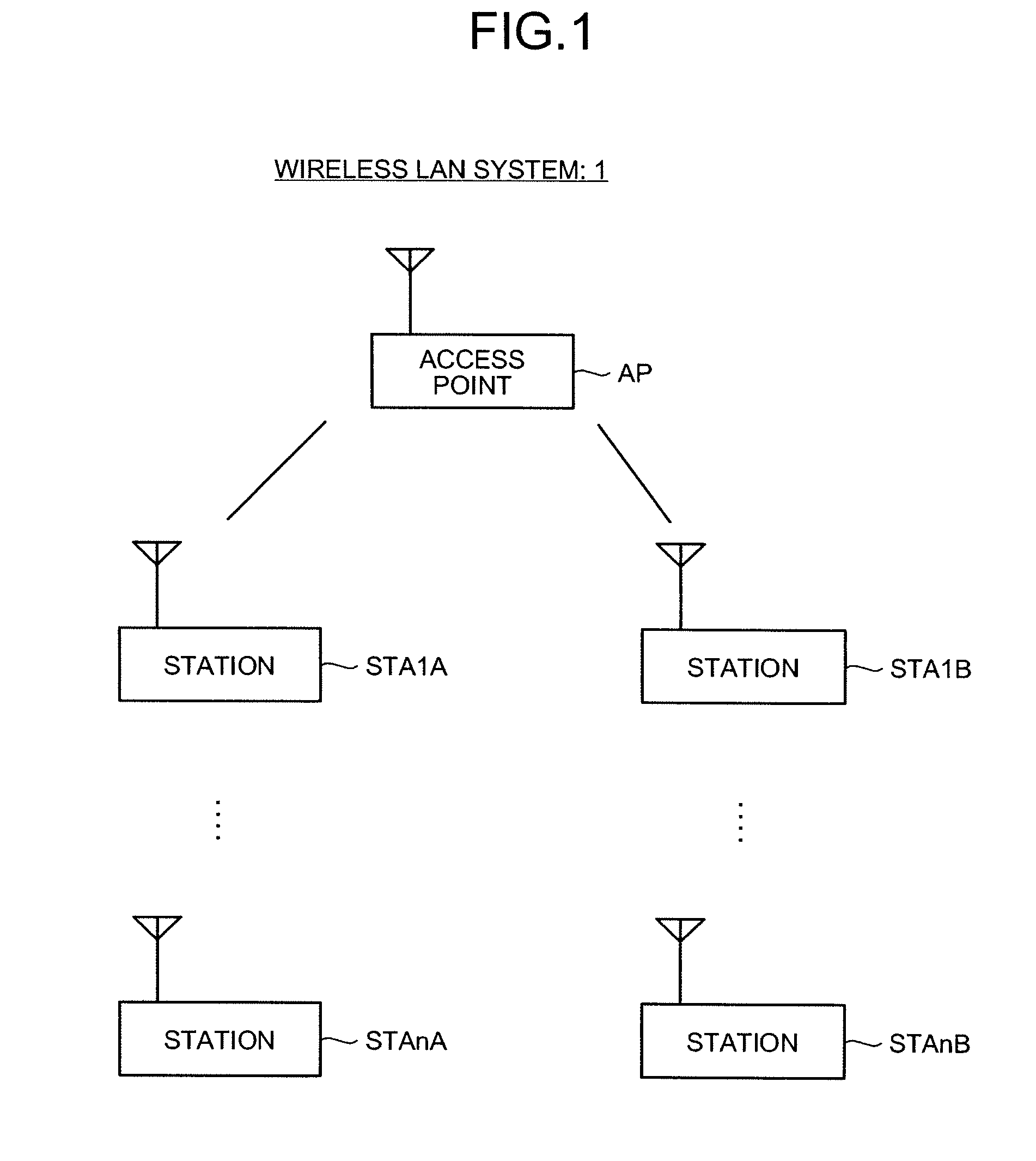
Radio Lan System, and Base Station and Terminal Station Thereof
InactiveUS20080259853A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesWireless lanData transmission
A wireless LAN system that includes a plurality of stations and an access point, interconnected via a network, and supports QoS has infrastructure mode and a Direct Link. In the infrastructure mode, data communication is performed between stations STA via an access point AP. In the Direct Link, data communication is performed directly between the stations STA. The access point AP performs a process for reserving a bandwidth 2W that is twice a bandwidth W required when the Direct Link is used, in response to a QoS bandwidth reservation request when the Direct Link is used from a station STA. As a result, the QoS of data transfer can be ensured even when the Direct Link is terminated.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
