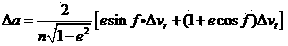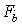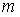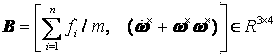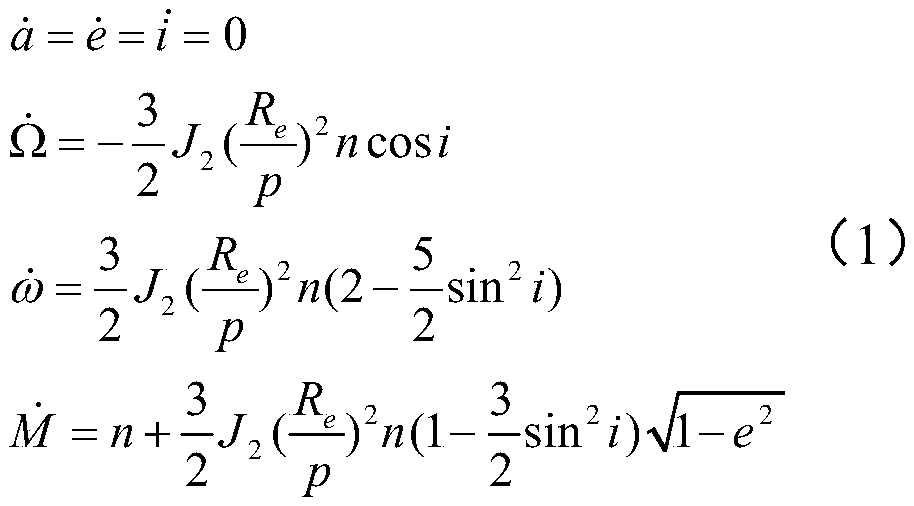Patents
Literature
126 results about "Orbit/Orbital" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
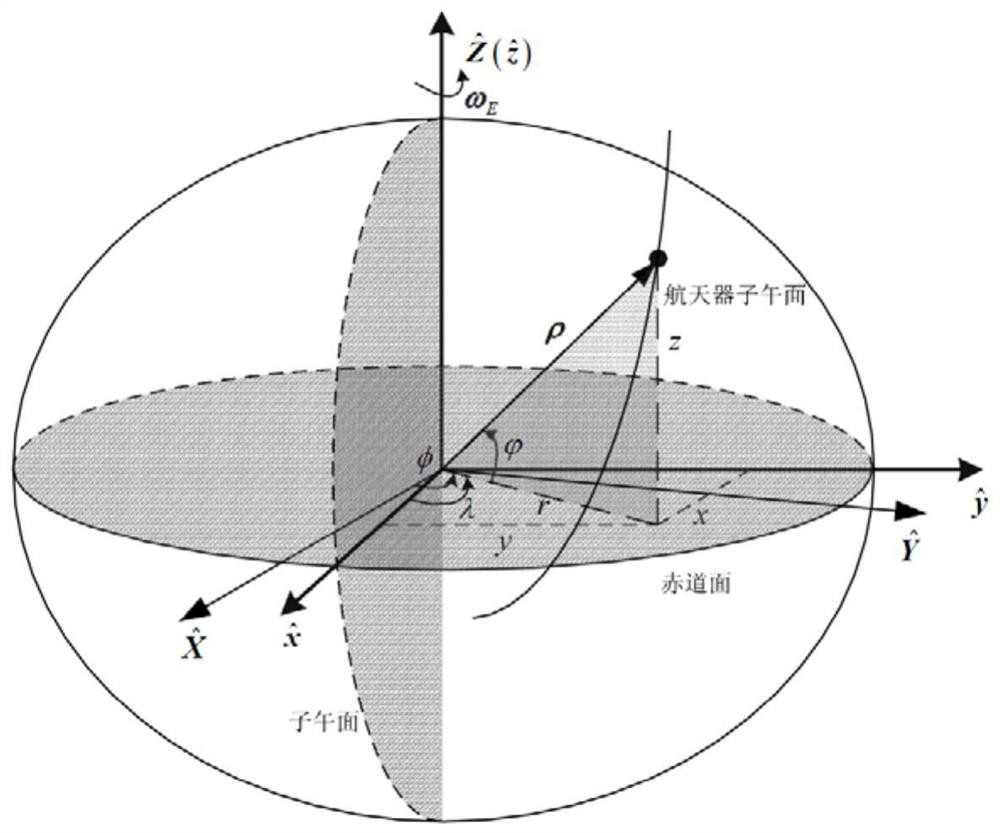
Orbit is basically 2d and orbital is 3d. Orbit is the concept of Bohr's atomic theory while orbital is the concept of the quntum theory. In an atom only orbital exists because as per heisenberg's uncertainity principle it is impossible to define the exact trajectory of electron and hence orbit cannot exist.
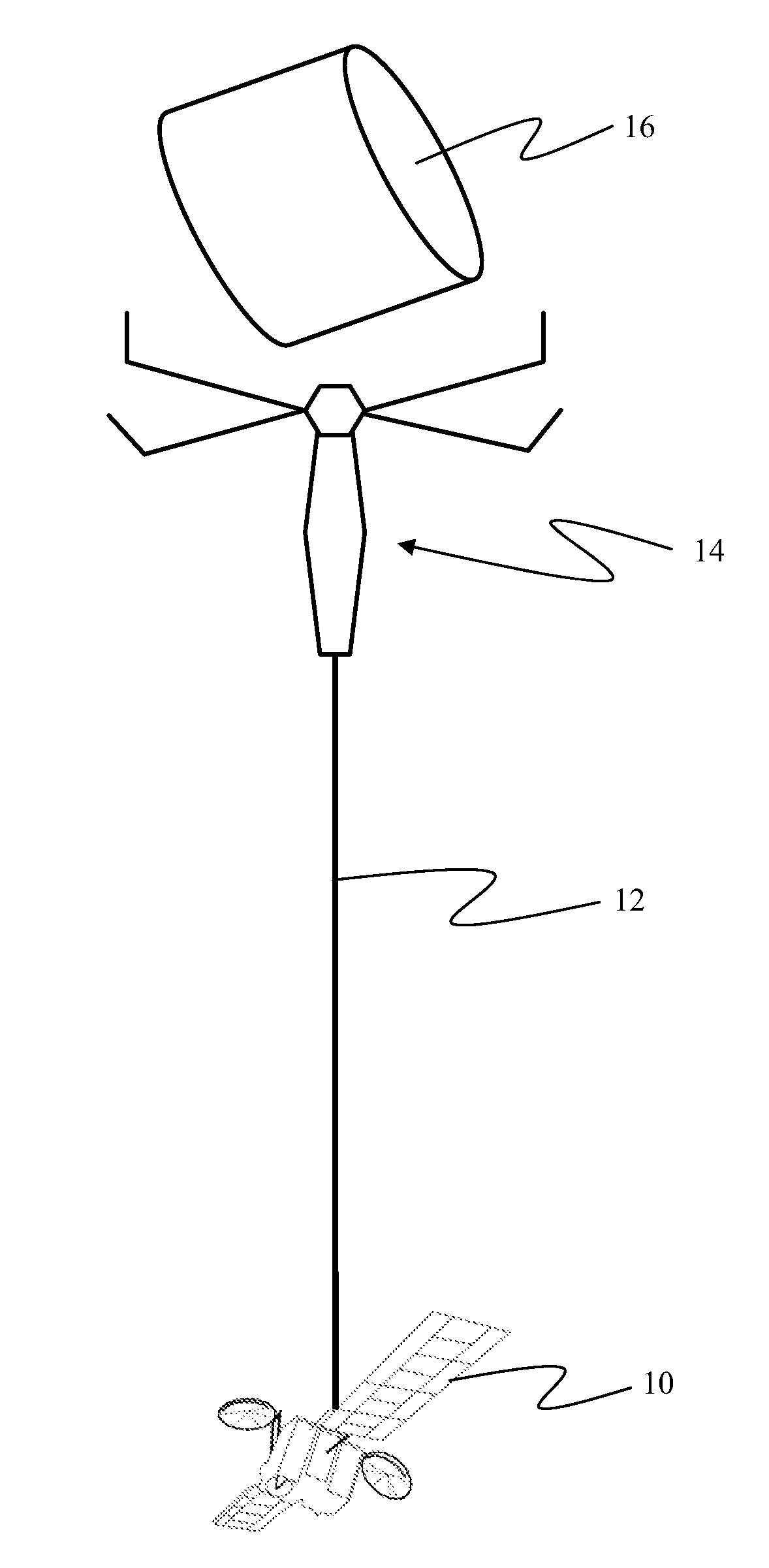
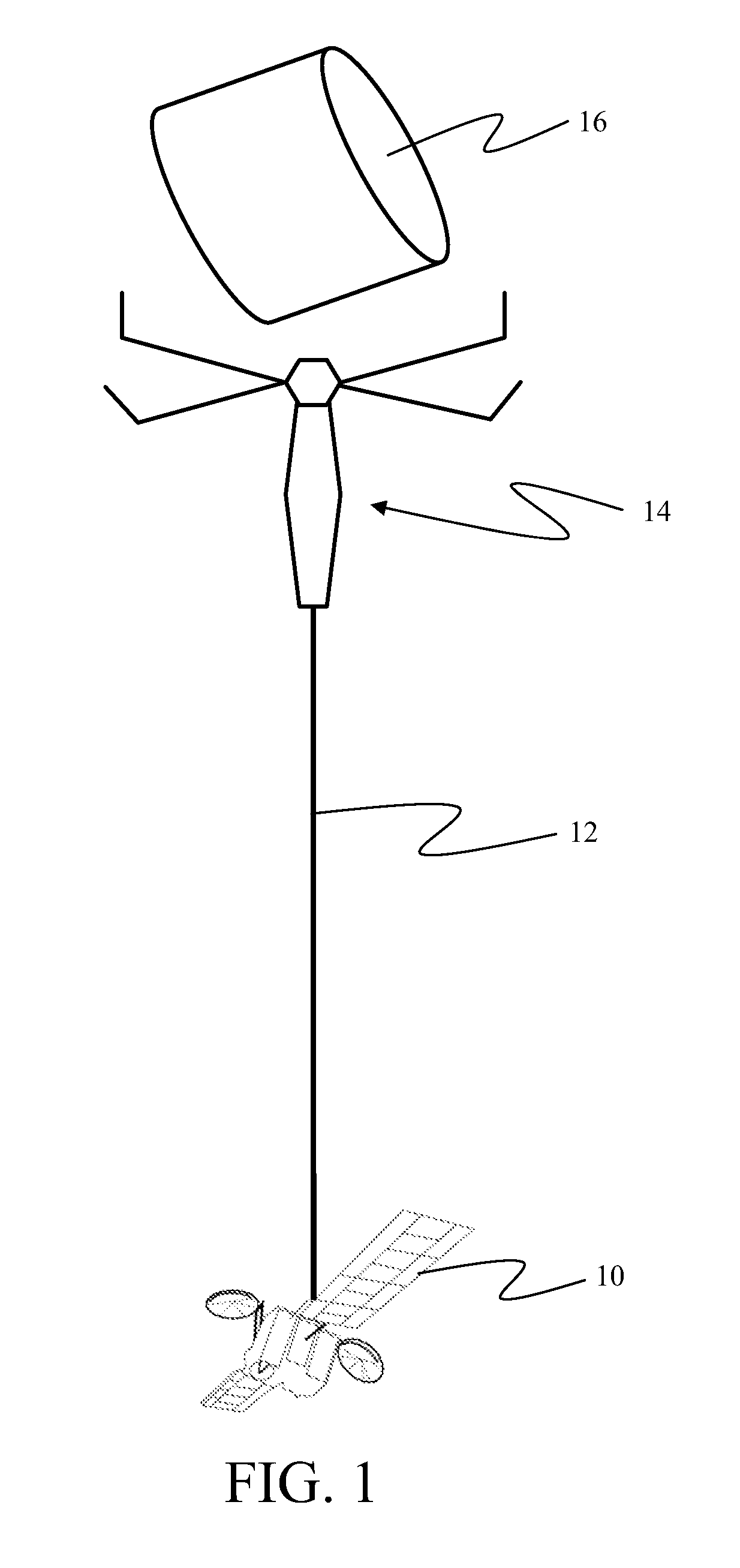
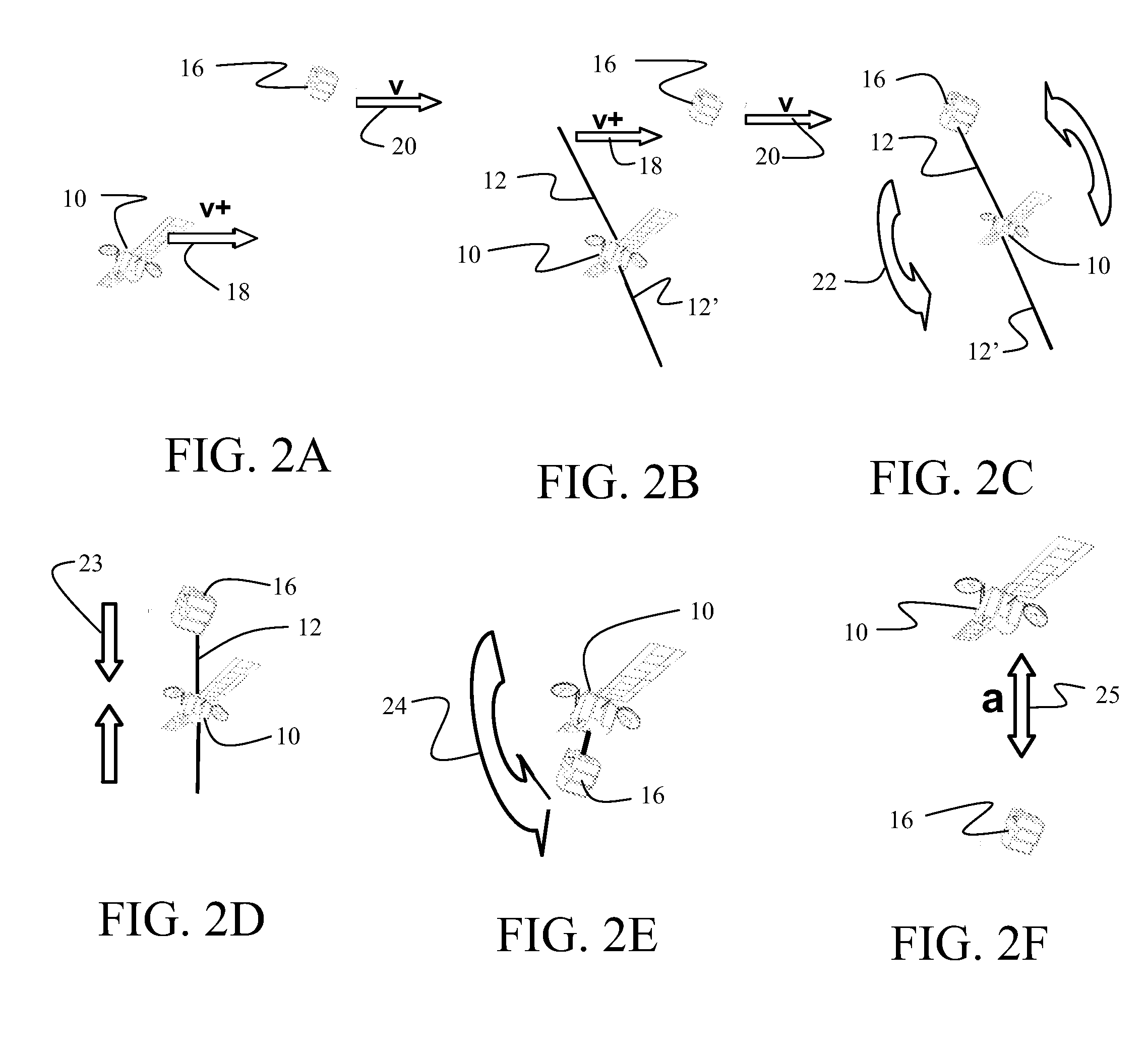
Method and apparatus for satellite orbital change using space debris
An apparatus for orbital change of a satellite incorporates a capture mechanism for space debris and a tether connecting the capture mechanism to a satellite. The tether is extendable to position the capture mechanism relative to the space debris. A controller is employed for timed release of the space debris by the capture mechanism for orbital change by the satellite.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method and device for cleaning space debris
InactiveCN103434658AEasy accessEfficient removalCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesAtmospheric layerEngineering
The invention discloses a method and device for cleaning space debris. According to the method, electromagnetic force is applied to the space debris running on an original orbit; the speed and / or direction of the space debris are / is changed under the action of the electromagnetic force; the space debris of which the speed is changed is changed to run on a new orbit under the action of gravity; at least the height of the perigee of the space debris on the new orbit is smaller than the height of the perigee of the space debris on the original orbit; the space debris running on the new orbit finally falls into the atmosphere of the earth under the action of atmosphere resistance. The device comprises a satellite bearing platform which is provided with an electric field device cleaning the space debris or a magnetic field device cleaning the space debris or a combination of the electric field device and the magnetic field device. The method and device for cleaning the space debris do not have high requirements for the accuracy of position detection of the space debris, micro space debris can be effectively cleaned, solar energy can be fully utilized for power generation, and self-carried energy is saved. The device for cleaning the space debris has the advantages of being simple in structure, low in manufacturing cost, and better in pulse action effect.
