Patents
Literature
150 results about "U-bit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In quantum mechanics, the u-bit or ubit is a proposed theoretical entity which arises in attempts to reformulate wave functions using only real numbers instead of the complex numbers conventionally used.
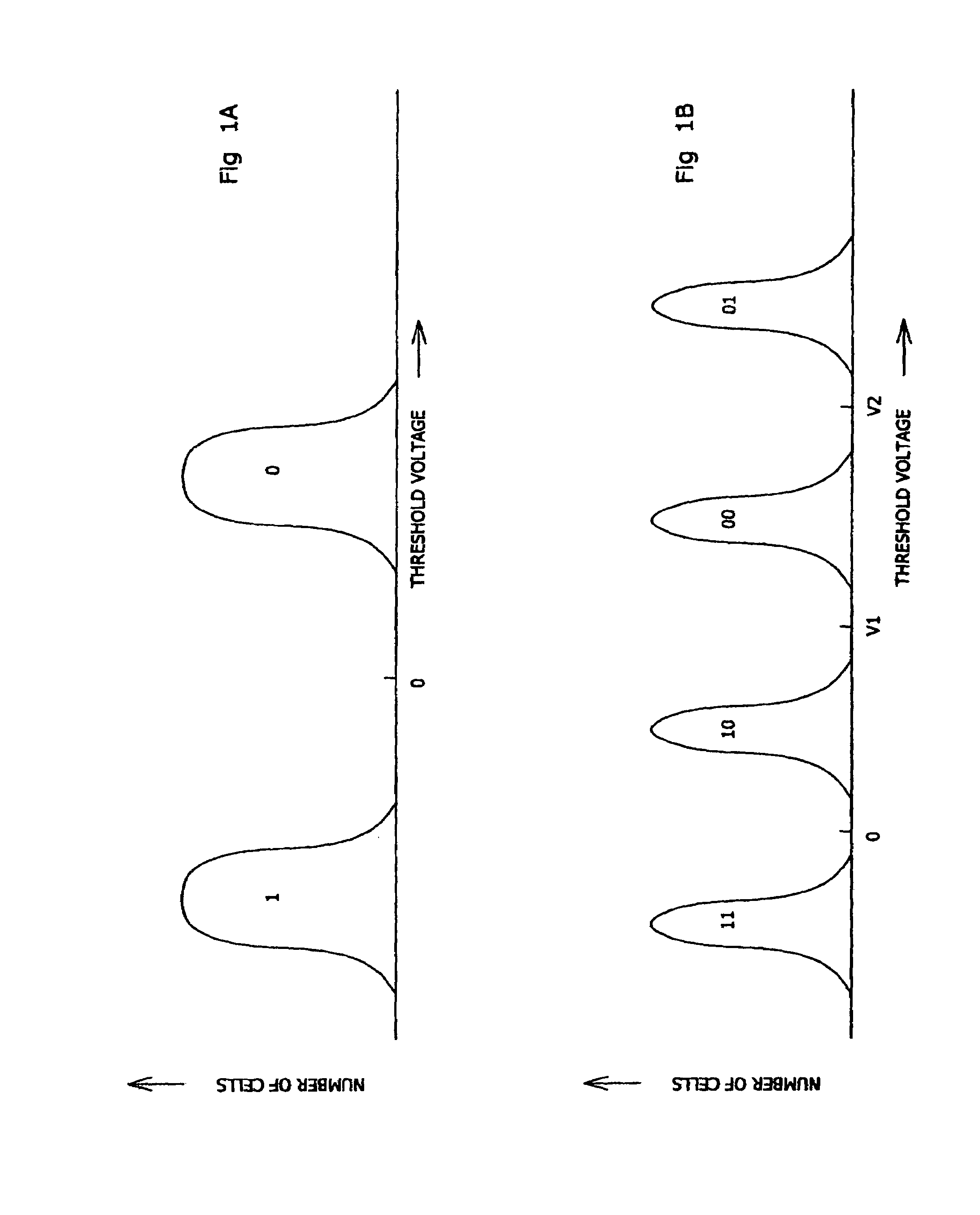
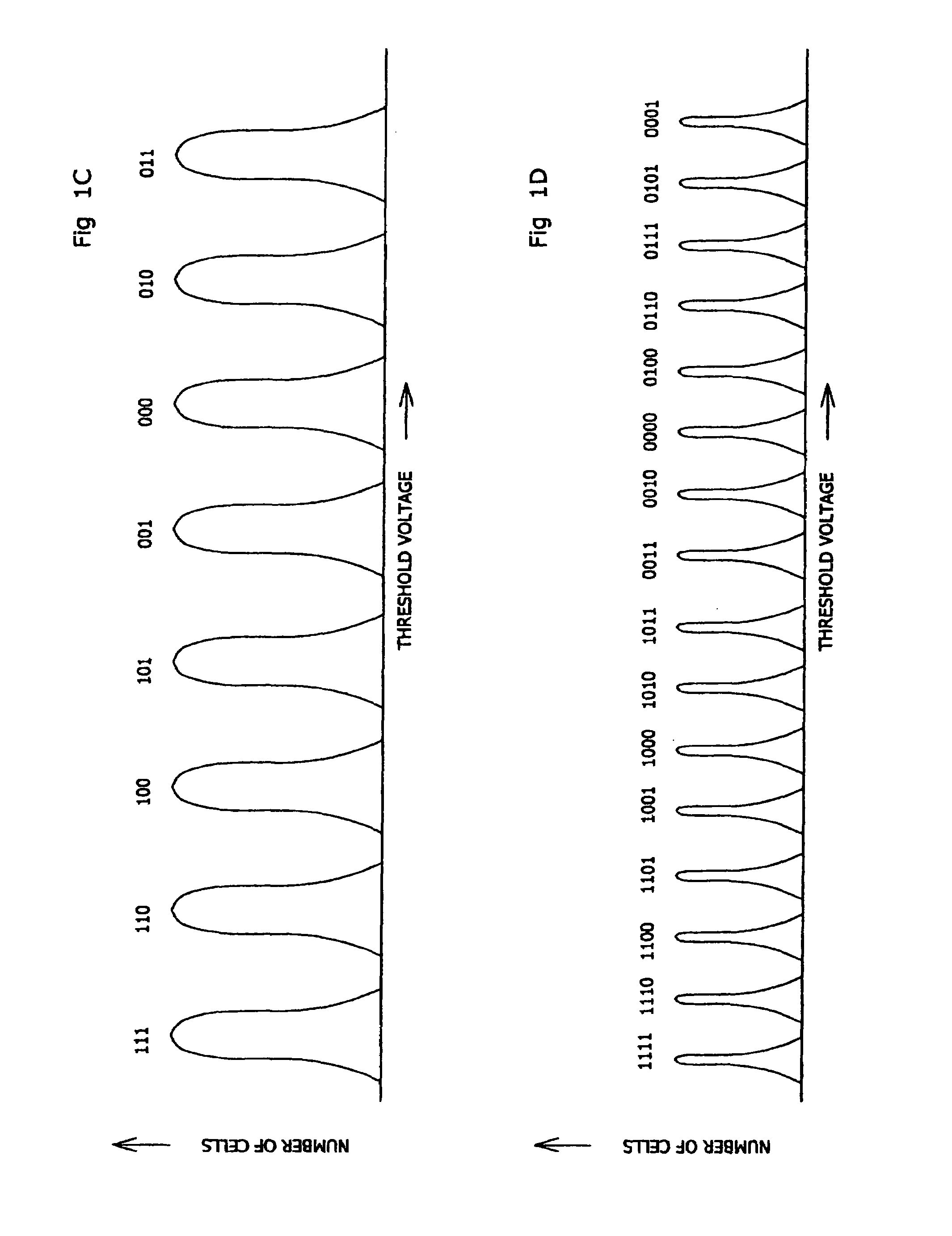
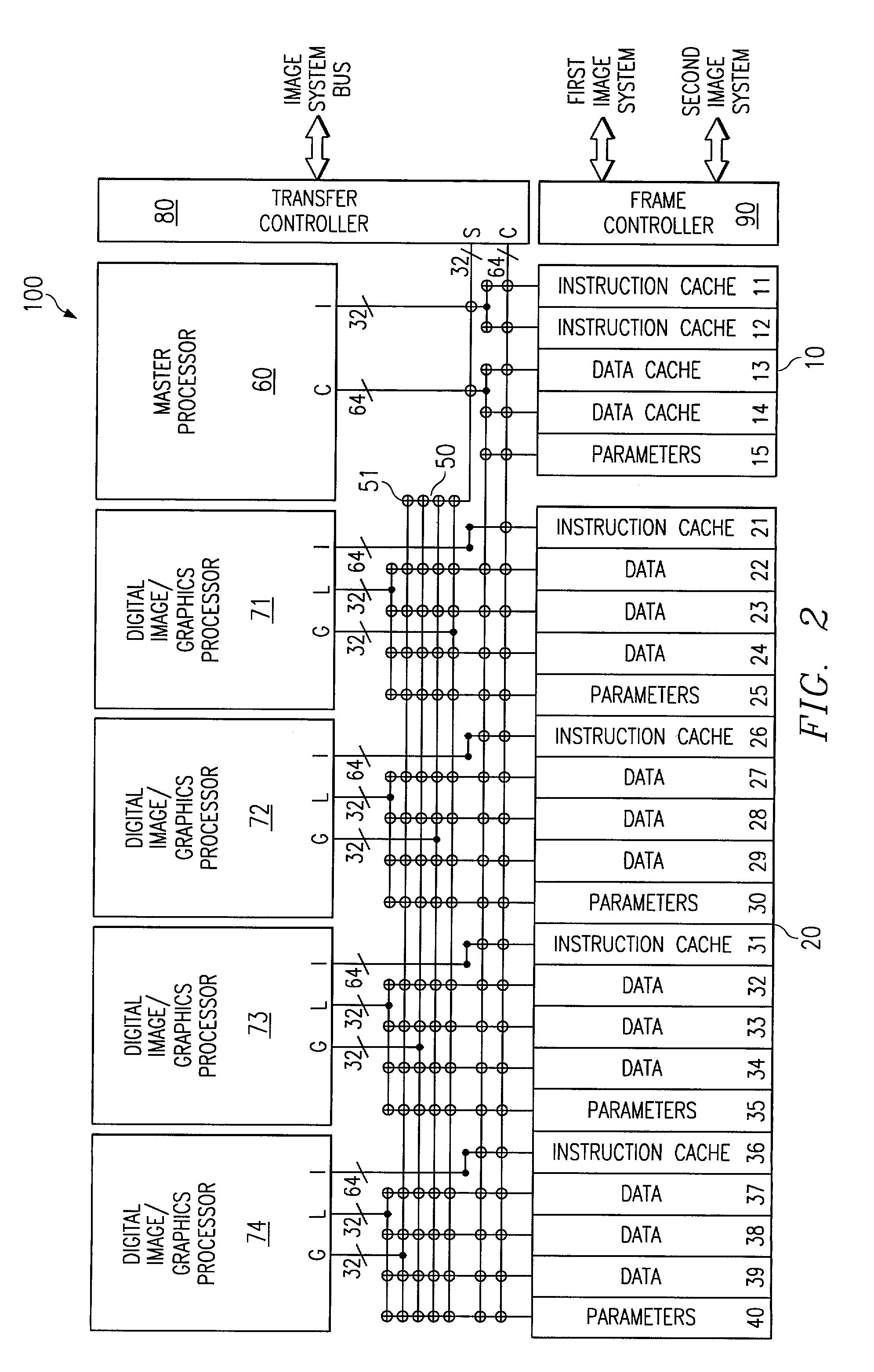
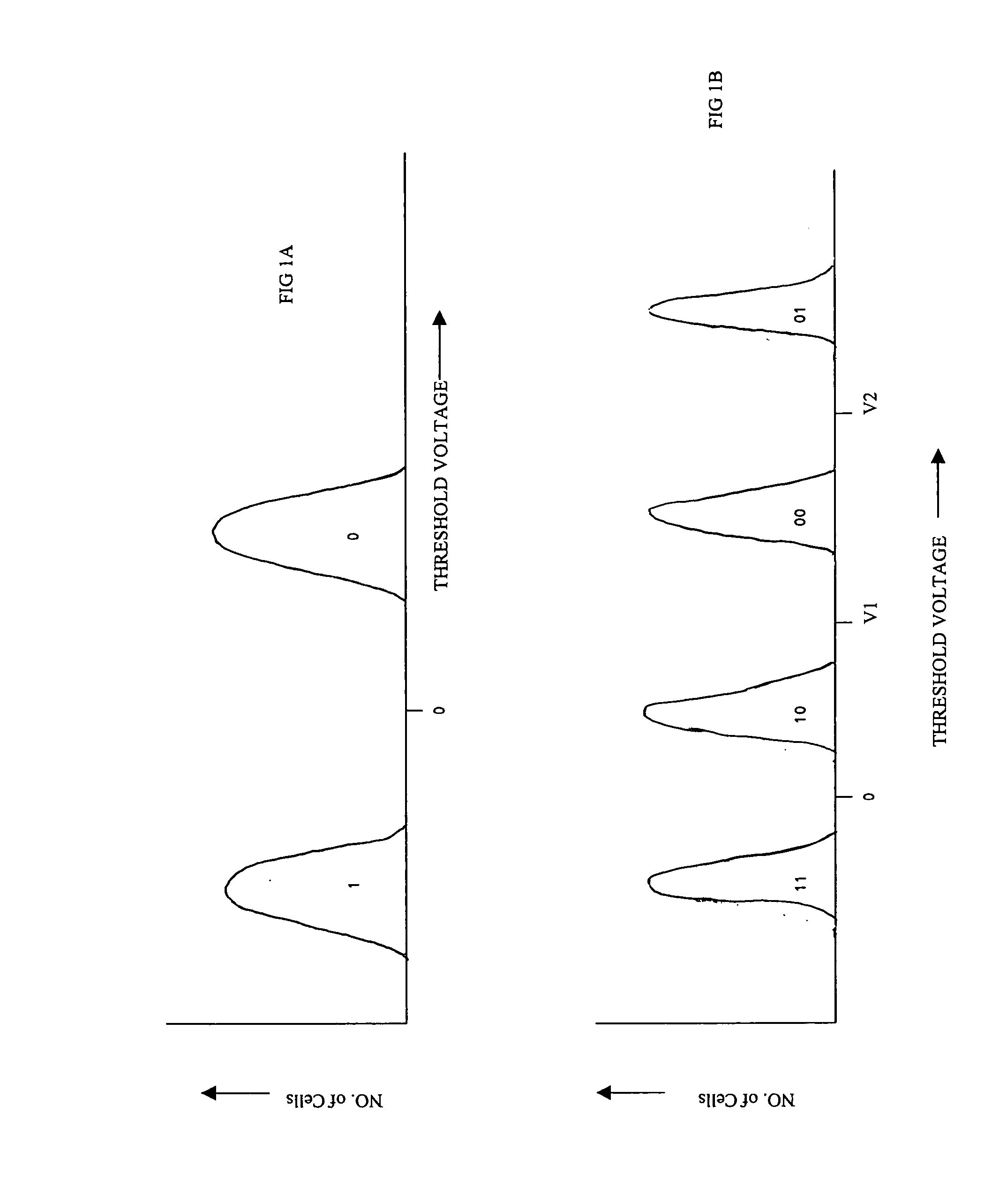
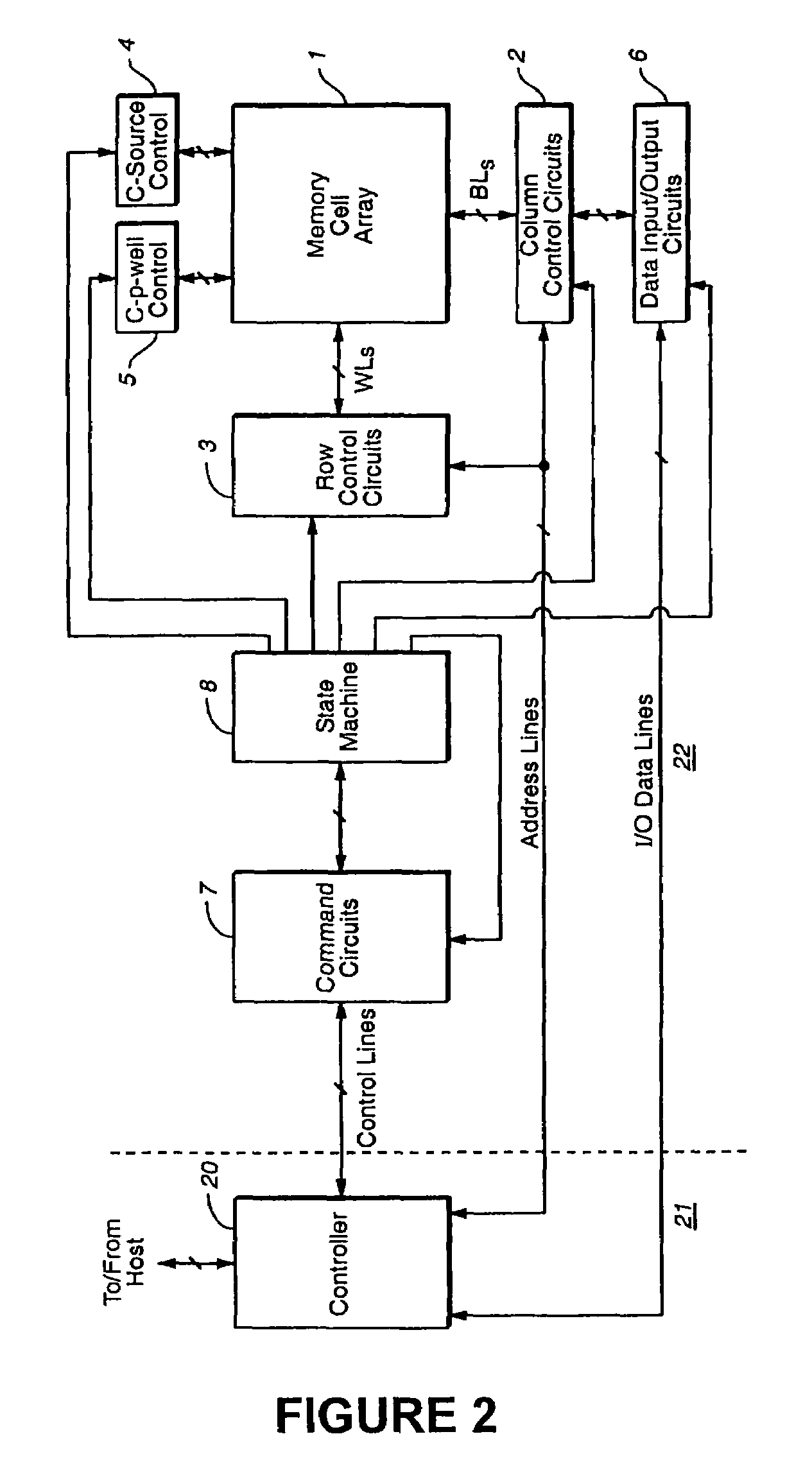
States encoding in multi-bit flash cells
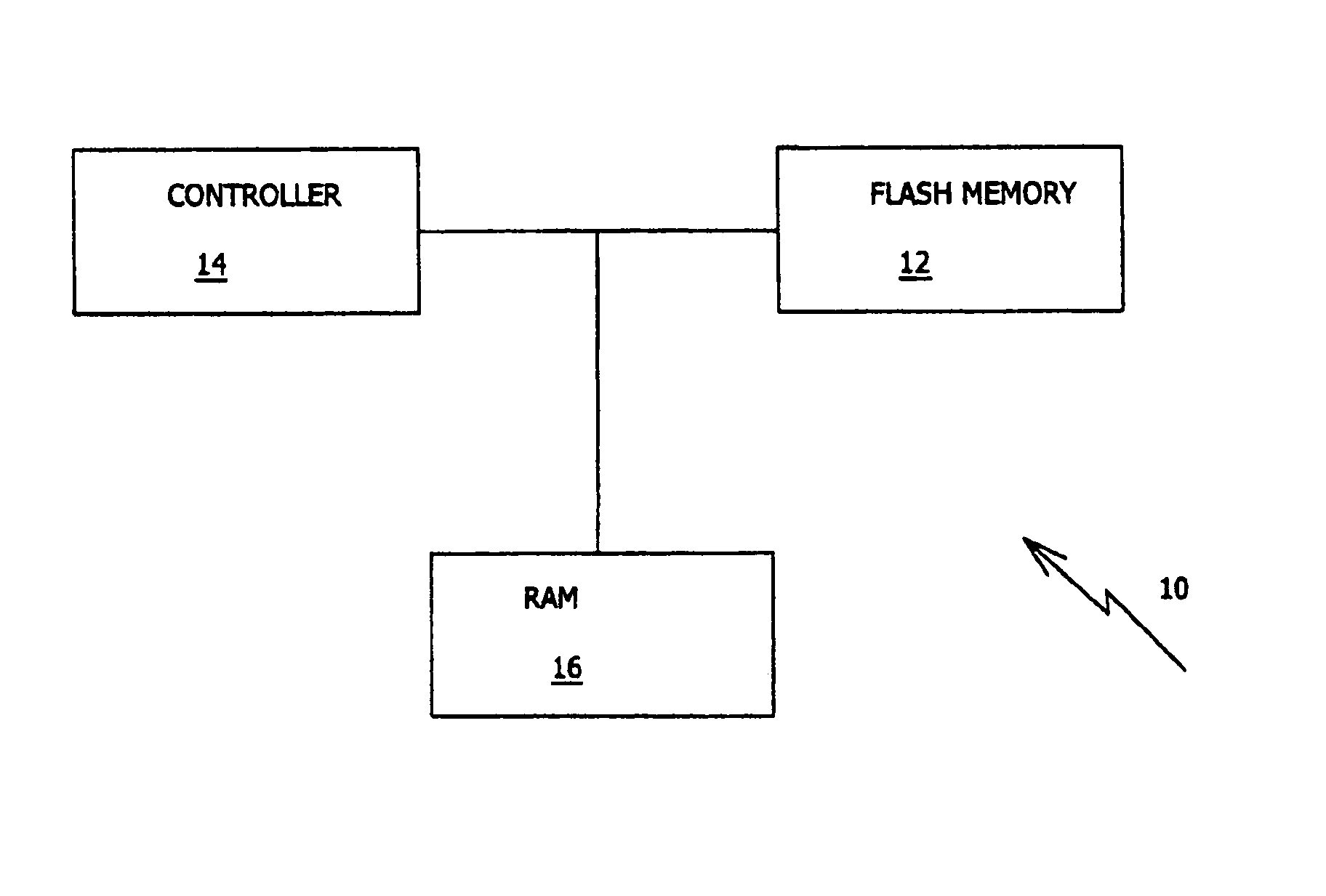
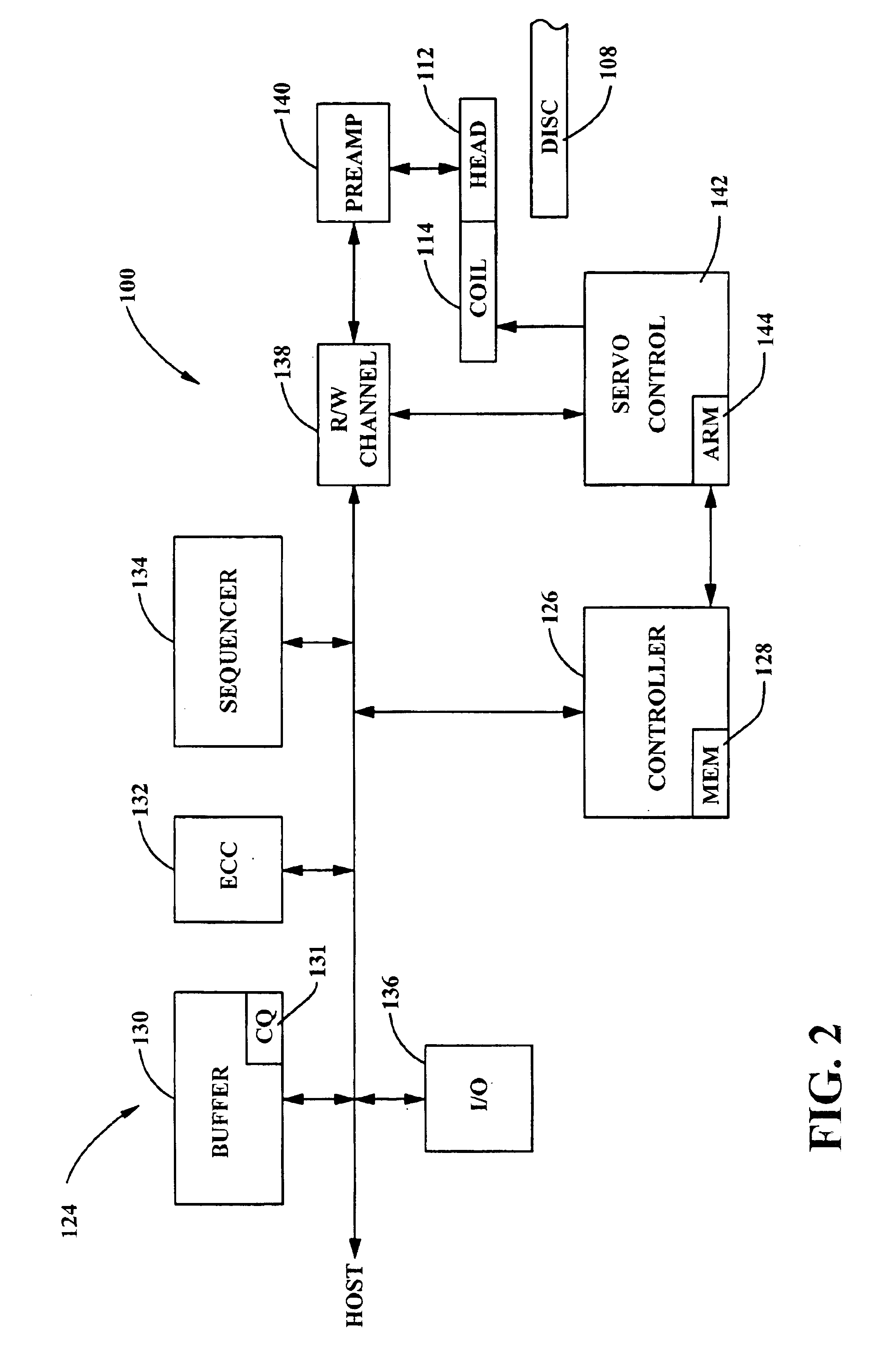
ActiveUS7310347B2Read-only memoriesData switching by path configurationComputer scienceThreshold voltage
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
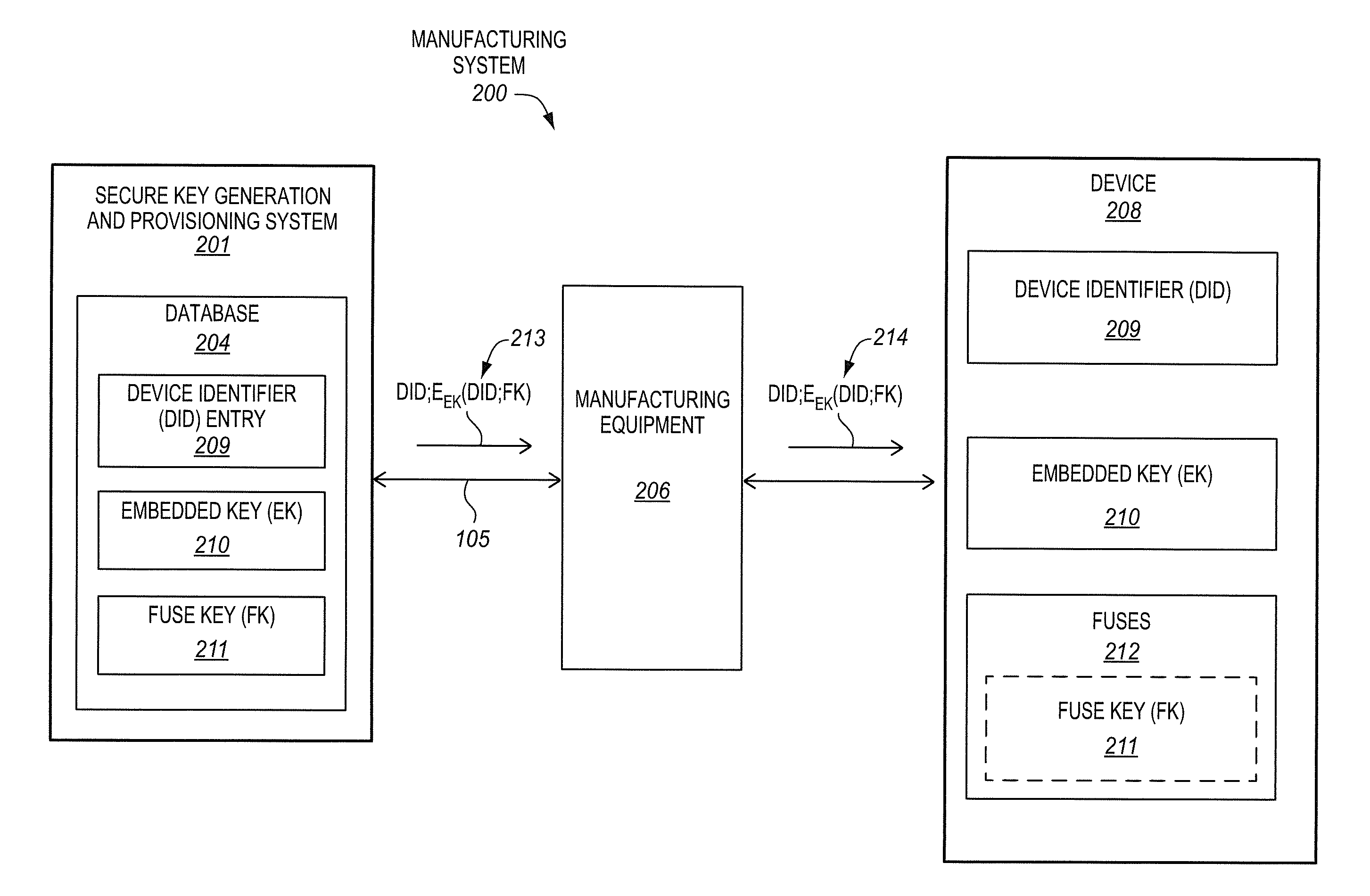
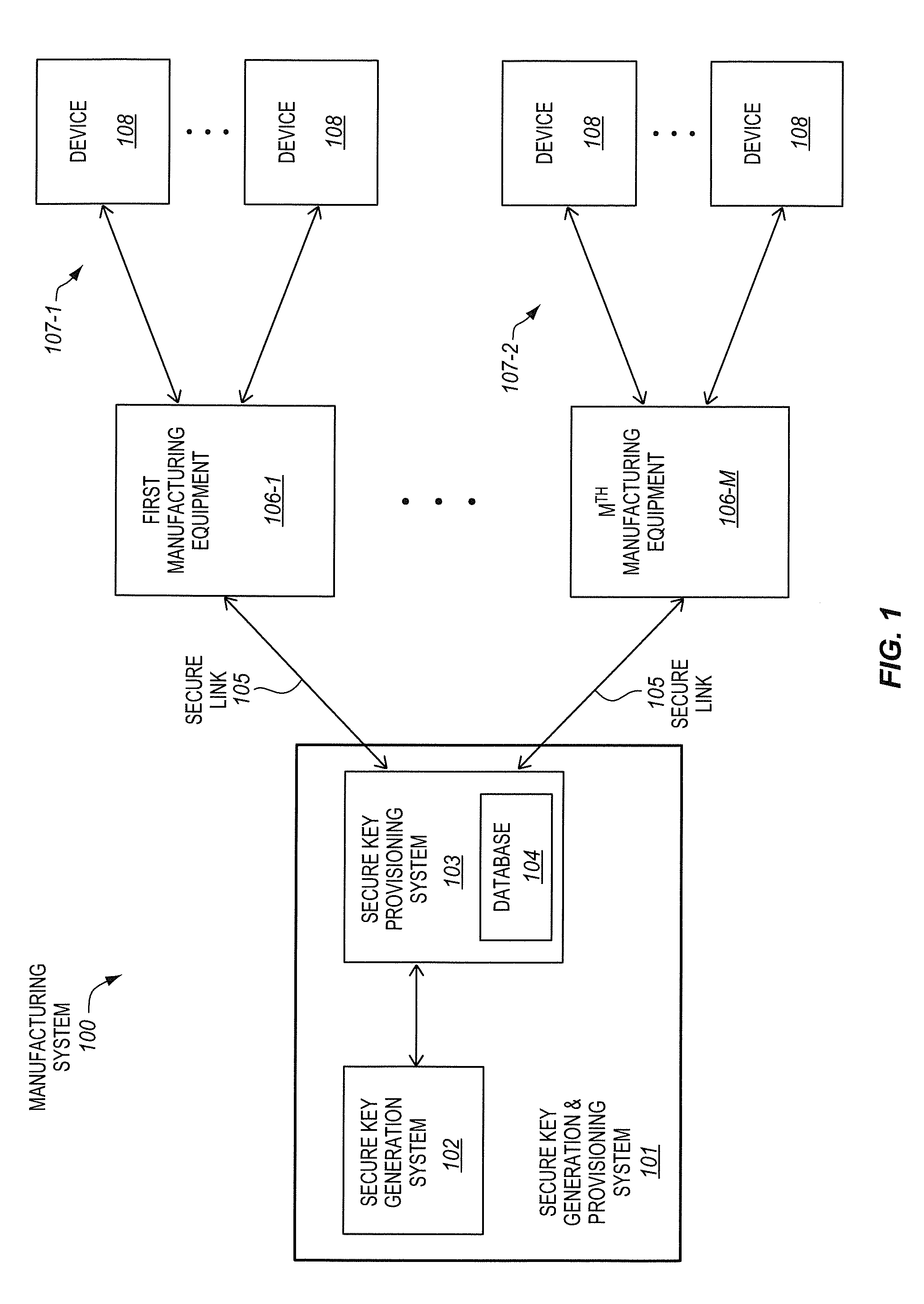
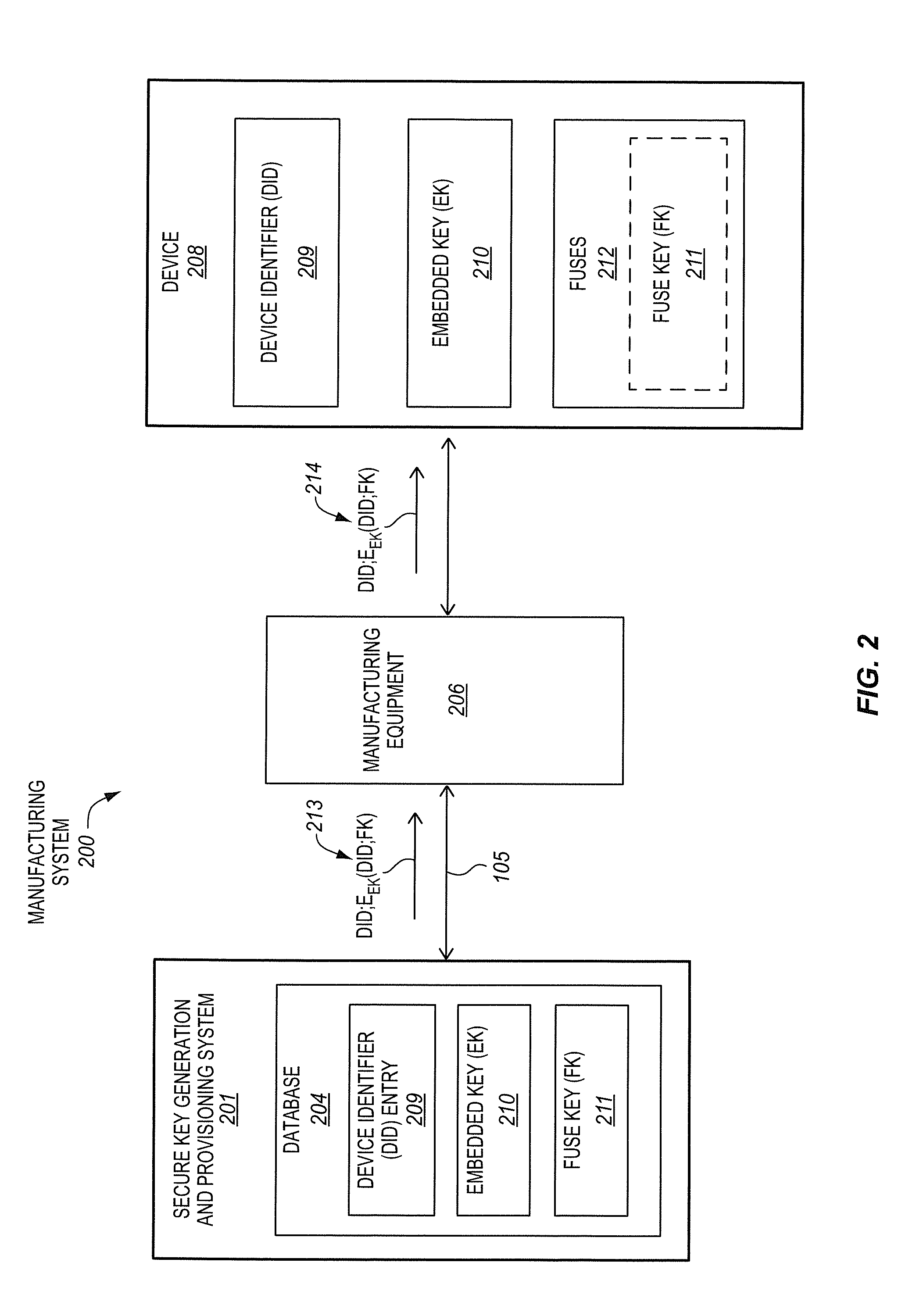
Secure provisioning of secret keys during integrated circuit manufacturing
ActiveUS20140093074A1Internal/peripheral component protectionSecuring communicationComputer hardwareIntegrated circuit manufacturing
A method, of an aspect, includes challenging a set of Physically Unclonable Function (PUF) cells, of an integrated circuit device, and receiving a set of PUF bits from the PUF cells in response. A PUF key is generated based on the set of PUF bits. An encryption of the PUF key with an embedded key is output from the integrated circuit device. The integrated circuit device receives an encryption of a fuse key with the PUF key. Fuses of the integrated circuit device are programmed with at least one of the fuse key and the received encryption of the fuse key with the PUF key. Other methods, apparatus, and systems are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
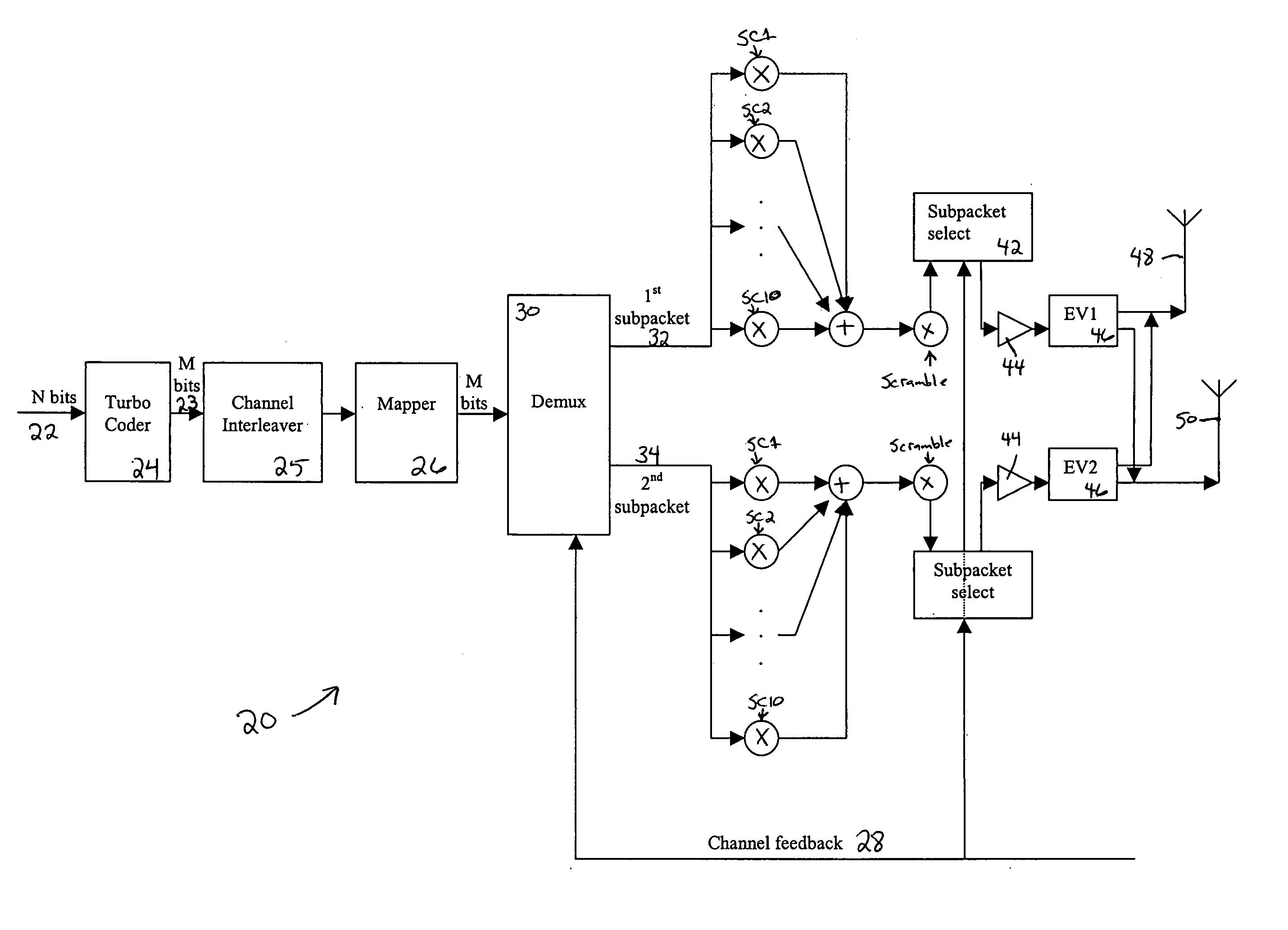
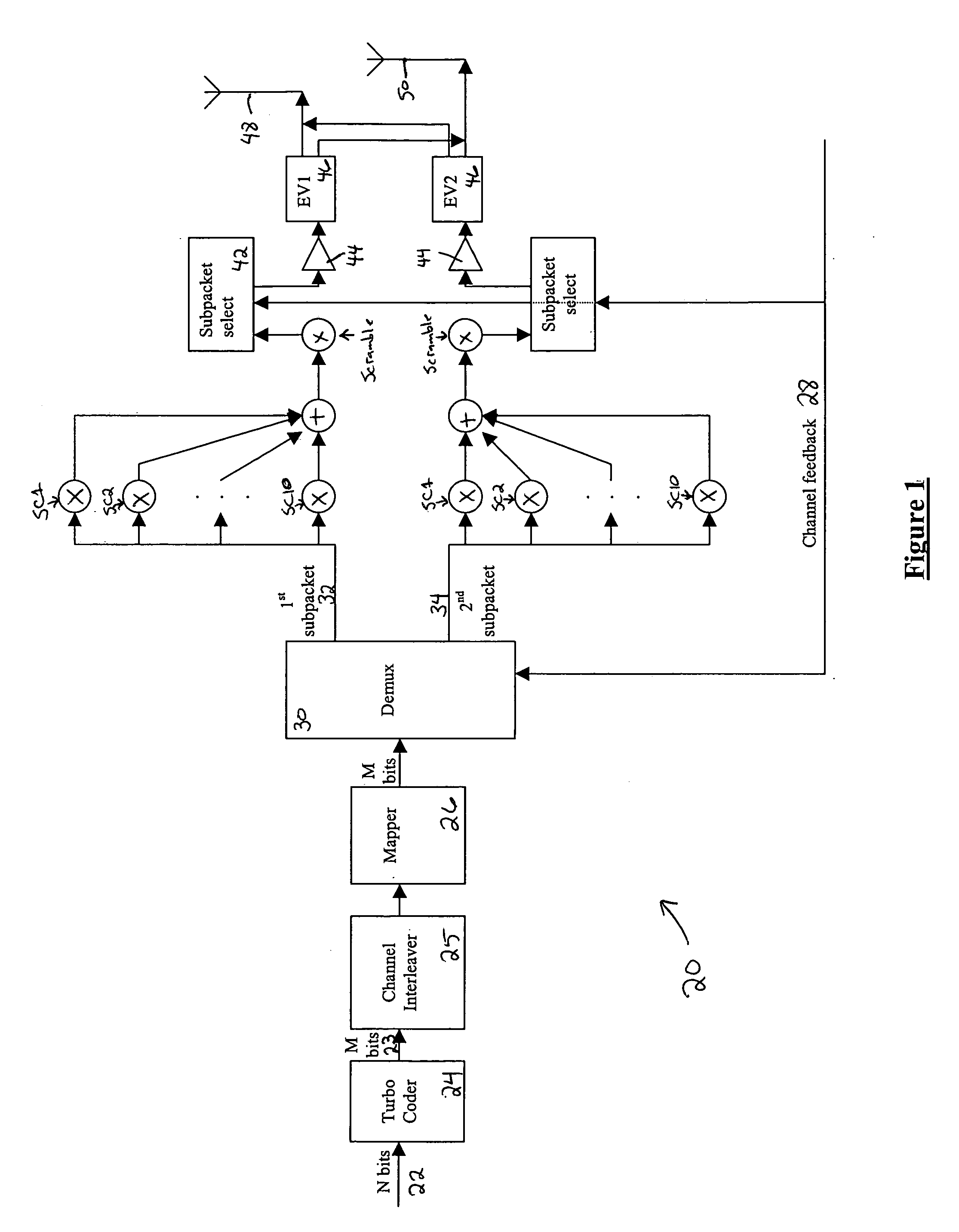
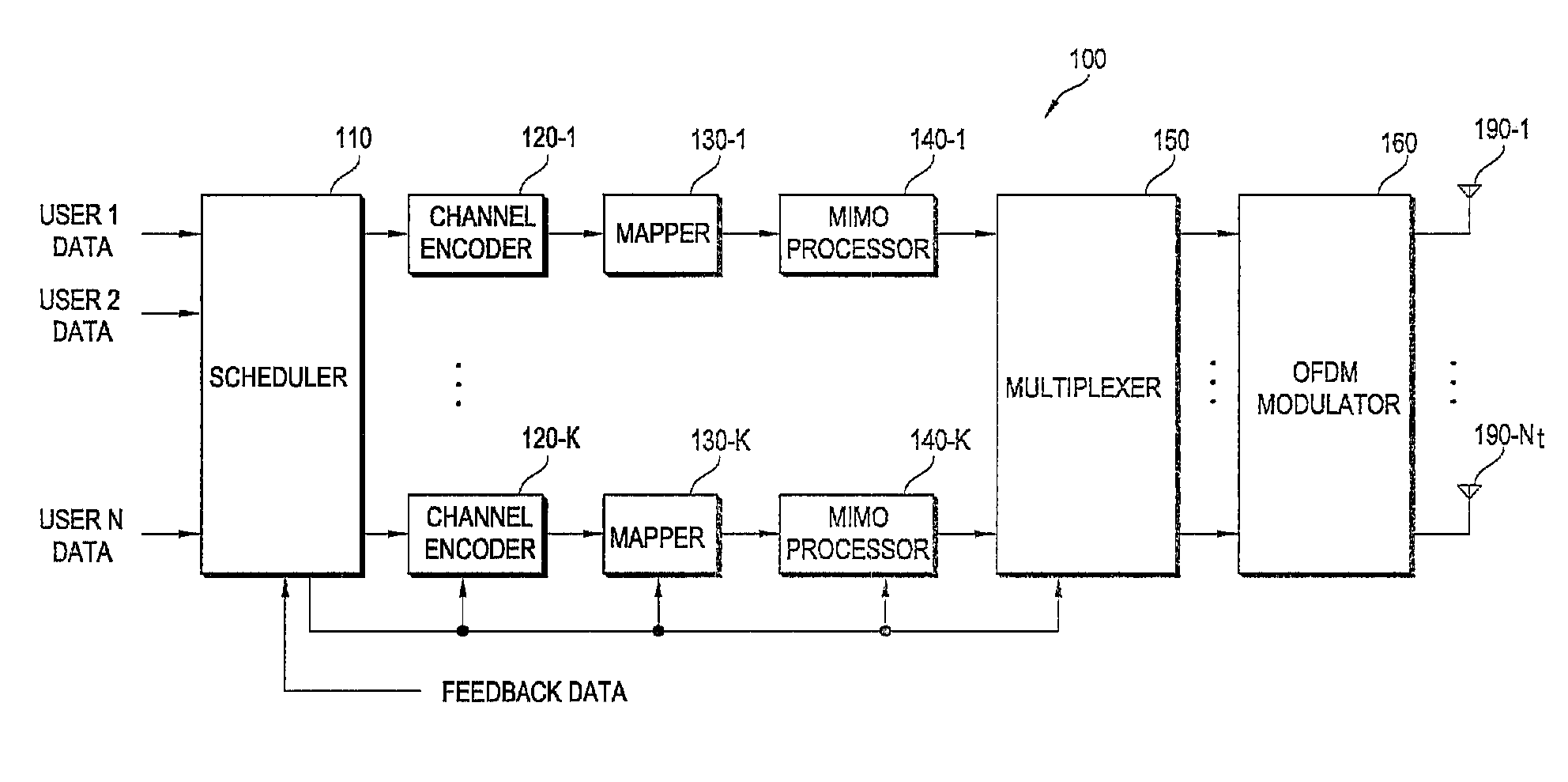
Flexible rate split method for MIMO transmission
InactiveUS20050111376A1Wide diversityReduce error rateSpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsMimo transmissionSelection system
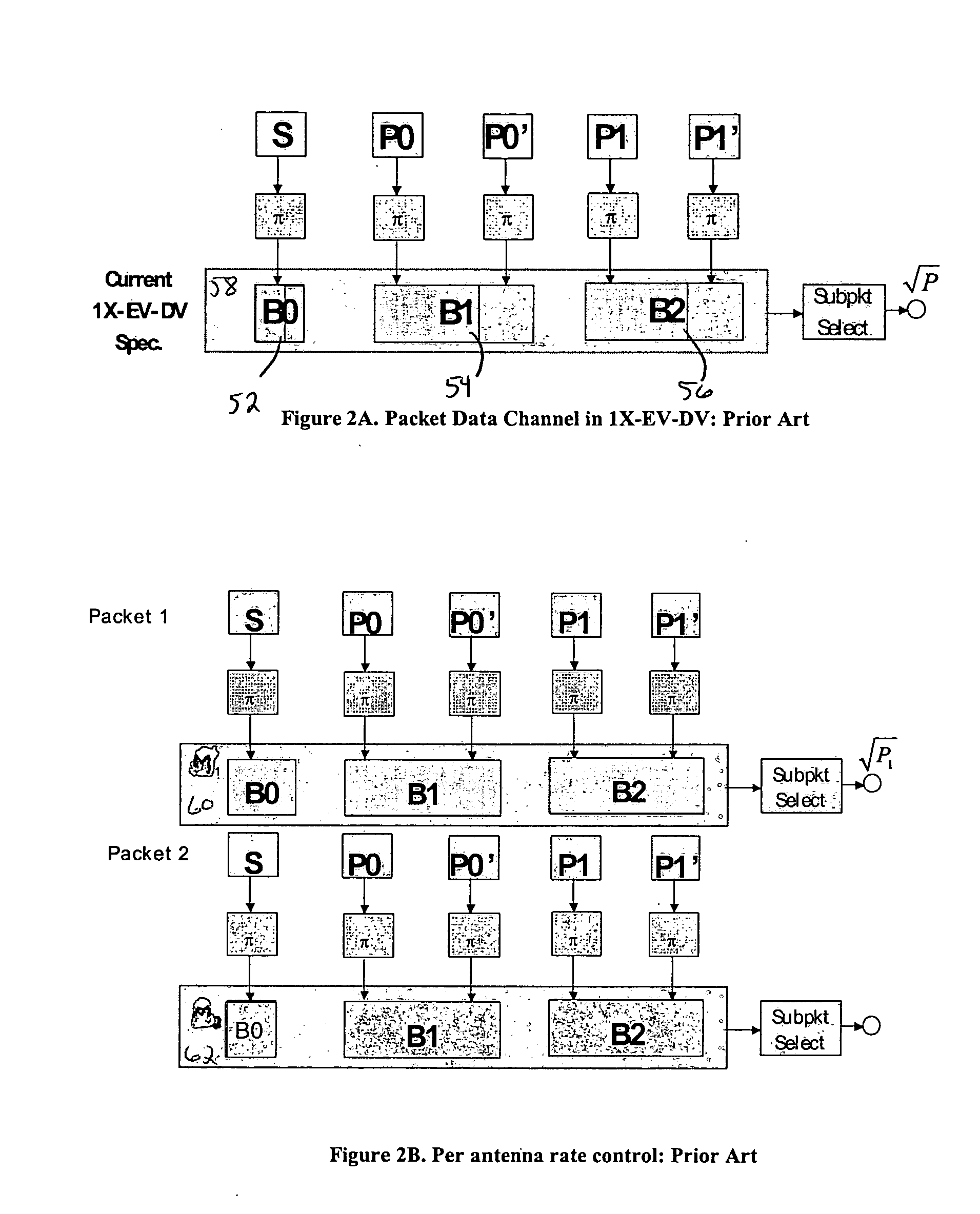
