Patents
Literature
45 results about "Radial line slot antenna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
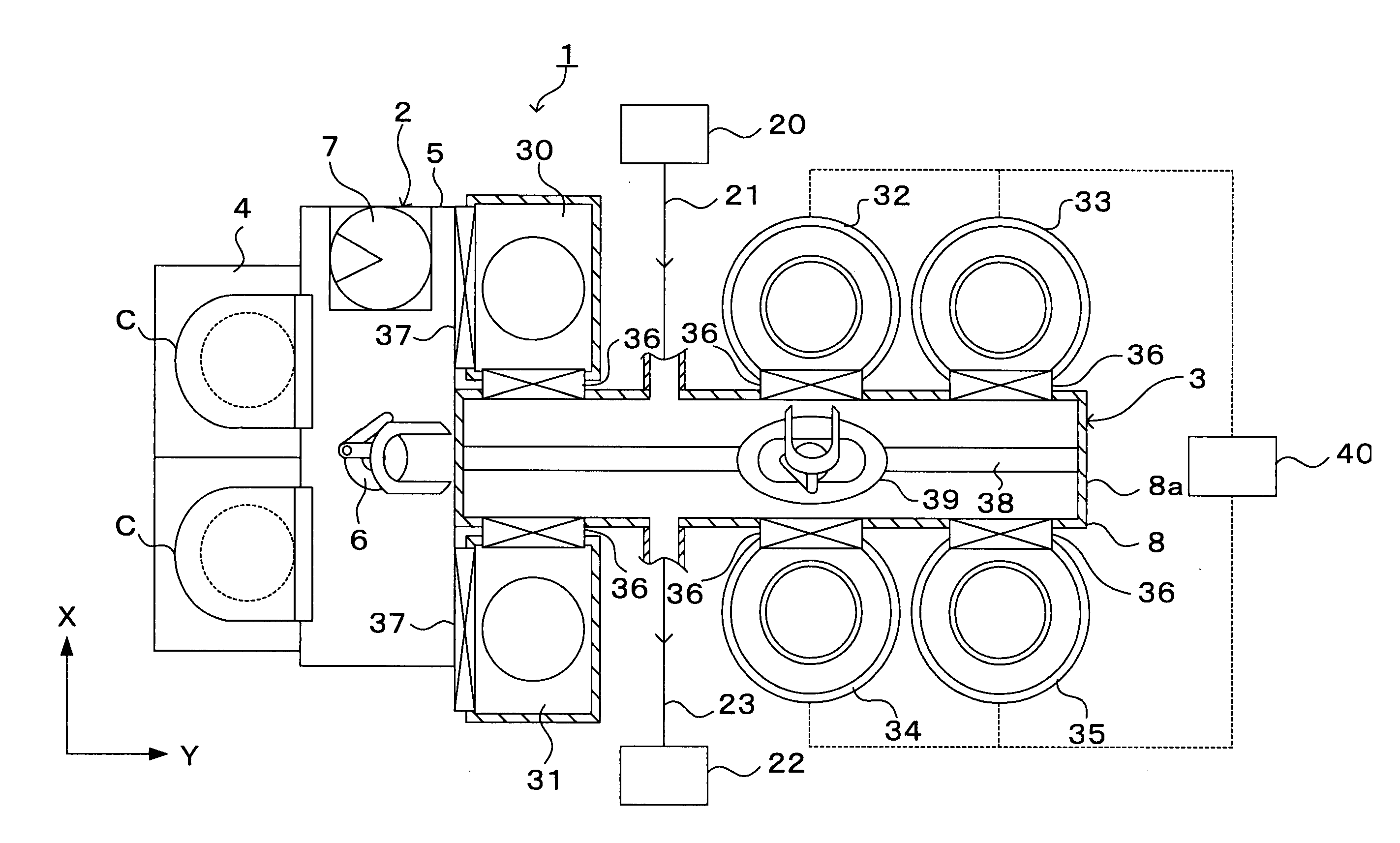
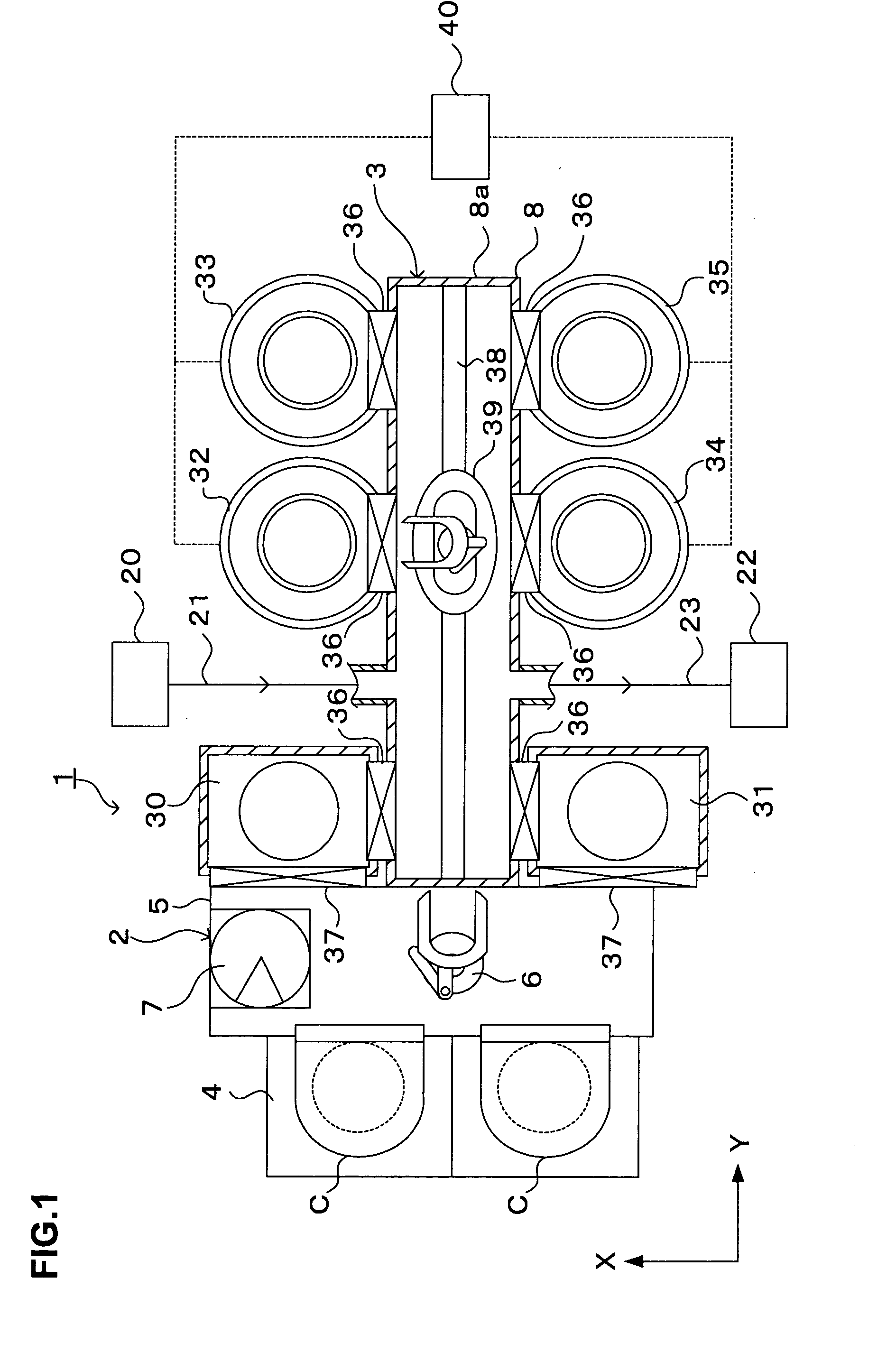
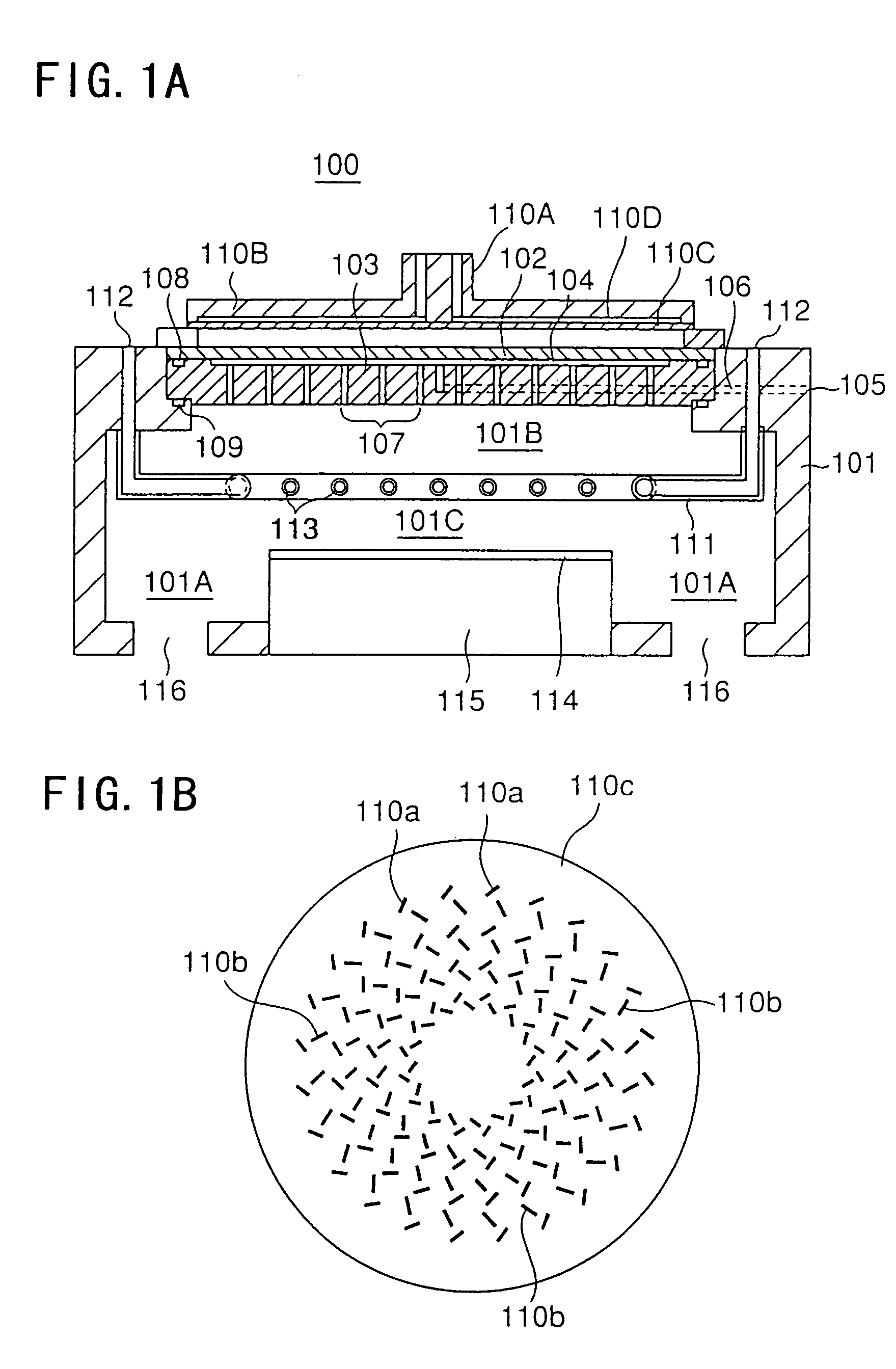
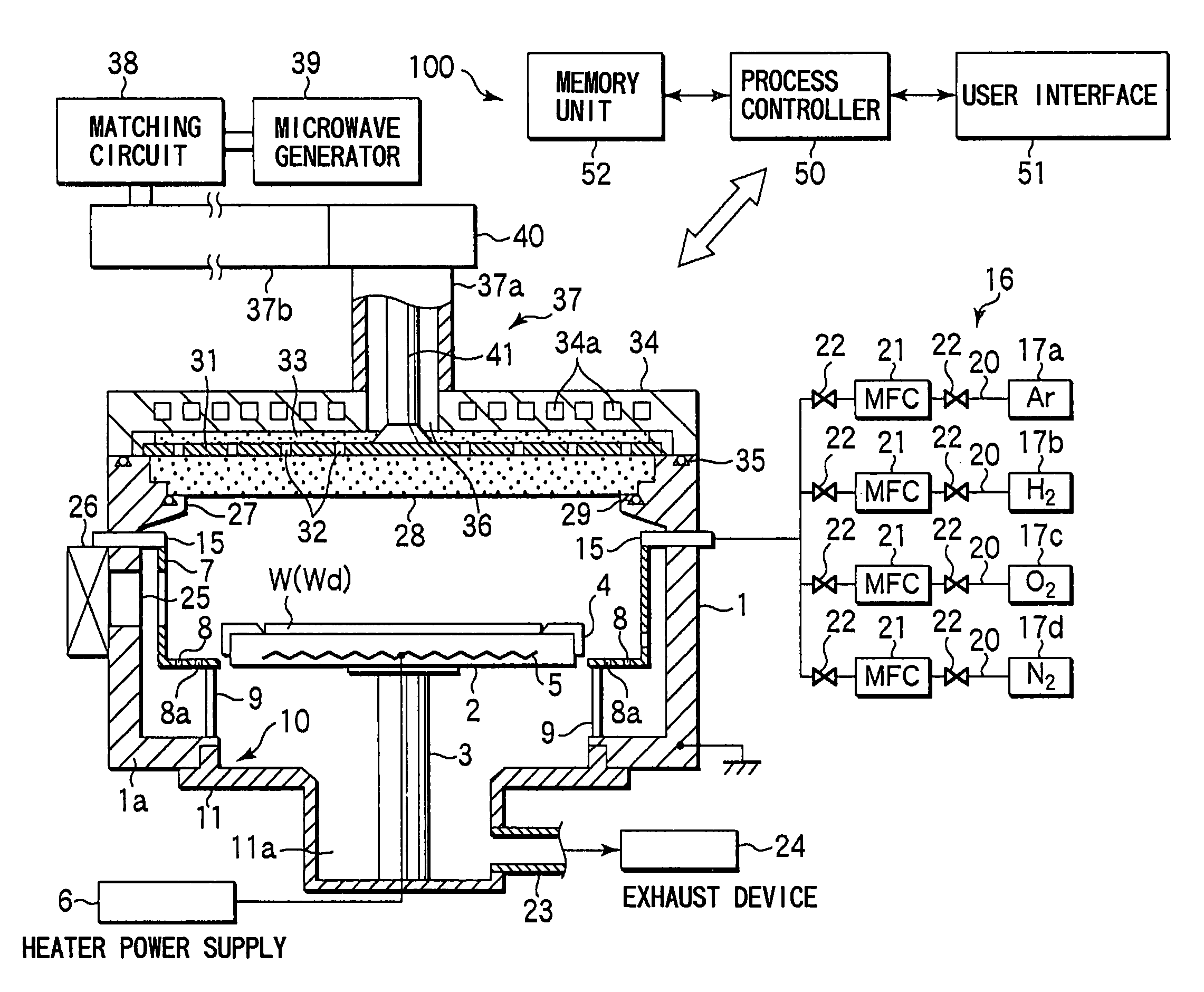
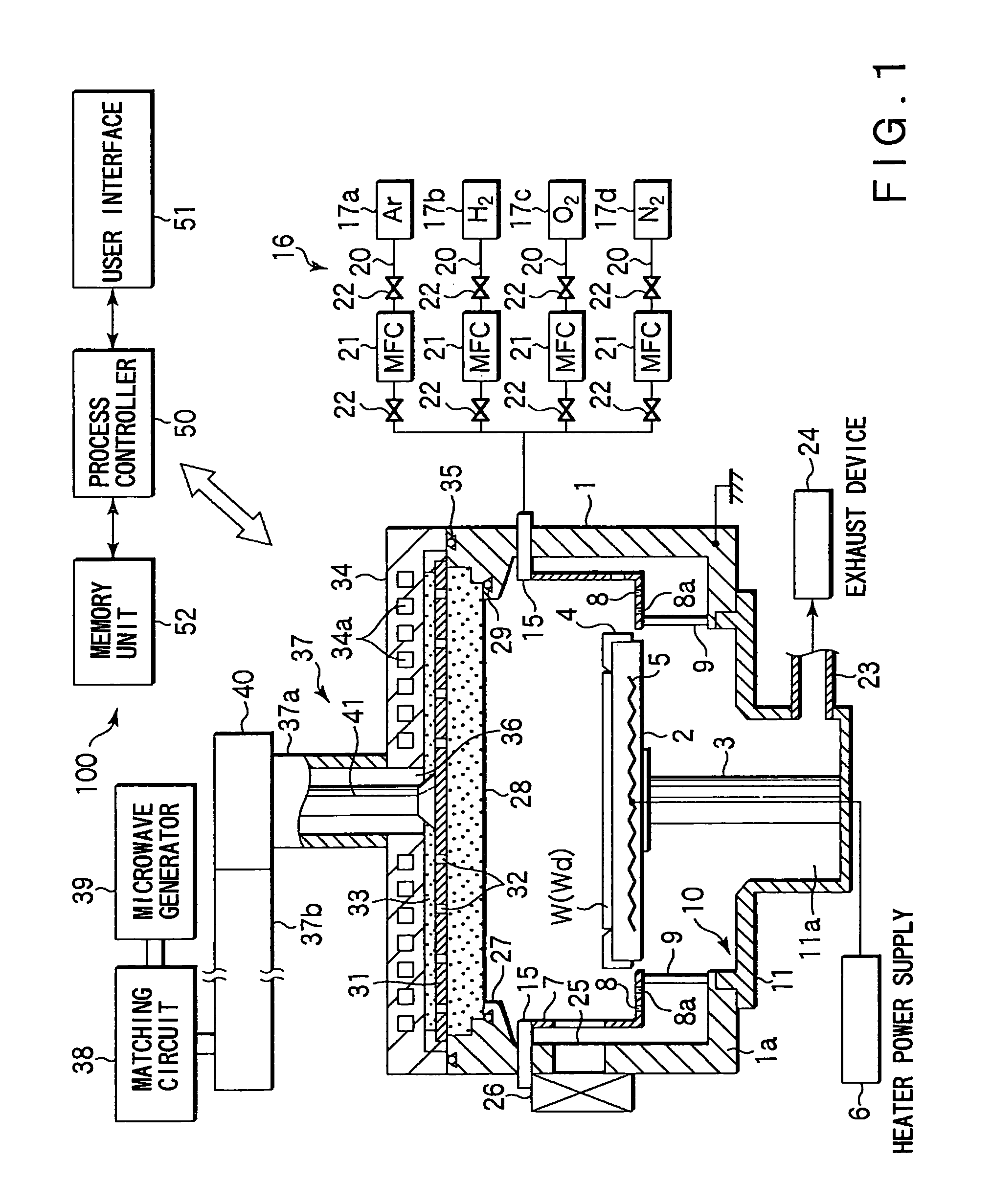
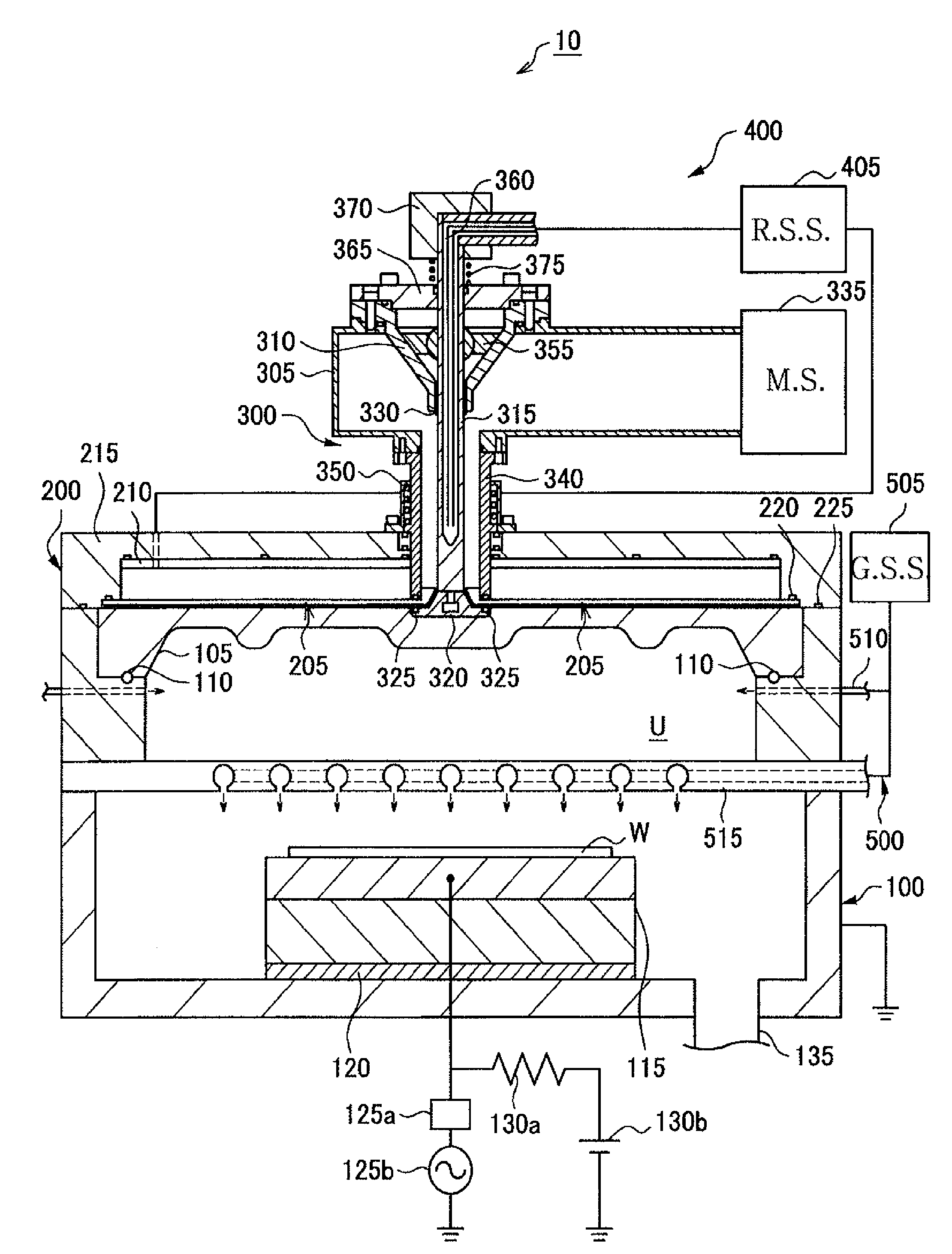
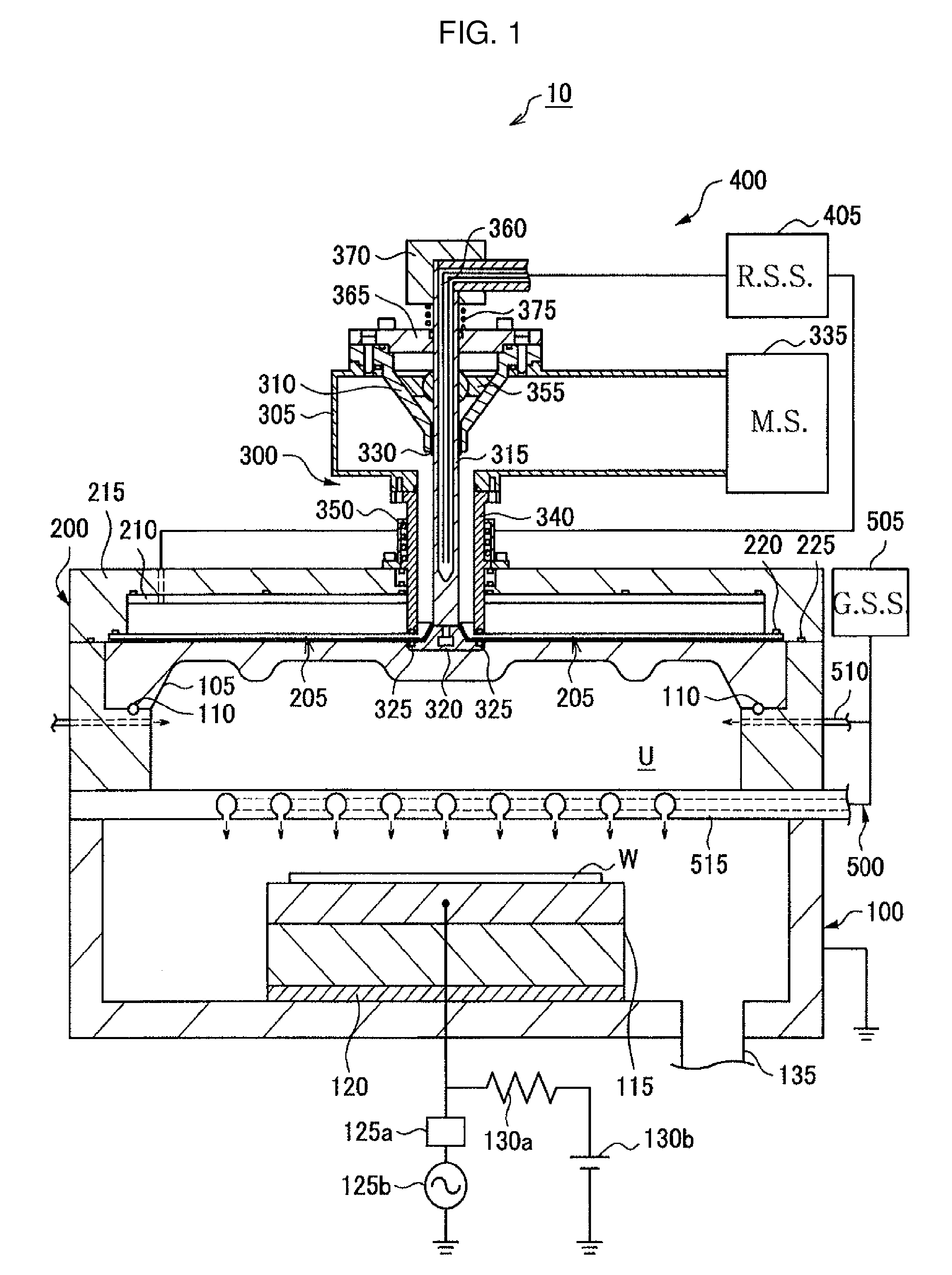
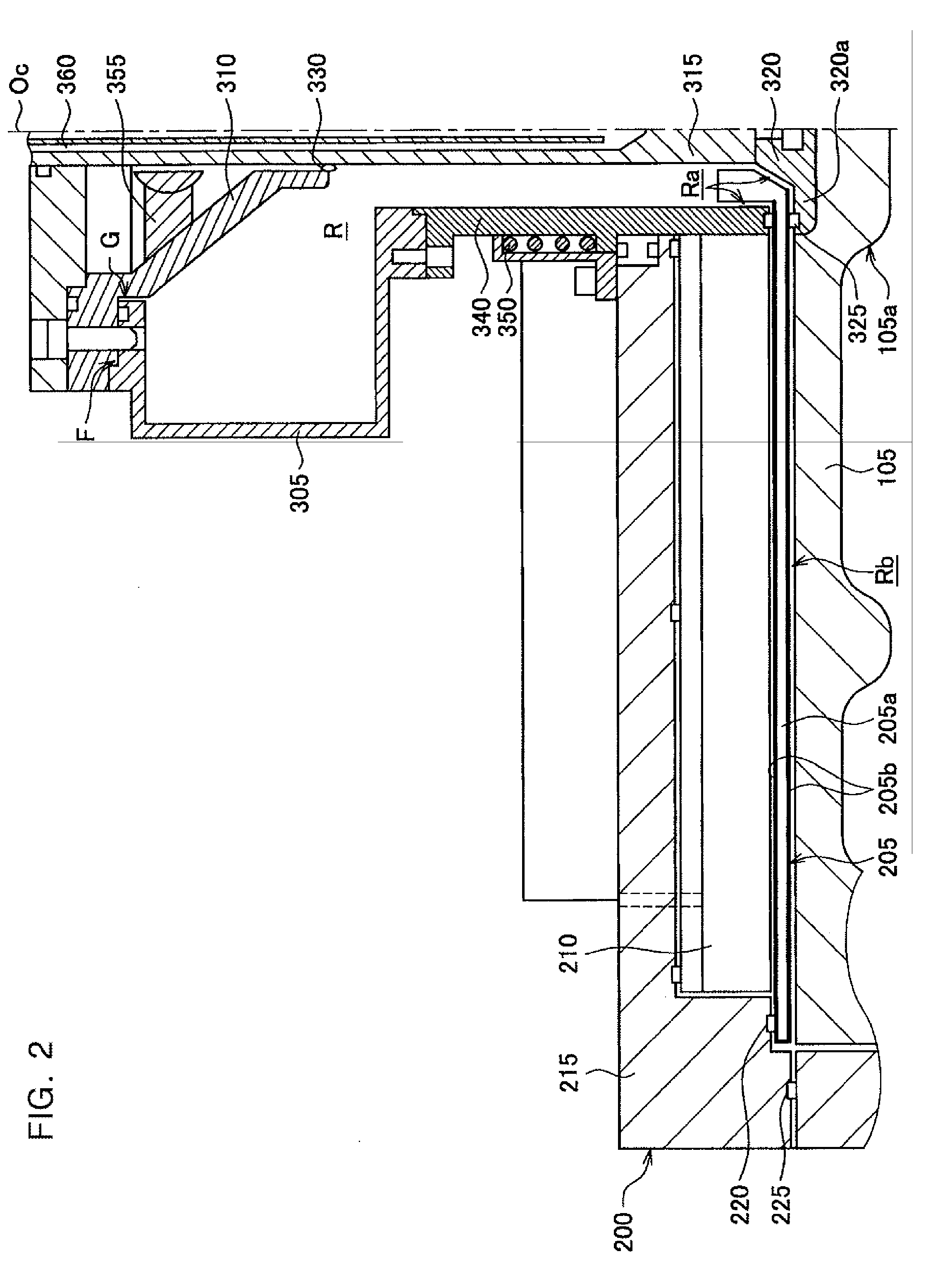
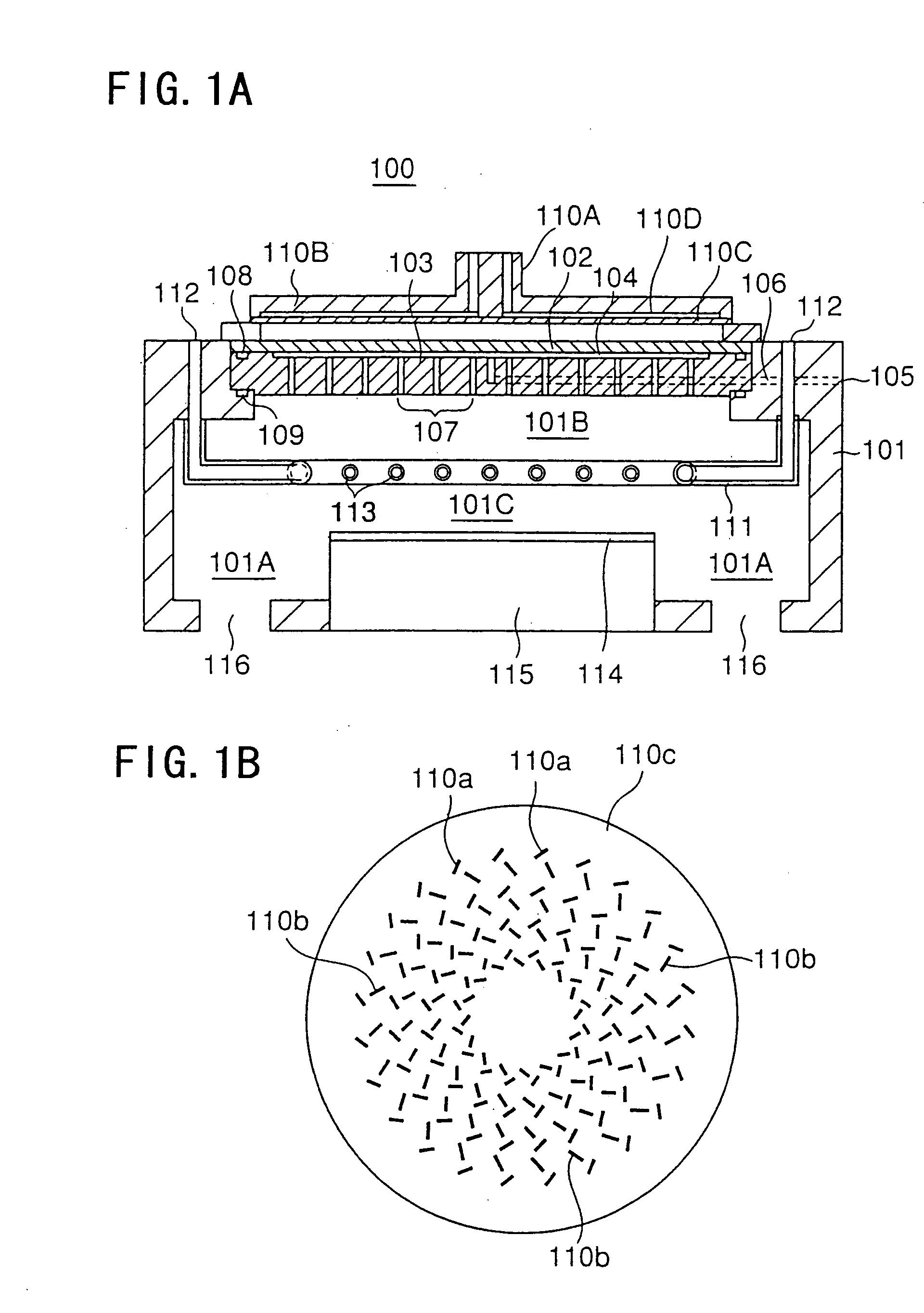
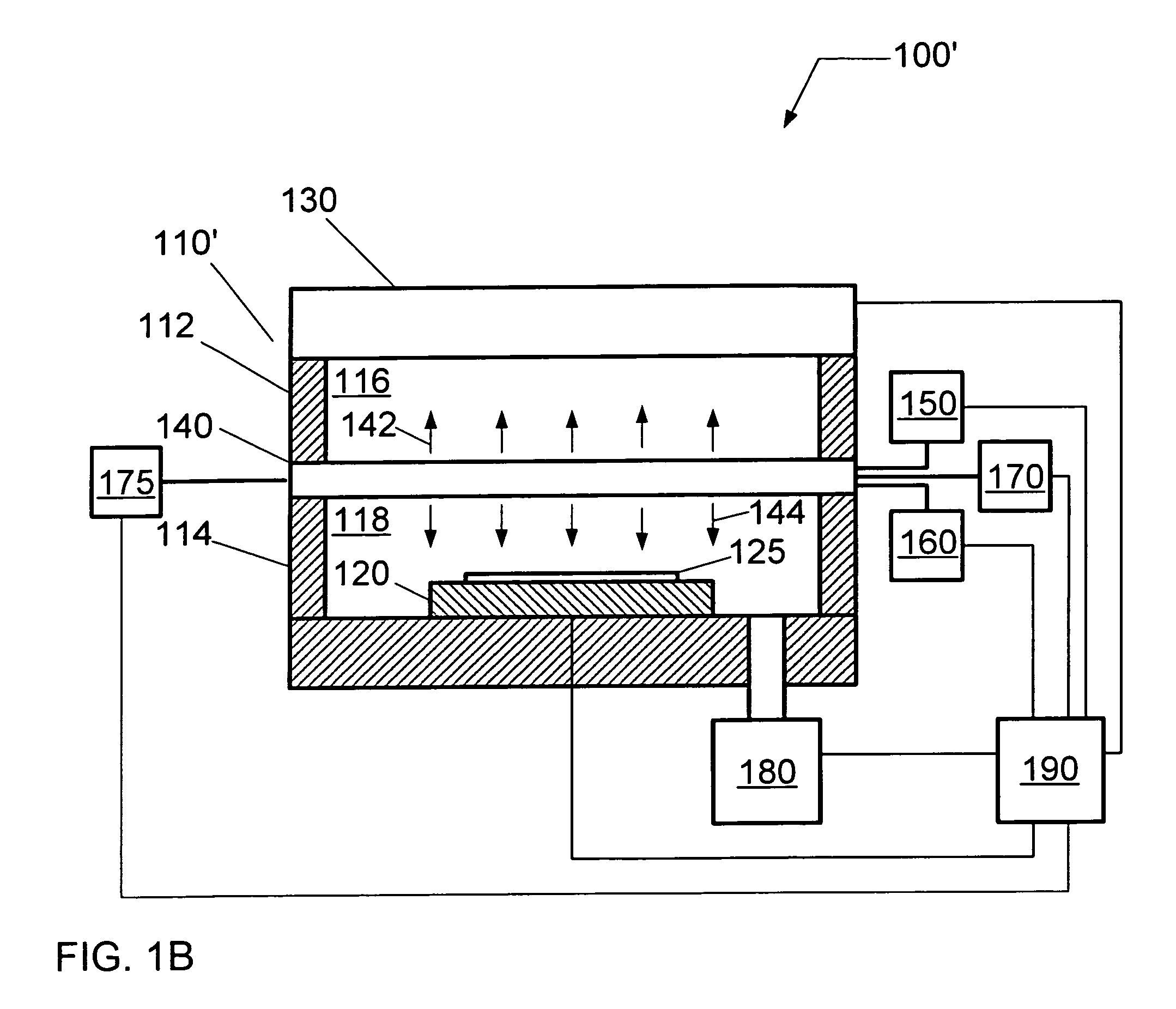
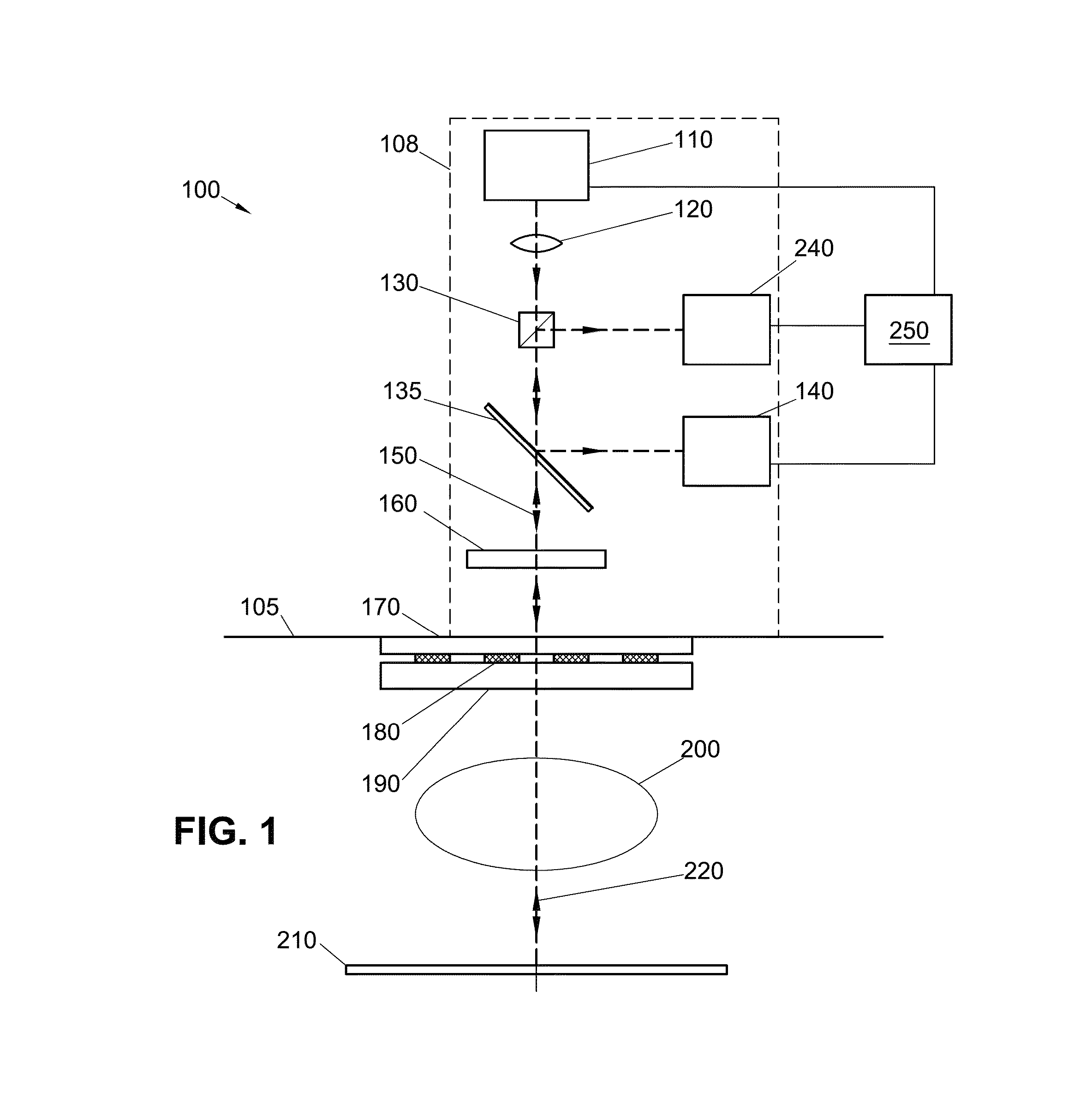
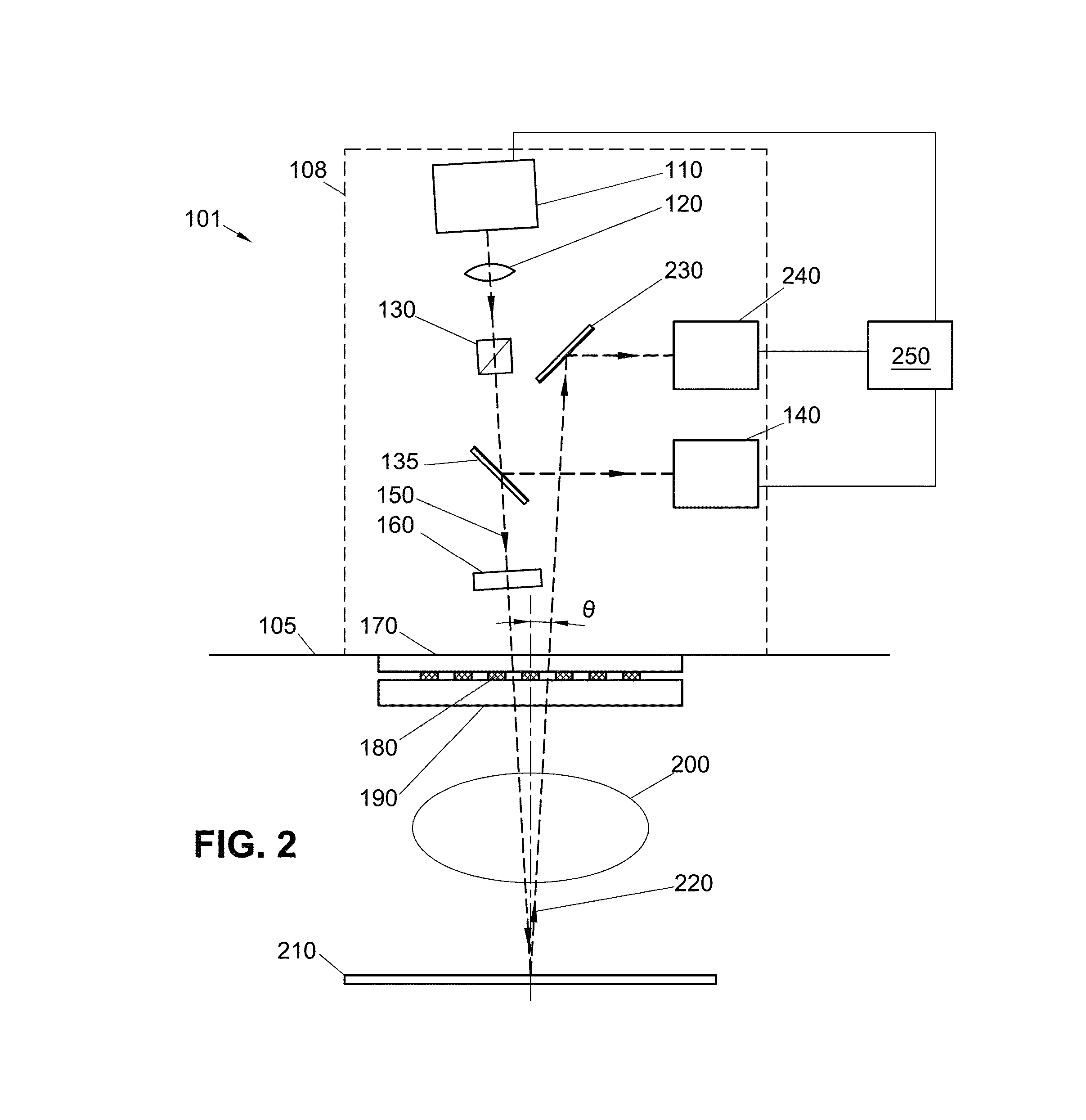
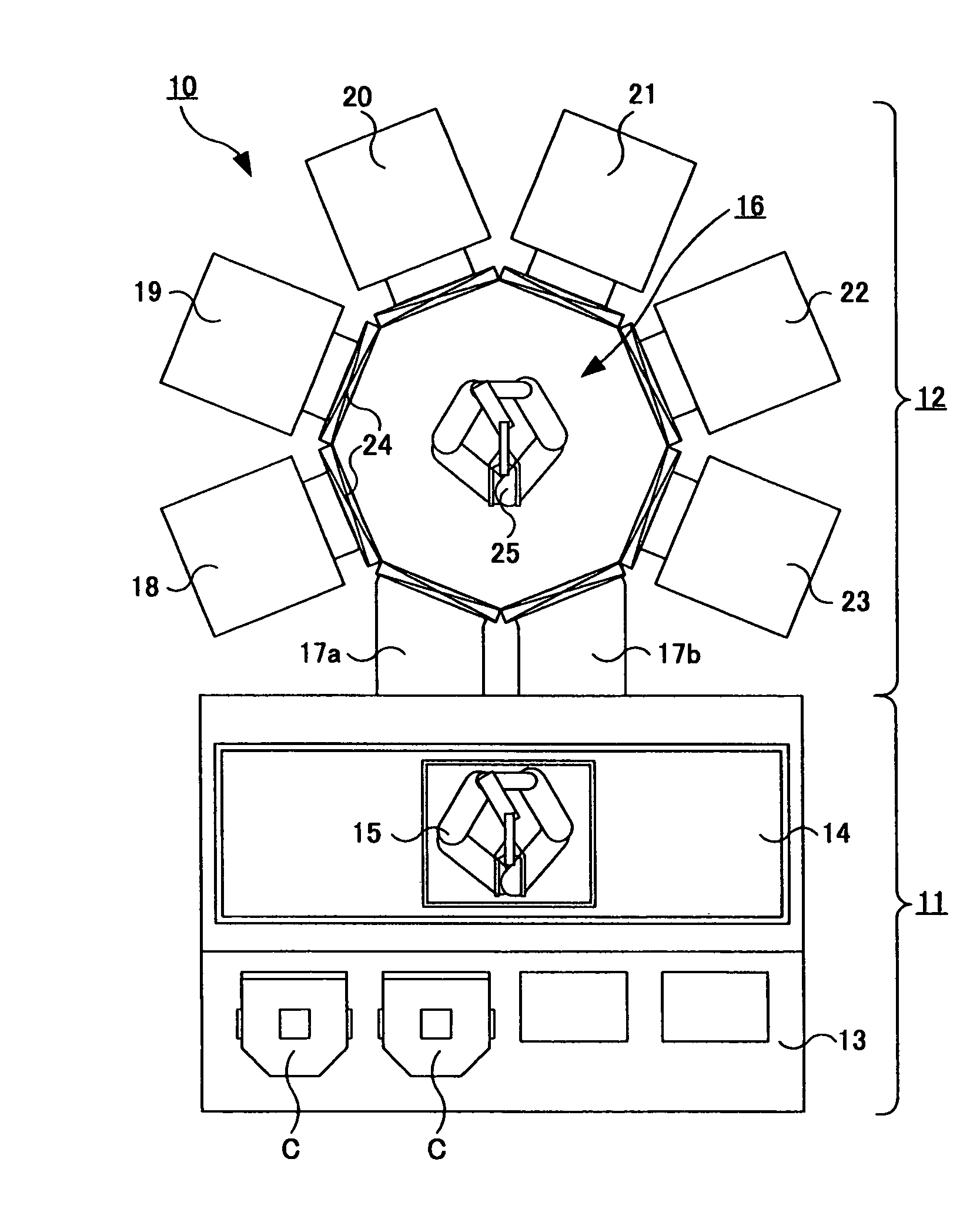
Substrate processing method, computer readable recording medium and substrate processing apparatus
InactiveUS20070062453A1Low dielectric constantImprove heat resistanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMicrowaveEngineering
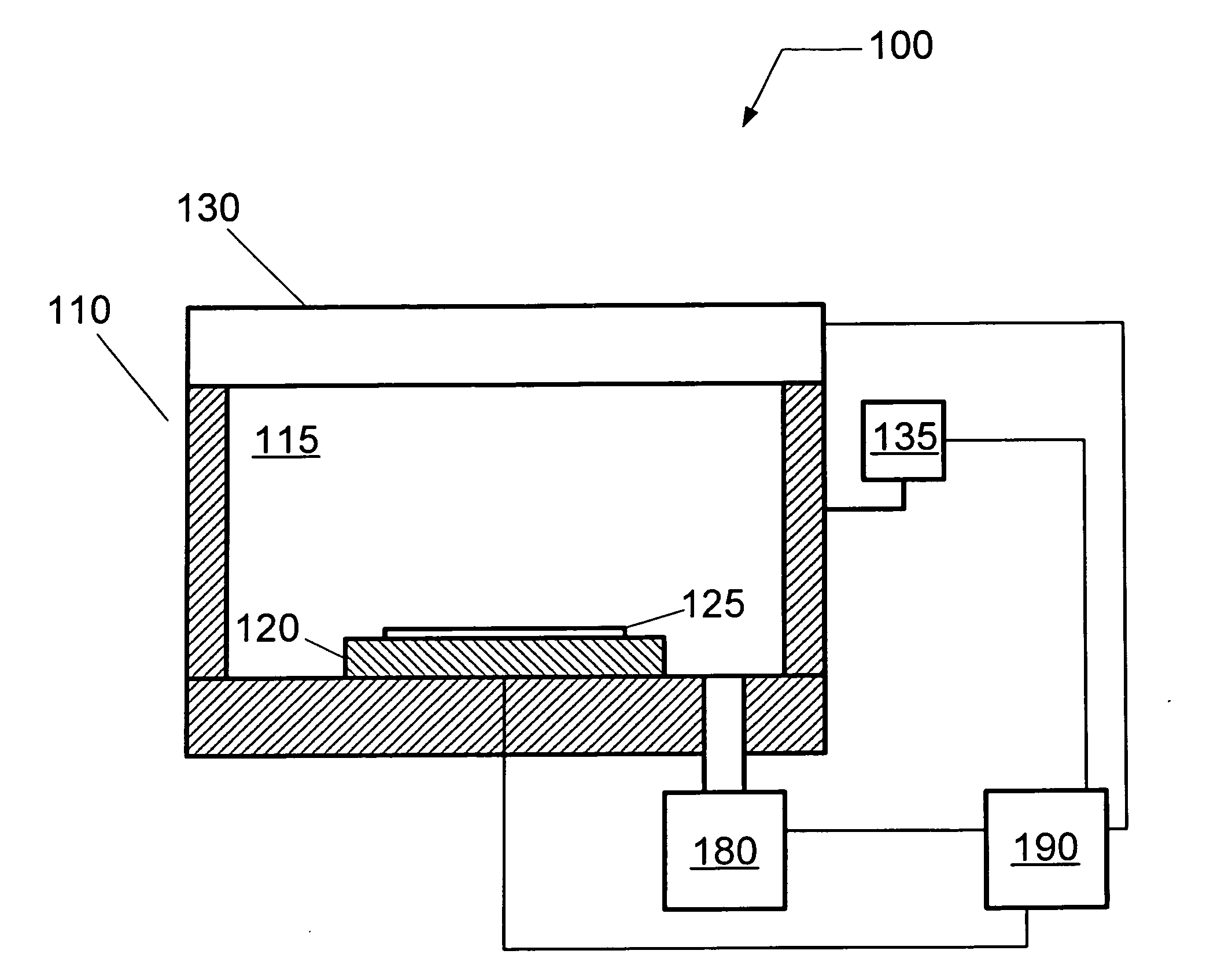
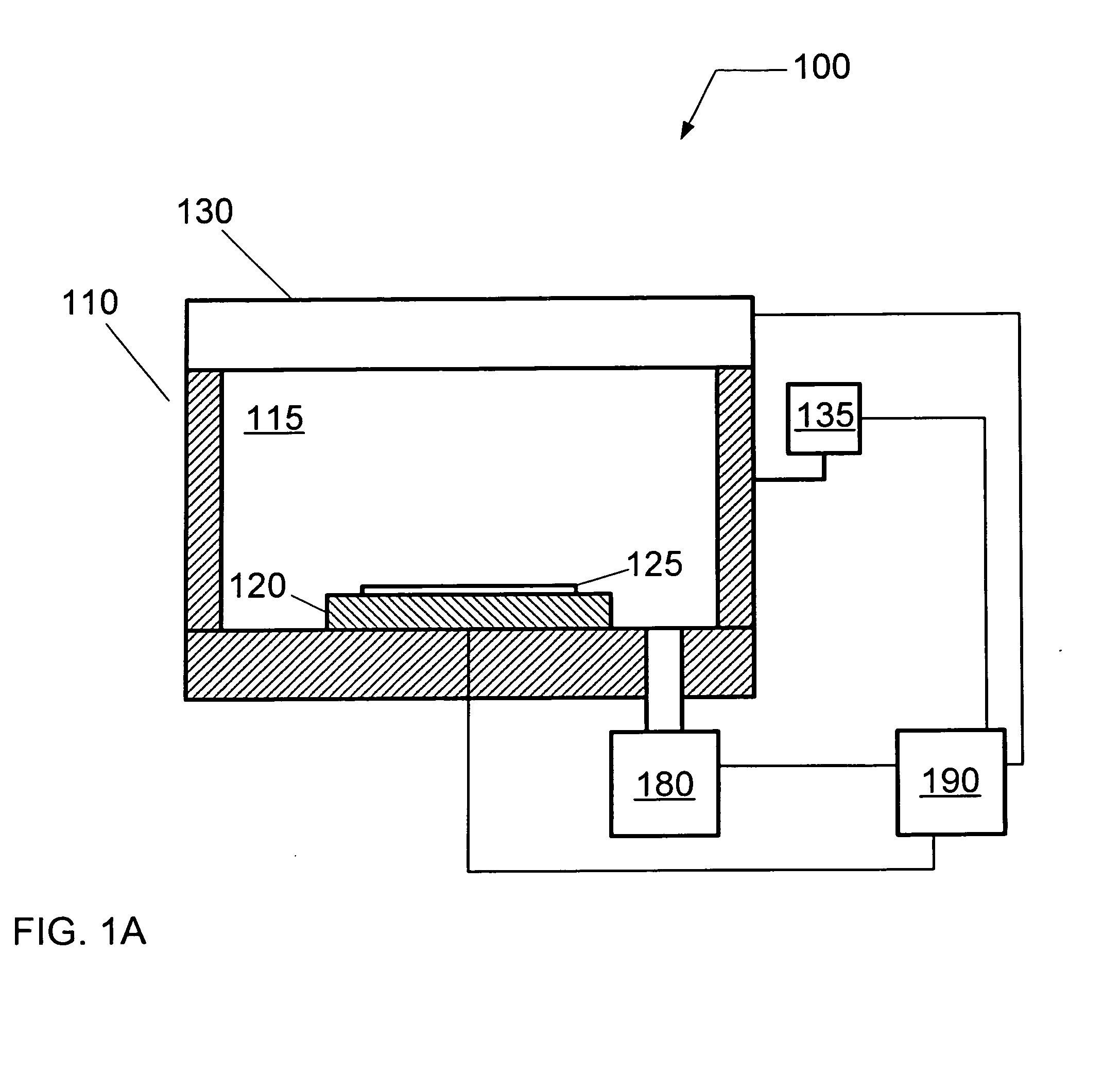
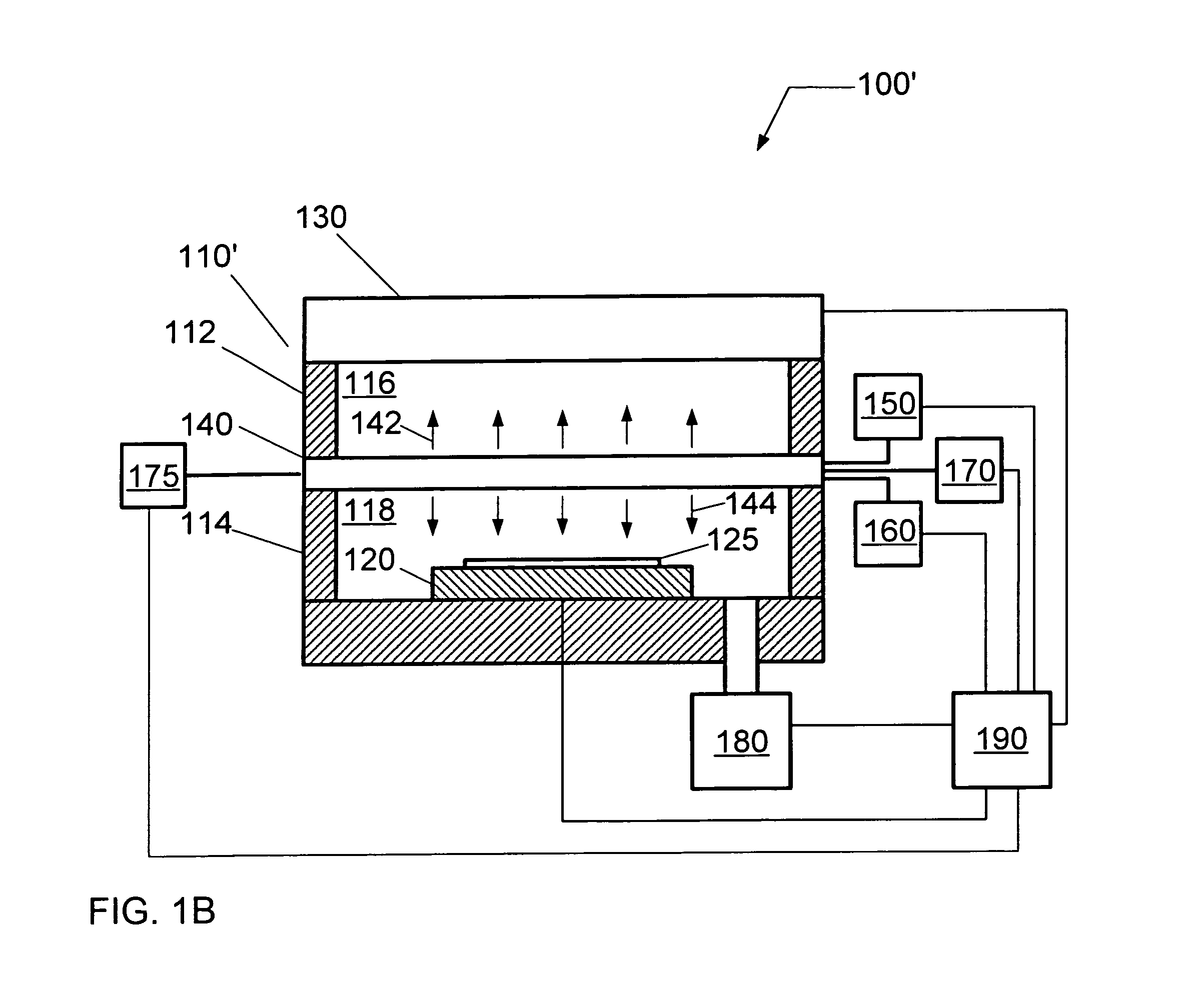
In the present invention, Ar gas for plasma generation is supplied to a plasma generation region and butyne gas having a multiple bond is supplied to a film formation region at a substrate side as source gas, inside of a process vessel in an insulating film forming apparatus. A microwave is supplied inside of the process vessel from a radial line slot antenna under a state in which a bias voltage is not applied to a substrate W. A plasma is thereby generated in the plasma generation region, the butyne gas in the film formation region is activated by the plasma, and an insulating film of amorphous carbon is formed on the substrate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