Owner:李怡勇 +3
Low-earth-orbit satellite orbit designing method for quickly revisiting discrete targets
InactiveCN103675832ARapid repeat reconnaissanceClarify requirements for side-looking pointing capabilityArtificial satellitesElectromagnetic wave reradiationHigh latitudeLongitude
Disclosed is a low-earth-orbit satellite orbit designing method for quickly revisiting discrete targets. The method includes (1), determining an inclination angle of a satellite orbit, wherein the inclination angle is not lower than the highest latitude Lmax of a ground target; (2), selecting a round orbit as the satellite orbit, wherein eccentricity ratio is 0; (3), executing a reconnaissance mission according to the ground target, determining a regression cycle of the orbit, utilizing the regression cycle to determine a semi-major axis of the satellite orbit, and then determining height of the orbit; (4), according to corresponding orbit ascending node longitude when sub-satellite points of an orbit ascending section and an orbit descending section of the satellite orbit pass the ground target, respectively determining ideal satellite orbit ascending node longitude of the orbit ascending section and the orbit descending section, performing optimization aiming at enabling the sum of designed satellite orbit ascending node longitude and a difference value of the ideal satellite orbit ascending node longitude of the orbit ascending section and the orbit descending section of the ground target, and determining ascending node longitude of the satellite orbit to be L; (5), utilizing the orbit inclination angle, the round orbit and the eccentricity ratio thereof, the orbit height and the ascending node longitude of the satellite orbit to complete designing of the satellite orbit.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
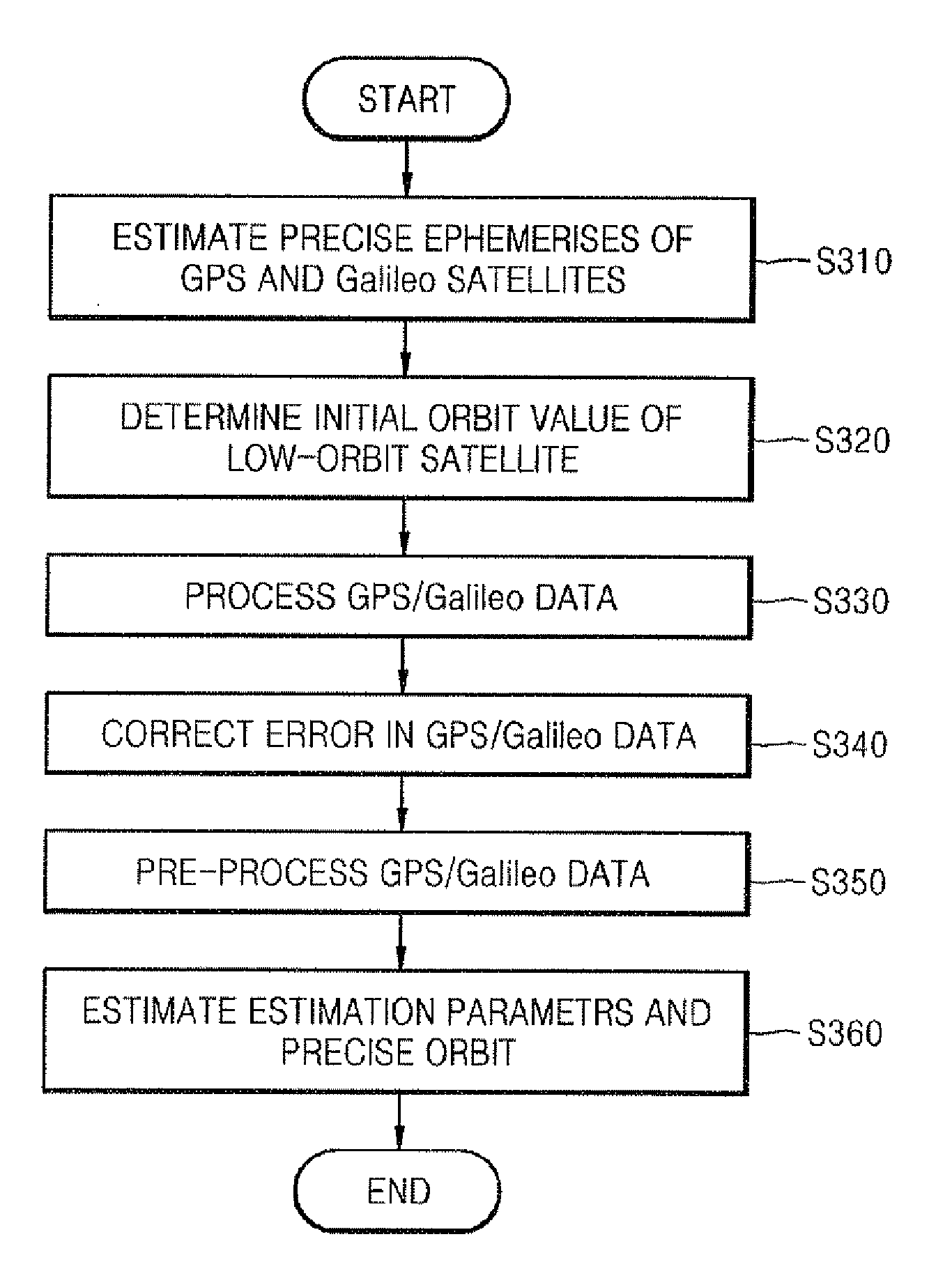
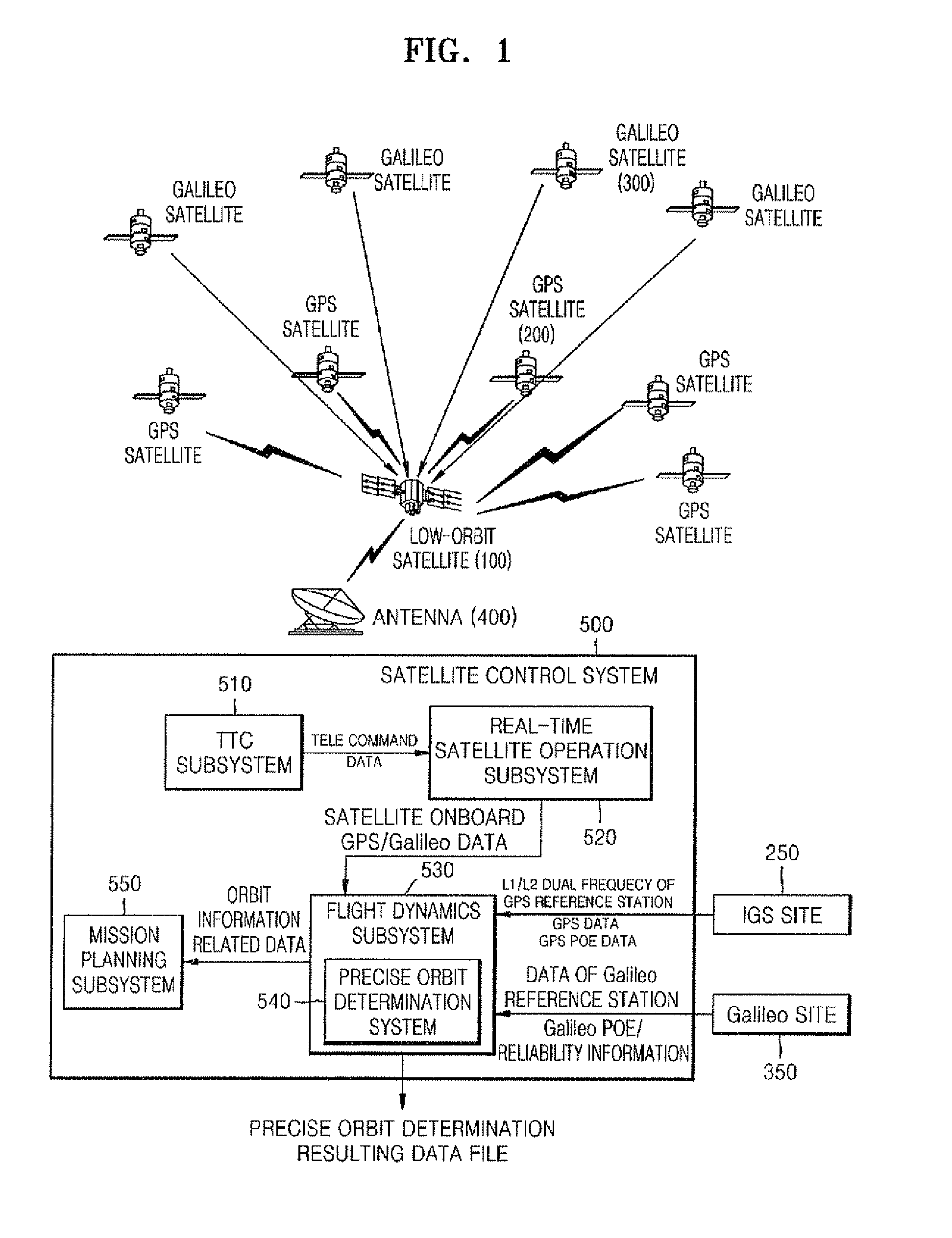
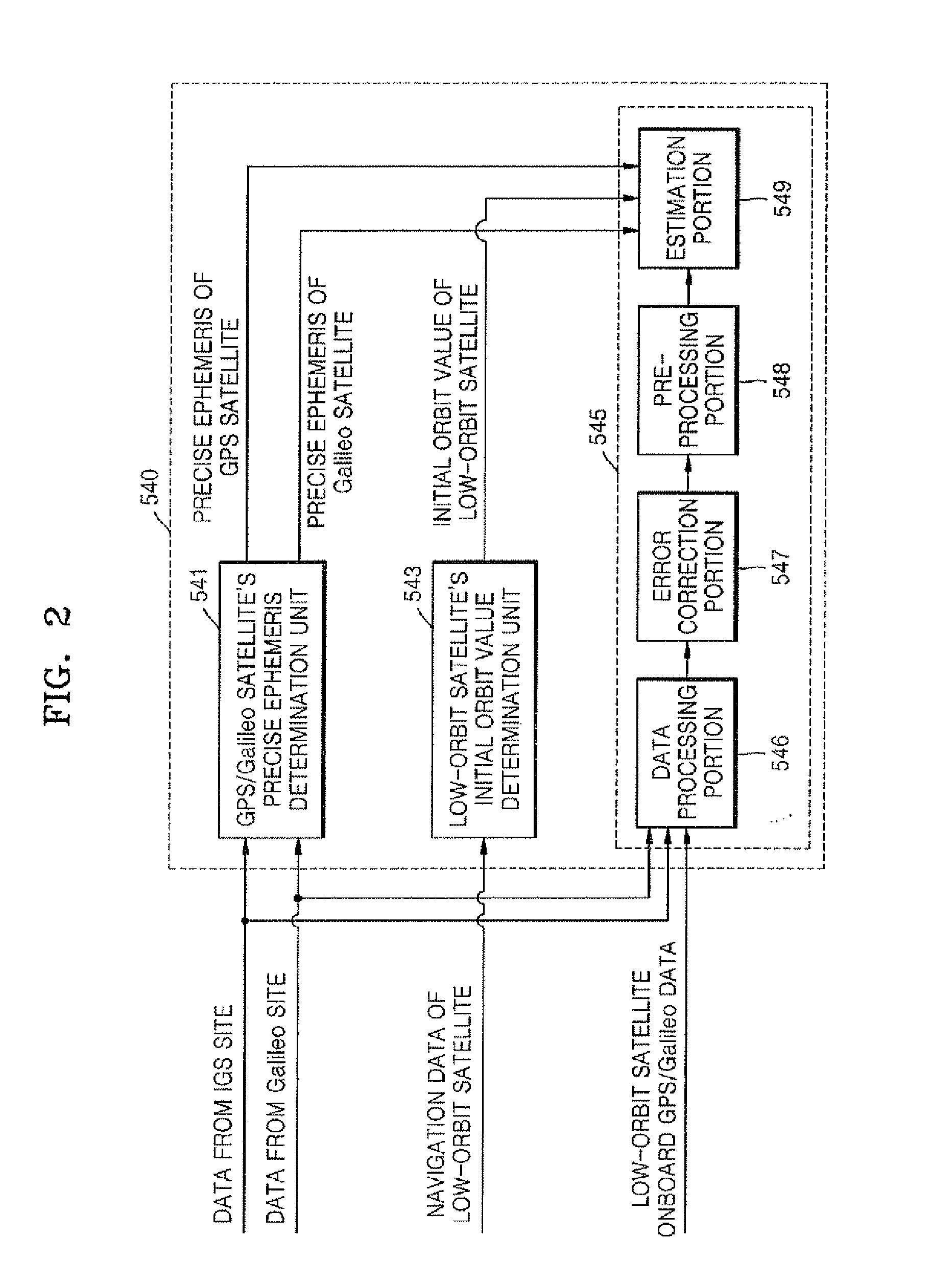
Precise orbit determination system and method using GPS data and galileo data
InactiveUS20100090889A1Improve convenienceAvoid disconnectionPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingOrbit perturbationDynamic models
Provided are a method and system for determining a precise orbit of a LEO satellite. The method includes: estimating a precise ephemeris of a global positioning system (GPS) satellite by fitting an orbit perturbation-based GPS dynamics model to observation data of the GPS satellite received from a GPS observatory and estimating a precise ephemeris of a Galileo satellite by fitting an orbit perturbation-based Galileo dynamics model to observation data of the Galileo satellite received from a Galileo observatory; determining an initial orbit value of a LEO satellite by fitting an orbit perturbation-based LEO satellite's basic dynamics model to navigation data received from the LEO satellite; and determining the precise orbit of the LEO satellite by calculating a difference between observation values, which are calculated based on a GPS and Galileo data received from the LEO satellite, the GPS observatory and the Galileo observatory, and calculated values, which are calculated based on an orbit perturbation-based LEO satellite's dynamics model that was calculated using the initial orbit value of the LEO satellite and the precise ephemeris of the GPS and Galileo satellites. Since both the GPS and Galileo data are received and used to determine the precise orbit of a LEO satellite, more precise orbit determination can be achieved.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for compositely controlling attitudes and orbits of in-orbit dragging combination spacecrafts
InactiveCN103970142AAchieving off-orbit maneuversClean operating environmentPosition/course control in three dimensionsMechanical engineeringOrbit/Orbital
The invention discloses a method for compositely controlling attitudes and orbits of in-orbit dragging combination spacecrafts. The method includes steps of identifying mass property parameters of the combination spacecrafts in an in-orbit manner; determining composite control on the attitudes and the orbits of the combination spacecrafts in orbit maneuver periods. The method has the advantages that abandoned spatial targets can be deorbited and maneuvered under the conditions of high disturbance torque and uncertain parameters; the method can be used for cleaning abandoned satellite or space debris in the earth orbit, and accordingly clean running environments can be provided for satellites which run normally.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE METER FACTORY
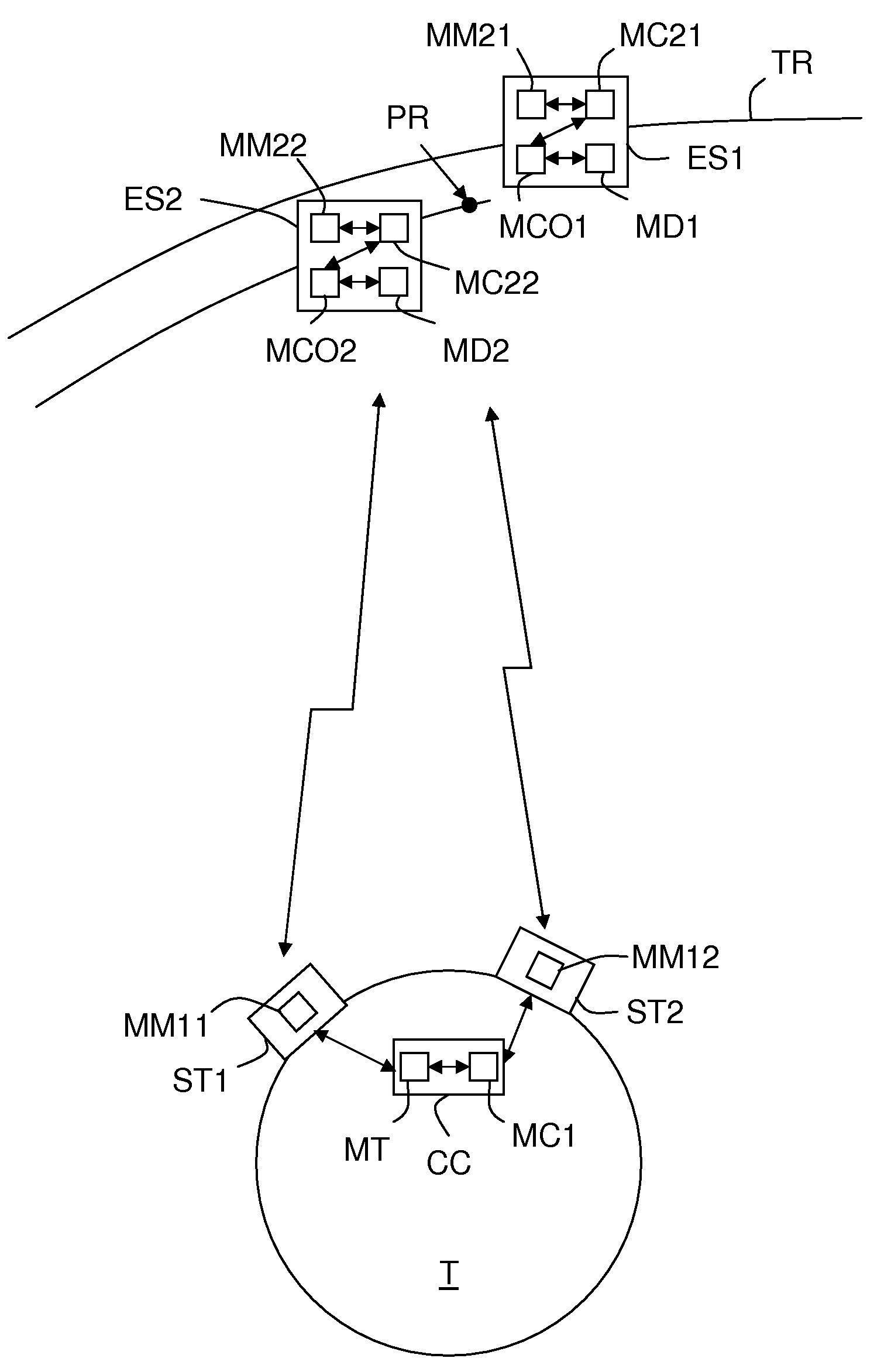
System for controlling the deployment of spacecraft required to fly in formation, by simultaneous and high-precision determination of their positions
ActiveUS20100032528A1Good conditionCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesMeasurement deviceEngineering
A system is dedicated to the control of the deployment of at least two spacecraft (ES1, ES2) which are provided with maneuvering means (MD1, MD2) and are intended to move according to a chosen formation. This system includes a control device (MM11, MM12, MT, MC1) comprising i) first measurement means (MM11, MM12, MT) responsible for determining substantially simultaneously and with high precision the orbital positions of the spacecraft (ES1, ES2), and ii) first calculation means (MC1) responsible for determining for each of the spacecraft, as a function of their orbital positions, maneuvers intended to position each of them at a chosen instant substantially in a chosen position with respect to a reference trajectory, having regard to the time law of a reference craft (ES1) on this reference trajectory (TR), so as to place the formation in a chosen configuration.
Owner:THALES SA
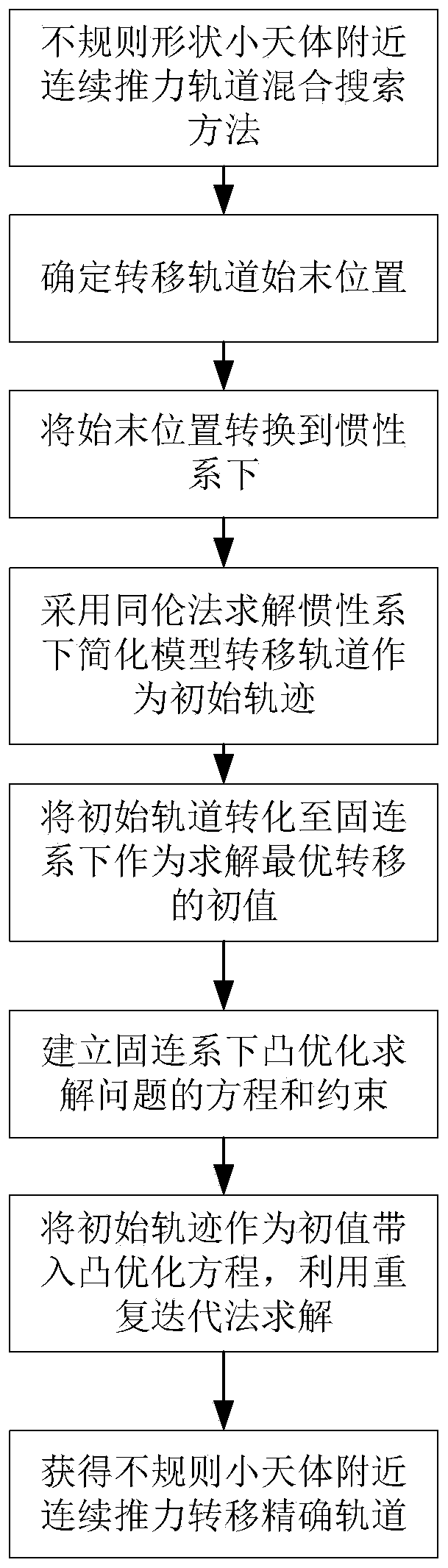
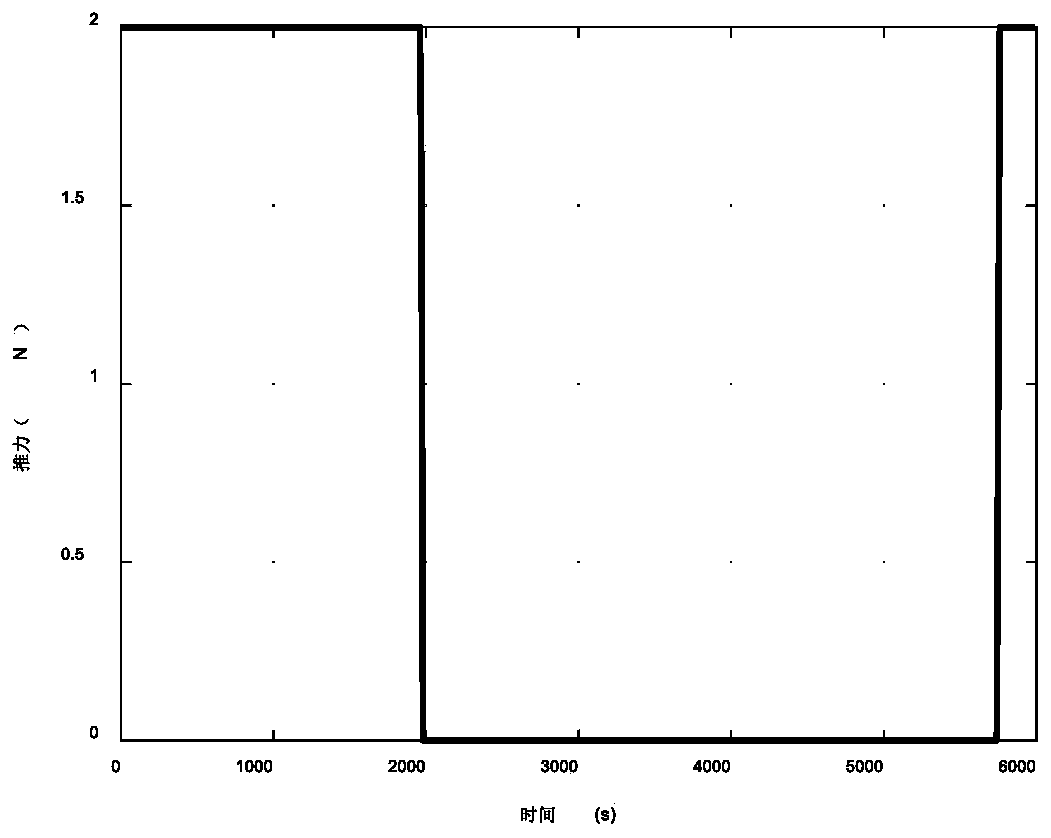
Hybrid search method for continuous thrust orbit near irregular-shaped small celestial body
ActiveCN110736470AHigh precisionSolved the inability to account for perturbations of irregular shapesInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsCelestial bodyComputational physics
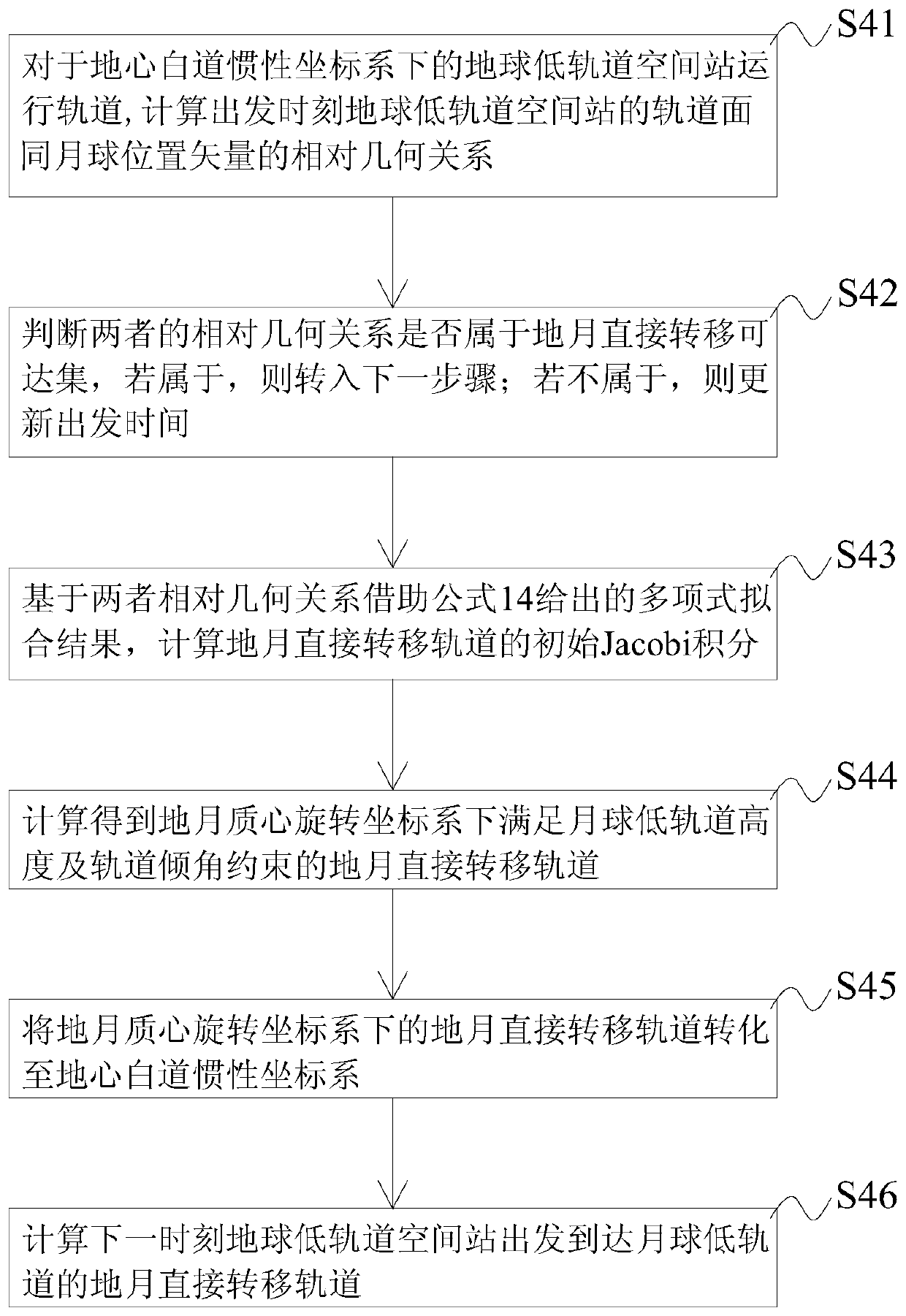