A method for transmitting a packet of N input bits includes encoding all of the N bits as a single entity, such as with an interleaver of length N within a turbo coder, outputting M encoded bits, channel interleaving the M bits, splitting the M encoded bits into a parallel first and second portion, and transmitting them over separate channels to achieve spatial diversity. The size of the first and second portion is determined based on a closed feedback loop that provides some knowledge of the channel, preferably a measure of channel capacity. The feedback loop may also provide channel knowledge to a subpacket selector associated with each transmit antenna, which determines an appropriate rate for that channel and selects subpackets to fill a transmission packet for that channel. The subpacket selectors choose a subpacket of systematic bits and fill the remaining transmission packet size with subpackets of parity bits. Eigenvectors may be employed to transmit each transmission packet over more than one channel with a power disparity between the channels. A transmitter according to the present invention is also described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Encoding scheme for producing magnetic field signals having desired spectral characteristics
ActiveUS6993088B2Constant energyLow component requirementsCode conversionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumHarmonic
Methods and systems for producing an encoded information signal having attenuated low frequency spectral components and a substantially constant average energy. An M bit code word is produced for each N bits of an information signal according to the following conditions: (a) each code word includes an equal number of logic zero bits and logic one bits; (b) each code word includes no more than two consecutive identical bits; and (c) M is greater than N. For example, M equals eight and N equals four. Such an encoded information signal is especially useful for generating a magnetic field signal usable for locating an underground object. This is in part because information sidebands of the magnetic field signal to have desired spectral characteristics that are useful in environments that often include harmonically derived interference signals at regular 50 Hz (±0.1 Hz) or 60 Hz (±0.1 Hz) intervals caused by power lines.
