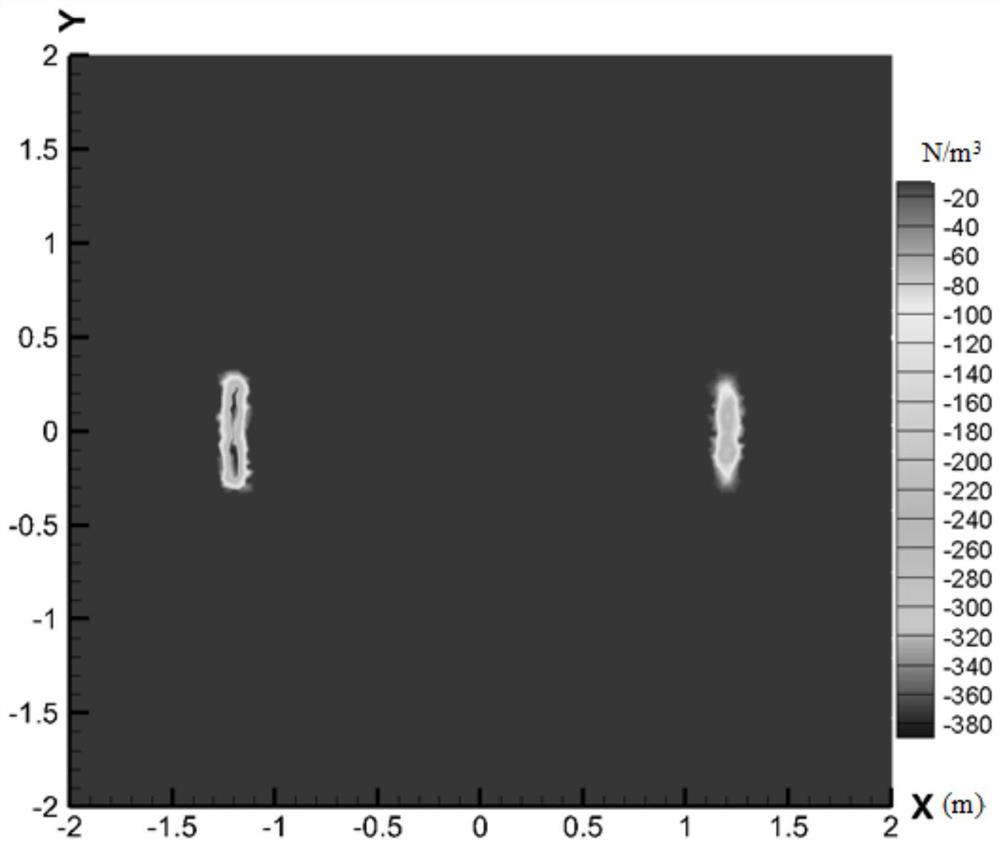
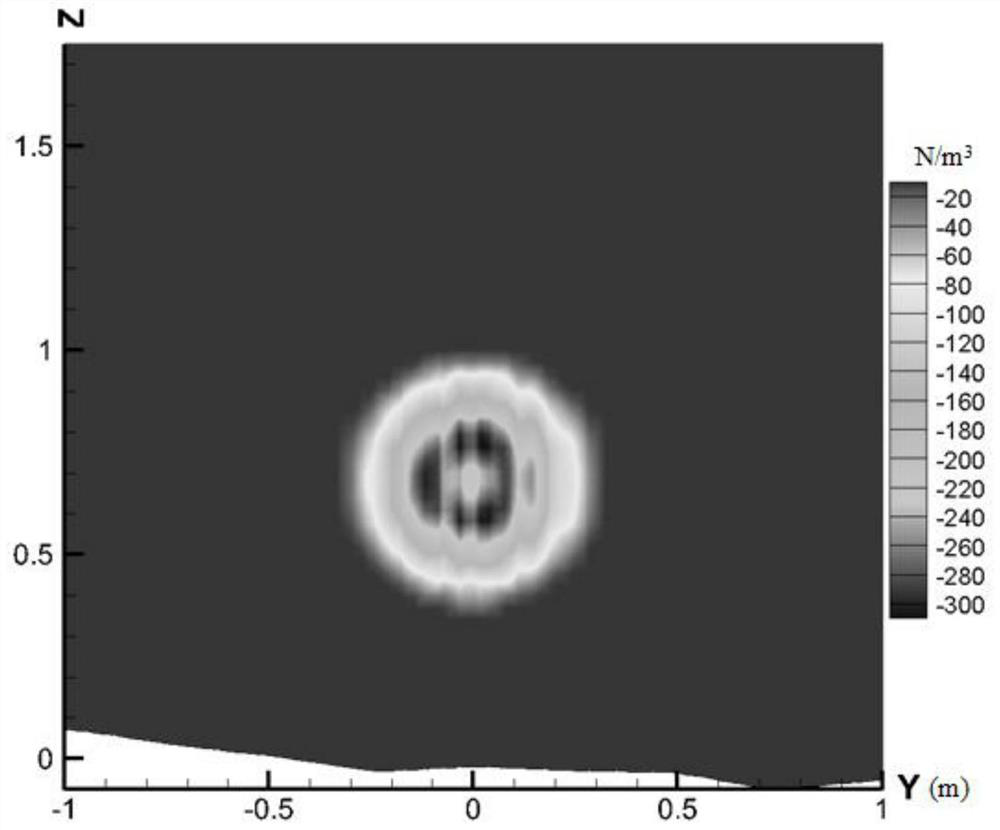
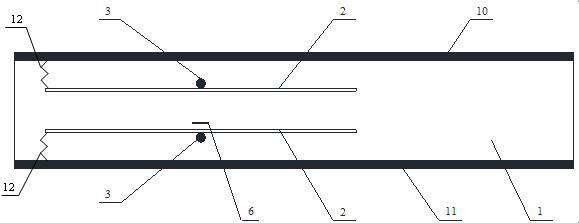
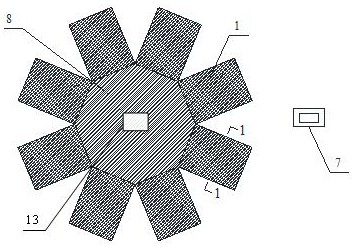
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Wind engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wind engineering is a subsets of mechanical engineering, structural engineering, meteorology, and applied physics to analyze the effects of wind in the natural and the built environment and studies the possible damage, inconvenience or benefits which may result from wind. In the field of engineering it includes strong winds, which may cause discomfort, as well as extreme winds, such as in a tornado, hurricane or heavy storm, which may cause widespread destruction. In the fields of wind energy and air pollution it also includes low and moderate winds as these are relevant to electricity production resp. dispersion of contaminants.
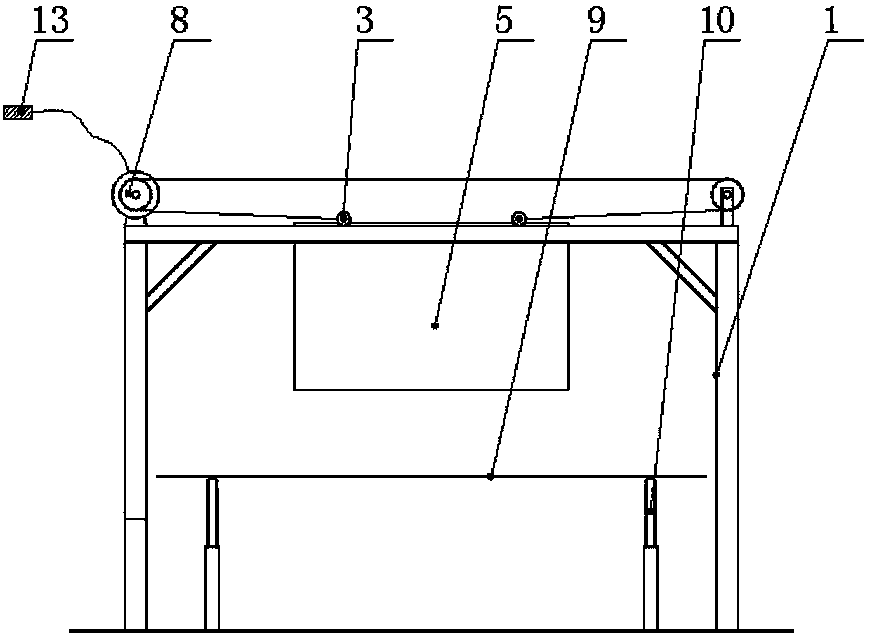
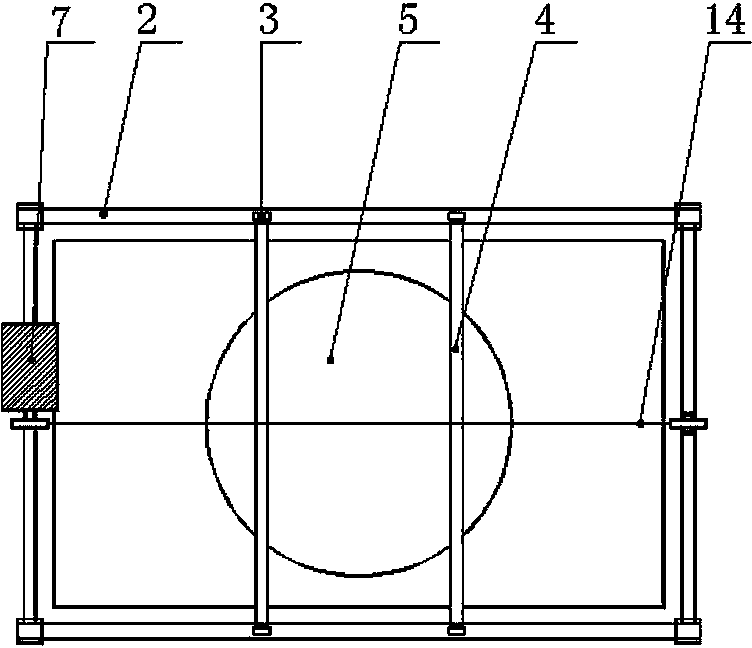
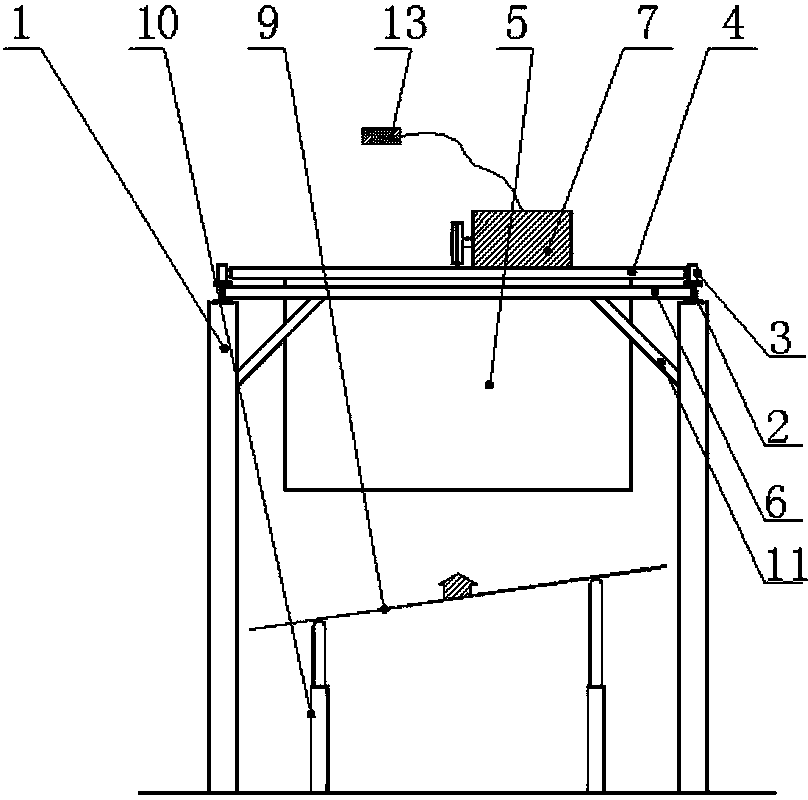
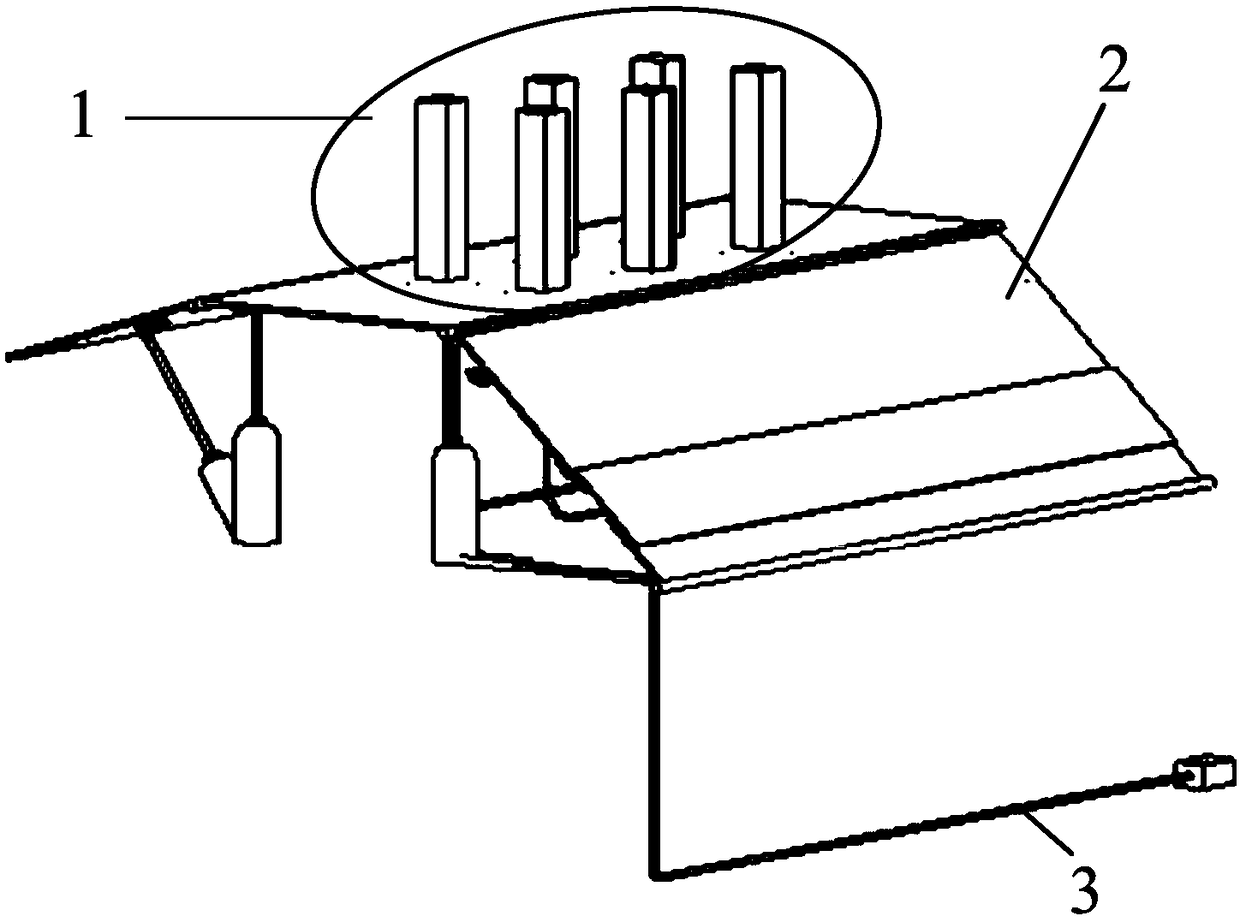
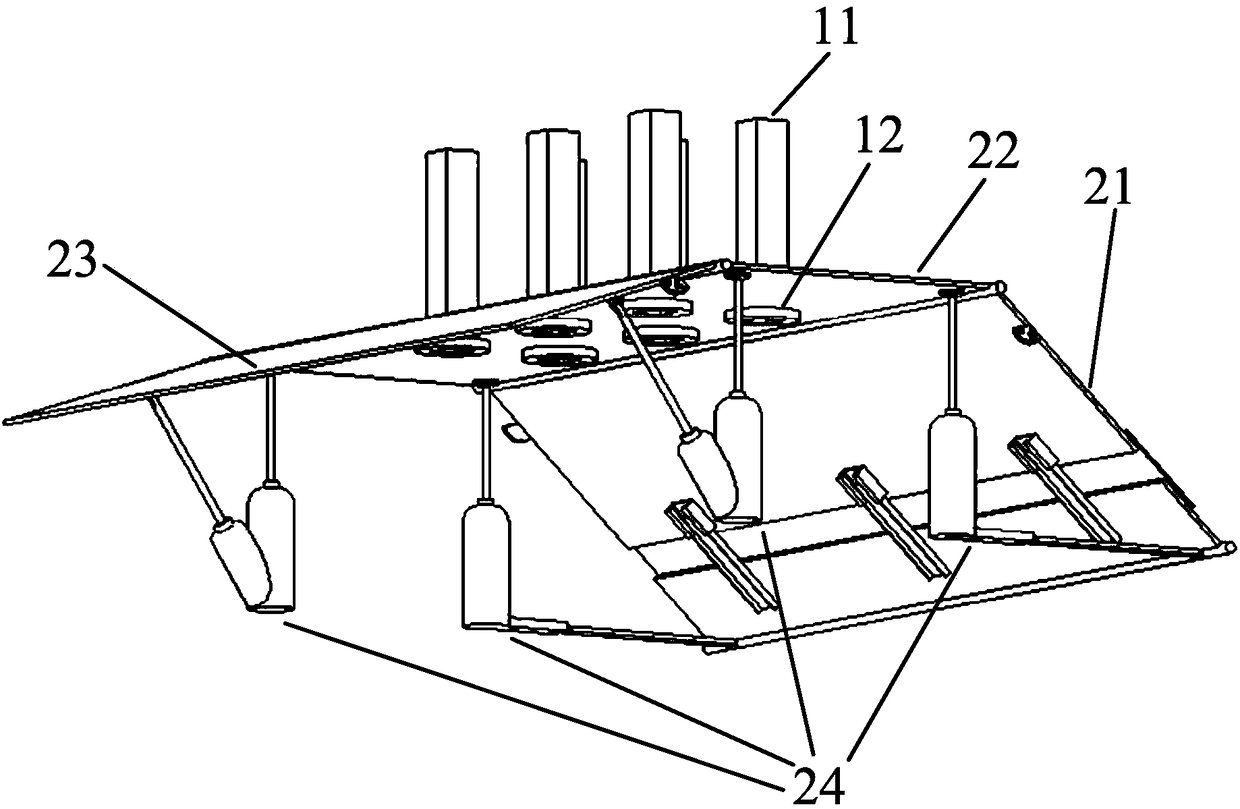
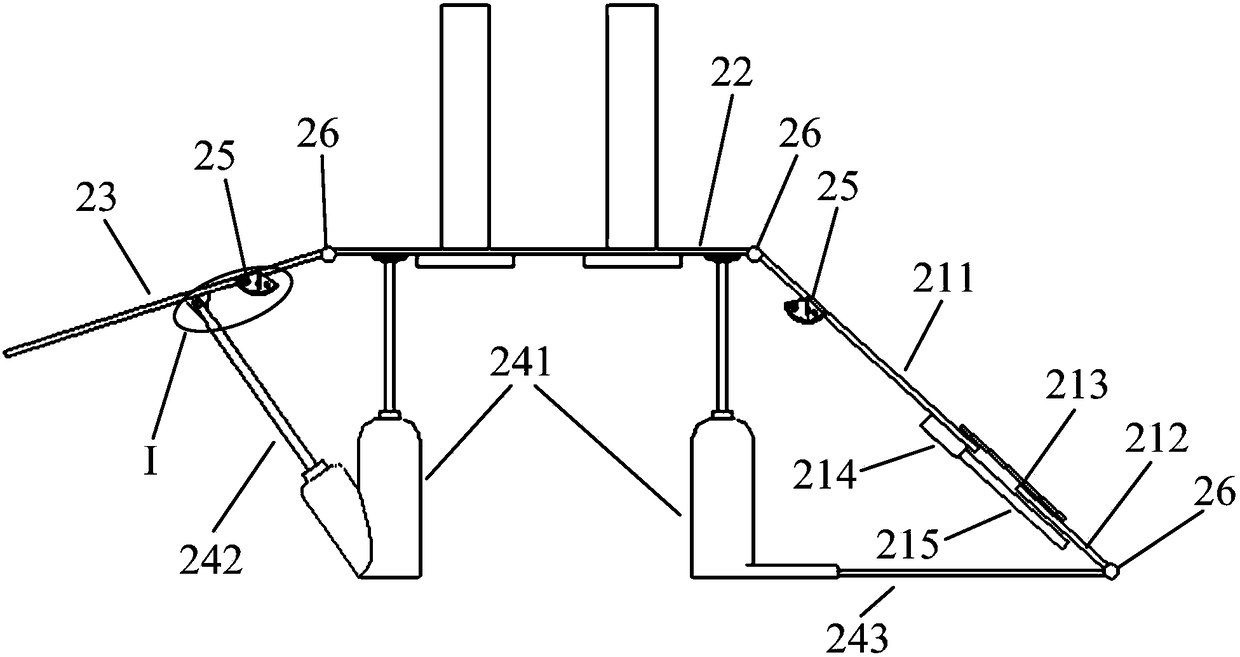
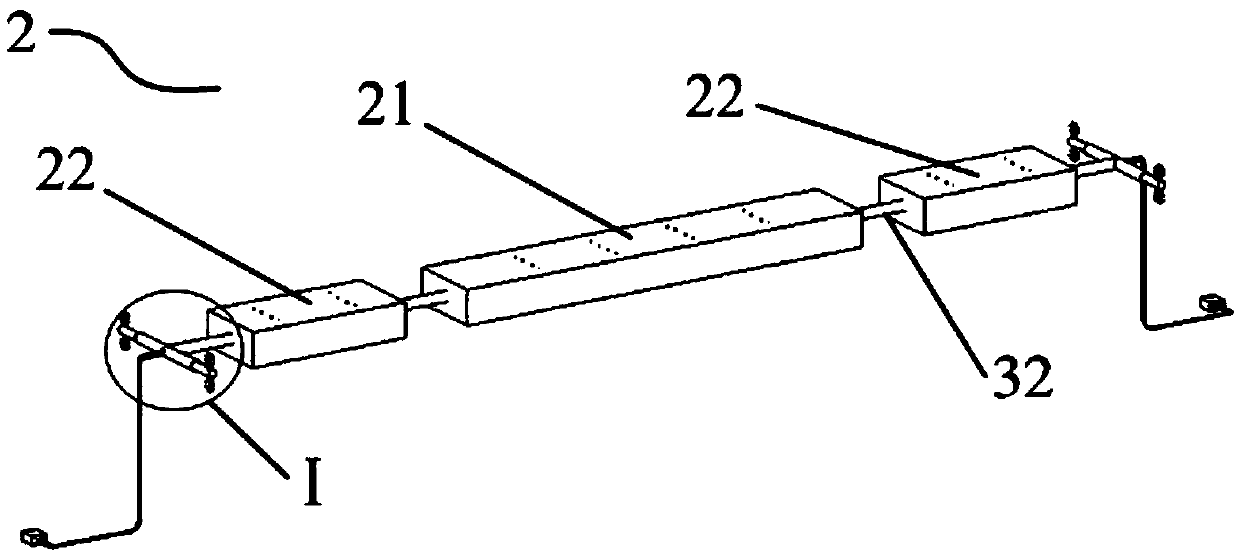
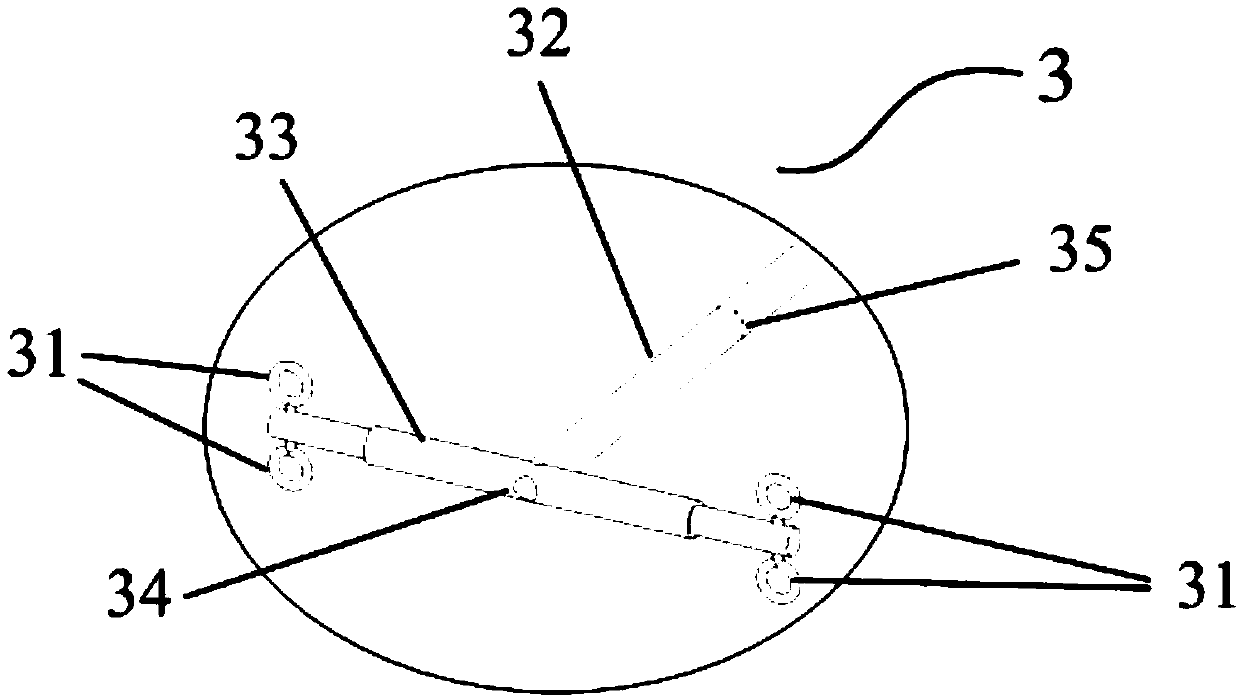
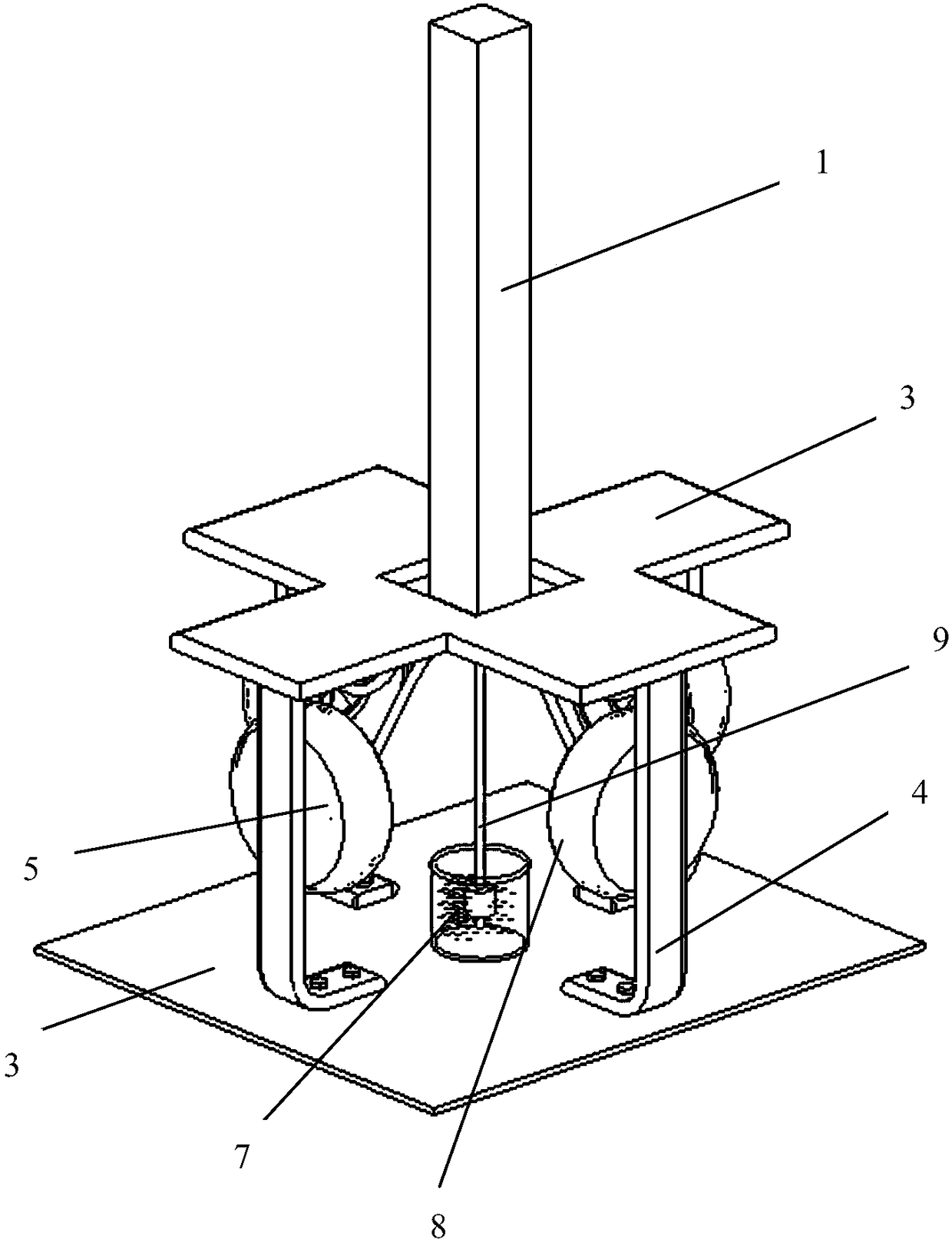
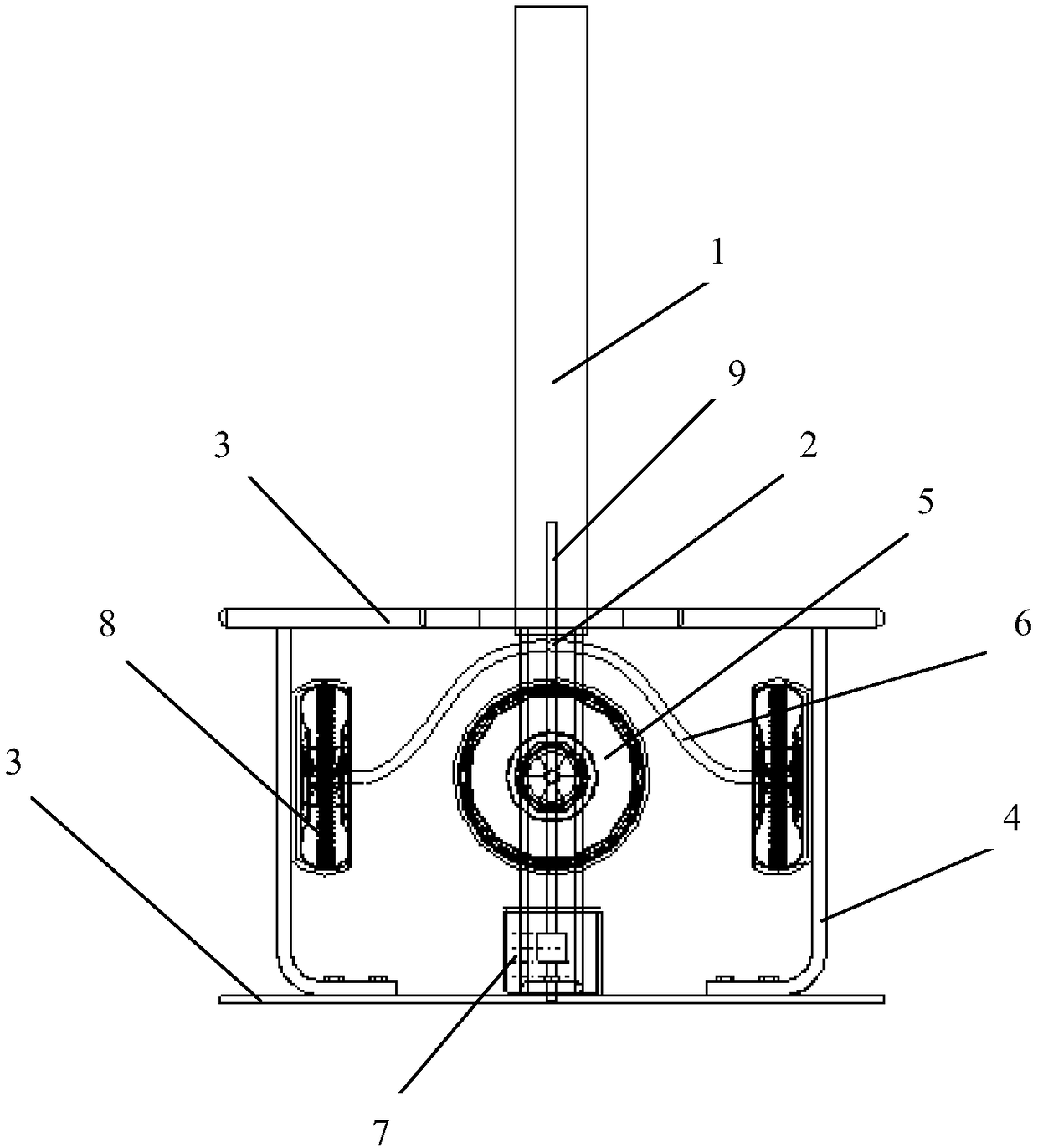
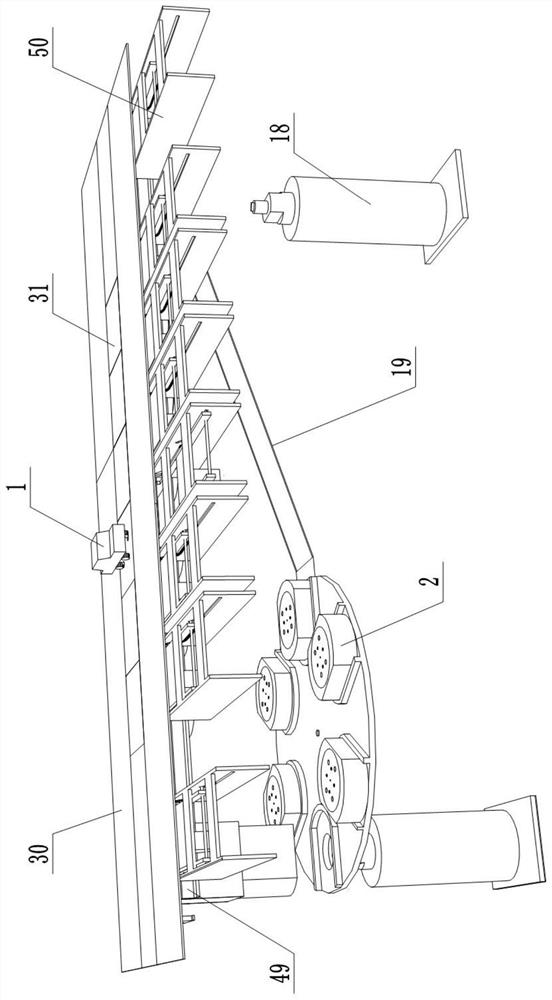
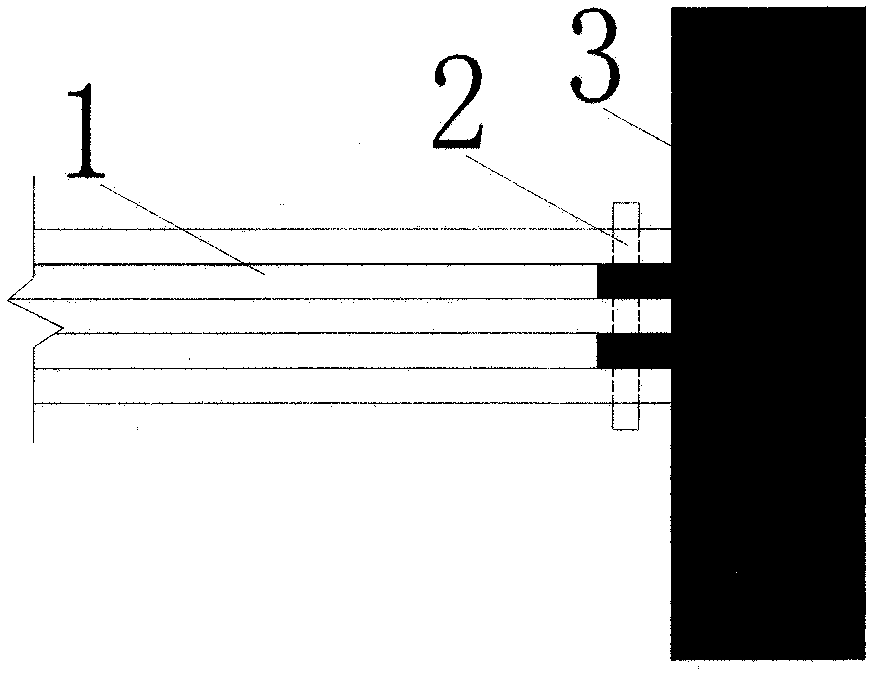
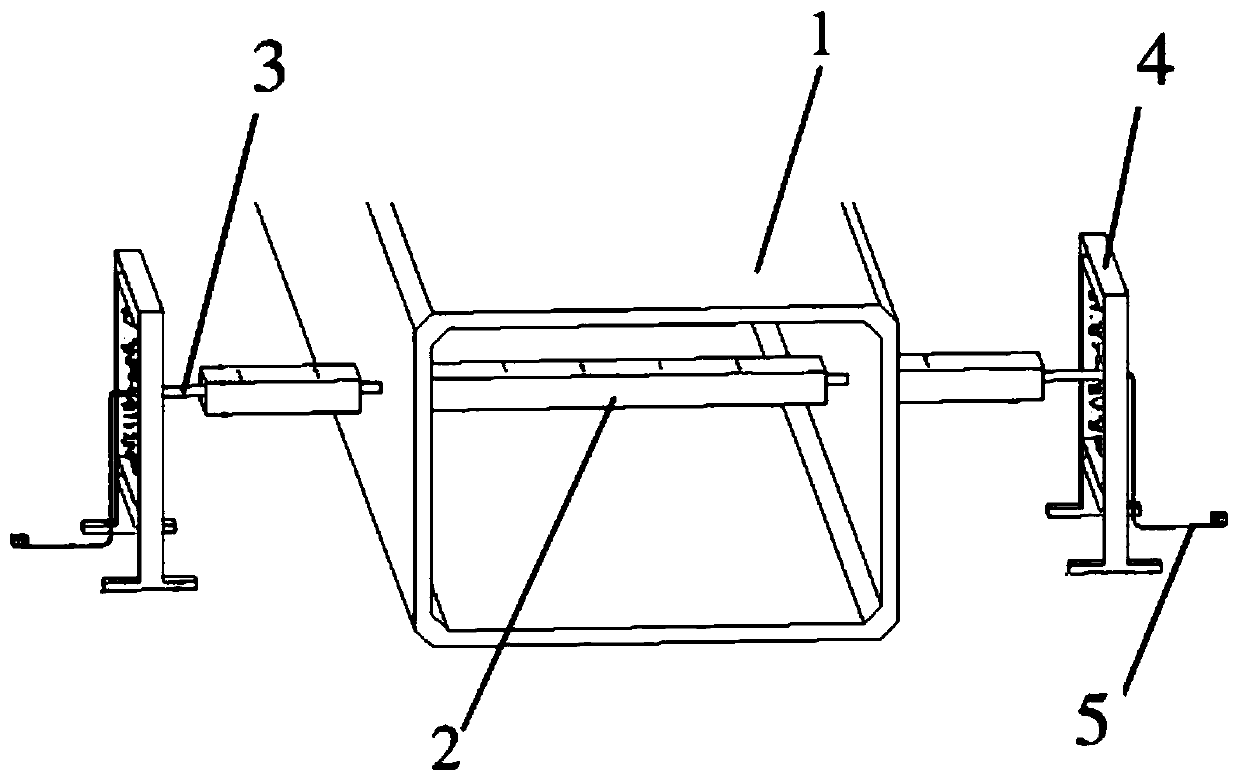
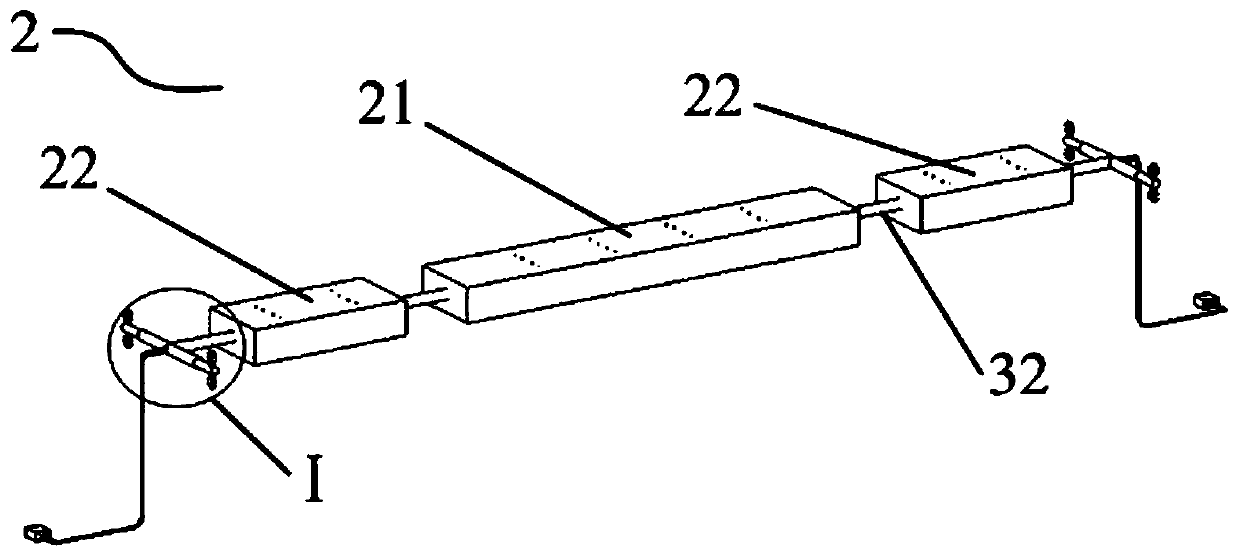
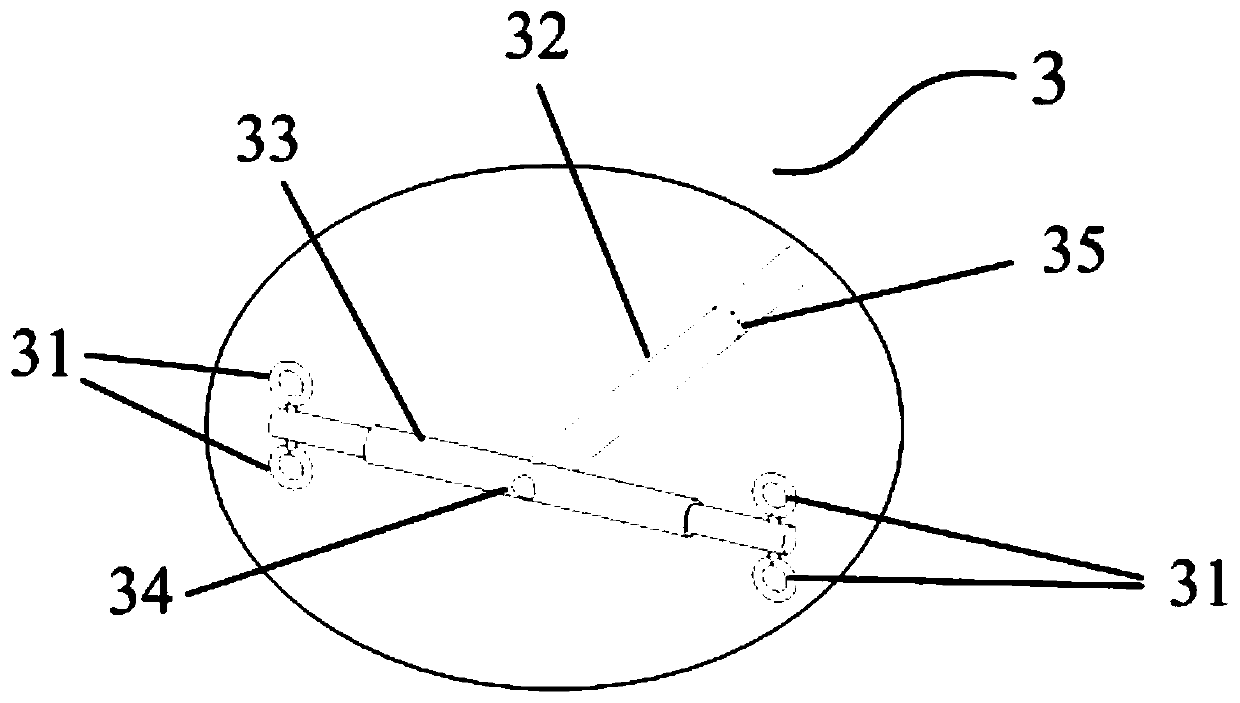
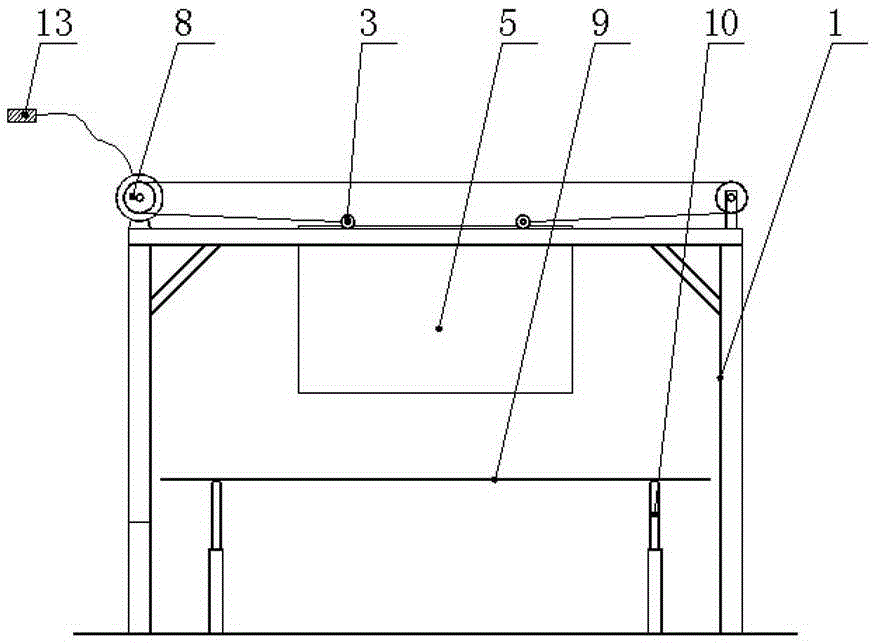
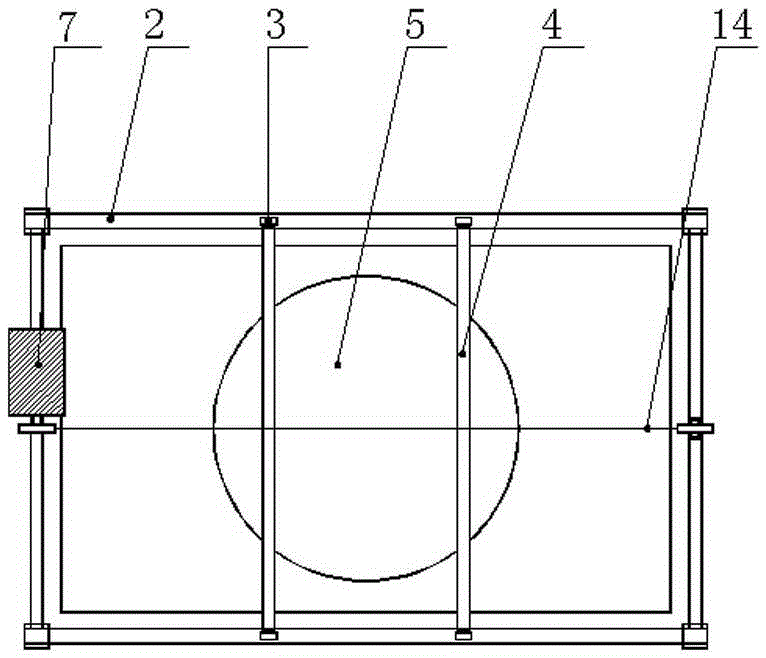
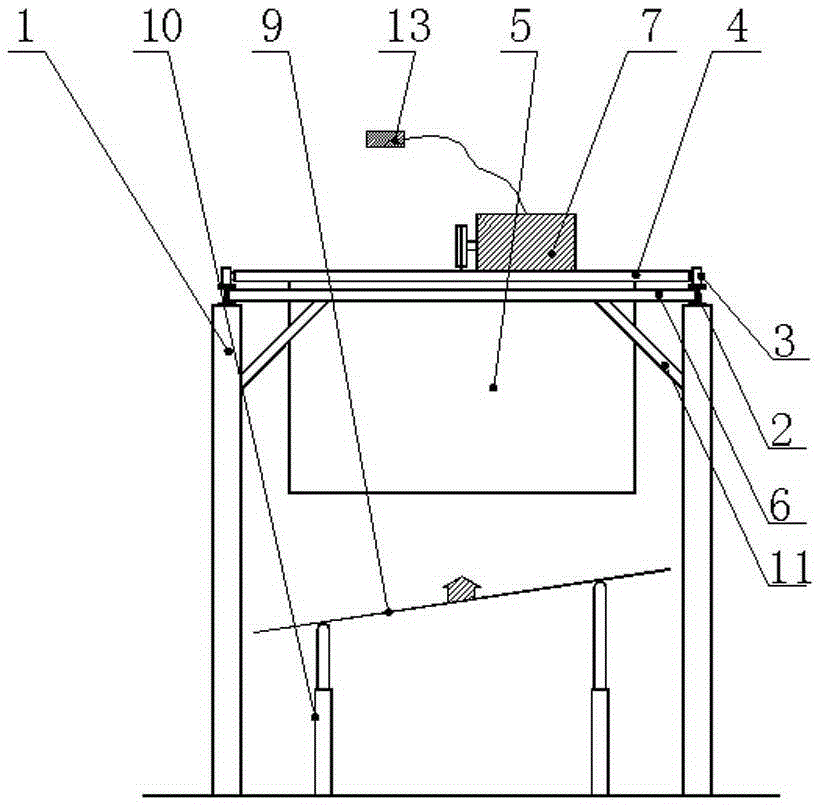
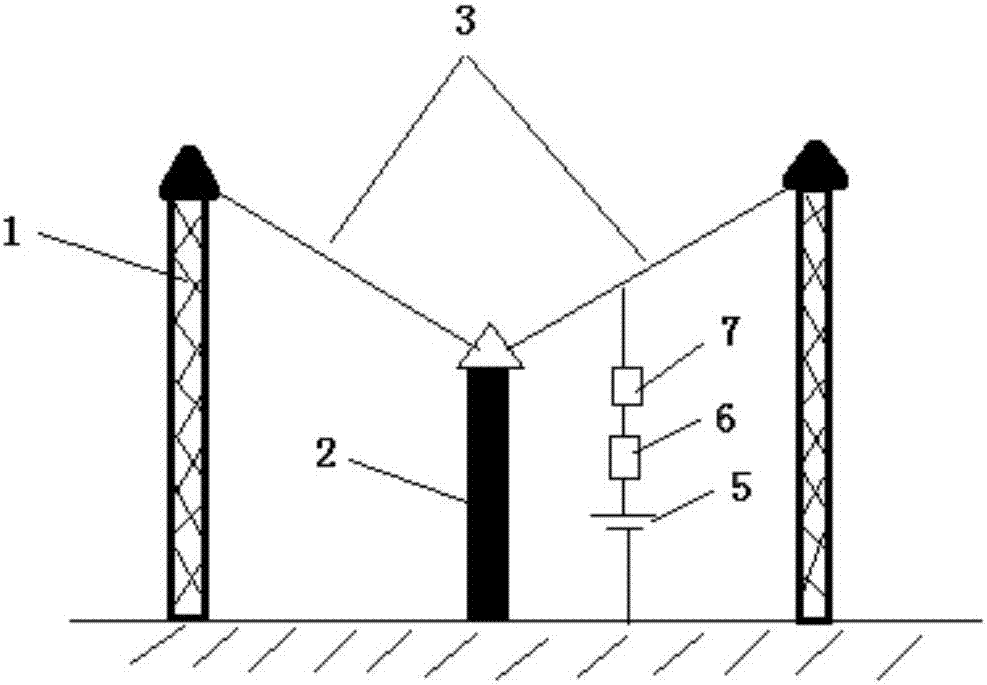
Tornado testing device for building wind engineering
The invention provides a tornado testing device for building wind engineering. The tornado testing device can accurately simulate a wind field of a tornado and the wind load effect of the tornado on a building. The tornado testing device comprises stand columns and a motor, wherein longitudinal beams are arranged on the tops of the stand columns, the longitudinal beams are connected with transverse beams, rolling wheels are arranged on the longitudinal beams and move along the longitudinal beams, the rolling wheels are connected with supporting beams, the supporting beams are connected with a vortex generator, the motor drives driving wheels to rotate, driven wheels matched with the driving wheels are arranged on the supporting beams, a platform is arranged