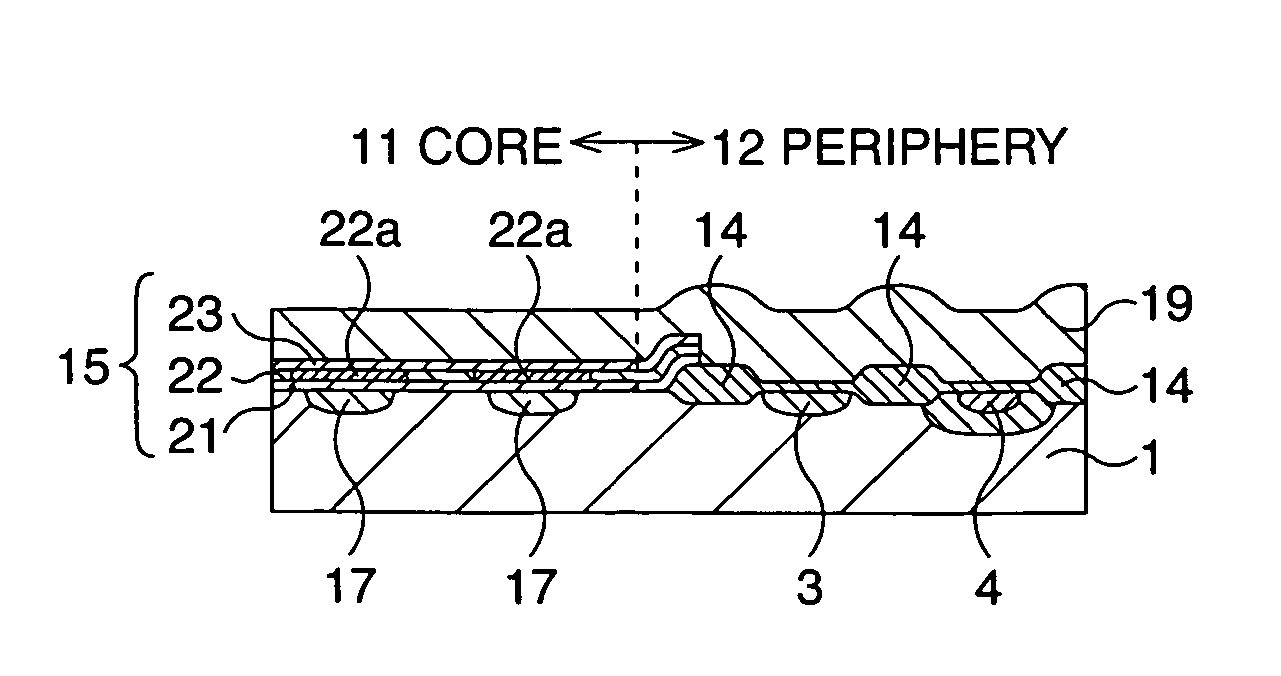
Semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
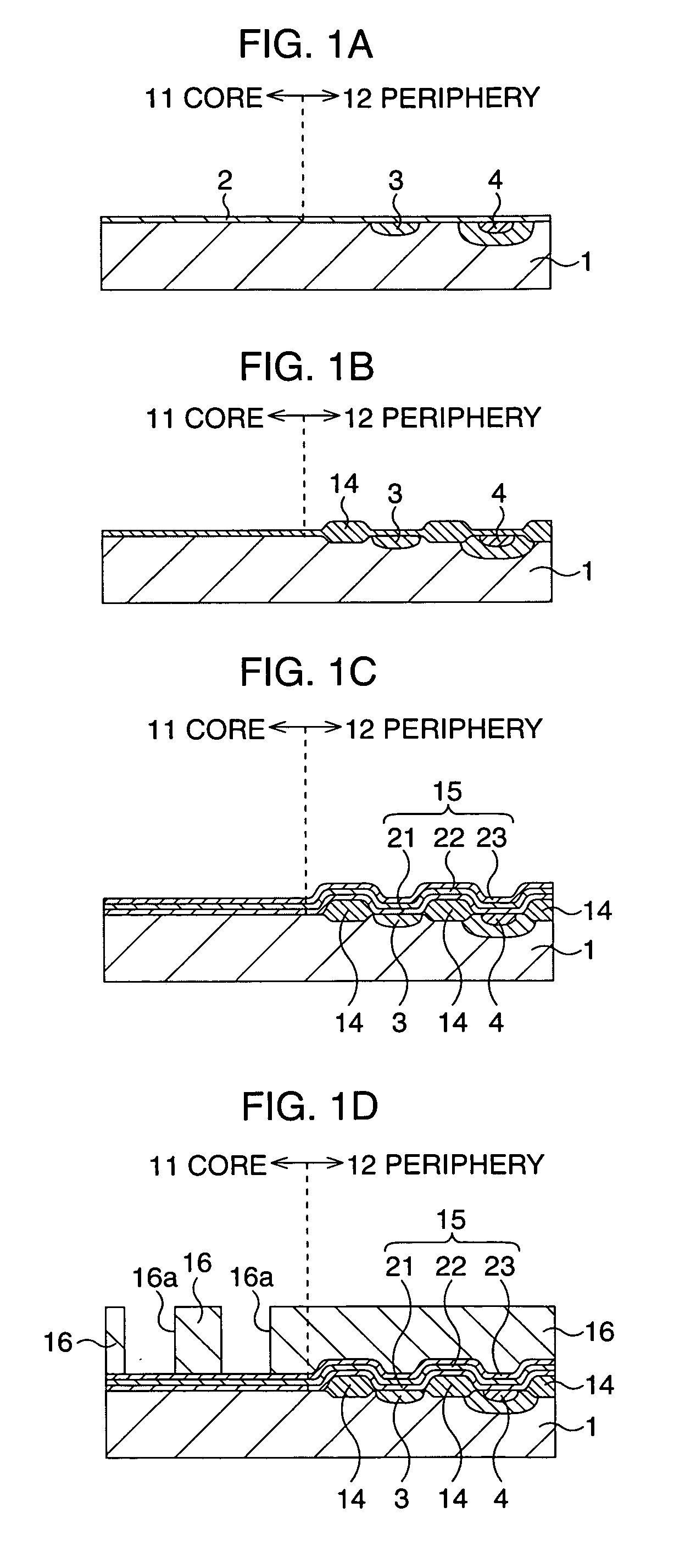
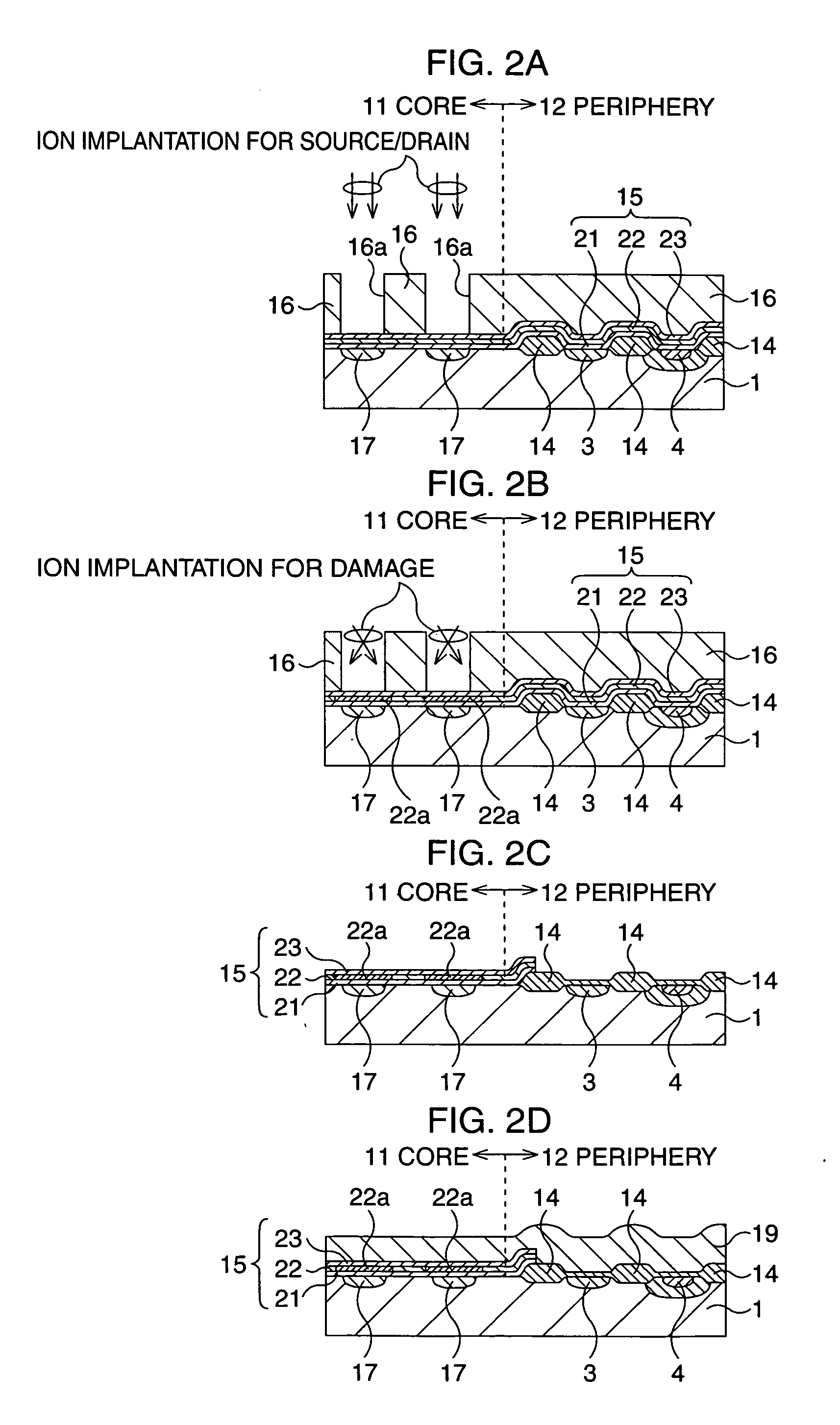
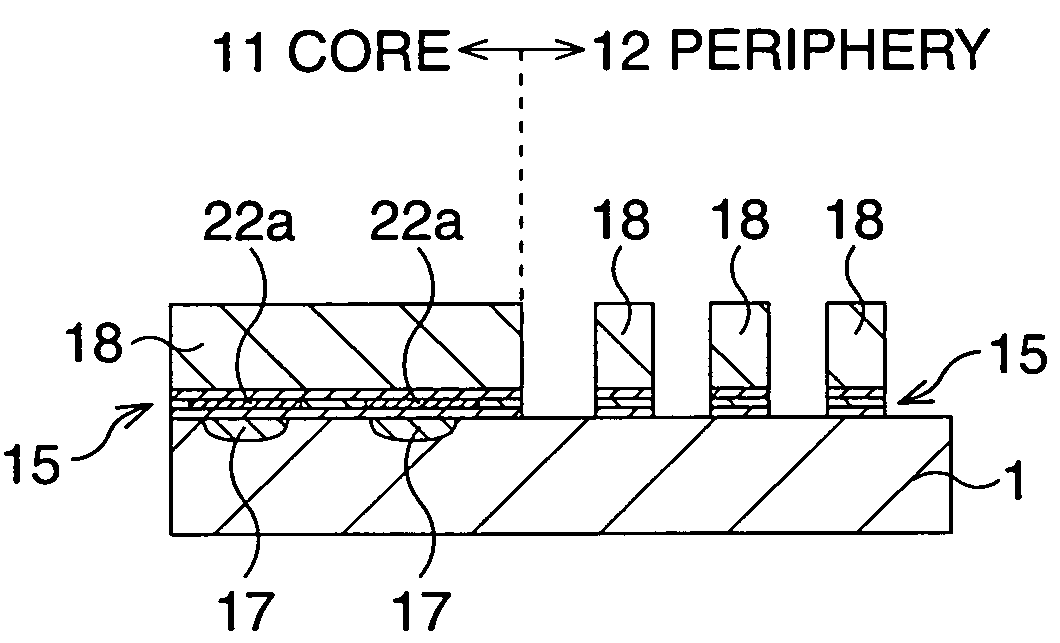
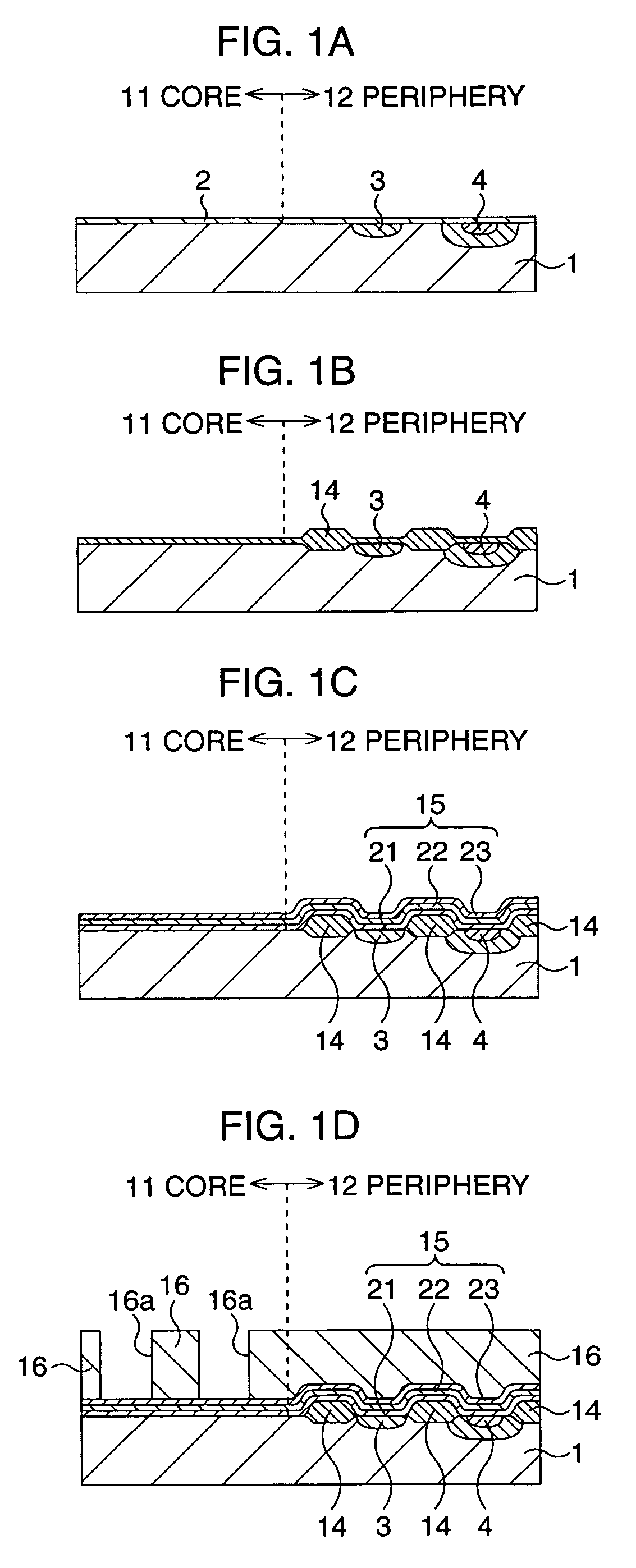
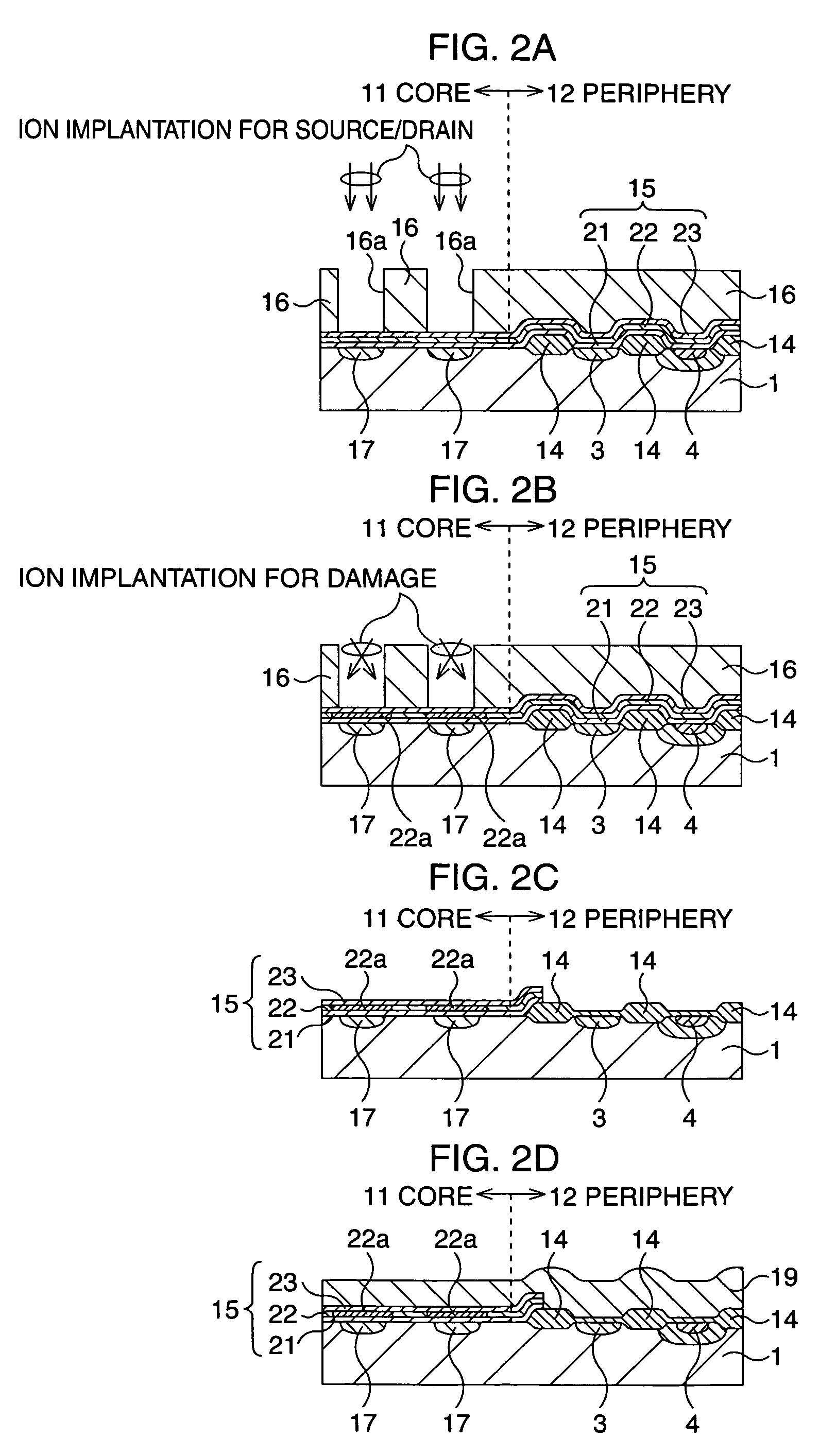
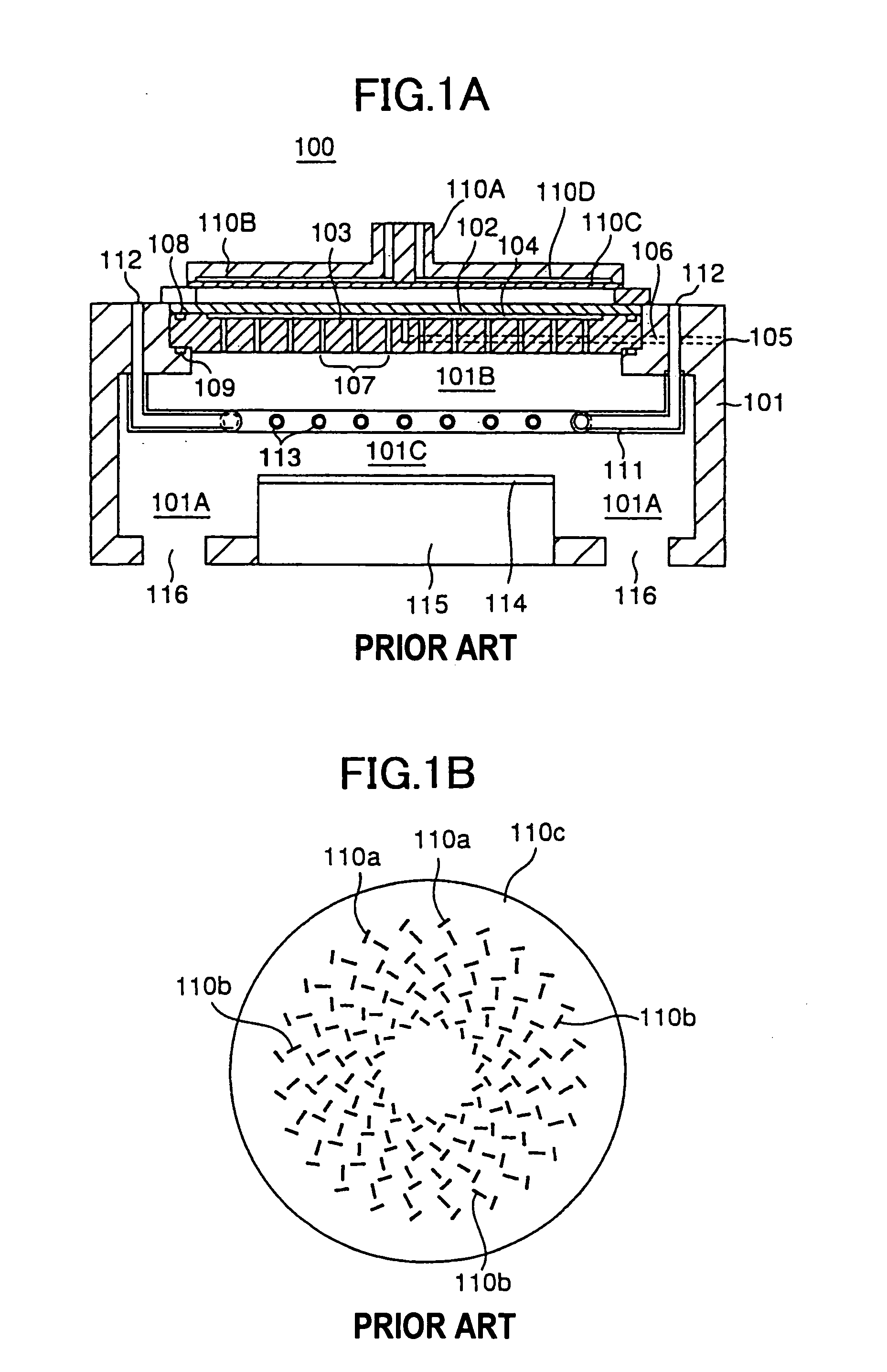
After an ONO film in which a silicon nitride film (22) formed by a plasma nitriding method using a plasma processor having a radial line slot antenna is sandwiched by silicon oxide films (21), (23), a bit line diffusion layer (17) is formed in a memory cell array region (11) by an ion implantation as a resist pattern (16) taken as a mask, then lattice defects are given to the silicon nitride film (22) by a further ion implantation. Accordingly, a highly reliable semiconductor memory device can be realized, in which a high quality nitride film is formed in a low temperature condition, in addition, the nitride film can be used as a charge trap film having a charge capture function sufficiently adaptable for a miniaturization and a high integration which are recent demands.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
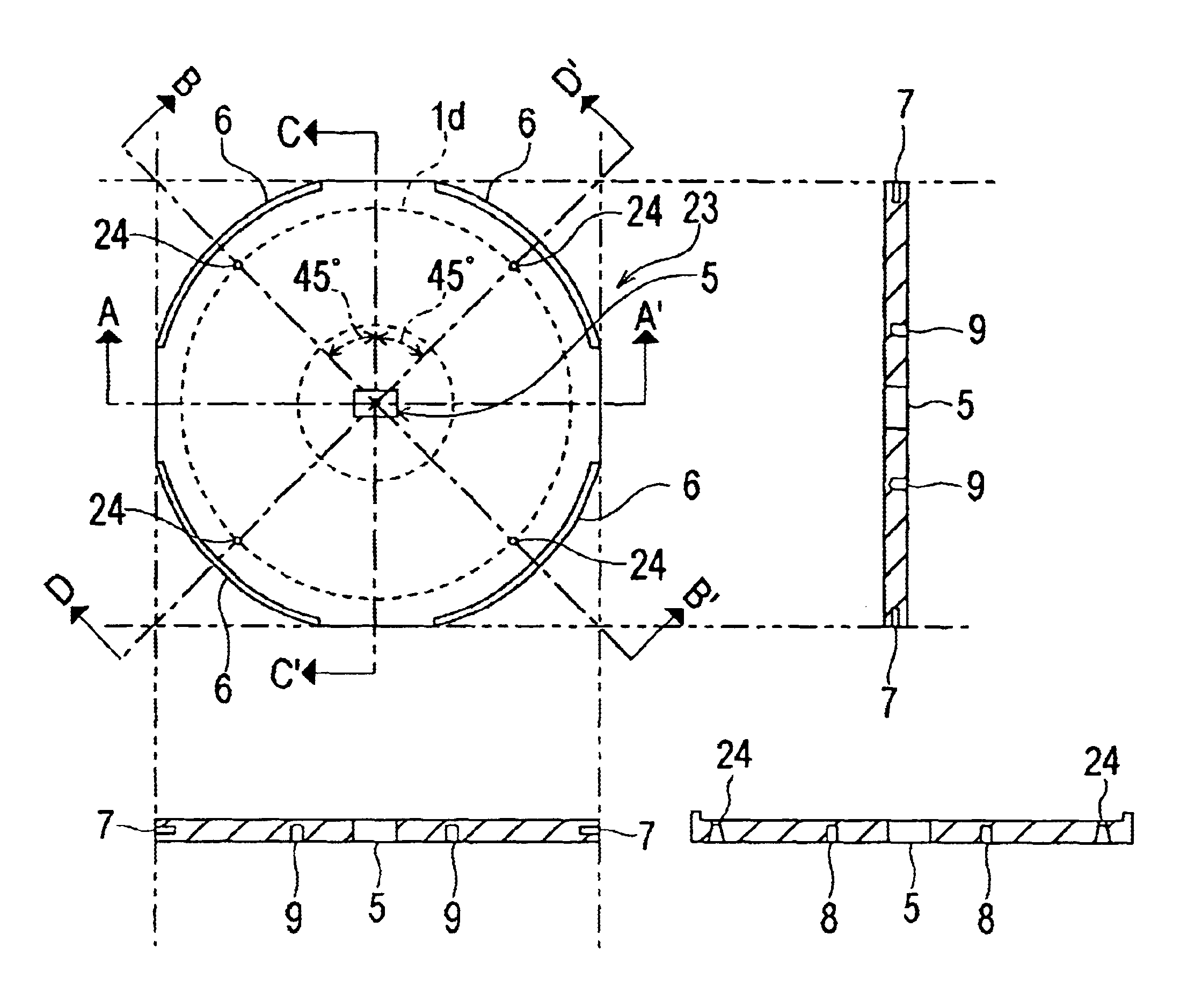
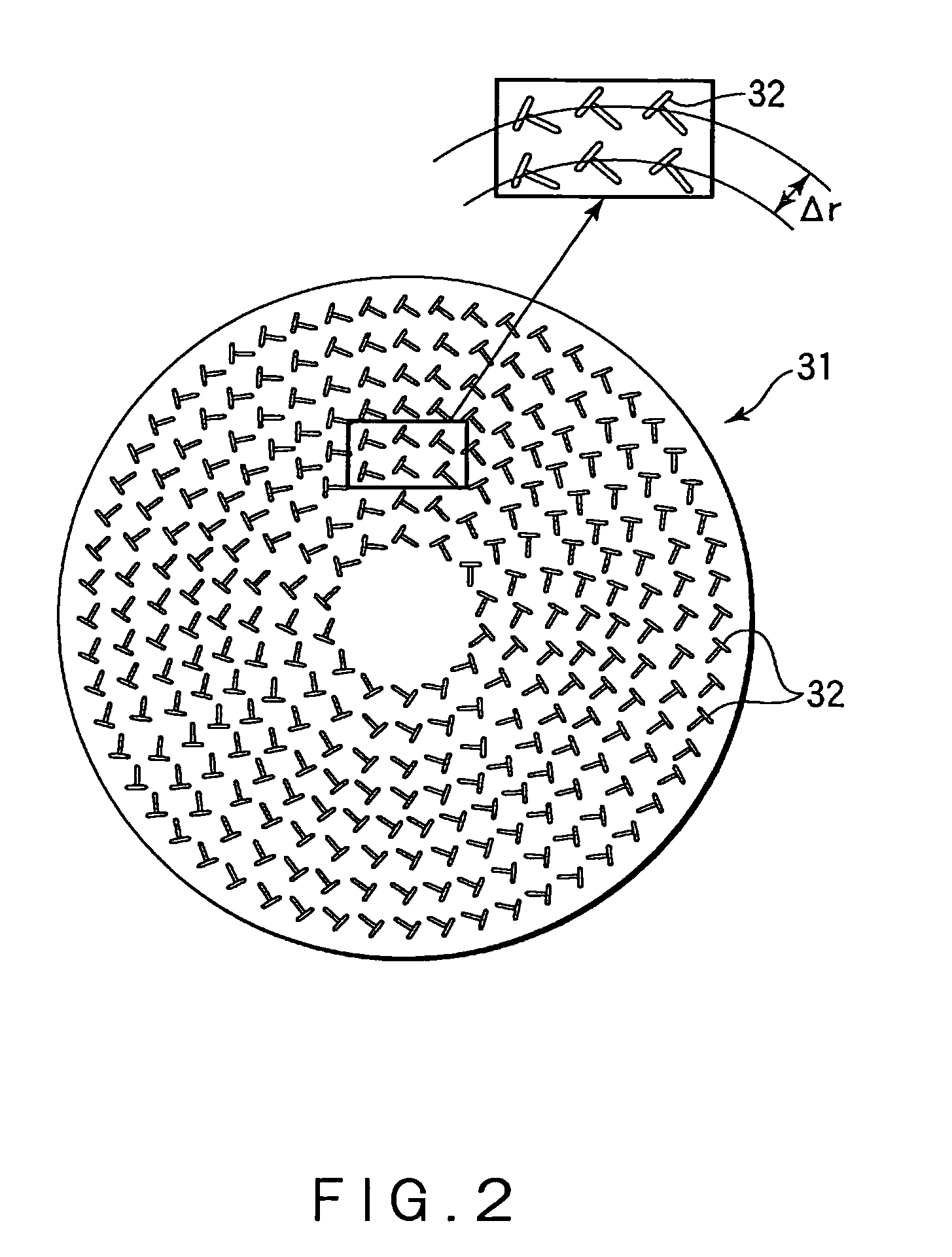
Steerable radial line slot antenna
InactiveUS7233297B1Improve efficiencyMaximum sensitivityIndividually energised antenna arraysSlot antennasBeam angleDielectric
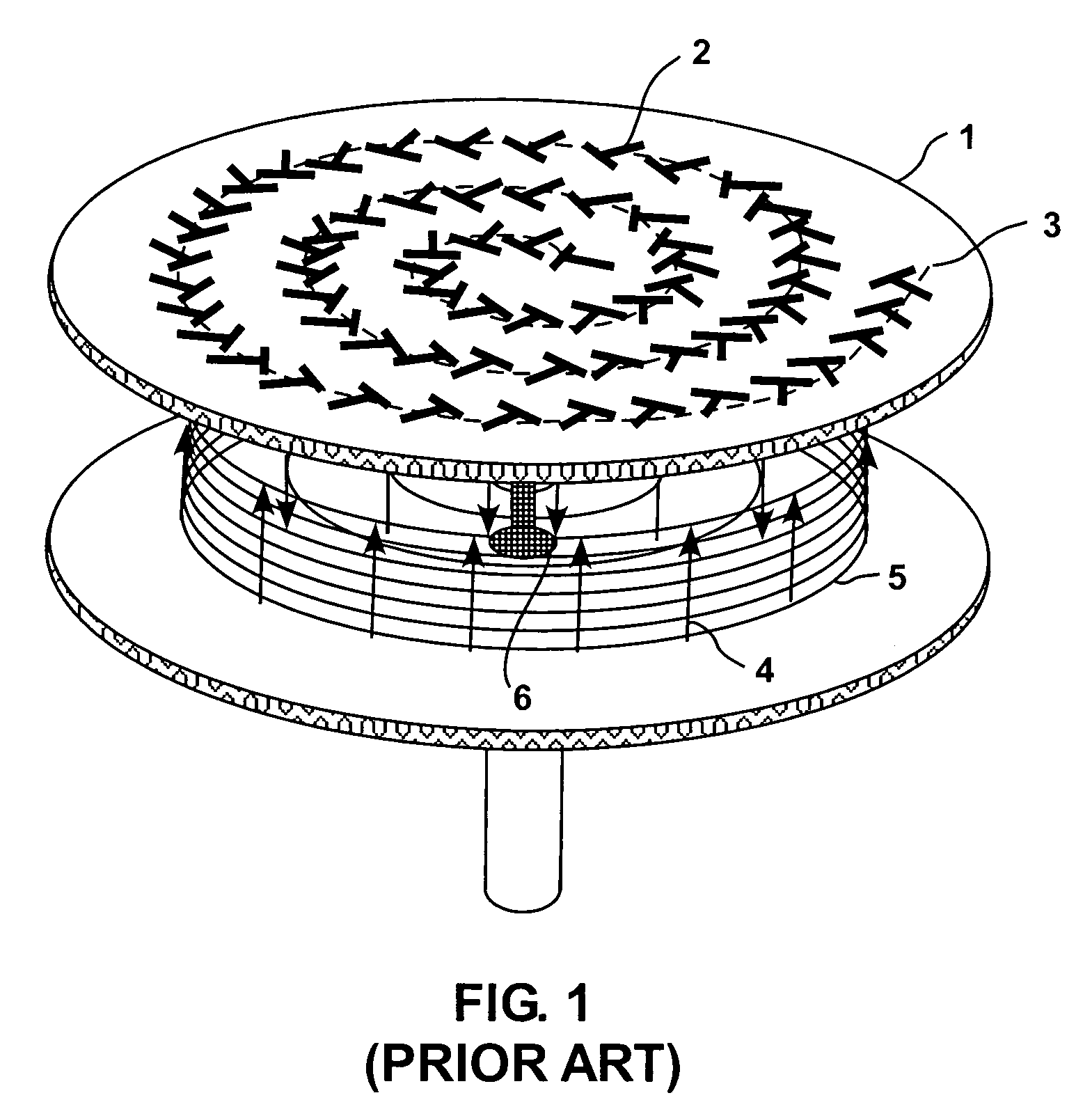