Owner:RADIODETECTION
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding n-bit data into 2n-bit codewords
InactiveUS6232895B1Simple and reliable processSimple dataParallel/series conversionError preventionBlock codeData encoding
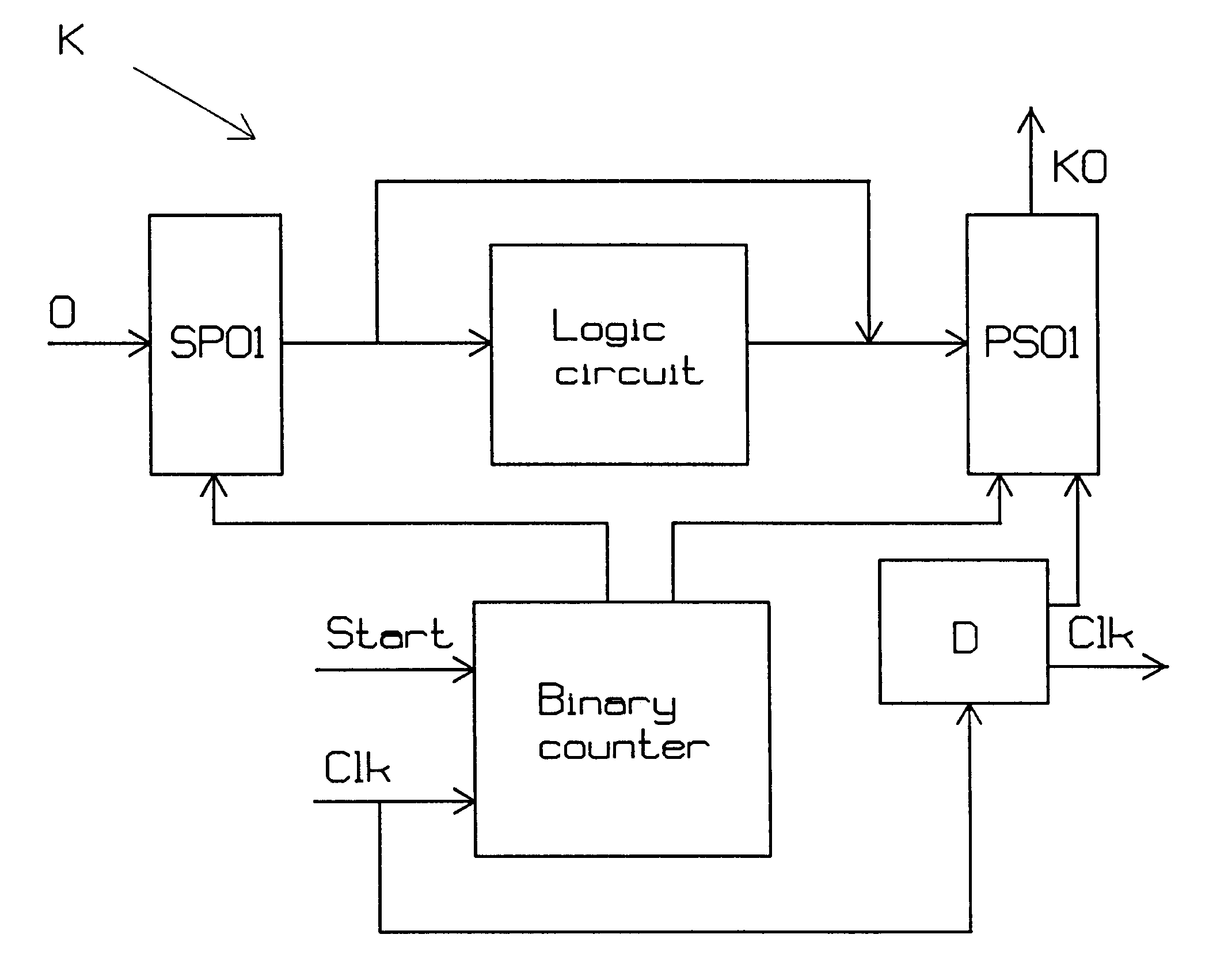
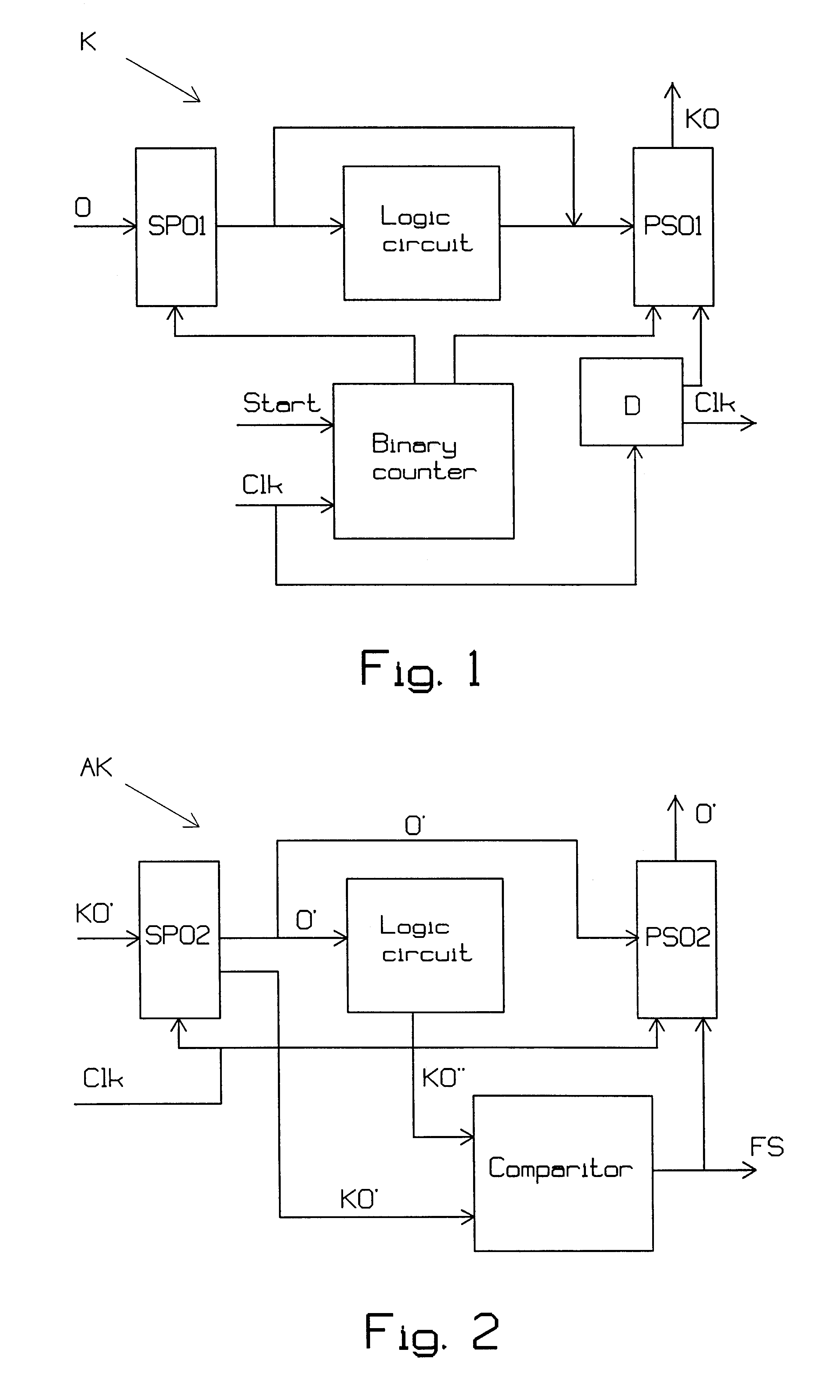
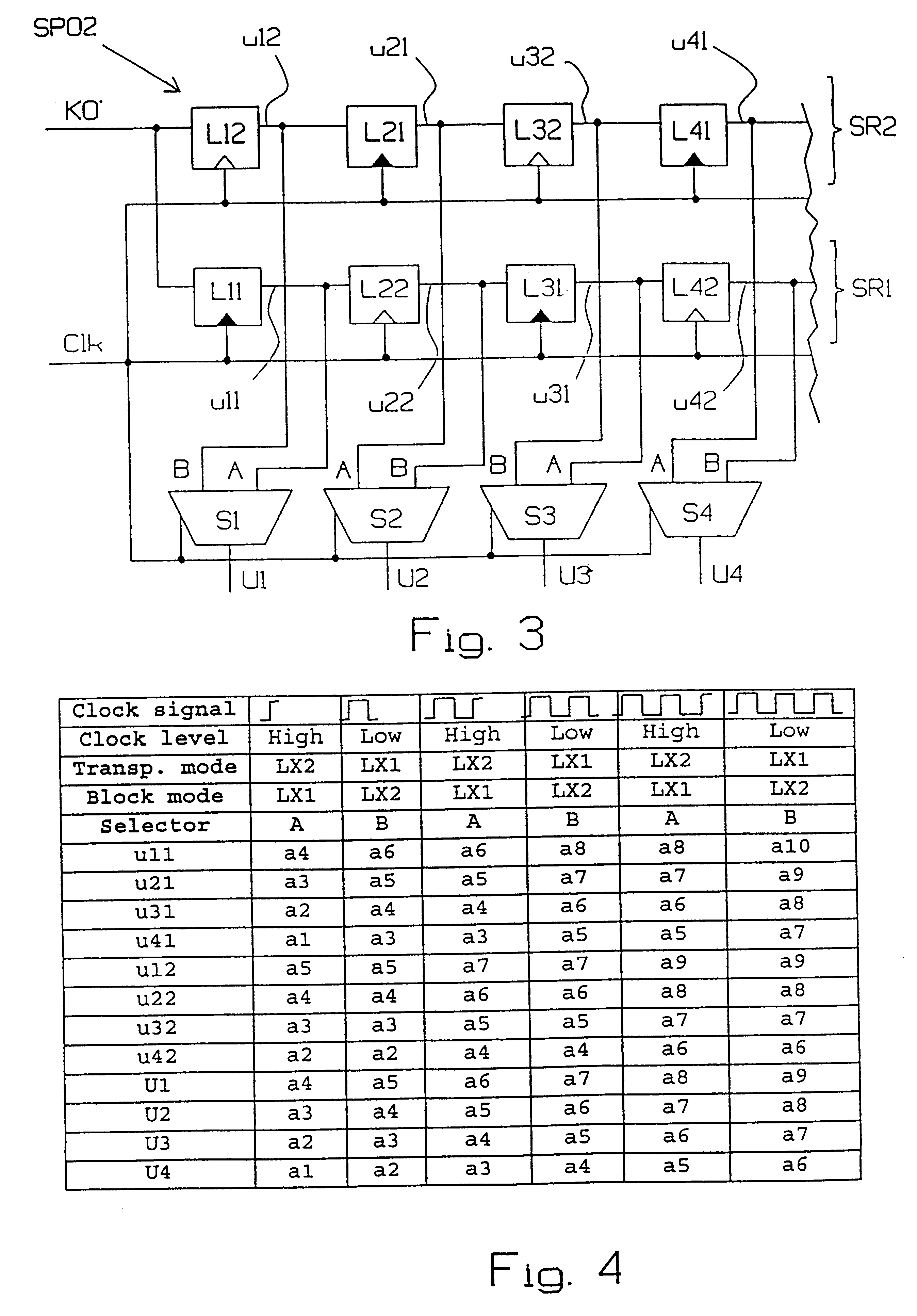
The present invention relates to the encoding and decoding respectively of serial data, using block codes. Encoding of a serial bit stream of input data in groups of N bits, so-called words (O), to serial output data in groups of 2N bits, so-called code words (KO), is preferably carried out by a logic circuit in a manner such that N of the 2N bits in the code words (KO) are comprised of the N bits input data, unchanged or inverted, and remaining bits in the code words (KO) are determined so that, seen statistically, the code words (KO) will include approximately as many zeros as ones, such that each code word (KO) will be unique for each word (O), and such that at least one of the code words (KO) will remain unique even in bit stream shifting processes. Decoding includes further encoding in a similar logic circuit and comparison of the incoming code words with the code words encoded in the logic circuit, in a predetermined manner.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
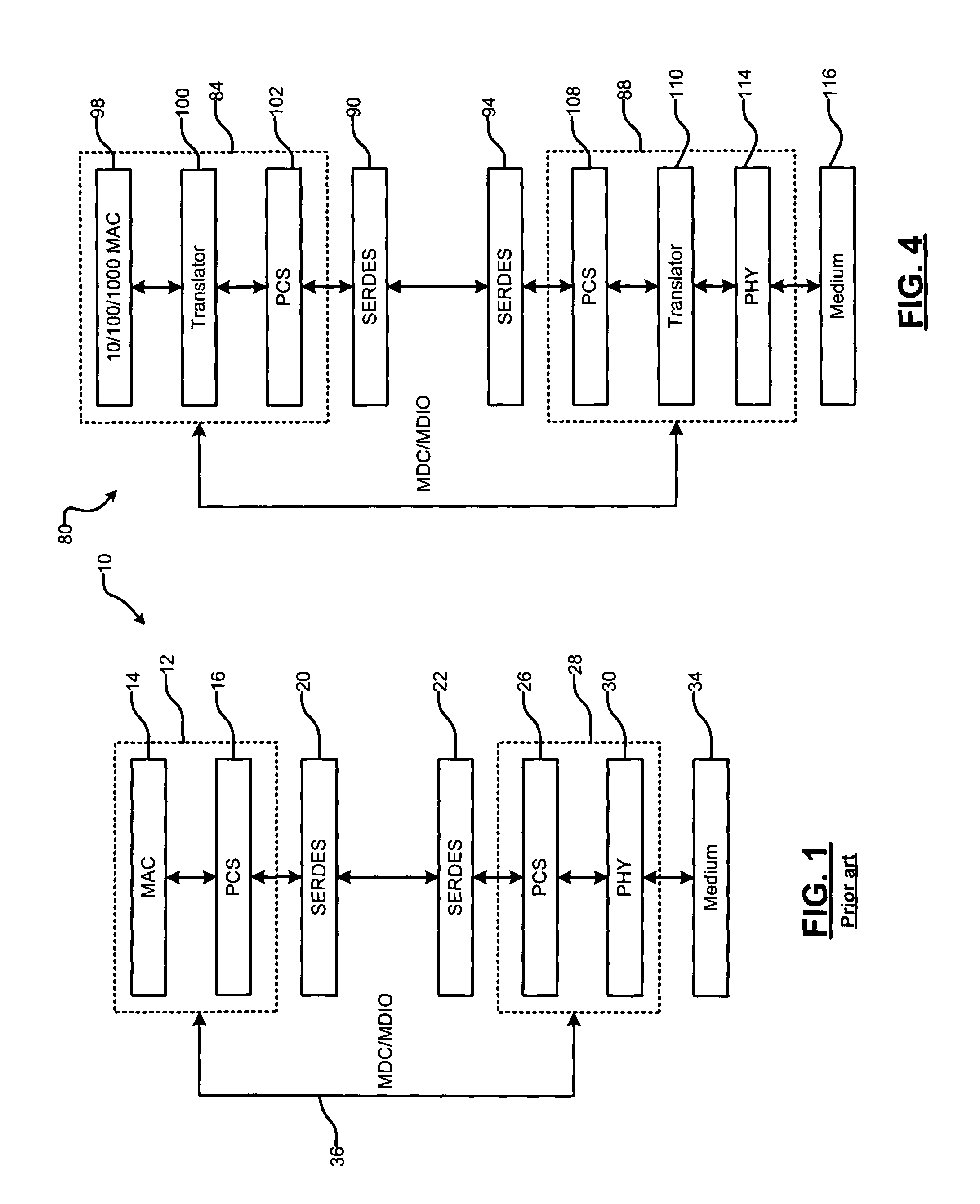
Multi-speed serial interface for media access control and physical layer devices
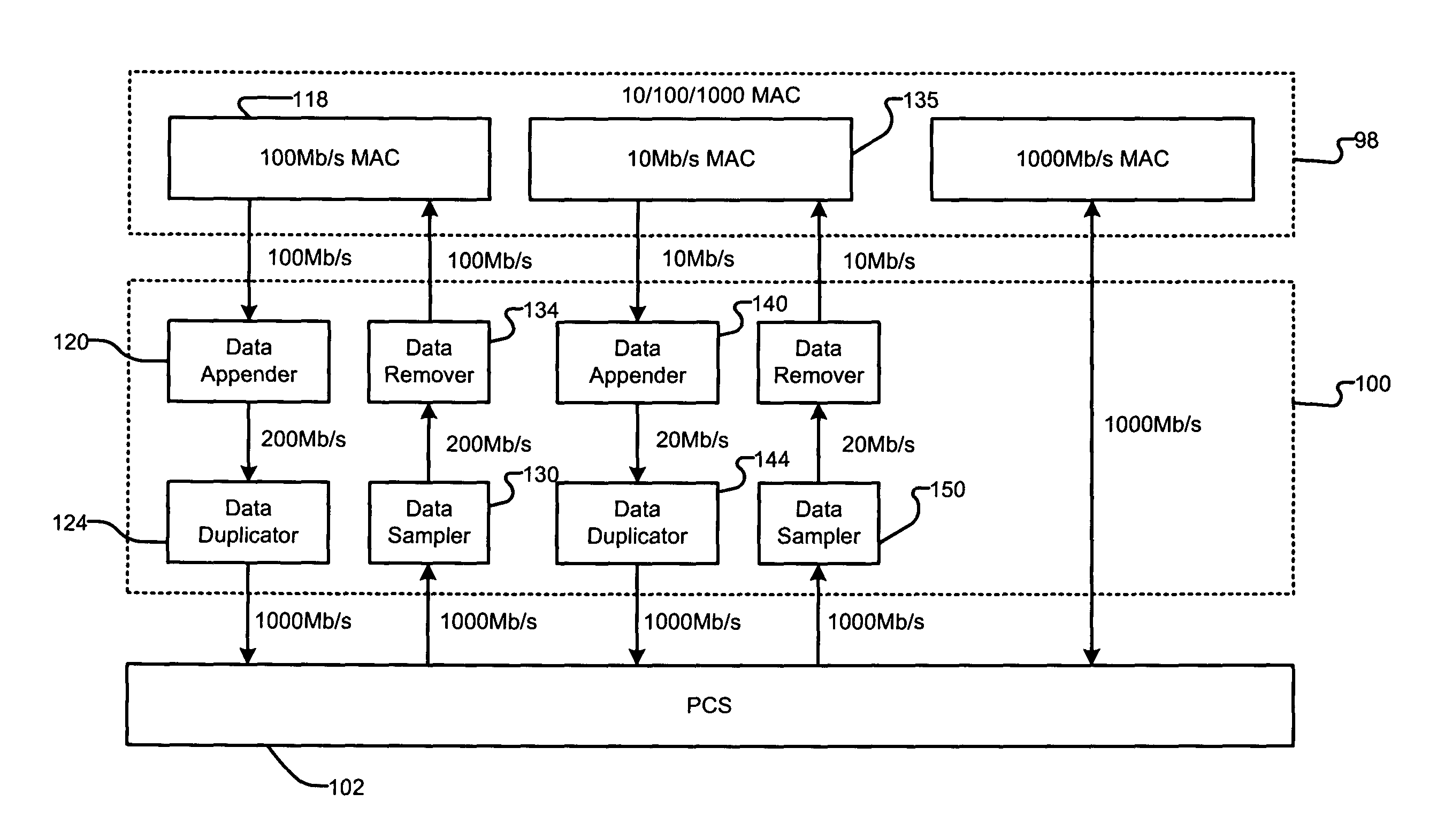
A network device includes a media access control (MAC) device that transmits a first data stream at a first data rate that includes symbols having M bits. A translator converts the first data stream to a second data stream at a second data rate. The translator includes a data appender that appends N bits to the symbols in the first data stream to generate second symbols having M+N bits. A data duplicator duplicates the second symbols X times to produce the second data stream at the second data rate.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Long instruction word controlling plural independent processor operations
InactiveUS7389317B2Instruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesArithmetic logic unitLeast significant bit
A data processing apparatus including a multiplier unit forming a product from L bits of each two data buses of N bits each N is greater than L. The multiplier forms a N bit output having a first portion which is the L most significant bits of the of product and a second portion which is M other bits not including the L least significant bits of the product, where N is the sum of M and L. In the preferred embodiment the M other bits are derived from other bits of the two input data busses, such as the M other bits of the first input data bus. An arithmetic logic unit performs parallel operations (addition, subtraction, Boolean functions) controlled by the same instructions. This arithmetic logic unit is divisible into a selected number of sections for performing identical operations on independent sections of its inputs. The multiplier unit may form dual products from separate parts of the input data. A single instruction controlling both the multiplier unit and the arithmetic logic unit permits addition of dual products. The dual products are temporarily stored in a data register permitting the multiply and add operations to be pipelined. The dual products are formed in one data word and added by a rotate / mask and add operation in a three input arithmetic unit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of avoiding errors in flash memory
Whenever N data bits are stored in a cell of a memory that programs each of its cells to represent any one of 2N different patterns of N>1 bits as a respective one of 2N ordered cell states, the N data bits are mapped to a transformed pattern of N bits according to a transformation that maps the pattern of the lowest state (typically all 1's) to a different pattern, and the cell is programmed to represent the transformed pattern. The transformation may invert all, some or only one of the bits of each pattern. Whenever the cells of the memory are read, the transformation is inverted.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
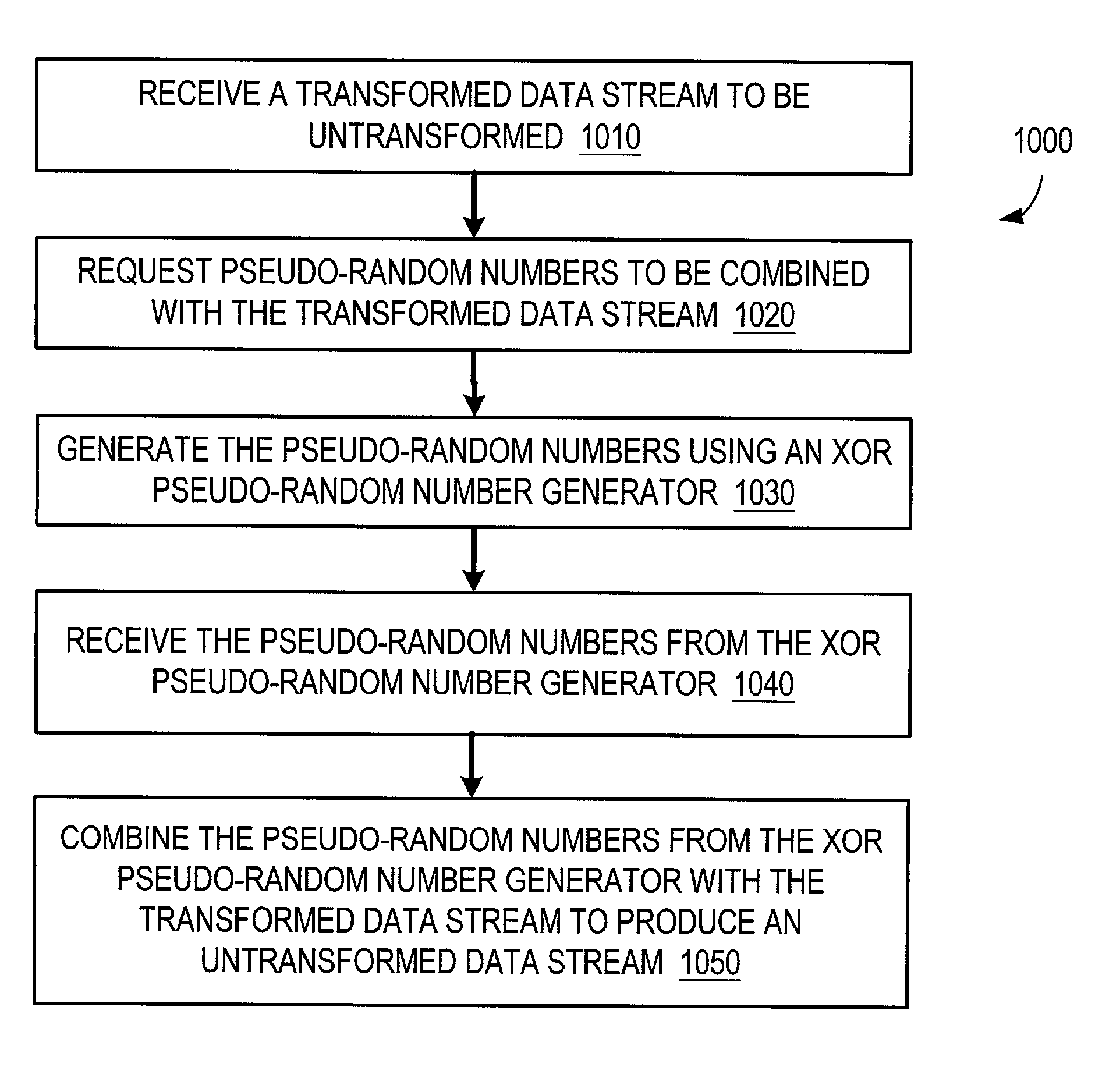
Method and apparatus for generating pseudo-random numbers
ActiveUS7082449B2Random number generatorsSecuring communicationRegister allocationProcessor register