The invention discloses a hybrid search method for a continuous thrust orbit near an irregular-shaped small celestial body, and belongs to the technical field of aerospace. The implementation method comprises the following steps: converting the initial state of an orbit from a small celestial body fixed connection system to an inertial system; obtaining an initial value of the continuous thrust transfer orbit by utilizing a homotopic method under the inertial system; establishing a continuous thrust equation under the fixed connection system by taking irregular-shaped perturbation of the of the small celestial body into consideration; transferring the initial orbit from the inertial system to the fixed connection system to serve as an initial value of the continuous thrust orbit; and solving an optimal transfer opportunity near the irregular small celestial body by adopting a convex optimization method by taking collision constraint into consideration. According to the invention, the problems that irregular-shaped perturbation cannot be considered in the homotopic method and that initial value searching is difficult in the convex optimization method are solved, searching for the continuous thrust transfer orbit near the irregular-shaped small celestial body is achieved, the searching convergence and precision of transfer orbit near the irregular-shaped small celestial body areimproved, and the method also has the advantages of high precision and convergence.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
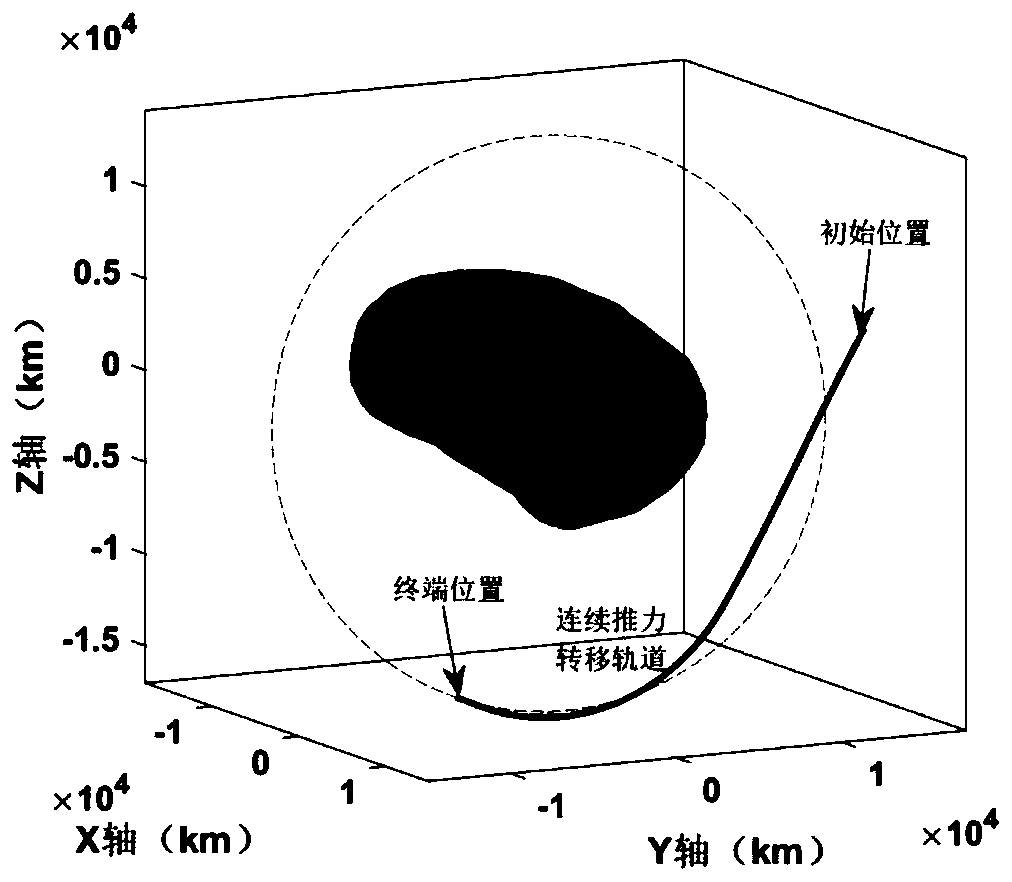
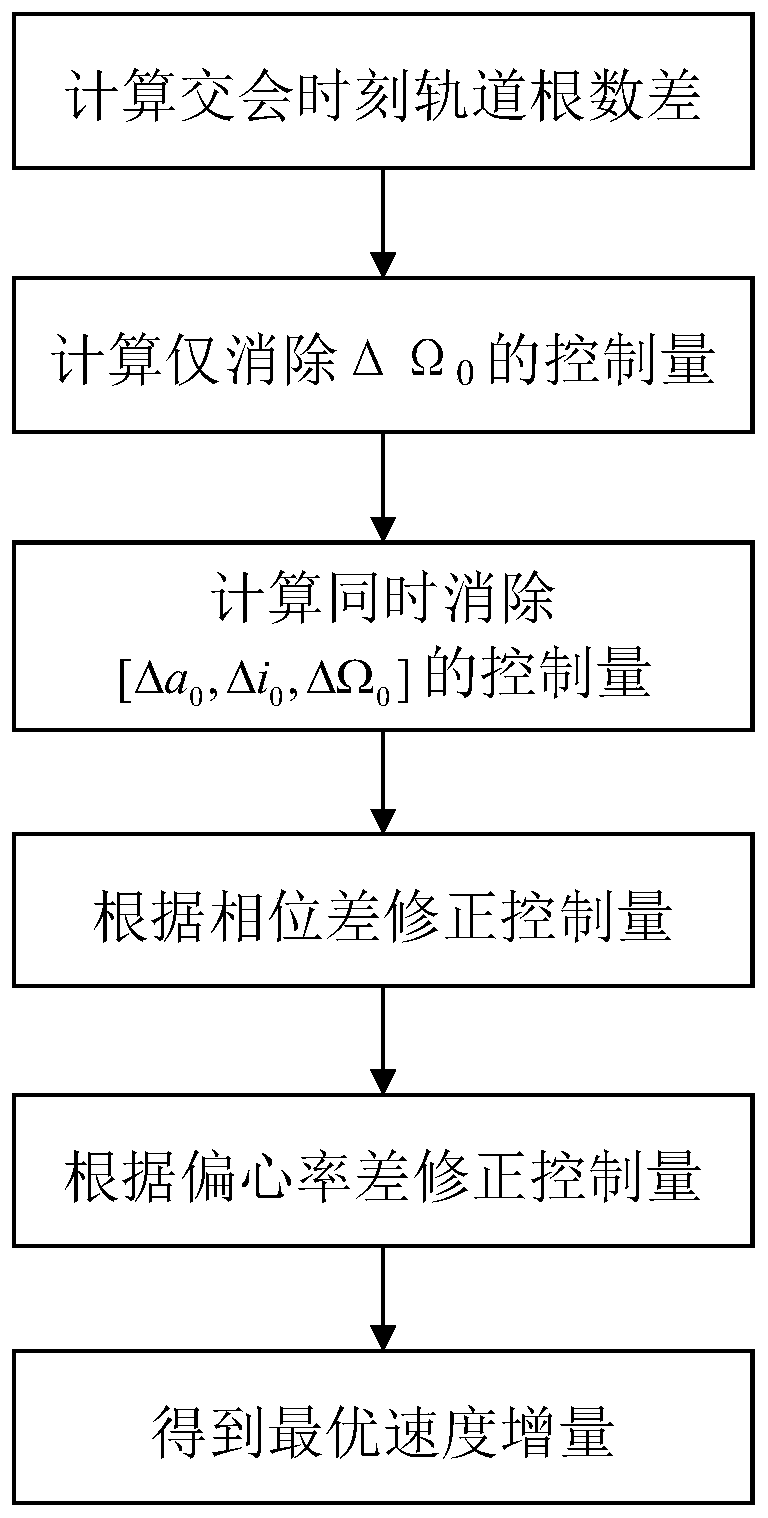
Method for rapidly estimating long-term orbital rendezvous optimal speed increment under J2 perturbation
ActiveCN110789739ADecrease speed incrementImprove optimization efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesLinear/angular speed measurementOrbital planeSimulation
The invention discloses a method for rapidly estimating a long-term orbital rendezvous optimal speed increment under J2 perturbation. The method includes the steps of calculating the orbital element difference of a non-maneuvering spacecraft and a target at the rendezvous moment, calculating an optimal control amount when only the ascending node ascensional difference is eliminated, substituting the optimal control amount as the initial value into a control amount optimizing model for eliminating the semi-major axis, dip angle and ascending node ascensional difference at the same time to obtain a new optimal control amount, modifying the control amount according to the phase difference in an orbital plane, modifying the control amount according to the eccentricity ratio vector difference,and finally obtaining the estimated optimal rendezvous speed increment. The method realizes the purpose of rapidly estimating the optimal rendezvous speed increment when precise solution is not neededand is high in estimating precision and suitable for the situations with large initial ascending node ascensional difference from a target orbit and small element differences from other orbits.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Planetary impact defense system
A system for defending a planet having a satellite against impact from an incoming body includes an explosive system and a propulsion system. The explosive system is adapted for deployment on the satellite and detonation thereon with sufficient explosive force to produce at least one ejectum to which is imparted a velocity increment sufficient for the ejectum to exceed the satellite's escape velocity and enter orbit about the planet. The propulsion system is adapted to be secured to at least one ejectum and impart a velocity increment to the ejectum sufficient to leave orbit about the planet and enter an orbit intercepting the incoming body.The system is used in a planetary defense method in which the explosive system is deployed at a deployment site on the satellite and detonated to produce at least one ejectum having a velocity that exceeds the escape velocity of the satellite. The ejectum enters into orbit around the planet, at which time the propulsion system is secured to the ejectum to produce a projectile. The propulsion system is then activated to increase the velocity of the projectile, causing the projectile to enter into an intercept orbit targeting the incoming body and subsequently intercept and impact the incoming body. The impact prevents the incoming body from impacting the planet.
Owner:PICCIONELLI GREGORY A
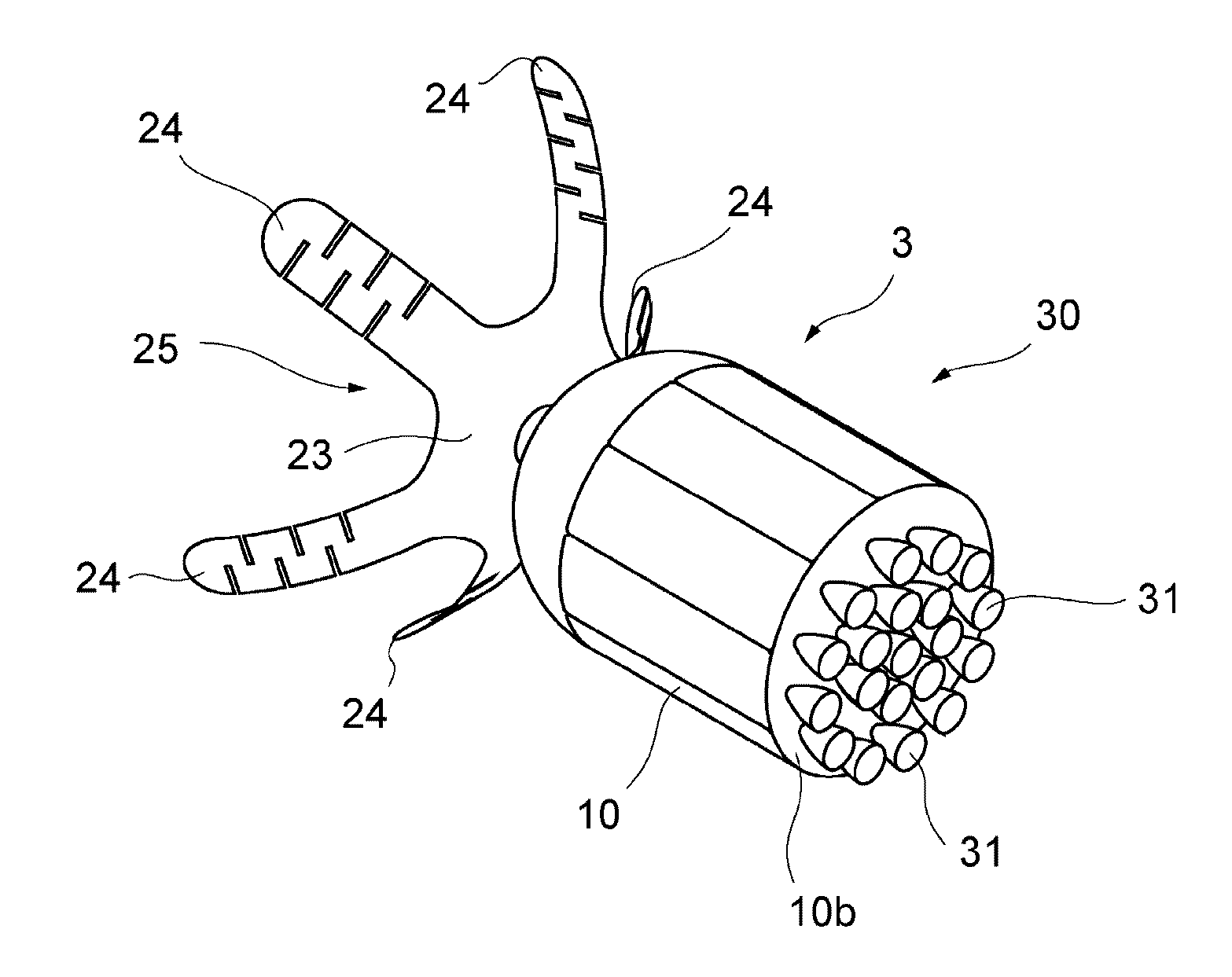
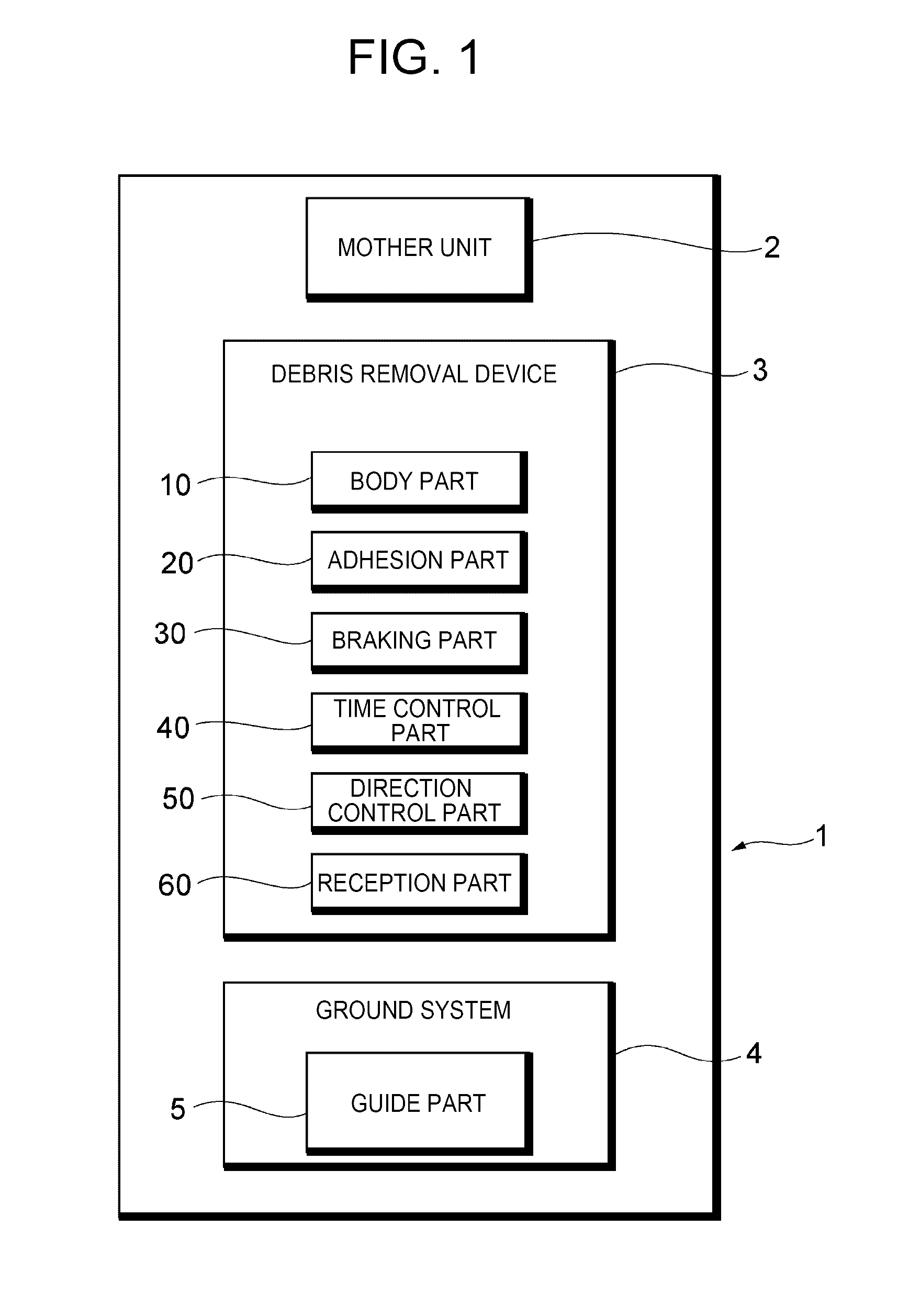
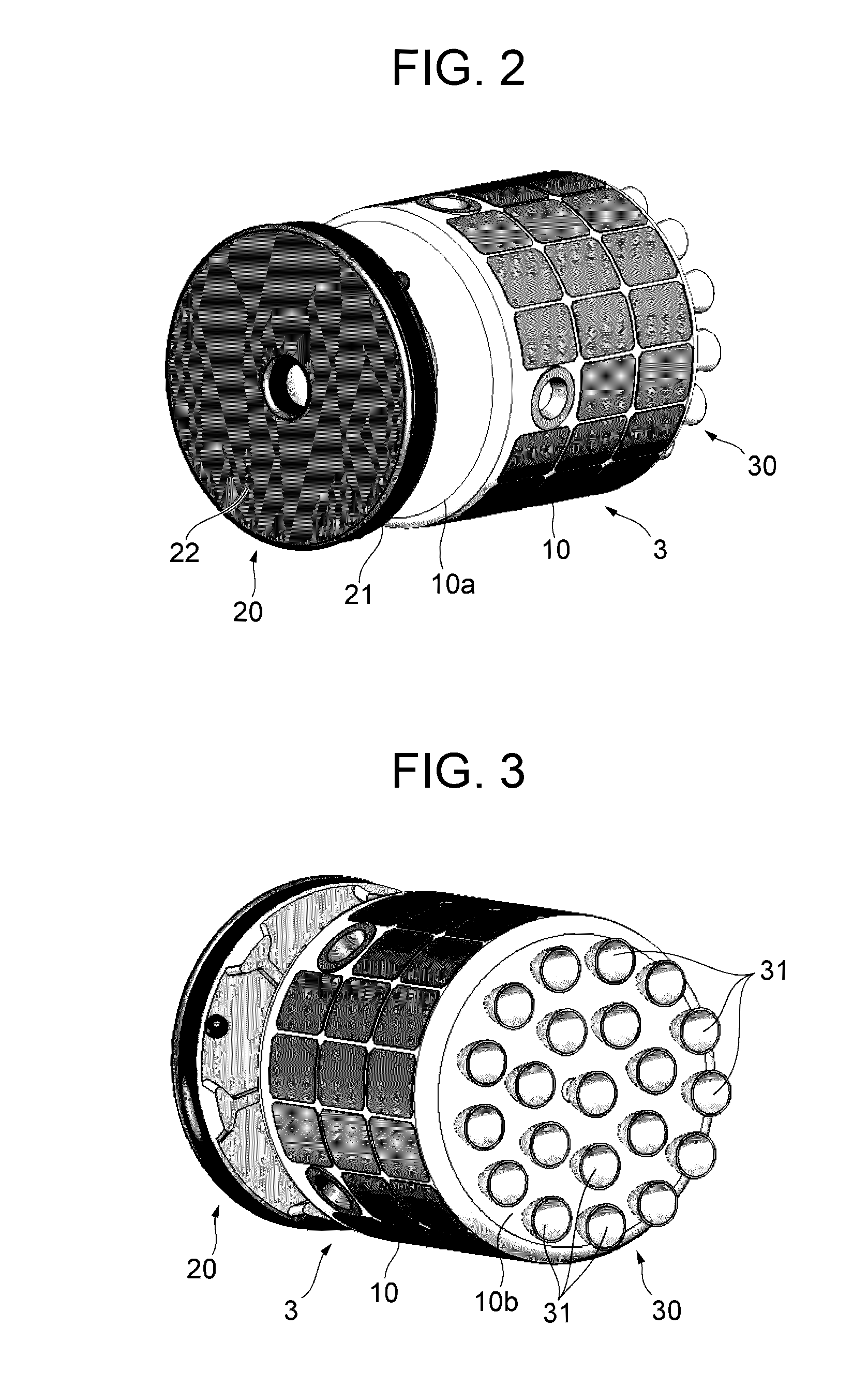
Debris removal device and debris removal system
InactiveUS20170015444A1Save spaceEfficient removalCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusEngineeringBrake force
A debris removal device includes: a body part; an adhesion part to let the space debris adhere to the body part; a braking part to generate braking force in a specific direction, to act on the space debris adhering to the body part via the adhesion part during circling of the body part around the orbit together with the space debris; and a timing control part to control generation timing of the braking force. The timing control part generates the braking force, during circling of the body part together with the space debris around the orbit, when the body part is located at a specific region on the orbit where a direction of the braking force is substantially parallel to an orbit plane including the orbit and substantially parallel to a tangential line of the orbit, and in substantially an opposite direction of a circling direction of the space debris.
Owner:ASTROSCALE JAPAN
Autonomous target recognition and early warning method of space debris based on radar
ActiveCN107529385BEarly warning and collision avoidanceAvoid harmElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarGoal recognition
The invention relates to satellite autonomous target identification, and discloses a radar-based space debris autonomous target identification and early warning method, including steps 1, capturing the target and performing high-precision relative navigation measurement; 2, according to the spacecraft orbit and relative measurement data Calculate the orbit of space debris; 3. Recursively predict the orbit of space debris and calculate the minimum relative distance; 4. Release early warning information; 5. Measure and update. The invention realizes the autonomous identification of space debris by the satellite, and provides early warning to avoid the impact of the space debris, and can effectively avoid the damage caused by the space debris to the spacecraft.