A steerable antenna comprising an array of T-shaped slots. The location of the slots is moved to define an array of ring- or spiral-patterned phase constant regions. Distortions or contractions of the pattern occur by repositioning some or all of the slots forming the array. The antenna also comprises an intermediate insulating layer and a lower plate. The insulating layer is formed by a deformable dielectric medium. Deformation of the dielectric medium allows the beam angle to be altered.
Owner:HRL LAB
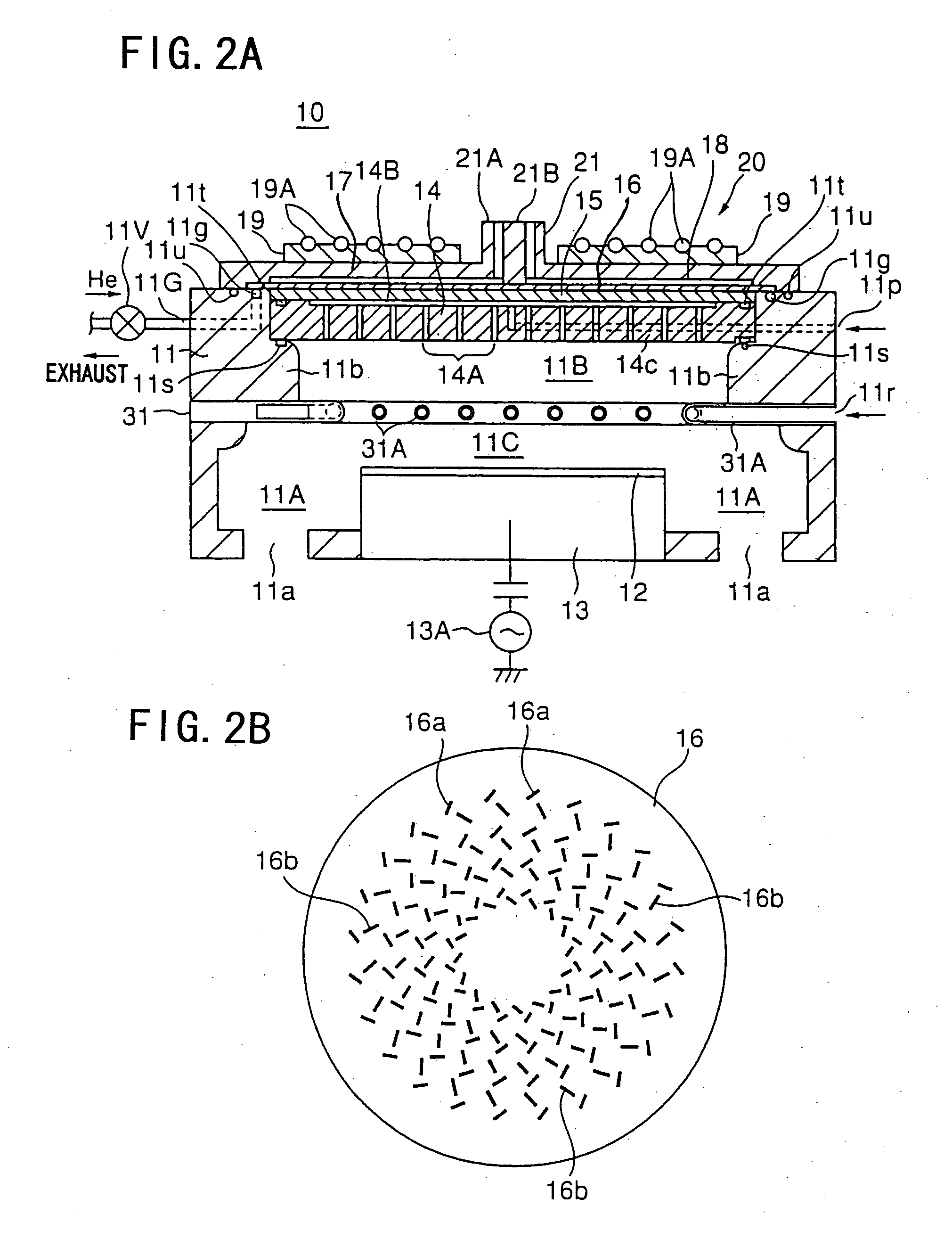
Low electron temperature, edge-density enhanced, surface wave plasma (SWP) processing method and apparatus
ActiveUS20130270997A1High degree of ionizationReduces temperature of electronElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceElectron temperature
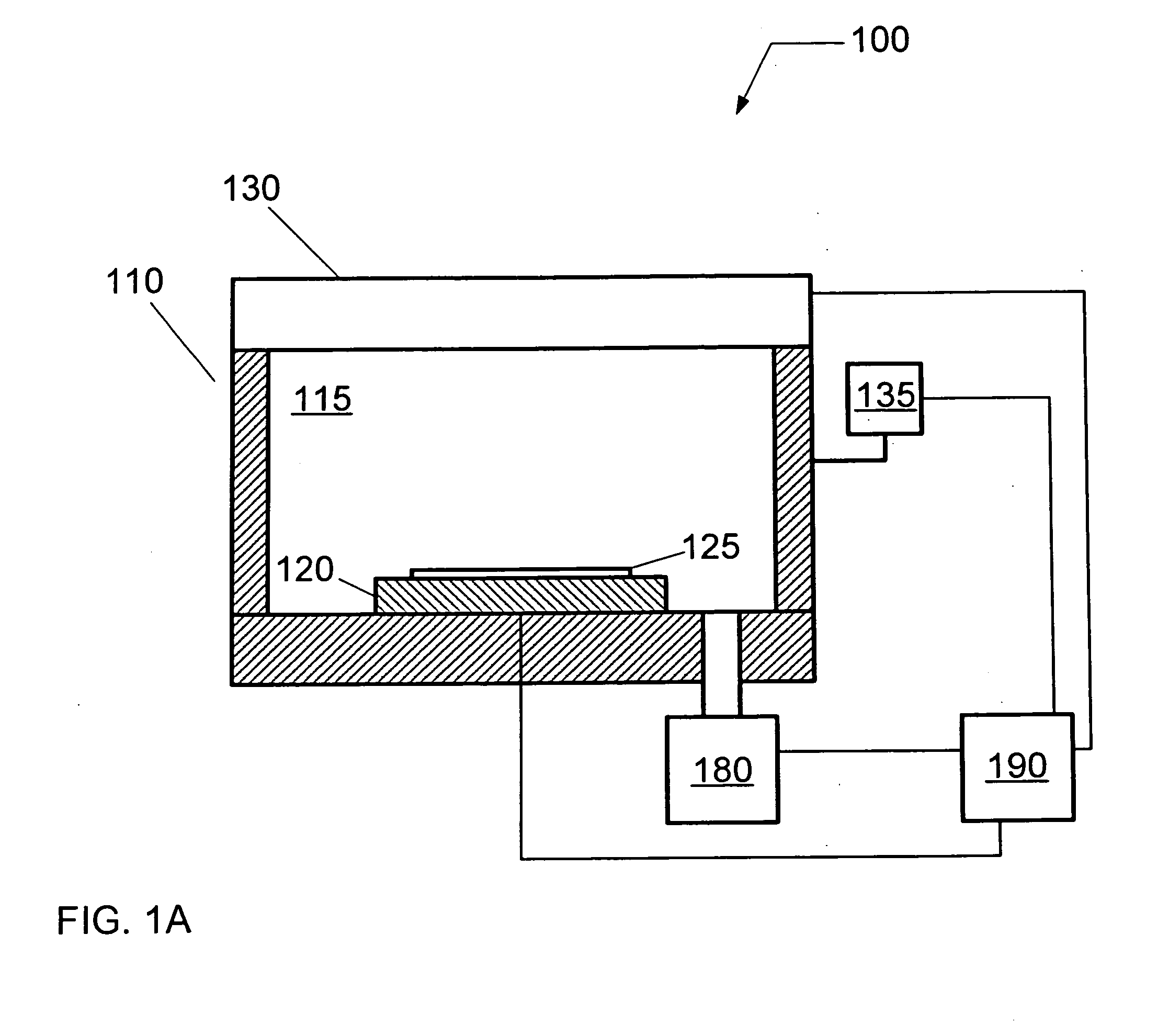
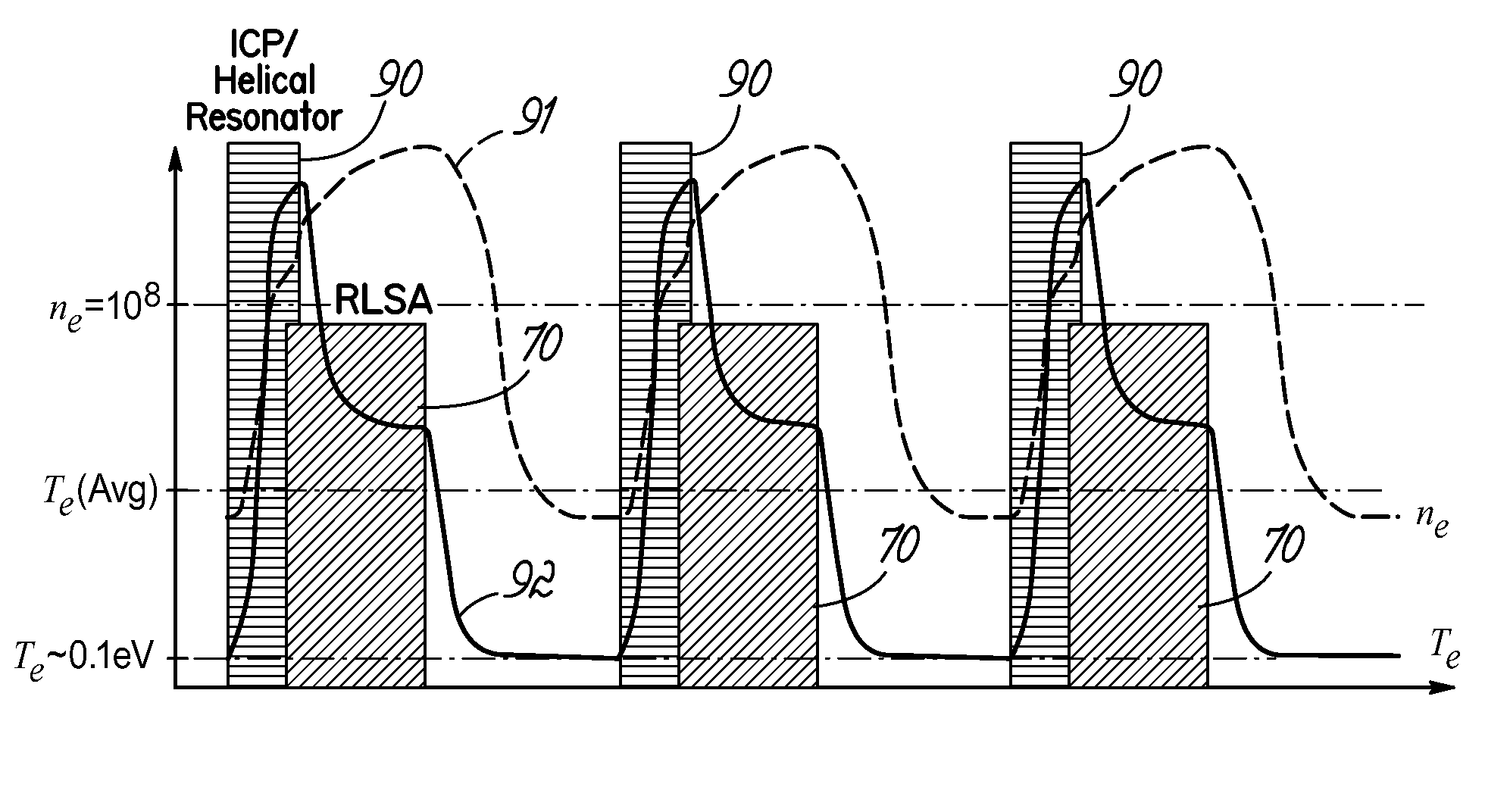
A surface wave plasma (SWP) source couples microwave (MW) energy into a processing chamber through, for example, a radial line slot antenna, to result in a low mean electron energy (Te). An ICP source, is provided between the SWP source and the substrate and is energized at a low power, less than 100 watts for 300 mm wafers, for example, at about 25 watts. The ICP source couples energy through a peripheral electric dipole coil to reduce capacitive coupling.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Electron beam enhanced surface wave plasma source
InactiveUS20080060759A1Improve robustnessCellsElectric discharge tubesRadial line slot antennaElectron
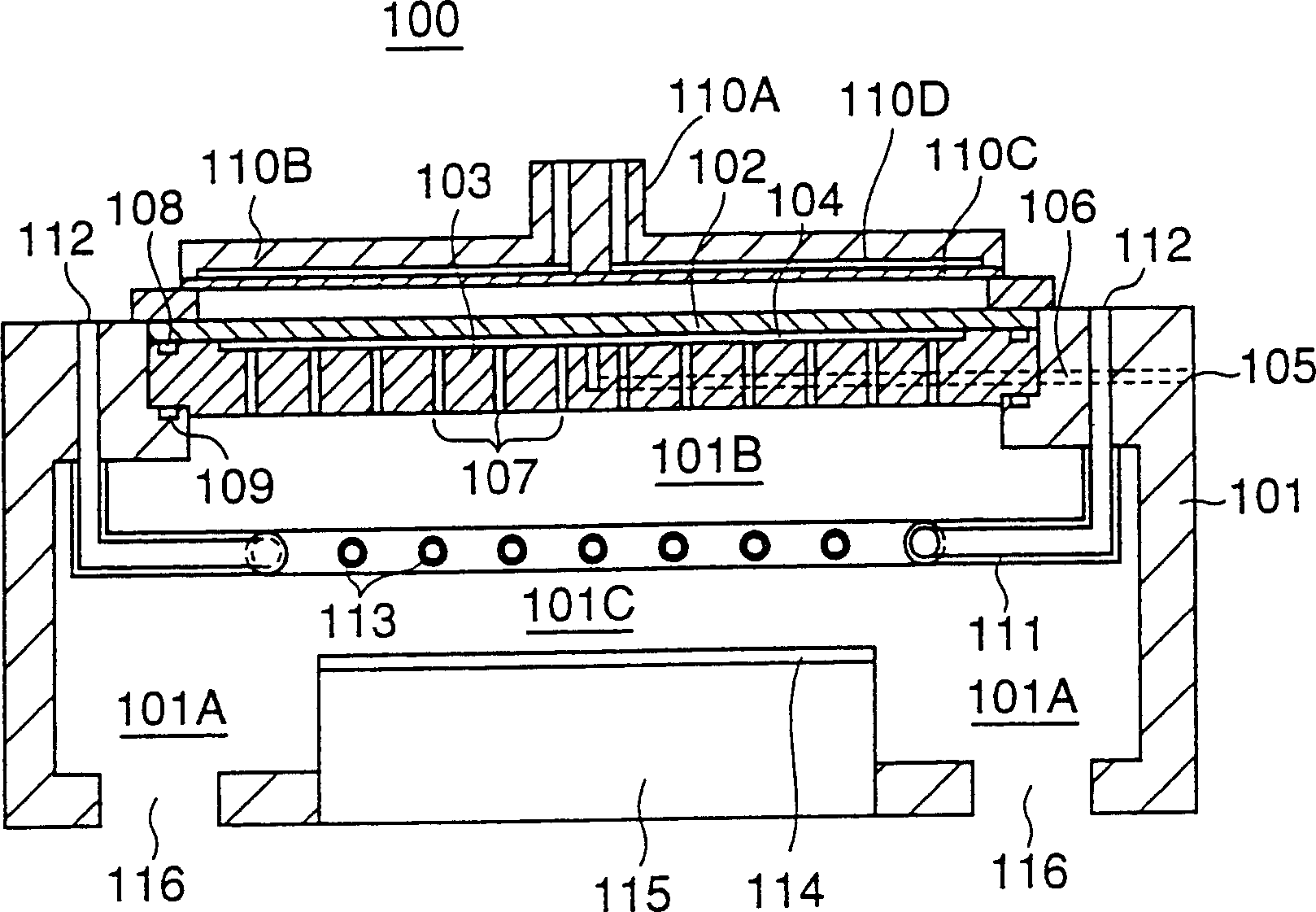
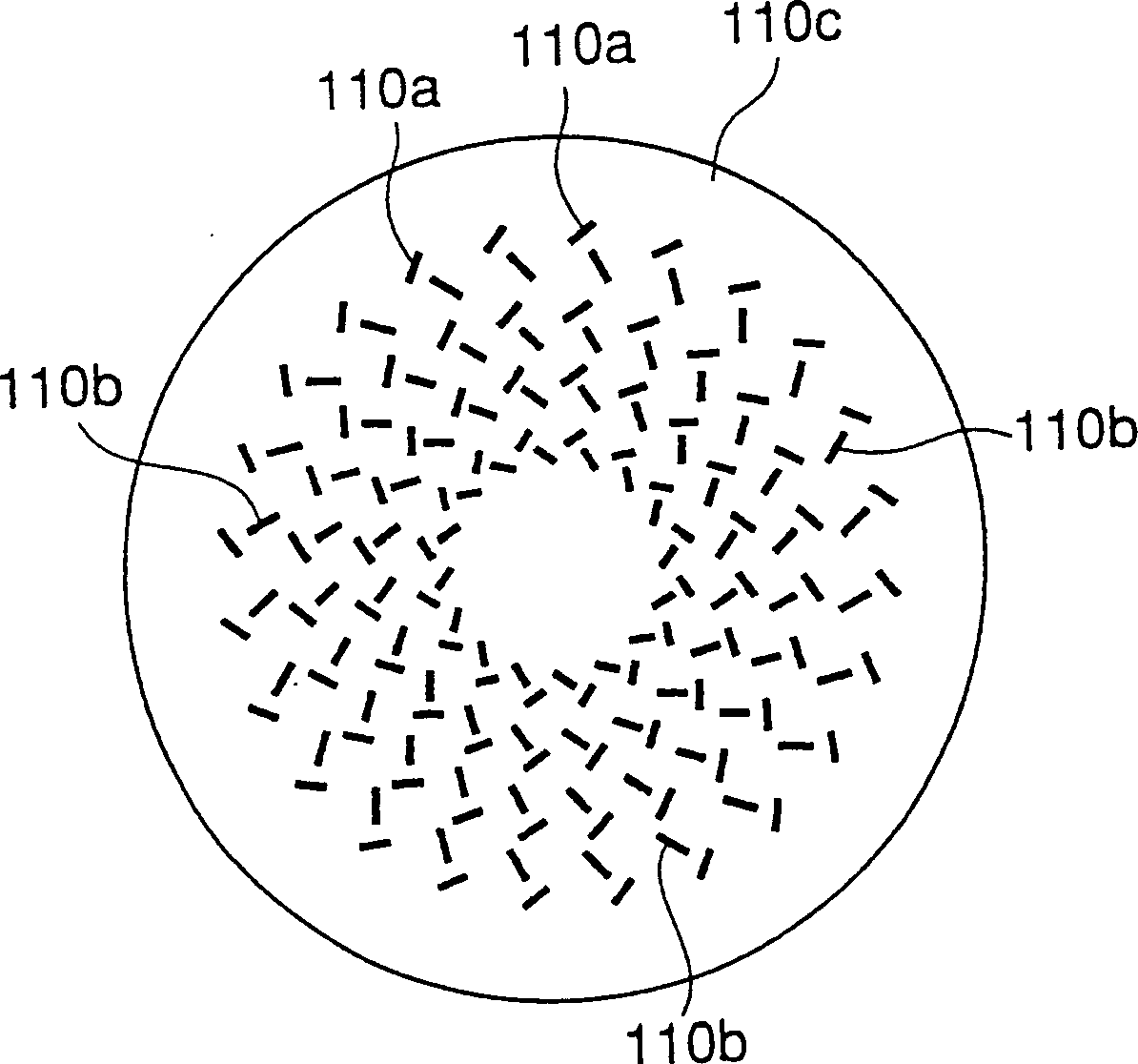
