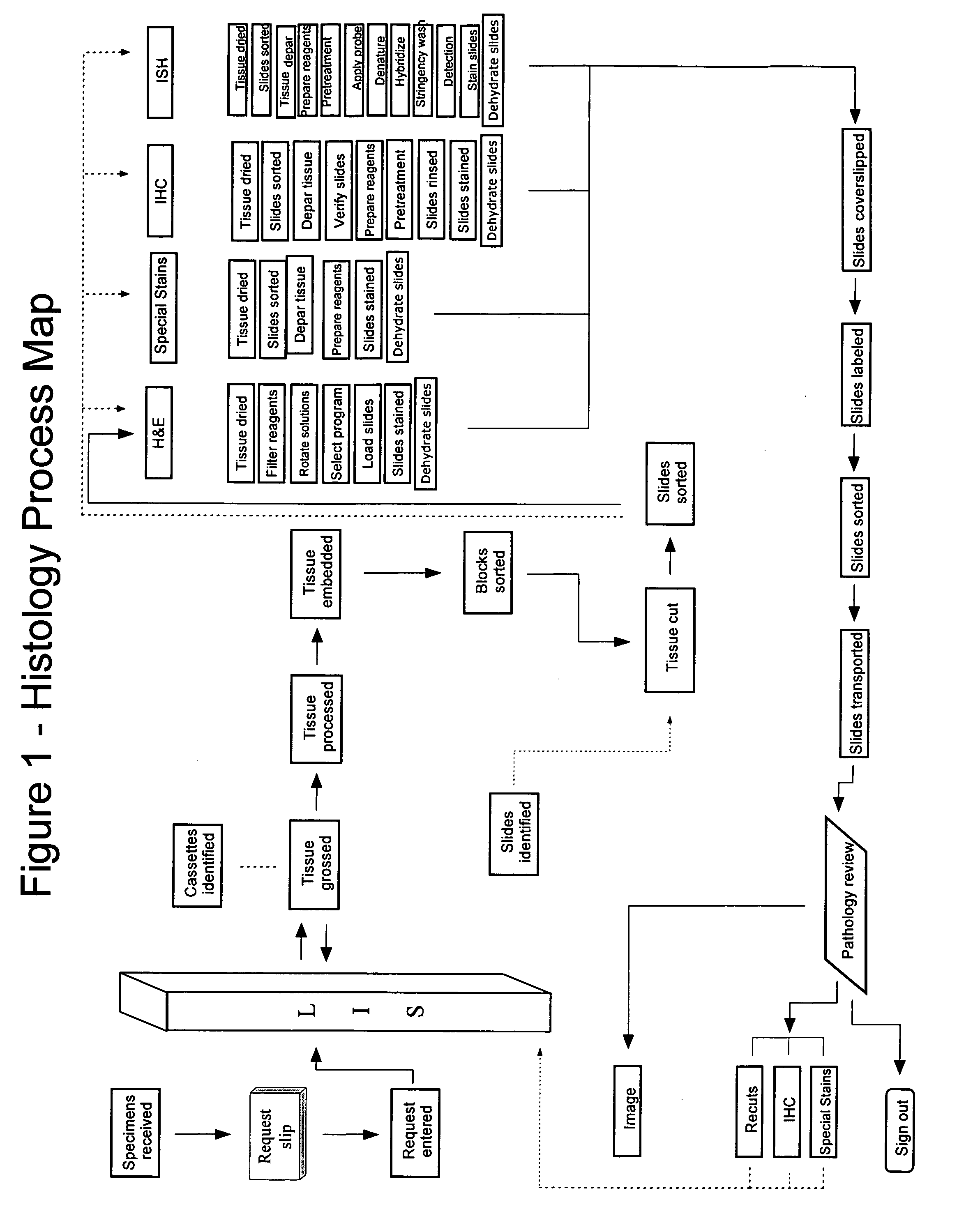
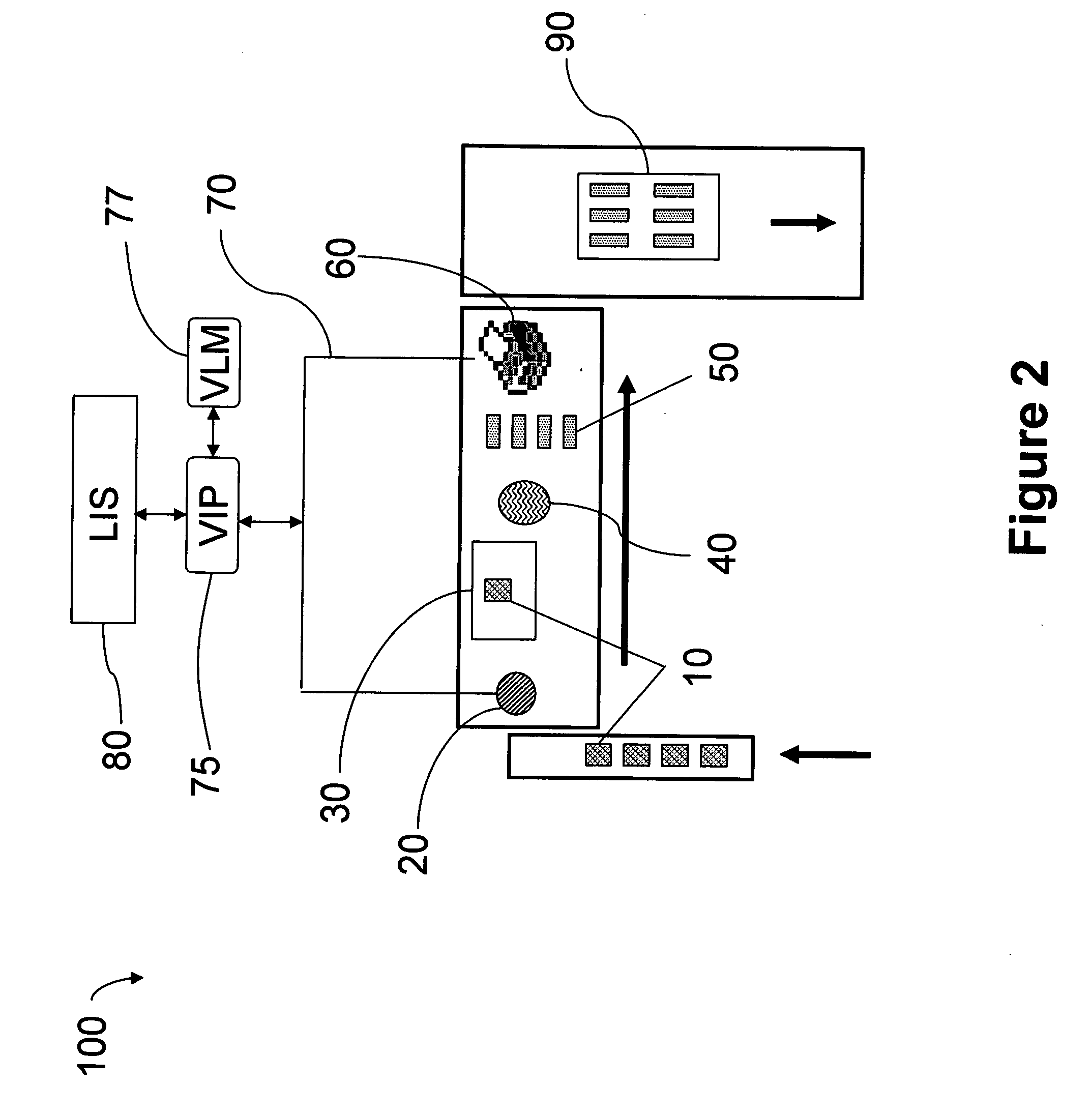
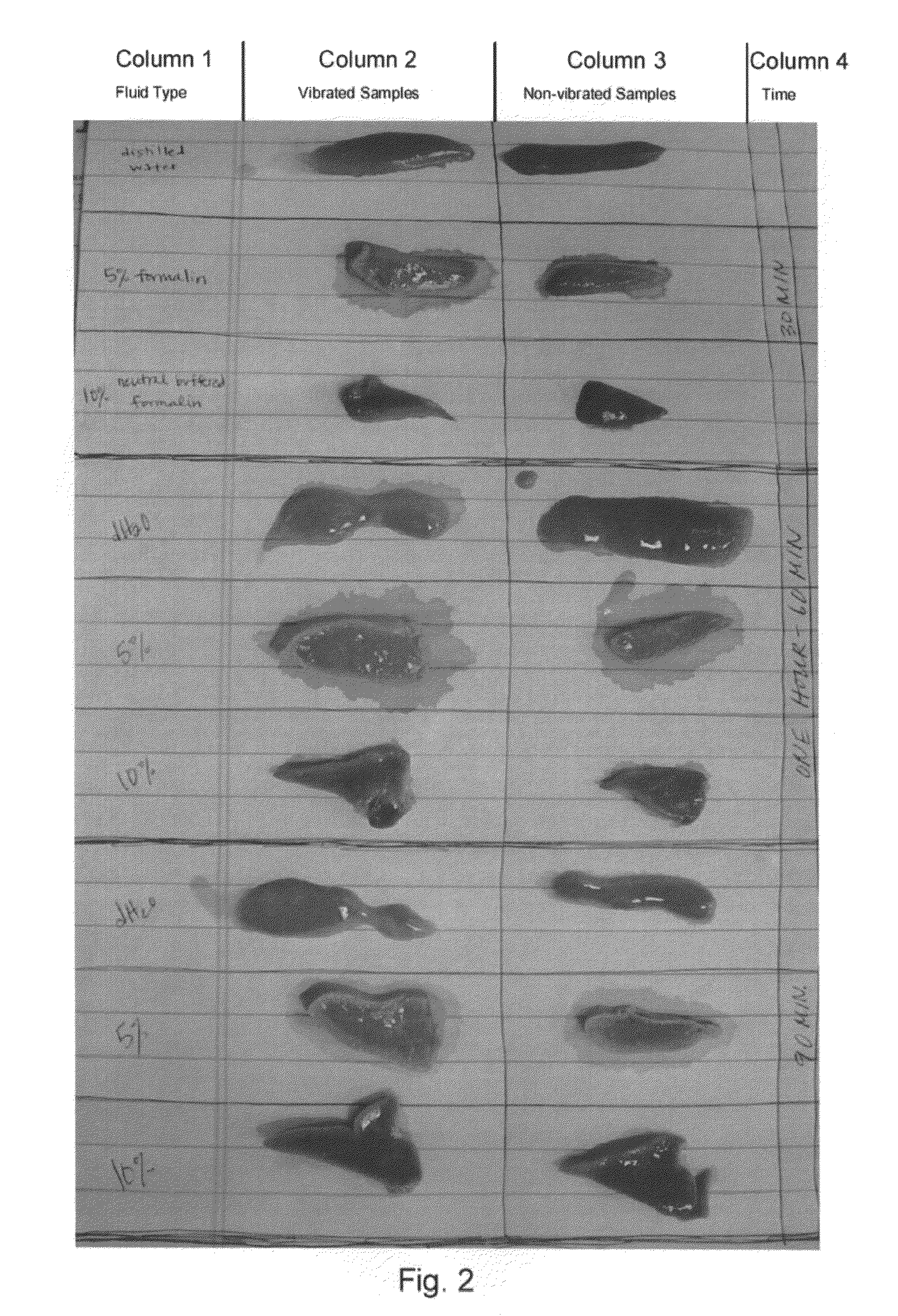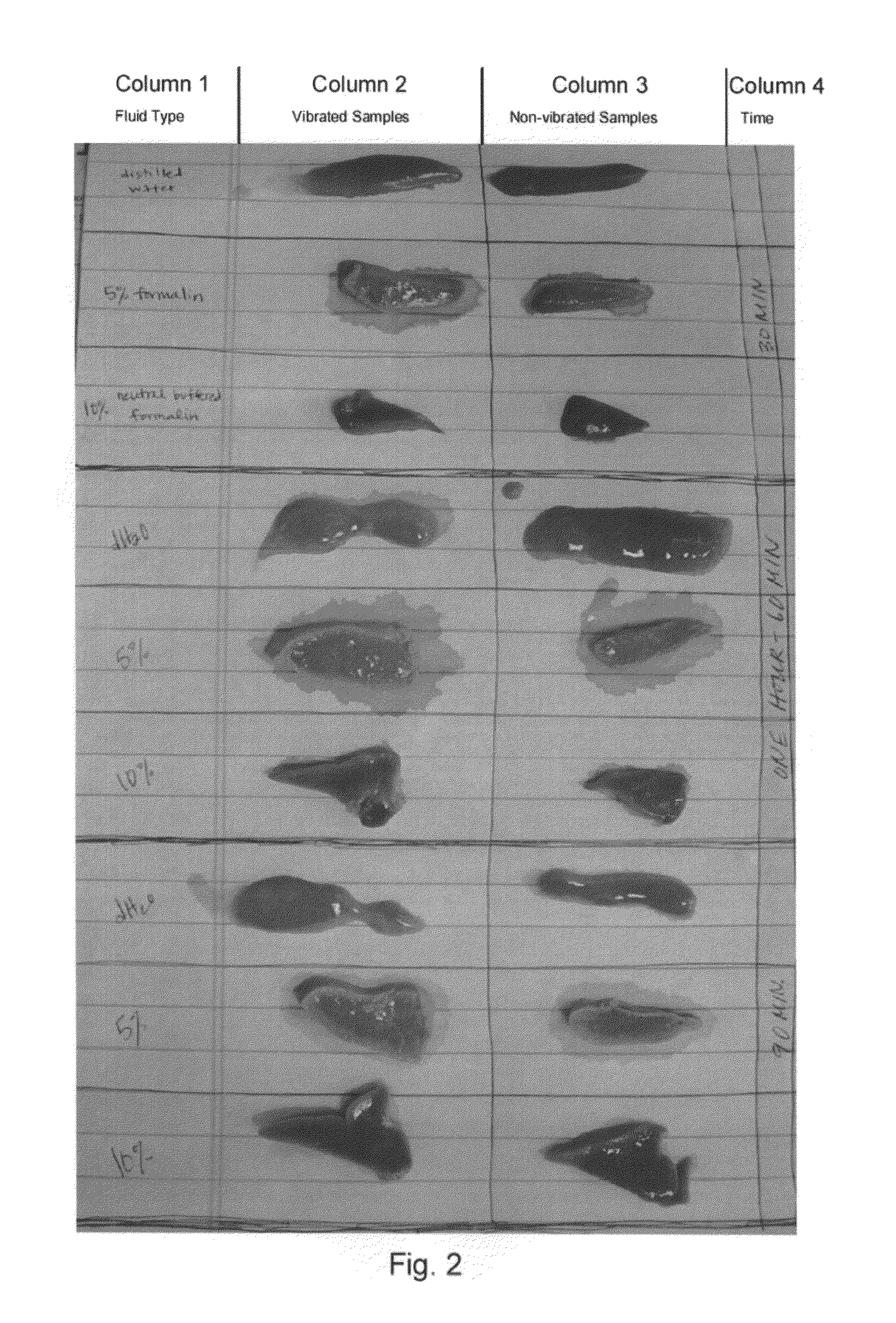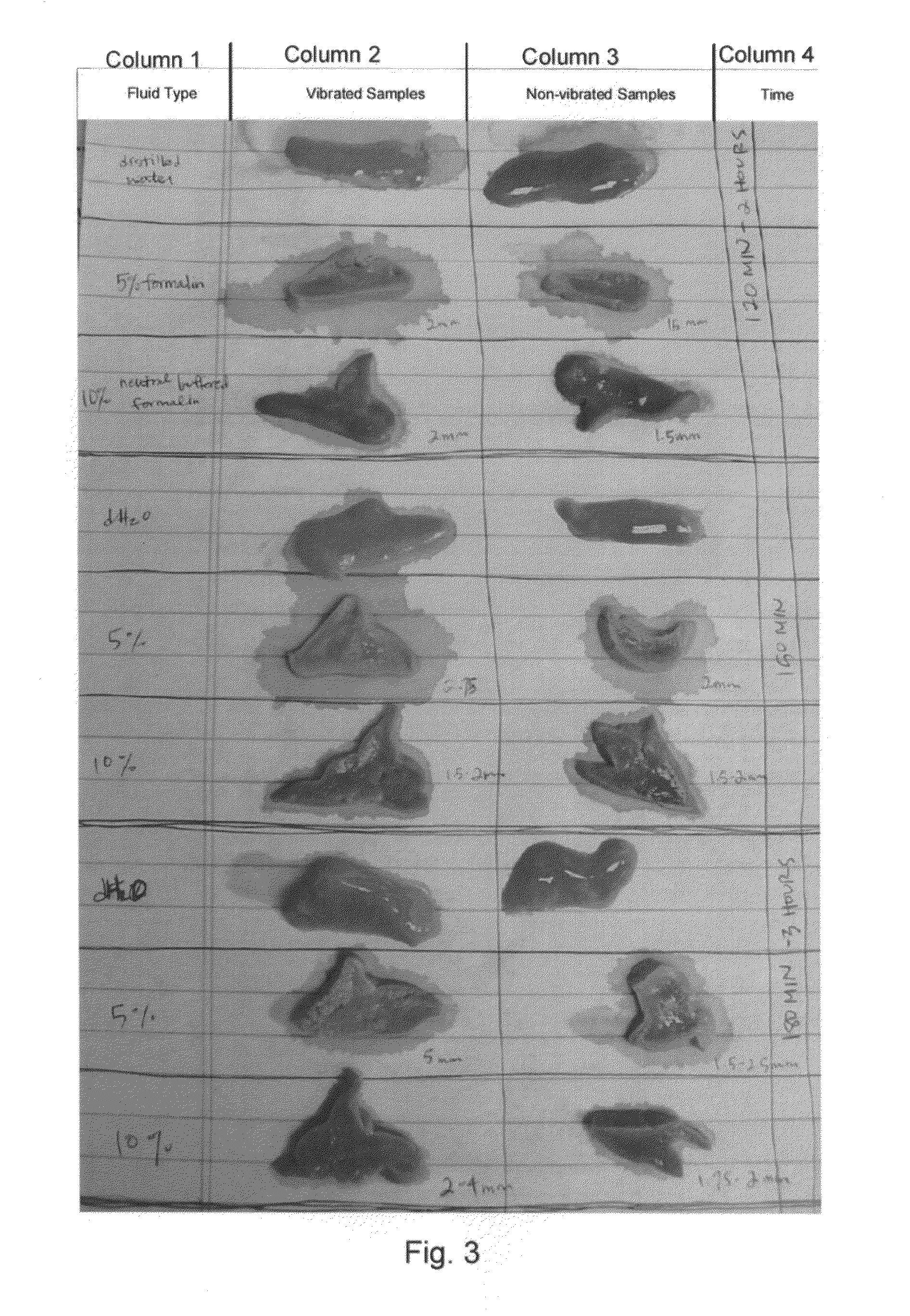Patents
Literature
44 results about "Tissue Stains" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
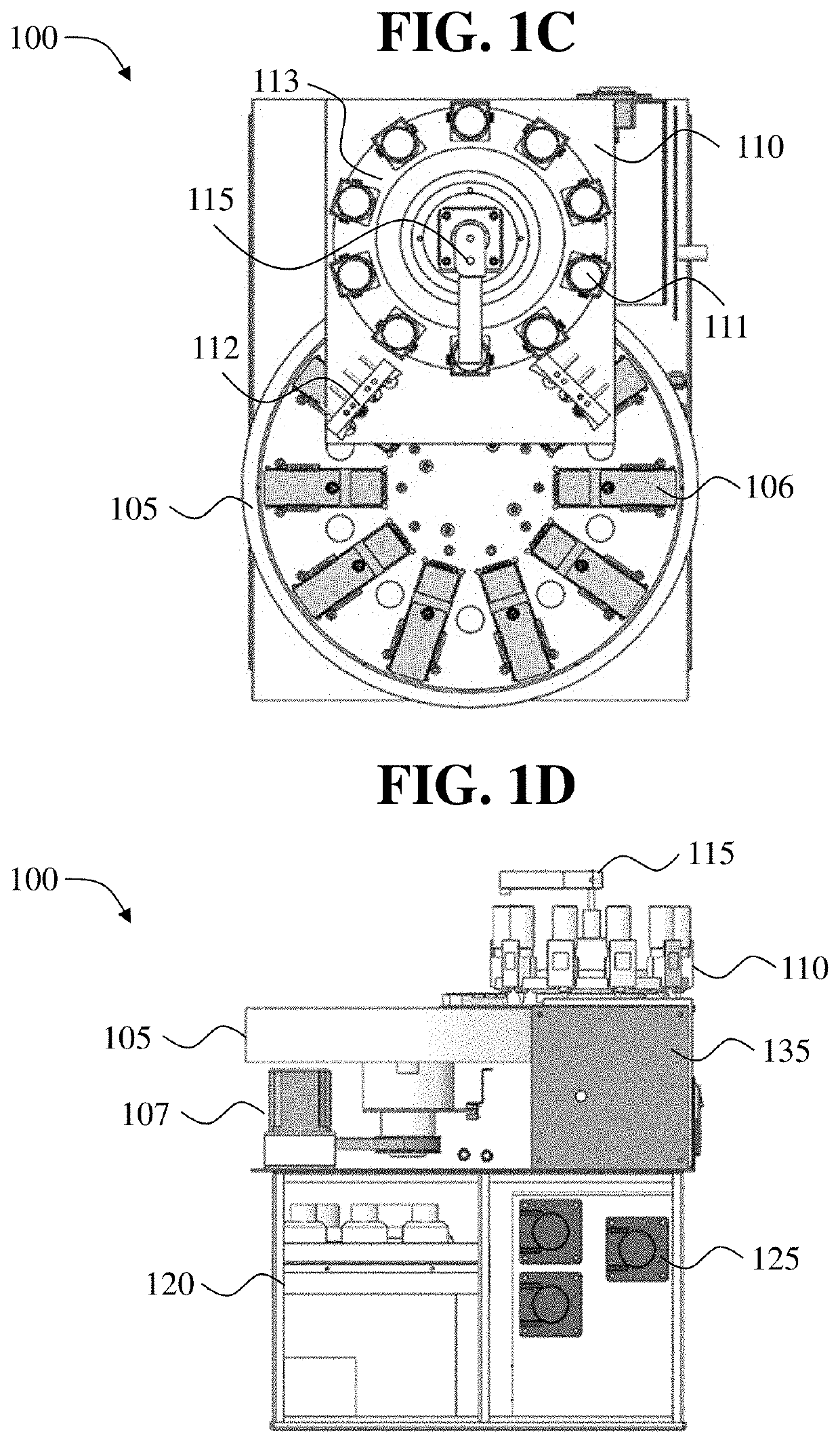
Automated tissue staining system and reagent container
InactiveUS6998270B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingEngineering
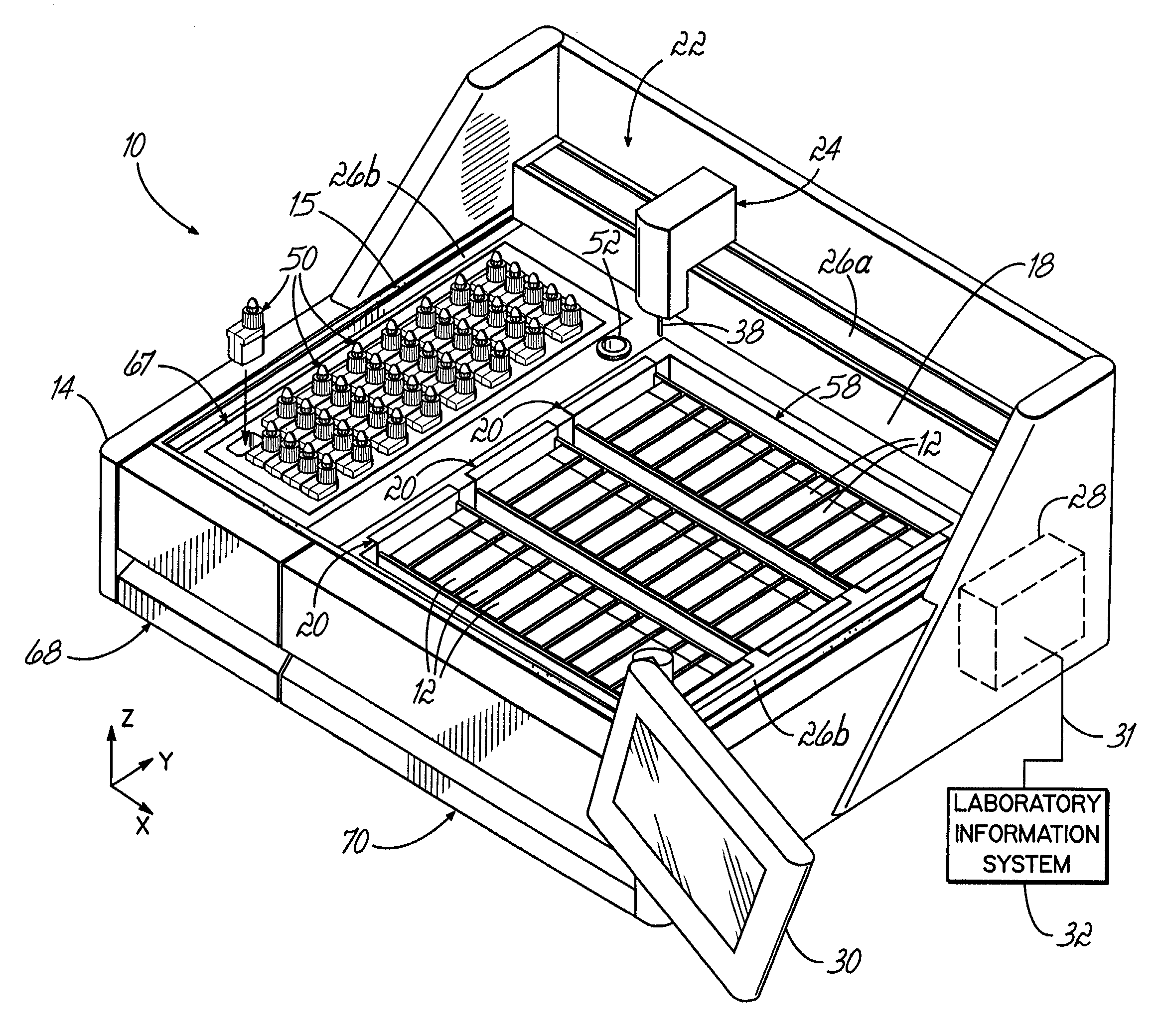
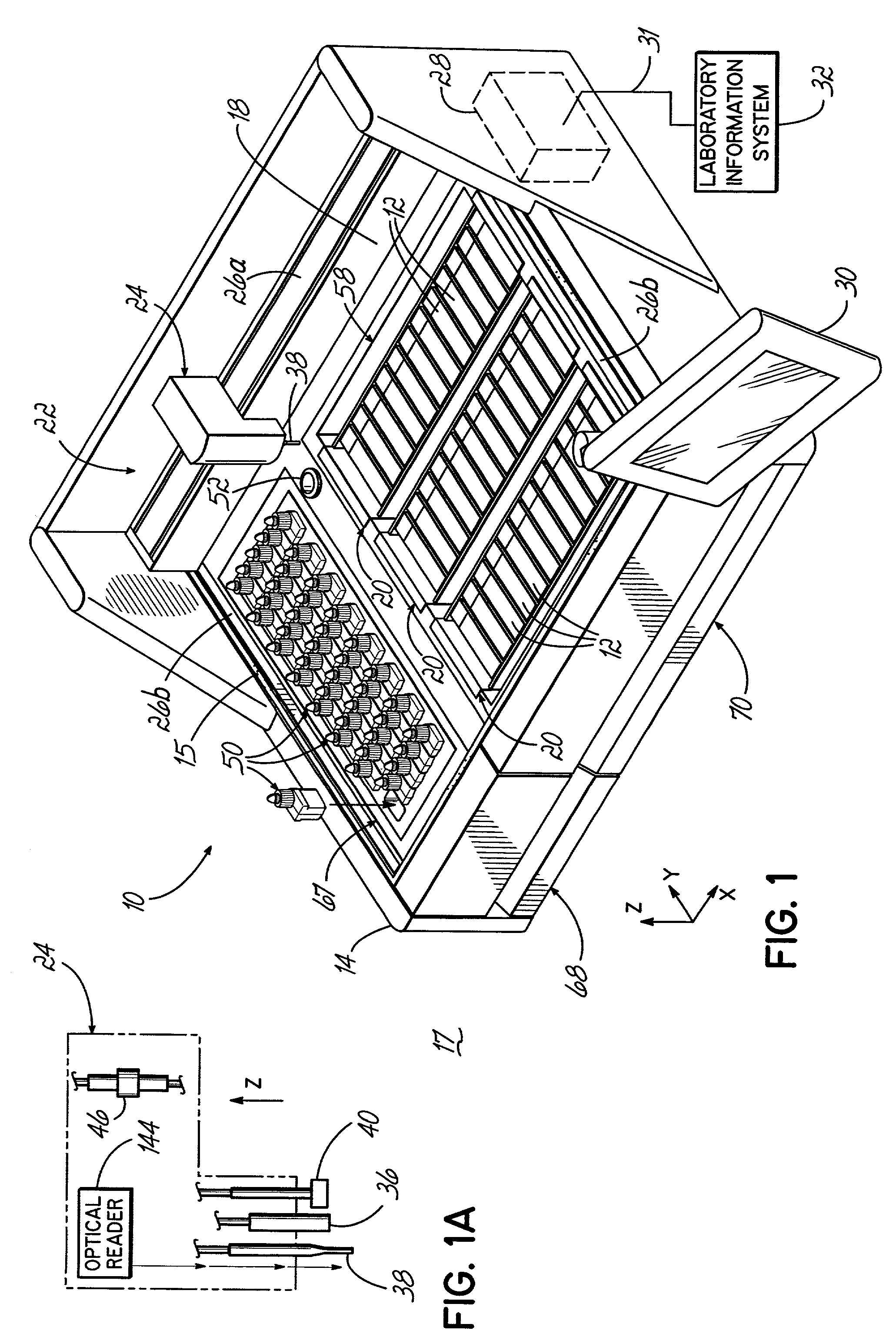
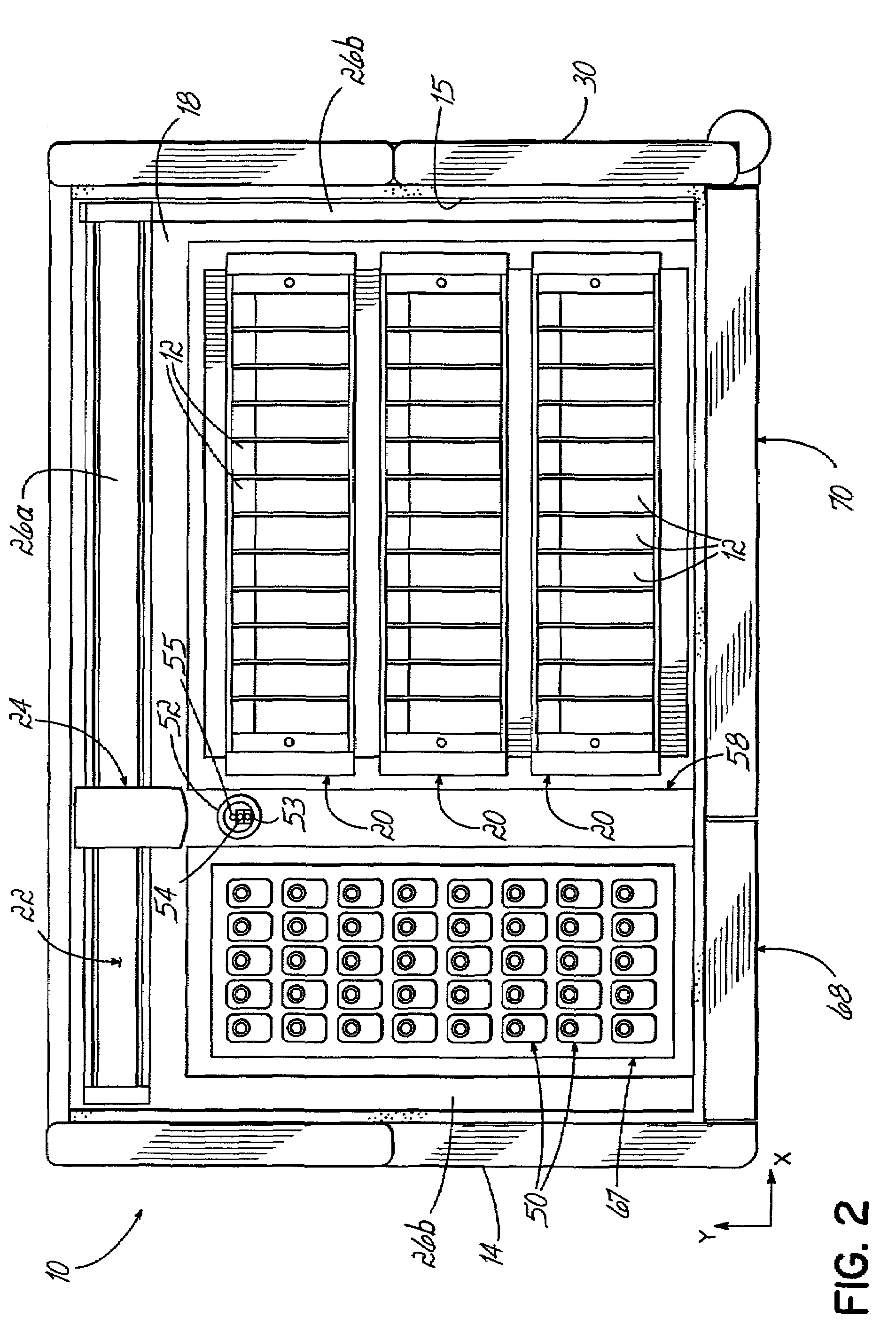
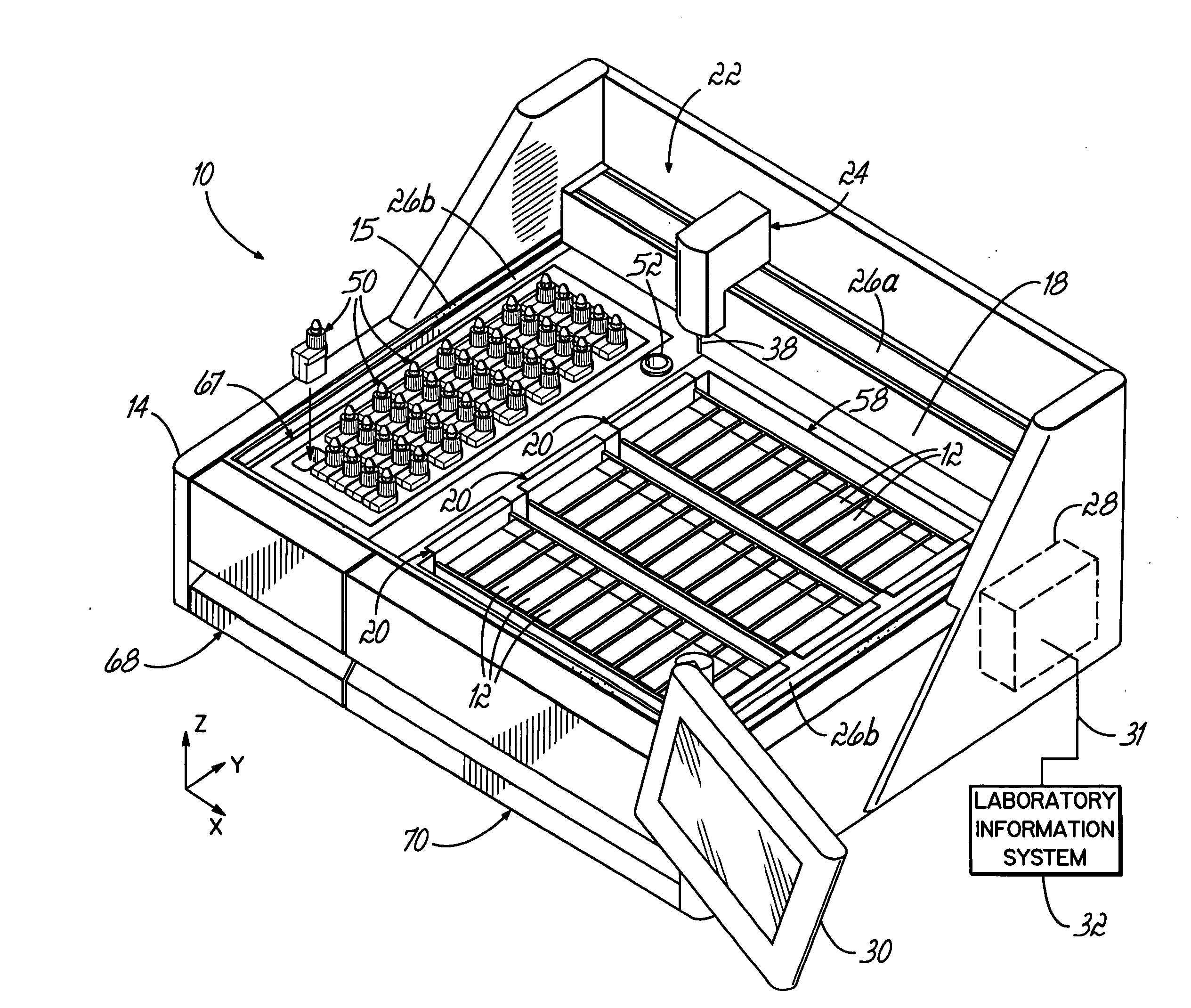
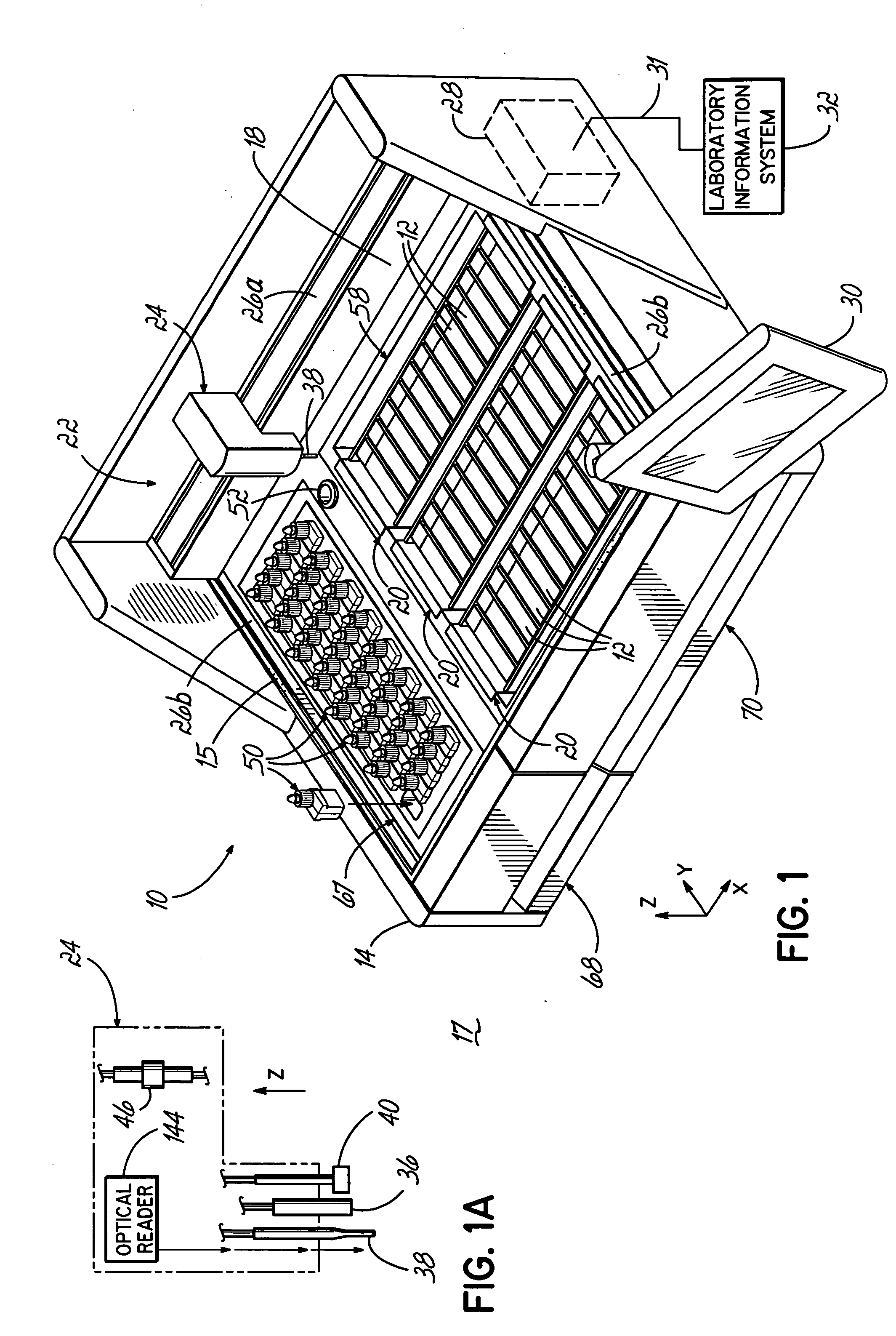
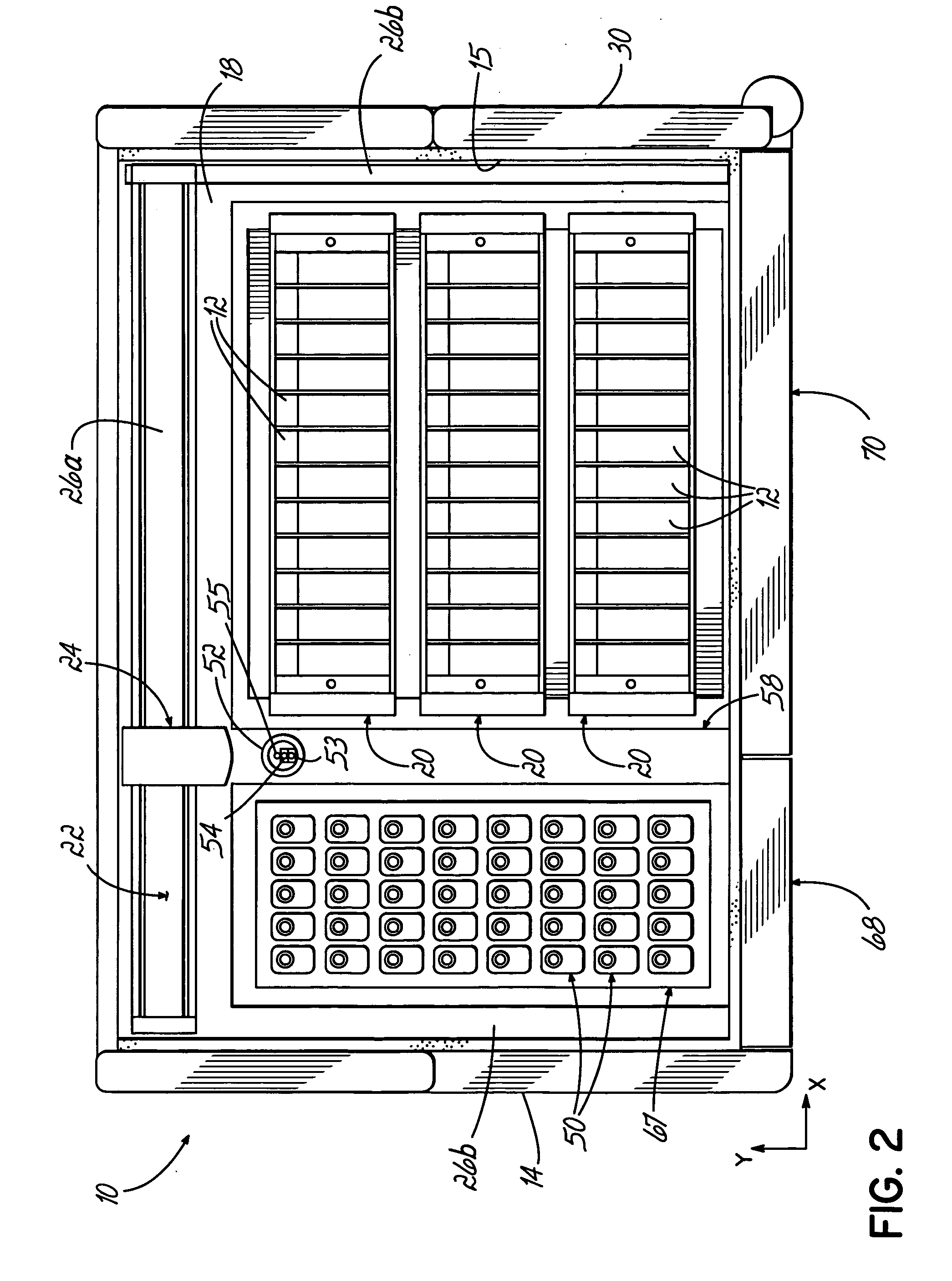
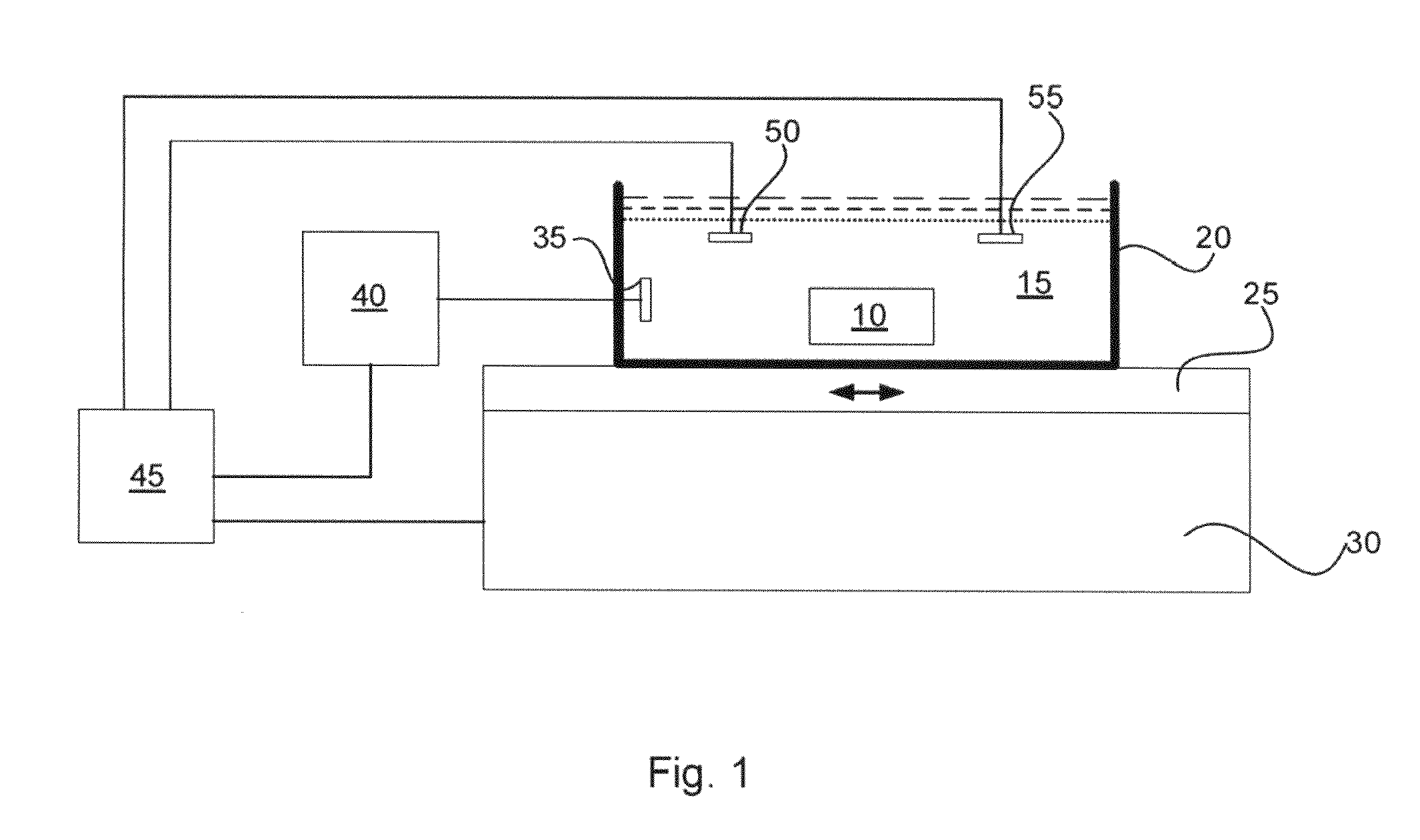
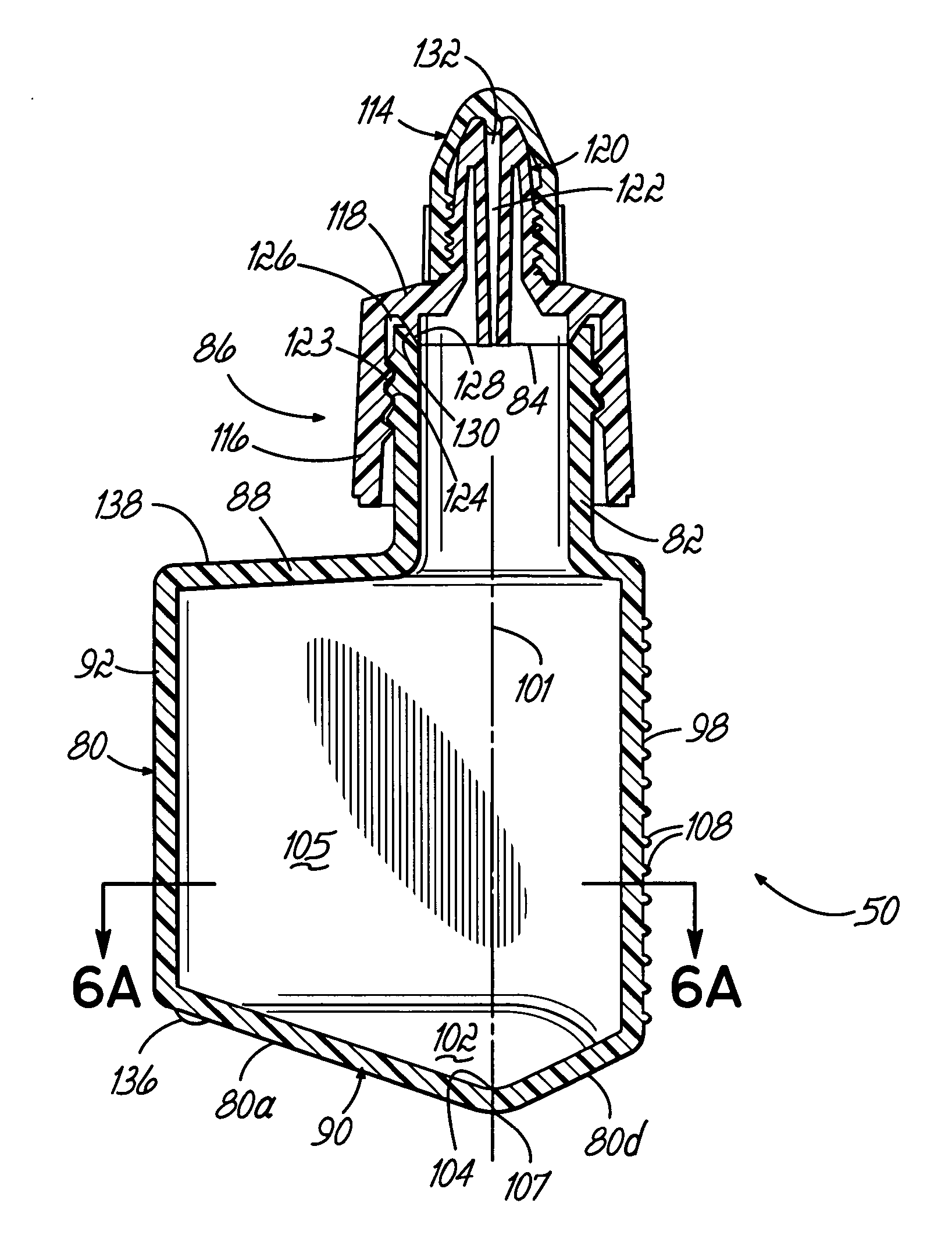
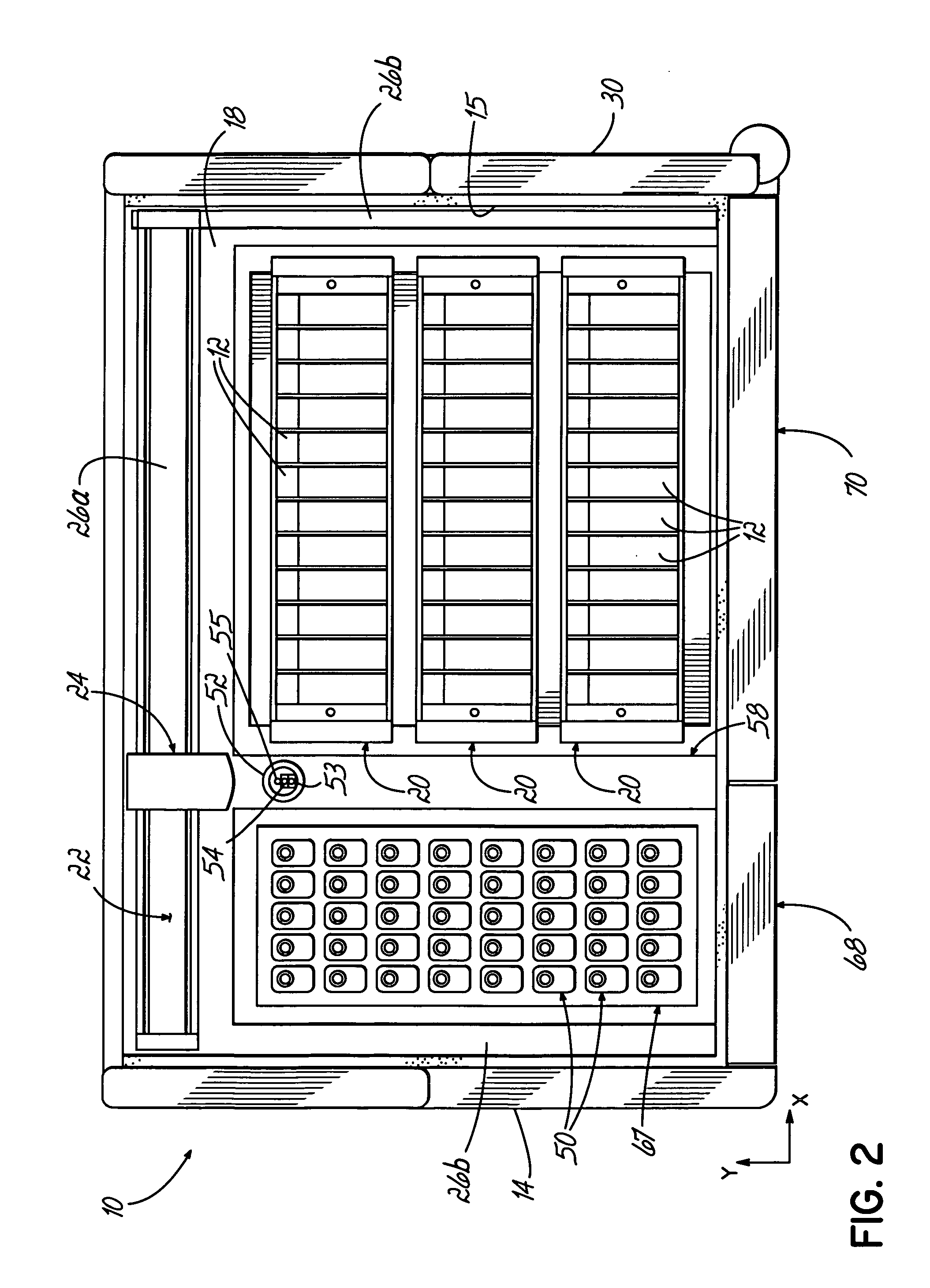
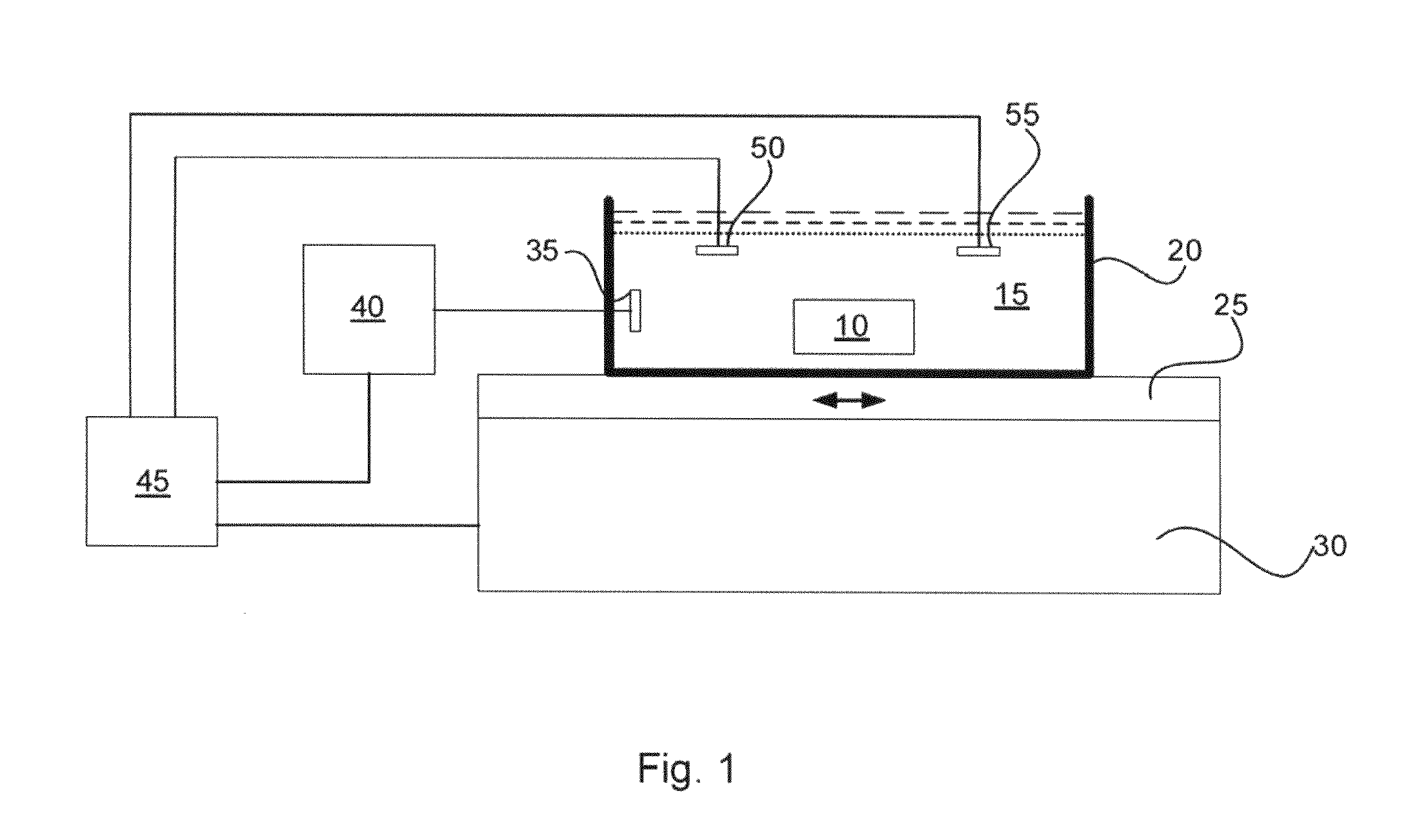
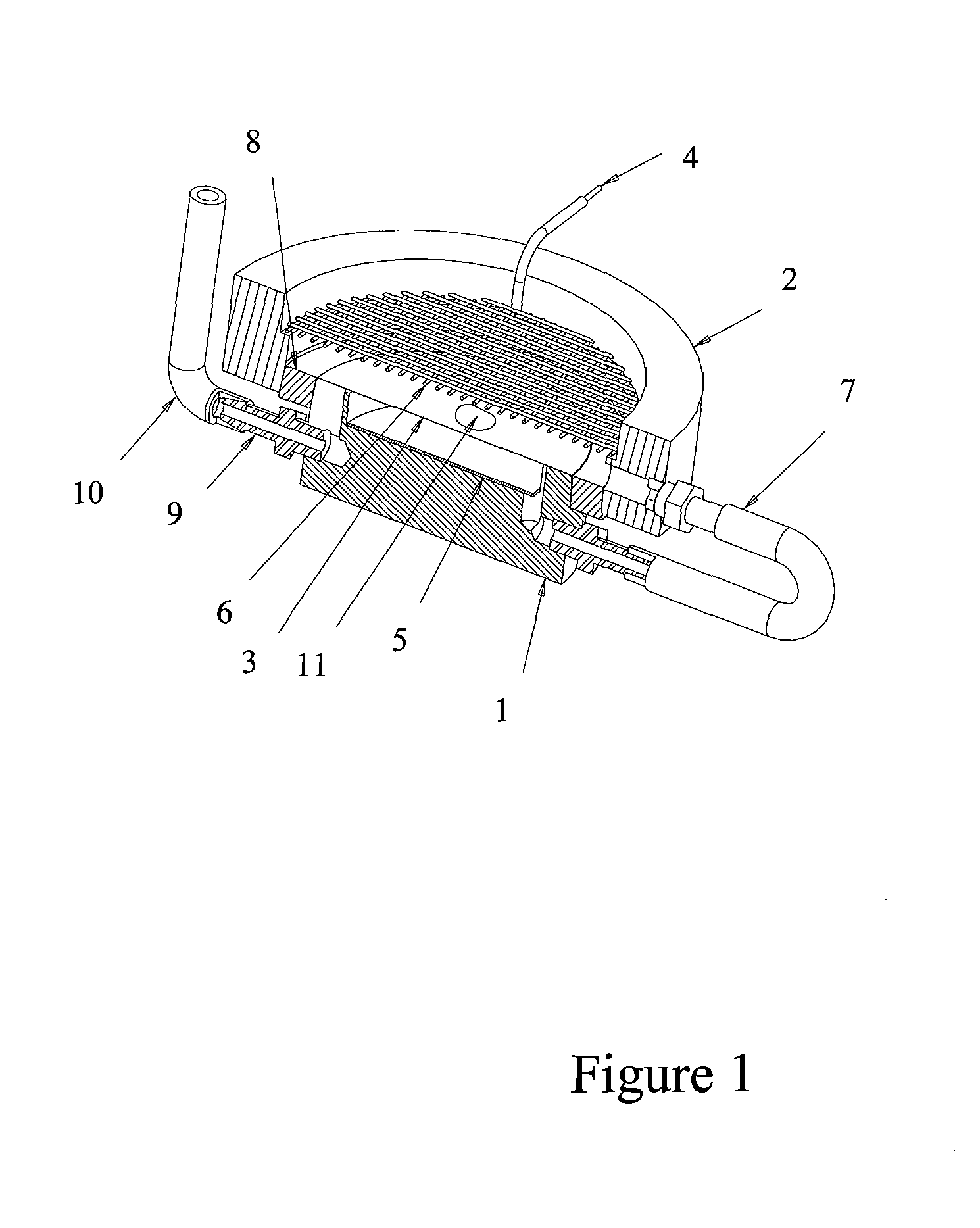
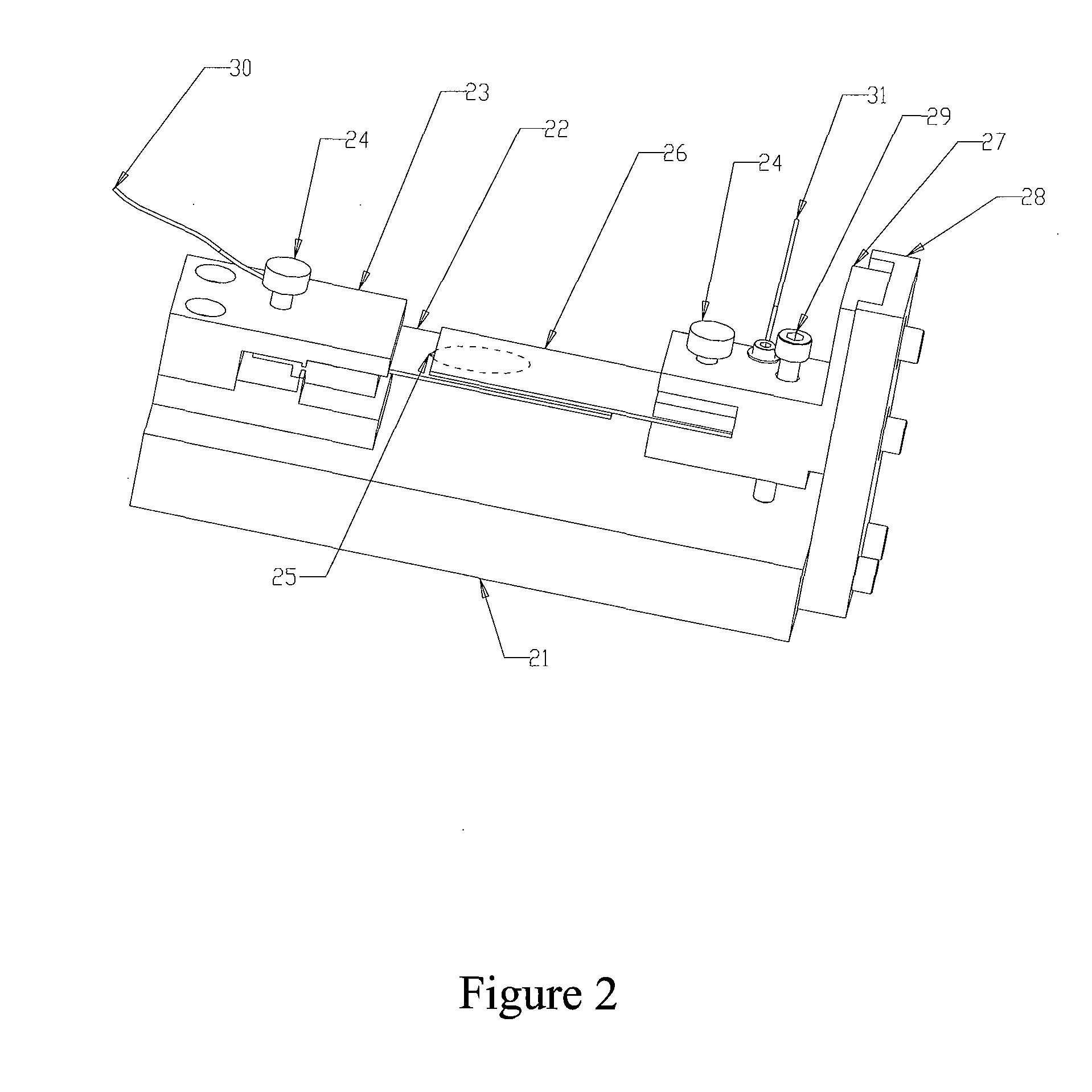
An automated staining system and a reagent container designed for use with the automated staining apparatus. The reagent container includes a reagent containment section capable of containing a volume of a reagent. The reagent containment section includes an upper wall and a base wall that are spaced apart along an axis. The base wall includes a well having a nadir that is aligned axially with an access opening in the upper wall so that a reagent probe entering the opening parallel to said axis will travel toward the nadir. In another aspect of the invention, the reagent container may include a two-dimensional data element containing reagent information. The staining apparatus may include one removable drawer for holding reagent containers and another removable drawer holding slides.
Owner:LAB VISION CORP
Automated lean methods in anatomical pathology
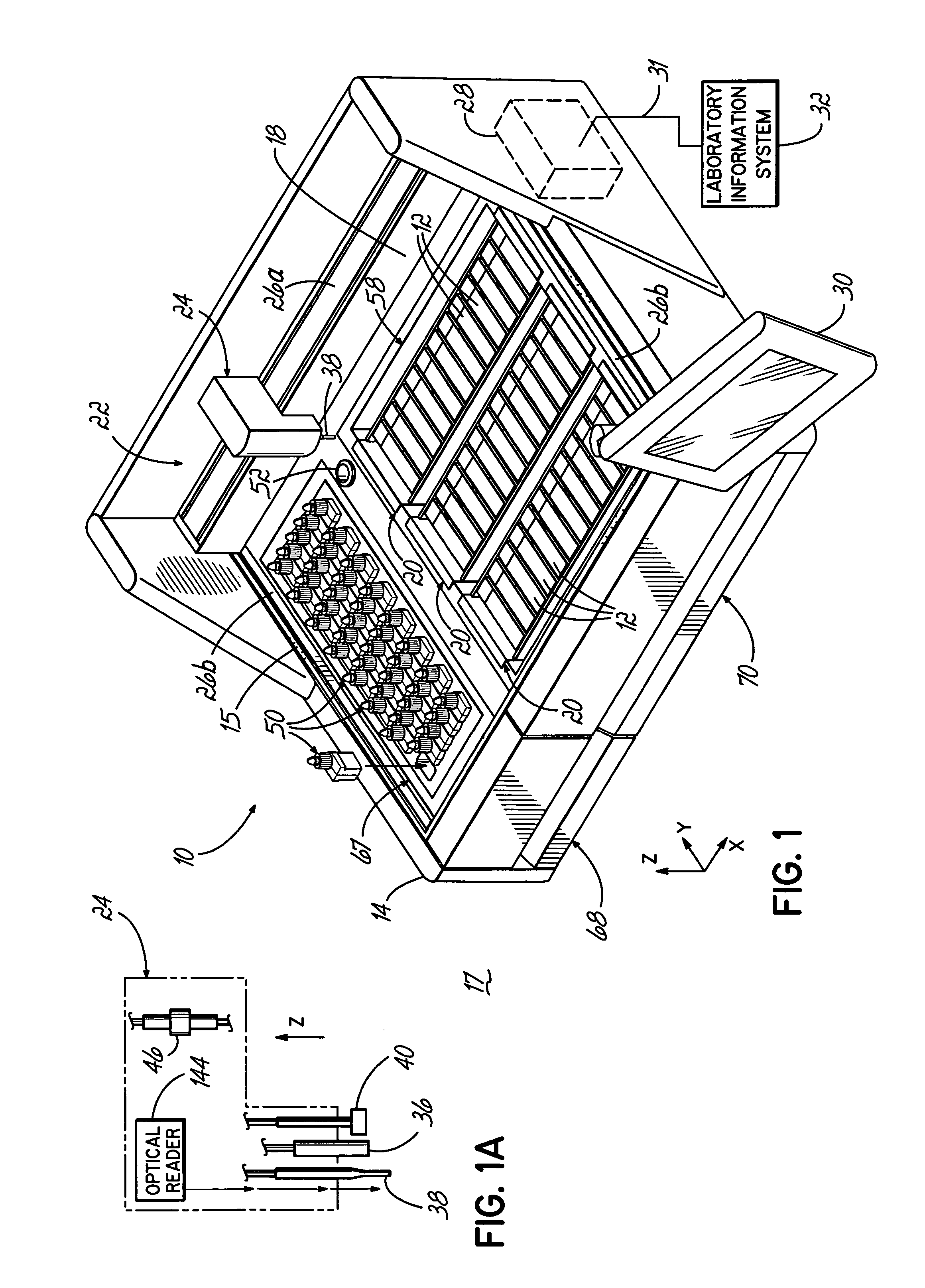
An embodiment of the method of the invention is a method of automating information flow in a laboratory performing tissue staining comprising positioning a networked label printer adjacent to a cutting station, the printer configured to access patient data directly or indirectly from the hospital LIS, the printer being configured with a data element scanner in electronic communication with said printer; inputting data from a tissue cassette-associated data element at said printer, whereby inputting data comprises reading