Owner:上海航天控制工程研究所
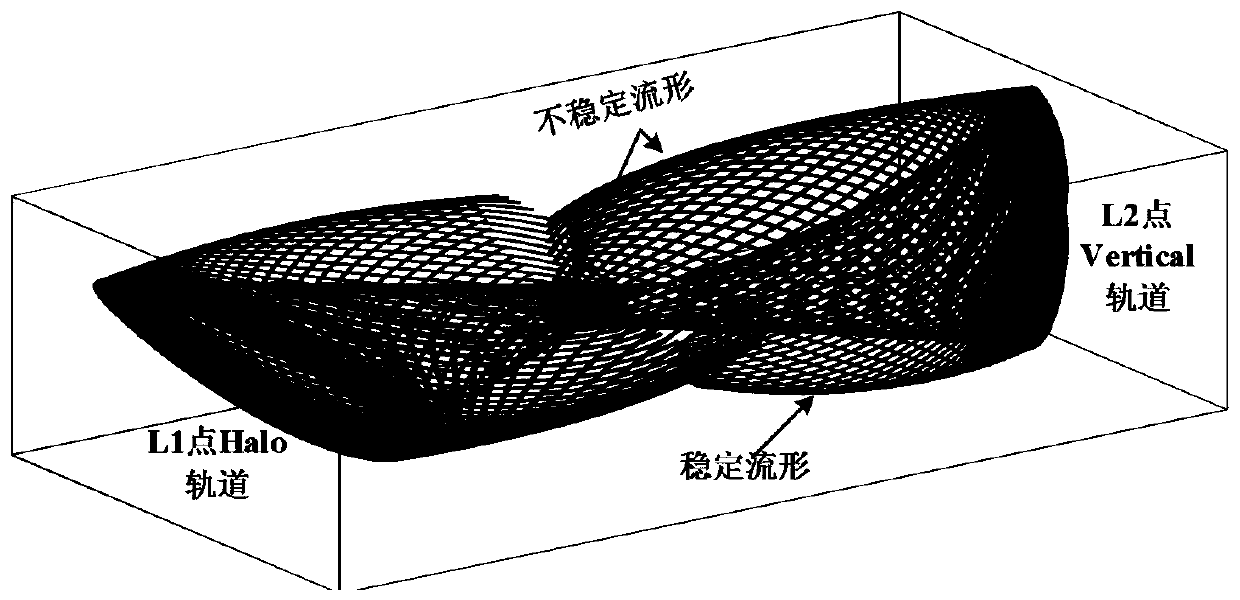
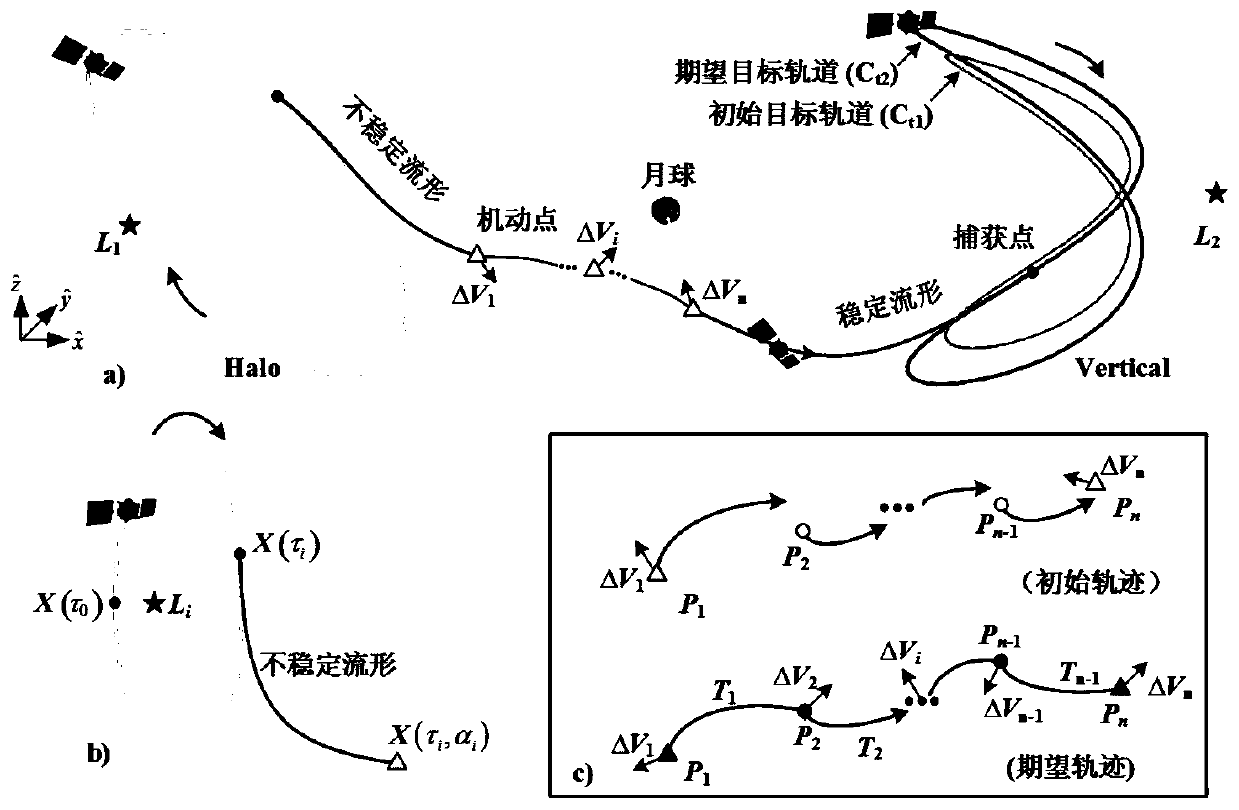
Earth-moon libration point interorbital transfer design method
ActiveCN110733667AEfficient determinationAvoid the effects of selection uncertaintyCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusComputational physicsTransfer orbit
The invention relates to an earth-moon libration point interorbital transfer design method. The method comprises the following steps that a, under the earth-moon mass center rendezvous coordinate system, an orbital kinetic equation of a detector is built; b, libration point invariant manifold data are stored; c, a transfer track splicing point range is searched; and d, a libration point interorbital optimal transfer track is determined. According to the libration point track invariant manifold state amount, splicing point positions of different track segments are rapidly determined, positionsof escape points and capture points are automatically adjusted, and the target track size are adjusted automatically, and the low-energy transfer track capable of meeting the task needs can be effectively designed.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
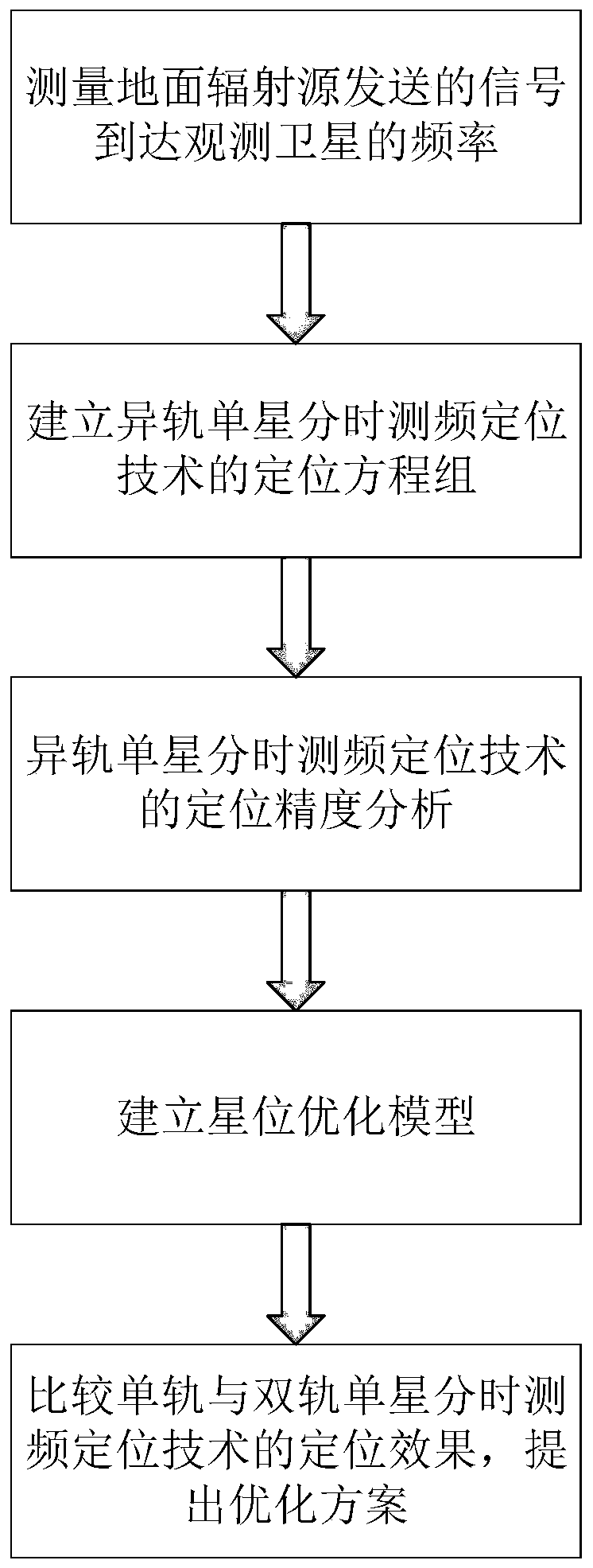
Different-orbit single-satellite time-sharing frequency measurement positioning method based on star position optimization
PendingCN110988851APrecise positioningHigh precisionUsing reradiationSingle starSatellite observation
The invention discloses a different-orbit single-satellite time-sharing frequency measurement positioning method based on star position optimization. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the frequency of a signal sent by a ground radiation source reaching an observation satellite; establishing a different-orbit single-satellite time-sharing frequency measurement positioning model, selecting a plurality of satellites with different orbits to respectively carry out frequency measurement at different moments, and establishing a positioning equation set according to a plurality of measured different signal frequencies; deriving geometric dilution precision factors, and analyzing the influence of various factors on the positioning precision; and establishing a star position optimization model, and optimizing the selection of orbit and satellite observation moments to improve the positioning precision. According to the invention, within a limited range of visibility, single satellites flying through different orbits of a positioning visual area at different moments are used for repeatedly and independently observing the same interference source; due to the difference in the aspects of flight direction, observation position distribution and the like, compared with a single-orbit single-satellite time-sharing frequency measurement positioning scheme, the positioning effect is stable, the precision is higher, the space between satellites is larger, and the selection of measurement positions can be more flexible.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
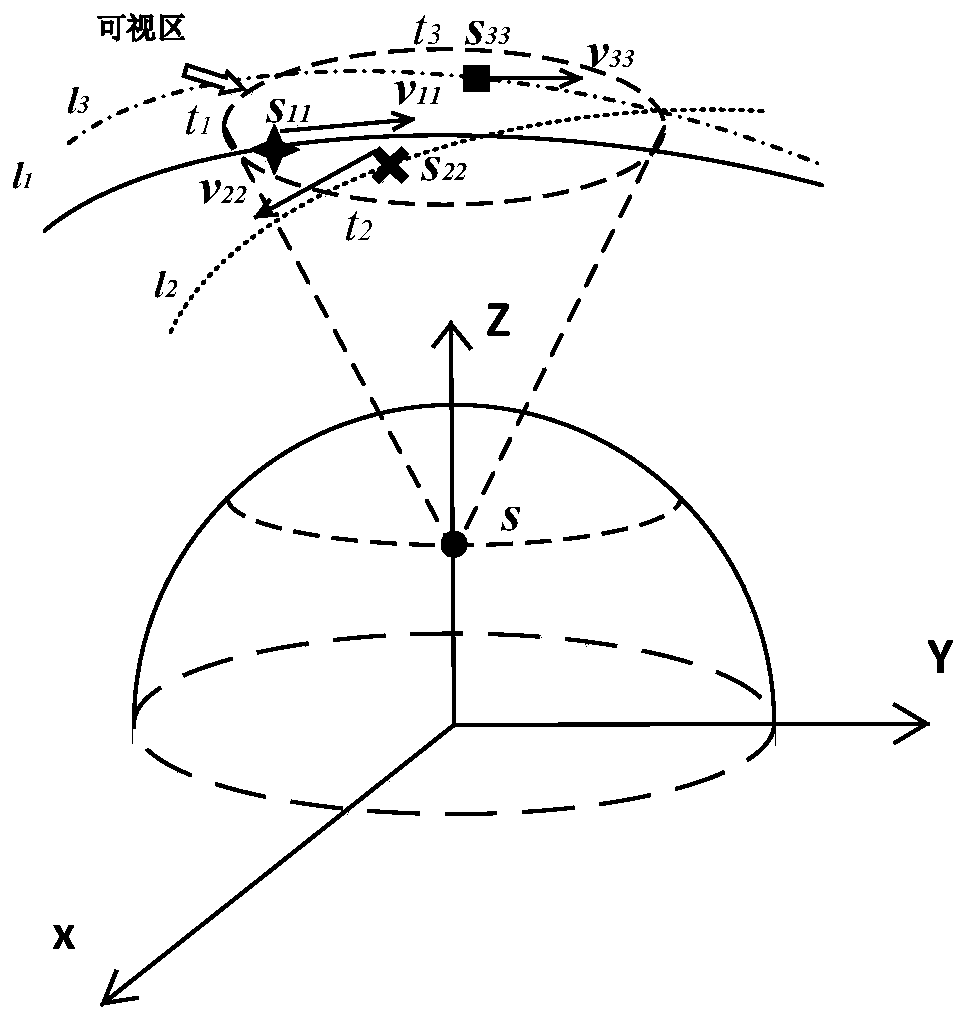
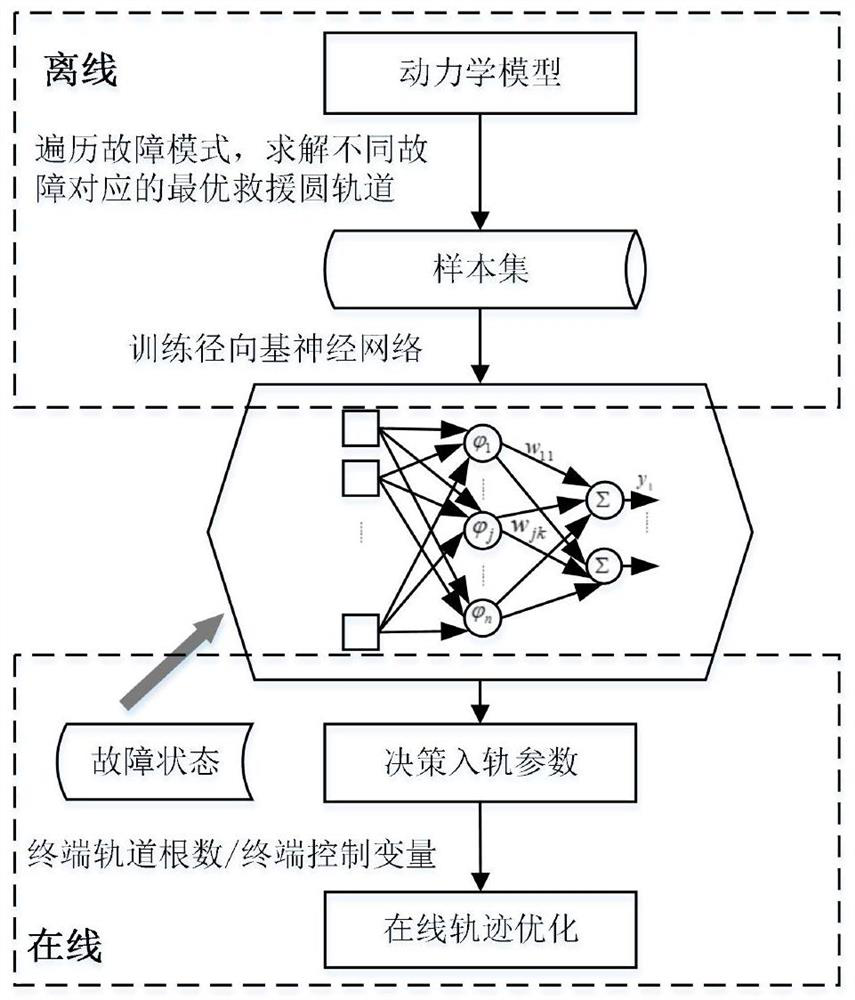
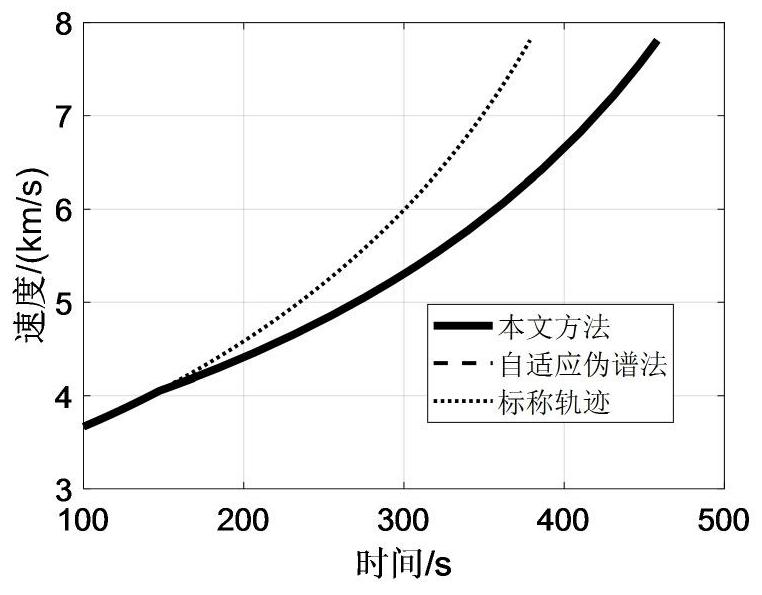
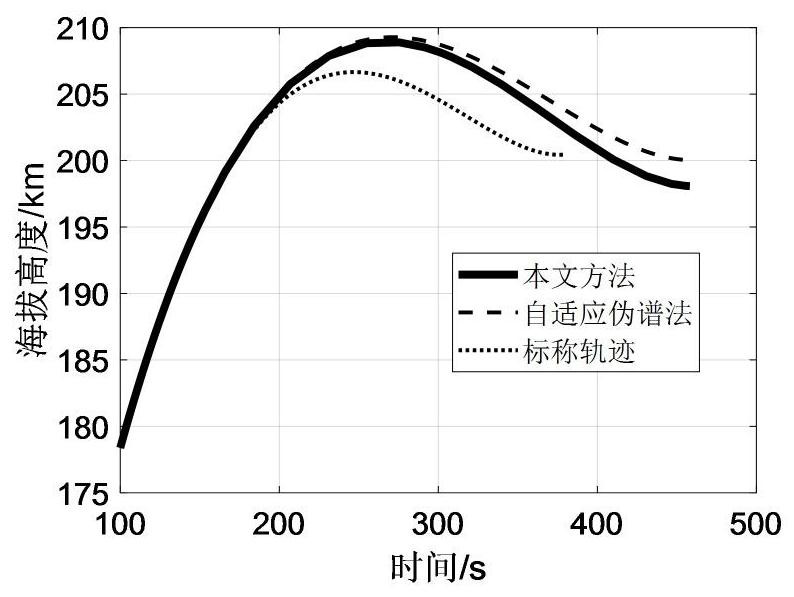
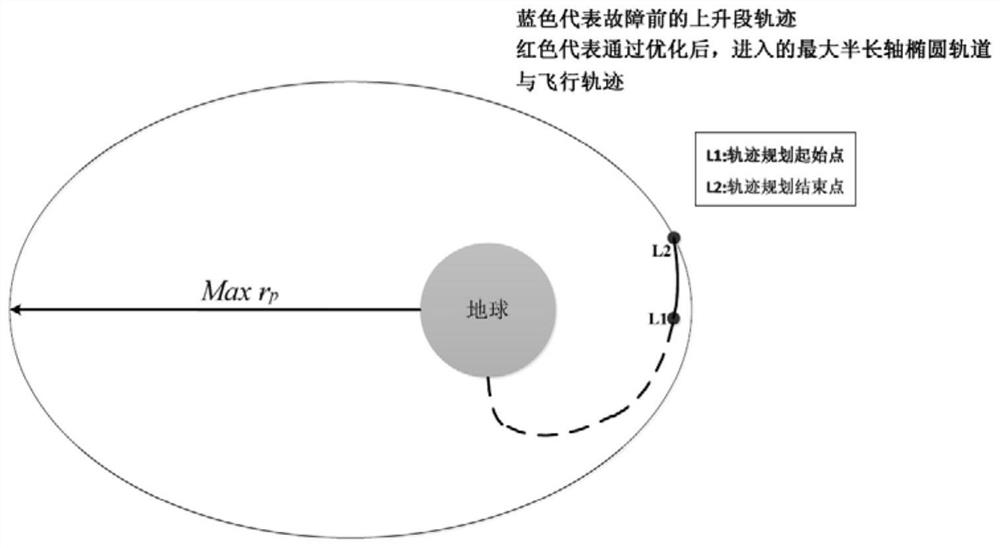
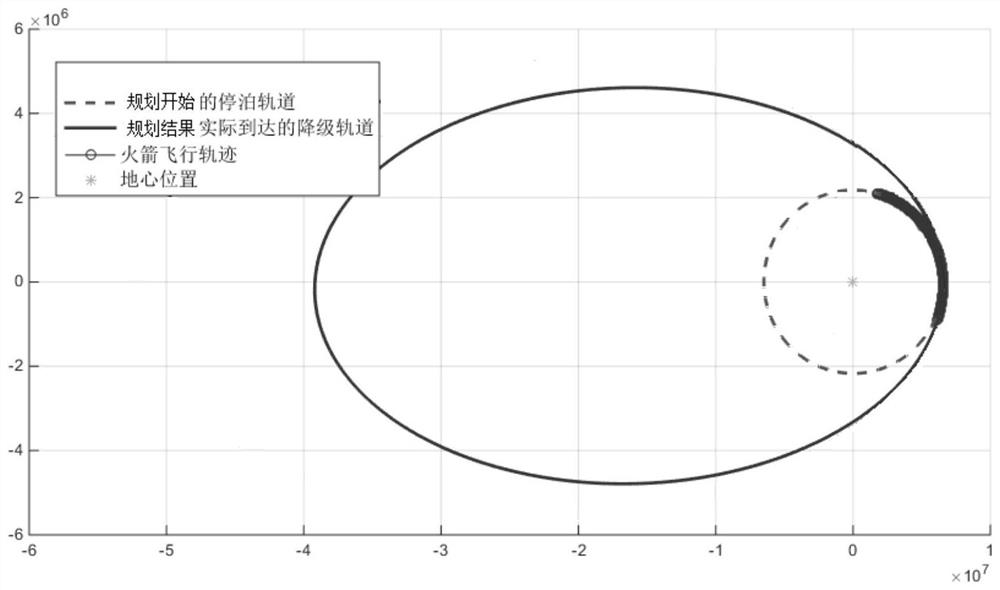
Trajectory re-planning method for elliptical rescue orbit under rocket thrust drop fault
PendingCN113189870AFast Online DecisionReasonable initial valueAdaptive controlData centerOrthogonal least squares
The invention discloses a trajectory re-planning method for an elliptical rescue orbit under rocket thrust drop faults. The trajectory re-planning method comprises the following steps: constructing trajectory optimization problems of an elliptical rescue orbit under various thrust drop faults; adopting an adaptive pseudo-spectral method to solve the trajectory optimization problem of the elliptical rescue orbit in an off-line mode so as to obtain a sample set of fault state-orbit injection parameters; performing normalization processing on the sample data by adopting a maximum-minimum method, selecting a radial basis function neural network data center through an orthogonal least square method, and training the radial basis function neural network in an off-line manner so as to establish a nonlinear mapping relation from a fault state to an orbit injection parameter, wherein theradial basis function is a Gaussian basis function; and solving an optimal propellant optimization problem on line by adopting a self-adaptive pseudo-spectral method to obtain a flight trajectory. According to the invention, the orbit injection parameters are decided through the radial basis function neural network, a reasonable initial value is provided for trajectory planning of the online elliptical rescue orbit, and the situation that the calculation efficiency is reduced due to conflicts among variables in the target function can be avoided.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Short arc initial orbit determining method based on gauss solution cluster
ActiveUS20210199439A1Degree of improvementEffectively solve multiple root problemCosmonautic vehiclesNavigational calculation instrumentsObservation dataState vector
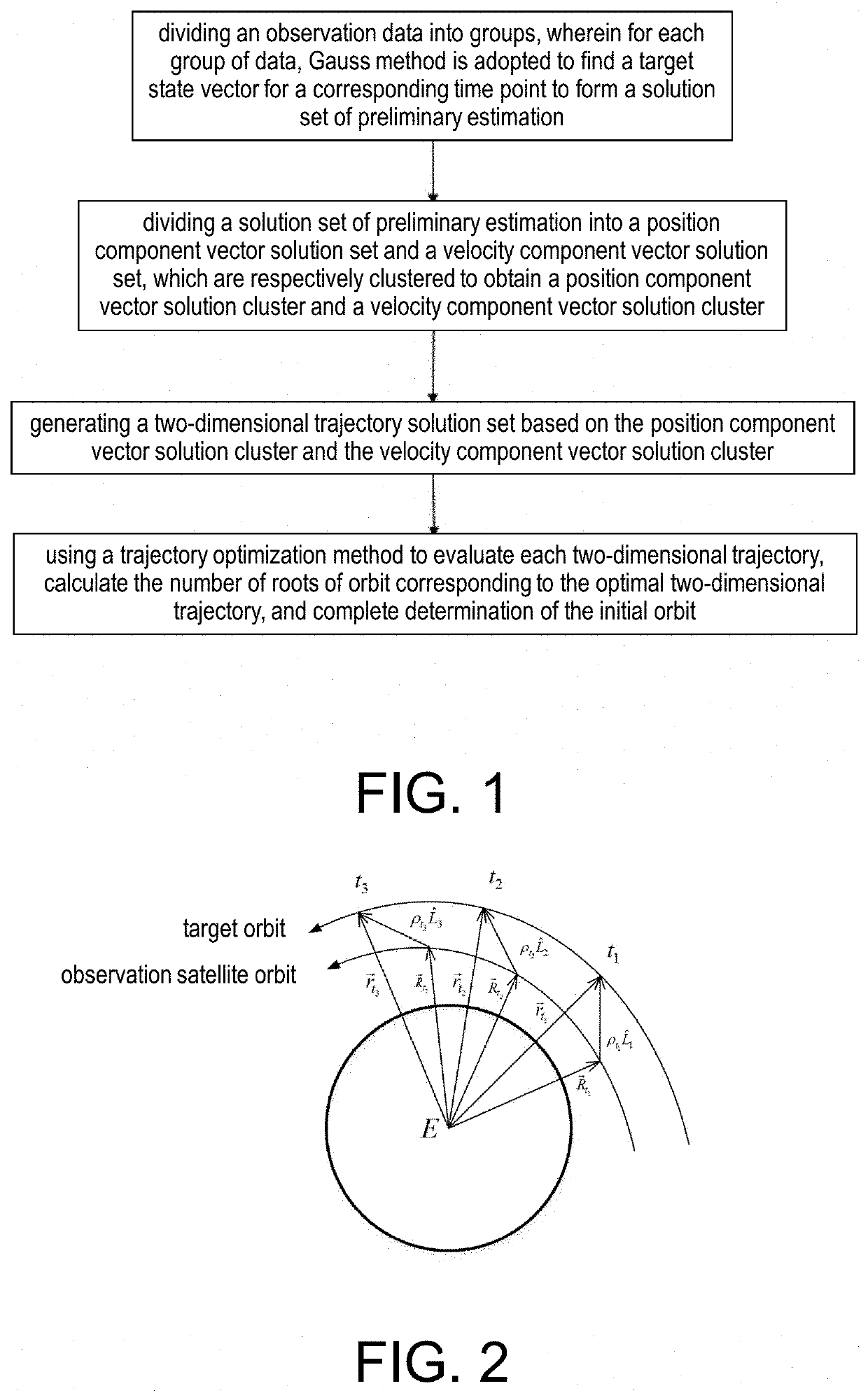
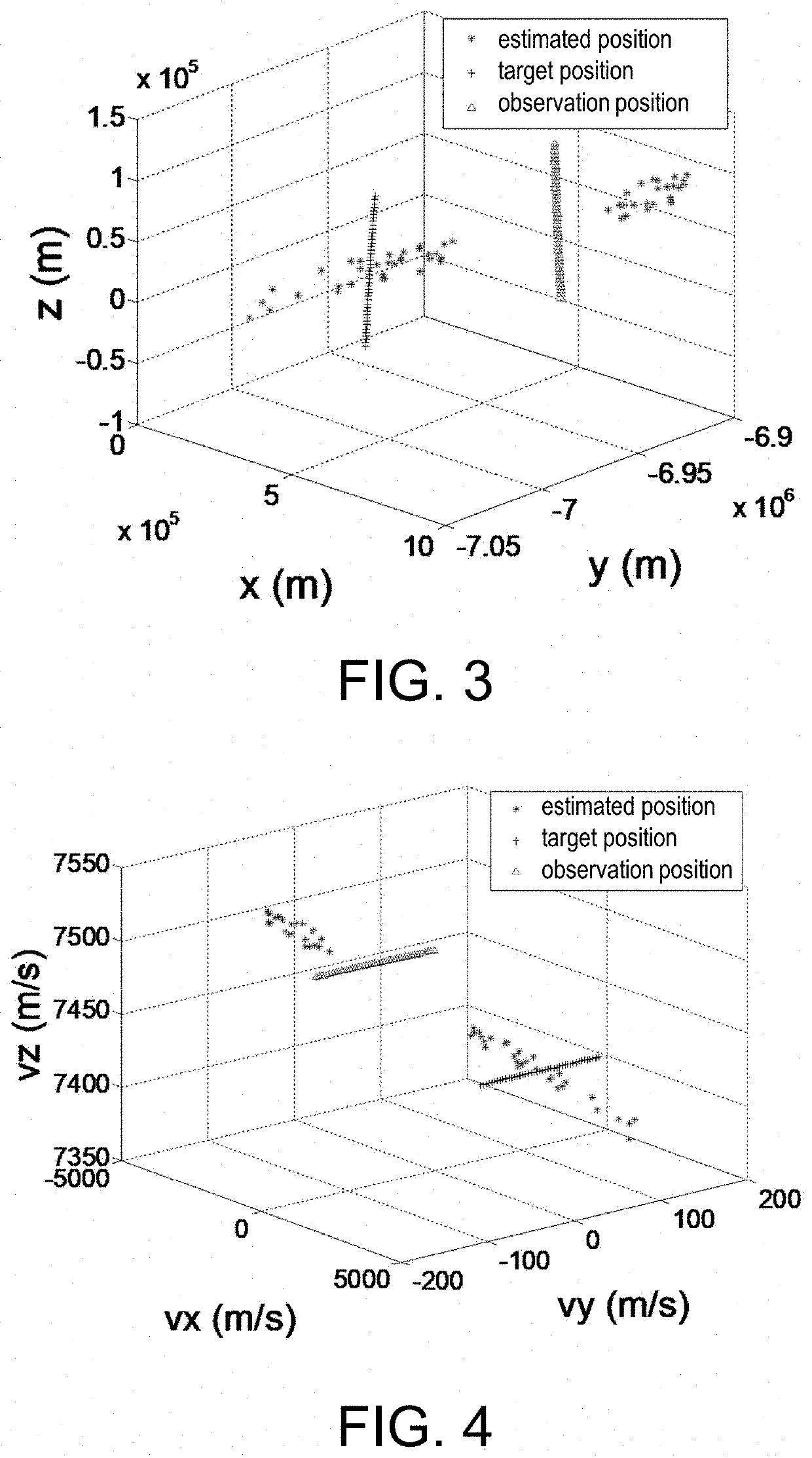
The invention discloses a preferable short arc orbit determining method based on Gauss solution cluster, and belongs to the astrodynamics field, including: grouping the observation data, using Gauss method to obtain the target state vector at the corresponding time point for each group of data, forming a solution set of preliminary estimation; dividing the solution set of preliminary estimation into a position component vector solution set and a velocity component vector solution set for clustering to obtain a position component vector solution cluster and a velocity component vector solution cluster; based on the position component vector solution cluster and the velocity component vector solution cluster, generating a two-dimensional trajectory solution set; evaluating each of the two-dimensional trajectories by using a trajectory optimal method, calculating the number of root of orbits corresponding to the optimal two-dimensional trajectory, thereby completing determination of initial orbit.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Orbit planning method of sun-synchronous circular orbit
PendingCN112649006AEfficient detectionInstruments for comonautical navigationComputational physicsSatellite orbit
The invention discloses an orbit planning method of a sun-synchronous circular orbit. A satellite launching orbit model, orbit regression characteristic constraints, target area illumination condition constraints and an accurate earth motion model (earth complex motion models such as age difference, nutation, rotation and polar movement are considered in the design) can be combined to design a sun-synchronous circular orbit scheme so as to realize rapid and effective detection of a target area. The problem to be solved by the satellite orbit planning design is to complete the planning design of a sun-synchronous circular orbit for different types of target area detection according to selected target area information, constraint conditions of orbit regression characteristics, constraint conditions of reconnaissance loads, launch deployment parameters, an accurate earth motion model and other data.
