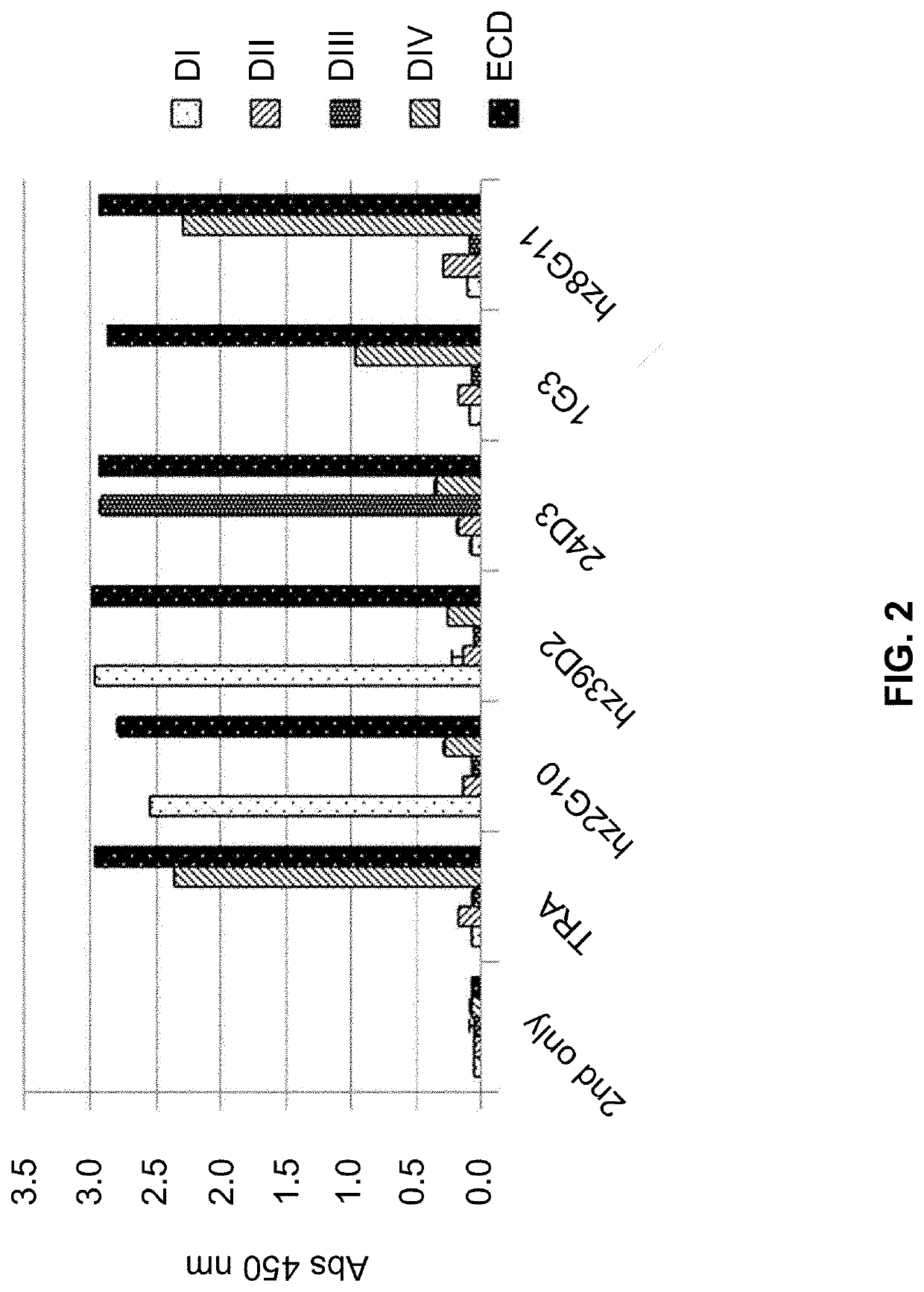
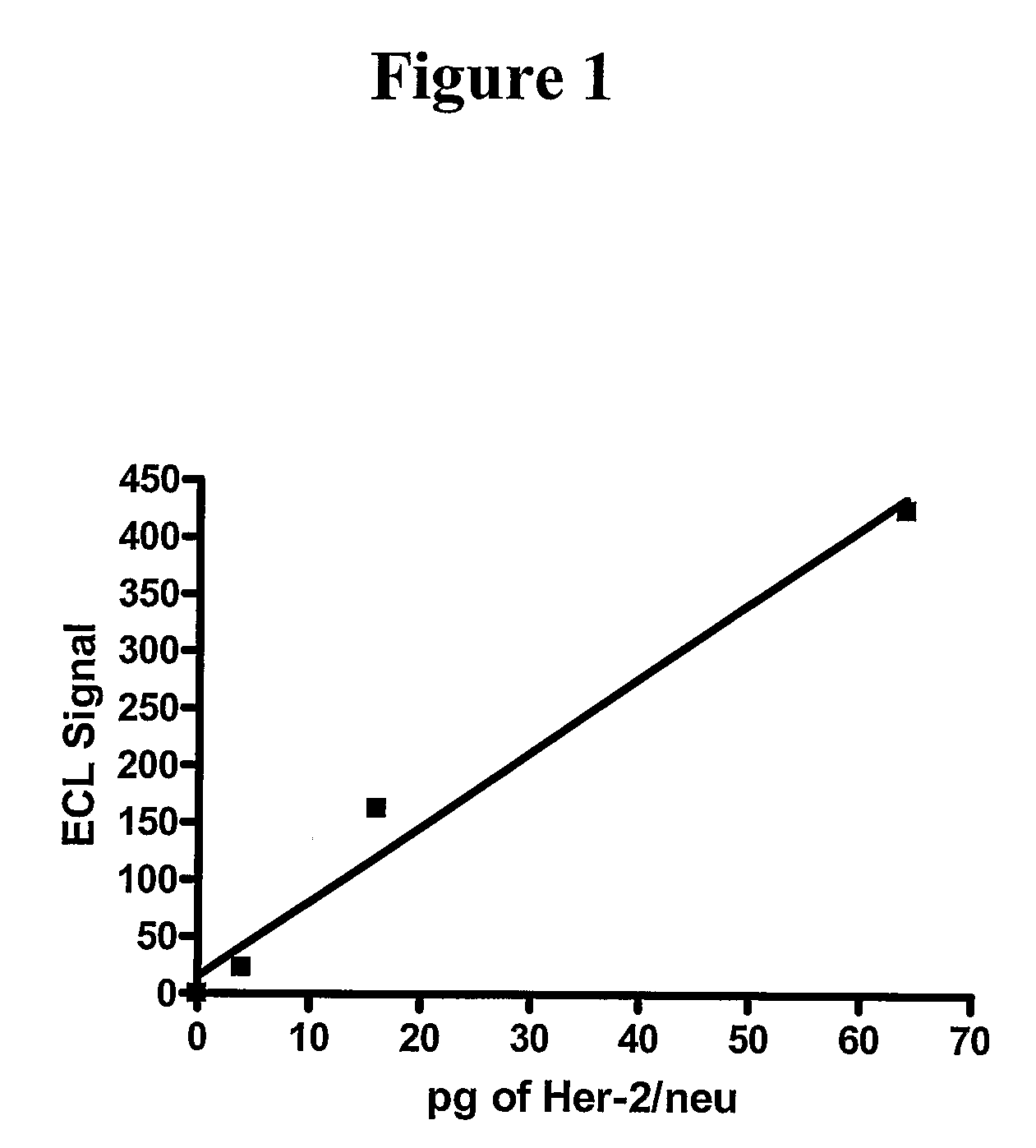
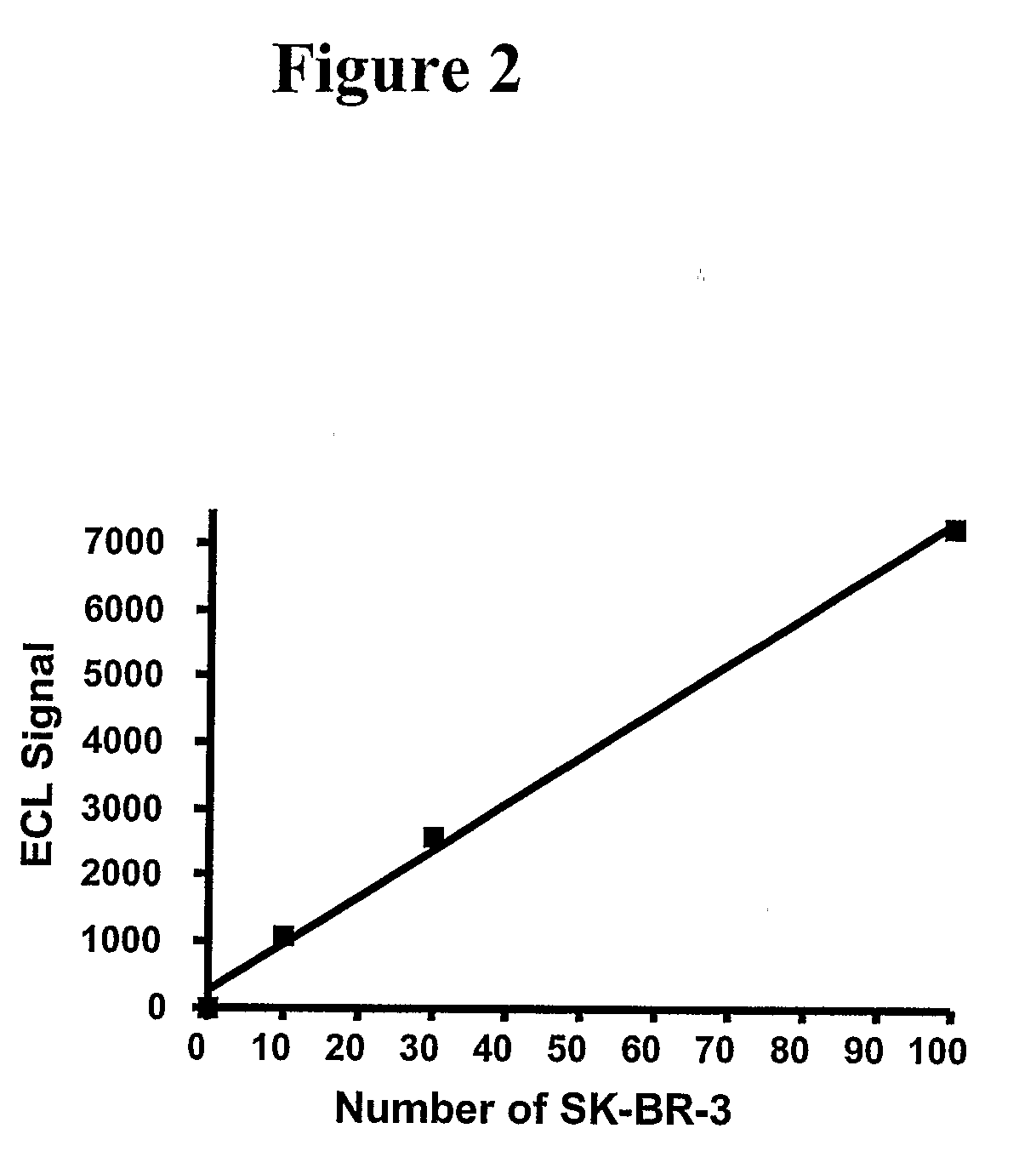
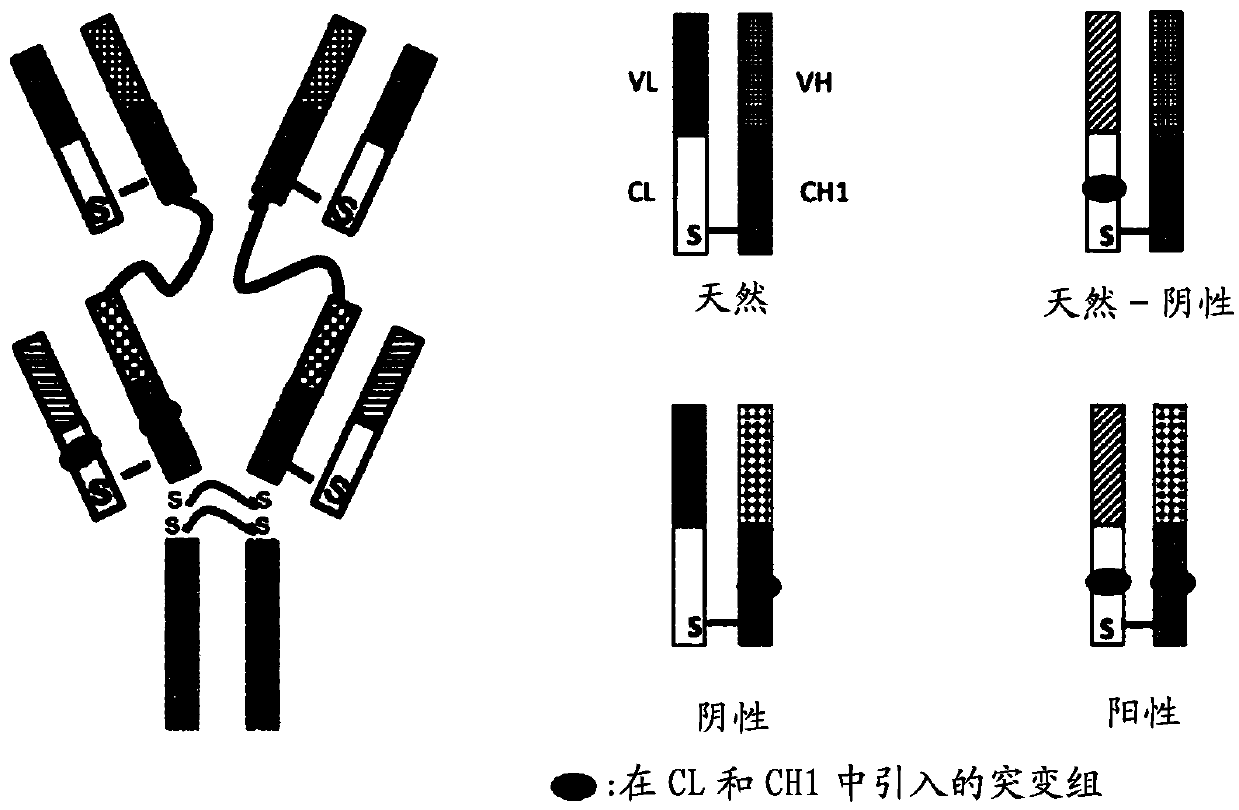
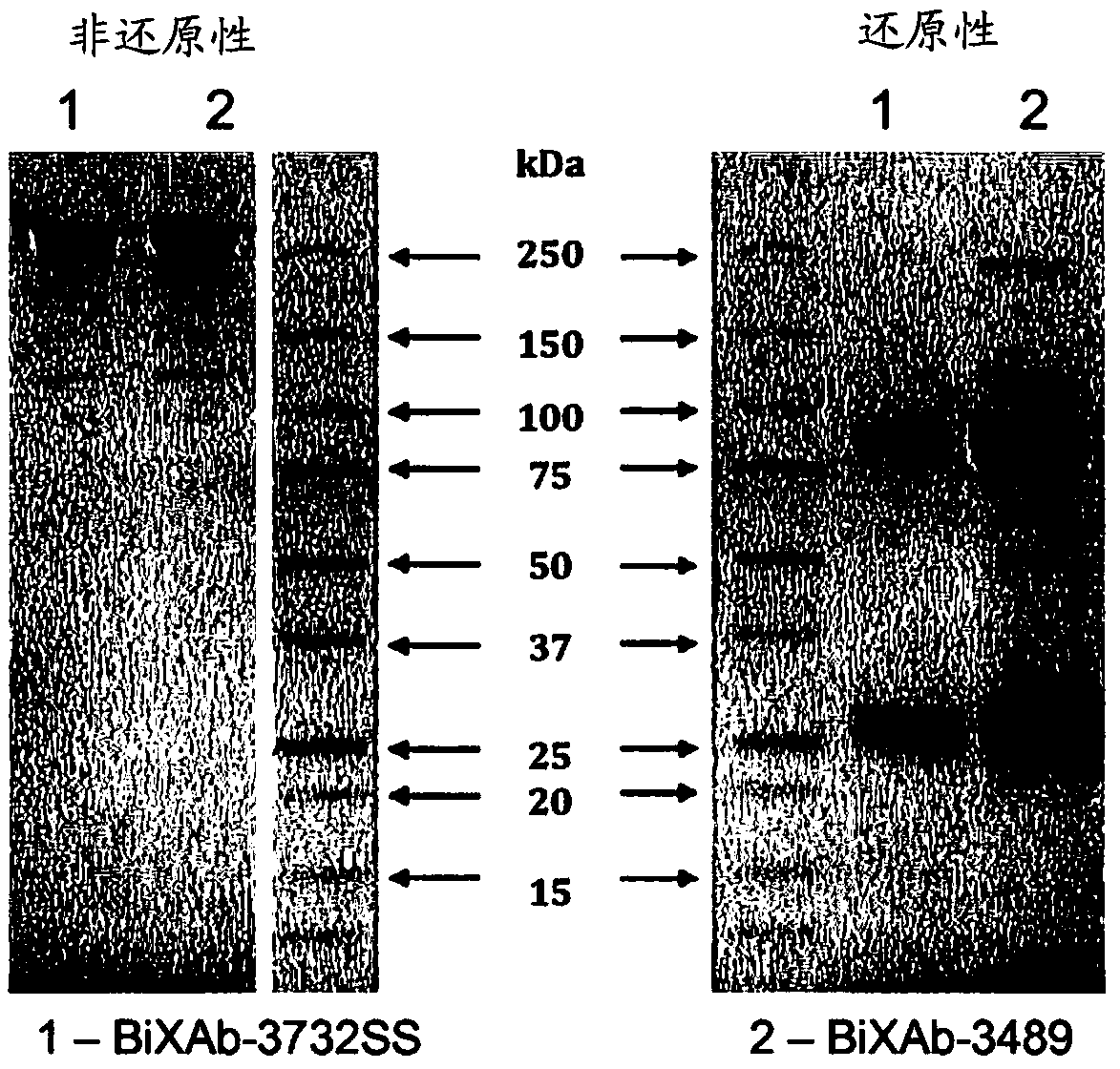
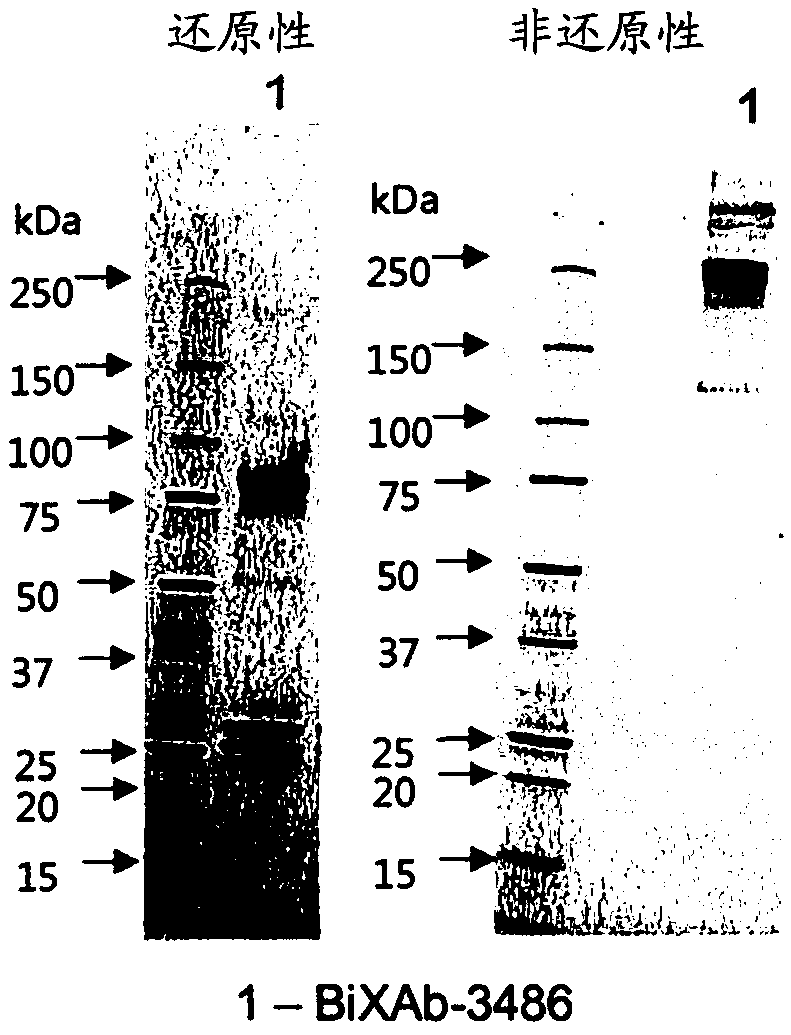
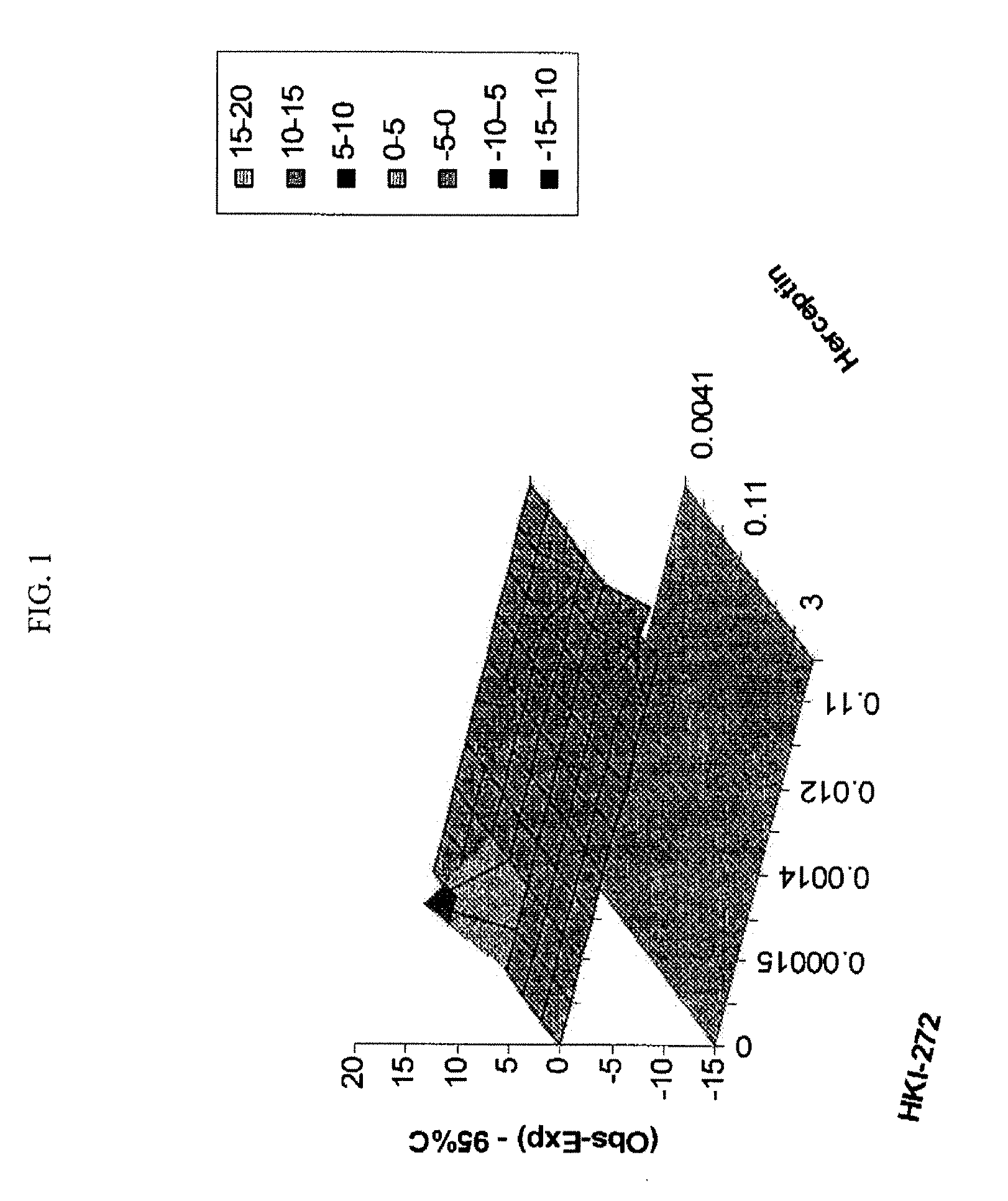
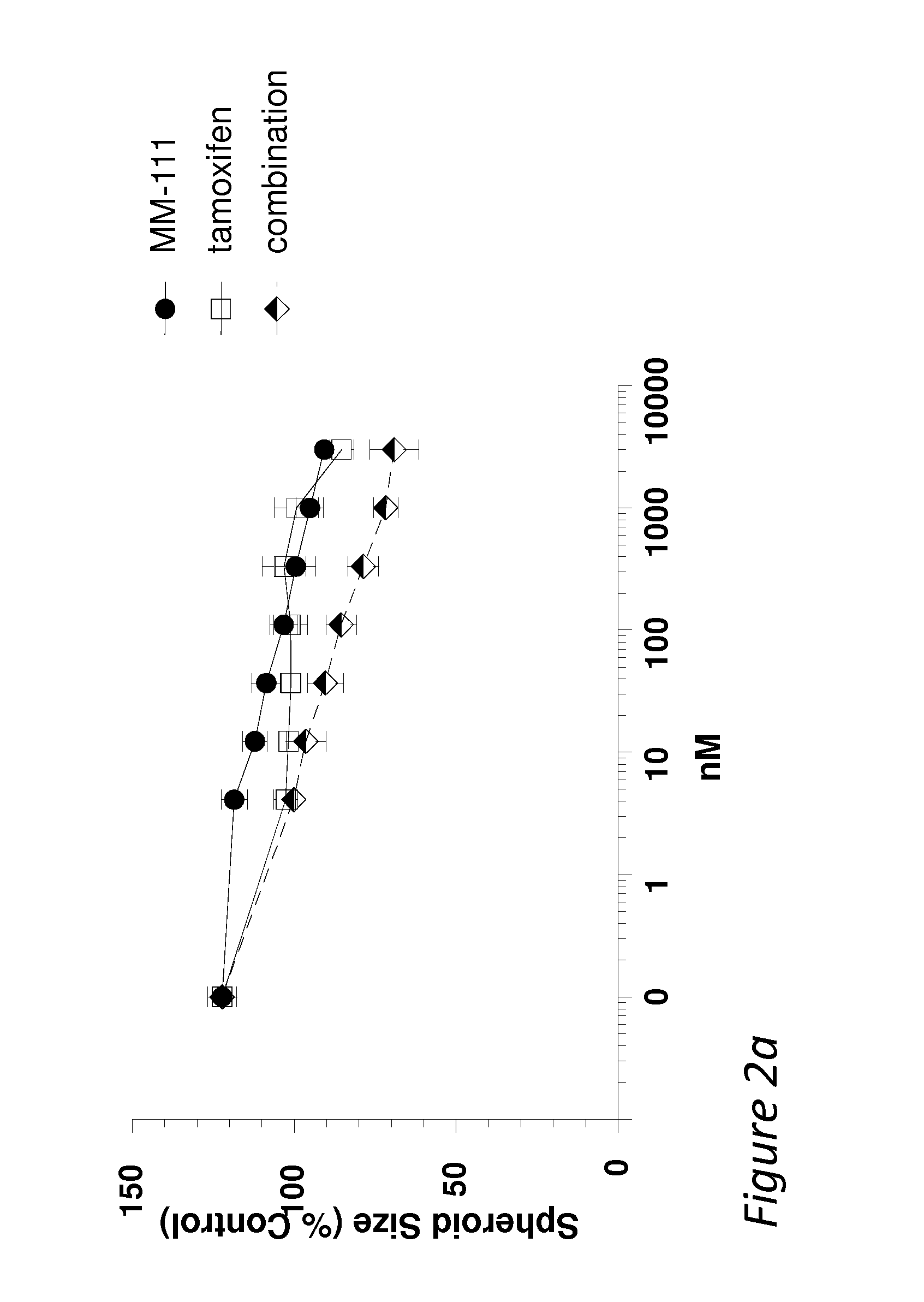
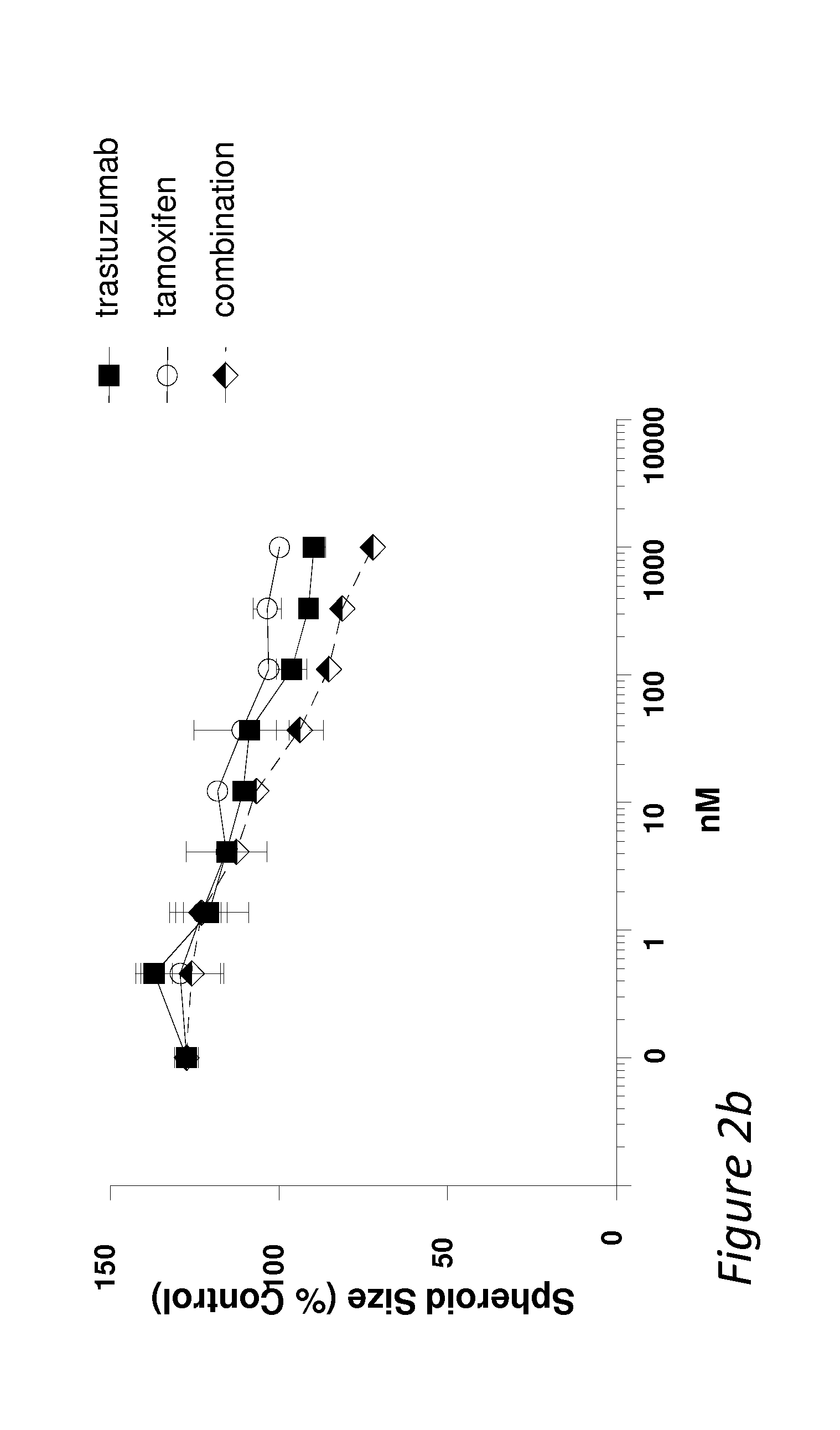
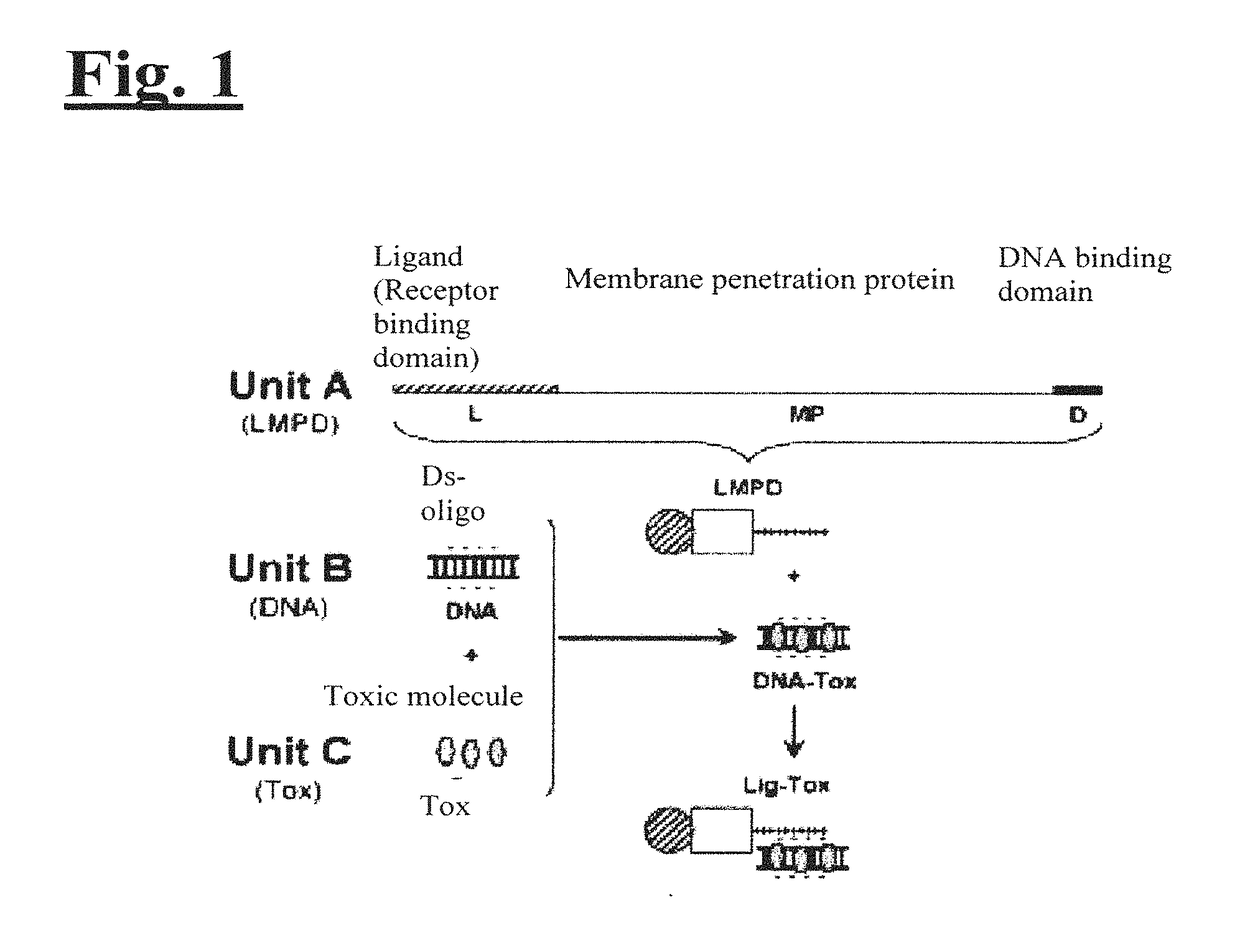
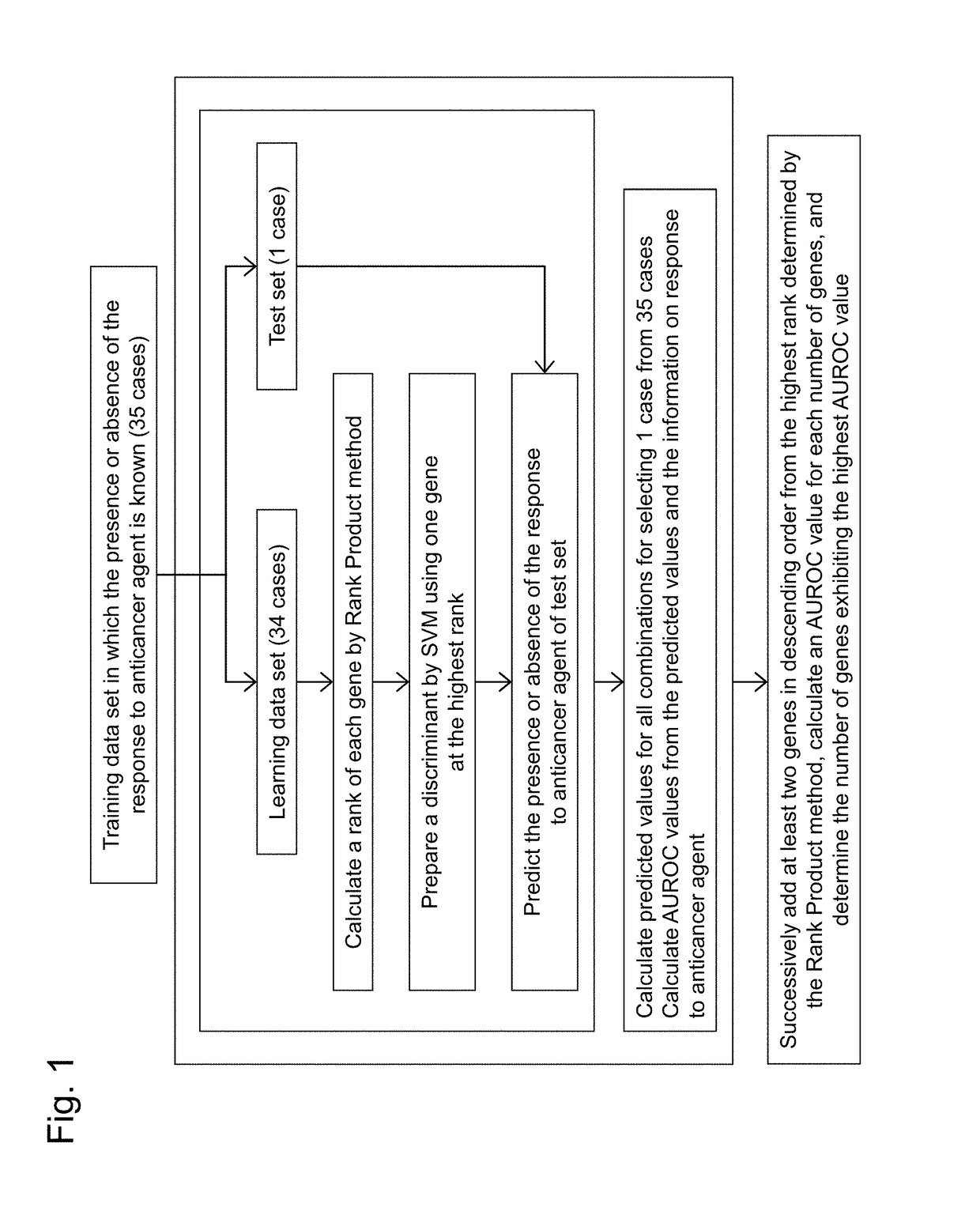
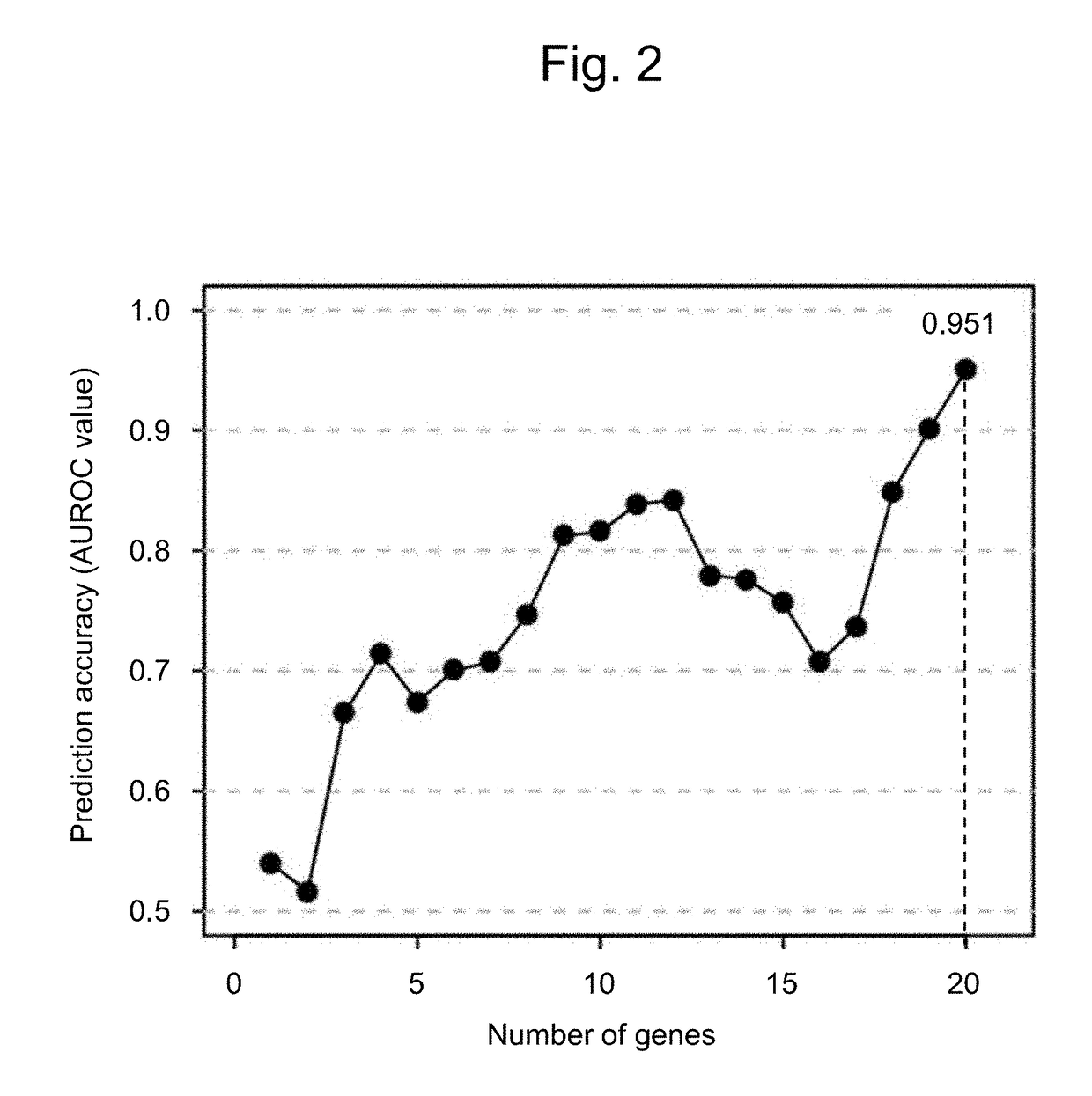
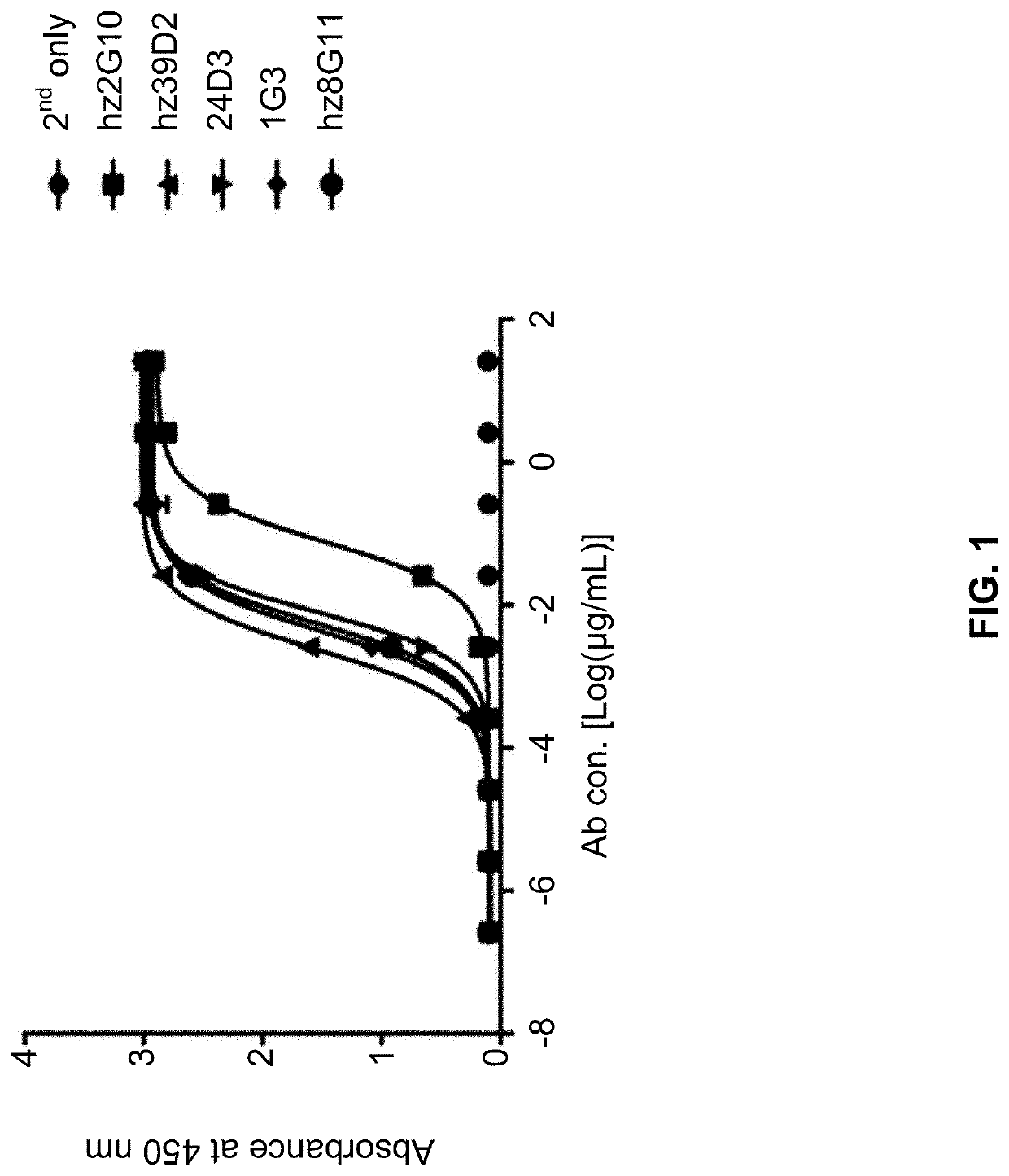
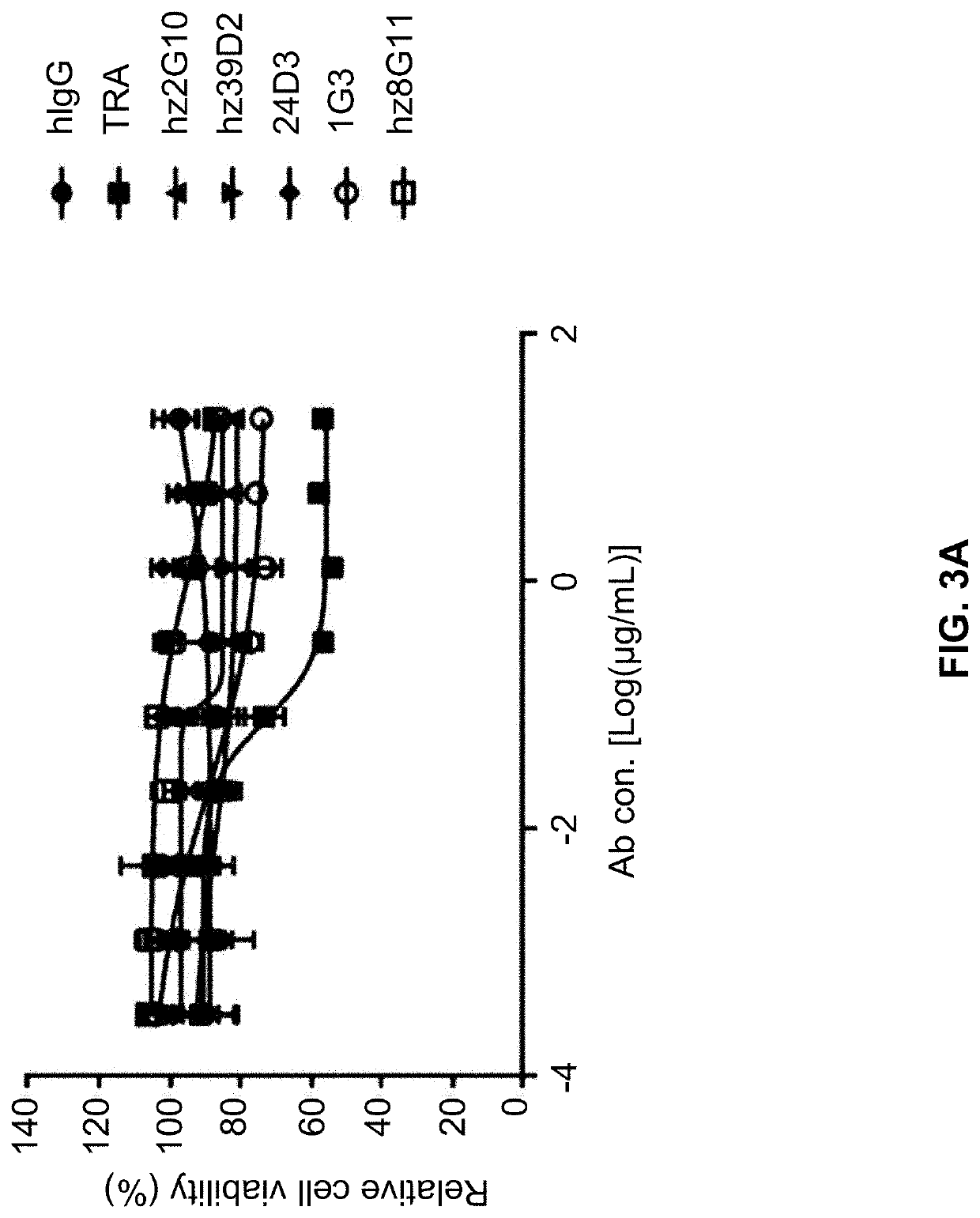
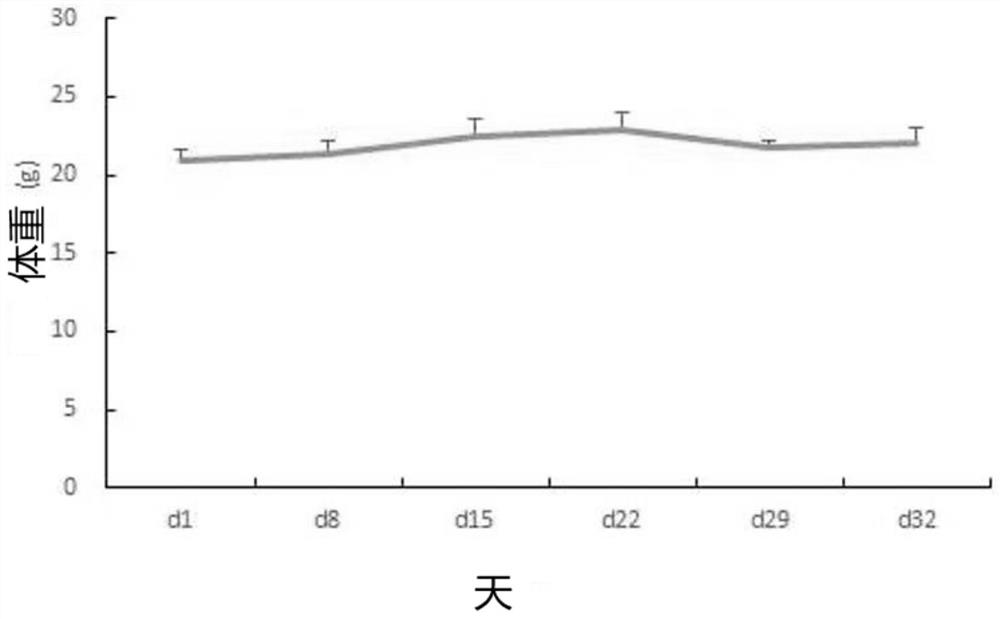
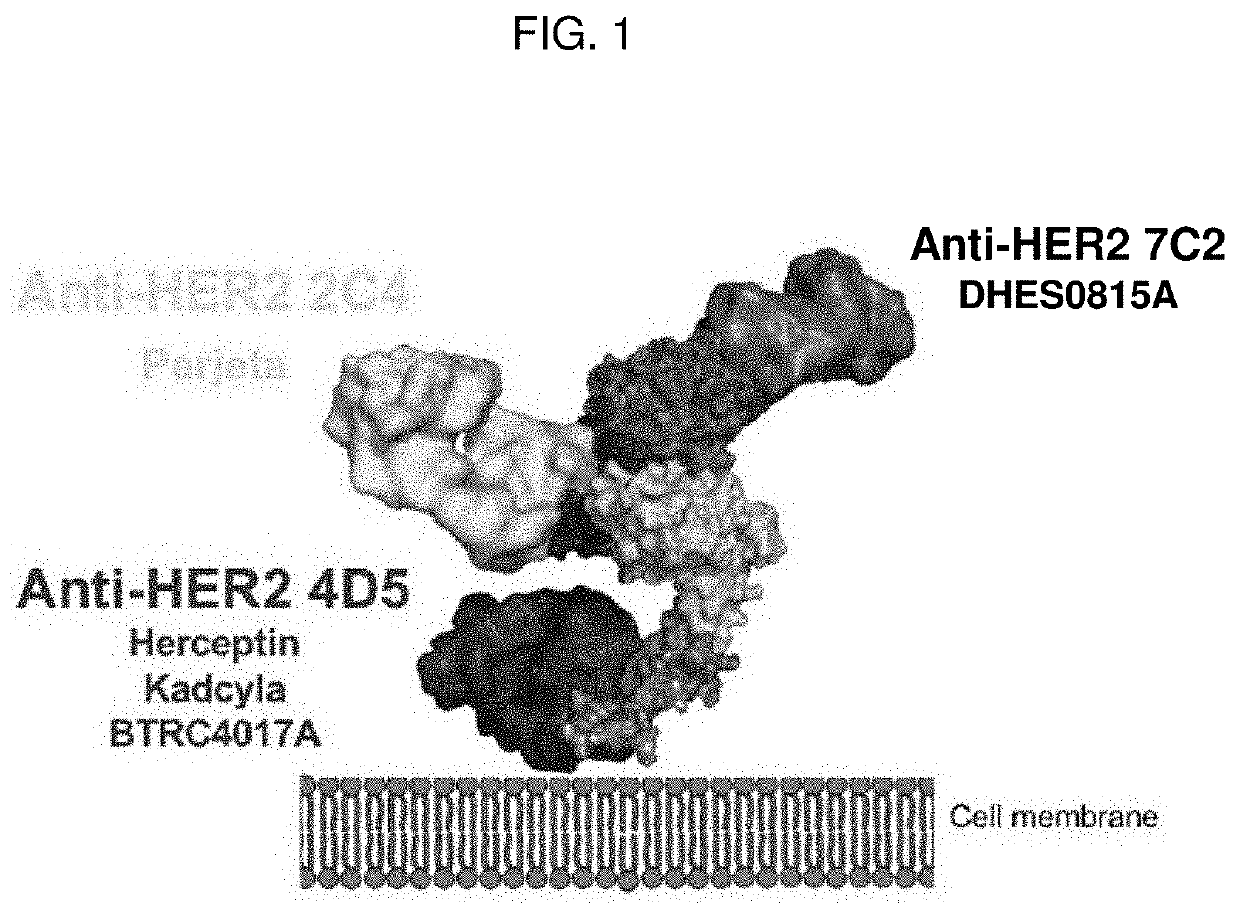
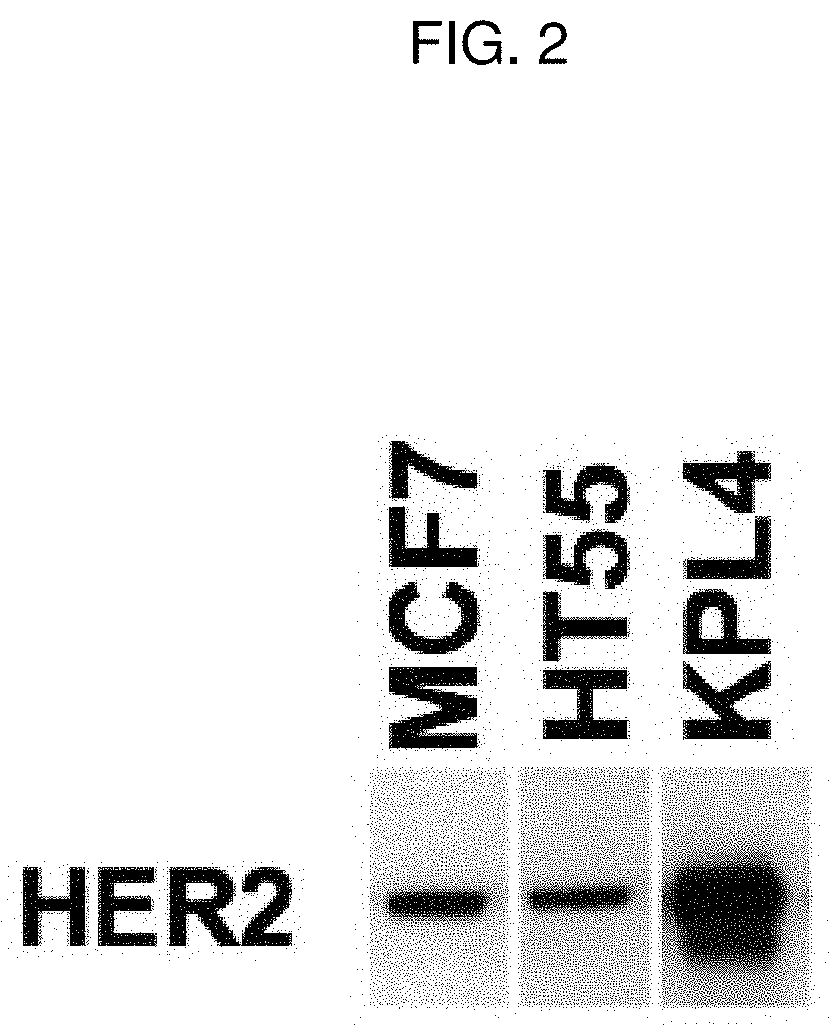
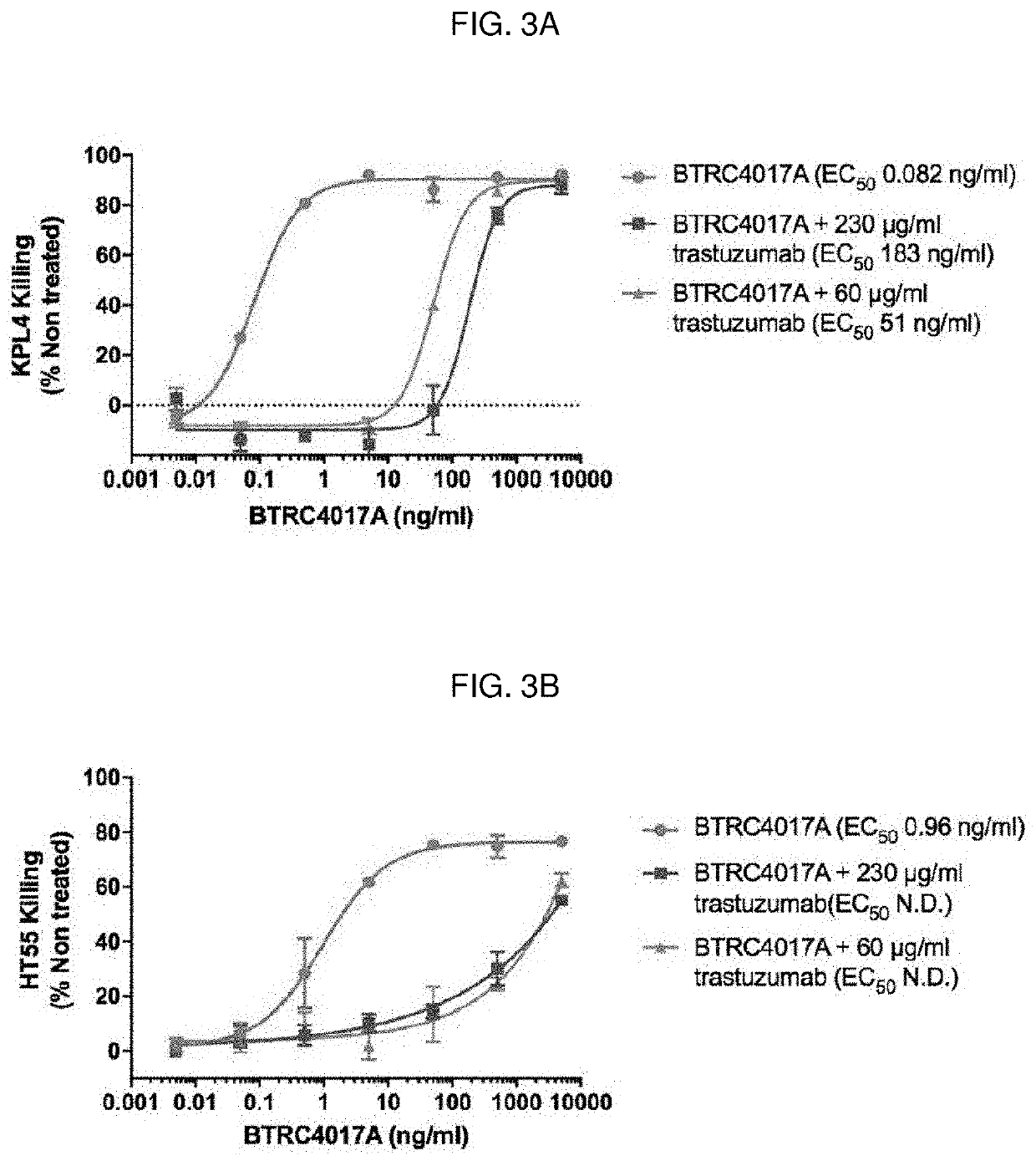
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Trastuzumab resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
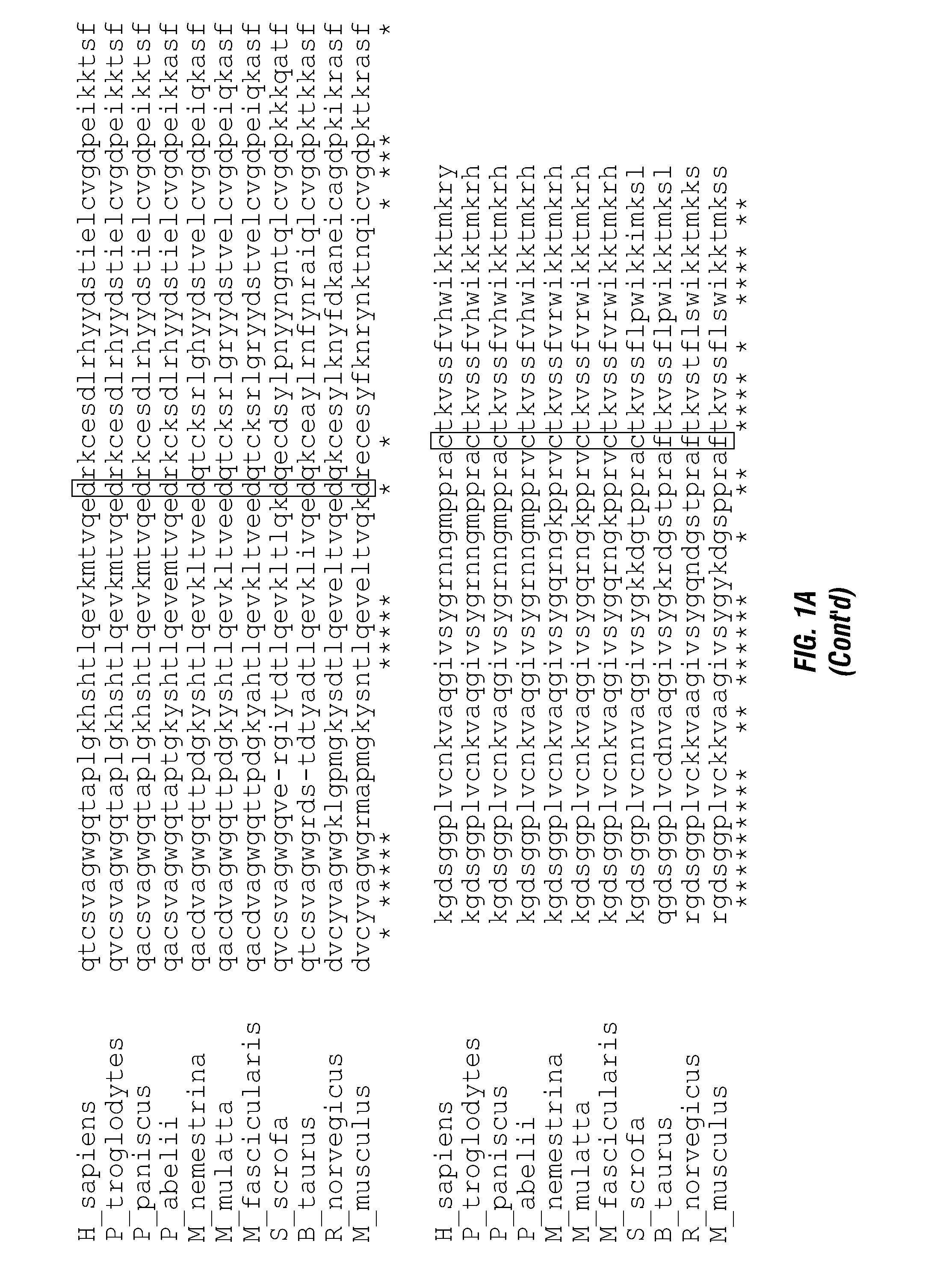
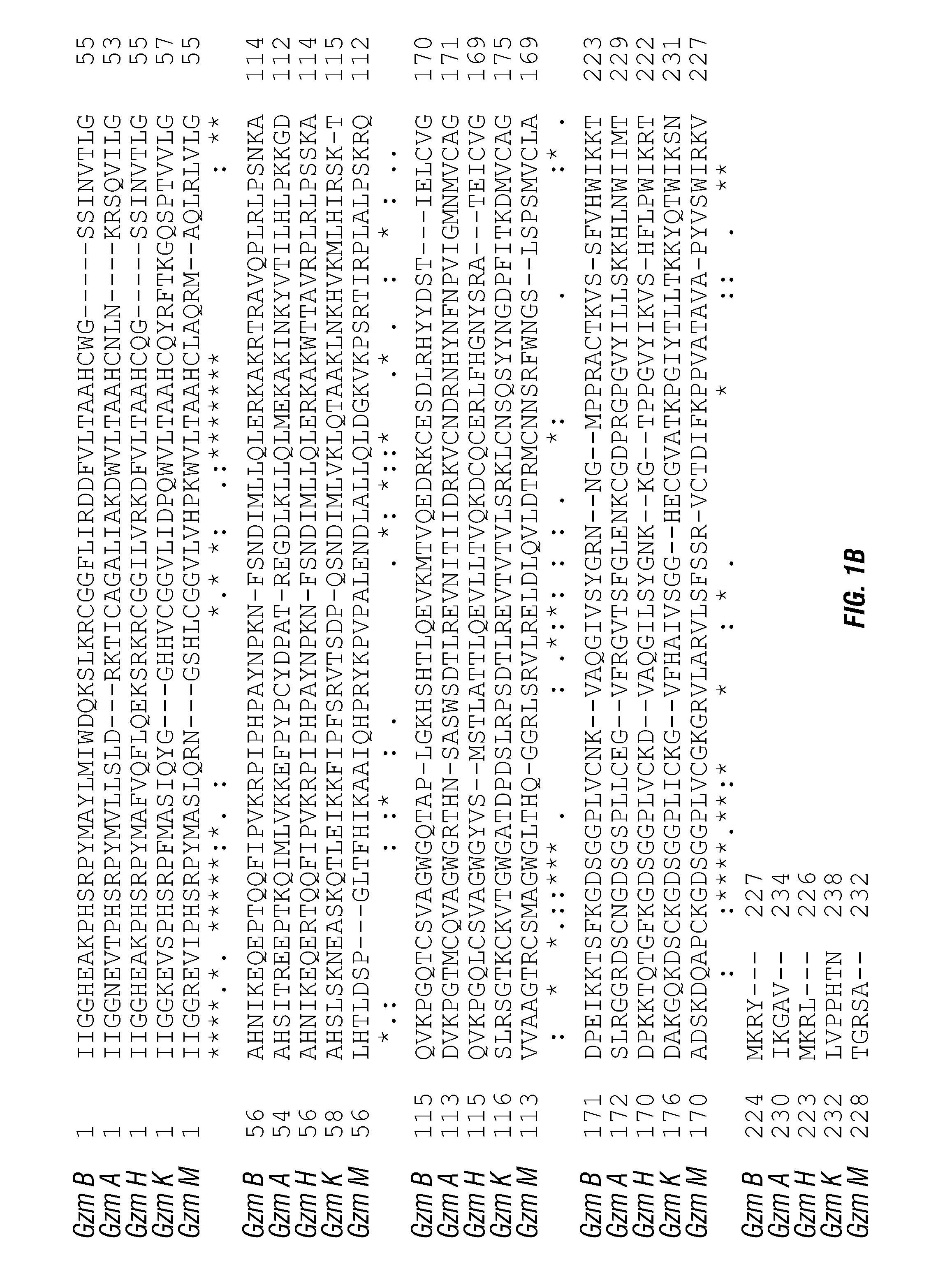