the data from the cassette-associated data element and uploading the cassette data to the LIS; identifying the corresponding test protocol identifier and then downloading the test protocol data to the printer; printing information on labels corresponding to each test specified in the LIS for the patient; attaching a single label to each slide; and cutting a tissue section for each labeled slide and mounting the section on the slide.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Endoscopy tissue stain
InactiveUS6599496B2Increase contrastLow viscosityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonDelivery vehicle
Owner:GI SUPPLY
Method for Determining Effectiveness of Medicine Containing Antibody as Component
InactiveUS20130230866A1High sensitivityWide rangeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingTreatment effect
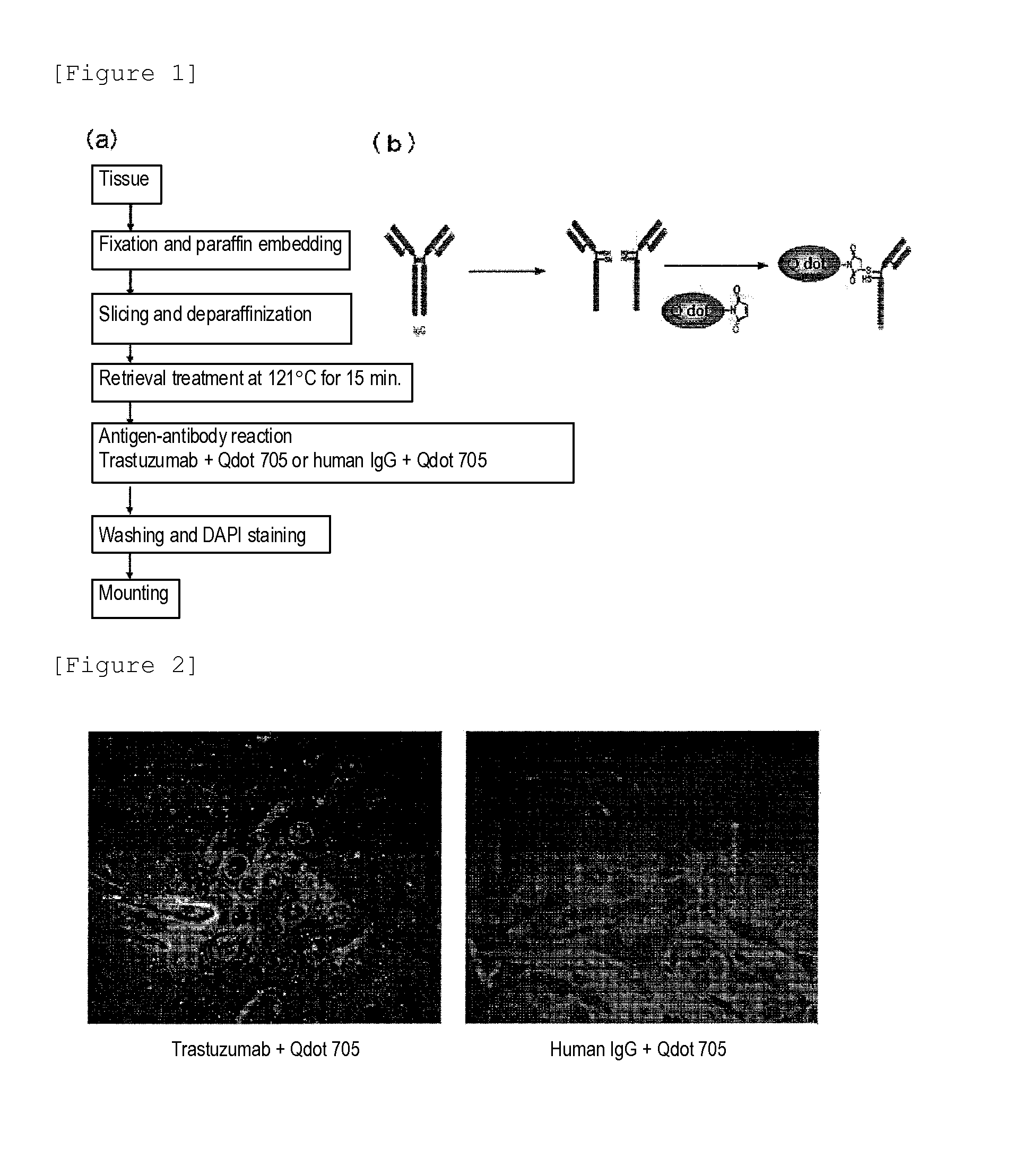
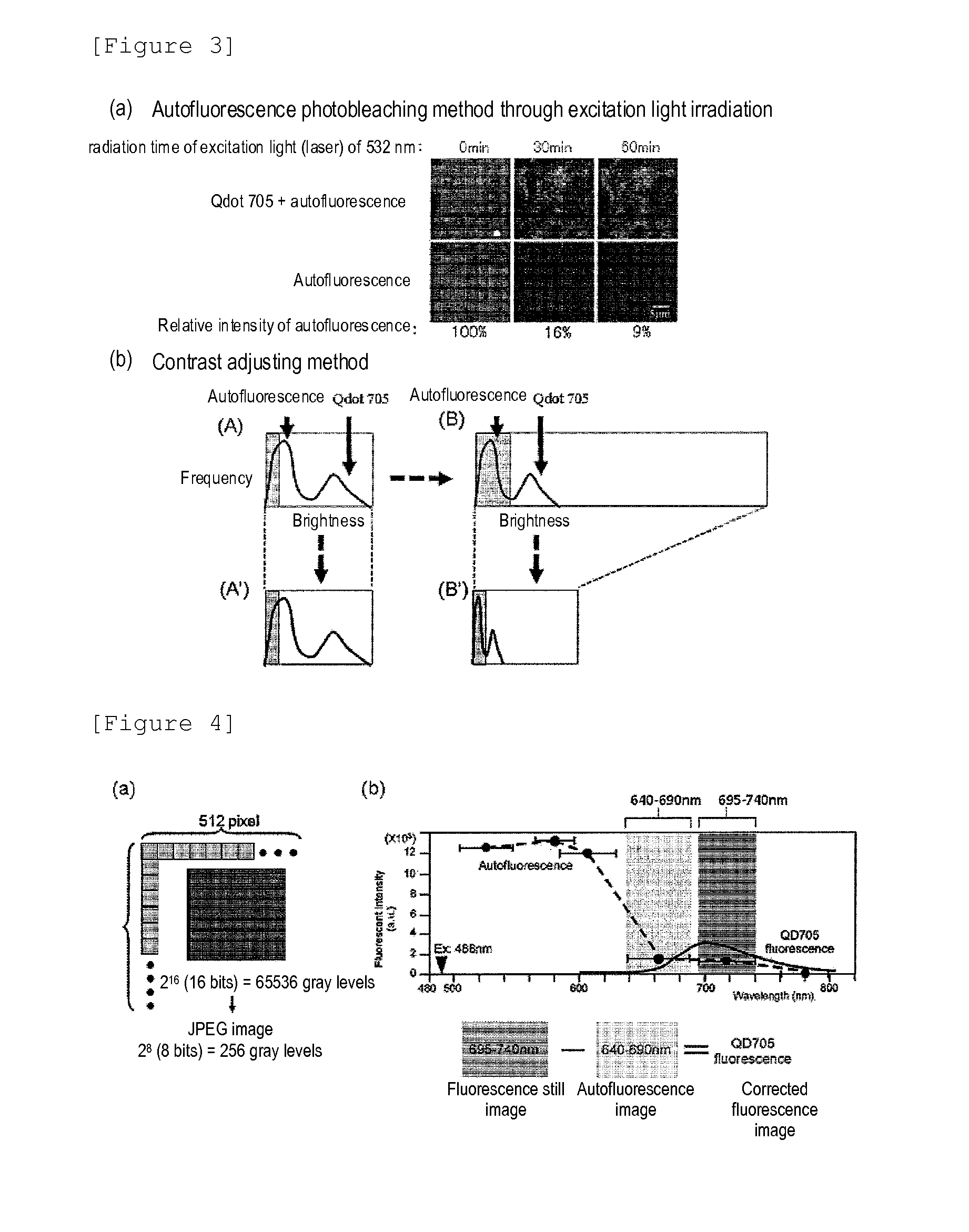
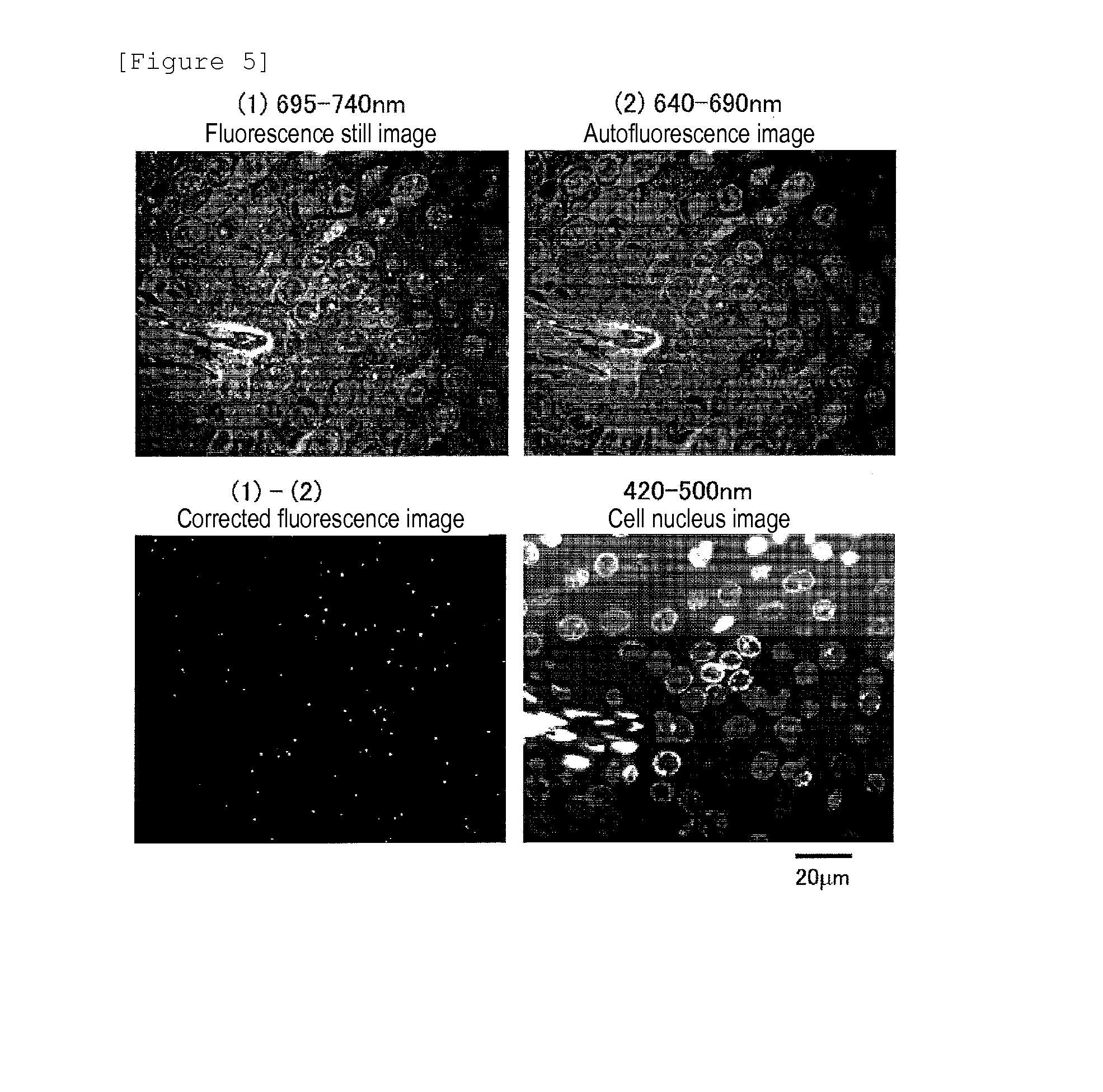
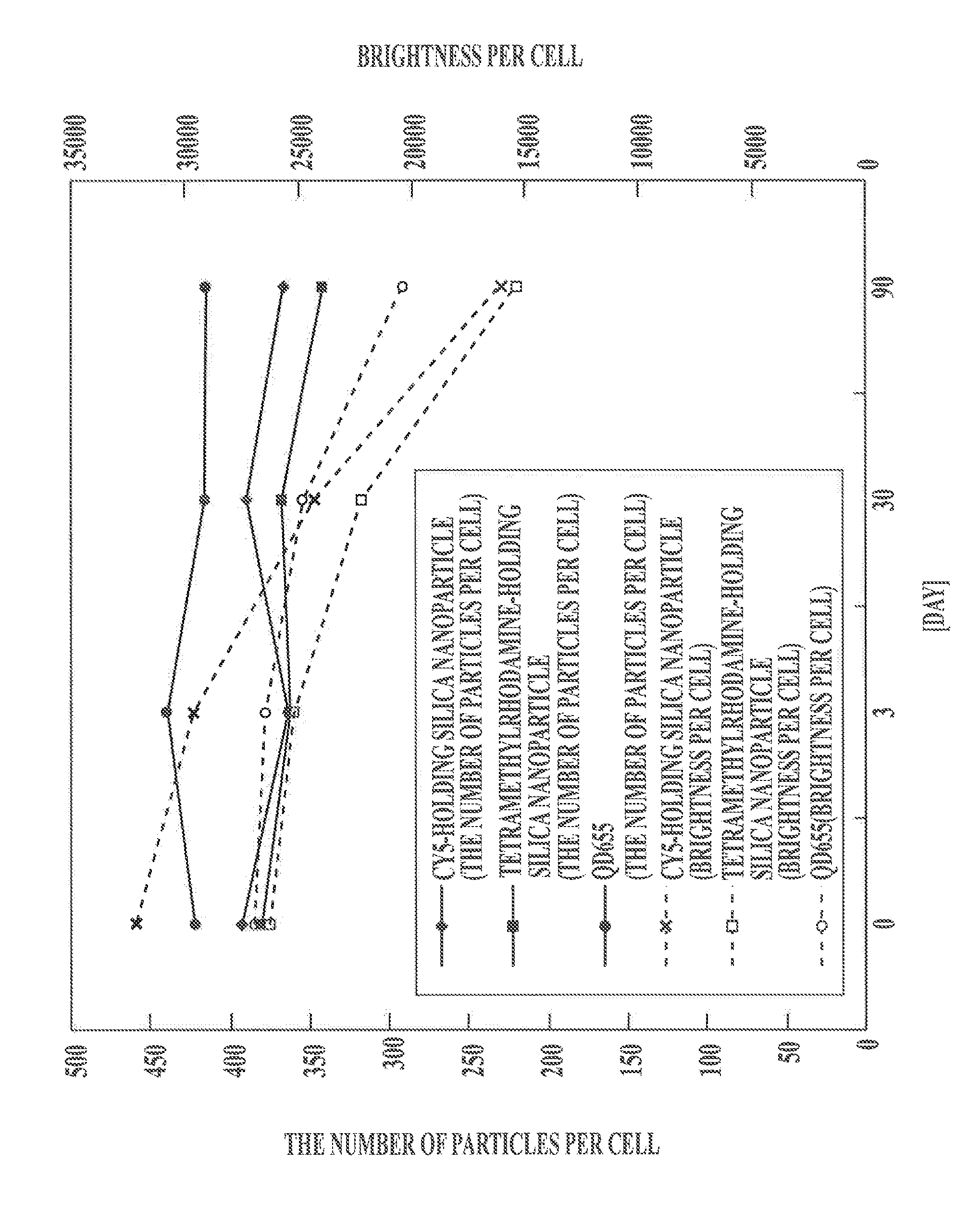
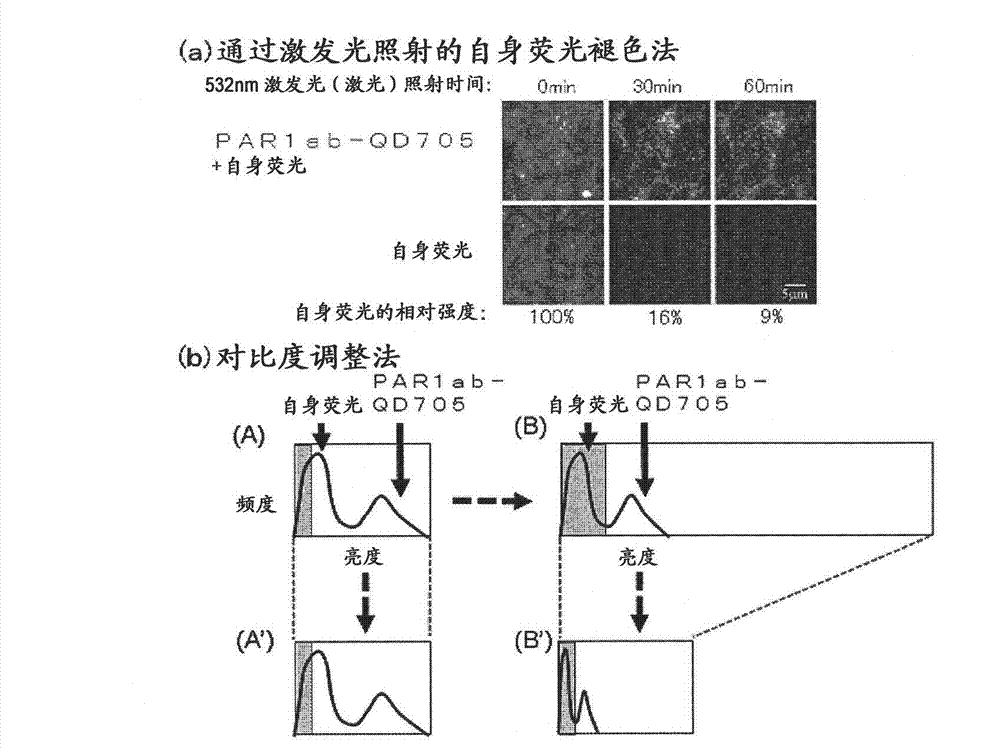
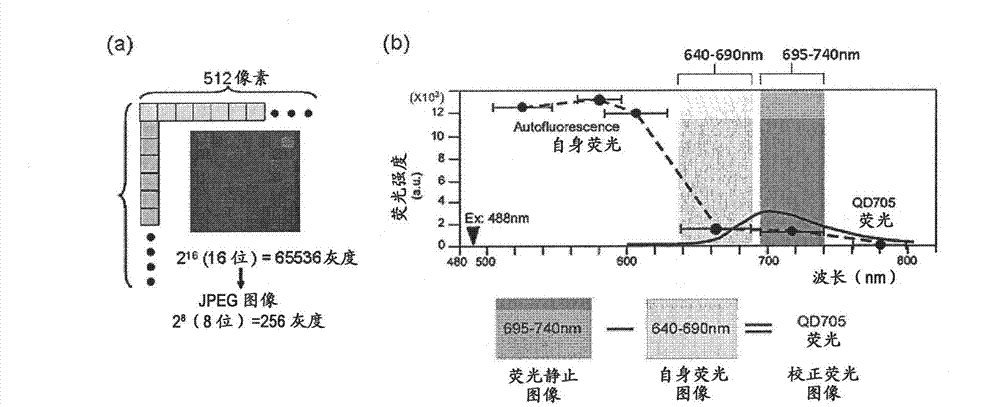
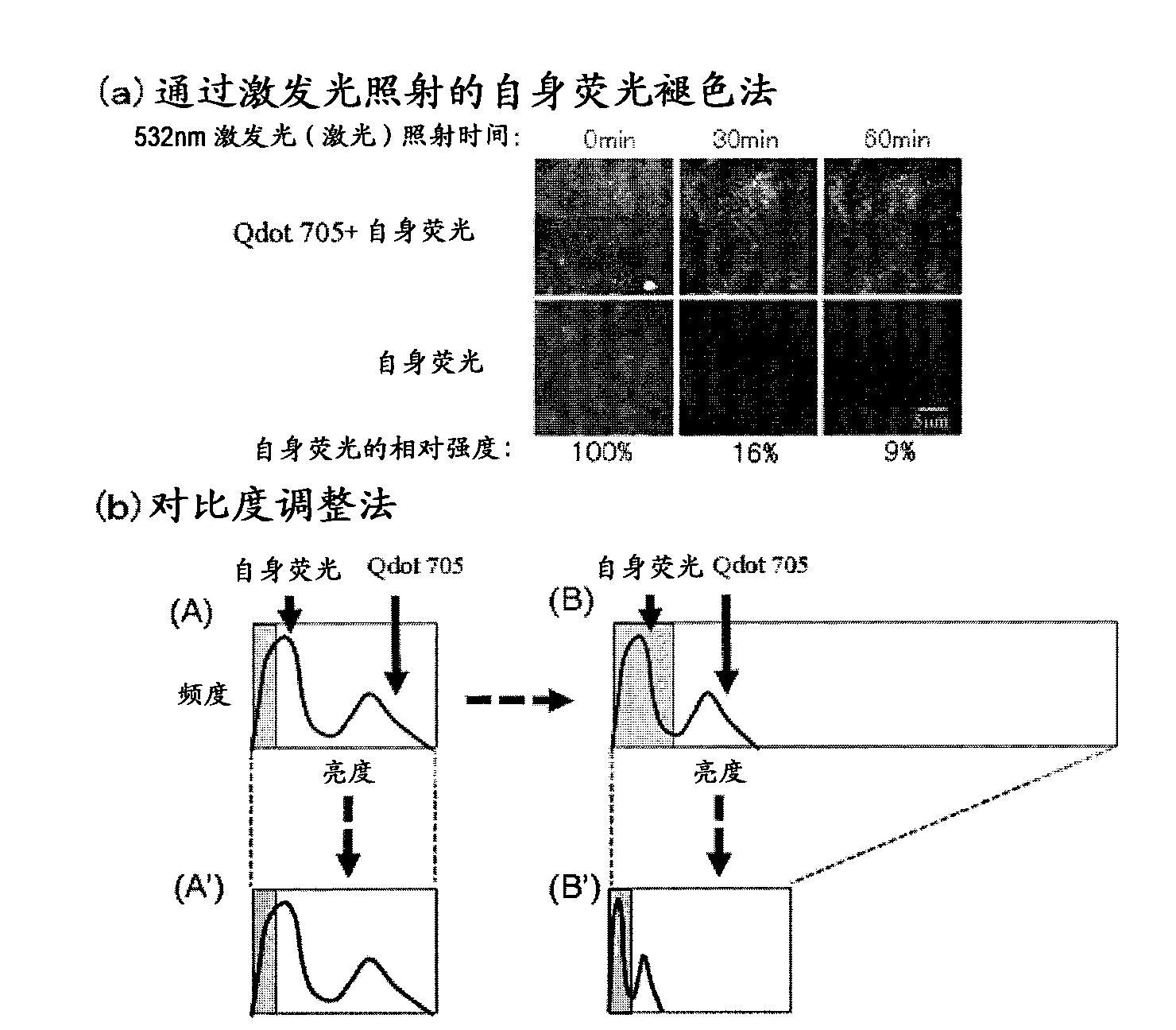
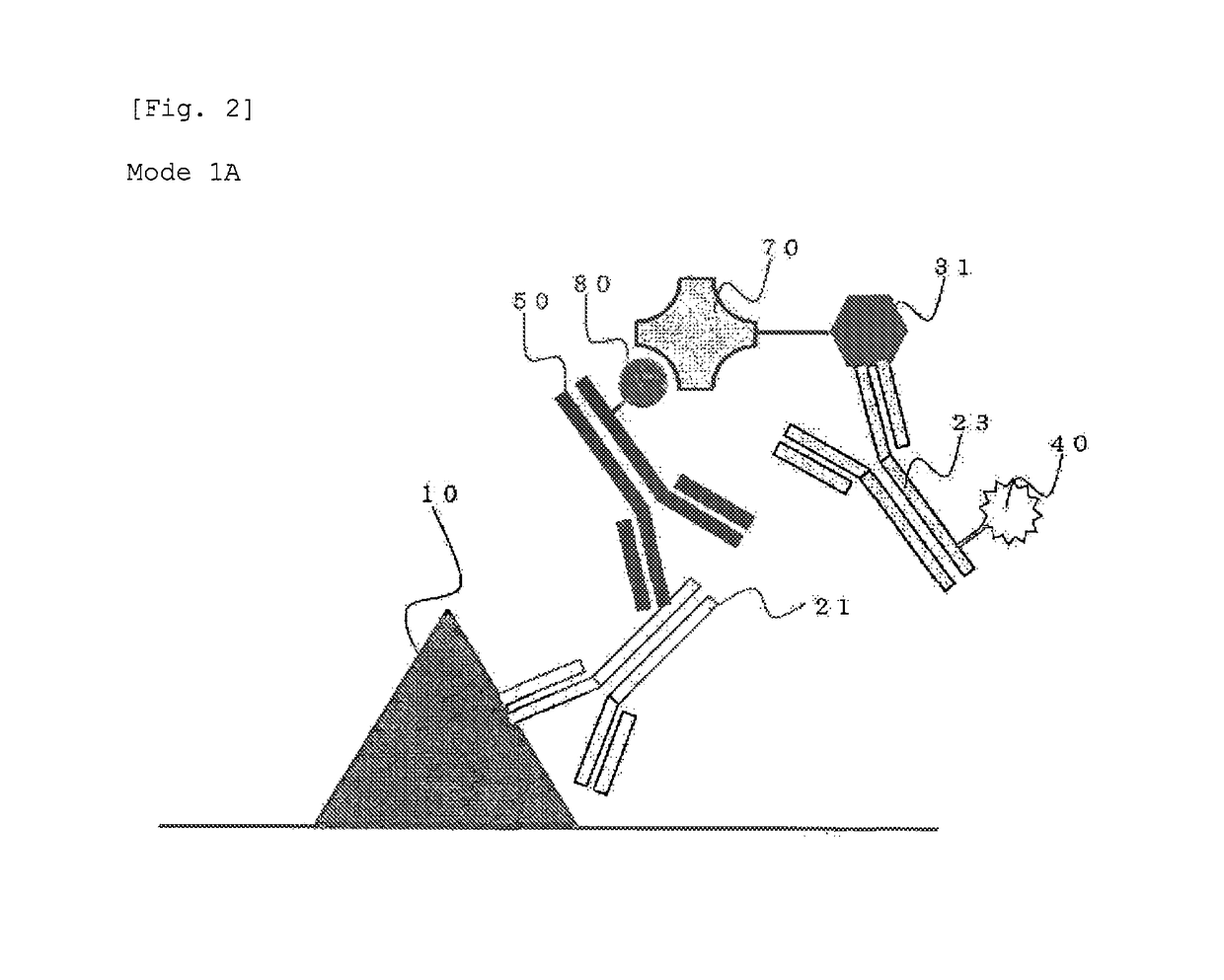
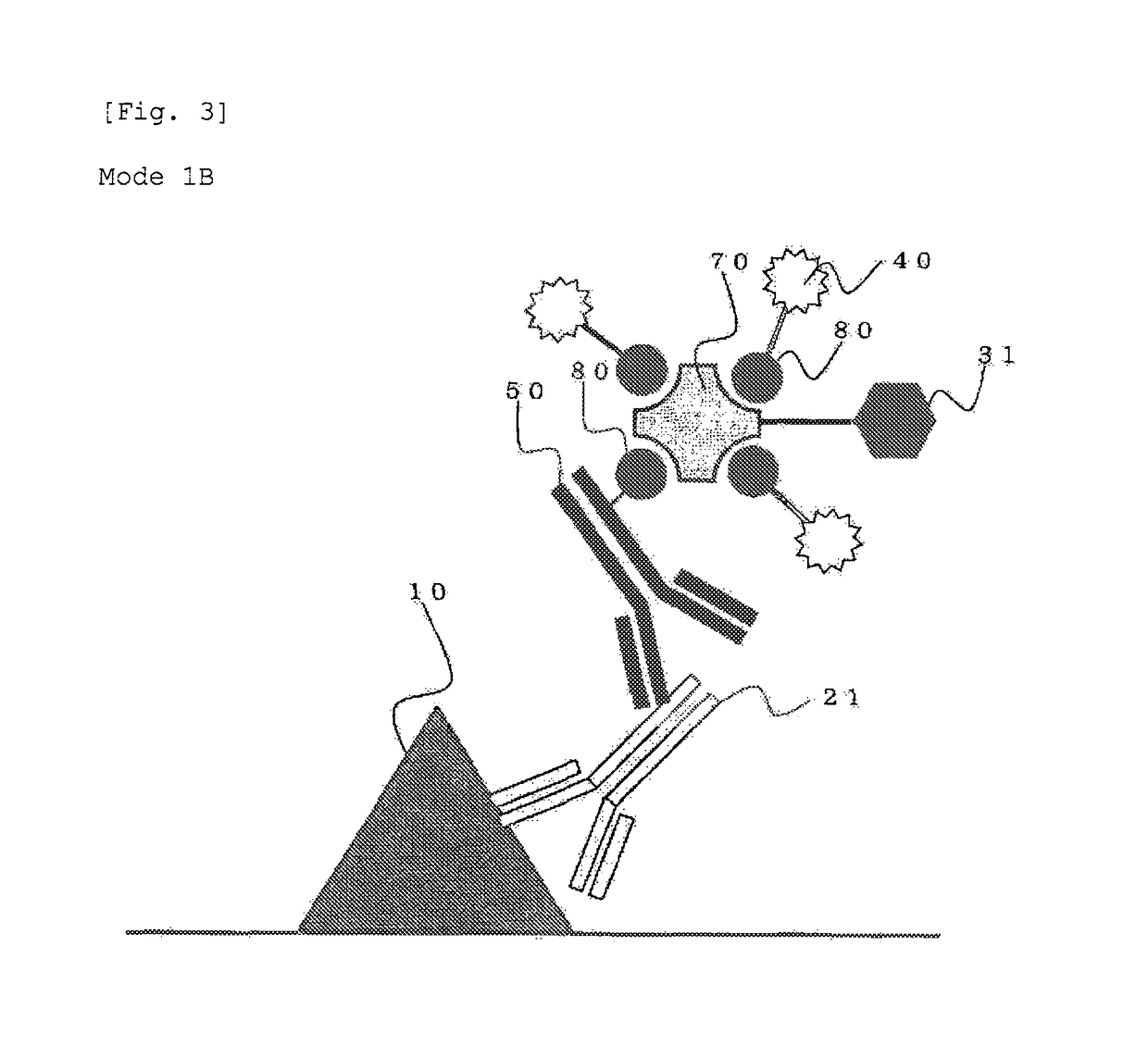
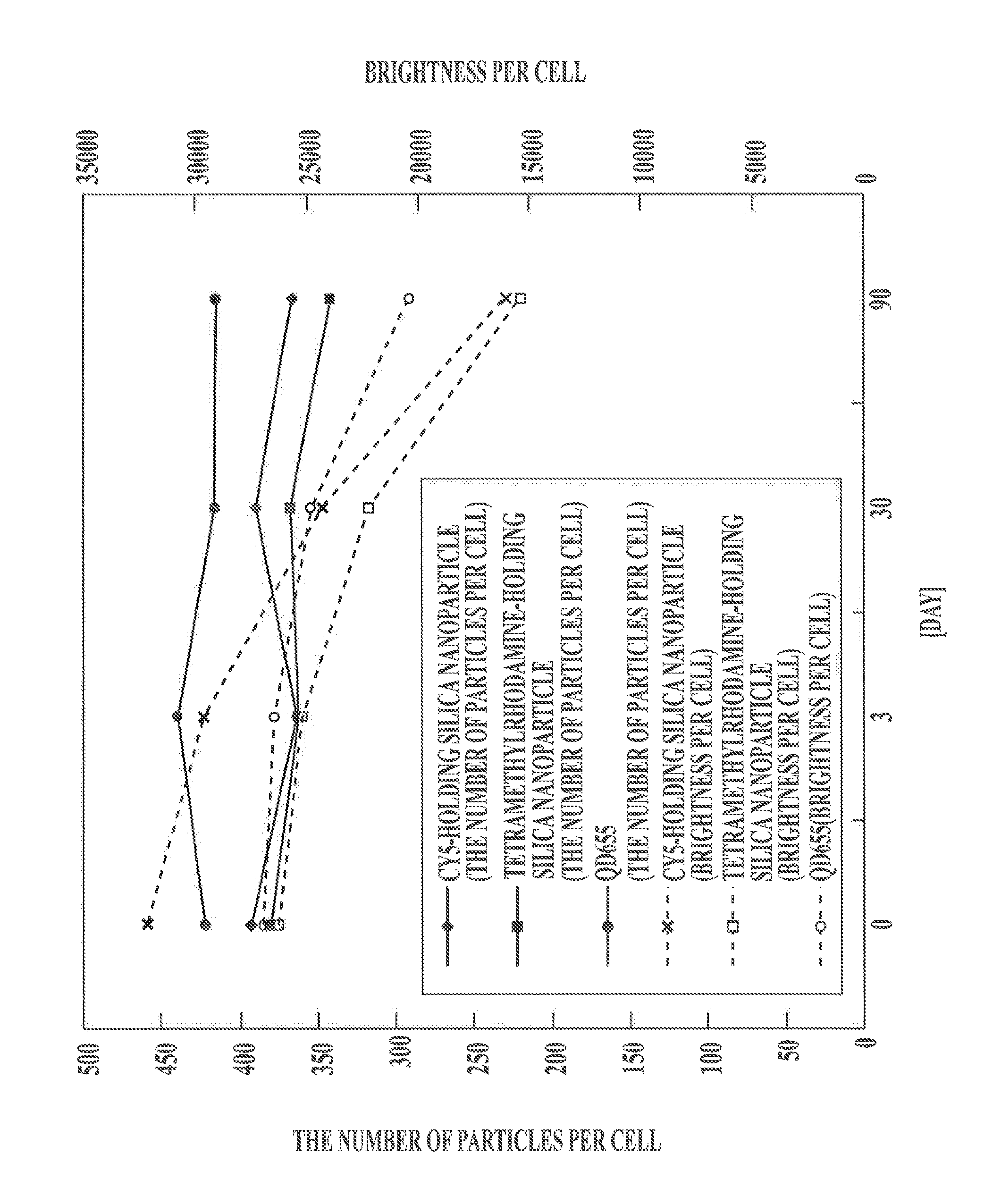
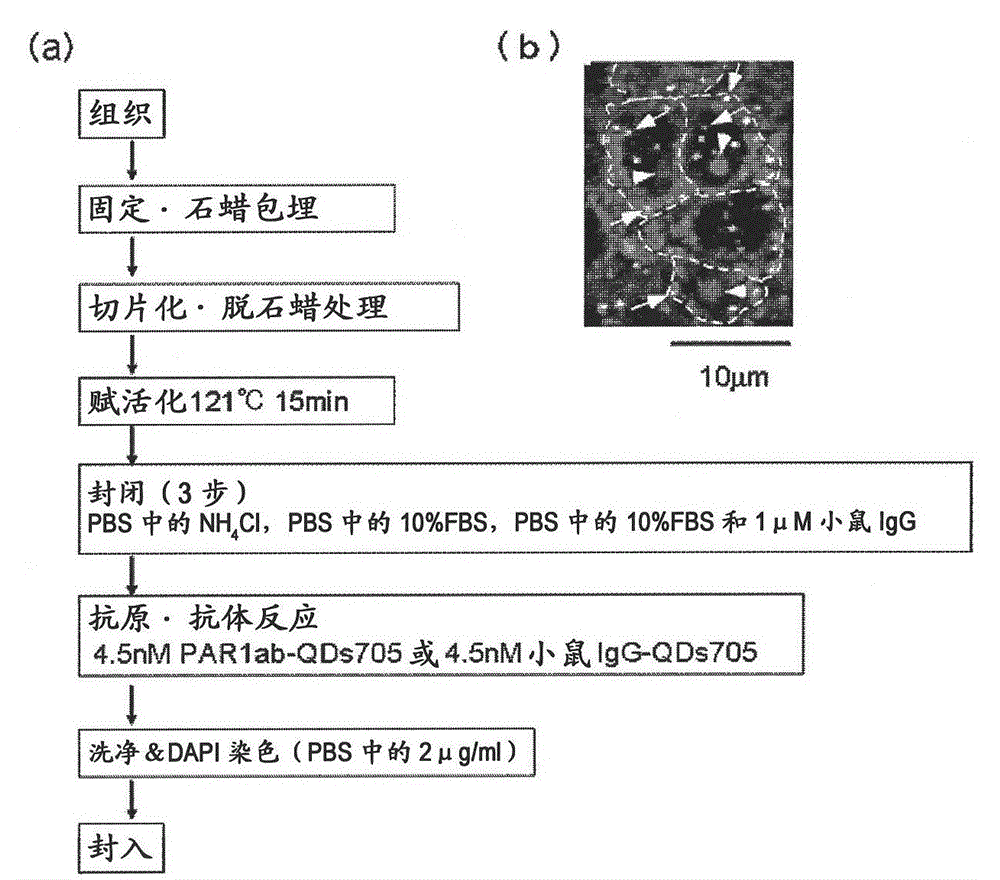
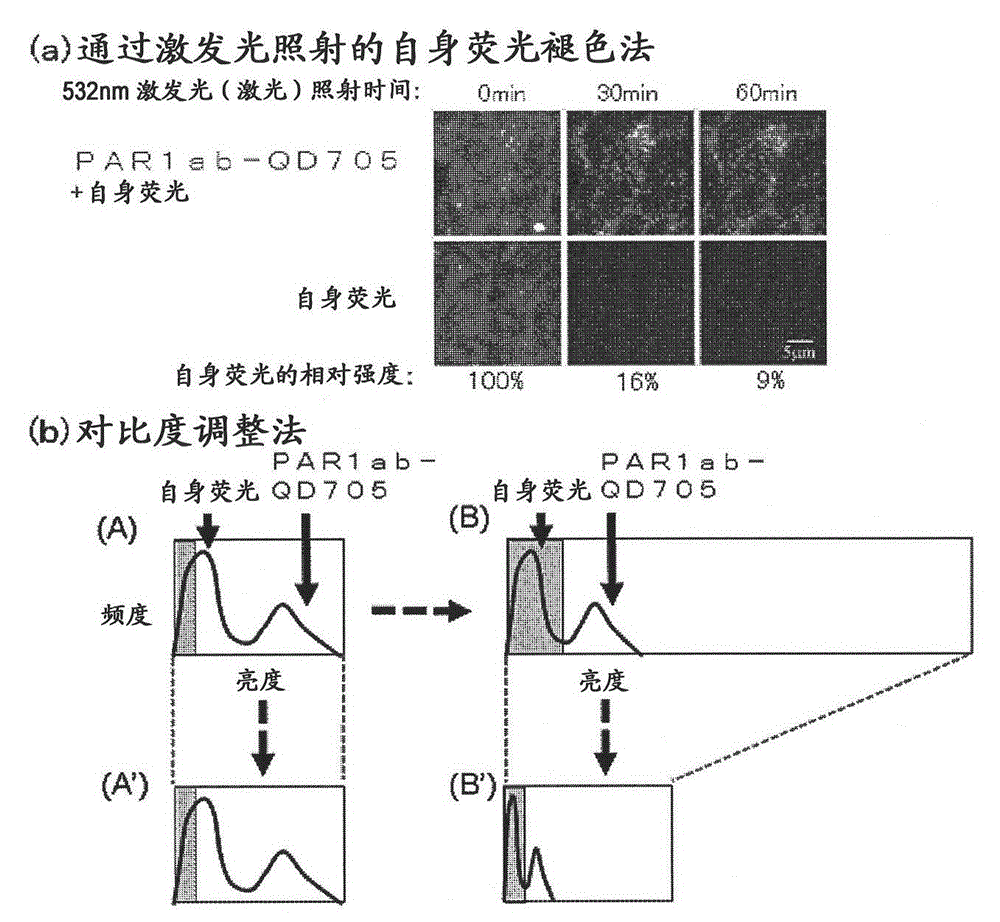
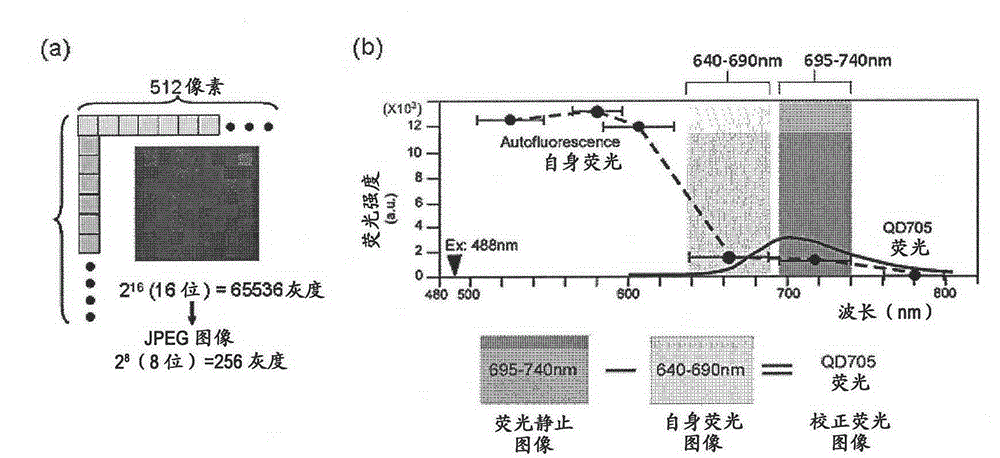
Protein recognized by an antibody used as an active ingredient of an antibody medicine such as trastuzumab or an antibody used for targeting a target site of an active ingredient is highly accurately quantitatively determined by employing a quantitative tissue staining method of biological tissues, thereby providing a method for determining therapeutic effectiveness of a medicine containing such an antibody as a component. The effectiveness of a medicine containing an antibody as a component is determined by employing a tissue staining method comprising the steps of: labeling the antibody in the medicine containing an antibody as a component with a fluorescent material and contacting the thus fluorescence-labeled antibody with a tissue sample; obtaining a fluorescence image by irradiating, with excitation light, a tissue site contacted with the antibody; obtaining an autofluorescence image in the same field of view and at the same focus as in the fluorescence image in a close region on a shorter wavelength