below the vortex generator, and the platform is arranged on a lifting device. According to the tornado testing device for the building wind engineering, the shape of vortex wind generated by the vortex generator is similar to the shape of the tornado, the wind speed and the wind direction of the vortex wind can be adjusted, the vertical distance between the vortex wind and a house model can be adjusted, the horizontal movement speed of the vortex wind can also be adjusted, and therefore the wind field of the tornados in different states and the effect of the wind load of the tornados on the building can be fully simulated.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Wind tunnel test device for simulating influence of wind on structure in mountain area
InactiveCN108168830AShorten test timeSolve the inadequacy of not being able to simulate mountainous buildingsAerodynamic testingBuilding simulationWind engineering
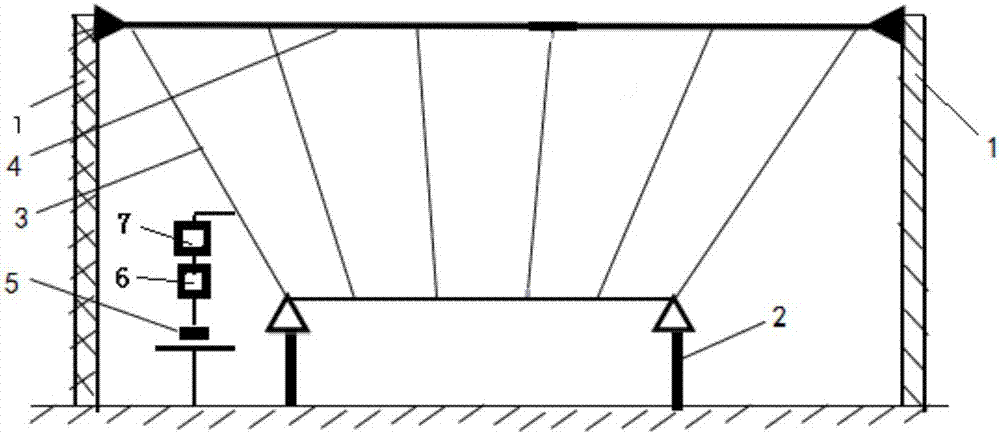
The invention discloses a wind tunnel test device for simulating influence of wind on a structure in a mountain area, and relates to the field of structural wind engineering. The wind tunnel test device comprises a building simulation system, a slope simulation system and a pressure measuring tube; the building simulation system is composed of a building model and a building base plate; the slopesimulation system is composed of a front slope subsystem, a building platform, a back slope subsystem and a driving subsystem, the front and back sides of the building platform are in rotatable connection with the front slope subsystem and the back slope subsystem respectively, the building model is mounted on the building platform via the building base plate, and the driving subsystem adjusts andcontrols the height of the building platform as well as the gradient of the front slope subsystem and the back slope subsystem; and the pressure measuring tube penetrates the building base plate andis laid in the building model. The wind tunnel test device can be used to overcome the disadvantage that test device at present does no research on the wind pressure characteristic of the building inthe mountain area, simulate mountain areas of different gradient and height-to-width ratio by changing the gradient of different landform simulated testers, and simulate different distribution forms of the buildings in the mountain area by changing the number and heights of building models.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Target track tracking calculation method of wind-driven rain amount