A plasma processing system is described for generating plasma with a ballistic electron beam using a surface wave plasma (SWP) source, such as a radial line slot antenna (RLSA) during semiconductor device fabrication. The antenna comprises a resonator plate having a partially open, electrically conductive layer coupled to a surface of the resonator plate. For example, the electrically conductive layer is formed at an interface between the resonator plate and the plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Low electron temperature microwave surface-wave plasma (SWP) processing method and apparatus
ActiveUS8968588B2High degree of ionizationImprove uniformityLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesElectron temperaturePlasma density
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST +1
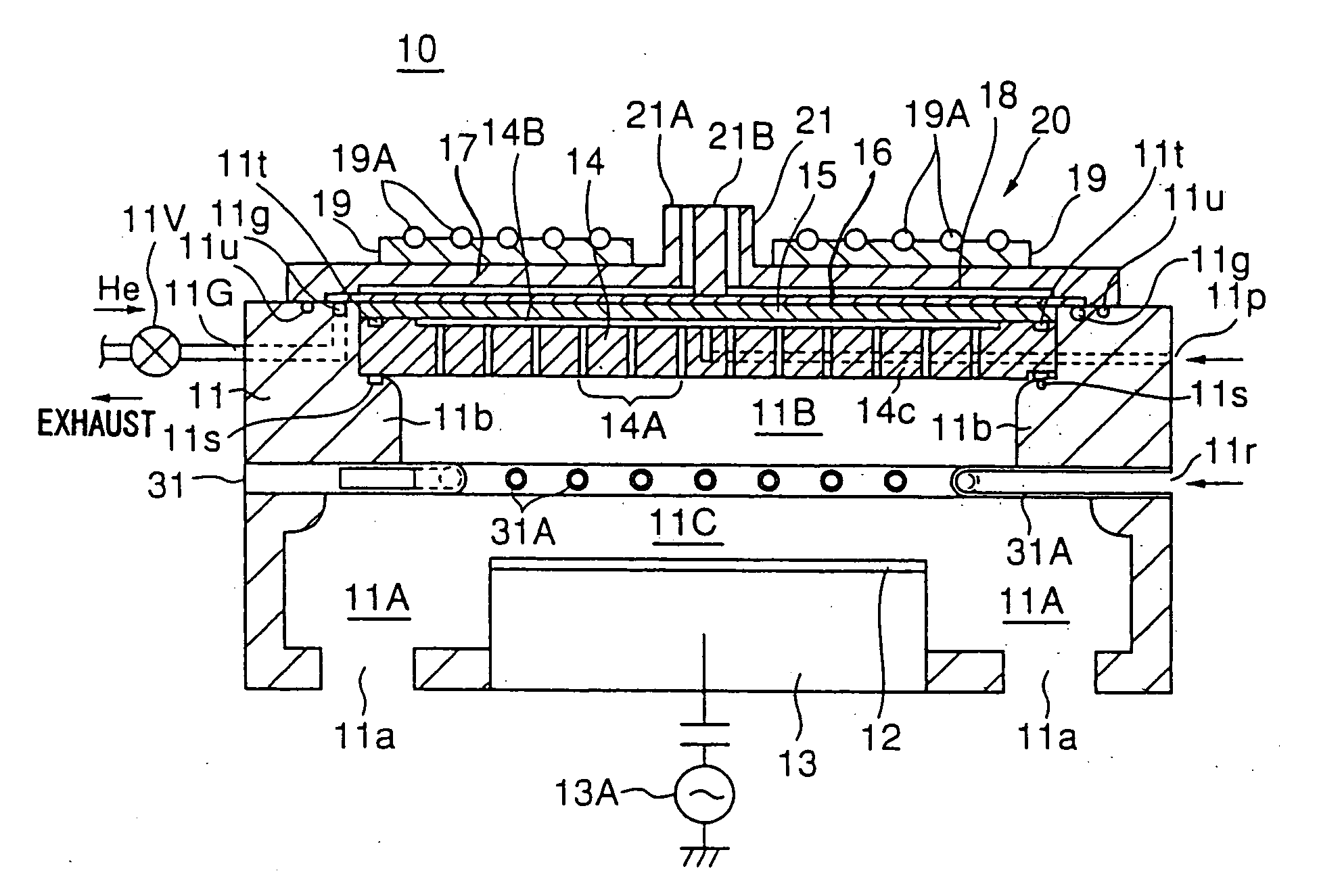
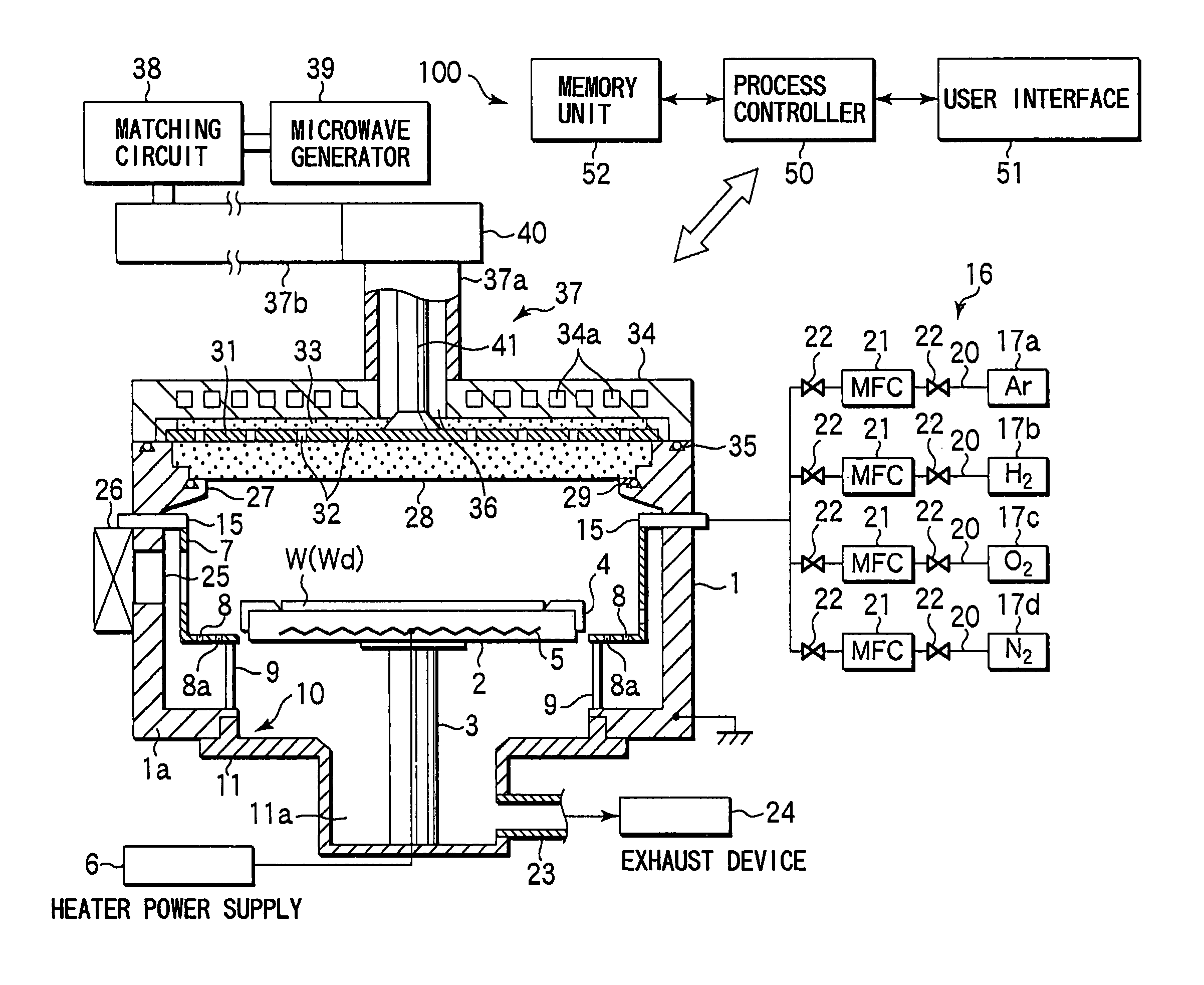
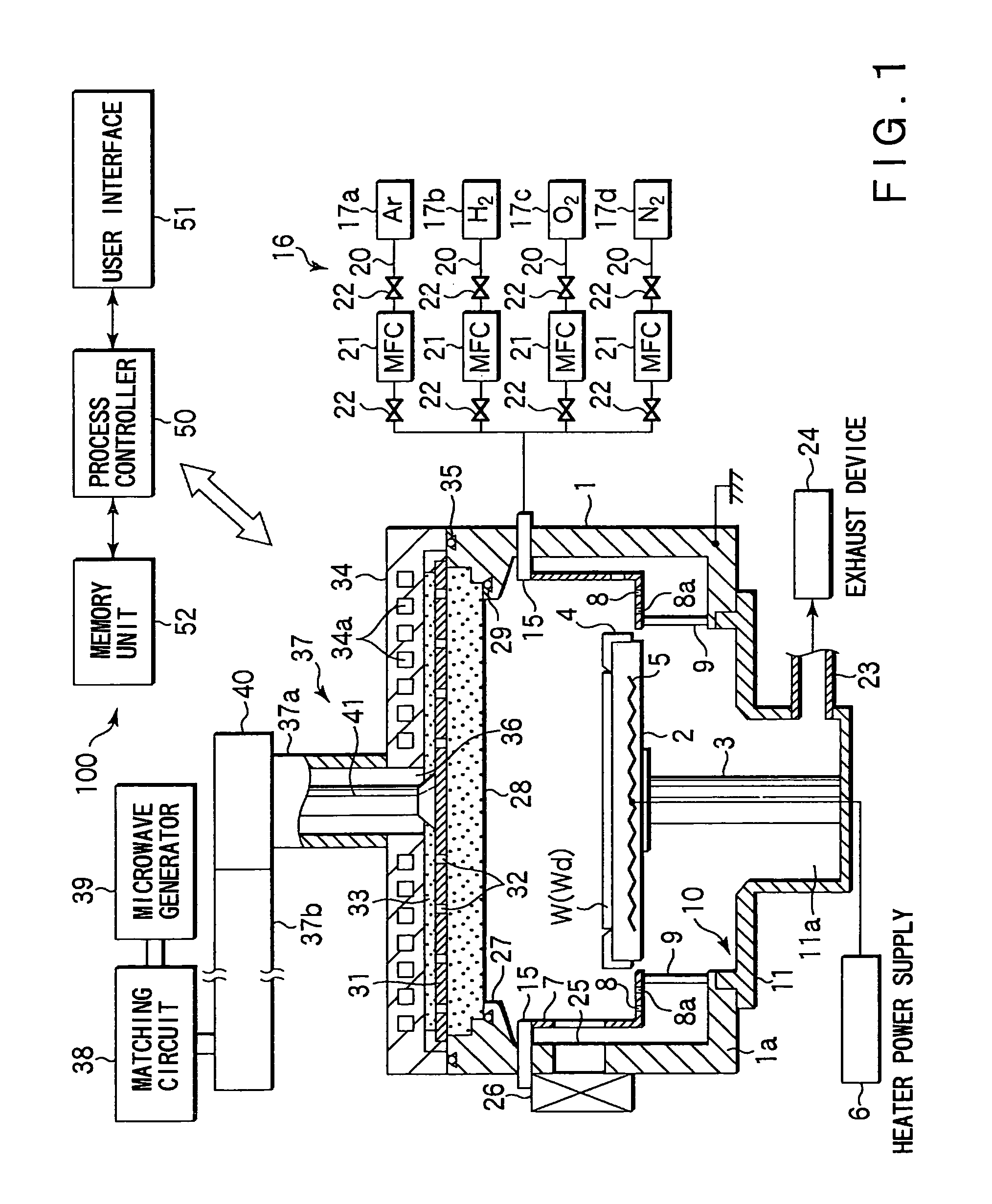
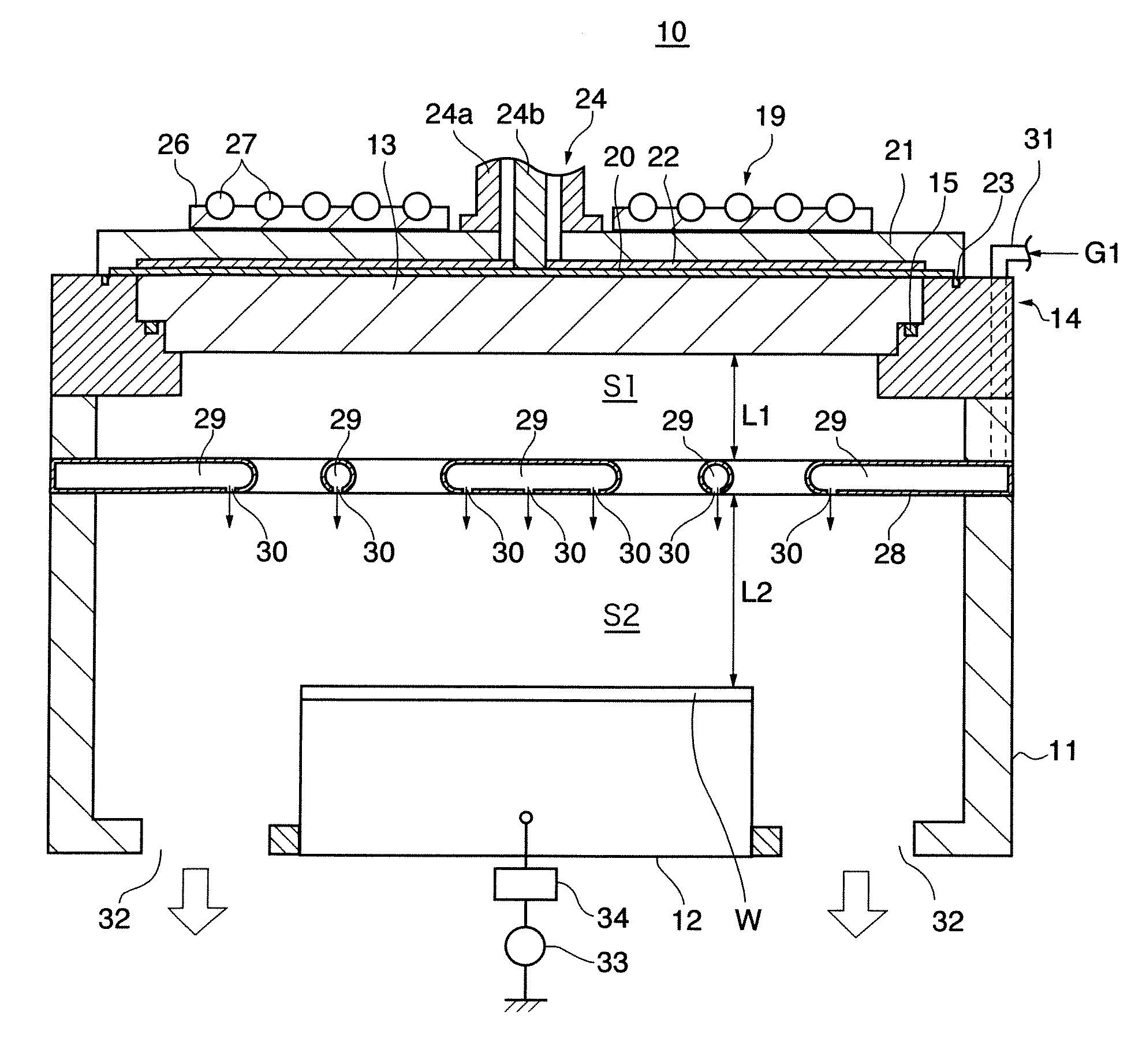
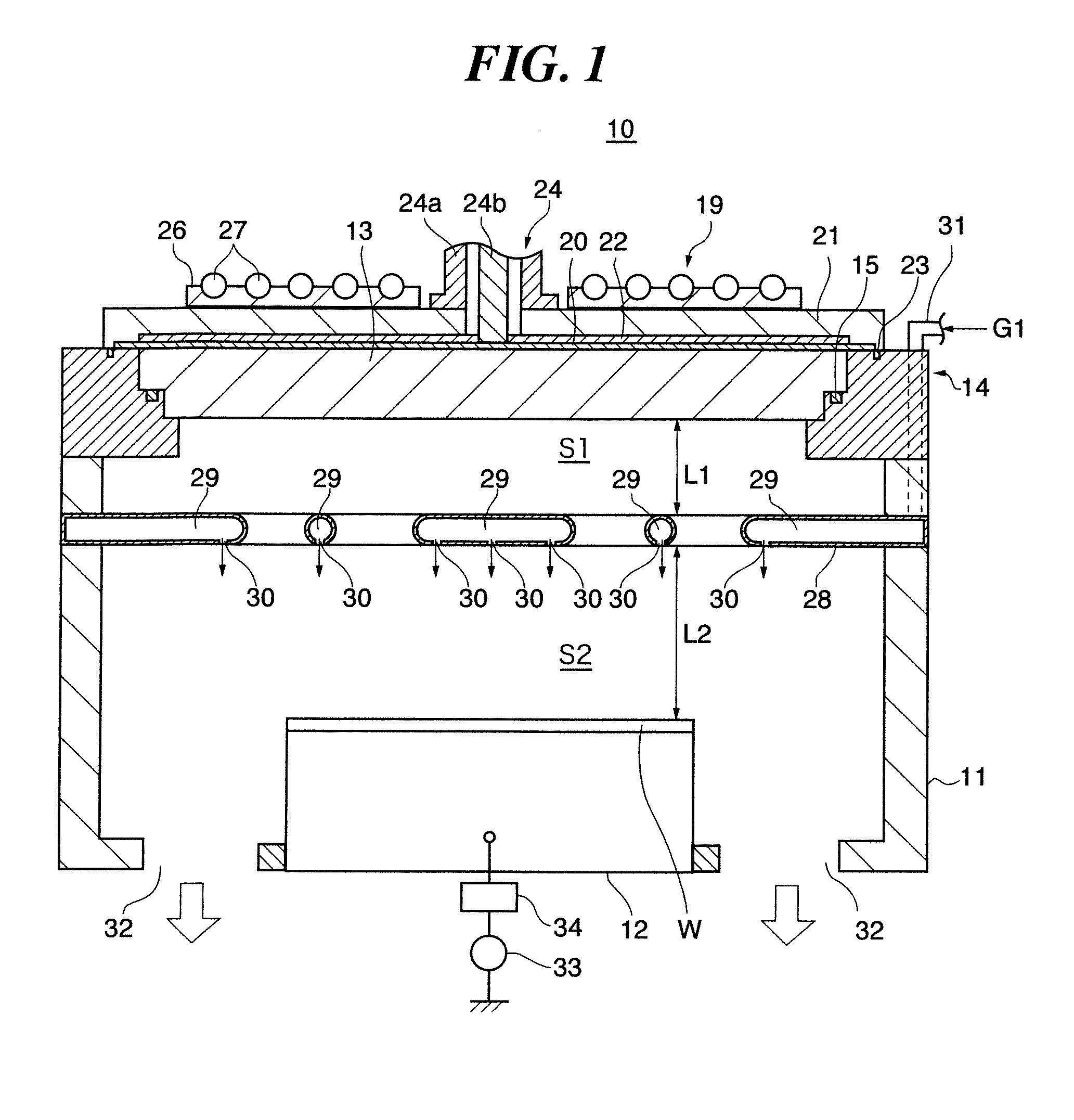
Device and method for plasma processing, and slow-wave plate
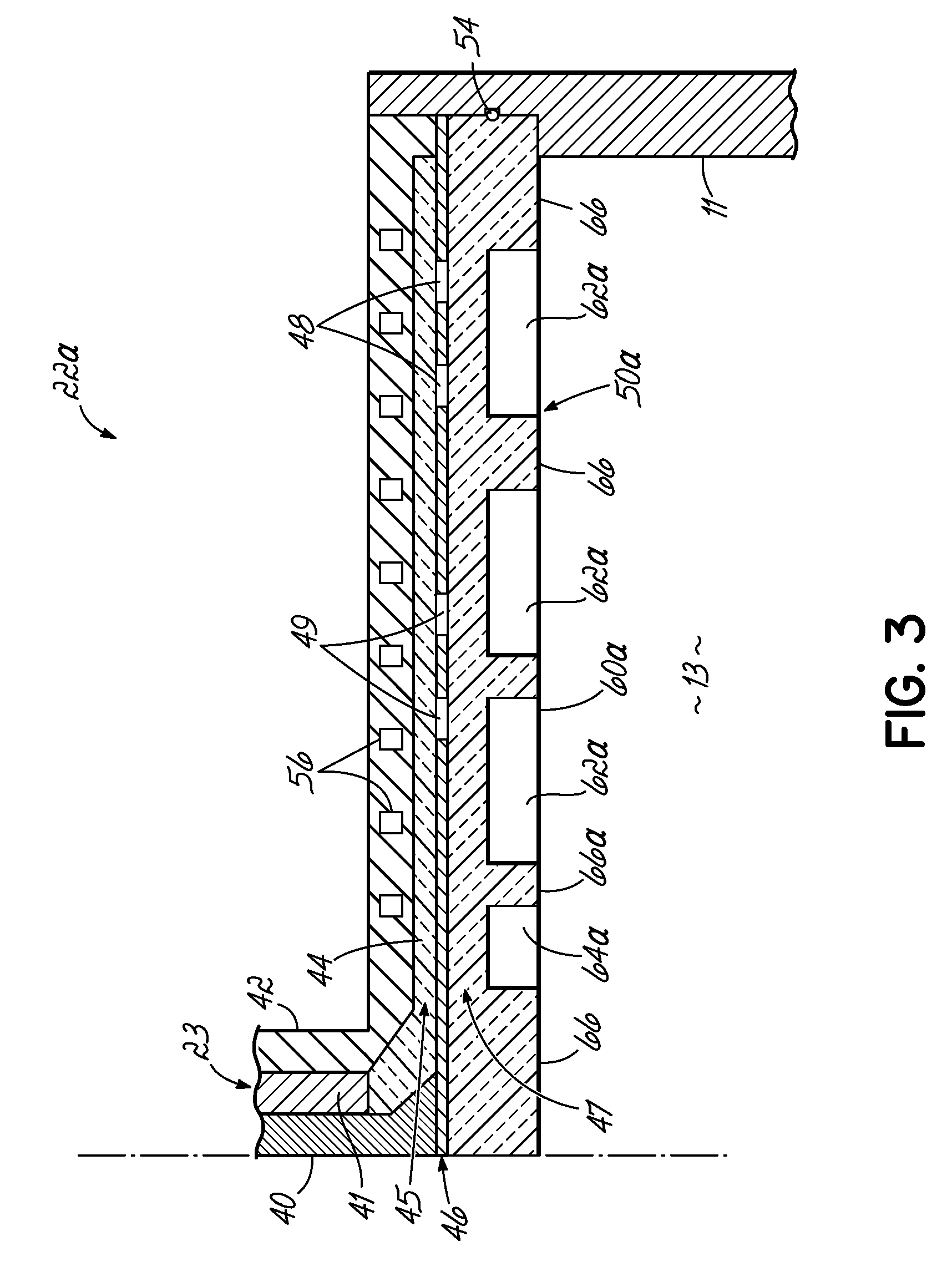
InactiveUS7083701B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityElectric discharge
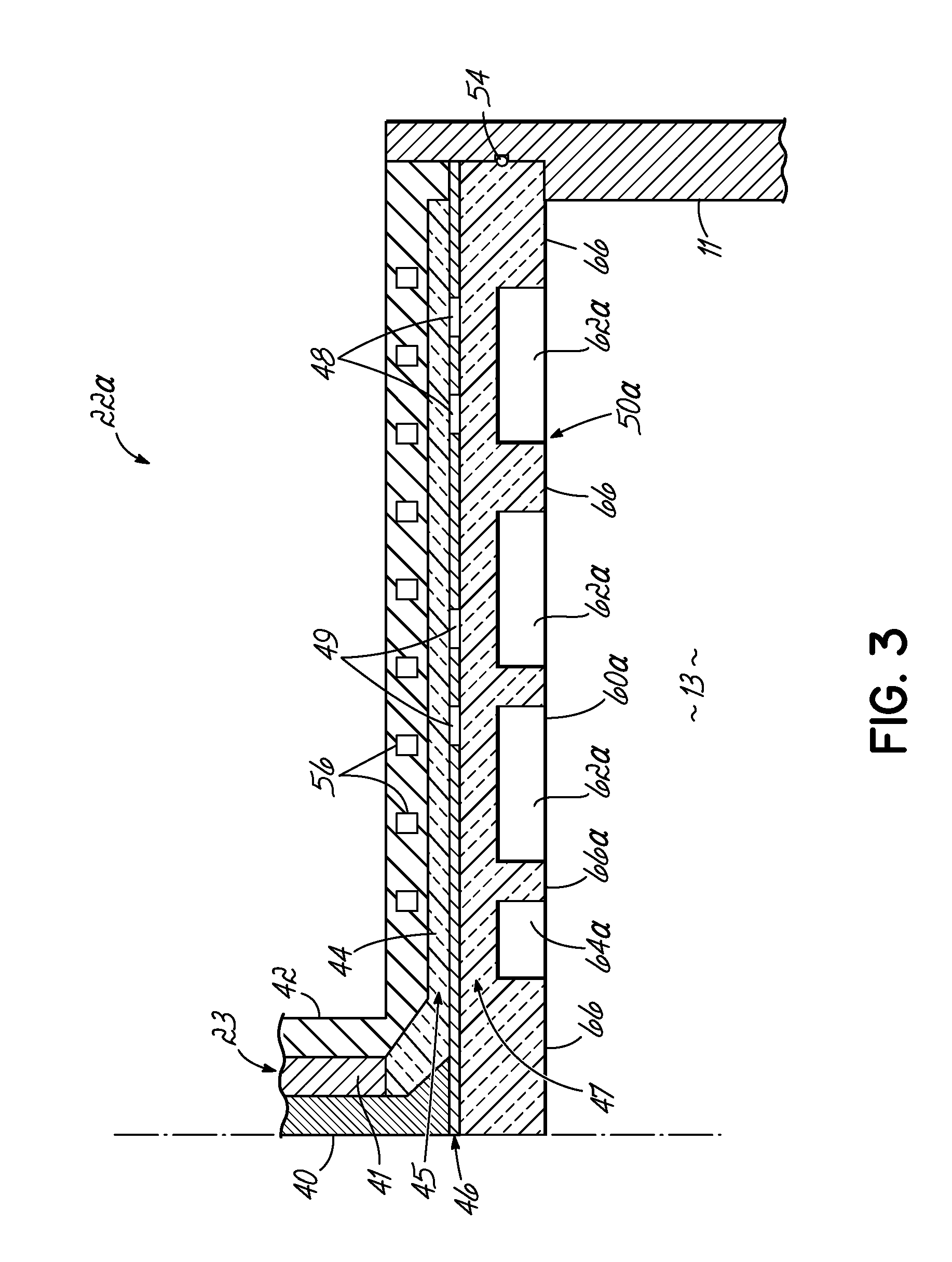
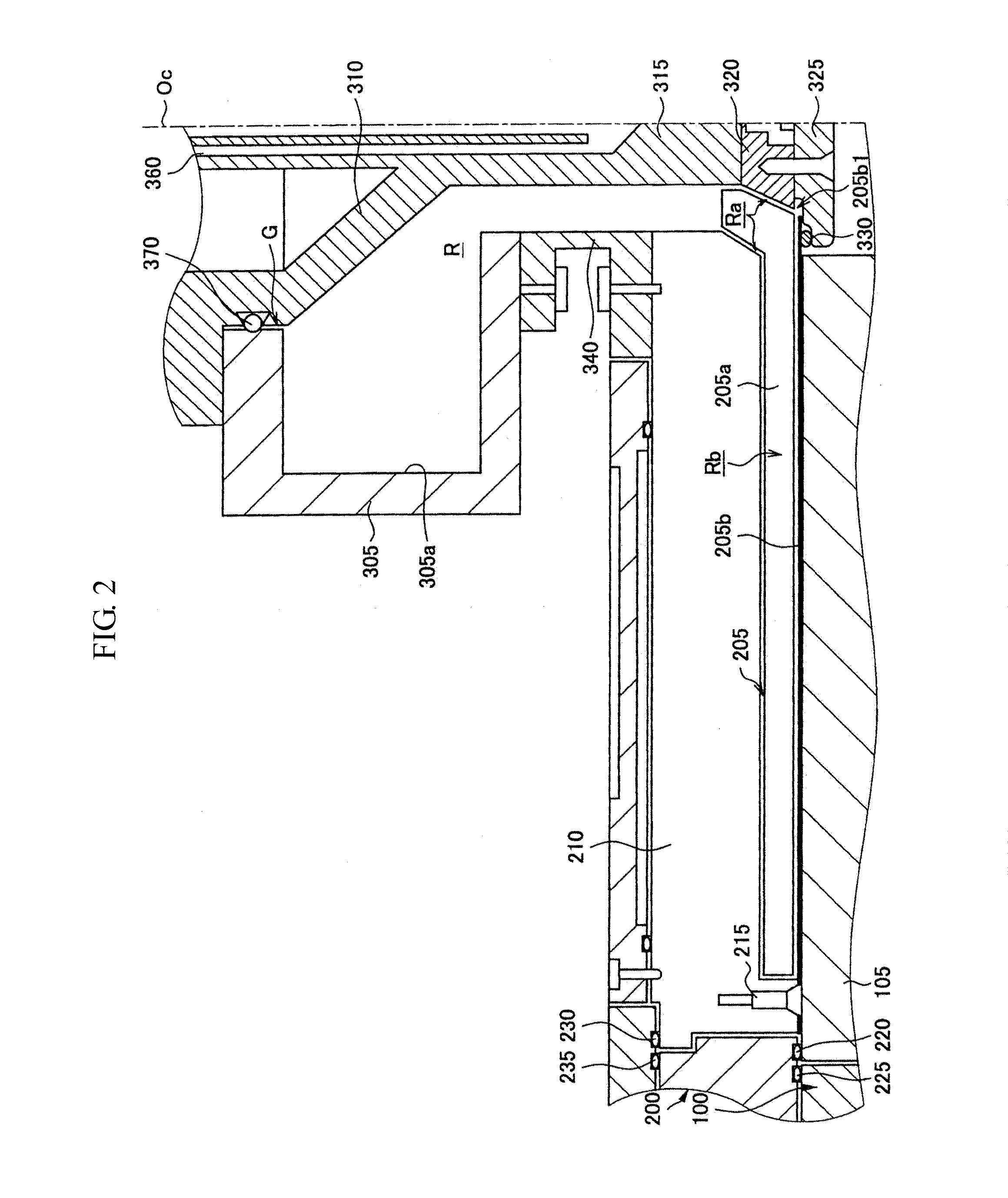
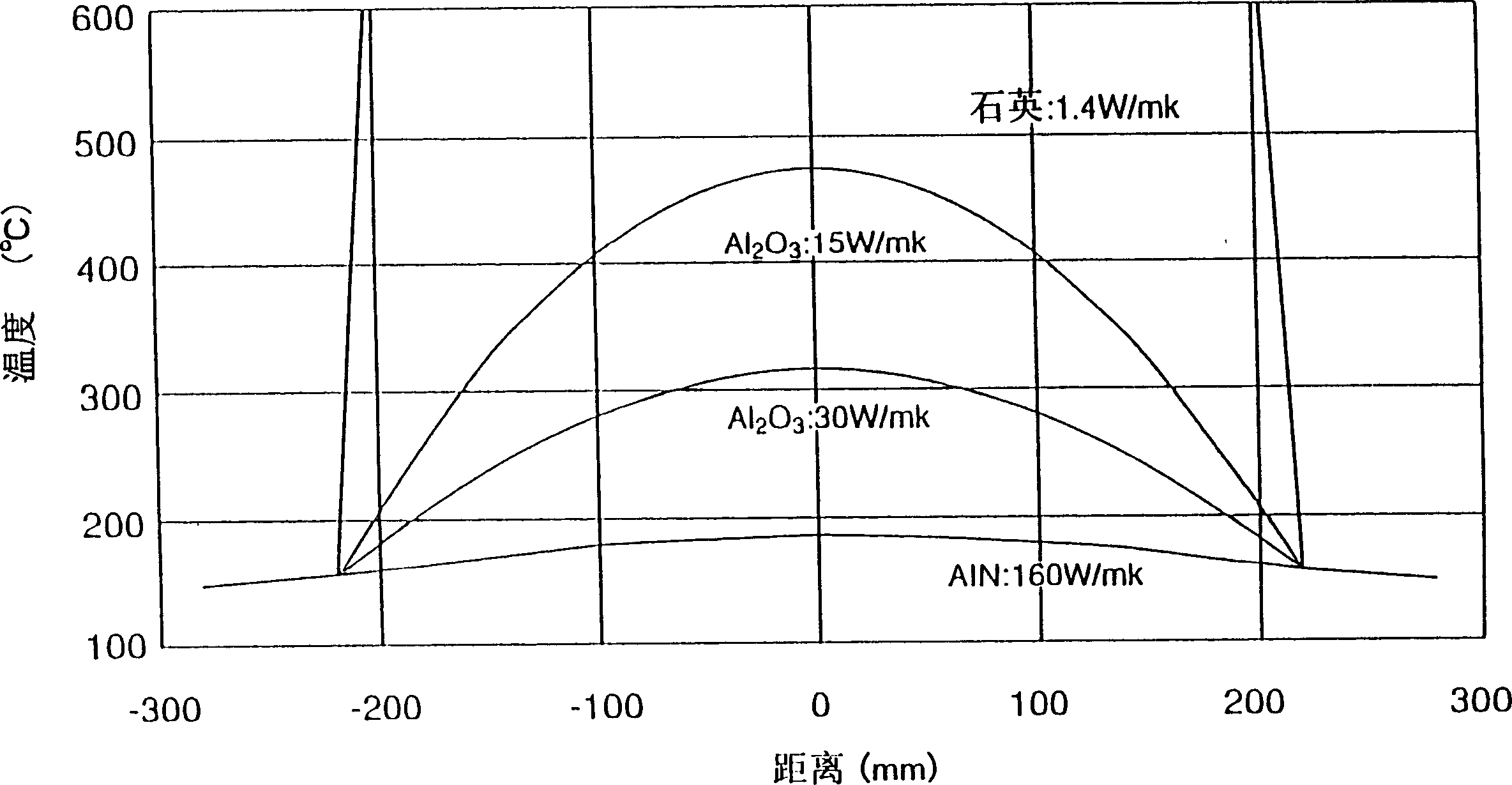
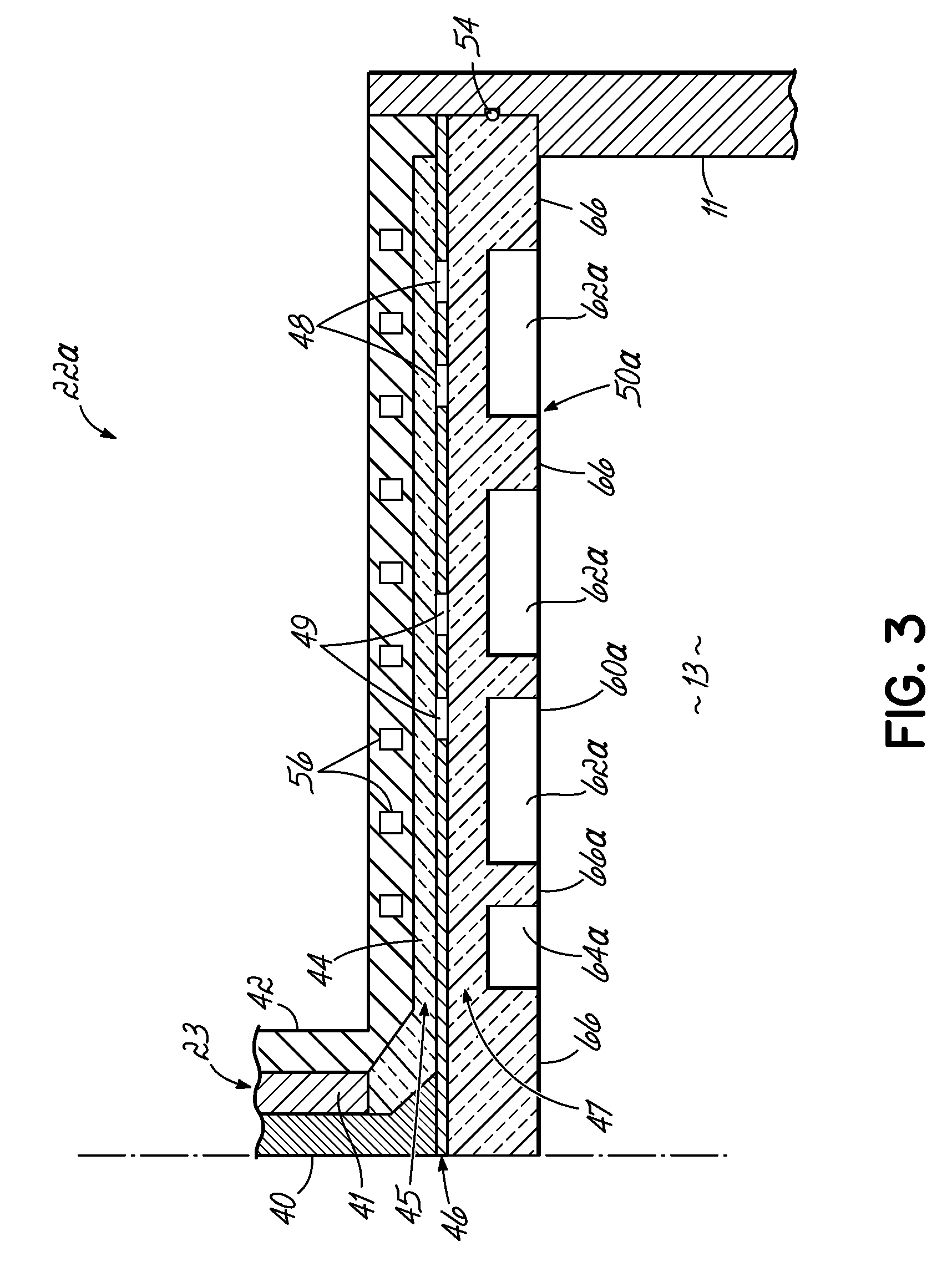
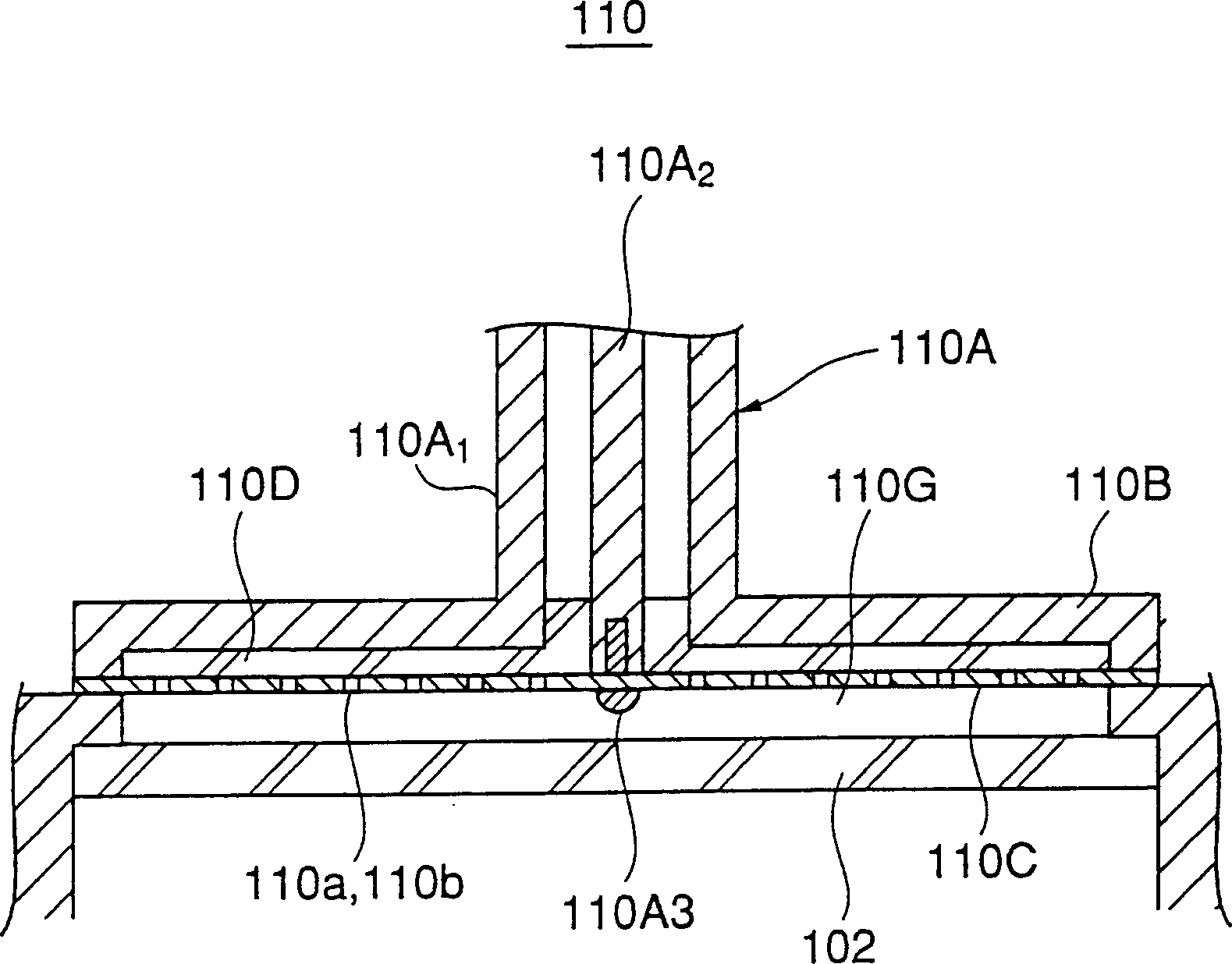