side or a longer wavelength side of an acquisition wavelength region of fluorescence emitted by the fluorescent material; obtaining a corrected fluorescence image by performing image processing for removing fluorescence brightness of the autofluorescence image from fluorescence brightness of the fluorescence image; counting the number of cells in the tissue site contacted with the antibody; measuring average fluorescence brightness per fluorescent particle; and calculating the number of fluorescent particles per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Electrophoretic in situ tissue staining
InactiveUS20050074890A1Easy to moveReduce background stainingElectrotherapyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsDiffusionTissue staining
The present invention introduces a radically different way of accelerating biomolecule conjugates into tissue, and hence towards their targets for purposes of tissue staining. The invention provides for an order of magnitude improvement over the prior art diffusion process used to stain tissue. The invention comprises a method of tissue staining by applying an electric field to a tissue sample in the presence of an electrolyte and biomolecular conjugates of interest suspended in the electrolyte. Typical staining times are reduced to seconds as opposed to 30-120 minutes common in the prior art. The invention is also directed to devices for performing the method.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Automated tissue staining system and reagent container
InactiveUS20050191214A1Container decorationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsTissue stainingEngineering
An automated staining system and a reagent container designed for use with the automated staining apparatus. The reagent container includes a reagent containment section capable of containing a volume of a reagent. The reagent containment section includes an upper wall and a base wall that are spaced apart along an axis. The base wall includes a well having a nadir that is aligned axially with an access opening in the upper wall so that a reagent probe entering the opening parallel to said axis will travel toward the nadir. In another aspect of the invention, the reagent container may include a two-dimensional data element containing reagent information. The staining apparatus may include one removable drawer for holding reagent containers and another removable drawer holding slides.