ActiveCN107016164AAccurate Collection Rate DistributionSmall amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWind drivenAngular point
The invention discloses a target track tracking calculation method of a wind-driven rain amount, and belongs to the technical field of wind engineering. The calculation method comprises the steps of on a given wind field incoming flow condition, solving a Reynolds average N-S equation to obtain a circle flow field of a building; according to an area to be calculated, establishing a virtual plane, and calculating a sample track end point of a sample track on the area to be calculated or the virtual plane; through a surrogate model method, and according to a sample track starting point and the sample track end point, establishing a function relation formula regarding the coordinate relation of a raindrop starting point and end point; given a raindrop track end point coordinate on the area to be calculated, calculating a raindrop track starting point coordinate; solving a raindrop motion equation to obtain an effective track, and according to the effective track, calculating collection rate distribution in the area to be calculated. According to the target track tracking calculation method of the wind-driven rain amount, accurate calculation of collection rates on the back face, lee side, the boundary and the corner point area of the building is achieved, and compared with an existing method, the needed raindrop track calculation amount is remarkably lowered.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
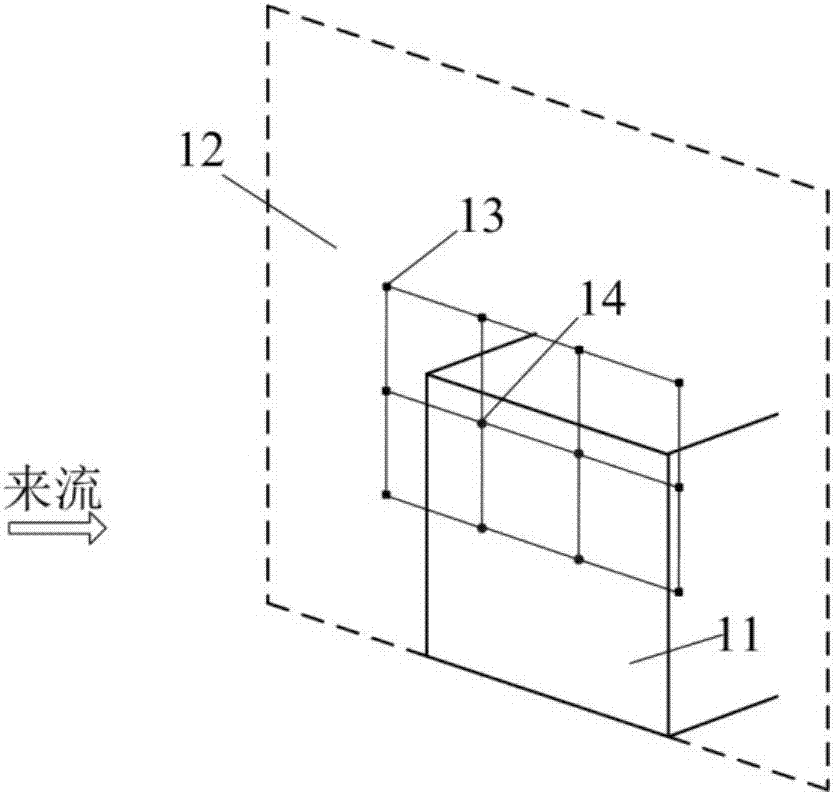
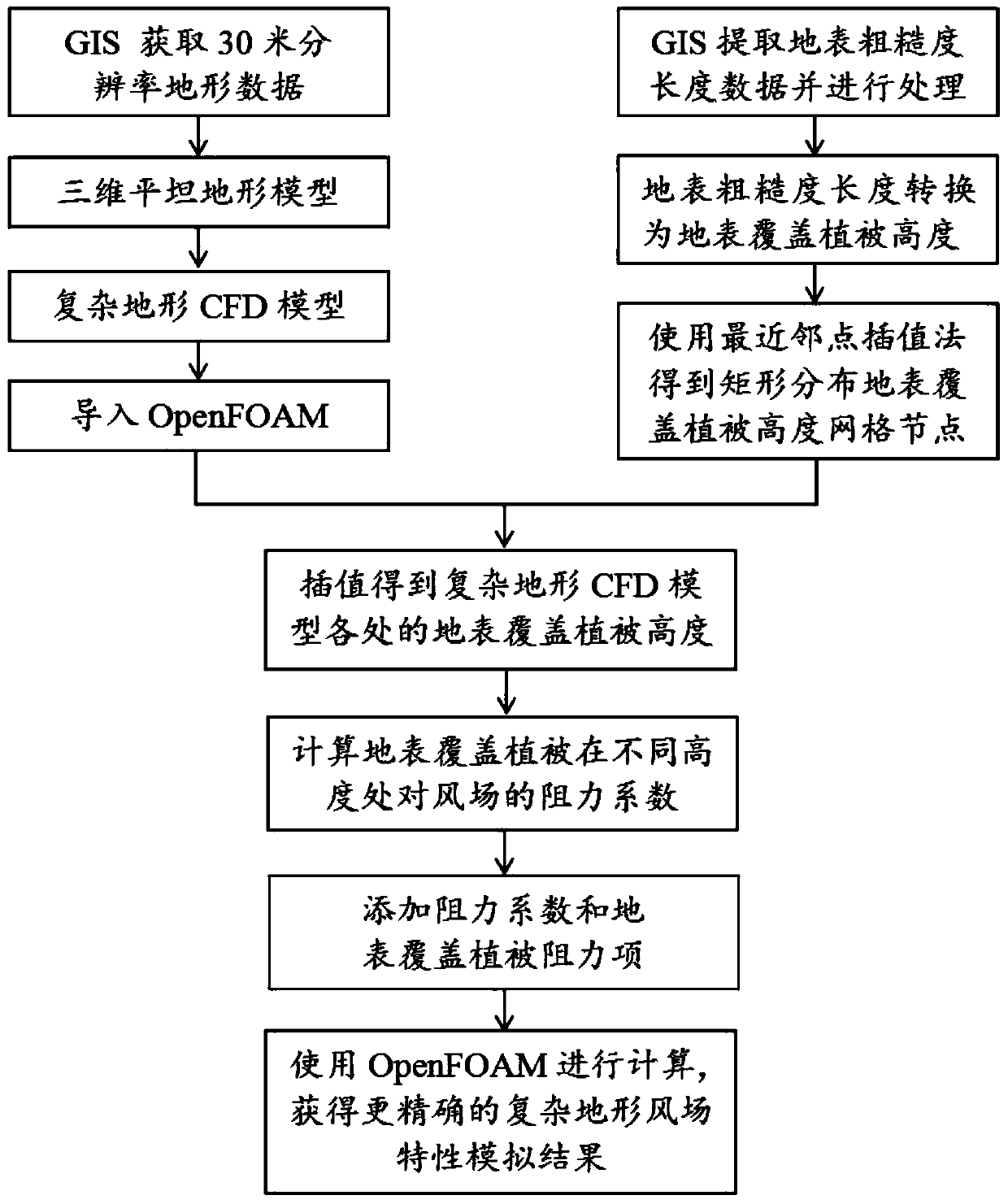
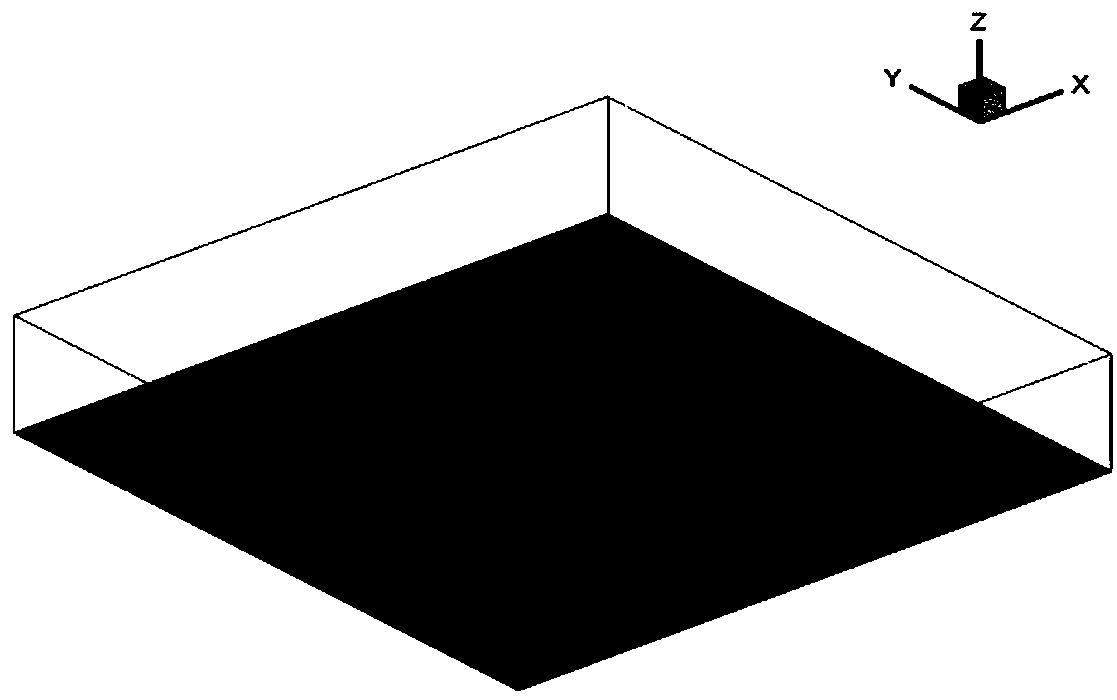
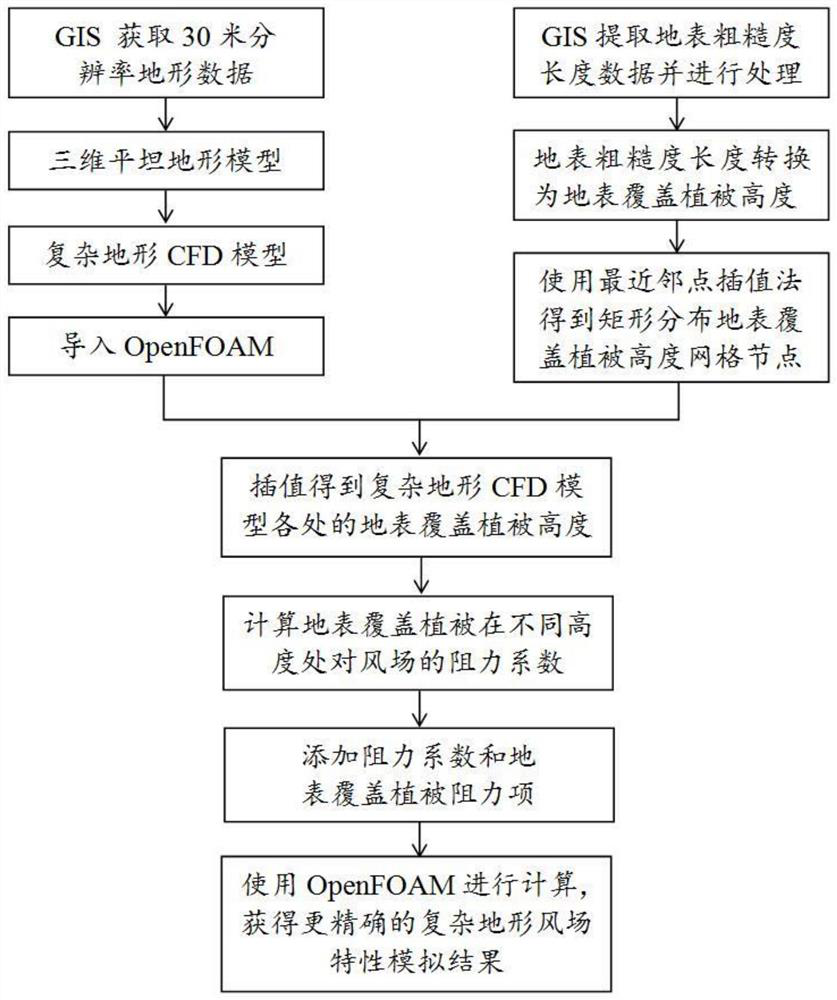
OpenFOAM-based method for simulating complex terrain surface roughness
ActiveCN108664705AAvoid manual processesSignificant distribution changeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTerrainWind engineering
The invention belongs to the field of computing wind engineering, and discloses an OpenFOAM-based method for simulating complex terrain surface roughness. The method comprises the following steps of 1) building a complex terrain CFD model, and generating a refined grid; 2) extracting surface roughness length data of the complex terrain CFD model, converting a surface roughness length into a surface cover vegetation height, and providing an accurate data basis for simulating an influence of a surface