Patents
Literature
124results about "Line combination usage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
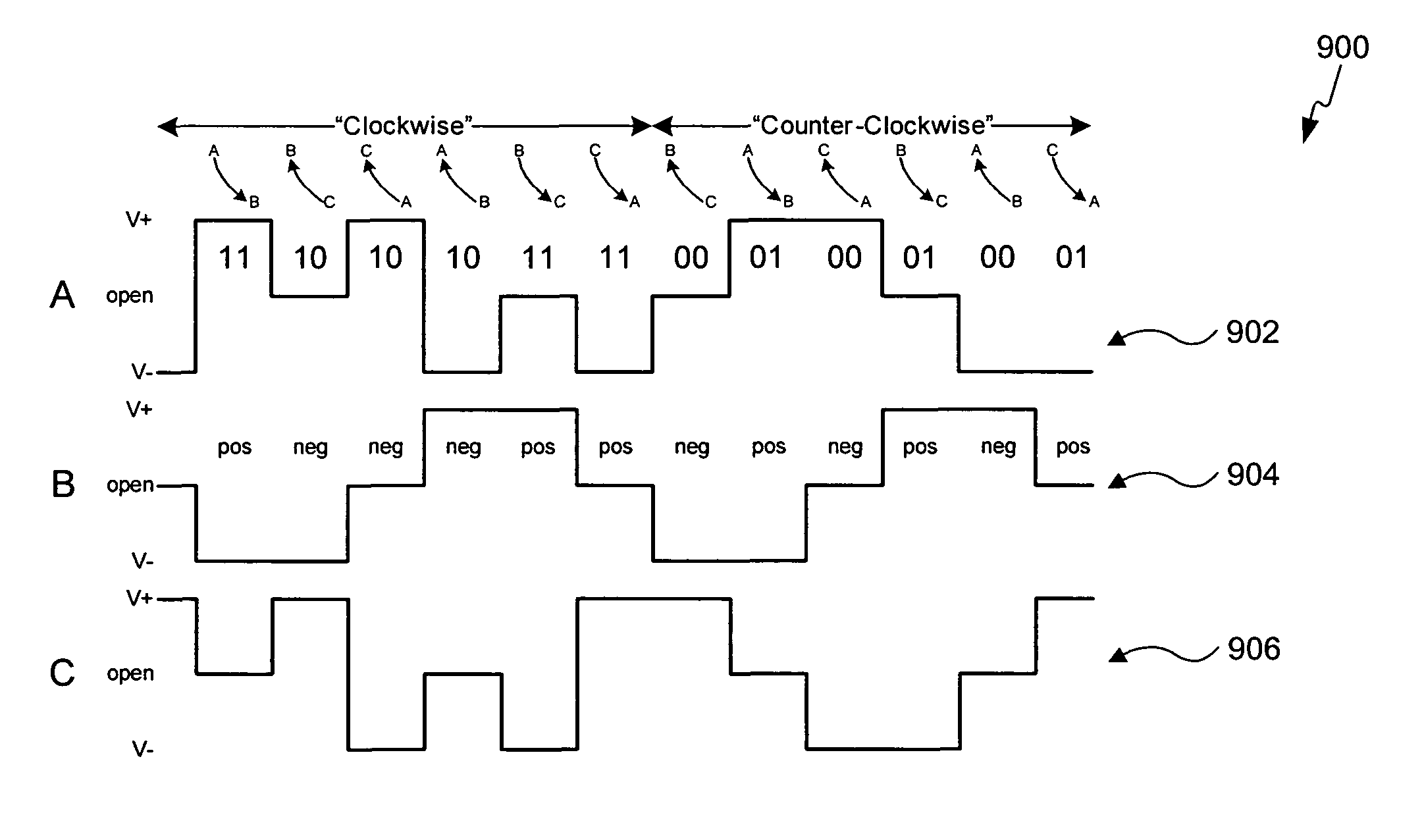
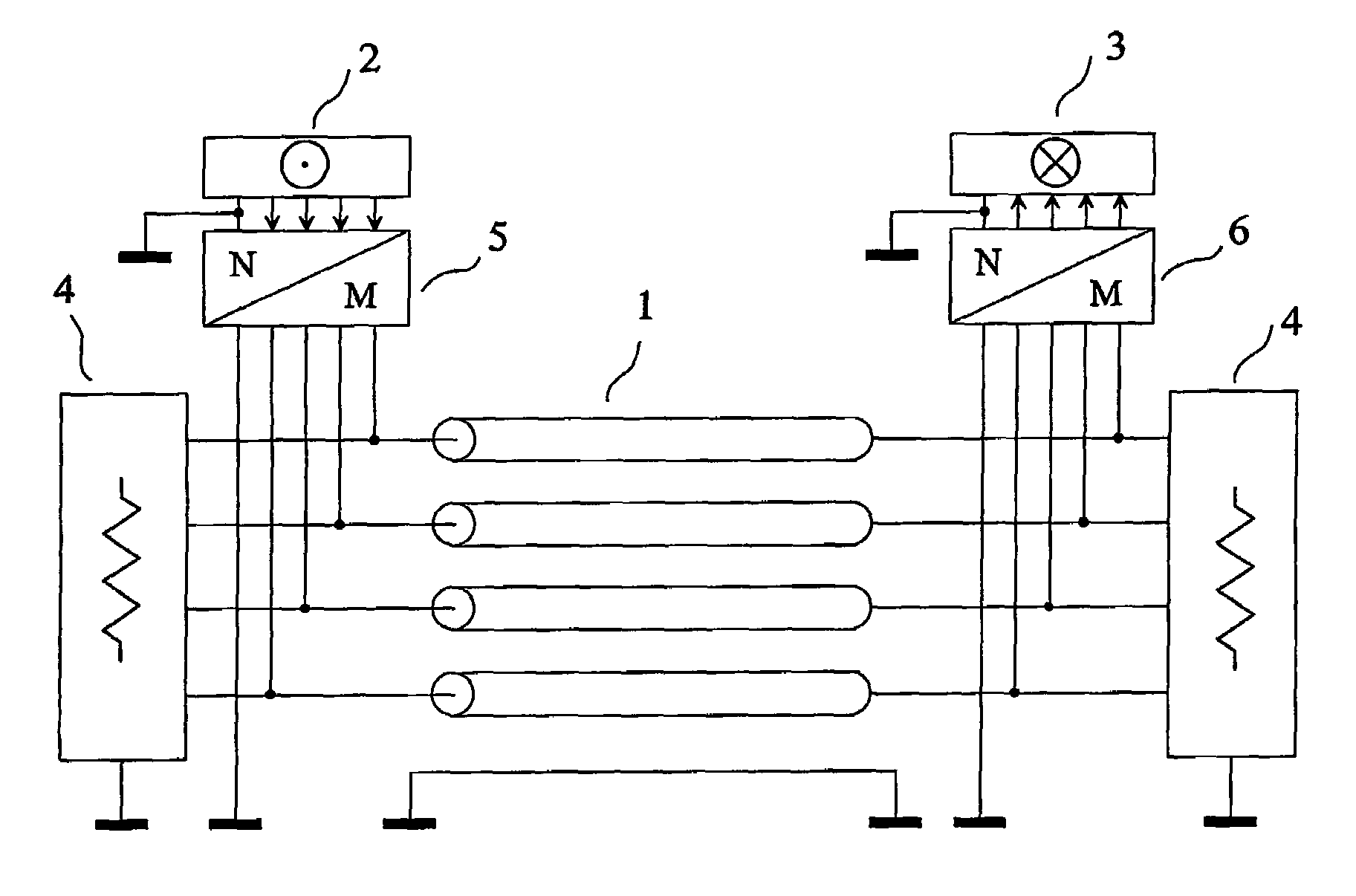
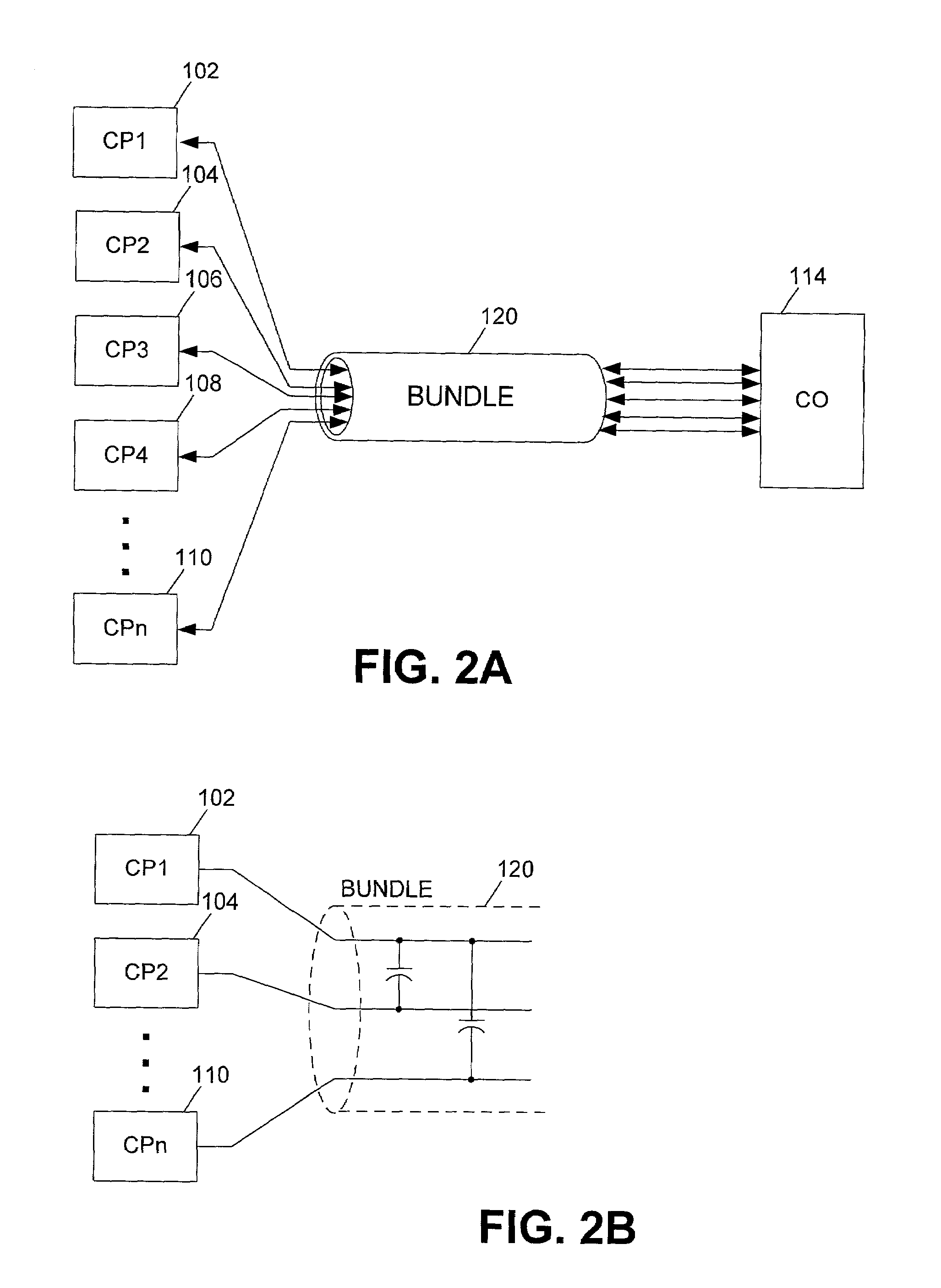
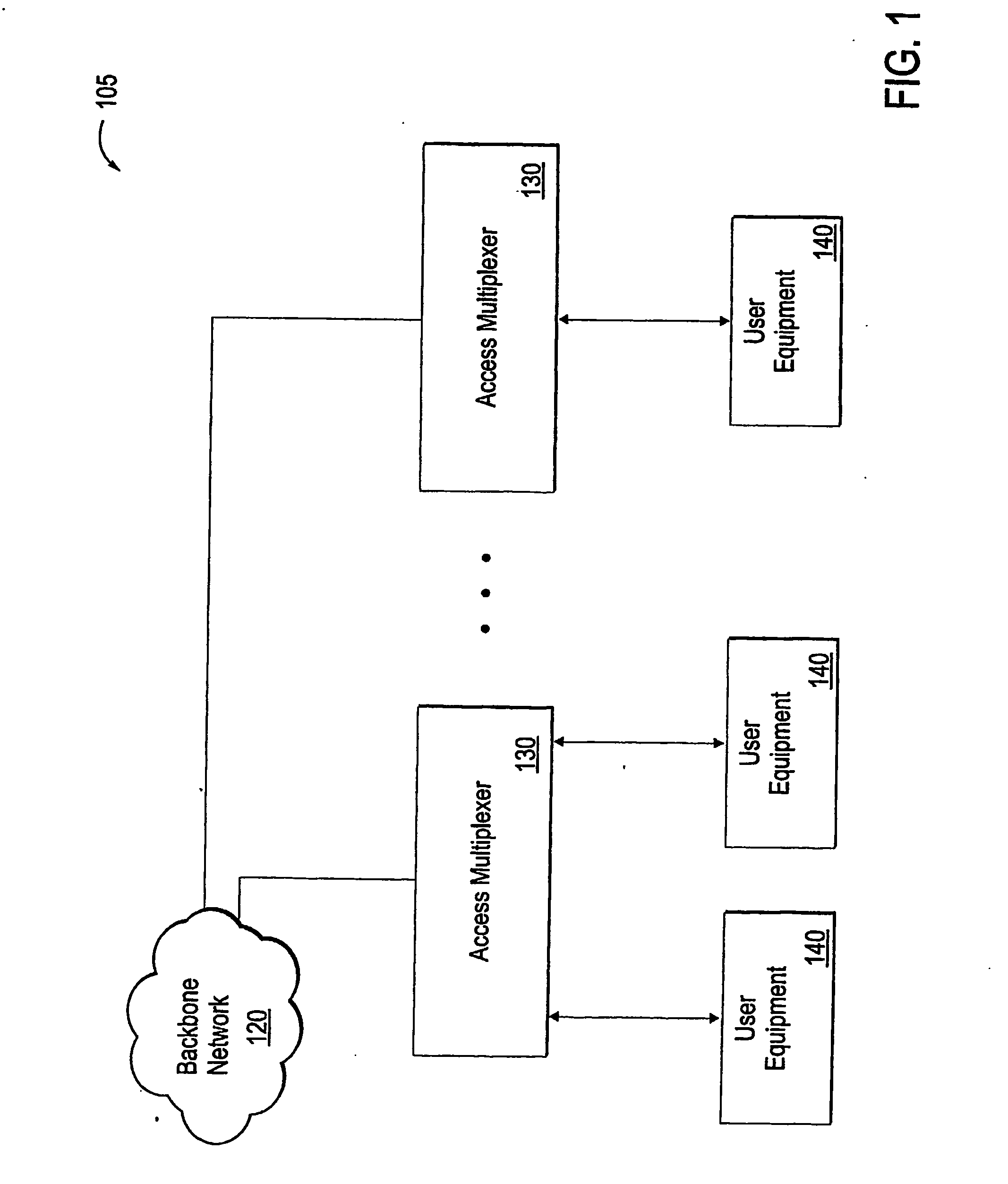
Three phase and polarity encoded serial interface
ActiveUS8064535B2Shorten the timeImprove efficiencyIndividual digits conversionPhase-modulated carrier systemsSerial digital interfaceElectrical conductor
A high speed serial interface is provided. In one aspect, the high speed serial interface uses three phase modulation for jointly encoding data and clock information. Accordingly, the need for de-skewing circuitry at the receiving end of the interface is eliminated, resulting in reduced link start-up time and improved link efficiency and power consumption. In one embodiment, the high speed serial interface uses fewer signal conductors than conventional systems having separate conductors for data and clock information. In another embodiment, the serial interface allows for data to be transmitted at any speed without the receiving end having prior knowledge of the transmission data rate. In another aspect, the high speed serial interface uses polarity encoded three phase modulation for jointly encoding data and clock information. This further increases the link capacity of the serial interface by allowing for more than one bit to be transmitted in any single baud interval.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adaptive pattern recognition based control system and method
A network media appliance, comprising at least one packet data network interface, adapted for communicating data packets with a data network according to an Internet Protocol; a media data interface, and a processor, having an associated memory for storing executable code, said code defining at least a remote virtual interface function, and a data transfer function for controlling transfer of data through said media data interface.
Owner:BLANDING HOVENWEEP
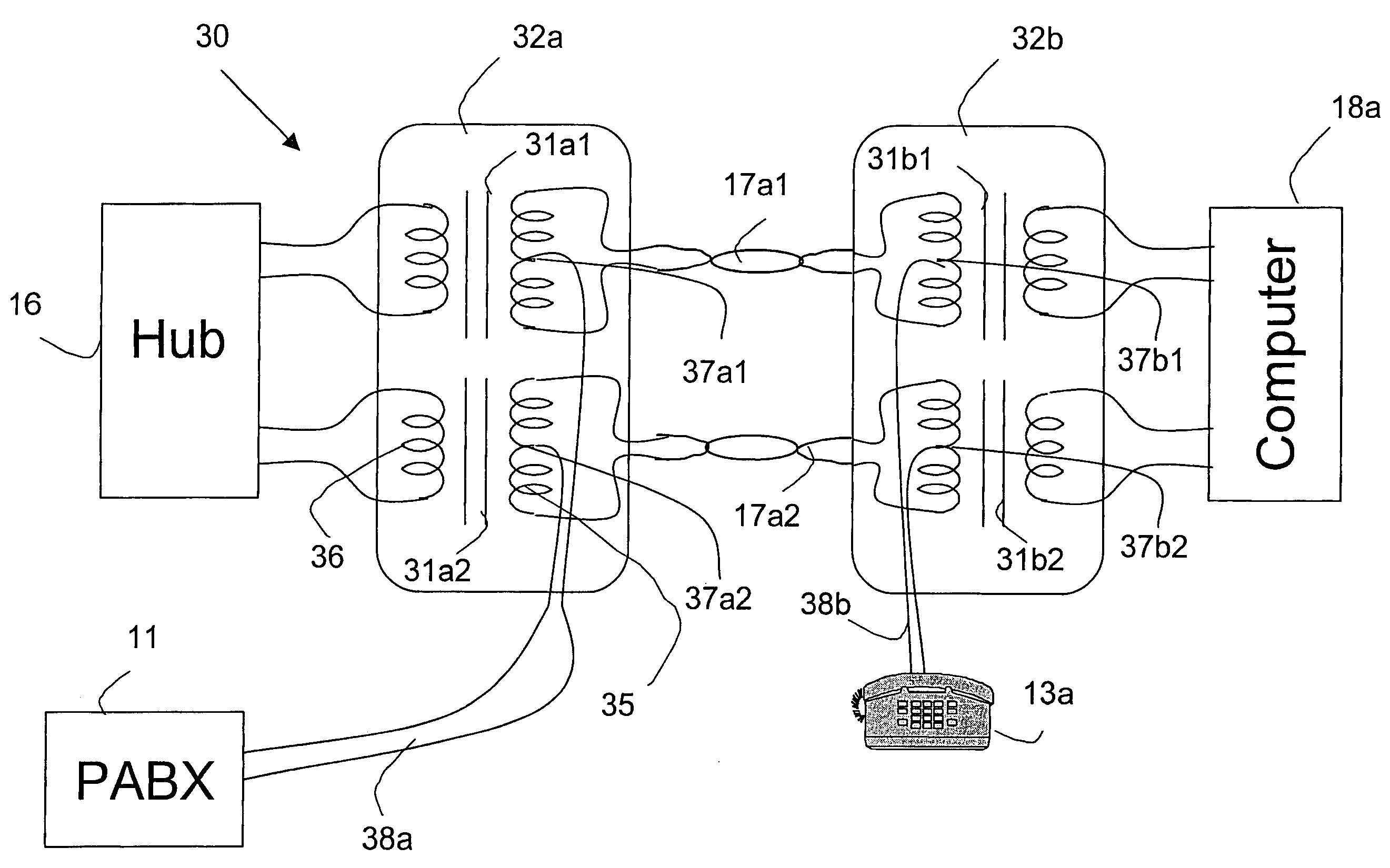
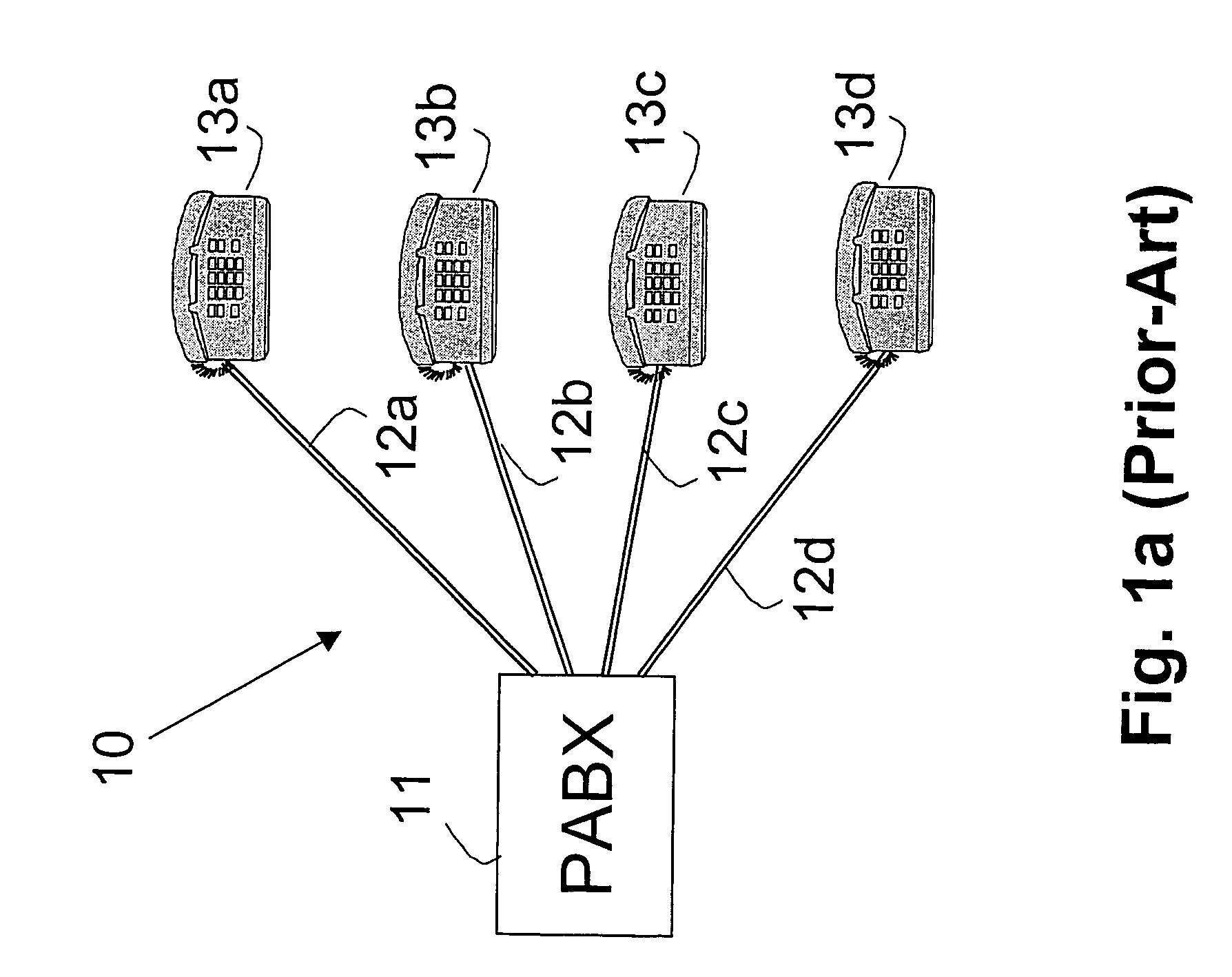
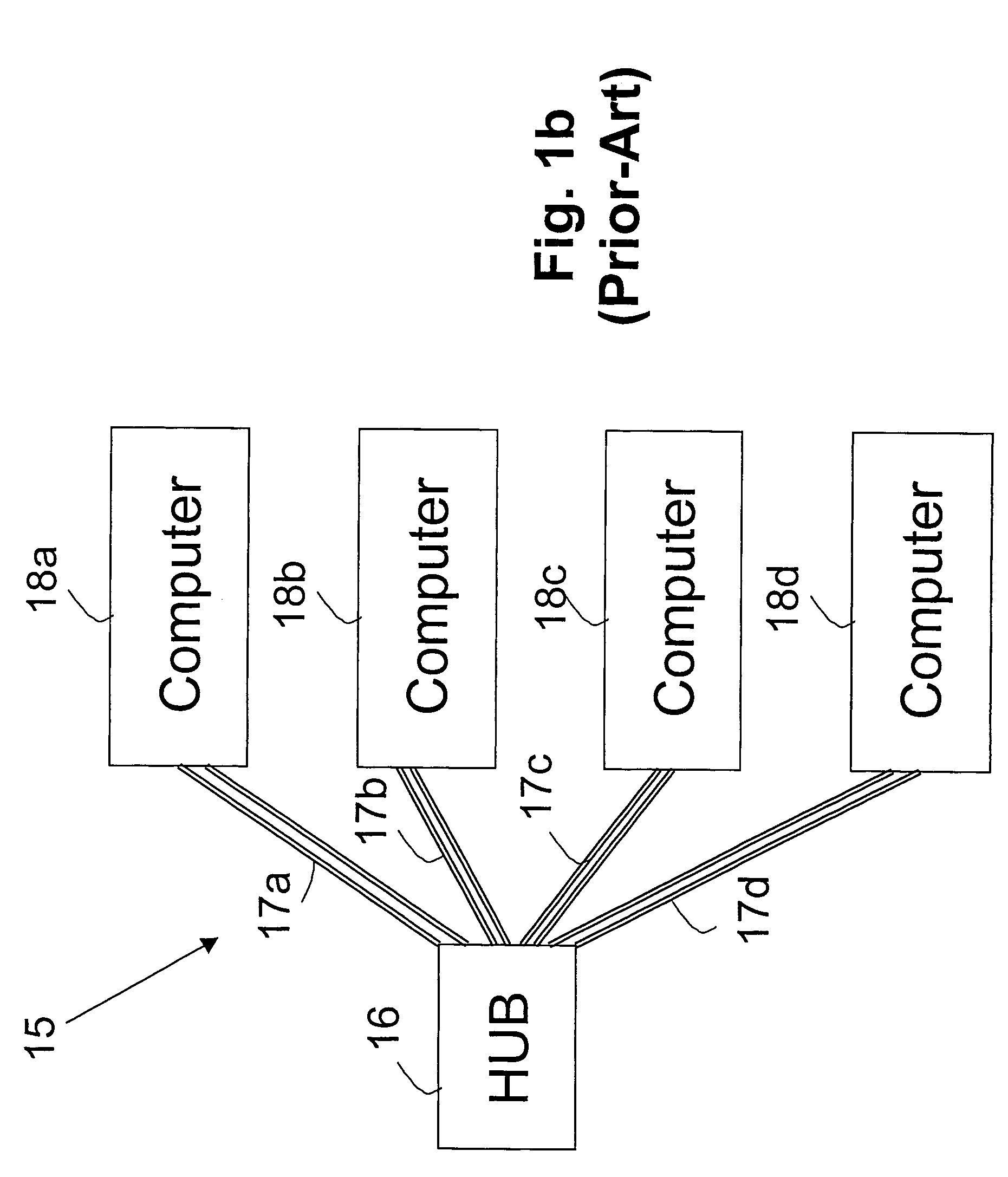
Telephone communication system and method over local area network wiring
A method and apparatus for enabling a local area network wiring structure to simultaneously carry digital data and analog telephone signals on the same transmission medium. It is particularly applicable to a network in star topology, in which remote data units (e.g. personal computers) are each connected to a hub through a cable comprising at least two pairs of conductors, providing a data communication path in each direction. Modules at each end of the cable provide a phantom path for telephony (voice band) signals between a telephone near the data set and a PBX, through both conductor pairs in a phantom circuit arrangement. All such communication paths function simultaneously and without mutual interference. The modules comprise simple and inexpensive passive circuit components.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
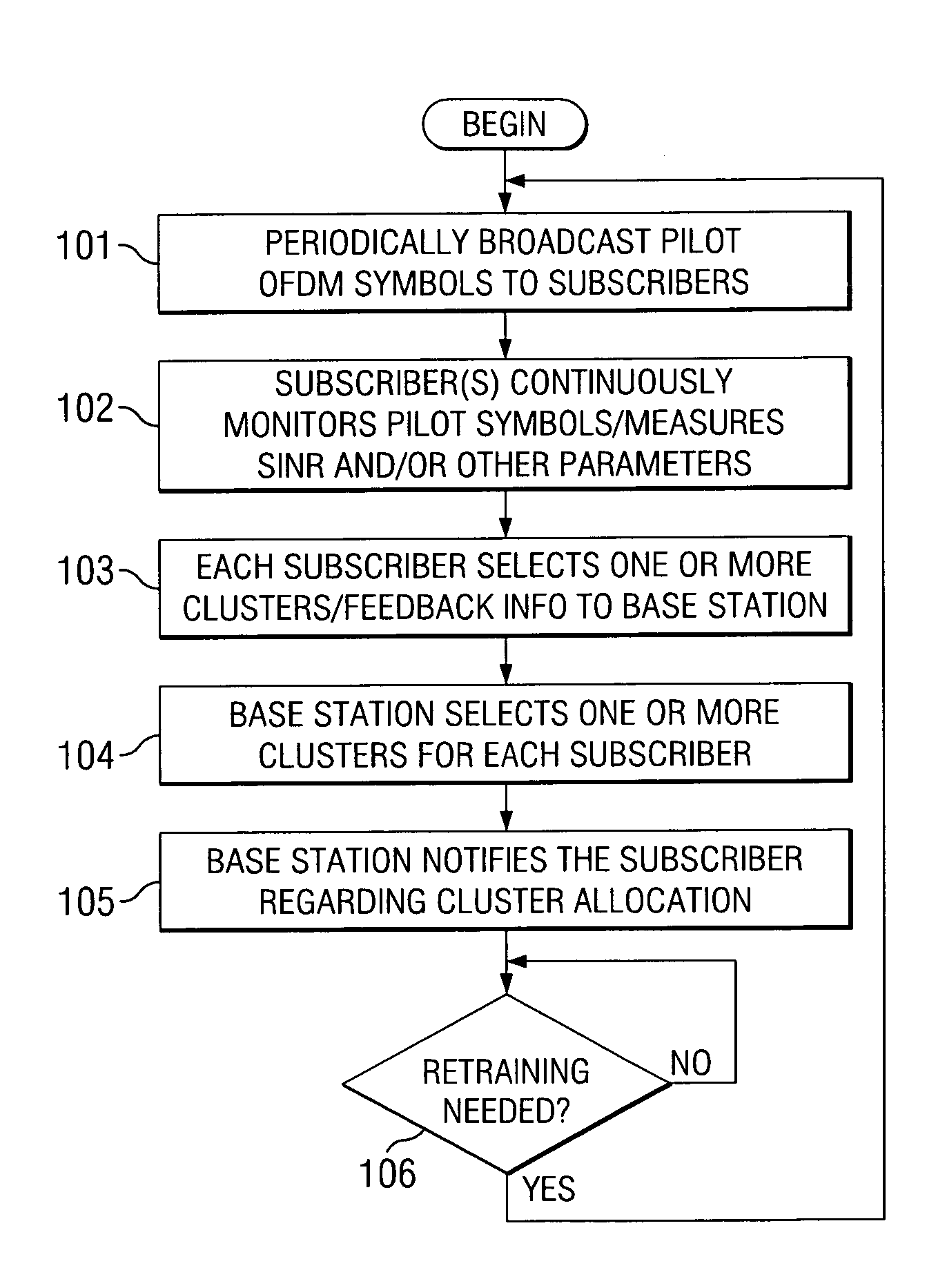
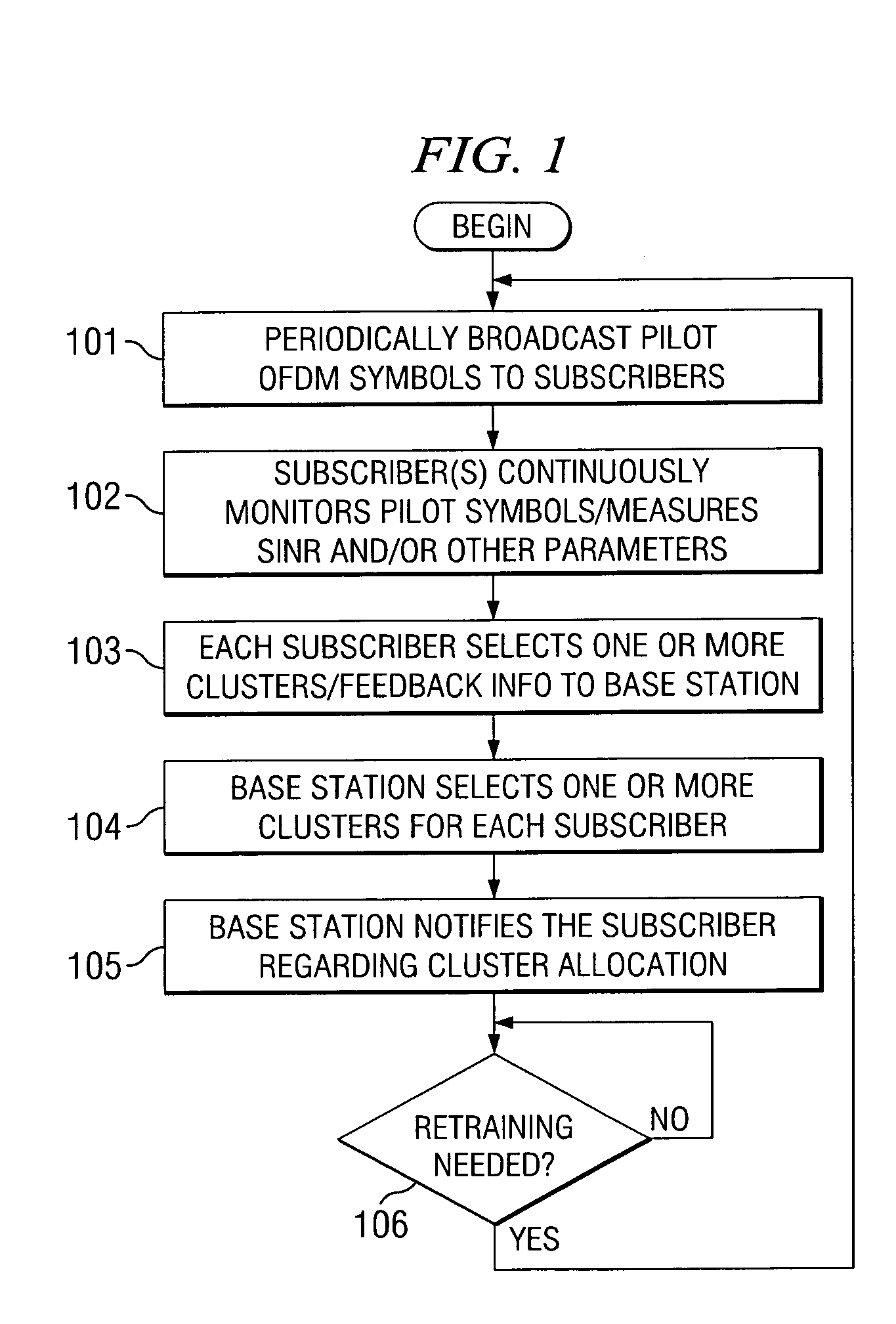
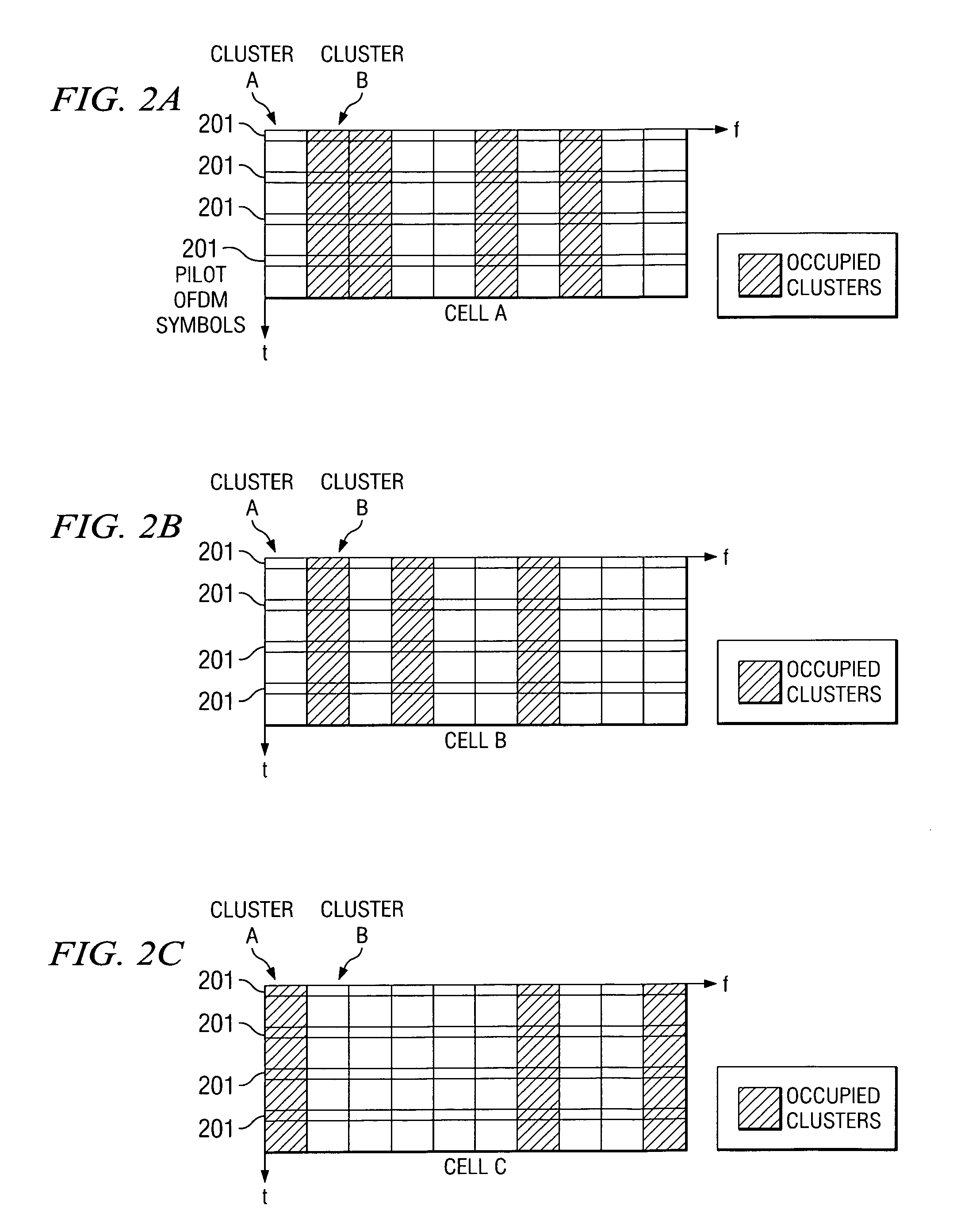
Multi-carrier communication with time division multiplexing and carrier-selective loading
ActiveUS7164669B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexStatistical time division multiplexingMultiuser system
A method for subcarrier allocation and loading for a multi-carrier, multi-subscriber system is described. At least one cluster in a first and second set of clusters of subcarriers is associated for use in communication with a first and second subscriber, respectively. Then, for each cluster associated for use in communication with the first subscriber and the second subscriber, usage of that cluster is multiplexed between the first subscriber during a first time division and the second subscriber during a second time division.
