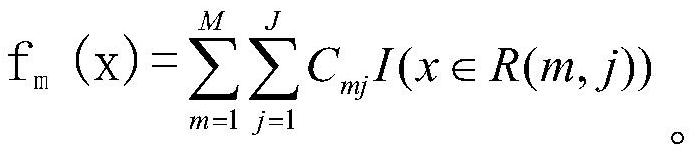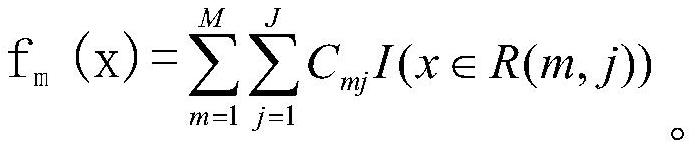Patents
Literature
30 results about "Sality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sality is the classification for a family of malicious software (malware), which infects files on Microsoft Windows systems. Sality was first discovered in 2003 and has advanced over the years to become a dynamic, enduring and full-featured form of malicious code. Systems infected with Sality may communicate over a peer-to-peer (P2P) network to form a botnet for the purpose of relaying spam, proxying of communications, exfiltrating sensitive data, compromising web servers and/or coordinating distributed computing tasks for the purpose of processing intensive tasks (e.g. password cracking). Since 2010, certain variants of Sality have also incorporated the use of rootkit functions as part of an ongoing evolution of the malware family. Because of its continued development and capabilities, Sality is considered to be one of the most complex and formidable forms of malware to date.
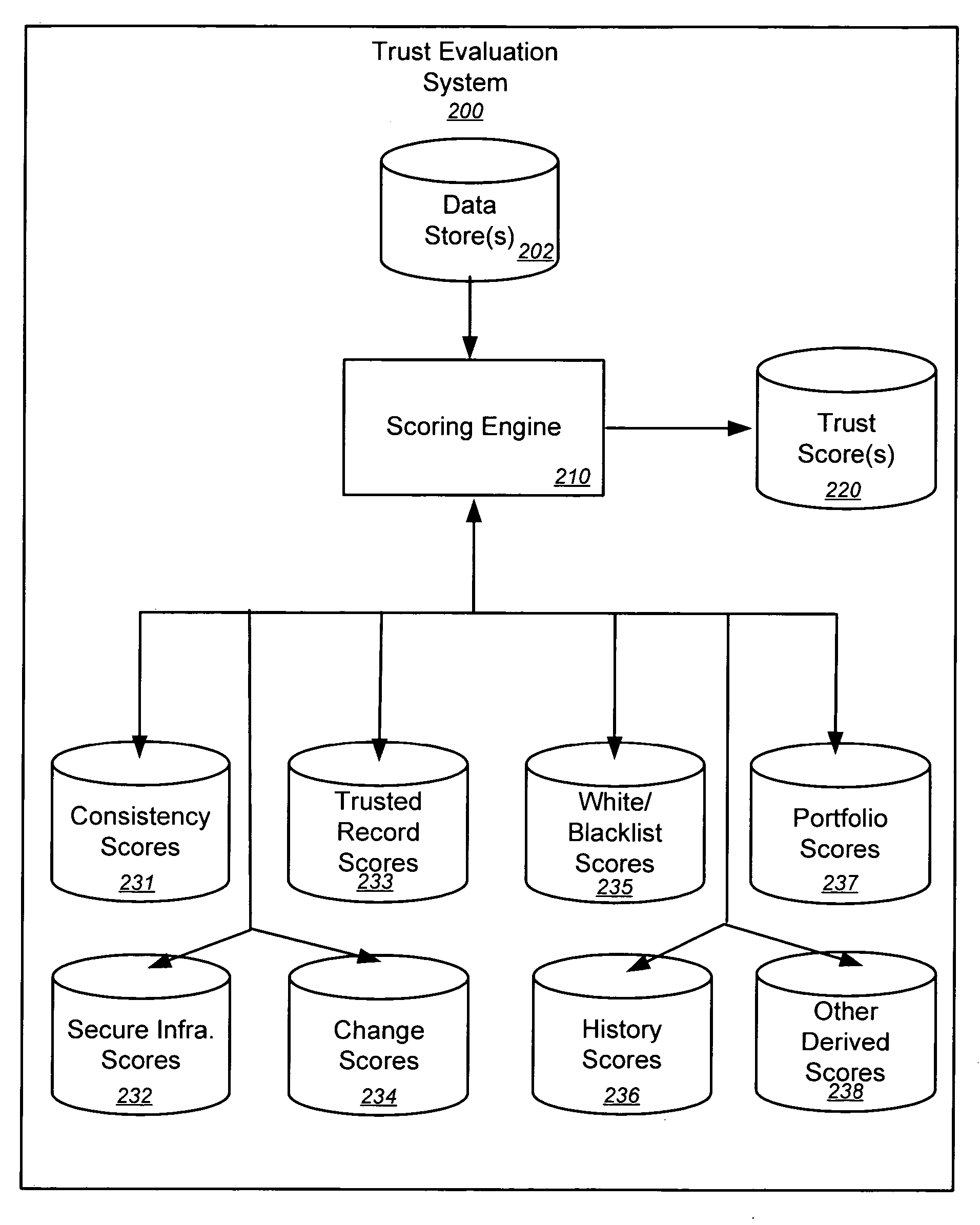
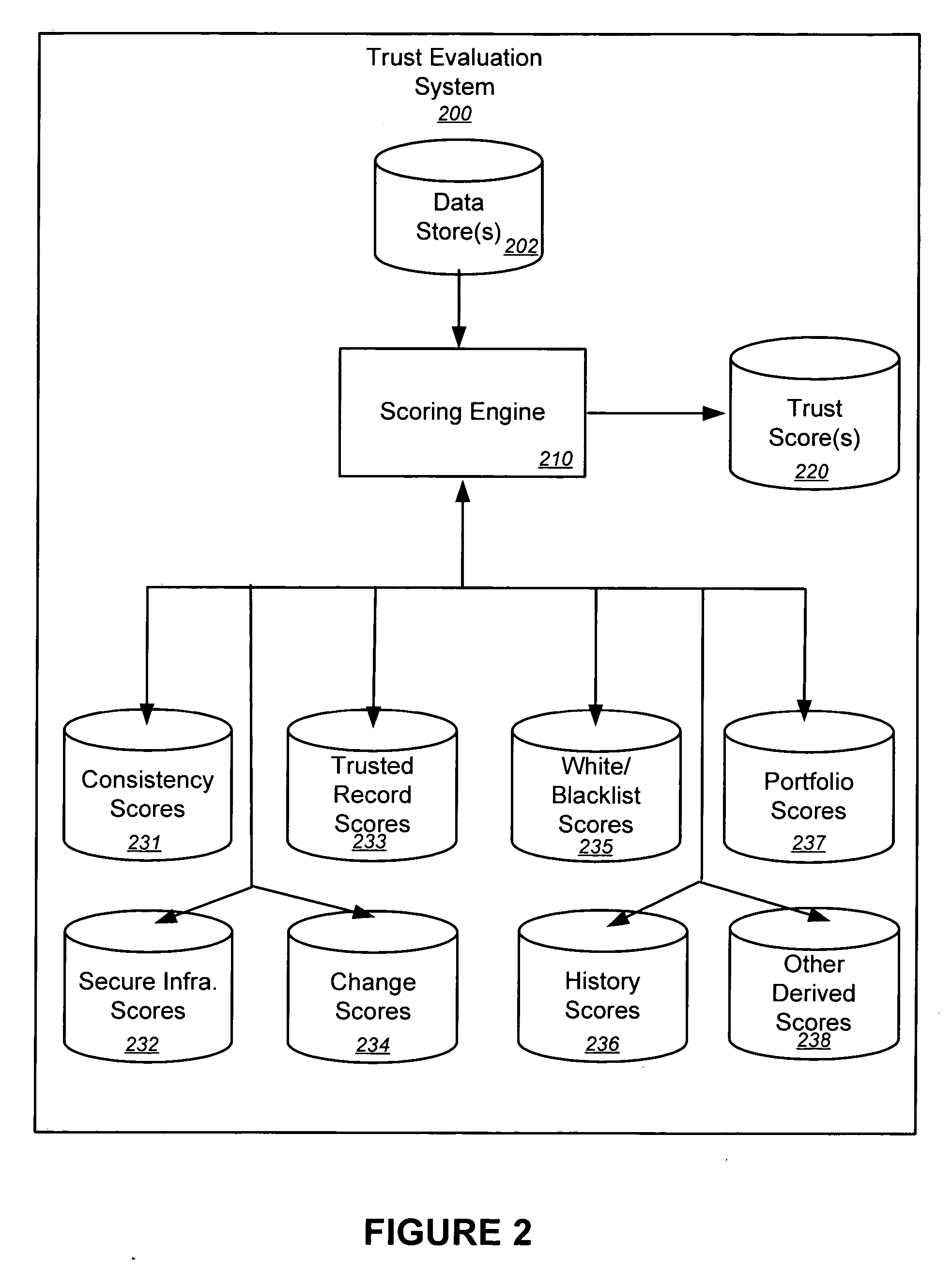
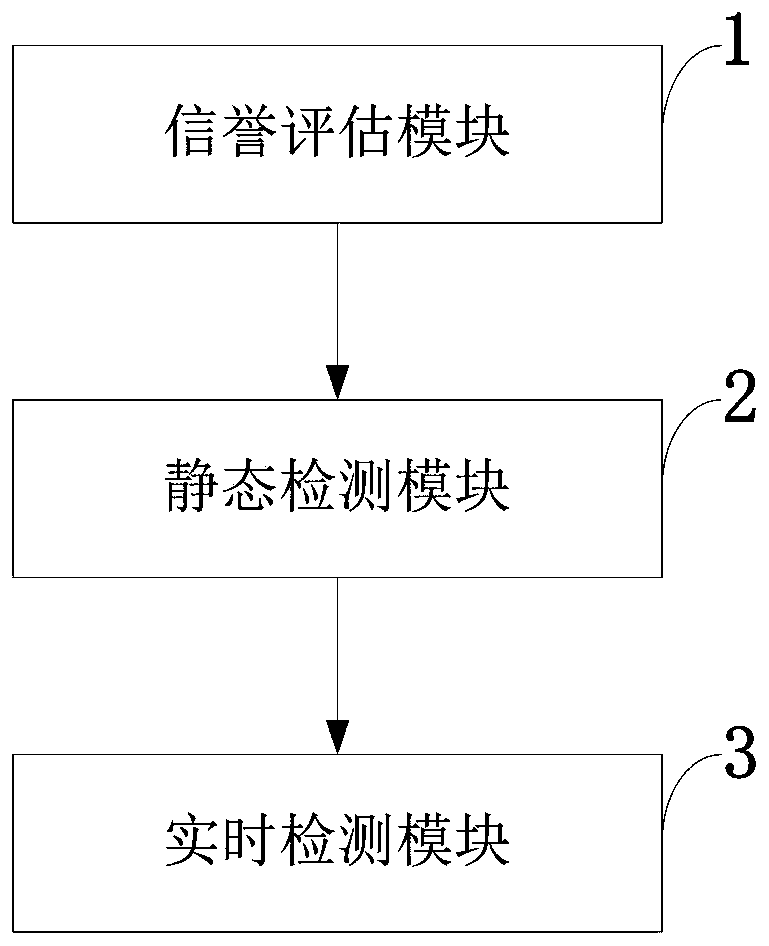
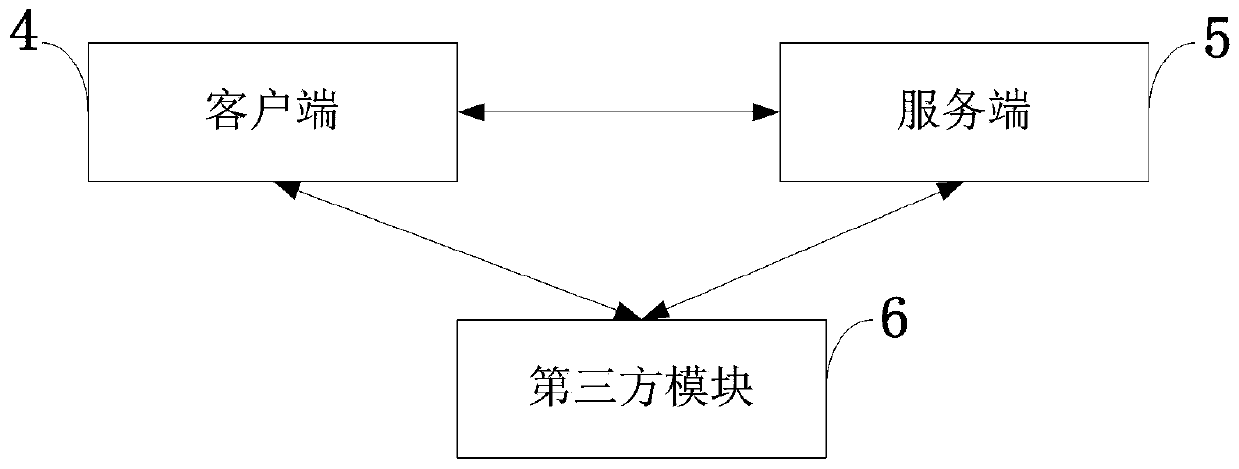
Implementing trust policies
InactiveUS20060212925A1Platform integrity maintainanceSpecial data processing applicationsInternet privacySality
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods, systems, and software for implementing trust policies. Such policies may be implemented in a variety of ways, including at one or more border devices, client computers, etc. In accordance with various embodiments, a communication between a client computer (and / or application) and an online entity may be monitored and / or otherwise detected. The online entity may be identified, and / or one or more trust scores associated with the online entity may be obtained. Based on the trust scores, as well, perhaps as the nature of the communication, an action (such as allowing the communication, blocking the communication, quarantining the communication, warning a user, administrator, etc.) may be taken. In some cases, a trust policy may be consulted to determine what action should be taken with respect to a given communication.
Owner:MARKMONITOR
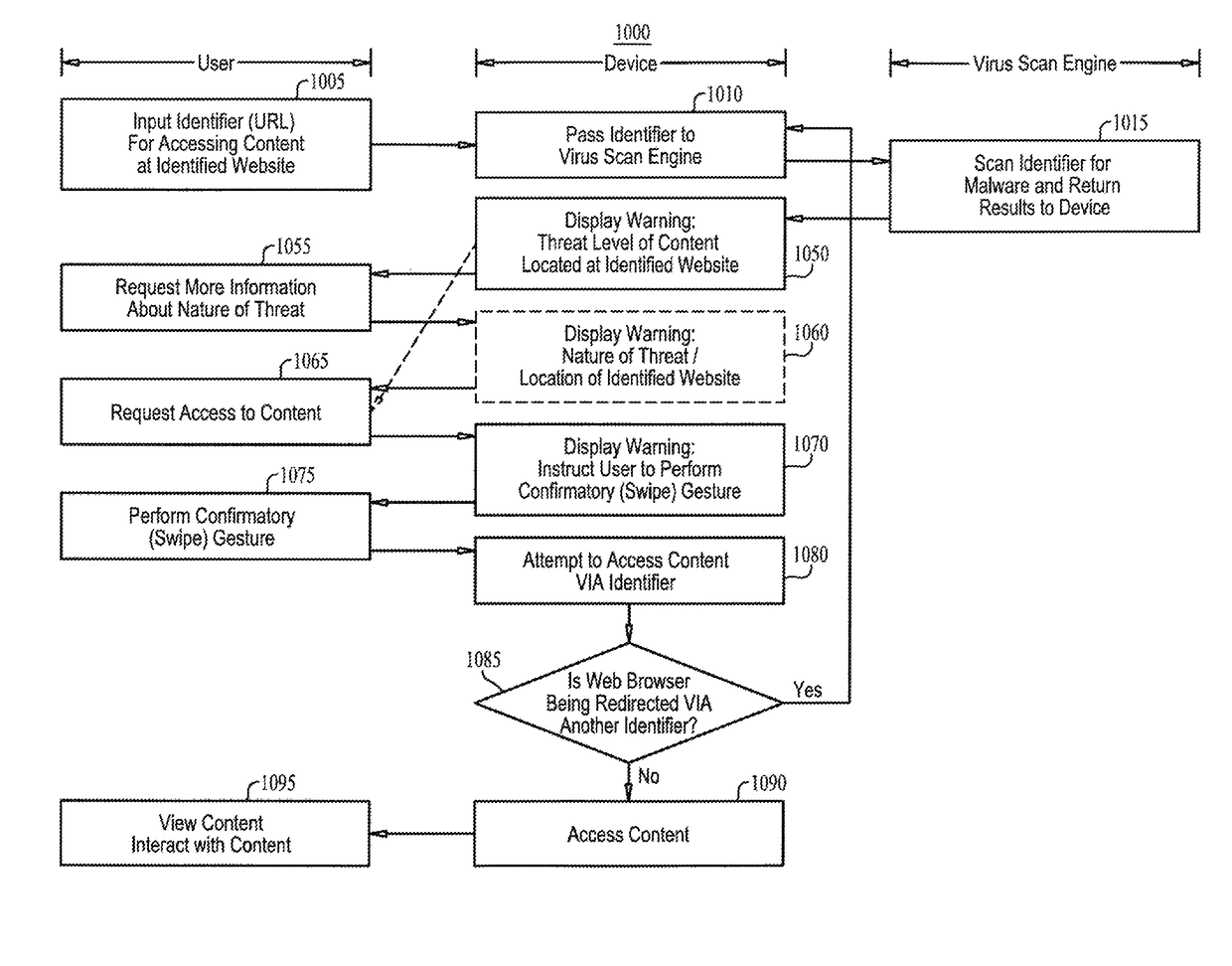
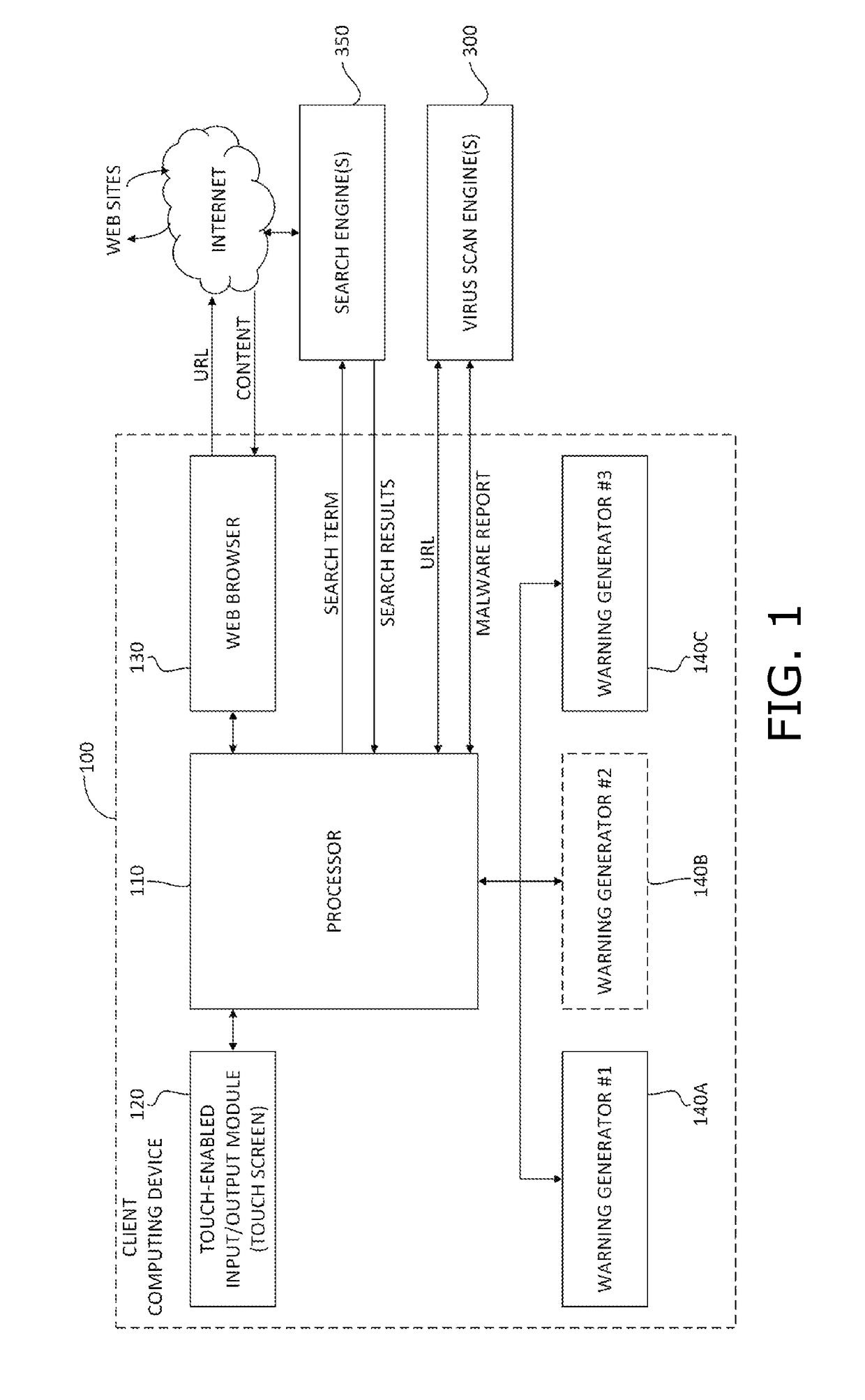
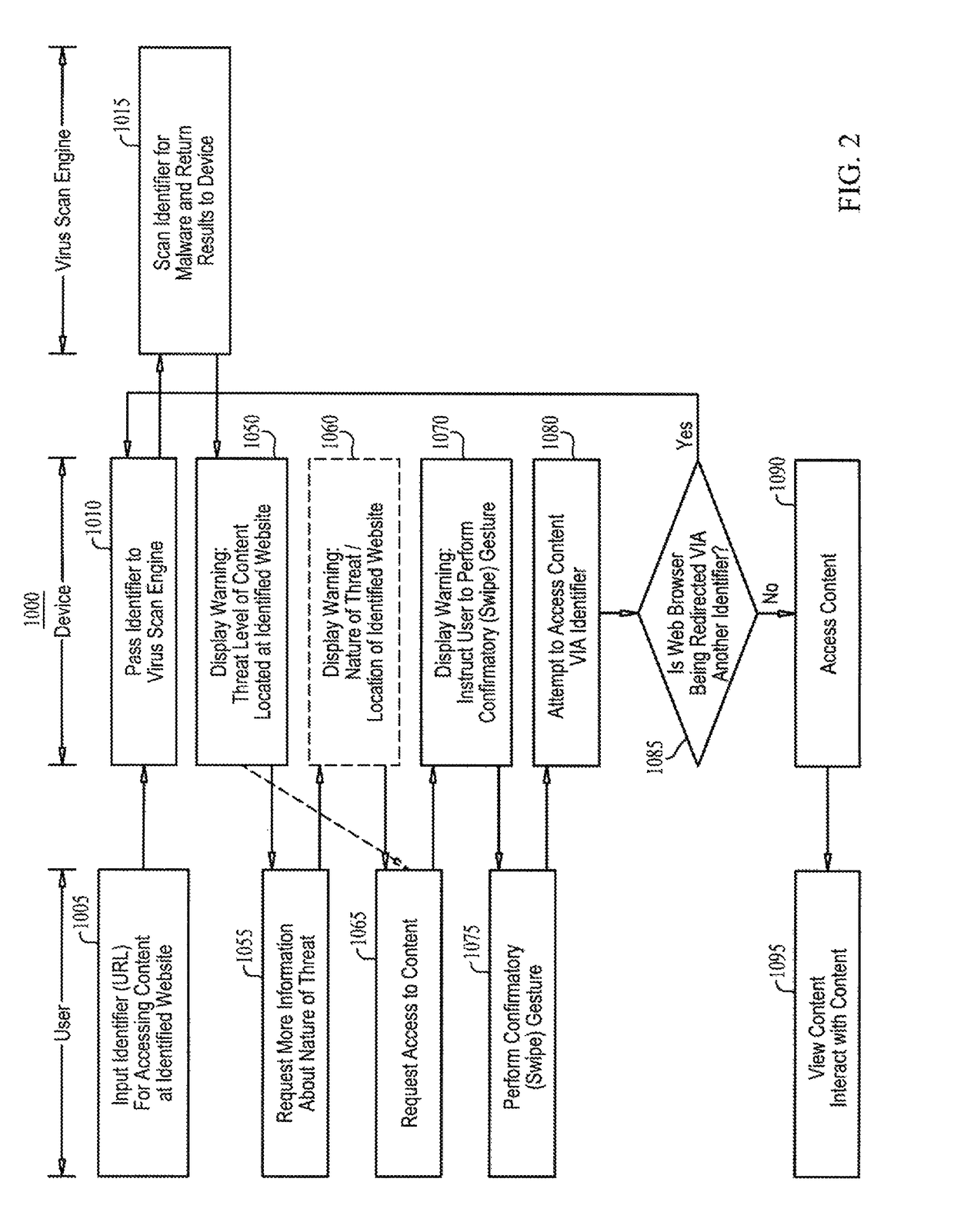
Malware warning
A malware warning system, including a client sending requests to and receiving replies from a server, and a server, including a first warning generator sending to the client a warning including a threat level of content located at a web site, in response to receiving from the client a URL for accessing content at the web site, a second warning generator sending to the client a warning including information about at least one of the nature of the threat of the content located at the web site and a location of the web site, in response to receiving from the client a request for more information about the nature of the threat, and a third warning generator, sending to the client a warning including an instruction to perform a swipe gesture to confirm a request to access the URL, in response to receiving that request from the client.