A method and apparatus for generating pseudo-random numbers. The method includes defining a first set of R bits and defining a second set of S bits different from the first set of R bits. The method also includes updating the second set of S bits using a predetermined process that operates on the first set of R bits and the second set of S bits to form an updated set of S bits. The method also includes updating the first set of R bits using another predetermined process. The apparatus may include a linear feedback shift register and a second register. The linear feedback shift register is configured to store R bits. The second register is configured to store S bits. Each bit of the S bits is updated using a function that operates on one or more of the R bits from the linear feedback shift register and one or more of the S bits.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
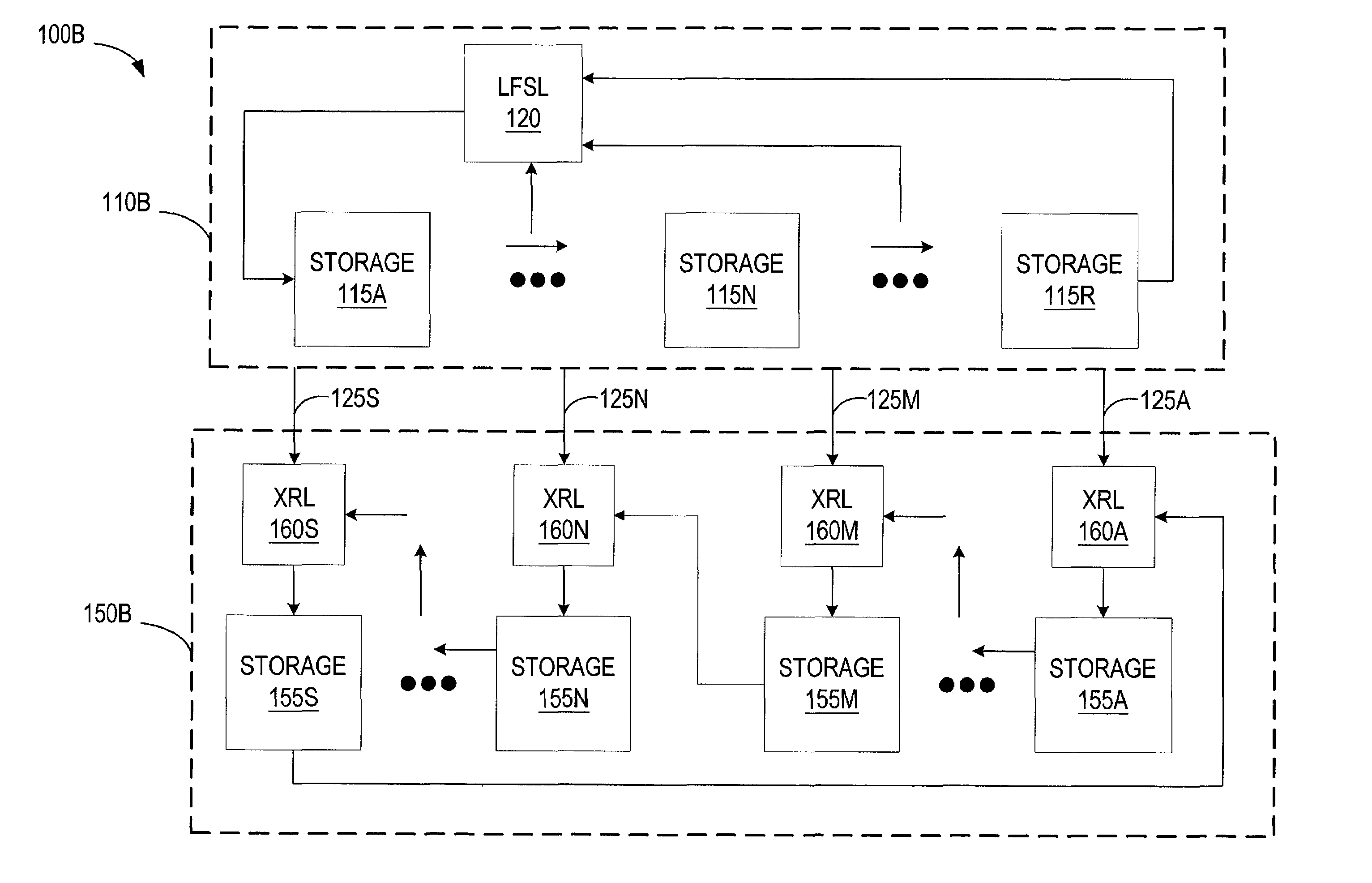
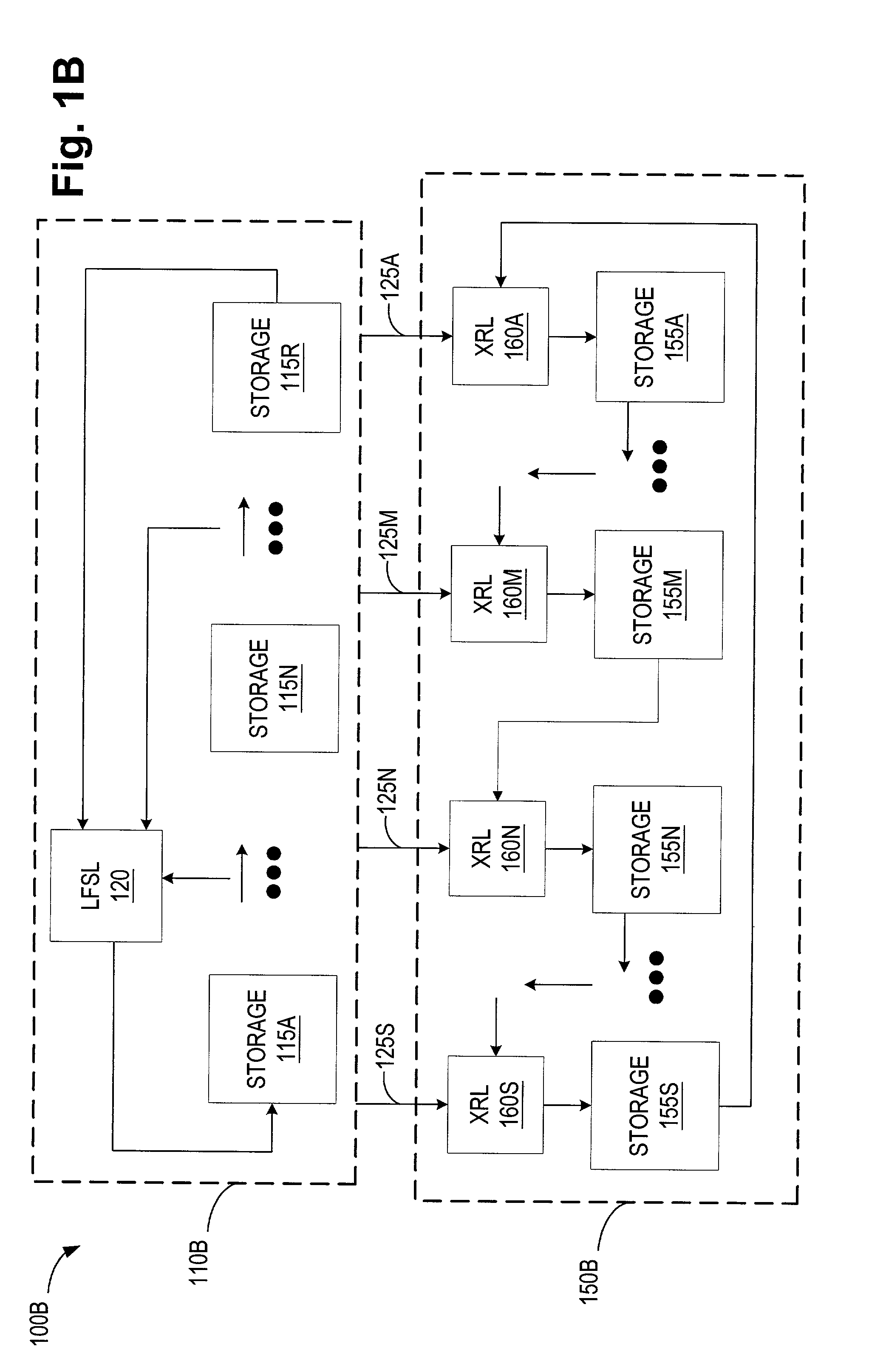
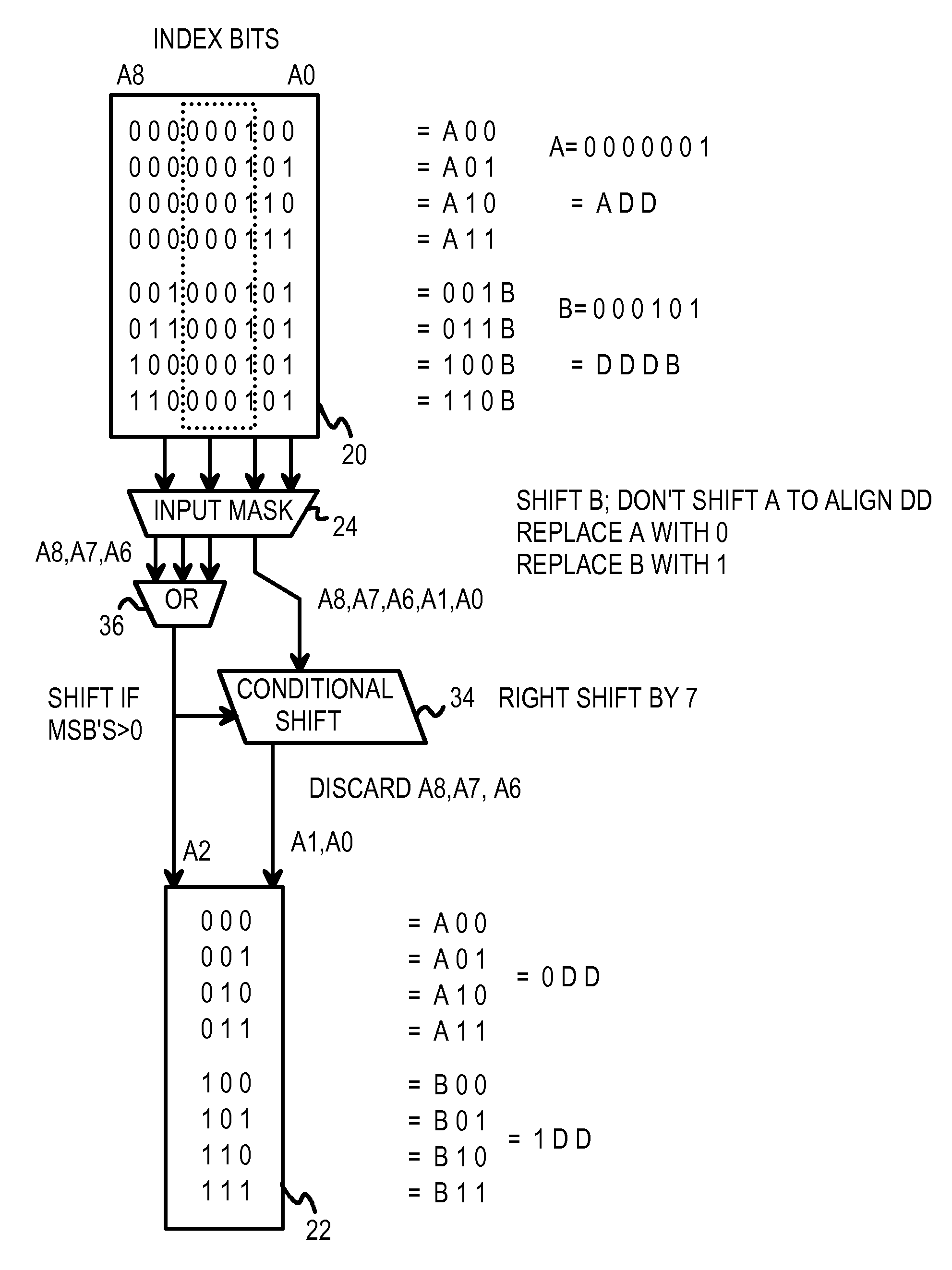
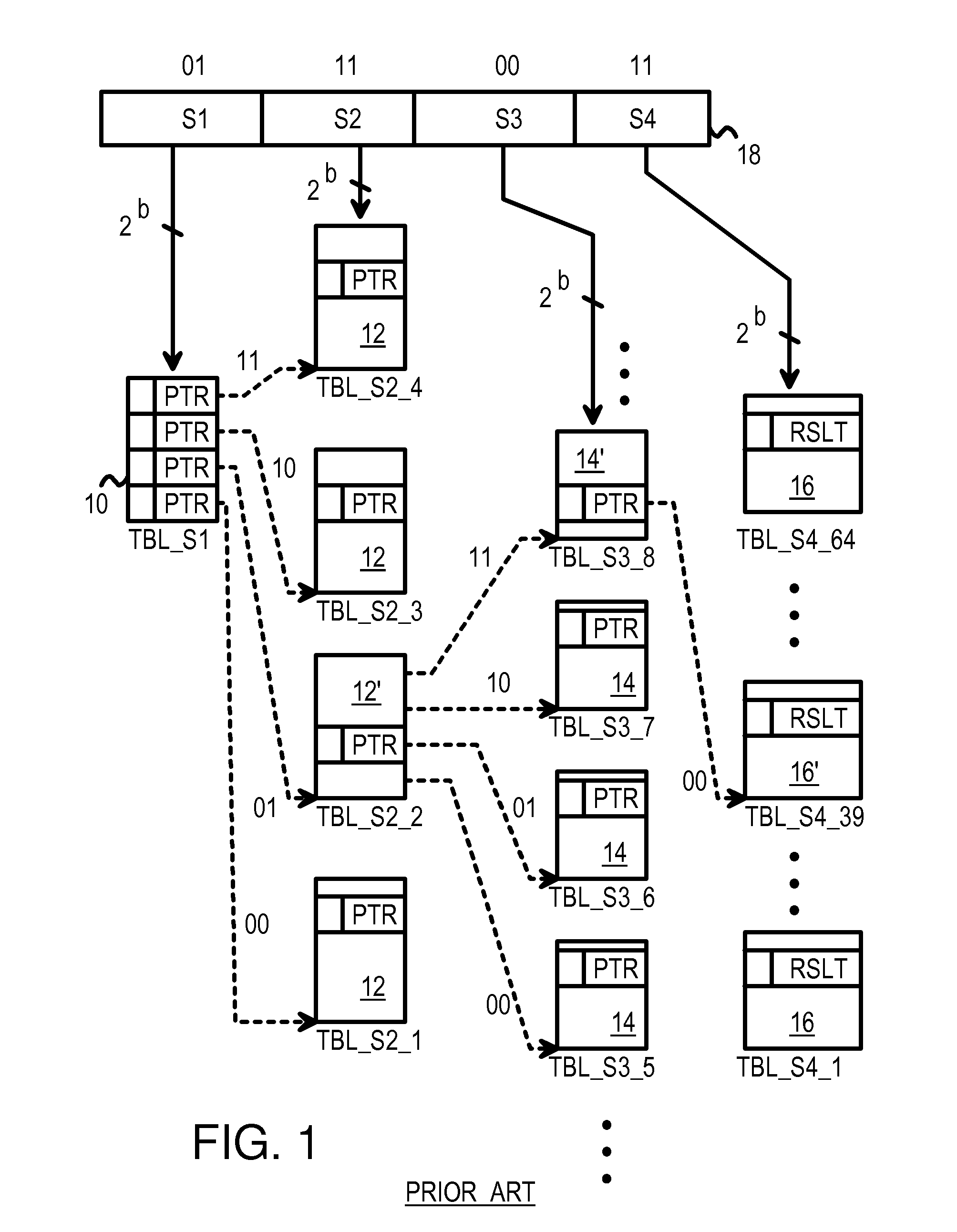
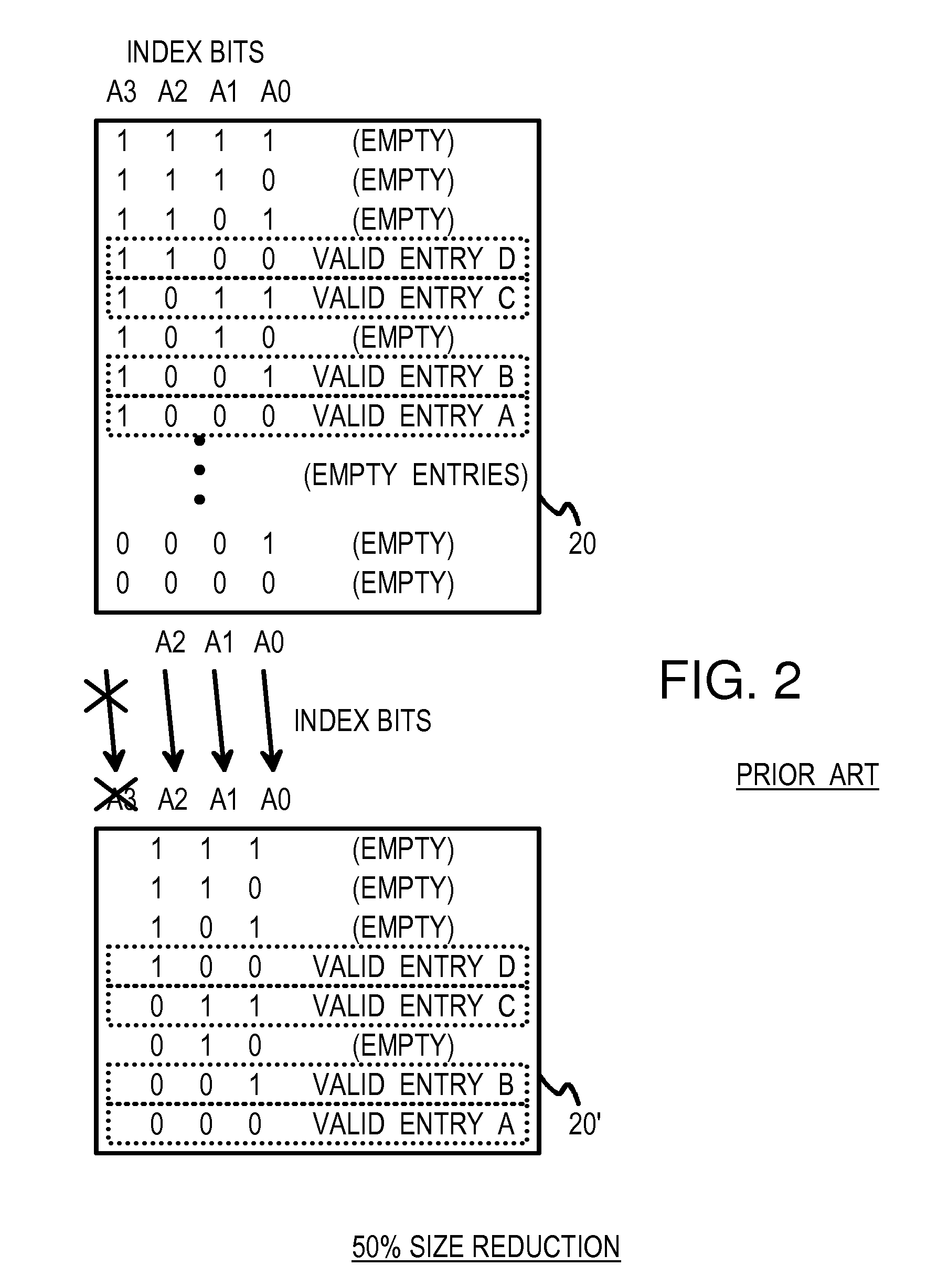
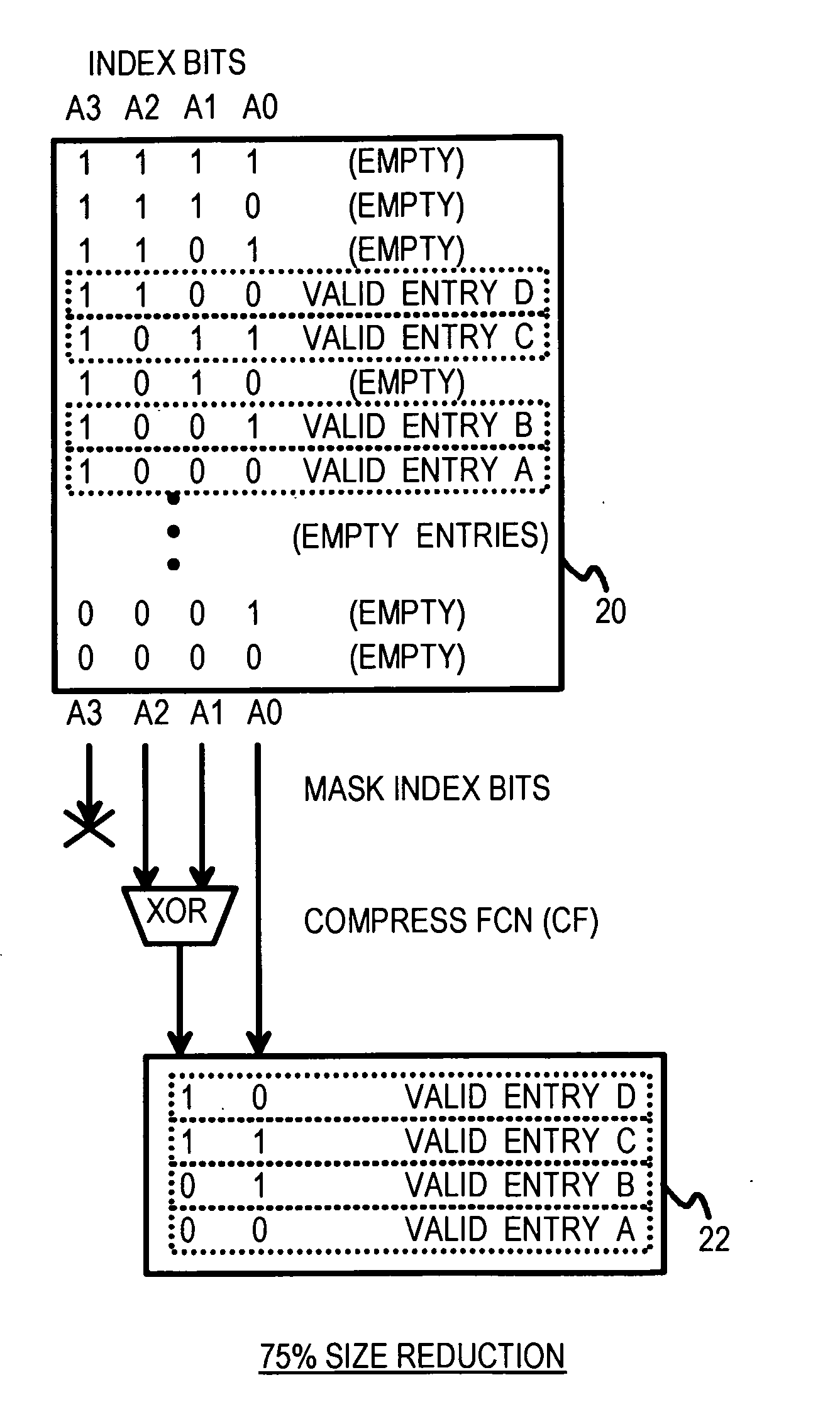
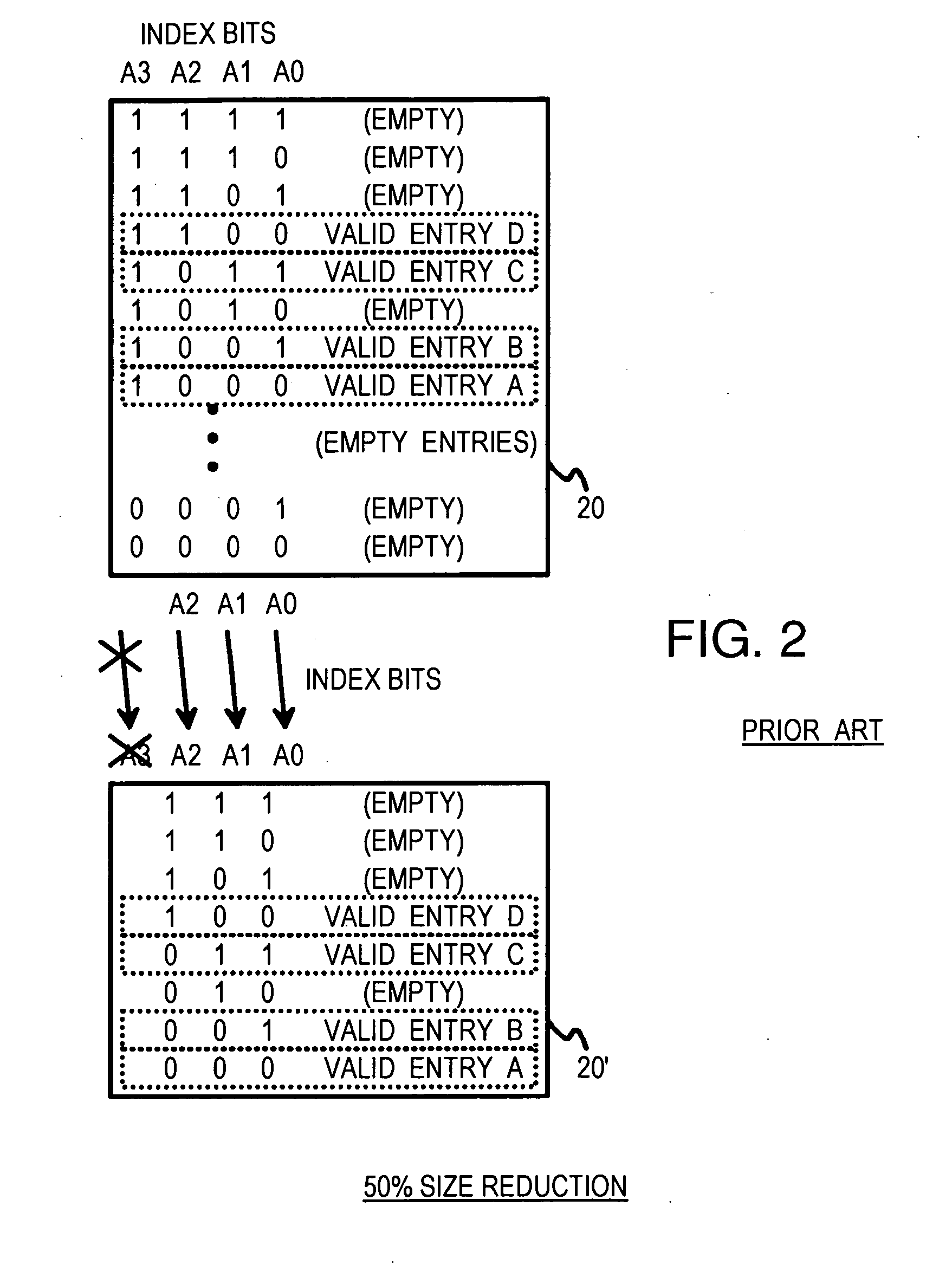
Multi-level compressed lock-up tables formed by logical operations to compress selected index bits
ActiveUS7430560B1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceLogical operations
A lookup is performed using multiple levels of compressed stride tables in a multi-bit Trie structure. An input lookup key is divided into several strides including a current stride of S bits. A valid entry in a current stride table is located by compressing the S bits to form a compressed index of D bits into the current stride table. A compression function logically combines the S bits to generate the D compressed index bits. An entry in a prior-level table points to the current stride table and has a field indicating which compression function and mask to use. Compression functions can include XOR, shifts, rotates, and multi-bit averaging. Rather than store all 2S entries, the current stride table is compressed to store only 2D entries. Ideally, the number of valid entries in the current stride table is between 2D−1 and 2D for maximum compression. Storage requirements are reduced.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Method of avoiding errors in flash memory
Whenever N data bits are stored in a cell of a memory that programs each of its cells to represent any one of 2N different patterns of N>1 bits as a respective one of 2N ordered cell states, the N data bits are mapped to a transformed pattern of N bits according to a transformation that maps the pattern of the lowest state (typically all 1's) to a different pattern, and the cell is programmed to represent the transformed pattern. The transformation may invert all, some or only one of the bits of each pattern. Whenever the cells of the memory are read, the transformation is inverted.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
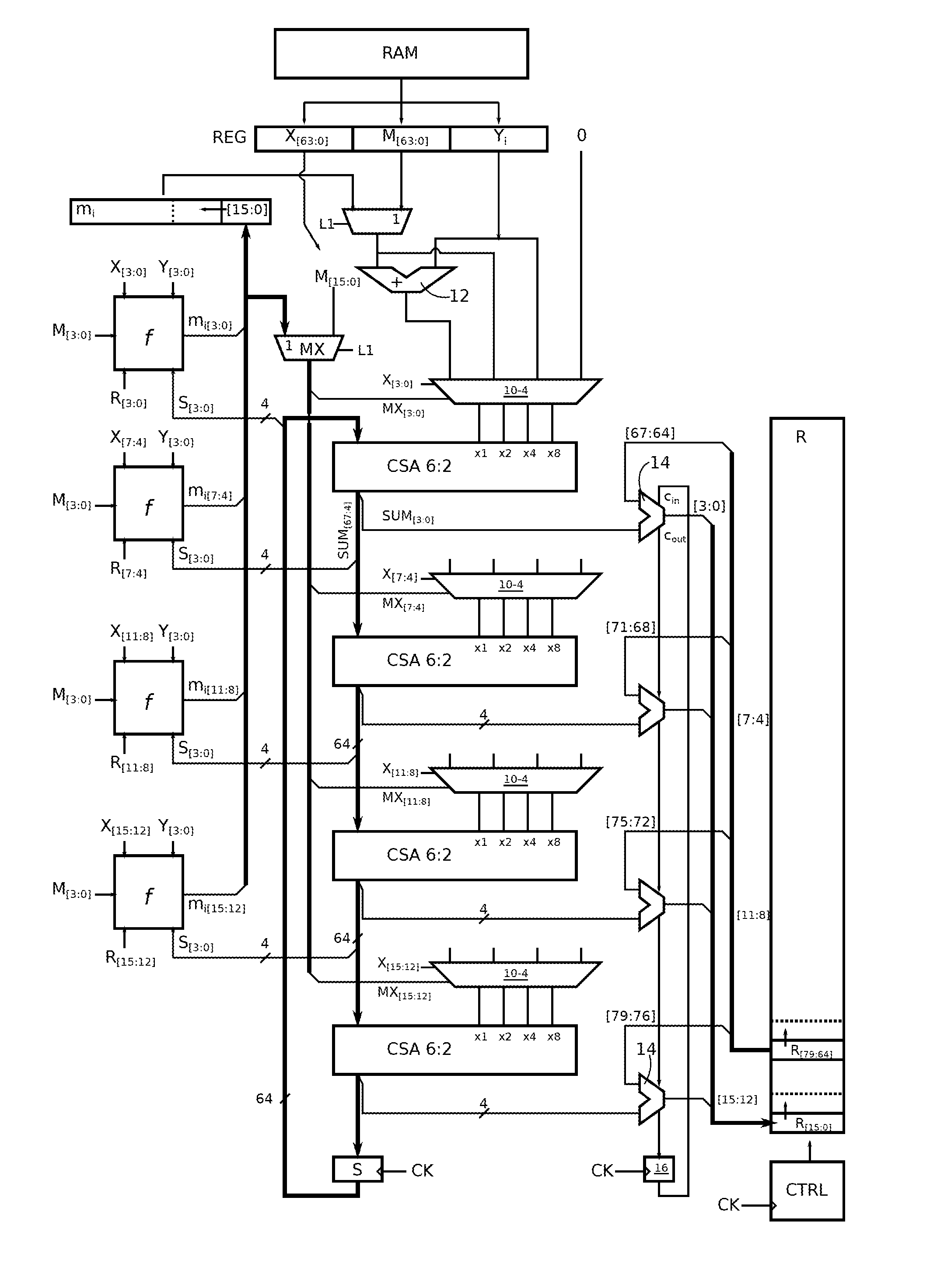
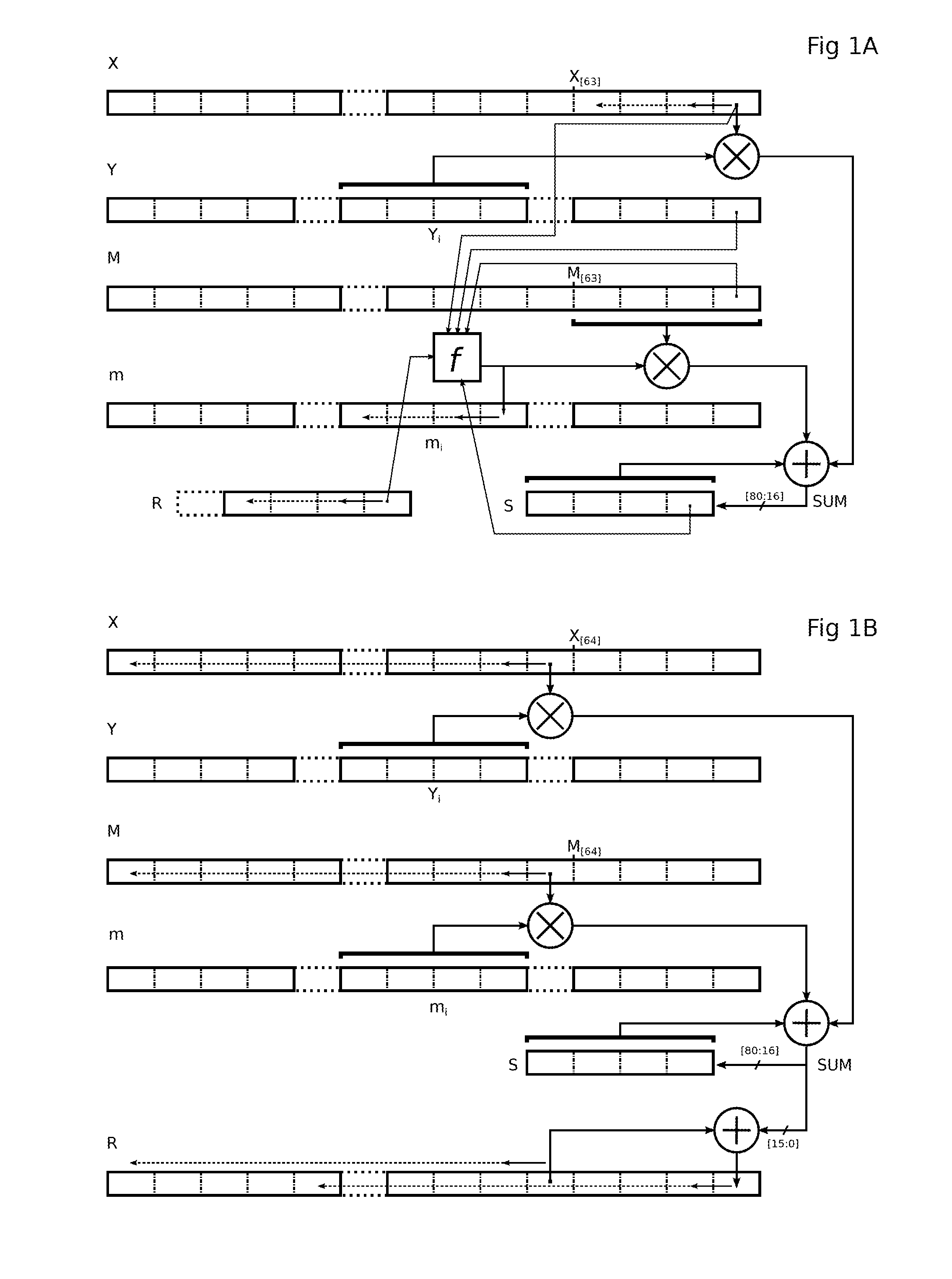
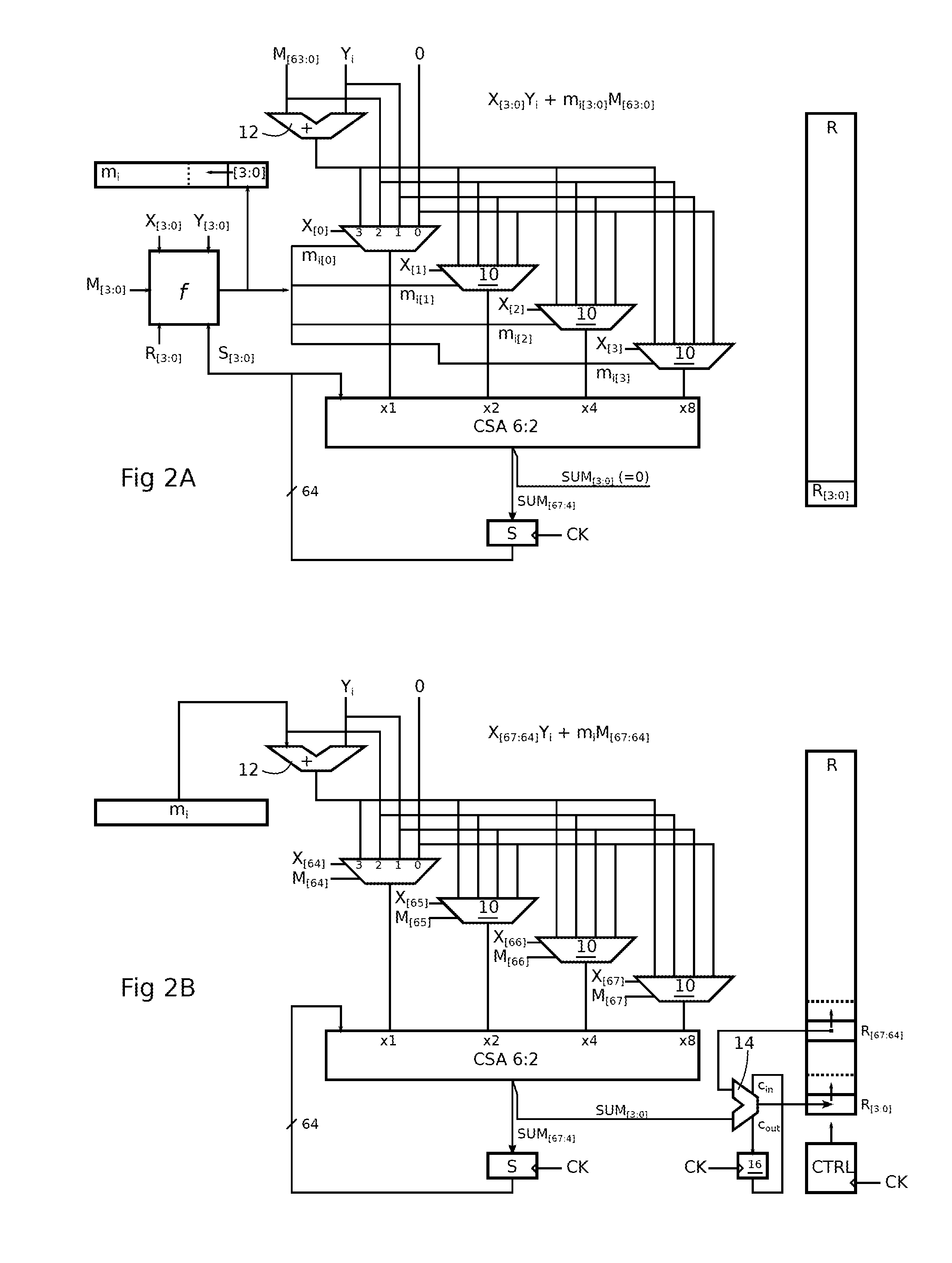
Montgomery multiplication method
Disclosed is a method of modular multiplication of two L-bit numbers (X, Y), the result defined from XY+mM, where M is the modulo, of L bits, and m is a number of L bits found and is divisible by 2L. L / k iterations are performed, an iteration i involving XYi+miM+R, Yi, mi being k-bit digits of rank i of Y, m from least significant bits, and R the previous iteration result. In each iteration, a first sub-loop of k / p iterations calculates a partial result of XYi+miM+R on k least significant bits of X, M, R, following decomposition of X, mi into p-bit digits. Starting each sub-loop iteration, the p bits of the current digit of mi are simultaneously produced. A second sub-loop calculates and sums the remaining partial results of XYi+miM+R using mi from the first sub-loop.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
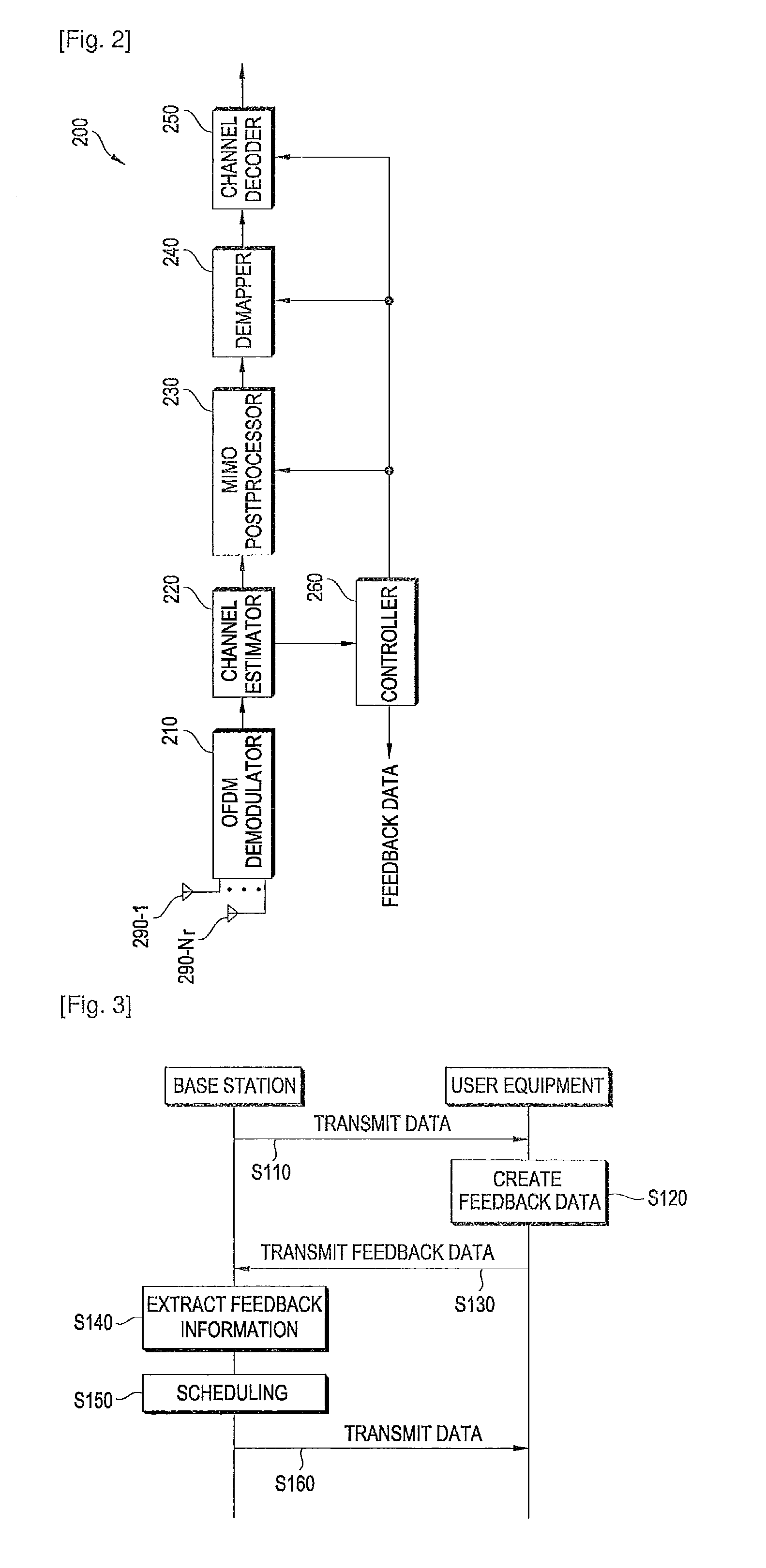
Method for transmitting feedback information
InactiveUS20100085912A1Reduce transmissionReceivers monitoringFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer scienceUser equipment
There is provided a method for enabling a user equipment to transmit feedback information. The method includes generating feedback data representing the feedback information, the feedback data expressed by a binary number having N bits, where N is an integer, the N bits comprising 2 levels, the feedback information represented by one of the 2 levels, wherein different types of the feedback information are assigned to different levels and transmitting the feedback data. Overheads incurred by transmission of feedback information can be reduced.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for generating pseudo-random numbers