cover vegetation on a wind field of a complex terrain; 3) calculating resistance coefficients of the surface cover vegetation to the wind field at different heights, and then converting the surface cover vegetation height into the corresponding resistance coefficient; and 4) adding the resistance coefficient and a resistance item of the surface cover vegetation by using OpenFOAM, thereby obtaining a more accurate complex terrain wind field characteristic simulation result. A program language supported by a computer is used; the influence of the surface roughness on the wind field of the complex terrain is considered; and therefore, the numerical simulation accuracy of the wind field ofthe complex terrain is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
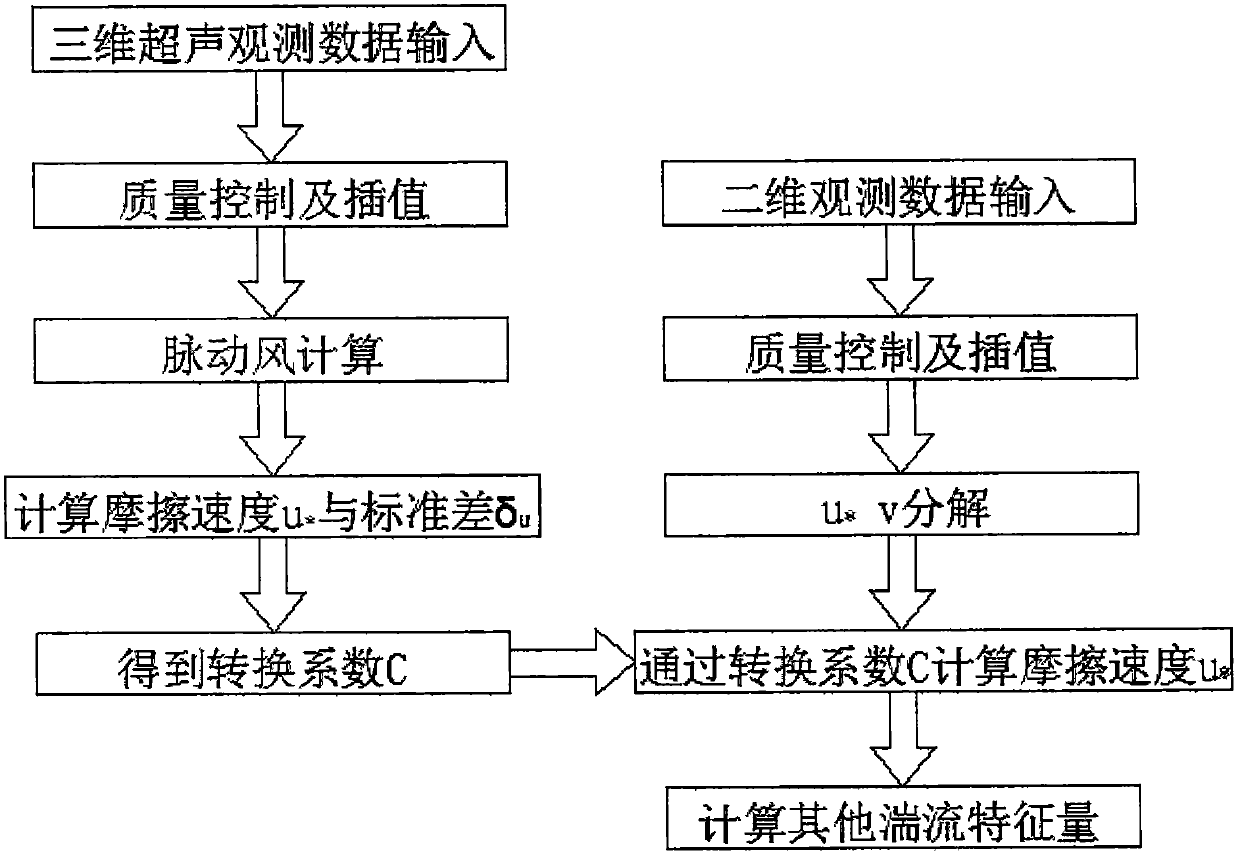
A turbulence characteristic calculation method for near-stratum strong wind
ActiveCN109902327AEffective use of utilizationIncrease the number of countable variablesSpecial data processing applicationsICT adaptationSonificationConversion coefficients
The invention discloses a turbulence characteristic calculation method for near-stratum strong wind, and relates to the technical field of weather and wind engineering. According to the turbulence characteristic calculation method for the near-stratum strong wind, a conversion coefficient inverted by observation data of an ultrasonic three-dimensional wind field is adopted to calculate Turbulencecharacteristics such as the friction speed, the underlying surface roughness, the momentum exchange coefficient and the heat induction exchange coefficient for surrounding two-dimensional wind field observation data, the number of calculable variables of the two-dimensional data is increased, and the data application scene is expanded. According to the method, the utilization rate of 1Hz two-dimensional near-surface wind field observation data is effectively utilized, the turbulence characteristics such as the friction speed, the underlying surface roughness, the momentum exchange coefficientand the heat induction exchange system which cannot be calculated in the prior art are increased, and the method has practical significance for turbulence characteristic analysis under the strong windcondition. And the near-surface turbulence observation data source in China is expanded, and the quality monitoring level and the data stability of the 10Hz three-dimensional ultrasonic data are further improved by comparing the data source with 1Hz data.