Owner:FINJAN MOBILE LLC
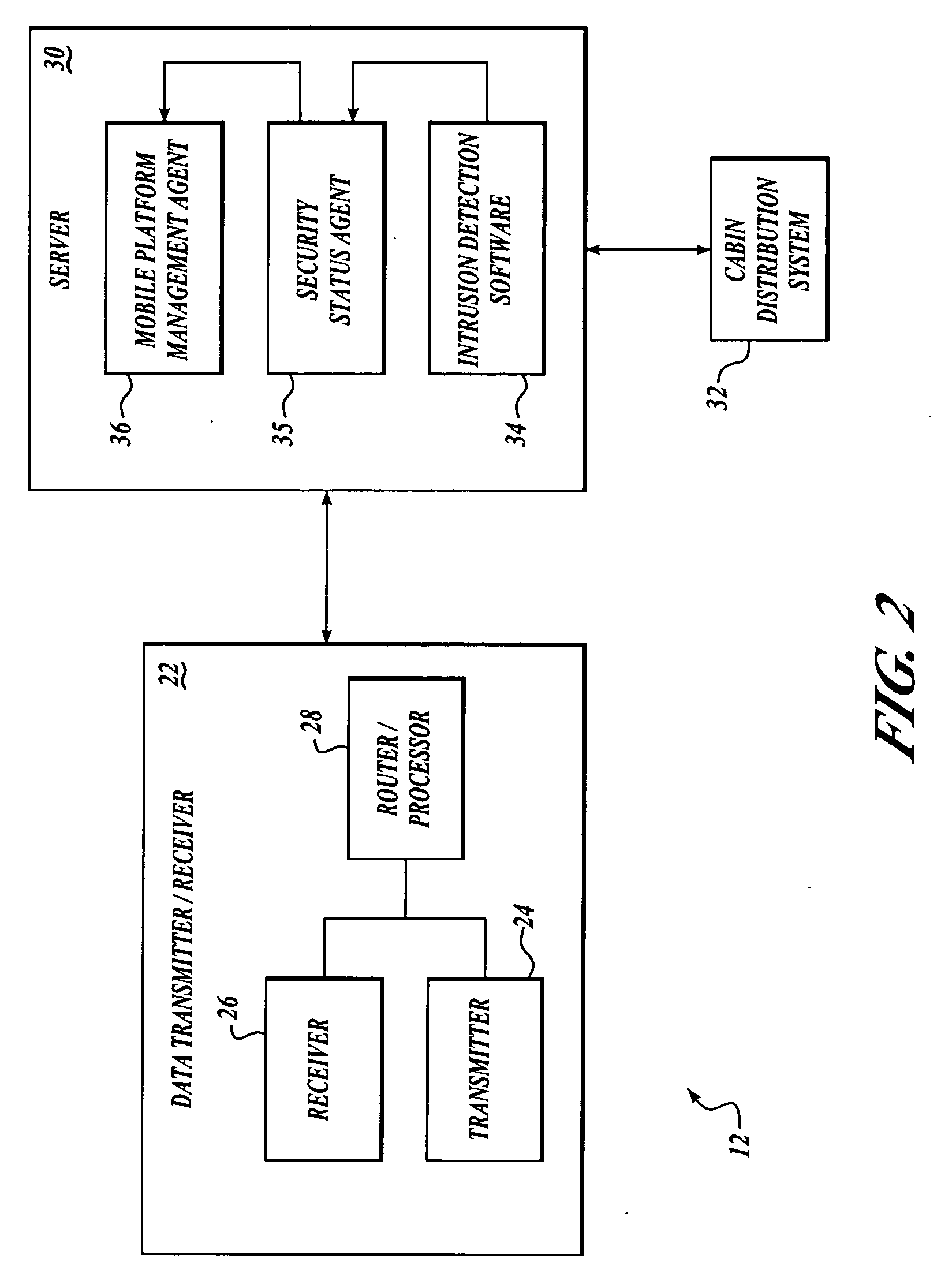
Security state vector for mobile network platform
ActiveUS20050254654A1Minimal amountMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionRolloverCyber operations
State of security in a mobile communications network is communicated. Data regarding nature and severity of security events onboard at least one mobile platform is generated and processed. A message that includes the processed data is generated and transmitted periodically. The processed data makes up a security state vector that includes the number of security events detected since power-up of the mobile platform node, sum of highest severity security events since power-up or counter rollover, sum of the second highest severity security events detected since power-up or counter rollover, sum of the third highest severity security events detected since power-up or counter rollover, highest security event classification, second-highest security event classification, and third-highest security event classification. The processed data may be used in a network operations center to prioritize mobile platforms from which logged data should be retrieved for further investigation and monitoring.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
A Method to Mitigate Distributed Denial of Service Attack
InactiveCN102281295AMitigate Distributed Denial of Service AttacksStrong noveltyTransmissionIp addressEngineering
The invention discloses a method for easing distributed denial of service attacks, which solves the defects in the prior detection or defense technologies. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: presetting a group of regional scope presented by an IP (Internet Protocol) address block, and a threshold of the number of messages of a protocol type or a message property allowed by each sub-region in the regional scope; when receiving one message of the corresponding protocol type or message property, searching the sub-region to which the message belongs according to a source IP address; if a cv (current value) of the number of the messages of the protocol type or message property corresponding to the sub-region to which the message belongs is more than 0, subtracting 1 from the cv, and further processing the received messages regularly according to the protocol type or message property; if the cv is equal to 0, or directly discarding the messages or discarding the messages after recording related information of the messages; aiming at the request on easing different types of distributed denial of service attacks, concurrently executing different recovery processing for the cv of the number of the messages of the corresponding protocol type or message property in corresponding sub-region within a given scope. The method is used in an IP network.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
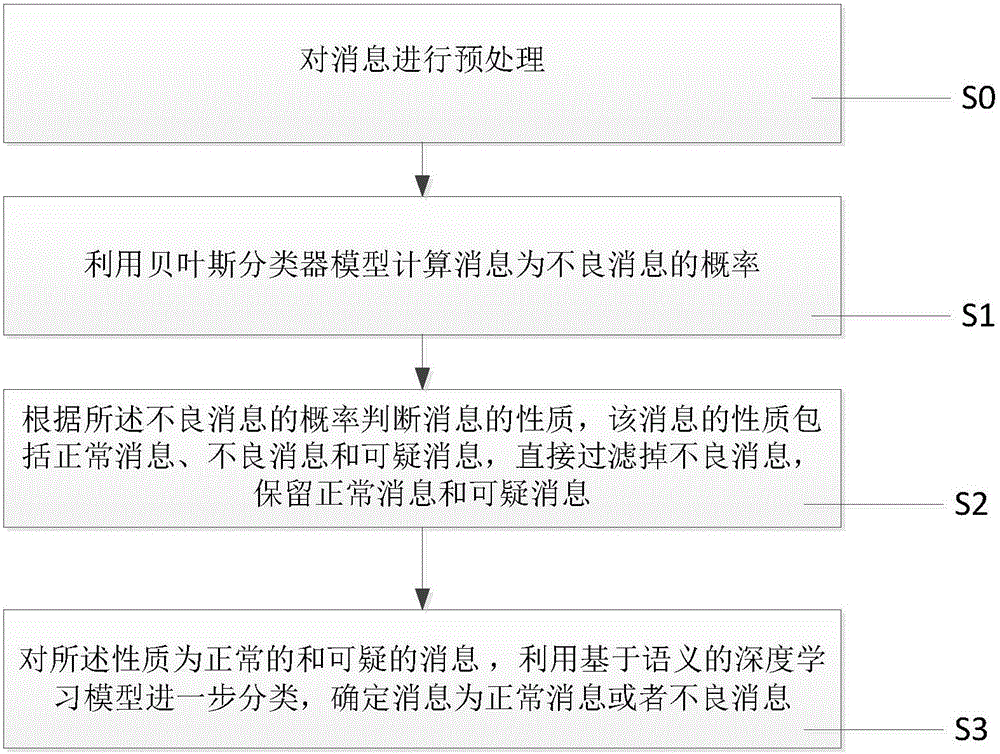
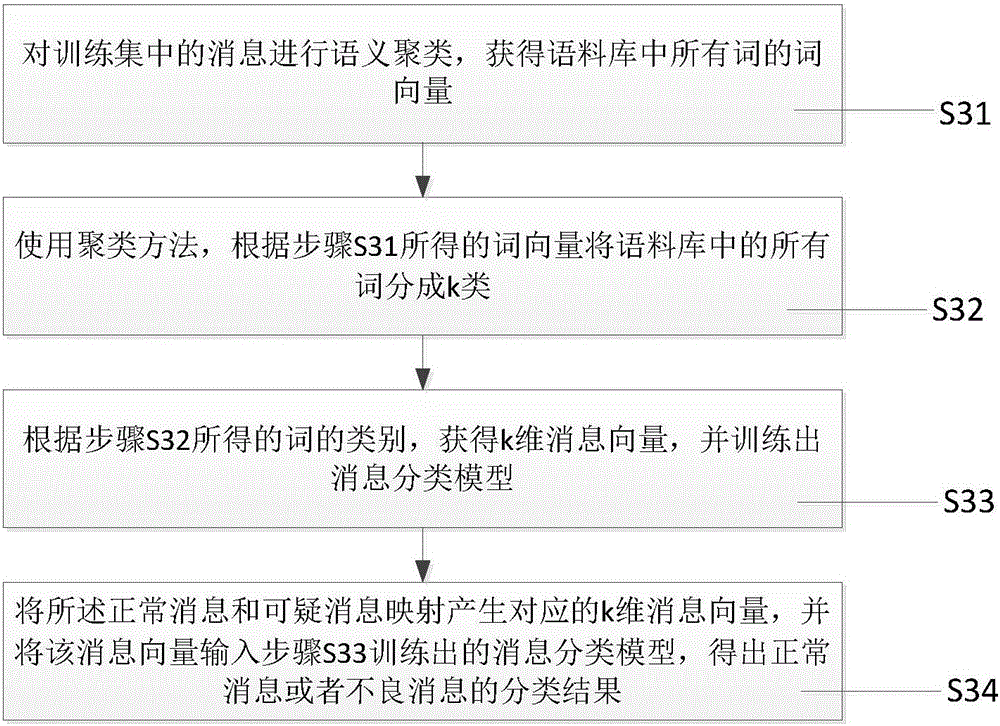
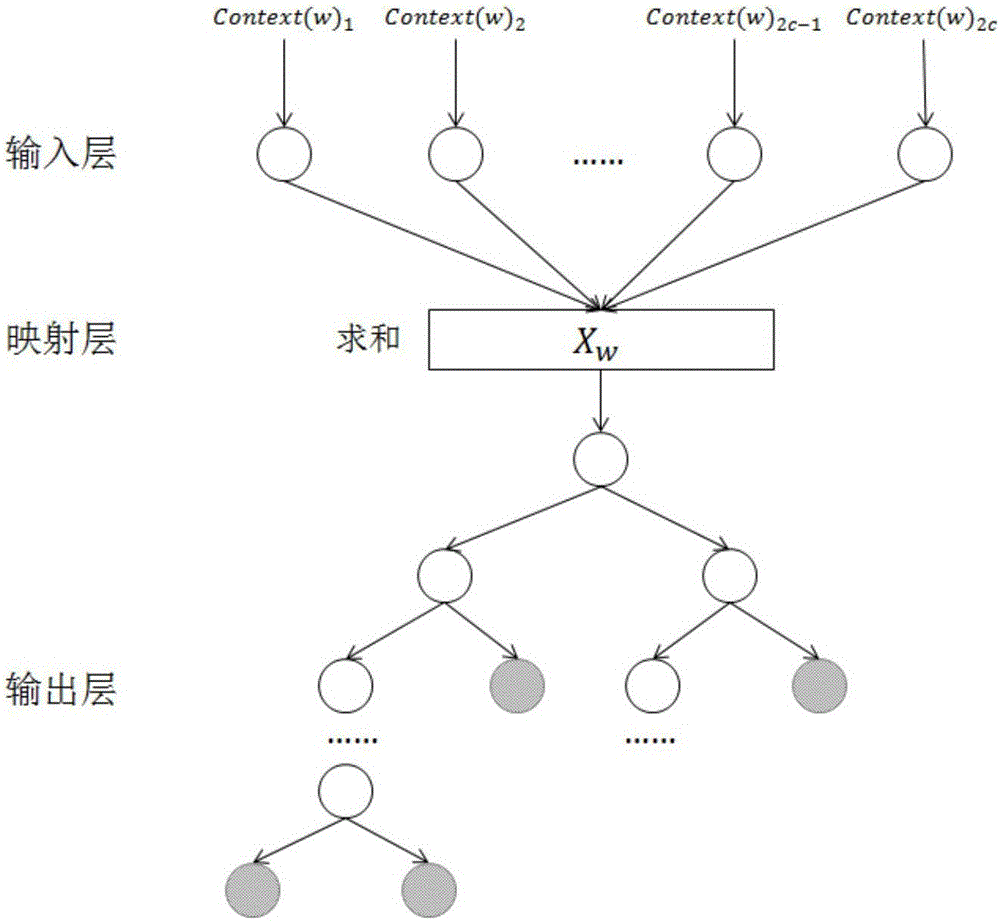
Message filtering method and device
The invention relates to a message filtering method. A Bayes classifier model is used for calculating the probability that a message is a rogue message; the property of the message is judged according to the probability of the rogue message, wherein the property of the message includes the normal message, the rogue message and the suspicious message; the rogue message is directly filtered away, and the normal message and the rogue message are remained; then, the further classification is performed by using a semanticbased deep study model; and the message is determined to be the normal message or the rogue message. Compared with the prior art, the method and the device have the advantages that the automatic study can be realized; a training set is regularly updated; the synonym is recognized; the manual annotation cost is greatly reduced; and high accuracy, robustness and stability are realized. In addition, the invention also provides a message filtering realization device.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Guarding against cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks
Cross-Site Request Forgery attacks are mitigated by a CSRF mechanism executing at a computing entity. The CSRF mechanism is operative to analyze information associated with an HTTP request for a resource. The HTTP request typically originates as an HTTP redirect from another computing entity, such as an enterprise Web portal. Depending on the nature of the information associated with the HTTP request, the HTTP request may be rejected because the CSRF mechanism determines that the request is or is likely associated with a CSRF attack. To facilitate this determination, the approach leverages a new type of “referer” attribute, a trustedReferer, which indicates that the request originates from a server that has previously established a trust relationship with the site at which the CSRF mechanism executes. The trustedReferer attribute typically is set by the redirecting entity, and in an HTTP request header field dedicated for that attribute.