Owner:NO 63921 UNIT OF PLA
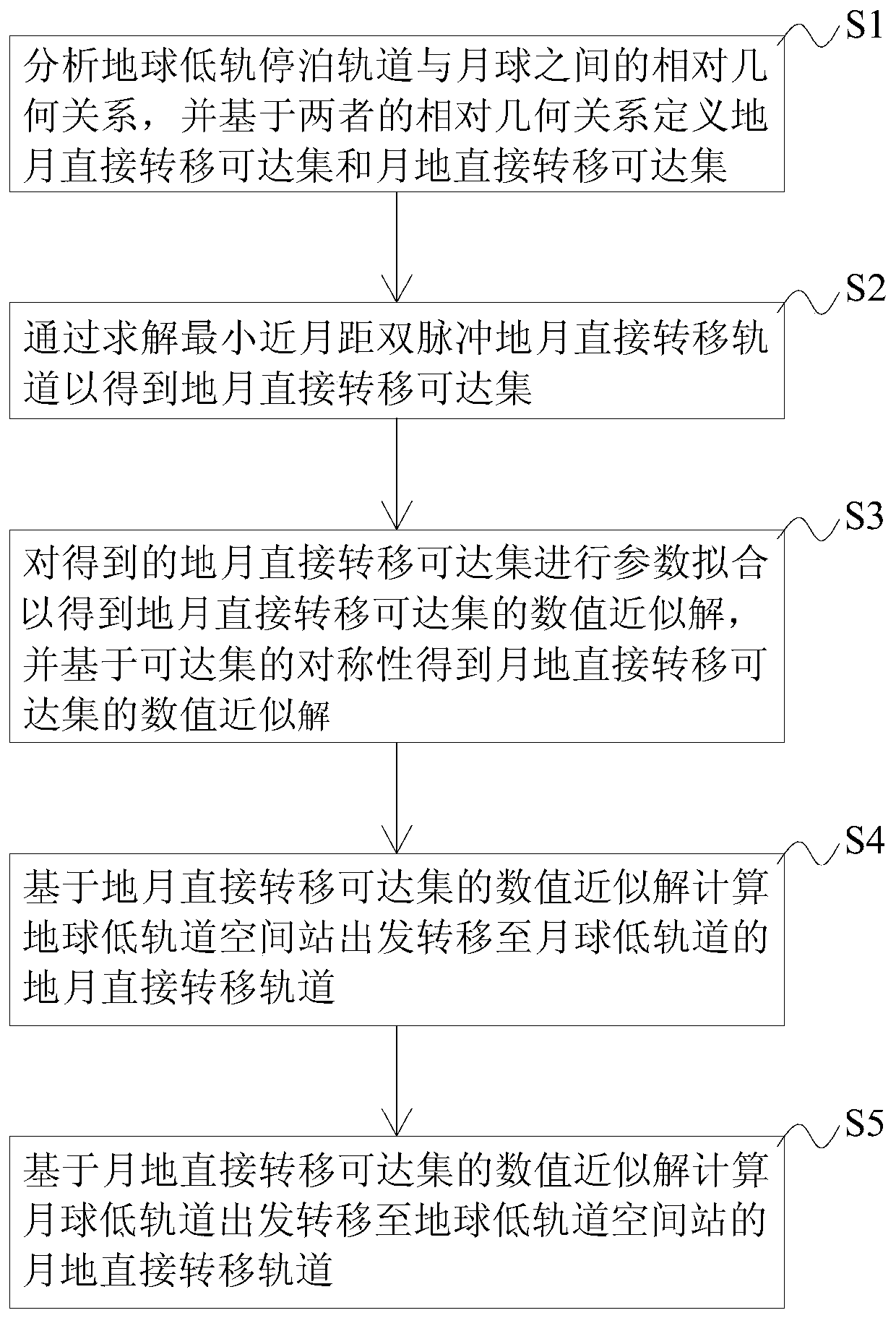
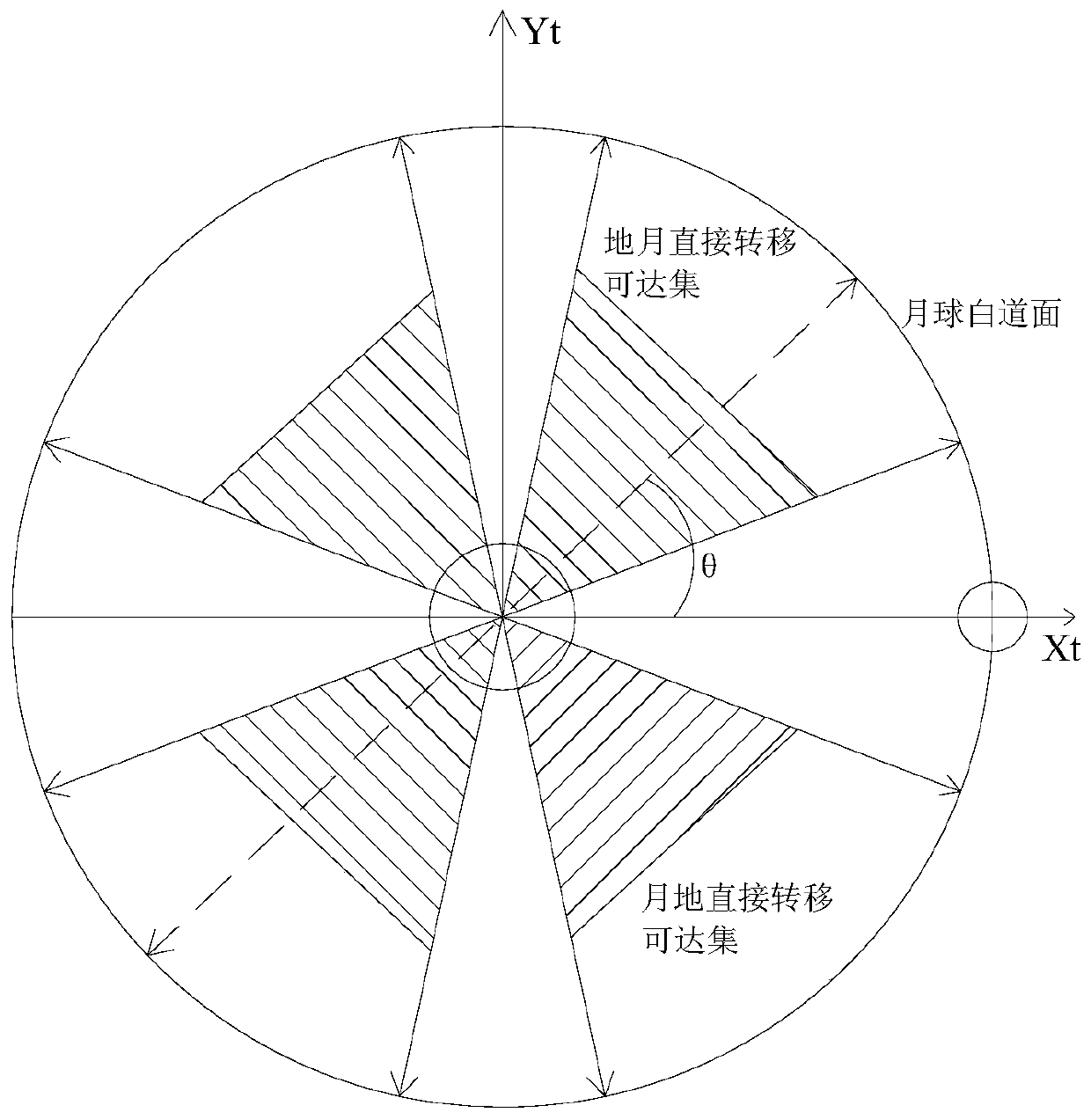
Earth-month/month-earth direct transfer orbit design method based on reachable set concept
ActiveCN110909461AHigh precisionQuick analysisDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingOrbital spaceTransfer orbit
The invention discloses an earth-moon / moon-earth direct transfer orbit design method based on a reachable set concept. According to the method, the relative geometrical relationship between the earthlow-orbit berthing orbit and the moon is analyzed; concepts of an earth-moon direct transfer reachable set and a moon-earth direct transfer reachable set are defined, then numerical solution is performed on the earth-moon direct transfer reachable set by introducing a minimum near-moon-distance double-pulse earth-moon direct transfer orbit, and the moon-earth direct transfer reachable set is obtained based on symmetry of the reachable set. The earth-month direct transfer reachable set and the month-earth direct transfer reachable set effectively disclose geometrical conditions for realizing earth-month / month-earth direct transfer, and can be used for quickly analyzing orbit transfer windows and transfer orbit characteristics of the earth low-orbit space station to and fro the moon low orbit, so that the method can be directly applied to moon detection task analysis based on the earth low-orbit space station. According to the method, the high-precision earth-moon / moon-earth direct transfer orbit can be obtained, and the method is rapid and effective.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Novel intelligent orbital transfer structure for tunnel inspection robot
The invention discloses a novel intelligent orbital transfer structure for a tunnel inspection robot, and belongs to the technical field of machinery manufacturing. The invention aims to solve the problems that the existing inspection robot in a tunnel cannot carry out multi-orbit orbital transfer inspection tasks and cannot select inspection routes in the inspection process. The novel intelligentorbital transfer structure comprises a front orbital-transfer orbit translation slide, a rear orbital-transfer orbit translation slide, orbital-transfer orbit sliding connection blocks, sliding connection block rolling wheels, a left orbital-transfer orbit, a right orbital-transfer orbit, a limit travel switch and a travel switch paddle. The novel intelligent orbital transfer structure is characterized in that the left orbital-transfer orbit and the right orbital-transfer orbit are respectively provided with two orbital-transfer orbit sliding connection blocks, the connecting blocks are provided with the sliding connection block rolling wheels, and the sliding connection block rolling wheels can translate along the orbital-transfer orbits; and after the robot identifies an orbital transfer position identification code, the left orbital-transfer orbit and the right orbital-transfer orbit move to the position overlapping with an original orbit, the limit travel switch is triggered, andorbital transfer is completed, so that the robot can continue to move. The novel intelligent orbital transfer structure has the advantages of simple structure, clever design and low cost and can effectively complete the orbital transfer movement of the tunnel inspection robot, and the orbital transfer precision is high.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
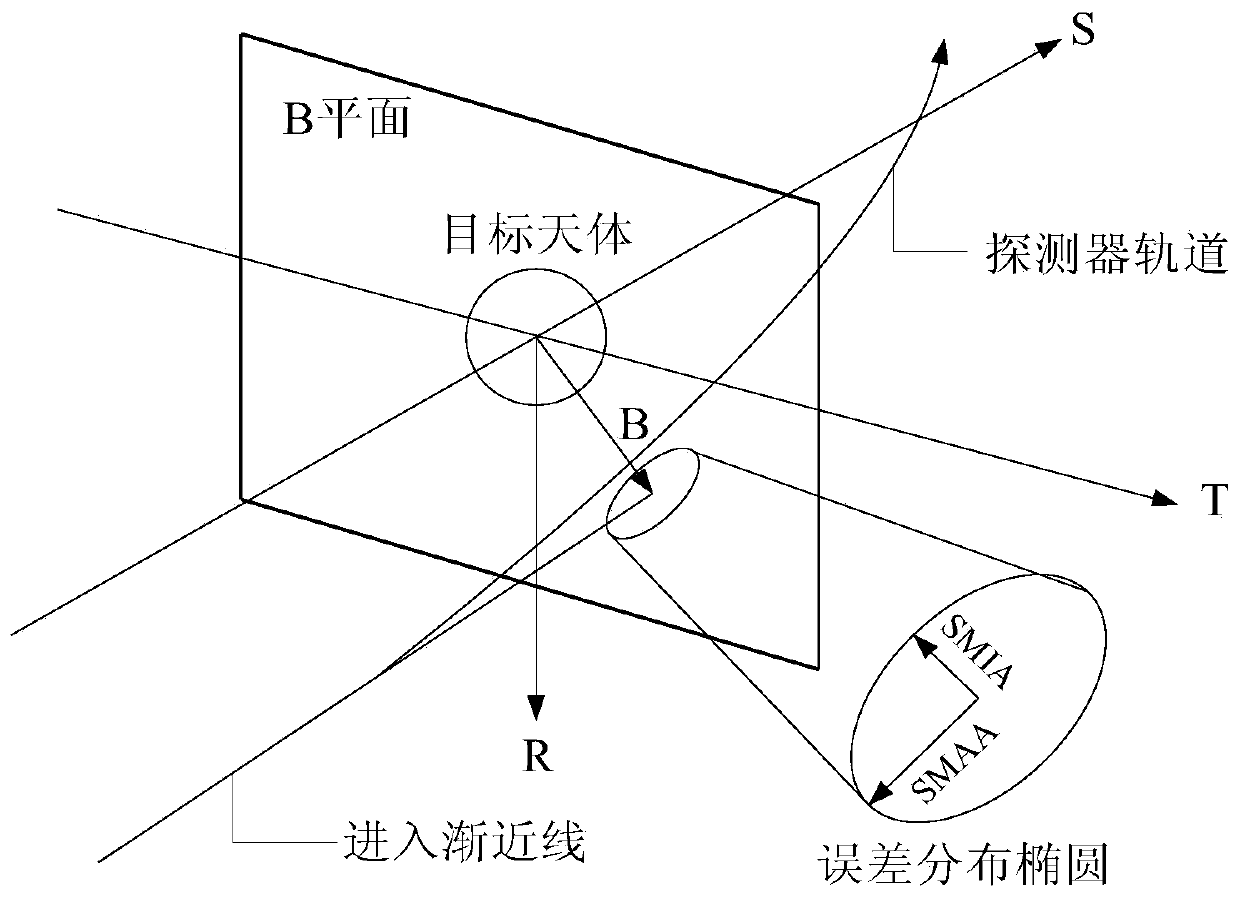
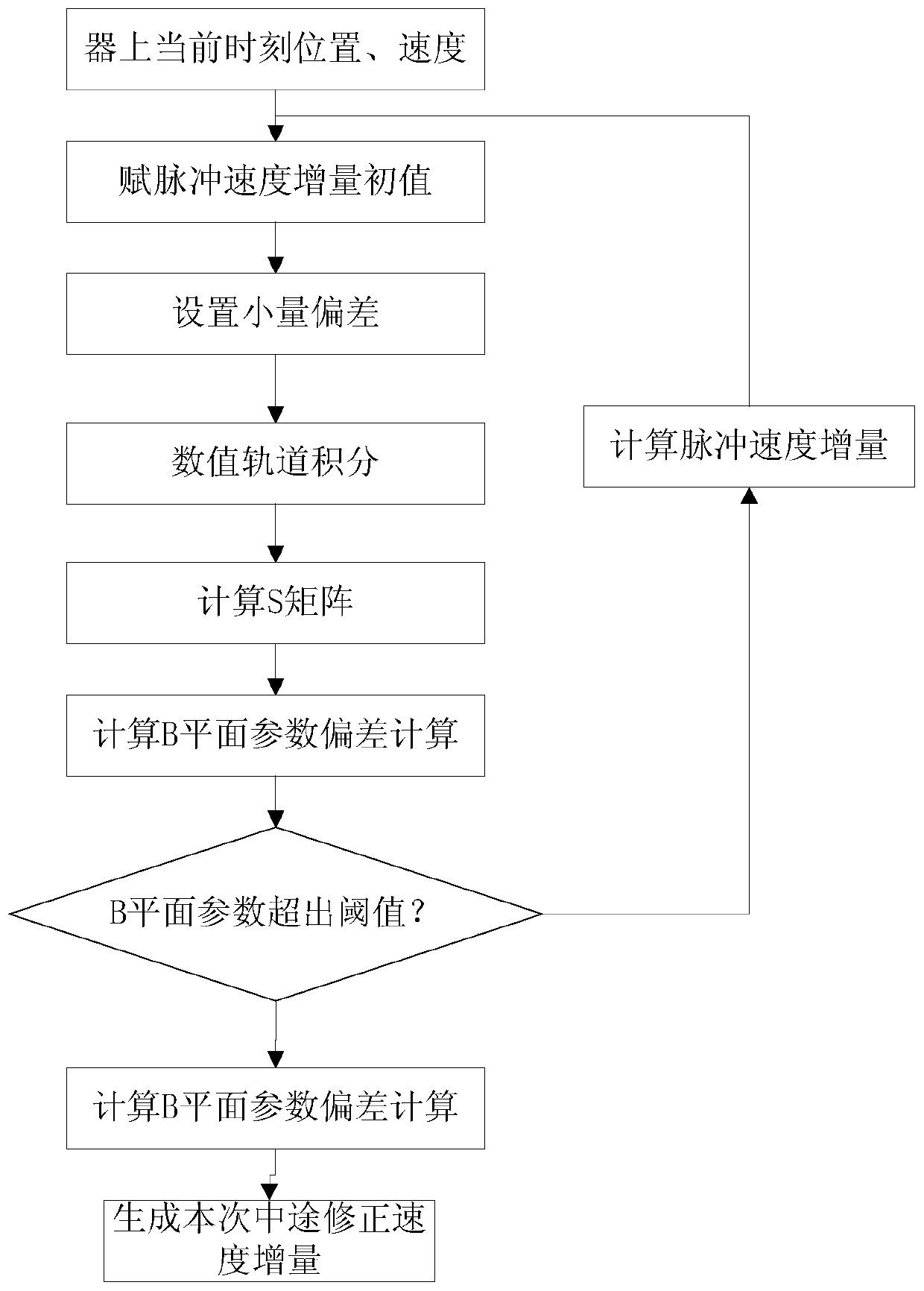
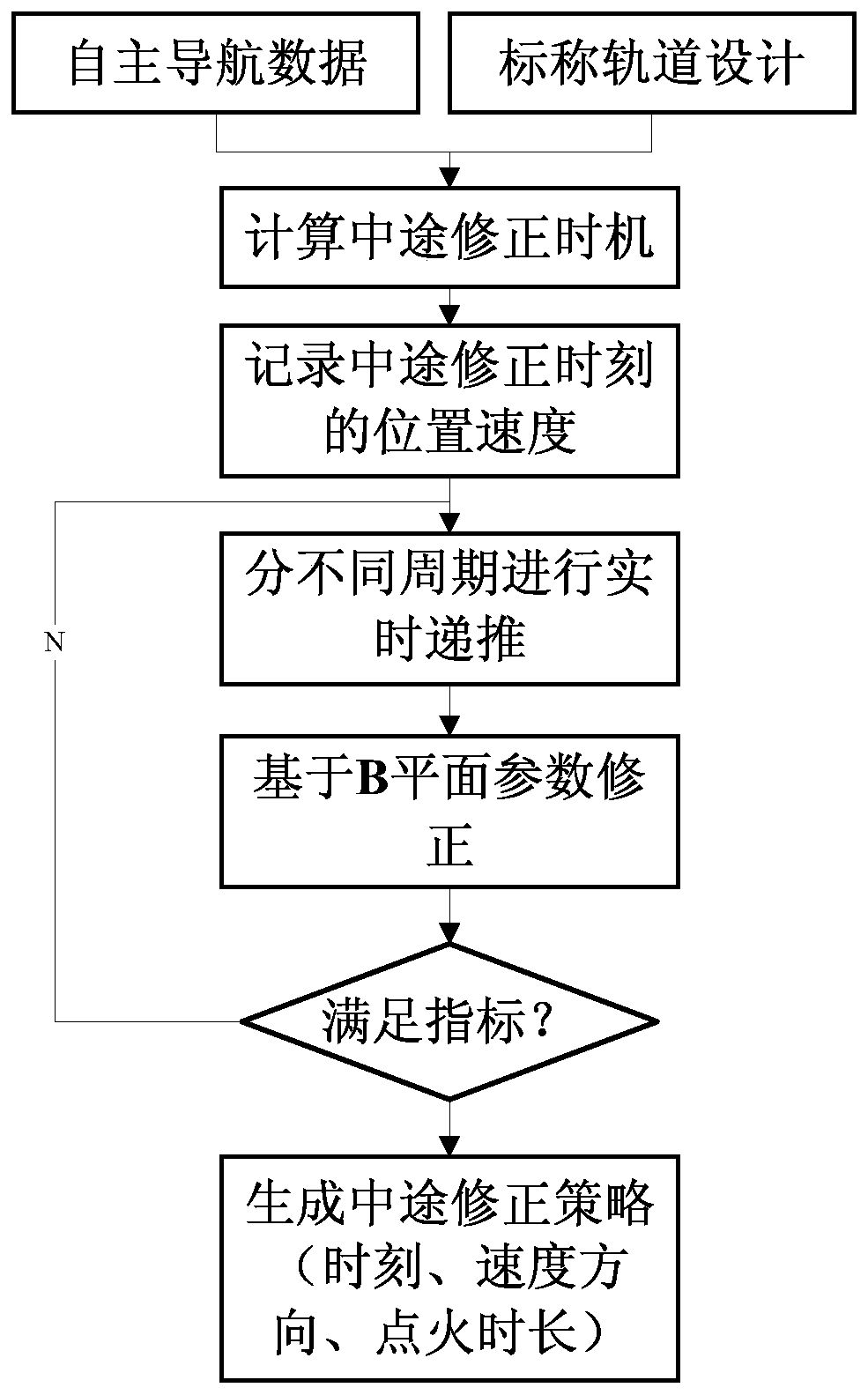
Midway correction strategy making and implementing method suitable for Mars detection
ActiveCN111319801AOccupy not muchReduce long-term surveillance stressCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusTransfer modelComputational physics
The invention relates to a midway correction strategy making and implementing method suitable for Mars detection. The method comprises the following steps that: S1, an error transfer model of a detector from any moment to the moment when the detector enters a Mars influence ball is established according to a limited three-body gravity orbit kinetic model, the orbit deviation of the detector arriving at the Mars at the current moment is calculated according to the error transfer model, and when the orbit deviation exceeds a deviation preset value, the method shifts to S2; S2, the speed error ofthe detector is corrected at the current moment by adopting a differential correction method with the parameter of entering the B-plane of the orbit of the Mars taken as a target, and iterative computation is performed with the error transfer model in the S1 to obtain pulse speed increment at the current moment; and S3, according to the pulse speed increment in the step S2, an orbit control duration and an orbit control ignition direction are obtained. With the method adopted, the autonomous formulation and implementation of a midway correction strategy under limited computing resources are realized. The method is simple and feasible, and Mars detection reliability under the condition of the absence of ground support is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Carrier rocket elliptical orbit online planning method
ActiveCN112270108AExactly satisfying terminal constraintsEasy to implementForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationGuidance controlClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a carrier rocket elliptical orbit online planning method, in particular to a rocket online trajectory planning method, and belongs to the field of aerospace guidance control.According to the method, the nonlinear constraint, namely the elliptical orbit injection constraint, can be converted into the convex constraint so that the elliptical orbit planning problem can be constructed into the convex planning problem, and online solving and implementation are facilitated. By updating the orbit injection point conjecture and establishing a new elliptical orbit convex programming model through the sequence, the orbit injection precision can be ensured, and the terminal constraint of elliptical orbit planning is accurately met.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
Mitigation of orbiting space debris by momentum exchange with drag-inducing particles
InactiveUS20130181061A1Shorten the timeLower relative altitudeAircraft componentsCosmonautic vehiclesMomentumEngineering
A cloud of small to medium-sized space debris is mitigated by releasing drag-reducing particles into the cloud from a dispenser vehicle, causing the particles to collide or otherwise interact with, and thereby exchange momentum with, the debris particles, reducing the orbiting velocity of the debris to a degree sufficient to cause the debris to de-orbit, or to accelerate the de-orbiting of the debris, to Earth. Certain embodiments also include a shepherd vehicle containing systems for identifying and tracking the debris cloud and for coalescing the debris cloud to increase the particles density in the cloud.