Owner:JIANGSU METEOROLOGICAL OBSERVATORY +1
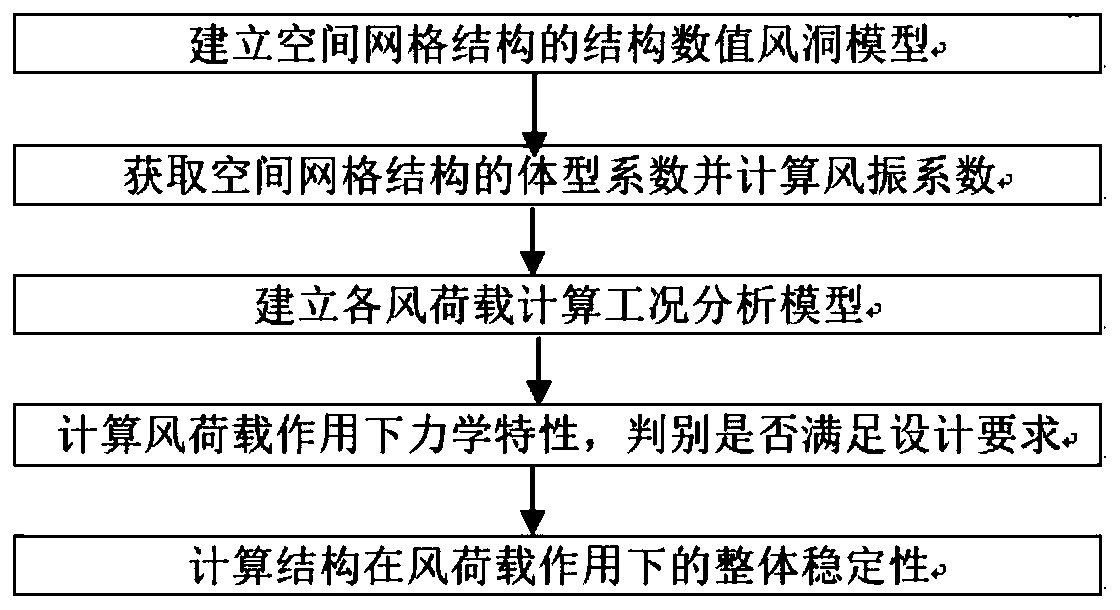
Wind engineering analysis method for large-span ultra-high space grid structure
InactiveCN110196990ANumerical wind tunnel methods are convenientNumerical Wind Tunnel Method FastGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsWind engineeringElastic plastic
The invention discloses a wind engineering analysis method for a large-span ultra-high space grid structure, and belongs to the technical field of special engineering design. The analysis method comprises the following implementation steps of firstly, establishing a structure numerical value wind tunnel model of a spatial grid structure; secondly, obtaining a body type coefficient of the space grid structure according to the structure numerical value wind tunnel model, and calculating a wind vibration coefficient of the space grid structure according to theoretical analysis; establishing a wind load calculation working condition analysis model according to the body type coefficient and the wind vibration coefficient; calculating the mechanical properties under the action of wind load according to a working condition analysis model, judging whether the mechanical properties meet design requirements or not, if so, performing the next step, and otherwise, performing structure optimization; and finally, analyzing the whole elastic-plastic process of the structure under the working condition of wind load calculation by adopting the low-order buckling mode of the structure, and calculating the overall stability of the structure under the action of wind load. The method can replace a wind tunnel test to obtain the shape coefficient of any position under any wind direction angle effect, the test period is short, and the cost is low.
Owner:NO 63921 UNIT OF PLA
Method for measuring blast time-frequency characteristic of structure roof of low-rise building
The invention relates to a method for measuring a blast time-frequency characteristic of a structure roof of a low-rise building, and belongs to the field of wind engineering. The method comprises thefollowing steps of S1) detecting the smoothness; S2) detecting the pulsated wind speed smoothness; S3) carrying out continuous and discrete wavelet transformation; and S4) analyzing the time-frequency characteristic. Thus, the blast time-frequency characteristic of the structure roof of the low-rise building is measured effectively, and determination basis is provided for construction of the structure roof of the low-rise building.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
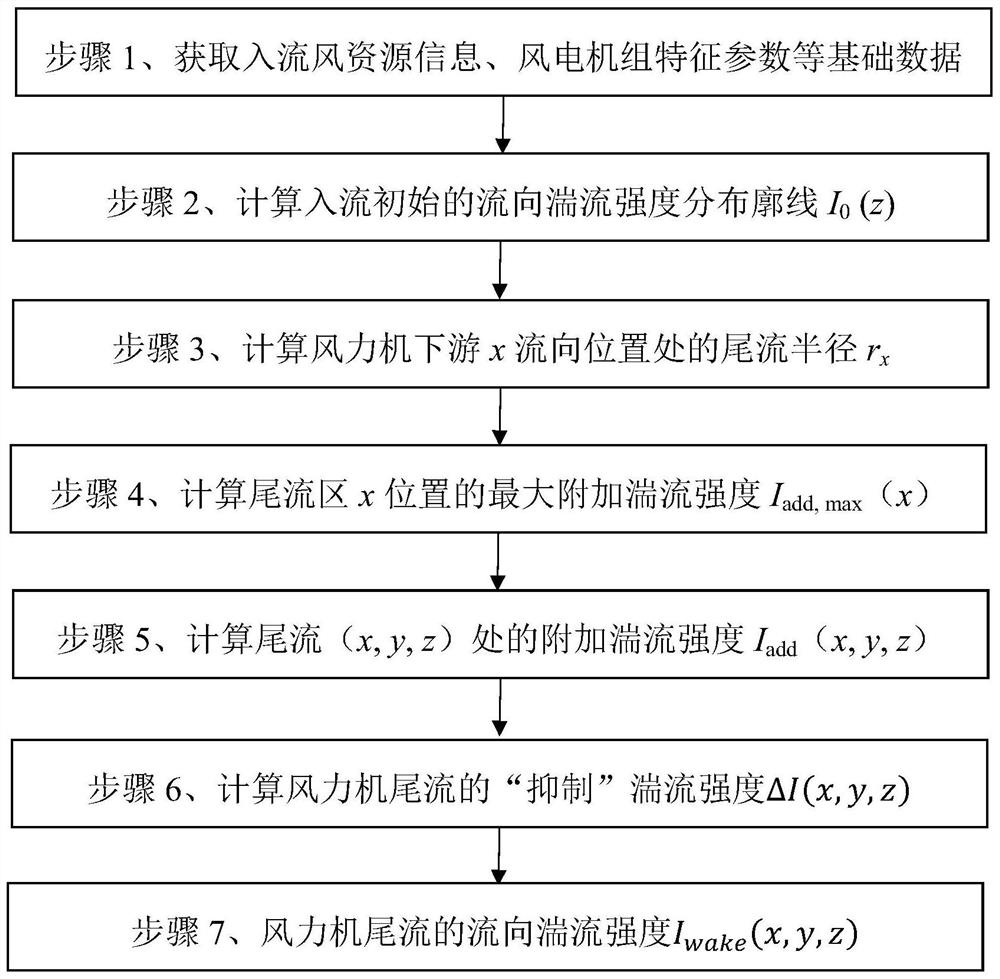
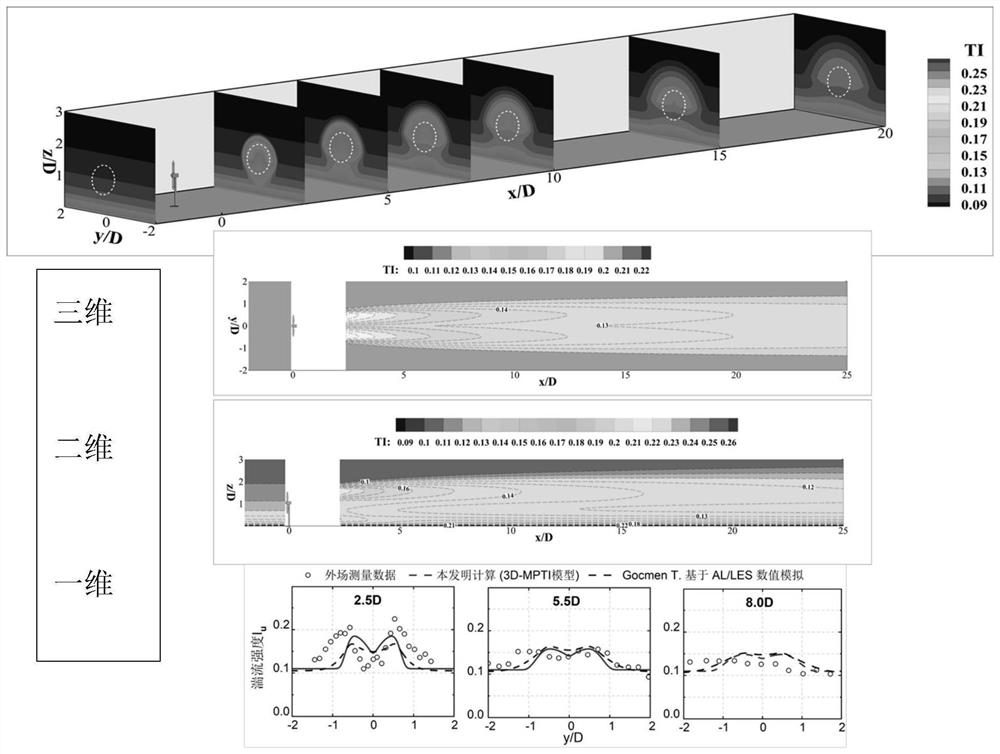
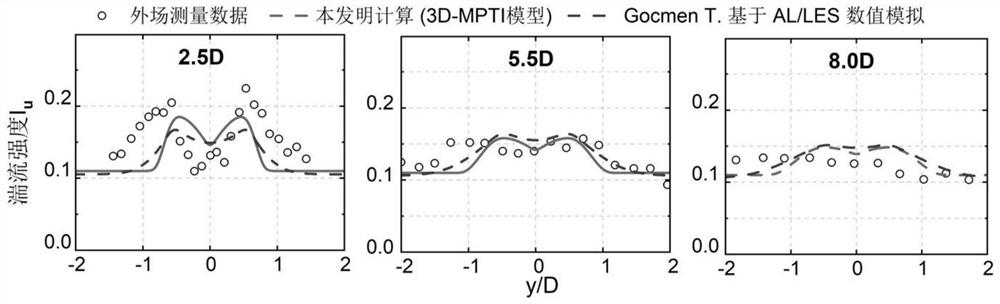
Method for calculating turbulence intensity of tail flow of wind turbine
PendingCN113705118AEffectively reflect the typicalEffectively reflect the characteristicsDesign optimisation/simulationWind engineeringAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses a method for calculating the turbulence intensity of the tail flow of a wind turbine. The method comprises the following steps: calculating a flow direction turbulence intensity vertical direction distribution type of inflow, a wake flow radius at any flow direction cross section position of a wake flow area and maximum additional turbulence intensity generated by a wake flow effect based on basic data such as inflow wind resource information and wind turbine generator characteristic parameters; calculating the additional turbulence intensity and the 'inhibition' turbulence intensity of the wake flow area position; and calculating the flow direction turbulence intensity of any position of the tail flow of the wind turbine based on the steps. According to the method, the flow direction turbulence intensity of any spatial position can be predicted with high precision, especially the 'double-peak' distribution of the near wake flow turbulence intensity and the 'turbulence weakening' effect of the near ground position, and the prediction precision is superior to that of a numerical simulation result based on computational fluid mechanics. And an accurate and efficient turbulence calculation tool is provided for wind turbine design and wind power plant unit layout optimization in a wind engineering project.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Novel wind tunnel test device for synchronously measuring aeroelasticity-pressure of inertia force
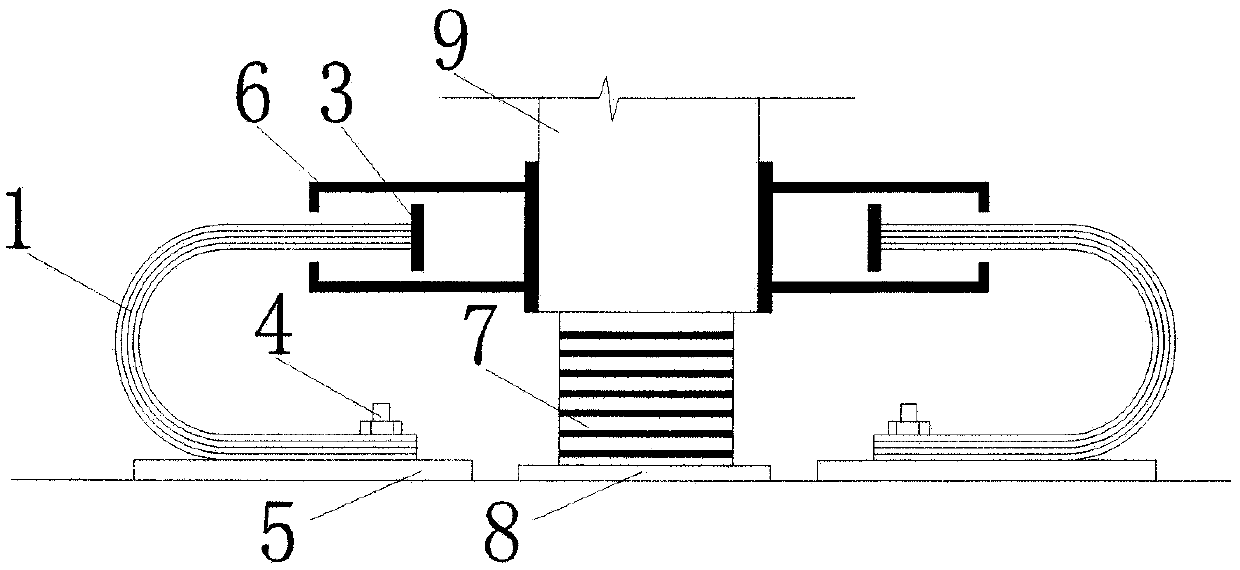
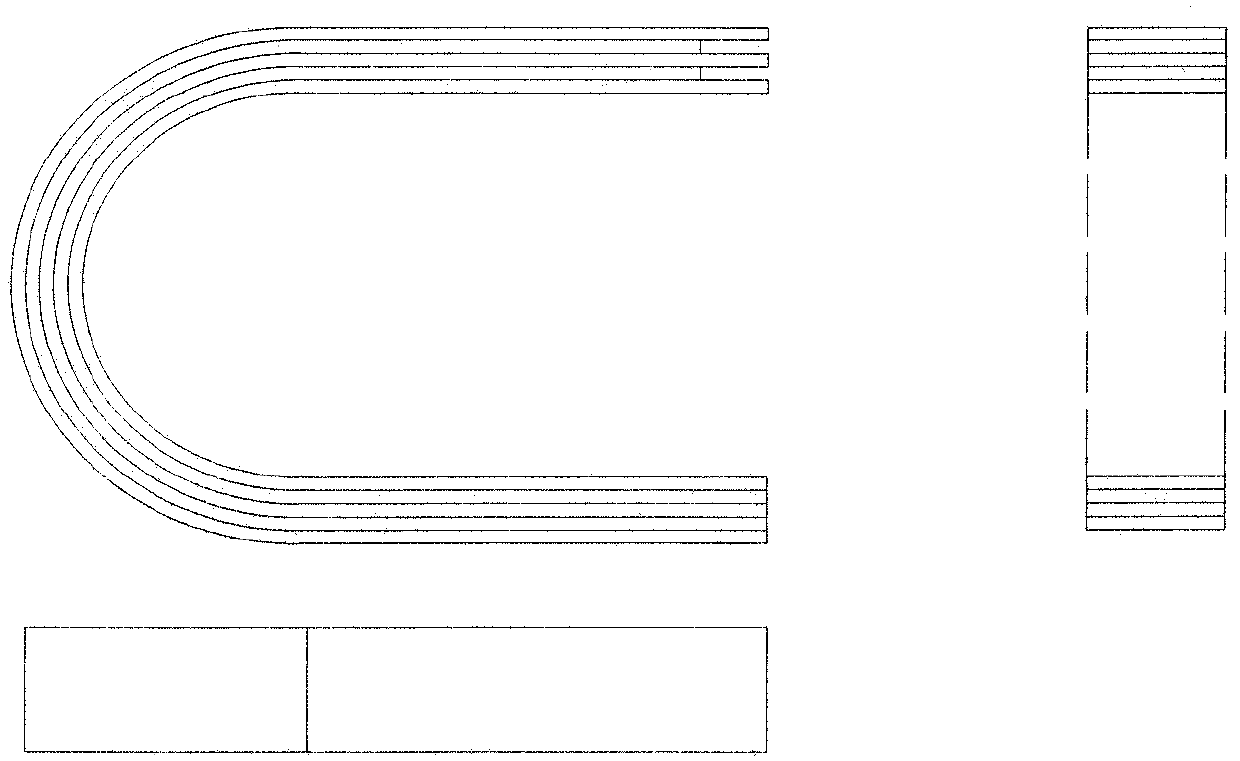
ActiveCN107894316AImprove accuracyGuaranteed accuracyAerodynamic testingAeroelasticityWind engineering
The invention belongs to the field of structural wind engineering and specifically discloses a novel wind tunnel test device for synchronously measuring aeroelasticity-pressure of inertia force. The test device comprises a wind tunnel body for testing a test member, a conduction member for fixing the test member, a stiffness control subsystem for changing stiffness of the test member and a data acquisition subsystem for collecting test data. The novel wind tunnel test device solves the problem that conventional wind tunnel test needs extra tests when considering fluid-solid coupling effect, and realizes test of different stiffness of members on the basis of not replacing the test member, thereby preventing waste of manpower and material resources, improving use efficiency of a wind tunneland reducing test cost.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Aeroelastic model testing device based on gas rigidity
ActiveCN108507750AMonitor inflationMonitor and control the inflation volumeSustainable transportationAerodynamic testingControl systemModel testing
The invention belongs to the field of aerodynamic wind tunnel tests in wind engineering and relates to an aeroelastic model testing device based on gas rigidity. The aeroelastic model testing device comprises a testing model, a fixing device, two vertically vertical shafts, four inflatable annular tires and a tire pressure monitoring system, wherein the fixing device comprises a base plate, at least four cantilevers and a connecting rod, the cantilevers are fixedly connected between an upper base plate and a lower base plate, one end of the connecting rod is fixed on the lower base plate, andthe other end of the connecting rod is inserted into the testing model through the two mutually vertical shafts; the tail ends of the two mutually vertical shafts are connected with the four inflatable annular tires and are fixed in a space formed by the upper base plate, the lower base plate and the cantilevers; and the inflatable annular tires are located on the inner sides of the cantilevers and are in contact with the inner sides of the cantilevers after being inflated; and the tire pressure monitoring system is connected with the inflatable annular tires. According to the aeroelastic model testing device, the rigidity of the model can be continuously, accurately and conveniently changed, and the structure of the aeroelastic model testing device is simple.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Turbulent flow field simulation device for structural wind engineering test
PendingCN107202676AEffective simulationSimulation is simple and effectiveAerodynamic testingWind engineeringAir pump