Owner:KAON SYST +1
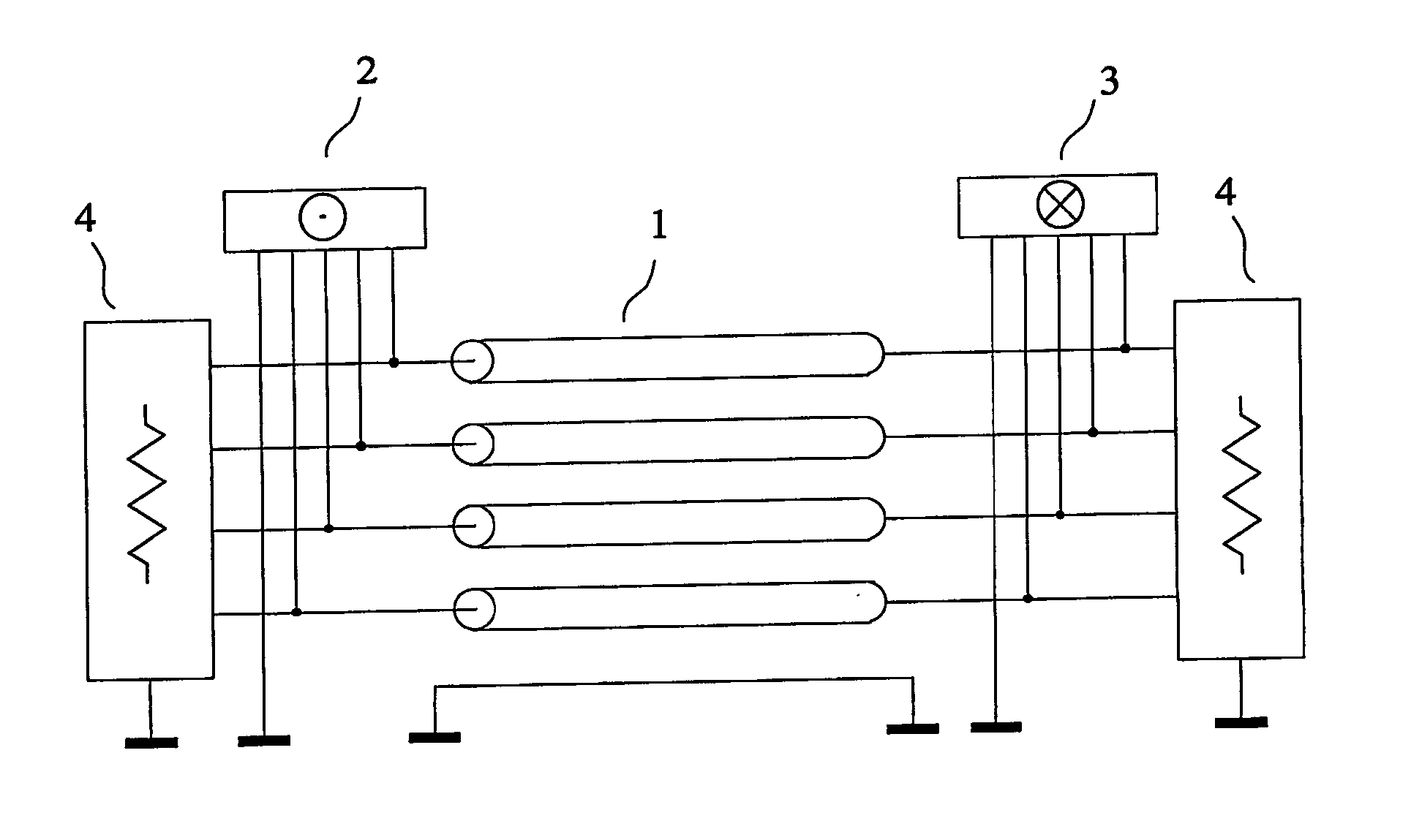
Method and device for transmission with reduced crosstalk
InactiveUS7167019B2Accurately determinedOptimize locationReliability increasing modificationsElectrically conductive connectionsElectrical conductorInterconnection
The invention relates to a method and a device for transmission with reduced crosstalk in interconnections used for sending a plurality of signals, such as the interconnections made with flat multiconductor cables, or with the tracks of a printed circuit board, or inside an integrated circuit. An interconnection with four parallel transmission conductors plus a reference conductor has each of its ends connected to a termination circuit. The transmitting circuit receives at its input the signals of the four channels of the source and its output terminals are connected to the conductors of the interconnection. The receiving circuit's input terminals are connected to the conductors of the interconnection, and its four output channels are connected to the destination. The signals of the four channels of the source are sent to the four channels of the destination, without noticeable crosstalk.
Owner:RAMBUS INC +1
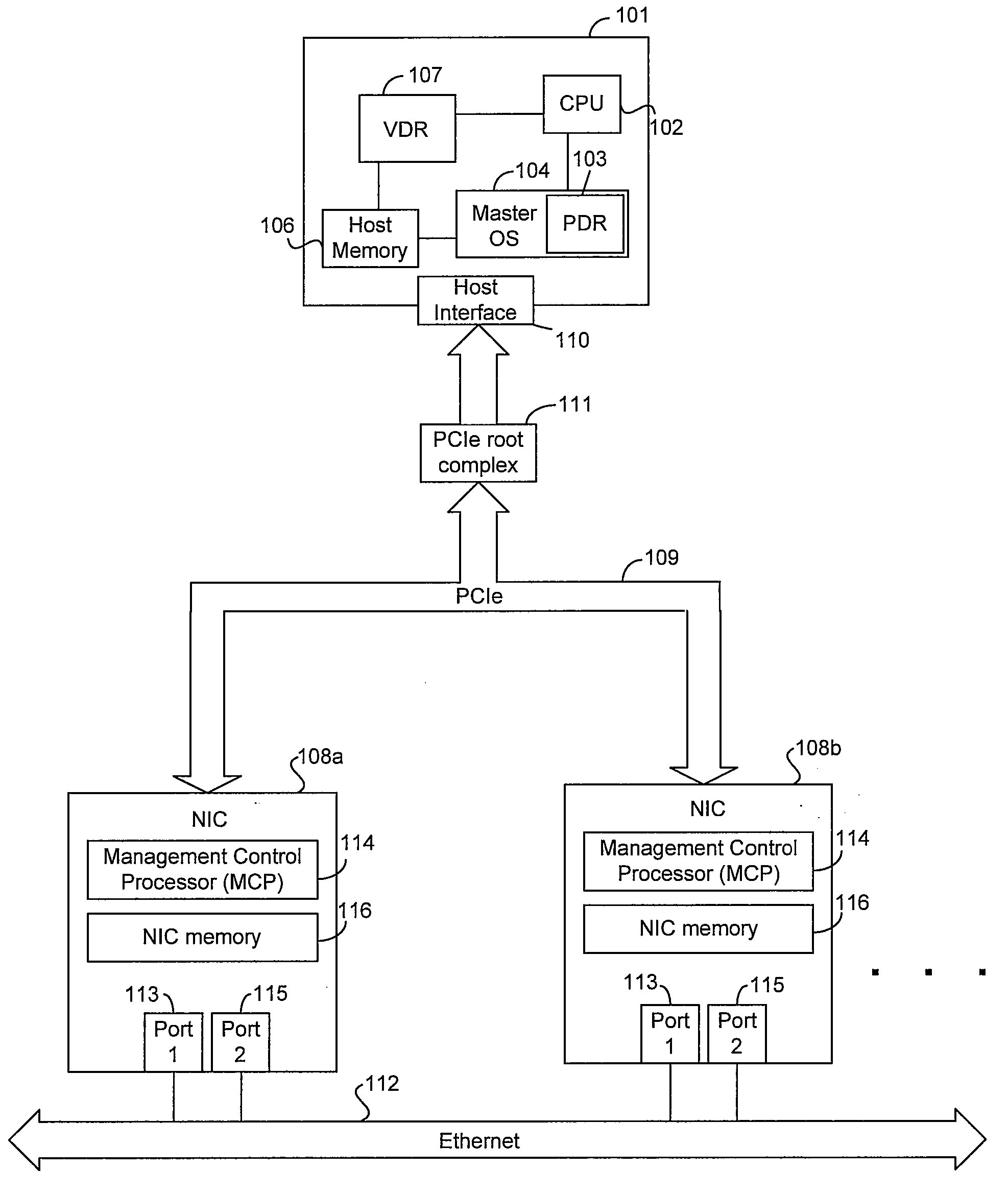
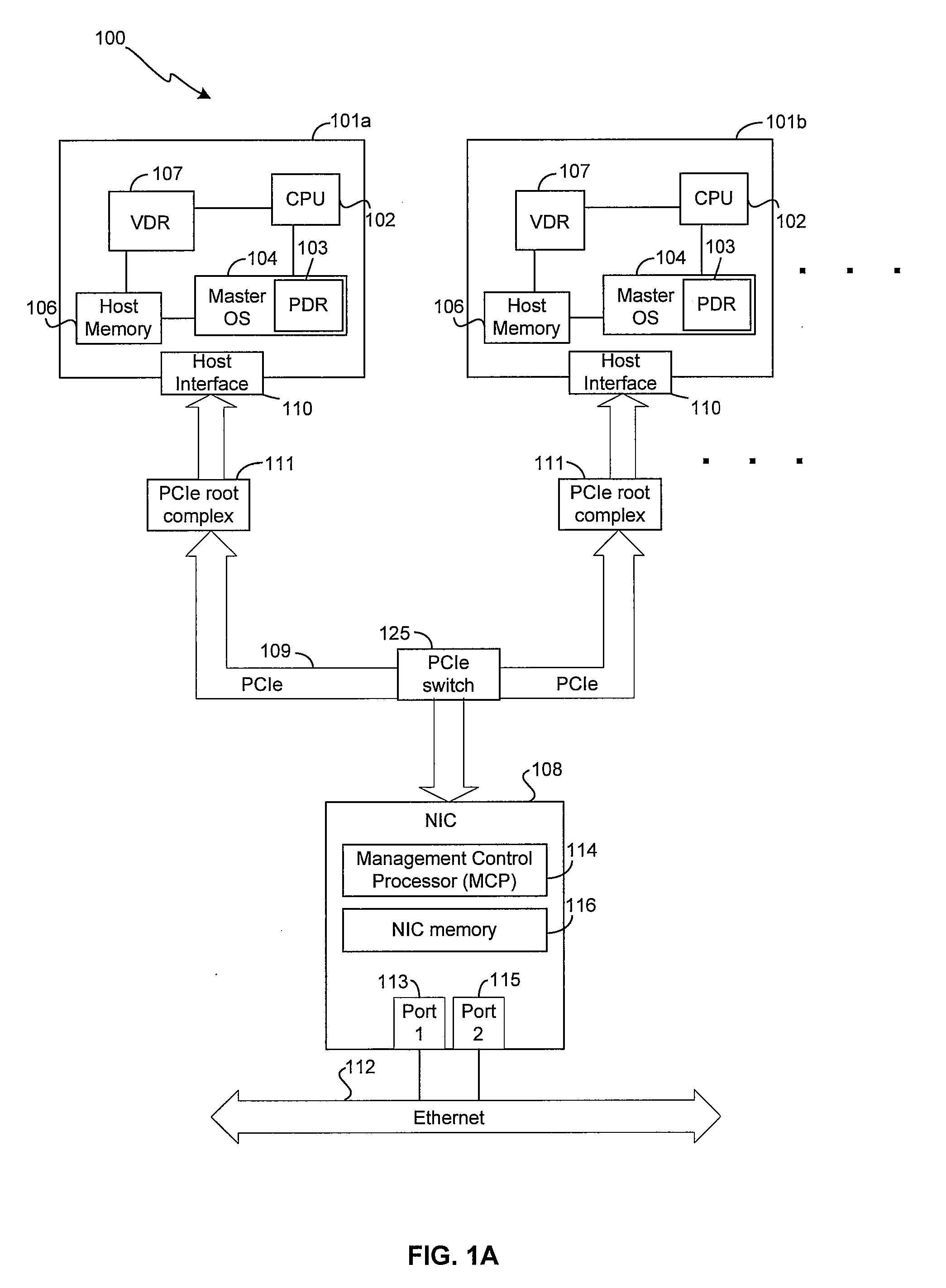
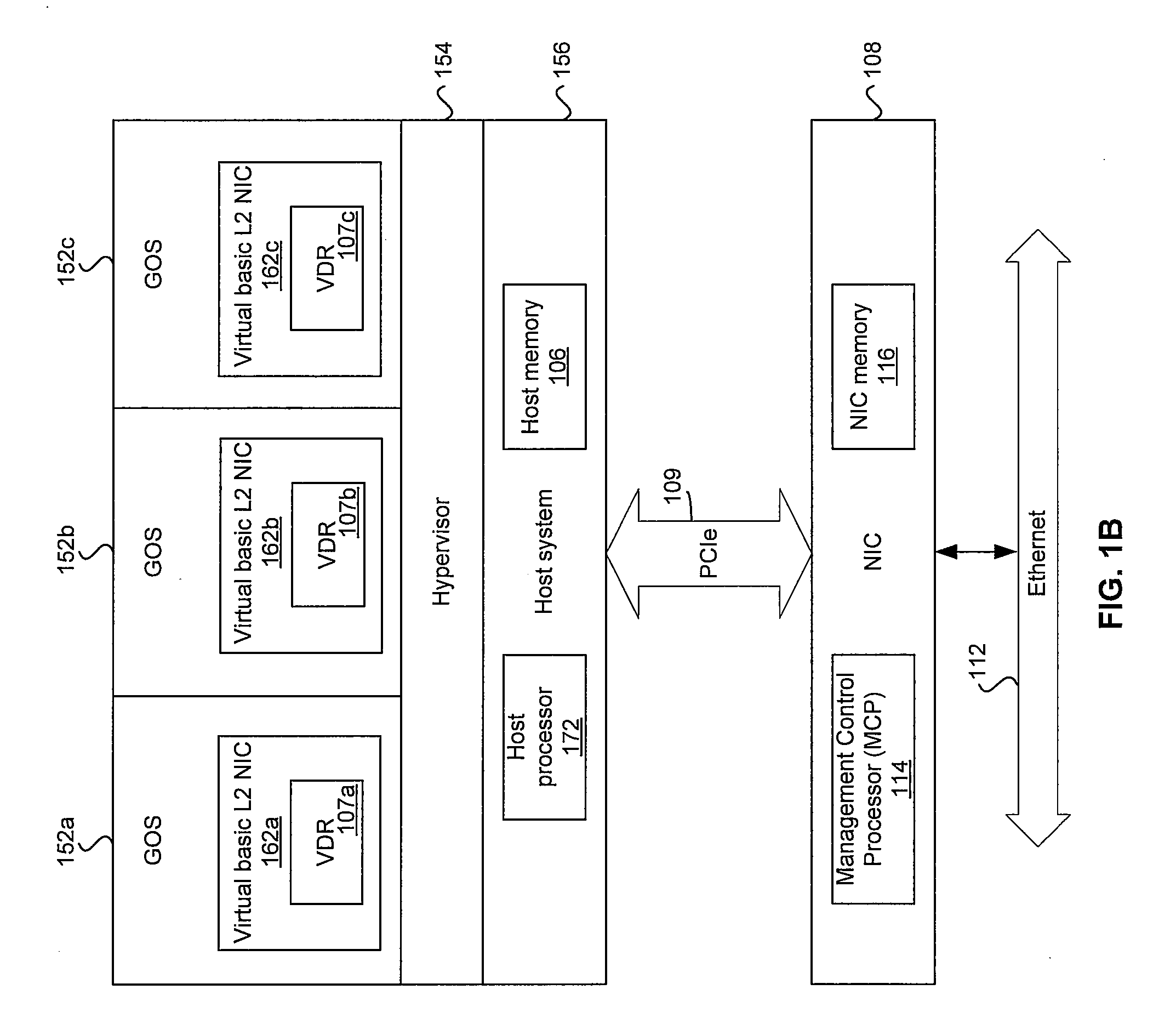
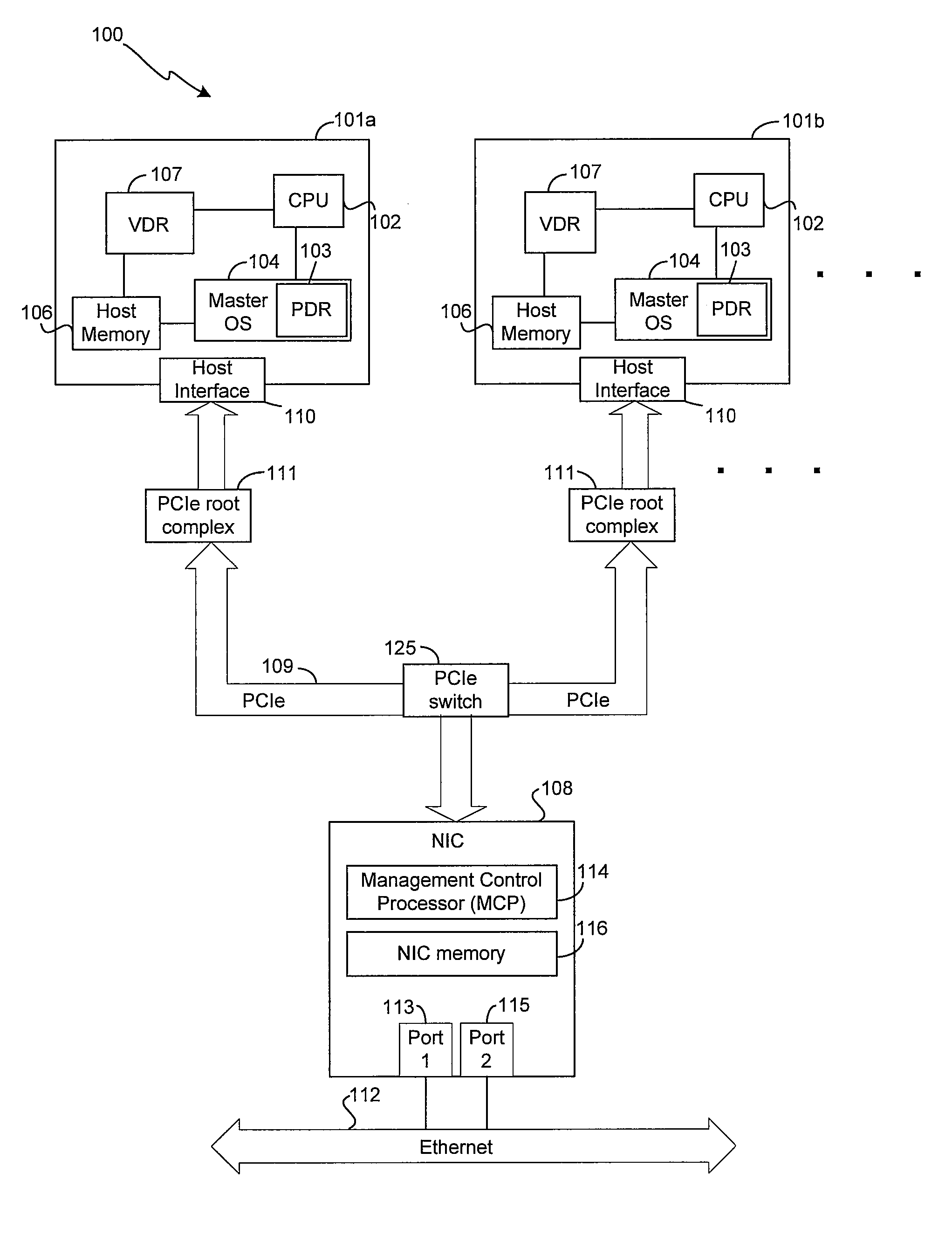
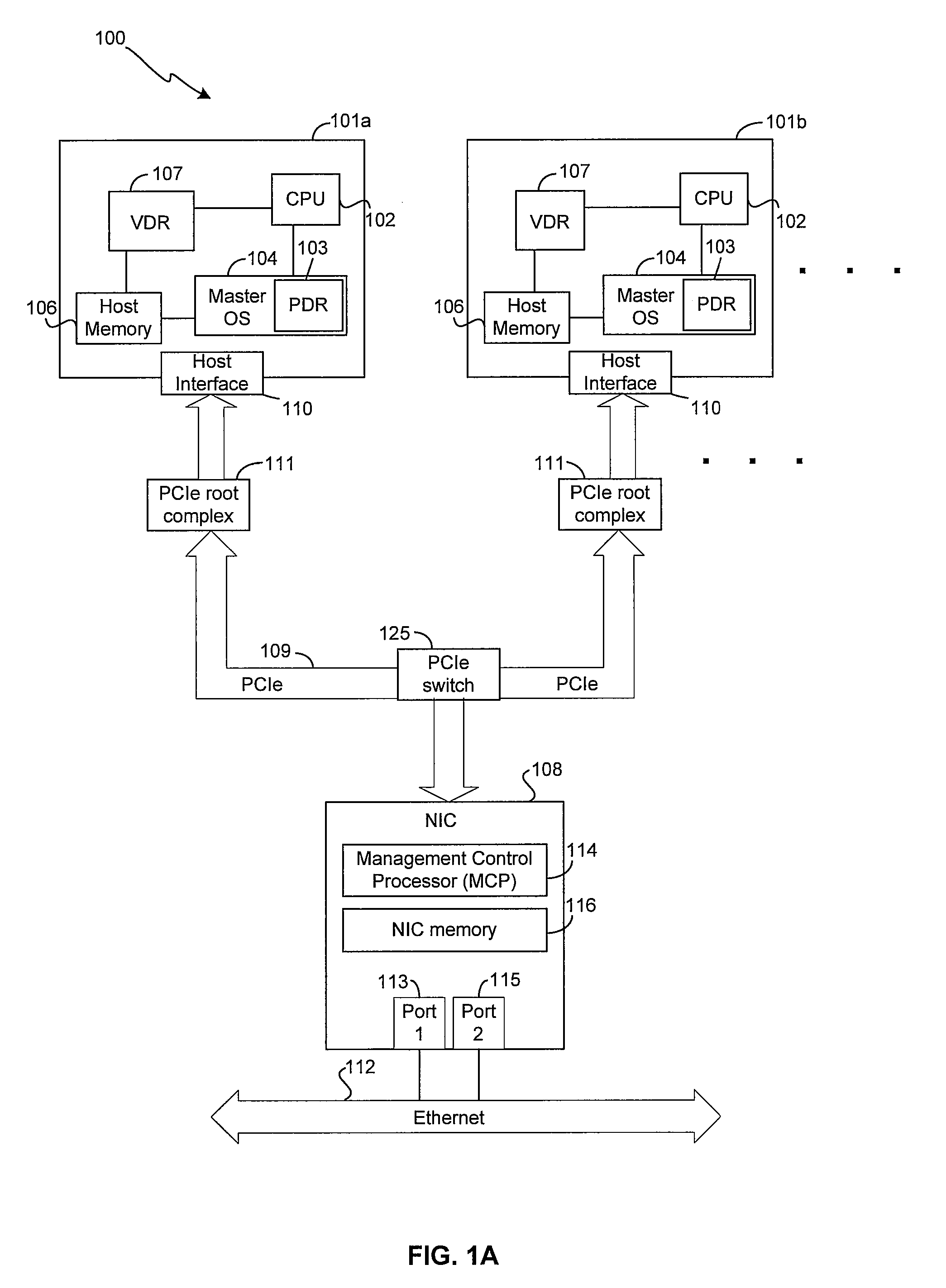
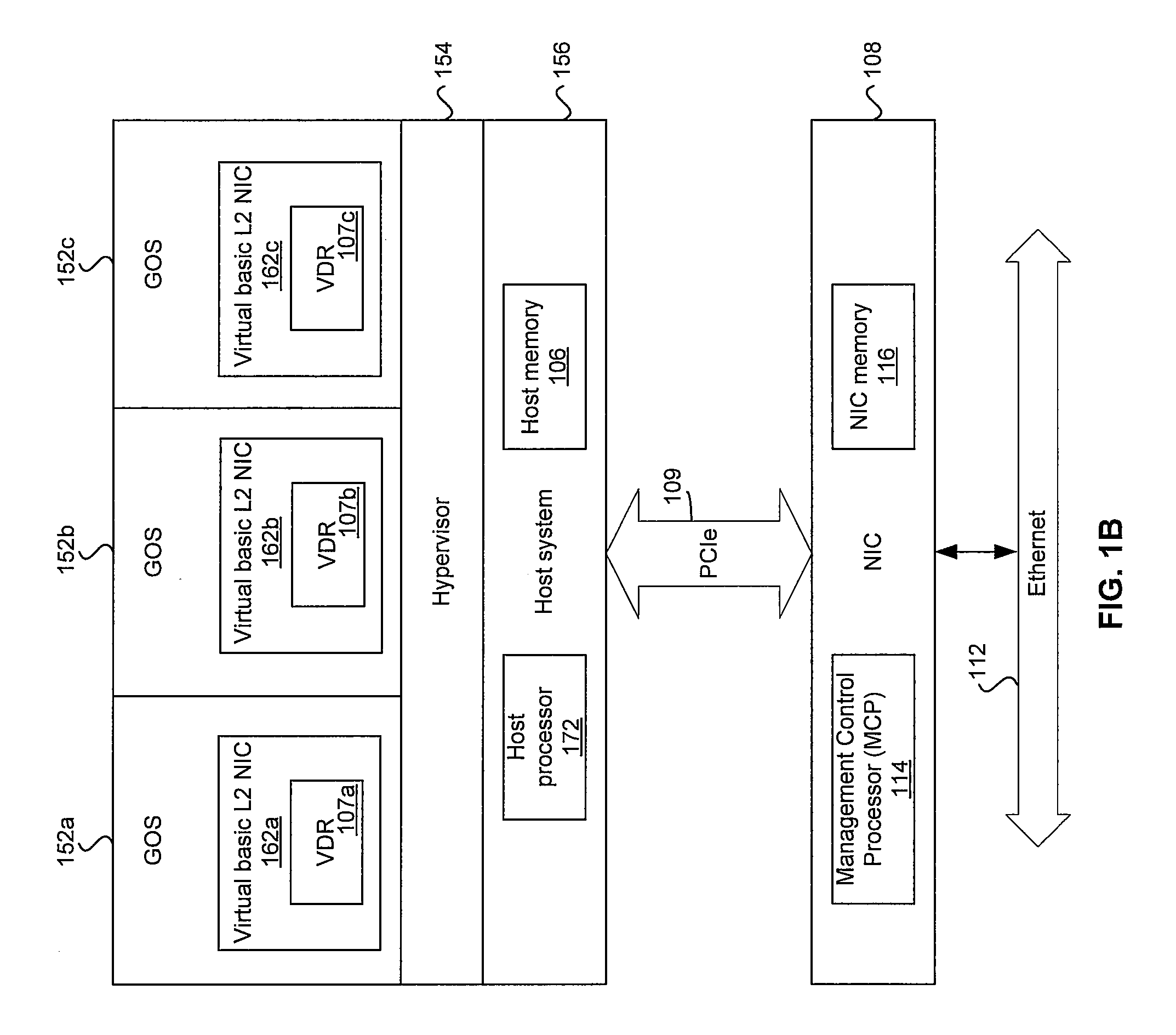
Method and system for configuring a plurality of network interfaces that share a physical interface
Certain aspects of a method and system for configuring a plurality of network interfaces that share a physical interface (PHY) may include a system comprising one or more physical network interface controllers (NICs) and two or more virtual NICs. One or more drivers associated with each of the virtual NICs that share one or more Ethernet ports associated with the physical NICs may be synchronized based on controlling one or more parameters associated with one or more Ethernet ports. One or more wake on LAN (WoL) patterns associated with each of the drivers may be detected at one or more Ethernet ports. A wake up signal may be communicated to one or more drivers associated with the detected WoL patterns. One of the drivers may be appointed to be a port master driver. If a failure of the appointed port master driver is detected, another driver may be appointed to be the port master driver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
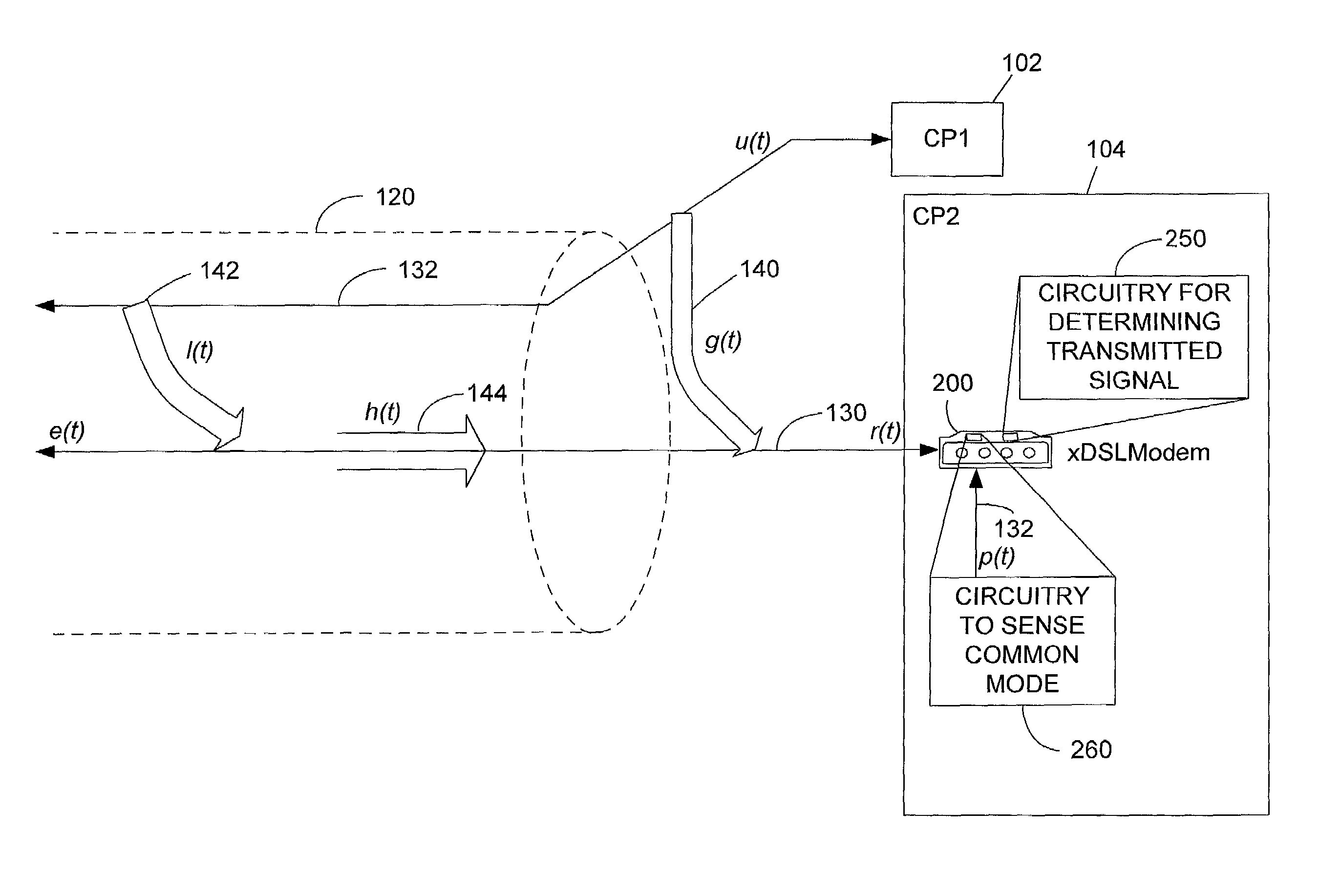
System and method for canceling crosstalk
ActiveUS6999504B1Improved crosstalk cancellation circuitryReduce crosstalkFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCrosstalk cancellationModem device
A method and apparatus are disclosed for reducing crosstalk in a telecommunication system. Broadly, the present invention utilizes a common mode signal to obtain additional information that can be used to better approximate the transmitted signal (by approximating and canceling crosstalk or otherwise). In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, a modem is provided having improved crosstalk cancellation circuitry for canceling crosstalk received on a local loop (or otherwise estimating the remotely transmitted signal) carrying modem communications. The modem includes a first input for receiving a signal carried on the local loop and a second input for receiving a signal obtained from the common mode. The modem further includes processing circuitry configured to either reduce crosstalk present in the signal carried on the local loop, or to otherwise closely approximate the remotely transmitted signal. Using both the first and second signals allows the processing circuitry of the modem to obtain more accurate results.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