Owner:IBM CORP
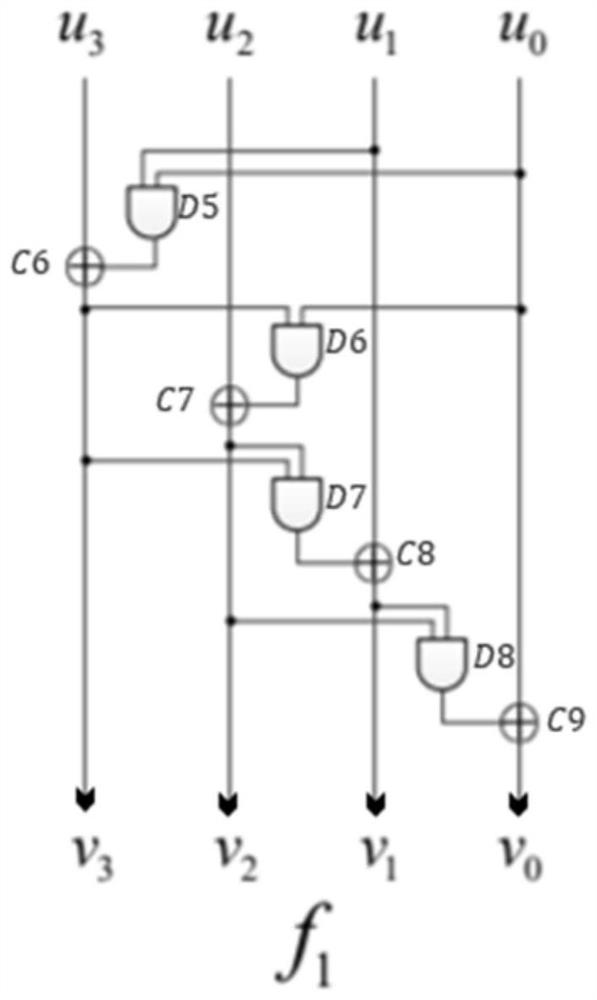
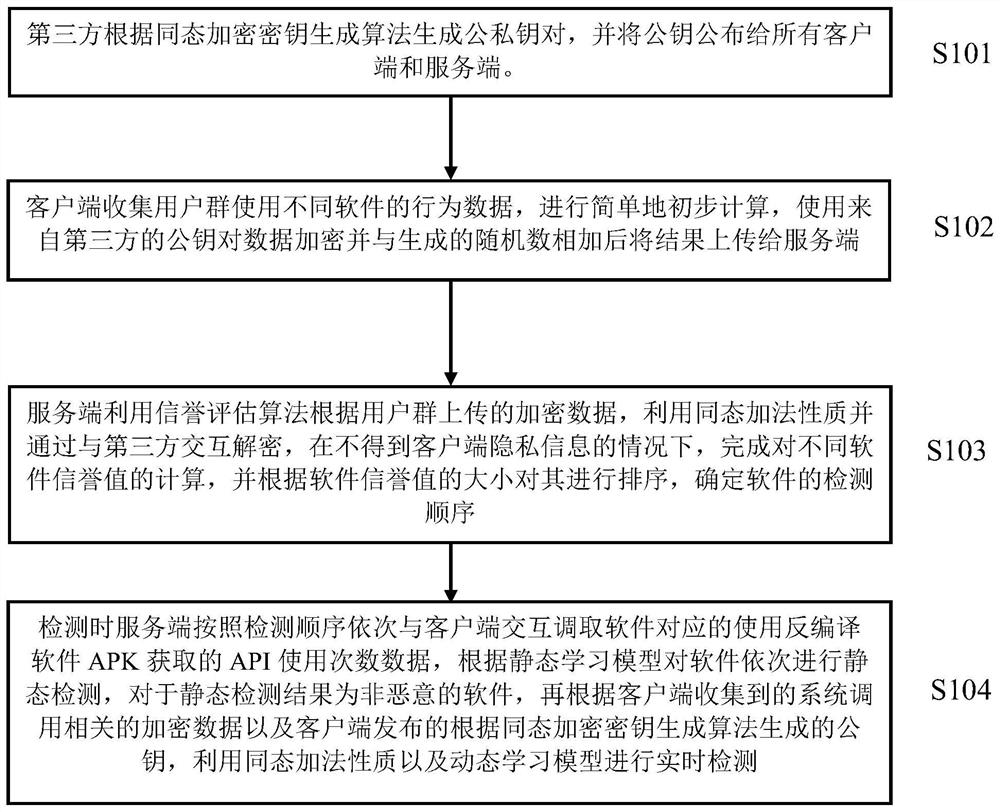
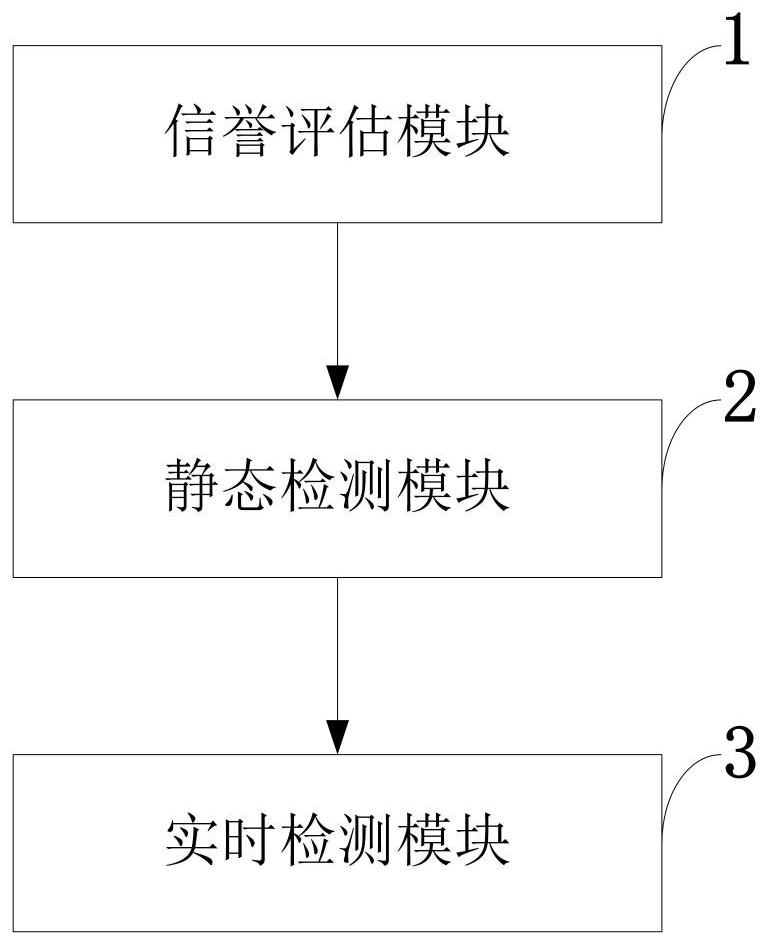
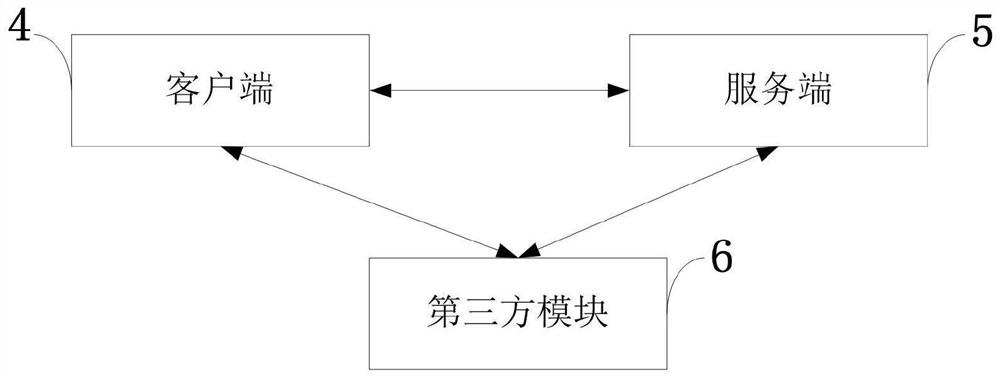
Multi-malicious-software hybrid detection method, system and device with privacy protection
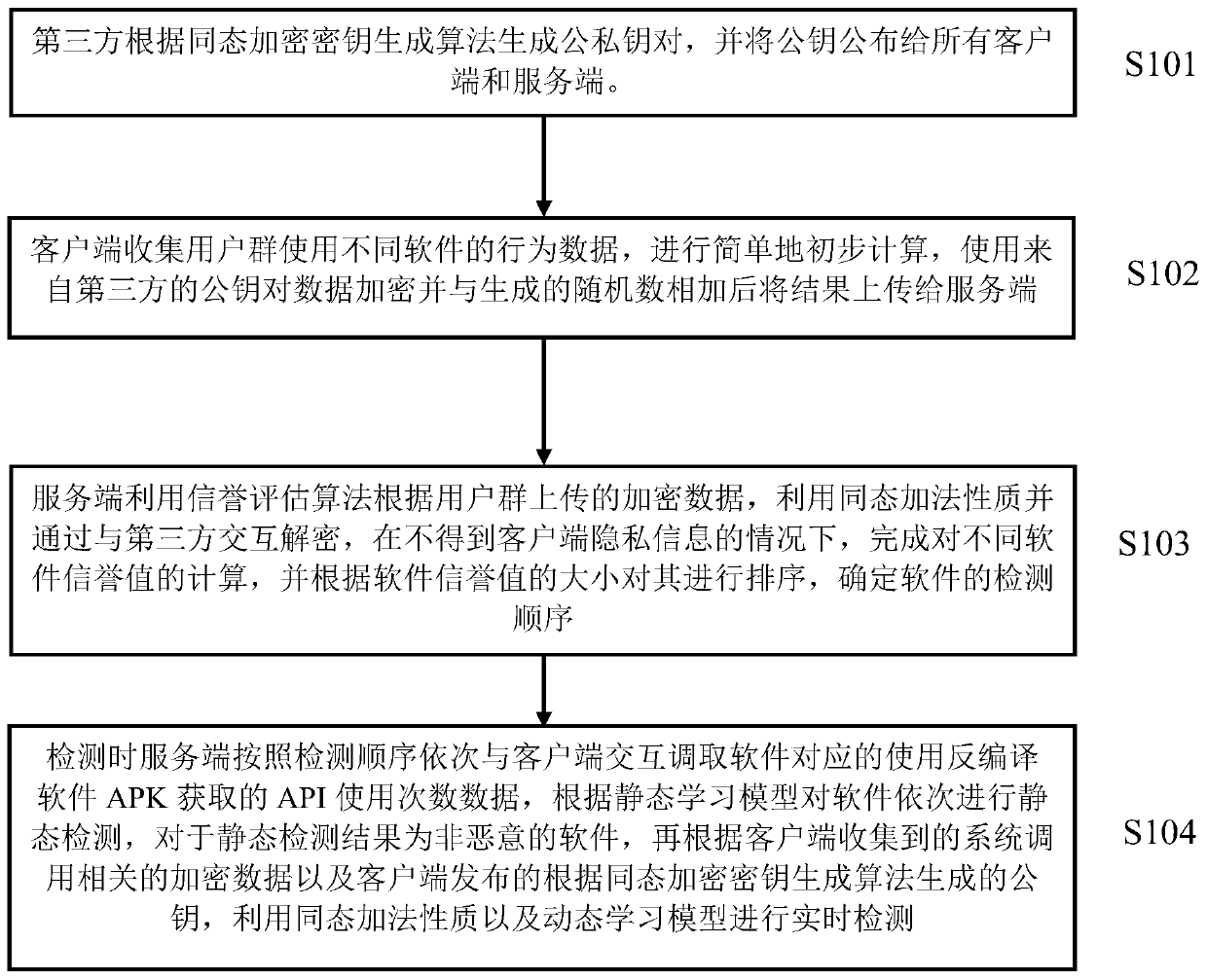
ActiveCN111417121AComprehensive detectionAvoid damageDigital data protectionPlatform integrity maintainancePrivacy protectionSality
The invention belongs to the technical field of malicious software detection, and discloses a multi-malicious-software hybrid detection method, system and device with privacy protection. The third party generates a public and private key pair according to a homomorphic encryption algorithm, and publishes a public key; the client collects behavior data of software used by the user group, carries out preliminary calculation, encrypts the behavior data by using a third-party public key, adds the behavior data to the generated random number and then uploads a result to the server; the server usesa reputation evaluation algorithm to complete calculation of different software reputation values by using homomorphic properties and interacting decryption with a third party according to the uploaded user group encryption data, and determines a software detection sequence according to the software reputation values; during detection, the server sequentially calls API use frequency data acquiredby decompilation software APK from the client according to a sequence; static detection is performed on the software according to the static learning model; if the detection result is non-malicious,related encrypted data and a public key thereof are called according to the system collected by the client, and real-time detection is performed by utilizing homomorphic properties and the dynamic learning model.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
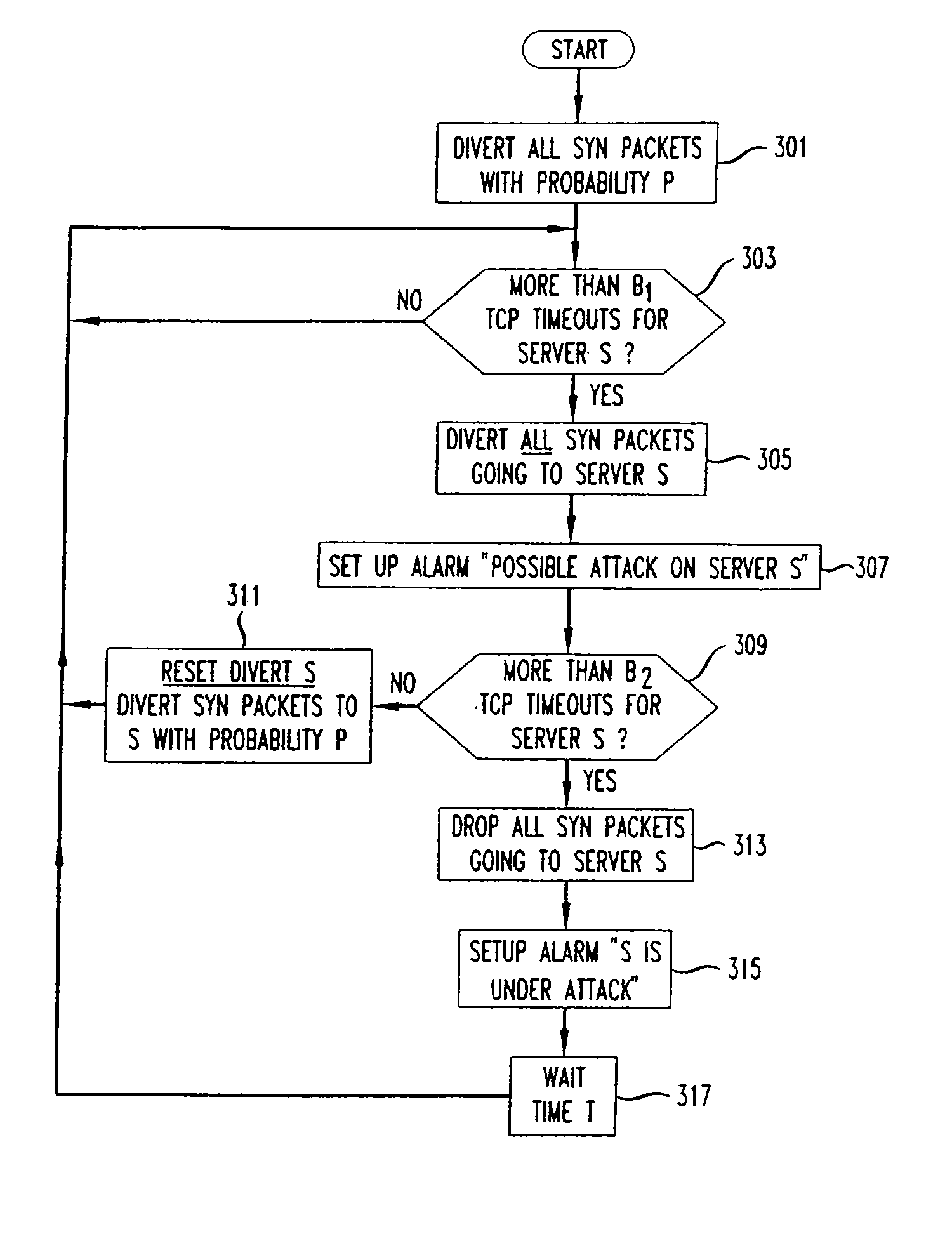
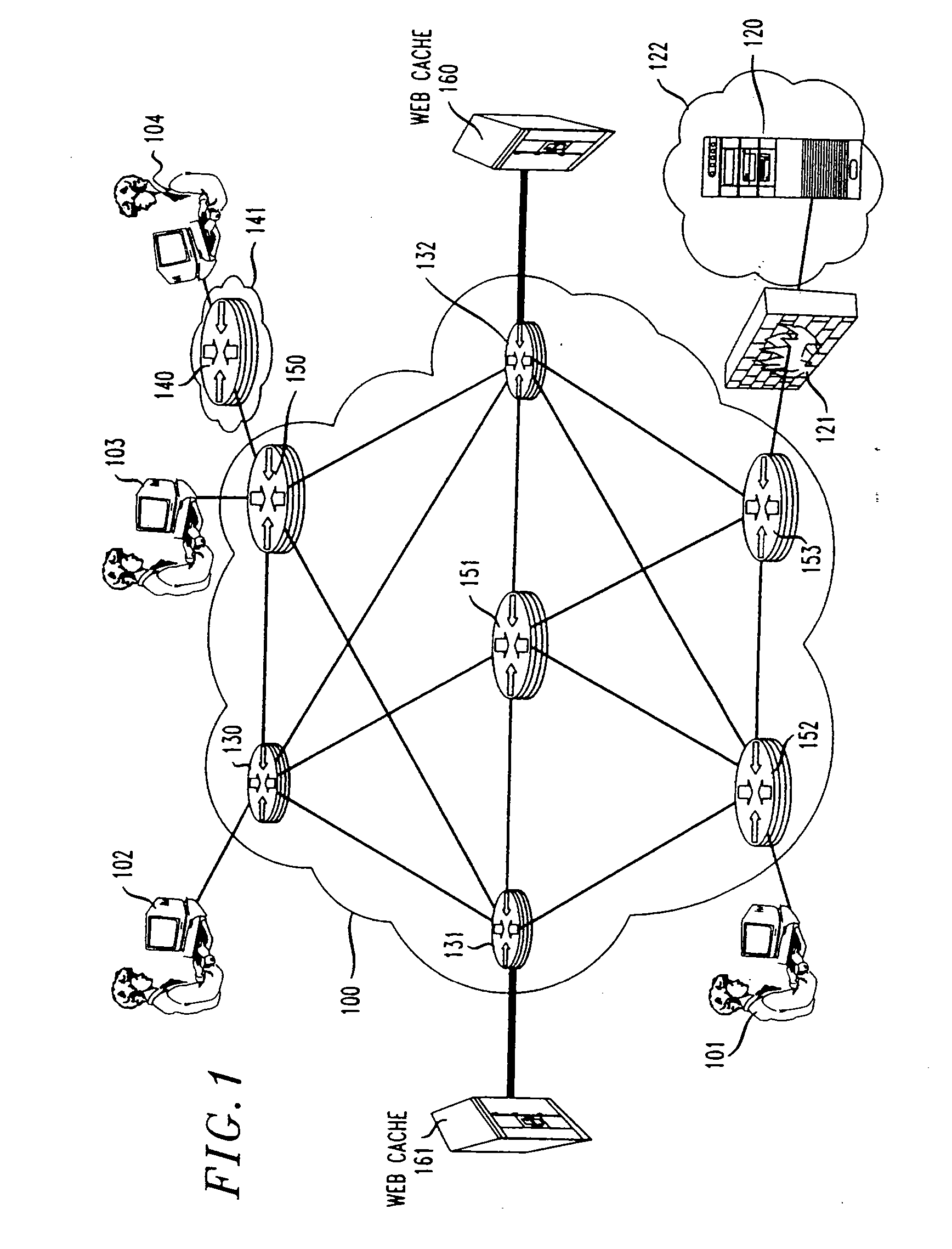
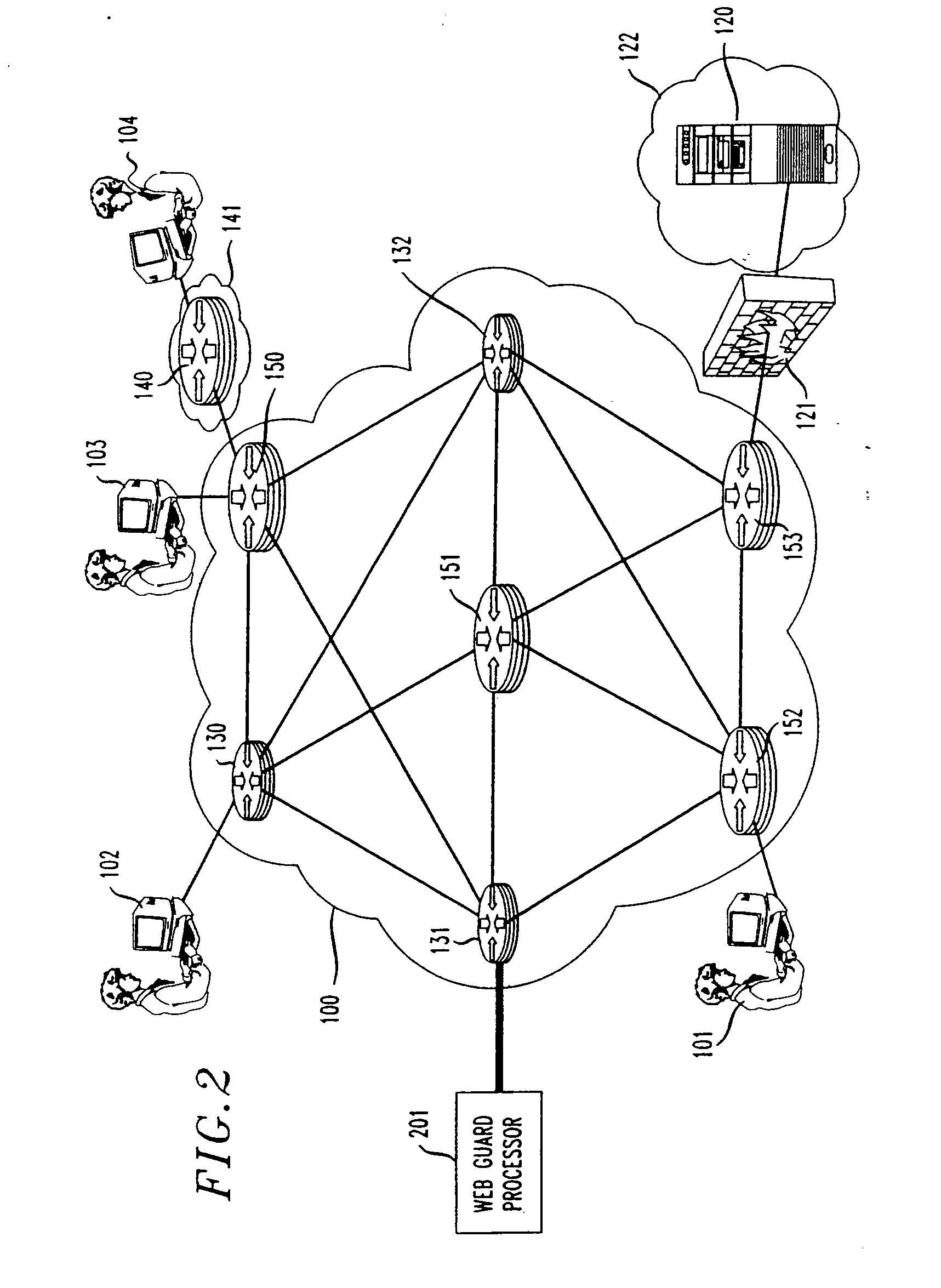
Process to thwart denial of service attacks on the internet
InactiveUS20080016566A1Installation economyGuaranteed economical operationMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionData packThe Internet
Coordinated SYN denial of service (CSDoS) attacks are reduced or eliminated by a process that instructs a layer 4-7 switch to divert a small fraction of SYN packets destined to a server S to a web guard processor. The web guard processor acts as a termination point in the connection with the one or more clients from which the packets originated, and upon the establishment of a first TCP connection with a legitimate client, opens a new TCP connection to the server and transfers the data between these two connections. It also monitors the number of timed-out connections to each client. When a CSDoS attack is in progress, the number of the forged attack packets and hence the number of timed-out connections increases significantly. If this number exceeds a predetermined threshold amount, the web guard processor declares that this server is under attack. It then reprograms the switch to divert all traffic (i.e. SYN packets) destined to this server to the web guard processor, or to delete all SYN packets to the server in question. If the number of timed-out connections increases, it can also inform other web guard processor arrangements, and / or try to find the real originating hosts for the forged packets. In either event, the server is thus shielded from, and does not feel the effects of, the DoS attack. Alternatively, a simpler approach is to arrange layer 4-7 switches to forward SYN packets to respective “null-cache” TCP proxies that each are arranged to operate without an associated cache, and therefore be inexpensive to install and operate. These null-cache TCP proxies, when subject to a CSDoS attack, will not successfully establish a TCP connection with a malicious host, due to the nature of the attack itself. Accordingly, no connections will be made from the null-cache TCP proxies to the server under attack, and the server will be protected.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
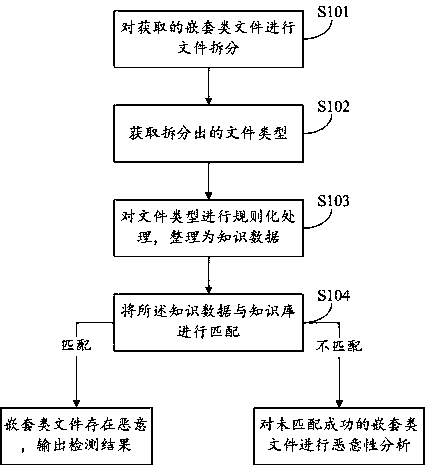
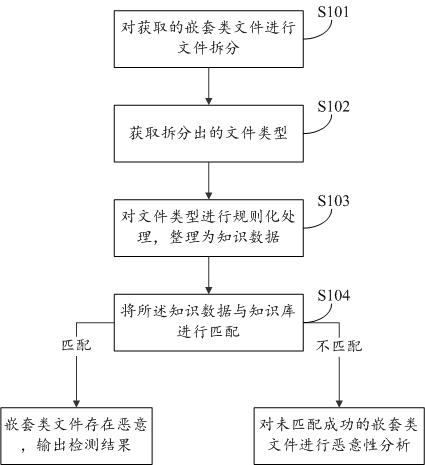
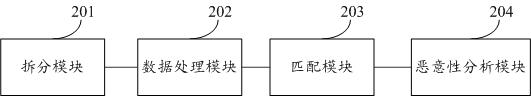
Heuristic detection method and system of nested file and storage medium
ActiveCN108229168AAccelerateDetection speedPlatform integrity maintainanceSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge baseLogic analysis
The invention provides a heuristic detection method and system of a nested file and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of dividing the obtained nested file; obtaining a divided file type, regularizing the file type and sorting the file type into knowledge data; matching the knowledge data with a knowledge base; if matching is successful, determining that the nested file is malignant,outputting the detection result and finishing the detection; if not, conducting malignance analysis on the unmatched nested file. Complex logic analysis is not needed, a virtual environment is not needed either to execute a script, instead, heuristic detection is conducted based on the property that a threat action will be generated based on the nested file in an abnormal environment, the detection speed can be effectively increased, and the detection accuracy can be effectively improved.