ActiveUS20030206630A1Random number generatorsSecuring communicationRegister allocationProcessor register
A method and apparatus for generating pseudo-random numbers. The method includes defining a first set of R bits and defining a second set of S bits different from the first set of R bits. The method also includes updating the second set of S bits using a predetermined process that operates on the first set of R bits and the second set of S bits to form an updated set of S bits. The method also includes updating the first set of R bits using another predetermined process. The apparatus may include a linear feedback shift register and a second register. The linear feedback shift register is configured to store R bits. The second register is configured to store S bits. Each bit of the S bits is updated using a function that operates on one or more of the R bits from the linear feedback shift register and one or more of the S bits.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Multi-Level Compressed Look-up Tables Formed by Logical Operations to Compress Selected Index Bits
ActiveUS20090024643A1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsLogical operationsTheoretical computer science
A lookup is performed using multiple levels of compressed stride tables in a multi-bit Trie structure. An input lookup key is divided into several strides including a current stride of S bits. A valid entry in a current stride table is located by compressing the S bits to form a compressed index of D bits into the current stride table. A compression function logically combines the S bits to generate the D compressed index bits. An entry in a prior-level table points to the current stride table and has a field indicating which compression function and mask to use. Compression functions can include XOR, shifts, rotates, and multi-bit averaging. Rather than store all 2S entries, the current stride table is compressed to store only 2D entries. Ideally, the number of valid entries in the current stride table is between 2D−1 and 2D for maximum compression. Storage requirements are reduced.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Information transmission method, sending terminal device and receiving terminal device
PendingCN107835063AAvoid lostAvoid delayNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionInformation transmissionTerminal equipment
The embodiment of the invention provides an information transmission method, a sending terminal device and a receiving terminal device. The information transmission method comprises the following steps: confirming the mother code length N of a Polar code according to the load of a first channel, wherein the load of the first channel is N bits, the N is 2<n>, and the n is a positive integer; performing Polar code coding on the target information to be transmitted to obtain N coded bits; and transmitting the N coded bits through the first channel. In the embodiment of the invention, the number of coded bits obtained after the Polar code coding is equal to the load length of the channel, therefore, the N coded bits is not required to perform a rate matching process when transmitted through the first channel, and the coding overhead of the channel is simplified; and because the rate matching is not required, the complexity and delay of the channel coding are greatly reduced, and the performance loss caused by the rate matching operation is avoided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
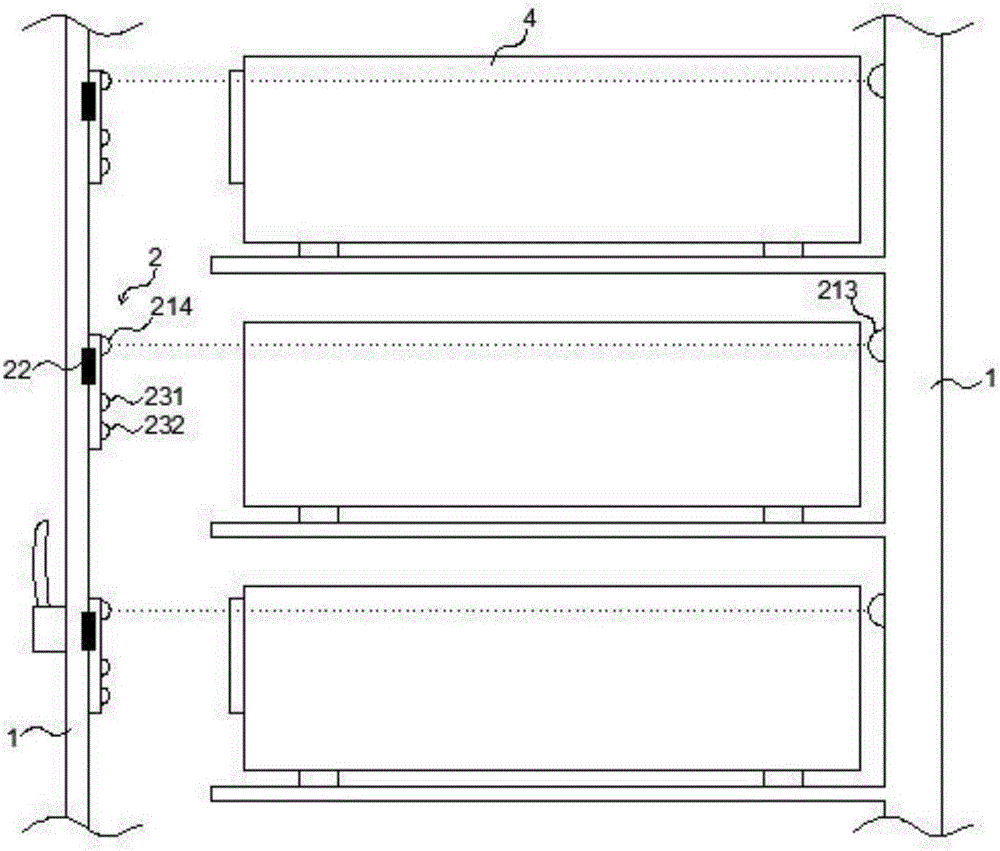
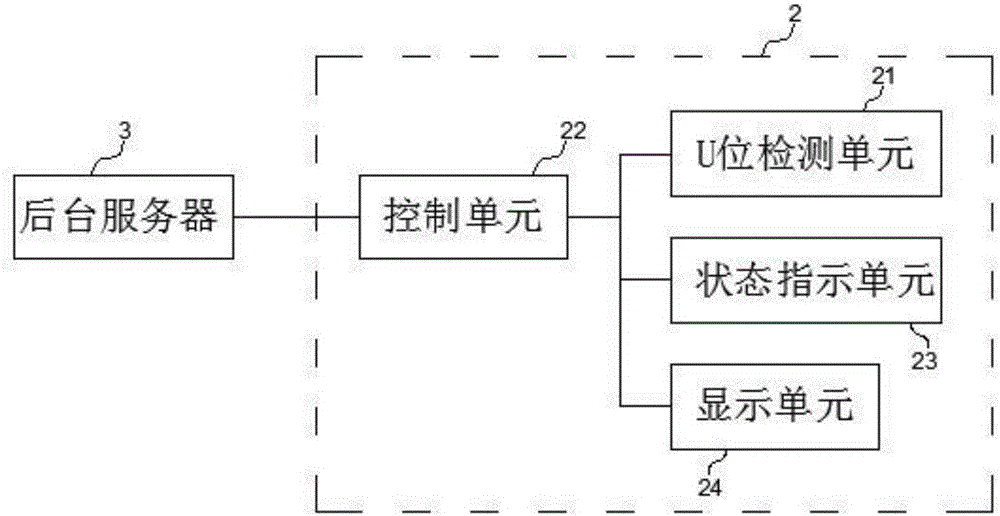
IT device cabinet U bit management method and U bit manager
ActiveCN105930250AImprove management efficiencyReduce demandHardware monitoringManagement efficiencyServer
The present invention discloses an IT cabinet U bit management method and a U bit manager. According to the method, a management terminal, i.e. a U bit manager is used to receive and store a background task, and then the task is compared with U bit state information, and then the U bit state information or preset information is sent to a background server according to a comparison result and the task or not. The U bit manager disclosed by the present invention is a management terminal with a self-determining function, wherein the U bit manager compares detected current U bit state information with stored last-time U bit state information, and returns state information of a U bit of which state information is changed to the background server, so as to update a U bit information list. Therefore, data returned from the management terminal to the background is greatly decreased, the demands for the communication network and the background server are reduced, and the IT device management efficiency is improved.