Owner:AEROJET ROCKETDYNE INC
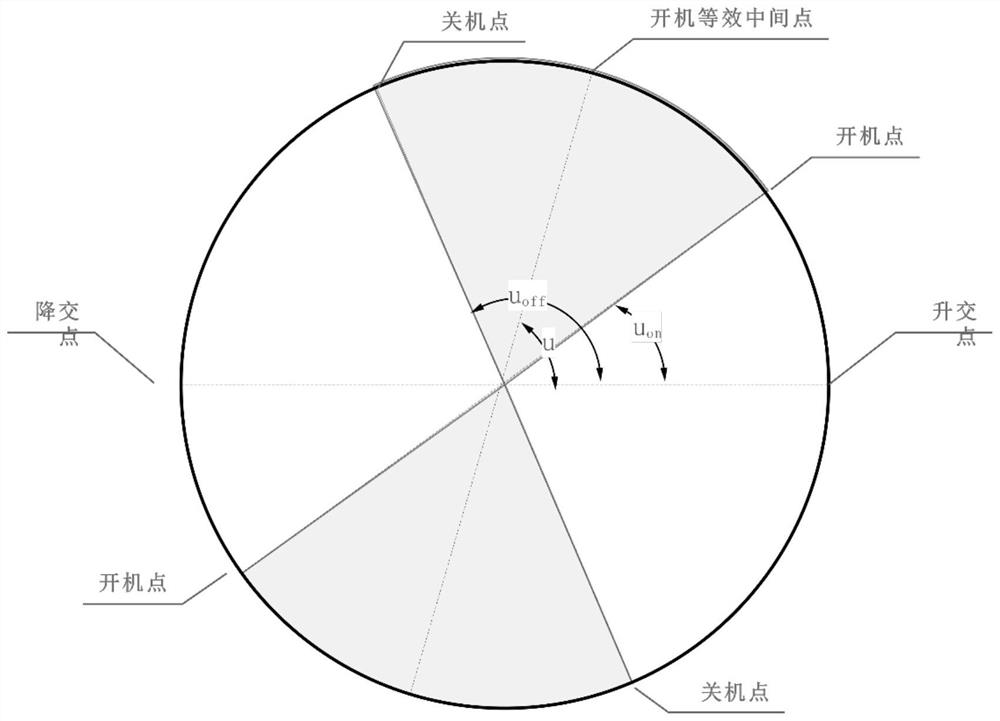
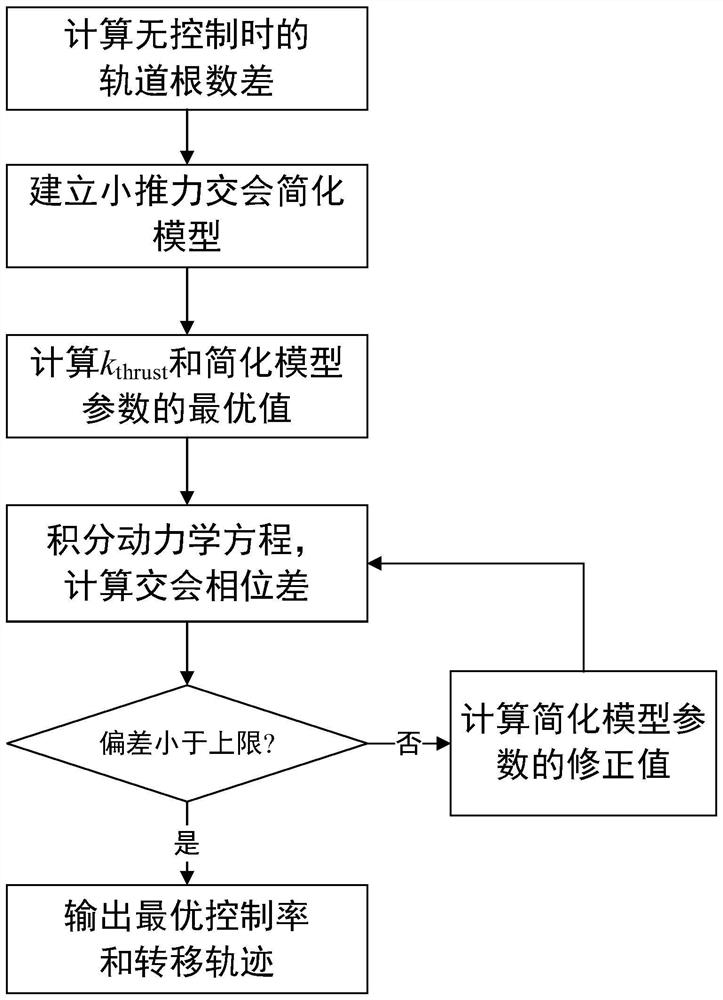
Analytic low-thrust circular orbit different-plane intersection optimization method
PendingCN114715435ASolve the problem of long rendezvous and large amount of calculationImprove solution efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesSustainable transportationReduced modelClassical mechanics
The invention discloses an analytic low-thrust circular orbit different-plane intersection optimization method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, obtaining an input spacecraft initial orbit, a target orbit needing to be intersected and a specified intersection moment, and calculating an orbit element difference between the spacecraft initial orbit and the target orbit needing to be intersected at the given intersection moment under the condition that the spacecraft is free of thrust and the target orbit needing to be intersected under the condition that the spacecraft is free of thrust; a simplified model for describing the intersection trajectory of the different planes of the small-thrust circular orbits is obtained; secondly, establishing a fixed thrust starting coefficient, and optimizing to obtain an optimal thrust starting coefficient, a semi-major axis, an inclination angle and right ascension variation of an ascending node; obtaining the phase difference of the rendezvous time relative to the target orbit needing rendezvous; obtaining a new dip angle and ascending node right ascension variation; and finally, outputting a corresponding small thrust control rate and a rendezvous transfer orbit. The method solves the problems that in the prior art, a parameter optimization method is time-consuming in integration and too many in solving variables, and the optimal rendezvous trajectory is not easy to obtain.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
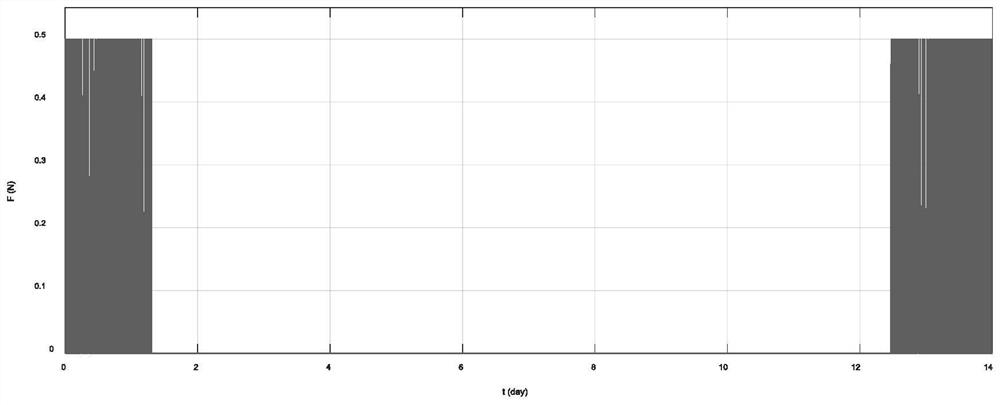
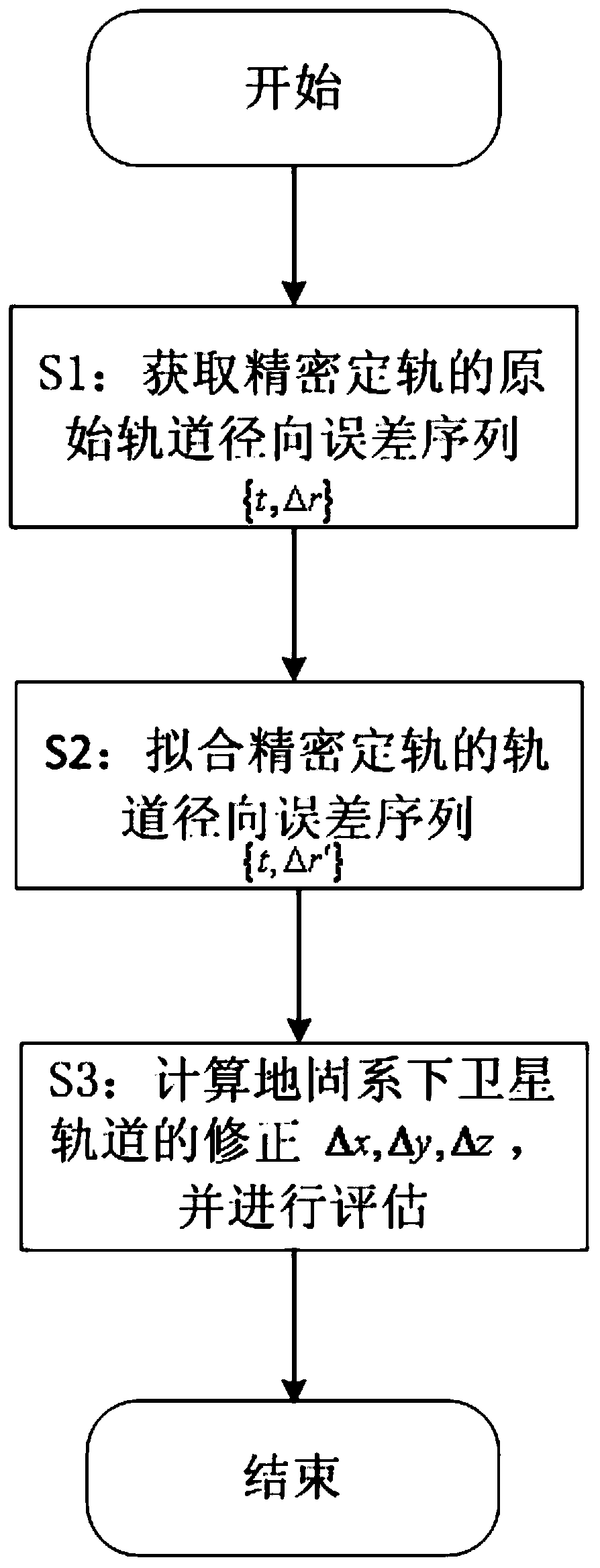
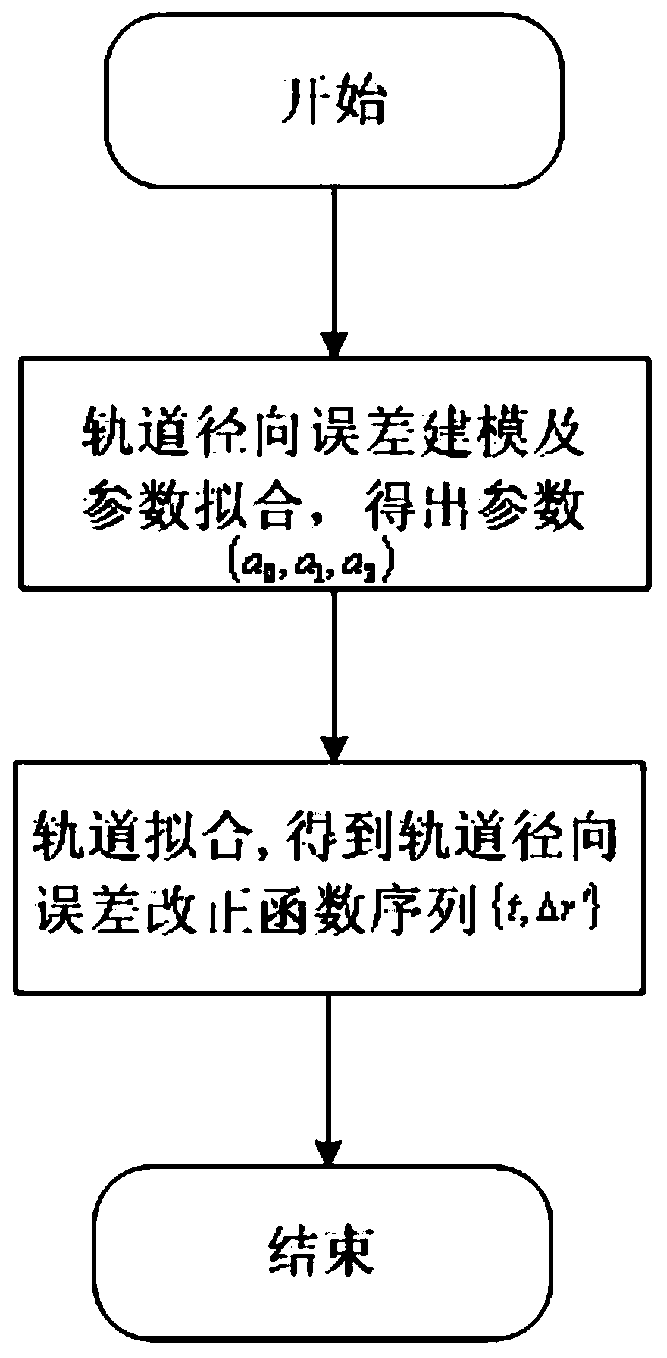
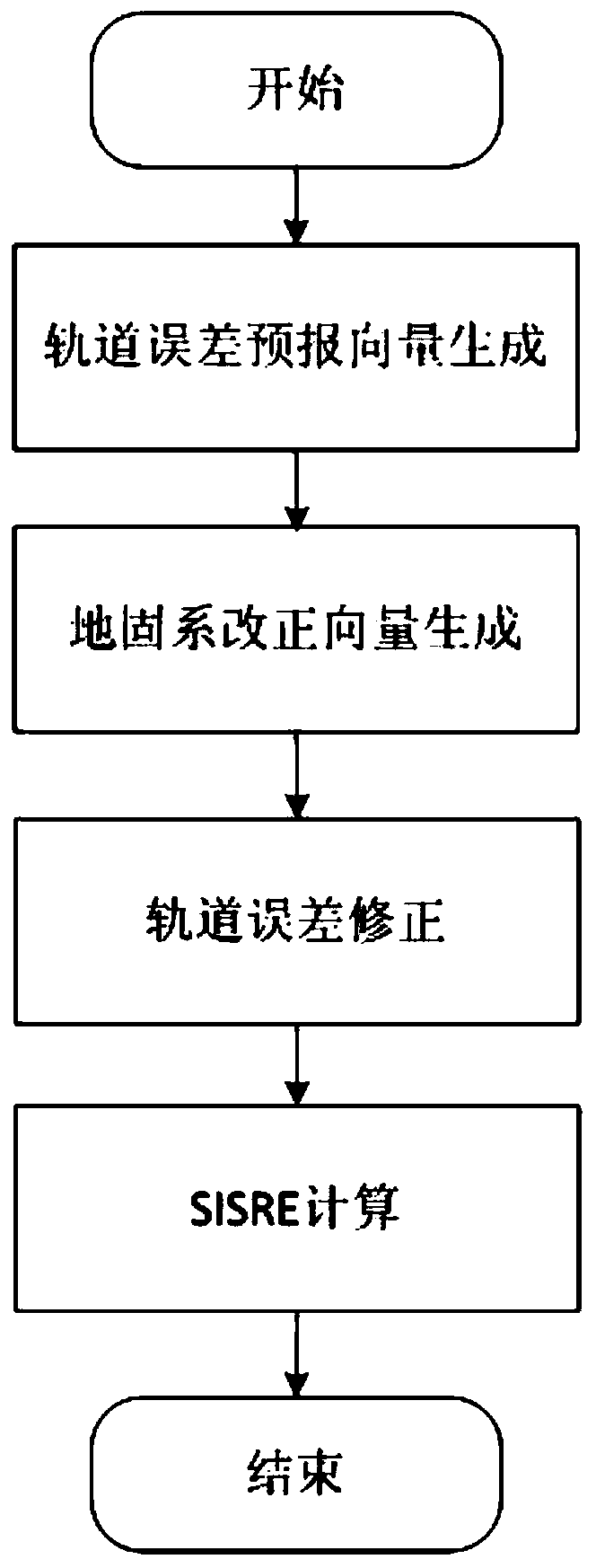
Satellite orbit error refinement method
ActiveCN111025341AThe error refinement method is simpleHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingComputational physicsSatellite orbit
The invention provides a satellite orbit error refinement method, which comprises the steps of respectively obtaining satellite-ground clock errors based on one-way and two-way time synchronization, comparing the clock errors, and obtaining an original orbit radial error sequence of precise orbit determination; based on the obtained original orbit radial error sequence, adopting a second-order polynomial to carry out orbit error fitting to obtain an orbit radial error correction sequence; and performing orbit error prediction based on a satellite orbit period by utilizing the orbit radial error correction sequence to obtain an orbit error prediction sequence, and converting the orbit error prediction sequence from an orbit coordinate system to an earth-fixed coordinate system to finish orbit error correction of precise orbit determination. According to the satellite orbit error refinement method, satellite orbit errors are effectively monitored, fitted, predicted and corrected under the conditions that dynamic factors are not considered and the range of a monitoring station is not expanded by means of comparing the two clock errors, and a practical Beidou satellite orbit performance improvement method is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
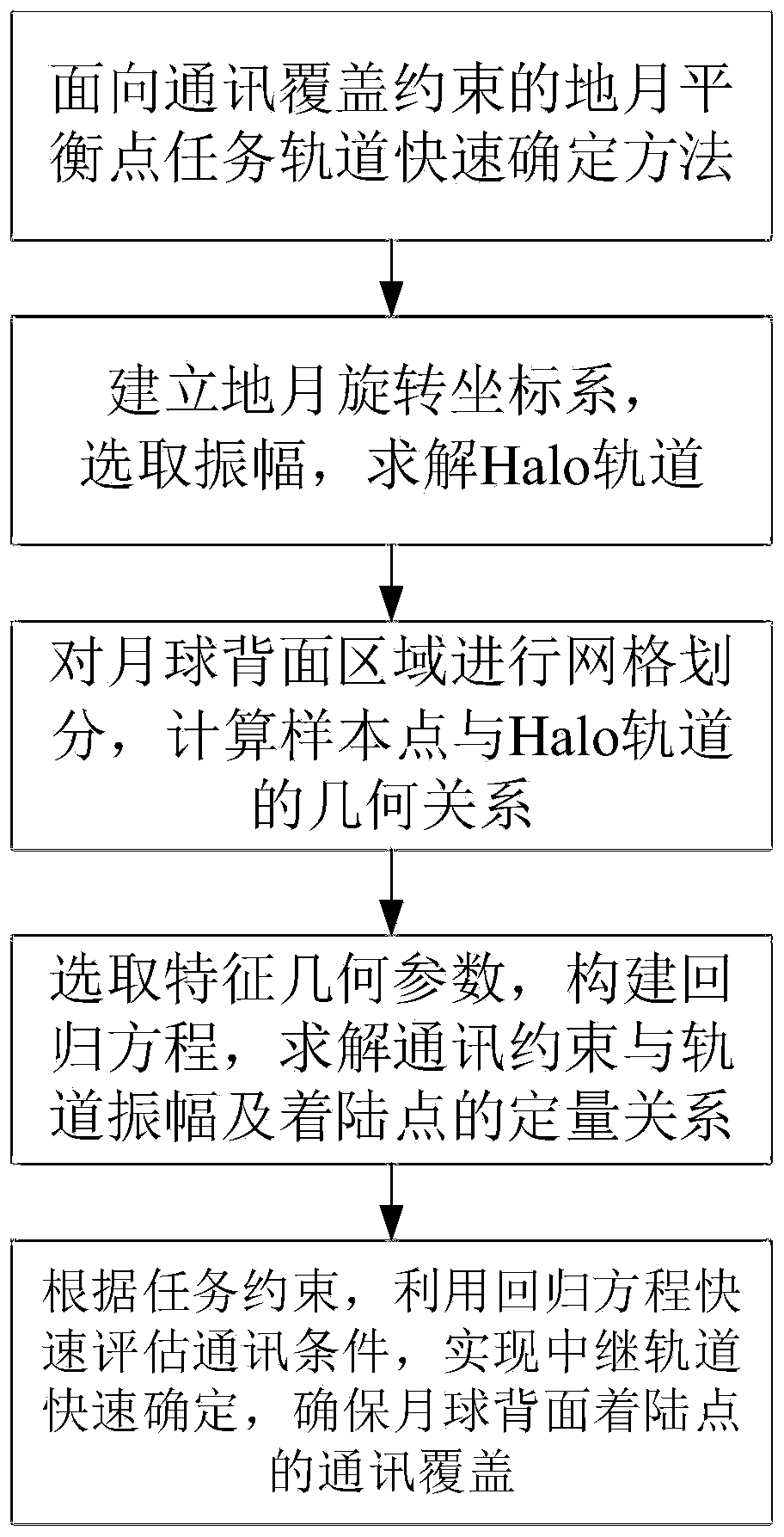
Communication coverage constraint-oriented earth-moon balance point task orbit rapid determination method
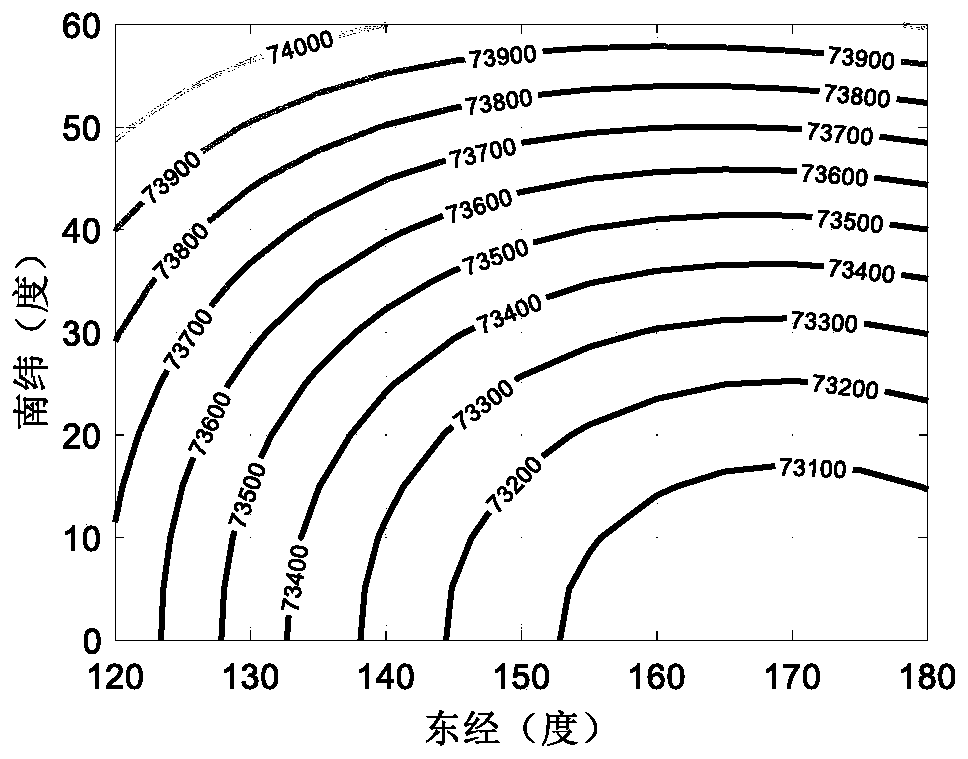
ActiveCN111559518AQuick fixCommunication Coverage EnsuresArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusFar side of the MoonEngineering
The invention discloses a communication coverage constraint-oriented earth-moon balance point task orbit rapid determination method, and belongs to the technical field of aerospace. The implementationmethod comprises the steps of establishing an earth-moon rotating coordinate system, determining an approximate analytical solution of a Halo orbit, obtaining an accurate solution by utilizing a differential correction method, and generating a plurality of Halo orbits for communication constraint amplitude calculation; conducting meshing on a back area of the moon, and calculating the geometricalrelationship between feature sample points and the Halo orbits; selecting characteristic geometric parameters according to communication constraint indexes, constructing a regression equation for thecommunication coverage constraint, and determining a quantitative relation between the communication constraint and the orbit amplitude as well as the landing point through the regression equation; and according to the task constraints, rapidly evaluating communication conditions by utilizing the regression equation, and realizing relay task orbit determination. The method can achieve the quick determination of task orbits with different communication constraints, guarantees the communication coverage of a landing point at the far side of the moon, and has the advantage of high orbit determination efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Regression track design method in high-precision gravitational field
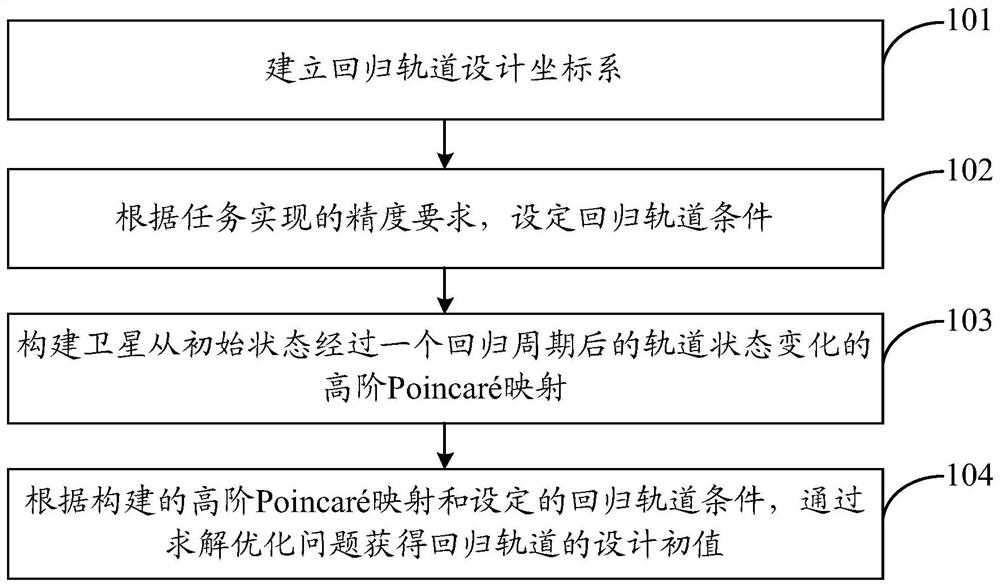
PendingCN111814313ANon-conservative gravitational increaseIncreased non-conservative gravitational perturbationDesign optimisation/simulationConstraint-based CADPoincare mappingOptimization problem