Owner:LAB VISION CORP
Tissue staining method, tissue evaluation method and biosubstance detection method
ActiveUS20130157895A1Good for observationHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyPreparing sample for investigationTissue stainingMedicine
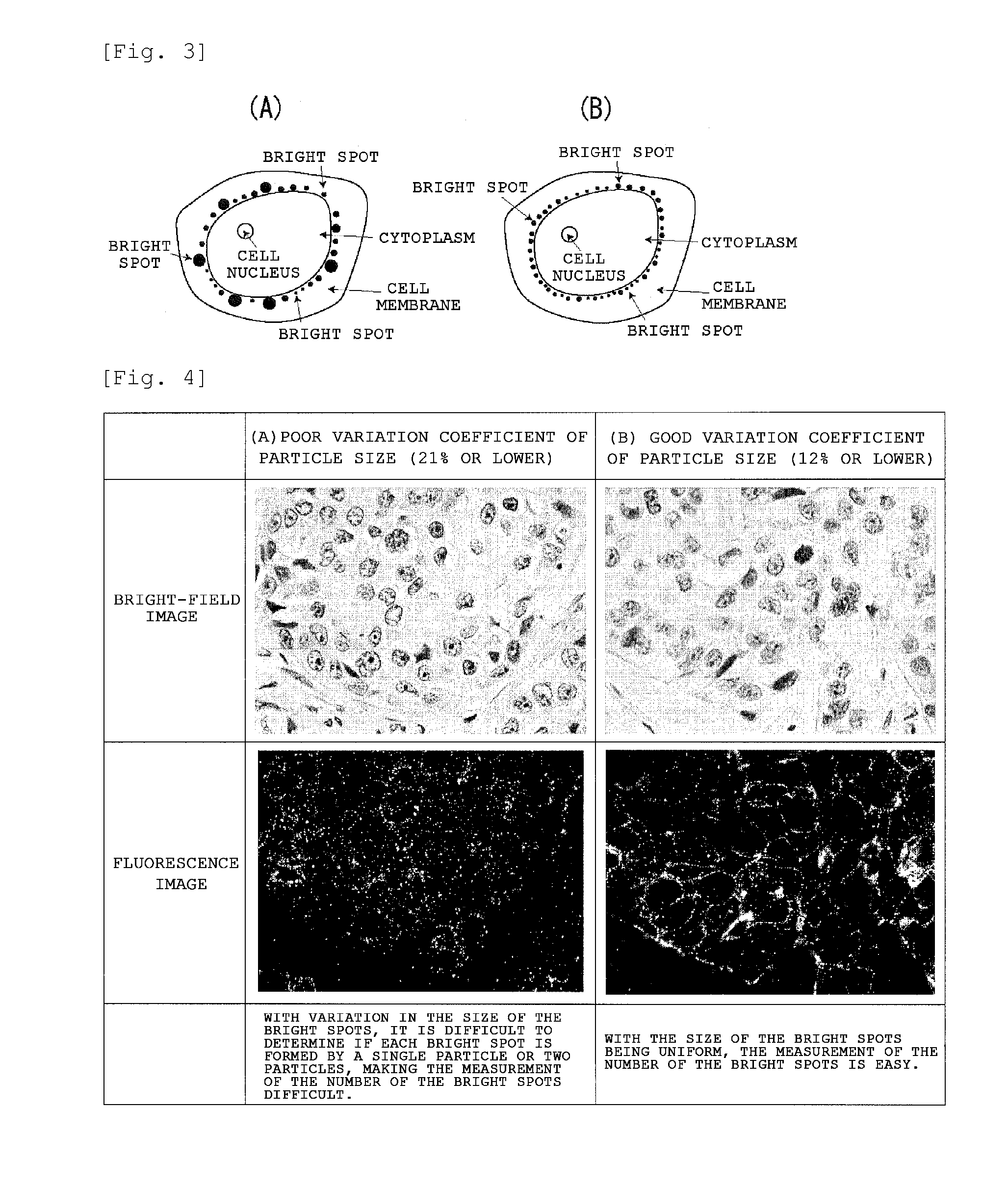
A tissue staining method which comprises: staining a tissue with a staining reagent wherein a biosubstance recognition site is bonded to particles carrying multiple fluorescent substances accumulated therein; in the stained tissue, counting fluorescent points or measuring fluorescent brightness; and evaluating the expression level of a biosubstance, which matches the biosubstance recognition site, in the aforesaid tissue on the basis of the number of the fluorescent points or fluorescent brightness that was measured.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method for determining cancer onset or cancer onset risk
InactiveUS20130203082A1High sensitivityExclude influenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingCancer cell
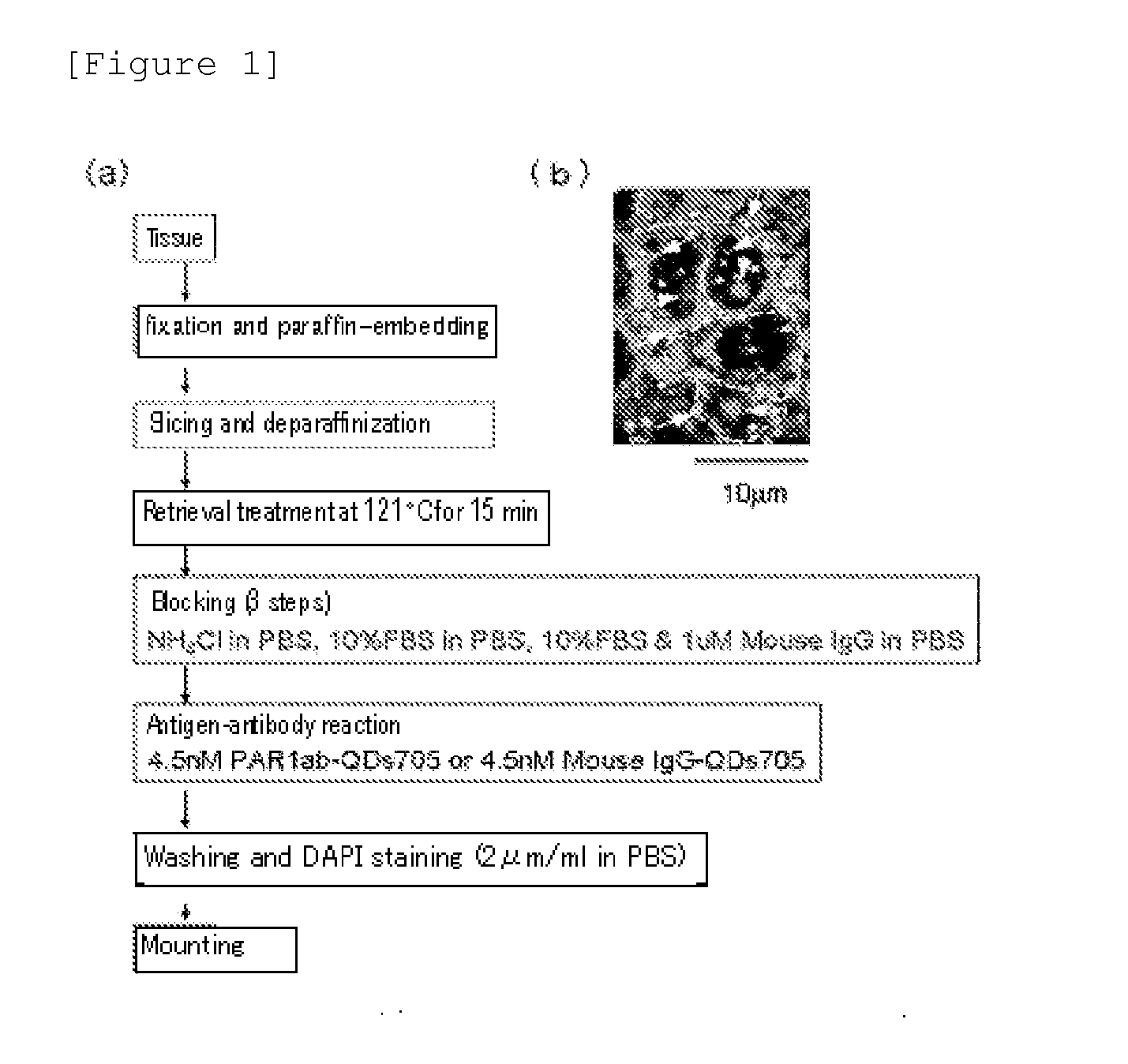
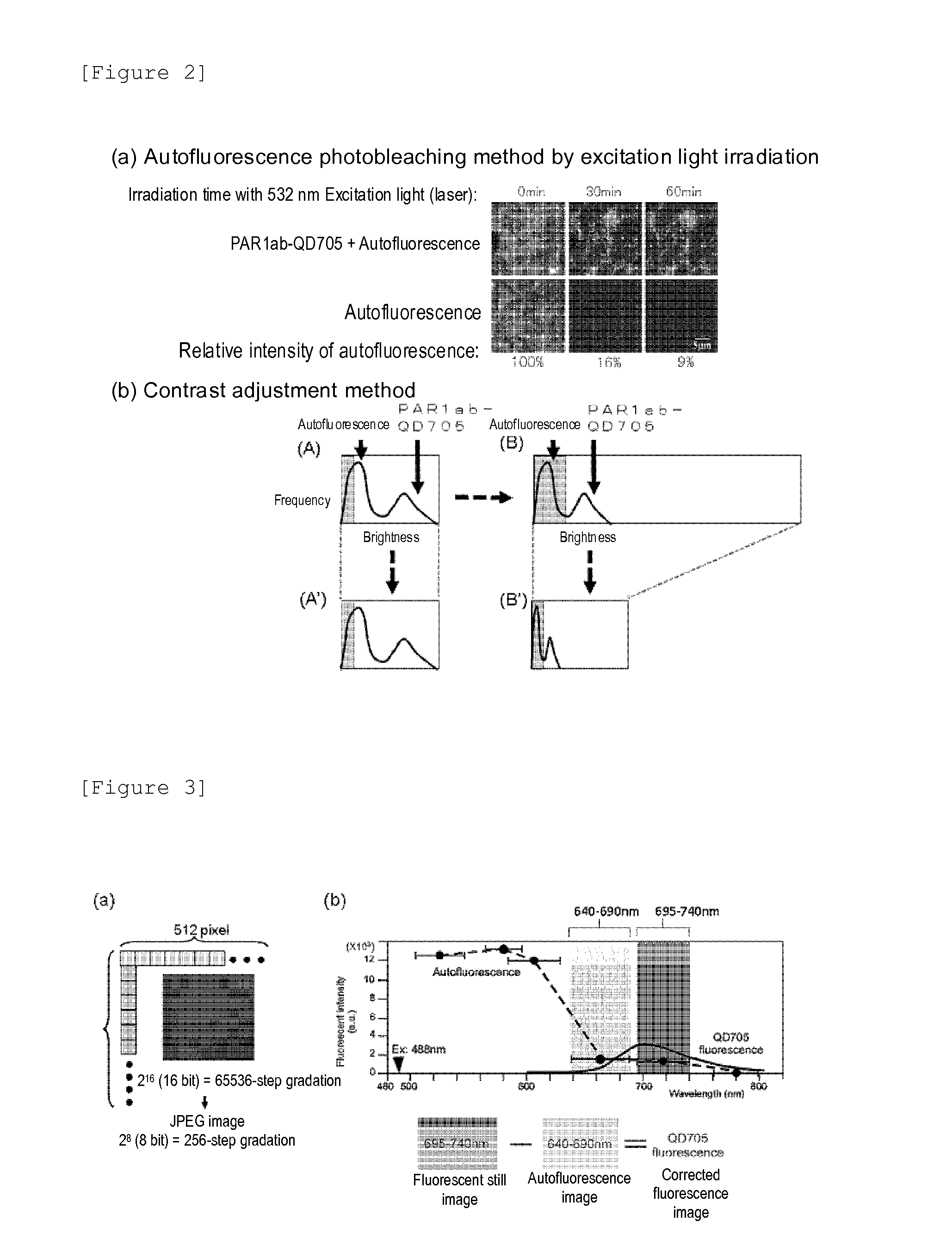
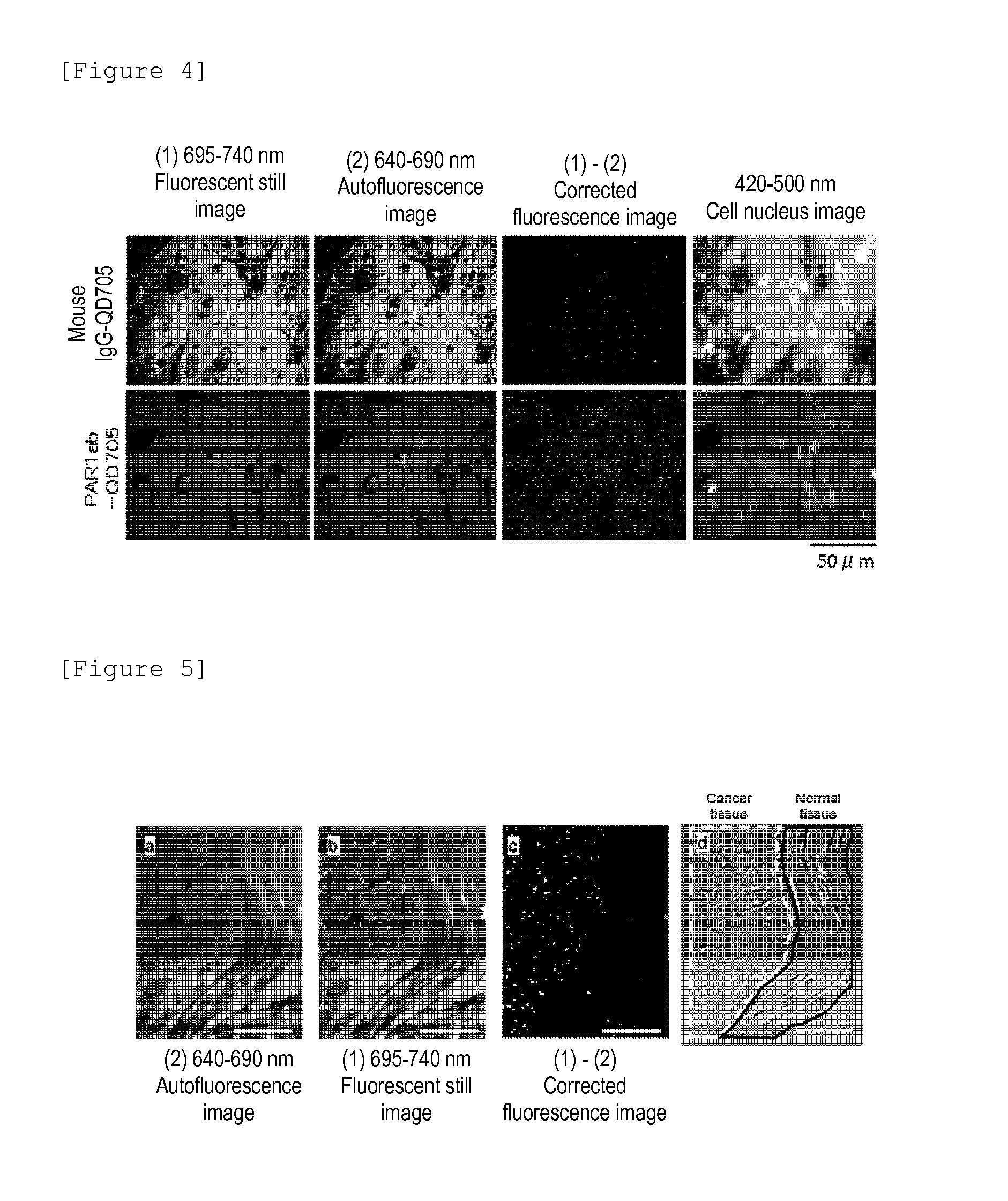
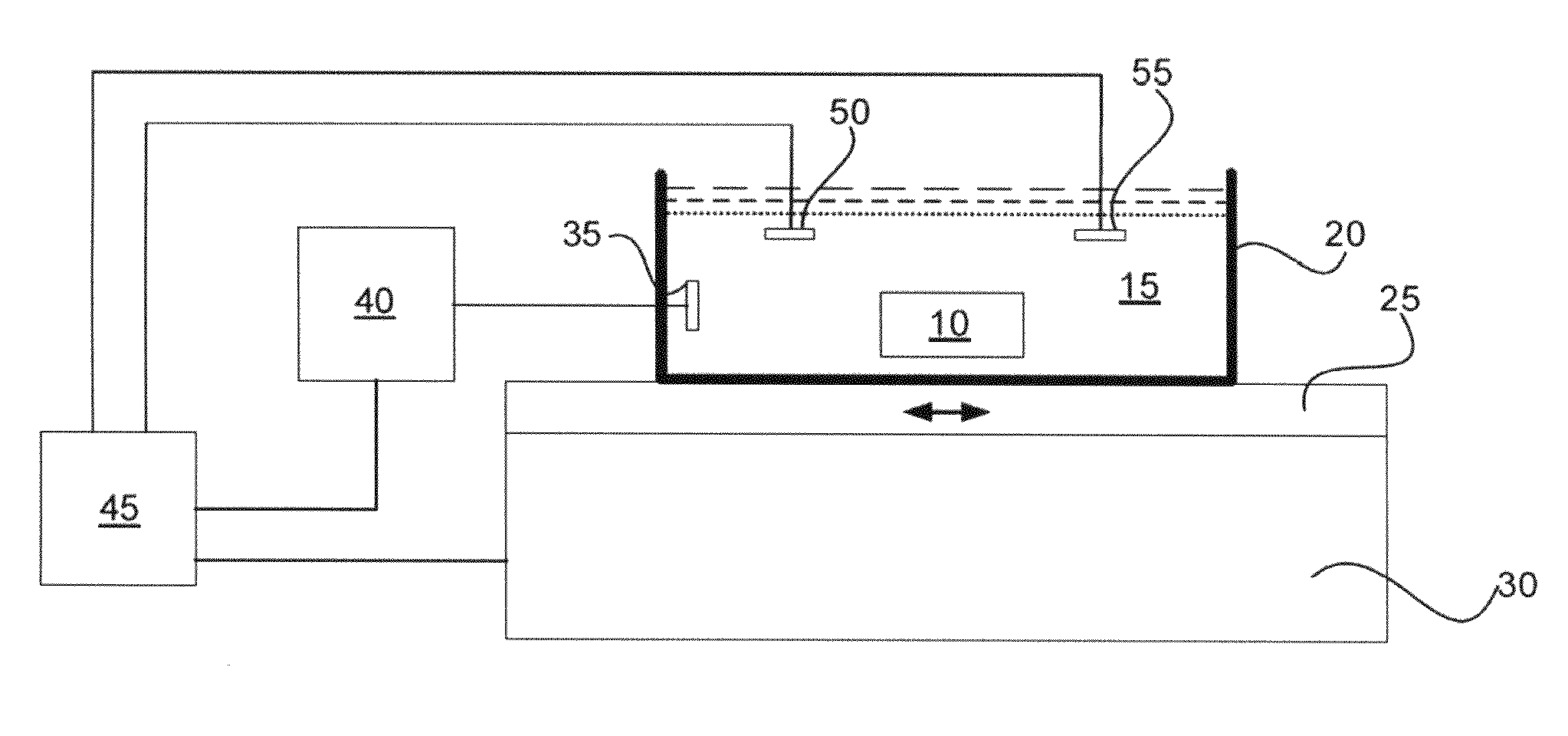
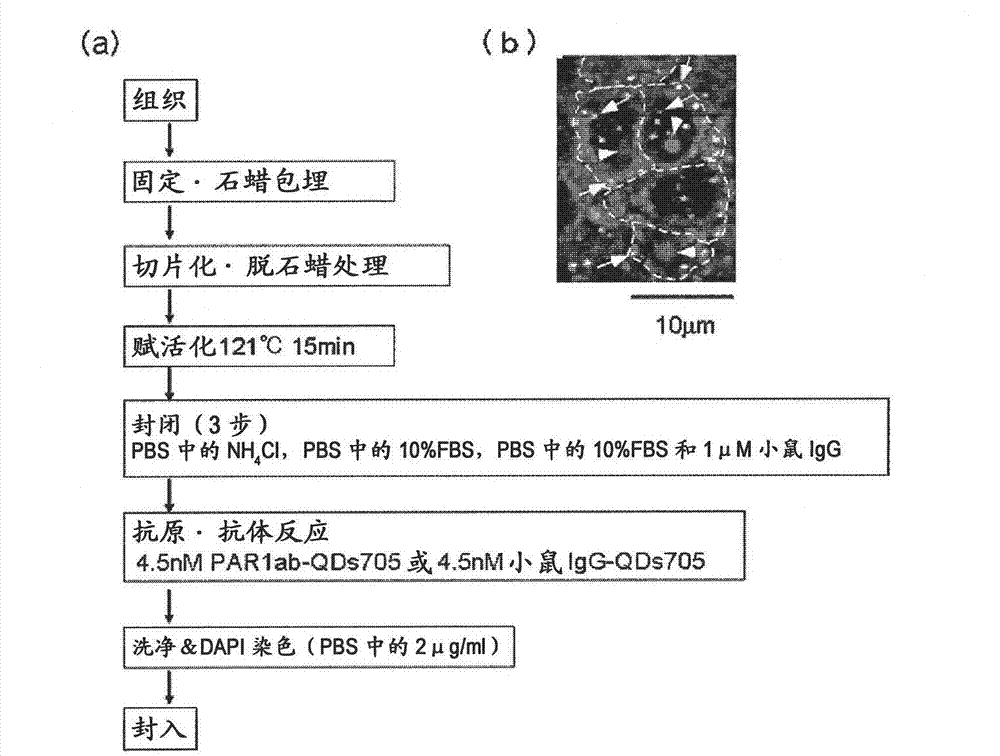
A highly accurate and quantitative method for determining cancer onset or cancer onset risk by a quantitative tissue staining method in biological tissues using an antibody capable of recognizing a cancer growth regulatory factor or cancer metastasis regulatory factor such as PAR1 antibody, which inhibits the cancer cell mobility and infiltration is provided. Cancer onset or cancer onset risk is determined using the tissue staining method comprising the steps of: labeling an antibody which recognizes a cancer growth regulatory factor or cancer metastasis regulatory factor with a fluorescent material, and contacting the fluorescent-labeled antibody with a tissue sample; irradiating a tissue site in contact with the antibody with excitation light to acquire a fluorescence image; acquiring an autofluorescence image in a vicinity region of a short wavelength side or long wavelength side of an acquisition region of fluorescence wavelength emitted by the fluorescent material, in the same field of vision and in the same focal point as those of the fluorescence image; acquiring a corrected