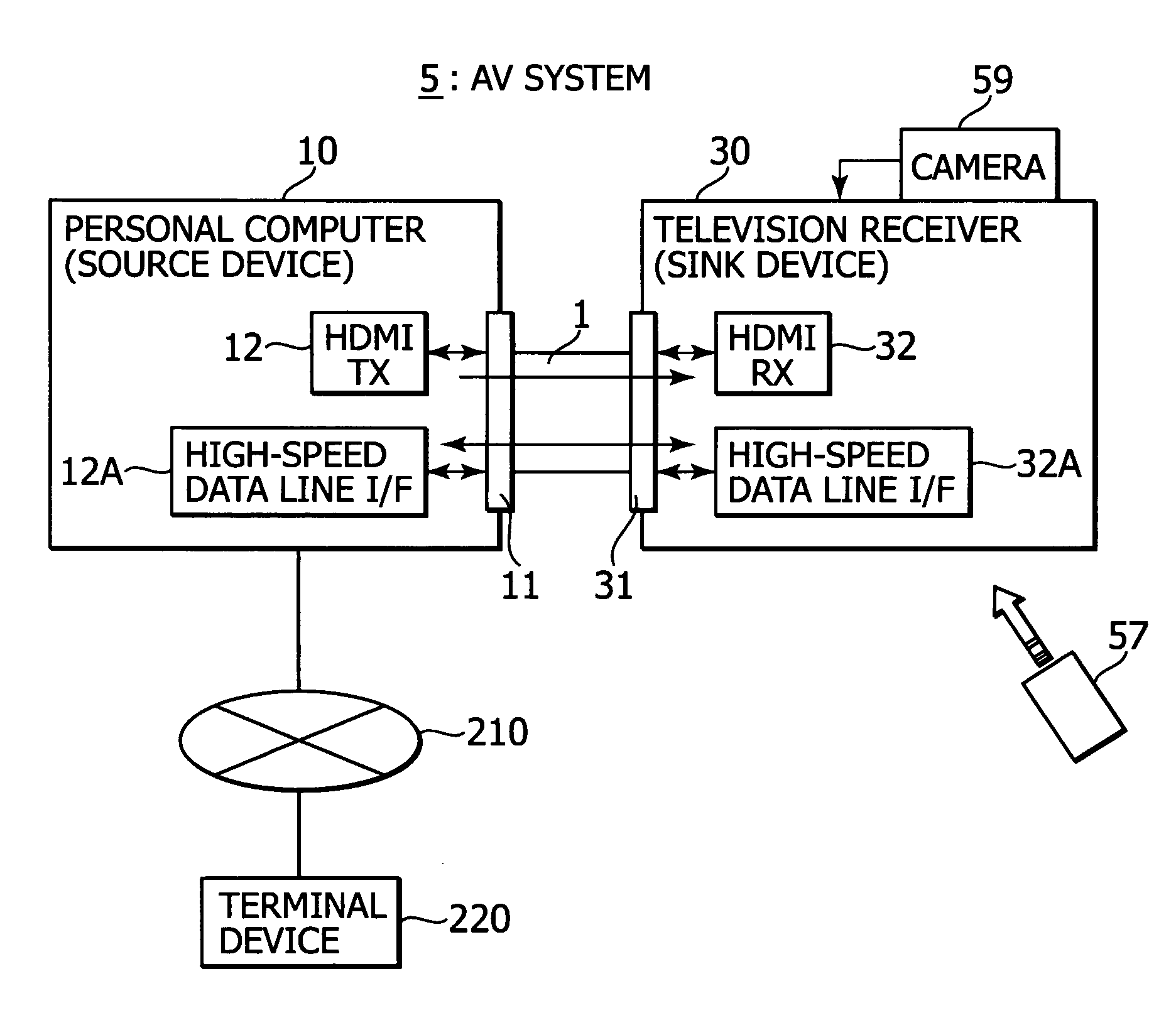
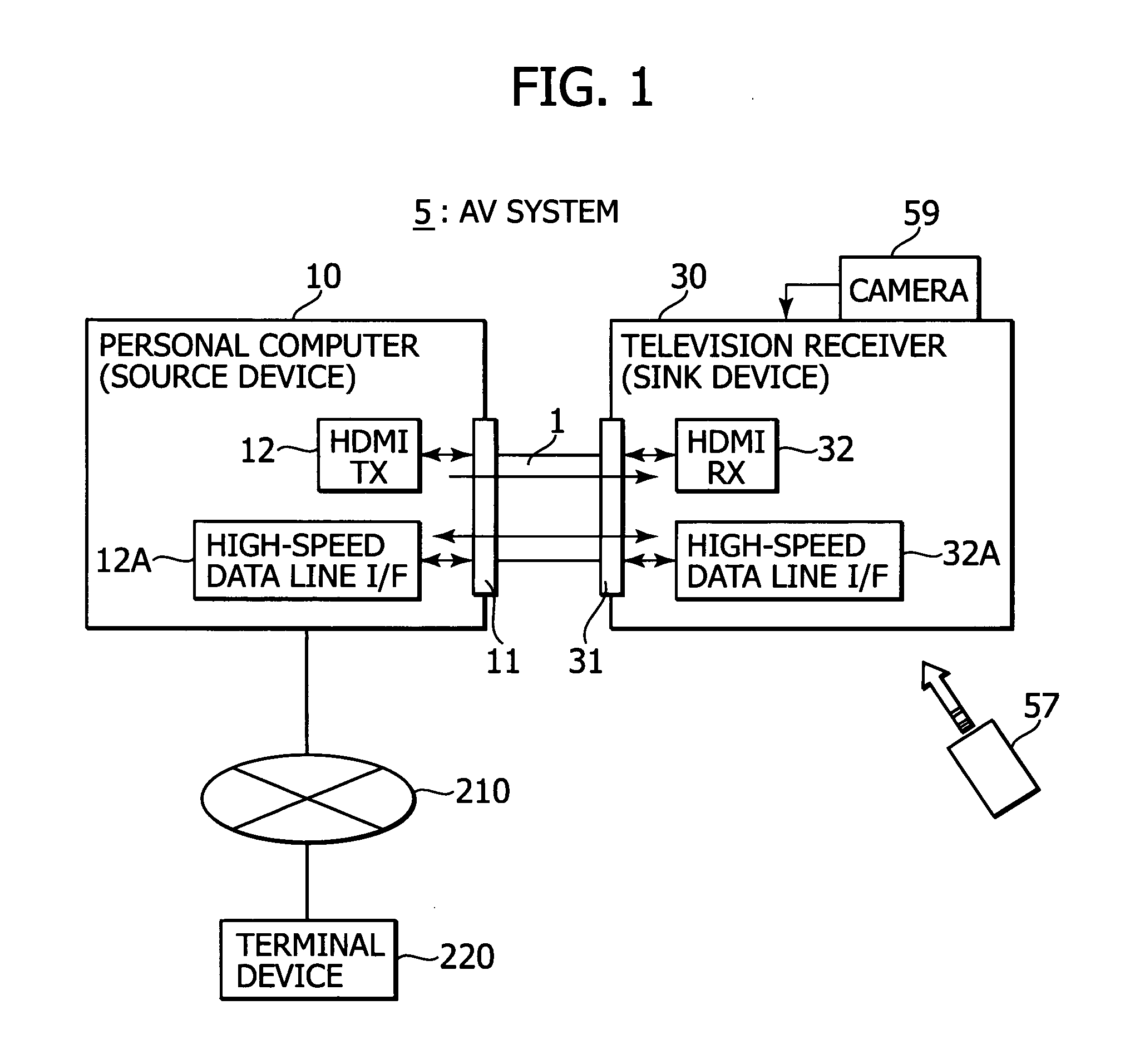
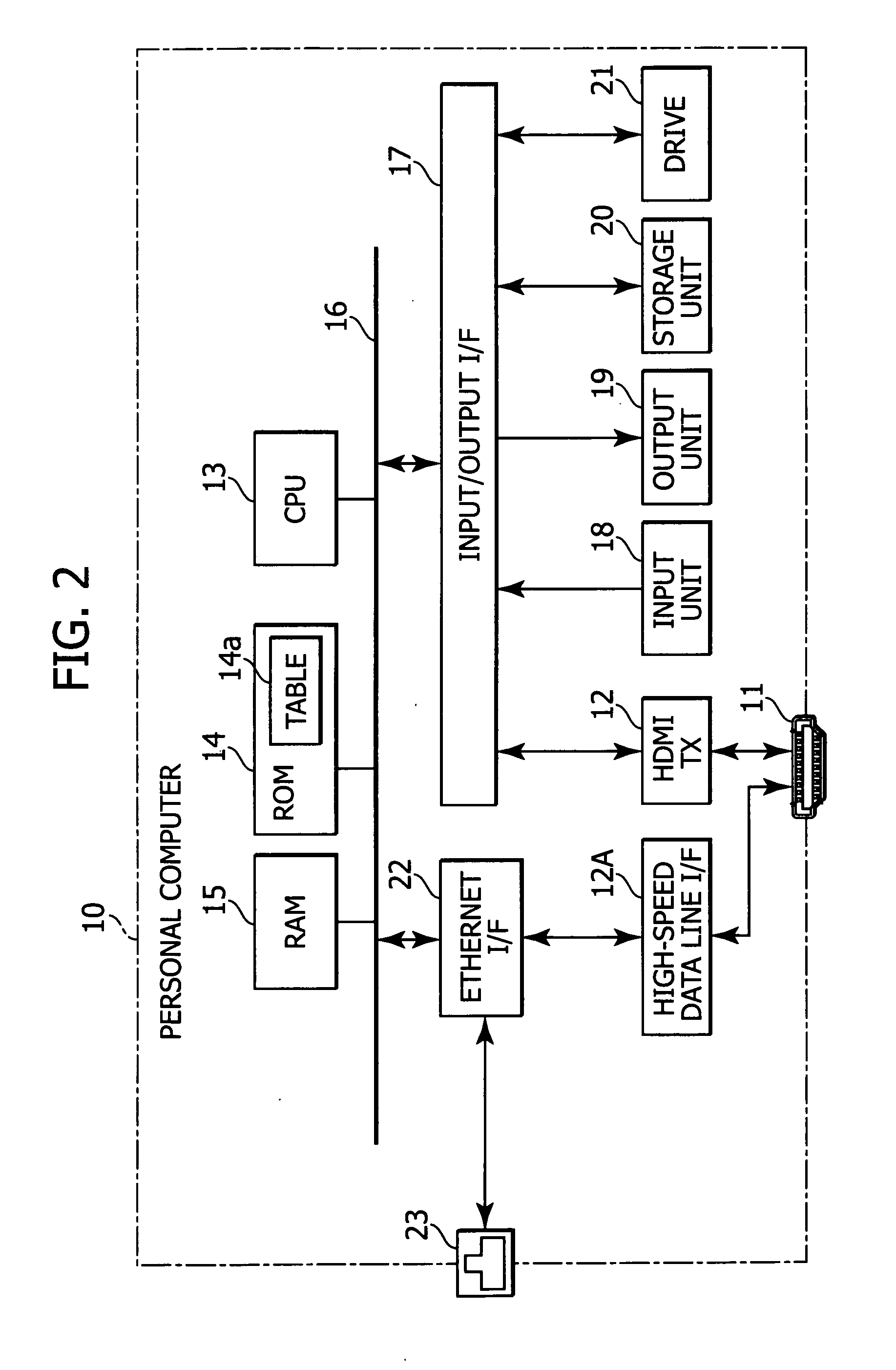
Display device and transmitting device
InactiveUS20090091656A1Miniaturization and low costLow costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDisplay deviceComputer science
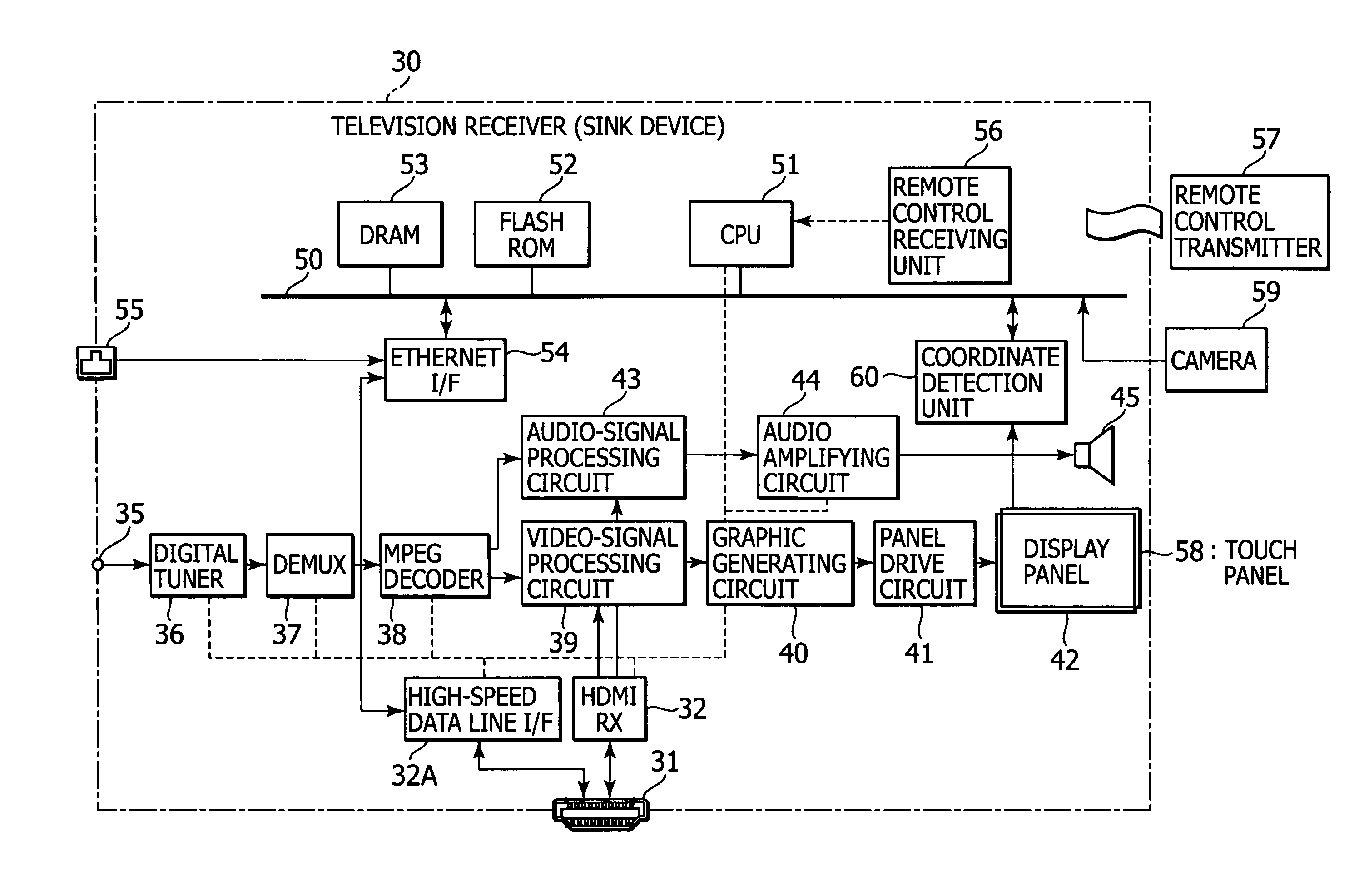
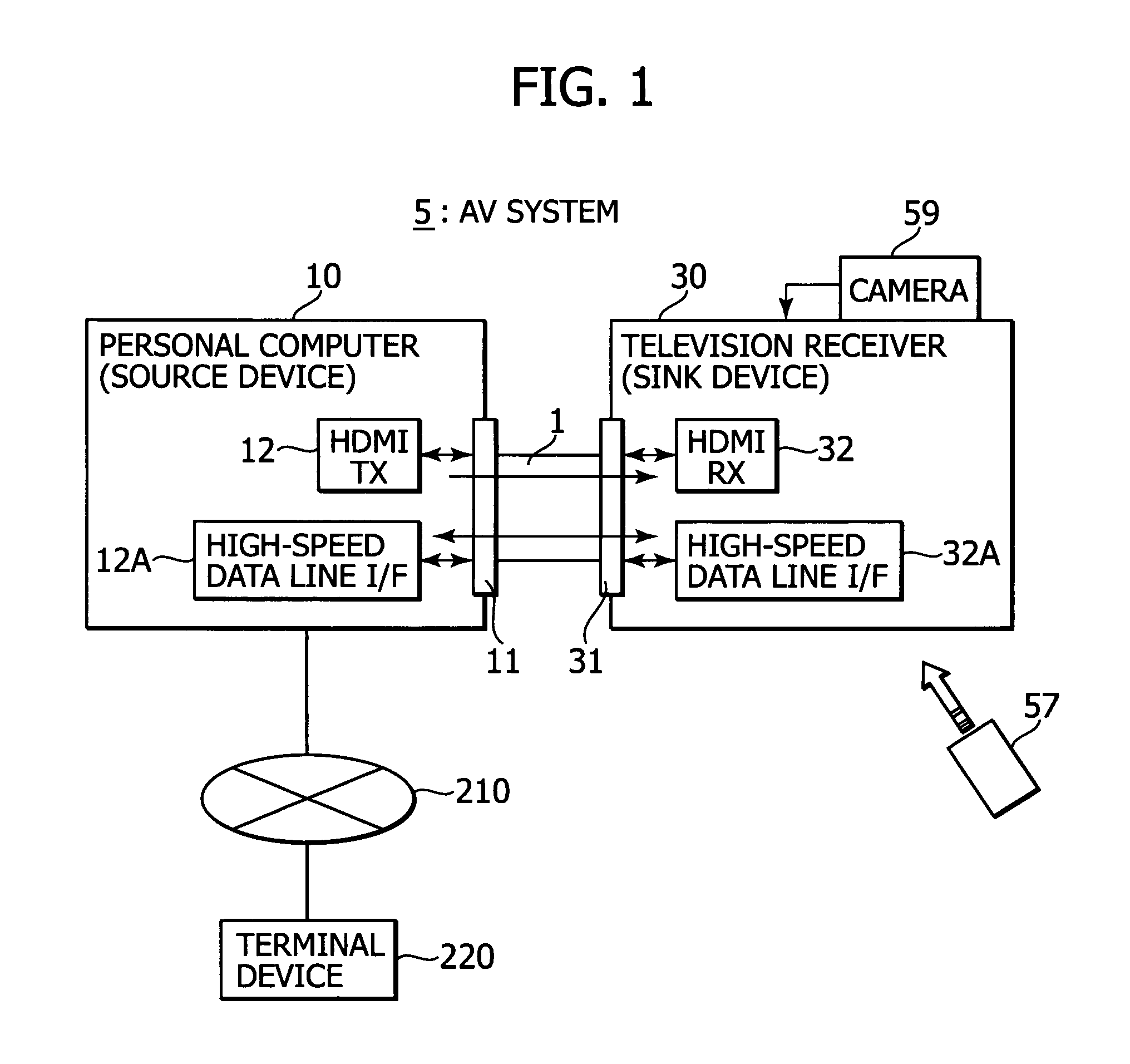
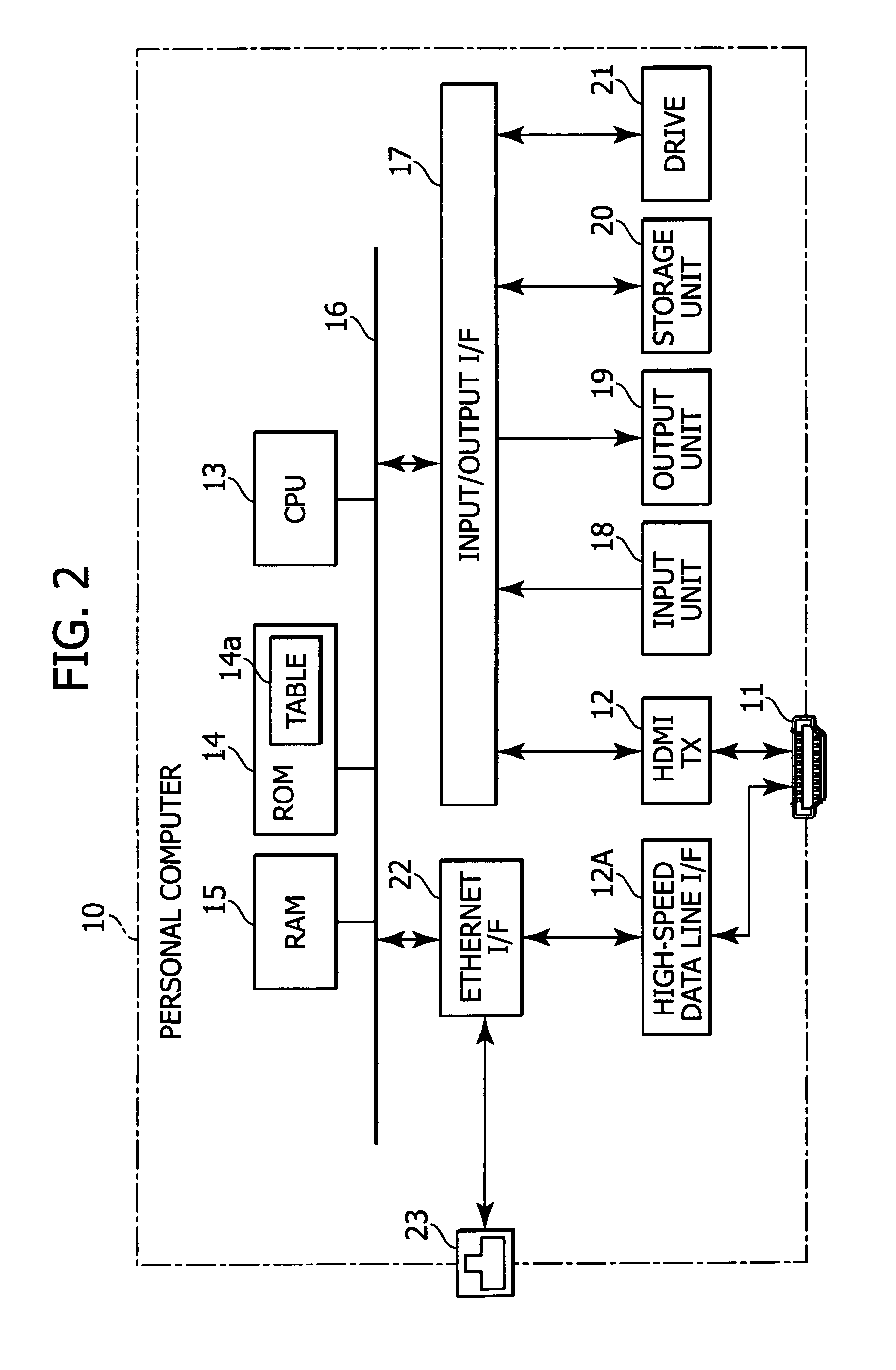
A display device includes a signal receiving unit, an image display unit, a communicating unit, a position designating unit, and an information transmitting unit. The signal receiving unit receives a video signal by a differential signal through a plurality of channels from an external apparatus via a transmission path. The image display unit processes the vide signal received in the signal receiving unit to display an image. The communicating unit performs a bi-directional communication by using a predetermined line which constitutes the transmission path. The position designating unit designates a position on a display screen of the image display unit. The information transmitting unit transmits, by the communicating unit, coordinate information on the position designated by the position designating unit to the external apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and system for configuring a plurality of network interfaces that share a physical interface
Certain aspects of a method and system for configuring a plurality of network interfaces that share a physical interface (PHY) may include a system comprising one or more physical network interface controllers (NICs) and two or more virtual NICs. One or more drivers associated with each of the virtual NICs that share one or more Ethernet ports associated with the physical NICs may be synchronized based on controlling one or more parameters associated with one or more Ethernet ports. One or more wake on LAN (WoL) patterns associated with each of the drivers may be detected at one or more Ethernet ports. A wake up signal may be communicated to one or more drivers associated with the detected WoL patterns. One of the drivers may be appointed to be a port master driver. If a failure of the appointed port master driver is detected, another driver may be appointed to be the port master driver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
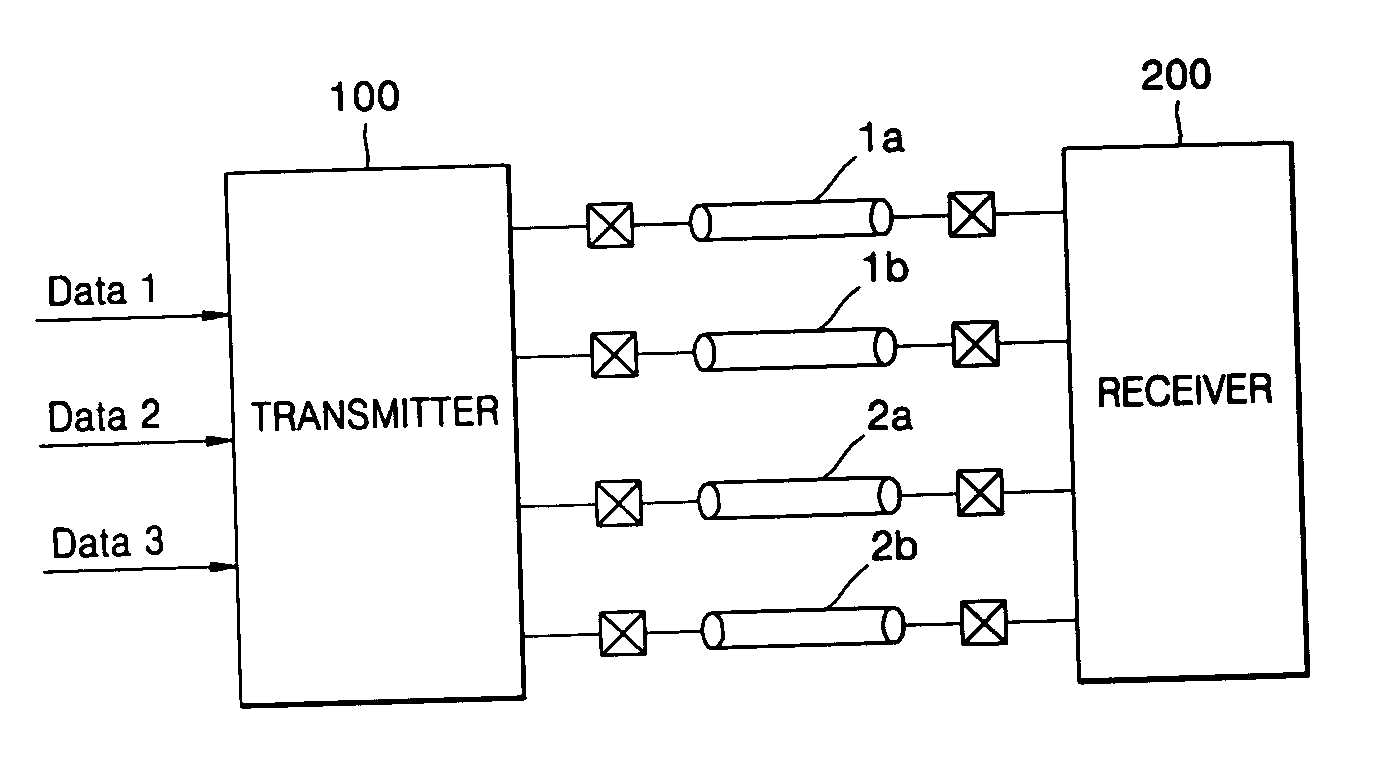
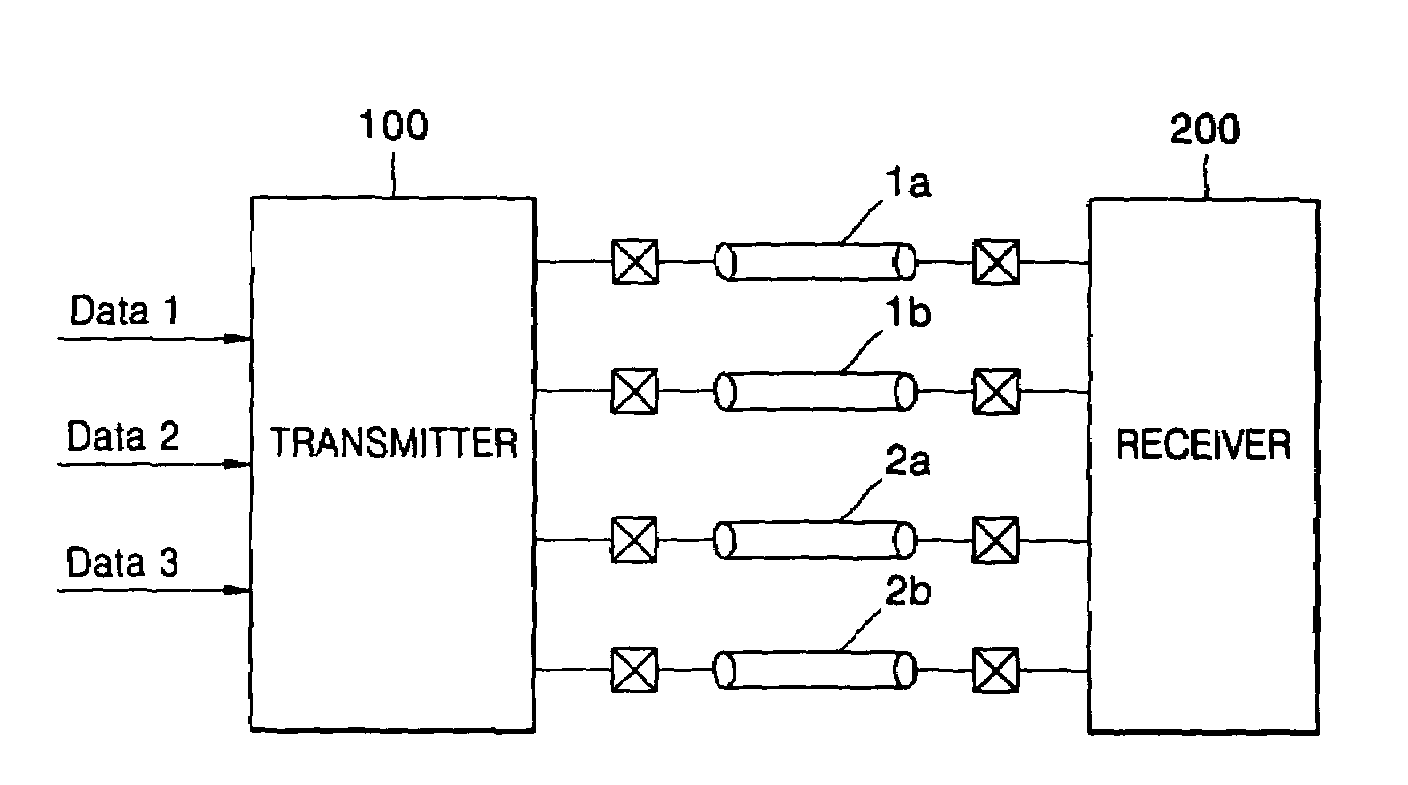
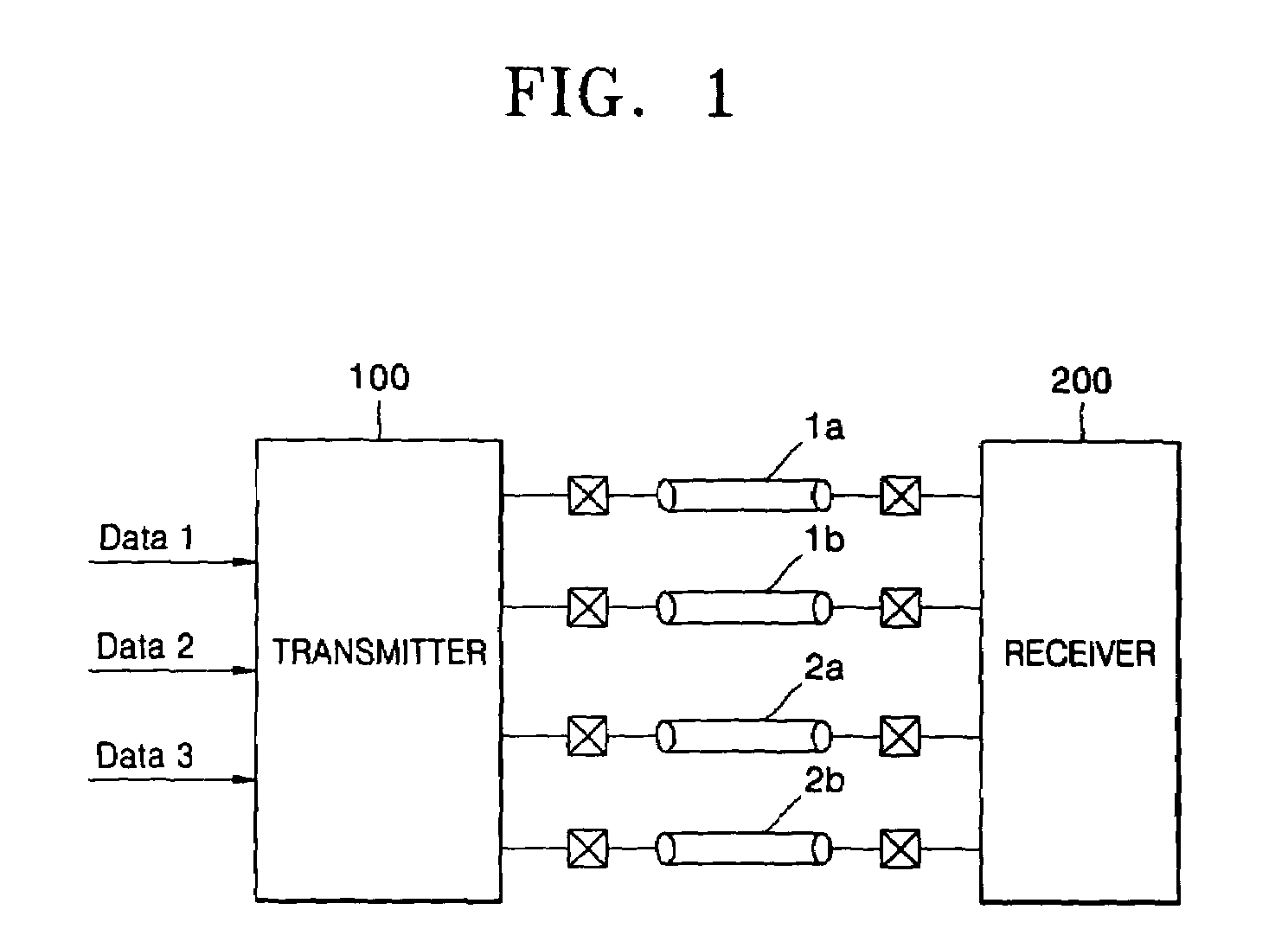
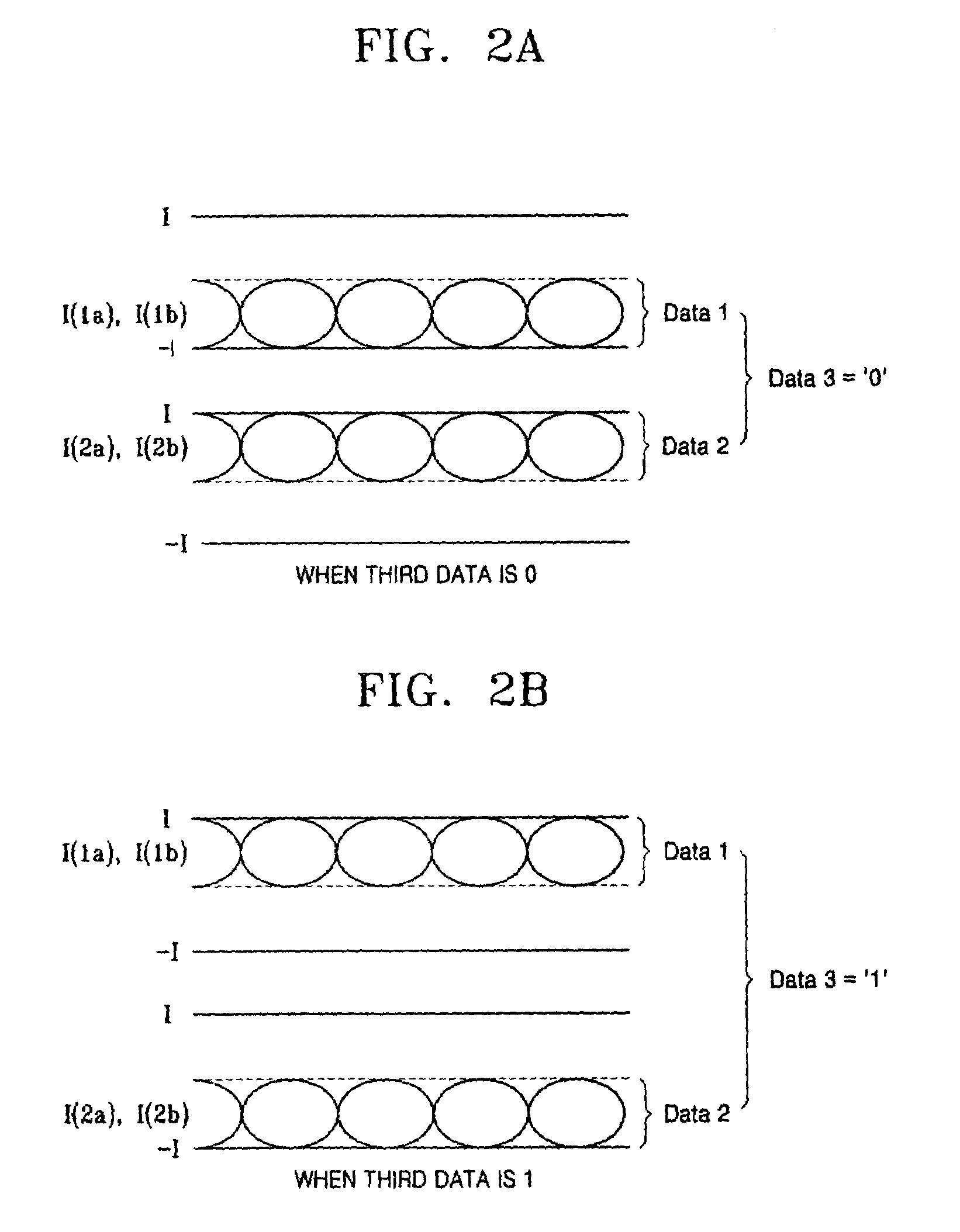
Current mode differential transmission method and system for transmitting three units of data using four signal lines
InactiveUS20060013331A1Reduce in quantityChannel dividing arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesDifferential transmissionEngineering
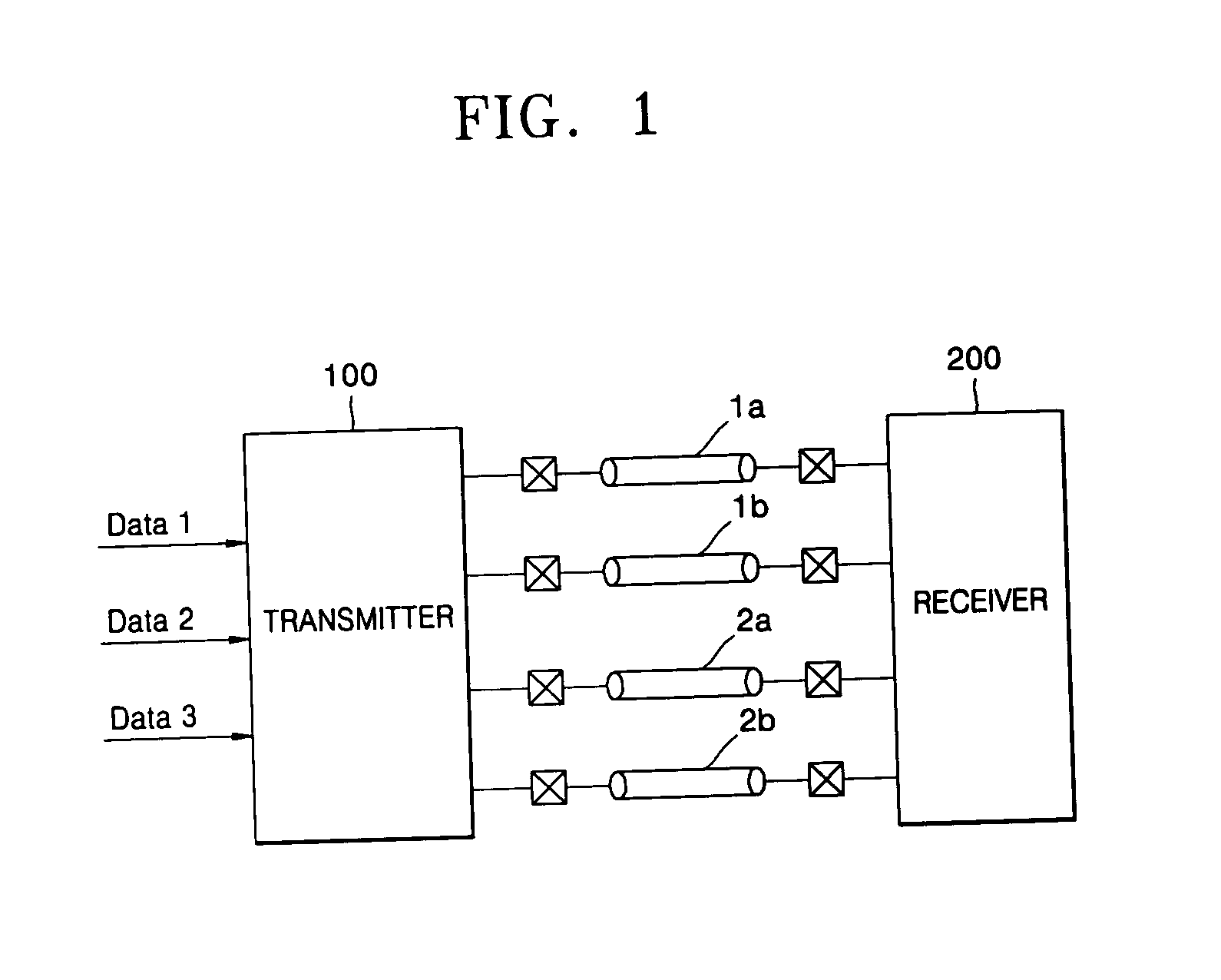
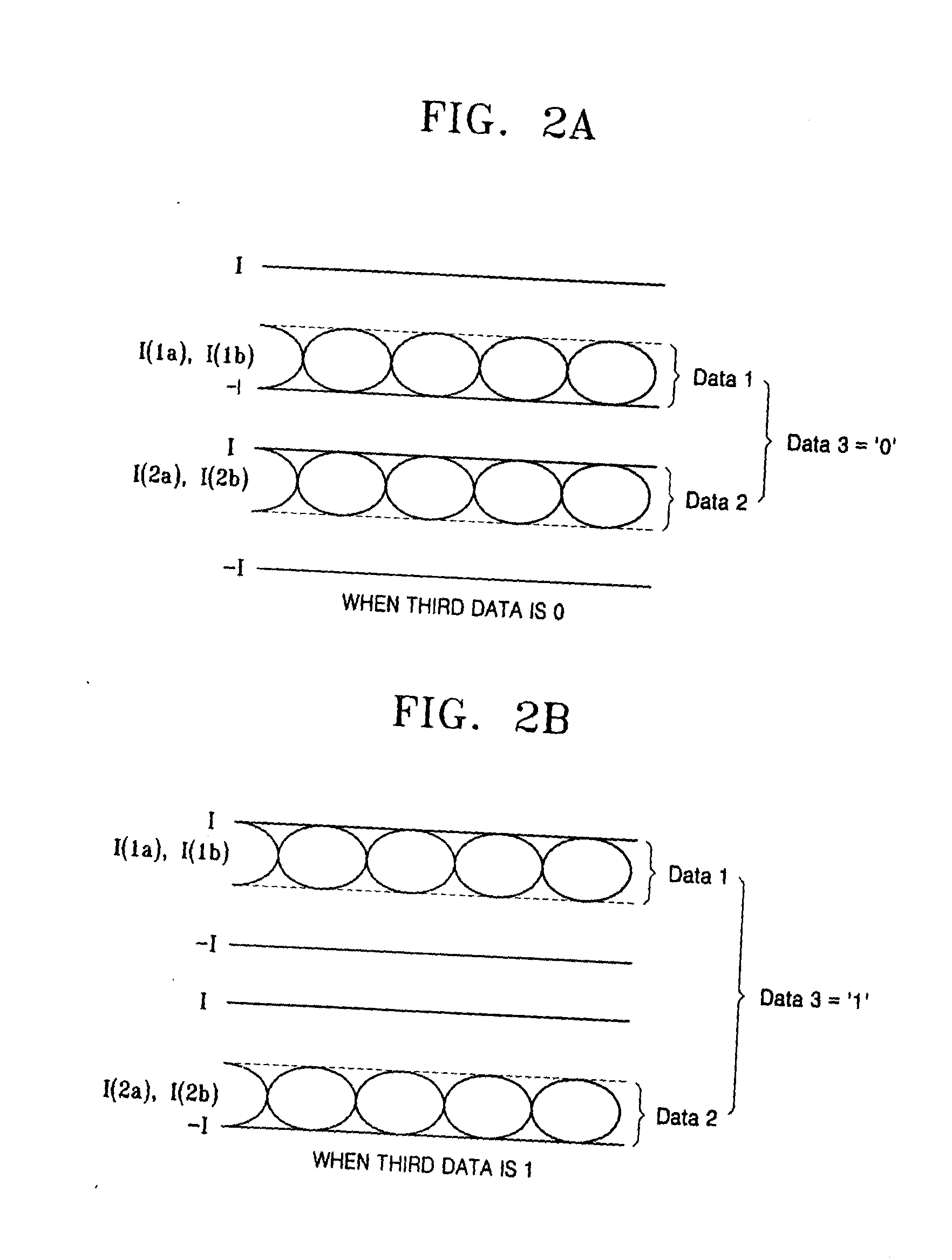