In a microwave plasma processing apparatus that uses a radial line slot antenna, a slot plate (16) is formed by a material having a thermal expansion rate close to the wave retardation plate (18), or depositing a metal on a dielectric plate constituting the wave retardation plate (18). An intimate contact between the wave retardation plate and a slot plate constituting a microwave radiation surface is improved so as to prevent an abnormal electric discharge.
Owner:OHMI TADAHIRO +1
Cleaning Method and Plasma Processing Method
ActiveUS20080317975A1Excellent Na reduction effectReliable cleaningElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningMicrowaveEngineering
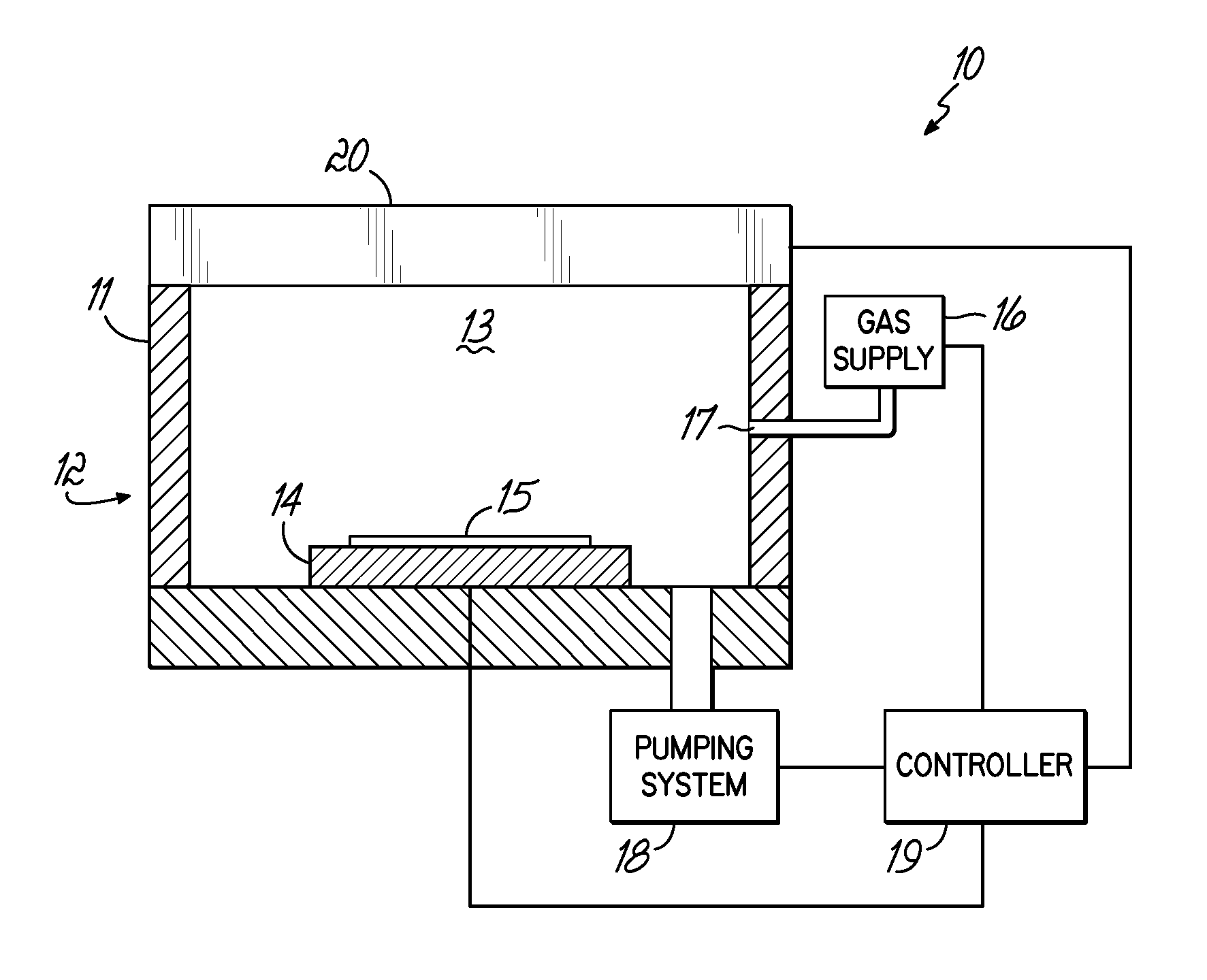
In a RLSA microwave plasma processing apparatus that radiates microwave from a microwave generator into a chamber by using a planer antenna (Radial Line Slot Antenna) having many slots formed according to a certain pattern, the chamber contaminated with Na or the like is cleaned by using a cleaning gas containing H2 and O2.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
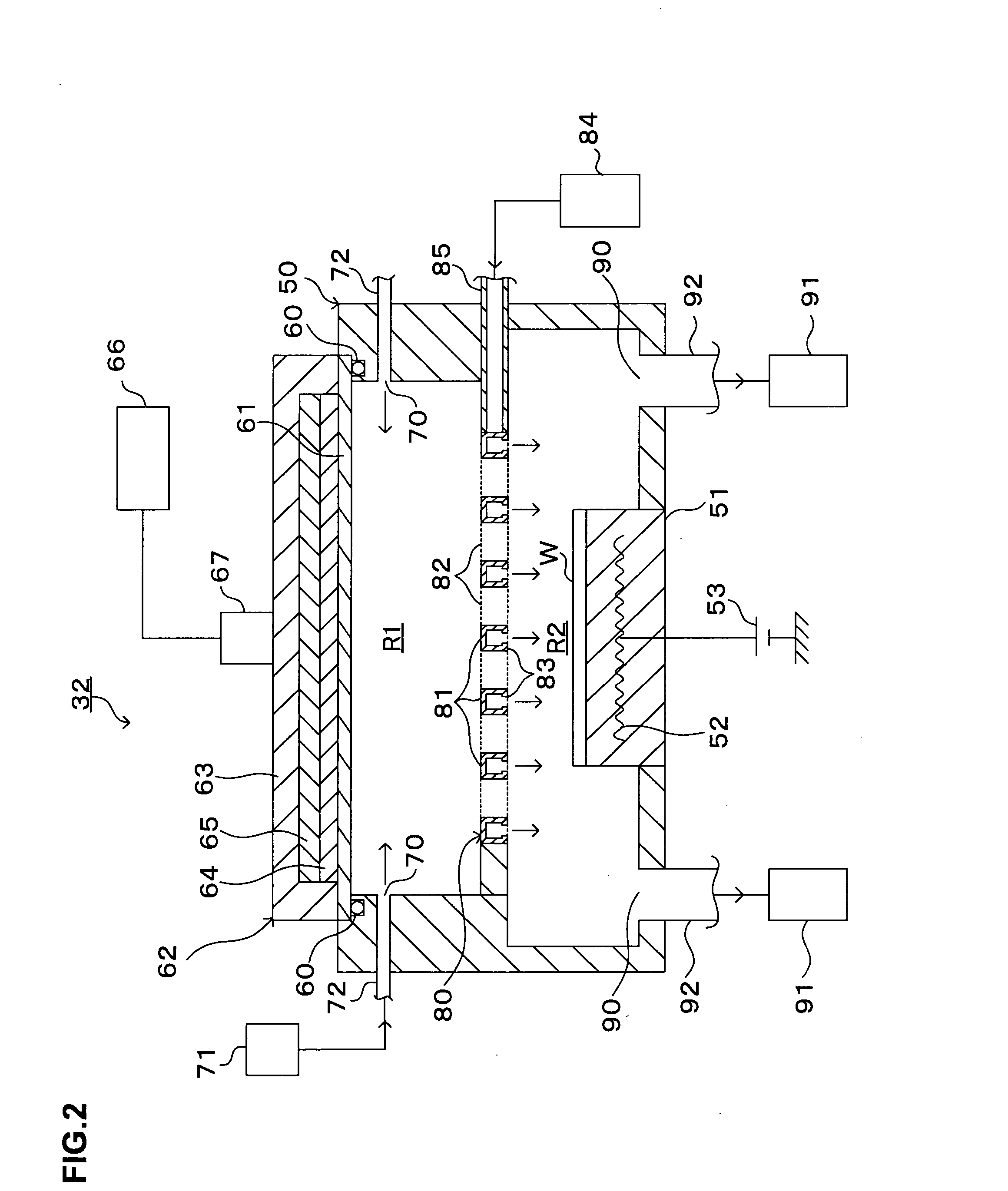
Plasma processing device
InactiveUS7097735B2Eliminate the problemImprove cooling efficiencyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowaveEngineering
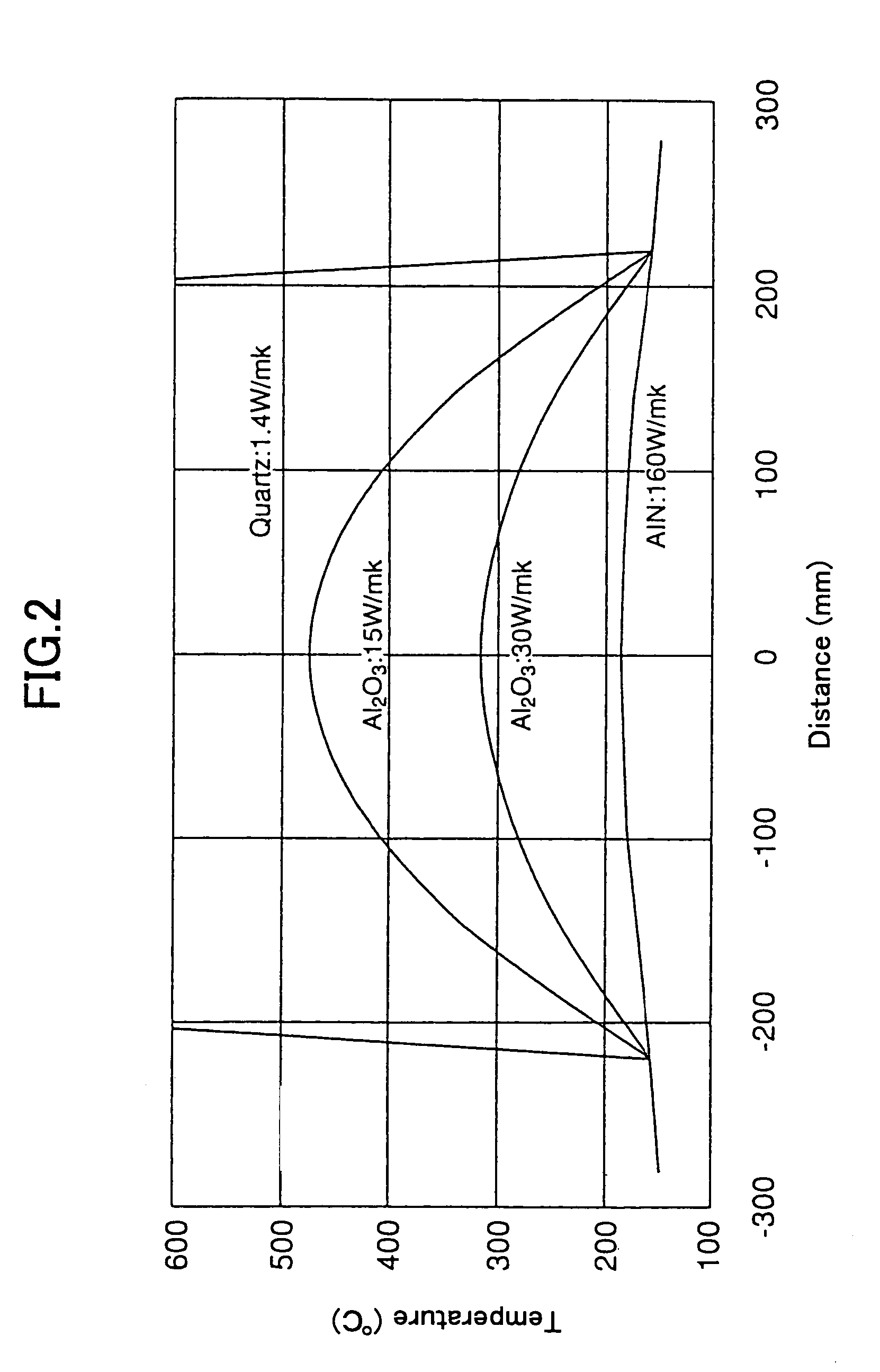
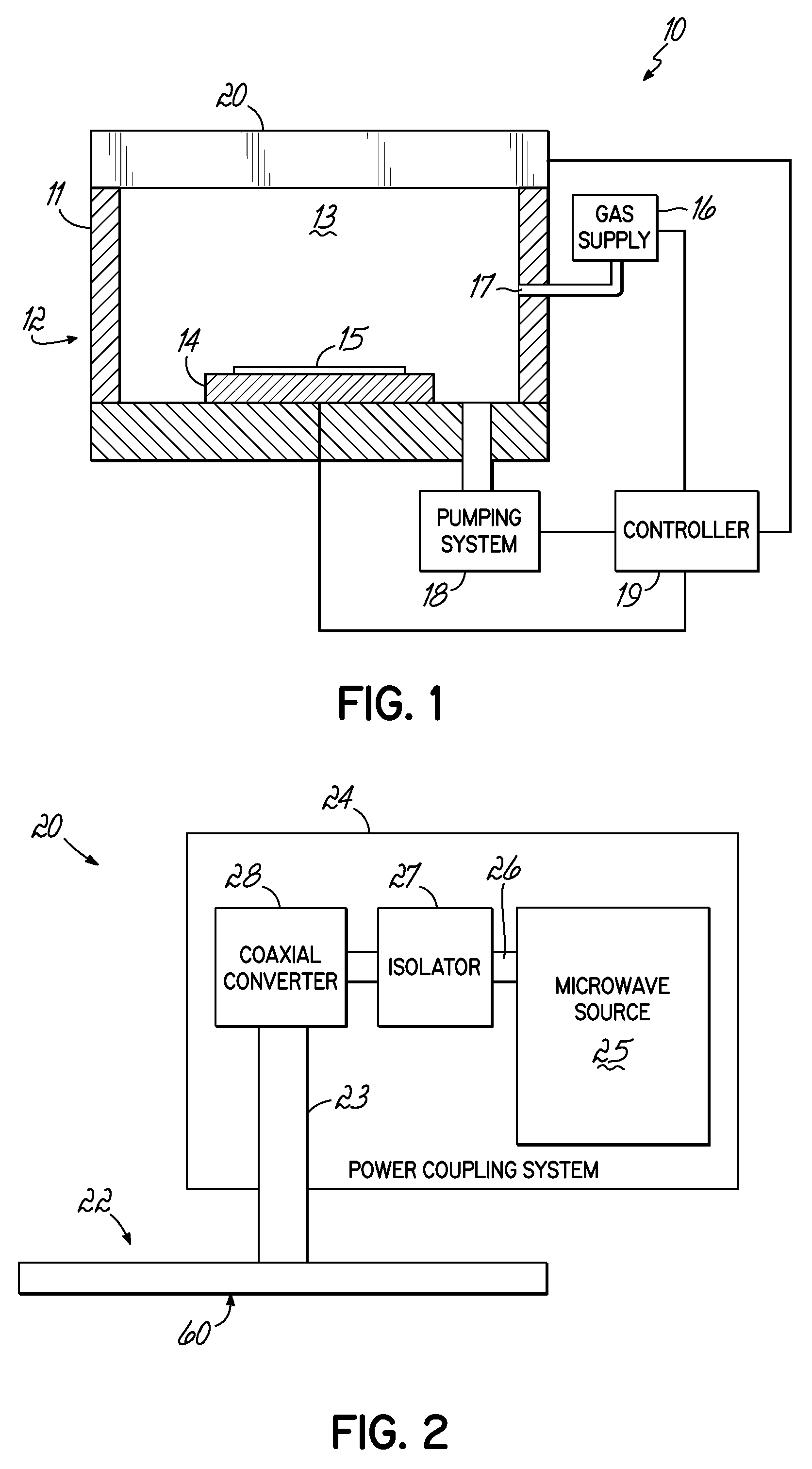
In a microwave plasma processing apparatus that uses a radial line slot antenna, the efficiency of cooling of a shower plate is optimized and simultaneously the efficiency of microwave excitation is optimized, by causing a radiation surface of the radial line slot antenna to make an intimate contact with a cover plate that forms a part of an outer wall of the processing chamber and makes an intimate contact with the shower plate.