fluorescence image by image processing to eliminate a fluorescent brightness of the autofluorescence image from the fluorescent brightness of the fluorescence image; counting the number of cells at the tissue site in contact with the antibody; measuring a mean fluorescent brightness of a single fluorescent particle; and calculating the number of fluorescent particles per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Methods for accelerating tissue processing
InactiveUS20100144002A1Effective diffusionPreparing sample for investigationElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentTissue sampleClearing Agent
Systems and methods for accelerating tissue processing by treating tissue samples and one or more tissue processing agents with infrasonic vibrations are discussed. Some non-limiting examples of tissue processing agents include a tissue fixative, dehydrating agent, clearing agent, impregnating agent, embedding agent, tissue stain, enzyme, or another chemical that diffuses into the tissue sample when the sample is being preserved or prepared for microscopic examination. The infrasonic vibrations can have a frequency from about 10 to about 600 Hz. The infrasonic vibrations can have an amplitude that is sufficiently high, when combined with the frequency, to induce turbulent mixing of the processing agent and accelerate tissue processing. The tissue sample may optionally be vibrated with ultrasonic vibrations. The ultrasonic vibrations can have a frequency and amplitude that are sufficiently high to induce turbulent mixing of the processing agent and to accelerate tissue processing.
Owner:DONNDELINGER THOMAS M
Endoscopy tissue stain
InactiveUS20020031474A1Increase contrastLow viscosityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonDelivery vehicle
An endoscopic stain is provided that includes a carbon pigment and a suspending / viscosity-increasing agent in a pharmaceutically acceptable delivery vehicle, wherein the carbon pigment has a total level of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) of not greater than 0.5 ppm. Methods of staining an internal site utilizing the stain of the invention and kits that include the stain of the invention are also provided.
Owner:GI SUPPLY
Methods and compositions for a microemulsion-based tissue treatment