Serine protease molecules and therapies
ActiveUS20140140976A1Enhanced intracellular activityReduce distractionsNervous disorderHydrolasesResistant cancerCancer research
Cell-targeted serine protease constructs are provided. Such constructs can be used in methods for targeted cell killing such as for treatment cell of proliferative diseases (e.g., cancer). In some aspects, recombinant serine proteases, such as Granzyme B polypeptides, are provided that exhibit improved stability and cell toxicity. Methods and compositions for treating lapatinib or trastuzumab-resistant cancers are also provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
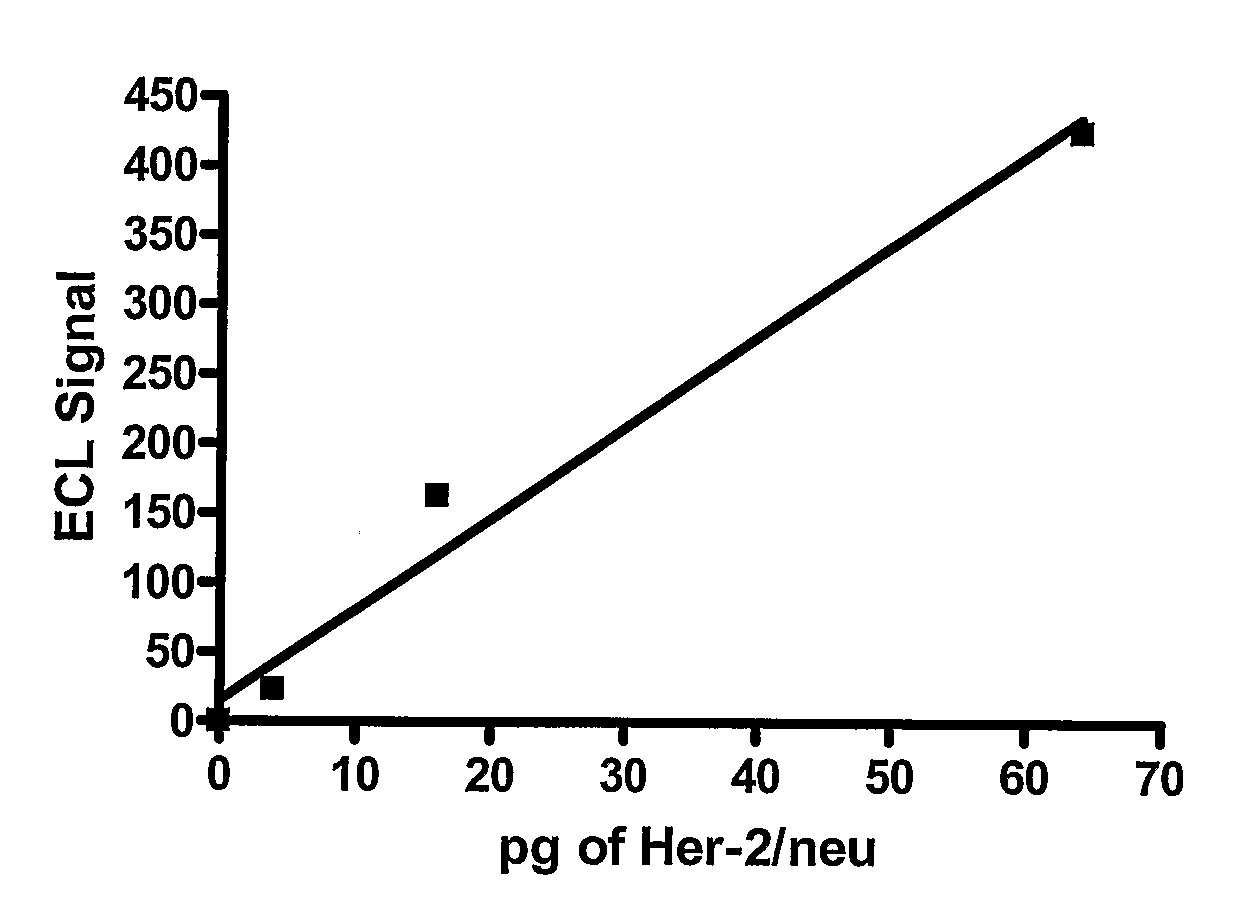
Detection of Elevated Levels of Her-2/Neu Protein on Circulating Cancer Cells and Treatment
InactiveUS20080261243A1Biological material analysisImmunoglobulinsAnticarcinogenCirculating cancer cell