Owner:HARBIN ANTIY TECH
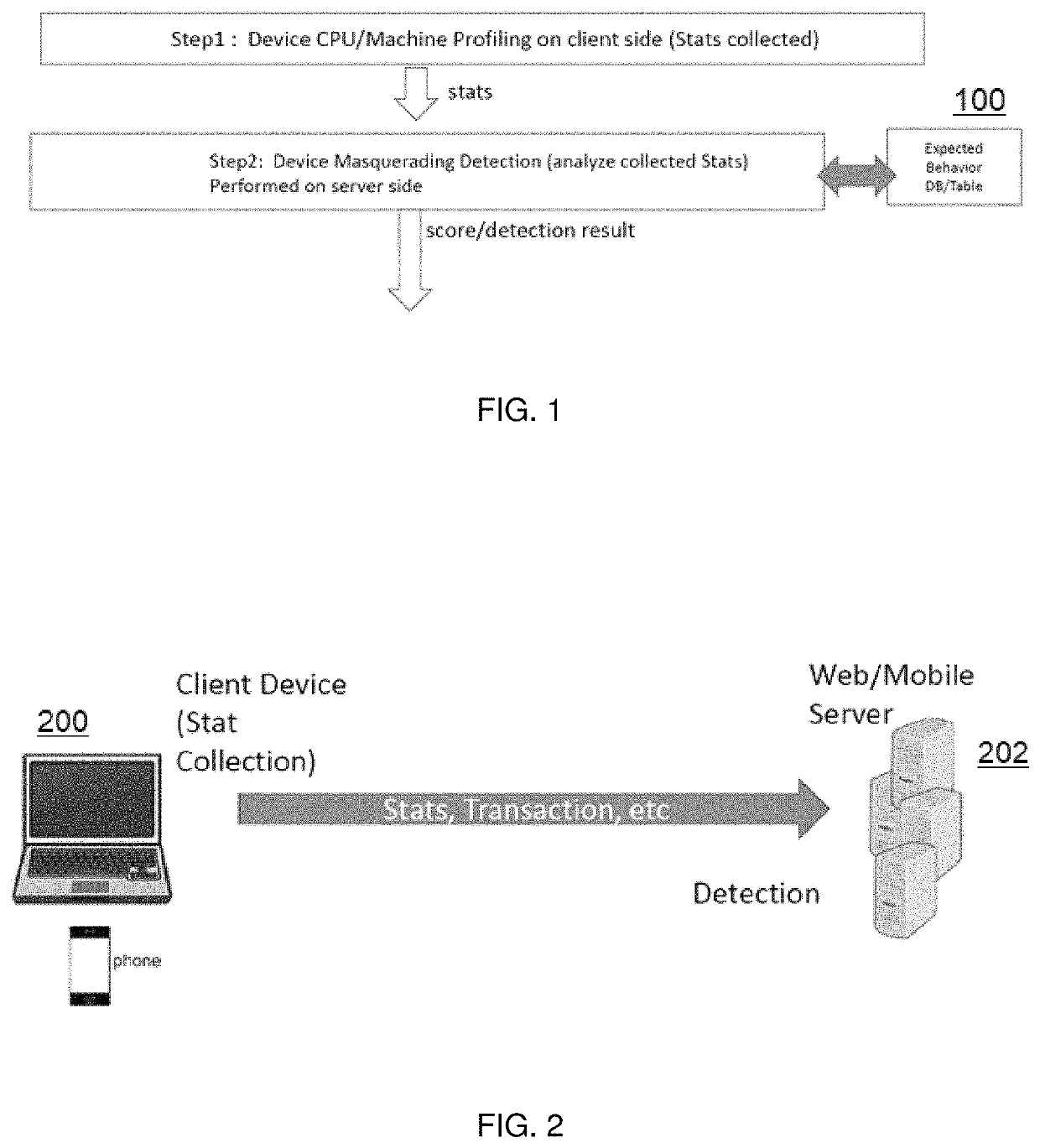
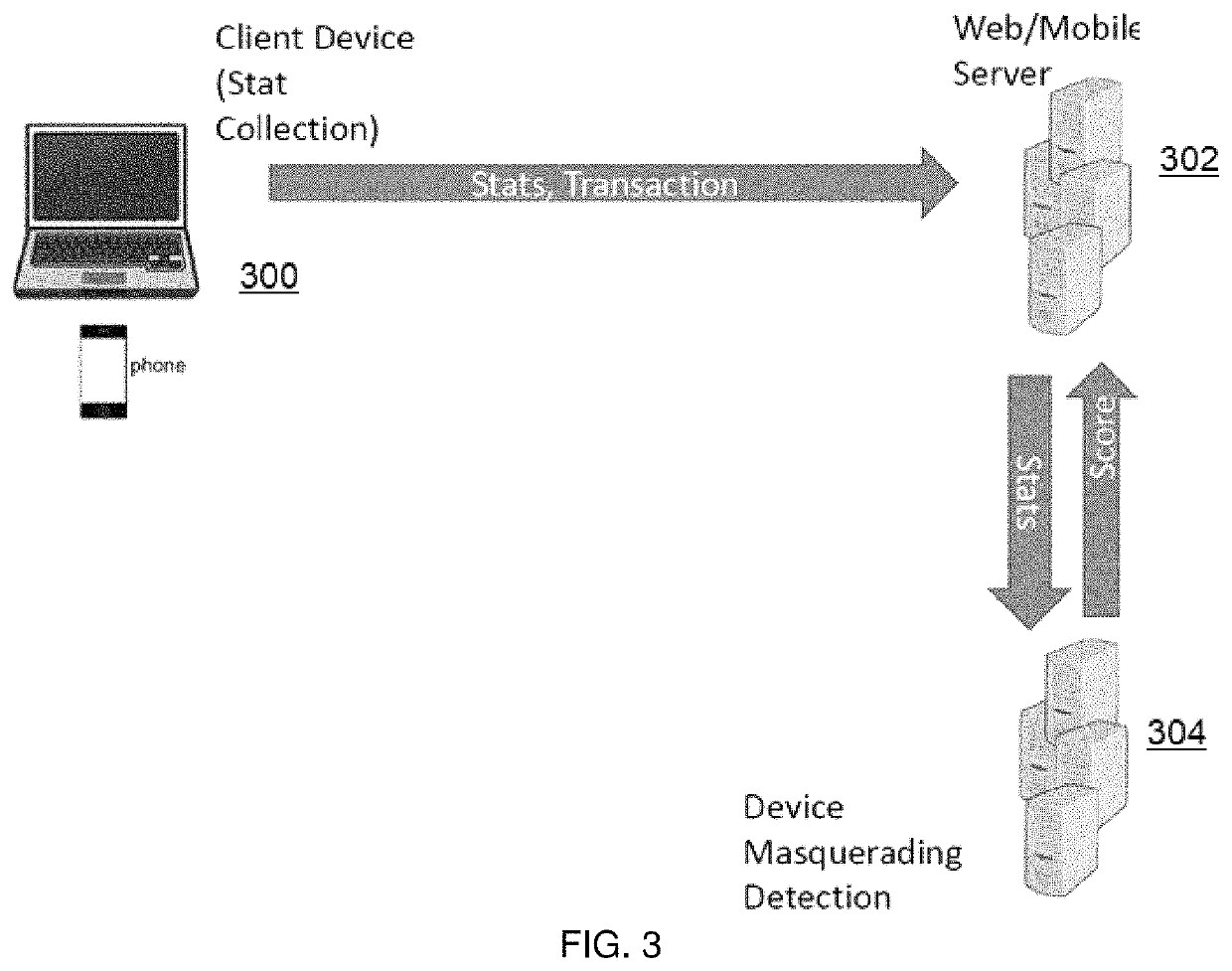
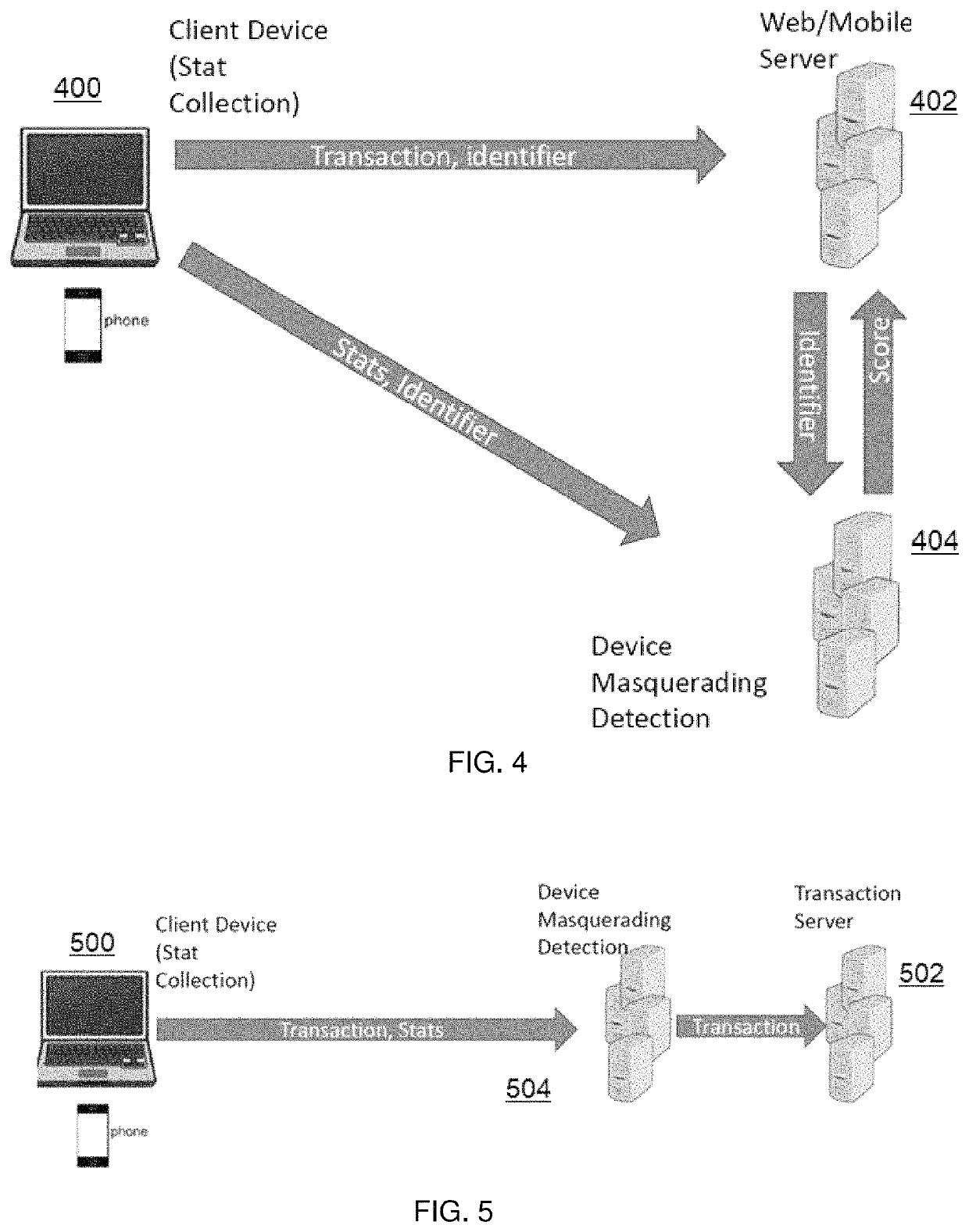
Detecting device masquerading in application programming interface (API) transactions
ActiveUS10715548B2Prevent or mitigate damageTransmissionDevice typeApplication programming interface
This disclosure describes a technique to determine whether a client computing device accessing an API is masquerading its device type (i.e., pretending to be a device that it is not). To this end, and according to this disclosure, the client performs certain processing requested by the server to reveal its actual processing capabilities and thereby its true device type, whereupon—once the server learns the true nature of the client device—it can take appropriate actions to mitigate or prevent further damage. To this end, during the API transaction the server returns information to the client device that causes the client device to perform certain computations or actions. The resulting activity is captured on the client computing and then transmitted back to the server, which then analyzes the data to inform its decision about the true client device type. Thus, when the server detects the true client device type (as opposed to the device type that the device is masquerading to be), it can take appropriate action to defend the site.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
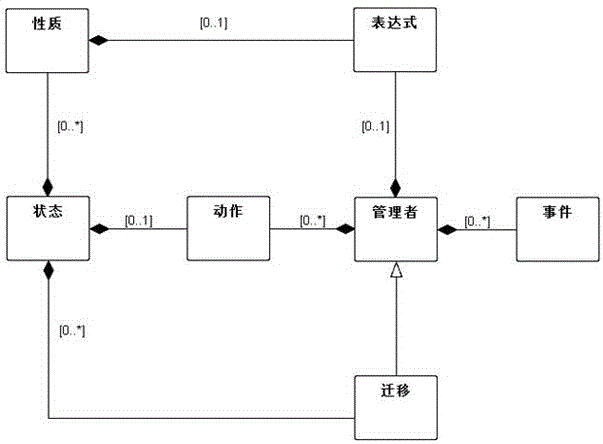
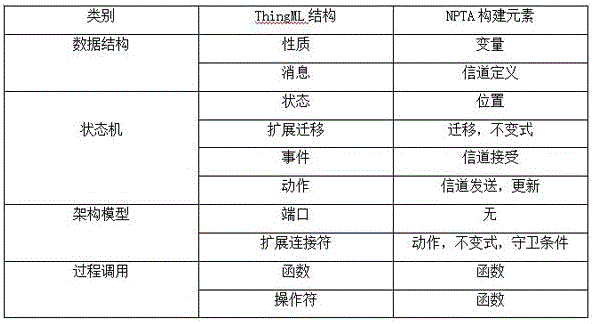
Quantitative analysis method of ThingML (Modeling Language) model under uncertain environment
ActiveCN105975695AImprove the effect of the modelReduce reworkSpecial data processing applicationsQuality of serviceStatistical model checking
The invention discloses a quantitative analysis method of a ThingML (Modeling Language) model under uncertain environment. The quantitative analysis method comprises the following steps: 1) expanding the language and the semantics of the ThingML, causing the ThingML to model uncertainty in the environment, and providing required quality-of-service requirements for a user; 2) utilizing Java to analyze to obtain the meta-model of the ThingML, and obtaining each required field of the ThingML; 3) converting the meta-model of the ThingML into a NPTA (Networks Priced Timed Automata) model, which includes foreground and back-end configuration; and 4) converting the quality-of-service property of the user into a query statement of UPPALL-SMC (Statistical Model Checking), and carrying out quantitative analysis on the system. The quantitative analysis method can evaluate the quality of service of the application of the Internet of Things so as to revise a corresponding design level to guarantee the quality of service.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
A heuristic detection method, system and storage medium for nested class files
ActiveCN108229168BDetection speedImprove accuracyDigital data information retrievalPlatform integrity maintainanceAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The present invention proposes a heuristic detection method, system, and storage medium for nested files. The method includes: splitting the obtained nested files; Regularized processing, sorting into knowledge data; matching the knowledge data with the knowledge base; if the matching is successful, the nested class file is malicious, output the detection result, and end the detection; otherwise, the nested class file that has not been matched successfully file for malicious analysis. The present invention does not need complex logical analysis, nor does it need a virtual environment to dynamically execute scripts, but performs heuristic detection based on the nature of threatening behaviors that will occur in abnormal environments based on nested class files, which can effectively improve detection speed, accuracy, etc.