The invention is directed to methods and compositions for deparaffinizing paraffin-embedded biological samples for subsequent tissue staining. The compositions are microemulsions that may include water / oil / surfactant microemulsions, and optionally a cosurfactant. The microemulsions enable deparaffinization without the use of xylene or toluene, and also enable solvent exchange without the use of intermediary alcohol dehydration or alcohol rehydration compositions.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Automated tissue staining system and reagent container
InactiveUS20060127283A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingEngineering
An automated staining system and a reagent container designed for use with the automated staining apparatus. The reagent container includes a reagent containment section capable of containing a volume of a reagent. The reagent containment section includes an upper wall and a base wall that are spaced apart along an axis. The base wall includes a well having a nadir that is aligned axially with an access opening in the upper wall so that a reagent probe entering the opening parallel to said axis will travel toward the nadir. In another aspect of the invention, the reagent container may include a two-dimensional data element containing reagent information. The staining apparatus may include one removable drawer for holding reagent containers and another removable drawer holding slides.
Owner:LAB VISION CORP
Compositions and methods for simultaneous inactivation of alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase enzymes during automated multiplex tissue staining assays
ActiveUS20180120202A1Short amount of timeHydrogen peroxideOrganic chemistryTissue stainingPeroxiredoxin
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
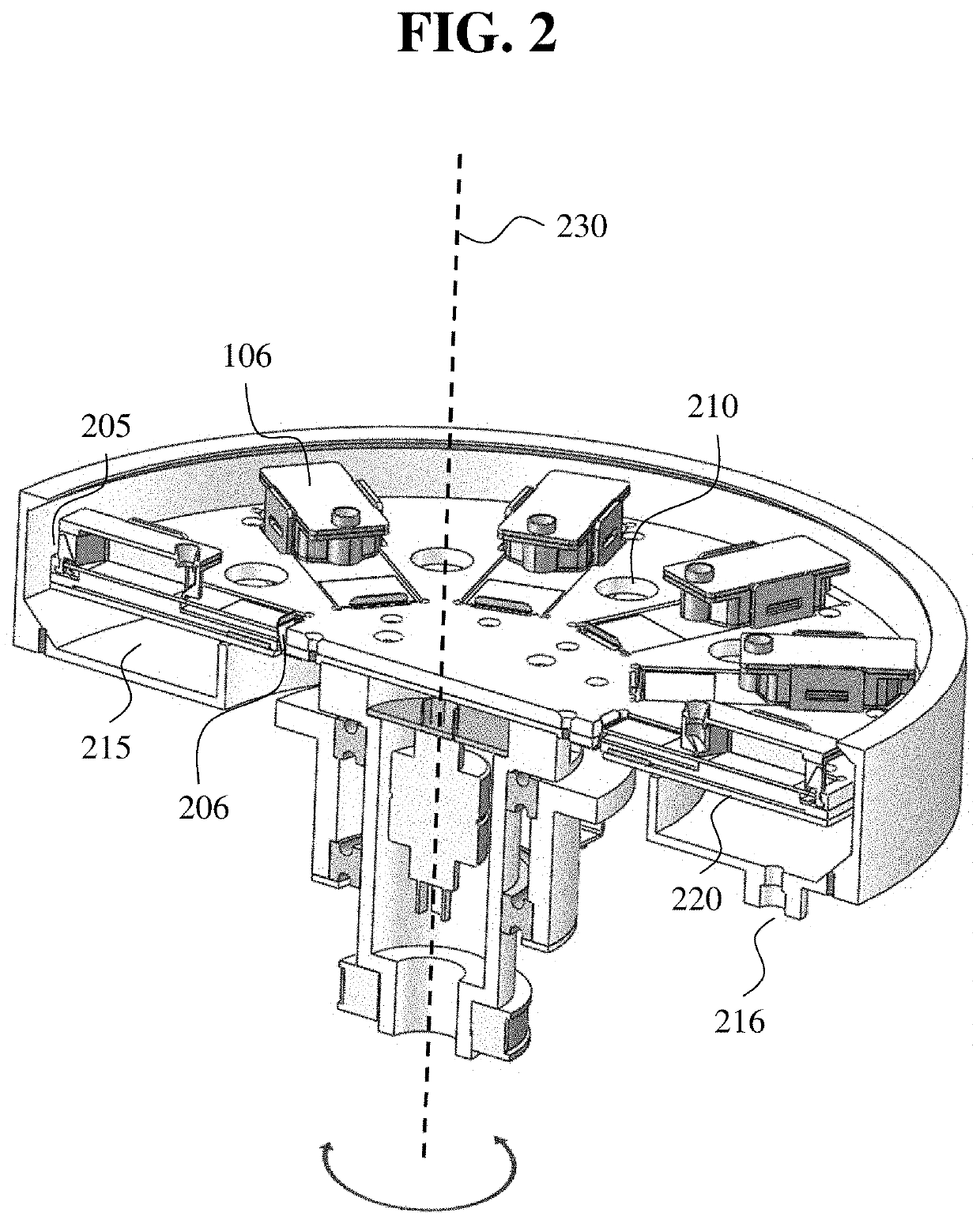
Devices and components for automated tissue processing and staining and uses thereof
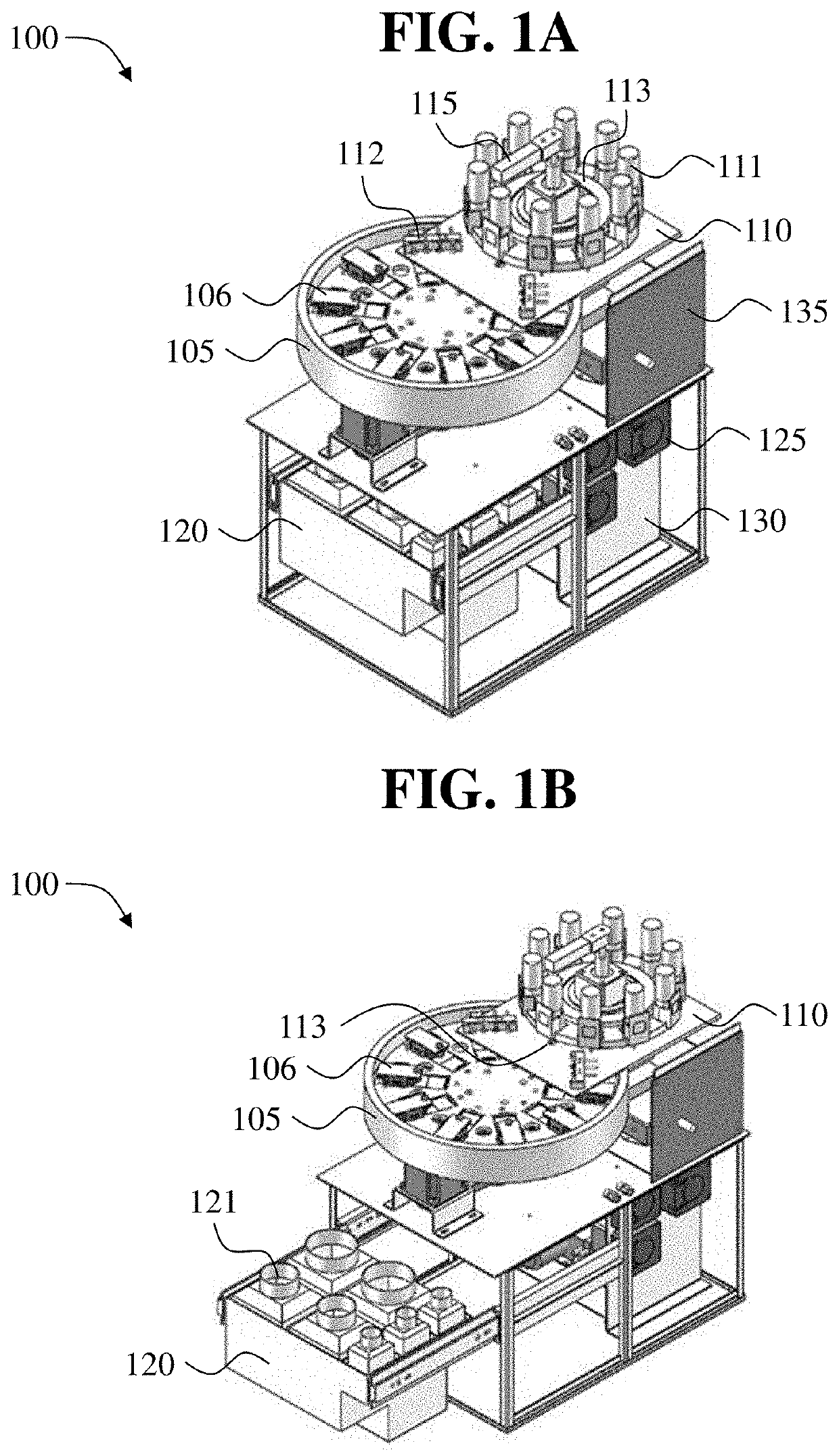
The present disclosure provides devices for processing, such as staining, a tissue sample on a microscope slide. In some embodiments, the tissue staining device described herein is capable of, e.g., automating, in whole or in part, a tissue staining protocol (including a chemical staining protocol and / or an immuno-based staining protocol) or a tissue dehydration protocol. Also provided in other aspects of the disclosure are components, methods of use, systems, and kits associated with the devices described herein.