The expression of Her-2 / neu protein on circulating cancer cells in a blood sample is detected by isolating the cancer cells from the blood sample and then performing on the isolated cancer cells a sensitive Her-2 / neu immunoassay. A positive result indicates the expression of Her-2 / neu on cancer cells in the blood sample. This method can be used to identify cancer patients who are likely to benefit from treatment with an anticancer agent that targets Her-2 / neu, such as trastuzumab (HERCEPTIN).
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOLOGICS CORP
Bispecific antibodies targeting EGFR and HER2
ActiveCN109563166AHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesCetuximab
The present disclosure relates to bispecific antibodies targeting EGFR and HER2, and methods for the production of these antibodies. The bispecific antibodies consist of one complete antibody on whichtwo VH-VL chains are attached via a linker to each NH terminal region of both VH chains of the antibody. The bispecific antibodies constructed use the amino acid sequences of the heavy chain (VH) andthe light chain (VL) variable regions of two monoclonal antibodies targeting EGFR and HER2, namely cetuximab and trastuzumab, respectively
Owner:BIOMUNEX PHARMA +3
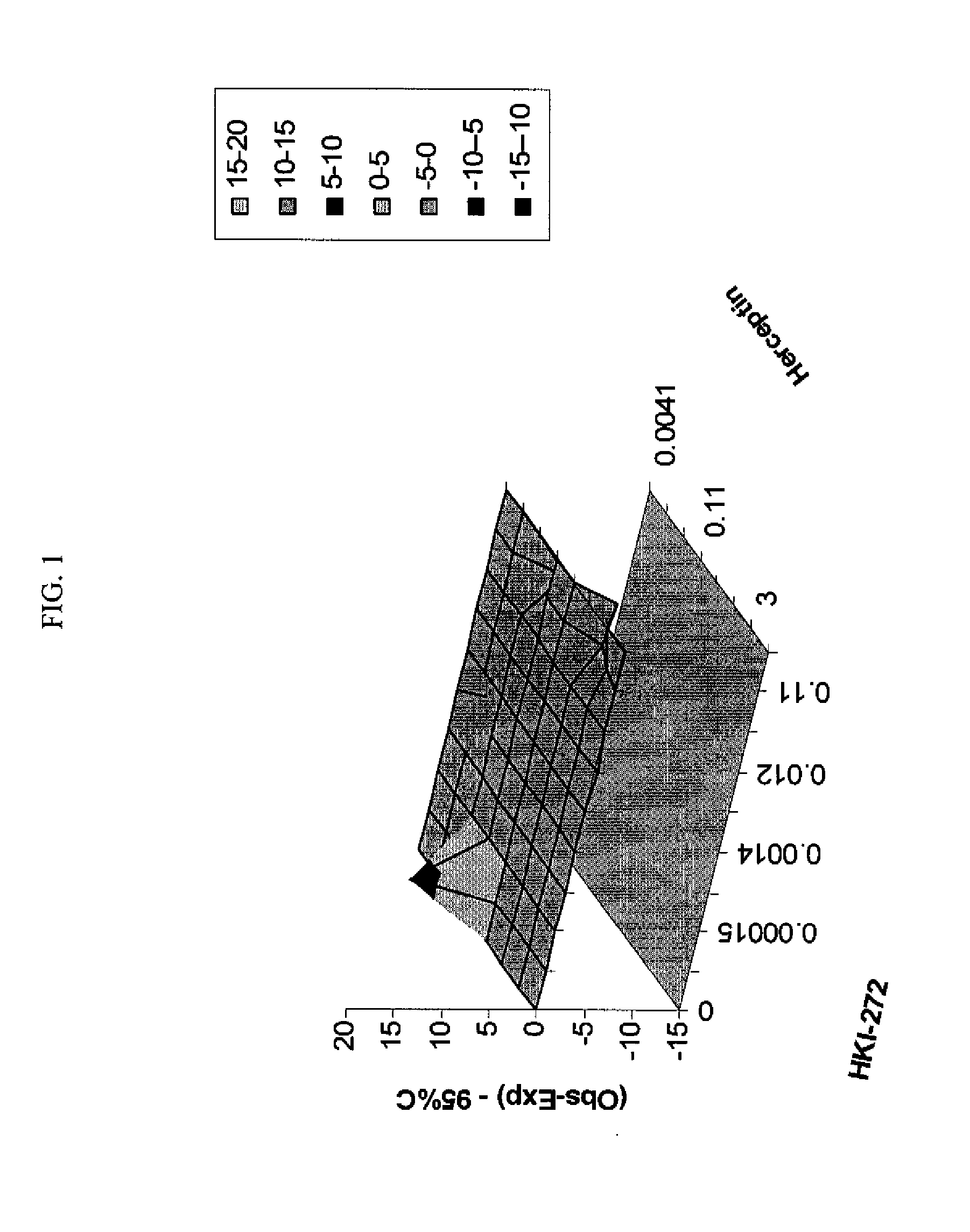
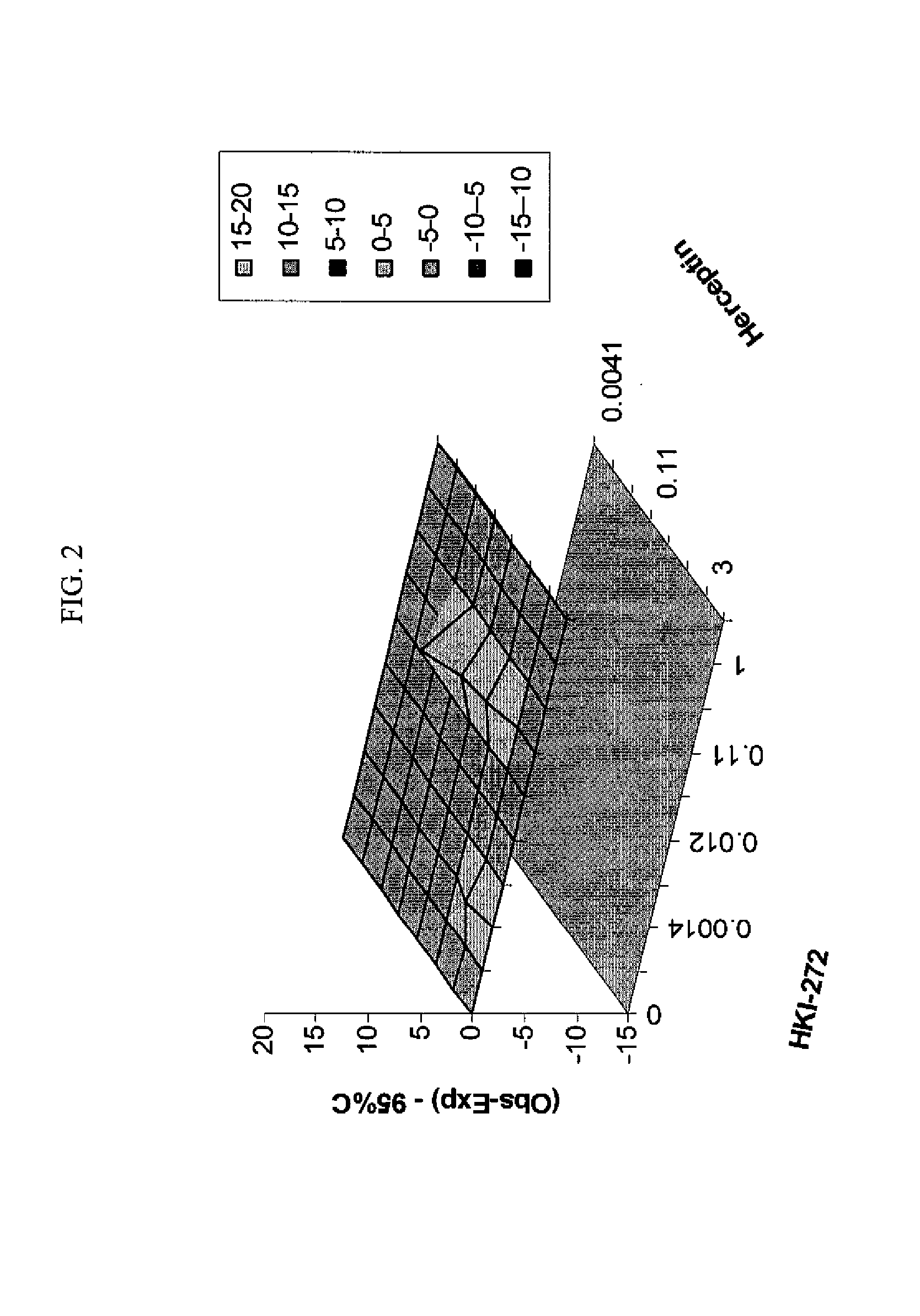
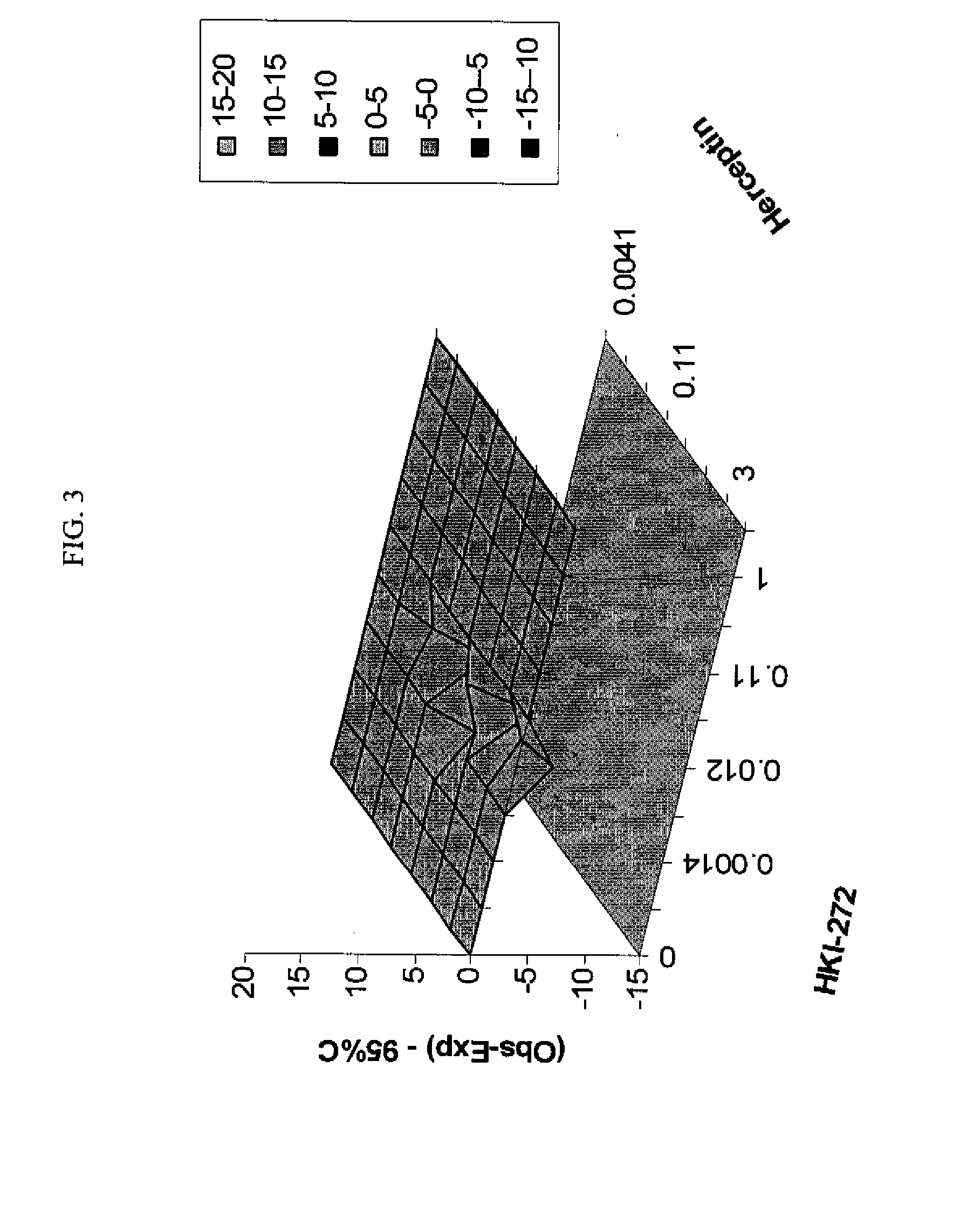
Antineoplastic Combinations with mTOR Inhibitor, Trastuzumab and/or HKI-272
A combination of temsirolimus and trastuzumab in the treatment of cancer is provided. A combination of temsirolimus and HKI-272 is provided. A combination of a trastuzumab and a HKI-272 is also provided. Regimens and kits for treatment of metastatic breast cancer, containing trastuzumab, temsirolimus and / or HKI-272, optionally in combination with other anti-neoplastic agents, or immune modulators are described.