Owner:OHMI TADAHIRO +1
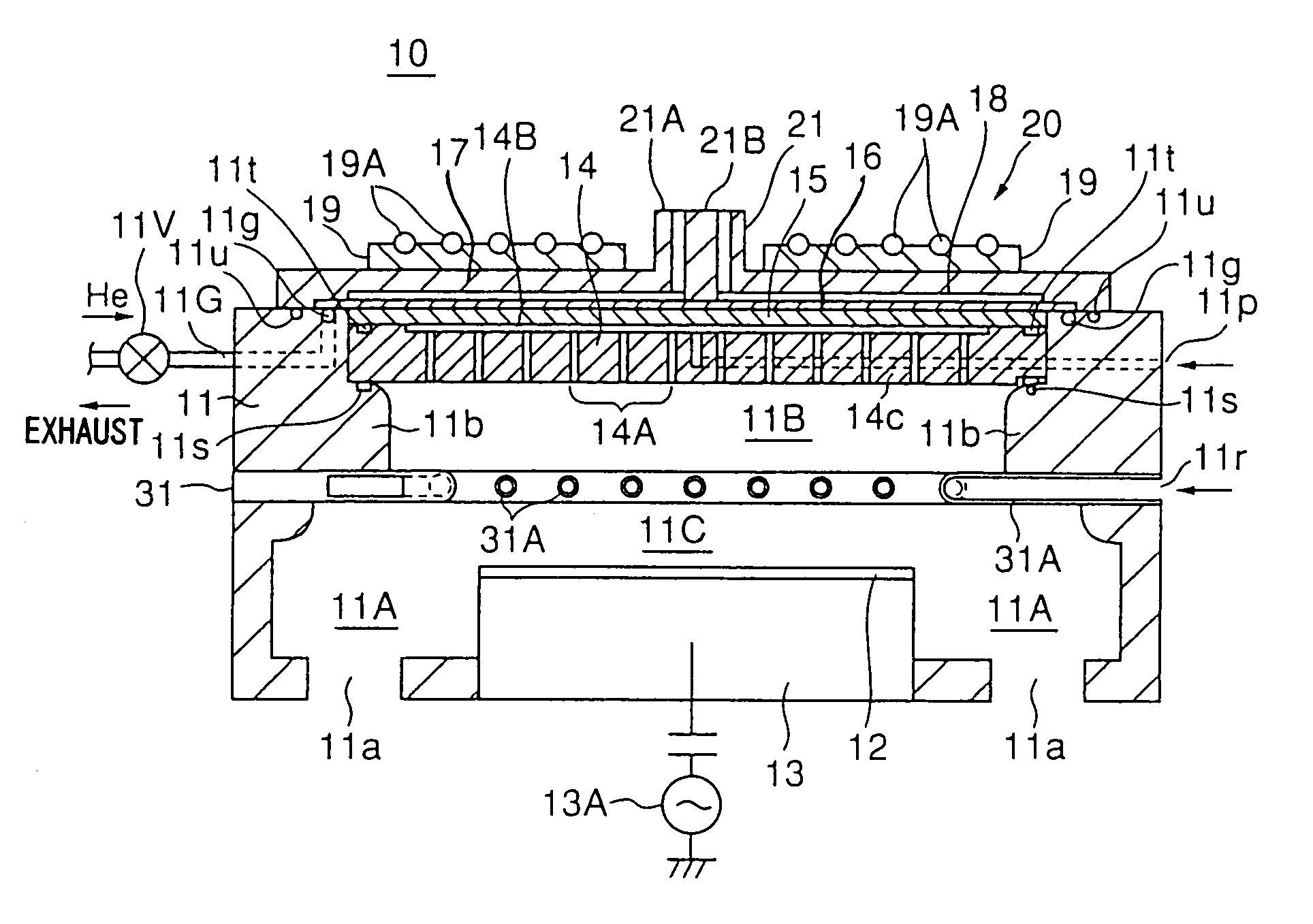
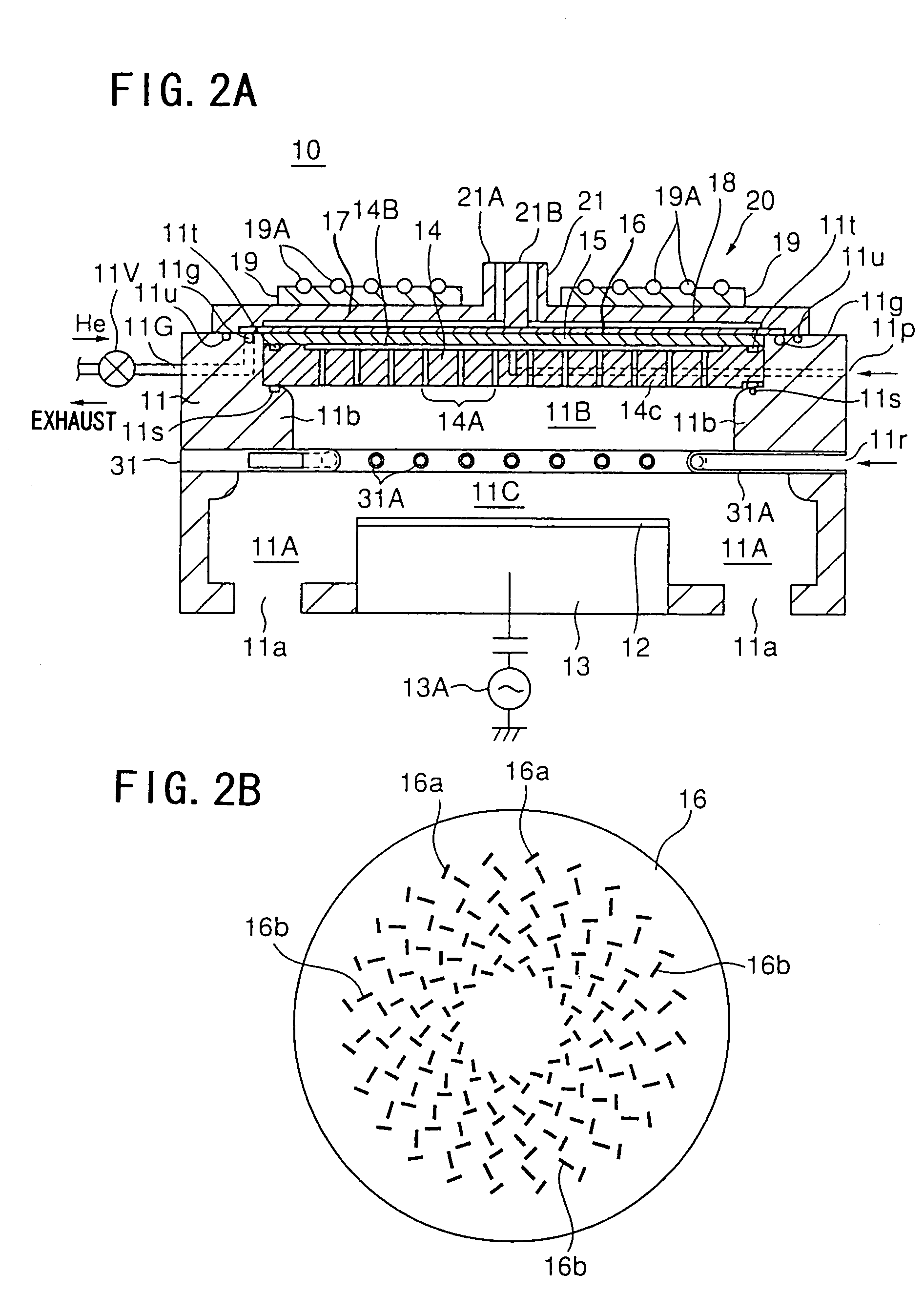
Microwave plasma processing apparatus and method of supplying microwaves using the apparatus
InactiveUS20090314629A1Uniform plasmaSuppress mutationElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElastomerElectricity
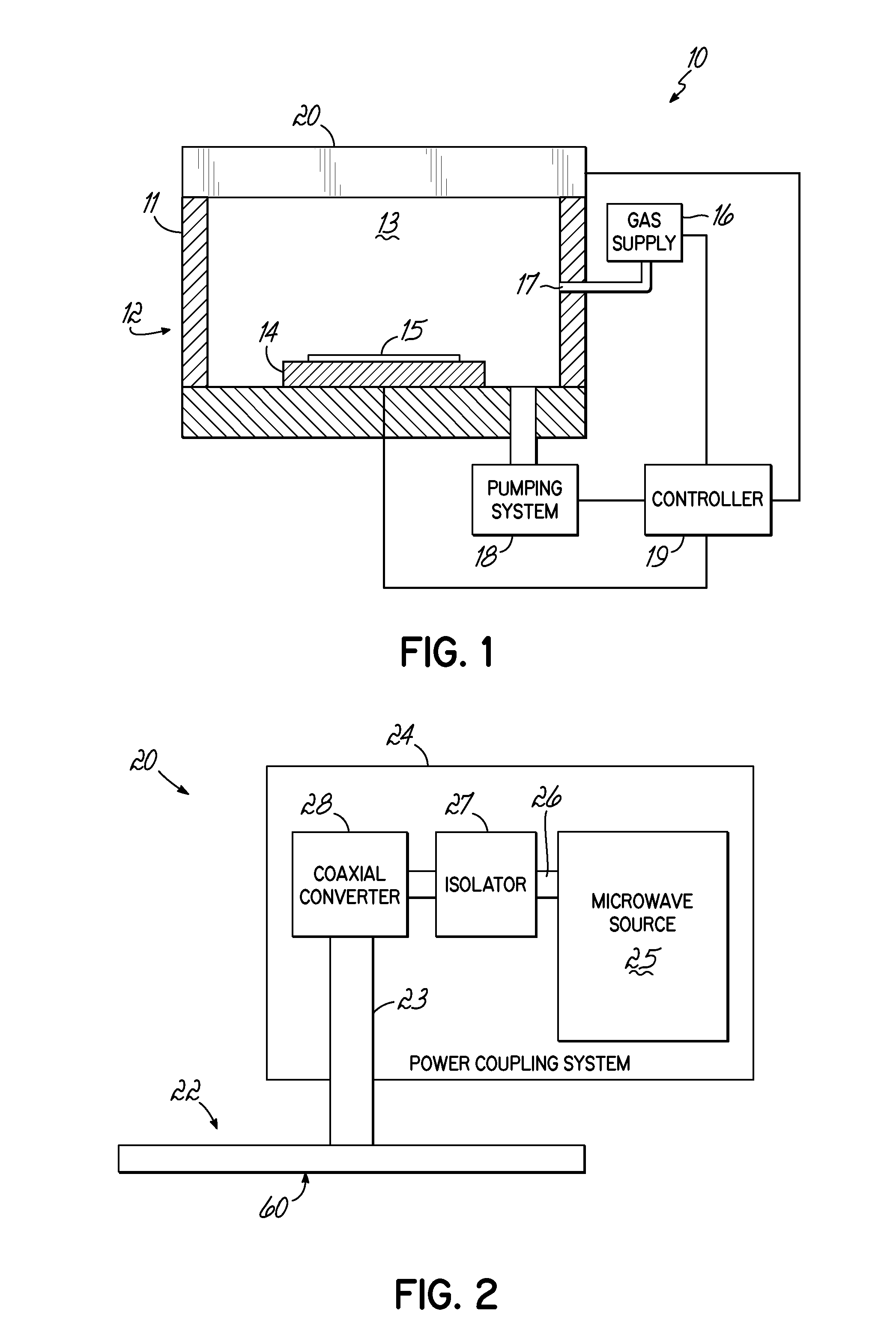
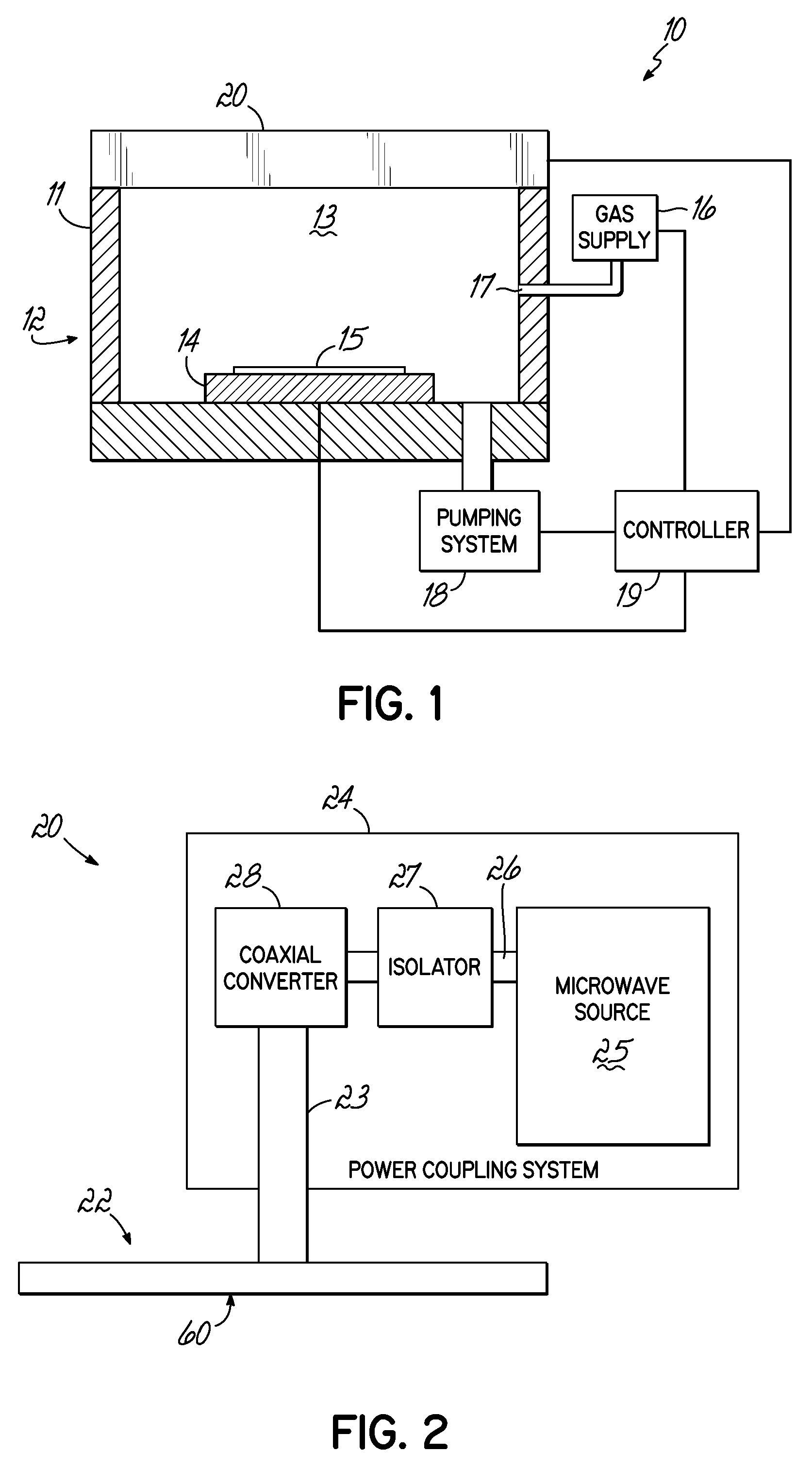
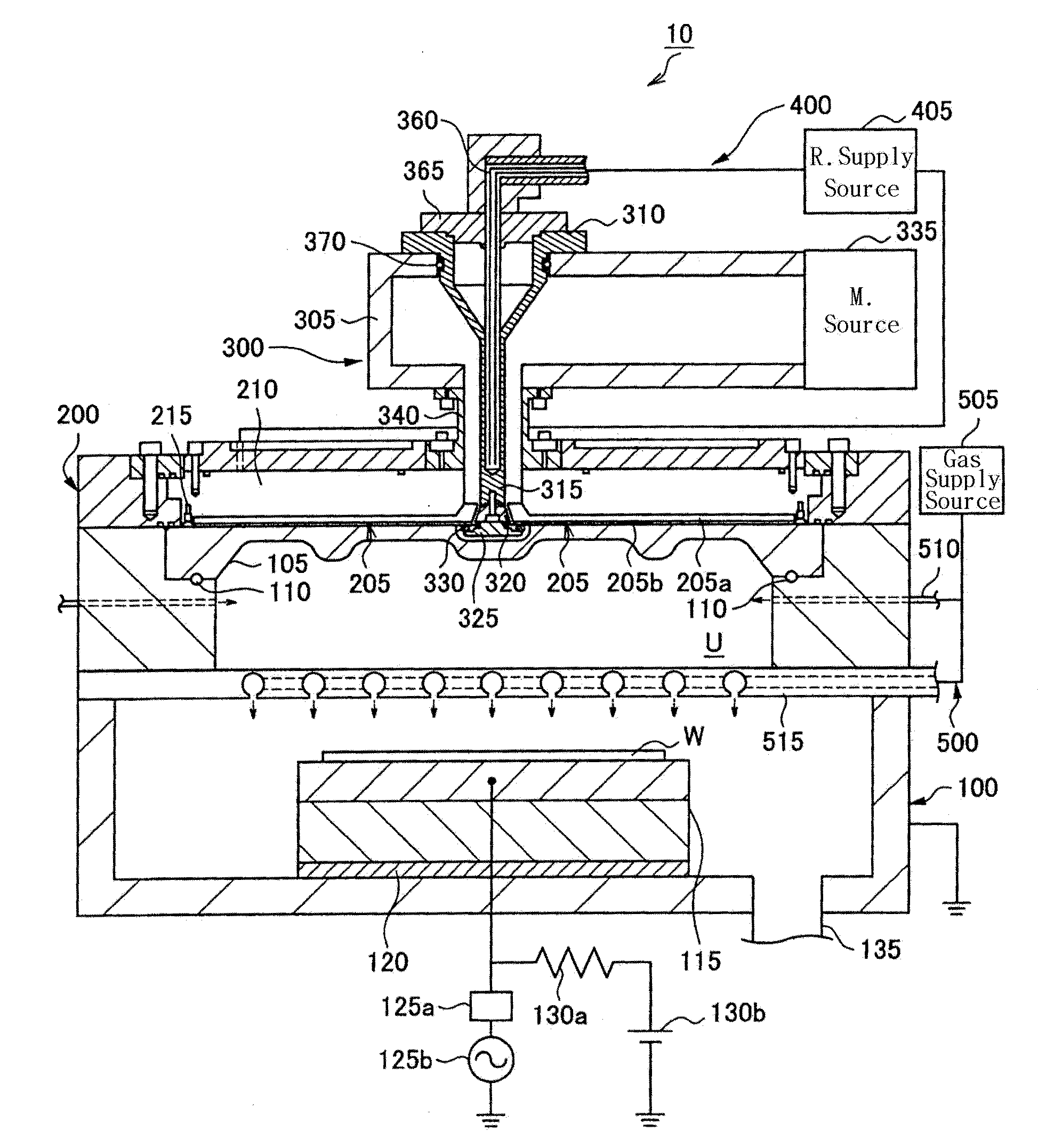
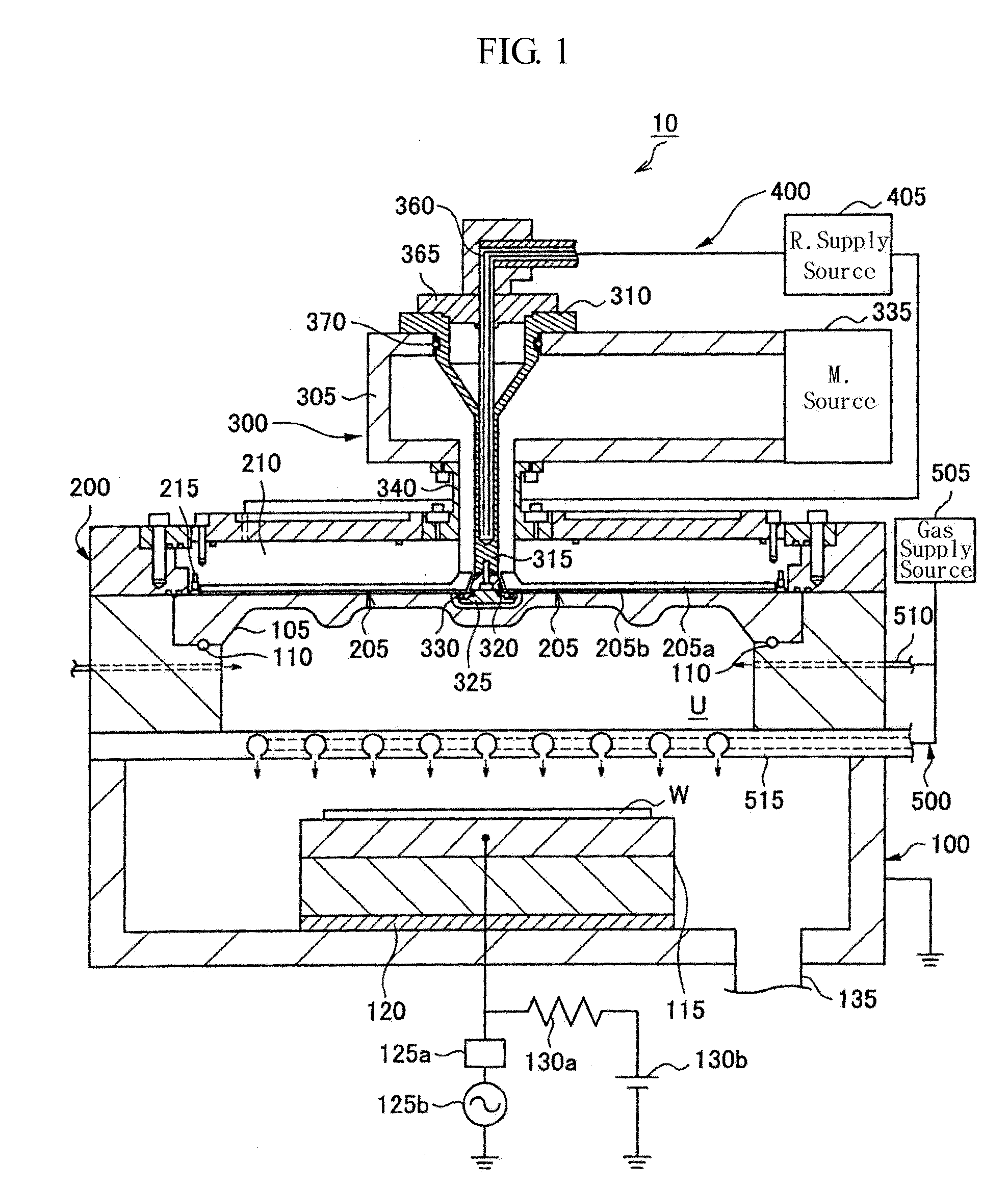
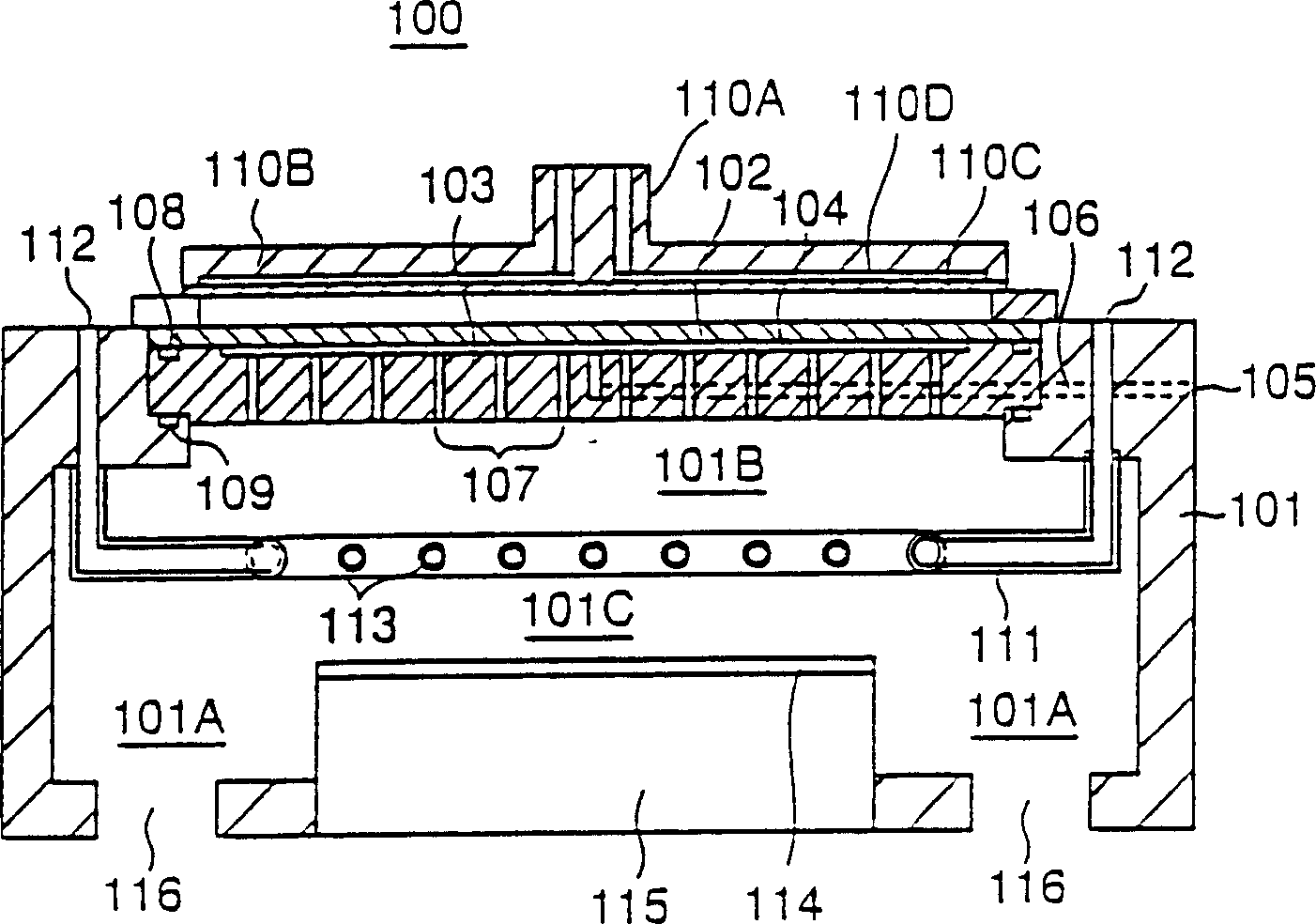
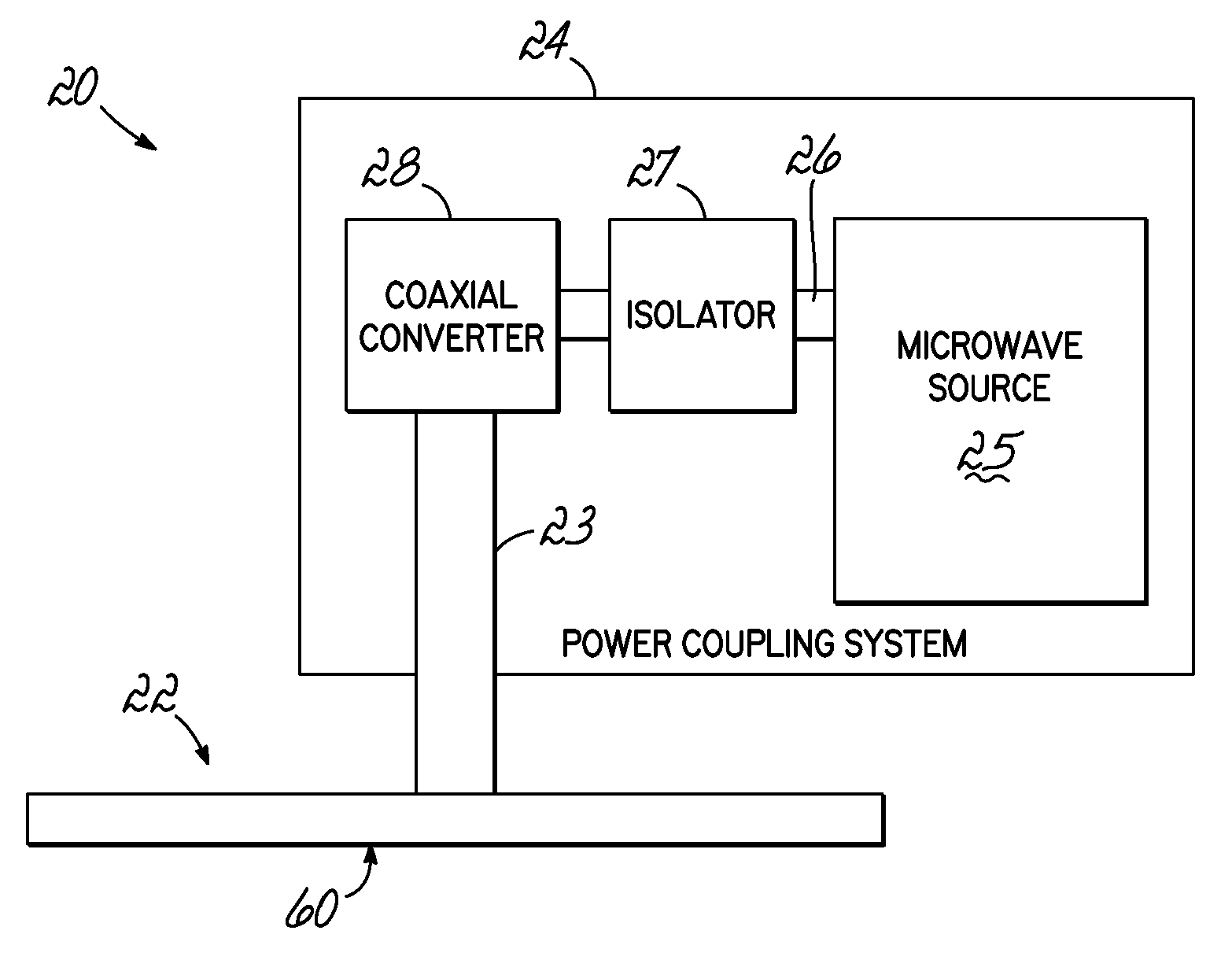
A transmission path of microwaves even after a temperature increases, is maintained in an appropriate state. A microwave plasma processing apparatus performs plasma processing on a substrate by exciting gas due to the electric field energy of microwaves emitted from a slot plate of a radial line slot antenna (RLSA). The microwave plasma processing apparatus includes: a processing container in which plasma processing is performed; a microwave source outputting microwaves; a rectangular waveguide transmitting the microwaves outputted from the microwave source; a coaxial converter converting a mode of the microwaves transmitted to the rectangular waveguide; a coaxial waveguide transmitting the microwaves of which the mode is converted by the coaxial converter; a taper-shaped connector attached to an inner conductor of the coaxial waveguide without contacting the slot plate; and an elastic body electrically connecting the taper-shaped connector and the slot plate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Electron beam enhanced surface wave plasma source
A plasma processing system is described for generating plasma with a ballistic electron beam using a surface wave plasma (SWP) source, such as a radial line slot antenna (RLSA) during semiconductor device fabrication. The antenna comprises a resonator plate having a partially open, electrically conductive layer coupled to a surface of the resonator plate. For example, the electrically conductive layer is formed at an interface between the resonator plate and the plasma, and a direct current (DC) voltage is applied to the electrically conductive layer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Microwave plasma processing apparatus and method of supplying microwaves using the apparatus
InactiveUS20090317566A1Suppress mutationEnsure electrical connectionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityElectrical conductor
A microwave plasma processing apparatus performs plasma processing on a substrate by exciting a gas by electric field energy of microwaves emitted from a radial line slot antenna (RLSA). The microwave plasma processing apparatus includes: a processing container in which plasma processing is performed; a microwave source outputting microwaves; a rectangular waveguide transmitting the microwaves outputted from the microwave source; a coaxial converter converting a mode of the microwaves transmitted to the rectangular waveguide; an inner conductor of a coaxial waveguide connected to the coaxial converter to be slidable; a first contact member joined with the coaxial converter and electrically connecting the coaxial converter and the inner conductor; and a first spring member absorbing displacement, due to thermal expansion, of the RLSA and a member disposed above the RLSA.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Plasma processing apparatus, plasma processing method and wave retardation plate
InactiveUS20060231208A1Electric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsElectric dischargeDielectric plate
In a microwave plasma processing apparatus that uses a radial line slot antenna, a slot plate (16) is formed by a material having a thermal expansion rate close to the wave retardation plate (18), or depositing a metal on a dielectric plate constituting the wave retardation plate (18). An intimate contact between the wave retardation plate and a slot plate constituting a microwave radiation surface is improved so as to prevent an abnormal electric discharge.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Radial line slot antenna having a conductive layer
InactiveUS7938081B2Improve robustnessElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadial line slot antennaSemiconductor
A radial line slot antenna (RLSA) is described for generating plasma during semiconductor device fabrication. The antenna comprises a resonator plate having a partially open, electrically conductive layer coupled to a surface of the resonator plate. For example, the electrically conductive layer is formed at an interface between the resonator plate and the plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Etching method and semiconductor device fabrication method
InactiveCN101154582AReduce etch rateImprove the selection ratioElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistMicrowave
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Plasma processing device and semiconductor mfg. device
InactiveCN1460289AElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowaveEngineering
Owner:大见忠弘 +1
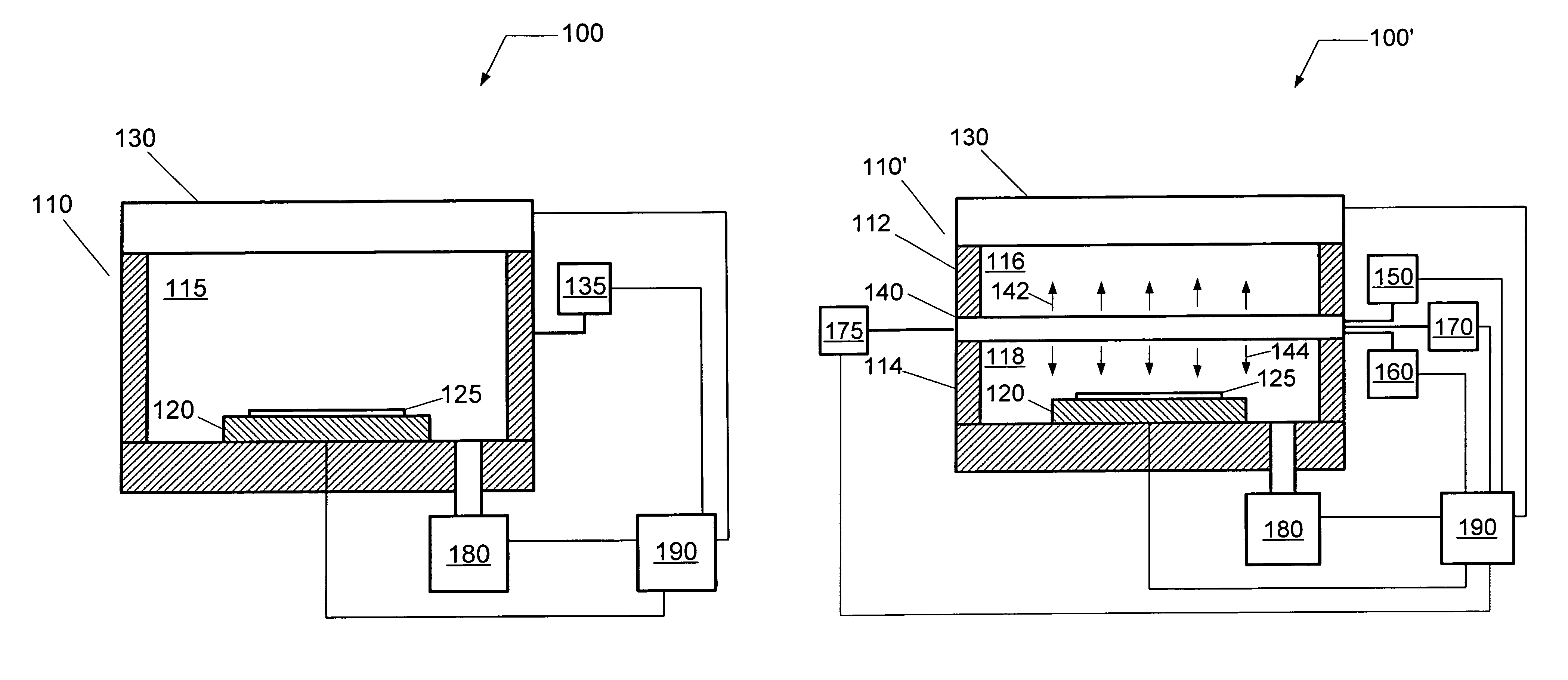
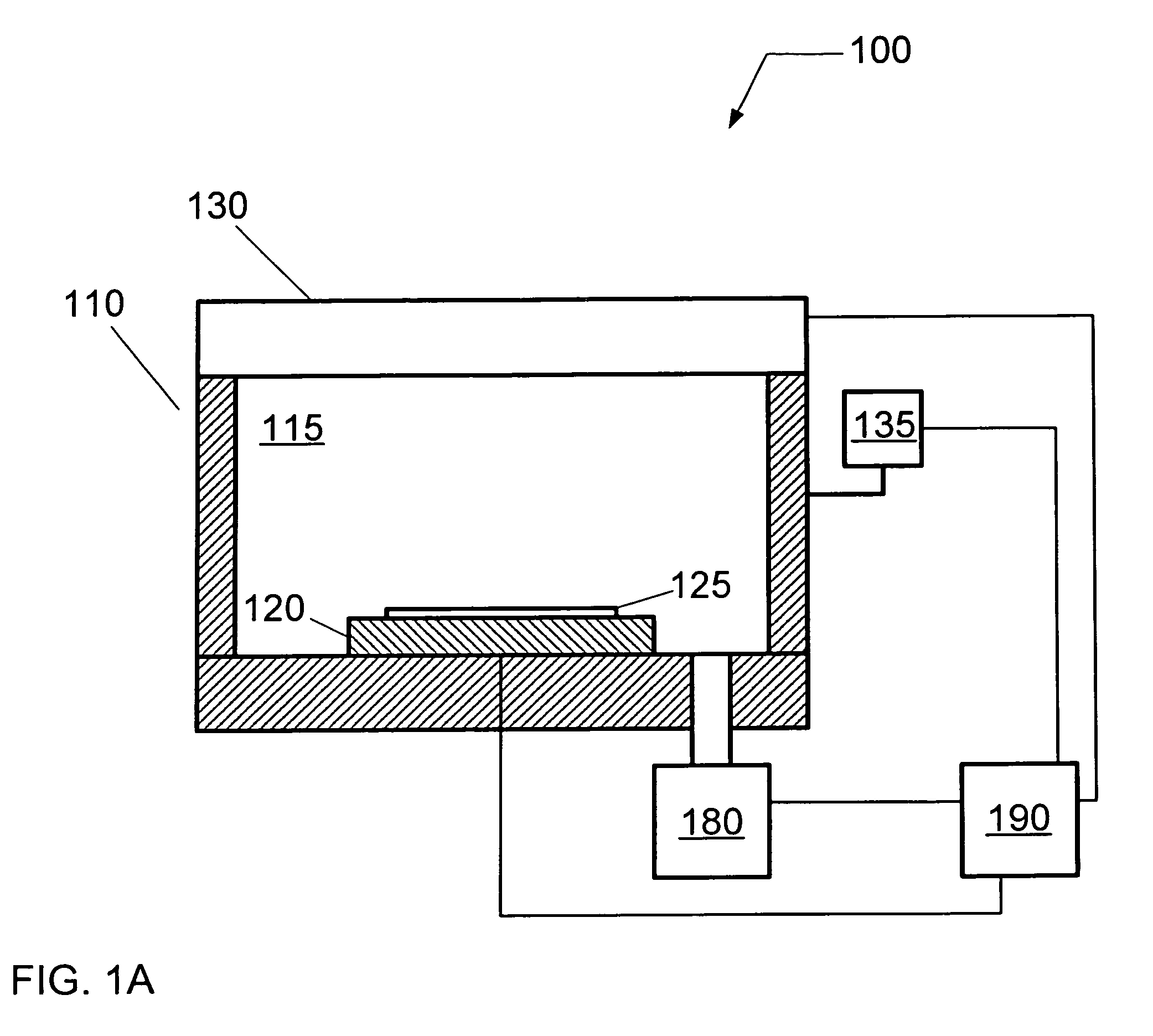
Low electron temperature microwave surface-wave plasma (SWP) processing method and apparatus
ActiveUS20130256272A1High degree of ionizationImprove uniformityLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesElectron temperaturePlasma density
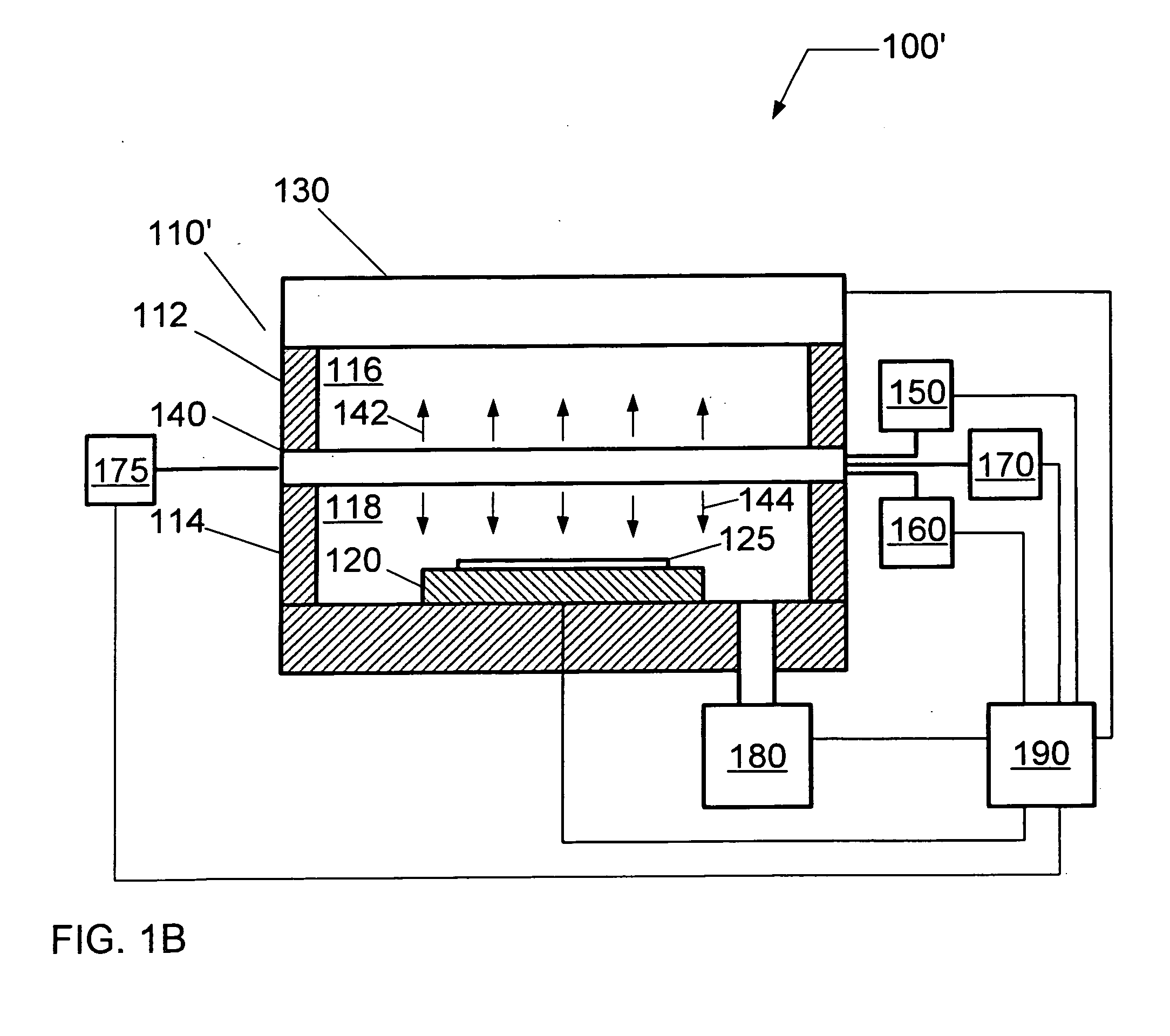
A surface wave plasma (SWP) source couples pulsed microwave (MW) energy into a processing chamber through, for example, a radial line slot antenna, to result in a low mean electron energy (Te). To prevent impingement of the microwave energy onto the surface of a substrate when plasma density is low between pulses, an ICP source, such as a helical inductive source, a planar RF coil, or other inductively coupled source, is provided between the SWP source and the substrate to produce plasma that is opaque to microwave energy. The ICP source can also be pulsed in synchronism with the pulsing of the MW plasma in phase with the ramping up of the MW pulses. The ICP also adds an edge dense distribution of plasma to a generally chamber centric MW plasma to improve plasma uniformity.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST +1
Plasma processing device
InactiveCN1460287ALow dielectric lossReduce heat transferElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoaxial waveguidesAbnormal discharge
In a microwave plasma processing apparatus that uses a radial line slot antenna, abnormal discharges are suppressed and the excitation efficiency of microwave plasma is improved simultaneously. In the joint between the radial line slot antenna and the coaxial waveguide, the point part of the power supplying line of the coaxial waveguide is separated from the slot plate constructing a radiation face.