Provided are a current mode differential transmission method and system for differentially transmitting three units of data using four signal lines. The method includes: dividing the four signal lines 1a, 1b, 2a and 2b into two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b, and differentially transmitting respective data (first data and second data) via the two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b; and transmitting the other data (third data) by differentially changing common mode currents of the two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Global positioning system (GPS) based secure access
ActiveUS20050213519A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsGlobal Positioning System
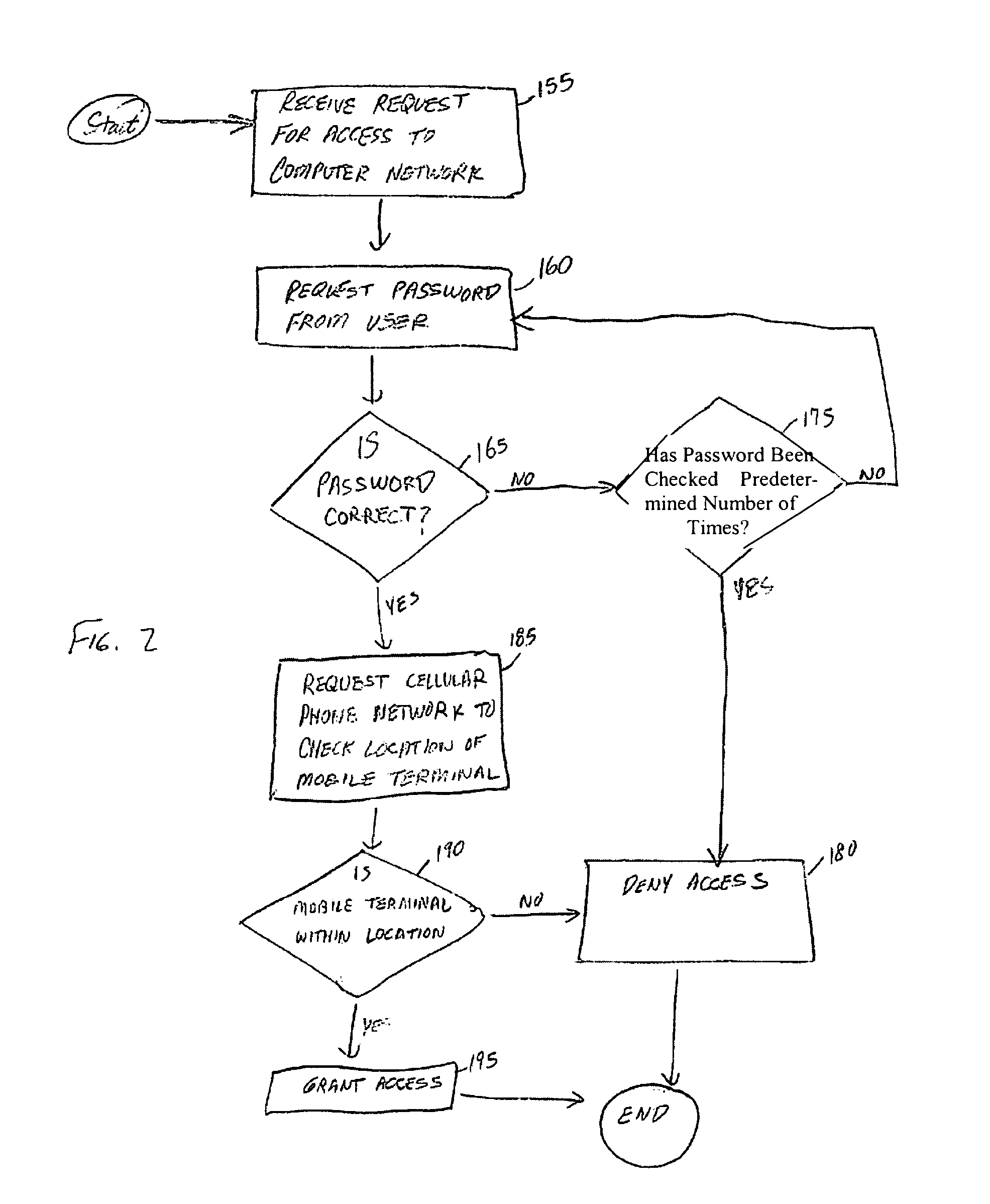
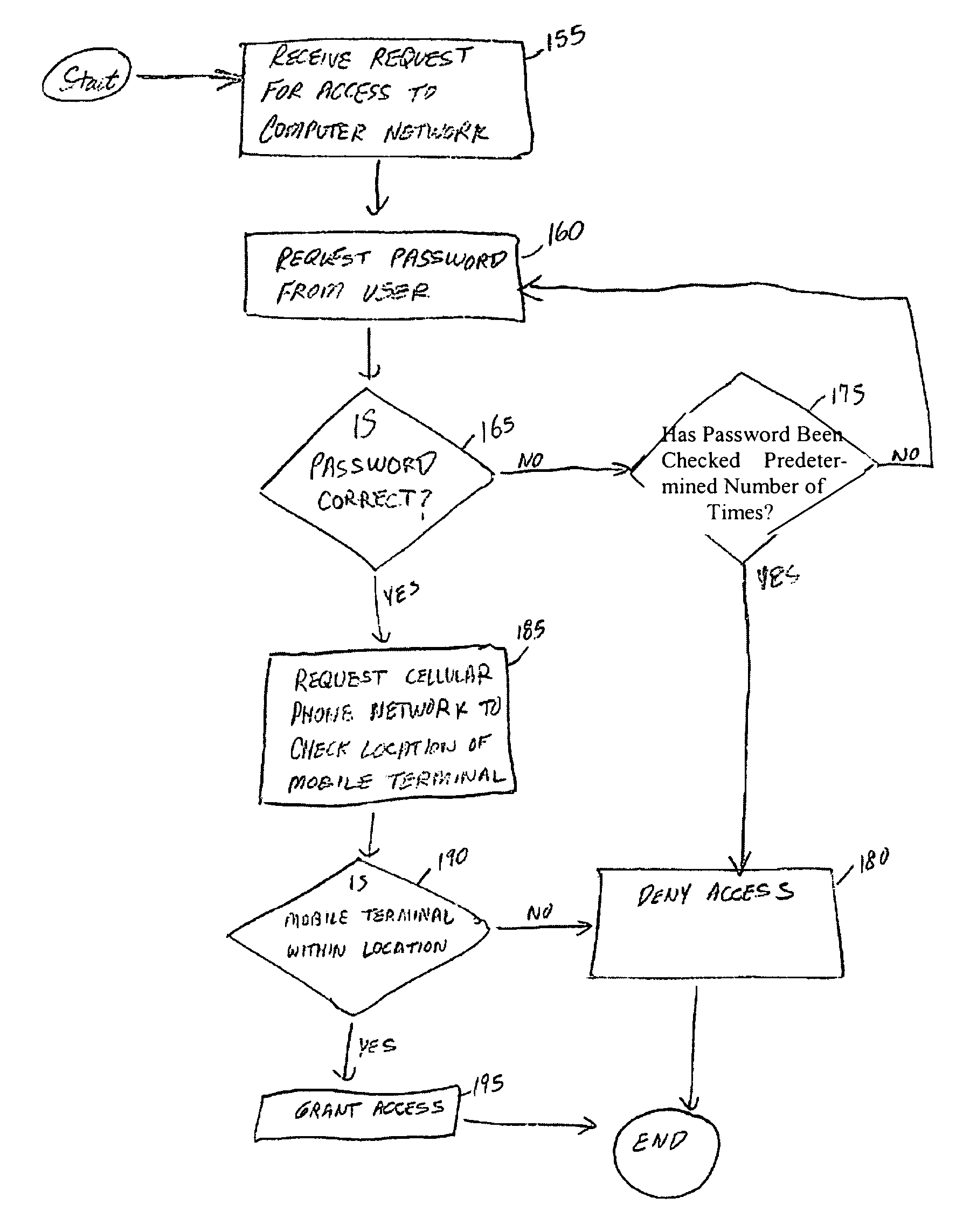
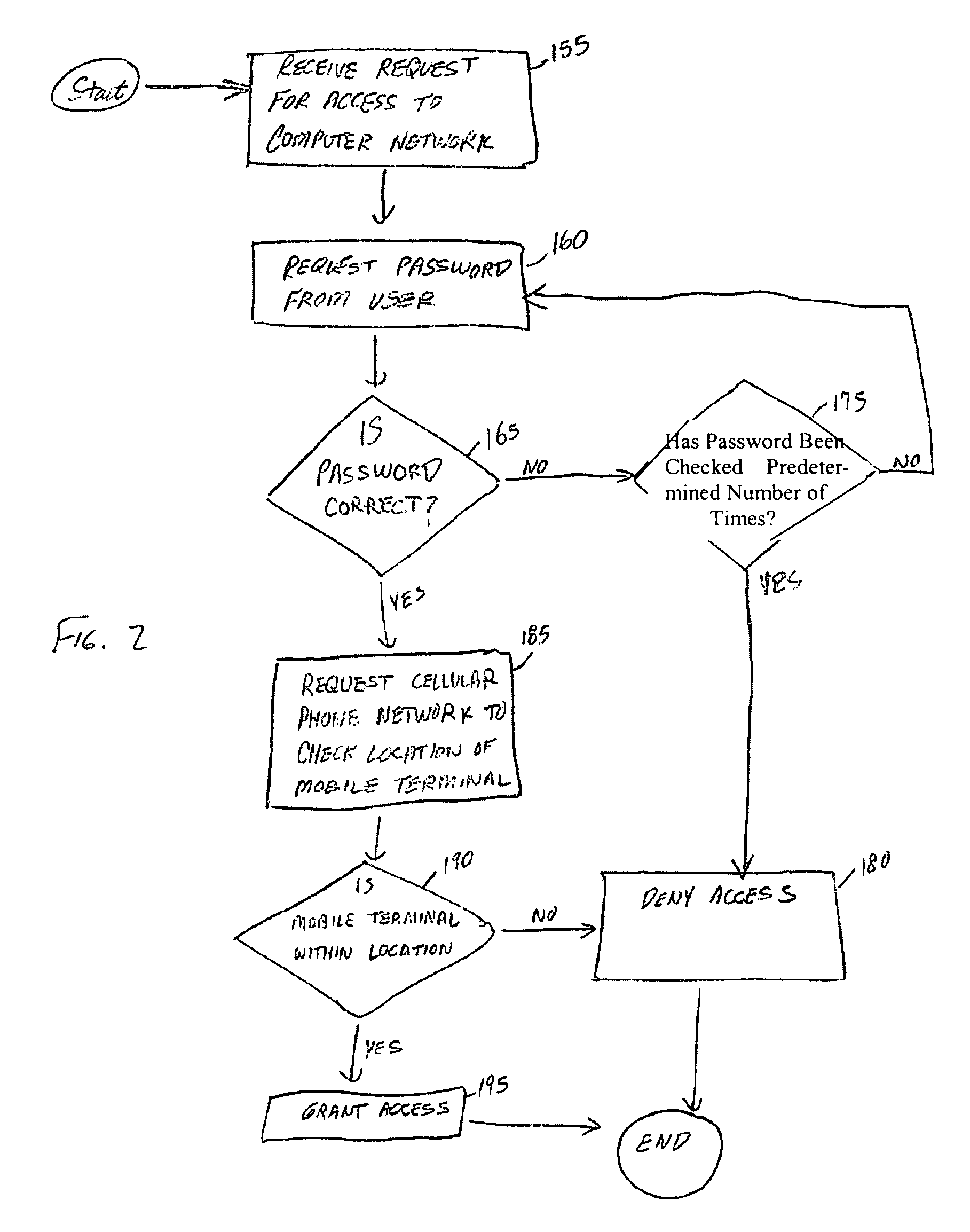
Presented herein are systems and methods for global positioning system based secure access. A request for access to a computer network is received. A determination is made whether a mobile terminal is within a predetermined location. If the mobile terminal is within the predetermined location, access is granted. If the mobile terminal is outside of the predetermined location, access to the computer network is denied.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Display device and transmitting device
InactiveUS8359628B2Low costImprove user convenienceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDifferential signalingDisplay device
A display device includes a signal receiving unit, an image display unit, a communicating unit, a position designating unit, and an information transmitting unit. The signal receiving unit receives a video signal by a differential signal through a plurality of channels from an external apparatus via a transmission path. The image display unit processes the vide signal received in the signal receiving unit to display an image. The communicating unit performs a bi-directional communication by using a predetermined line which constitutes the transmission path. The position designating unit designates a position on a display screen of the image display unit. The information transmitting unit transmits, by the communicating unit, coordinate information on the position designated by the position designating unit to the external apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
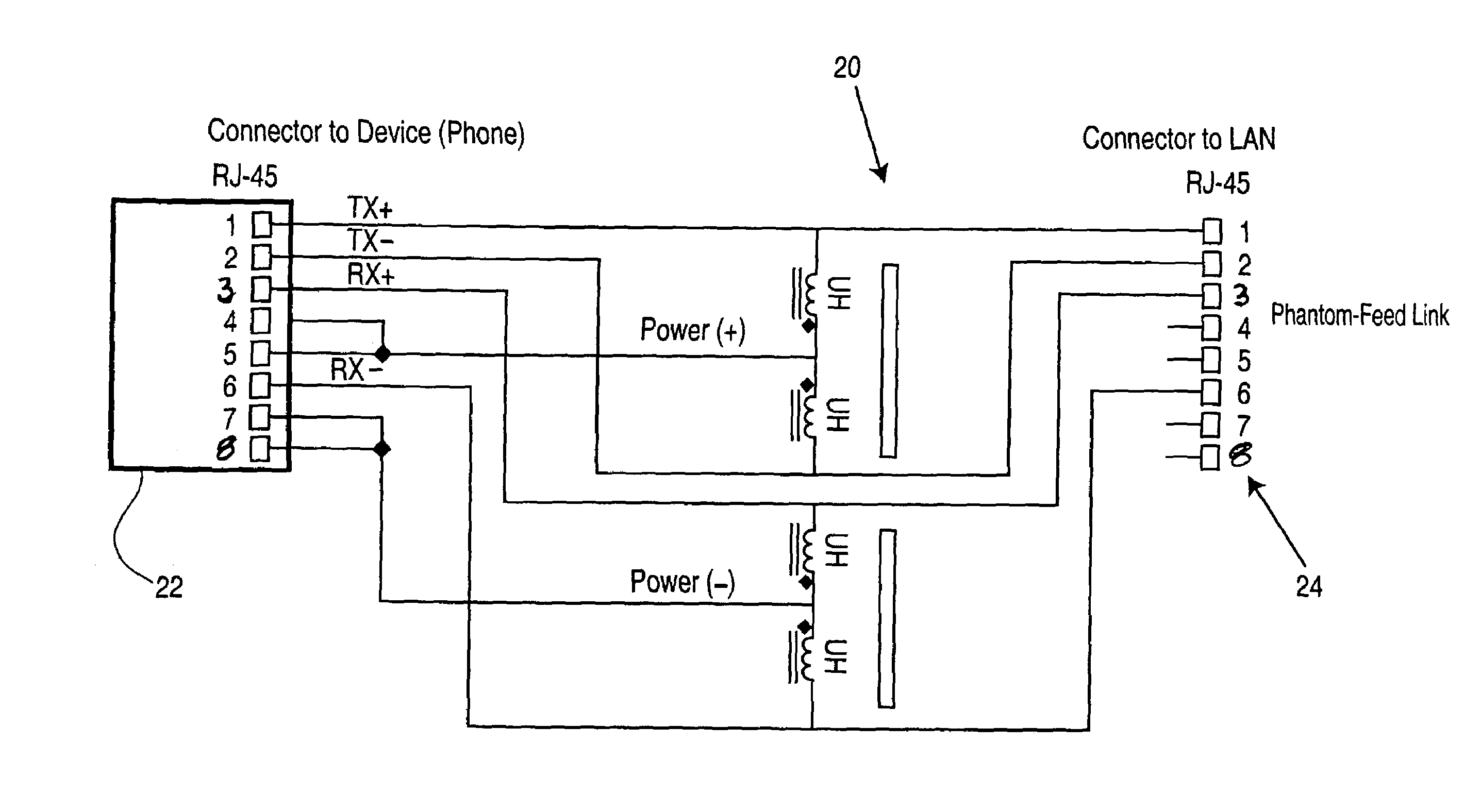
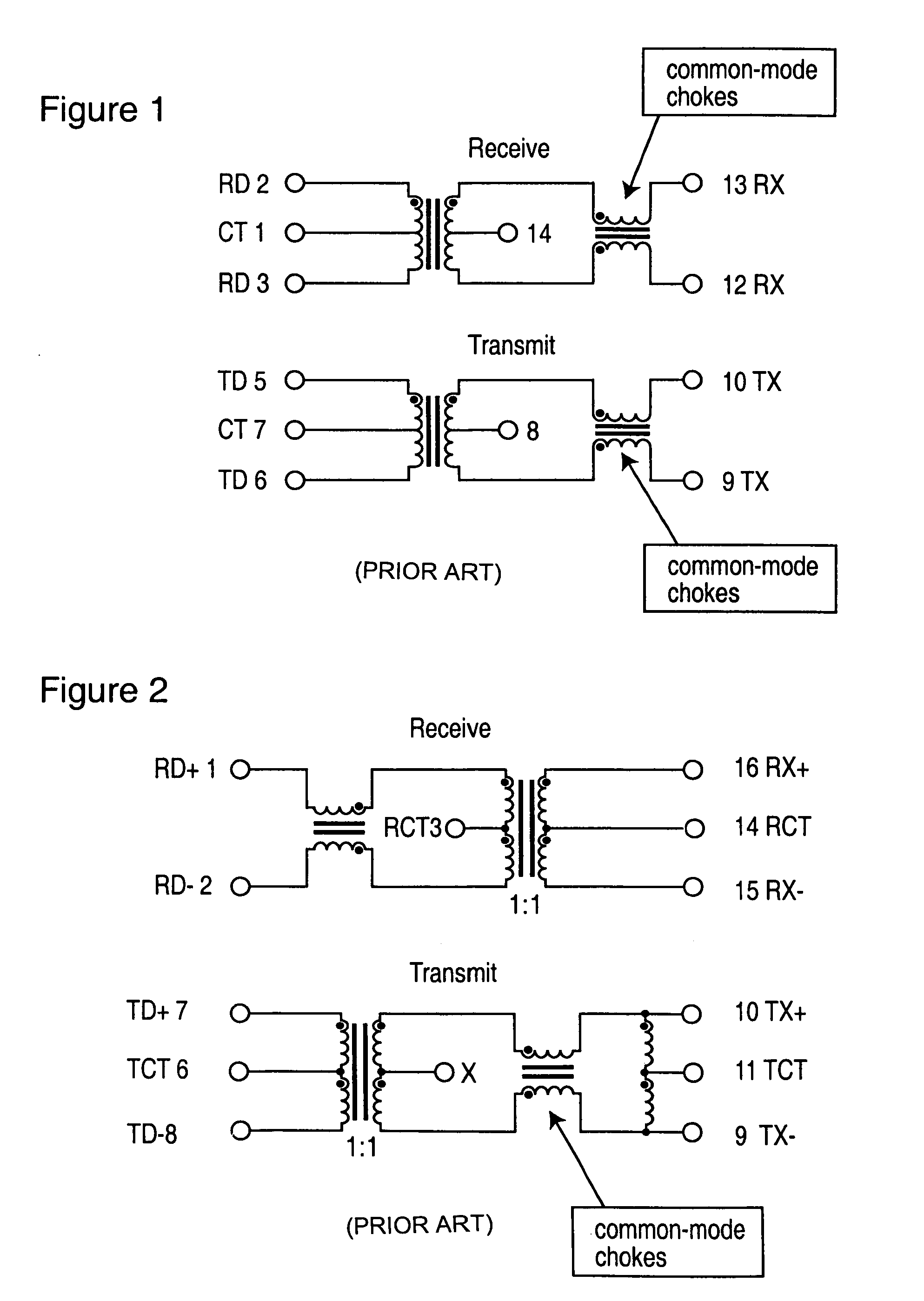
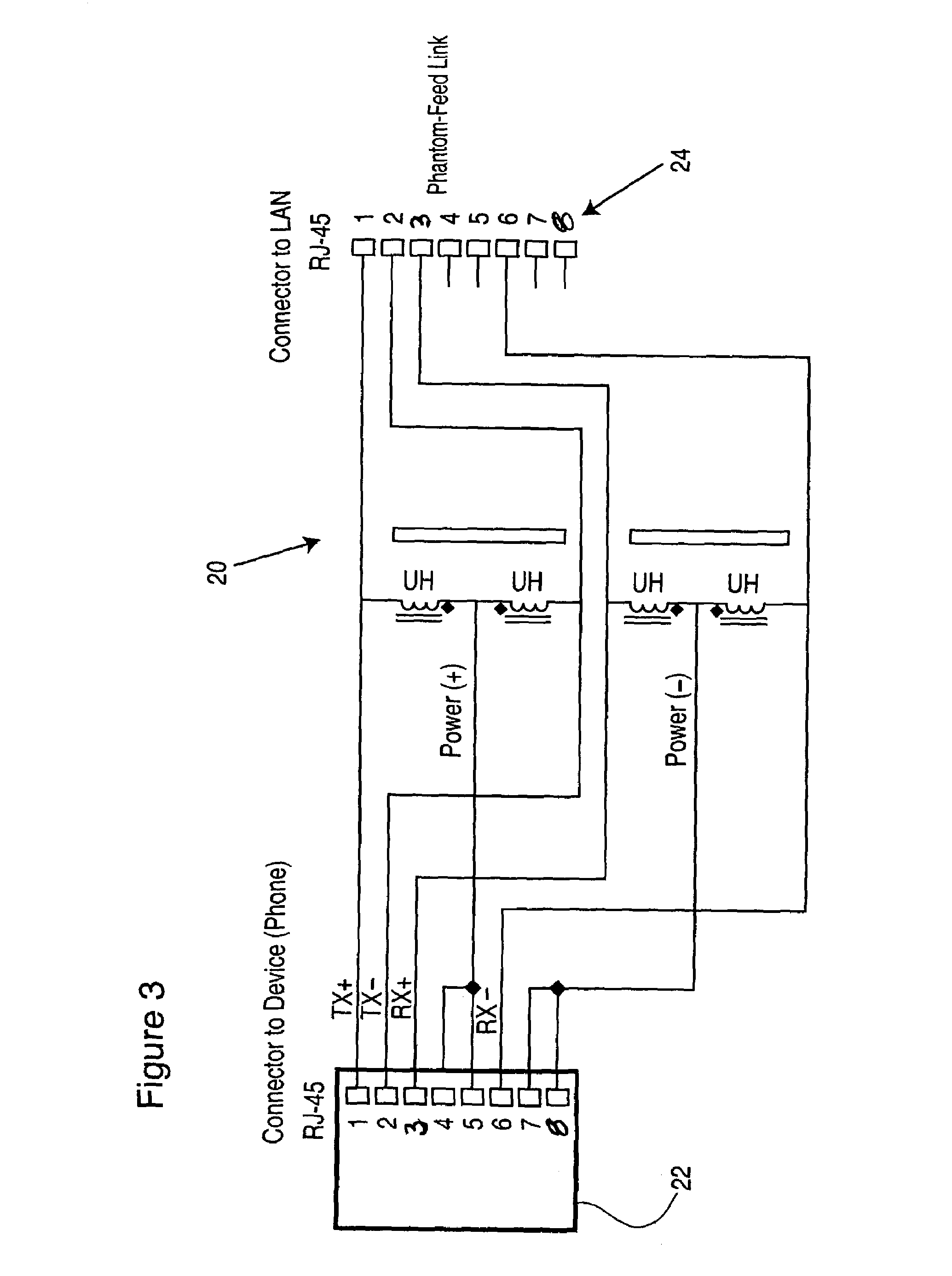
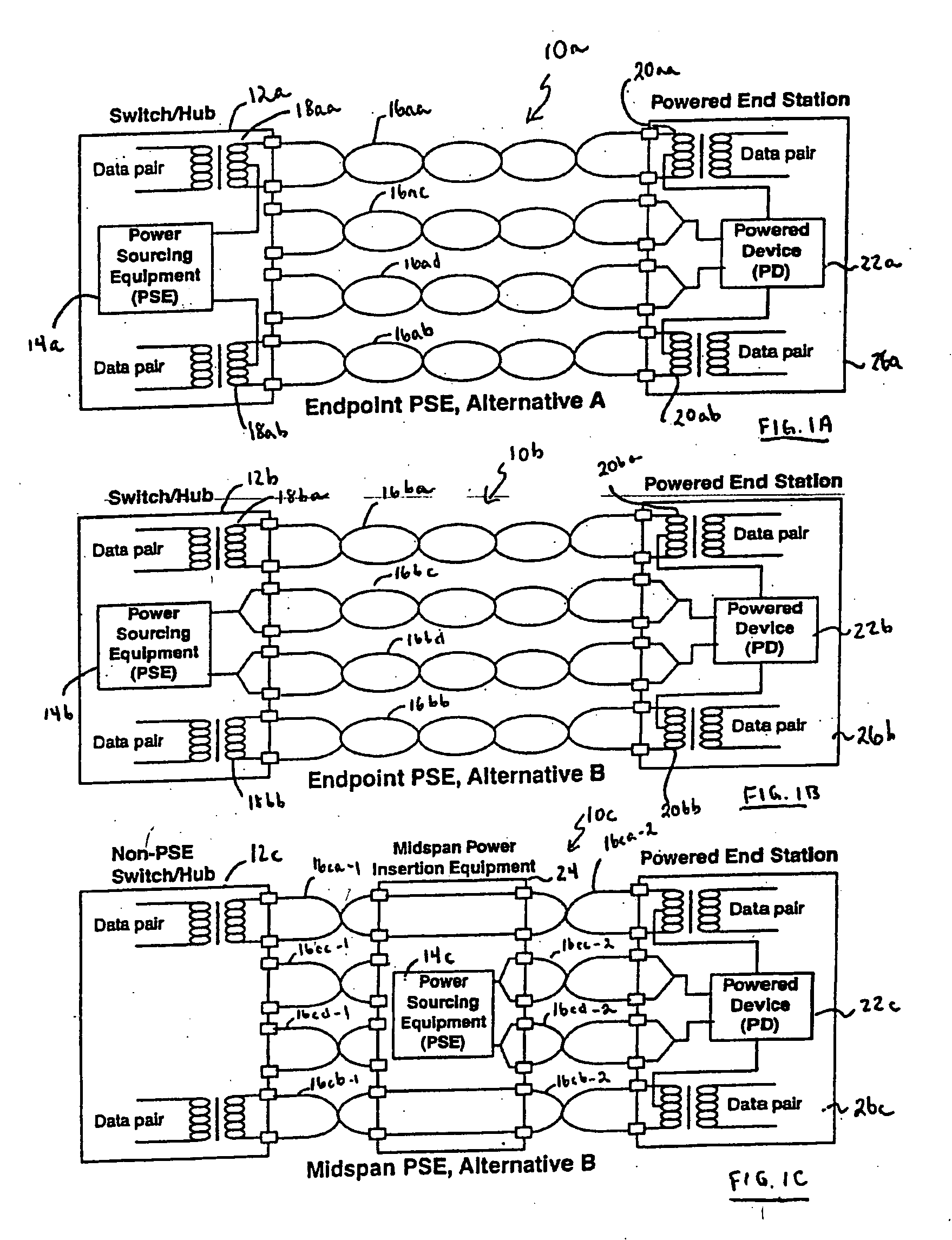
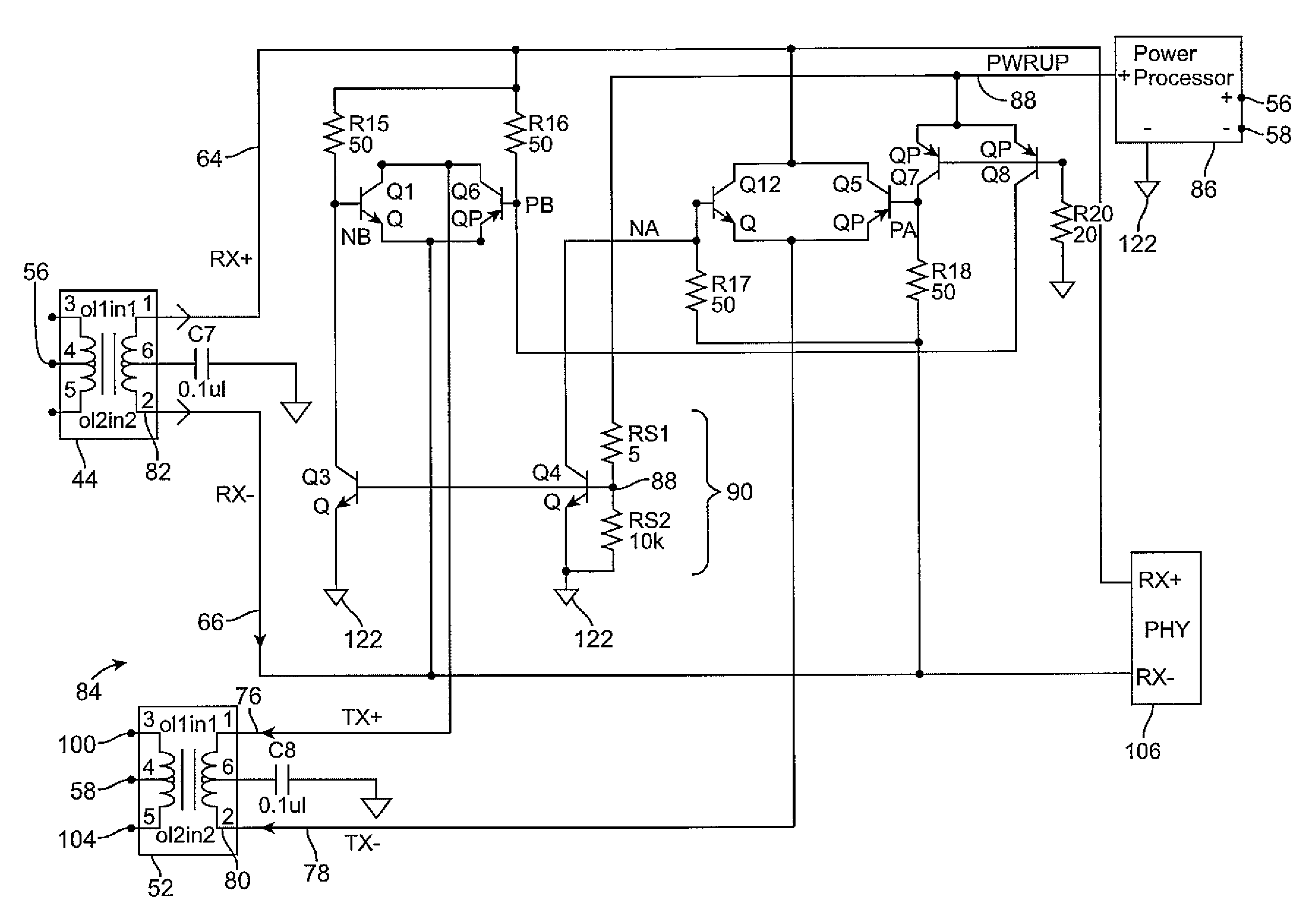
Power supply for phantom-feed LAN connected device using spare-pair powering
ActiveUS7030733B2Interconnection arrangementsElectrically conductive connectionsStandby powerConnected device
A system for providing power to a local area network LAN connected device via spare wire pairs from a phantom feed LAN, the system comprising a first connector for connecting to the LAN connected device; a second connector for connecting to a LAN hub; and means for redirecting current from signaling wires of said second connector to at least one spare wire pair of said first connector.
Owner:MITEL
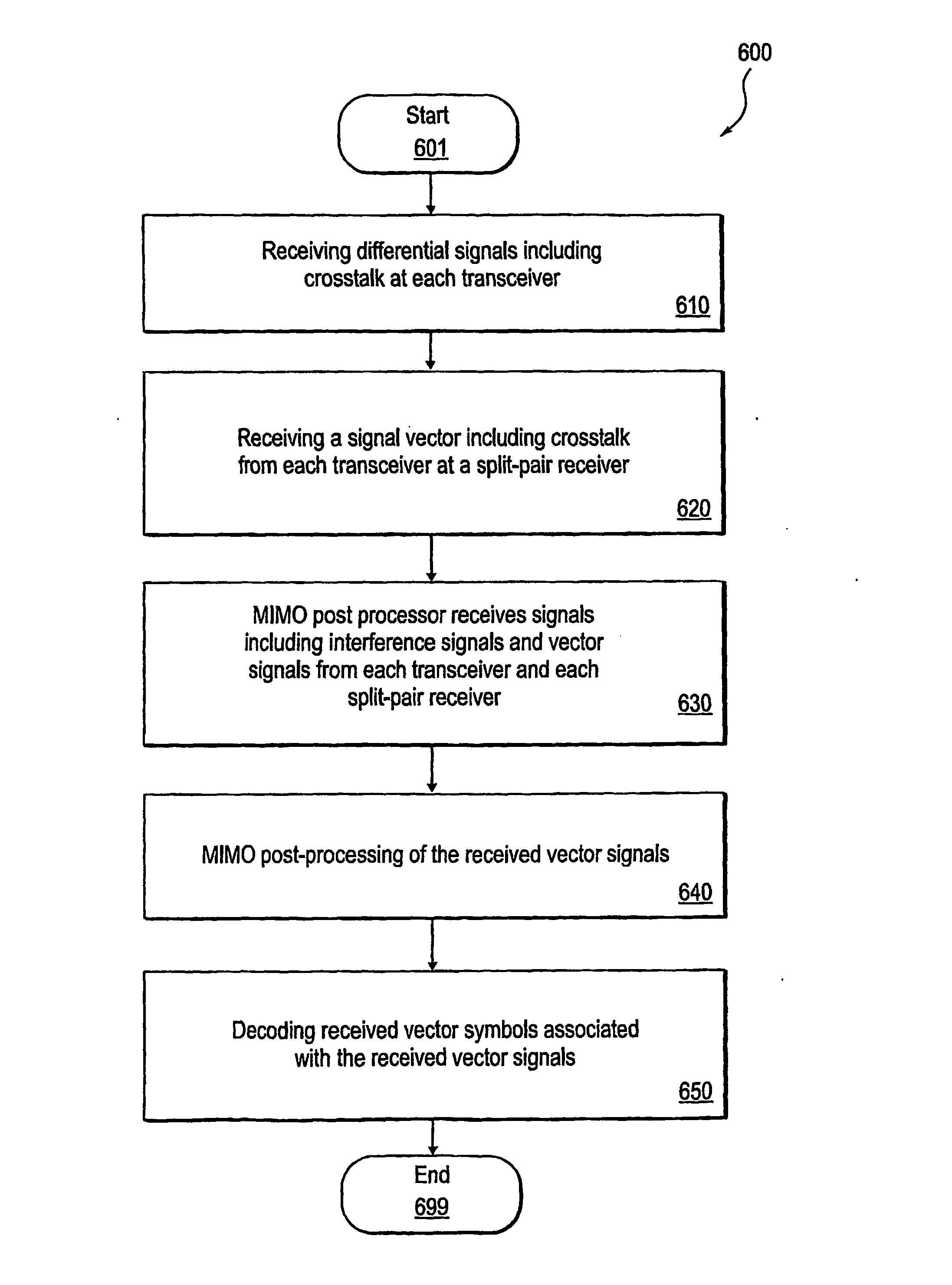
Method and system for split-pair reception in twisted-pair communication systems
InactiveUS20060109779A1Improve performanceAdd dimensionChannel dividing arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemTransceiver
A method and system are disclosed for improving the performance of a multiline transmission system by using one or more split-pair receivers in a multiline communications system to identify crosstalk on a pair of transceivers coupled to the split pair receivers, wherein each split pair receiver receives a signal including the crosstalk from each transceiver and provides a corresponding signal vector to a post processing unit, and performing MIMO post-processing on signal vectors received at a receiver from each transceiver and each split-pair receiver while minimizing crosstalk on pairs of lines in the multiline communications system with a frequency equalizer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
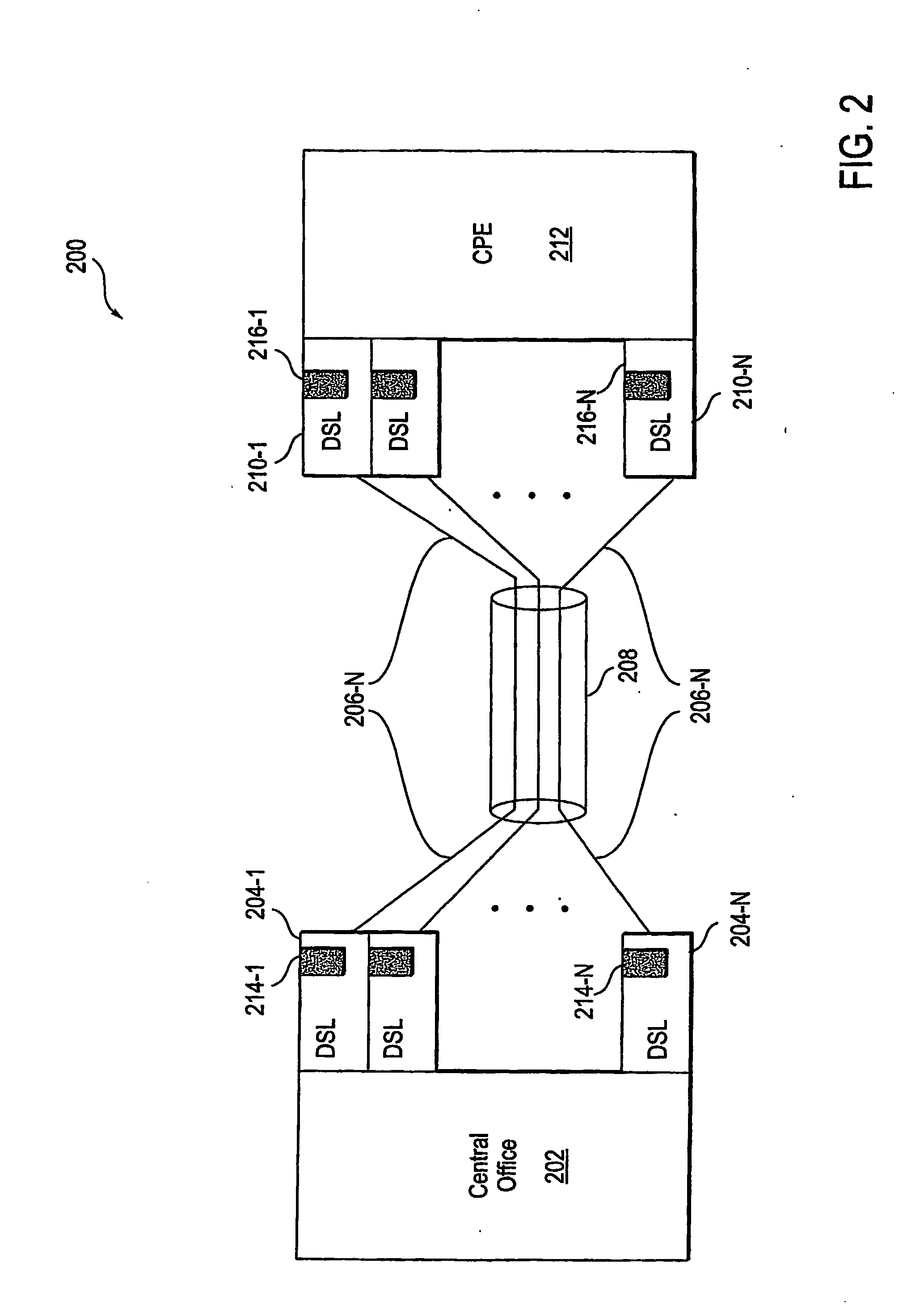
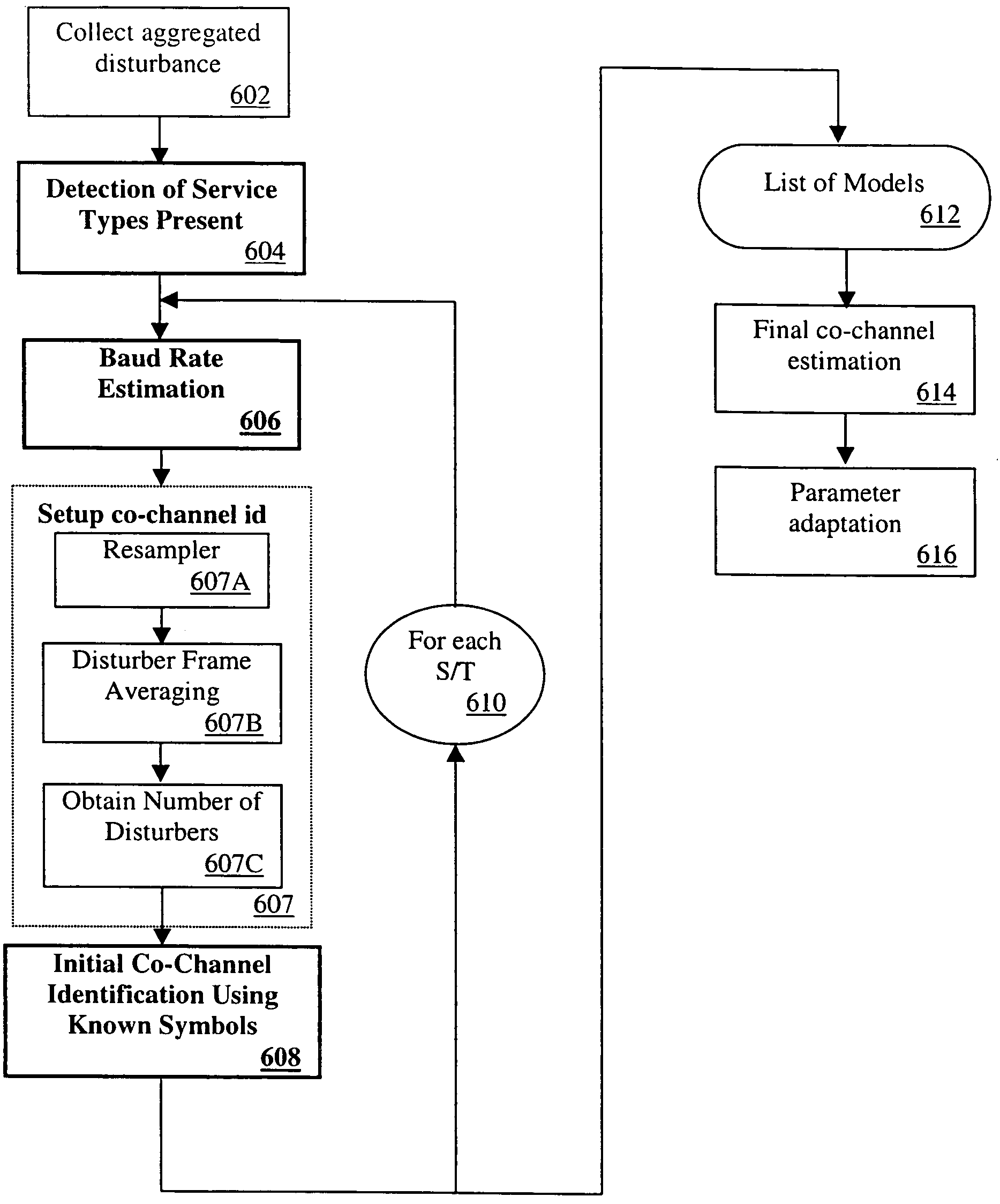
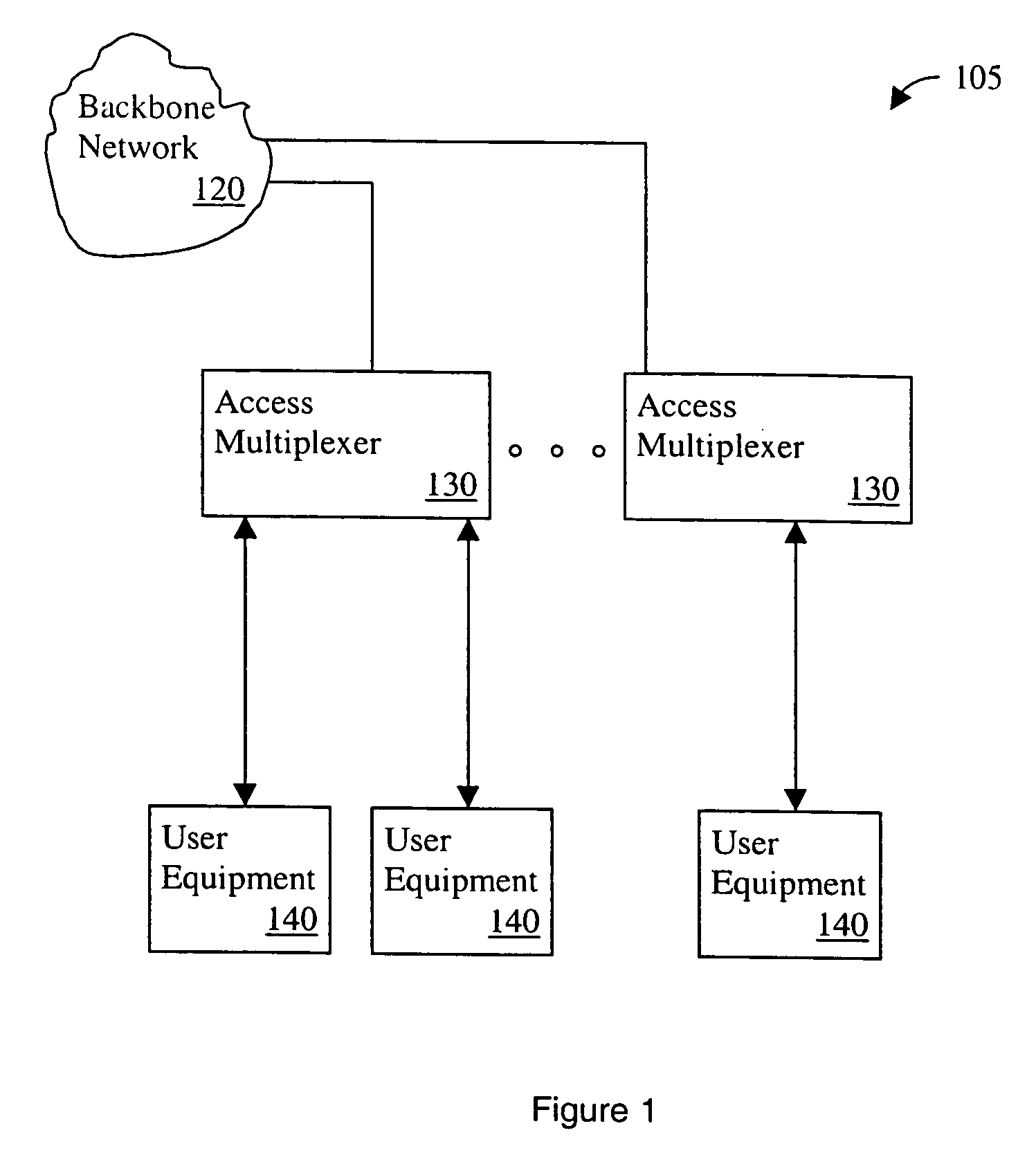
Method and apparatus for characterization of disturbers in communication systems
InactiveUS6970415B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemEngineering
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Global positioning system (GPS) based secure access
ActiveUS7372839B2Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsComputer terminalGlobal Positioning System
Presented herein are systems and methods for global positioning system based secure access. A request for access to a computer network is received. A determination is made whether a mobile terminal is within a predetermined location. If the mobile terminal is within the predetermined location, access is granted. If the mobile terminal is outside of the predetermined location, access to the computer network is denied.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
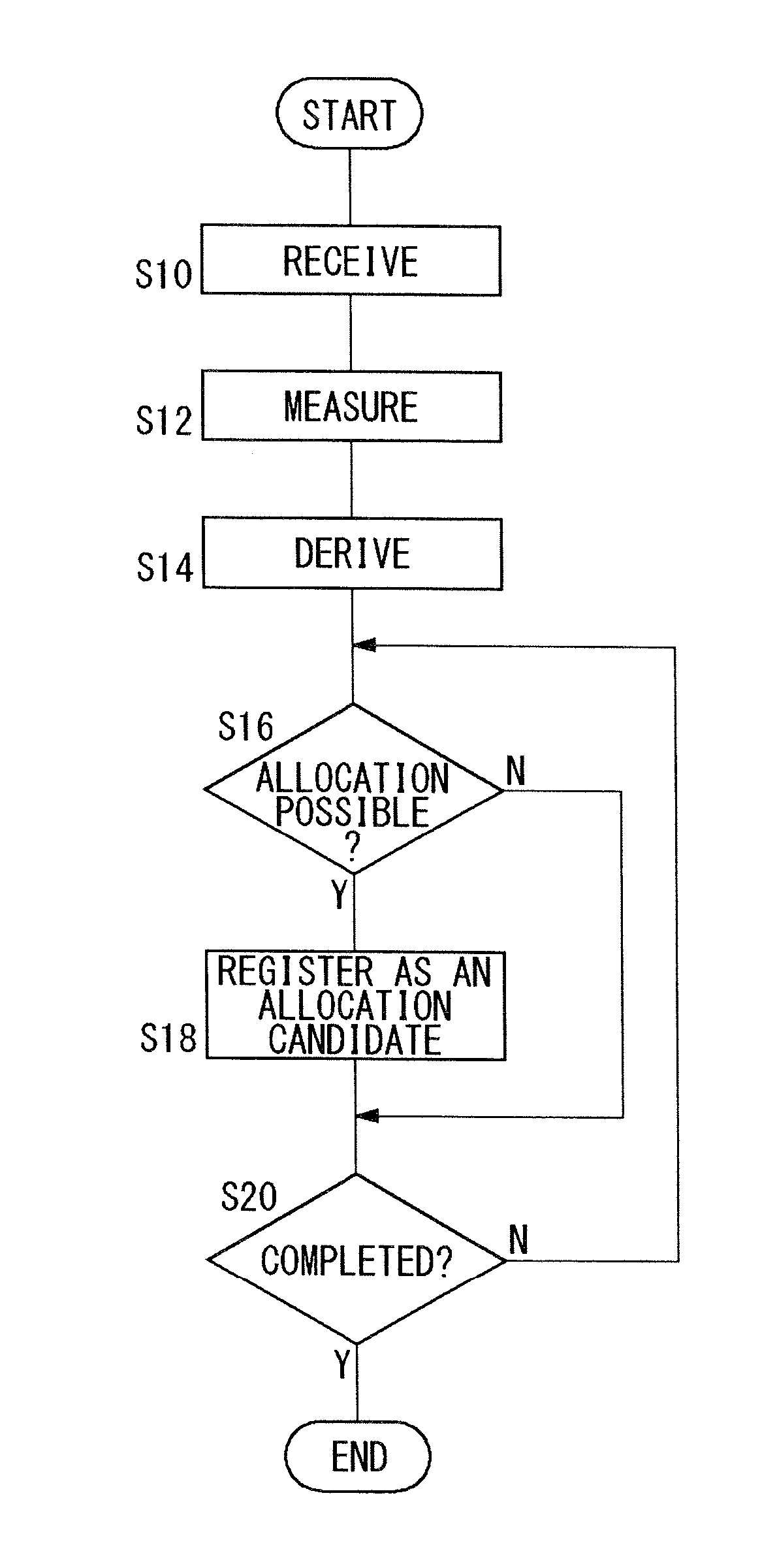
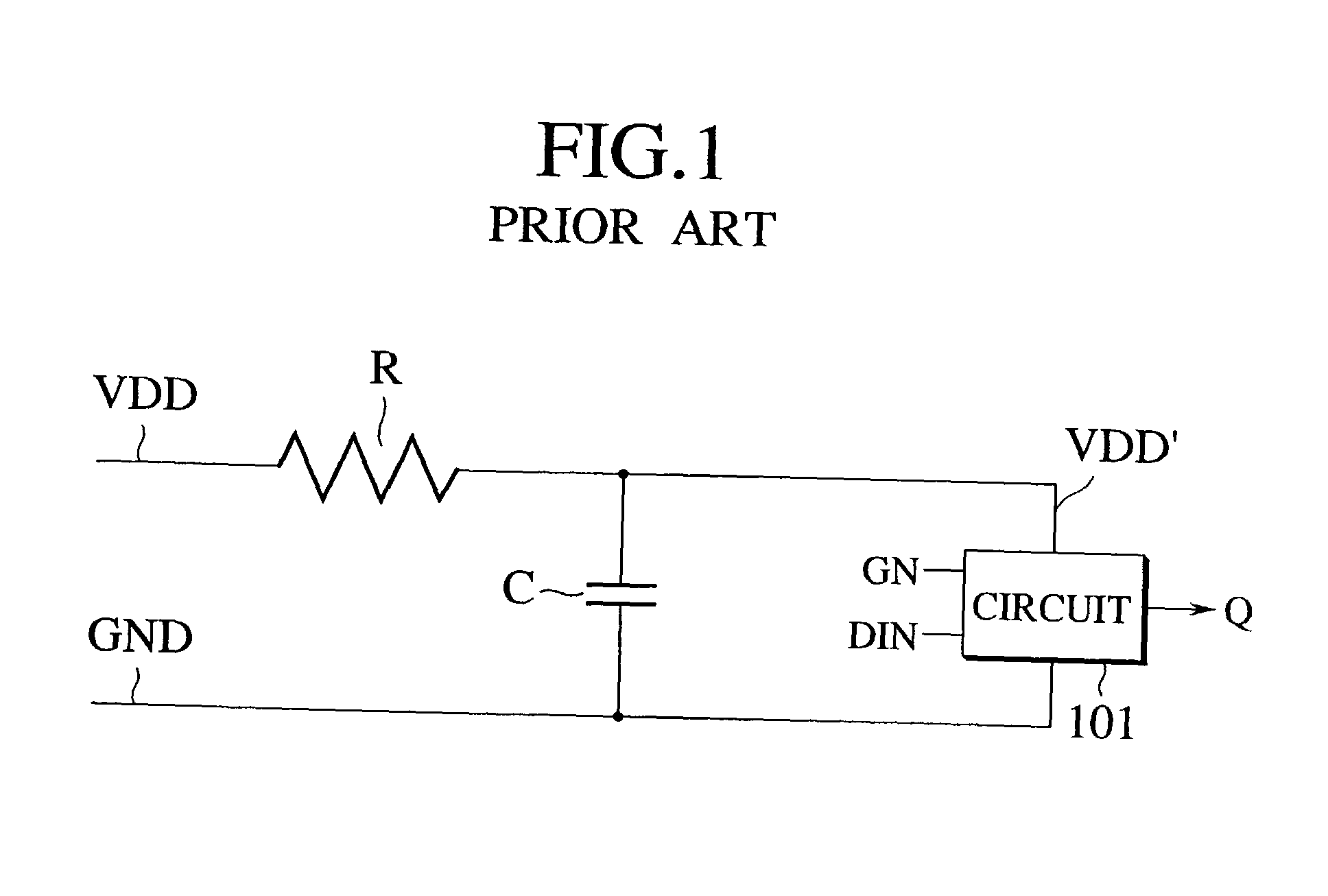
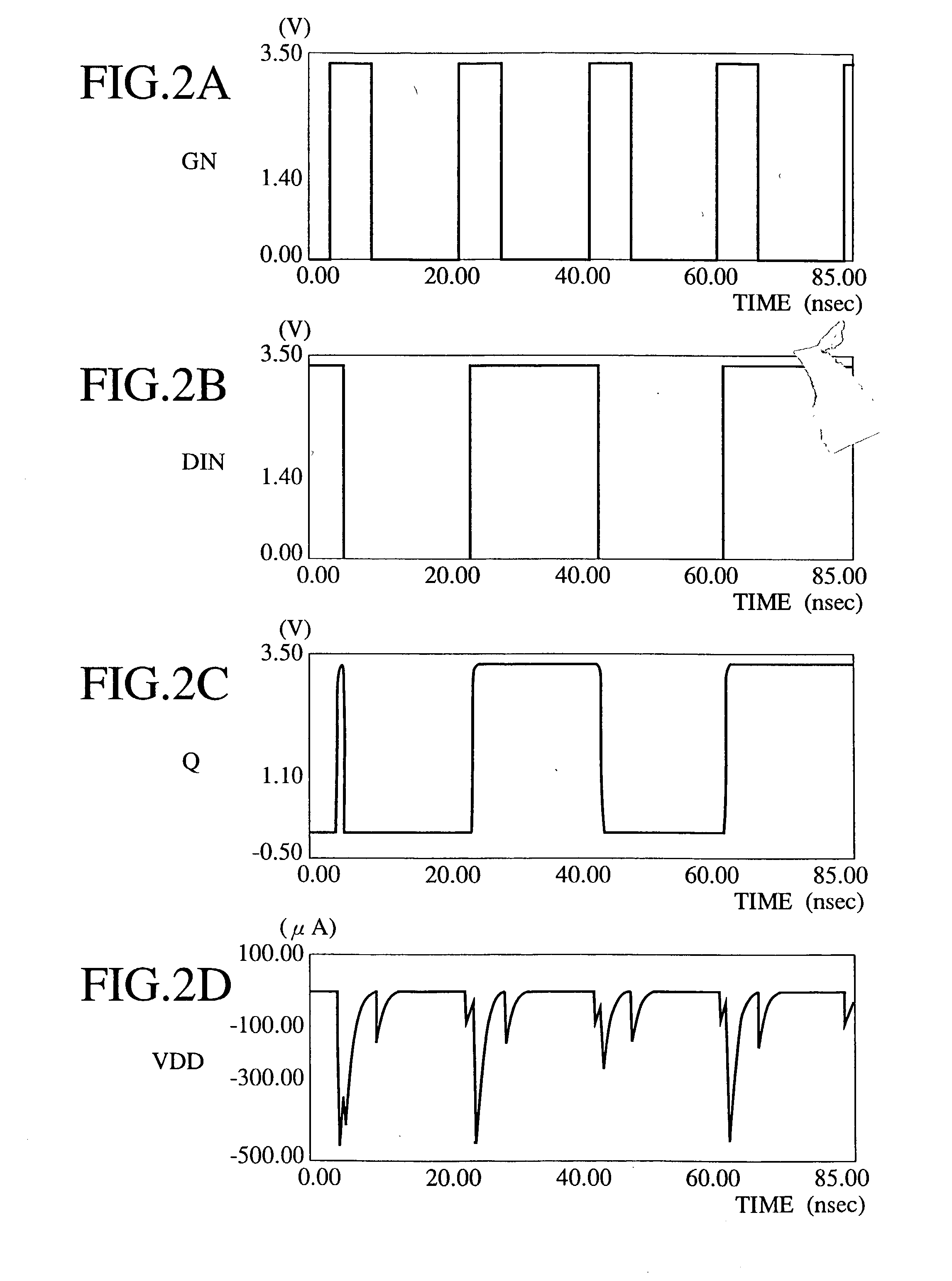
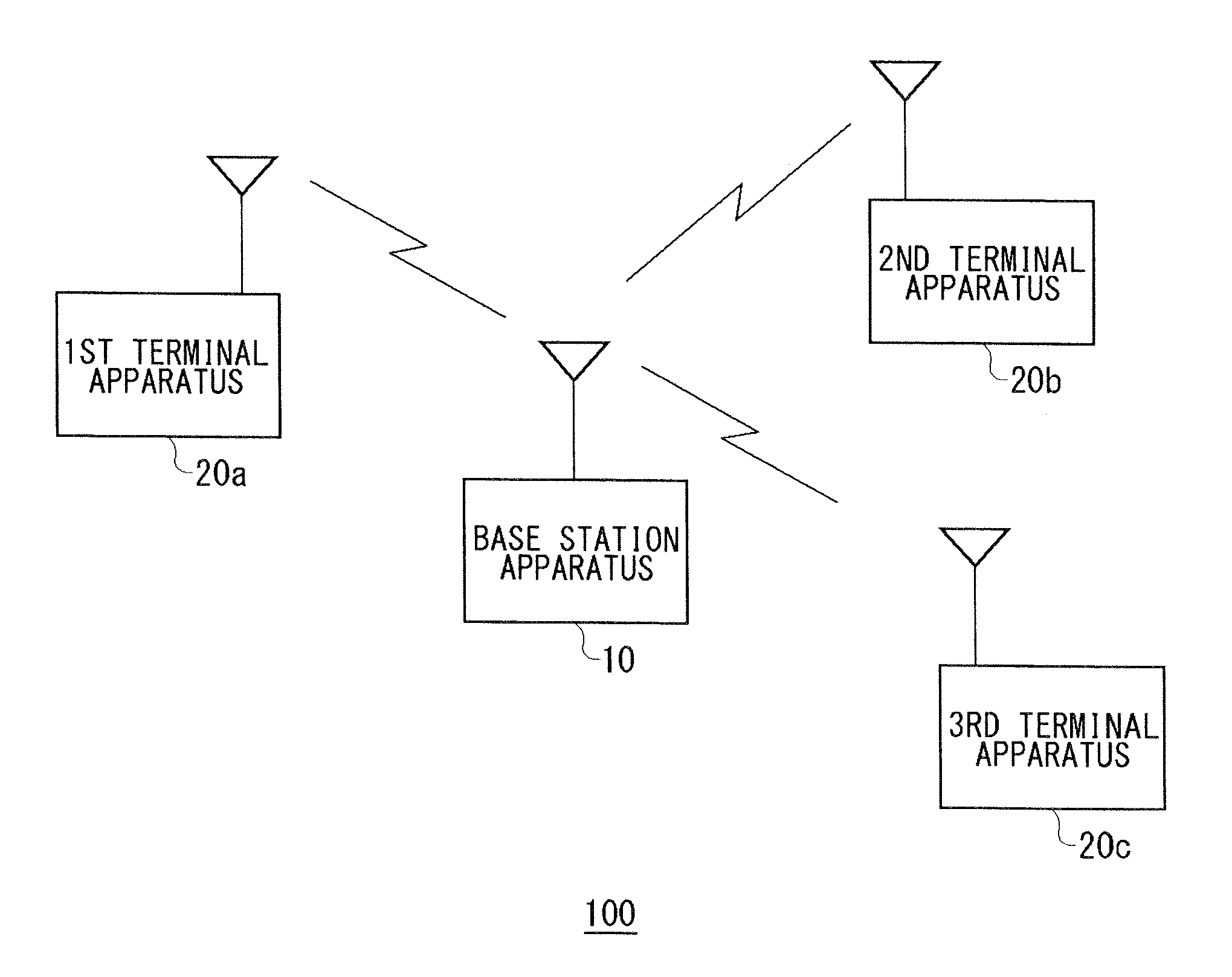
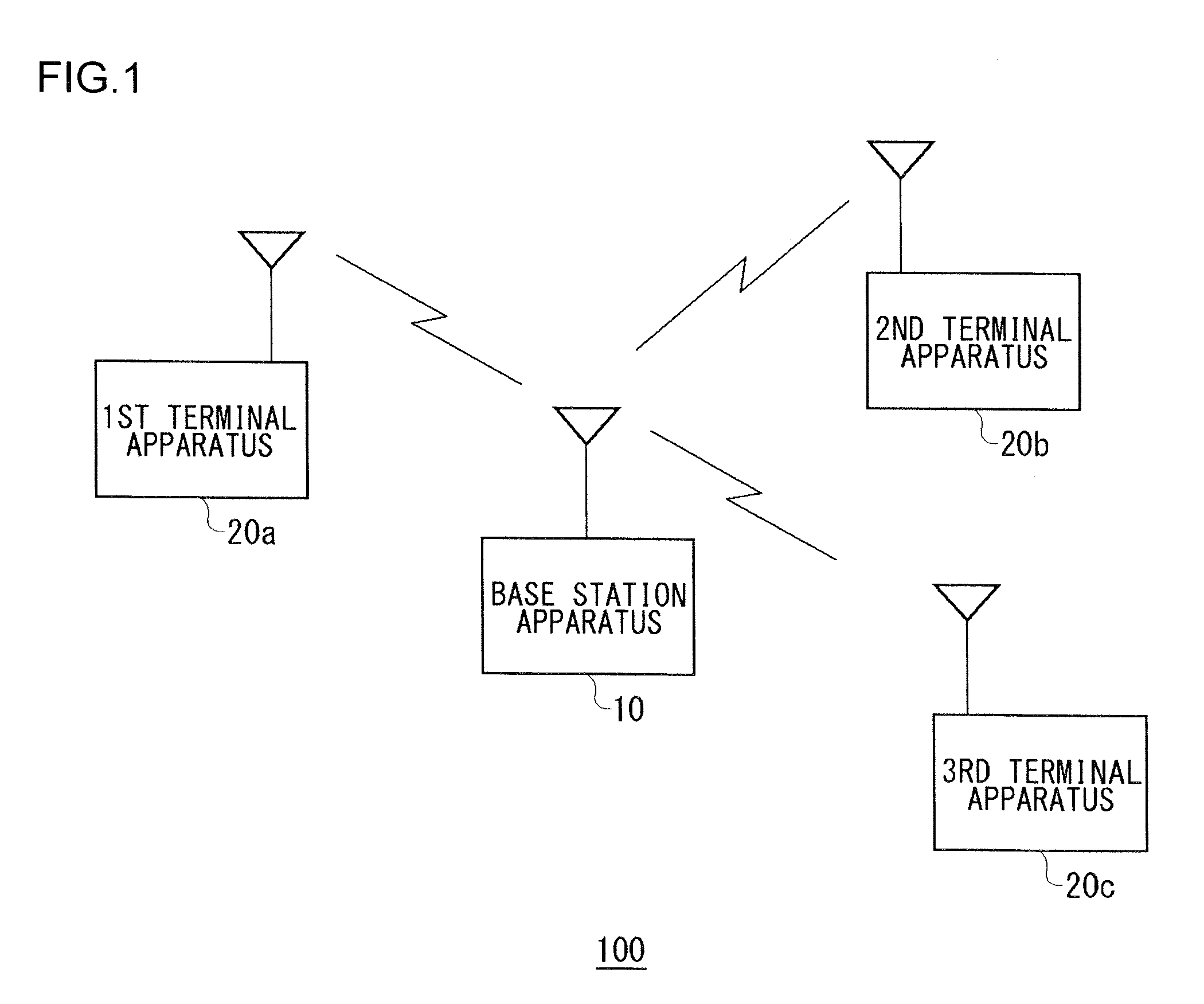
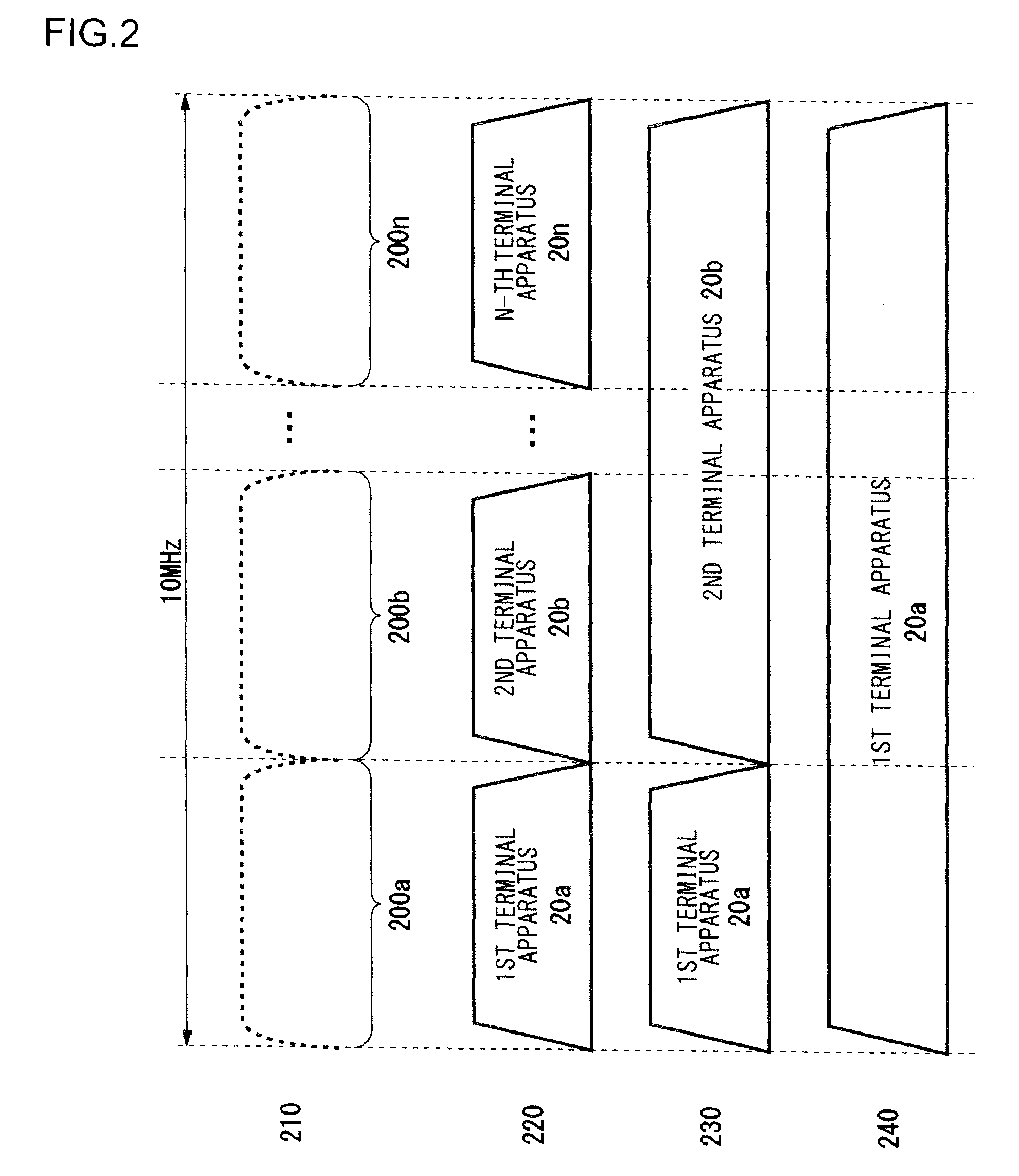
Method for allocating radio channels and base station apparatus utilizing the same
ActiveUS20080045227A1Efficient use ofFrequency-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTerminal equipmentCarrier signal
A base station apparatus includes a measurement unit, a derivation unit and an allocation unit. A base station apparatus allocates at least one subcarrier block, in a frequency band containing a plurality of subcarrier blocks composed of a plurality of subcarriers, to a terminal apparatus. The measurement unit measures an interference power of at least part of subcarriers among a plurality of subcarriers in each of the plurality of subcarrier blocks. The derivation unit derives, from the interference power of subcarriers measured by the measurement unit, an average value of the interference power for each of the plurality of subcarrier blocks and a statistical value indicating a degree of variation in the interference power relative to the average value. The allocation unit allocates at least one subcarrier block to the terminal apparatus, based on the average value and the statistical value derived by the derivation unit.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Current mode differential transmission method and system for transmitting three units of data using four signal lines
InactiveUS7508881B2Reduce in quantityChannel dividing arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesDifferential transmissionEngineering