Owner:华西信息工程江苏有限公司
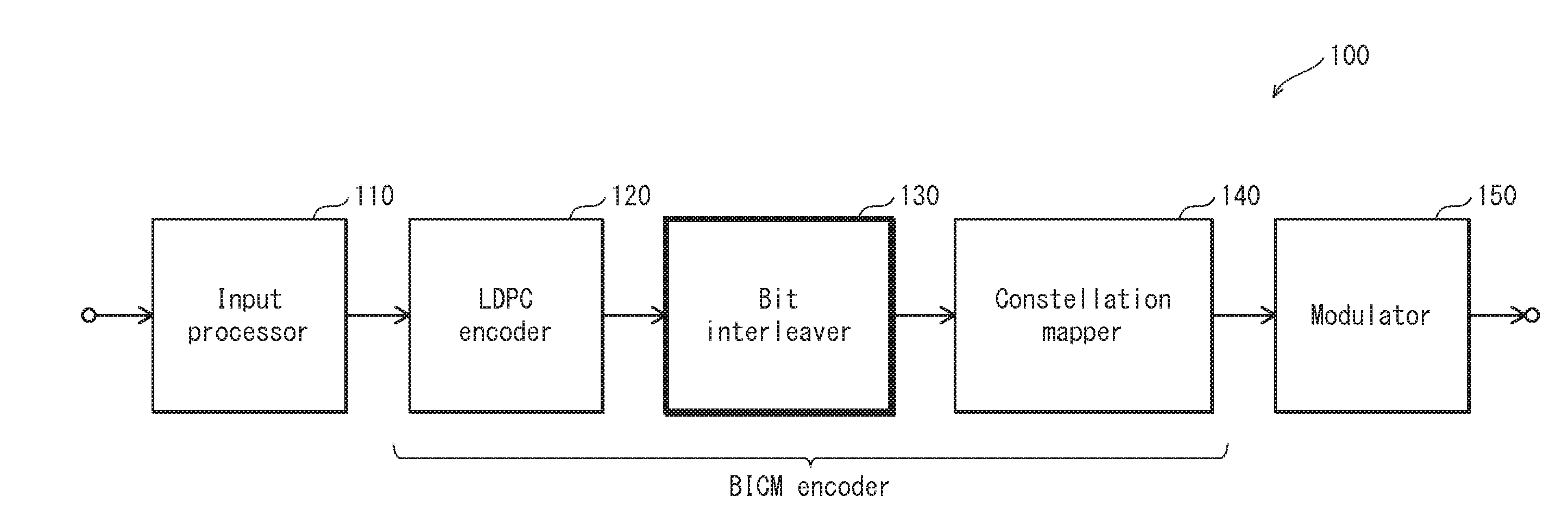
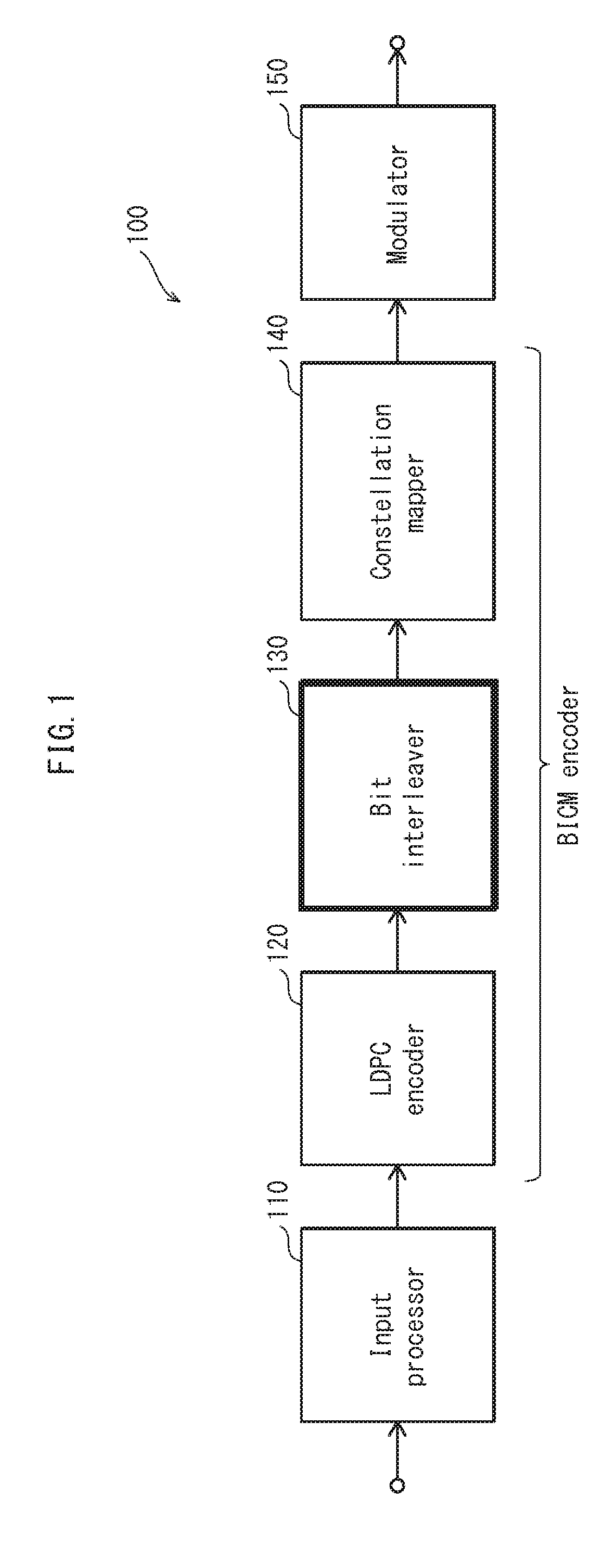
Parallel bit interleaver
ActiveUS20150381207A1Effective interleavingError correction/detection using LDPC codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceConstellation
A bit interleaving method involves applying a bit permutation process to a QC LDPC codeword made up of N cyclic blocks each including Q bits, and dividing the codeword, after the bit permutation process, into a plurality of constellation words each imade up of M bits, the codeword being divided into N / M sections, each constellation word being associated with one of the N / M sections, and the bit permutation process being performed such that each of the constellation words includes one bit from each of M different cyclic blocks associated with a given section.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
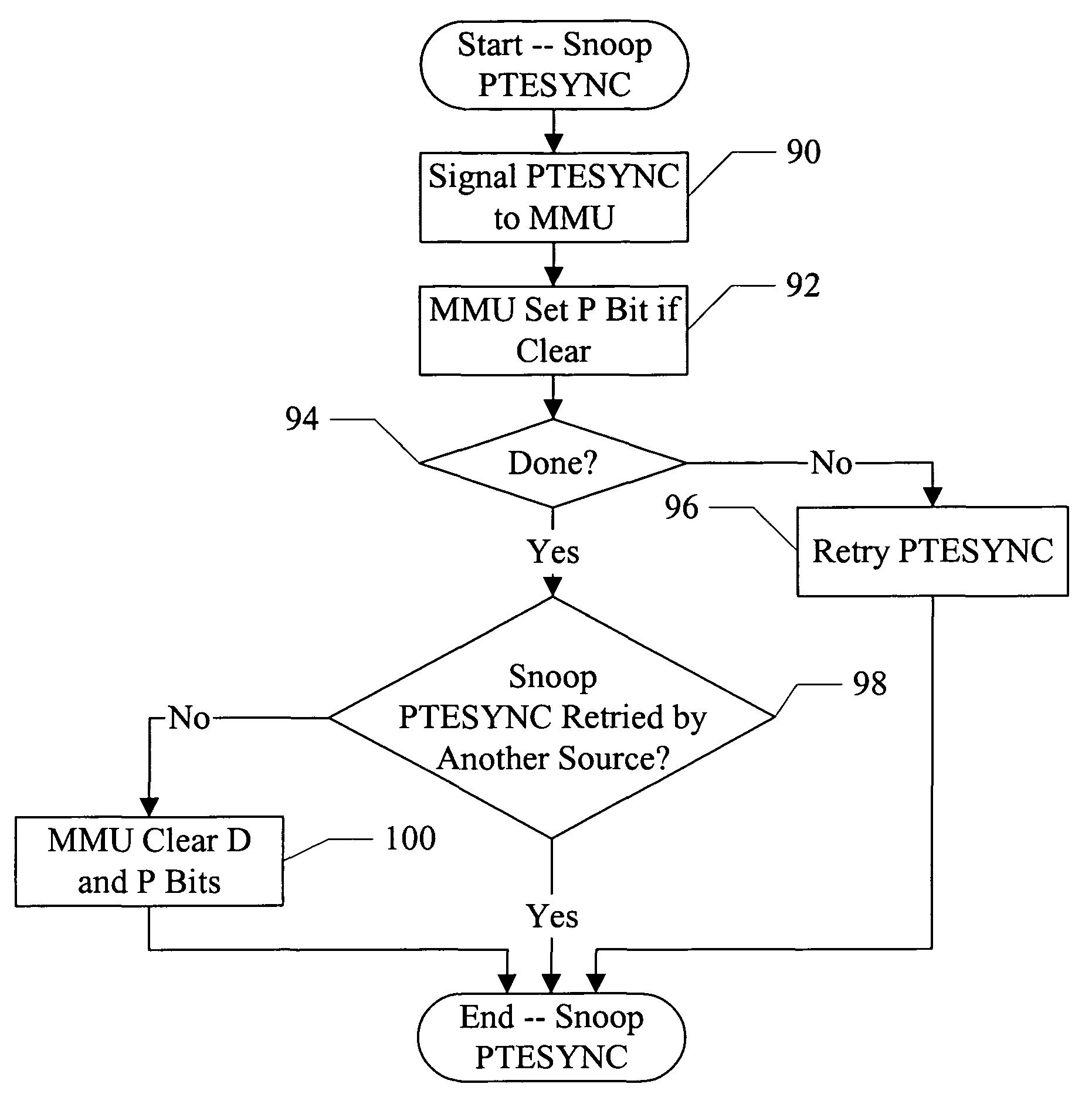
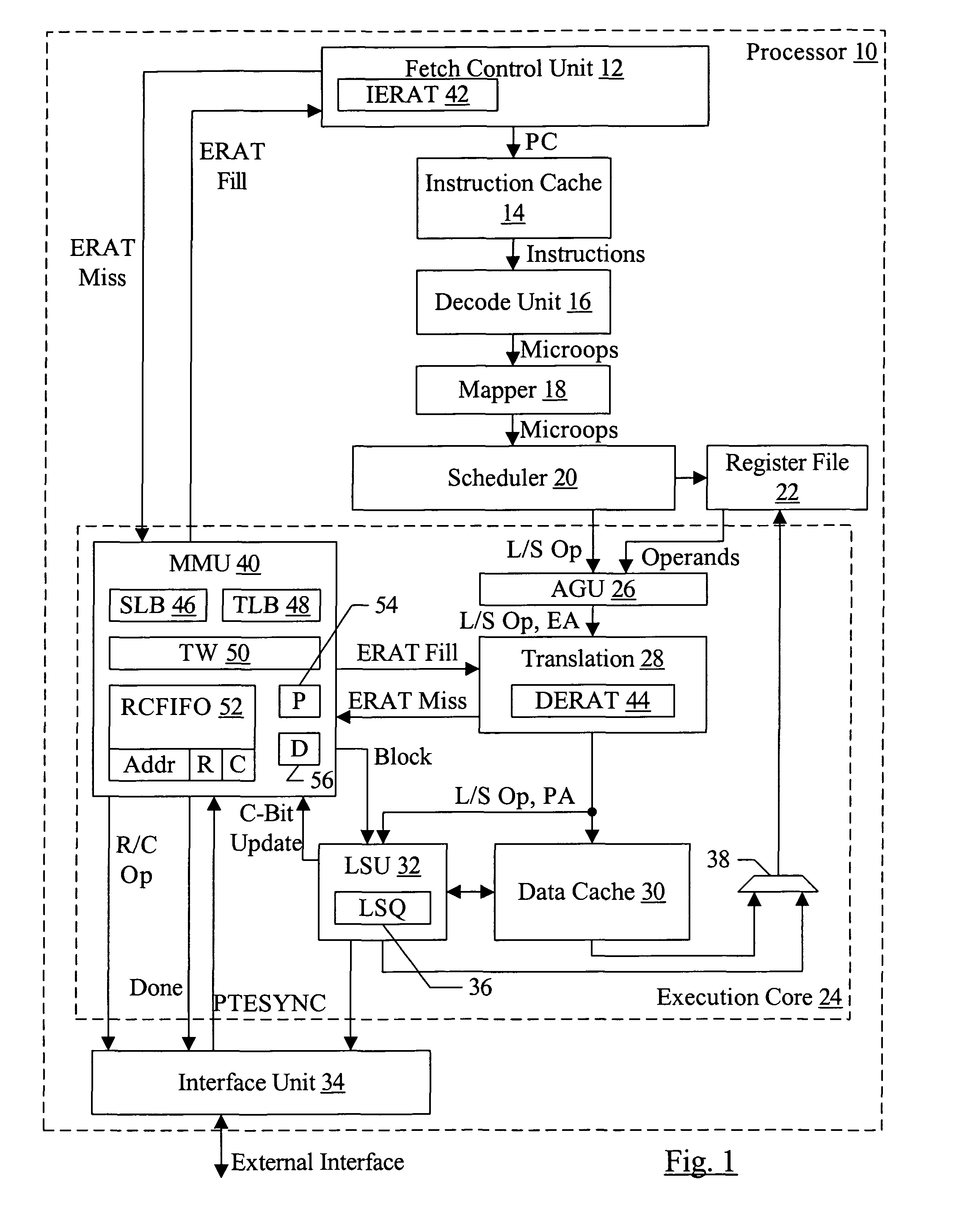
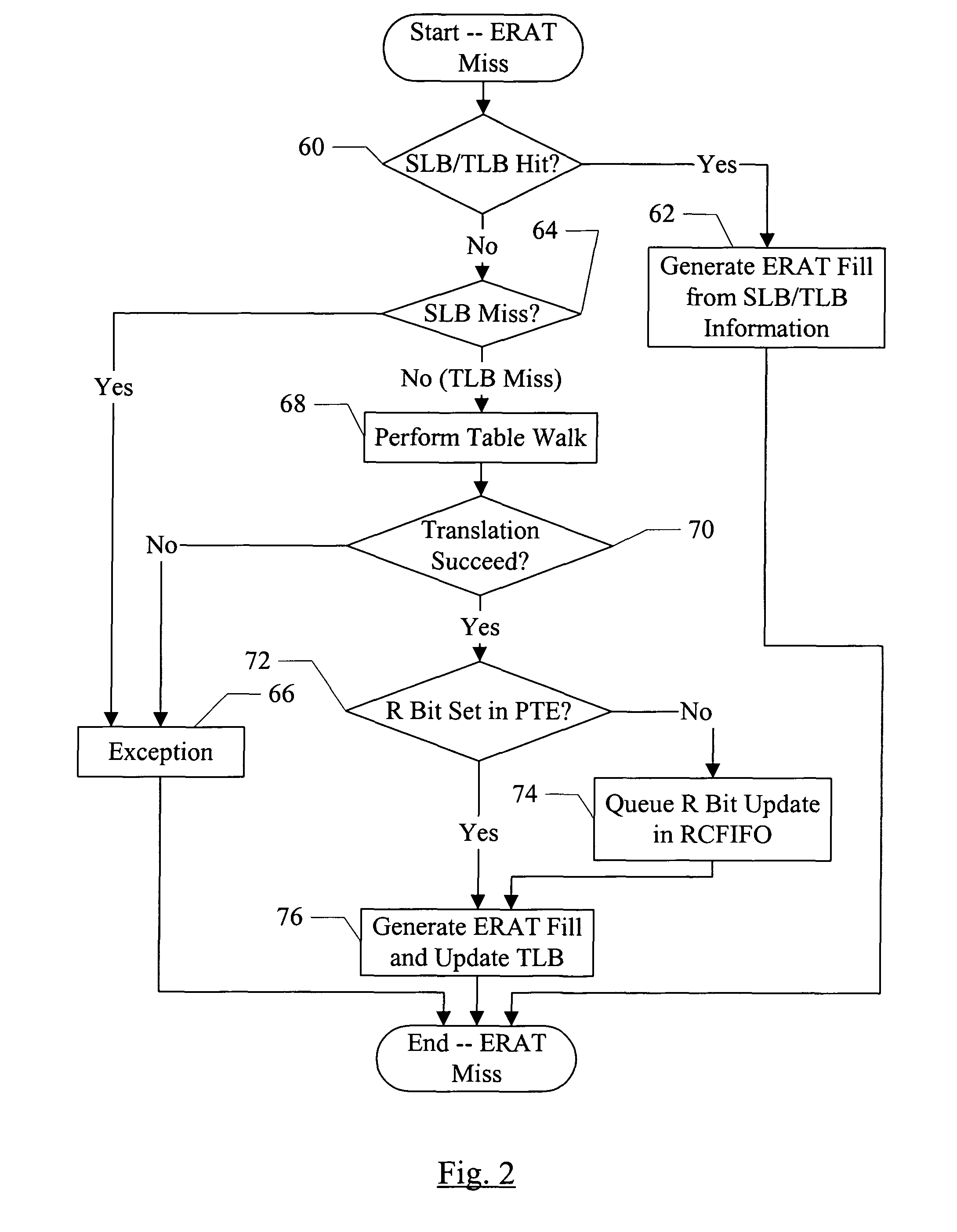
R and C bit update handling
InactiveUS7739476B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple digital computer combinationsPage tableMemory management unit
Owner:APPLE INC
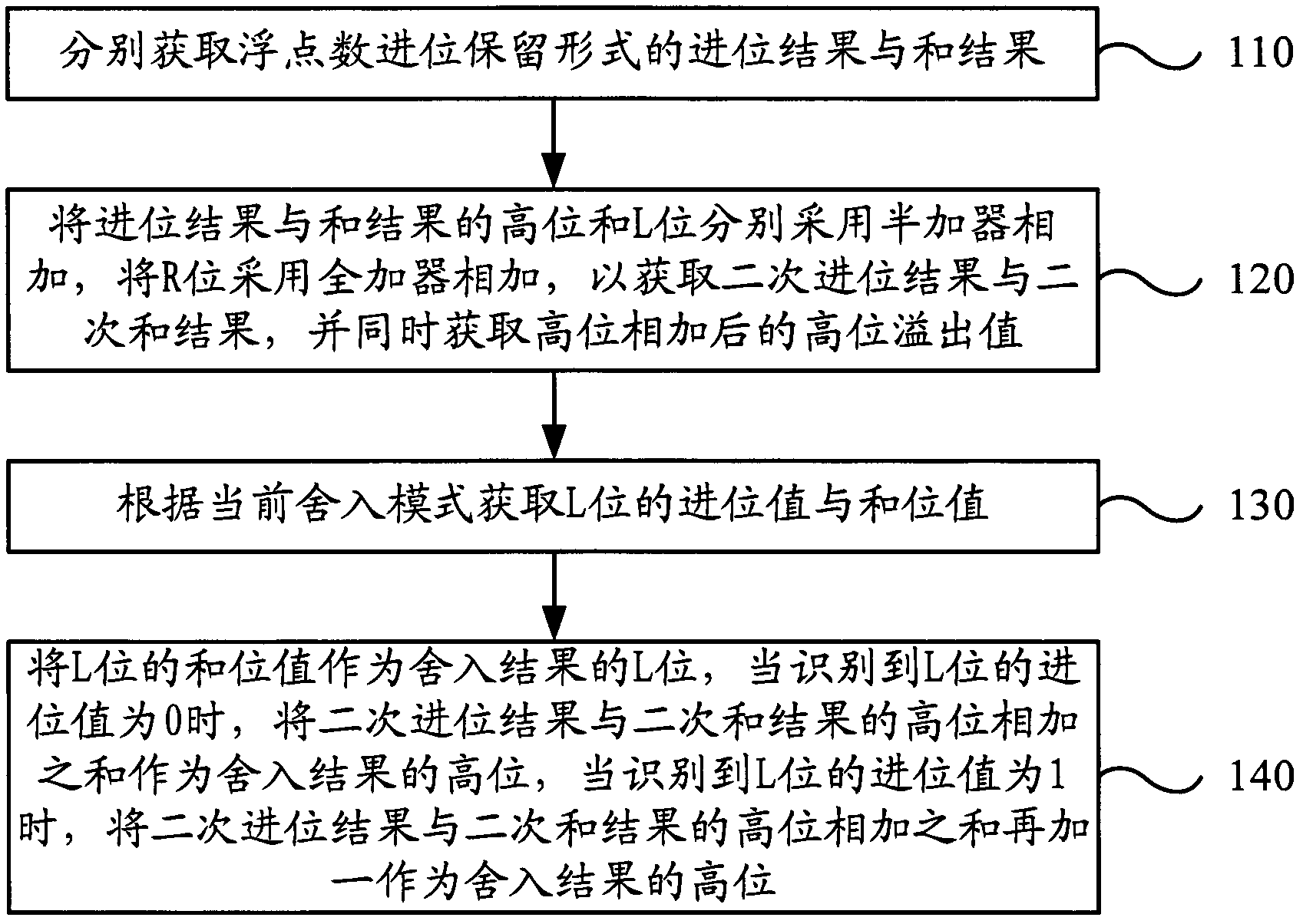
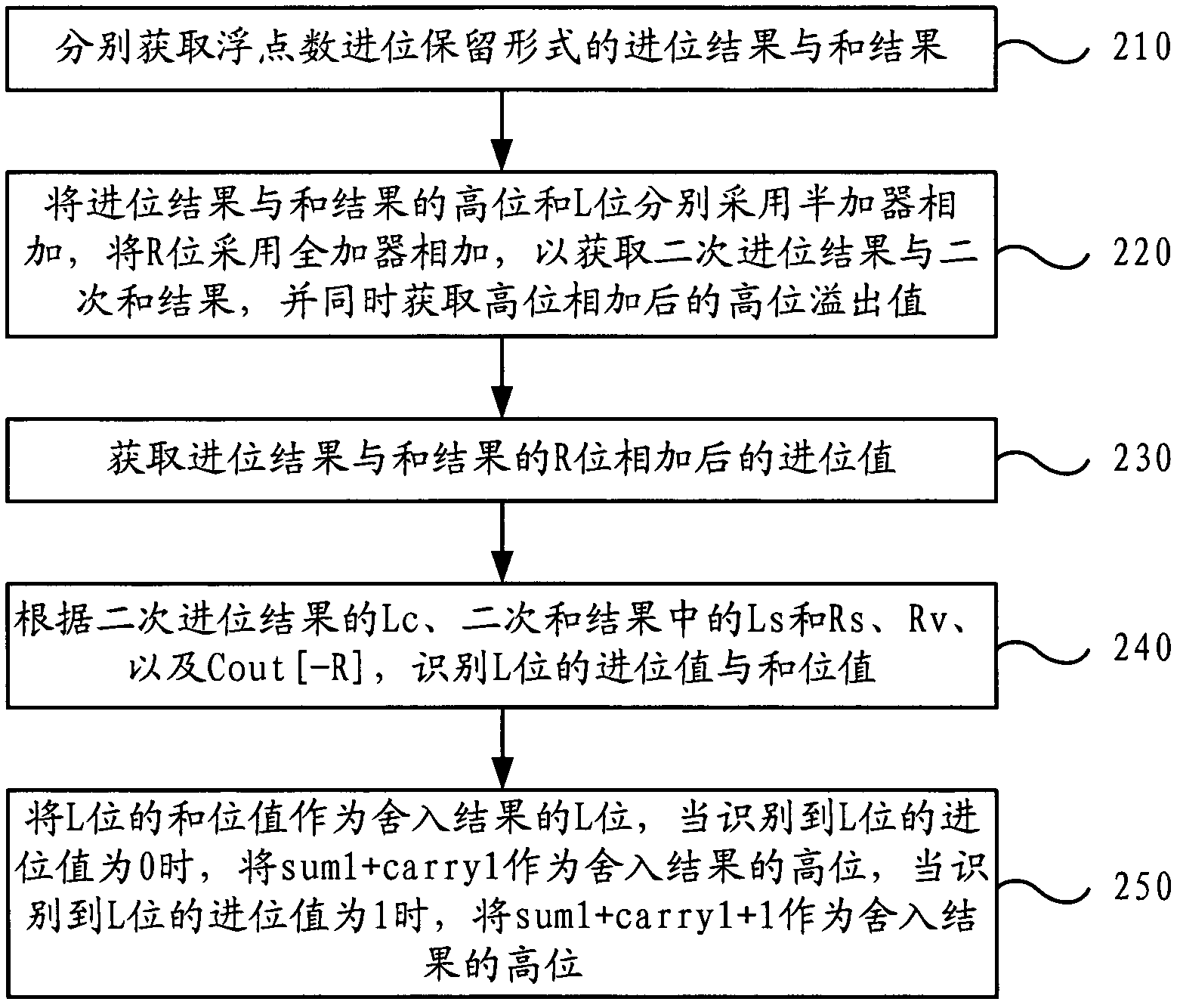
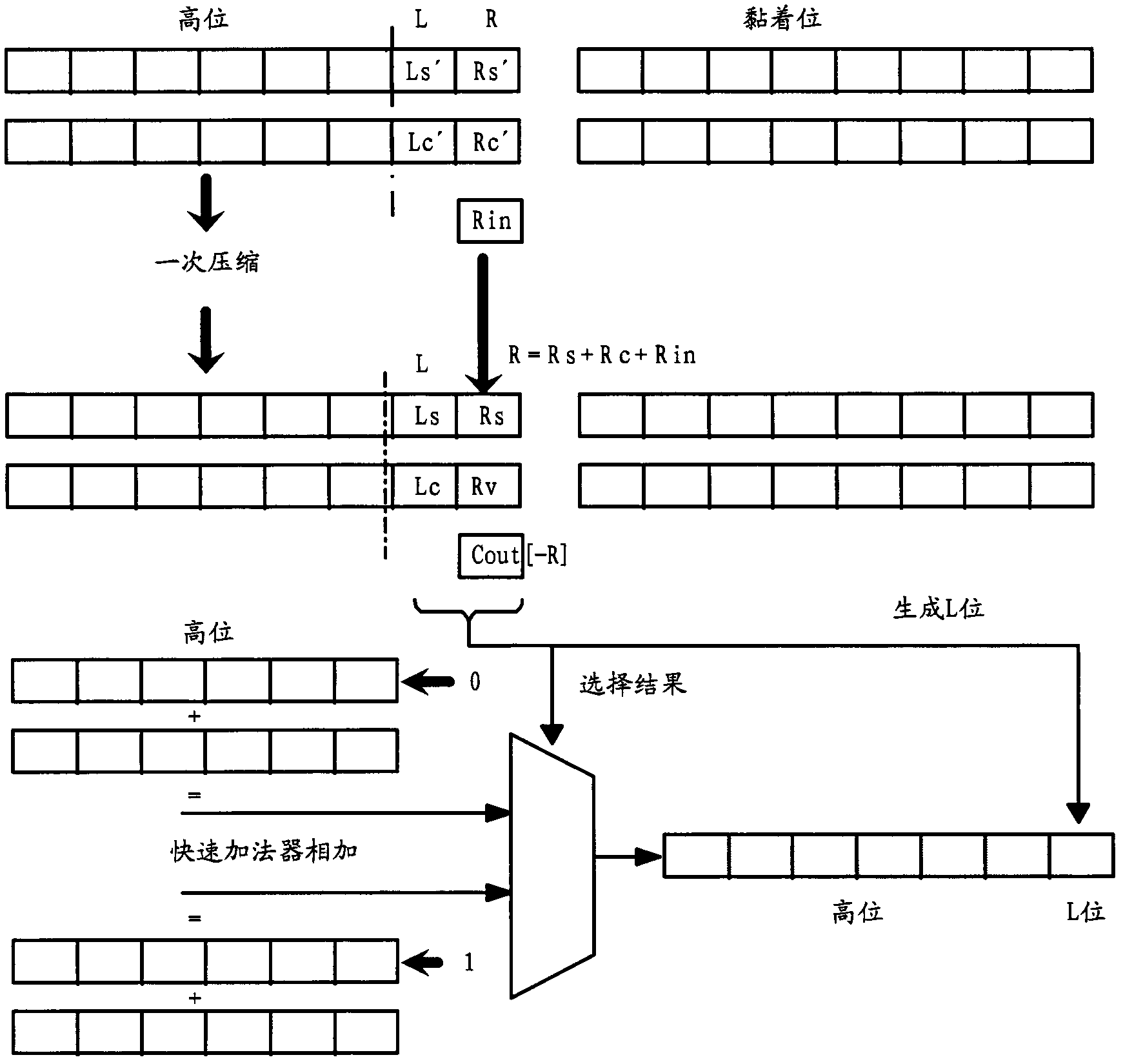
Multiplication rounding implementation method and device
InactiveCN102004627AImprove performanceImprove execution efficiencyDigital data processing detailsFloating point multiplierComputer engineering
The invention discloses a multiplication rounding implementation method and a device. The method comprises the following steps: respectively obtaining carry result and sum result in the floating point number carry save form; adopting a half-adder to respectively add the high bit and the L bit of the carry result and the sum result, adopting a full adder to add the R bit to obtain secondary carry result and secondary sum result, and simultaneously obtaining high bit overflow value after high bit adding; obtaining carry value and sum value of the L bit in the current rounding mode; taking the sum value of the L bit as the L bit of rounding result, taking the sum of the high bit of the secondary carry result and the high bit of the secondary sum result as the high bit of the rounding result when the carry value of the L bit is identified to be 0, and taking the sum of the high bit of the secondary carry result and the high bit of the secondary sum result plus 1 as the high bit of the rounding result when the carry value of the L bit is identified to be 1. The method and the device can improve the execution efficiency of the rounding operation of a floating-point multiplier and improve the performances of a floating-point processing unit.
Owner:HISILICON TECH
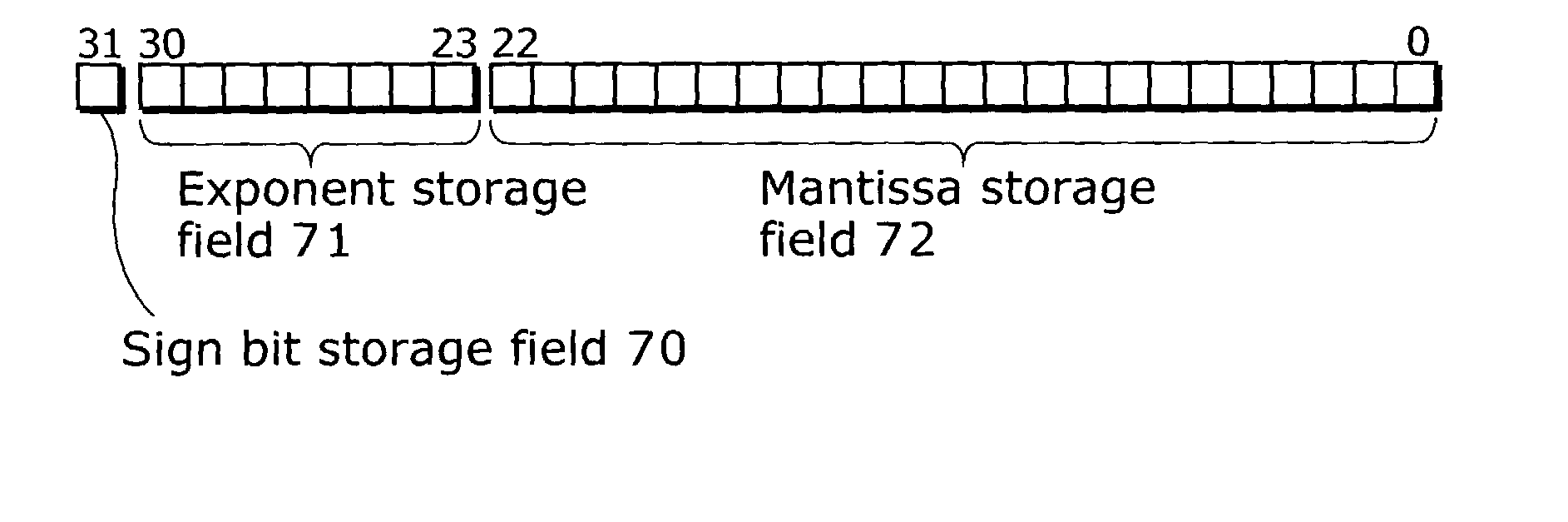
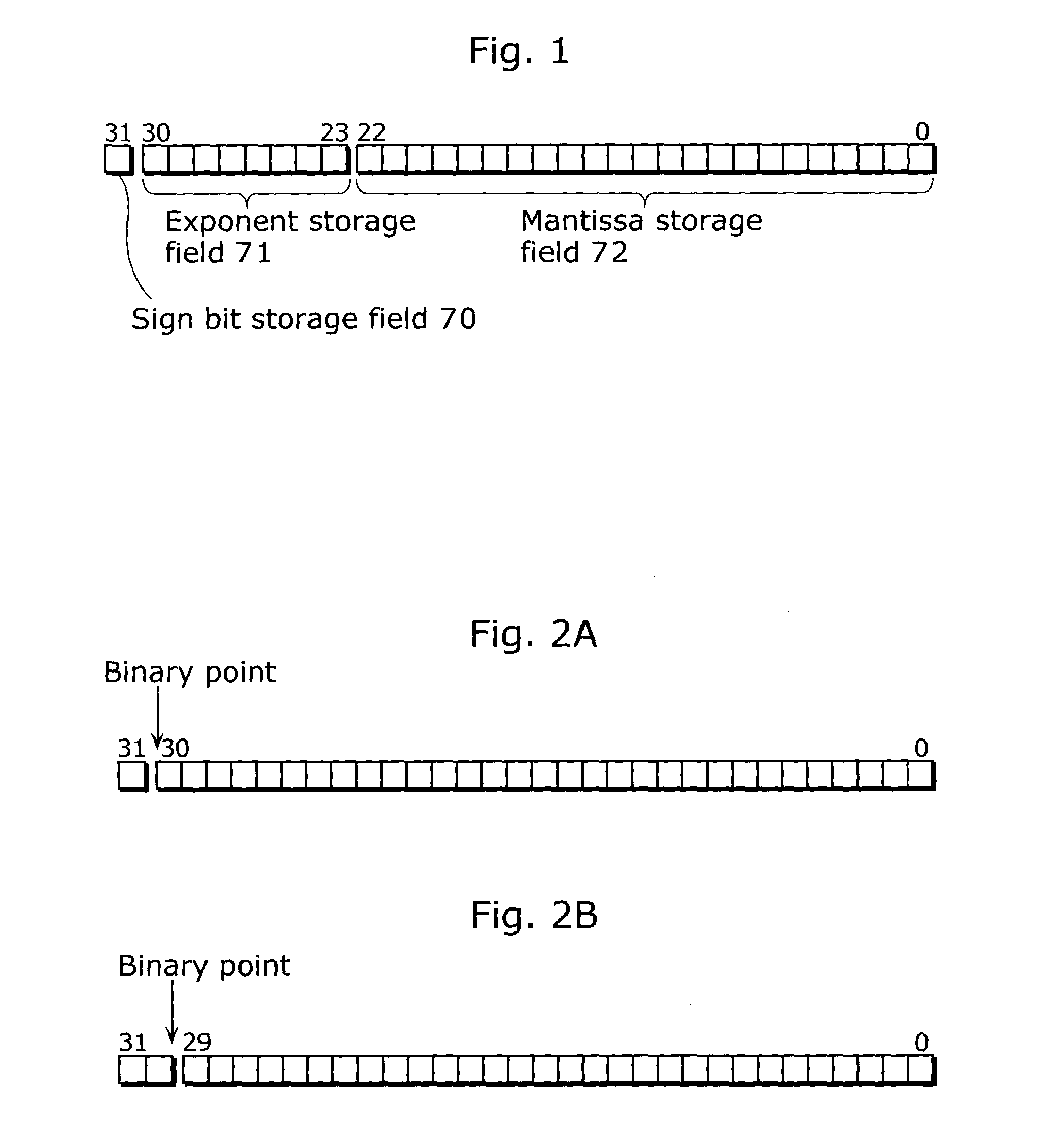
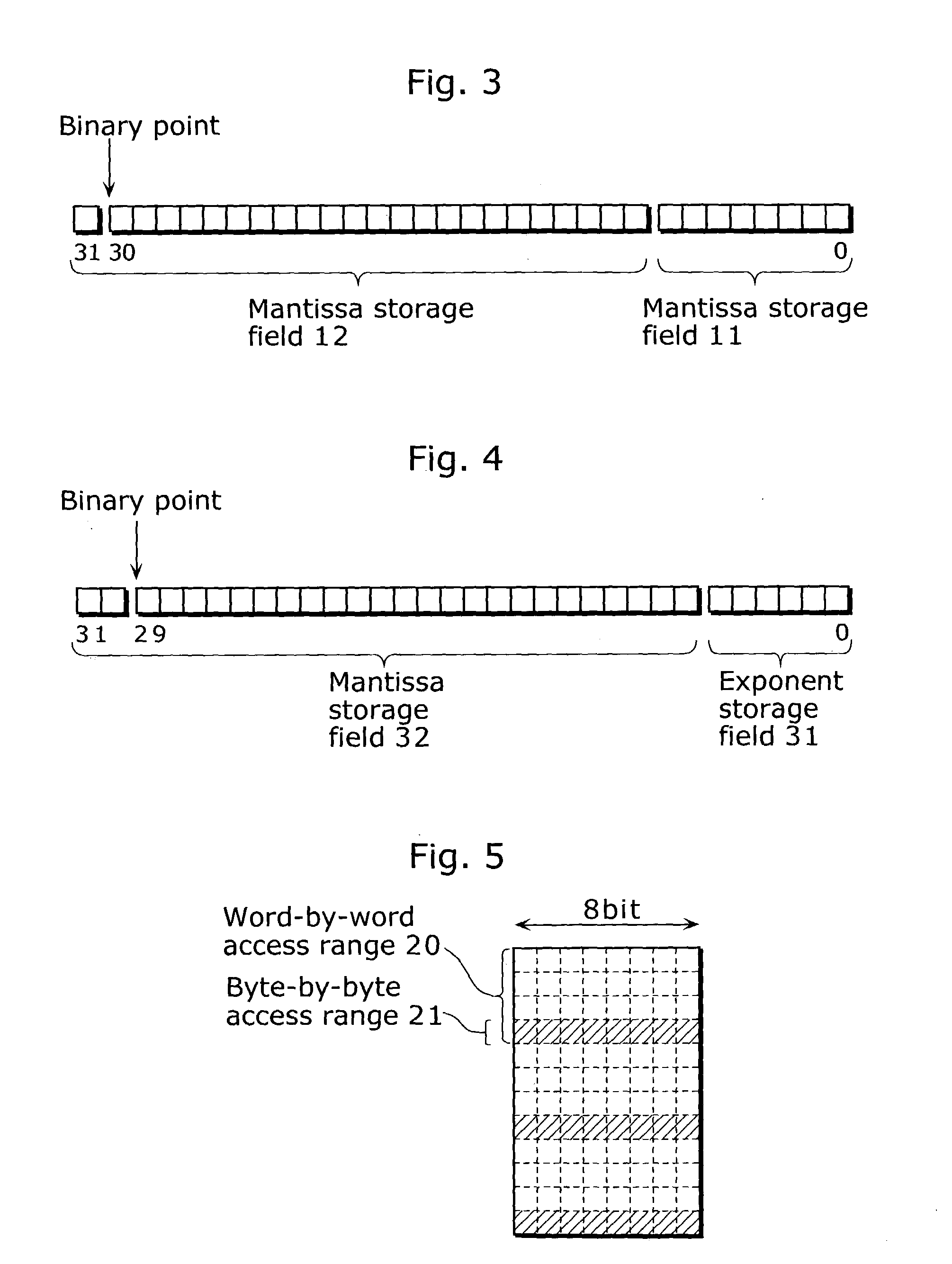
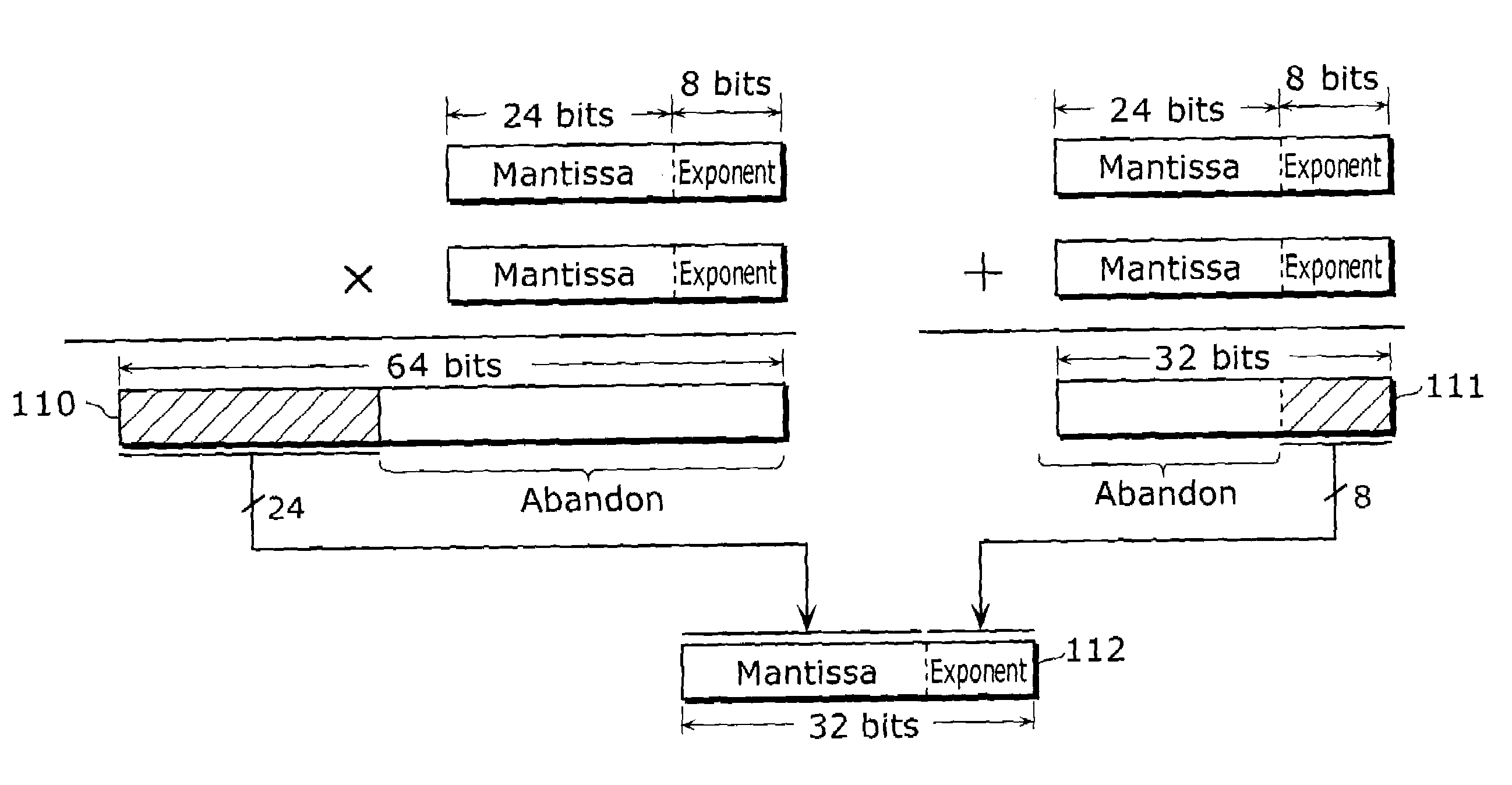
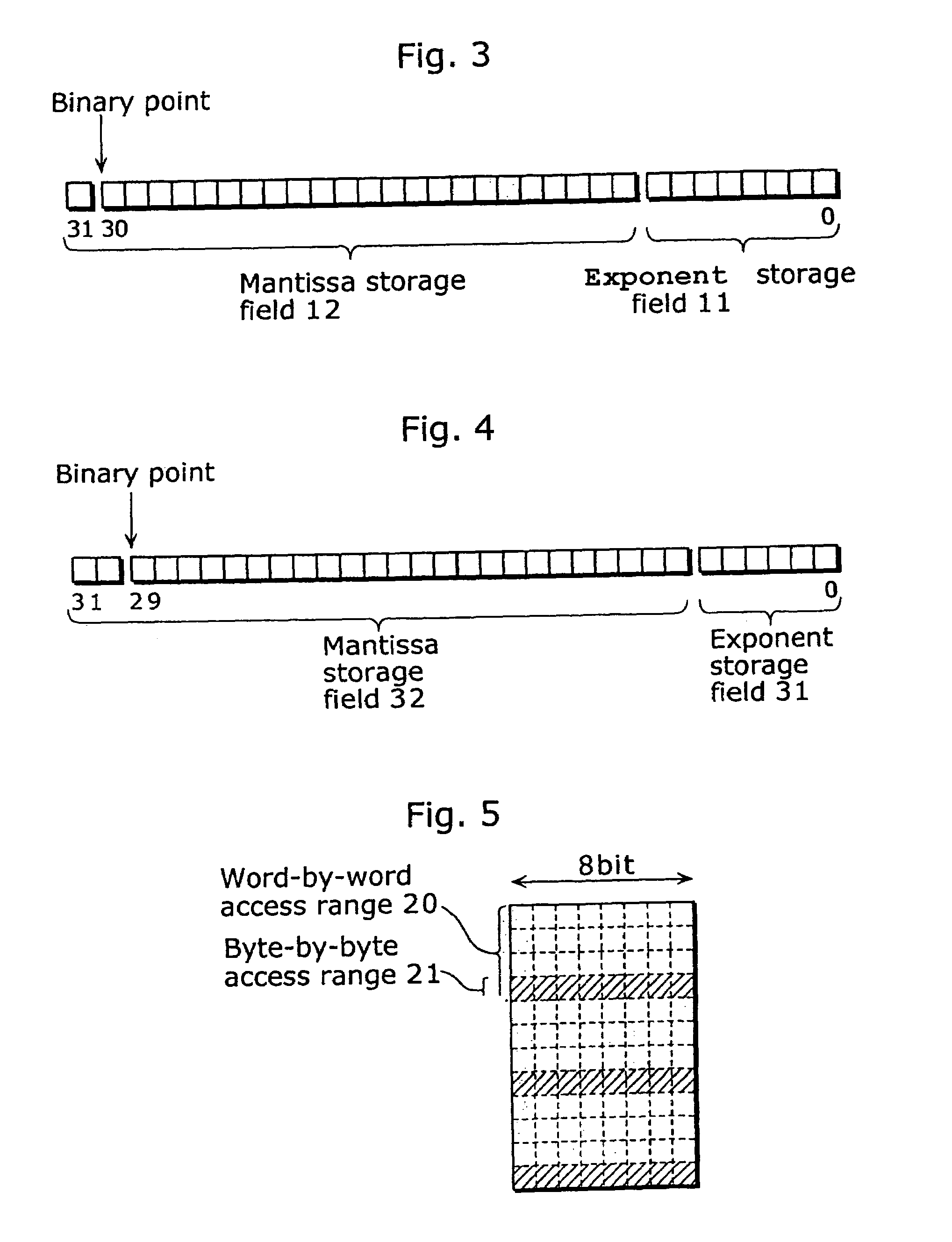
Floating point number storage method and floating point arithmetic device
ActiveUS20030236651A1High speed machiningHigh-speed extractionComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-denominational number representationBit fieldLeast significant bit
In order to provide a method or the like for storing floating point numbers to make it easier to manage the floating point numbers using a fixed point processor, when a real number x is represented by a*(2{circumflex over ( )}n) where a mantissa is a and an exponent is n, the mantissa is stored as a fixed point number in the upper U bits of N-bit field (N>=(U+L)) and the exponent is stored as an integer in the lower L bits. For the multiplication of two real numbers represented in such a format, these two real numbers are multiplied as fixed point numbers so as to make only the upper significant bits of the multiplication result a mantissa, while these two real numbers are added as integers so as to make only the lower significant bits of the addition result an exponent. As a result, the multiplication result can be obtained in a floating point format.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
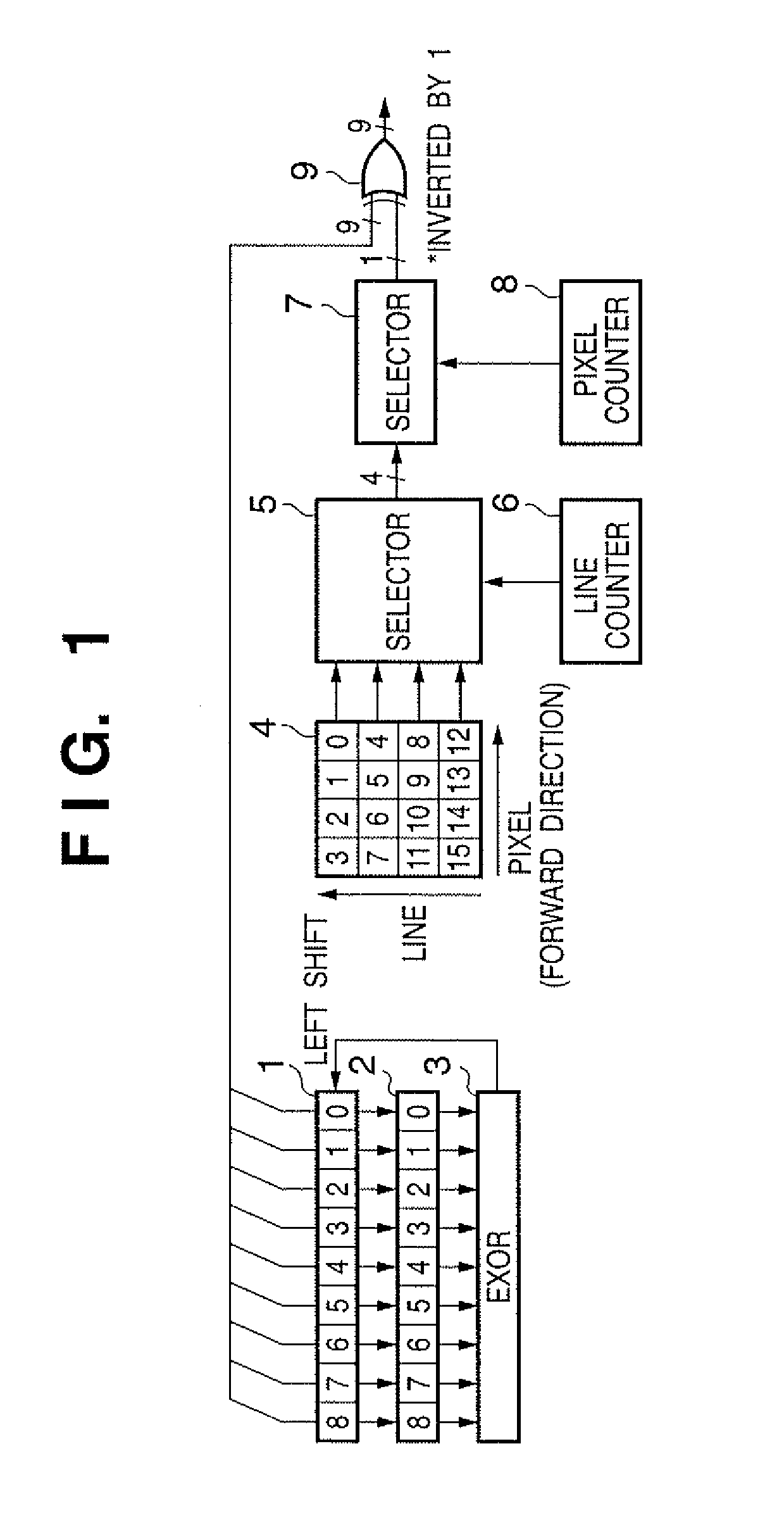
Random number generating method and random number generating apparatus
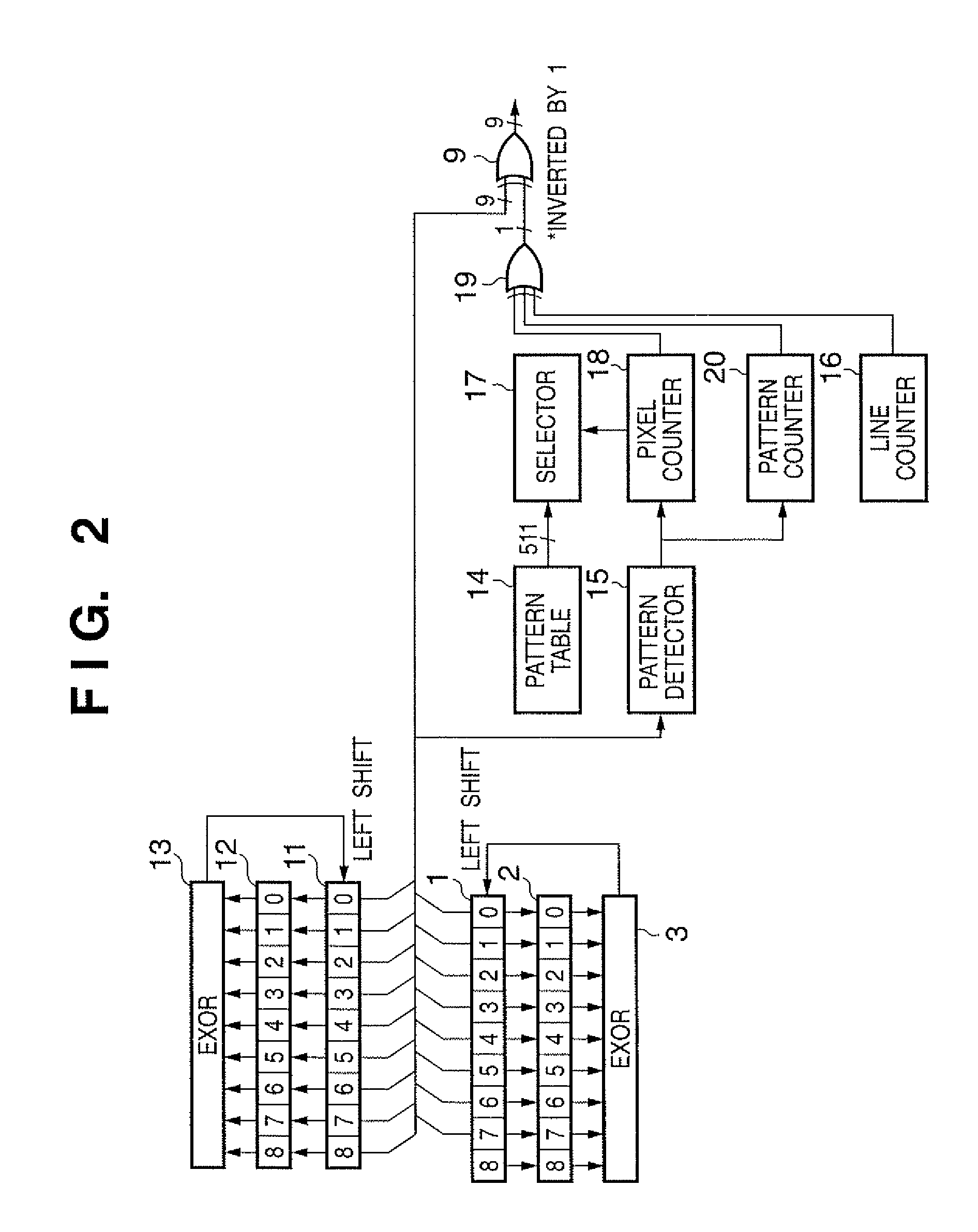