Owner:WYETH LLC
ANTINEOPLASTIC COMBINATIONS WITH mTOR INHIBITOR, TRASTUZUMAB, AND/OR HKI-272
A combination of temsirolimus and trastuzumab in the treatment of cancer is provided. A combination of temsirolimus and HKI-272 is provided. A combination of a trastuzumab and a HKI-272 is also provided. Regimens and kits for treatment of metastatic breast cancer, containing trastuzumab, temsirolimus and / or HKI-272, optionally in combination with other anti-neoplastic agents, or immune modulators are described.
Owner:WYETH LLC
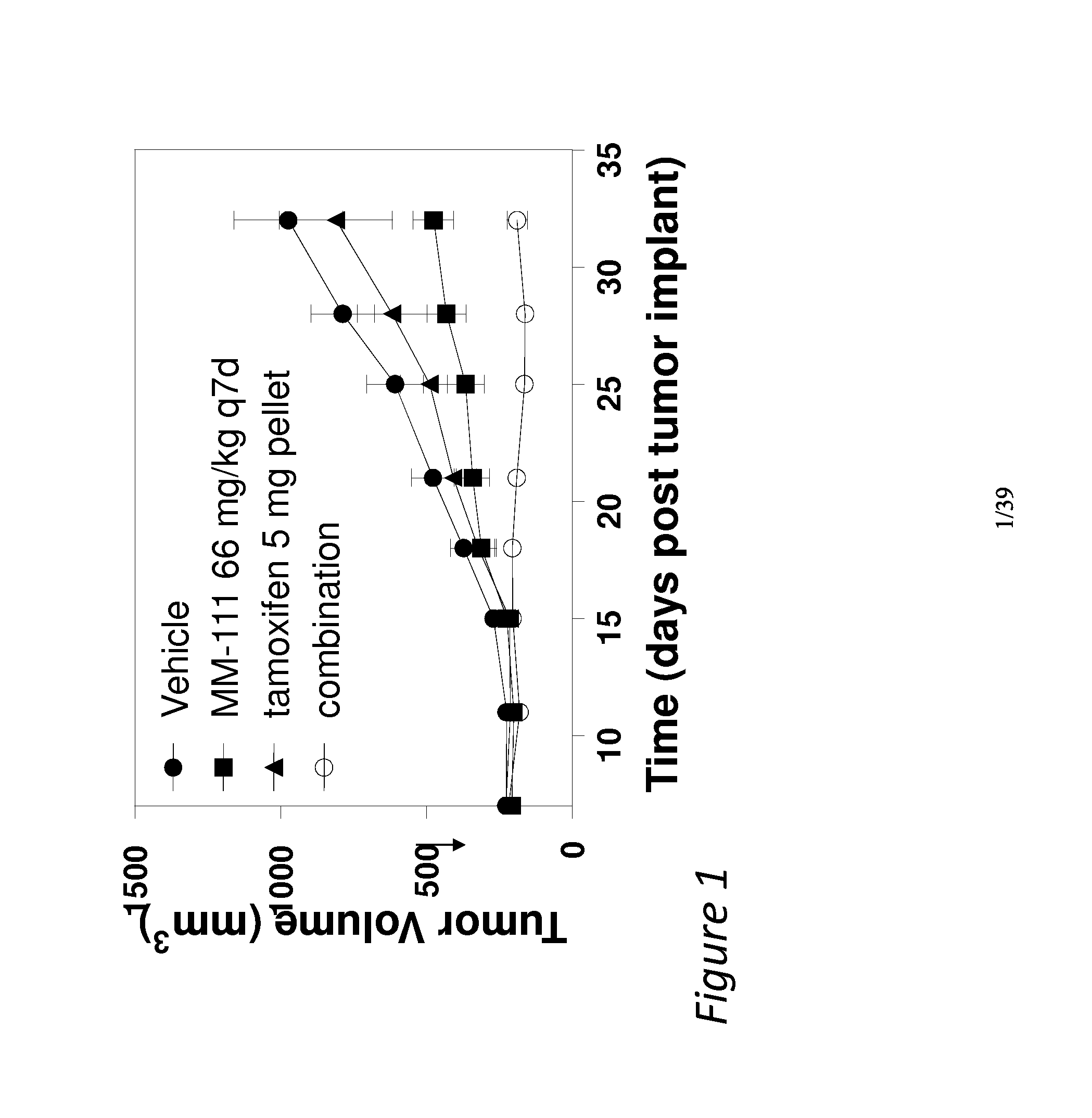
Combination therapies comprising Anti-erbb3 agents
Disclosed are methods and compositions for inhibiting the growth of a tumor (e.g., a malignant tumor) in a subject. In particular, combination therapies for treating a tumor in a subject by co-administering an agent selected from i) an effective amount of an anti-estrogen agent; ii) an effective amount of a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor; iii) an effective amount of a MEK / PI3 kinase / AKT inhibitor; iv) an effective amount of MM-151; v) an effective amount of an mTOR inhibitor; and / or vi) an effective amount of trastuzumab or TMD1, and / or combinations thereof; and an effective amount of a bispecific anti-ErbB2 / anti-ErbB3 antibody. Also disclosed is a bispecific anti-ErbB2 / anti-ErbB3 antibody for use in the therapy of a tumor in combination with an agent selected from i) an effective amount of an anti-estrogen agent; ii) an effective amount of a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor; iii) an effective amount of a MEK / PI3 kinase / AKT inhibitor; iv) an effective amount of MM-151; v) an effective amount of an mTOR inhibitor; and / or vi) an effective amount of trastuzumab or TMD1, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:14NER ONCOLOGY INC
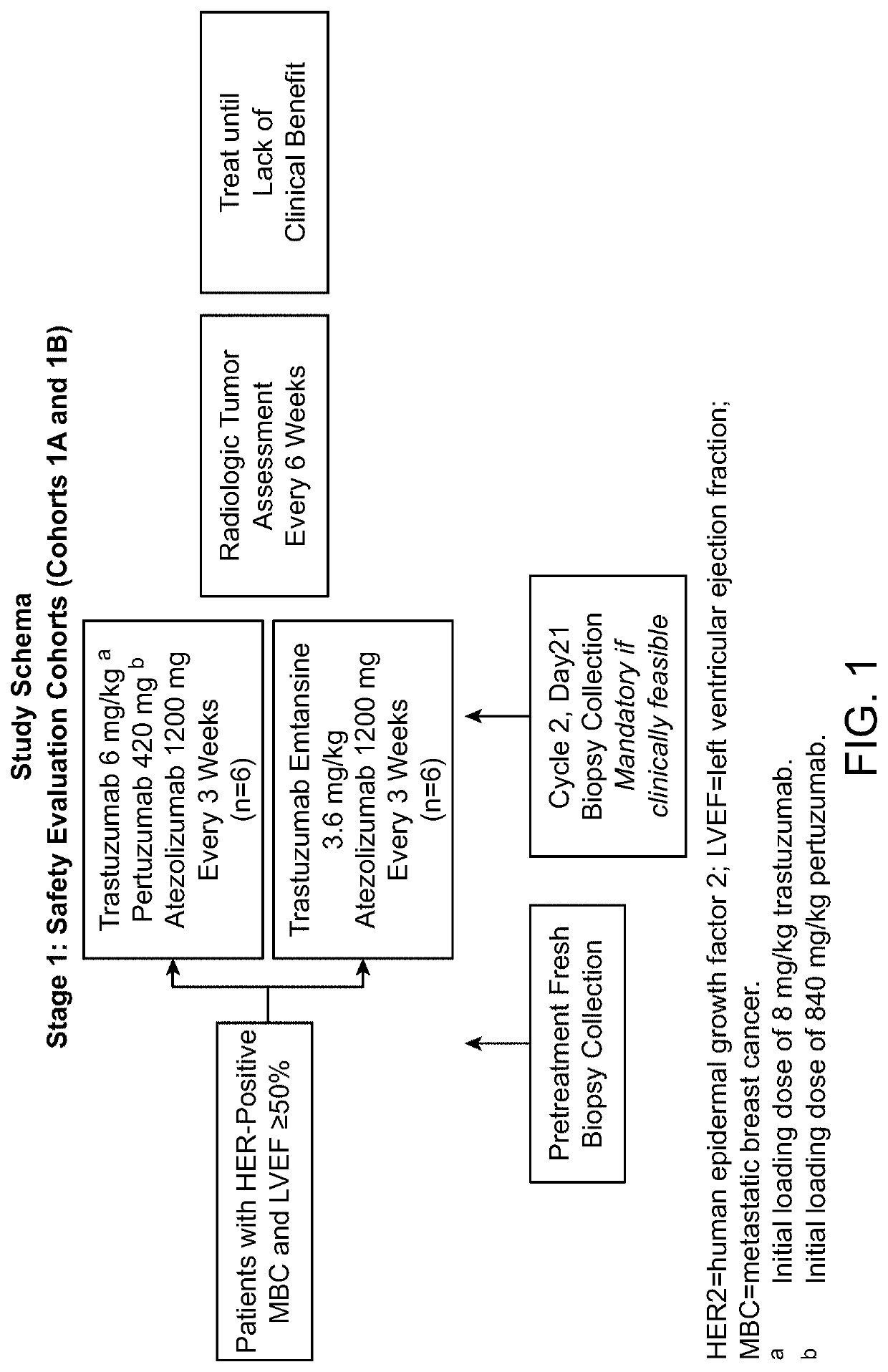
Treatment of advanced her2 expressing cancer
InactiveUS20200237910A1High response rateImprove responseAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsProstate cancerBiliary tract
Methods for the treatment of patients with HER2-positive, HER2-amplified and / or HER2-mutated advanced cancer by administration of pertuzumab plus trastuzumab are disclosed. In one aspect, the cancer is advanced HER2-positive, HER2-amplified and / or HER2-mutated colorectal, biliary, bladder, urothelial, salivary, lung, pancreatic, ovarian, prostate, or skin cancer. In another aspect, the cancer is HER2-positive, HER2-amplified and / or HER2-mutated colorectal, biliary, bladder, urothelial, salivary, lung, pancreatic, ovarian, prostate, or skin cancer that is refractory to one or more other treatment regimens.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
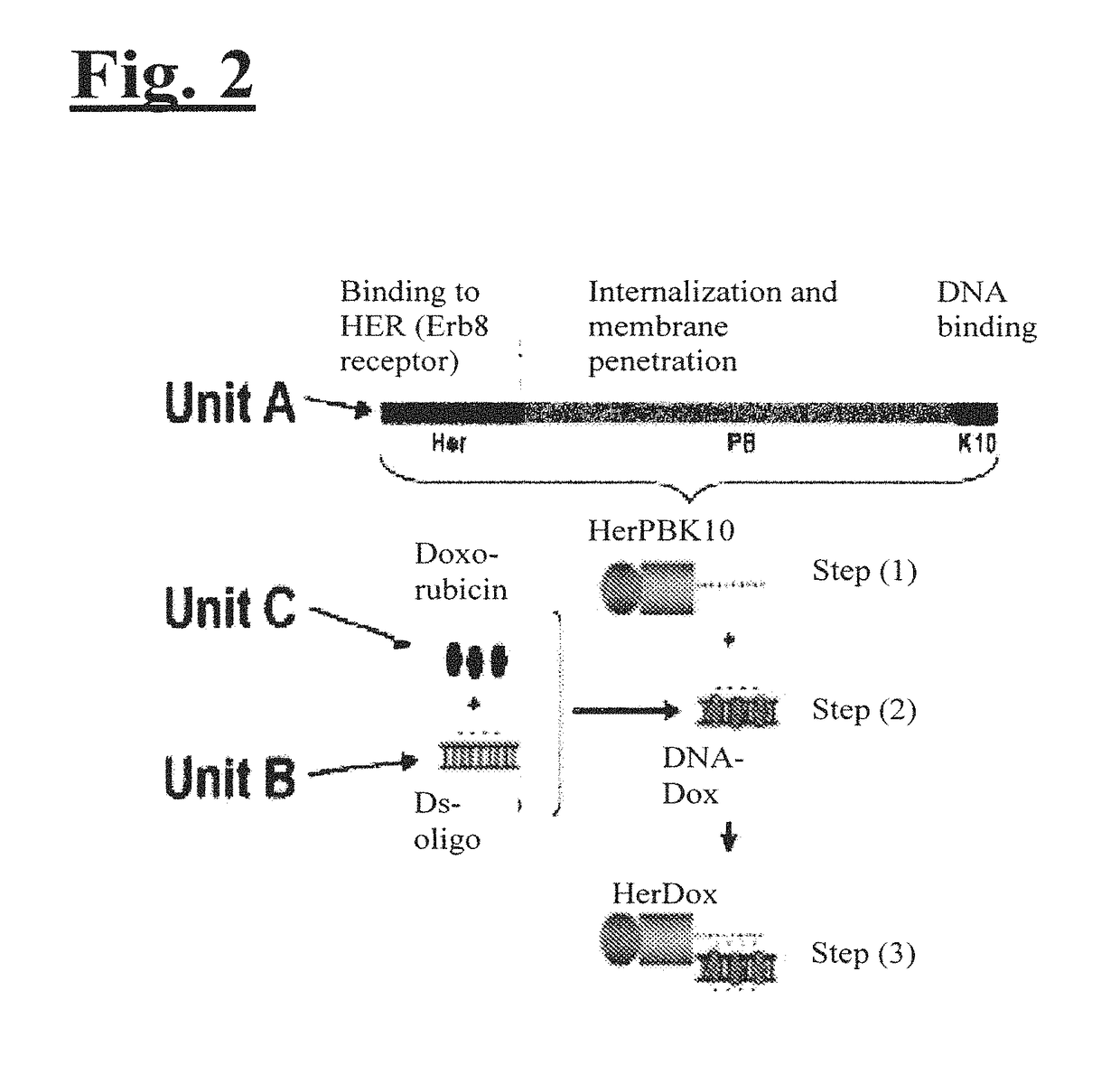
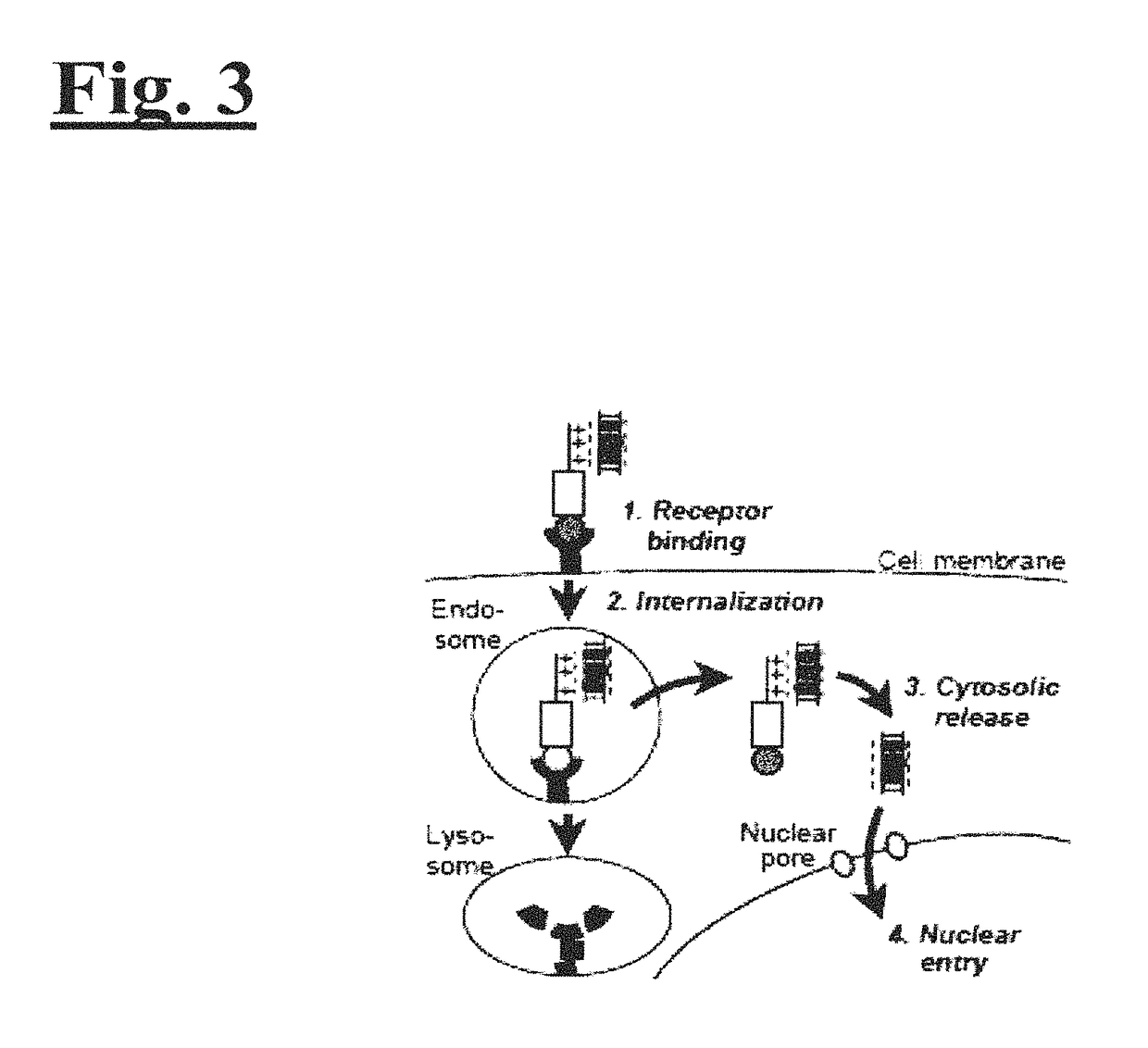
Targeting trastuzumab-resistant her2+ breast cancer with a her3-targeting nanoparticle
InactiveUS20180066033A1Organic active ingredientsFusion with DNA-binding domainTherapy resistantApoptosis
Disclosed herein are methods of treating cancer in a patient, the method comprising identifying a patient who is resistant to treatment with an anti-HER2 therapy; and administering to the patient a drug delivery molecule, comprising a polypeptide molecule adapted to target and / or penetrate a type of cell; a nucleic acid molecule bound to the polypeptide sequence via electrostatic interactions; and a chemical agent non-covalently linked to the nucleic acid sequence. Also disclosed are methods of inducing apoptosis in an anti-HER2 therapy resistant HER2+ breast cancer cell, the method comprising contacting the anti-HER2 therapy resistant HER2+ breast cancer cell with the drug delivery molecule. Further disclosed herein are methods of treating cancer in a patient, the method comprising identifying a patient who is resistant to anti-HER2 therapy; and administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of a drug delivery molecule, comprising a polypeptide molecule adapted to target and / or penetrate a type of cell; and a sulfonated corrole molecule bound to the polypeptide sequence. Finally disclosed herein are methods of inducing apoptosis in an anti-HER2 therapy resistant HER2+ breast cancer cell, the method comprising contacting the anti-HER2 therapy resistant HER2+ breast cancer cell with a drug delivery molecule, comprising a polypeptide molecule adapted to target and / or penetrate a type of cell; and a sulfonated corrole molecule bound to the polypeptide sequence.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
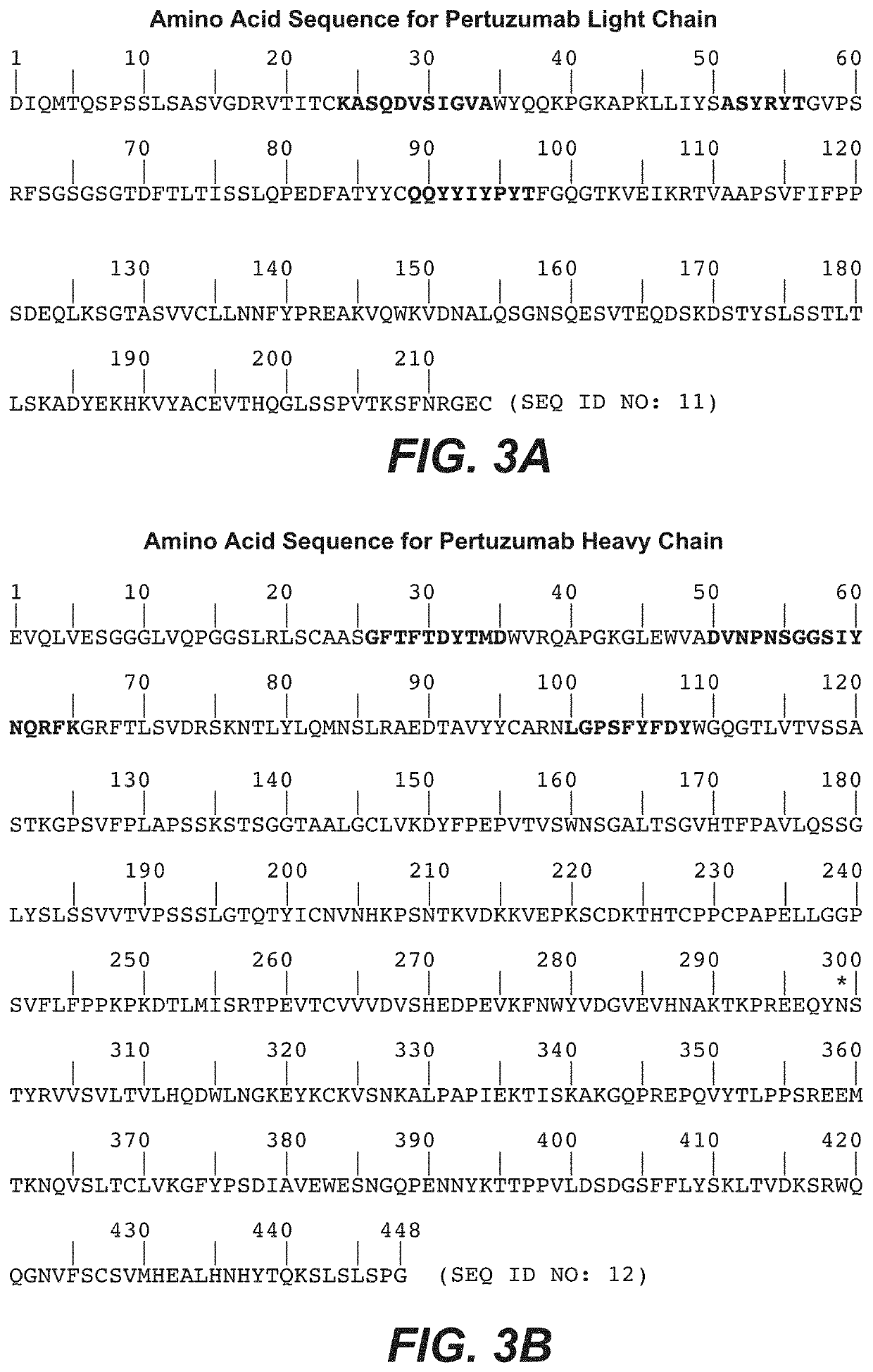
Adjuvant treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer
ActiveUS11077189B2Reduce riskReduce deathOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPrimary breast cancerIV Chemotherapy
Methods are provided for the adjuvant treatment of operable HER2-positive primary breast cancer in human patients by administration of pertuzumab in addition to chemotherapy and trastuzumab. The methods reduce the risk of recurrence of invasive breast cancer or death for a patient diagnosed with HER2-positive early breast cancer (eBC) compared to administration of trastuzumab and chemotherapy, without pertuzumab.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Serine protease molecules and therapies
Cell-targeted serine protease constructs are provided. Such constructs can be used in methods for targeted cell killing such as for treatment cell of proliferative diseases (e.g., cancer). In some aspects, recombinant serine proteases, such as Granzyme B polypeptides, are provided that exhibit improved stability and cell toxicity. Methods and compositions for treating lapatinib or trastuzumab-resistant cancers are also provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Adjuvant treatment of her2-positive breast cancer
ActiveUS20210330789A1Reduce riskReduce deathOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPrimary breast cancerIV Chemotherapy
Methods are provided for the adjuvant treatment of operable HER2-positive primary breast cancer in human patients by administration of pertuzumab in addition to chemotherapy and trastuzumab. The methods reduce the risk of recurrence of invasive breast cancer or death for a patient diagnosed with HER2-positive early breast cancer (eBC) compared to administration of trastuzumab and chemotherapy, without pertuzumab.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Methods of treating her2-positive cancer
InactiveUS20210040216A1Organic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHER2 Positive Breast CancerProgrammed death
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Cell strain for expressing HER2 gene, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN104017772AStable expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionMultiple cloning siteNude mouse
The invention provides a cell strain for expressing HER2 gene, and a construction method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) inserting HER2 gene into the polyclone site of the expression vector to obtain a recombinant expression vector; and 2) transfecting a cell strain by using the recombinant expression vector to obtain the monoclonal cell strain for expressing HER2 gene. The cell strain can efficiently and stably express the HER2 gene, has resistance to the existing HER2 targeted antibody drug trastuzumab, can successfully construct a human breast cancer transplantation tumor model in the nude mouse body, and can be used for screening novel breast cancer drugs.