Provided are a current mode differential transmission method and system for differentially transmitting three units of data using four signal lines. The method includes: dividing the four signal lines 1a, 1b, 2a and 2b into two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b, and differentially transmitting respective data (first data and second data) via the two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b; and transmitting the other data (third data) by differentially changing common mode currents of the two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
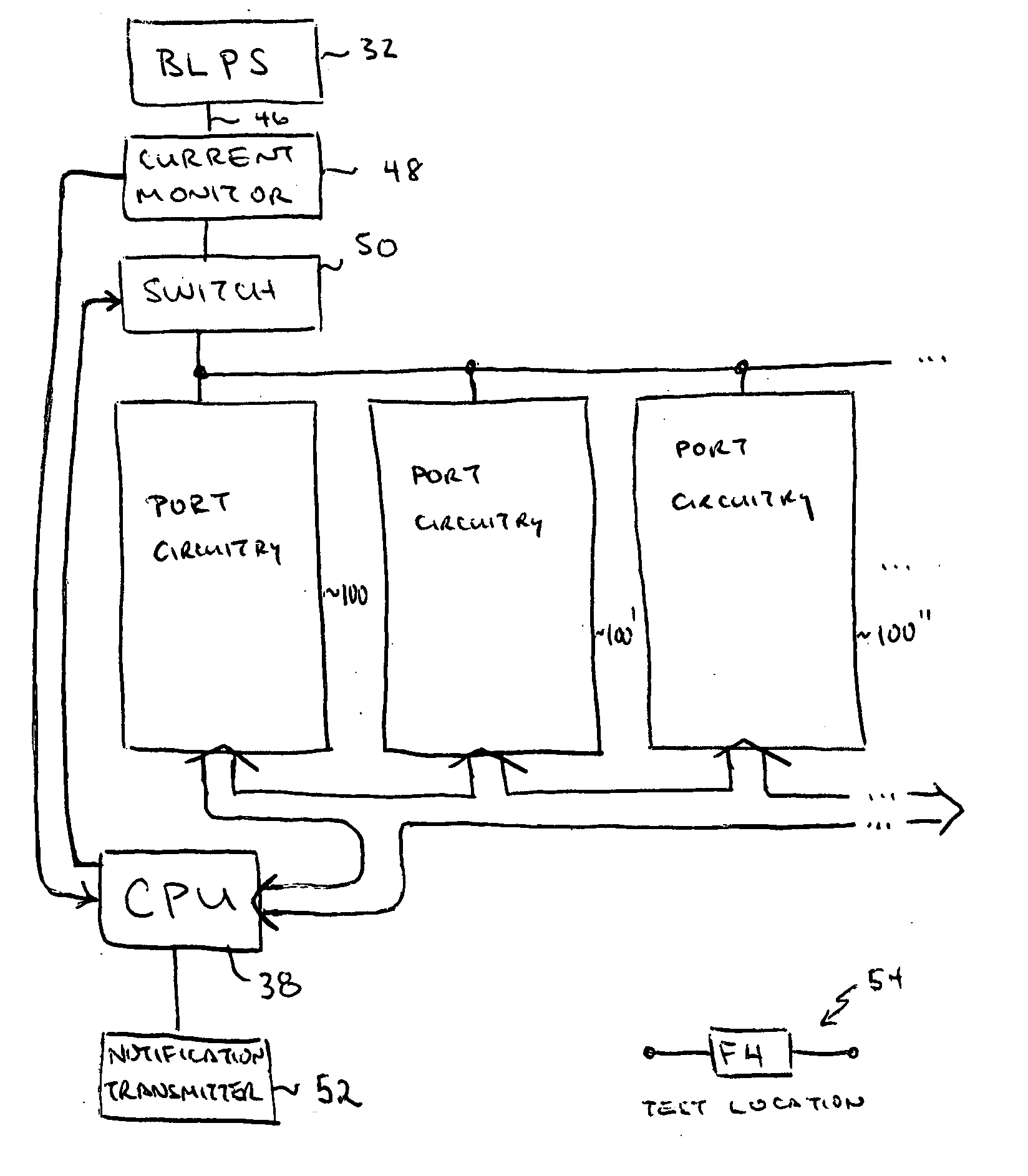
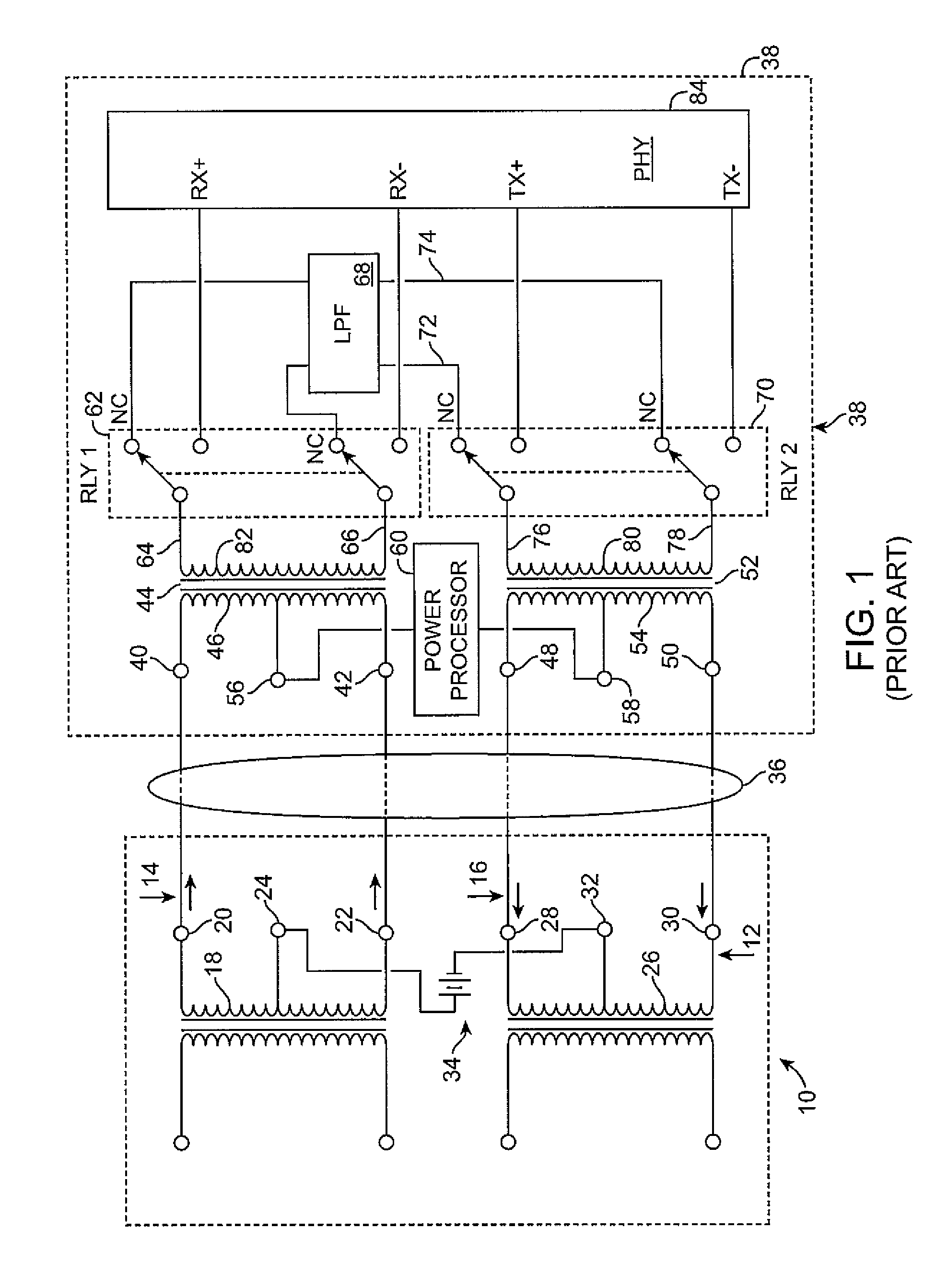
Fail-safe inline power in a wired data telecommunications network
ActiveUS20060262713A1Multiplex communicationData switching current supplyTelecommunications networkEngineering
A dynamic fuse element is provided in an inline power circuit to provide an electrical current protection level that varies in accordance with allocated current levels and that can respond to current spikes that are not expected. The dynamic fuse element comprises a processor aware of allocated current levels and an inline switch controlled by the processor to turn OFF in the event of a fault. In another aspect ferrite fuses may be provided for relatively low-current applications. In yet another aspect test fuses may be placed on the circuit board to verify that fuses used in manufacture operate at a certain current level.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Differential signal receiving device and differential signal transmission system
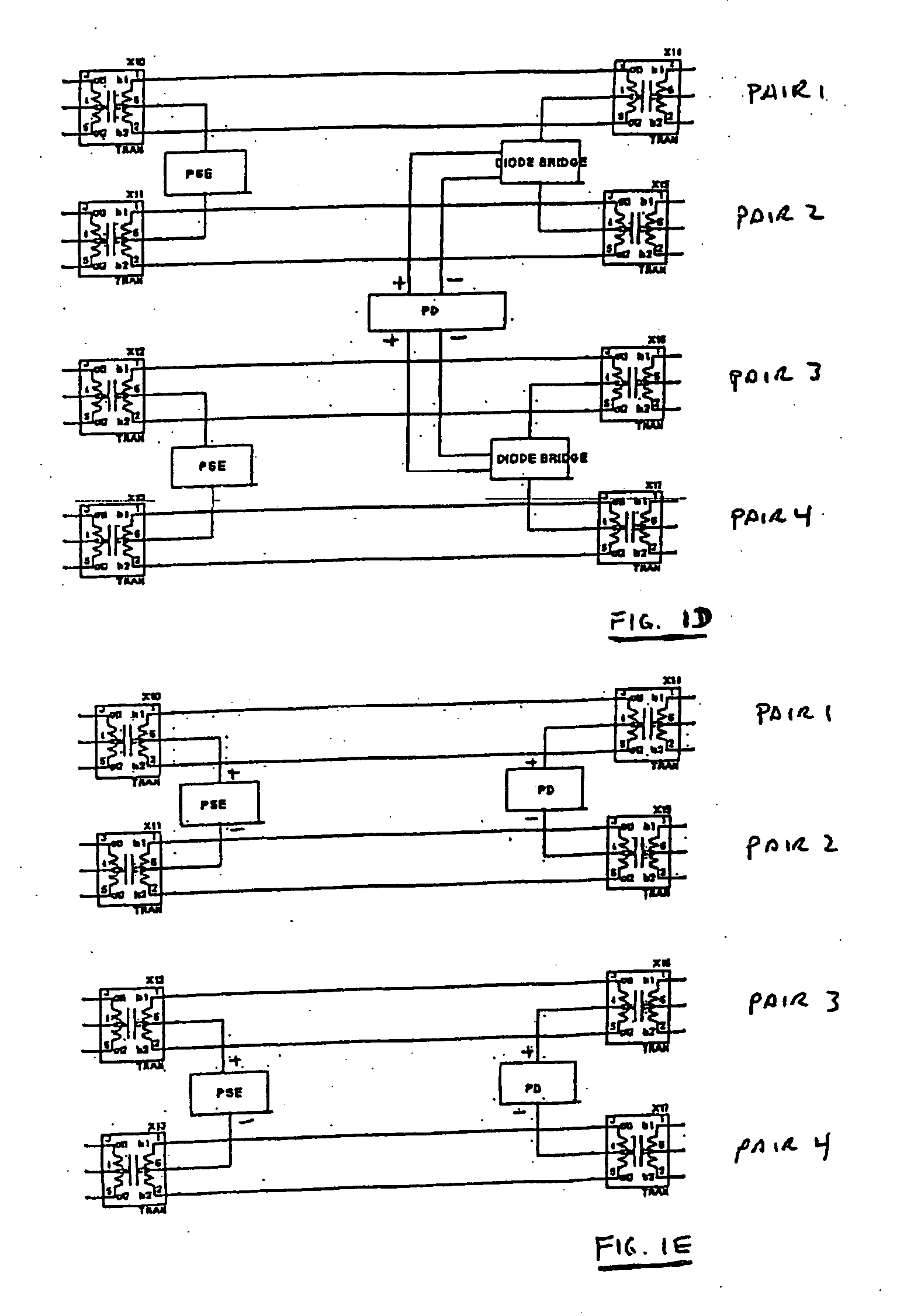
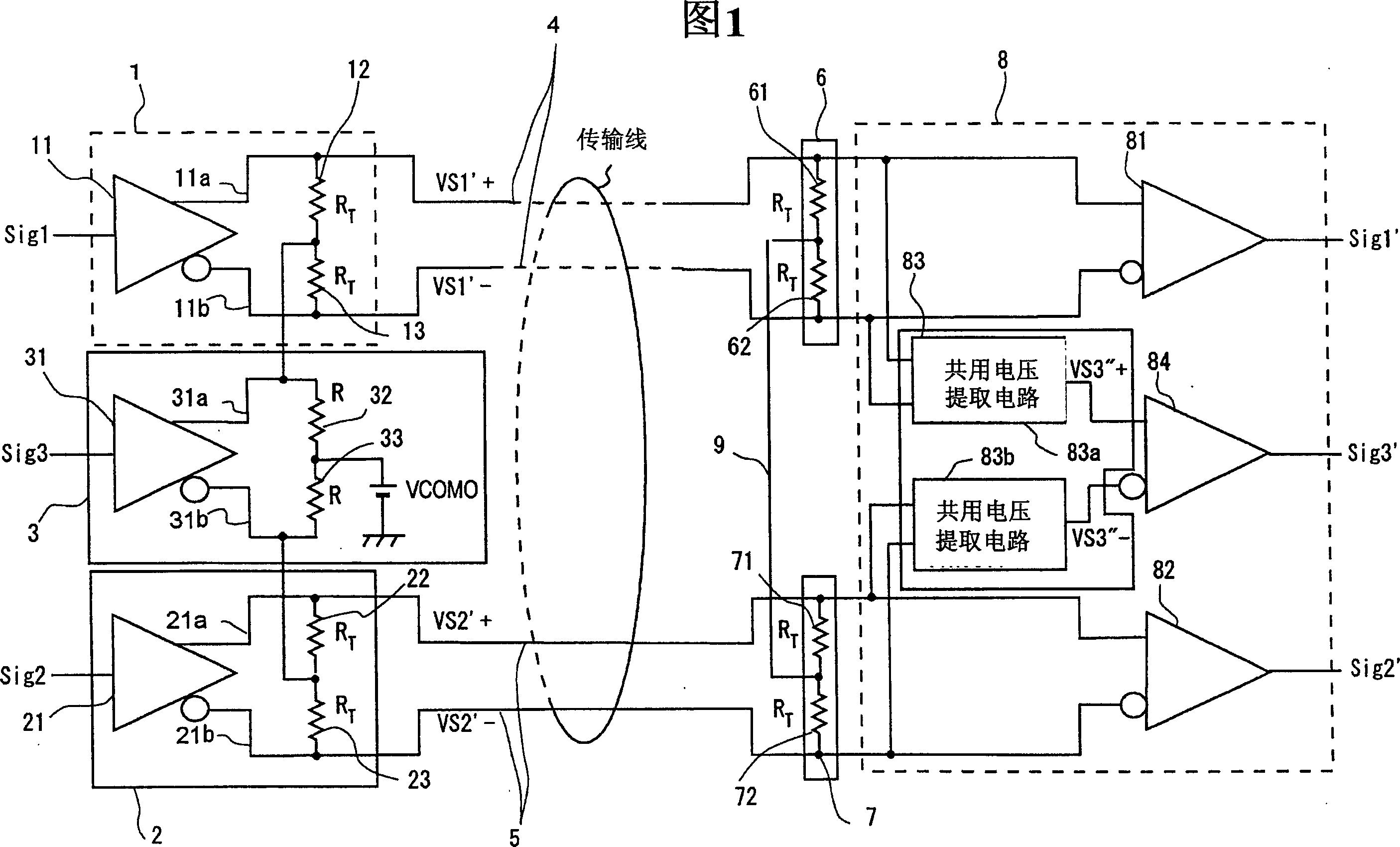
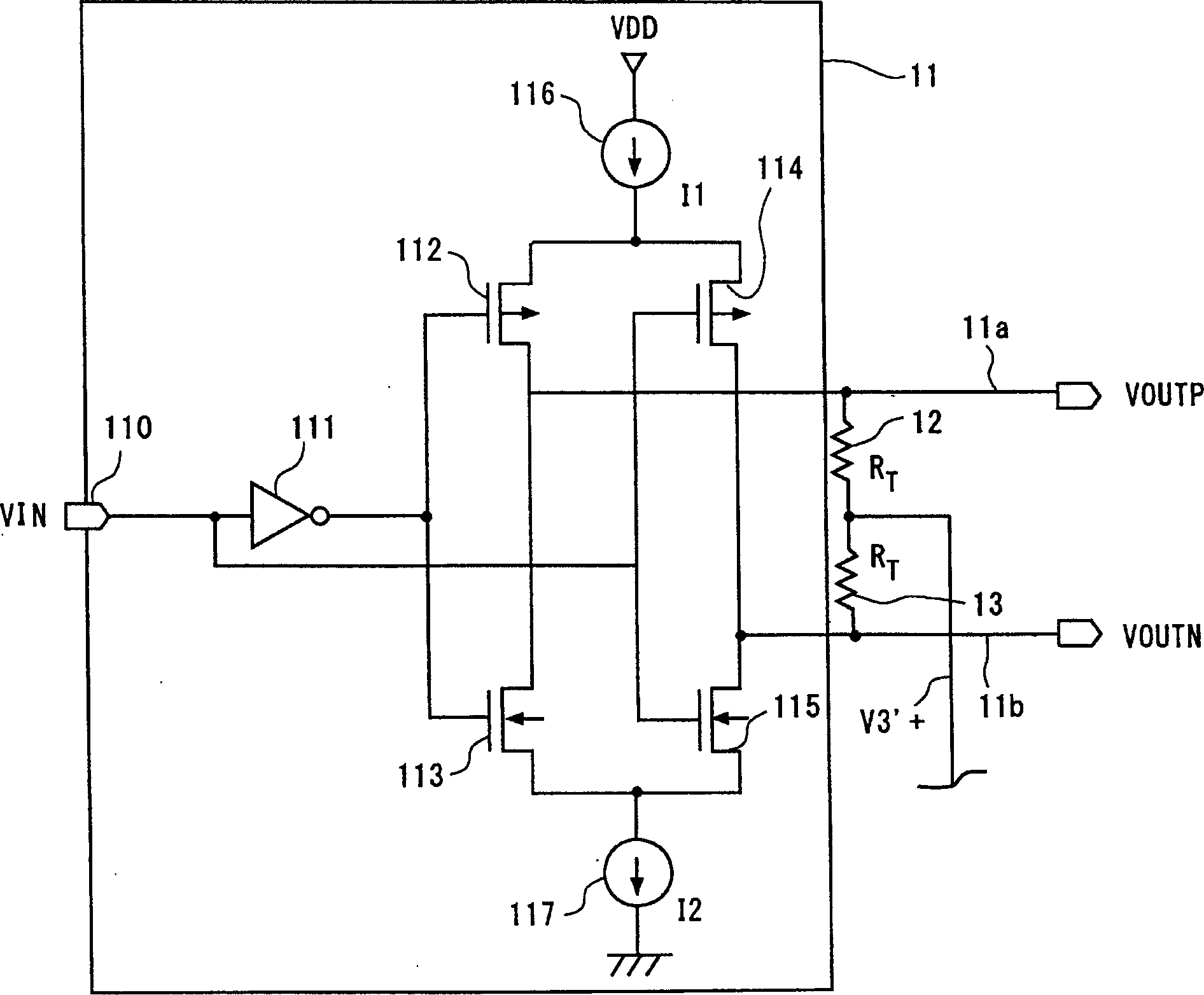
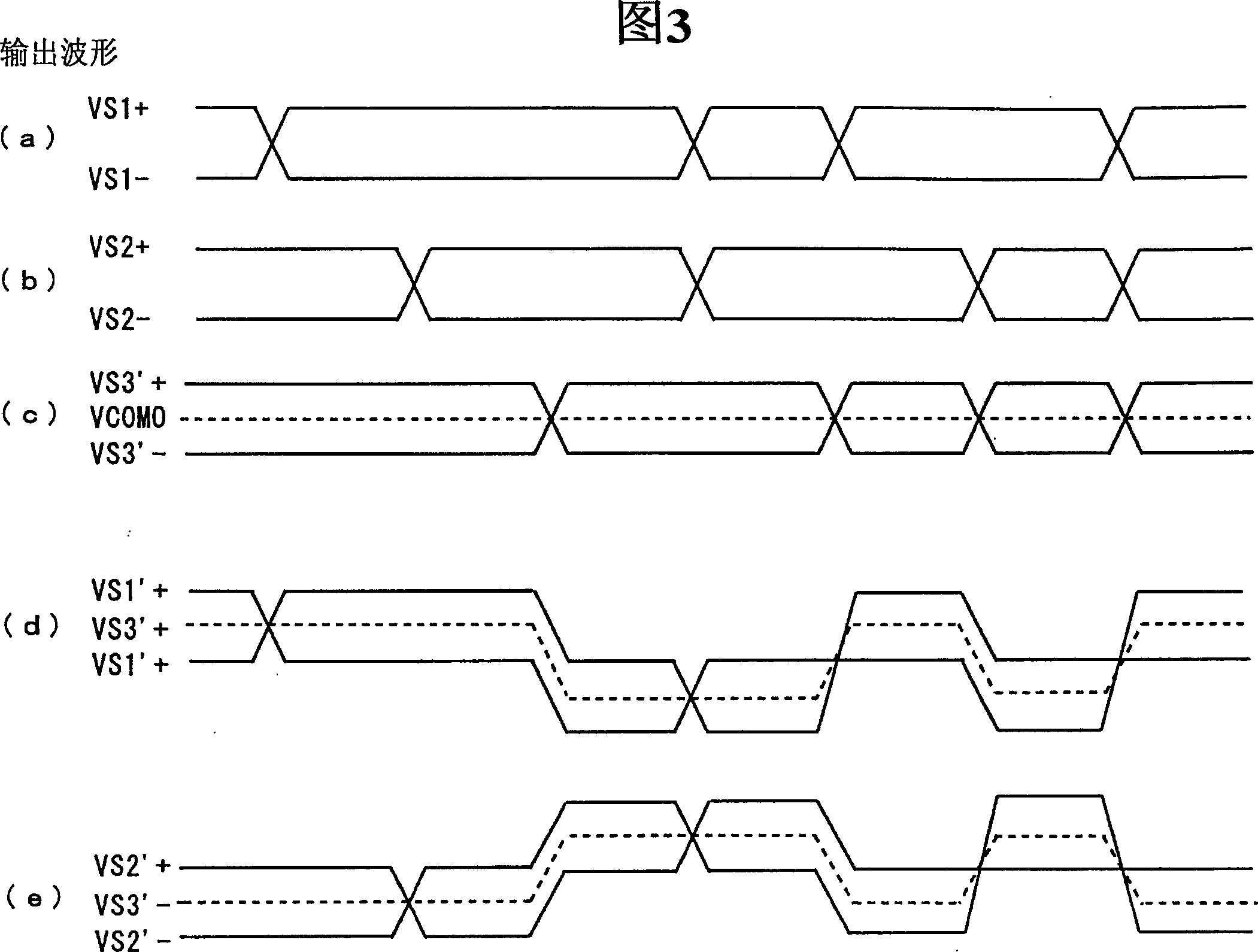
InactiveCN1574800AFully understandMultiple input and output pulse circuitsLine-faulsts/interference reductionDifferential signalingEngineering
The intermediate node of the first terminator connected between a pair of signal lines transmitting the first differential signal with one side of the third differential signal as a common voltage and the intermediate node of the second terminator connected between a pair of signal lines transmitting the second differential signal with the other side of the third differential signal as a common voltage are connected by the intermediate connection. Thus, the intermediate node of the first terminator and the intermediate node of the second terminator act as a virtual ground of the third differential signal, enabling the matching of the impedance of the terminators related to the third differential signal and the impedance of the signal lines related to the third differential signal. It is thus able to prevent the reflection of the third differential signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
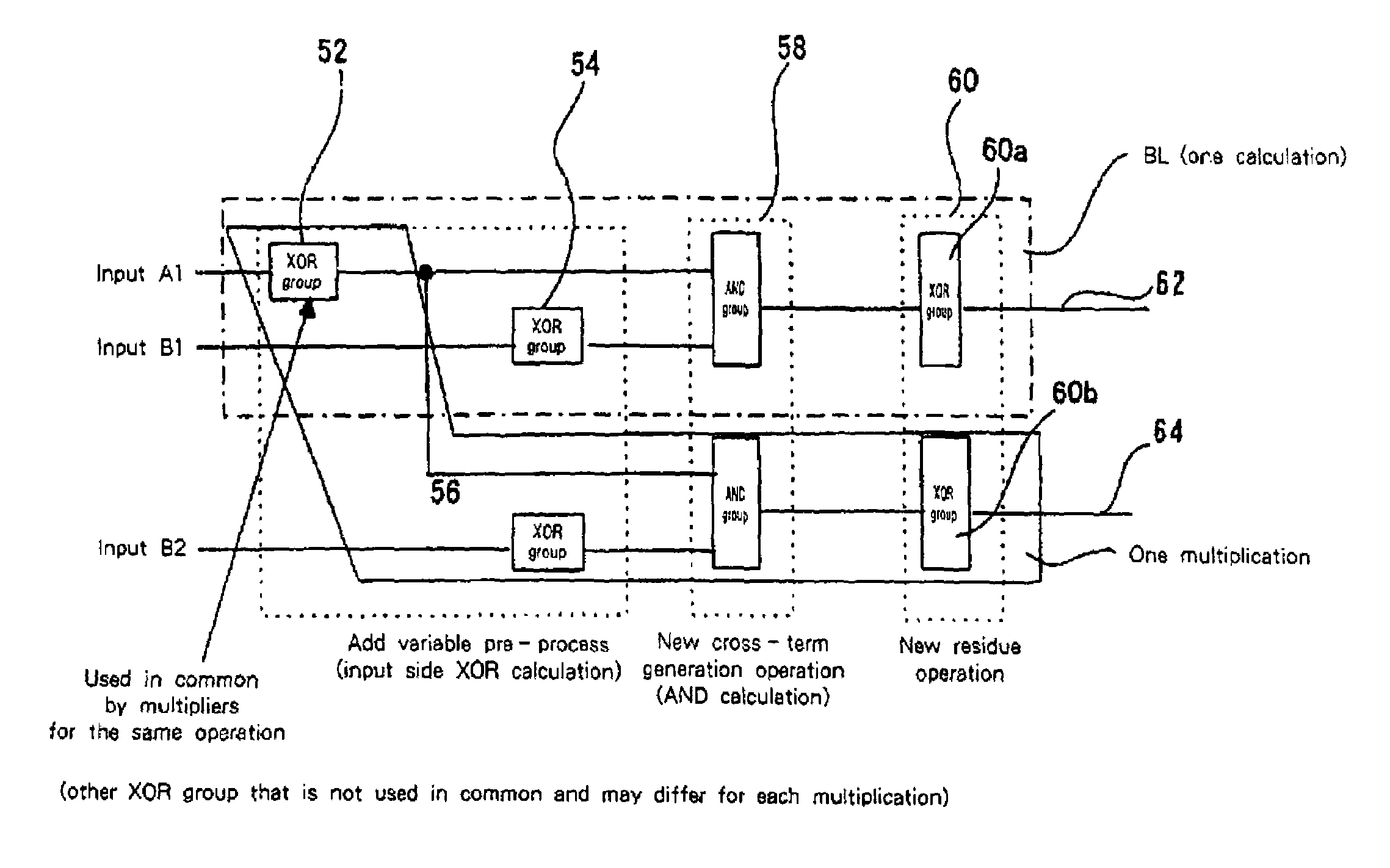
Combinational circuit, and encoder, decoder and semiconductor device using this combinational circuit
InactiveUS7010738B2Efficient configurationSmall sizeOther decoding techniquesDigital data processing detailsBinary multiplierComputer science