The invention provides a turbulent flow field simulation device for a structural wind engineering test. The turbulent flow field simulation device for the structural wind engineering test comprises a base, a gas outlet pipe, a gas cavity, a gas inlet and a gas pump; the gas cavity is arranged in the base; the gas outlet pipe is connected with the gas cavity and the outer side of the base; the gas pump is connected with the gas inlet; the gas inlet is connected with the gas cavity; and a test model is arranged on the base. A turbulent flow field is simulated by blasting gas flow on the lower surface of an incoming flow field, so that effective simulation of the wind field of the actual engineering structure is realized, a double-way pulsating turbulent flow field can be simulated simply and effectively, and the device is flexible in form and high in applicability and can serve as effective supplementation of the existing technical scheme.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
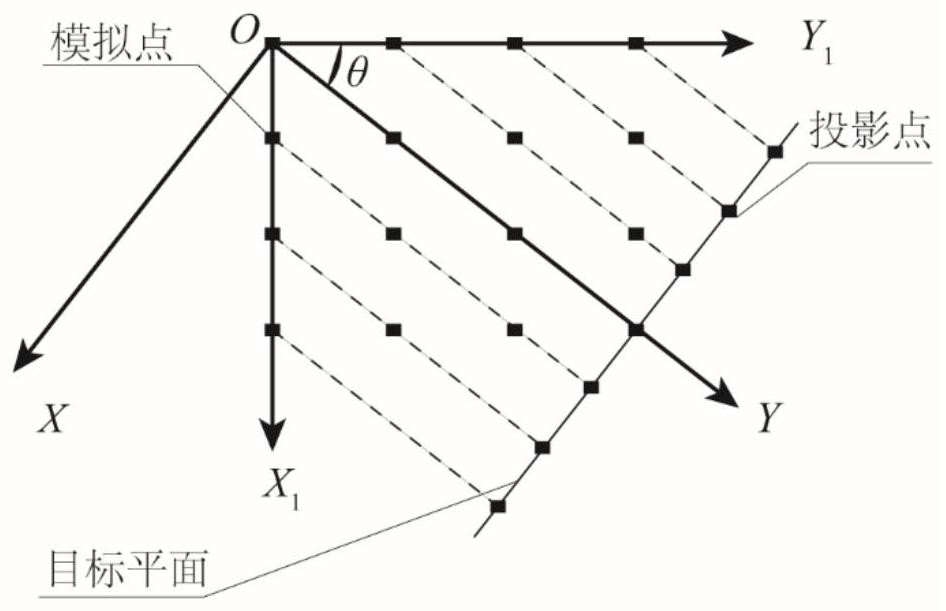
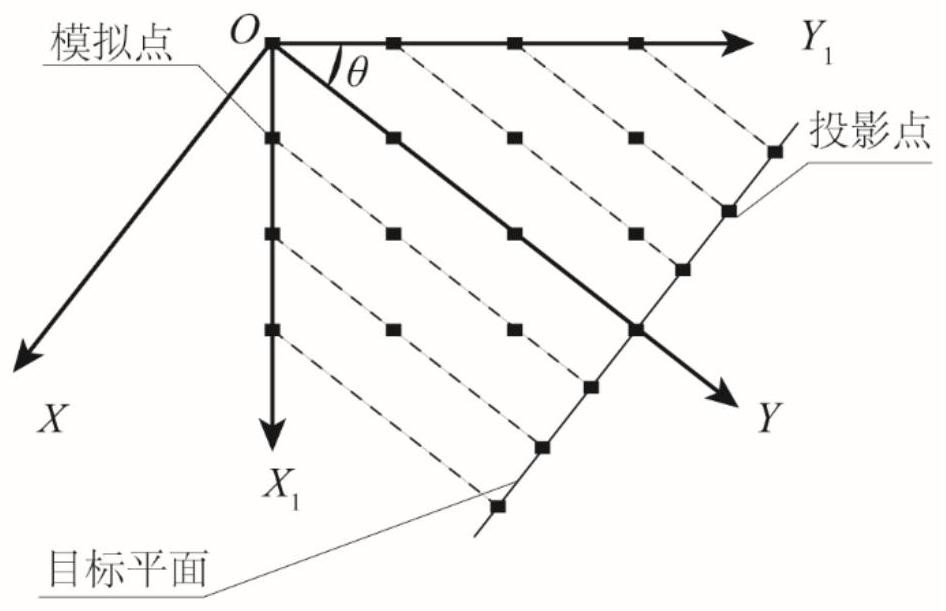
Three-dimensional wind field efficient simulation method based on delay effect
ActiveCN113468692AReduce dimensionalityImprove decomposition efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationClassical mechanicsWind engineering
The invention discloses a three-dimensional wind field efficient simulation method based on a delay effect, and belongs to the technical field of structural wind engineering. The method for generating the wind speed time history mainly comprises the steps of determining coordinates and an initial coordinate system of simulation points according to a structural drawing, transforming the coordinate system to enable a Y axis to be parallel to the wind speed direction, obtaining a three-dimensional model of N structural simulation points, projecting all the simulation points of the three-dimensional model to a target two-dimensional plane, converting the simulation points into projection points in a two-dimensional plane, calculating wind speed delay time, namely required time from each point to the projection points on the target plane, adopting a two-dimensional coherence function to consider spatial correlation of different simulation points in the transverse direction and the vertical direction, generating fluctuating wind speed by using a harmonic superposition method, and obtaining wind speed time histories of all the points by using the delay time. The statistical characteristics of the data obtained by the time delay method are similar to the result of the traditional three-dimensional method, but the simulation efficiency is greatly improved; and meanwhile, the method is simple to operate and has a reasonable theoretical background.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
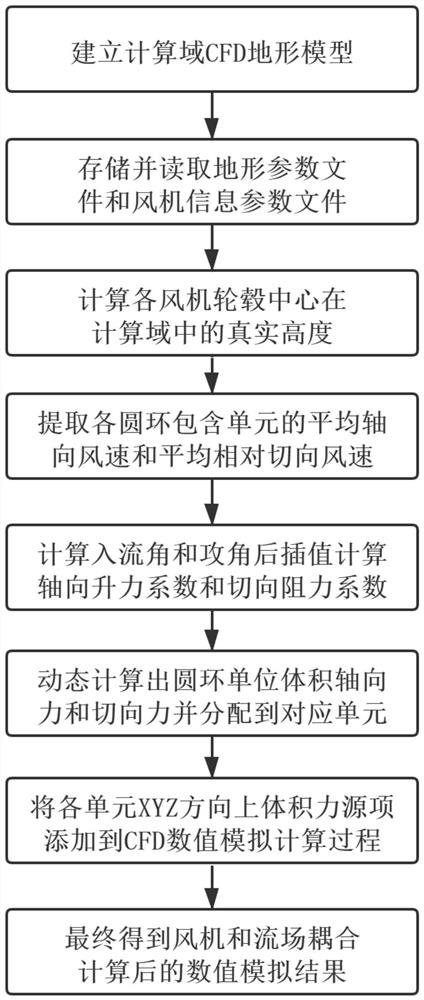
Wind power plant fan wake flow dynamic coupling simulation method
PendingCN112966454ASimulation is accurateReal wake effectsDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingWind engineeringEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of computational wind engineering, and particularly discloses a wind power plant fan wake flow dynamic coupling simulation method, which comprises the following steps of: S1, dividing a computational domain into a plurality of grid units, further establishing a computational domain grid model, and simultaneously obtaining relevant parameters of a fan; s2, dividing the fan actuating disc into a plurality of radially equidistant circular rings, respectively calculating axial force and tangential force corresponding to each circular ring according to the wind speed, distributing the axial force and tangential force to each grid unit contained in the circular rings to obtain a resistance item of each grid unit, and establishing a corresponding relation model of the wind speed and the resistance item; and S3, based on the computational domain grid model, carrying out numerical simulation on the fan wake flow, adding a resistance item to a corresponding grid unit during simulation, and dynamically calculating and updating the resistance item according to the changed wind speed and the corresponding relation model. The resistance item is correspondingly and dynamically added according to the incoming flow wind speed, the disturbance effect of the flow field and the draught fan on the flow field can be calculated in a coupling mode, and the wake flow distribution condition of the draught fan is truly reflected.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Intelligent control device and method for inlet attack angle of tornado test
PendingCN114722718AMake up for the defect that the entrance angle of attack cannot be changedSimple structureHuman health protectionAerodynamic testingClassical mechanicsWind engineering
The invention discloses a tornado test inlet attack angle intelligent regulation and control device and method, and belongs to the field of structural wind engineering test equipment.The device comprises a main control computer, an attack angle regulation and control device, an inlet wind speed test module and a tornado simulator internal PIV module, the main control computer is wirelessly connected with the attack angle regulation and control device, the inlet wind speed test module and the internal PIV module of the tornado simulator to transmit data; the main control computer receives the internal wind field structure parameters of the tornado simulator provided by the PIV module in real time, analyzes the actual attack angle of the internal wind field based on a wind field characteristic parameter analysis algorithm, performs autonomous optimization analysis of the entrance attack angle through a machine learning optimization algorithm, and transmits the attack angle regulation and control quantity to the attack angle regulation and control device; therefore, accurate regulation and control of the inlet attack angle of the visual test tornado test are realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
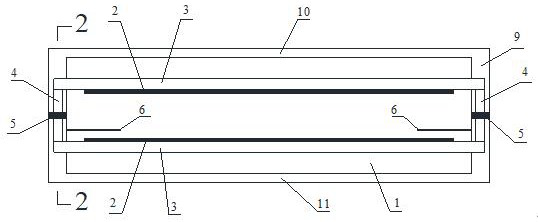
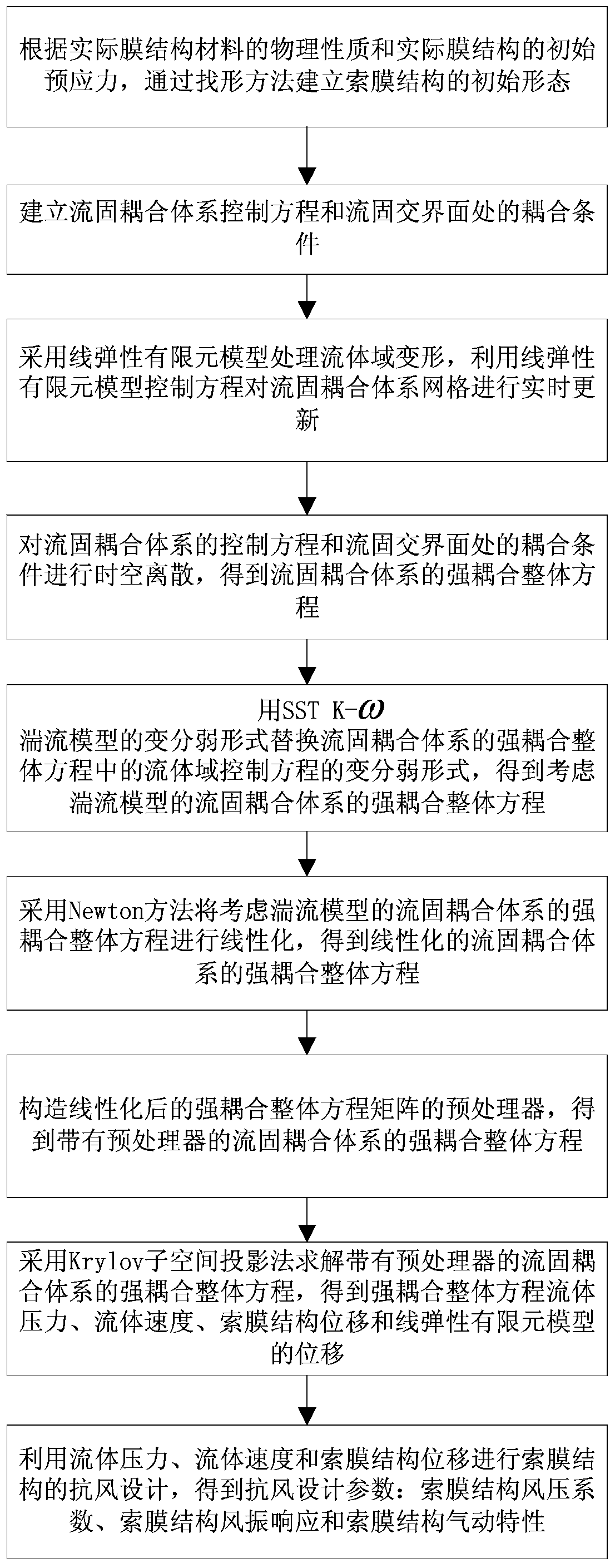
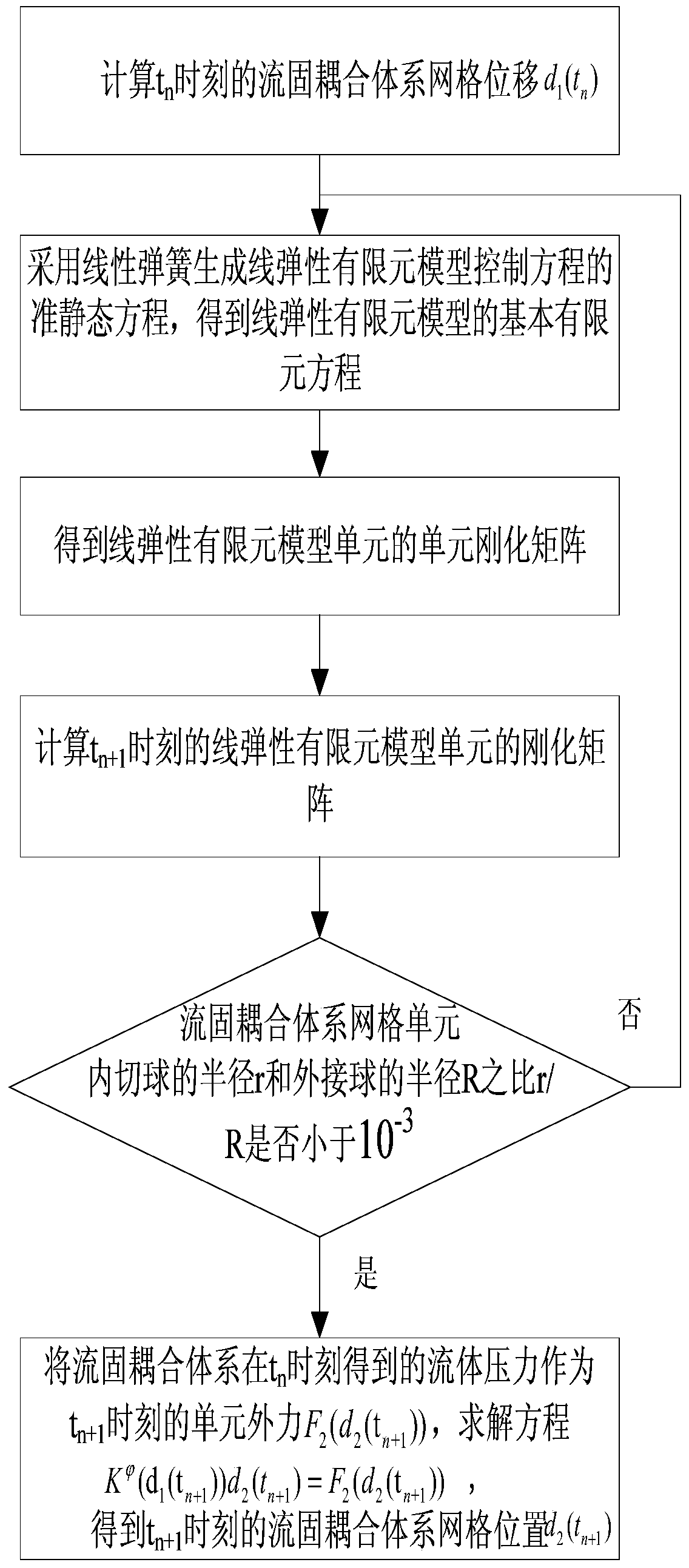
A wind-resistant design method for cable-membrane structures based on strong coupling integral technology
ActiveCN104573269BSolve the problem of data exchange transmissionSolving Convergence ProblemsSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical engineering technologyElement model
The invention relates to a wind-resistant design method of a cable-membrane structure based on strong coupling overall technology, which establishes the initial form of the cable-membrane structure; establishes the control equation of the fluid-solid coupling system and the coupling conditions at the fluid-solid interface, and performs time-space discretization on it, Obtain the strong coupling overall equation of the fluid-solid coupling system; use the SST K‑ω turbulence model to simulate turbulence, obtain the strong coupling overall equation of the fluid-solid coupling system considering the turbulence model, and use the Newton method to linearize it; after constructing the linearized The preprocessor of the strong coupling global equation matrix, obtains the strong coupling global equation of the fluid-solid coupling system with the preprocessor, uses the Krylov subspace projection method to solve it, and obtains the strong coupling global equation fluid pressure, fluid velocity, The displacement of the cable-membrane structure and the displacement of the linear elastic finite element model; thus, the wind-resistant design of the cable-membrane structure is carried out, and the wind-resistant design parameters are obtained.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Bridge wind tunnel wind speed and vehicle force measurement test system and method
PendingCN112268683AReduced adjustabilityReduce the number of devicesVehicle testingAerodynamic testingMeasurement testMarine engineering