Owner:HARBIN ANTIY TECH
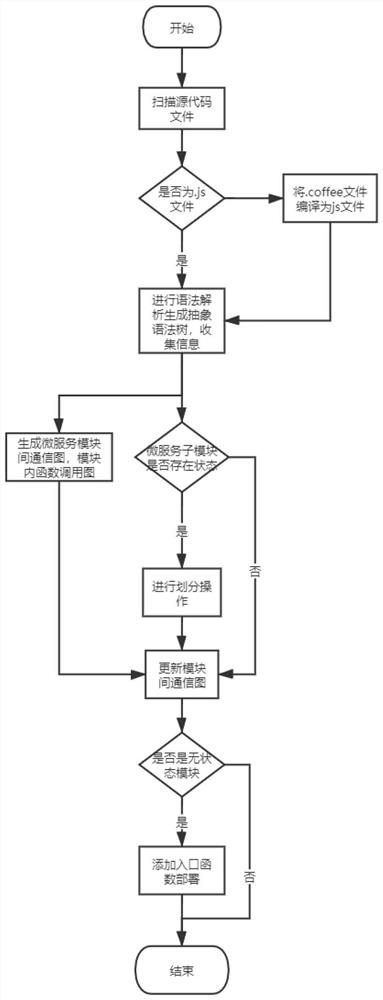
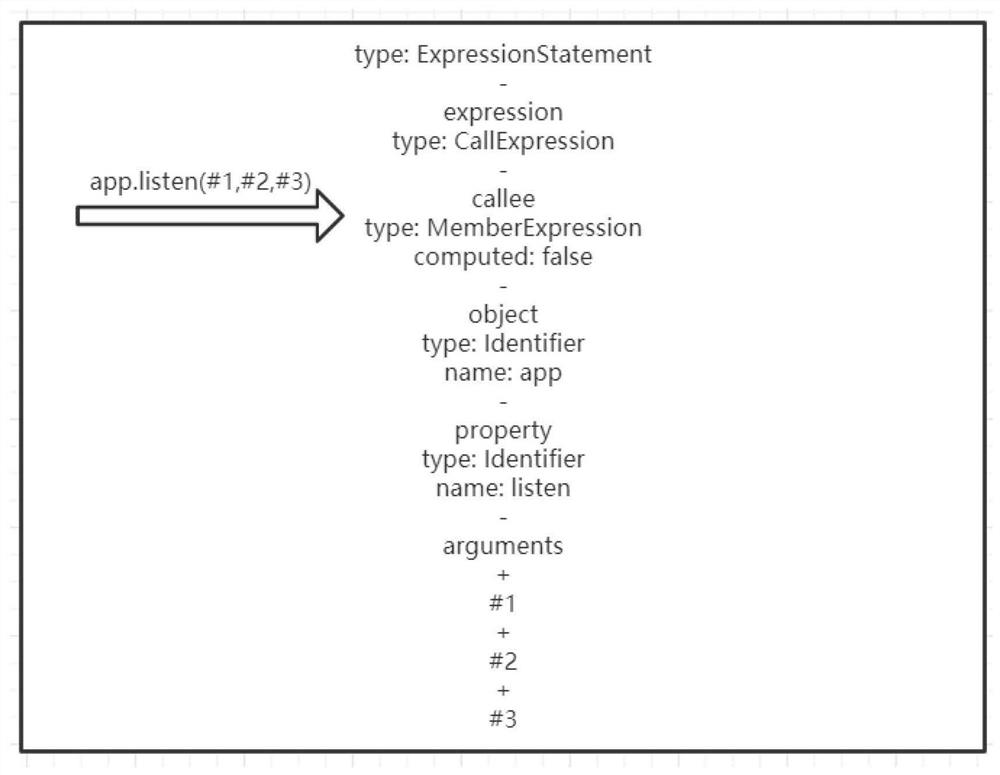
An openwhisk serverless framework migration method for microservice applications
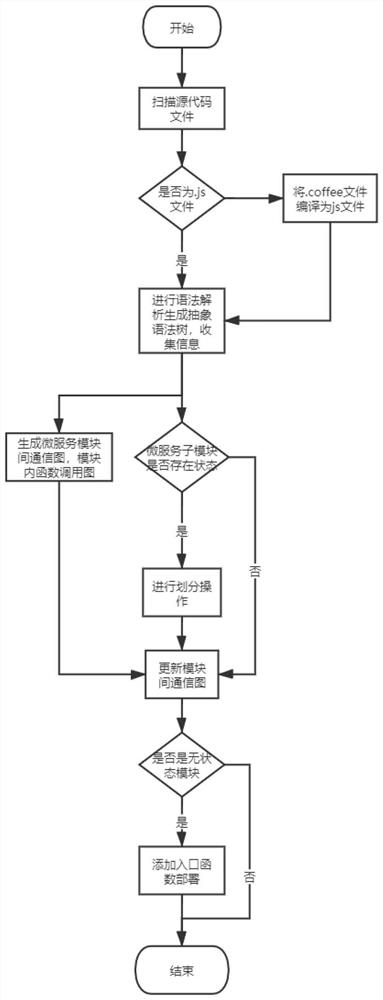
ActiveCN112817567BAutomate migrationImprove efficiencySoftware designExecution paradigmsSource code fileCall graph
The invention discloses an openwhisk serviceless framework migration method for microservice applications, which utilizes the exprima syntax parsing tool of Node.js language to generate abstract syntax tree nodes, and extracts key information from them to generate function call graphs. Communication diagram and judgment of the nature of microservice submodules, and try to divide stateful microservice modules to maximize automatic migration. Parse project source code files, project package files, configuration files, etc. from the level of abstract syntax tree, which is simple and efficient. At present, there is no similar technical solution, and the emergence of the present invention will help developers to improve the migration efficiency of applications to the serverless computing platform.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
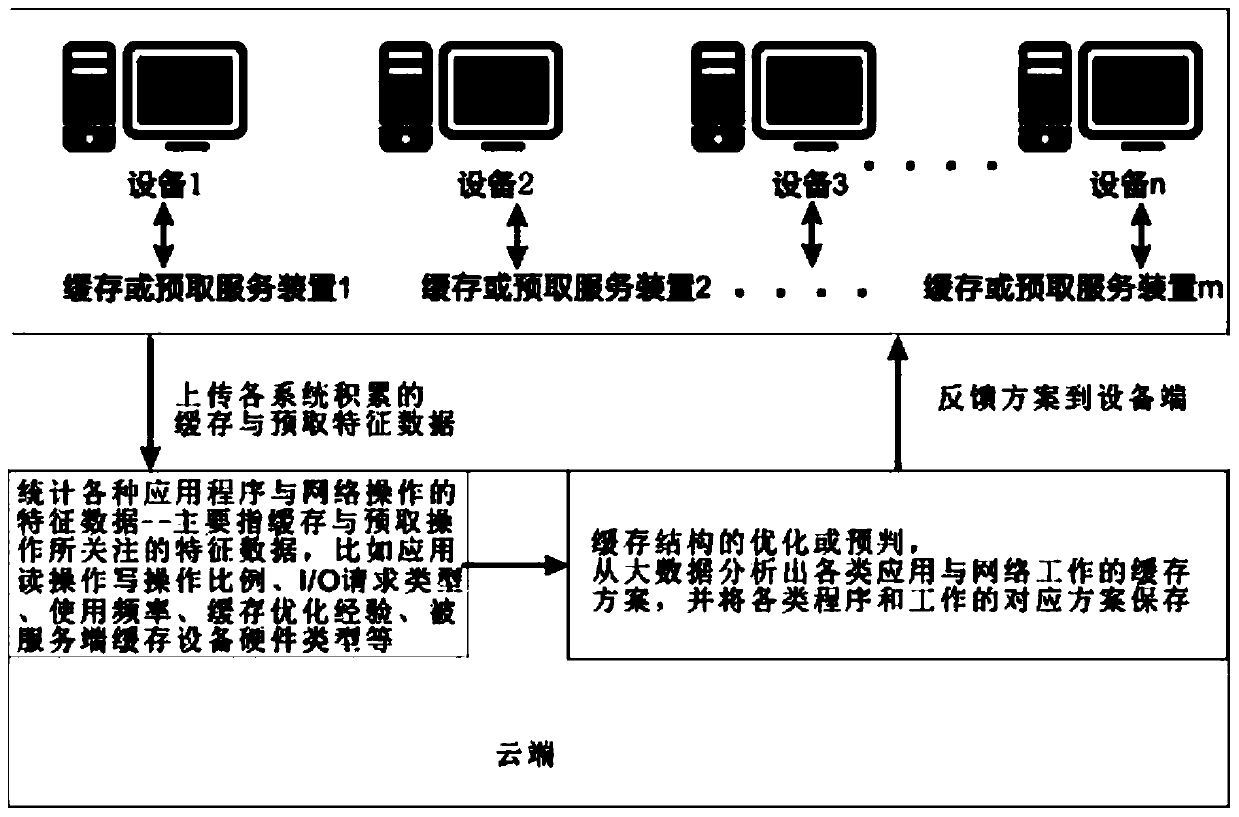
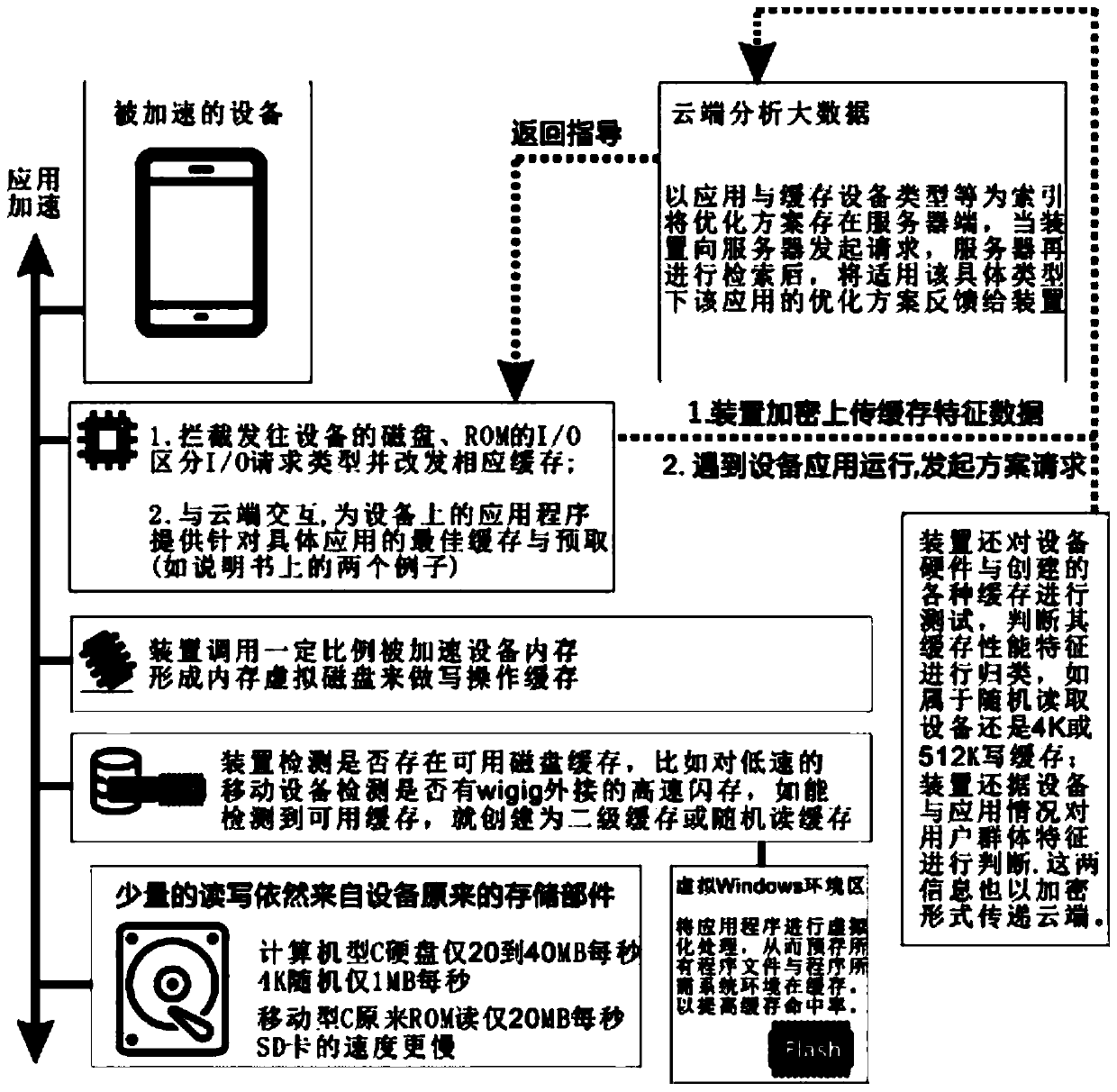
A caching and prefetching acceleration method and device for computing equipment based on big data
ActiveCN104320448BImprove the effectImprove caching accelerationTransmissionActive feedbackWeb operations
A caching and prefetching acceleration method and device for computing equipment based on big data, which is different from the traditional caching mode in which equipment is optimized, in that the method submits data to the cloud by a large number of caching or prefetching service devices, including these Part of the characteristic data of various applications or network operations on the service device served by the service device. The so-called characteristic data mainly refers to the characteristic data concerned by the cache and prefetch operations, such as the proportion of application read and write operations, I / O Request type, file size, frequency of use, cache optimization experience, hardware type of the cached device on the server side, user group characteristics, etc., the cloud will perform statistics and analysis after receiving the data, dig out optimized cache or prefetch solutions for different applications, and then By means of active feedback or passive response, the optimized caching scheme and prediction scheme are returned to the caching service device for processing, so that the work of the nature of prediction and targeted optimization can be directly performed without re-accumulating cache data for a long time.
Owner:张维加
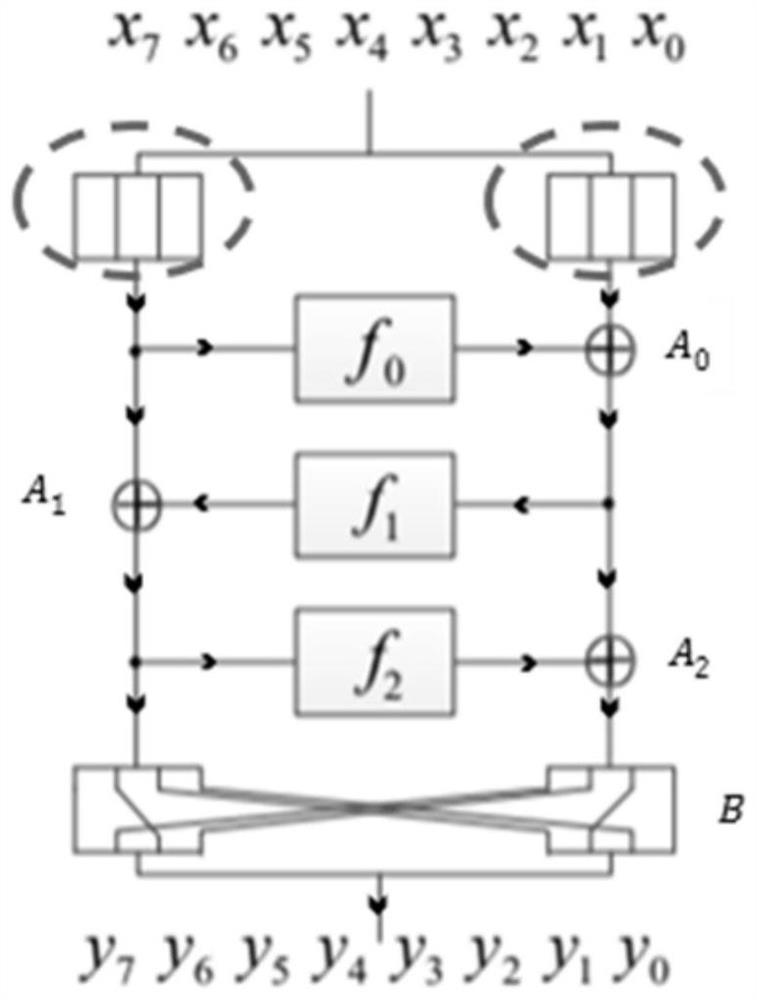
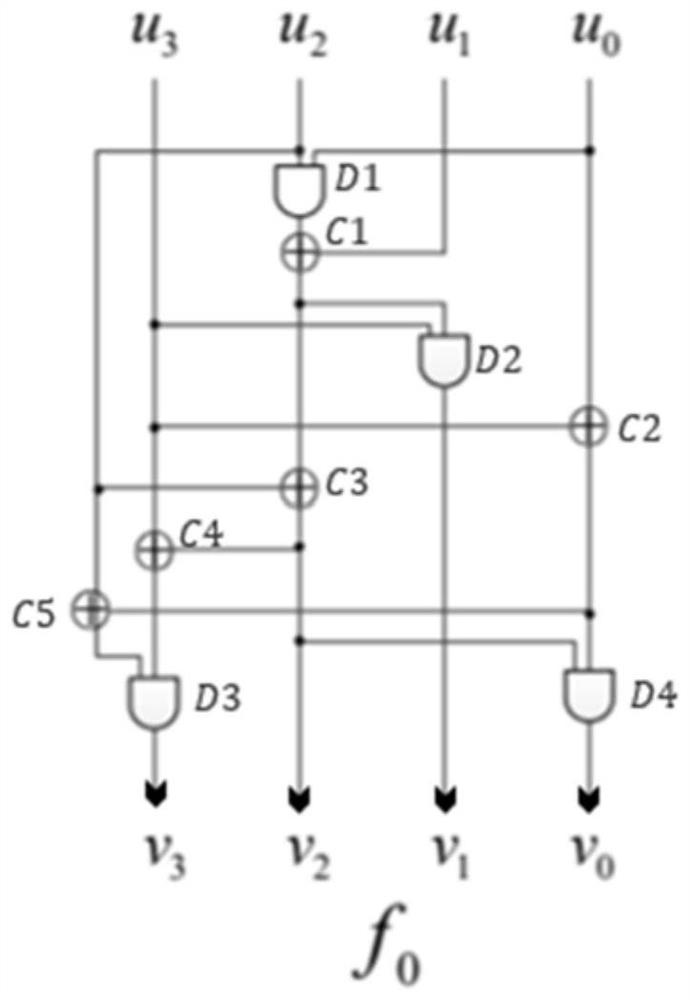
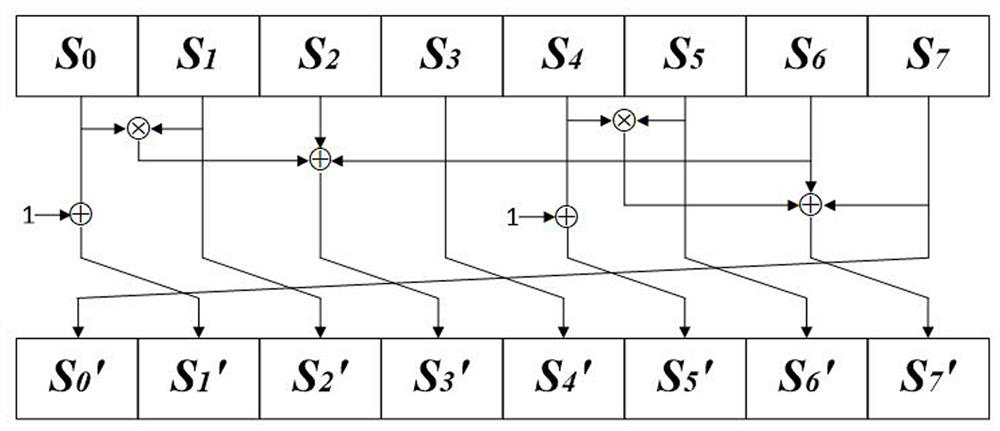
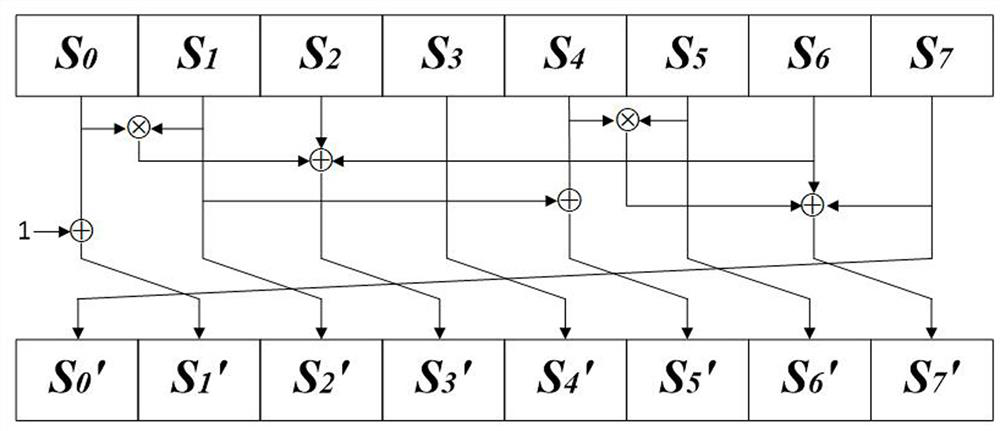
Construction method and circuit of lightweight 8-bit S box
ActiveCN113162755AIncrease speedGood cryptographic propertiesEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesS-boxPassword
The invention relates to a construction method of a lightweight 8-bit S box and a circuit thereof. According to the method, on the basis of 4*4 function iteration construction, a bit transformation mode is adopted to construct an 8*8 S box, a three-round balanced Feistel structure is used, and the Feistel structure uses three different functions of 4-bit input and 4-bit output and bit-level position transformation to ensure the distribution uniformity. The S-box design concept constructed by the invention pays attention to improvement of hardware implementation efficiency, particularly to reduction of the area occupied by hardware implementation, and meanwhile, other password security indexes of the S-box design can be kept to have good performance. According to the method, the S box which is low in hardware implementation cost, high in speed and good in cryptographic property can be found, and the method has great advantages in byte design-oriented algorithms in scenes such as 5G and the like.
Owner:北京信息科学技术研究院
Multi-malware hybrid detection method, system and device with privacy protection
ActiveCN111417121BComprehensive detectionAvoid damageDigital data protectionPlatform integrity maintainancePrivacy protectionSality
The invention belongs to the technical field of malicious software detection, and discloses a mixed detection method, system and device for multiple malicious software with privacy protection. The third party generates a public-private key pair according to the homomorphic encryption algorithm, and publishes the public key; the client collects the behavior data of the user group using the software, conducts preliminary calculations, encrypts with the third-party public key, adds it to the generated random number, and uploads the result to Server: The server uses the reputation evaluation algorithm to encrypt data according to the uploaded user group, utilizes the homomorphic nature and interacts with the third party to decrypt, completes the calculation of different software reputation values, and determines the software detection sequence according to the software reputation value; Call the API usage data obtained by the decompiled software APK from the client in order, and perform static detection on the software according to the static learning model. Public key, using homomorphic properties and dynamic learning model for real-time detection.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Secure calling convention system and methods
PendingCN113056737AEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesInterprogram communicationSoftware engineeringSality
The present disclosure is directed to systems and methods for protecting software application information that is passed between a caller of an API and the logic contained within the API by using a Secure Calling Convention (SCC). The SCC involves performing a cryptographic operation on the information such that the true nature of the information is obfuscated. The SCC prevents a hacker from using the information to reverse-engineer the software application to behave as desired.