A combinational circuit comprises: a plurality of multipliers, independently performing two or more multiplications for coded digital signals in a Galois extension field GF(2m) (m is an integer equal to or greater than 2), wherein the multipliers include an input side XOR calculator, an AND calculator, and an output side XOR calculator, and wherein the multipliers share the input side XOR calculator. Further, according to the present invention, these multipliers each include an adder connected between an AND calculator and an output side XOR calculator, wherein the output side XOR calculator is used in common, and wherein the outputs of the AND calculators in the multipliers are added by the adders, and the addition results are calculated by the output side XOR calculator that is used in common.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and device for transmission with reduced crosstalk
InactiveUS20060099926A1Accurately determinedOptimize locationReliability increasing modificationsStatic indicating devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
The invention relates to a method and a device for transmission with reduced crosstalk in interconnections used for sending a plurality of signals, such as the interconnections made with flat multiconductor cables, or with the tracks of a printed circuit board, or inside an integrated circuit. An interconnection with four parallel transmission conductors plus a reference conductor has each of its ends connected to a termination circuit. The transmitting circuit receives at its input the signals of the four channels of the source and its output terminals are connected to the conductors of the interconnection. The receiving circuit's input terminals are connected to the conductors of the interconnection, and its four output channels are connected to the destination. The signals of the four channels of the source are sent to the four channels of the destination, without noticeable crosstalk.
Owner:RAMBUS INC +1
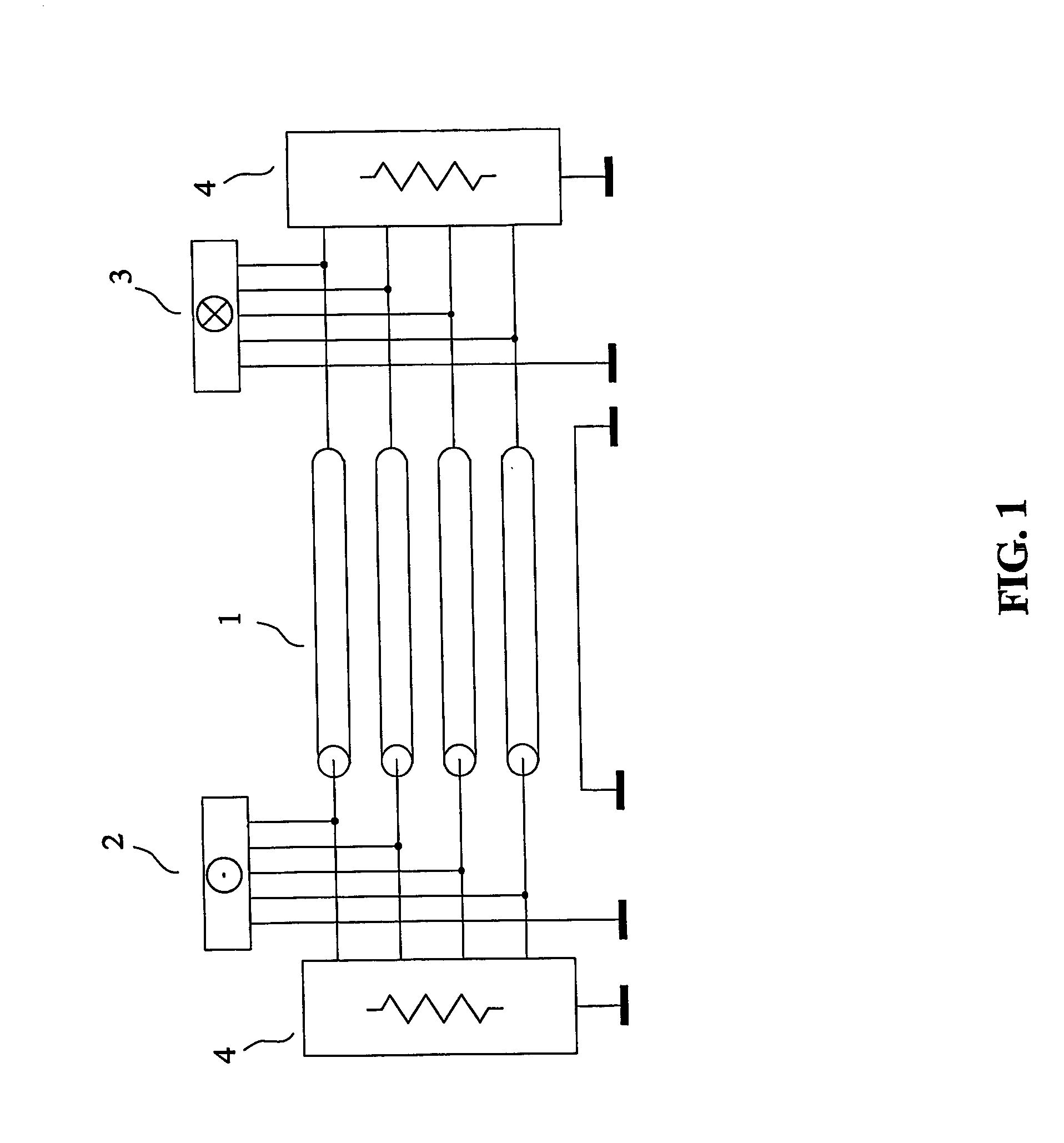
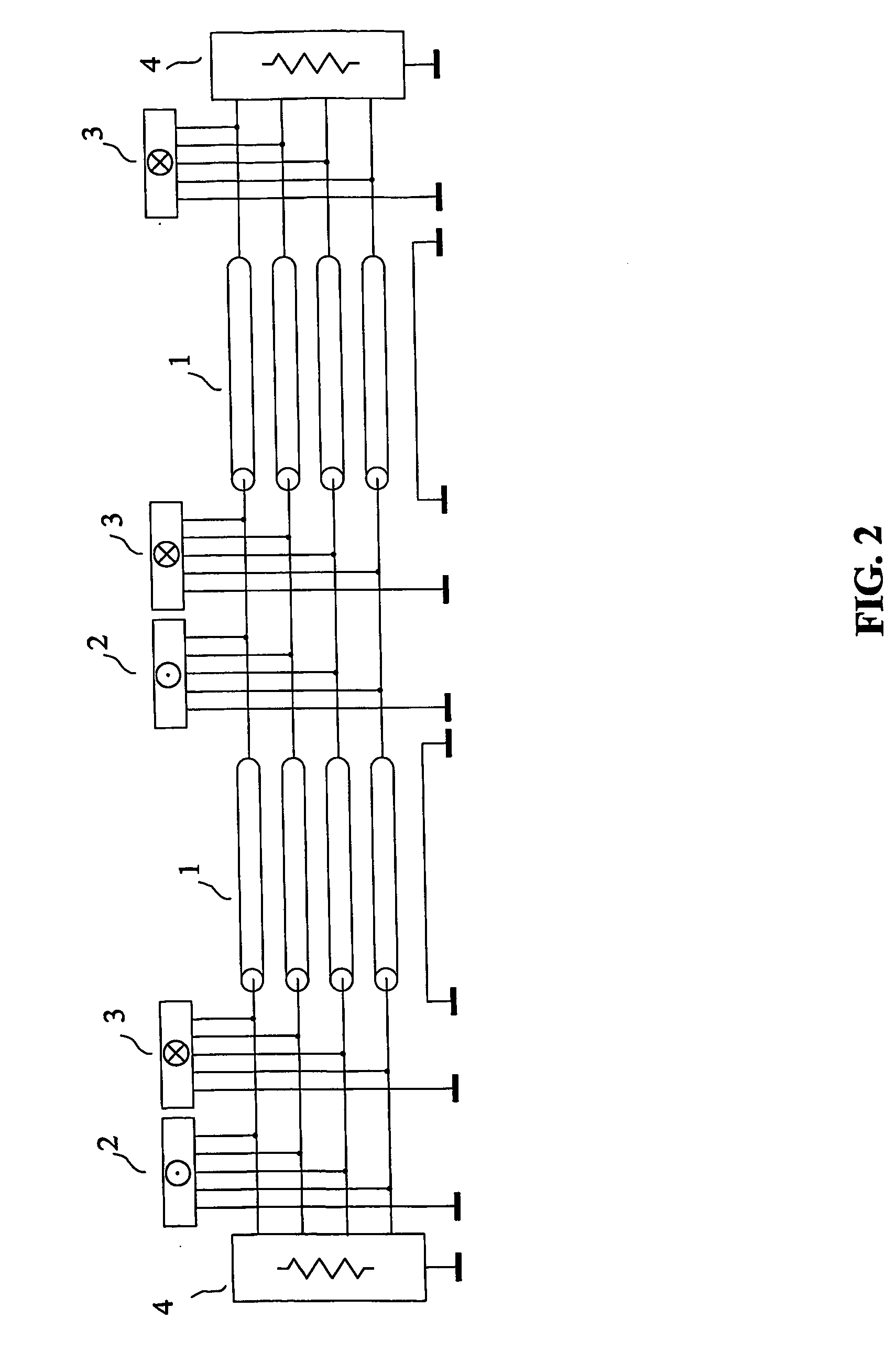
Method and device for injecting a noise signal into a paired wire communication link
InactiveUS7260152B2High impedanceLower impedanceCorrect operation testingFrequency-division multiplexTelecommunications linkWired communication
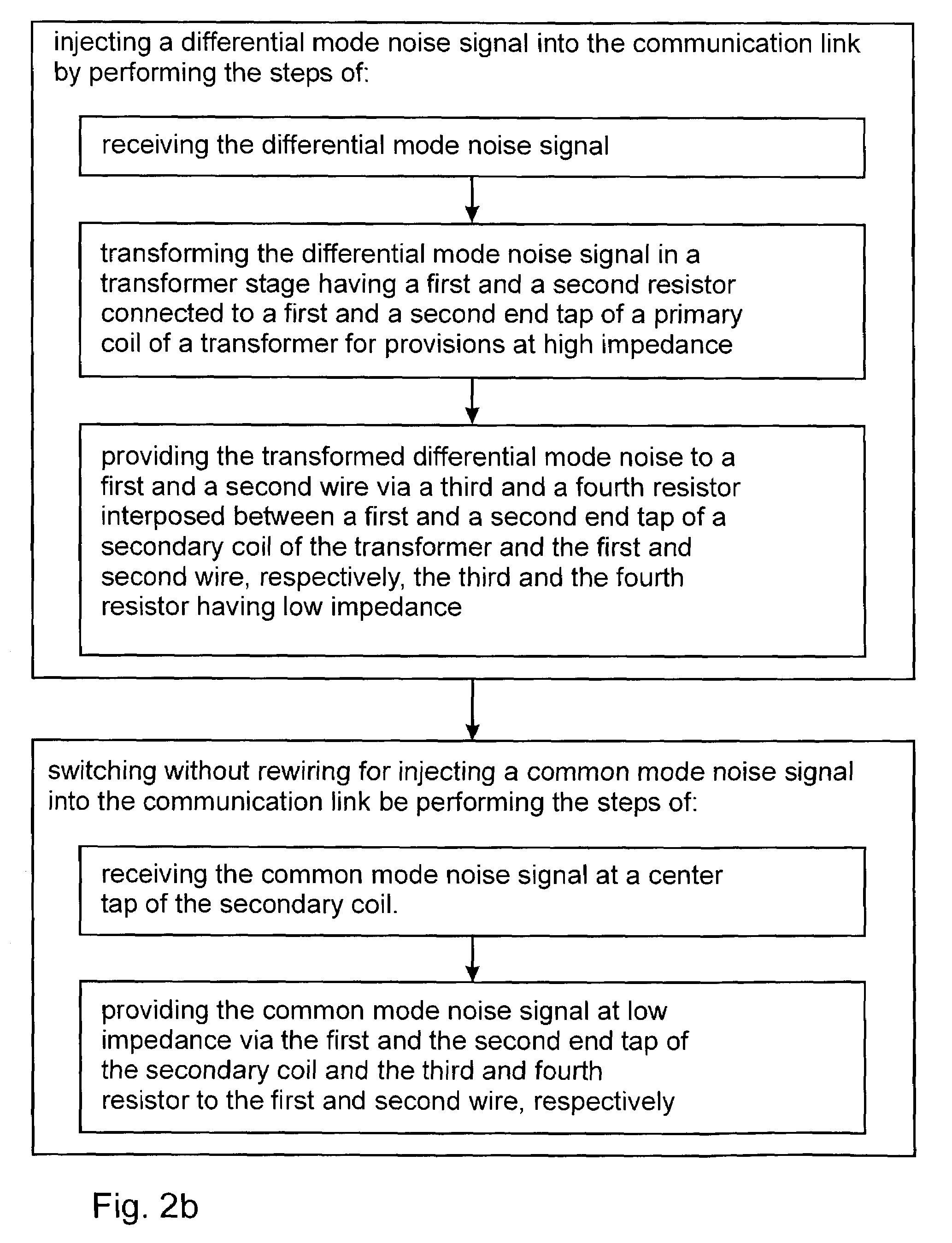
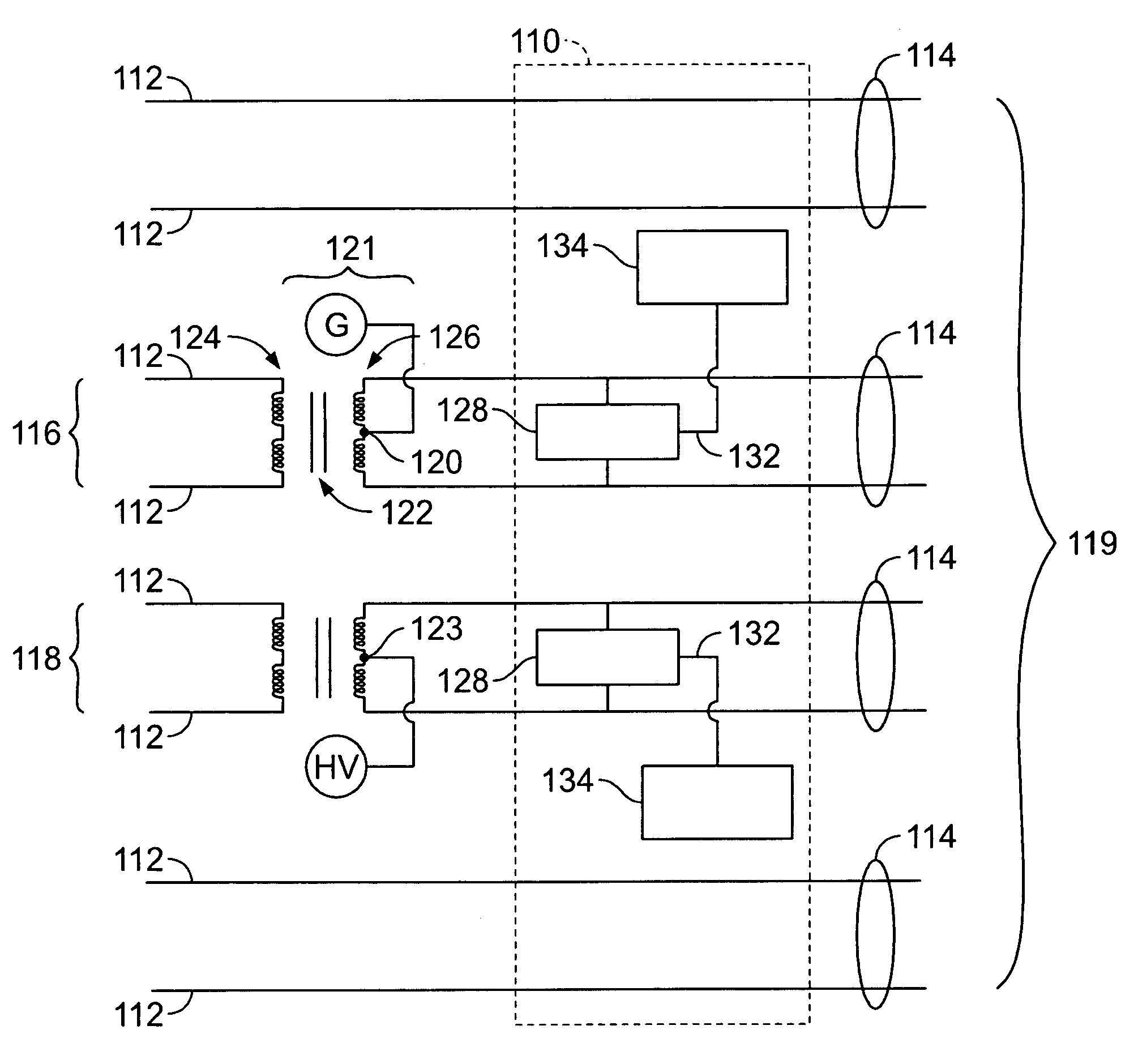
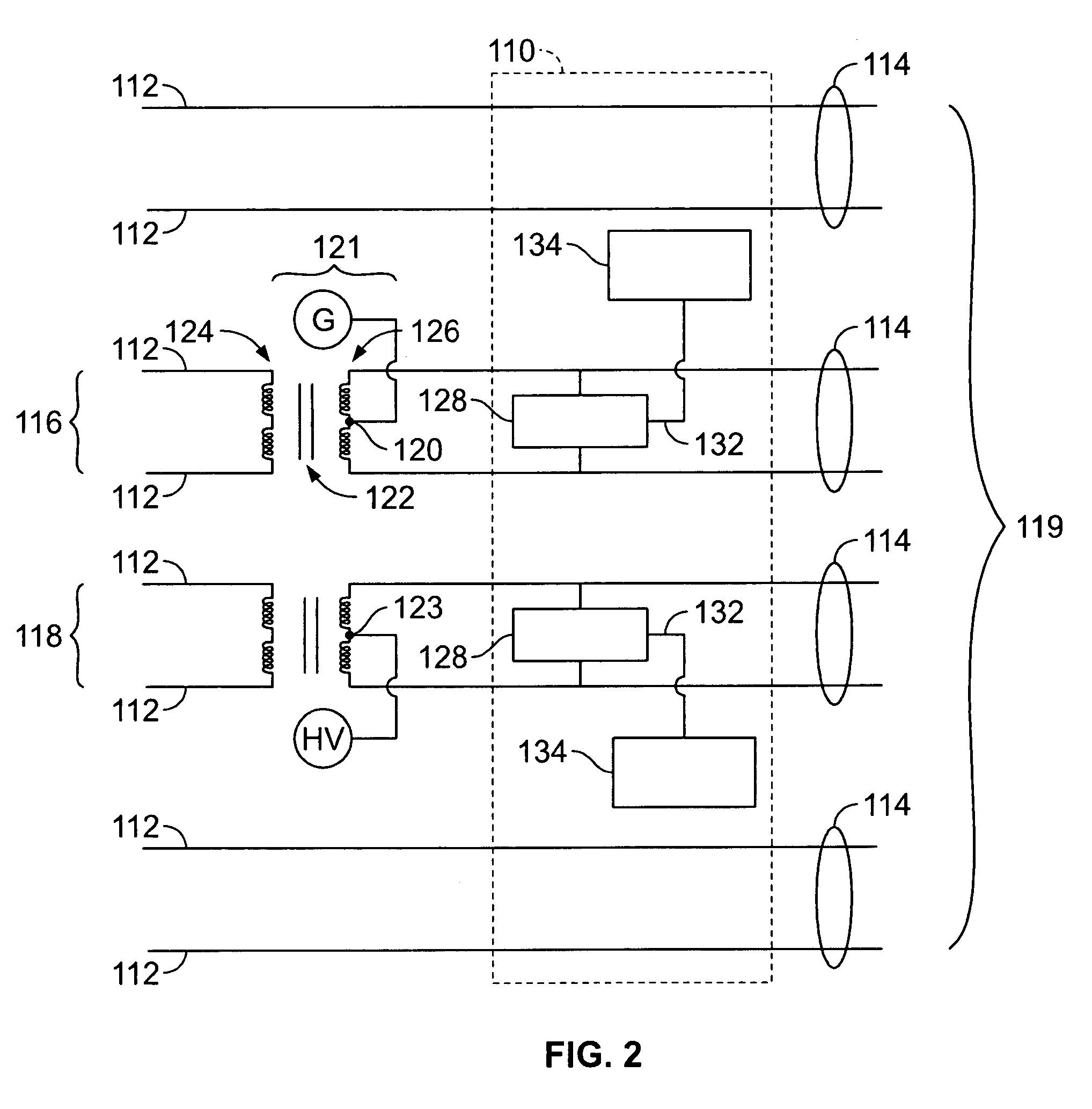
The present invention relates to a device and method for injecting a noise signal into a wire pair of a communication link. In operation a differential mode noise signal is received at a first and a second input port, which are connected via a first and a second resistor to a first and a second end tap of a primary coil of a transformer, respectively. The transformed differential mode noise signal is then transmitted via a first and a second end tap of a secondary coil of the transformer and a third and a fourth resistor to a first and a second output port for injection at high impedance into a first and a second wire of the communication link. Optionally, the device comprises a third input port connected to a center tap of the secondary coil for receiving a common mode noise signal. The common mode noise signal is then provided at low impedance to the first and the second wire via the first and the second end tap of the secondary coil and via the third and fourth resistor having low impedance, respectively. The device allows injection of a noise signal into the communication link at a desired location without splitting the same. Furthermore, the device allows injection of differential mode noise signals and common mode noise signals using same circuitry without switching and / or rewiring between different electrical circuits.