Owner:NOVODIAX
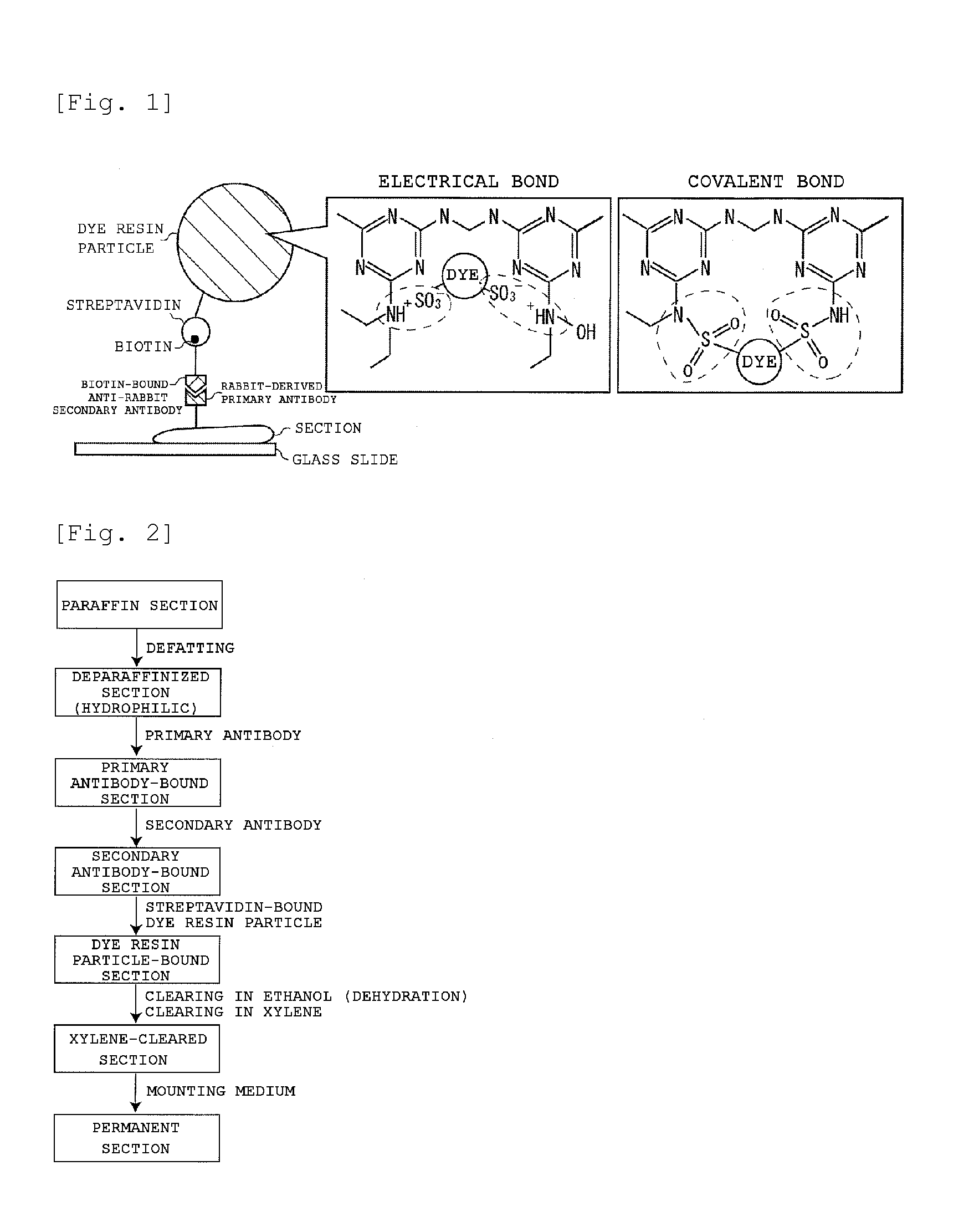
Staining agent for staining tissue, production method for staining agent for staining tissue and tissue staining kit including staining agent for staining tissue
ActiveUS20160018300A1Fluorescent signal enhancementAvoid bleedingPreparing sample for investigationOrganic dyesTissue stainingFluorescence
An object of the present invention is to provide: a staining agent for tissue staining which has an improved fluorescence signal evaluation accuracy; and a tissue staining kit comprising the staining agent. The staining agent for tissue staining contains, as a staining component, dye-resin particles comprising thermosetting resin particles and a fluorescent dye immobilized on the resin particles, wherein the resin particles contains a substituent having an electric charge opposite to that of the fluorescent dye and forms an ionic bond or a covalent bond with the fluorescent dye, and the dye-resin particles have a particle size variation coefficient of 15% or less.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method for staining tissue
ActiveUS20150064717A1High quantitativityImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansTissue stainingFluorescence
Provided is a method for staining a tissue enabling highly precise staining, by which the expression amount and / or the location of a biological substance in a tissue sample can be detected with a high quantitativity together with detailed information that can be obtained by bright field observation.The tissue staining method of the present invention is a method for staining a tissue, in which both staining that allows bright field observation and fluorescence staining are carried out for the same specific biological substance.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method for determining cancer onset or cancer onset risk
Provided is a method for highly accurately and quantitatively determining cancer onset or cancer onset risk by quantitative tissue-staining which is conducted in a biotissue with the use of an antibody capable of recognizing a cancer proliferation inhibitor or a cancer metastasis inhibitor, for example, PAR1 antibody inhibiting the mobility and infiltrating properties of cancer cells. Cancer onset or cancer onset risk is determined by a tissue staining method, said method comprising: a step for labeling an antibody, which is capable of recognizing a cancer proliferation inhibitor or a cancer metastasis inhibitor, with a fluorescent substance and then contacting the fluorescent-labeled antibody with a tissue sample; a step for irradiating a tissue site, which has been contacted with said antibody, with an excitation light to give a fluorescence image; a step for acquiring an intrinsic fluorescence image in a neighborhood region on a shorter or longer wavelength side, compared with the region wherein the wavelength of the fluorescence emitted by the fluorescent substance is acquired, in the same visual field at the same focus point as said fluorescence image; a step for conducting an image processing for removing the fluorescent brightness of said intrinsic fluorescence image from the fluorescent brightness of said fluorescence image to give a corrected fluorescence image; a step for counting cells at the tissue site which has been contacted with the antibody; a step for measuring the average fluorescent brightness per fluorescent particle; and a step for calculating the fluorescent particle count per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Method for determining effectiveness of medicine containing antibody as component
InactiveCN103154741APromote cancer treatmentMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDisease diagnosisTissue stainingTrastuzumab
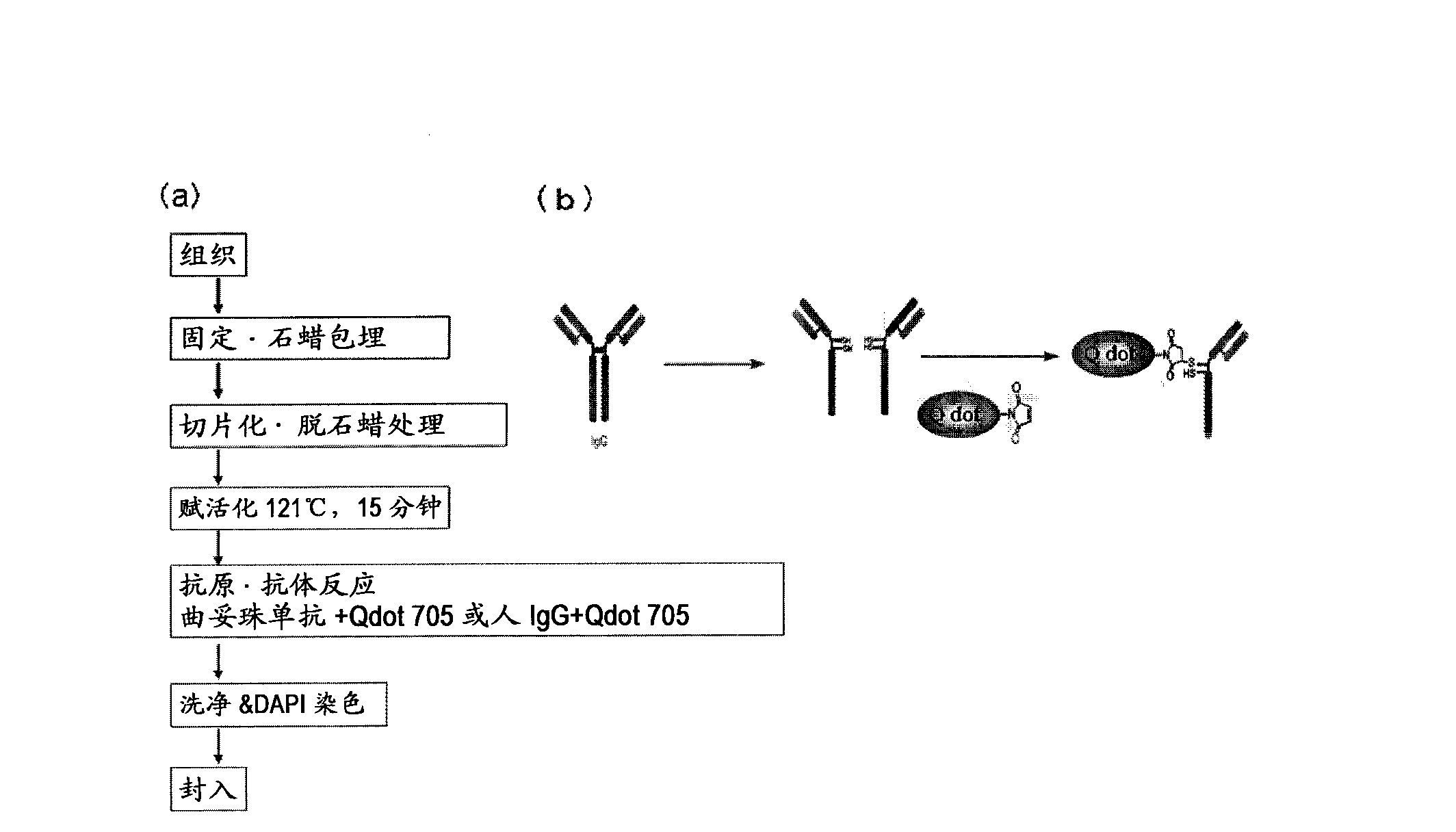
Provided is a method for determining effectiveness of medicine containing, as components, antibodies that are active components of an antibody preparation such as trastuzumab, or antibodies for a target to a target site of active component, by determining the quantity of the protein recognized by the antibodies with high accuracy, in a quantitative tissue staining method for biological tissue. The effectiveness of the medicine containing antibodies as components is determined by using the tissue staining method including the following steps: a step of labeling the antibodies in a medicine that contains antibodies as components with a fluorescent substance, and bringing the fluorescently labeled antibodies into contact with a tissue sample; a step of irradiating the tissue site contacted with the antibodies with excitation light to obtain a fluorescence image; a step of obtaining an intrinsic fluorescence image in the vicinity of the short-wavelength side or long-wavelength side of the acquisition area of fluorescence wavelength emitted from the fluorescent substance, in the same field of vision and in the same focus as those of the fluorescence image; a step of obtaining a collected fluorescence image by image-processing to eliminate the fluorescent intensity of the intrinsic fluorescence image from the fluorescent intensity of the fluorescence image; a step of counting the number of cells at the tissue site contacted with the antibodies; a step of measuring the average fluorescent intensity of one particle of fluorescent particles; and a step of calculating the number of fluorescent particles per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Automated lean methods in anatomical pathology
ActiveUS20170030810A1Withdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationTissue stainingPatient data
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Methods for accelerating tissue processing
InactiveUS8216808B2Effective diffusionPreparing sample for investigationElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentTissue sampleClearing Agent
Systems and methods for accelerating tissue processing by treating tissue samples and one or more tissue processing agents with infrasonic vibrations are discussed. Some non-limiting examples of tissue processing agents include a tissue fixative, dehydrating agent, clearing agent, impregnating agent, embedding agent, tissue stain, enzyme, or another chemical that diffuses into the tissue sample when the sample is being preserved or prepared for microscopic examination. The infrasonic vibrations can have a frequency from about 10 to about 600 Hz. The infrasonic vibrations can have an amplitude that is sufficiently high, when combined with the frequency, to induce turbulent mixing of the processing agent and accelerate tissue processing. The tissue sample may optionally be vibrated with ultrasonic vibrations. The ultrasonic vibrations can have a frequency and amplitude that are sufficiently high to induce turbulent mixing of the processing agent and to accelerate tissue processing.
Owner:DONNDELINGER THOMAS M
Tissue staining method
ActiveUS10551378B2Diagnostic precision is enhancedImprove conveniencePreparing sample for investigationAntigenTissue staining
It is an object of the present invention to provide a tissue staining method that makes it possible to observe both information on the morphology of a tissue and information on a biological substance such as an antigen molecule to be detected on a single section and in a single view field. The present invention provides a tissue staining method, including carrying out (A) a HE (hematoxylin-eosin) staining, and (B) a histochemical staining, serially on a single tissue section, wherein the histochemical staining is defined as a histochemical technique for detecting a biological substance to be detected in a tissue in a visible manner by use of a binding reaction between the biological substance to be detected and a probe biological substance capable of binding specifically to the biological substance to be detected.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method for staining tissue
ActiveUS9970847B2High quantitativityImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingTissue stainingFluorescence
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Tissue staining protocol and composition
InactiveUS20050202524A1New informationEasy to checkPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingTissue stainingHistological staining
An enhanced and particularly quick histological staining method is expressed in which a frozen tissue or deparafffinized tissue sample is briefly immersed in an eosin solution, used as a first dye, and then in a hematoxylin solution, used as a second die. The slide is rinsed and air-dried to make ready for assessment.
Owner:BRUSILOVSKIY ARKADIY I
Tissue staining method, tissue evaluation method and biosubstance detection method
ActiveUS20150160103A1Good for observationHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyLibrary screeningTissue stainingFluorescence
A tissue staining method which comprises: staining a tissue with a staining reagent wherein a biosubstance recognition site is bonded to particles carrying multiple fluorescent substances accumulated therein; in the stained tissue, counting fluorescent points or measuring fluorescent brightness; and evaluating the expression level of a biosubstance, which matches the biosubstance recognition site, in the aforesaid tissue on the basis of the number of the fluorescent points or fluorescent brightness that was measured.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Apparatus for Electrophoretic In Situ Tissue Staining
InactiveUS20080020450A1Additional movementReduce concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyDiffusionTissue staining
The present invention introduces a radically different way of accelerating biomolecule conjugates into tissue, and hence towards their targets for purposes of tissue staining. The invention provides for an order of magnitude improvement over the prior art diffusion process used to stain tissue. The invention comprises a method of tissue staining by applying an electric field to a tissue sample in the presence of an electrolyte and biomolecular conjugates of interest suspended in the electrolyte. Typical staining times are reduced to seconds as opposed to 30-120 minutes common in the prior art. The invention is also directed to devices for performing the method.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
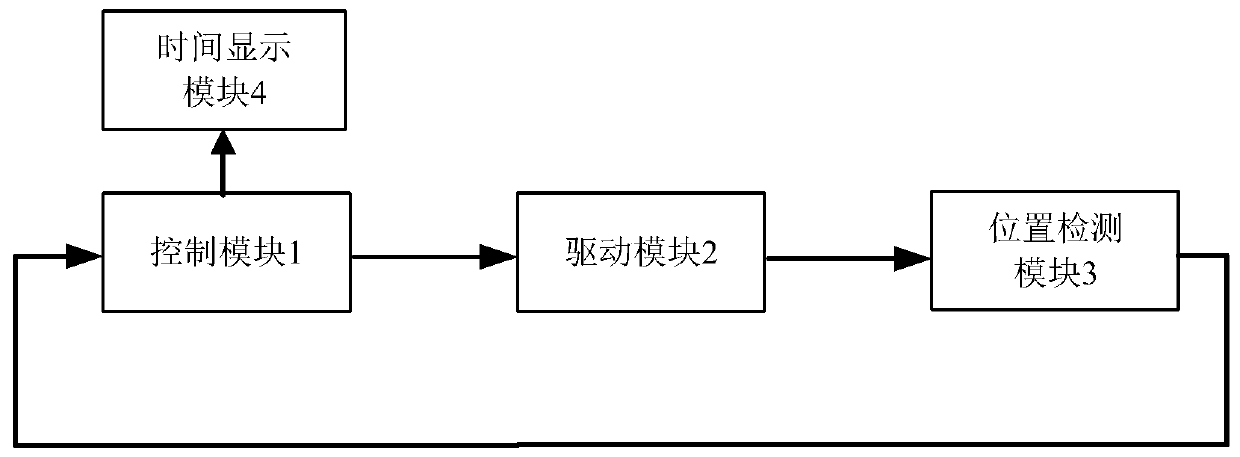
Method and device for intelligent timing of tissue staining machine
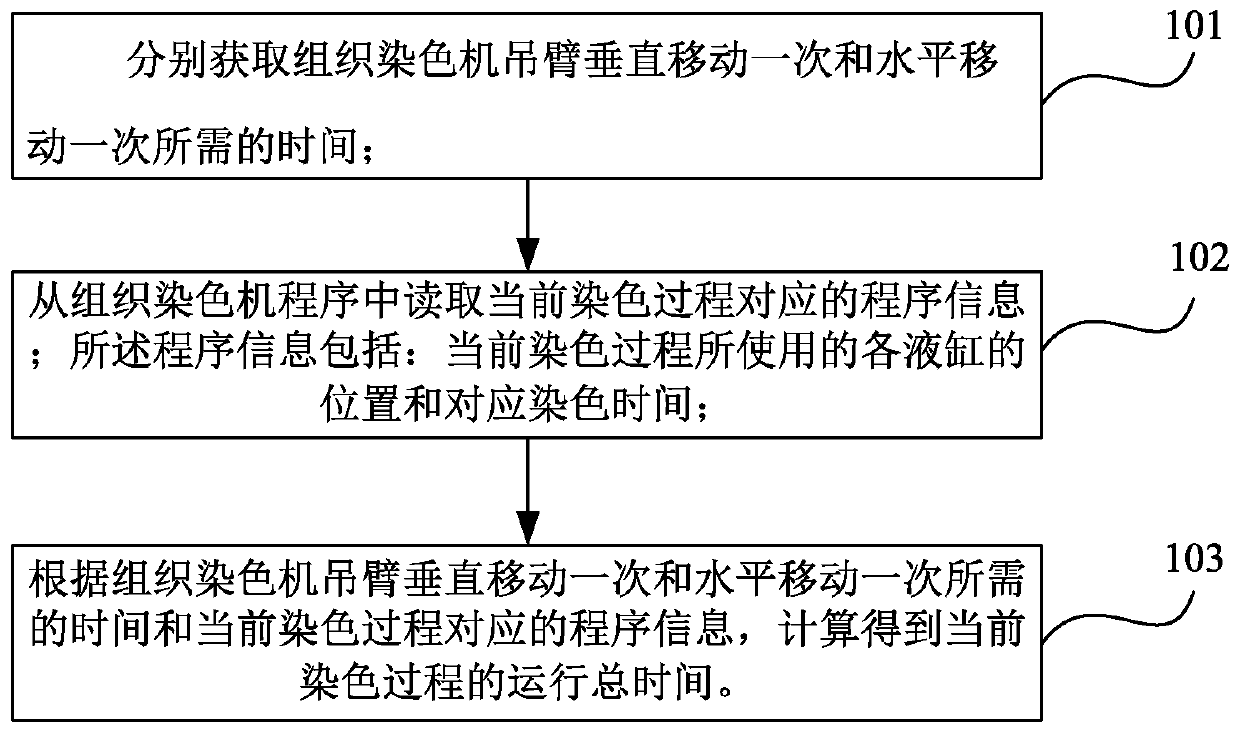
InactiveCN110836804AImprove work efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationTissue stainingMedical equipment
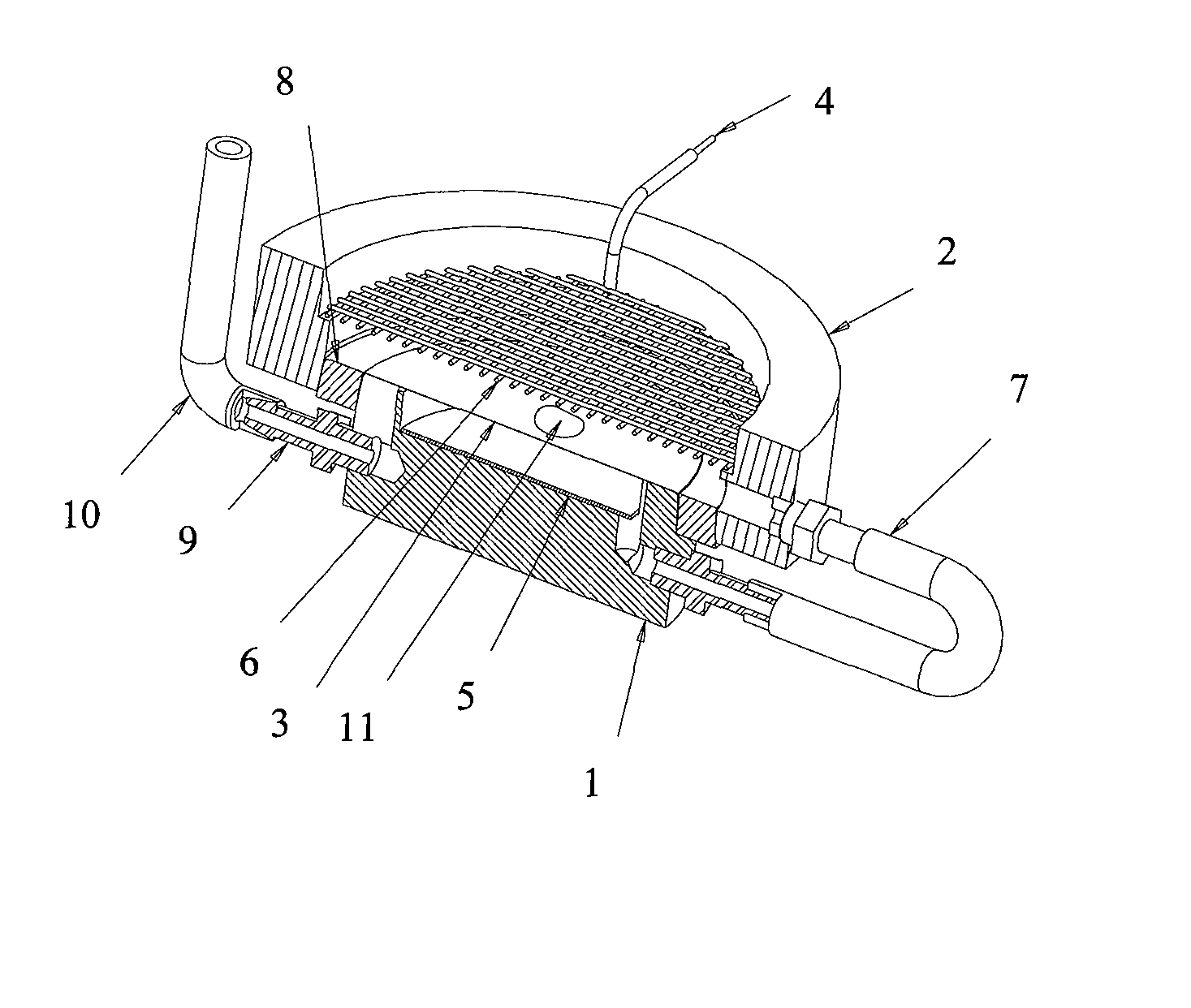
The invention relates to the field of new medical equipment, and in particular to a method and device for intelligent timing of a tissue staining machine. The method comprises the following steps of respectively obtaining the time required for the boom of the tissue staining machine to move vertically once and horizontally once; reading program information corresponding to the current staining process from the tissue staining machine, wherein the program information includes the position of each cylinder used in the current staining process and the corresponding staining time; and calculatingto obtain the total running time of the current staining process according to the time required for the boom of the tissue staining machine to move vertically once and horizontally once and the program information corresponding to the current staining process. The invention can predict the time required for the staining process.