Owner:阿韦瓦软件有限责任公司
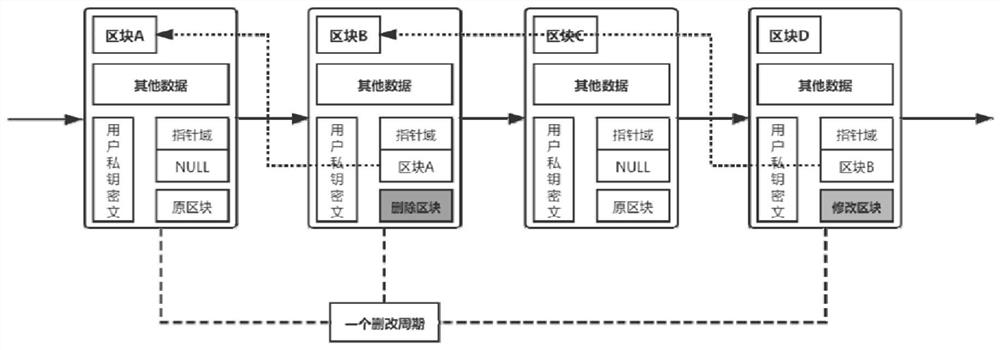
A Recordable and Traceable Blockchain Security Deletion Method
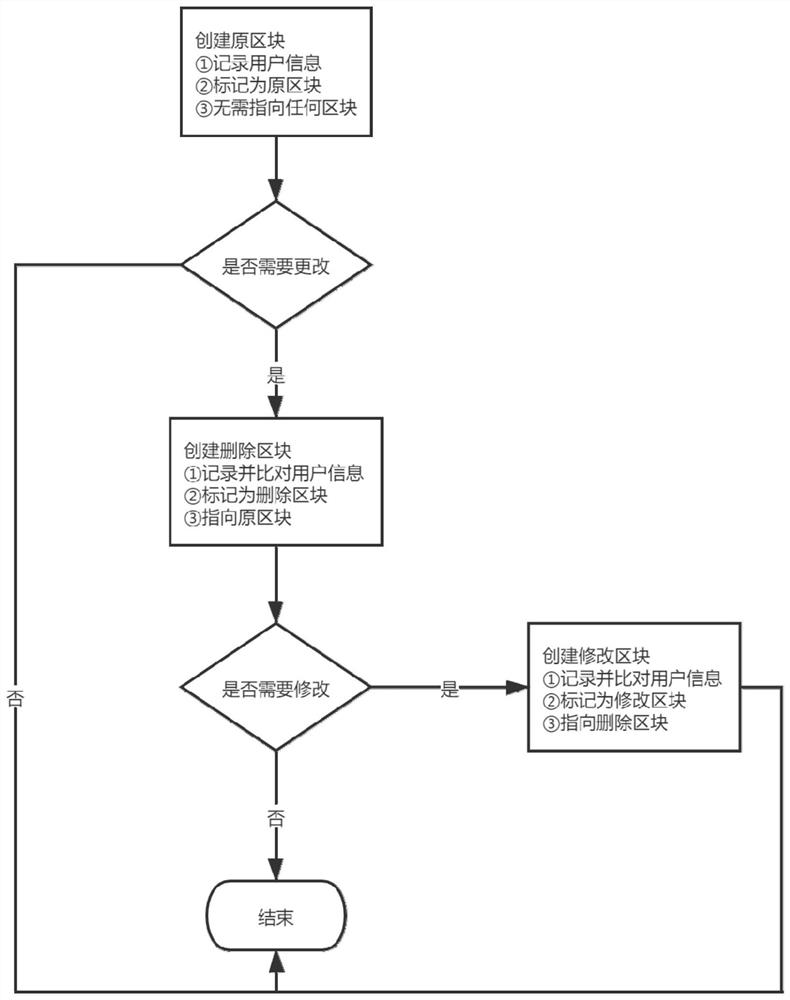
ActiveCN113378213BPreserve immutable propertiesGuaranteed flexibilityDigital data protectionSalityDatabase
The invention discloses a recordable and traceable block chain security deletion method, the process is: create a block with arbitrary data according to the requirements of different applications; the block contains fields that record the nature of the block, and the identification Divided into: original block, deleted block, modified block; deleted block and modified block also contain pointers to other blocks, which are used to connect the original block, deleted block and modified block; When deleting, the user creates a deleted block with a deleted block identifier. The deleted block contains a pointer to the original block that needs to be deleted, indicating that the deleted block deletes the original block; the rest of the data is the same as the original block The user data is completely consistent; after the deletion is completed, the block needs to be modified. The modification process is as follows: the user creates a modified block with a modification identifier, and the modification points to the deleted block. The rest of the data is the same as or different from the original block. At the same time, the original block information is saved for the undo deletion process; otherwise, the modification is completed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
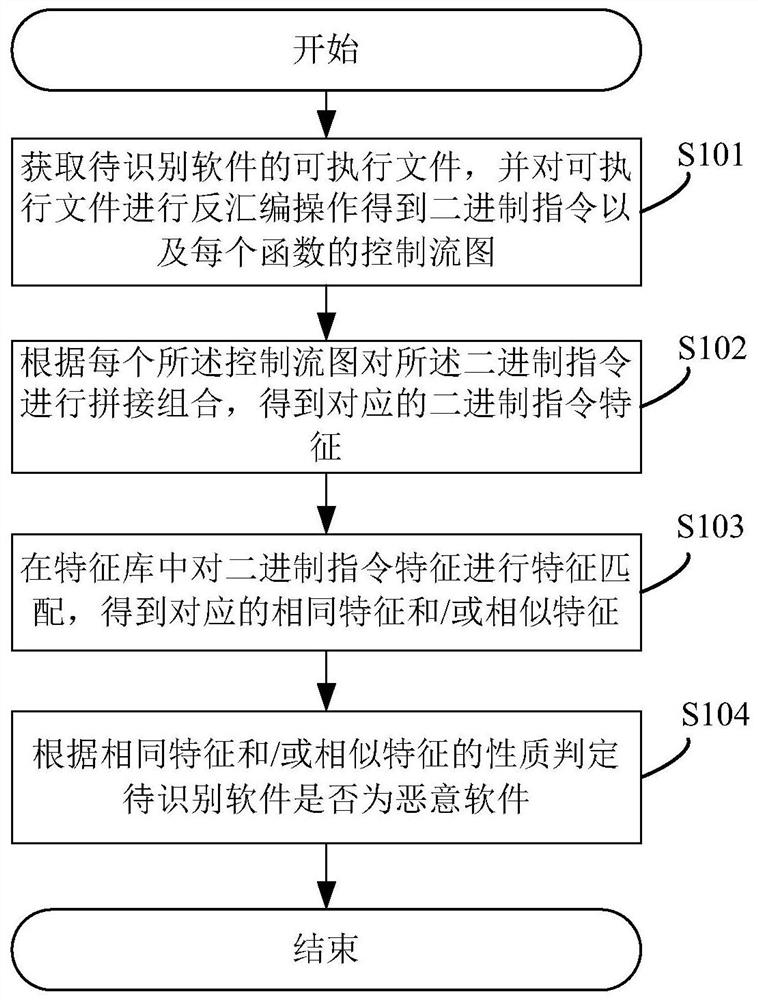
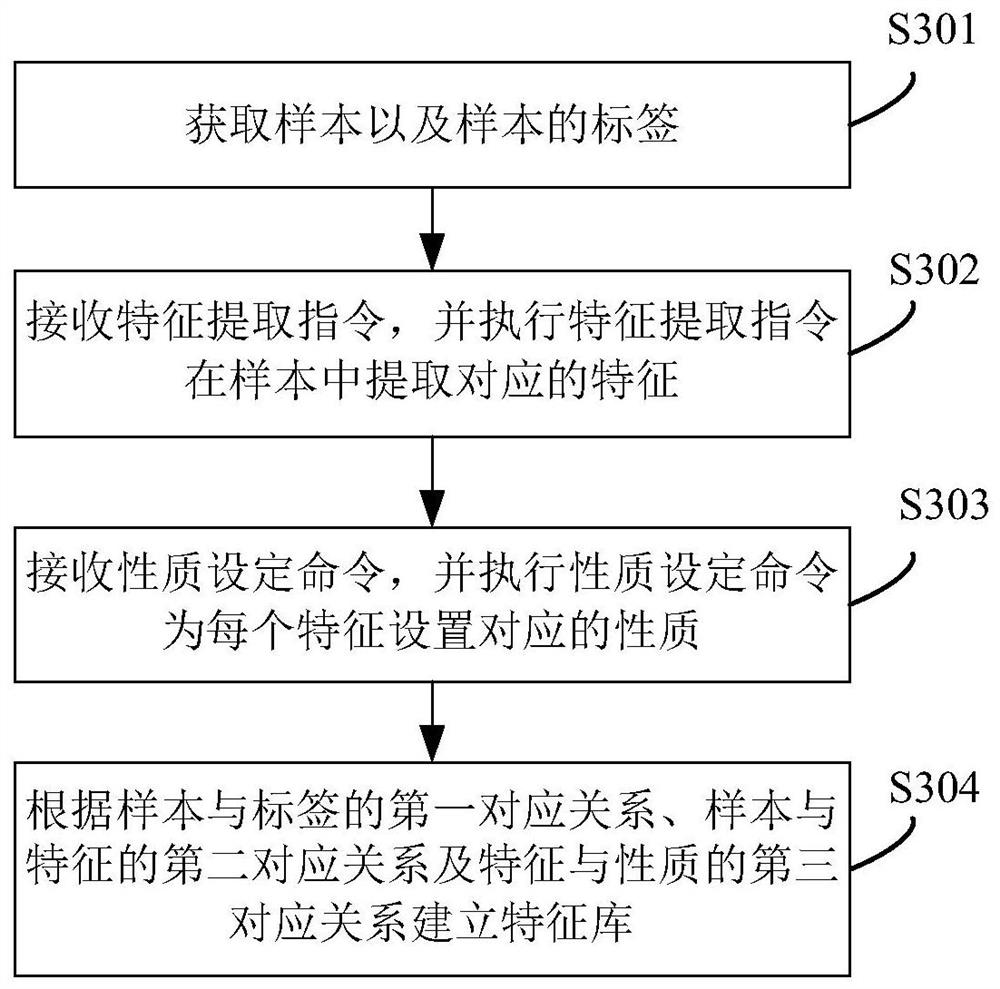
Malicious software identification method, system and device and readable storage medium
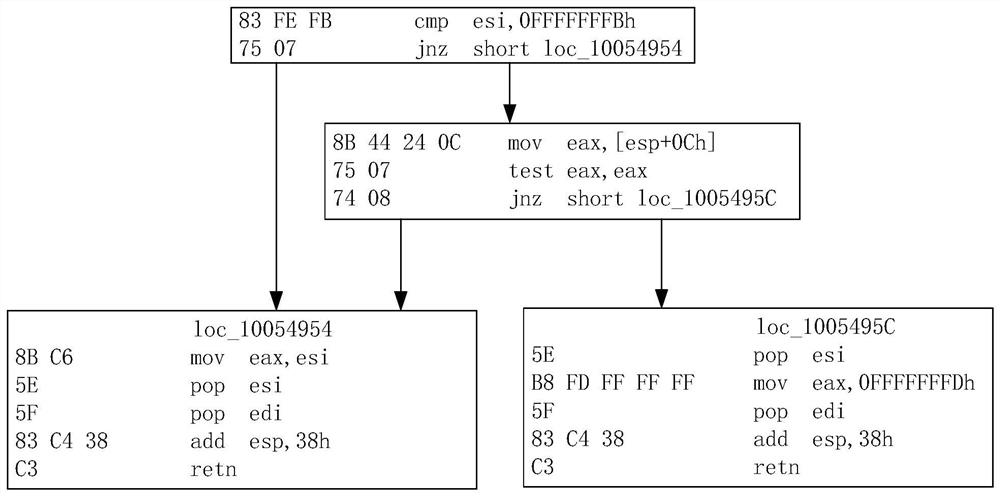
PendingCN113901457AHigh precisionSmall granularityPlatform integrity maintainanceTheoretical computer scienceEngineering
The invention discloses a malicious software identification method, which comprises the following steps: obtaining an executable file of software to be identified, and extracting binary instruction characteristics in the executable file; performing feature matching on the binary instruction features in a feature library to obtain corresponding same features and / or similar features; and judging whether the to-be-identified software is malicious software or not according to the properties of the same features and / or similar features. Because the control flow diagram is an abstract data structure of the minimum control logic in the program execution process, the binary instruction feature obtained by splicing and combining the binary instructions according to each control flow diagram has smaller granularity than the function, and the real-time execution process of the control flow of the function can be reflected; therefore, similarity matching is carried out by utilizing the binary instruction characteristics of the executable file, and the malicious software identification precision can be obviously improved. The invention also provides a malicious software identification system and device and a readable storage medium, which have the above beneficial effects.
Owner:SANGFOR TECH INC
System and method for realizing lightweight application burying point
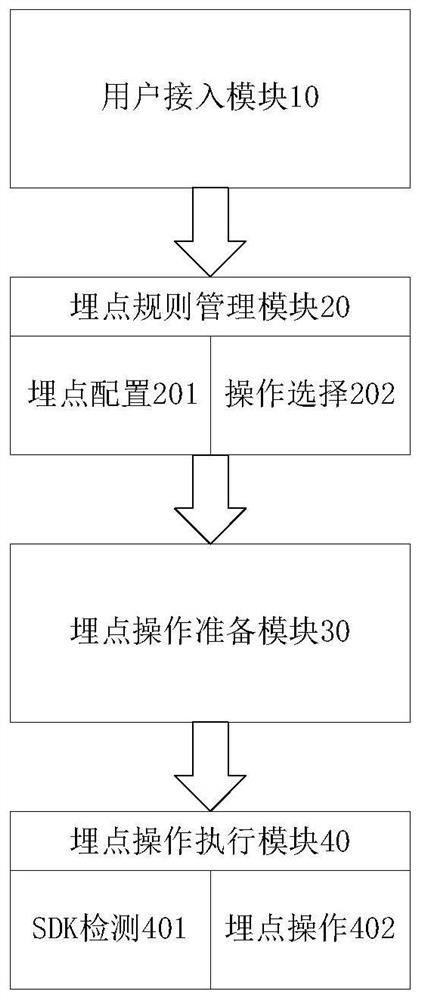
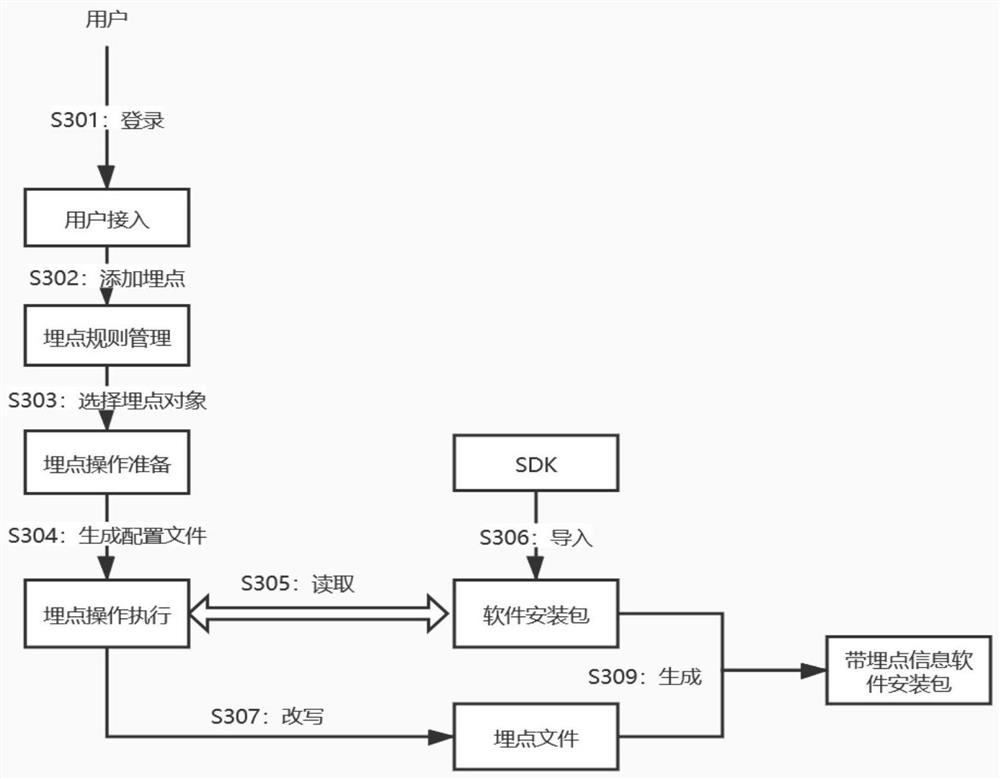
PendingCN113010434AAvoid writingImprove readabilitySoftware testing/debuggingExecution paradigmsMaintainabilityConfigfs
The invention discloses a system for realizing lightweight application point burying, which comprises a user access module, a point burying rule management module, a point burying operation preparation module and a point burying operation execution module, and is characterized in that the point burying rule management module comprises a point burying configuration component and an operation selection component; and after the software installation package of the lightweight application embedded with the burying point information is installed and operated, related statistical results can be read through the user access module. According to the technical scheme, writing of non-service burying point codes in service codes can be avoided, the readability of the codes is improved, and the development difficulty is reduced; Meanwhile, the compatibility, the expandability and the maintainability of the point burying scheme are improved based on the point burying mode of the configuration file.