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
Method and apparatus for providing out of band communications over structured cabling
An out of band communications apparatus includes first and second data lines arranged in a differential pair. The data lines convey high speed data within a first frequency range and out of band data within a second frequency range that differs from the first frequency range. The apparatus also includes a band pass filter coupled to the first and second data lines. The filter only passes the out of band data and blocks the high speed data. The apparatus also includes a device coupled to the band pass filter and configured to at least one of transmit and receive out of band data.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS UK INFRASTRUCTURE +1
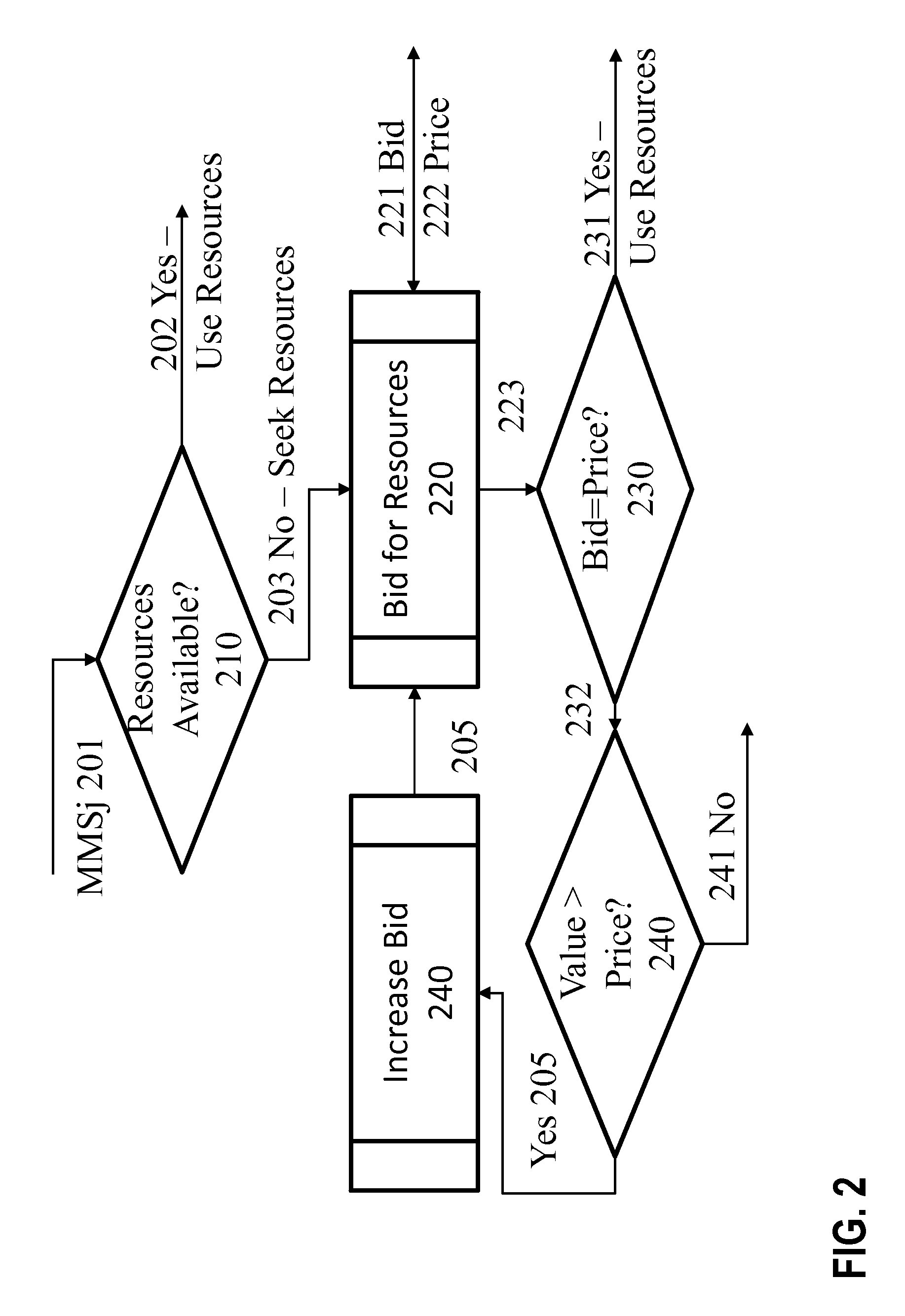
Method for administering radio resources by monitoring the interference situation
ActiveUS7197316B2Good conditionAccurately informedRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringMobile radioRadio signal
In a method for administering radio resources in a mobile radio cell, which includes a plurality of mobile terminals which are distinguishable by their radio signals, and a base station, the administration of radio resources of a mobile radio cell is improved to such an extent that the available radio resources are utilized more economically. A mobile terminal is requested by the base station to send out a signal, currently present at a receiver of the mobile terminal, which is representative of an interference situation at the location of the mobile terminal. This is sent together with information for estimating the channel between the mobile terminal and the base station so that the base station receives raw data at the location of the mobile terminal, and evaluates the signal received from the mobile terminal and the information for estimating the channel between the mobile terminal and the base station for determining the radio sources forming the basis of the signal and the intensities of at least some of the radio sources. Further, the base station in the mobile radio cell adapts the distribution of the radio resources for improving the interference situation at the location of the mobile terminal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
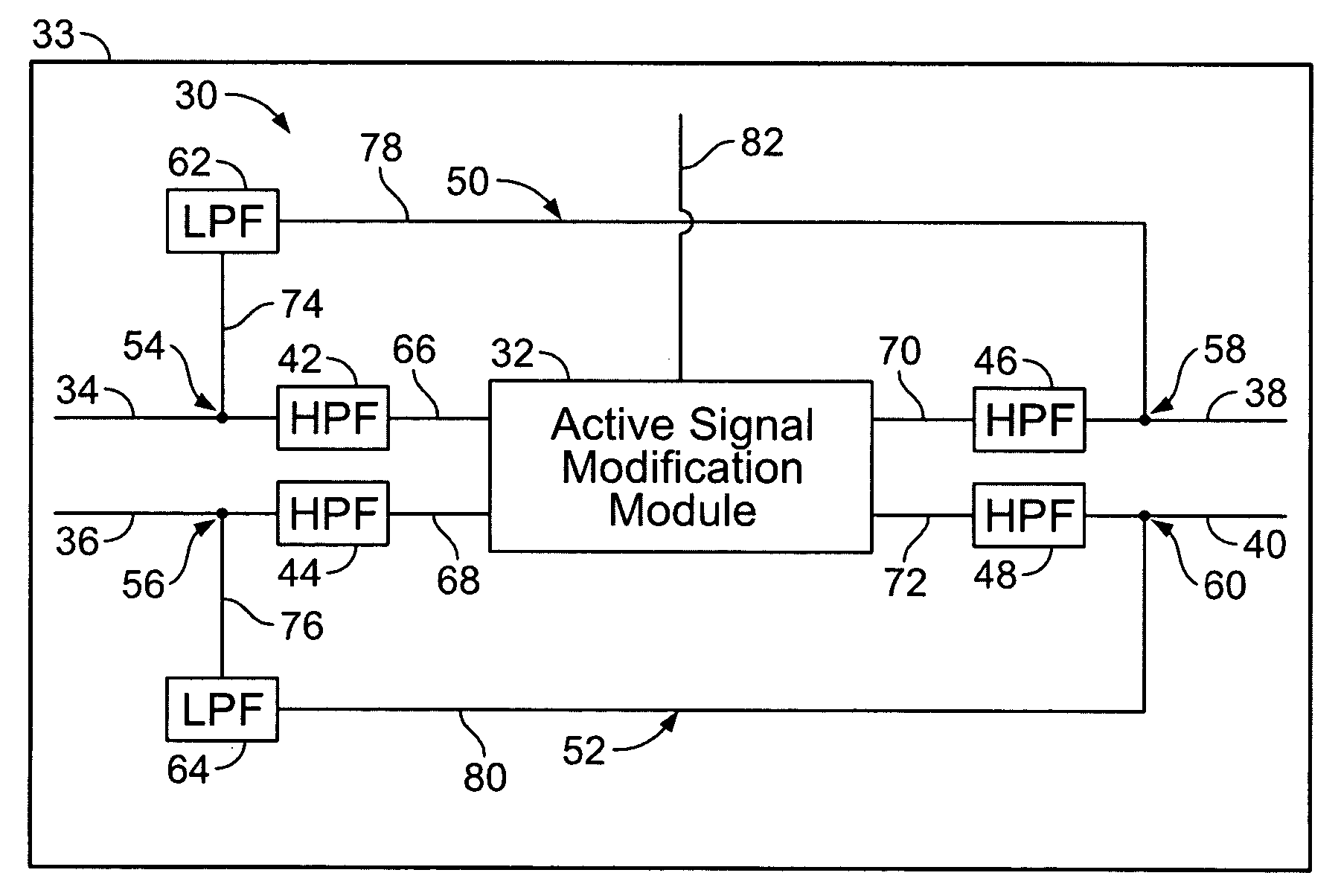
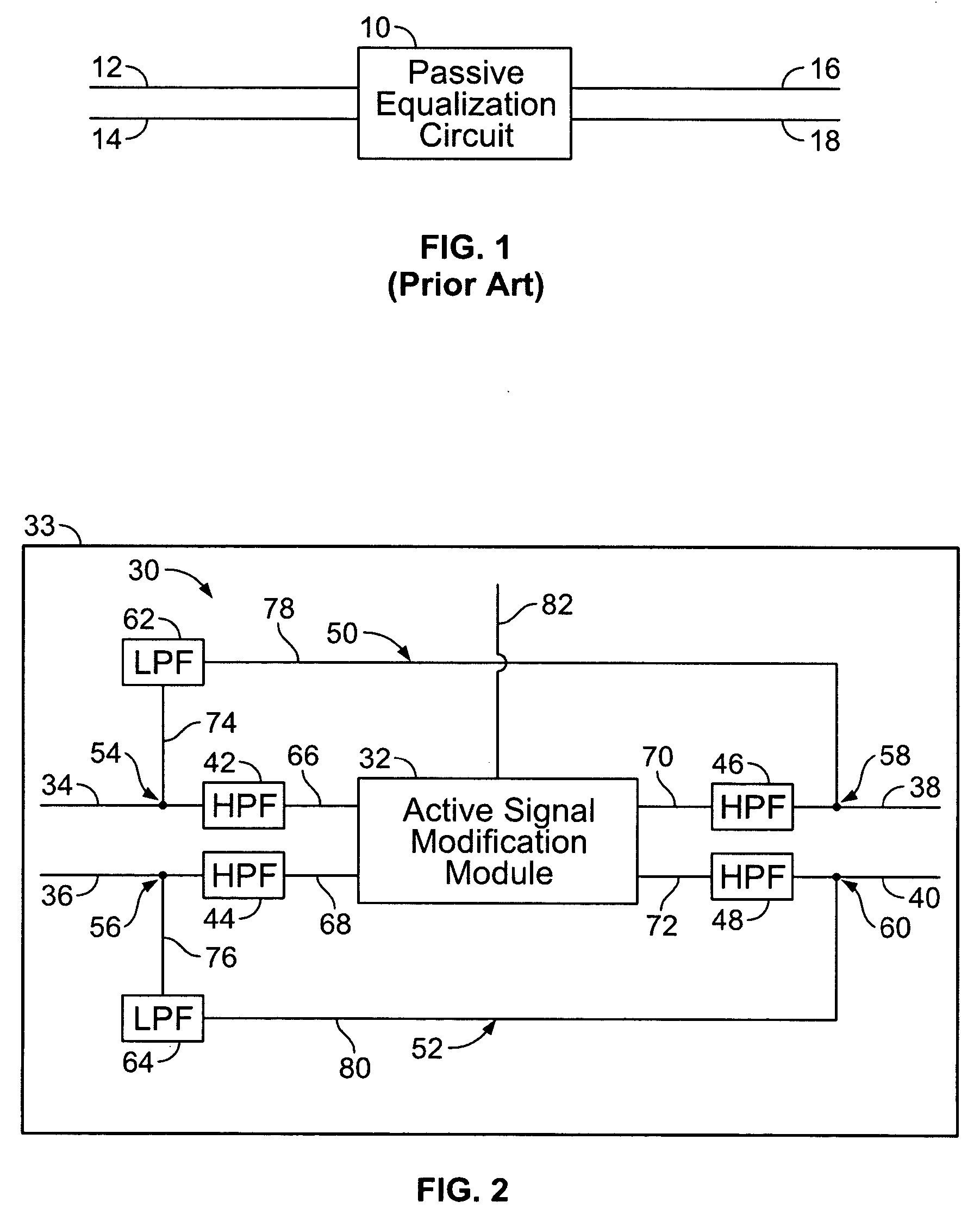
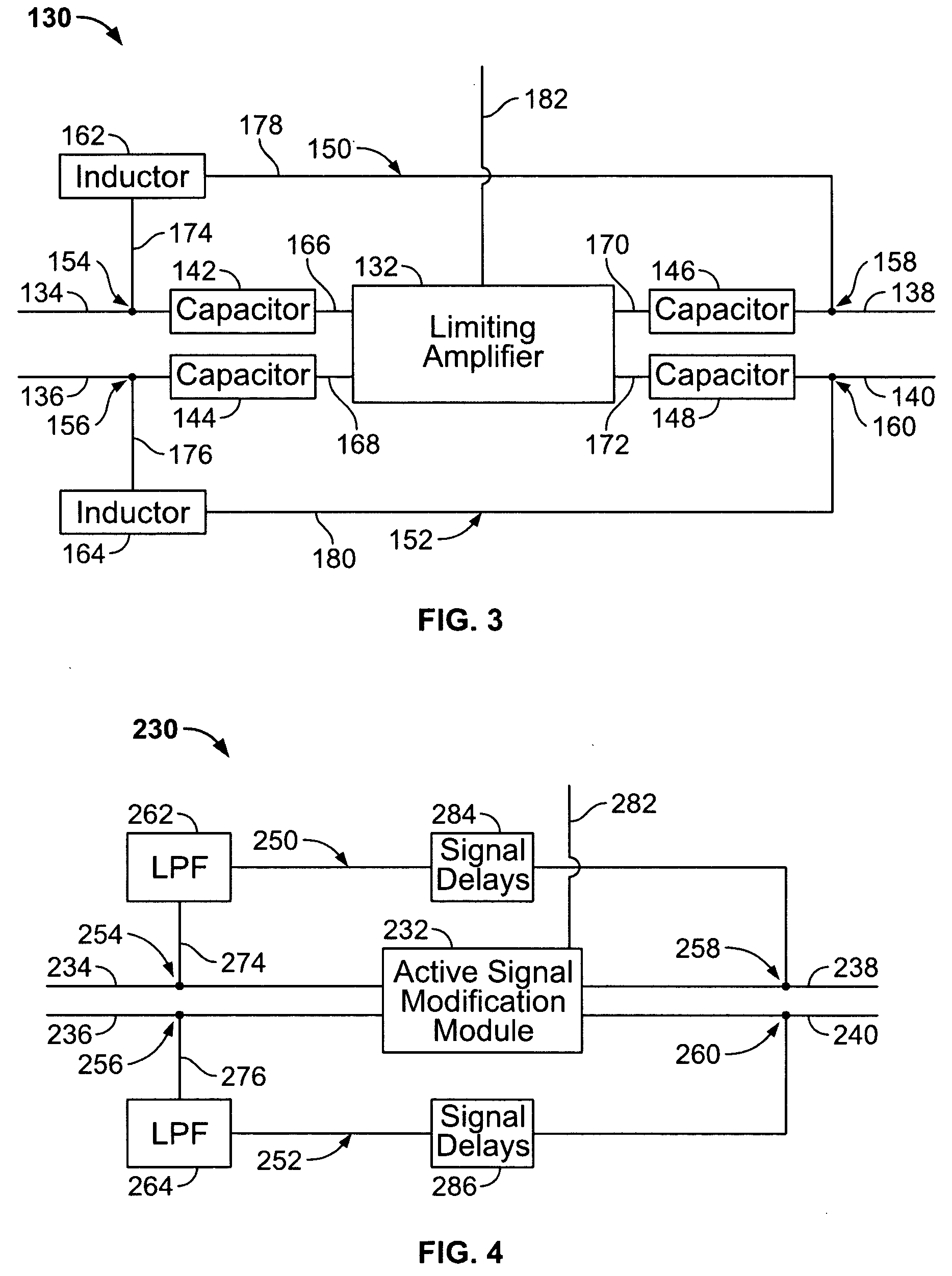
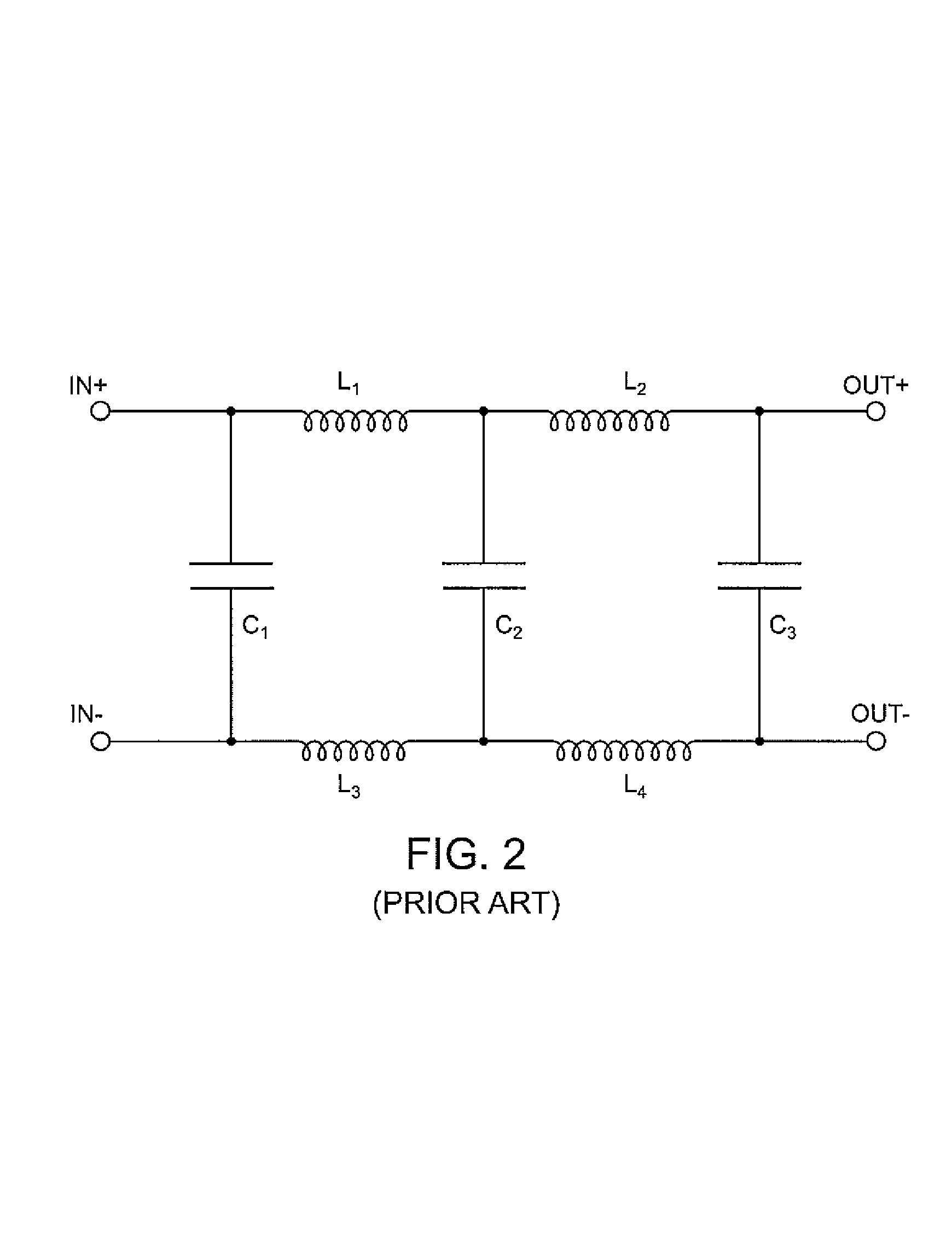
Multi-mode signal modification circuit with common mode bypass
InactiveUS20060146921A1Electric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsLow-pass filterHigh frequency
A signal modification circuit is provided for use with multi-mode formatted data in accordance with a common mode component and a high frequency component formatted in accordance with a differential mode. The circuit includes an active module that modifies the high frequency component to generate a modified and enhanced high frequency component at an output thereof. A bypass line interconnects the inputs and outputs of the active module to bypass the active module. A low pass filter is provided along the bypass line blocking passage of the high frequency component along the bypass line.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
Noise suppression circuit, asic, navigation apparatus, communication circuit, and communication apparatus having the same
InactiveUS20030011500A1Electric signal transmission systemsElectronic switchingCapacitanceTelecommunications
The present invention provides an noise suppression circuit comprises an internal circuit which has a high and a low level terminals. The low level terminal is connected to a low level power supply (GND) line. The noise suppression circuit further comprises a first transistor in which one main electrode is connected to the high level terminal of the circuit, a bypass capacitor connected between the other main electrode of the first transistor and the low level power supply line, and a second transistor connected between the other main electrode of the first transistor and a high level power supply (VDD) line. The first transistor is conductive when the internal circuit is active, and is not conductive when the internal circuit is inactive. The second transistor is not conductive when the internal circuit is active, and is conductive when the internal circuit is inactive. Moreover, a communication circuit for setting the number of data buses to be newly added to be less than two times a transmission data, then encoding the data to be sent so as to make the numbers of "0" and "1" in the data to be sent through the data buses equal to each other and accordingly reducing the increase of the number of the data buses to a minimum and thereby suppressing the common phase power supply noise is provided. A communication apparatus comprising the communication circuit is also provided. Furthermore, the bypass capacitor C for noise suppression circuit is formed in an empty space in a ASIC. A polysilicon layer constituting one electrode of the bypass capacitor is formed in the substrate contact region formed between basic cells regularly arranged, each including a plurality of nMOS and pMOS transistors. This bypass capacitor C is connected between the high and the low level power supply lines to reduce the current running through the power supply line to suppress the EMI noise.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for allocating radio channels and base station apparatus utilizing the same
ActiveUS8068875B2Efficient use ofFrequency-division multiplexSubstation equipmentCarrier signalTerminal equipment
A base station apparatus includes a measurement unit, a derivation unit and an allocation unit. A base station apparatus allocates at least one subcarrier block, in a frequency band containing a plurality of subcarrier blocks composed of a plurality of subcarriers, to a terminal apparatus. The measurement unit measures an interference power of at least part of subcarriers among a plurality of subcarriers in each of the plurality of subcarrier blocks. The derivation unit derives, from the interference power of subcarriers measured by the measurement unit, an average value of the interference power for each of the plurality of subcarrier blocks and a statistical value indicating a degree of variation in the interference power relative to the average value. The allocation unit allocates at least one subcarrier block to the terminal apparatus, based on the average value and the statistical value derived by the derivation unit.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Unpowered twisted pair loopback circuit for differential mode signaling
ActiveUS7447307B2Multiple input and output pulse circuitsInterconnection arrangementsTelecommunications linkEngineering
A method and apparatus provide an IP telephone or similar device with a mechanism to receive and at least briefly loop back discovery signals received from a telecommunications device such as an Ethernet switch while not permitting the loop back of data packet signals. No mechanical relays are required and the circuitry can be fully integrated on an integrated circuit using commonly available techniques, if desired.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
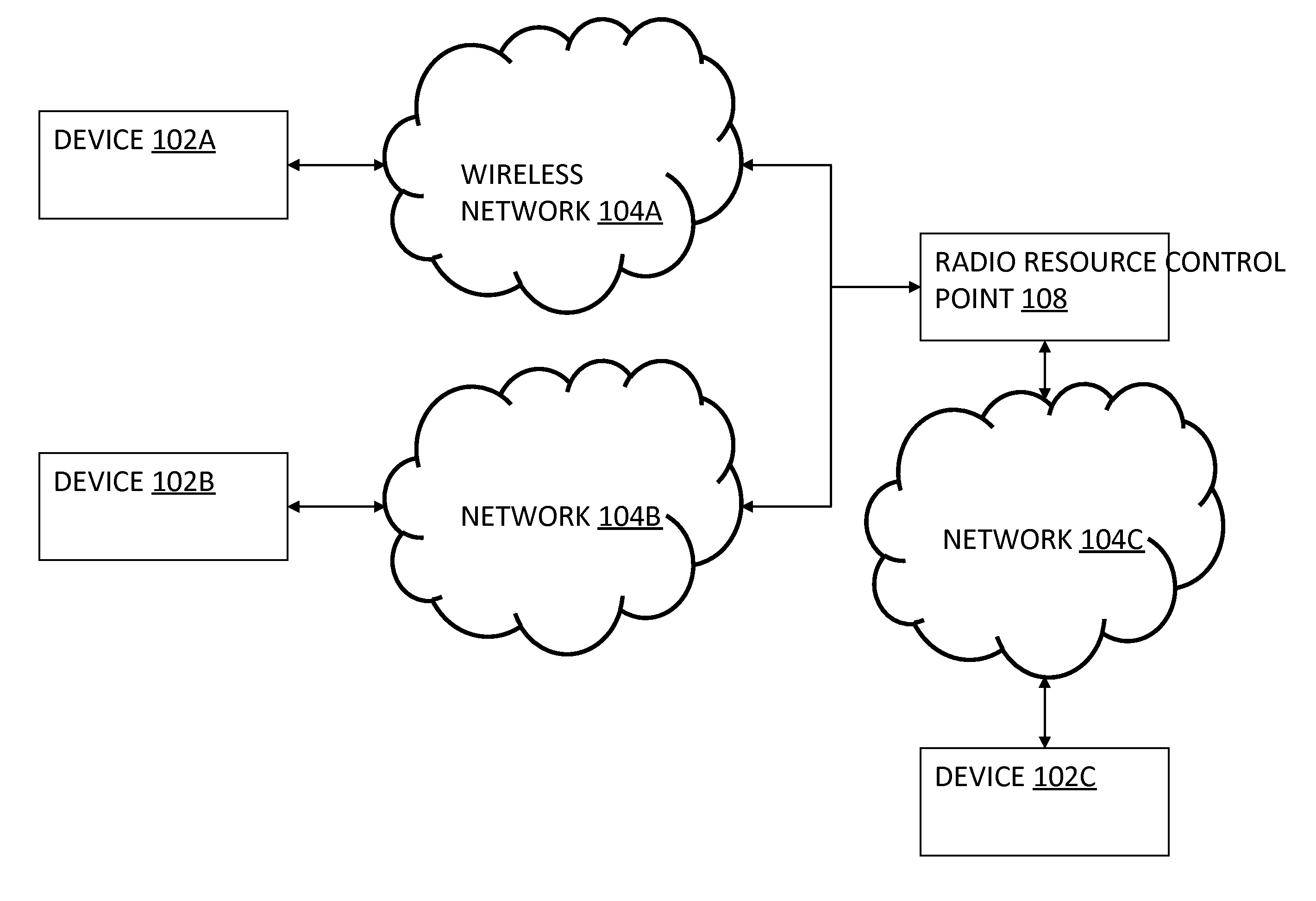
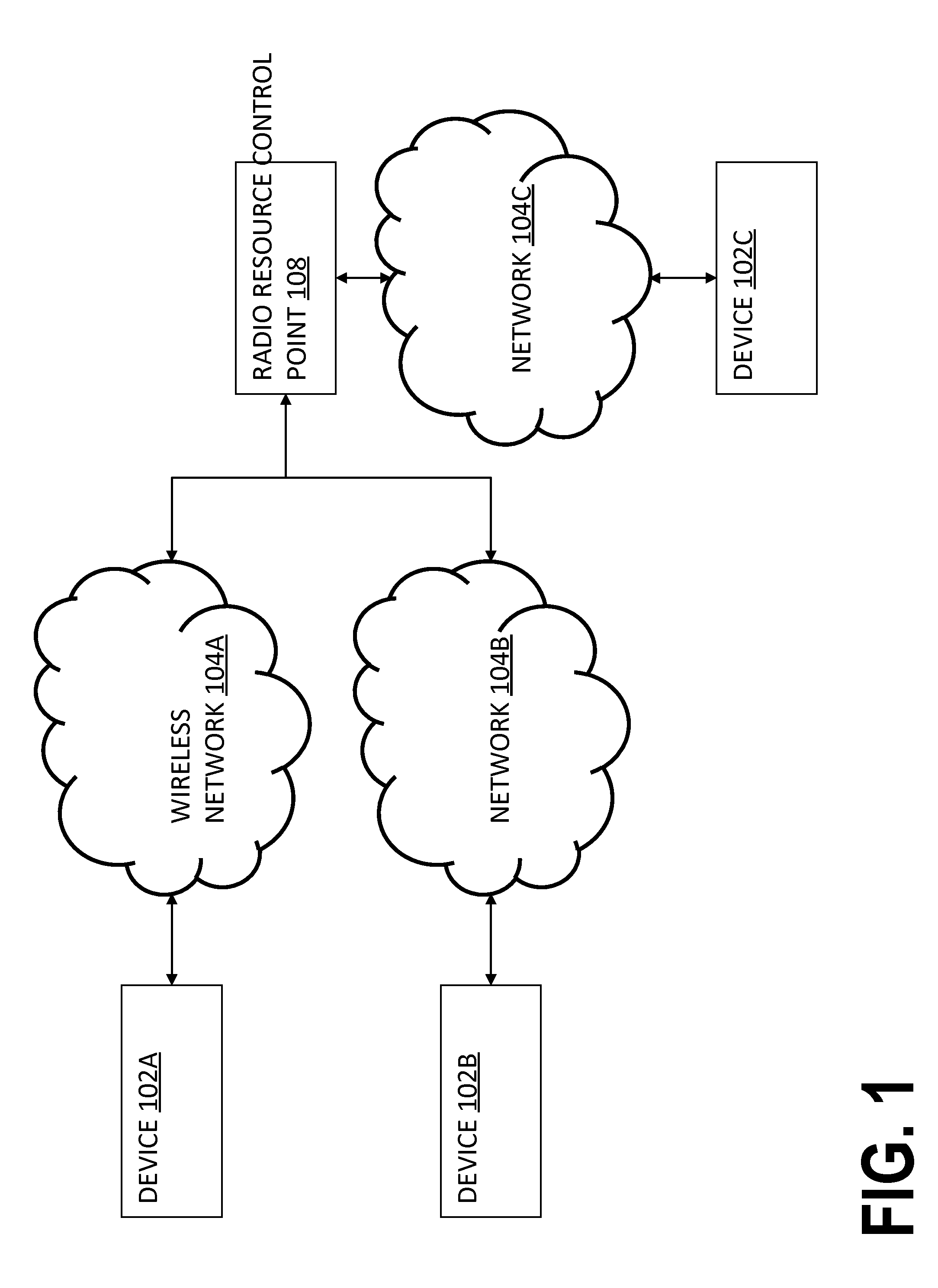
Radio resource managment
ActiveUS9325468B2Maximize aggregate user quality of experienceIncrease resourcesTelephonic communicationInter user/terminal allocationRadio access networkResource management
Methods and systems described herein relate to more optimally allocating and scheduling radio resources simultaneously in space, time and frequency to enhance user quality of experience (QoE) according to use context within the constraints of maximizing long term service provider revenue expectation for a given investment in radio access network infrastructure for improved radio resource management, such methods optionally including use of heat maps of user trajectories as a factor in a process for resource allocation.
Owner:FEDERATED WIRELESS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com