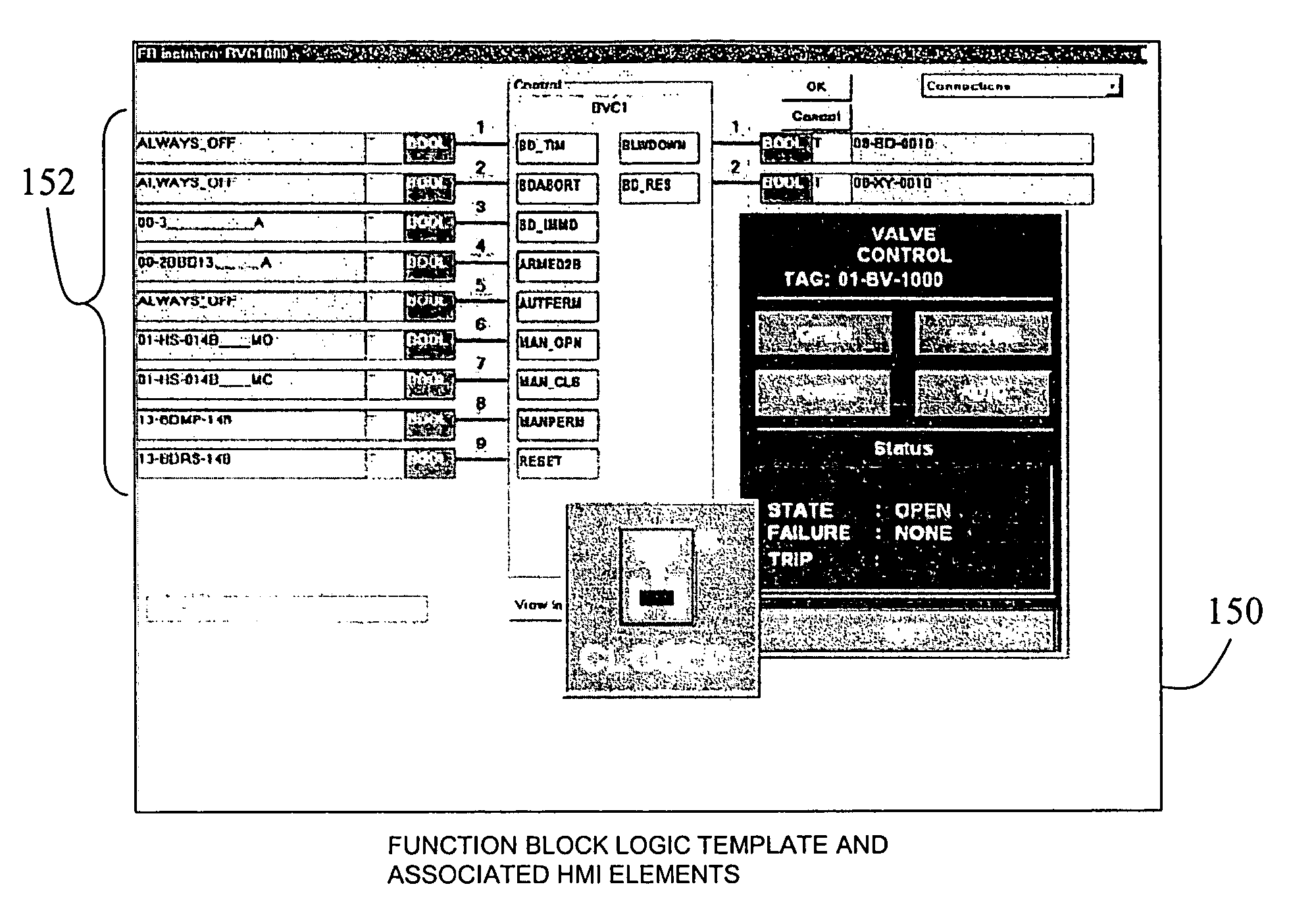
Cause and effect logic application implementation
InactiveUS6941261B1Software simulation/interpretation/emulationProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersComputer aidComputer-aided
A method for Cause and Effect application logic implementation includes defining a formal methodology for specification of functional requirements for a target system based upon Cause and Effect notation and function blocks and employing a computer-aided specification tool-set to support capture and validation of functional requirements. The method further includes employing a software module to directly execute Cause and Effect application logic.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
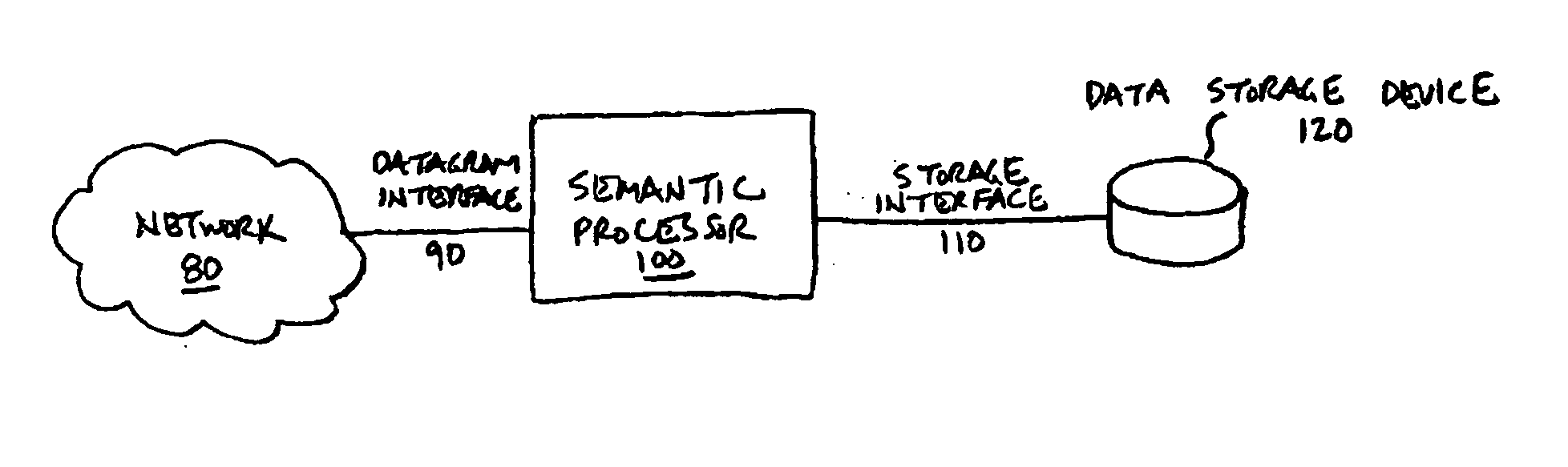
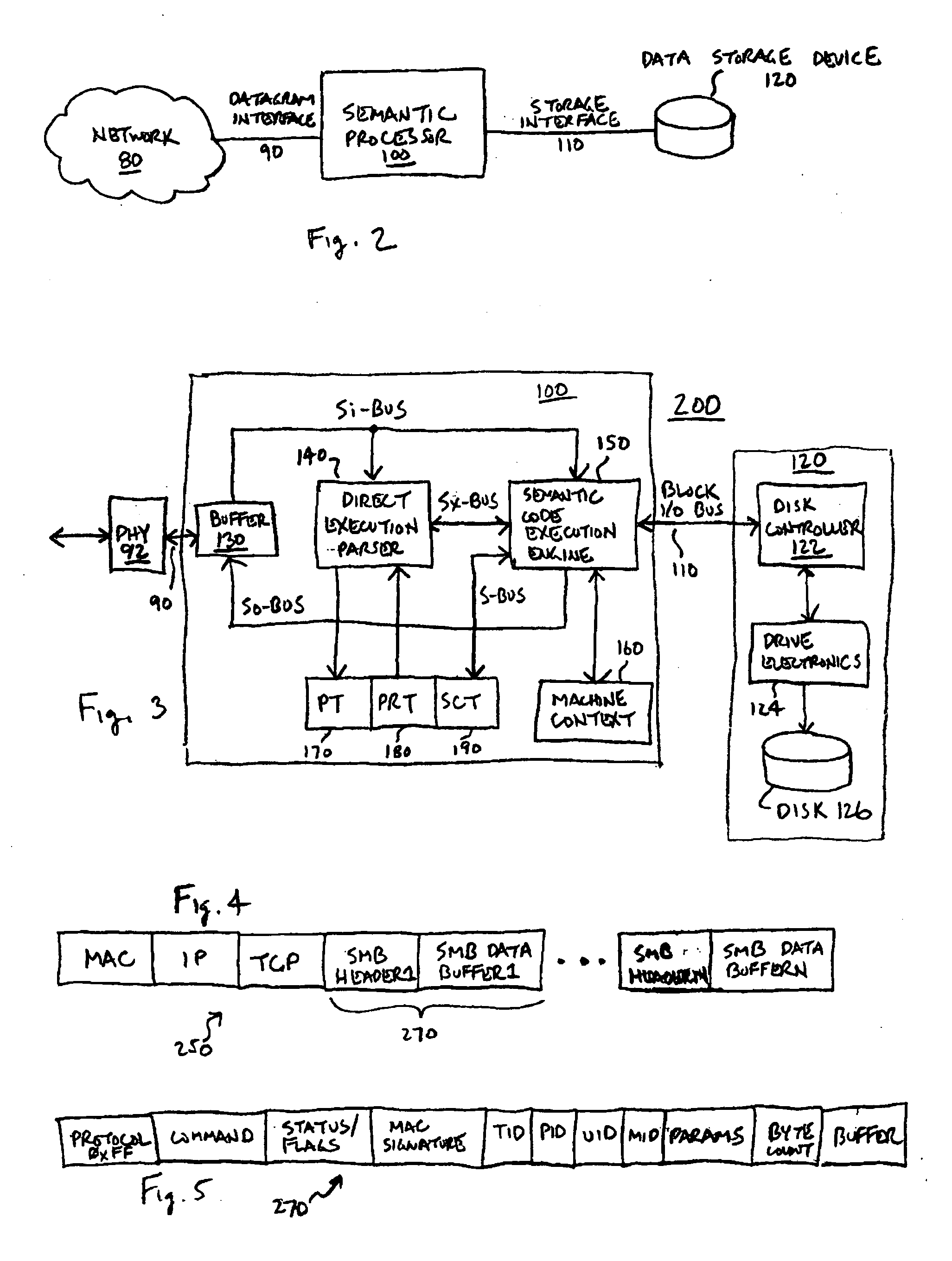
Semantic processor storage server architecture