Owner:GUANGZHOU QISHENG INFORMATION TECH
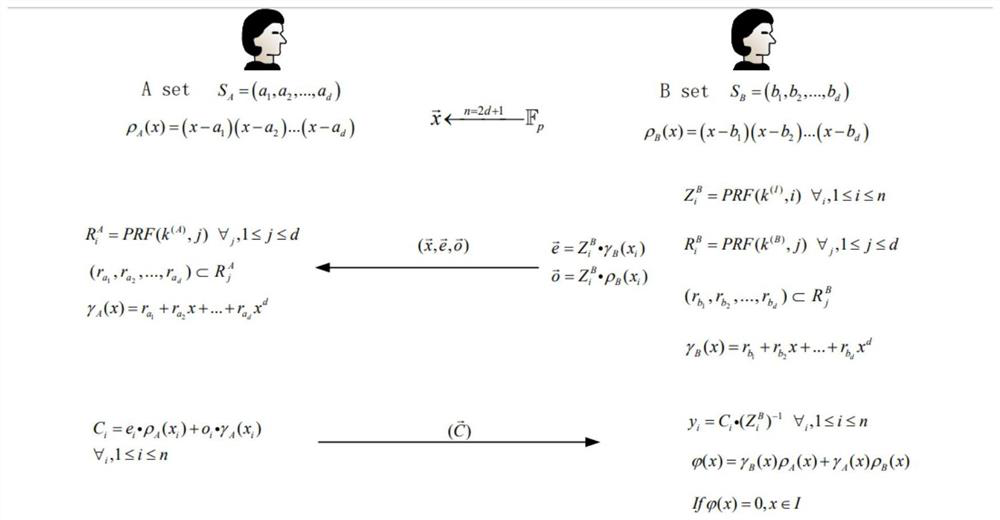
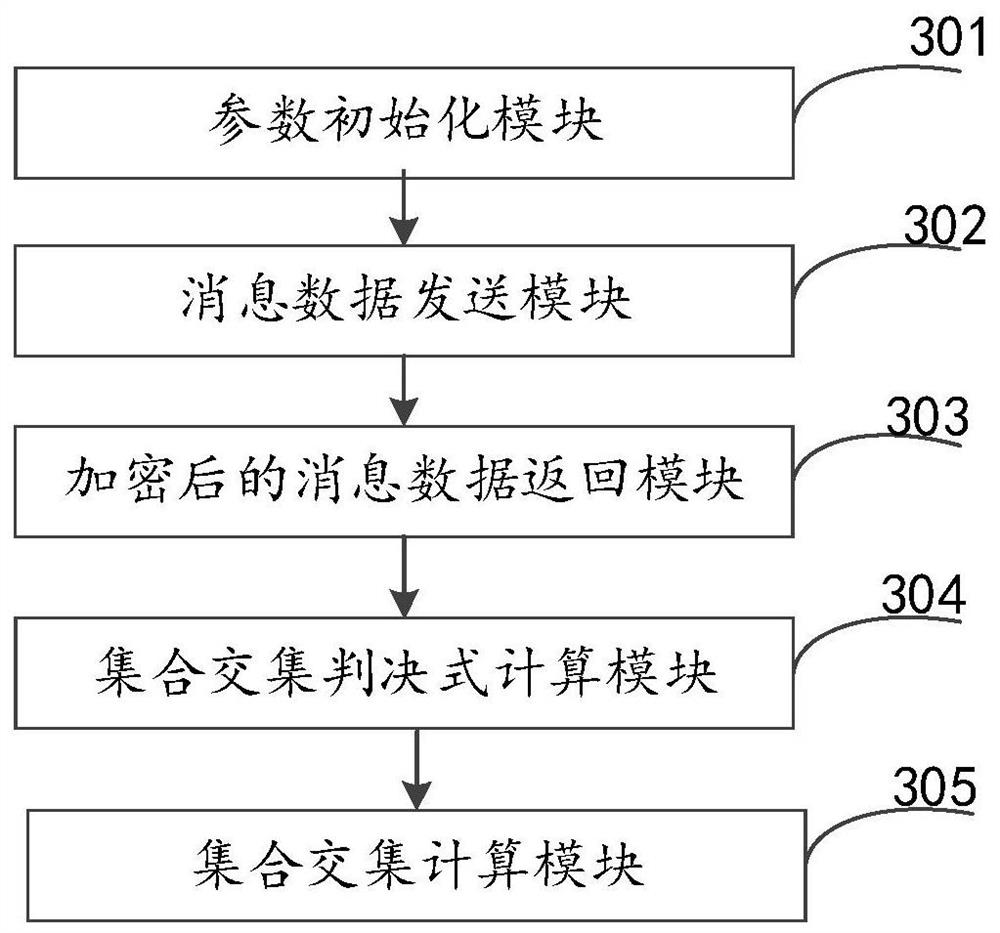
Method and system for computing intersection of privacy-preserving sets based on polynomial representation
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Node Property Identification Method Based on Distributed System
ActiveCN108810030BEfficient identificationFighting against Sybil attacksMachine learningNeural architecturesEngineeringSality
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
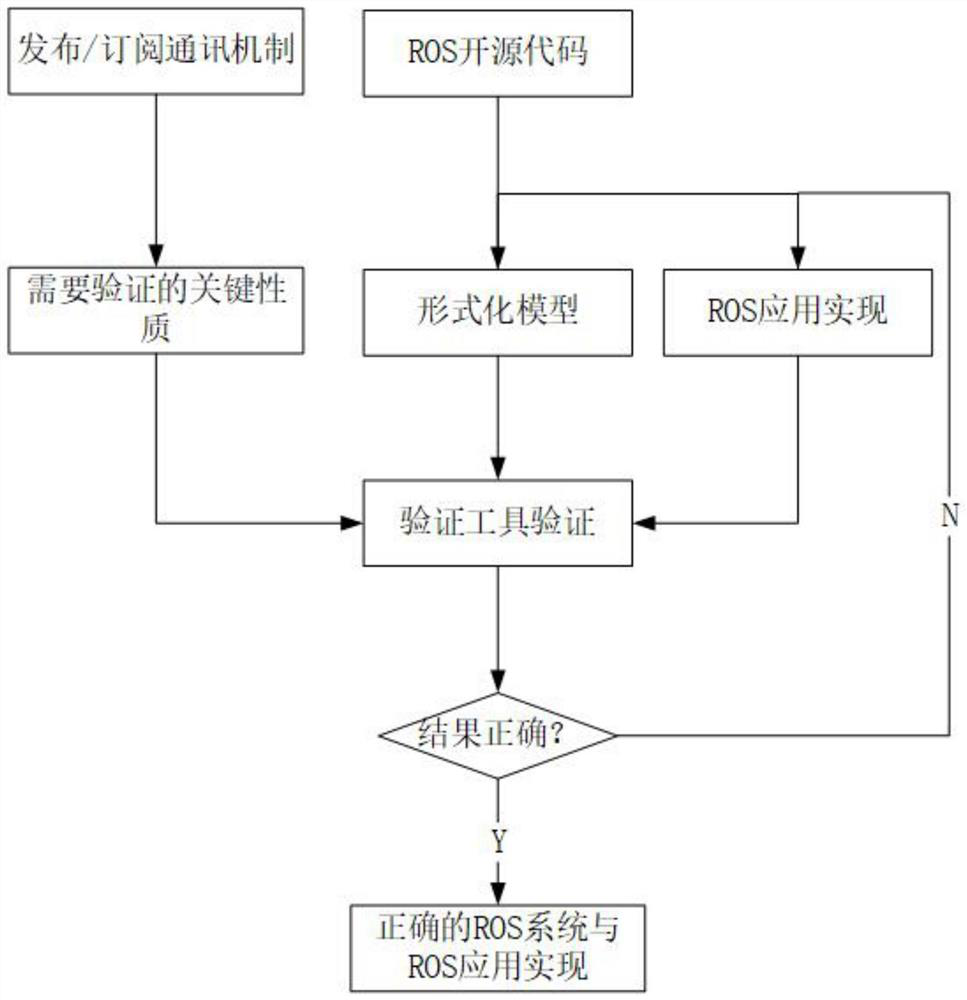
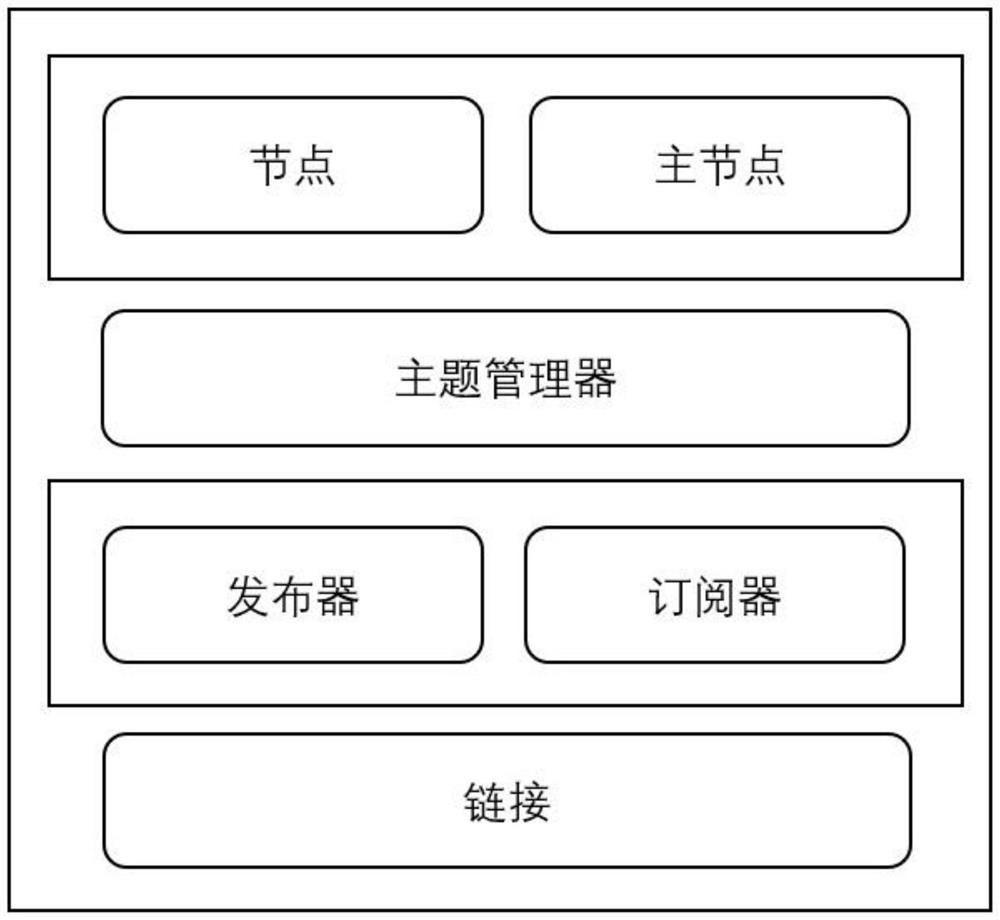
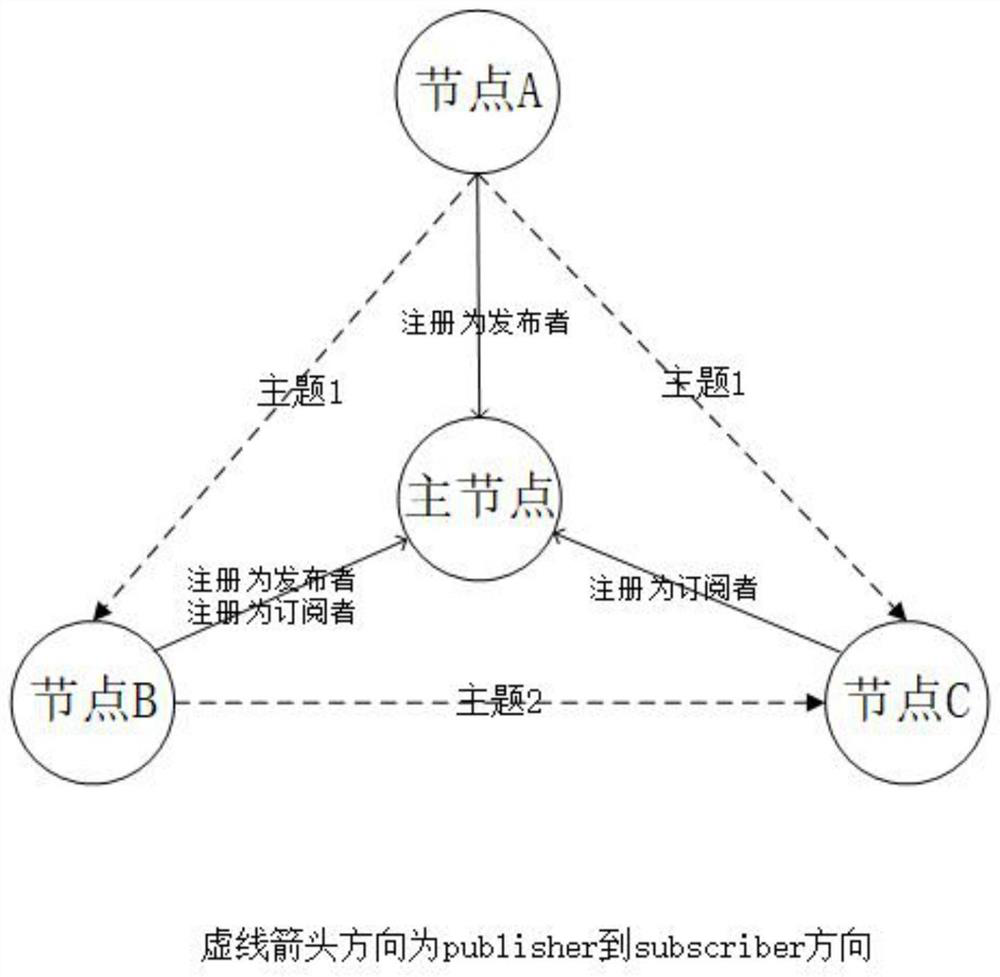
Formalized modeling and verification method of ROS underlying communication mechanism and application thereof
ActiveCN113127344AQuick fixSoftware testing/debuggingEnergy efficient computingTense logicTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a formalized modeling and verification method for an ROS underlying communication mechanism, and the method comprises the steps: firstly extracting modules, functions and rules of the ROS underlying communication mechanism according to an open source code of an ROS; establishing a formalized model about an underlying theme communication mechanism; extracting key properties according to a 'publishing / subscribing' communication mechanism, and describing he properties by using a tense logic language; designing an ROS application example, and verifying the key properties described by the tense logic language by using a formalized verification tool and combining the application example with the established formalized model; and analyzing a 'publishing / subscribing' communication mechanism of the ROS according to the verification result and process. The method is applied to the specific implementation of the ROS comprising three mutually subscribed nodes, and the deadlock-free property, accessibility, activity and correctness of the ROS and ROS application implementation are improved through formalized verification.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
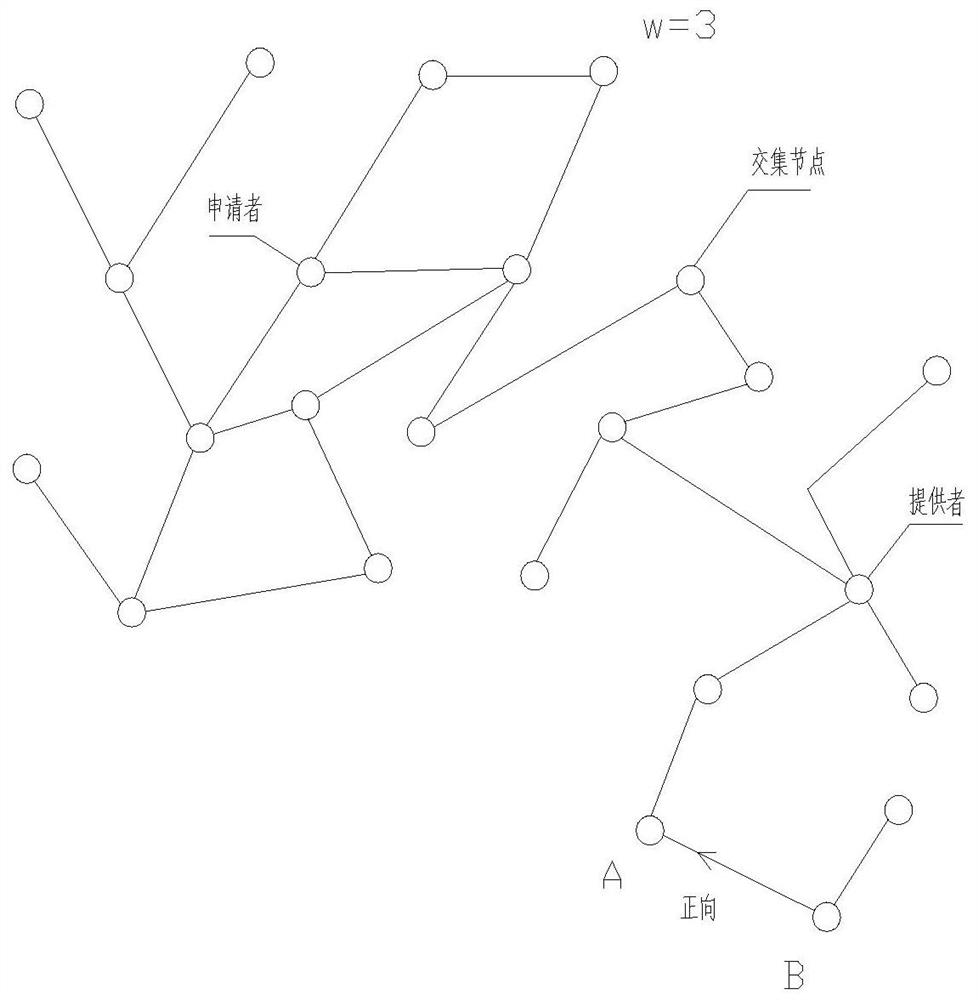
A Distributed System Based Node Property Identification Method
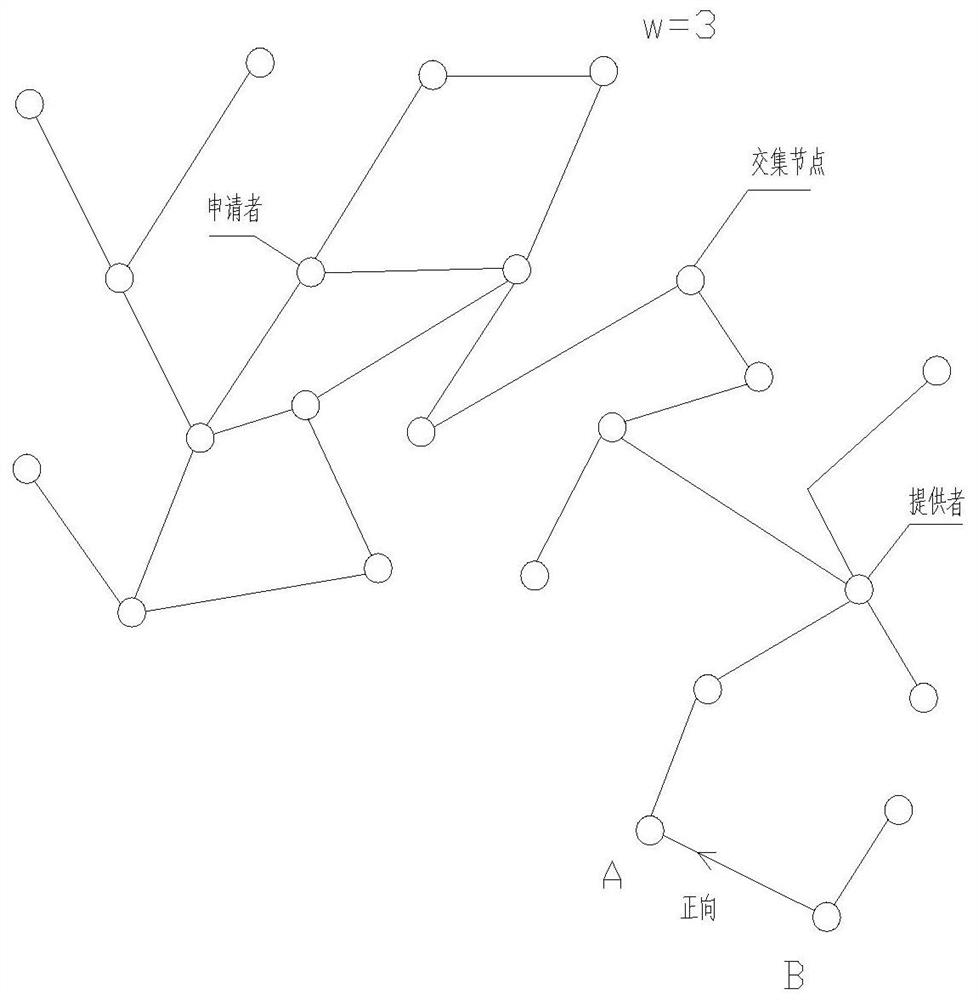
ActiveCN109088862BEfficient identificationFight against attackKernel methodsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer networkEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for identifying node properties based on a distributed system, comprising the following steps: treating participants who apply for resources or provide resources in the distributed system as nodes; the nodes include good faith nodes and Sybil nodes (malicious nodes) and pending nodes; if there is a record of providing resources or obtaining resources between nodes, it is considered to form a connection edge; when the pending node sends out a resource application as the applicant, it is assumed that the participant that receives the resource application and provides resources is a bona fide node. In the random routing, the characteristics of the applicant node are extracted, and based on this, the nature of the pending node that sends out the resource application is identified, so as to decide whether to provide resources to it. The invention can effectively identify Sybil nodes, so as to resist Sybil attacks.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
A Quality Control Method for Crowdsourcing Classification Data Based on Self-paced Learning
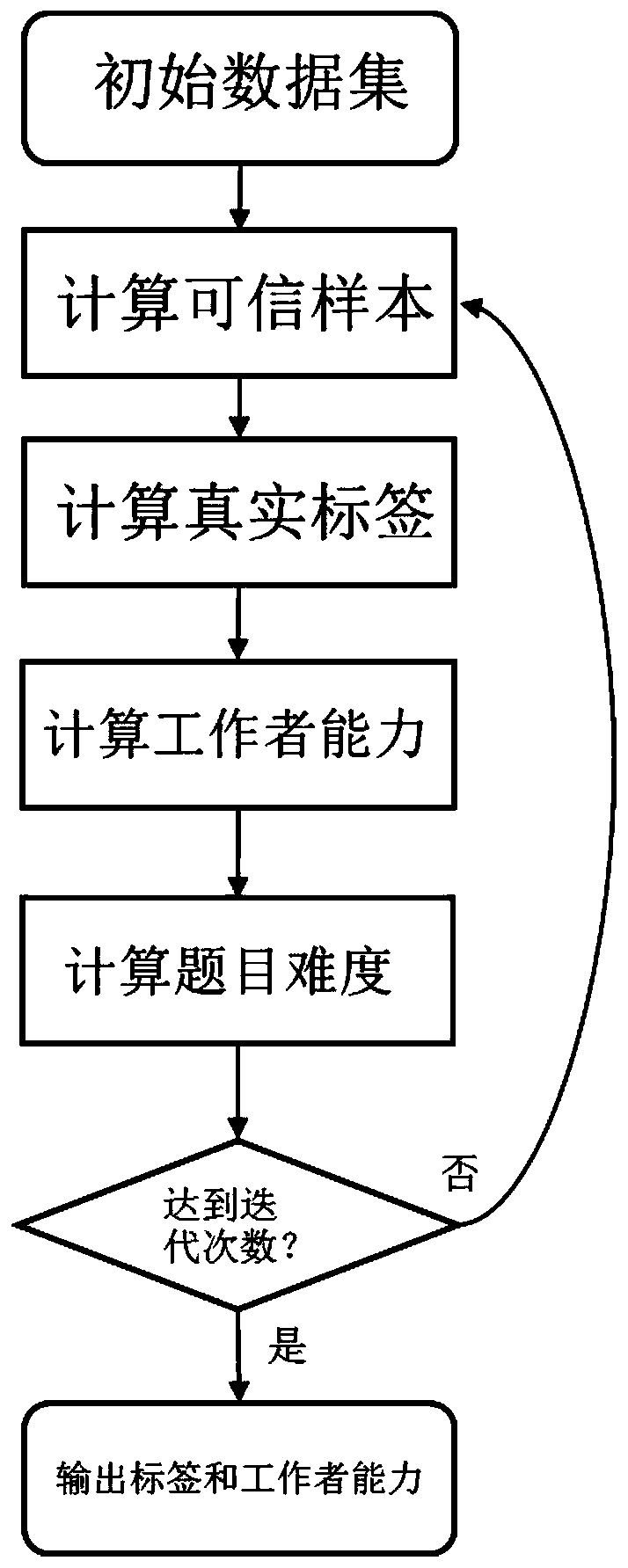
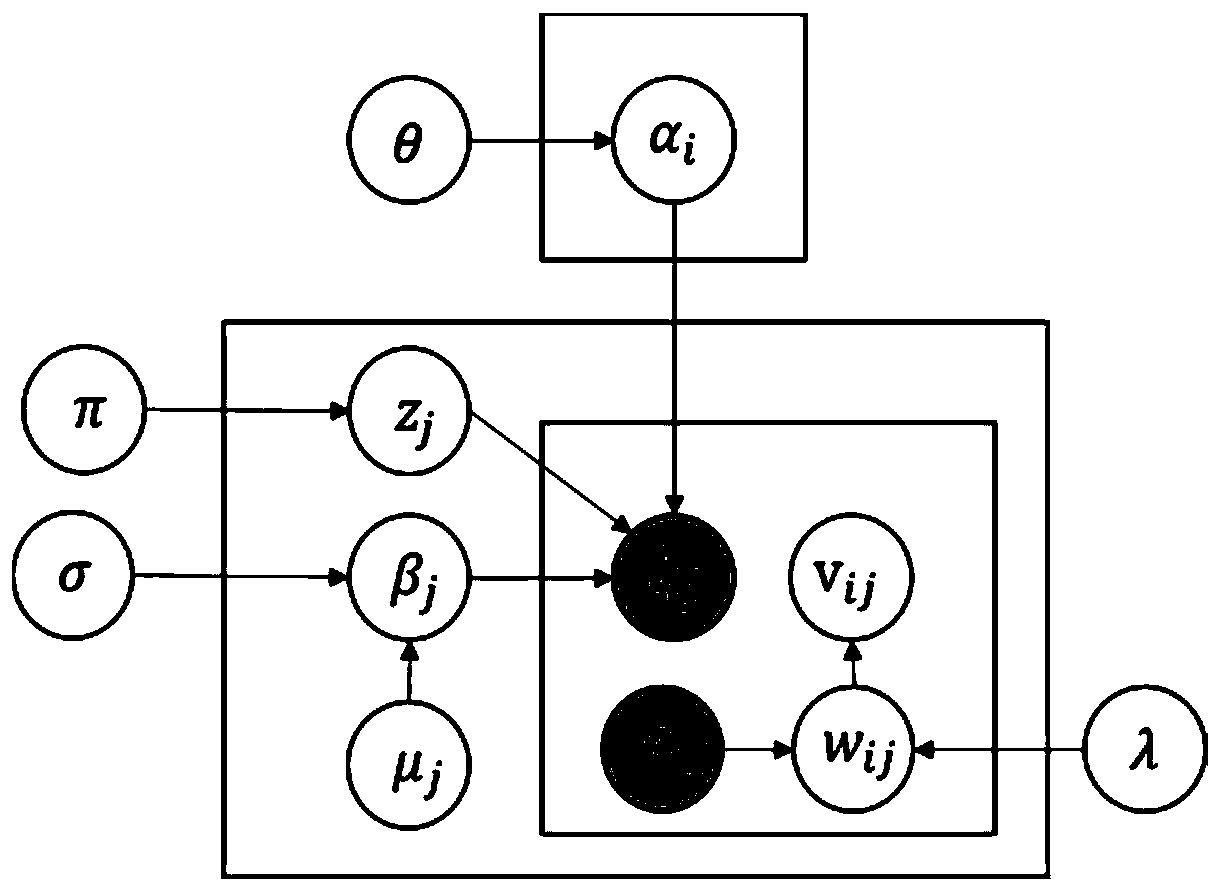
ActiveCN107357763BAccurate estimateEasy Distribution ControlResourcesComplex mathematical operationsData setSality
The invention discloses a crowdsourcing classification data quality control method based on self-learning and belongs to the field of computer scientific data mining technology. The method is used for true classification discovery of multiple classification crowdsourcing annotation tasks and recognition of a malicious worker. According to the method, first, sample credibility is calculated according to initial dataset nature; second, a sample is selected; third, a true tag and the ability of a worker are calculated; fourth, another sample is selected according to updated ability and the true tag; fifth, after all sample points are completely selected, further optimization is performed; and finally an annotated true answer and recognition results of the ability of the worker and a malicious and passive worker are acquired at the same time. Experiments prove that a better result can be obtained through the method compared with a traditional method.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
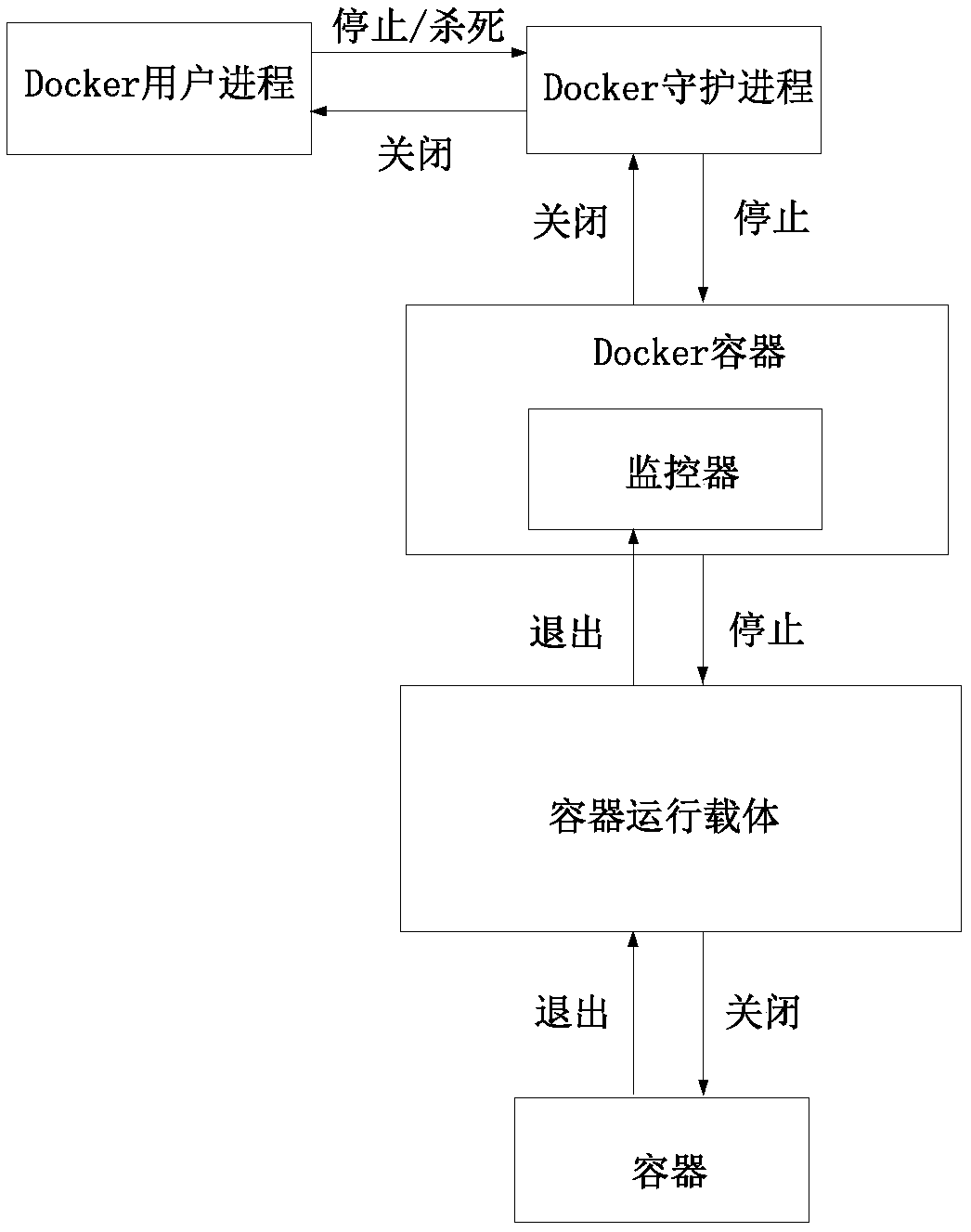
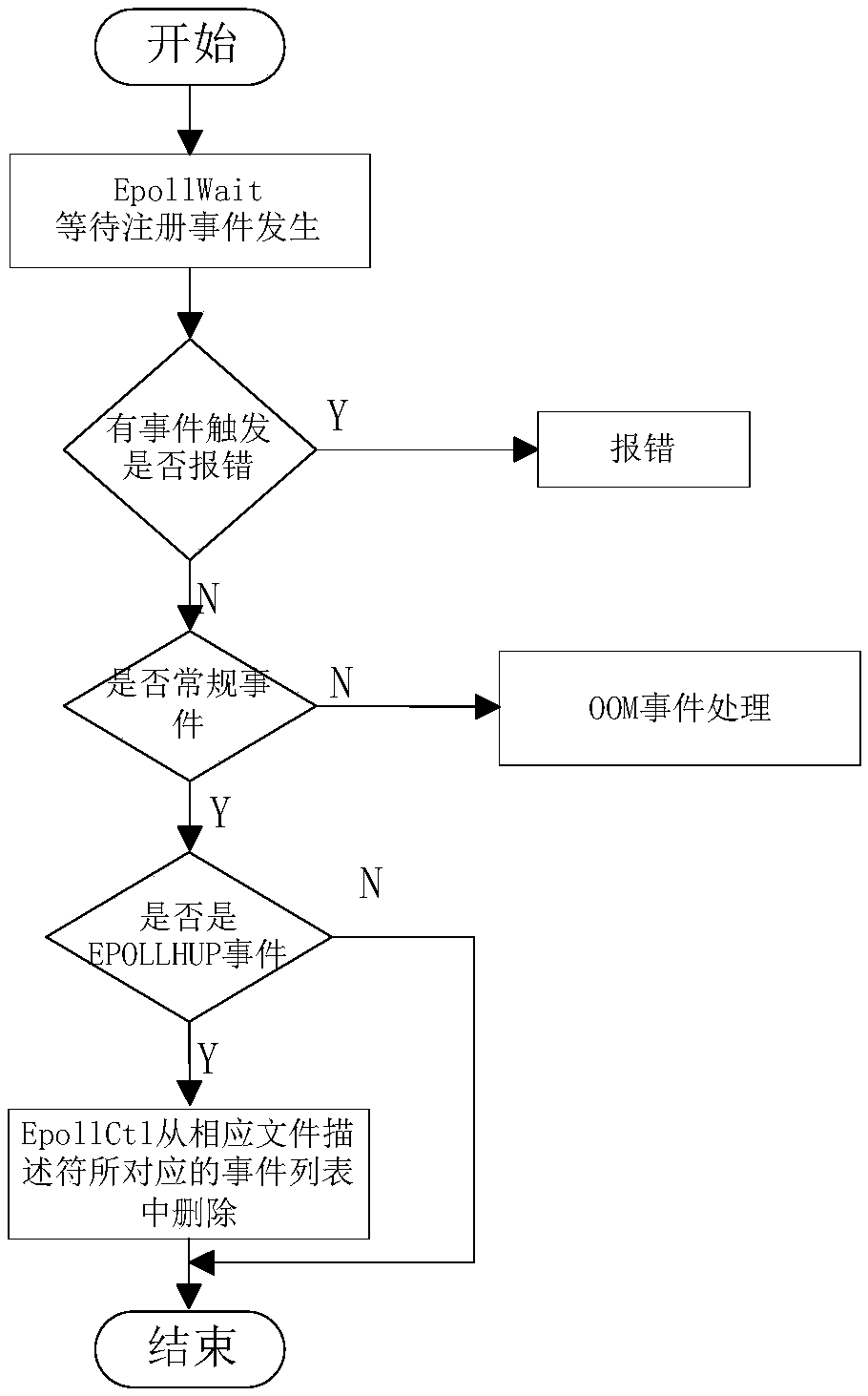
Method for executing Epoll system calling by Docker
ActiveCN110795092AOvercome the defect of slow execution exit speedQuick responseEnergy efficient computingSoftware reuseSoftware engineeringSystem call
The invention relates to a method for executing Epoll system calling by a Docker and application of the method, and the method comprises the following steps: creating an Epoll instance, and returninga file descriptor of the instance; registering a required specific file descriptor; waiting for a registration event; after monitoring that a certain event occurs, detecting whether an error is reported in the event occurrence process or not; detecting the property of the event, if the event is an OOM event, entering an OOM event processing flow, and if the event is a conventional event, performing the next operation; judging whether the event is an EPOLLHUP event or not, if not, ending, and if yes, performing the next operation; and deleting the EPOLLHUP event from the event list corresponding to the corresponding file descriptor, and reporting an error if the deletion fails. According to the method and the device, the defect that the executive quit speed of an existing Docker container is low is overcome, and the response speed of the Docker container is increased.