Owner:HUBEI ENG UNIV
Methods for Determining Cancer Incidence or Risk of Cancer Incidence
The present invention provides a high-accuracy and quantitative determination method of cancer onset or cancer risk by performing a quantitative tissue staining method using, for example, an inhibitor of cancer cells in living tissue. Motility and invasive PAR1 antibodies and other antibodies that recognize cancer growth control factors or metastasis control factors. The present invention uses the following tissue staining method to determine the incidence of cancer or the risk of cancer incidence. The tissue staining method includes the following steps: labeling an antibody that recognizes a cancer proliferation control factor or metastasis control factor with a fluorescent substance, making the fluorescently labeled antibody A step of contacting a tissue sample; a step of irradiating excitation light to the tissue site in contact with the antibody to obtain a fluorescent image; obtaining fluorescence emitted by the fluorescent substance in the same field of view and at the same focus as the fluorescent image A step of obtaining an autofluorescence image in a region near the short wavelength side or the long wavelength side compared to the wavelength region; performing image processing, removing the fluorescence brightness of the autofluorescence image from the fluorescence brightness of the fluorescence image, and obtaining a corrected fluorescence image The process; the process of counting the number of cells in the tissue site contacted by the antibody; the process of calculating and measuring the average fluorescence brightness of one fluorescent particle; the process of calculating the number of fluorescent particles per one cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Tissue stain and use thereof
ActiveUS11452783B2Easy to useEasily observable during injection into tissuePowder deliveryLuminescence/biological staining preparationTissue stainingActive agent
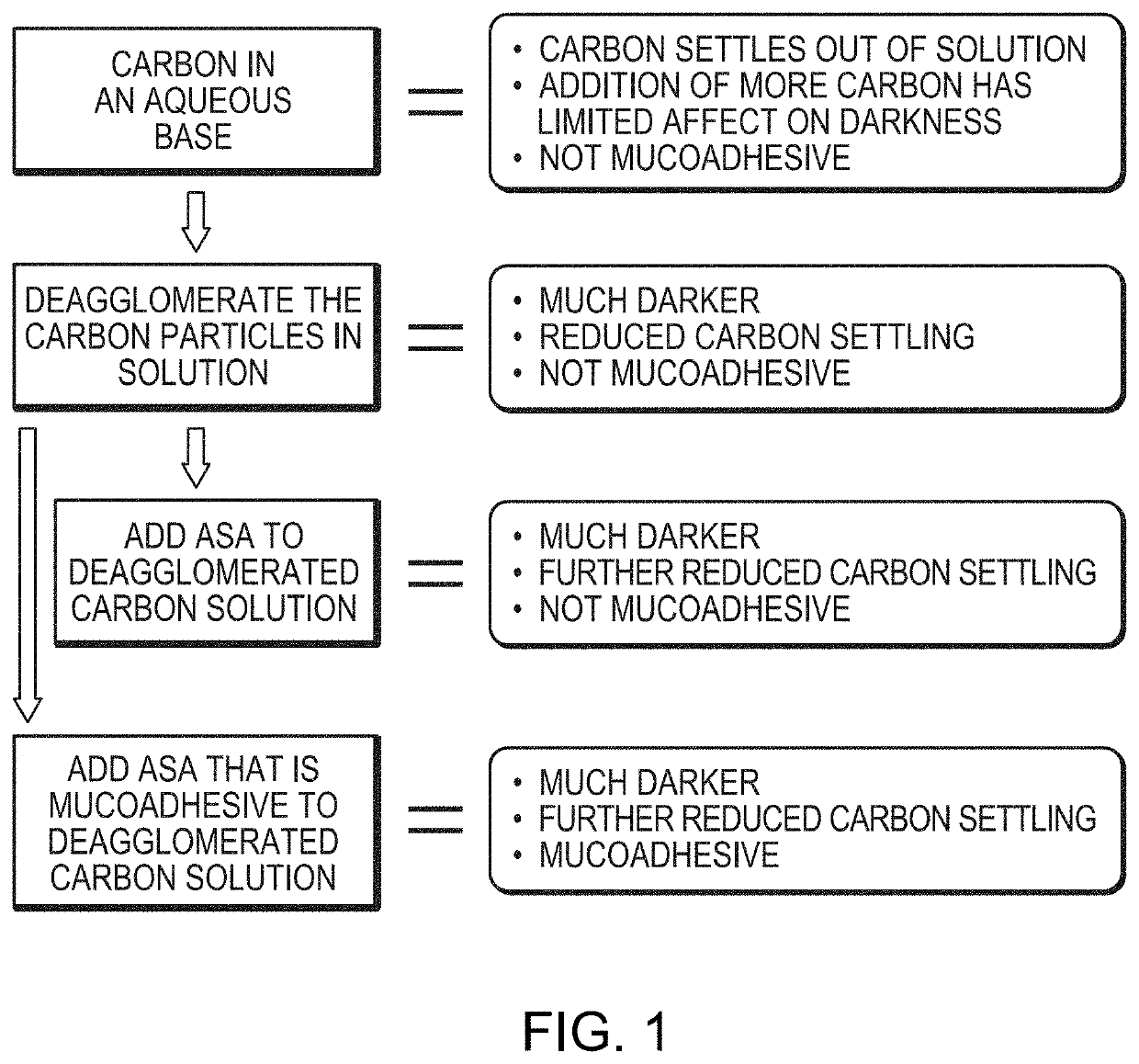
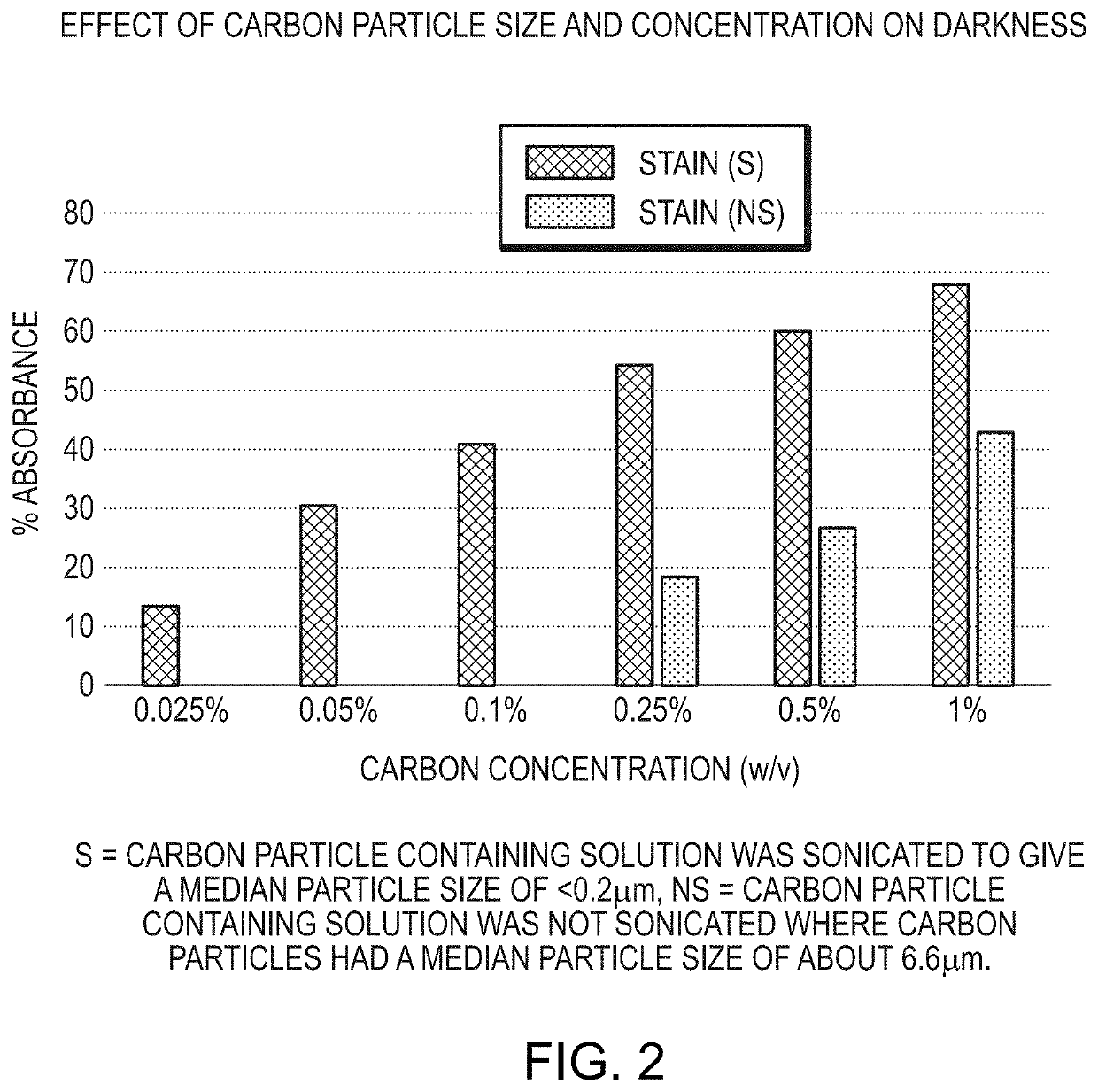
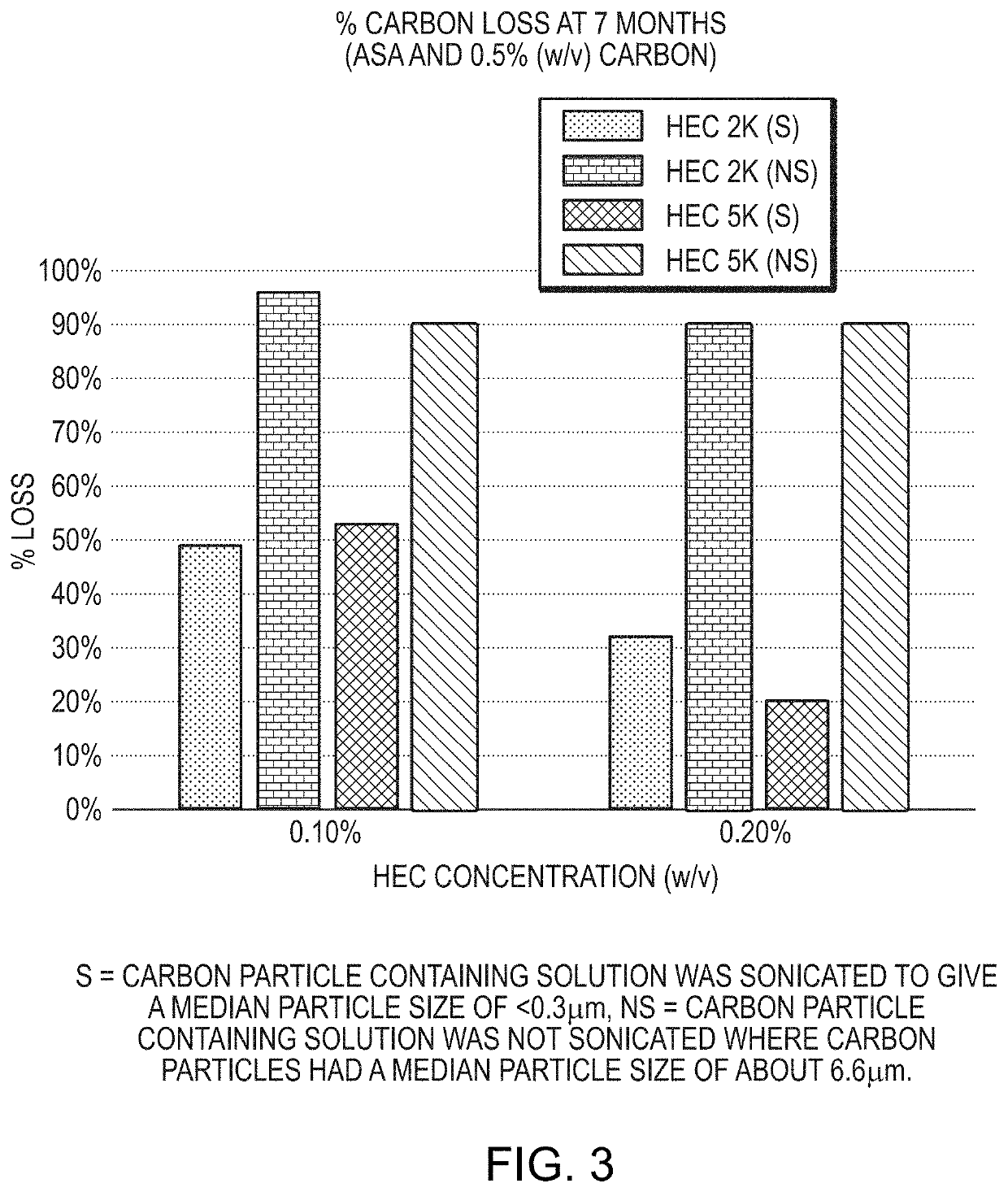
Provided is a tissue staining composition containing carbon particles having a mean particle diameter less than 0.3 μm in diameter (optionally less than 0.2 μm in diameter) together with one or more agents that maintain the carbon particles in suspension (for example, an anti-settling agent and / or surfactant). In certain circumstances, the anti-settling agent may also have mucoadhesive properties. The tissue staining composition is visually dark and does not disperse rapidly when introduced into regions of tissue of interest making it ideal for marking the regions that can be visualized clearly and over prolonged periods of time via, for example, direct visualization, endoscopic or laparoscopic inspection. The invention also provides methods of making and using the tissue staining composition for marking regions of tissue of interest, for example, gastrointestinal tissue, as well as other tissues.
Owner:GI SUPPLY
Banana fruit differential high efficient starter and plant expressing carrier
InactiveCN1279169CFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionTissue stainingAgricultural science
The invention relates to a banana fruit-specific high-efficiency expression promoter and a plant expression vector thereof. The promoter is 748 bp long, and a new plant expression vector named pBIL2 is constructed by replacing the constitutive 35S promoter on the plant expression vector pBI121. The GUS gene transient expression method was used to detect the promoter activity of the promoter containing this segment and the pBI121 promoter. GUS tissue staining showed that the promoter had expression tissue specificity, that is, it was only expressed in fruit. The activity of GUS was determined to be 100-300 times higher than that of other organs in each banana fruit, and it was slightly higher than that of 35S promoter. The acquisition of the promoter provides a powerful tool for banana transgene and molecular biology research on banana fruit, especially creates conditions for the research and development of using banana as a bioreactor. Therefore, the acquisition of the promoter has important theoretical and practical significance.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +1
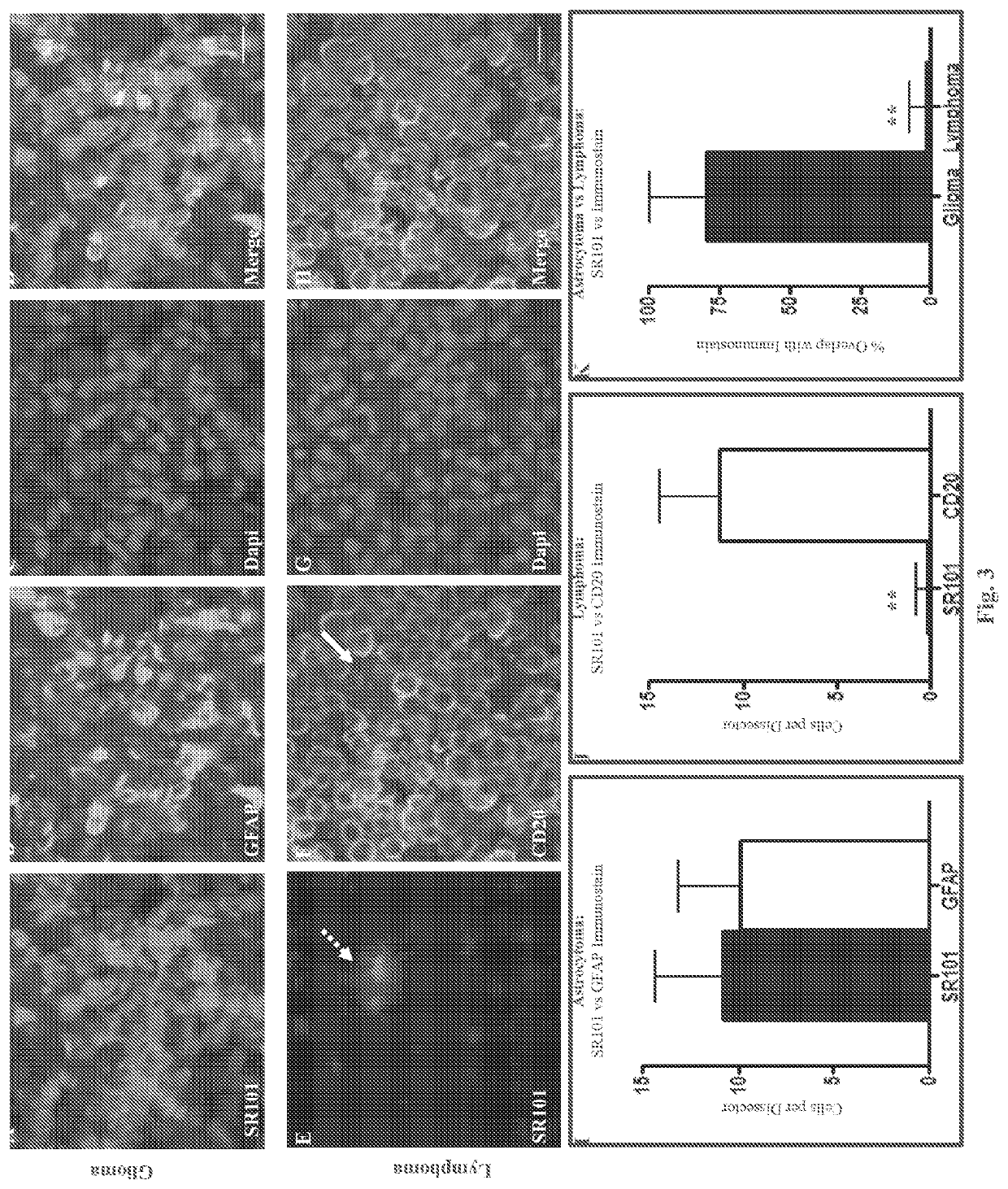
System and method for diagnosis of astrocytic brain tumor
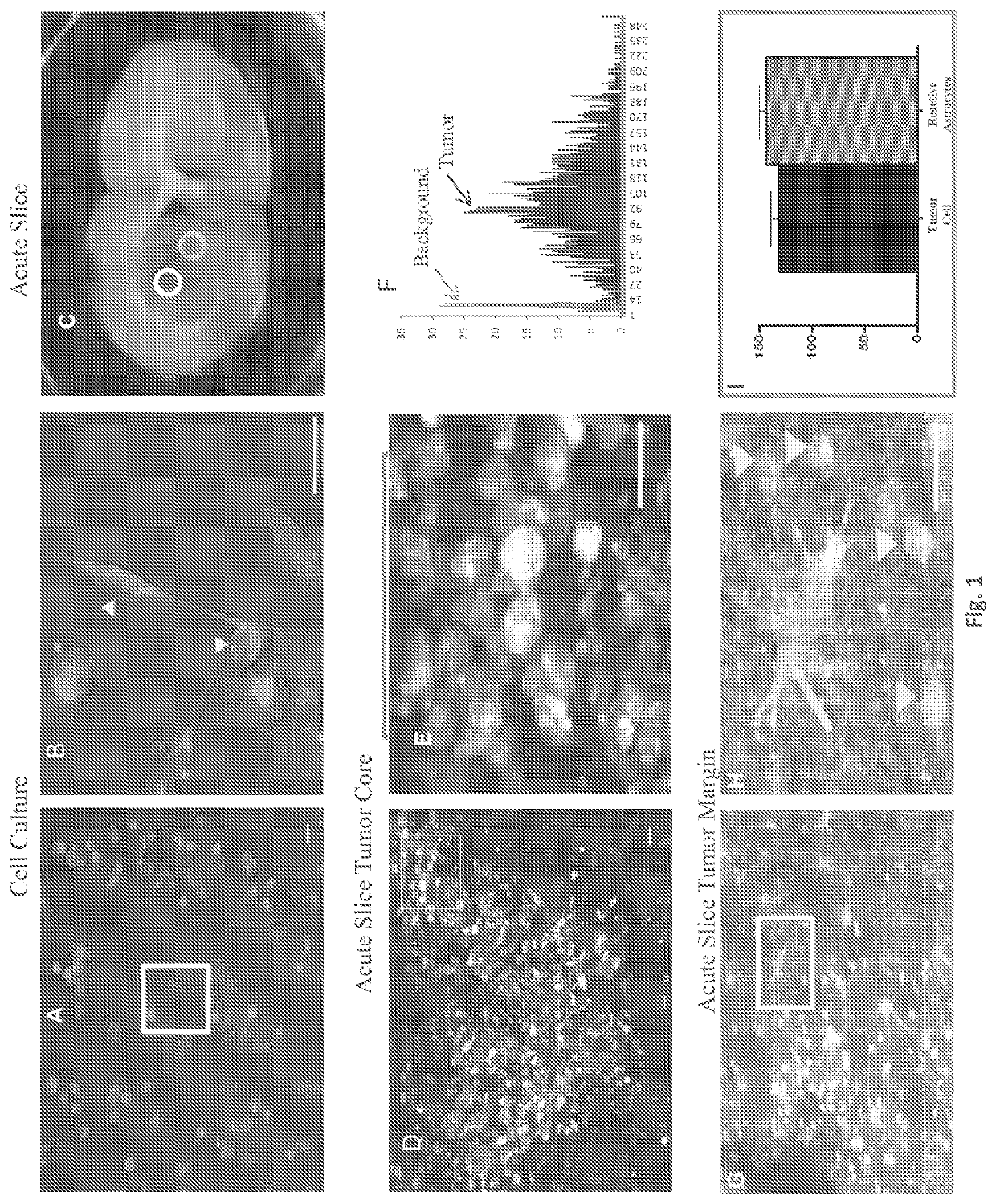
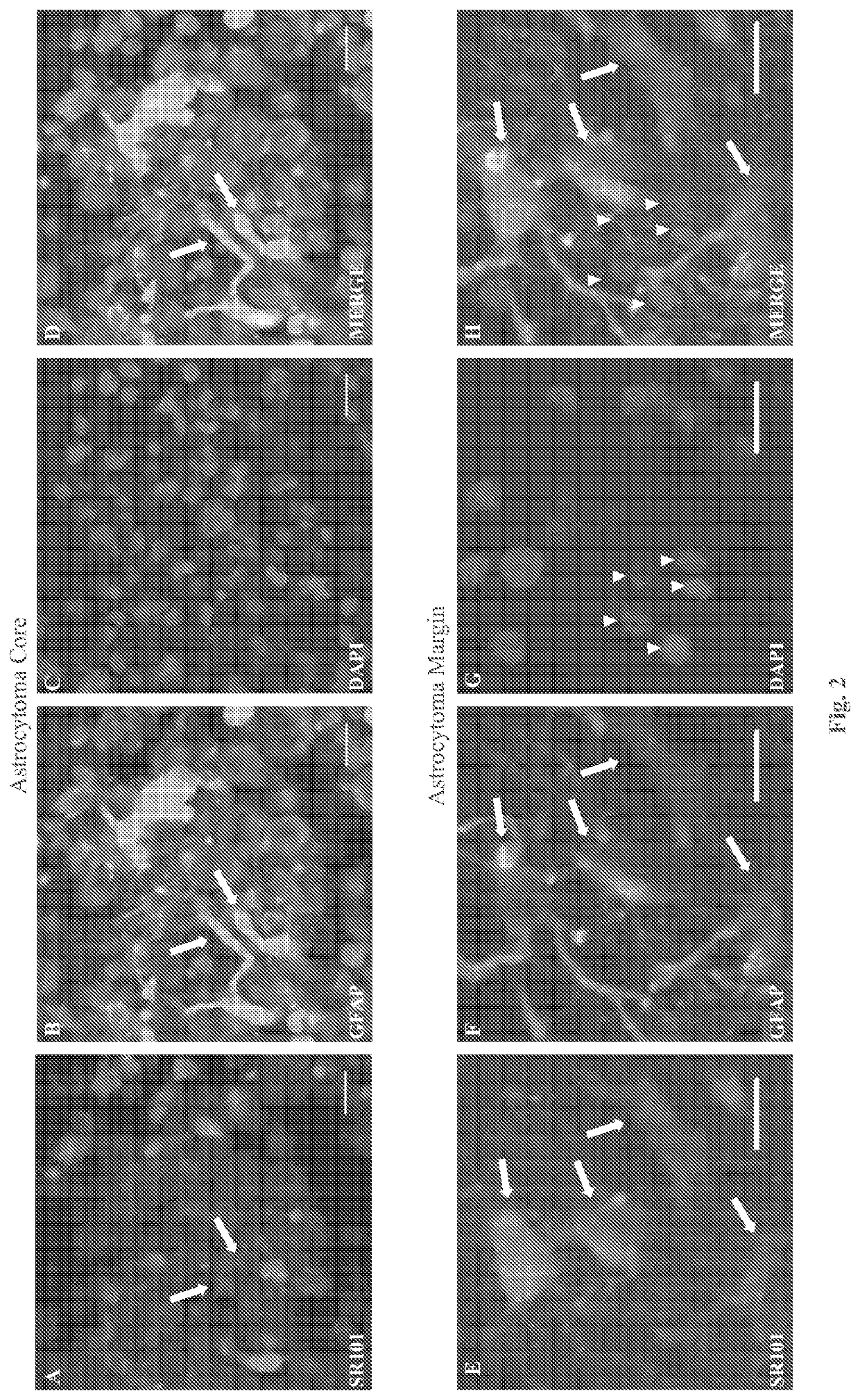
ActiveUS10675363B2Minimize and eliminate needIn-vivo testing preparationsMaterial analysisHuman brain tumorRadiology
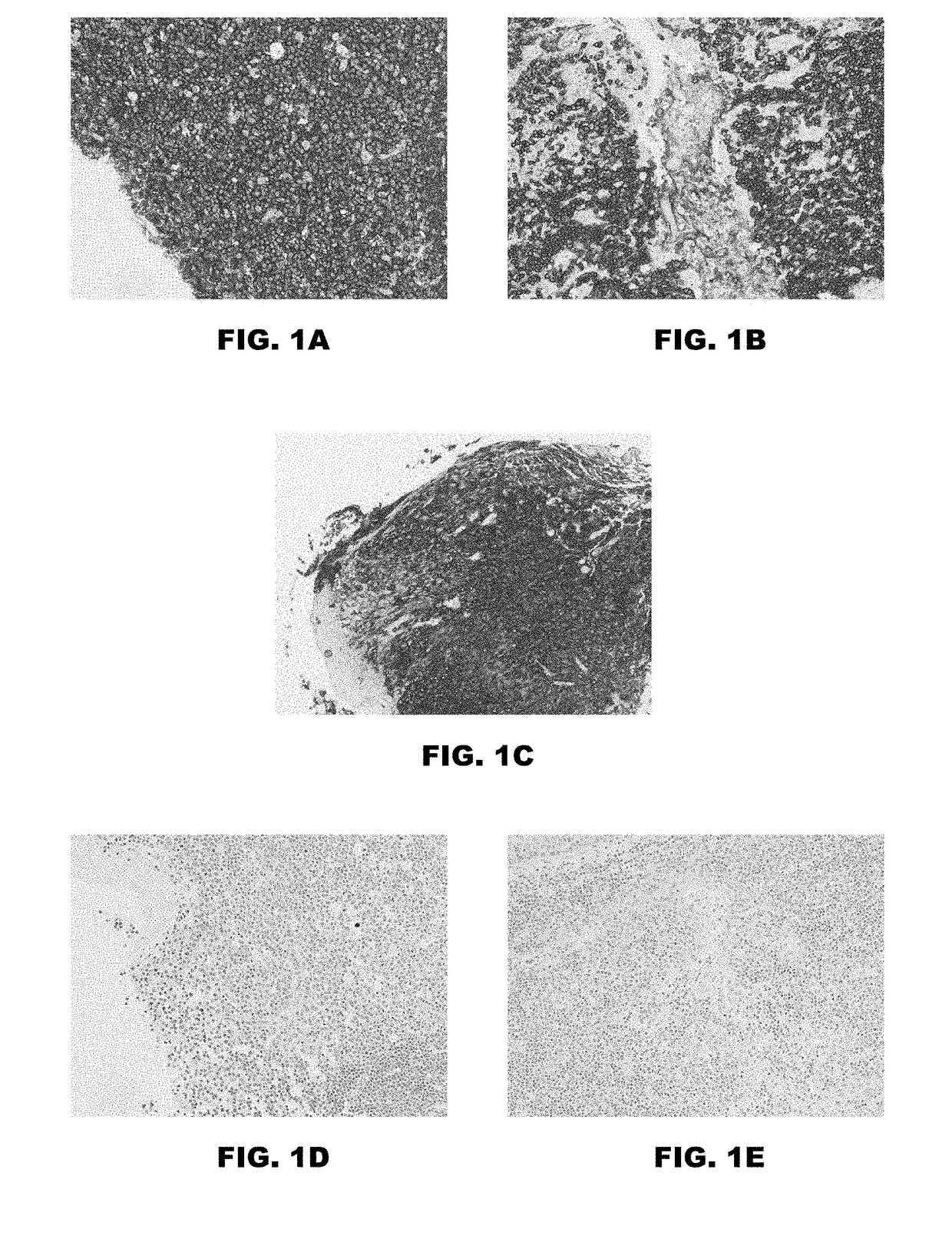
Methods and systems for distinguishing an astrocytic human brain rumor from a non-astrocytic human brain tumor (FIG. 4). In one embodiment a method includes the steps of staining tumor tissue from a subject suspected of having a brain tumor with SR101 and visualizing the tissue stained with SR101 with a fluorescence imaging device to confirm an astrocytic or non-astrocytic tumor type. Advantageously, rumor tissue from a subject is stained ex vivo, and the staining and visualizing steps are performed intraoperatively so as to guide the surgeon and thereby minimize or eliminate the need for a subsequent surgery.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com