Owner:HEFEI HANKEMAB BIOTECH CO LTD
Trastuzumab-mediated cis-platinum targeting conjugate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104857523ASimple preparation processImprove stabilityHeavy metal active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsHER2 Positive Breast CancerCarboxyl radical
The invention relates to medicine technical field, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a trastuzumab-mediated cis-platinum targeting conjugate and application of the trastuzumab-mediated cis-platinum targeting conjugate in the preparation of a breast cancer resistant drug. Amphiphilic block copolymer methoxy polyethylene glycol-polyglutamic acid (mPEG-PGA) prepared from methoxypolyethylene glycol amine and 5-benzyl L-glutamate N-carboxyanhydrie is used as a base material for preparation of cis-platinum loading nano balls through the membrane dialysis method, and a carrier is connected with trastuzumab by carrier surface carboxyl group to prepare the trastuzumab-mediated cis-platinum targeting conjugate. The trastuzumab-mediated cis-platinum targeting conjugate can be targeted to enrich chemotherapy drugs in tumor site so as to directly kill tumor cells, reduce the side and toxic effects of traditional antitumor drugs, and trastuzumab targeting therapy of HER2 positive breast cancer patients can be implemented. The trastuzumab-mediated cis-platinum targeting conjugate can cleverly realize trastuzumab and cis-platinum combined targeted drug delivery way, and has good application prospect in treatment of breast cancer by combination of trastuzumab and chemotherapy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for knocking out FUT8 gene
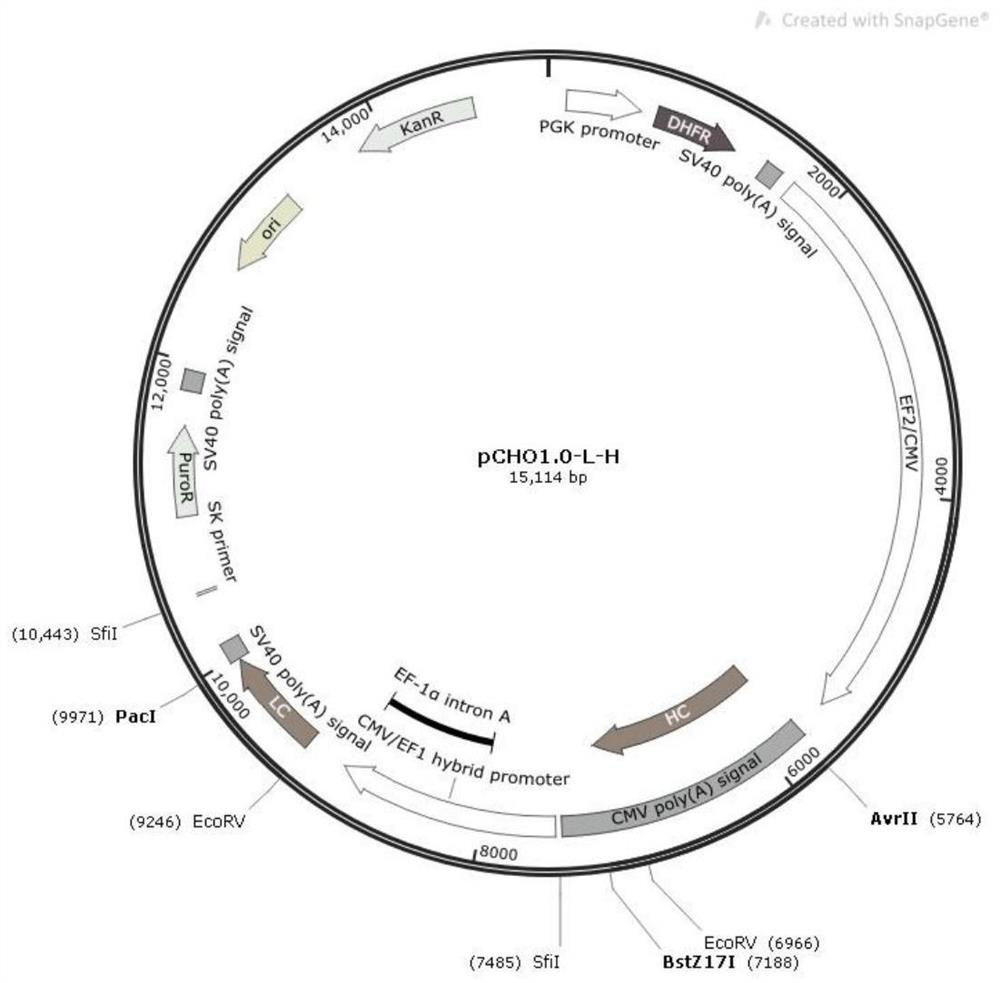
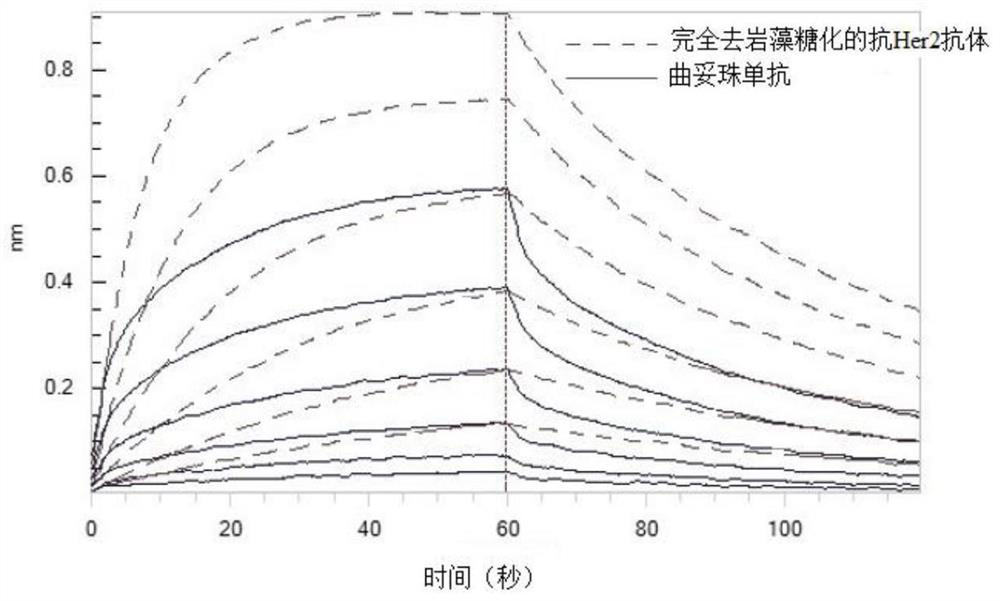
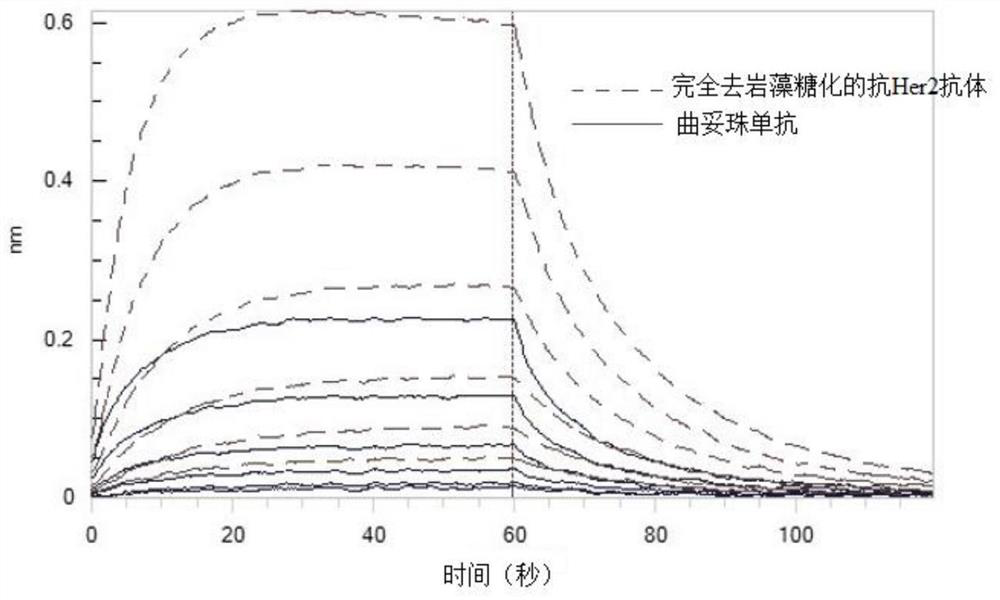
PendingCN114457110ASimple and fast operationSave time and costGenetically modified cellsAntibody ingredientsGene silencingTrastuzumab resistance
The invention discloses a method for knocking out an FUT8 gene to improve the ADCC activity of an antibody. And coding the FUT8 gene of the CHO cell by using a CRISPR / Cas9 technology to obtain the CHO cell silenced by the FUT8 gene. Through detection of physicochemical properties and biological activity of the engineered cell expression antibody, a glycoform detection result shows that fucose of the engineered cell expression antibody is completely eliminated, and by taking trastuzumab as a contrast, the affinity of the engineered cell expression complete fucose-free antibody and Fc gamma Rs antigen is improved by 20 times, and the ADCC effect is improved by 19 times.
Owner:SHENGHE CHINA BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Compositions and methods for treatment of her2 positive metastatic breast cancer
InactiveCN109475576AOrganic active ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAntigenAntiendomysial antibodies
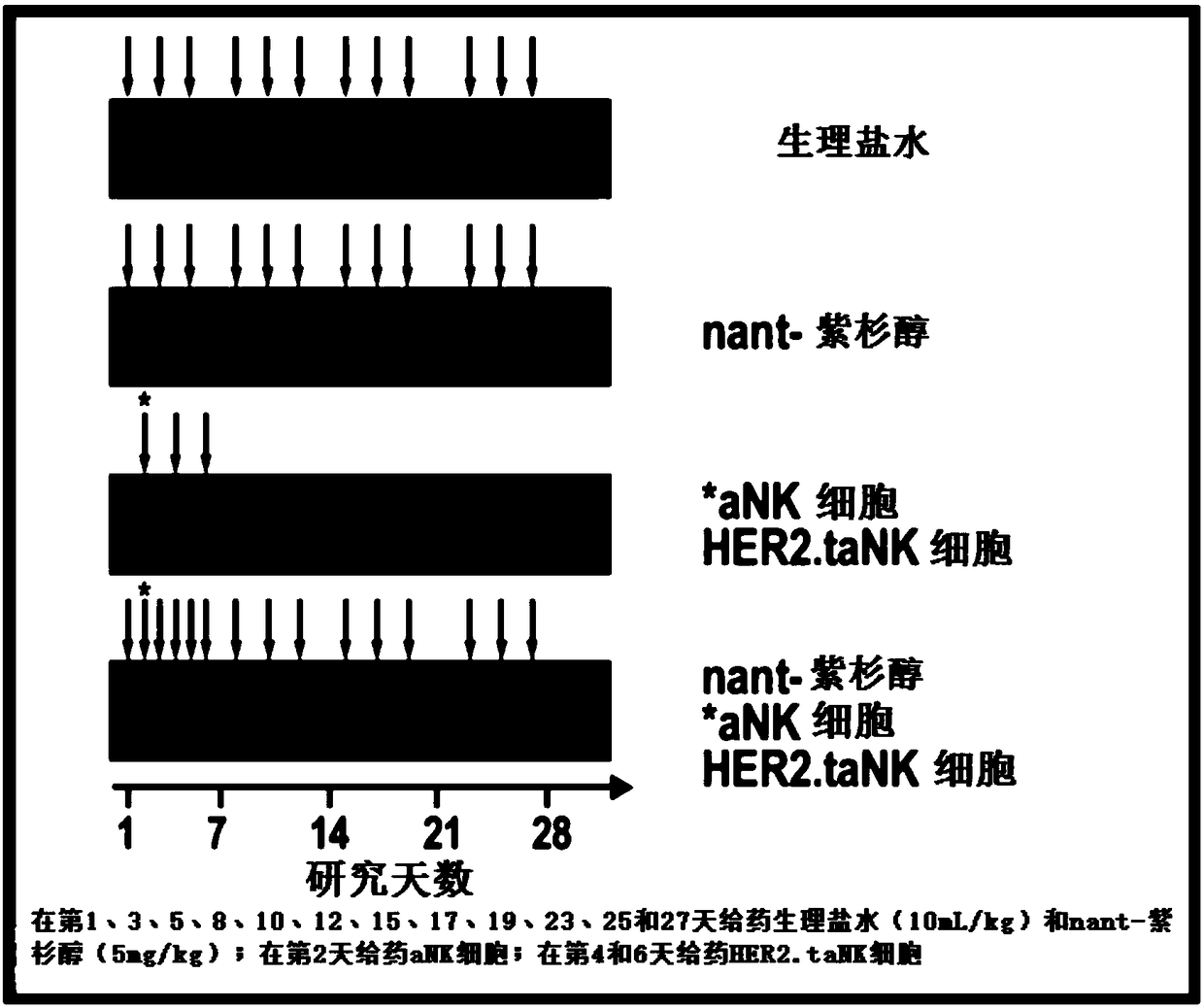
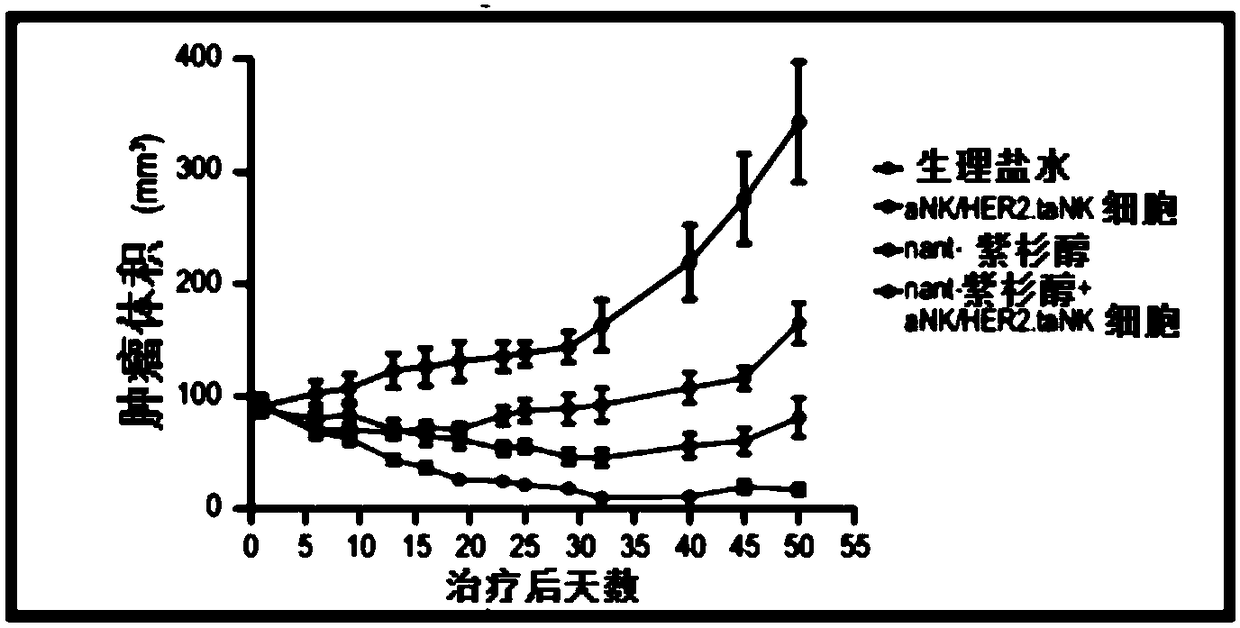
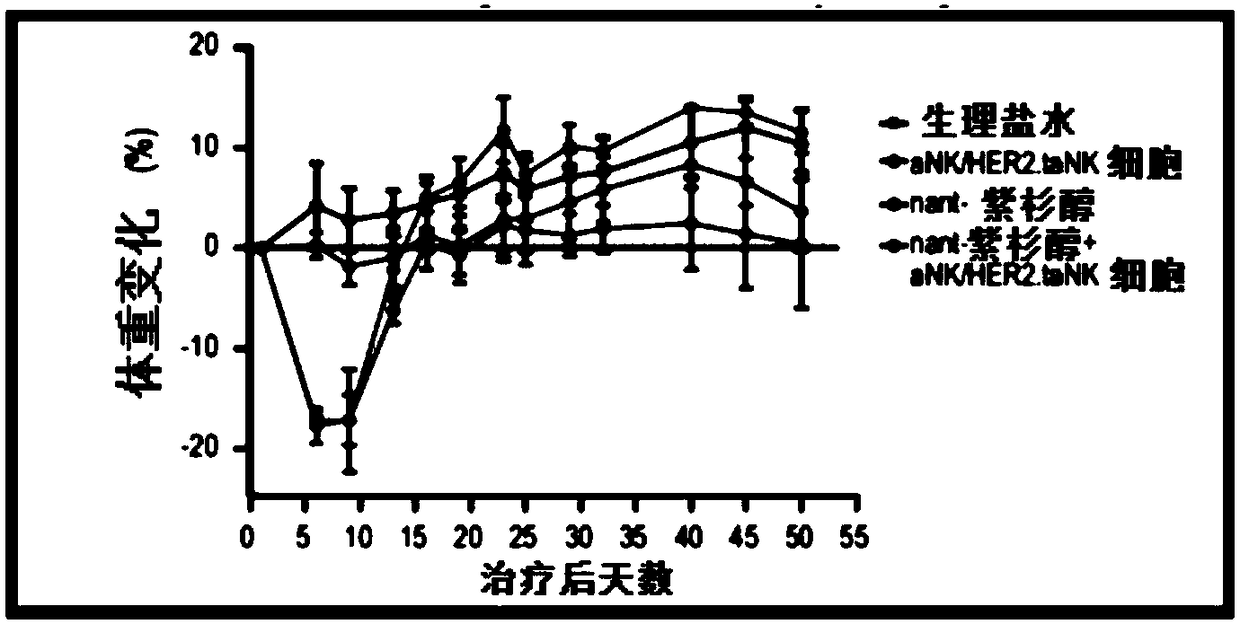
Contemplated immunotherapies include co-administration of an activated NK cell that is further genetically modified and a cancer therapeutic agent. In preferred embodiments, activated NK cells are further modified to taNK cells, which include a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) with affinity for a cancer specific antigen, a cancer associated antigen, or a tumor specific antigen. Activated NK cells can also be further genetically modified to include high affinity Fc receptor CD16a (V158). Appropriate cancer therapeutic agents include chemotherapeutic drugs (e.g., nant-paclitaxel) or cancer targeted antibodies (e.g., trastuzumab).