Owner:CHINA STANDARD SOFTWARE
PHP static code analysis method based on taint analysis
PendingCN113836532AReduce false positivesReduce false alarm ratePlatform integrity maintainanceData streamAlgorithm
The invention relates to a PHP static code analysis method based on taint analysis. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing lexical analysis and grammatical analysis on PHP static codes, and constructing an abstract syntax tree corresponding to the codes; secondly, segmenting the abstract syntax tree into different sub-functions, and marking taint data streams in each function by using a taint analysis technology; and finally, judging whether a vulnerability exists or not according to the convergent point parameter property of the taint data stream. In addition, when the taint data stream is marked, the variable range is narrowed by limiting the data type of the newly added variable, and the vulnerability false alarm rate is reduced by combining measures such as conditions when the safety threat function is utilized. According to the method, automatic tool vulnerability detection can be achieved, and under the condition that no branch exists in the code, vulnerability detection of the Web application can be completed more efficiently and more accurately.
Owner:CHINA YOUKE COMM TECH
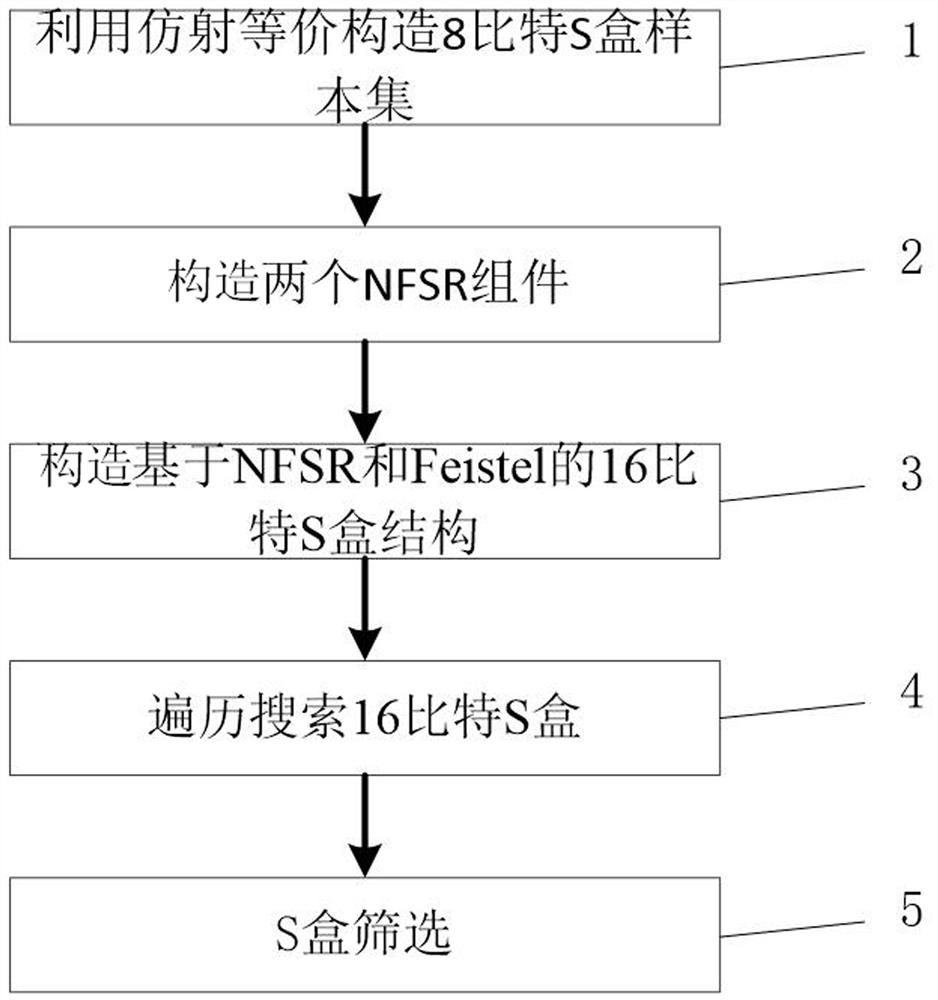
16-bit S box construction method based on NFSR and Feistel structure
ActiveCN113783684ASimple structureExcellent cryptographic propertiesEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesS-boxNonlinear feedback shift register
The invention discloses a 16-bit S box construction method based on NFSR and an Feistel structure. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an 8-bit S box sample set; constructing two NFSR components by using an eight-stage nonlinear feedback shift register; combining the two constructed NFSR components with a Feistel structure, carrying out multi-round iteration based on the 8-bit password S box sample set, and carrying out output after iteration so as to construct a 16-bit password S box; and finally, testing the constructed 16-bit S box, performing screening according to difference uniformity, nonlinearity, algebraic times and signal-to-noise ratio in sequence, and screening out the 16-bit S box with better password property for outputting. The method is based on an NFSR and Feistel structure, an S box is used for replacing a round function, and the construction structure is simple; the 16-bit S box with better cryptographic properties can be constructed, and S box support with high security is provided for a block cipher algorithm.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
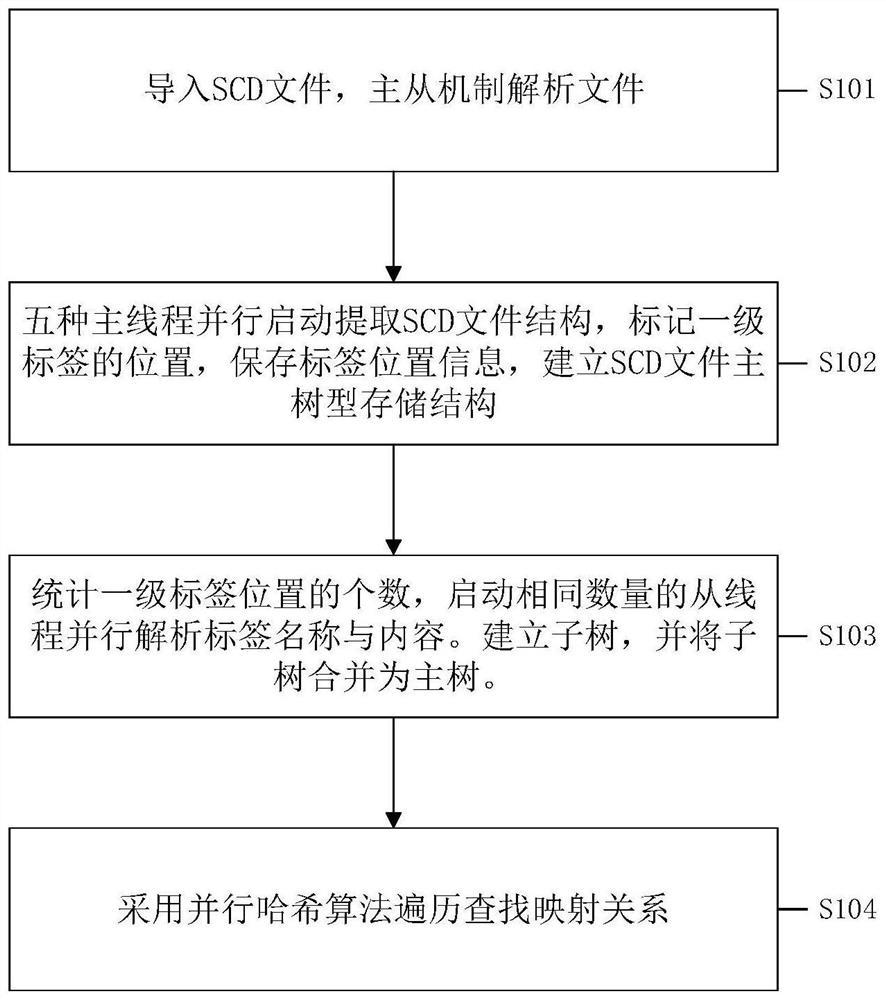
A parallel parsing method for scd files in smart substations
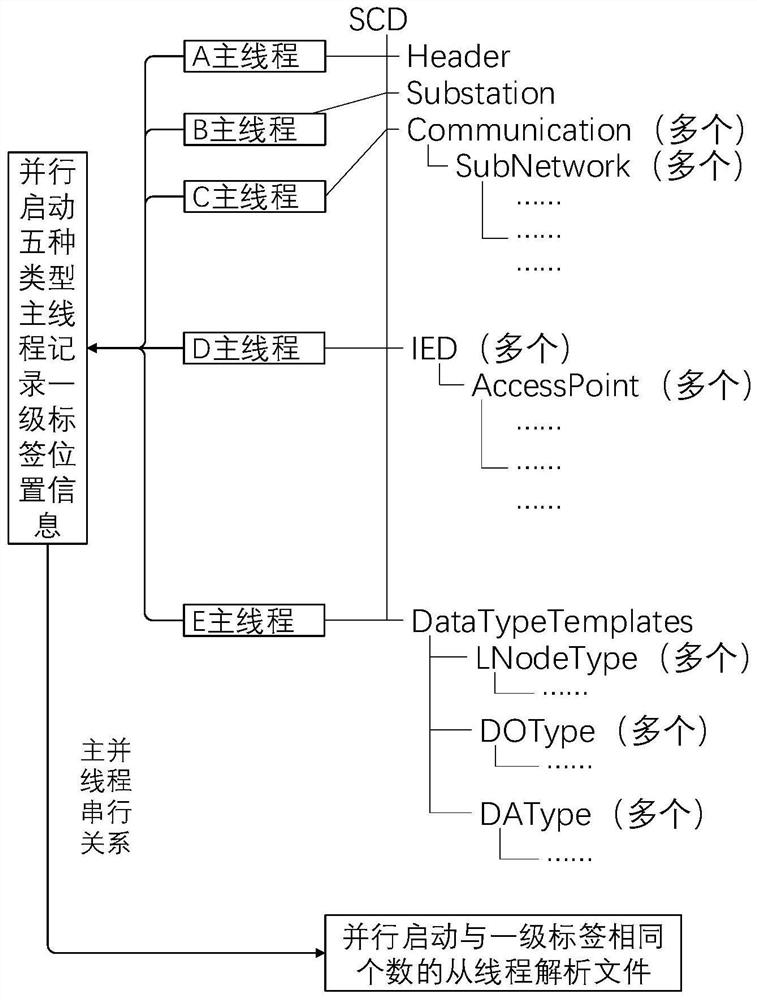
ActiveCN109800209BOn-site commissioning work is convenientShorten the timeFile access structuresComputer architectureSmart substation
The invention relates to a parallel parsing method for SCD files of an intelligent substation. A master-slave parsing mechanism is adopted, the main thread extracts the structure of the SCD file, and the slave threads parse the names and properties of labels. The main thread and the slave thread are in a serial relationship; the main thread and the main thread, and the slave thread and the slave thread are in a parallel relationship. Start five types of main threads in parallel according to the SCD file structure, mark the first-level label position of the SCD file, and save the label position information; count the number of first-level label positions, and start the same number of slave threads to analyze the first-level label and the labels it contains The name and nature of the analysis result of each slave thread is stored in a tree structure, and a type subtree is established, and each subtree is integrated into a complete main tree according to the SCD file structure; the parsing process uses a parallel hash algorithm to realize the tree structure Quick Search. The invention adopts the parallel multi-thread technology to greatly reduce the analysis time of the SCD file and improve the result query efficiency.
Owner:HUBEI CENT CHINA TECH DEV OF ELECTRIC POWER
Openwhisk service-free framework migration method for micro-service application
ActiveCN112817567AAutomate migrationImprove efficiencySoftware designExecution paradigmsSource code fileCall graph
The invention discloses an openwhisk service-free framework migration method for a micro-service application, which comprises the following steps of: generating abstract syntax tree nodes by utilizing an exprima grammar analysis tool of a Node.js language, extracting key information from the abstract syntax tree nodes to generate a function call graph and a communication graph between micro-service sub-modules, judging the properties of the micro-service sub-modules, trying to divide stateful micro-service modules, and achieving automatic migration to the greatest extent. Project source code files, project package files, configuration files and the like are analyzed from the level of the abstract syntax tree, implementation is easy, and efficiency is high. At present, no similar technical scheme exists, and developers can be helped to improve the efficiency of migrating the application to the server-free computing platform by using the method.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com