InactiveUS20050268032A1Low costDigital data information retrievalMemory loss protectionLogical operationsSchema for Object-Oriented XML
A storage server uses a semantic processor to parse and respond to client requests. A direct execution parser in the semantic processor parses an input stream, comprising client storage server requests, according to a defined grammar. A semantic processor execution engine capable of manipulating data (e.g., data movement, mathematical, and logical operations) executes microcode segments in response to requests from the direct execution parser in order to perform the client-requested operations. The resulting operational efficiency allows an entire storage server to be collapsed in some embodiments into a few relatively small integrated circuits that can be placed on a media device's printed circuit board, with the semantic processor itself drawing perhaps a few Watts of power.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
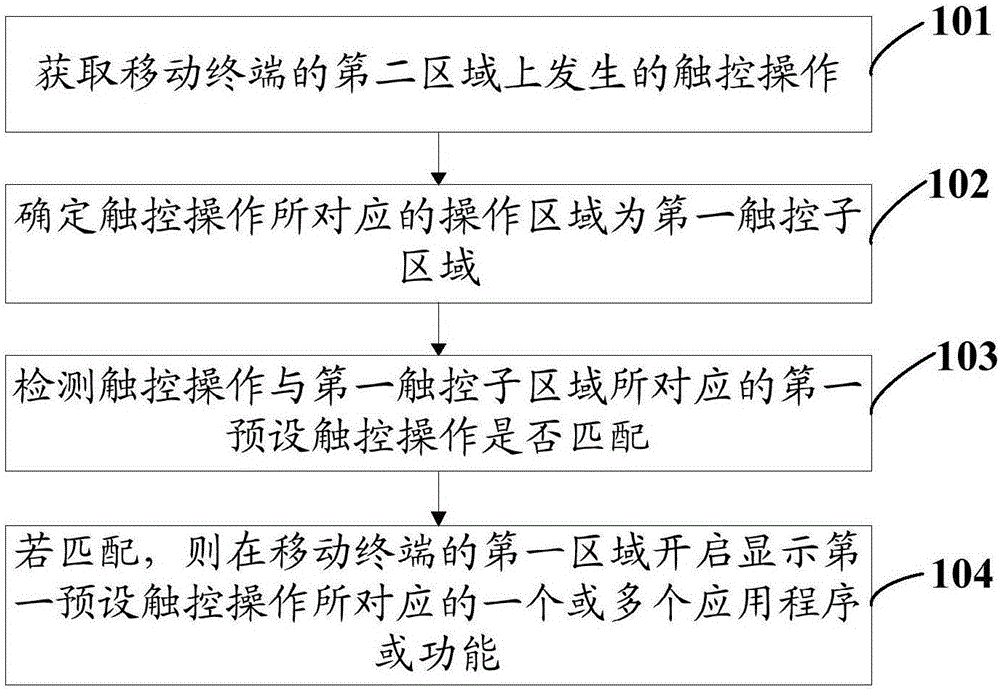