The invention discloses a regression track design method in a high-precision gravitational field. The method comprises the steps of building a regression track design coordinate system; setting a regression orbit condition according to the precision requirement of task implementation; constructing high-order Poincare mapping of orbital state change of the satellite after a regression period from an initial state; and according to the constructed high-order Poincare mapping and set regression orbit conditions, solving an optimization problem to obtain a design initial value of a regression orbit. According to the invention, high-precision and rapid track design is realized.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
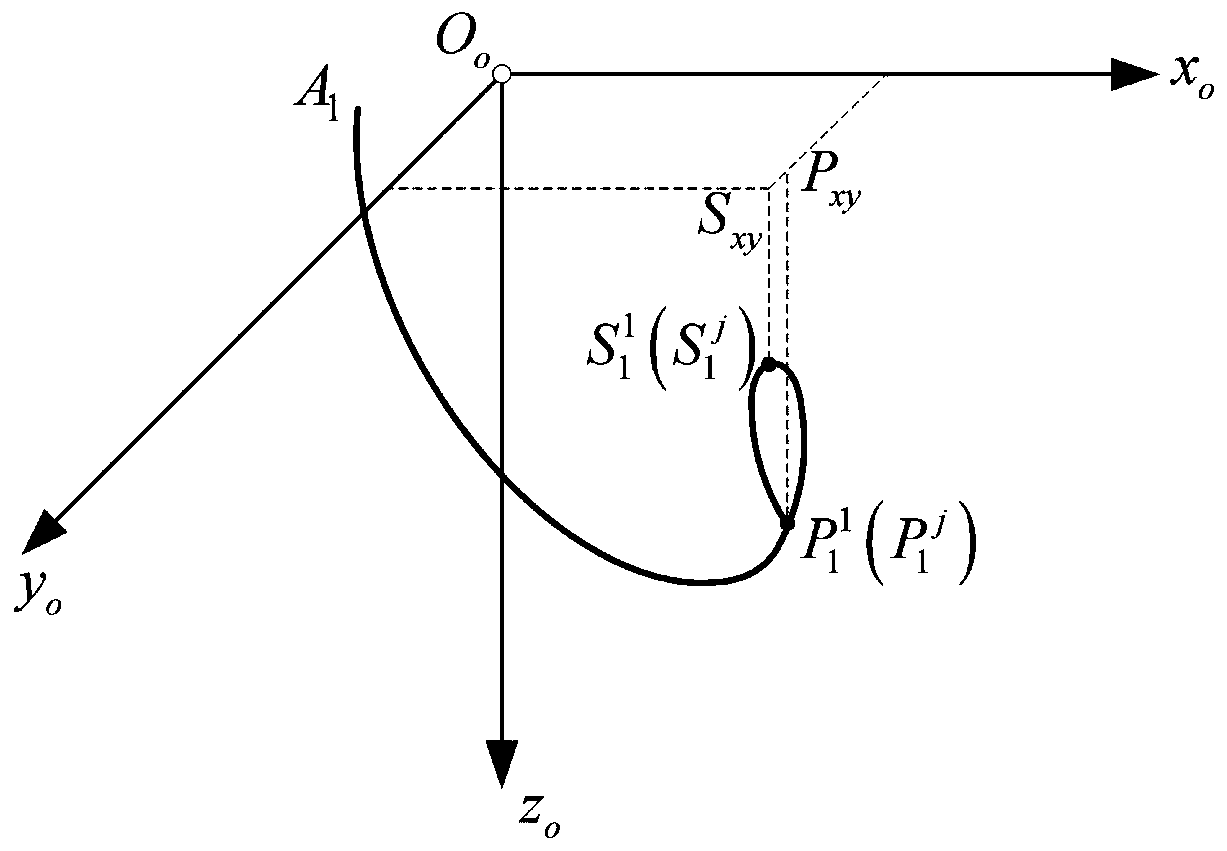
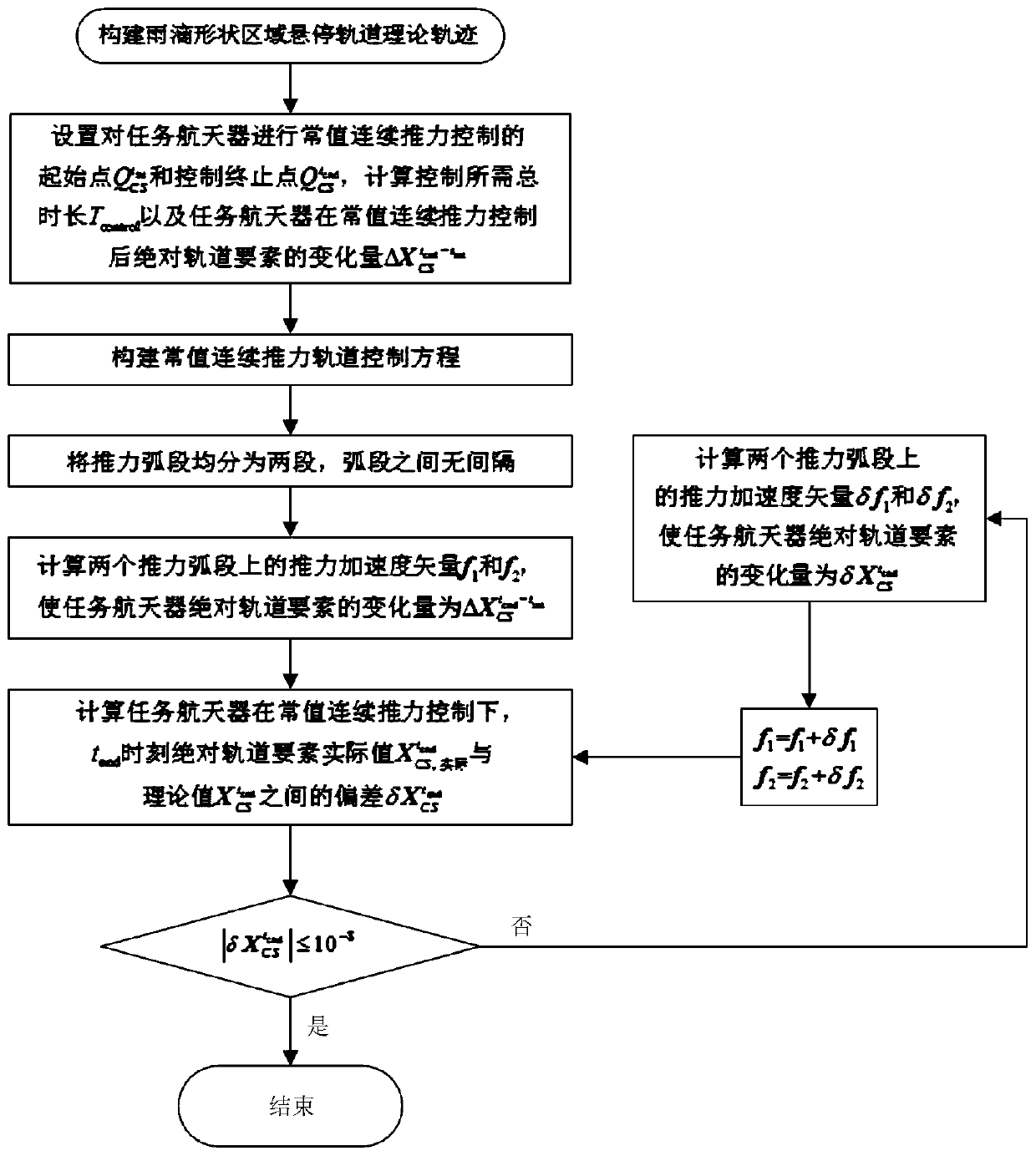
Regional hovering orbit control method based on constant continuous thrust
ActiveCN111324137ASolve control problemsFast solutionCosmonautic vehiclesAttitude controlClassical mechanicsOrbital control
The invention discloses a regional hovering orbit control method based on constant continuous thrust, and the method comprises the steps: giving a theoretical track of a regional hovering orbit according to a raindrop shape hovering configuration design method; then selecting two points from the two sides of the raindrop sharp point to serve as a starting point and an ending point for constant continuous thrust control over the task spacecraft orbit, and calculating the total control duration and the theoretical value of the absolute orbit element variation of the task spacecraft after control; and finally, by constructing a constant continuous thrust orbit control equation, calculating a regional hovering orbit control strategy based on constant continuous thrust, and achieving long-termhovering of the mission spacecraft relative to the target spacecraft in a specified region. Aiming at the requirement of an on-orbit service task for a hovering technology, the invention provides a constant continuous thrust control strategy for realizing spacecraft regional hovering, and solves the problem that the existing regional hovering orbit pulse control method is not applicable under thecondition that a spacecraft is equipped with a continuous thrust engine.
Owner:GENERAL ENG RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
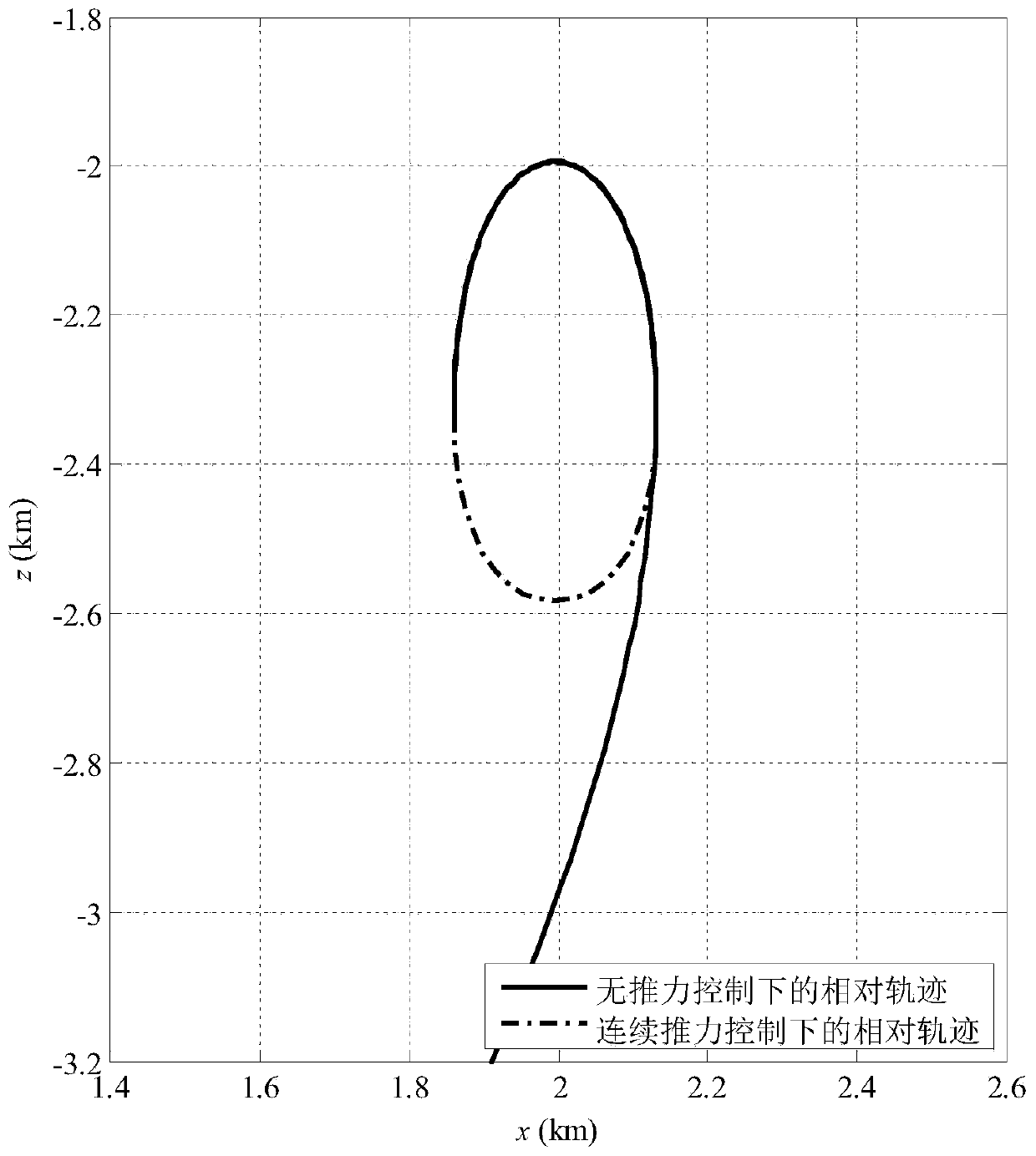
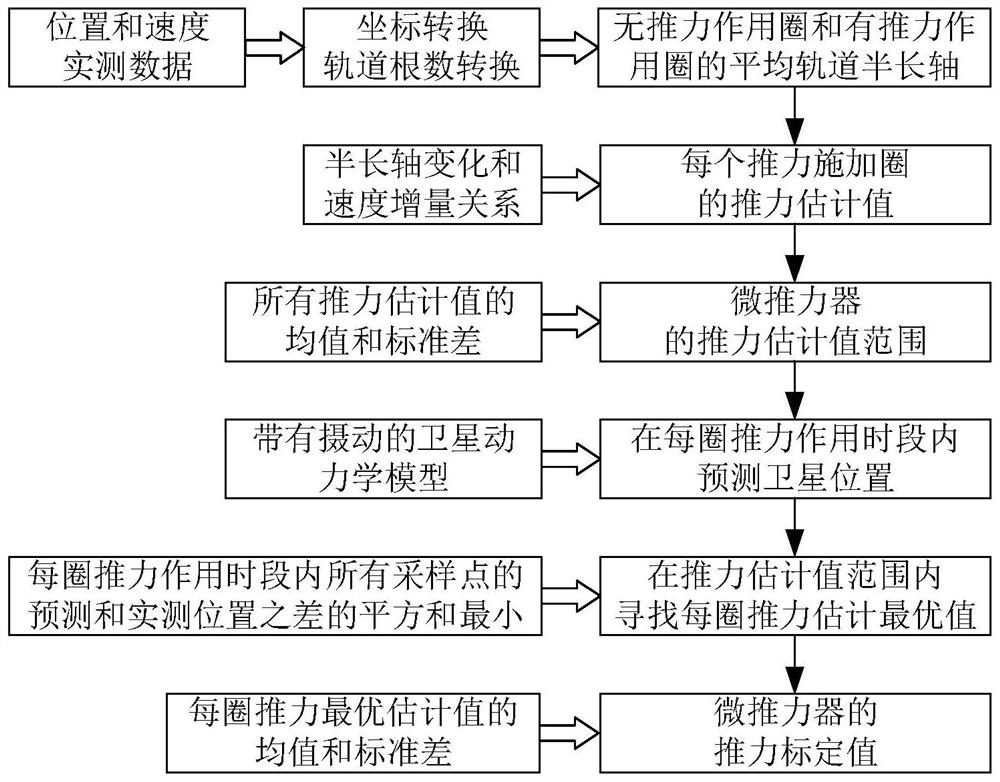
Thrust on-orbit calibration test method
ActiveCN112298614AHigh control precisionCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic vehicle trackingClassical mechanicsControl theory
The invention discloses a thrust on-orbit calibration test method, belongs to the technical field of spacecraft electric propulsion, and can solve the problem that an existing on-orbit calibration test method is relatively large in deviation, so that the control precision of a micro thruster on an orbit is relatively low. The method comprises the following steps: when the number of running turns of a satellite is an even number of turns, applying thrust to the satellite to obtain a non-thrust acting ring and a thrust acting ring of the satellite; obtaining a thrust estimated value range of thethruster according to the average orbit semi-major axis of the thrust-free action ring and the thrust action ring adjacent to the thrust-free action ring; obtaining prediction positions of all sampling points according with the thrust estimation value range according to the orbit dynamics model; according to the prediction positions and the actual measurement positions of all the sampling pointsin each thrust application time period, obtaining a thrust optimal estimation value in each thrust application time period; and obtaining thrust calibration information of the thruster according to the thrust optimal estimation value. The on-orbit calibration test method is used for on-orbit calibration of the thrust of the satellite thruster.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
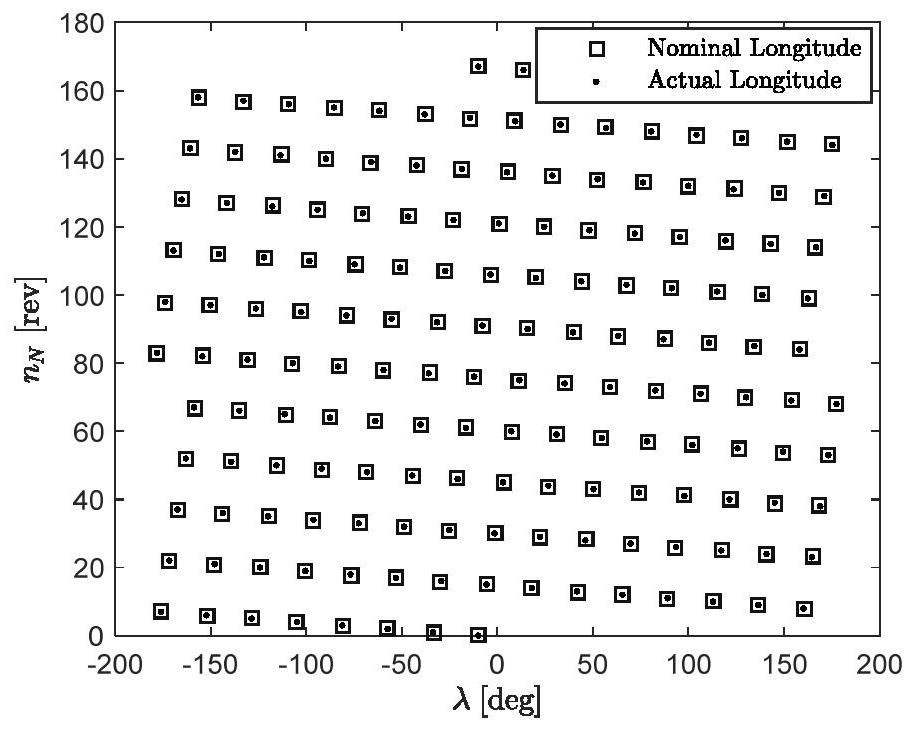
Orbit planning method for sun-synchronous circular regression orbit
The invention discloses an orbit planning method for a sun-synchronous circular regression orbit. The design of the sun-synchronous circular regression orbit needs to meet two index requirements of ascending node right ascension derivative constraint and regression coefficient constraint of the sun-synchronous orbit. According to the two index requirements, the two important parameters of the orbit semi-major axis and the orbit inclination angle of the sun-synchronous circular regression orbit can be obtained through iterative calculation; the position of a launching point near the central position of a launching area is traversed and selected according to the calculated semi-major axis of the orbit, the calculated inclination angle of the orbit, the central position of the designated launching area and other parameters; and deviation distribution of subsatellite point geocentric longitude and target point geocentric longitude are calculated when the sun-synchronous circular regression orbit subsatellite point passes through the target latitude circle for multiple times corresponding to different launching point positions, the orbit design with the minimum deviation value is selected to carry out threshold judgment, and the effective orbit design is stored. According to the invention, rapid and effective detection of the target area can be realized.