Owner:NANTCELL INC +1
Methods of determining acute myeloid leukemia response to treatment with farnesyltransferase inhibitors
ActiveCN103328971APredictive validityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGene expressionPaclitaxel
The disclosed method rapidly identifies with desired accuracy AML patients, including elderly AML patients, likely to respond to treatment with a combination of a farnesyltransferase inhibitor and one or more of etoposide, teniposide, tamoxifen, sorafenib, paclitaxel, temozolomide, topotecan, trastuzumab and cisplatinum. In an embodiment, the improvements include the use of whole blood rather than the customary bone marrow sample, thus making the assay more accurate, rapid, less intrusive, less expensive as well as less painful. The method includes evaluation of a two-gene expression ratio (RASGRP1 :APTX), which with a corresponding threshold, provides sufficient accuracy for predicting the response to the combination treatment. In the preferred embodiment the combination treatment combines tipifarnib (Rl 15777, ZARNESTRA TM ) with etoposide. Further, the elderly AML patients identified as being likely responsive to the combination treatment with tipinifarb and etoposide have a complete recovery rate comparable to the best therapy available for younger patients.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Anti-her2 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof, and chimeric antigen receptor comprising same
ActiveCN111655732ALow homologyGood killing effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntiendomysial antibodiesAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention relates to a novel anti-HER2 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof used in the prevention or treatment of cancer, a chimeric antigen receptor comprising the same, and usesthereof. The antibody of the present invention is an antibody that specifically binds to HER2 which is highly expressed in cancer cells (particularly, breast cancer or gastric cancer cells), and binds to an epitope that is different from an epitope to which conventional trastuzumab binds. Compared to transtuzumab, the antibody of the present invention exhibits a better killing ability with respect to kill HER2-unexpressed cancer cells which have non reactivity (or resistance) to a trastuzumab antibody or have reduced sensitivity. In addition, when the anti-HER2 antibody of the present invention is administered in combination with trastuzumab, a synergistic killing ability with respect to a cancer cell line on which the trastuzumab antibody acts. Therefore, a composition of the present invention can be very usefully used for combined administration with a trastuzumab antibody for the treatment of cancer, and for the treatment of cancer not treated by trastuzumab.
Owner:GREEN CROSS LAB CELL CORP
Bispecific antibodies targeting EGFR and her2
PendingUS20190153104A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesCetuximab
The present disclosure relates to bispecific antibodies targeting EGFR and HER2, and methods for the production of these antibodies. The bispecific antibodies consist of one complete antibody on which two VH-VL chains are attached via a linker to each NH terminal region of both VH chains of the antibody. The bispecific antibodies constructed use the amino acid sequences of the heavy chain (VH) and the light chain (VL) variable regions of two monoclonal antibodies targeting EGFR and HER2, namely cetuximab and trastuzumab, respectively.
Owner:INST REGIONAL DU CANCER DE MONTPELLIER +3
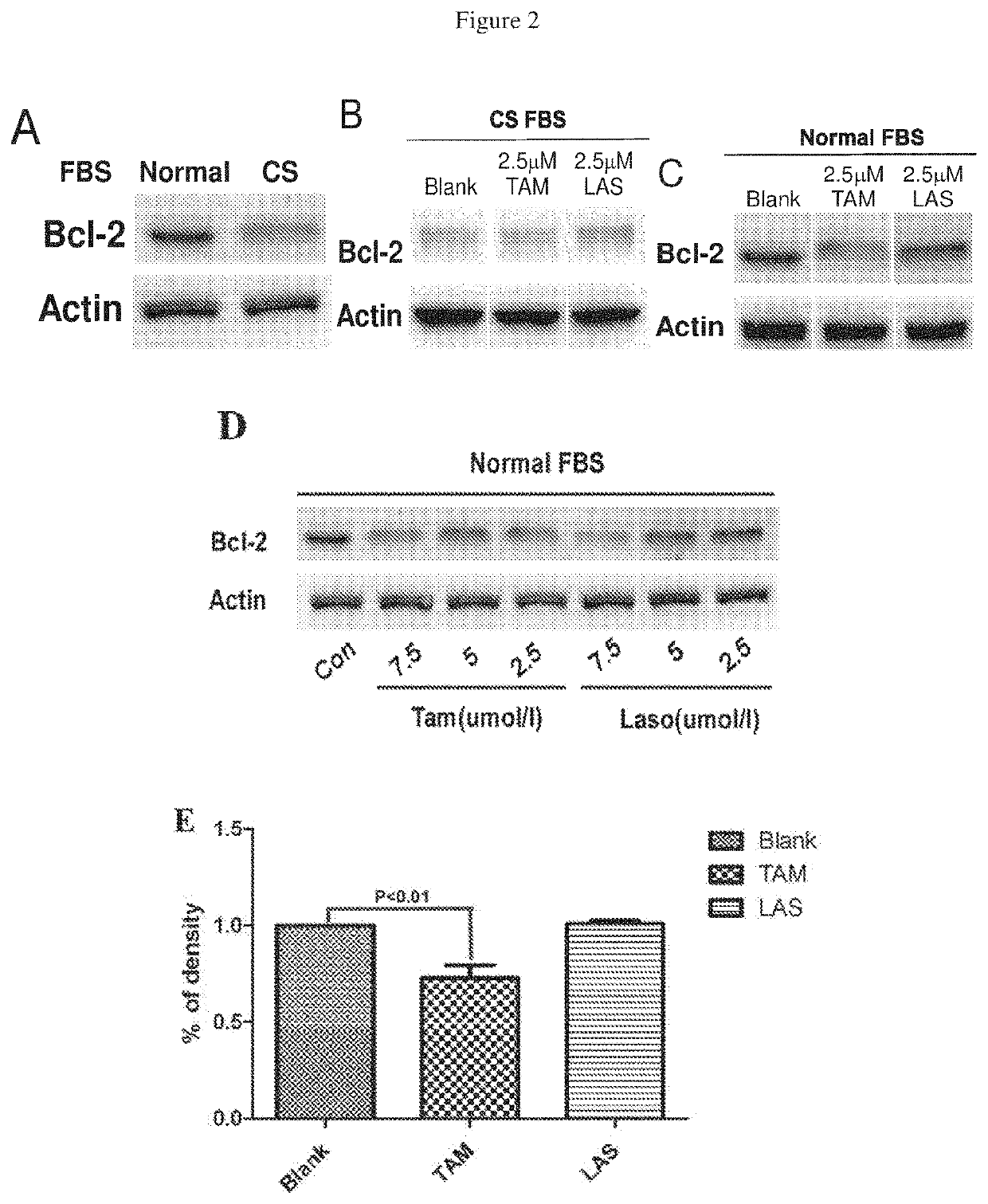
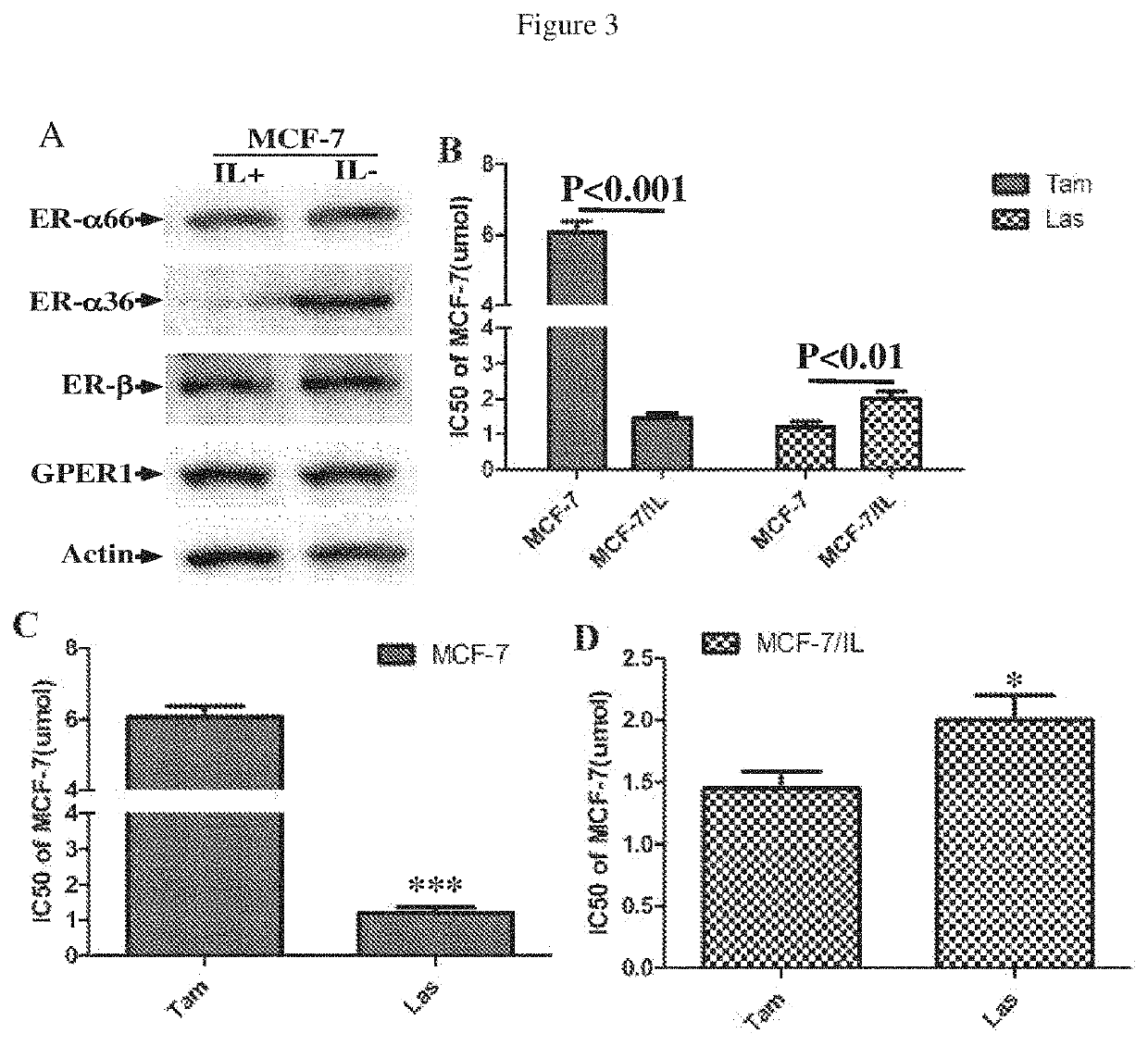
Lasofoxifene modulation of membrane-initiated estrogen signals and methods for tumor treatment
The present invention found that lasofoxifene is an antagonist of ER-α36. It not only inhibits the growth of ER-α36 positive lung, colon and gastric cancers, and also it can inhibit the growth of acquired or de novo tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 cells. Our finding also provides methods and compositions for treating cancer comprising lasofoxifene alone or in combination with at least one other agent selected from the group consisting of gefitinib and / or trastuzumab or functional equivalent thereof, and an inhibitor in hormonal or epidermal growth factor signal transduction pathways.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIACHI PHARMA DEV LTD
System and Method for Cold Plasma Therapy with HER-Family Receptors
PendingUS20200069958A1Promote resultsEnhance specific killingElectrotherapySurgical instrument detailsCancer cellReceptor
A system and method for using a concomitant effect of cold atmospheric plasma and Trastuzumab to overcome Trastuzumab invalidity or resistance and enhances the outcome of breast cancer therapy in both HER2-positive and negative cancer cells.
Owner:JEROME CANADY RES INST FOR ADVANCED BIOLOGICAL & TECHCAL SCI
Combination therapies comprising anti-ERBB 3 agents
InactiveCN103547598AHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesTyrosine
Disclosed are methods and compositions for inhibiting the growth of a tumor (e.g., a malignant tumor) in a subject. In particular, combination therapies for treating a tumor in a subject by co-administering either i) an effective amount of an anti-estrogen agent or ii) an effective amount of a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor and an effective amount of a bispecific anti-ErbB2 / anti-ErbB3 antibody, and optionally an effective amount of trastuzumab. Also disclosed is a bispecific anti-ErbB2 / anti-ErbB3 antibody for use in the therapy of a tumor in combination with either i) an anti-estrogen agent or ii) a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and optionally in use with trastuzumab.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
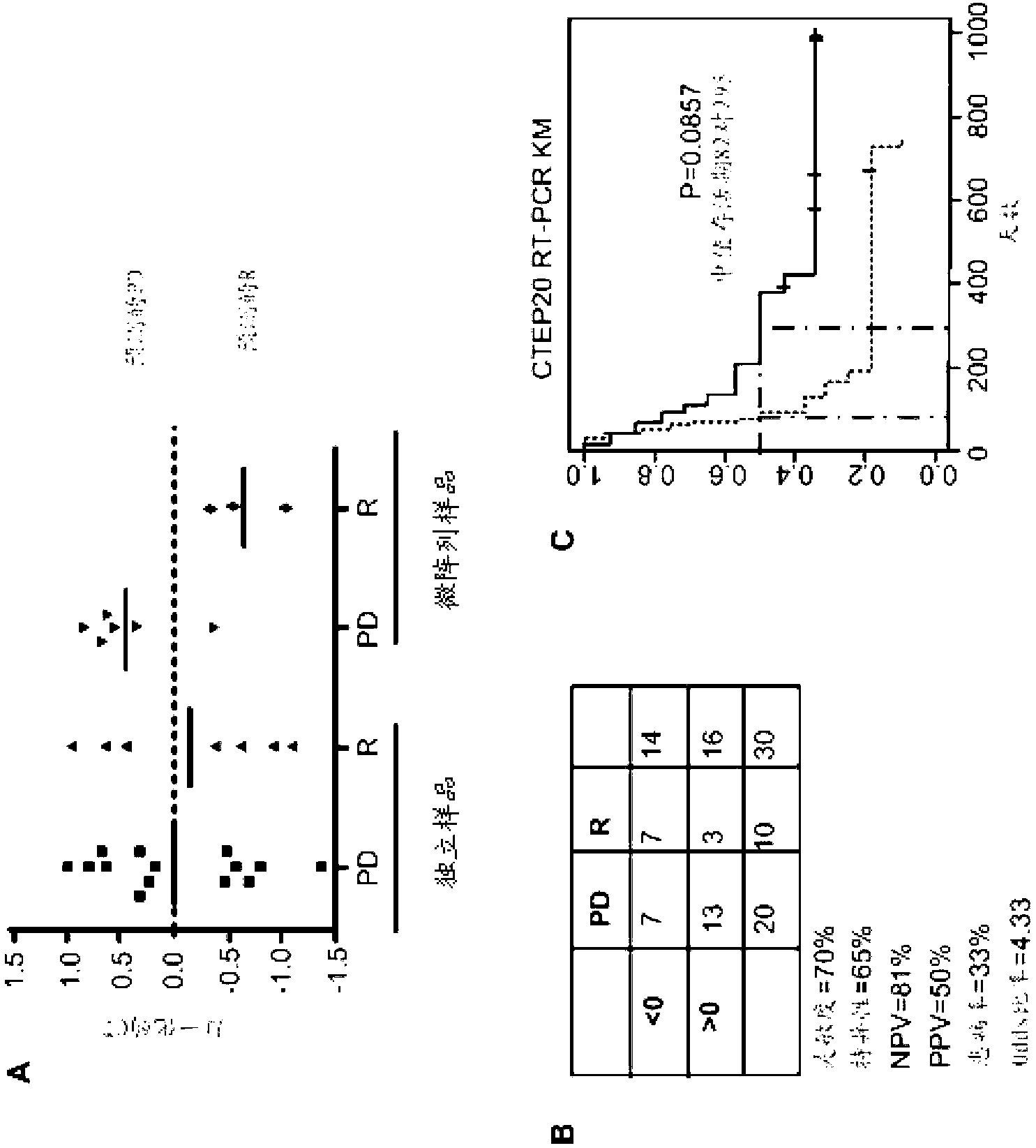
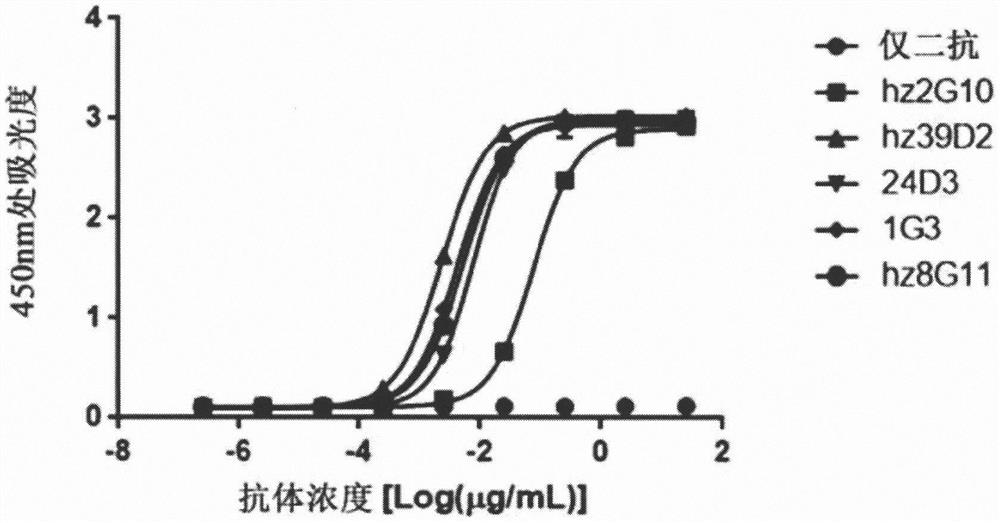
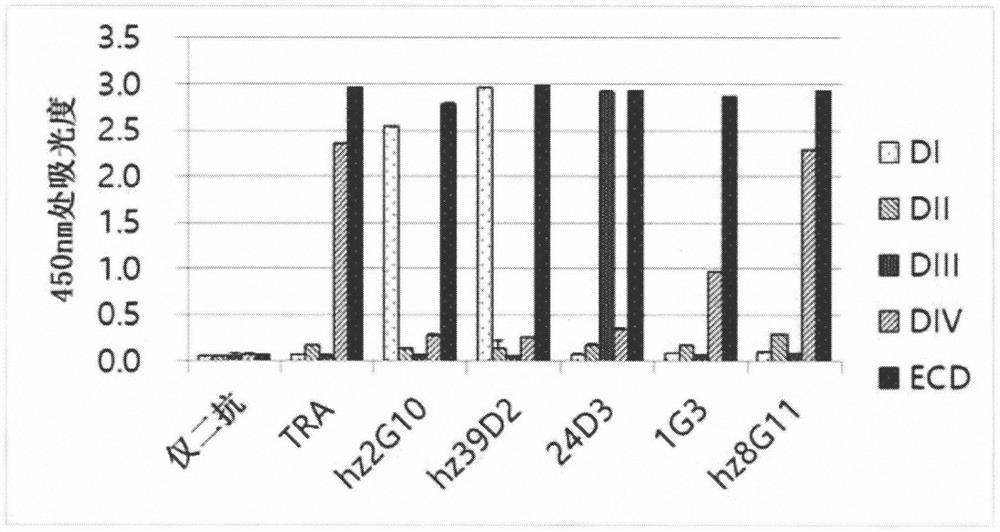
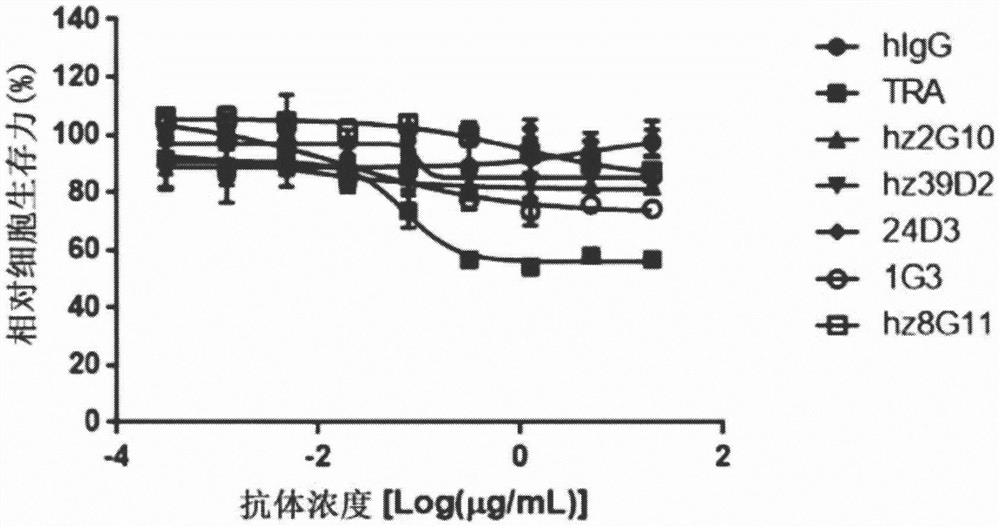
Method for predicting response to trastuzumab therapy in breast cancer patients
InactiveUS9873916B2Strong specificityImprove forecast accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsA-DNANucleotide sequencing
This invention relates to a composition and a method for prediction of a response to Trastuzumab therapy in a breast cancer patient, and more specifically, a composition, a kit, a DNA chip, and a method for predicting a response to Trastuzumab therapy by using polynucleotides each comprising a nucleotide sequence represented by any of SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 9, 11 to 19, and 21 to 23 in the Sequence Listing or a nucleotide sequence derived therefrom by substitution of u with t, mutants thereof, derivatives thereof, or fragments thereof comprising at least 16 continuous nucleotides, or a polynucleotide comprising a complementary sequence thereof, and using an increase or decrease in Her2 protein expression level as an indicator.