Operation method of mobile terminal, and mobile terminal
InactiveCN106325749AWill not affect the normal displayImprove operating experienceInput/output processes for data processingHuman–computer interactionMultiple applications
The invention discloses an operation method of a mobile terminal, and the mobile terminal. A touch control display panel of the mobile terminal comprises a first area forming a flat surface, and a second area arranged on the side edge of the first area and forming a curved surface. The shortcut operation method comprises the steps of acquiring touch control operation on the second area of the mobile terminal, wherein the second area comprises a plurality of touch control sub areas; determining an operation area corresponding to the touch control operation as a first touch control sub area; detecting whether the touch control operation and first preset touch control operation corresponding to the first touch control sub area are matched or not; if yes, opening and displaying one or more application programs or functions corresponding to the first preset touch control operation on the first area of the mobile terminal. According to the operation method provided by the invention, a user only needs to execute a touch control action corresponding to expected operation so as to directly execute corresponding shortcut operation, so that unnecessary man-machine interaction steps are reduced, and the operation experience of the user is improved.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Multi-partition-table inquiring and processing method and device
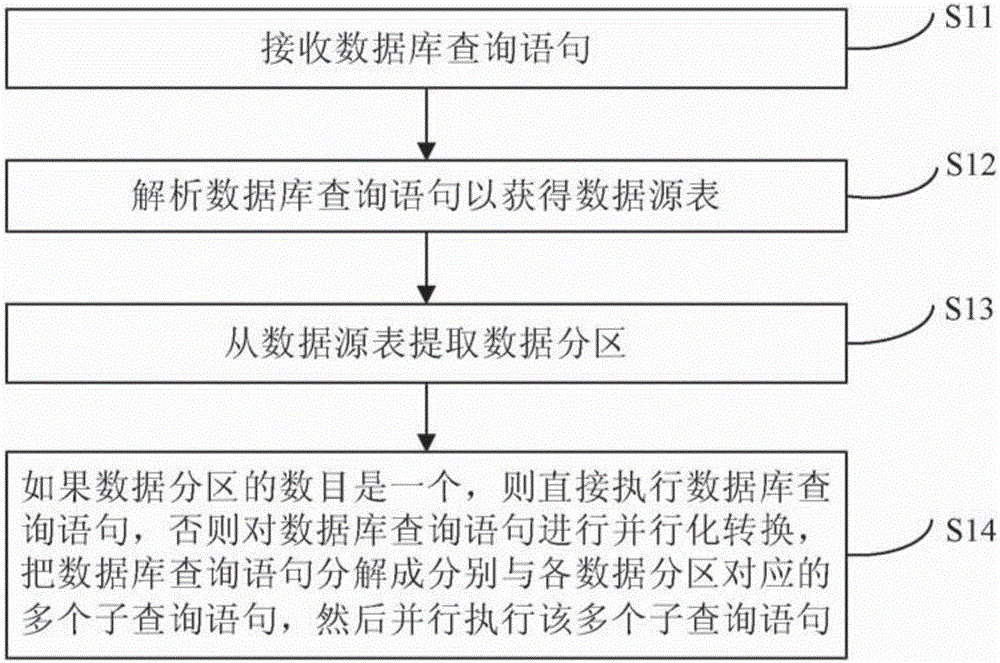
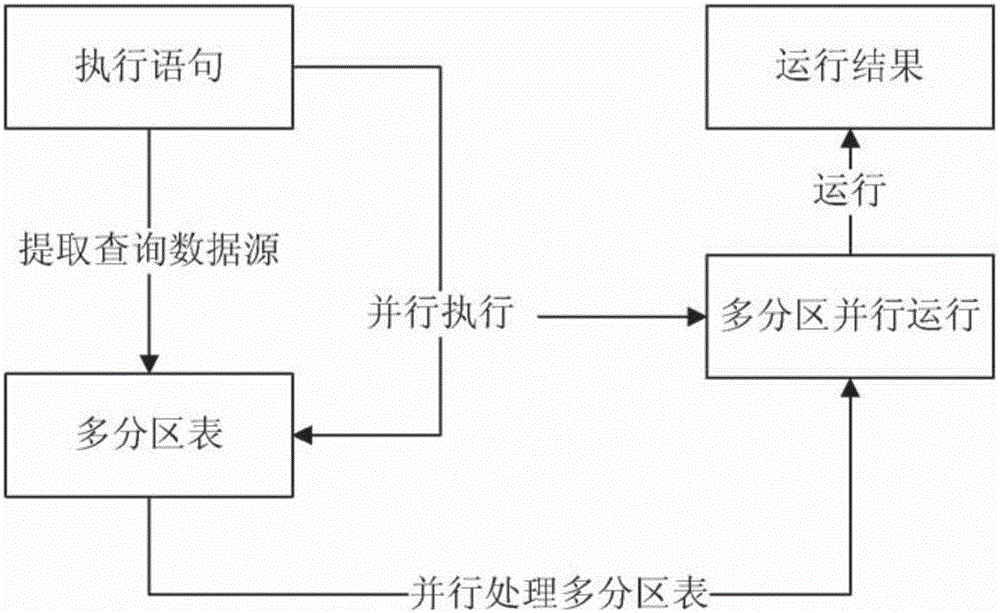
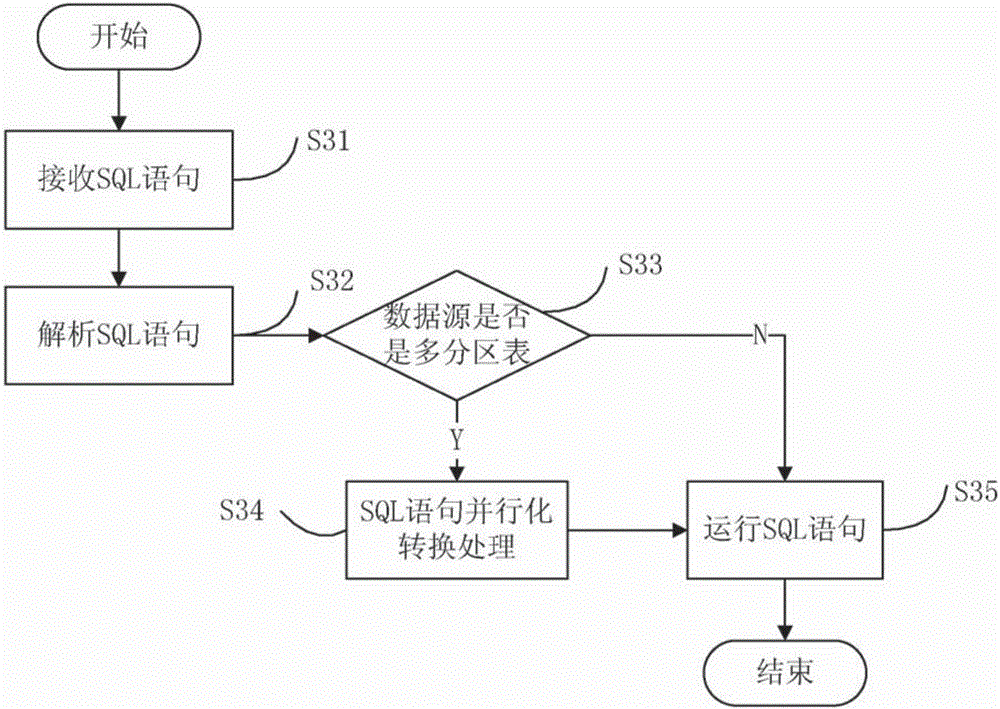
InactiveCN105975617AIncrease input and outputImprove operational efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsData sourceQuery statement
The invention provides a multi-partition-table inquiring and processing method and device. Data of all partition tables can be executed and inquired in parallel, the input and output data amount is increased, and the execution efficiency of Presto is improved. The method includes the steps of receiving a database inquiring statement, analyzing the database inquiring statement to obtain a data source table, extracting data partitions from the data source table, if the number of data partitions is one, directly executing the database inquiring statement, otherwise, conducting parallel conversion on the database inquiring statement, decomposing the database inquiring statement into multiple sub inquiring statements corresponding to all the data partitions respectively, and then executing the sub inquiring statements in parallel.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG SHANGKE INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com