Owner:NO 63921 UNIT OF PLA
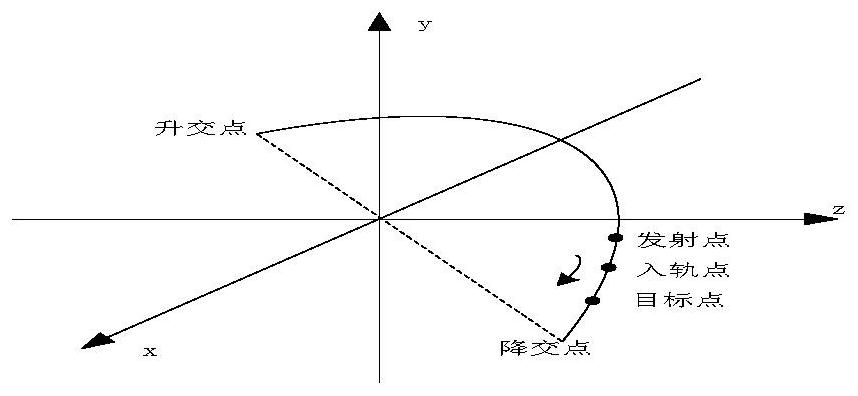
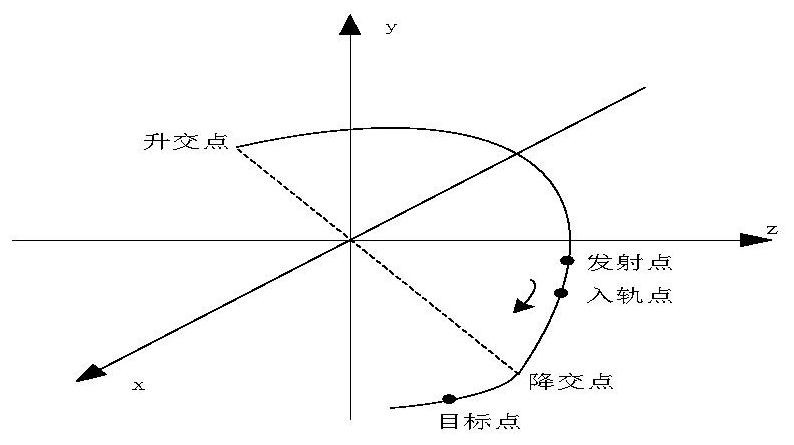
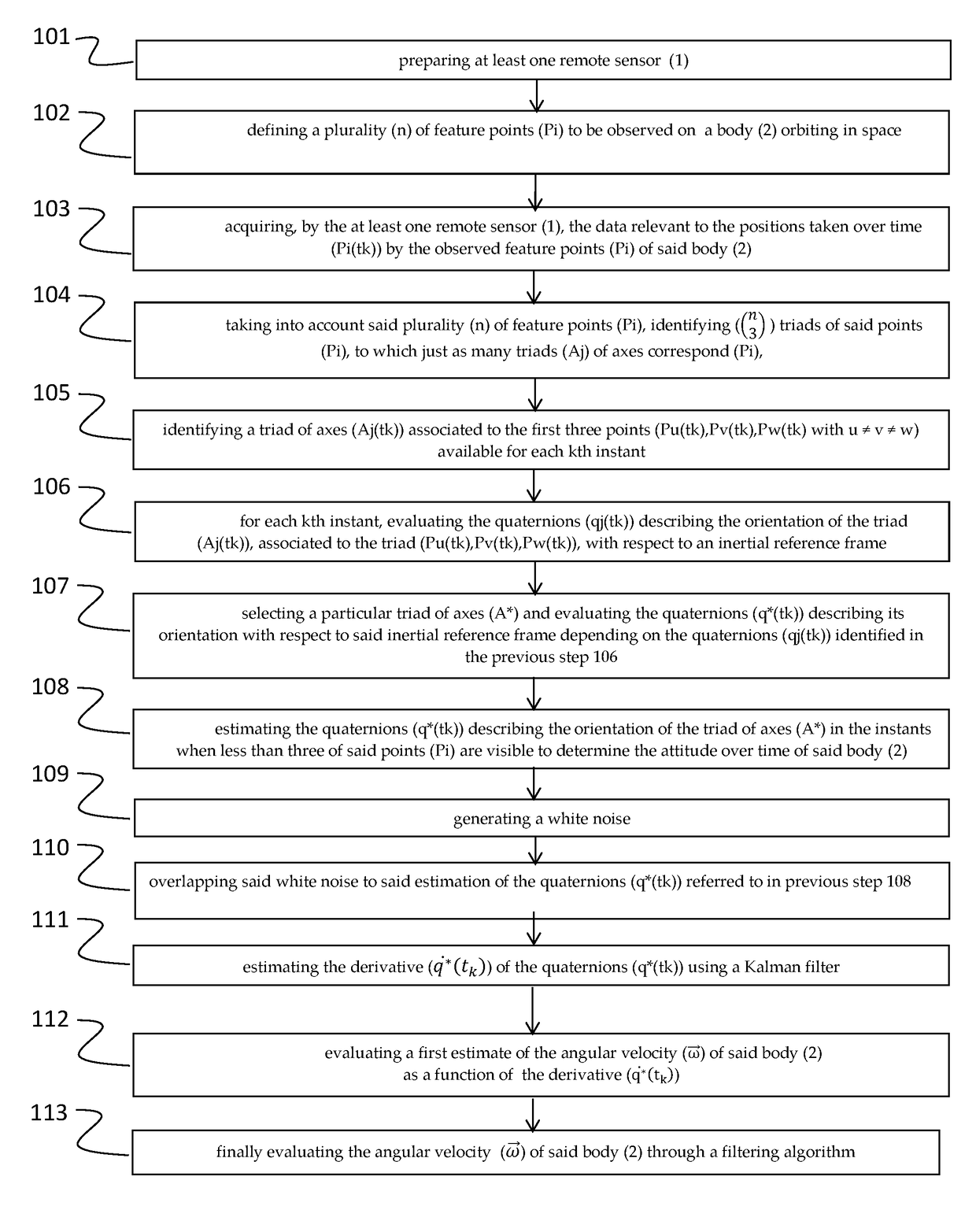
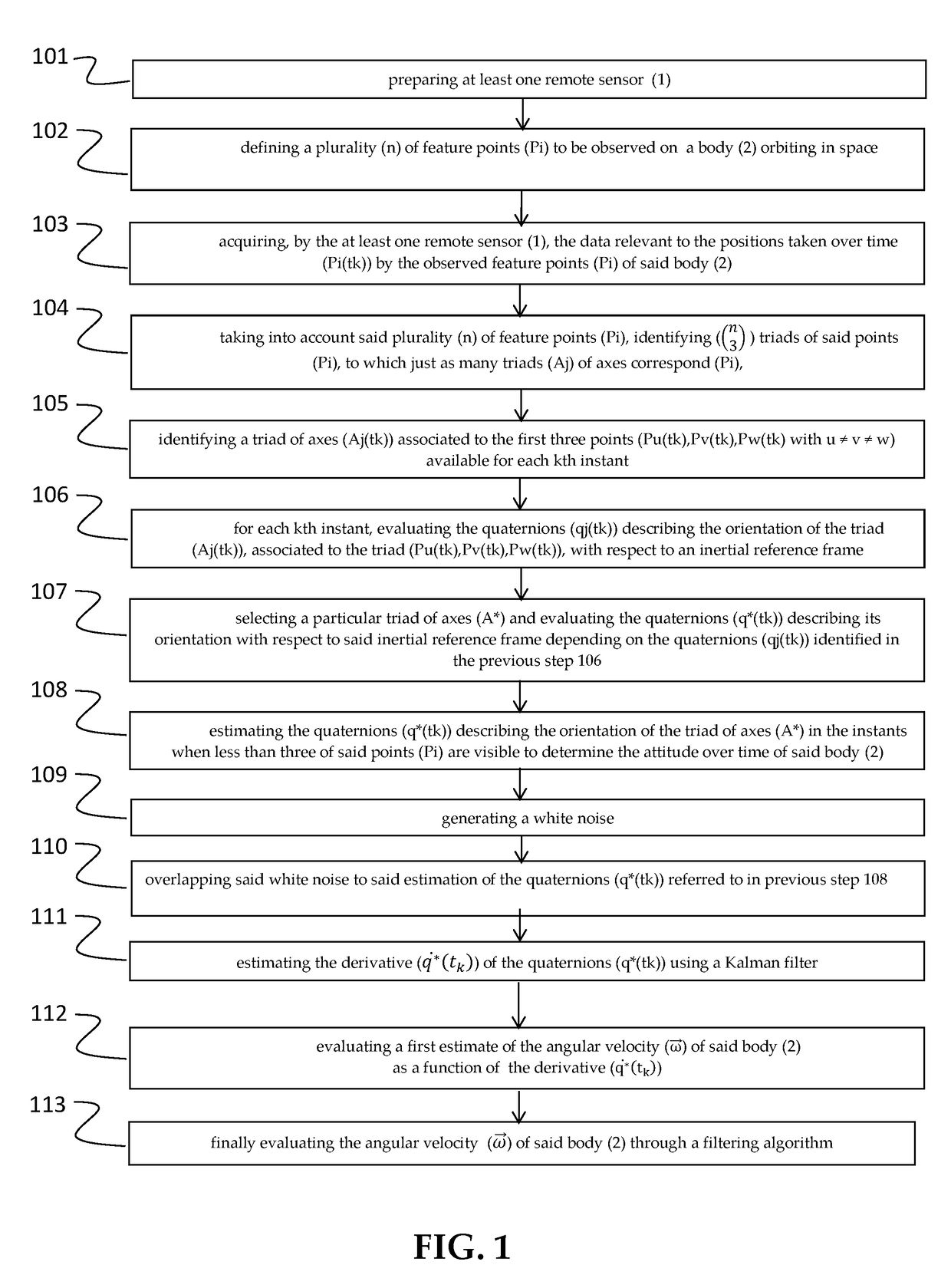
Method and system for measuring the angular velocity of a body orbiting in space
The invention relates to a method for measuring the angular velocity ({right arrow over (ω)}) of a body (2) orbiting, or in motion anyway, in space depending on the detection of the trajectory of a plurality (n) of feature points (Pi) to be observed of said body (2), said trajectory being detected on the basis of data acquired by at least one remote sensor (1); the invention relate also to the related system for measuring the angular velocity ({right arrow over (ω)}) of a body (2) orbiting, or in motion anyway, in space using such method and that comprises at least one remote sensor (1), it being possible for said at least one sensor (1) to be installed on board a spacecraft (3) or to be housed in a earth station (5).The present invention has a preferred application for measuring the angular velocity in fields such as for recovering and de-orbiting space debris.
Owner:POLITECNICO DI TORINO
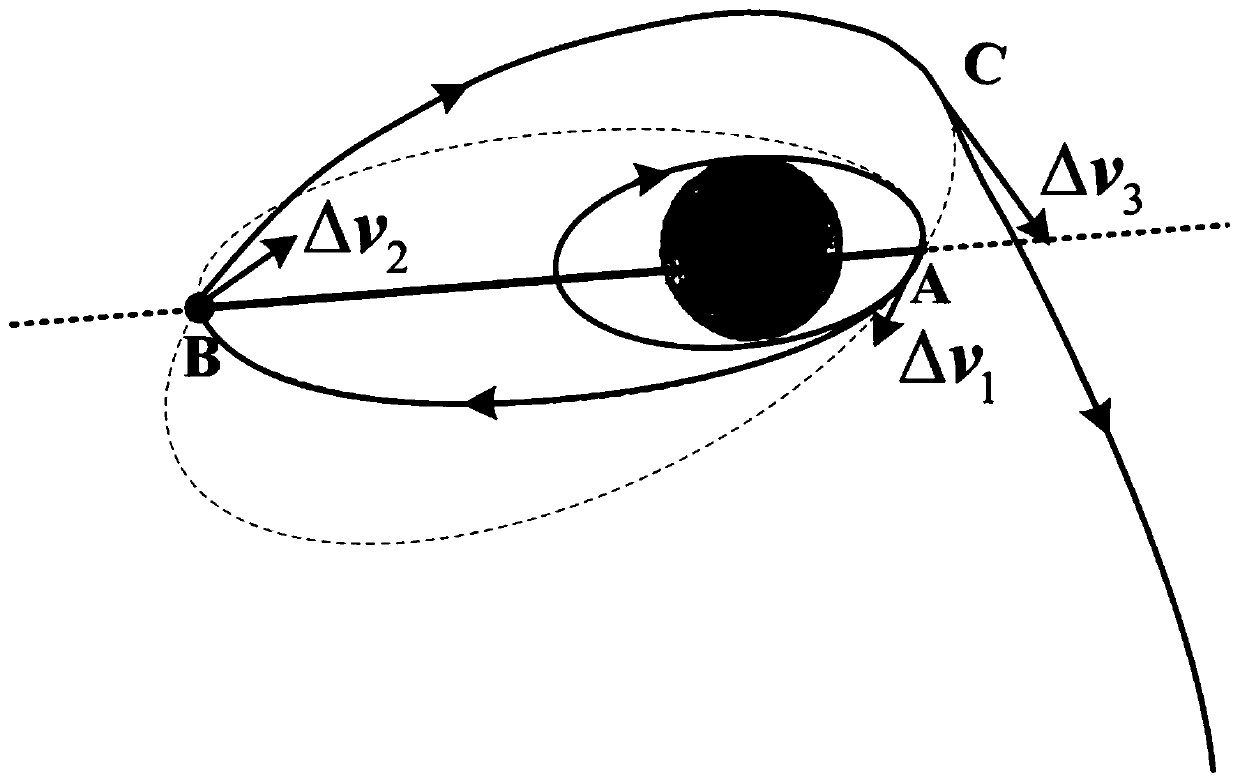
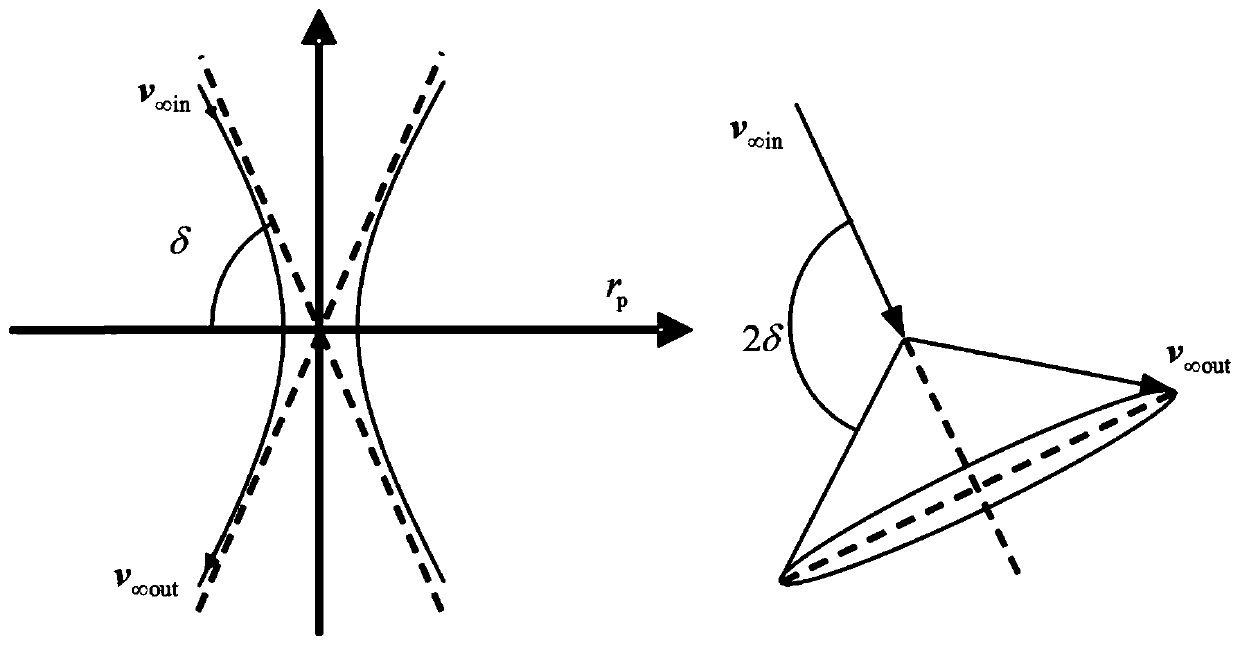
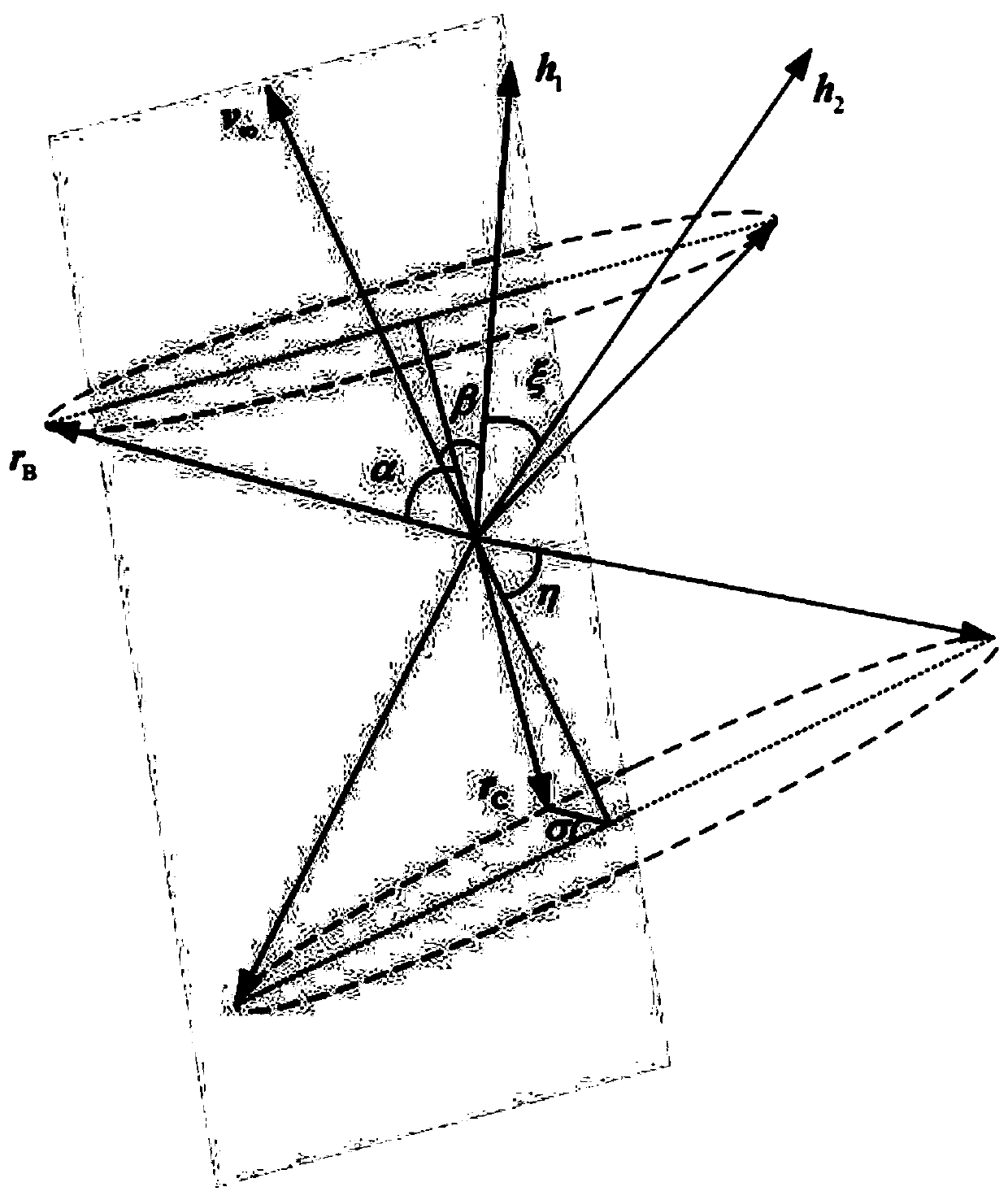
Month-earth three-pulse return orbit speed increment analysis method
ActiveCN110704952AFast and efficient preliminary approximation analysisIntuitive and concise preliminary approximate analysisGeometric CADDelta-vEngineering
The invention discloses a moon-earth three-pulse return orbit speed increment analysis method, which comprises the following steps: A, obtaining a normal unit vector h1 of a lunar orbit plane, a normal unit vector h2 of a lunar escape orbit plane and positions rA, rB and rC for applying three pulses by taking a moon center as an original point; B, obtaining a conical surface S1 with the lunar escape orbit aiming v infinity out as the axis, wherein the half cone angle of the conical surface S1 is eta; C, enabling the plane where v infinity out and h1 are located to serve as the datum plane, setting the rotating angle sigma of rC around the straight line where v infinity out is located, and determining rC and a lunar escape orbit plane; D, obtaining a conical surface S2 with the straight line where rC is located as the axis, wherein the half cone angle of the conical surface S2 is alpha; E, obtaining the included angle beta between h1 and v infinity out and the different-plane differencexi between the lunar orbit and the lunar escape orbit; F, solving the sizes delta v1, delta v2 and delta v3 of the three pulses; G, solving a total speed increment delta v; and H, changing the independent variable influencing the delta v to obtain a change rule of the delta v. According to the method, the spatial geometrical relationship is utilized, and preliminary approximate analysis can be rapidly, effectively, visually and simply carried out on the speed increment required by the three-pulse maneuvering process.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com