Owner:大见忠弘 +1
Radial line slot antenna having a conductive layer
InactiveUS20080060760A1Improve robustnessElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadial line slot antennaSemiconductor
A radial line slot antenna (RLSA) is described for generating plasma during semiconductor device fabrication. The antenna comprises a resonator plate having a partially open, electrically conductive layer coupled to a surface of the resonator plate. For example, the electrically conductive layer is formed at an interface between the resonator plate and the plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
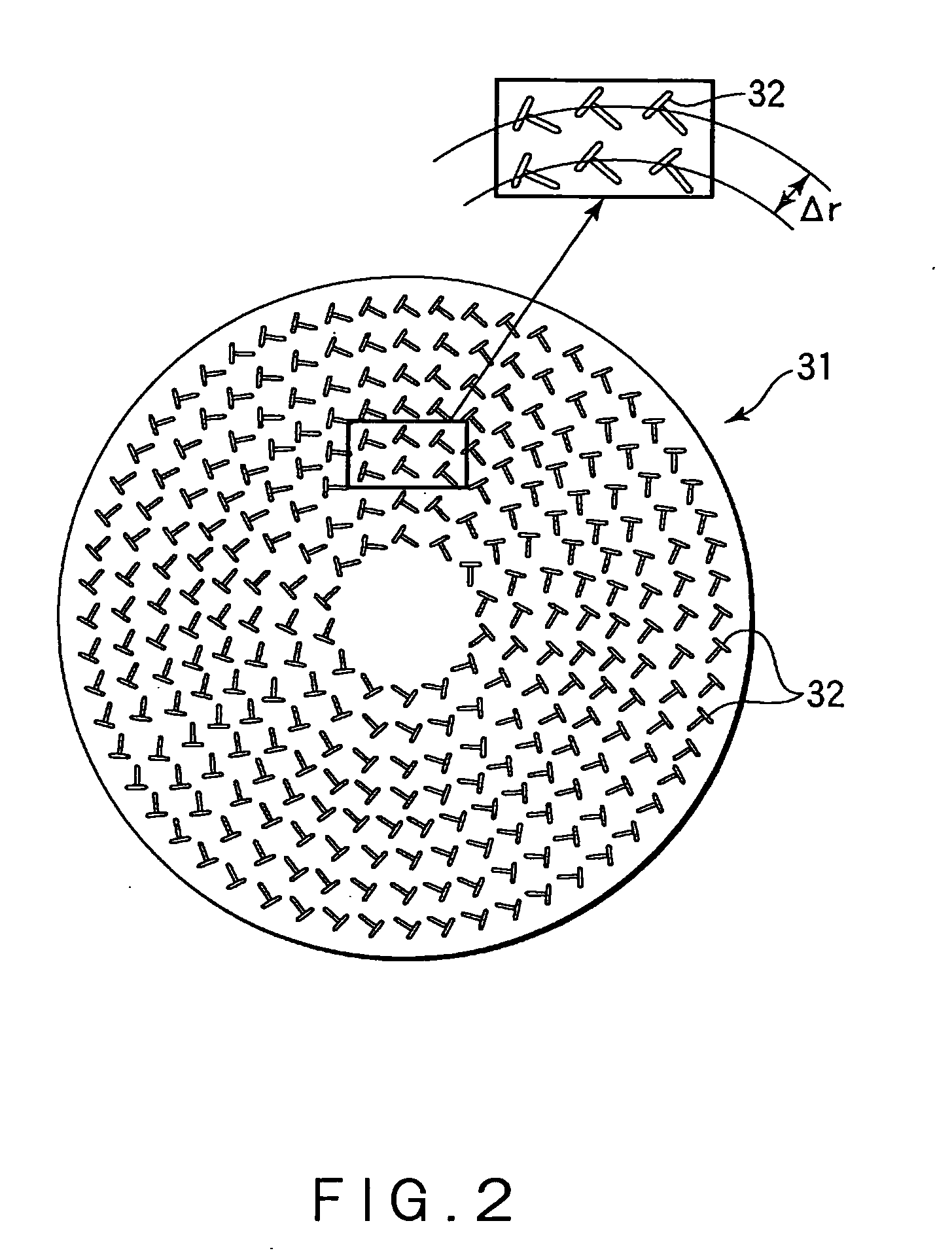
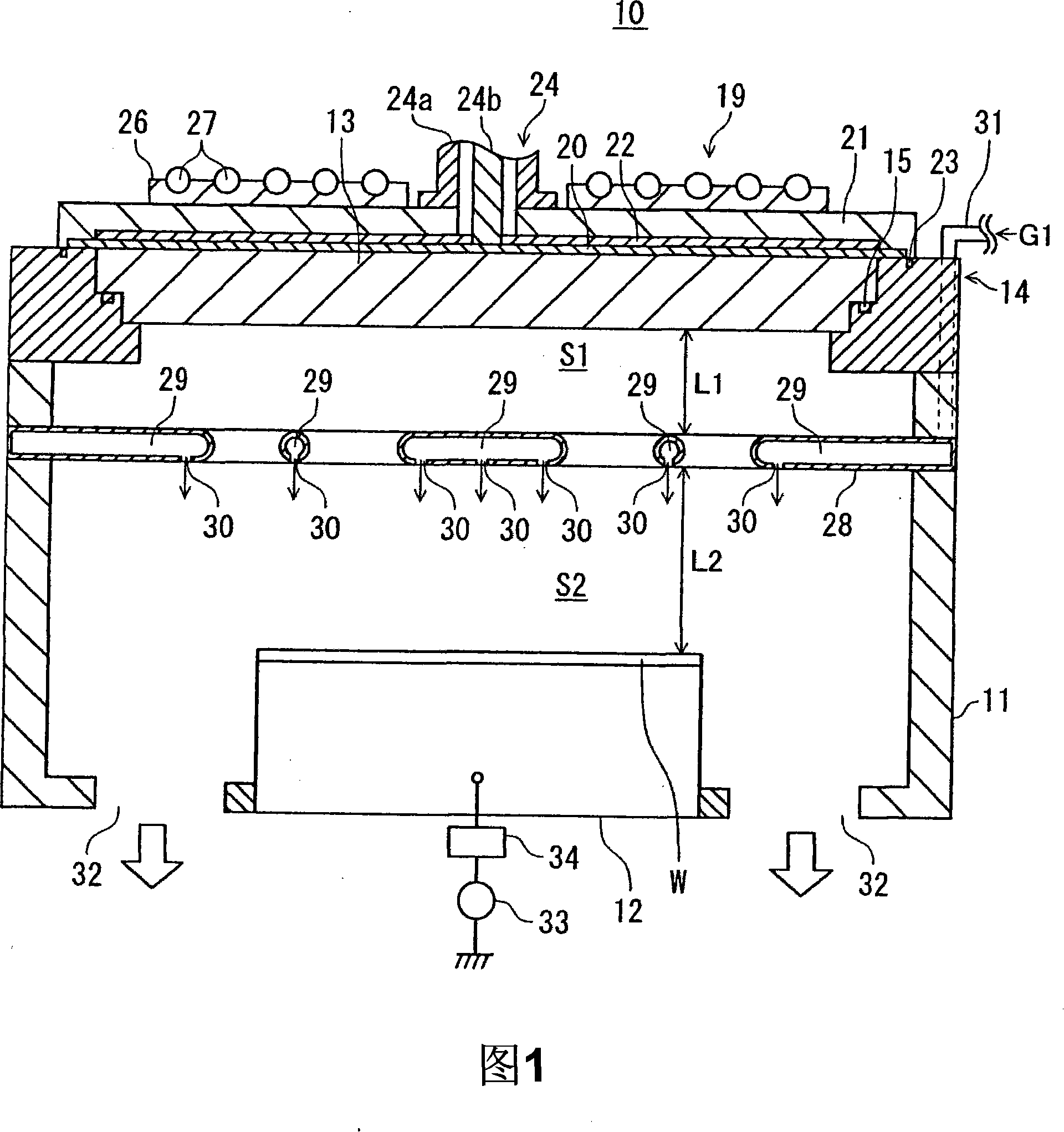
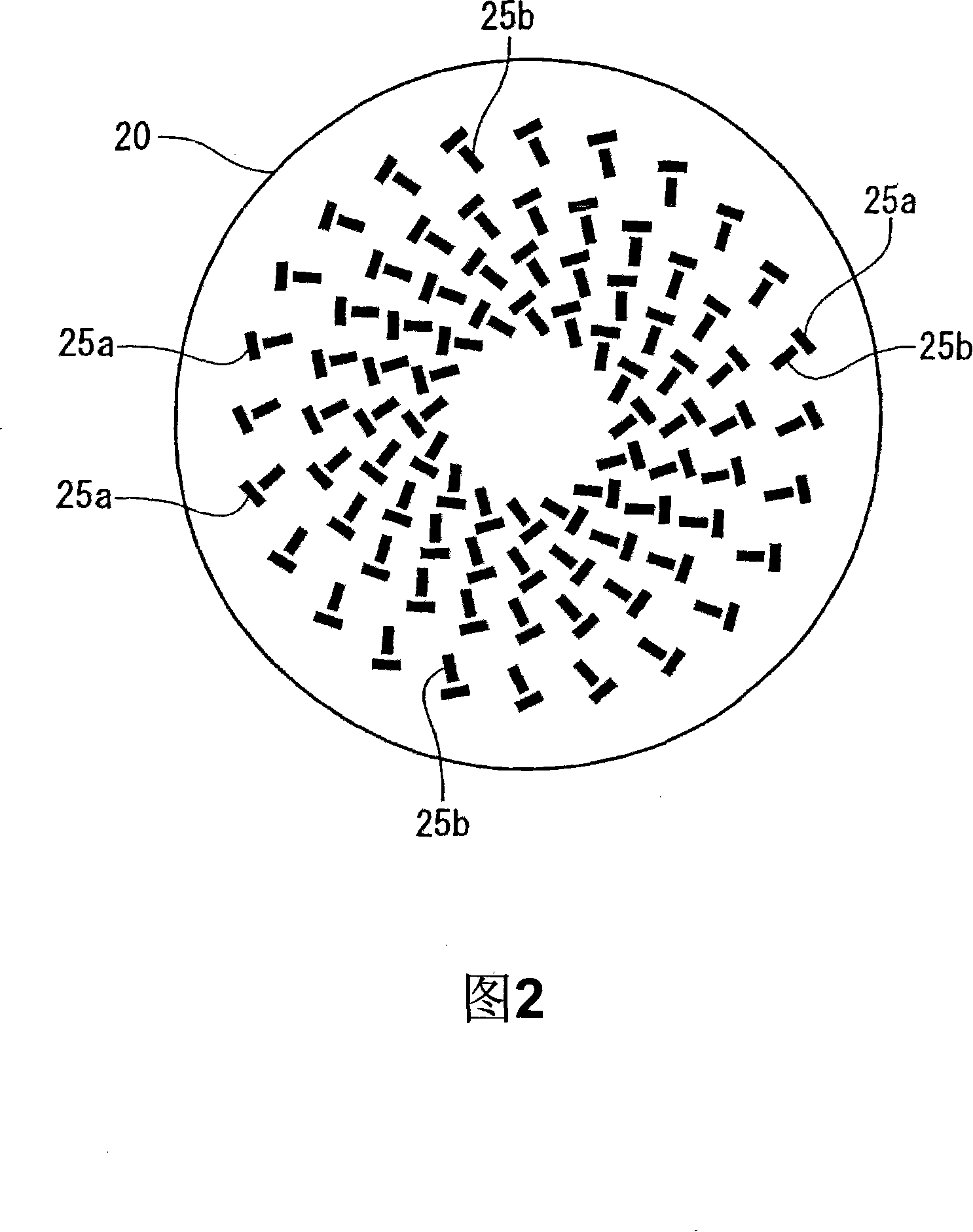
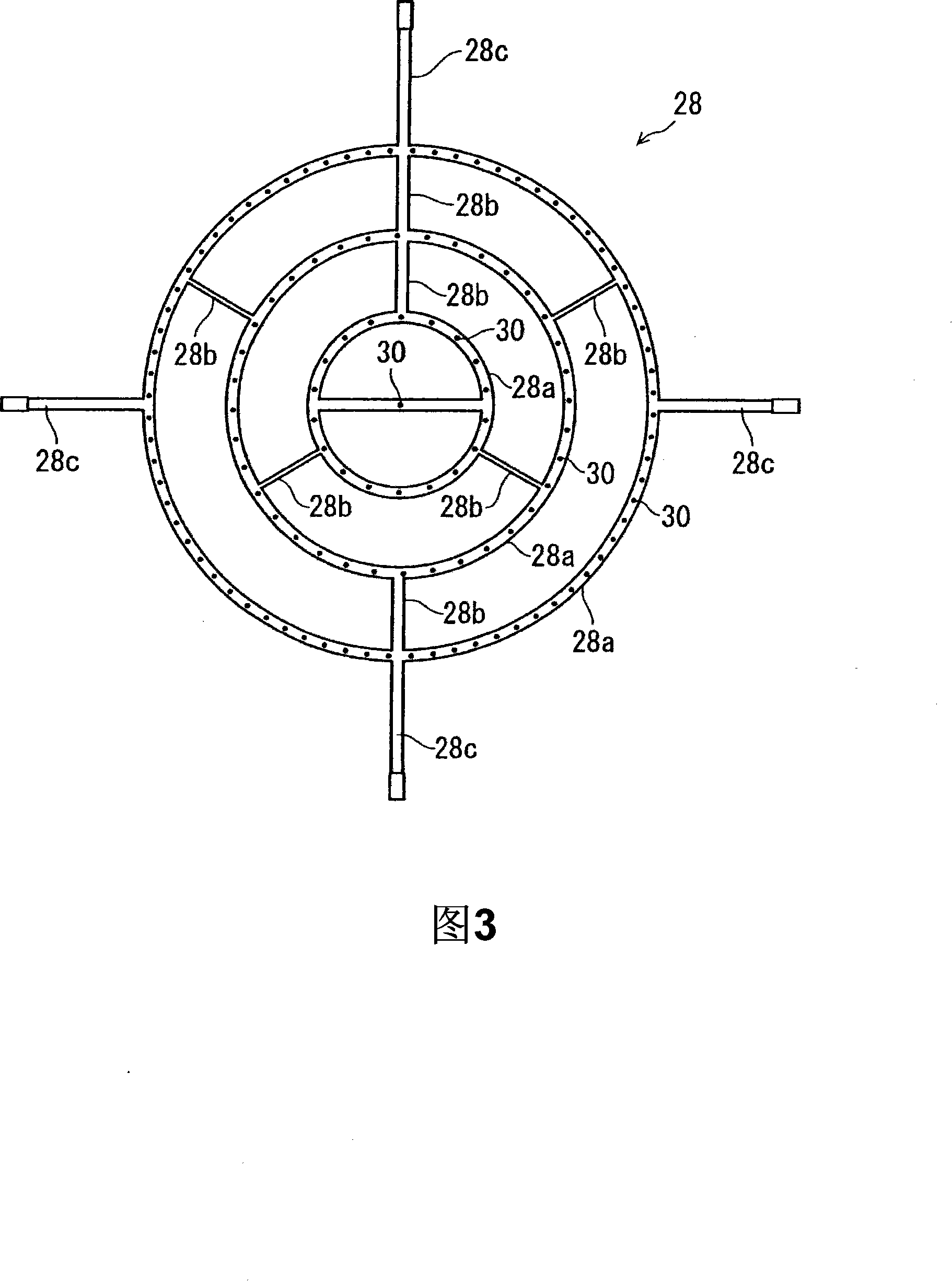
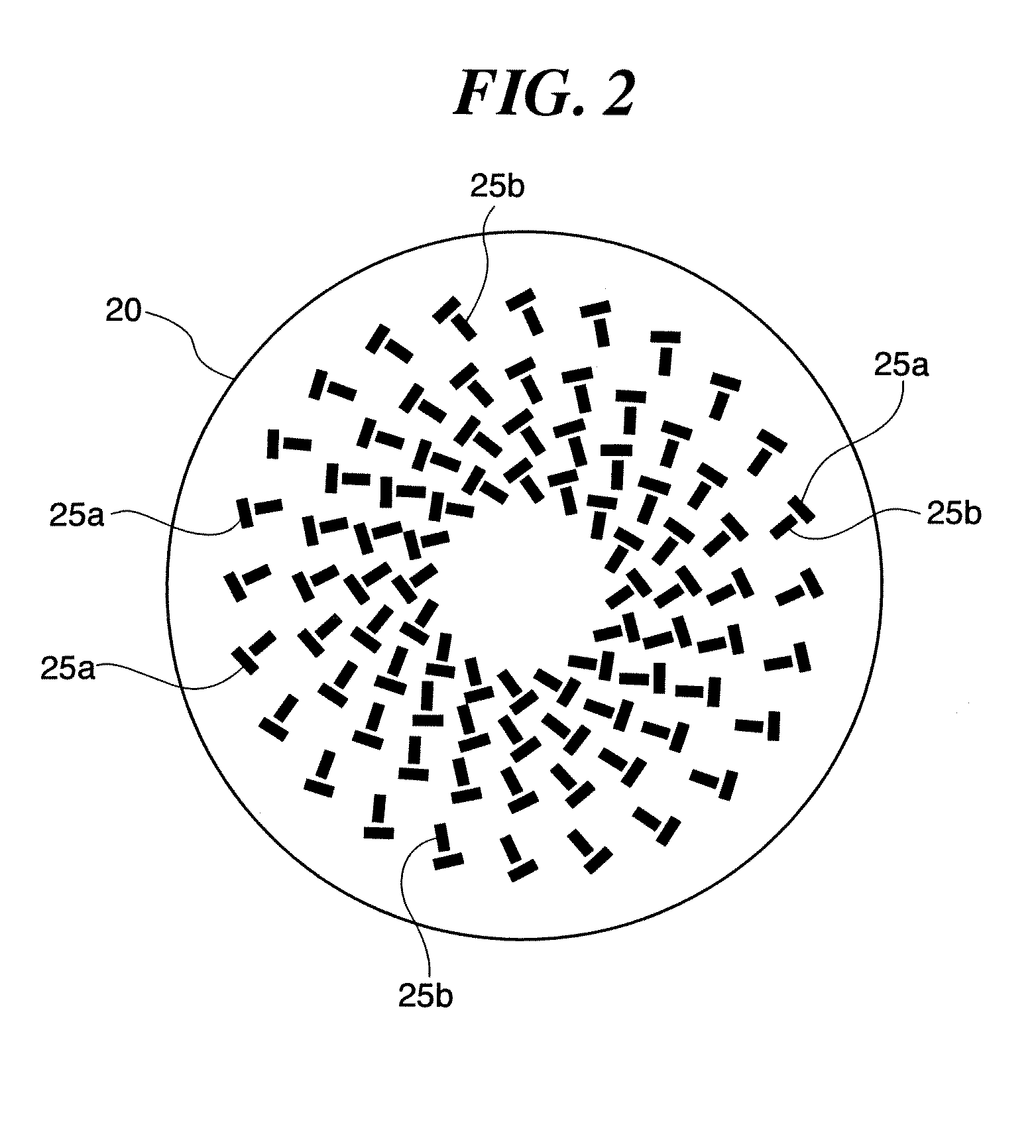
Radial line slot antenna
InactiveUS6853344B2Improve performanceLow costIndividually energised antenna arraysCoupling devicesEngineeringLength wave
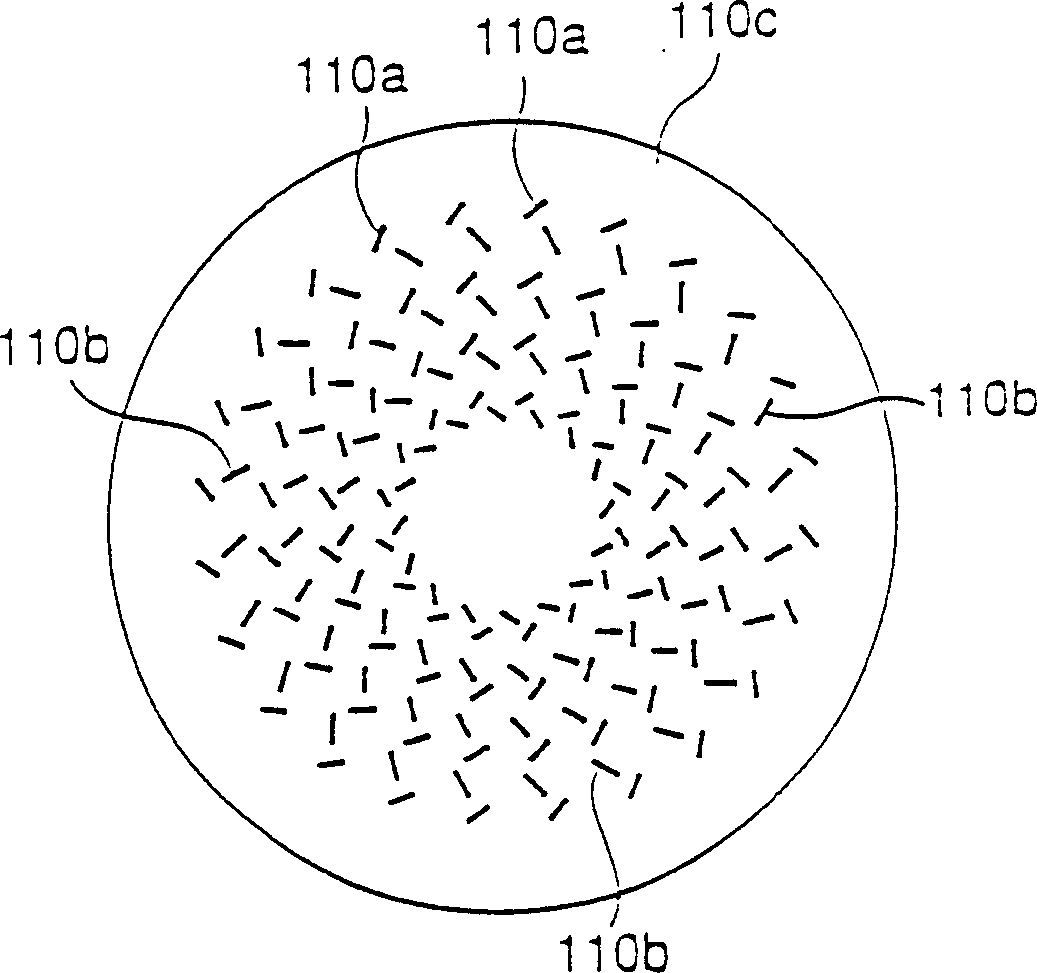
In an RLS antenna, the present invention allows adjusting the optimum positional relationship between the feeder section of the feeder disk and the feeder section of the antenna disk, simply, quickly and at high accuracy by a visual check, so that mass production becomes possible, and an increase in performance and a decrease in cost are implemented. When the diameter of the antenna disk is D and the wavelength of the central frequency is λ, a marker of about 0.10λ or less is disposed in an area of 0.5 (D−4λ)−0.5D distant from the center. A through hole with a size (opening area) through which the marker can be viewed is disposed at a position the same as the position of the marker on the feeder disk. By visually confirming that the marker is positioned at the center of the through hole, the antenna disk is positioned and secured on the feeder disk.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
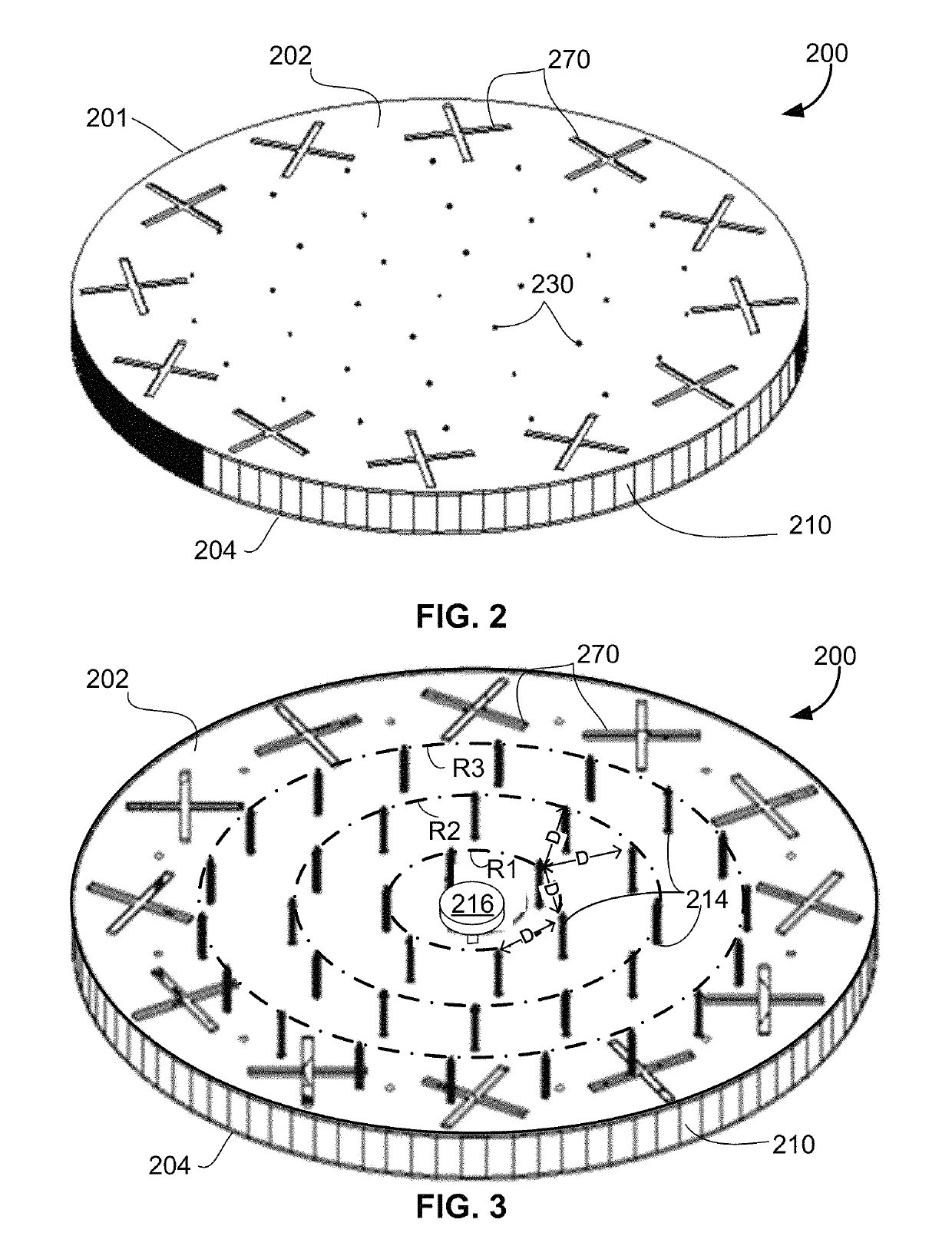
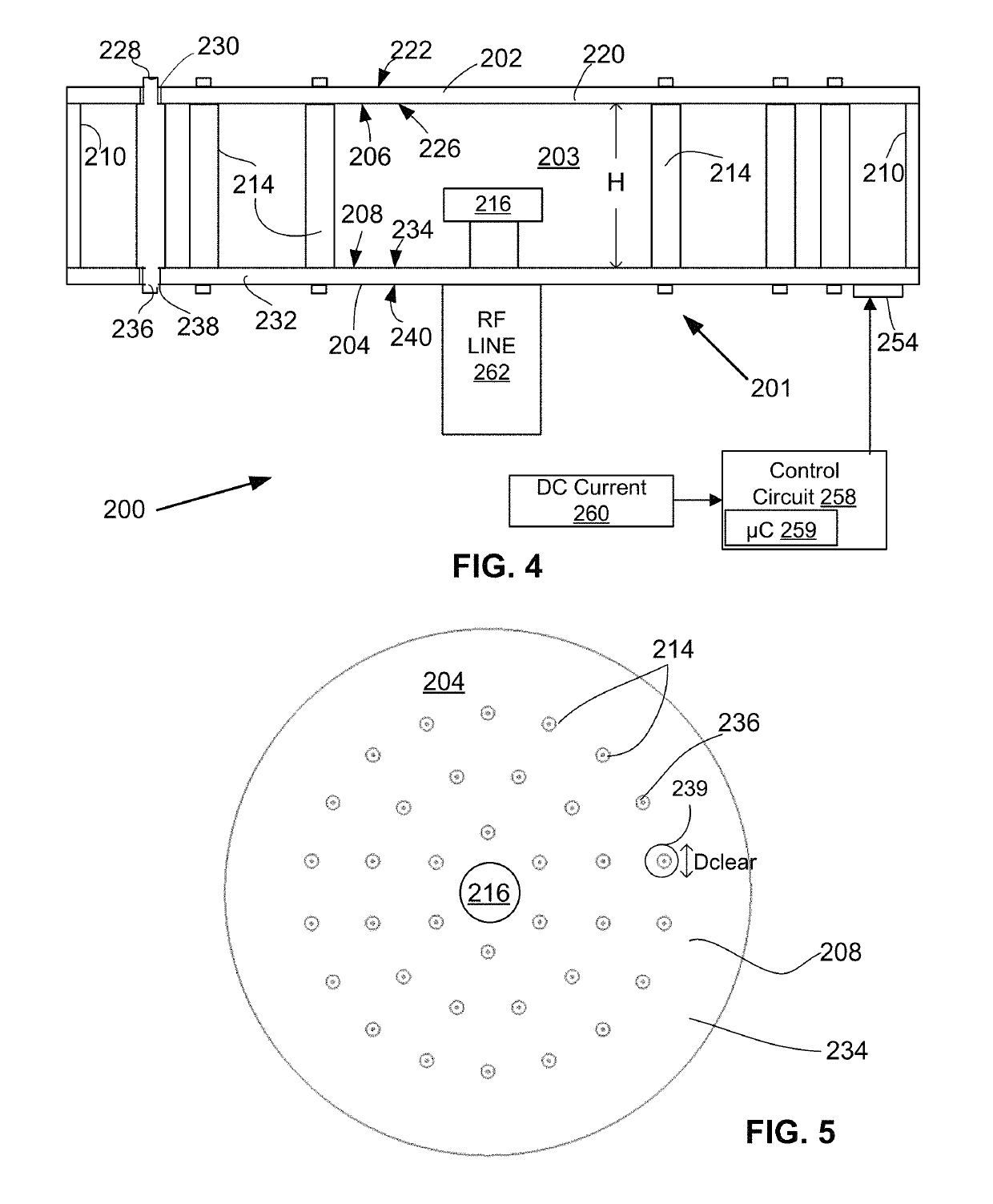
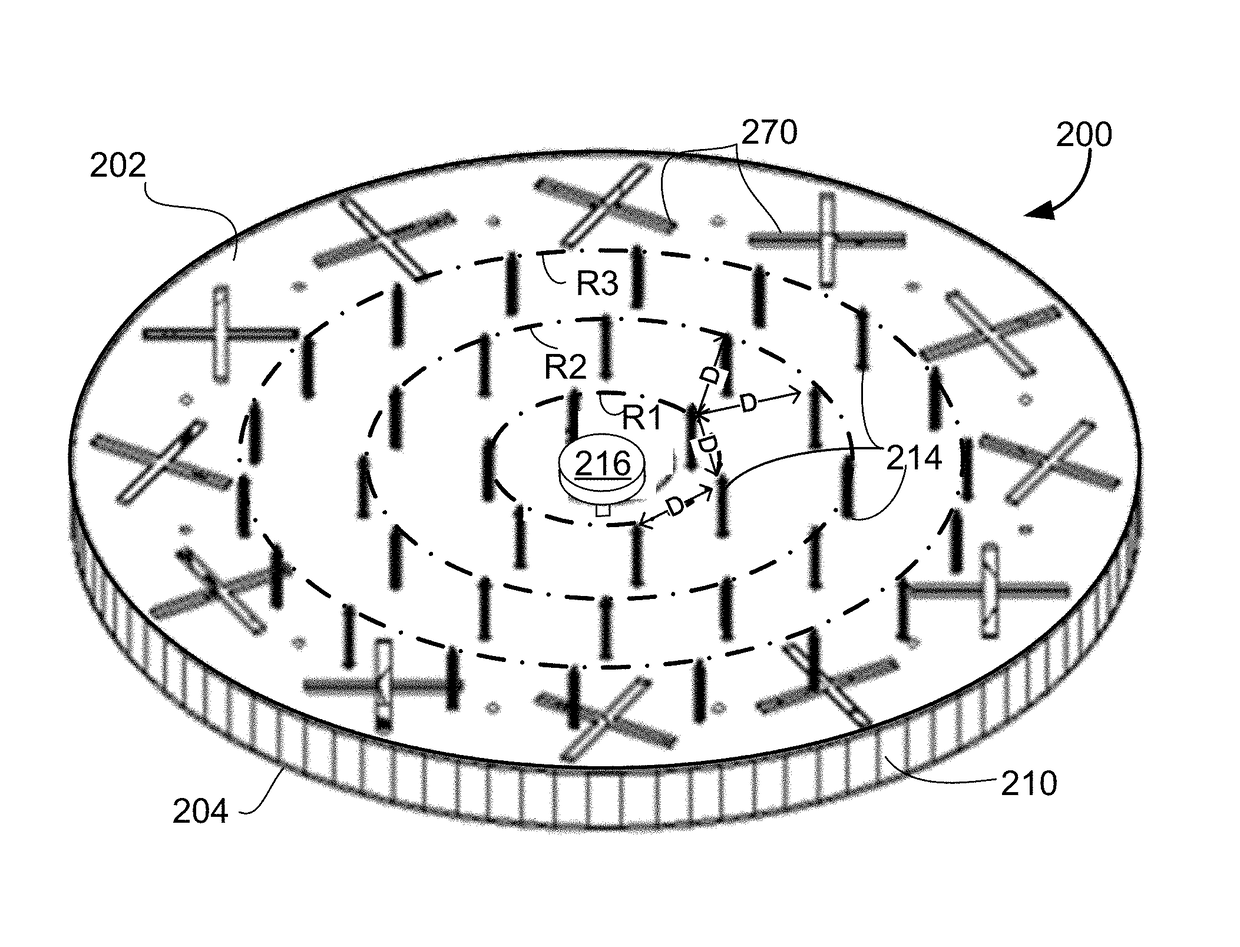
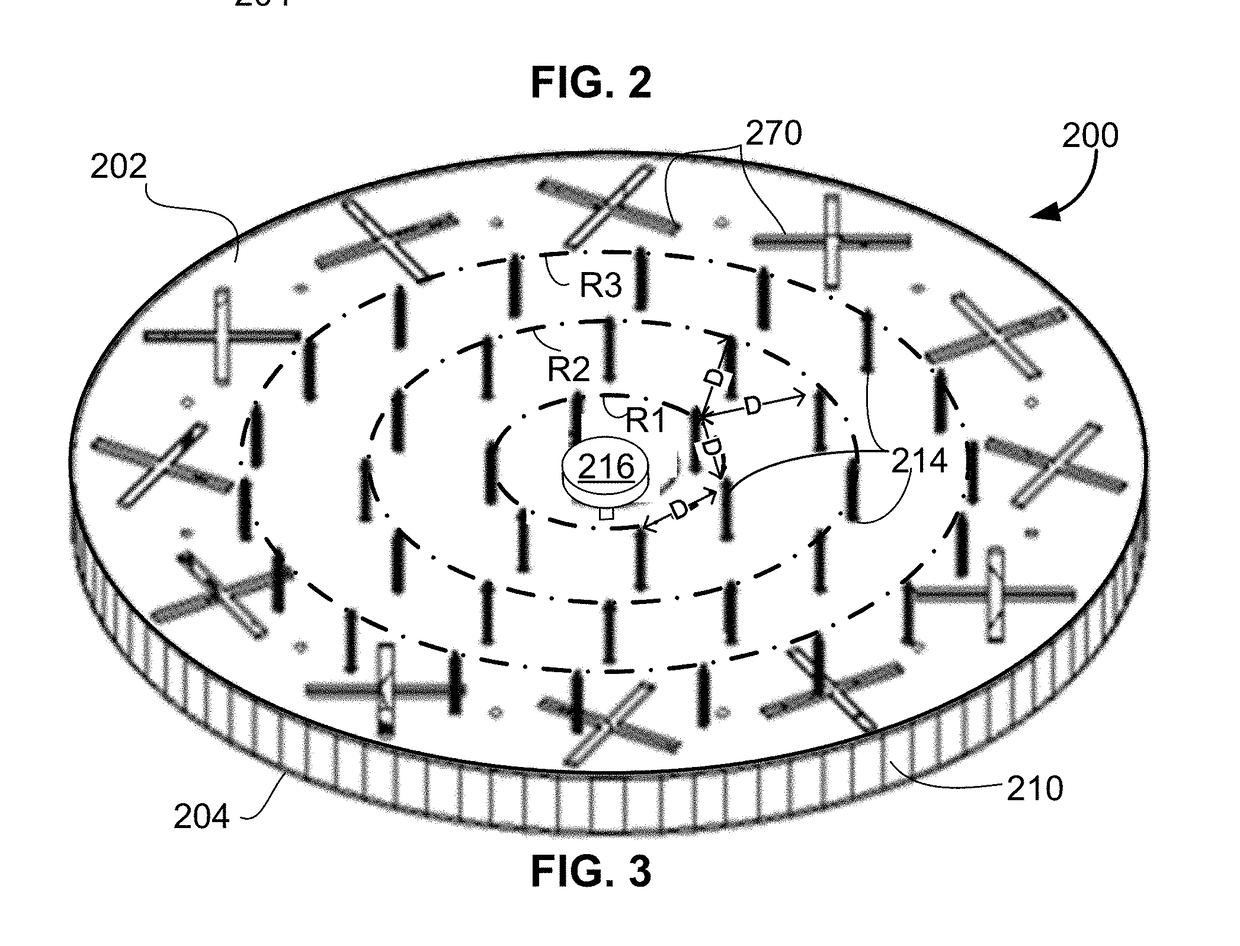
Reconfigurable radial-line slot antenna array
ActiveUS10454184B2Simultaneous aerial operationsParallel-plate/lens fed arraysRadial waveguideCapacitance
An antenna that includes a radial waveguide defining a waveguide region between opposed first and second surfaces. A radio frequency (RF) probe is disposed in the waveguide region for generating RF signals, and a plurality of radiating slot antenna elements are disposed on the first surface for emitting the RF signals from the waveguide region. A plurality of spaced apart conductive elements are disposed within the waveguide region. The antenna includes tunable elements that each include a quarter wavelength RF choke coupled through a variable capacitance and an inductive line to a respective one of the conductive elements. A plurality of DC control lines are provided, with each DC control line being connected to at least one of the tunable elements to adjust the variable capacitance thereof. A control circuit is coupled to the DC control lines and configured to selectively apply DC current values to adjust the variable capacitances of the tunable elements to control a propagation direction of the RF signals from the RF probe.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
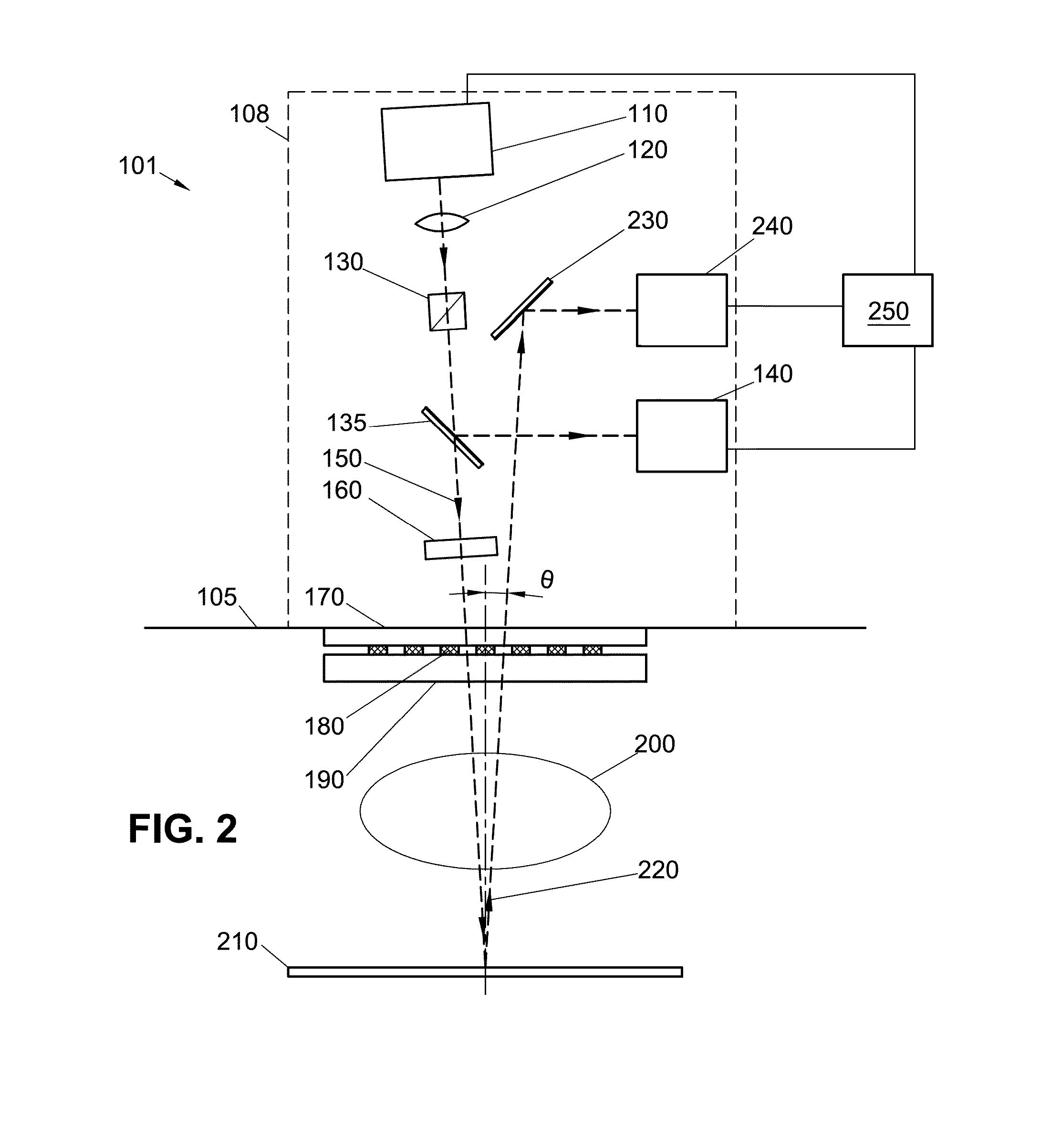
System for in-situ film stack measurement during etching and etch control method
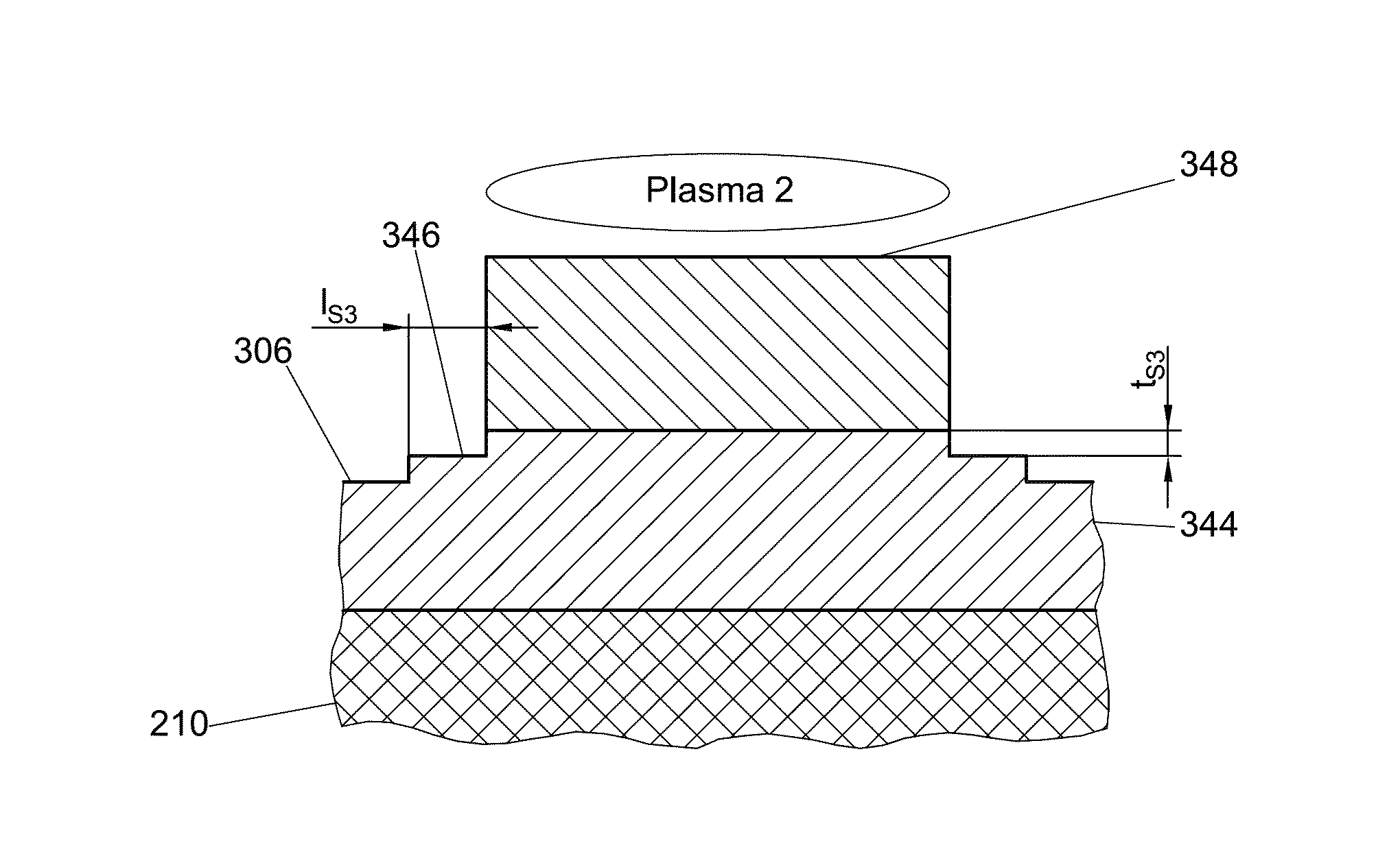
ActiveUS20140024143A1Reduce pruningReduce horizontal sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesLateral recessRadial line slot antenna
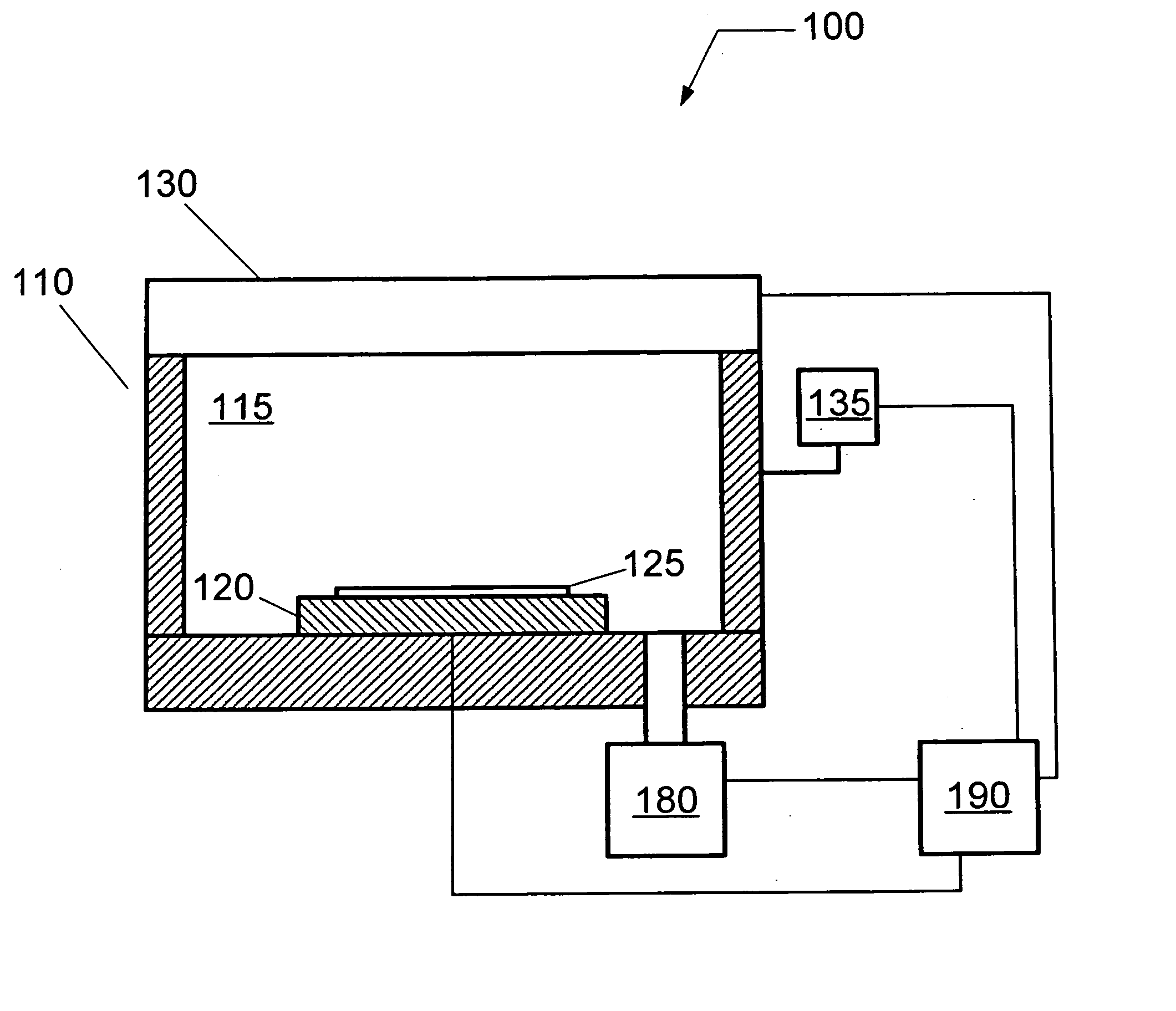
Disclosed is an in-situ optical monitor (ISOM) system and associated method for controlling plasma etching processes during the forming of stepped structures in semiconductor manufacturing. The in-situ optical monitor (ISOM) can be optionally configured for coupling to a surface-wave plasma source (SWP), for example a radial line slotted antenna (RLSA) plasma source. A method is described to correlate the lateral recess of the steps and the etched thickness of a photoresist layer for use with the in-situ optical monitor (ISOM) during control of plasma etching processes in the forming of stepped structures.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Reconfigurable radial-line slot antenna array
ActiveUS20180219299A1Simultaneous aerial operationsParallel-plate/lens fed arraysCapacitanceRadial waveguide