InactiveUS20110119321A1Random number generatorsCoding/ciphering apparatusShift registerComputer science
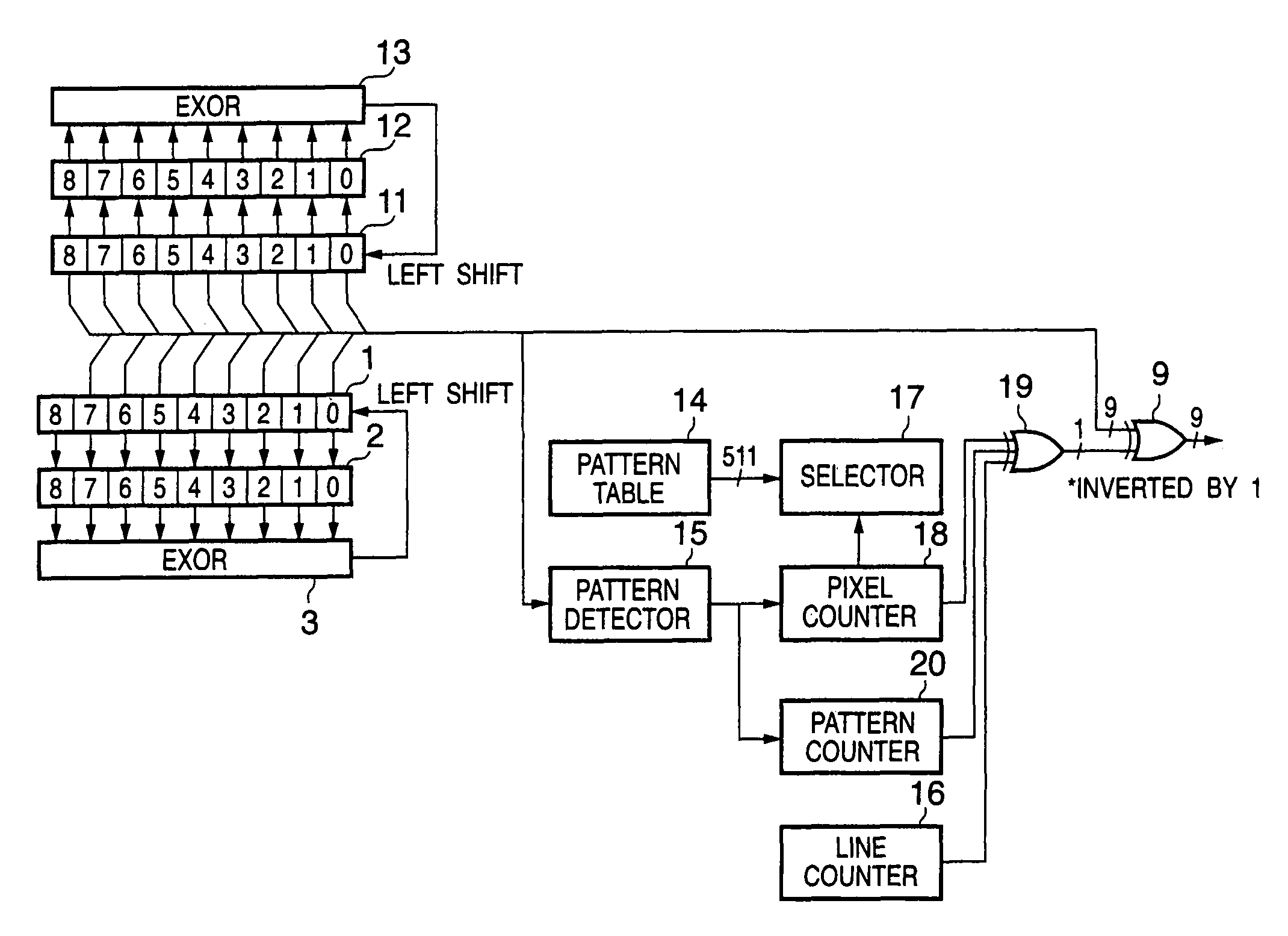
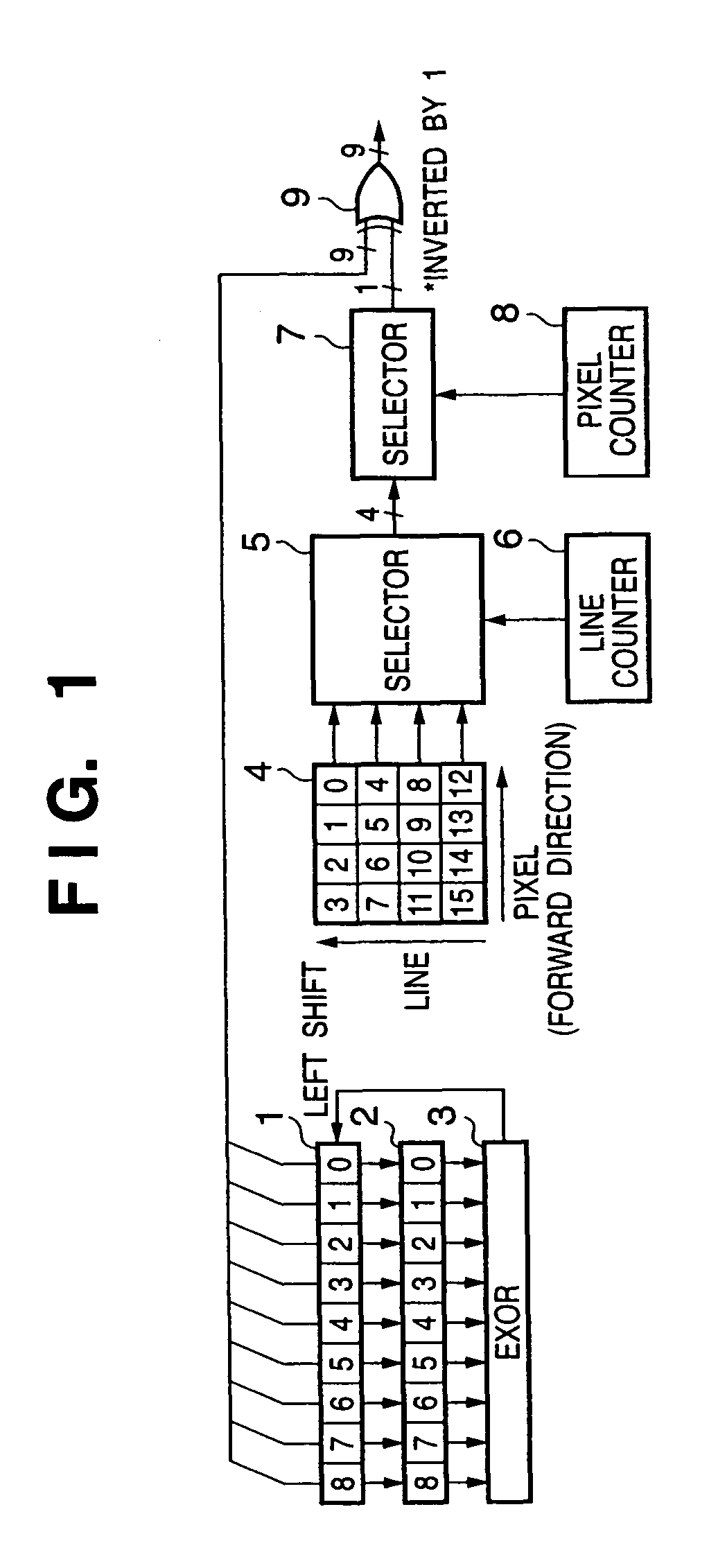
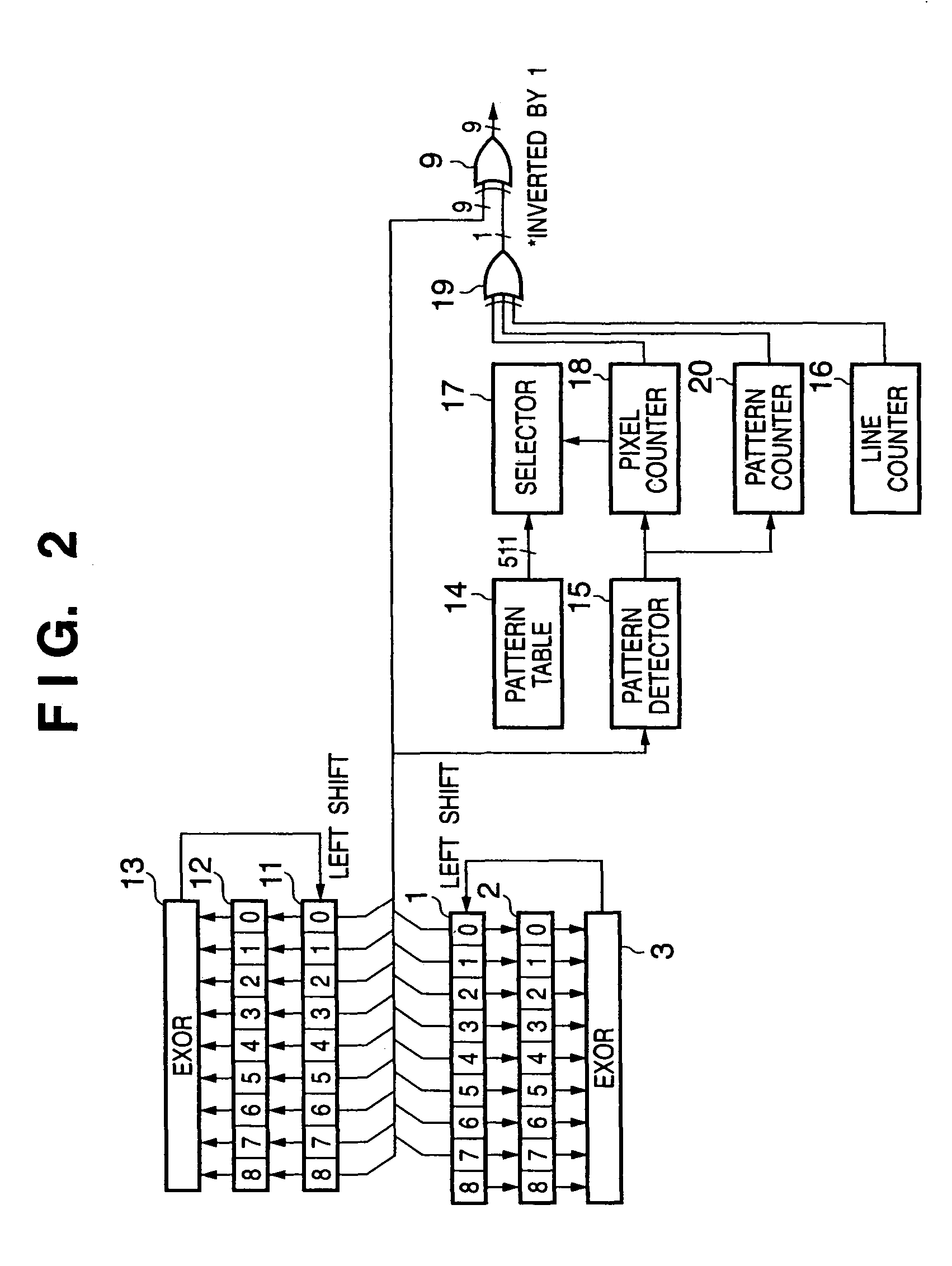
A mask circuit (2) masks a bit sequence of K bits by a predetermined bit pattern. An EXOR circuit (3) EXORs the masked bit sequence. An inverter (9) controls inversion / non-inversion of values of bits of a bit sequence which includes a bit value indicating the EXOR result in a result obtained by shifting the bit sequence of K bits held in a shift register (1), in accordance with a designated bit value in a pattern table (14). A bit sequence as the control result is output as a random number expressed by K bits.
Owner:CANON KK
Floating point number storage method and floating point arithmetic device
ActiveUS7188133B2High-speed extractionHigh speed machiningComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-denominational number representationBit fieldLeast significant bit
In order to provide a method or the like for storing floating point numbers to make it easier to manage the floating point numbers using a fixed point processor, when a real number x is represented by a*(2^n) where a mantissa is a and an exponent is n, the mantissa is stored as a fixed point number in the upper U bits of N-bit field (N≧(U+L)) and the exponent is stored as an integer in the lower L bits. For the multiplication of two real numbers represented in such a format, these two real numbers are multiplied as fixed point numbers so as to make only the upper significant bits of the multiplication result a mantissa, while these two real numbers are added as integers so as to make only the lower significant bits of the addition result an exponent. As a result, the multiplication result can be obtained in a floating point format.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
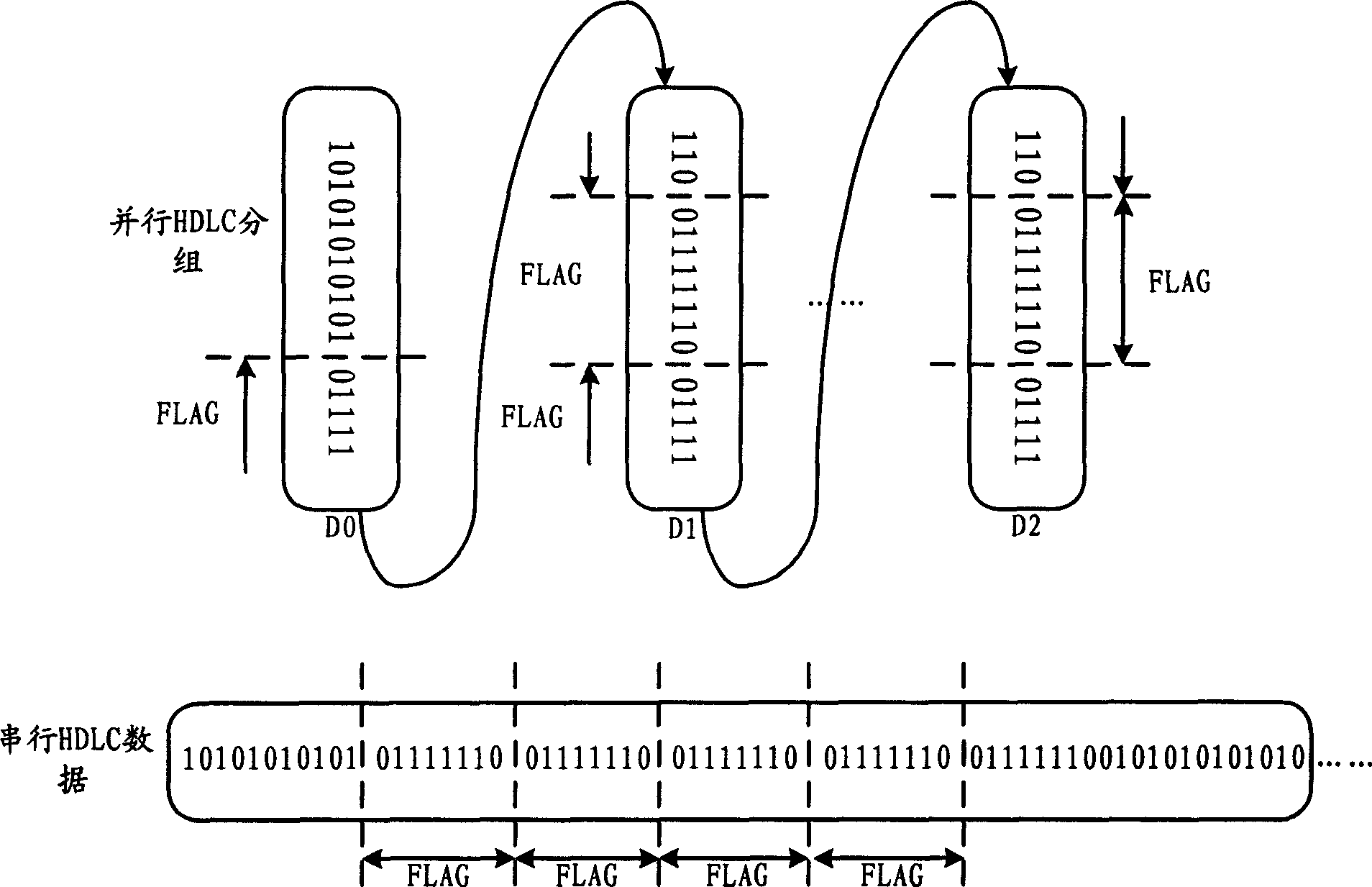
Method and system for parallel transmitting serial data according to high level data link control
ActiveCN1917519AAvoid it happening againReduce complexityData switching networksShift registerData stream
The invention can effectively reduces the occupation on redundancy bandwidth, avoid the generation of flag bit sequence of segments and lower the load of CPU. In the invention, reading the k bits of next group to the shift register from serial HDLC data stream; if the valid data only have C bits, C<K, then the front K-C bits in flag bit sequence are filled into the remaining space of shift register; sending the data in the shift register, and recording C; when needing to send next HDLC frame, the rear K-C+A bits in flag bit sequence are filled into the shift register, and then reading the valid data of the next HDLC frame from the serial HDLC data stream; wherein, A represents the bit numbers in flag bit sequence.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
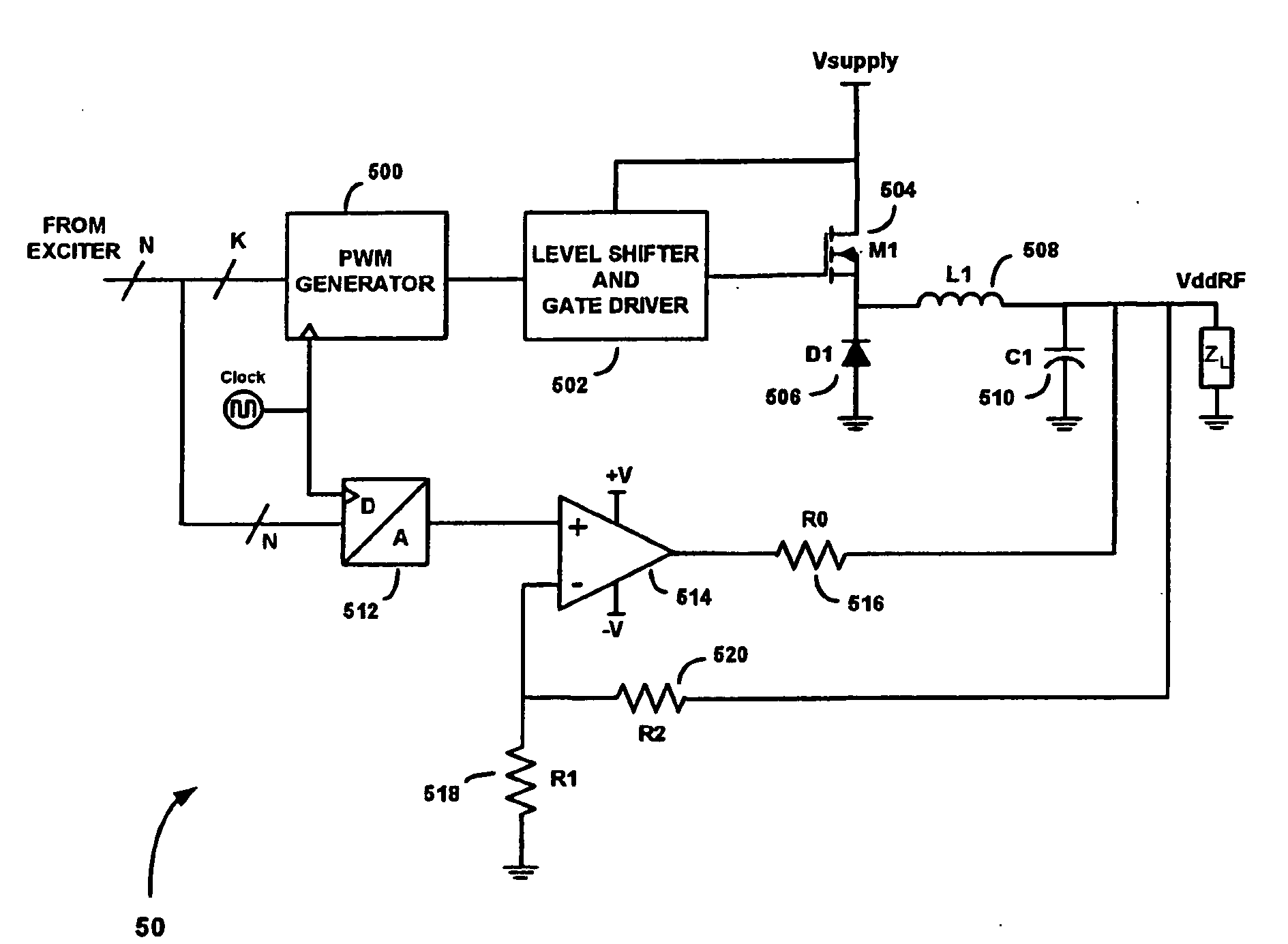
Enhanced hybrid class-S modulator
ActiveUS20080074207A1Eliminate errorsReduce errorsSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAmplitude modulation detailsAudio power amplifierBuck converter
A highly-efficient hybrid class-S modulator circuit for a polar modulator includes a class-S path having a digital pulse-width modulator (PWM) generator, which receives the K most significant bits (MSBs) of N-bit digital input words to generate a discrete set of PWM signals. The discrete set of PWM signals drives a buck converter, to provide a modulated power supply voltage signal having a plurality of quantized voltage levels. An error generated by using only K of the N bits of each N-bit word is reduced by dithering the input drive and converting the error to an AC signal. Dithering is performed by feeding the N−K least significant bits (LSBs) of each N-bit input word to an input of a digital oscillator, while feeding the K most significant bits (MSBs) of each word to the PWM generator. The digital oscillator converts the N−K LSBs of each input word into an oscillating single LSB. An oscillating error signal appearing at the output of the modulator is fed to the inverting input of an op-amp connected in parallel with the class-S path. At the same time, the desired output voltage, which is represented by the full N bits of the N-bit input words, is coupled to the non-inverting input of the op-amp. The op-amp responds to the input signals by sourcing or sinking current into or out of the modulator output terminal, thereby removing the error attributable to using only K of the N bits at the PWM generator.