The invention discloses a bridge wind tunnel wind speed and vehicle force measurement test system and method, and relates to the technical field of bridge wind engineering. The system comprises a vehicle model, a wind measurement platform and a force measurement platform, wherein the wind measurement platform is arranged in the wind tunnel, comprises a wind measurement crown block and is used formeasuring wind speeds and wind directions at different positions; the force measurement platform is arranged in the bridge model and comprises a force measurement balance and a mechanical servo system, and the vehicle model is locked on the force measurement balance, so that the six-component force of the vehicle model can be conveniently collected in time in the test process; and the mechanical servo system is used for conveying and moving the force measurement balance. Through the cooperation of the wind measurement platform and the force measurement platform, the wind speed and direction ofeach lane and the corresponding vehicle model six-component force under each working condition can be continuously and synchronously acquired at any time, the frequency of adjusting the working condition and equipment by stopping a wind tunnel is reduced, the manual interference is reduced, and the test efficiency and precision are improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV OF TECH
A method of simulating the surface roughness of complex terrain based on openfoam
ActiveCN108664705BAvoid manual operationSignificant distribution changeDesign optimisation/simulationGeographical information databasesTerrainVegetation height
The invention belongs to the field of computing wind engineering, and discloses an OpenFOAM-based method for simulating complex terrain surface roughness. The method comprises the following steps of 1) building a complex terrain CFD model, and generating a refined grid; 2) extracting surface roughness length data of the complex terrain CFD model, converting a surface roughness length into a surface cover vegetation height, and providing an accurate data basis for simulating an influence of a surface cover vegetation on a wind field of a complex terrain; 3) calculating resistance coefficients of the surface cover vegetation to the wind field at different heights, and then converting the surface cover vegetation height into the corresponding resistance coefficient; and 4) adding the resistance coefficient and a resistance item of the surface cover vegetation by using OpenFOAM, thereby obtaining a more accurate complex terrain wind field characteristic simulation result. A program language supported by a computer is used; the influence of the surface roughness on the wind field of the complex terrain is considered; and therefore, the numerical simulation accuracy of the wind field ofthe complex terrain is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A two-way limit mechanism of laminated U-shaped steel plates
InactiveCN105178463BImprove seismic performanceLarge amount of deformationShock proofingSheet steelIsolation layer
A bidirectional limit mechanism of laminated U-shaped steel plates, belonging to the field of anti-seismic, shock-absorbing and wind-resistant technologies for engineering structures, comprising laminated U-shaped steel plates (1), U-shaped steel plate fixing plates (5), push-pull plates (3), Push-pull groove (6) etc. The push-pull groove (6) is fixed on the upper structure of the shock-isolation layer, and the laminated U-shaped steel plate (1) goes deep into the inside of the push-pull groove, so that the push-pull plate (3) is in the middle of the push-pull groove (6). There is a certain distance between the push-pull plate (3) and the left and right ends of the push-pull groove (6). When the shock-isolation bearing undergoes large deformation, the limiter can limit the deformation of the shock-isolation layer in two directions of push and pull, and play a role in protecting the shock-isolation facilities.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CIVIL ENG & ARCHITECTURE
A new type of wind tunnel test device for aeroelasticity-pressure measurement with synchronous inertial force measurement
ActiveCN107894316BImprove accuracyGuaranteed accuracyAerodynamic testingAeroelasticityData acquisition
The invention belongs to the field of structural wind engineering and specifically discloses a novel wind tunnel test device for synchronously measuring aeroelasticity-pressure of inertia force. The test device comprises a wind tunnel body for testing a test member, a conduction member for fixing the test member, a stiffness control subsystem for changing stiffness of the test member and a data acquisition subsystem for collecting test data. The novel wind tunnel test device solves the problem that conventional wind tunnel test needs extra tests when considering fluid-solid coupling effect, and realizes test of different stiffness of members on the basis of not replacing the test member, thereby preventing waste of manpower and material resources, improving use efficiency of a wind tunneland reducing test cost.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
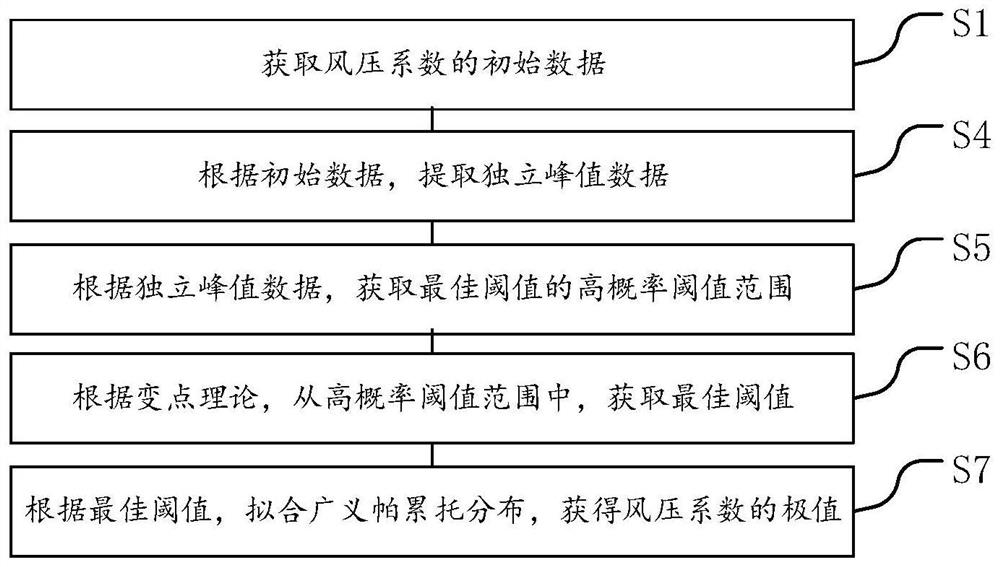
Improved threshold exceeding extreme value estimation method and device, equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114266091AImplement automatic selectionLess original sampleGeometric CADComplex mathematical operationsData ingestionEstimation methods
The embodiment of the invention provides an improved beyond-threshold extreme value estimation method and device, equipment and a storage medium, and relates to the technical field of structural wind engineering research. The extreme value estimation method comprises the steps of S1, obtaining initial data of a wind pressure coefficient, S4, extracting independent peak value data according to the initial data, S5, obtaining a high probability threshold range of an optimal threshold value according to the independent peak value data, S6, obtaining the optimal threshold value from the high probability threshold range according to a change point theory, S7, fitting generalized Pareto distribution according to the optimal threshold value, and obtaining an extreme value of the wind pressure coefficient. Automatic selection of the optimal threshold value is achieved through the change point theory, small deviation can be obtained with few original samples, and the method has good practical significance.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
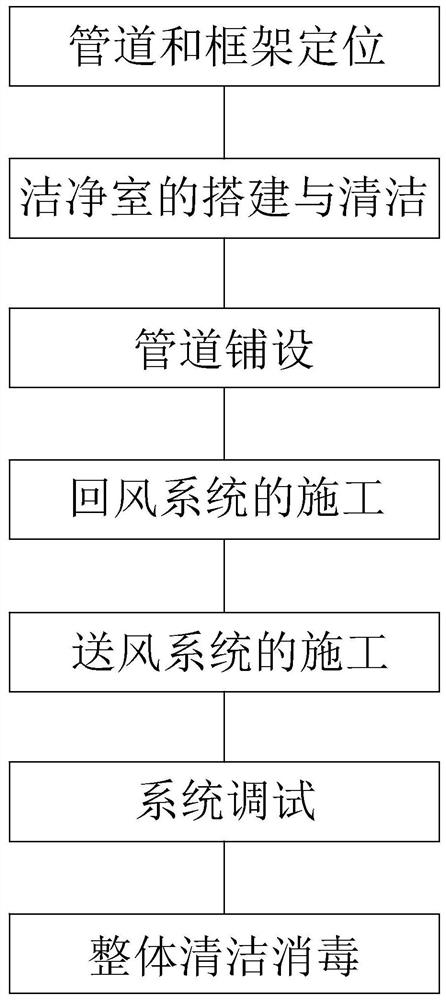
High-efficiency air supply and return engineering construction method for low-stable-speed and auxiliary-flow clean air conditioner
InactiveCN112902347ASlow down the spreadLow costDucting arrangementsMechanical apparatusSuspended particlesBusiness enterprise
The invention discloses a high-efficiency air supply and return engineering construction method for a low-stable-speed and auxiliary-flow clean air conditioner. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a pipeline and a frame are positioned; 2, a clean room is built and cleaned; 3, the pipeline is laid; 4, an air return system is constructed; 5, an air supply system is constructed; 6, the system is debugged; and 7, overall cleaning and disinfection are performed. The construction process is reasonable in design, the construction sequence follows the principle of 'first large, second small and first inside and second outside', orderly and effective installation of the system is guaranteed, and the project constructed through the construction method can enable the diffusion speed of harmful suspended particles in the clean room to reach the minimum, so that the cleanliness in the clean room reaches the higher grade, in addition, the construction cost and the operation cost of a project constructed and completed through the method are low, and the method is more suitable for enterprise production.