Owner:TORAY IND INC +1
Anti-her2 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof, and chimeric antigen receptor comprising same
PendingUS20210179733A1Low homologyStrong killing abilityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntiendomysial antibodiesAntigen Binding Fragment
The present disclosure relates to a novel anti-HER2 antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof used in the prevention or treatment of cancer, a chimeric antigen receptor including the same, and uses thereof. The antibody of the present disclosure is an antibody that specifically binds to HER2 which is highly expressed in cancer cells (particularly, breast cancer or gastric cancer cells), and binds to an epitope that is different from an epitope to which trastuzumab binds. When compared with trastuzumab, the antibody of the present disclosure exhibits better killing ability for HER2-unexpressed cancer cells which have non-reactivity (or resistance) to the trastuzumab antibody or have reduced sensitivity. In addition, when the anti-HER2 antibody of the present disclosure is administered in combination with trastuzumab, a synergistic killing ability is achieved for cancer cells on which the trastuzumab antibody acts. Therefore, a composition of the present disclosure can be very usefully used for combined administration with the trastuzumab antibody for the treatment of cancer, or for the treatment of cancer not treated with trastuzumab.
Owner:GC CELL CORP
Antibody Library and Method
PendingUS20210388063A1Raise the ratioHigh affinityPeptide librariesHydrolasesComplementarity determining regionNucleotide
This disclosure relates to methods of generating antibody libraries, antibody libraries produced using such methods, and variant antibodies. Presently, methods of improving antibody binding (affinity maturation assays) require the screening of vast libraries of antibody variants (often >1010) to identify a small fraction of variants with improved characteristics. The present invention involves taking the nucleotide sequence of the framework and complementarity determining region of a target antibody and identifying motifs which would be recognised by deamination somatic hypermutation enzymes. A small library of variants is then created which incorporate one or more of these mutations. It was found that a relatively high proportion of the variants have an increased affinity. The technique of the present invention was demonstrated on the trastuzumab and Cathepsin S antibodies, and the variants produced are also claimed.
Owner:FUSION ANTIBODIES PLC
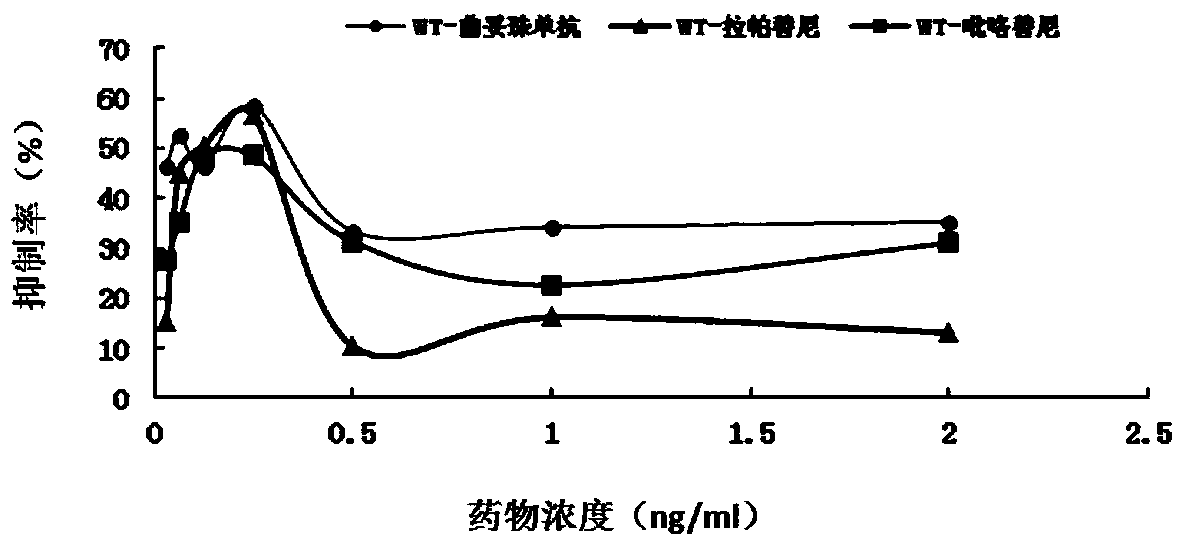
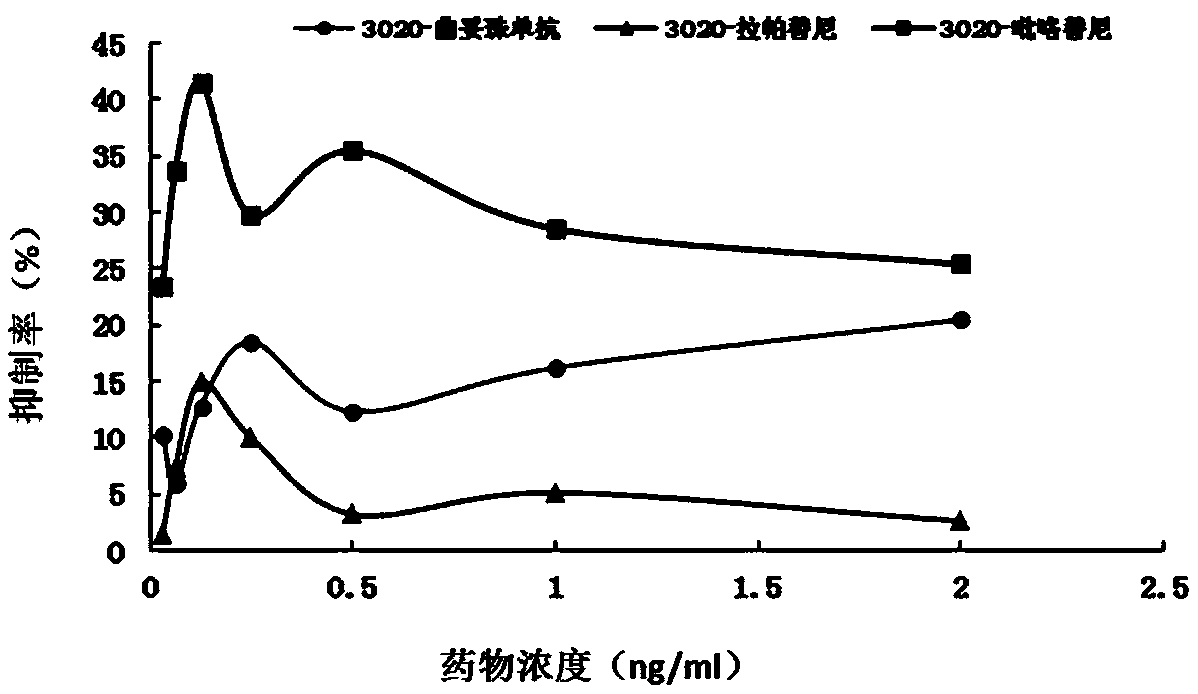
Gene mutation site for predicting anti-HER2 therapeutic drug reactivity of patients with breast cancer and application thereof
ActiveCN108949998ALearn about drug resistanceEffective guidanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMedicineAnti her2
The invention discloses a gene mutation site for predicting the anti-HER2 therapeutic drug reactivity of patients with breast cancer and application thereof. By a large scale of screening, the inventor discovers for the first time that the 3020 site of the HER2 gene coding sequence is related to the drug reactivity of patients with breast cancer on trastuzumab, lapatinib or pyrotinib. Based on theresearch result, a product for predicting the drug reactivity of a patient with breast cancer on trastuzumab, lapatinib or pyrotinib is developed. The product can be widely applied to clinical application by detecting the function of the 3020 site genome of the HER2 gene coding sequence.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
P97 fusion proteins
Provided are p97 (melanotransferrin)-trastuzumab fusion proteins and related methods of use thereof, for instance, to facilitate delivery of trastuzumab across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and / or improve tissue penetration of the antibody in CNS and peripheral tissues, and thereby treat and / or diagnose HER2-positive cancers, including those of the central nervous system (CNS).
Owner:BIOASIS TECH
Antibody-drug conjugates based on gold compounds
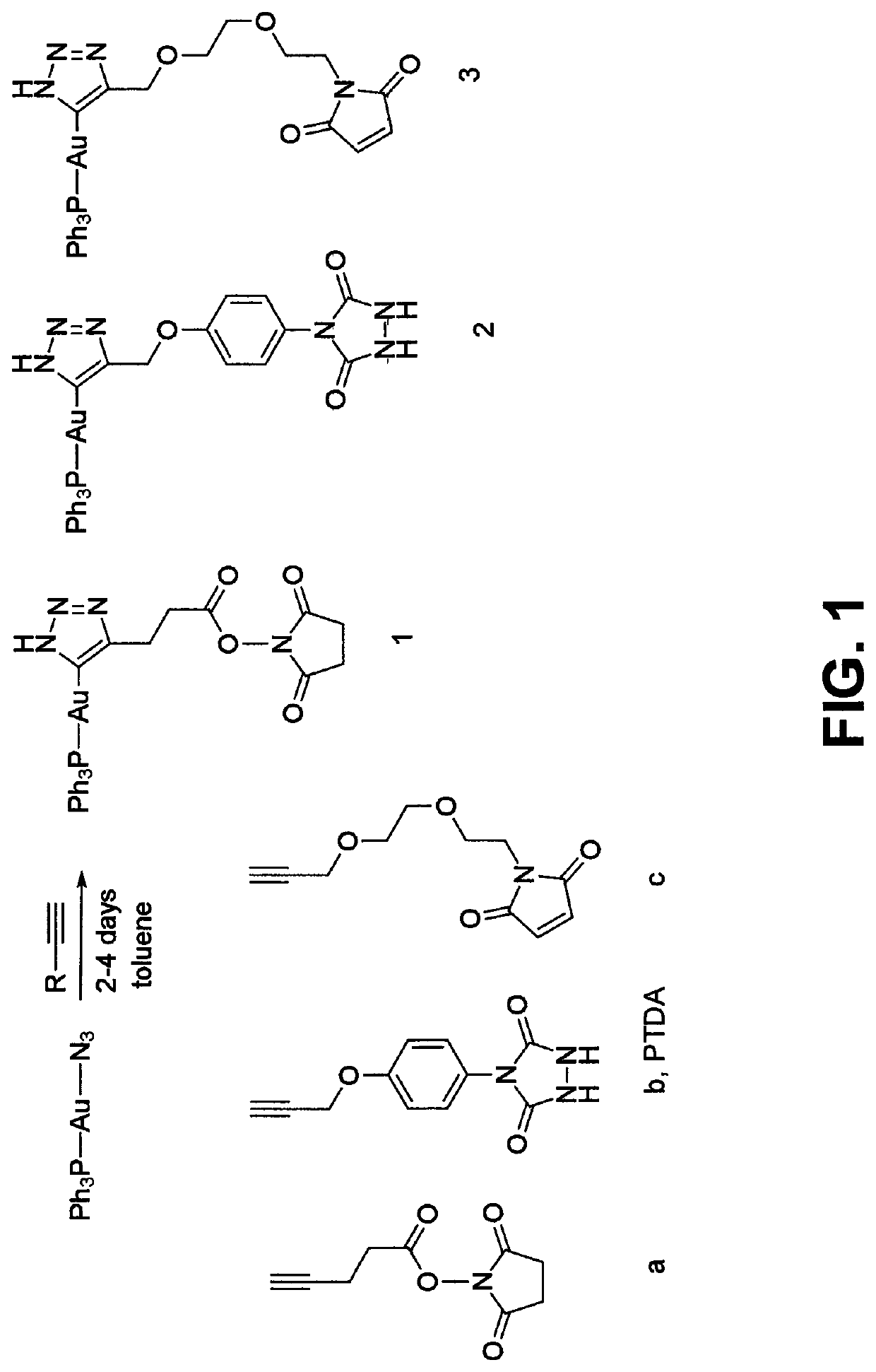
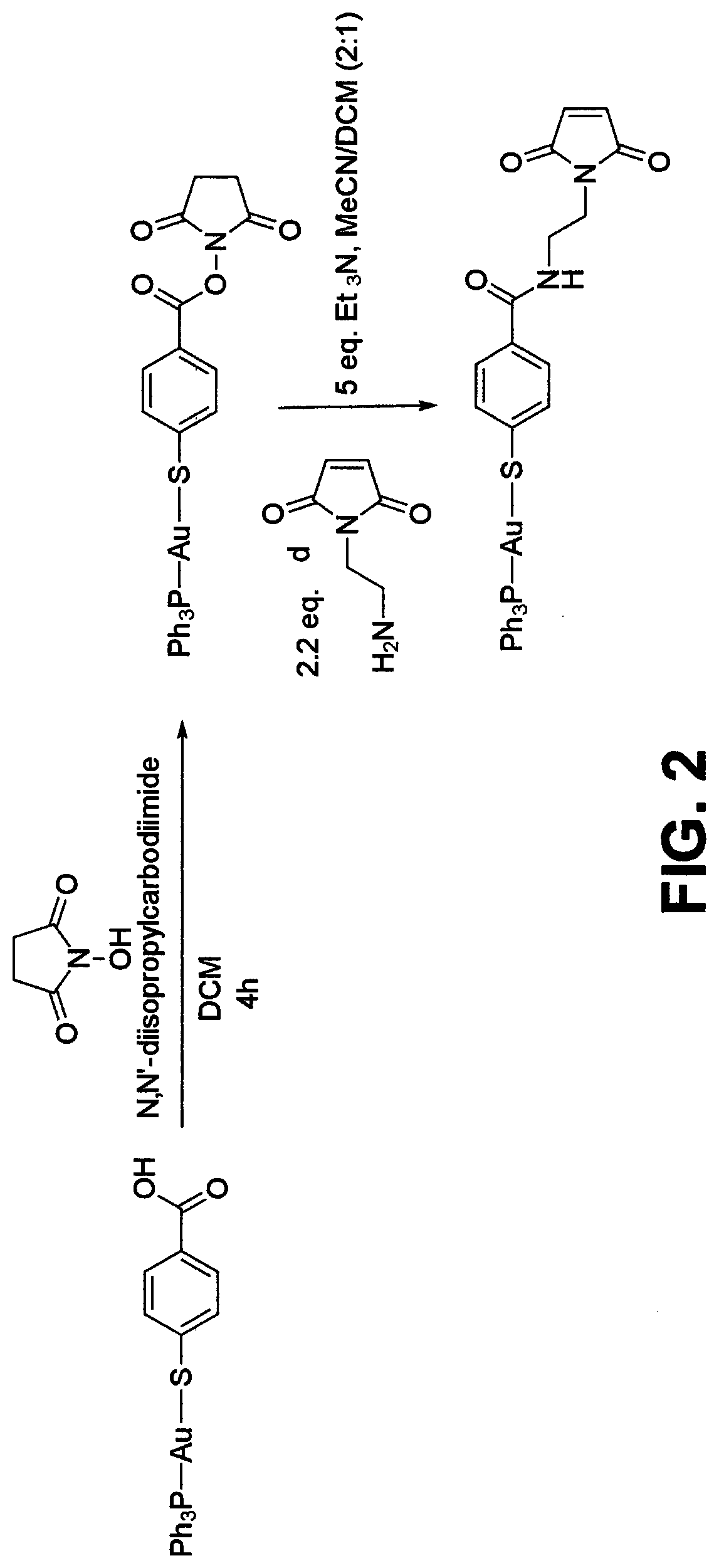
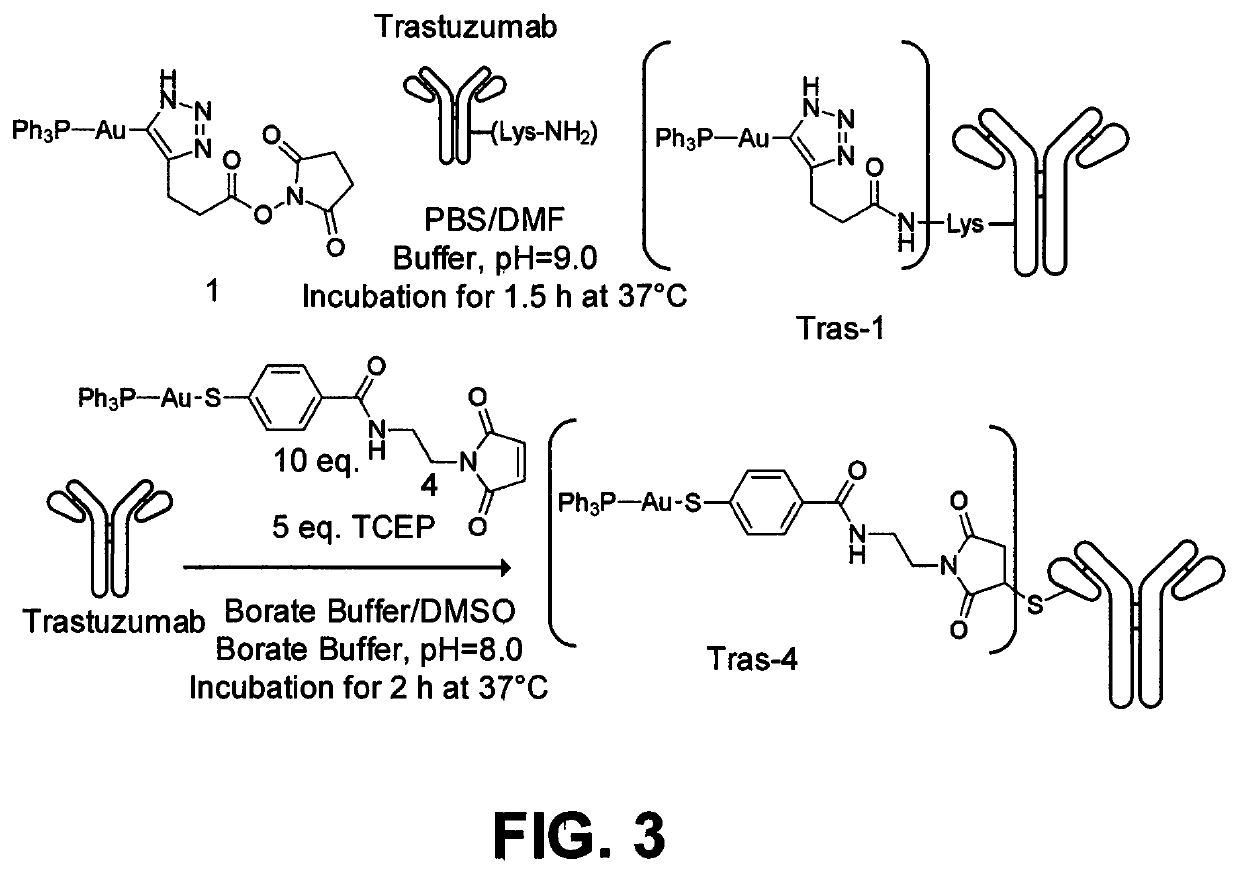
ActiveUS20200016276A1Well formedOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesChemical compound
Antibody-drug-conjugates (ADC) are provided having a structure of:wherein L is PR3 ligand. The ADC has n drug moieties bound to the Trastuzumab antibody such that the ADC has a drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) between 2 and 4 and the drug moieties are bound to the Trastuzumab antibody through cysteine (S) or lystine (Lys) residues. The disclosed ADCs are particularly useful in treating breast cancer.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT +1
HER2 positive gastric cancer drug-resistant PDX model as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to a construction method of an HER2 positive gastric cancer drug-resistant PDX model, which comprises the step of transplanting fresh gastric cancer tissues of a drug-resistant HER2 positive gastric cancer patient after drug treatment to the subcutaneous part of a mouse. The gastric cancer tissue of the drug-resistant patient treated by HER2 positive trastuzumab is clinically obtained, and the gastric cancer PDX model is successfully established. The scheme provided by the invention plays a crucial role in understanding a potential molecular mechanism of acquired drug resistance of trastuzumab, searching a new treatment strategy for overcoming drug resistance and formulating a next effective treatment scheme.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CANCER HOSPITAL
Treatment of cancer with her2xcd3 bispecific antibodies in combination with Anti-her2 mab
PendingUS20220098325A1Convenient treatmentDecreased likelihoodImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesBispecific antibody
The present invention provides methods of treating of HER2-positive cancers (such as HER2-positive breast cancer and HER2-positive gastric cancers) using HER2 antibodies, such as a combination of a HER2 T cell-dependent bispecific antibody (TDB) with an additional HER2 antibody (e.g., trastuzumab).
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com