Owner:MCCUNE EARL W JR DR
Entropy processor for decoding
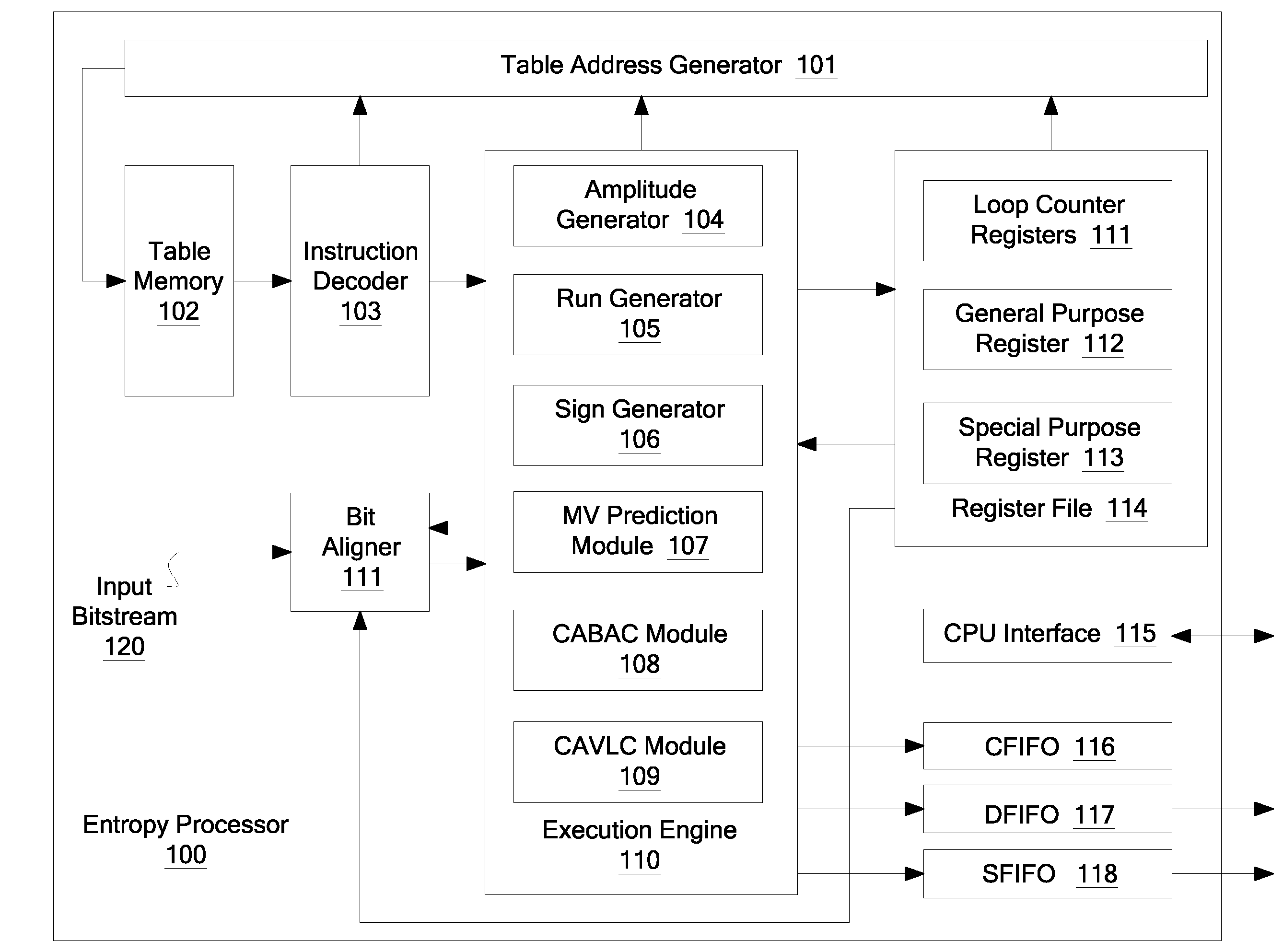
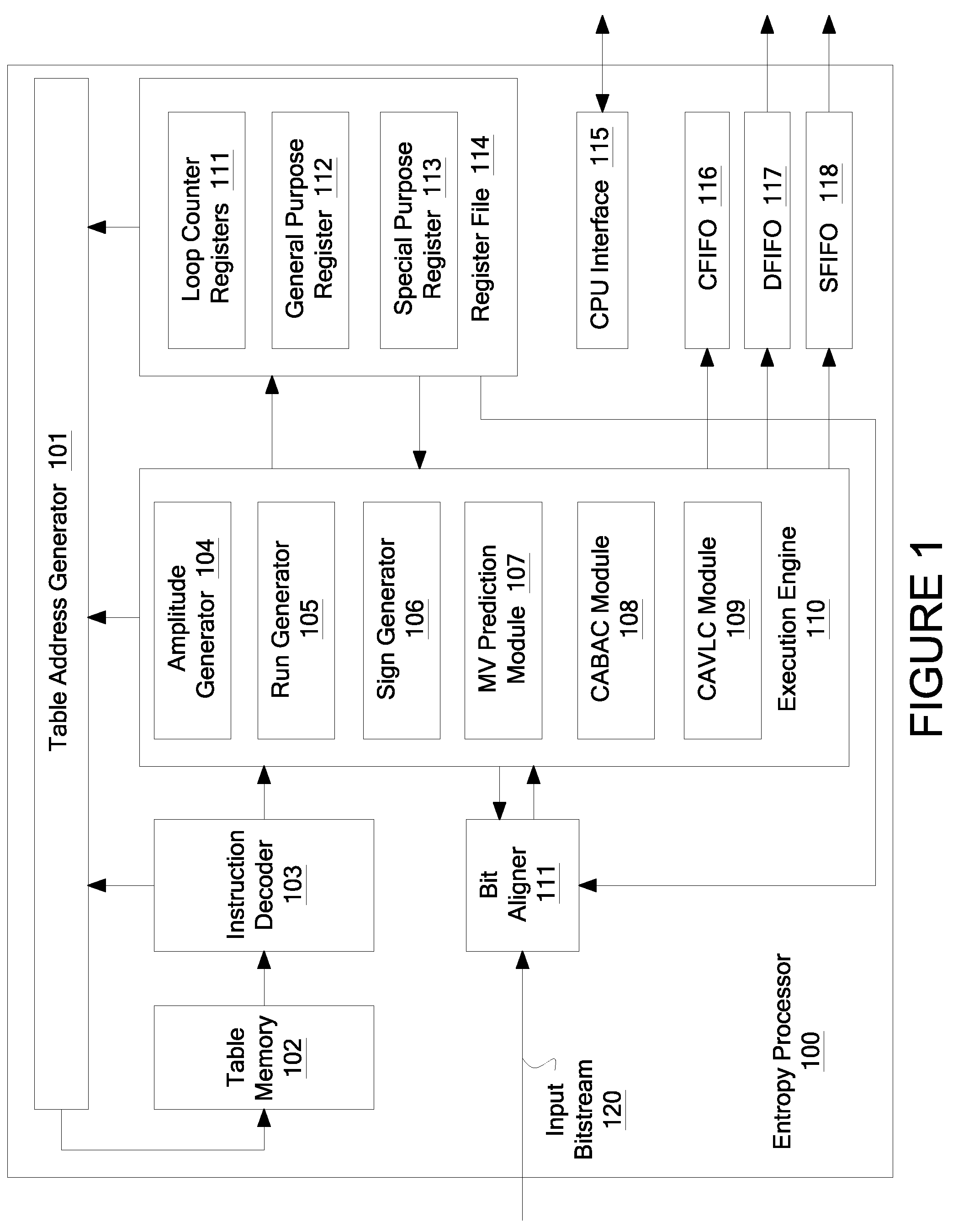
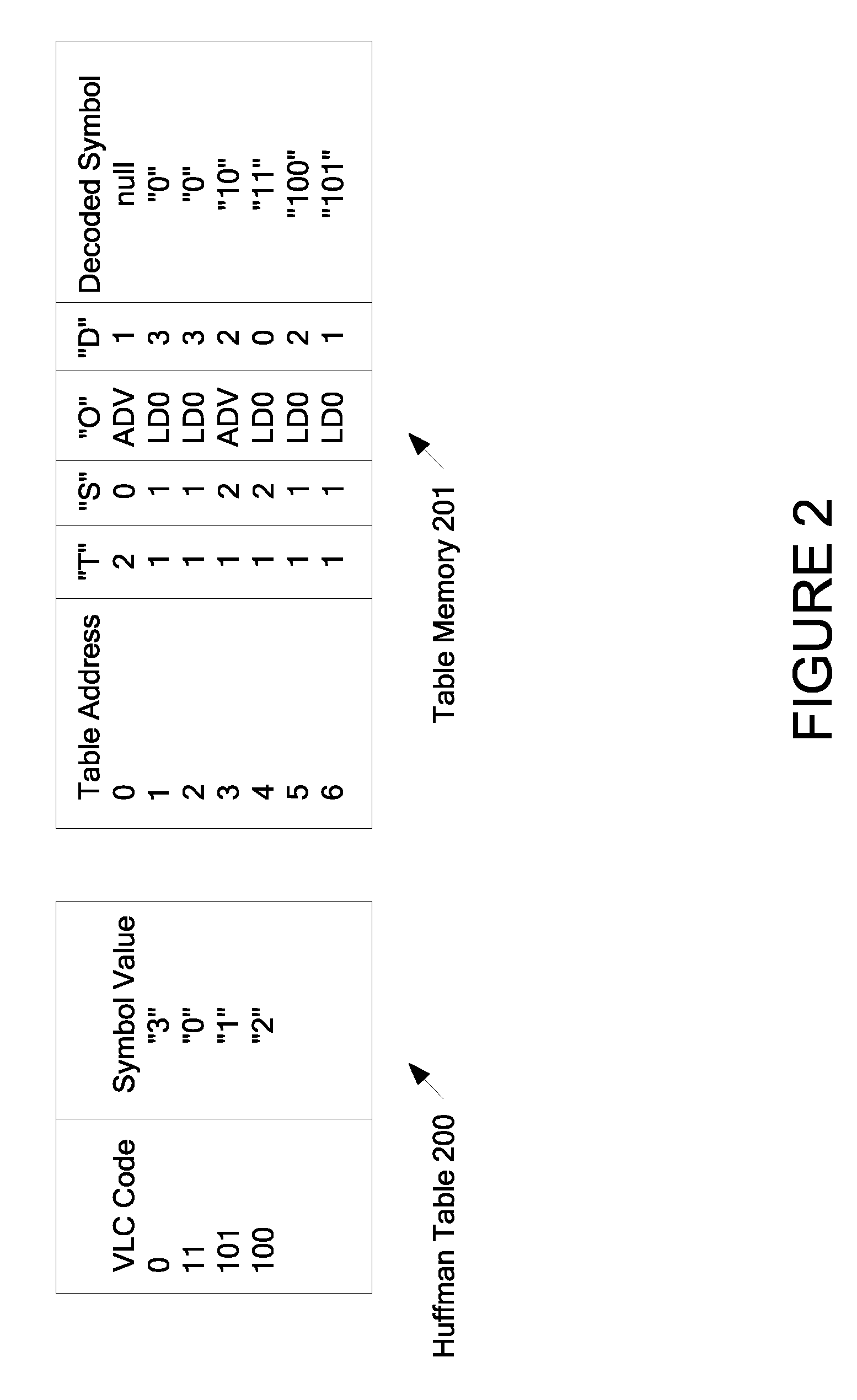
InactiveUS7508328B2Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionVariable-length codeTheoretical computer science
A method for processing a variable length code comprising: determining a first address; decoding opcodes from the at least one table starting at a first address; in response to each of the opcodes: receiving a portion of a sequence of bits, the sequence of bits comprising a first variable length code; receiving S from the second table at the current address; flushing S bits in the sequence of bits; receiving T corresponding to one of the stages; determining a value of a set of T bits in the sequence of bits; receiving D from the second table at the current address; and computing the next address, the next address being the sum of the current address, D, and the value of the set of T bits; and retrieving the next opcode, the next opcode being retrieved from the next address; and determining the decoded syntax element.
Owner:APUSONE TECH
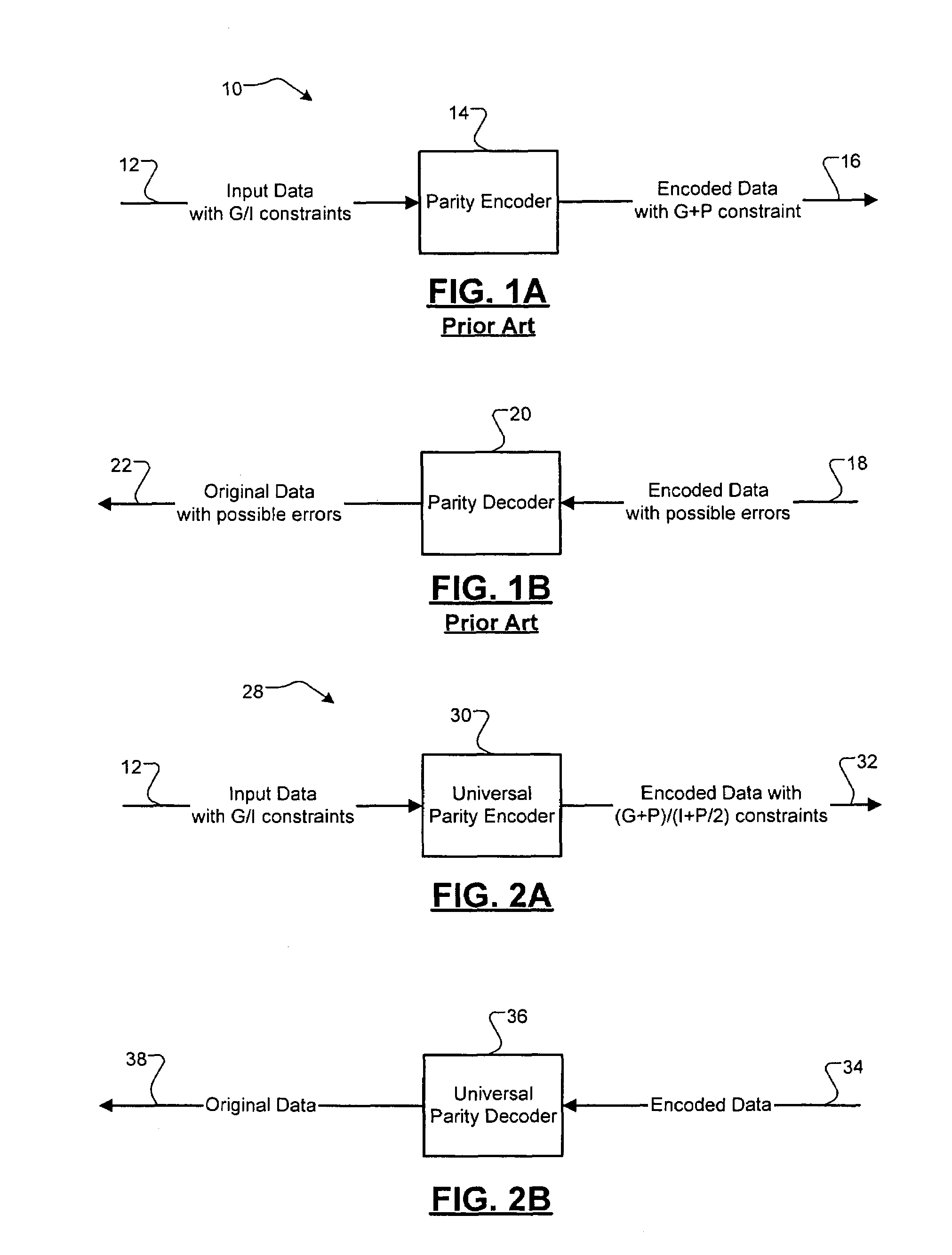
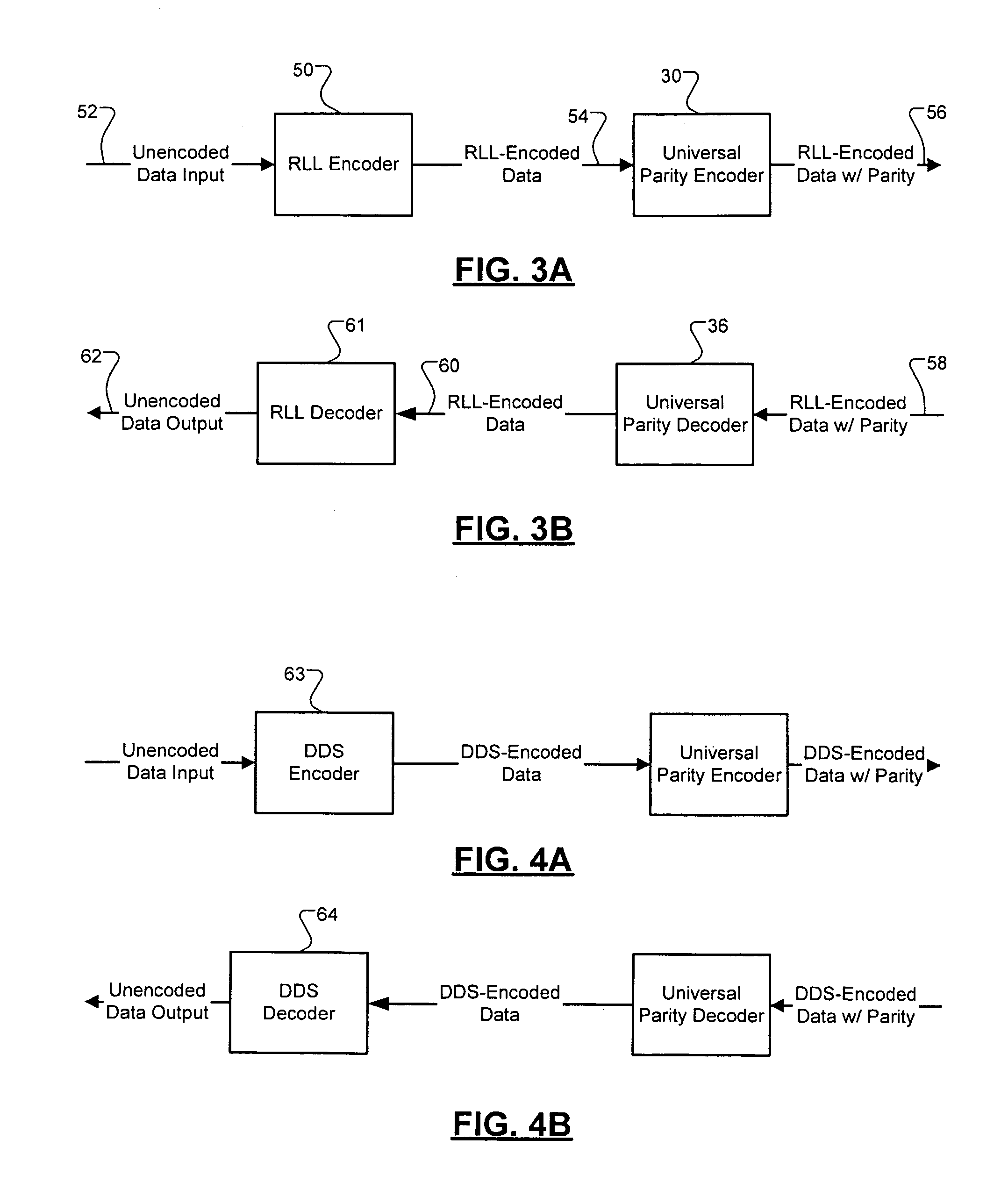
Universal parity encoder
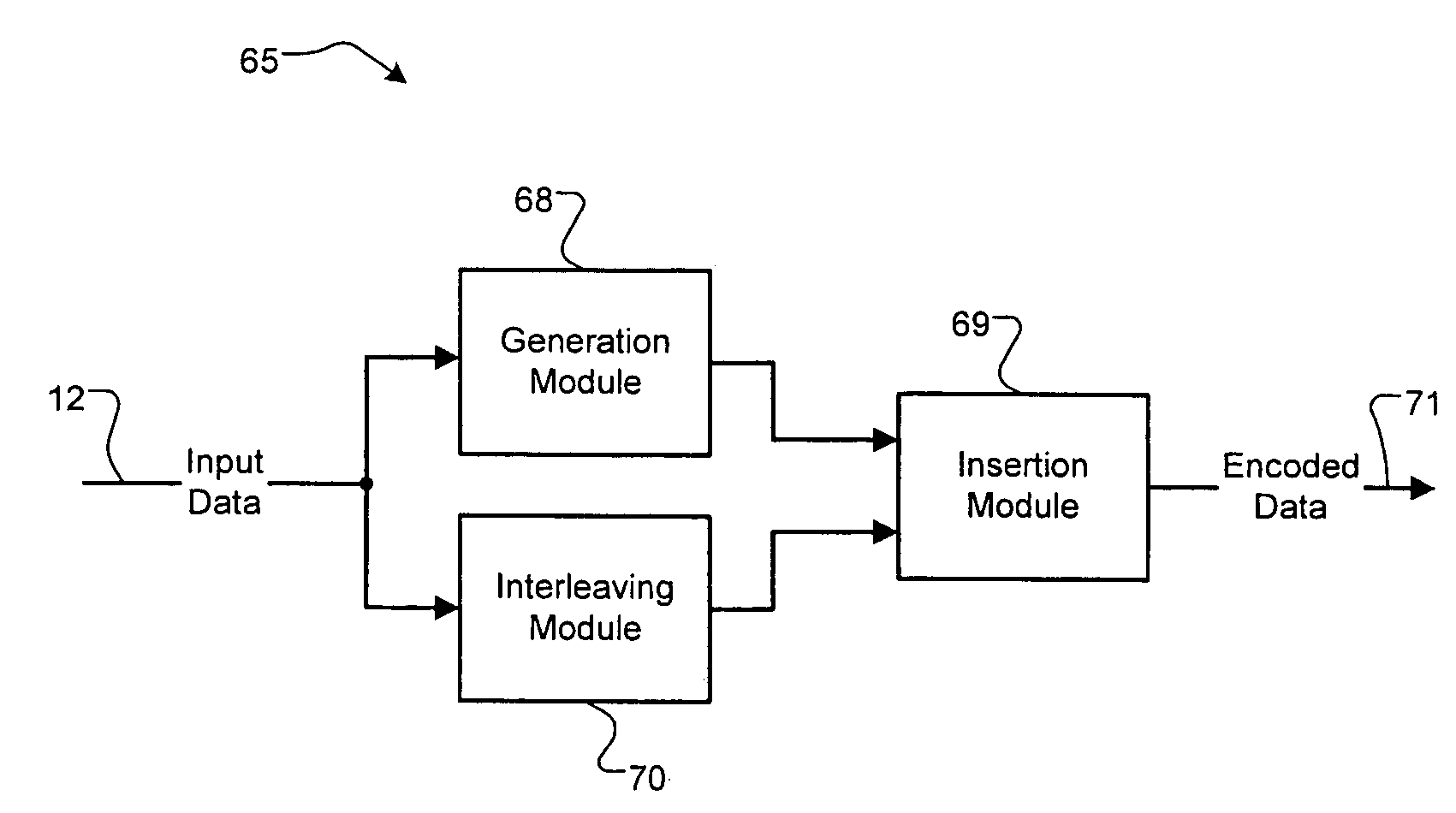
A data encoding system for a data stream comprises an interleaving module that receives the data stream as N bit data blocks and that reverses positions of at least two of the N bits of selected ones of the data blocks. A generating module generates P error checking bits for each of the N bit data blocks. An insertion module receives the P error checking bits from the generating module and inserts the P error checking bits into the corresponding data block received from the interleaving module.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
High rate run length limited code
InactiveUS6839004B2Increase valueRecord information storageImage codingHigh rateCommunications system
Methods of encoding and decoding, as well as an encoding system and a digital communications system are provided for encoding data words into code words and decoding code words into data words. The data words are encoded according to a run-length-limited (RLL) code of “k” constraint, the encoding producing u-bit non-zero code words. The “k” constraint can be increased to a higher value by extending the u-bit non-zero code words to generate q-bit non-zero code words.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
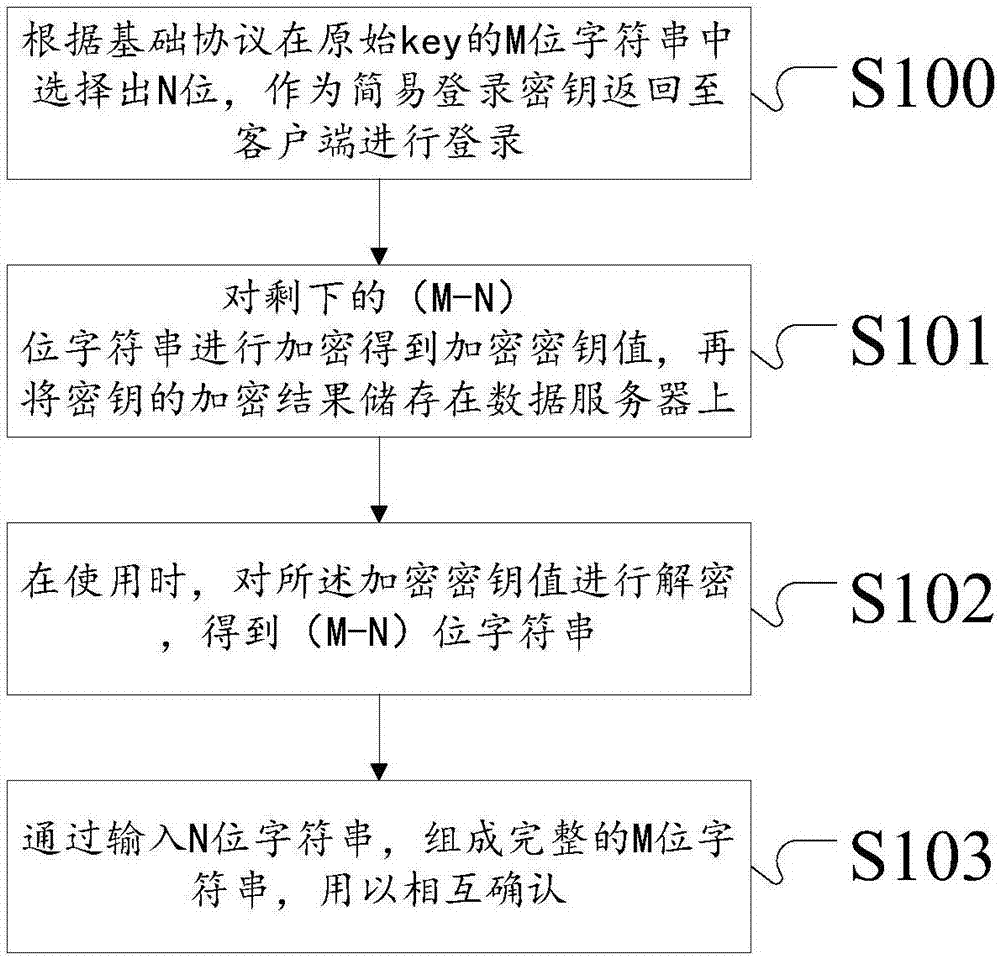
Secure and efficient block chain customization login method and security reinforcing system
ActiveCN107070896AFew digitsEasy to customizeKey distribution for secure communicationClient-sideChain network
The invention discloses a secure and efficient block chain customization login method and security reinforcing system. The method logs in a block chain network and comprises the following steps: selecting N bits from M bits of a character string of an original key according to a basic protocol to take as a simple login key to return to a client for logging in, performing encryption on the rest (M-N) bits of the character string to obtain an encrypted key value, then storing an encrypted result of the key to a data server, performing decryption on the encrypted key value in use to obtain the (M-N) bits of the character string, and forming the complete M bits of the character string by inputting the N bits of the character string for mutual confirmation. According to the secure and efficient block chain client login method and security reinforcing system disclosed by the invention, when the client logs in, the digits are few and are easy to be remembered, thereby being convenient for customization; and meanwhile, the character string is encrypted and stored in segments, so the security capability is high; and thus, the problems that the existing block chain private key is lost and stolen easily are solved well.
Owner:智牛股权投资基金(平潭)合伙企业(有限合伙)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com