An antenna that includes a radial waveguide defining a waveguide region between opposed first and second surfaces. A radio frequency (RF) probe is disposed in the waveguide region for generating RF signals, and a plurality of radiating slot antenna elements are disposed on the first surface for emitting the RF signals from the waveguide region. A plurality of spaced apart conductive elements are disposed within the waveguide region. The antenna includes tunable elements that each include a quarter wavelength RF choke coupled through a variable capacitance and an inductive line to a respective one of the conductive elements. A plurality of DC control lines are provided, with each DC control line being connected to at least one of the tunable elements to adjust the variable capacitance thereof. A control circuit is coupled to the DC control lines and configured to selectively apply DC current values to adjust the variable capacitances of the tunable elements to control a propagation direction of the RF signals from the RF probe.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
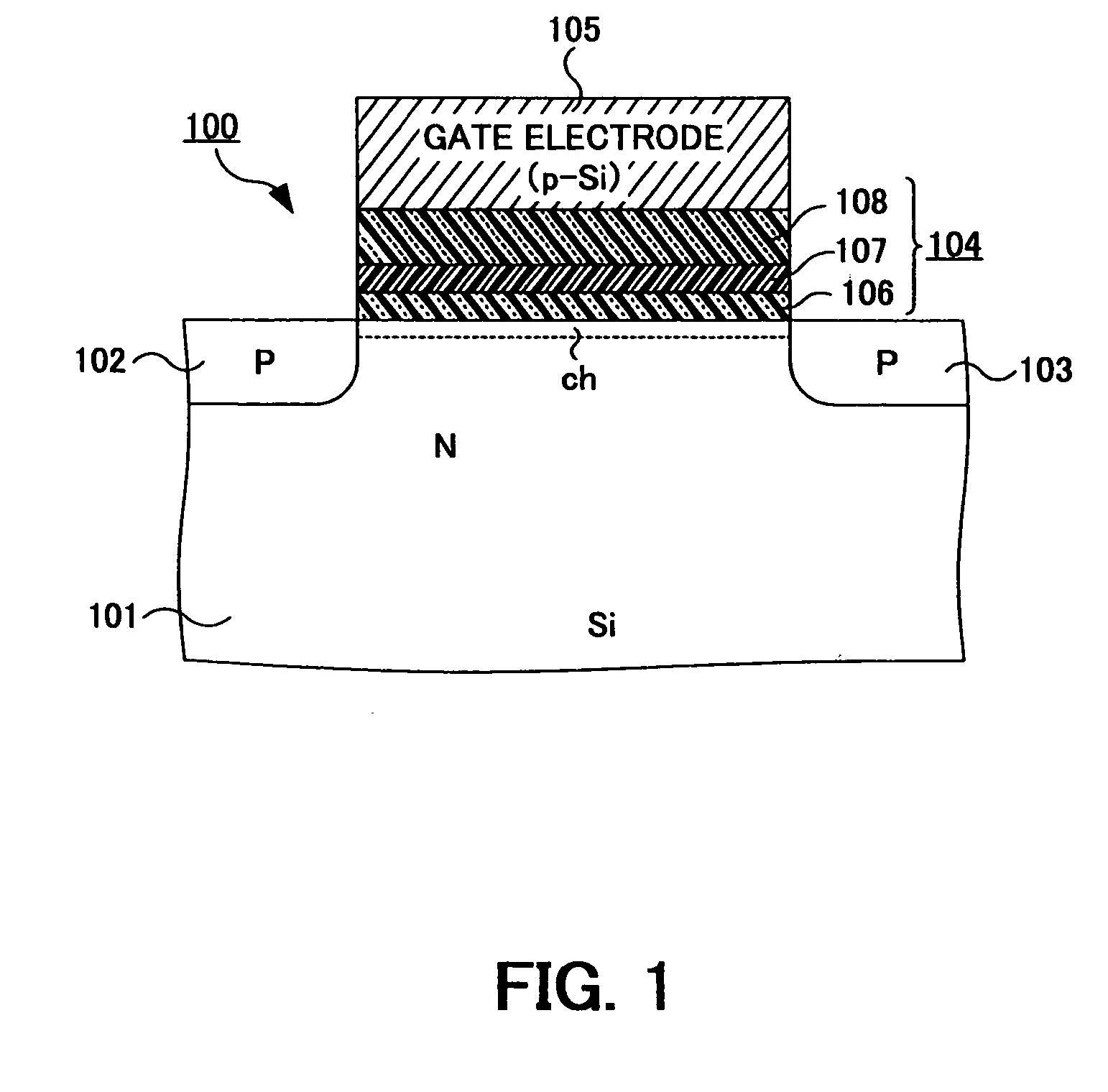
Forming method and forming system for insulation film
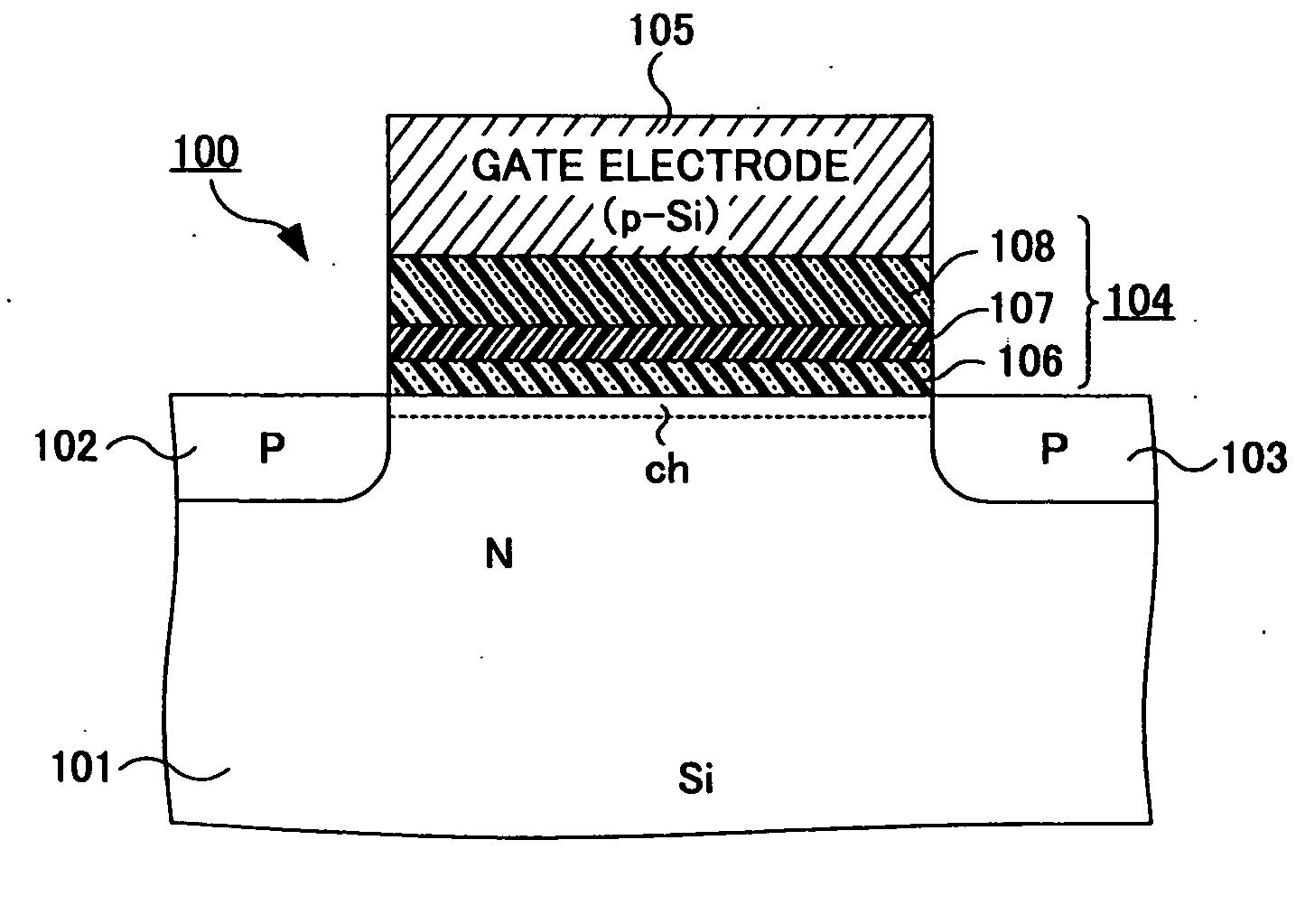
InactiveUS20070085154A1Improve reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsMicrowaveOptoelectronics
A gate insulation film (104) of a MISFET (100) is constituted of a silicon oxide film (106), silicon nitride film (107), and high-permittivity film (108). The silicon oxide film (106) and silicon nitride film (107) are formed by microwave plasma processing with a radial line slot antenna.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
System for in-situ film stack measurement during etching and etch control method
ActiveUS9059038B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesLateral recessRadial line slot antenna
Disclosed is an in-situ optical monitor (ISOM) system and associated method for controlling plasma etching processes during the forming of stepped structures in semiconductor manufacturing. The in-situ optical monitor (ISOM) can be optionally configured for coupling to a surface-wave plasma source (SWP), for example a radial line slotted antenna (RLSA) plasma source. A method is described to correlate the lateral recess of the steps and the etched thickness of a photoresist layer for use with the in-situ optical monitor (ISOM) during control of plasma etching processes in the forming of stepped structures.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Cleaning method and plasma processing method
ActiveUS8034183B2Remove pollutantsEfficient removalElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningMicrowaveEngineering
In a RLSA microwave plasma processing apparatus that radiates microwave from a microwave generator into a chamber by using a planer antenna (Radial Line Slot Antenna) having many slots formed according to a certain pattern, the chamber contaminated with Na or the like is cleaned by using a cleaning gas containing H2 and O2.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Etching method and semiconductor device fabrication method
InactiveUS20080261406A1High selectivityAvoid recessionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistMicrowave
An etching method capable of increasing the selectivity of a polysilicon film to a silicon oxide film and suppressing recess formation on a silicon base layer. That part of the polysilicon film of a wafer transferred into a processing vessel which is exposed through an opening is etched so as to slightly remain on a gate oxide film. The pressure in a processing space is set to 66.7 Pa, HBr gas and He gas are supplied to the processing space, and a microwave of 2.45 GHz is supplied to a radial line slot antenna. The polysilicon film is etched by plasma generated from the HBr gas so as to be completely removed, the exposed gate oxide film is etched, and a resist film and an anti-reflection film are etched.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Forming method and forming system for insulation film
InactiveUS7374635B2Improve reliabilityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowavePermittivity
A gate insulation film (104) of a MISFET (100) is constituted of a silicon oxide film (106), silicon nitride film (107), and high-permittivity film (108). The silicon oxide film (106) and silicon nitride film (107) are formed by microwave plasma processing with a radial line slot antenna.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
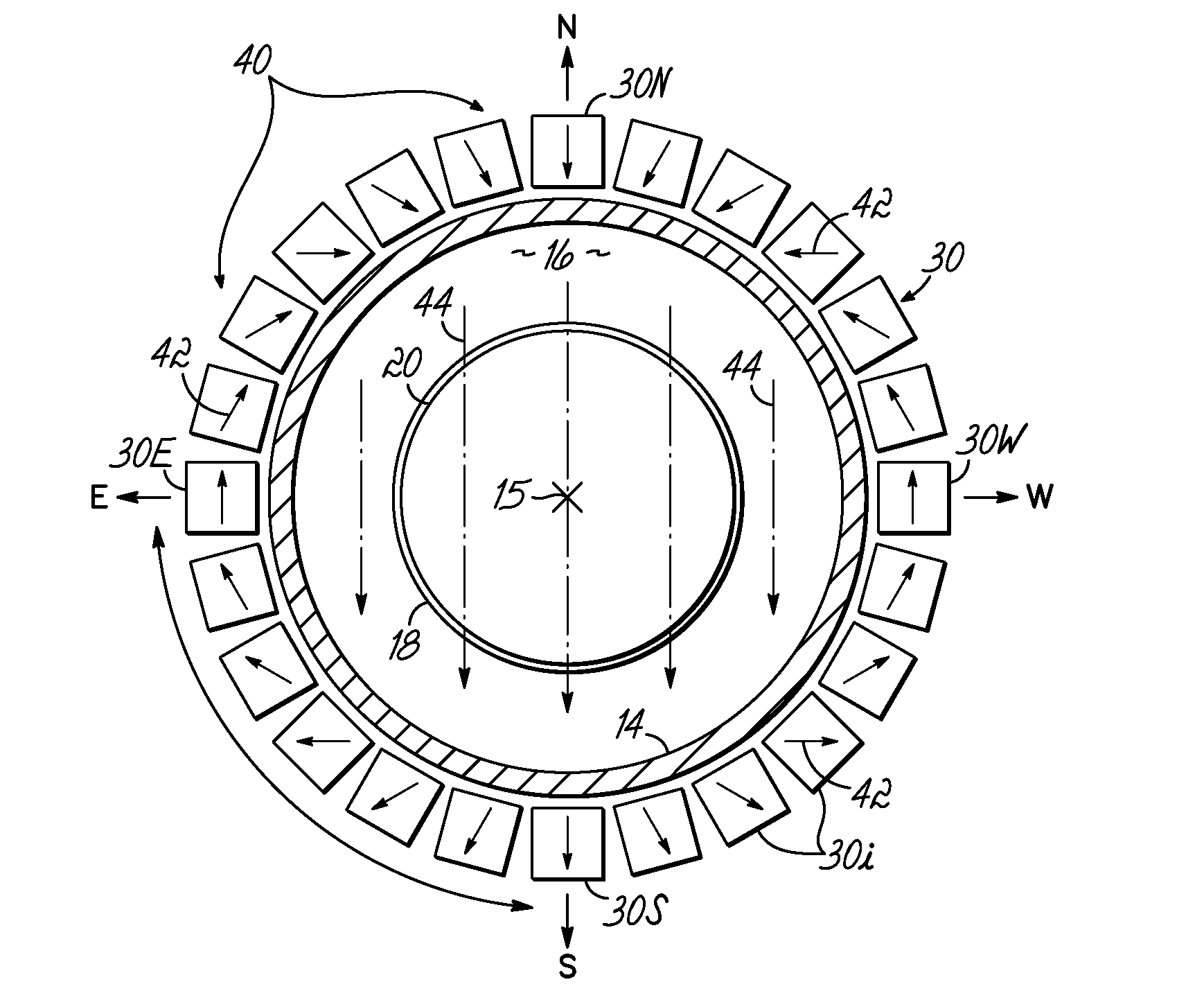
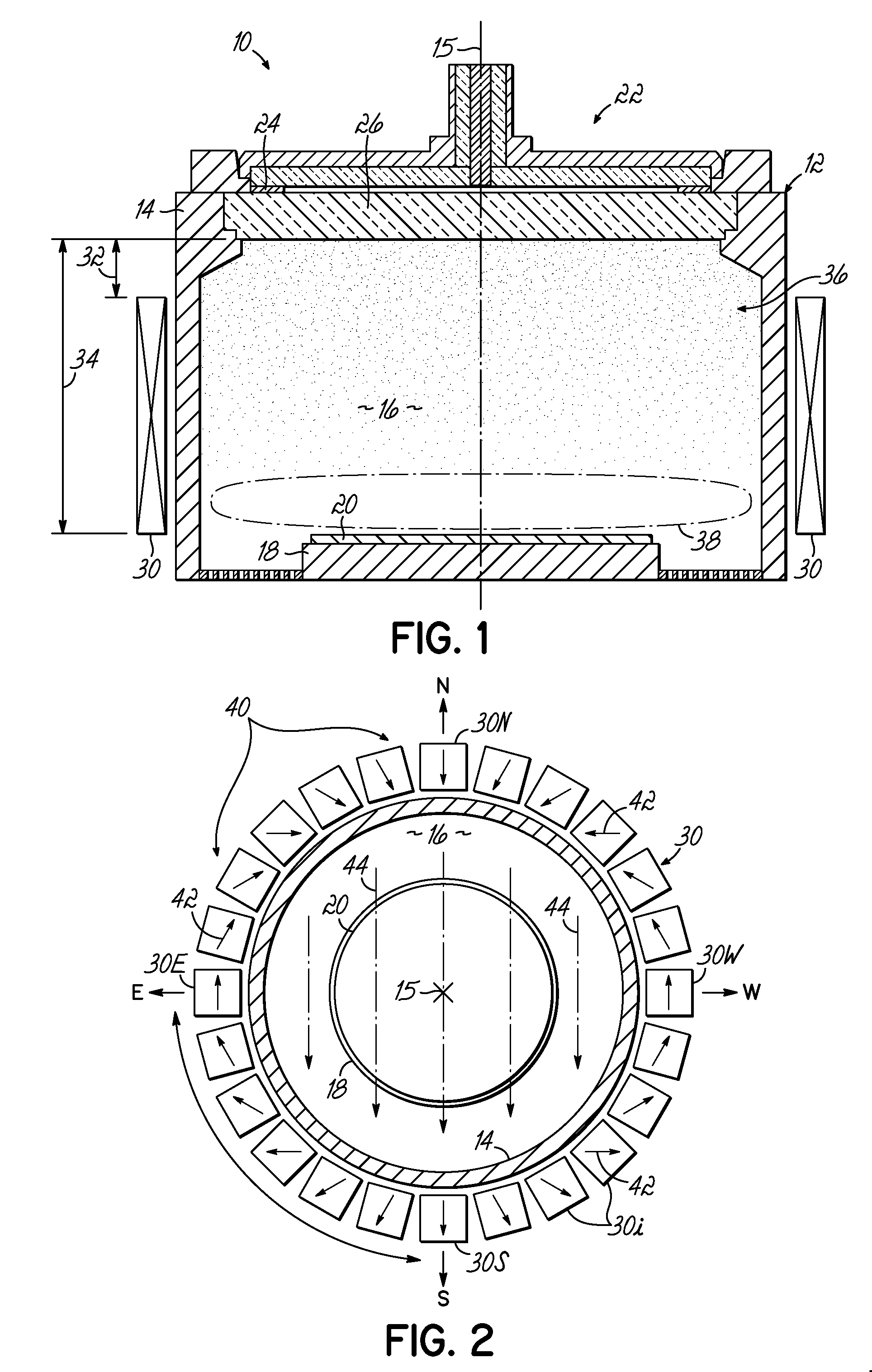
Dipole ring magnet assisted microwave radial line slot antenna plasma processing method and apparatus
ActiveUS20160293389A1Lower average energyEnhance azimuthal uniformityElectric discharge tubesChemical treatmentPlasma electron
A method and apparatus is provided for obtaining a low average electron energy flux onto a substrate in a processing chamber. A processing chamber includes a substrate support therein for chemical processing. An energy source induced plasma, and ion propelling means, directs energetic plasma electrons toward the substrate support. A dipole ring magnet field is applied perpendicular to the direction of ion travel, to effectively prevent electrons above an acceptable maximum energy level from reaching the substrate holder. Rotation of the dipole magnetic field reduces electron non-uniformities.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com