Owner:济南润德医用工程有限公司
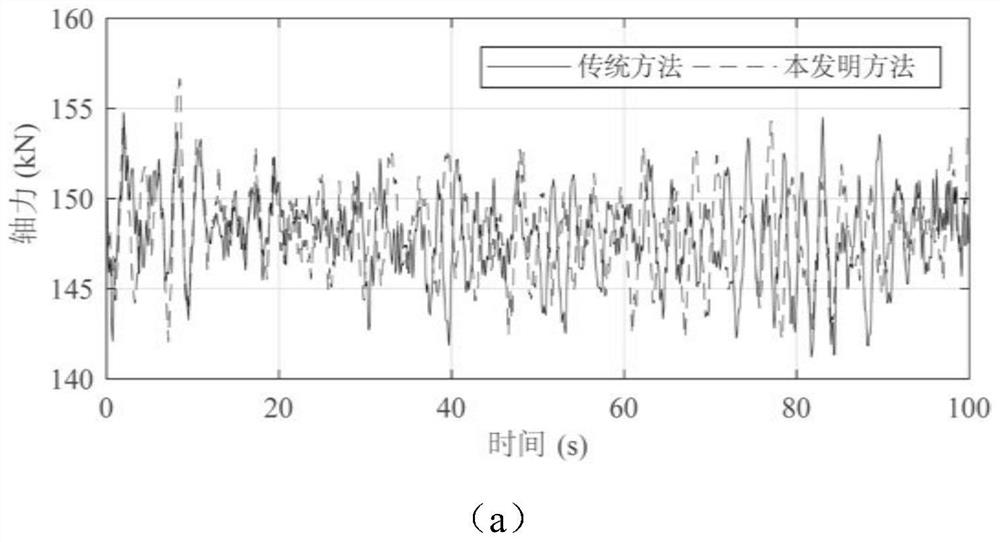
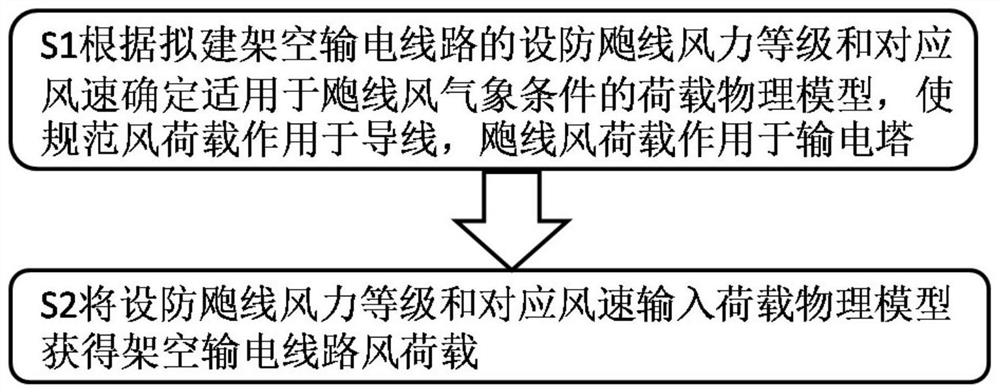
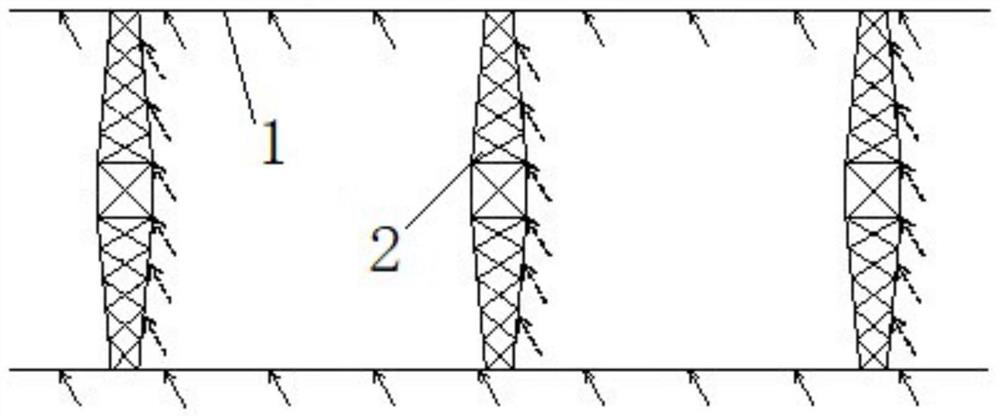
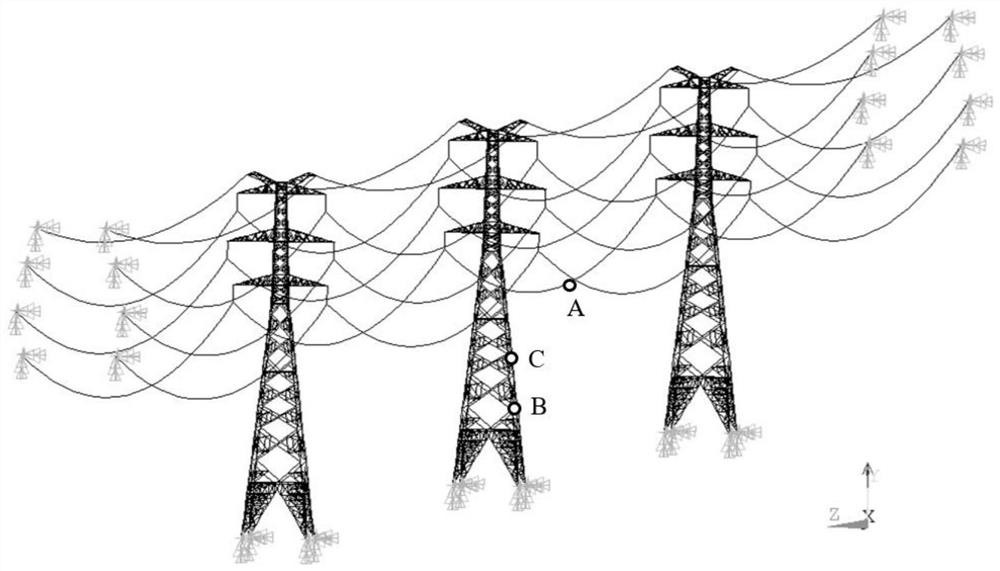
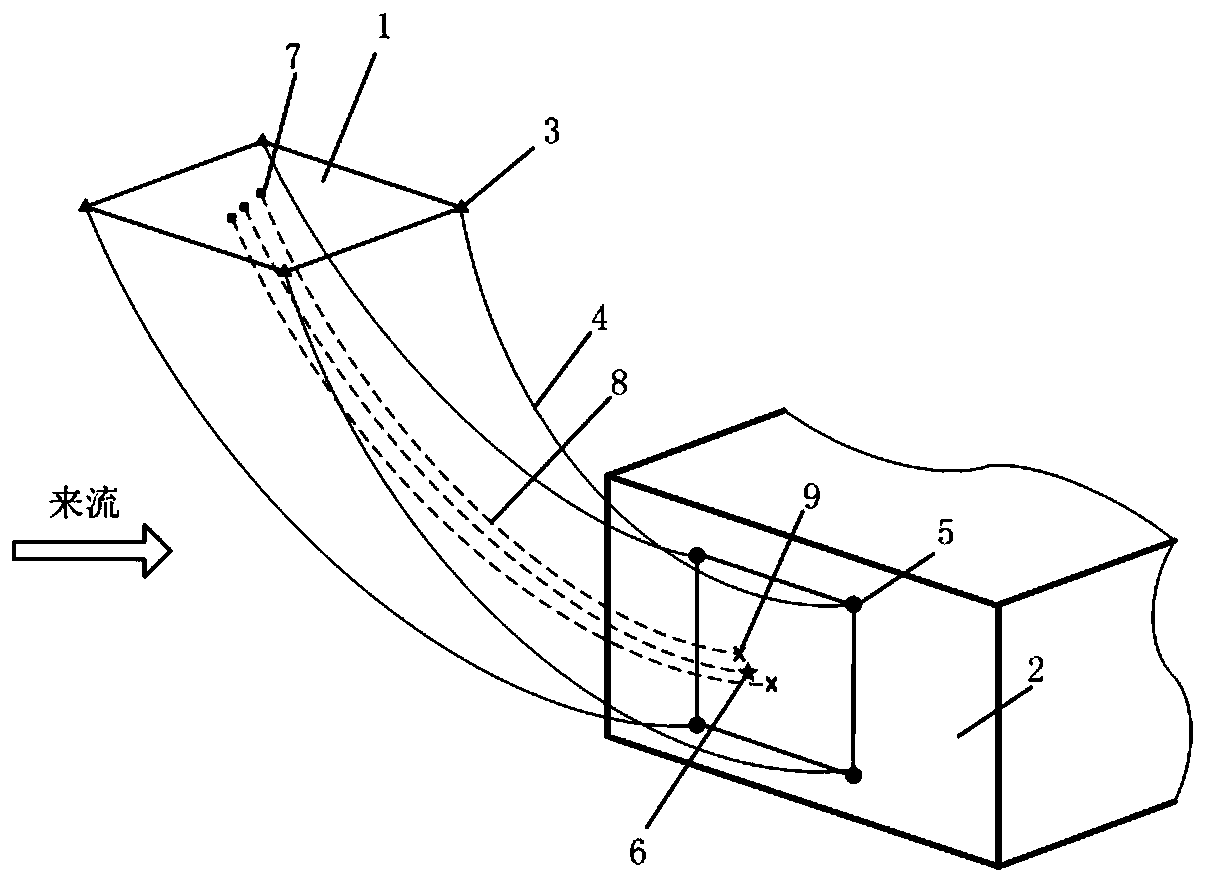
Overhead transmission line squall line wind load calculation method, system, medium and equipment
ActiveCN114492044AImprove structural strengthImprove ability to resist squall line windData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationTransmission towerWind engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication, and relates to an overhead transmission line squall line wind load calculation method, system, medium and equipment, and the overhead transmission line squall line wind load calculation method comprises the following steps: determining a load physical model suitable for squall line wind meteorological conditions according to a fortification squall line wind power level of a planned overhead transmission line and a corresponding wind speed, the standard wind load acts on the conductor, and the squall line wind load acts on the power transmission tower; and inputting the fortified squall line wind power grades and the corresponding wind speeds into the load physical model to obtain the overhead transmission line wind load. According to the invention, reasonable evaluation of the squall line wind load of the power transmission line is realized on the basis of the basic principle of structural wind engineering and measured data of squall line wind meteorology.
Owner:STATE GRID ECONOMIC TECH RES INST CO +4
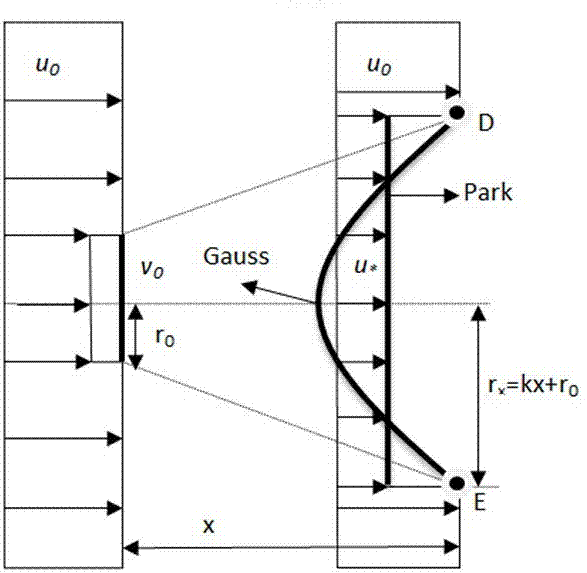
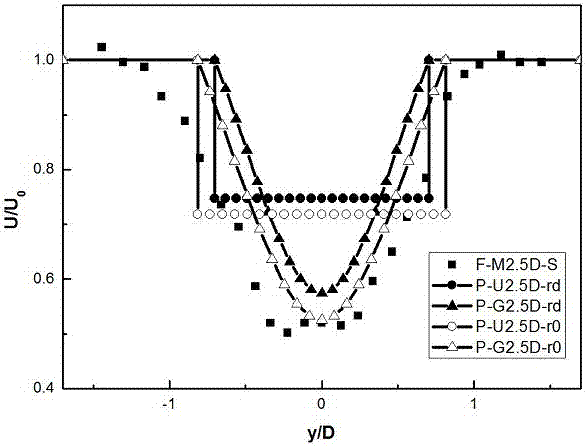
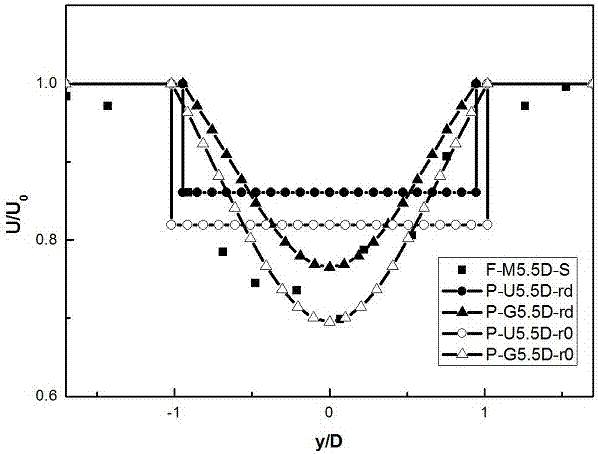
A Wake Calculation Method for Wind Engineering
ActiveCN104794287BImprove forecast accuracyHigh simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWind engineeringEngineering
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Calculating method for limited area of wind-driven rain amount
InactiveCN107066810AReduce in quantitySmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsWind drivenCenter of area
The invention discloses a calculating method for a limited area of wind-driven rain amount, which belongs to the technical field of wind engineering. The method of the invention comprises the following steps of solving a flow field around buildings; choosing a wall surface to be calculated of the building, performing limited area division on the wall surface to be calculated, and calculating a raindrop trace with each limited area corner point as a raindrop trace end-point; calculating a collection rate of each limited area according to the raindrop trace, and employing the collection rate as a collection rate at the center point of the limited area; and constructing a reconstructed function according to a coordinate of each center point of the limited area and the collection rate thereof, and then calculating the collection rate of each corner point of the limited area according to the reconstructed function. The calculating method for the limited area of the invention only needs to calculate the collection rates of a small amount of the corner points of the limited areas to accurately provide a collection rate result of a wall surface boundary and each inner point. The calculation result indicates that according to the calculating method for the limited area of wind-driven rain amount, more than 90% of raindrop trace calculating amount can be decreased under the same condition of collection rate accuracy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
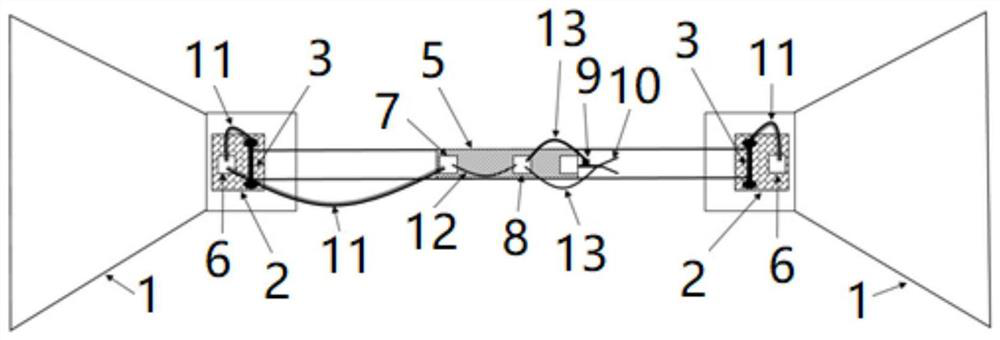
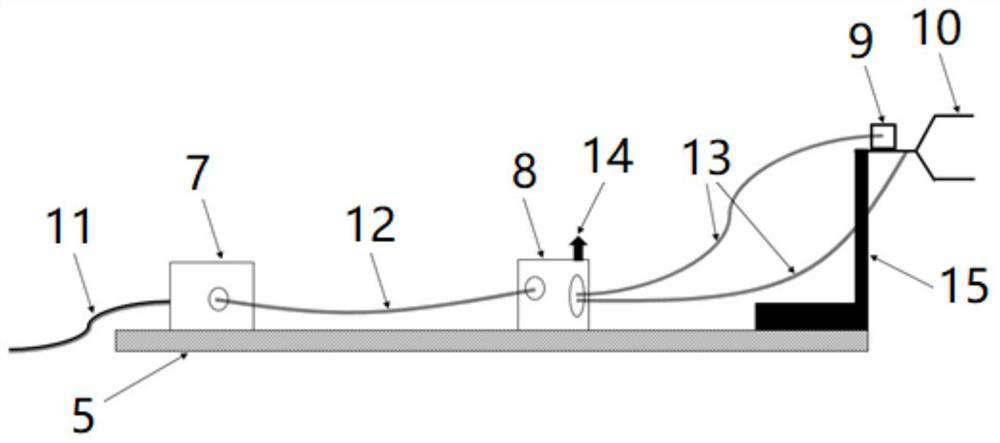
Bridge type wind measurement system
InactiveCN113155403ASolve the problem that the real high-frequency three-dimensional wind observation data of the preset bridge deck position cannot be obtainedAerodynamic testingMarine engineeringBridge type
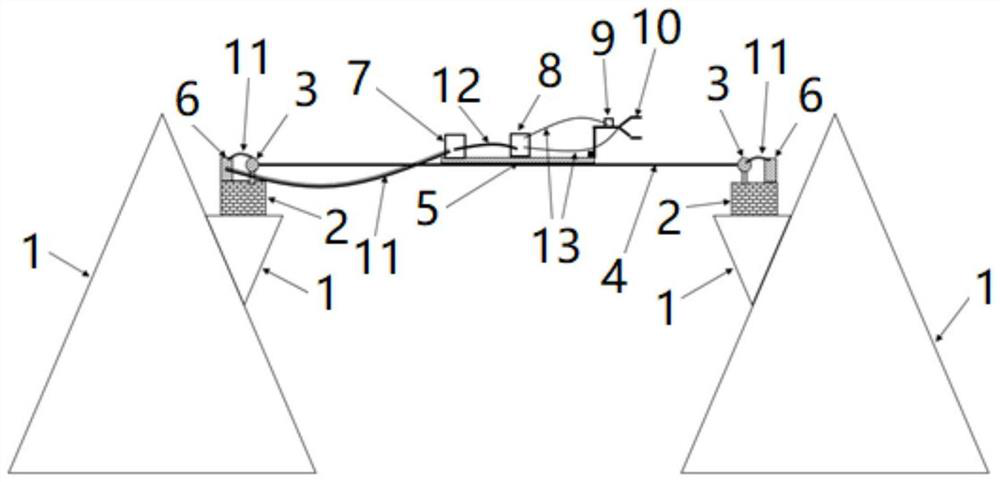
The invention discloses a bridge type wind measurement system which comprises a connecting cable and a power supply assembly. The two ends of the connecting cable are connected to the two ends of a preset bridge respectively, at least one observation platform is arranged on the connecting cable, and a wind observation part is arranged on the observation platform and used for measuring high-frequency three-dimensional wind data, collecting the high-frequency three-dimensional wind data and outputting the high-frequency three-dimensional wind data. The power supply assembly is electrically connected with the wind observation part. According to the embodiment, the observation part is directly installed at the real position of the preset bridge deck through the connecting cable and the observation platform, and then the three-dimensional turbulent flow fluctuating wind speed is directly observed, so that high-frequency three-dimensional wind at the real positions of the bridge decks on canyons, valleys and rivers can be measured before the bridge is built; accurate and reliable three-dimensional wind observation data are provided for bridge wind resistance design, and the data is used for calculating bridge wind engineering parameters.
Owner:INST OF ATMOSPHERIC PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY SCI
An Efficient Simulation Method of 3D Wind Field Based on Delay Effect
ActiveCN113468692BReduce dimensionalityImprove decomposition efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationComputational scienceWind engineering
The invention discloses a three-dimensional wind field high-efficiency simulation method based on delay effect, and belongs to the technical field of structural wind engineering. The main steps of generating the time history of wind speed in the present invention are as follows: determine the coordinates of the simulation point and the initial coordinate system according to the structural drawing, transform the coordinate system so that the Y axis is parallel to the wind speed direction, and obtain the three-dimensional model of N structural simulation points, and All the simulation points of the 3D model are projected onto the target two-dimensional plane, and the simulation points are transformed into projection points in the two-dimensional plane. The wind speed delay time is calculated, that is, the time required for each point to project on the target plane, and the two-dimensional coherence function is used to consider To simulate the horizontal and vertical spatial correlation of different points, use the "harmonic superposition method" to generate fluctuating wind speed, and use the delay time to obtain the time history of wind speed at all points. The statistical characteristics of the data obtained by the time delay method of the present invention are similar to the results of the traditional three-dimensional method, but the simulation efficiency is greatly improved, and the method is simple to operate and has a reasonable theoretical background.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Wind creation device and method
Owner:TAIYI ENVIRONMENT TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Tornado test device for construction wind engineering
The invention provides a tornado testing device for building wind engineering. The tornado testing device can accurately simulate a wind field of a tornado and the wind load effect of the tornado on a building. The tornado testing device comprises stand columns and a motor, wherein longitudinal beams are arranged on the tops of the stand columns, the longitudinal beams are connected with transverse beams, rolling wheels are arranged on the longitudinal beams and move along the longitudinal beams, the rolling wheels are connected with supporting beams, the supporting beams are connected with a vortex generator, the motor drives driving wheels to rotate, driven wheels matched with the driving wheels are arranged on the supporting beams, a platform is arranged below the vortex generator, and the platform is arranged on a lifting device. According to the tornado testing device for the building wind engineering, the shape of vortex wind generated by the vortex generator is similar to the shape of the tornado, the wind speed and the wind direction of the vortex wind can be adjusted, the vertical distance between the vortex wind and a house model can be adjusted, the horizontal movement speed of the vortex wind can also be adjusted, and therefore the wind field of the tornados in different states and the effect of the wind load of the tornados on the building can be fully simulated.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Wind generating device and method
Owner:TAIYI ENVIRONMENT TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Calculation method of target trajectory tracking for wind-driven rainfall
ActiveCN107016164BSmall amount of calculationGet collection rate distributionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWind drivenWind engineering
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com